Patents
Literature
526 results about "Phonon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, specifically in solids and some liquids. Often designated a quasiparticle, it represents an excited state in the quantum mechanical quantization of the modes of vibrations of elastic structures of interacting particles.
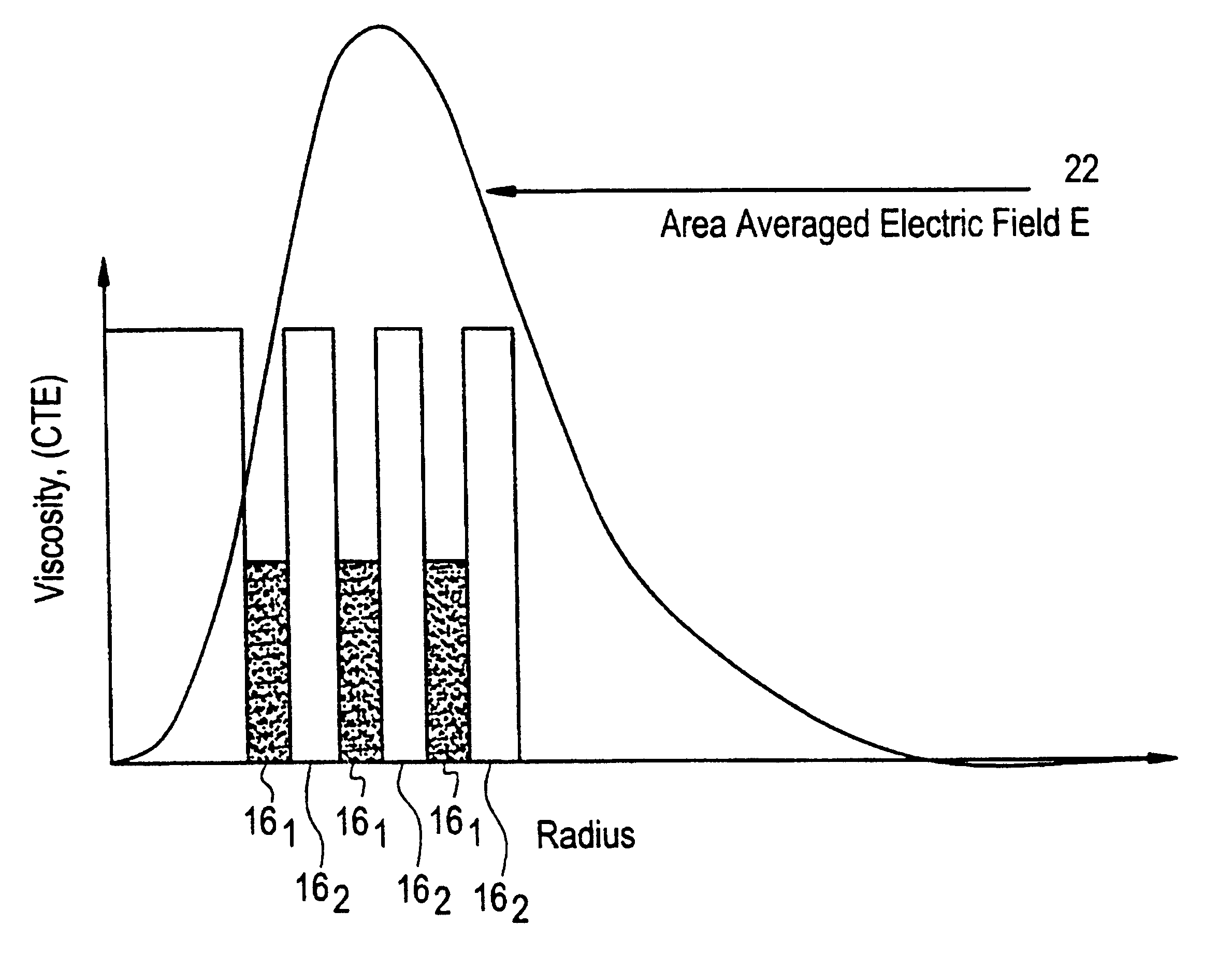
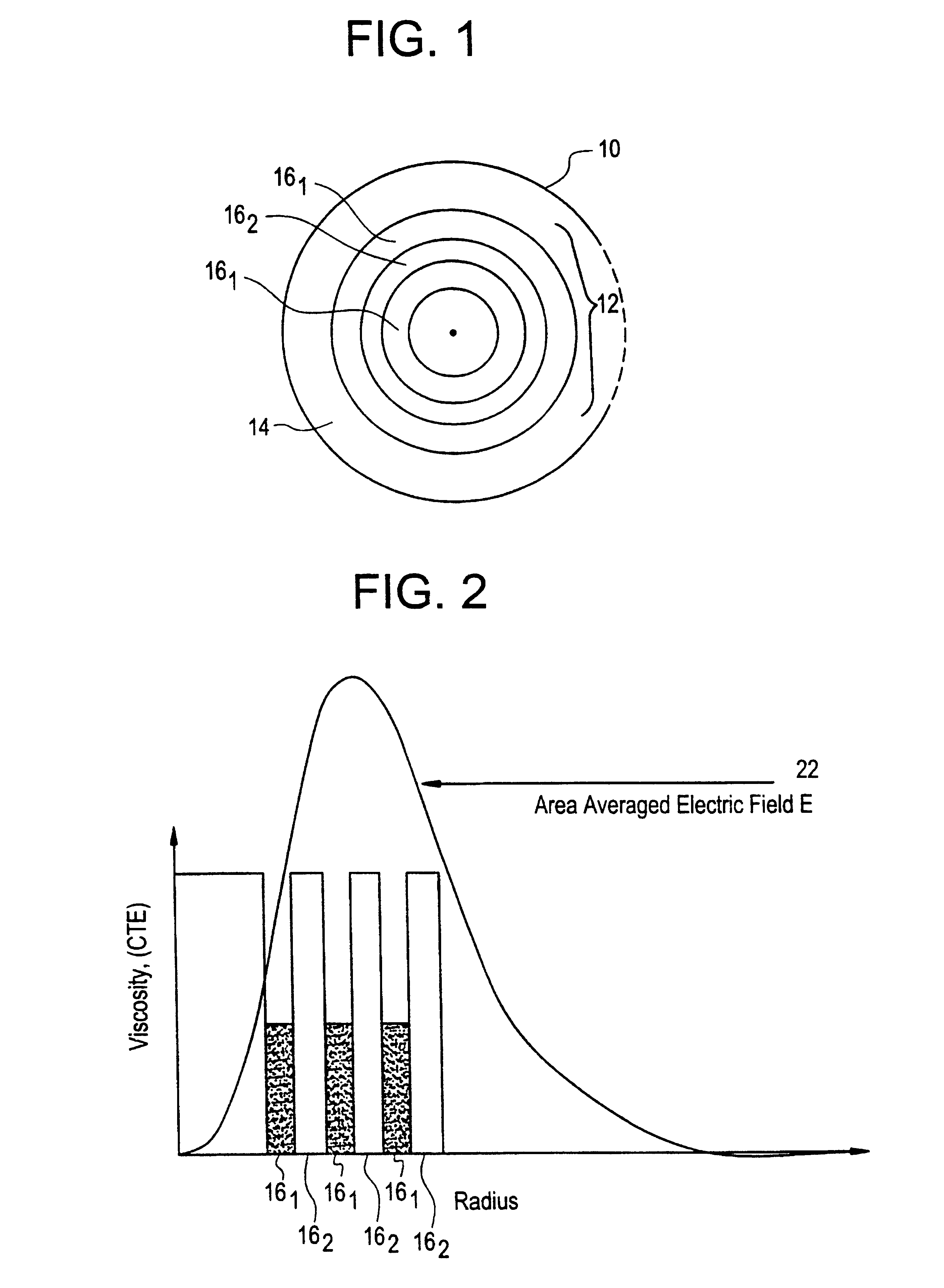
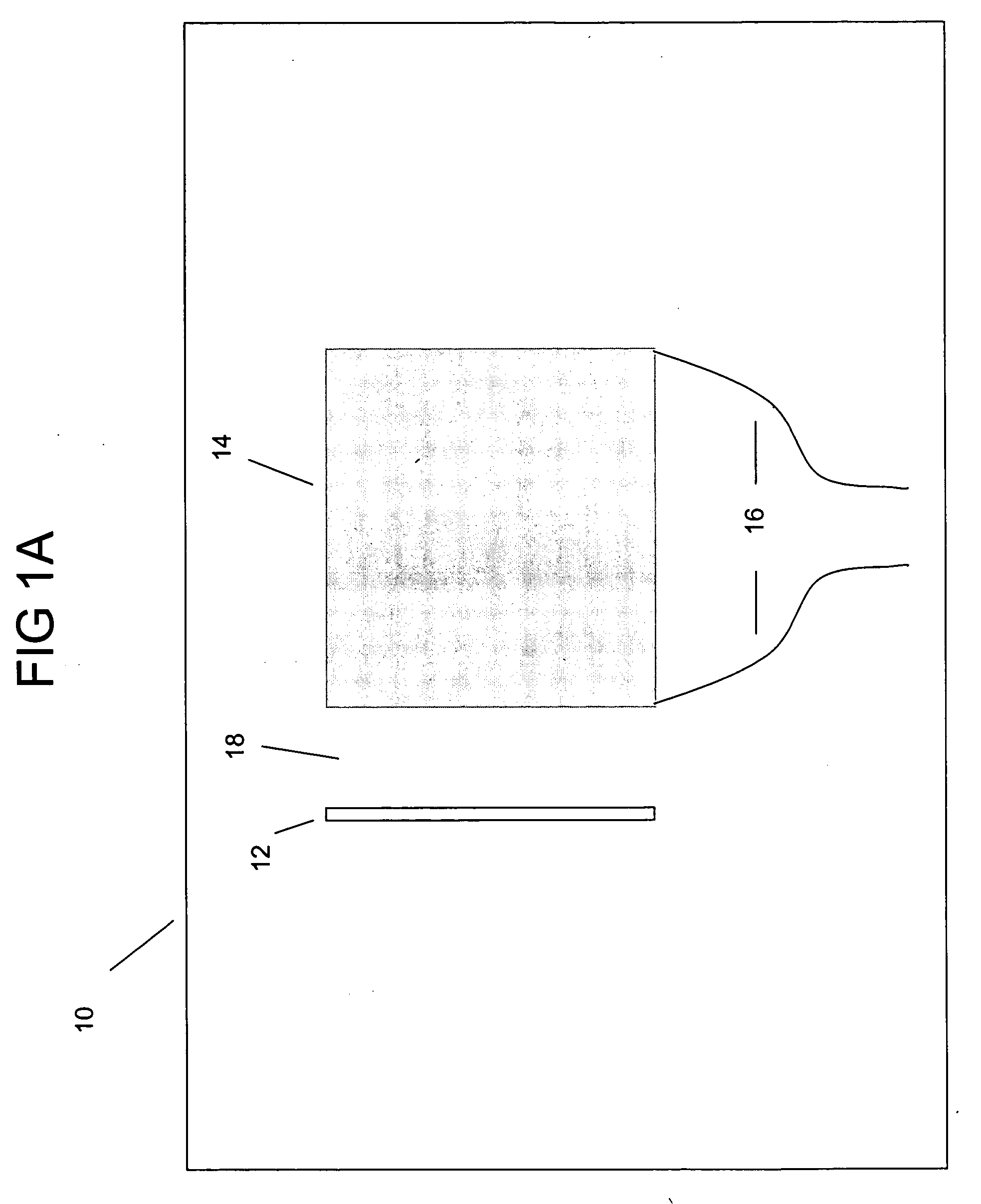
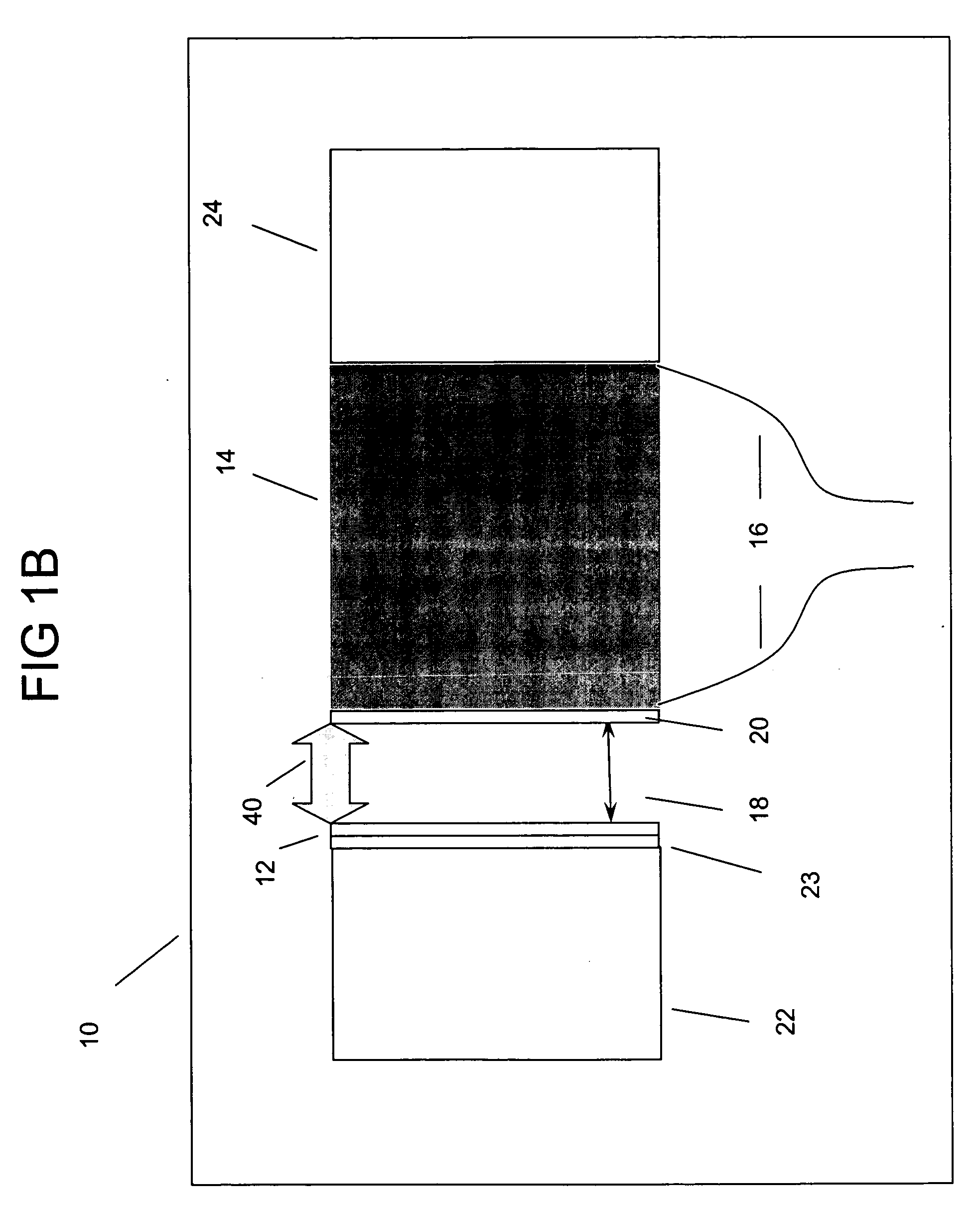
Suppression of stimulated Brillouin scattering in optical fiber
InactiveUS6542683B1Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGlass fibre drawing apparatusFiberDopant
Suppression of stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) by broadening the energy spectrum of participating SBS photons and / or phonons is achieved in an optical fiber having a core with both radially nonuniform viscosity and CTE profiles provided by alternating layers of glass modifying dopants such as phosphorous and fluorine. The nonuniform thermal expansion and viscosity profiles impart a residual, permanent, nonuniform stress in the fiber. The SBS suppressing effect provided by the nonuniform stress can be controlled and enhanced by applying a uniform or nonuniform tensile force to the fiber as it is being drawn. A preform for the fiber is also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method for forming a thin-film thermoelectric device including a phonon-blocking thermal conductor
InactiveUS20050150535A1Reduce needReduction in electron thermal conductivityThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentElectrical conductorLiquid metal
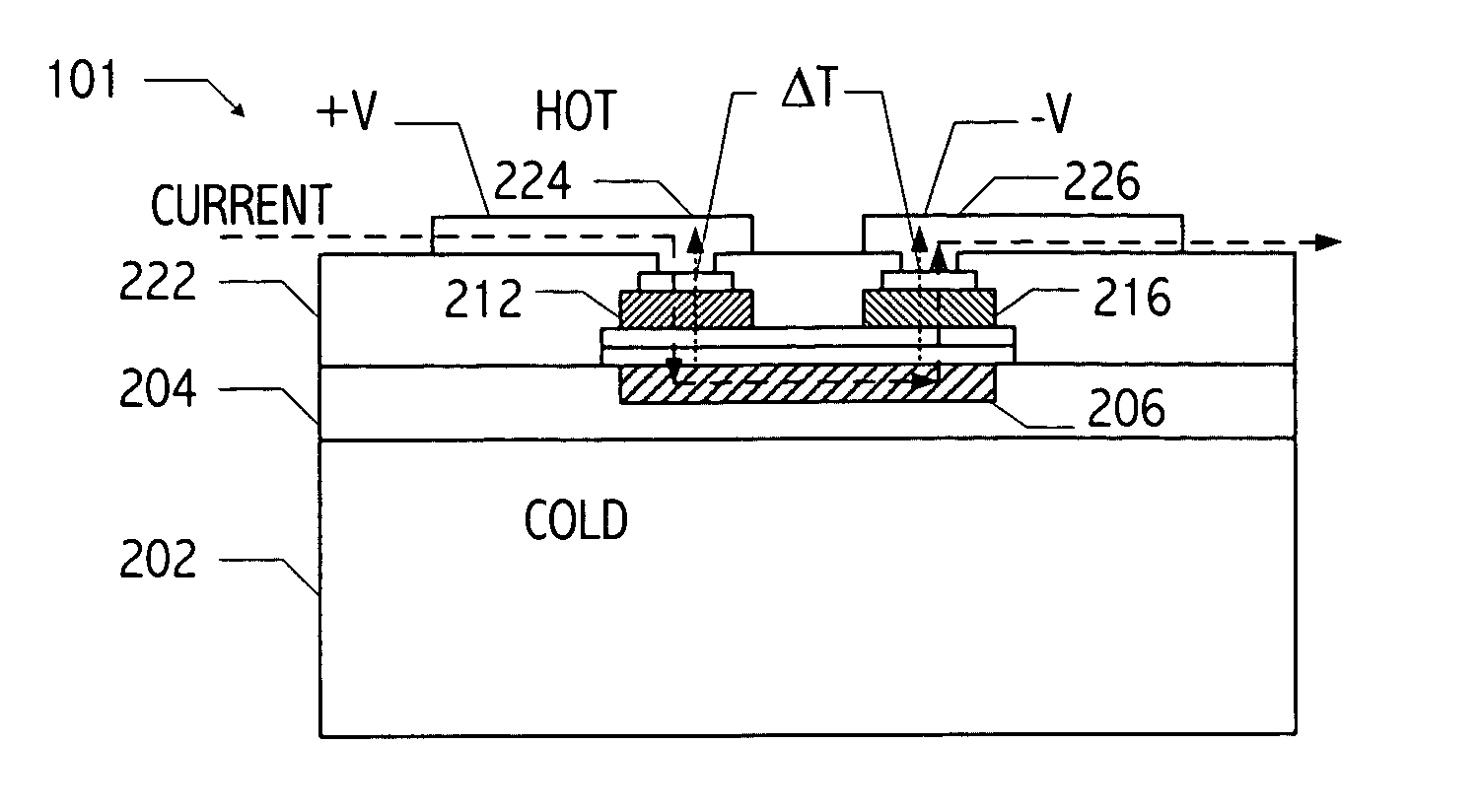
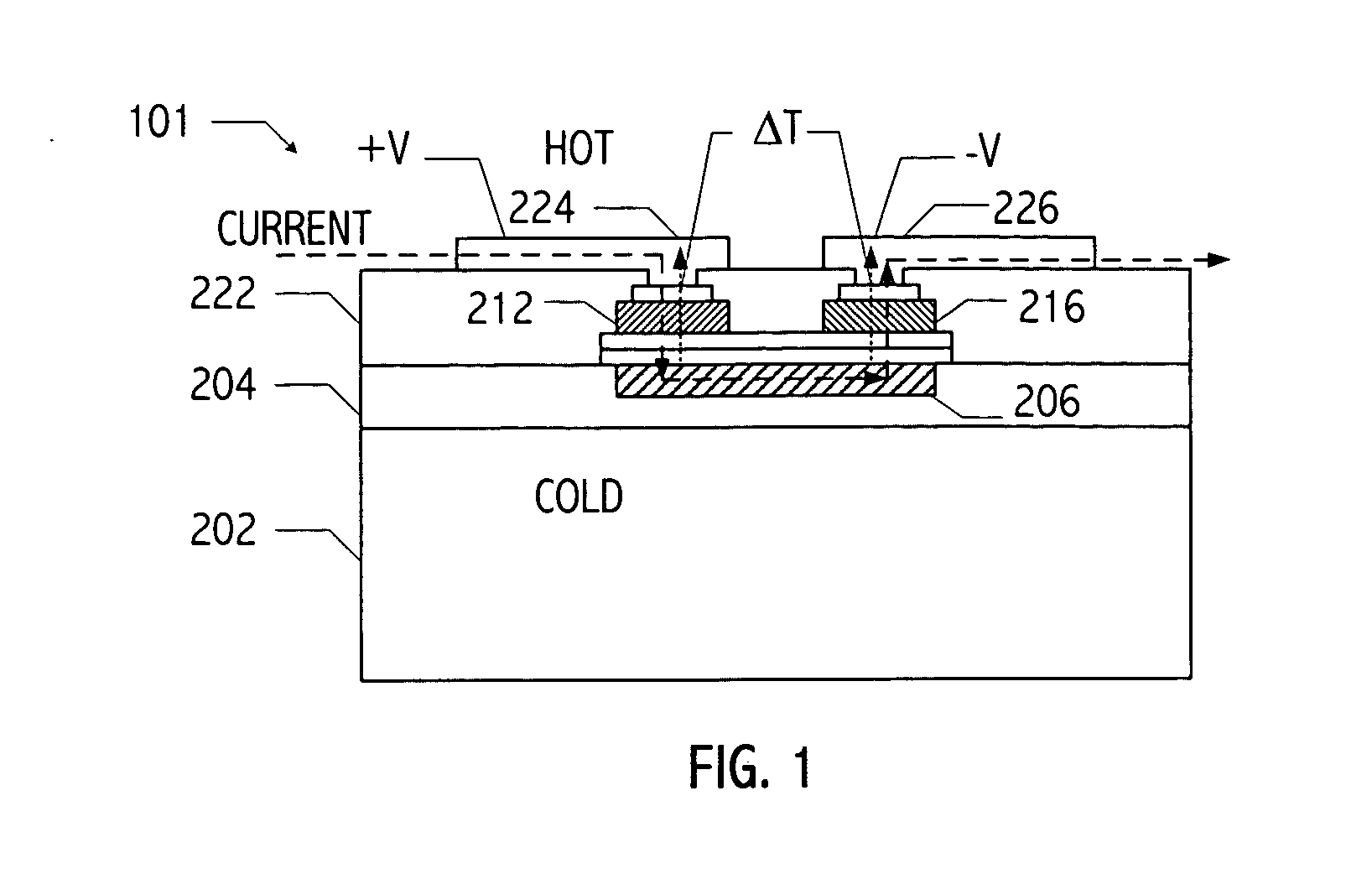
A vertical, monolithic, thin-film thermoelectric device is described. Thermoelectric elements of opposing conductivity types may be coupled electrically in series and thermally in parallel by associated electrodes on a single substrate, reducing the need for mechanisms to attach multiple substrates or components. Phonon transport may be separated from electron transport in a thermoelectric element. A thermoelectric element may have a thickness less than an associated thermalization length. An insulating film between an electrode having a first temperature and an electrode having a second temperature may be a low-thermal conductivity material, a low-k, or ultra-low-k dielectric. Phonon thermal conductivity between a thermoelectric element and an electrode may be reduced without a significant reduction in electron thermal conductivity, as compared to other thermoelectric devices. A phonon conduction impeding material may be included in regions coupling an electrode to an associated thermoelectric element (e.g., a liquid metal).
Owner:NANOCOOLERS
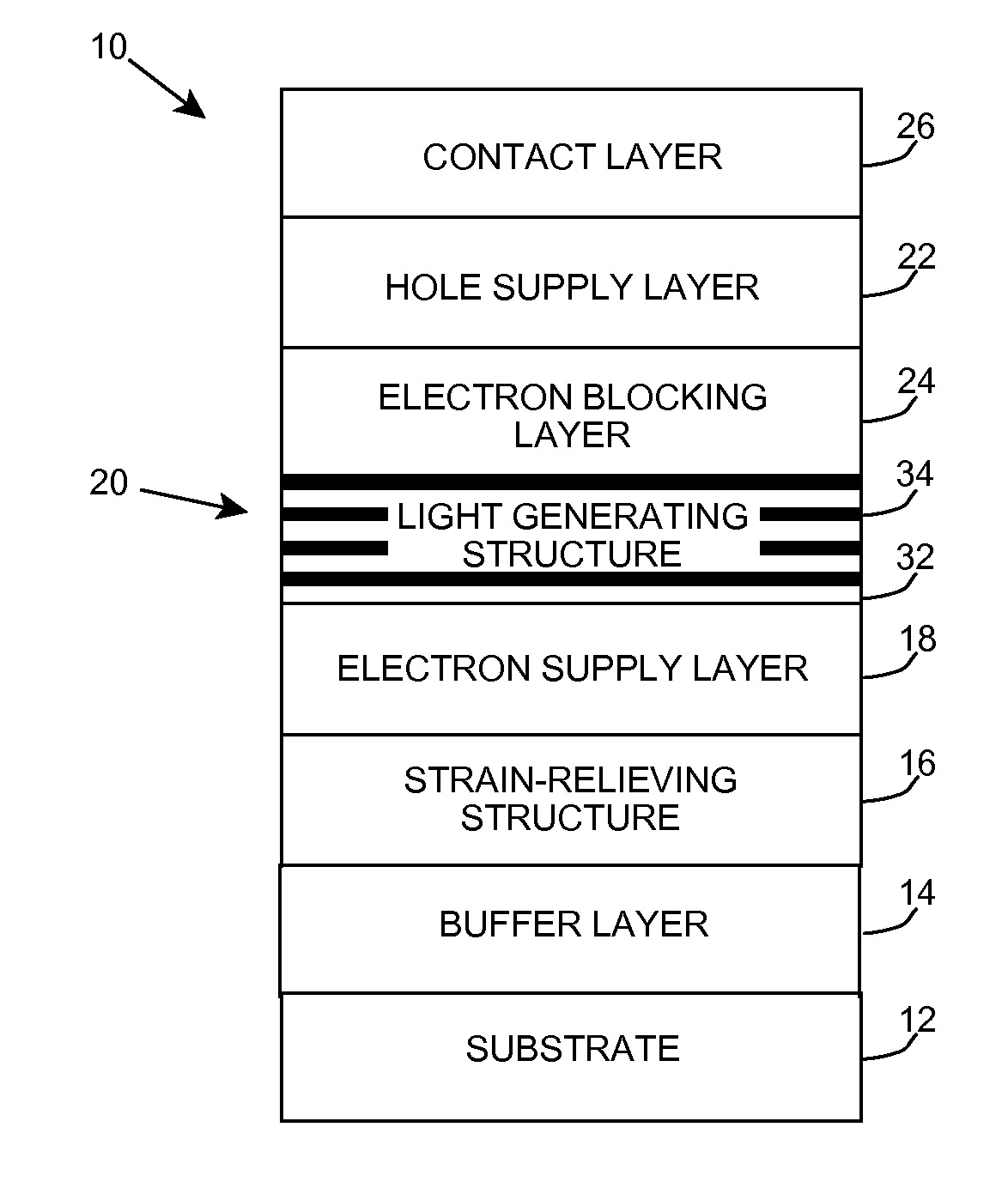
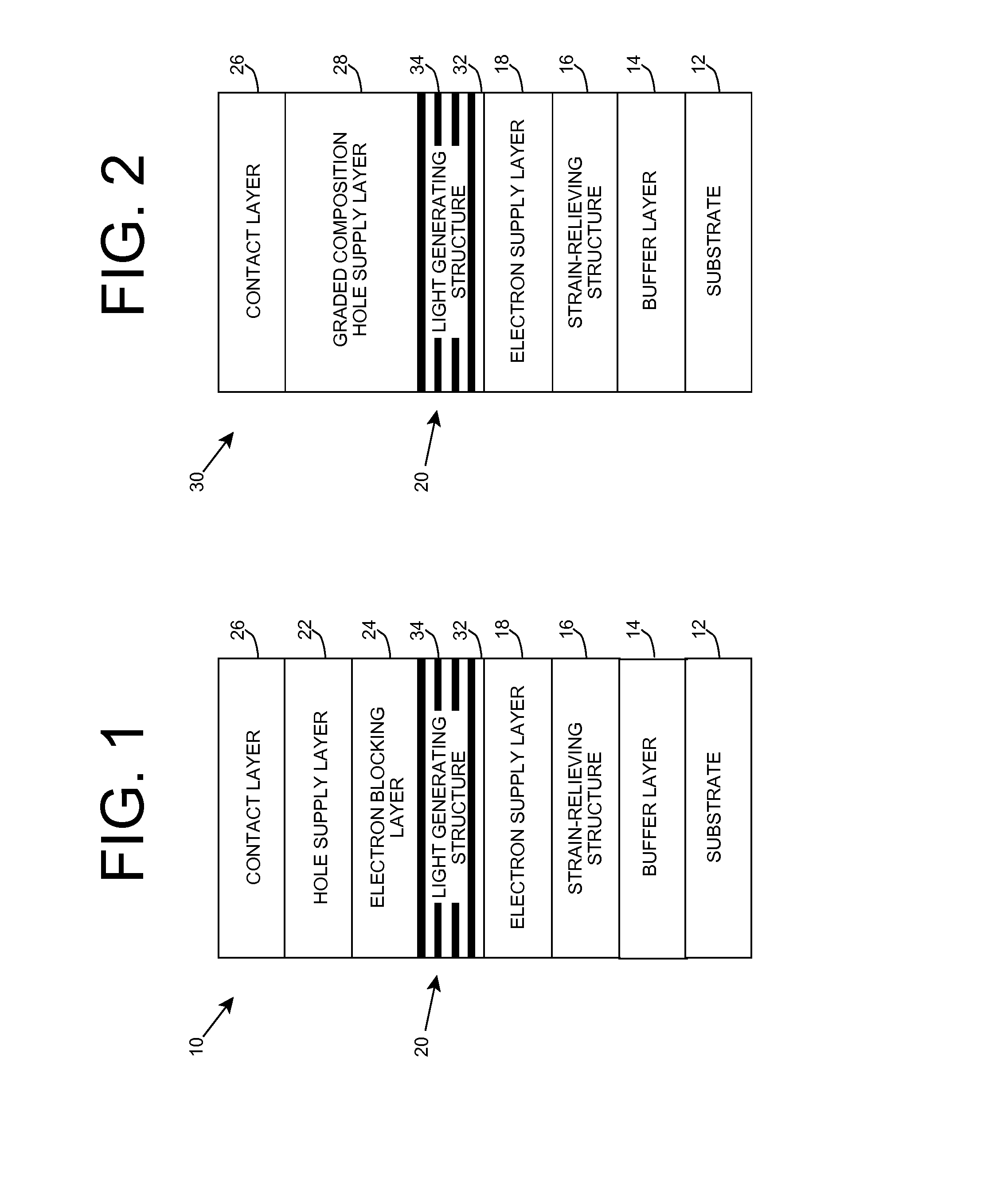
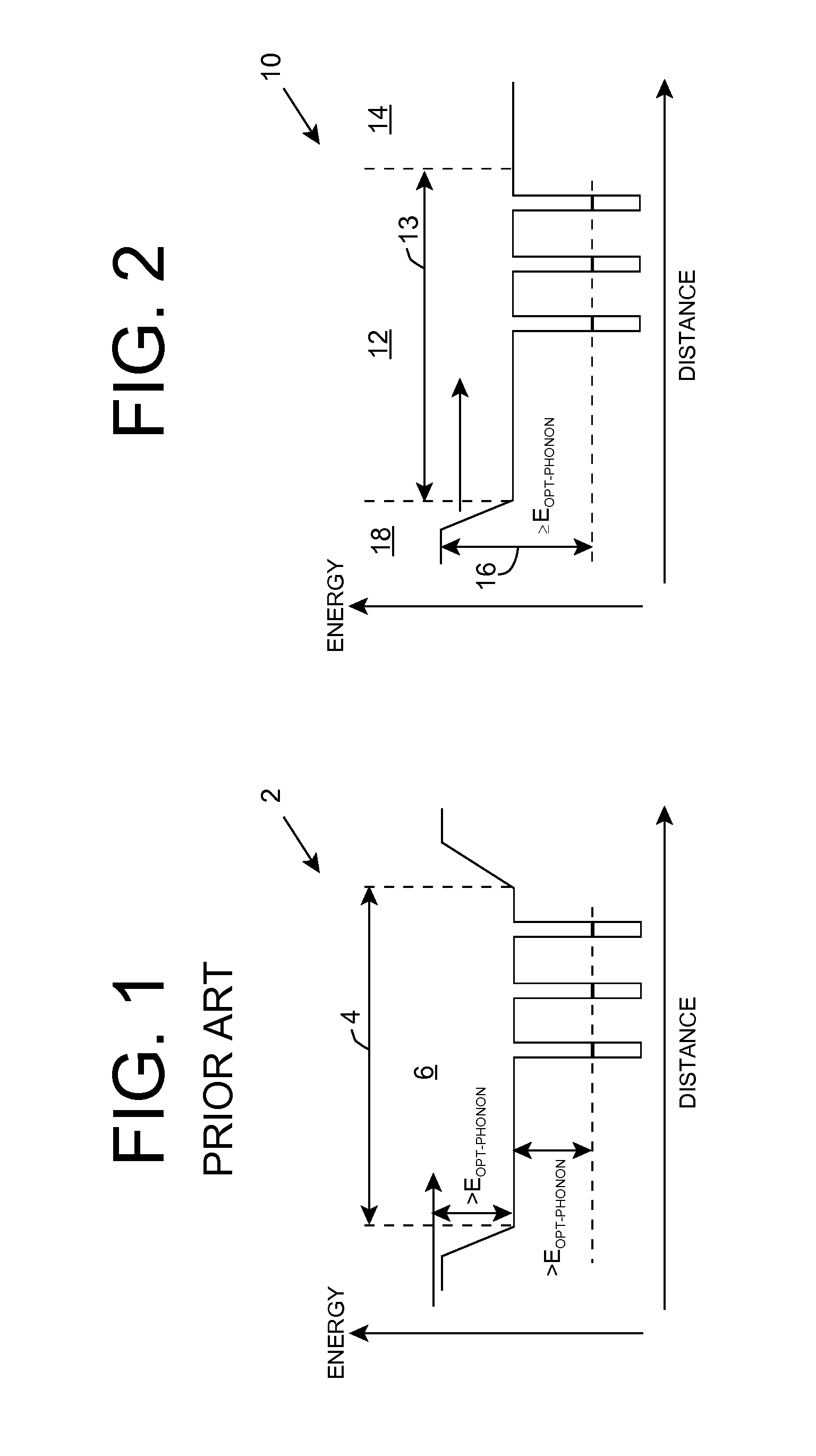
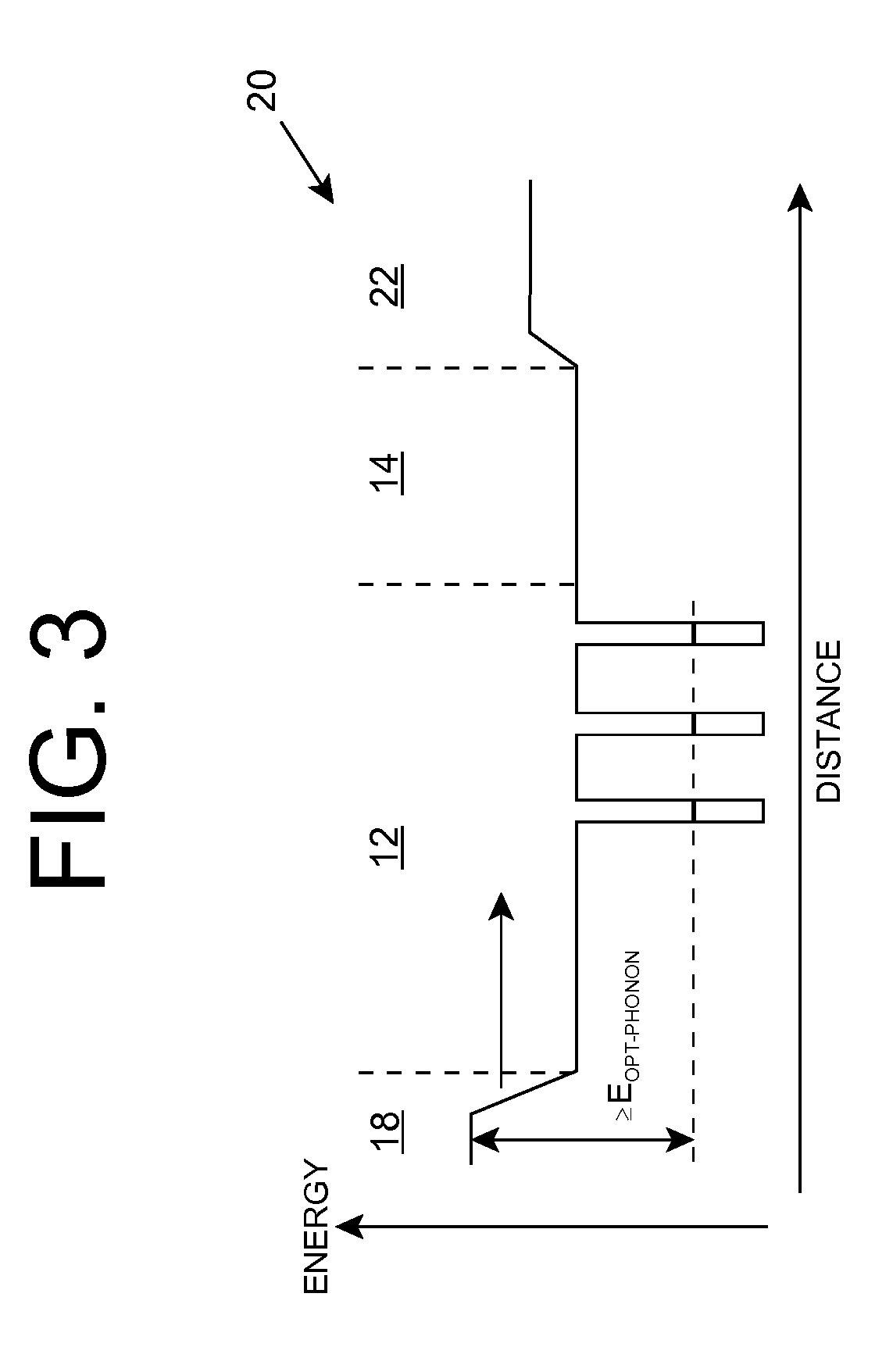
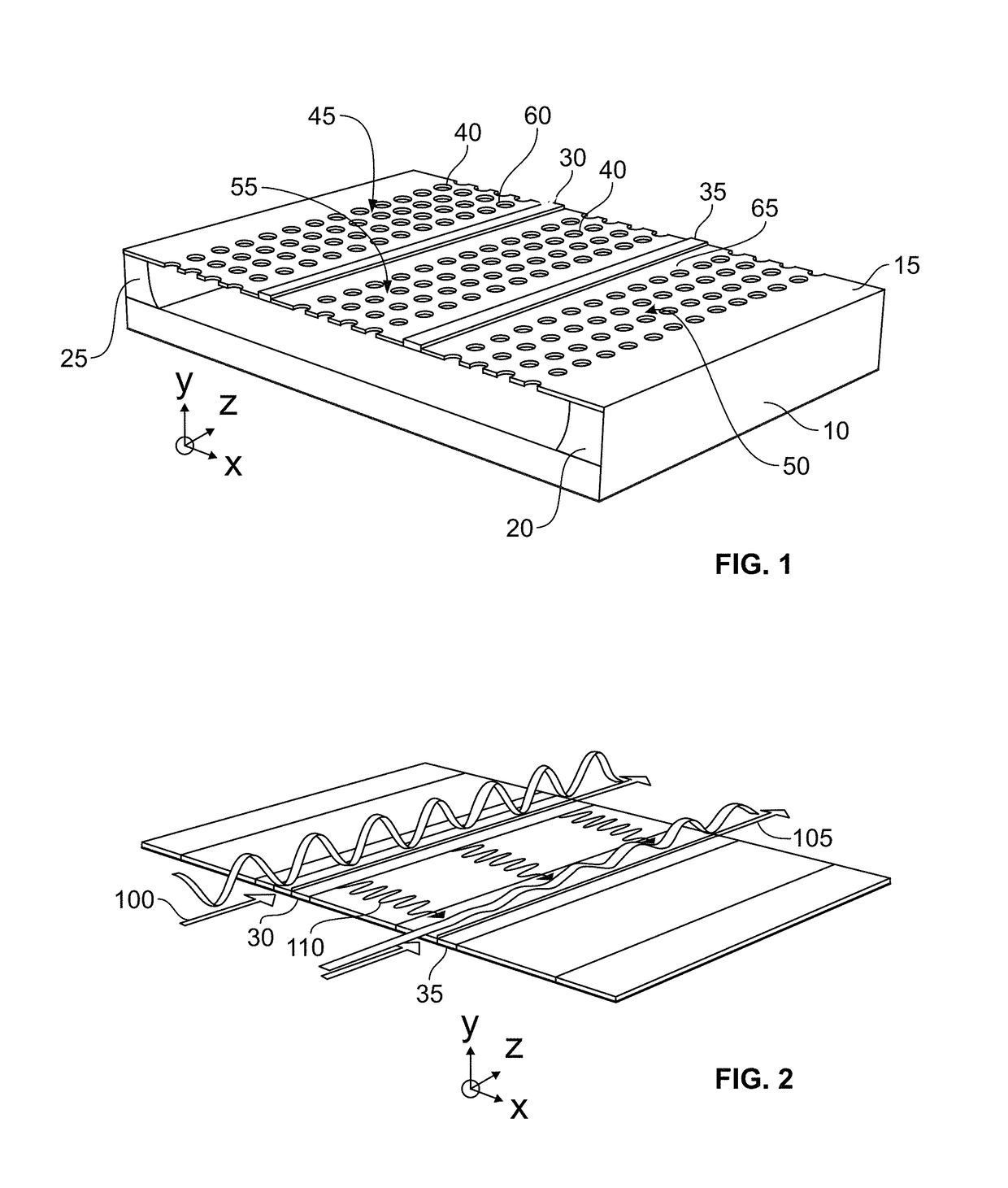
Heterostructure including light generating structure contained in potential well
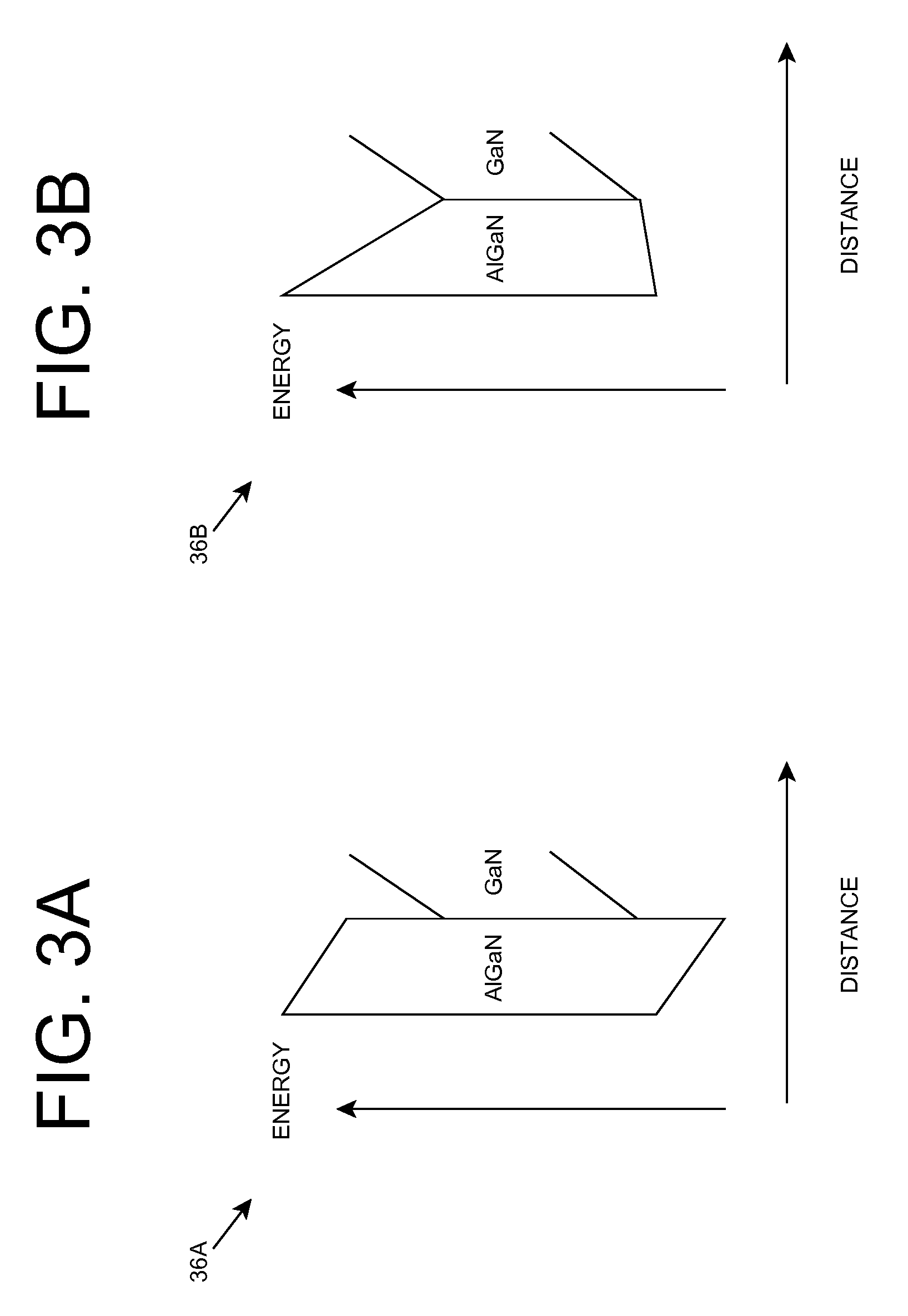
ActiveUS20070181869A1Improve featuresConvenient lightingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsPotential wellElectron hole
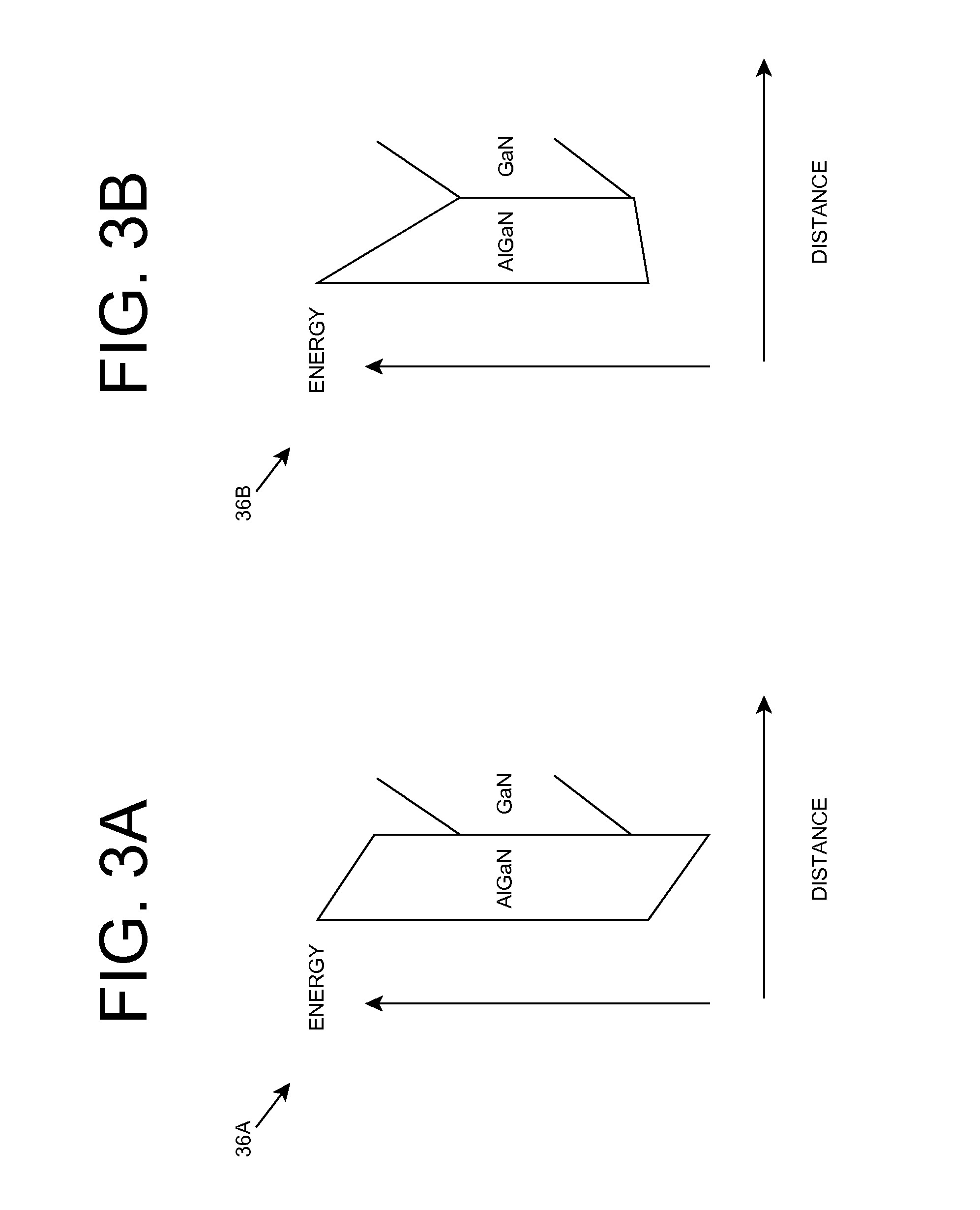
A light emitting heterostructure and / or device in which the light generating structure is contained within a potential well is provided. The potential well is configured to contain electrons, holes, and / or electron and hole pairs within the light generating structure. A phonon engineering approach can be used in which a band structure of the potential well and / or light generating structure is designed to facilitate the emission of polar optical phonons by electrons entering the light generating structure. To this extent, a difference between an energy at a top of the potential well and an energy of a quantum well in the light generating structure can be resonant with an energy of a polar optical phonon in the light generating structure material. The energy of the quantum well can comprise an energy at the top of the quantum well, an electron ground state energy, and / or the like.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Phonon-blocking, electron-transmitting low-dimensional structures
ActiveUS7342169B2Lower lattice thermal conductivityImprove ZTThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentLattice mismatchCharge carrier
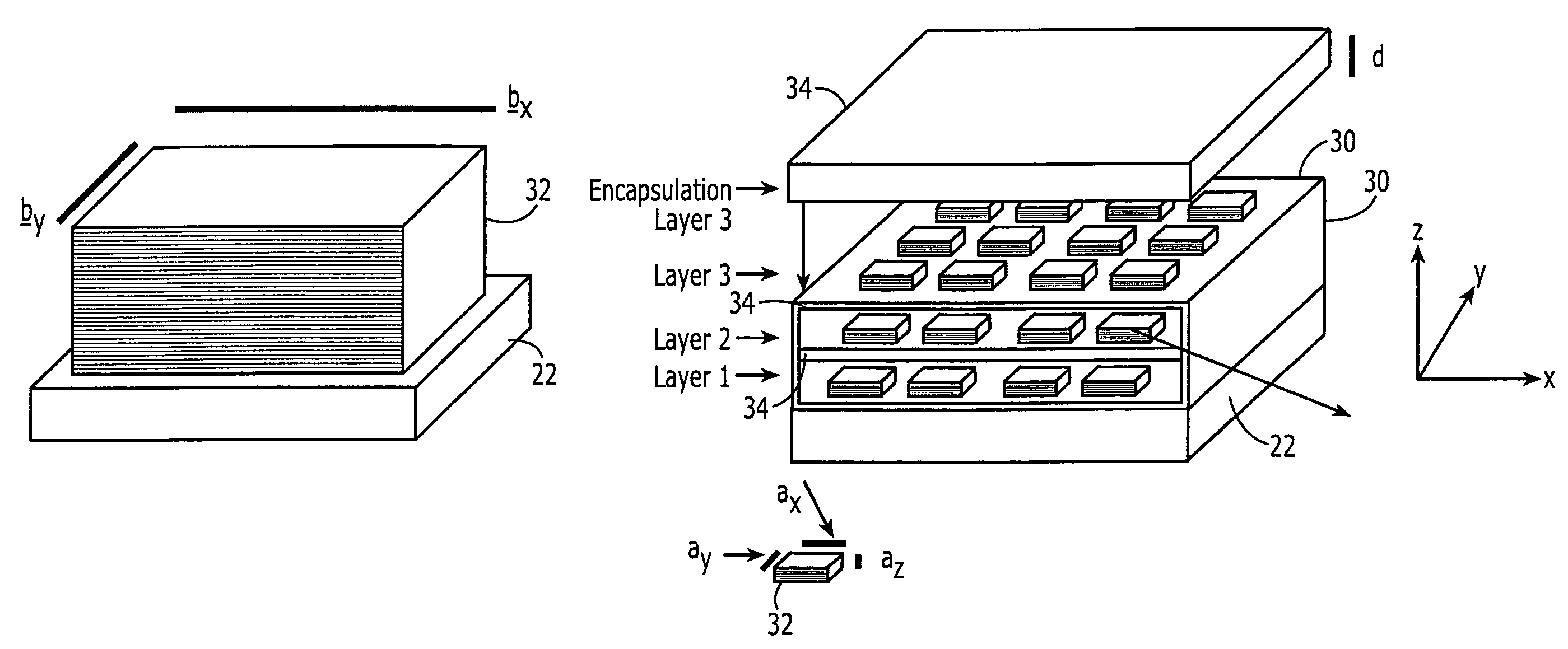
A thermoelectric structure and device including at least first and second material systems having different lattice constants and interposed in contact with each other, and a physical interface at which the at least first and second material systems are joined with a lattice mismatch and at which structural integrity of the first and second material systems is substantially maintained. The at least first and second material systems have a charge carrier transport direction normal to the physical interface and preferably periodically arranged in a superlattice structure.
Owner:LAIRD THERMAL SYST INC
Noise suppression method for wave filter
ActiveUS7057476B2Eliminate signalWeaken energyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesImpedence networksThin-film bulk acoustic resonatorHarmonic vibration
A noise suppression method of a wave filter used to eliminate standing wave signal interferences in the acoustic wave filter consisted by a plurality of film bulk acoustic resonators (FBARs). The method is to provide a plurality of scatterers in the structured consisted by the FBARs, thereby creating an band-gap structure due to the material characteristics difference, which consequently generates a destructive interfering effect to the transverse higher harmonics vibration within a specific operating frequency range, and ultimately decreases or even eliminates any parasitic effects. Therefore, within the operation frequency range of this band-gap structure, abnormal signals created by any transverse wave modes cannot exist. In addition, an acoustic shield can be provided by phononic crystal structures between different FBARs, thus acoustic shielding any mutual interference within the operation frequency range.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Phononic metamaterials for vibration isolation and focusing of elastic waves
ActiveUS20130025961A1Reduce throughputMore complexity in manufacturingNon-rotating vibration suppressionSound producing devicesWaveform shapingBroadband
A methodology for designing structured metamaterials that can reflect, absorb and focus the propagation of both scalar acoustic and vector elastic waves is described. Three exemplary representative inventions based on the disclosed invention are described, illustrating i) compact ultra-wide broadband isolation, ii) sub-wavelength gaps and negative index propagation utilizing a single material platform, and iii) a fundamentally new method of producing multiple high frequency spectral gaps. Such metamaterial designs possess a wide range of potential applications, ranging from but not limited to, isolating an entity from external mechanical or acoustical vibrations, compact focusing lenses as well as cascaded high frequency filters for wave shaping and nonlinear wave propagation control.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
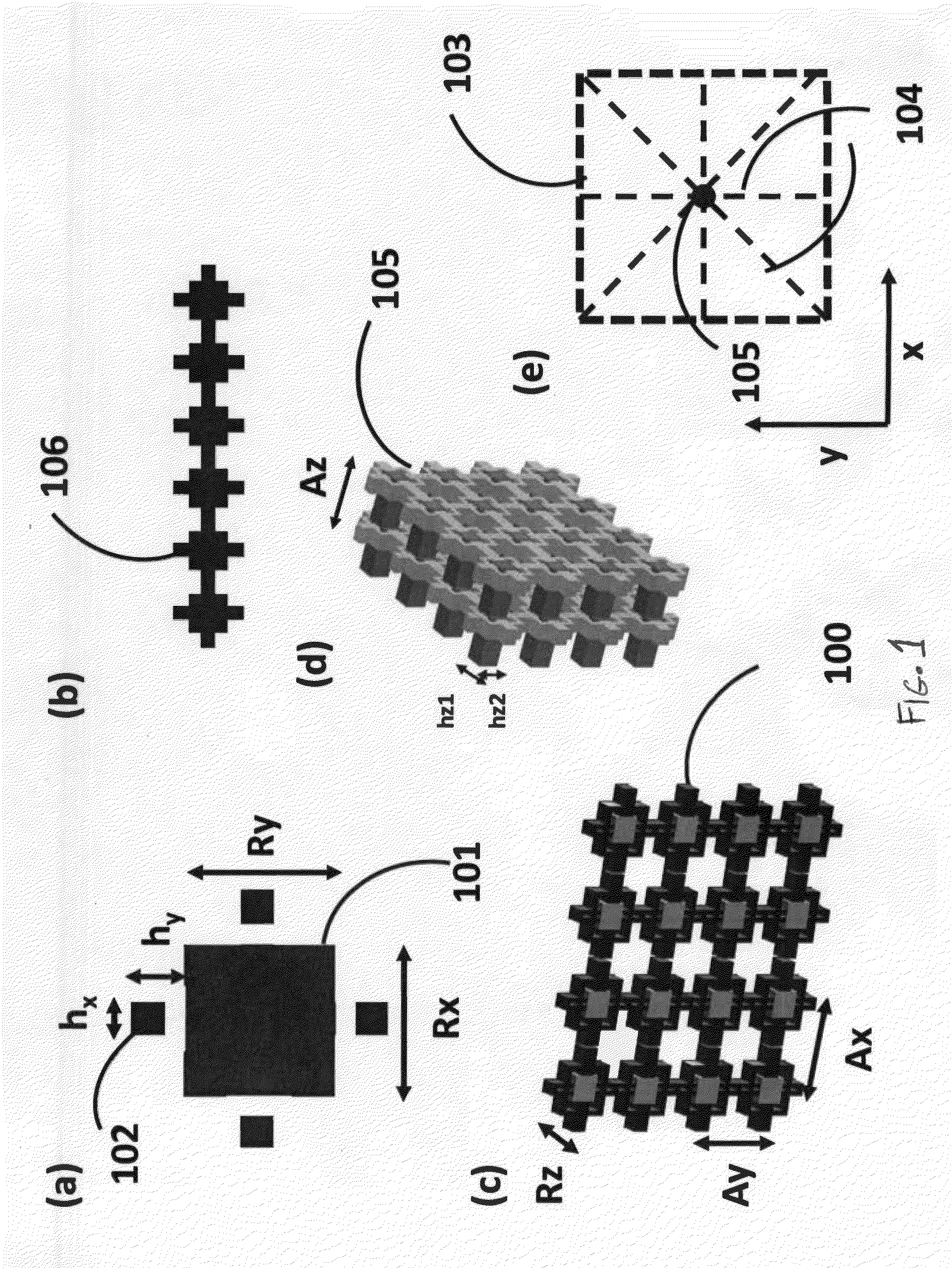
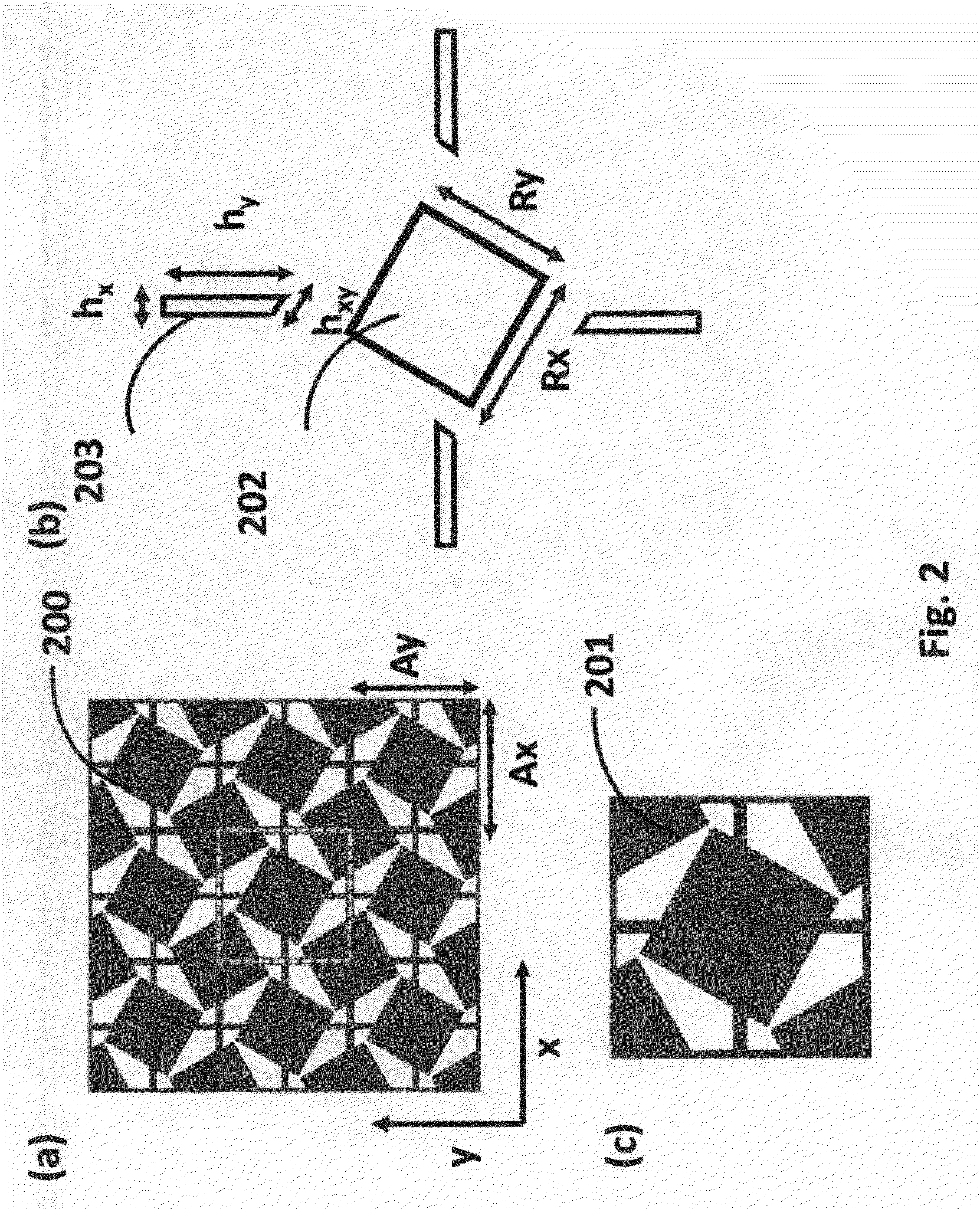
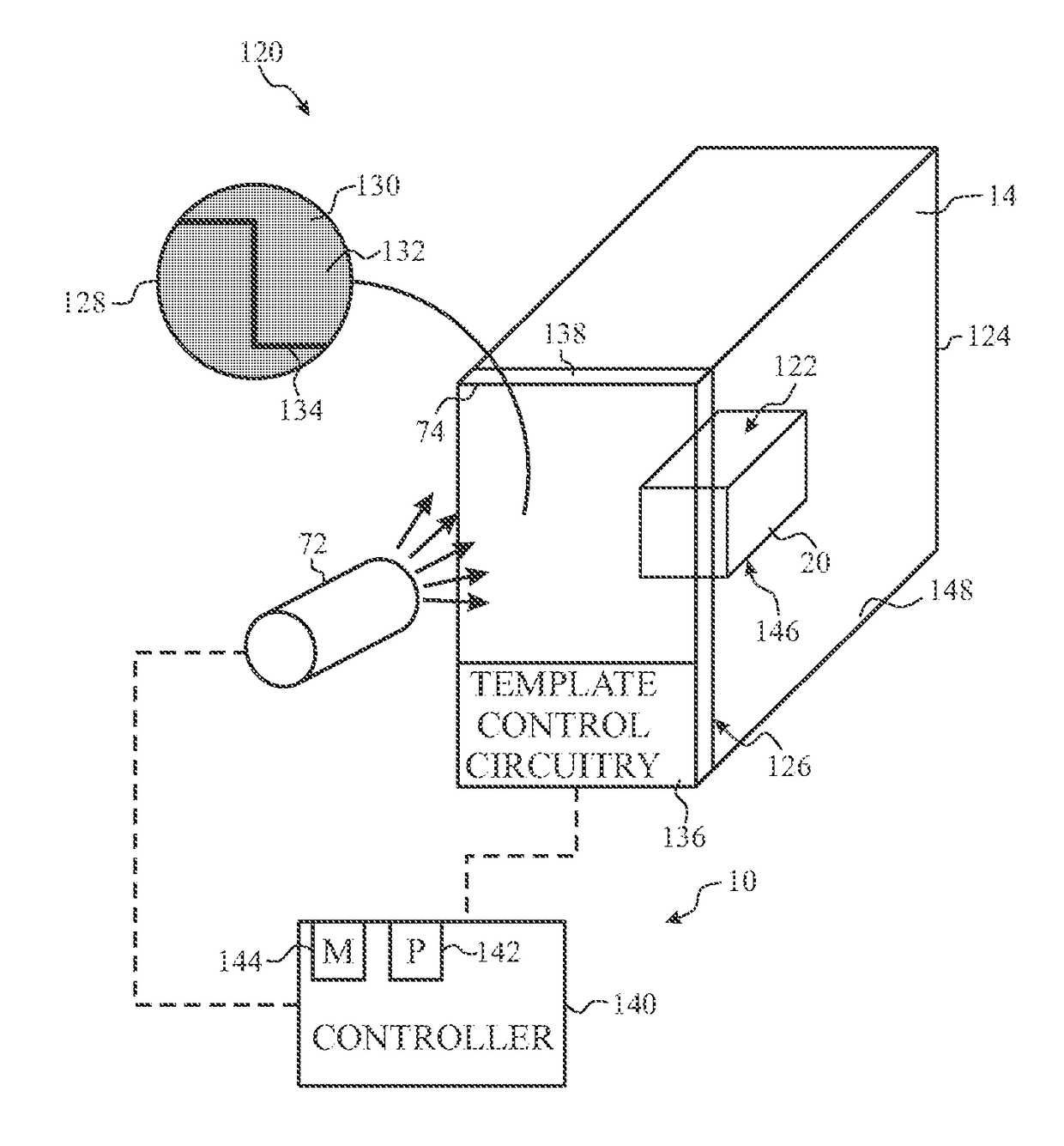
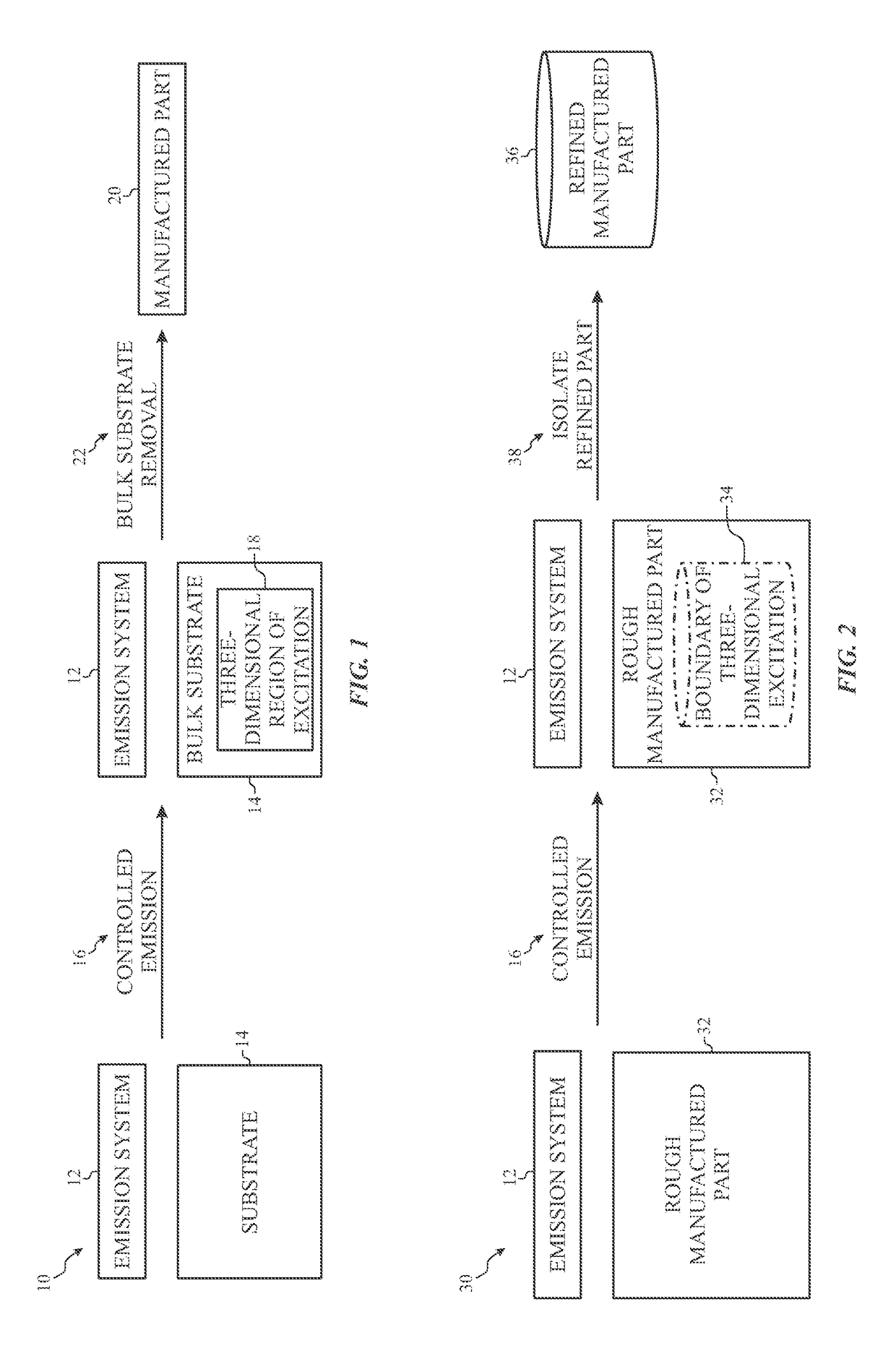
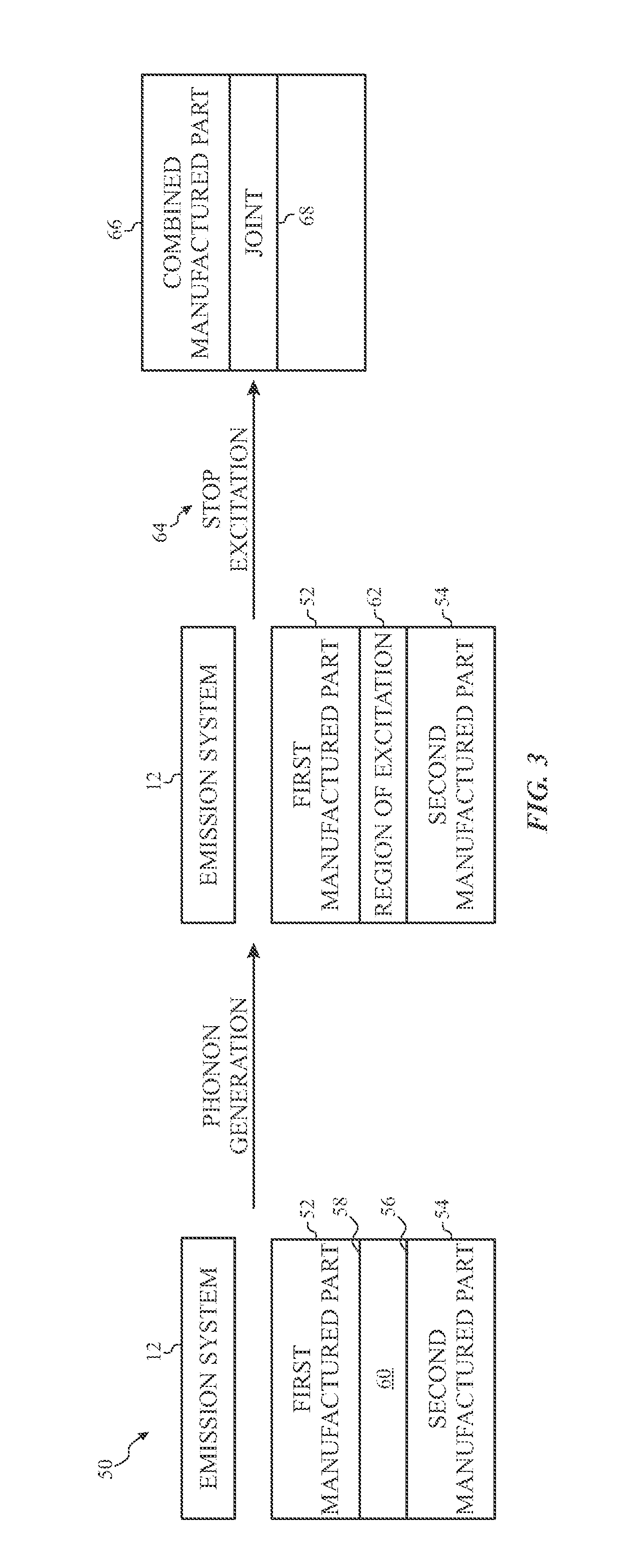
Phonon generation in bulk material for manufacturing
ActiveUS10065367B2Manufacturing irradiation arrangementsCeramic shaping apparatusEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:CHEVRON PHILLIPS CHEMICAL CO LP
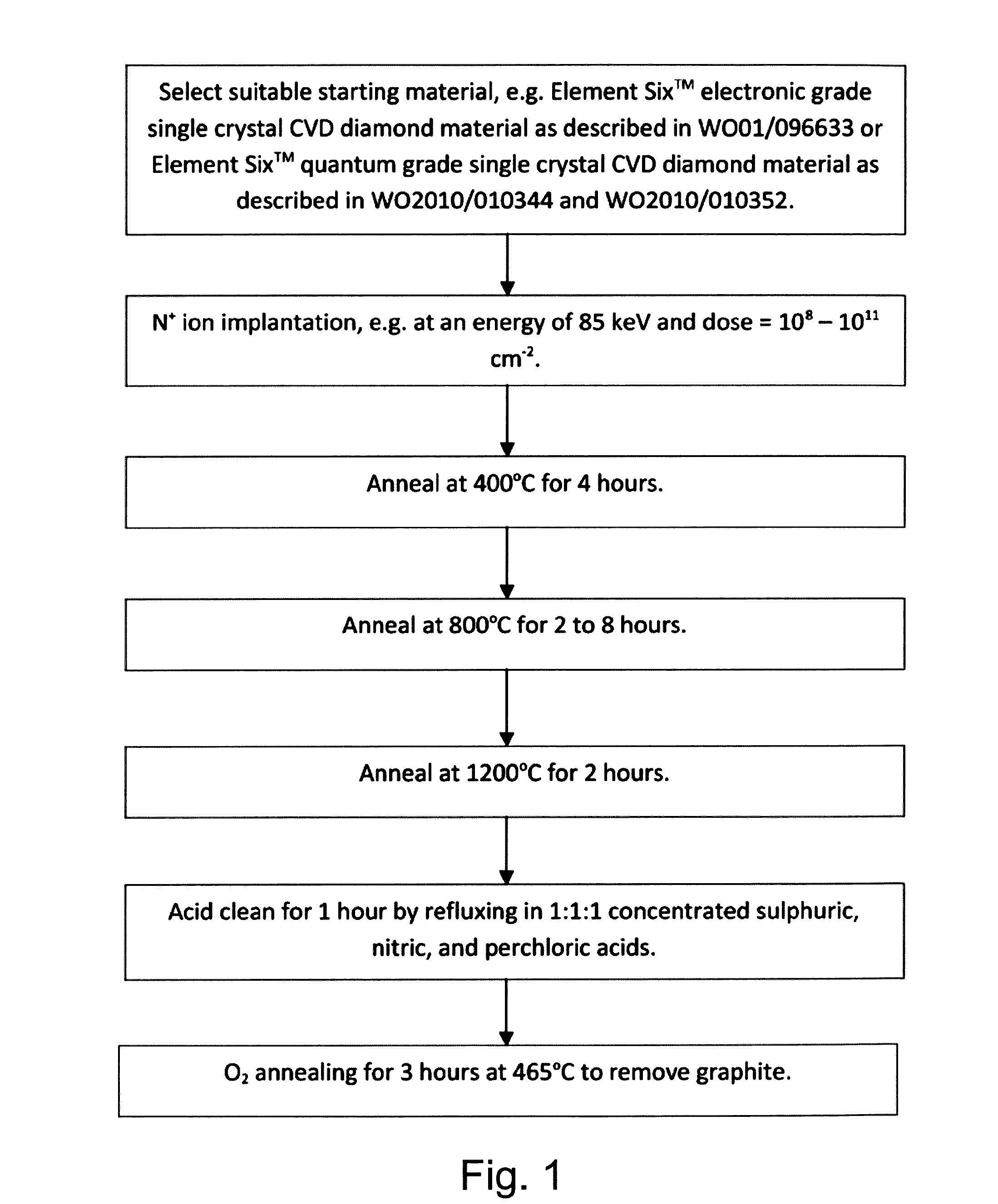
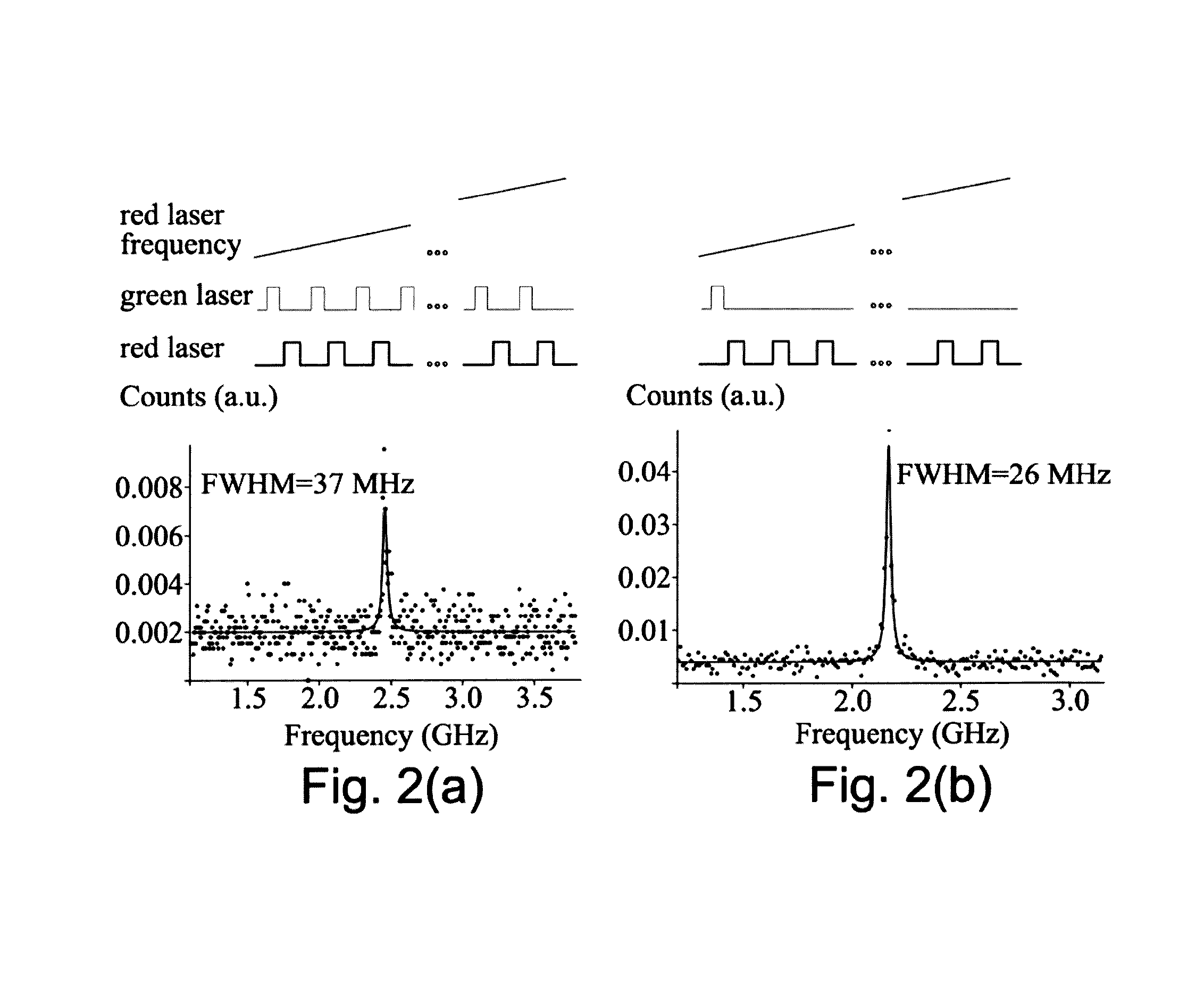
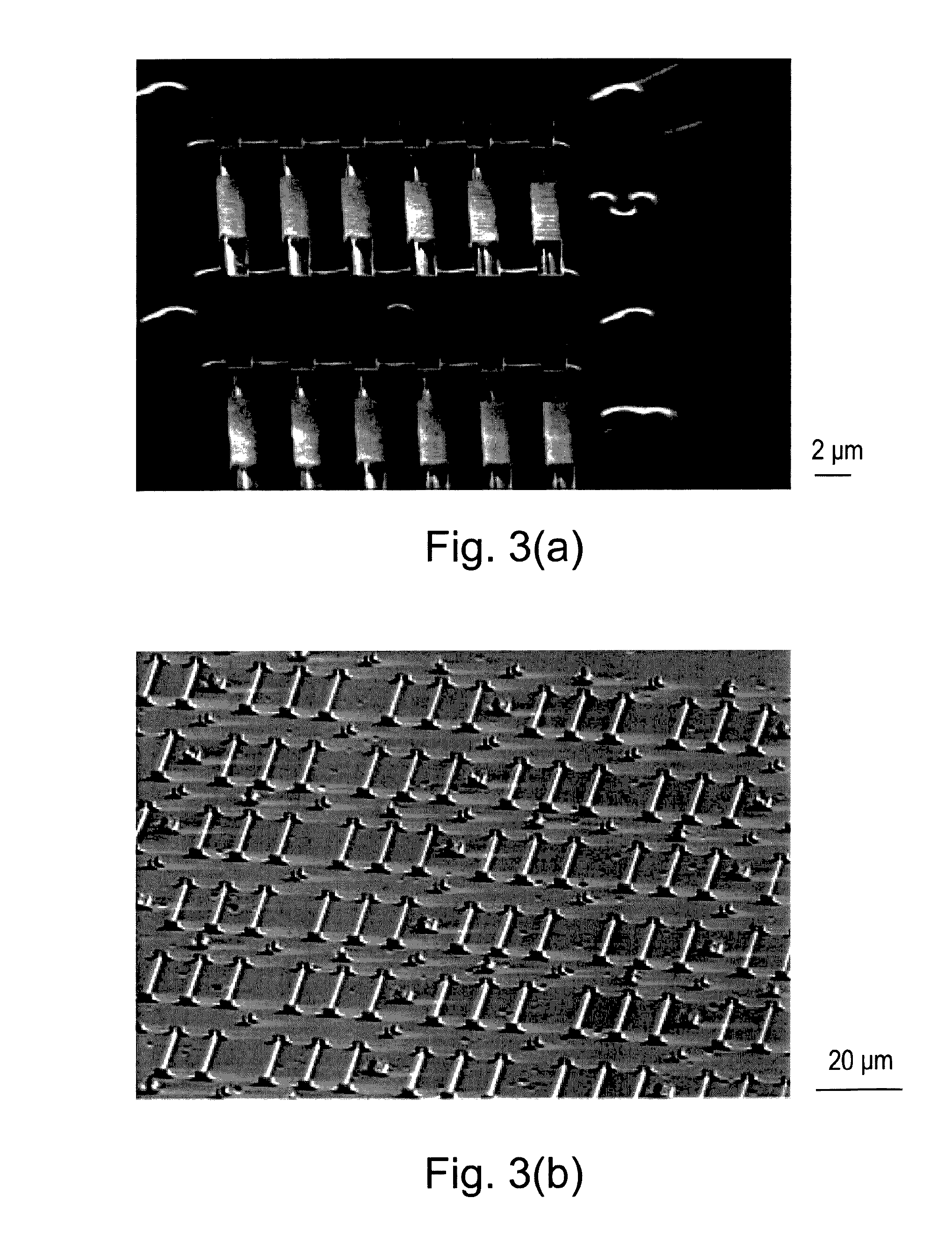
Synthetic diamond materials for quantum and optical applications and methods of making the same
A synthetic diamond material comprising one or more spin defects having a full width half maximum intrinsic inhomogeneous zero phonon line width of no more than 100 MHz. The method for obtain such a material involves a multi-stage annealing process.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
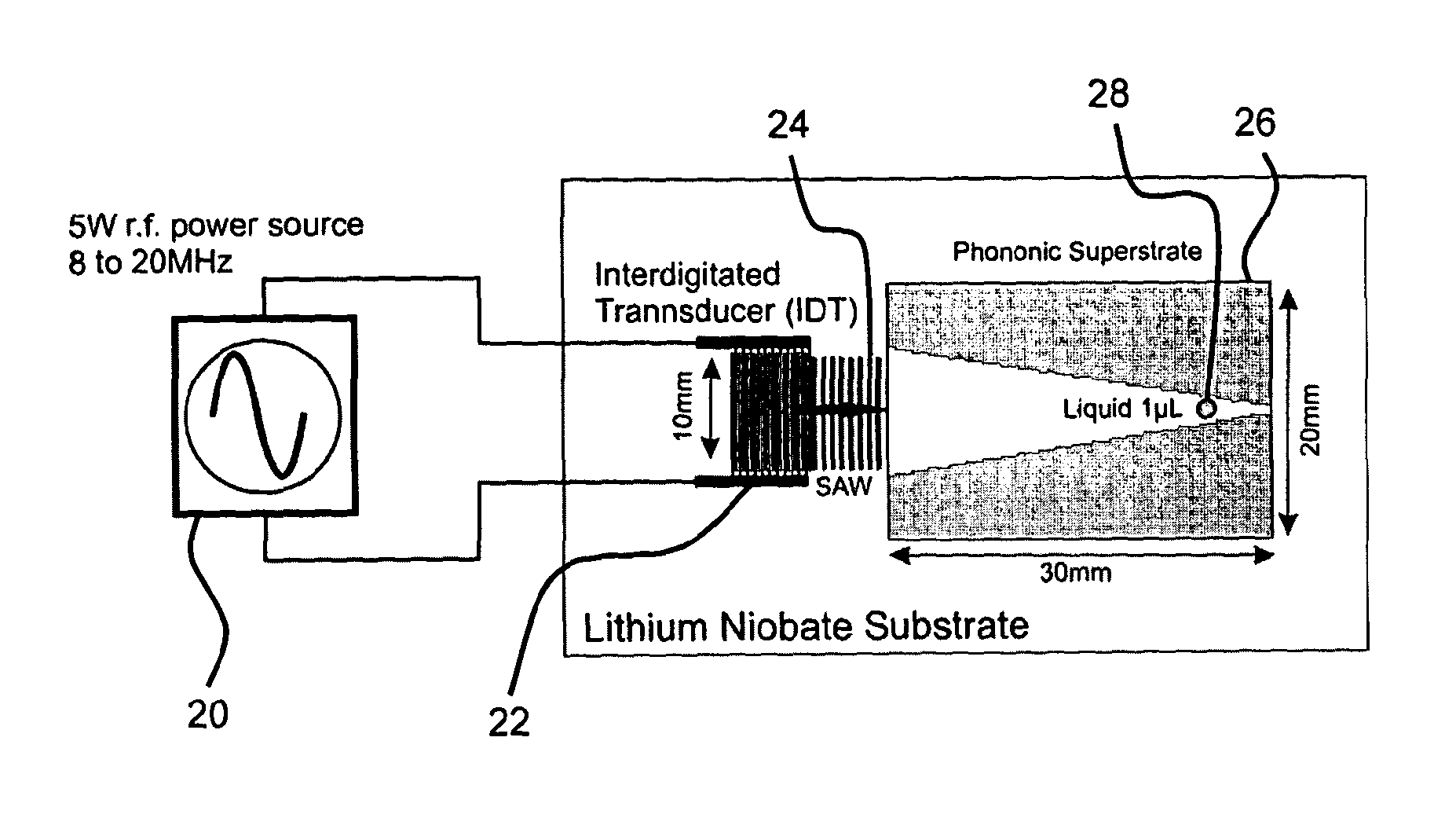
Fluidics Apparatus for Surface Acoustic Wave Manipulation of Fluid Samples, Use of Fluidics Apparatus and Process for the Manufacture of Fluidics Apparatus
ActiveUS20130330247A1Cost-effectiveEfficient preparationElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementFluidicsTransducer
A fluidics apparatus for manipulation of at least one fluid sample is disclosed. A manipulation surface locates the fluid sample. A surface acoustic wave (SAW) generation material layer is provided. This is a polycrystalline material, textured polycrystalline material, biaxially textured polycrystalline material, microcrystalline material, nanocrystalline material, amorphous material or composite material. A transducer electrode structure arranged at the SAW generation material layer provides SAWs at the manipulation surface for interaction with the fluid sample. The manipulation surface has a phononic structure, for affecting the transmission, distribution and / or behaviour of SAWs at the manipulation surface. The apparatus is typically manufactured by reel-to-reel processes, to reduce the unit cost to a level at which the apparatus can be considered to be disposable after a single use.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
Monolithic thin-film thermoelectric device including complementary thermoelectric materials
InactiveUS20050150539A1Reduce needReduction in electron thermal conductivityThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentLiquid metalThermoelectric element
A vertical, monolithic, thin-film thermoelectric device is described. Thermoelectric elements of opposing conductivity types may be coupled electrically in series and thermally in parallel by associated electrodes on a single substrate, reducing the need for mechanisms to attach multiple substrates or components. Phonon transport may be separated from electron transport in a thermoelectric element. A thermoelectric element may have a thickness less than an associated thermalization length. An insulating film between an electrode having a first temperature and an electrode having a second temperature may be a low-thermal conductivity material, a low-k, or ultra-low-k dielectric. Phonon thermal conductivity between a thermoelectric element and an electrode may be reduced without a significant reduction in electron thermal conductivity, as compared to other thermoelectric devices. A phonon conduction impeding material may be included in regions coupling an electrode to an associated thermoelectric element (e.g., a liquid metal).
Owner:NANOCOOLERS
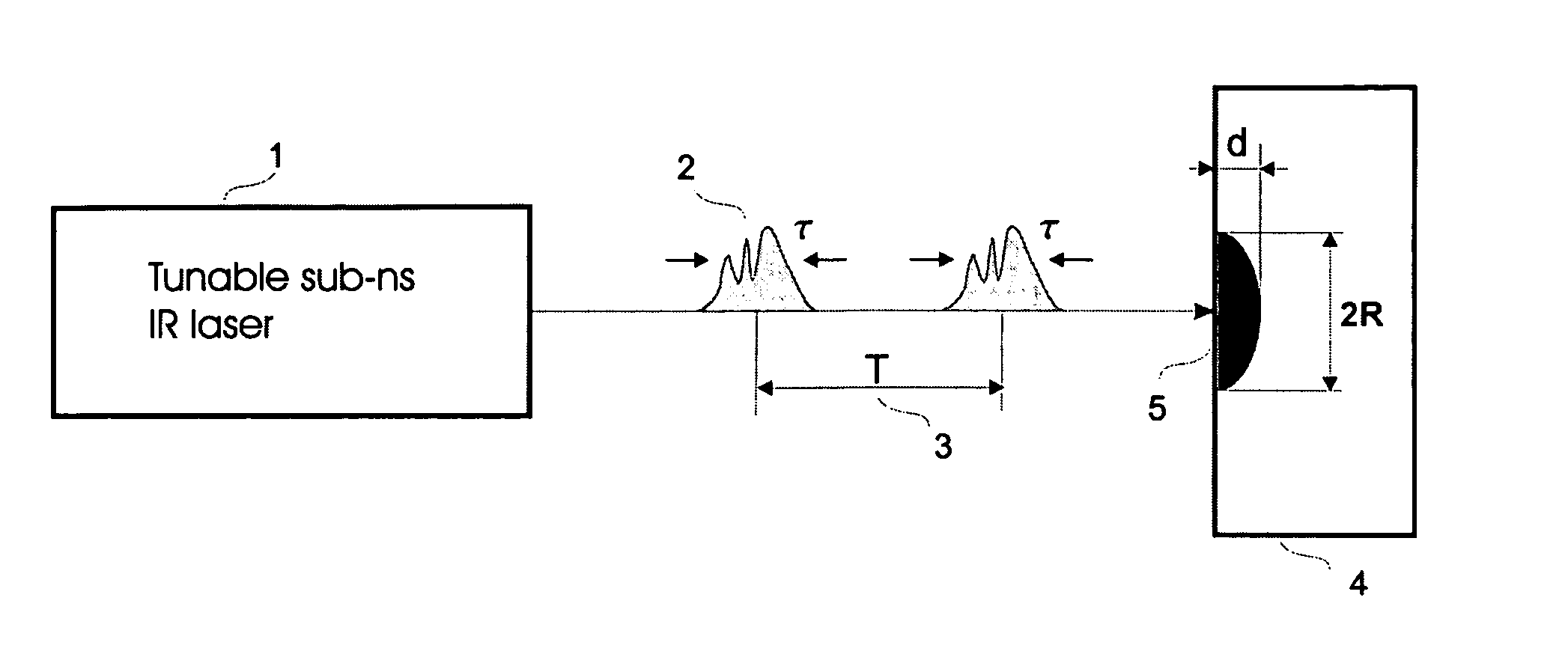
Laser selective cutting by impulsive heat deposition in the IR wavelength range for direct-drive ablation
ActiveUS20060195072A1Material efficiencyImprove efficiencySurgical instrument detailsLight therapyHeat depositionThermal expansion
The present invention provides a method of laser processing of materials, specifically laser induced ablation processes for laser removal of material particularly important in medical and dental applications in which the laser removal of material should be done in such a way as to not damage any of the surrounding soft or hard biomaterial. The ablation process is achieved by impulsive heat deposition (IHD) by direct and specific excitation of short lived vibrations or phonons of the material in such a way as to not generate highly reactive and damaging ions through multiphoton absorption. The heat deposition and ensuing ablation process under prescribed time and wavelength conditions for laser irradiation is achieved faster than heat transfer to surrounding tissue by either acoustic or thermal expansion or thermal diffusion that otherwise would lead to excess heat related damage. The result is that all the deposited laser energy is optimally channelled into the ablation process in which the inertially confined stresses from both photomechanical expansion forces and thermally driven phase transitions and associated volume changes constructively interfere to drive the most efficient ablation process possible with minimal damage to surrounding areas by either ionizing radiation or heat effects. By choosing a specific range of wavelengths, spatial and temporal shaping of infrared laser pulses, the energy can be optimally deposited in a manner that further increases the efficiency of the ablation process with respect to minimizing collateral damage.
Owner:LIGHT MATTER INTERACTION
Phononic metamaterials for vibration isolation and focusing of elastic waves
ActiveUS8833510B2Non-rotating vibration suppressionSound producing devicesWaveform shapingAcoustic wave
A methodology for designing structured metamaterials that can reflect, absorb and focus the propagation of both scalar acoustic and vector elastic waves is described. Three exemplary representative inventions based on the disclosed invention are described, illustrating i) compact ultra-wide broadband isolation, ii) sub-wavelength gaps and negative index propagation utilizing a single material platform, and iii) a fundamentally new method of producing multiple high frequency spectral gaps. Such metamaterial designs possess a wide range of potential applications, ranging from but not limited to, isolating an entity from external mechanical or acoustical vibrations, compact focusing lenses as well as cascaded high frequency filters for wave shaping and nonlinear wave propagation control.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Surface plasmon coupled nonequilibrium thermoelectric devices
InactiveUS20050247337A1Easy maintenanceEasy to manufactureThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectElectric discharge tubesThermal energyElectron temperature
A surface-plasmon-coupled thermoelectric apparatus includes a first surface-plasmon substrate and a thermoelectric substrate electrically coupled to a plurality of electrodes. The substrates are electrically isolated from each other, and a first face of the thermoelectric substrate opposes a first face of the first surface-plasmon substrate to define a phonon insulating gap. A method of transferring thermal energy across the phonon insulating gap includes creating a first surface-plasmon polariton at the first surface-plasmon substrate when the first surface-plasmon substrate is coupled to a first thermal reservoir. Also included is creating a nonequilibrium state between the electron temperature and the phonon temperature at a first face of the thermoelectric substrate, when a second face of the thermoelectric substrate is coupled to a second thermal reservoir. Also included is coupling the first surface plasmon polariton with electrons in the thermoelectric substrate across the phonon insulating gap, thereby transferring thermal energy between the thermal reservoirs through the phonon insulating gap.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD +1
Thermoelectric semiconductor compound and method of making the same
InactiveUS6225548B1Thermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsMean free pathSingle crystal
A thermoelectric semiconductor compound is provided whose performance index Z is remarkably improved without sacrificing Seebeck coefficient, electrical conductivity or thermal conductivity. The thermoelectric semiconductor compound includes a first thermoelectric semiconductor which is in the form of matrix and a second thermoelectric semiconductor which is in the form of particles dispersed in the matrix. The first thermoelectric semiconductor and the second thermoelectric semiconductor have a common element. The average diameter D of the dispersed particles complies with a formula of A<D<B, where A is the mean free path of a carrier in a single crystal of the second thermoelectric semiconductor and B is the mean free path of a long wave length phonon in the single crystal of the second thermoelectric semiconductor. A method for making the a thermoelectric semiconductor compound is provided.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
Nano-optomechanical transducer
A nano-optomechanical transducer provides ultrabroadband coherent optomechanical transduction based on Mach-wave emission that uses enhanced photon-phonon coupling efficiencies by low impedance effective phononic medium, both electrostriction and radiation pressure to boost and tailor optomechanical forces, and highly dispersive electromagnetic modes that amplify both electrostriction and radiation pressure. The optomechanical transducer provides a large operating bandwidth and high efficiency while simultaneously having a small size and minimal power consumption, enabling a host of transformative phonon and signal processing capabilities. These capabilities include optomechanical transduction via pulsed phonon emission and up-conversion, broadband stimulated phonon emission and amplification, picosecond pulsed phonon lasers, broadband phononic modulators, and ultrahigh bandwidth true time delay and signal processing technologies.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Reinforcement Element With Sensor Fiber, Monitoring System, And Monitoring Method
A reinforcement element, comprises at least one sensor fiber adapted for strain measurements based on stimulated Brillouin scattering within said sensor fiber. Furthermore, a system for monitoring strain within a structure comprises a reinforcement element comprising at least one sensor fiber adapted for strain measurements based on stimulated Brillouin scattering within said sensor fiber, a pump laser for coupling in laser radiation of a pump frequency into said at least one sensor fiber, a Stokes laser for coupling in laser radiation of a Stokes laser radiation into said at least one sensor fiber, wherein the pump frequency and the Stokes frequency are different from one another and wherein the frequency difference between the pump and Stokes frequencies is within the range of acoustical phonons within said sensor fiber, a sensor adapted to obtain a stimulated Brillouin backscattering signal, and a network analyzer adapted for determining the complex transfer function of the sensor fiber to determine a spatially resolved strain measurement.
Owner:GLOTZL GES FUR BAUMESSTECHN +2
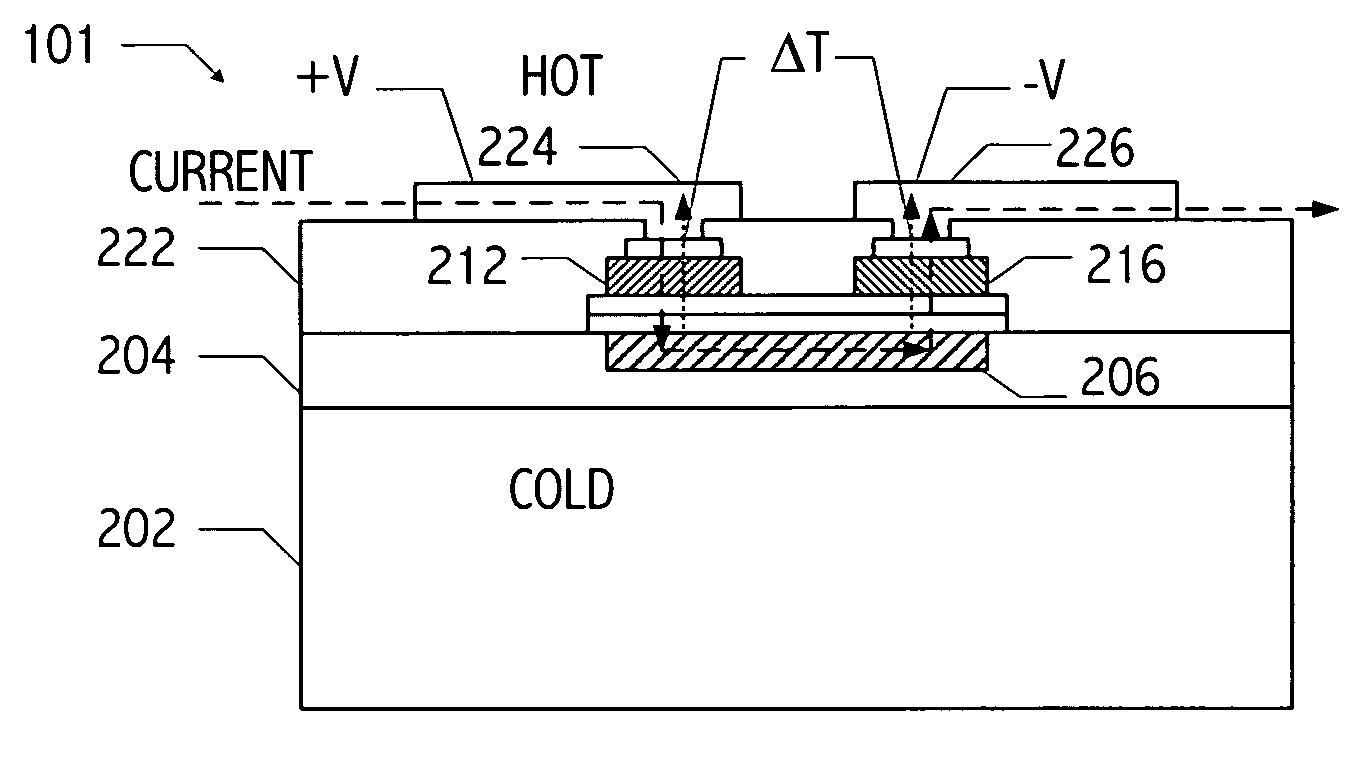
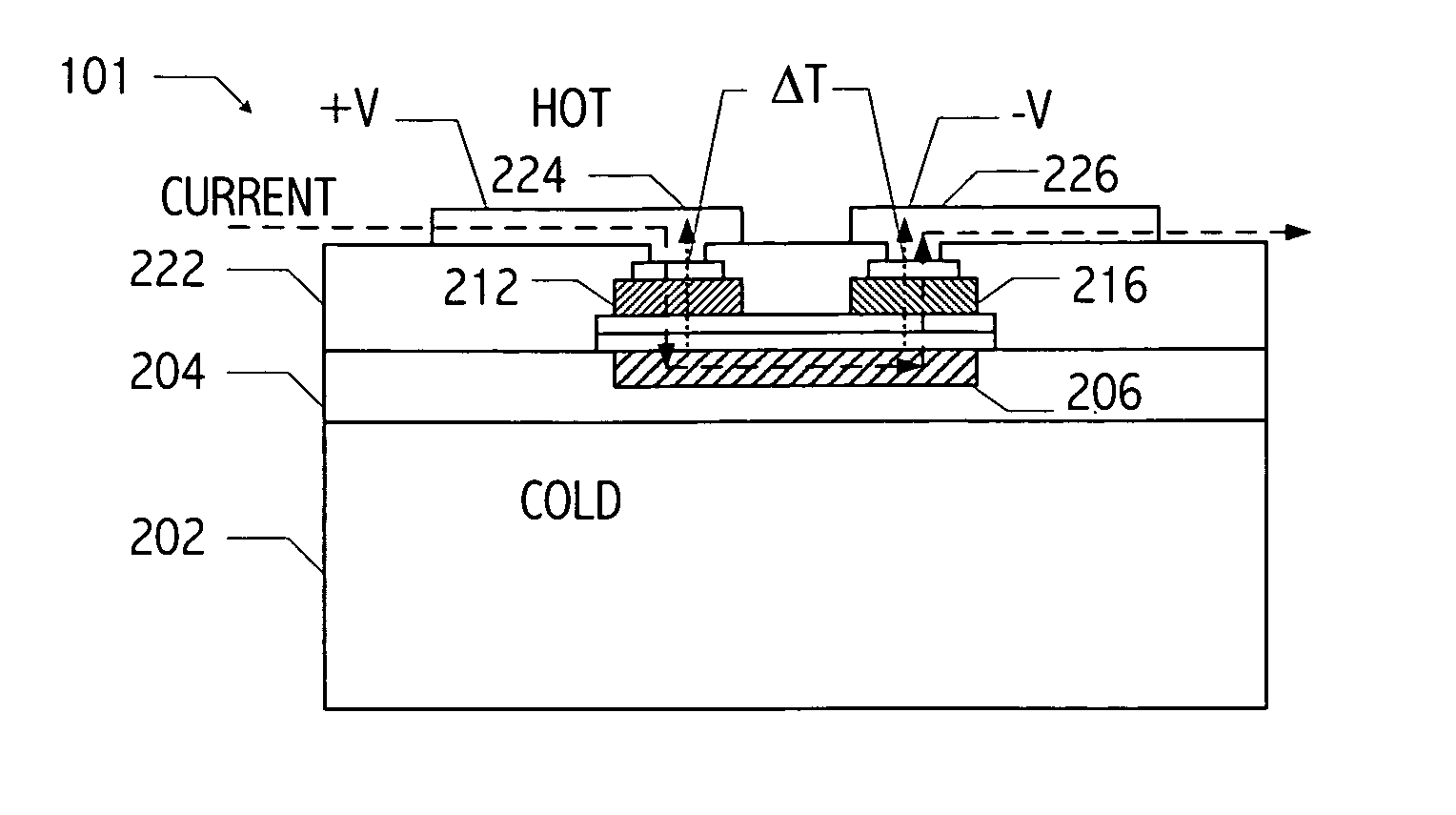
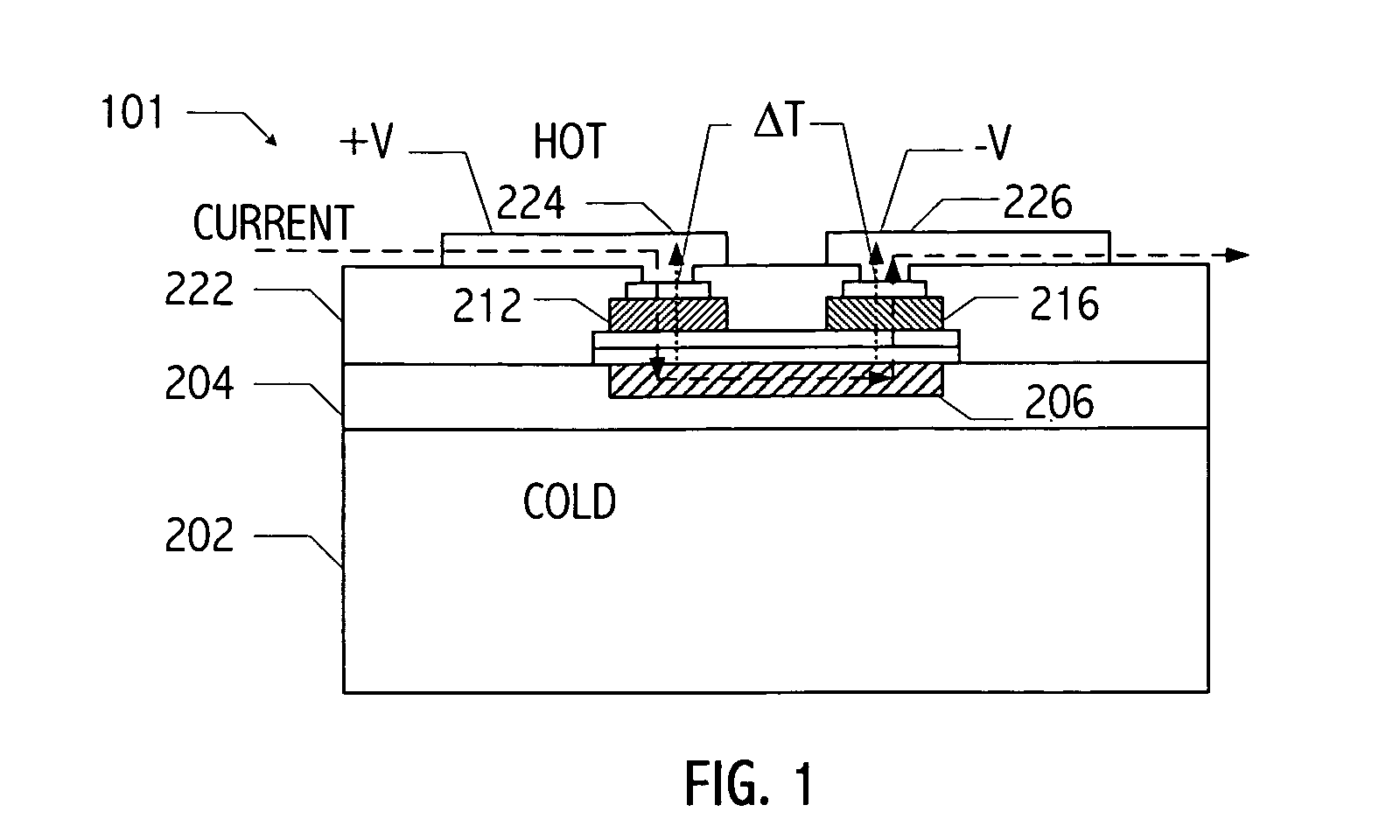
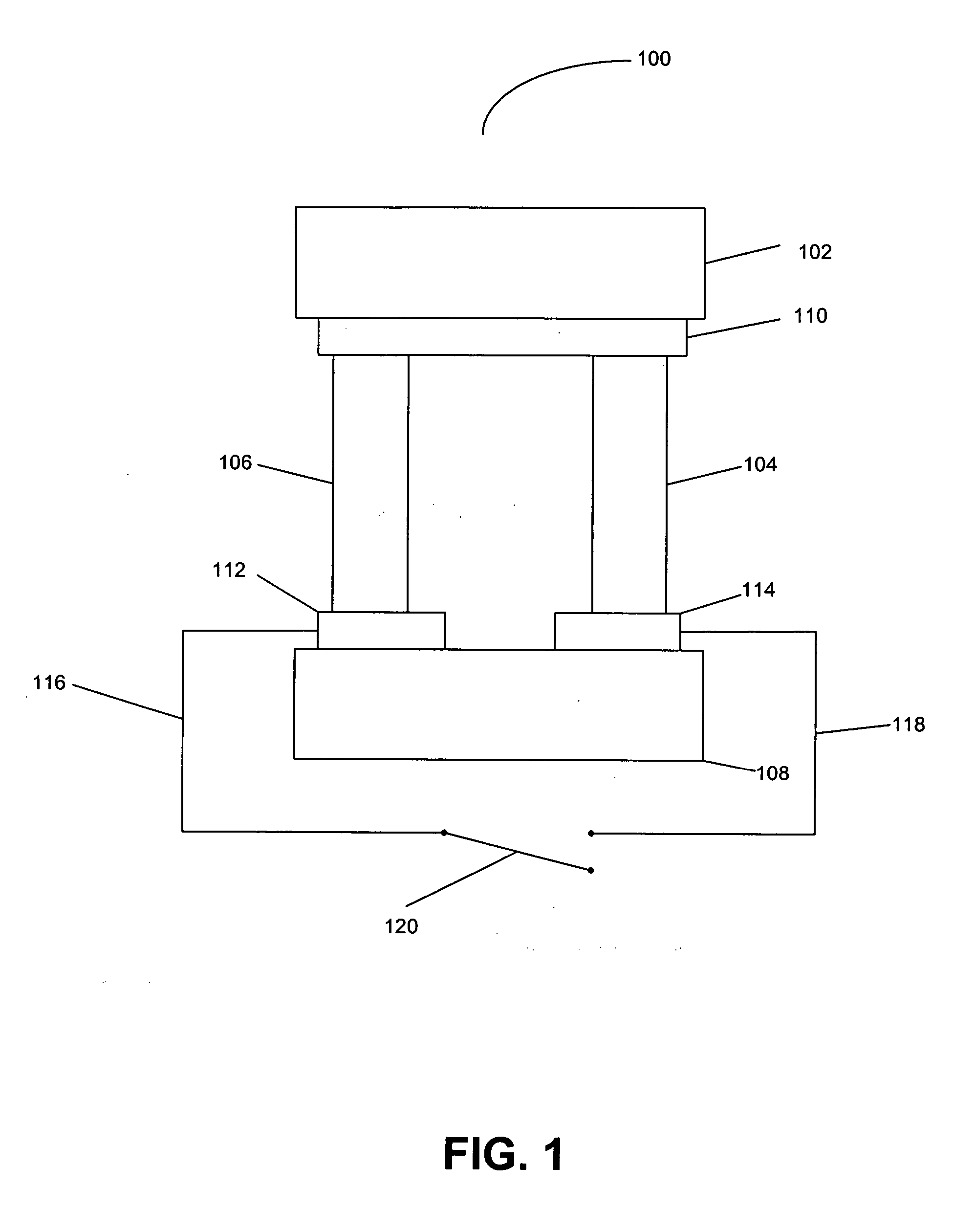
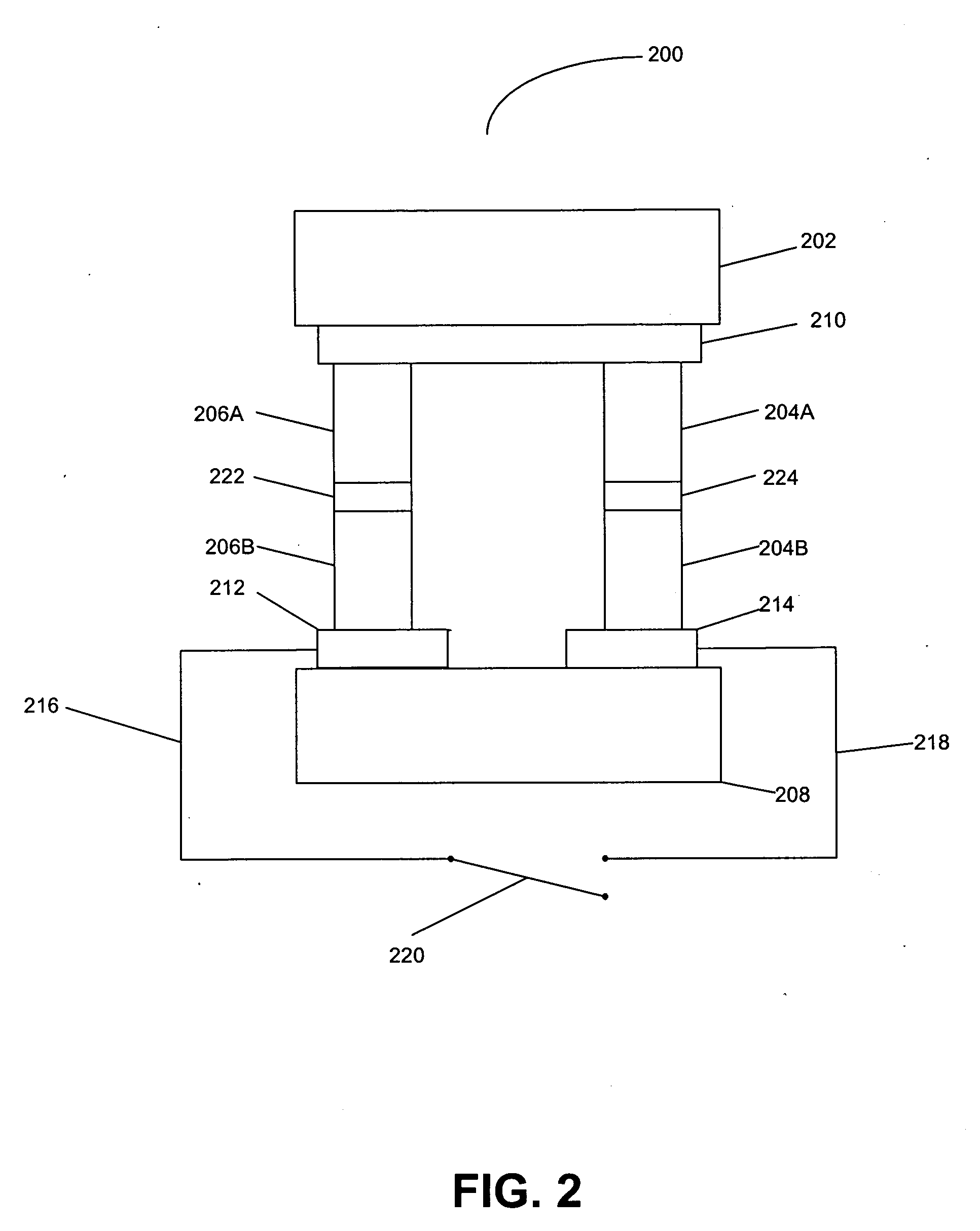
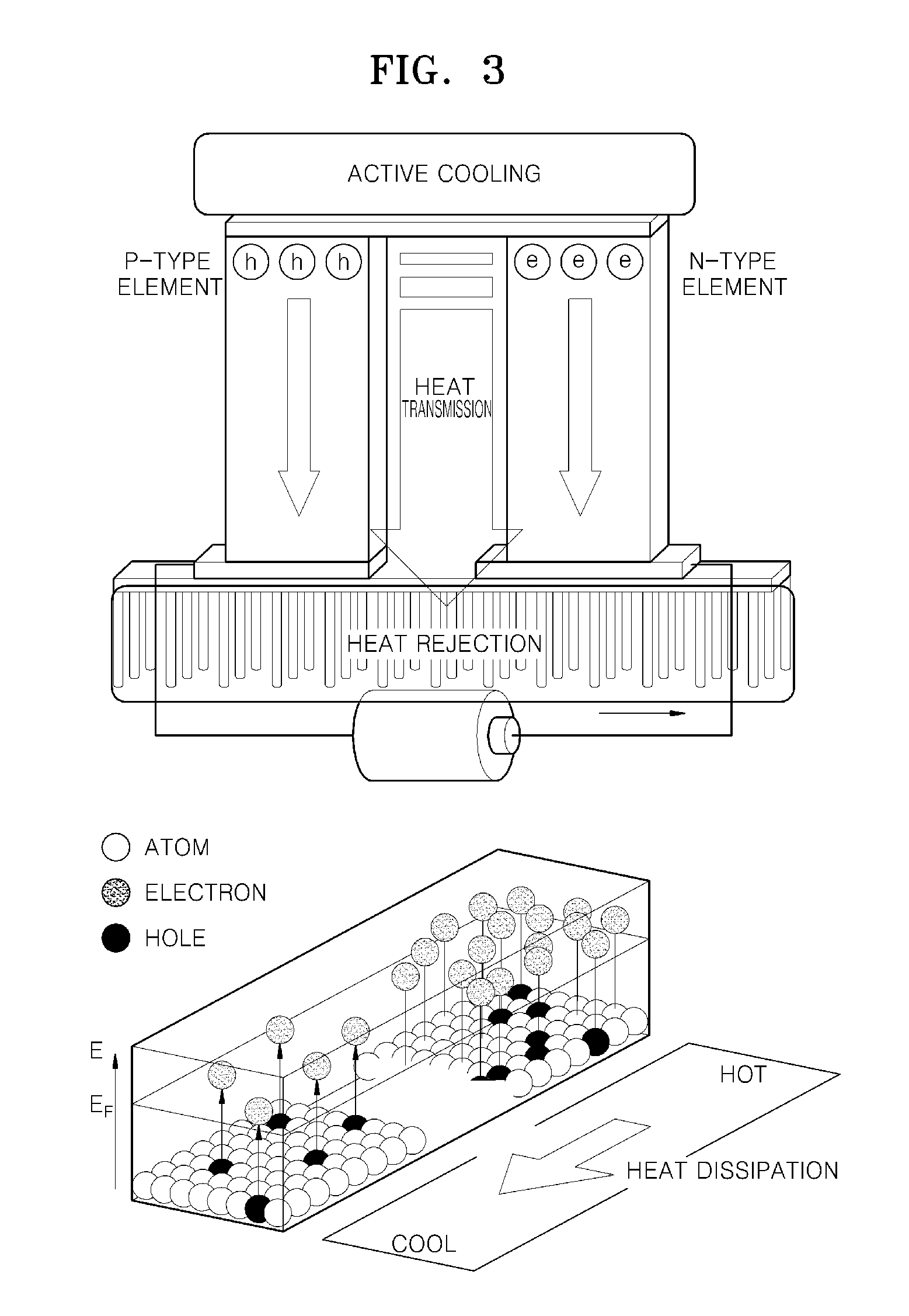
Thermoelectric tunnelling device
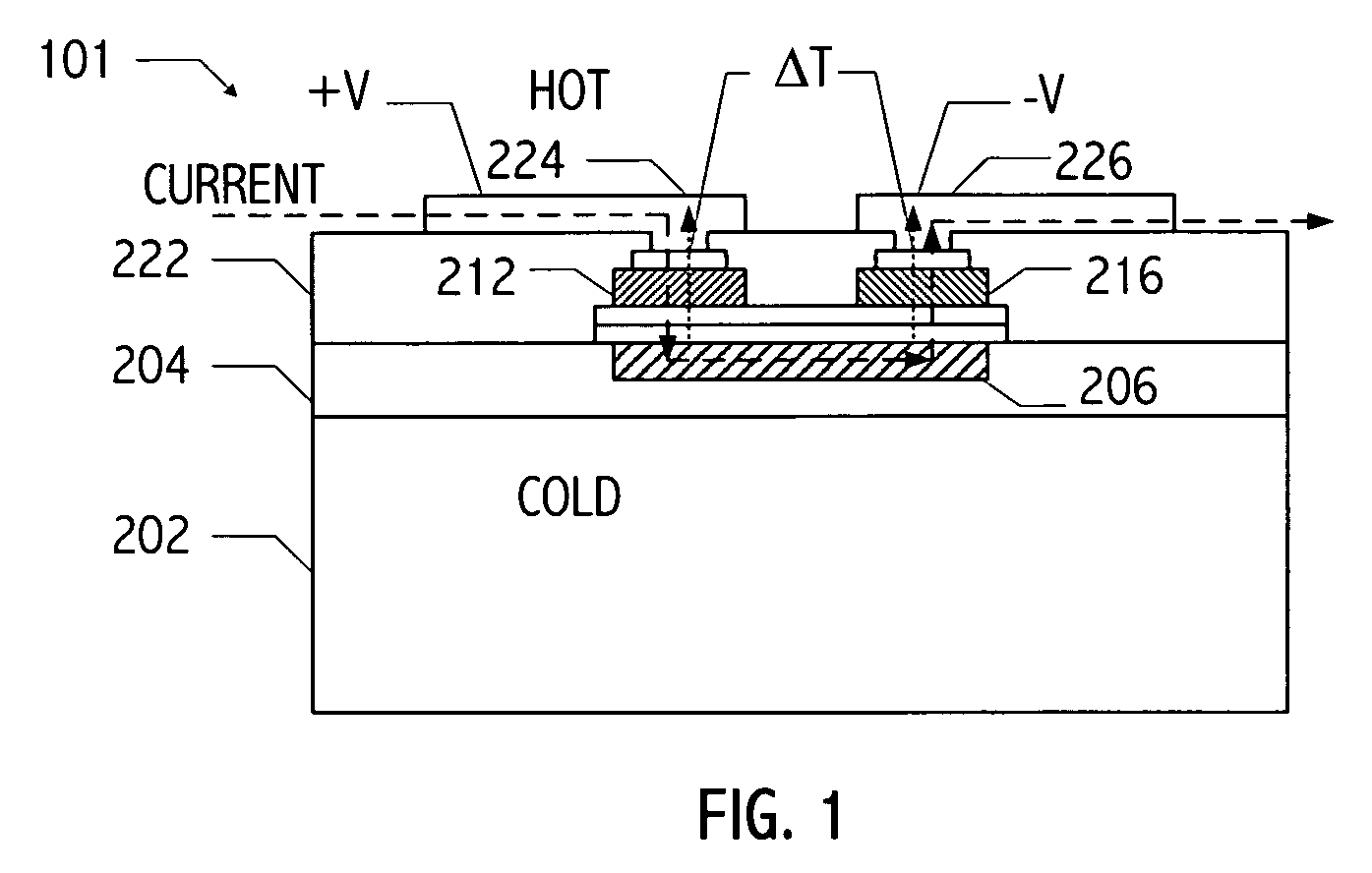
InactiveUS20070137687A1Thermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectElectric discharge tubesCold platePhonon
Methods and apparatuses for making a thermotunneling device. A method in accordance with the present invention comprises metal / semiconductor or semiconductor / semiconductor bonded material combinations that allows current flow between a hot plate and a cold plate of a thermoelectric device, and interrupting a flow of phonons between the hot plate and the cold plate of the thermoelectric device, wherein the interrupted flow is caused by a nanogap, said nanogap being formed by applying a small voltage or current between the two sides of the thermoelectric device.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
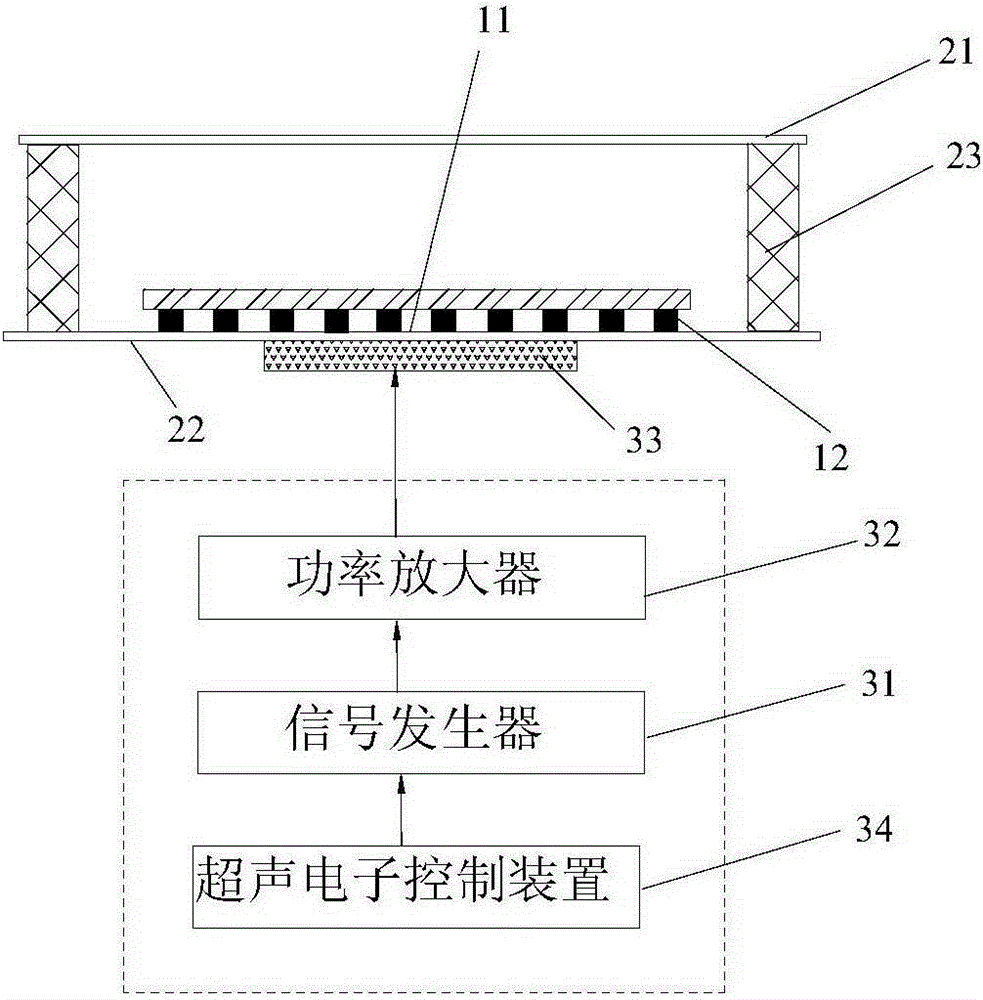
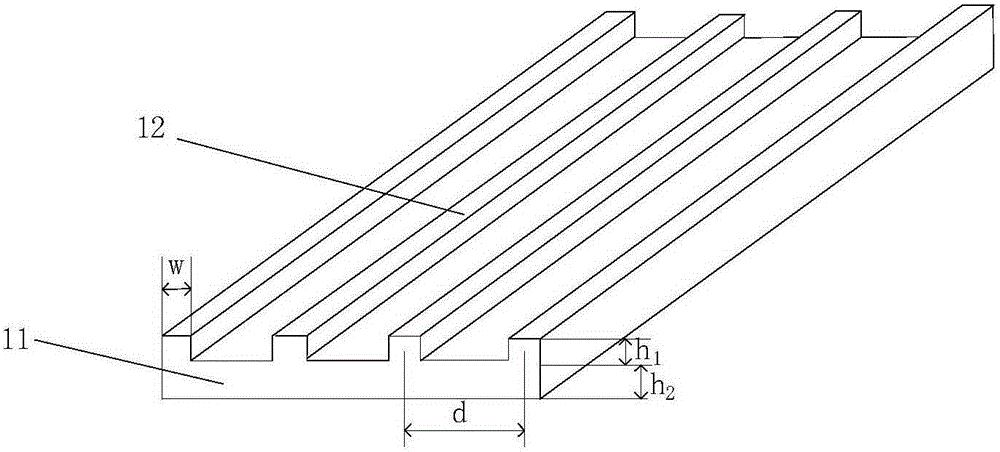
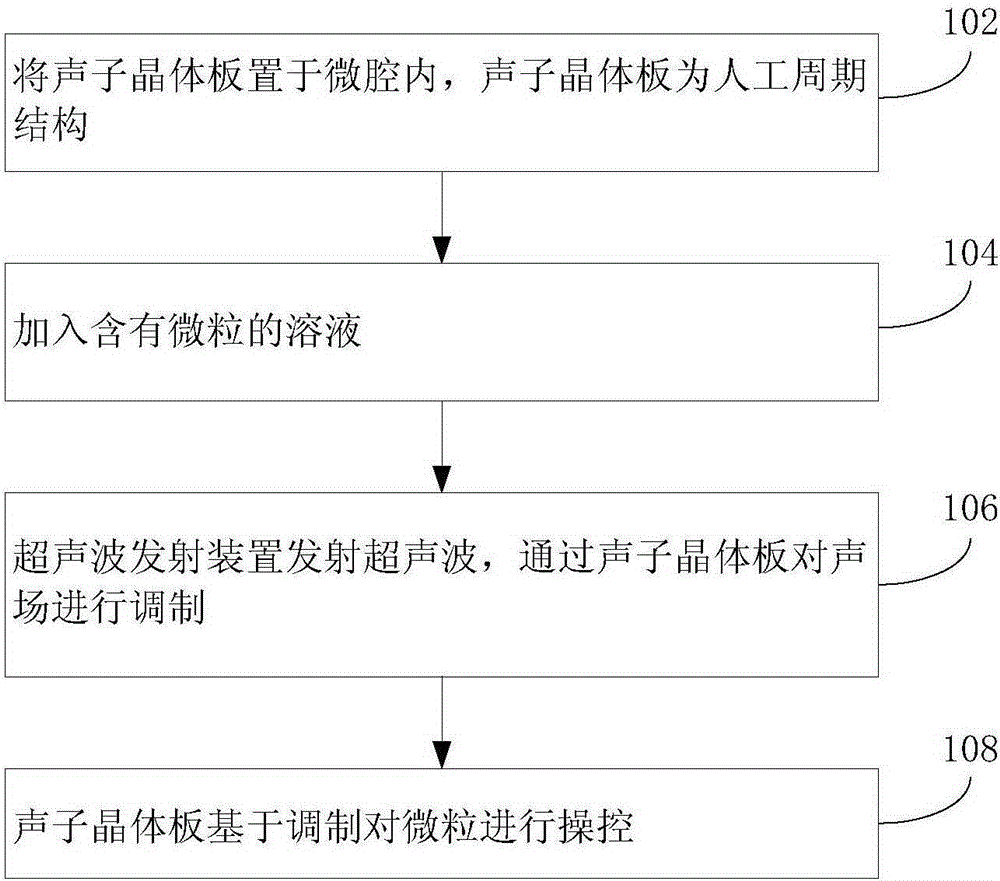
Artificial structural acoustic field based micro-fluid system and particle control method
ActiveCN105214742AFlexible design of transport routesShipping route changesLaboratory glasswaresEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesPhotonic crystalFluid system
The invention discloses an artificial structural acoustic field based micro-fluid system which comprises a micro-cavity and an ultrasonic transmitting device. The micro-cavity is used for containing a particle-containing solution, and the ultrasonic transmitting device is used for transmitting ultrasonic waves. The artificial structural acoustic field based micro-fluid system is characterized by further comprising a photonic crystal slab arranged in the micro-cavity, the photonic crystal slab is of an artificial periodic structure and is used for modulating an acoustic field to control particles. The invention further discloses a particle control method for an artificial structural acoustic field based micro-fluid. In the preferred embodiment of the invention, due to the fact that the micro-fluid system comprises the micro-cavity, the ultrasonic transmitting device and the photonic crystal slab, the ultrasonic transmitting device is used for transmitting the ultrasonic waves and the photonic crystal slab is of the artificial periodic structure and is used for modulating the acoustic field to control particles, a new medicine delivery means is provided, and technical support is provided for research and development of drugs.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bulk thermoelectric material and thermoelectric device comprising the same
InactiveUS20100108115A1Material nanotechnologyThermoelectric device junction materialsThermoelectric materialsNanoparticle
Owner:CHUNGJU NAT UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION +1
Lateral acoustic wave resonator comprising a suspended membrane of low damping resonator material
ActiveUS8525619B1High frequencyMinimize impactImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesHarmonicTransducer
A very high-Q, low insertion loss resonator can be achieved by storing many overtone cycles of a lateral acoustic wave (i.e., Lamb wave) in a lithographically defined suspended membrane comprising a low damping resonator material, such as silicon carbide. The high-Q resonator can sets up a Fabry-Perot cavity in a low-damping resonator material using high-reflectivity acoustic end mirrors, which can comprise phononic crystals. The lateral overtone acoustic wave resonator can be electrically transduced by piezoelectric couplers. The resonator Q can be increased without increasing the impedance or insertion loss by storing many cycles or wavelengths in the high-Q resonator material, with much lower damping than the piezoelectric transducer material.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
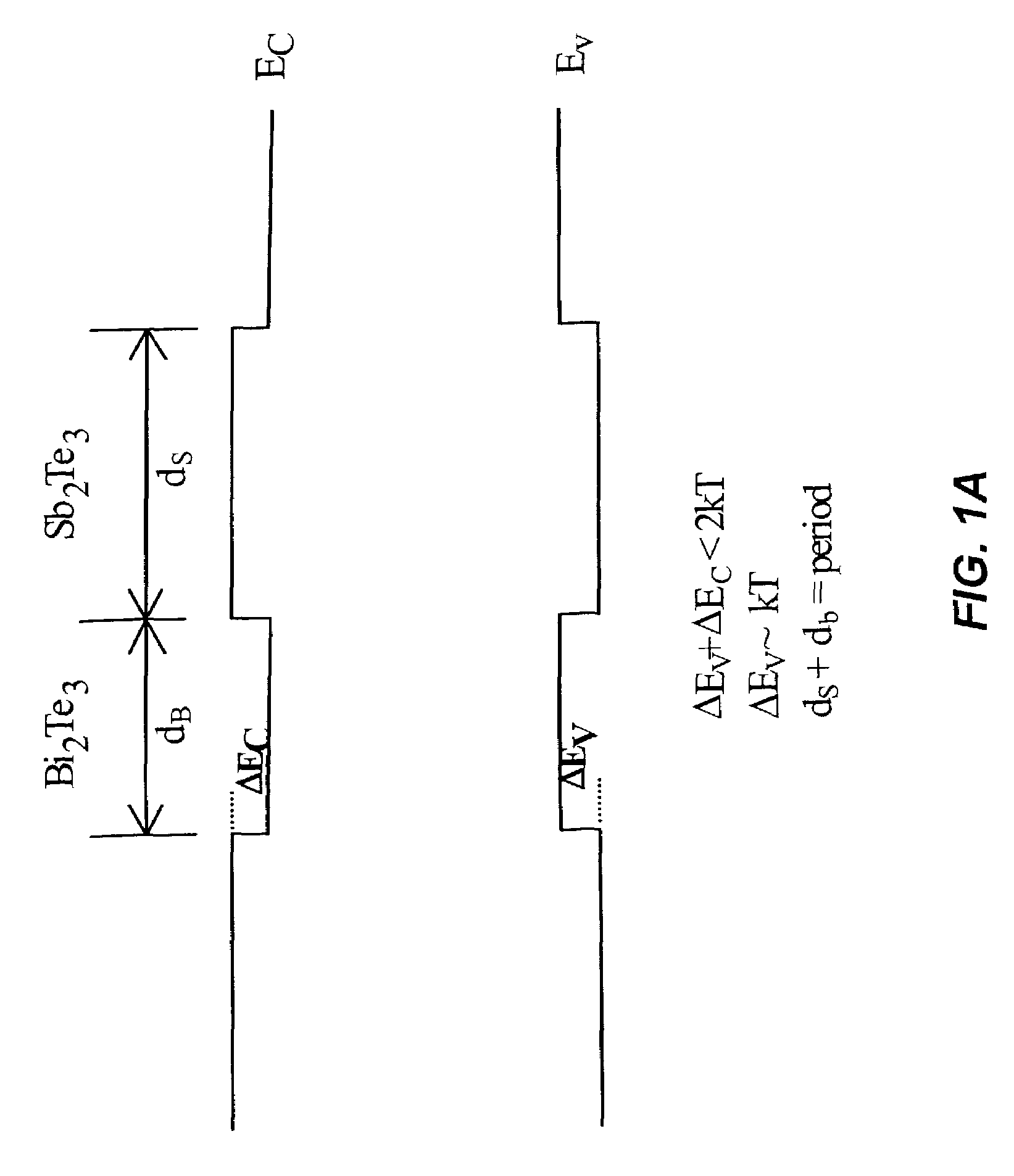
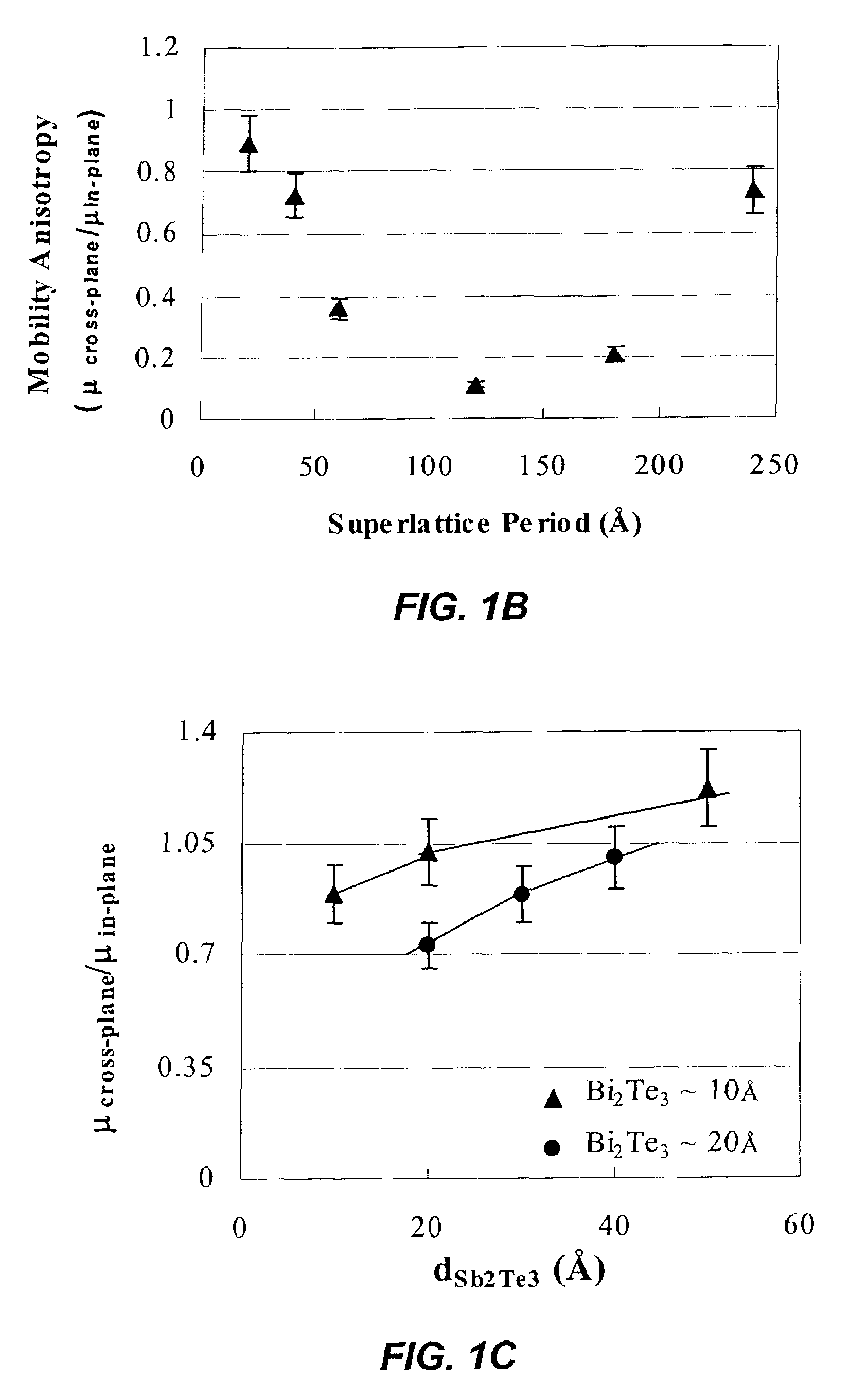
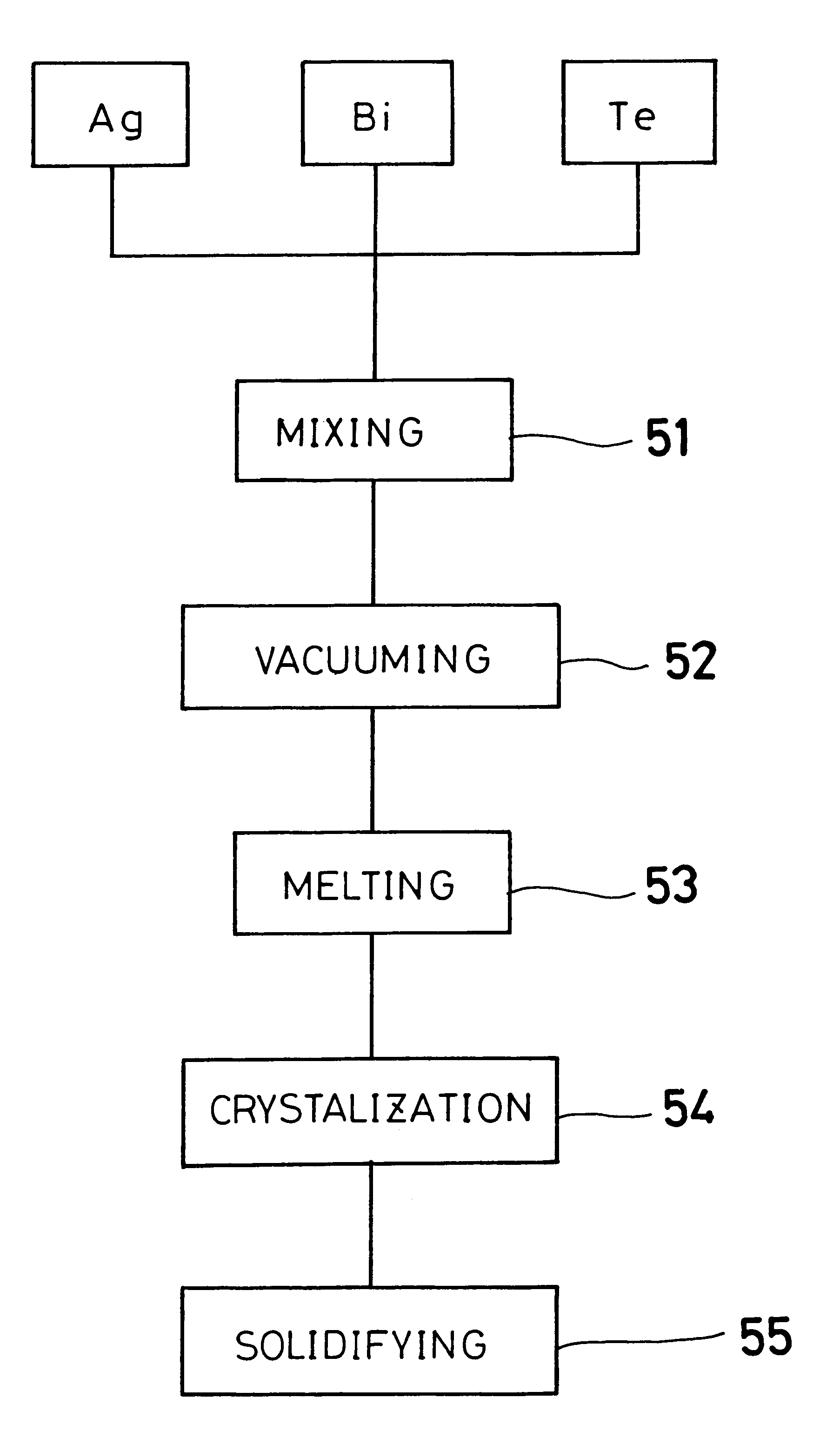
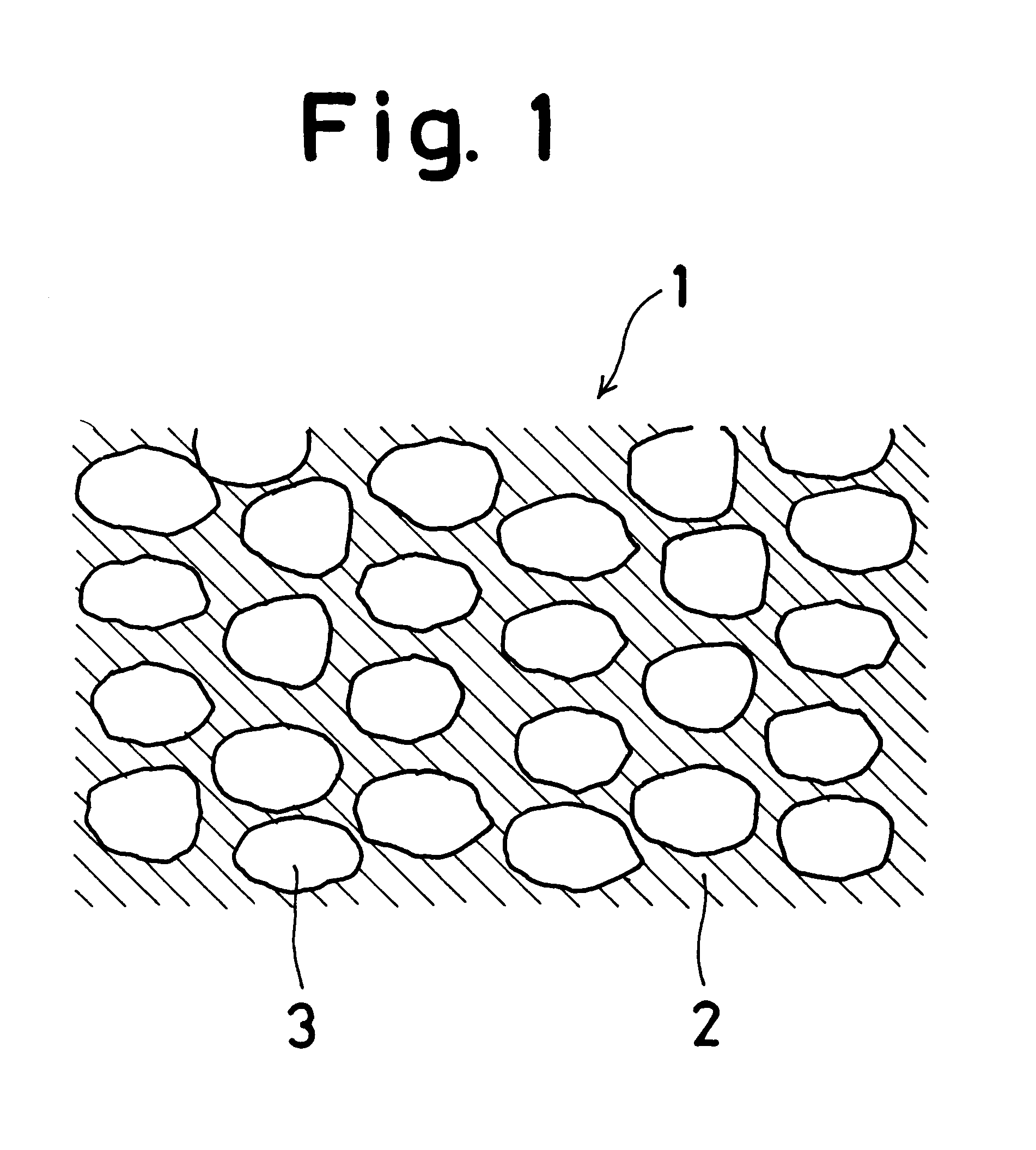
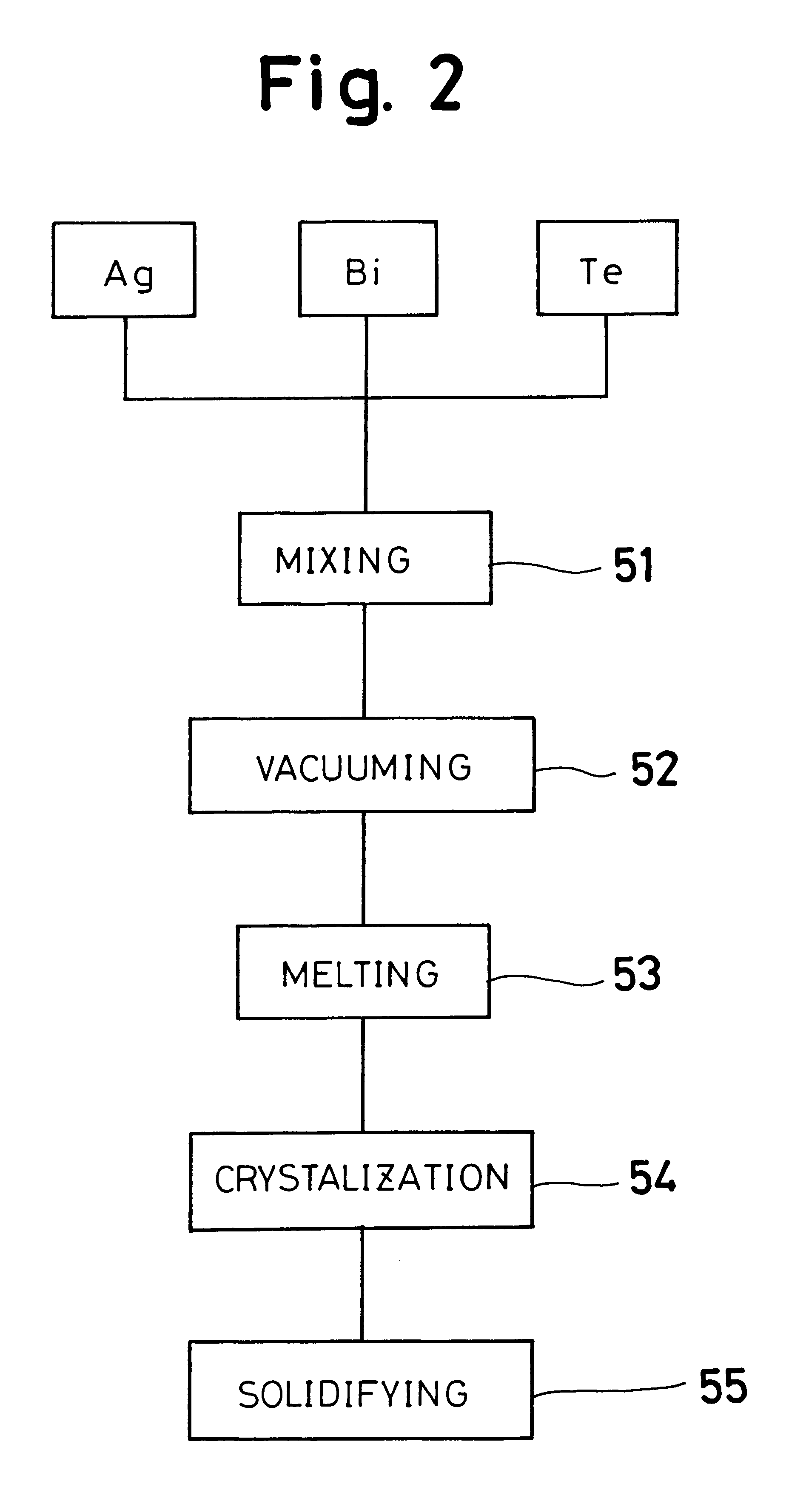
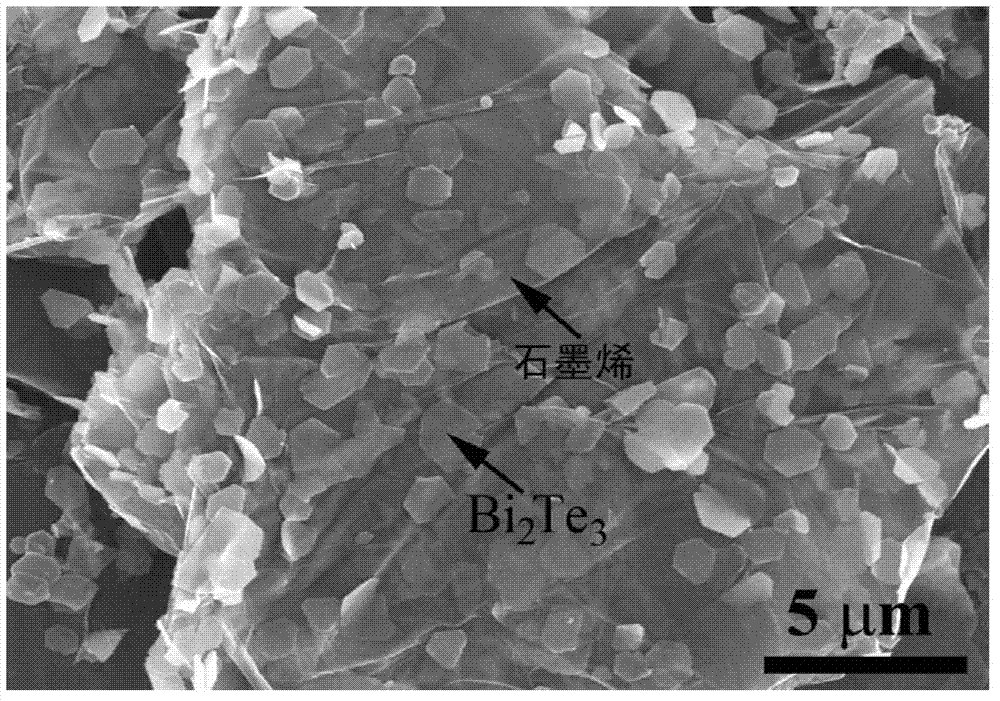
Bi2Te3 thin-piece/graphene composite material, preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN102760827AImprove thermoelectric performanceAvoid reunionGrapheneThermoelectric device junction materialsSolventCvd graphene
The invention discloses a Bi2Te3 thin-piece / graphene composite material. The Bi2Te3 thin-piece / graphene composite material consists of a micron-sized Bi2Te3 thin sheet and graphene. Due to the actions of dispersion, bearing and isolation of the graphene, the sintering of the micron-sized Bi2Te3 thin sheet in the heat-treatment process can be effectively prevented for maintaining effective scattering of the crystal boundary to phonons, and the great significance for improving the thermoelectric properties of the Bi2Te3 material is embodied. The composite material can be used as a thermoelectric material. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the composite material by a one-step hydrothermal method or a one-step solvothermal method, and has the advantages of simple process, low cost, short period and low energy consumption and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
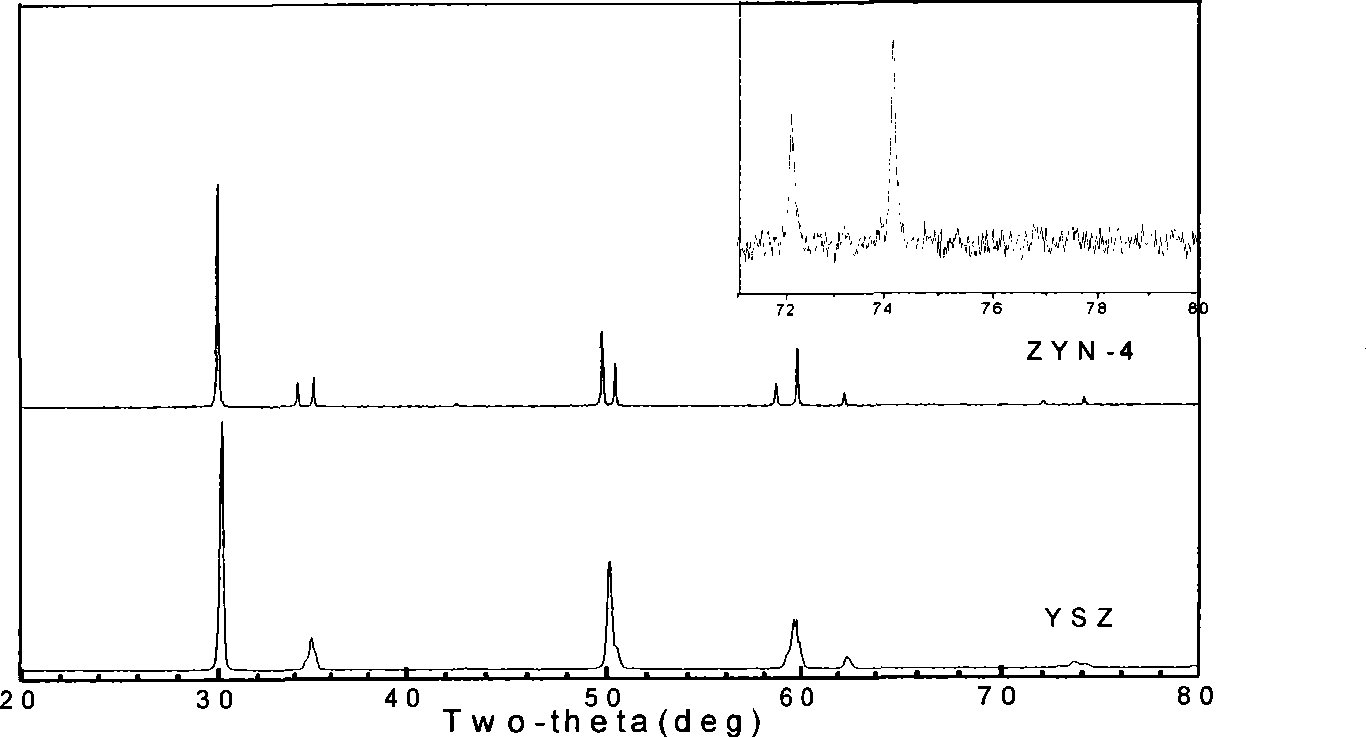
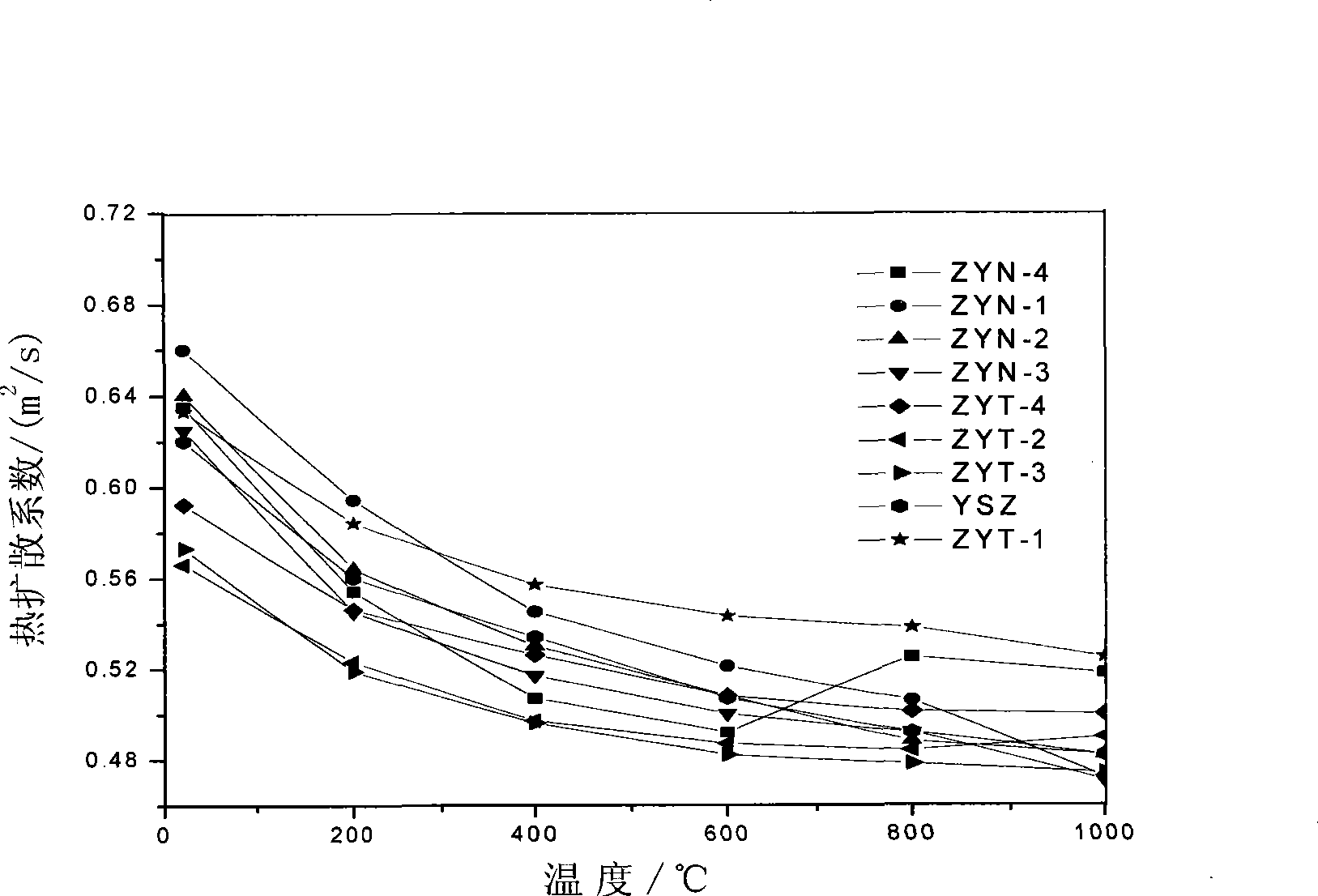
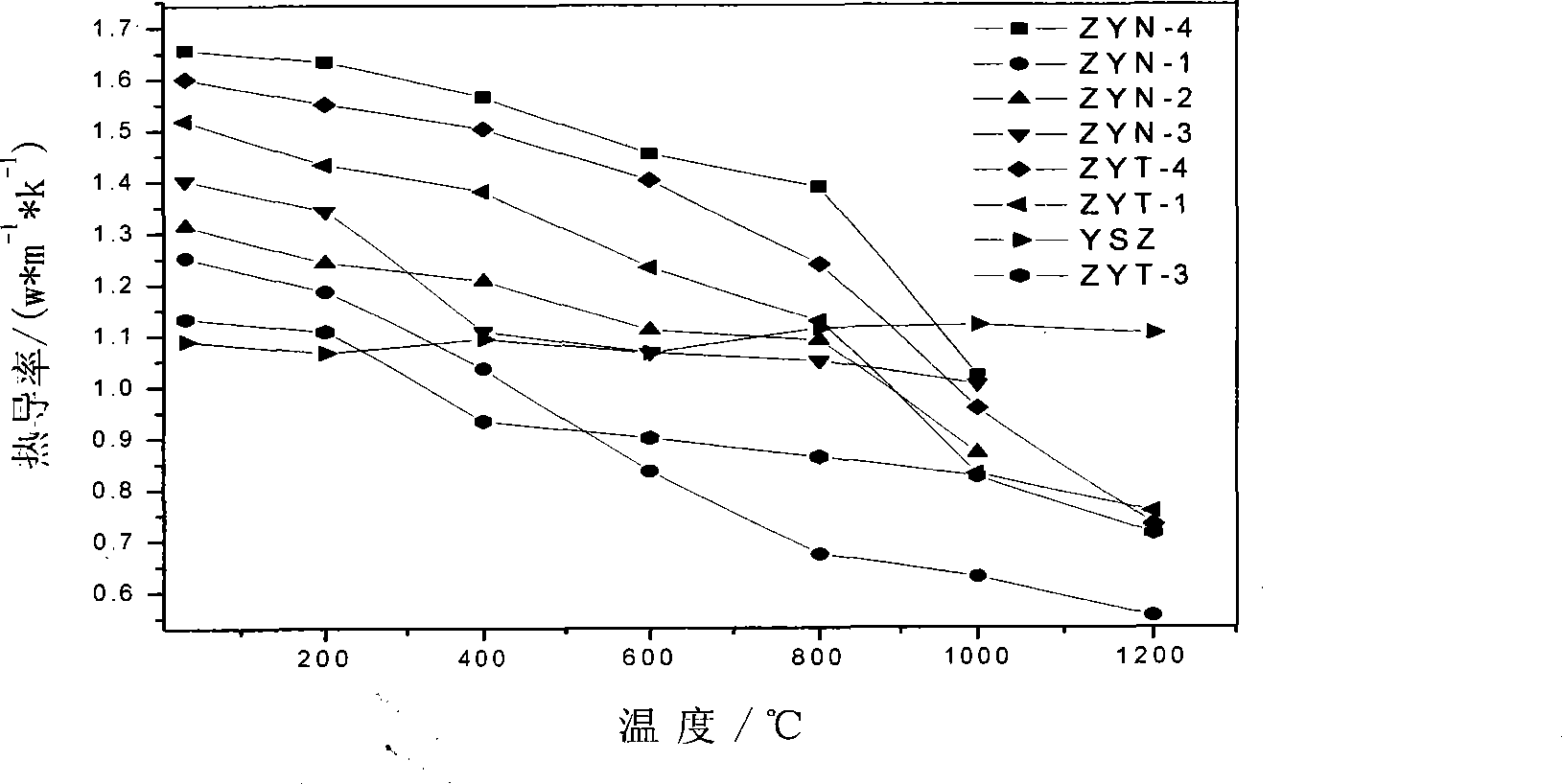
Multi-element co-stabilizing zirconia of heat barrier coat material and preparation method
The invention relates to a multivariant co-stable zirconia thermal barrier coating material and a preparation method which belong to the field of materials. The multivariant co-stable zirconia thermal barrier coating material is characterized by consisting of the following materials according to mole fractions: zirconia, yttria, niobium oxide or tantalum oxide and rare earth oxide. The preparation method comprises the following steps: a zirconia ball is ground by wet process, dried and molded; a pre-burnt block is obtained by pre-burning; the pre-burnt block is smashed and further carried out with the wet ball milling to obtain slurry; the slurry is dried, granulated and mould pressed to obtain a green body, the green body is sintered to obtain the multivariant co-stable zirconia thermal barrier coating material; the ceramic material can be used as a target material for preparing a thermal barrier coating by using the EB-PVD method. A third phase of Nb2O5 / Ta2O5 is introduced in YSZ to develop the stable existence interval of t-ZrO2 to further obtain non-transition t'-ZrO2, and the rare earth oxide is added to increase the defects to further improve the phonon or photon scattering on the basis, thereby improving the using temperature of the ZrO2 thermal barrier coating and reducing the thermal conductivity of the material.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
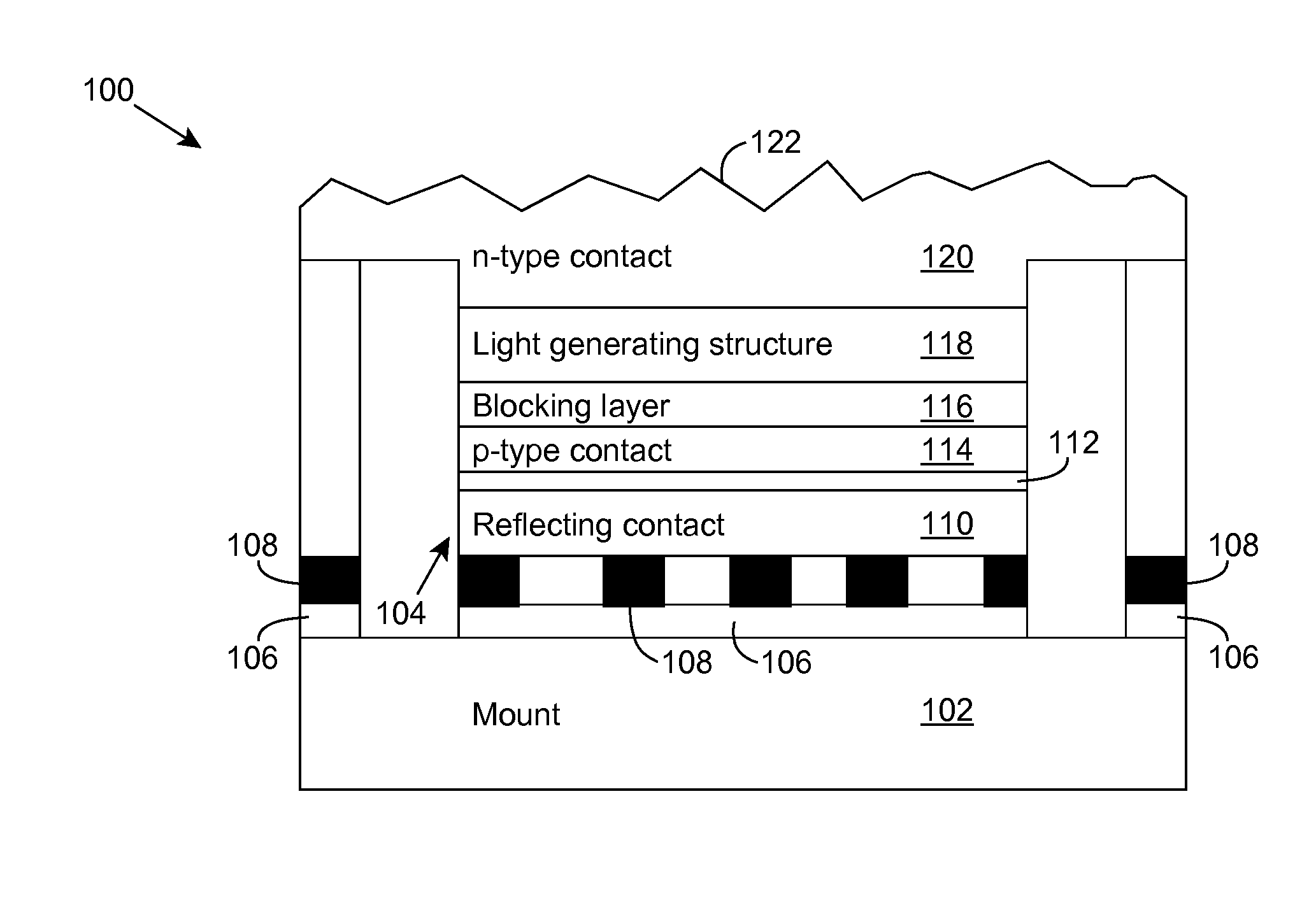
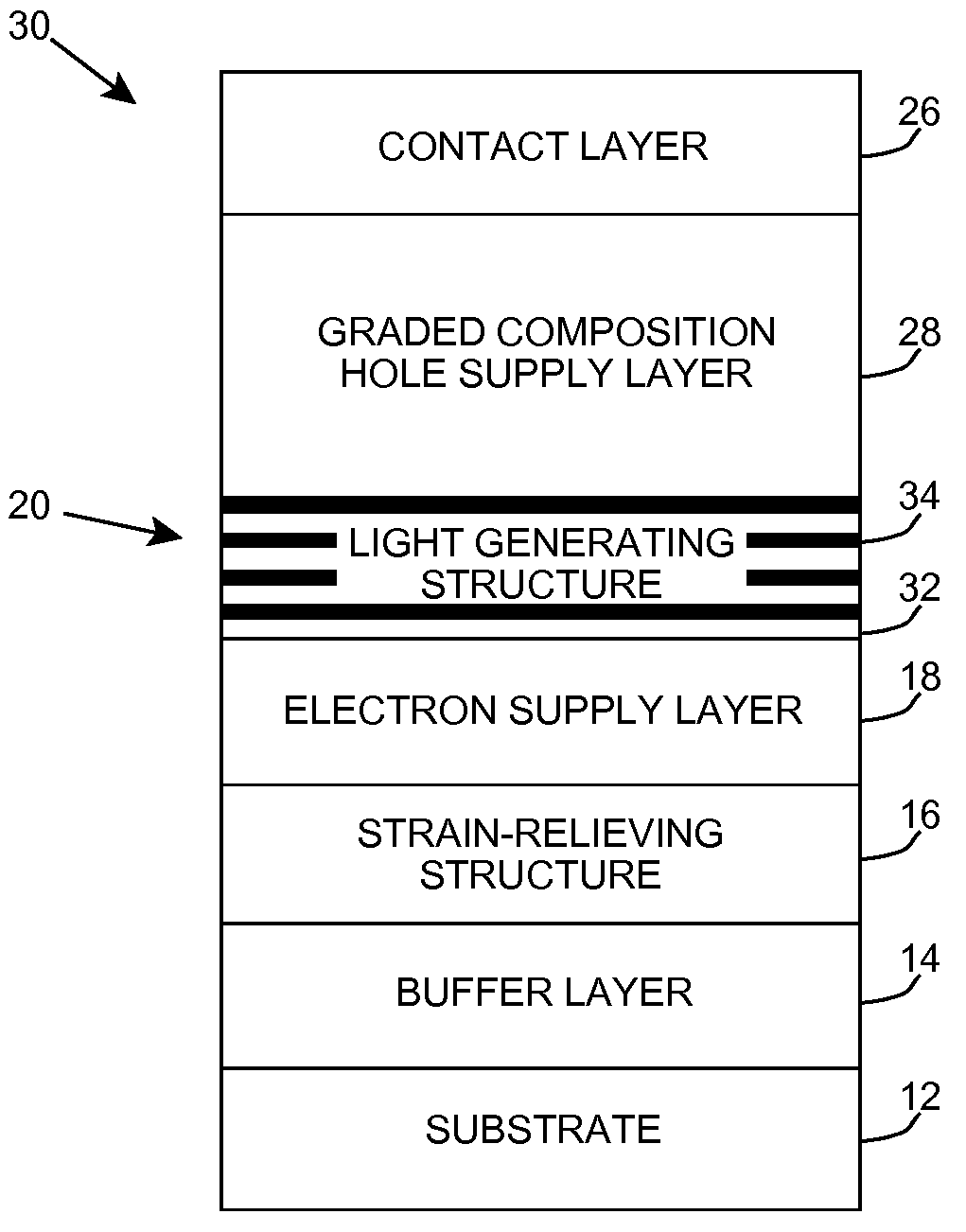
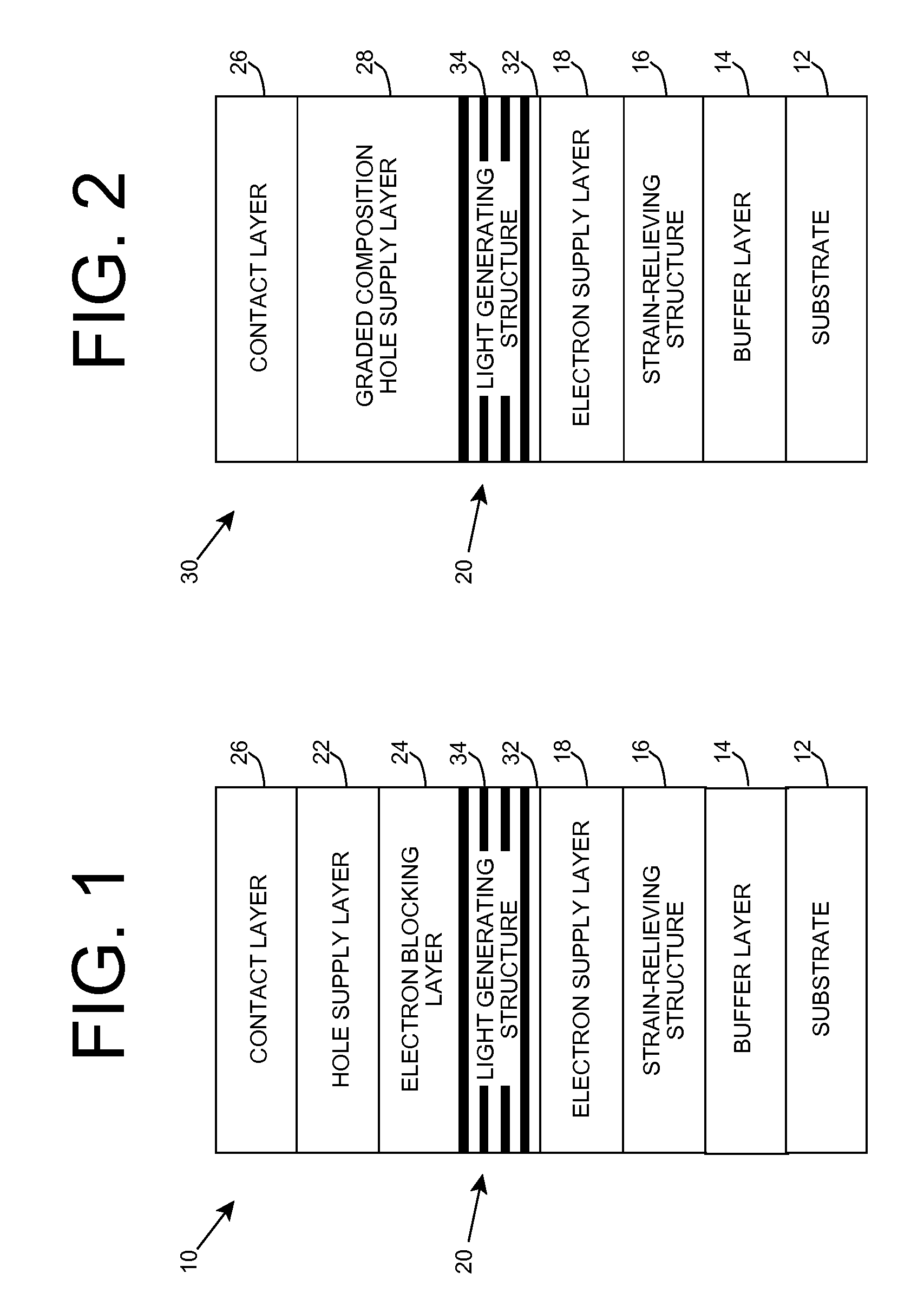
Deep ultraviolet light emitting diode
A light emitting diode is provided, which includes an n-type contact layer and a light generating structure adjacent to the n-type contact layer. The light generating structure includes a set of quantum wells. The contact layer and light generating structure can be configured so that a difference between an energy of the n-type contact layer and an electron ground state energy of a quantum well is greater than an energy of a polar optical phonon in a material of the light generating structure. Additionally, the light generating structure can be configured so that its width is comparable to a mean free path for emission of a polar optical phonon by an electron injected into the light generating structure. The diode can include a blocking layer, which is configured so that a difference between an energy of the blocking layer and the electron ground state energy of a quantum well is greater than the energy of the polar optical phonon in the material of the light generating structure. The diode can include a composite contact, including an adhesion layer, which is at least partially transparent to light generated by the light generating structure and a reflecting metal layer configured to reflect at least a portion of the light generated by the light generating structure.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Low-frequency vibration-isolation combined sandwiched structure
InactiveCN103514873AGood vibration isolationSmall sizeSound producing devicesRubber layered productsRubber materialVibration control
The invention discloses a low-frequency vibration-isolation combined sandwiched structure. The low-frequency vibration-isolation combined sandwiched structure comprises a lower uniform layer, a middle layer and an upper uniform layer sequentially from bottom to top, wherein the middle layer is of a limited two-dimension photonic crystal structure, the limited two-dimension photonic crystal structure comprises a base body and a plurality of scatters embedded into the base body, the scatters are respectively connected with the upper uniform layer and the lower uniform layer into a whole, and the lower uniform layer, the scatters and the upper uniform layer (3) are all made of rubber materials. The scatters, the upper layer and the lower layer are combined into an integrated body and are made of the same materials. The base body needs to be fixed. The low-frequency vibration-isolation combined sandwiched structure can block incident vibration along a plate and low-frequency vibration perpendicular to the plate through the designed structure, be applied to vibration control within the frequency range of hundreds of hertz, and serve as a low-frequency vibration-isolation facility of projects such as foundations and inner walls of buildings, ships and warships, and high-speed rails.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
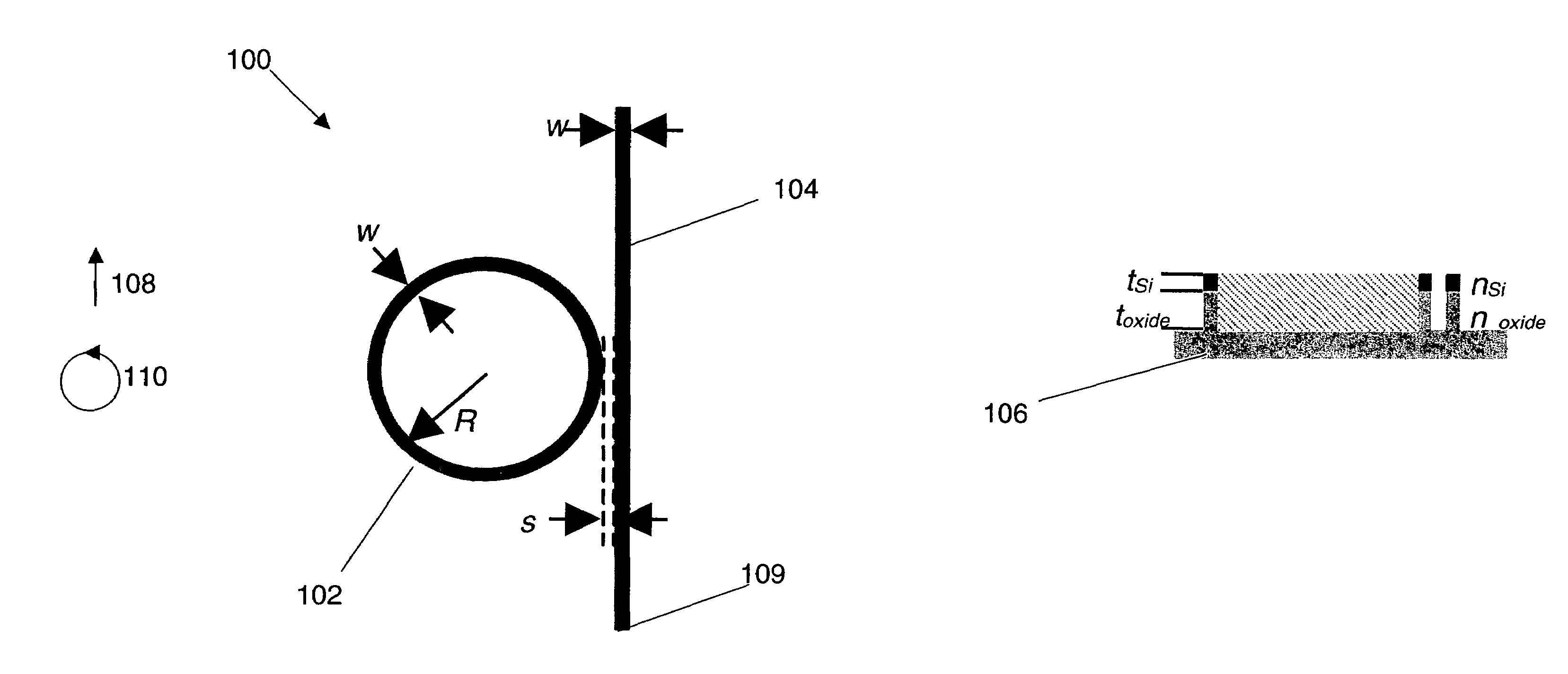
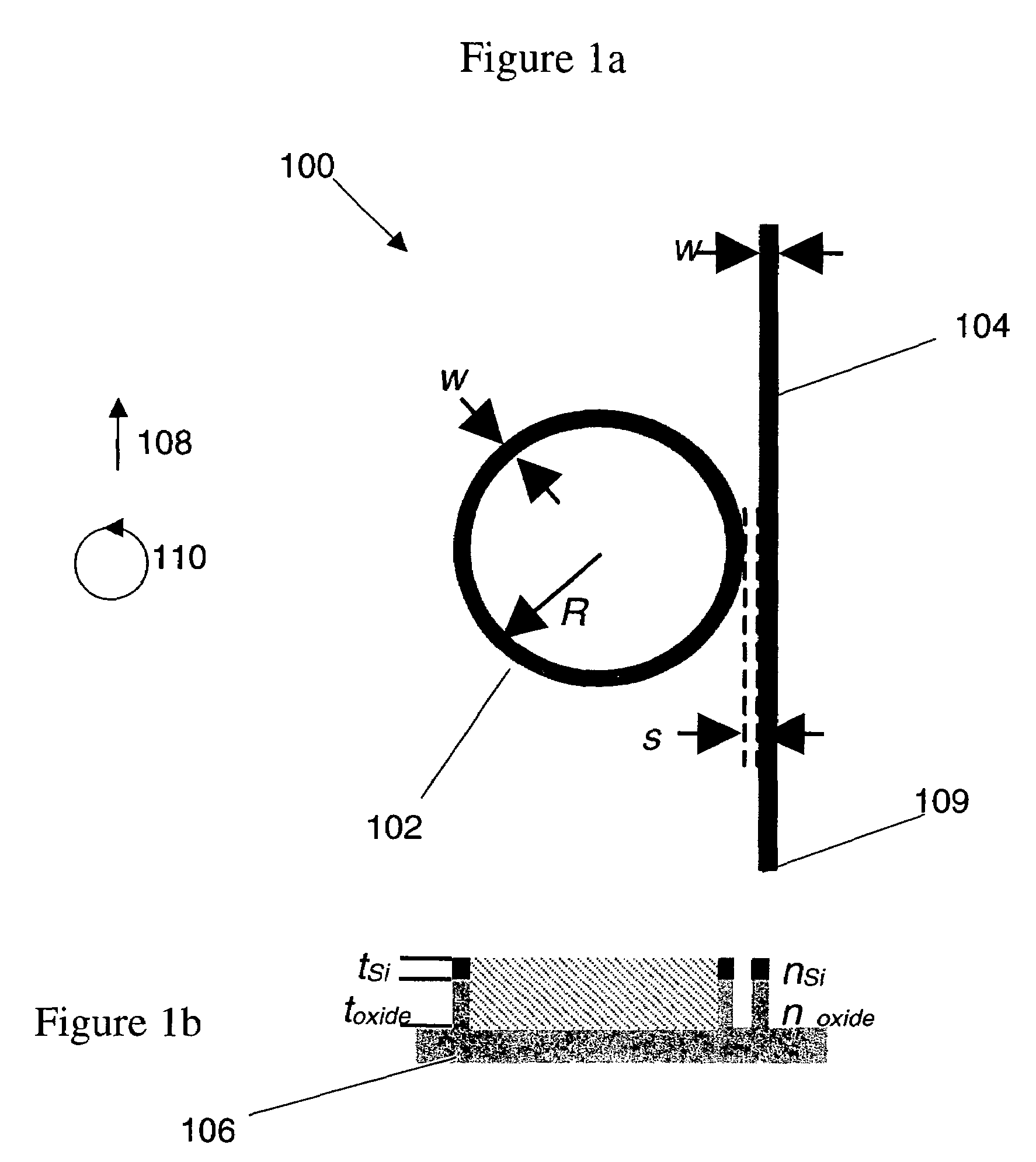
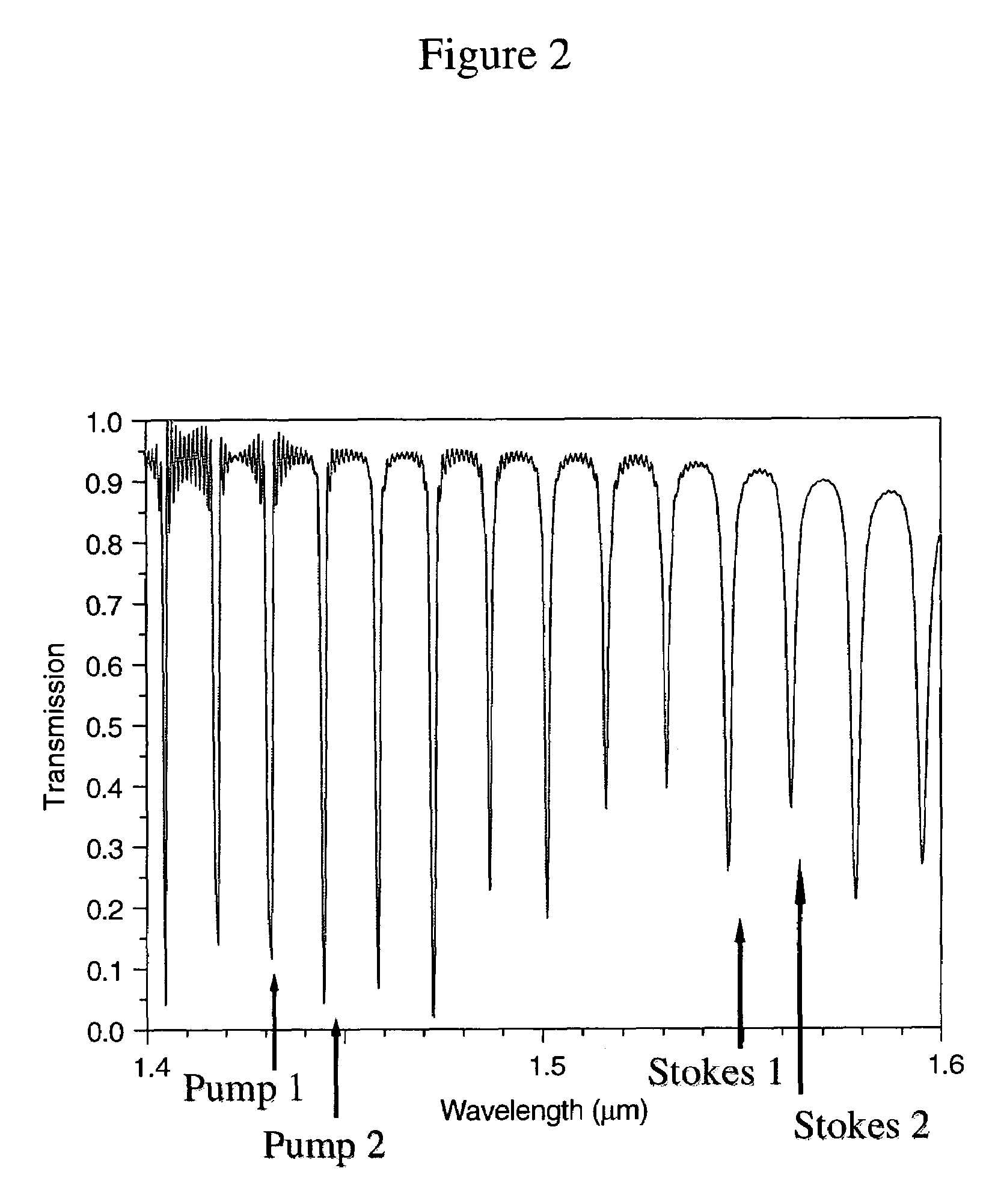
Enhanced raman amplification and lasing in silicon-based photonic crystals
Tunable laser devices and methods of manufacturing such devices are disclosed. air-holes with defects that form an optical waveguide. The waveguide has a cross-sectional area whose dimensions are in sub-wavelength ranges, wherein the cross-sectional area is perpendicular to the propagation direction of light in the waveguide. The waveguide receives pump light and outputs Stokes light through Raman scattering. The laser device may include a photonic crystal made from silicon having air-holes with defects forming a pair of optically coupled cavities. The geometries of the cavities can be substantially identical to each other. The cavities are defined to cause a frequency-splitting difference between a frequency of pump light and a frequency of Stokes light to correspond to an optical phonon frequency in silicon through Raman scattering.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
All-silicon raman amplifiers and lasers based on micro ring resonators
InactiveUS7532656B2Laser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionMicrowaveWhispering gallery
Devices for generating a laser beam are disclosed. The devices include a silicon micro ring having at least one silicon optical waveguide disposed at a distance from the micro ring. The radius and the cross-sectional dimension of the microring, the cross-sectional dimension of the waveguide, and the distance between the micro ring and the waveguide are determined such that one or more pairs of whispering gallery mode resonant frequencies of the micro ring are separated by an optical phonon frequency of silicon. Methods of manufacturing a lasing device including a silicon micro ring coupled with a silicon waveguide are also disclosed.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method for forming a monolithic thin-film thermoelectric device including complementary thermoelectric materials
InactiveUS20050150536A1Reduce needReduction in electron thermal conductivityThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentLiquid metalThermoelectric element
A vertical, monolithic, thin-film thermoelectric device is described. Thermoelectric elements of opposing conductivity types may be coupled electrically in series and thermally in parallel by associated electrodes on a single substrate, reducing the need for mechanisms to attach multiple substrates or components. Phonon transport may be separated from electron transport in a thermoelectric element. A thermoelectric element may have a thickness less than an associated thermalization length. An insulating film between an electrode having a first temperature and an electrode having a second temperature may be a low-thermal conductivity material, a low-k, or ultra-low-k dielectric. Phonon thermal conductivity between a thermoelectric element and an electrode may be reduced without a significant reduction in electron thermal conductivity, as compared to other thermoelectric devices. A phonon conduction impeding material may be included in regions coupling an electrode to an associated thermoelectric element (e.g., a liquid metal).
Owner:NANOCOOLERS
On-chip photonic-phononic emitter-receiver apparatus
A radio-frequency photonic devices employs photon-phonon coupling for information transfer. The device includes a membrane in which a two-dimensionally periodic phononic crystal (PnC) structure is patterned. The device also includes at least a first optical waveguide embedded in the membrane. At least a first line-defect region interrupts the PnC structure. The first optical waveguide is embedded within the line-defect region.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Heterostructure including light generating structure contained in potential well
ActiveUS7619238B2Convenient lightingImprove featuresSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanoopticsPotential wellElectron hole
A light emitting heterostructure and / or device in which the light generating structure is contained within a potential well is provided. The potential well is configured to contain electrons, holes, and / or electron and hole pairs within the light generating structure. A phonon engineering approach can be used in which a band structure of the potential well and / or light generating structure is designed to facilitate the emission of polar optical phonons by electrons entering the light generating structure. To this extent, a difference between an energy at a top of the potential well and an energy of a quantum well in the light generating structure can be resonant with an energy of a polar optical phonon in the light generating structure material. The energy of the quantum well can comprise an energy at the top of the quantum well, an electron ground state energy, and / or the like.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
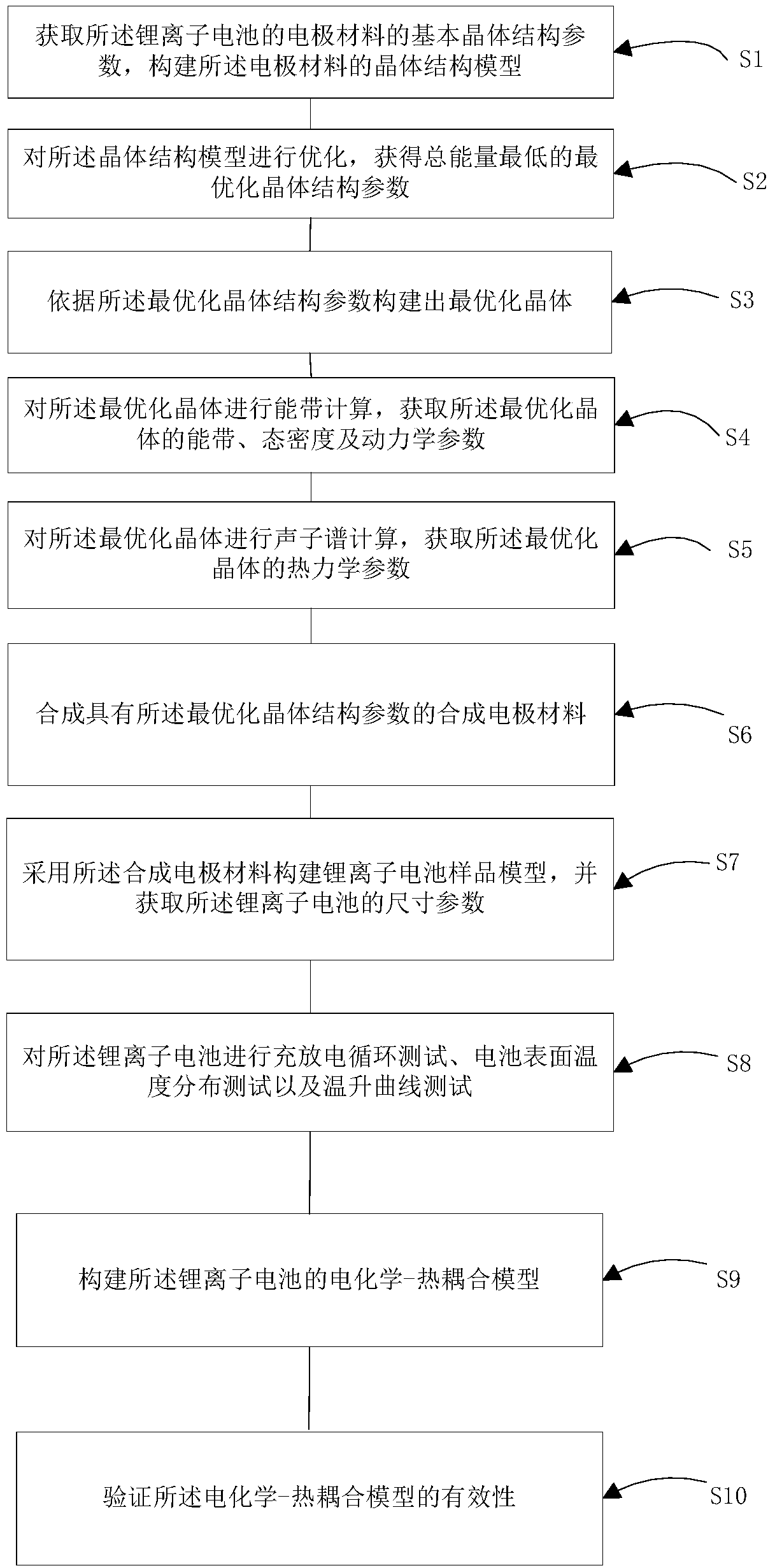
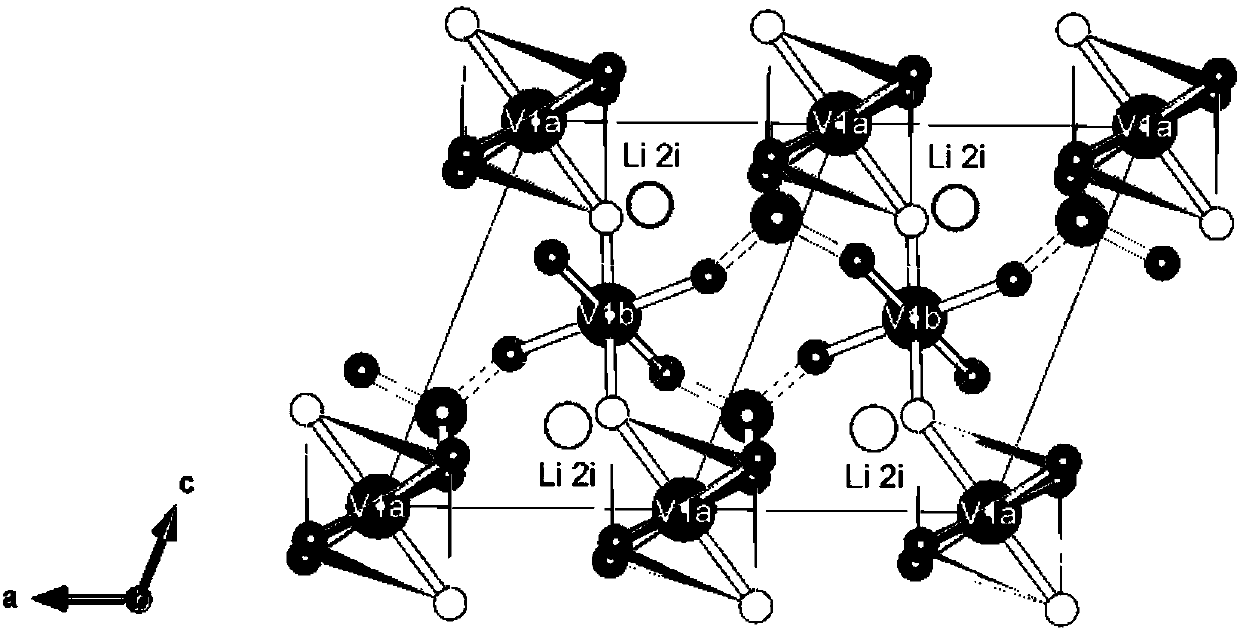
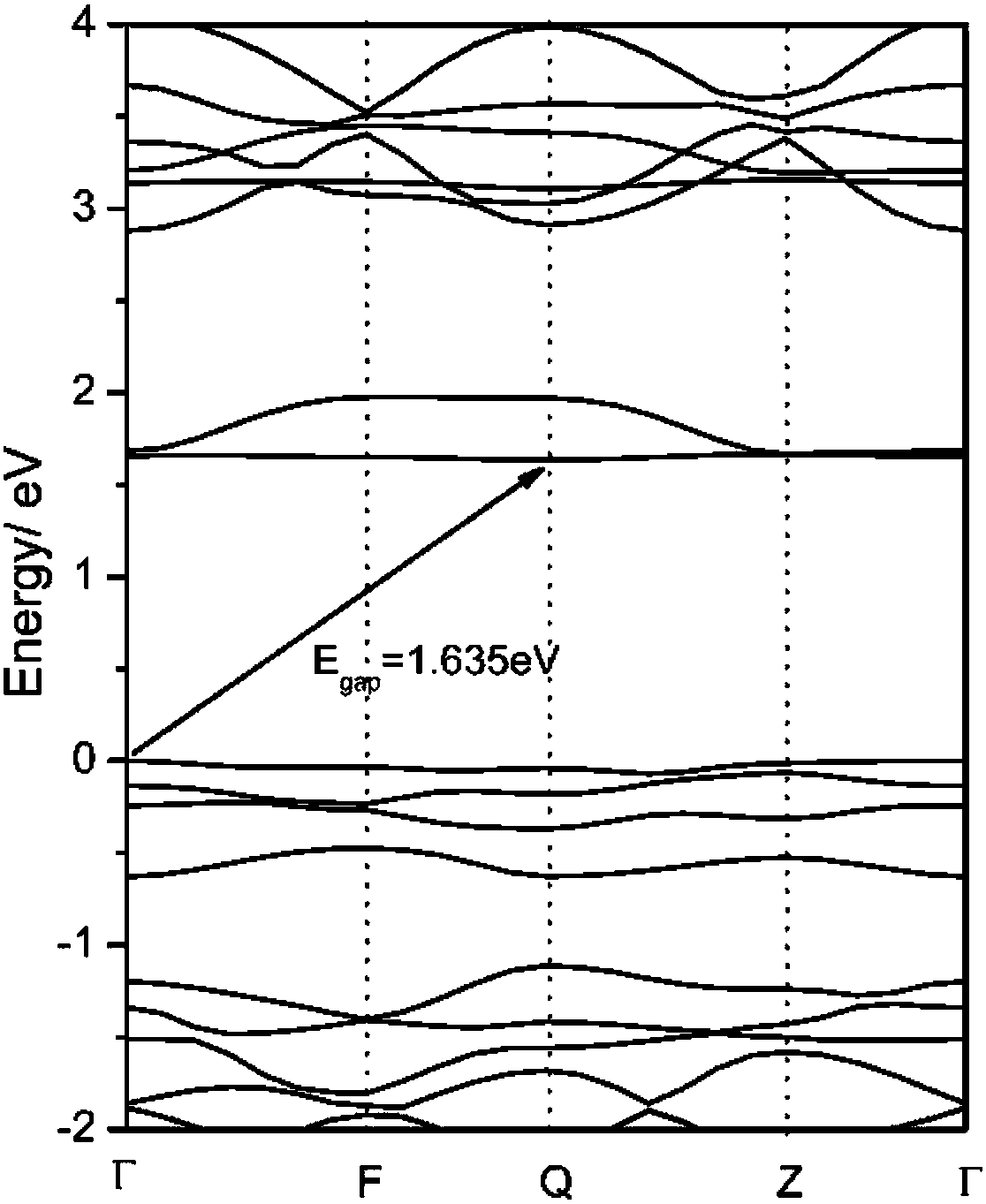
Simulation method and device for predicting lithium-ion battery material electrochemical performance and equipment
ActiveCN108009397AEfficient analysisChemical property predictionSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringCharge discharge
The embodiment of the invention provides a simulation method and device for predicting lithium-ion battery material electrochemical performance and equipment. The simulation method comprises the stepsthat basic crystal structure parameters of an electrode material of a battery are acquired, and a crystal structure model of the electrode material is constructed; the crystal structure model is optimized, and optimal crystal structure parameters with minimum total energy are obtained; an optimal crystal is constructed according to the optimal crystal structure parameters; energy band calculationis performed on the optimal crystal, and an energy band, density of states and dynamic parameters of the optimal crystal are acquired; phonon spectrum calculation is performed on the optimal crystal,and thermodynamic parameters of the optimal crystal are acquired; a synthetic electrode material with the optimal crystal structure parameters is synthesized; the synthetic electrode material is adopted to construct a battery sample model, and dimension parameters of the battery are acquired; charge-discharge loop testing, battery surface temperature distribution testing and temperature rise curve testing are performed on the battery; an electrochemical-thermal coupling model of the battery is constructed; and the effectiveness of the electrochemical-thermal coupling model is verified.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com