Patents
Literature
93 results about "Heat deposition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
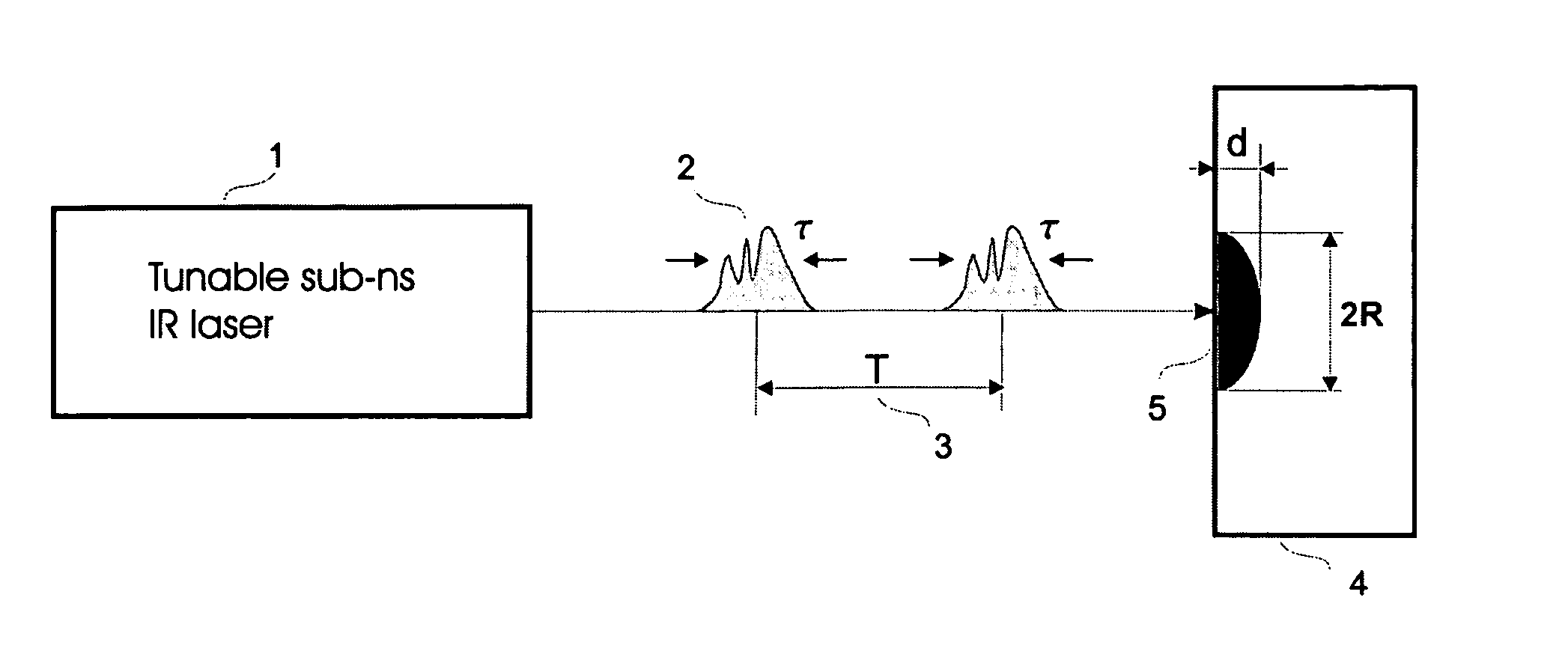
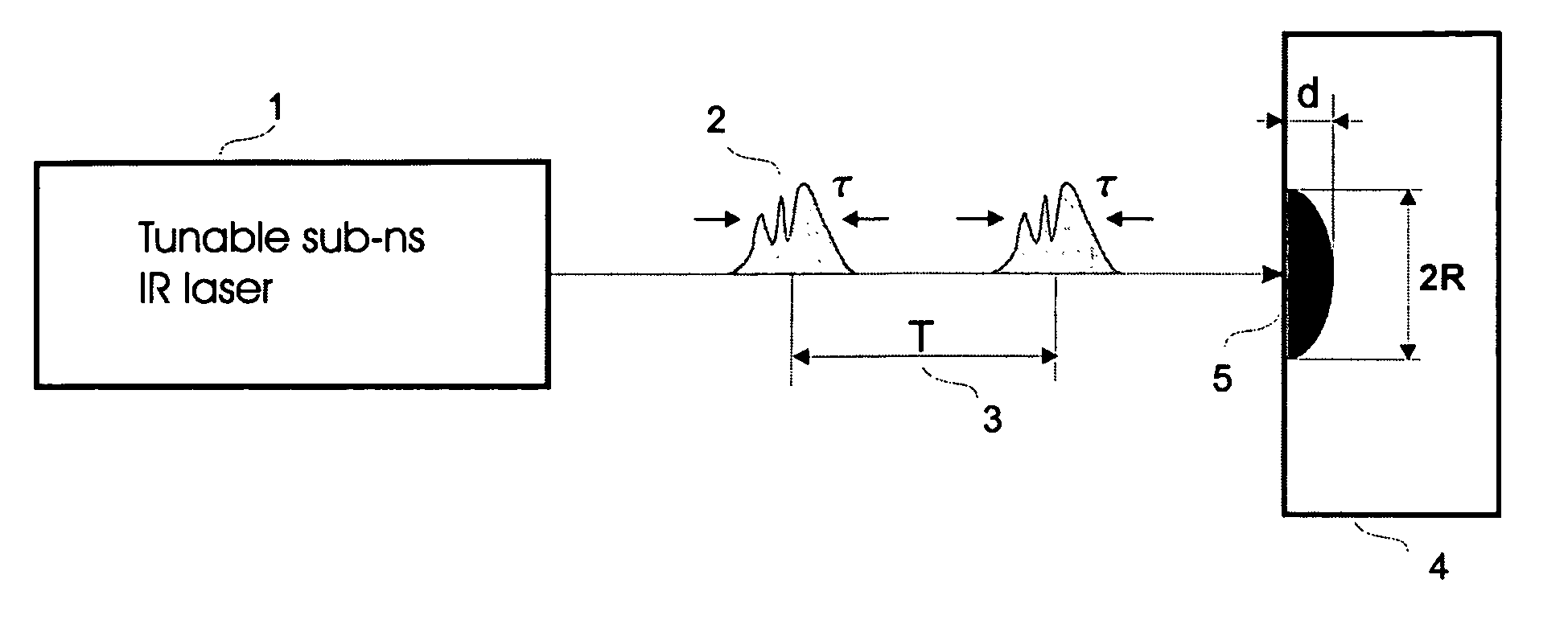
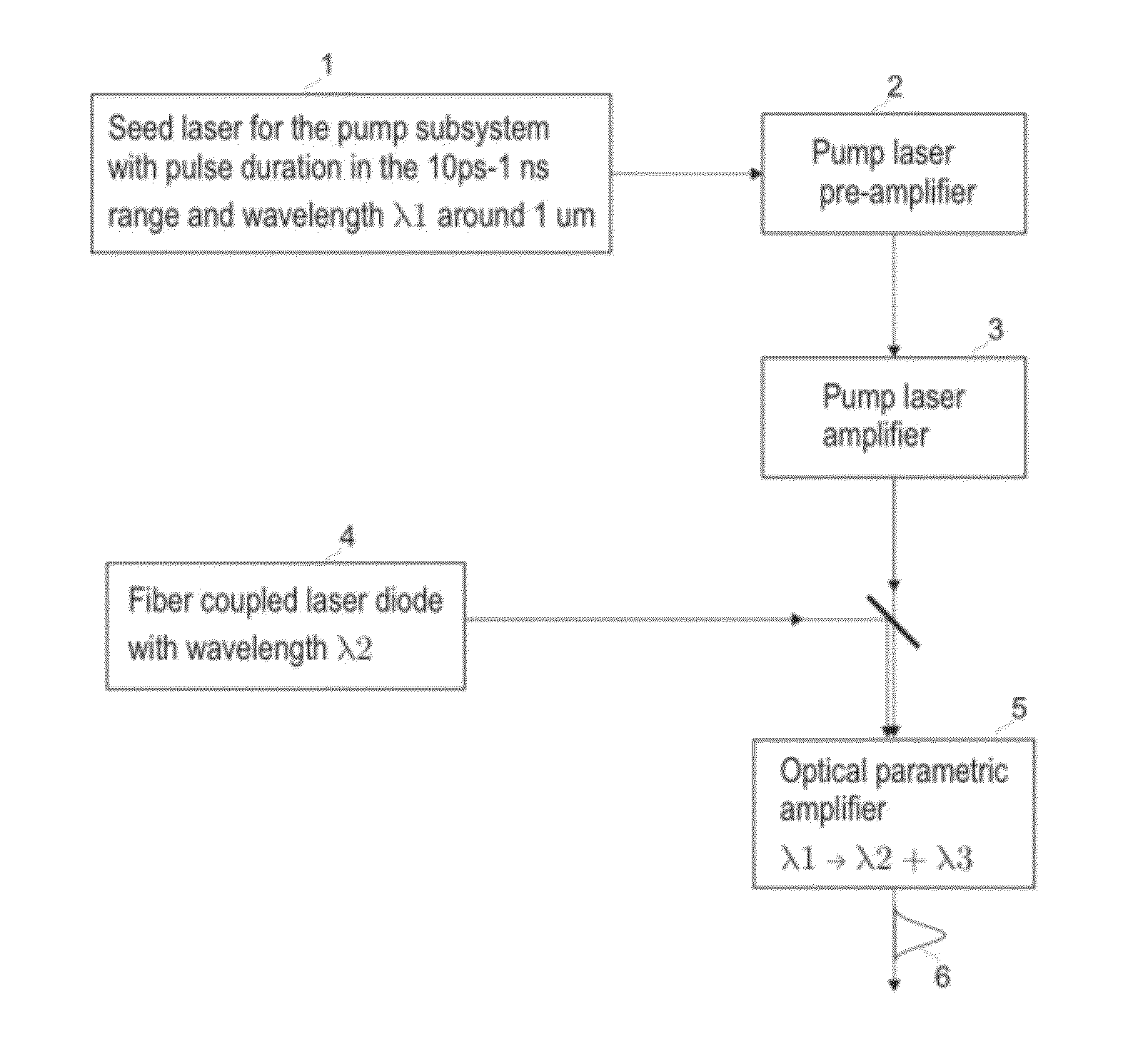
Laser selective cutting by impulsive heat deposition in the IR wavelength range for direct-drive ablation
ActiveUS20060195072A1Material efficiencyImprove efficiencySurgical instrument detailsLight therapyHeat depositionThermal expansion
The present invention provides a method of laser processing of materials, specifically laser induced ablation processes for laser removal of material particularly important in medical and dental applications in which the laser removal of material should be done in such a way as to not damage any of the surrounding soft or hard biomaterial. The ablation process is achieved by impulsive heat deposition (IHD) by direct and specific excitation of short lived vibrations or phonons of the material in such a way as to not generate highly reactive and damaging ions through multiphoton absorption. The heat deposition and ensuing ablation process under prescribed time and wavelength conditions for laser irradiation is achieved faster than heat transfer to surrounding tissue by either acoustic or thermal expansion or thermal diffusion that otherwise would lead to excess heat related damage. The result is that all the deposited laser energy is optimally channelled into the ablation process in which the inertially confined stresses from both photomechanical expansion forces and thermally driven phase transitions and associated volume changes constructively interfere to drive the most efficient ablation process possible with minimal damage to surrounding areas by either ionizing radiation or heat effects. By choosing a specific range of wavelengths, spatial and temporal shaping of infrared laser pulses, the energy can be optimally deposited in a manner that further increases the efficiency of the ablation process with respect to minimizing collateral damage.
Owner:LIGHT MATTER INTERACTION
Method for preparing tungsten/copper functional gradient material by infiltration - weld method
InactiveCN1593818AEasy to prepare and effectiveSolve thermal stressMetal layered productsFritGradient material
The invention relates to a new method of making tungsten-copper functional gradient material, which consists of pure tungsten layer and tungsten-copper gradient transit layer. First, make the gradient hole-framework with boring fluid of percent 5~80 volume ratio and tungsten powder of 1~20 micron. Infiltrate copper fluid to make the tungsten-copper gradient transit layer. Weld the W / Cu gradient layer and the pure tungsten by hot pressure. The process is following: mix the material and mould them, then frit framework, Infiltrate copper, weld and check. The method has both the advantage of melt-casting technique and jointing technique. The tungsten-copper functional gradient material made by this method is better heatproof and suited to electric sealing material, heat sinking material, and anti-high temperature plasma scouring unit such as the first layer material in nuclear fusion.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Laser selective cutting by impulsive heat deposition in the IR wavelength range for direct-drive ablation
ActiveUS8029501B2Material efficiencyImprove efficiencySurgical instrument detailsLight therapyThermal dilatationHeat deposition
The present invention provides a method of laser processing of materials, specifically laser induced ablation processes for laser removal of material particularly important in medical and dental applications in which the laser removal of material should be done in such a way as to not damage any of the surrounding soft or hard biomaterial. The ablation process is achieved by impulsive heat deposition (IHD) by direct and specific excitation of short lived vibrations or phonons of the material in such a way as to not generate highly reactive and damaging ions through multiphoton absorption. The heat deposition and ensuing ablation process under prescribed time and wavelength conditions for laser irradiation is achieved faster than heat transfer to surrounding tissue by either acoustic or thermal expansion or thermal diffusion that otherwise would lead to excess heat related damage. The result is that all the deposited laser energy is optimally channelled into the ablation process in which the inertially confined stresses from both photomechanical expansion forces and thermally driven phase transitions and associated volume changes constructively interfere to drive the most efficient ablation process possible with minimal damage to surrounding areas by either ionizing radiation or heat effects. By choosing a specific range of wavelengths, spatial and temporal shaping of infrared laser pulses, the energy can be optimally deposited in a manner that further increases the efficiency of the ablation process with respect to minimizing collateral damage.
Owner:LIGHT MATTER INTERACTION INC
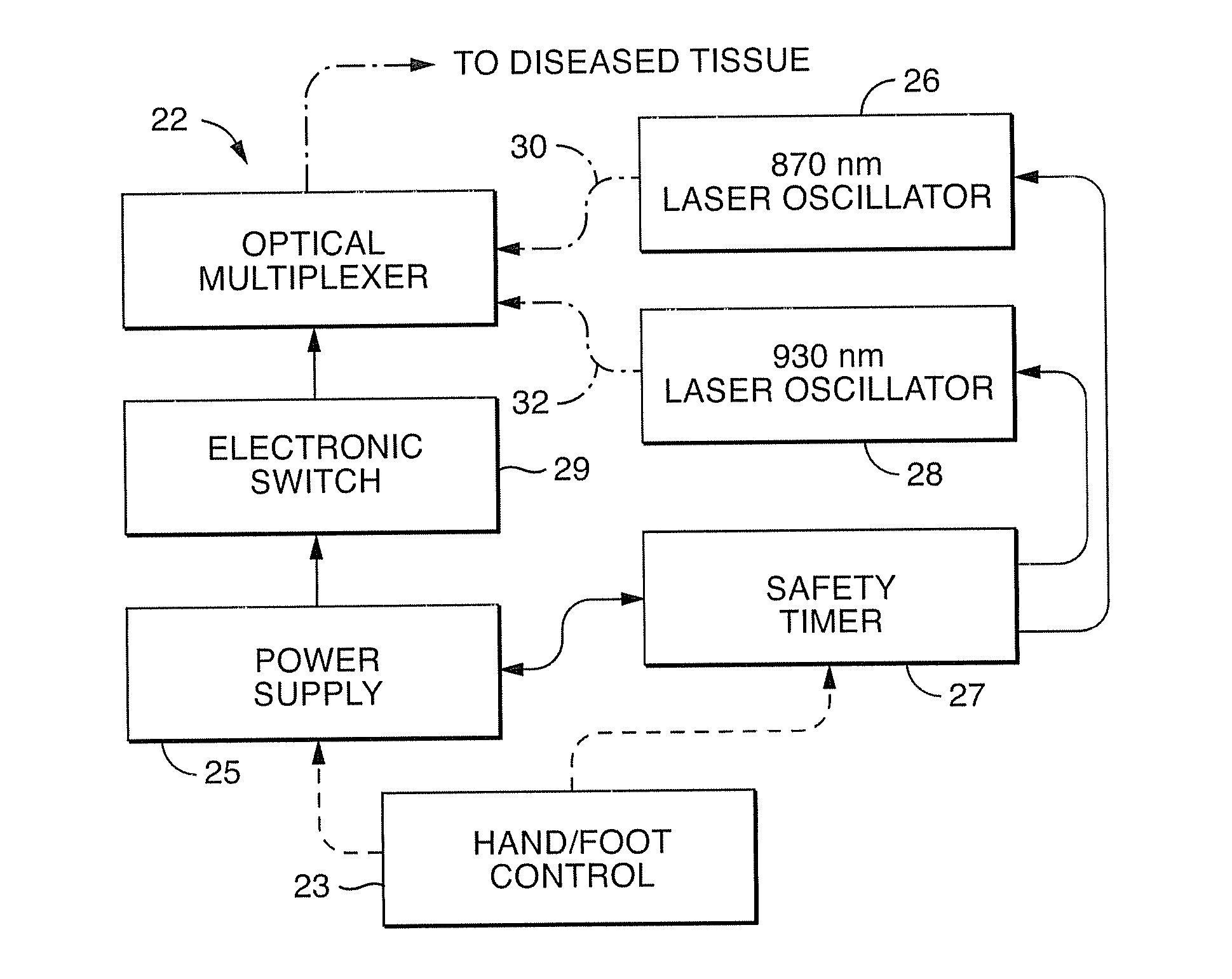
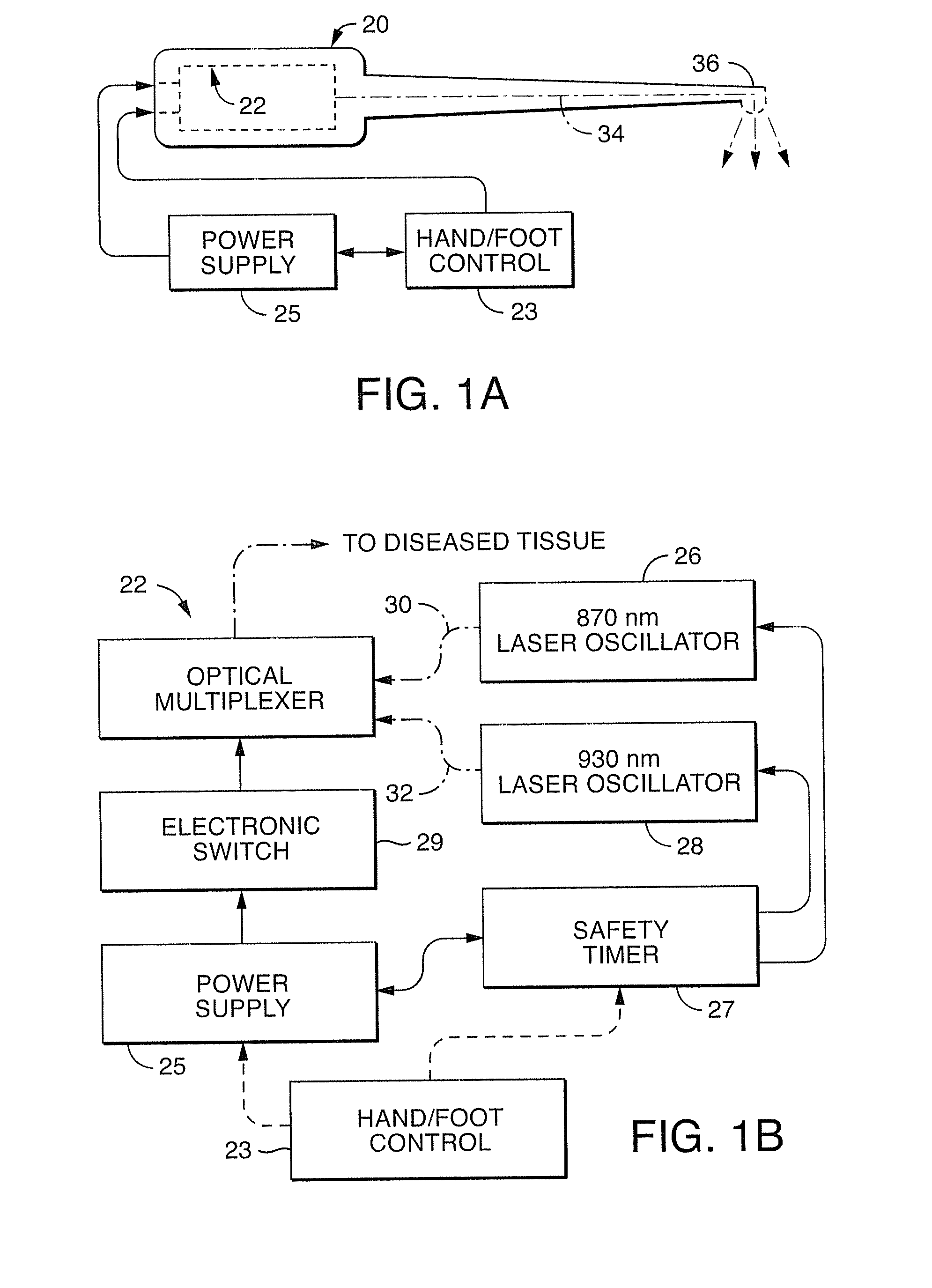
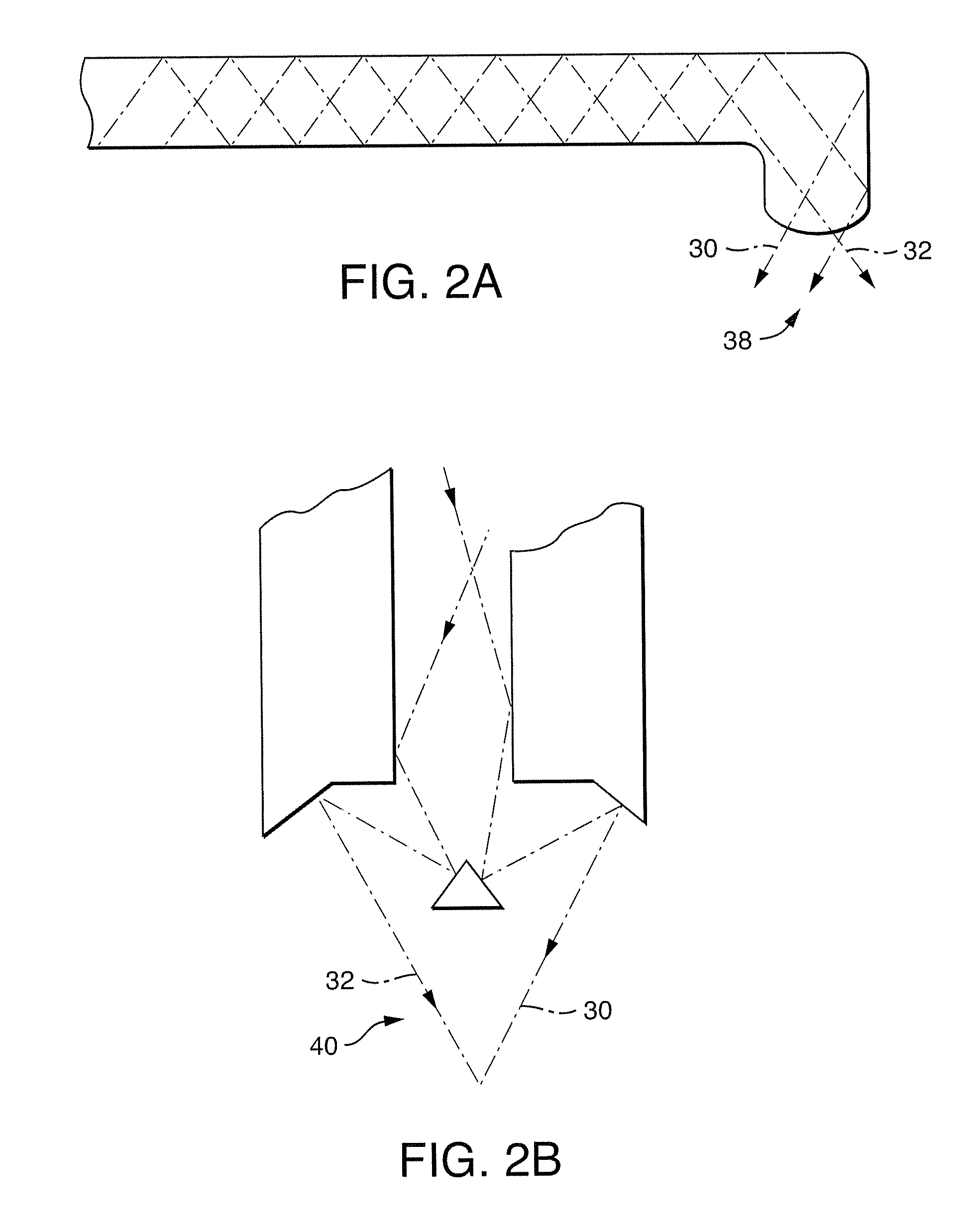
Near infrared microbial elimination laser system
InactiveUS20080021370A1Minimal heat depositionElectrotherapyGum massageOptical interactionHeat deposition
Dual wavelength laser energy in the near infrared electromagnetic spectrum is described as destroying bacteria via photo-damage optical interactions through direct selective absorption of optical energy by intracellular bacterial chromophores. Use of various dual wave length laser systems include use of optical assembly including two distinct diode laser ranges (including 870 nm and 930 nm) that can be emitted to achieve maximal bacterial elimination without intolerable heat deposition. Related processes for medical procedures are also described.
Owner:NOMIR MEDICAL TECH
Carbon nanotube modified titanium based fluorine-containing lead dioxide electrode and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103508517AImprove electrocatalytic activityImprove conductivityWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatmentLead dioxideActive agent
The invention relates to a carbon nanotube modified titanium based fluorine-containing lead dioxide electrode and a preparation method thereof. The carbon nanotube modified titanium based fluorine-containing lead dioxide electrode is prepared by: taking a titanium plate as a substrate, polishing and etching the titanium plate substrate, performing thermal deposition of a tin antimony oxide base layer, then conducting electrodeposition of an alpha-PbO2 intermediate layer in an alkaline plating solution, and finally performing electrodeposition of a beta-PbO2 active layer in an acidic plating solution containing fluoride ions, a surfactant and a carbon nanotube. Compared with ordinary titanium based fluorine-containing lead dioxide electrodes, the carbon nanotube modified titanium based fluorine-containing lead dioxide electrode has high catalytic activity and long service life. The electrode can be used as an anode to treat organic wastewater, can achieve a good degradation effect, and can realize mineralization on poisonous and harmful organic matters that are difficult to degrade. Being easy and convenient to operate, the electrode provided by the invention is a potential electrode suitable for water treatment.
Owner:JILIN NORMAL UNIV
Low-radiation self-cleaning composite function glass and producing method
This invention relates to a low radiation self-cleaning complex function glass. This glass has trilamellar membrane structure, membranous layer from glass outward in turns is : SiO2 transition layer, ion adulterated SnO2 layer, ion adulterated SiO2 - TiO2 layer. The on-line preparation method is sol-gel method, combine with atomizing sedimentation, utilize thermal decomposition and coagulation process of collosol at 450 to 550 deg to proceed heat sedimentation, in turns form membranous layer on the on-line glass plate surface. This invention through controlling the coating material concentration, dopant ion variety, thermal decomposition temperature and membranous layer thickness bring low radiation to the glass coated this membrane, execute stable uniwafer low emissivity glass, reduce cost, and realize reprocessing treatment of low radiation steeling and hot bending. This invention applies to common building and shield glass.
Owner:CHINA LUOYANG FLOAT GLASS GROUP
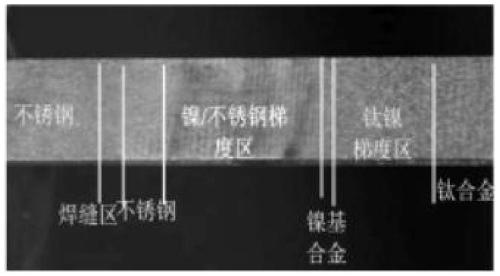
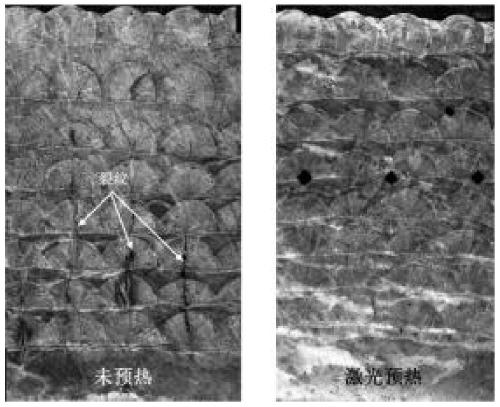
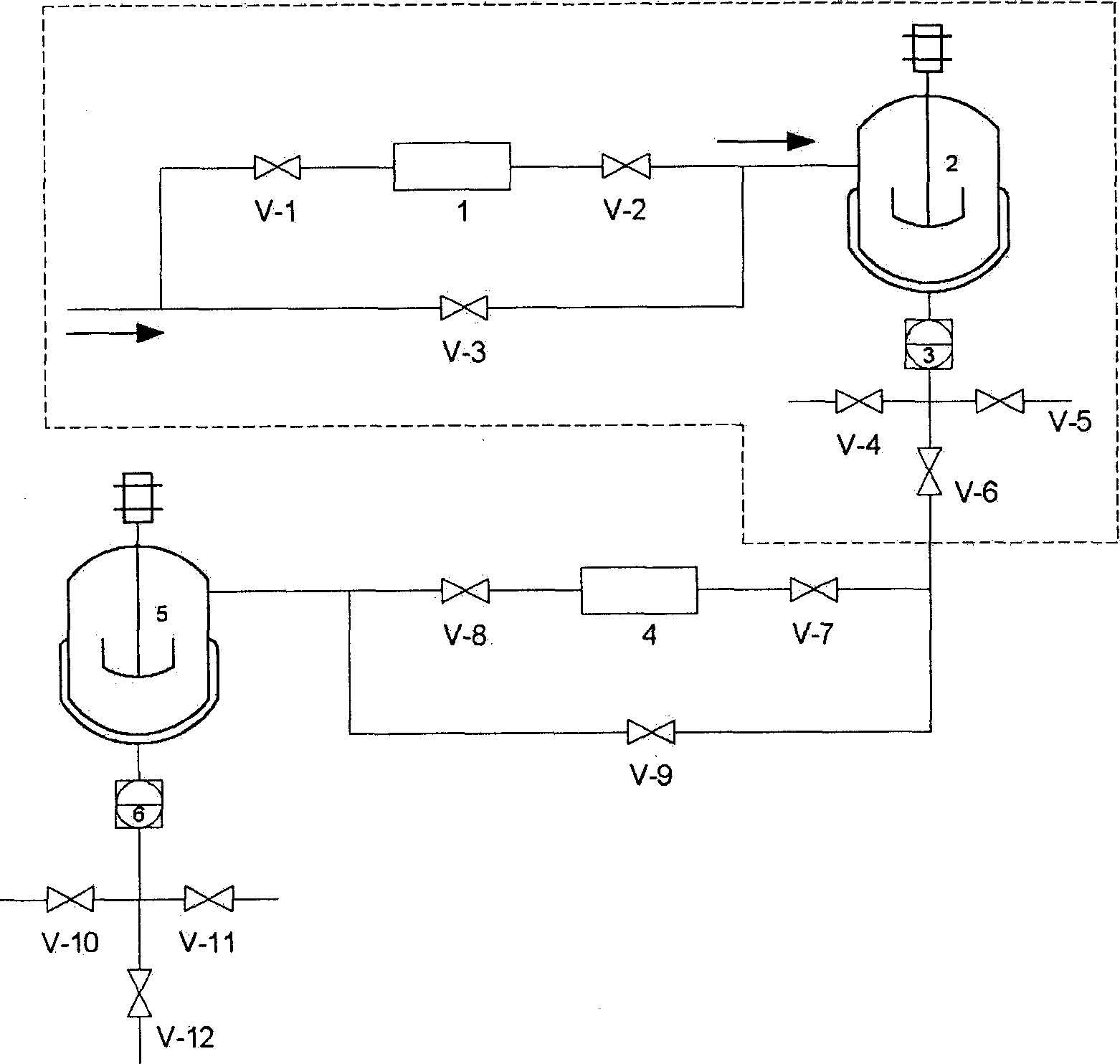
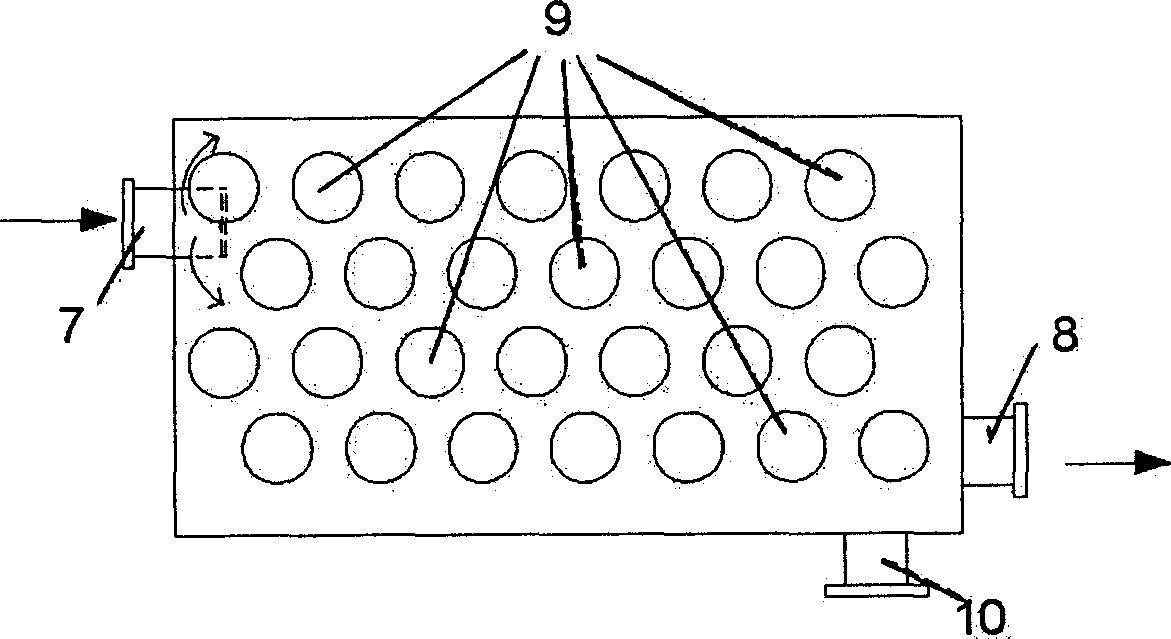
Gradient transition connection method of steel/titanium dissimilar metal based on laser synchronous preheating deposition
InactiveCN111151880AAvoid heat stressFirmly connectedAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyHeat depositionTitanium alloy
The invention relates to the technical field of laser machining, in particular to a gradient transition connection method of steel / titanium dissimilar metal based on laser synchronous preheating deposition. The method comprises the following steps of (1) machining and cleaning a substrate, wherein the joint form is butt joint or corner joint; (2) preheating, specifically, preheating the cross section of the deposition position of a titanium alloy base material by adopting laser; (3) powder preparation, specifically, weighing the stainless steel and the titanium alloy, and separately mixing theweighed stainless steel and titanium alloy with a nickel-based alloy; (4) laser deposition and synchronous preheating, specifically, preheating a deposition layer after laser deposition for a certainperiod of time, then continuously depositing, and alternately performing; (5) post-heating, specifically, continuously running the laser to perform post-heat treatment on the deposition layer; and (6) welding, specifically, obtaining the titanium / nickel / steel gradient deposition layer and performing welding. The method solves the problems of low strength and poor toughness of a welding joint caused by the fact that a continuous and high-brittleness intermetallic compound is extremely easy to form at an interface in the traditional fusion welding, high-energy beam welding and solid-phase connection process of the titanium alloy and the stainless steel at present.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Dirty oil dewatering process for refinery and oil field
The present invention relates to dirty oil dewatering process, and is especially ultrasonic treatment process of dewatering dirty oil in refinery and oil field to recover oil. Water containing dirty oil is first ultrasonic treated in ultrasonic treater with ultrasonic field of standing wave and traveling wave before being oil-water separated in a heat deposition tank, or water containing dirty oil is oil-water separated in a heat deposition tank with standing wave and traveling wave ultrasonic treater. The technological process adopts physical demulsifying process to dewater, has high dirty oil adaptability, no influence of dirty oil property, fast oil-water separation, high dewatering rate, and low operation cost. The present invention is significant in dirty oil recovering and reducing environmental pollution.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Fused filament fabrication extruder
InactiveUS20160354977A1Additive manufacturing with liquids3D object support structuresFused filament fabricationTemperature control
3D Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) is improved by heating the deposition nozzle with one or more non-contact heat sources. 3D FFF is also improved by cooling the deposition nozzle with one or more active cooling elements. Temperature control of the deposition nozzle is improved due to the reduction in mass of the nozzle by eliminating conductive heat elements and their associated devices, such as thermal transfer blocks. Responsiveness of the nozzle is improved by using lasers as non-contact heating sources, allow for rapid changes in temperature when necessary.
Owner:GORDON MARK CHRISTOPHER
Preparation method and application method of electrocatalysis electrode
ActiveCN105776431ALarge specific surface areaExtended service lifeWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsHeat depositionTitanium
The invention provides a preparation method and an application method of an electrocatalysis electrode. The preparation method includes: taking titanium as a substrate, depositing Bi-SnO2-Sb2O3-CNT on the titanium substrate by means of heat deposition, and then depositing a PbO2 active surface layer on a Bi-SnO2-Sb2O3-CNT interlayer by the aid of electrodeposition to prepare a Ti / Bi-SnO2-Sb2O3-CNT / PbO2 electrocatalysis electrode. The electrocatalysis electrode is used for ultrasound electrocatalysis algae killing and microcystin degradation. The electrocatalysis electrode is taken as an anode, a stainless steel or copper sheet is taken as a cathode, microcystis aeruginosa solution added with electrolyte is subjected to electrolysis, and ultrasonic treatment is applied in the electrolytic process. The preparation method and the application method of the electrocatalysis electrode have the advantages that the electrode has more catalytic activity sites, and catalytic activity of the electrode is improved; electrical conductivity of the electrode can be improved, and energy consumption can be lowered; electrocatalytic activity is high, and service life is long; ultrasonic oxidation and electrocatalytic oxidation are combined, synergistic effect is generated, and efficiency of algae killing and microcystin degradation is highly increased.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Three-dimensional comprehensive test mining system for large-scale full-size mining well
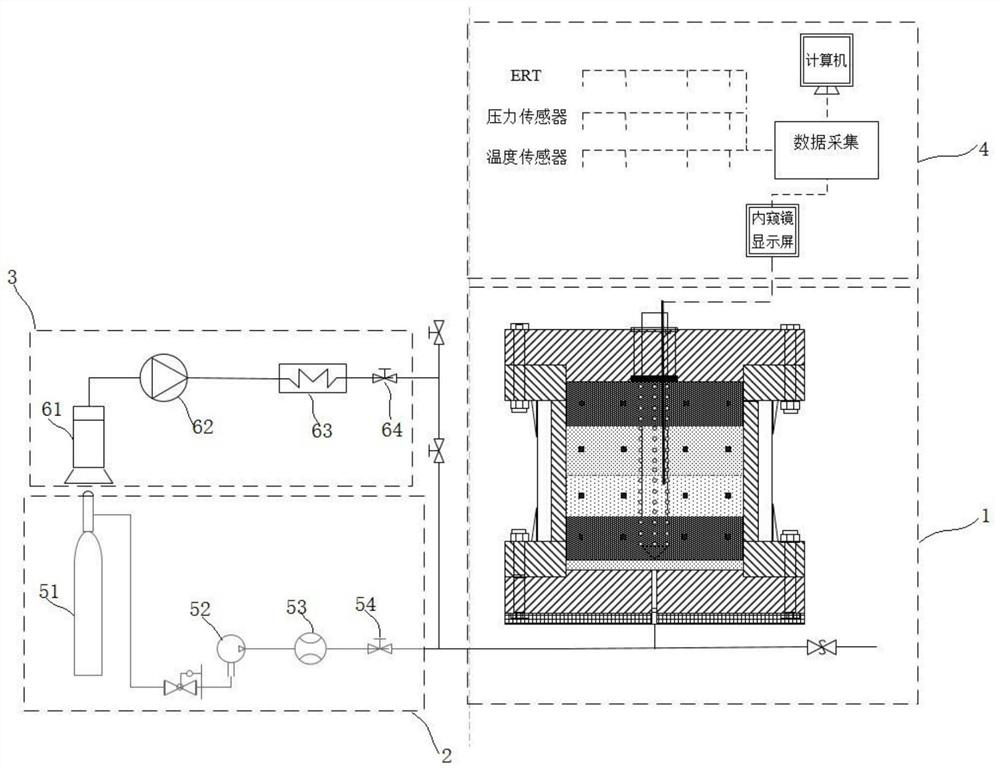
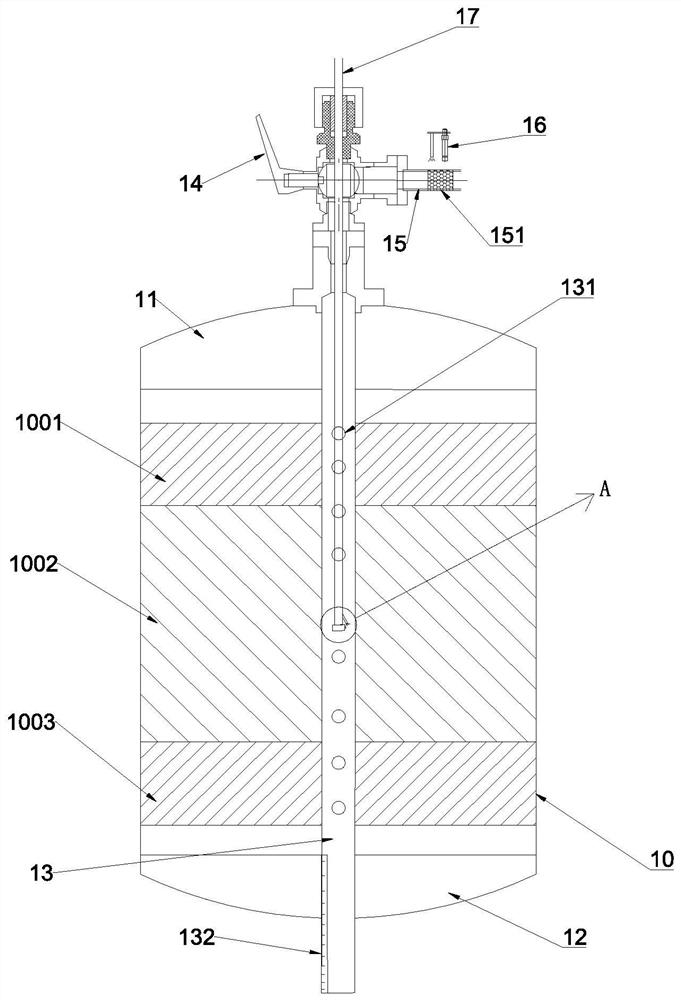
ActiveCN112031714AOptimize production well structureOptimizing sand production and sand control methodsSurveyConstructionsTemperature controlData acquisition
The invention discloses a three-dimensional comprehensive test mining system for a large-scale full-size mining well. The three-dimensional comprehensive test mining system comprises a reaction kettle, a gas injection module, a liquid injection module, a temperature control module and a data acquisition, processing and display module, wherein the reaction kettle is used for preparing a natural gashydrate sample and truly simulating a natural gas hydrate reservoir forming environment in a seabed settled layer; the reaction kettle comprises a reaction kettle body, an upper kettle cover mountedon the upper end face of the reaction kettle body and a lower kettle cover mounted on the lower end face of the reaction kettle body; the gas injection module is used for quantitatively injecting gasinto the reaction kettle in a hydrate synthesis process; the liquid injection module is used for quantitatively injecting liquid into the reaction kettle in the hydrate synthesis process; the temperature control module is used for controlling the temperature in the reaction kettle; and the data acquisition, processing and display module is used for acquiring, storing, processing and displaying data when the test mining system is used for testing. The system disclosed by the invention can be used for preparing the natural gas hydrate sample and carrying out simulation researches on mining testsincluding pressure reduction, heat injection and the like under different well pattern arrangement forms; and hydrate decomposition, gas-liquid seepage and heat transfer and sediment stability in a mining process are researched.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
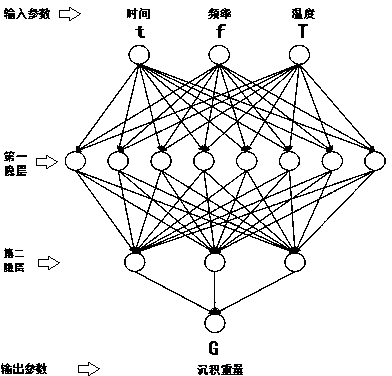
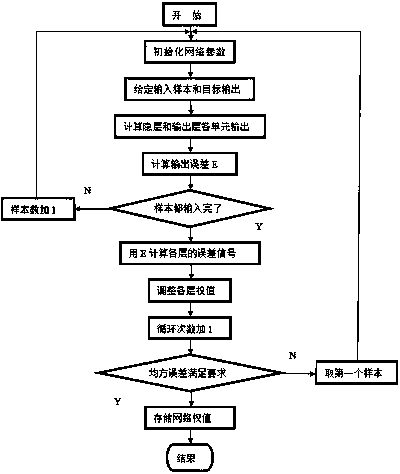
Forecasting method for induction thermal deposition calcium-phosphate coating process on basis of neural network
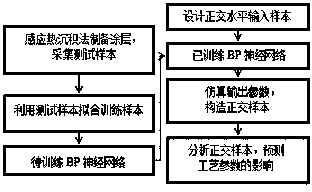
InactiveCN103745271AEffective studyEnrich the knowledge base of induction thermal deposition process parametersBiological neural network modelsForecastingTest sampleEngineering
The invention discloses a forecasting method for an induction thermal deposition calcium-phosphate coating process on the basis of a neural network, which comprises the following steps of preparing a calcium-phosphate coating by utilizing an induction thermal deposition method and collecting a test sample; fitting out a training sample by the test sample; establishing the BP (Back Propagation) neural network, training the network by adopting a Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm and utilizing the training sample, and testing the generalization ability of the network by the test sample; designing orthogonal horizontal process parameters, using the orthogonal horizontal process parameters as input parameters, simulating output parameters by utilizing the trained network and constructing an orthogonal sample; and carrying out analyzing calculation on the obtained orthogonal sample and forecasting influence of the process parameters on the deposition process. According to the invention, the data mining ability of the neural network is successfully utilized and the relation between three process parameters of time, frequency and temperature of induction thermal deposition and the deposition rate is analyzed, so that design of the calcium-phosphate coating preparation process is effectively guided.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV +1
Method for making gallium nitride crystal
InactiveCN1434482AReduce the number of defectsSimple methodPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsHeat deposition
This invention relates to a process method for semiconductor materials of gallium nitride crystals including the following steps: (1) epitaxial growth of Ga nitride or Al nitride on a substrate (2) heat-deposition of crystal particles of silicon, silicon carbide, silicon nitride or silicon oxide (3) continuation of epitaxial growth of Ga nitride further growing undoped and doped Ga nitride film Dor LED, LD, HEMT etc. photoelectronic and electronic apparatus. The said substraet can be sapphire, SiC SiL GaAs, ZnO, MgO, LiAlO2 or Li GaO2 effectively reducing dislocation, overcoming mismatch of the substrate and epitaxial layer.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for enhancing aluminum interconnect properties
InactiveUS6200894B1Enhanced aluminum interconnect propertyImprove propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHeat depositionSurface conditions
A method of enhancing the aluminum interconnect properties in very fine metalization patterns interconnecting integrated circuits that improves the texture and electromigration resistance of aluminum in thin films. Enhanced performance can be obtained by forming a smooth oxide layer in situ, or by surface conditioning a previously formed oxide layer in an appropriate manner to provide the requisite surface smoothness, then by refining the aluminum microstructure by hot deposition or ex-situ heat treatment.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Technology for brewing dry type red date wine
InactiveCN103320259APromote technological progressExpand production scaleMicroorganism based processesAlcoholic beverage preparationPectinaseDistillation
The invention provides a technology for brewing dry type red date wine, comprising: selecting fresh red dates without mildew and moth, cleaning with clear water of 50 DEG C, depitting the red dates, boiling the red dates in water at 100 DEG C in a mass ratio of 1:2-3 for 30-40min, cooling to room temperature, and then squeezing the red dates to obtain a stock solution with pulp; treating the stock solution with 72-110V of voltage by microelectrolysis for 20-30h, to obtain a red date liquid; adding citric acid into the red date liquid for regulating a pH value of the red date liquid to make it be 3.5-4; adding high active dry yeast of wine with mass being 0.03-0.05% of that of the red date liquid, uniformly mixing in a fermentation cylinder, and fermenting for 14-30 days at 15-20 DEG C; adding pectase into the fermented red date liquid according to 0.15-0.25g / L, clarifying for 5-6h at 40-50 DEG C, separating slurries, placing the slurries in a distillation container, and distilling the slurries with strong fire until a distilled fluid is half of the original slurries, to obtain the red date wine stock solution; heat-treating at 70-80 DEG C to precipitate heat deposition in the wine, reducing the temperature to 1-4 DEG C after heat treatment to precipitate cold deposition in the wine, filtrating with a 0.2-0.5pm microfilm after removing the deposition to obtain stoke wine; and finally heating to disinfect the stoke wine at 120-130 DEG C for 2-3s to obtain the dry type red date wine.
Owner:NINGXIA SHENGKANGYUAN JUJUBE WINE BIOTECH
Electromagnetic inductive heating device
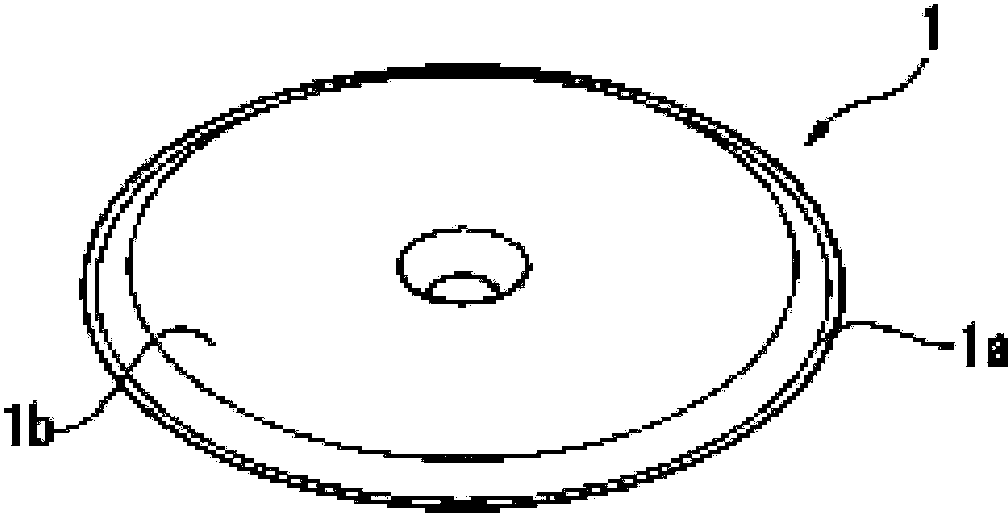
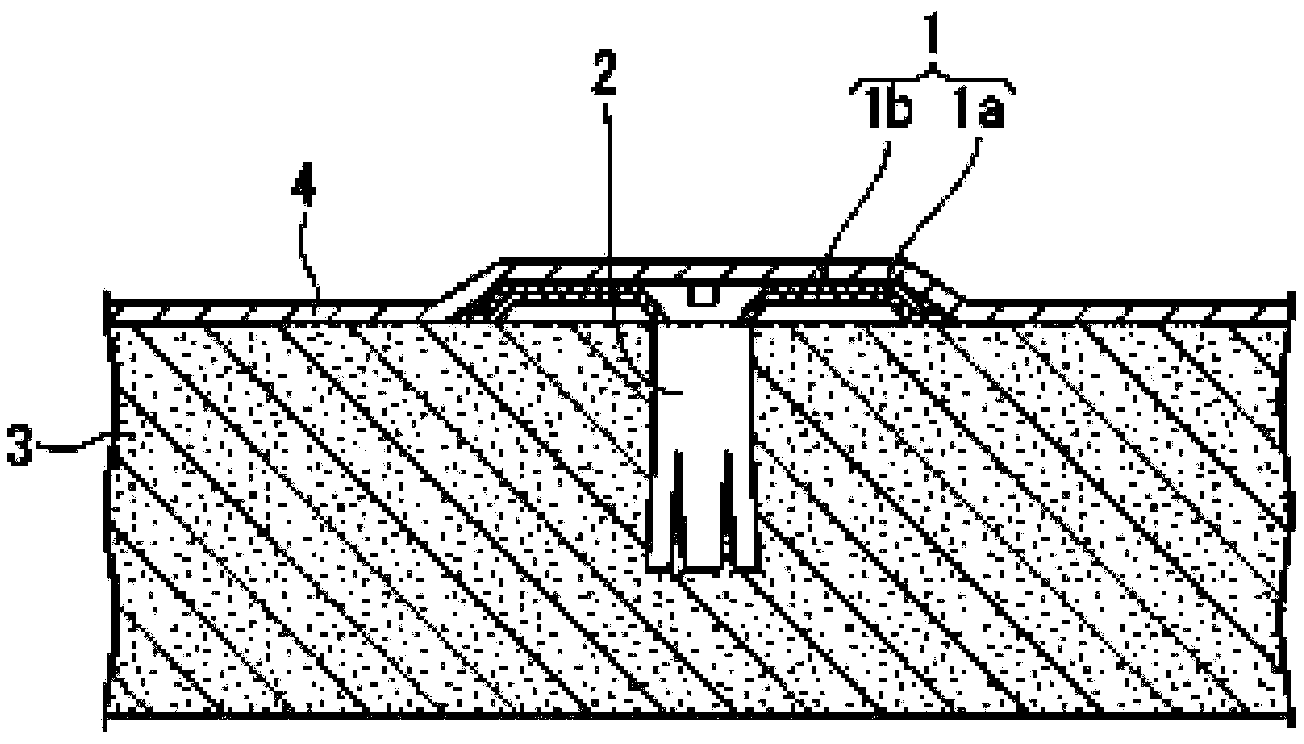
InactiveCN104054393AFixed indifferenceFixed uniformRoof covering using flexible materialsRoof toolsHeating timeHeat deposition
The present invention relates to an electromagnetic inductive heating device for bonding a sheet to anchoring members comprising a conductive base and a thermoplastic resin layer, characterized by bonding the anchoring members to the sheet by heat deposition of the thermoplastic resin layer by heating of the conductive base, said device comprising: a heating means for heating the conductive base via the sheet by electromagnetic induction; a temperature measurement means for measuring the temperature of the sheet; and a heating time setting means for setting heating time by the heating means according to the temperature of the sheet. With the present invention, it is possible to provide an electromagnetic inductive heating device with which it is possible to desirably bond the anchoring members and the sheet even if there are large temperature changes in a covering surface due to seasons, weather, etc., and to reliably anchor a sheet, uniformly and without unevenness, to all anchoring members even if time is required to lay down the sheet.
Owner:SIKA TECH AG
Preparation method for patterned film with gradually changed thickness
ActiveCN106591787AGreat potentialEasy to joinVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringSoft magnet
The invention discloses a preparation method for a patterned film with a gradually changed thickness. The preparation method mainly comprises the following steps of: designing magnetic fields by utilizing software such as ANSYS and COMSOL according to a to-be-obtained pattern with a gradually changed thickness, wherein the magnetic fields consist of permanent magnets or soft magnets; then, fixing a substrate with the permanent magnets or the soft magnets onto a sample stage on a positive electrode of a magnetron sputtering apparatus, and enabling one surface, without a magnet, of the substrate to face towards a magnetic metal target; and fixing the magnetic metal target onto a target stage on a negative electrode of the magnetron sputtering apparatus, starting sputtering, observing reading of a film thickness meter in a sputtering process, stopping sputtering when the displayed film thickness reaches a proper thickness, thereby obtaining a metal film with a thickness in patterned distribution on the substrate. The method disclosed by the invention can be flexible and can obtain various patterned films, and the thicknesses of the films are in stepless gradual change; and meanwhile, the magnetic fields can be conveniently added into film preparation processes such as magnetic-control sputtering and vacuum heat deposition, magnets can be repeatedly used, and operations are flexible, so that the preparation method is simple and reliable, and is low in cost.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Method for preparing reflection-reduction film element of light P with thickness of 193nm in large angle mode
InactiveCN102928894AReduce residual reflection lossImprove output efficiencyVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingBeam expanderComputer module
The invention discloses a method for preparing a reflection-reduction film element of light P with thickness of 193nm in a large angle mode, and relates to the technical field of application of ArF excimer laser, and the method is used for solving the problem that the oversize optical loss is caused by surplus reflection when a 193nm laser beam in a P polarization state is incident to a beam expander prism group in a large angle mode. By utilizing the method, an LaF3 film layer and an MgF2 film layer are alternately deposited on a substrate in a vacuum heat deposition method; optical constant analysis on the LaF3 film layer and the MgF2 film layer are performed, and particularly, the thickness of the LaF3 film layer is optimized; the thickness of each LaF3 film layer is extremely compressed; and the total thickness of the multilayered LaF3 film layer is less than 40nm, so that the preparation of the reflection-reduction film element is realized. By utilizing the method, the ArF laser in the P polarization-state has extremely-low reflection ratio when being incident to 71o, and the output efficiency of the ArF laser is greatly improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Furnace temperature control method for thermal budget balance
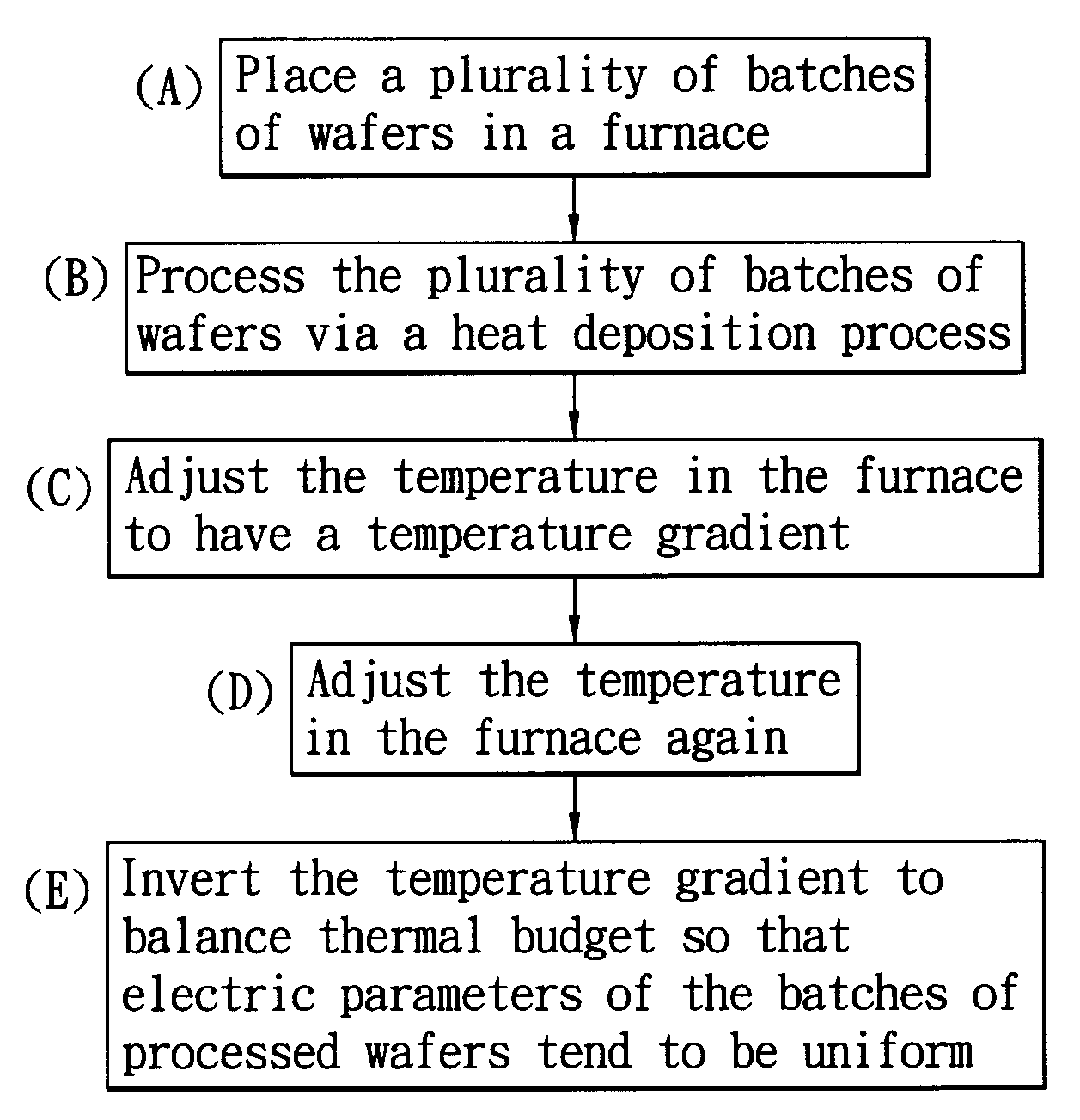
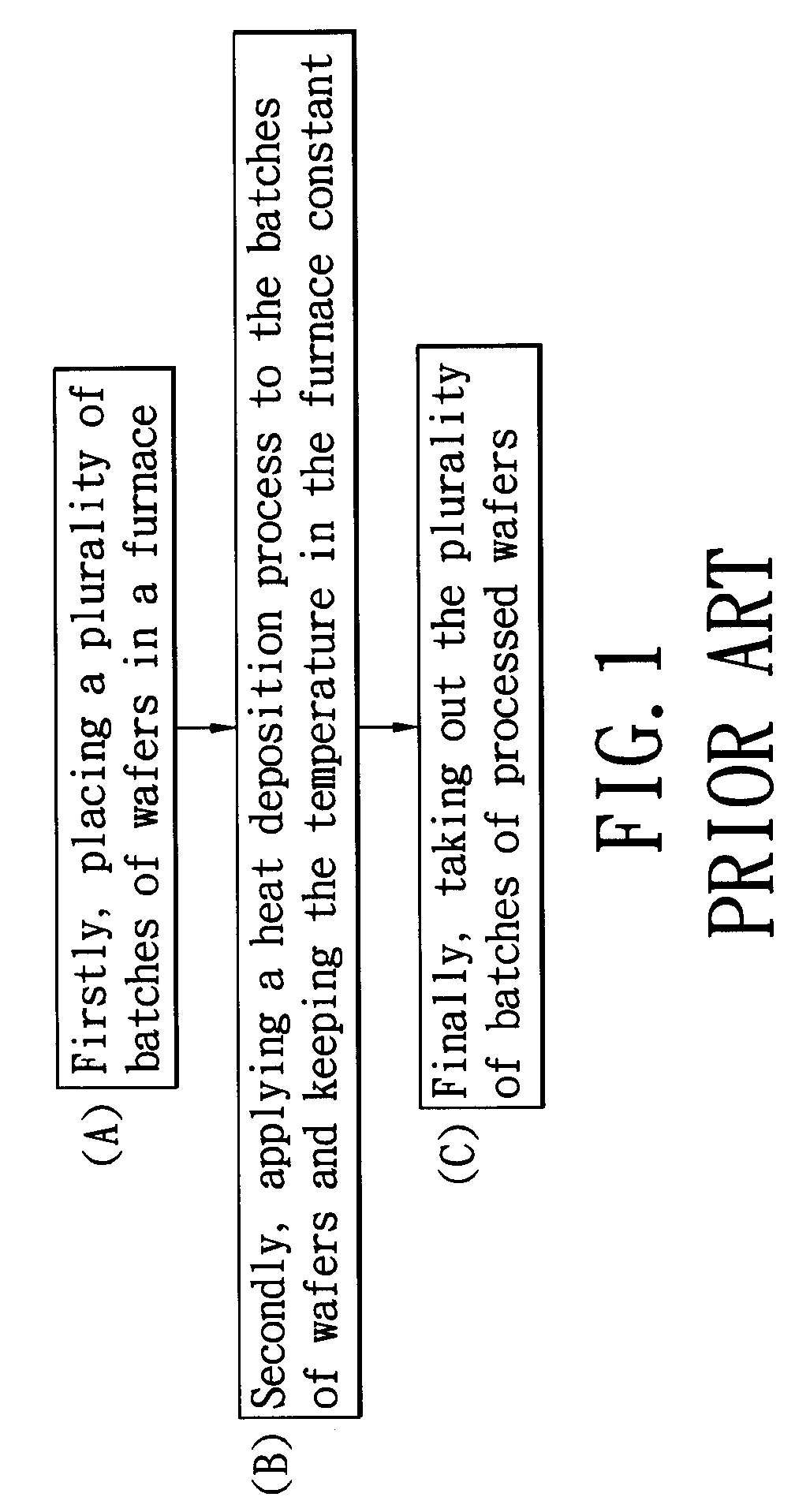
InactiveUS20100098855A1Low yieldSuppress mutationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingElectricityFurnace temperature
A furnace temperature control method for thermal budget balance includes the steps of: placing a plurality of batches of wafers in the furnace; processing the wafers in the furnace via a heat deposition process; adjusting temperature in the furnace during the heat deposition process so that the temperature in the furnace has a temperature gradient; and controlling and inverting the temperature gradient so that the wafers in the furnace have the same thermal budget, whereby the electric parameters of the processed wafers tend to become uniform. Accordingly, considering the influence of the thermal budget, the present invention adjusts the temperature in the furnace and balances the thermal budget of the wafers in the furnace to avoid that the electric parameters of the processed wafers have extreme values, thereby improving the yield rate.
Owner:INOTERA MEMORIES INC
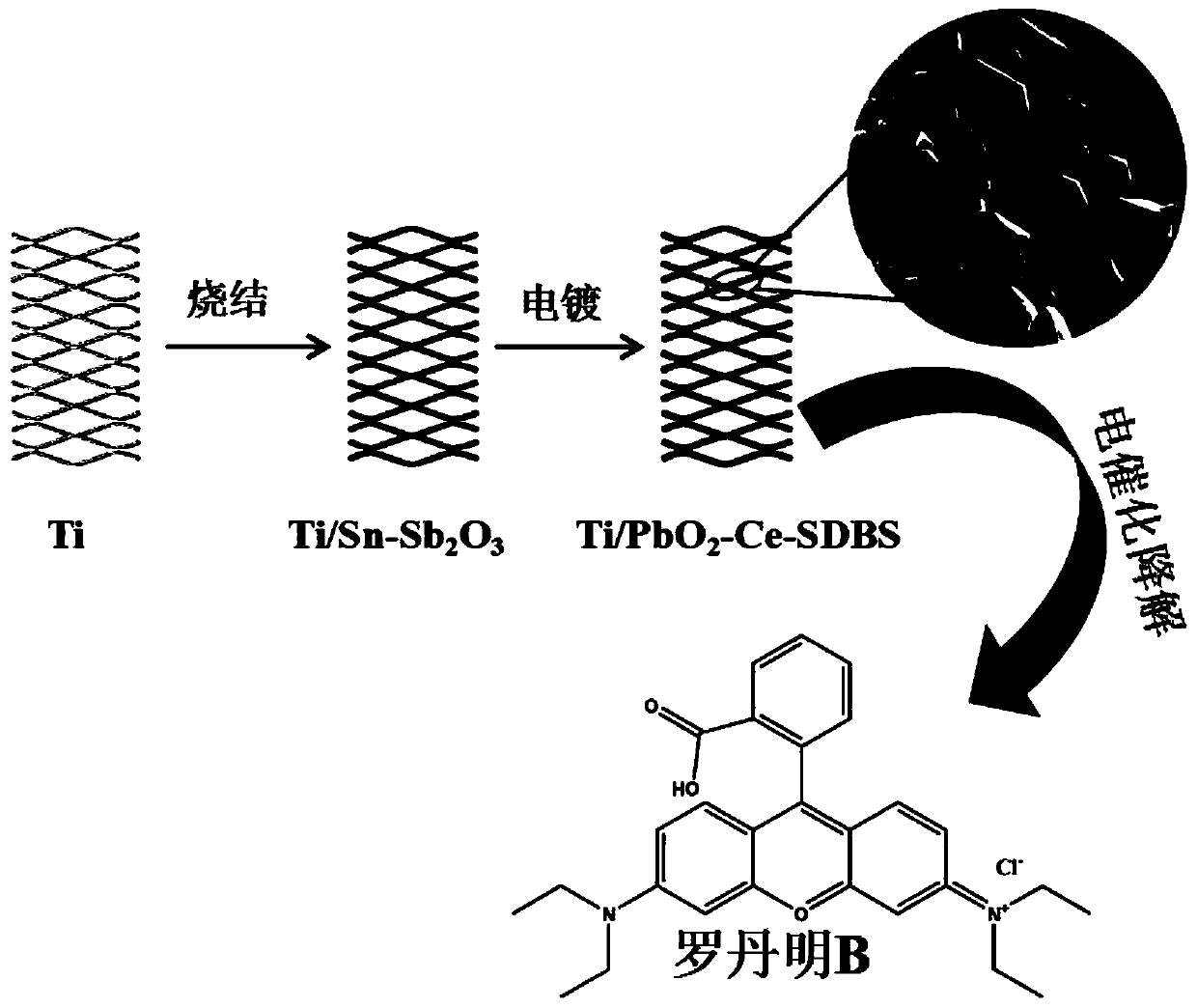
Titanium-based lead dioxide electrode for degrading rhodamine B, and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN110980890ASimplify the manufacturing processImprove production efficiencyWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processLead dioxideCatalytic oxidation
The invention belongs to the field of electrochemical catalytic oxidation water treatment, and relates to a titanium-based lead dioxide electrode for degrading rhodamine B, and a preparation method and application thereof. The electrode includes a titanium matrix, a tin-antimony oxide layer, and an active layer (co-doped with Ce and SDBS). The preparation method includes direct deposition of a PbO2 active layer on the titanium matrix thermally deposited with the tin-antimony oxide bottom layer, a step of preparing an alpha-PbO2 layer is cancelled and preparation of the titanium-based lead dioxide electrode is simplified, thus improving the preparation efficiency of the titanium-based lead dioxide electrode. As the step of preparing an alpha-PbO2 layer is cancelled, and process parameters requiring adjustment and control in the step are cancelled, thus facilitating improvement of the percent of pass of finished products, reducing the production cost and greatly improving high oxygen evolution potential, catalytic activity, and service lifetime of the titanium-based lead dioxide electrode.
Owner:XIAN TAIJIN NEW ENERGY & MATERIALS SCI TECH CO LTD
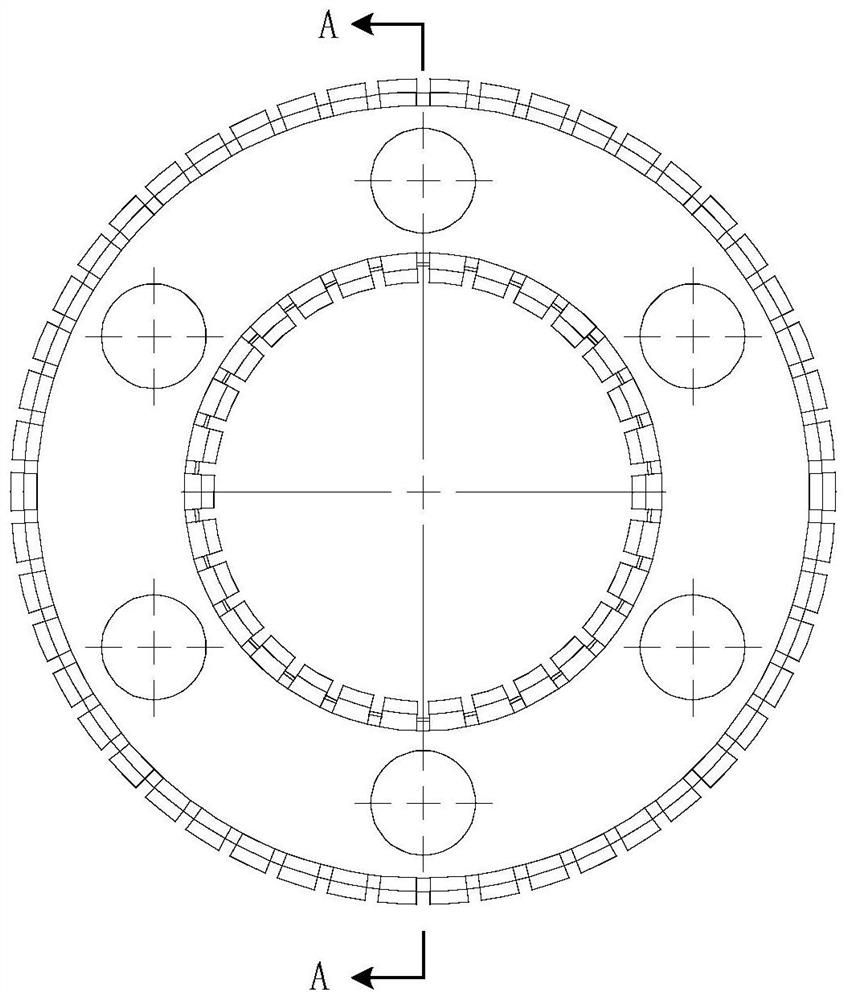
Superconductive proton cyclotron beam deflector
ActiveCN107333379ASimple structureImprove work performanceMagnetic resonance acceleratorsManufacturing cost reductionProton
The invention discloses a superconductive proton cyclotron beam deflector, which comprises a space formed by a grounding housing, a beam cutting board, an outer beam cutting board clamp ring and an inner beam cutting board clamp ring. The space is internally provided with a high-voltage electrode; and the high-voltage electrode is fixedly arranged to the grounding housing through an insulator. The thickness of the beam cutting board is 0.1-0.3 mm at a beam inlet end, the thickness of the middle portion of the beam cutting board changes continuously, and the thickness of the beam cutting board is 1-3 mm at a beam outlet end. A sine gap is designed on the beam cutting board; and the outer beam cutting board clamp ring is provided with a water cooling loop. The structure of the beam deflector in a superconductive proton cyclotron is optimized; and through design of the cutting board structure provided with a replaceable striking plate and the water cooling loop and capable of resisting beam heat deposition, work capability of the beam deflecting mechanism can be improved, meanwhile, processing difficulty of beam deflecting mechanism can be reduced and manufacture cost is reduced.
Owner:HEFEI CAS ION MEDICAL & TECHNICAL DEVICES CO LTD
Carbon nanotube modified lead dioxide electrode and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106809918ASimple processGood effectElectrolytic inorganic material coatingWater contaminantsLead dioxideCarbon nanotube
The invention provides a carbon nanotube modified lead dioxide electrode in an electrocatalytic oxidation process, and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method for the lead dioxide electrode comprises the following steps: preprocessing a titanium plate, and carrying out heat deposition on a tin-antimony oxide bottom layer, an electrolytic deposition alpha-PbO2 intermediate layer, an electrolytic deposition beta-PbO2 internal layer, an electrophoresis carbon nanotube interlayer and an electrolytic deposition beta-PbO2 surface layer. The carbon nanotube modified lead dioxide electrode prepared with the preparation method has the advantages of large specific surface area, high hydroxyl radical production ability, high electrocatalytic oxidation activity and long service life, and is an electrode material which has a development potential and is suitable for an electrocatalytic oxidation process.
Owner:JILIN NORMAL UNIV
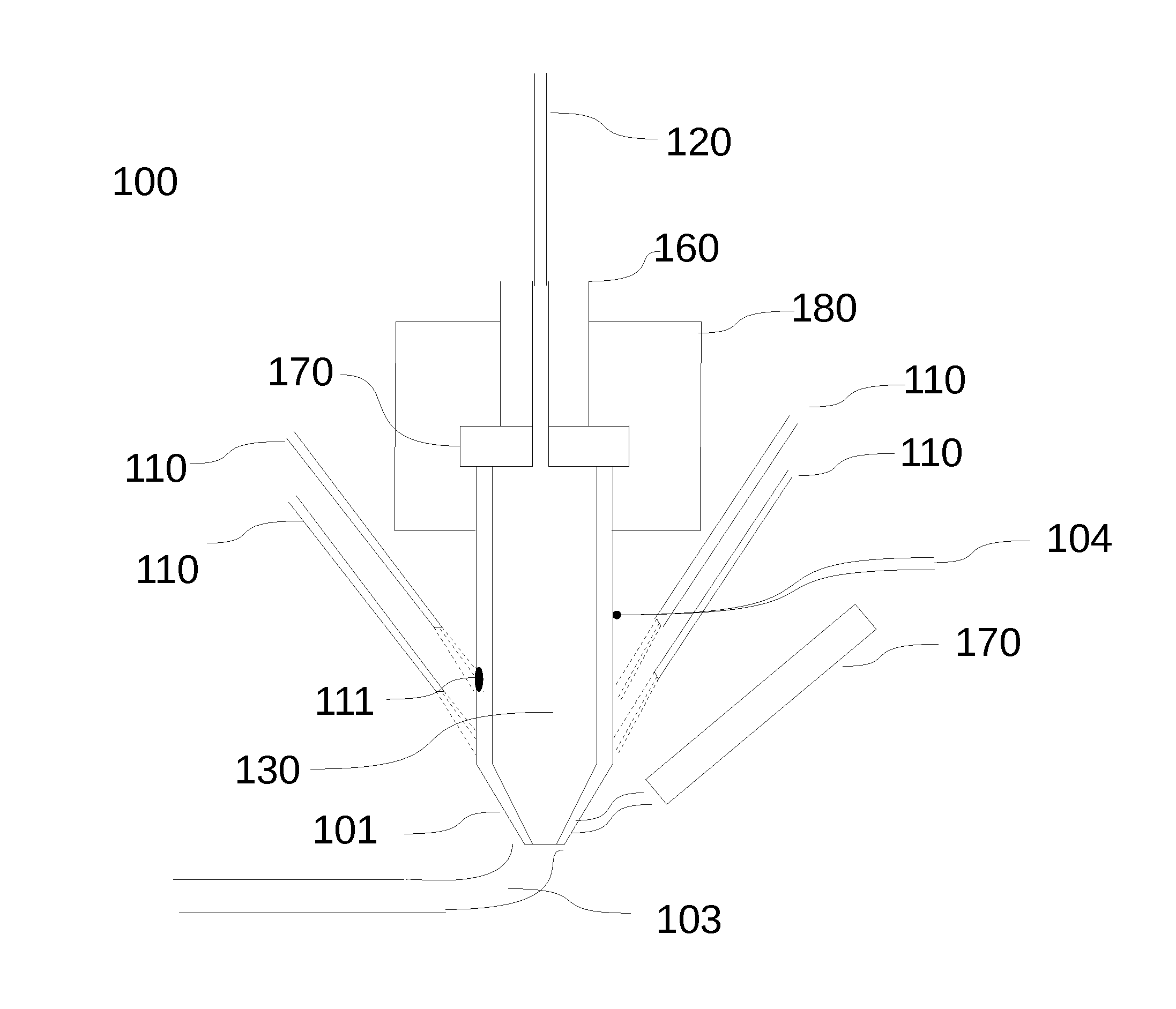
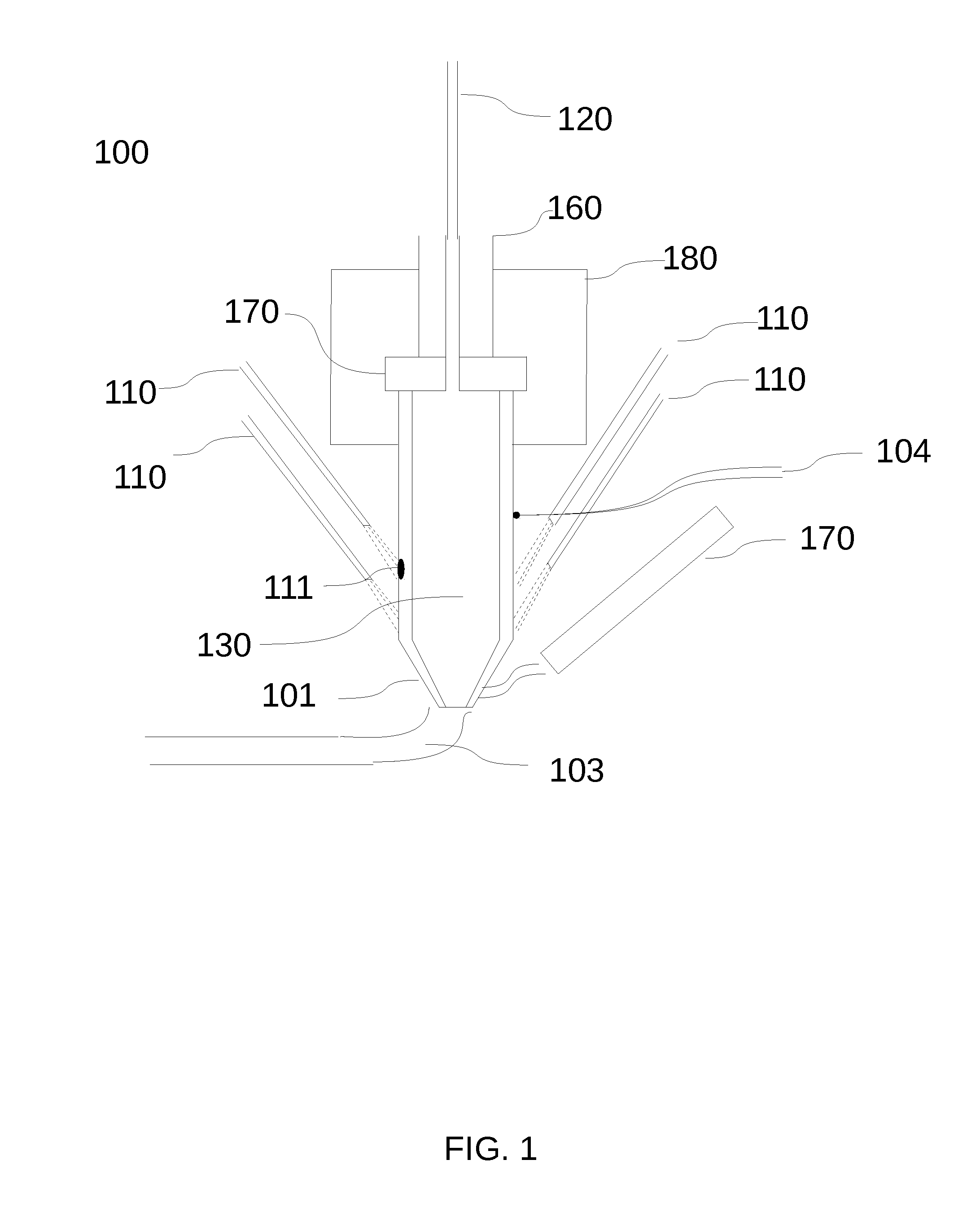
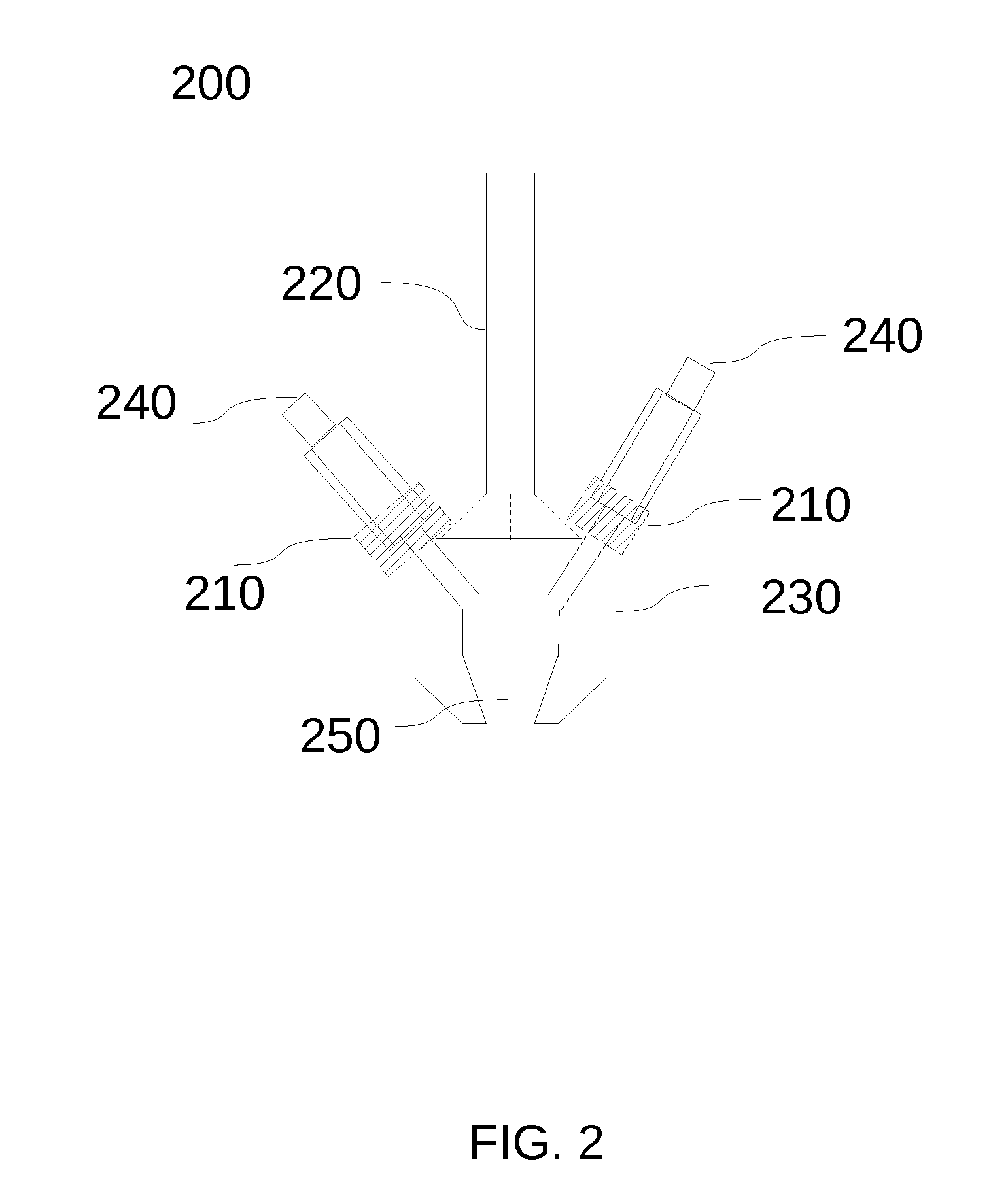
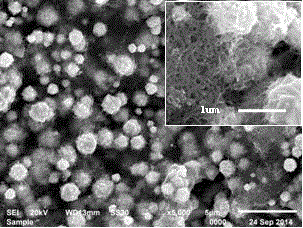
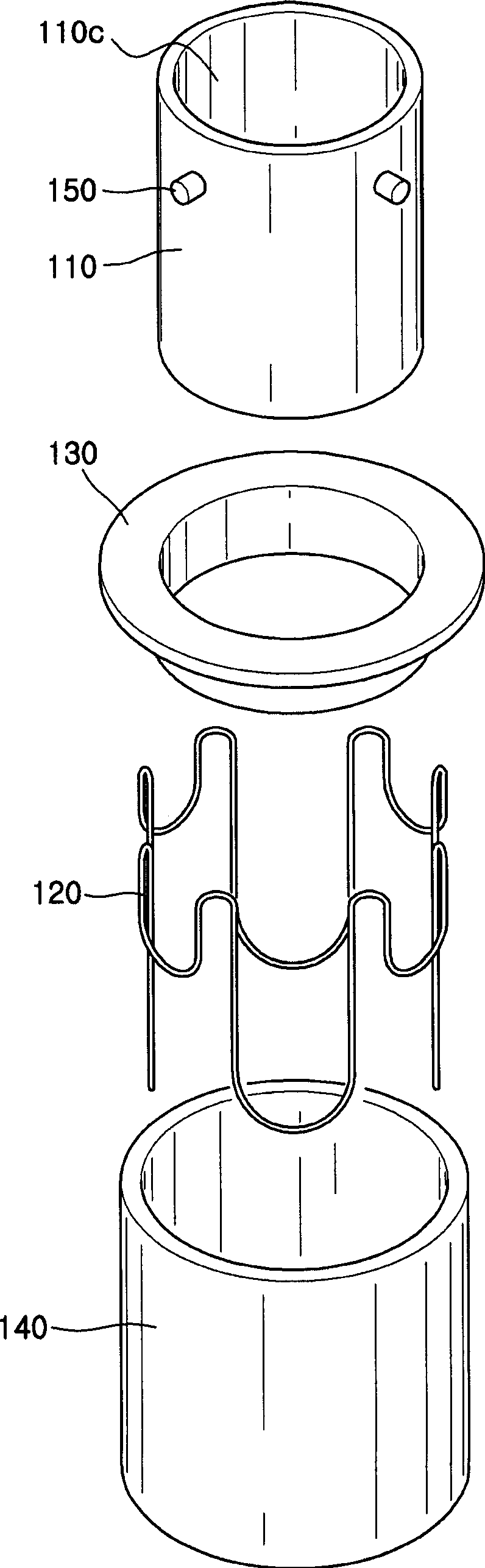
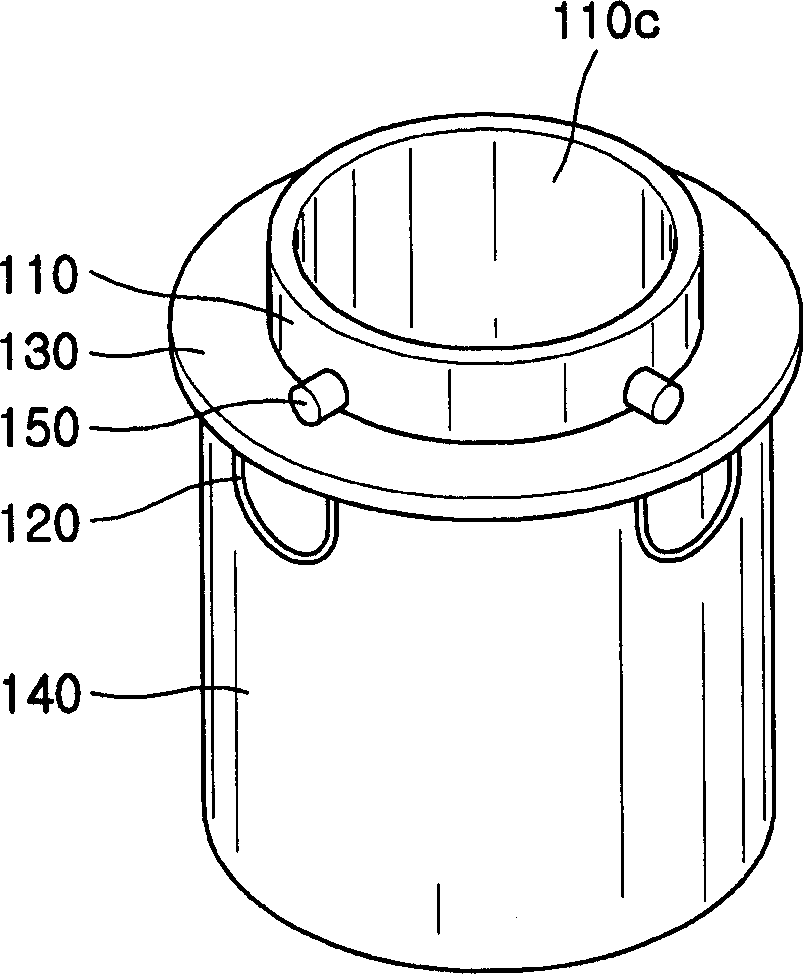
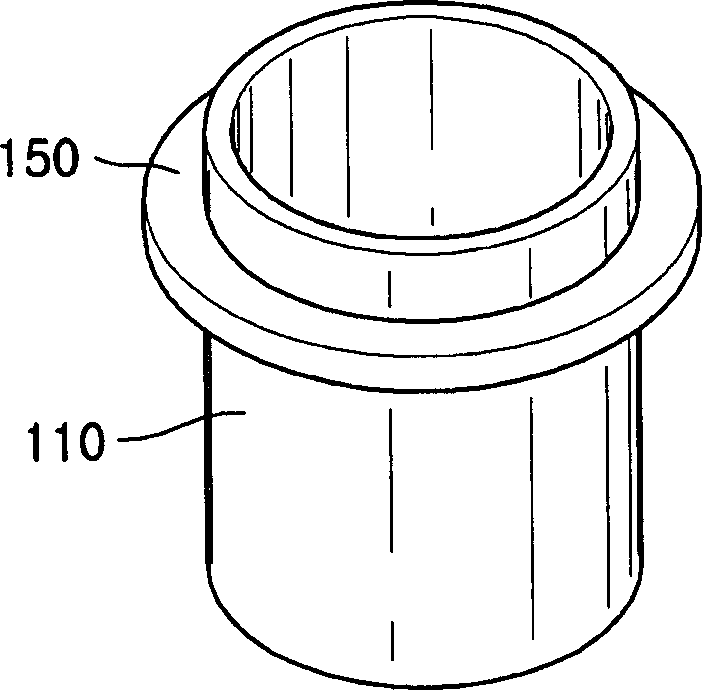
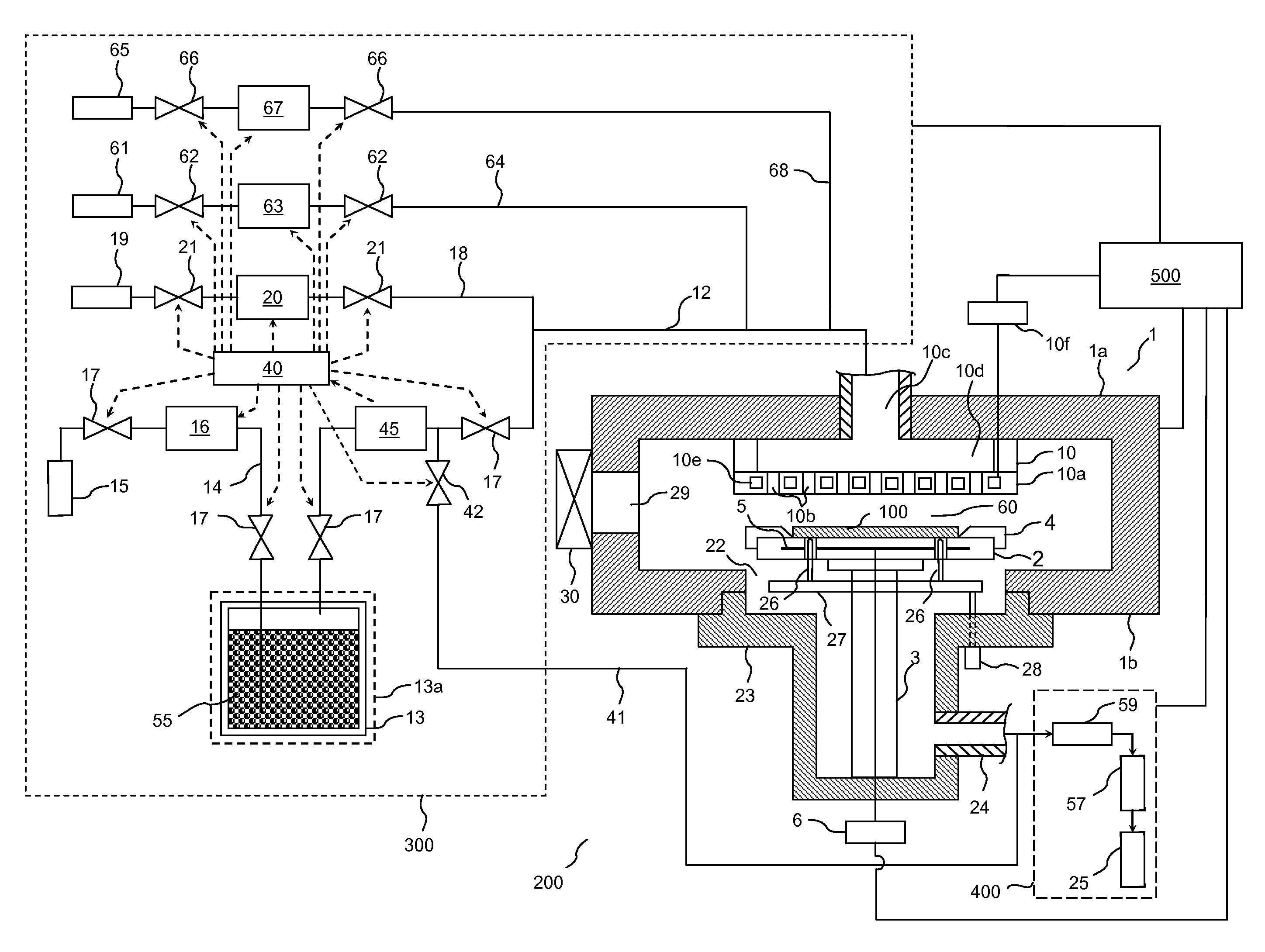
Heating crucible and deposition apparatus including the same
The invention provides a heating crucible and a deposition device. The heating crucible has uniform deposition rate and excellent repeatability. The heating crucible of the deposition device includes: a titanium body with an inner cavity and an opening, the inner cavity is used to accommodate the material to be deposited, and the opening is used to spray the material to be deposited; a wire is used to heat the main body; an insulator is used to Insulate the body from the wires.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Laser selective cutting by impulsive heat deposition in the ir wavelength range for direct-drive ablation
InactiveUS20120041428A1Material efficiencyImprove efficiencySurgical instrument detailsBoring toolsLaser processingThermal expansion
A method of laser processing of materials and specifically laser induced ablation processes for laser removal of material by impulsive heat deposition (IHD) by direct and specific excitation of short lived vibrations or phonons of the material in such a way as to not generate highly reactive and damaging ions through multiphoton absorption. The heat deposition and ensuing ablation is achieved faster than heat transfer to surrounding tissue by either acoustic or thermal expansion or thermal diffusion. The deposited laser energy is channeled into the ablation process to drive the most efficient ablation process possible with minimal damage to surrounding areas by either ionizing radiation or heat effects.
Owner:LIGHT MATTER INTERACTION INC
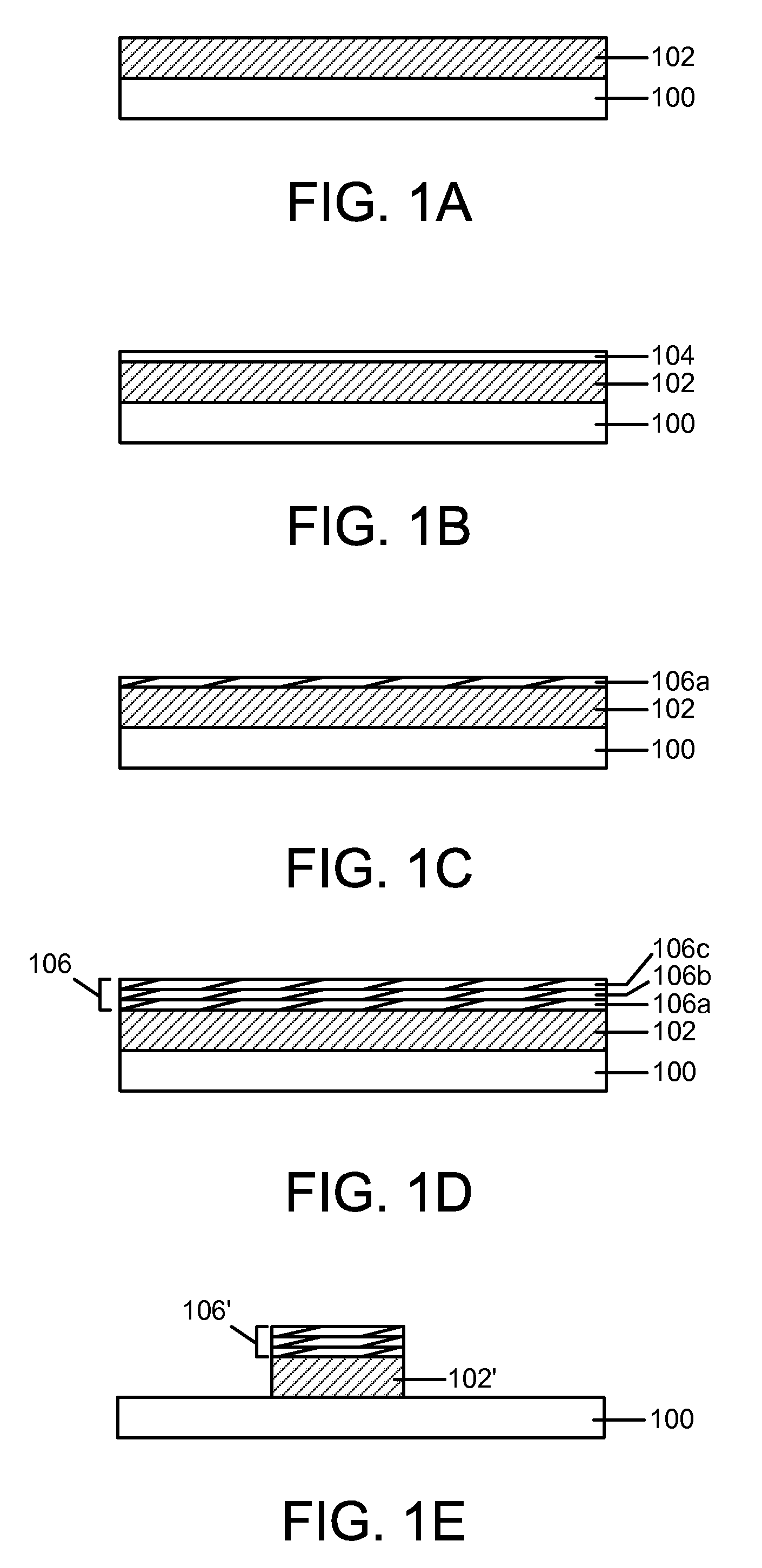
Sequential flow deposition of a tungsten silicide gate electrode film
InactiveUS20090087550A1Preventing or causing only small increases in the EOT of the gate stacks during processingSpecial surfacesChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon filmDevice material
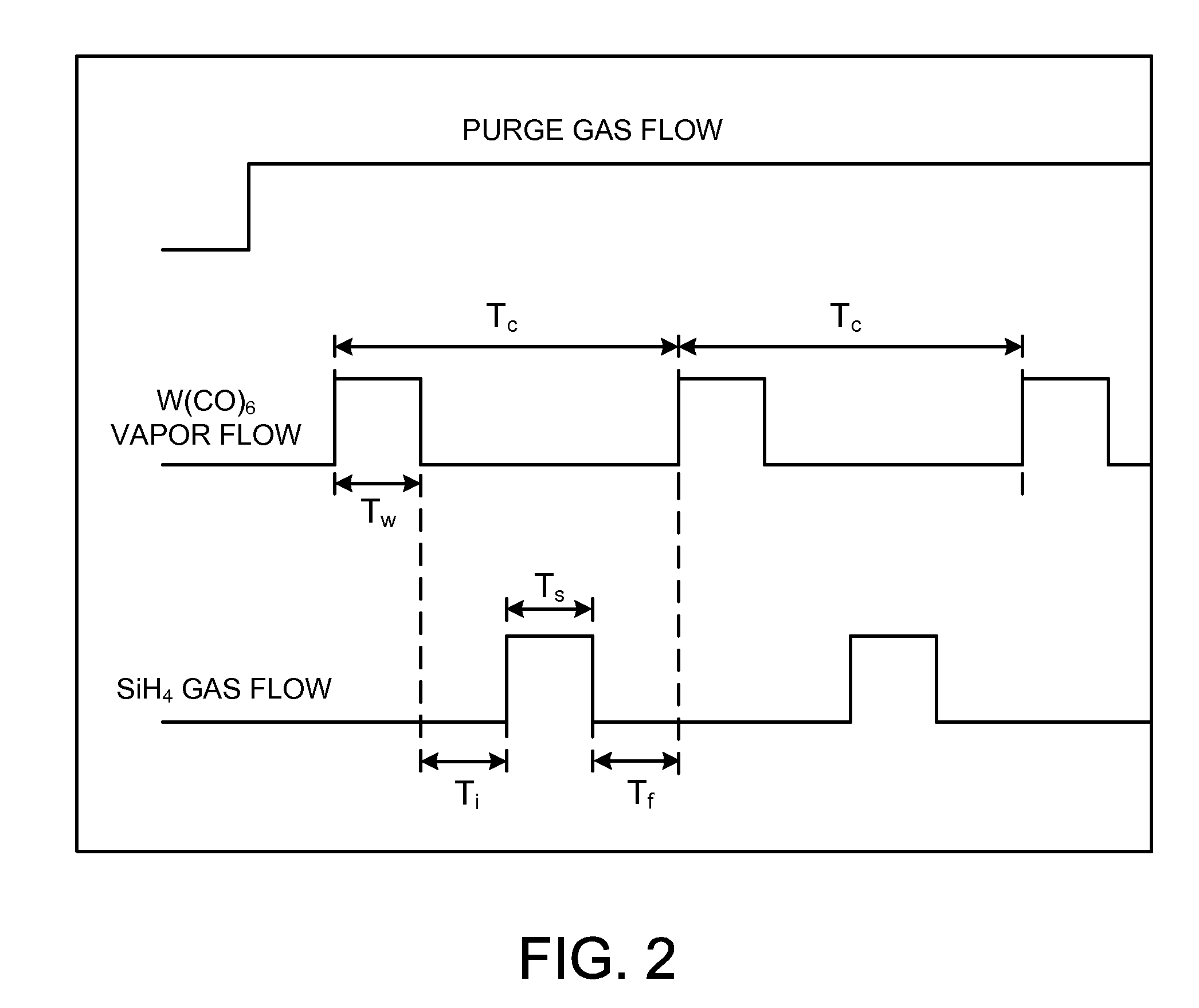
A method is provided for forming WSix gate electrode films with tunable Si / W atomic ratios, low oxygen and carbon film impurities, and work functions suitable for advanced semiconductor devices. The method includes providing a substrate containing a high-k film in a process chamber, maintaining the substrate at a temperature between 450° C. and 550° C., and performing a plurality of deposition cycles to form a WSix gate electrode film on the high-k film. According to embodiments of the invention, each deposition cycle includes exposing the substrate to a first process gas containing W(CO)6 vapor to thermally deposit a W metal film with a thickness between 0.1 nm and less than 2 nm, and exposing the W metal film to a second process gas containing SiH4 to form a WSix film having a Si / W atomic ratio controlled by self-limited Si incorporation into the W metal film. The method further includes patterning the WSix gate electrode film and high-k film to form a gate stack.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
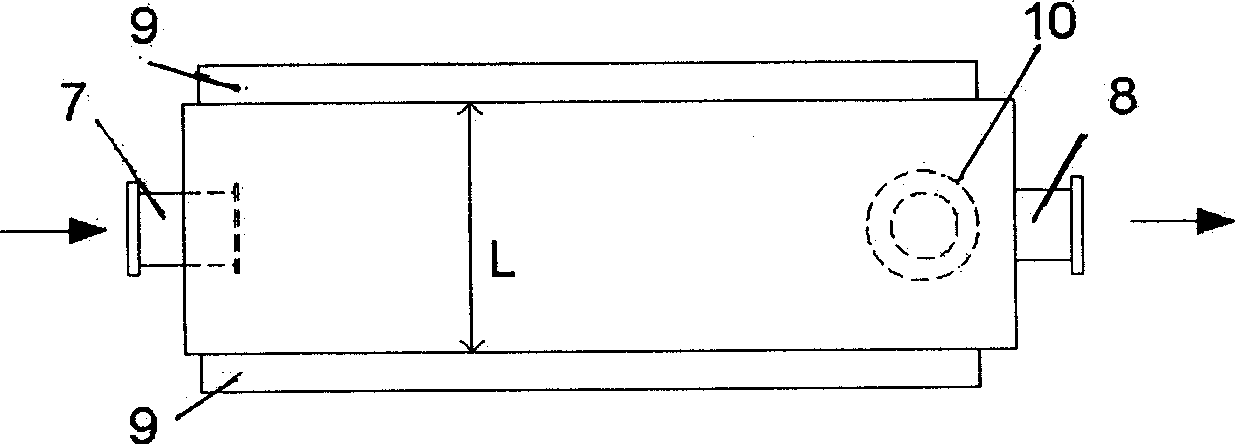
Automobile emission inhalable particulate matter removing device
InactiveCN1632294AImproved thermophoretic effectImproved thermophoretic deposition efficiency due to thermophoretic effectExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusFully developedHeat deposition
The utility model relates to a device for removing inhalable particles of automobile tail gas, which belongs to a device for removing ultrafine particles in the car tail gas. The device is composed of a group of parallel arranged thermophoresis working sections and upper and lower cascade boxes; The inlet and outlet of the thermophoresis working section are connected. The cold air outside the car is used to cool the pipe wall of the thermophoresis working section, and the inhalable particles contained in the exhaust gas will be deposited on the inner wall of the thermophoresis working section pipe due to the thermophoresis effect caused by the temperature difference. The invention utilizes the non-fully developed flow effect, and under the action of the thermophoretic effect, the thermophoretic deposition efficiency is continuously advanced in each link, and finally achieves a higher total deposition efficiency, and has the advantages of low construction and operation costs, convenient implementation, and controllability. The advantage of simplicity; efficient removal of inhalable particulate matter can be achieved under different installation conditions.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Hall thruster heat conduction support and Hall thruster comprising same
ActiveCN112483341AFast heat conductionReduce depositionMachines/enginesUsing plasmaPhysicsHeat deposition
The invention discloses a Hall thruster heat conduction support and a Hall thruster comprising the same, and relates to a heat dissipation structure of the Hall thruster. The invention aims to solve the problem of low heat stability of an existing high-specific-impulse high-power Hall thruster. The Hall thruster heat conduction support comprises two cylinders which are the same in length and are coaxially nested inside and outside, wherein the same ends of the two cylinders are connected through a bottom plate; a plurality of through holes are formed in the bottom plate; a plurality of gaps with one ends open and the other ends closed are formed in the cylinder walls of the two cylinders; the plurality of gaps are evenly distributed in the circumferential direction of the cylinder; the trend of the gaps is the same as the axial direction of the cylinders; and the open ends of the gaps are communicated with the open ends of the cylinders. According to the Hall thruster heat conduction support, most wall surface deposition heat flow is conducted to an external member with high heat dissipation capacity of the Hall thruster, so that heat deposition of an internal magnetic circuit of the Hall thruster is reduced, the overall heat dissipation capacity of the Hall thruster is enhanced, and finally the overall heat stability of the Hall thruster is improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +1
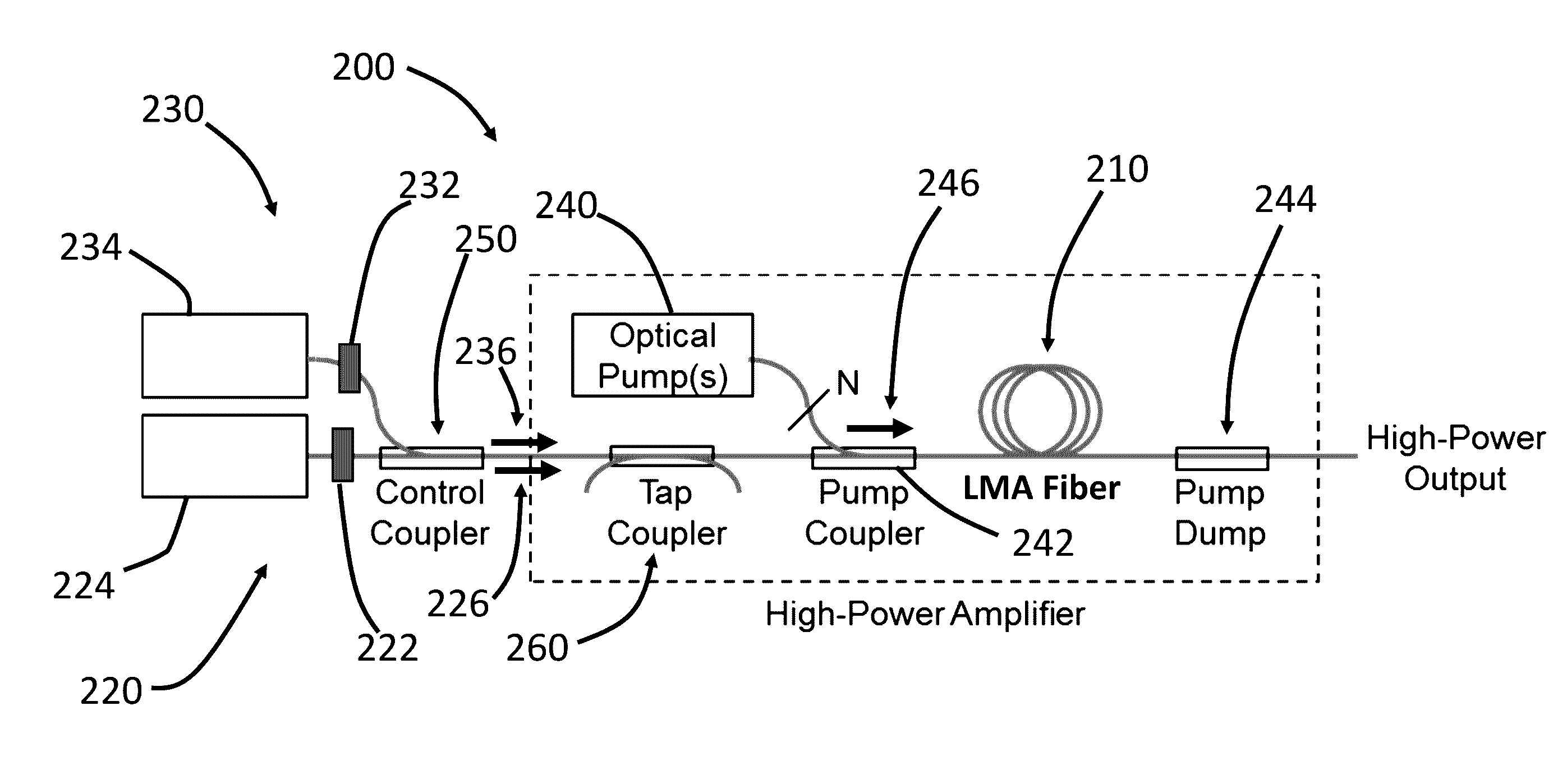
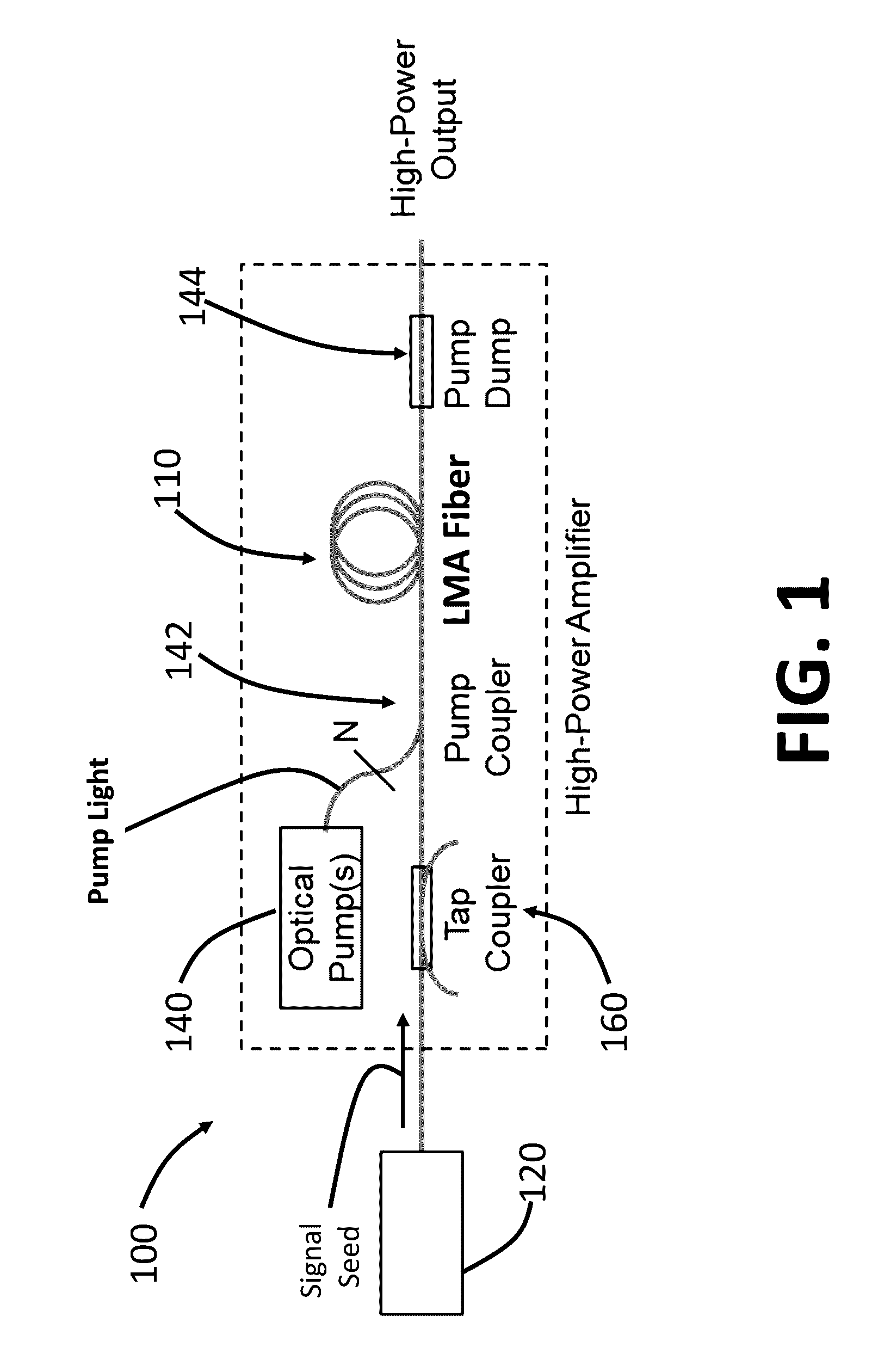
Systems and methods for light amplification
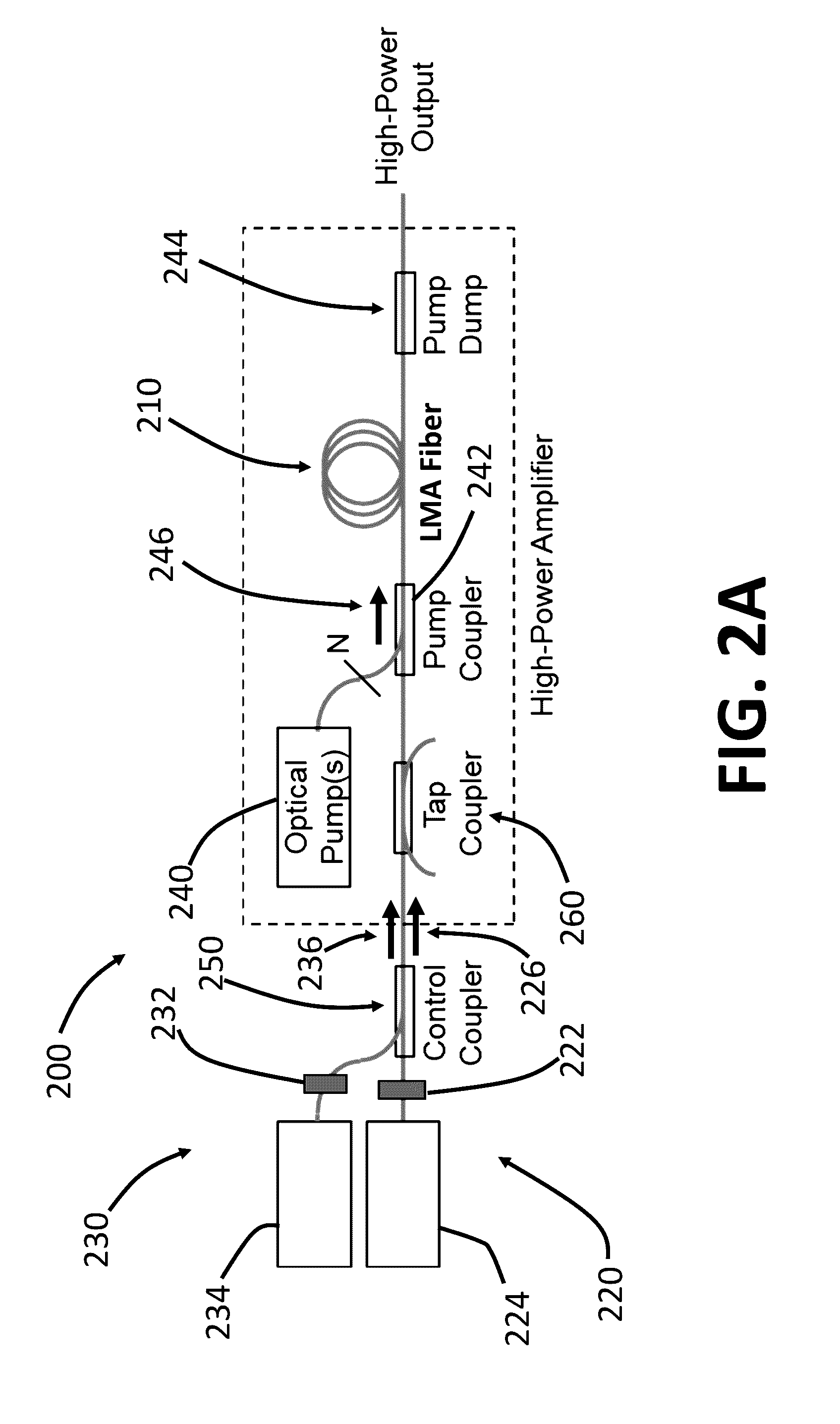
ActiveUS9515451B2Reduce rateMitigate multimode instabilityOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialFiberHeat deposition
A system for optical amplification includes an optical fiber with a core containing a gain medium surrounded by a cladding, a seed light source, a control light source, and a pump source. The seed light source transmits seed light, at a first wavelength and having a first linewidth greater than 100 MHz, into the core of the fiber. The control light source transmits control light, at a second wavelength shorter than the first wavelength, into the core where it interacts with the pumped gain medium so as to reduce the peak rate of heat deposition per unit length along the fiber. The control light has a second linewidth greater than 100 MHz. The pump source transmits pump light at a pump wavelength, shorter than the second wavelength, into the fiber so as to pump the gain medium and amplify the seed light.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Optical fiber device and manufacturing method and application thereof
InactiveCN104242027AHeat dissipation fastSuitable for a wide temperature rangeActive medium shape and constructionLaser cooling arrangementsHeat depositionLaser source
The invention provides an optical fiber device and a manufacturing method and application of the optical fiber device. Inorganic heat superconducting materials are packaged in the optical fiber device and closed space in any shape of an optical component in the optical fiber device, and heat deposition of a fiber laser and key devices and modules in the fiber laser can be removed fast and effectively. The sealing space in different shapes can be used under multiple conditions, the method is simple, manufacturing is easy, and fast heat radiation can be achieved easily. Through the method, the stability of the optical fiber device can be improved, and the service life of a laser source can be prolonged.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Method of manufacturing organic light-emitting device and organic light-emitting device manufactured using the method
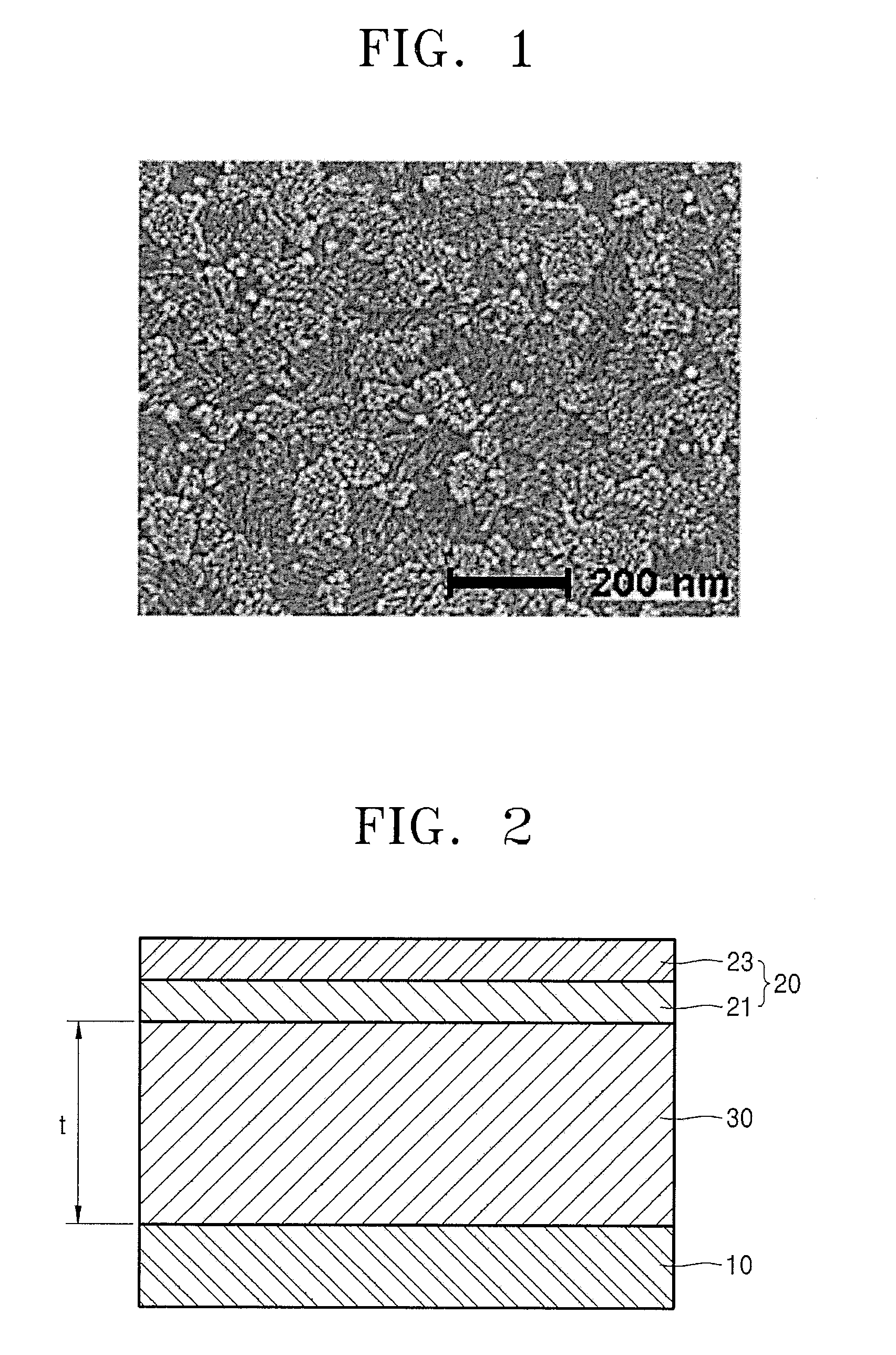
InactiveUS20080254306A1High light coupling efficiencyReduce the ratioMolten spray coatingElectroluminescent light sourcesIndiumOrganic light emitting device
Provided is a method of manufacturing an organic light-emitting device, the method including: forming an anode; forming an intermediate layer including an emission layer on the anode; and forming a cathode on the intermediate layer, wherein the forming the cathode includes: thermally depositing indium oxide with plasma generated in a chamber; and surface-treating with plasma an indium oxide layer formed by the thermal depositing of the indium oxide.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com