Patents
Literature
2698results about "Water/sewage treatment by electrochemical methods" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
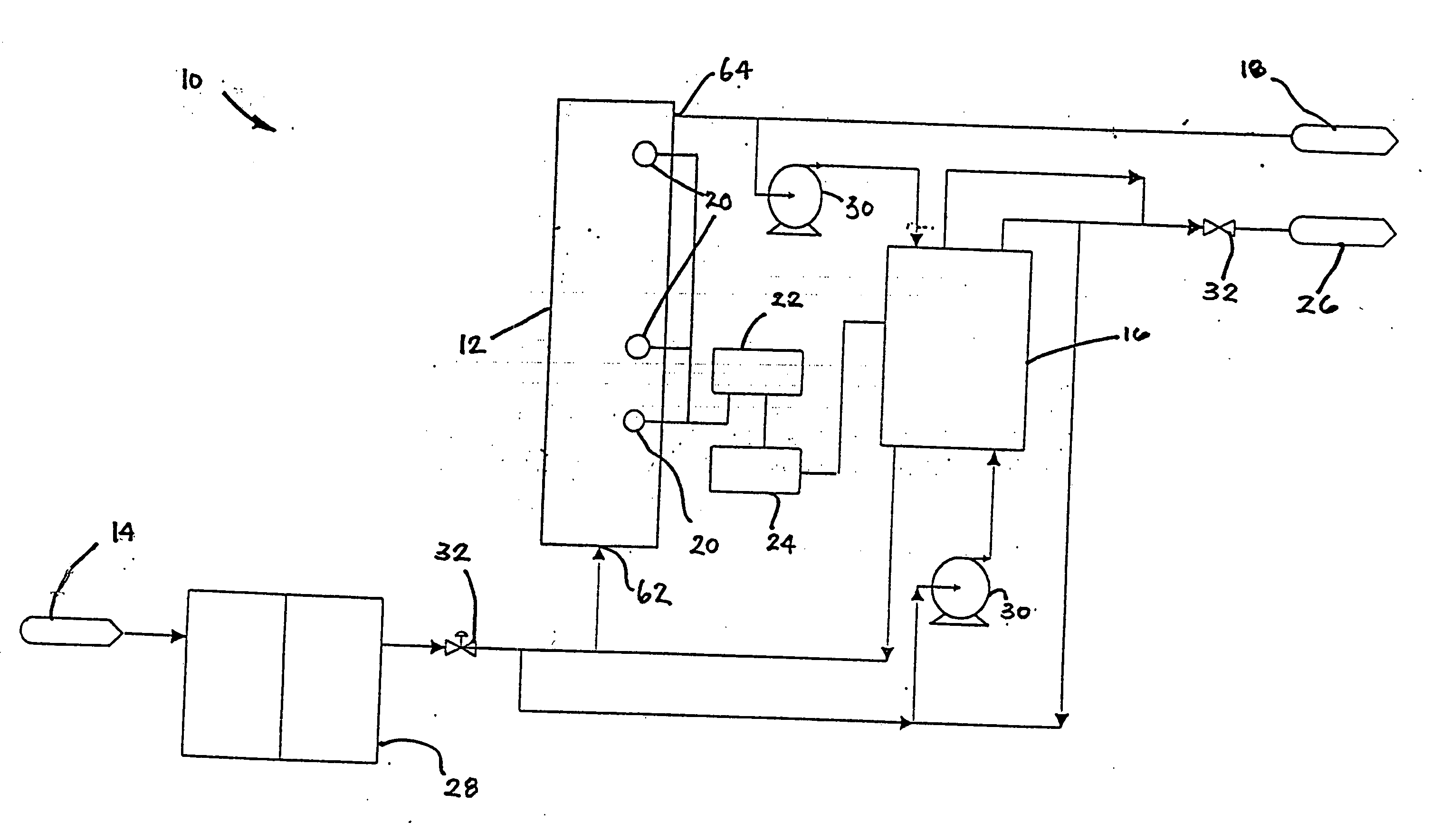
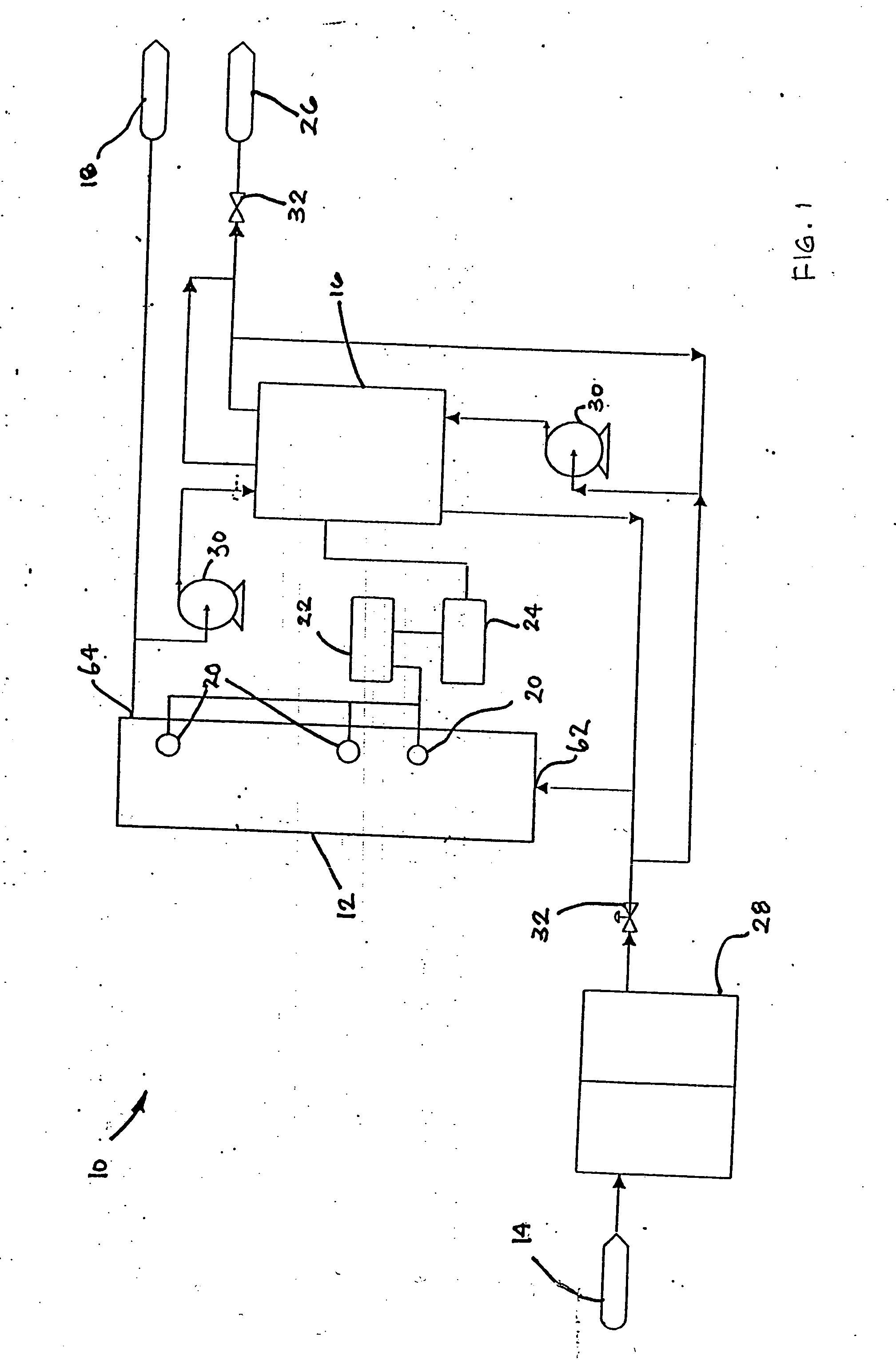
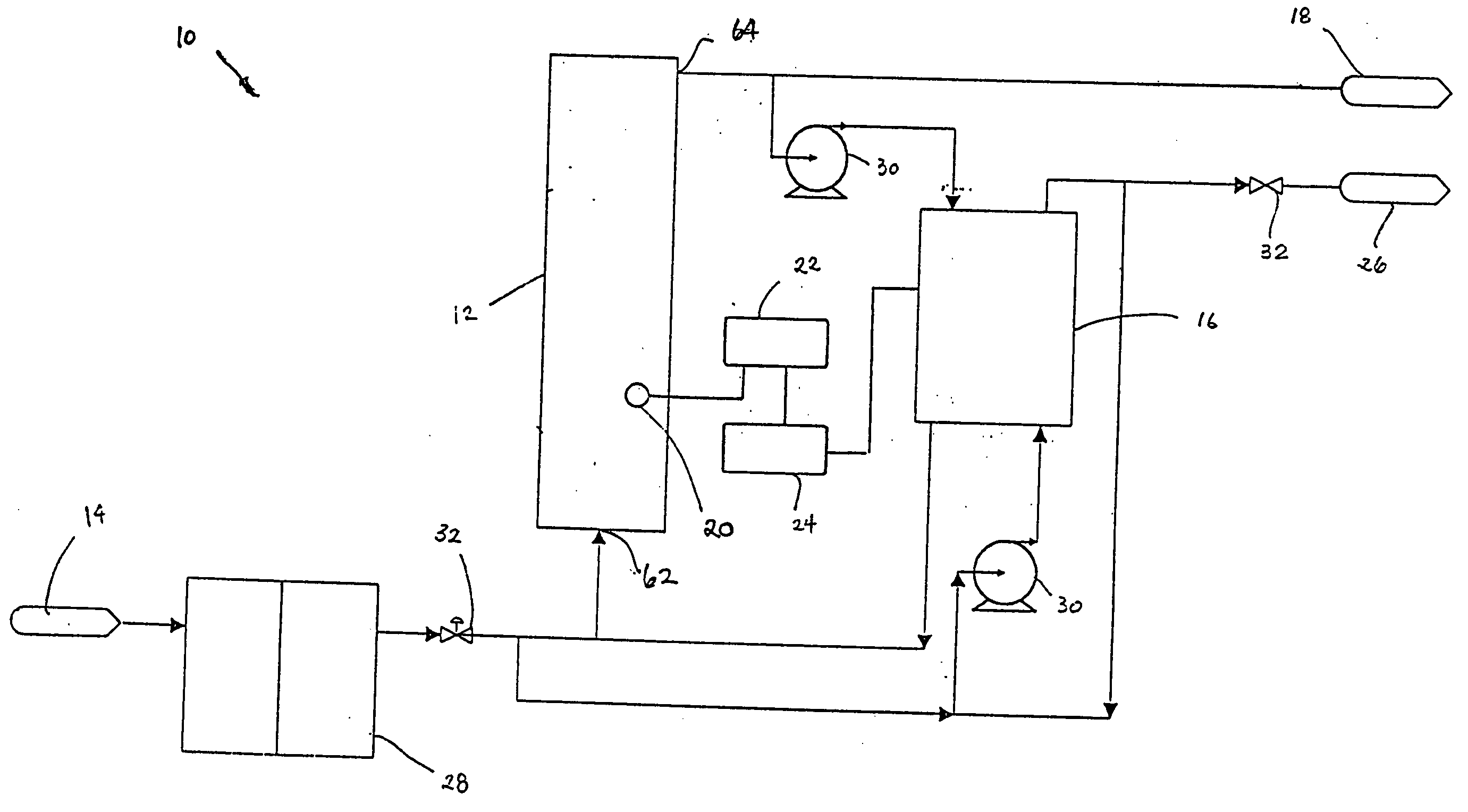
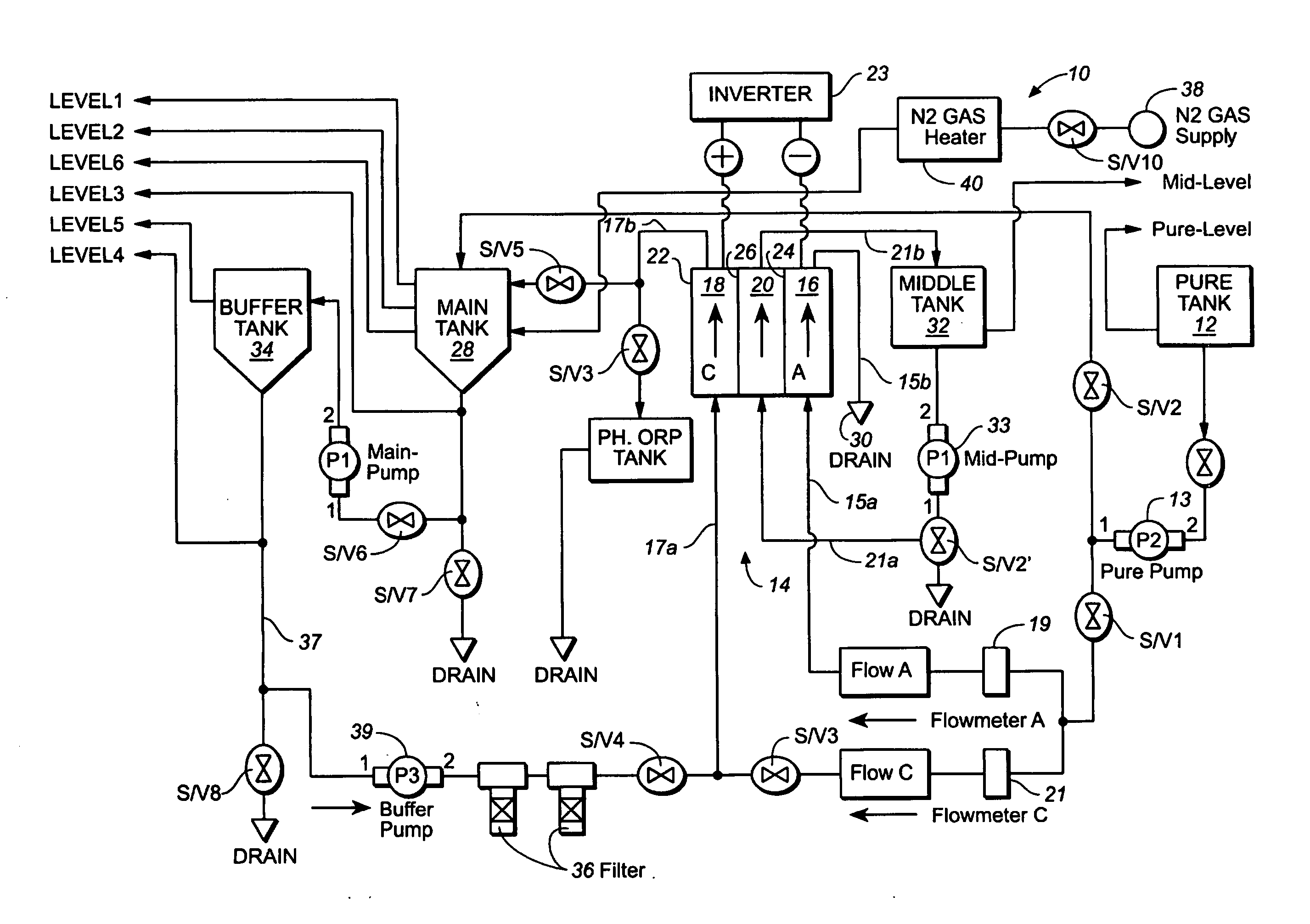
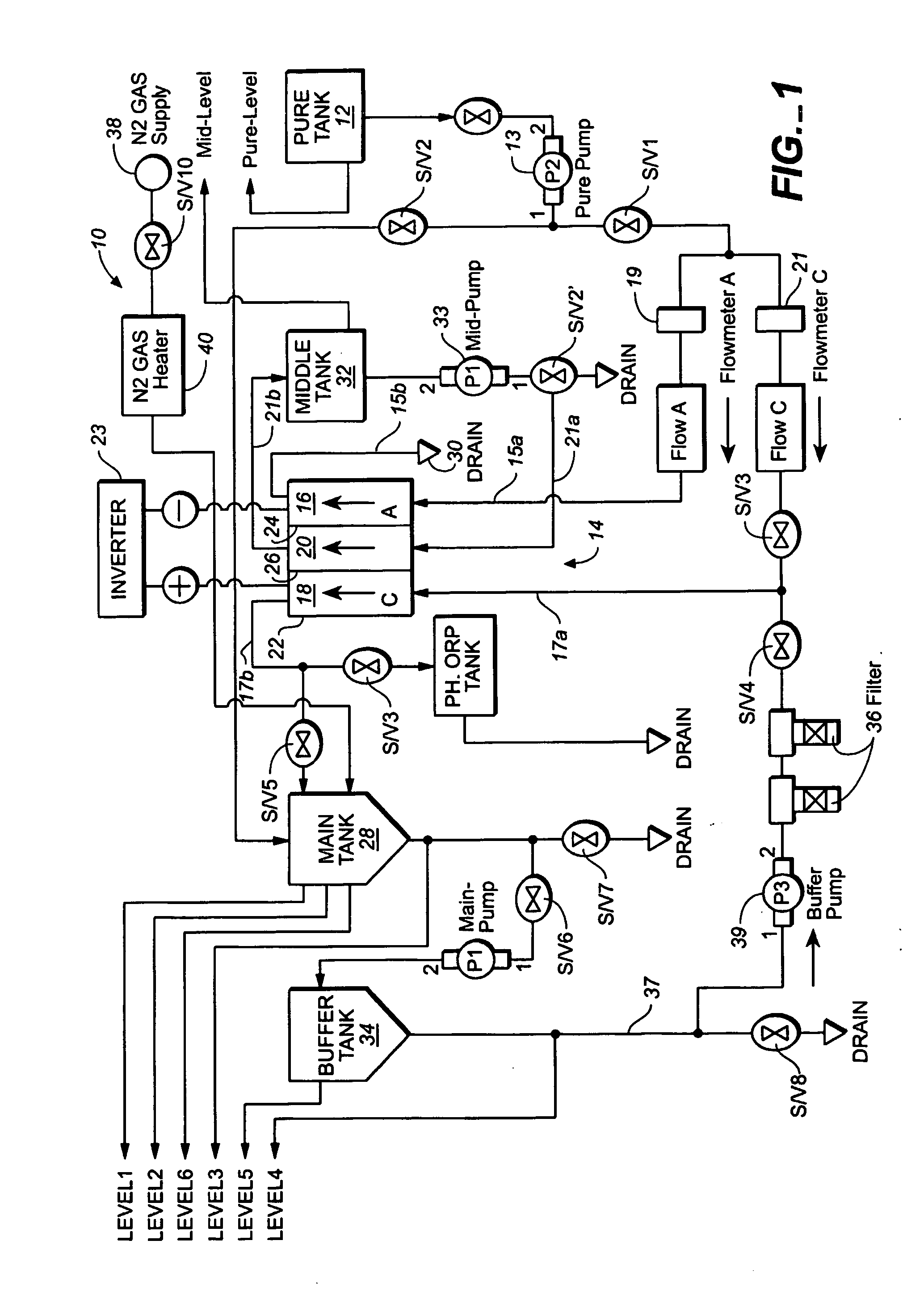
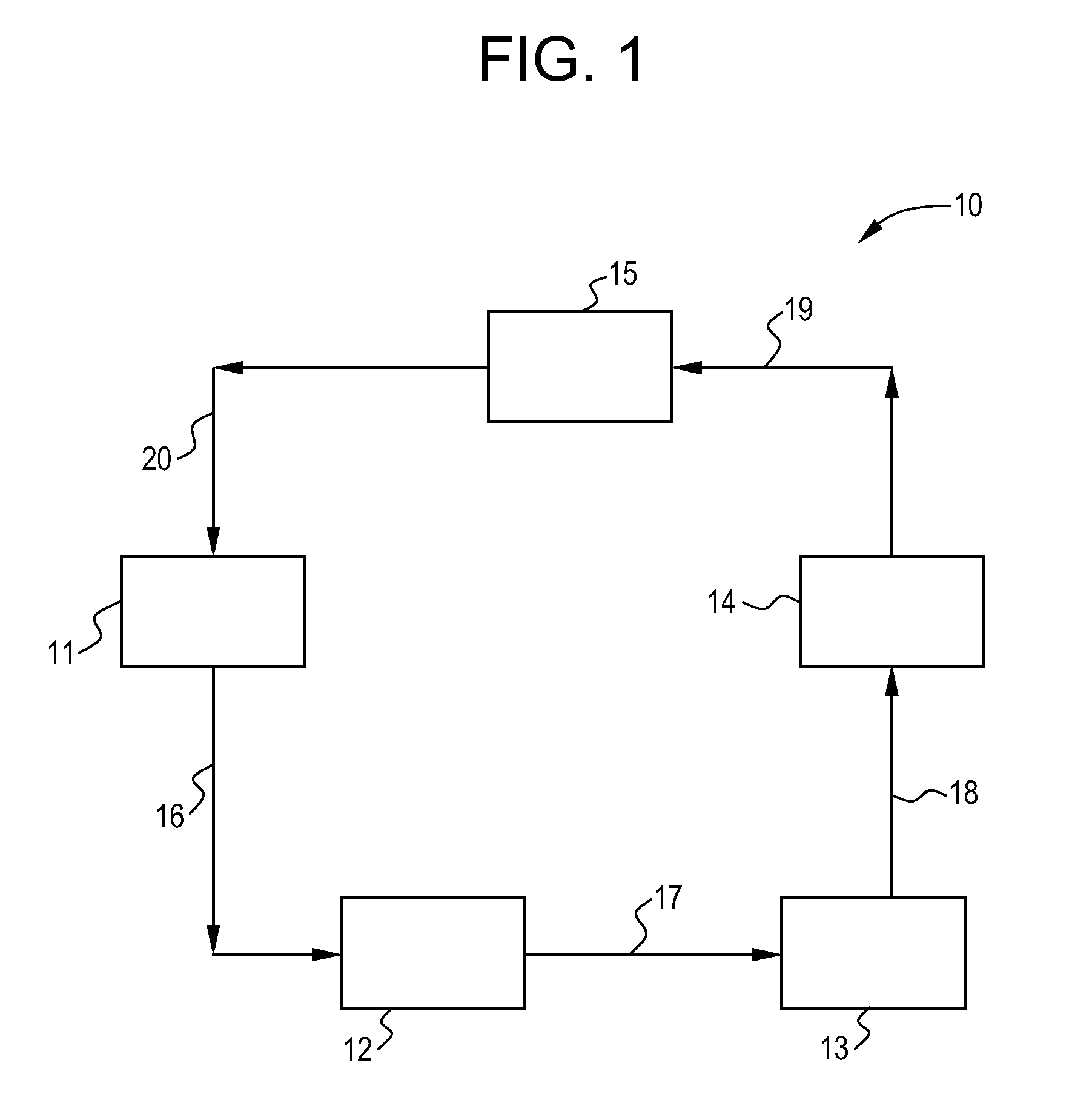
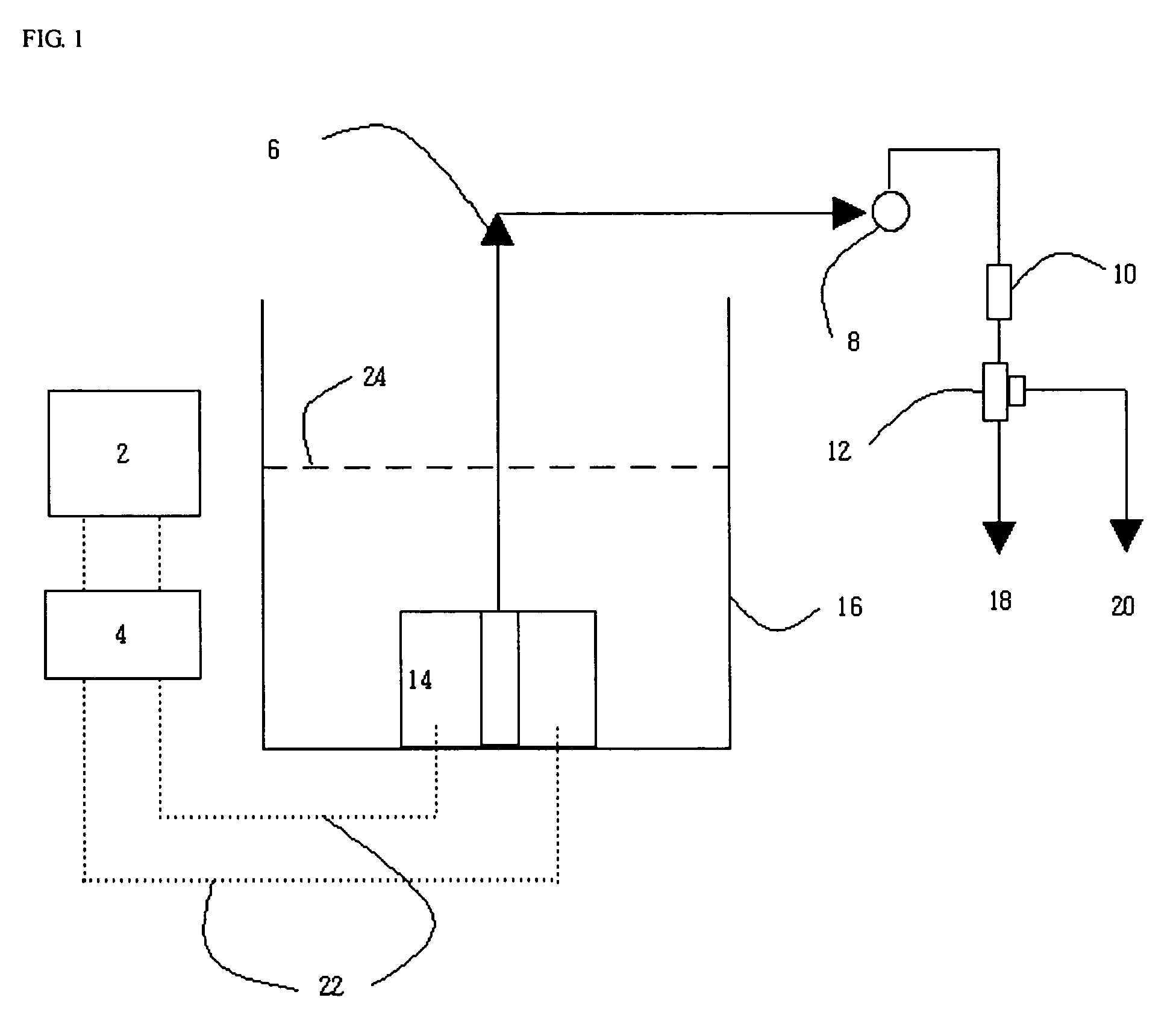
Water treatment system and method
ActiveUS20050103722A1Water treatment parameter controlIon-exchange column/bed processesWater treatment systemWater source
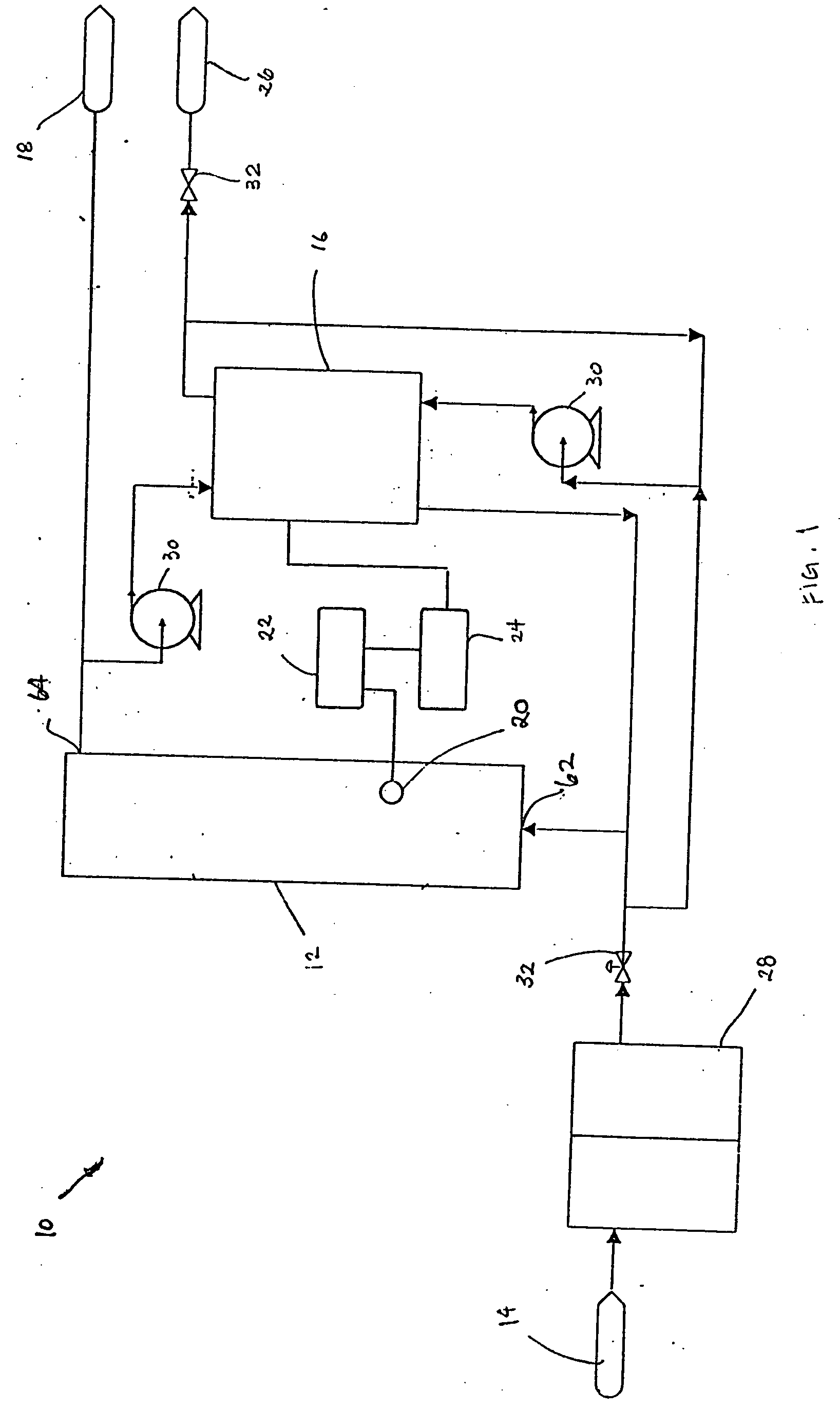
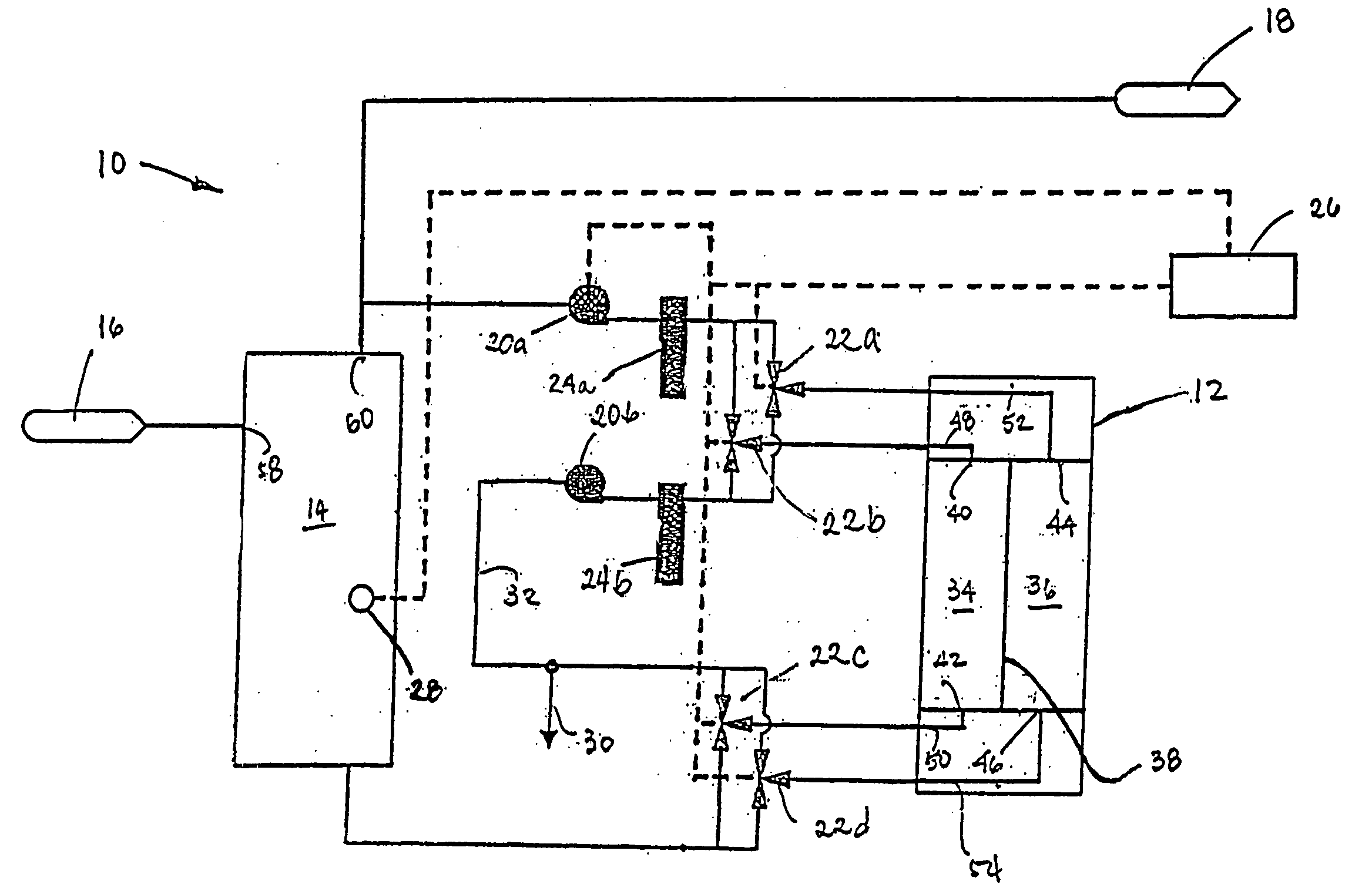
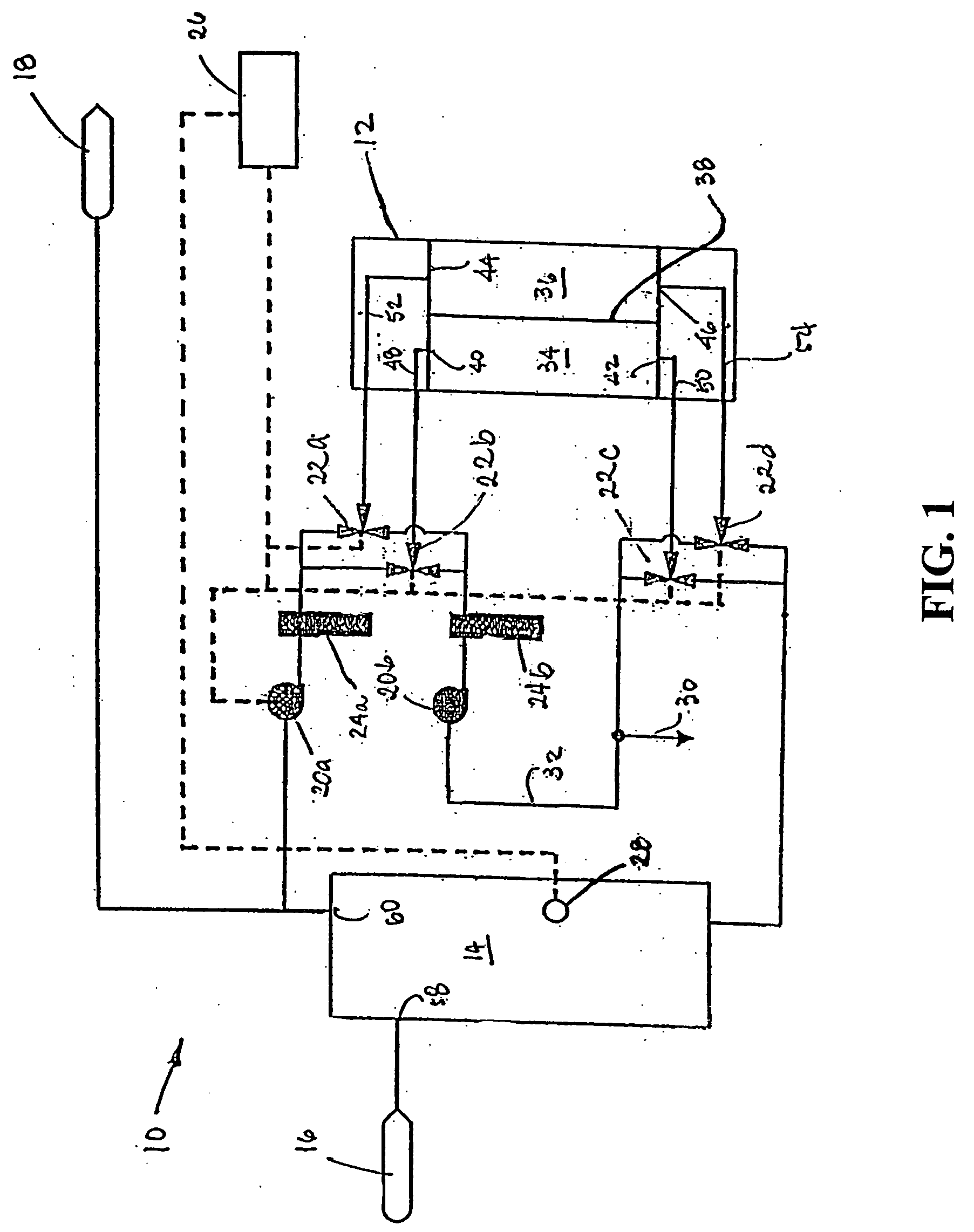
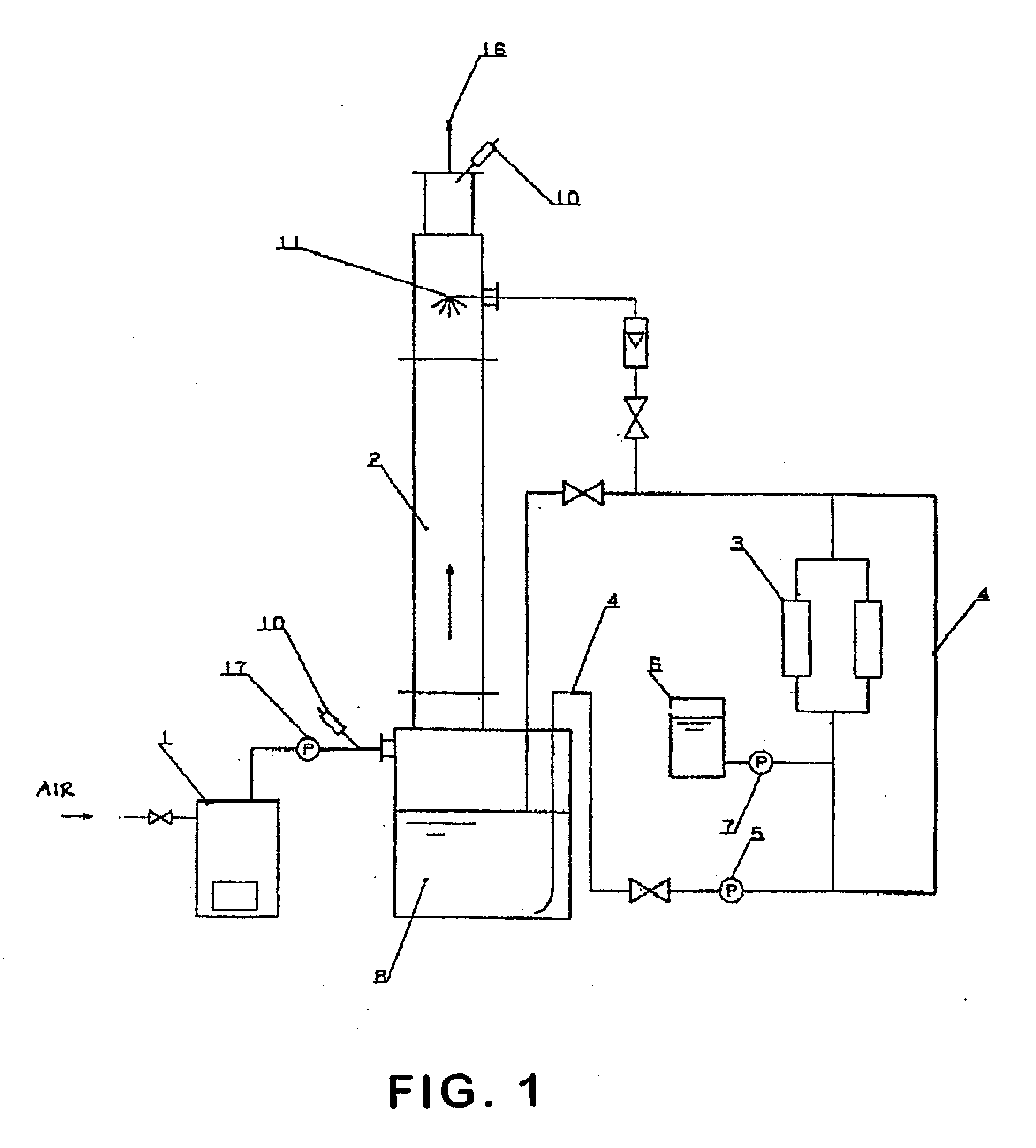
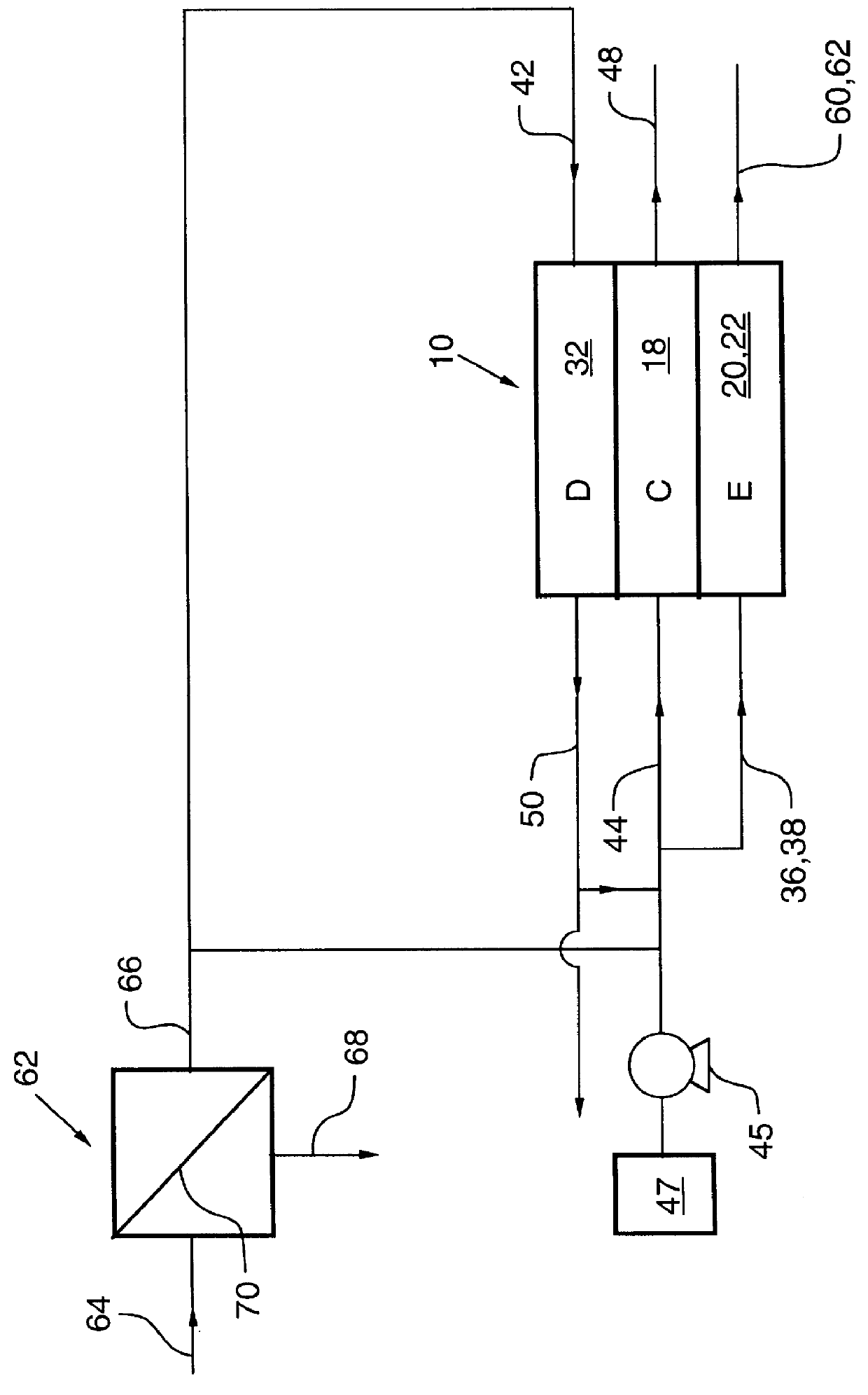
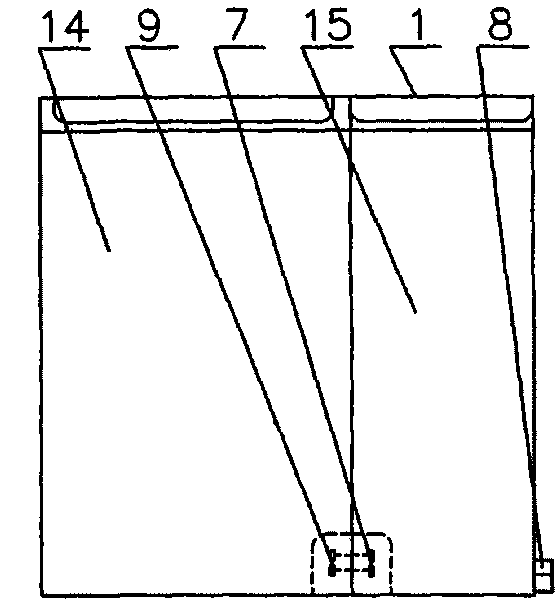
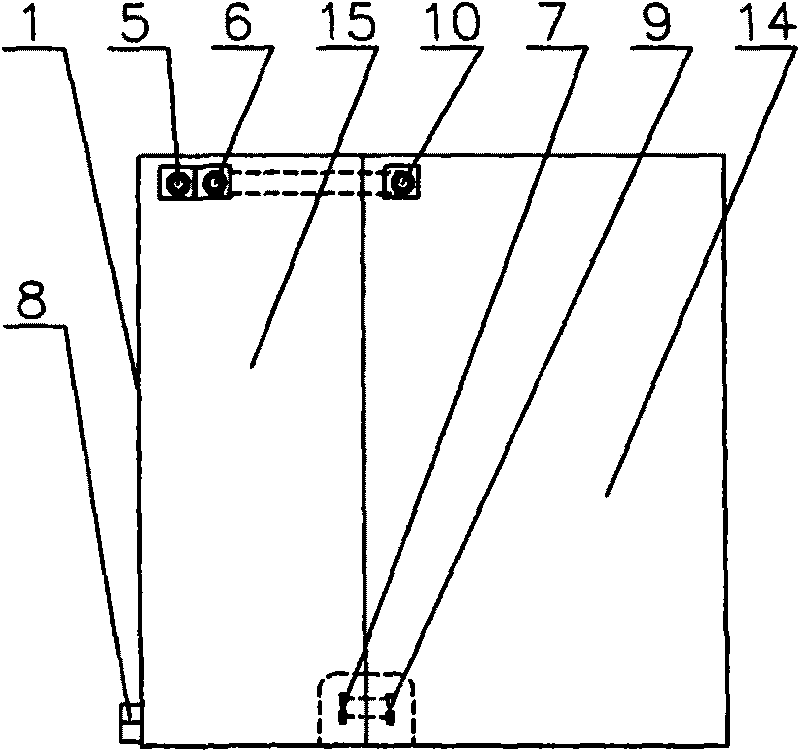
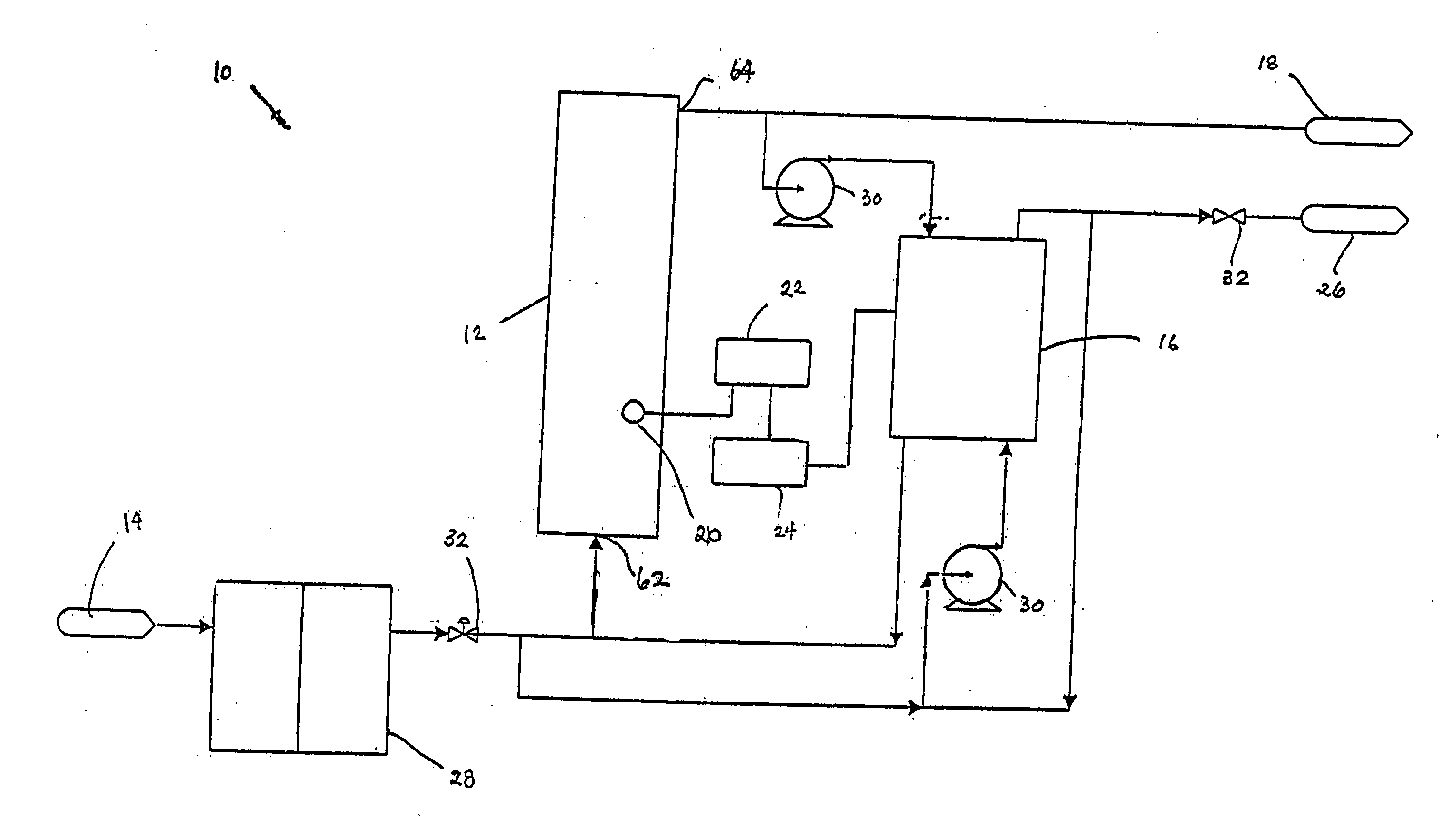
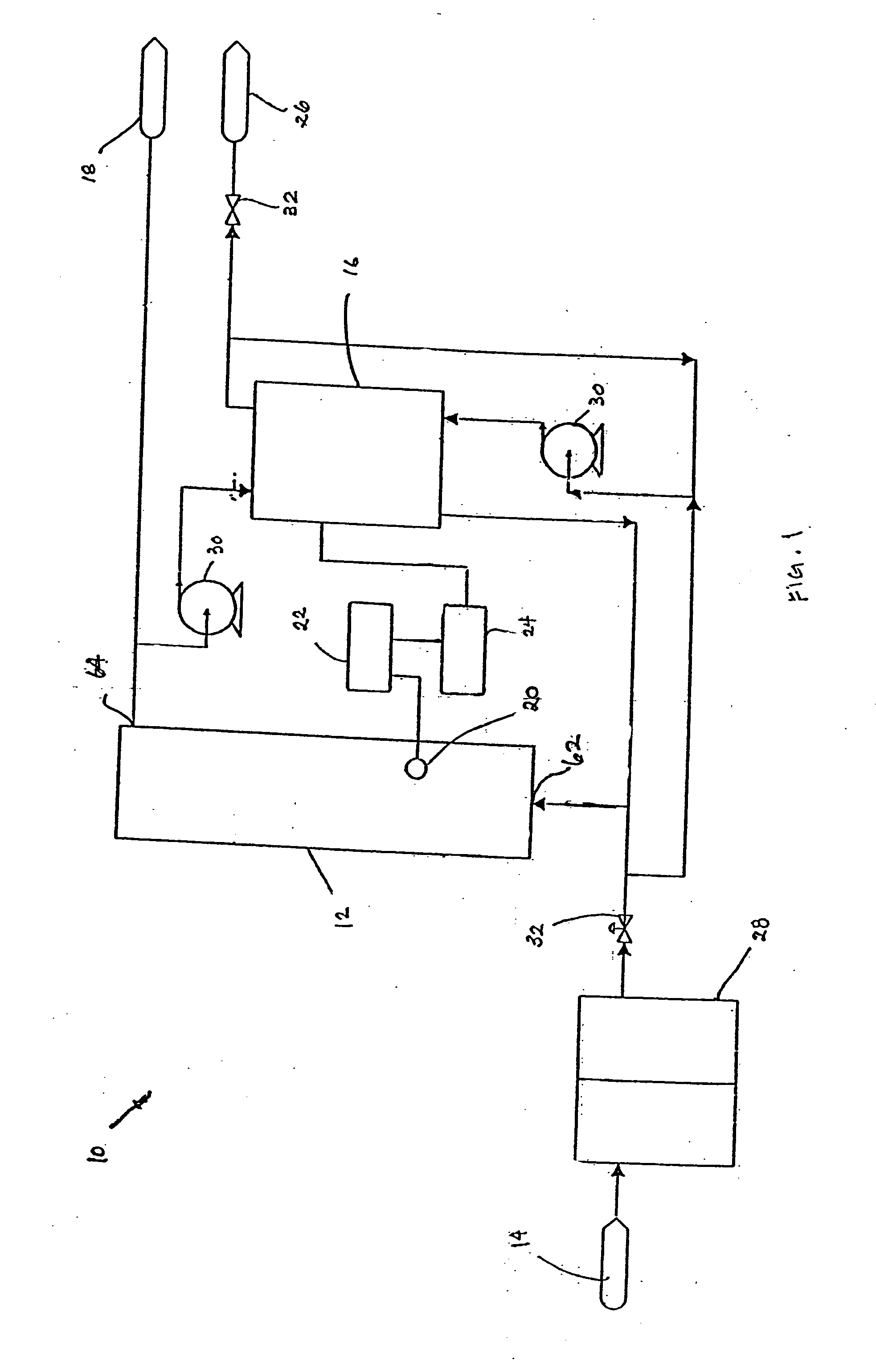
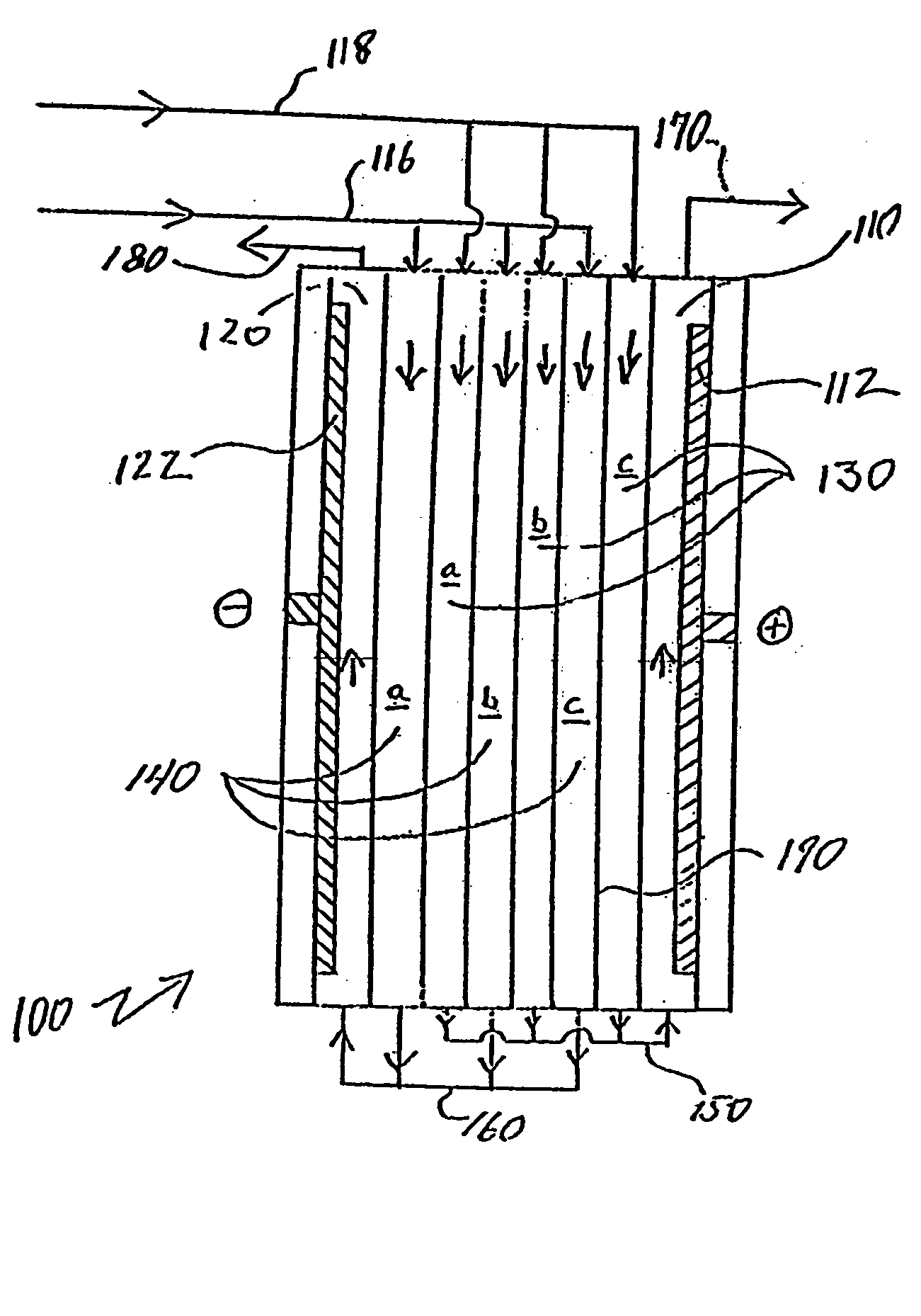
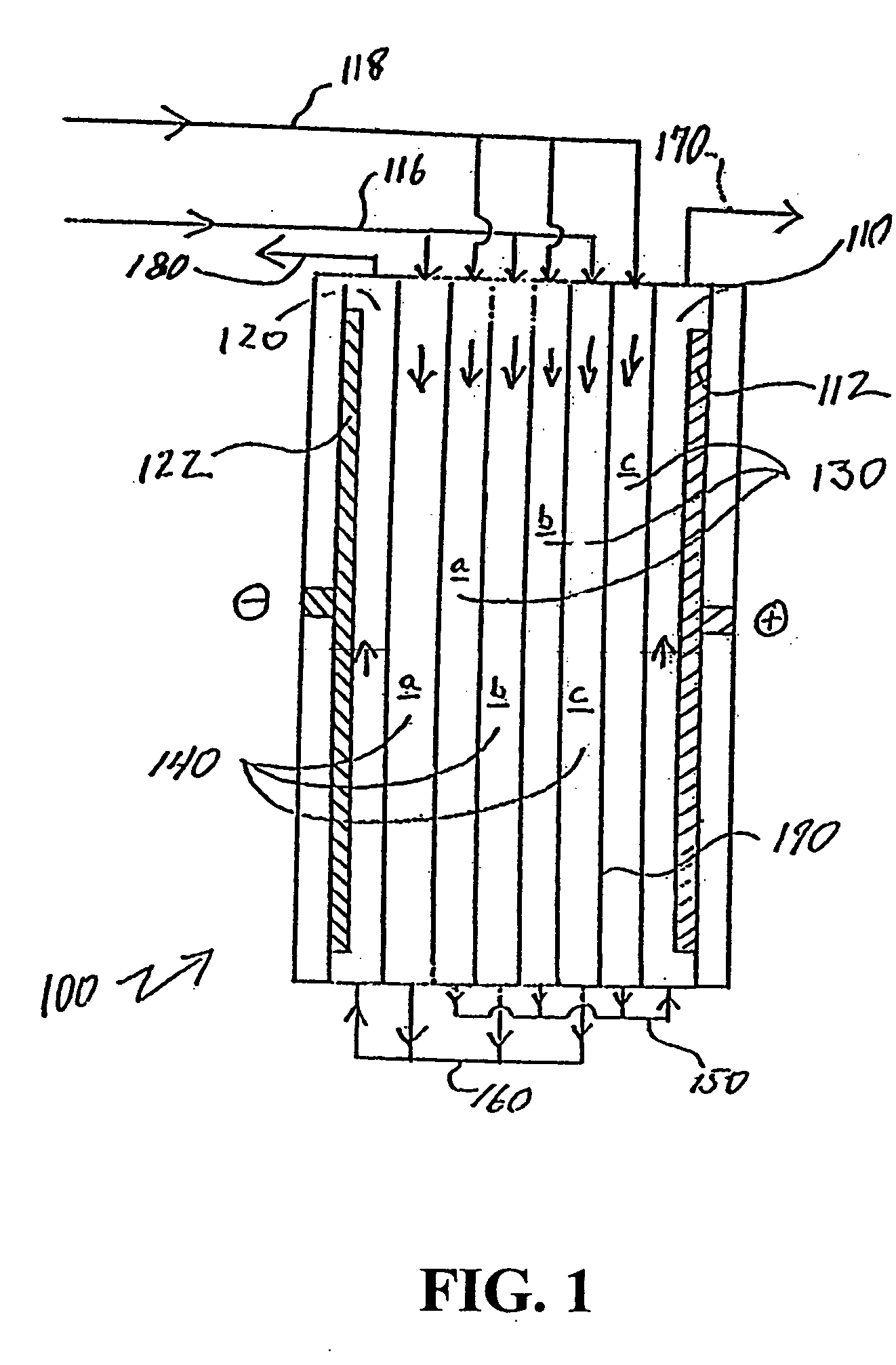
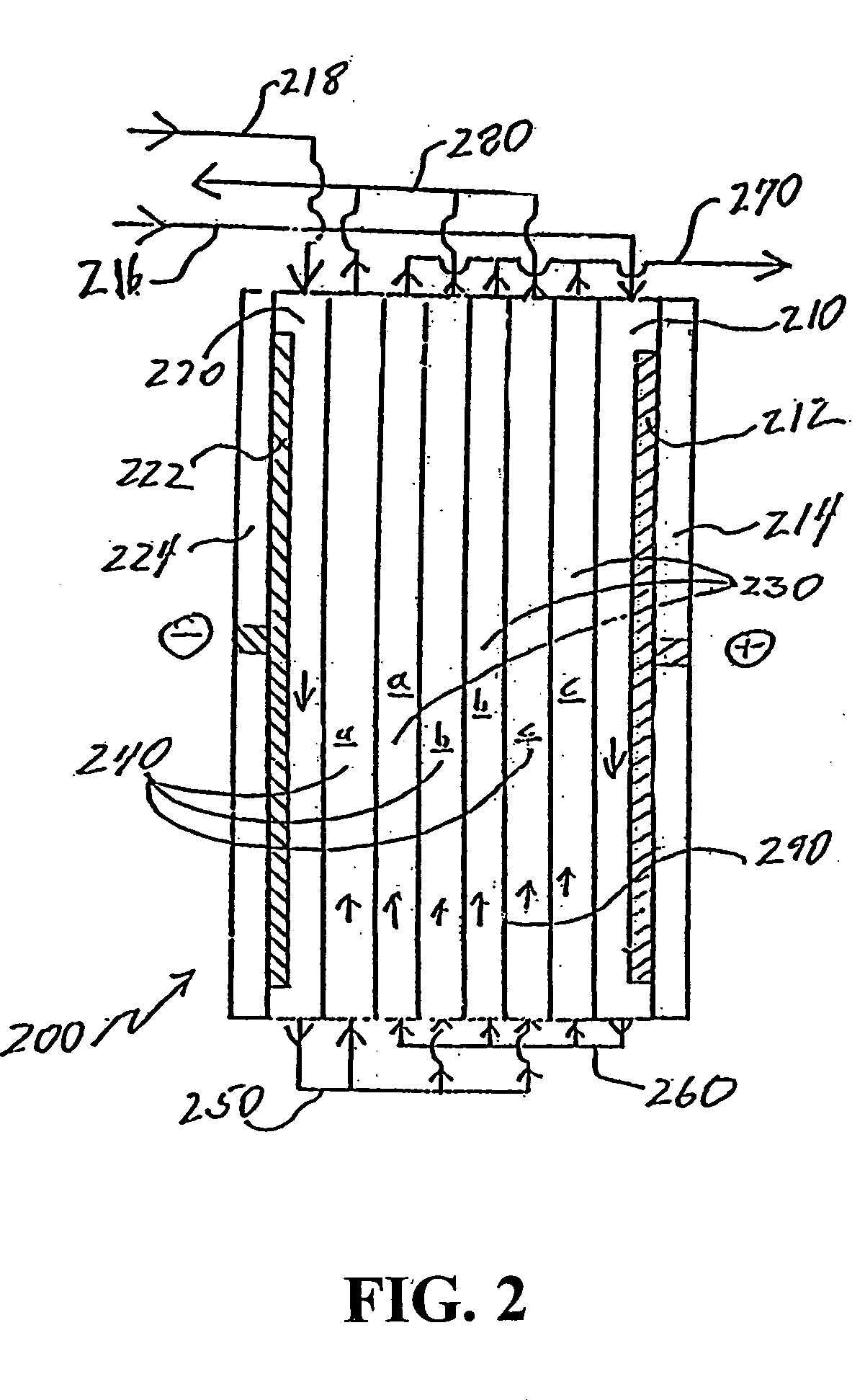
A water treatment system provides treated or softened water to a point of use by removing a portion of any hardness-causing species contained in water from a point of entry coming from a water source, such as municipal water, well water, brackish water and water containing foulants. The water treatment system typically treats the water containing at least some undesirable species before delivering the treated water to a point of use. The water treatment system has a reservoir system in line with an electrochemical device such as an electrodeionization device. The water treatment system has a sensor or a set of sensors for measuring at least one property of the water or an operating condition of the treatment system. The water treatment system also has a controller for adjusting or regulating at least one operating parameter of the treatment system or a component of the water treatment system to optimize the operation and performance of the system or components of the system to supply water tailored to quality requirements.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
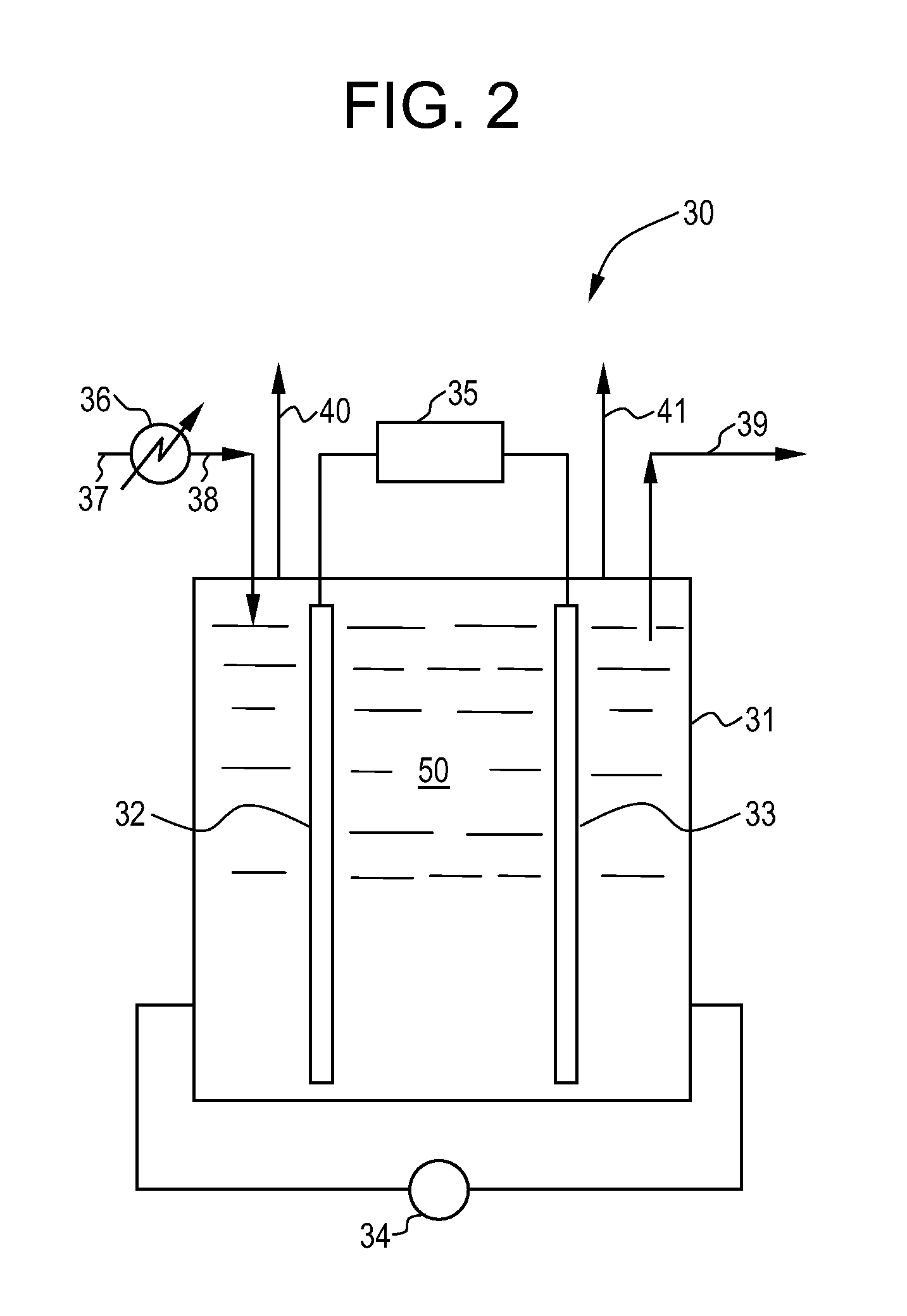
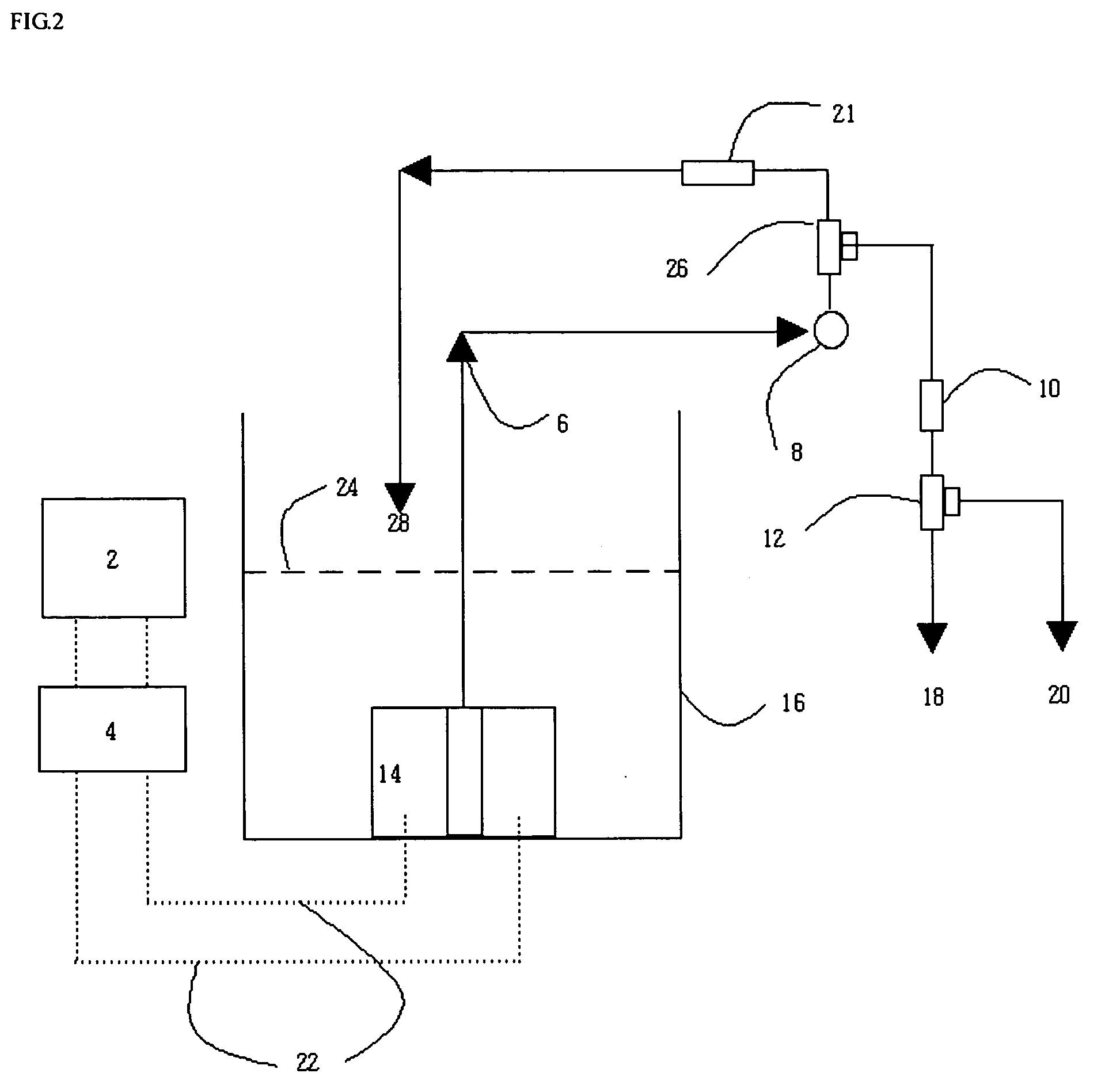
Water treatment system and method
InactiveUS20050103717A1Water treatment parameter controlWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsElectricityWater treatment system
A water treatment system provides treated water to a point of use by removing at least a portion of any hardness-causing species contained in water from a water source, such as municipal water, well water, brackish water and water containing foulants. The water treatment system typically receives water from the water source or a point of entry and purifies the water containing at least some undesirable species before delivering the treated water to a point of use. The water treatment system has a pressurized reservoir system in line with an electrochemical device such as an electrodeionization device. The water treatment system can have a controller for adjusting or regulating at least one operating parameter of the treatment system or a component of the water treatment system.
Owner:SIEMENS WATER TECH HLDG CORP
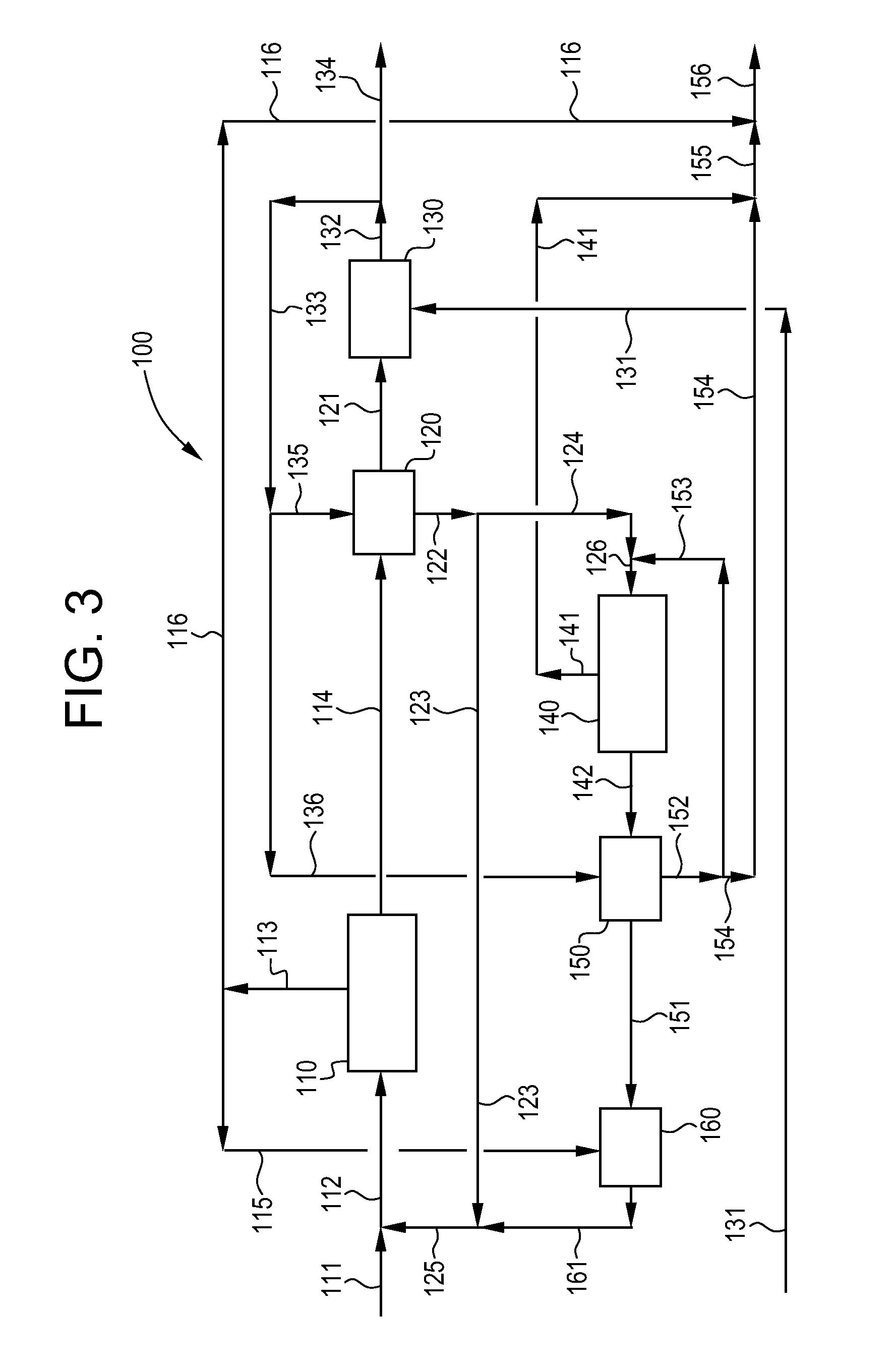
Water treatment system and method
ActiveUS20050103622A1Improve water purification abilitySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementWater treatment systemSoftened water
A treatment system provides treated or softened water to a point of use by removing at least a portion of any undesirable species contained in water from a water source. The treatment system can be operated to reduce the likelihood of formation of any scale that can be generated during normal operation of an electrochemical device. The formation of scale in the treatment system, including its wetted components, may be inhibited by reversing or substituting the flowing liquid having hardness-causing species with another liquid having a low tendency to produce scale, such as a low LSI water. Various arrangements of components in the treatment system can be flushed by directing the valves and the pumps of the system to displace liquid having hardness-causing species with a liquid that has little or no tendency to form scale.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for producting negative and positive oxidative reductive potential (orp) water
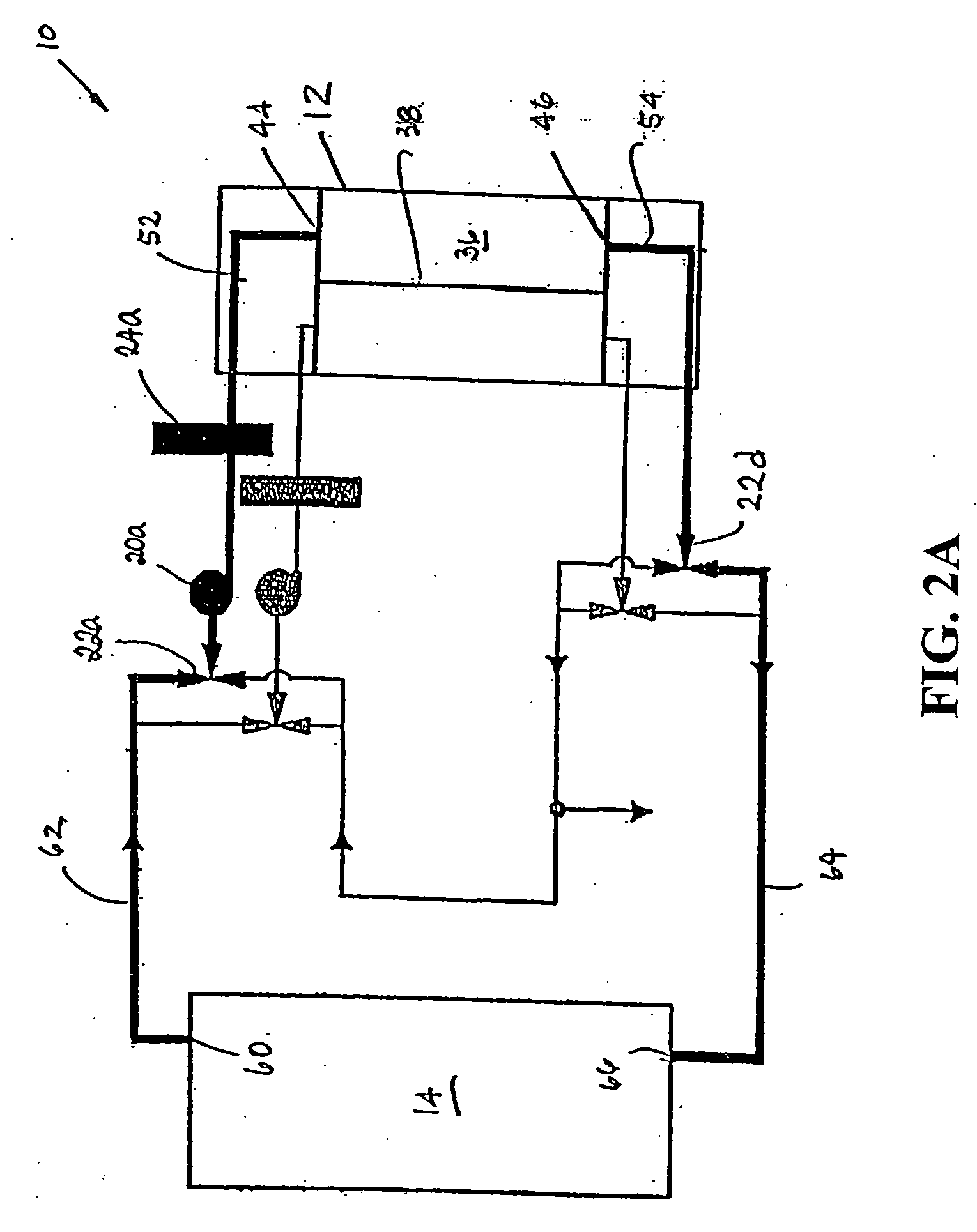
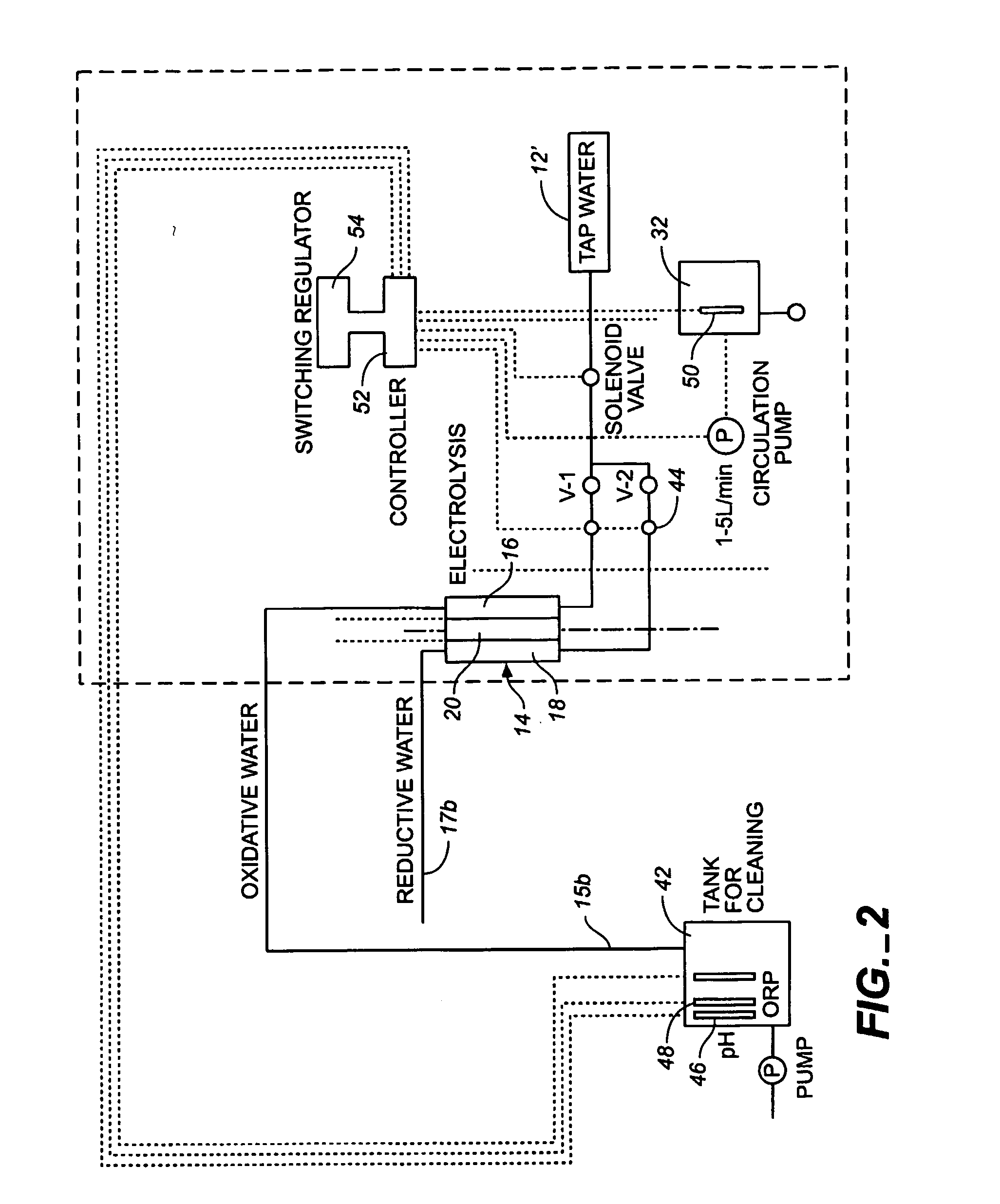
ActiveUS20050121334A1Effective and efficient and economicalCellsWater treatment parameter controlParticulatesElectrolysis
A method and apparatus for electrolytically producing oxidation reduction potential water from aqueous salt solutions for use in disinfection, sterilization, decontamination, wound cleansing. The apparatus includes an electrolysis unit having a three-compartment cell (22) comprising a cathode chamber (18), an anode chamber (16), and a saline solution chamber (20) interposed between the anode and cathod chambers. Two communicating (24, 26) membranes separate the three chambers. The center chamber includes a fluid flow inlet (21a) and outlet (21b) and contains insulative material that ensures direct voltage potential does not travel through the chamber. A supply of water flows through the cathode and anode chambers at the respective sides of the saline chamber. Saline solution flows through the center chamber, either by circulating a pre-prepared aqueous solution containing ionic species, or, alternatively, by circulating pure water or an aqueous solution of, e.g., aqueous hydrogen chloride and ammonium hydroxide, over particulate insulative material coated with a solid electrolyte. Electrical current is provided to the communicating membranes separating the chambers, thus causing an electrolytic reaction that produces both oxidative (positive) and reductive (negative) ORP water.
Owner:SONOMA PHARMA INC
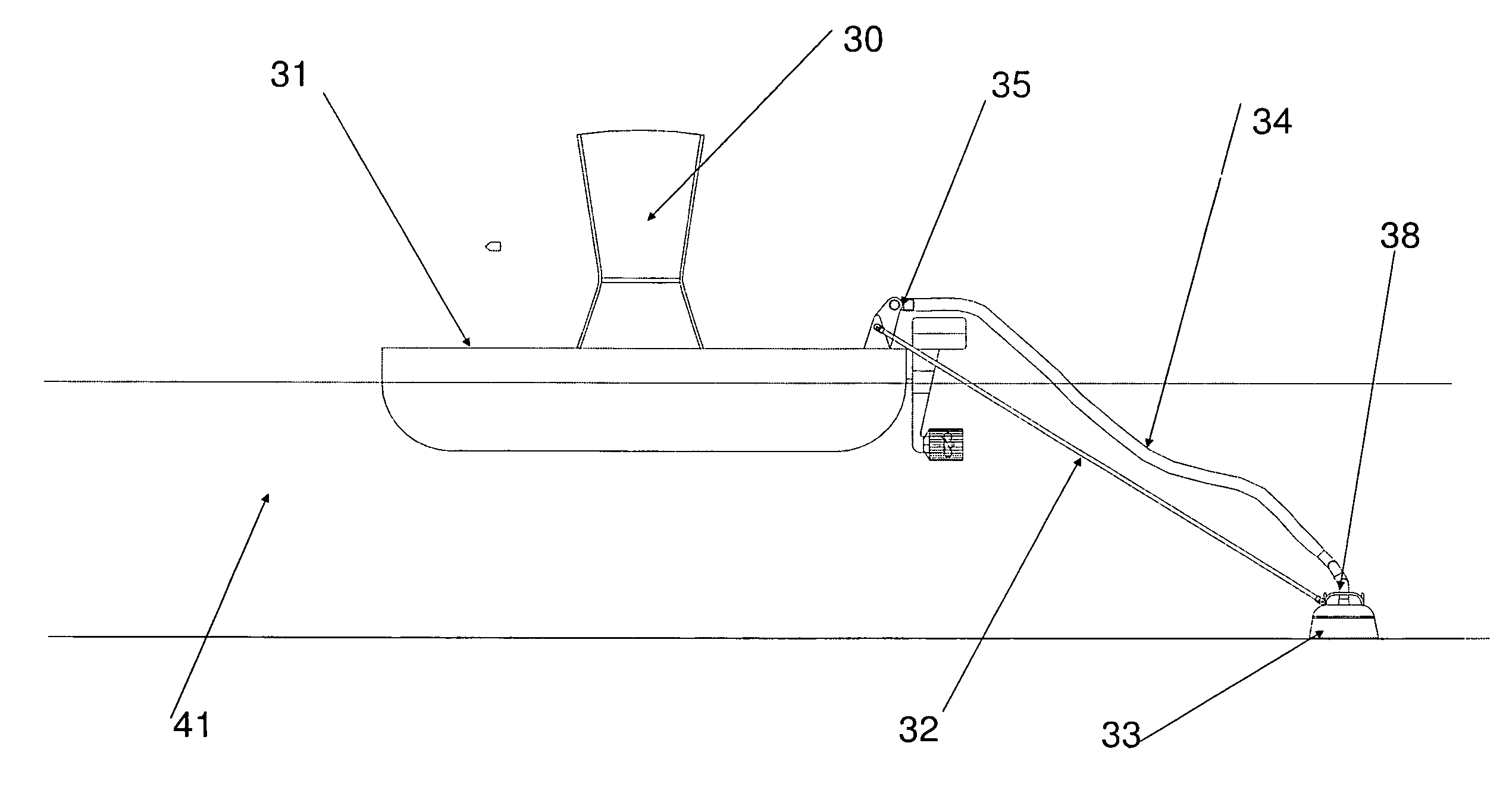
Process to obtain water bodies larger than 15,000 m3 for recreational use with color, transparency and cleanness characteristics similar to swimming pools or tropical seas at low cost
The invention discloses a process to implement and maintain water bodies larger than 15,000 m3 for recreational use, such as lakes or artificial lagoons, with excellent color, transparency and cleanness properties at low cost, which comprises the following steps:a.—providing a structure able to contain a large water body larger than 15,000 m3;b.—feeding the structure of step (a) with inlet water having iron and manganese levels lower than 1.5 ppm and turbidity lower than 5 NTU;c.—measuring water pH, ideally it should be within a range lower than 7.8;d.—adding an oxidizing agent to the water contained in the structure of step (a), with which a 600 mV minimal ORP is controlled in water for a minimal period of 4 hours and in maximal cycles of 48 hours;e.—adding a flocculating agent in concentrations within 0.02 and 1 ppm with maximal frequencies of 6 days and cleaning the bottom of the structure of step (a) with a suction device to remove precipitated impurities from the bottom of said structure, together with the additional flocculants and;f.—generating a displacement of surface water containing impurities and surface oils by means of the injection of inlet water according to step (b), which generates said displacement in such a way to remove said surface water by means of a system for impurities and surface oils removal arranged in the structure of step (a), which together with step (e) replaces traditional filtering.The present invention also discloses a structure to contain large water bodies comprising a system for the removal of impurities and surface oils by means of skimmers and the suction device to clean said structure.
Owner:CRYSTAL LAGOONS TECH INC
Method and device for deodorization and purification of exhaust gas or flue gas
InactiveUS20030164309A1Easy can be electrolyzedHigh densityCyanogen compoundsLighting and heating apparatusHazardous substancePotassium hydroxide
A method and device for removing, deodorizing and purifying odor, smoke and harmful substances from exhaust gas or flue gas employs a water solution containing hypohalogen acid such as hypochlorous acid soda, an alkaline electrolyte such as potassium hydroxide or sodium hydroxide and a saline electrolyte such as sodium chloride, potassium chloride, sodium bromide or potassium bromide which is electrolyzed to produce an electrolytic water solution which is fed to a deodorizing tower and brought into contact with exhaust gas or flue gas to remove odor, smoke and harmful substances in the exhaust gas or flue gas.
Owner:OMEGA CO LTD
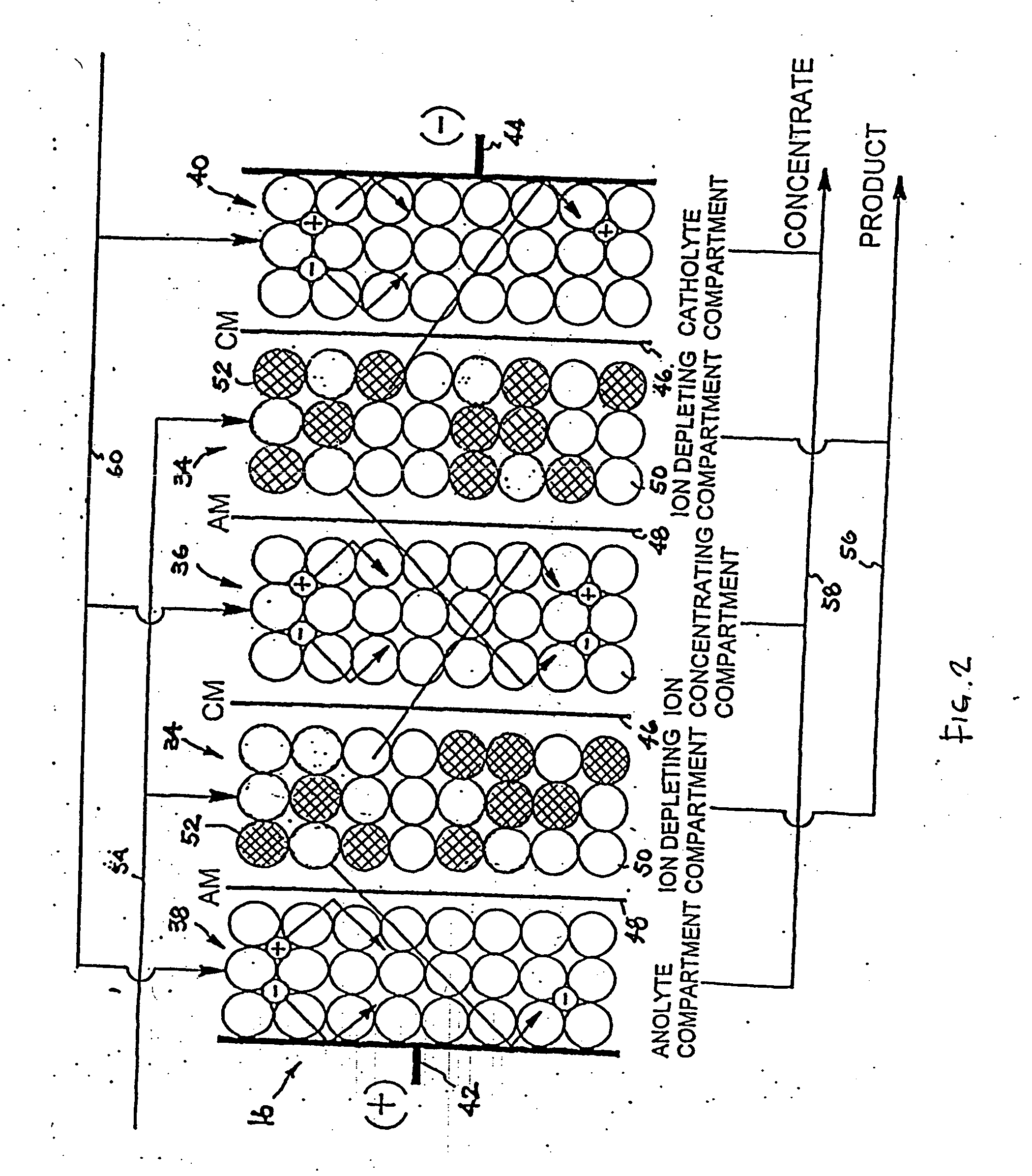
Method and apparatus for preventing scaling in electrodeionization units
InactiveUS6149788AAvoid mixingImprove conductivitySludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectricityIncreased tolerance
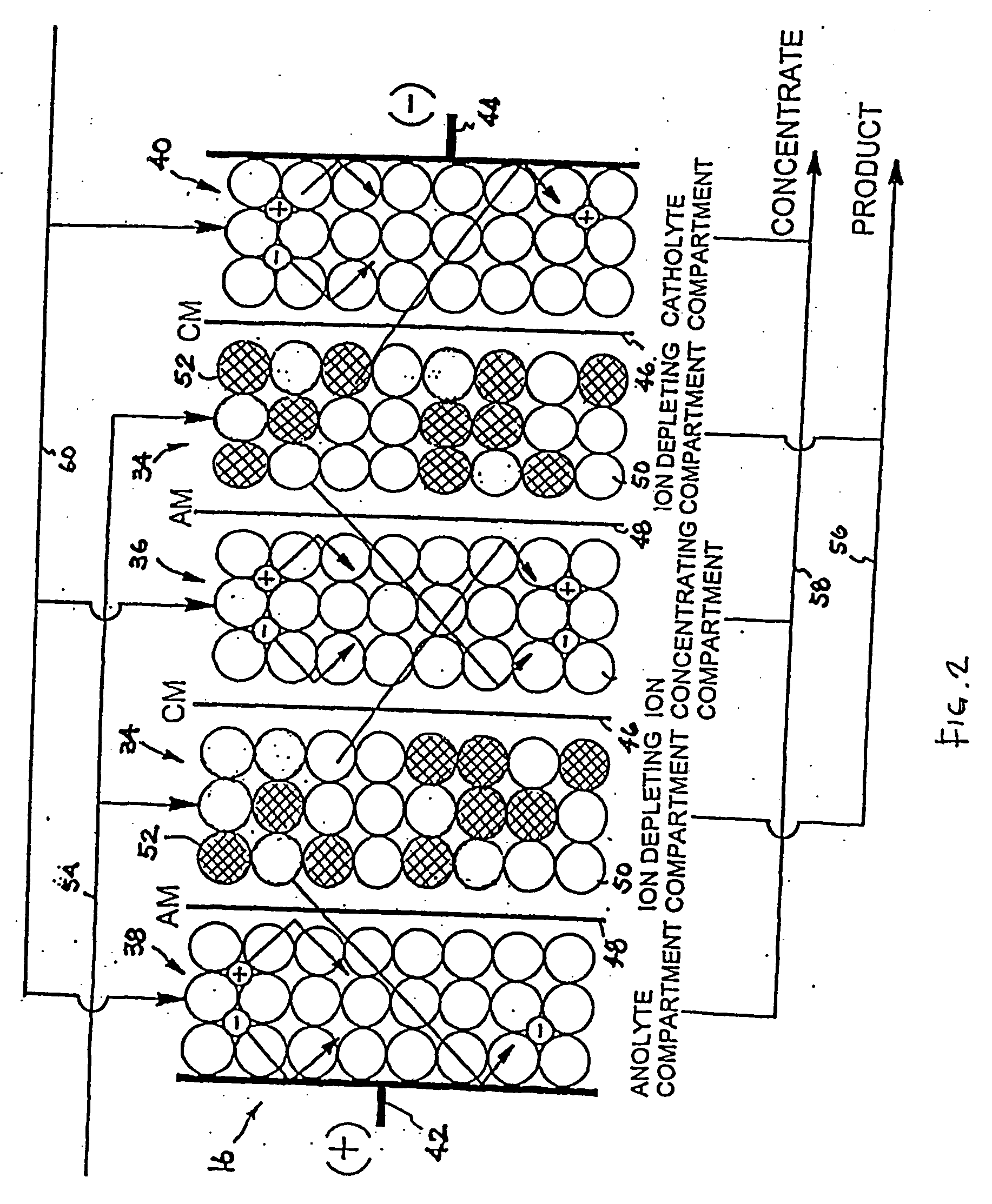
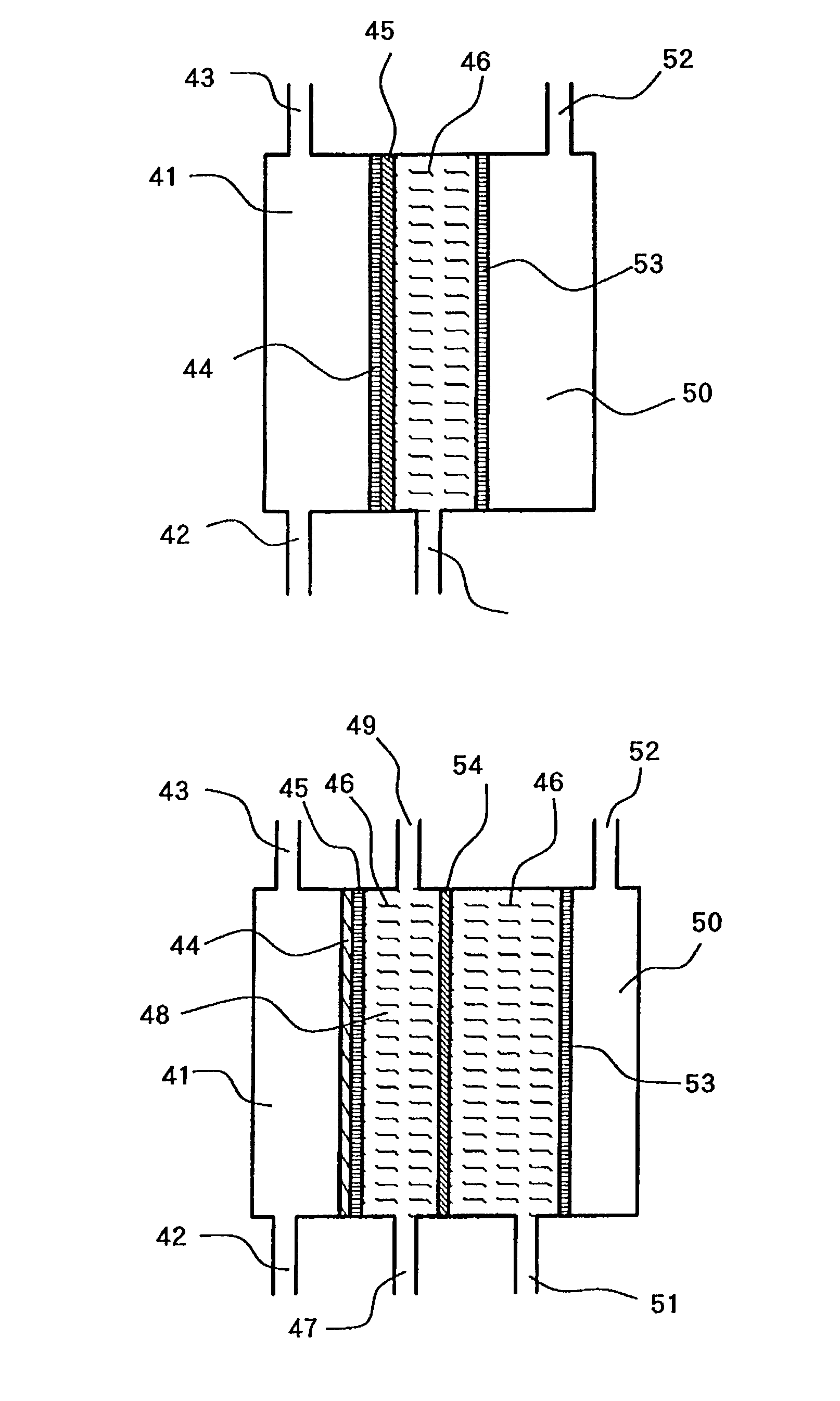
A method and apparatus is provided for inhibiting scaling in an electrodeionization system and, more particularly, for increasing tolerance to hardness in the feed water to an electrodeionization unit by inhibiting precipitation of scale-forming metallic cations contained in the feed water and thereby increasing efficiencies of the electrodeionization system. Water to be purified is passed through an electrodeionization unit in which the flow in the diluting compartment is countercurrent to the flow in the concentrating compartment. This is to impede the migration of scale-forming metallic cations from the diluting compartment, through the cation exchange membrane, into the concentrating compartment and towards the concentrating compartment side of the anion exchange membrane, thereby preventing scale formation on the anion exchange membrane. The electrodeionization unit may be further modified by dividing the concentrating compartments into first and second compartments by a porous diaphragm or ion-conducting membrane. The porous diaphragm or ion-conducting membrane effectively eliminates convective transport of scale-forming metallic cations from the cation exchange membrane side of the concentrating compartment to the anion exchange membrane side of the concentrating compartment, thereby inhibiting scale formation on the anion exchange membrane.
Owner:E CELL
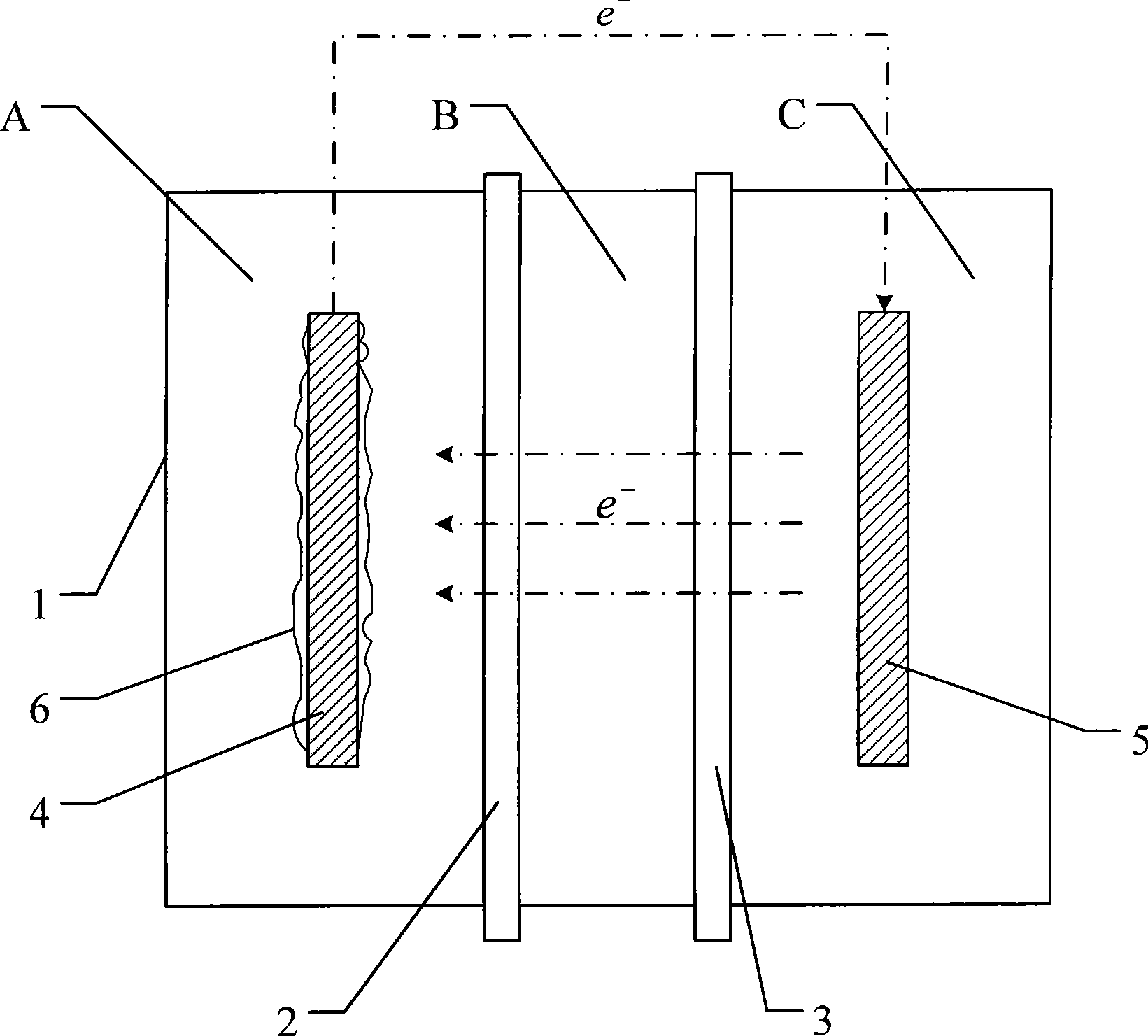
Electrolytic cell for producing charged anode water suitable for surface cleaning or treatment, and method for producing the same and use of the same
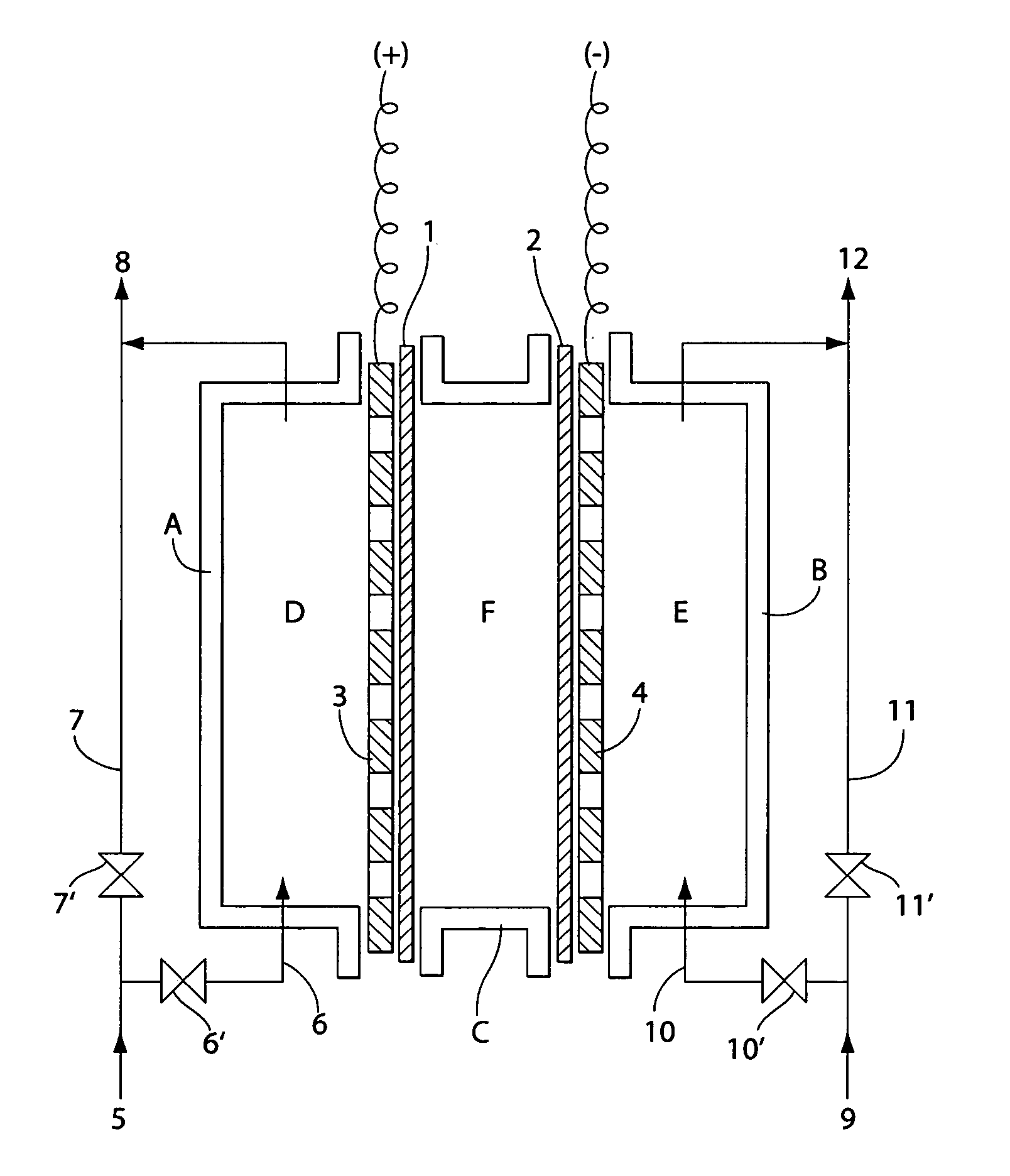
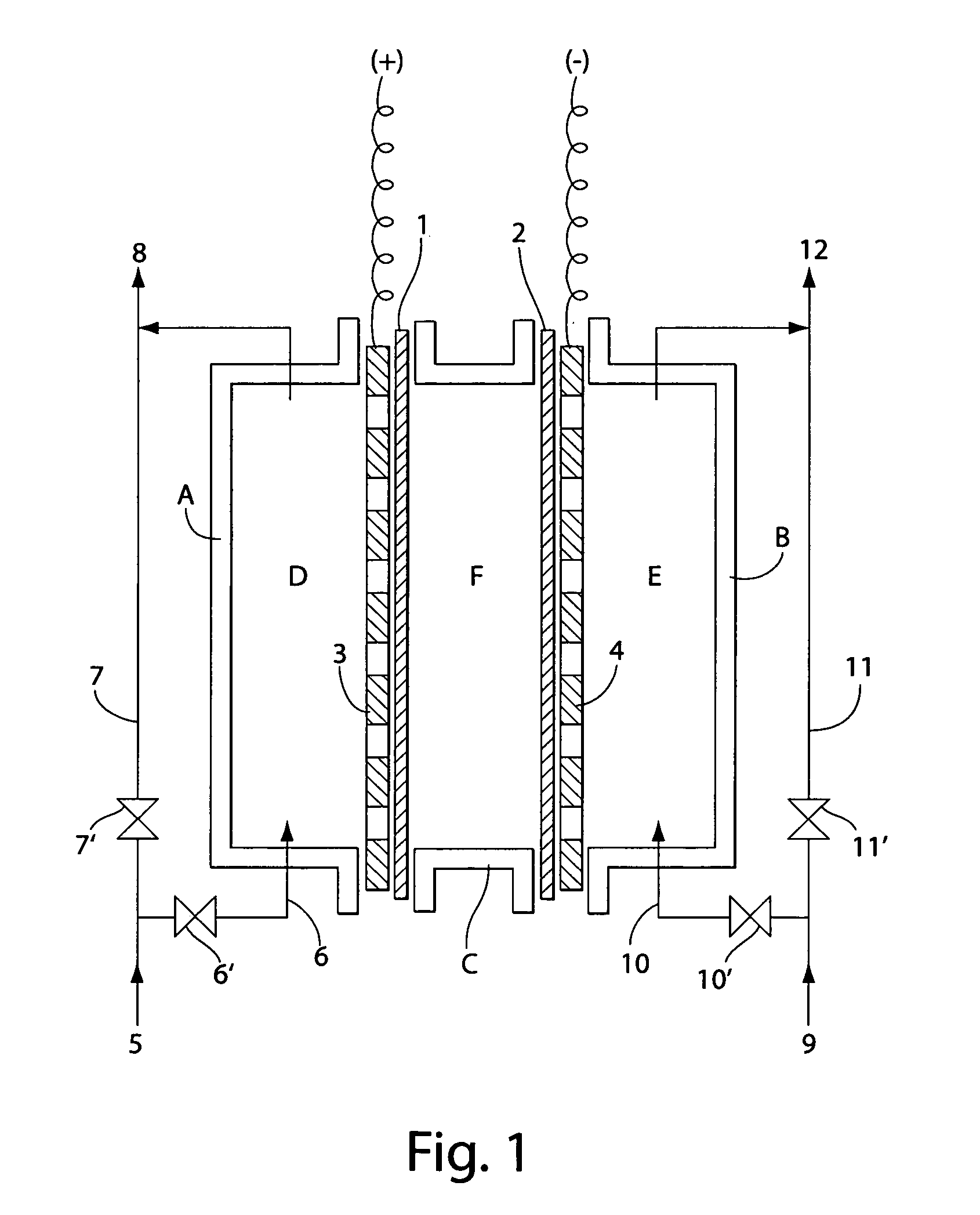
InactiveUS7090753B2Reduce the binding forceEasy to cleanCellsWater treatment parameter controlSurface cleaningElectrical battery
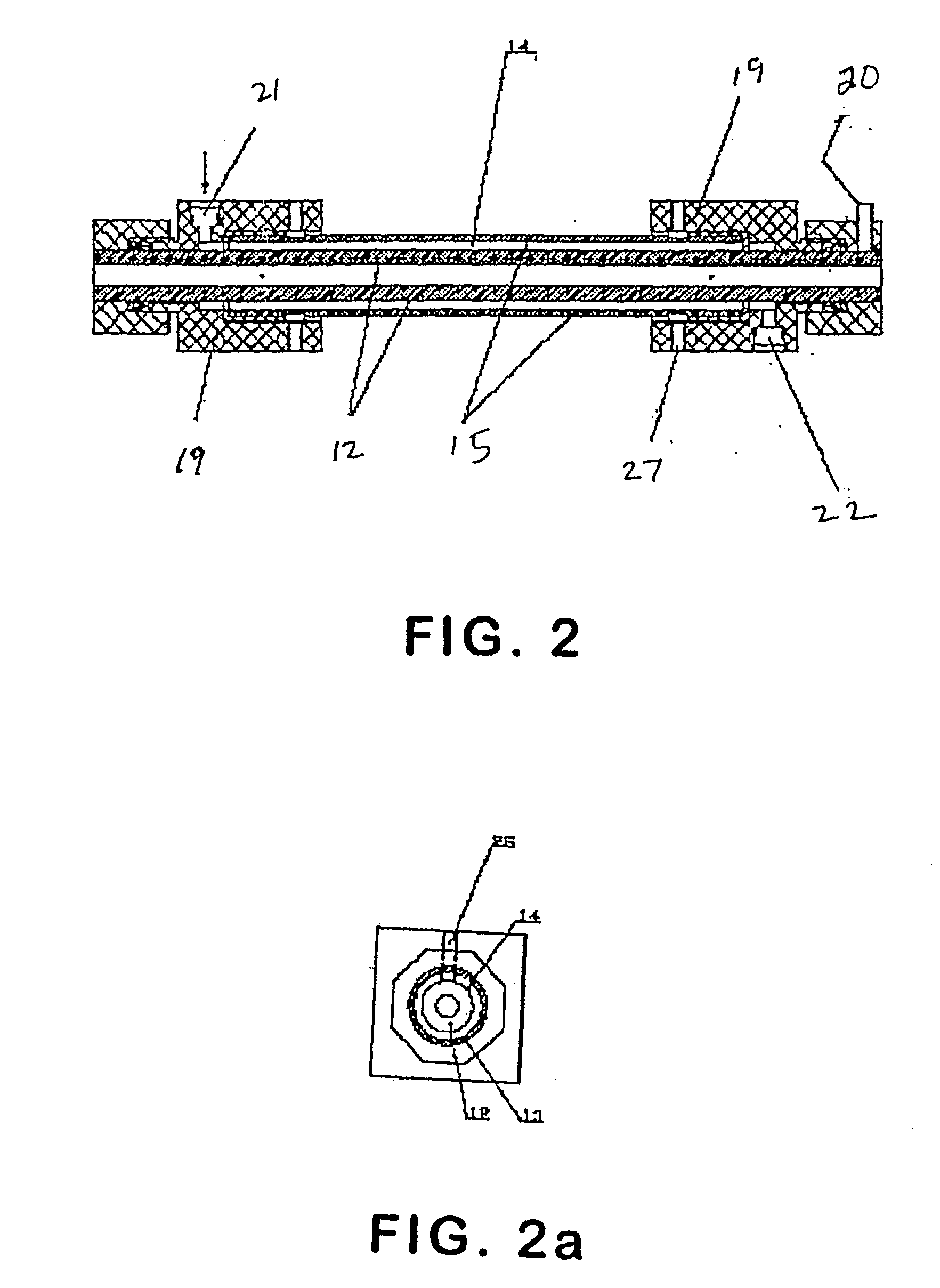
The present invention provides an electrolytic cell, which can efficiently produce, charged water having an excellent performance of improving surface cleaning or treatment of an object, e.g., semiconductor, glass, or resin and of cleaning and sterilizing medical device.The electrolytic cell of the present invention is for producing charged anode water suitable for surface cleaning or treatment, including the cathode chamber 41 and anode chamber 50, fluorinated cation-exchange membrane 46 provided to separated these chambers from each other, cathode 44 closely attaché to the cation-exchange membrane 45 on the side facing the cathode chamber 41, and middle chamber 48 filled with the cation-exchange resin 46, provided on the other side of The cation-exchange membrane 46, the cation-exchange resin 46 being arranged in such a way to come into contact with the fluorinated cation-exchange membrane 45, wherein the feed water is passed into the middle chamber 48 and passed thorough The anode chamber 50 to be recovered as the charged anode water.
Owner:SONOMA PHARMA INC
Recycling water saving device of washing machine
InactiveCN101748581AReduce manufacturing costCheap production supplyWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsOther washing machinesWater savingSalt content
The invention relates to a recycling water saving device of a washing machine, which belongs to the technical field of environmentally-friendly water treatment, comprises a shell, and is characterized in that a recycling water bucket, a water treatment device, a circuit integrated control operation actuator and a control circuit are respectively arranged in the shell, wherein the water treatment device is connected onto the recycling water bucket in parallel, a tap water inlet and a water outlet I of the water saving device are respectively arranged on the upper side of the shell, a water inlet and a water outlet II of the water saving device are respectively arranged on the lower side thereof, and the water treatment device consists of a double pole film and double liquid flow type hydroxyl free-radical generator, an aeration device and a filter unit. The invention comprehensively utilizes the initial discharged washing fluid, keeps the mixed liquid of a first rinsing and a second rinsing to repeatedly wash the clothing, not only the existence and accumulation of the salt content can be neglected, but also the purpose of saving the water resource is achieved. The water saving device is designed into an independent component so as to be compatible to various types of washing machines and detergents. In addition, a program control valve is designed and manufactured to realize the automation of the water saving device.
Owner:薛廷芳
Water treatment system and method
ActiveUS20050103630A1Inhibit migrationPromote migrationSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementWater sourceSoftened water
The present invention is directed to a water treatment or purification system and method for providing treated water in industrial, commercial and residential applications. The treatment system provides treated or softened water to a point of use by removing at least a portion of any hardness-causing species contained in water from a water source, such as municipal water, well water, brackish water and water containing foulants. The water treatment system includes an electrochemical device, such as an electrodeionization device, that can have at least one compartment that generates and traps hydrogen ions which can be used in another compartment of the electrochemical device such as, an electrode compartment, to reduce or at least dissolve any scale. Other applications of the system would be in the treatment and processing of foods and beverages, sugars, various industries such as the chemical, pharmaceutical, waste water treatment and power generating industries.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Production of electrolytic water
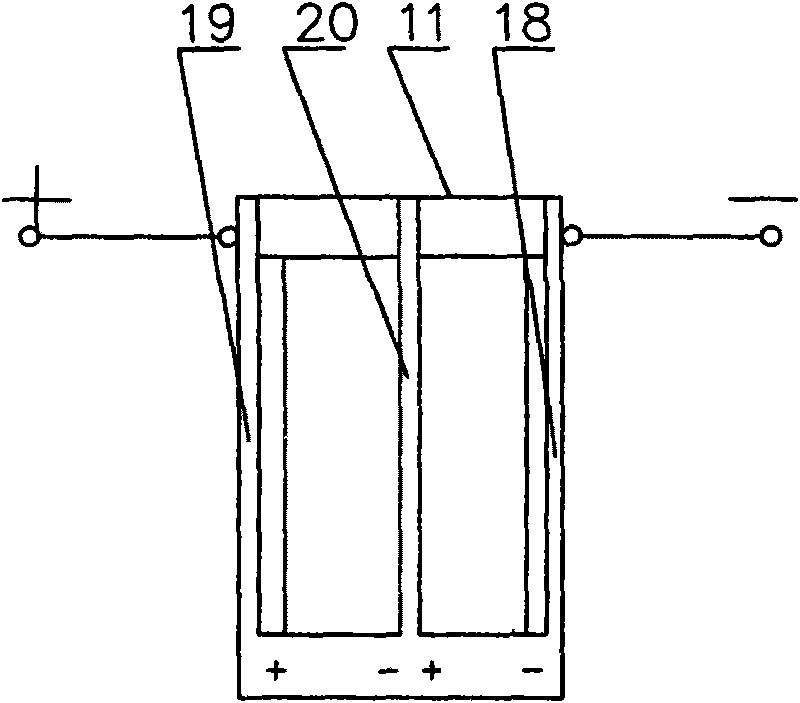
InactiveUS7238272B2Prevent adhesionIncrease productivityCellsLiquid separation by electricityWater useElectrolysed water
Apparatus and methods are provided for producing electrolytic water using three chambers, rigid plates and ion exchange membranes. Benefits include reduced scale production and increased long-term bactericidal effects of the water produced.
Owner:ELECTROLYZER
Process method for treating hardly-biodegradable organic wastewater
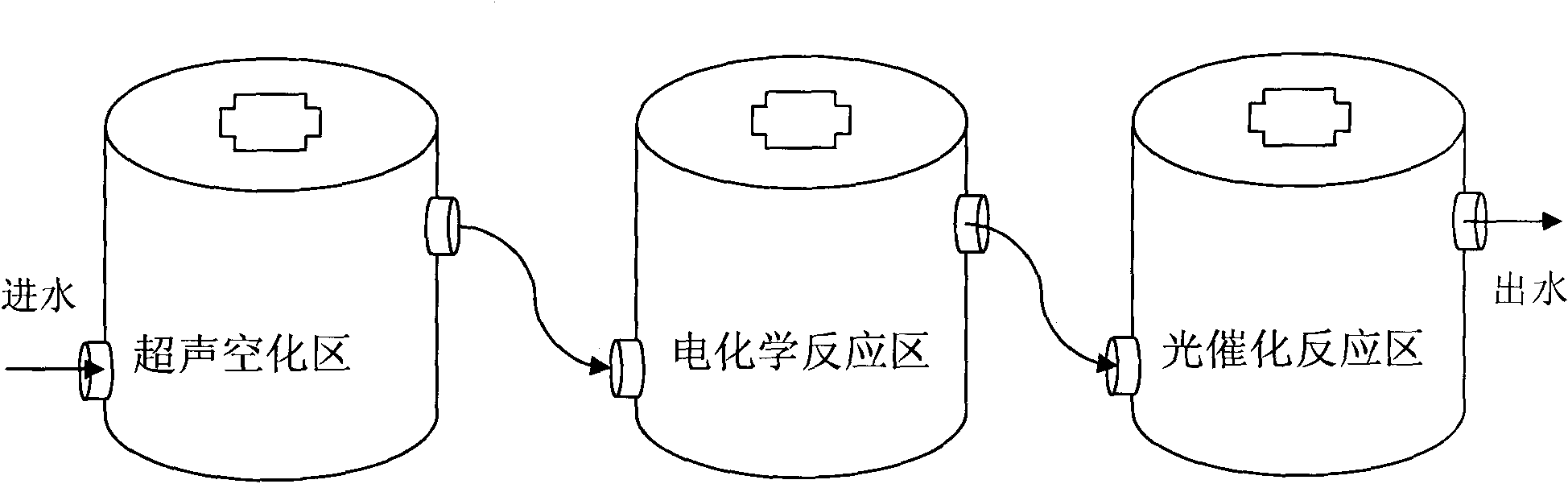
ActiveCN101786756AReduce dosageReduce generationWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsElectrochemical responseUltrasonic cavitation
The invention relates to a process method for treating hardly-biodegradable organic wastewater, and the method comprises the following steps: mainly utilizing the combination of ultraviolet light, electrochemistry, ultrasonic waves and oxidation-reduction chemical reaction for treating the hardly-biodegradable organic wastewater, and treating the wastewater by three reaction units of an ultrasonic cavitation zone, an electrochemical reaction zone and an ultraviolet light catalytic reaction zone, thereby realizing the high-efficient multi-stage deep wastewater oxidation reaction which combines the ultrasonic wastewater treatment method, the ultrasonic light and the collaborative Fenton reagent oxidation wastewater treatment, as well as the electrochemistry and the collaborative Fenton reagent oxidation wastewater treatment, effectively treating a variety of types of hardly-biodegradable organic wastewater and leading the COD removal rate of the wastewater after the treatment to be more than 90%.
Owner:GUANGXI BOSSCO ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Process to maintain large clean recreational water bodies
The invention discloses a process to implement and maintain water bodies larger than 15,000 m3 for recreational use, such as lakes or artificial lagoons, with excellent color, transparency and cleanness properties at low cost, which comprises the following steps:a.—providing a structure able to contain a large water body larger than 15,000 m3;b.—feeding the structure of step (a) with inlet water having iron and manganese levels lower than 1.5 ppm and turbidity lower than 5 NTU;c.—measuring water pH, ideally it should be within a range lower than 7.8;d.—adding an oxidizing agent to the water contained in the structure of step (a), with which a 600 mV minimal ORP is controlled in water for a minimal period of 4 hours and in maximal cycles of 48 hours;e.—adding a flocculating agent in concentrations within 0.02 and 1 ppm with maximal frequencies of 6 days and cleaning the bottom of the structure of step (a) with a suction device to remove precipitated impurities from the bottom of said structure, together with the additional flocculants and;f.—generating a displacement of surface water containing impurities and surface oils by means of the injection of inlet water according to step (b), which generates said displacement in such a way to remove said surface water by means of a system for impurities and surface oils removal arranged in the structure of step (a), which together with step (e) replaces traditional filtering.The present invention also discloses a structure to contain large water bodies comprising a system for the removal of impurities and surface oils by means of skimmers and the suction device to clean said structure.
Owner:CRYSTAL LAGOONS TECH INC
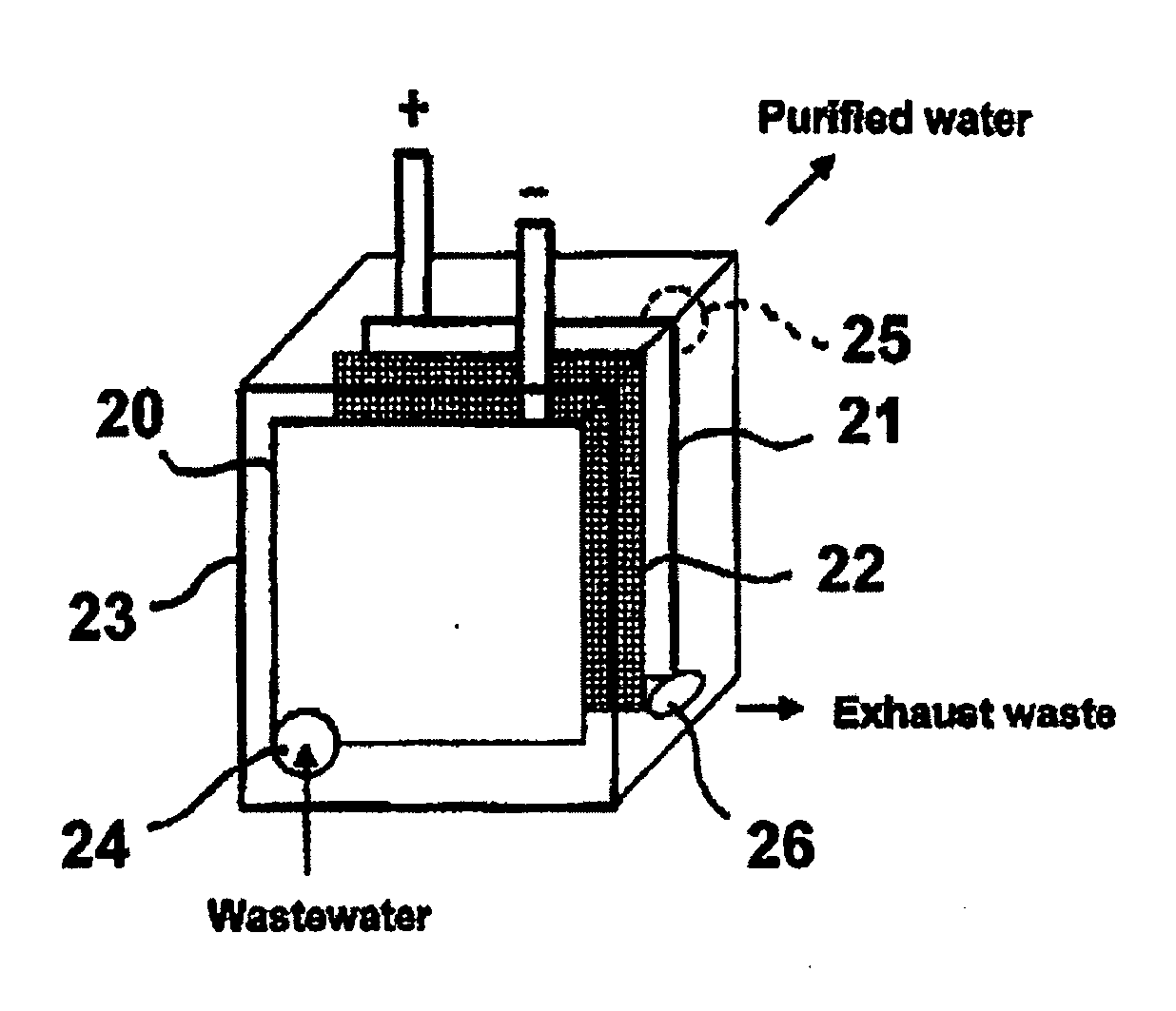
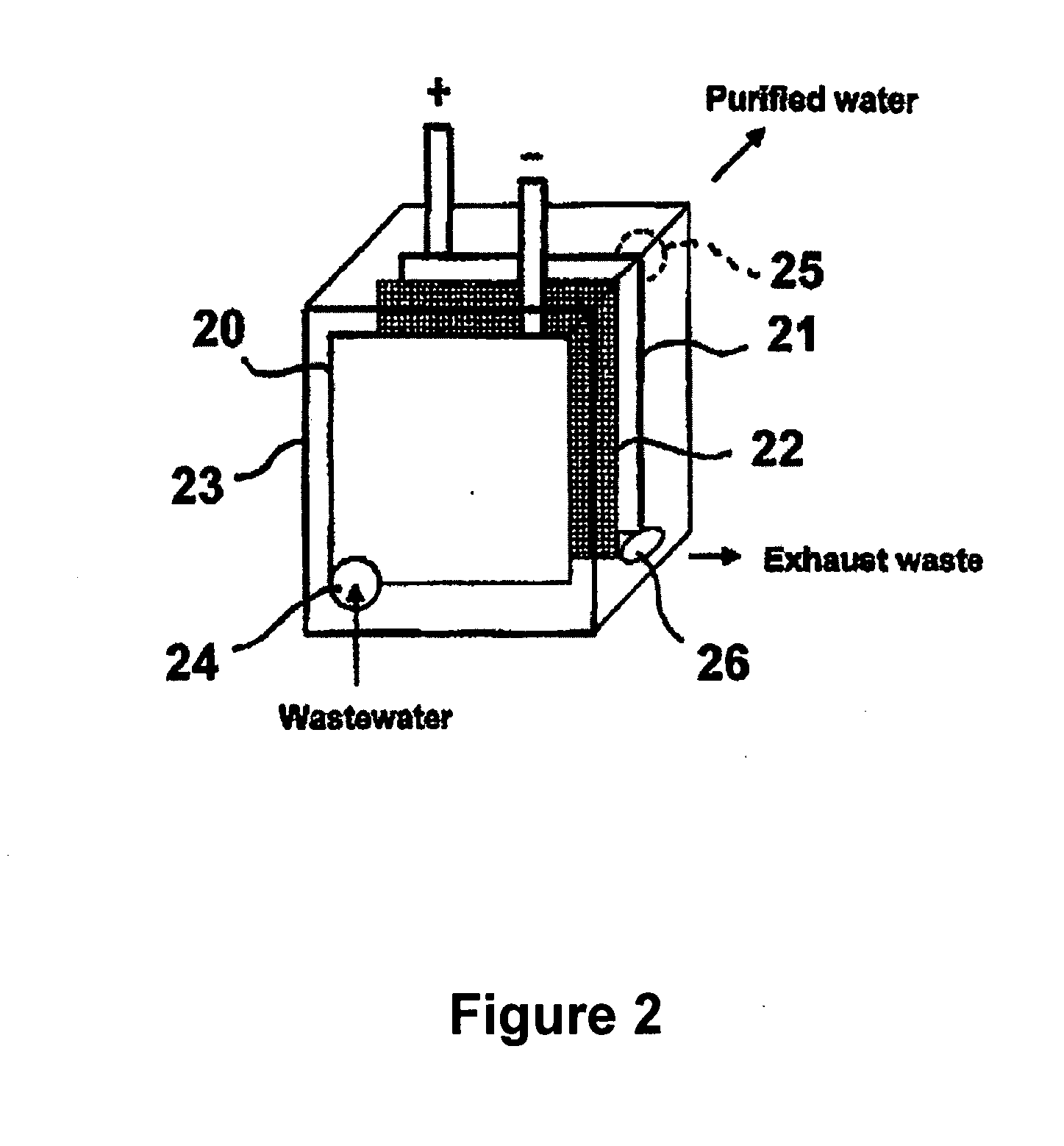
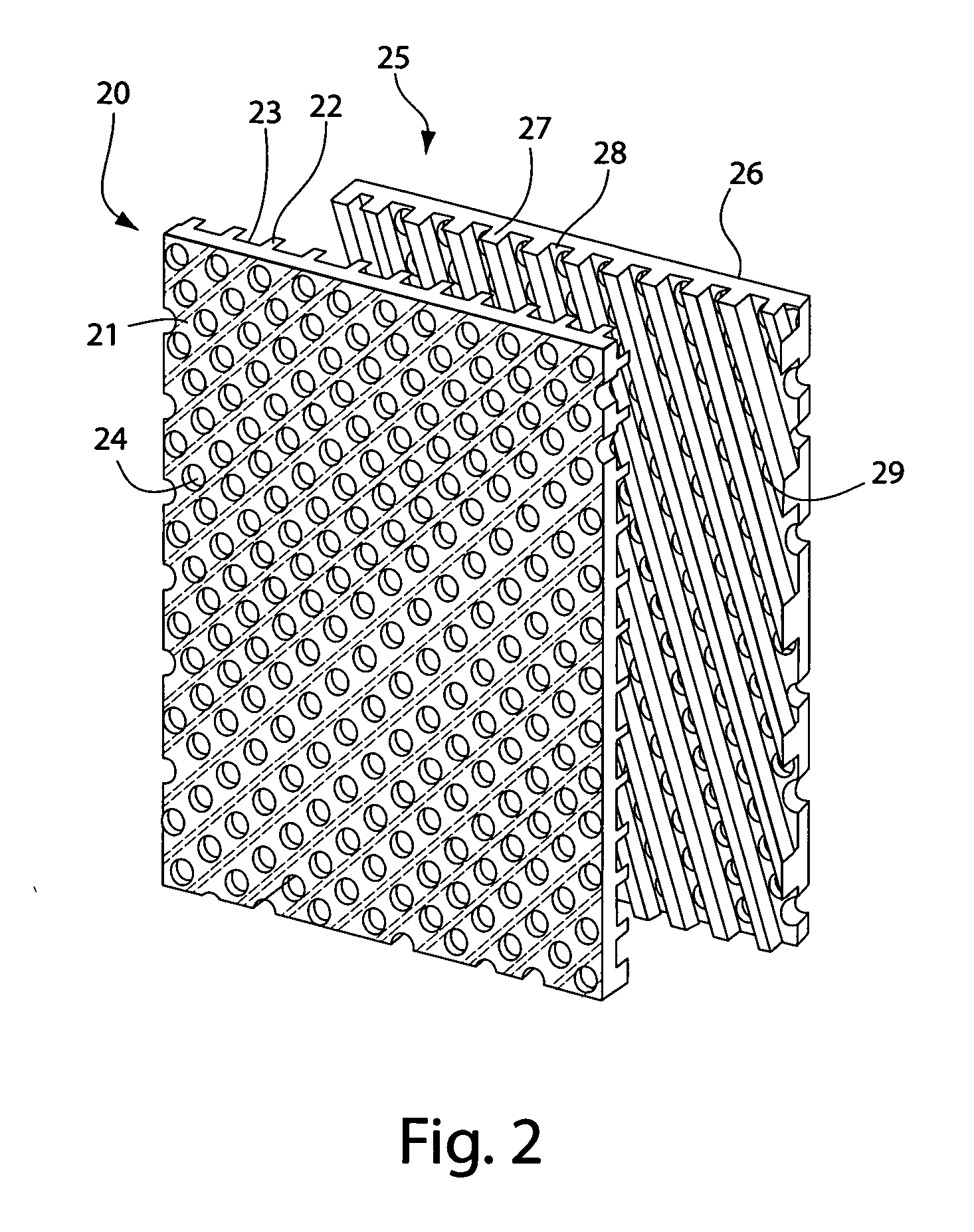
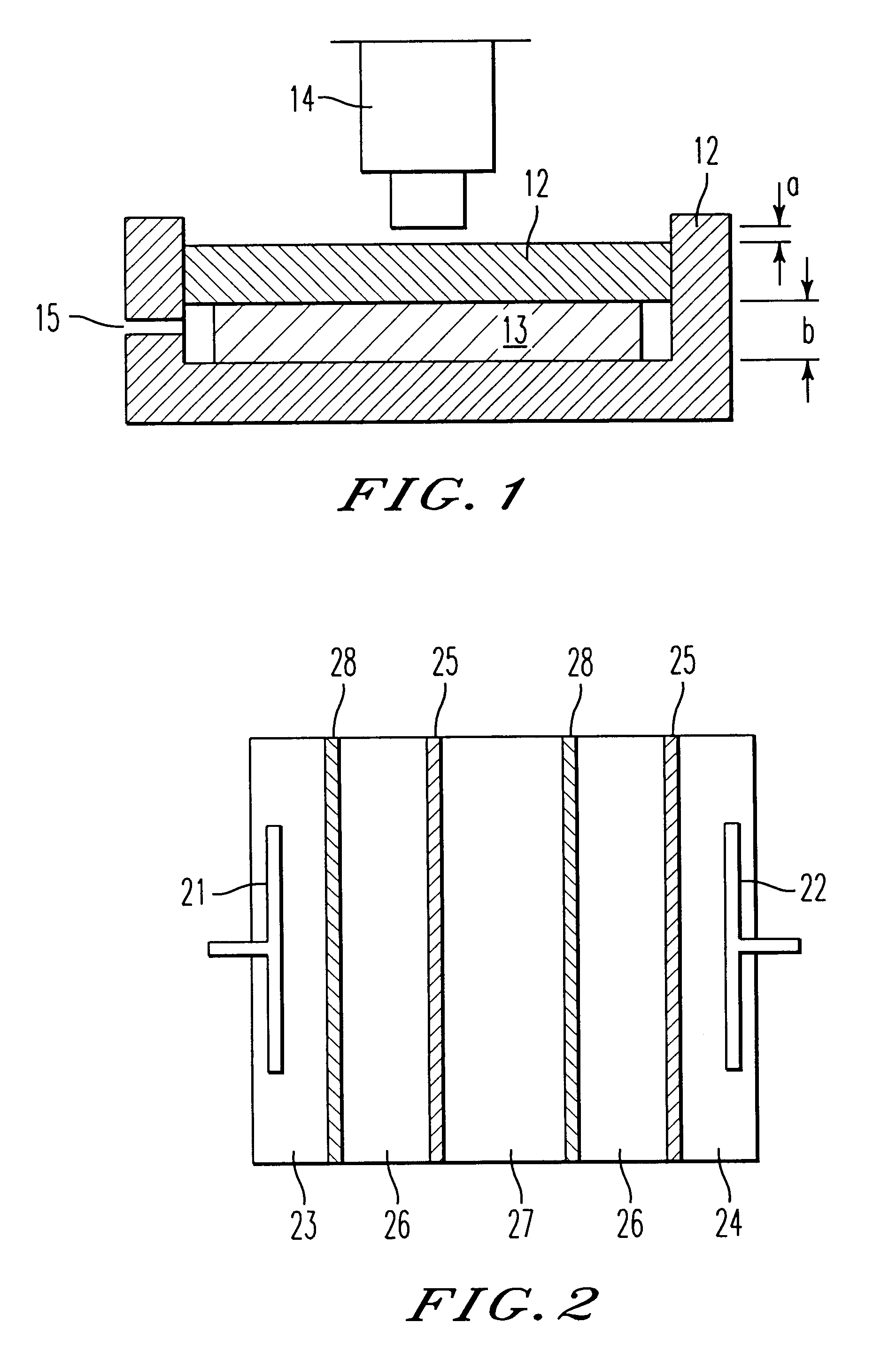
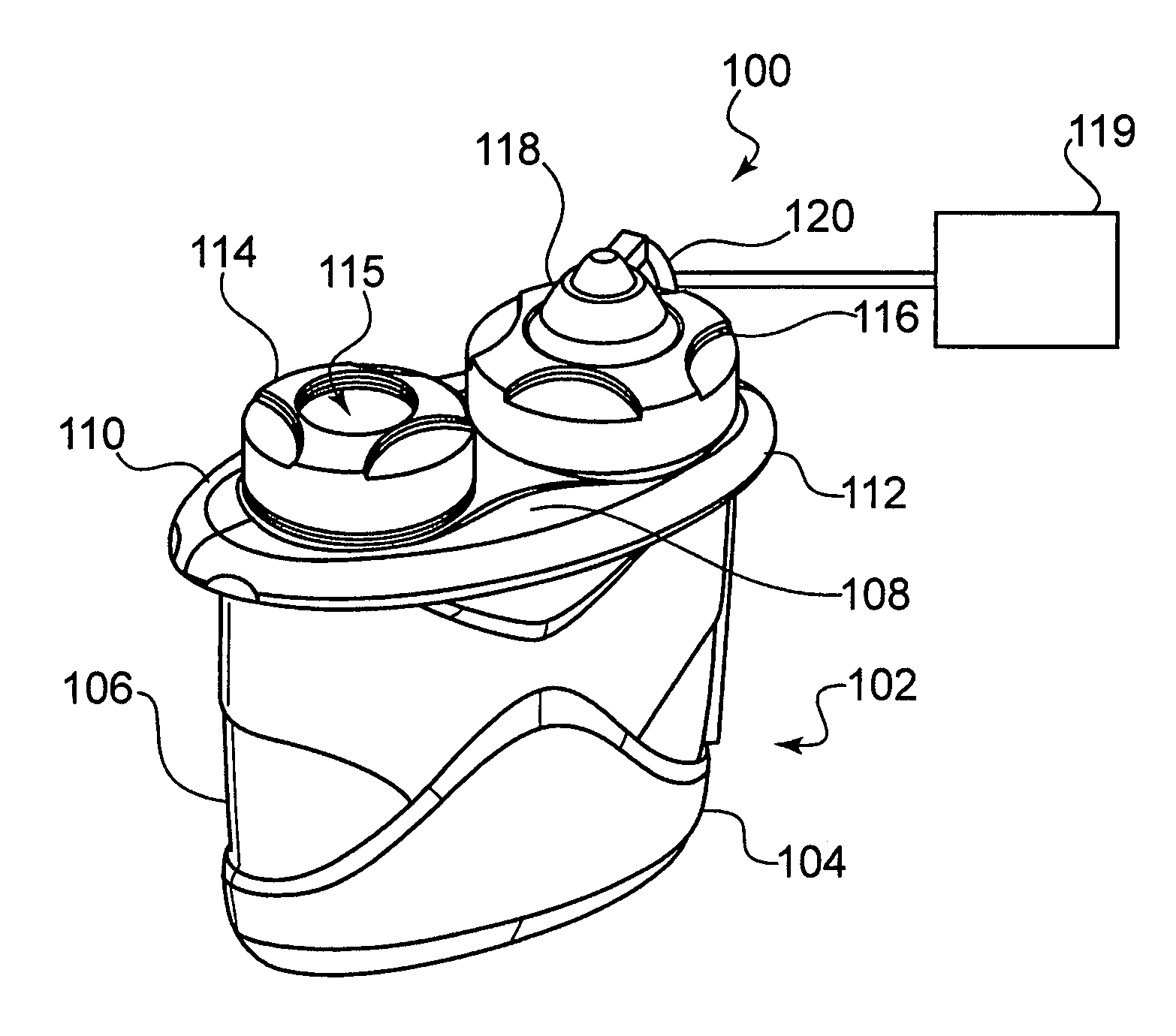
Multifunctional filtration and water purification systems
InactiveUS20080073288A1Waste water treatment from quariesElectrolysis componentsCross-linkFiltration
A water purification system having a porous anode electrode (21) and a porous cathode electrode (20), each of which is made of graphite, at least one metal oxide, and an ion-exchange, cross-linked, polarizable polymer, and optionally comprises microchannels. Disposed between the electrodes is a non-electron conductive, fluid permeable separator element (22), whereby wastewater is able to flow from one electrode to the other electrode. The electrodes and separator may be disposed within a housing (23) having a wastewater inlet opening (24), and exhaust waste outlet opening (26) and a purified water outlet opening (25). In this way, components of the system are easily replaced should the need arise.
Owner:QUOS
Dental equipment and method of operating such equipment
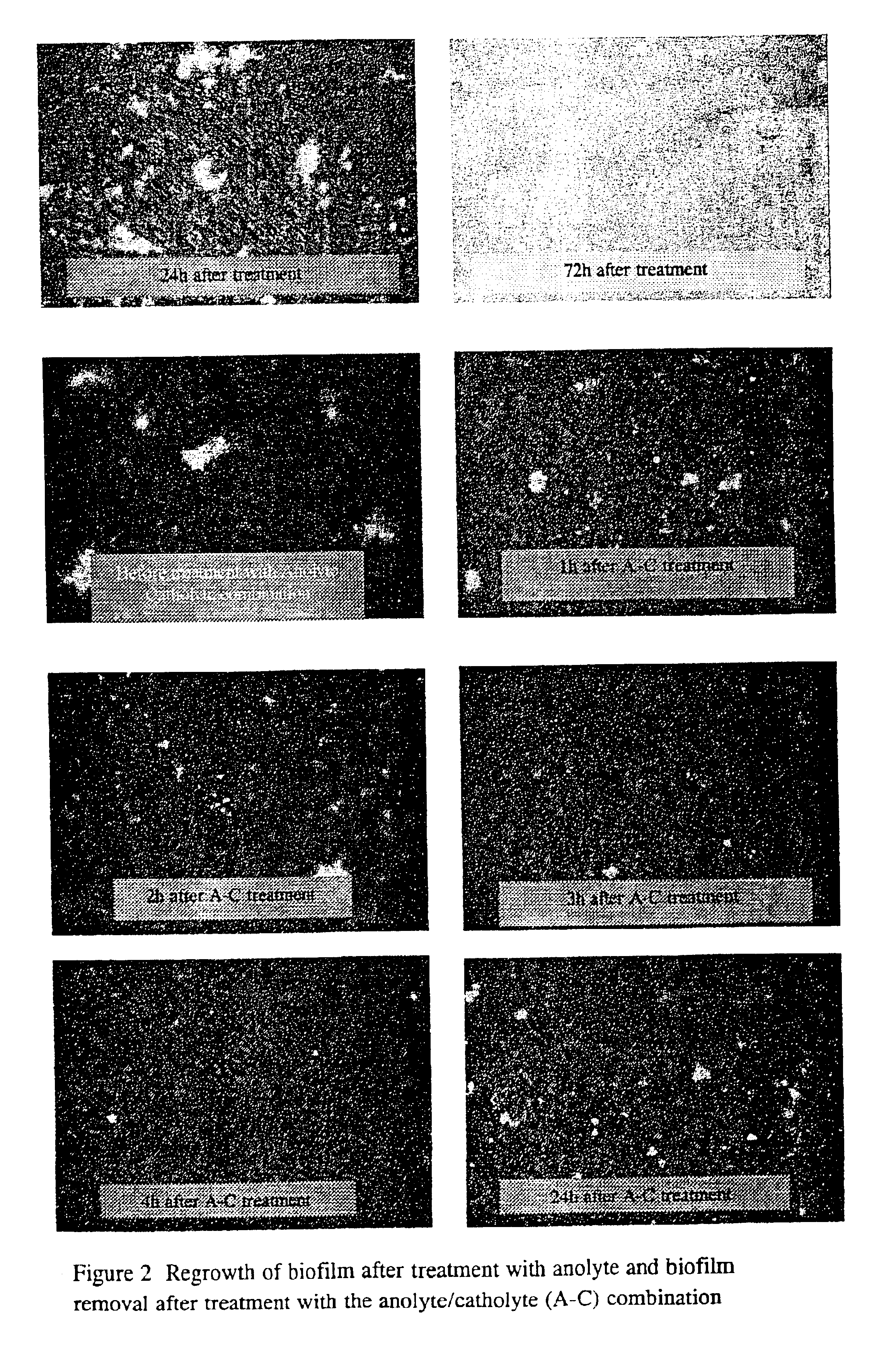
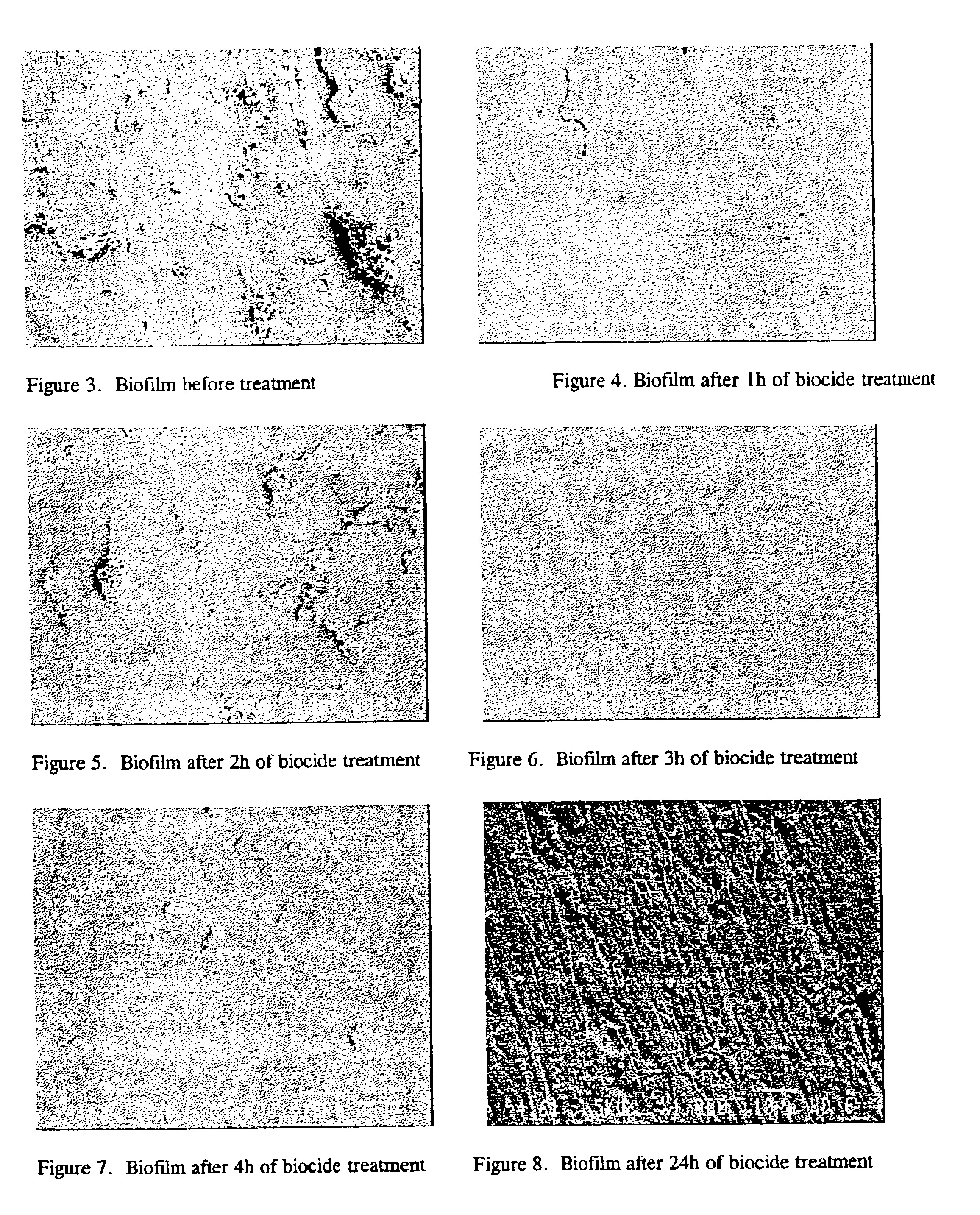
InactiveUS6878287B1Suitable for useEliminate biofilmElectrostatic separatorsElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisDental Equipment
An electrolytically activated, microcidal aqueous solution is disclosed which is used in the elimination and control of biofilm in dental unit water lines. The solution has a pH between 6.75 and 10 with microcidal as well as anti-oxidising, dispersing and surfactant properties, rendering the solution bio-compatible and non-corrosive, as well as capable of eliminating biofilm in dental unit water lines, while simultaneously dispersing and dislodging the biofilm from the water lines so as reduce the micro-organisms in the dental water to a predetermined level. The aqueous solution is produced using an electrolytic device that allows the independent manipulation of specific individual properties of two separate product streams (a cation-rich stream and an anion-rich stream), the manipulation being performed by separate and independent recirculation through the same electrode chamber or counter-electrode chamber of the electrolytic device to modulate the respective properties of the anion-containing and the cation-containing solutions.
Owner:RADICAL WATERS IP
Production of electrolytic water
InactiveUS20050189237A1Increase free chlorine production efficiencyPrevent adhesion of scaleCellsLiquid separation by electricityWater useElectrolysed water
Apparatus and methods are provided for producing electrolytic water using three chambers, rigid plates and ion exchange membranes. Benefits include reduced scale production and increased long-term bactericidal effects of the water produced.
Owner:ELECTROLYZER
Sewage treatment process and apparatus for synchronous electrogenesis desalinisation
ActiveCN101481178ARealize three effects in oneSimple processFinal product manufactureWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsElectronChemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of water resource processing, and in particular relates to a technology and a device for processing sewage from synchronous electricity generation and desalting, which comprises an anode chamber, an anion exchange membrane, a middle desalting chamber, a cation exchange membrane and a cathode chamber. An electric generation microorganism membrane is arranged on an anode. Sewage flows into the anode chamber and is removed by oxidization under the action of electric generation microorganisms, and electrons are conducted to the anode. Anions in the middle desalting chamber penetrate the anion exchange membrane to reach the anode, and cations penetrate the cation exchange membrane to reach the cathode to realize the desalting processing and form internal currents. The electrons reach the cathode by external circuit loading to generate reduction reaction to realize the electricity generation process. The internal currents of the microorganism fuel battery are used for sewage processing, electric generation and desalting. The technology of the invention is simple and easy to operate and has low energy consumption and high efficiency. The device is simple in structure and is convenient for industrial production and utilization.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Water treatment
InactiveUS20060000784A1Good removal effectReduce needWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsSludgePotable water
This is a method of water and wastewater treatment for removal of pollutants in at least two-step process comprising (a) treatment of water producing at least partially treated intermediate effluent, (b) treatment of the intermediate effluent with a sacrificial metal and producing ions of said sacrificial metal, and providing very thoroughly treated effluent, (c) recuperating sacrificial metal ions generated in the step (b) and recycling the recuperated ions in the step (a), the recuperated and recycled ions from the step (c) improve treatment efficiency of step (a) by additionally removing pollutants from the intermediate effluent using recuperated ions, resulting in cleaner intermediate effluent, and, therefore, the pollutant loading rate in step (b) is reduced, intermediate effluent is further treated more thoroughly, and the demand for the sacrificial metal in step (b) is reduced. Step (a) can preferably be a biological, biological-abiotic, physical chemical, or combination of these steps. Step (b) is preferably a spontaneous cementation-driven electrochemical process. The combination of said steps (a), (b) and (c) produces a synergistic effect resulting in improved removal of said pollutants and in reduced need in said sacrificial metal. For example, a drinking quality water can be very economically and reliably obtained from wastewater. In addition to the superb treatment efficiency and reduced reagent requirements, the waste sludge from the system is beneficially disposed in-sewers, in sanitary landfills or on land.
Owner:KHUDENKO BORIS
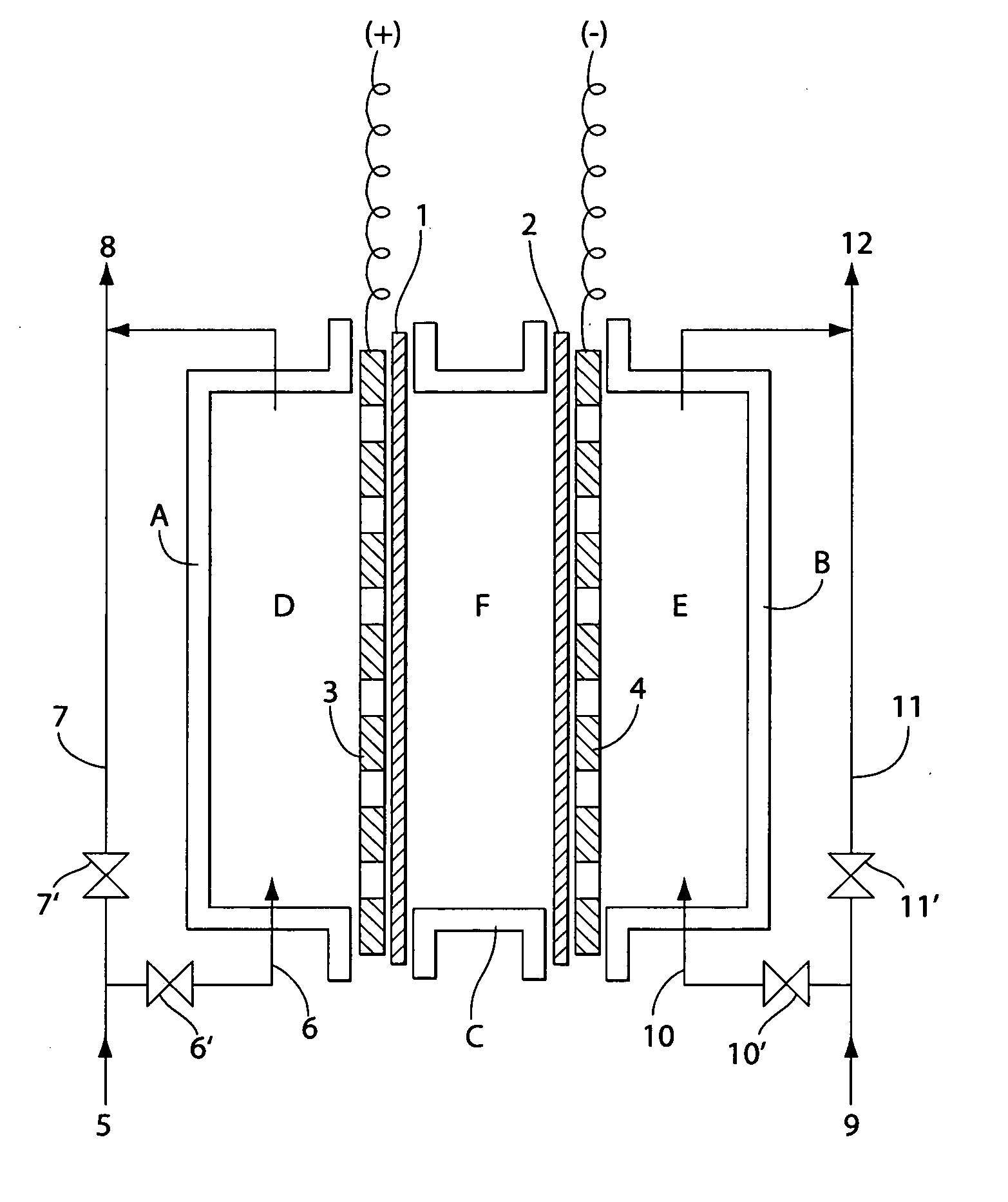
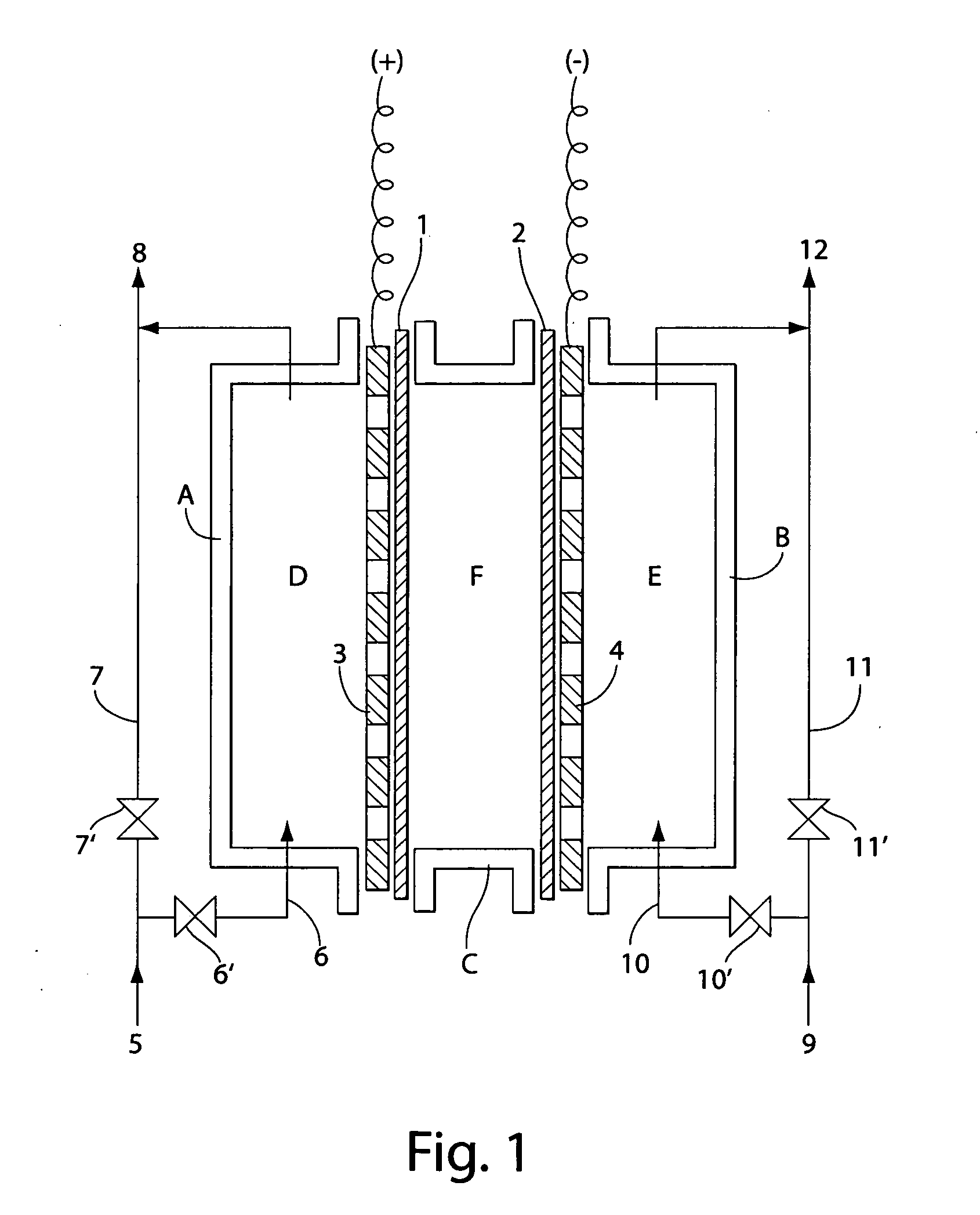
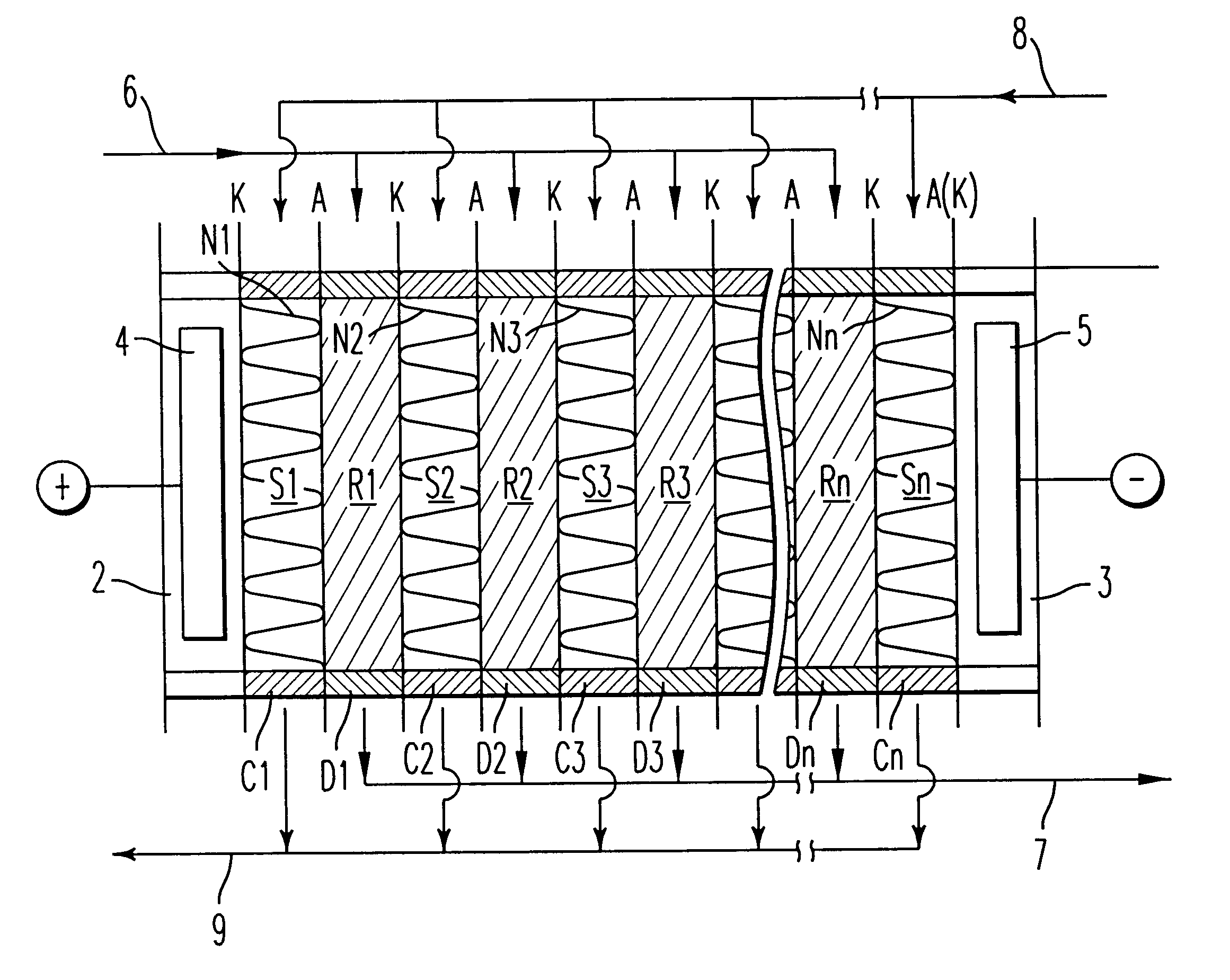
Method and apparatus for producing deionized water
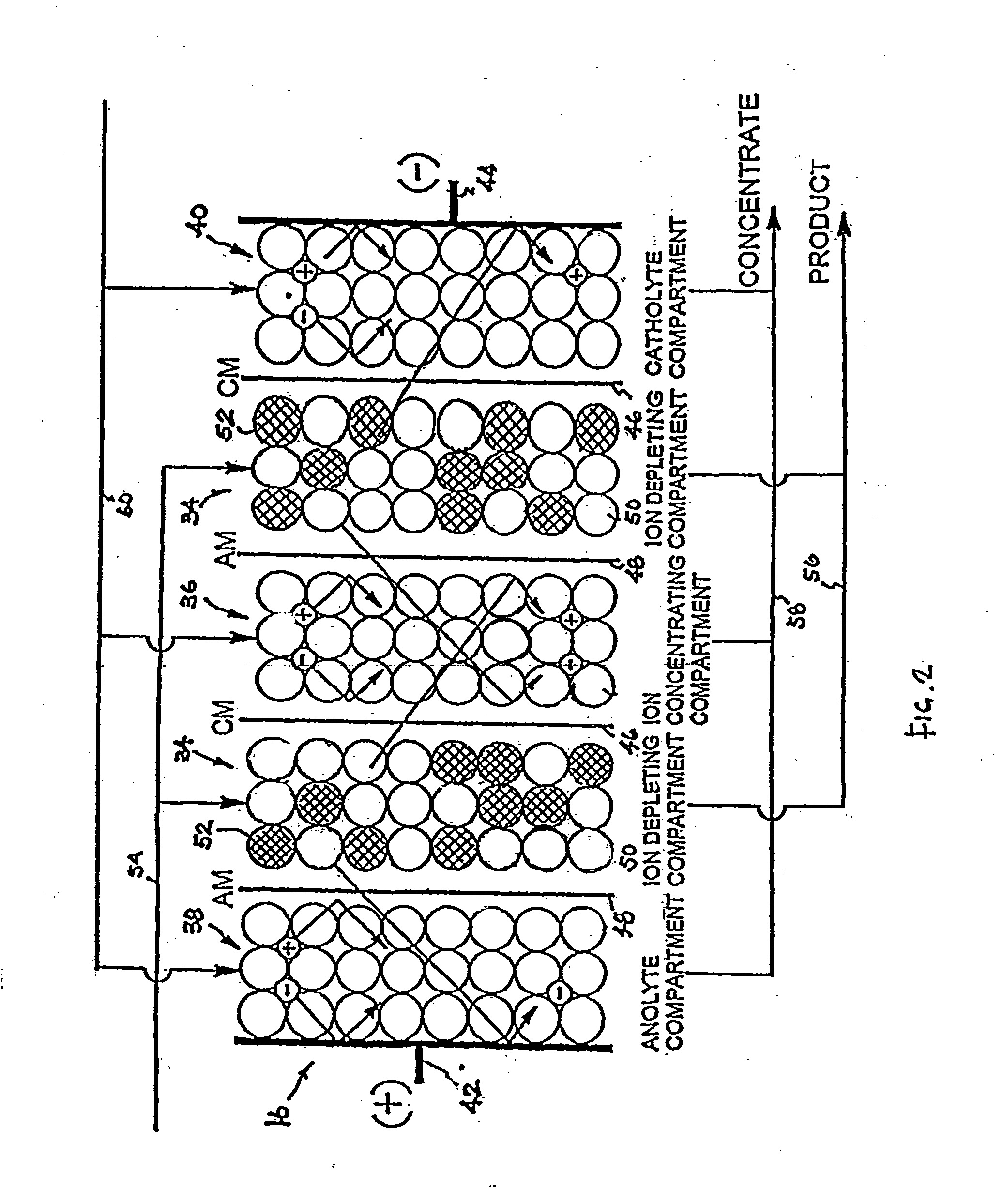
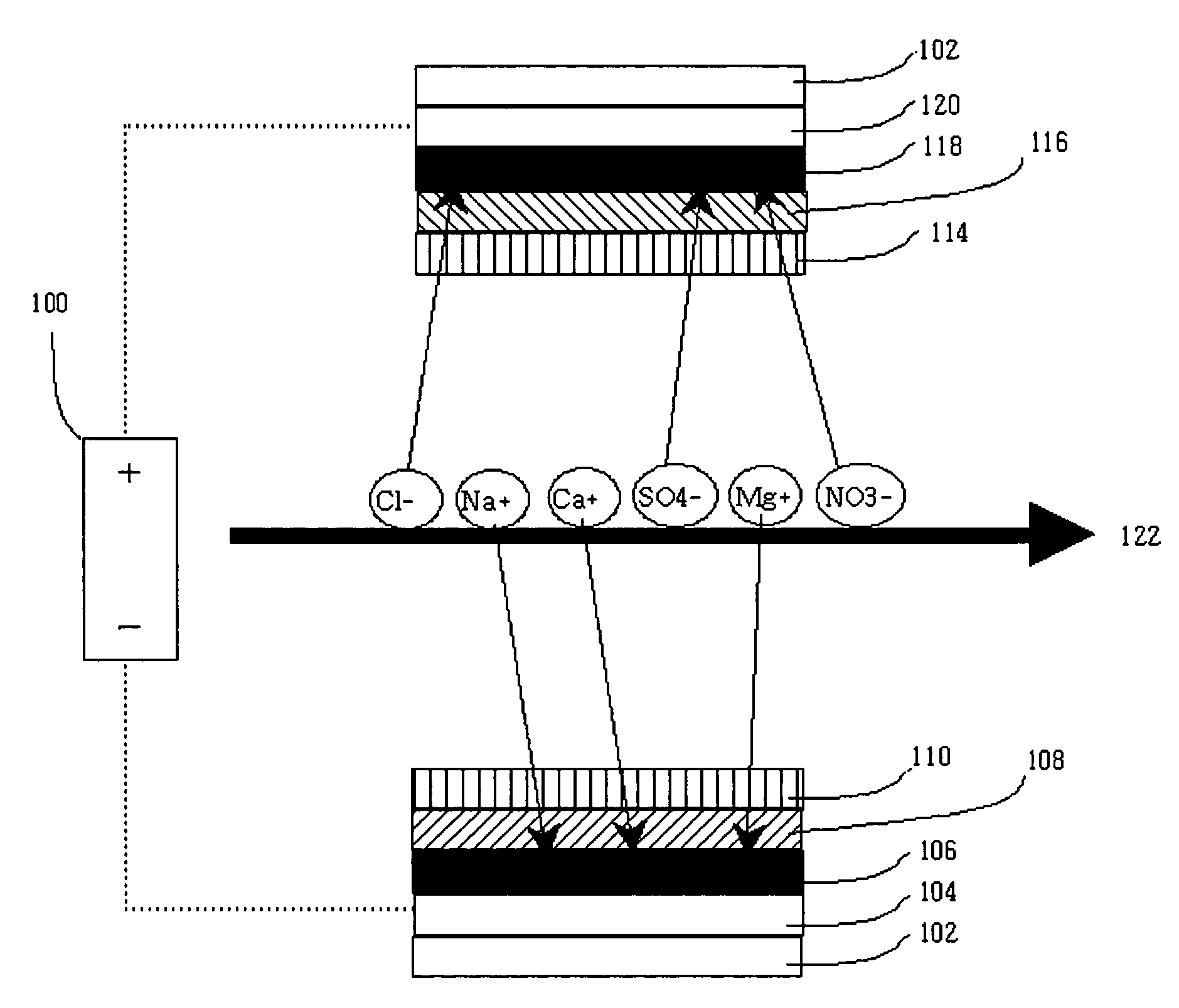
InactiveUS6228240B1Improve the immunityPure waterSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementIon-exchange membranesChemistry
An apparatus for producing deionized water consisting essentially of an electrodialyzer having cation exchange membranes and anion exchange membranes alternately arranged between a cathode and an anode to form demineralizing compartments and concentrating compartments, and ion exchangers accommodated in the demineralizing compartments, wherein a pressure of from 0.1 to 20 kg / cm2 is exerted between the ion exchangers accommodated in the demineralizing compartments and the cation exchange membranes and anion exchange membranes defining the demineralizing compartments.
Owner:GE WATER
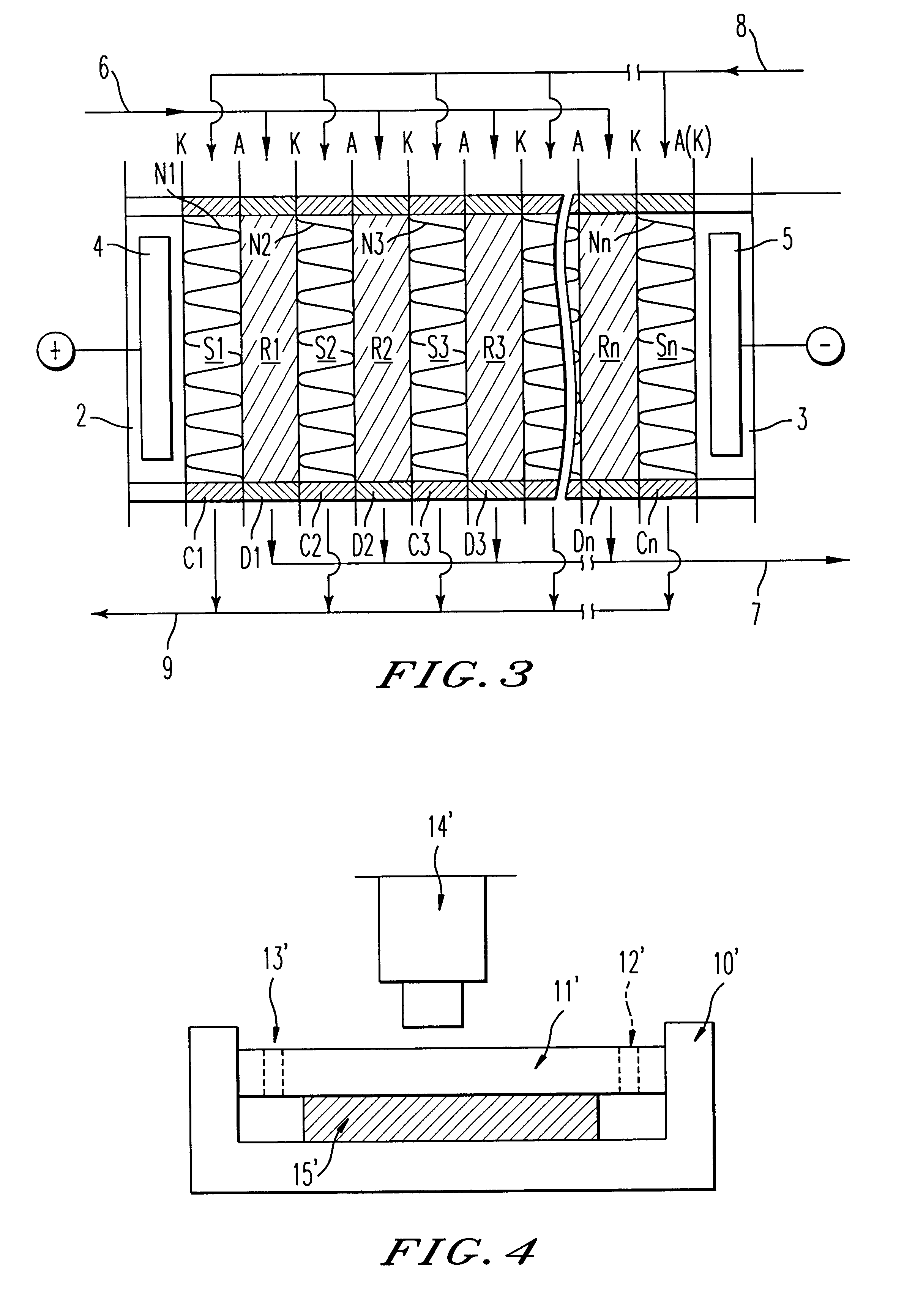
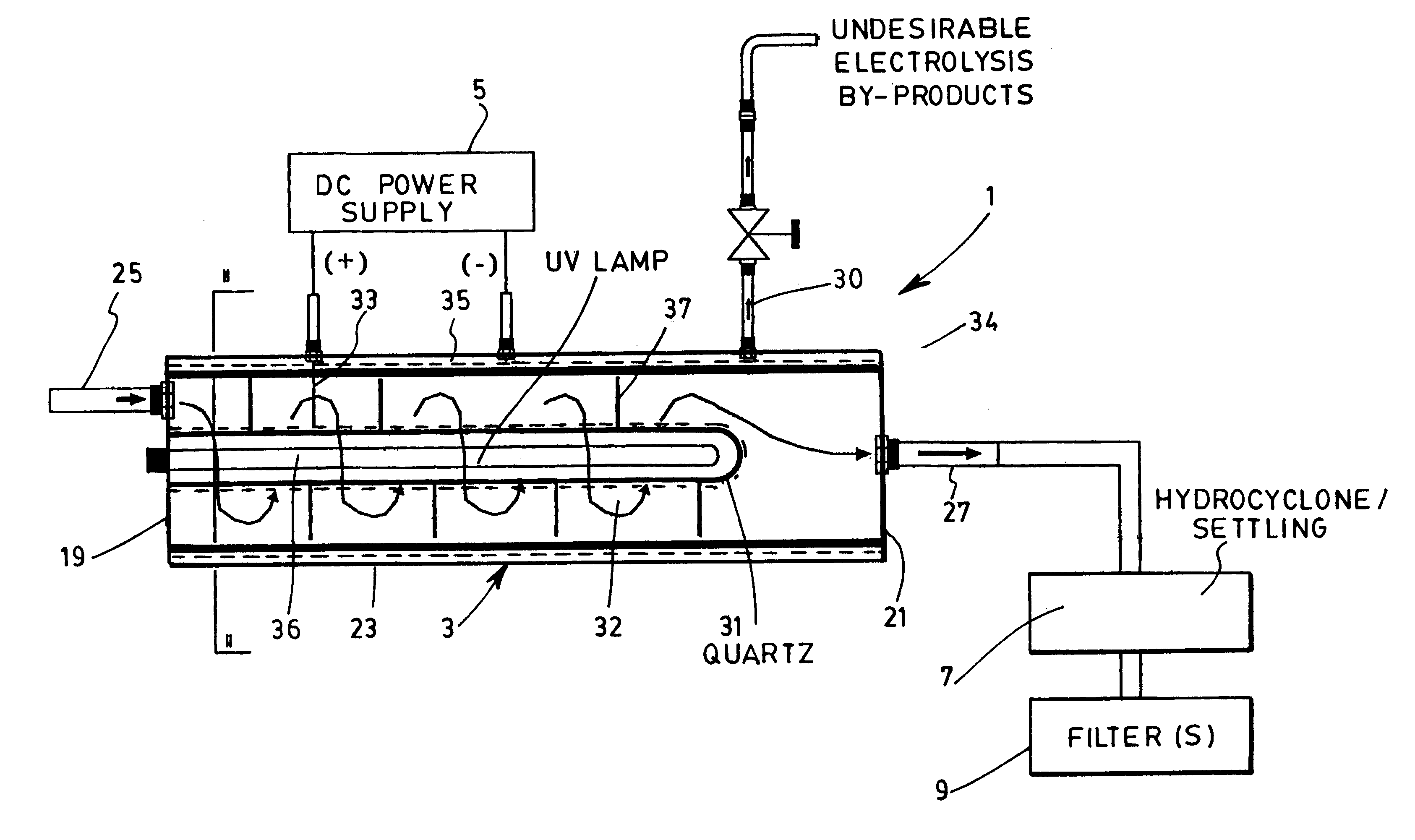
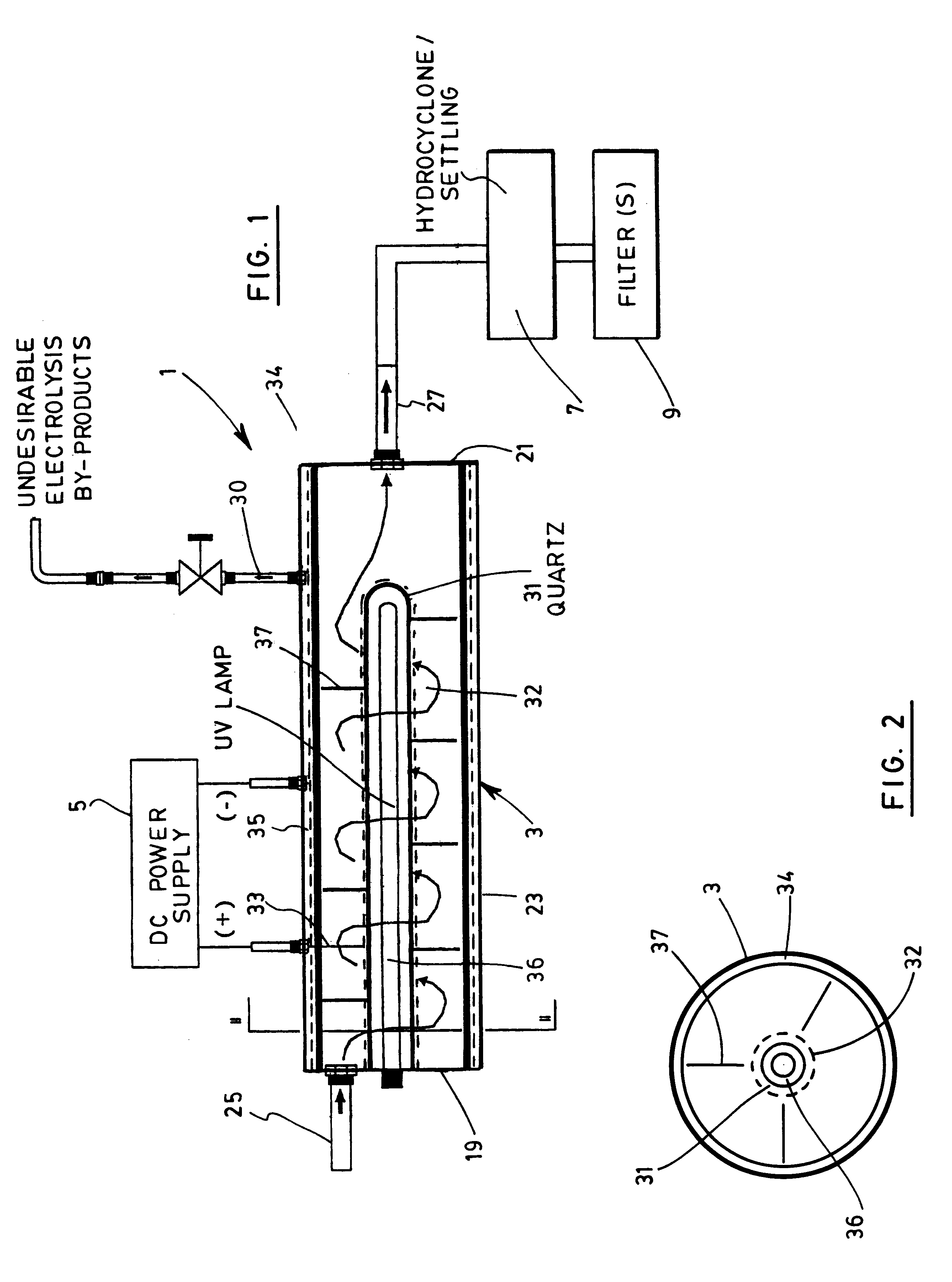
Device and method for treating water with ozone generated by water electrolysis
InactiveUS6180014B2Economical and efficient methodPhotography auxillary processesDisinfectionHigh concentrationElectrolysis
A process and a device for the treatment of water, especially for removing therefrom a large variety of pollutants, especially organic, inorganic and biological pollutants through in situ generation of ozone. Ozone is economically produced in situ at a high concentration through the interaction of electrolytically produced oxygen and UV light having a wavelength of 189 nm. The device has a set of anode and cathode for electrolytically producing nascent oxygen which reacts with UV light at a wavelength of 189 nm to produce ozone "in situ" within a vessel where the polluted water is submitted to the combinative action of ozone and other oxidation reactions. The device also has a hydrocyclone or retention tank of removing cationic pollutants such as heavy metals, free radicals as well as undesirable electrolysis byproducts such as nascent hydrogen through a secondary outlet. Oxidation by-products are subsequently removed from the exiting water stream by means of decantation, flocculation, coagulation or filtration.
Owner:SALAMA AMIR
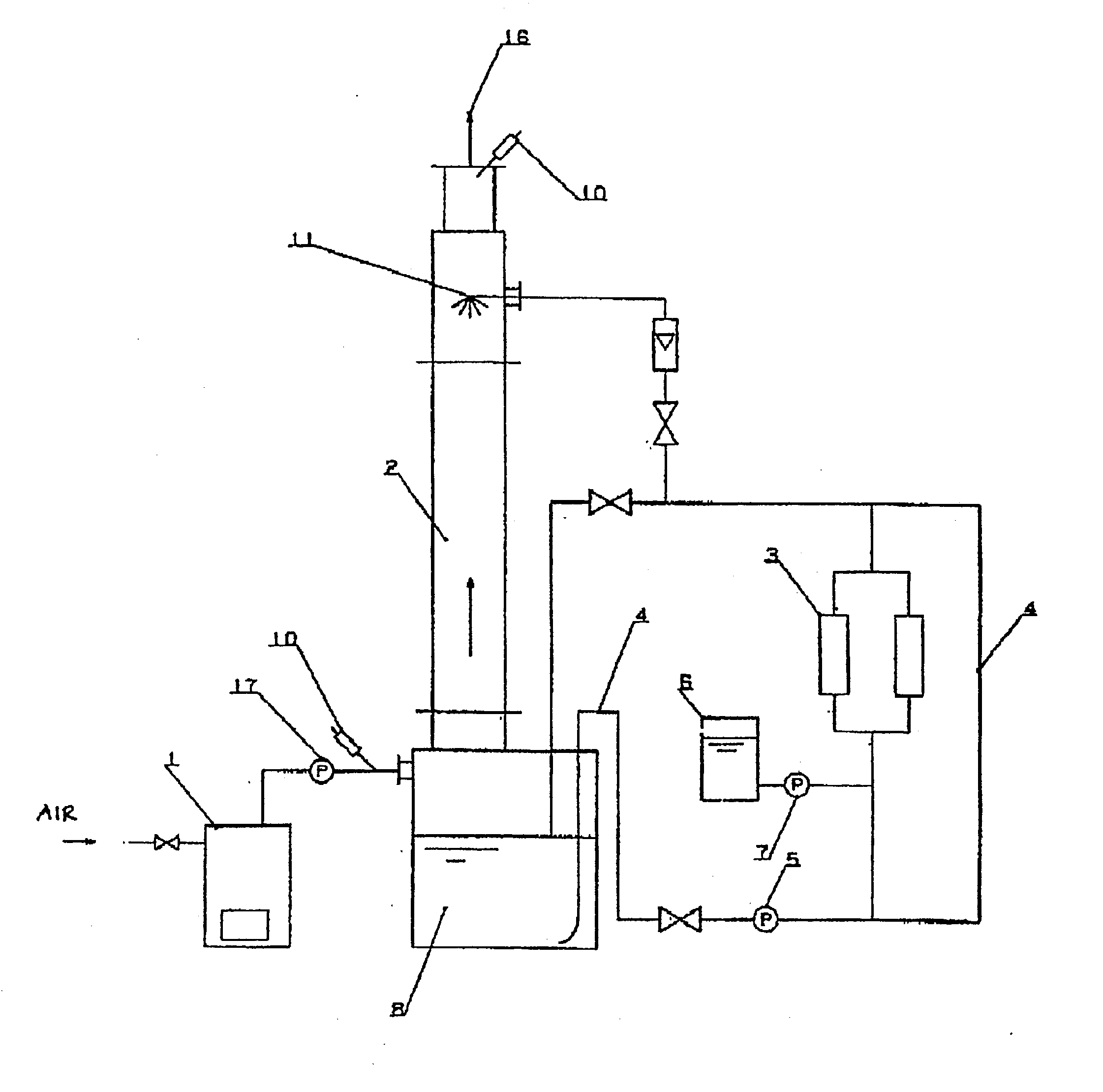
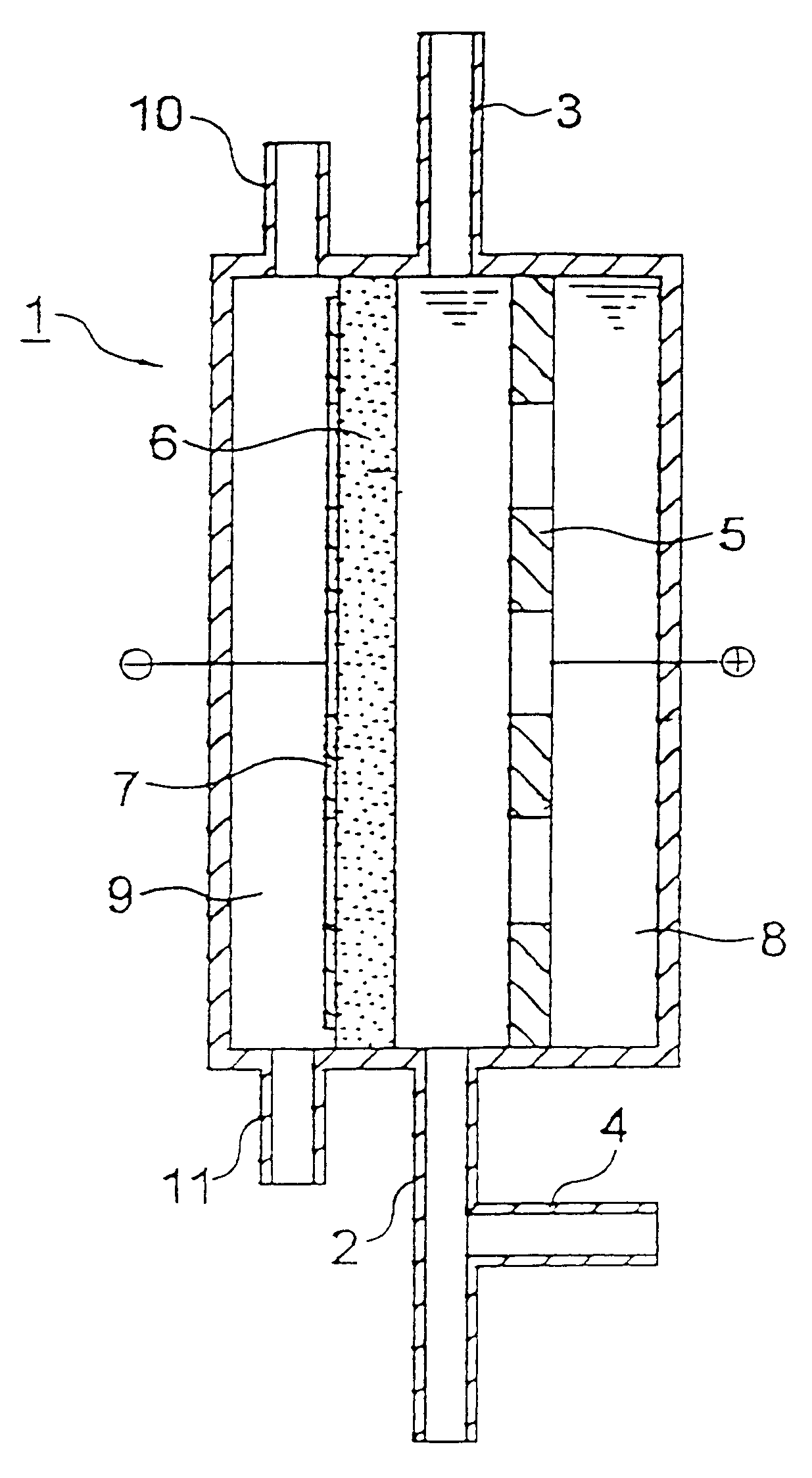
Method and apparatus for water treatment
A method and apparatus for water treatment. The method comprises supplying an oxygen-containing gas to cathode 6 to yield hydrogen peroxide, supplying an inorganic acid to anode 5 through an acid solution addition opening 4 to yield an oxidation product, e.g., hypochlorous acid, and using both the hydrogen peroxide and oxidation product thus generated to treat a liquid to be treated. The atmosphere around the cathode surface is kept neutral to acidic due to the acidity of the coexisting oxidation product to thereby inhibit the deposition of metal hydroxides.
Owner:DE NORA PERMELEC LTD
Treatment of a waste stream through production and utilization of oxyhydrogen gas
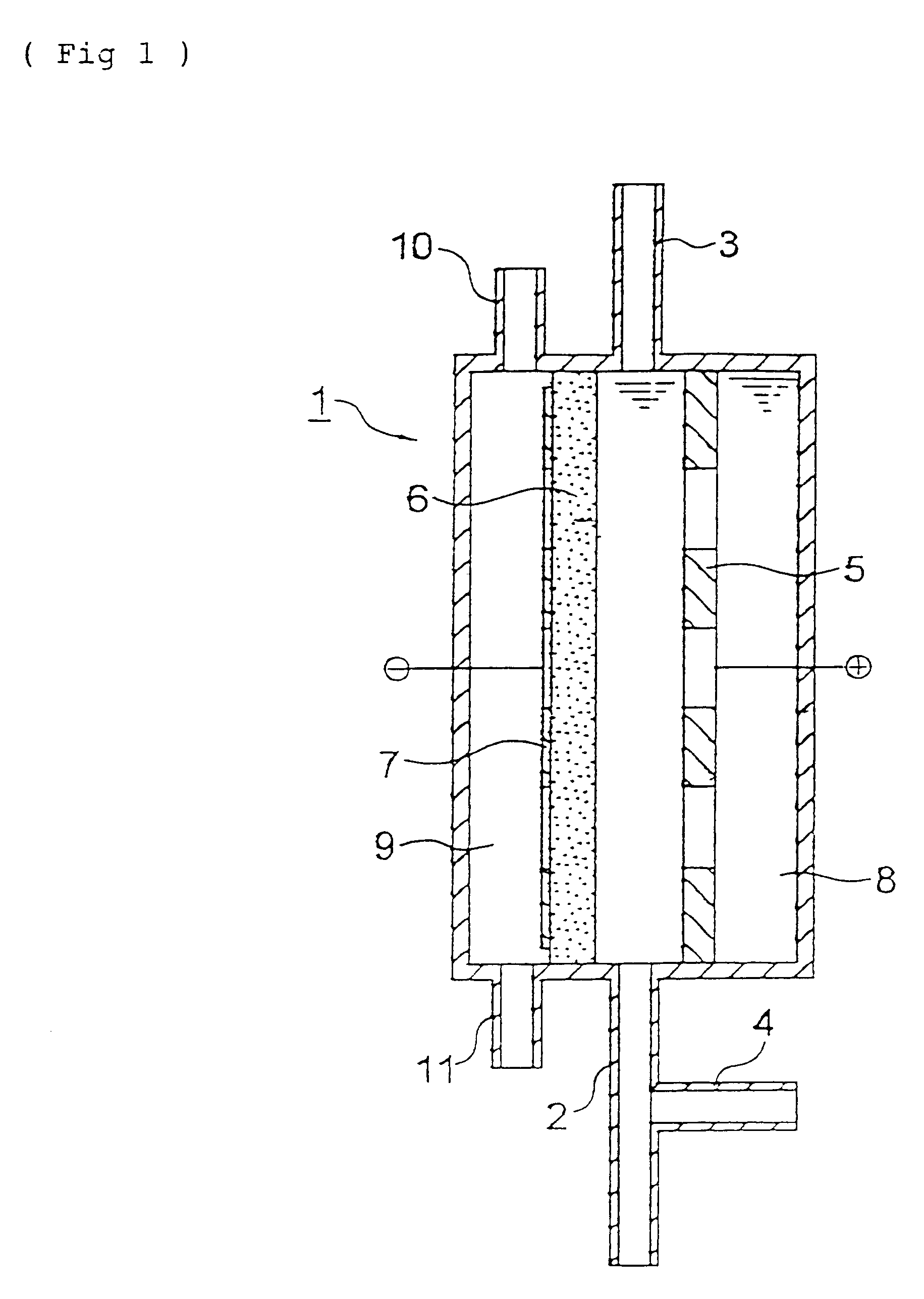
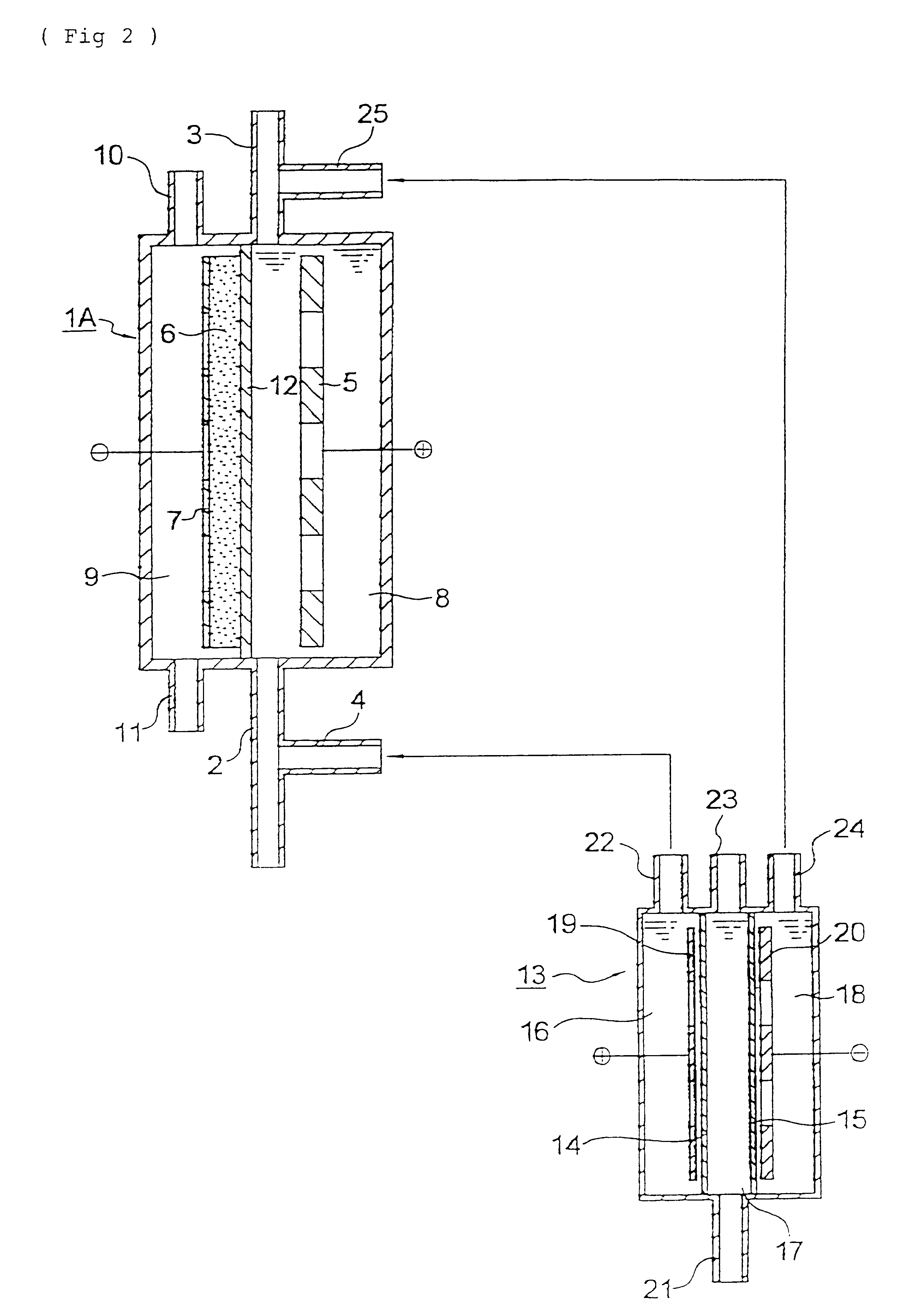
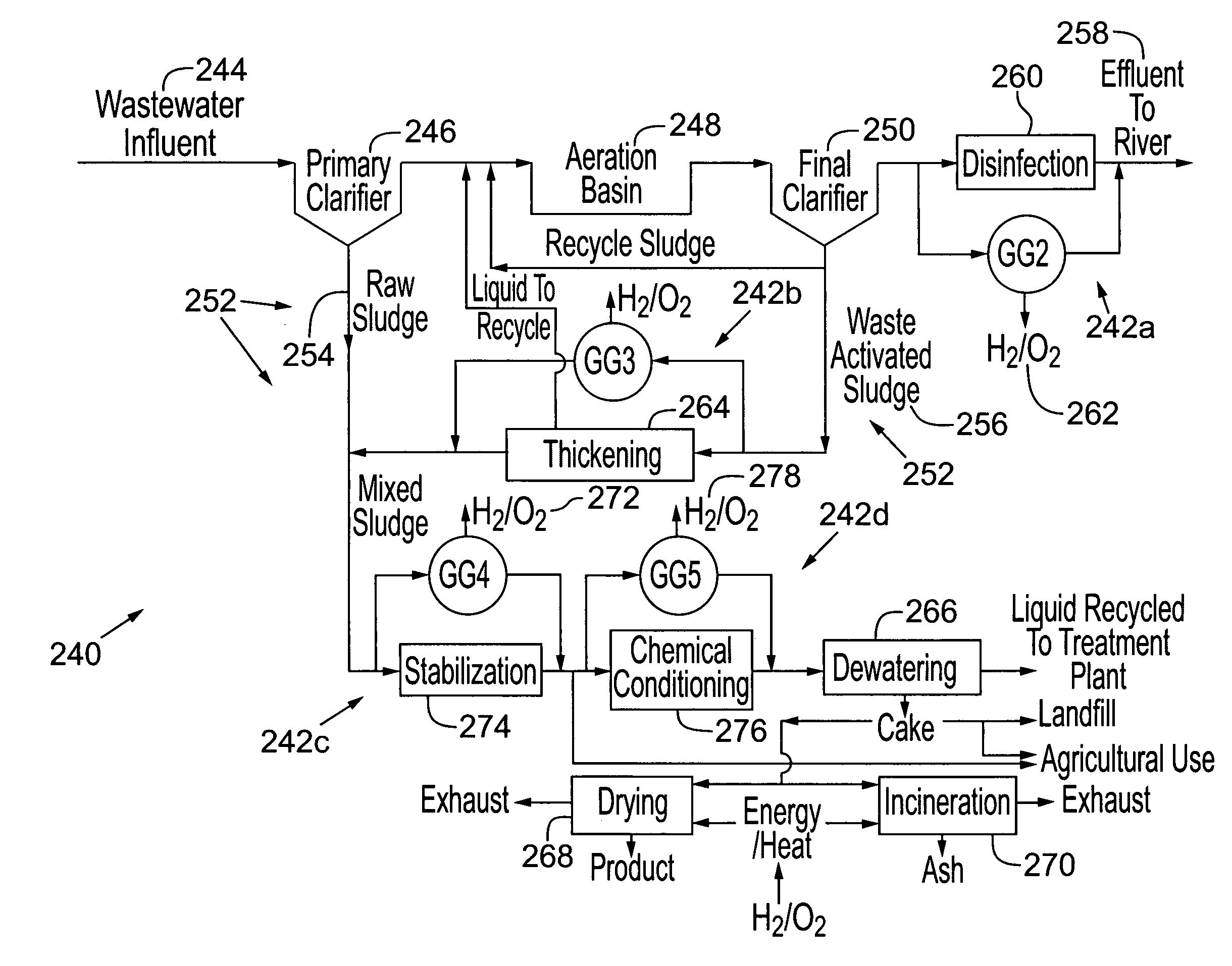
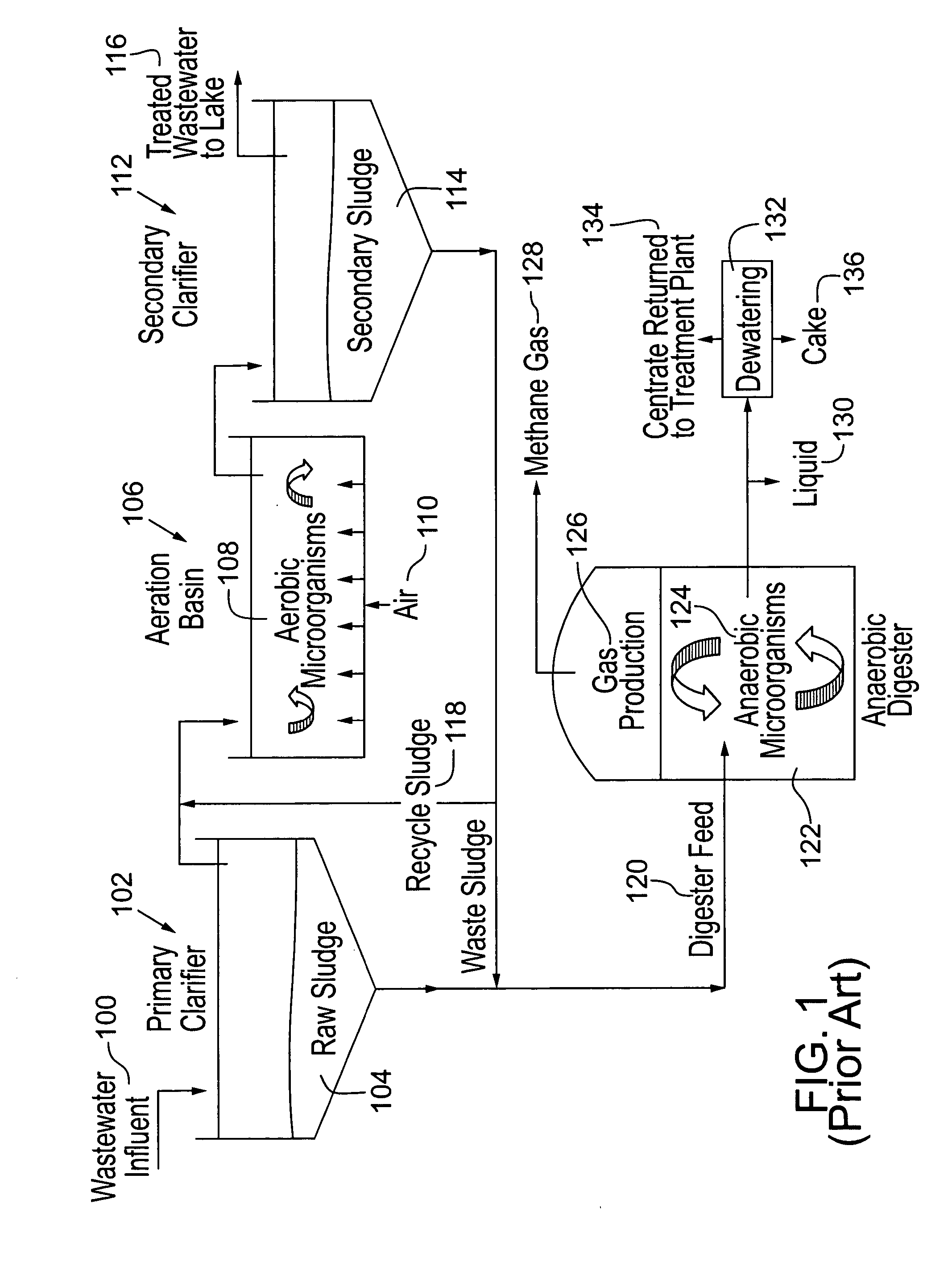
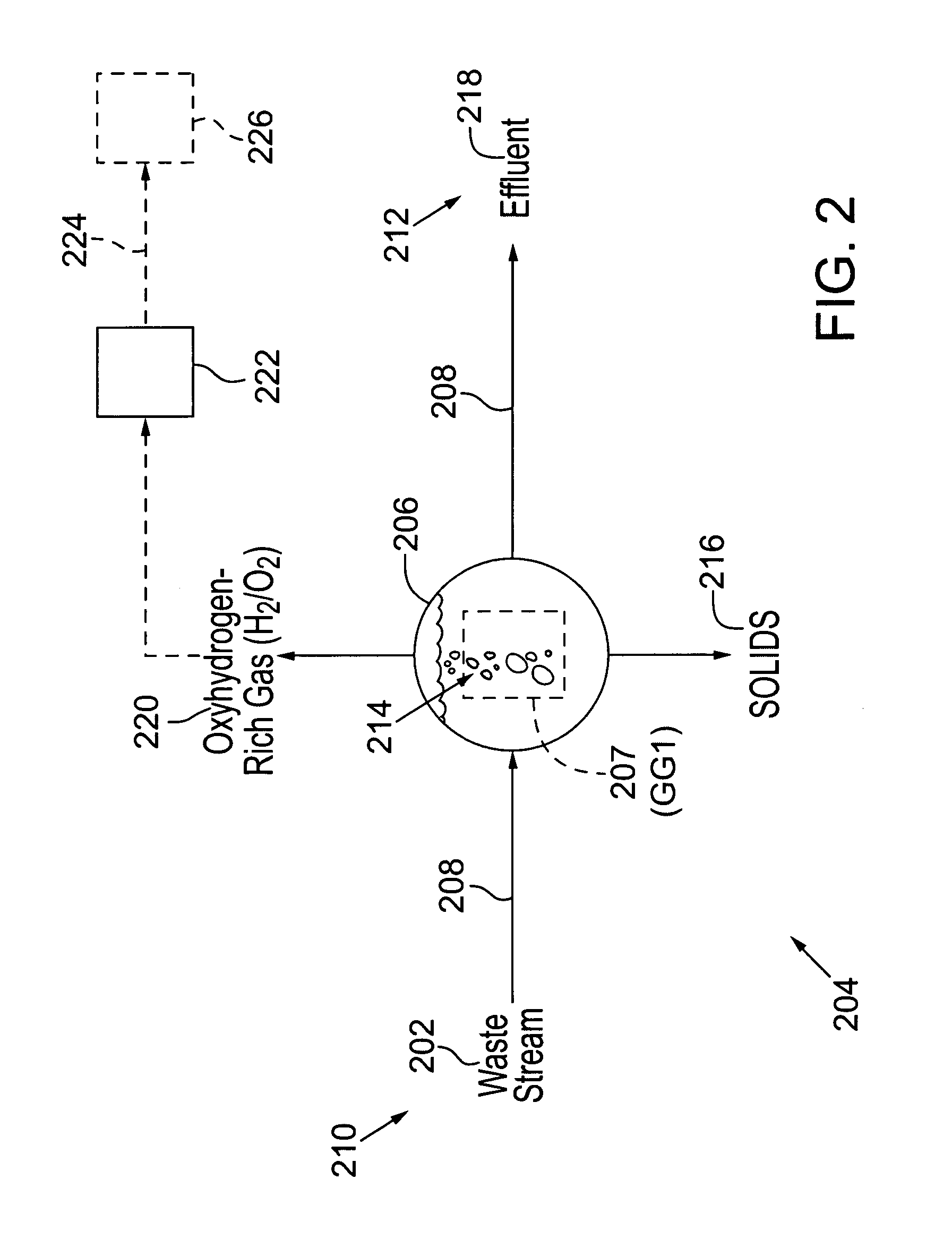
Methods and systems for treating a waste stream in a waste treatment system involve performing a unit process of the waste treatment system by contacting the waste stream with oxyhydrogen-rich gas generated on-site by an oxyhydrogen gas generator that implements water dissociation technology. In a preferred embodiment, the oxyhydrogen gas generator involves applying a pulsed electrical signal to a series of closely-spaced electrodes that are submerged in the waste stream to produce oxyhydrogen-rich gas from a water component of the waste stream. Operation of the oxyhydrogen gas generator in the waste stream may accomplish one or more unit processes for waste treatment, such as conditioning, stabilization, thickening, and dewatering, among others. At least a portion of the oxyhydrogen-rich gas can be conveyed for a second use in the waste treatment system, such as a source of combustible fuel for incineration or power generation, for example.
Owner:XOGEN TECH
Sanitization system and system components
InactiveUS7767168B2Easy to adaptUsing liquid separation agentMixing methodsOzone generatorVapor–liquid separator
A multi-use sanitization system is disclosed which includes one or more containers in fluid communication with other system components. Components of the system include an ozone contacting device, such as a vortex-venturi or a sparger, for incorporating ozone into a liquid, an ozone generator to provide ozone to the vortex-venturi, a fluid transfer valve to allow simultaneous flow of liquid into and out of the container, and a pump to promote fluid flow through the system. Optionally, a gas-liquid separator with an optional integral gas release valve, an ozone destructor, an oxidation-reduction potential ozone sensor, or a pour-through type pre-filter may be incorporated into the system.
Owner:TERSANO INC
Brine purification
InactiveUS20100219372A1Increase contentLower levelTreatment using aerobic processesIsotope separationSaline waterCarbon adsorption
Process and apparatus for reducing organic content of brine comprising subjecting a brine solution to at least two purification treatments selected from electrochemical treatment, chlorinolysis, or other chemical oxidation treatment, carbon adsorption, extraction, biological treatment and chrystallizing treatment; wherein the organic content of purified brine is sufficiently low to enable sense of the purified brine in an industrial process.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Apparatus for purifying water
InactiveUS7238278B2Reduce concomitant disadvantageEconomical purification processLiquid solutions solvent extractionLoose filtering material filtersHypohaliteMetal salts
The invention relates to a method for purifying water by forming in an electrolytic cell molecular halogen, hypohalic acid, hypohalite ions or combinations thereof, from halide ions dissolved in the water; and dissolving one or more soluble metal salts in the water to provide corresponding metal ions. The invention also relates to a system for purifying water, having an electrolytic cell comprising a plurality of electrodes sufficient to electrolytically convert halide ion in the water into molecular halogen, hypohalic acid, or hypohalite ions, or combinations thereof; and a metal generator, which provides concentrations of one or more metals to the water.
Owner:ZODIAC POOL SYST LLC
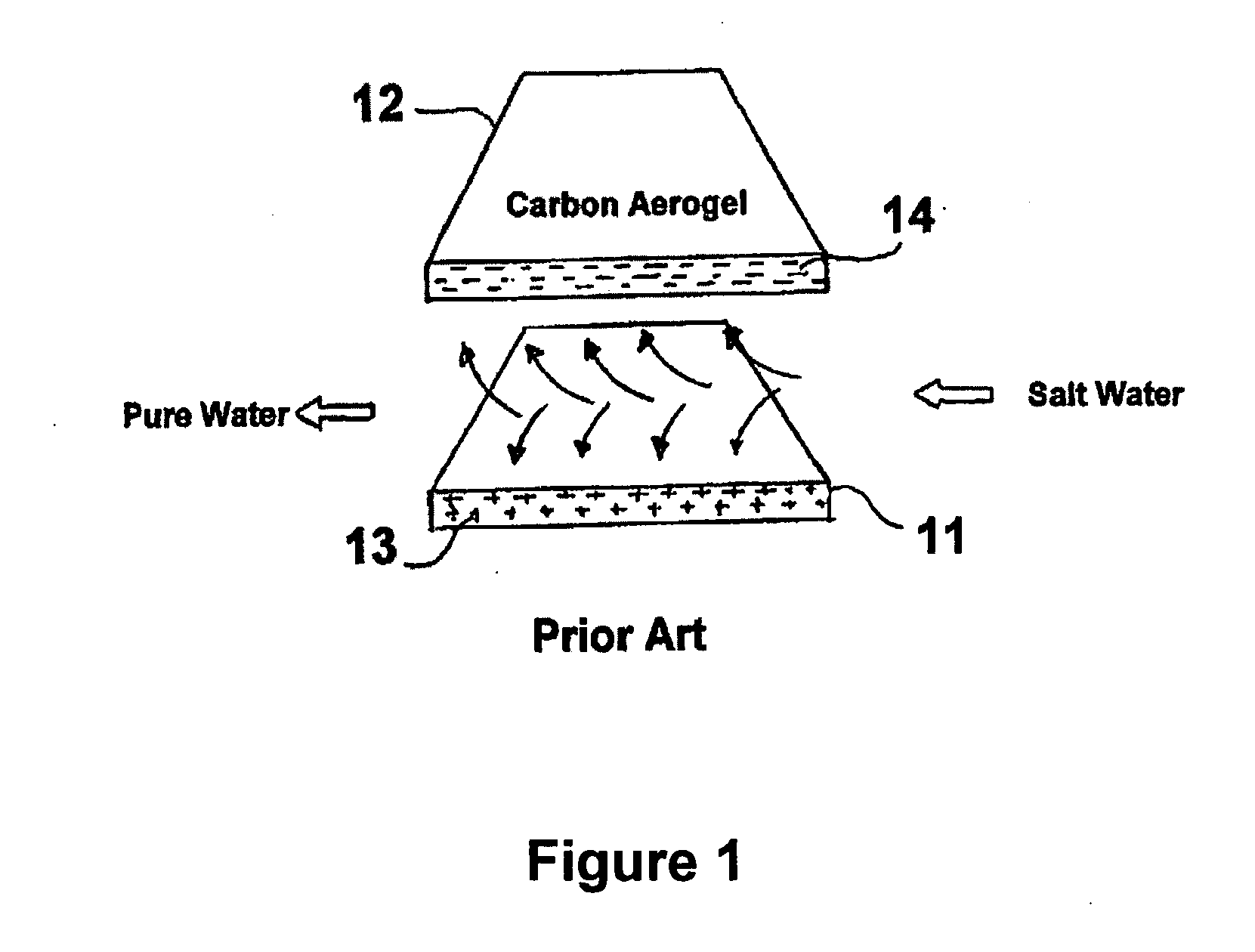
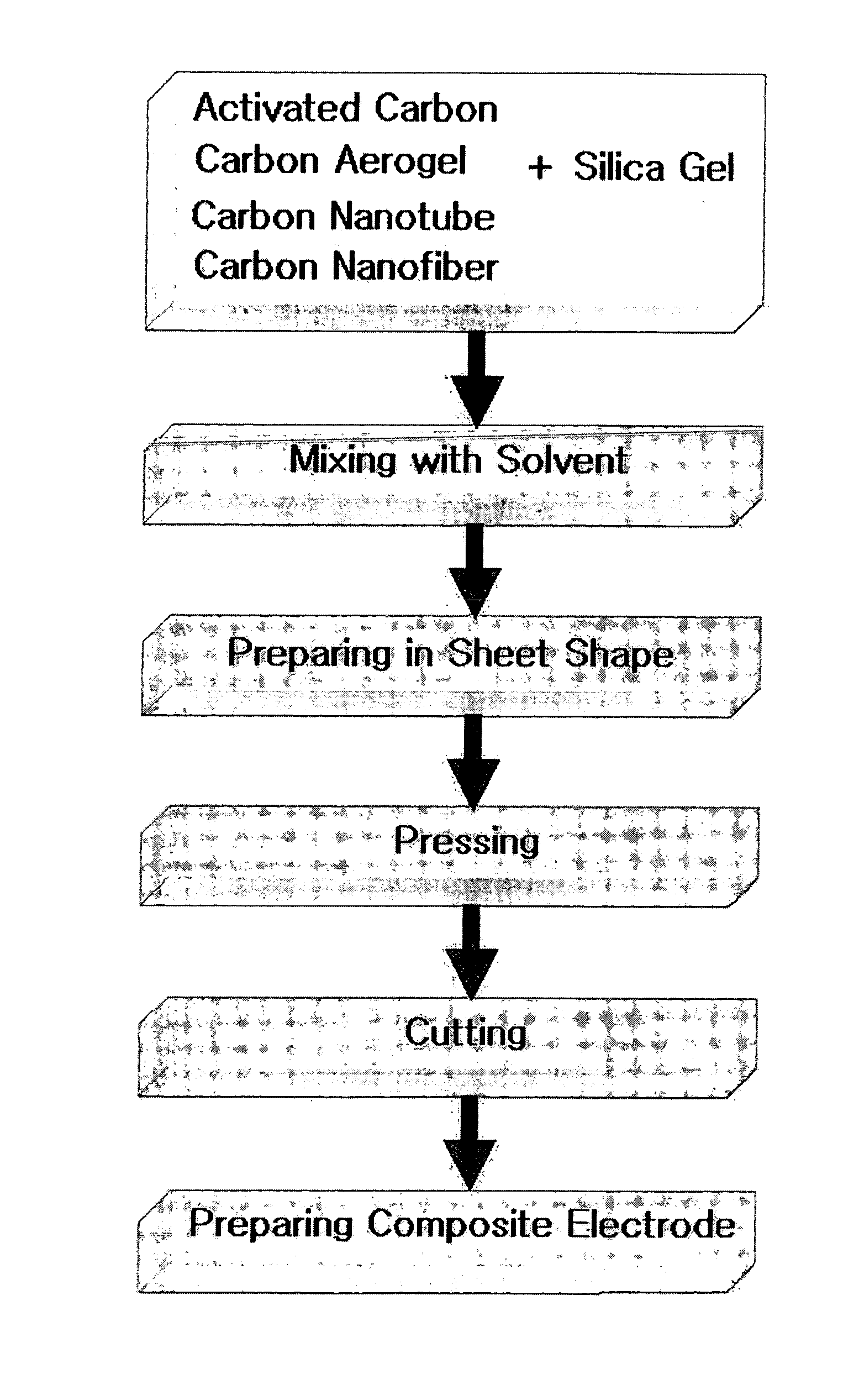
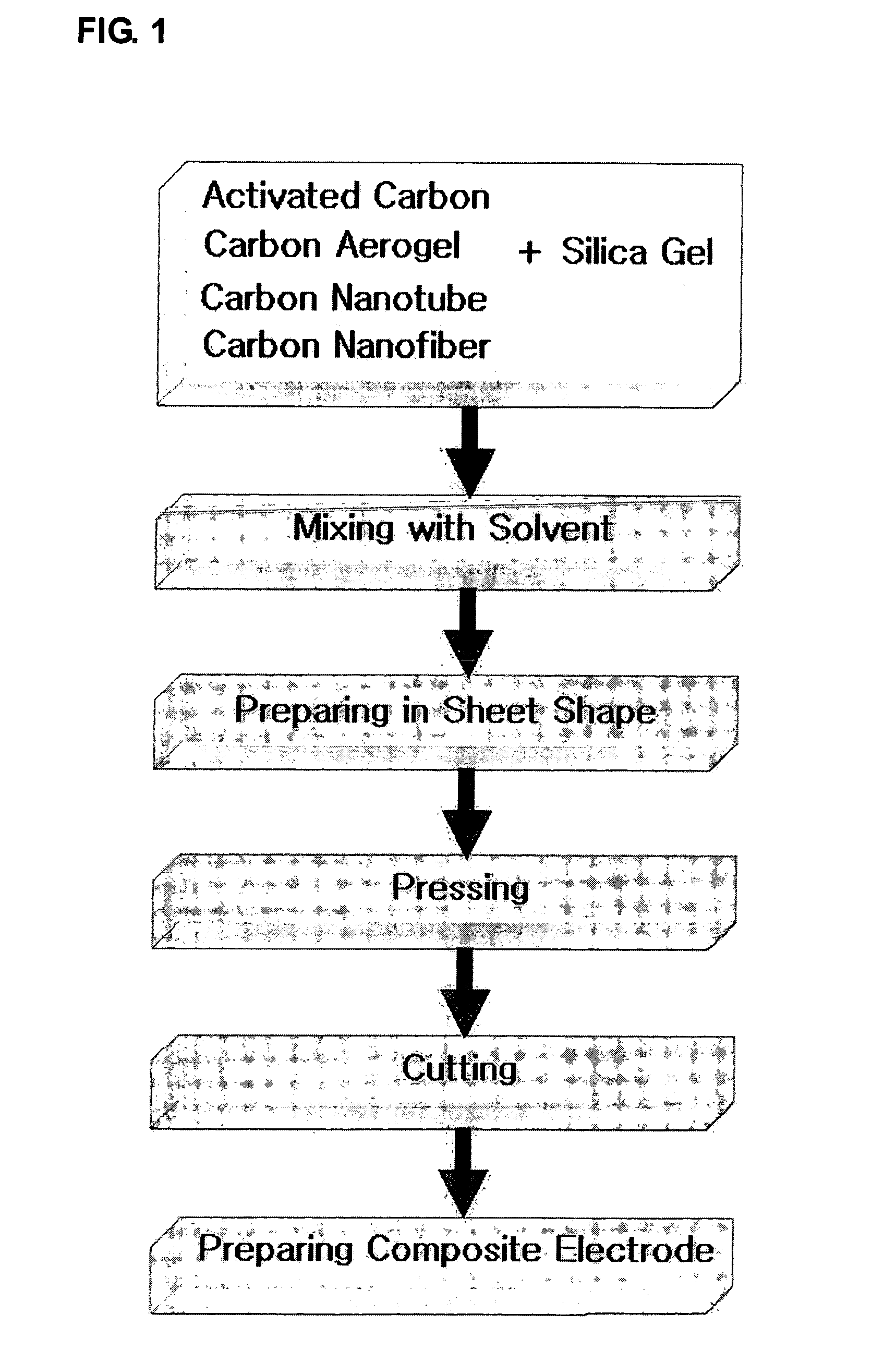
Carbon-porous media composite electrode and preparation method thereof
InactiveUS20050155216A1Improve hydrophilicitySimple processMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolytic capacitorsWater useCapacitance
The present invention discloses a carbon-porous media composite electrode material, a composite electrode using the same and a preparation method thereof. The carbon-porous media composite electrode can be applied for a device such as a secondary battery, a capacitor or the like, or for preparing ultra pure water using a capacitive deionization process, purifying salty water or the like.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Treatment of humans with colloidal silver composition
Owner:AMERICAN SILVER LLC
Mediated electrochemical oxidation process used as a hydrogen fuel generator
InactiveUS20050161342A1Improve efficiencyLiquid separation by electricityWater/sewage treatment using germicide/oligodynamic-processFuranUltraviolet
A mediated electrochemical oxidation process and apparatus are used to process biological and organic materials to provide hydrogen and oxygen for use as fuel in numerous types of equipment. Waste materials are introduced into an apparatus for contacting the waste with an electrolyte containing the oxidized form of one or more reversible redox couples, at least one of which is produced electrochemically by anodic oxidation at the anode of an electrochemical cell. The oxidized species of the redox couples oxidize the organic waste molecules and are themselves converted to their reduced form, whereupon they are reoxidized and the redox cycle continues until all oxidizable waste species have undergone the desired degree of oxidation. The entire process takes place at temperatures to avoid any possible formation of either dioxins or furans. The oxidation process may be enhanced by the addition of ultrasonic energy and / or ultraviolet radiation.
Owner:SCIMIST LNC
Water treatment system and method
ActiveUS20050103723A1Less corrosiveVolume/mass flow measurementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsWater treatment systemTreated water
A method and apparatus for producing purified water. Treated water may be provided for domestic use wherein the water may be treated by removing selected dissolved species while retaining properties that may improve the properties or aesthetics of the water.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Submerged-type electrosorption-based water purification apparatus and method thereof
ActiveUS20070284313A1Improve efficiencyPromote recoverySeawater treatmentCell electrodesElectricityIndustrial effluent
Provided is a submerged-type, electrosorption-based desalination apparatus for water purification and method, comprising applying a DC voltage of 0.1 to 2.0 volts to a carbon electrode of the reactor to thereby adsorb inorganic ions on the carbon electrode, and reversely applying the same DC voltage having opposite polarity to recycle regeneration solution to the outside of the apparatus or into the treatment tank, thereby enhancing a recovery rate. In addition, in order to improve desalination efficiency, the reactor used in the desalination apparatus may be embodied in various forms of T-shaped, linear type, single, composite, and ion exchange membrane electrodes. Therefore, the present invention may be applied to remove inorganic ions from industrial wastewater, sea water, and brackish water, which contain large amounts of inorganic ions.
Owner:KOREA ELECTRIC POWER CORP
Popular searches
Dispersed particle separation Scale removal and water softening Water/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fields Water/sewage treatment by ion-exchange Water/sewage treatment by degassing Electrodialysis Water/sewage treatment apparatus Reverse osmosis Water/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysis Multistage water/sewage treatment
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com