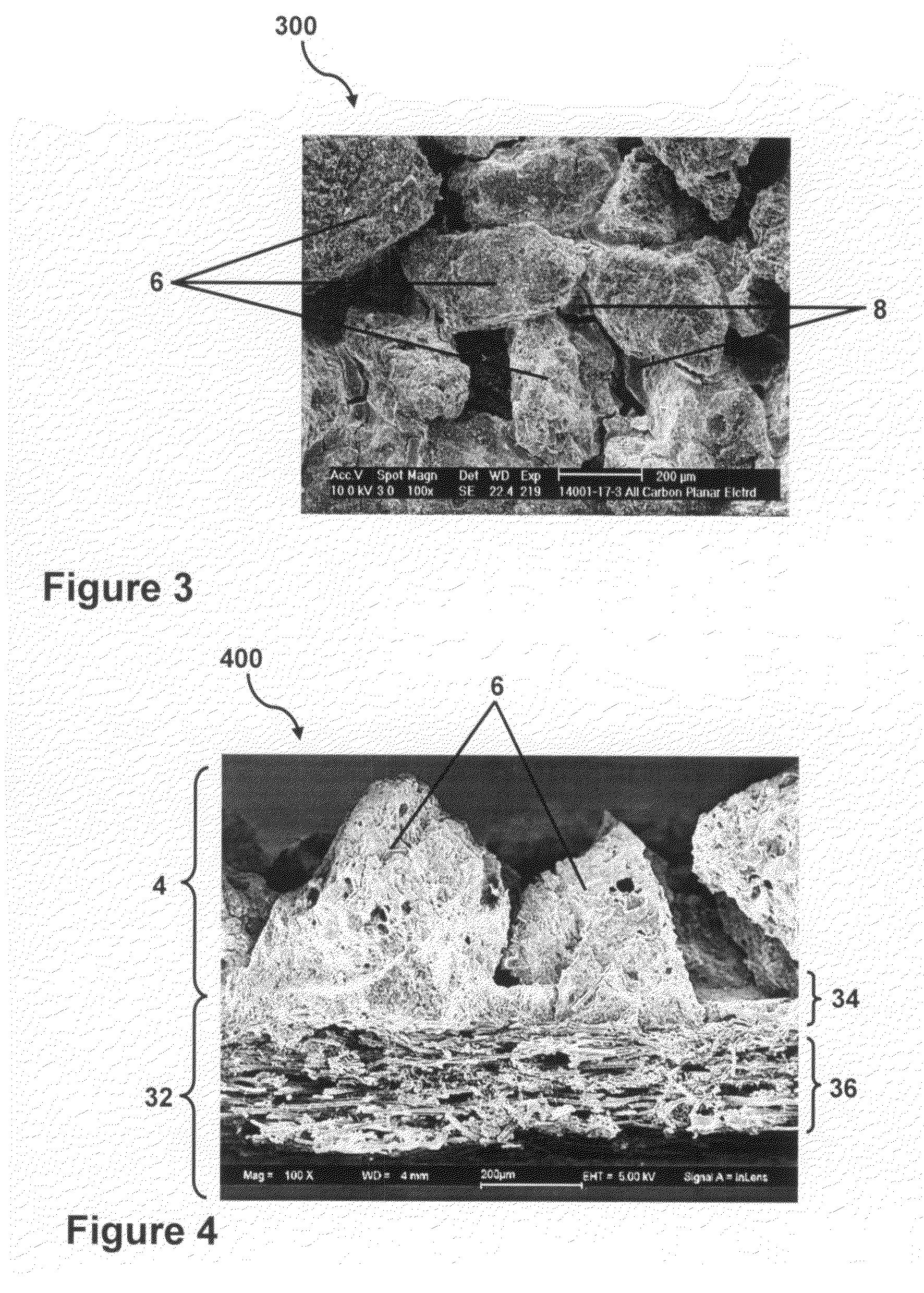
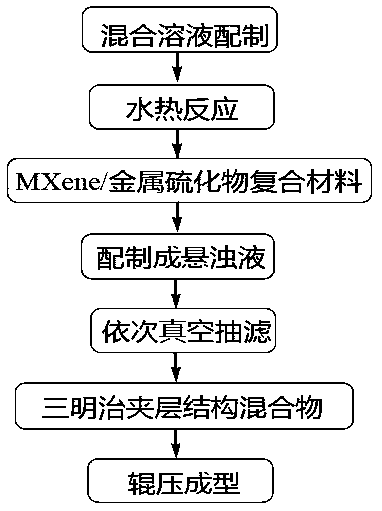
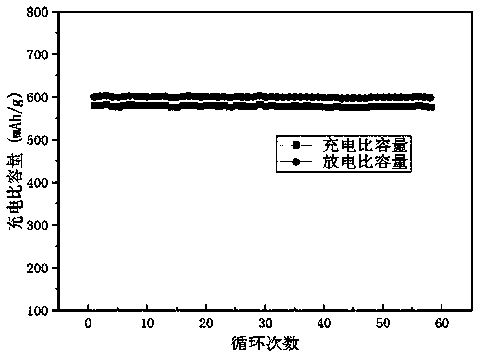
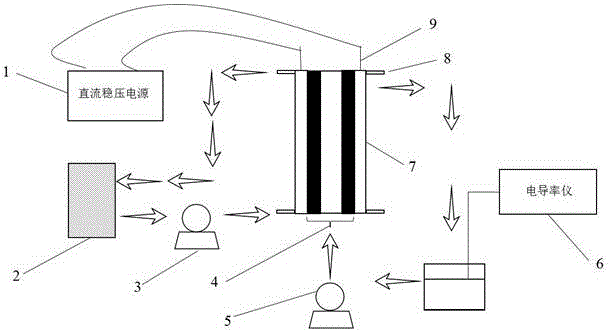
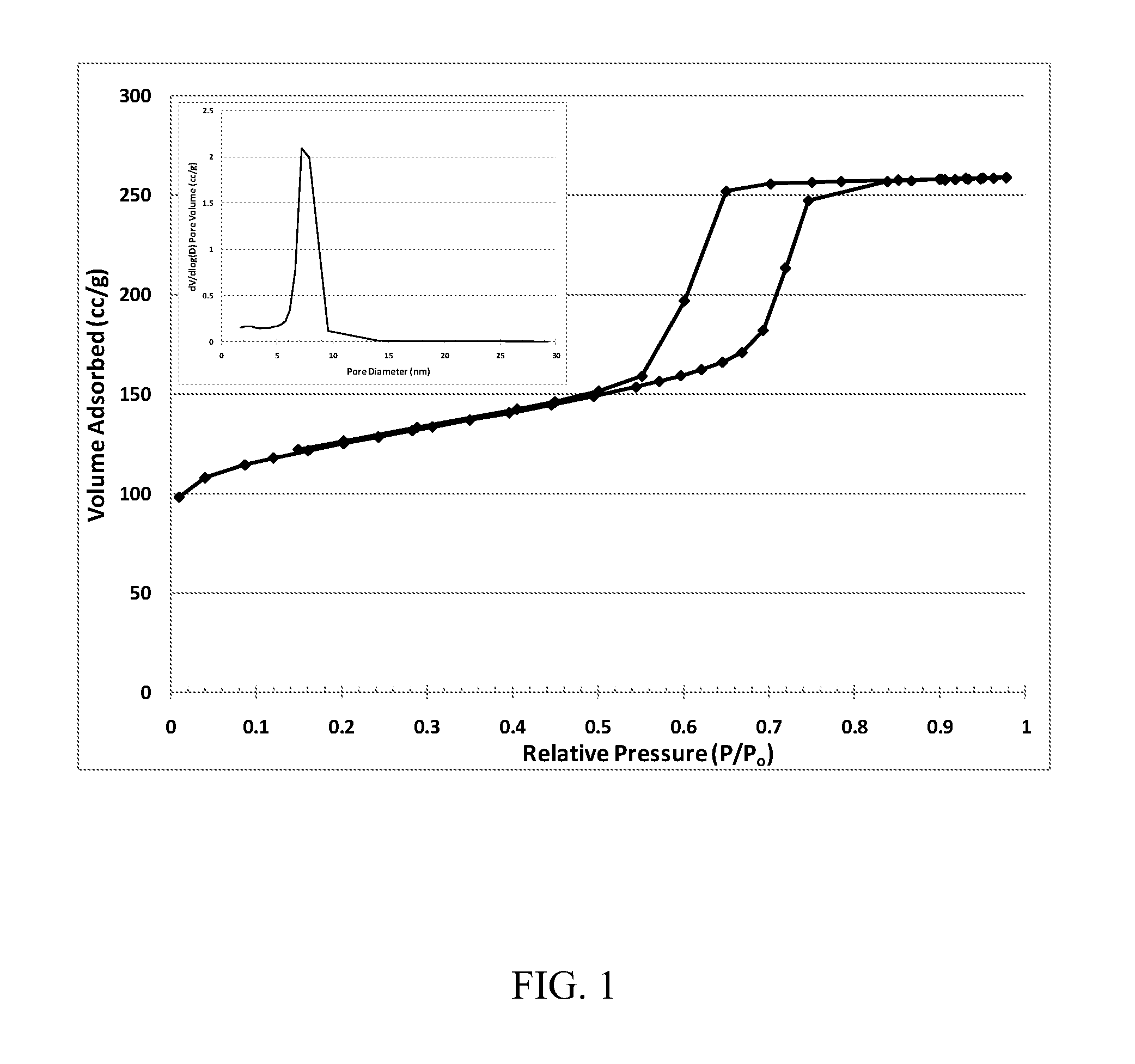
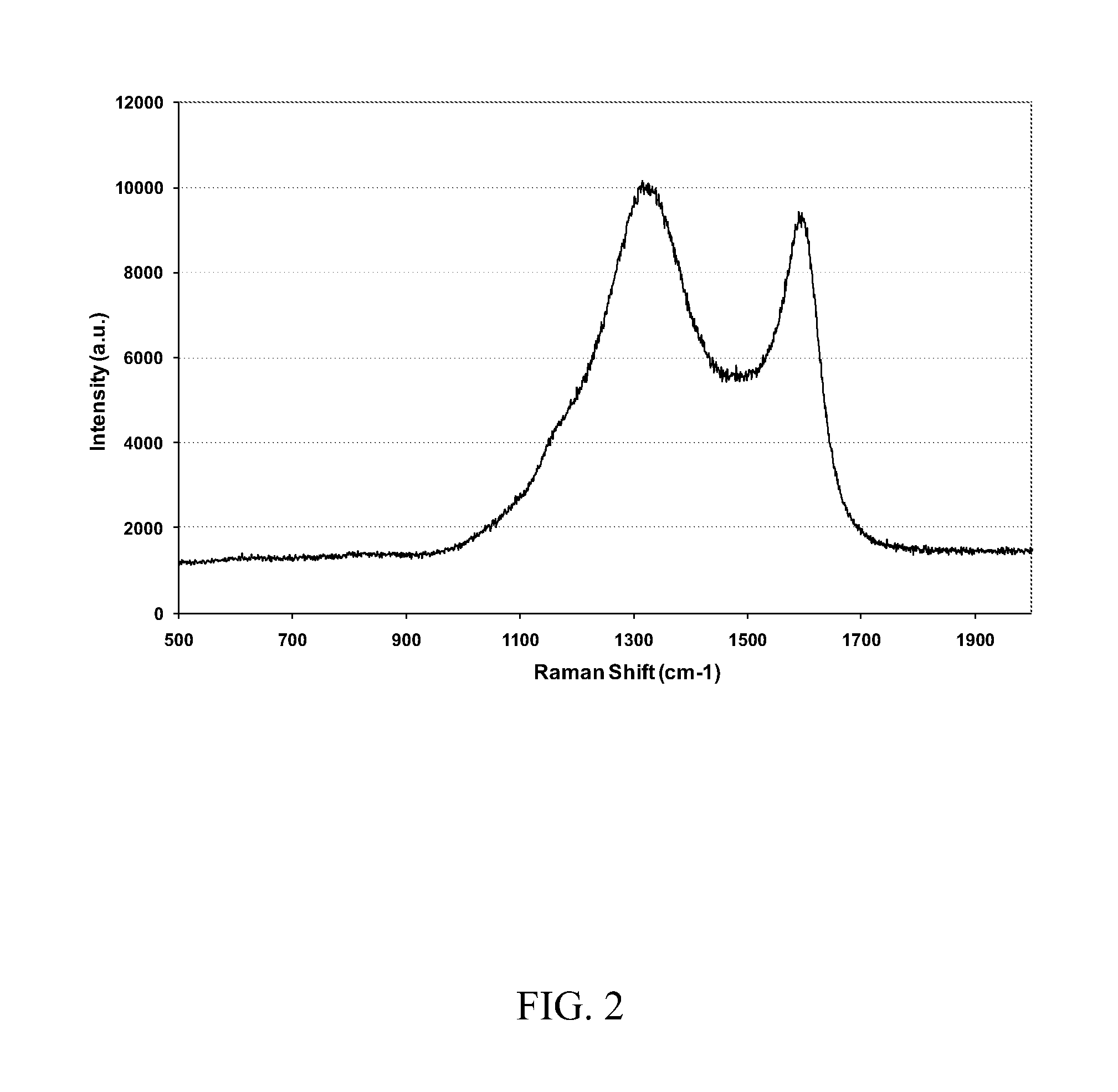
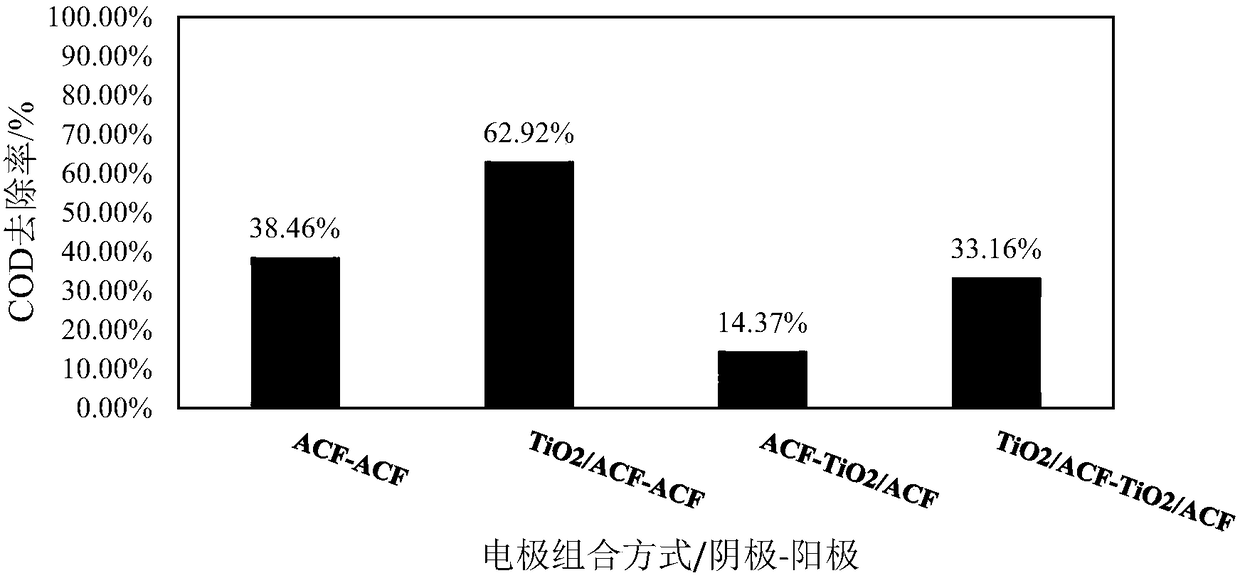
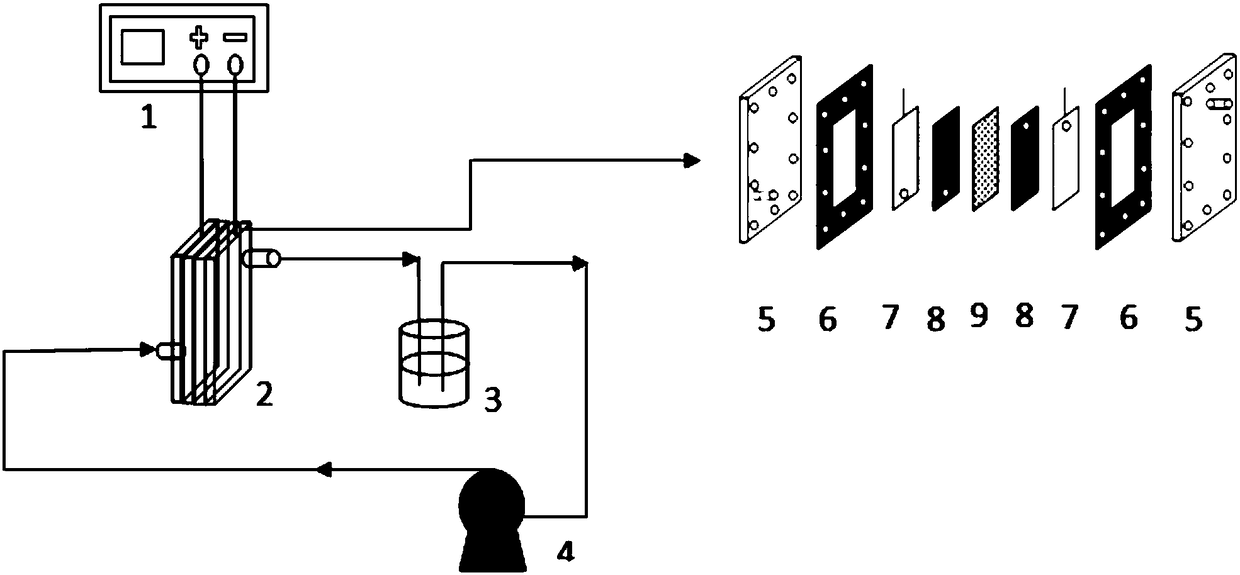
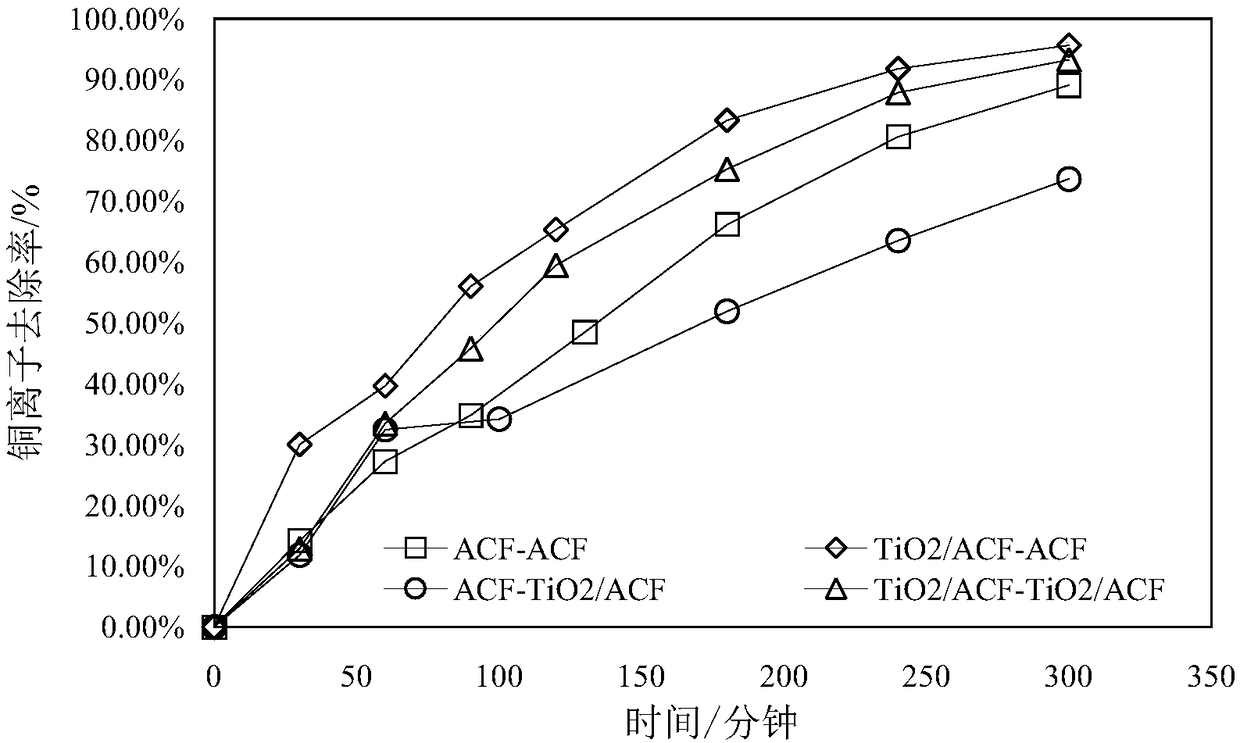
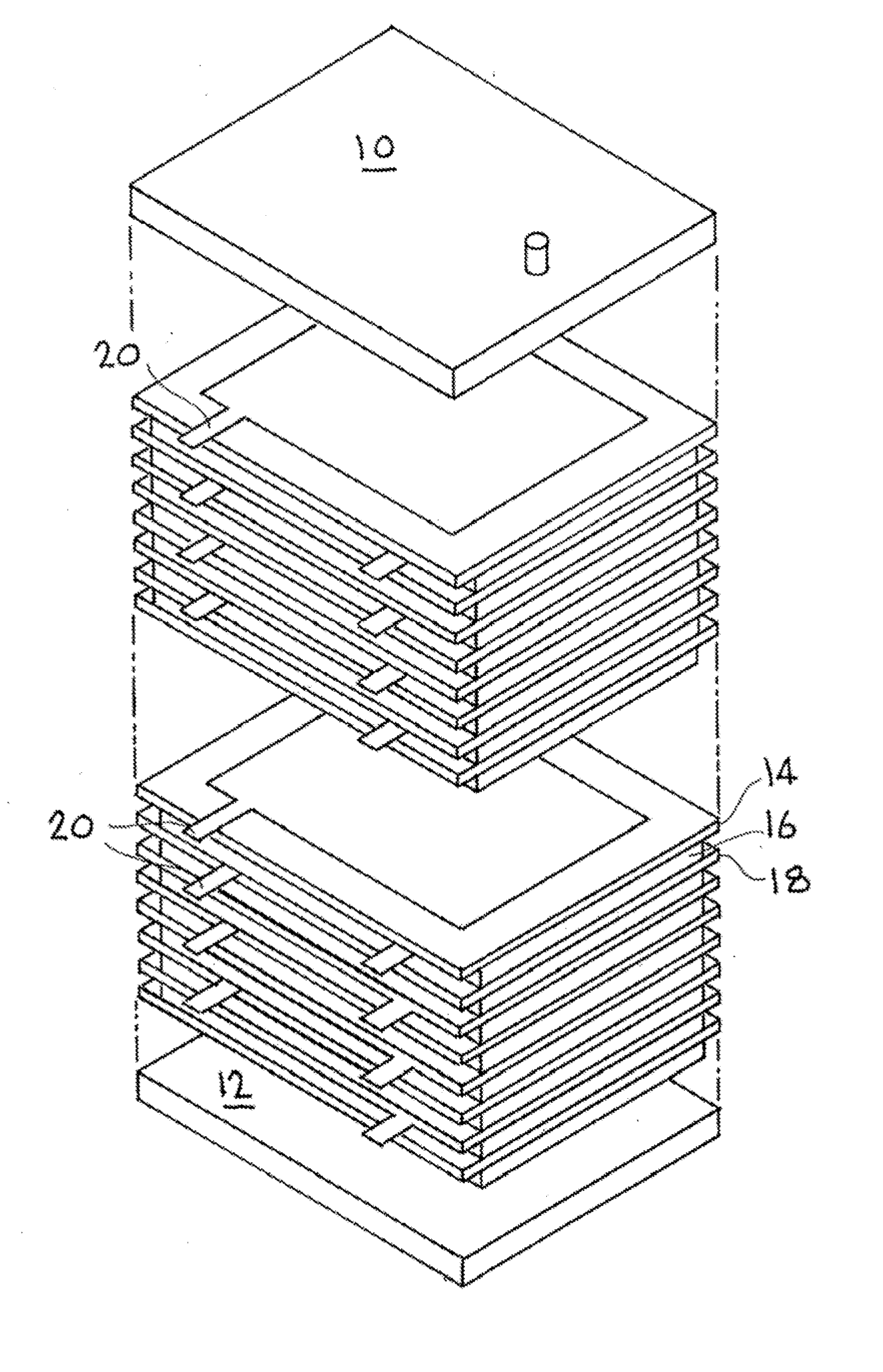
Patents
Literature
327 results about "Capacitive deionization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
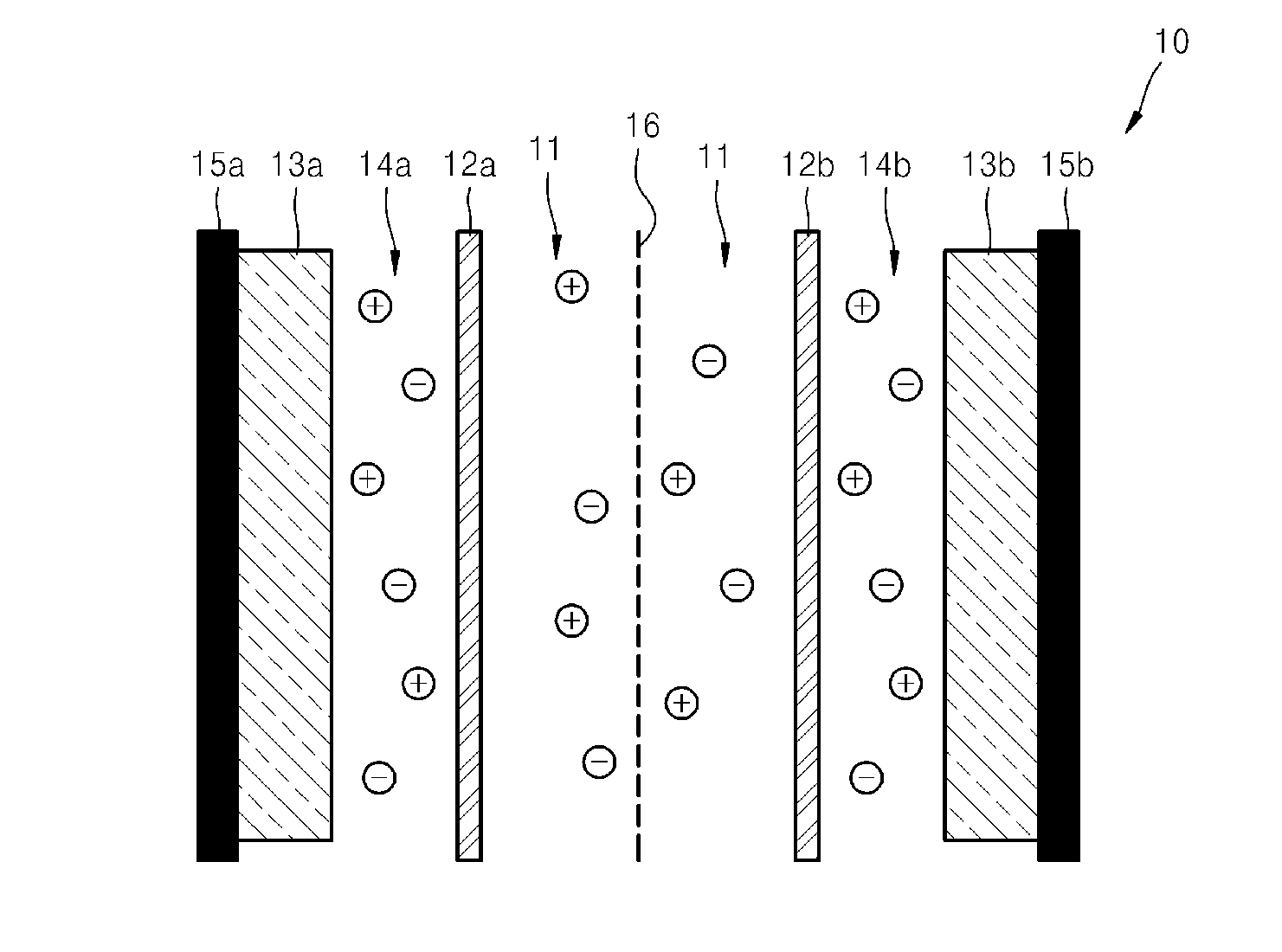
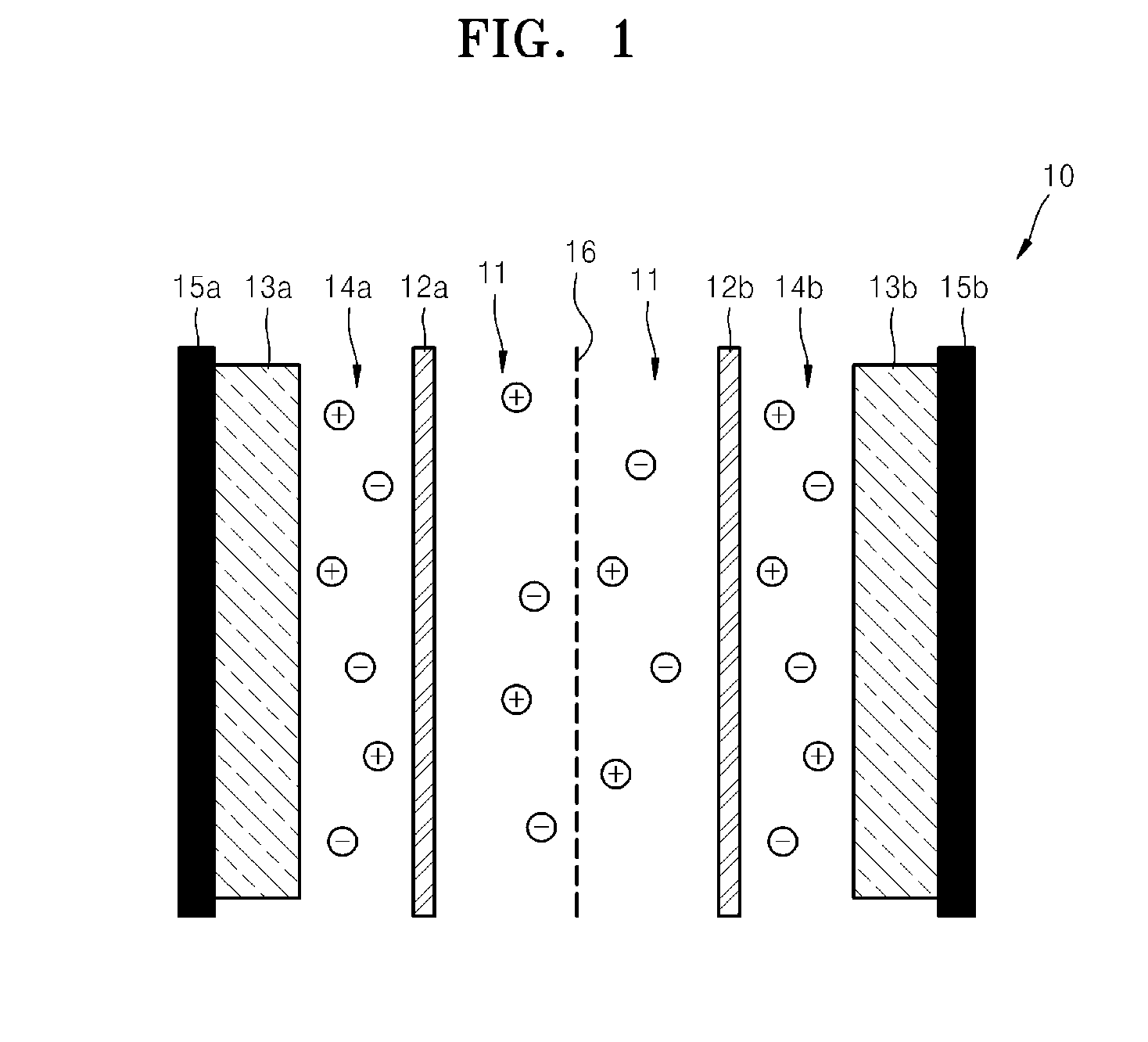
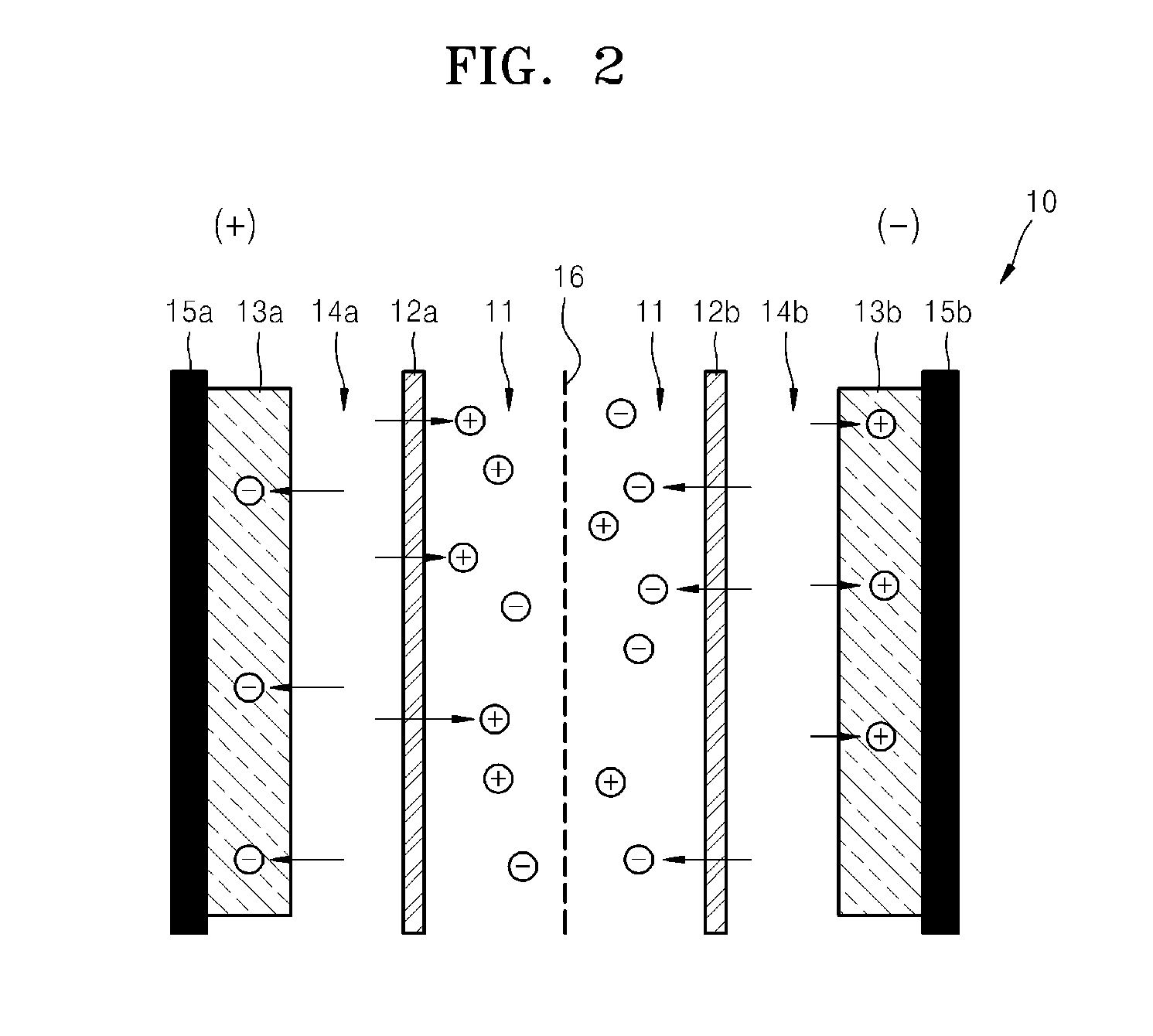
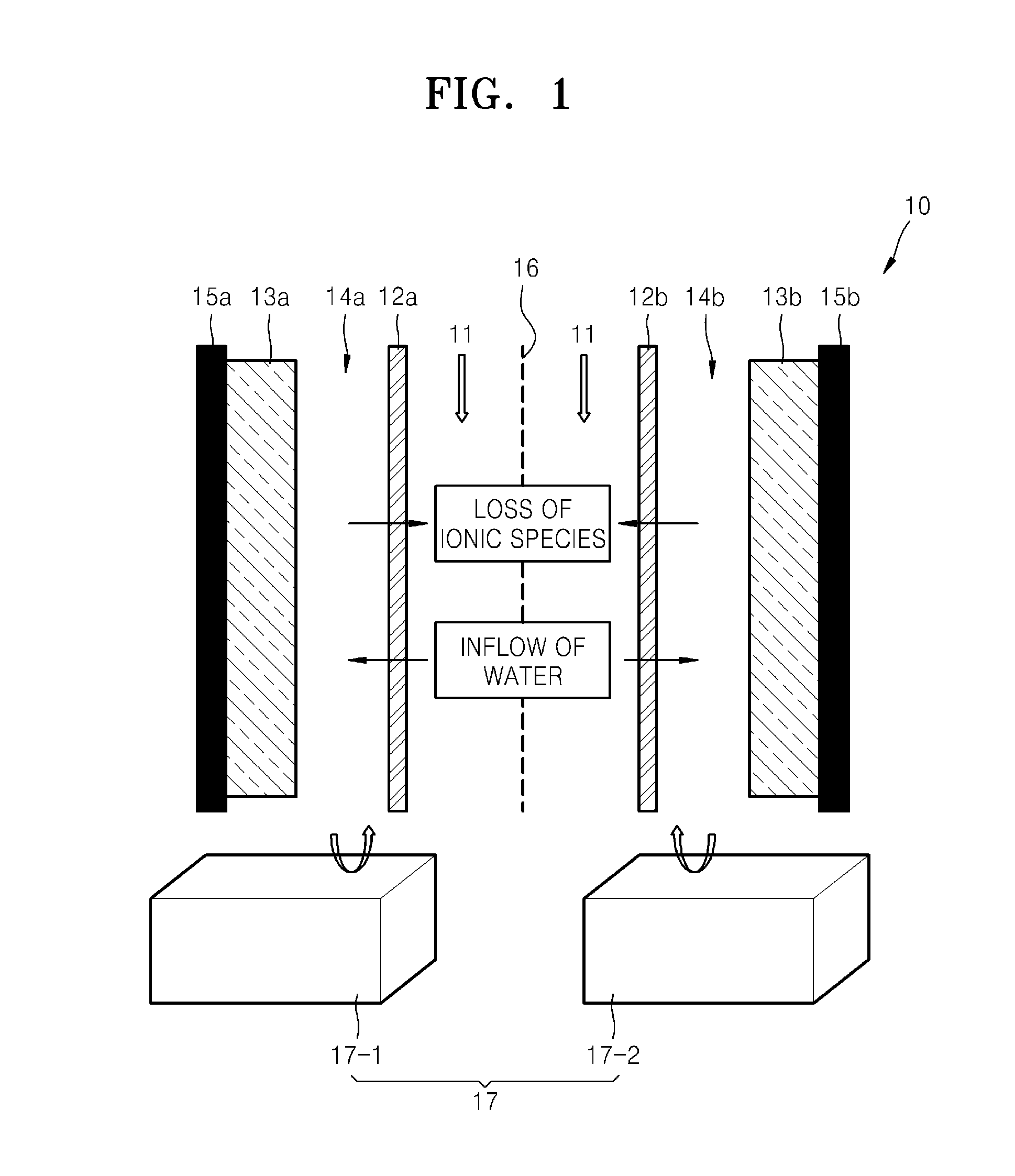
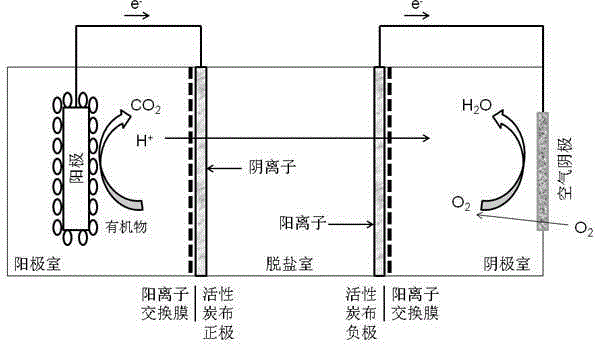
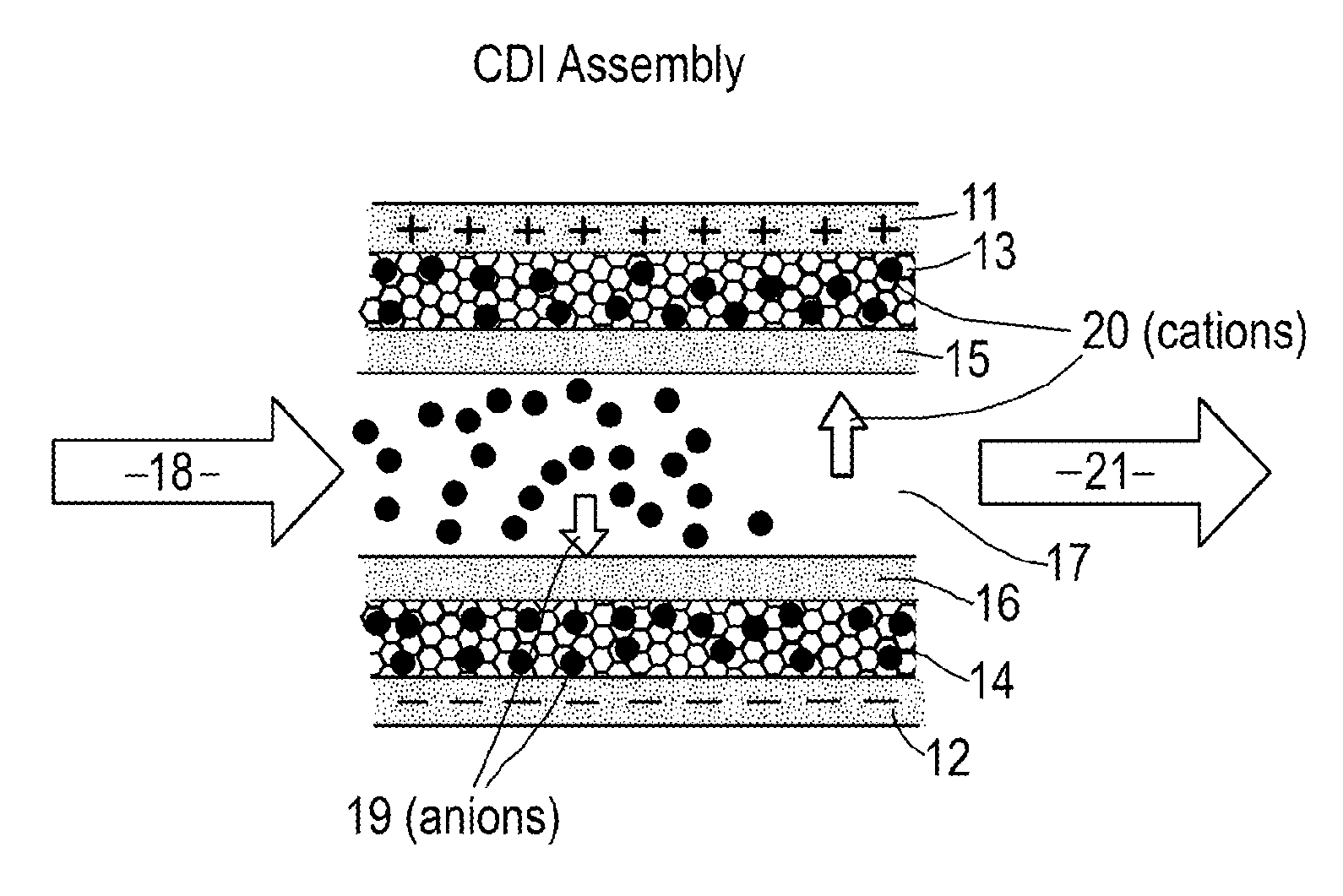
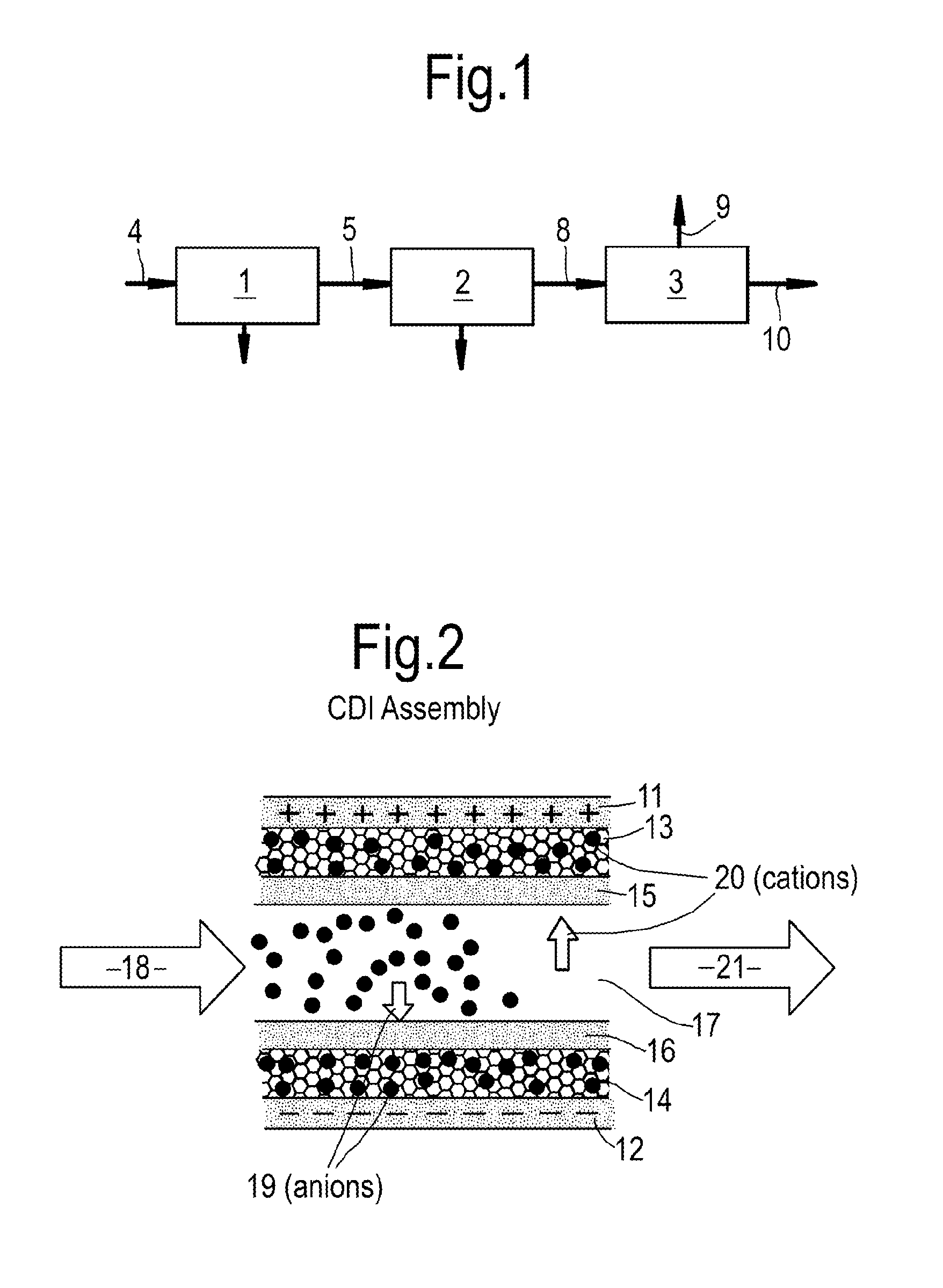
Capacitive deionization (CDI) is a technology to deionize water by applying an electrical potential difference over two electrodes, which are often made of porous carbon. Anions, ions with a negative charge, are removed from the water and are stored in the positively polarized electrode. Likewise, cations (positive charge) are stored in the cathode, which is the negatively polarized electrode.
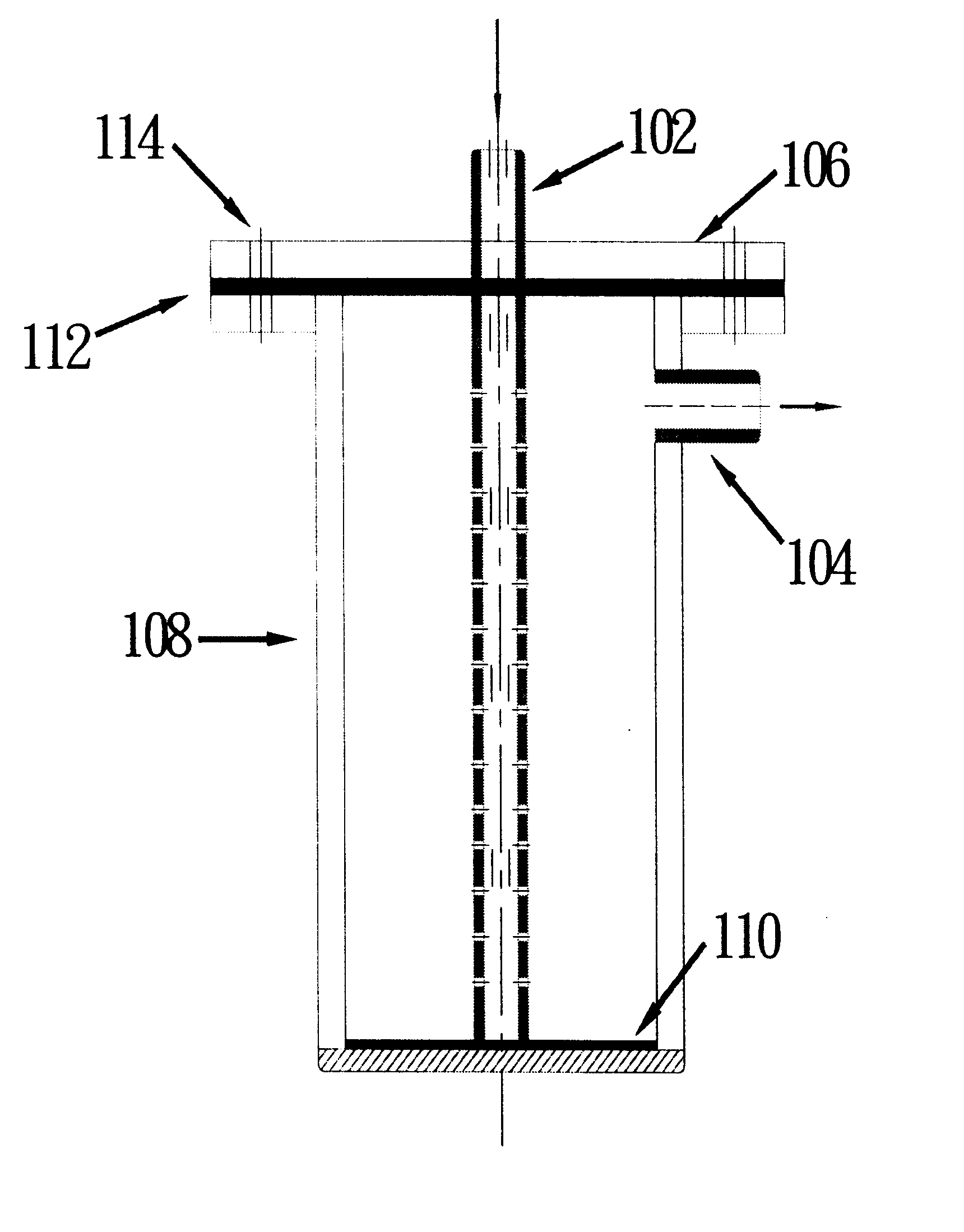
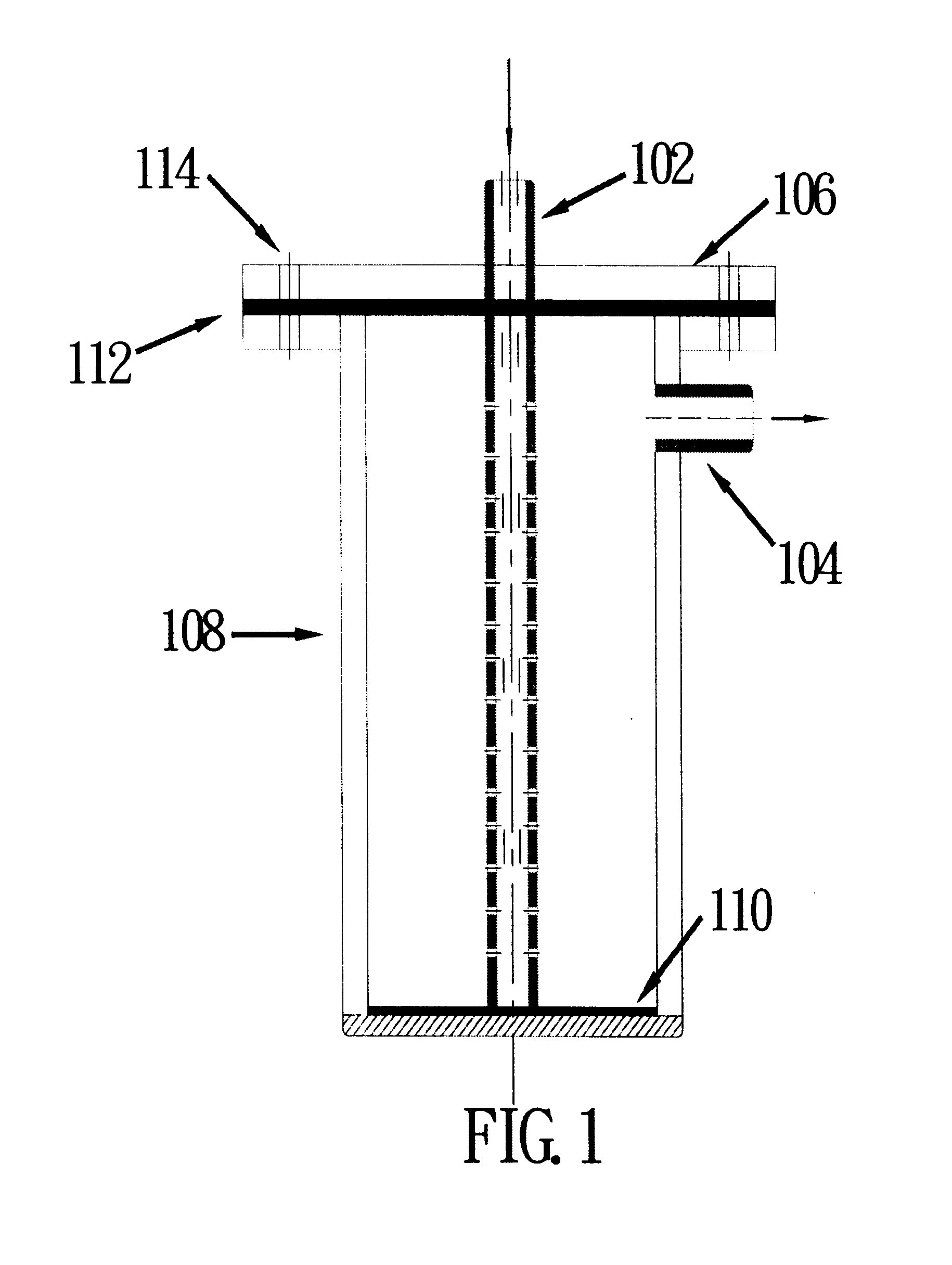
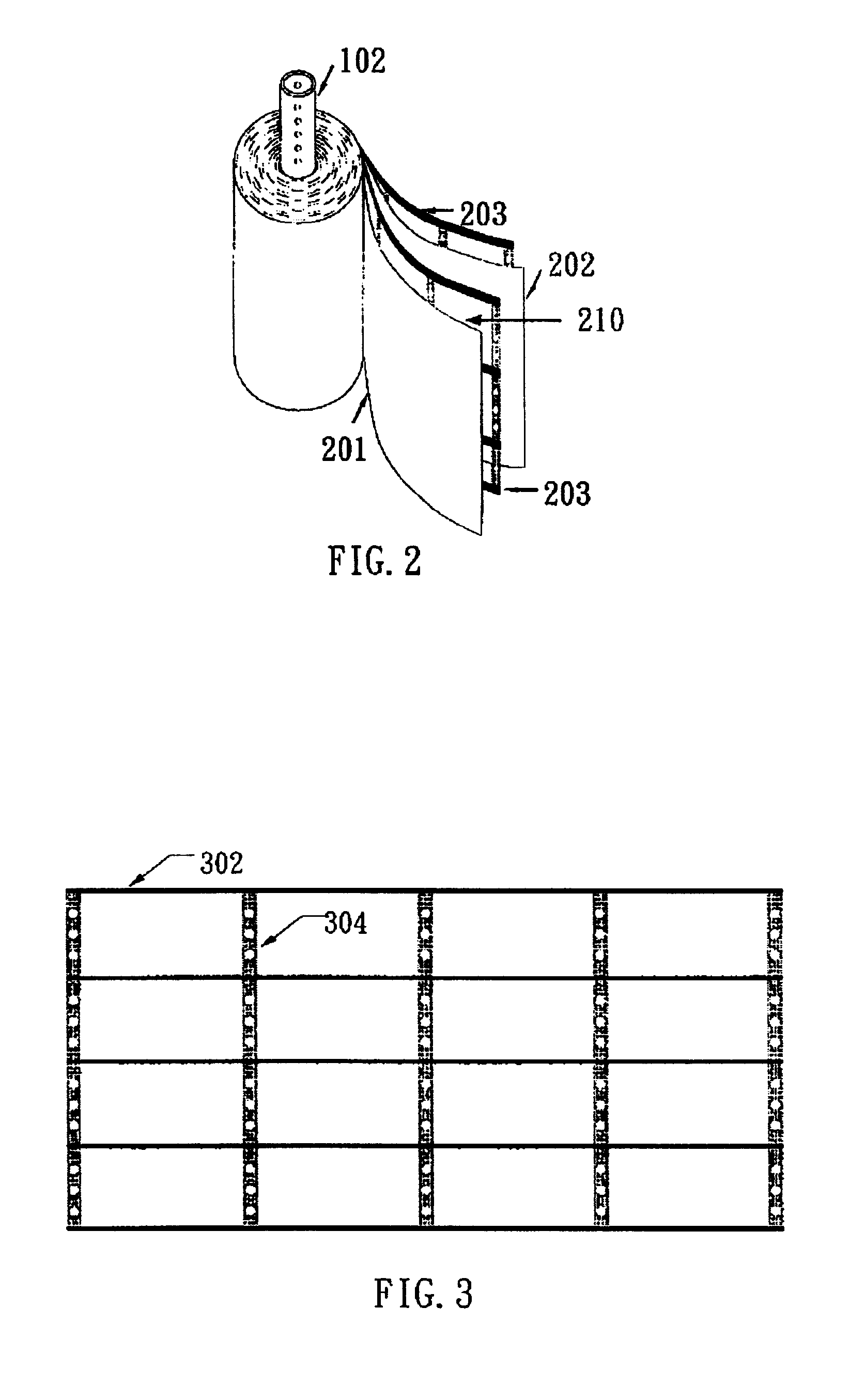
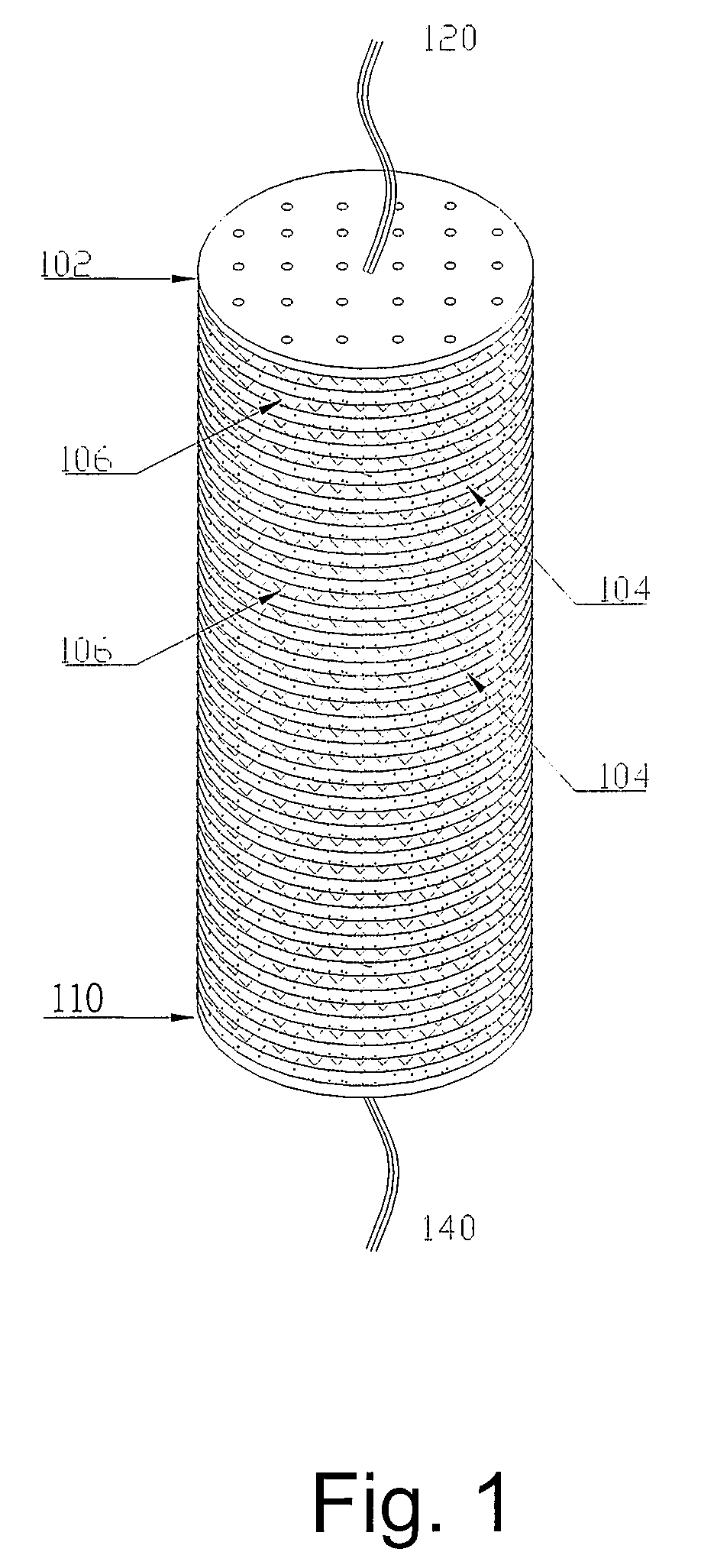
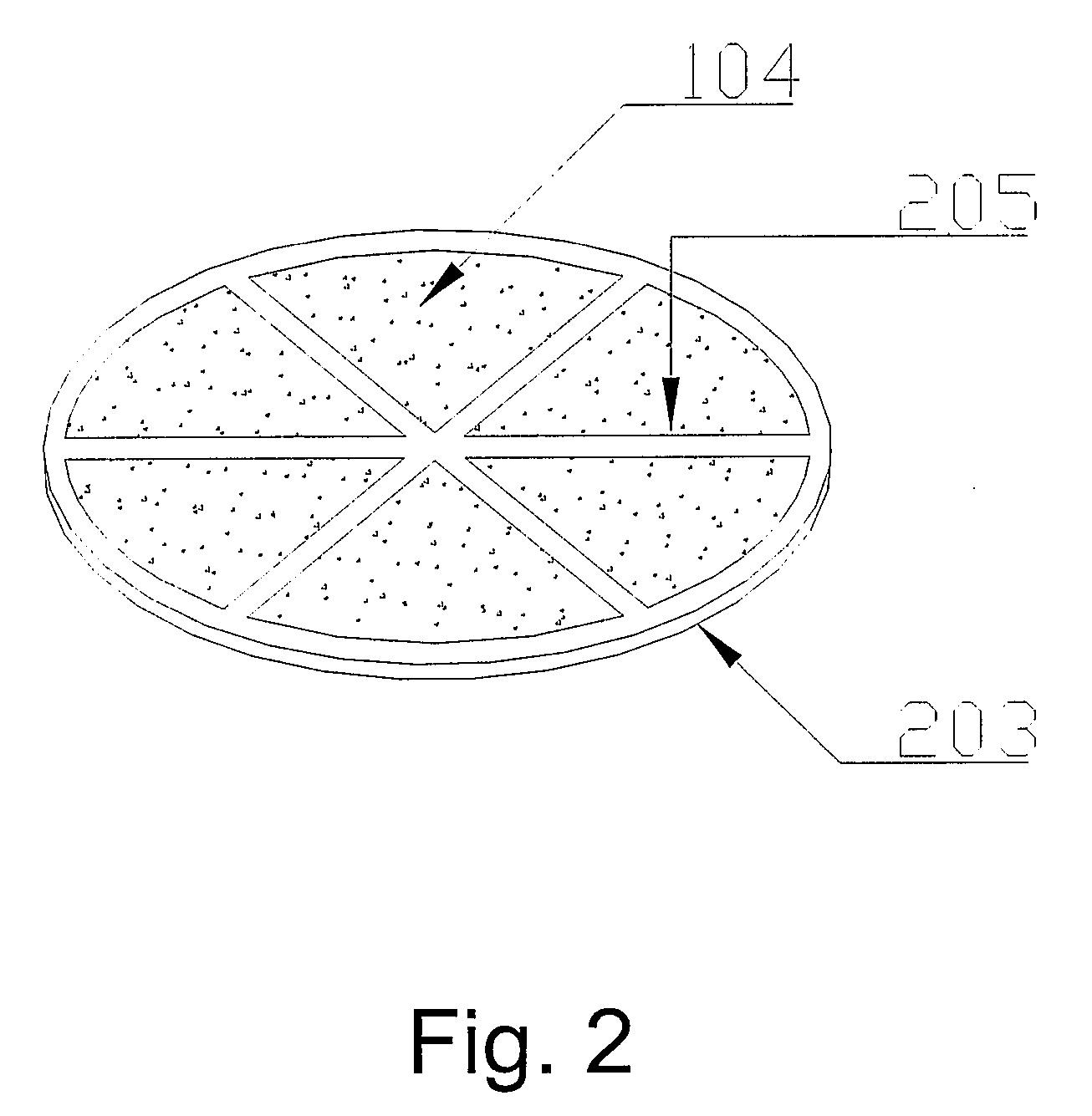
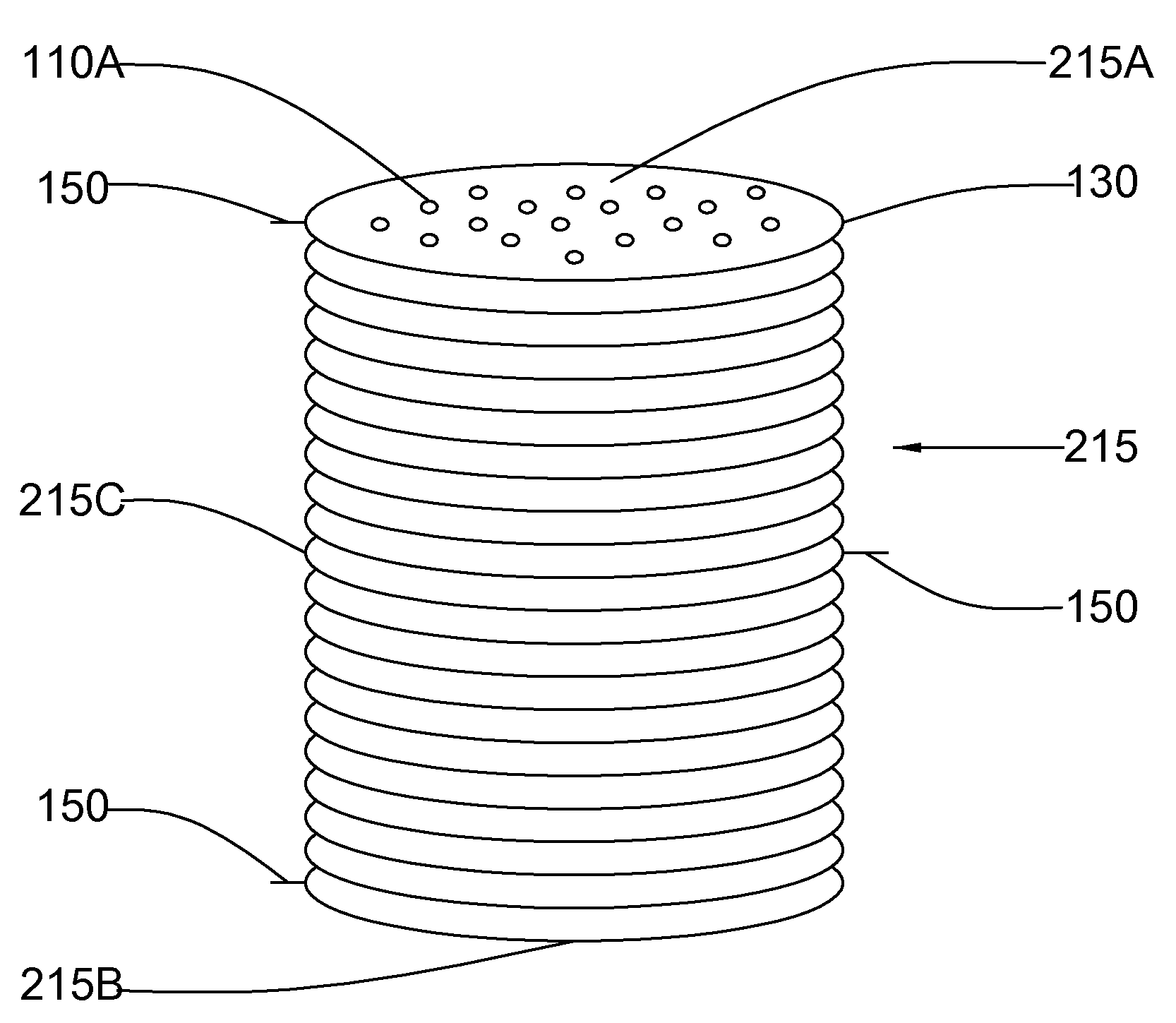
Replaceable flow-through capacitors for removing charged species from liquids
InactiveUS6462935B1Material nanotechnologyWater treatment parameter controlCapacitanceCapacitive deionization
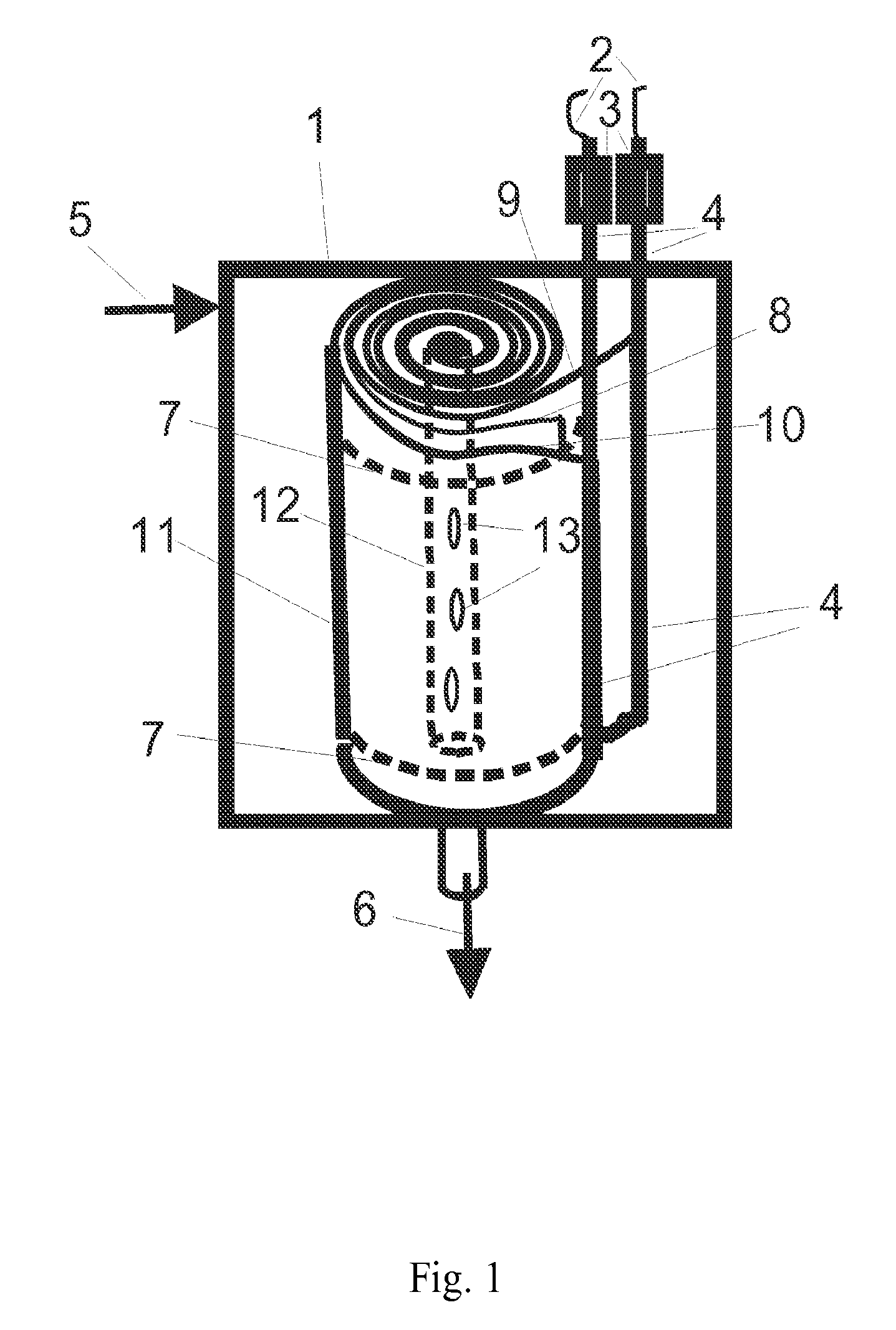
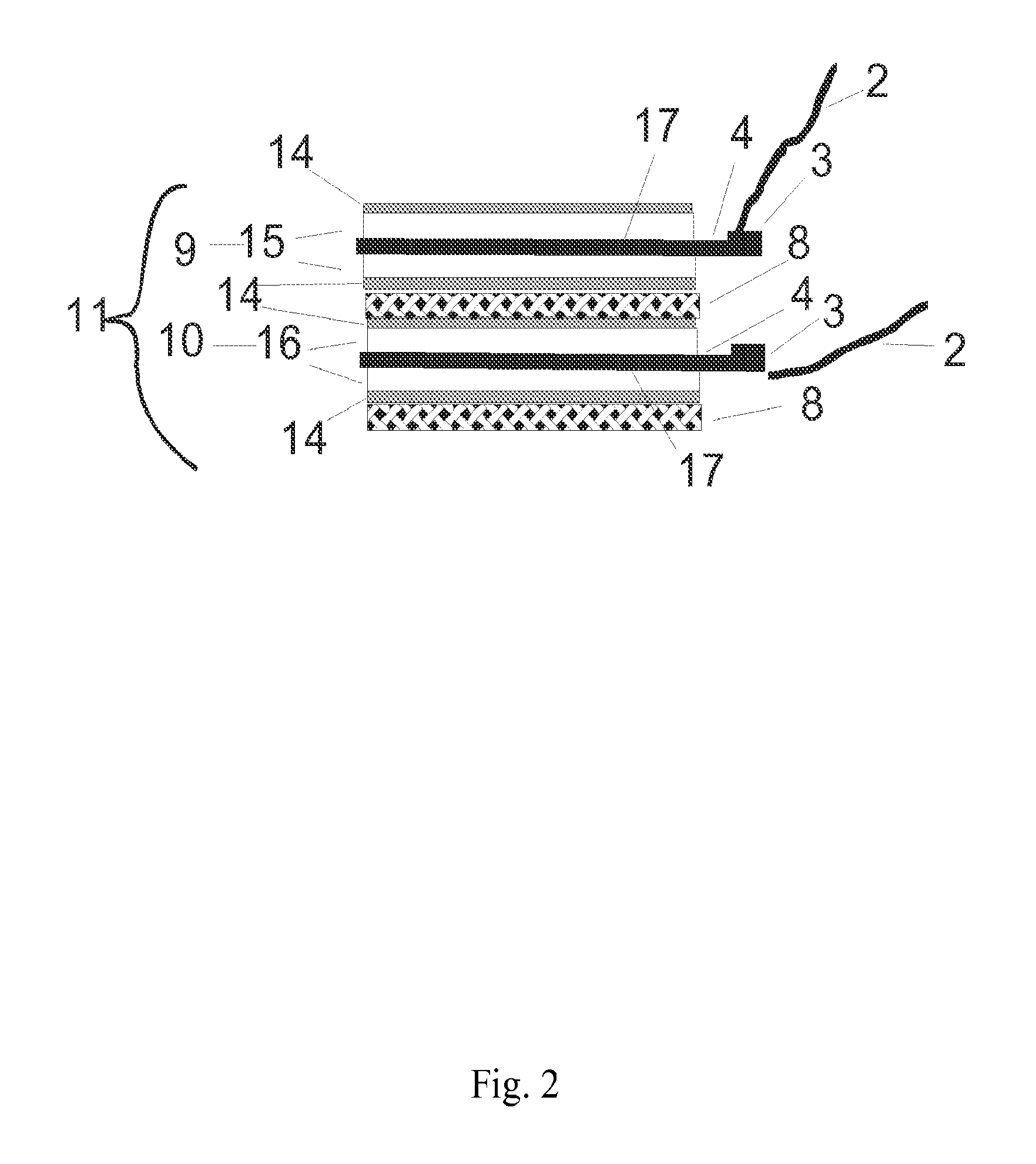
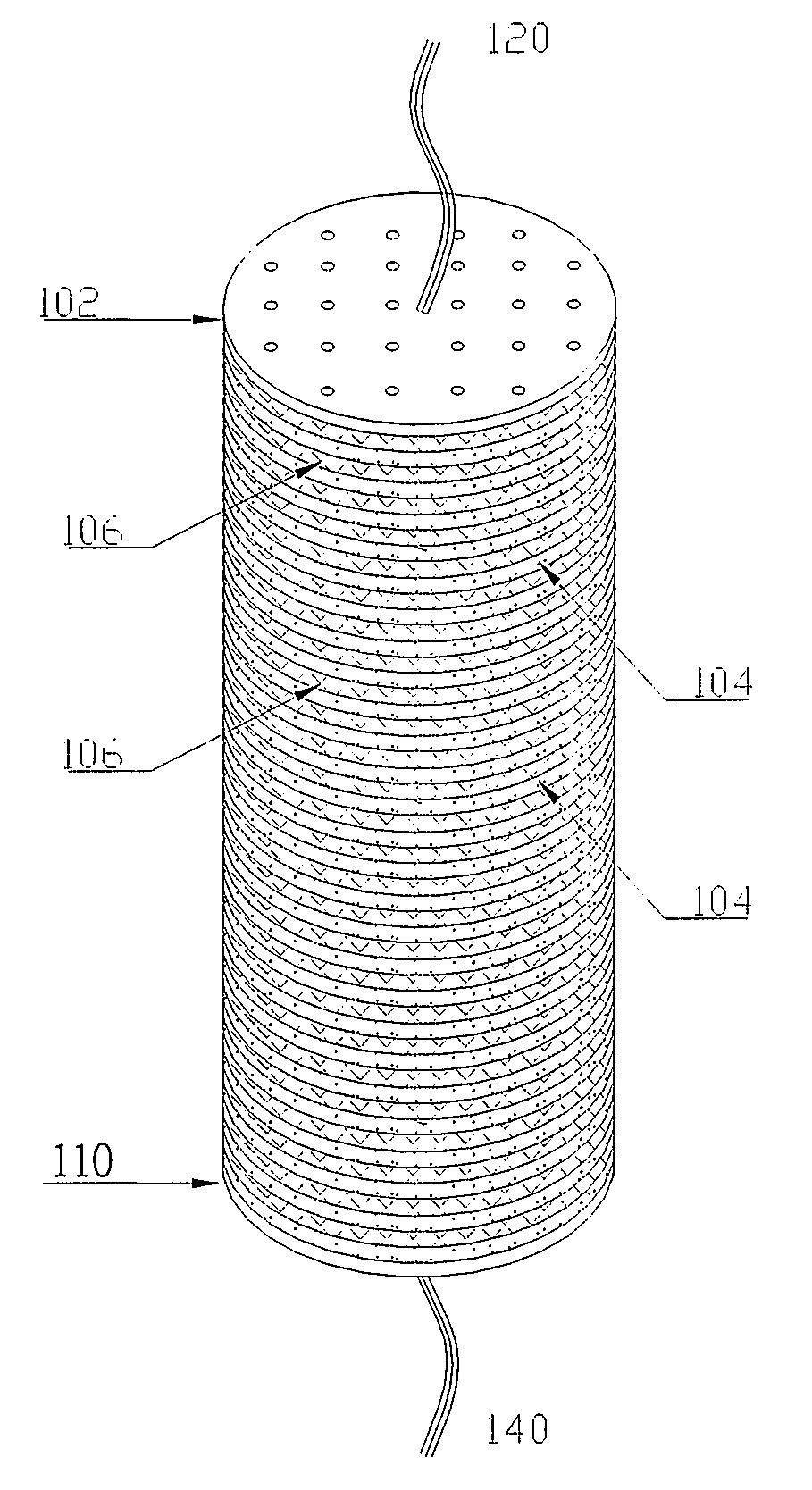
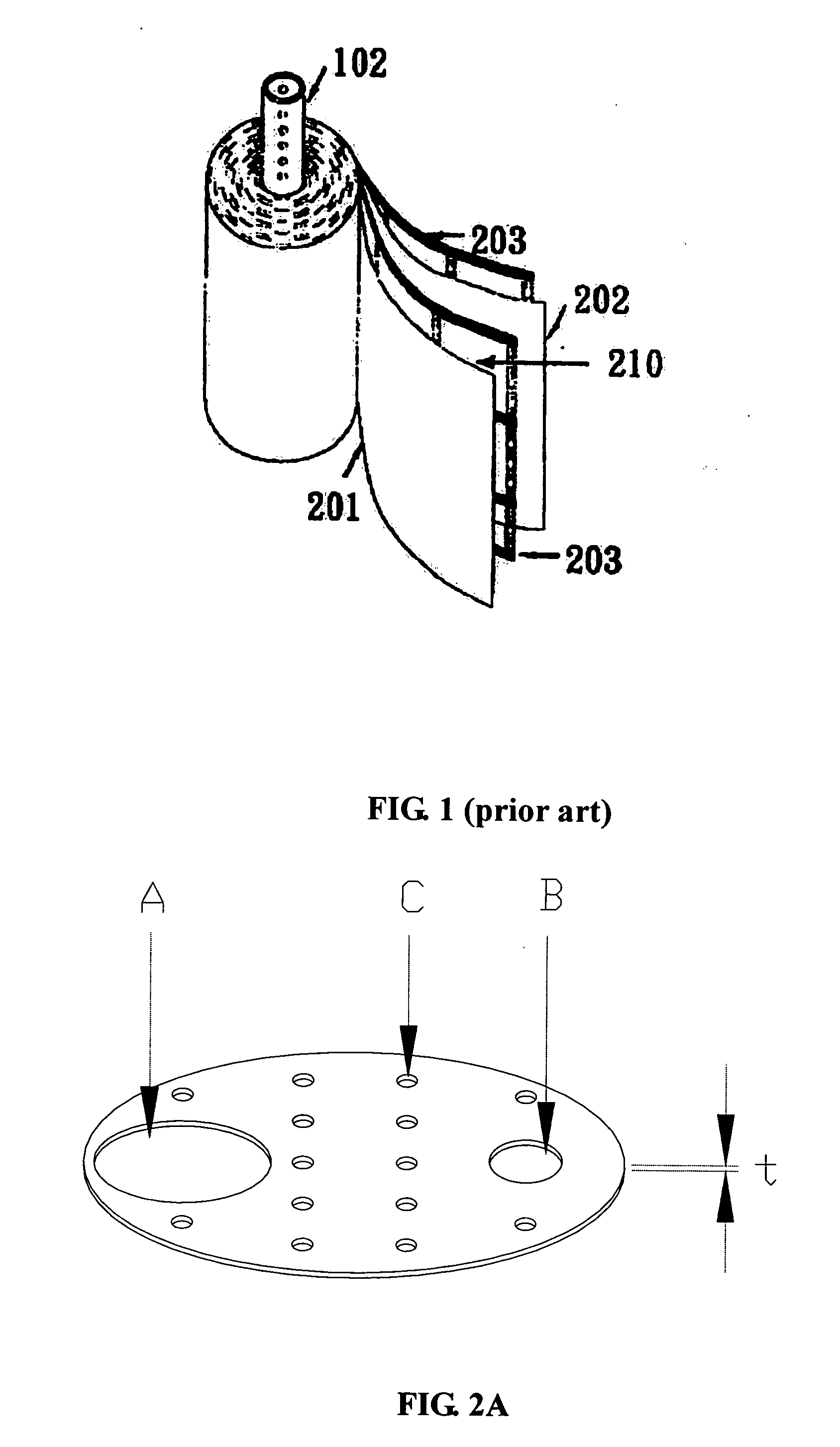
A free-standing flow-through capacitor (FTC) is constructed by concentrically winding two electrodes and two dividers into a hollow-center roll. A liquid-feeding pipe is inserted to the central opening for delivering fluids to the FTC. Nanoparticles of hydrated iron compound with Fe3O4 as the main component or its composite powders are used as the active materials for the electrodes. With channels crated by the dividers assembled in the roll, fluids injected from the feed pipe are confined inside the FTC, and flow outwardly and transversely through the entire length of the electrodes. Under an application of a low DC voltage to the electrodes, charged species are adsorbed and removed from the treated liquids as soon as they are in contact with the electrodes. Capacitive deionization using FTC of the present invention is applicable to waste-streams reduction, water purification and desalination at low costs and easy operation.
Owner:SHIUE LIH REN
Polarized Electrode for Flow-through Capacitive Deionization
ActiveUS20140346046A1Improve Coulombic efficiencyImprove purification effectElectrolysis componentsElectrostatic separatorsCapacitanceCapacitive deionization
The polarized electrode flow through capacitor comprises at least one each electrode material, with a pore volume that includes meso and micropores, with contained anionic or cationic groups. The polarized electrodes are in opposite polarity facing pairs, separated by a flow path or flow spacer. Both polarities of the particular attached ionic groups used are ionized at the working pH or composition of the particular feed solution supplied to inlet of the flow through capacitor. The contained groups cause the electrodes to be polarized so that they are selective to anions or cations. The polarized electrode flow through capacitor has better performance compared to identical flow through capacitors made from non-derivitized carbon. The capacitor electrode materials so derivitized provide this polarization function directly without need for a separate charge barrier material.
Owner:MESPILUS
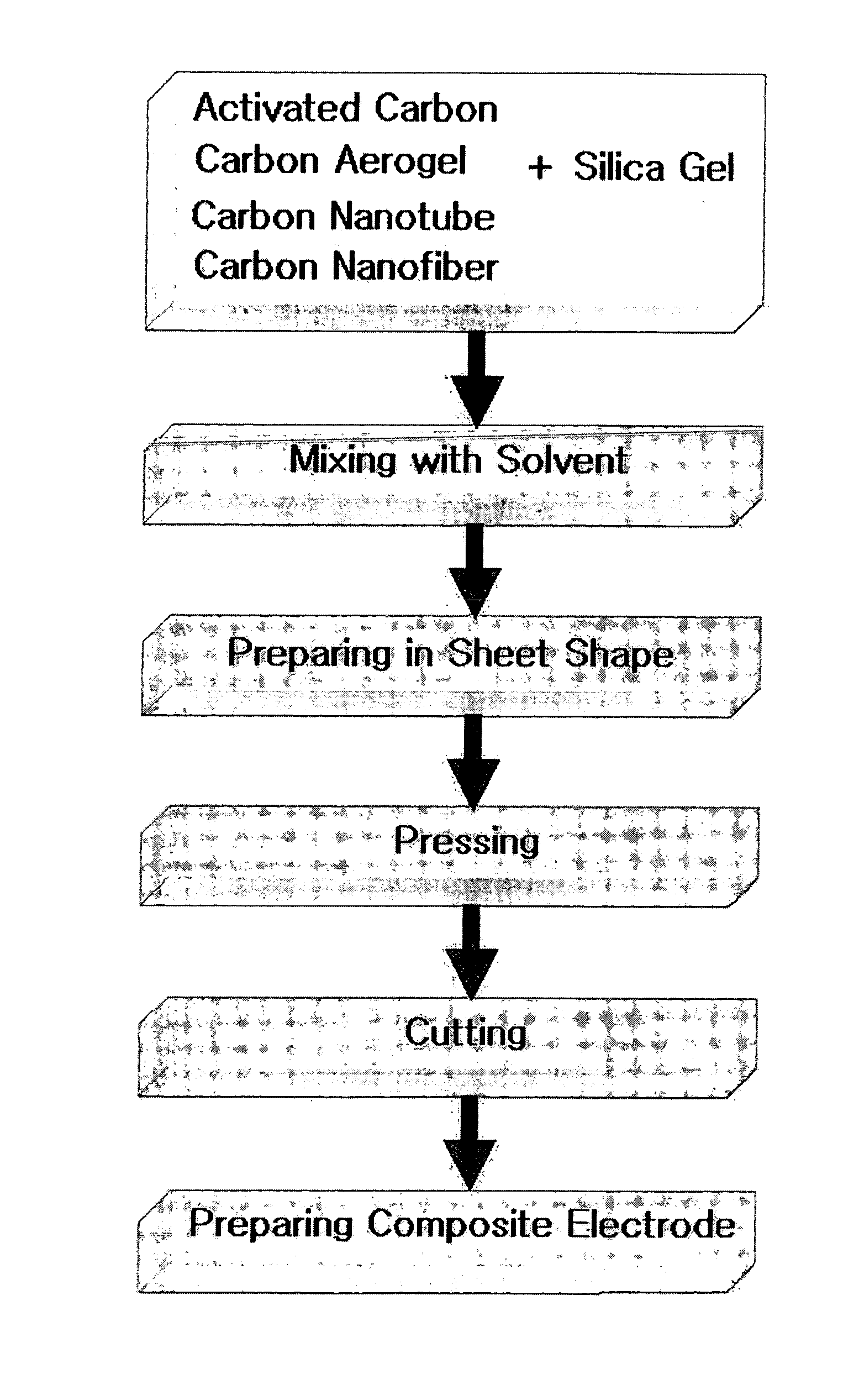
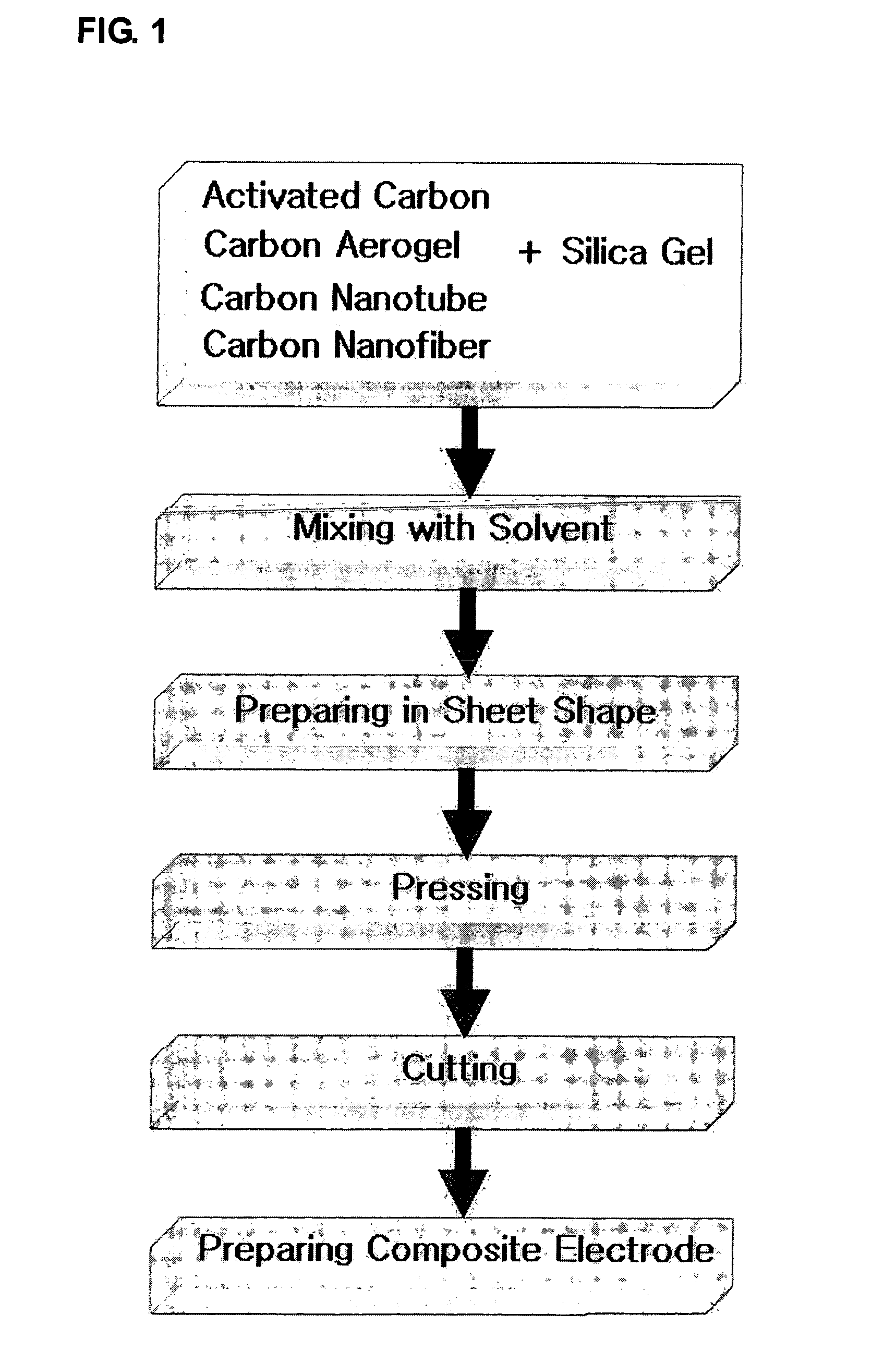
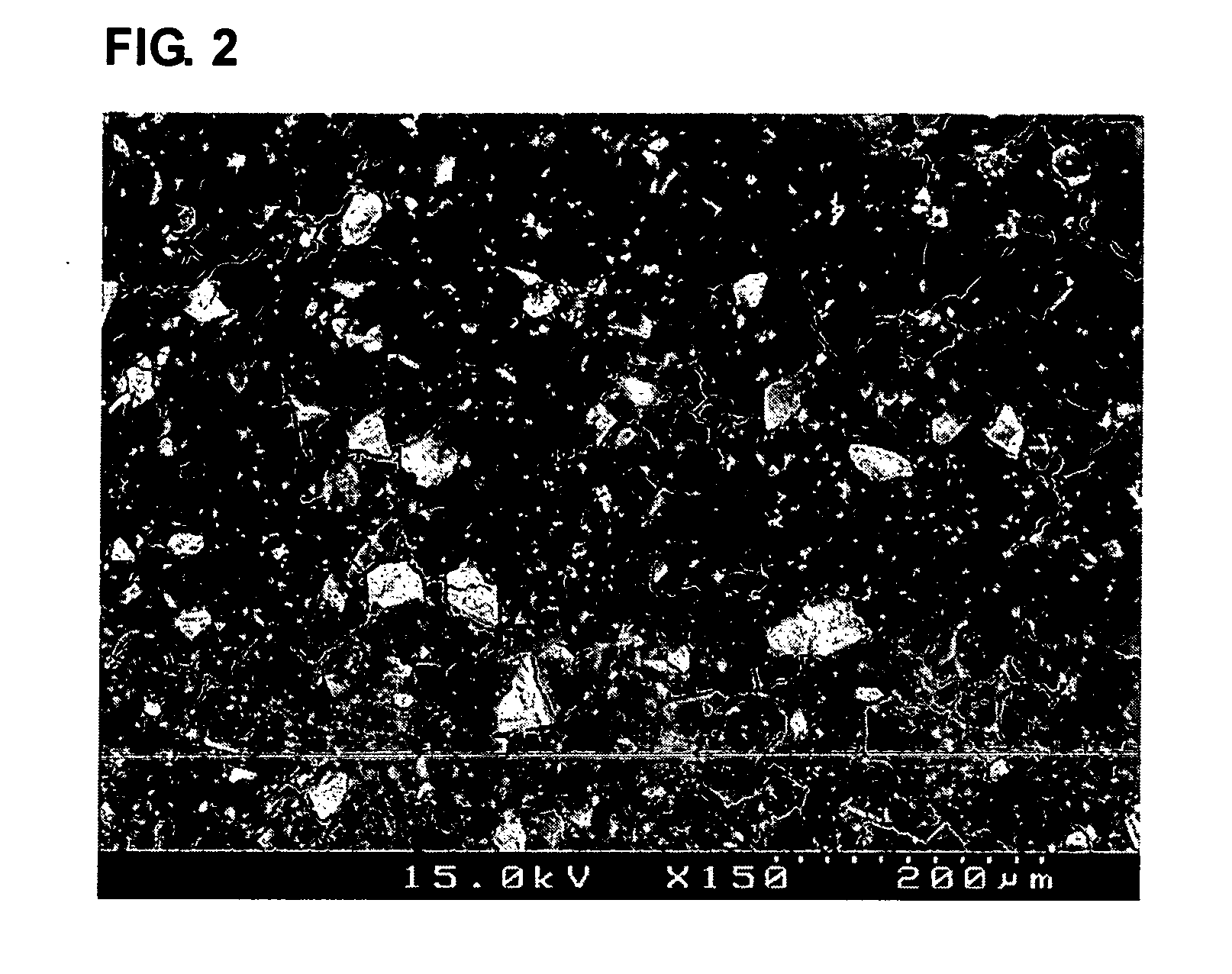
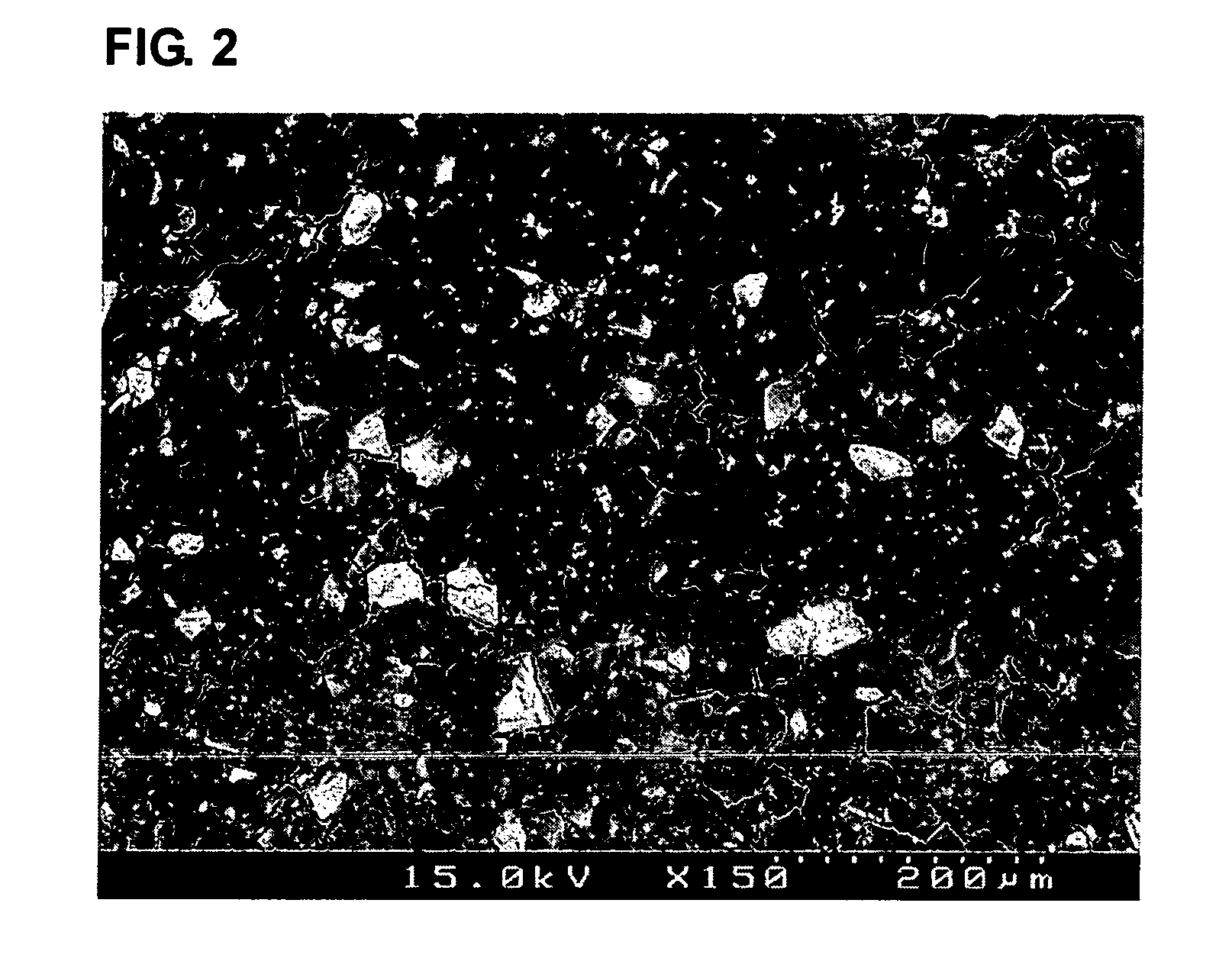
Carbon-porous media composite electrode and preparation method thereof
InactiveUS20050155216A1Improve hydrophilicitySimple processMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolytic capacitorsWater useCapacitance
The present invention discloses a carbon-porous media composite electrode material, a composite electrode using the same and a preparation method thereof. The carbon-porous media composite electrode can be applied for a device such as a secondary battery, a capacitor or the like, or for preparing ultra pure water using a capacitive deionization process, purifying salty water or the like.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Metal-carbon composites and methods for their production
InactiveUS20150306570A1Similar and improved propertyHigh activityCarbon compoundsInorganic active ingredientsCarbon compositesCapacitive deionization
A method of forming a metal-carbon composite, the method comprising subjecting a precursor composition to a curing step followed by a carbonization step, the precursor composition comprising: (i) a phenolic component, (ii) a crosslinkable aldehyde component, (iii) a polymerization catalyst, and (iv) metal-containing particles, wherein said carbonization step comprises heating the precursor composition at a carbonizing temperature of at least 300° C. for sufficient time to convert the precursor composition to said metal-carbon composite. The produced metal-carbon composite, devices incorporating them, and methods of their use (e.g., in capacitive deionization and lithium ion batteries) are also described.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Carbon-porous media composite electrode and preparation method thereof
InactiveUS7505250B2Improve hydrophilicitySimple processMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolytic capacitorsCapacitanceWater use
The present invention discloses a carbon-porous media composite electrode material, a composite electrode using the same and a preparation method thereof. The carbon-porous media composite electrode can be applied for a device such as a secondary battery, a capacitor or the like, or for preparing ultra pure water using a capacitive deionization process, purifying salty water or the like.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
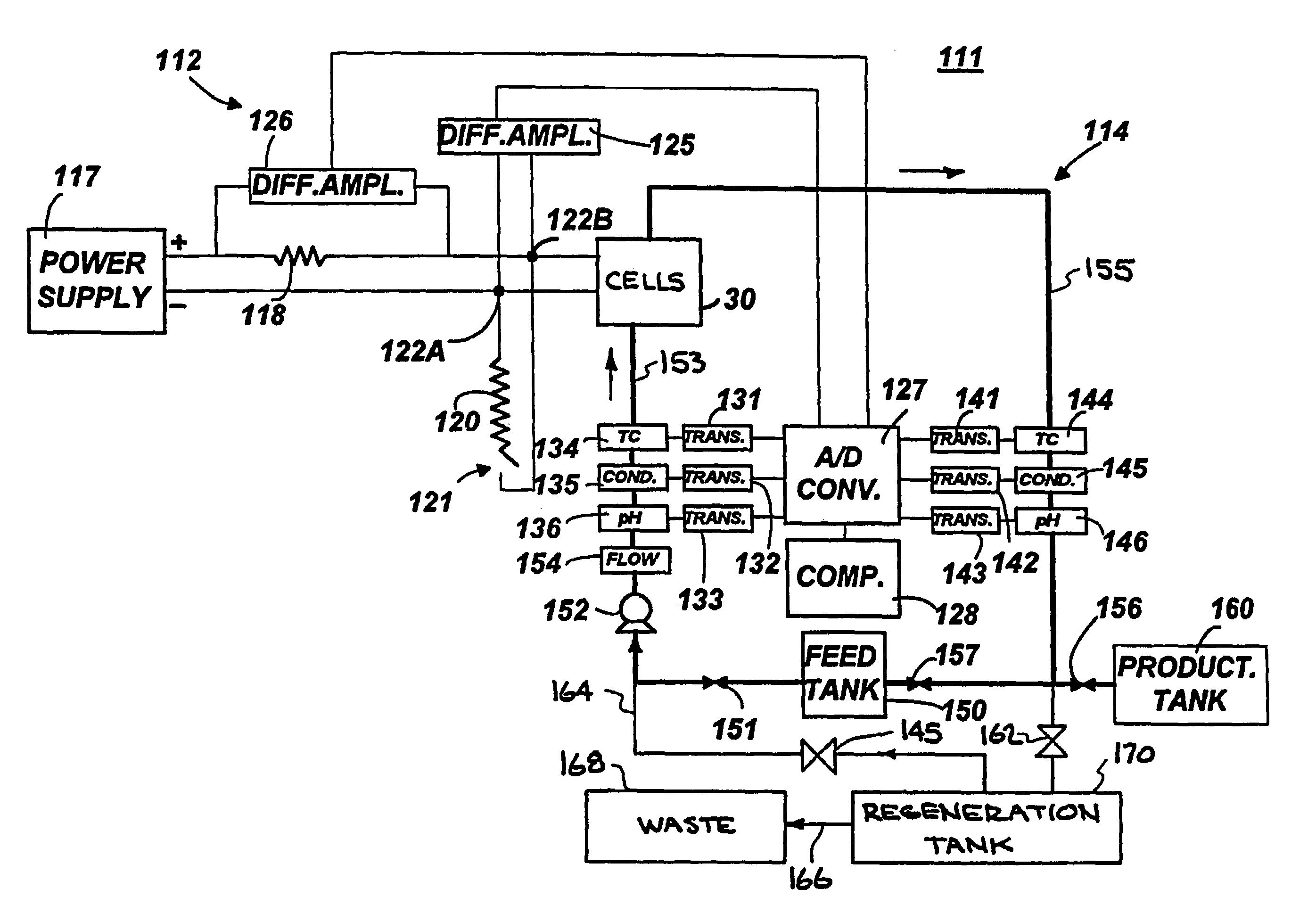
Capacitive deionization system for water treatment
InactiveUS20080198531A1Suitable for reuseHigh electrode-utilization efficiencySeawater treatmentElectrolytic capacitorsCapacitanceCapacitive deionization
A capacitive deionization (CDI) system for deionizing water is disclosed. The CDI system comprises at least a flow through capacitor (FTC) module, at least a first supercapacitor, at least a second supercapacitor, at least a third supercapacitor and a controller. The FTC module comprises a plurality electrodes for removing ions from water flowing between the electrodes under an electric field applied between the electrodes. The first supercapacitor is connected between the potential source and the FTC module for amplifying energy provided by the potential source. The second supercapacitor is connected to the FTC module for receiving energy from the FTC module for regenerating the electrodes of the FTC module. The third supercapacitor is adapted for exchanging energy with the FTC module for regenerating the electrodes of the FTC module. The controller is adapted for regulating deionization rate of the water and regeneration of the electrodes of the FTC module.
Owner:SHIUE LIH REN
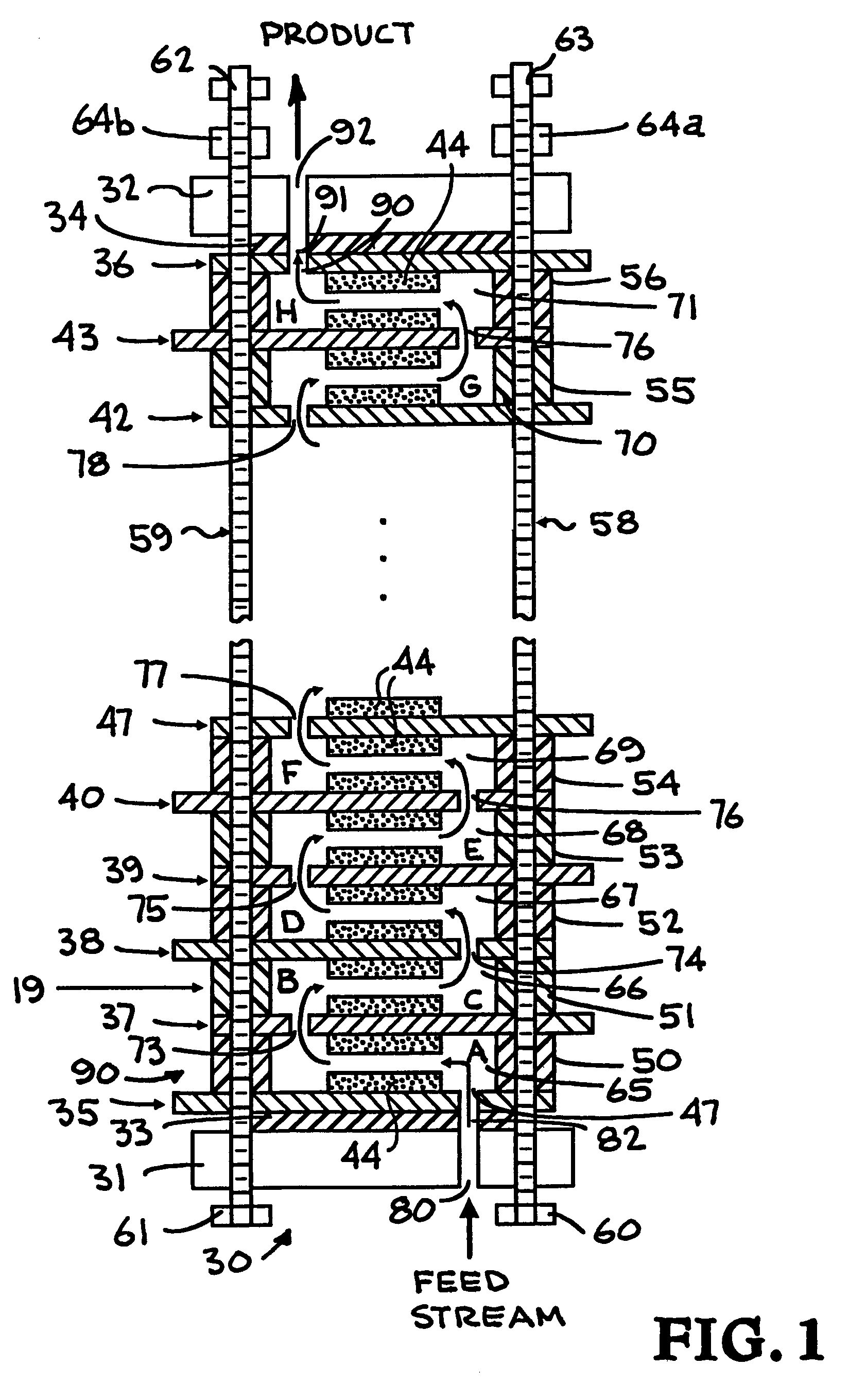
Alternating-polarity operation for complete regeneration of electrochemical deionization system
InactiveUS7138042B2Volume of waste can be minimizedConductivity maximizedCellsMaterial nanotechnologyCapacitanceElectrical battery
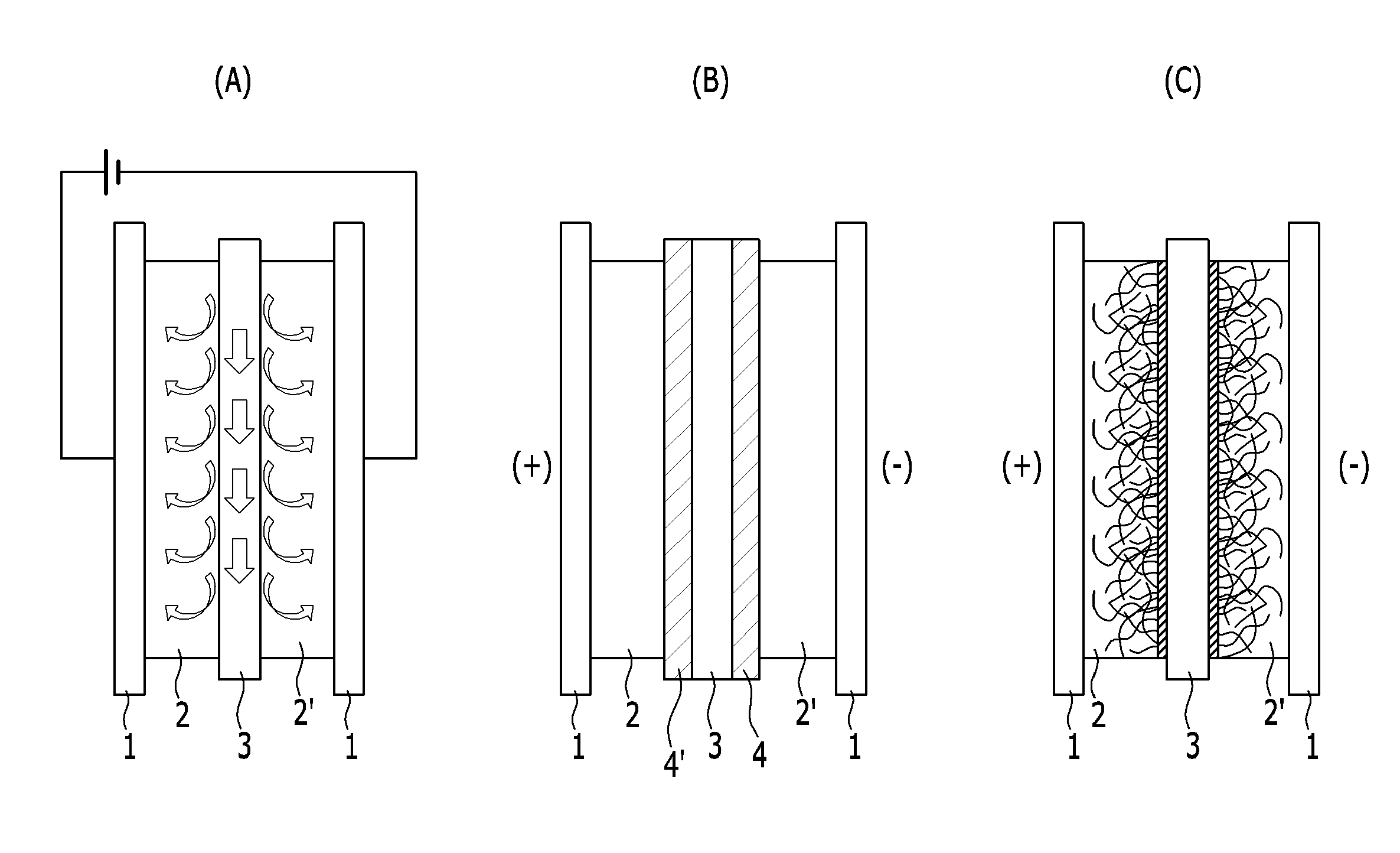
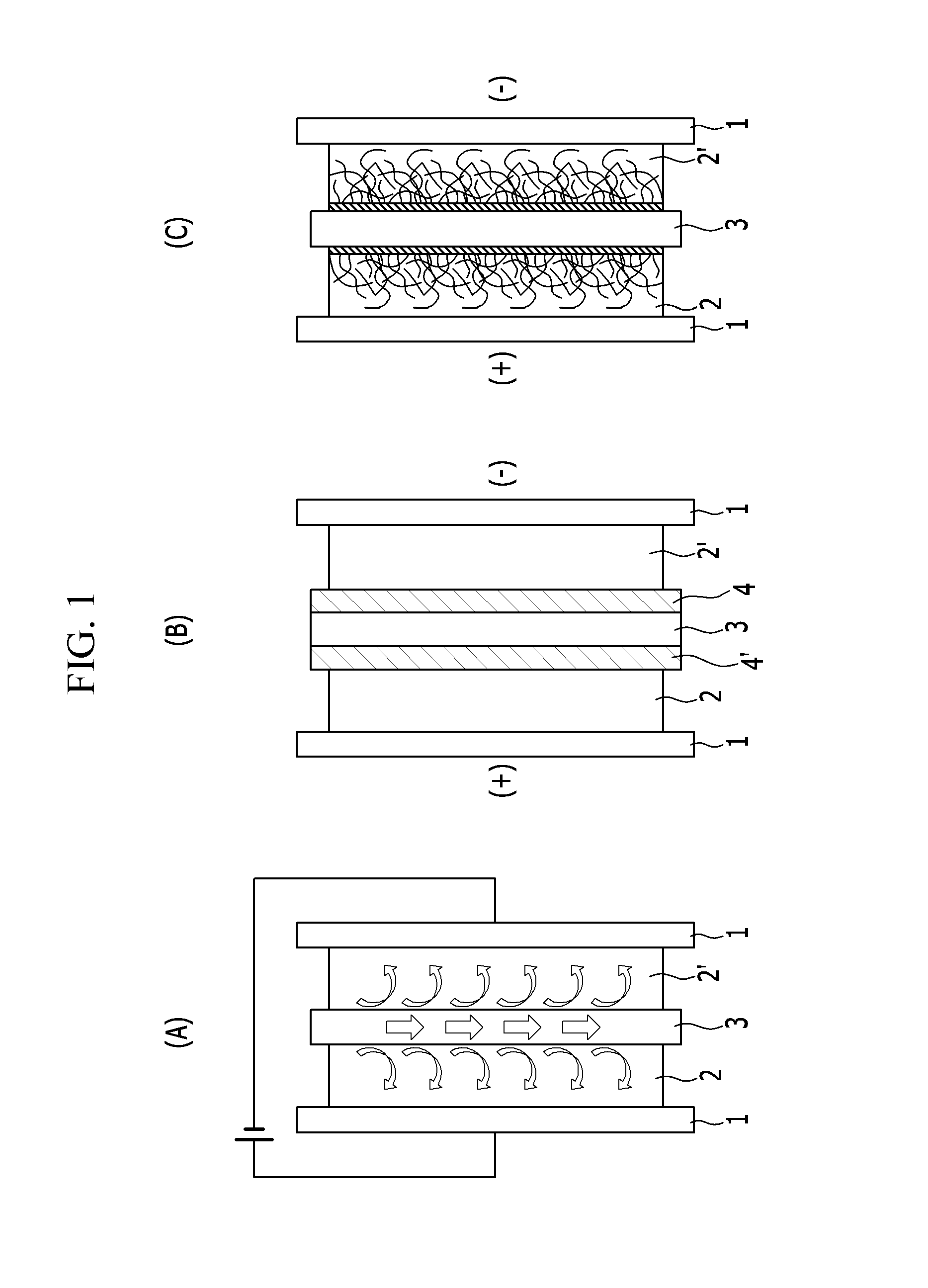
An electrically regeneratable battery of electrochemical cells for capacitive deionization (including electrochemical purification) and regeneration of electrodes is operated at alternate polarities during consecutive cycles. In other words, after each regeneration step operated at a given polarity in a deionization-regeneration cycle, the polarity of the deionization step in the next cycle is maintained. In one embodiment, two end electrodes are arranged one at each end of the battery, adjacent to end plates. An insulator layer is interposed between each end plate and the adjacent end electrode. Each end electrode includes a single sheet of conductive material having a high specific surface area and sorption capacity, preferably a sheet formed of carbon aerogel composite. The batter further includes a plurality of generally identical double-sided intermediate electrodes that are equidistally separated from each other, between the two end electrodes. As the electrolyte enters the battery of ells, t flows through a continuous open serpentine channel defined by the electrodes, substantially parallel to the surfaces of the electrodes. By polarizing the cells, ions are removed from the electrolyte and are held in the electric double layers formed at the carbon aerogel surfaces of the electrodes. As the electrodes of each cell of the battery are saturated with the removed ions, the battery is regenerated electrically at a reversed polarity from that during the deionization step of the cycle, thus significantly minimizing secondary wastes.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
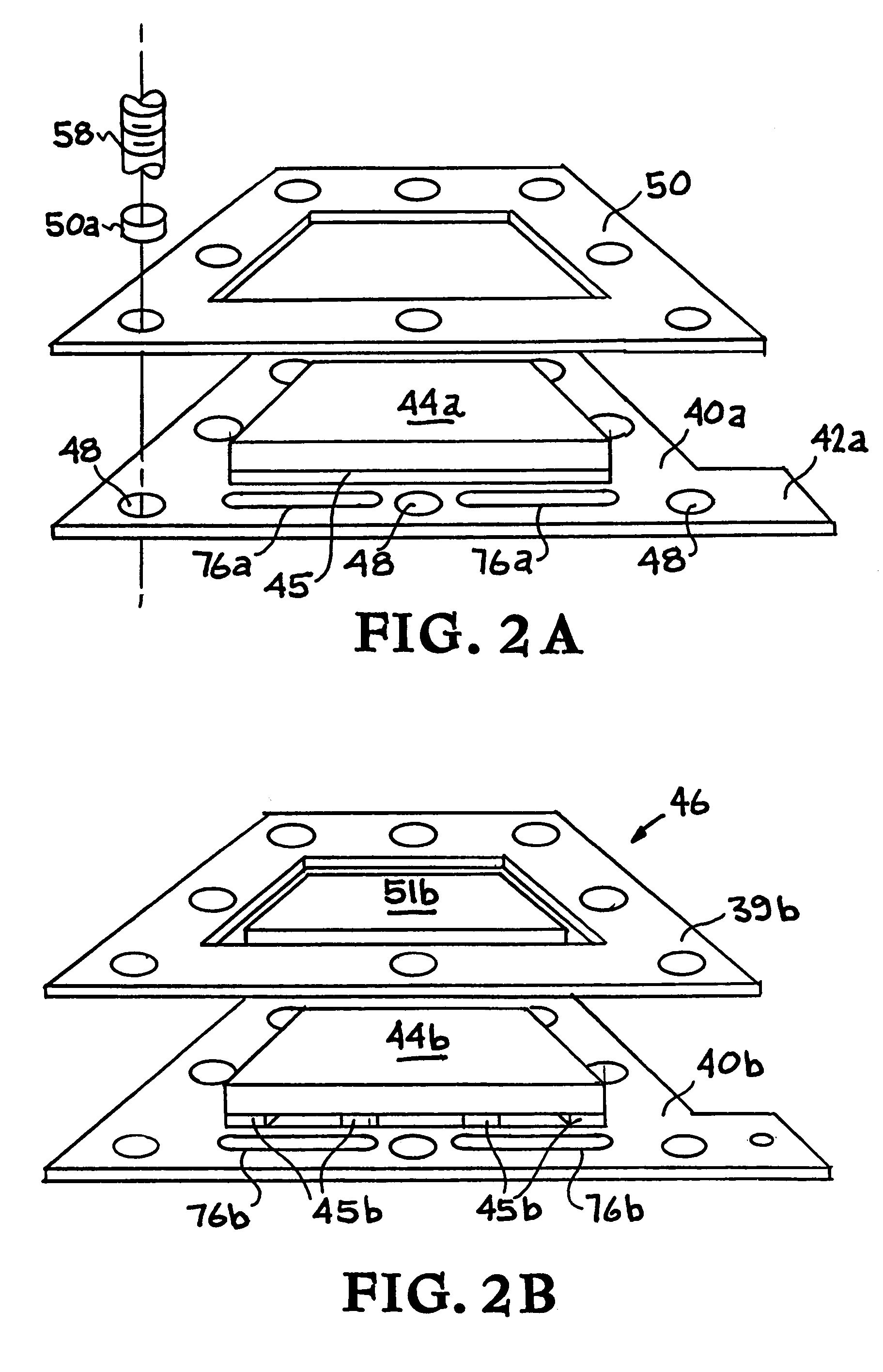
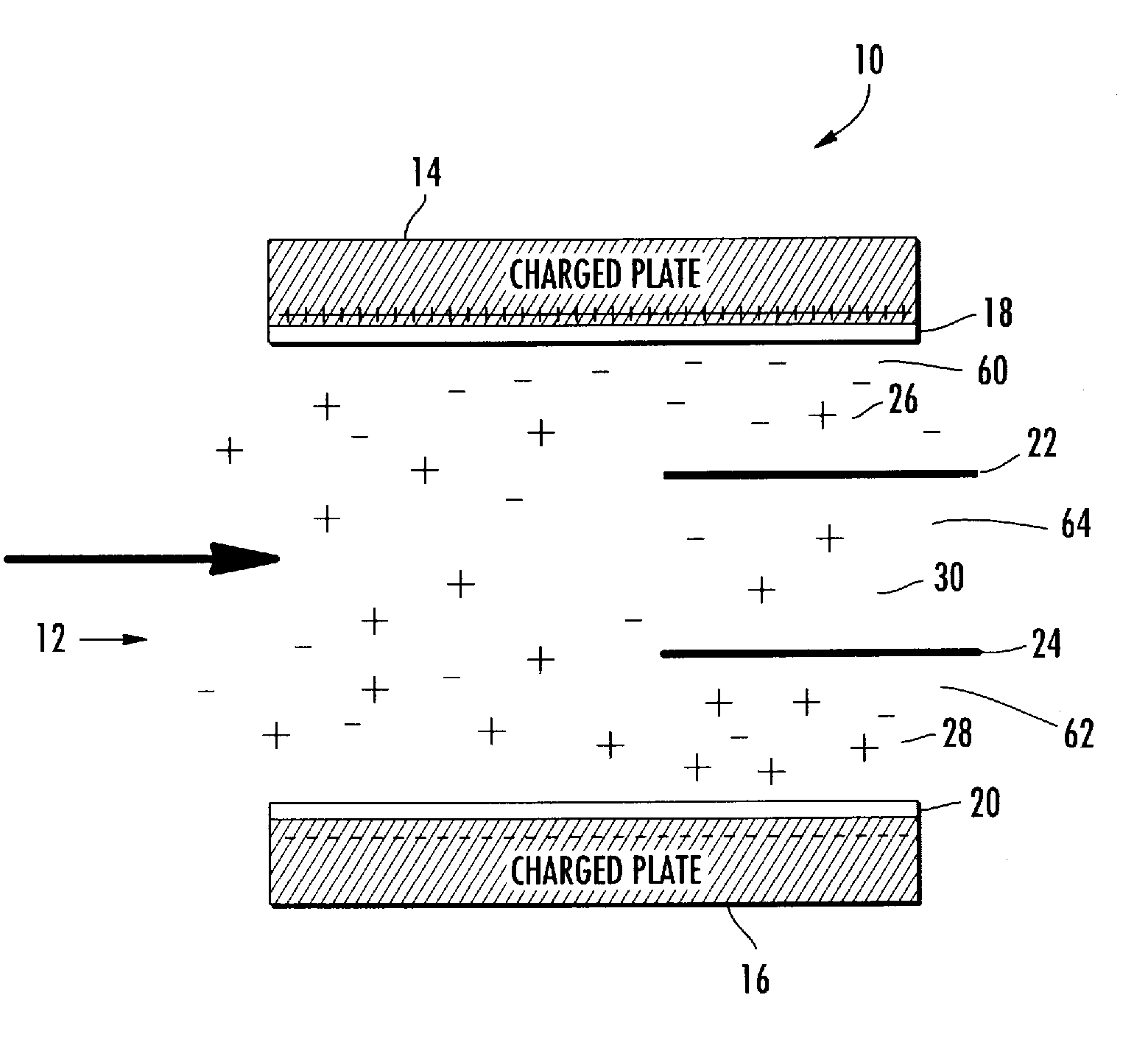
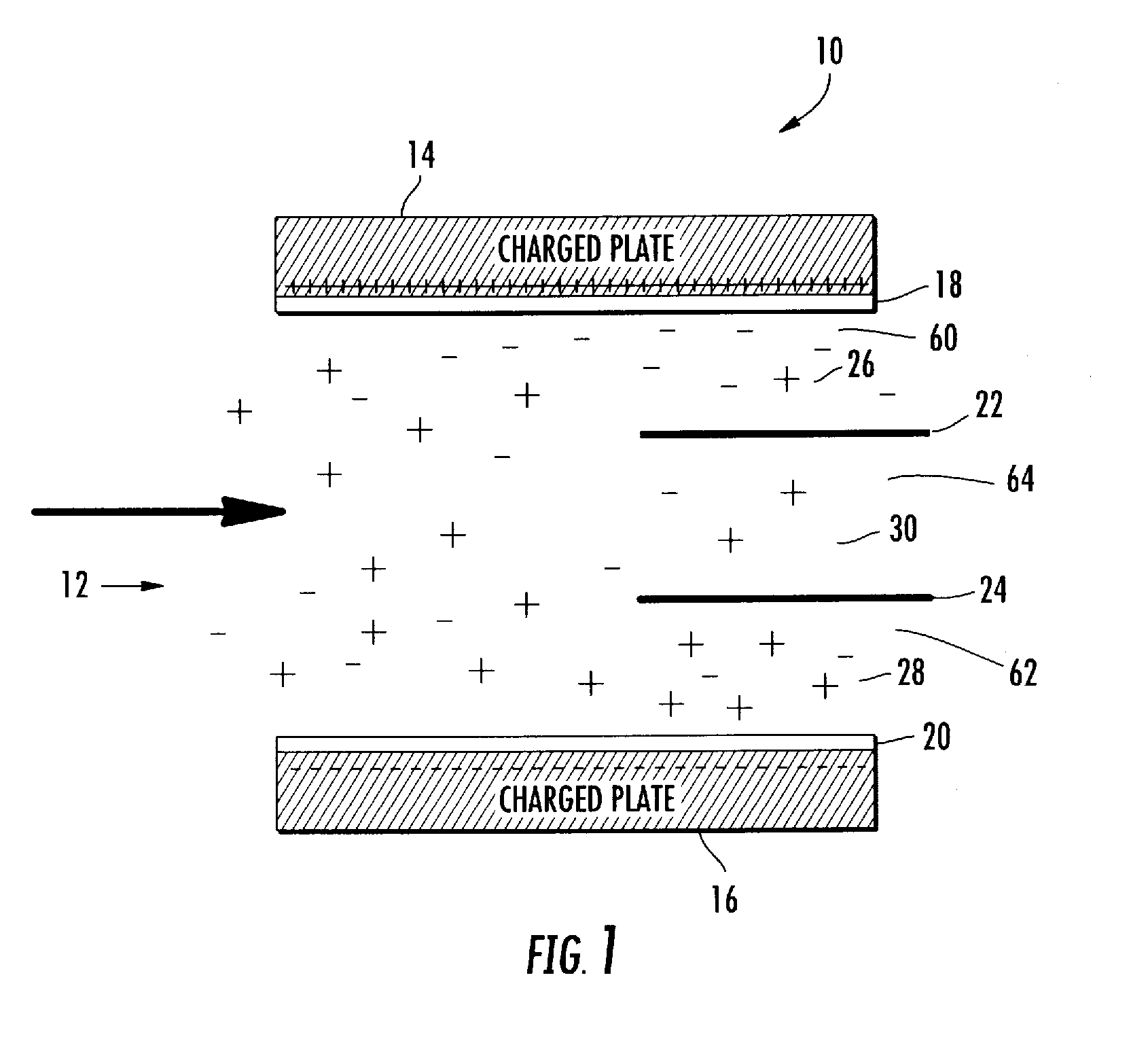
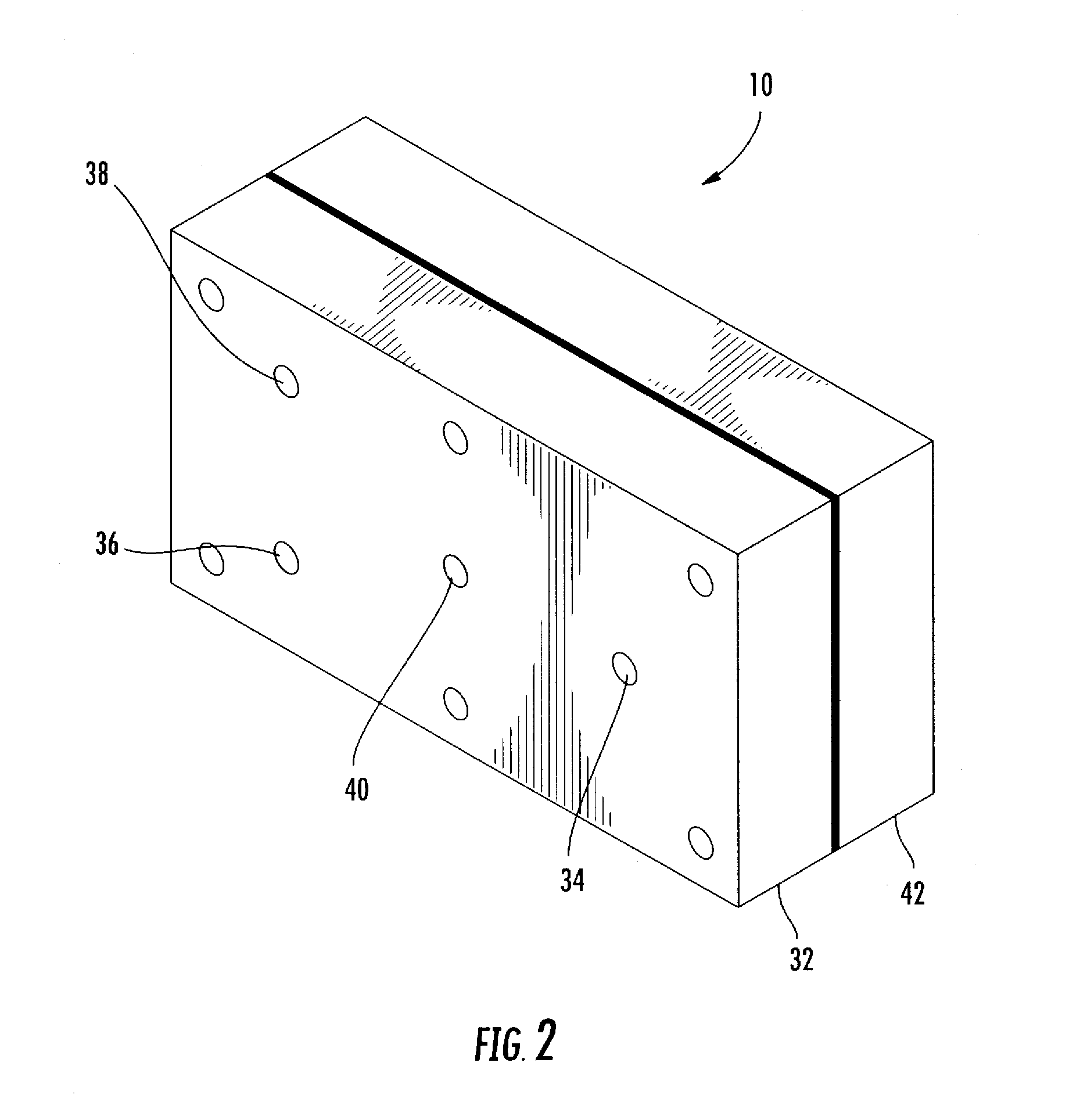
Microscale capacitive deionization apparatus
ActiveUS20080023333A1Little chanceFlexibility in production sizeElectrolysis componentsElectrostatic separatorsCapacitanceCapacitive deionization
The present device is a microchannel separator that uses a separation driving force created by an electric field. An ionic fluid flows through the microchannels and is subjected to an electric field by two spaced apart parallel electrodes possessing an electric charge. The ions in the ionic fluid are attracted towards the charged electrodes and thus are concentrated in the region of flow near the charged electrodes and depleted from the central region of flow between the charged electrodes. The charged electrodes are insulated from the ionic fluid by an impermeable barrier which prevents arcing and adherence of the ions to the charged electrodes. After a sufficient length of passage of the ionic fluid through a main channel two blocking plates separate the flow into a central and two outer output channels. The central channel draws a portion of the ionic fluid from the central region of the main channel that has fewer ions than the ionic fluid in the regions near the charged electrodes. The concentrated ionic fluid in the outer channels is discharged separately from the central channel.
Owner:VECENERGY AEGIR
Deionization apparatus and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090218227A1Reduce contact resistanceImprove conductivityElectrostatic separatorsFrom normal temperature solutionsElectricityCapacitance
A capacitive deionization apparatus, wherein a spacing distance between electrodes of cells is uniformly maintained and a flow in the cells is optimized to improve efficiency of the deionization apparatus and contact resistance between a carbon material and a collector is reduce to improve electrical conductivity, is disclosed. The capacitive deionization apparatus which includes a plurality of electrode modules, each having a collector and electrodes disposed on upper and lower surfaces of the collector to electrically and chemically remove ions from liquid, includes a plurality of plates made of a stiff material are alternately stacked with the electrode modules such that the electrode modules are spaced at specific intervals, wherein the collector and the electrodes are pressed by a pair of adjacent plates among the plurality of plates to maintain a contact therebetween.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Carbon composition with hierarchical porosity, and methods of preparation
ActiveUS20120234695A1Without usingSimple processMaterial nanotechnologyCellsCapacitanceSufficient time
A method for fabricating a porous carbon material possessing a hierarchical porosity, the method comprising subjecting a precursor composition to a curing step followed by a carbonization step, the precursor composition comprising: (i) a templating component comprised of a block copolymer, (ii) a phenolic component, (iii) a dione component in which carbonyl groups are adjacent, and (iv) an acidic component, wherein said carbonization step comprises heating the precursor composition at a carbonizing temperature for sufficient time to convert the precursor composition to a carbon material possessing a hierarchical porosity comprised of mesopores and macropores. Also described are the resulting hierarchical porous carbon material, a capacitive deionization device in which the porous carbon material is incorporated, as well as methods for desalinating water by use of said capacitive deionization device.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Layered carbon electrodes useful in electric double layer capacitors and capacitive deionization and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20080297980A1Improve performanceGood mechanical integrityElectrolytic capacitorsHybrid capacitor electrodesCapacitanceCapacitive deionization
Carbon electrodes for use in, for example, Capacitive Deionization (CDI) of a fluid stream or, for example, an electric double layer capacitor (EDCL). Methods of making the carbon electrodes are also described. The carbon electrode comprises an electrically conductive porous carbon support and a carbon cover layer comprising carbon particles in contact with the electrically conductive porous carbon support. A carbonizable material is within the electrically conductive porous carbon support and provides a bond to the carbon particles at the interface of the electrically conductive porous carbon support and the carbon cover layer. The electrically conductive porous support in some embodiments is a layered structure, where one of the layers is a carbonizable paste layer having electrically conductive particles mixed therein.
Owner:CORNING INC
MXene-based flexible composite negative electrode material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109671949AIncrease energy densityImprove conductivityCell electrodesGrapheneCapacitanceCharge discharge
The invention discloses an MXene-based flexible composite negative electrode material and a preparation method thereof. According to the MXene-based flexible composite negative electrode material andthe preparation method thereof, a transition metal sulfide is loaded on a two-dimensional layered structure of the MXene material through a hydrothermal method. The agglomeration effect of the MXene material is overcome, and the collapse of a layered structure is prevented. Meanwhile, the energy density of the composite material is improved. The MXene material with high conductivity acts as a three-dimensional conductive network skeleton, so that the conductivity and the mechanical strength of the composite material are enhanced. The volume expansion of the transition metal polysulfide material in the charging process is buffered. Meanwhile, the material has good charge-discharge cycle stability. The composite material and expanded graphite are combined to prepare a self-supporting high-flexibility negative electrode material. In the charging and discharging process, the hydrophilic MXene material has high affinity to polysulfides. The electrochemical performance and the capacitive deionization performance of the composite negative electrode material can be further improved. Sulfides generated by transition metal sulfides are eliminated. The shuttle effect of the polysulfides is limited, and the service life of the negative electrode material is prolonged.
Owner:FUJIAN XFH NEW ENERGY MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for flow-electrode capacitive deionization (FCDI)-based desalination and application
InactiveCN106044970AReduce manufacturing costSimple structureDispersed particle separationWater/sewage treatmentPeristaltic pumpAutomatic control
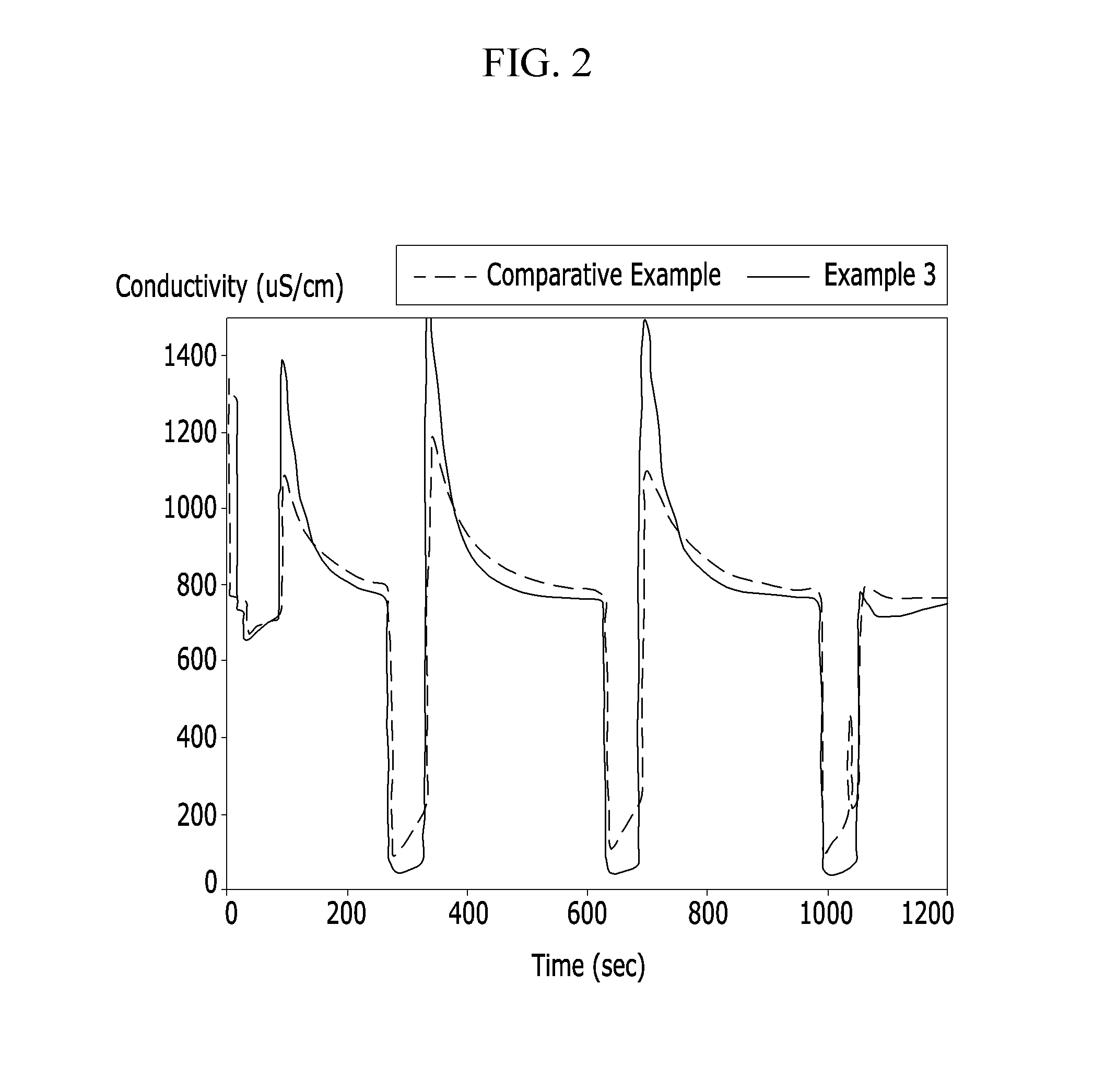
The invention discloses a method for flow-electrode capacitive deionization (FCDI)-based desalination and application. According to the method, a direct current voltage stabilization power supply, a flow electrode, a dual-channel peristaltic pump, an FCDI module unit, a small-size peristaltic pump, a conductivity meter, an organic glass fixing device, a stainless steel interface and an electrode connection splice are involved; one end of each of two pump pipes of the dual-channel peristaltic pump is arranged in each of anode chamber flow electrode liquid and cathode chamber flow electrode liquid, and the other end of the pump pipe is connected with the stainless steel interface in the lower part of the organic glass fixing device; the flow electrode enters the FCDI unit module through the stainless steel interface through pressure provided by the dual-channel peristaltic pump; incoming water is pumped into the FDCI unit module with a prepared sodium chloride solution with different concentration at certain flow speed through the small-size peristaltic pump; the conductivity meter is used for measuring the conductivity concentration of discharged water. A reaction device used in the method is simple in structure, low in operation cost and easy to operate, and no chemicals is fed; automatic control and on-line monitoring are easy to implement; the method is low in energy consumption, and the preparation cost of the electrode is lowered; the method can be applied to the technical field of environmental engineering and water treatment.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Total solution for water treatments
InactiveUS20070272550A1Improve power efficiencyHigh recovery rateCellsEnergy based wastewater treatmentCapacitanceElectrolysis
All pollutants dissolved or existed in water can be grossly classified as ionized and neutral species. The former includes inorganic and organic ions, while the latter contains inorganic molecules, organic molecules and organisms. Using flow through capacitor for performing capacitive deionization (CDI), the ionic contaminants can be effectively and economically removed from water. Whereas the neutral contaminants are not retained in the static electric field of CDI, they can be decomposed upon flowing through an electrolytic ozonator. Either gaseous or ionic products will be generated at the ozone treatment, and the ionic byproducts can be subsequently removed by CDI. By integrating the electrolytic ozone reactor with flow through capacitor, the O3 / CDI hybrid technique becomes a total solution for eliminating hazardous materials in water. Both the reactor of in-situ ozone and the flow-through capacitor (FTC) of CDI are operated in energy conservative and pollution free conditions, so the detoxification of water is highly cost effective.
Owner:GAINIA INTELLECTUAL ASSET SERVICES
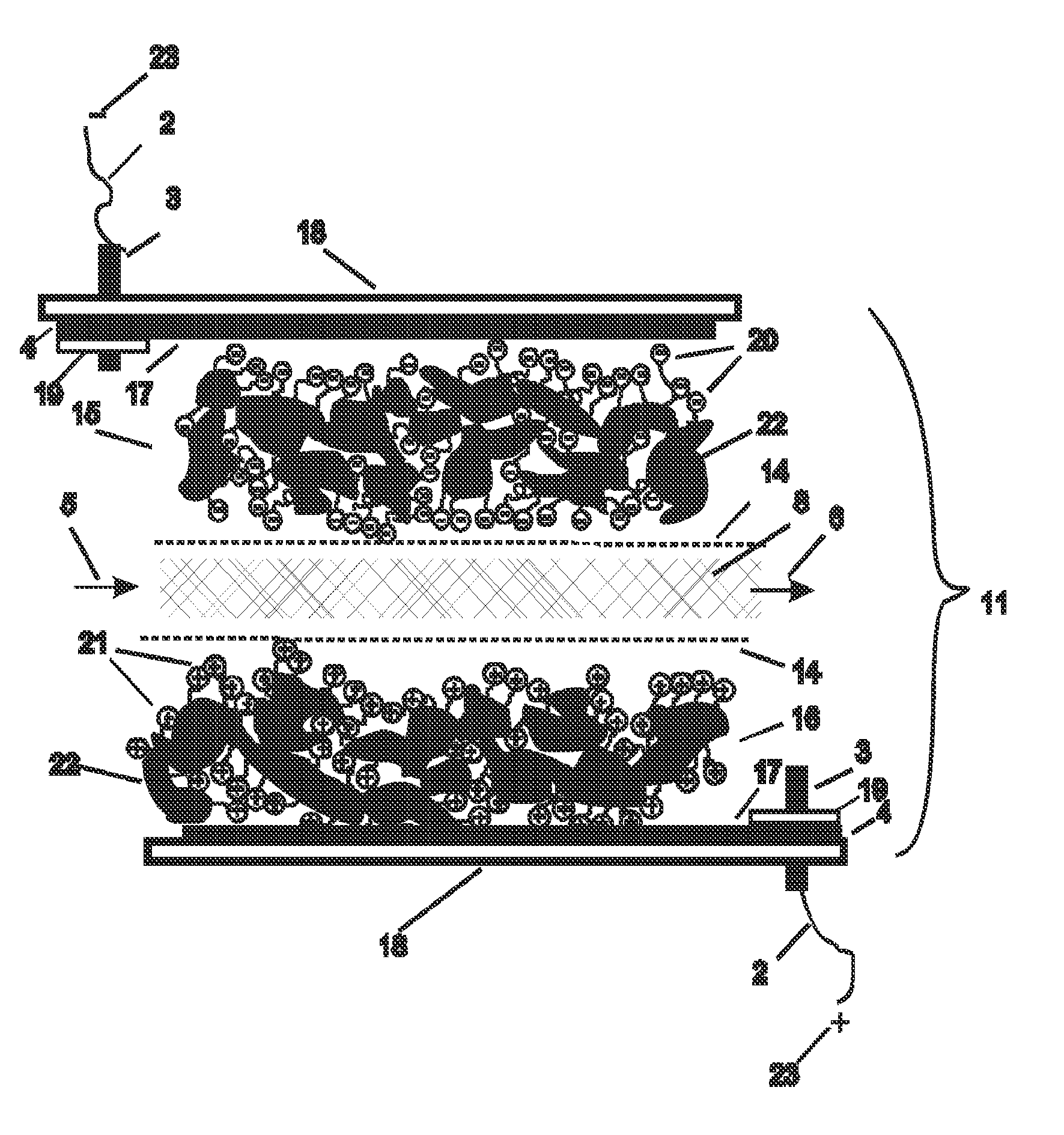
Electrode for capacitive deionization device, method of manufacturing the electrode, and capacitive deionization device having the electrode
ActiveUS20090020430A1Easy to operateImprove conductivityFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesElectrostatic separatorsCapacitanceCapacitive deionization
Disclosed herein is an electrode for capacitive deionization device including an active material, a waterborne polyurethane, and a conducting agent. Disclosed herein too is a method of manufacturing the electrode and a capacitive deionization device employing the electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Capacitive deionization device
InactiveUS20110042205A1Increase concentrationCellsLine/current collector detailsCapacitanceCapacitive deionization
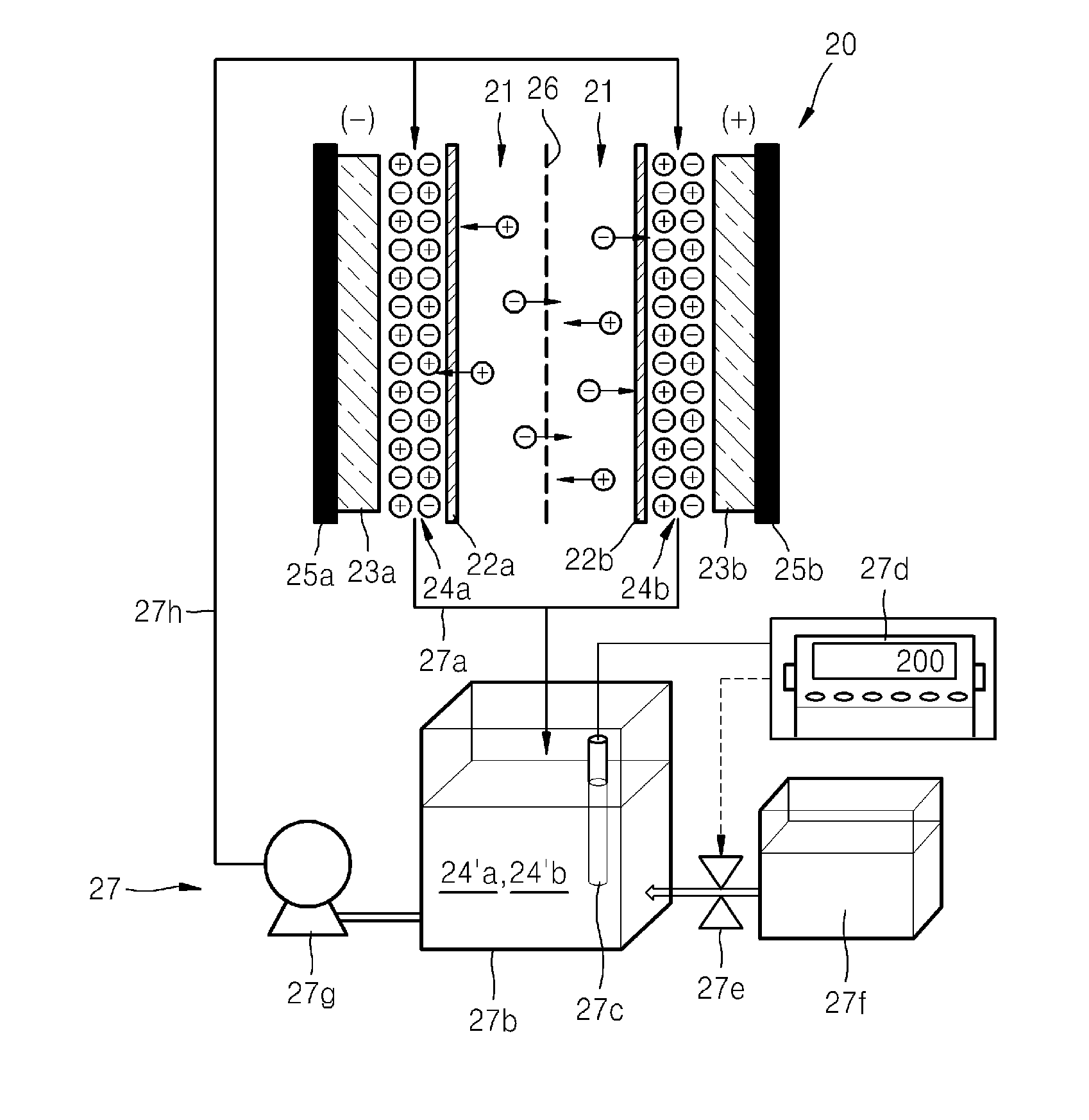
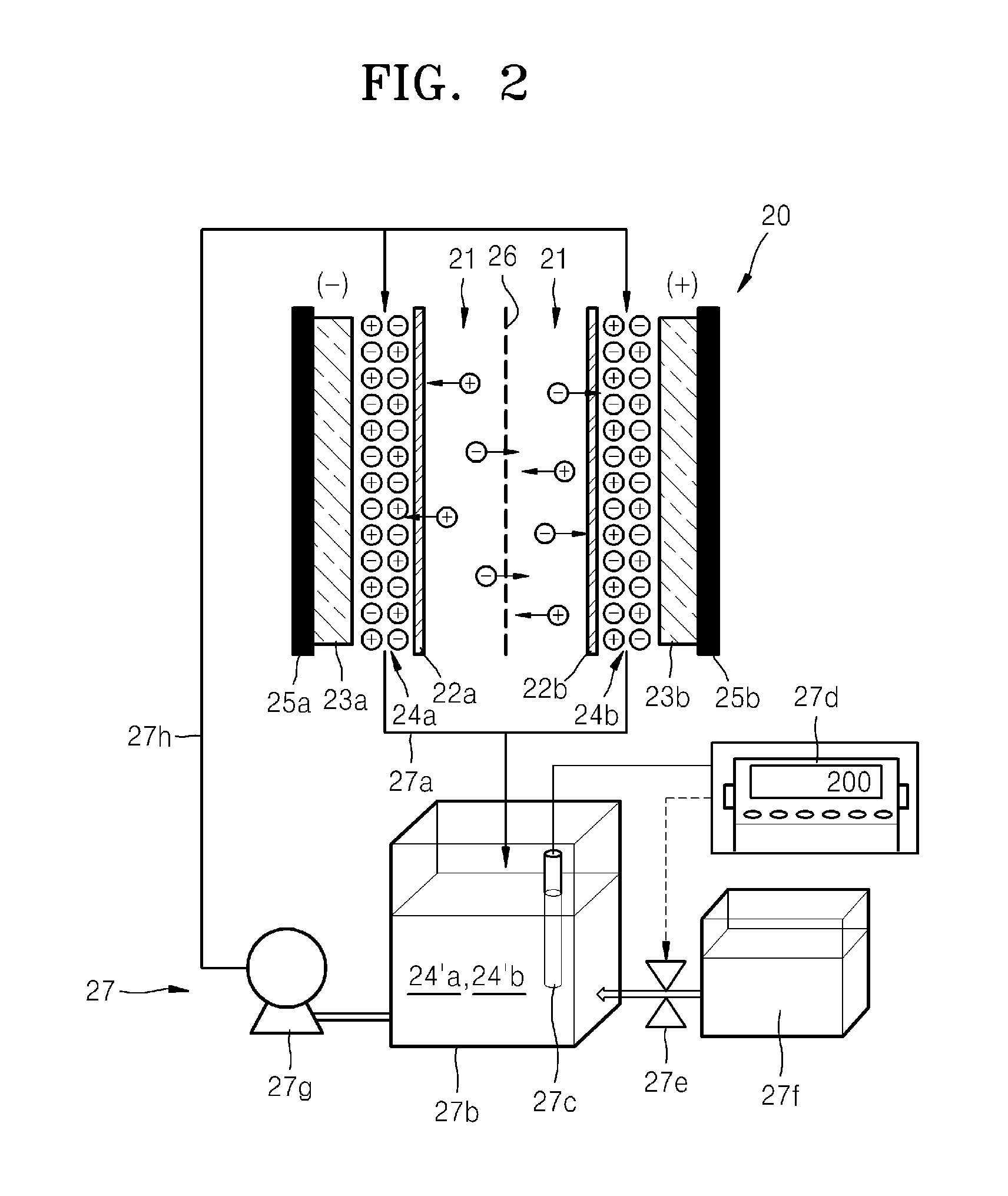
A capacitive deionization device includes; at least one flow path configured for influent water flow, at least one pair of electrodes, at least one charge barrier disposed between the at least one flow path and a corresponding electrode of the at least one pair of electrodes, and at least one electrolyte solution disposed between the at least one electrode of the at least one pair of electrodes and a corresponding charge barrier of the at least one charge barrier, wherein the at least one electrolyte solution is different in at least one of ionic concentration and ionic species from the influent water.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Capacitive deionization device
A capacitive deionization device includes; at least one flow path configured to receive influent fluid, at least one pair of electrodes, at least one charge barrier disposed between the at least one flow path and a corresponding electrode of the at least one pair of electrodes, at least one electrolyte solution disposed between at least one of the at least one pair of electrodes and a corresponding charge barrier of the at least one charge barrier, and at least one electrolyte compensation device in fluid communication with the at least one electrolyte solution, wherein the at least one electrolyte solution differs from the influent fluid.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
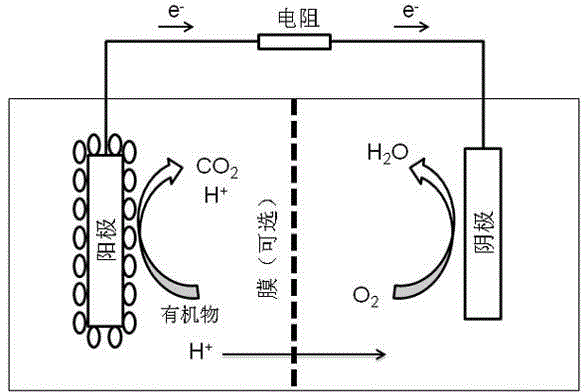
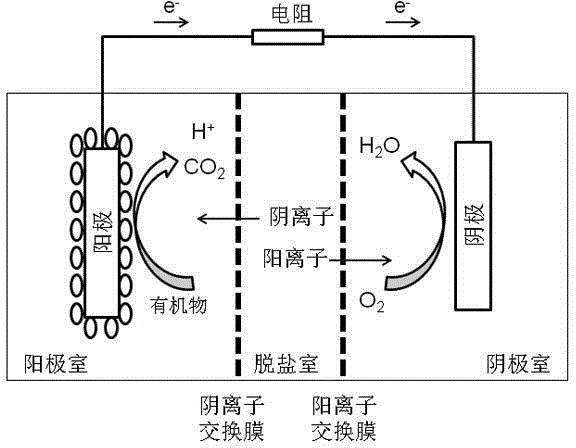
Microbial capacitive desalination fuel cell technology
InactiveCN104617322AIncrease resistanceLower resistanceFinal product manufactureCell electrodesBiologyOrganopónicos
The invention discloses a microbial capacitive desalination fuel cell technology for supplying power to a capacitive deionization unit by virtue of electric energy generated by microbial treatment of sewage and relates to the technical field of microbial treatment of sewage, microbial power generation and capacitive deionization desalination. The desalination technology consists of a microbial fuel cell and a capacitive deionization unit. The technology is characterized in that two cation exchange membranes and two active carbon cloth electrodes are added between an anode chamber and a cathode chamber of a microbial fuel cell to form a desalination chamber. The problem in the prior art is that microorganisms oxidize organic pollutants to release protons which are accumulated to lead to decrease of pH value of the anode chamber so as to affect the yield and desalination. The anode chamber, the desalination chamber and the cathode chamber are divided by using the two cation exchange membranes and two active carbon cloth electrodes, so that protons can be freely transferred among the three chambers by virtue of the cation membranes and the active carbon cloth so as to stabilize the pH values of the chambers. The invention aims to provide the method for operating microbial capacitive desalination fuel cell in a long term, wherein the activity of electrochemically active microorganisms is maintained and the electricity production capacity and the desalination efficiency are improved.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV +1
Capacitive deionization electrodes, capacitive deionization apparatuses including the same, and production methods thereof
ActiveUS20150175449A1Enhanced charge separation efficiencyIncreased ion removal capacityElectrostatic separatorsFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesCapacitanceCapacitive deionization
A capacitive deionization electrode may include a conductive material and a polymer on a surface of the conductive material. The polymer may have at least one functional group in a single polymer chain.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Capacitive Deionization Using Hybrid Polar Electrodes
InactiveUS20090255815A1Reduce energy costsShort turnaround timeFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesElectrostatic separatorsCapacitanceEngineering
Capacitive deionization (CDI) is a non-membrane and chemical-free technique for water purification, used-water recycling, and seawater desalination. Ionic contaminants in the waters are retained by a static electric field built within the critical component of CDI, which is known as flow through capacitor (FTC). Apparently, parameters enhancing the field strength of FTC and electrode efficiency are the keys to the performance of CDI. The FTC of the present invention is formed by a plurality of monopolar and a plurality of bipolar electrodes, and a plural number of perforated holes are disposed on the FTC electrodes in a pattern that allows certain water flow rate and residence time to yield the highest efficiency of electrode utilization.
Owner:GAINIA INTELLECTUAL ASSET SERVICES +1
Method and system for enhancing oil recovery (EOR) by injecting treated water into an oil bearing formation
ActiveUS20130168097A1Reduce salinityEnhanced overall recoveryMembranesGeneral water supply conservationCapacitive deionizationElectric capacity
A process and a system for enhancing recovery of oil from an oil-bearing formation are provided in which water having a total dissolved solids content is filtered to remove some solids in a filter assembly, the filtered water is treated to remove some ions in a capacitive deionization assembly, and the filtered deionized water is injected into the oil-bearing formation to mobilize crude oil and enhance oil recovery from the formation.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Continuous wastewater treatment device utilizing membrane capacitive deionization
ActiveCN103991937ALower resistanceLarge capacityDispersed particle separationWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeCapacitanceProcess module
The invention relates to a continuous wastewater treatment device utilizing membrane capacitive deionization. An upper cover plate and a lower cover plate are coaxially installed at the upper end and the lower end of a cylindrical shell, a water inlet nozzle and a water outlet nozzle which are communicated with the interior of the shell are respectively formed in the axis part of the upper cover plate and the axis part of the lower cover plate, a water collecting plate is coaxially installed on the upper cover plate in the shell, conducting rods are uniformly and axially distributed on the periphery of the shell at intervals, a lower distribution board and an upper distribution board are coaxially installed in the shell between the water collecting plate and a water distributing plate and are of a pair of metal boards, and a plurality of groups of processing module components are coaxially installed between the two distribution boards, wherein each group of processing module component comprises an upper current collecting plate, a membrane carbon positive electrode, a diaphragm, a membrane carbon negative electrode and a lower current collecting plate. According to the continuous wastewater treatment device, the membrane electrode is integral and is prepared by a carbon electrode and an ion membrane through spraying a cation exchange coating on a cathode and spraying an anion exchange coating on an anode, the thickness of the ion exchange layer is less than 10mu, and the membrane electrode has small resistance and large capacitance compared with those of a membrane electrode on which an ion membrane is directly added.
Owner:BEIJING HUA YAN BANG SCI & TECH +1
Ion-Selective Capacitive Deionization Composite Electrode, and Method for Manufacturing a Module
InactiveUS20120199486A1Gap minimizationAvoid dirt buildupSludge treatmentPretreated surfacesCapacitive deionizationComposite electrode
Provided are a CDI electrode and a method for manufacturing a module using the same. A composite electrode manufactured by the manufacturing method of the present invention can manufacture a CDI electrode capable of increasing adsorption efficiency and rate of ions and selectively adsorbing cation and anion, thereby simply and inexpensively manufacturing the CDI electrode module without using a cation-exchange membrane and an anion-exchange membrane.
Owner:SIONTECH
Carbon composition with hierarchical porosity, and methods of preparation
ActiveUS8865351B2Alleviating mass-transport limitationLess time without compromising salt removal efficiencyCellsMaterial nanotechnologyCapacitive deionizationSufficient time
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Membrane capacitive deionization device for circulation treatment and treatment method
InactiveCN106830227AEfficient use ofRealize the collectionDispersed particle separationWater/sewage treatmentCapacitanceWater storage tank
The invention discloses a membrane capacitive deionization device for circulation treatment and a treatment method. The membrane capacitive deionization device comprises a membrane capacitance deionization component, a step-up / step-down converter, a direct-current (DC) power supply, a raw water storage tank, a middle liquid storage tank, a regenerated water storage tank, a fresh water storage tank, a conductivity monitor, a water pump, a power valve, a check valve and a DC / DC converter. Based on a technique of double-electrode layer desalting principles, the membrane capacitive deionization device is capable of removing salt and storing energy; and in the regeneration process of a capacitive deionization unit, the stored energy can be released. Collection of the part of energy can be achieved, and the collected energy can be used as an external power supply of the capacitive deionization unit for desalting operation. In order to achieve the purpose of maximization of energy storage, the step-up / step-down converter is introduced, energy recycling can be achieved, and the energy consumption can be reduced. Due to the design of the experiment device disclosed by the invention, an effect of multi-level treatment on strong brine can be achieved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
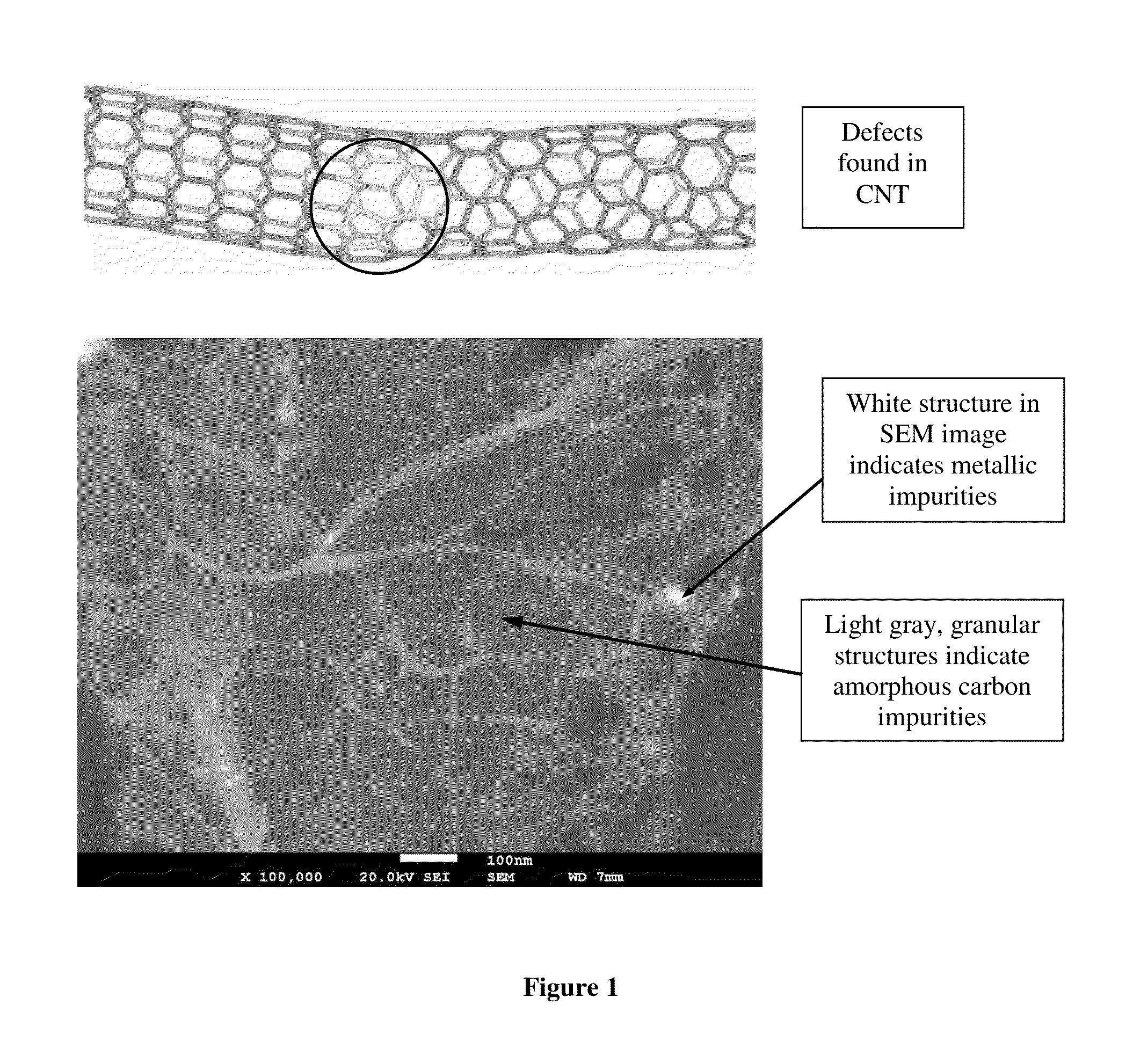
Method of purifying carbon nanotubes and applications thereof
ActiveUS20130222975A1Material nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor separatorsCapacitive deionizationOrganic solvent
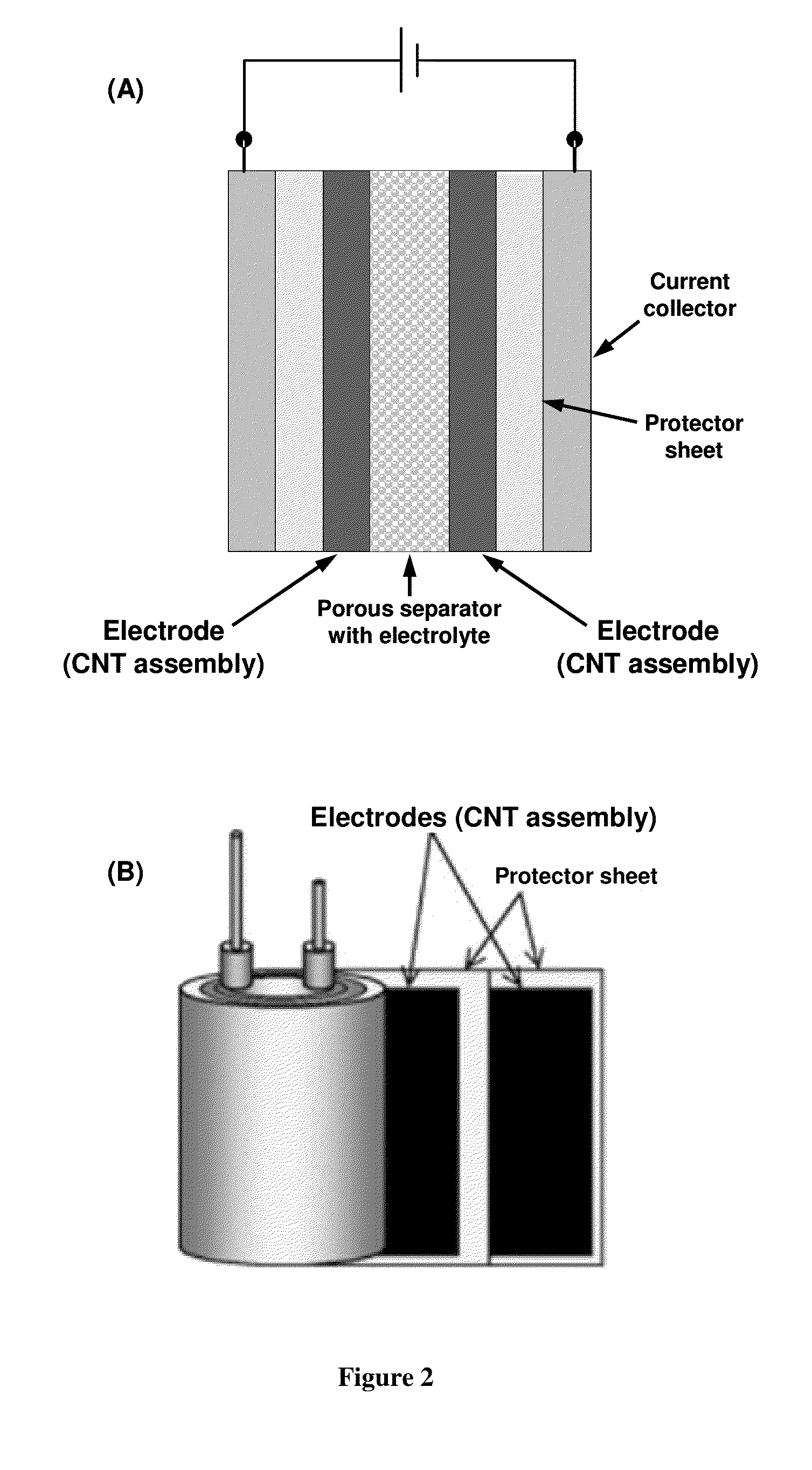
The present invention relates to a method of preparing purified carbon nanotubes (CNTs) comprising mixing starting CNTs with an organic solvent in the presence of sonication; substantially removing the organic solvent to obtain a CNT composition; and heating the CNT composition at 200° C. or higher to obtain the purified carbon nanotubes. The present invention further relates to the purified CNTs and cohesive CNT assemblies prepared from the method described herein, and articles (e.g. capacitor, energy storage device or capacitive deionization device) comprising the purified CNTs.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
Method for cooperatively removing heavy metal and organic matters by capacitive deionization coupling electrocatalysis
ActiveCN108423776AHigh catalytic activityAchieve degradationWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsCapacitancePollution
The invention belongs to the fields of water treatment and resource recycling and discloses a capacitive deionization (CDI) coupling electrocatalysis system and a method for cooperatively removing heavy metal and organic pollutants in water by using the CDI coupling electrocatalysis system. Under the conditions of an external electric field (smaller than 2V), a capacitive electrostatic adsorptioneffect is coupled with an electrocatalytic oxidation degradation effect, and the heavy metal and the organic pollutants are simultaneously moved. The CDI coupling electrocatalysis system disclosed bythe invention has the beneficial effects cooperative removal of the heavy metal and the organic pollutants in the water is realized by using electrodes with catalytic activity, and the defect and theproblem that a traditional water treatment technology only treats a single pollution system is overcome / solved. The reaction system has the advantages of simplifying a treatment technology, shorteningthe flow, reducing secondary pollution and facilitating scale and industrial application.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Capacitive de-ionization electrode
ActiveUS20100025247A1Easy to replaceLess expensiveSludge treatmentElectrolysis componentsCapacitanceCapacitive deionization
An electrode “cell” for use in a capacitive deionization (CDI) reactor consists of the electrode support structure, a non-reactive conductive material, the electrode accompaniment or substrate and a flow through screen / separator. These “layers” are repeated and the electrodes are sealed together with gaskets between two end plates to create stacked sets of alternating anode and cathode electrodes in the CDI reactor.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Hybrid Capacitive Deionization and Electro-Deionization (CDI-EDI) Electrochemical Cell for Fluid Purification
InactiveUS20080078672A1Function increaseShort regeneration timeCellsEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesCapacitanceCapacitive deionization
Systems and methods are described that combine capacitive deionization (CDI) and electro-deionization (EDI) mechanisms for deionizing aqueous or non-aqueous solutions. The inventive systems and methods modify certain known coatings or films by perforating the films with pin holes and using spacers that separate the coatings from the electrodes. Benefits derived from these improvements include: (a) maintaining a high level of purification; (b) increasing by as much as 25% the rate of expulsion of ions during regeneration; (c) increasing by as much as 50% the rate of electrical discharge of the cell; (d) decreasing the regeneration time (producing as much as 33% more purified water per unit of time); (e) reducing by as much as 25% the power required; and (f) improving the recovery of the system to as much as 85%.
Owner:ATLAS ROBERT D
Pretreatment method for deacidification and impurity removal of acid leaching liquid of vanadium extracted from stone coal
The invention relates to a pretreatment method for deacidification and impurity removal of acid leaching liquid of vanadium extracted from stone coal. Ion exchange resin and carbon materials are used for being prepared into a composite electrode plate which is placed in a capacitive deionization assembly, a direct-current power source is powered on, the acid leaching liquid of vanadium extracted from stone coal is subjected to pretreatment of deacidification and impurity removal, the treated composite electrode plate is in short connection or reverse connection, and the desorption process is performed. The method is little in energy consumption, the pretreatment efficiency is improved, loss of precipitated and mixed V in the solid and liquid separating process is reduced, and therefore the using amount of chemical agents is small, the V loss rate is low, and the impurity removal effect is obvious. The pretreatment method further has the advantages that the technology is flexible, and the method can be used for pretreatment of deacidification and impurity removal of acid leaching liquid of vanadium extracted from stone coal and can also be used for treatment of other high-acid multi-impurity leaching liquid.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com