Patents
Literature
1280results about How to "Without using" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Drug releasing coatings for medical devices
ActiveUS20080118544A1Avoid dependenceAvoid disadvantagesOrganic active ingredientsBiocideControlled releaseDrug release
The invention relates to a medical device for delivering a therapeutic agent to a tissue. The medical device has a layer overlying the exterior surface of the medical device. The layer contains a therapeutic agent and an additive. The additive has a hydrophilic part and a hydrophobic part and the therapeutic agent is not enclosed in micelles or encapsulated in particles or controlled release carriers.
Owner:LUTONIX INC
Monitor for an optical fibre and multi-guide optical fibre circuits and methods of making them
InactiveUS20050074208A1Easy to controlHigh yield preparationOptical measurementsCoupling light guidesEngineeringEvanescent wave
The invention relates to a monitor for monitoring at least one optical signal parameter in an opticl fibre having an access region of reduced cladding sufficient to allow access to the evanescent field. The monitor includes an optical element mountable adjacent to the access region of an optical fibre which optical element is capable of obtaining access to the evanescent field to enable use of the data therein to derive the at least one optical signal parameter.
Owner:BADCOCK RODNEY +2
Distraction instrument and method for distracting an intervertebral site
InactiveUS20070123904A1Minimize impactReduce amountSpinal implantsOsteosynthesis devicesDistractionCircular disc
A distraction instrument includes a drive rod, a driver mechanism coupled to the drive rod, and a pair of arms linked to the driver mechanism. A method of implanting an artificial disc or a fusion implant in an intervertebral site includes preparing the intervertebral site, actuating a gear mechanism of a distraction instrument to distract the intervertebral site, and inserting at least a core of the artificial disc or fusion implant into the intervertebral site.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Drug releasing coatings for medical devices
ActiveUS20080255508A1Avoid lipolysis dependence and other disadvantageRapid elutionStentsBiocideWater solubleCompound (substance)
Owner:LUTONIX INC
Method and system for determining an imaging direction and calibration of an imaging apparatus
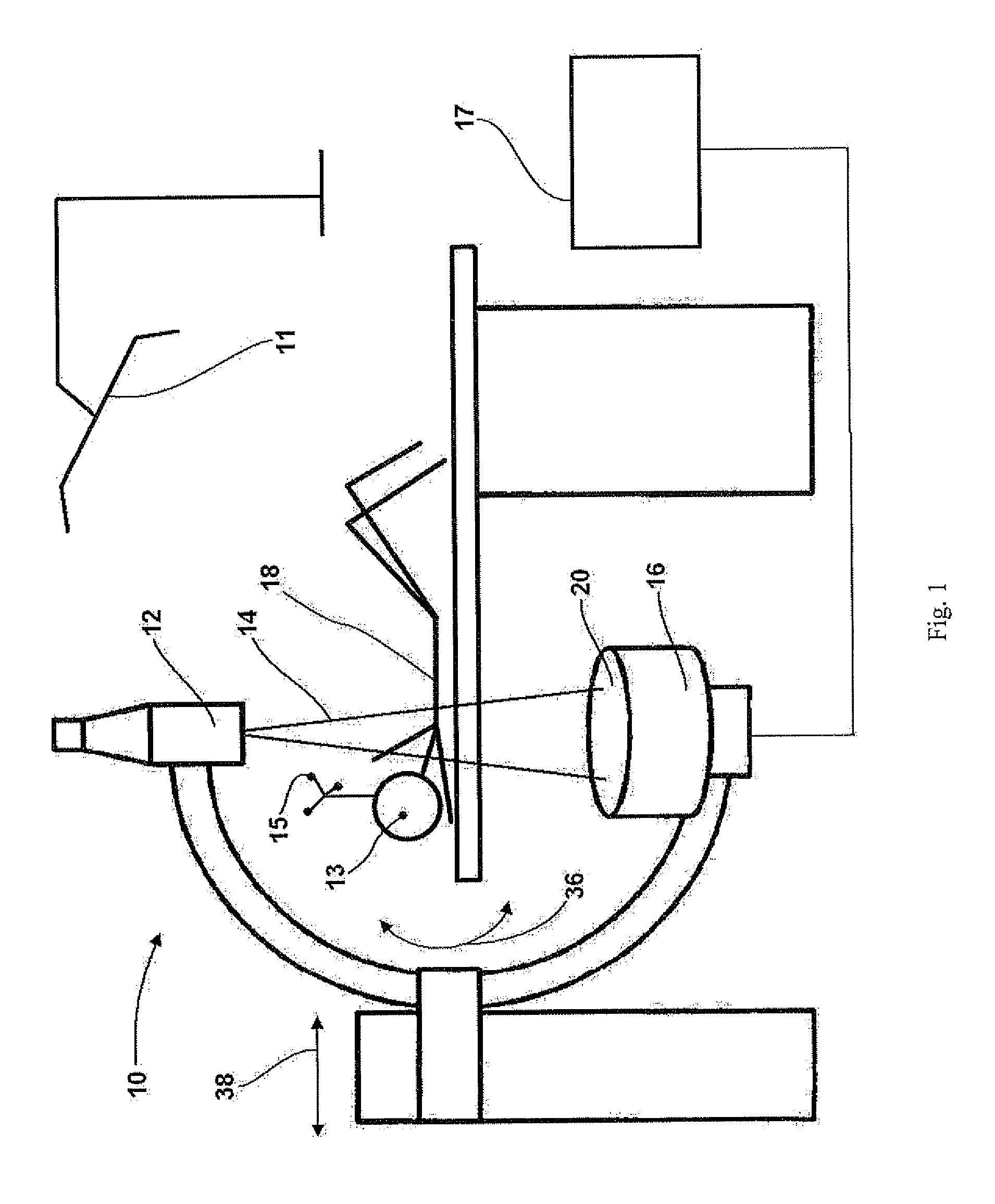
The present invention relates to a method for determining an imaging direction of an imaging apparatus (10), such as an x-ray apparatus, with a radiation source or an imaging source (12) that emits an imaging beam (14) to an imaging detector (16) along a beam path, comprising the steps of imaging an object (18) from a first direction to obtain a first 2D image; providing 3D reference data, for example a generic or statistical 3D model or an earlier obtained 3D data set, of the imaged object (18); performing a 2D / 3D matching of the first 2D image with the 3D reference data to determine a position of an imaging plane (20, 22, 24) of the first 2D image relative to the 3D reference data; and determining the imaging direction of the imaging apparatus (10) relative to the object (18) based on the position of the imaging plane (20, 22, 24) relative to the 3D reference data, as well as to a navigation system for computer-assisted surgery comprising the imaging system of the preceding claim; a tracking system (11), such as optical or IR tracking means; detection devices (13, 15) such as e.g. radiopaque markers (13) detectable by the imaging system and markers (15) detectable by the tracking system (11) attachable to an object (18), wherein the navigation system is adapted to detect a position of the object (18) based on the detection devices (13, 15), in order to generate detection signals and to supply the detection signals to the computer (17) such that the computer can determine point data on the basis of the detection signals received; a calibration object such as a patient body or a phantom bearing detection devices for calibrating the navigation system.
Owner:BRAINLAB
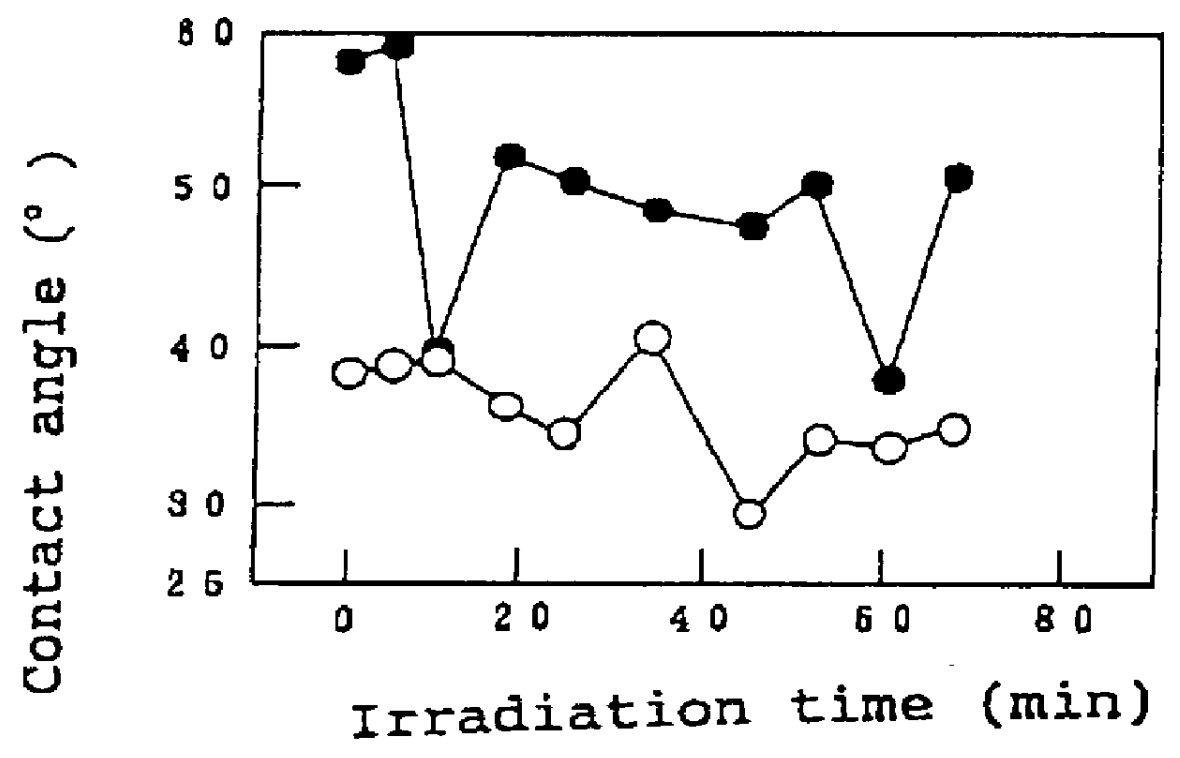
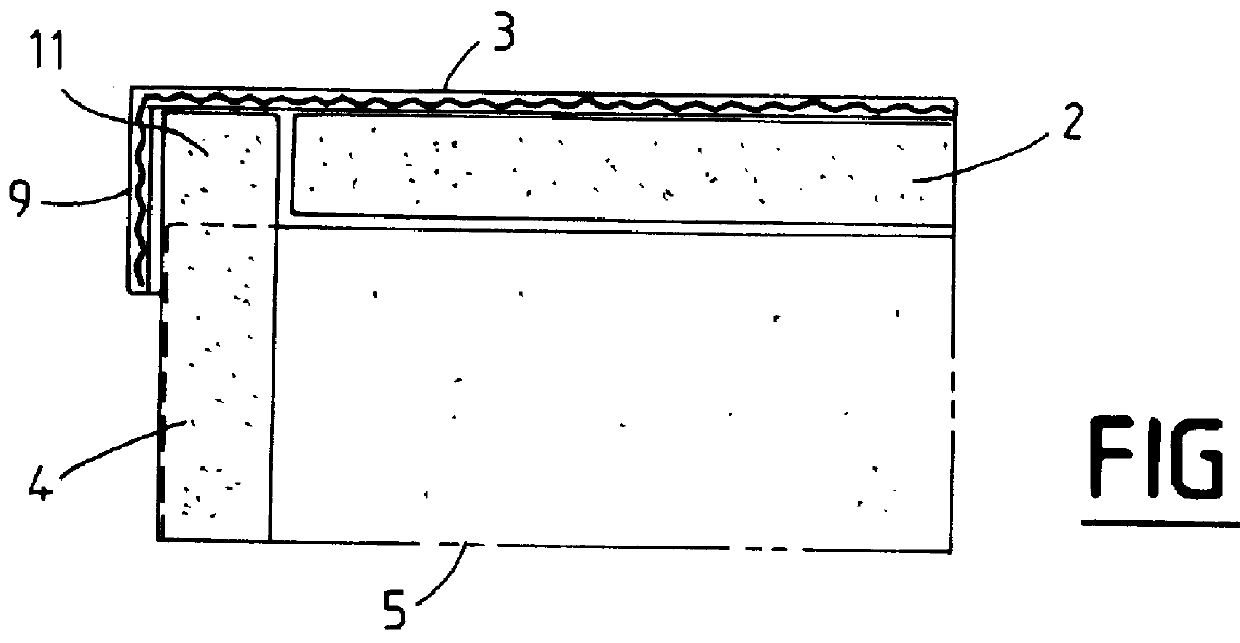
Method for photocatalytically hydrophilifying surface and composite material with photocatalytically hydrophilifiable surface
InactiveUS6090489AImproved oil repellencyEasy to disassembleOther chemical processesPretreated surfacesAtmospheric airSolid acid
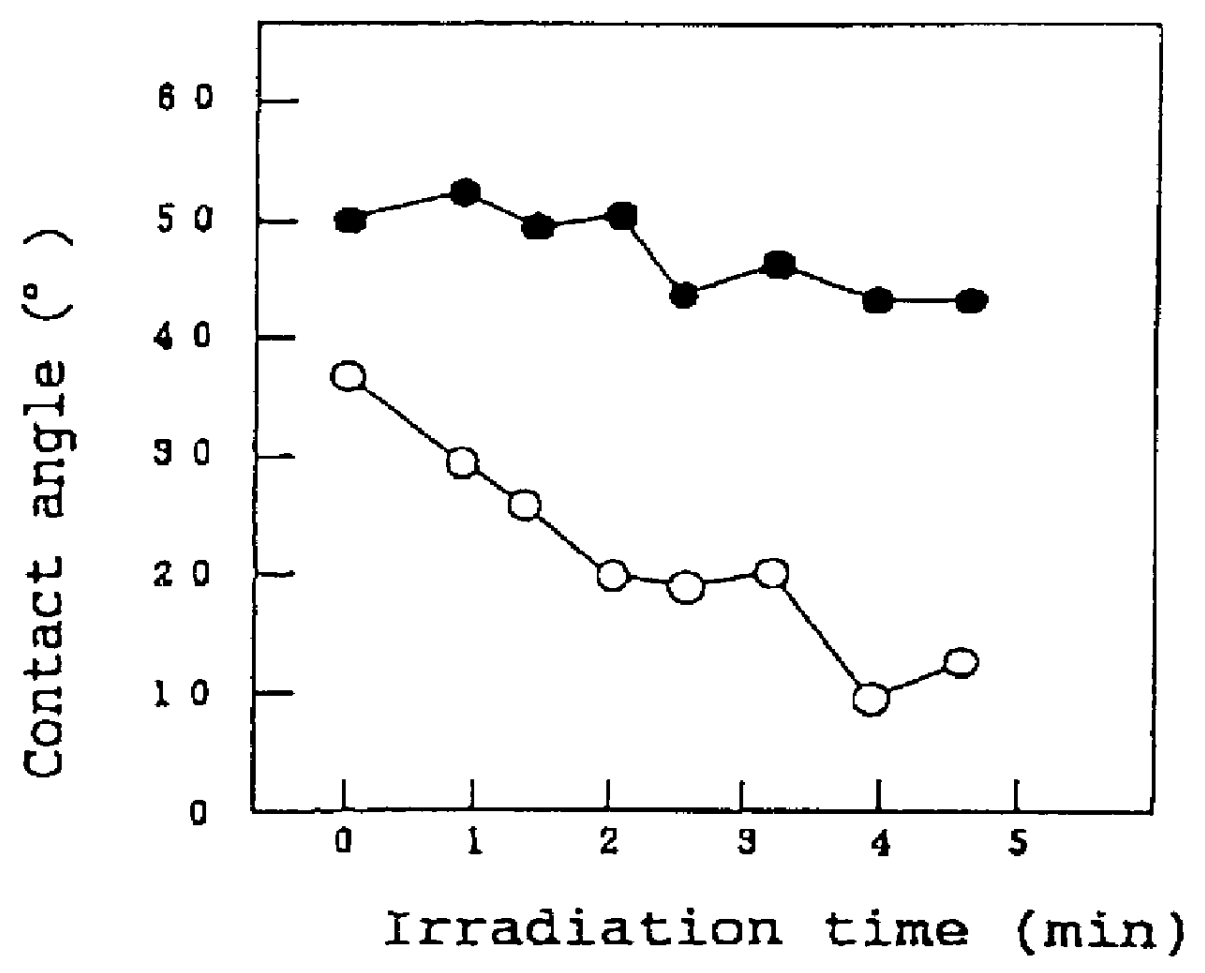
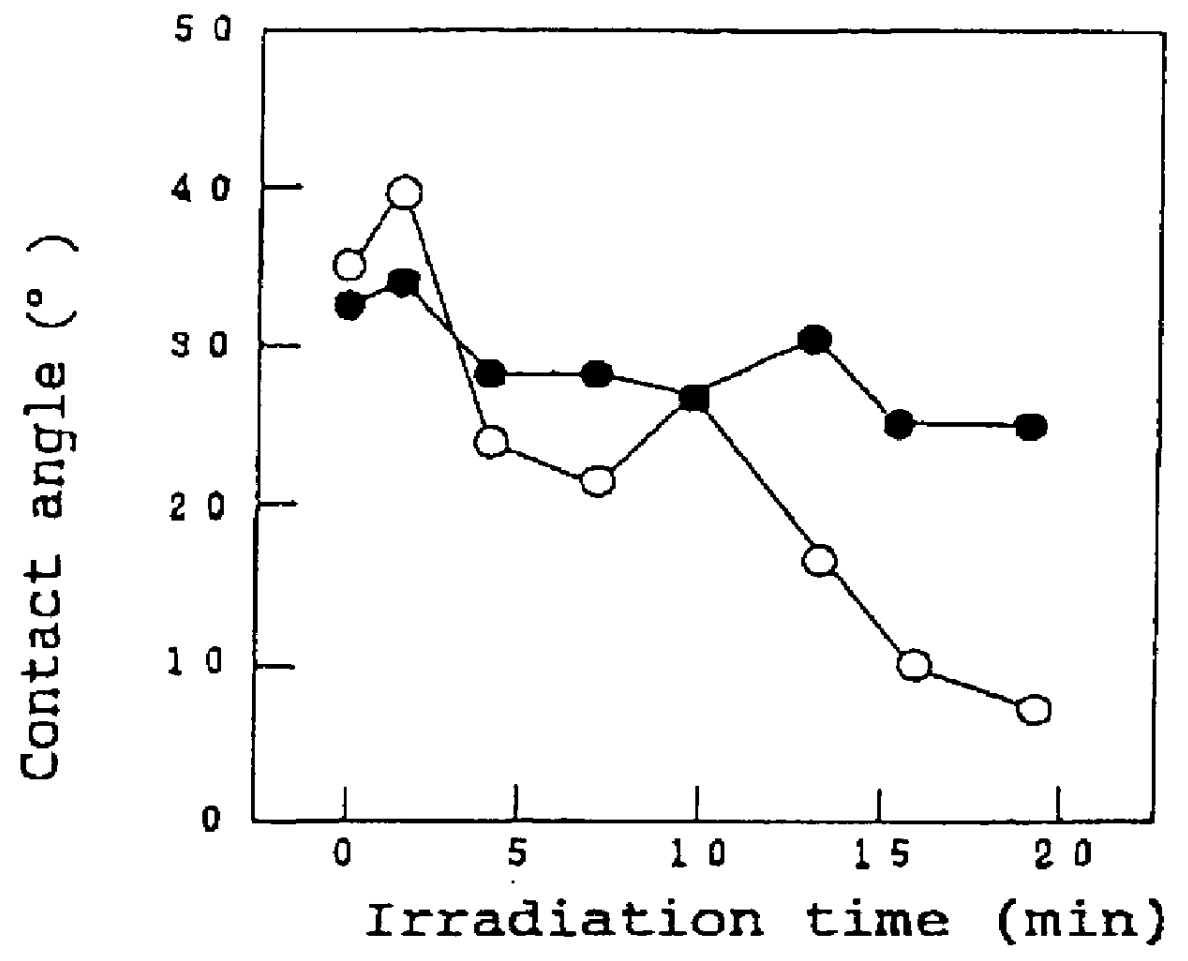
A method for hydrophilifying the surface of a substrate by taking advantage of photocatalytic action. The substrate has a photocatalytic titania coating (10). The surface of the photocatalytic coating (10) bears the solid acid that increases a hydrogen bond component ( gamma Sh) in the surface energy in the solid / gas interface of the coating. Photoexcitation of the photocatalyst enhances the hydrogen bond component ( gamma Sh) in the surface energy of the photocatalytic coating (10), accelerating the physical adsorption of molecules of water in the atmosphere through a hydrogen bond (16) onto hydrogen atoms in a terminal OH group (12), bonded to a titanium atom, and a bridge OH group (14) on the surface of the coating. This results in the formation of a high density, physically adsorbed water layer (18) on the surface of the photocatalytic coating (10), thus permitting the surface of the substrate to be easily hydrophilified. The method is applicable to antifogging, antifouling, selfcleaning and cleaning of articles.
Owner:TOTO LTD
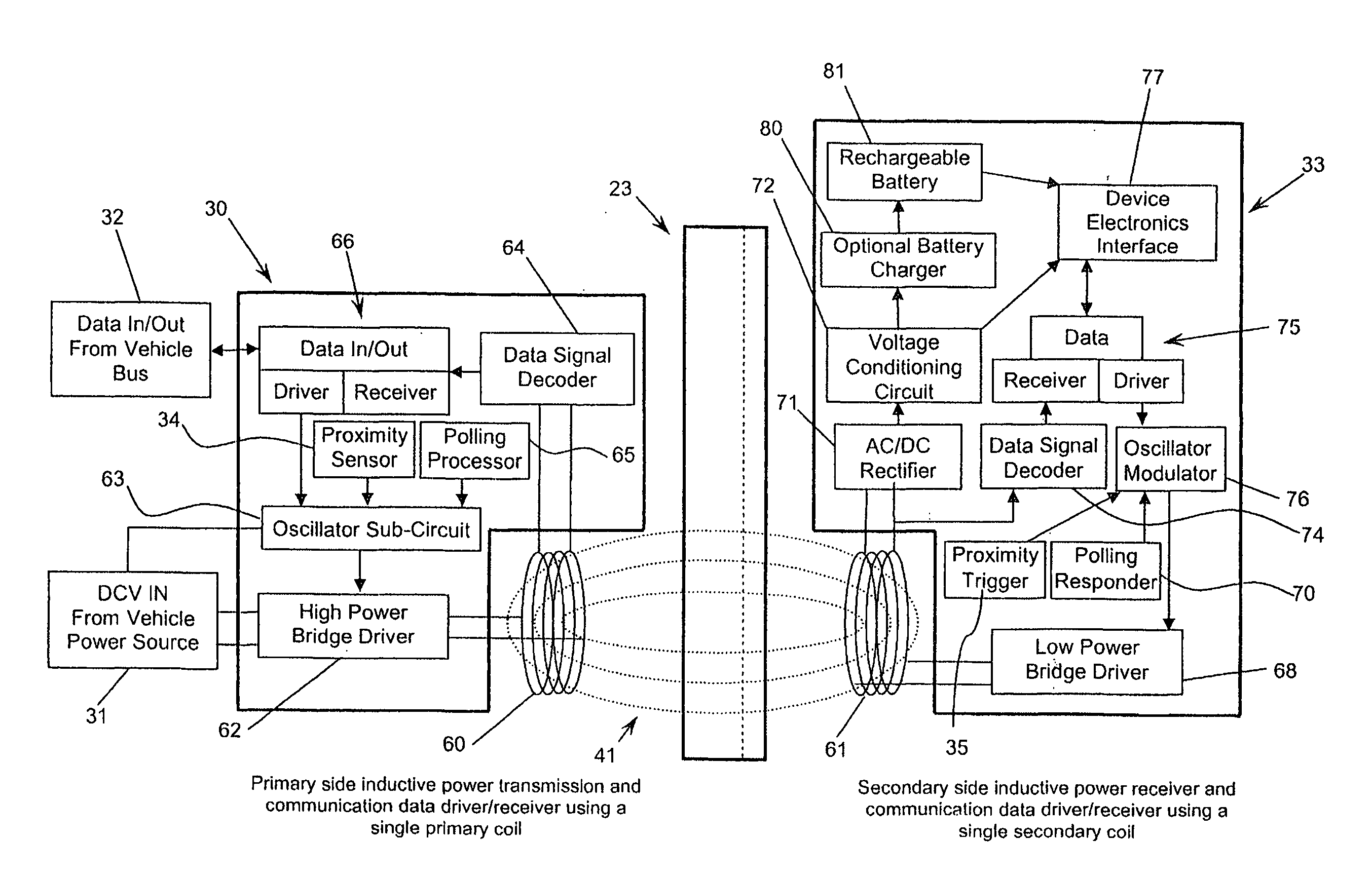
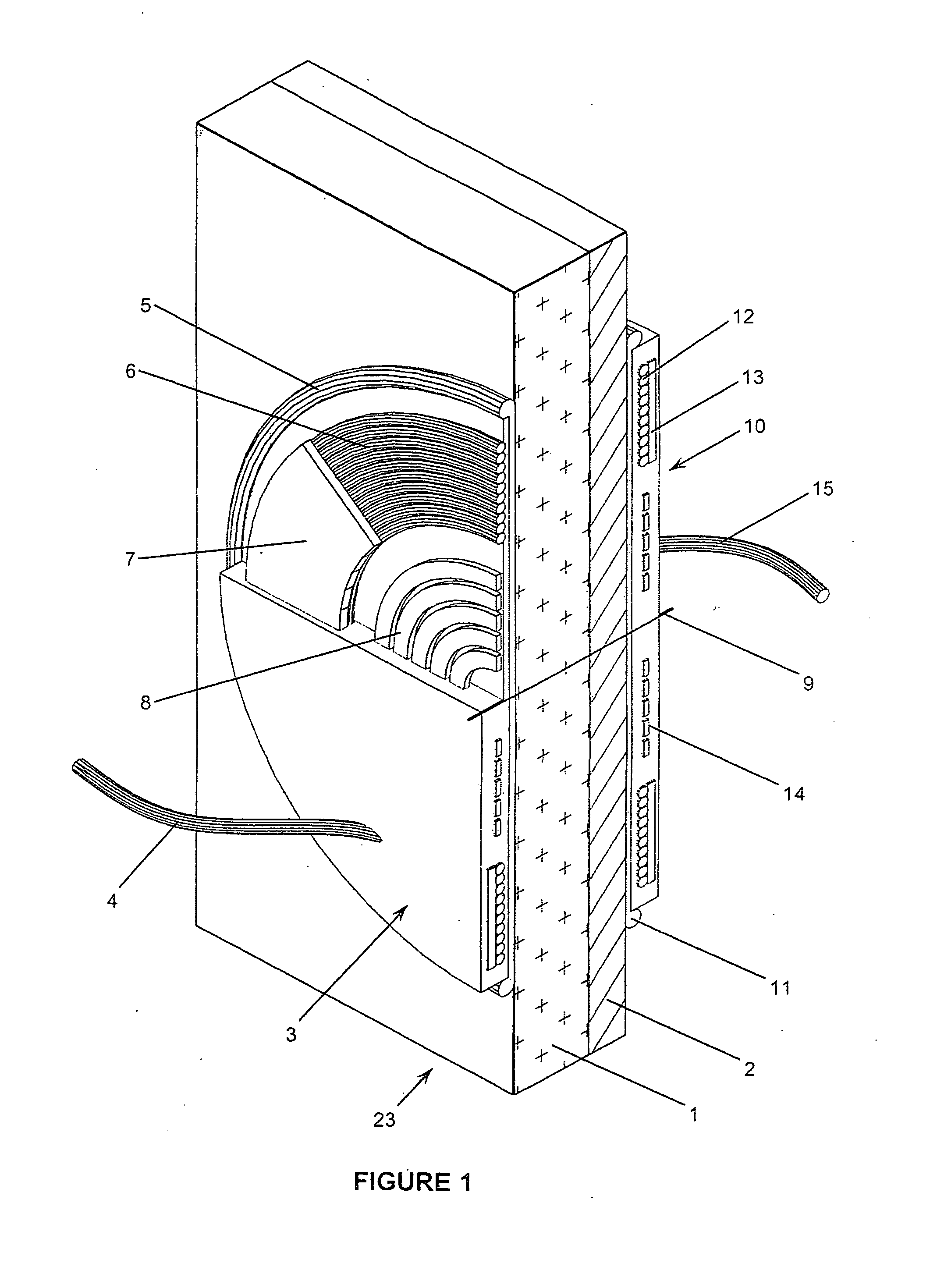
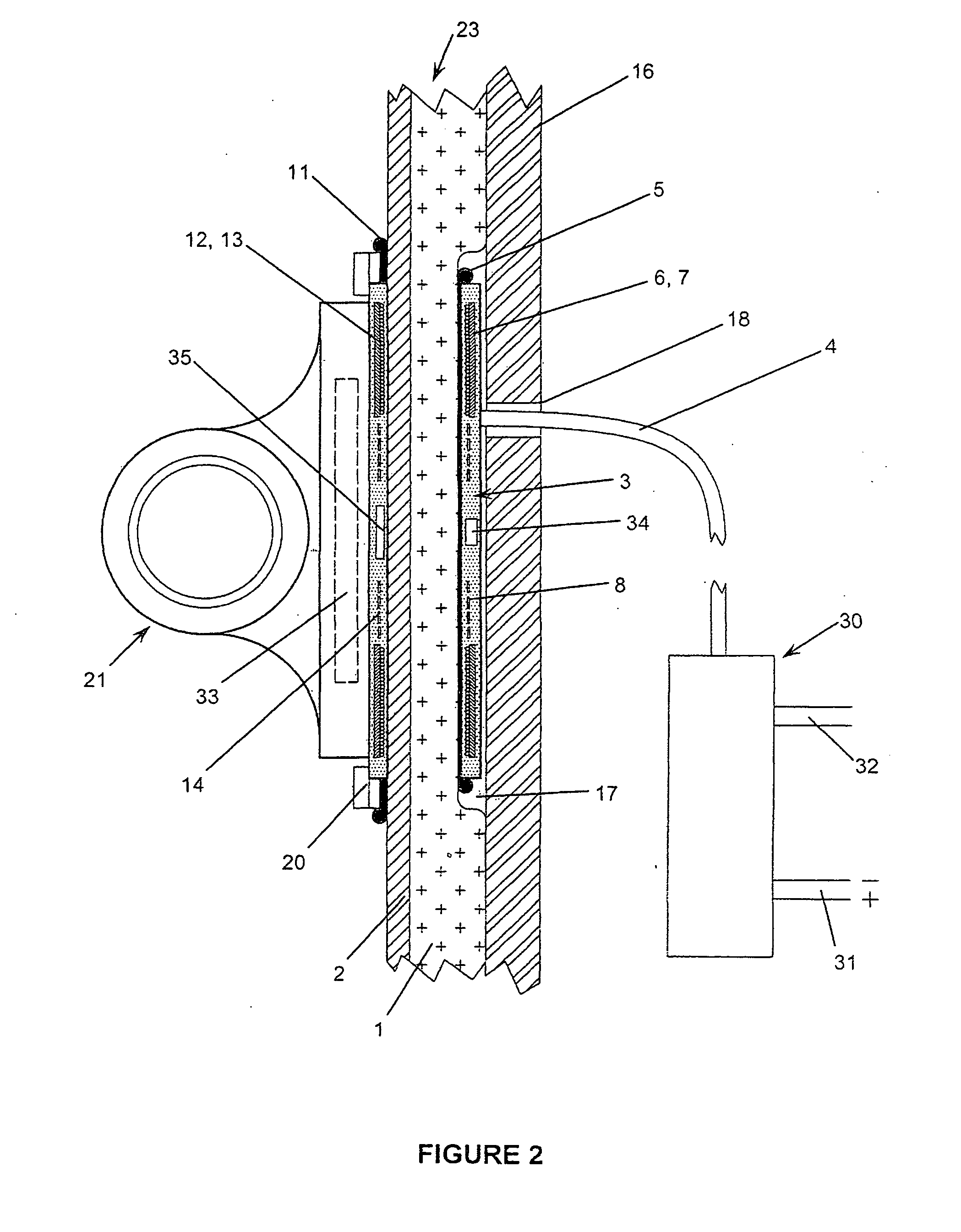
Inductive transmission of power and data through ceramic armor panels
ActiveUS20120032632A1Decreasing its survivabilityCompromising their effectivenessCircuit authenticationElectromagnetic wave systemElectrical devicesData transmission
A system for the inductive transmission of power and data through large caliber ballistic appliqué composite armor panels mountable to military vehicle includes a large caliber ballistic appliqué composite armor panel and a quick-release base mounted to the outer face of the panel and a primary coil mounted to the inner face of the panel so as to be opposite to and aligned with the base; and, a portable electrical device having a secondary coil mounted in its base end, and wherein the armor thickness is no greater than substantially the range of 30 to 50 percent of the diameter of the secondary coil. The base end of the portable electrical device is adapted to releasably mount onto the quick release base for power transfer to the electrical device and for data transfer between the primary coil and the secondary coil by inductive coupling between the primary and secondary coils.
Owner:CYNETIC DESIGNS
Device, head mounted display, control method of device and control method of head mounted display
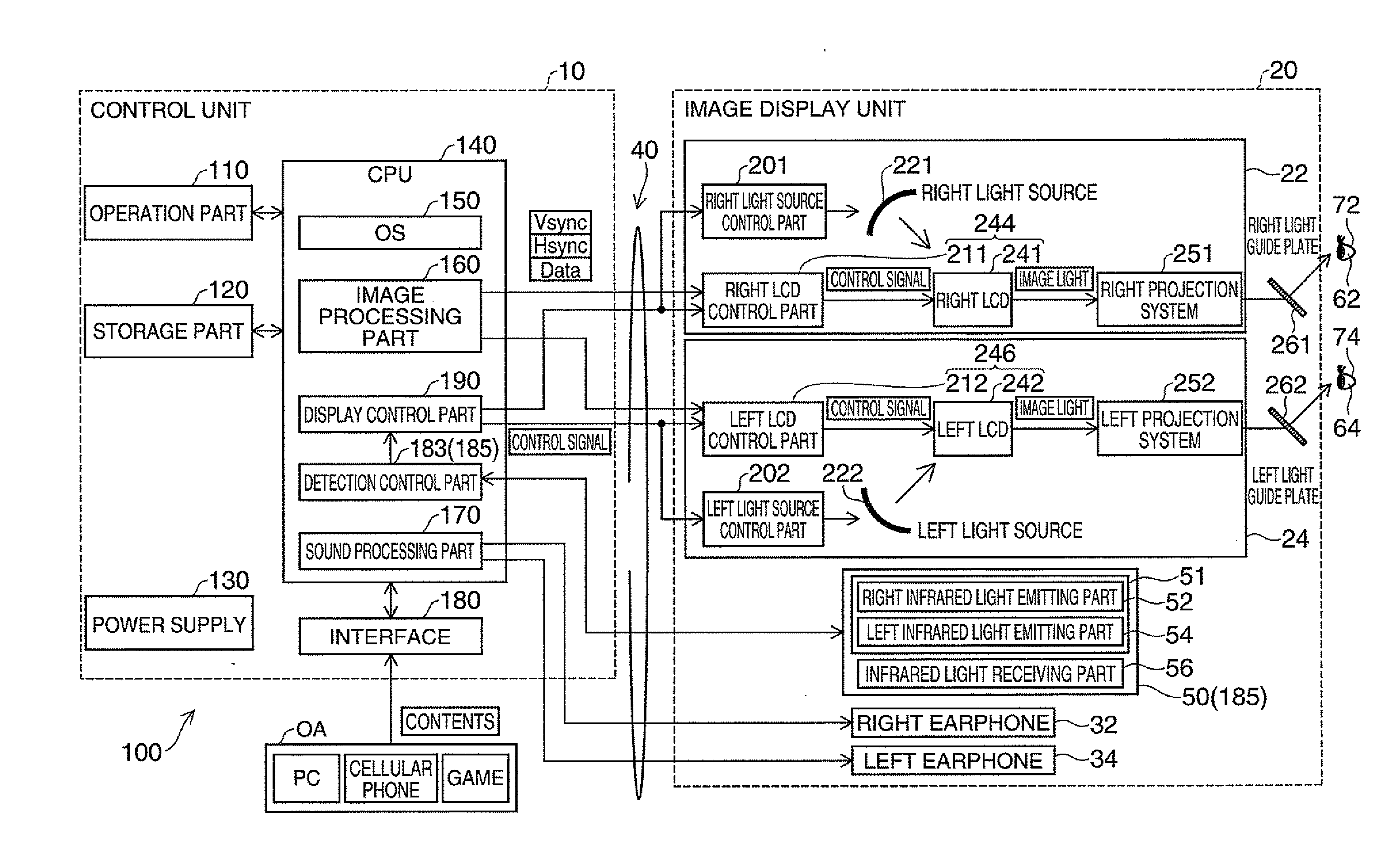
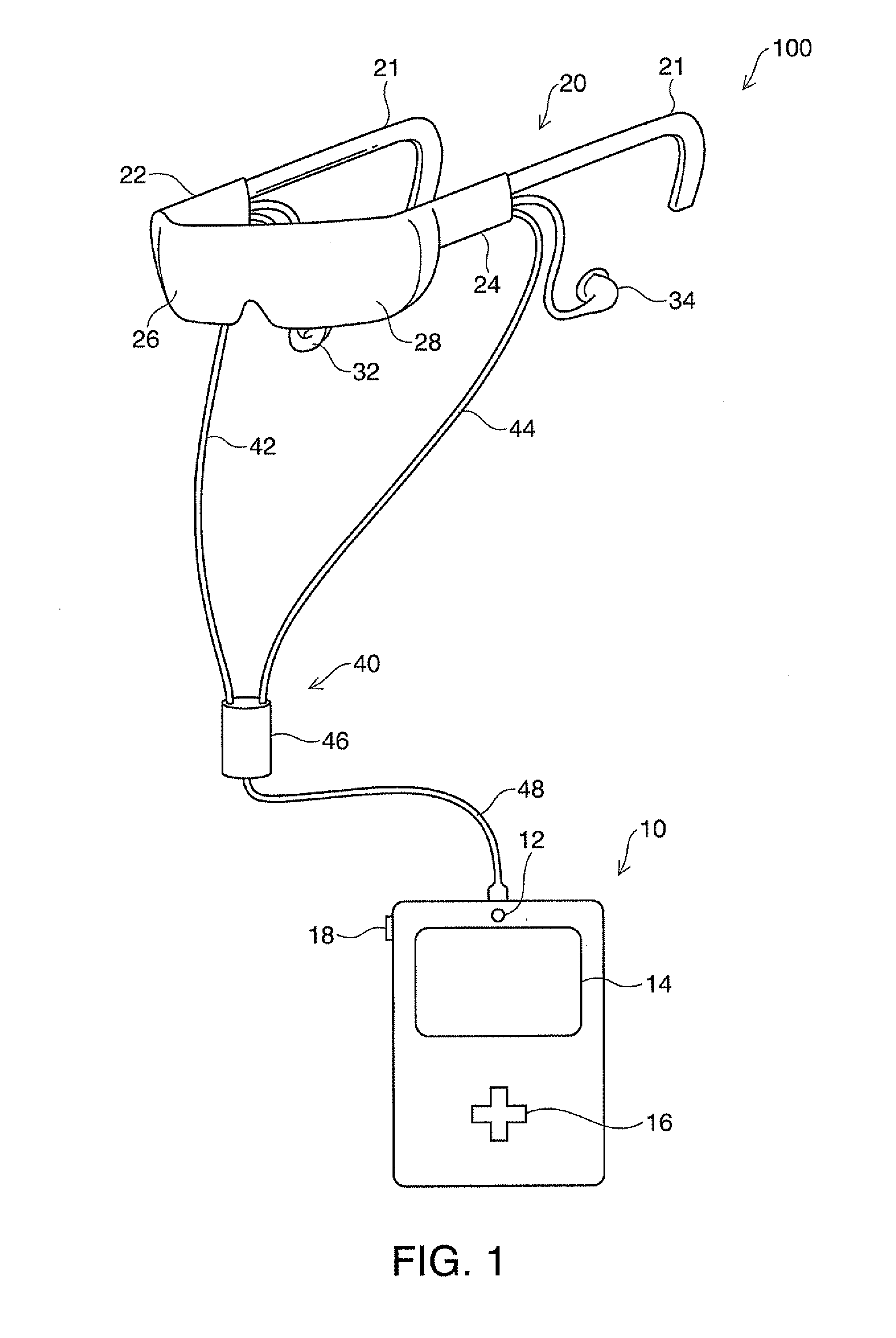
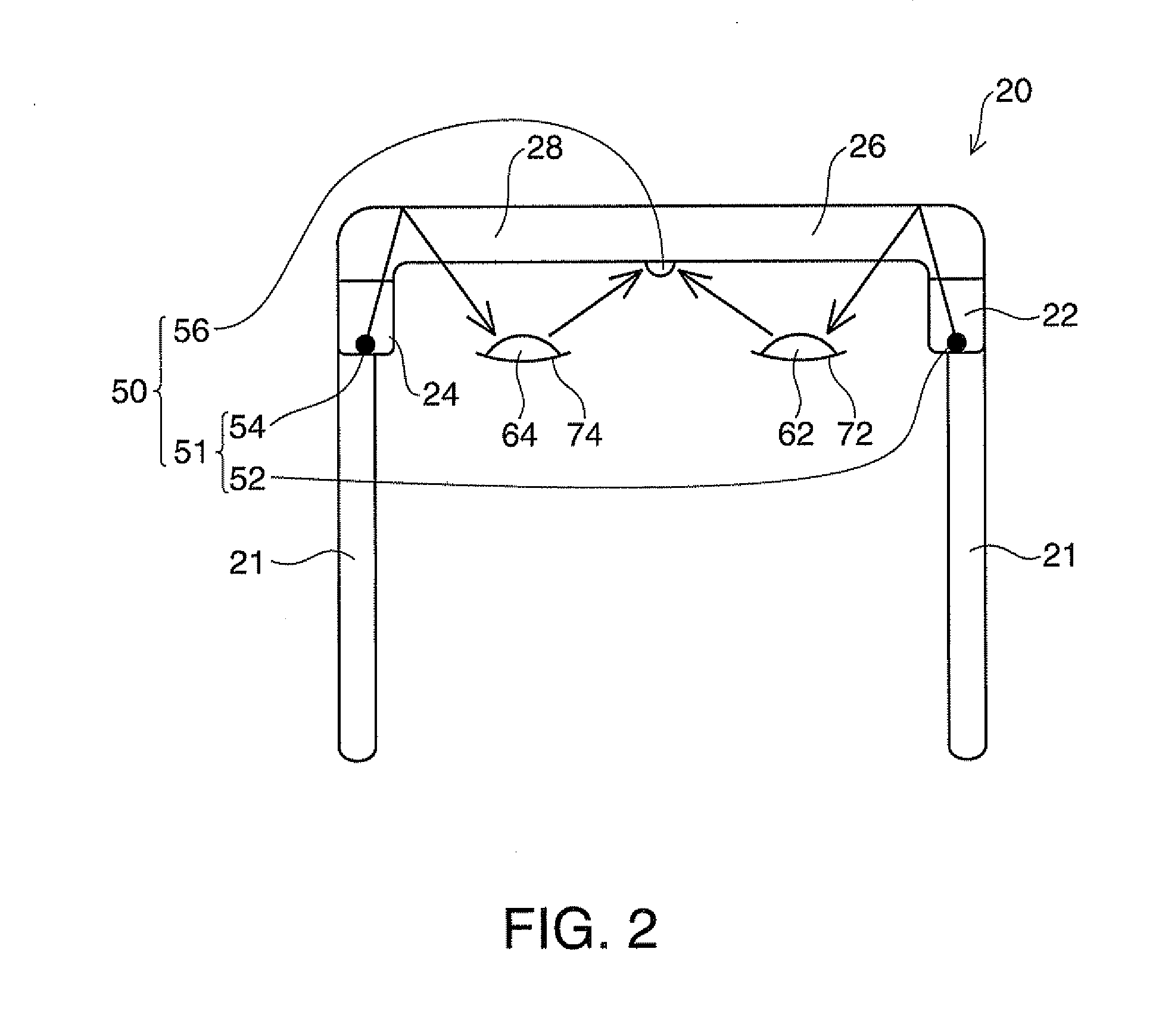
ActiveUS20120242570A1Without usingReduce light outputCathode-ray tube indicatorsDetails for portable computersDisplay deviceEmbedded system
A device includes a detection unit that detects states of eyelids of a user, and a control unit that performs operations in response to the states of the eyelids of the user detected by the detection unit.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method and apparatus to reduce variation of excess fiber length in buffer tubes of fiber optic cables
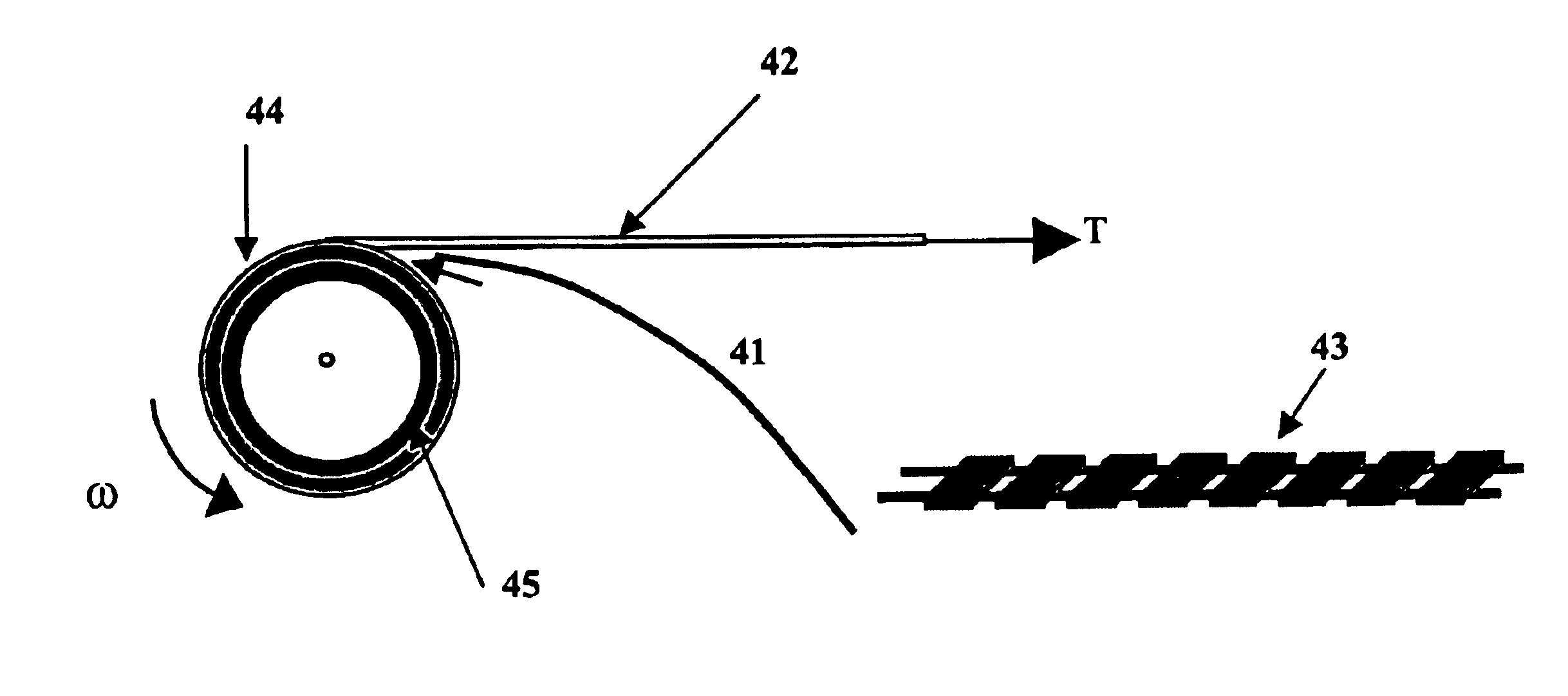
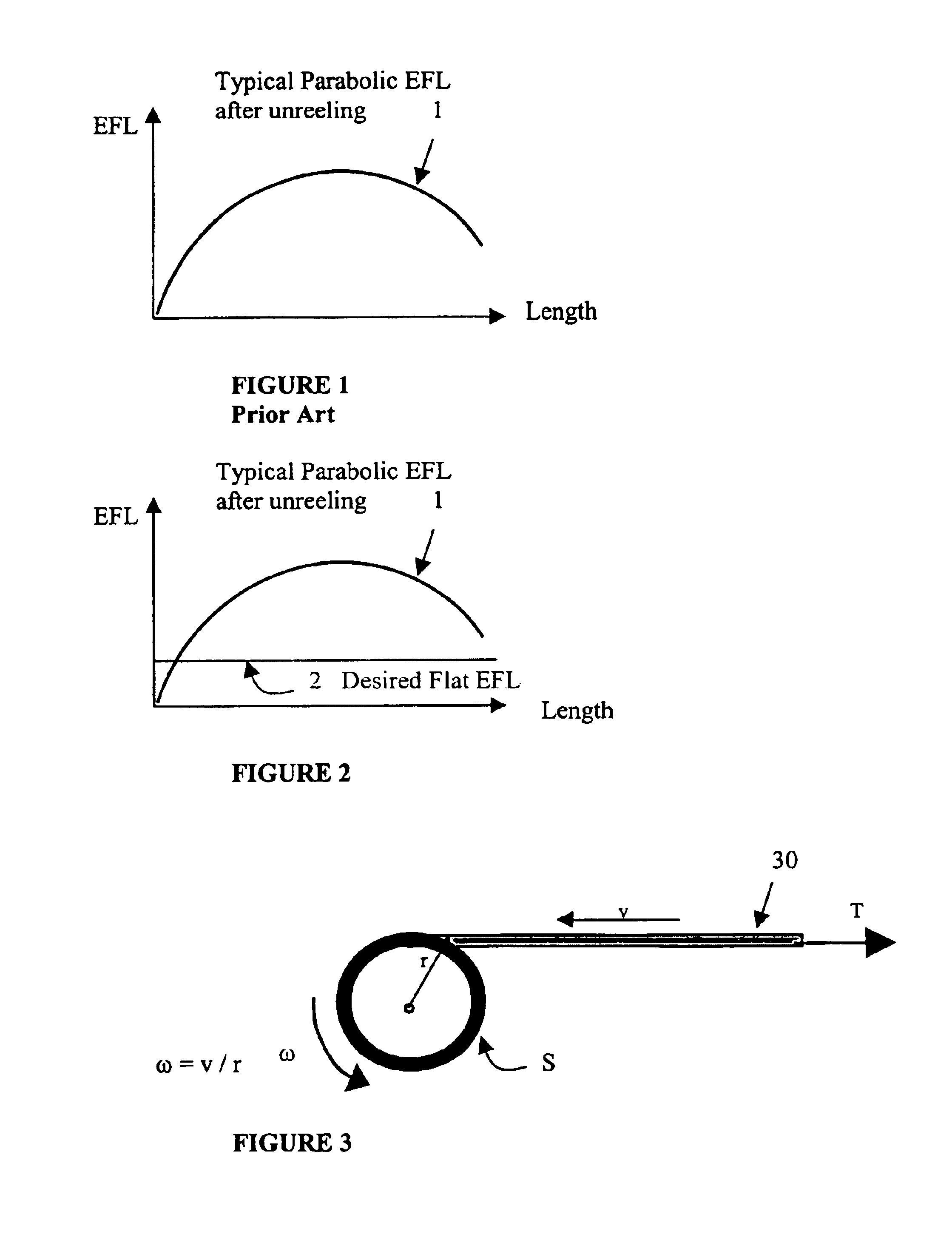
InactiveUS6922515B2Evenly distributedEliminating and greatly reducing impactFilament handlingFibre mechanical structuresConductor CoilFiber
The present invention provides a method for reducing and / or controlling the variations of excess fiber length along the length of reeled fiber optic buffer tubes during the manufacture of the buffer tubes. The present invention varies any number, or combination, of parameters during the manufacture of buffer tubes to achieve a substantially uniform excess fiber length along a reeled buffer tube. One embodiment of the inventive method uses monotonically decaying draw or take-up tension of the buffer tubes during winding, combined with a stiffness-compliant pad placed on the reel core to aid in providing a substantially uniform excess fiber length in the tube, while another embodiment uses a monotonically increasing angular speed of the reel in combination with the stiffness-compliant pad on the reel core. In yet another embodiment a pad is placed either periodically or continuously in the windings of the buffer tube to provide an absorbing layer for the residual stresses existing in the buffer tube as it is reeled and after the reeling is complete, combined with re-reeling the buffer tube onto a second reel after the buffer tube has cooled (after manufacture), where the pad is removed during the re-reeling process. Additionally, the present invention can have the layers of buffer tube separated with rigid, cylindrical panels separating the layers. The present inventive method also combines any, or all, of the above steps to aid in achieving a substantially uniform excess fiber length along the length of the reeled buffer tube.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Multilayer printed wiring board and method for producing multilayer printed wiring board
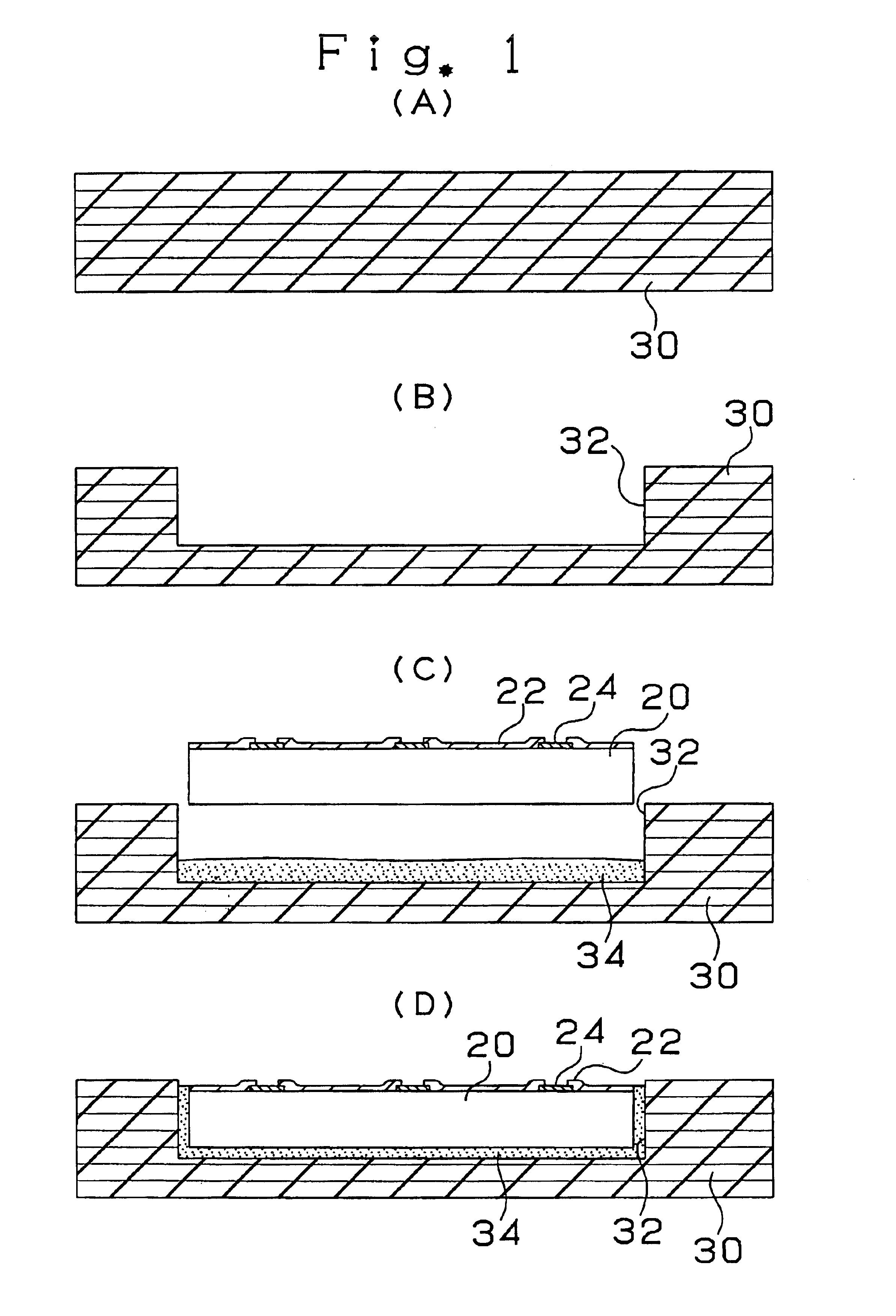
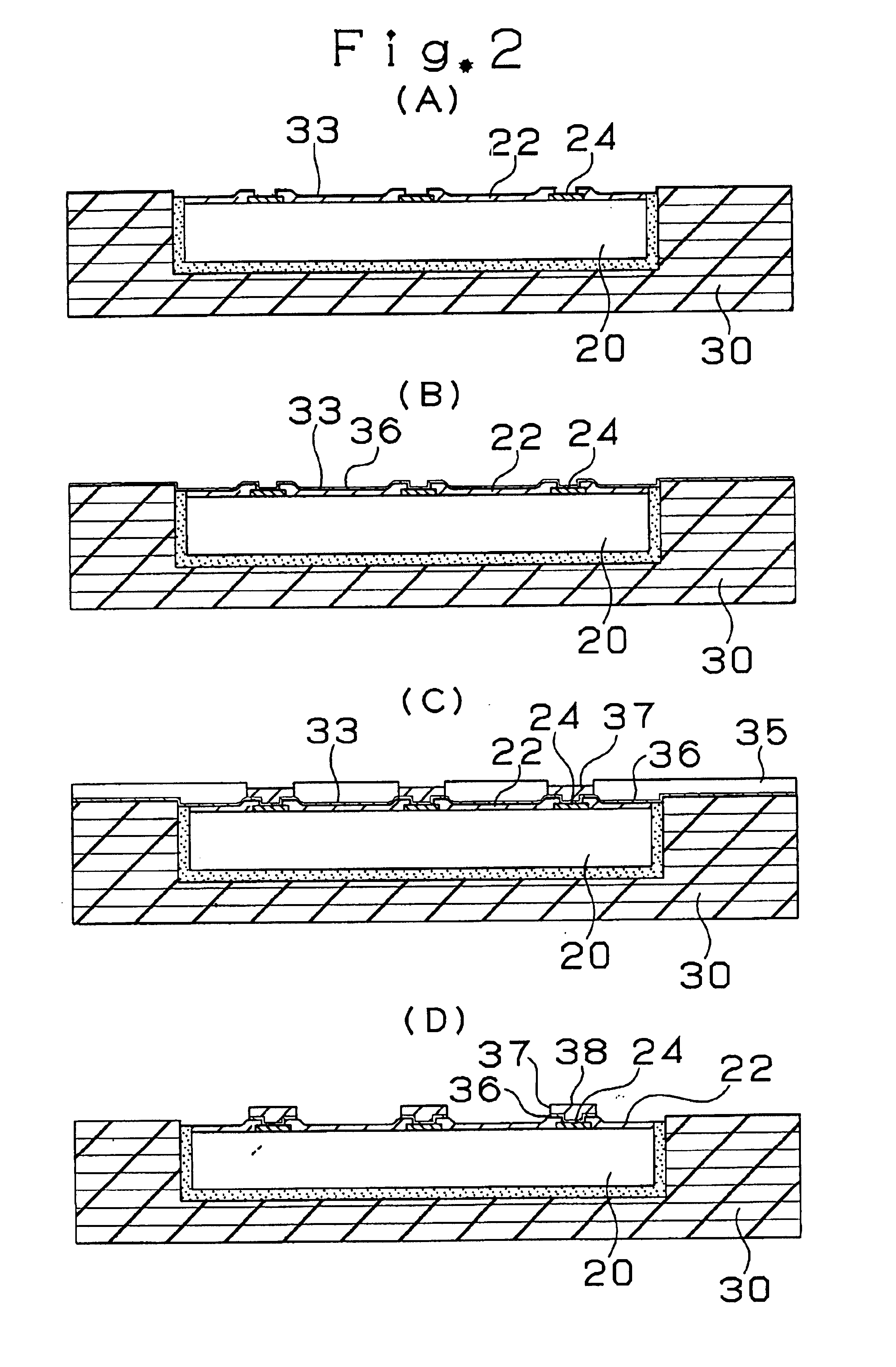
InactiveUS6909054B2Low yieldWithout usingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted electric component incorporationCopperPrinted circuit board
A multilayer printed circuit board has an IC chip 20 included in a core substrate 30 in advance and a transition layer 38 provided on a pad 24 of the IC chip 20. Due to this, it is possible to electrically connect the IC chip to the multilayer printed circuit board without using lead members and a sealing resin. Also, by providing the transition layer 38 made of copper on the die pad 24, it is possible to prevent resin residues on the pad 24 and to improve connection characteristics between the pad 24 and a via hole 60 and reliability.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
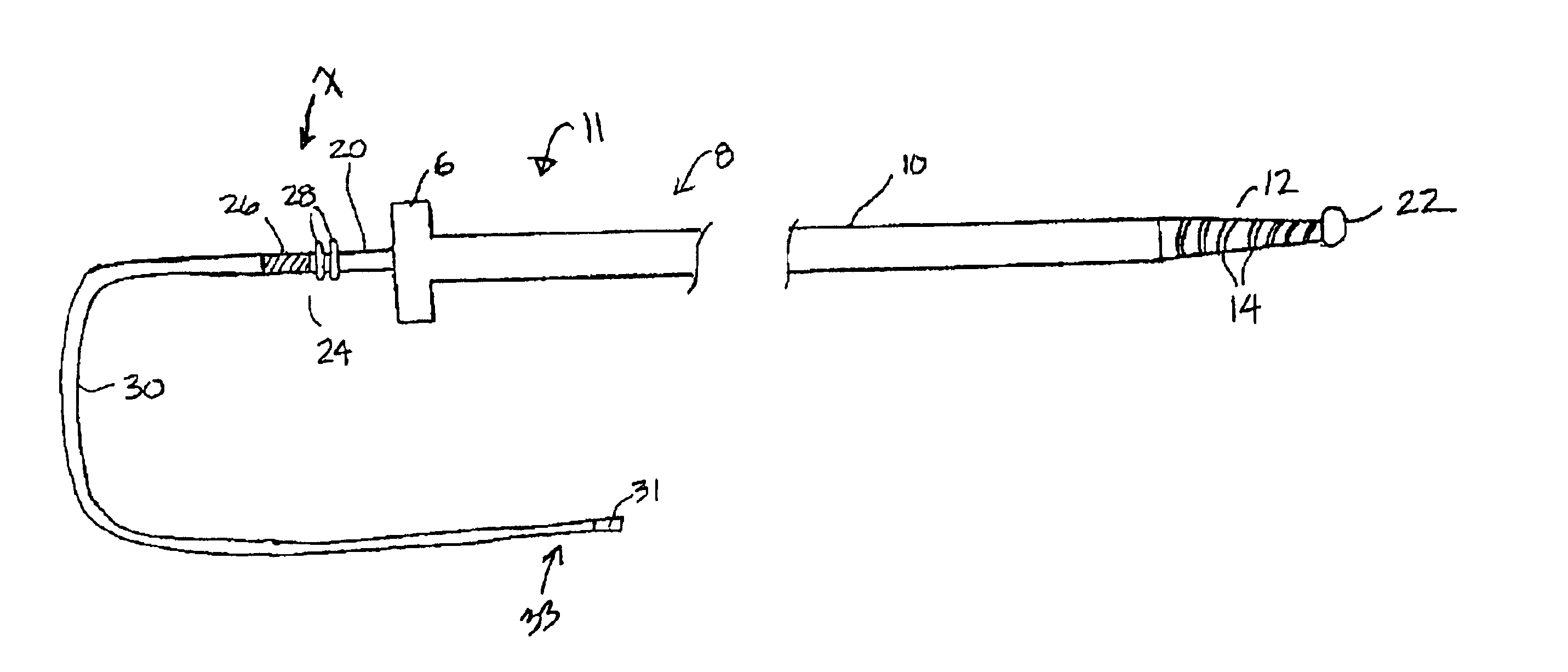
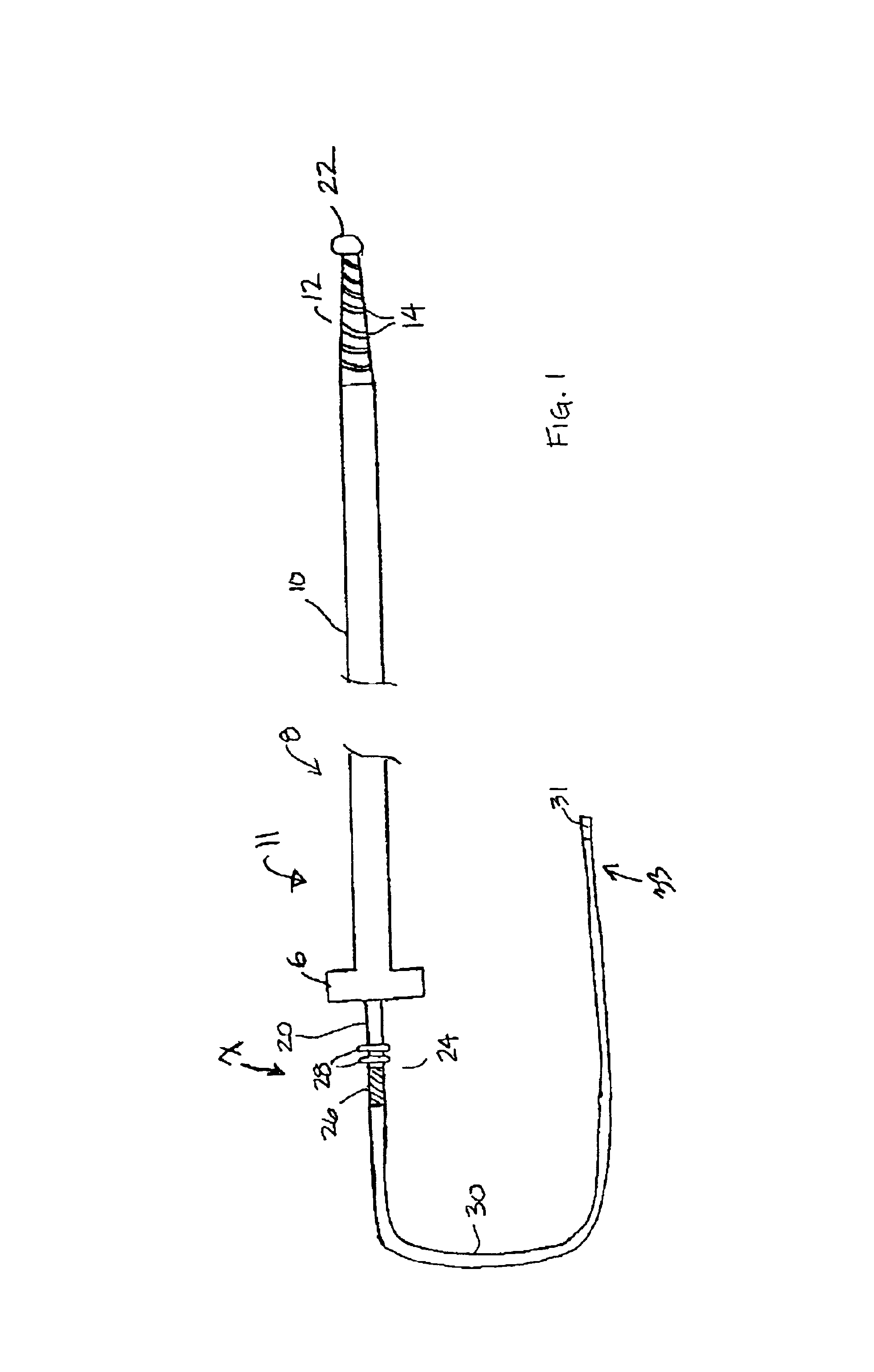
Cardiac vein lead and guide catheter
InactiveUS6871085B2Easy steeringSmall sizeTransvascular endocardial electrodesSurgical instrument detailsWalking around obstaclesDistal segment
A guide catheter and medical lead are provided wherein the lead may be used as a pull wire to steer the guide catheter. The guide catheter is provided with a flexible distal segment and the lead is provided with a distal engaging member, which may also serve as an electrode. The distal engaging member interacts with the distal catheter end such that traction applied to the proximal lead end causes flexion of the distal segment of the catheter to advance the flexible distal segment between a non-flexed position and a flexed position, allowing the catheter to be steered around obstacles.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
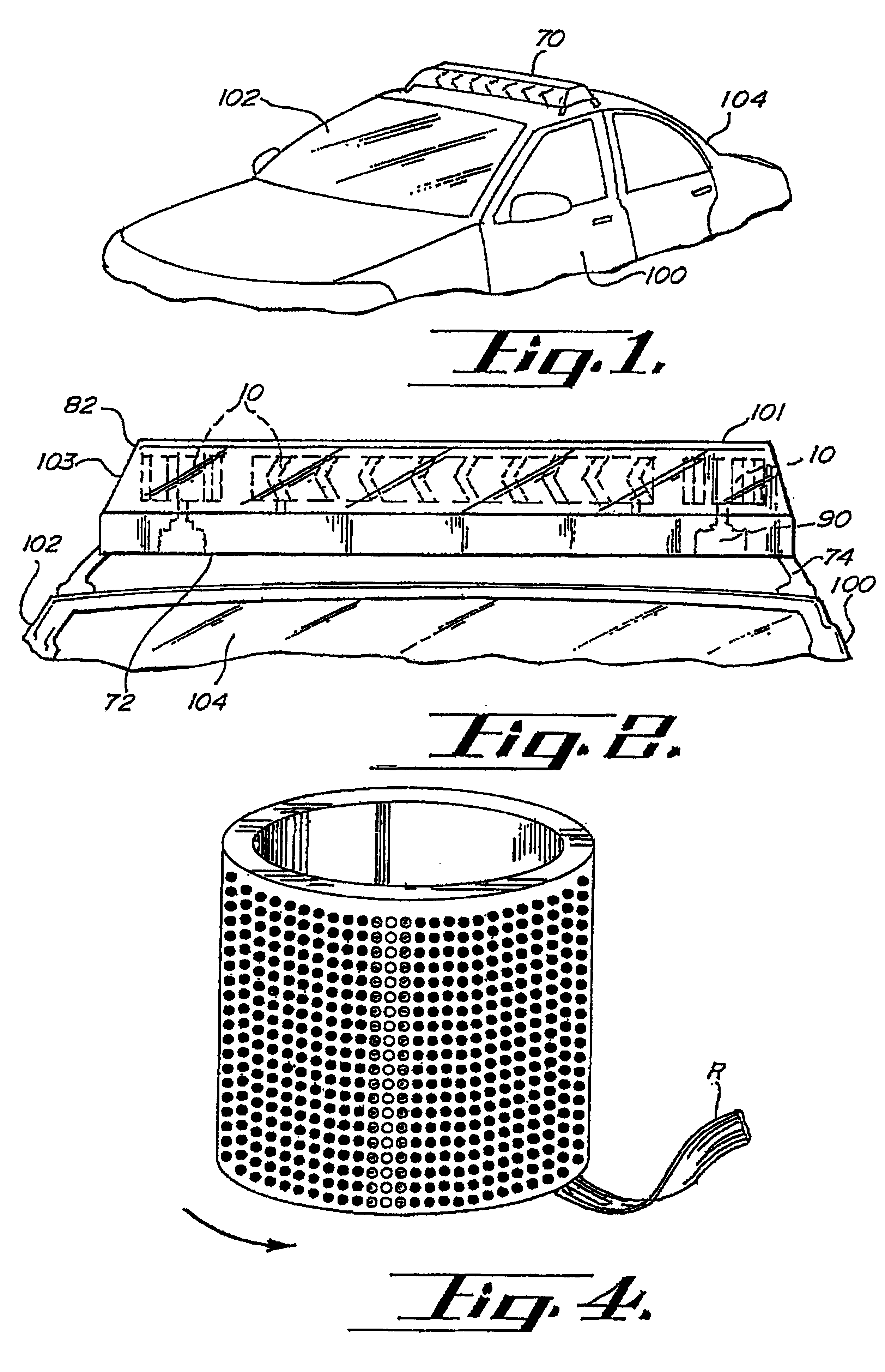
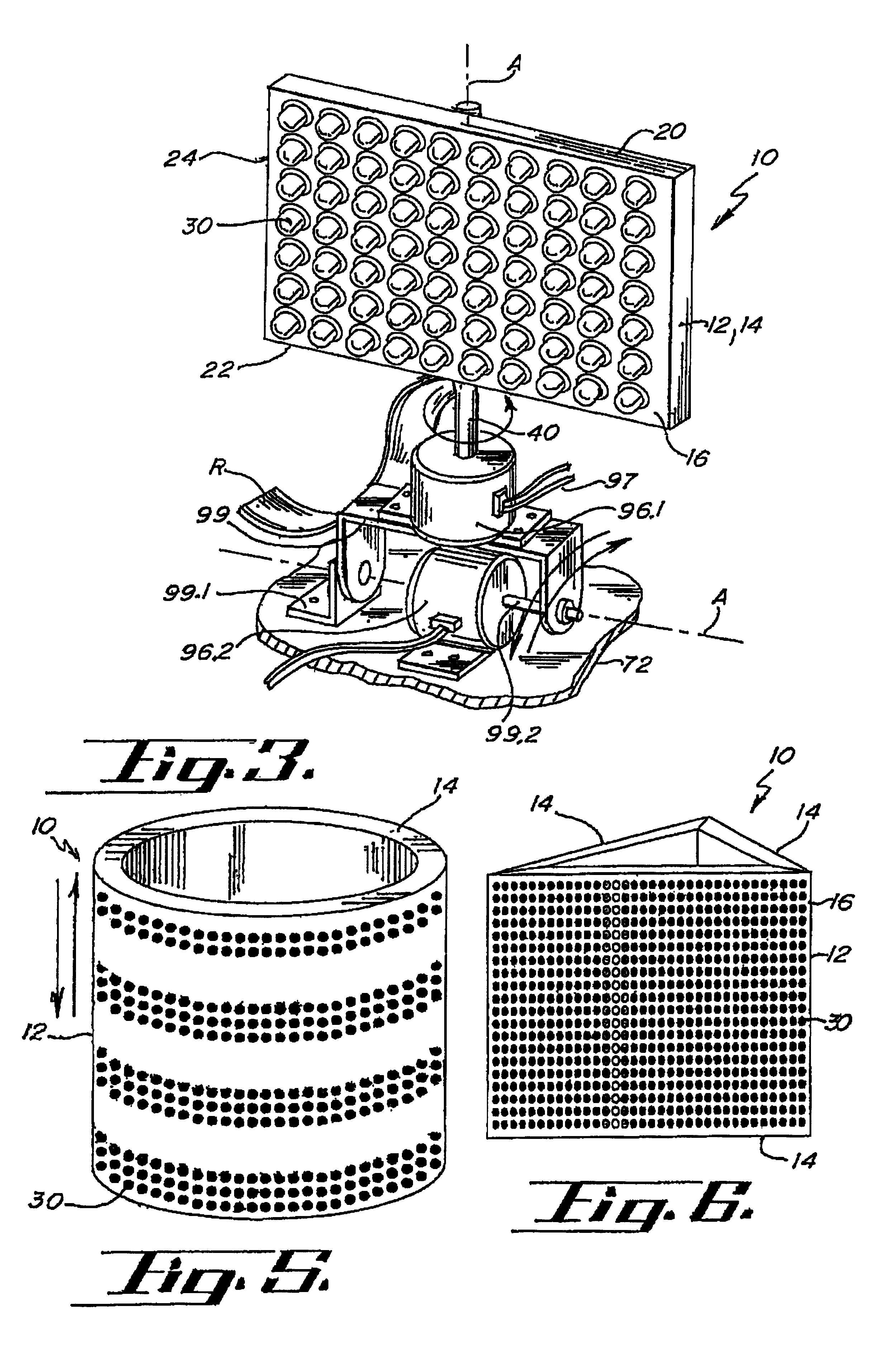
Replaceable LED modules
A modular warning signal light system comprising at least one support. The at least one support having at least one module receiving port. The module receiving ports constructed and arranged to removably receive the support engagement member of a module. Each module having at least one visible side. The at least one visible side having at least one light emitting diode light source engaged thereto. The at least one light emitting diode light source, module and support all in independent electrical communication with a controller. The controller constructed and arranged to selectively activate the at least one support, the at least one module, the at least one light emitting diode light source, and any combinations thereof to create at least one warning light signal.
Owner:911 EMERGENCY PRODS
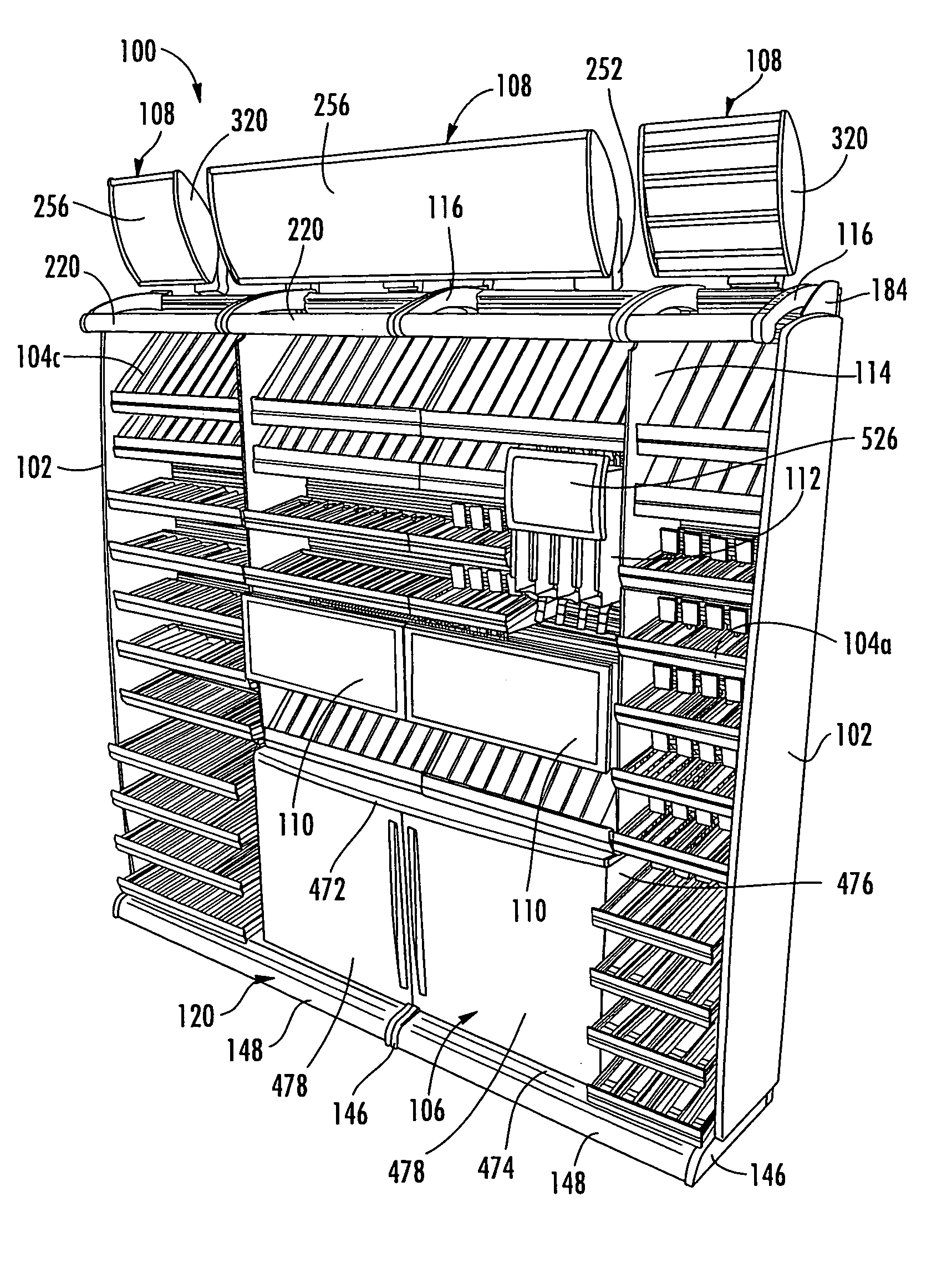
Modular, adjustable display rack
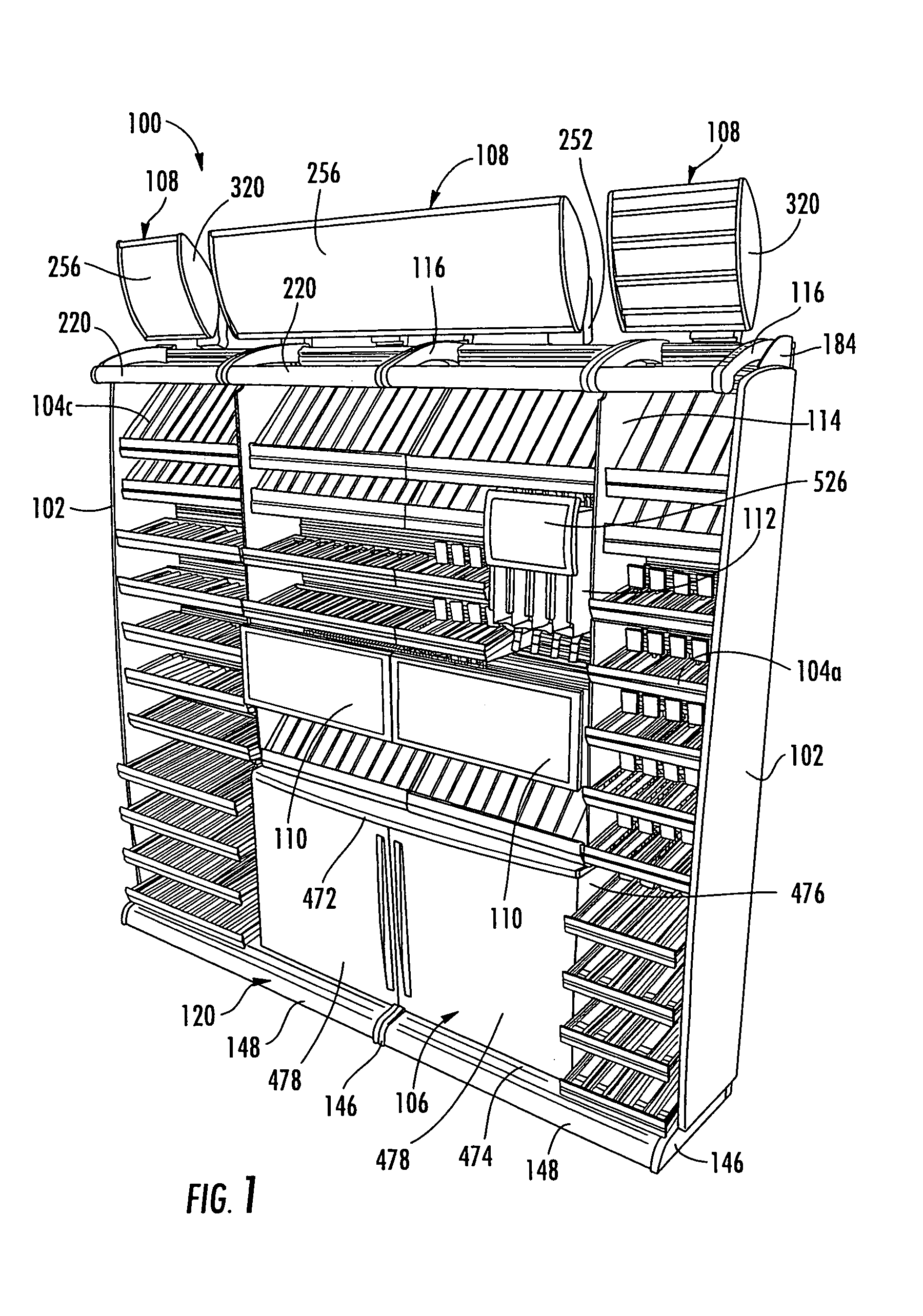
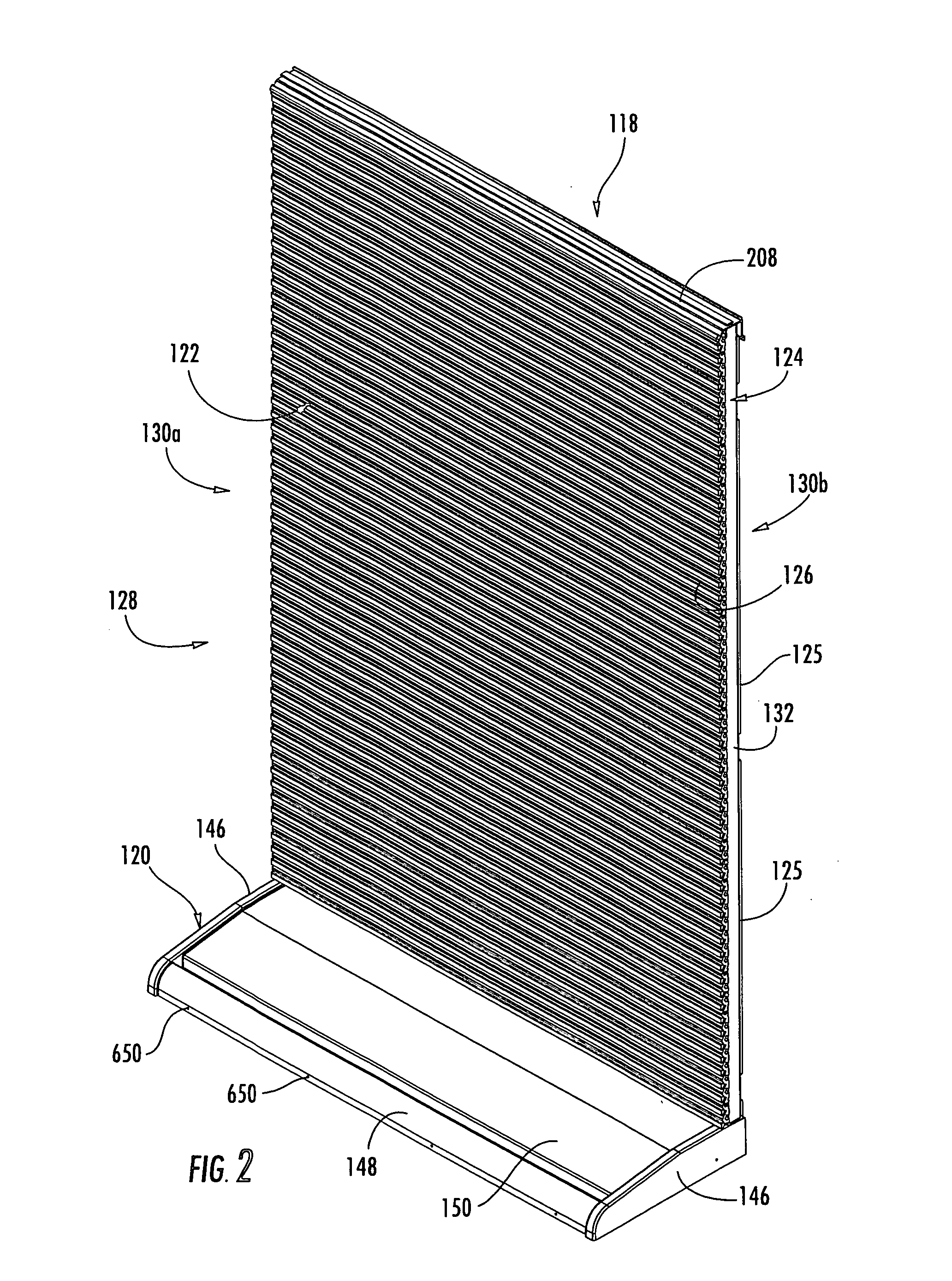
ActiveUS7175034B2Easy to assembleIncrease flexibilityFolding cabinetsDismountable cabinetsModularityEngineering
A point of purchase display stand for displaying products includes shelving, lights, cabinets, signs, baskets, and other items that may be supported on a slot wall positioned in the back of the stand. The slot wall may be made up of horizontal slots that allow the aforementioned items to be positioned at a plurality of vertical locations and a virtually infinite number of horizontal locations. End panels and doors may also be added to the display stand for providing security to the contents of the display stand. The shelves may only require a small amount of rotation to be removed from the slot wall. The shelves may be oriented in a plurality of different angular orientations, and they may be optionally connected with adjacent shelves so that any sagging of a given shelf is transmitted to the adjacent shelves, thereby maintaining the shelves in horizontal alignment with each other.
Owner:ALTRIA GRP DISTRIBUTION
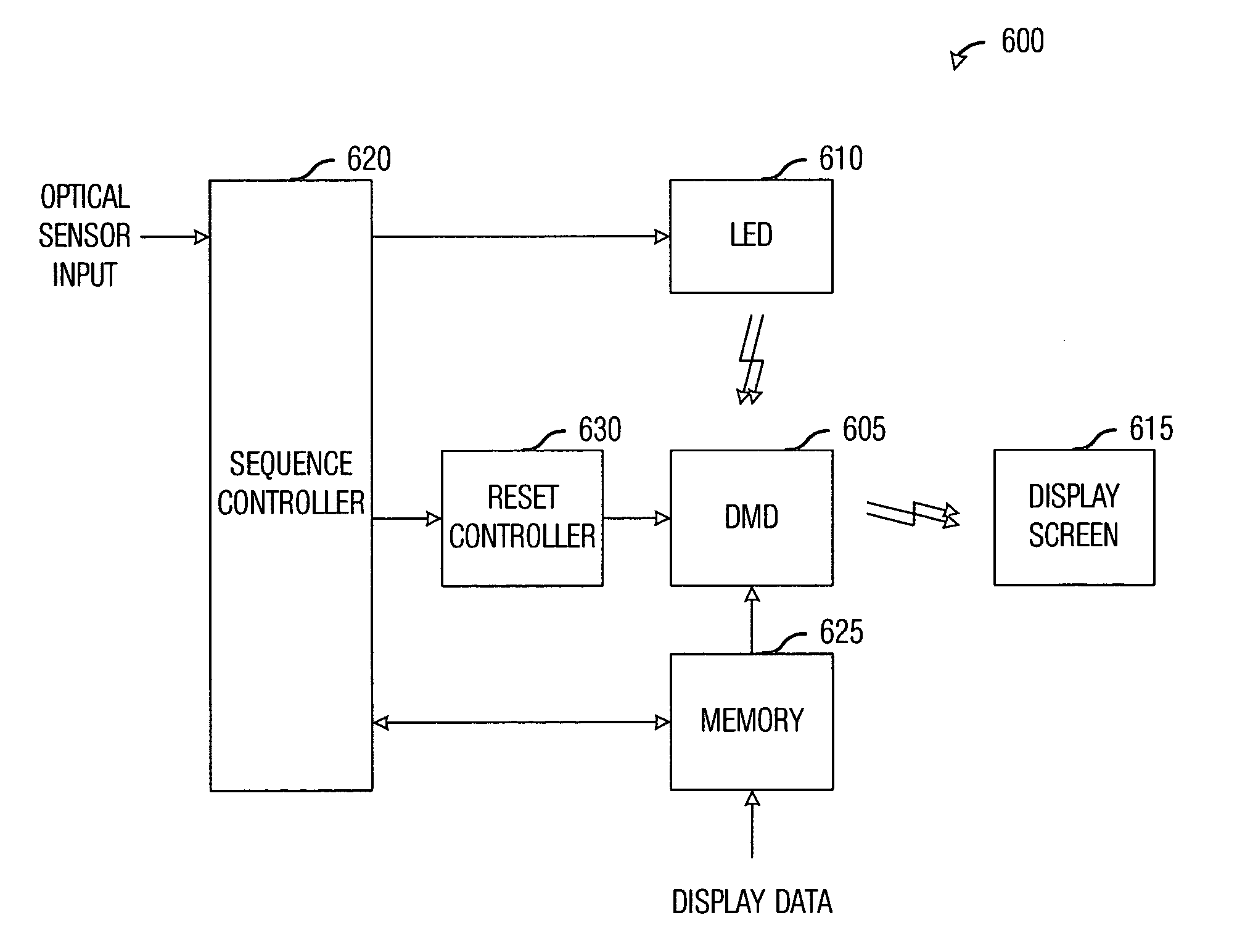
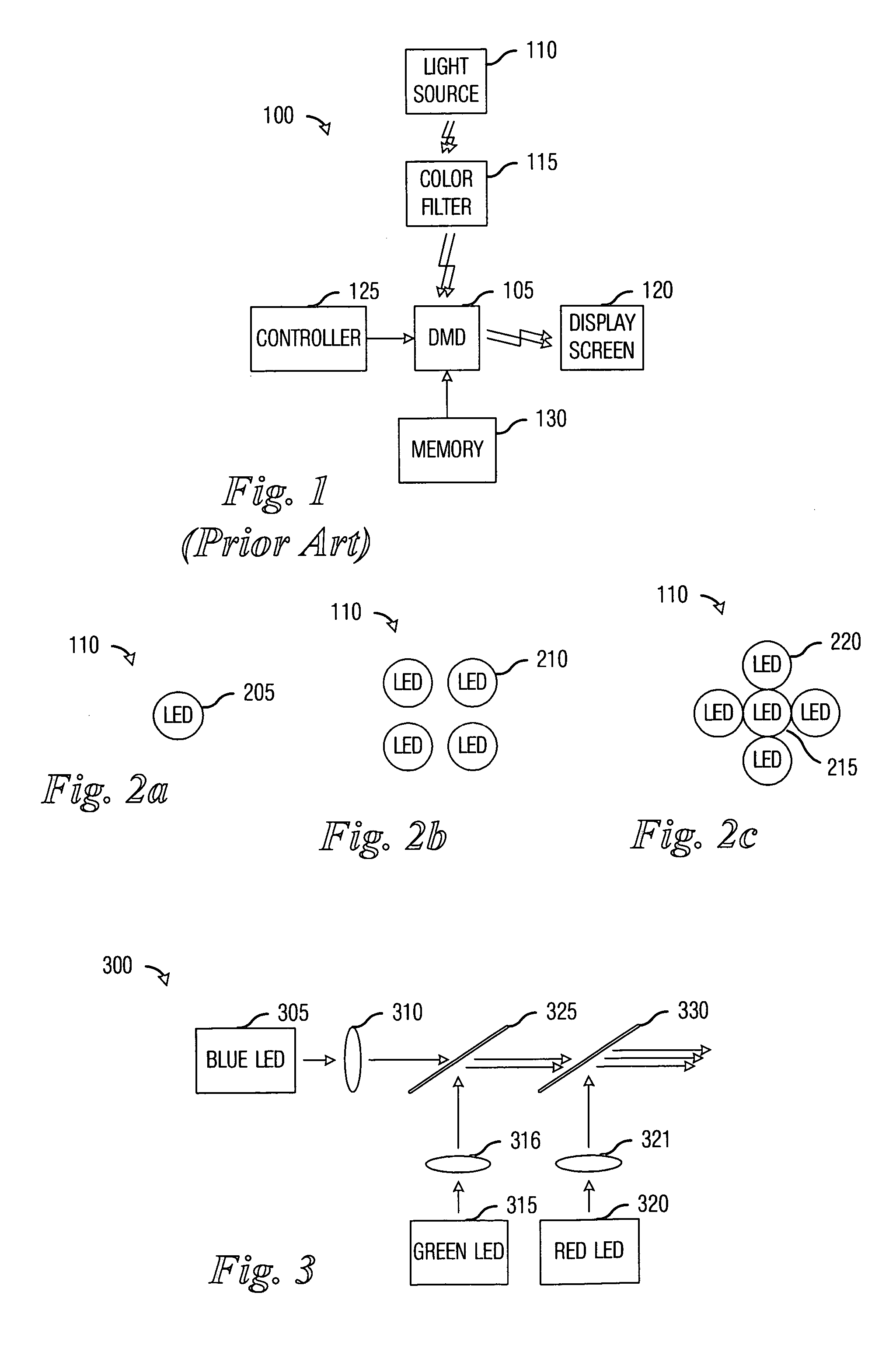
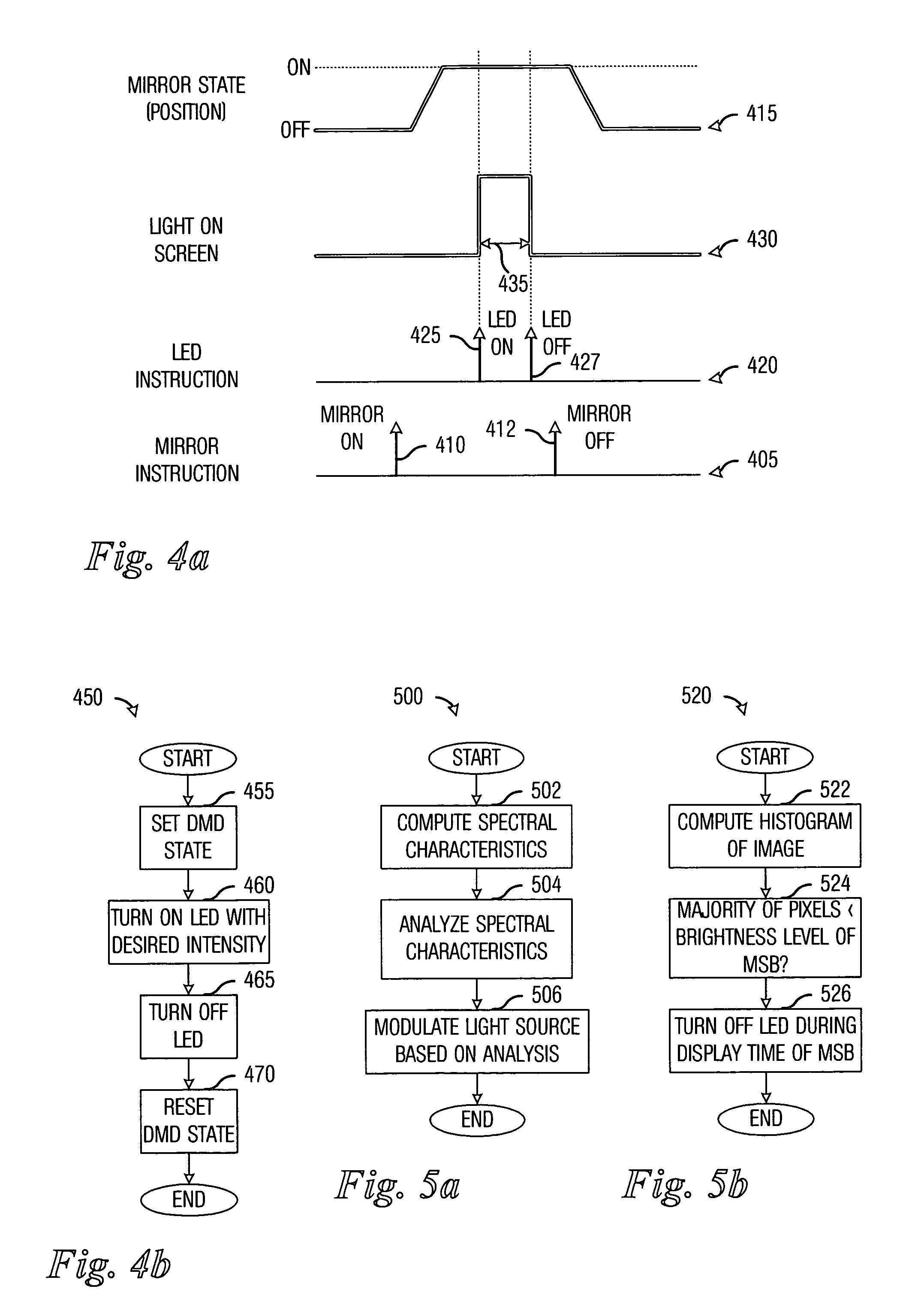
Light-emitting diode (LED) illumination in display systems using spatial light modulators (SLM)
InactiveUS20070013871A1Quick switchEasy to adjustProjectorsColor television detailsSpatial light modulatorImage quality
System and method for enhancing performance in an SLM display system using LED illumination. A preferred embodiment comprises computing a set of spectral characteristics, analyzing the set of spectral characteristics, and modulating a light produced by a light source of a display system based upon the analysis, wherein the light source comprises one or more light-emitting diodes. The spectral characteristics can provide information regarding either the images being displayed by the display system or an operating environment of the display system. Either can have an impact upon the quality of the images being displayed on the display system and can be used to make adjustments to the light source.
Owner:MARSHALL STEPHEN WESLEY +1
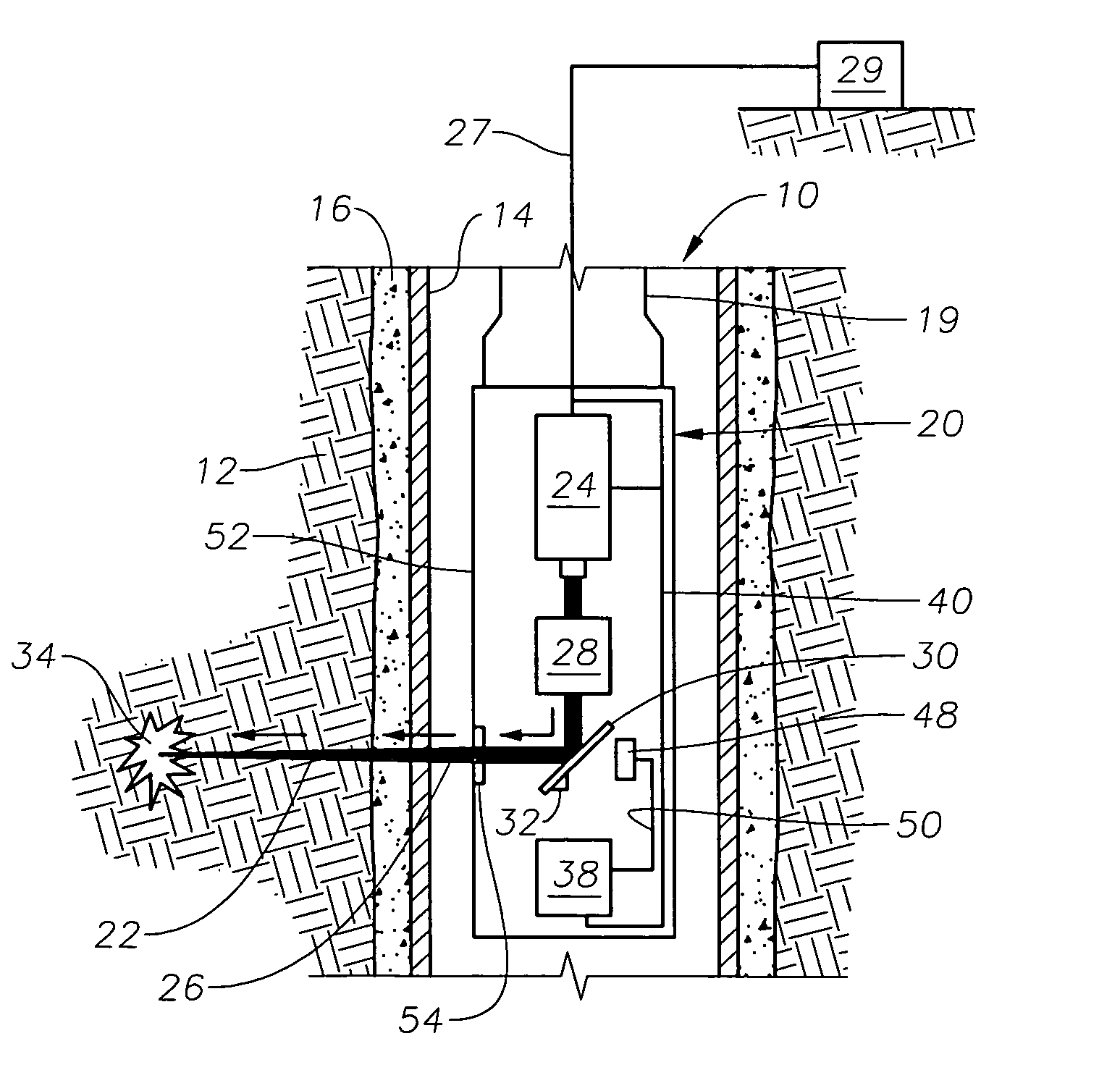
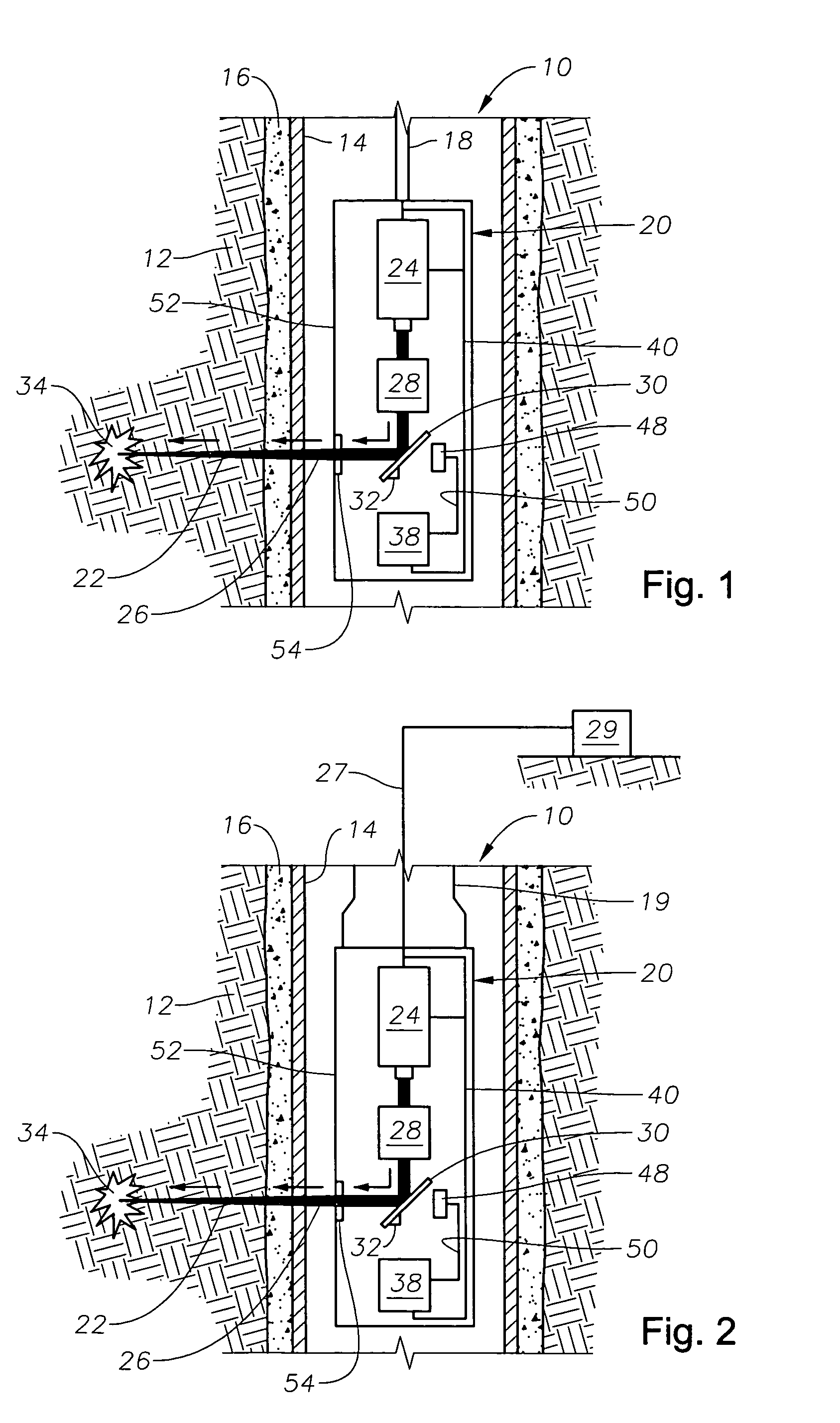
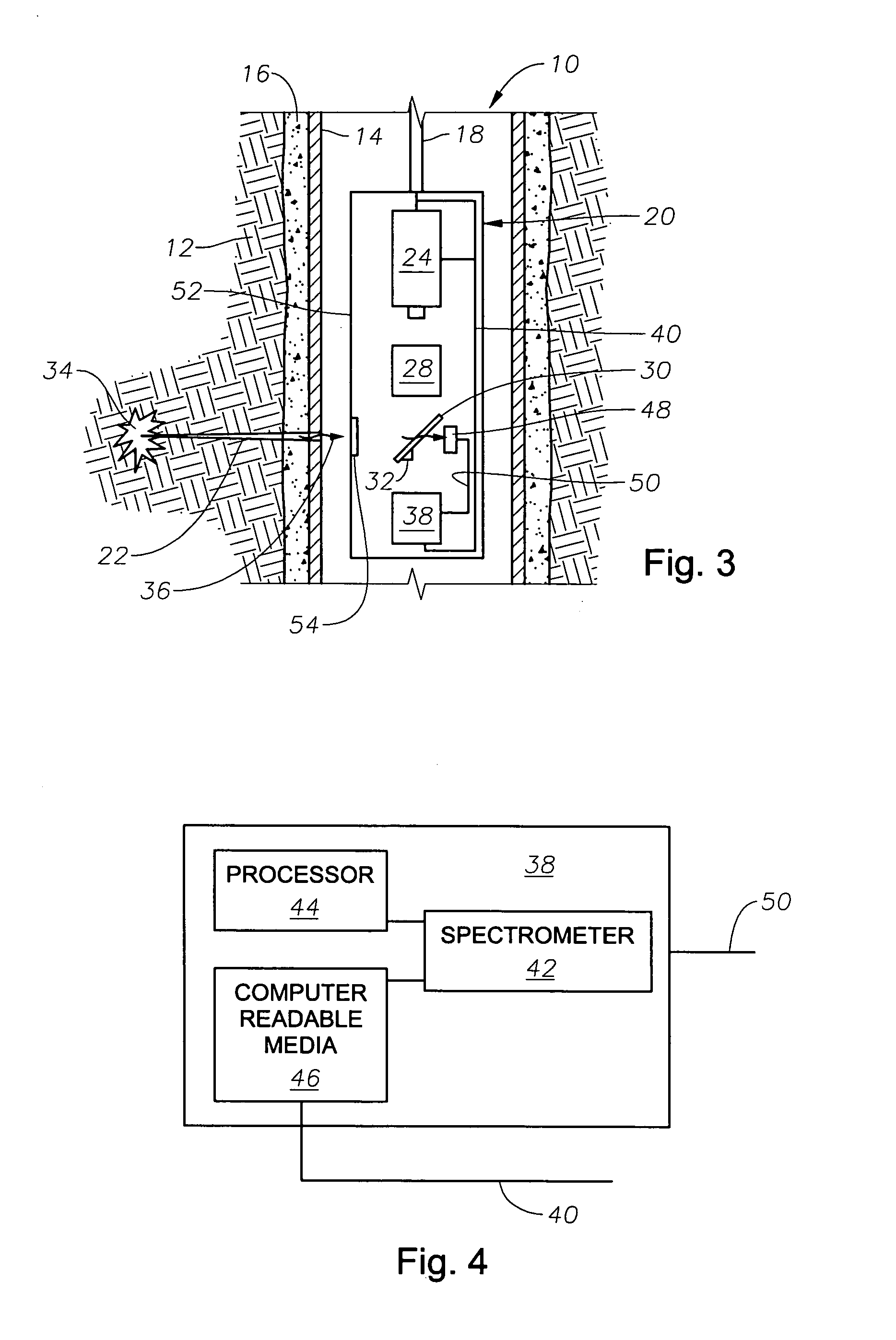
Drilling, perforating and formation analysis
ActiveUS7490664B2Easy to useWithout usingSpectrum investigationConstructionsMaterial removalWell drilling
A system and method of drilling and / or perforating uses a laser beam to remove material, such as to perforate the casing, cement and formation or drill a well bore. The system and method can further or alternately encompass material analysis that can be performed without removing the material from the well bore. The analysis can be performed apart from or in connection with drilling operations and / or perforating the casing, cement and formation. The analysis can be used in a feed back loop to adjust material removal, adjust material analysis, determine the location of future material removal, and for other uses.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Snap-in float-mount electrical connector
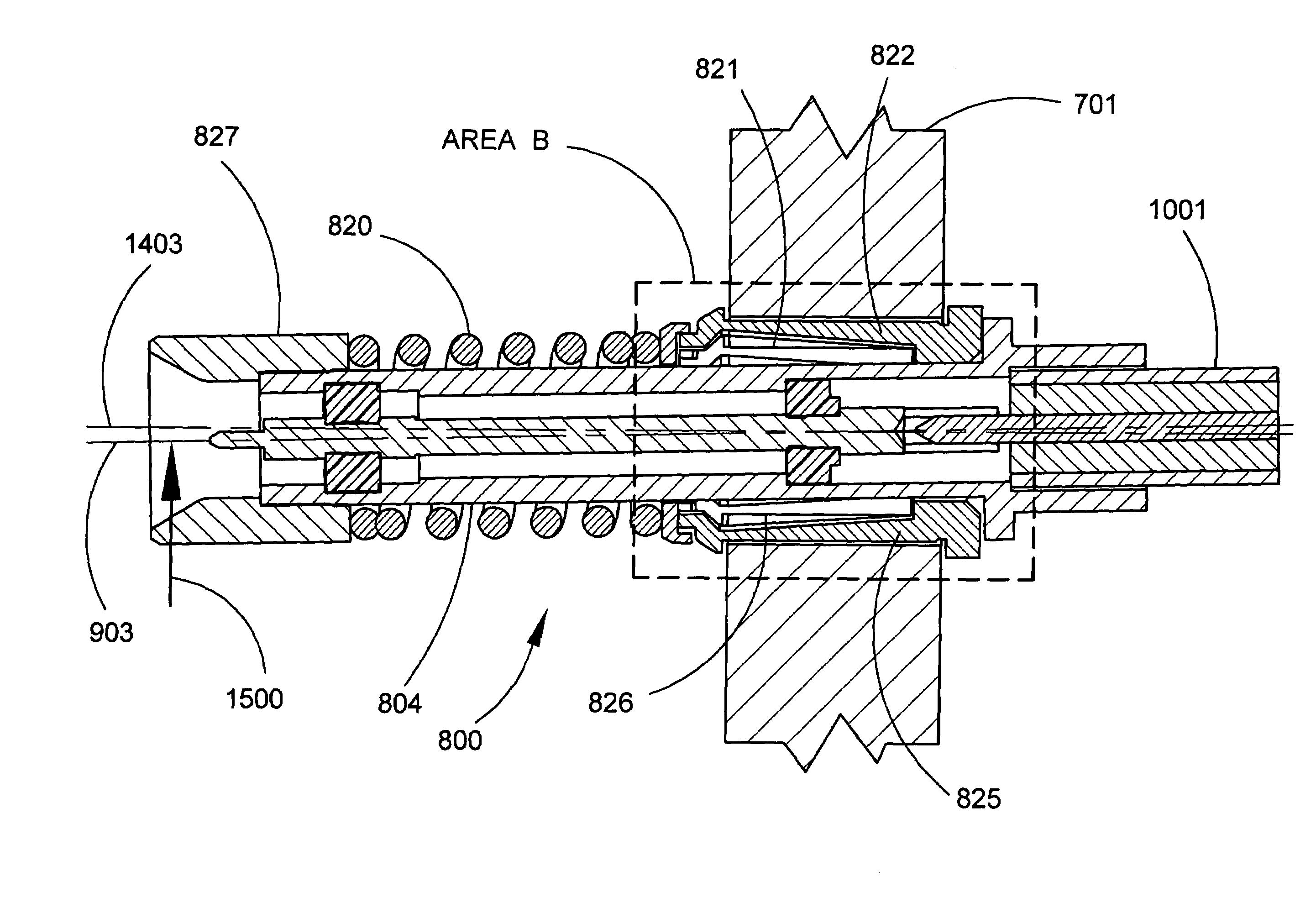
ActiveUS7077697B2Overcome disadvantagesReduce usageEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsElectrically conductive connectionsCoil springEngineering
An electrical connector (800) for mounting in a mounting hole includes a body (804) and a mounting mechanism. The mounting mechanism includes a spring finger basket (806) that includes a base portion (808) and a plurality of spring fingers (809). Each spring finger (821–826) is commonly connected at the base portion and has a tip (812) at a free end opposite the base portion. The base portion is attached to an outer surface of the body adjacent to a flange (805) in the outer surface. The tip of each spring finger is spaced apart from the body. An end cap (818) is attached to the outer surface of the body. The end cap has an outer lip (819) limiting outward radial movement and permitting inward radial movement of the tip of each spring finger during radial movement of the body with respect to the mounting mechanism. A coil spring (404) is attached to the outer surface of the body. A shroud (827) is attached to the body adjacent to a front side of the coil spring. The mounting mechanism permits simultaneous radial and axial movement of the body relative to the mounting mechanism.
Owner:CORNING OPTICAL COMM LLC
Methods, systems and apparatuses for dual-camera based zooming
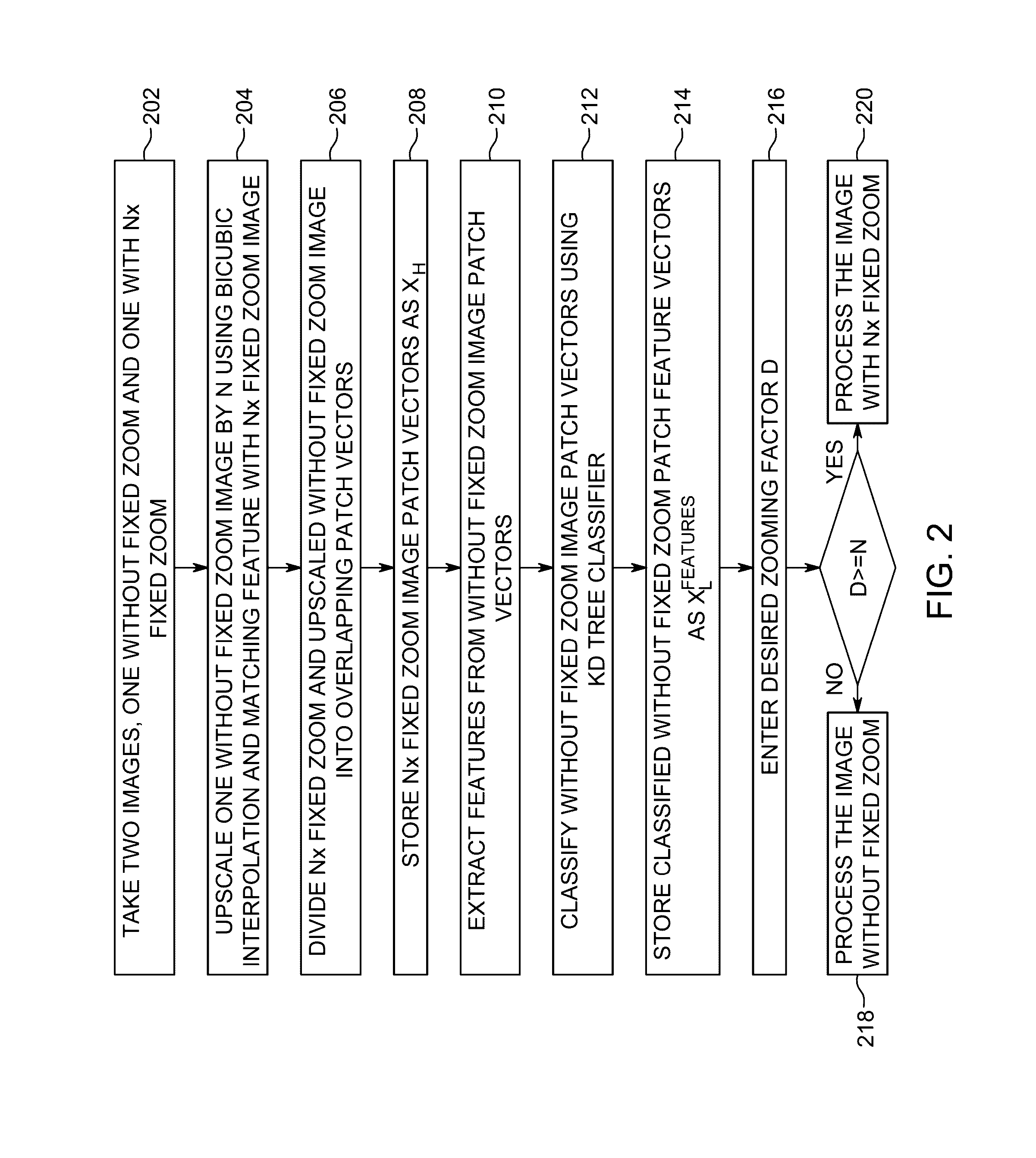
ActiveUS9485432B1Without usingGreat zoomingTelevision system detailsGeometric image transformationImage resolutionHigh resolution
A method and apparatus for zooming an image by a zoom factor wherein a first image without zoom and a second image with fixed optical zoom are processed to find a mapping between low resolution patches and high resolution patches that are then used for zooming the first image if the zoom factor is less than the fixed optical zoom else the mapping between low resolution patches and high resolution patches are used for zooming the second image with fixed optical zoom.
Owner:UURMI SYST
Microstream injector
InactiveUS20070043320A1Quick distinctionPrevent accidental contactJet injection syringesMicroneedlesNeedle Free InjectionInjection site
The present invention provides a micromachined or microsized component-based needleless injector for delivering a dose of a liquid formulation containing a biologically active agent to tissue by way of a high pressure liquid microstream that penetrates the skin and deposits the agent at an optimal depth in the tissue. The device is appropriate for subcutaneous, intramuscular, or mucosal injection sites, as well as intracellular injection. Embodiments include micromachined or microsized components such as valves, jets, and MEMS pumps. Some embodiments of the invention are modular, with interchangeable parts, other embodiments are integrated in a unitary design. Embodiments with a unitary design are typically single use, however modular features also create embodiments with components that provide multiple instances of use.
Owner:KENANY SAAD AL
Insulating foldable box for transportation and packaging purposes
InactiveUS6041958AReduce in quantityEasy to disassembleDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusLateral elementElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:ENTHALPY
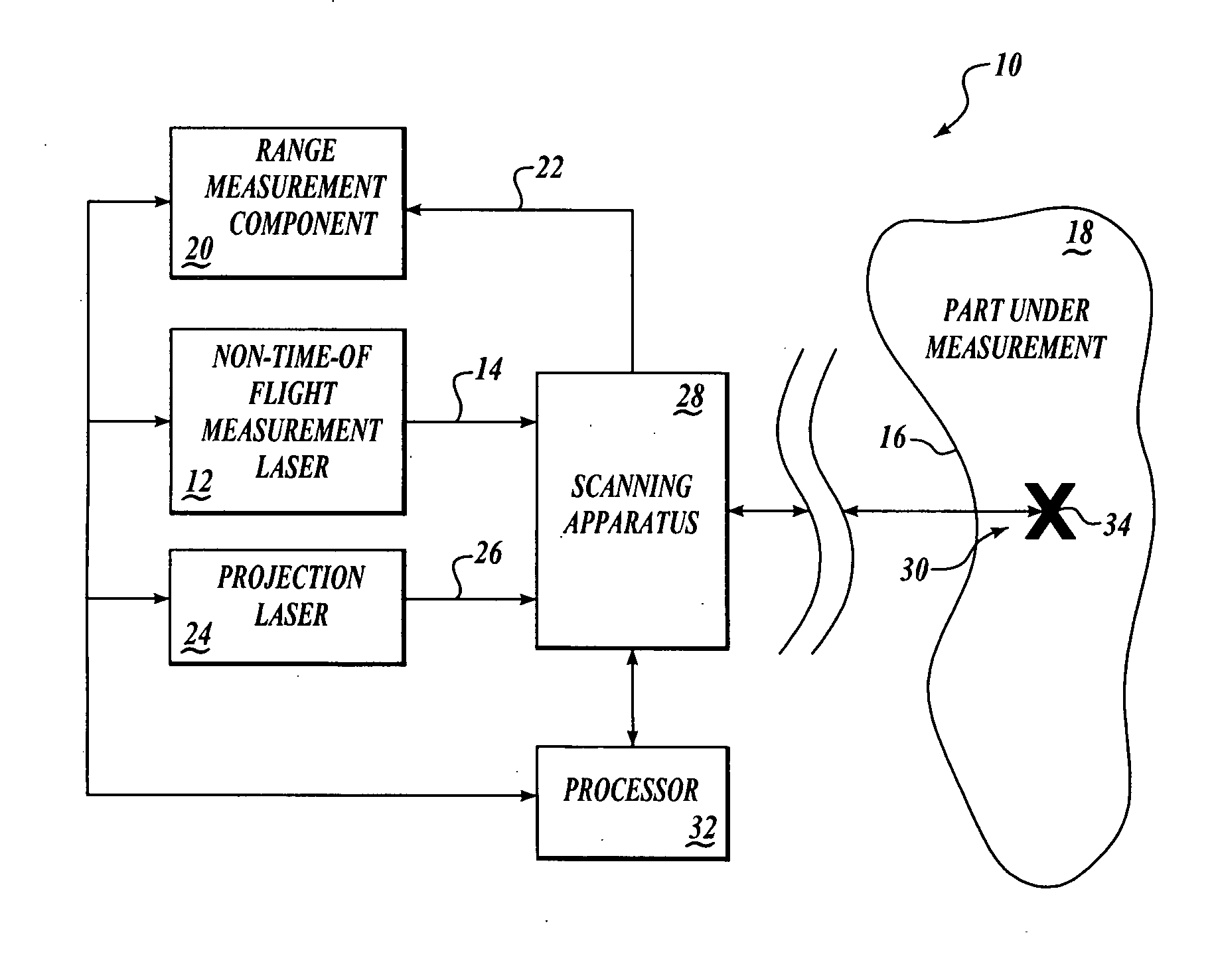
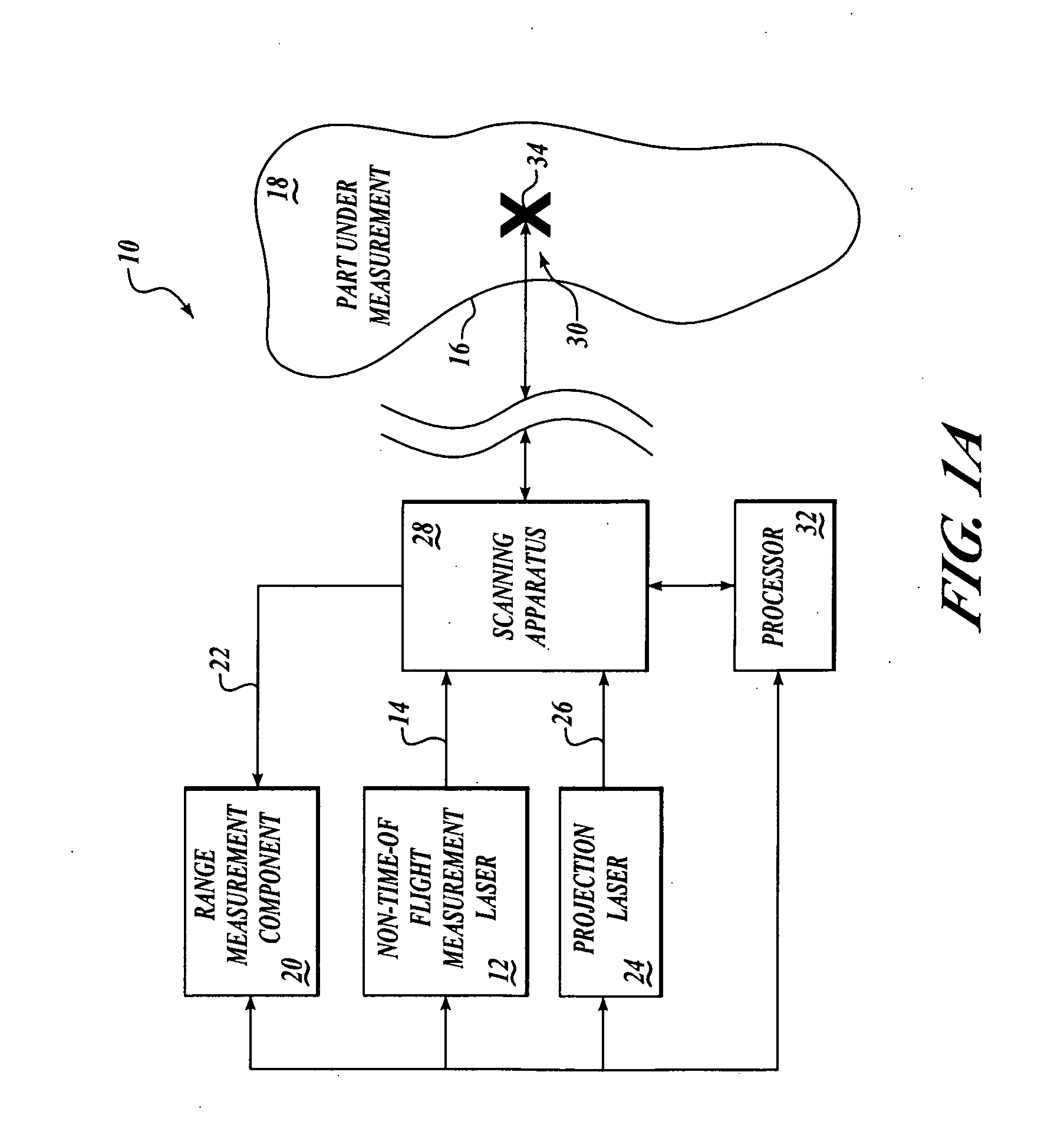
Method and apparatus for combining a targetless optical measurement function and optical projection of information
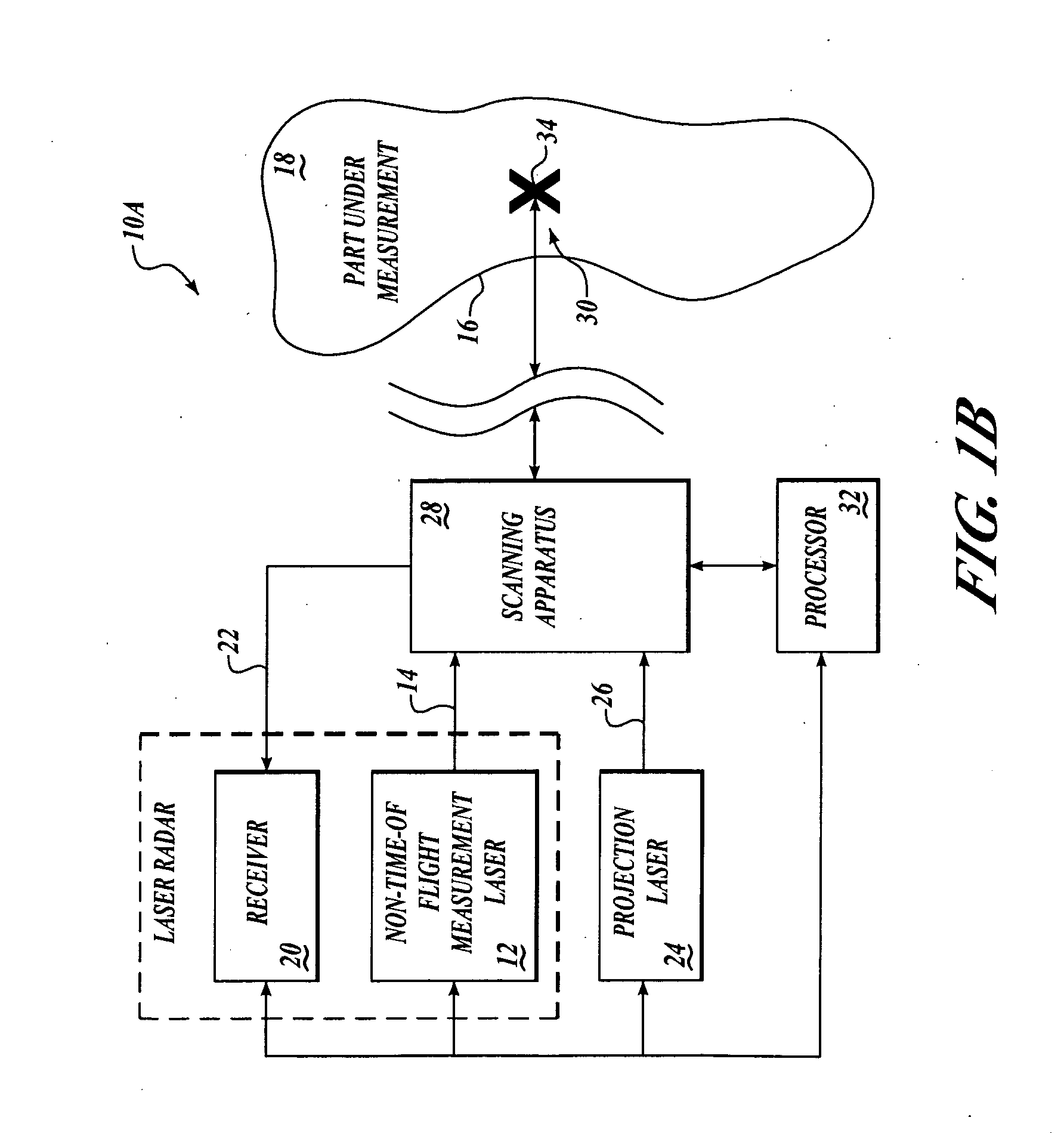
ActiveUS20060132803A1Low costEliminate errorsOptical rangefindersUsing optical meansLight beamOptical measurements
Systems and methods are provided for targetless optical measurement and optical information projection. A non-contact optical measurement device is provided for determining at least one of position and orientation of a workpiece. A projector is provided for projecting a part definition on the workpiece. Advantageously, beams from the non-contact optical measurement device and the projector pass through common optics.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Booting an operating system or running other pre-boot code from a file stored under a different operating system
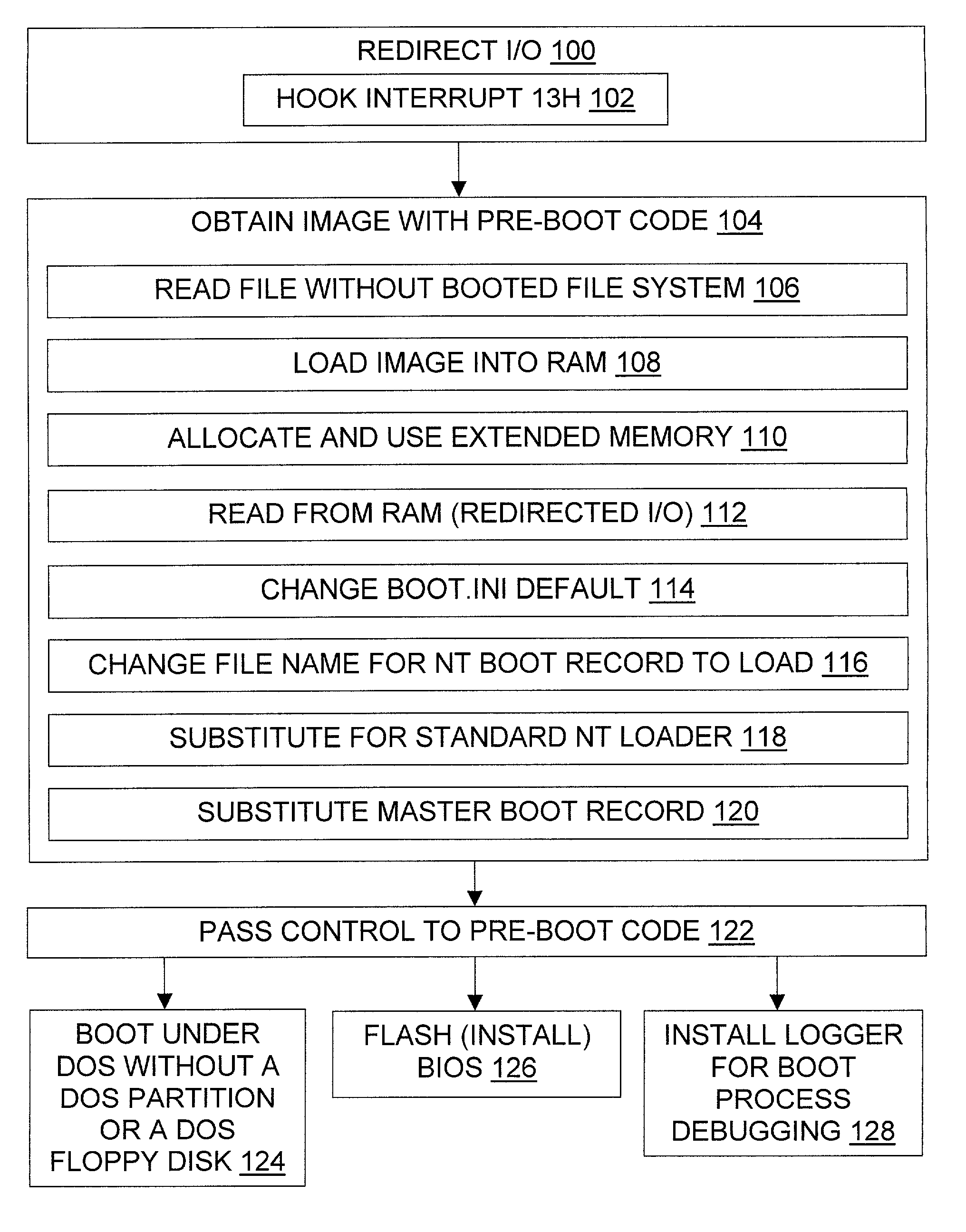
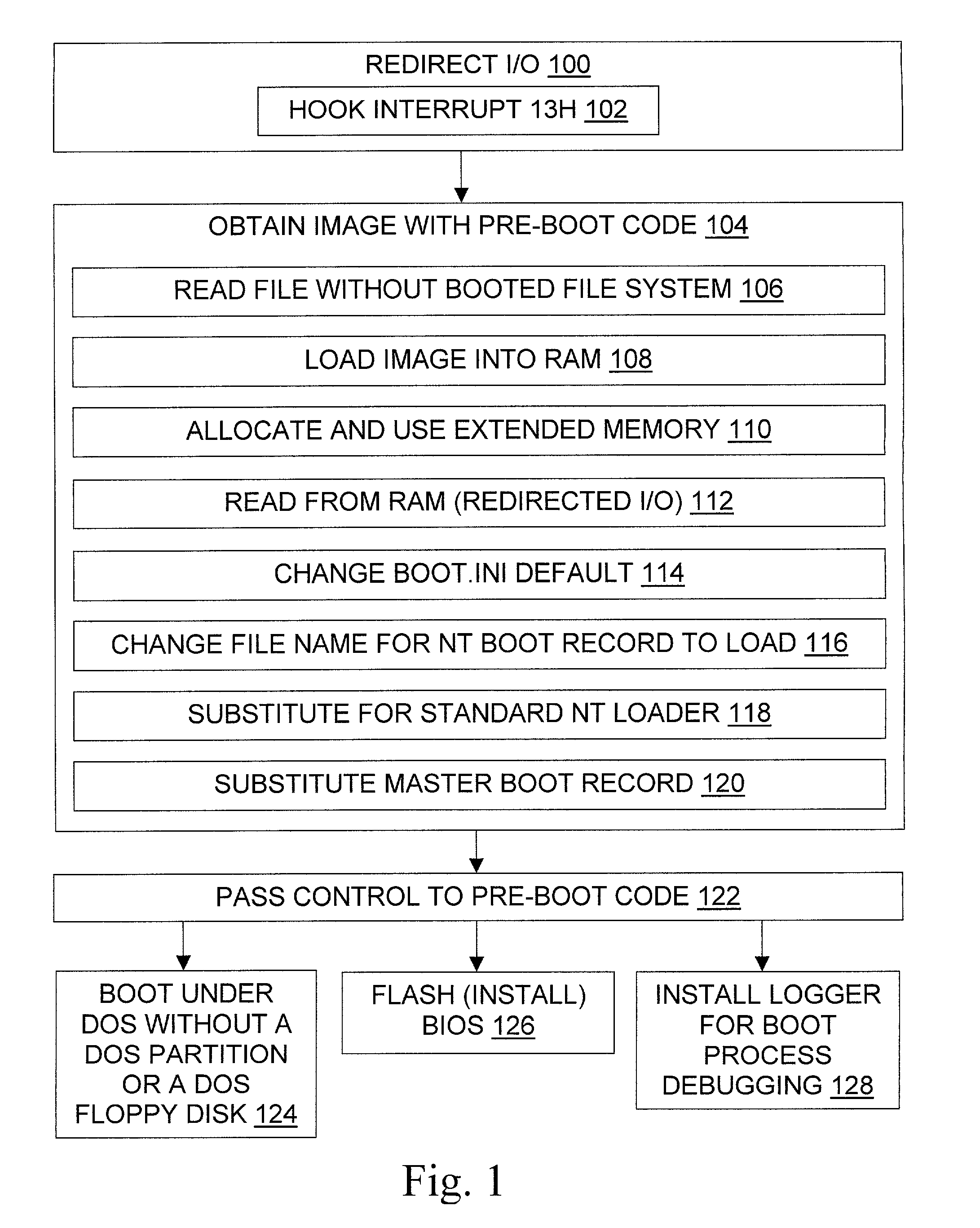
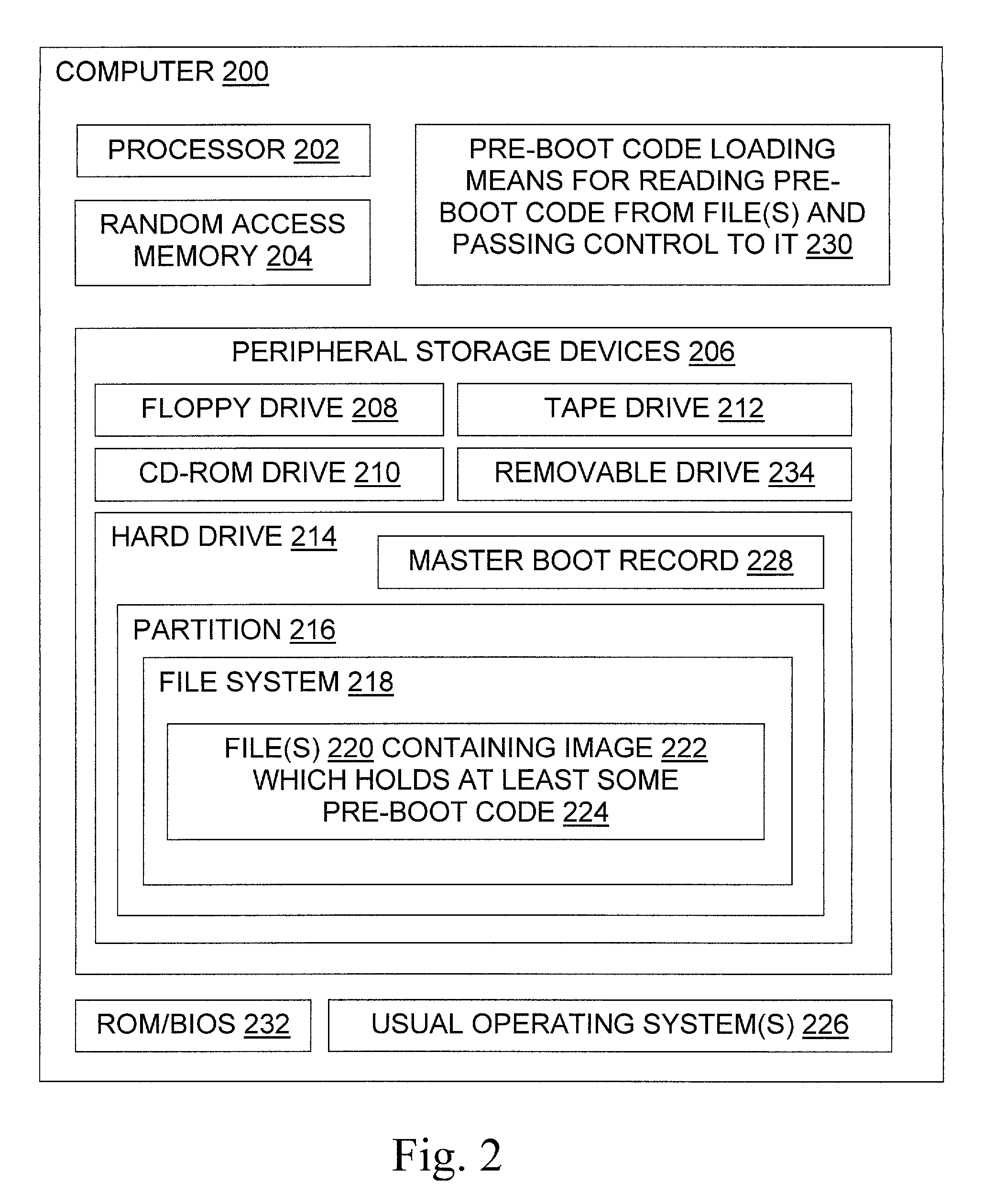
InactiveUS6996706B1Increase flexibilityWithout usingDigital computer detailsBootstrappingOperational systemFile system
The invention provides tools and techniques for running pre-boot code on a computer from a file stored in a file system on the computer. The pre-boot code may include an operating system which is not otherwise installed on the system. For instance, the pre-boot code may be used to boot a DOS operating system on a computer which lacks a DOS hard disk partition. The pre-boot code may contain code to perform operations that are difficult to perform after the operating system is booted, such as code for monitoring the boot process to help debug it. The pre-boot code is obtained from the file without using booted file system code, and is then executed. The code may be obtained by redirecting floppy drive I / O to read the pre-boot code from a copy in memory, or to read it as needed from one or more files on the hard disk.
Owner:GEN DIGITAL INC
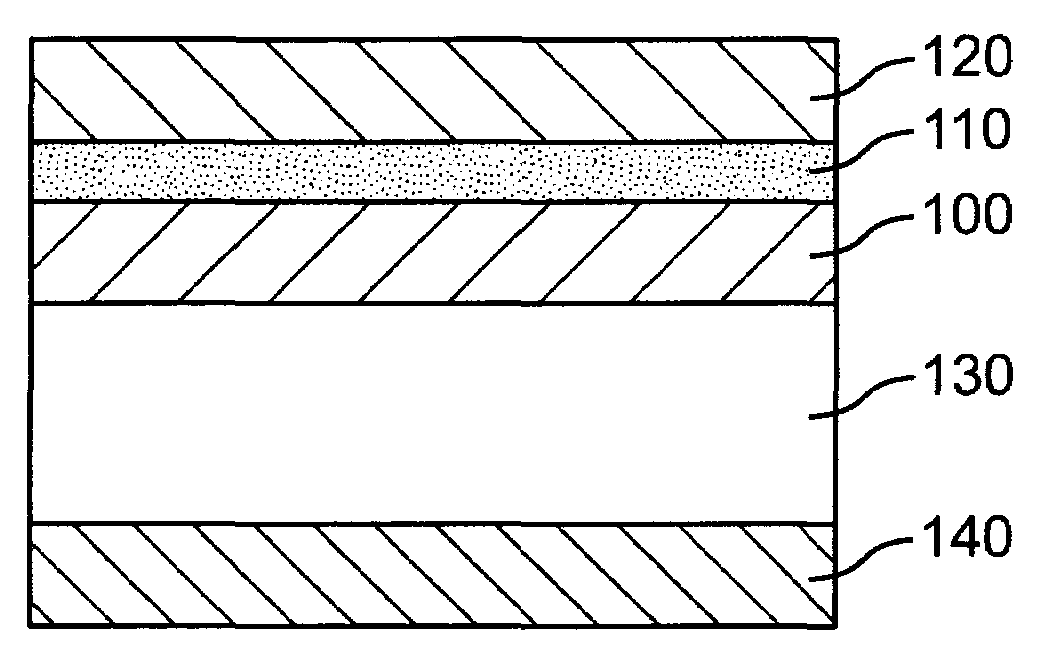
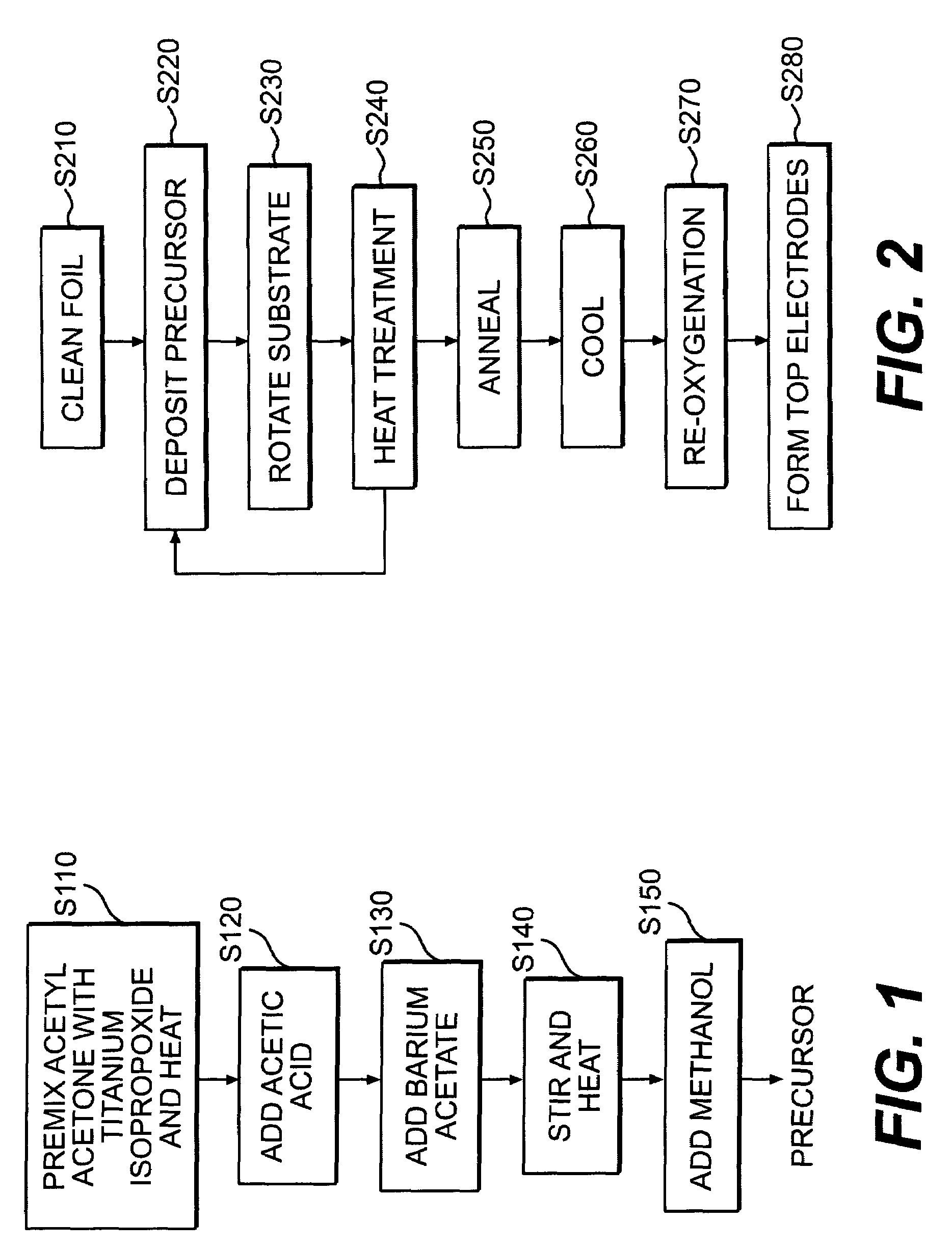
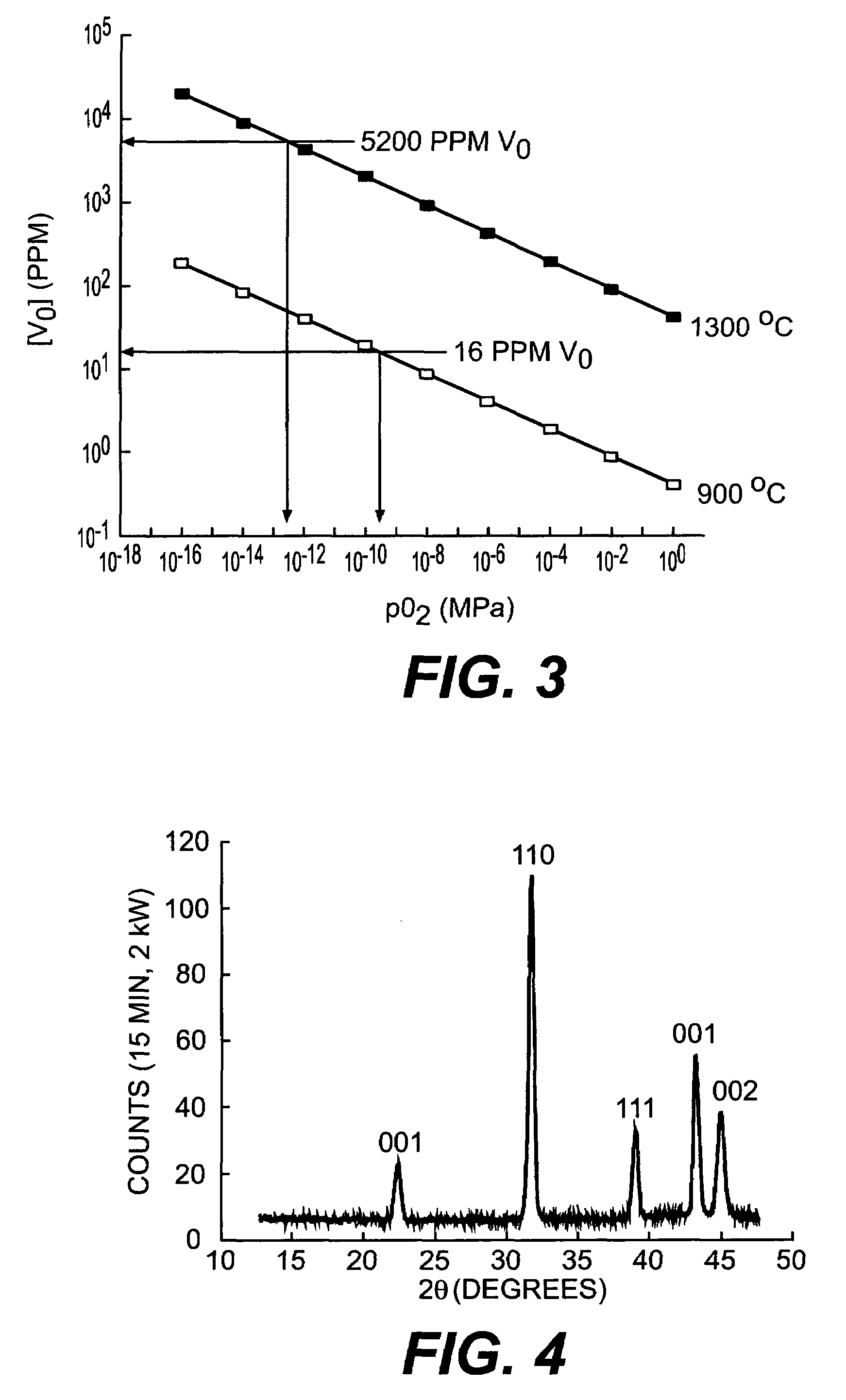
Thin film dielectrics for capacitors and methods of making thereof
ActiveUS7029971B2Increase capacitance densityLow loss tangentFixed capacitor dielectricPrinted circuit aspectsDielectricCopper foil
Dielectrics are formed having high dielectric constants, low loss tangents, and other desirable electrical and physical properties. The dielectrics are annealed at temperatures allowing the use of copper foil substrates, and at low oxygen partial pressures.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
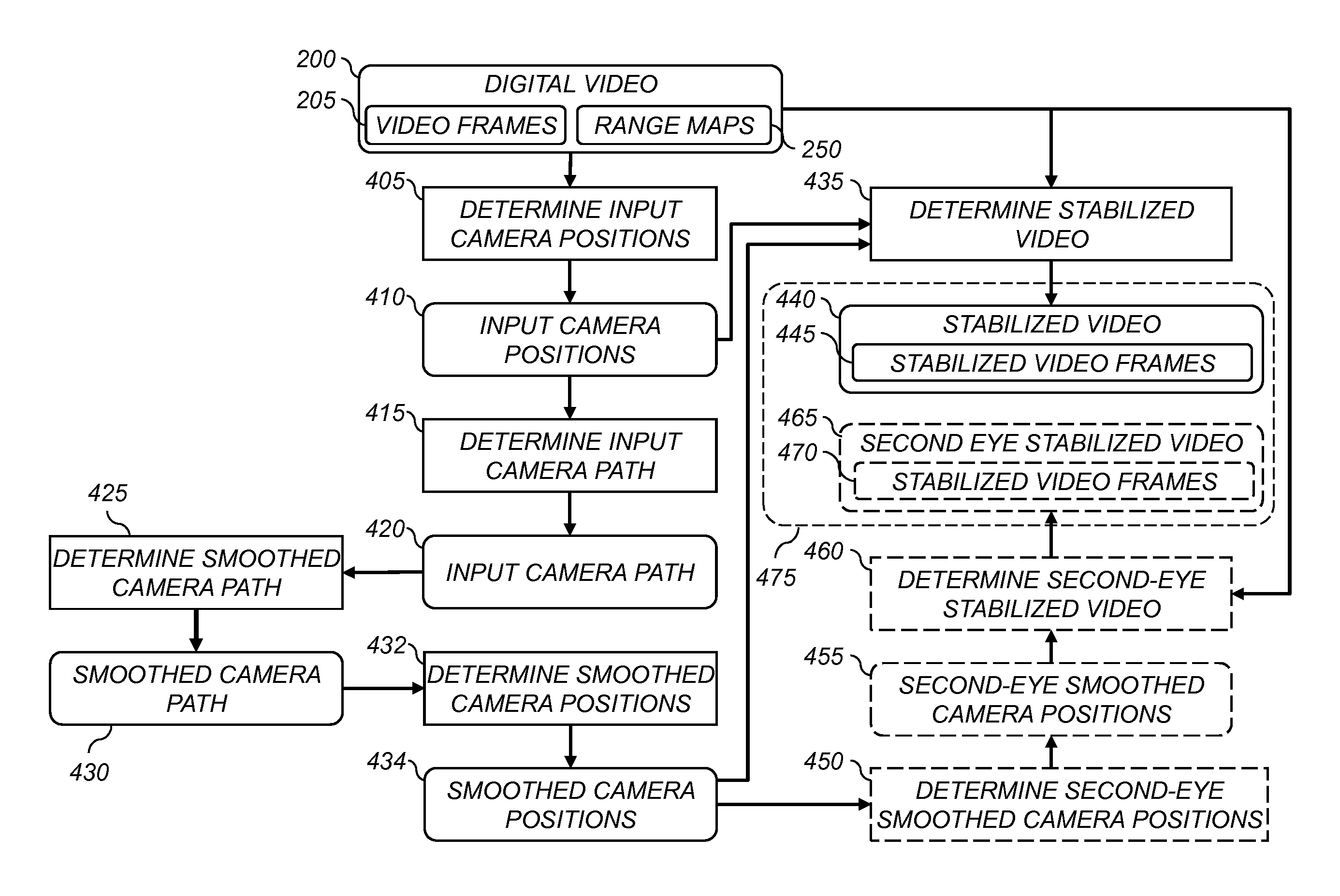
Forming a stereoscopic video
A method for forming a stereoscopic video of a scene from first and second input digital videos captured using respective first and second digital video cameras, wherein the first and second input digital videos include overlapping scene content and overlapping time durations. The method includes determining camera positions for each frame of the first and second input digital videos, and determining first-eye and second-eye viewpoints for each frame of the stereoscopic video. First-eye and second-eye images are formed for each frame of the stereoscopic video responsive to the corresponding video frames in the first and second input digital videos and the associated camera positions.
Owner:MONUMENT PEAK VENTURES LLC
Multilayer printed circuit board and multilayer printed circuit board manufacturing method
InactiveUS20070227765A1Low yieldWithout usingPrinted electric component incorporationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCopperPrinted circuit board
A multilayer printed circuit board has an IC chip 20 included in a core substrate 30 in advance and a transition layer 38 provided on a pad 24 of the IC chip 20. Due to this, it is possible to electronically connect the IC chip to the multilayer printed circuit board without using lead members and a sealing resin. Also, by providing the transition layer 38 made of copper on the die pad 24, it is possible to prevent resin residues on the pad 24 and to improve connection characteristics between the pad 24 and a via hole 60 and reliability.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Method and apparatus for facilitating efficient authenticated encryption
InactiveUS20060285684A1Efficient processLow costSecret communicationSecuring communicationComputer hardwareCiphertext
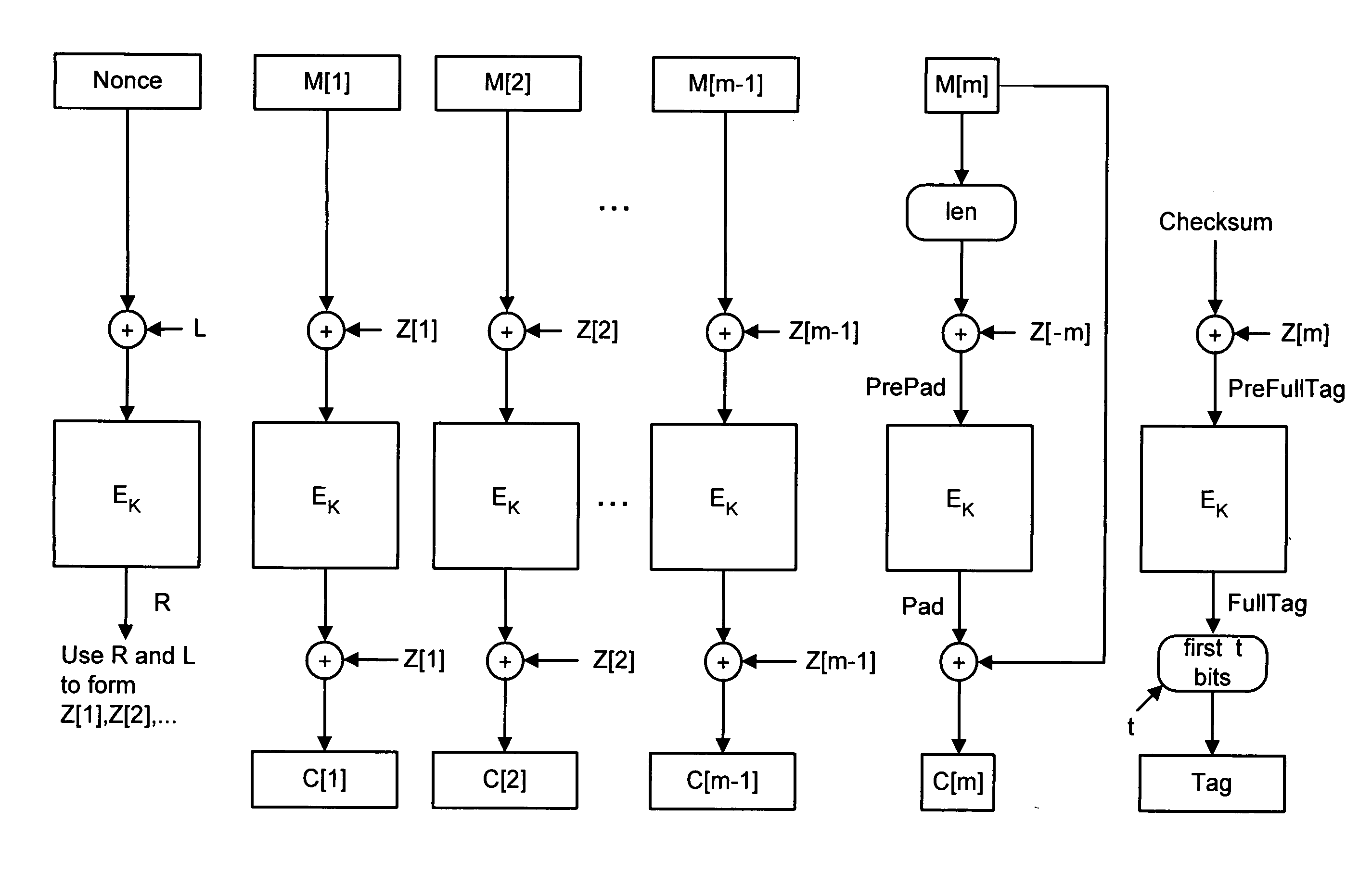
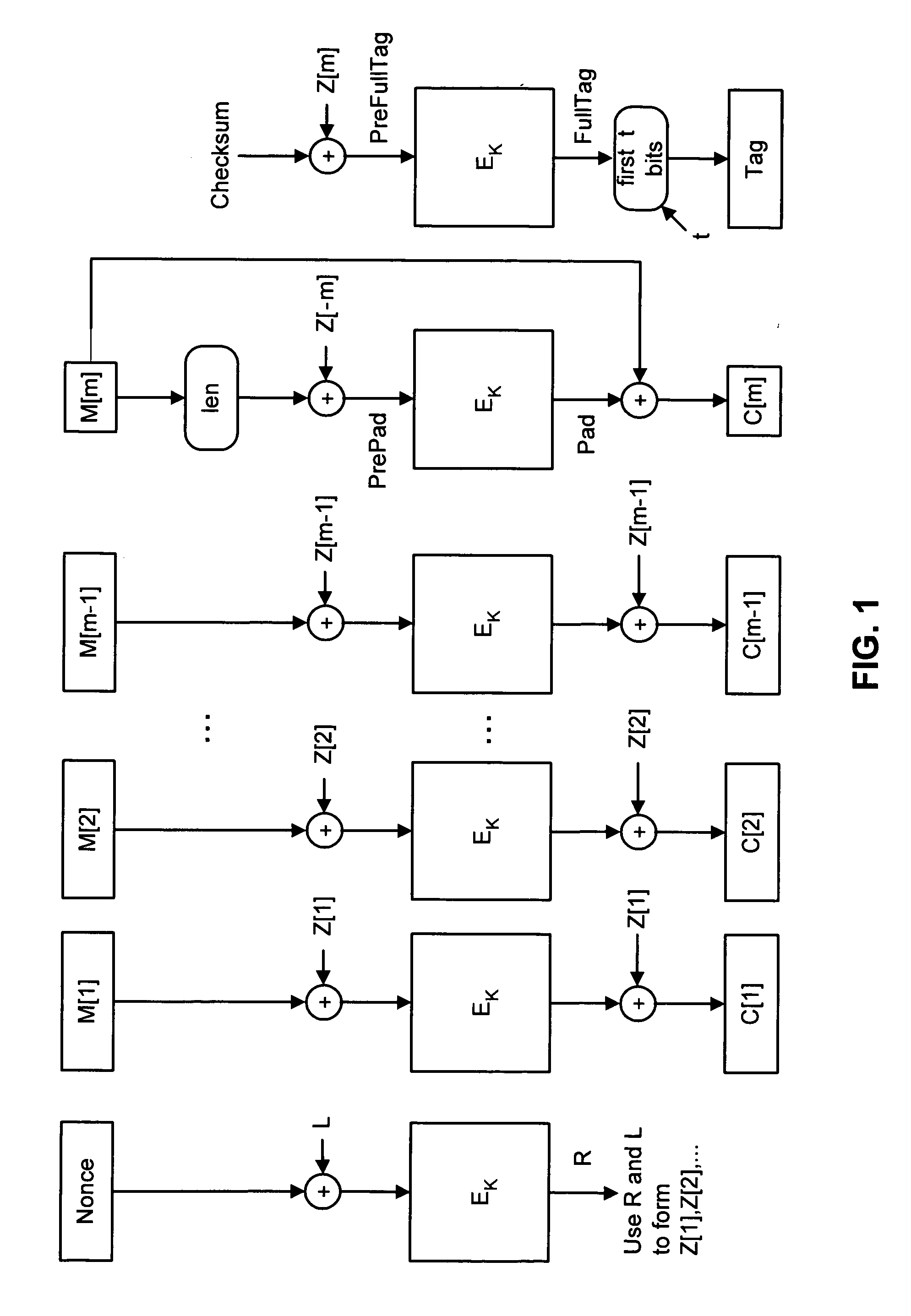
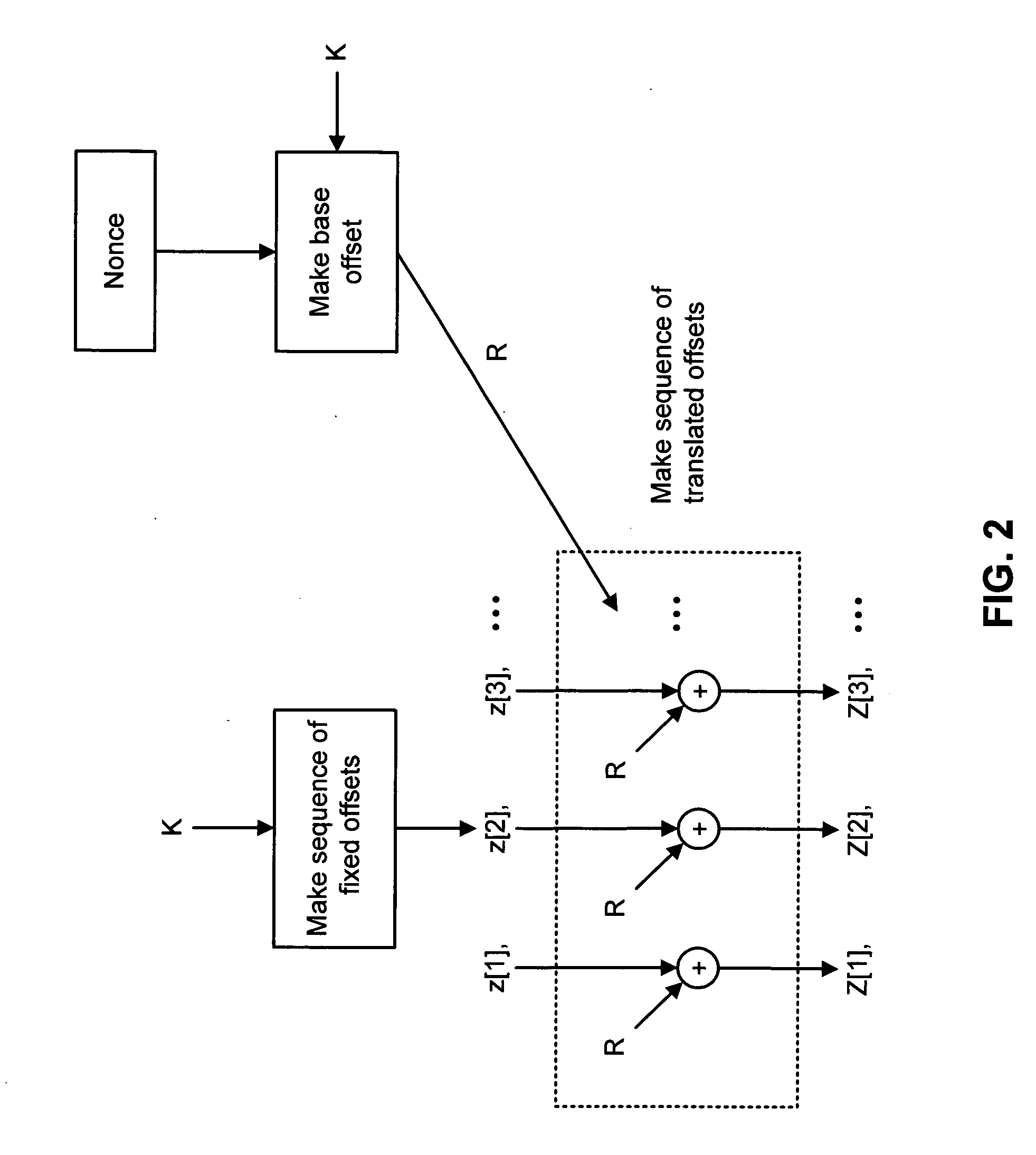
A shared-key encryption scheme that uses identically keyed block-cipher calls, low additional overhead, supports the encryption of arbitrary-length strings, produces a minimal-length-ciphertext, and is fully parallelizable. In one embodiment, “OCB”, a key shared between communicating parties is mapped to a key variant using the block cipher. The key variant is mapped into a sequence of basis offsets using shifts and conditional xors. To encrypt a message using a nonce, a nonce-dependent base offset is formed, and then a sequence of offsets is constructed by starting with the base offset and then xoring, for each offset, an appropriate basis offset. The message is partitioned into message blocks of the same length as the block length of the block cipher, along with a message fragment that may be shorter. Each message block is combined with a corresponding offset, enciphered, and then combined again with the offset, yielding a ciphertext block. The message fragment is xored with an appropriately computed pad to give a ciphertext fragment. A checksum is formed using the message blocks, the message fragment, and the pad. The checksum is combined with an offset and enciphered to yield a tag. The encrypted message includes the ciphertext blocks, the ciphertext fragment, and the tag.
Owner:ROGAWAY PHILLIP
Battery-powered light source device for endoscope
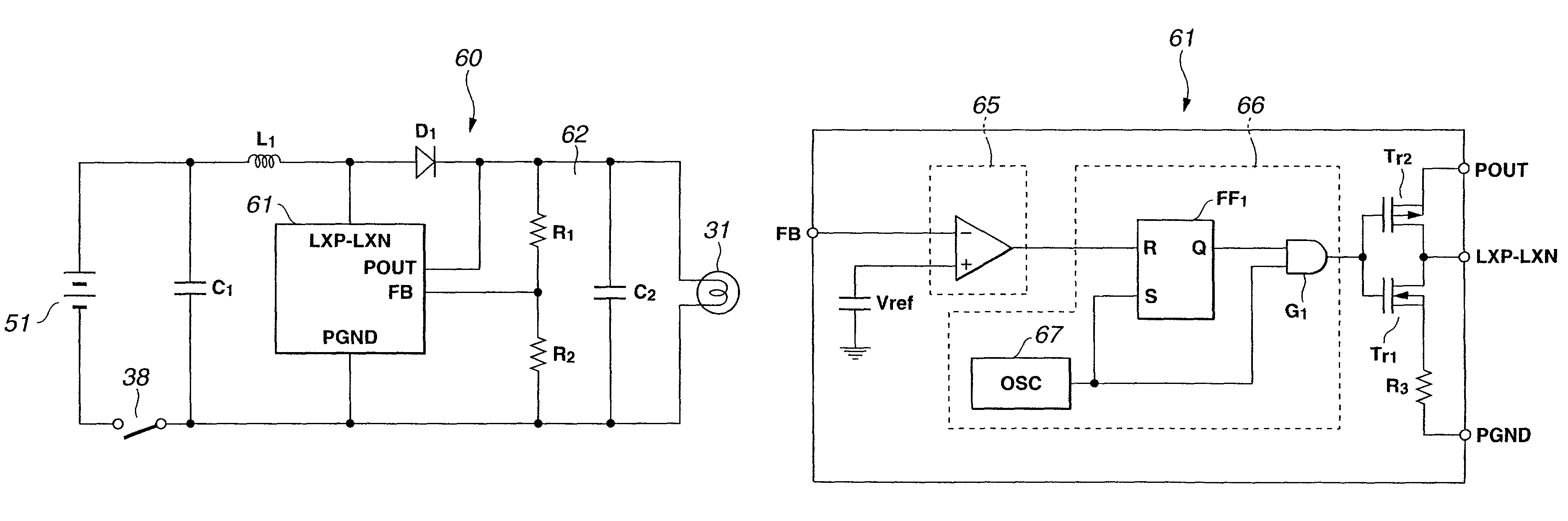
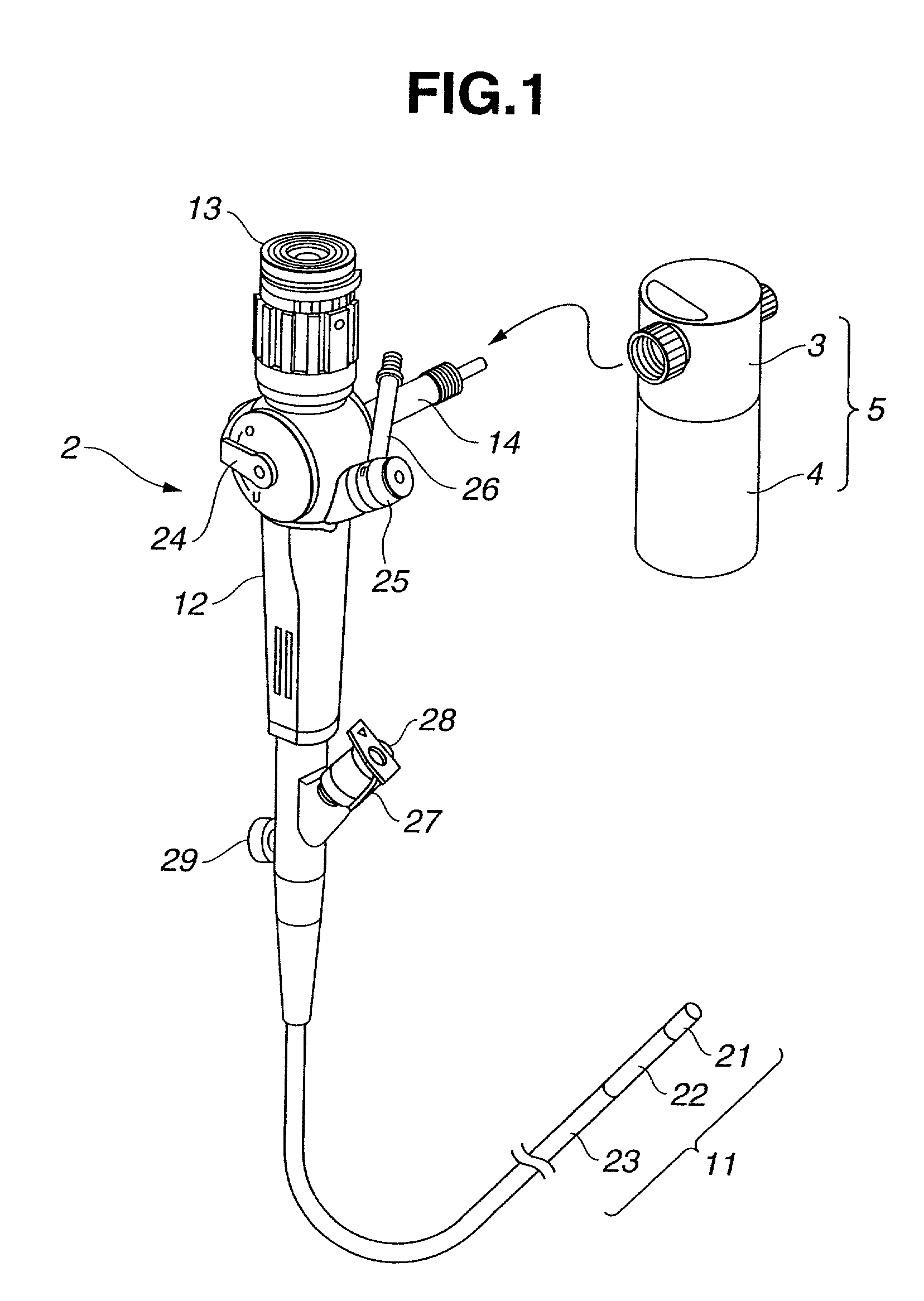
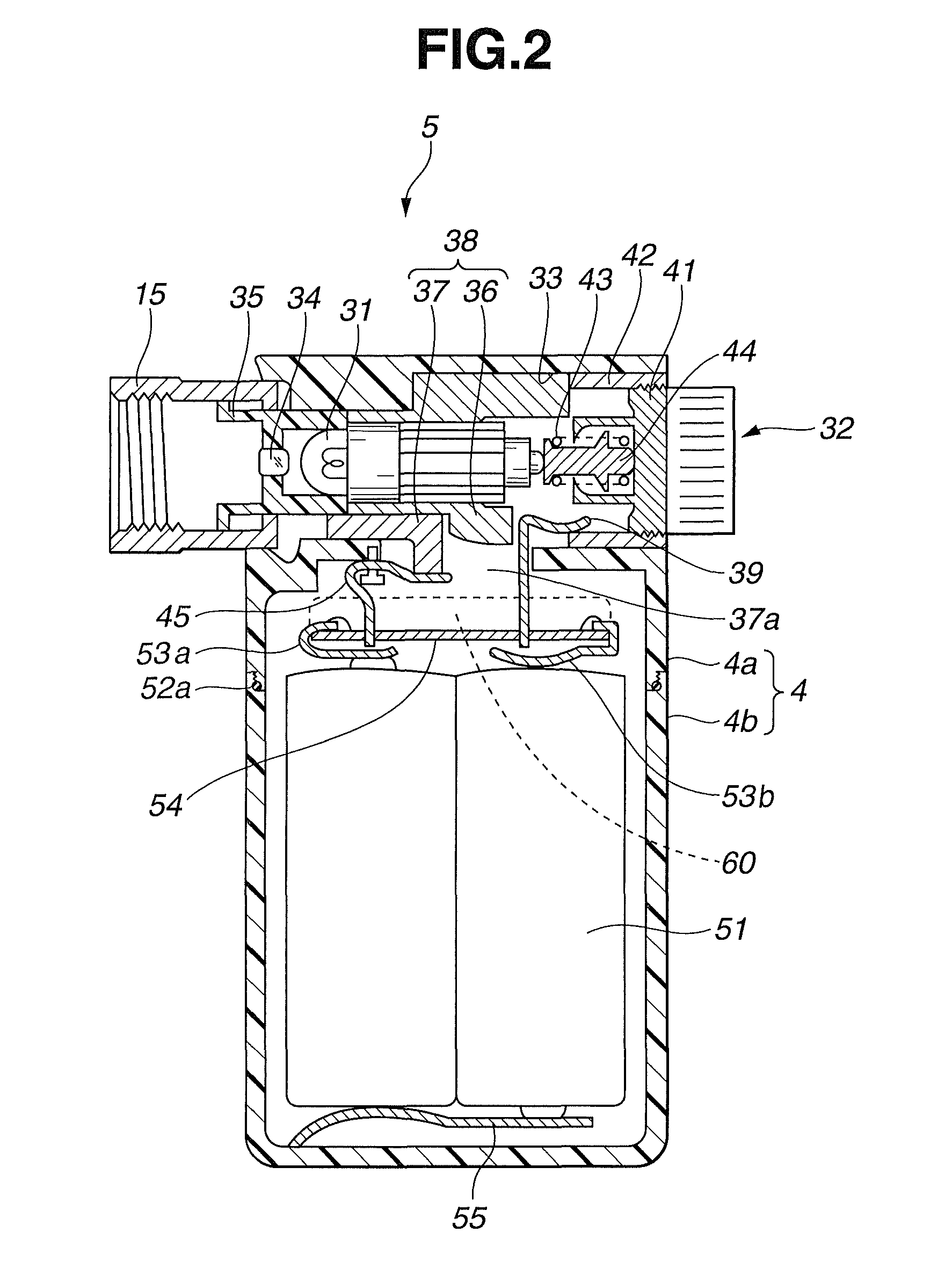
A battery-powered light source device 5 has an DC / DC converter 61 that boosts the supply voltage of a battery 51 and supplies electrical power to a lamp 31, and, inside this DC / DC converter 61, are provided a comparator 65 that compares a specific reference voltage to the output voltage of a DC / DC converter 61, and a control component 66 that keeps the output voltage from the DC / DC converter 61 at a specific lamp voltage on the basis of the comparison result of this comparator 65, whereby the supply voltage of the battery 51 is boosted and the optimal lamp voltage is obtained. Consequently, the battery-powered light source device 5 allows the brightness of the lamp to be adjusted and a high step-up efficiency to be obtained, and the battery can therefore be used more efficiently, and a more convenient use of the endoscope is possible.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
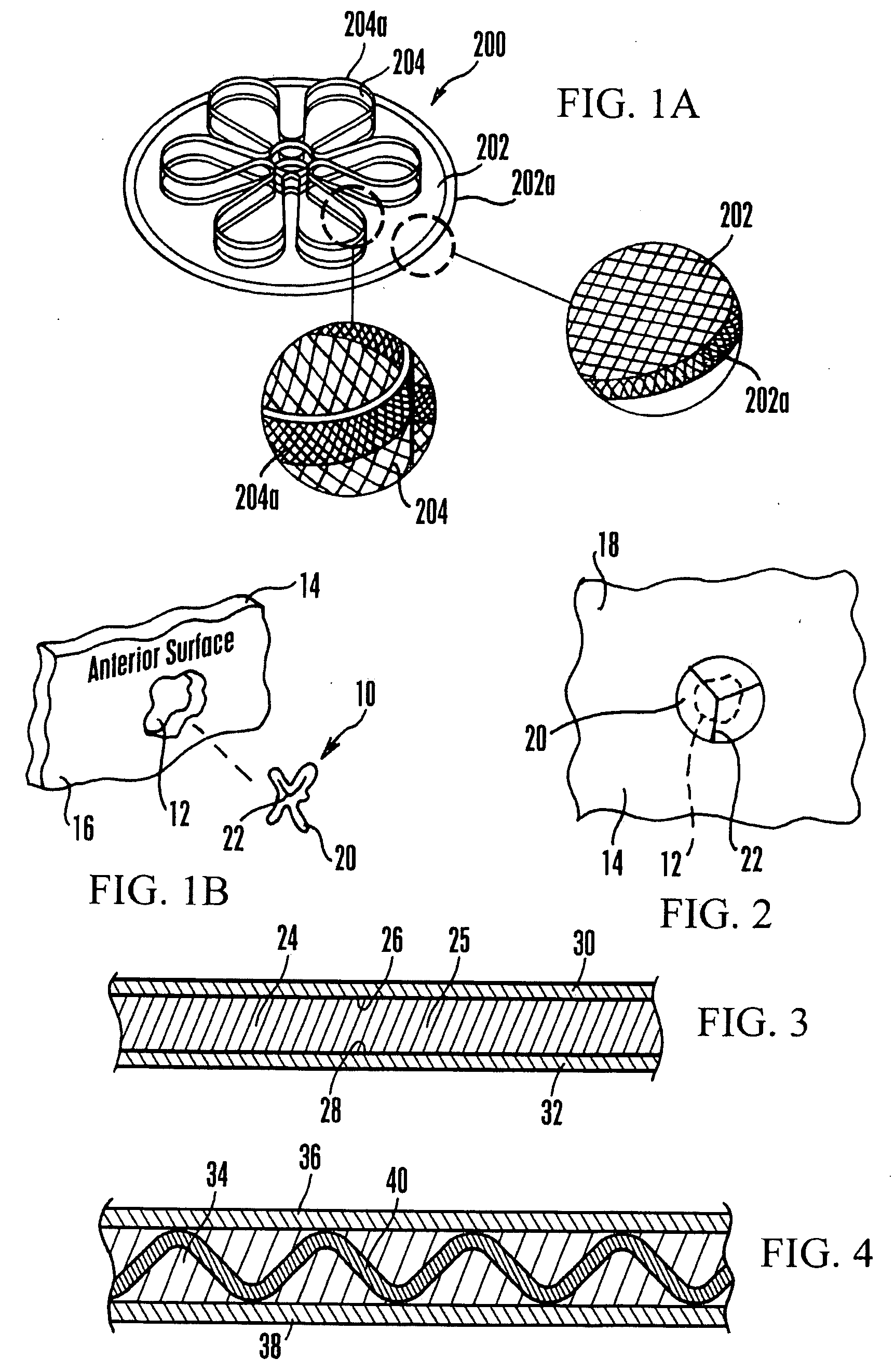
Fortified mesh for tissue repair
InactiveUS20090192530A1Decrease in resiliencyQuality improvementProsthesisWound clampsTissue repairEngineering
A mesh to repair a hole in a muscle wall includes a resilient mesh body and fortifying structure such as mesh portions of thicker weave than other portions, or strengthening members that can be engaged with the mesh and then removed from the mesh once the mesh is place over the hole. The same principles can be applied to a plug that is engaged with the mesh for filling the hole.
Owner:AMATO
Interventional medical closure device
ActiveUS20060287673A1Reduce traumaSimple yet effectiveSuture equipmentsExcision instrumentsNoseBlood vessel
An interventional medical closure device is suitable for assisting closure of an opening through a blood vessel wall after completion of an interventional procedure within the internal lumen of the blood vessel. The device comprises a closure element, a grasping element for grasping the closure element, and a delivery element for delivering the closure element into the internal lumen of the blood vessel. The closure element comprises a suture, and an engagement foot at a distal end of the suture. The grasping element is inter-engageable with the closure element to grasp the closure element. The delivery element comprises a main body portion, and a distal nose. The distal nose defines a reception space for carrying the engagment foot of the closure element. The delivery element also comprises an engagement foot which is movable relative to the main body portion between a low-profile delivery configuration and a protruding engagement configuration.
Owner:VIVASURE MEDICAL LTD
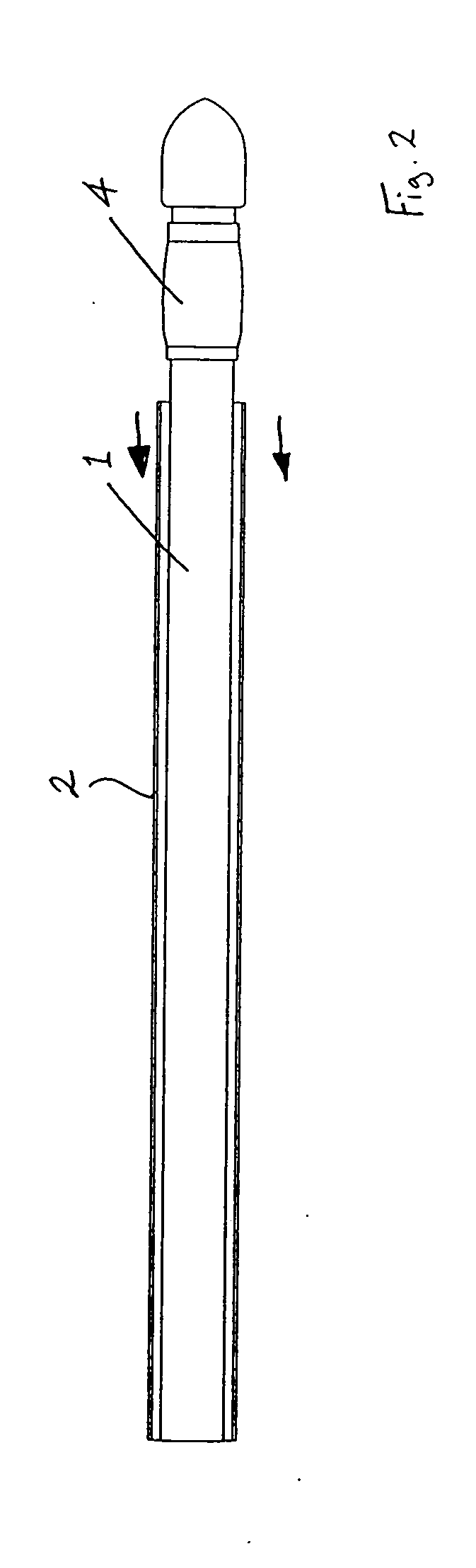
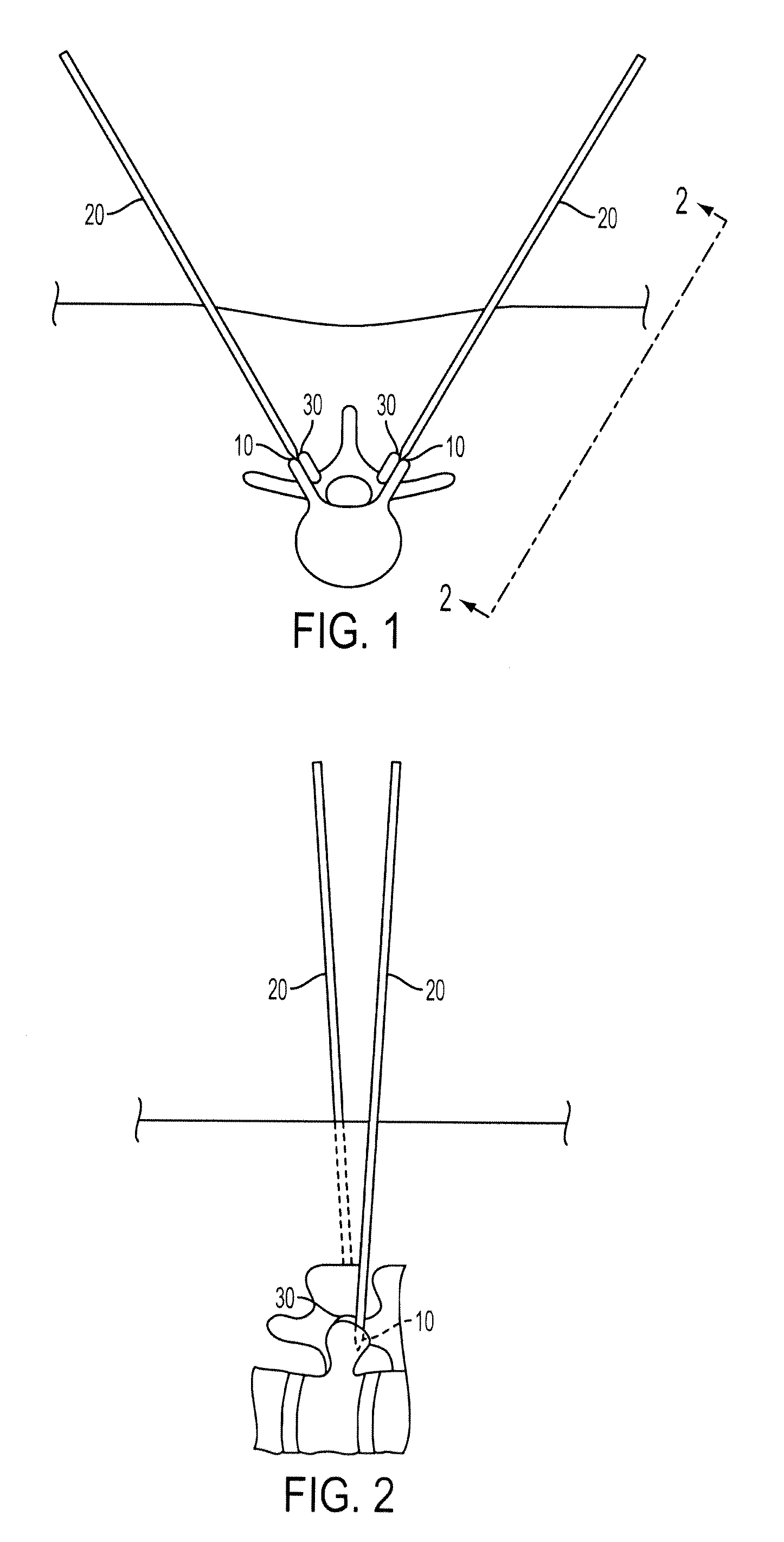
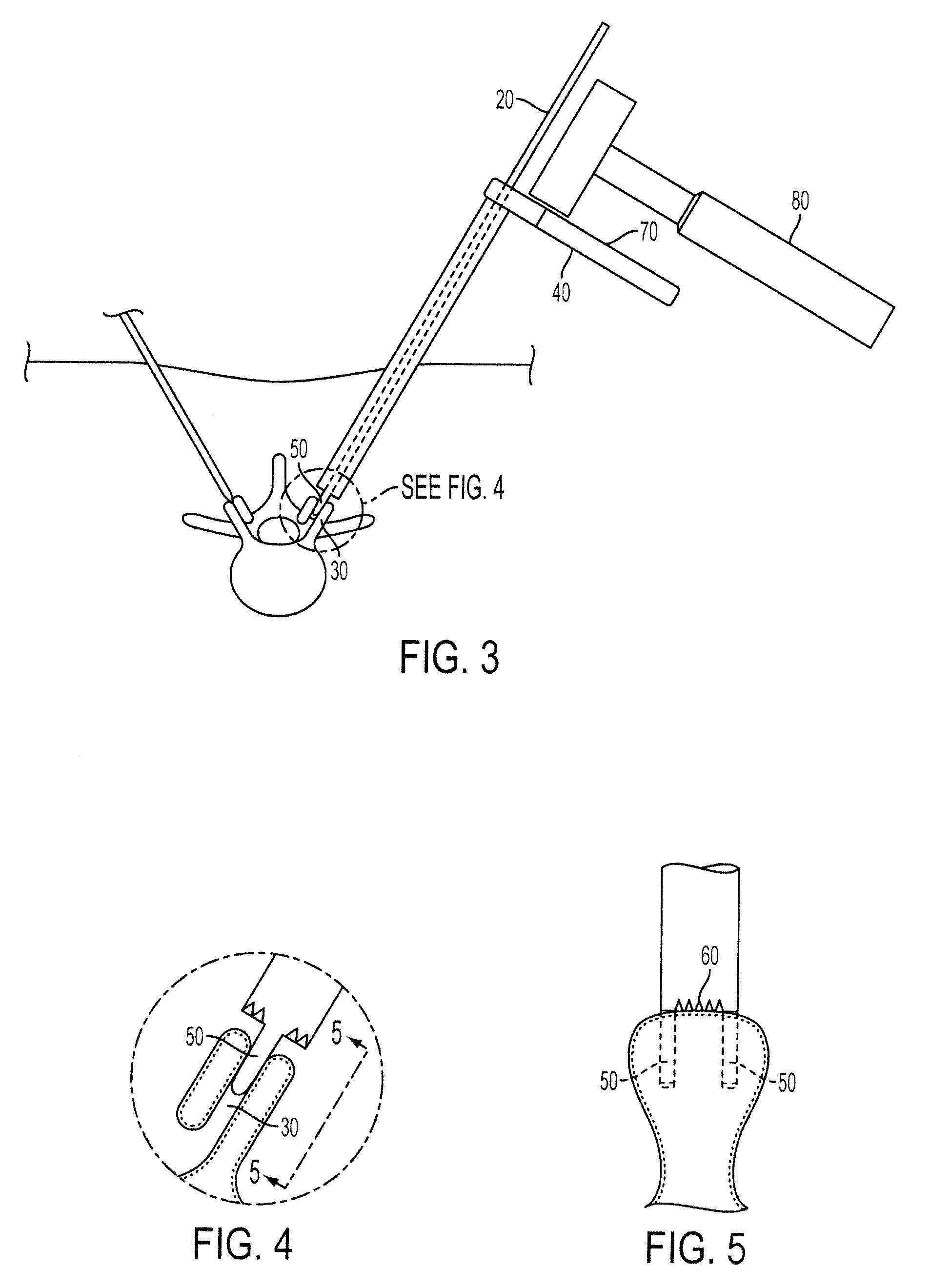
Methods and Surgical Kits for Minimally-Invasive Facet Joint Fusion
InactiveUS20090234397A1Prevent over-insertionMinimally-invasiveInternal osteosythesisSurgical furnitureLess invasive surgeryArthroscopy
Disclosed herein are methods and surgical kits that can be used to fuse facet joints via a minimally invasive procedure (including an arthroscopic or percutaneous procedure). An exemplary method includes creating an incision; locating a facet joint with a distal end of a pin; sliding a substantially hollow drill guide over said pin wherein said drill guide comprises a proximal end, a distal end; removing said pin from within said drill guide; inserting a drill bit into said drill guide; drilling a hole into a bone of said facet joint; removing said drill bit; inserting a facet joint bone plug into said hole using a bone plug inserter having a raised portion at or near is proximal end, wherein said raised portion prevents over-insertion of said bone plug; and removing said drill guide.
Owner:MINSURG INT
Methods and apparatus for secure online access on a client device
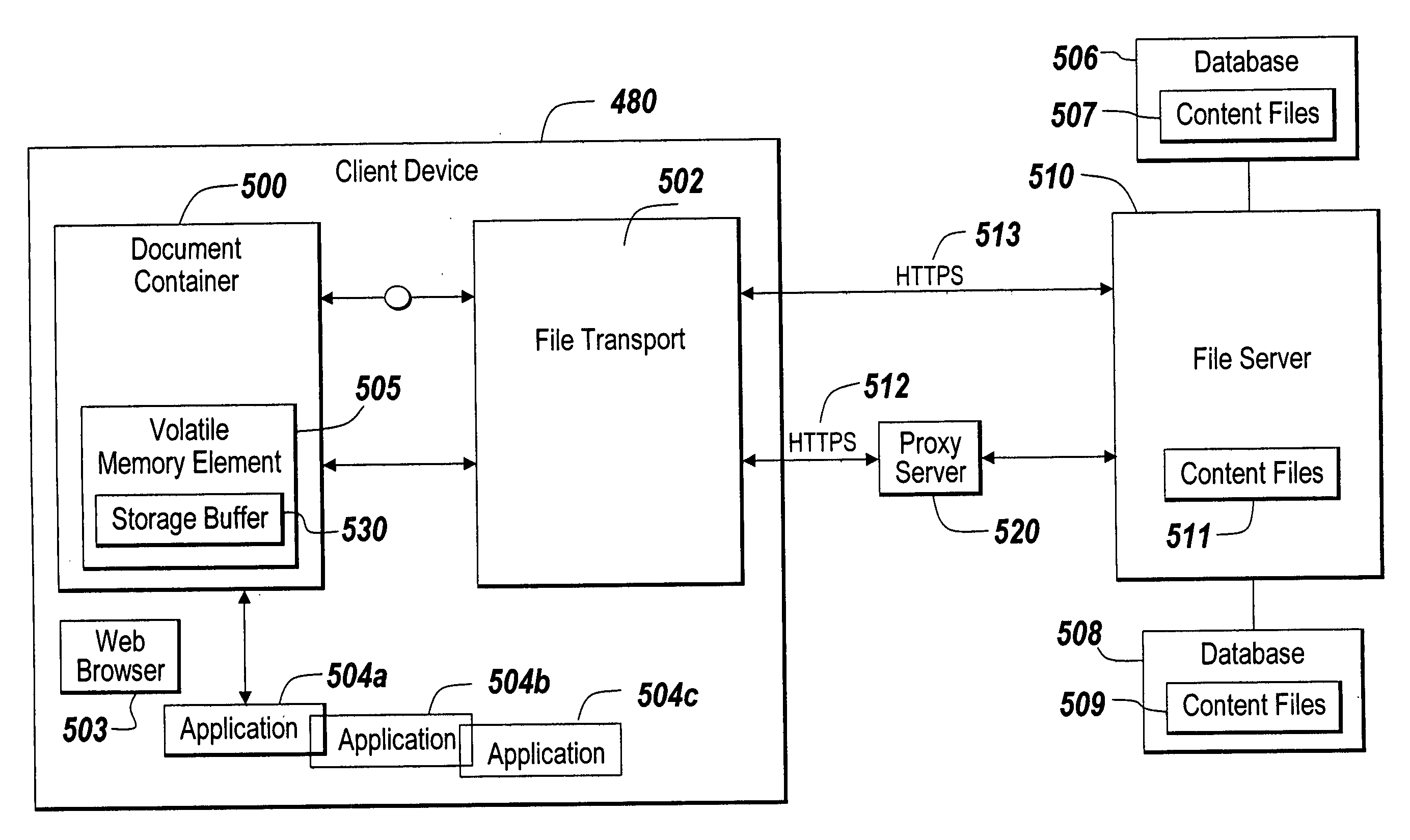
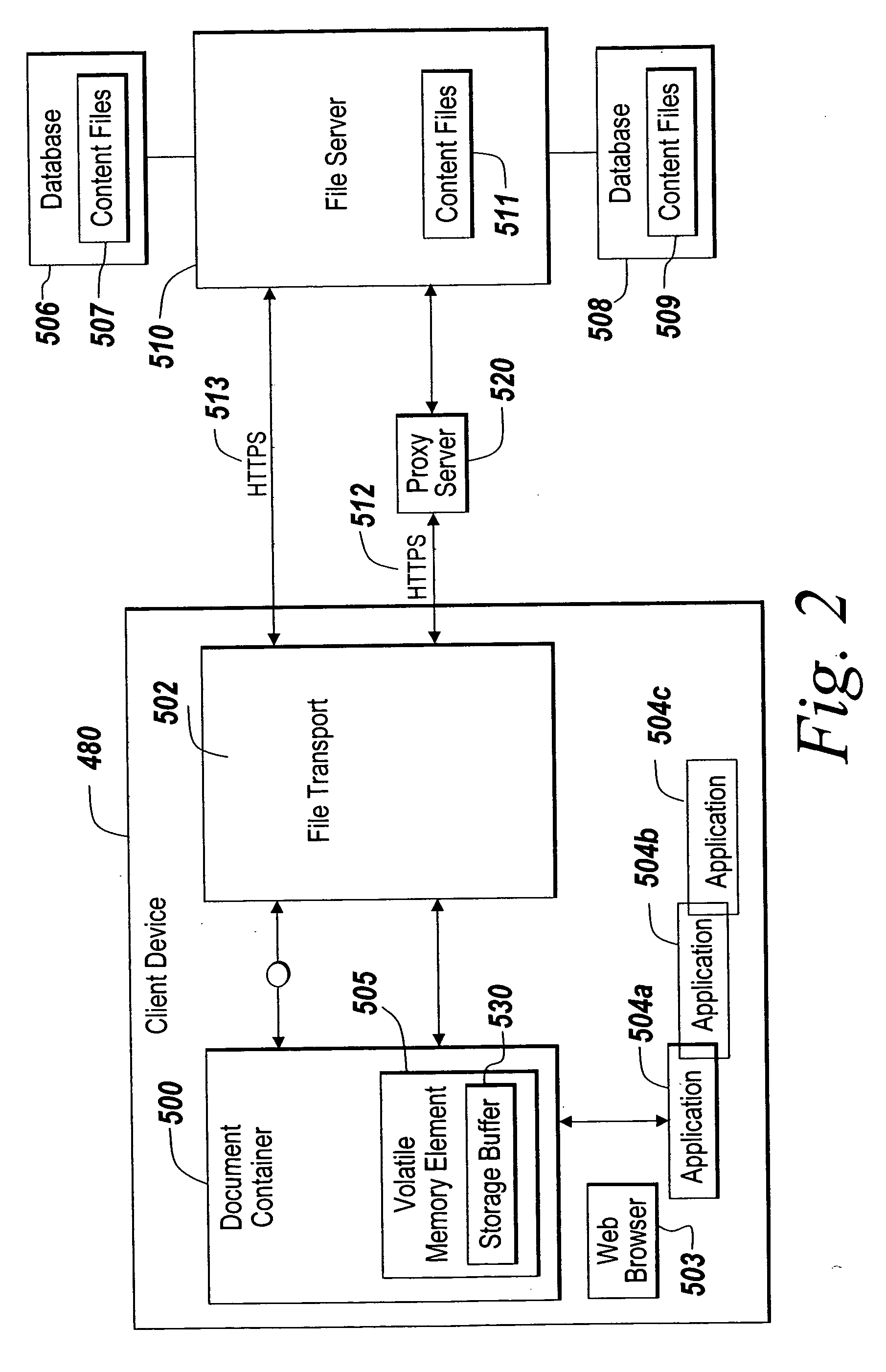
ActiveUS20060047956A1Prevent unwanted disclosure of confidential informationManipulation is limitedComputer security arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsPaper documentDocument preparation
A method of securely accessing at a client device content from a server without using the non-volatile memory of the client device is disclosed. The bypassing of non-volatile memory lessens the security risk of unauthorized viewing of the server originated content. An transport mechanism is initiated on a client device and creates a document container. Downloaded documents from a server are mapped into the document container and saved within the document container in volatile memory. Substitute menus are generated within the container to replace application menus. User documents are saved directly to the originating server via the substitute menus. The downloaded copies in volatile memory automatically delete when the document container is destroyed thereby reducing security concerns of unauthorized viewing of the content at the client device.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com