Patents
Literature
223results about How to "Prevent accidental contact" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
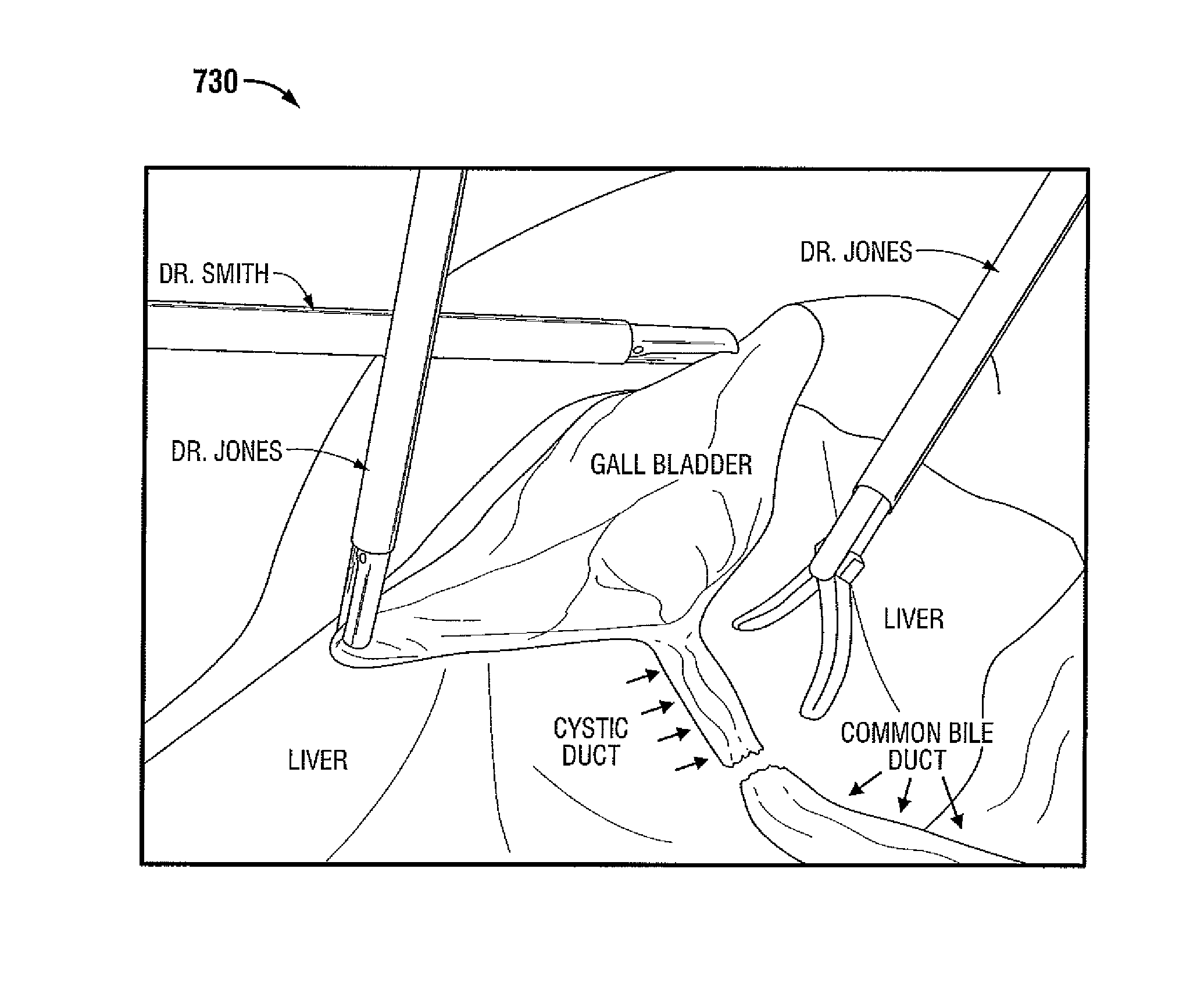
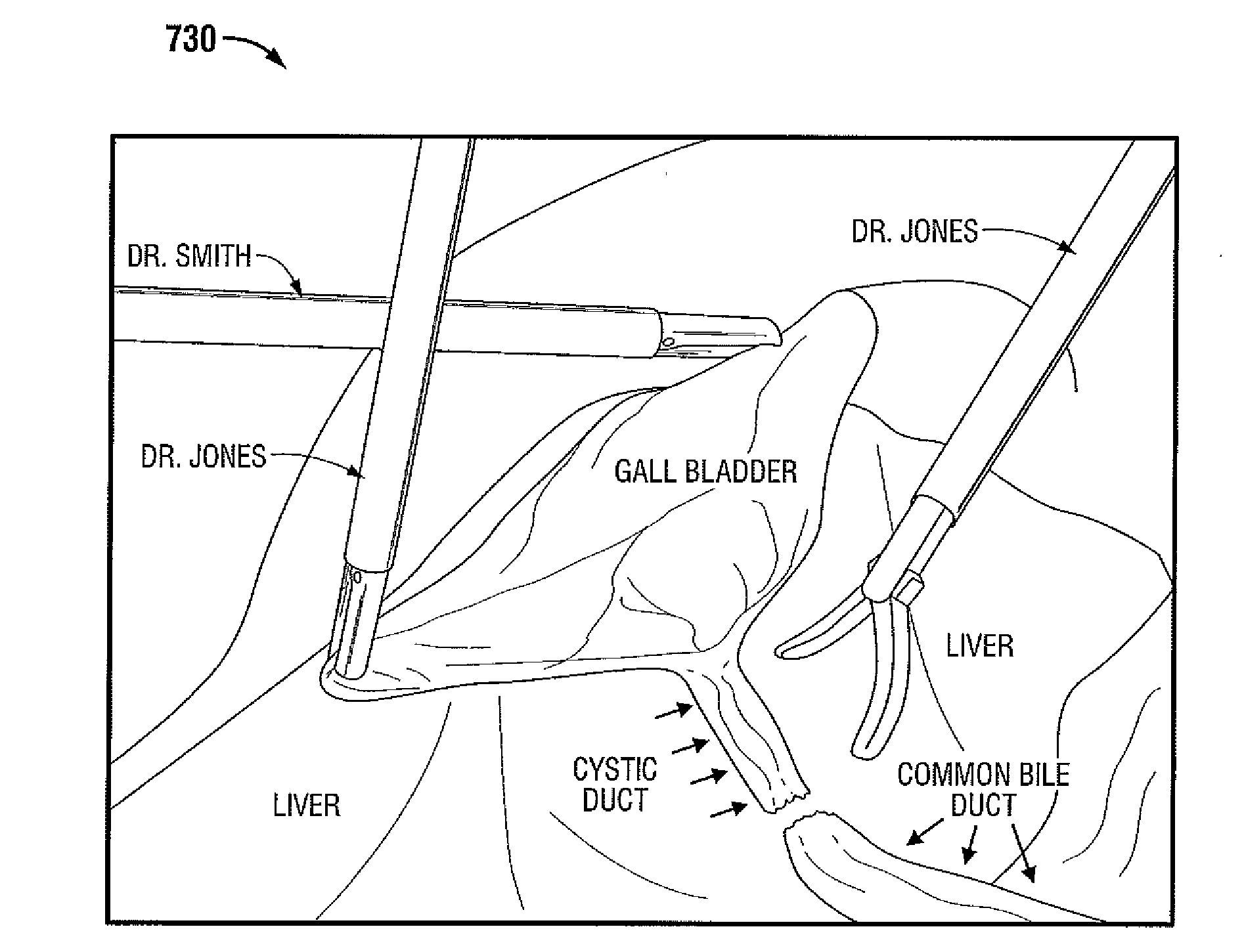
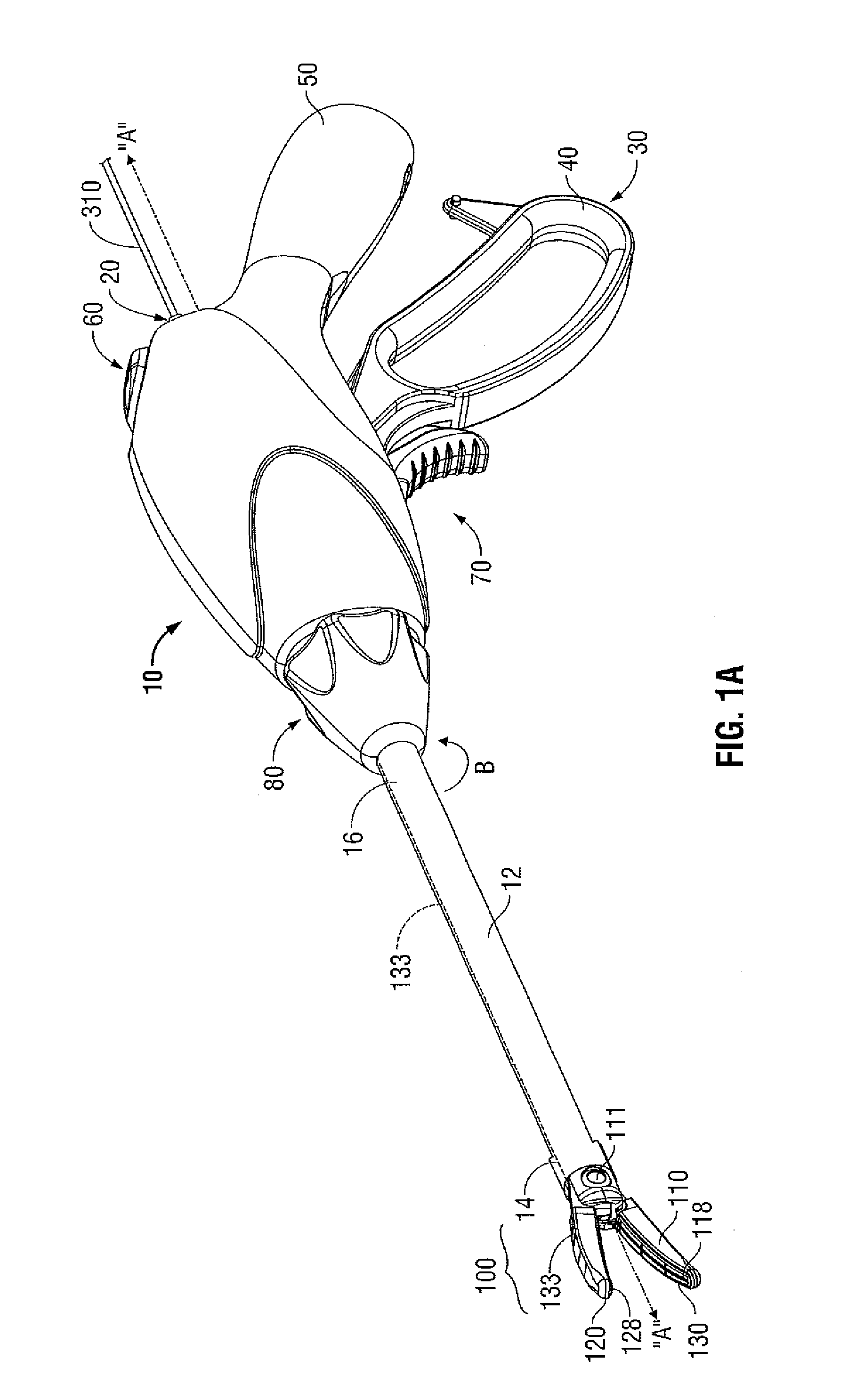
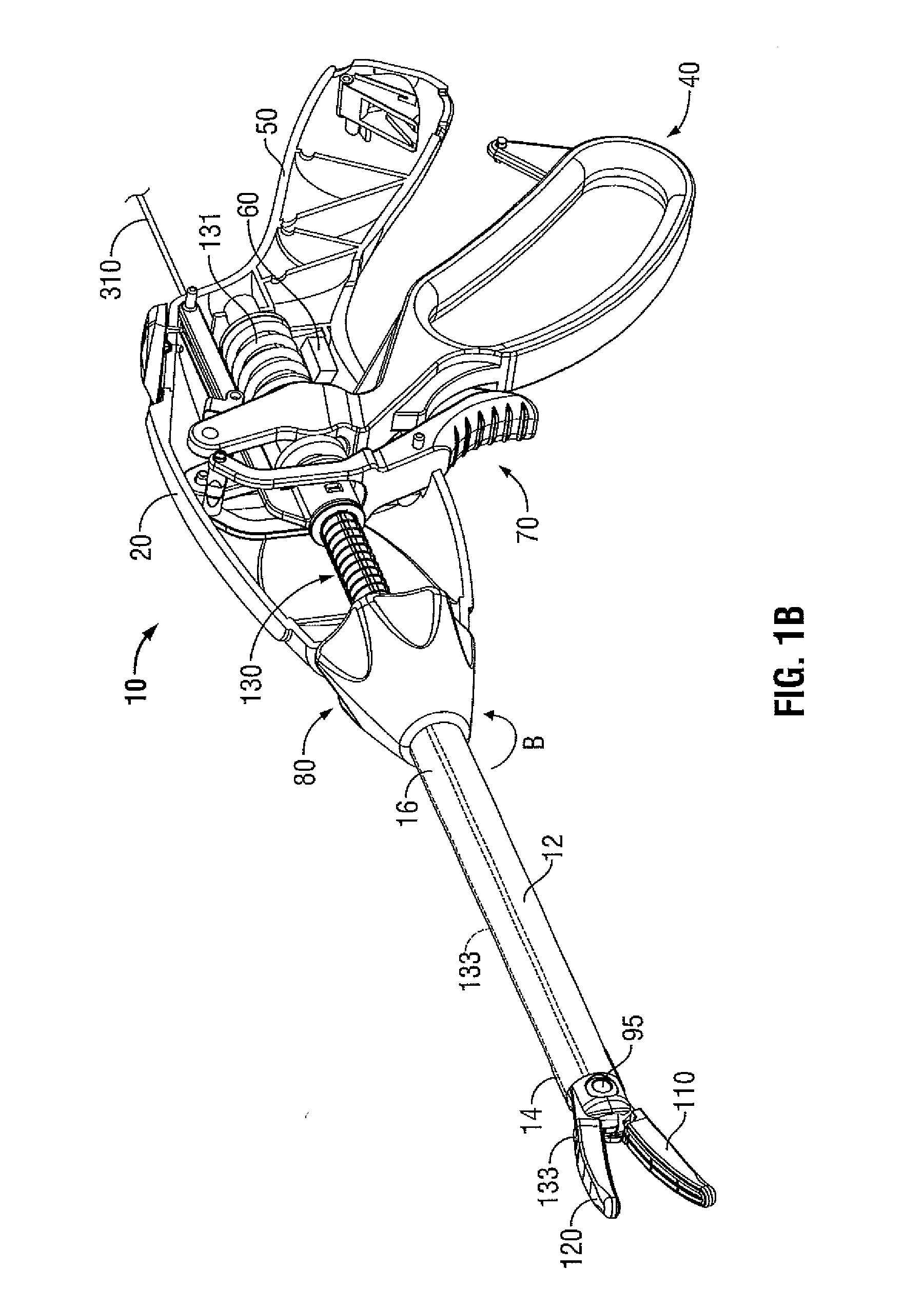
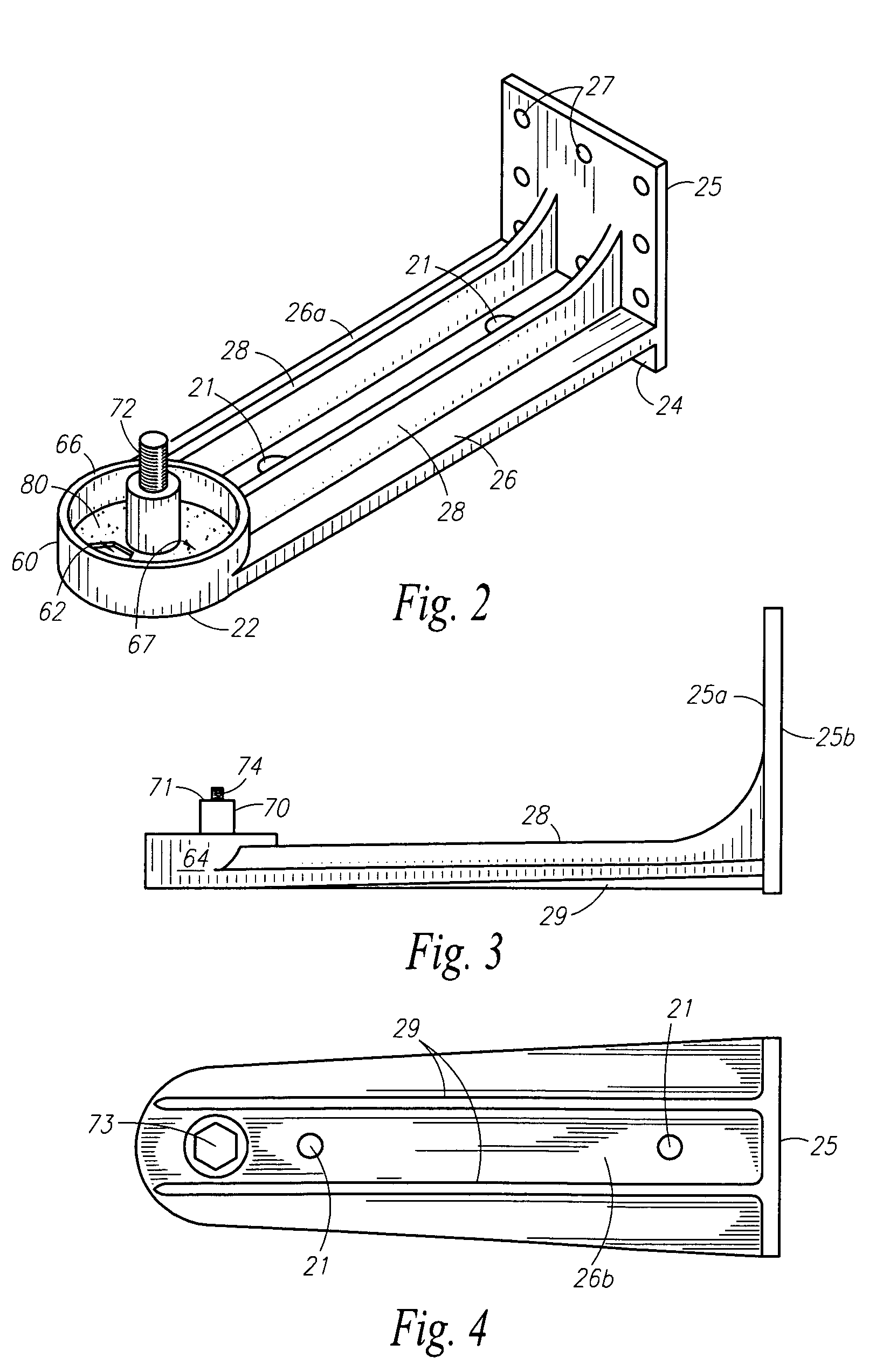
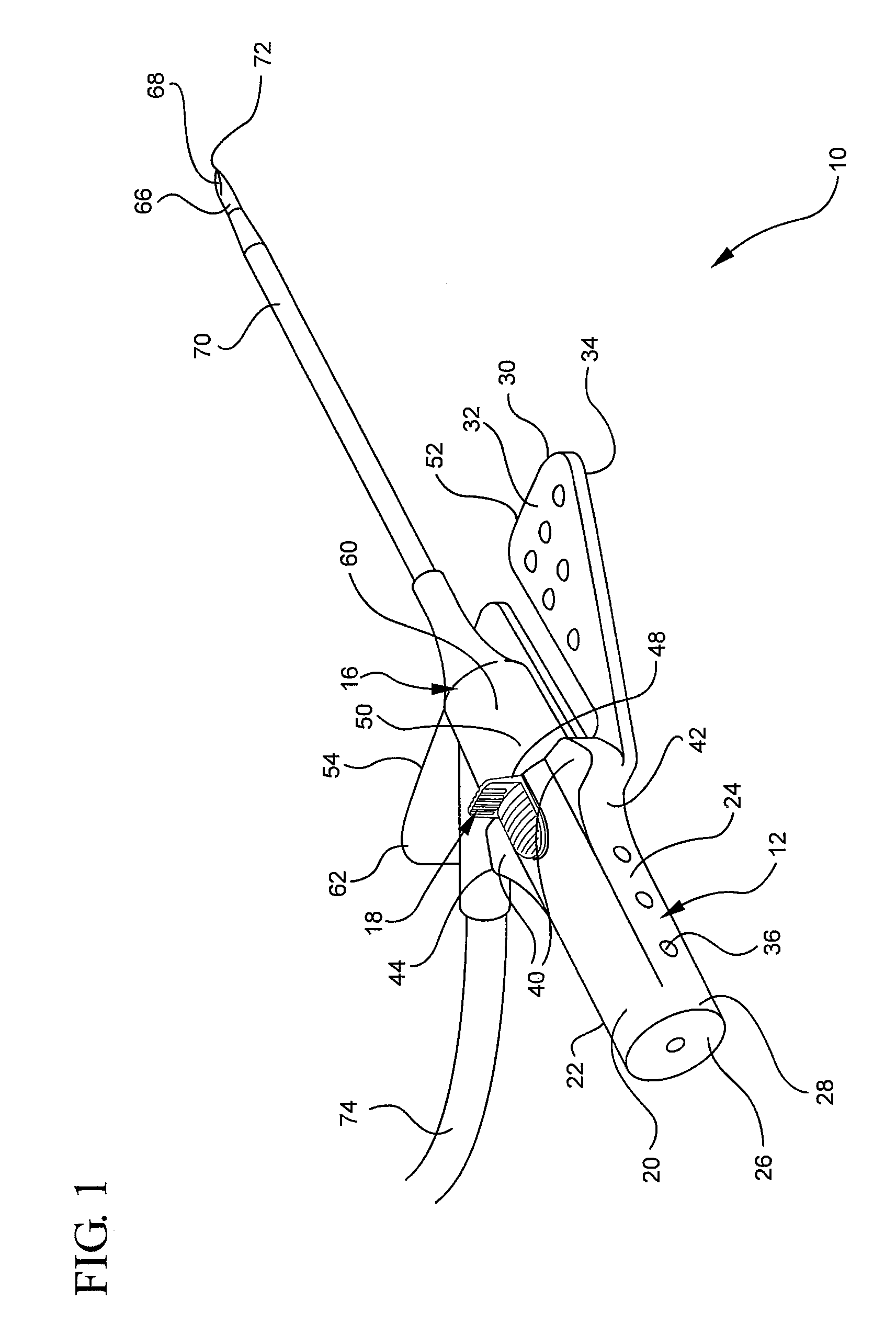
Apparatus and method for using augmented reality vision system in surgical procedures
ActiveUS9123155B2Improve eyesightAvoid enteringMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesSurgerySurgical siteX-ray
A system and method for improving a surgeon's vision by overlaying augmented reality information onto a video image of the surgical site. A high definition video camera sends a video image in real time. Prior to the surgery, a pre-operative image is created from MRI, x-ray, ultrasound, or other method of diagnosis using imaging technology. The pre-operative image is stored within the computer. The computer processes the pre-operative image to decipher organs, anatomical geometries, vessels, tissue planes, orientation, and other structures. As the surgeon performs the surgery, the AR controller augments the real time video image with the processed pre-operative image and displays the augmented image on an interface to provide further guidance to the surgeon during the surgical procedure.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
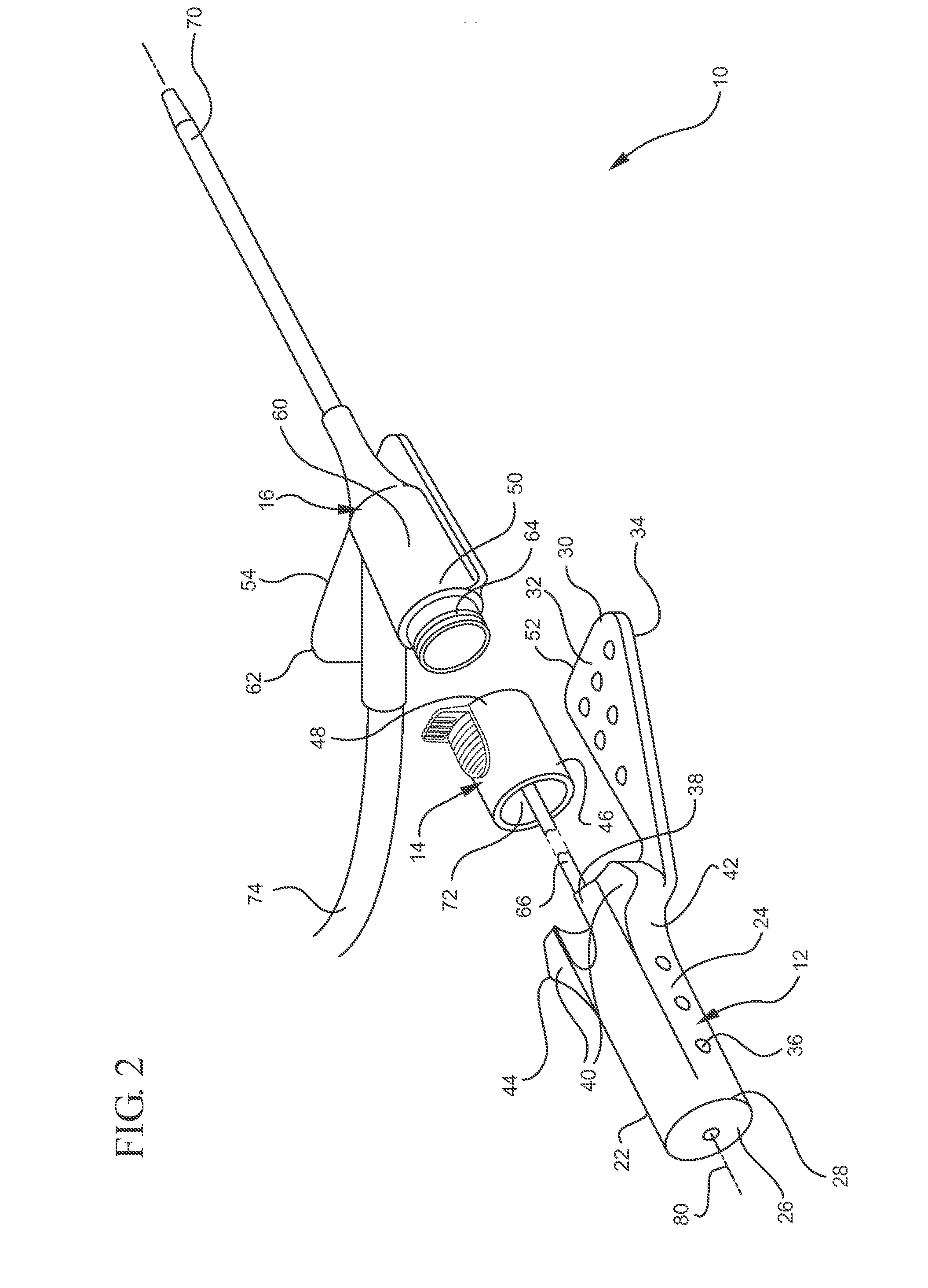
Apparatus and Method for Using Augmented Reality Vision System in Surgical Procedures
ActiveUS20130038707A1Improve eyesightAvoid enteringMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesSurgeryImaging technologySurgical site
A system and method for improving a surgeon's vision by overlaying augmented reality information onto a video image of the surgical site. A high definition video camera sends a video image in real time. Prior to the surgery, a pre-operative image is created from MRI, x-ray, ultrasound, or other method of diagnosis using imaging technology. The pre-operative image is stored within the computer. The computer processes the pre-operative image to decipher organs, anatomical geometries, vessels, tissue planes, orientation, and other structures. As the surgeon performs the surgery, the AR controller augments the real time video image with the processed pre-operative image and displays the augmented image on an interface to provide further guidance to the surgeon during the surgical procedure.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
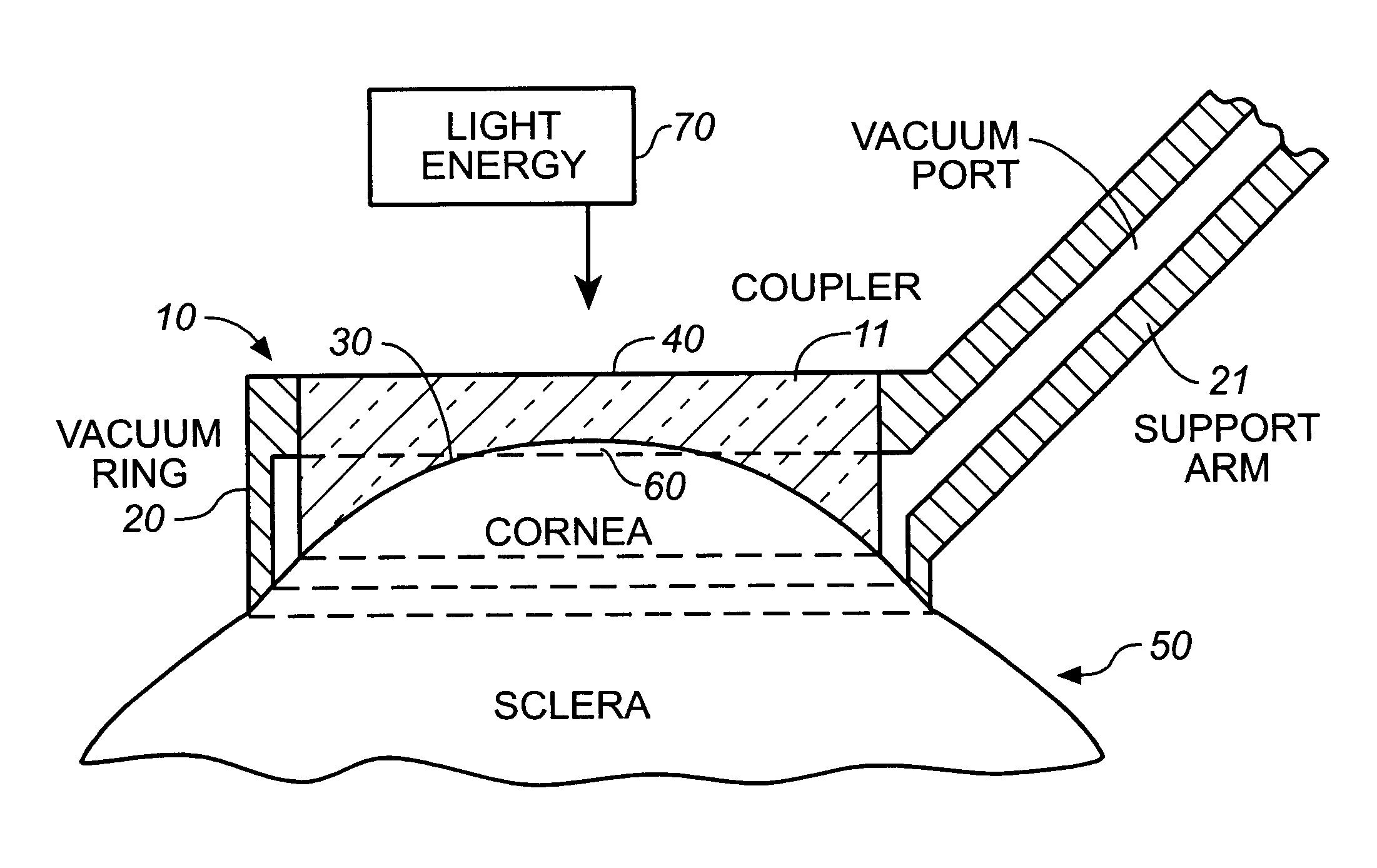
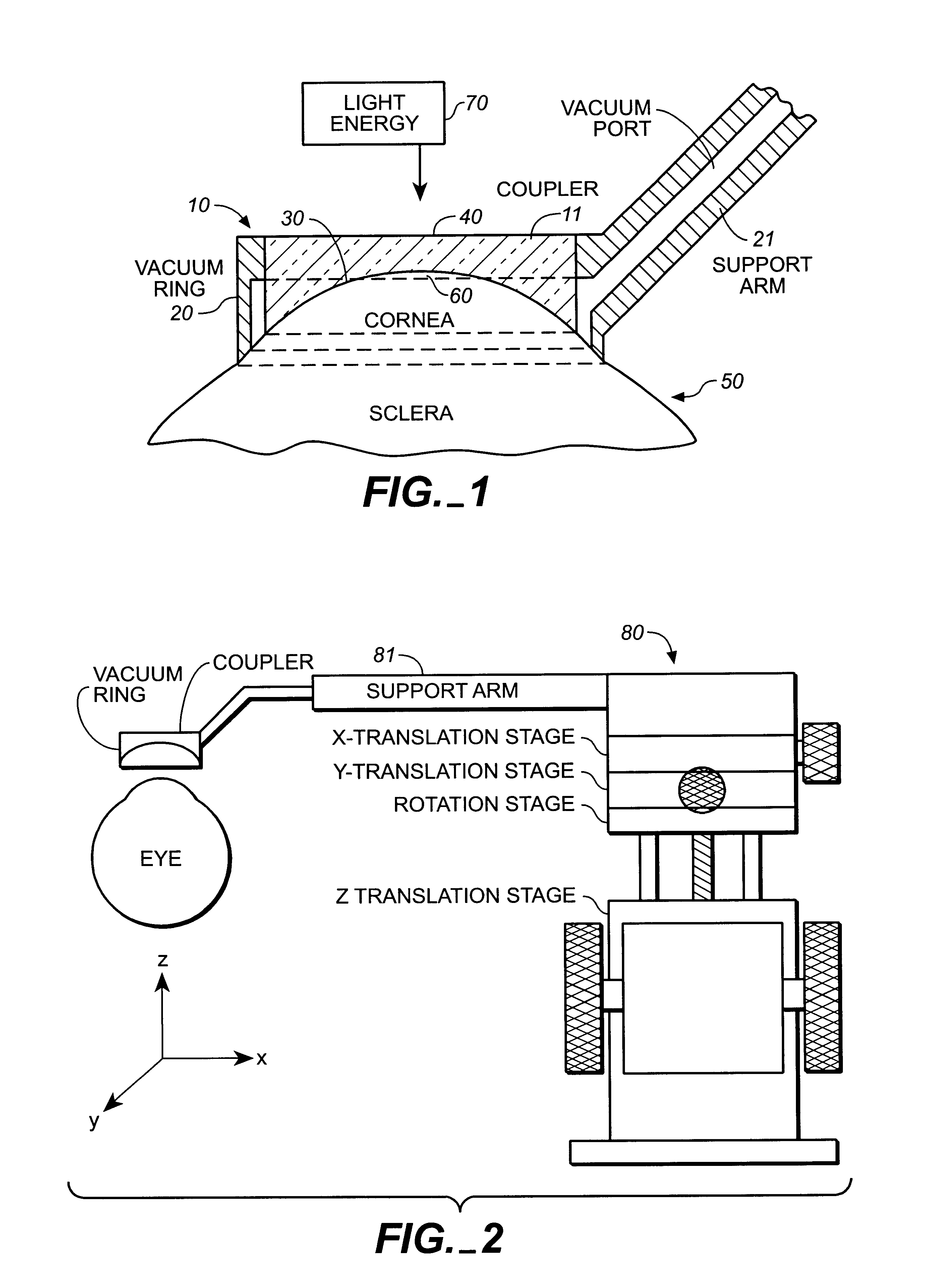
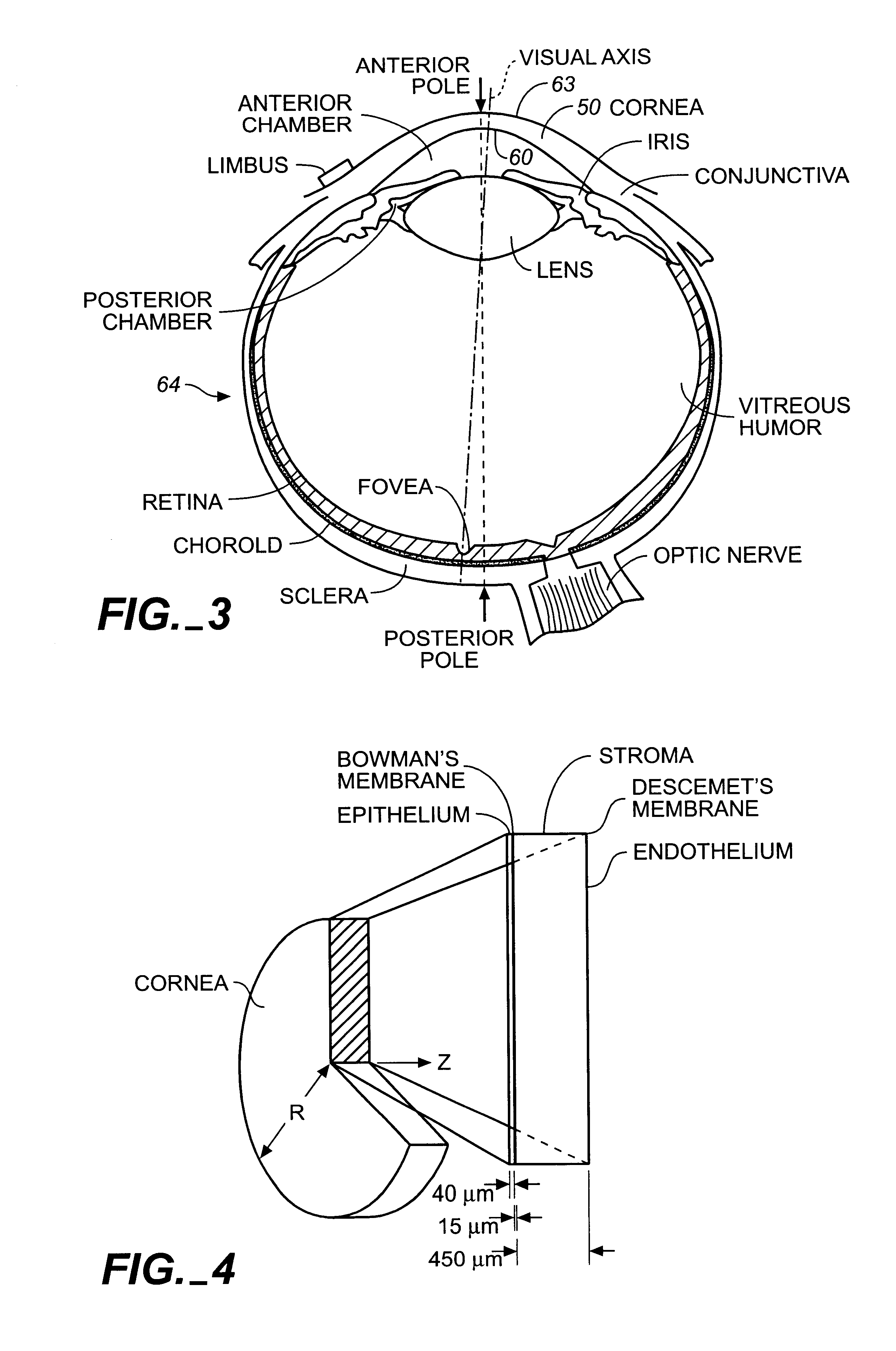
Apparatus for cornea reshaping
InactiveUS6342053B1Prevent accidental contactImprove protectionLaser surgerySurgical instruments for heatingOcular refractionOptical energy
An apparatus is described for use in combination with a noninvasive ophthalmological method for cornea reshaping in order to correct ocular refractive errors such as myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness), and astigmatism. This apparatus is called a coupler and it is made of a material which is substantially transparent to the light energy used to reshape the cornea. The coupler conducts heat from the anterior portion of the cornea during the heating of the stroma by the light energy. The reshaping is enhanced by the coupler as it has a corneal engaging surface with a radius of curvature which approximates the desired emmetropic shape of the cornea. In addition to being a heat sink and template for the eye, the coupler also acts as a positioner and restrainer of the eye by attaching itself to the eye via an annular suction ring. Finally, the coupler also acts as a mask to prevent accidental exposure of the central optic zone to any light energy during the cornea reshaping procedure.
Owner:LASER BIOTECH +1
Ultrasound probe positioning immersion shell
ActiveUS20050101869A1Improve operator visualizationMinimizes formation of air bubbleInfrasonic diagnosticsTomographyClosed chamberRadiology
An ophthalmologic appliance being an ultrasound prob positioning immersion shell for use in ultrasonic measurement of axial length of the eye ophthalmology and other procedures. Support members in an upper chamber and a lower chamber each provides accommodating support along and about a central axis of the ultrasound probe positioning immersion shell and about vertically spaced regions of ultrasound probes to provide for perpendicular alignment of ultrasound probes to the corneal plane. Vents in the chamber structure allow for introduction of fluid medium and for the expelling of air from the chambers to inhibit bubble formation.
Owner:ESI
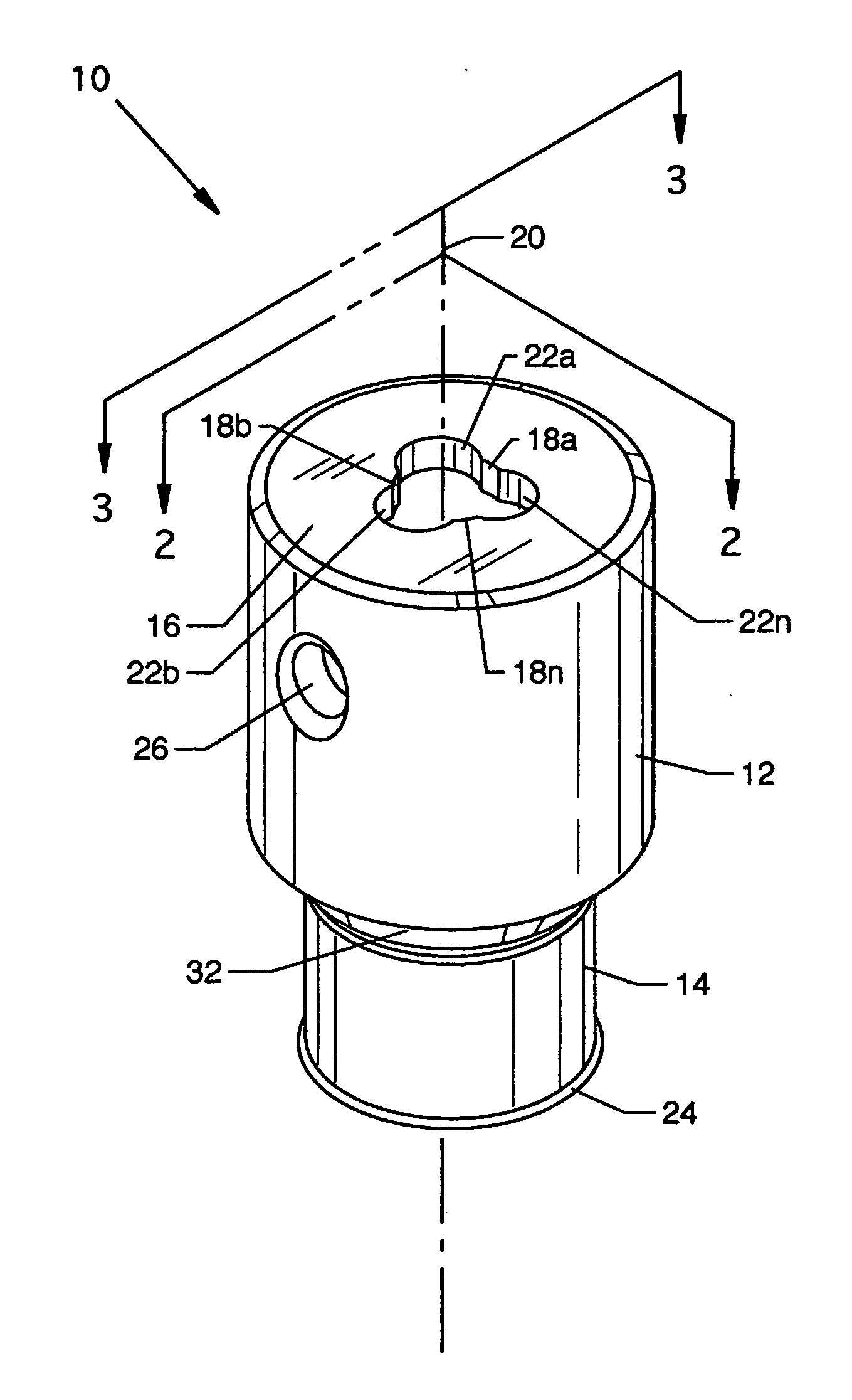
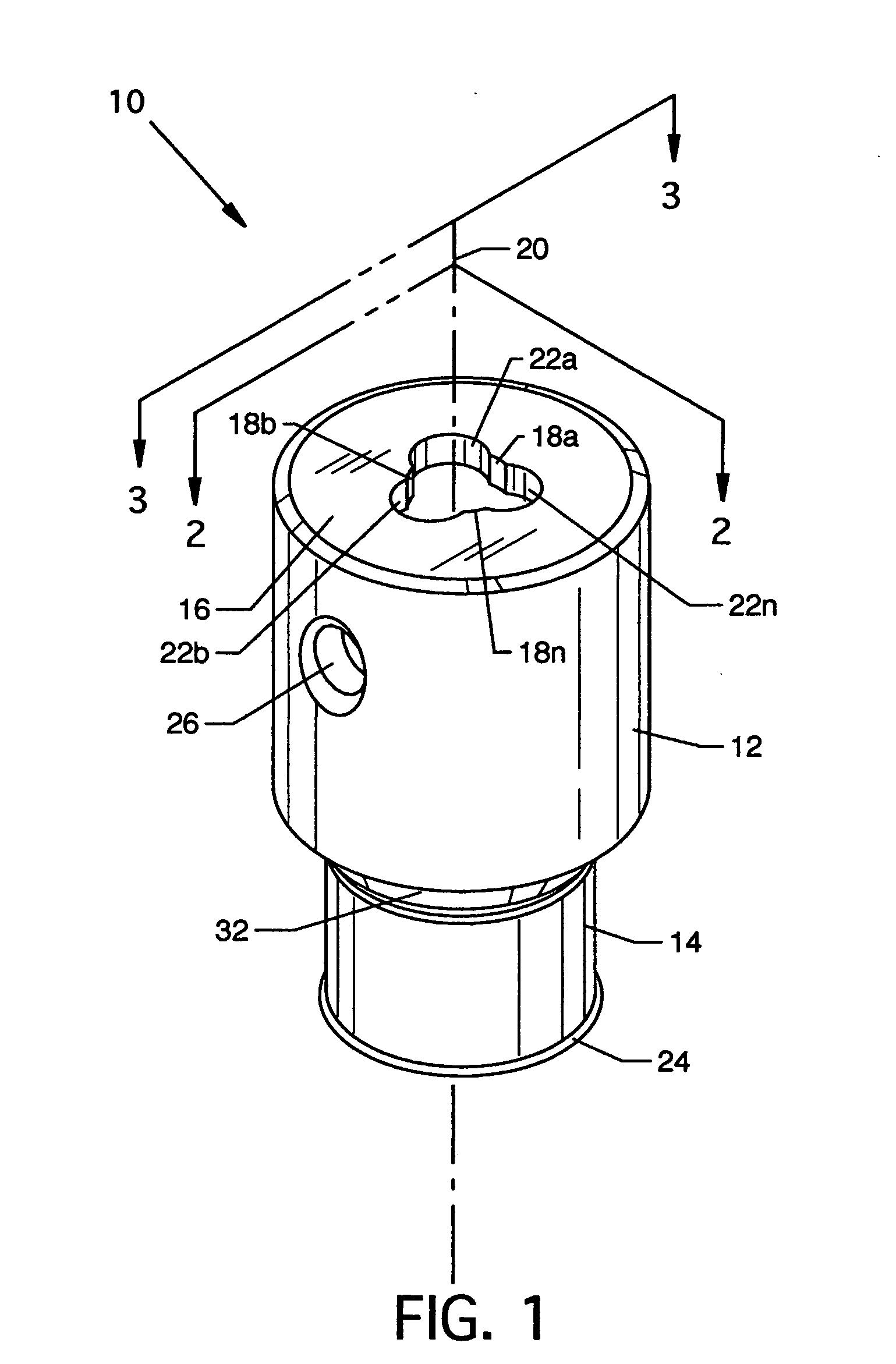
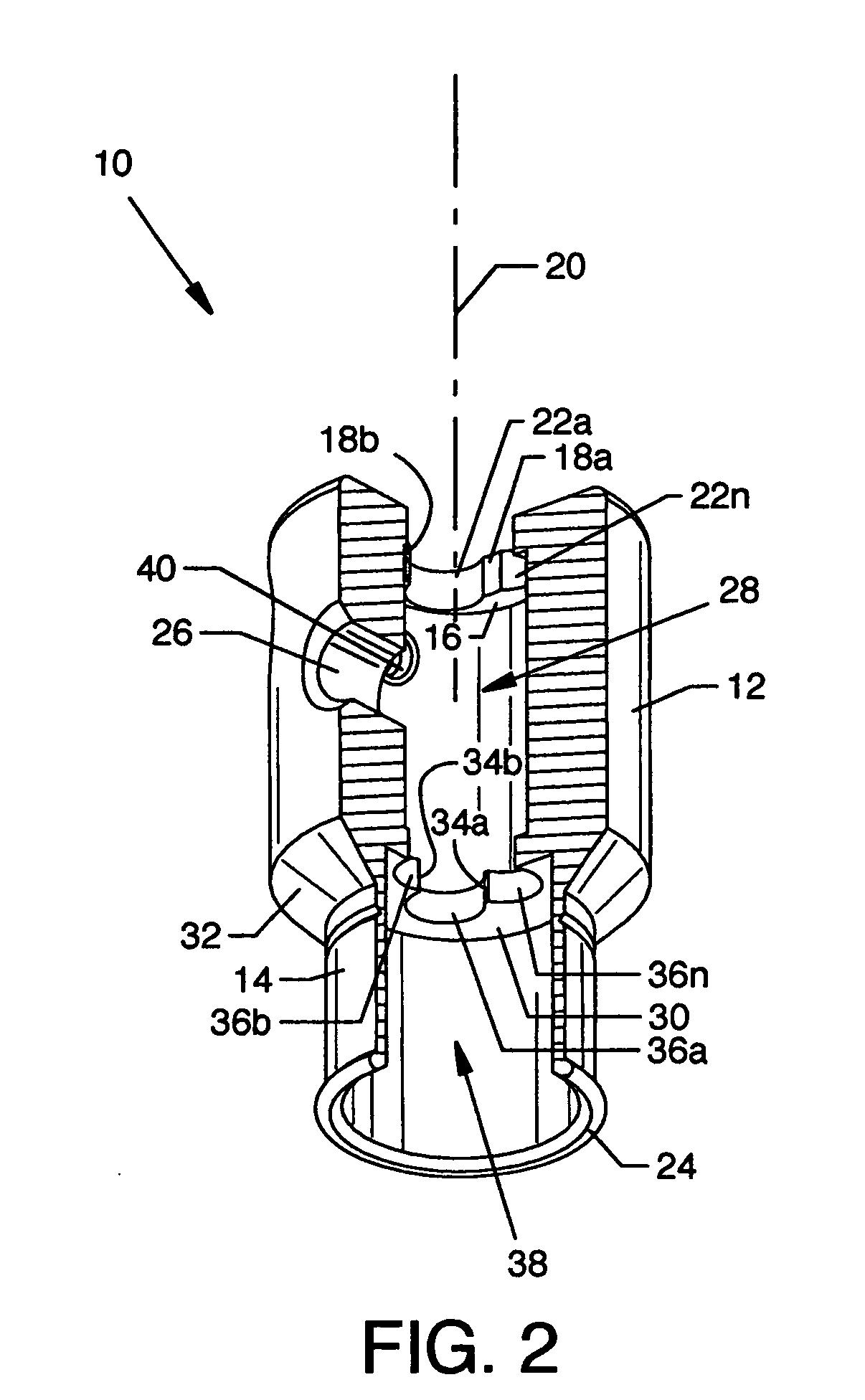
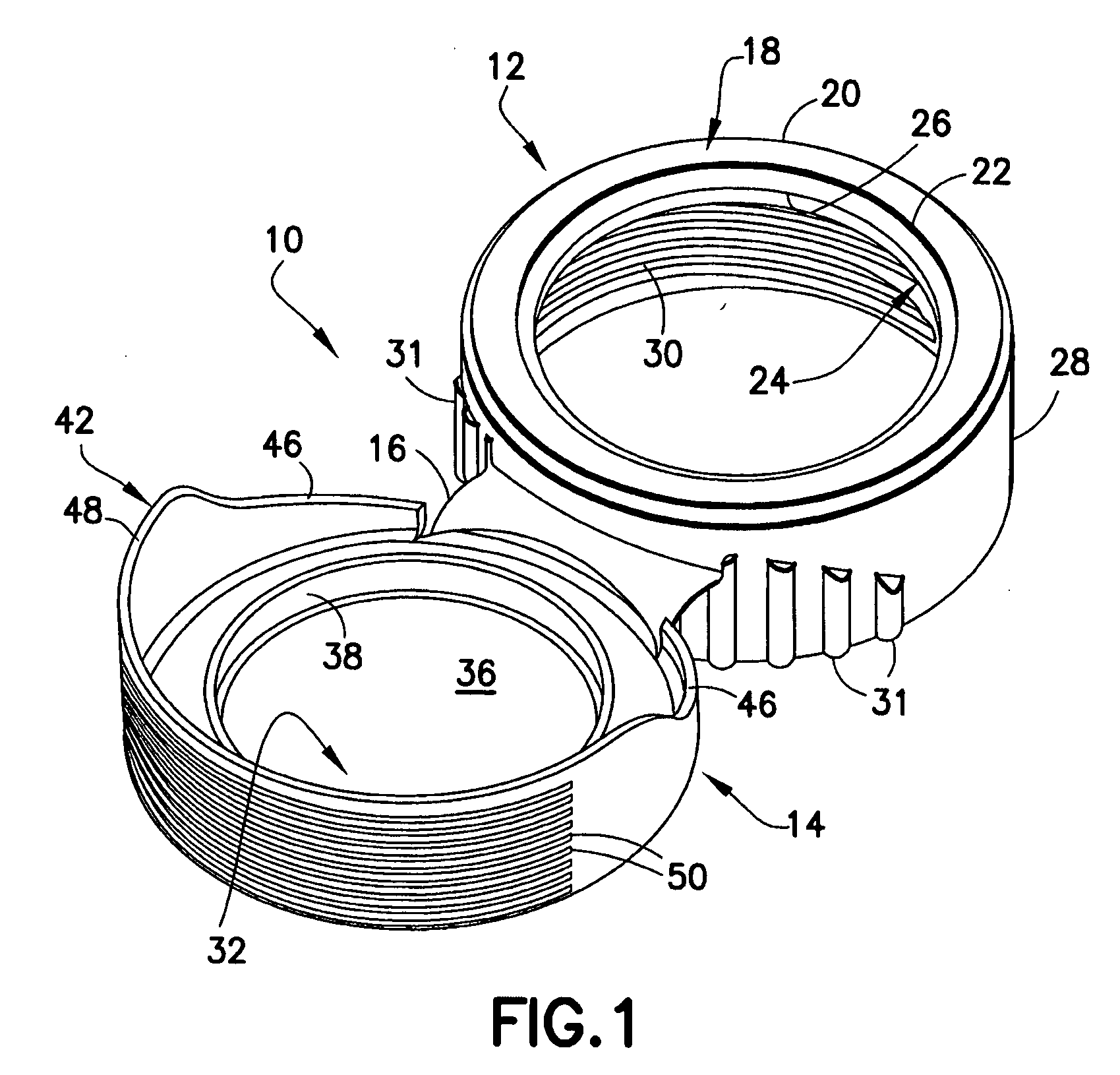
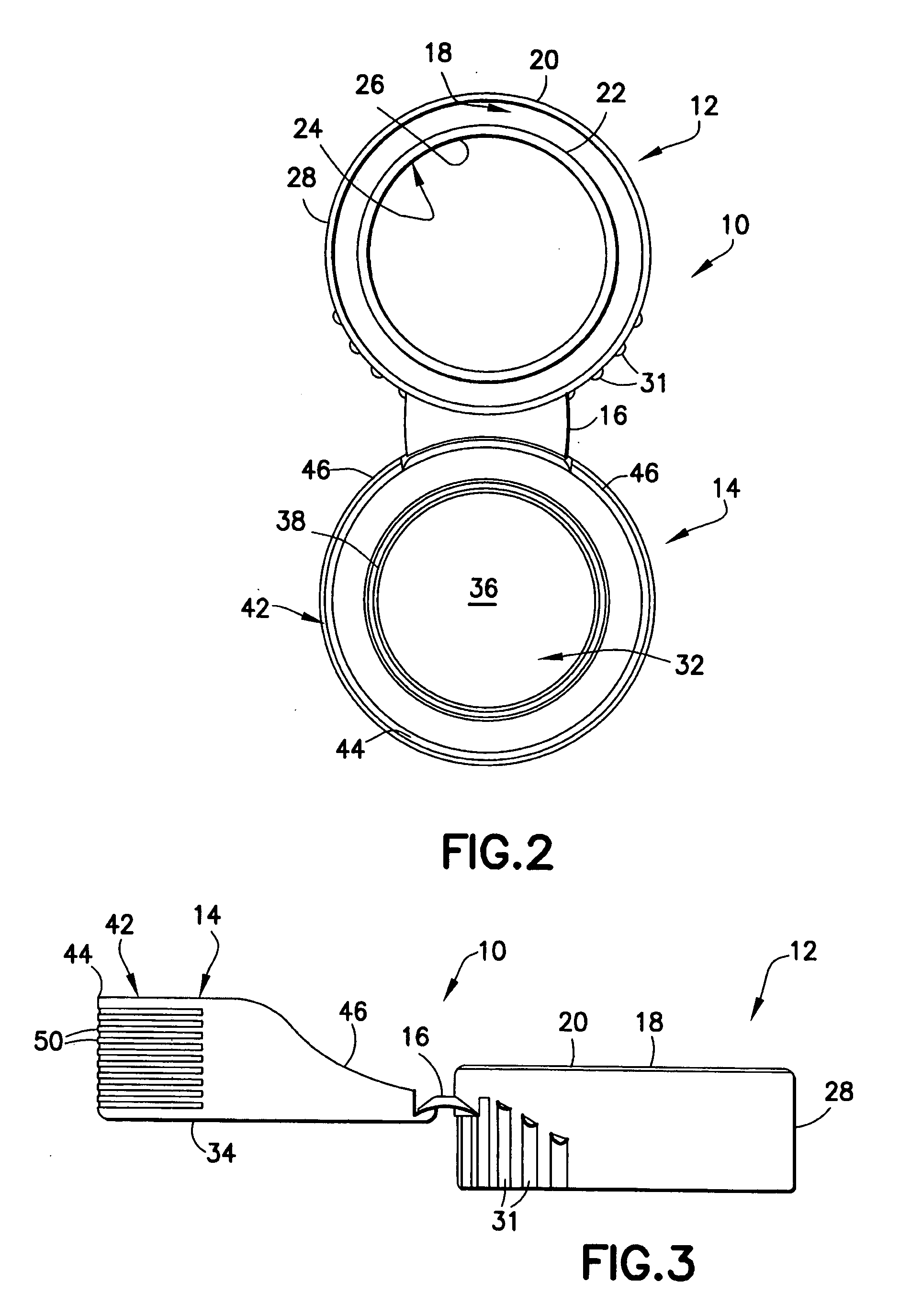
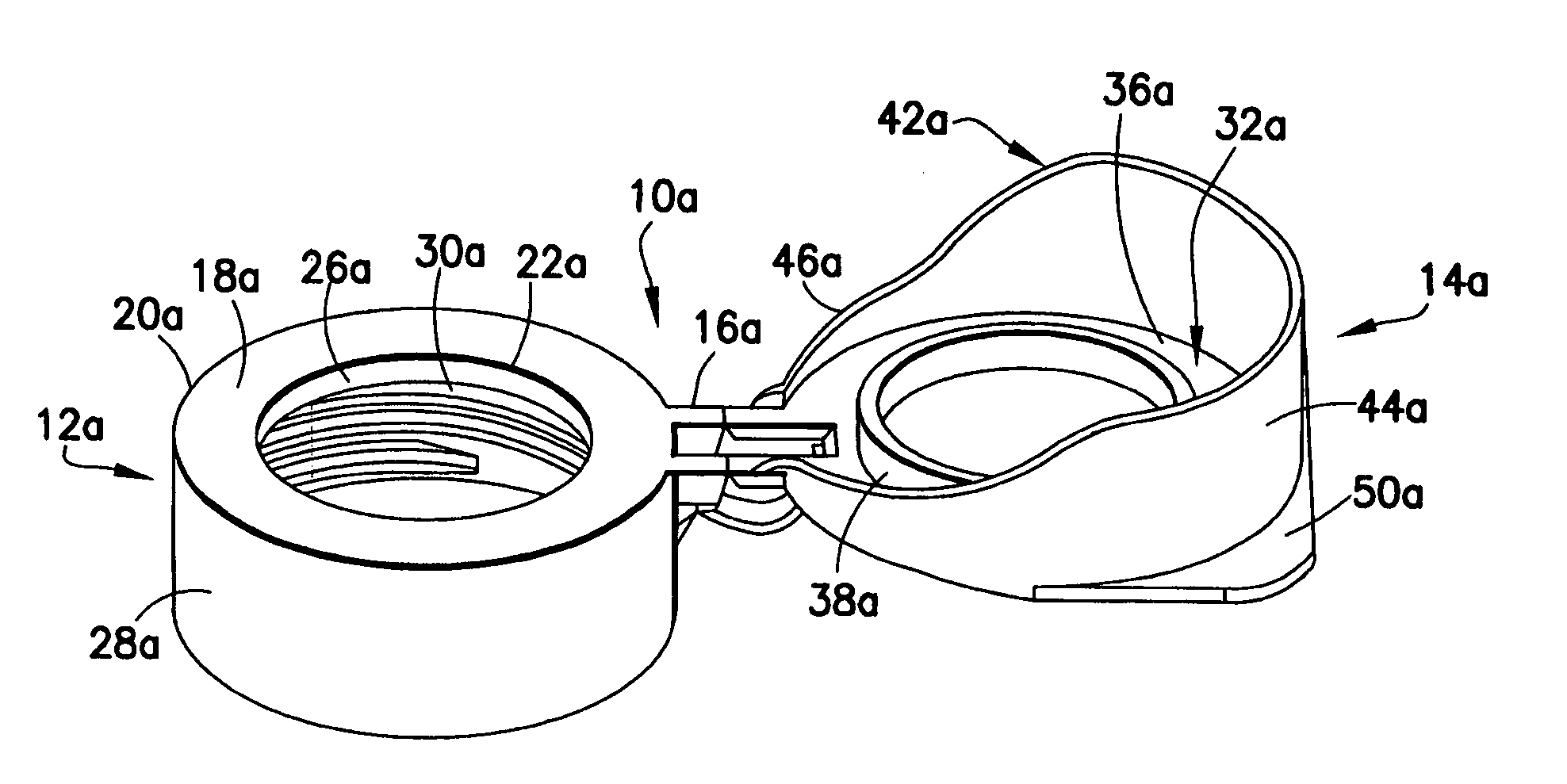
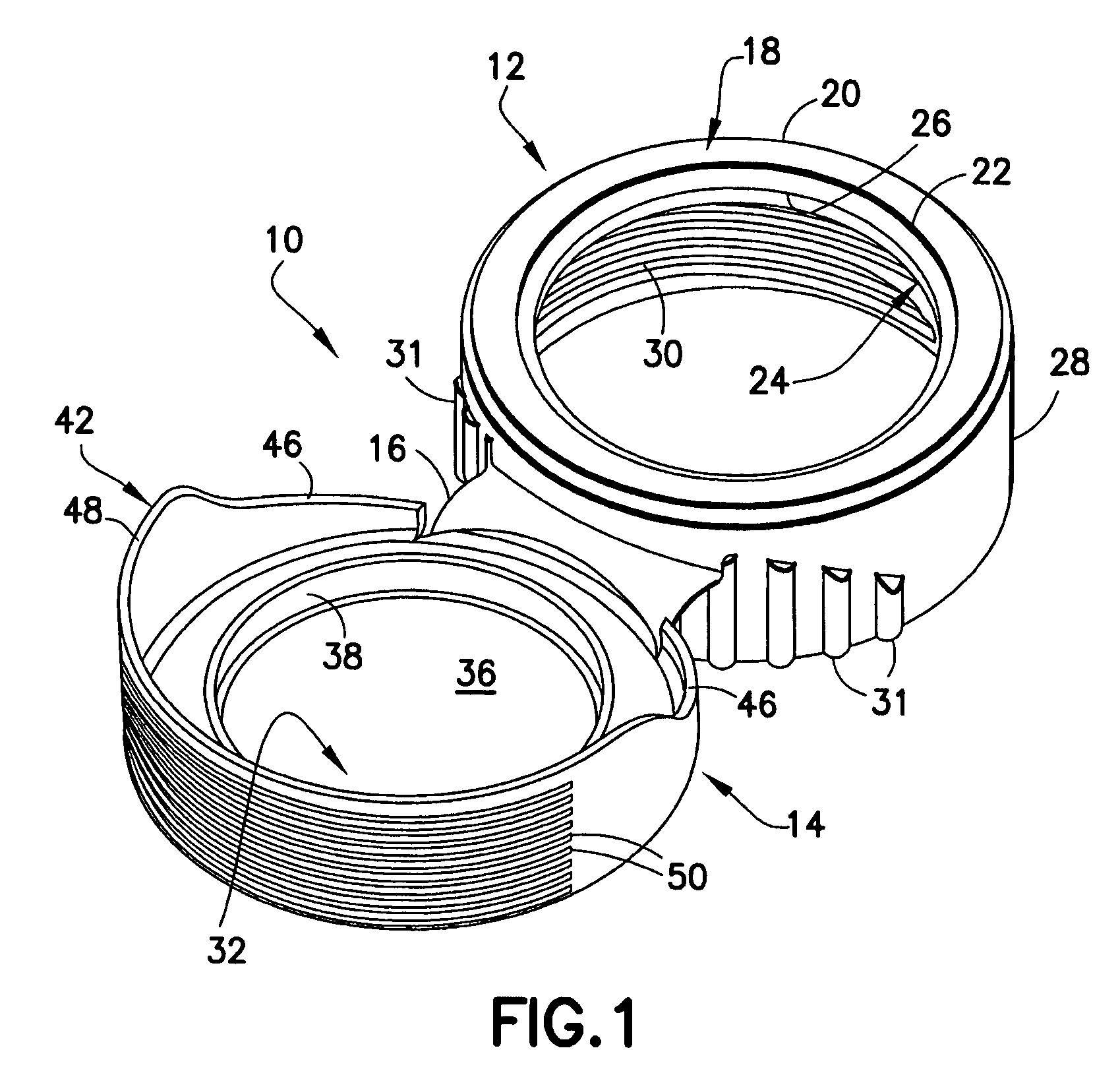
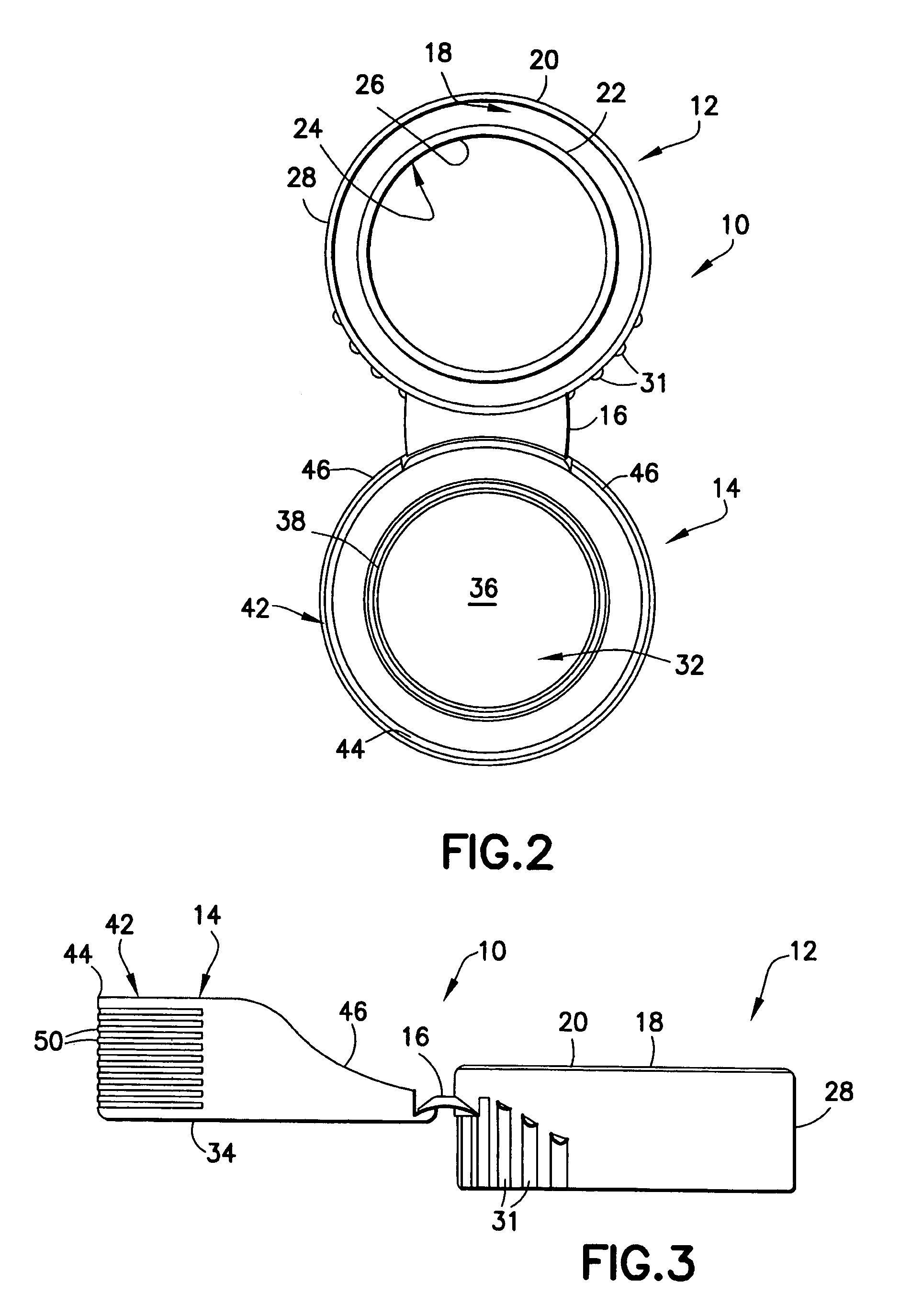
Piercing member protection device
ActiveUS8075550B2Avoid turningIncrease engagementCatheterTube connectorsClassical mechanicsEngineering
Owner:CARMEL PHARMA
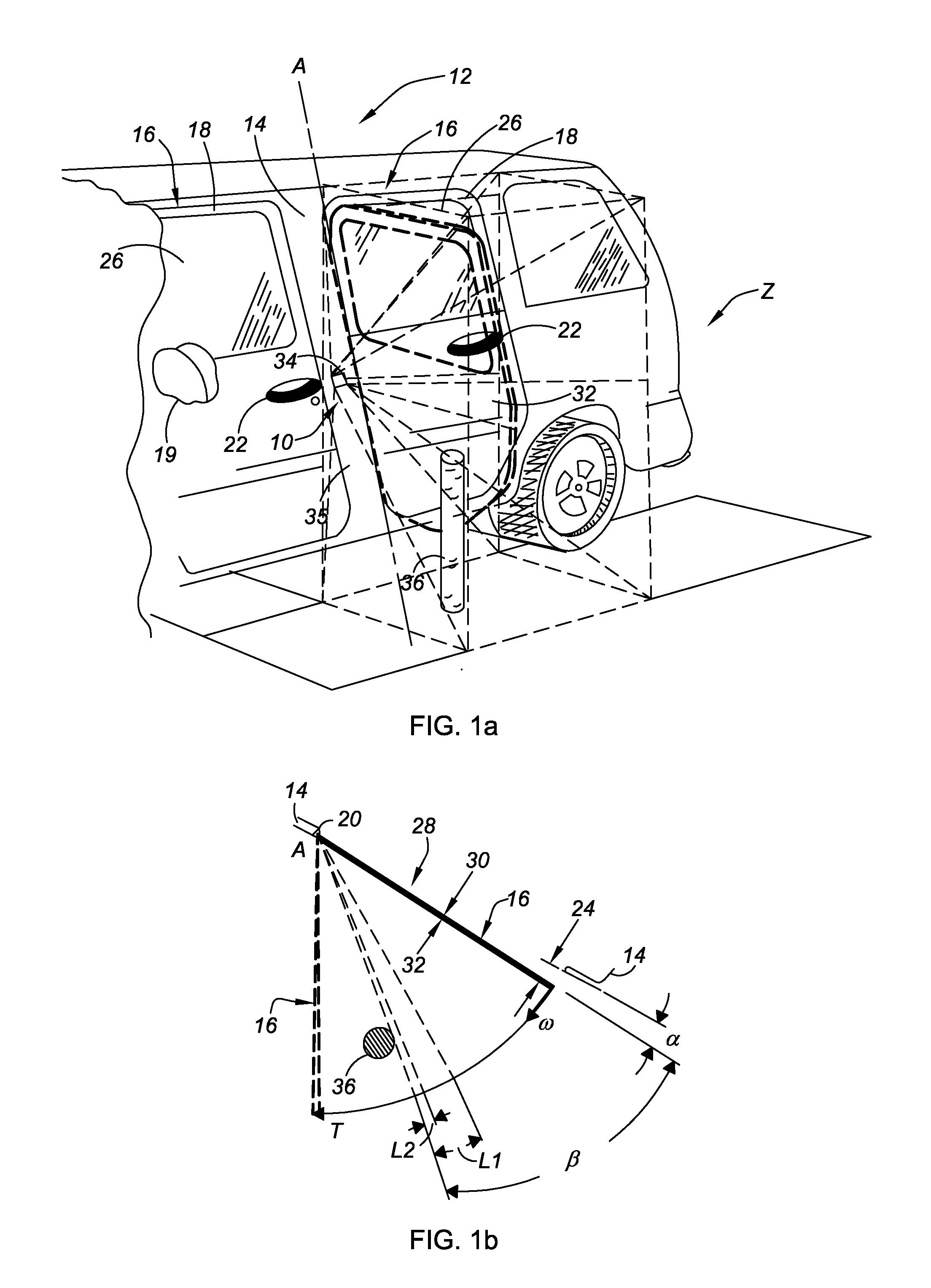
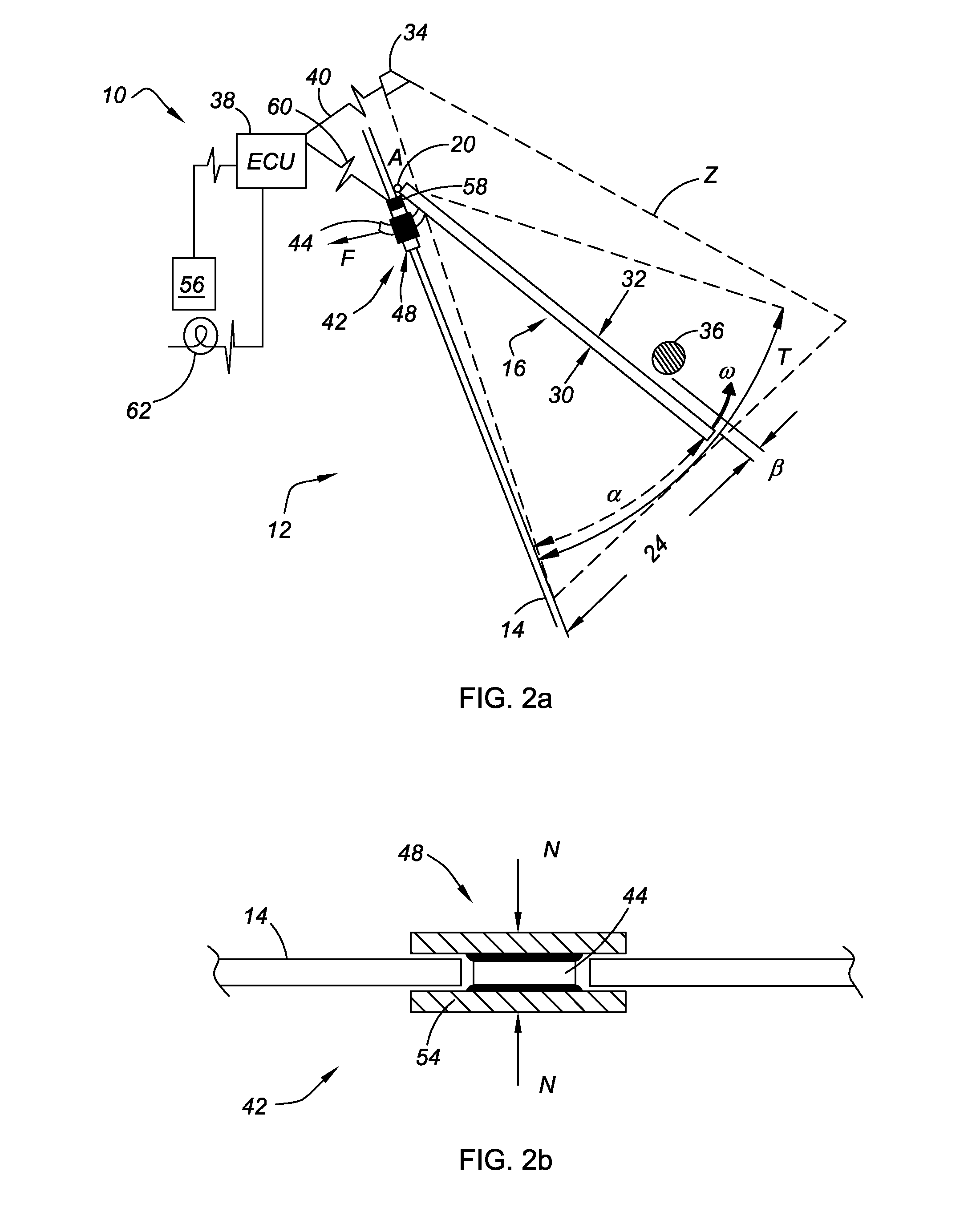
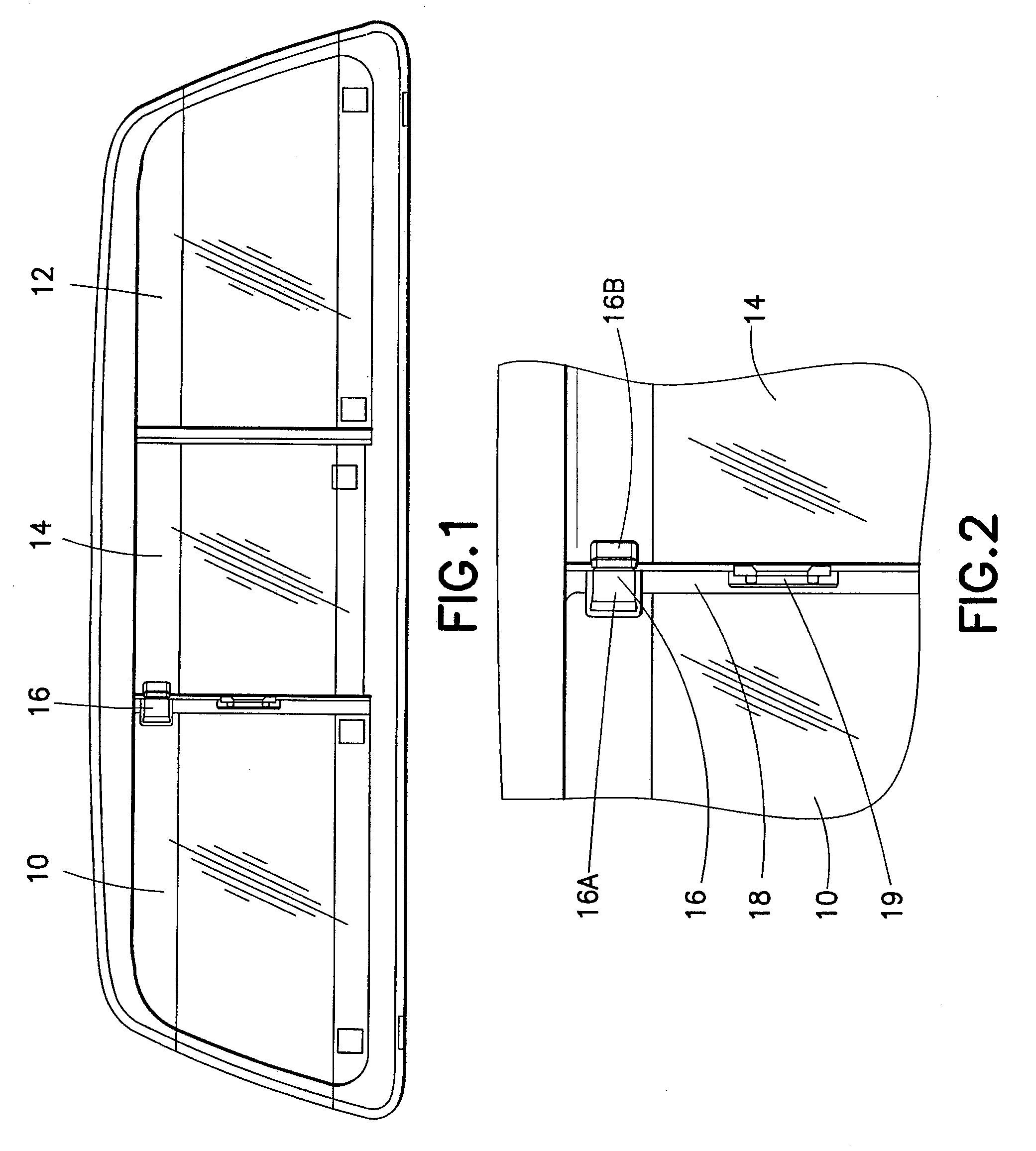
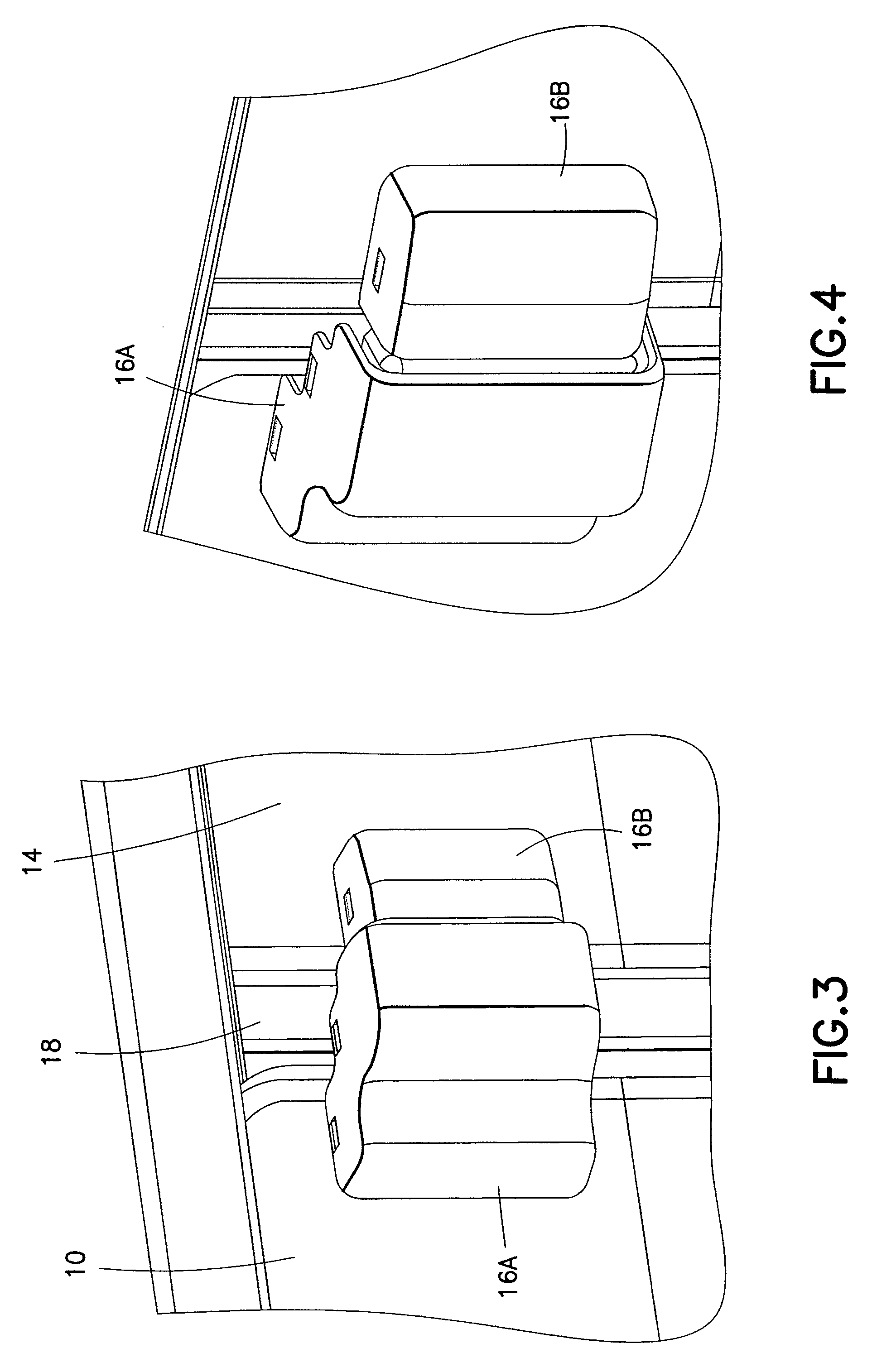
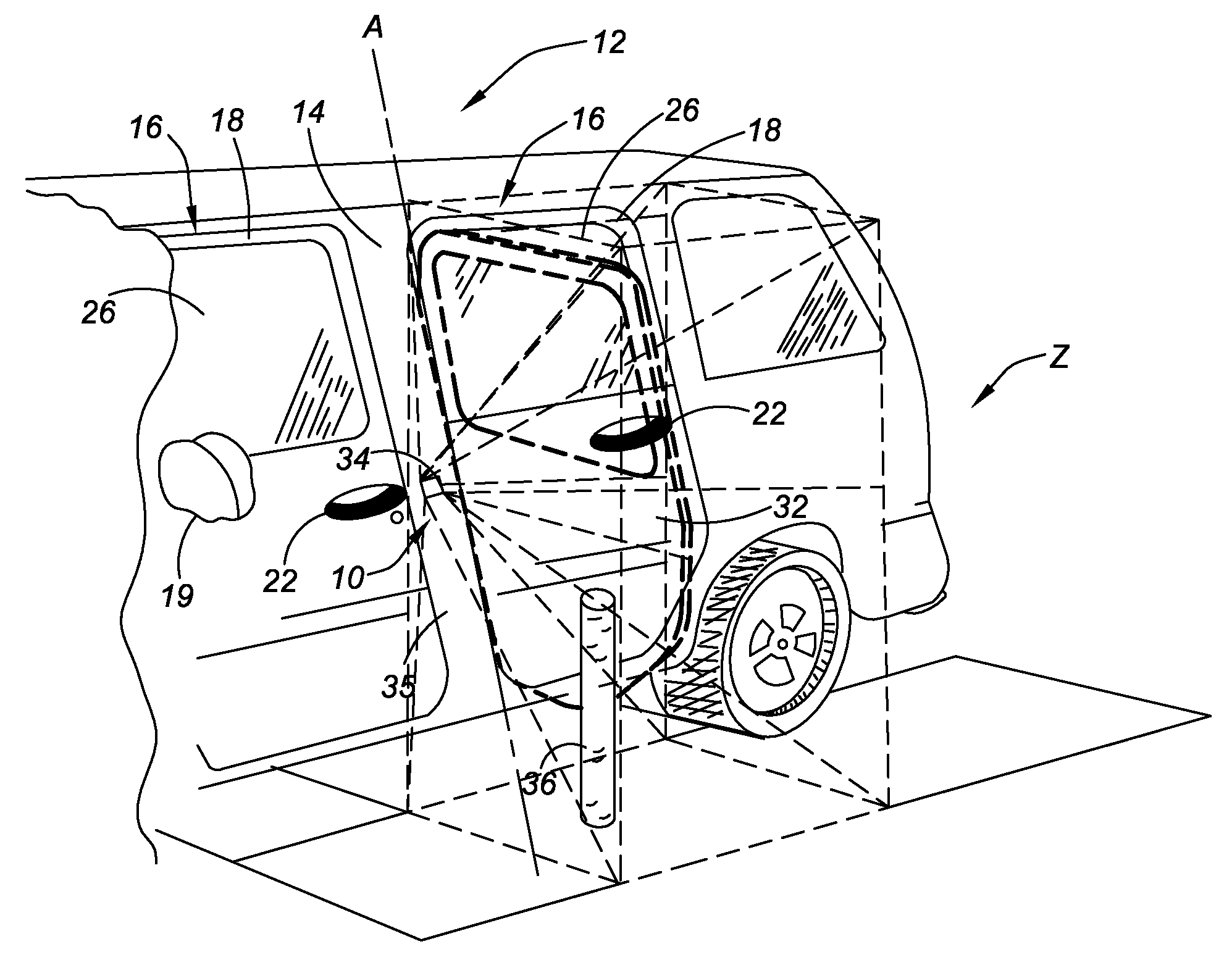
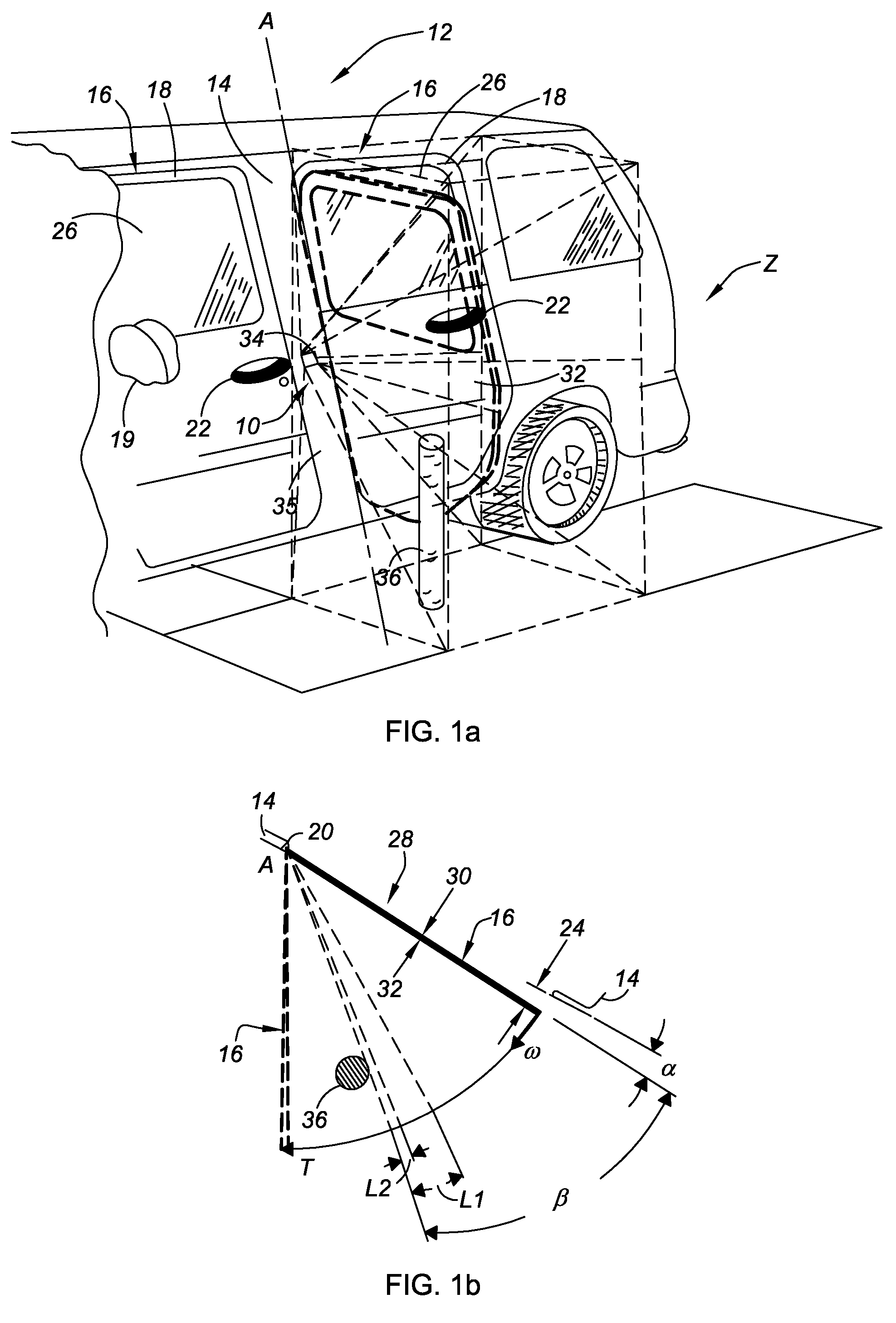
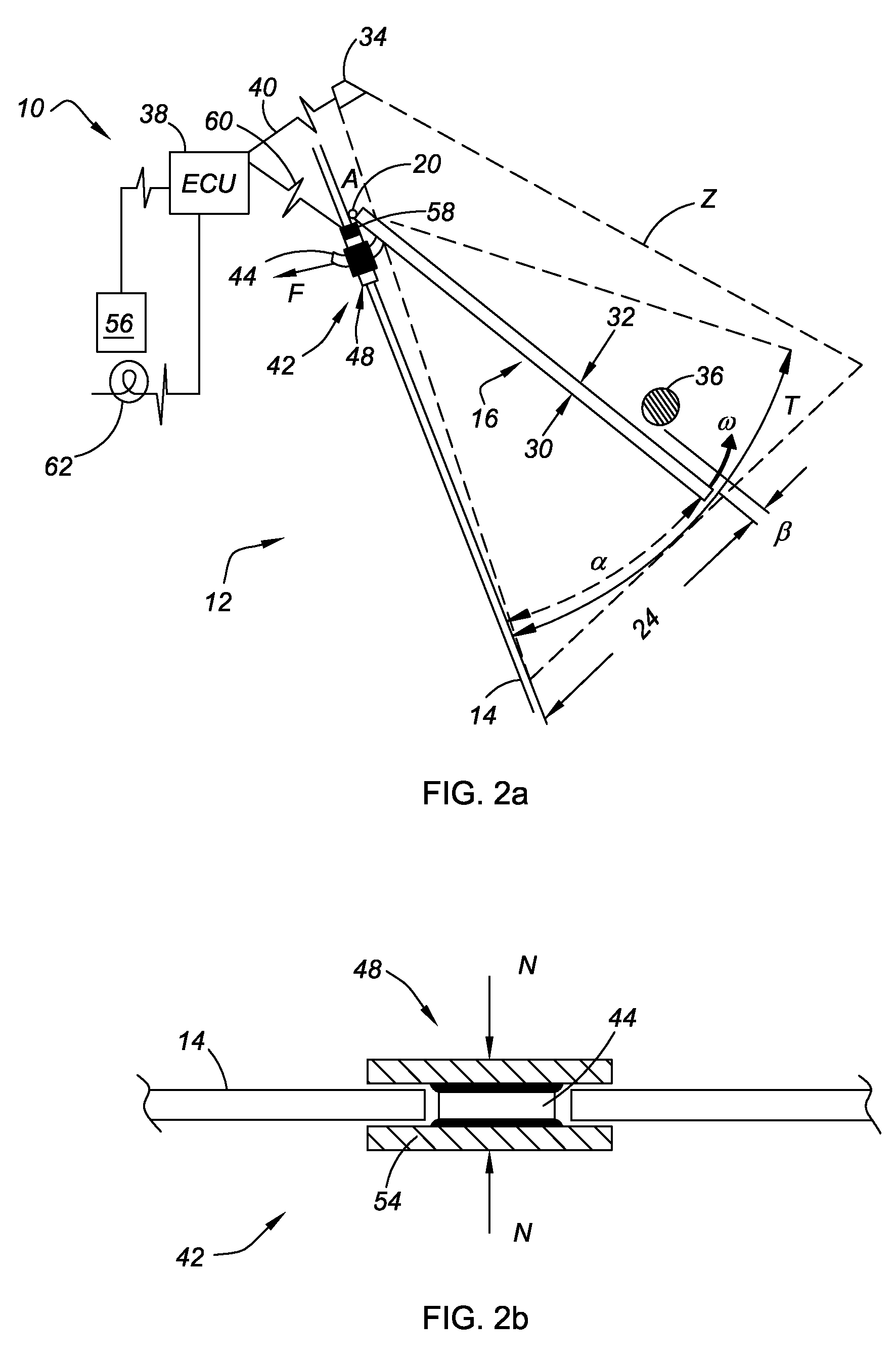
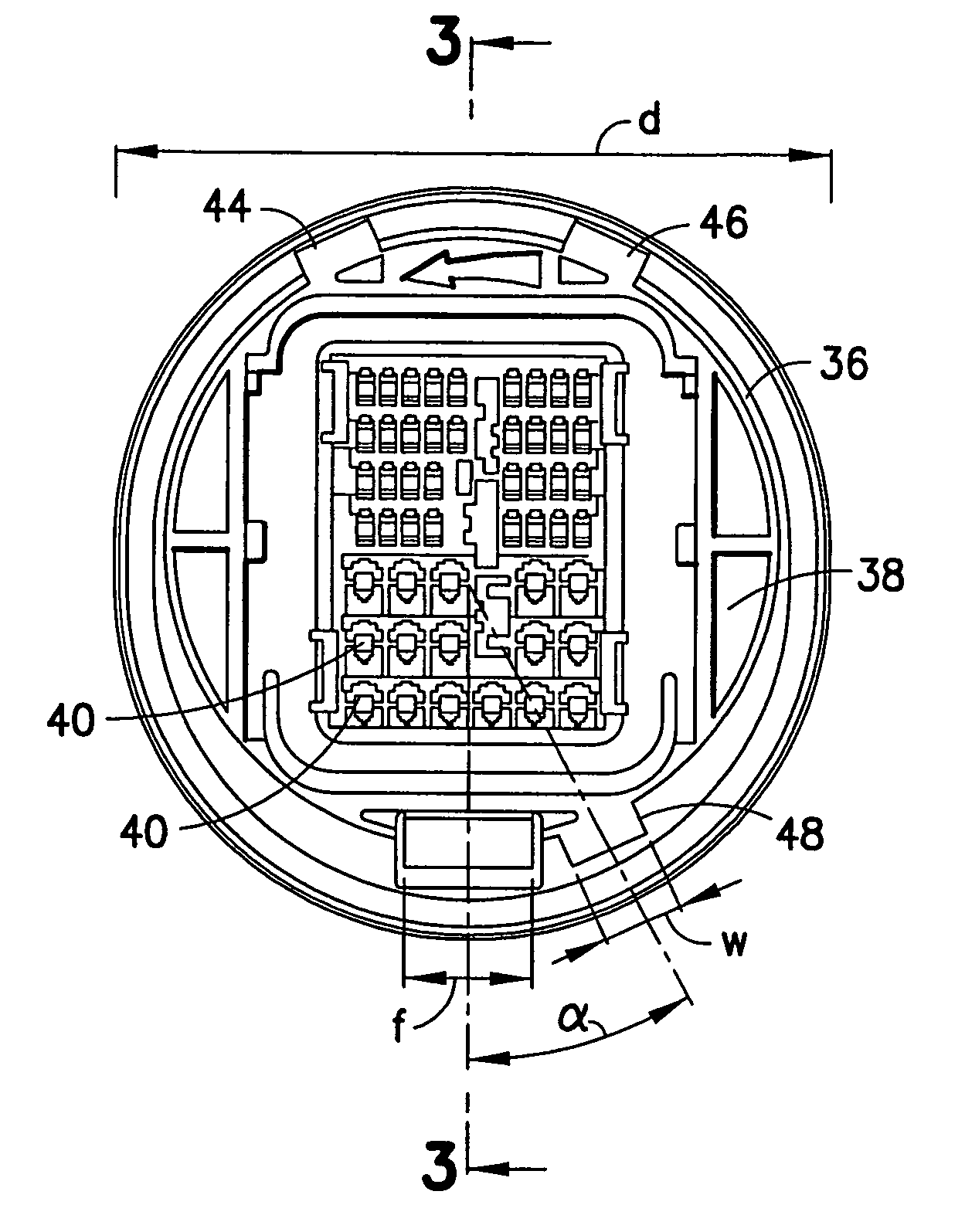
Obstruction Detection Device for Vehicle Door and Method
ActiveUS20080294314A1Avoid contactPrevent accidental contactDigital data processing detailsRoad vehicles traffic controlMobile vehicleActuator
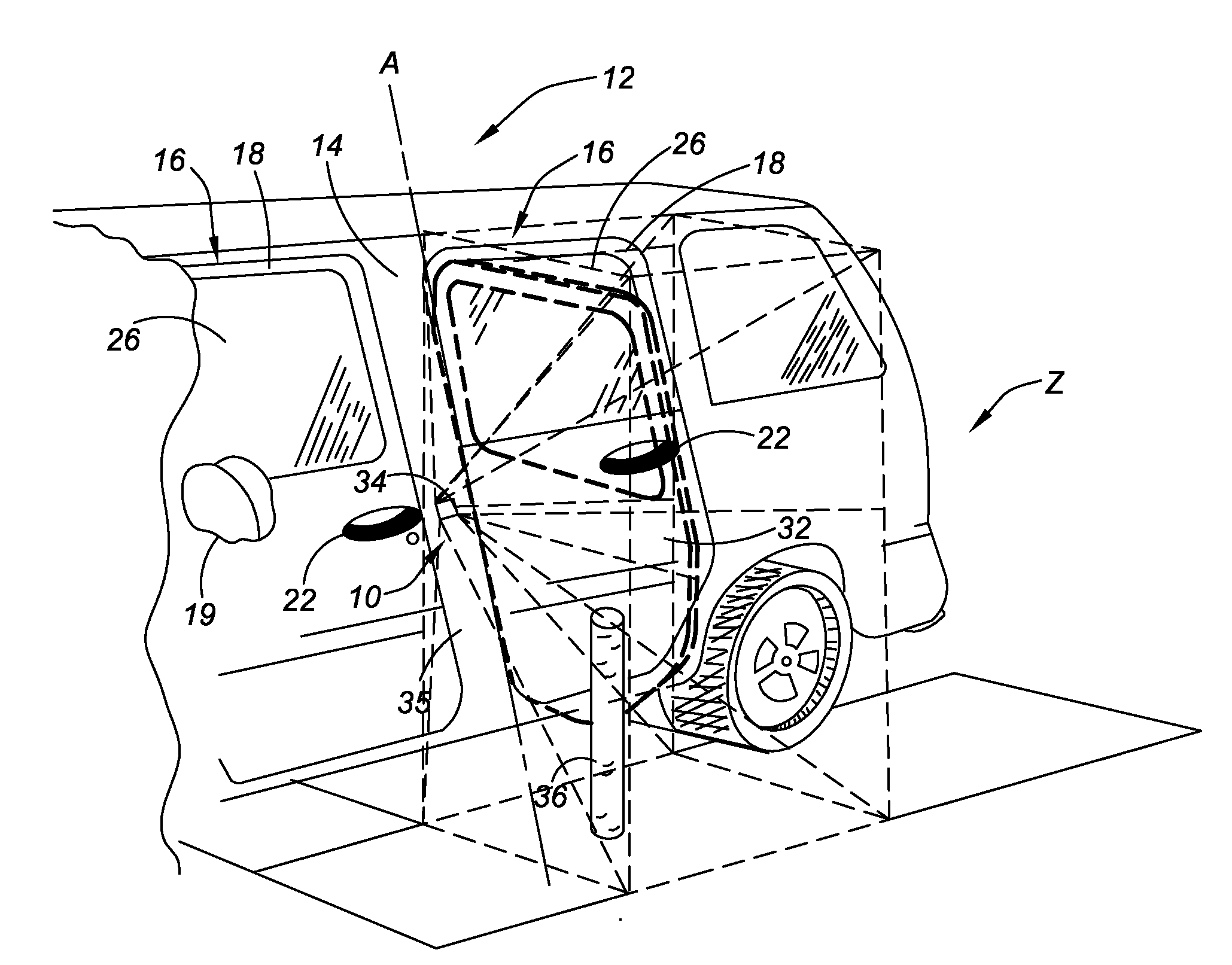
An obstruction detection device for a motor vehicle having a door assembly movably connected to a vehicle body is provided. The device controls the vehicle door's opening angle to prevent inadvertent contact with an object foreign to the vehicle, while providing the largest opening for vehicle ingress and egress. The obstruction detection device includes a controller that is operatively connected to at least one sensor configured to actively monitor and transmit signals to the controller indicative of the presence and corresponding proximity of the object relative to the door assembly. An actuator is operatively connected to and controlled by the controller. The actuator is configured to apply a selectively variable force that restricts the movement of the vehicle door assembly with respect to the vehicle body when the door is a predetermined distance from the object.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
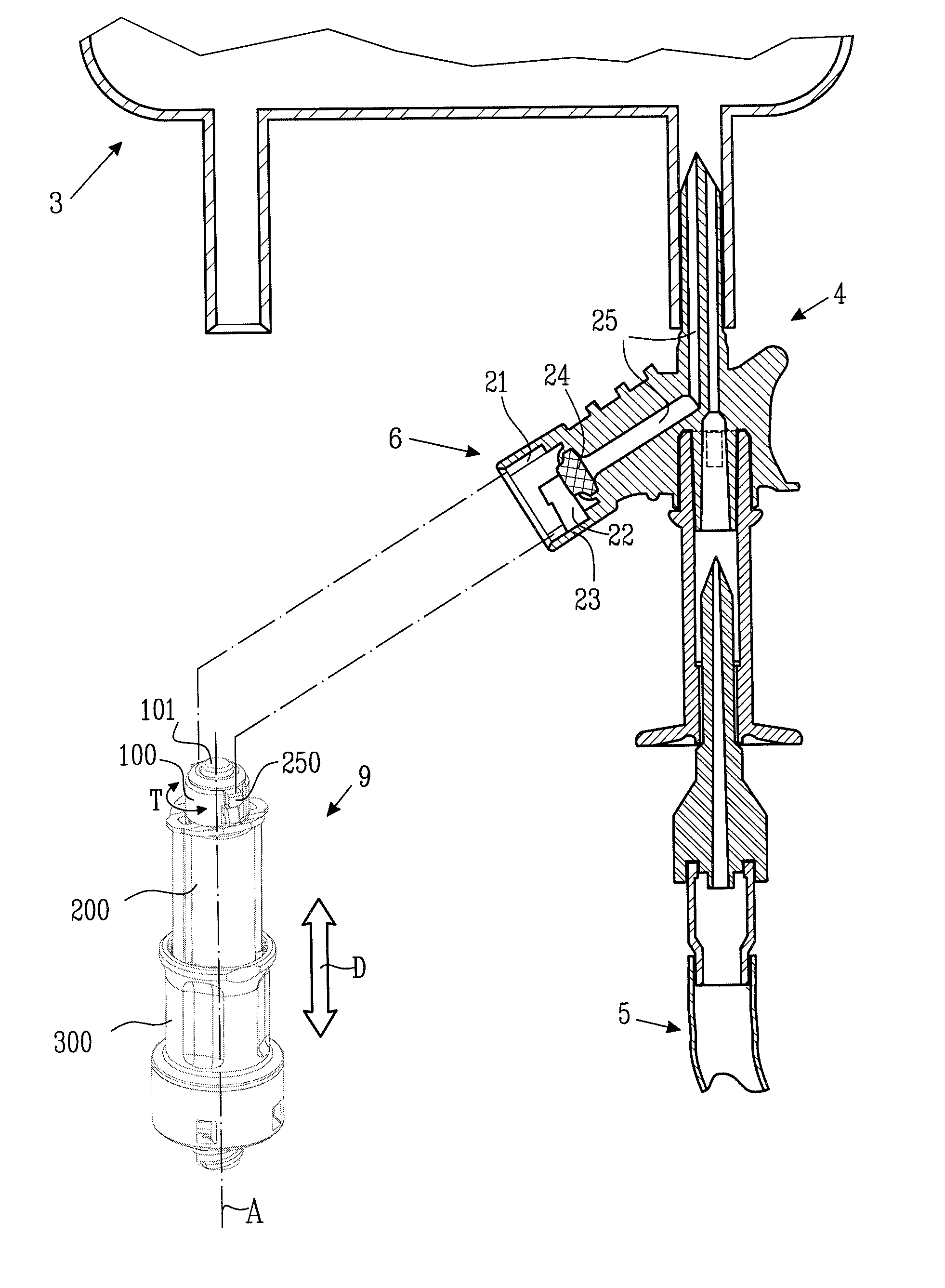
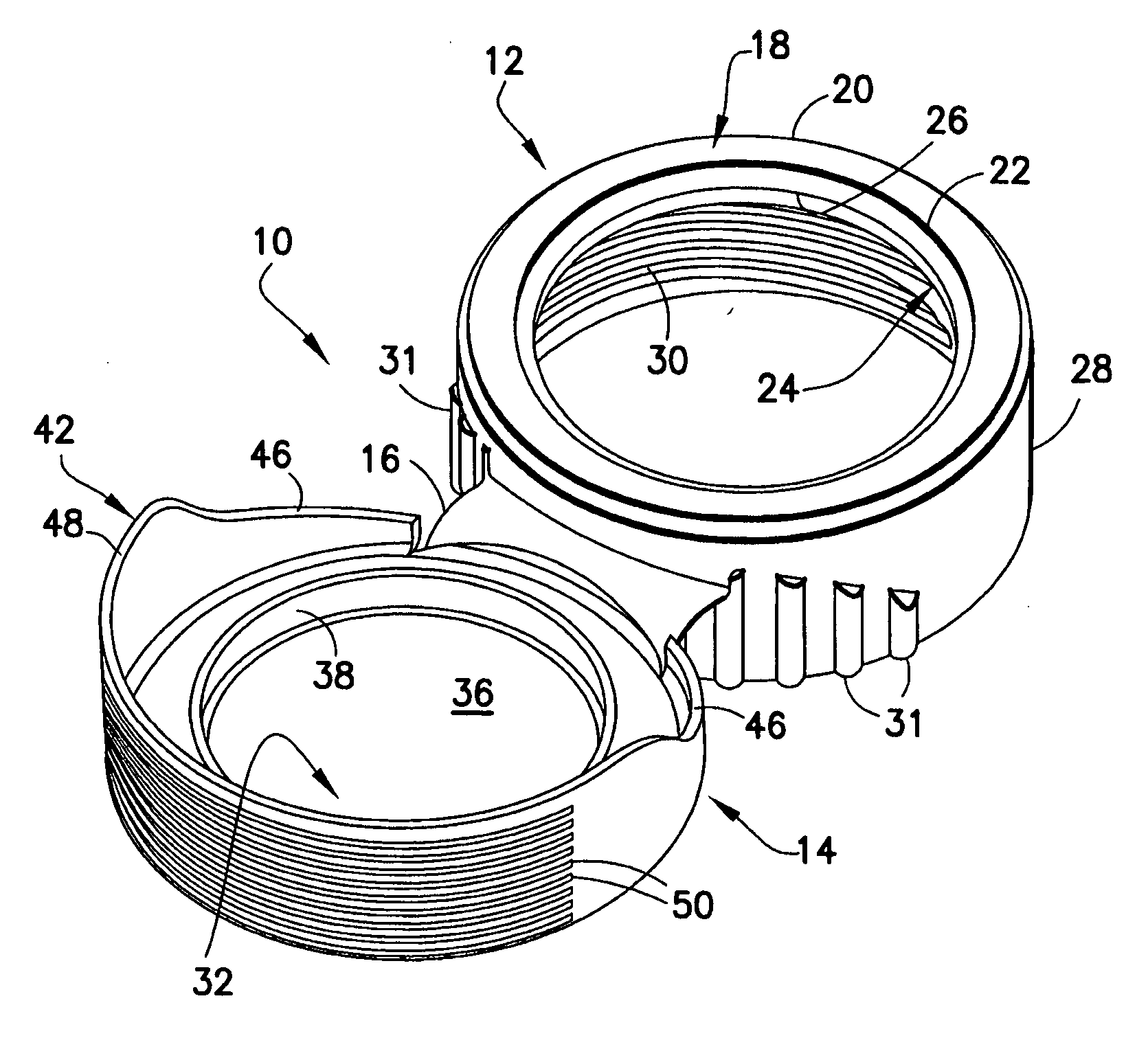
Piercing Member Protection Device
ActiveUS20100004602A1Avoid turningIncrease engagementCatheterTube connectorsMechanical engineeringAccidental exposure
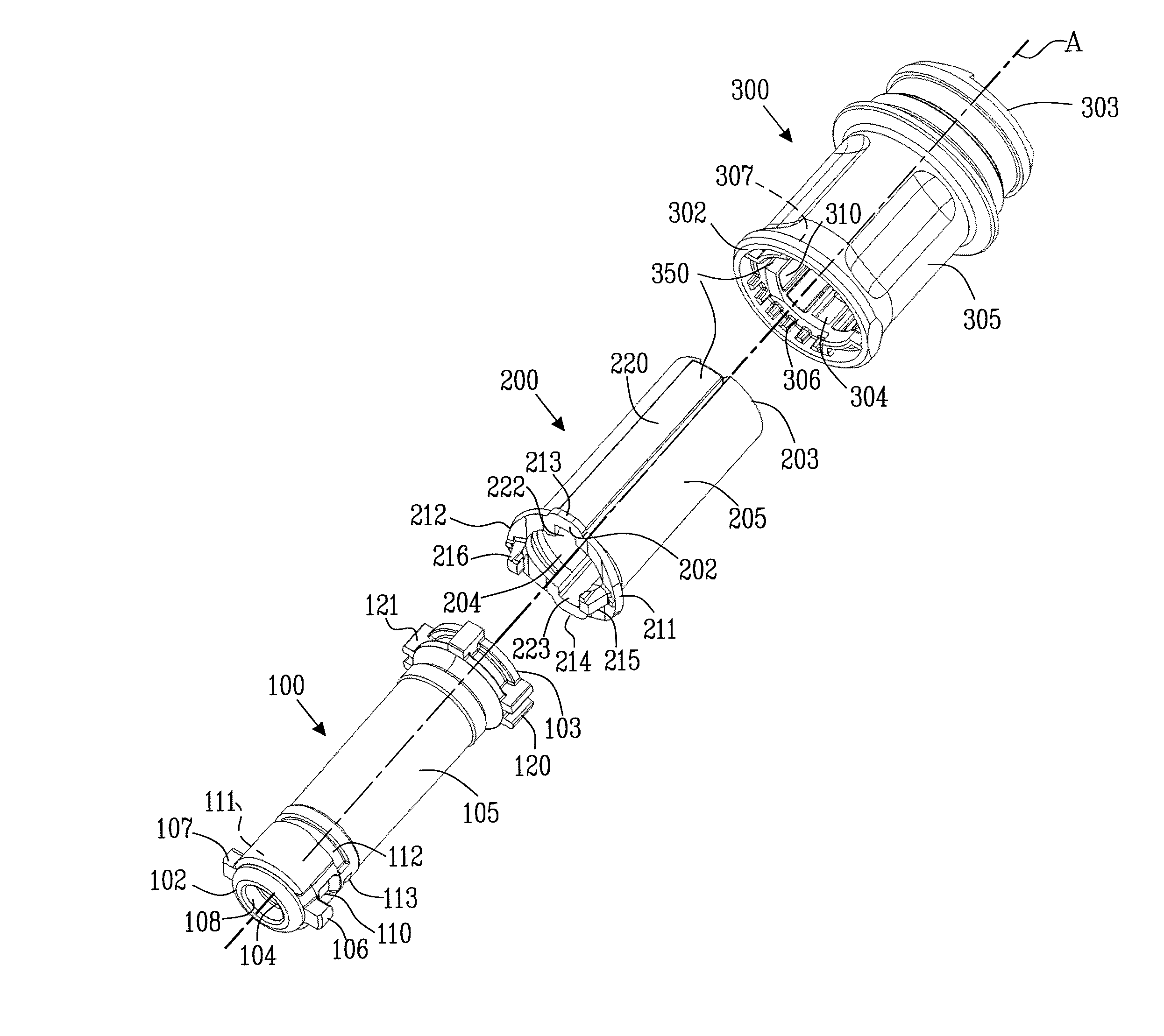
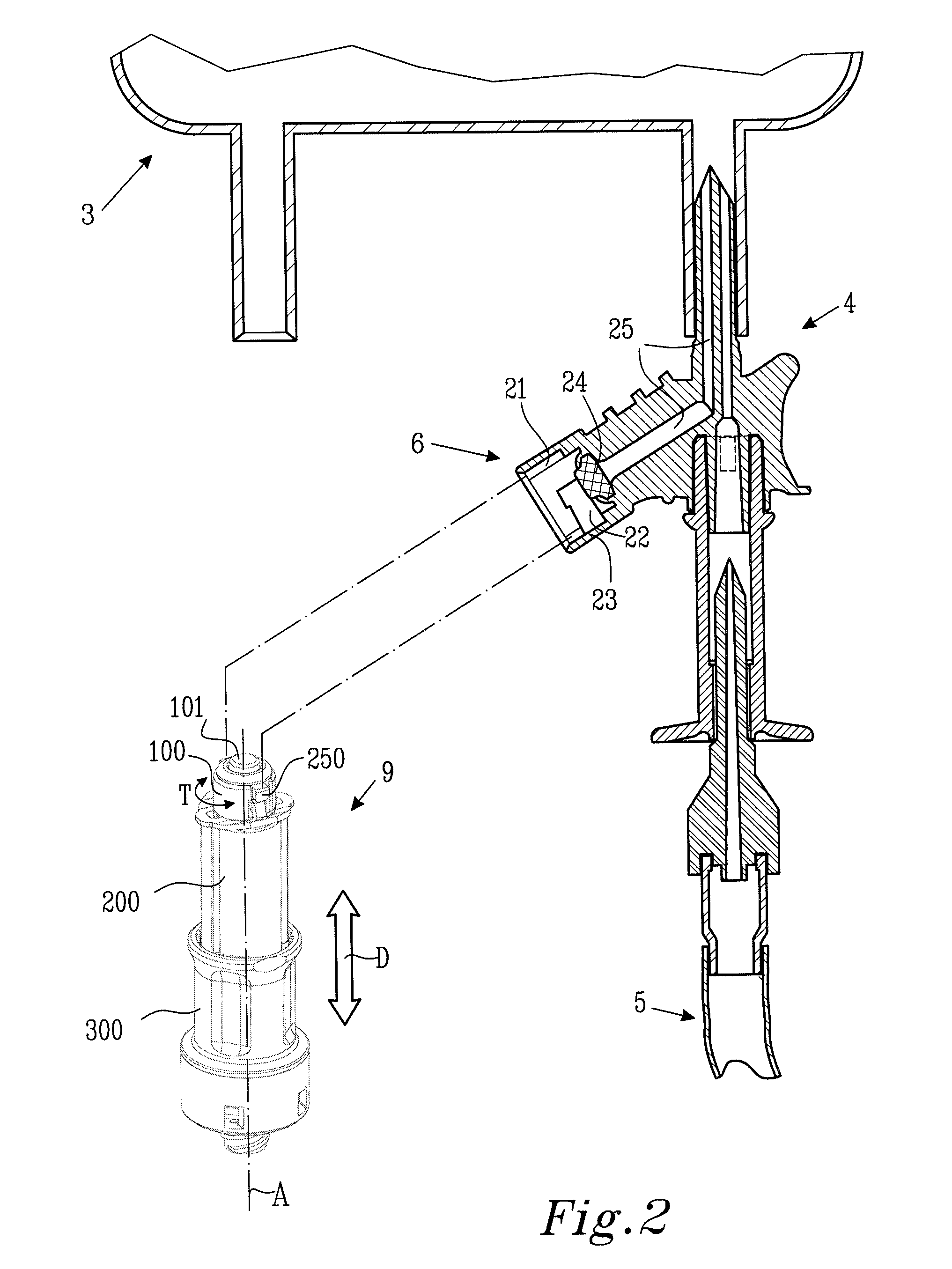
The present invention relates to a piercing member protection device (9) which comprises a first, a second and a third cylindrical member (100, 200, 300). The first cylindrical member (100) is at least partly encompassed by the second cylindrical member (200), and the second cylindrical member (200) is at least partly encompassed by the third cylindrical member (300). The third cylindrical member (300) comprises a piercing member (400) having a piercing tip (401). A first locking arrangement (250) is arranged to enable or prevent the turning of the first and third cylindrical member, with respect to the second cylindrical member, while a second locking arrangement (350) is arranged to enable or prevent movement of the piercing member (400) along the longitudinal centre axis A, so as to expose the piercing tip (401) of the piercing member (400). The piercing member protection device (9) provides a safe device which reduces the risk of accidental exposure of the piercing tip (401) and contamination for a user.
Owner:CARMEL PHARMA
Fluid collection device having tilting retractable needle
InactiveUS7513887B2Prevent accidental contactInfusion syringesSensorsMedical deviceBiomedical engineering
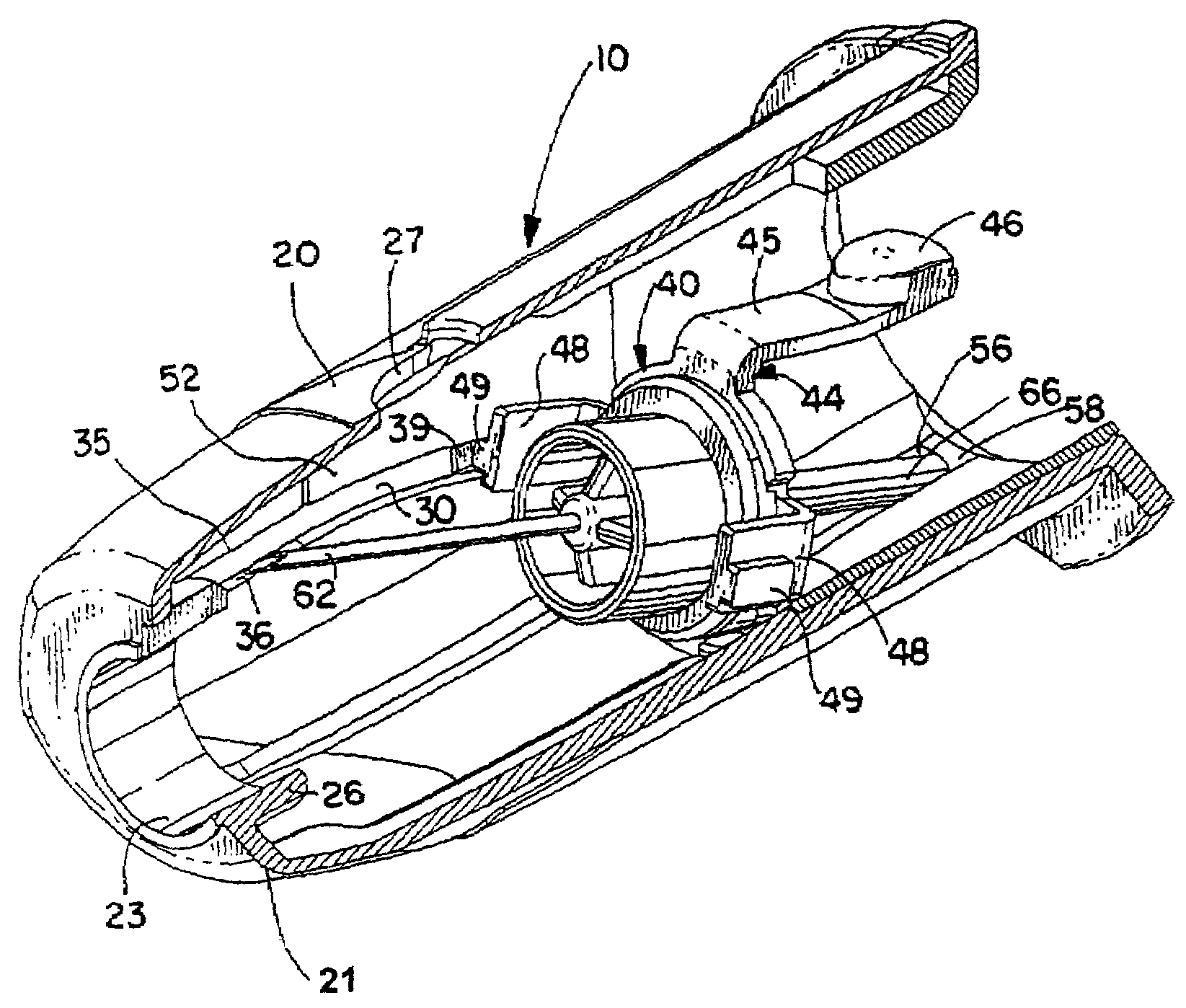
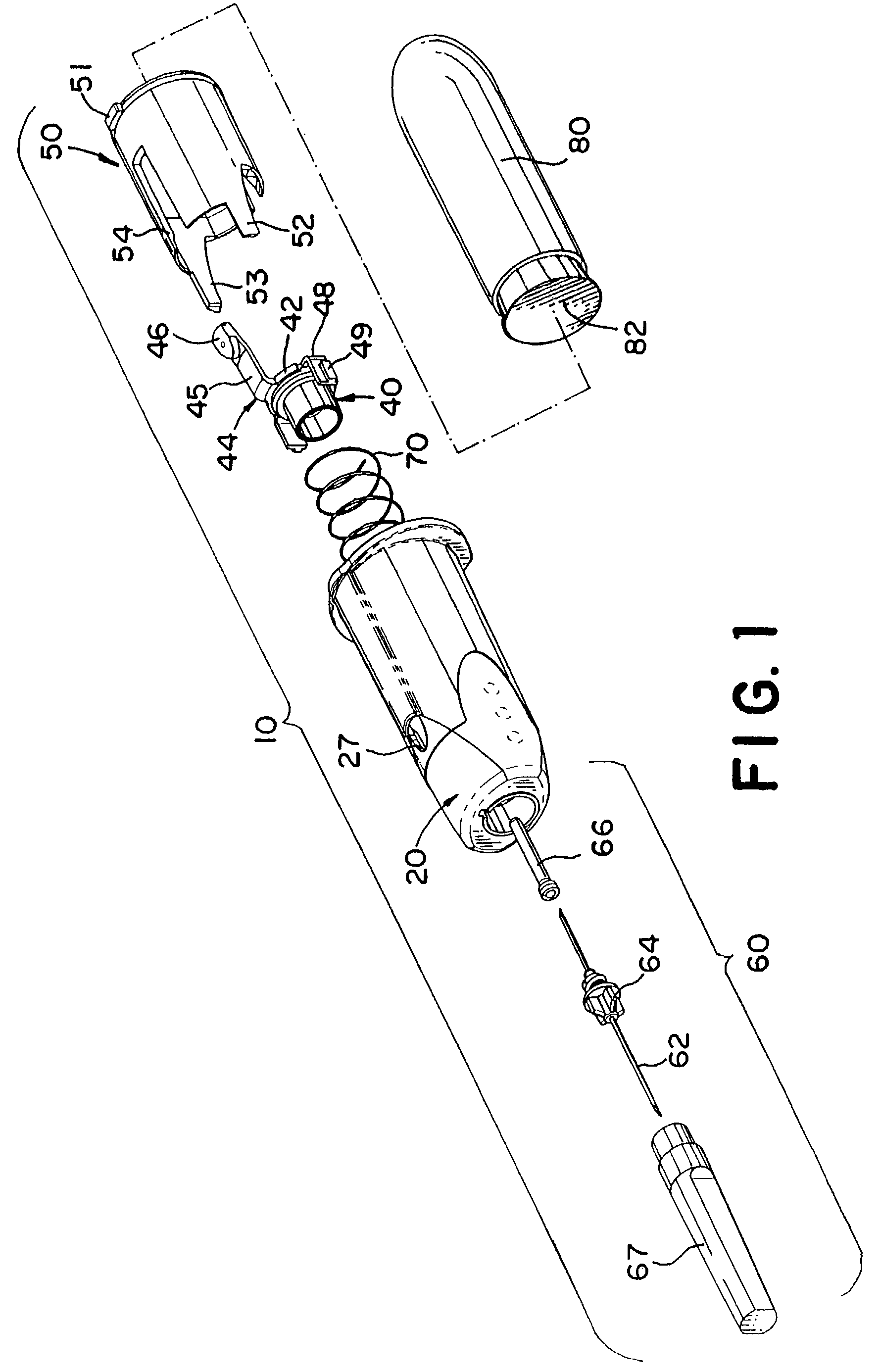
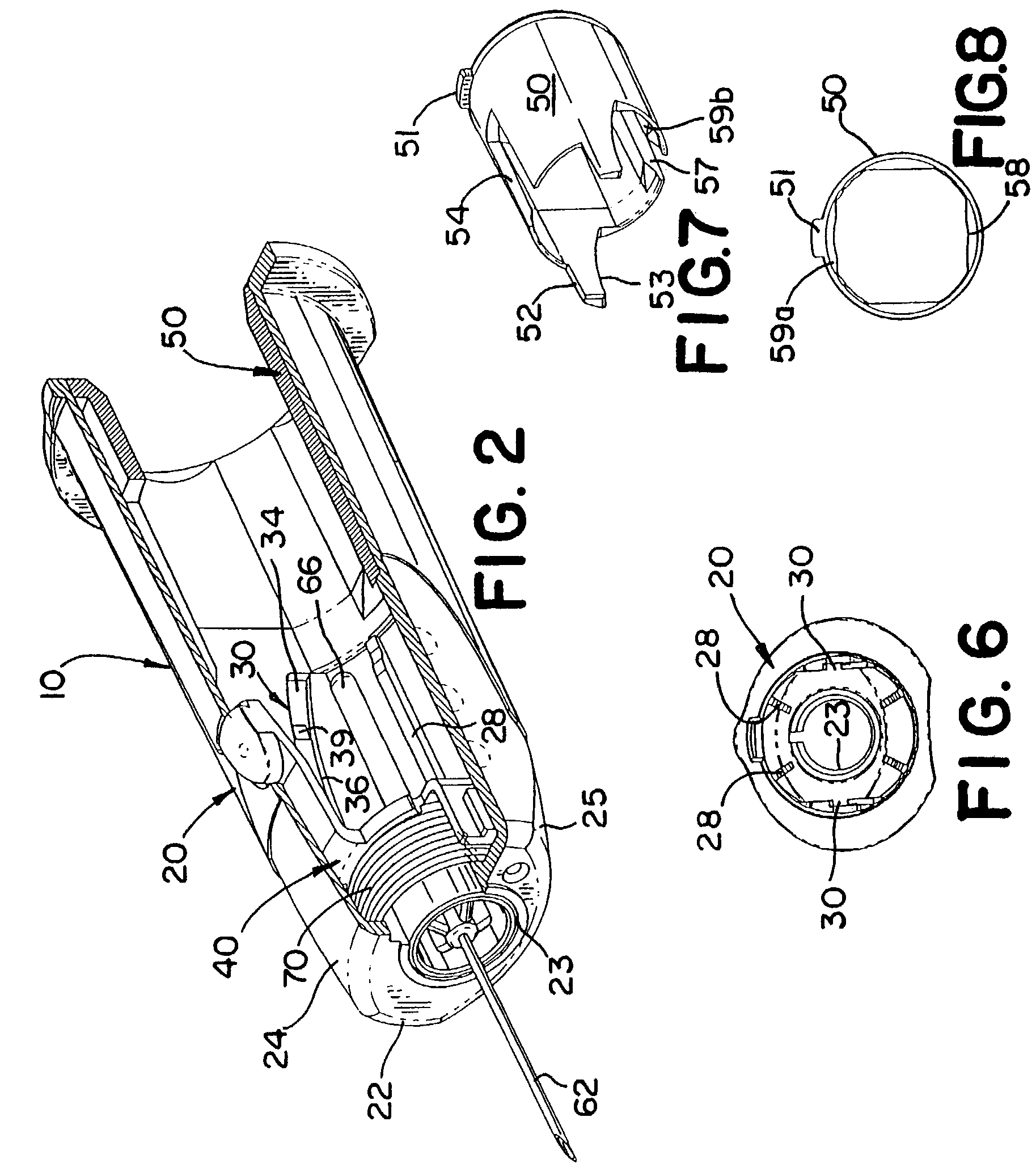
A medical device is provided for collecting fluid samples from a patient, such as blood samples. The device includes a needle having a forward sharpened tip that is retracted into the housing of the device after use to prevent exposure to the contaminated needle. The rearward end of the housing is open, forming a socket for receiving a fluid container, such as a vacuum tube, that will receive the fluid sample. A needle retainer releasably retains the needle in the extended position against the rearward bias of a biasing element. After use, the medical professional retracts the needle by pressing an actuation button, allowing the biasing element to displace the needle rearwardly. A guide track guides the needle during retraction, tilting the needle off-axis.
Owner:MDC INVESTMENT HLDG
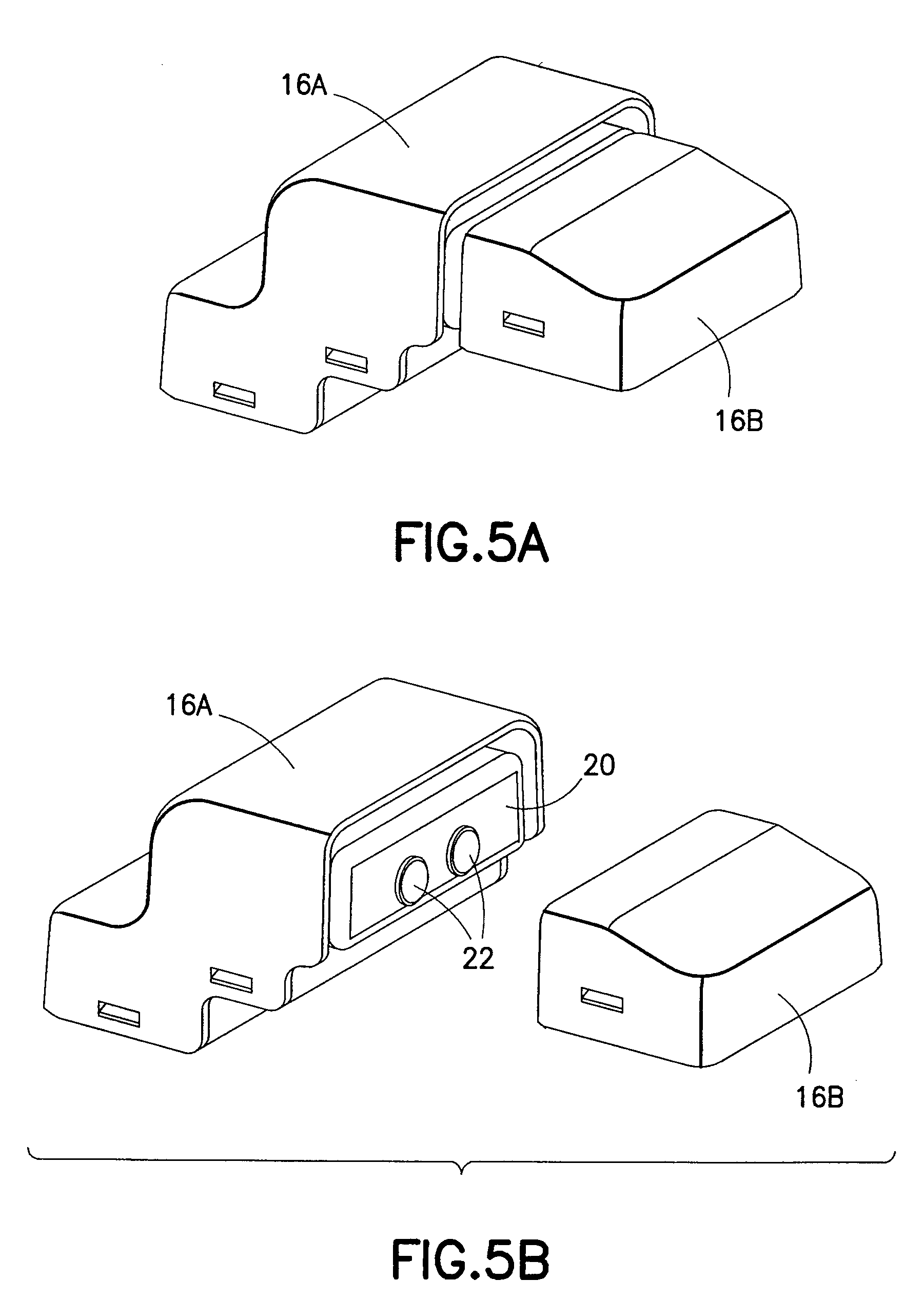
Sliding window magnetic electrical connector
InactiveUS7871272B2Restrict movementMaintain alignmentVehicle connectorsElectric discharge tubesSlide windowEngineering
An electrical connector for supplying electrical power from a fixed member to a movable member that moves with respect to the fixed member, the movable member bearing an electrical load. The electrical connector has a first connector part fixed to the fixed member and connected to a source of electrical power. A second connector part is fixed to the movable member and is connected to the electrical load. The first connector part and second connector part are movable into electrical engagement when the movable member is moved adjacent the fixed member. The first connector part has a first housing, a movable enclosure in the housing, having first external electrical contacts, and a movable carriage bearing second electrical contacts. The movable carriage has first magnets or magnet attractive components, the second contacts being movable with the carriage by a first magnetic force into electrical engagement with the first contacts.
Owner:CASCO PRODUCTOS CORP
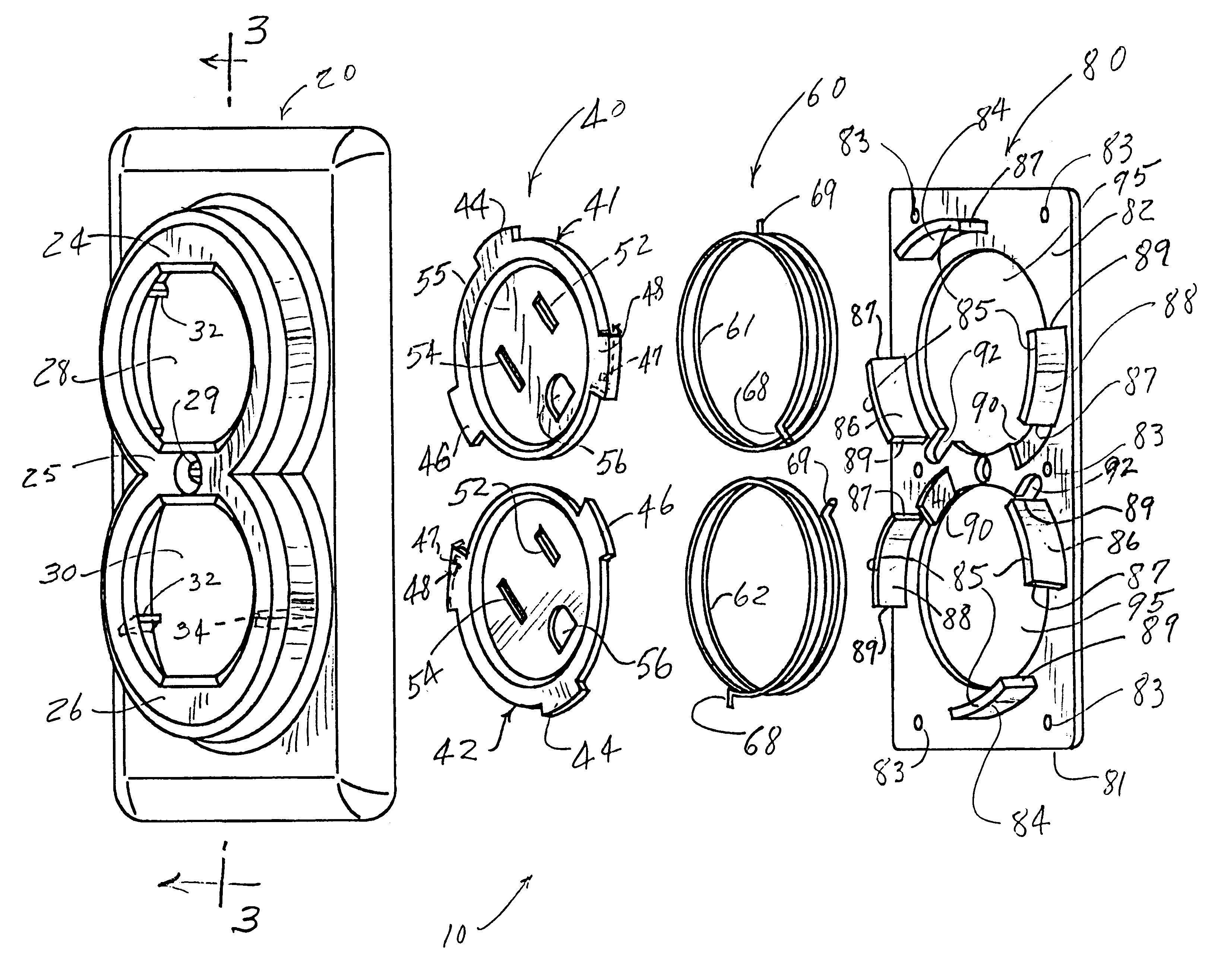
Electrical outlet cover
InactiveUS6364673B1Prevent accidental contactCasings/cabinets/drawers detailsLive contact access preventionMechanical engineeringElectrical shock
An electrical outlet cover having a pair of floating socket covers which are resiliently urged toward a first position wherein holes in the floating socket covers are not aligned with holes in the electrical outlet. The floating socket cover must be rotated from the first position to a second position wherein holes in the socket cover are aligned with holes in the cover and then pushed toward the socket for moving prongs on the plug into holes in the socket. While prongs on the plug are moving into holes on the socket the prongs are covered by the floating socket covers to prevent electrical shock resulting from touching prongs of a plug that is partially plugged into the electrical socket.
Owner:LEE HAN YOUNG
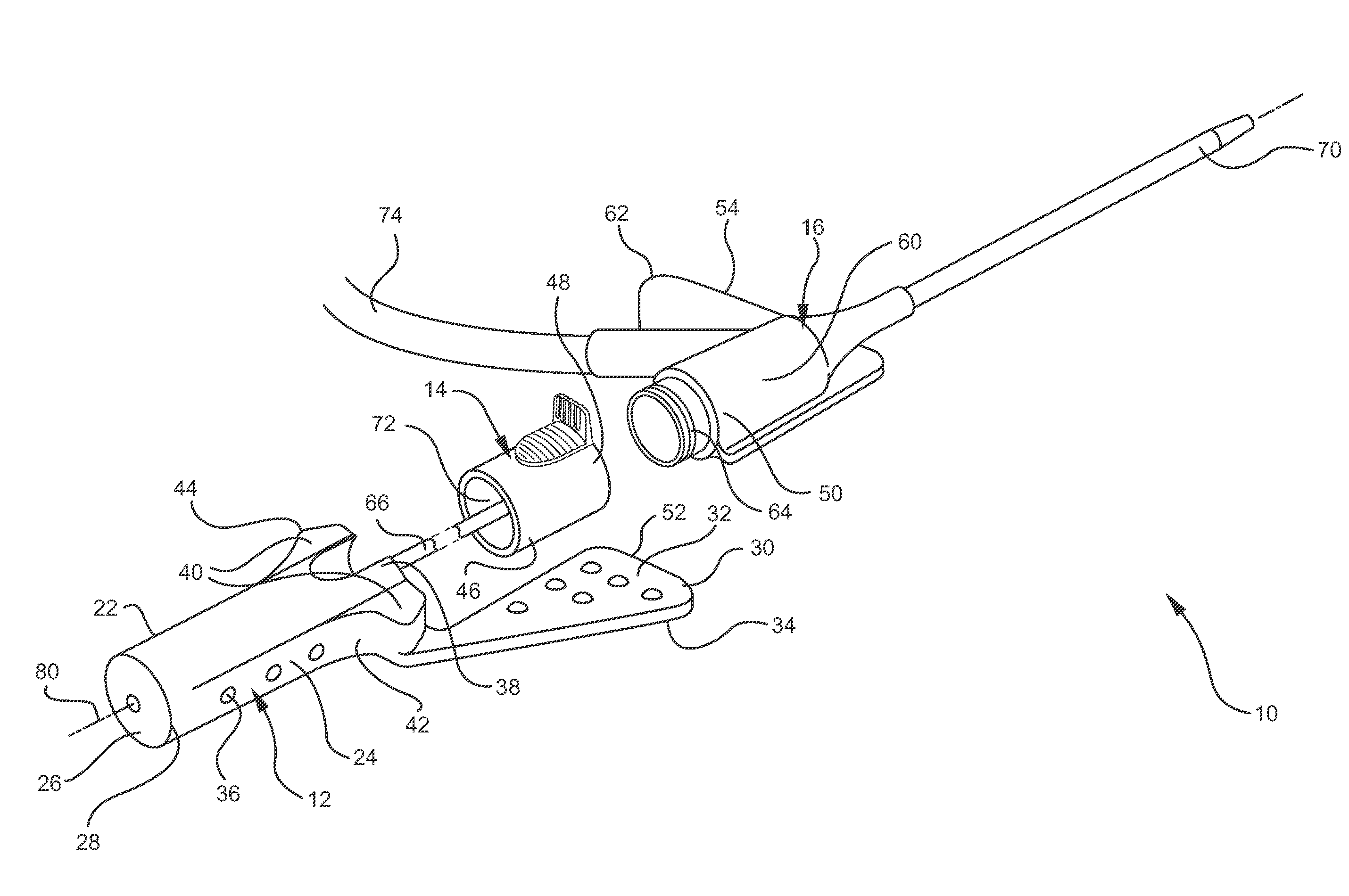
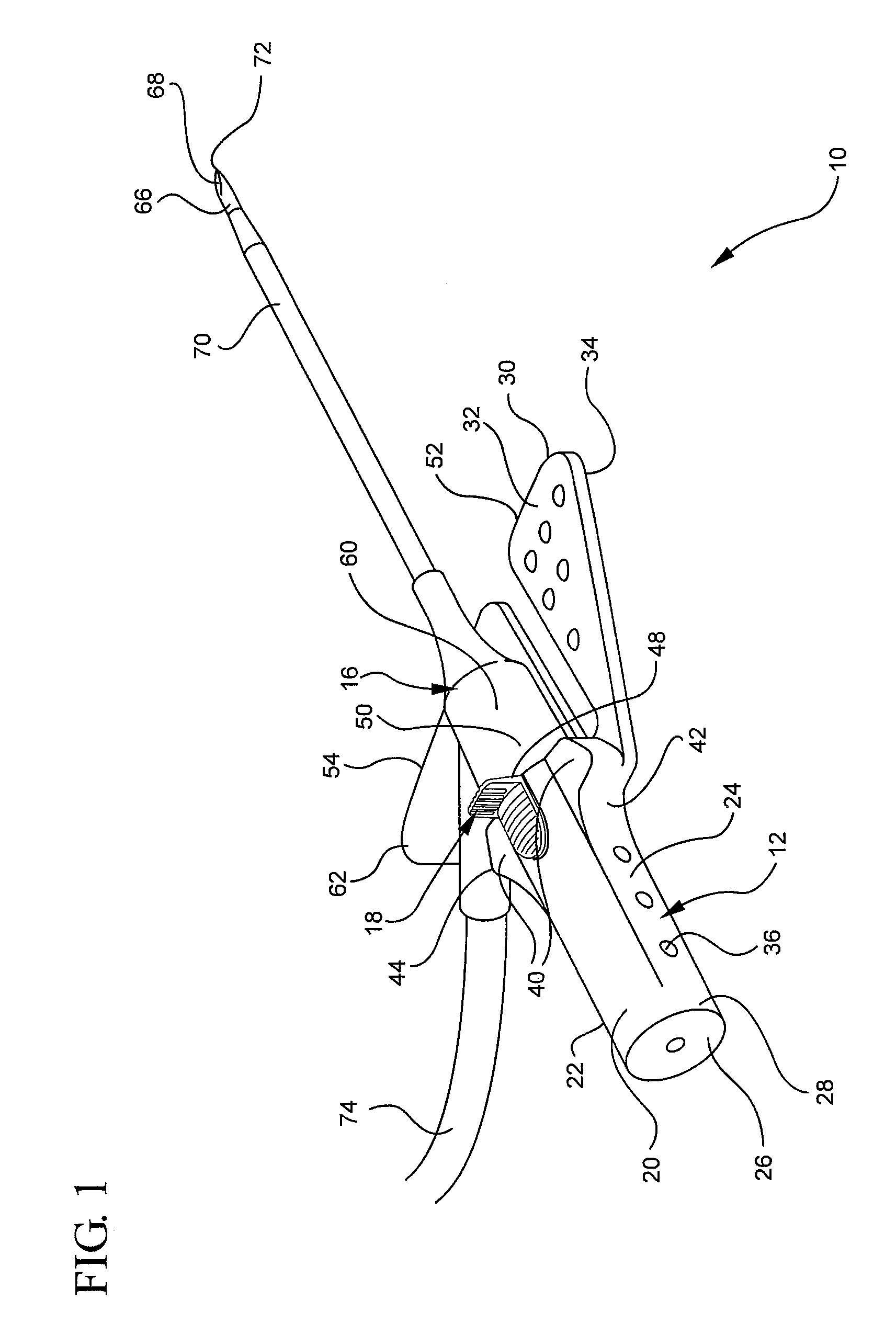
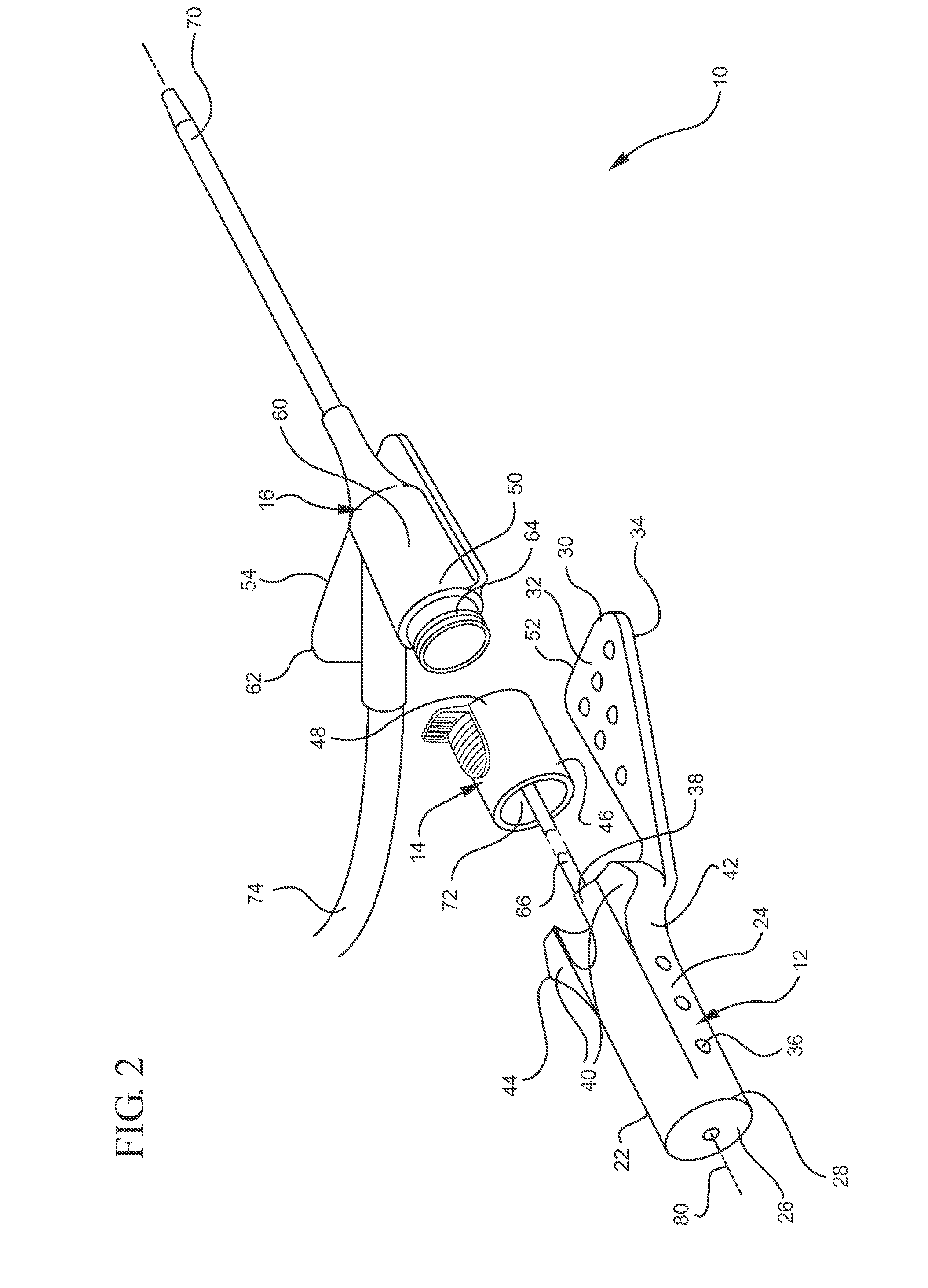
Endoscopic suturing system
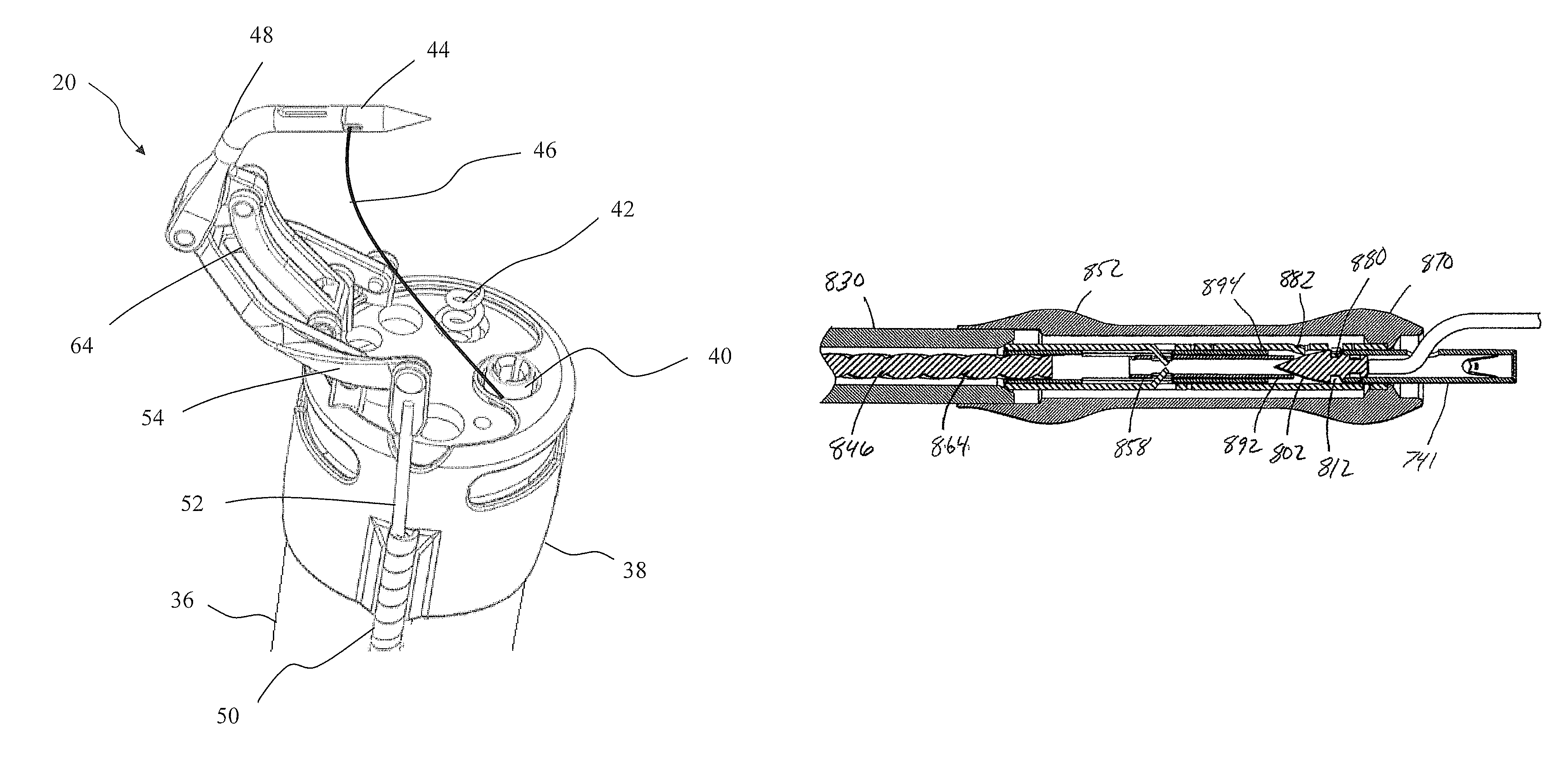
ActiveUS8287556B2Prevent accidental contactImprove visualizationSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesNeedle punctureEndoscope
An endoscopic suturing system and method are disclosed as are devices for use with the system and method such as a suture dispenser, a cinch device, and a tissue grasper. In one embodiment the suturing system includes a cap assembly arranged at the distal end portion of an endoscope or guide member, with the cap assembly including a rotatable needle holder. The needle holder is actuated through a transmission element extending outside the endoscope or guide member. A needle capture device may be inserted through a channel of the endoscope or guide member in order to capture a needle held in the needle holder when the needle holder is rotated so that the needle punctures tissue.
Owner:APOLLO ENDOSURGERY INC
Flip top cap
InactiveUS7717284B2Easy to installReduce the likelihood of exposureCapsClosure capsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A cap is provided for a laboratory vessel. The cap includes a lid that can be rotated relative to the laboratory vessel from a closed position to an open position. The lid includes at least one tab dimensioned and disposed for receiving manual digital pressure for opening and / or closing the lid. The tab is in an offset position to prevent a thumb or forefinger from passing over and in contact with the opening to the vessel. Additionally, the lid includes a shield inwardly from the tab for further preventing contact between a finger and the open top of the vessel.
Owner:CORNING INC
Obstruction detection device for vehicle door and method
ActiveUS7761209B2Avoid contactPrevent accidental contactDigital data processing detailsRoad vehicles traffic controlMobile vehicleActuator
An obstruction detection device for a motor vehicle having a door assembly movably connected to a vehicle body is provided. The device controls the vehicle door's opening angle to prevent inadvertent contact with an object foreign to the vehicle, while providing the largest opening for vehicle ingress and egress. The obstruction detection device includes a controller that is operatively connected to at least one sensor configured to actively monitor and transmit signals to the controller indicative of the presence and corresponding proximity of the object relative to the door assembly. An actuator is operatively connected to and controlled by the controller. The actuator is configured to apply a selectively variable force that restricts the movement of the vehicle door assembly with respect to the vehicle body when the door is a predetermined distance from the object.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Twist lock panel-mounted connector
ActiveUS7090533B1Less manufacturing precisionEasy to shapeSubstation/switching arrangement detailsCoupling parts mountingFlange
A connector (10) is configured for mounting to a panel (12). The panel (12) has a mounting aperture (18) formed with a keyway (22). The connector (10) has a housing (24) with a front end (26) dimensioned to pass through the mounting aperture (18). However, keys (44, 46, 48) project out in proximity to the front end (26) of the housing (24). At least one of the keys (48) is dimensioned to pass through the keyway (22). A stop flange (50) projects out from the housing (24) rearward of the keys (44, 46, 48). A resiliently deflectable locking finger (60) projects forward of the stop flange (50) and is dimensioned to engage in the keyway (22).
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
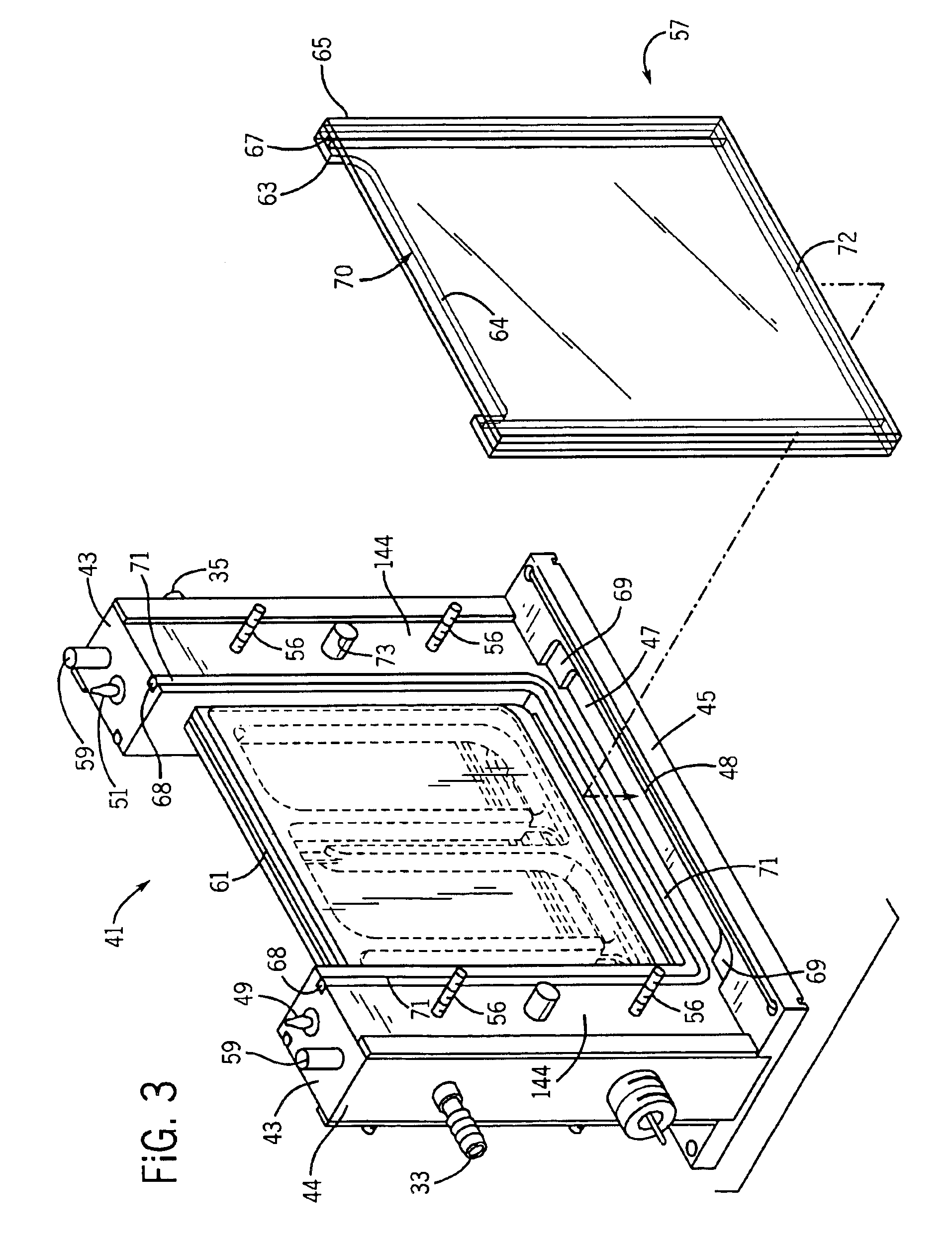
Vertical electrophoresis system
InactiveUS6942775B1Facilitate electrophoresisPrevent accidental contactSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementElectrophoresisEngineering
A plugging medium is used to block the bottom opening of cassettes for vertical electrophoresis in order to facilitate filling the cassettes with separation media. Cassettes can be filled within a vertical electrophoresis system in which electrophoresis is conducted without further manipulation of the cassettes. The system includes a frame assembly mounted on a base containing a basin for plugging solution. The cassette is mounted to the frame assembly in a substantially vertical position such that a bottom opening of the empty cassette resides below the rim of the basin. The plugging solution (e.g. agarose gel) forms a plug within the bottom of the cassette to contain the separation medium.
Owner:OWL SEPARATION SYST
Flip top cap with contamination protection
ActiveUS8172101B2Easy to installReduce the likelihood of exposureCapsLaboratory glasswaresEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:CORNING INC
Needle capture device
ActiveUS8679136B2Prevent accidental contactImprove visualizationSuture equipmentsSurgical furnitureEndoscopeBiomedical engineering
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Guard for connection point of adjoined wire connectors
ActiveUS8408929B2Prevent accidental contactEasy to useEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsElectrical junctionEngineering
A cylindrical guard is used for protecting the electrical junction between connectors. The guard is essentially two split cylindrical sections oriented end-to-end with breakaway tabs therebetween. The split cylindrical pieces are hinged, and substantially irreversibly lock together in a “clamshell” like fashion. The resulting guarded junction is less likely to be accidentally disengaged, thereby protecting both property and life. The guard can be removed by cutting, or broken and moved to expose the underlying junction by severing the breakaway tabs.
Owner:SHOALS TECH GROUP
Position and pathway lighting system for a vehicle or combination of vehicles sides undersides rear or trailing wheels and rear or trailing body portion
InactiveUS20150203026A1Improve securitySufficient lightingPoint-like light sourceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsDriver/operatorConductive materials
The invention describes a lighting system apparatus intended to increase safety during operation of mainly large or lengthy vehicles and combination vehicles in darkness and poor visibility. The lighting system is comprised of a single or plurality of light sources designed for vehicular use and housed in a durable thermally conductive material having a lens through which light is projected. Said light source housings are attached to the vehicle whereby, when actuated by a controller, sufficient illumination is directed onto the specific areas on the vehicle(s) and ground surface peripheral to said vehicle or combination of vehicles at one or more areas along the sides and rear or trailing portions to the extent that the driver can more safely control said vehicle(s) because of increased visual cognition of the aforementioned areas via the rear-view mirrors. Persons proximate are also more aware of said vehicle(s) position and pathway by means of said illumination and can more readily avoid dangerous contact.
Owner:SCHOTANUS TODD A
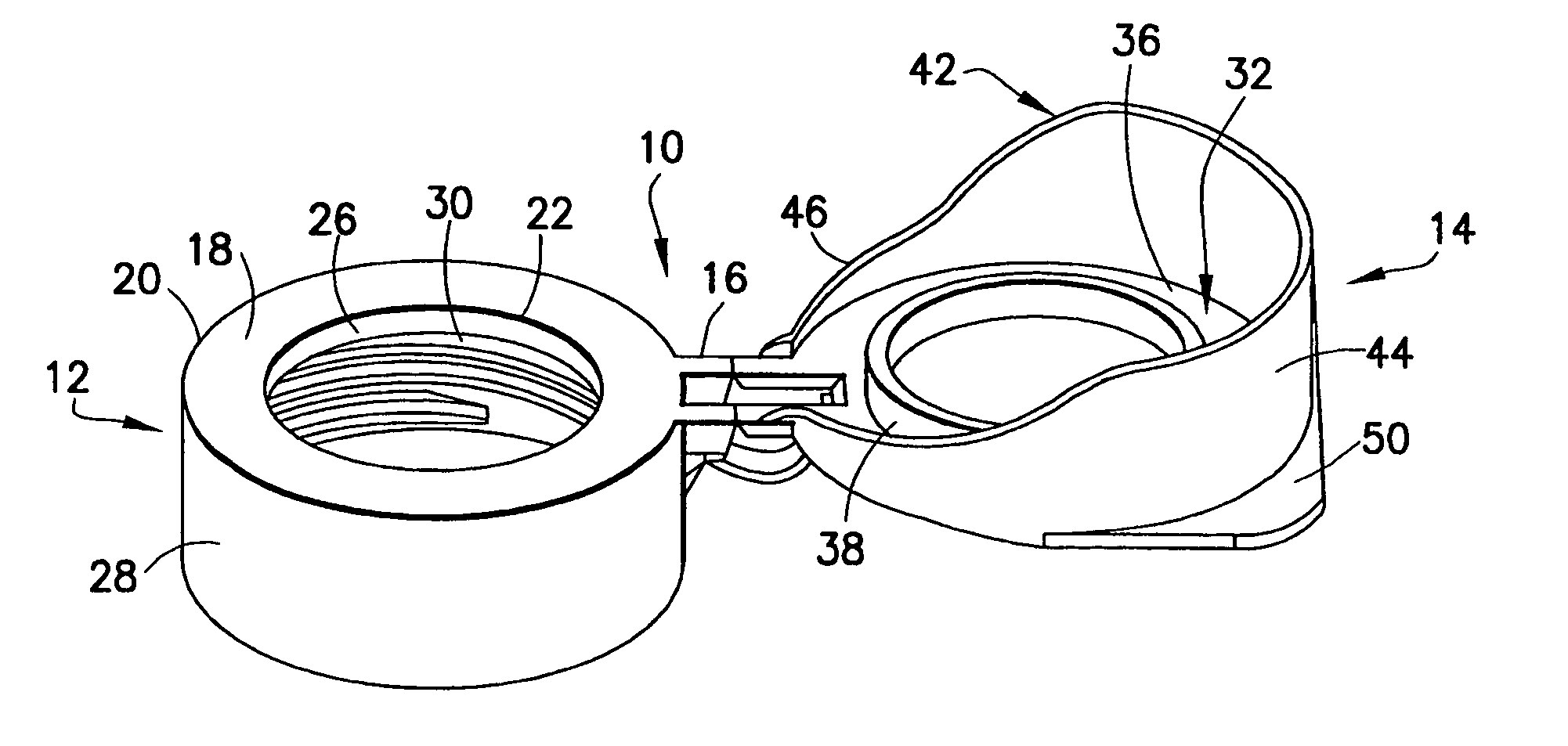
Ocular positioning droplet dispencing device with a recessed dispensing oriface
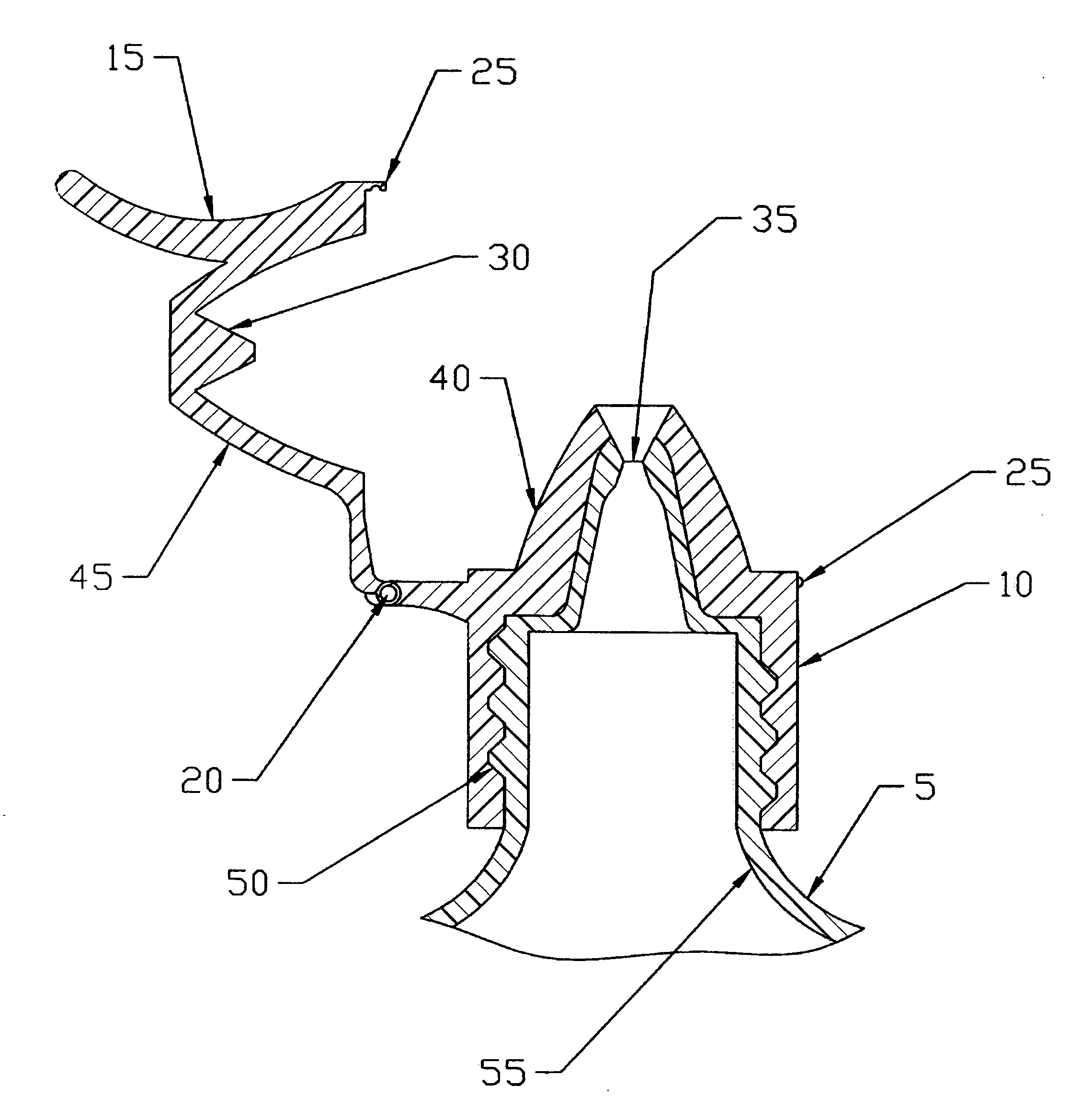
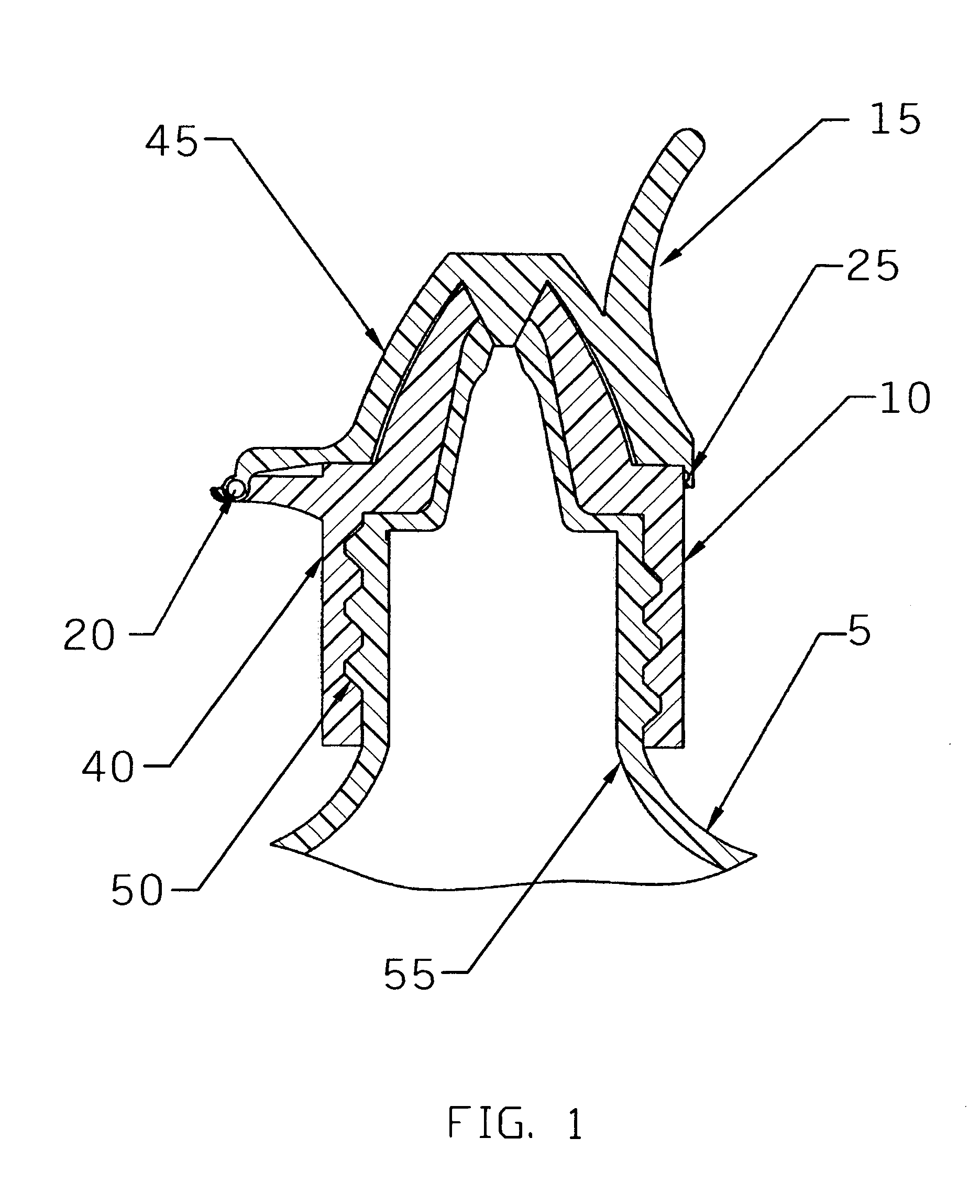
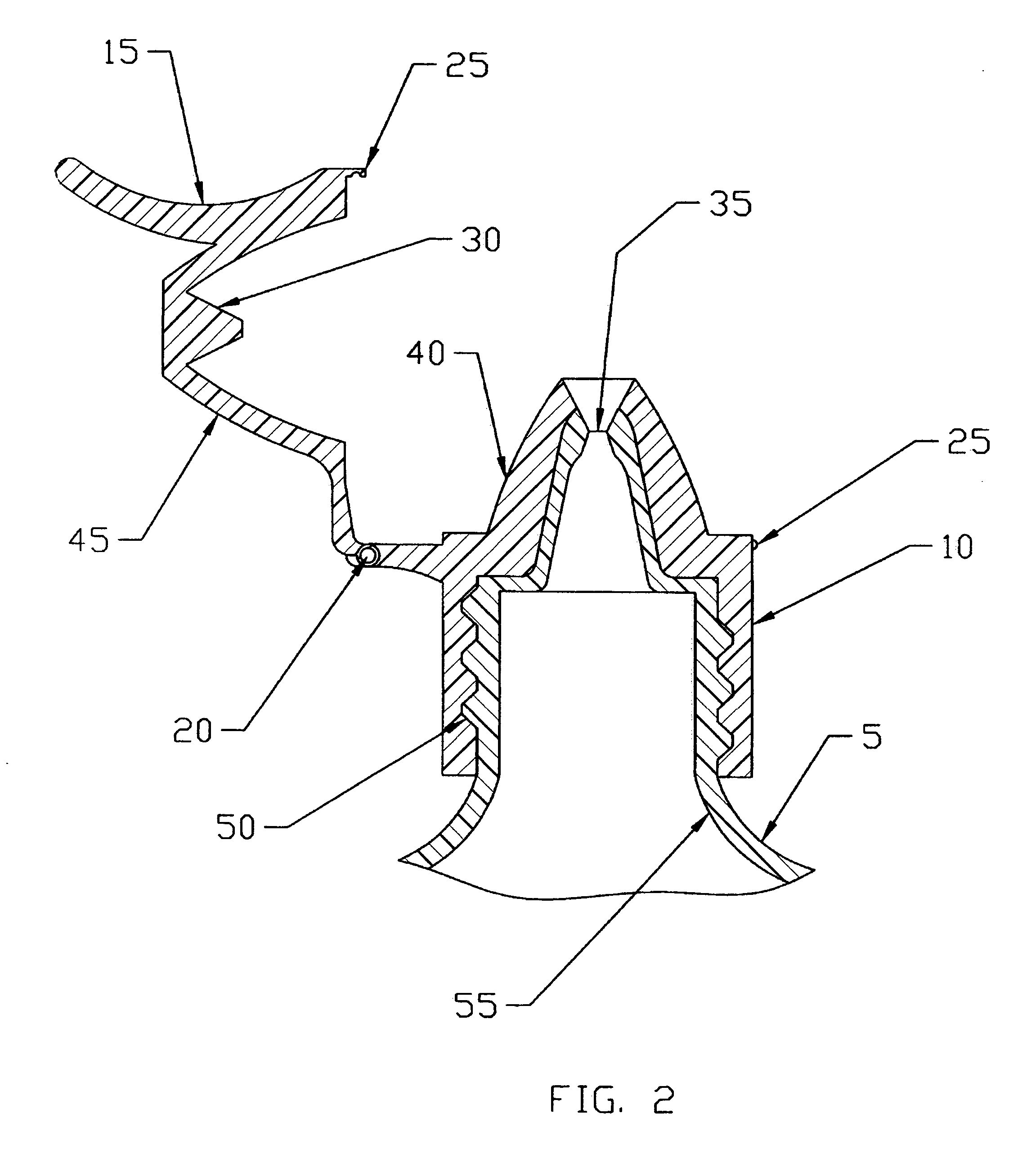
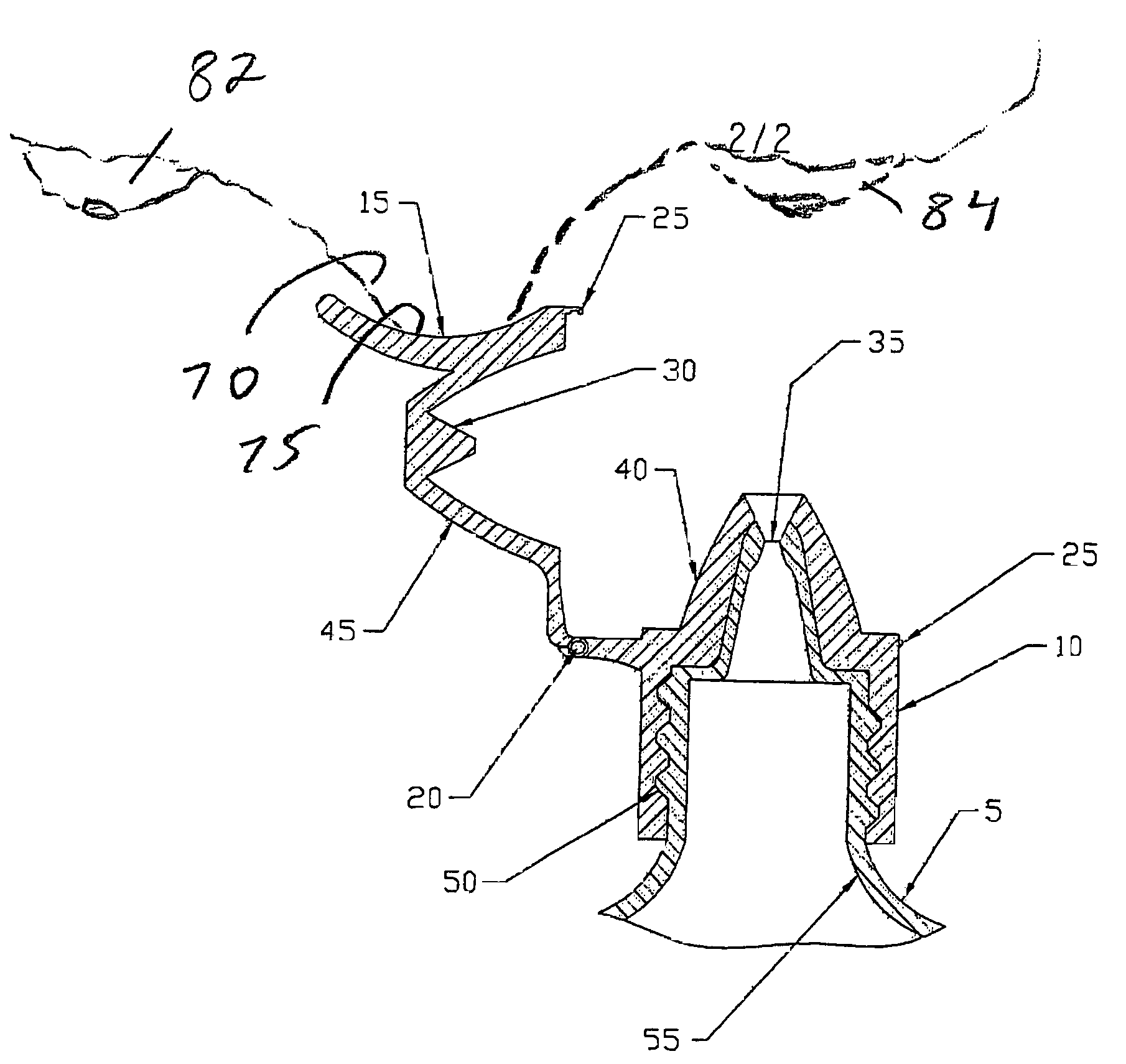
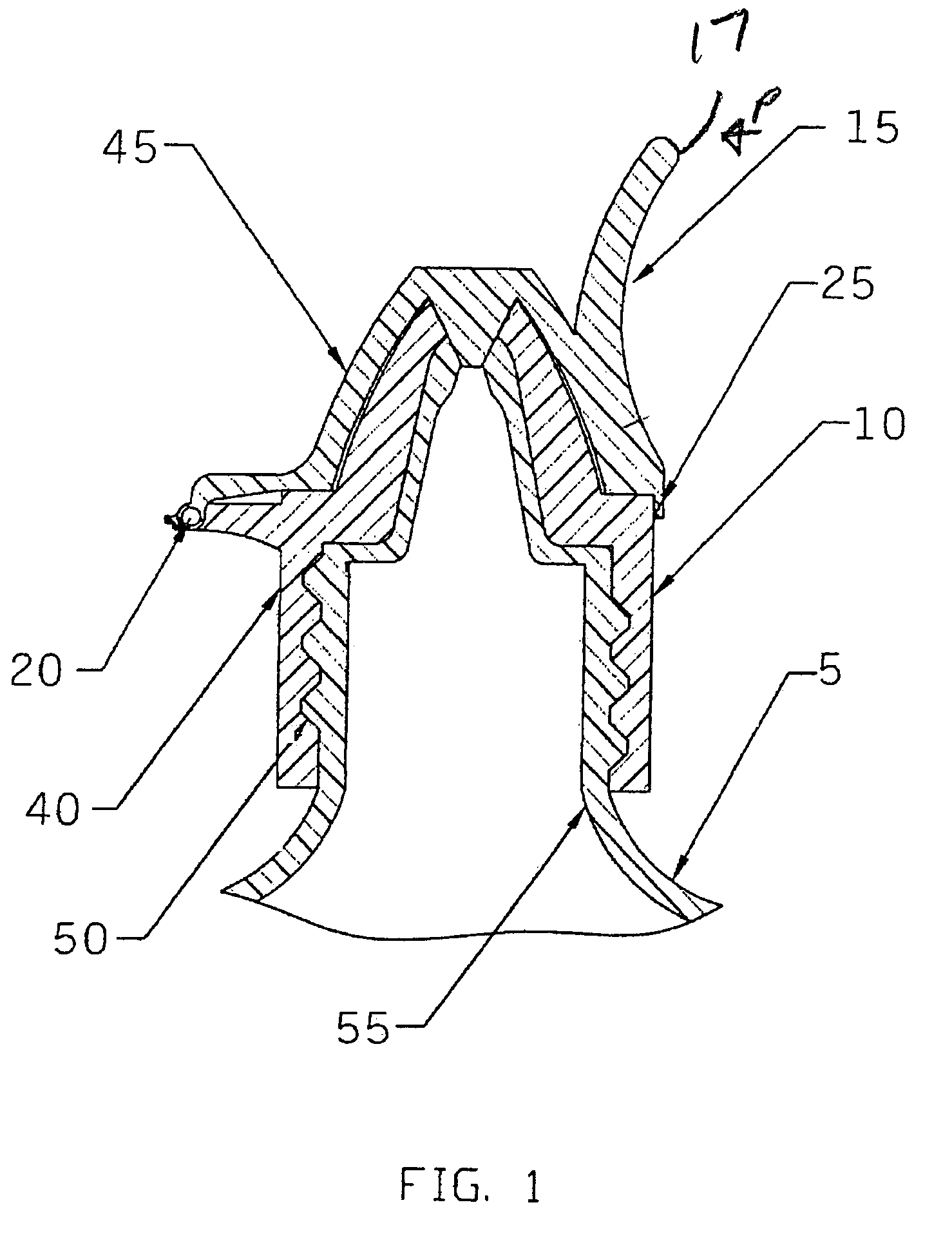
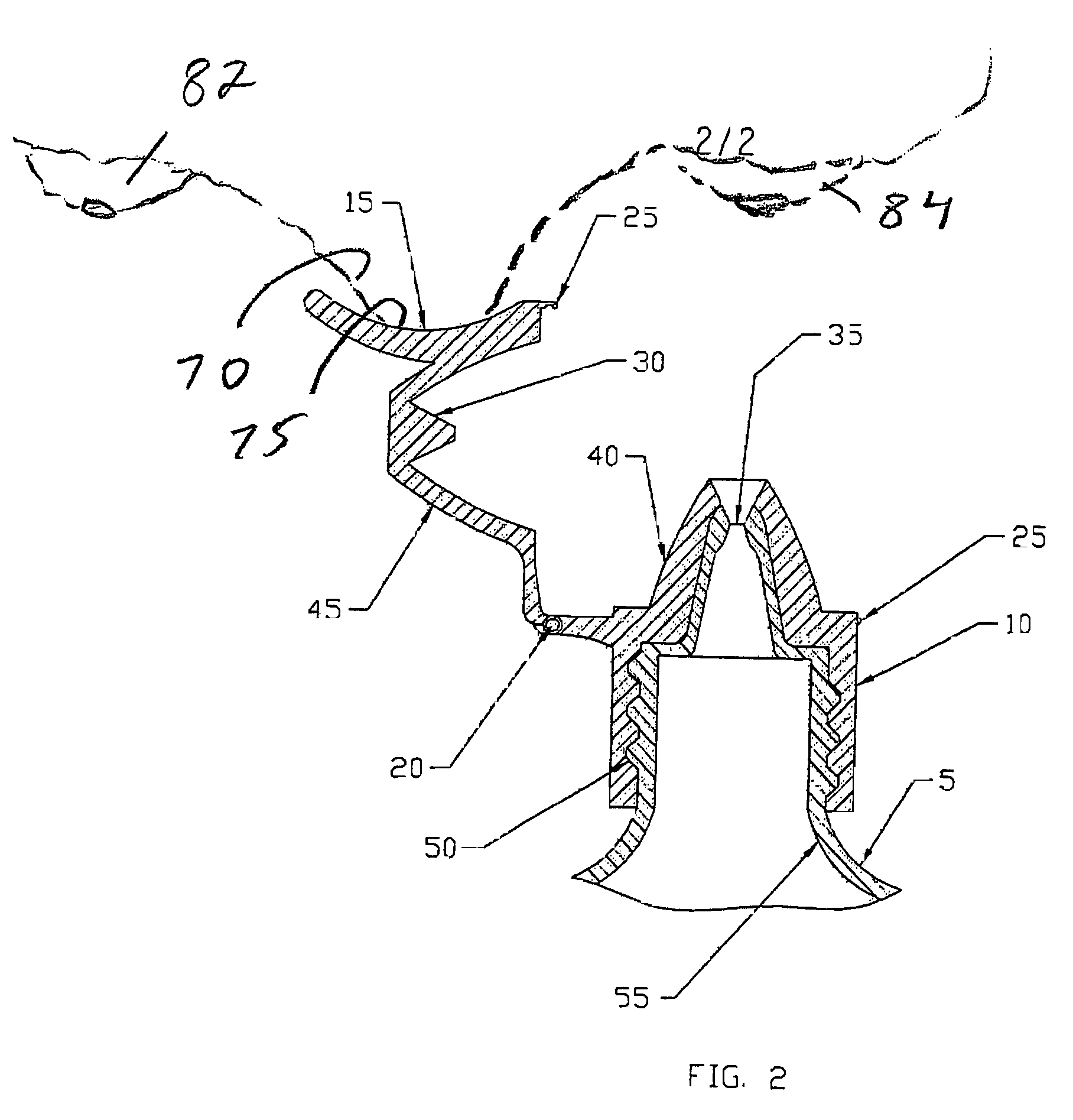
ActiveUS20060157516A1Prevent accidental contactPositioning is simple and fastClosuresLiquid flow controllersEngineeringScrew thread
An ocular positioning device threadably attached to a standard soft sided squeeze bottle of ophthalmic fluid. The device consists of two parts, an attaching mechanism and a sealing mechanism, connected by a hinge with motion limited to ninety degrees of arc. The sealing mechanism is fitted with a nose bridge saddle designed to rest on the bridge of the users nose and to align the discharge nozzle with the central portion of the ocular opening of either of the users eyes when the attaching hinge is in the fully open position. The sealing mechanism is also fitted with a manually operated latch to maintain the sealing mechanism in the closed and sealed condition to prevent leakage when not in use.
Owner:BARBER RORY
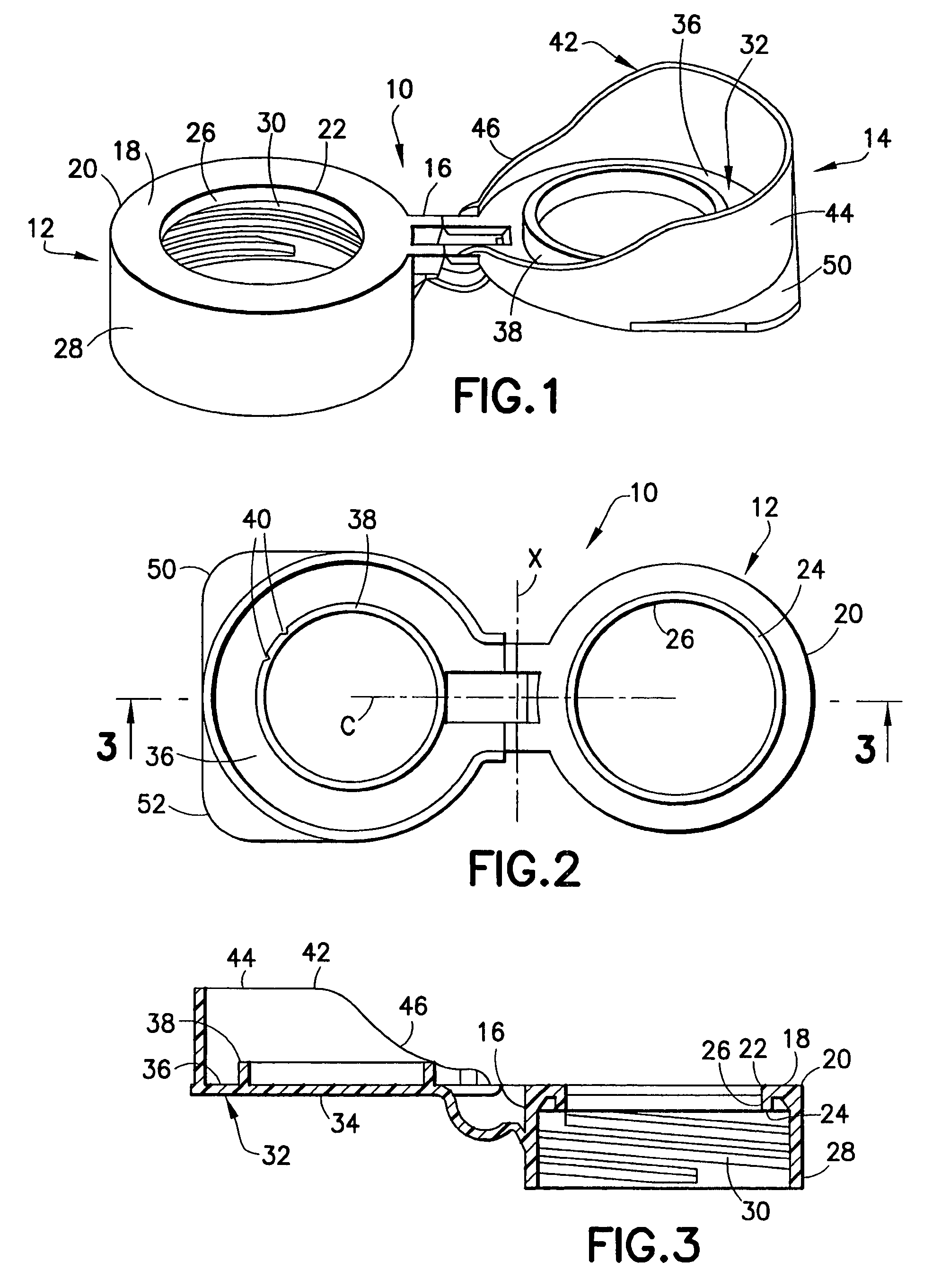
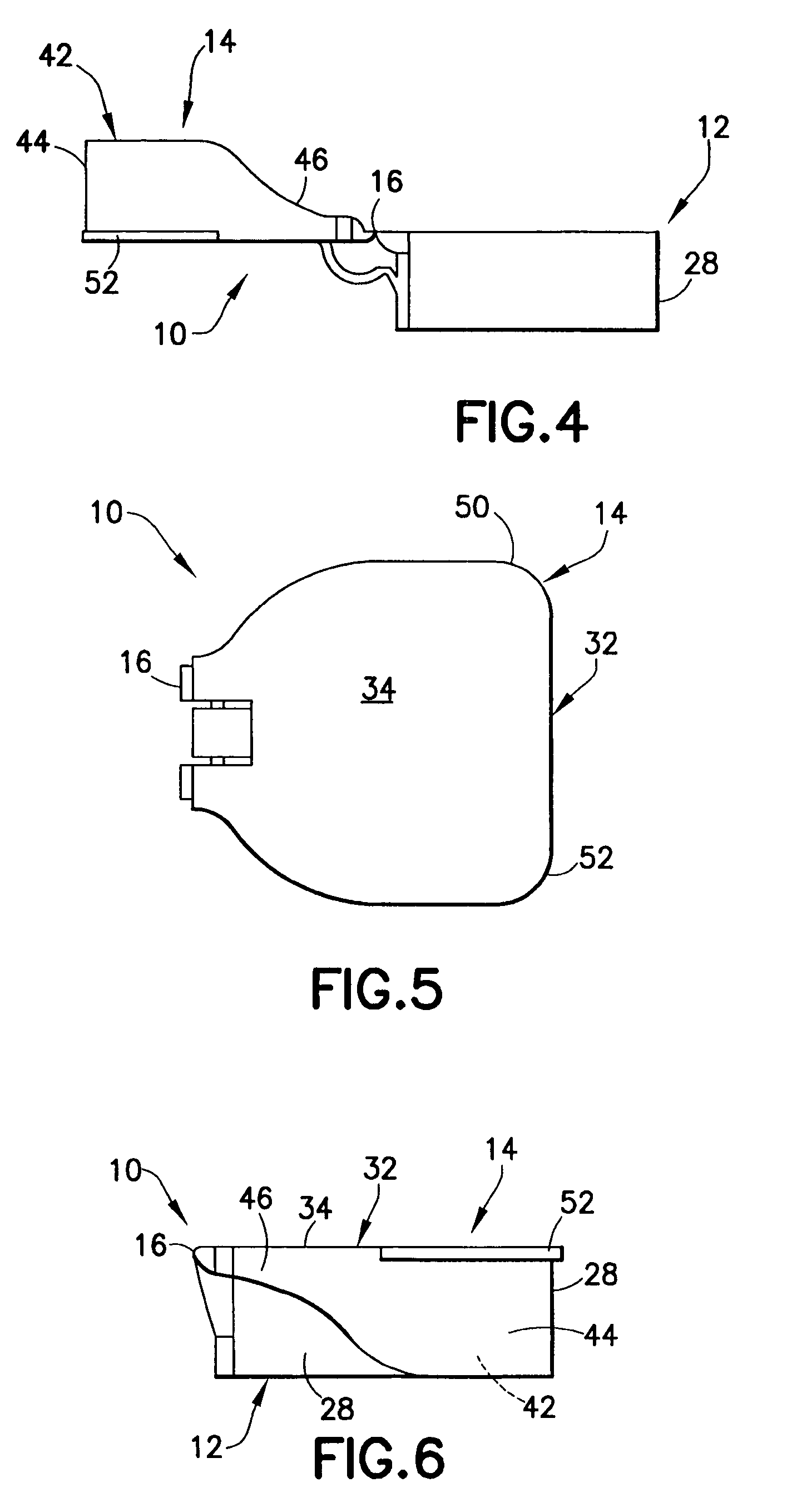
Ocular positioning droplet dispensing device with a recessed dispensing orifice
ActiveUS7325708B2Prevent accidental contactPositioning is simple and fastClosuresLiquid flow controllersScrew threadNose bridge
An ocular positioning device threadably attached to a standard soft sided squeeze bottle of ophthalmic fluid. The device consists of two parts, an attaching mechanism and a sealing mechanism, connected by a hinge with motion limited to ninety degrees of arc. The sealing mechanism is fitted with a nose bridge saddle designed to rest on the bridge of the users nose and to align the discharge nozzle with the central portion of the ocular opening of either of the users eyes when the attaching hinge is in the fully open position. The sealing mechanism is also fitted with a manually operated latch to maintain the sealing mechanism in the closed and sealed condition to prevent leakage when not in use.
Owner:BARBER RORY
Method of determining axial alignment of the centroid of an edge gripping end effector and the center of a specimen gripped by it
InactiveUS20060045719A1Minimizes specimen damage and production of contaminant particleQuickly and accurately transferMechanical apparatusData processing applicationsEngineeringActuator
A method determines axial alignment between the centroid of an end effector and the effective center of a specimen held by the end effector. The method is implemented with use of an end effector coupled to a robot arm and having a controllable supination angle. A condition in which two locations of the effective center of the specimen measured at 180° displaced supination angles do not lie on the supination axis indicates that the centroid is offset from the actual effective center of the specimen.
Owner:BOOKS AUTOMATION US LLC
Pet feeder with insect repellent
InactiveUS8001931B2Highly accuratePrevent accidental contactCandle holdersLighting support devicesInsect repellantsCompanion animal
Owner:DEESE RANDY C +1
Systems and methods for providing a safety integrated catheter with universal grip
ActiveUS8357121B2“choked up” gripAvoid adjustmentInfusion syringesCatheterIntravenous catheterEngineering
A universal gripping surface is provided on an intravenous catheter assembly. The universal gripping surface provides a plurality of surfaces whereby a user may grip the catheter assembly in a desired gripping configuration for improved balance and control of the catheter assembly during insertion of the catheter. Additionally, the universal gripping surface includes a guard feature to prevent a user's unintended contact with various components of the catheter assembly whereby the contact may result in an undesirable “over the bevel” condition.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Specimen sensing and edge gripping end effector
InactiveUS6898487B2Minimizes specimen damage and production of contaminant particleQuickly and accurately transferJointsTemperatue controlFiberActuator
Robot arm end effectors rapidly transfer semiconductor wafers between a wafer cassette and a processing station. Preferred embodiments of the end effectors include proximal and distal rest pads, the latter having pad and backstop portions that support and grip the wafer at its peripheral edge or within an annular exclusion zone that extends inward from the peripheral edge of the wafer. Preferred embodiments of the end effectors also include fiber optic light transmission sensors for determining various wafer surface, edge, thickness, tilt, and location parameters. The sensors provide robot arm extension and elevation positioning data supporting methods of rapidly and accurately placing and retrieving a wafer from among a stack of closely spaced wafers stored in the wafer cassette.
Owner:BOOKS AUTOMATION US LLC
Systems and methods for providing a safety integrated catheter with universal grip
ActiveUS20100249713A1“choked up” gripAvoid adjustmentGuide needlesInfusion syringesIntravenous catheterEngineering
A universal gripping surface is provided on an intravenous catheter assembly. The universal gripping surface provides a plurality of surfaces whereby a user may grip the catheter assembly in a desired gripping configuration for improved balance and control of the catheter assembly during insertion of the catheter. Additionally, the universal gripping surface includes a guard feature to prevent a user's unintended contact with various components of the catheter assembly whereby the contact may result in an undesirable “over the bevel” condition.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Flip top cap
ActiveUS20070009390A1Easy threaded installationSmooth rotationCapsClosure capsTop capLaboratory facility
Owner:CORNING INC
Flip top cap
ActiveUS7546931B2Easy threaded installationFacilitate gripping and rotationCapsClosure capsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:CORNING INC
Wheel cover device
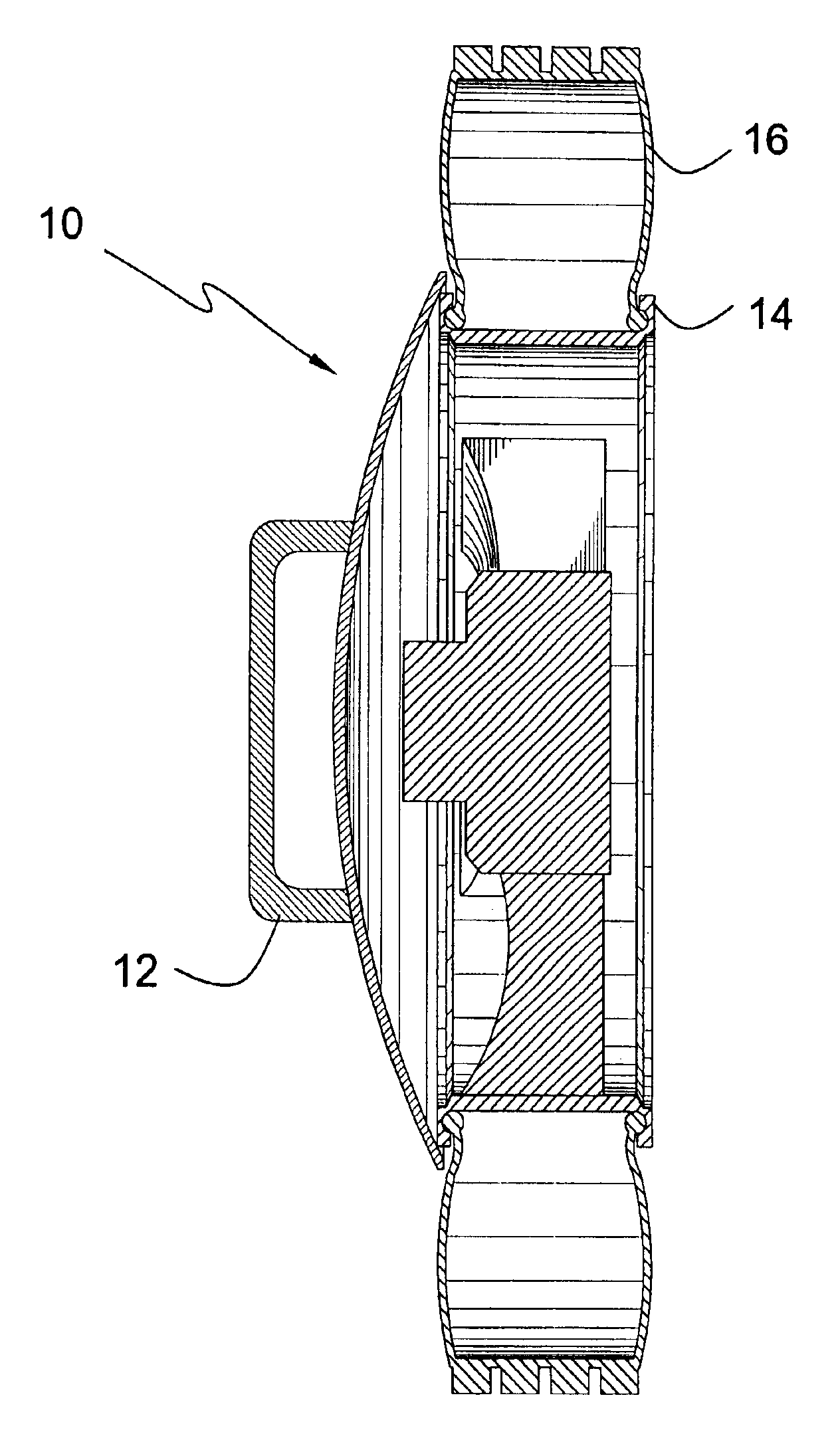
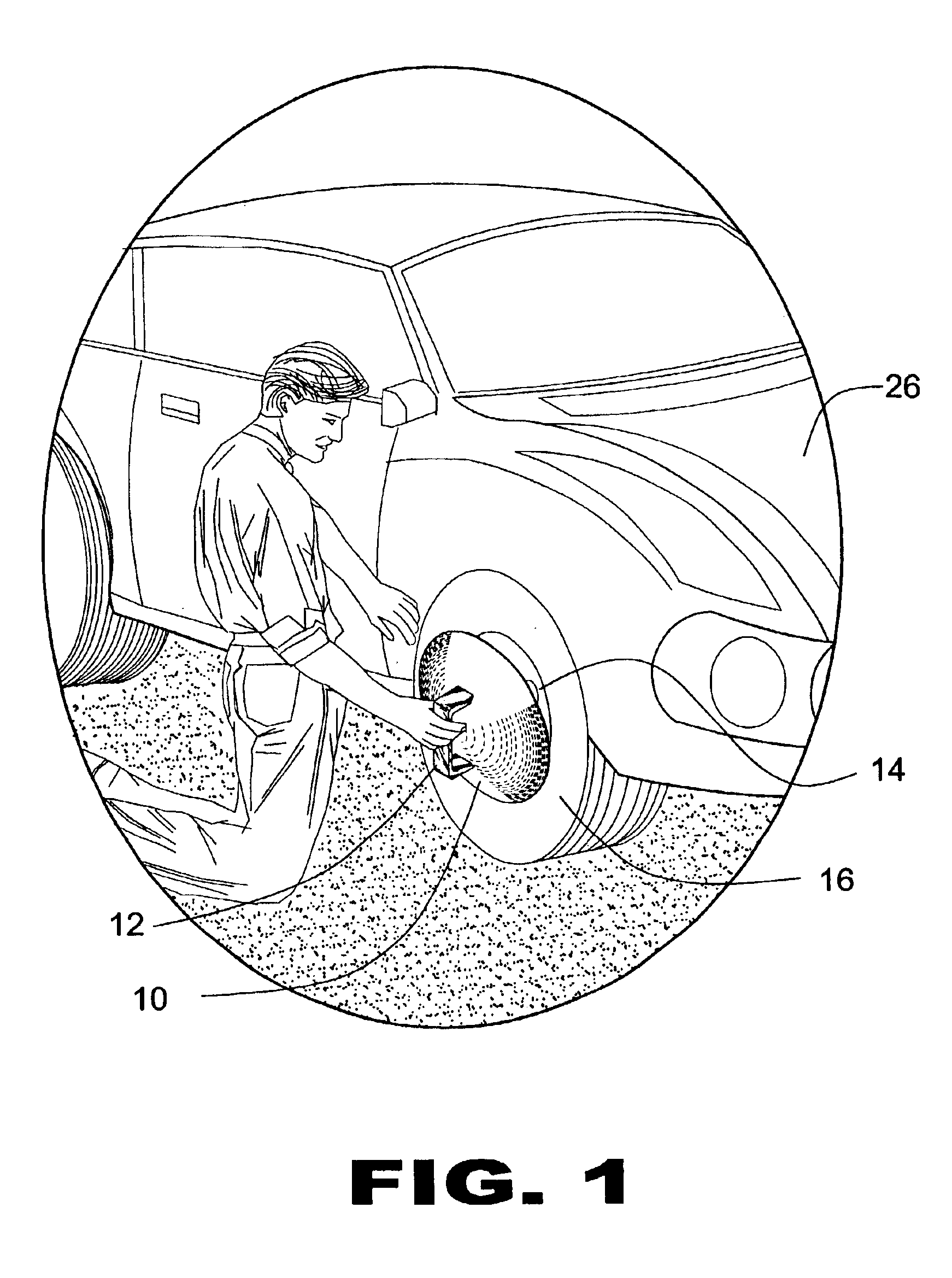
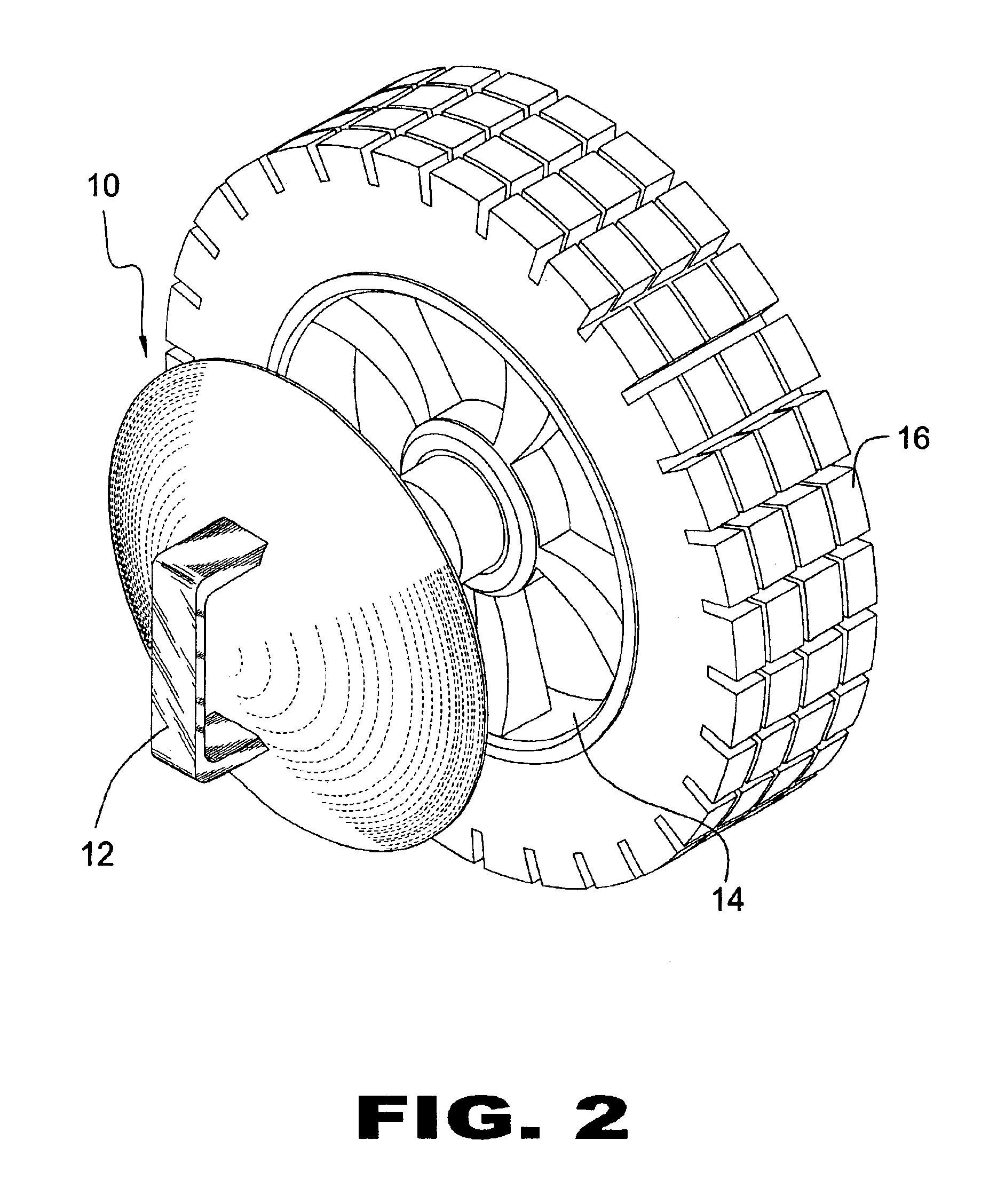
InactiveUS6863353B1Easily and rapidly putPrevent accidental contactCleaning apparatus for vehicle exteriorsWheel protectionConvex sideGasket
The present invention 10 discloses a domed covering element sized to cover and protect the entire wheel rim 14 while leaving the tire 16 fully exposed. A handle member 12 is fixedly attached to a central portion of the convex side of the covering element 10 to allow the user 18 to easily and rapidly put the present invention 10 into position and maintain it there with the use of just one hand so the other is free to spray or brush on the tire dressing 20. The domed shape of the covering element 10 keeps the user's hand 18 away from the dressing solution 20 during the application thereof as well as protecting the wheel rim 14 from getting scuffed from contact with the surface of the covering element. The present invention may include a resilient, compressible gasket 24 which encompasses the periphery of the covering element 10 to form an impermeable seal when a slight pressure is applied thereto. The gasket 24 assures that no solution 20 will pass therethrough and contact the wheel rim 14 even when heavily applied.
Owner:BUCKNER GEORGE
Medical Connecting Device
ActiveUS20160262982A1Risk minimizationPrevent accidental contactPharmaceutical containersMedical packagingBottleBiomedical engineering
A bottle connector for use in a medical fluid transfer arrangement, the bottle connector having an axial direction and a radial direction and comprising a first part and a second part, the first part comprising a hollow piercing member comprising an inner gas channel and extending in the axial direction beyond the end of the first part. The second part comprises a bottle coupling member, for coupling the bottle connector to a medical bottle. The first and second parts are pre-connected and are concentrically arranged with respect to each other and the bottle connector has a transport configuration with a first, maximum length in which the piercing member is completely located within the bottle connector, and a fluid transfer configuration with a second, minimum length.
Owner:CARMEL PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com