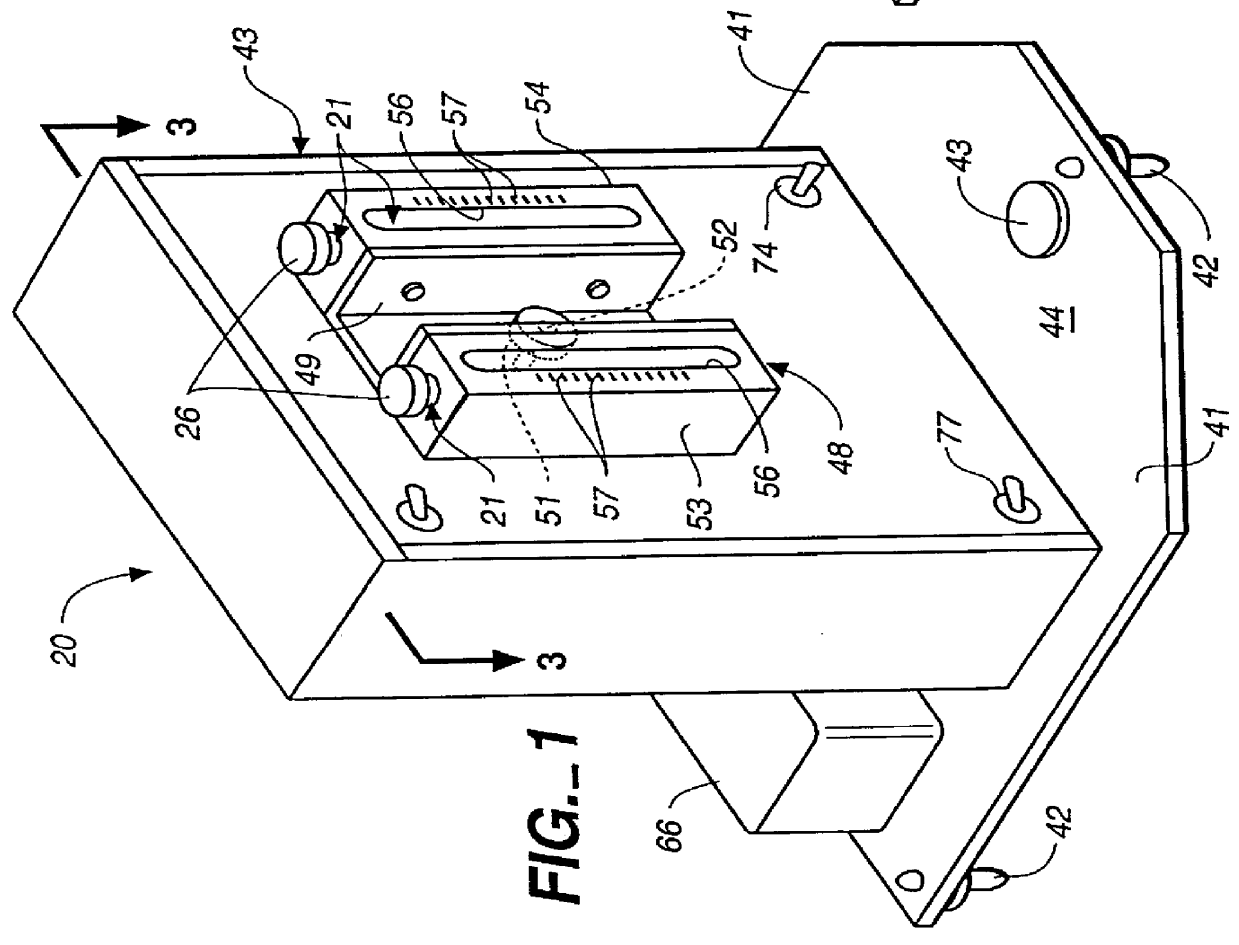
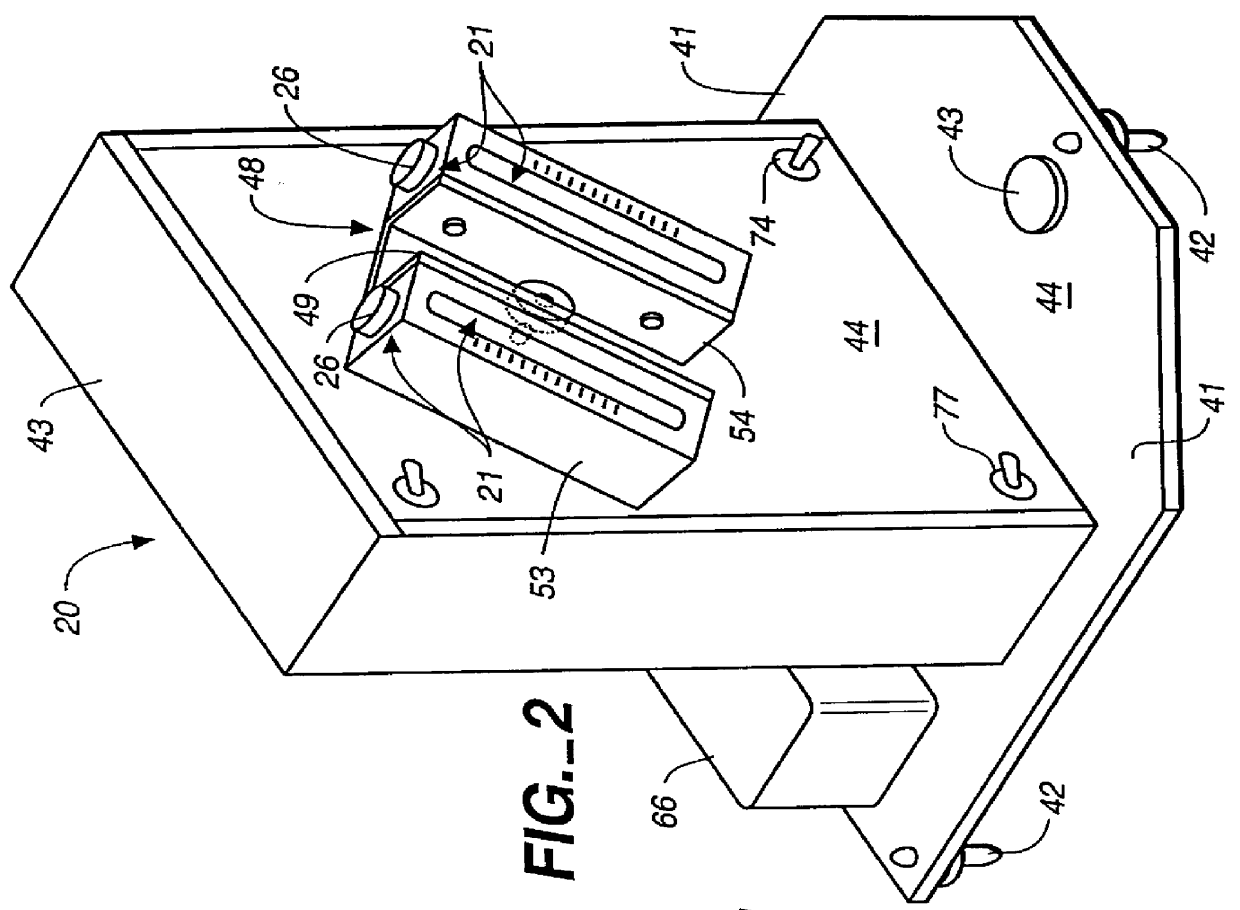
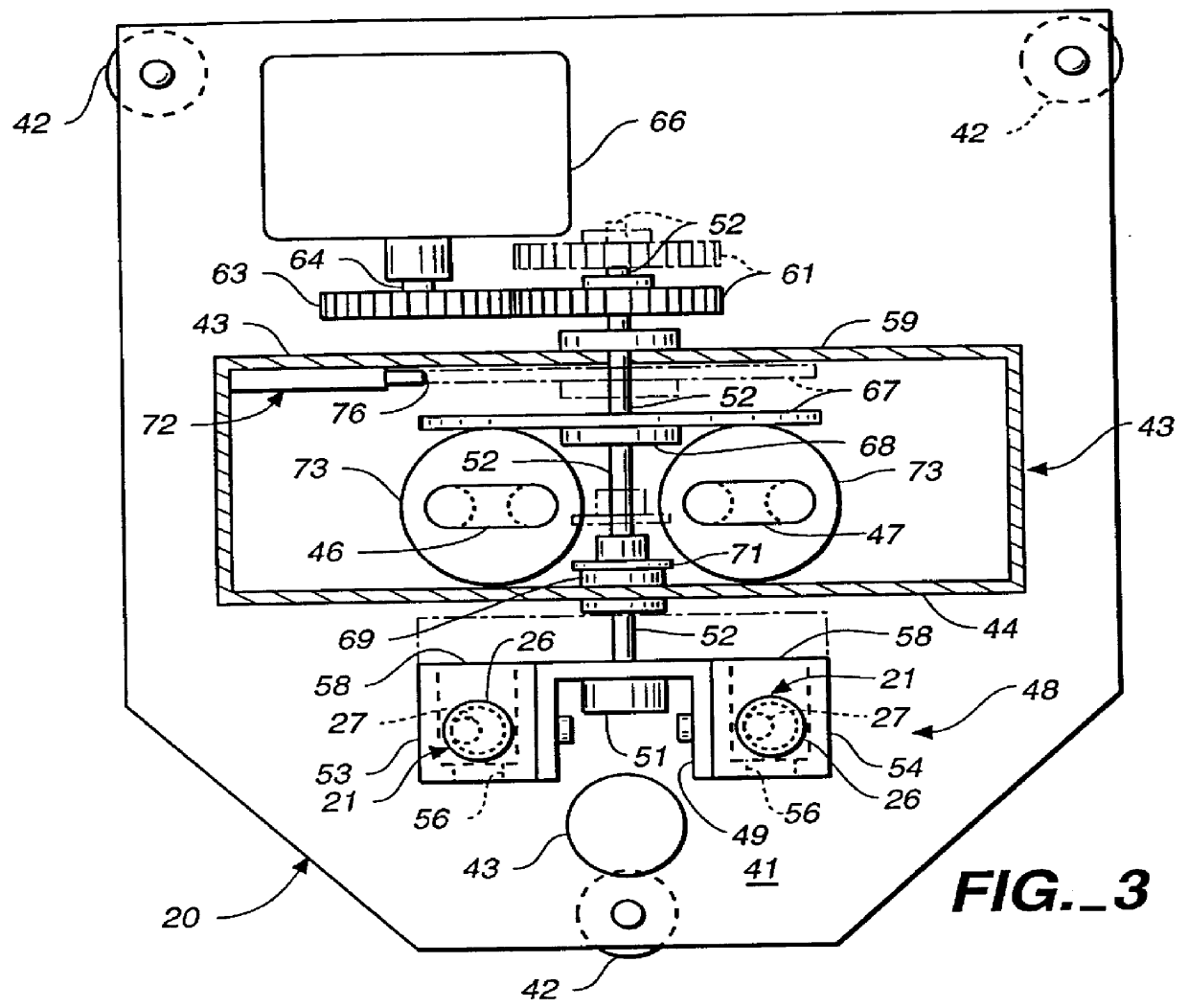
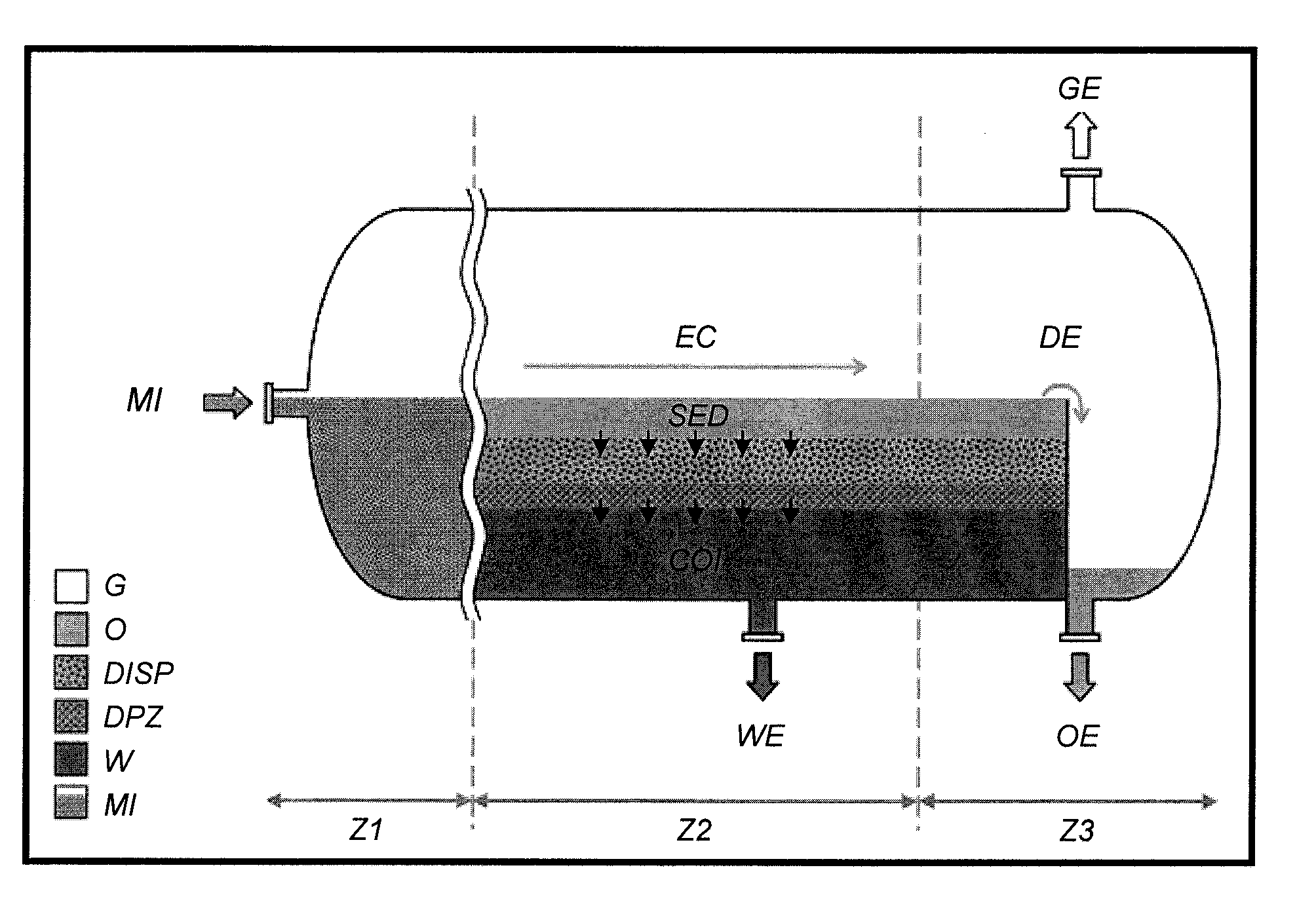
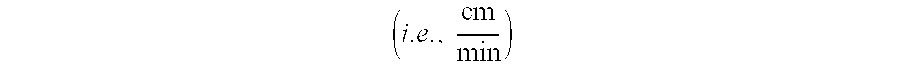Patents
Literature
140 results about "Decantation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Decantation is a process for the separation of mixtures of immiscible liquids or of a liquid and a solid mixture such as a suspension. The layer closer to the top of the container—the less dense of the two liquids, or the liquid from which the precipitate or sediment has settled out—is poured off, leaving the other component or the more dense liquid of the mixture behind. An incomplete separation is witnessed during the separation of two immiscible liquids.
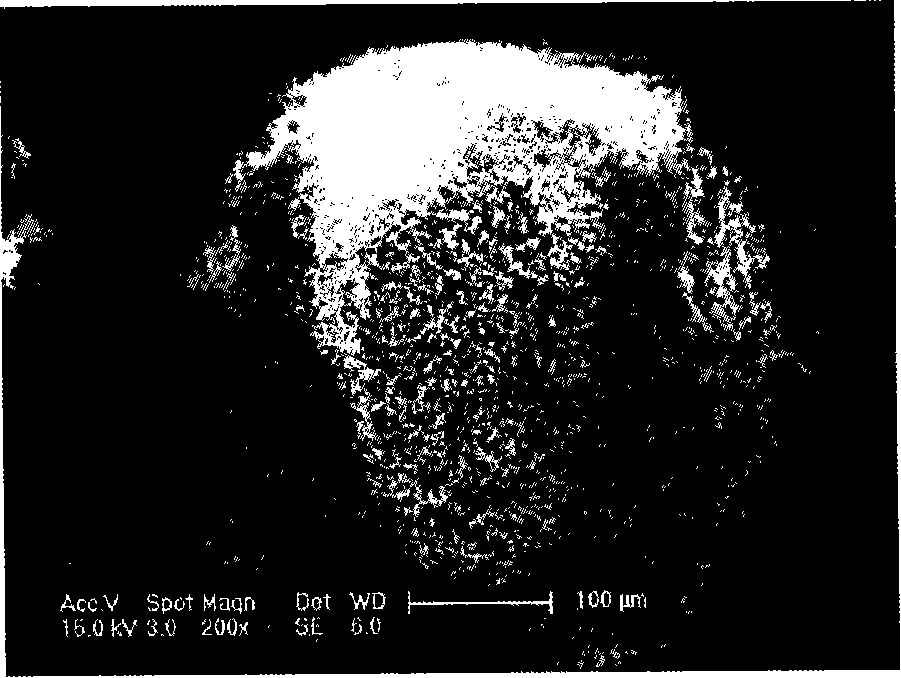
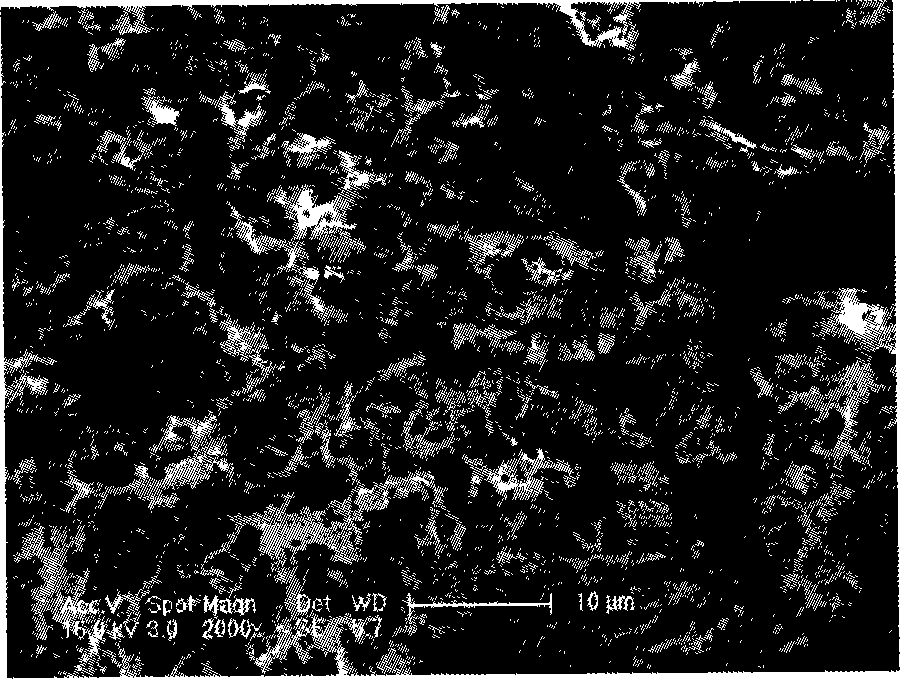
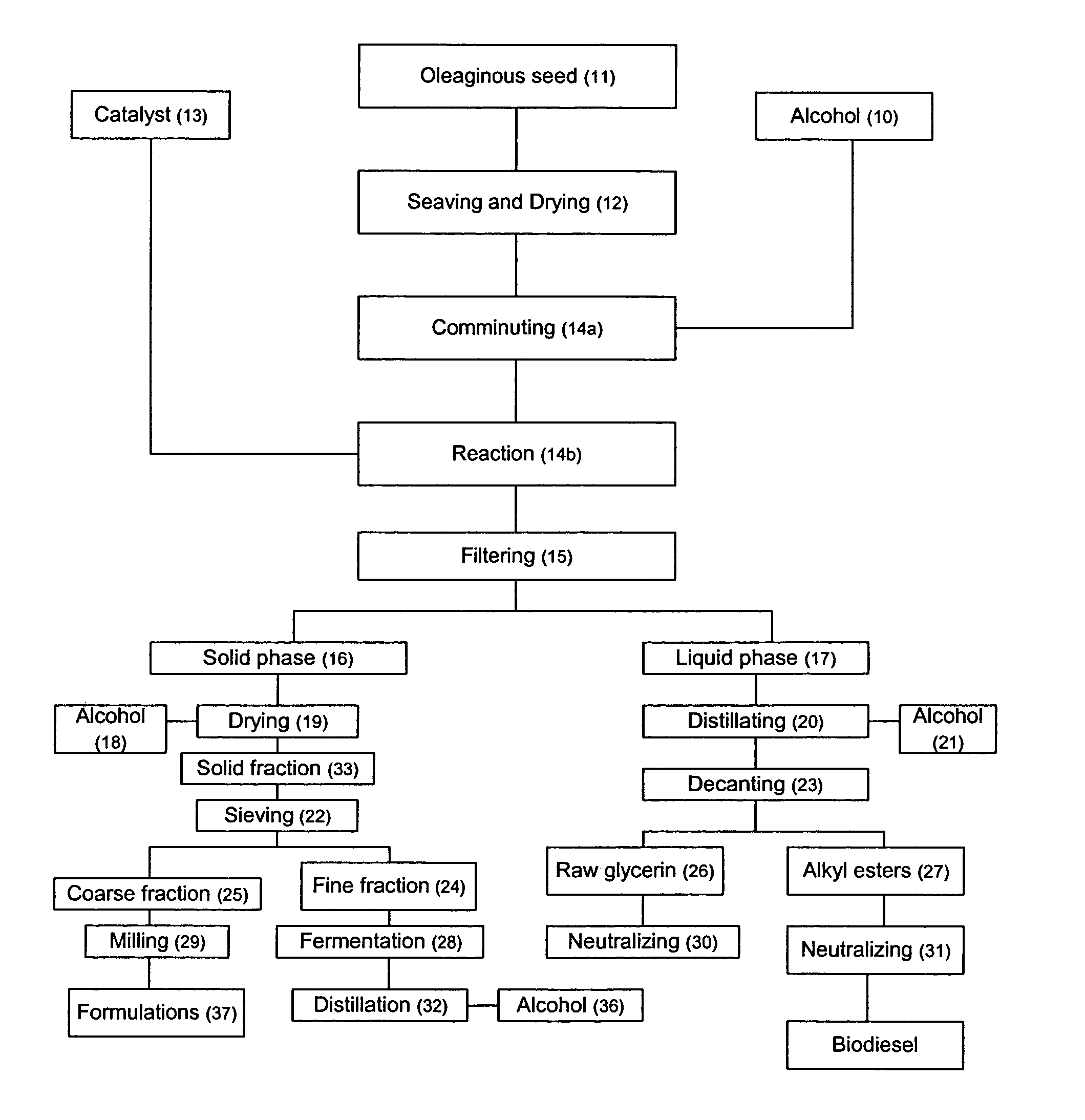
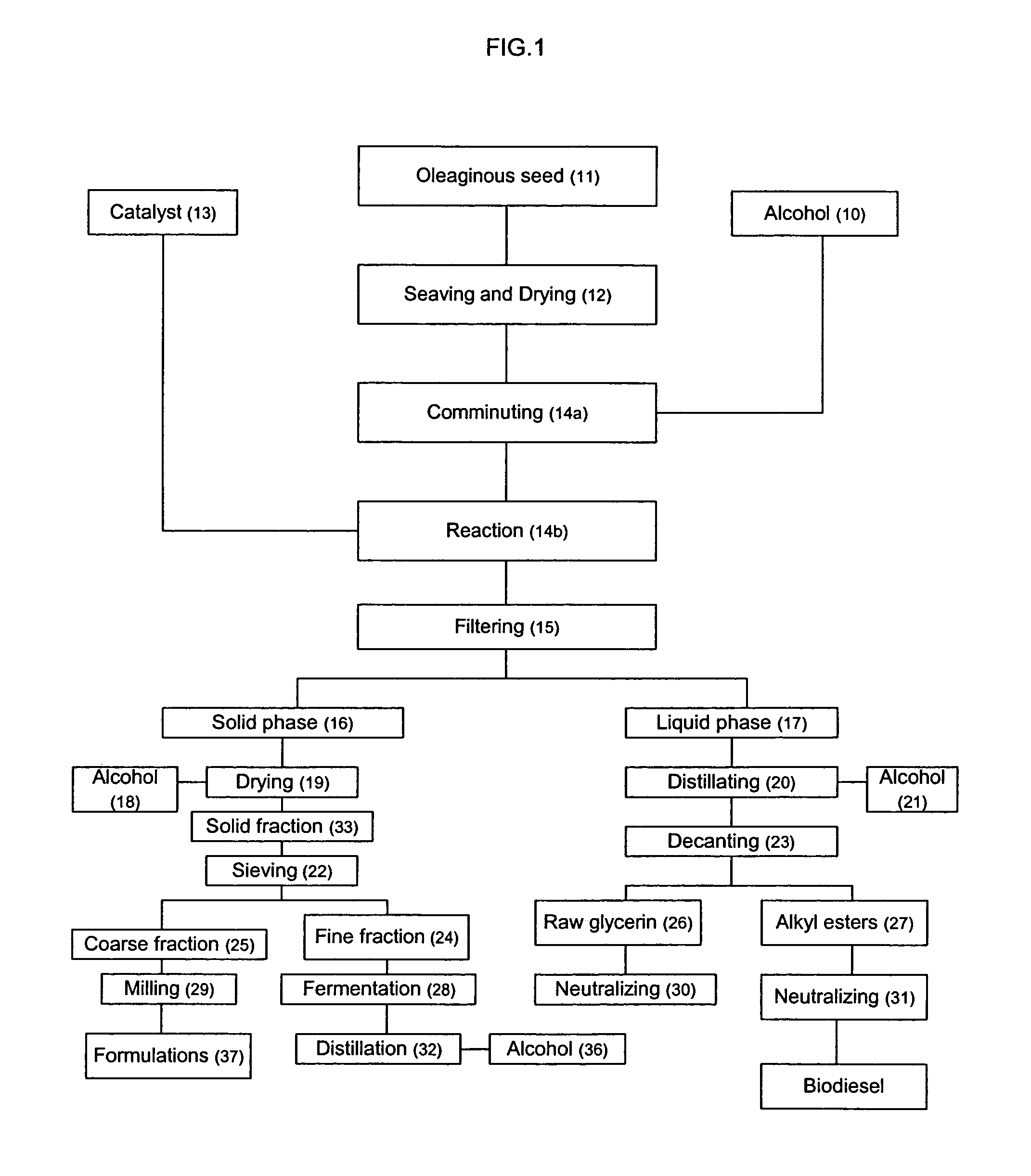
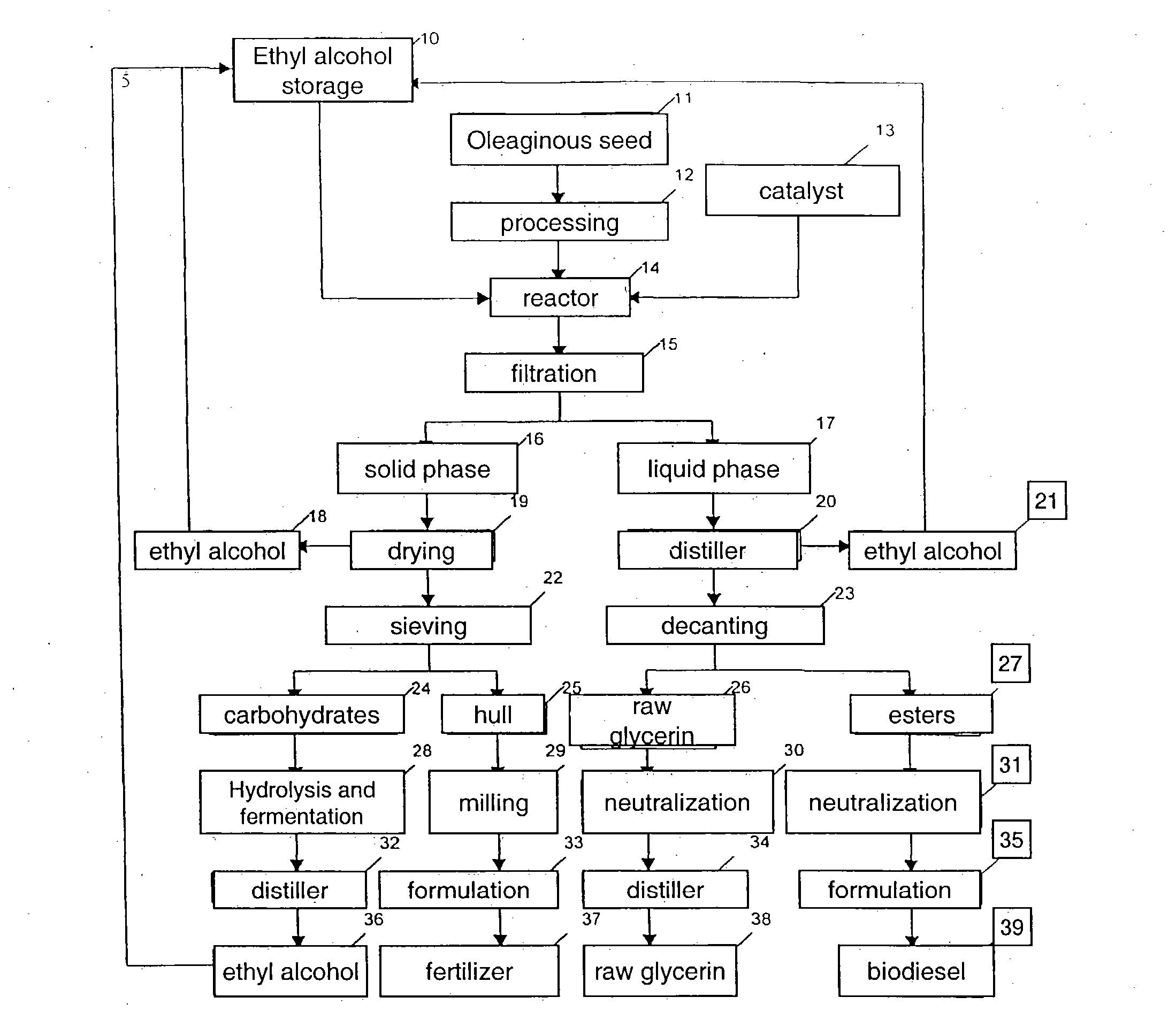
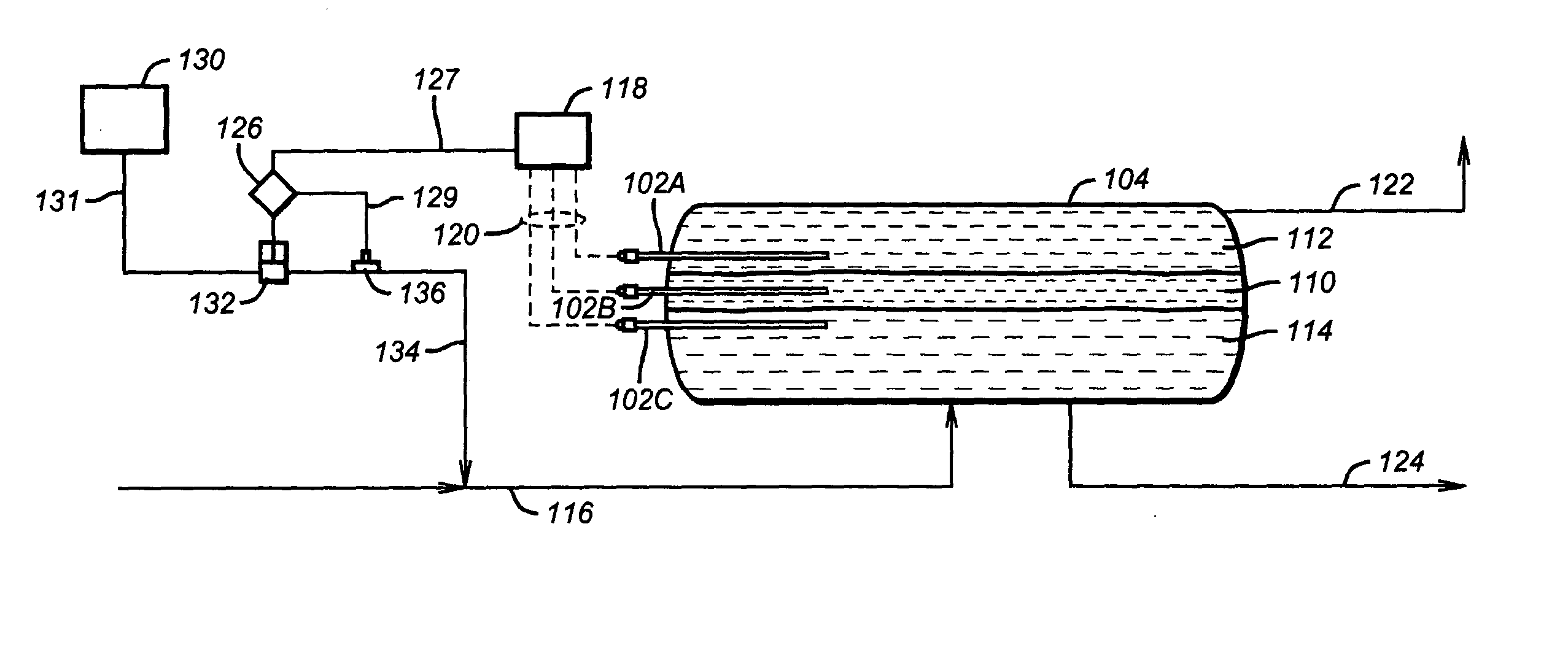
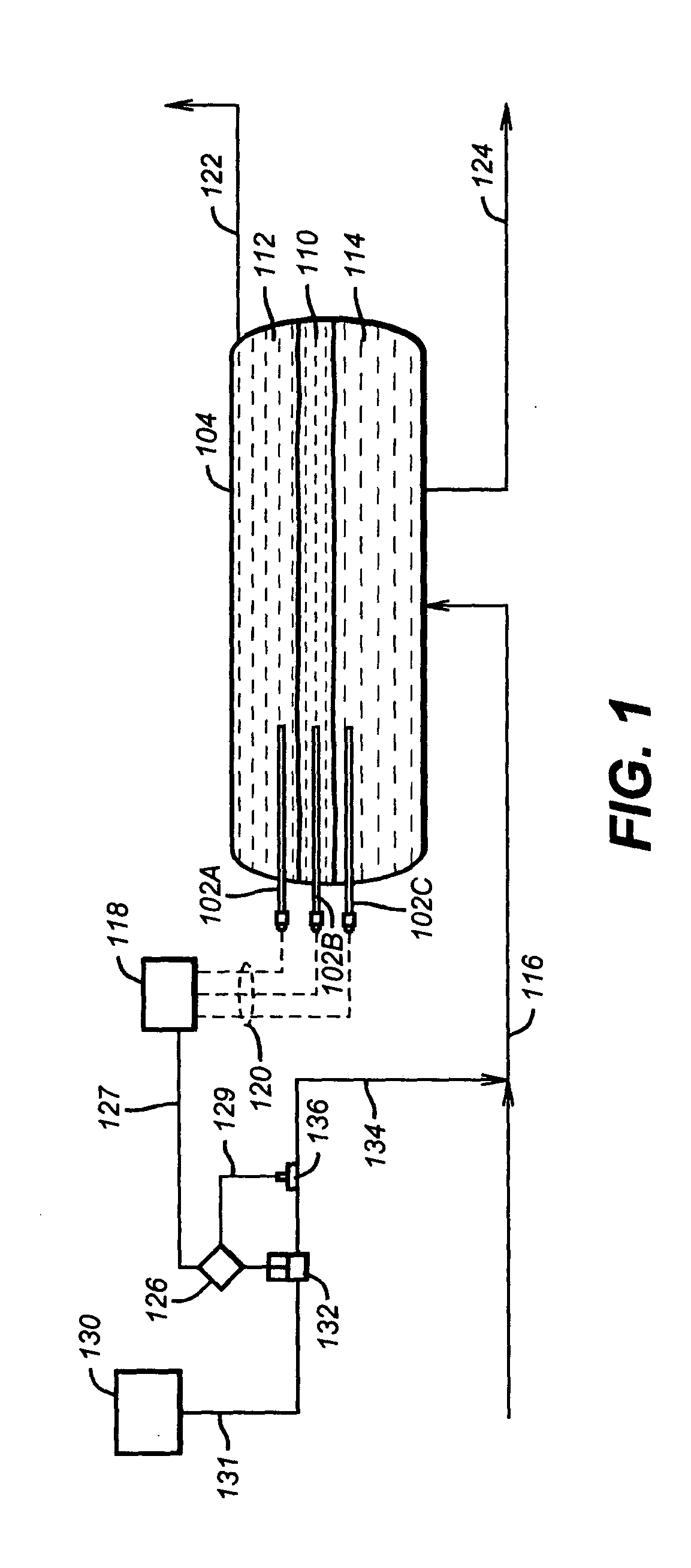
Process for producing biodiesel fuel using triglyceride-rich oleagineous seed directly in a transesterification reaction in the presence of an alkaline alkoxide catalyst
InactiveUS7112229B2Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationOil and greaseBiodiesel
An integrated process is described for producing biodiesel from oleaginous seeds, preferably castor bean seeds. The inventive process includes a transesterification reaction where the seeds themselves react with anhydrous ethyl alcohol in the presence of an alkaline catalyst. The resulting ethyl esters are then separated by decantation and neutralized and used as fuel for diesel engines, co-solvents for diesel and gasoline mixtures with anhydrous or hydrated ethyl alcohol. The solid fractions may be used as fertilizers, for feeding cattle and as a raw material for producing ethyl alcohol.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
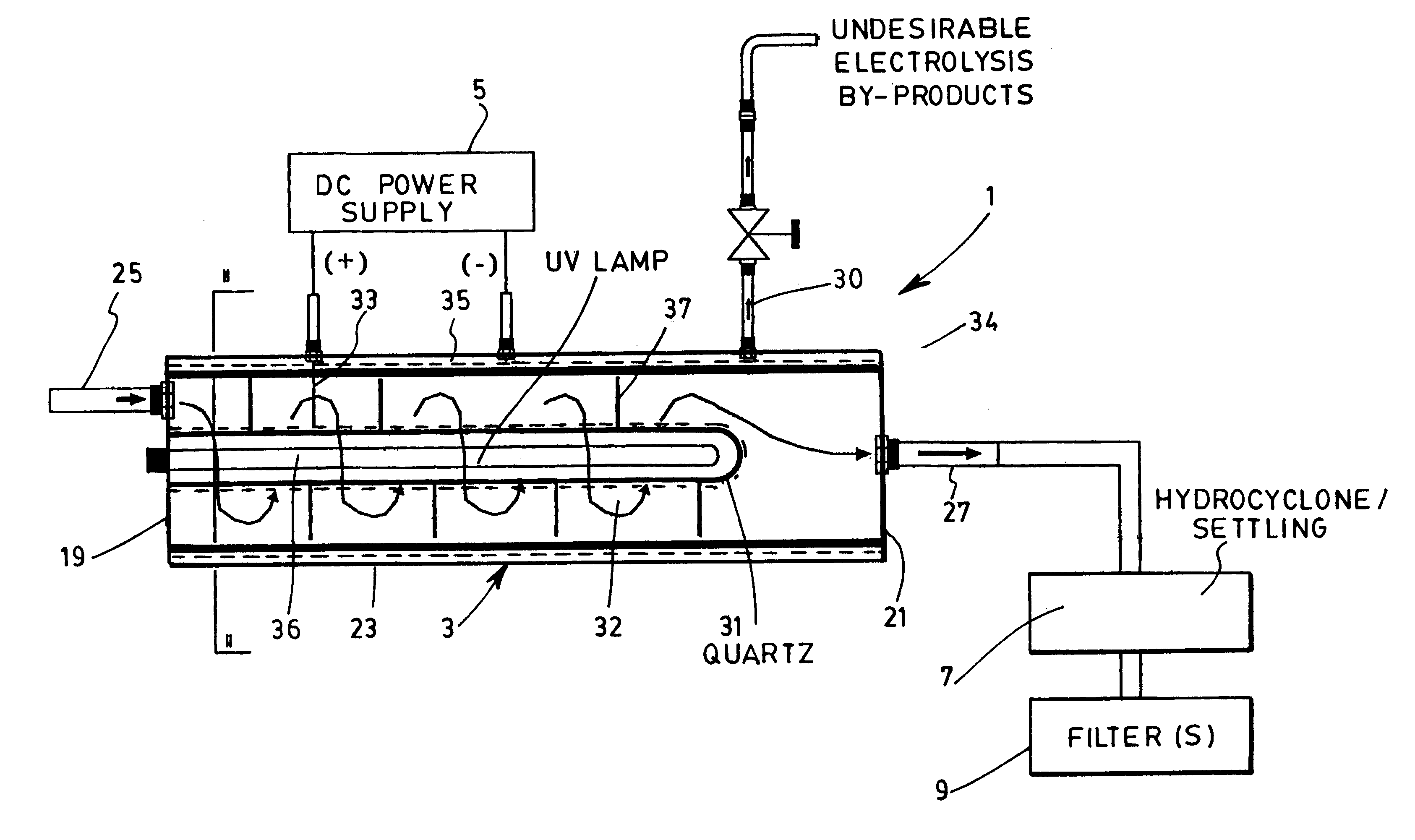
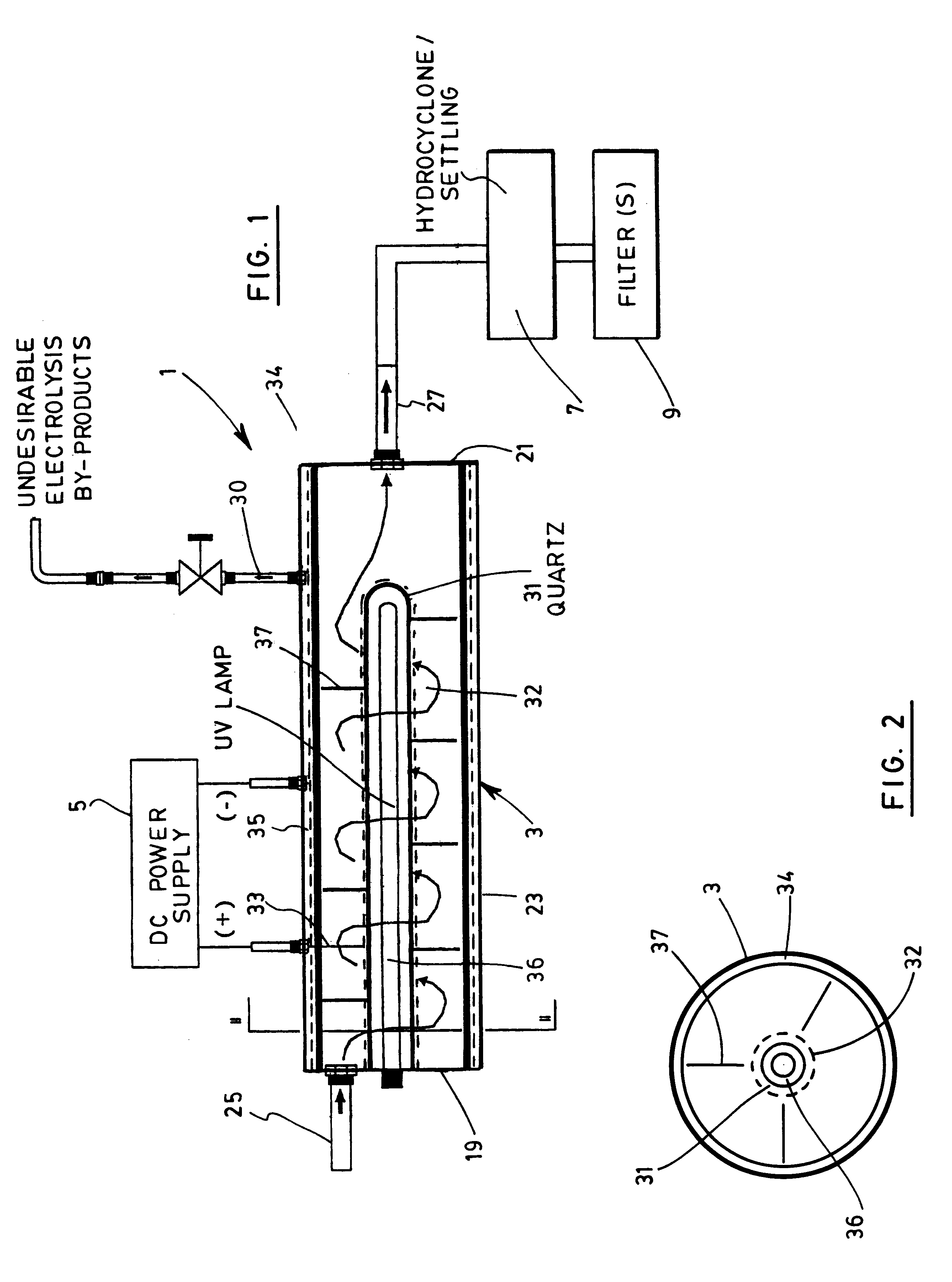
Device and method for treating water with ozone generated by water electrolysis
InactiveUS6180014B2Economical and efficient methodPhotography auxillary processesDisinfectionHigh concentrationElectrolysis
A process and a device for the treatment of water, especially for removing therefrom a large variety of pollutants, especially organic, inorganic and biological pollutants through in situ generation of ozone. Ozone is economically produced in situ at a high concentration through the interaction of electrolytically produced oxygen and UV light having a wavelength of 189 nm. The device has a set of anode and cathode for electrolytically producing nascent oxygen which reacts with UV light at a wavelength of 189 nm to produce ozone "in situ" within a vessel where the polluted water is submitted to the combinative action of ozone and other oxidation reactions. The device also has a hydrocyclone or retention tank of removing cationic pollutants such as heavy metals, free radicals as well as undesirable electrolysis byproducts such as nascent hydrogen through a secondary outlet. Oxidation by-products are subsequently removed from the exiting water stream by means of decantation, flocculation, coagulation or filtration.
Owner:SALAMA AMIR
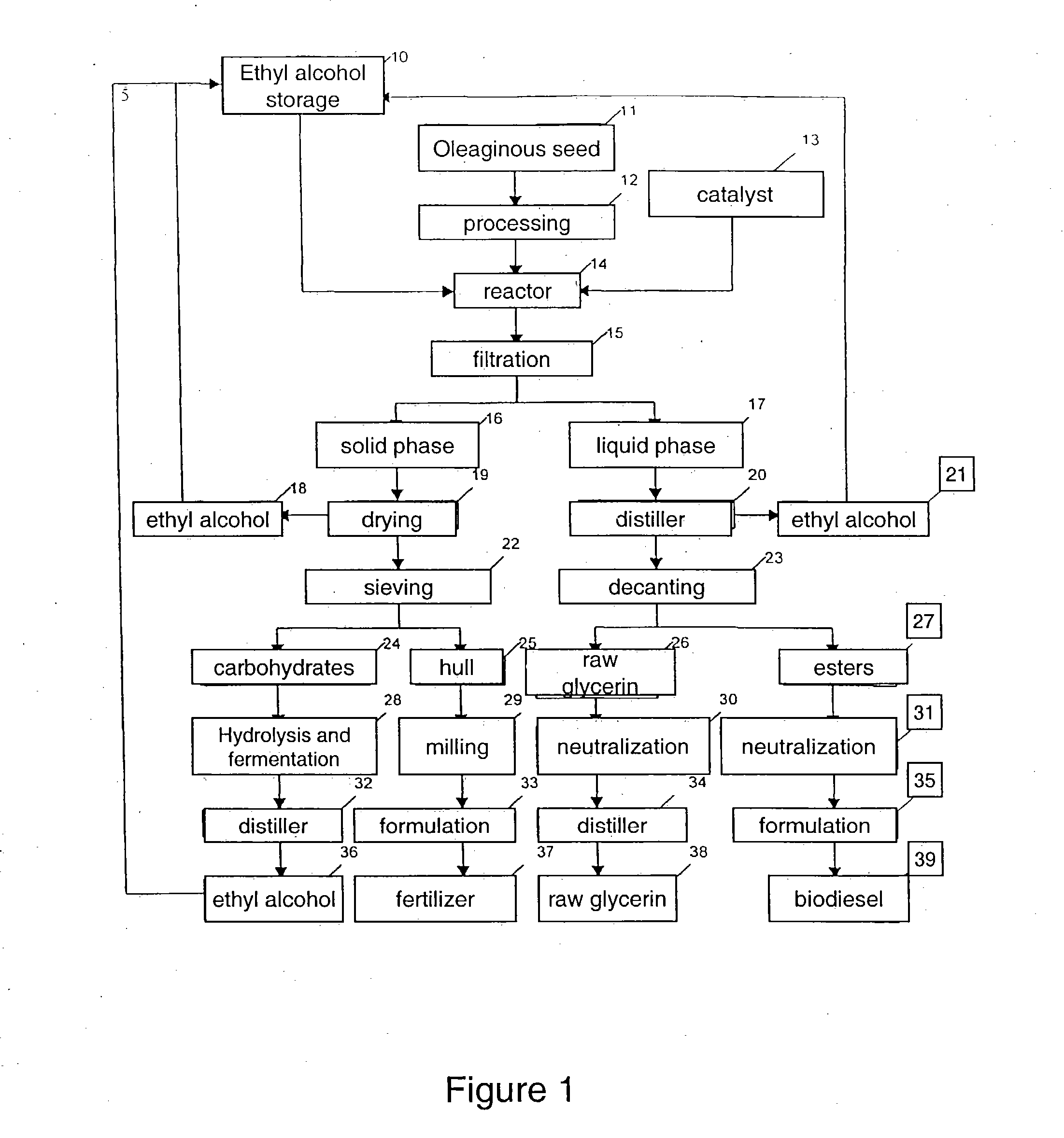
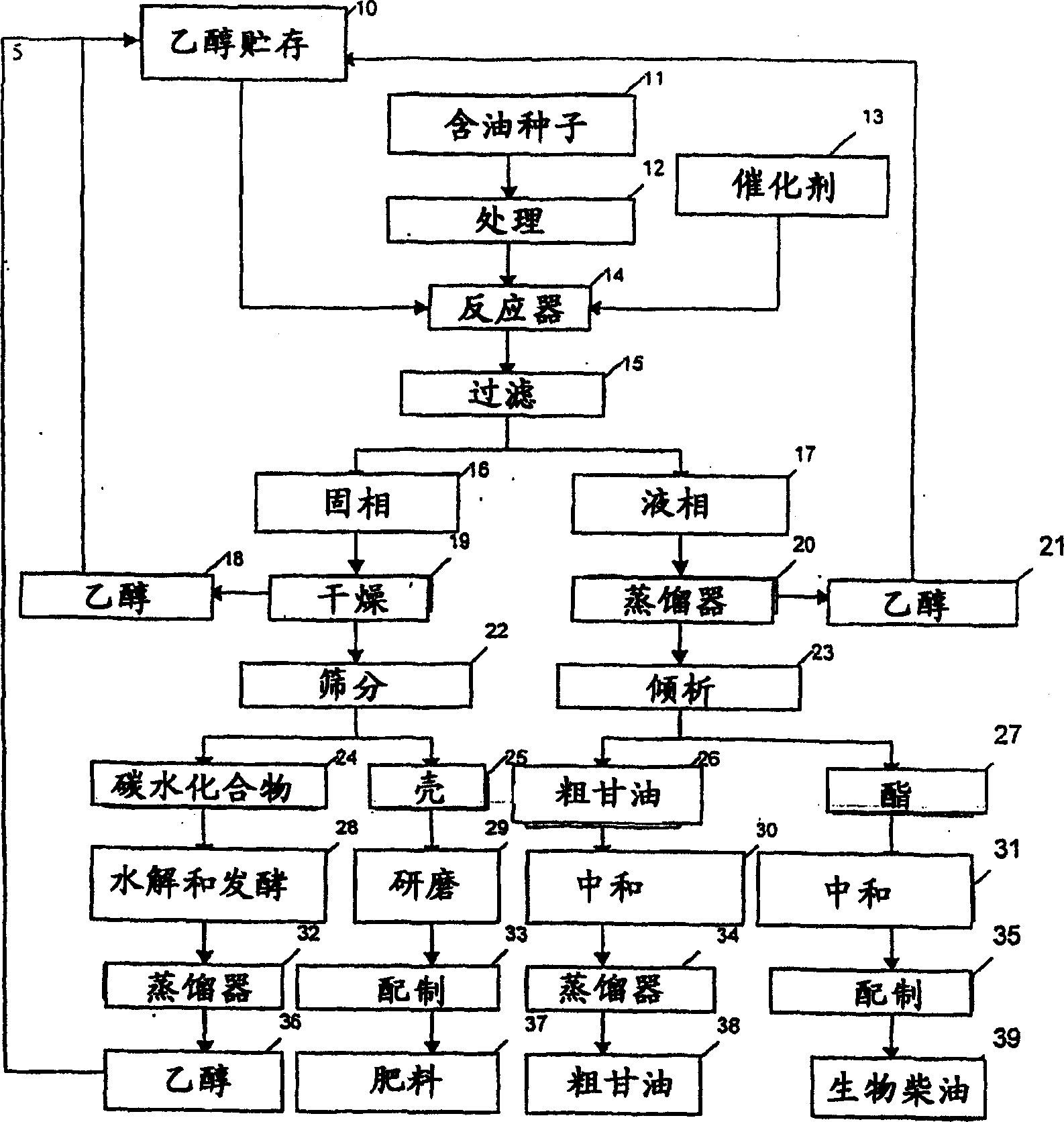
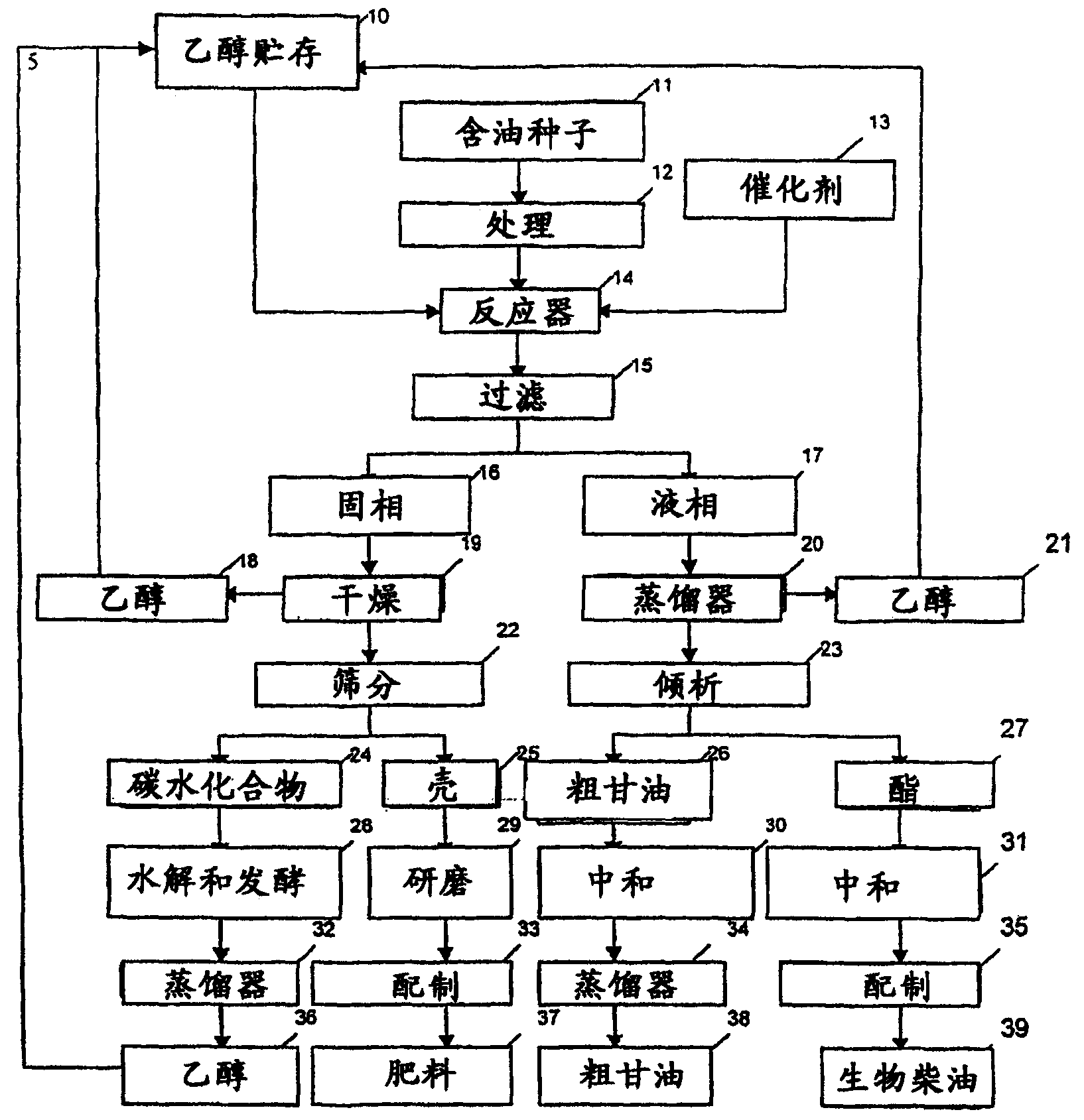
Process for producing biodiesel
InactiveUS20050011112A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationBiodieselSolid fraction
An integrated process is described for producing biodiesel from oleaginous seeds, preferably castor bean seeds, comprising a transesterification reaction where the seeds themselves react with anhydrous ethyl alcohol in the presence of an alkaline catalyst. The resulting ethyl esters are then separated by decantation and neutralized and used as fuel for diesel engines, co-solvents for diesel and gasoline mixtures with anhydrous or hydrated ethyl alcohol. The solid fractions may be used as fertilizers, for feeding cattle and as a raw material for producing ethyl alcohol.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Cellulose microsphere as well as preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN101250267ALarge specific surface areaGood biocompatibilityOther chemical processesOther blood circulation devicesCelluloseOrganic solvent
The invention discloses cellulose microsphere, and a preparation process and the application. The cellulose microsphere is prepared through dispersing cellulose solution in organic solvent which comprises emulsifier or composite emulsifier, solidifying in constant temperature for 1-10hr to shape after stirring to evenly disperse drops, then adding diluted acid to make cellulose regenerate into microsphere, standing and stratifying, filtering to obtain cellulose particles, finally obtaining cellulose microsphere after decantation. The solution of cellulose and the preparation of cellulose microsphere are physical processes without chemical reaction. The whole preparation technology is simple, has short time consumption, and organic solvent can be repeatedly used. The process has low device demand, which is convenient for industrial production. The cellulose microsphere which is prepared through adopting the process has favorable mechanical property, excellent flow-ability, heat stability and swelling resistance property, oxidation resistance ability, biodegrability resistance and acidic and alkali degradation capability, and has extensive usage.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Process for the production of biodiesel in continuous mode without catalysts
InactiveUS20070010681A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationBiodieselVegetable oil
A continuous, non catalytic process for producing biodiesel from vegetable oils and ethanol or methanol includes pumping a mixture of vegetable alcohol through a pump towards a tube shaped reactor, wherein the mixture is submitted to high pressure and temperature, where the resulting product is non reacted alcohol, glycerin and a mixture of esters (biodiesel) which is directed to the reservoir at the reactor outlet where an upper phase of alcohol is redirected through an alcohol return pipe to the pump inlet, and the intermediate phase, biodiesel, and the lower phase (mostly of glycerin) are led to the separation reservoir or decantation tank, where the alcohol is removed through the alcohol return pipe, being biodiesel and glycerin the final products, which are then collected for the end to which they were aimed.
Owner:INTECNIAL +1
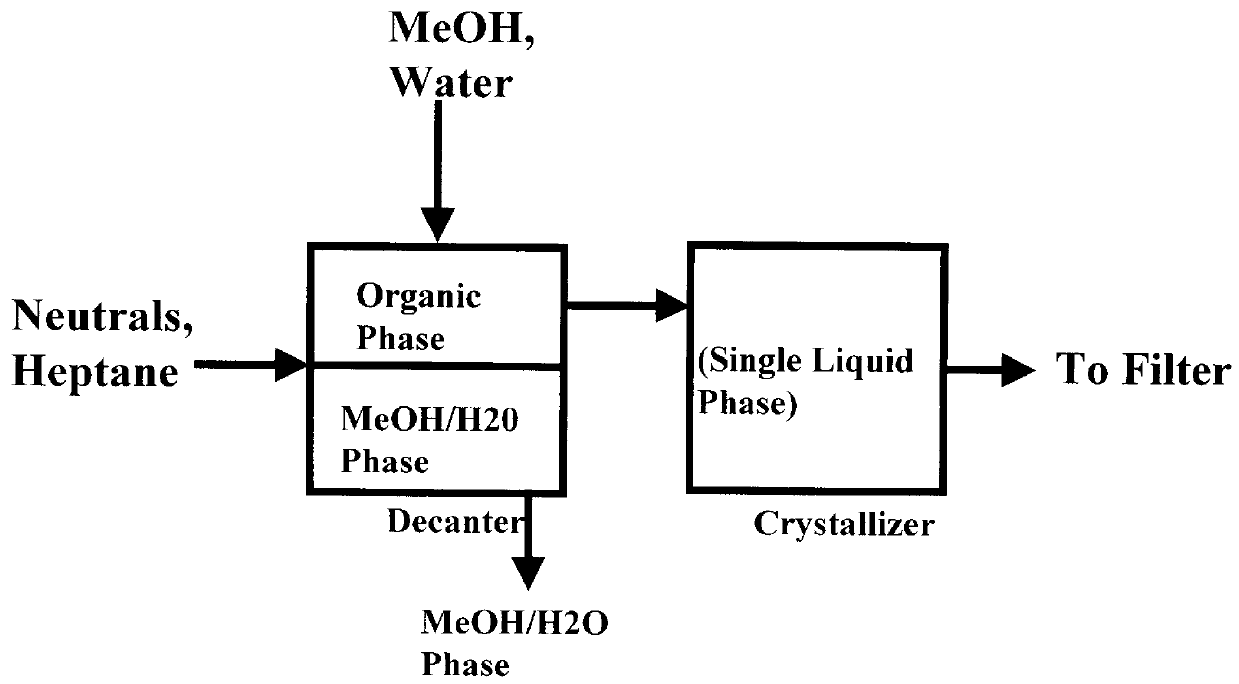
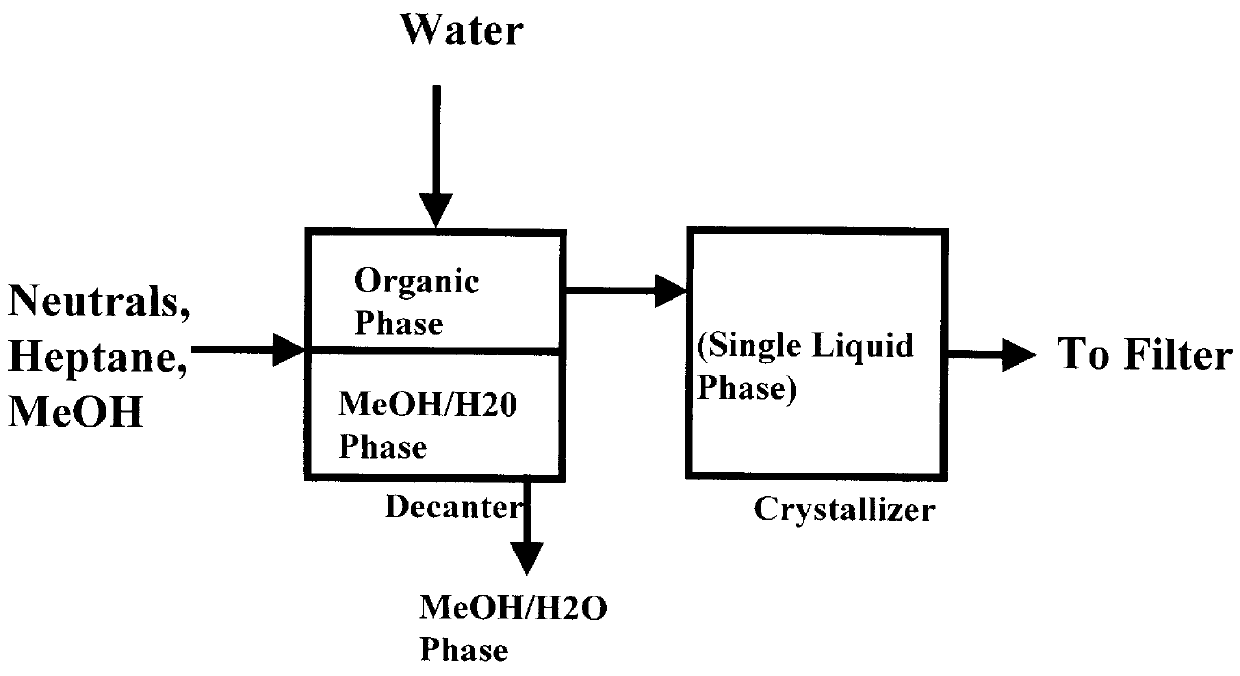
Isolation and purification of sterols from neutrals fraction of tall oil pitch by single decantation crystallization
Sterols from the solvent-extracted or distilled neutrals of saponified tall oil pitch are disclosed to be isolated and purified by a process of a liquid-liquid extraction where the hydrocarbon extraction stream is washed with an aqueous methanol solution to remove methanol-soluble impurities by adding the methanol and water, sequentially or as a blend. The resulting hydrocarbon / neutrals / methanol / water solution separates into an upper organic phase and a lower methanol / water phase, which lower phase is removed. The remaining organic phase is allowed to cool to from about 20-30 DEG C., with agitation, to facilitate crystallization of sterols, which crystals are recovered by filtering.
Owner:MEADWESTVACO CORP
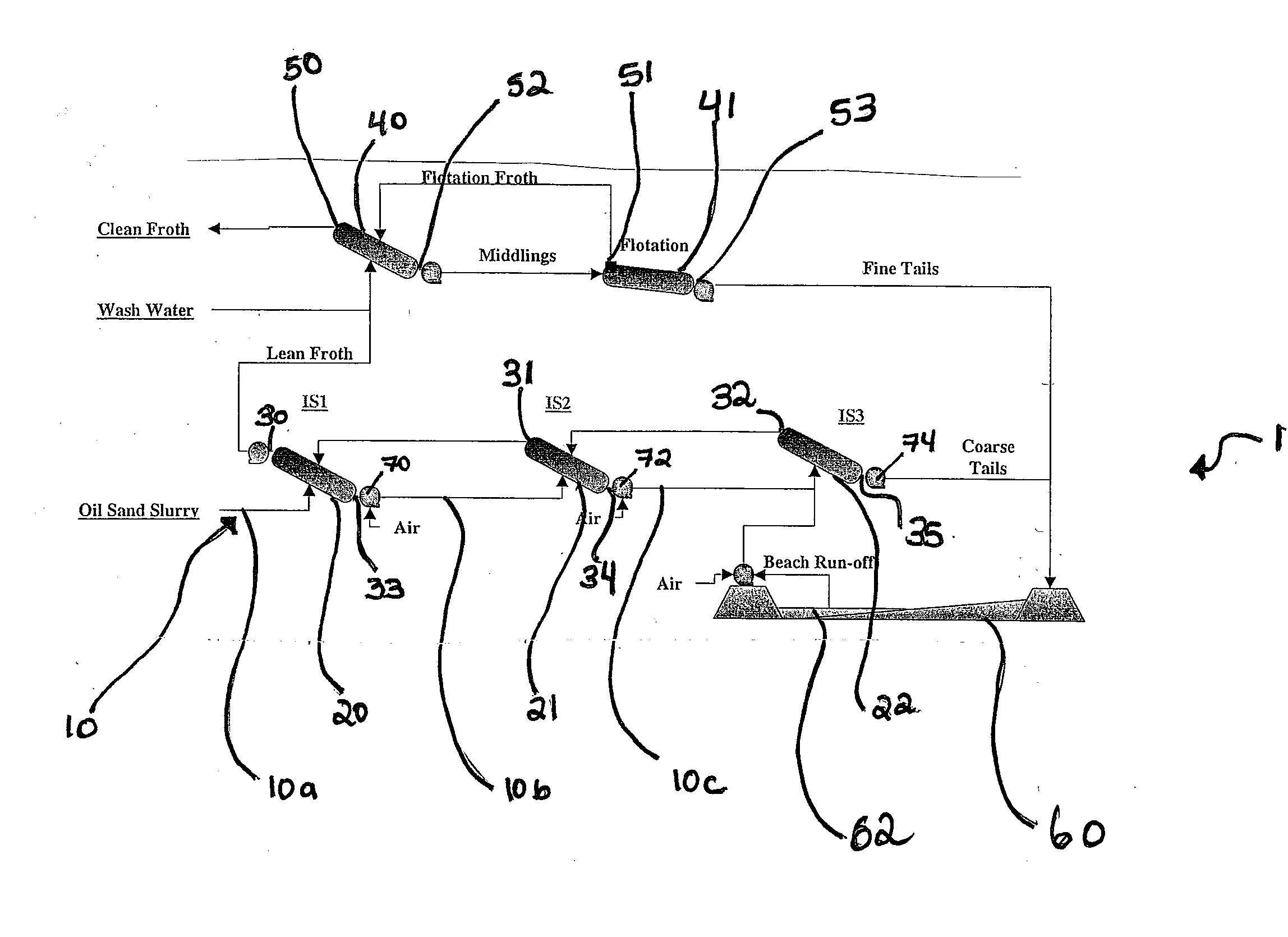
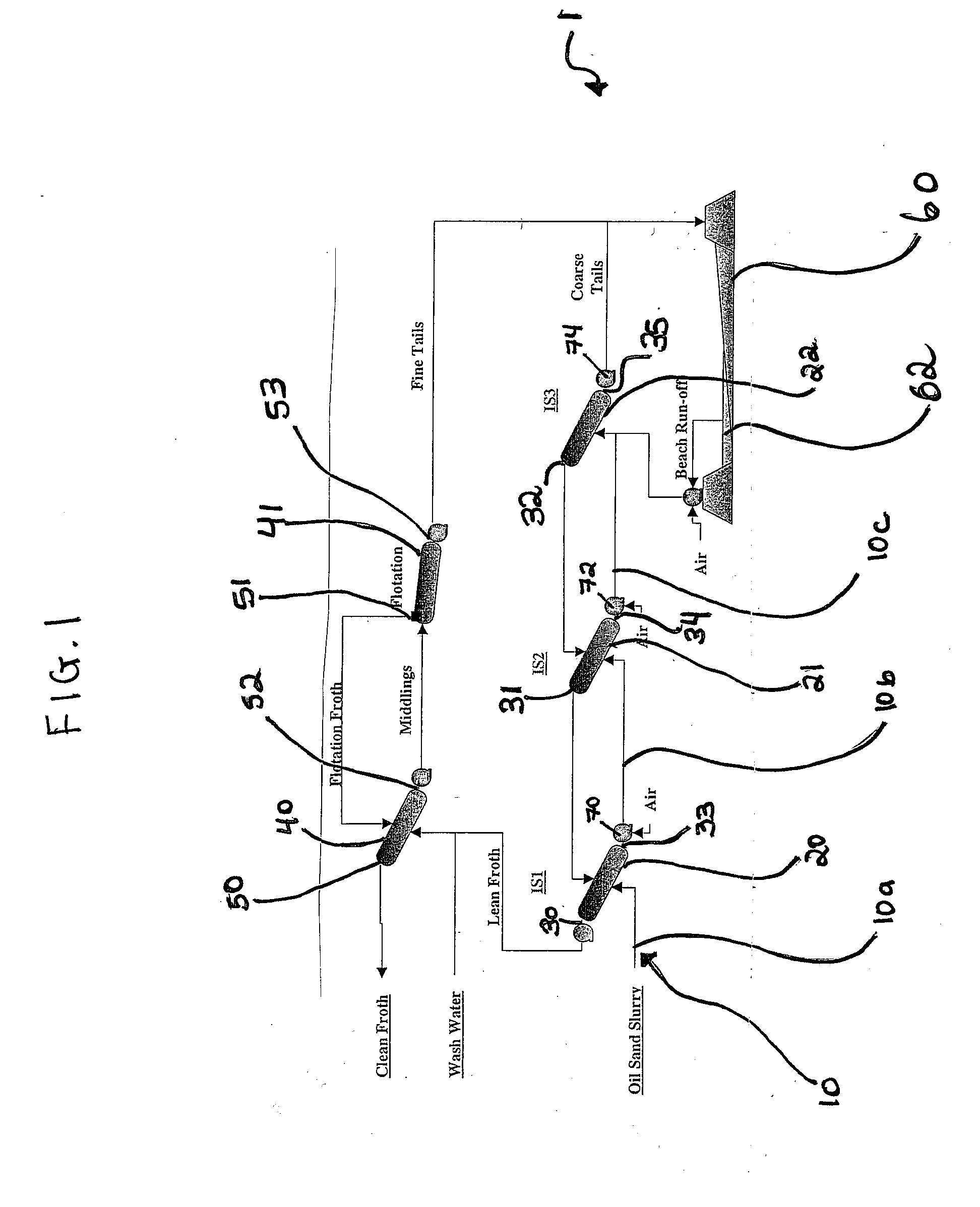
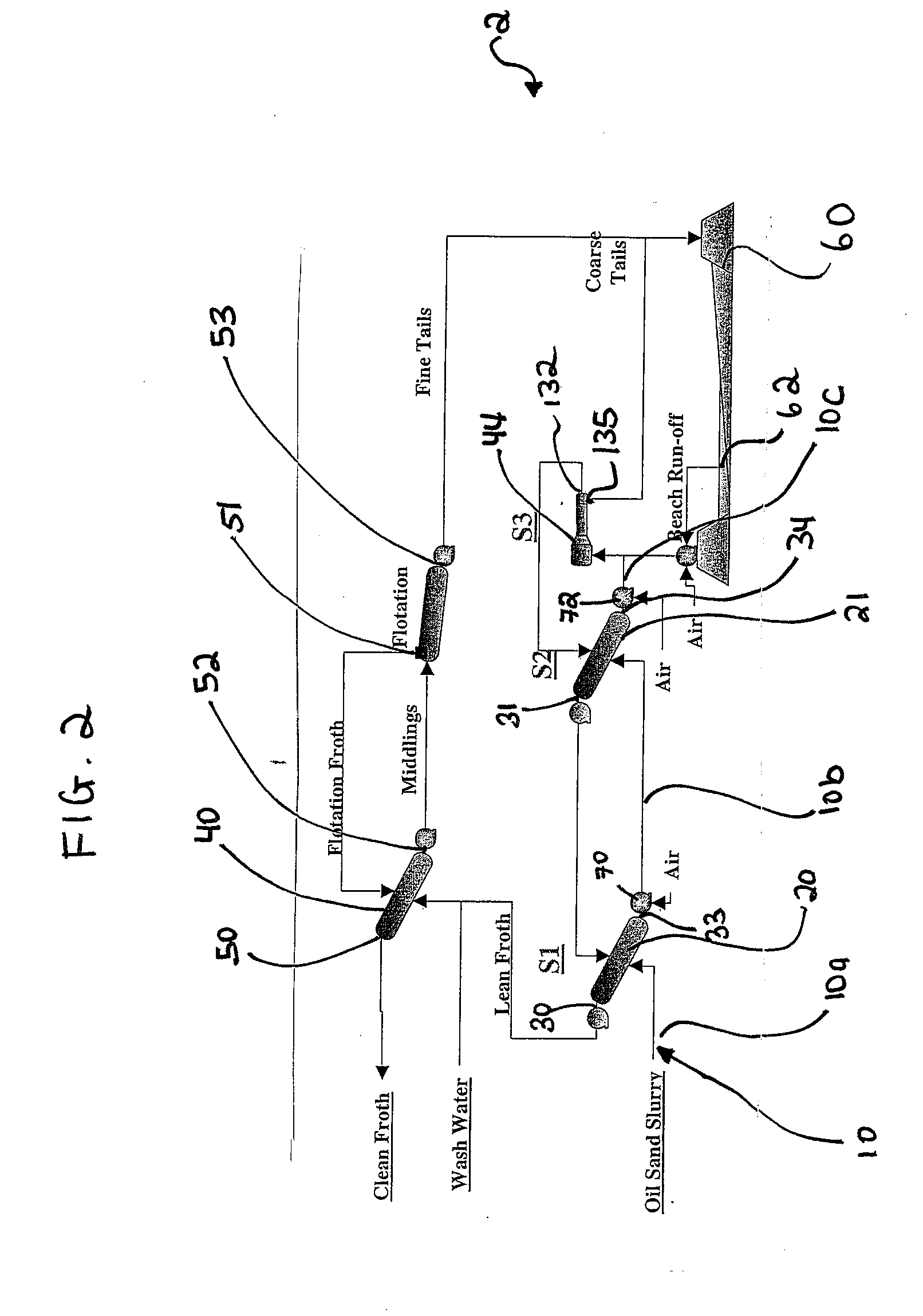
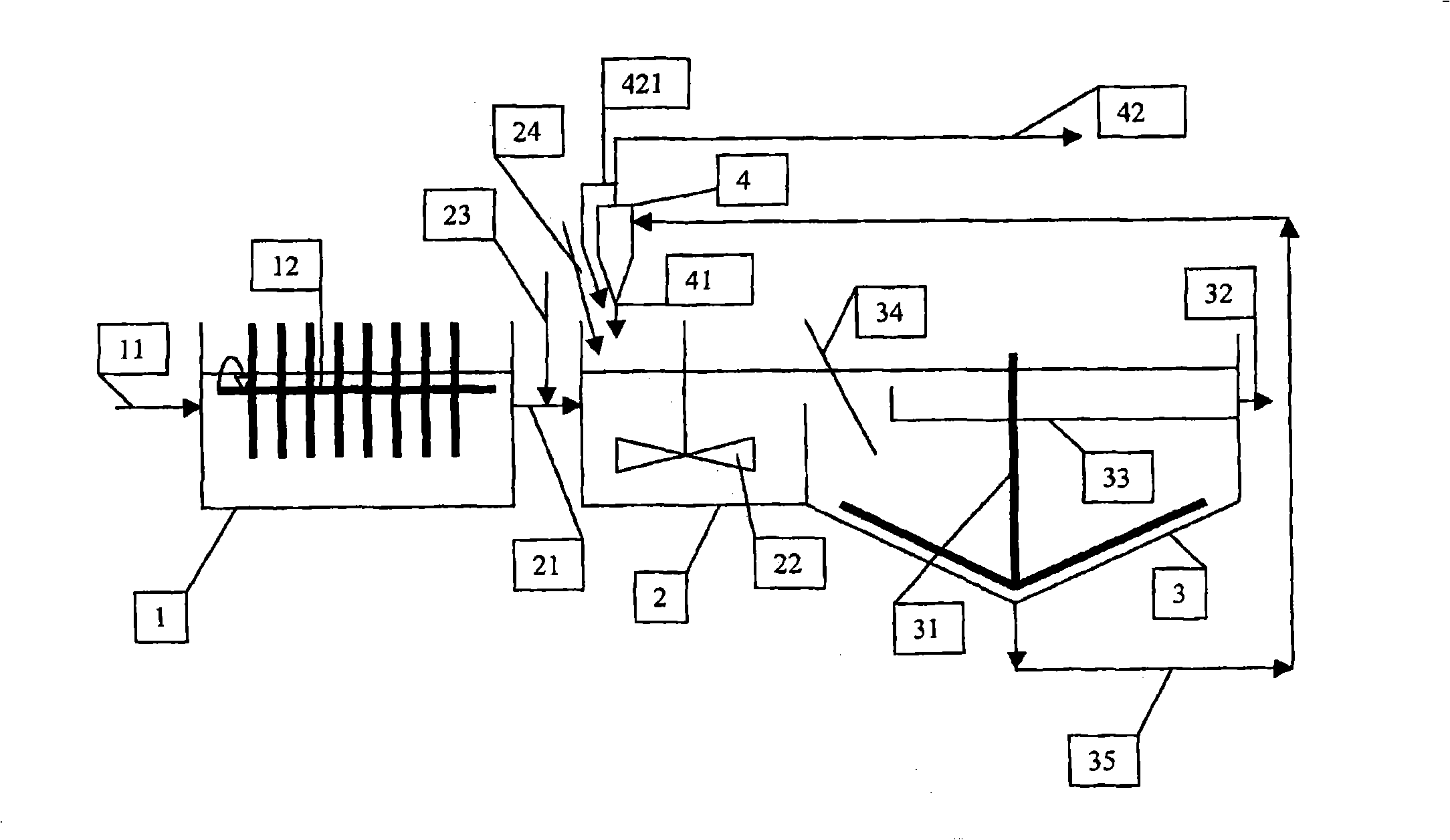
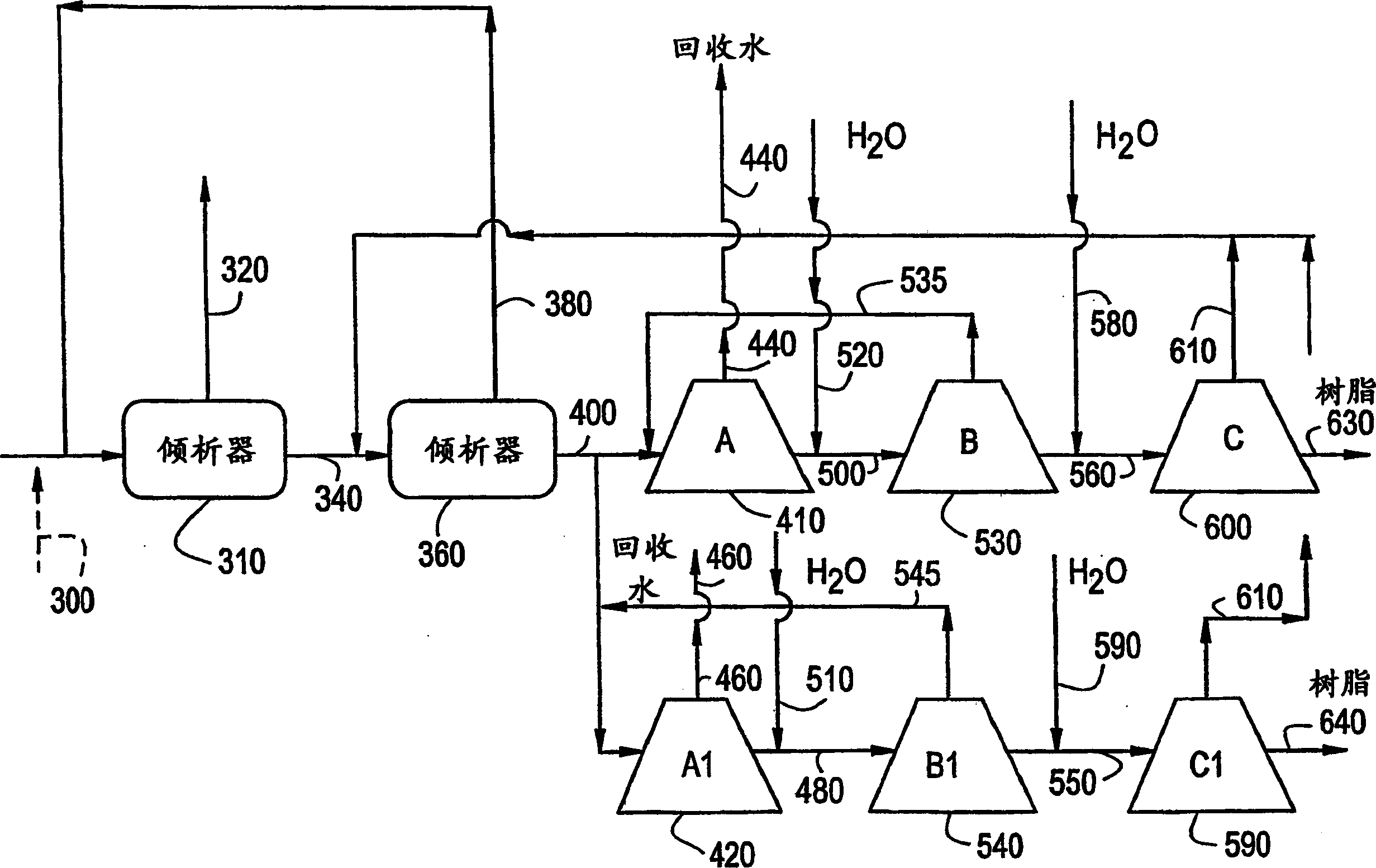
Relocatable countercurrent decantation system
InactiveUS20070289911A1Liquid separation auxillary apparatusReversed direction vortexProcess engineeringSlurry
A process line for separating oil sand slurry comprising coarse solids, fines, bitumen and water, into a first product comprising bitumen, fines and water and a second product comprising coarse solids, fines and water is provided comprising a plurality of countercurrently operating solid / liquid separators arranged in series along a pipeline, wherein the underflow of one separator is fed to the next separator in series and the overflow of each separator is fed to the preceding separator, the underflow of the last separator being the second product and the overflow from the first separator being the first product.
Owner:CANADIAN OIL SANDS +6
Method for preparing immobilized enzyme by using spherical bacterial cellulose as carrier
InactiveCN101705222ASignificant progressSignificant positive effectMicroorganism based processesOn/in organic carrierWater bathsFermentation
The invention relates to a method for preparing immobilized enzyme by using spherical bacterial cellulose as a carrier. The method comprises the following steps of: inoculating activated slant strains into a seed culture medium for cultivation to obtain a liquid seed, shifting the liquid seed into a fermentation medium under a condition of 80 to 200 rpm at the temperature between 25 and 30 DEG C for 48 to 96 hours, and carrying out decantation to obtain bacterial cellulose balls; processing the bacterial cellulose balls in a water bath at the temperature between 80 and 90 DEG C for 30 to 120 min with 0.1 percent NaOH, rinsing the balls with deionized water, collecting the balls, neutralizing residual alkali liquor in the balls with 0.1 percent acetic acid, standing, rinsing the balls with the deionized water, taking the balls out, absorbing surface moisture, and freezing and drying the balls to obtain cellulose balls; and finally, preparing the immobilized enzyme by a physical adsorption method or an adsorption-crosslinking method. The spherical bacterial cellulose balls can effectively adsorb biological enzyme, maximally keep enzyme activity, and have safety and environmental protection. The method is simple and easy to operate and has strong controllability.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Improved process for treating gases containing hydrogen sulfur and sulfur dioxide
InactiveCN1840470AOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsDispersed particle separationCarboxylic acidSolvent
A process for treating a gas containing hydrogen sulphide (H2S) and sulphur dioxide (SO2) is described in which: said gas is brought into contact at a suitable temperature with an organic solvent containing at least a soluble catalytic system, comprising at least one compound comprising at least one functional group A consisting of a carboxylic acid function and at least one functional group B comprising at least one nitrogen atom and which can produce an acid-base type reaction with at least one functional group A under the operating conditions of said process; a gaseous effluent substantially depleted in hydrogen sulphide and sulphur dioxide is recovered, along with liquid sulphur separated from the solvent by liquid-liquid decantation; said catalytic system which is employed slowing by-product formation.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Real-time on-line sensing and control of emulsions in formation fluids
ActiveUS20050018176A1Efficient demulsificationReduce presencePhase-affecting property measurementsScattering properties measurementsEmulsionEngineering
Real time determination of the presence of emulsion in a formation fluid is accomplished using an optical probe, preferably an attenuated total reflectance probe. The determination can then be used to appropriately increase, decrease or leave unchanged the use of demulsification additives or other means to control emulsion formation. The method is particularly useful for free water knock-out separations, where a plurality of probes can be used to distinguish the location and / or volume of emulsion, or “rag”, layer and thereby to facilitate decantation of relatively pure oil and water fractions. It can also be effectively used in pipelines, and can optionally determine the degree of emulsification and trends toward emulsification or demulsification.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Process for producing biodiesel
An integrated process is described for producing biodiesel from oleaginous seeds, preferably castor bean seeds, comprising a transesterification reaction where the seeds themselves react with anhydrous ethyl alcohol in the presence of an alkaline catalyst. The resulting ethyl esters are then separated by decantation and neutralized and used as fuel for diesel engines, co-solvents for diesel and gasoline mixtures with anhydrous or hydrated ethyl alcohol. The solid fractions may be used as fertilizers, for feeding cattle and as a raw material for producing ethyl alcohol.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Method for producing crude tall oil by soap washing with calcium carbonate removal
ActiveUS20120123087A1Avoid confusionAvoid accumulationFatty oils/acids recovery from wastePulp liquor regenerationBlack liquorFiltration
A method for producing crude tall oil from black liquor soap while removing calcium carbonate and lignates is disclosed. Black liquor soap is first combined with an alkaline ash medium having a lower concentration of lignates and inorganic solids than the black liquor soap, to form washed tall oil soap, fortified brine, lignates, and calcium carbonate. The washed tall oil soap is then separated from the fortified brine, lignates, and calcium carbonate, by centrifugation, decantation, filtration, settling, or a combination of these techniques. Acidification of the washed tall oil soap gives crude tall oil and a spent acid mixture. The crude tall oil is separated from the spent acid. The spent acid is made alkaline, and at least a portion of it is returned for use as alkaline wash medium. The method avoids accumulation of calcium sulfate in acidulation units.
Owner:KRATON CHEM LLC
Real-time on-line sensing and control of emulsions in formation fluids
InactiveUS6927846B2Reduce presenceSmooth connectionPhase-affecting property measurementsScattering properties measurementsEmulsionWater fraction
Real time determination of the presence of emulsion in a formation fluid is accomplished using an optical probe, preferably an attenuated total reflectance probe. The determination can then be used to appropriately increase, decrease or leave unchanged the use of demulsification additives or other means to control emulsion formation. The method is particularly useful for free water knock-out separations, where a plurality of probes can be used to distinguish the location and / or volume of emulsion, or “rag”, layer and thereby to facilitate decantation of relatively pure oil and water fractions. It can also be effectively used in pipelines, and can optionally determine the degree of emulsification and trends toward emulsification or demulsification.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
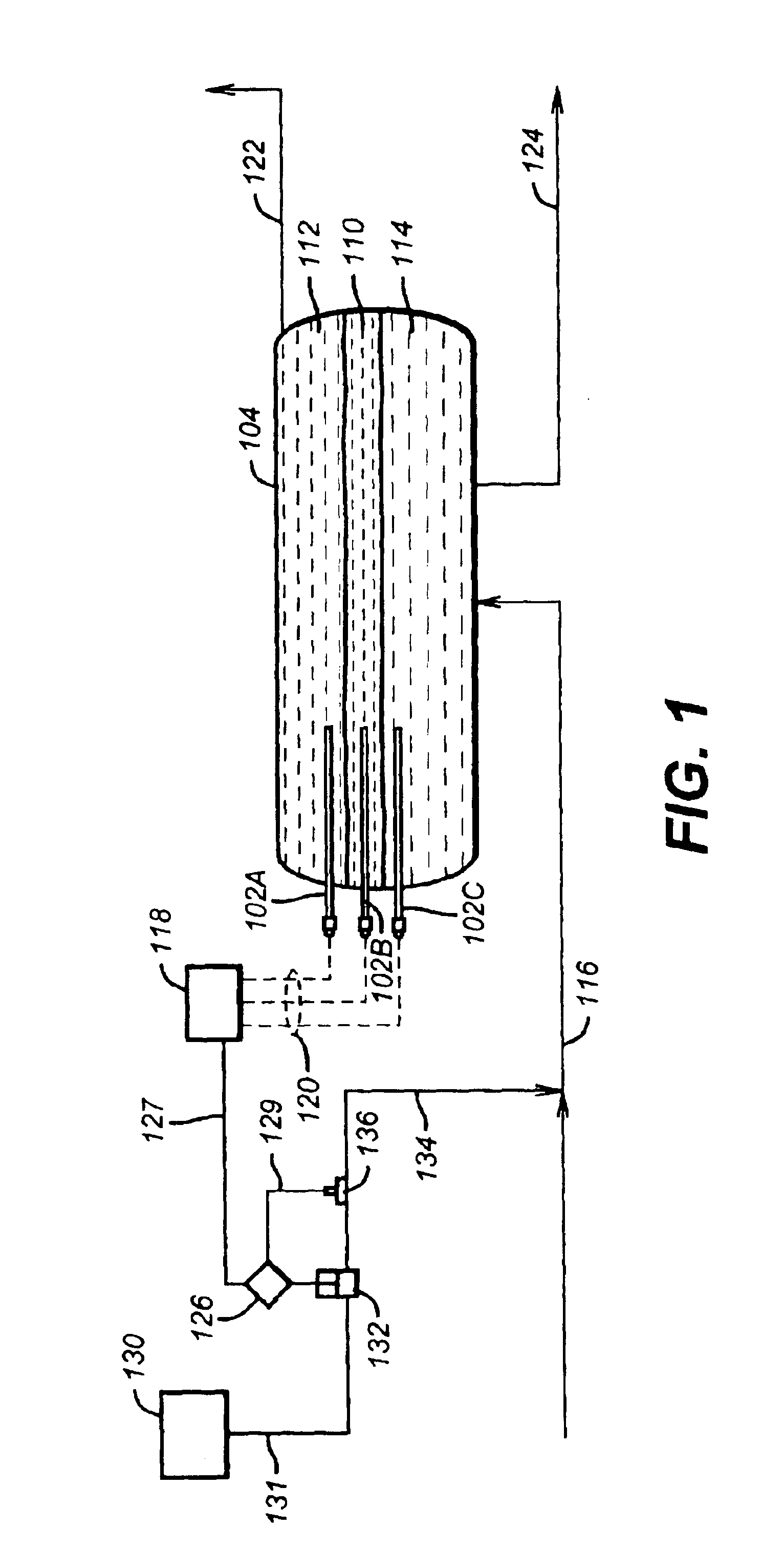
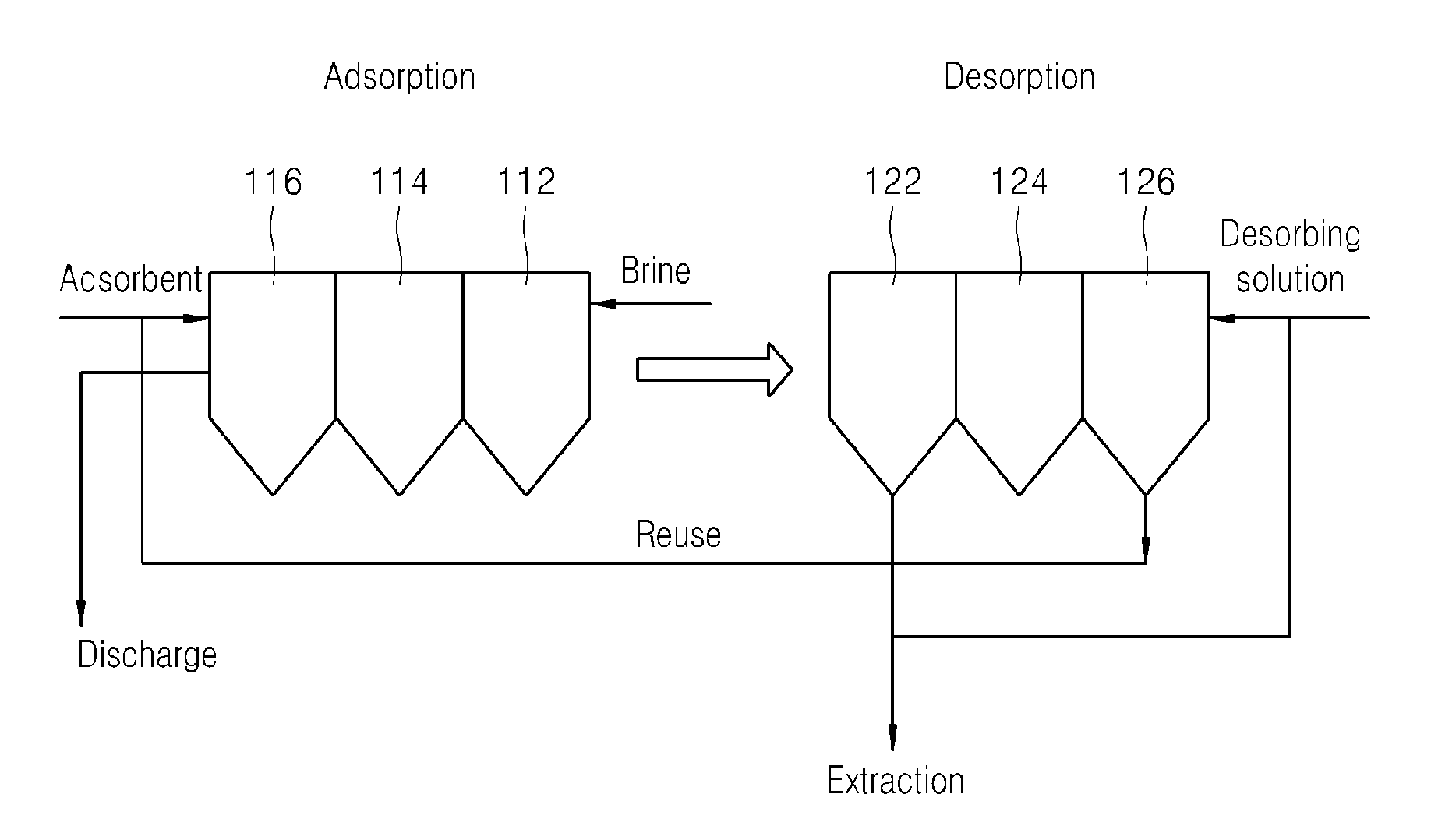
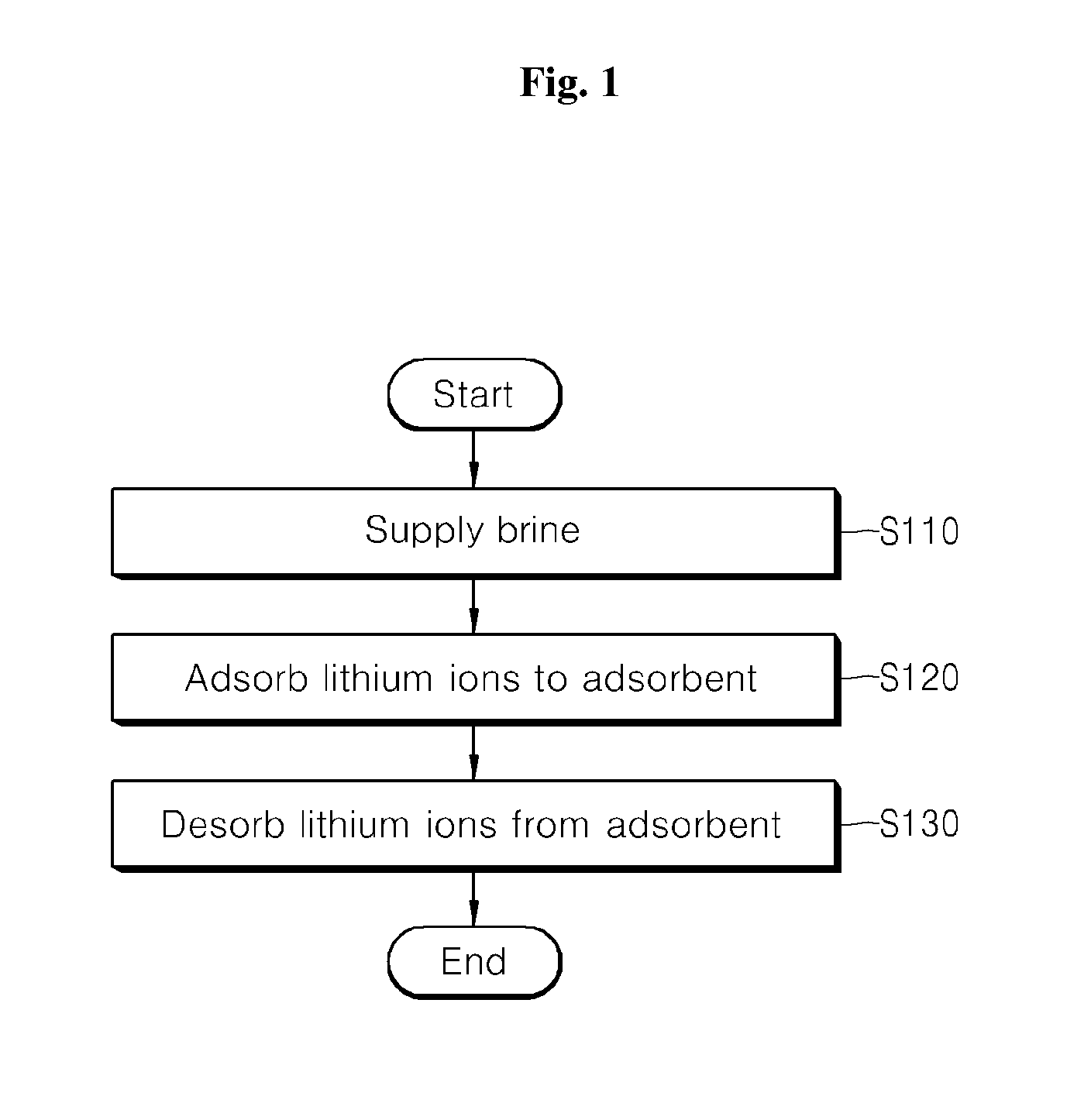
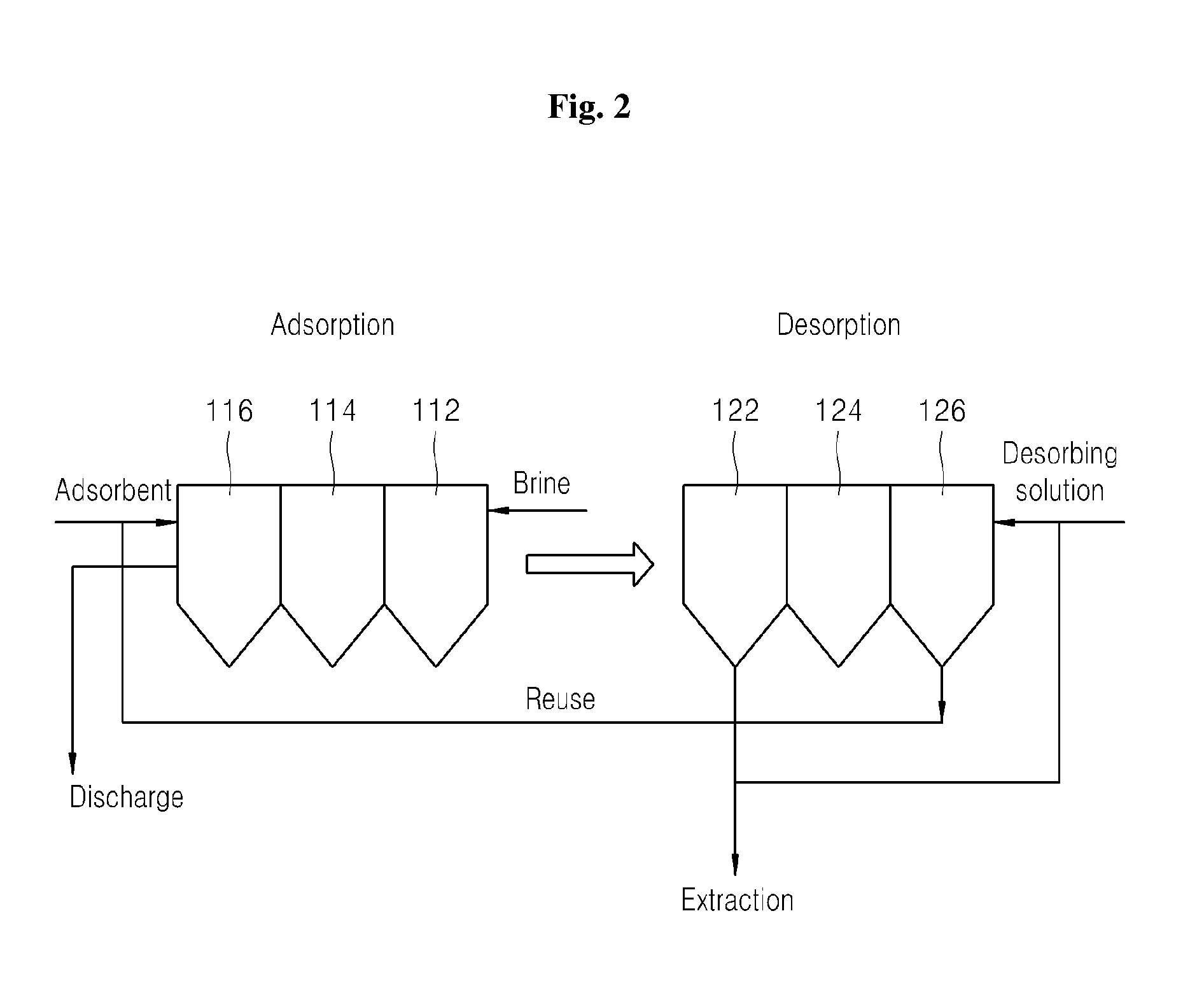
Apparatus and method for adsorbing and desorbing lithium ions using a ccd process
ActiveUS20130001168A1Efficient and economically feasible extractionEffective and economically feasible extractionIon-exchange process apparatusIon-exchanger regenerationLithiumDesorption
The present disclosure provides a method for adsorption / desorption of lithium ions from brine, which employs a counter current decantation process in adsorption / desorption of lithium ions, thereby achieving an adsorption rate of 65±5% and a desorption rate of 95±3%. The method includes supplying brine into one of a plurality of adsorption reactors, adsorbing lithium ions to an adsorbent by supplying the adsorbent to the adsorption reactor to which the brine is supplied and forcing the brine and the adsorbent to sequentially flow backwards inside the respective adsorption reactors, and desorbing the lithium ions from the brine by forcing the adsorbent to which the lithium ions are adsorbed to sequentially flow backwards inside a plurality of desorption reactors. Here, the brine and the adsorbent are stirred by a stirrer to maintain the adsorbent in an intermediate state instead of settling or floating inside the respective adsorption reactors.
Owner:KOREA INST OF GEOSCI & MINERAL RESOURCES
Synchronous grouting grout for shield construction control and grouting method thereof
InactiveCN103396065AEasy to controlMeet security needsUnderground chambersTunnel liningMass ratioFilling rate
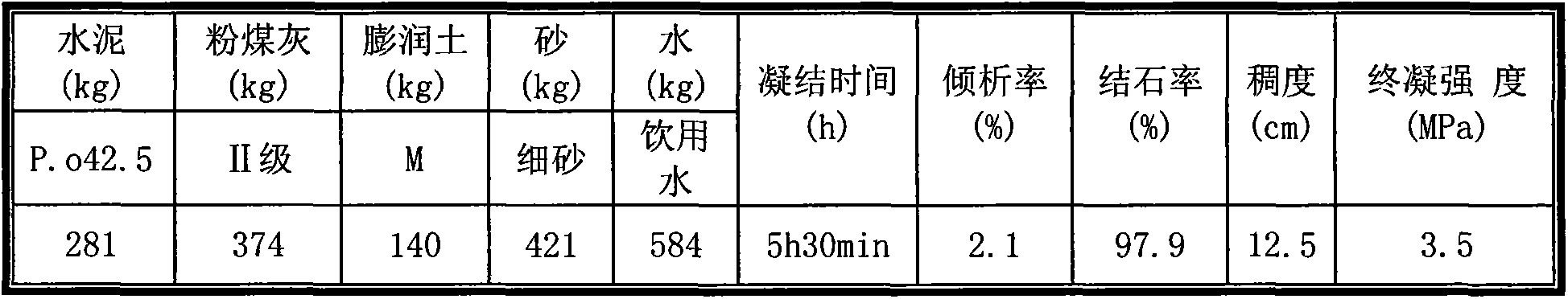
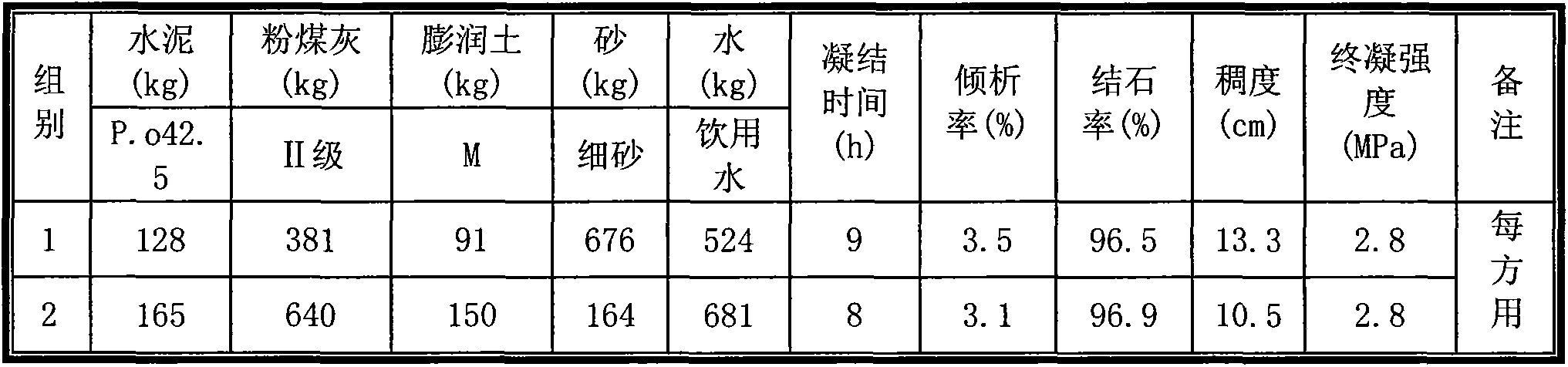
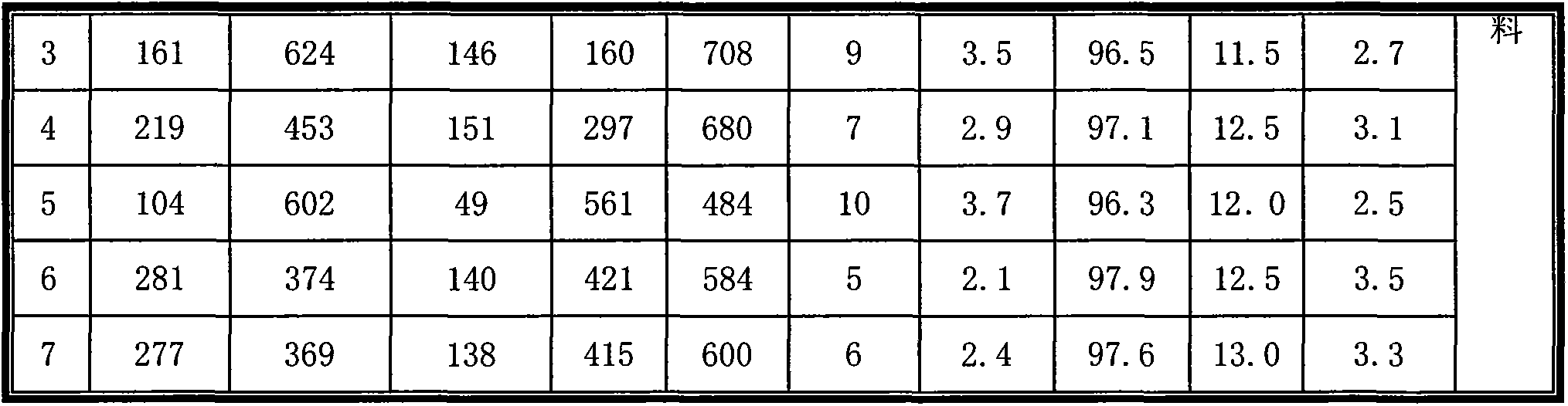
The invention relates to high-performance synchronous grouting active grout for shield construction control. The high-performance synchronous grouting grout is characterized in that the mass ratio of cement to pulverized fuel ash to bentonite to sand to water is 281:374:140:421:584, wherein the cementer is P.O42.5, the pulverized fuel ash is II-stage, the bentonite is sodium-stage, the sand is fine sand, the water is drinking water; the initial setting time of the grouting active grout prepared at a mass ratio is 5.5 hours, the final setting strength is 3.9MPa, the decantation rate is 3%, the stone rate is 3%, and the thickness is 11cm. The grouting active grout has the characteristics of short setting time, high solidification strength, good stability and high filling rate and can be used for effectively controlling ground surface settlement above tunnels, and a synchronous grouting system of a shield tunneling machine does not need to be specially transformed.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY SHISIJU GROUP CORP +1
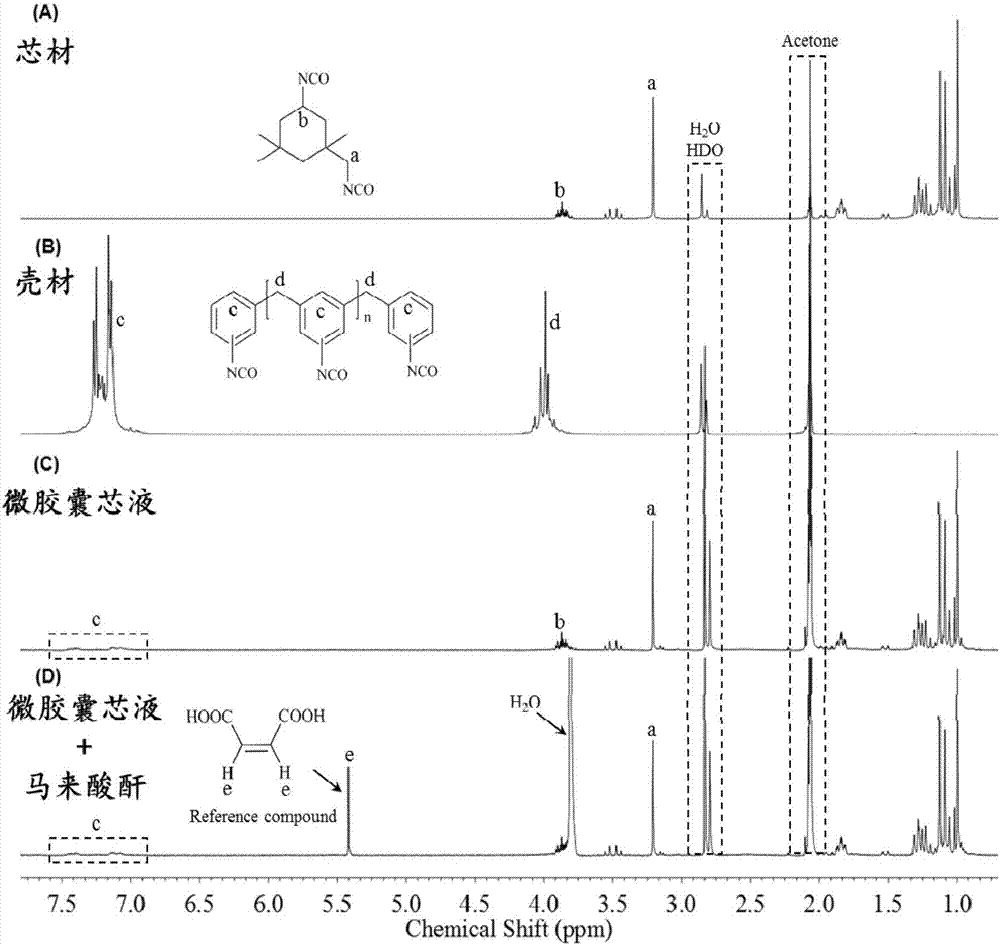
Preparation method of composite shell coated liquid isocyanate self-repairing microcapsule
InactiveCN106943969ASmooth appearanceGood particle size controllabilityMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationCross-linkHigh concentration
A preparation method of a composite shell coated liquid isocyanate self-repairing microcapsule comprises the following steps: adding a polyisocyanate shell material and a low-activity liquid isocyanate core material into a polyvinyl alcohol-water solution to form a core material and shell material mixed oil phase, emulsifying the oil phase to form a stable oil-in-water emulsion, dividing an amine cross-linking agent into six parts, respectively adding the six parts of the amine cross-linking agent into deionized water to prepare six amine solutions with the same volume, sequentially dropwise adding the six solutions into the emulsion from low concentration to high concentration, carrying out a heating reaction, cooling the obtained emulsion to room temperature, washing the cooled emulsion, carrying out decantation to obtain a microcapsule, and drying the separated microcapsule at room temperature to obtain the self-repairing microcapsule. The preparation method has the advantages of simple synthesis steps, low cost, high cladding rate, controllable dimension and high composite shell strength.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
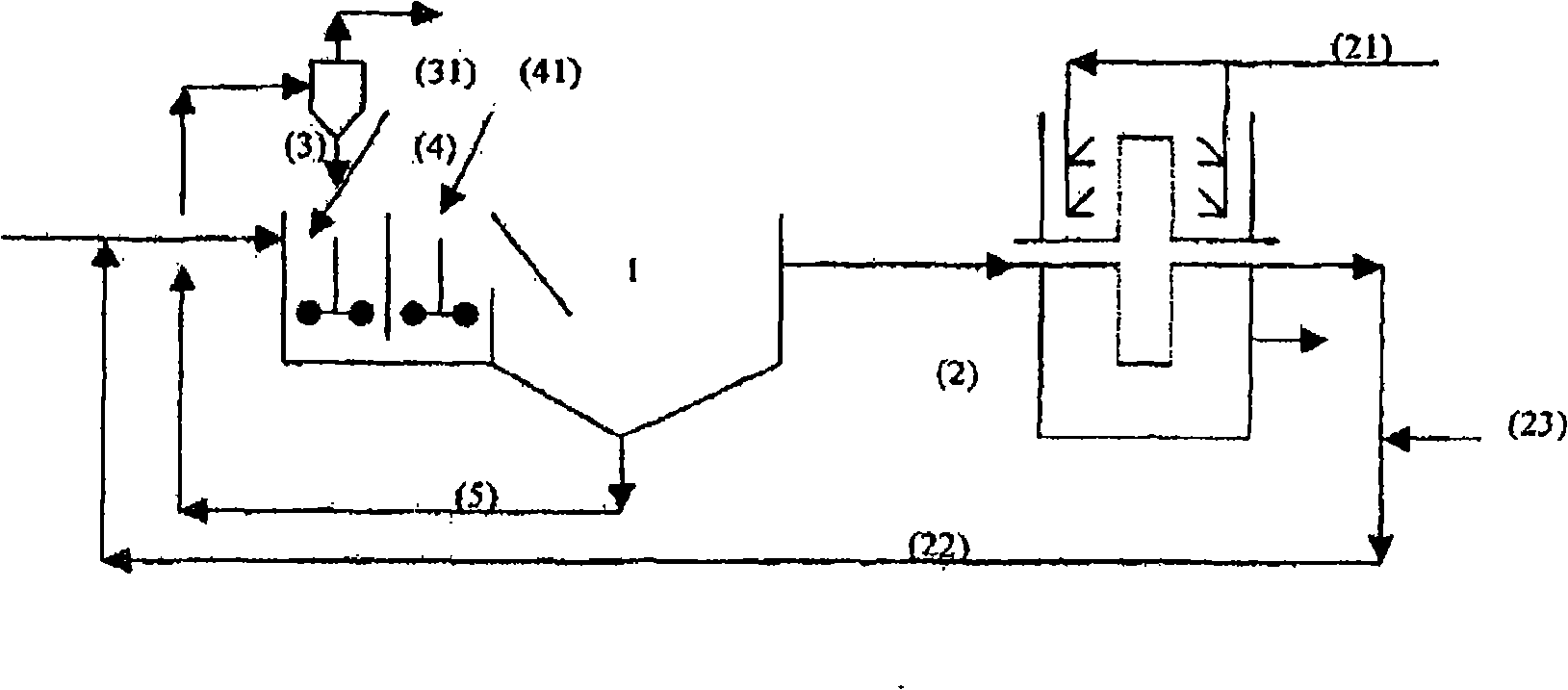
Water treating method and arrangement integrating a fixed-bacteria biological treatment and flocculation-decantation
InactiveCN101296870ASmall sizeLess quantityTreatment using aerobic processesWater treatment compoundsSludgeWater insoluble
The inventive water treating method and arrangement successively combine at least one step consisting in biological treating at least one part of pollution contained in said waters by a fixed biomass, wherein a bio-cleaned flow logically obtainable at the and of said step, prior to the entry thereof to a next step, contains less than 2 mg / l of MES, and at least one stage for carrying out a flocculation-decantation by ballasted flocs consisting in transferring biologically treated flow to a mixing area (2), preferentially at a velocity gradient ranging from 10 s-<1> to 1000 s<-1>, wherein at least one type of denser than water insoluble granulated material is injected and suspended matters are aggregated around said granulated material particles, in transferring the flow issued from the mixing area (2) to a decantation area, wherein the clarified flow and decantation sludges mixed with the granulated material are separated, in extracting granulated material from the decantation sludges, in recycling major part thereof is in the mixing area (2) and in removing the decantation sludges separated form the granulated material.
Owner:ODISHA TV
Process for purification of polycarbonate-containing solutions by plate decantation
InactiveCN1461322AEfficient and economical separationEfficient and economical purificationCentrifugal force sediment separationSedimentation settling tanksInterfacial reactionCentrifugation
This invention relates to an economical and efficient process for purifying a reaction mixture obtained in a two-phase interfacial reaction for the preparation of polycarbonate. More particularly, the method of the invention provides for separating the reaction mixture into an organic phase, which includes the desired polycarbonate and undesirable impurities, and an aqueous phase. The organic phase is further purified by using a plate decanter in combination with coalescence and centrifugation.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Method for preparing novel porous honeycomb mesoporous titanium dioxide material
InactiveCN101830503AGood photocatalytic effectThree wastes less pollutionPhysical/chemical process catalystsTitanium dioxideSolventMaterials science
The invention discloses a method for preparing a novel porous honeycomb mesoporous titanium dioxide material, which relates to a method for preparing a mesoporous titanium dioxide material, and belongs to the technical field of a titanium dioxide photocatalyst. Organic acid and alcohol and an inorganic titanium source of C2-C9, and organic acid and an organic titanium source of C2-C9 are used as the raw materials in the method. The method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing the organic acid and the titanium source in the molar ratio of 1-10:1, reacting for 0.5-1.0h at the temperature of 10 DEG C-80 DEG C, and evaporating the solvent to obtain a honeycomb puffing solid; roasting for 1-5h at the temperature of 200-700 DEG C to obtain the porous honeycomb mesoporous titanium dioxide material. The invention has the advantages of easily obtained raw materials, simple preparation method, short preparation time, and no need of adding templates. The obtained mesoporous titanium dioxide has both visible pores and the mesopores, the distribution of pore diameters is narrow, the micropore diameter is 20-30nm, and the specific area is 90-160m<2> / g. The mesoporous titanium dioxide material has certain hardness, is easy to separate from liquid phase, can achieve good separation effect by decantation, has high photocatalytic activity, and is especially suitable for the fields of photocatalysis.
Owner:SHENYANG INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
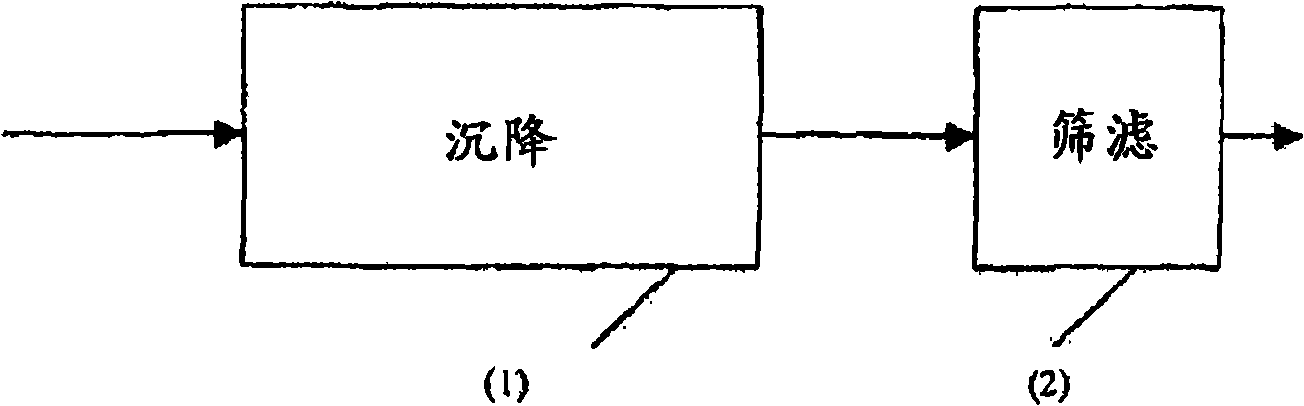
Wastewater treatment method comprising decantation and fine screening stages and device for carrying out said method
InactiveCN101309870AEasy to handleSmall sizeWater treatment parameter controlWater/sewage treatment by irradiationMicrometerWastewater
The invention relates to a wastewater treatment method for reducing the content thereof in suspended materials, in particular in parasites, comprising a decantation stage consisting in transferring said waters to a decanter at a treating rate greater than 10 m / h, wherein said decantation stage is followed by a fine screening stage carried out with the aid of a screen whose mesh size ranges from approximately 5 micrometers to approximately 25 micrometers.
Owner:VEOLIA WATER SOLUTIONS & TECH SUPPORT
Method and apparatus for rapid determination of blood sedimentation rate
InactiveUS6098451AImprove trustAccelerates the lag phaseRead-only memoriesSedimentation analysisGravitational sedimentationBiology
An apparatus and method for rapid determination of erythrocyte sedimentation rates for a blood specimen (29) which can be linearly transposed to Westergren sedimentation rates. The method includes the steps of inducing accelerated rouleaux formation in the specimen (29) in an amount sufficient to begin settling at substantially the decantation rate for the specimen. In one embodiment a structure (27) which produces a very thin cross-sectional region (37) of the specimen (29) inside the lumen (23) of a specimen container (21) is provided to accelerate rouleaux formation. In an alternative embodiment (120), accelerated rouleaux formation is accomplished using a centrifuge (122). A third embodiment employs a movable rod (223) mounted inside the specimen tube (221) to induce accelerated rouleaux formation. All embodiments of the process next employ gravity settling the specimen in a near horizontal oriented container (21, 121, 221). Thereafter, the amount of settling occurring is determined. A sealed specimen container (21, 121, 221) which permits thorough mixing of blood in a very small diameter container for use in performing the method also is provided.
Owner:BULL BRIAN S
Method of separating two dispersed-phase immiscible liquids
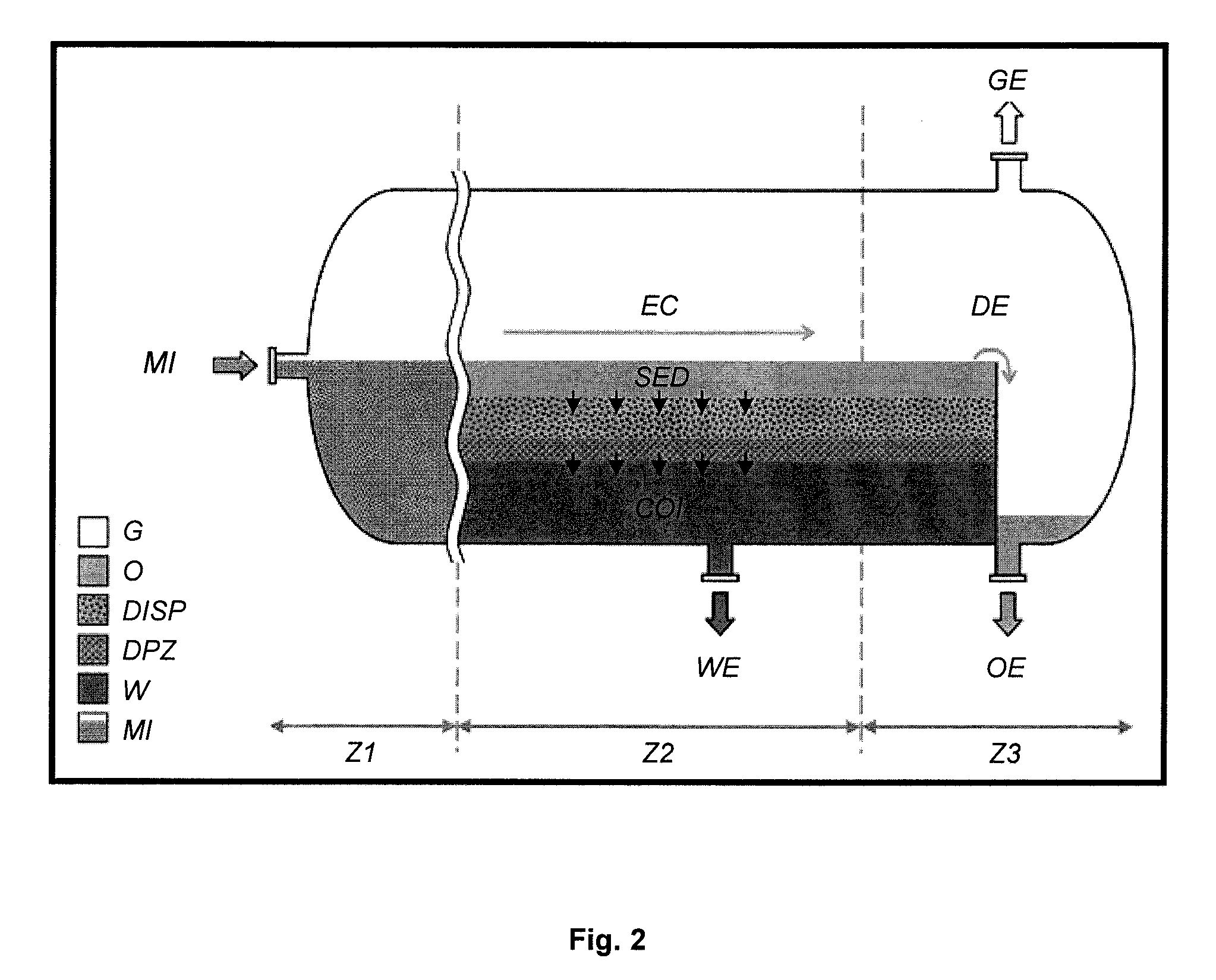
InactiveUS20120125868A1Water/sewage treatmentSedimentation separationStationary conditionsPhysical separation
Method of separating two dispersed-phase immiscible liquids. The two liquids are fed into a gravity separator where both liquids are separated by decantation. A first phase consisting of a first liquid is obtained at the bottom of the separator, a second phase consisting of the second liquid is obtained at the tap of the separator, a third phase containing the two dispersed-phase immiscible liquids and a fourth phase containing the two immiscible liquids in a dense bed are obtained. Physico-chemical properties of the liquids and of the dispersed phase are measured, and a physical separation model is defined. This model is defined considering that the separator works under stationary conditions, using a matter conservation balance for the first fluid within the dense bed, while taking account of a first phenomenon of coalescence between water drops within the third phase, and of a second phenomenon of coalescence between water drops of the fourth phase and the first phase. This model is then used to optimize implementation of the separation. Application to the separation of petroleum effluents for example.
Owner:FALAPPI STEFANO +4
Biodiesel process
InactiveUS20100186289A1High yieldPromote conversionFatty acid esterificationFatty acids production/refiningBiodieselDistillation
Processes for producing biodiesel compositions are disclosed. FFAs present in the triglycerides can be removed by reaction with isobutylene, or by Kolbe electrolysis. The Kolbe electrolysis can be performed on the starting material, or on the crude glycerol. The triglycerides are transesterified to form alkyl esters of the fatty acids and glycerol. The transesterification reaction can be catalyzed by an alkoxide, rather than a hydroxide, to help keep the glycerol by-product dry. The alkoxide salt can be neutralized by reaction with a dry acid, such as gaseous hydrogen chloride or sulfuric acid, and the resulting alcohol removed by distillation, and at least a portion of the neutralized salt can be removed by filtration or decantation. The process can provide improved biodiesel yields, and glycerol pure enough for use directly in glycerol ether manufacture.
Owner:CPS BIOFUELS INC
Improved method for quick detection of Ramaria root spore density
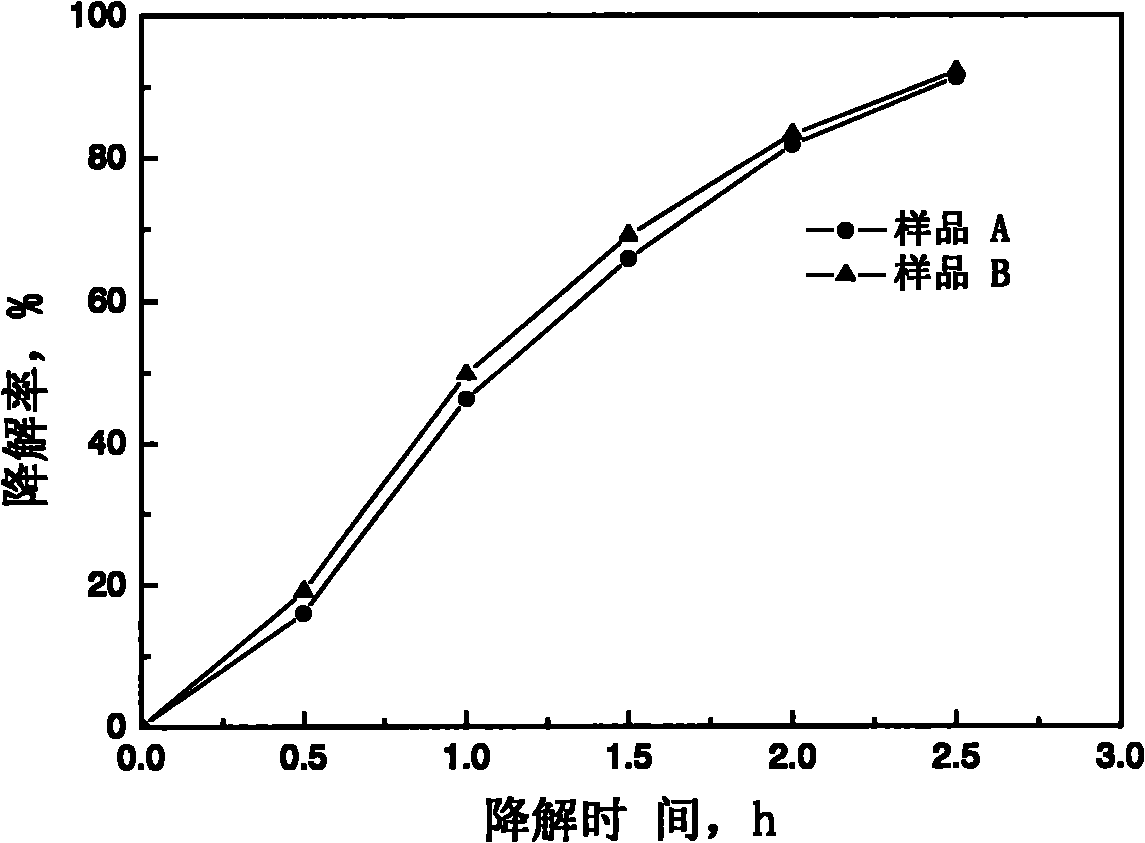
InactiveCN1979127AHigh precisionHigh speedMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationSporeImproved method
The invention relates to mycorhiza biotechnology that is a new method of ecological management for coal field. Mycorhiza spore density is a standard to measure mycorhiza annidation. It adopts optimized method--wet sieve decantation decoration method to test spore density. It could improve testing accuracy and speed, and lowers the human error in spore density testing process. It supplies a spore density rapid testing method for ecological application of mycorhiza biotechnology.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
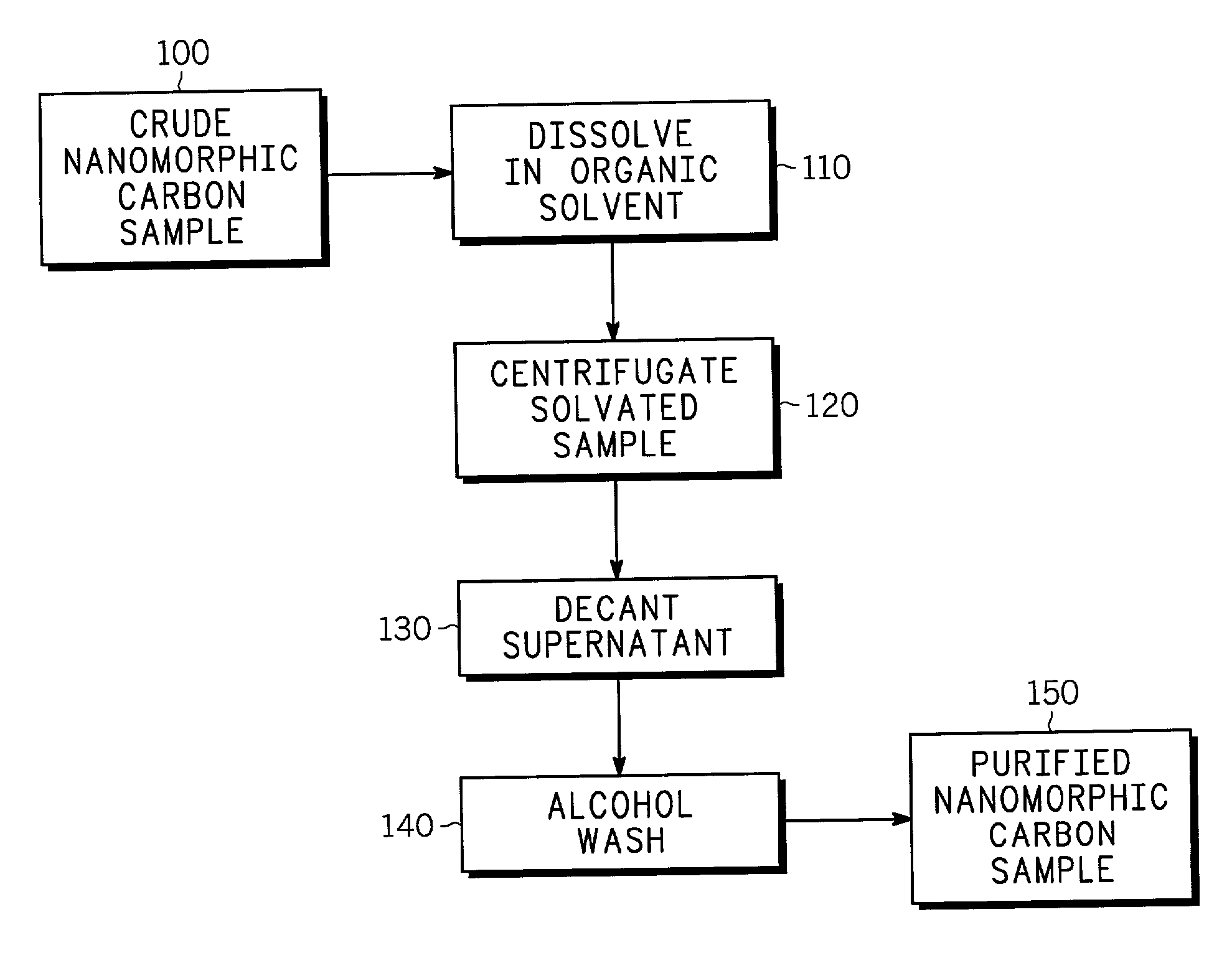
Method for non-reactive separation of nanomorphic carbon species
An exemplary method for substantially non-chemically-reactive separation of nanomorphic carbon species (150) comprises inter alia the steps of dissolving a crude nanomorphic carbon sample (100) in an organic solvent (110), centrifugation of the solvated sample (120) and decantation of the resulting supernatant (130). Disclosed features and specifications may be variously controlled, adapted or otherwise optionally modified to improve carbon nanospecies purification. An exemplary embodiment of the present invention representatively provides for non-oxidative cleaning of carbon nanotubes.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Method for purifying raffinate
The invention discloses a method for purifying raffinate, which comprises the following steps: preheating the raffinate containing 40.0% (by weight)-47.0% (by weight) of P2O5 and 1.6% (by weight)-2.8% (by weight) of magnesium to 50-75 DEG C, then adding 3-5 times of the volume of mixed solvent under stirring, keeping the feeding time to be 0-40min, continuously carrying out reaction for 30-90min after completing the feeding, standing, cooling to room temperature-35 DEG C, and using filtration or decantation for obtaining clear solution. The clear solution is further distilled at the vacuum degree of 0.08MPa and the temperature of 60 DEG C-80 DEG C for recovering alcohol, thereby obtaining the purified raffinate. The method is characterized by good magnesium removal effect, low energy consumption and small solvent loss.
Owner:WENGFU (GRP) CO LTD
Process for resin phase separation by plate decantation
InactiveUS6420517B1Efficient separationEfficient and economical mannerNon-miscible liquid separationInterfacial reactionCentrifugation
This invention relates to an economical and efficient process for purifying a reaction mixture obtained in a two-phase interfacial reaction for the preparation of polycarbonate. More particularly, the method of the invention provides for separating the reaction mixture into an organic phase, which includes the desired polycarbonate and undesirable impurities, and an aqueous phase. The organic phase is further purified by using a plate decanter in combination with coalescence and centrifugation.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
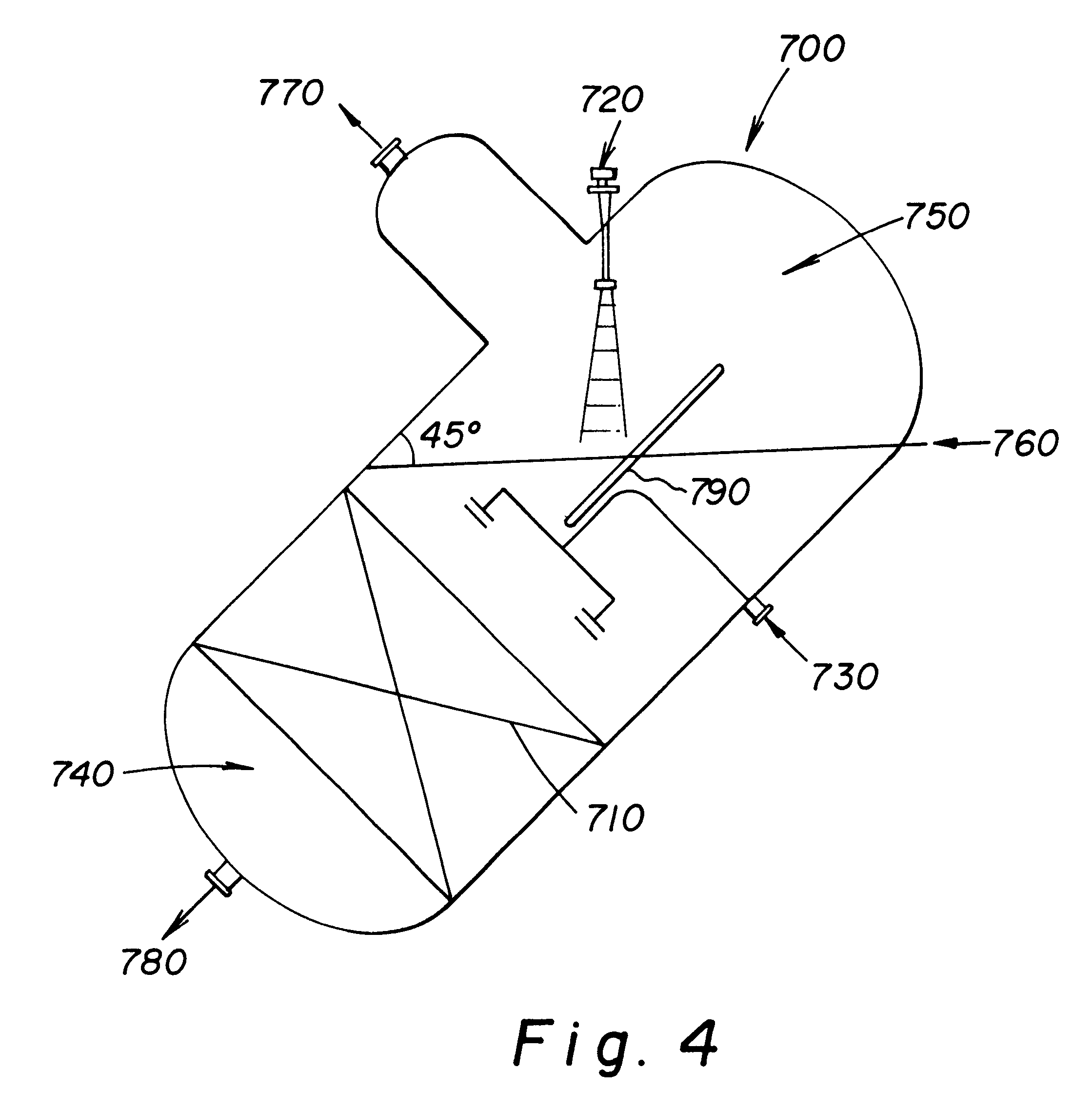
System and device for mass transfer and elimination of contaminants
ActiveUS20060011062A1Mechanical apparatusLighting and heating apparatusSuspended particlesMembrane cell
A system and a device that are used for liquid-gas phase mass transfer with elimination of contaminants. The systems includes a plurality of liquid membrane-producing cells. Upon contact, the liquid membranes collapse with a gas stream and the collapsed liquid material covers the suspended particles, and eliminates them by decantation. Moreover, the membrane cells increase the speed of the gas stream and cause the gas stream to hit the surface of the liquid at an incident angle of 45°, which serves to improve the transfer of vapor into the gas.
Owner:RAMOS DE LA FUENTE RUBEN
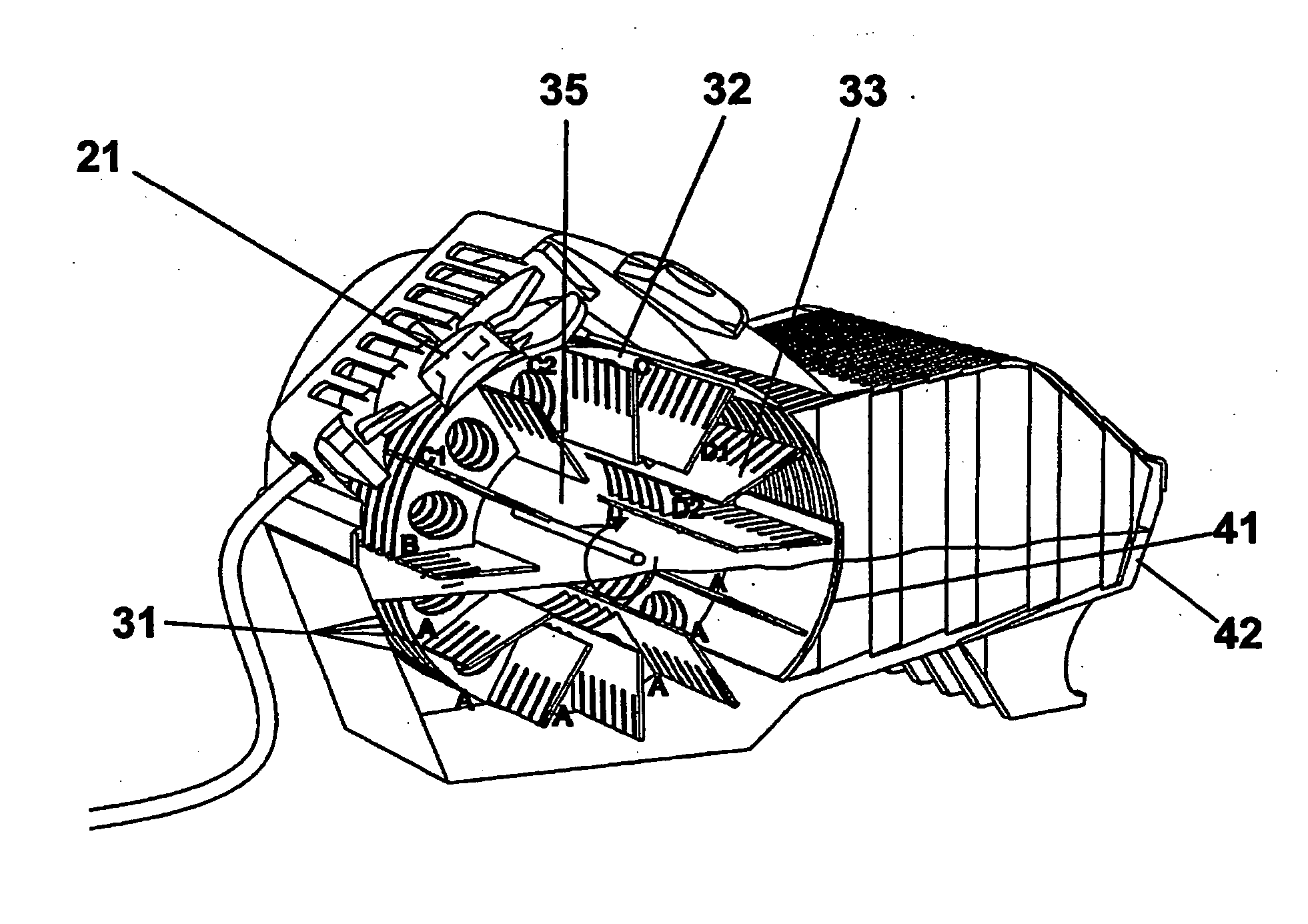
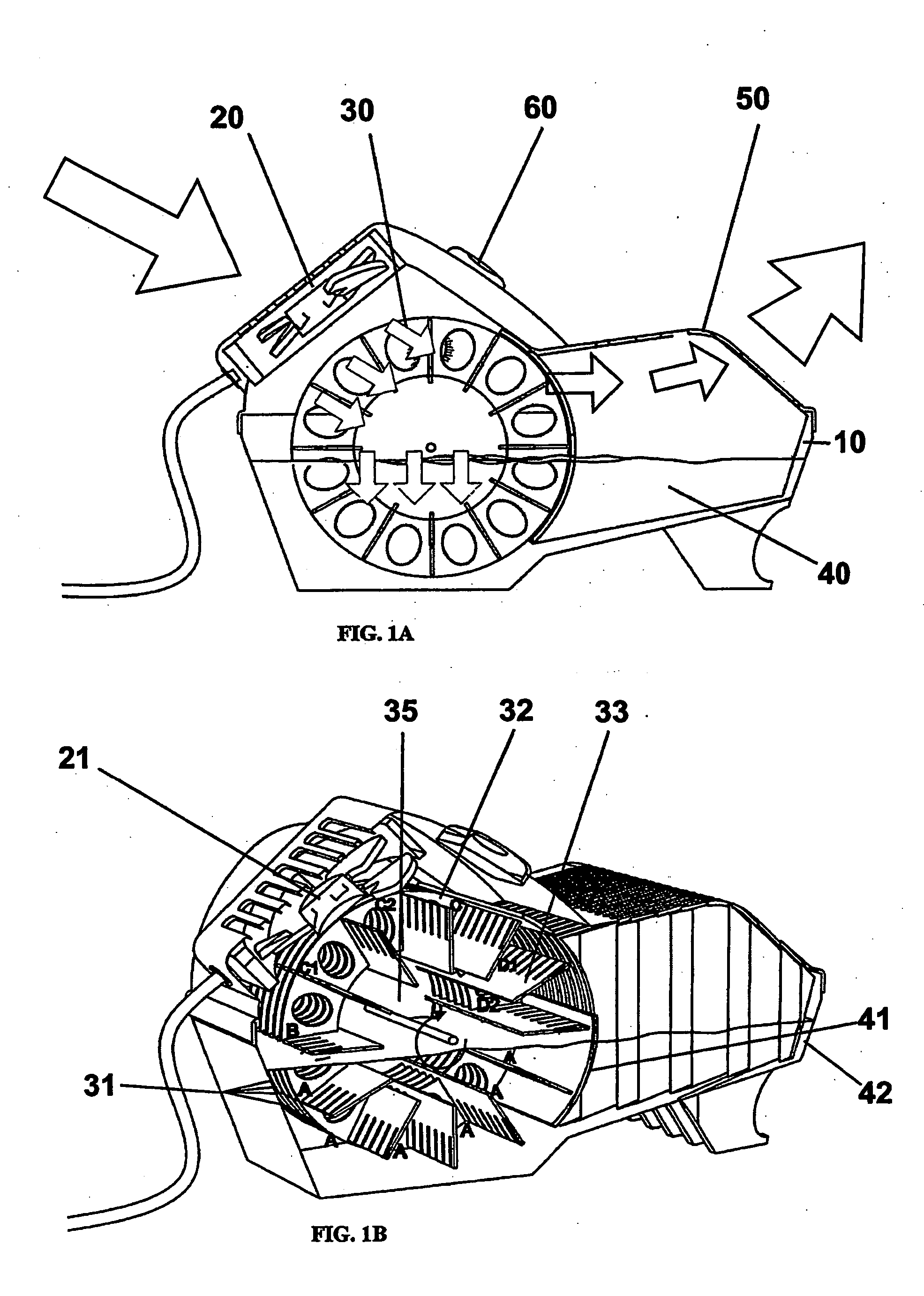
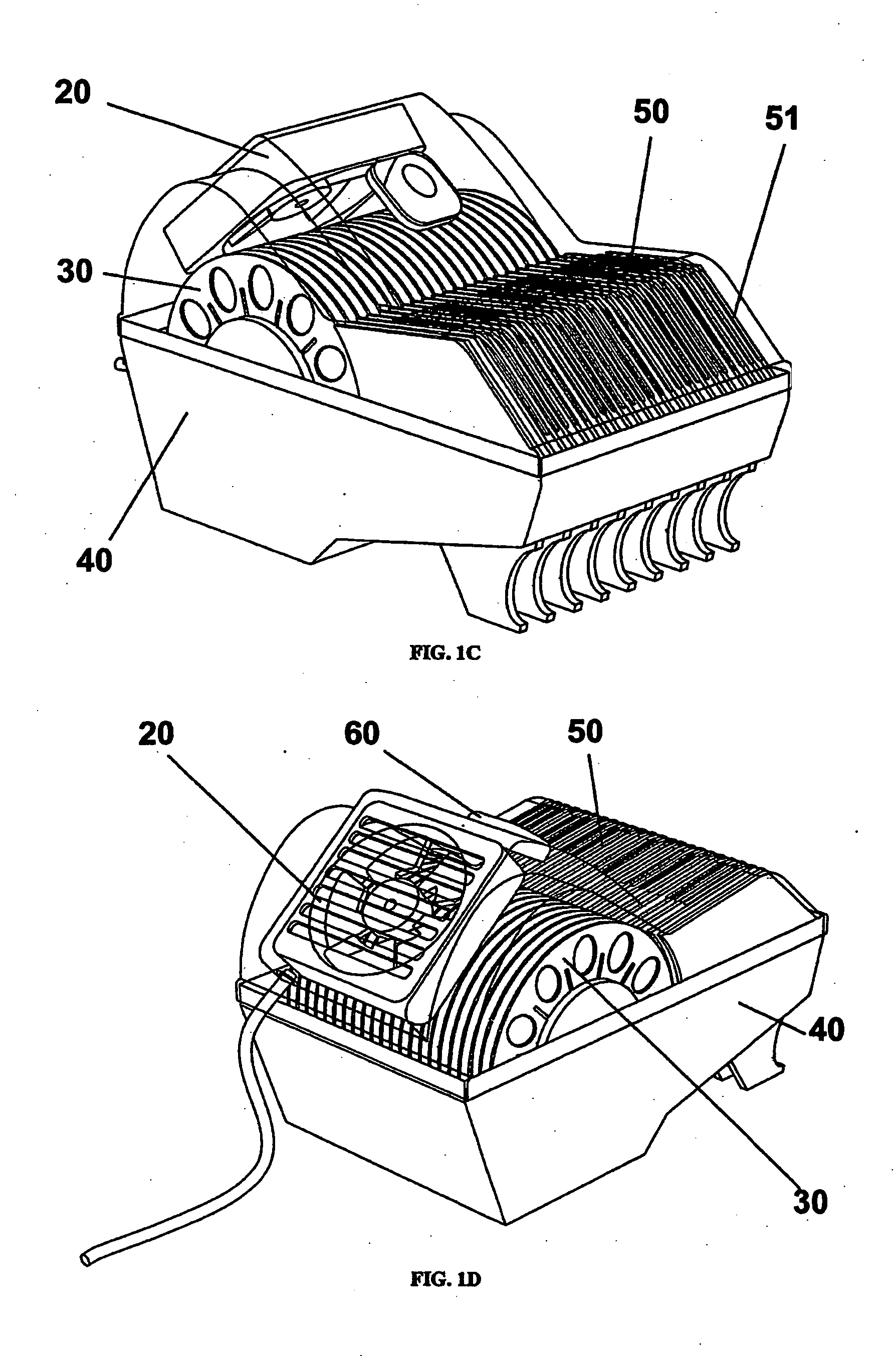
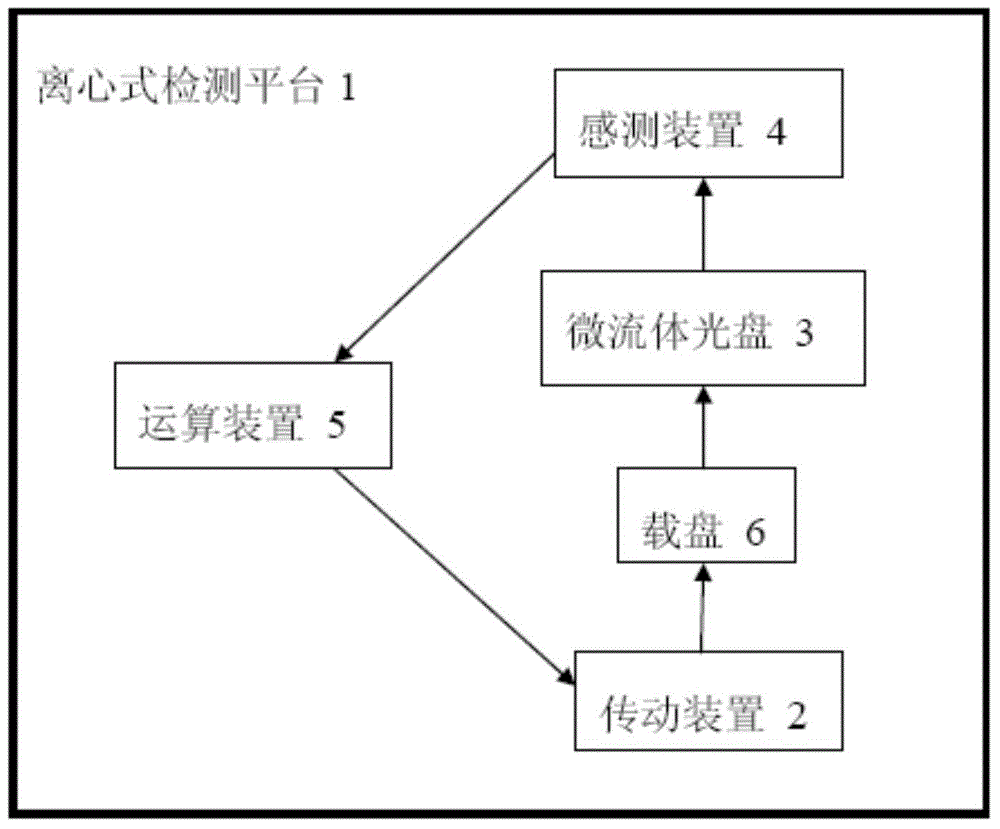
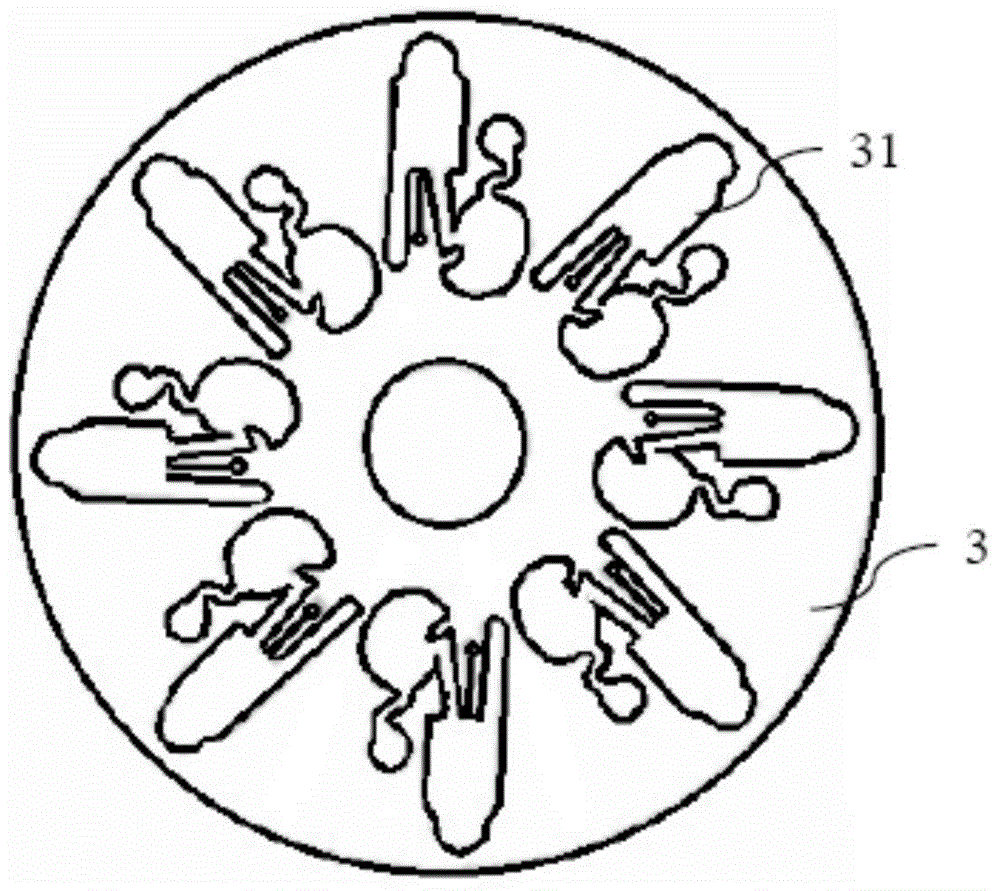
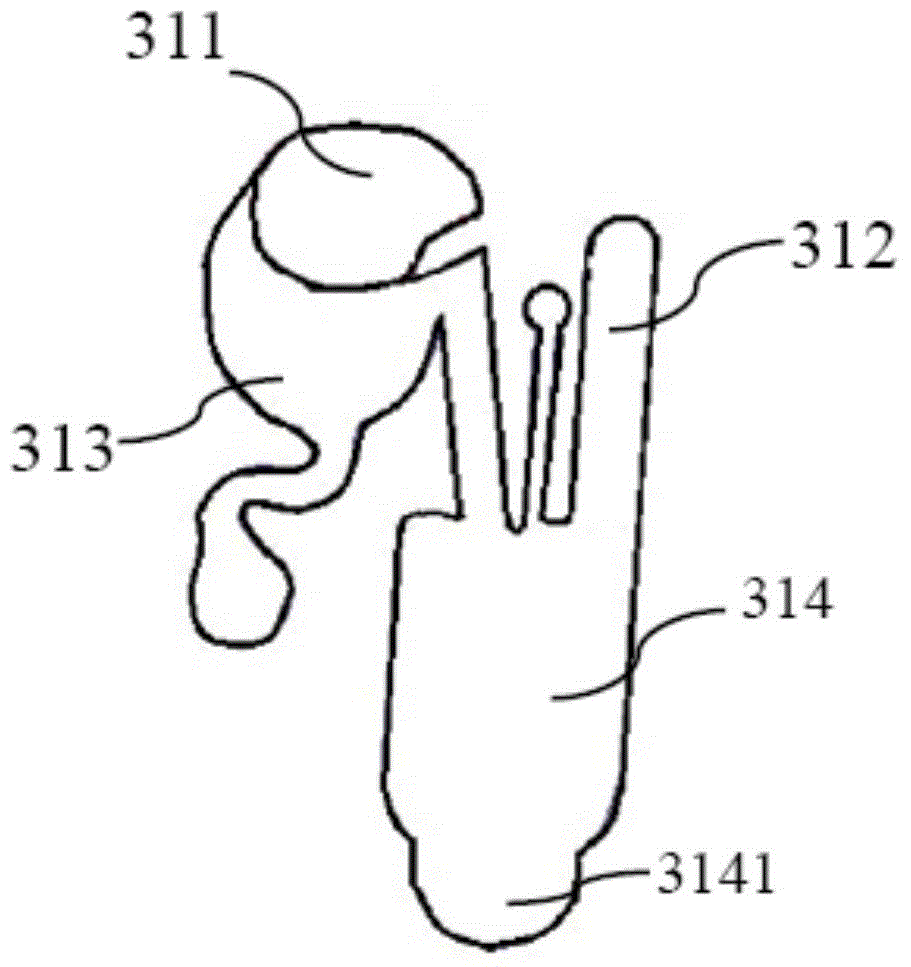
Centrifugal-type detection platform and operating process thereof
The invention discloses a centrifugal-type detection platform, which comprises a microfluid optical disc, a transmission device capable of controlling rotation and the rotation mode of the microfluid optical disc, a sensing apparatus used for sensing reaction of the microfluid optical disc, and an operation apparatus used for receiving a reaction signal and generating a result. The transmission device drives the microfluid optical disc to rotate for generating centrifugal force, thereby a sample or a reagent can be transmitted, the sample is separated, or the microfluid optical disc is driven for alternative rotation by clockwise and anticlockwise directions, so that the separated sample enables quantitative decantation and is mixed with the reagent, and a purpose of rapid detection completion can be reached. According to the invention, at least a micro channel is placed in the microfluid optical disc, and comprises a sample storage groove, a reagent storage groove, a decantation tank, a mixing tank and a detecting zone.
Owner:常德普施康生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com