Process for purification of polycarbonate-containing solutions by plate decantation
A polycarbonate and tray technology, which is applied in the field of purifying polycarbonate-containing solutions by tray decantation, can solve the problems of slow efficiency, time-consuming and expensive centrifuge installation and operation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] A tray decanter was tested in a polycarbonate resin separation line consisting of three centrifuges. The first centrifuge is used for resin and brine separation. The second centrifuge is used for pickling the resin solution, reducing the chloride ion concentration in the third centrifuge, and preventing the third centrifuge from being excessively corroded.
[0034] To test the use of a tray decanter, a 200 liter decanter unit (ex Esmitec / FIB) was tested on the discharge of the feed pump of the resin separation line. The separated light and heavy organic phases from the top and bottom of the decanter are conveyed back to the inlet of the centrifuge feed pump.
[0035] The feed mixture to the decanter consisted of an aqueous phase (brine or wash water) and an organic phase (polycarbonate in dichloromethane). The feed mixture enters the decanter through the feed tube. The aqueous, ie light phase flows to the top of the decanter and the resin solution to the bottom. The...
Embodiment 2
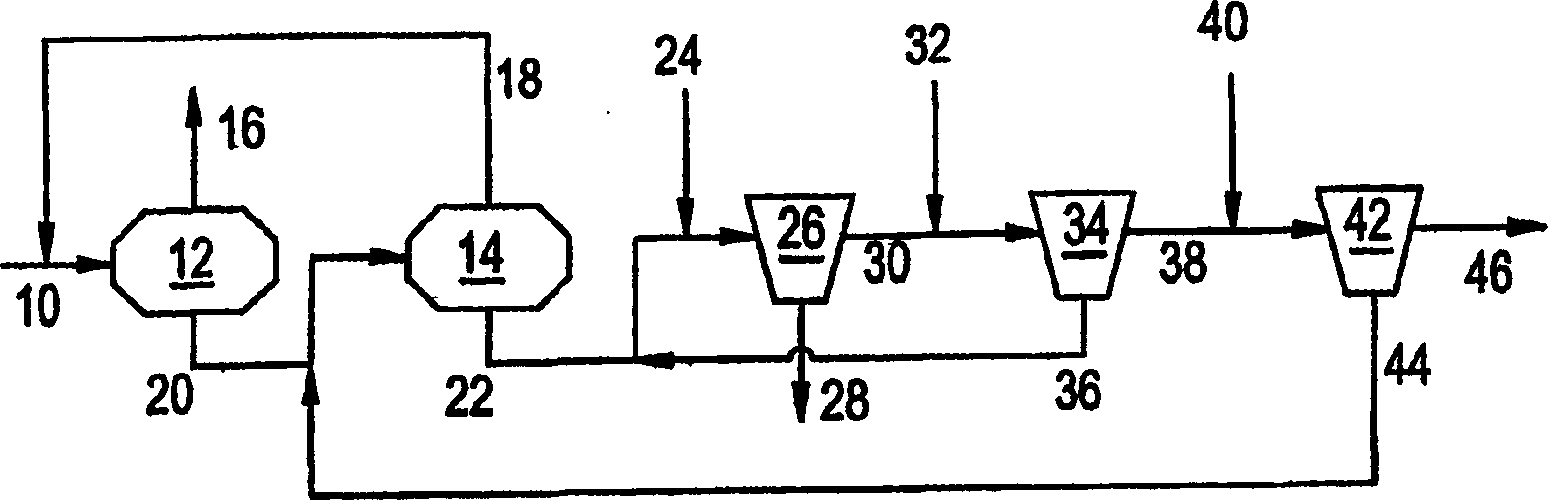
[0041] The polycarbonate-containing reaction mixture can be prepared using an interfacial reaction method. Such a reaction mixture can use two tray decanters and three centrifuges, such as figure 1 Isolation and purification were carried out as indicated. Calculations were made using mass balances according to Example 1 assuming feed stream composition, entrained brine and polycarbonate content.
[0042] The results are summarized in Table 1, where PC = polycarbonate, MeCl 2 = dichloromethane, BPA = bisphenol A, TEA = triethylamine. The final effluent of the purified organic phase contained 0.5% by weight of water.
[0043] 10
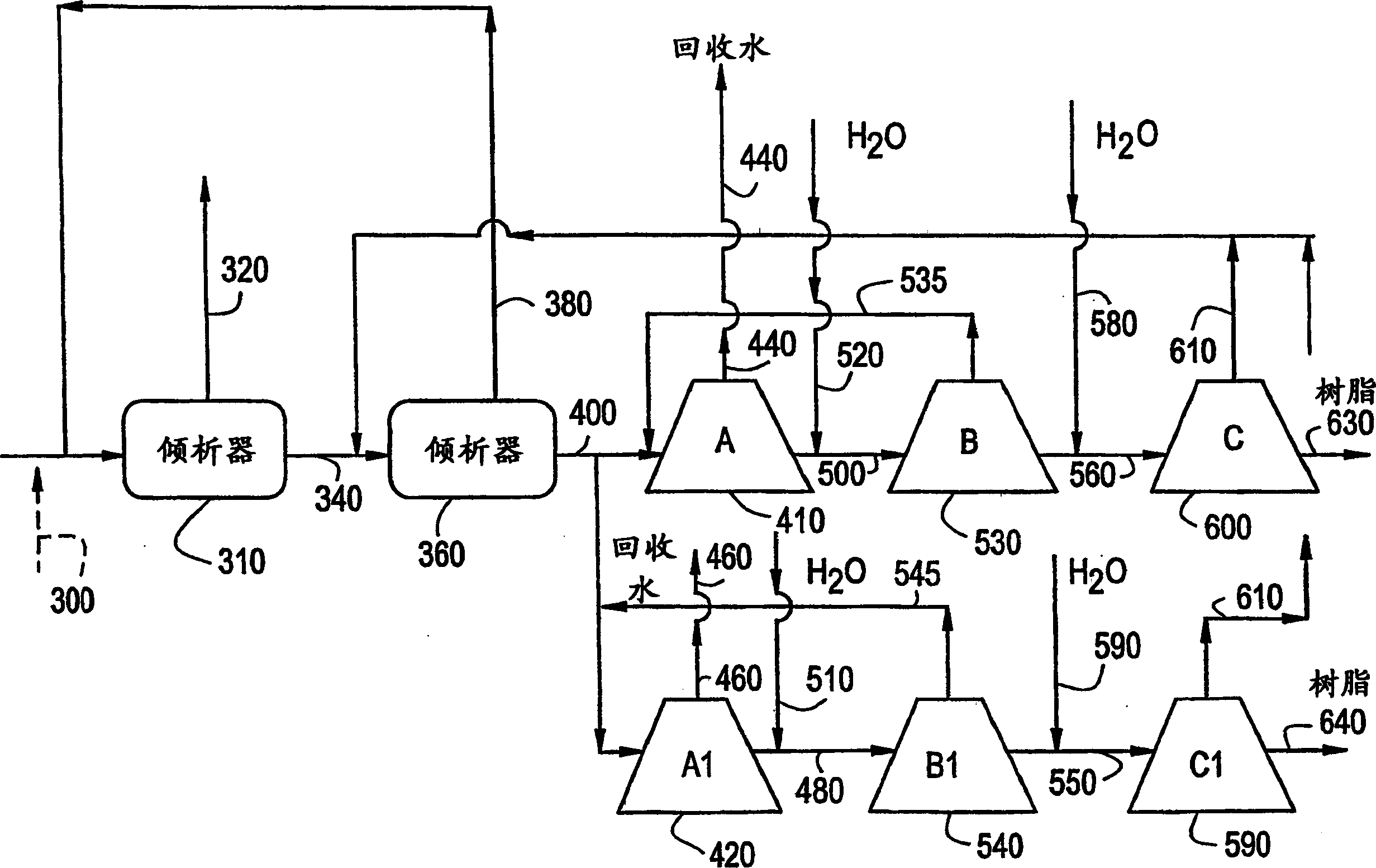
[0044] image 3 An alternative separation network is shown comprising two tray decanters in series followed by two centrifuge trains each comprising 3 centrifuges arranged in parallel. The effluent 300 from a tray reactor producing polycarbonate using a two-phase interface process is introduced into a tray decanter 310 where the effl...
Embodiment 4
[0046] A reactor effluent solution with a polycarbonate concentration in the organic phase of 10-18% by weight and a brine or aqueous phase in a specific gravity of 1.0-1.16 is fed into a tray decanter and discharged continuously. The feed rate was maintained such that the retention time in the decanter was 10-30 minutes. Continuous operation and defined retention times create waves and turbulence around the interface, making observation of the interface difficult. Such as Figure 4 As shown, decanter 700 is fitted with a top-down sonar probe 720 (available from Accu-Gage Corporation). The effluent solution enters decanter 700 through feed port 730 . The effluent separates into an organic phase 740 and a brine phase 750 with an interface 760 therebetween. The lighter brine phase exits through brine outlet 770 at the top of the decanter and the heavier organic phase exits through organic phase outlet 780 at the bottom of the decanter. Optionally, additional trays can be ins...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com