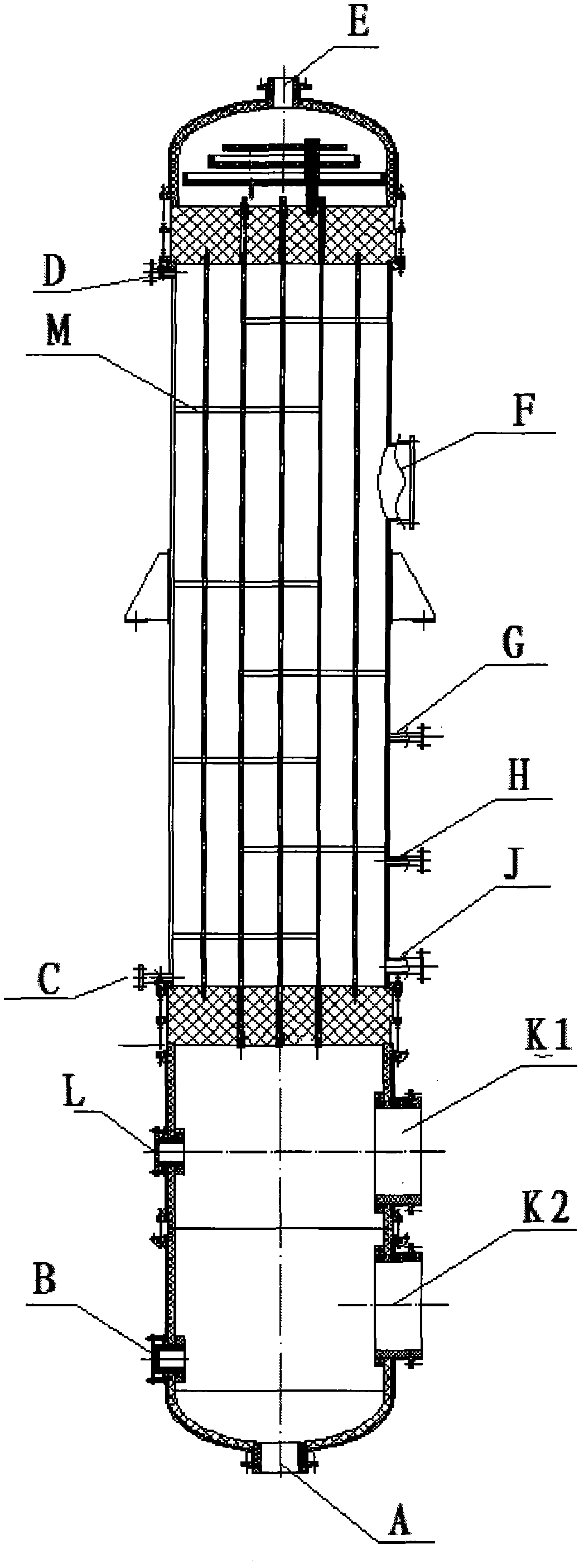
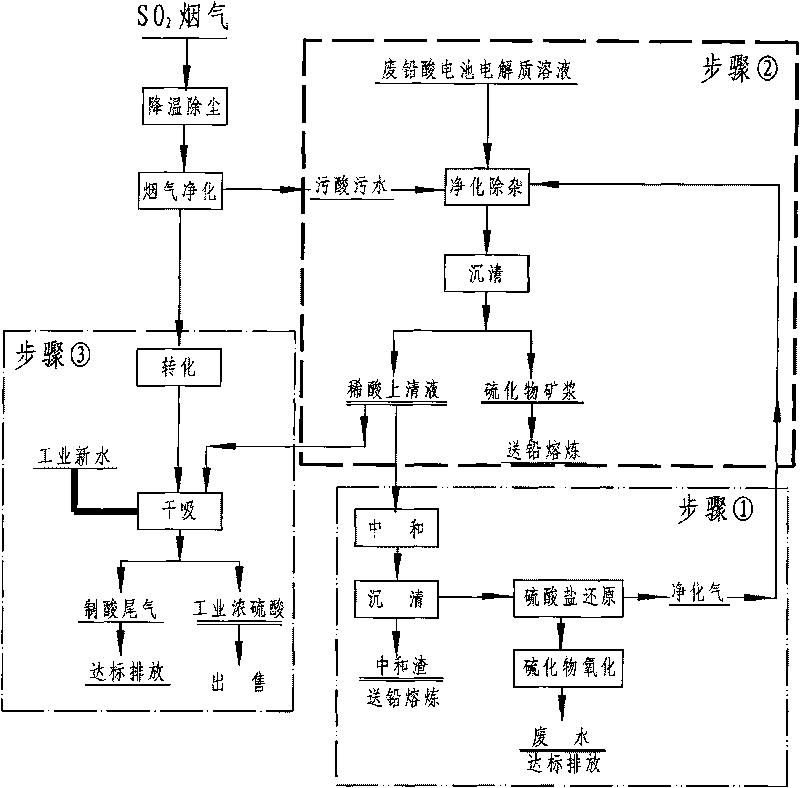
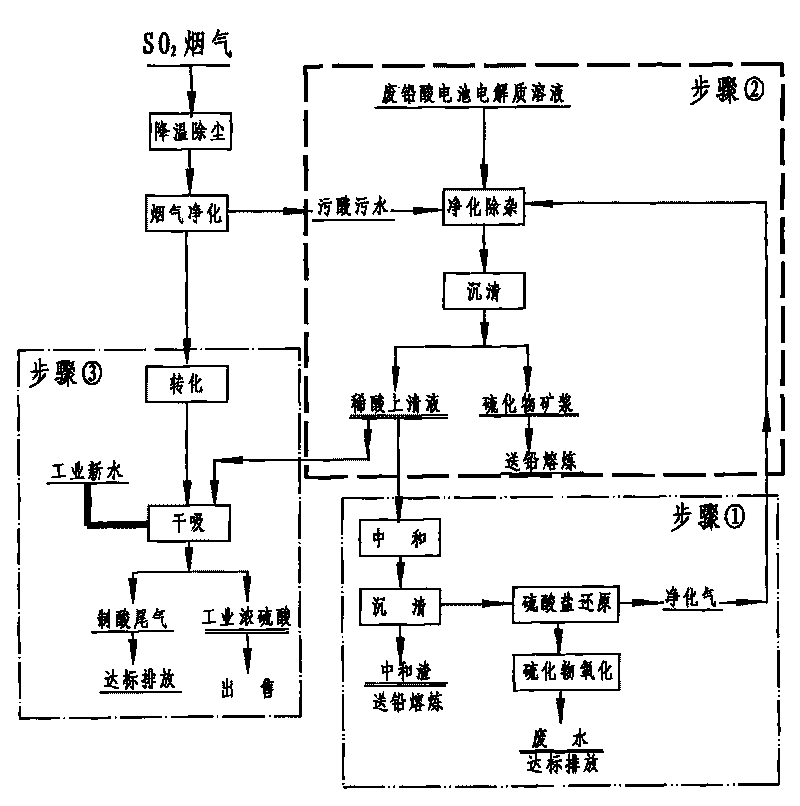
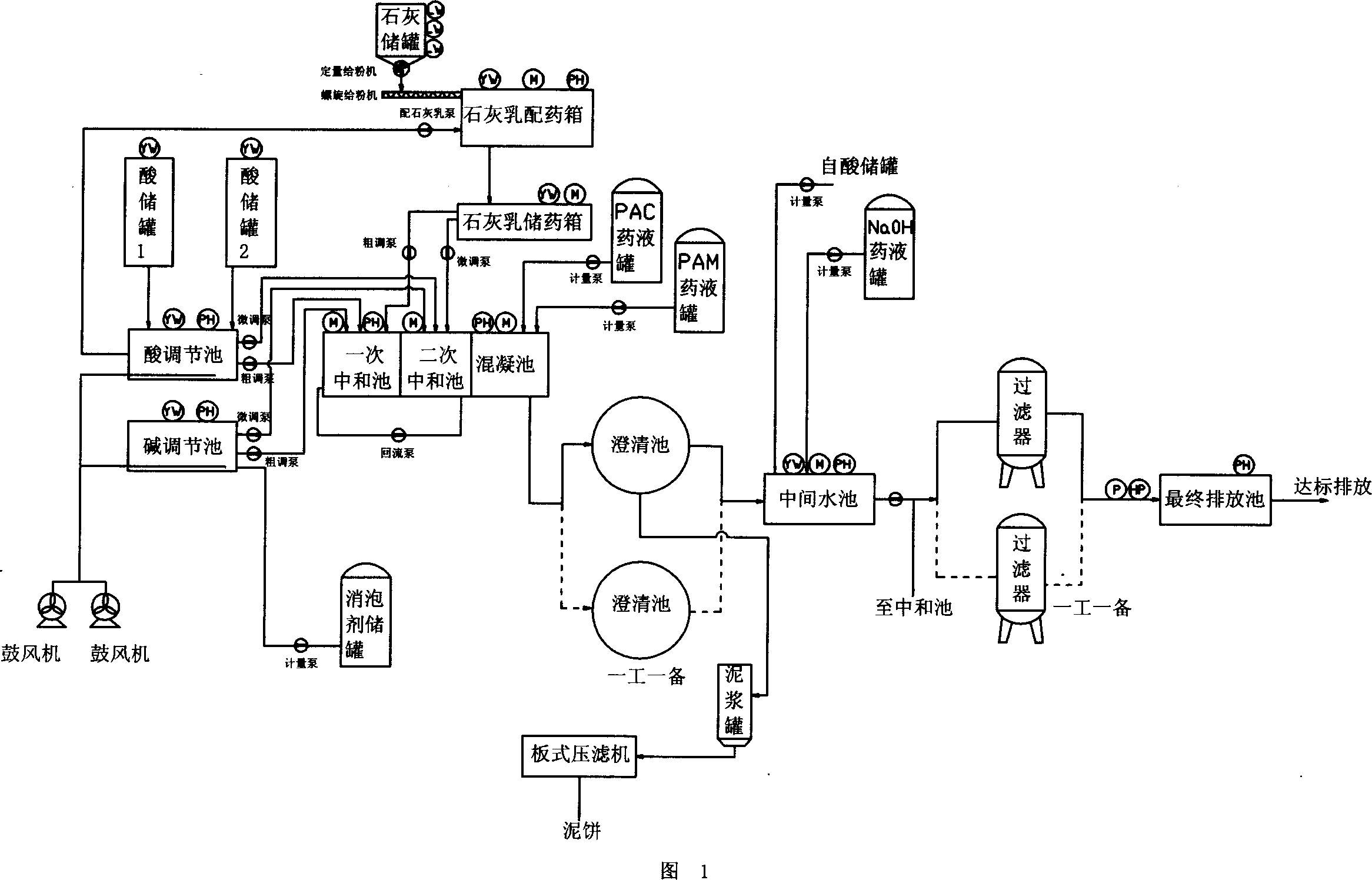
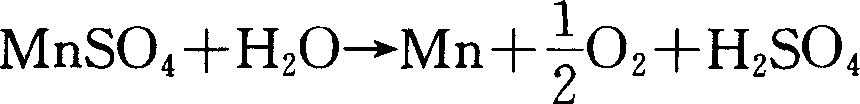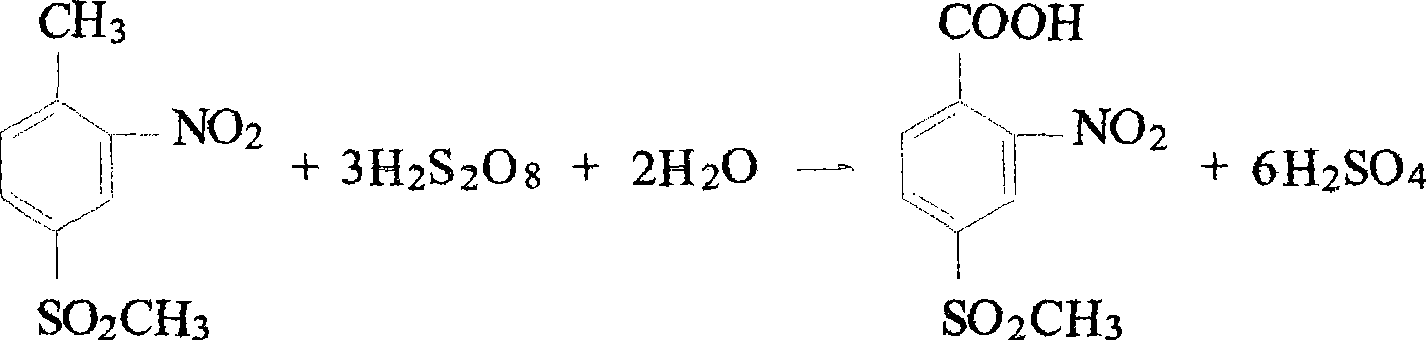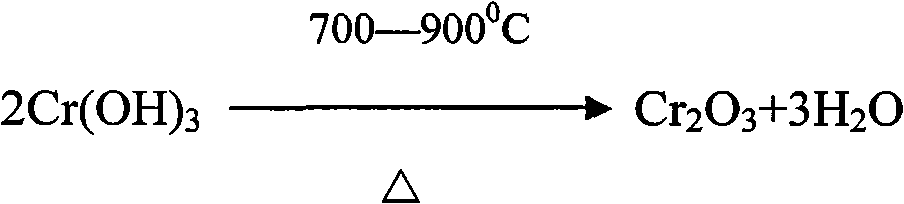Patents
Literature
2003 results about "Spent acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition of spent acid. : acid weakened by use: such as. a : mixed acid that has been used in nitration. b : acid that has been used in pickling metal articles.
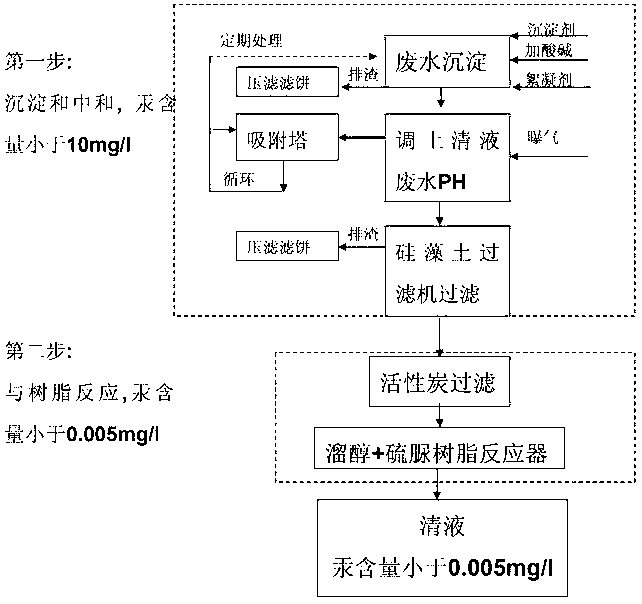
Method for treating mercury-containing wastewater during PVC (Polyvinyle Chloride) production through two-step process
InactiveCN102936070AEnsuring a circular economyImprove processing efficiencyMultistage water/sewage treatmentNature of treatment waterSlagGas phase
The invention discloses a method for treating mercury-containing wastewater during PVC (Polyvinyle Chloride) production through a two-step process. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, completing primary removal of mercury, copper, ferrous and ferric iron, cadmium, zinc, manganese, lead and suspending impurities of above 10mg / l by using a precipitator and a flocculating agent, regulating PH to 6-8 and then adding the flocculating agent and stirring for 30 minutes, standing for above 1 hour, discharging slag and aerating, absorbing mercury carried away by a gas phase through a sulfide adsorber, purifying water by using a plate type kieselguhr filter, removing residual suspended matters; and 2, carrying out complete reaction on the mercury in the wastewater by using an active carbon and a mercaptan and thiourea resin combining method again for being removed, and finally reaching the standard that the content of the mercury is less than 0.005mg / l. The treated wastewater can be recycled to salt melting or an acetylene generator, so that zero emission of the treated wastewater is achieved; and the mercury-containing waste acid water of hydrochloric acid desorption in the industry of chlor-alkali can be treated, the consumption of acid is reduced, and the great popularization significance is achieved in the industry of chlor-alkali.
Owner:赵建军
Treatment technology of producing sulfuric acid from alkylated spent sulfuric acid through high temperature decomposition
ActiveCN1751984ARealize lysis treatmentAvoid secondary pollutionSulfur-trioxide/sulfuric-acidDecompositionContact method
A process for preparing sulfuric acid from used alkylating sulfuric acid by high-temp cracking includes such steps as heating to 1000-1100 deg.C, cracking, acid washing for cleaning, converting twice by contact method, and absorbing twice to obtain qualified sulfuric acid for reuse. It has high recovering rate.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
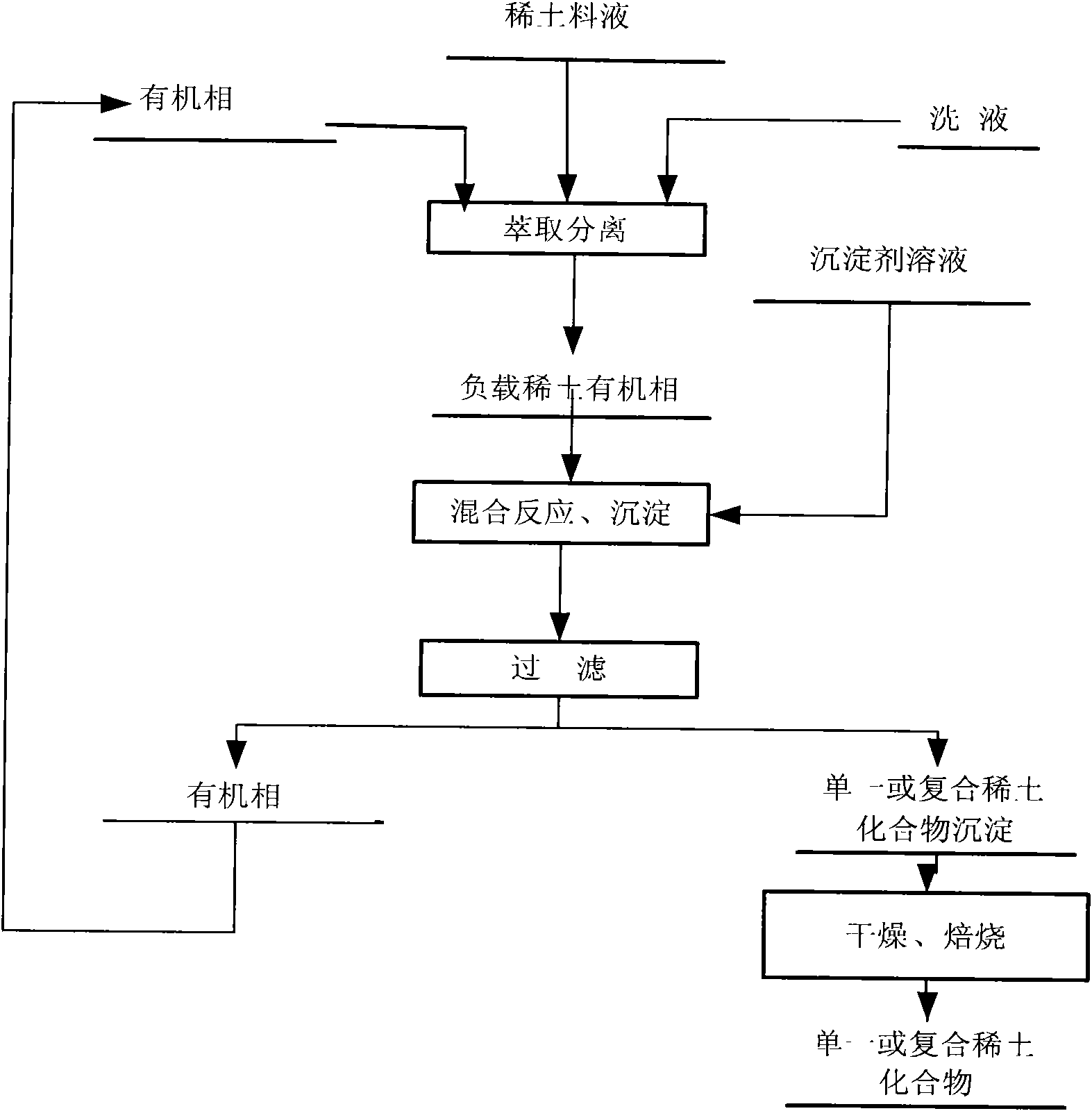
Process of directly preparing rare-earth compound from extraction separation load organic phase
InactiveCN101602519ASolve the problem of high residual acid and large acid consumptionEliminate the step of stripping rare earthRare earth metal compoundsProcess efficiency improvementDispersityRare earth
The invention provides a process of directly preparing a rare-earth compound from an extraction separation load organic phase. The process comprises following steps: carrying out a mixed precipitation reaction between a precipitator solution and the load organic phase which is obtained from extraction separation and contains rare-earth; post-treating the filter cake obtained by filtering slurry liquid so as to obtain the rare-earth compound with good dispersity and uniform particle size distribution; and returning the organic phase to the extraction separation working procedure for recycling use. The process of extracting and separating rare-earth omits the rare-earth stripping step, saves a great amount of acid needed by the rare-earth in a stripping load organic phase and solves the problems of stripping difficulty of medium-heavy rare-earth, high spent acid of a stripping solution, and the like. The invention uses the precipitator to precipitate the rare-earth from the organic phase, and the whole precipitation reaction is carried out on an oil-water interface to effectively control the grain size. Meanwhile, a trace organic phase is attached to grain surfaces and is used as a surface active agent to reduce the mutual adsorption action of grains for deflocculation. The invention can obtain products with good dispersity and uniform grain size distribution, thereby being a new method for preparing a high-quality rare-earth compound material. The invention has simple process, is easy to realize the industrialized production and has low production cost.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG +1
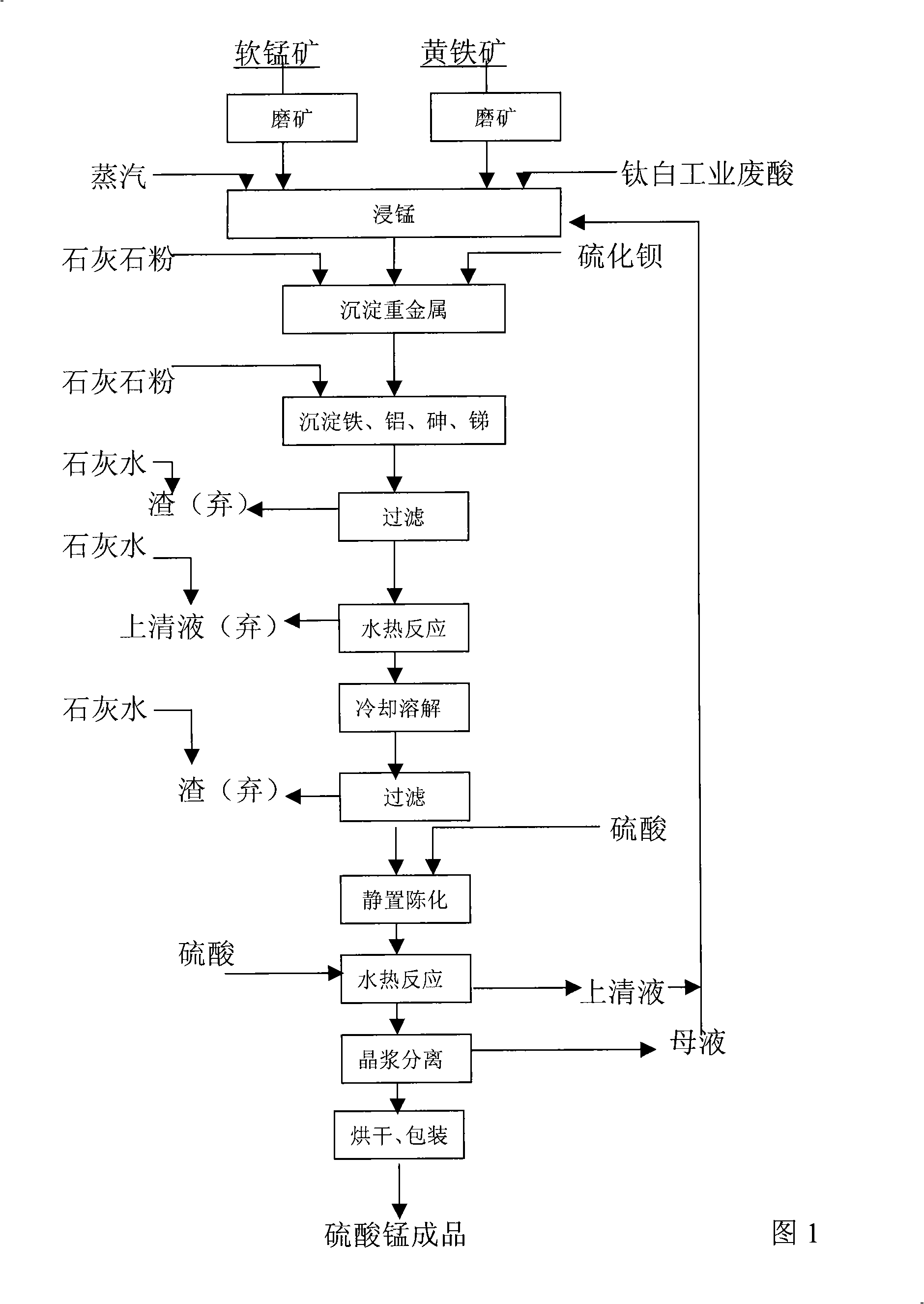
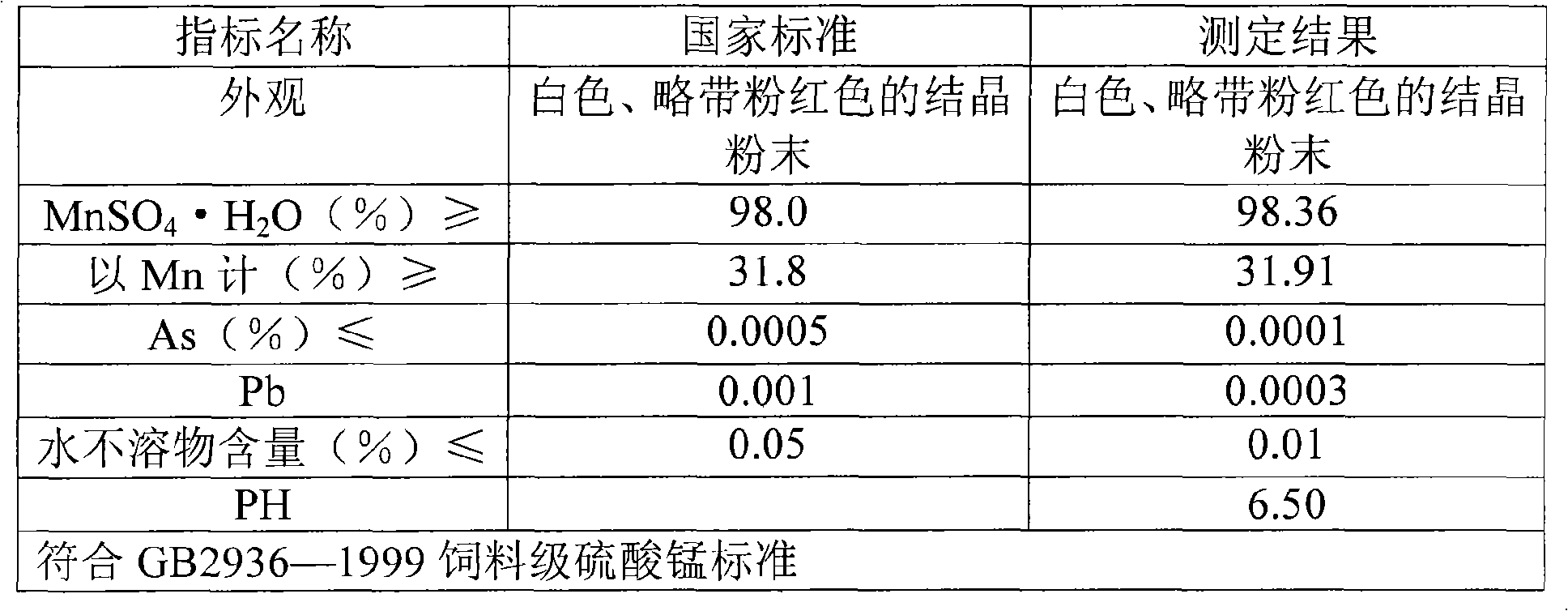
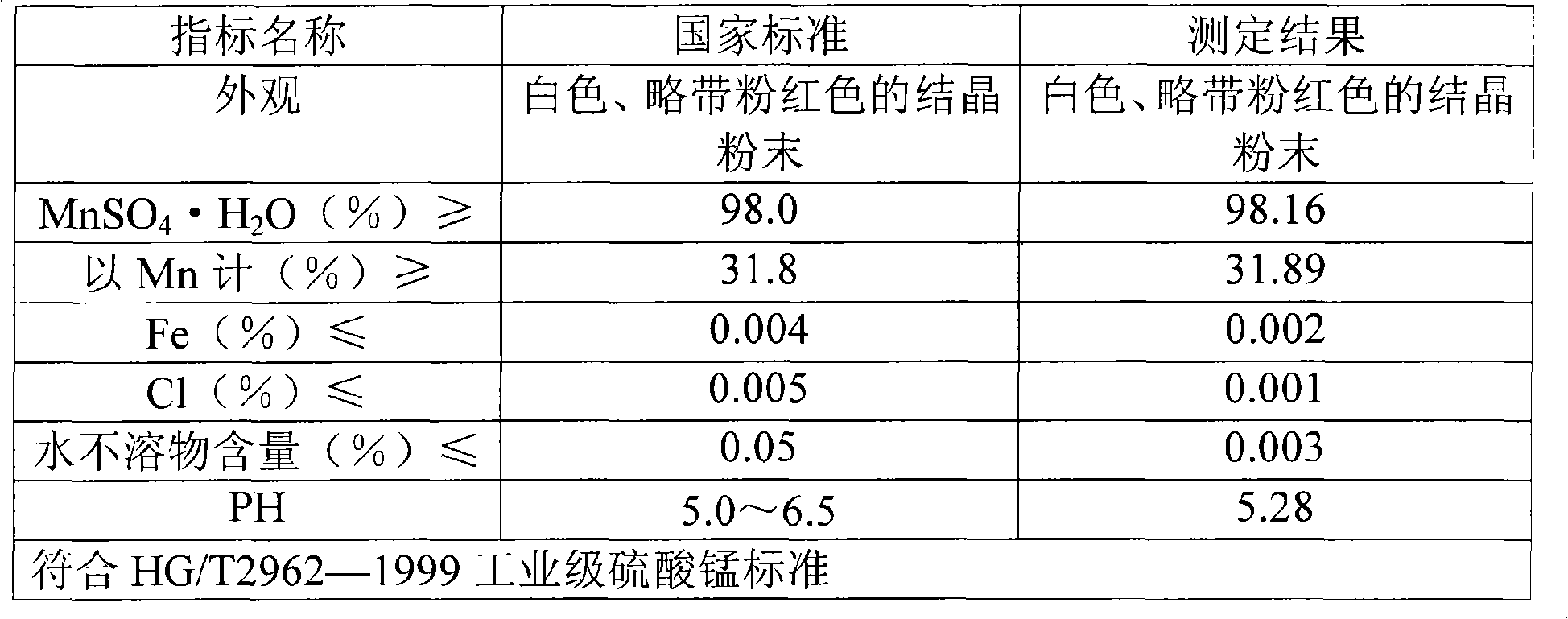
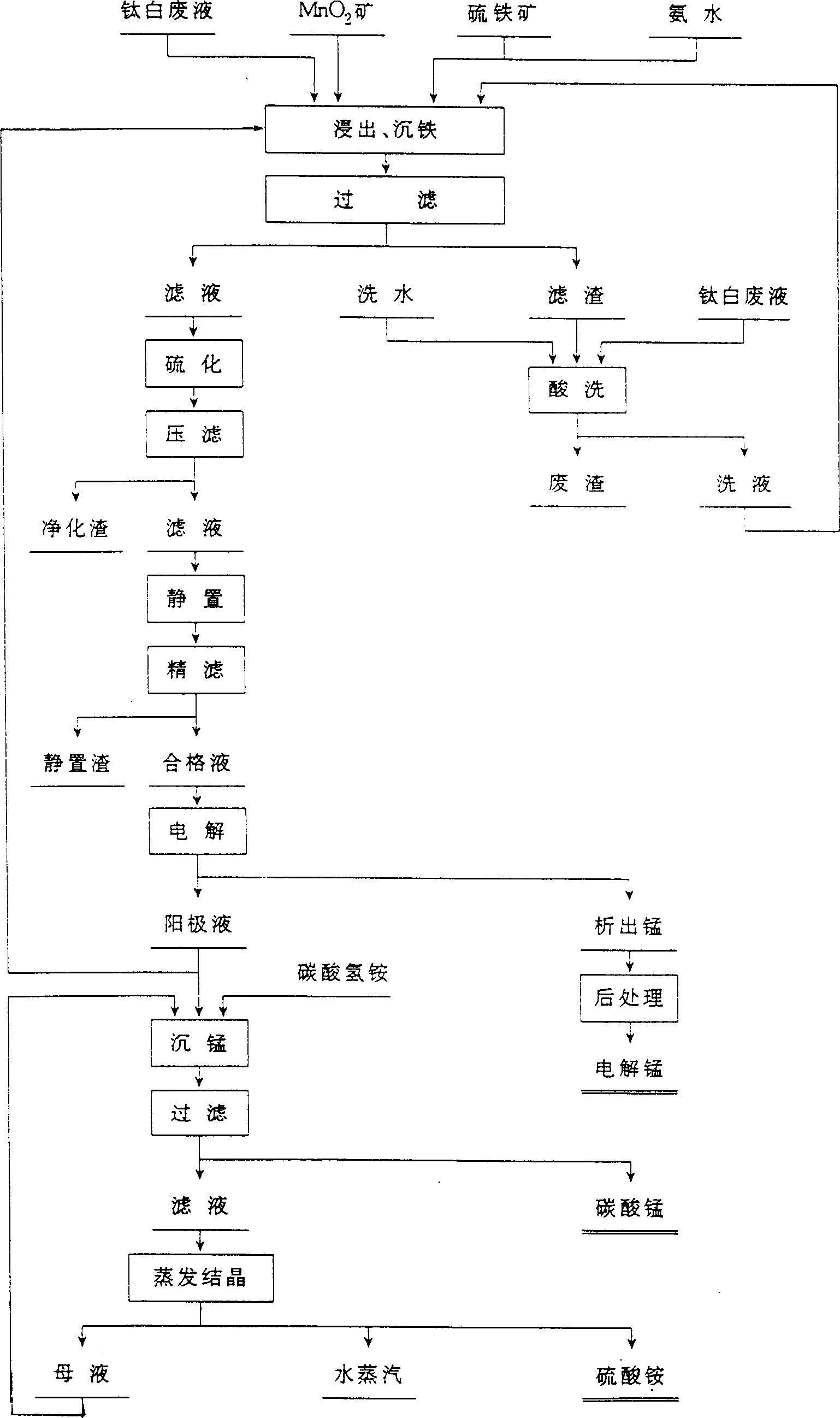
Method for producing manganese sulfate monohydrate crystal using pyrolusite and waste acid as raw material
InactiveCN101337692ASimple production processProduct quality is stableManganese sulfatesHeavy metalsPyrite
A method for producing monohydrate manganous sulfate crystals comprises the steps of (1) finely grinding pyrolusite and iron pyrites; (2) using industrial acid sludge of titanium white as a manganese leaching agent; (3) leaching manganese; (4) adjusting the pH value of a suspension liquid after leaching manganese, adding barium sulfide to deposit heavy metal; (5) adjusting the pH value of the suspension liquid after the deposition of the heavy metal, depositing iron, aluminum, arsenic, and stibium, and filtering; (6) conducting hydro-thermal reaction for a filtrate after filtering to obtain a solution containing coarse particles of manganous sulfate crystals; filtering the solution; and adjusting the pH value of the filtrate; (9) enabling the filtrate to conduct standing, seasoning and filtering; (10) adjusting the pH value of the filtrate to conduct hydro-thermal reaction to obtain a coarse particle manganous sulfate crystal solution; removing a supernatant fluid to obtain crystal mush containing coarse particles of manganous sulfate crystals; (11) separating the crystal mush to obtain the monohydrate manganous sulfate crystals.
Owner:广西远辰新能源材料有限责任公司 +4
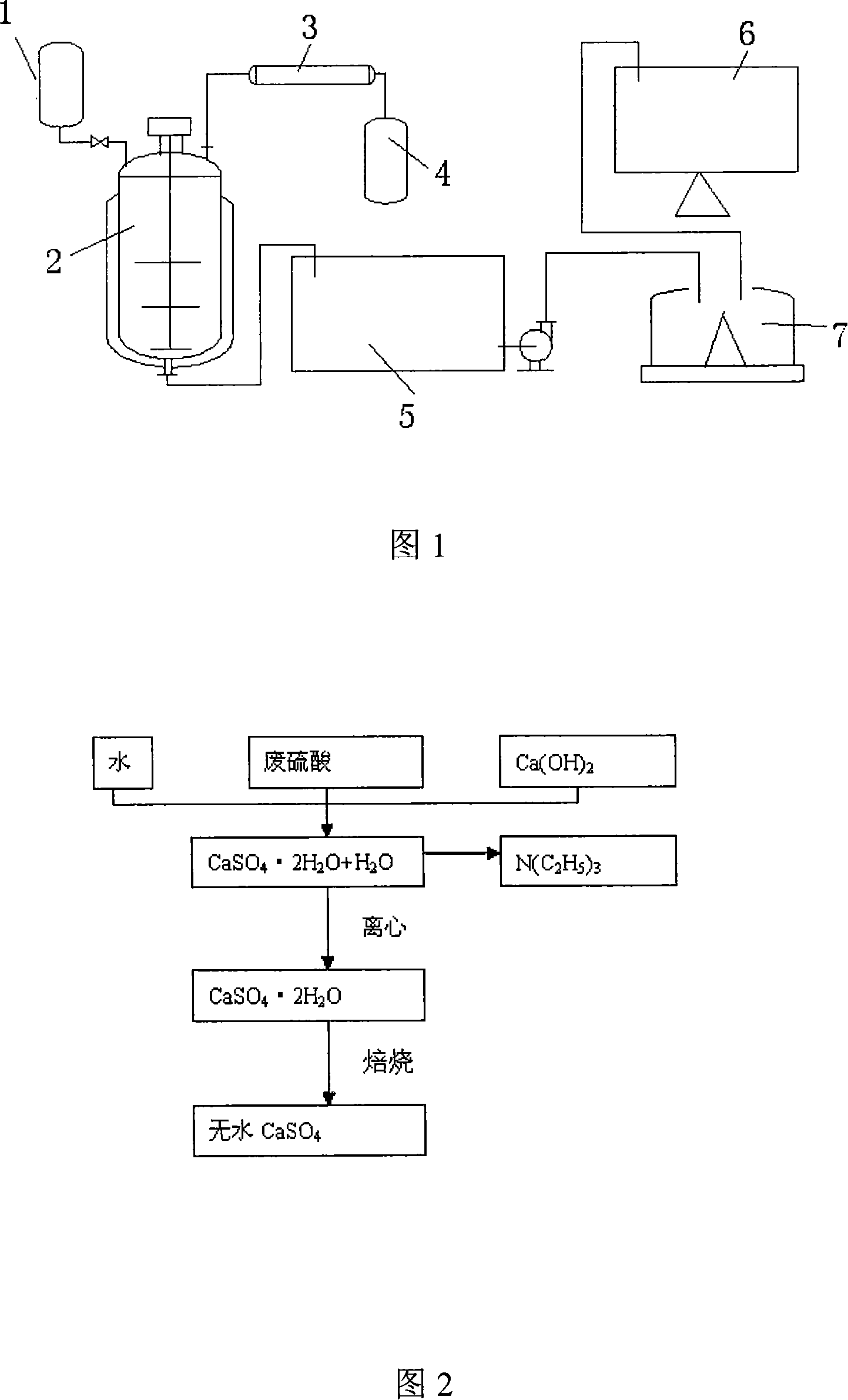
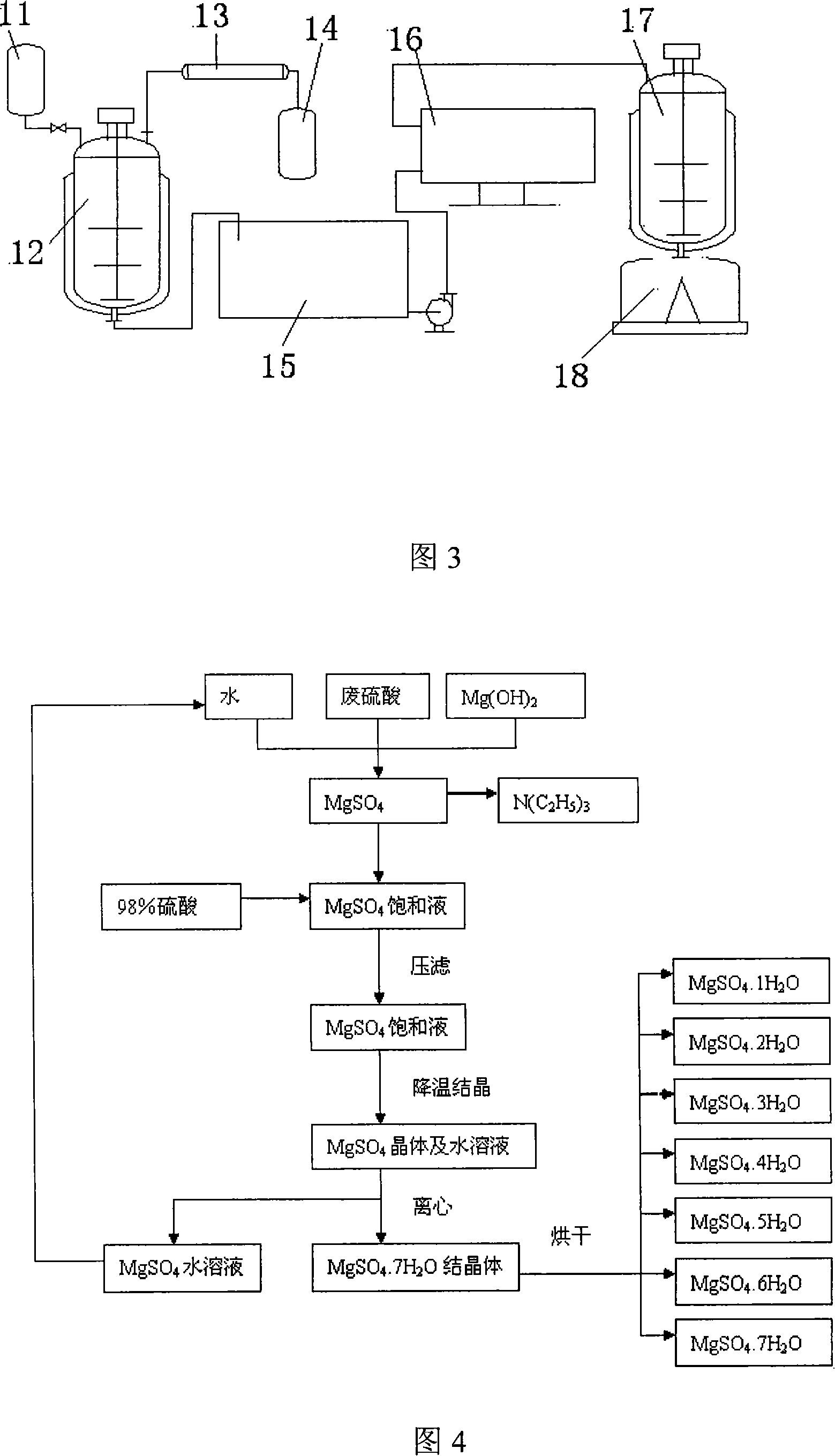
Waste acid treatment method and treatment system for acesulfame preparation technique by sulphuric anhydride cyclization method
ActiveCN101148300ASolve environmental problemsAchieve recyclingMagnesium sulfatesMultistage water/sewage treatmentSewageAcesulfame potassium
The present invention is process of treating waste acid solution from Acesulfame potassium preparing sulfuric anhydride cyclizing process. The process of treating waste acid solution includes the reaction of the waste acid solution and the mixture comprising Mg(OH)2 or MgO and water in a neutralizing reactor to produce triethylamine gas, cooling triethylamine gas in a cooler into triethylamine liquid and collecting in a tank, regulating the pH value of neutralizing reaction resultant in a regulating tank with 98 % concentration sulfuric acid solution into 5-7, filtering, cooling the filtrate in a MgSO4 cooling reactor to separate out MgSO4 hydrate. The present invention has MgSO4 yield up to 95 % and N(C2H5)3 recovering rate up to 95 % and can eliminate environmental pollution caused by Acesulfame potassium production.
Owner:ANHUI WEIDUO FOOD INGREDIENTS CO LTD
Process for recovering sulfuric acid and sulfate from waste acid generated in preparation of titanium dioxide by using sulfuric acid method
InactiveCN102079512AImprove recycling ratesIncrease concentrationSulfur-trioxide/sulfuric-acidIron sulfatesHigh concentrationWater vapor
The invention relates to a process for recovering sulfuric acid and sulfate from waste acid generated in the preparation of titanium dioxide by using a sulfuric acid method, belonging to the technical field of waste acid treatment in the industrial production. The invention recovers sulfuric acid and sulfate products from waste acid generated in the production process for preparing the titanium dioxide by using the sulfuric acid method through the sedimentation pretreatment and the simple process including the first segment of flash evaporation-crystallization, concentration and separation, the second segment of vacuum evaporation, concentration and separation and the third segment of vacuum evaporation, concentration and separation. The invention has simple process, convenience of operation, simple equipment, high performance price ratio and high yield, high concentration and less impurities of the product acid, can recycle resources without waste liquid or waste residue emission and can be favorable to environmental protection and energy saving, and emitted exhaust mainly contains air and less vapor, is non-toxic to the environment and can effectively overcome the difficulties of fouling and clogging of the equipment. The invention can be widely applied to the recovery of waste acid in the industrial production and be particularly suitable for recovering the waste acid generated in the preparation of titanium dioxide by using the sulfuric acid method.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
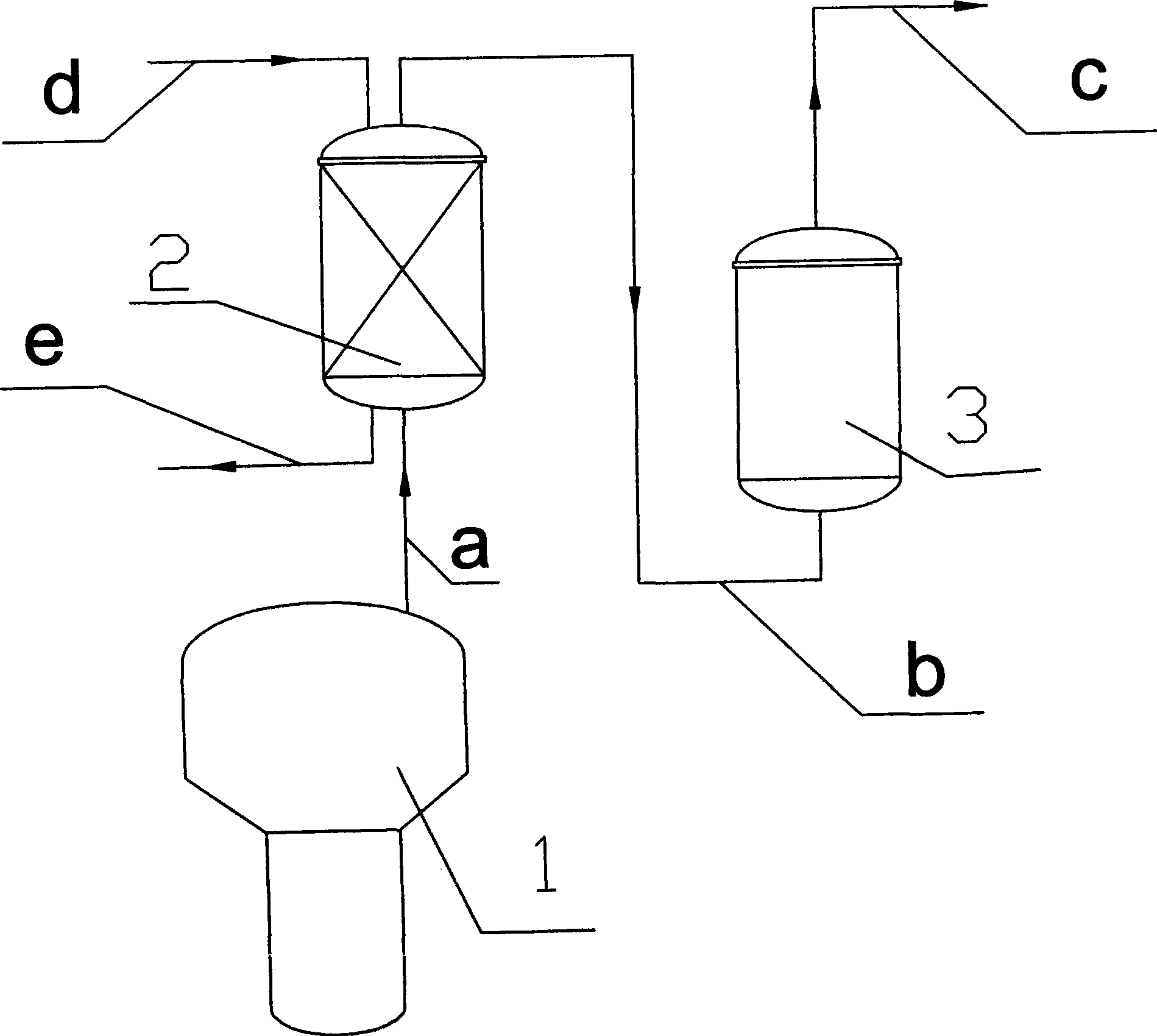
Technique for reducing impurity content in gas phase hydrogenchloride from hydrolysis of dimethyldichlorosilane
InactiveCN101423193ALow impurity contentHigh yieldChlorine/hydrogen-chloride purificationGas phaseHydrolysate
The invention discloses a process method used for reducing the content of impurities in gas-phase hydrogen chloride after hydrolysis of dichlorodimethyl silane, comprising the steps as follows: a two-step device is used for separating the impurities; a vapour liquid separator leads the mixed hydrogen chloride gas generated after the hydrolysis of dichlorodimethyl silane to enter a washing tower of a guide structure so as to remove most of impurities; subsequently, the hydrogen chloride gas with most of impurities removed is arranged into the bottom of a demister; the adsorption medium at the internal layer of the demister is porous fiber which is used to adsorb the siloxane impurity in the hydrogen chloride gas; and the hydrogen chloride gas with the siloxane impurity removed is sent to a methyl chloride device to carry out the subsequent process. The method reduces the content of the impurities in the hydrogen chloride gas, improves the yield of hydrolysate of the dichlorodimethyl silane, keeps the pressure of the hydrogen chloride gas at a high level after purification, does not generate a great deal of waste acid, avoids the disposal of waste acid, and has low energy consumption and low equipment expense.
Owner:浙江恒业成有机硅有限公司
Metal surface treatment agent
InactiveCN1786281ANo "hydrogen embrittlement" phenomenonGood effectSurface-active agentsNuclear chemistry
The invention relates to a deoiling, derusting and rust preventing metal surface treating compound. It is made up of ammonia or amine, organic acid, auxiliary agent, surface active agent, chelating agent. Its pH value is 7-8. The organic acid belongs to food, participating reaction, and has no waste acid and water after using. The treated metal surface appears virgin metal natural color. It will not corrode the metal. And the í‹hydrogen embrittlementíŒ will never happen.
Owner:王开平
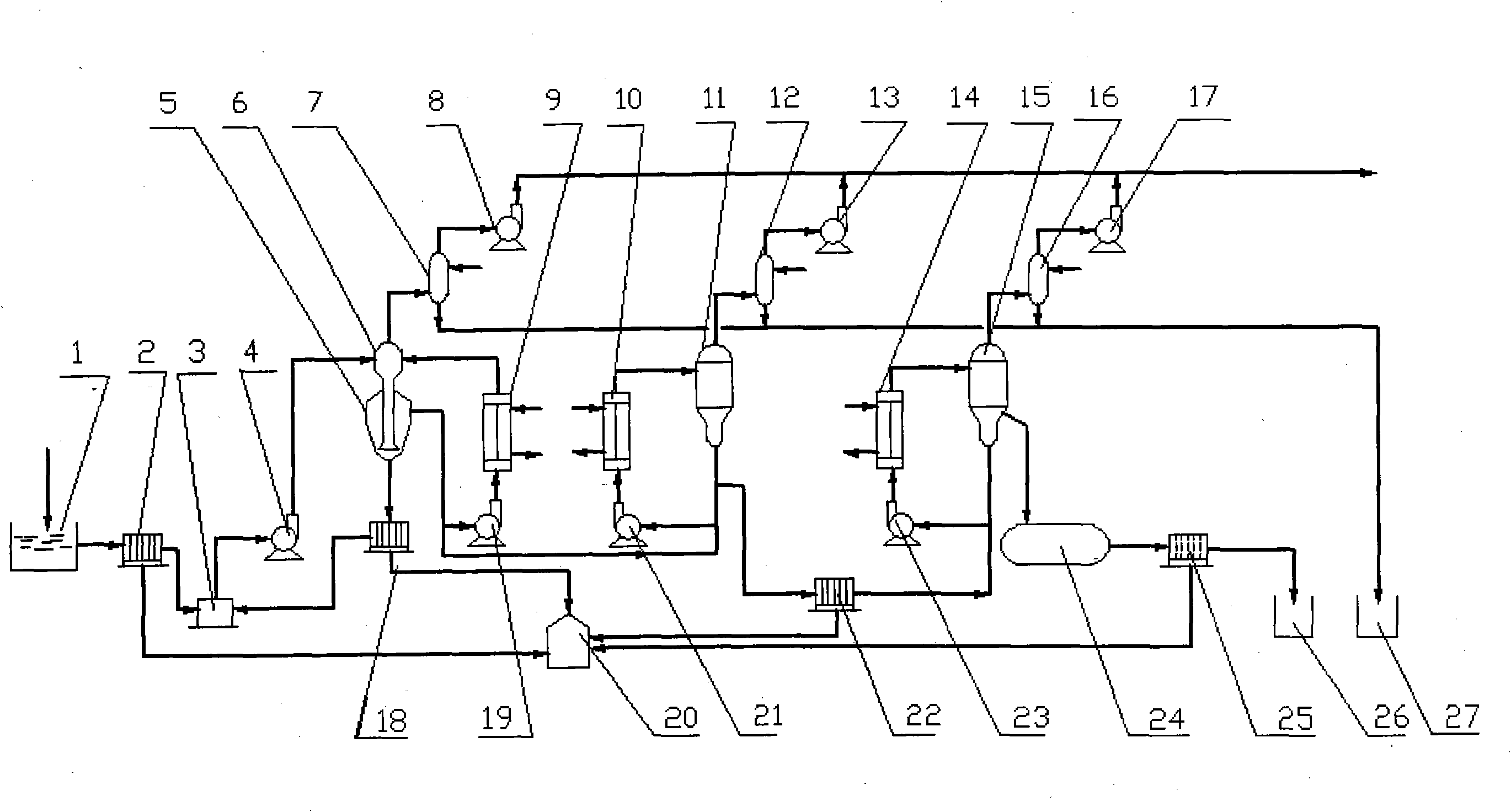
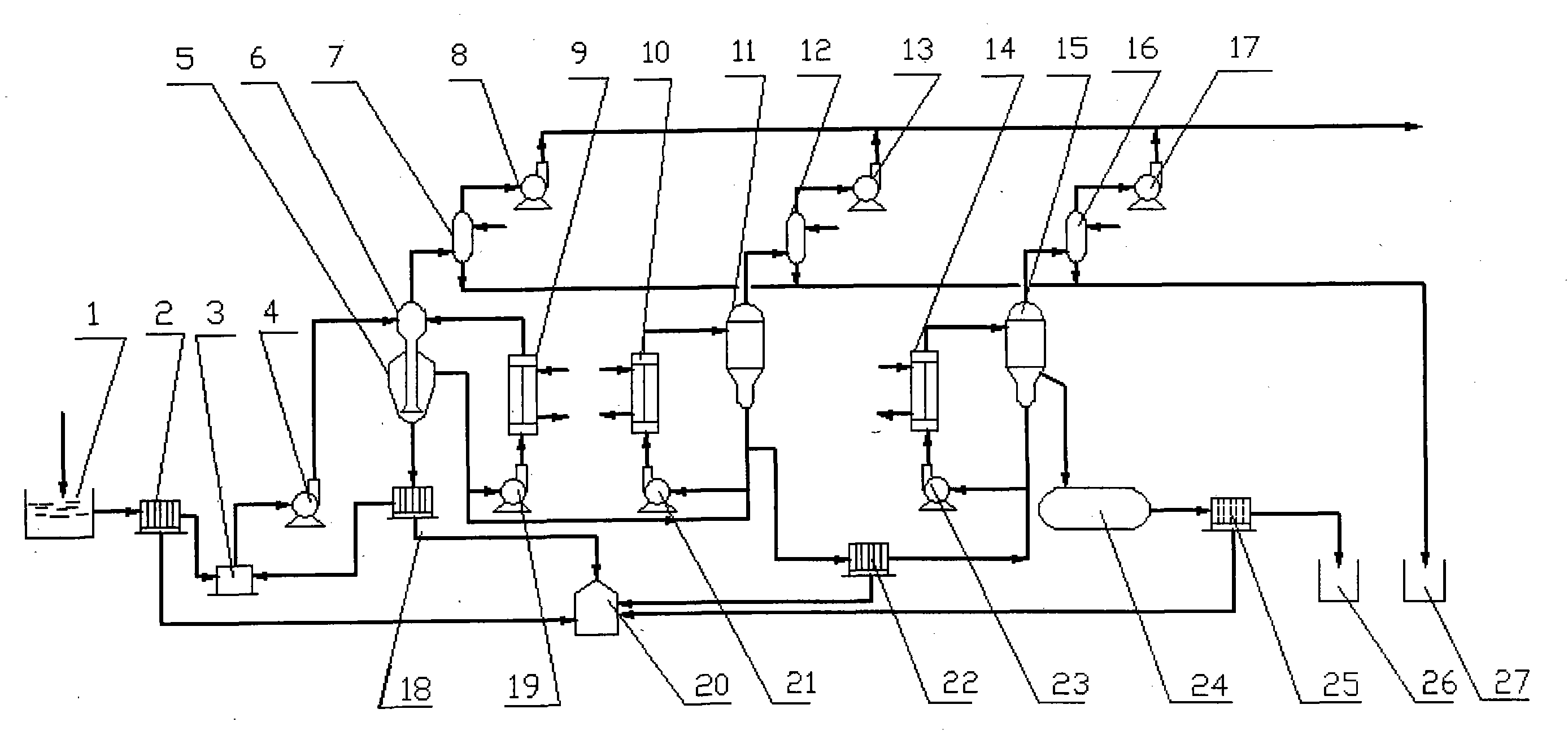
Method of manufacturing electrolytic metal manganese using titanium white waste acid and manganese dioxide ore
InactiveCN1724697ASolve pollutionImprove filtering effectPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisSulfur
The invention relates to a method to make electrolysis manganese metal by titan white spent acid and manganese dioxide mine. The feature is that it uses the H2SO4 and Fe2+ in the titan white spent acid as assistant material, adds manganese dioxide mine and sulfur iron ore to make electrolysis manganese metal. The invention solves the environment pollution problem caused by titan white spent acid. The electrolysis manganese metal has high quality and reaches the YB / T051-2003DJMnA high purity production standard.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Method for treating waste acid produced from titanium dioxide production using vitriol method
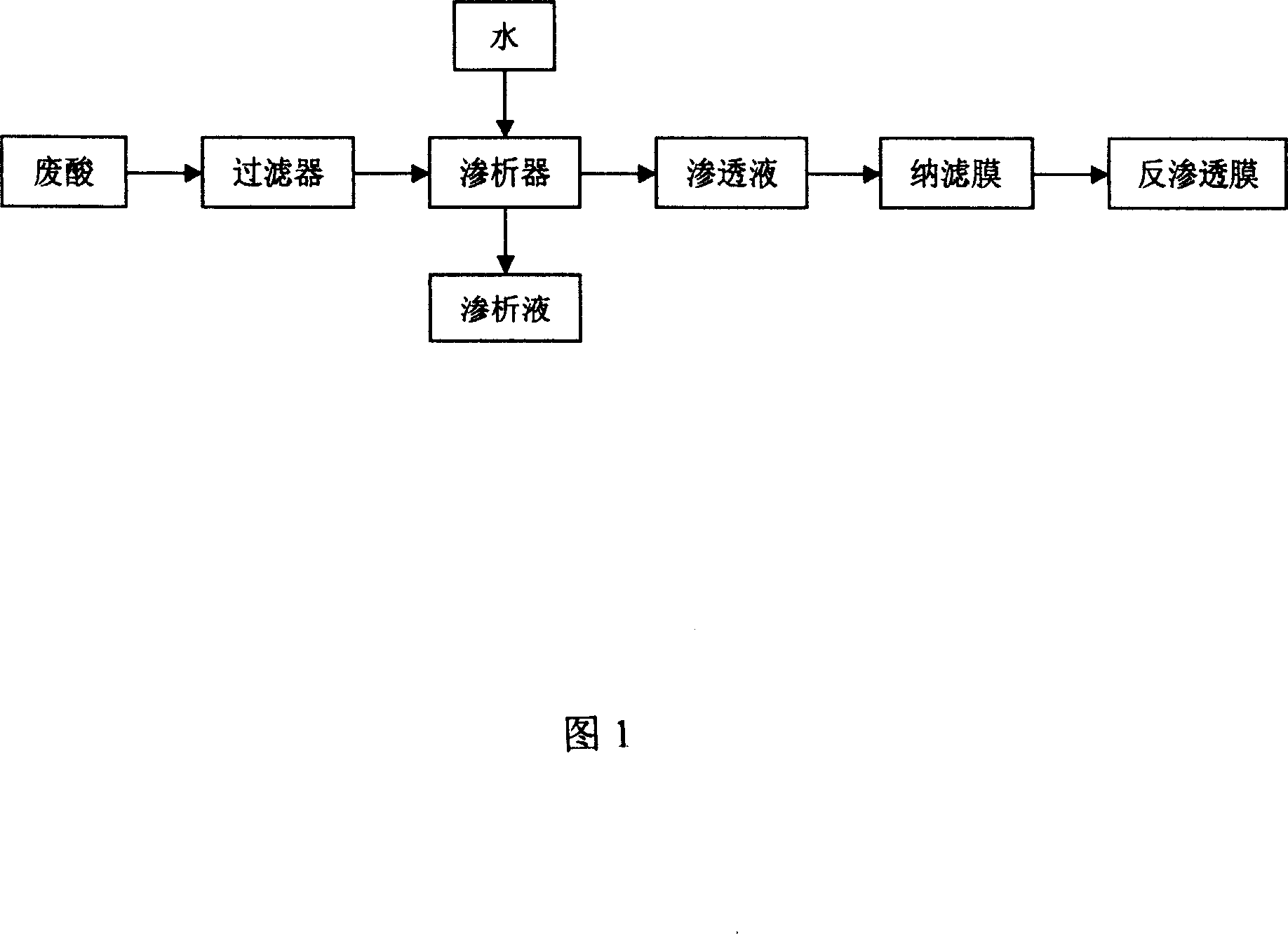
InactiveCN1966400AReduce pollutionEfficient separationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisSulfur-trioxide/sulfuric-acidReverse osmosisTitanium
The invention relates to a way to treat spent acid in the sulfuric acid method to produce titanium pigment. The characteristic of the invention: the method includes the following steps: pulping the spent acid into the sophisticated filtrator through the high pressure anti-corrosion pulp, the filtrate entering the container; the tap water and filtered spent acid going separately into the two inlets of the diffuse dialyzator, separating for the first time the strong H2SO4 from FeSO4 in the permeating solution, the separated strong permeating solution is pulped into the nano-filter membrane to separate H2SO4 for the second time, the content of FeSO4 in the solution is 0.1% or less; the separated permeating solution H2SO4 goes into the reverse osmosis membrane device and the concentrated solution is the dilute sulfuric acid product. The advantage of the invention includes high spent acid recovery rate, high purity, low processing cost and high holding-up rate.
Owner:上海闵欣环保设备工程有限公司
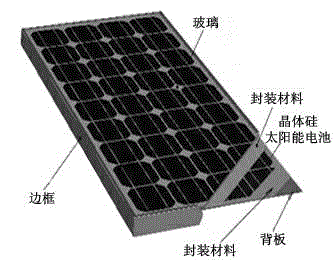
Acid corrosion solution for preparing multicrystal silicon pile surface and its using method
ActiveCN1821446AEliminate hazardsSuitable for mass productionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationCorrosion reactionHydrofluoric acid
The present invention discloses acid corrosion solution for preparing polycrystalline silicon pile surface and its usage. The solution is compounded with oxidant and hydrofluoric acid and through mixing, and the oxidant is nitrate or nitrite. During use, the cut polycrystalline silicon chip is set inside the corrosion solution for corrosion at the temperature of -10 to +25 deg.c for 0.5-20 min to eliminate damage surface caused by wire electrode cutting, with the acid corrosion time and temperature being dependent on the solution concentration. The present invention is suitable for both intermittent production and continuous production, and has easy treatment of the produced waste acid.
Owner:WUXI SUNTECH POWER CO LTD
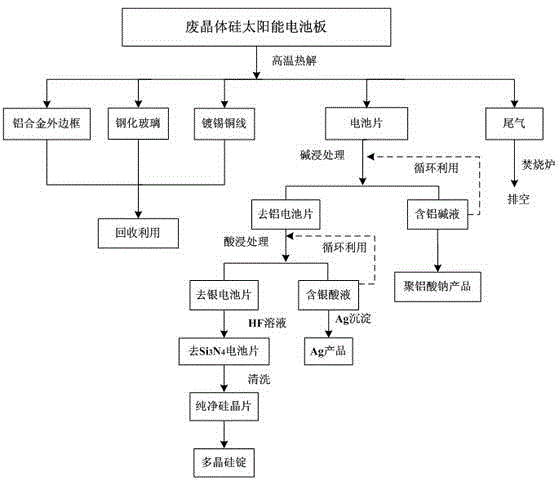
Waste crystalline silicon solar cell panel disassembling and recovering method
ActiveCN103978021AIncrease added valueRealize sorting and recyclingWaste processingSolid waste disposalWaferingPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a waste crystalline silicon solar cell panel disassembling and recovering method. The method can realize the classification recovery of aluminum frames, toughened glass, silicon wafers, aluminum, silver and copper of waste crystalline silicon solar cell panels. The method adopts a heat treatment technology and a chemical technology combination technique to realize the frame and glass recovery of the waste crystalline silicon solar cell panels, the silicon wafer separation, and the valuable metal and silicon wafer recovery. The method has the advantages of recovery treatment difficulty reduction, tail gas harmlessness realization, secondary pollution control and environment protection; and an alkali dipping treatment and acid dipping treatment solution can be recycled, so the reagent consumption is reduced, the waste acid and waste alkali generation amount is reduced, and the final waste treatment cost is reduced.
Owner:刘景洋
Method for recovering metal from molybdenum-containing spent catalyst
ActiveCN102050492AImprove solubilityHigh recovery rateMolybdeum compoundsProcess efficiency improvementSpent acidMetal
The invention discloses a method for recovering metal from a molybdenum-containing spent catalyst, which comprises the following steps of: degreasing and crushing the spent catalyst, mixing the spend catalyst and sodium carbonate, and calcining; after calcining, leaching by water, recovering molybdenum from the spent catalyst by adopting an organic extracting agent; and preparing solution of mixed acid by utilizing spent acid discharged in the method to treat solid residues after water leaching, and recovering metal in the spent acid and the residues further. By the method, the recovery rate of the metal in the spent catalyst can be improved further, the severity of the operation condition is lowered simultaneously, and the method has low energy consumption and can be in the metal recovery process of the molybdenum-containing spent catalyst.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
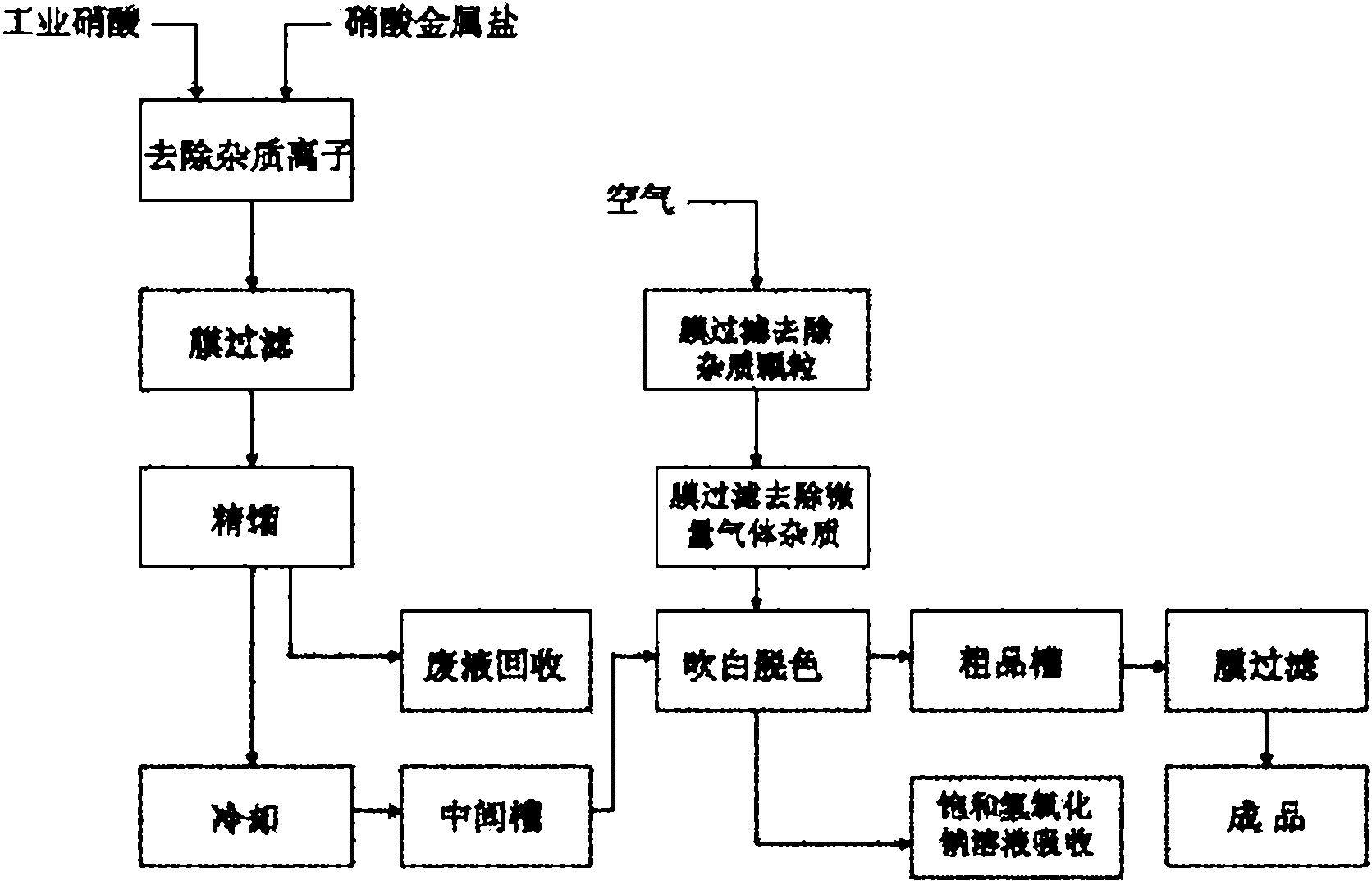
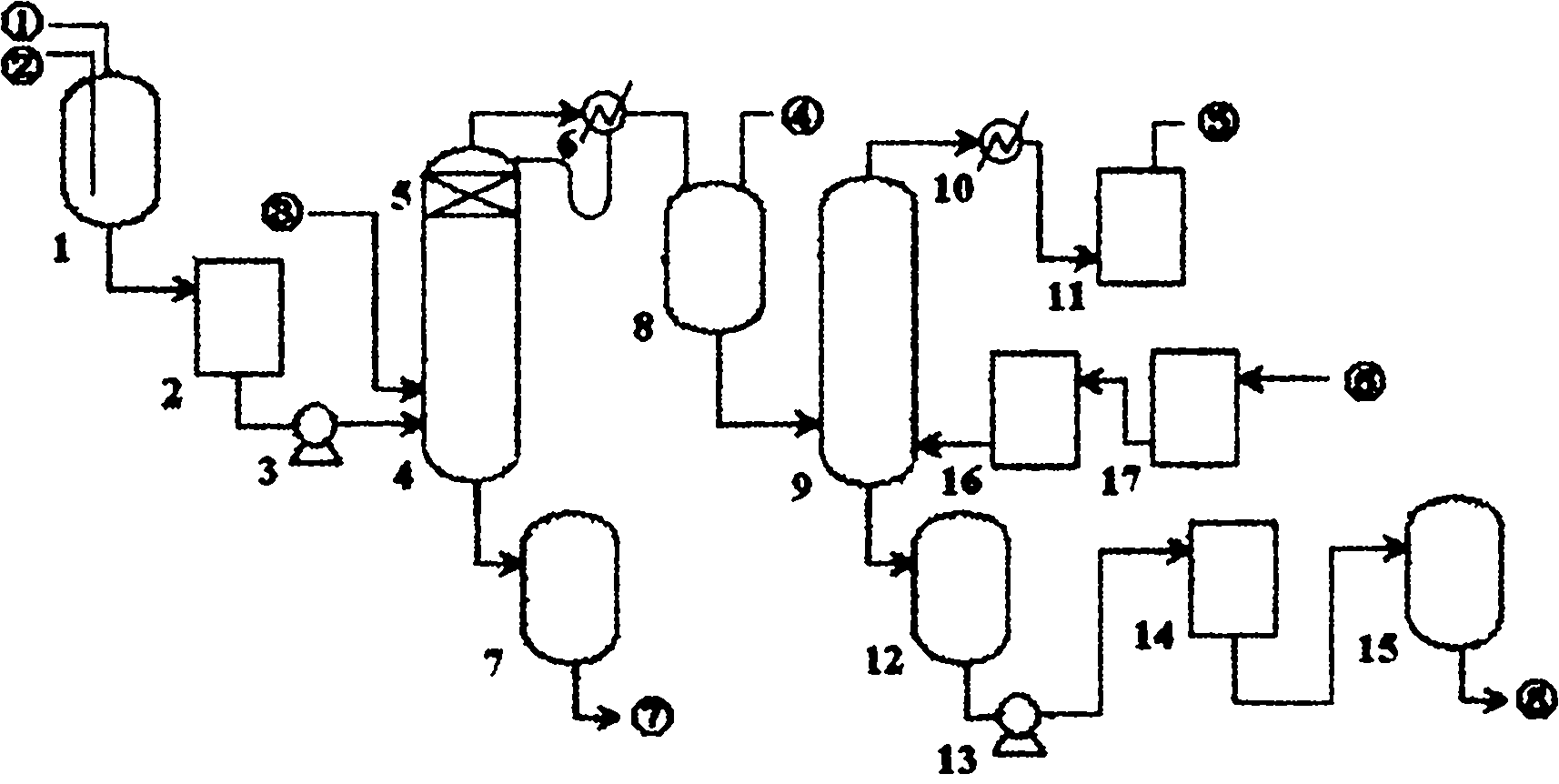
Process for preparing ultrapure nitric acid
InactiveCN102001635AEfficient removalSolve the problem of high content of impurity ionsNitric acidInorganic saltsNitrogen oxides
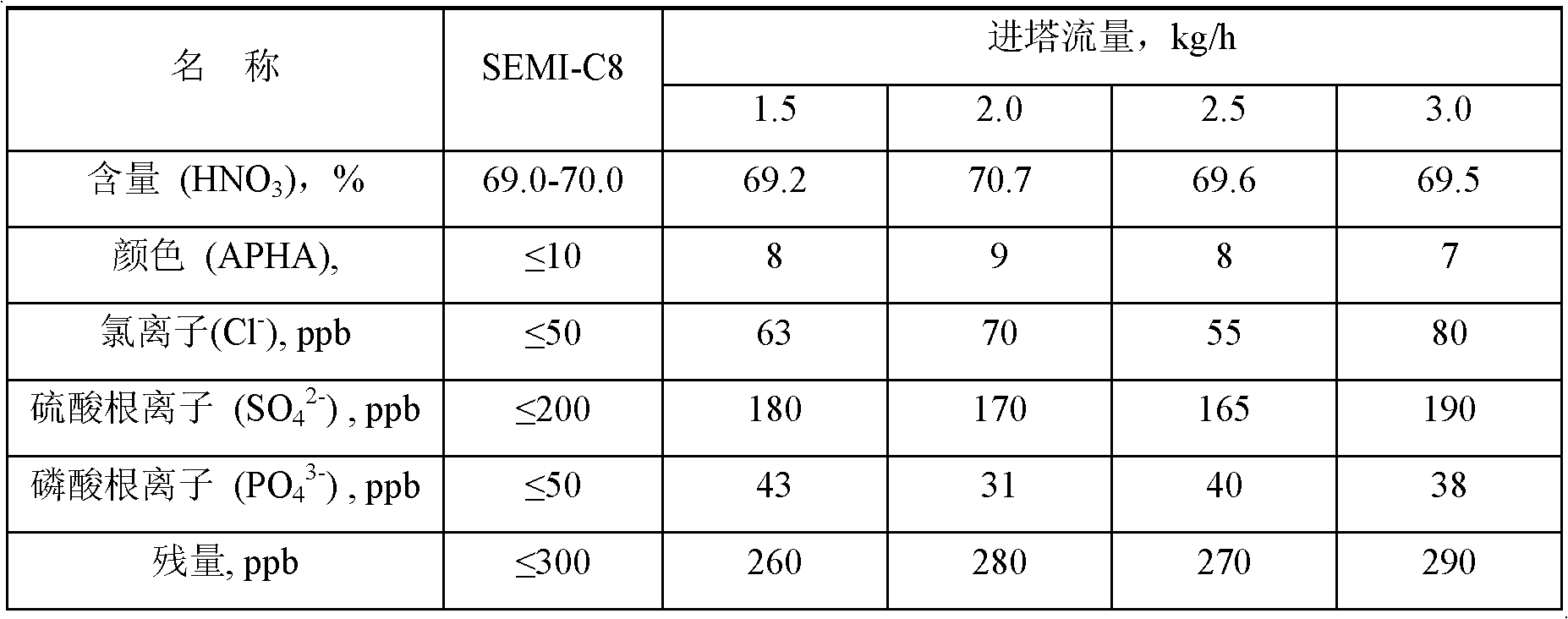
The invention discloses a process for preparing ultrapure nitric acid. The method comprises the following steps of: adding nitric acid metal salt to react with impurity anions, namely Cl<-> and SO4<2-> in industrial nitric acid serving as a raw material, precipitating, performing membrane filtration purification, rectifying to remove inorganic salt, regulating rectification liquid to form 69 to 70 weight percent nitric acid by using ultrapure water, white-blowing by using purified air in a white-blowing tower, absorbing blown nitrogen oxide by using saturated aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide, adding white-blowing liquid into a crude product groove, and performing membrane filtration to obtain the ultrapure nitric acid. The detection shows that: the content of the ultrapure nitric acidprepared by the process reaches 69 to 70 weight percent and various indexes of the product all meet the semiconductor equipment and material international (SEMI) C8 standard. The rectification is performed and waste acid is collected simultaneously, and the waste acid is treated and recycled, so that the quality and productivity of the product are improved; and the product has stable quality, lowimpurity content and high purity and is suitable for large-scale and continuous production.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHEM REAGENT RES INST
Environmentally-friendly lithographic printing plate base and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN102407653AAvoid pollutionMeet the requirements of energy saving and environmental protectionPrinting pre-treatmentForme preparationElectrolysisBiochemical engineering
The invention relates to an environmental friendly lithographic printing plate base and a preparation process thereof and belongs to the technical field of printing platemaking. The environmentally-friendly lithographic printing plate base comprises a metal or nonmetal plate base and is characterized in that an adhesion layer and a hydrophilic layer are sequentially adhered to the plate base, the adhesion layer is formed by solidifying an adhesion layer coating liquid, and the hydrophilic layer is formed by solidifying a hydrophilic layer coating liquid. The hydrophilic layer is connected with a base body material through the adhesion layer so as to be firmly integrated to form the lithographic printing plate base, thus the fastness of the plate base is improved. The environmentally-friendly lithographic printing plate base is machined and then can be printed on a printing machine. According to the preparation process disclosed by the invention, the condition that the traditional plate base preparation needs electrolysis coursing and anodic oxidation treatment processes is improved, thus environment pollution caused by the consumption of a large amount of electric energy and the exhaust of a large amount of waste acid is avoided, and the requirements on energy conservation and environment conservation are realized.
Owner:石深泉
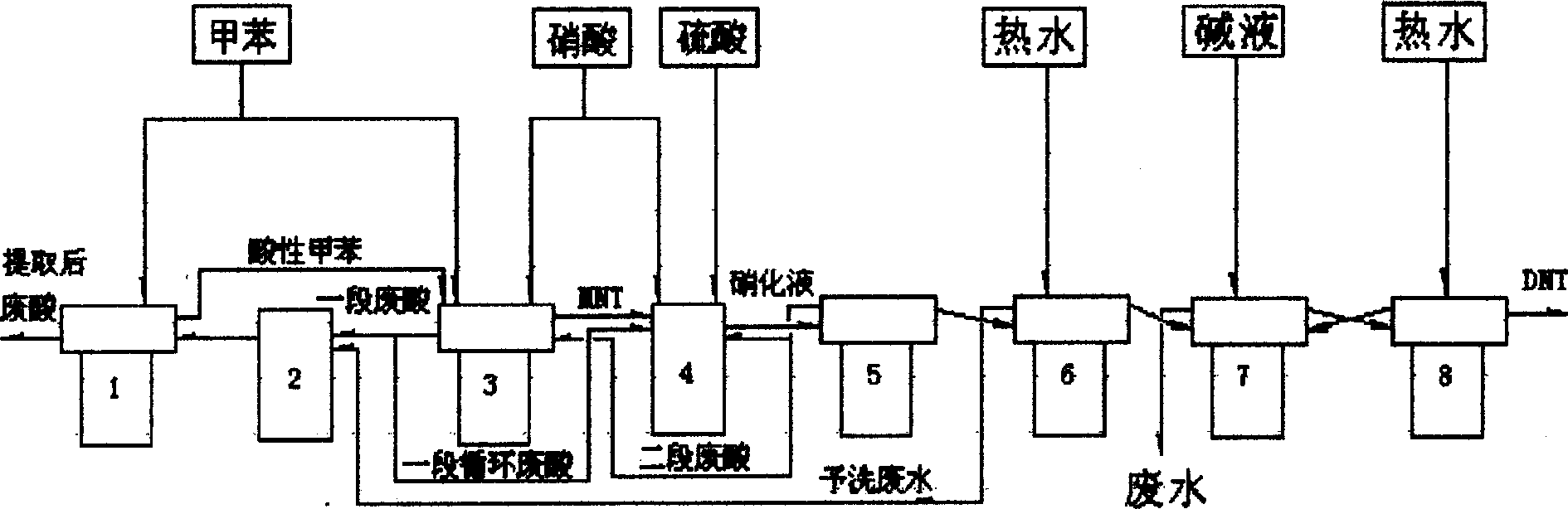
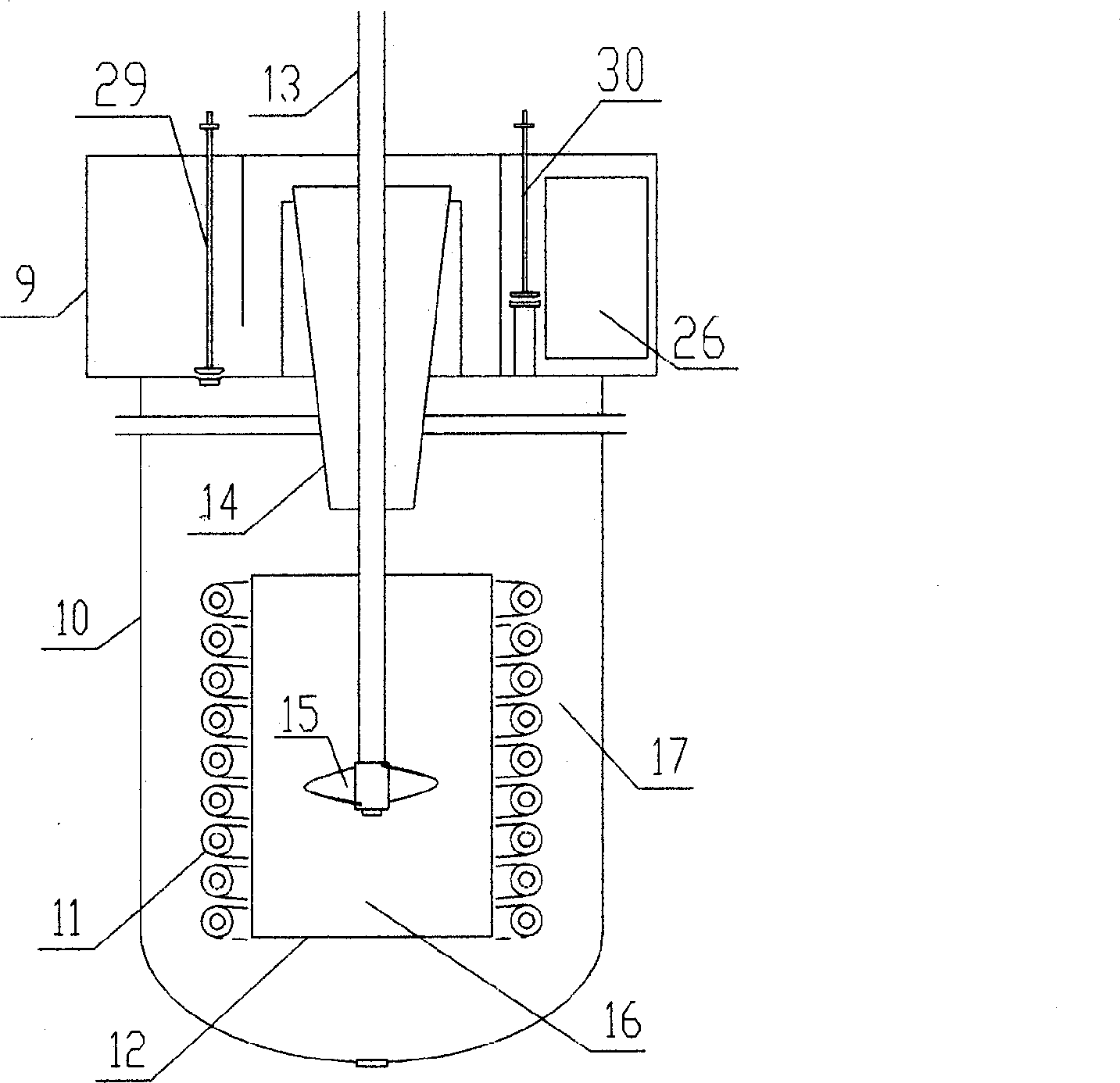
Process for continuous preparing diruitro methylbenzele and apparatus thereof
ActiveCN1793106AEnsure and improve qualityReduce quota consumptionNitro compound preparationTolueneSpent acid
The invention relates to a method to continuously produce dinitrotoluene and the device that is suited to the method. The method adopts two steps to make dinitrotoluene and organic phase and spent acid phase are separated. The acid phase is cycling used in the first and the second stage; toluene, nitric acid and mixture acid are added into the center of draft tube of reactor synchronously, mixing fully, cycling in the center and outside of the draft tube; after fully reacting, the taking gravity settling separation in the separator where spent acid cycling device, stop cycling device, and disc type separating device are installed.
Owner:GANSU YINGUANG CHEM IND GRP CO LTD
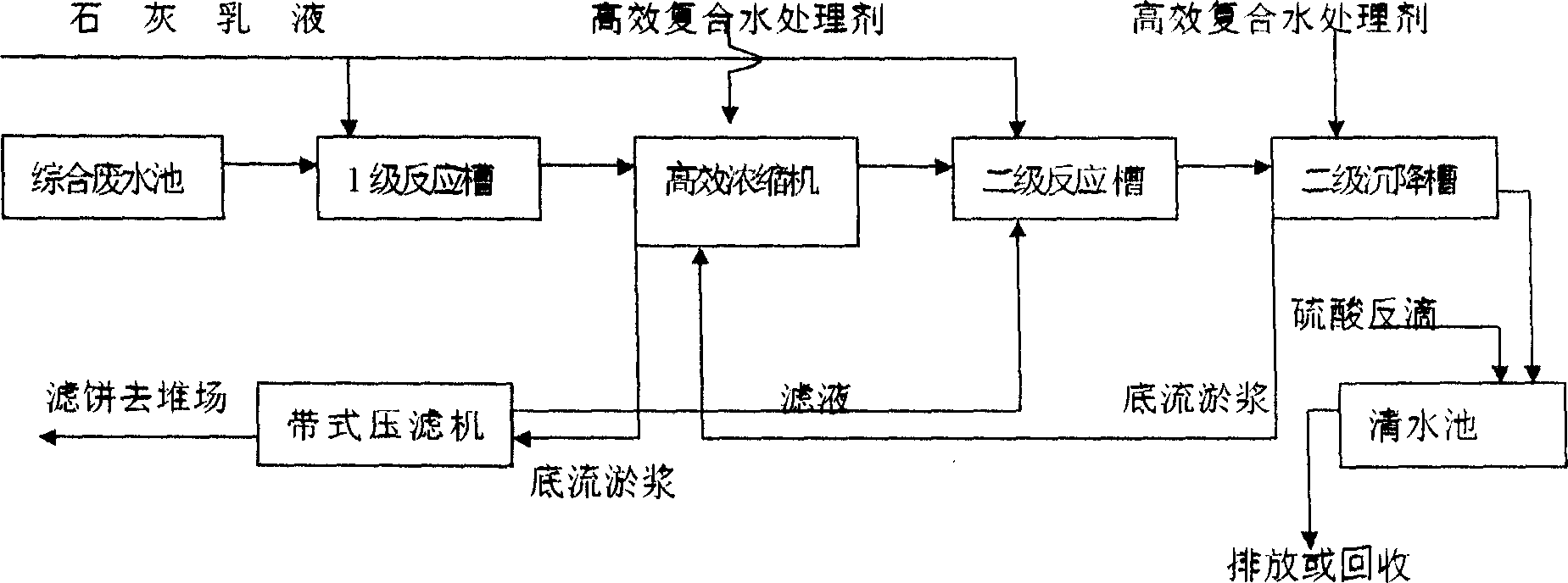
Process for treating and controlling acid waste water containing fluorine
InactiveCN1724405AReduce dosageReduce consumptionWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationSludgeWastewater
A process for treating the F-contained acidic sewage generated by producing P fertilizer includes such steps as pumping the sewage in class-one reaction pool, adding lime milk, neutralizing, mixing it with efficient composite water treating agent in an efficient concentrating machine, depositing, pumping the supernatant in the class-two reaction pool, adding lime milk for regulating pH value, press filtering the sludge, transporting the cake to stack yard, pumping the filtrate in the class-one reaction pool, mixing the slurry of the class-two reaction pool with said water treating agent in class-two slant depositing pool, depositing, regulating the pH value of its supernatant for draining, and regulating the pH value of its sludge for returning it back to the class-one depositing pool.
Owner:WENGFU (GRP) CO LTD
Acid pickling and waste acid treatment process for improving purity of powdery quartz sand
The invention provides an acid pickling and waste acid treatment process for improving purity of powdery quartz sand. The process includes the steps: putting the powdery quartz sand in an acid pickling purification device, and using an acid pump for pumping acid pickling solution into the acid pickling purification device, wherein the acid pickling solution is composed of hydrofluoric acid, fluorosilicic acid, oxalic acid and water or composed of fluorosilicic acid, oxalic acid and water; removing the acid pickling solution after acid pickling, and collecting; delivering the powdery quartz sand to a washing device by clear water after acid pickling, washing to neutral, and dewatering to obtain a finished product of powdery quartz sand; transferring waste acid into a neutralization tank for neutralization, delivering into a sedimentation tank by the pump, and allowing calcium fluosilicate and calcium oxalate to precipitate; delivering the clear water into a regulation tank after precipitation to realize pH adjustment for precipitation of iron ions; using oxalic acid or fluorosilicic acid to adjust pH, precipitating calcium fluosilicate and calcium oxalate again, filtering to obtain clear water, and delivering the clear water to a workshop for recycling. The acid pickling and waste acid treatment process for improving purity of the powdery quartz sand has the advantages of remarkable purity improvement and impurity reduction and simplicity and convenience in subsequent treatment.
Owner:HUANGGANG NORMAL UNIV +1
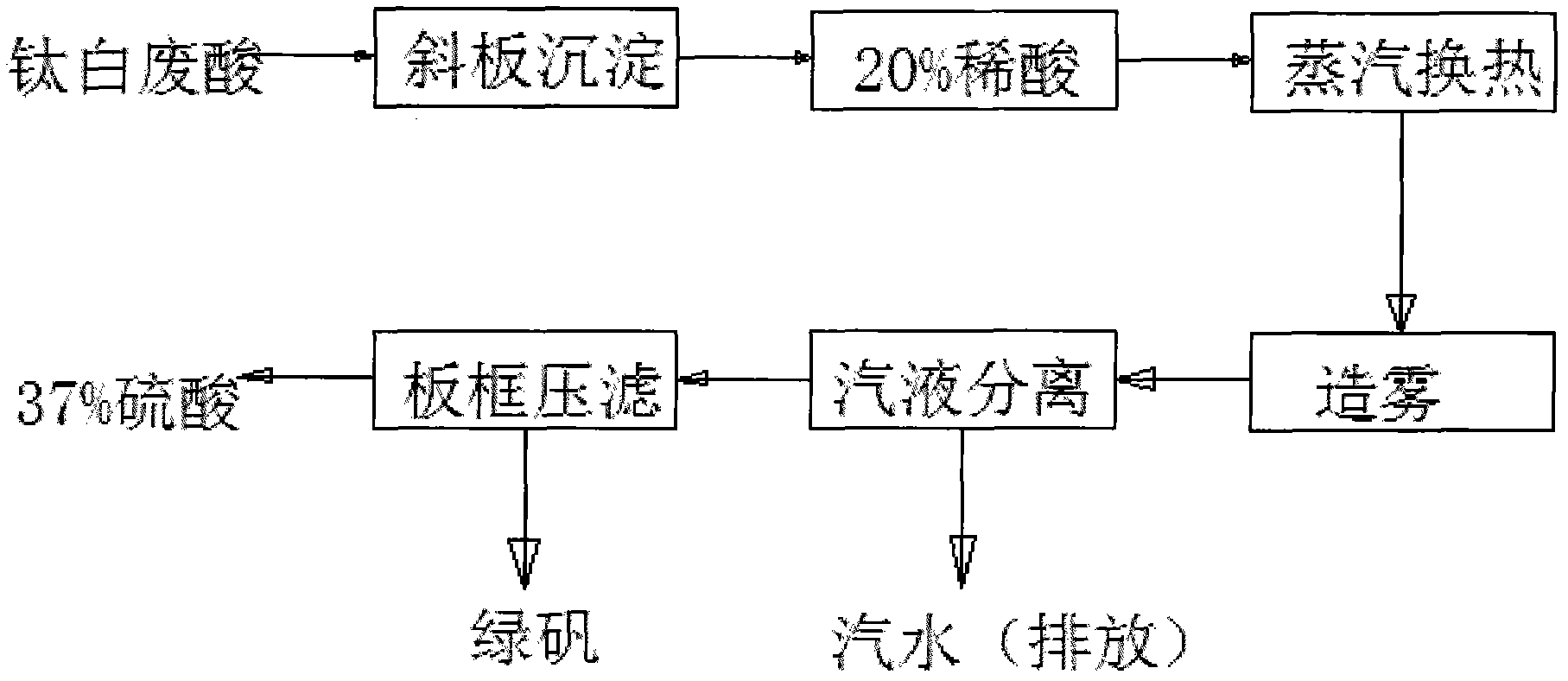
Process of industrialize for waste acid concentrition recovering used in titanium white production by sulfuric acid method
ActiveCN1724339AReduce energy consumptionReduce dosageSulfur-trioxide/sulfuric-acidTitanium dioxideWhite powderTitanium
An industrial process for reclaiming the waste acid in the production of titanium white powder by sulfuric acid method features that the waste acid is concentrated by fume and then by steam. Its advantages are high efficiency, low cost, and no environmental pollution.
Owner:潜江方圆钛白有限公司
Preparation of o-nitro p-methylsulfonylbenzoic acid
ActiveCN101503383AIncrease concentrationSlow down decompositionOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationBenzoic acidOleum
The invention relates to a preparation method of o-nitro-p-methysulfonyl benzoic acid. O-nitro-p-methylsulfonyl toluene is oxidized by persulphuric acid to obtain the o-nitro-p-methysulfonyl benzoic acid. The preparation method comprises the following processes: (a) oxyful and oleum are mixed at a low temperature to prepare persulphuric acid; (b) o-nitro-p-methylsulfonyl toluene is dissolved in sulphuric acid; and (c) the persulphuric acid obtained from the step (a) is dripped into the liquid obtained from the step (b) for purpose of reaction to obtain the o-nitro-p-methysulfonyl benzoic acid. In the method, the reaction of the oleum and the oxyful relatively improves the concentration and the oxidization capability of the oxyful and reduces the decomposition speed of the oxyful; as vanadic oxide is not used, waste acid treatment, recovery and the like are omitted; and the persulphuric acid in use is automatically transformed into sulphuric acid after the oxidization is finished and can finally be used indiscriminately with a mother liquid. Compared with the prior art, the amount of the oxyful in use is greatly reduced, and the production cost remarkably decreases. Compared with the nitric acid oxidization process, the preparation method is safer, environment-friendly and clean.
Owner:浙江嘉福新材料科技有限公司
Method capable of recycling acids for preparing 2,5-dichloronitrobenzene (DCNB) through continuous nitration
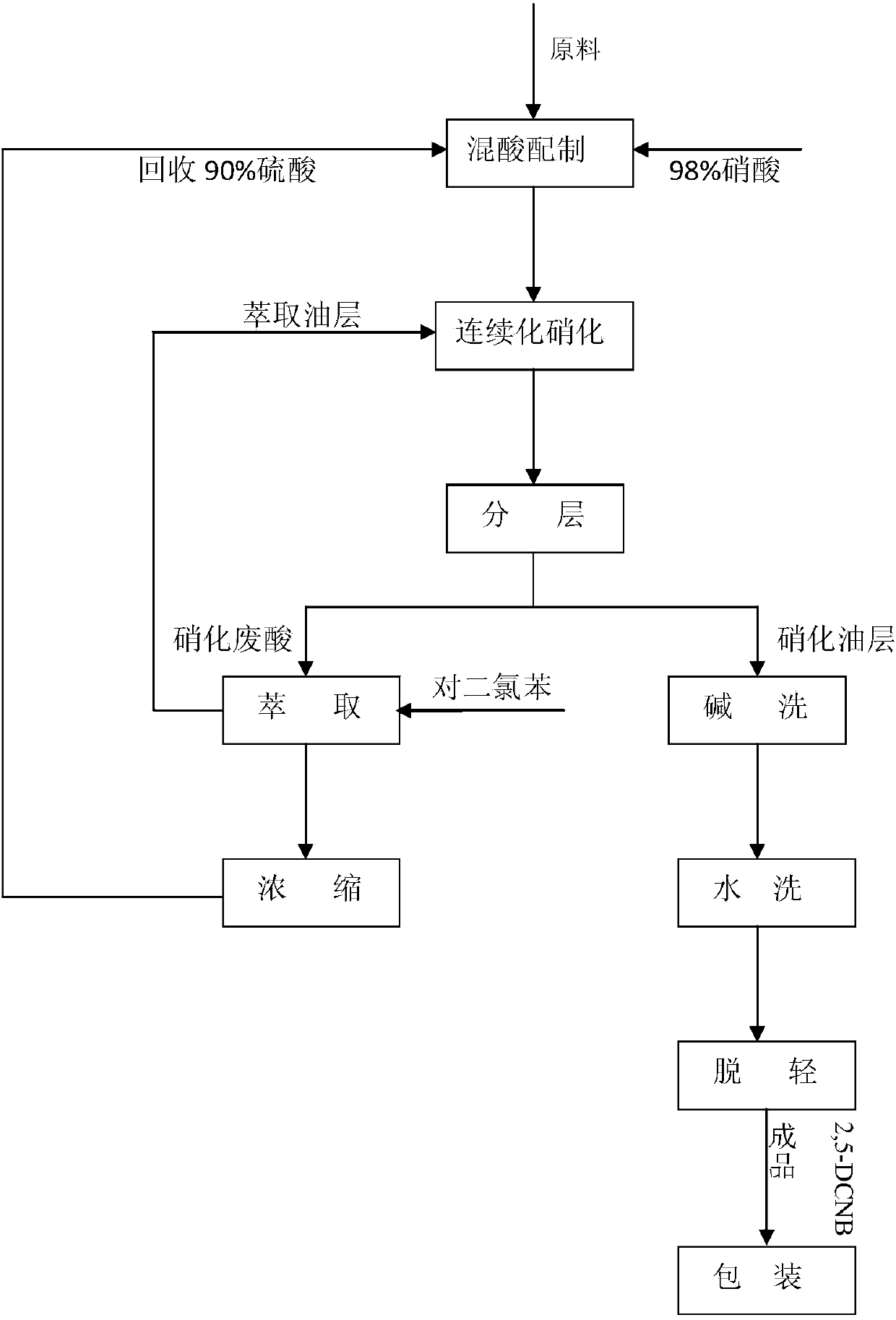
ActiveCN104649910AReduce labor intensitySimple processNitro compound preparationContinuous reactorEmulsion
The invention relates to a production method for preparing 2,5-dichloronitrobenzene (DCNB) through continuous nitration, which particularly realizes the recycling of waste acids in the preparing process. The invention provides a technological program capable of recycling acids for preparing 2,5-dichloronitrobenzene (DCNB) through the continuous nitration, which is characterized in that sulfuric acid and nitric acid are prepared into a mixed acid, the mixed acid and paradichlorobenzene are simultaneously fed into a three-stages kettle (ring) type continuous reactor to carry out nitration reaction, a nitration reaction solution discharged form the third-stage kettle (ring) type continuous reactor is stood for layering so as to obtain a nitrifying oil layer and a nitrifying waste acid, and the nitrifying oil layer is subjected to alkali cleaning, water washing and light component removal so as to obtain a 2,5-DCNB finished product; paradichlorobenzene is added into the nitrifying waste acid to extract organic matters in the acid layer, residual HNO3 in the acid layer is consumed, after the extraction is completed, the obtained product is layered so as to obtain an extraction oil layer and an extracted residual waste acid, the extraction oil layer is used for next-batch nitrification, the extracted residual waste acid after being concentrated and nitric acid are prepared into the waste acid for next-batch nitrification, a small amount of emulsion layer is produced in the process of recycling, and the emulsion layer after being combined with the nitrifying oil layer is subjected to alkali cleaning and water washing.
Owner:JIANGSU YANGNONG CHEM GROUP +2
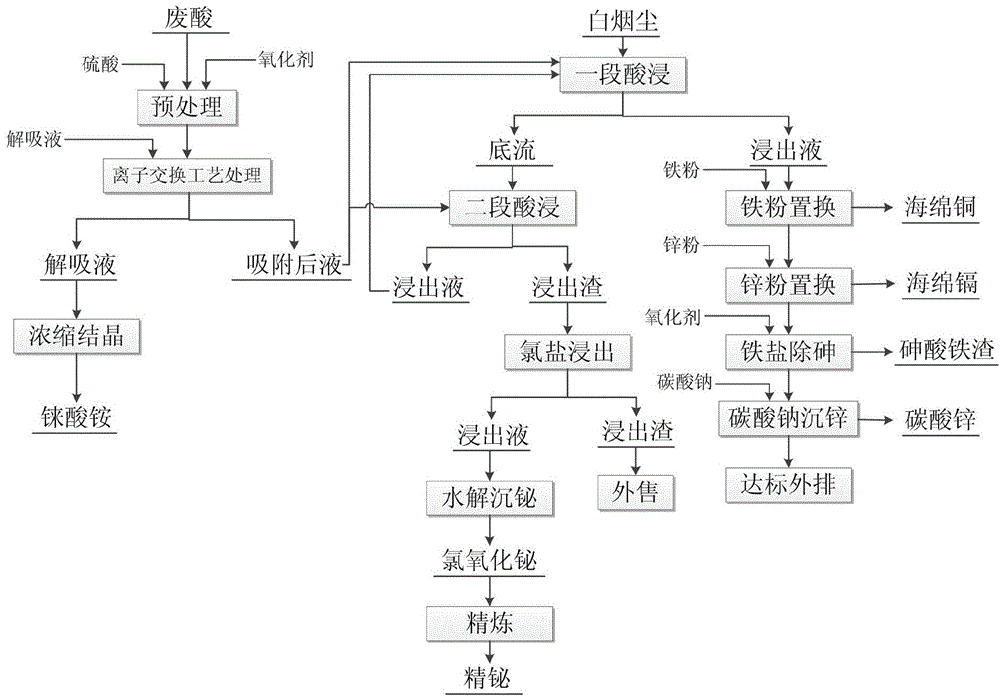
Process of recovering copper smelting waste acid and white smoke dusts
InactiveCN104593604AEfficient selective adsorptionEasy to handleProcess efficiency improvementParticulatesWater treatment
The invention provides a process of recovering copper smelting waste acid and white smoke dusts. The process comprises the following steps: removing suspended particulate matters in the waste acid, regulating the acidity and the redox potential of the liquid, and enabling ions including molybdenum ions in the liquid to exist in a high positive ion mode; then selectively adsorbing rhenium by utilizing ion exchange resin, after adsorption is saturated, carrying out desorption to obtain a rhenate liquid, and carrying out concentration and crystallization to obtain rhenate; using the waste acid after adsorbing the rhenium for leaching the white smoke dusts; treating the white smoke dusts by adopting two segments of countercurrent acid leaching-chloride leaching process, recovering valuable metals including copper, zinc and cadmium of an acid leaching liquid, carrying out harmless treatment on harmful elements including arsenic by virtue of a molysite method, recovering valuable metals including bismuth of a chloride leaching liquid, and selling lead sulfate, serving as a main component of chloride leaching residues, to a lead smelting plant. According to the process provided by the invention, the rhenium in the waste acid can be efficiently separated and recovered, the leaching white smoke dusts of the waste acid can be fully utilized, and the waste acid and white smoke dust leaching liquids can be comprehensively treated by utilizing a set of copper recovering and arsenic harmless treatment system, so that the process matching ability is good, the comprehensive recovery rate of the valuable metals is high, the waste water treatment effect is good, the investment is little, the production cost is low, and the economical benefit is good.
Owner:ZIJIN MINING GROUP
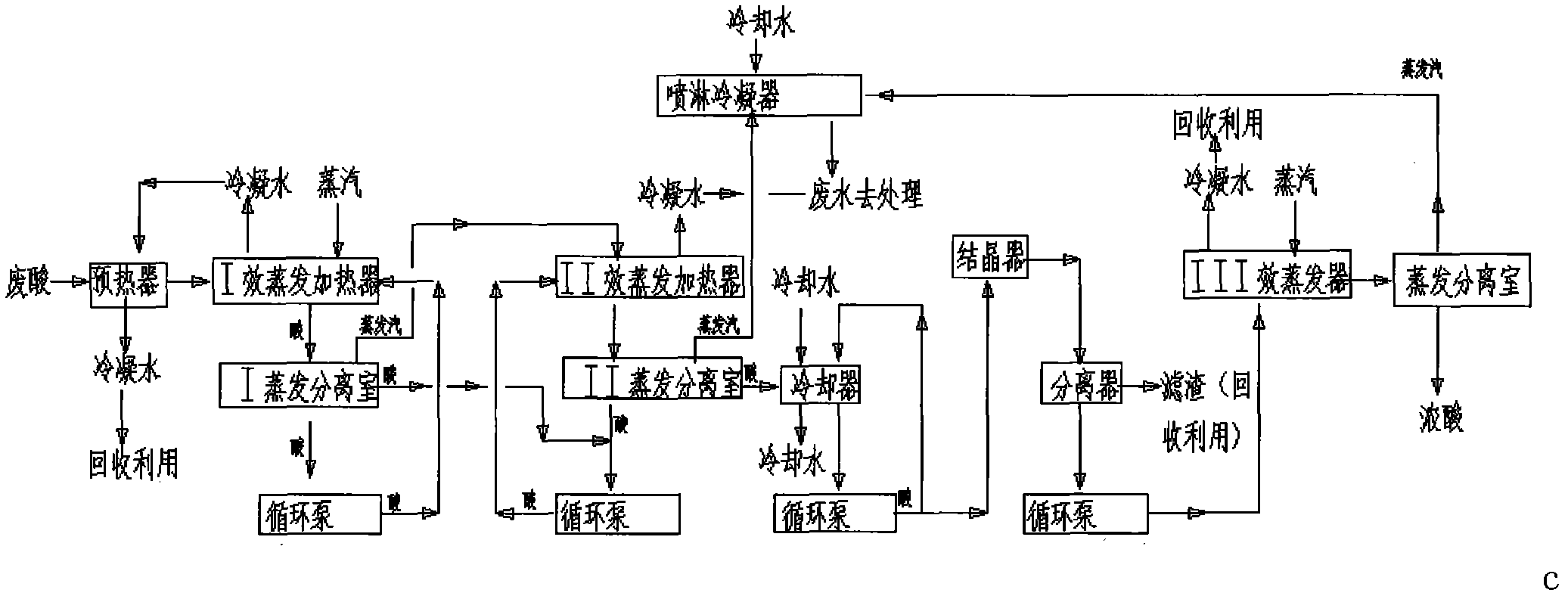
Waste acid concentration multistage treatment method
ActiveCN101935077ATake advantage ofReduce heat transfer areaMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by heatingSteam condensationSpray cooling
The invention relates to a waste acid concentration multistage treatment method which comprises the following steps of: heating 20-22% waste acid by a preheater, evaporating by a one-effect evaporation heater and a double-effect evaporation heater, cooling by a cooler and crystallizing by a crystallizer; heating by a triple-effect evaporation heater and separating by a separator to obtain 65% concentrated acid. The secondary steam part is used as a heat source part of the next stage heater and is condensed by spraying cooling water, wherein the one-effect evaporation heater and the double-effect evaporation heater are falling film graphite tube array evaporation heaters; the triple-effect evaporation heater is a floating head tube array graphite heat exchange. The water evaporation capability of the method is increased from 2.5 tons to 10 tons, and the stage number is 3 or more. A large amount of steam and cooling water is saved, and the pollution to the environment is reduced. The heat exchange area of equipment is reduced by 30%, and materials are saved and manufacturing cost is reduced correspondingly. The heat of steam is fully utilized, more than 35% of steam is saved, and more than 30% of cooling water can be saved. The condensed water part of the steam is used as the hear source part of the preheater and is recycled for other uses.
Owner:NANTONG JINGTONG GRAPHITE EQUIP
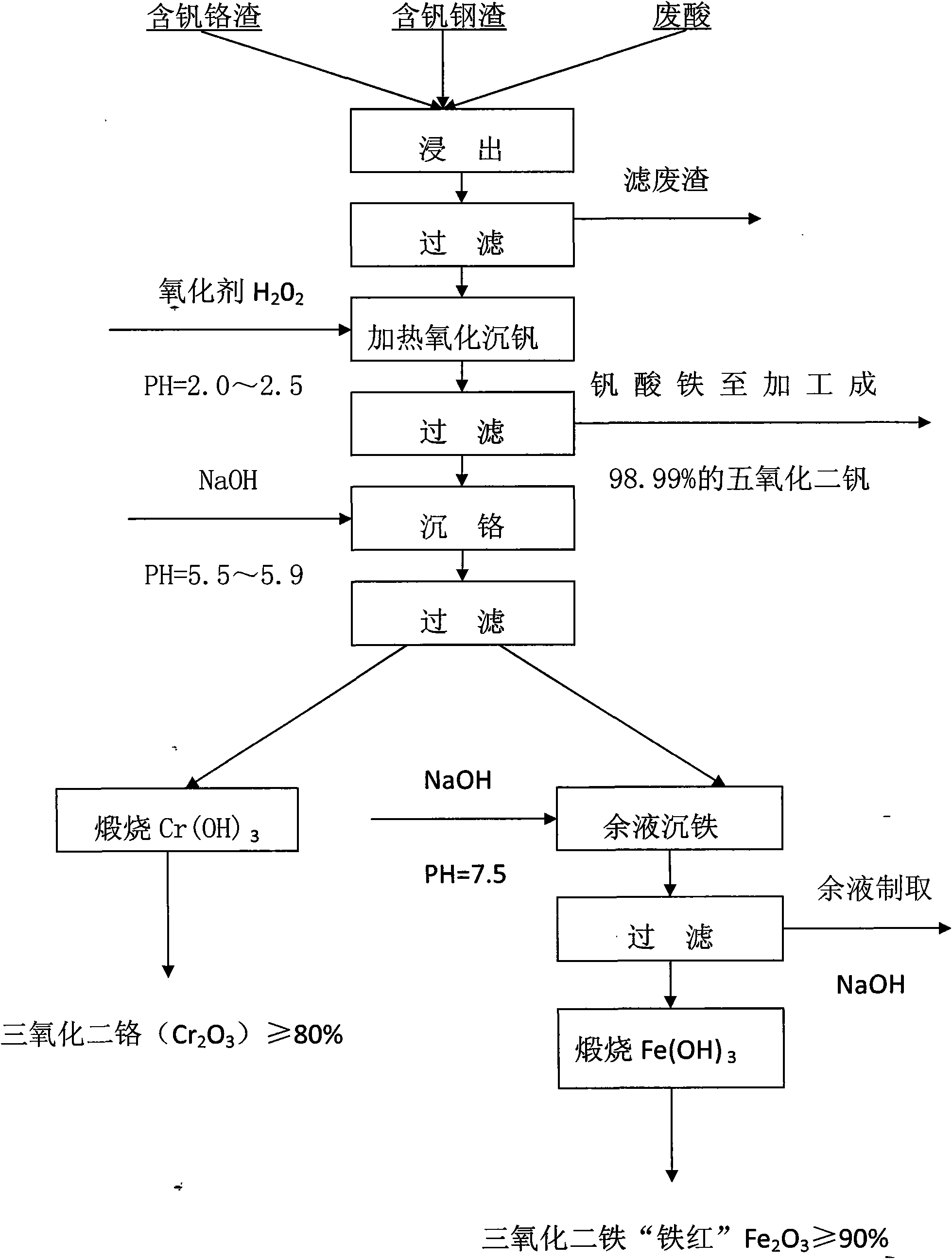
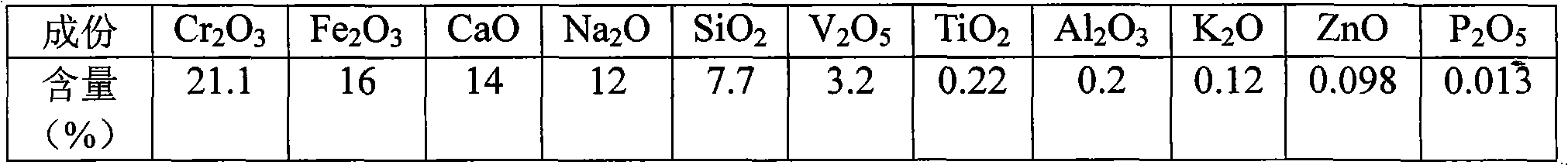
Process for extracting vanadium and chromium from chromic slag by using waste acid of titanium powder plant
InactiveCN101979683AFiltration process goes wellAchieve the purpose of separationProcess efficiency improvementChromium(III) hydroxideSlag
The invention discloses a method for separating and extracting vanadium and chromium. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) producing chromium fine sand (Cr2O3) of which the content is over 80 percent and ferric vandate of which the content is over 20 percent from two waste materials by taking waste acid of a titanium powder plant as a leaching agent and vanadium-chromium slag (containing 2.5 to 4.5 percent of vanadium and 14 to 25 percent of chromium) as a raw material; (2) putting the vanadium-chromium slag into the waste acid to allow the chromium and the vanadium in the slag to form chromium sulfate and vanadyl sulfate which can be dissolved in water very easily, wherein the leaching time is about 6 hours; (3) adding a certain amount of steel making steel slag during leaching to fulfill the aim of generating a great deal of calcium sulfate when a great deal of calcium oxide meets the acid during filtration, and wrapping, adsorbing or and stopping 'silica gel' formed by silicon dioxide in the chromium slag by the calcium sulfate which is used as a filter medium to ensure that the filtration is performed smoothly; (4) adjusting the pH value of the filtrate to be 2.5 by using sodium hydroxide, and then adding an oxidant and oxydol to ensure that the chromium in the solution is oxidized to be hexavalent, the iron is oxidized to be trivalent, and the vanadium is oxidized to be pentavalent; (5) heating the leaching solution to the temperature of between 70 and 90 DEG C to ensure that the vanadium and the iron is combined together to generate water-fast 'ferric vandate', wherein the time for thermal precipitation is about one hour, and the vanadium residual in the solution is not more than 0.4 g / L; (6) adding sodium hydroxide into the solution of which the ferric vandate is filtered out, and fully stirring the mixture until the pH value of the solution is between 5.5 and 5.9 to ensure that the chromium in the solution is completely converted into chromium.
Owner:PANZHIHUA SHUOSHENG IND & TRADING
Method for recycling iron and zinc containing waste hydrochloric acid solution
ActiveCN105696010ATake advantage ofSolve the problem of no separation and recyclingProcess efficiency improvementZinc hydroxideChloride
The invention discloses a method for recycling an iron and zinc containing waste hydrochloric acid solution. The method specifically comprises the following steps that 1, acid consuming and reducing are carried out, acidity is made to meet the requirement, and ferric iron in waste acid is reduced into ferrous iron; 2, zinc and iron are extracted and separated, and a ferrous chloride solution is obtained; 3, an organic phase transfers zinc into a strip liquor through reverse extraction, and the organic phase is extracted for reuse; and 4, the strip liquor is subjected to subsection kalizing treatment, zinc hydroxide is obtained, and the strip liquor is reused. According to the method, iron and zinc are separated through different extracting capacities of N235 to the ferrous iron and zinc, and therefore pure ferrous chloride liquid and zinc hydroxide solids are obtained. Ferrous chloride can be oxidized into ferric trichloride, and ferrous chloride and ferric trichloride both can be used as a water treatment agent; and zinc hydroxide can be used as a raw material for preparing zinc oxide or zinc chloride.
Owner:3R ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD
Titanium ore acidolysis method through sulfuric acid process
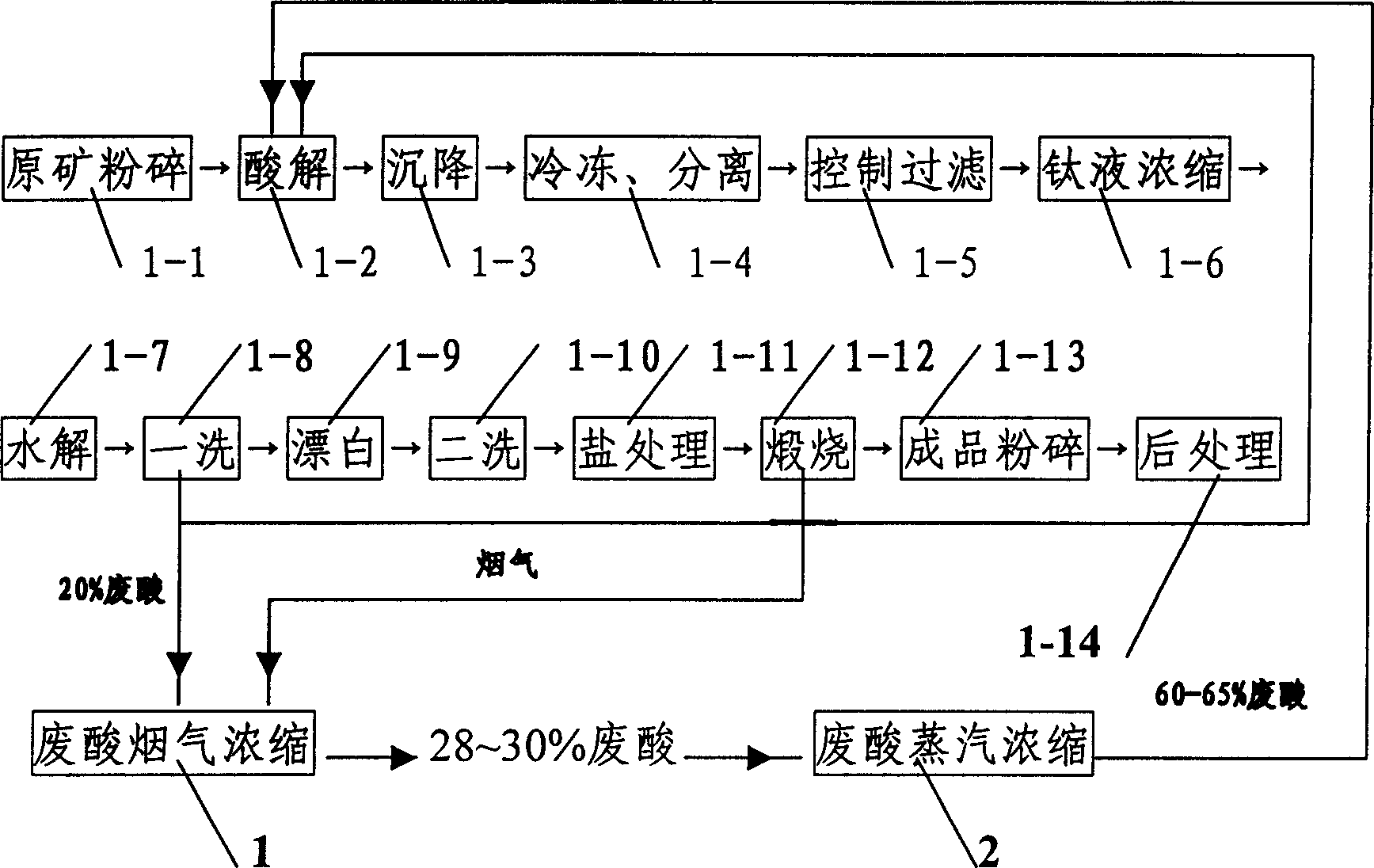
The invention relates to an improved method for the titanium ore acidolysis through sulfuric acid in the process of producing titanium white through a sulfuric acid process. The method is characterized in that: the method comprises the following steps: firstly premixing dilute waste acid produced by titanium white production after concentration and trash extraction with the titanium ore; and then adding the premixed ore slurry into an acidolysis pot, and then adding concentrated sulfuric acid so as to initiate a main reaction through the dilution heat produced by the added concentrated acid. The method has the advantages of: 1) improving the reutilization amount of titanium white waste acid and reducing the cost of concentrated waste acid; 2) removing a sulfuric acid cooling link so as to simplify the operation; 3) improving the operational conditions of premixing and acidolysis so as to reduce the risk of technical accidents; and 4) strengthening the premixing intensity, improving the premixing effect, so that the acidolysis reaction is sufficient and the acidolysis rate is remarkably improved.
Owner:XIANGYANG LOMON TITANIUM IND CO LTD
Treatment of an aqueous mixture containing an alkylene oxide with an ion exchange resin
InactiveUS20060189833A1Organic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationEthylene oxideIon exchange
A process for separating an alkylene oxide from an aqueous mixture is provided in which no detectable dioxane byproduct is formed. An aqueous mixture containing an alkylene oxide is contacted with a carboxylic acid ion exchange resin to separate the alkylene oxide from the aqueous mixture. The ion exchange capacity of the resin is regenerated with an acid wash at a temperature of at least 60° C., wherein regeneration of the resin does not result in the formation of dioxane in the spent acid wash. The process is particularly useful in purifying an aqueous 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde solution derived from an aqueous extraction of a hydroformylation reaction mixture containing ethylene oxide.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Method for enriching scandium, titanium and vanadium from sulfuric acid method titanium dioxide waste acid, and for treating waste acid
InactiveCN103540752ARealize environmental protectionReduce extraction costsNature of treatment waterWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationDissolutionHydrolysis
The invention relates to a method for enriching scandium, titanium and vanadium from sulfuric acid method titanium dioxide waste acid, and for treating waste acid. The method comprises the steps that: titanium dioxide waste acid is subjected to two-stage neutralization by using calcium carbonate, such that white gypsum is obtained, and two-stage neutralization slag with enriched scandium, titanium and vanadium are obtained; the two-stage neutralization slag is dissolved by using titanium dioxide waste acid; the dissolution liquid is subjected to scandium extraction and stripping, such that crude scandium slag is obtained; scandium extraction residue liquid is subjected to titanium hydrolysis, such that high-titanium slag is obtained; the hydrolysis filtrate is subjected to neutralization vanadium precipitation by using sodium carbonate, such that vanadium slag is obtained; the liquid after vanadium precipitation is subjected to aeration and further neutralization with the two-stage neutralization filtrate, and can reach a discharge standard and can be discharged. With the method provided by the invention, scandium, titanium and vanadium can be effectively enriched from titanium dioxide waste acid, and the treated waste acid tail liquid can reach a discharge standard and can be discharged.
Owner:广西冶金研究院有限公司
Method for regenerating and recovering sulfuric acid from waste acid
ActiveCN101759158AAvoid pollutionReduce processing costsWater contaminantsSulfur-trioxide/sulfuric-acidFlue gasNuclear chemistry
The invention relates to a method for regenerating and recovering sulfuric acid from waste acid generated in the production of the sulfuric acid or waste acid collected from waste lead-acid storage batteries, comprising the following steps of: firstly preparing purified gas containing H2S with volume percent of 2.5%-5%, CO2 with volume percent of 20%-45% and N2 with volume percent of 50%-77.5; supplying the purified gas to a waste acid solution with the flow rate of 10-20 m3 / h and the stirring speed of 300-400 rpm at the speed of 400-600 L / h so that heavy metal impurities in the waste acid solution and S2+ react to generate a sulfide; precipitating, filtering and separating the generated sulfide so that the sulfide is purified and removed from a dilute sulfuric acid solution; and replenishing the filtered dilute sulfuric acid solution which replaces new water into the dry-adsorbing procedure of a flue gas acid making systemso that the sulfuric acid in the waste acid solution is recovered into industrial sulfuric acid. The method has the advantages of low production cost, short flow, high cyclic utilization rate, low energy consumption, treatment of wastes by using wastes, small environmental pollution and high level of automation.
Owner:HENAN YUGUANG GOLD & LEAD
Method and apparatus for treating acid and alkaline waste water
InactiveCN1951839ANo consumptionGuaranteed unobstructedMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationWastewaterIndustrial water
The invention discloses a disposing technique of industrial acid-base waste water, which is characterized by the following: adopting industrial acid waste water and industrial alkaline waste water as raw material; neutralizing; condensing; sedimenting; dehydrating for sludge; making the water reach draining standard (COD<=100mg / l;SS<=mg / l); calculating flow of waste acid and base through PLC mathematical mould; reducing the consumption of industrial water; introducing self-adjusting K coefficient in the system fluctuating condition; generating more rational value automatically; improving system intelligence; interfering artificially according to experience.
Owner:辽宁三和环境工程有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com