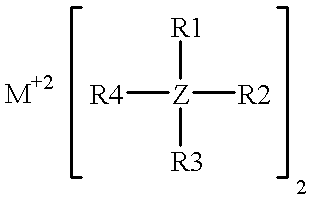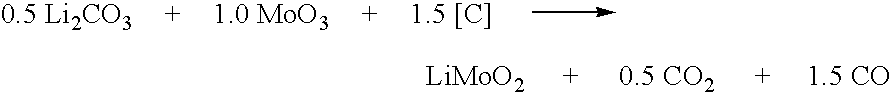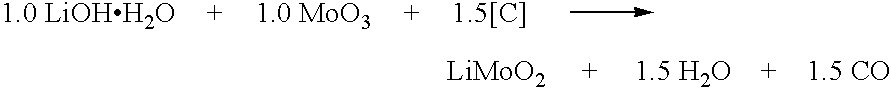Patents
Literature
912results about "Molybdeum compounds" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
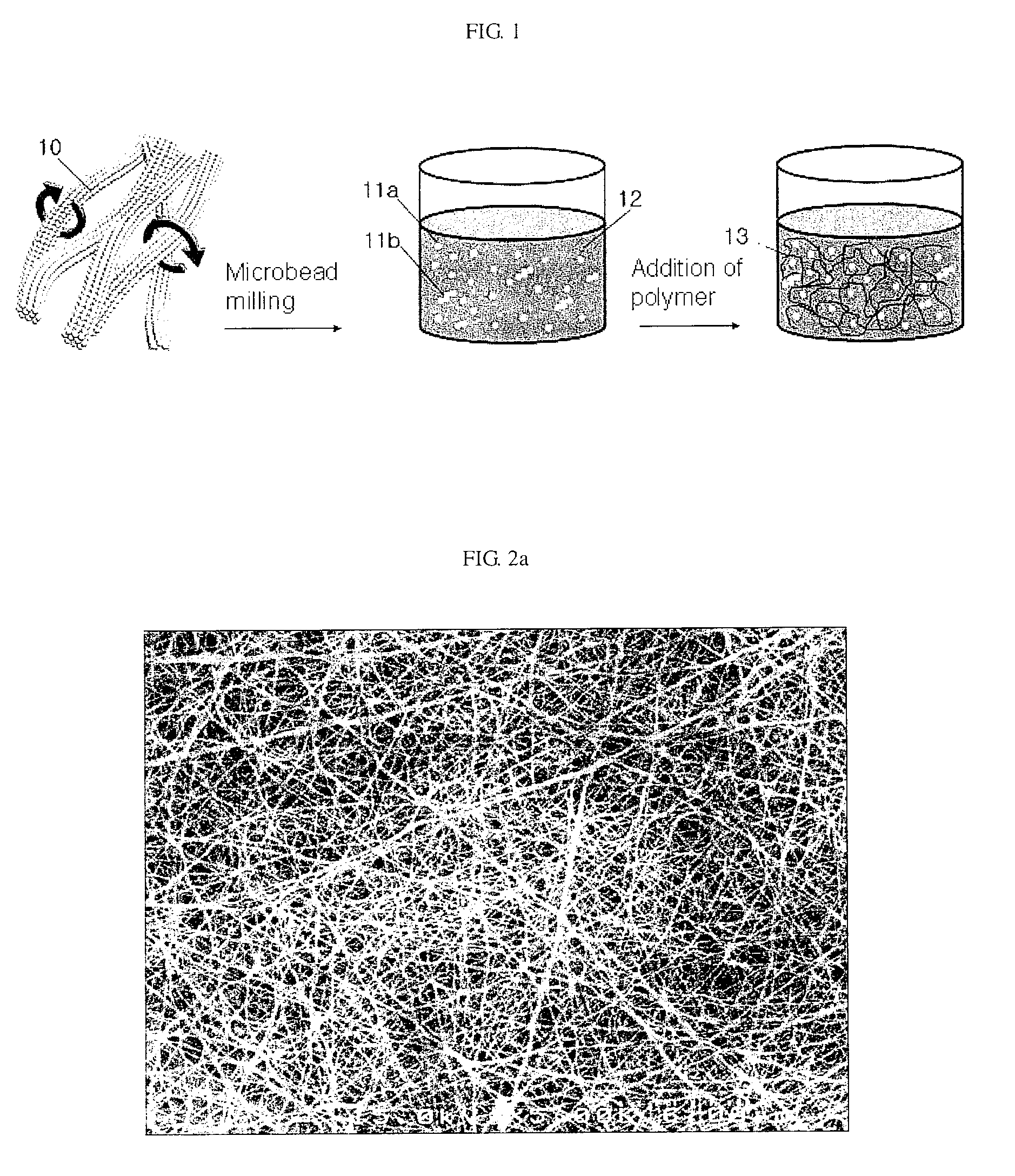
Solid chemical hydride dispenser for generating hydrogen gas
InactiveUS20070020172A1Molybdeum compoundsSynthetic resin layered productsCompound (substance)Hydrogen evolution
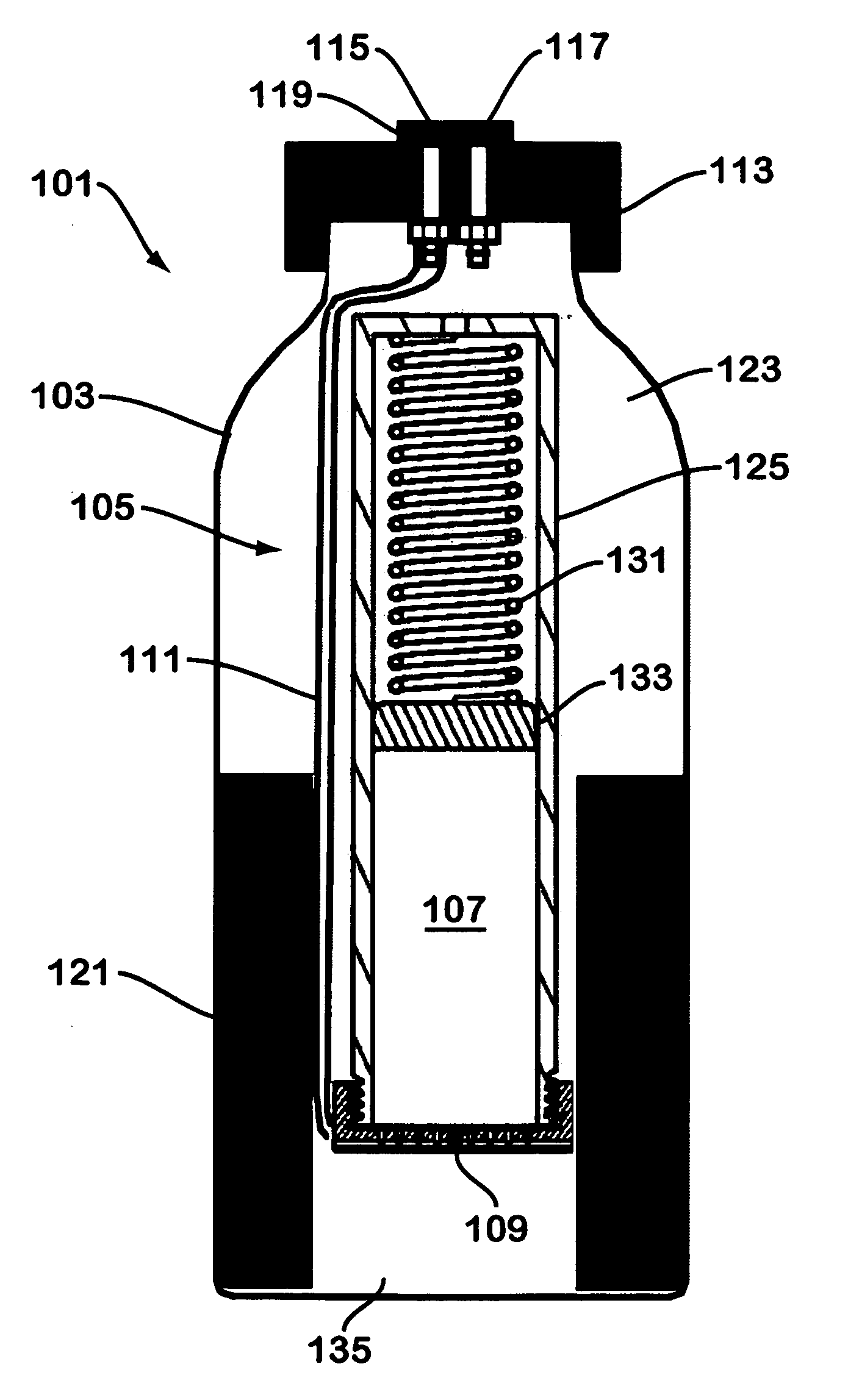
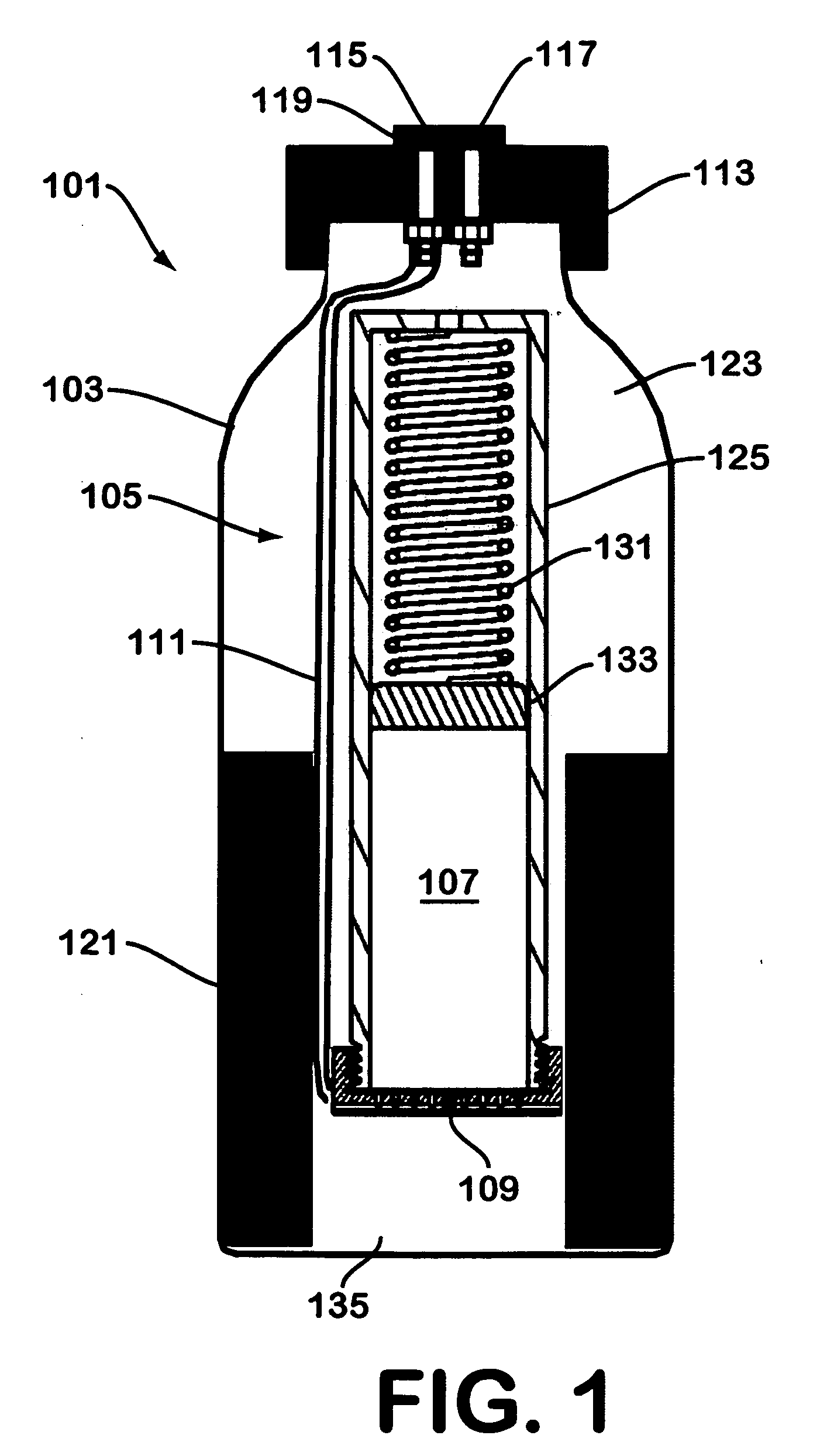
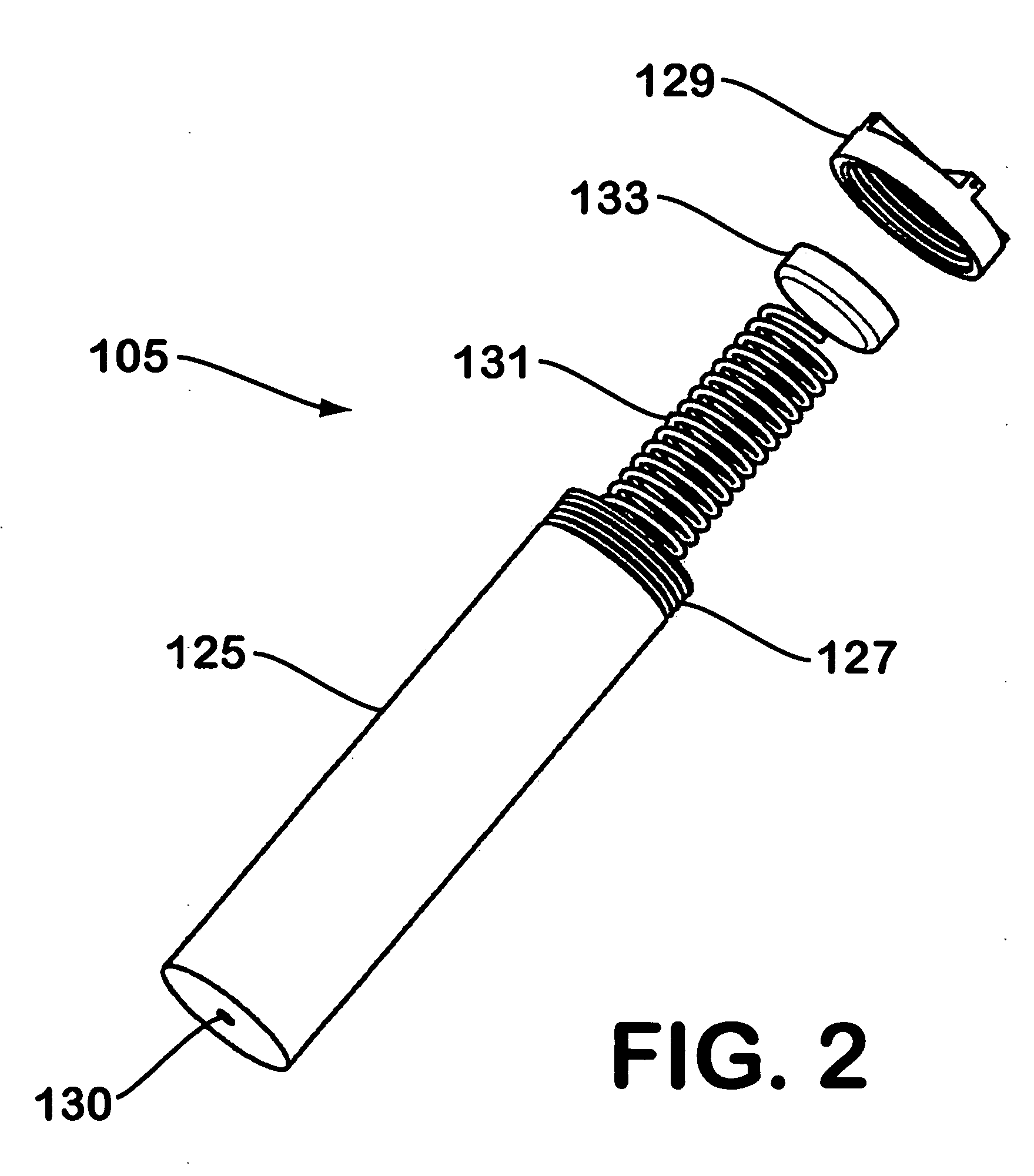
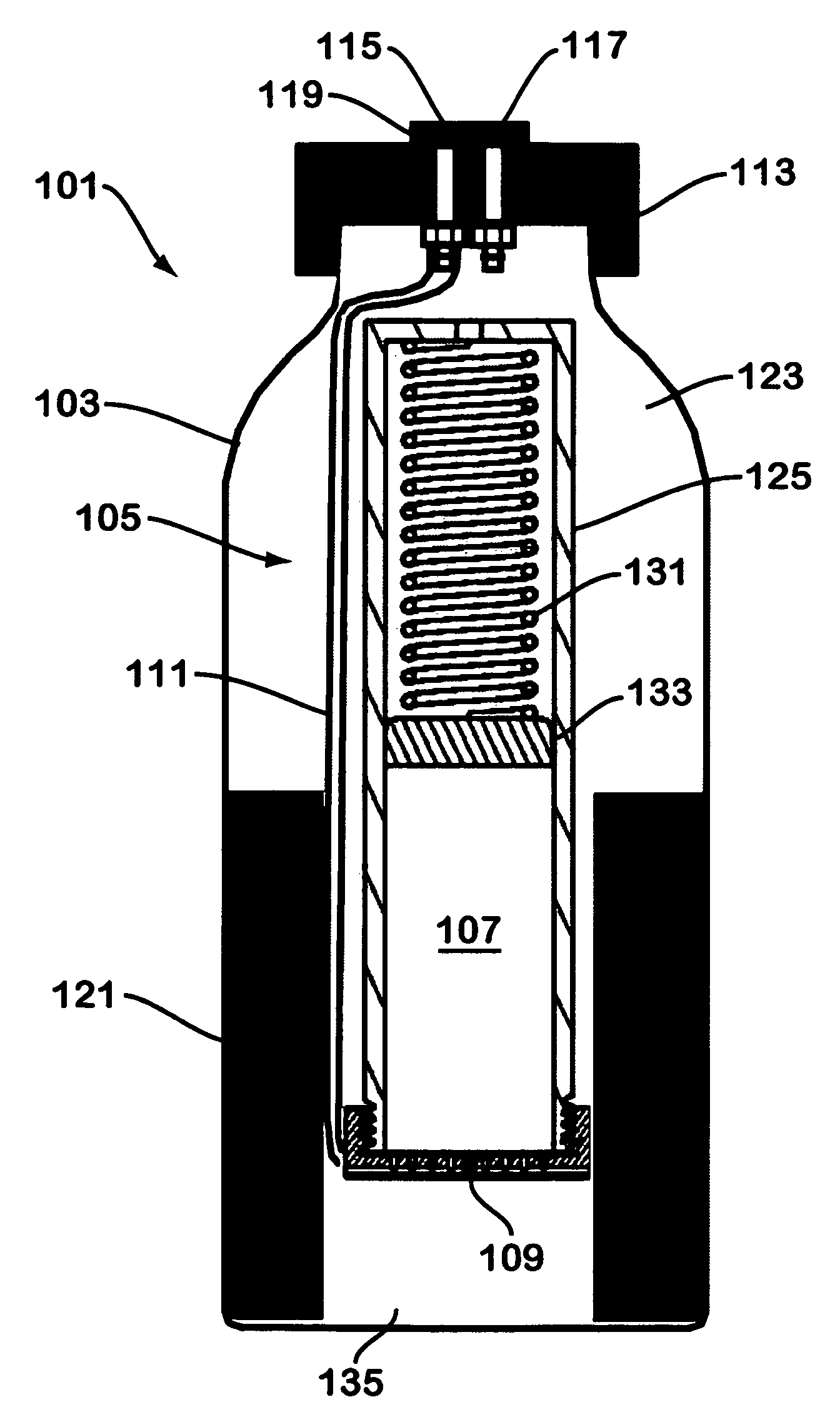
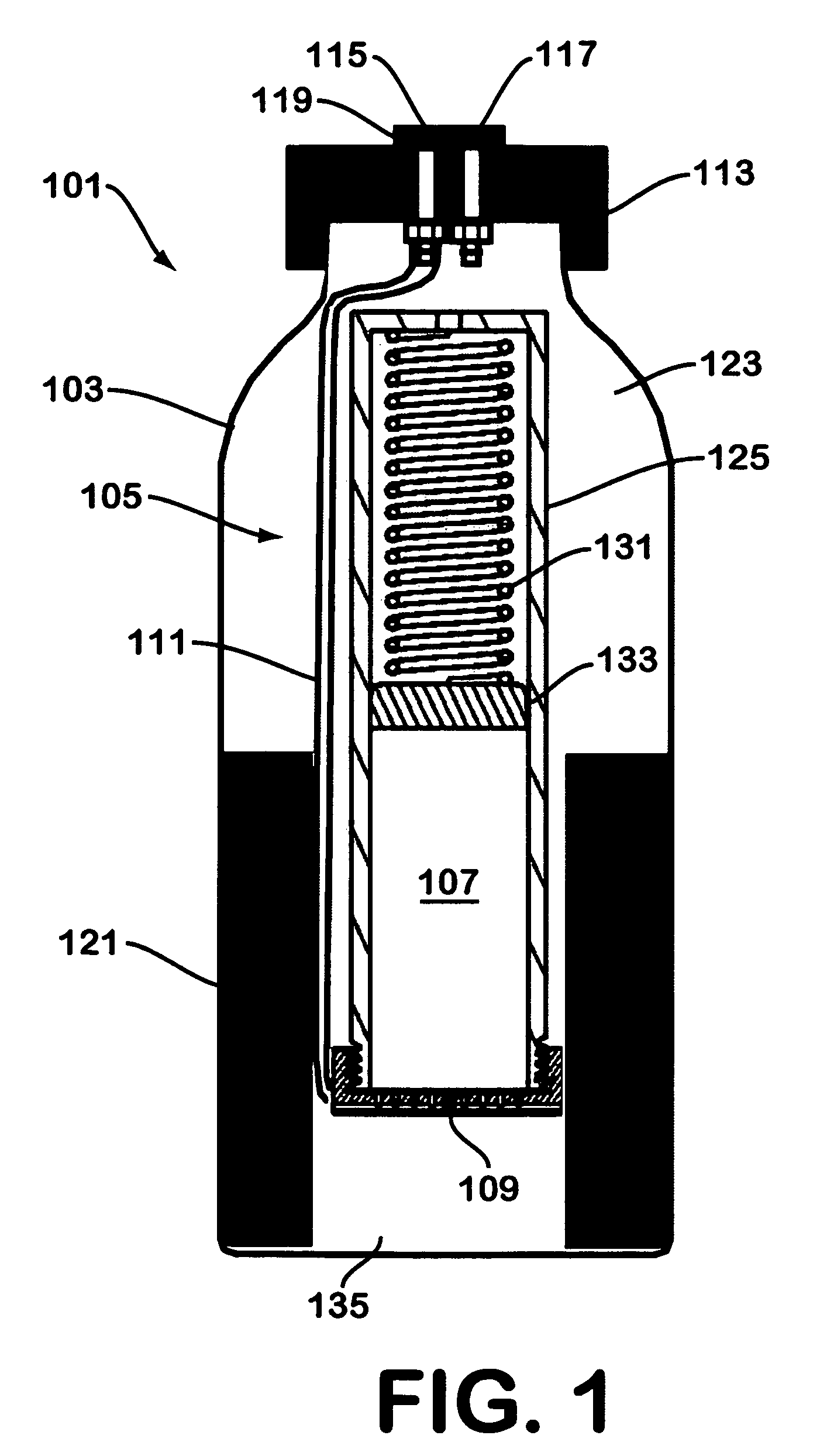
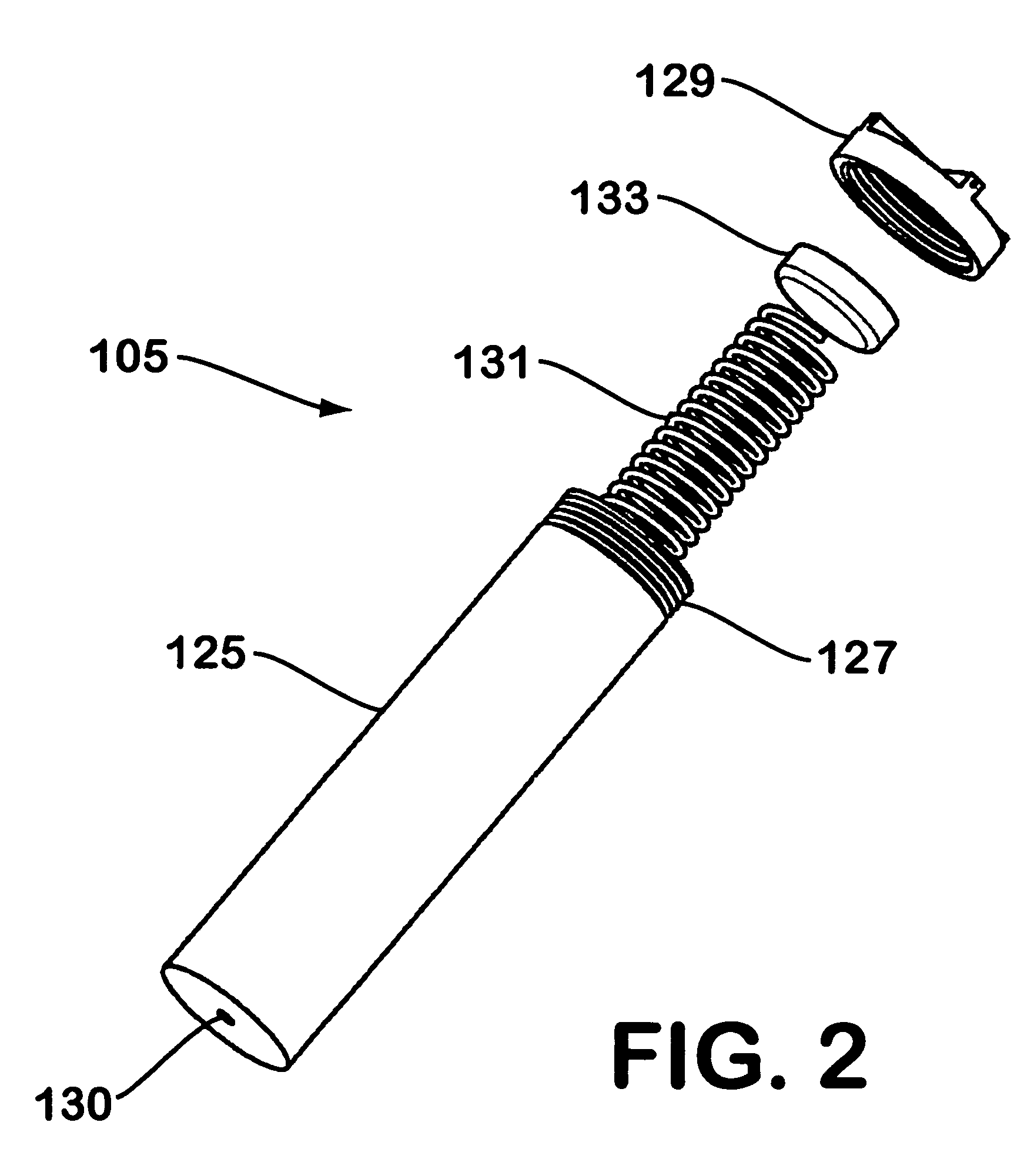
A device for generating hydrogen gas is provided. The device (101) comprises a first hydrogen-containing composition (107) that reacts with a second composition to evolve hydrogen gas; a dispenser (105) adapted to apply the first composition to a first porous member (109); and a conduit (111) adapted to supply the second composition to the first porous member. In a preferred embodiment, the first composition is selected from the group consisting of hydrides, borohydrides and boranes, the second composition is water, and the dispenser is spring-loaded and is charged with the first composition. As the first composition reacts with water at the interface to evolve hydrogen gas, the dispenser forces the reaction product across the interface and out of the dispenser, where it will not interfere with the progress of the hydrogen evolution reaction.
Owner:LYNNTECH POWER SYST
Conductive particle, visible light transmissive particle dispersed conductor, method for producing same, transparent conductive thin film, method for producing same, transparent conductive article using same, and infrared shielding article
ActiveUS20070187653A1Improve conductivityGood visible light transmittanceMaterial nanotechnologyConductive materialInfraredRare-earth element
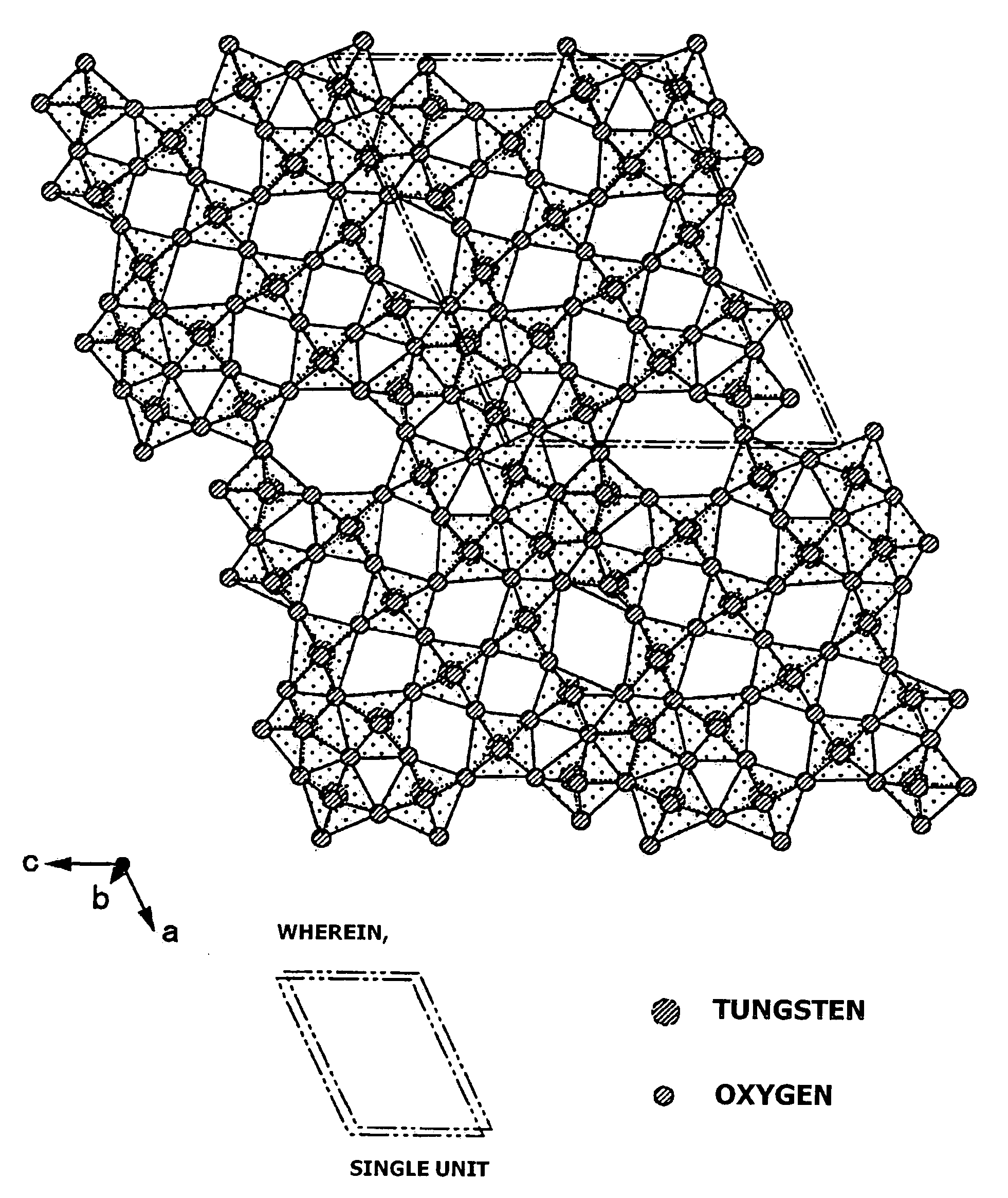
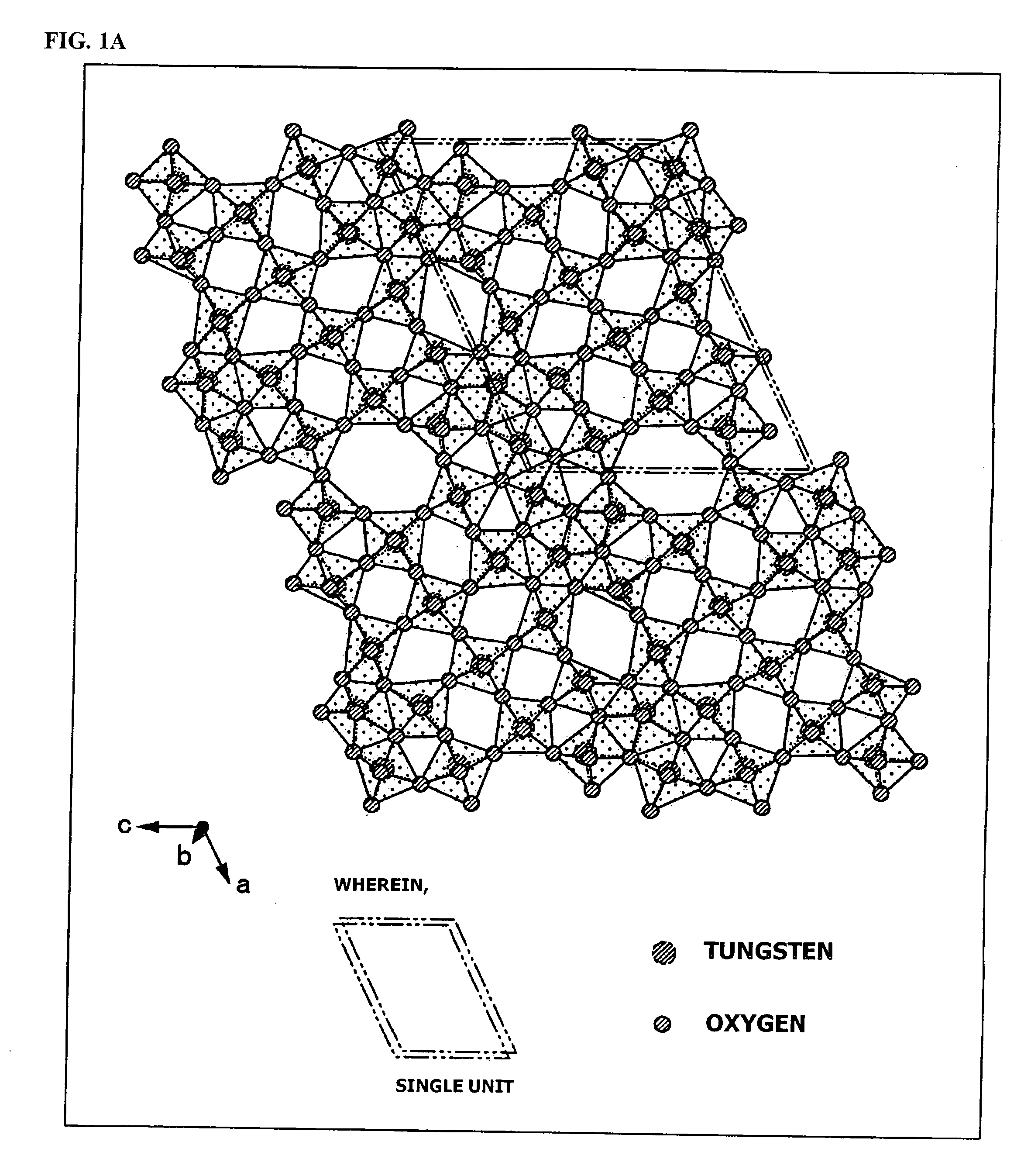
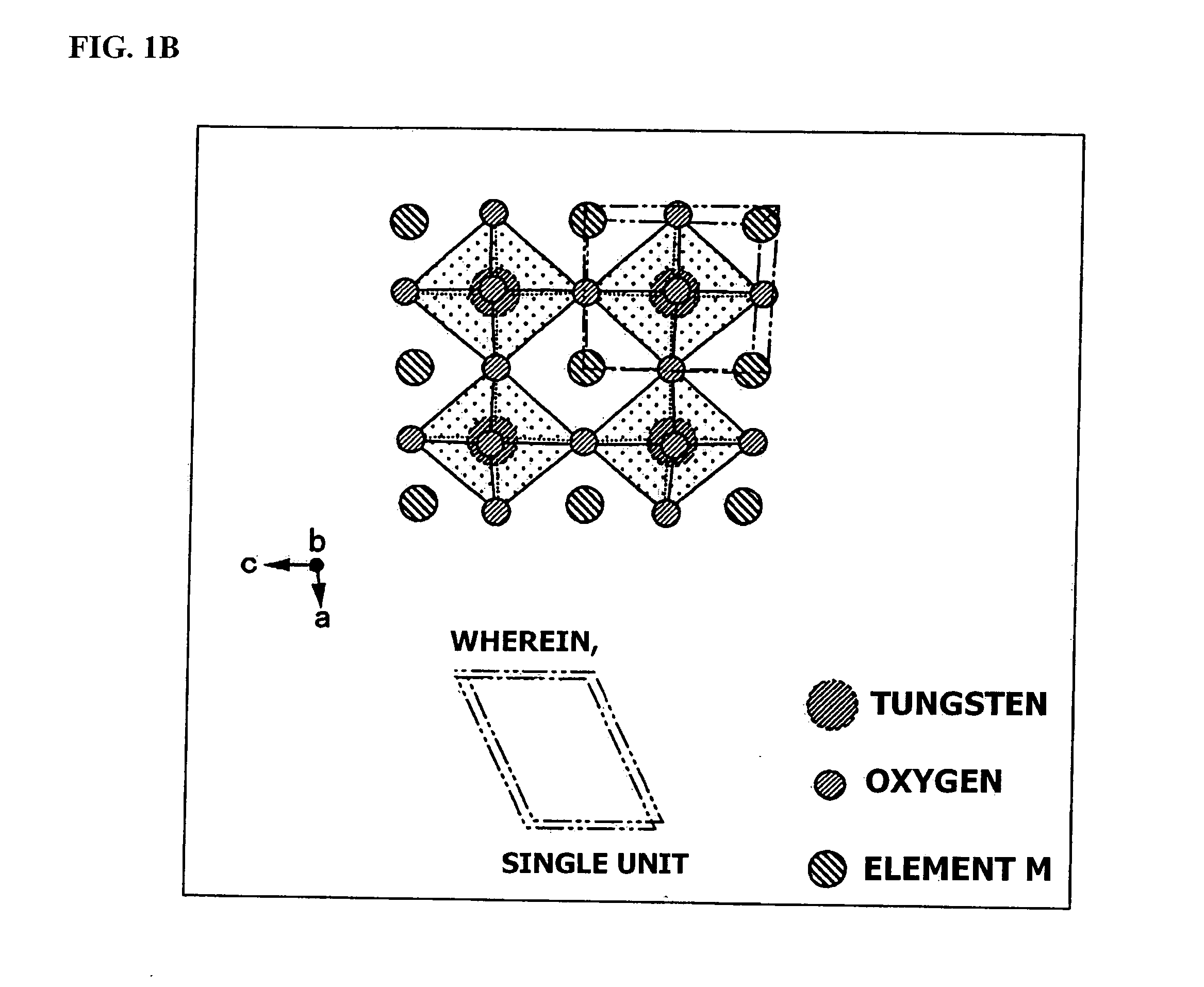
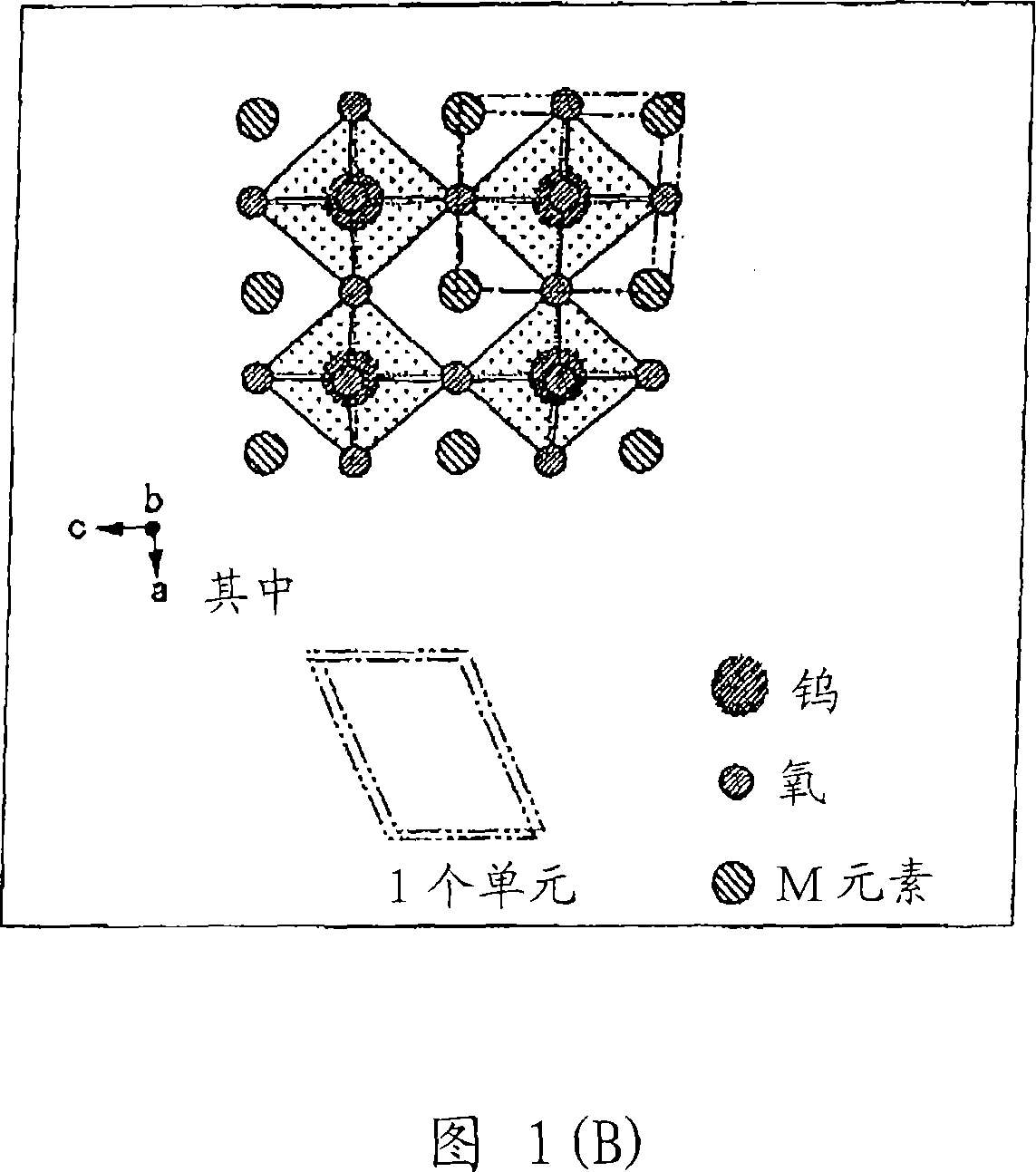
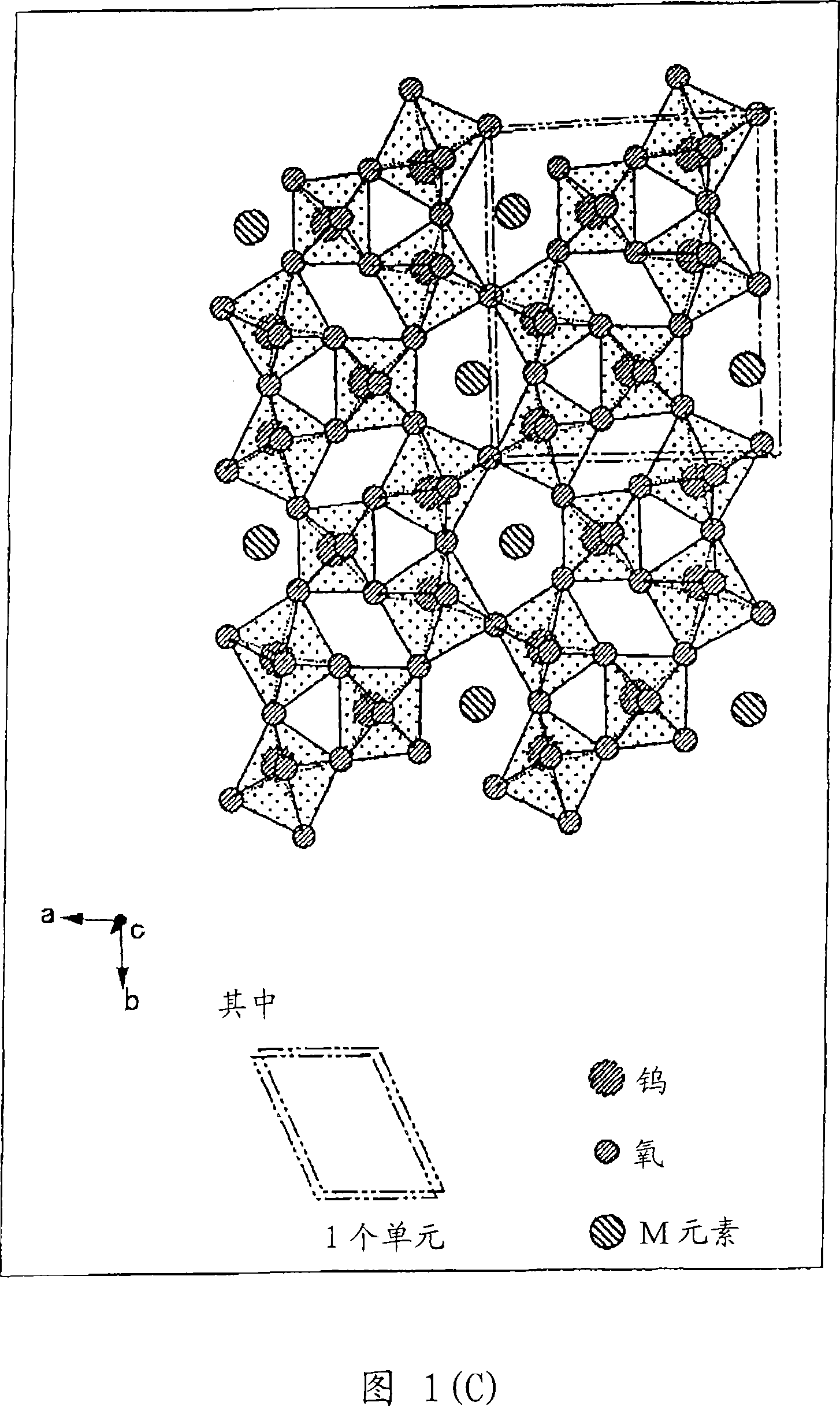
An object of the present invention is to provide an infrared-shielding nanoparticle dispersion that has a property whereby visible light is adequately transmitted, and light in the near-infrared region is adequately shielded; an infrared-shielding body manufactured using the infrared-shielding nanoparticle dispersion; a method for manufacturing infrared-shielding nanoparticles that are used in the infrared-shielding nanoparticle dispersion; and infrared-shielding nanoparticles manufactured using the method for manufacturing infrared-shielding nanoparticles. The present invention is a method for manufacturing infrared-shielding nanoparticle dispersion obtained by dispersing infrared-shielding nanoparticles in a medium, an infrared-shielding body manufactured by using the infrared-shielding nanoparticle dispersion, and infrared-shielding nanoparticles used in the infrared-shielding nanoparticle dispersion, wherein the infrared-shielding nanoparticles include a substance expressed by the general formula MXAYW(1-Y)O3 (where M is one or more elements selected from H, He, alkali metals, alkaline-earth metals, rare earth elements, Mg, Zr, Cr, Mn, Fe, Ru, Co, Rh, Ir, Ni, Pd, Pt, Cu, Ag, Au, Zn, Cd, Al, Ga, In, Tl, Si, Ge, Sn, Pb, Sb, B, F, P, S, Se, Br, Te, Ti, Nb, V, Mo, Ta, Re, Be, Hf, Os, Bi, and I; A is one or more elements selected from Mo, Nb, Ta, Mn, V, Re, Pt, Pd, and Ti; W is tungsten; O is oxygen; 0<X≦1.2; 0<Y≦1).
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
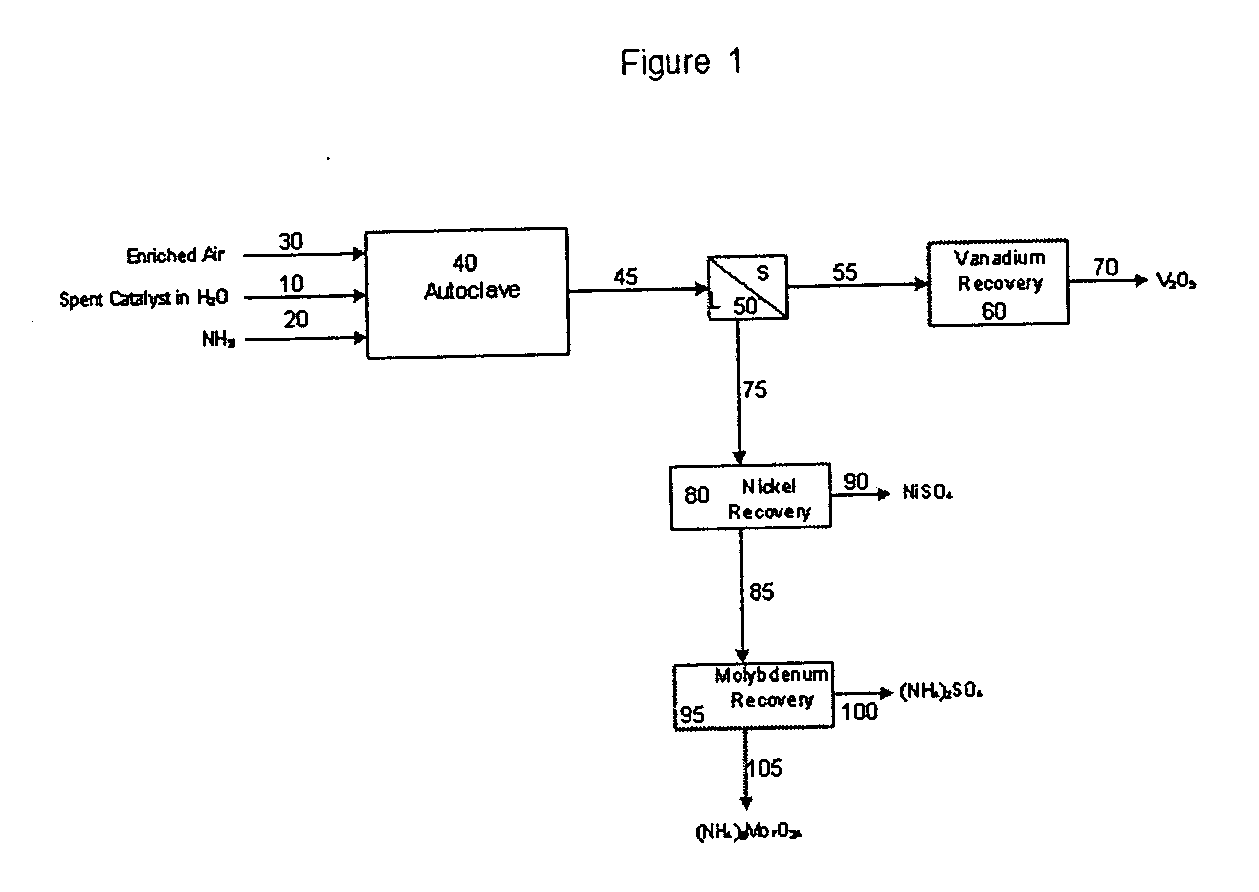
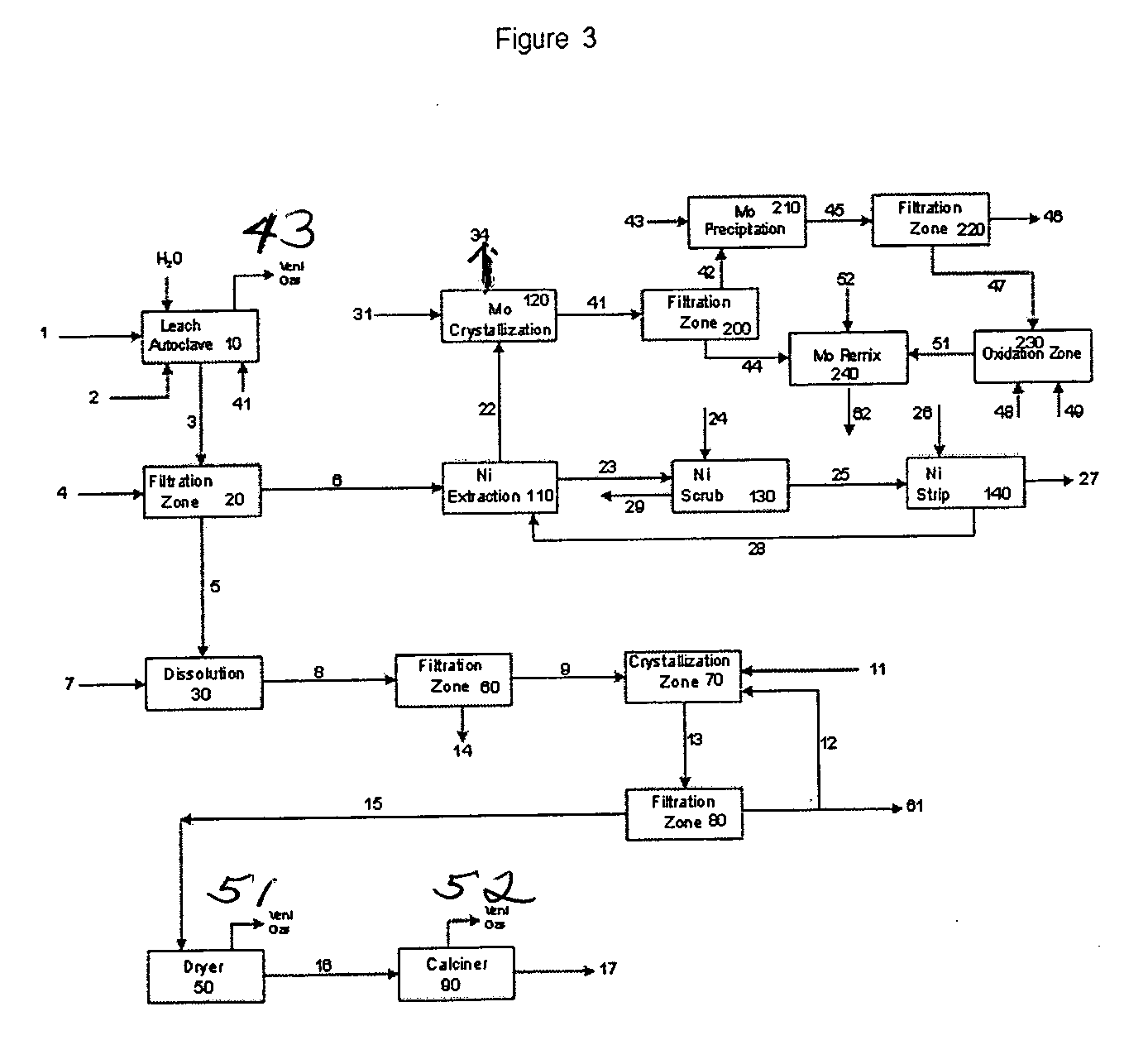
Process for metals recovery from spent catalyst
The process of this invention is directed to the removal of metals from an unsupported spent catalyst. The catalyst is subjected to leaching reactions. Vanadium is removed as a precipitate, while a solution comprising molybdenum and nickel is subjected to further extraction steps for the removal of these metals. Molybdenum may alternately be removed through precipitation.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
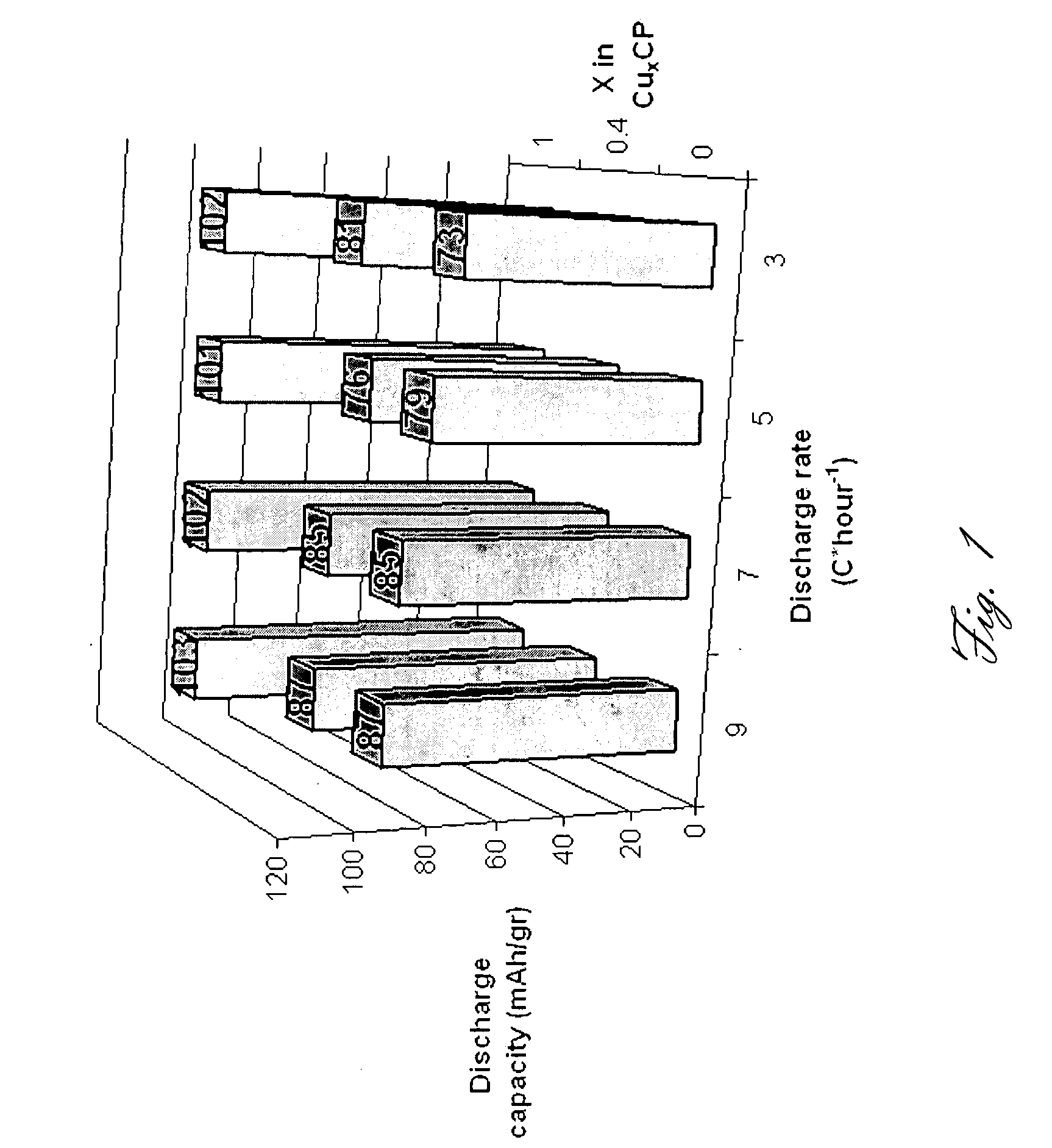
Rechargeable magnesium battery
ActiveUS20080182176A1Improved kineticsImprove conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyPhosphorus sulfur/selenium/tellurium compoundsElectrochemical windowCopper
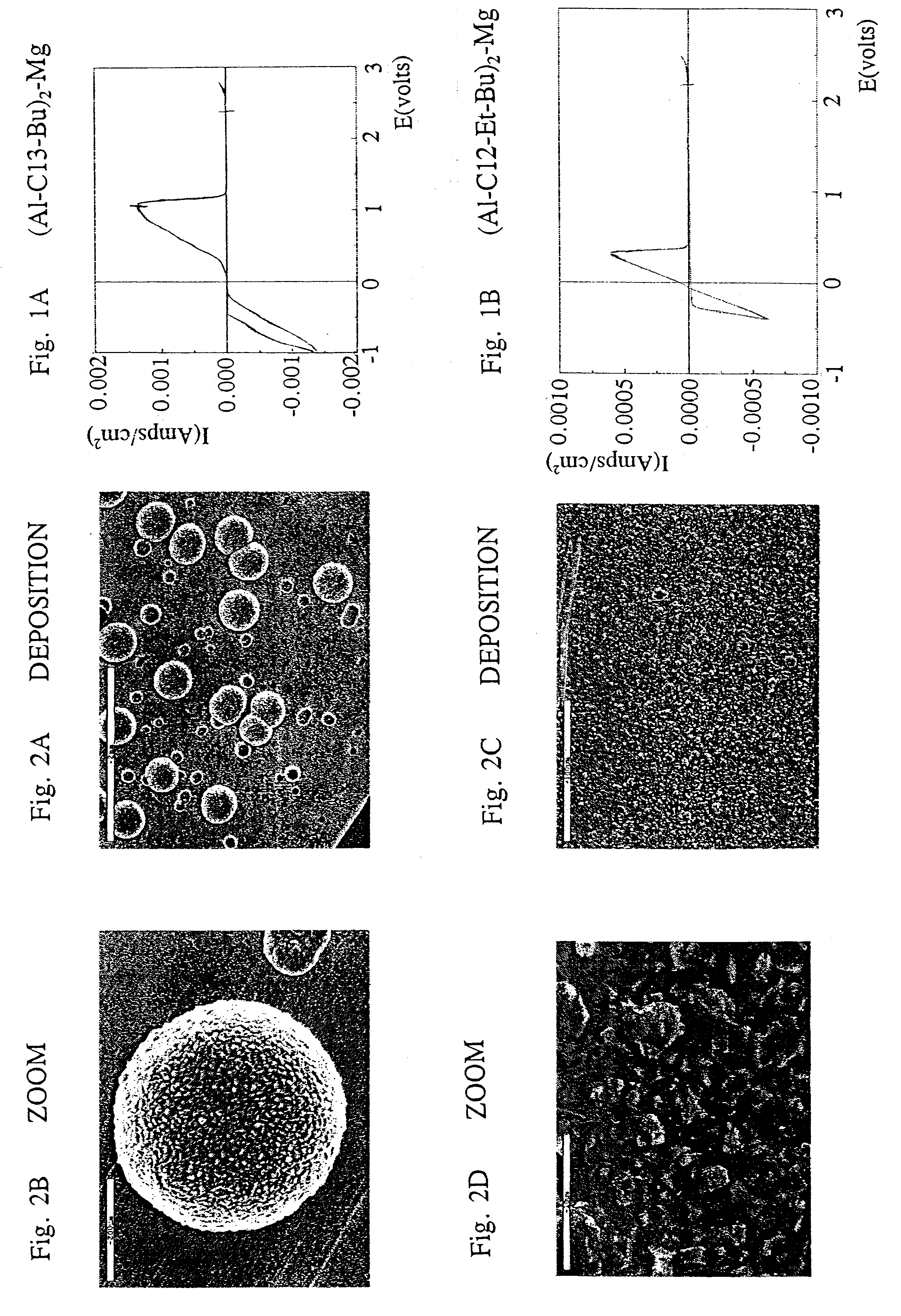
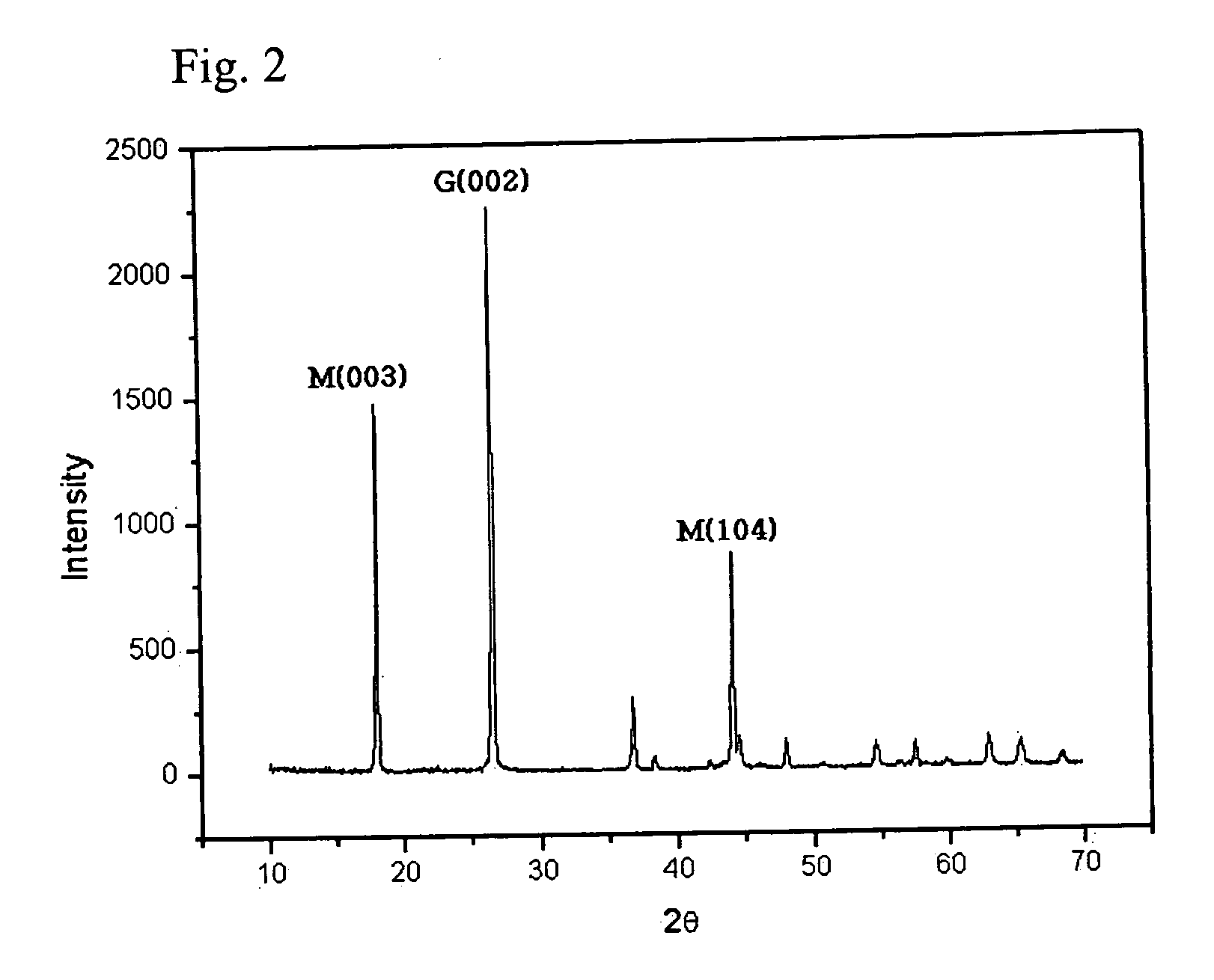
This invention generally relates to electrochemical cells utilizing magnesium anodes, new solutions and intercalation cathodes. The present invention is a new rechargeable magnesium battery based on magnesium metal as an anode material, a modified Chevrel phase as an intercalation cathode for magnesium ions and new electrolyte solution from which magnesium can be deposited reversibly, which have a very wide electrochemical window. The Chevrel phase compound is represented by the formula Mo6S8-YSeY in which y is higher than 0 and lower than 2 or by the formula MXMo6S8 in which M is selected from the group comprising of copper (Cu), nickel (Ni), silver (Ag) and / or any other transition metal; further wherein x is higher than 0 and lower than 2.
Owner:BAR ILAN UNIV
Nano-sized particles, processes of making, compositions and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070140951A1Economical and efficientQuality improvementMaterial nanotechnologyToilet preparationsSolventPharmaceutical formulation
The present invention describes methods for preparing high quality nanoparticles, i.e., metal oxide based nanoparticles of uniform size and monodispersity. The nanoparticles advantageously comprise organic alkyl chain capping groups and are stable in air and in nonpolar solvents. The methods of the invention provide a simple and reproducible procedure for forming transition metal oxide nanocrystals, with yields over 80%. The highly crystalline and monodisperse nanocrystals are obtained directly without further size selection; particle size can be easily and fractionally increased by the methods. The resulting nanoparticles can exhibit magnetic and / or optical properties. These properties result from the methods used to prepare them. Also advantageously, the nanoparticles of this invention are well suited for use in a variety of industrial applications, including cosmetic and pharmaceutical formulations and compositions.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Negative active material for a rechargeable lithium battery,a method of preparing the same, and a rechargeable lithium battery including the same
ActiveUS20080118834A1Improve stabilityImprove cycle lifeElectrode manufacturing processesMolybdeum compoundsArylHigh rate
A negative active material for a rechargeable lithium battery includes a core including an active material being capable of performing reversible electrochemical oxidation and reduction, and a coating layer on the surface of the core. The coating layer includes a reticular structure including —O-M-O— wherein M is selected Si, Ti, Zr, Al, or combinations thereof and an organic functional group linked to the M as a side chain. The organic functional group is selected from the group consisting of an alkyl group, a haloalkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, and combinations thereof. The negative active material for a rechargeable lithium battery according to the present invention can be applied along with an aqueous binder, and improve high capacity, good cycle-life, and particularly high capacity during charge and discharge at a high rate.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
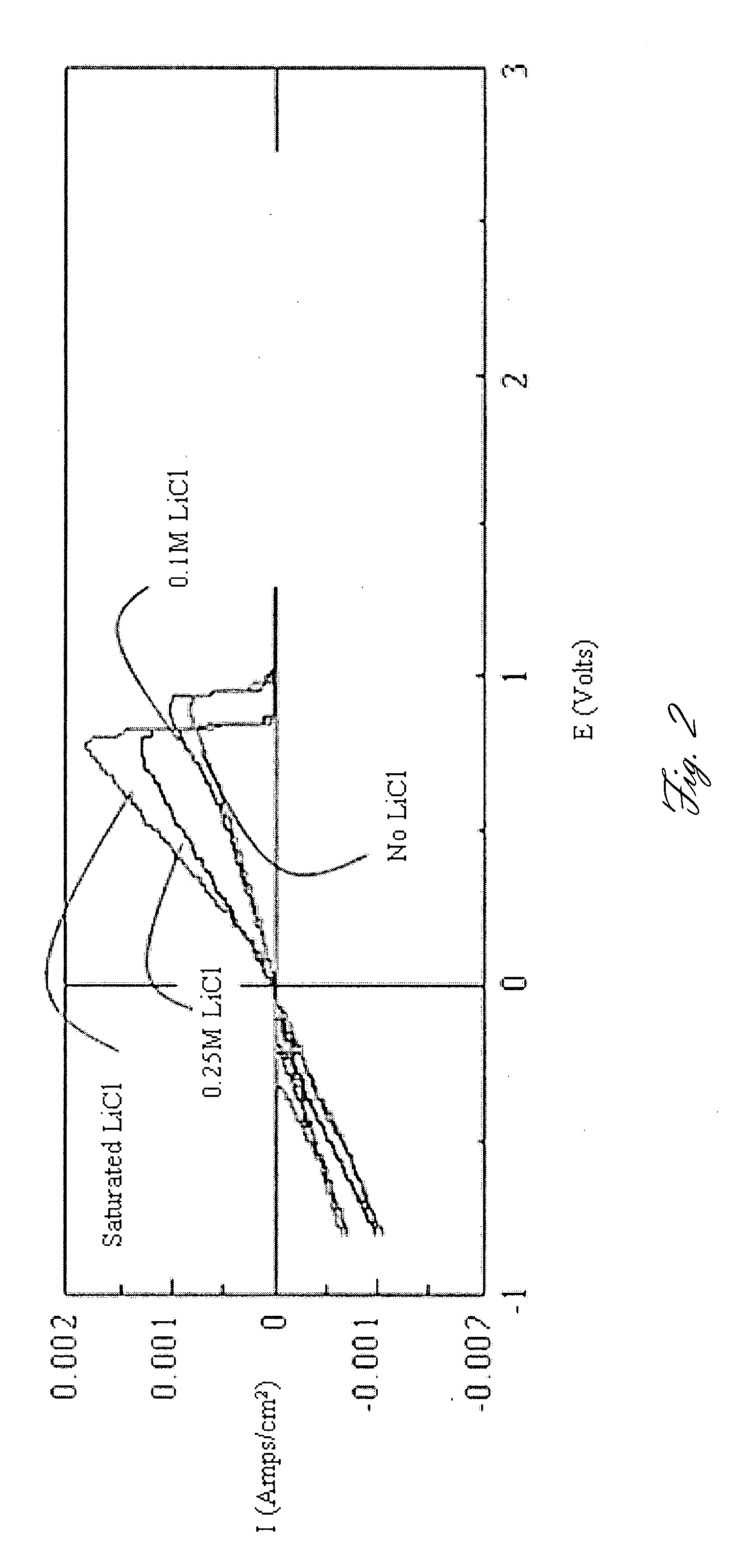
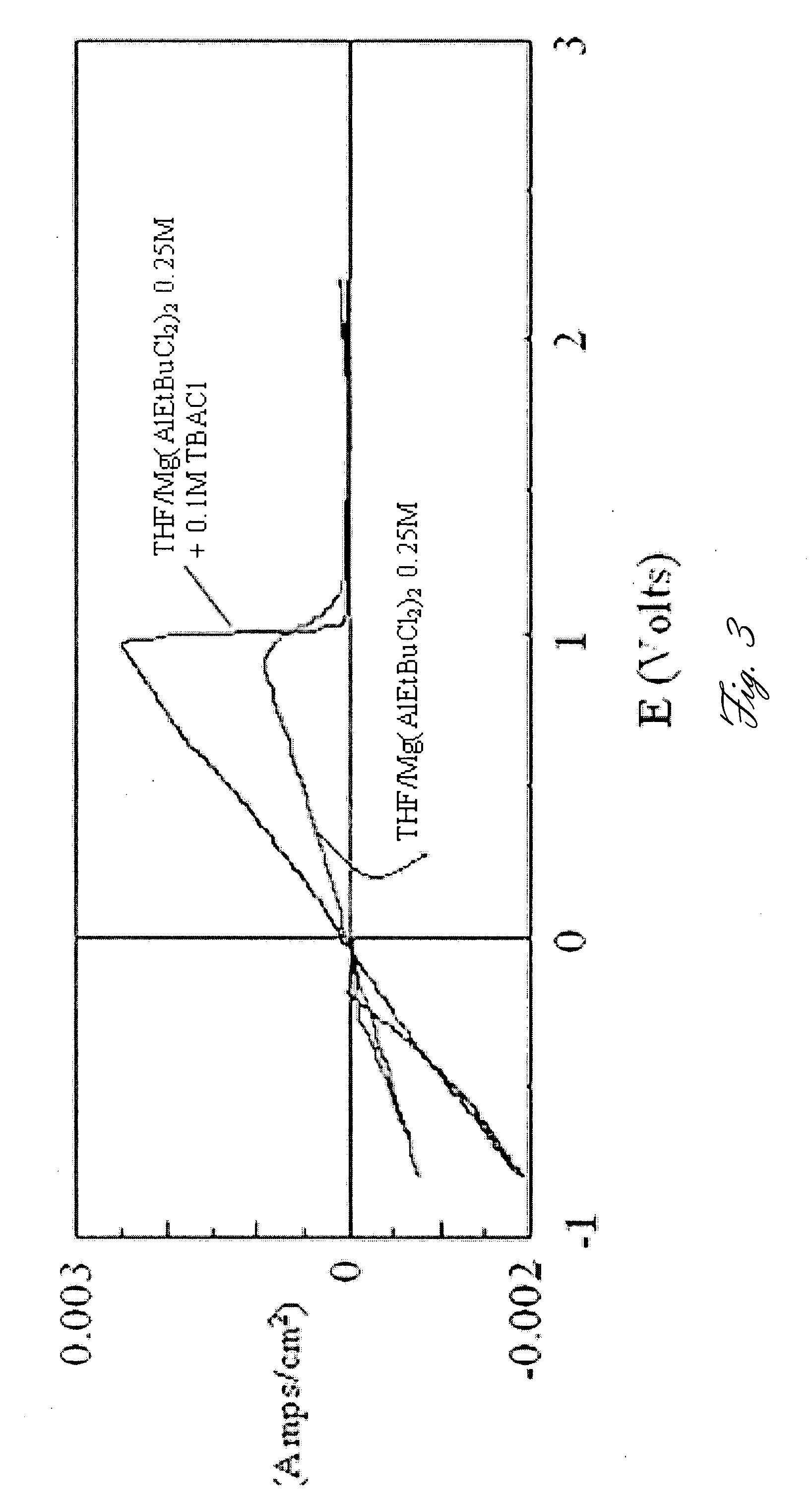
High-energy, rechargeable, electrochemical cells with non-aqueous electrolytes
InactiveUS6316141B1Non-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsElectrolysisHigh energy
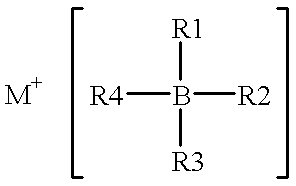
A non-aqueous electrolyte for use in an electrochemical cell comprising: (a) at least one organic solvent; (b) at least one electrolytically active salt represented by the formula:in which: M' is selected from a group consisting of magnesium, calcium, aluminum, lithium and sodium; Z is selected from a group consisting of aluminum, boron, phosphorus, antimony and arsenic; R represents radical selected from the following groups: alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, phenyl, benzyl, and amido; X is a halogen (I, Br, Cl, F); m=1-3; and n=0-5 and q=6 in the case of Z=phosphorus, antimony and arsenic, and n=0-3 and q=4 in the case of Z=aluminum and boron. Rechargeable, high energy density electrochemical cells containing an intercalation cathode, a metal anode, and an electrolyte of the above-described type are also disclosed.
Owner:BAR ILAN UNIV
Negative active material for a lithium secondary battery, a method of preparing the same, and a lithium secondary battery comprising the same
InactiveUS20050164090A1Increase chanceElectrode manufacturing processesNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsLithiumHigh rate
The present invention relates to a negative active material for a lithium secondary battery which includes a metal oxide-based core material and a carbon material disposed on the surface of the core material, a method of preparing the same, and a lithium secondary battery including the negative active material. According to the present invention, a negative active material for a lithium secondary battery is prepared by coating a core material having good energy density per unit volume with a carbon material, thereby improving the cycle life and charge-discharge characteristics of a lithium secondary battery at a high rate.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Thermoelectric material and thermoelectric converting element using the same
Compounds are expressed by general formula of AxBC2-y where 0<=x<=2 and 0<=y<1, and have CdI2 analogous layer structures; A-site is occupied by at least one element selected from the group consisting of Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Zr, Nb, Mo, Ru, Rh, Pd, Ag, Cd, Hf, Ta, W, Re, Ir, Pt, Au, Sc, rare earth elements containing Y, B, Al, Ga, In, Tl, Sn, Pb and Bi; B-site is occupied by at least one element selected from the group consisting of Ti, V, Cr, Zr, Nb, Mo, Hf, Ta, W, Ir, and Sn; C-site is occupied by at least one element selected from the group consisting of S, Se and Te; the compounds exhibit large figure of merit so as to be preferable for thermoelectric generator / refrigerator.
Owner:NEC CORP
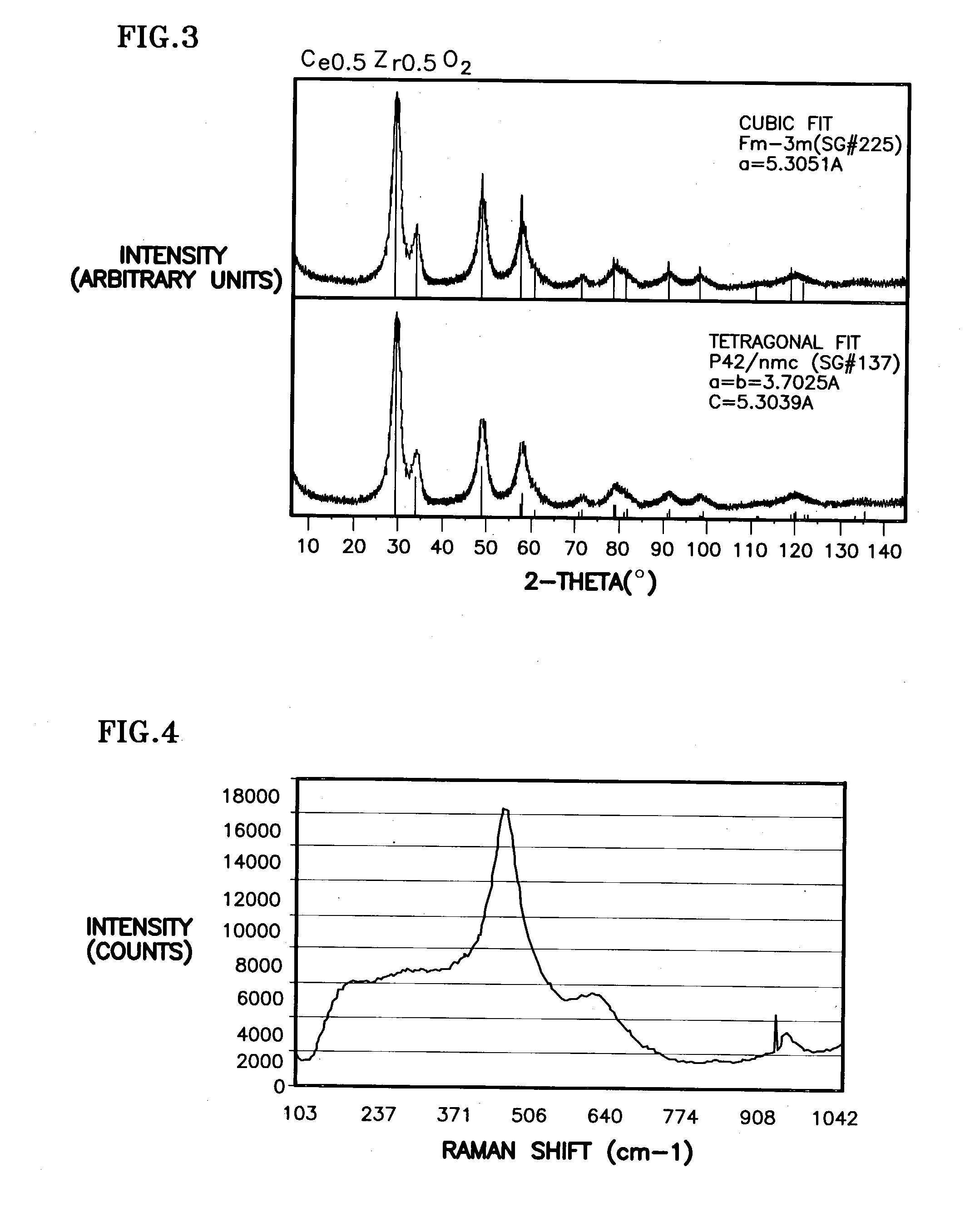
Ceria-based mixed-metal oxide structure, including method of making and use
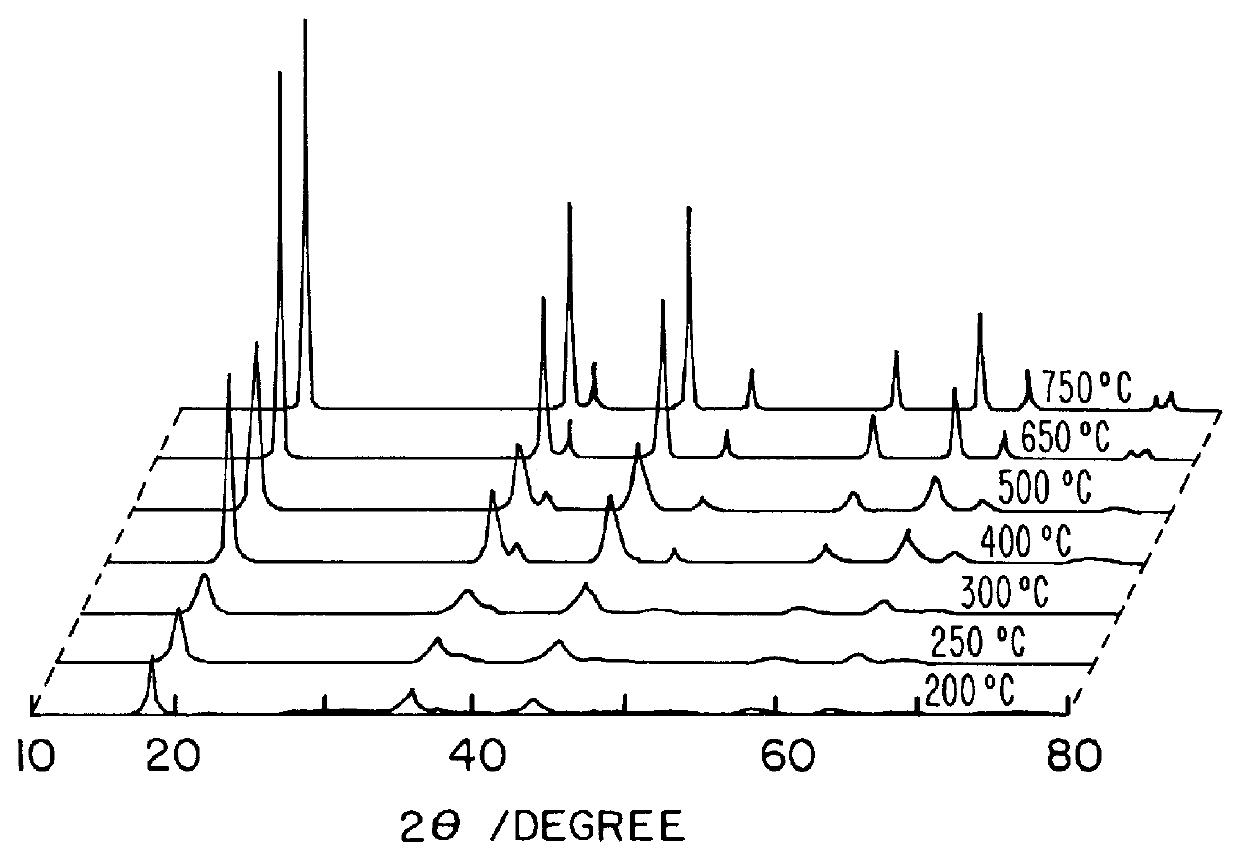
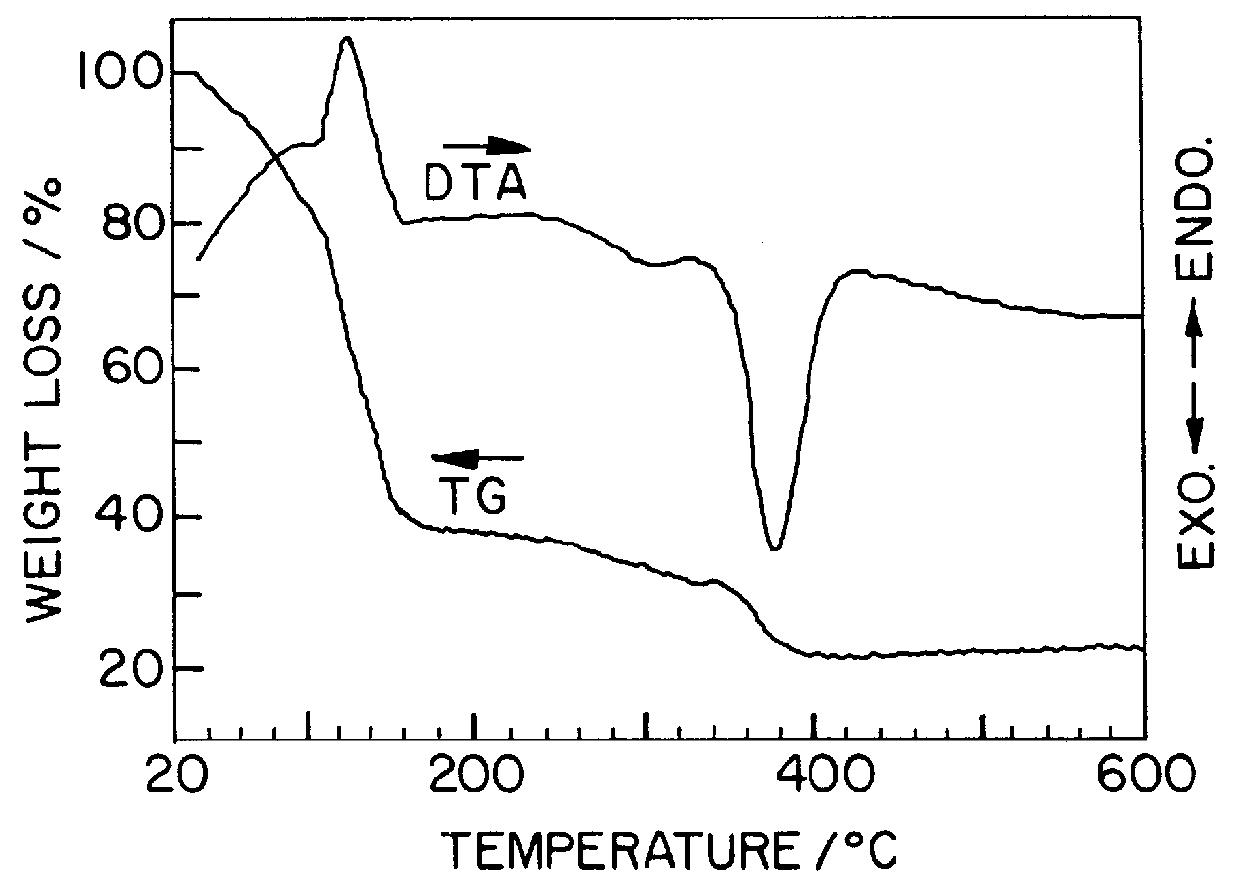
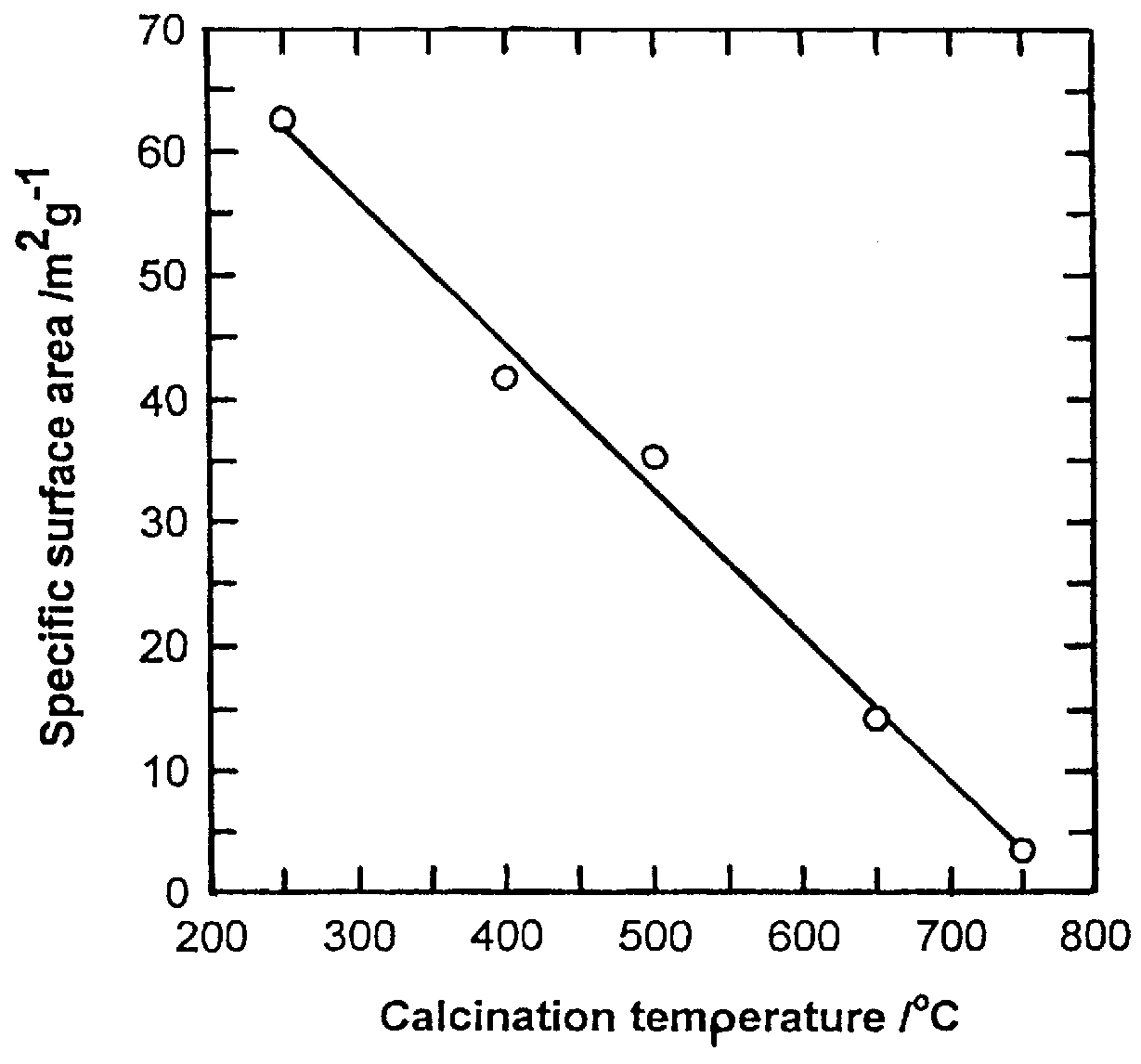
InactiveUS20030186805A1Increase surface areaSimple structureRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMaterial nanotechnologyPtru catalystCerium(IV) oxide
A homogeneous ceria-based mixed-metal oxide, useful as a catalyst support, a co-catalyst and / or a getter, is described. The mixed-metal oxide has a relatively large surface area per weight, typically exceeding 150 m<2> / g, a structure of nanocrystallites having diameters of less than 4 nm, and including pores larger than the nanocrystallites and having diameters in the range of 4 to about 9 nm. The ratio of the pore volumes, VP, to skeletal structure volumes, VS, is typically less than about 2.5, and the surface area per unit volume of the oxide material is greater than 320 m<2> / cm<3>, such that the structural morphology supports both a relatively low internal mass transfer resistance and large effective surface area for reaction activity of interest. The mixed metal oxide is made by co-precipitating a dilute metal salt solution containing the respective metals, which may include Zr, Hf, and / or other metal constituents in addition to Ce, replacing water in the co-precipitate with a water-miscible low surface-tension solvent, and relatively quickly drying and calcining the co-precipitate at moderate temperatures. A highly dispersive catalyst metal, such as Pt, may be loaded on the mixed metal oxide support from a catalyst-containing solution following a selected acid surface treatment of the oxide support. The mixed metal oxide, as catalyst support, co-catalyst or getter, is applied in various reactions, and particularly water gas shift and / or preferential oxidation reactions as associated with fuel processing systems, as for fuel cells and the like.
Owner:INT FUEL CELLS
Methods of preparing cathode active materials for lithium secondary battery
InactiveUS6071489AEasy to optimizeHigh crystallinityMaterial nanotechnologyNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsManganeseEthyl acetate
The LixMn2O4 powder for cathode active material of a lithium secondary battery of the present invention is prepared by a method of comprising the steps of mixing an acetate aqueous solution using Li acetate and Mn acetate as metal precursors, and a chelating agent aqueous solution using PVB, GA, PAA or GC as a chelating agent; heating the mixed solution at 70 DIFFERENCE 90 DEG C. to form a sol; further heating the sol at 70 DIFFERENCE 90 DEG C. to form a gel precursor; calcining the produced gel precursor at 200 DIFFERENCE 900 DEG C. for 5 DIFFERENCE 30 hours under atmosphere. The cathode active material, LixMn2O4 powder for a lithium secondary battery in accordance with the present invention has a uniform particle size distribution, a high crystallinity and a pure spinel-phase, and a particle size, a specific surface area, a lattice of a cubic structure and the like can be controlled upon the preparing conditions. The present invention also provides a method of preparing LiNi1-xCoxO2 powder, which comprises the steps of providing a gel precursor using PAA as a chelating agent and hydroxide, nitrate or acetate of Li, Co and Ni as metal precursors; heating the gel precursor at 200 DIFFERENCE 900 DEG C. for 5 DIFFERENCE 30 hours to form a powder. The LixMn2O4 and LiNi1-xCoxO2 powder of the present invention can be used for a cathode active material of a lithium secondary battery such as a lithium ion battery or lithium polymer battery.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY DEVICES CO LTD
Ceria-based mixed-metal oxide structure, including method of making and use
InactiveUS20030235526A1Increased internal surface areaHigh catalytic activityRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMaterial nanotechnologyRheniumFuel cells
A homogeneous ceria-based mixed-metal oxide, useful as a catalyst support, a co-catalyst and / or a getter has a relatively large surface area per weight, typically exceeding 150 m<2> / g, a structure of nanocrystallites having diameters of less than 4 nm, and including pores larger than the nanocrystallites and having diameters in the range of 4 to about 9 nm. The ratio of pore volumes, VP, to skeletal structure volumes, VS, is typically less than about 2.5, and the surface area per unit volume of the oxide material is greater than 320 m<2> / cm<3>, for low internal mass transfer resistance and large effective surface area for reaction activity. The mixed metal oxide is ceria-based, includes Zr and or Hf, and is made by a novel co-precipitation process. A highly dispersed catalyst metal, typically a noble metal such as Pt, may be loaded on to the mixed metal oxide support from a catalyst metal-containing solution following a selected acid surface treatment of the oxide support. Appropriate ratioing of the Ce and other metal constituents of the oxide support contribute to it retaining in a cubic phase and enhancing catalytic performance. Rhenium is preferably further loaded on to the mixed-metal oxide support and passivated, to increase the activity of the catalyst. The metal-loaded mixed-metal oxide catalyst is applied particularly in water gas shift reactions as associated with fuel processing systems, as for fuel cells.
Owner:AUDI AG
Negative active material for non-aqueous electrolyte battery, method of preparing same, and non-aqueous electrolyte battery comprising same
InactiveUS20050079417A1Improve security featuresNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsMolybdeum compoundsPhysical chemistryNon aqueous electrolytes
A negative active material of a non-aqueous electrolyte battery includes a compound represented by formula 1: LixMyVzO2+d (1) where 0.1≦x≦2.5, 0<y≦0.5, 0.5≦z≦1.5, 0≦d≦0.5, and M is at least one element selected from the group consisting of Al, Cr, Mo, Ti, W, and Zr.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
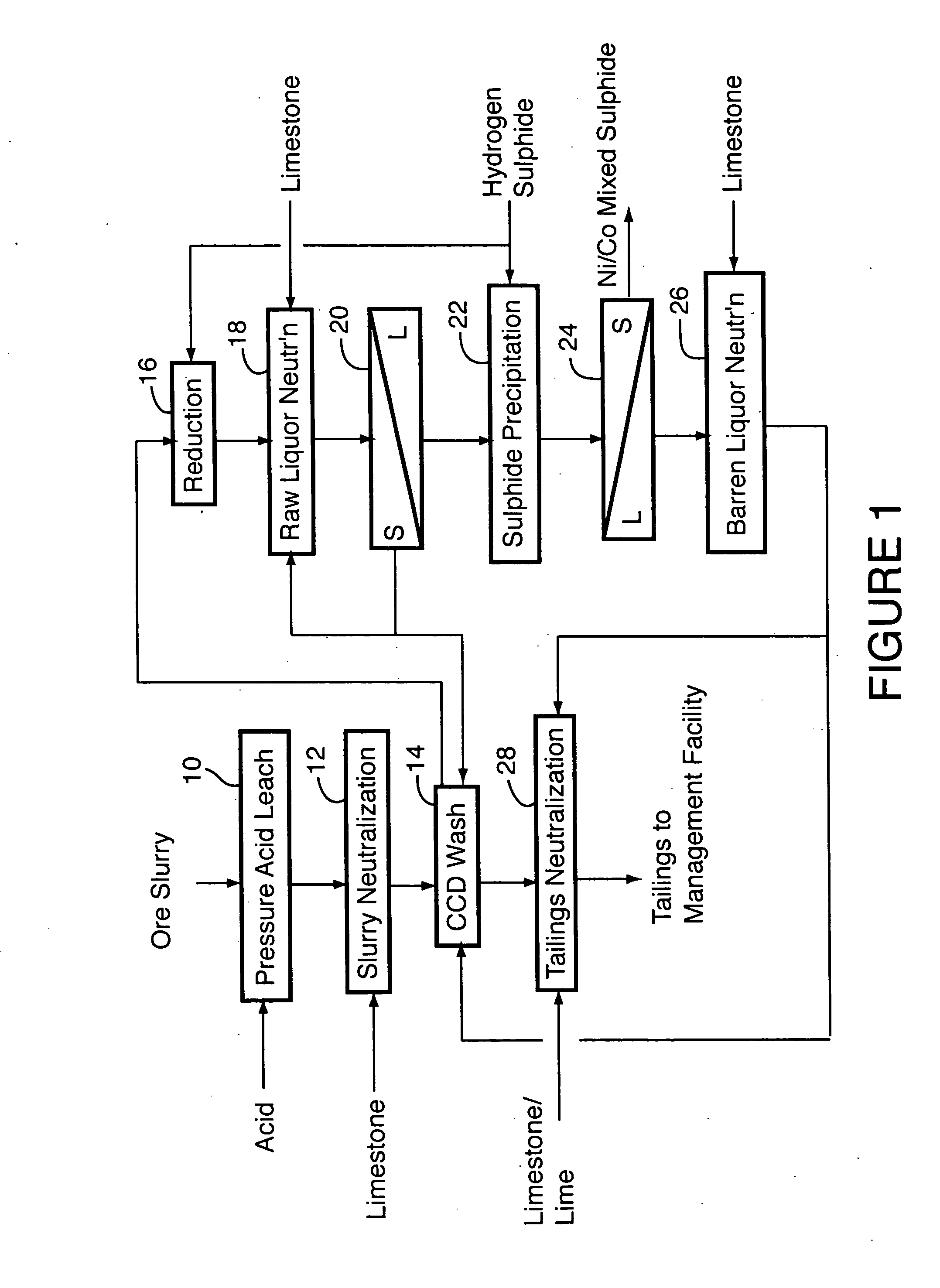
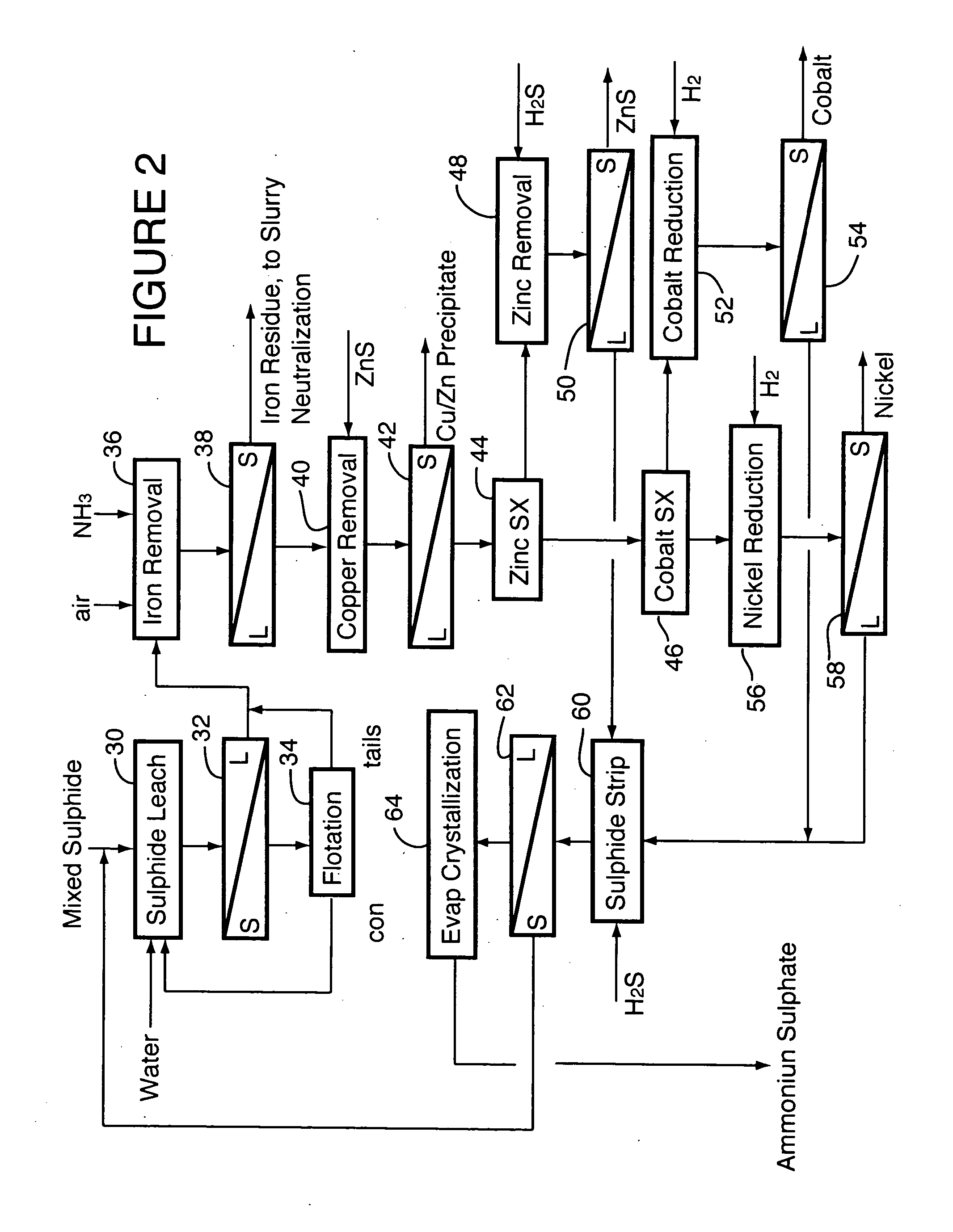
Process for recovery of nickel and cobalt from laterite ore
ActiveUS20060228279A1Efficient separation and recoveryHigh purityCobalt sulfidesSolvent extractionFree solutionSlurry
A process for recovering nickel and cobalt values from nickel- and cobalt-containing laterite ores as an enriched mixed nickel and cobalt sulphide intermediate and for producing nickel and cobalt metal from the nickel and cobalt sulphide intermediate. The laterite ore is leached as a slurry in a pressure acid leach containing an excess of aqueous sulphuric acid at high pressure and temperature, excess free acid in the leach slurry is partially neutralized to a range of 5 to 10 g / L residual free H2SO4 and washed to yield a nickel- and cobalt-containing product liquor, the product liquor is subjected to a reductant to reduce any Cr(VI) in solution to Cr(III), the reduced product liquor is neutralized to precipitate ferric iron and silicon at a pH of about 3.5 to 4.0, and the neutralized and reduced product liquor is contacted with hydrogen sulphide gas to precipitate nickel and cobalt sulphides. The precipitated nickel and cobalt sulphides can be leached in a water slurry in a pressure oxidation leach, the leach solution subjected to iron hydrolysis and precipitation, the iron-free solution contacted with zinc sulphide to precipitate copper, the iron- and copper-free solution subjected to zinc and cobalt extraction by solvent extraction to produce a nickel raffinate, the nickel raffinate contacted with hydrogen gas to produce nickel powder and the cobalt strip solution from the solvent extraction step contacted with hydrogen gas to produce cobalt powder.
Owner:SHERRITT INTERNATIONAL
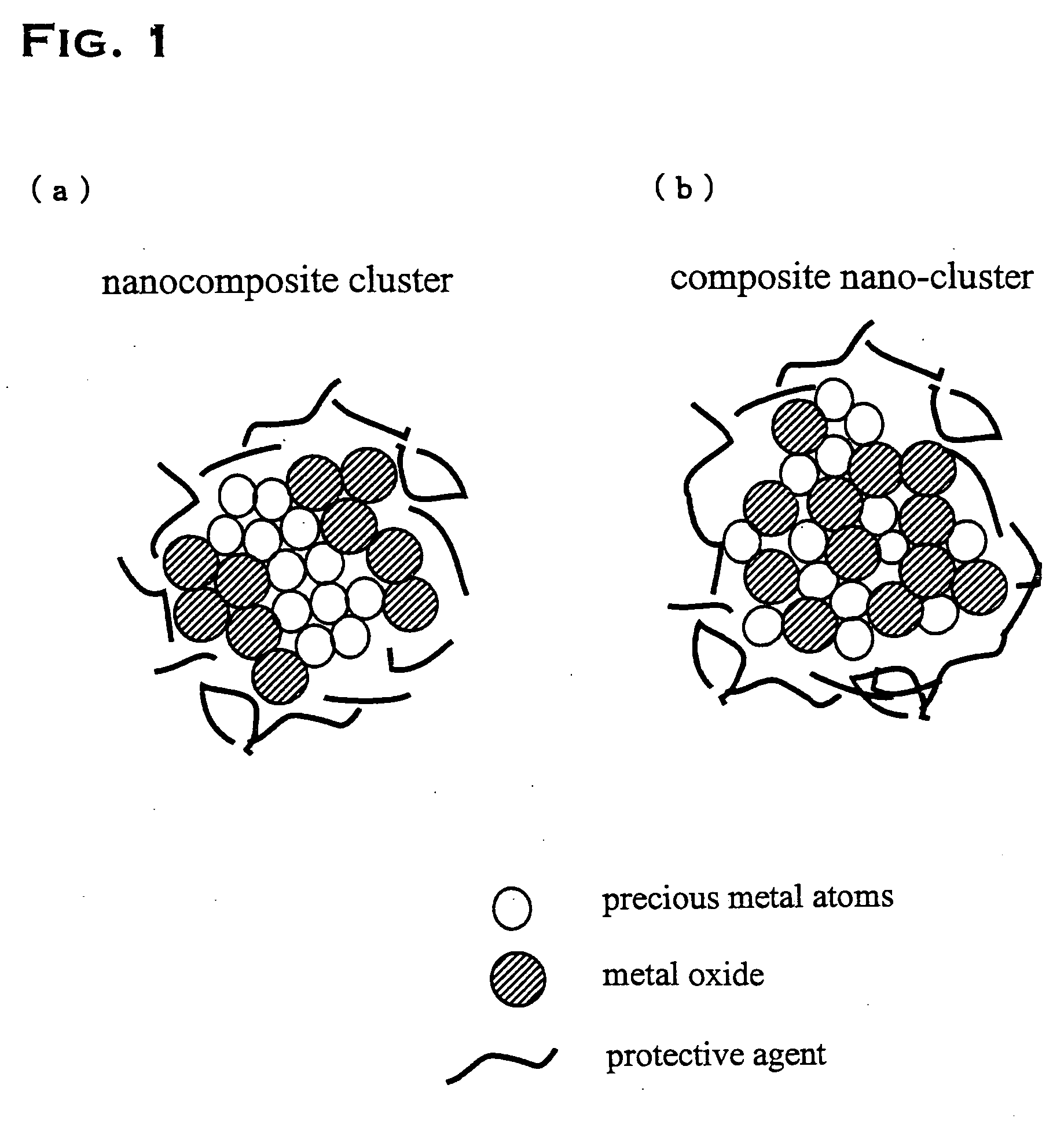
Precious metal - metal oxide composite cluster
InactiveUS20050065026A1Increase the effective surface areaSmall granularityMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingOxide compositeMaterials science
The present invention provides a precious metal—metal oxide composite cluster, wherein said cluster is formed as a single particle by combining a precious metal portion comprising a single atom or an aggregate of a plurality of atoms consisting of one or more precious metals, and a metal oxide portion comprising a single molecule or an aggregate of a plurality of molecules consisting of one or more metal oxides, and wherein said particle has a particle size between 1 and 100 nm.
Owner:TANAKA PRECIOUS METAL IND
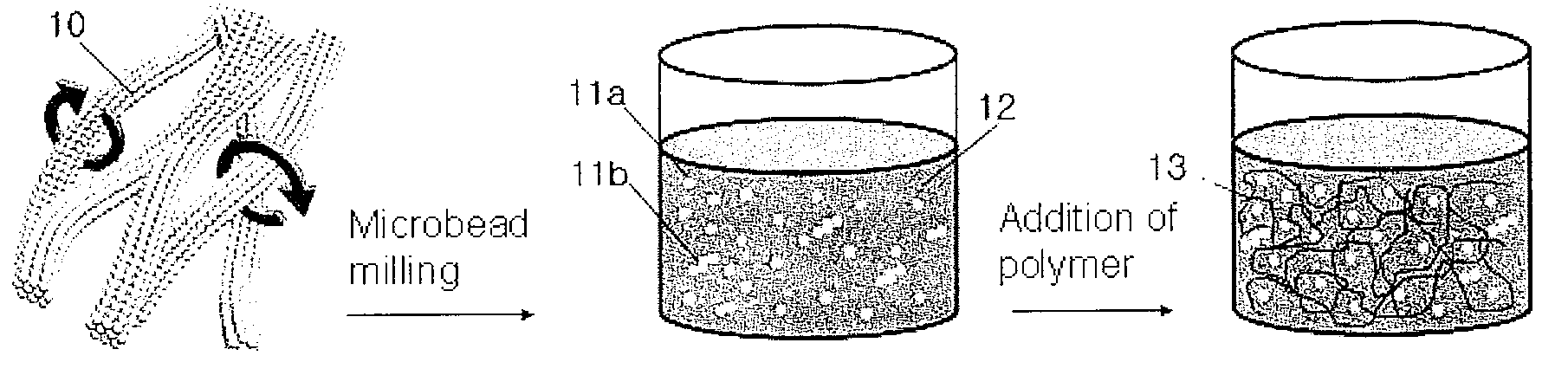
NANO powder, NANO ink and micro rod, and the fabrication methods thereof
InactiveUS20100167078A1Easy to makeOvercome problemsAlkaline earth titanatesPigmenting treatmentFiberMicro rods
Disclosed are a method for fabricating nanopowders, nano ink containing the nanopowders and micro rods, and nanopowders containing nanoparticles, nano clusters or mixture thereof, milled from nano fiber composed of at least one kind of nanoparticles selected from a group consisting of metal, nonmetal, metal oxide, metal compound, nonmetal compound and composite metal oxide, nano ink containing the nanopowders and microrods, the method comprising spinning a spinning solution containing at least one kind of precursor capable of composing at least one kind selected from a group consisting of metal, nonmetal, metal oxide, metal compound, nonmetal compound and composite metal oxide, crystallizing or amorphizing the spun precursor to produce nano fiber containing at least one kind of nanoparticles selected from a group consisting of metal, nonmetal, metal oxide, metal compound, nonmetal compound and composite metal oxide, and milling the nano fiber to fabricate nanopowders containing nanoparticles, nano clusters or mixture thereof.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Negative active material for rechargeable lithium battery, method of preparing thereof, and rechargeable lithium battery including the same
ActiveUS20080118840A1Improve stabilityExcellent charge and discharge efficiency and cycle-lifeMaterial nanotechnologyMolybdeum compoundsDischarge efficiencyVanadium oxide
A negative active material for a rechargeable lithium battery of the present invention includes a lithium-vanadium oxide core material being capable of performing reversible electrochemical oxidation and reduction, and an inorganic oxide coating layer disposed on the surface of the core material. The negative active material can improve stability at the interface between a negative electrode and an electrolyte, charge and discharge efficiency, and cycle-life, and can be applied along with all kinds of aqueous and non-aqueous binders.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Synthesis of Metal Compounds Under Carbothermal Conditions
InactiveUS20050255026A1Economical and convenient processLower capability requirementsPhosphatesLithium compoundsOxidation stateGraphite
Active materials of the invention contain at least one alkali metal and at least one other metal capable of being oxidized to a higher oxidation state. Preferred other metals are accordingly selected from the group consisting of transition metals (defined as Groups 4-11 of the periodic table), as well as certain other non-transition metals such as tin, bismuth, and lead. The active materials may be synthesized in single step reactions or in multi-step reactions. In at least one of the steps of the synthesis reaction, reducing carbon is used as a starting material. In one aspect, the reducing carbon is provided by elemental carbon, preferably in particulate form such as graphites, amorphous carbon, carbon blacks and the like. In another aspect, reducing carbon may also be provided by an organic precursor material, or by a mixture of elemental carbon and organic precursor material.
Owner:LITHIUM WERKS TECH BV +1
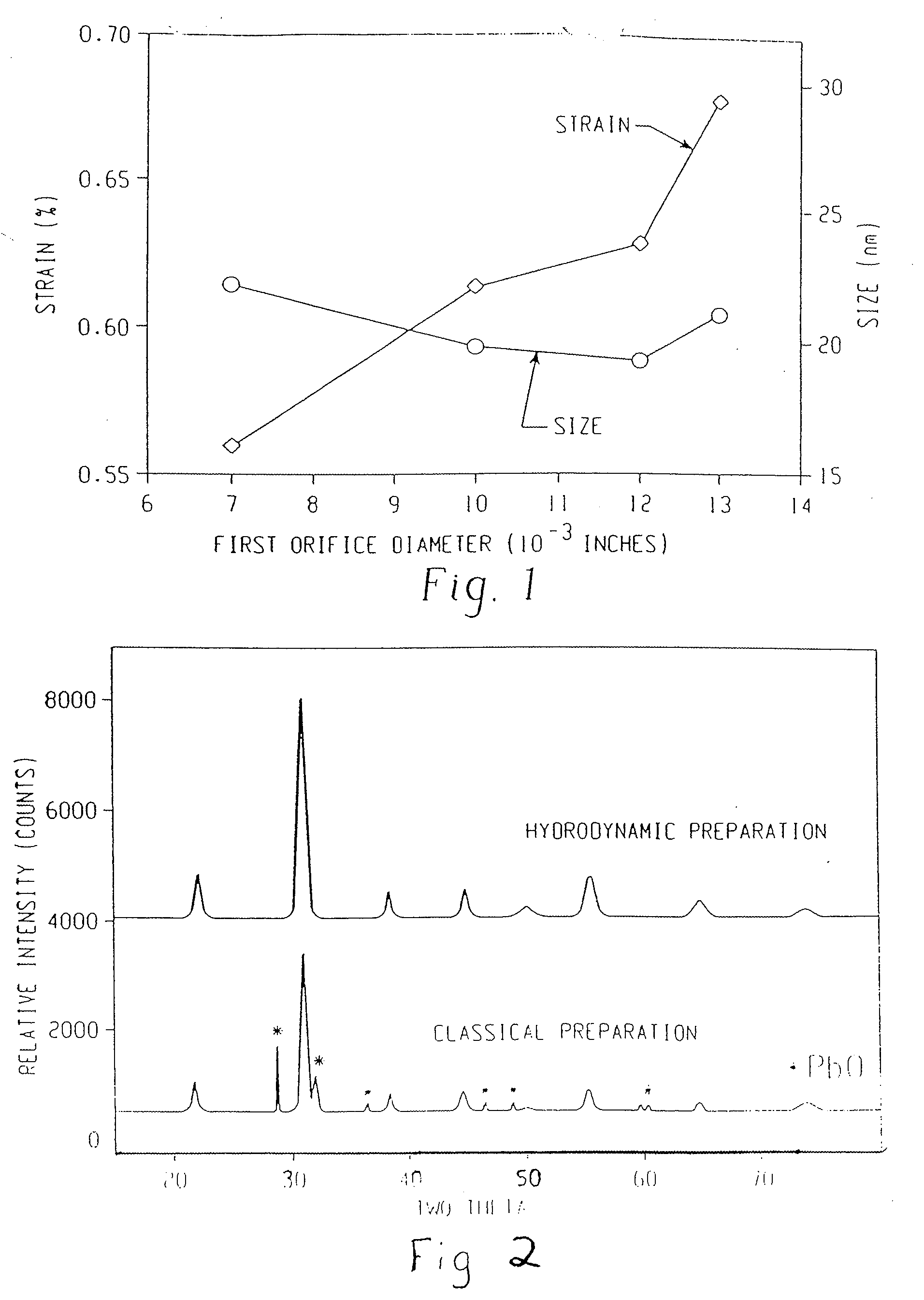
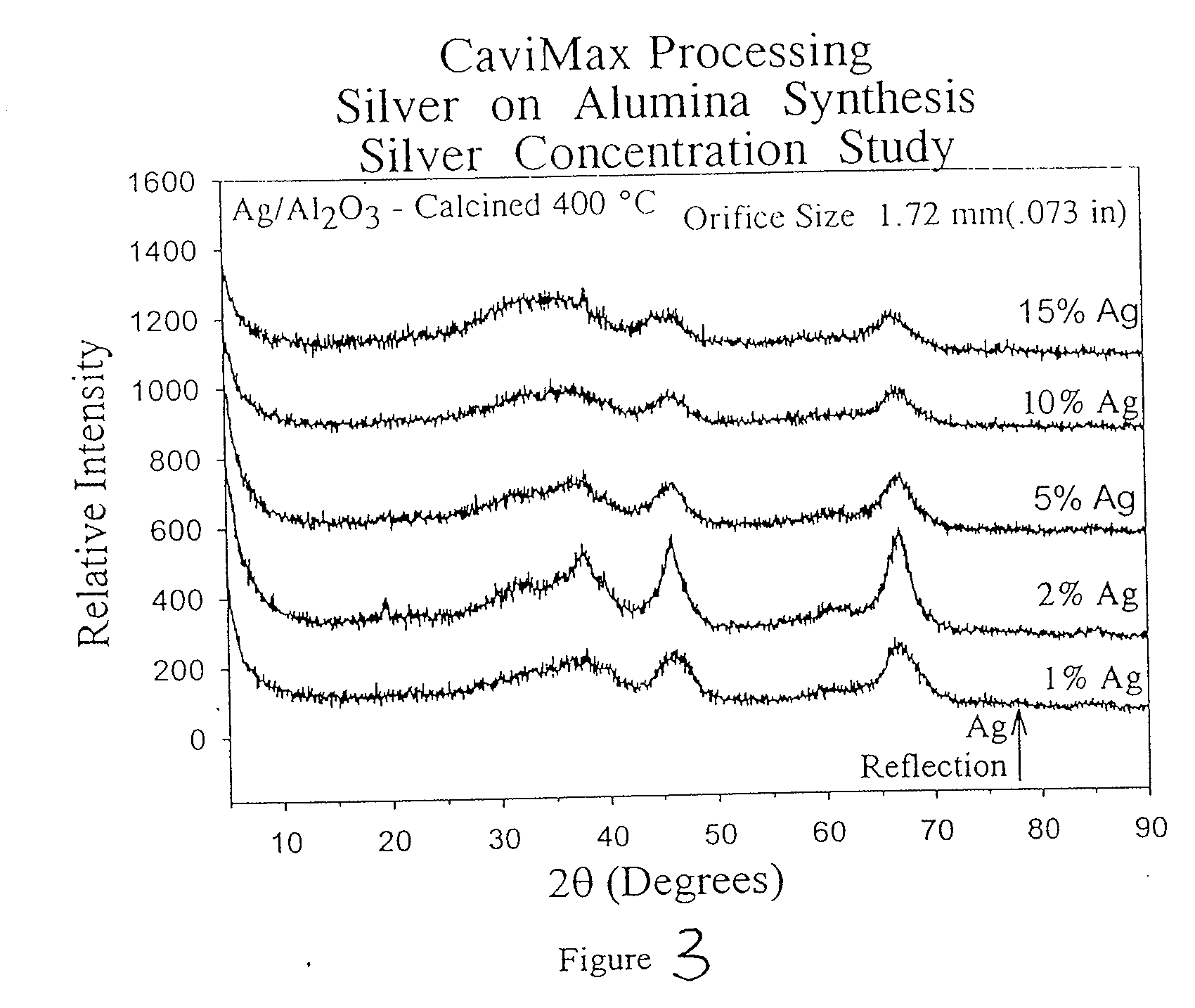
Method of preparing compounds using cavitation and compounds formed therefrom
InactiveUS20070066480A1Efficient modificationEasy to adjustMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingCompound (substance)Nanostructured materials
Nanostructured materials and processes for the preparation of these nanostructured materials in high phase purities using cavitation is disclosed. The method preferably comprises mixing a metal containing solution with a precipitating agent and passing the mixture into a cavitation chamber. The chamber consists of a first element to produce cavitation bubbles, and a second element that creates a pressure zone sufficient to collapse the bubbles. The process is useful for the preparation of catalysts and materials for piezoelectrics and superconductors.
Owner:WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE +1
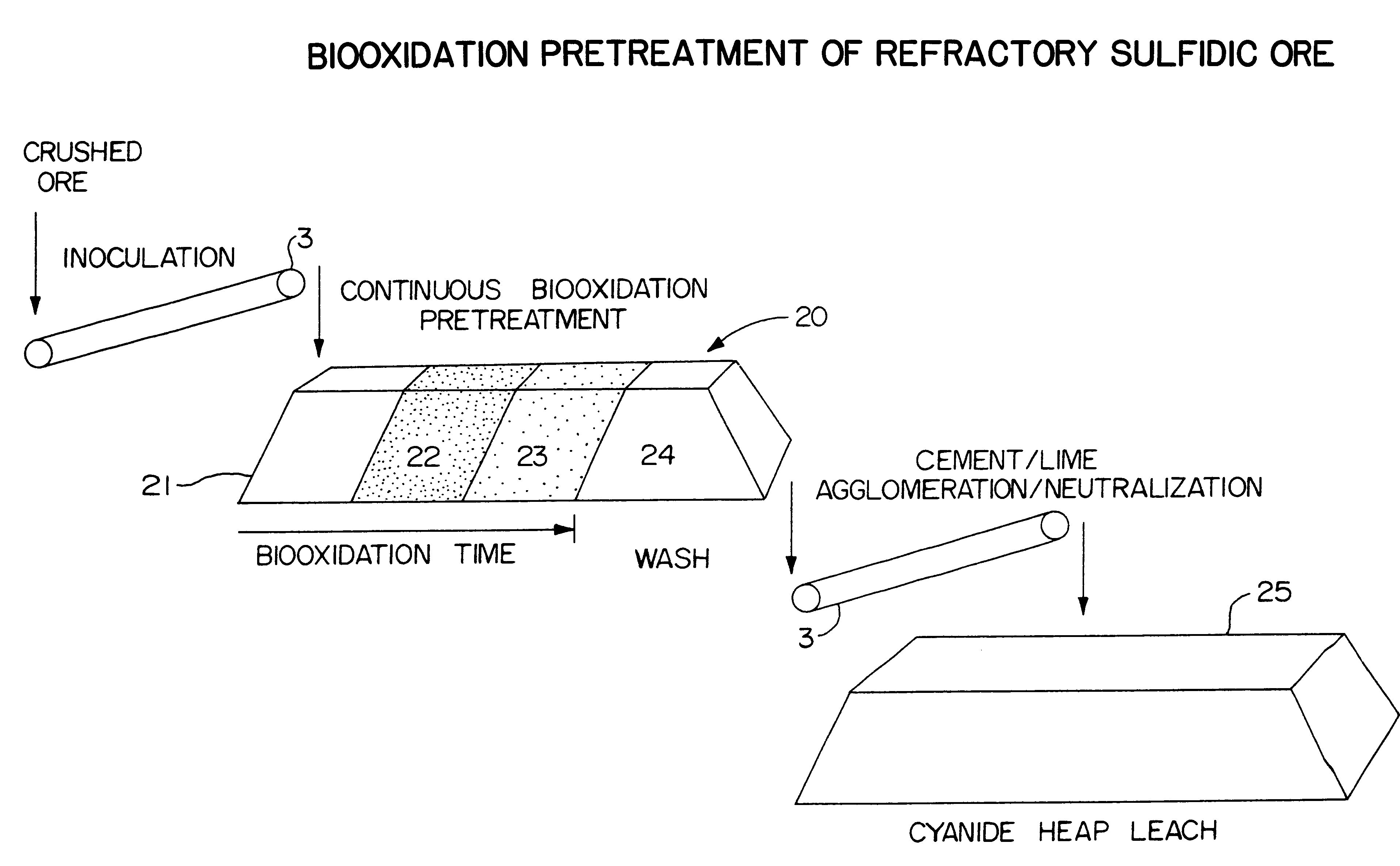
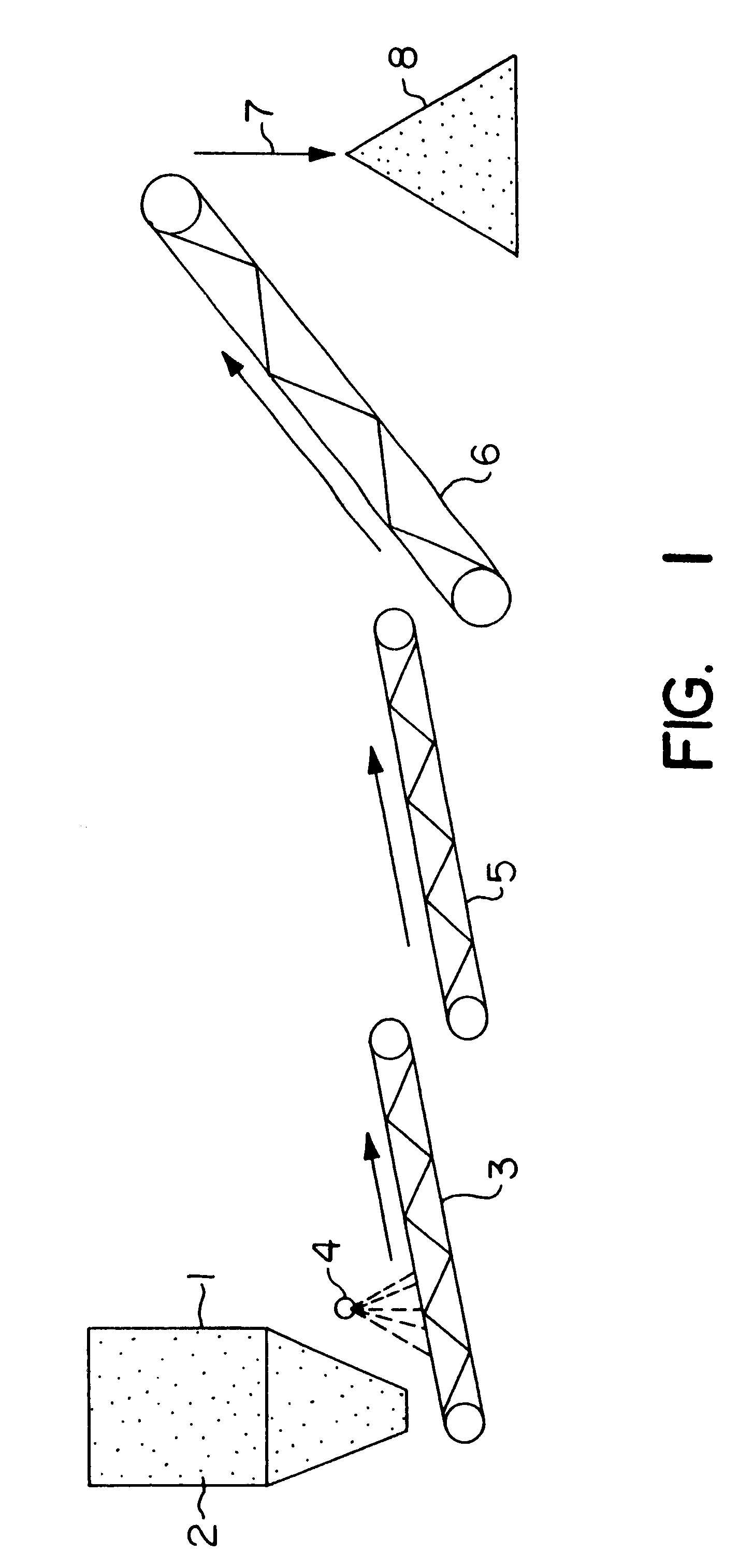
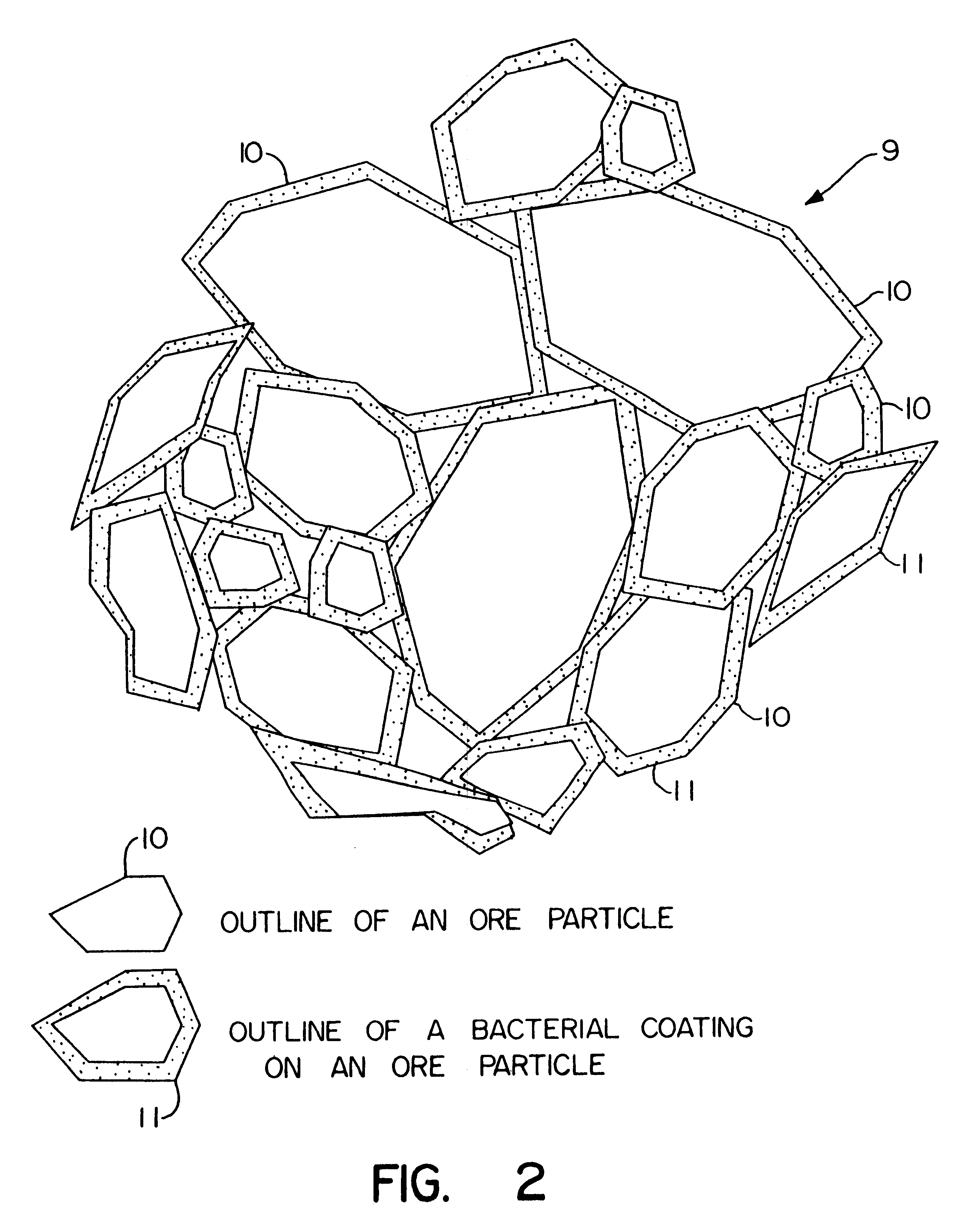
Biooxidation process for recovery of metal values from sulfur-containing ore materials
InactiveUS6383458B1Increase ratingsIncrease attractivenessTransuranic element compoundsSolvent extractionParticulatesPartial oxidation
A process for the recovery of one or more metal values from a metal ore material comprising those of one or more values and a matrix material having a sulfur content wherein the sulfur is present in an oxidation-reduction state of zero or less comprisinga. forming particulates from particles of said ore and an inoculate comprising bacteria capable of at least partially oxidizing the sulfur content;b. forming a heap of said particulates;c. biooxidizing the sulfur content andd. recovering those one or more metal values.
Owner:NEWMONT USA LTD
Solid chemical hydride dispenser for generating hydrogen gas
InactiveUS7666386B2Molybdeum compoundsSynthetic resin layered productsCompound (substance)Hydrogen evolution
A device for generating hydrogen gas is provided. The device (101) comprises a first hydrogen-containing composition (107) that reacts with a second composition to evolve hydrogen gas; a dispenser (105) adapted to apply the first composition to a first porous member (109); and a conduit (111) adapted to supply the second composition to the first porous member. In a preferred embodiment, the first composition is selected from the group consisting of hydrides, borohydrides and boranes, the second composition is water, and the dispenser is spring-loaded and is charged with the first composition. As the first composition reacts with water at the interface to evolve hydrogen gas, the dispenser forces the reaction product across the interface and out of the dispenser, where it will not interfere with the progress of the hydrogen evolution reaction.
Owner:LYNNTECH POWER SYST
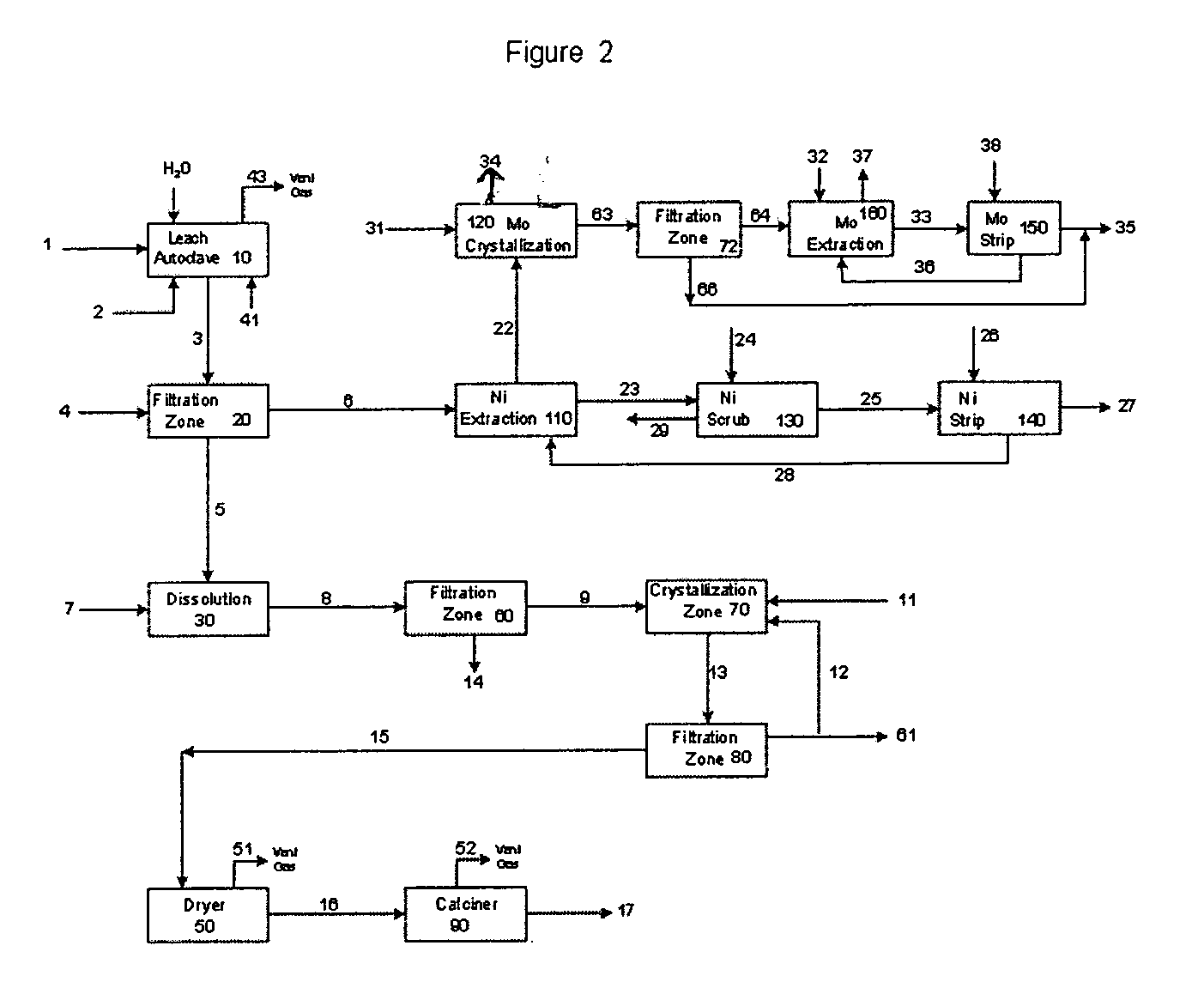
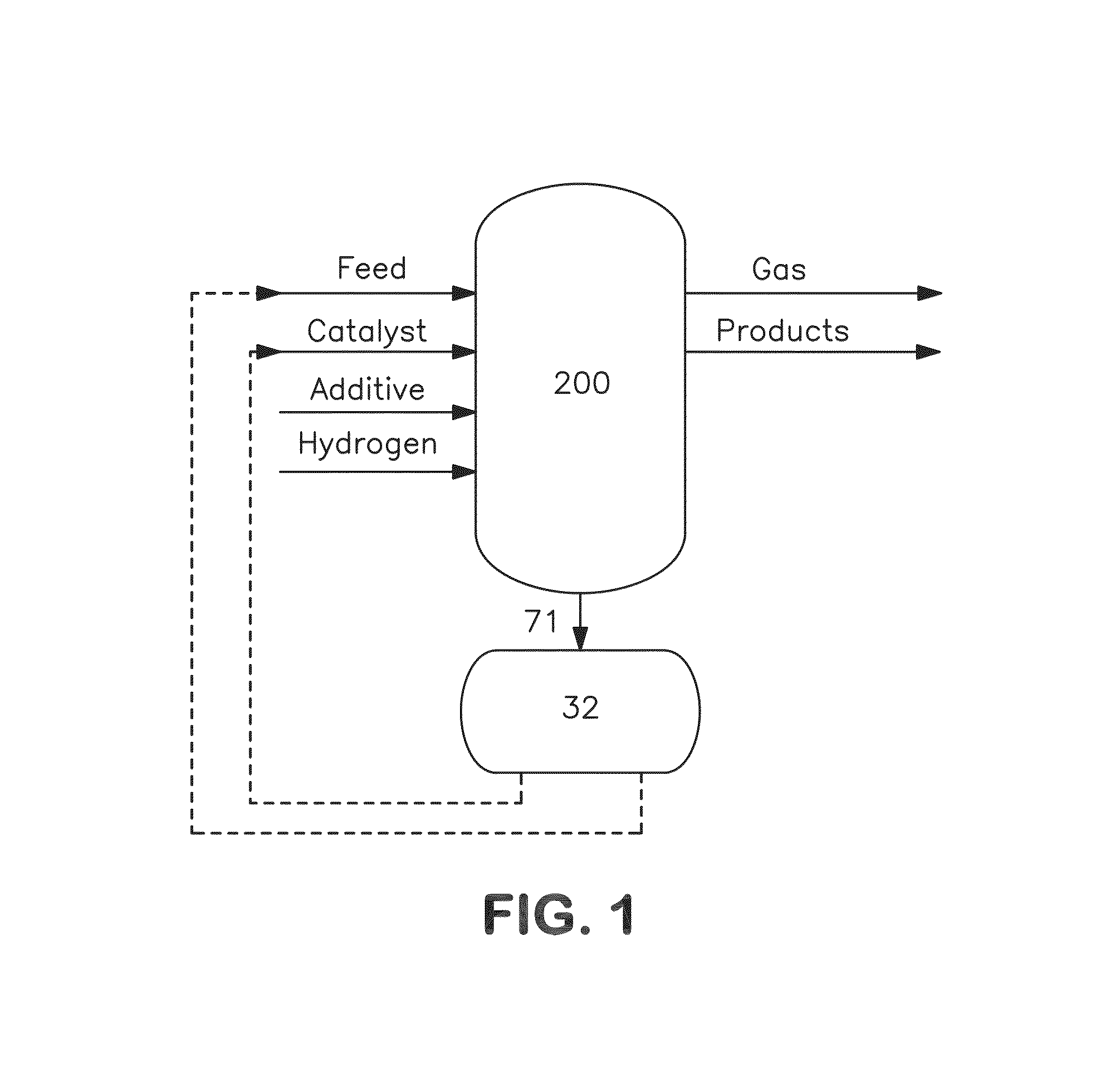
Process for separating and recovering base metals from used hydroprocessing catalyst
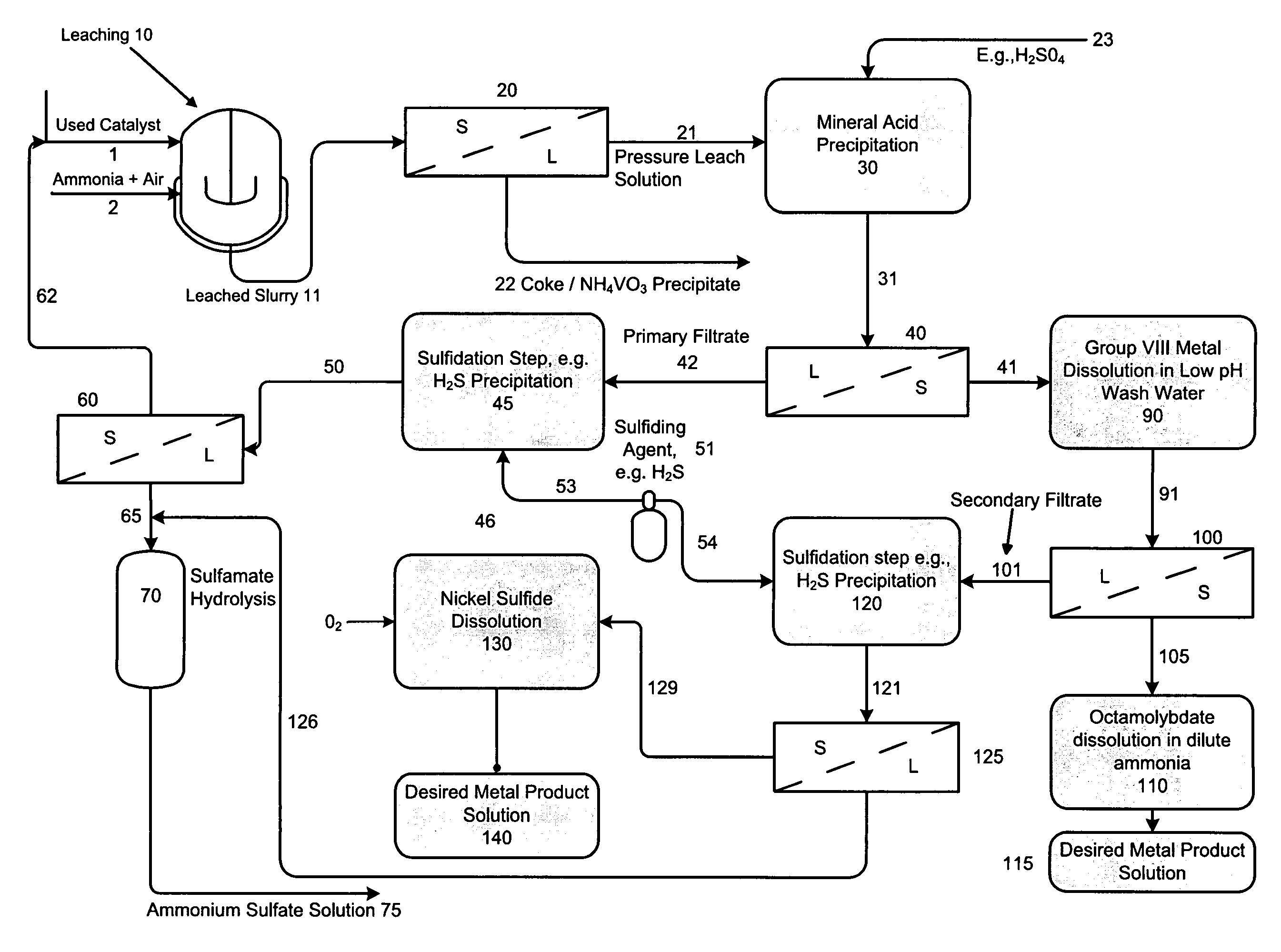
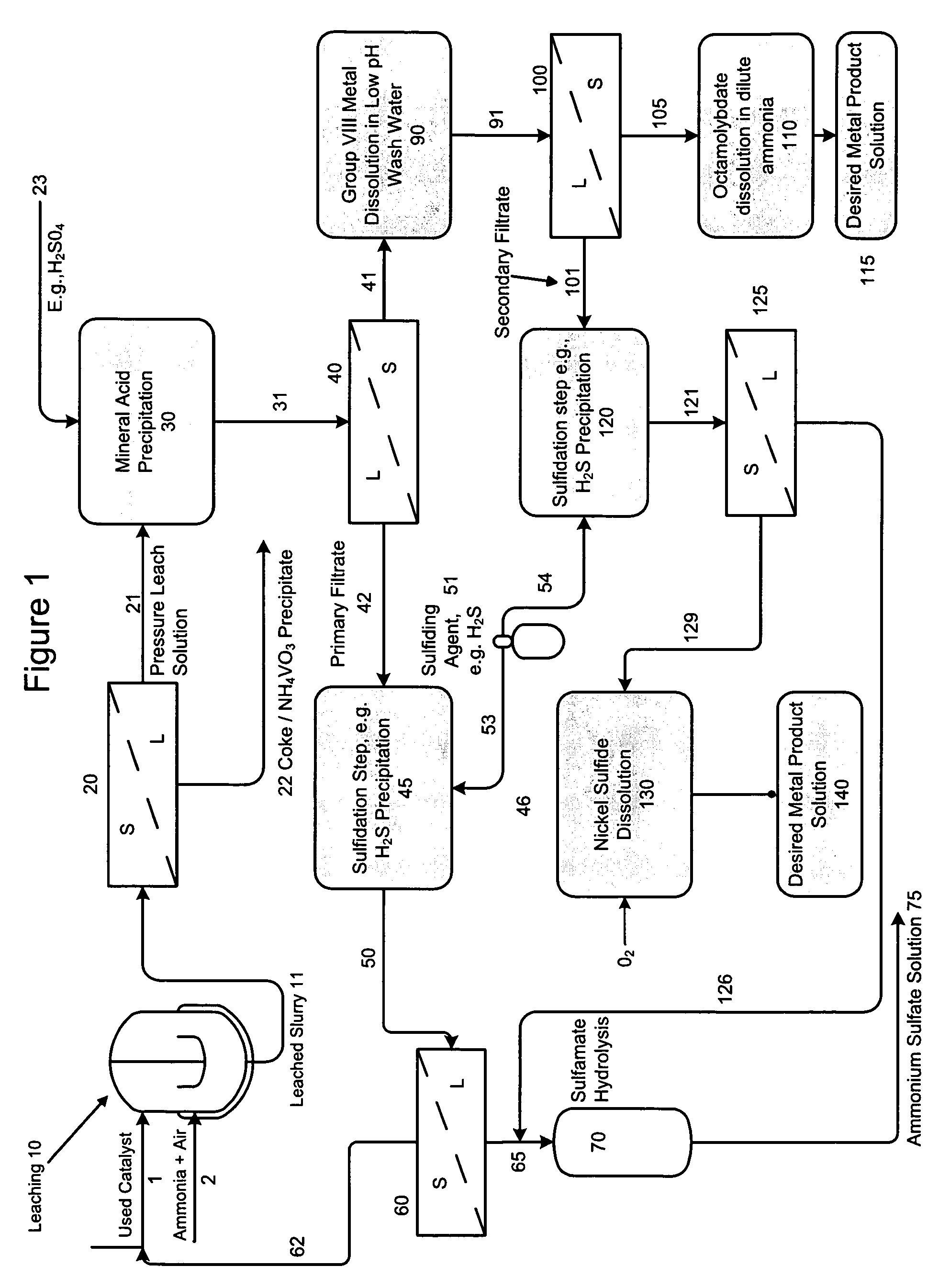
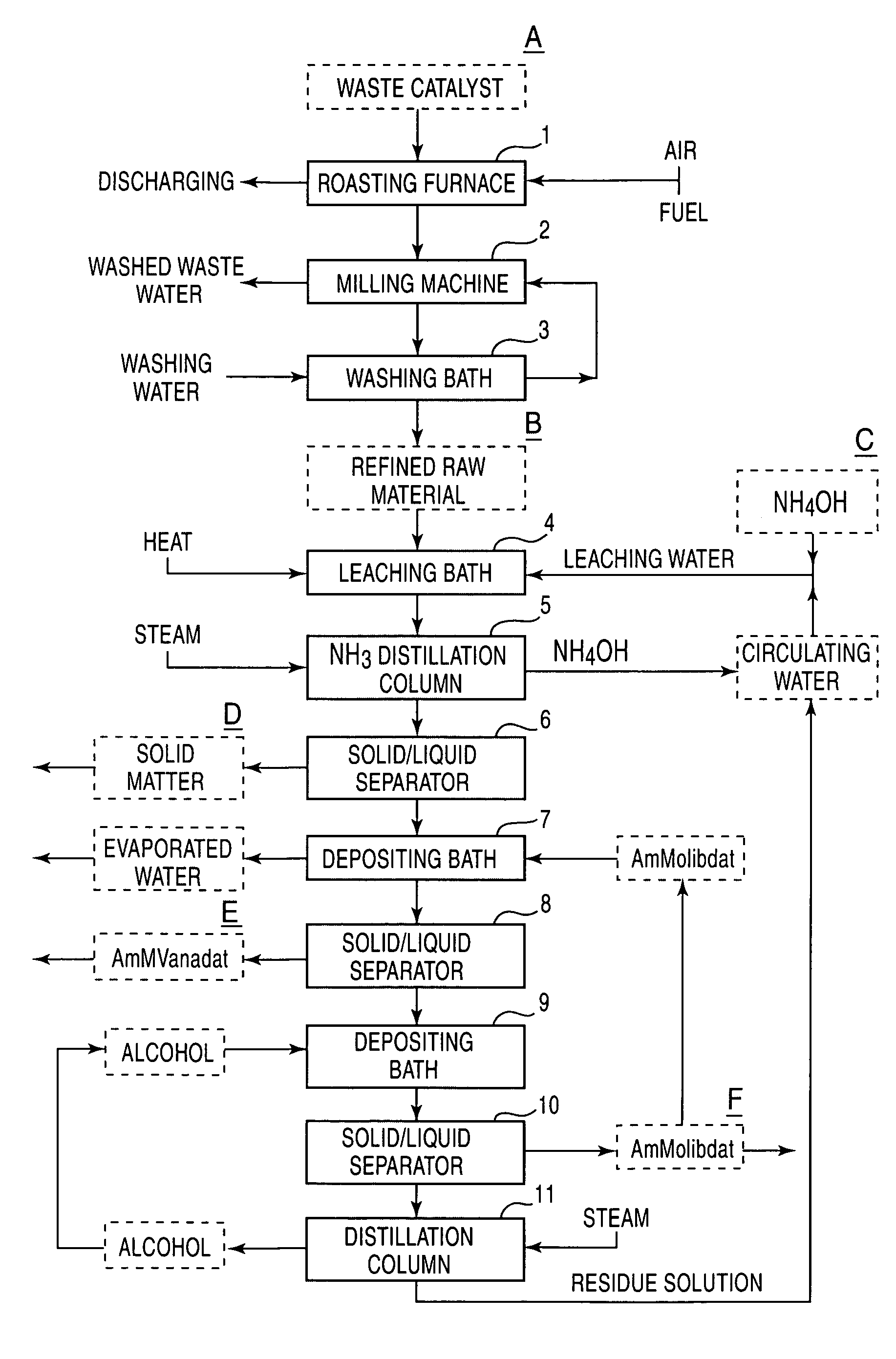
A method is disclosed for separating and recovering base metals from a used hydroprocessing catalyst originating from Group VIB and Group VIII metals and containing at least a Group VB metal. In one embodiment, the used catalyst is contacted with an ammonia leaching solution to dissolve and separate the Group VIB and VIII metals from the Group VB metal complex and coke associated with the used catalyst. The resulting Group VIB and VIII metal containing solution is processed through at least two additional precipitation and liquid / solid separation steps to produce, in separate processing streams, a Group VIB metal product solution (such as ammonium molybdate) and a Group VIII metal product solution (such as nickel sulfate). Additionally, two separate filtrate streams are generated from liquid-solid separation steps, which filtrate streams are combined and subjected to hydrolysis and oxidation (oxydrolysis) to generate a purified ammonium sulfate solution for further processing, such as for fertilizer.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
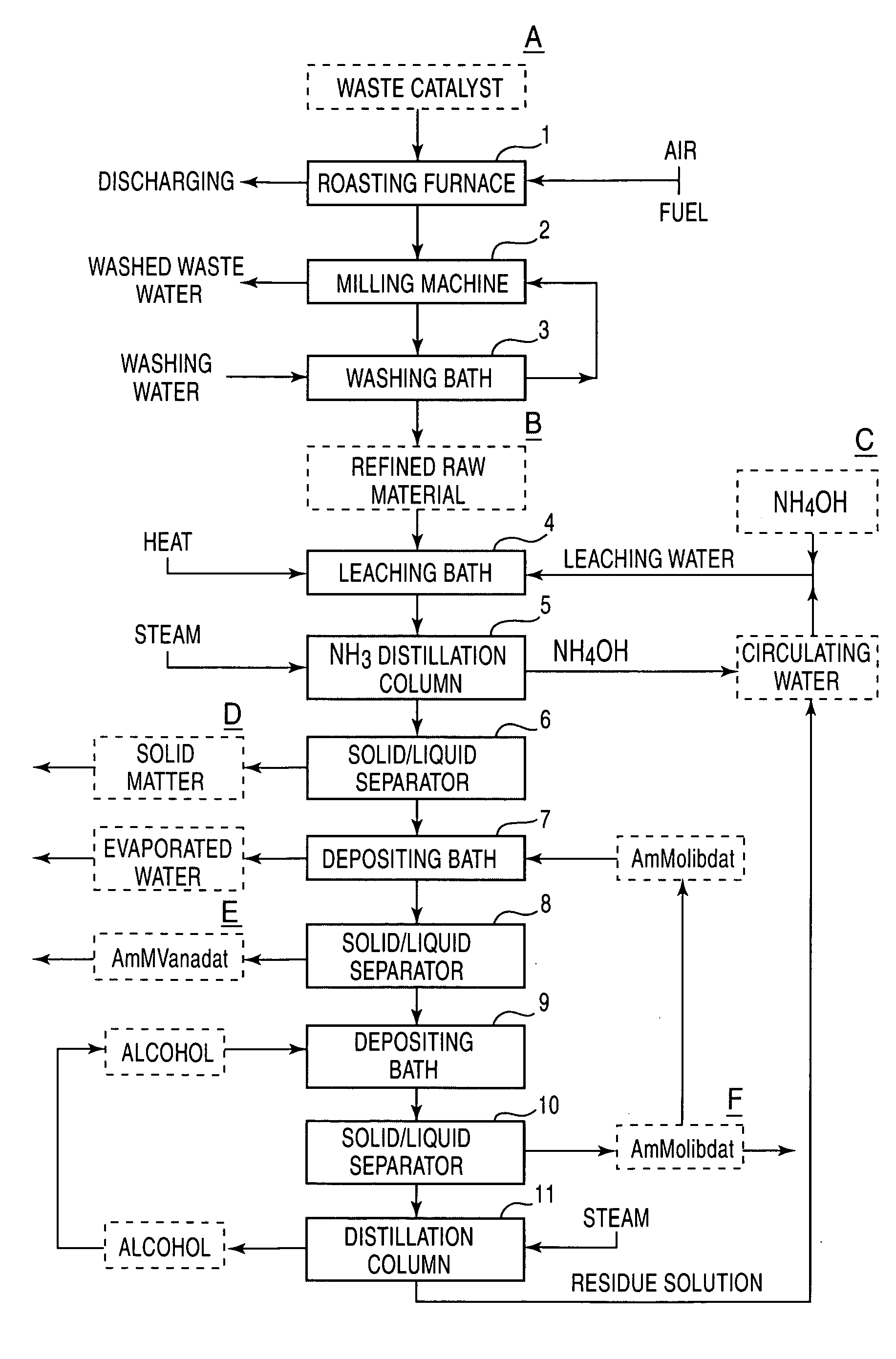
Recovery of the transition metal component of catalyst used in heavy feed hydroconversion
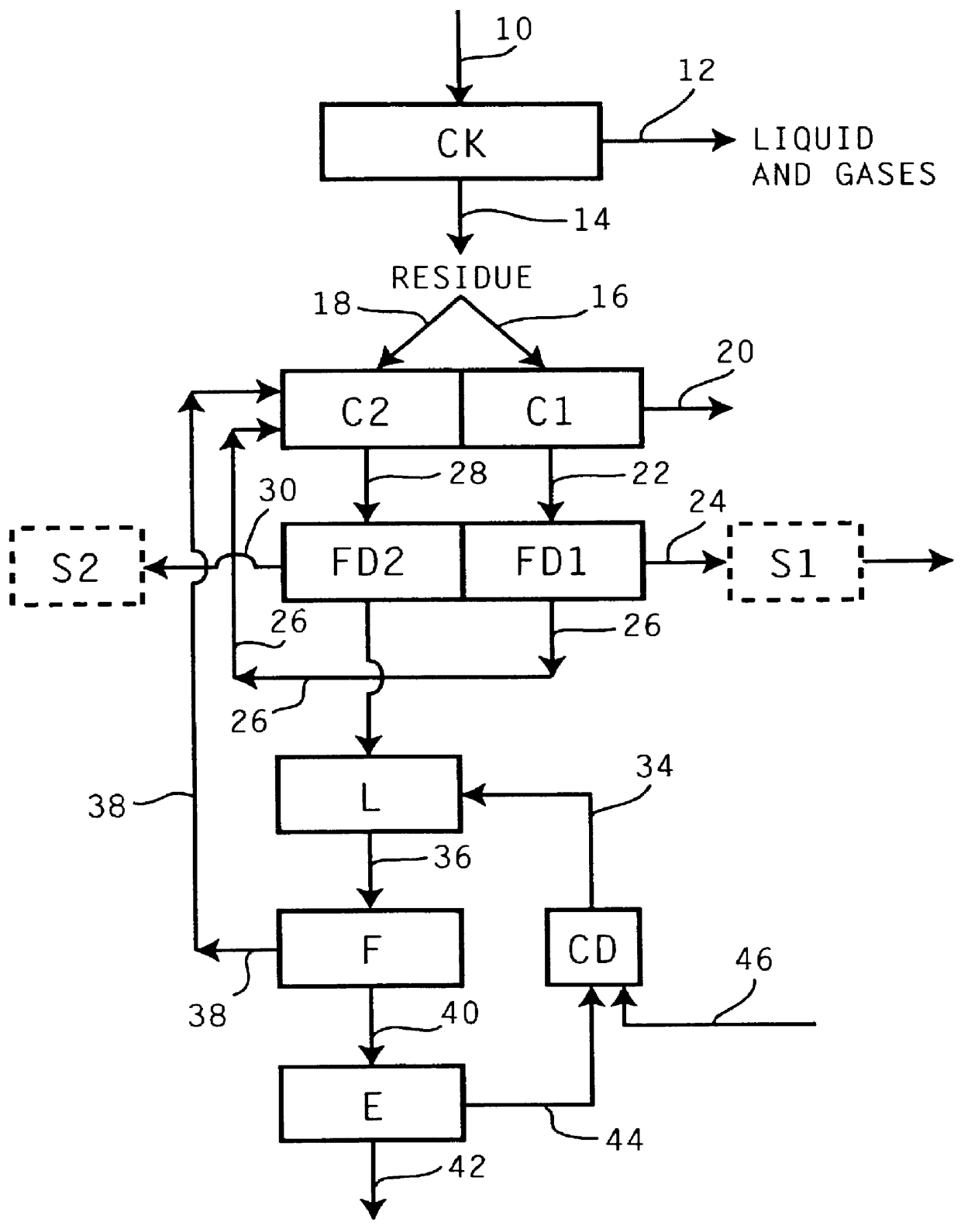
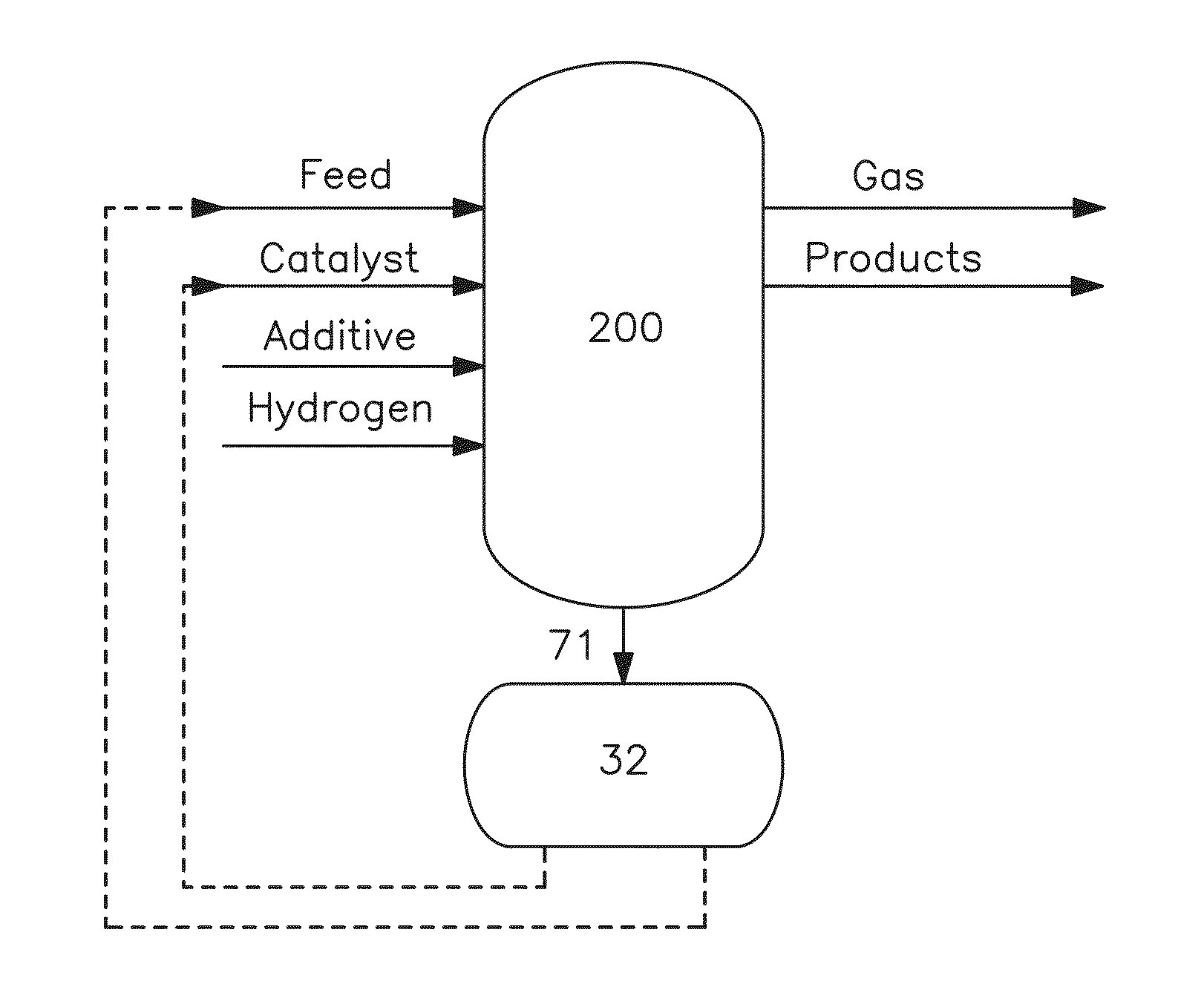
The invention relates to a process for recovering the transition metal component of catalysts used in the hydroconversion of heavy hydrocarbonaceous materials. In accordance with the invention, a slurry of a transition metal catalyst and hydrocarbon is catalytically desulfurized resulting in a desulfurized product and a solid residue containing the transition metal. The transition metal may be recovered by coking the residue and then dividing the coker residue into two portions are combusted with the flue dust from the first combustion zone being conducted to the second combustion zone. The flue dust from the second combustion zone is treated with ammonia and ammonium carbonate in order to obtain ammonium molybdate.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Thermally dissolving and catalytic method for preparing liquid fuel by lignite as well as catalyst and solvent used therefor
ActiveCN101182421AMild operating conditionsSimple preparation equipmentOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMolybdeum compoundsLiquid productForming gas
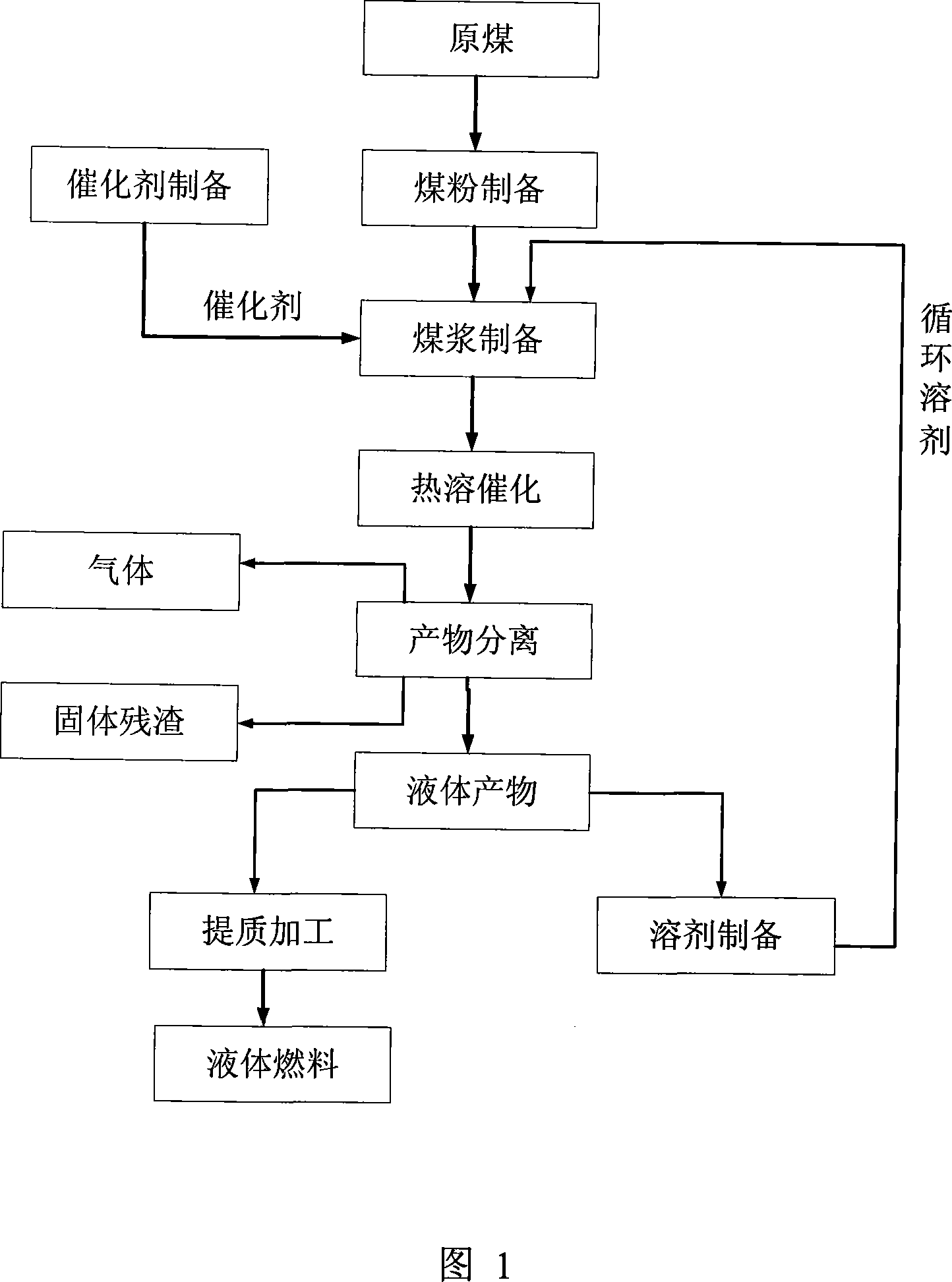
The invention belongs to the technological field of coal chemical processing and discloses a heat dissolving and catalyzing method using brown coal to prepare liquid fuel. The method comprises the following steps: 1) the brown coal is smashed and dried to prepare pulverized coal; 2) the pulverized coal, solvent and catalyst are stirred and mixed well to prepare coal slurry; wherein, the weight percent of the pulverized coal is 30 percent to 40 percent; the weight percent of the solvent is 60 percent to 70 percent; the quantity of the added catalyst is 0.5 percent to 1 percent of the weight of the pulverized coal; 3) the coal slurry is dissolved by heat and catalyzed to prepare heat dissolved and liquefied products; wherein, the temperature is 390 DEG C to 450 DEG C; the pressure is 5.0MPa to 9.0MPa; the reaction time is 30 minutes to 60 minutes; 4) the heat dissolved and liquefied products are separated to form gas-phase, liquid-phase and solid-phase products; 5) the liquid products are extracted and processed to form liquid fuel. The invention also discloses catalyst and solvent used in the method. The operation condition of the method of the invention is mild; the conversion ratio of the organic substances in the brown coal can achieve a higher level; after being processed, the liquid fuel product can be used for preparing engine fuel suiting national standards; and the preparation equipment is simple; the investment is small; the cost is low; and the invention is a coal liquefaction method suiting the national conditions of China.
Owner:ZHAOQING SHUNXIN COAL CHEM TECH
Process for simultaneous recovery of chromium and iron from Chromite Ore Processing Residue
InactiveUS20040086438A1Simple eco-friendlySolvent extractionMolybdeum compoundsIron saltsChromate salt
The present invention relates to a process for simultaneous recovery of chromium and iron from Chromite Ore Processing Residue (COPR) and more particularly, the present invention relates to an economical and environment-friendly process for recovering chromium as a chromate salt and iron as an iron salt from non-leachable Chromite Ore Processing Residue and avoids landfilling of toxic metals.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method for recovering metal from molybdenum-containing spent catalyst
ActiveCN102050492AImprove solubilityHigh recovery rateMolybdeum compoundsProcess efficiency improvementSpent acidMetal
The invention discloses a method for recovering metal from a molybdenum-containing spent catalyst, which comprises the following steps of: degreasing and crushing the spent catalyst, mixing the spend catalyst and sodium carbonate, and calcining; after calcining, leaching by water, recovering molybdenum from the spent catalyst by adopting an organic extracting agent; and preparing solution of mixed acid by utilizing spent acid discharged in the method to treat solid residues after water leaching, and recovering metal in the spent acid and the residues further. By the method, the recovery rate of the metal in the spent catalyst can be improved further, the severity of the operation condition is lowered simultaneously, and the method has low energy consumption and can be in the metal recovery process of the molybdenum-containing spent catalyst.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Process for separating and recovering valuable metals
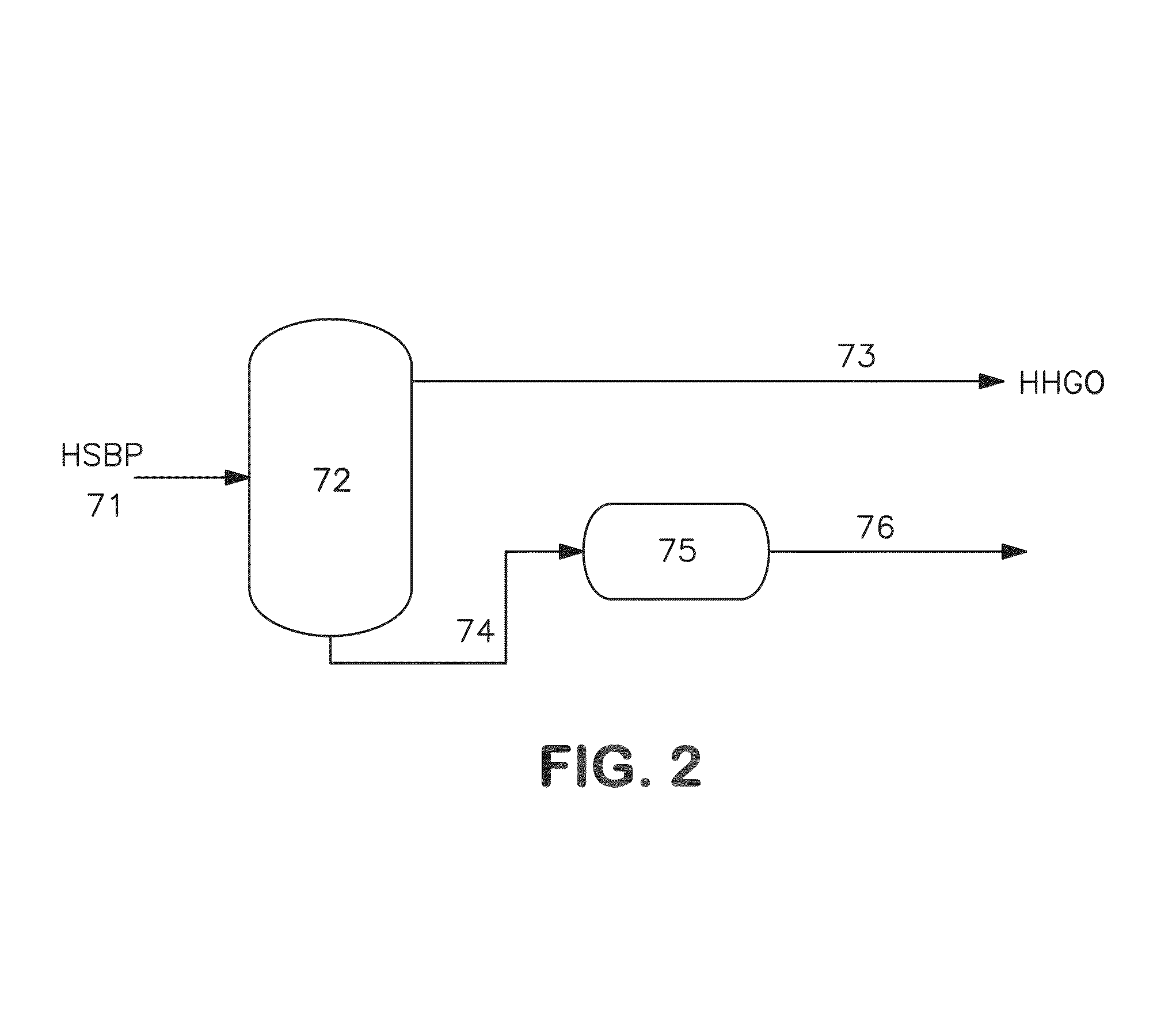
InactiveUS20040213717A1Speed up leachingProceed efficientlyOther chemical processesTantalum compoundsVanadium CompoundsAlcohol
The present invention provides a process for economically separating and recovering valuable metal components, with no many kinds of chemicals being used, with no waste water that causes environmental pollution being discharged, and also perfectly no by-products being formed by means of simple steps. The present invention includes a step of leaching a raw material containing at least vanadium oxides and molybdenum oxides with ammonia-containing leaching water to obtain a leached solution containing a vanadium compound and a molybdenum compound, a step of adding ammonium orthomolybdate to the leached solution to separate and recover the deposited ammonium metavanadate from a first solution for separation, a step of adding a water-soluble alcohol to the separated solution to separate and recover the deposited ammonium orthomolybdate from a second solution for separation, a step of distilling the second solution for separation to separate and recover the water-soluble alcohol and a residue-solution, a step of adding at least a portion of the residue solution to the ammonia-containing leaching water as the portion thereof, and a step of returning a portion of the recovered ammonium orthomolybdate and a total of a recovered, water-soluble alcohol to the system for reusing.
Owner:Y K YSK TECHNOSYST
Conductive particle, visible light transmissive particle dispersed conductor, method for producing same, transparent conductive thin film, method for producing same, transparent conductive article usi
ActiveCN101023498AImprove permeabilityImprove conductivityConductive layers on insulating-supportsMolybdeum compoundsInfraredElectrical resistance and conductance
Disclosed is a visible light transmissive particle dispersed conductor using conductive particles containing a tungsten oxide or / and a composite tungsten oxide. Also disclosed are a visible light transmissive conductive article made of such a visible light transmissive particle dispersed conductor, conductive particles used for such a visible light transmissive particle dispersed conductor and visible light transmissive conductive article, and a method for producing such conductive particles. For providing a visible light transmissive particle dispersed conductor having excellent visible light transmittance and excellent conductivity at low cost, there are used conductive particles containing a tungsten oxide represented by the general formula: WyOz (wherein 2.2 = z / y = 2.999) or / and a composite tungsten oxide represented by the general formula: MxWyOx (wherein 0.001 <= x / y <= 1.1 and 2.2 <= z / y <= 3.0) and having a particle diameter of not less than 1 nm, visible light transmissivity, and a powder resistivity measured at a pressure of 9.8 MPa of not more than 1.0 O.cm.
Owner:SUMITOMO METAL MINING CO LTD
Process for separating and recovering valuable metals
InactiveUS7182926B2Control generationSuitable for useOther chemical processesTantalum compoundsAmmonium orthomolybdateAmmonium metavanadate
A process for economically separating and recovering valuable metal components, with few kinds of chemicals being used, with no waste water that causes environmental pollution being discharged, and also perfectly no by-products being formed by means of simple steps. The process includes a step of leaching a raw material containing at least vanadium oxides and molybdenum oxides with ammonia-containing leaching water to obtain a leached solution containing a vanadium compound and a molybdenum compound, a step of adding ammonium orthomolybdate to the leached solution to separate and recover the deposited ammonium metavanadate from a first solution for separation, a step of adding a water-soluble alcohol to the separated solution to separate and recover the deposited ammonium orthomolybdate from a second solution for separation, a step of distilling the second solution for separation to separate and recover the water-soluble alcohol and a residue solution, a step of adding at least a portion of the residue solution to the ammonia-containing leaching water as the portion thereof, and a step of returning a portion of the recovered ammonium orthomolybdate and a total of a recovered, water-soluble alcohol to the system for reusing.
Owner:Y K YSK TECHNOSYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com