Patents
Literature
96 results about "Pressure oxidation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
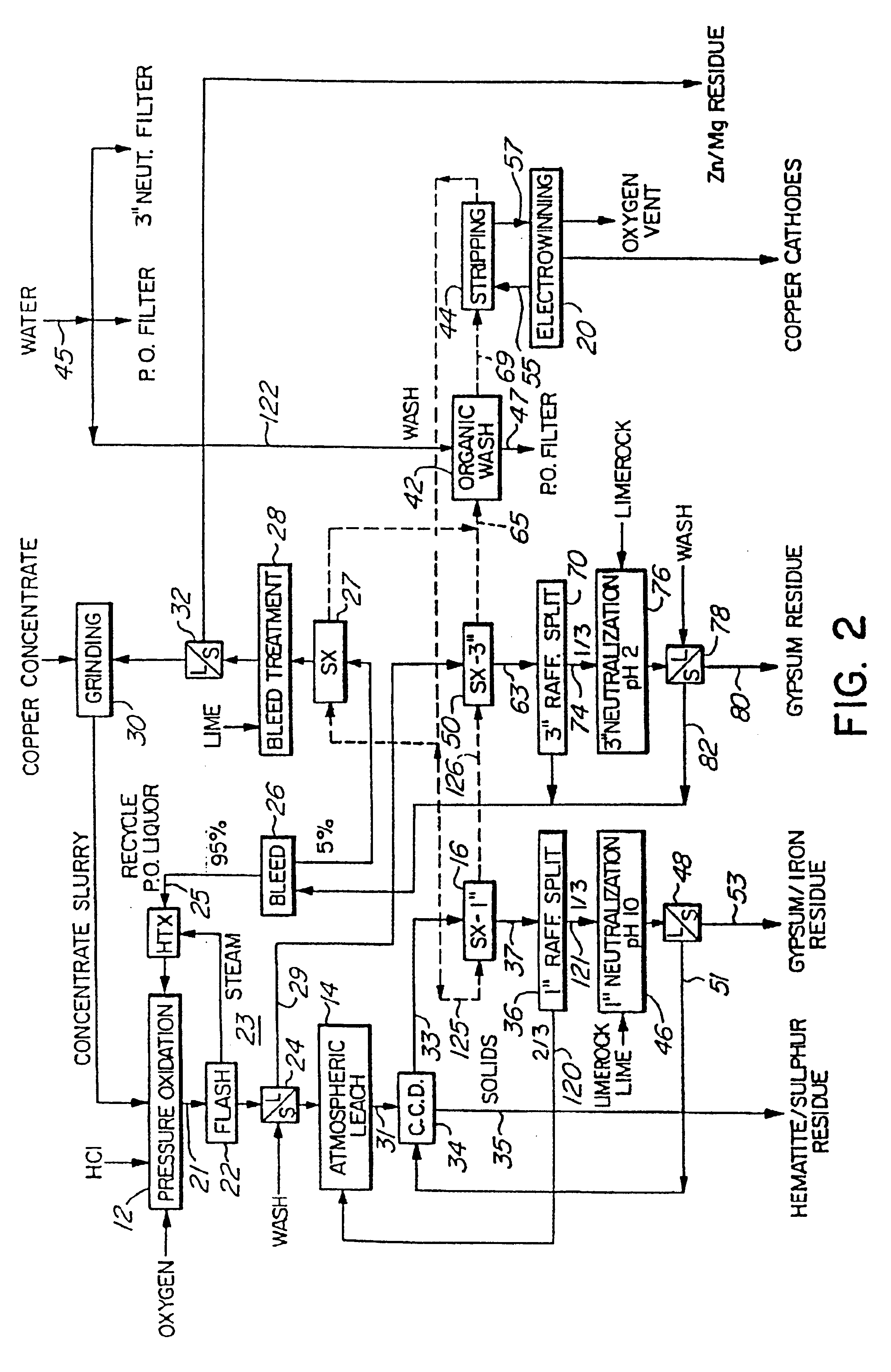
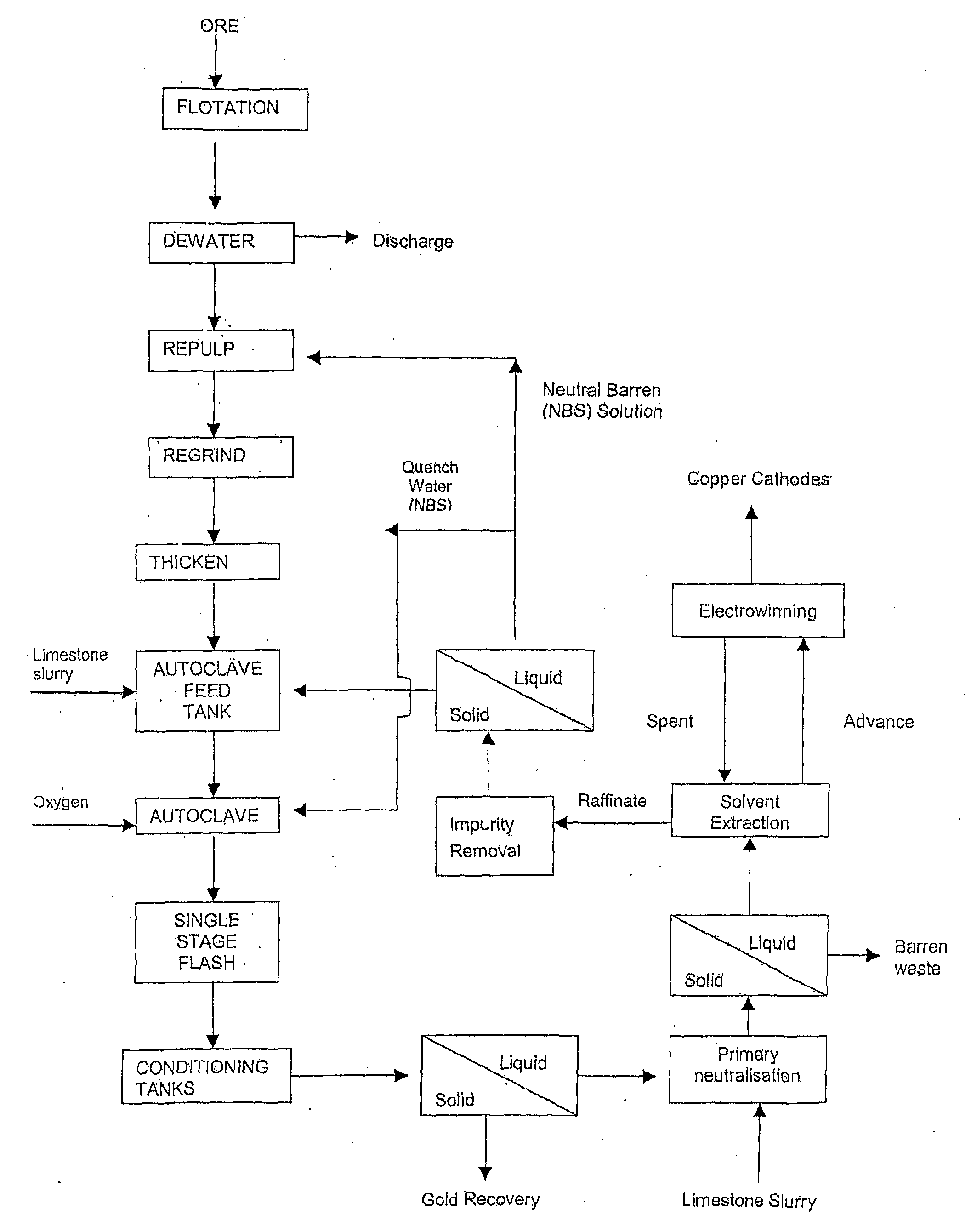
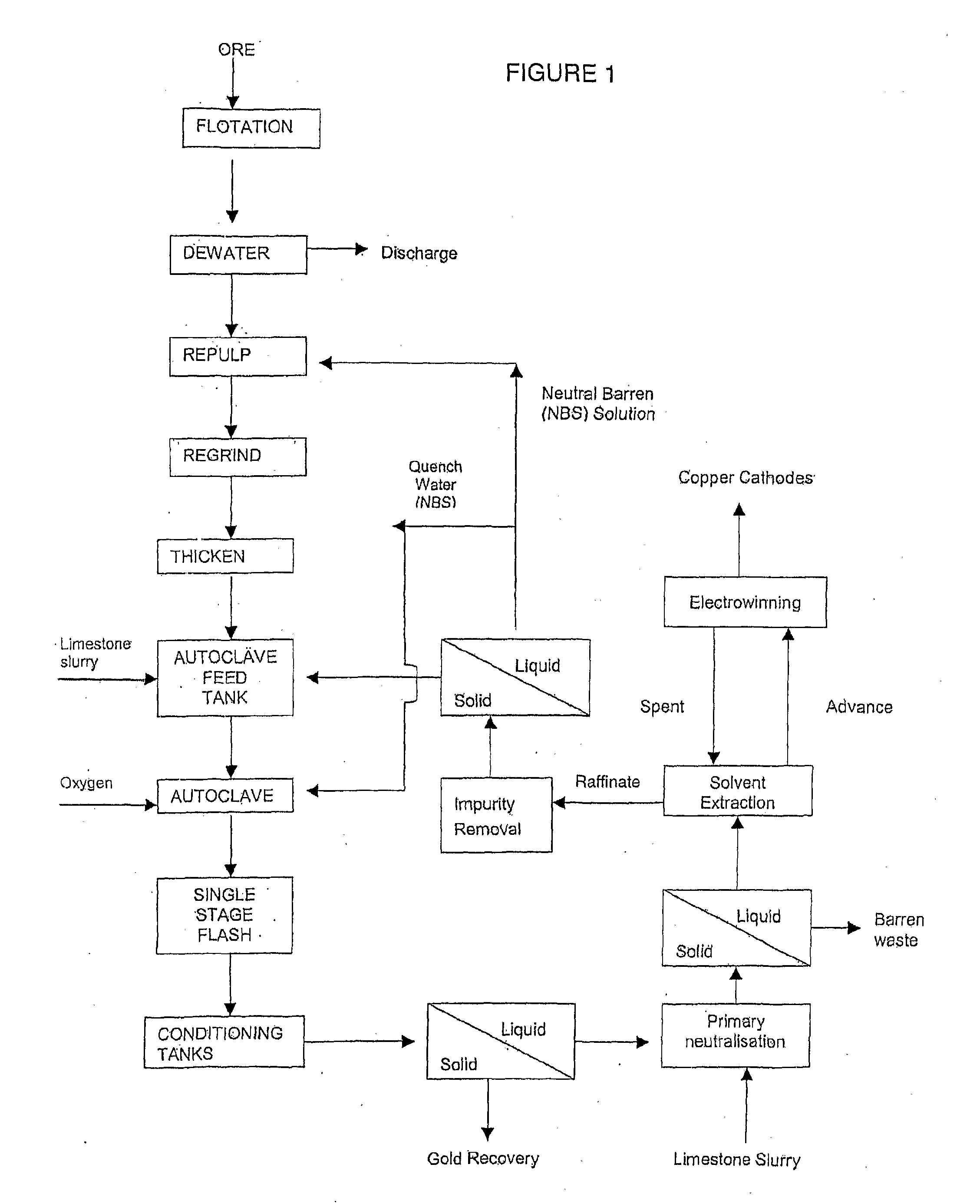
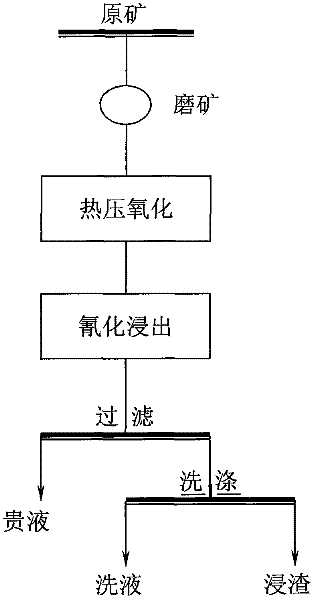
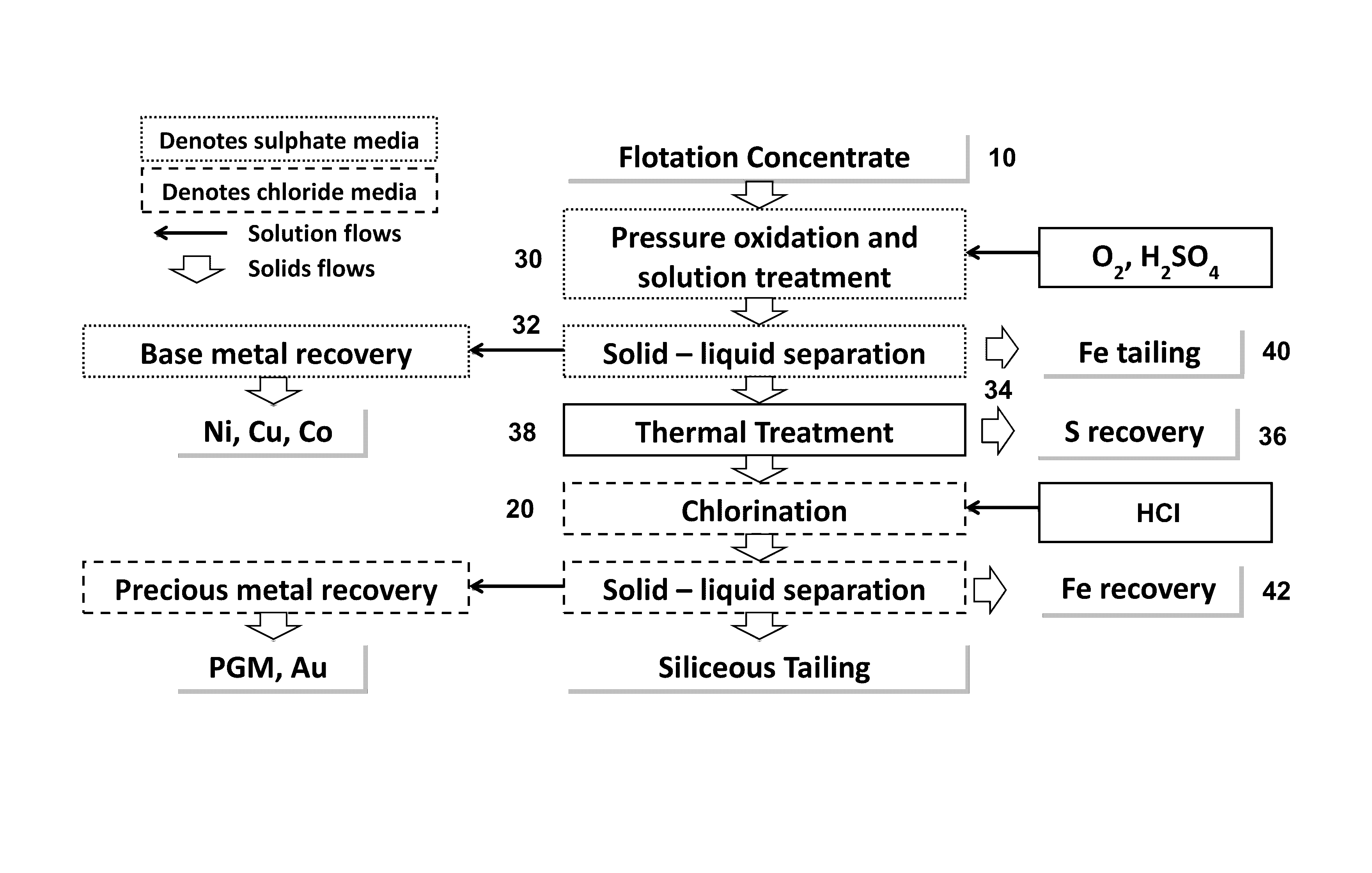
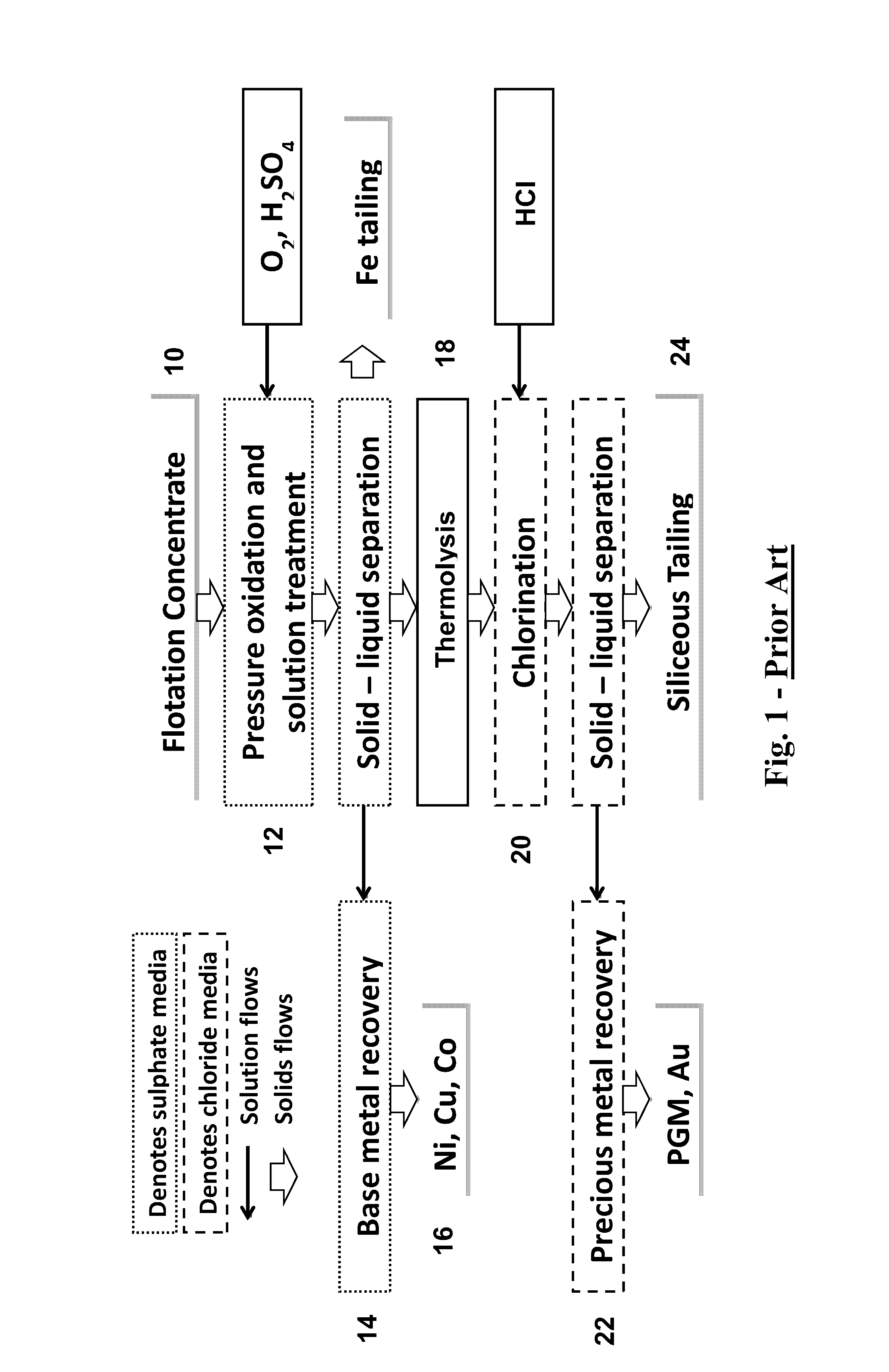
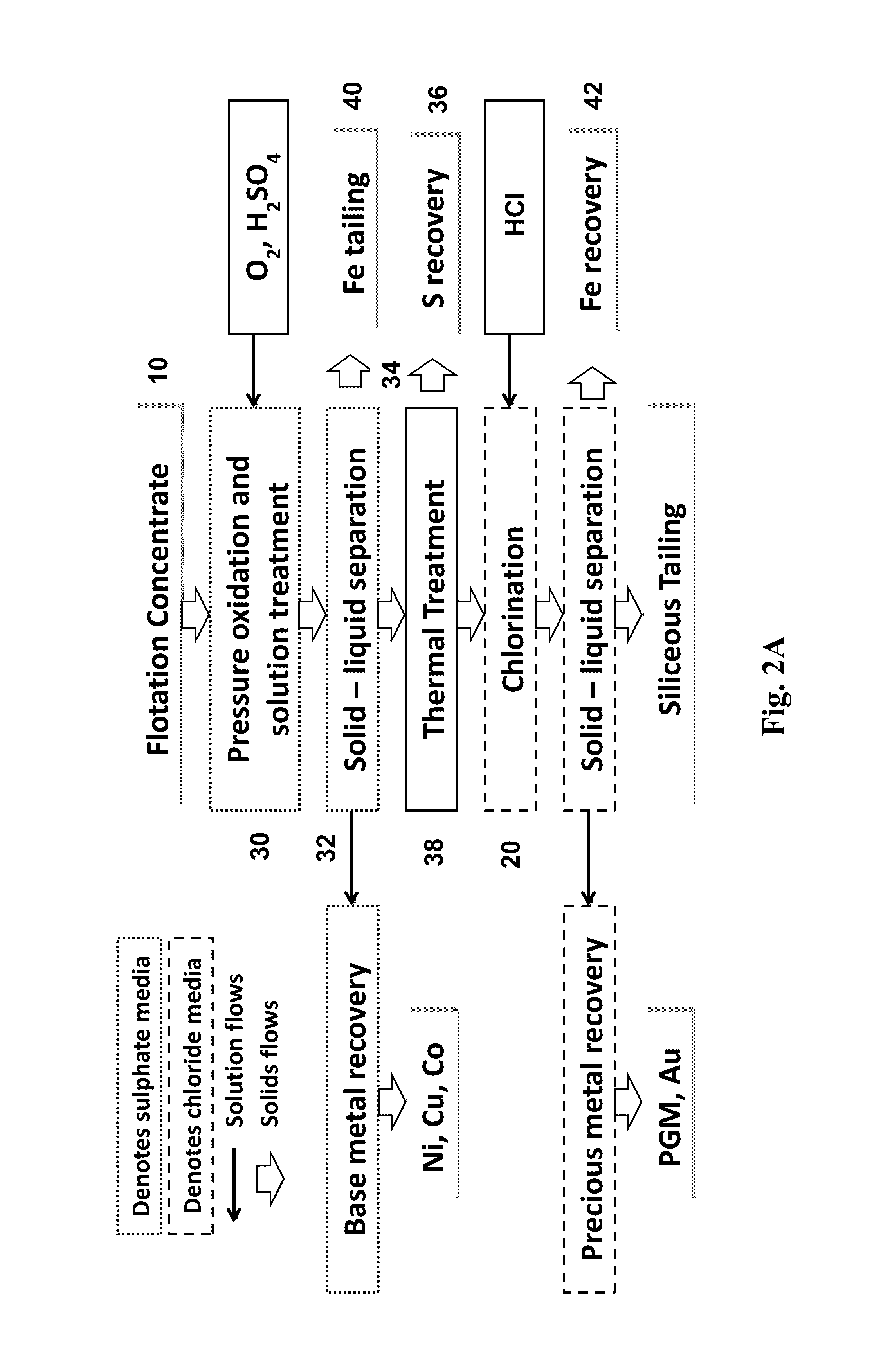
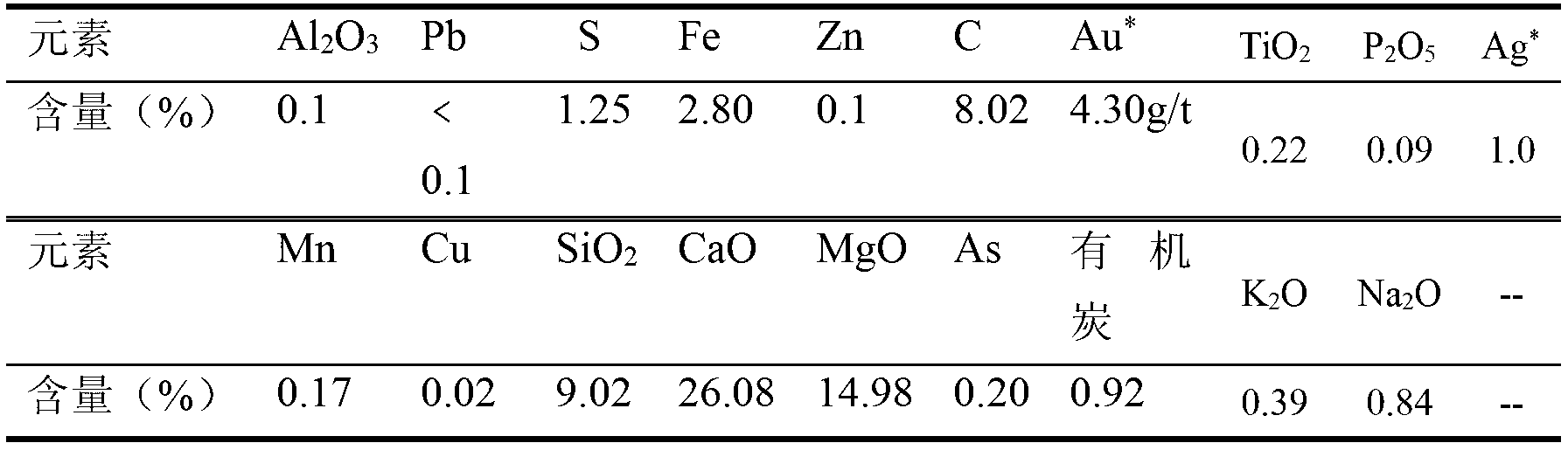
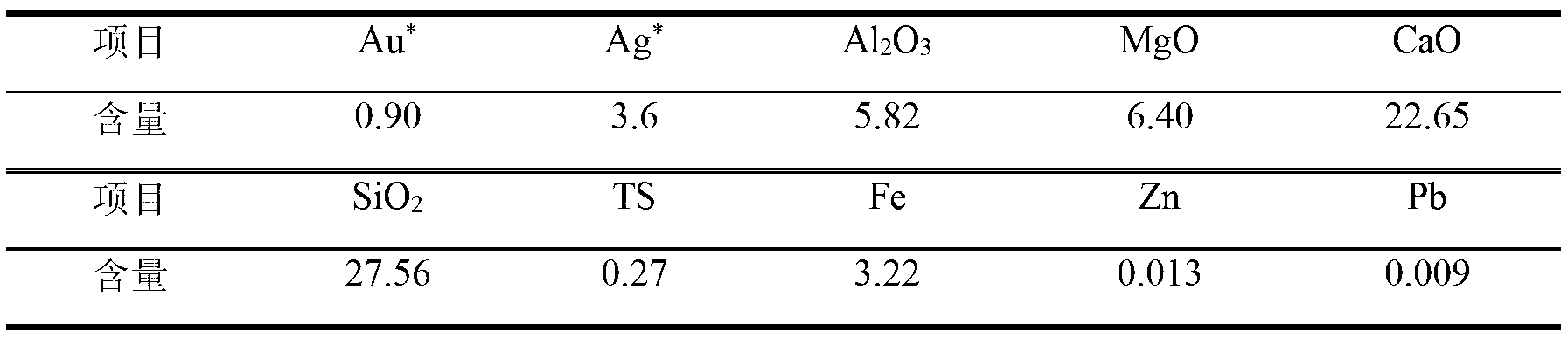
Pressure Oxidation is a process for extracting gold from refractory ore. The most common refractory ores are pyrite and arsenopyrite, which are sulfide ores that trap the gold within them. Refractory ores require pre-treatment before the gold can be adequately extracted. The pressure oxidation process is used to prepare such ores for conventional gold extraction processes such as cyanidation. It is performed in an autoclave at high pressure and temperature, where high-purity oxygen mixes with a slurry of ore.
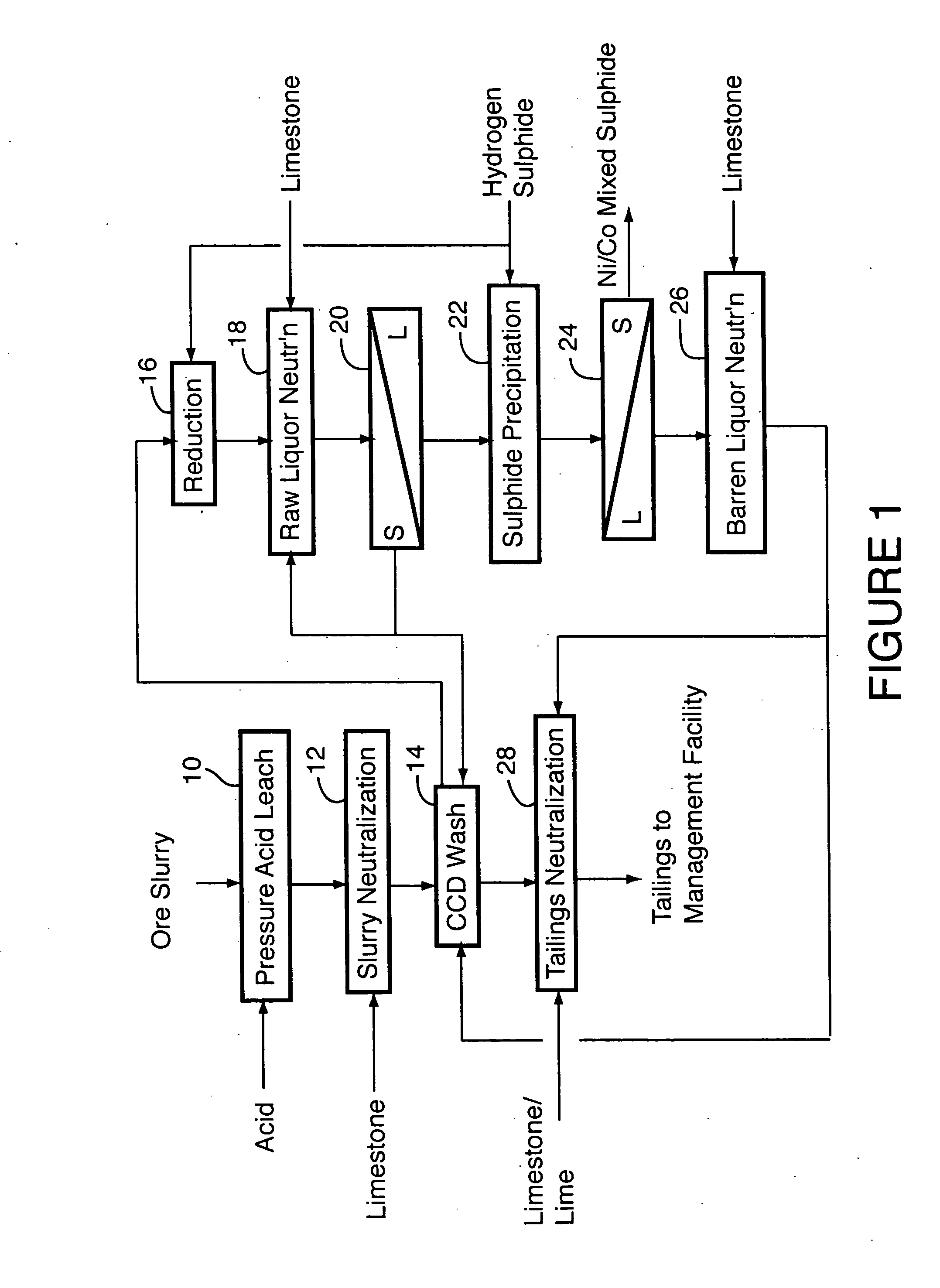
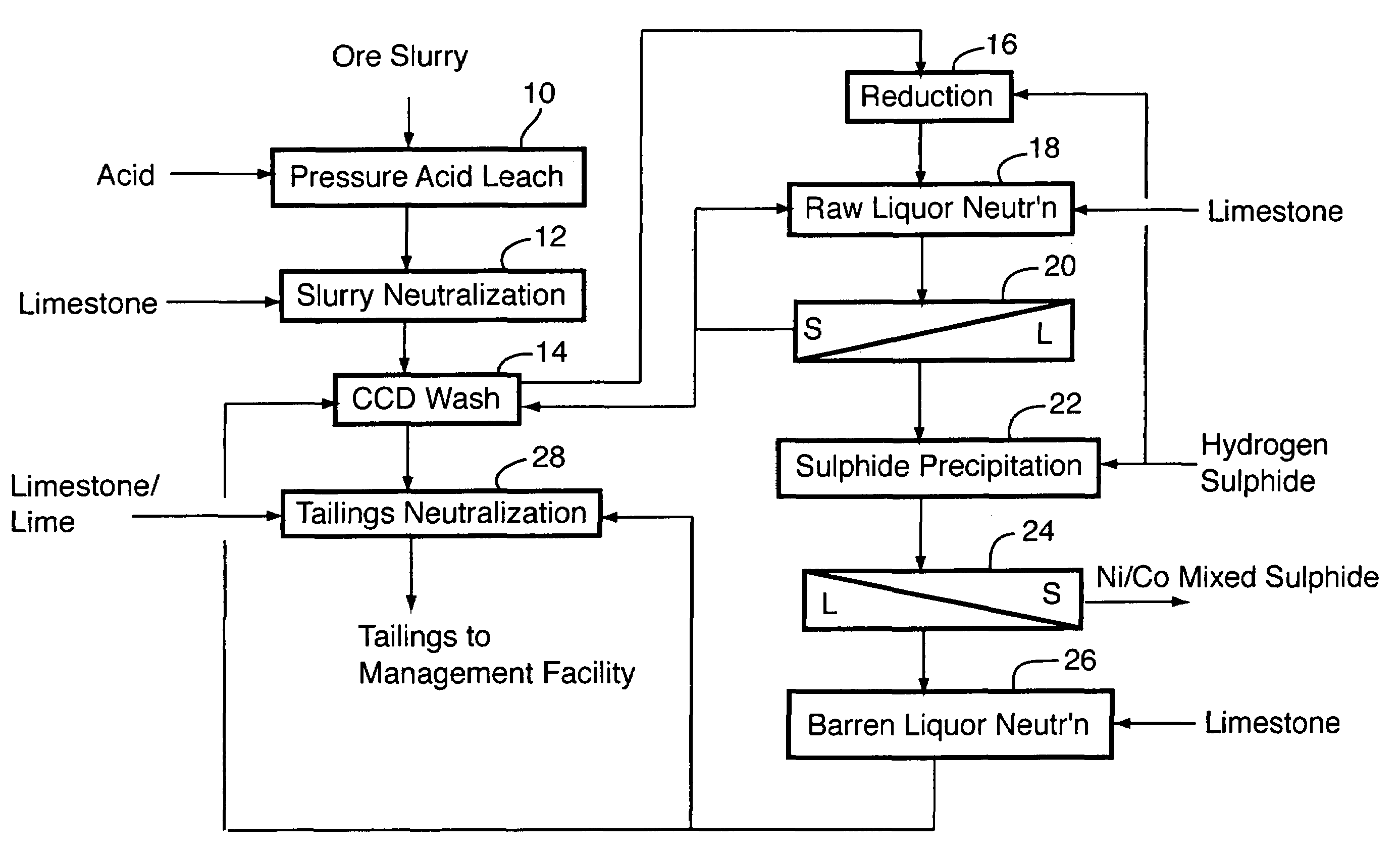
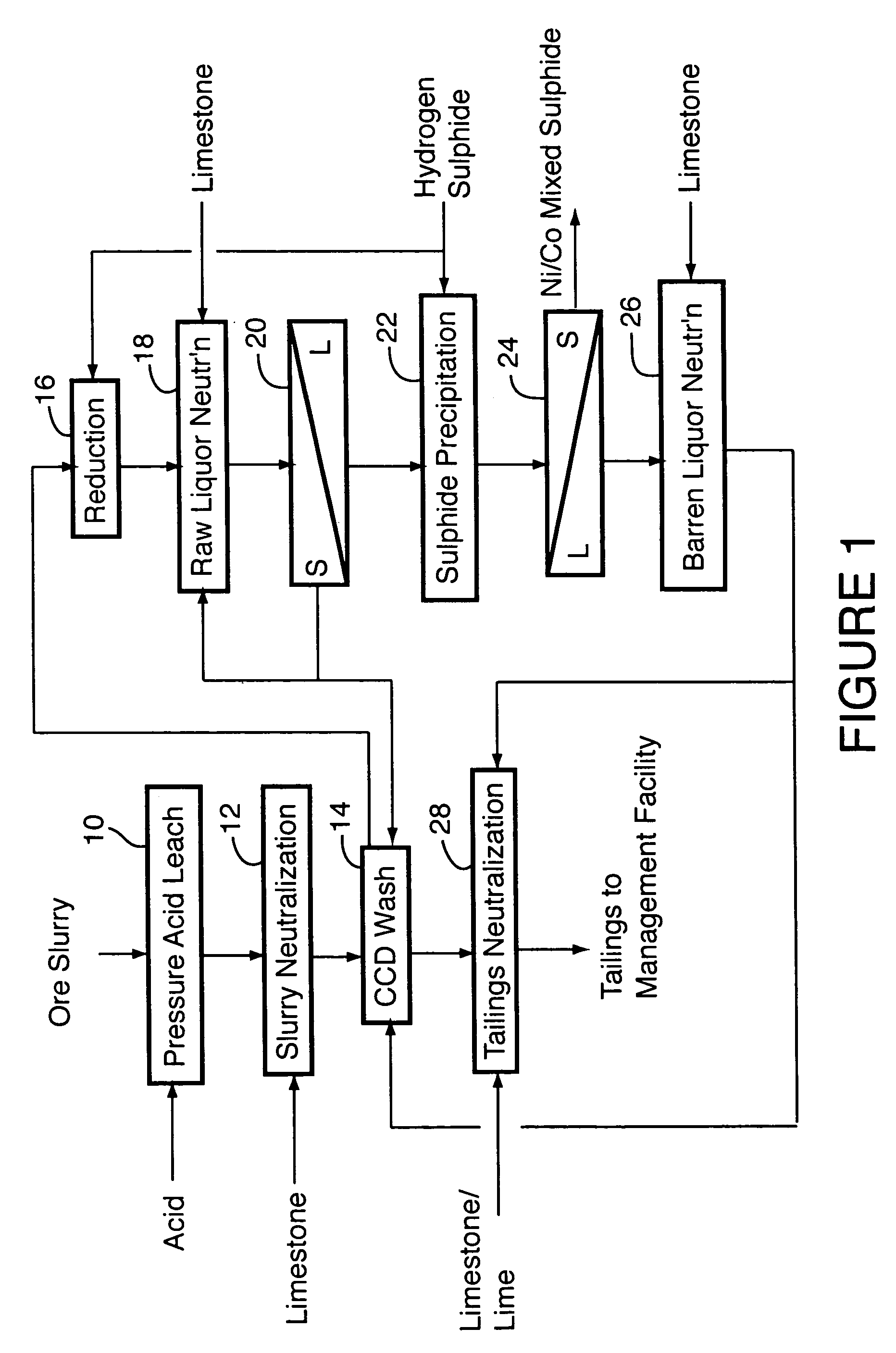
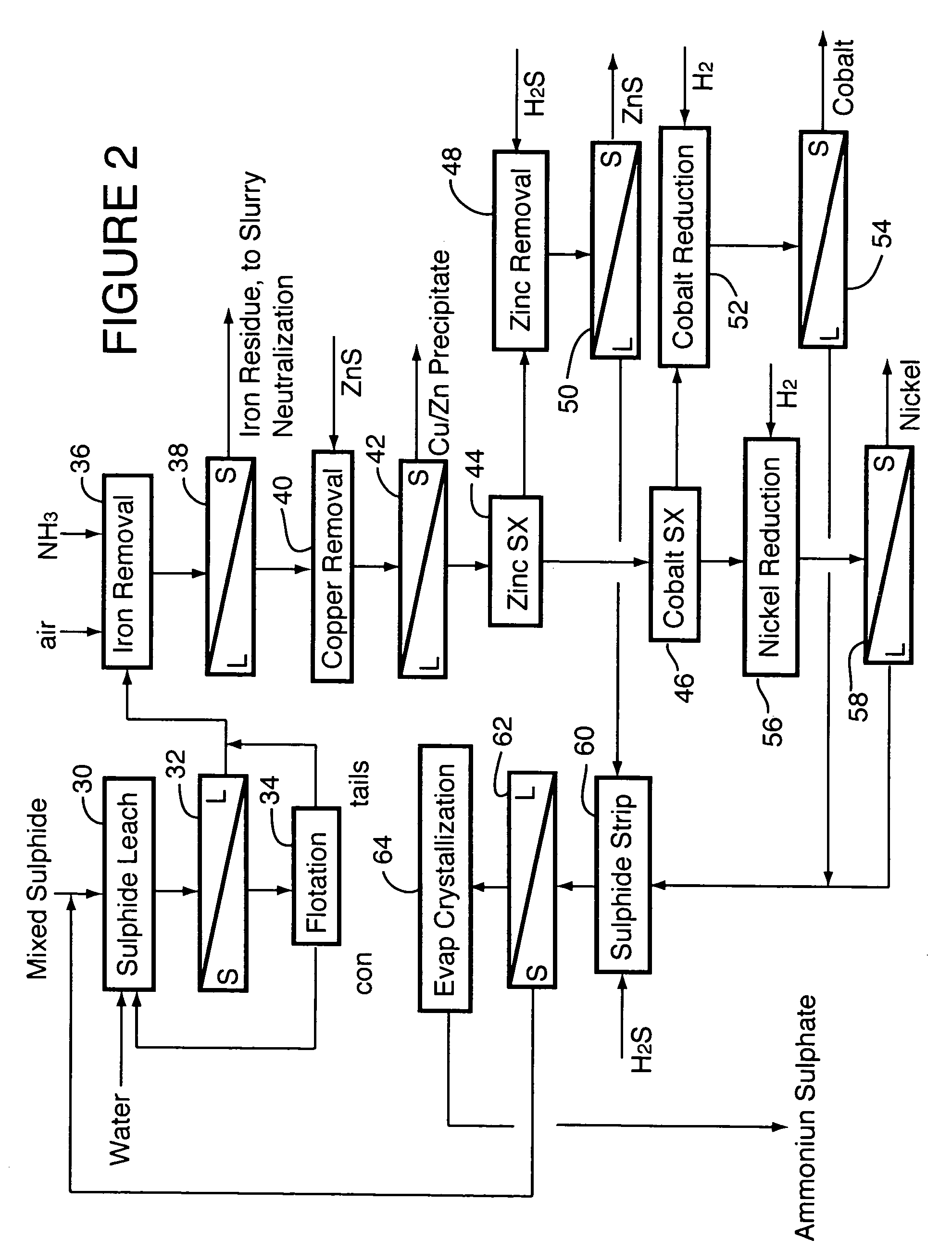
Process for recovery of nickel and cobalt from laterite ore
ActiveUS20060228279A1Efficient separation and recoveryHigh purityCobalt sulfidesSolvent extractionFree solutionSlurry
A process for recovering nickel and cobalt values from nickel- and cobalt-containing laterite ores as an enriched mixed nickel and cobalt sulphide intermediate and for producing nickel and cobalt metal from the nickel and cobalt sulphide intermediate. The laterite ore is leached as a slurry in a pressure acid leach containing an excess of aqueous sulphuric acid at high pressure and temperature, excess free acid in the leach slurry is partially neutralized to a range of 5 to 10 g / L residual free H2SO4 and washed to yield a nickel- and cobalt-containing product liquor, the product liquor is subjected to a reductant to reduce any Cr(VI) in solution to Cr(III), the reduced product liquor is neutralized to precipitate ferric iron and silicon at a pH of about 3.5 to 4.0, and the neutralized and reduced product liquor is contacted with hydrogen sulphide gas to precipitate nickel and cobalt sulphides. The precipitated nickel and cobalt sulphides can be leached in a water slurry in a pressure oxidation leach, the leach solution subjected to iron hydrolysis and precipitation, the iron-free solution contacted with zinc sulphide to precipitate copper, the iron- and copper-free solution subjected to zinc and cobalt extraction by solvent extraction to produce a nickel raffinate, the nickel raffinate contacted with hydrogen gas to produce nickel powder and the cobalt strip solution from the solvent extraction step contacted with hydrogen gas to produce cobalt powder.
Owner:SHERRITT INTERNATIONAL
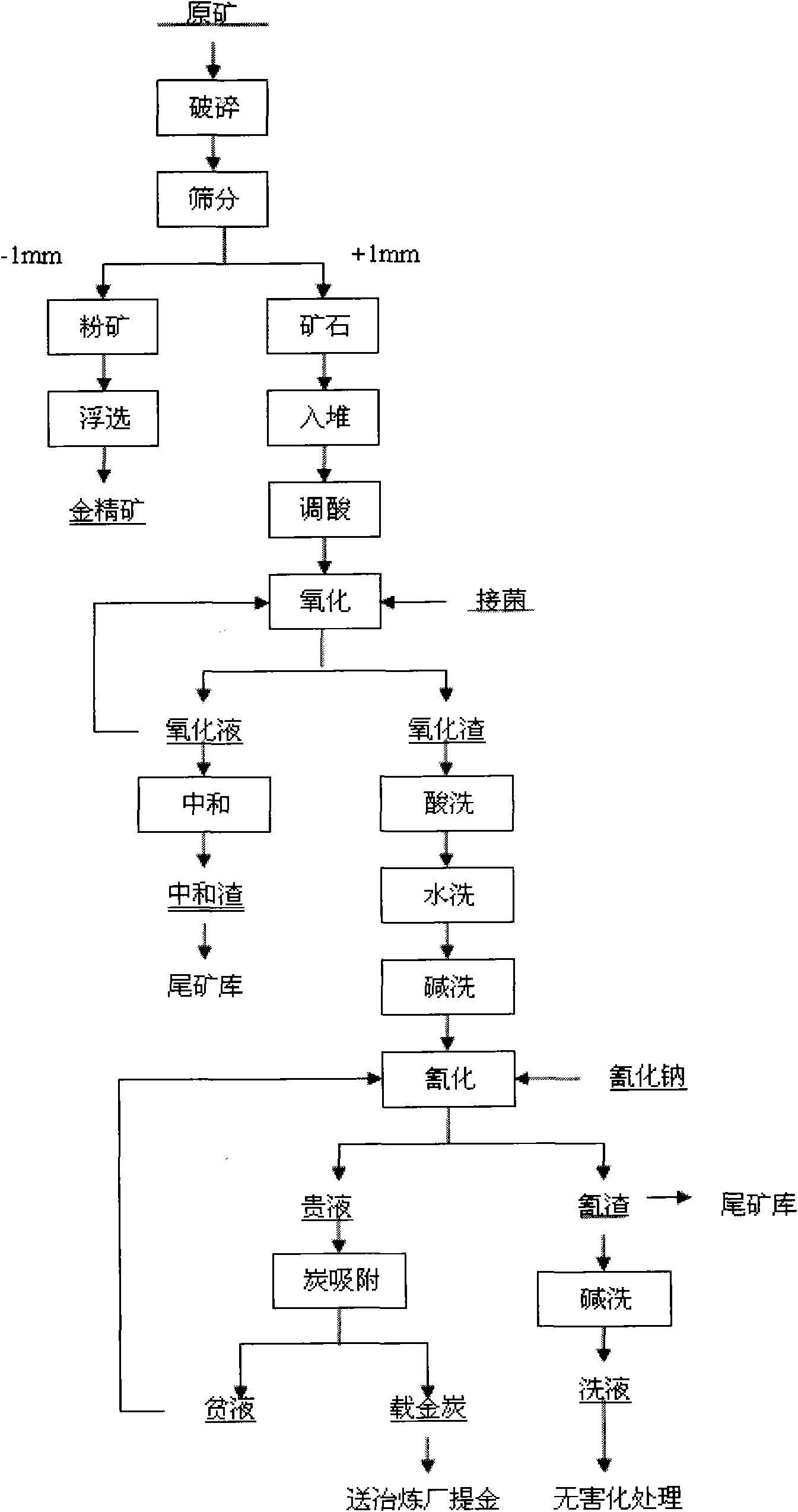
Process for extracting gold from low-grade difficultly-treatable gold ore containing arsenic and carbon
The invention relates to a process for extracting gold from low-grade difficultly-treatable gold ore containing arsenic and carbon. The process is characterized in that: the gold ore has the characteristics of high clay mineral content, large fine ore amount after grinding, and the like. The process comprises the following steps of: grinding raw ore to 10 to -30 millimeters; sieving ore through a sample sieve of 1 to -2 millimeters or washing the ore with water so as to separate fine ore from the ore; floating gold concentrate by using the obtained fine ore; performing direct heap leaching on ore of +2 millimeter and performing biological oxidation; performing medium transformation such as acid washing, water washing, alkali washing and the like on the biologically-oxidized ore and cyaniding directly so as to extract gold, wherein gold is extracted from the floated gold concentrate by biological oxidation-cyaniding and carbon soaking-pressure oxidation-cyaniding and gold extraction or baking, oxidation and cyaniding. Due to the adoption of the process, the problem of permeability of gold ore is solved and the gold extracting rate is effectively increased from 2 to 5 percent during direct heap leaching and cyaniding to 55 to 65 percent. The process has the advantages of simple process, high gold extracting rate, low pollution, high benefit and the like.
Owner:ZIJIN MINING GROUP
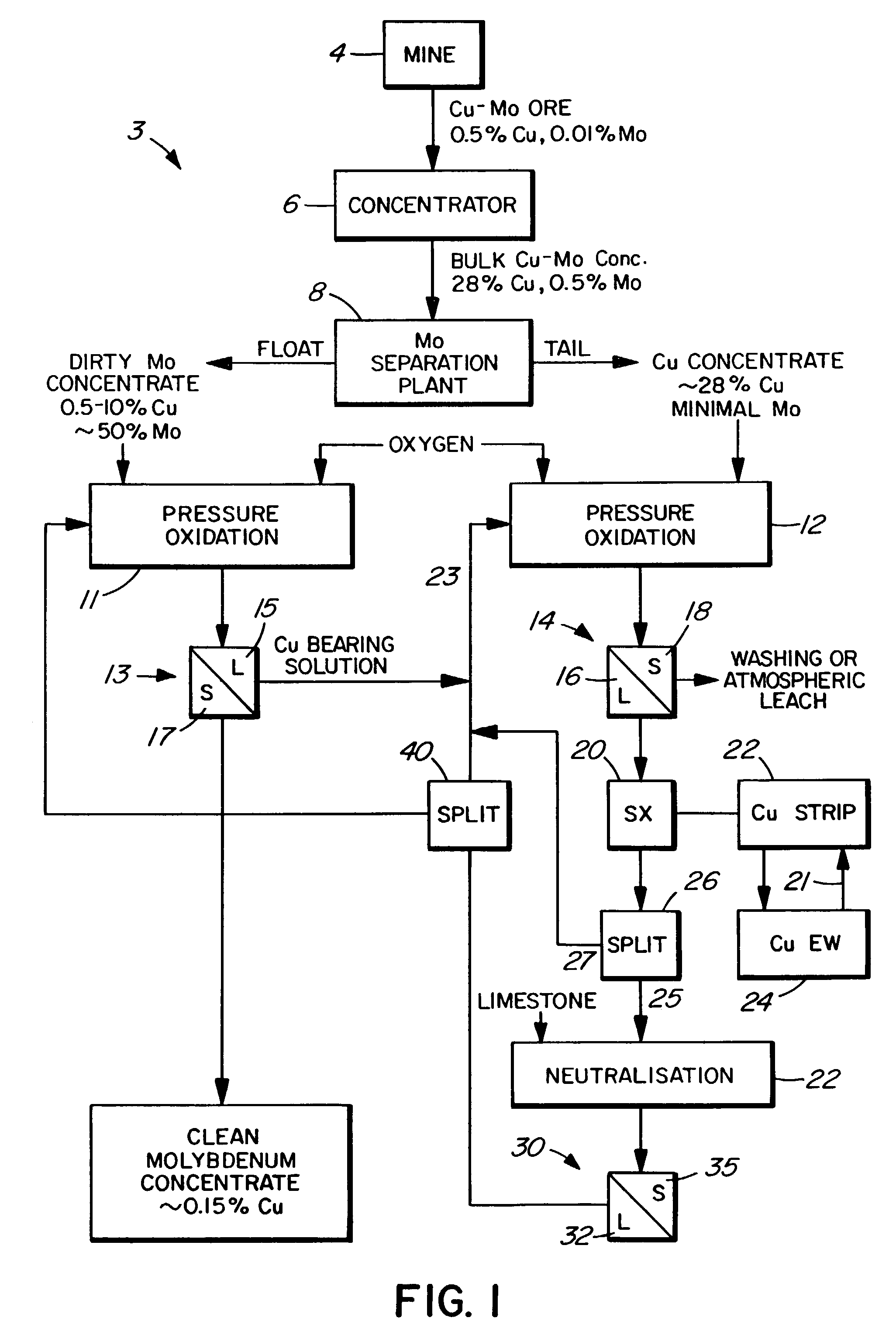
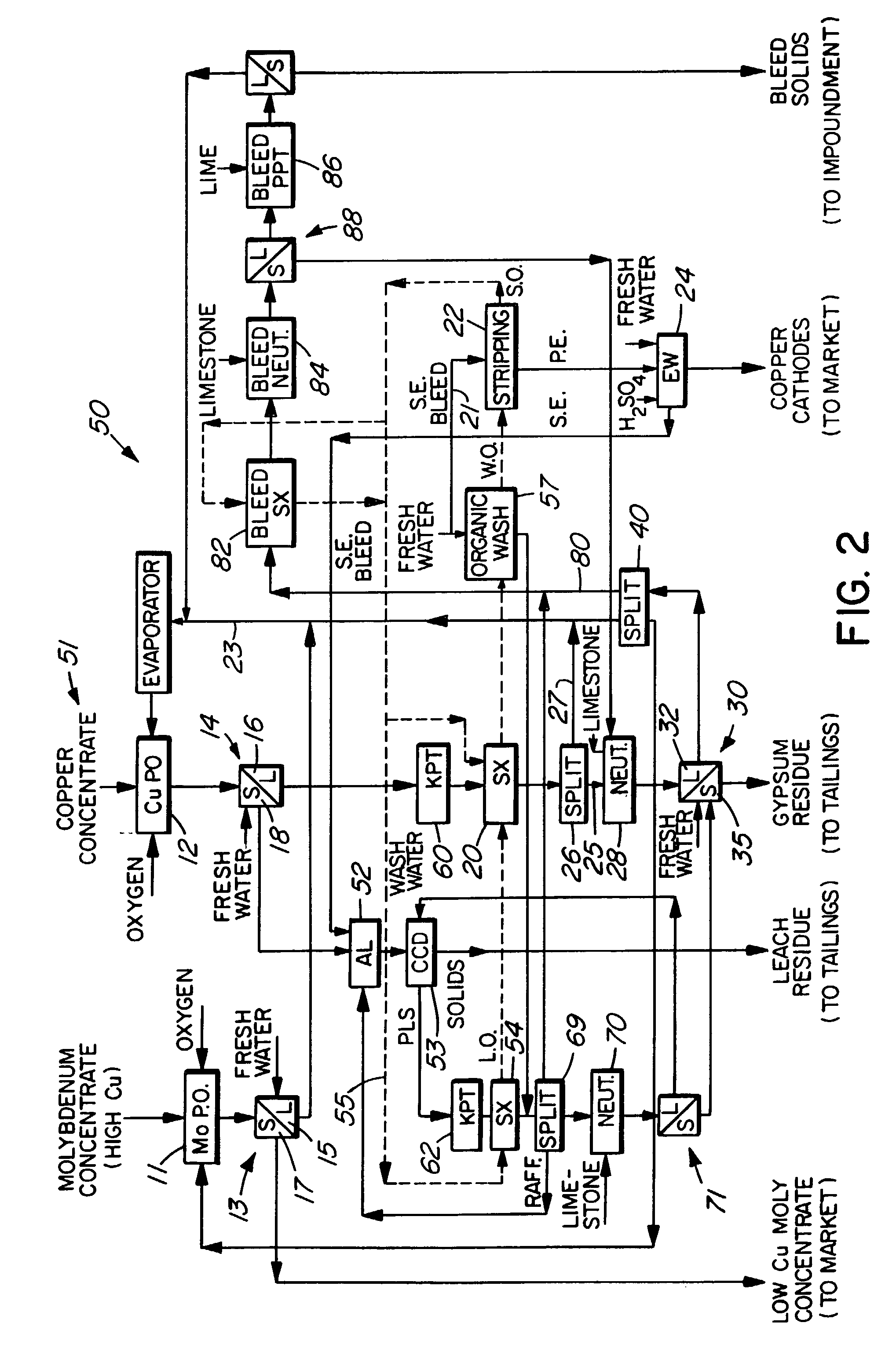
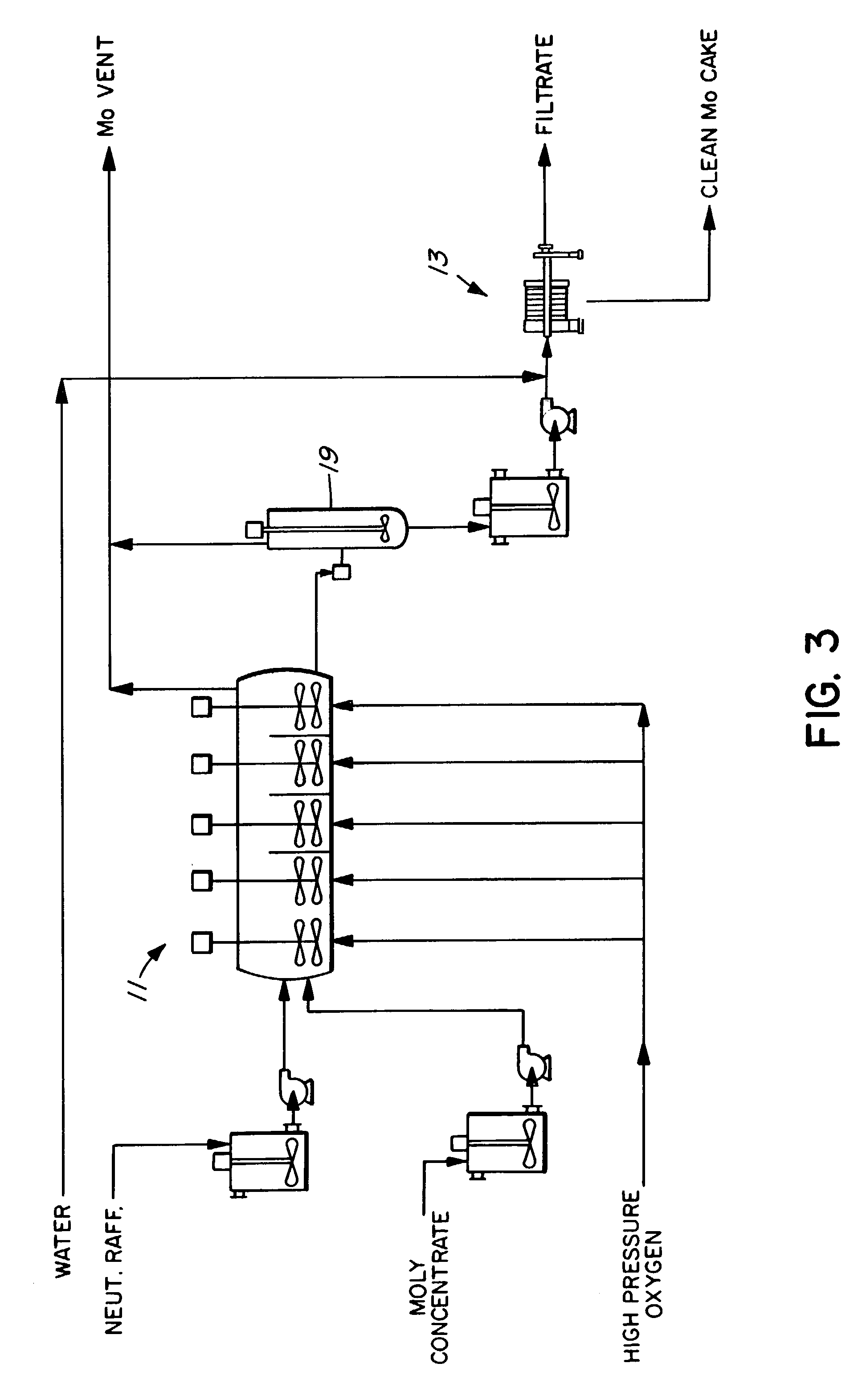
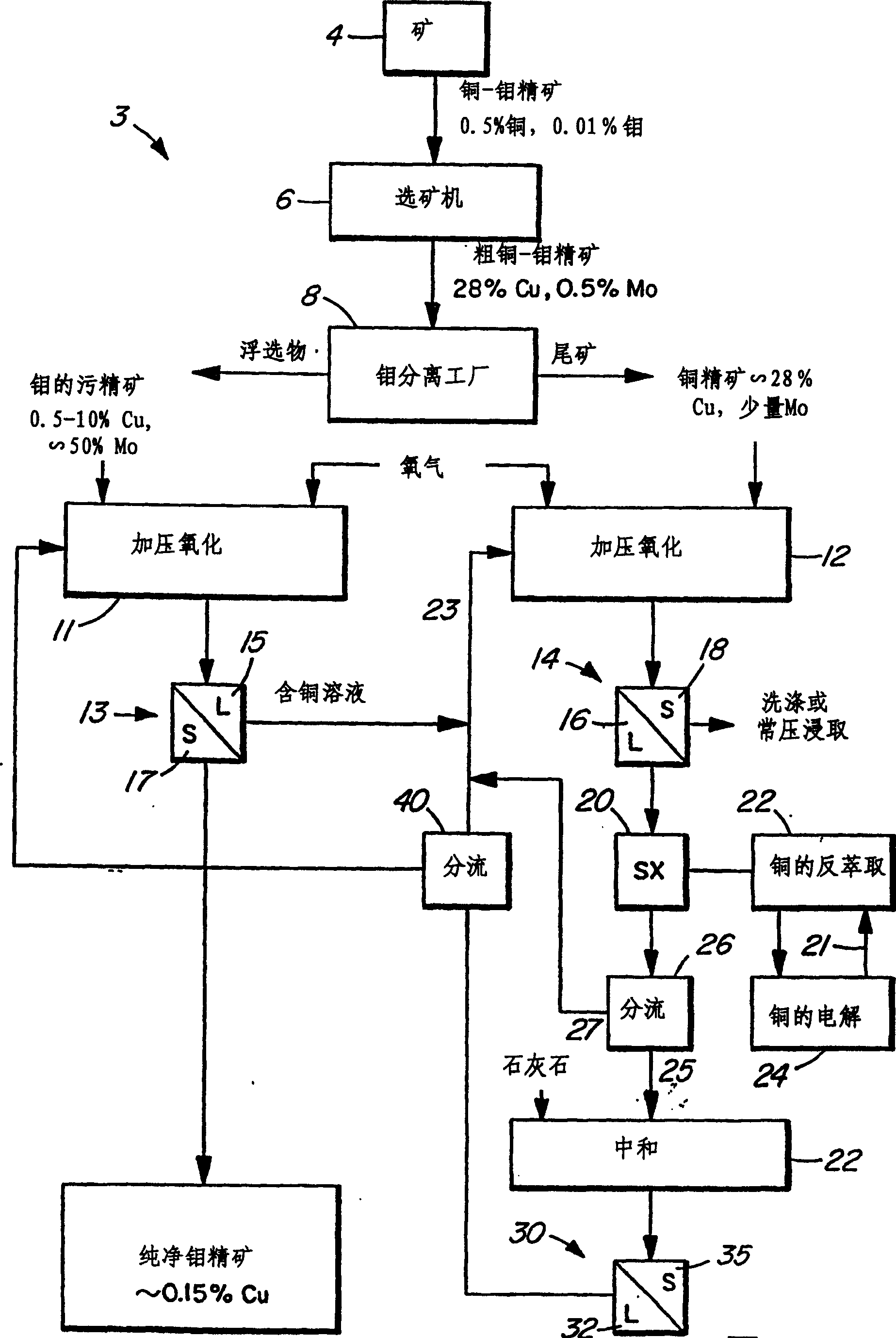
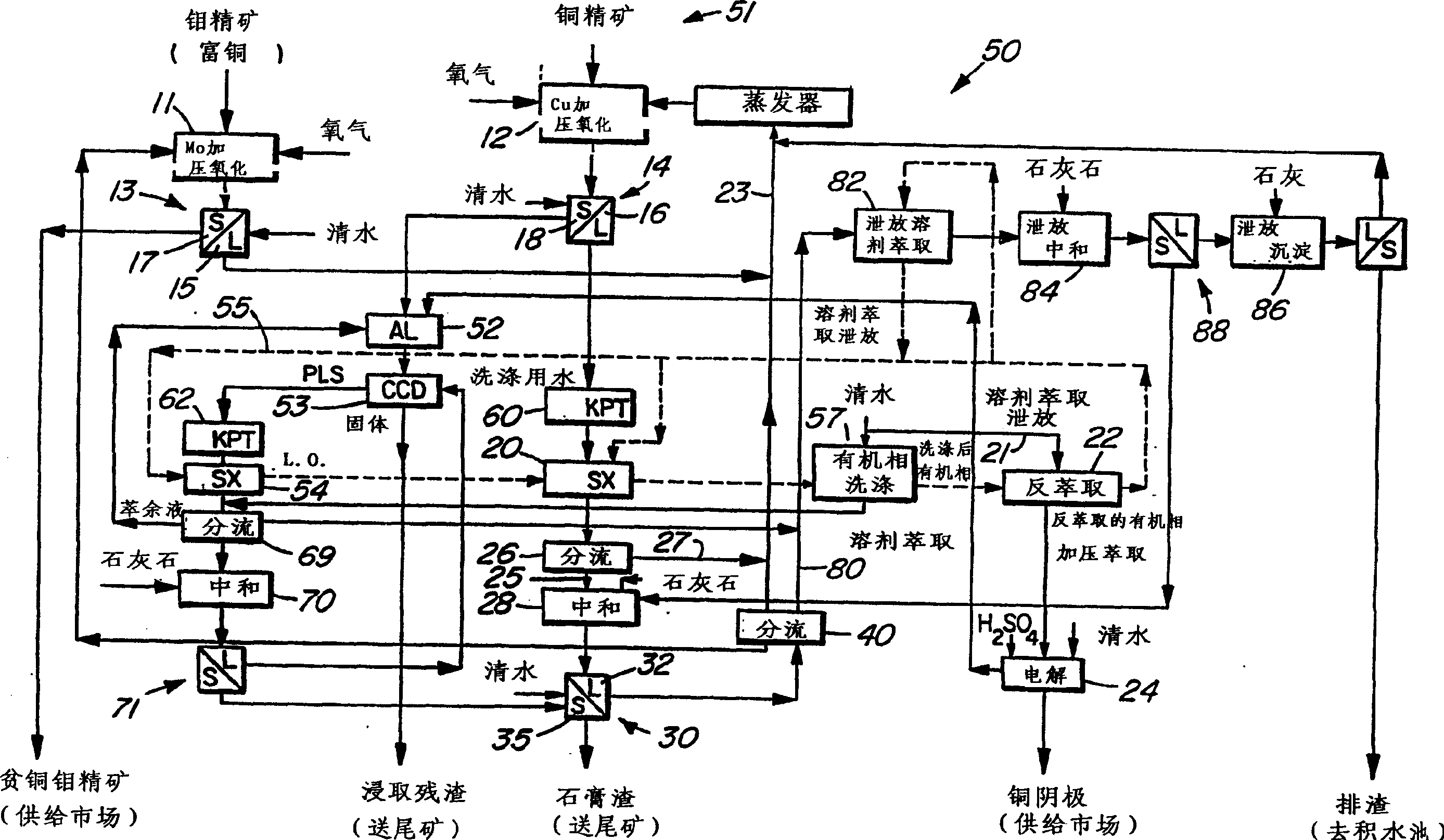
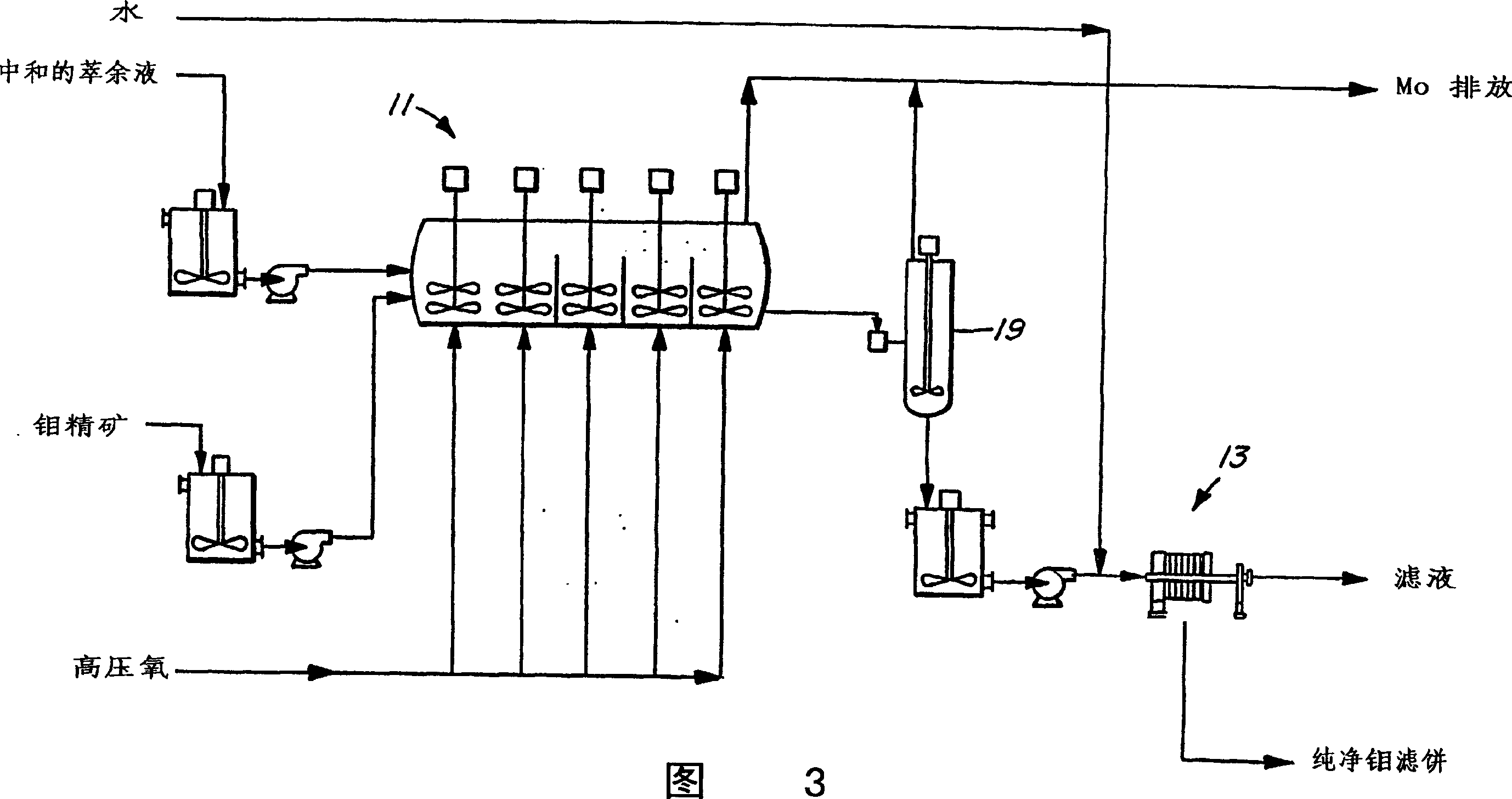
Process for the treatment of molybdenum concentrate
A method of treatment or purification of a molybdenum concentrate also containing copper, comprises the step of subjecting the molybdenum concentrate to pressure oxidation in the presence of oxygen and a feed solution containing copper (e.g. CuSO4) and halide (e.g. CuCl2) to produce a pressure oxidation solution containing copper and a solid residue containing molybdenum. The pressure oxidation solution may be combined with feed solution to a second pressure oxidation in which a copper concentrate is treated for the recovery of copper therefrom.
Owner:CESL LIMITED
Chloride assisted hydrometallurgical extraction of metal
A process for the extraction of a metal from an ore or concentrate comprises subjecting the ore or concentrate to pressure oxidation in the presence of oxygen and an acidic solution containing halogen ions and a source of bisulphate or sulphate ions, such as H2SO4. The metals which can be extracted by the process comprises copper as well as non-cuprous metals such as zinc, nickel and cobalt. During pressure oxidation the metal may be precipitated as an insoluble basic salt, such as basic copper sulphate, or substantially completely solubilized and precipitated later as the basic metal salt.
Owner:CESL LIMITED
Process for controlling acid in sulfide pressure oxidation processes
ActiveUS20090071296A1Reduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementMaterials scienceInorganic sulfide
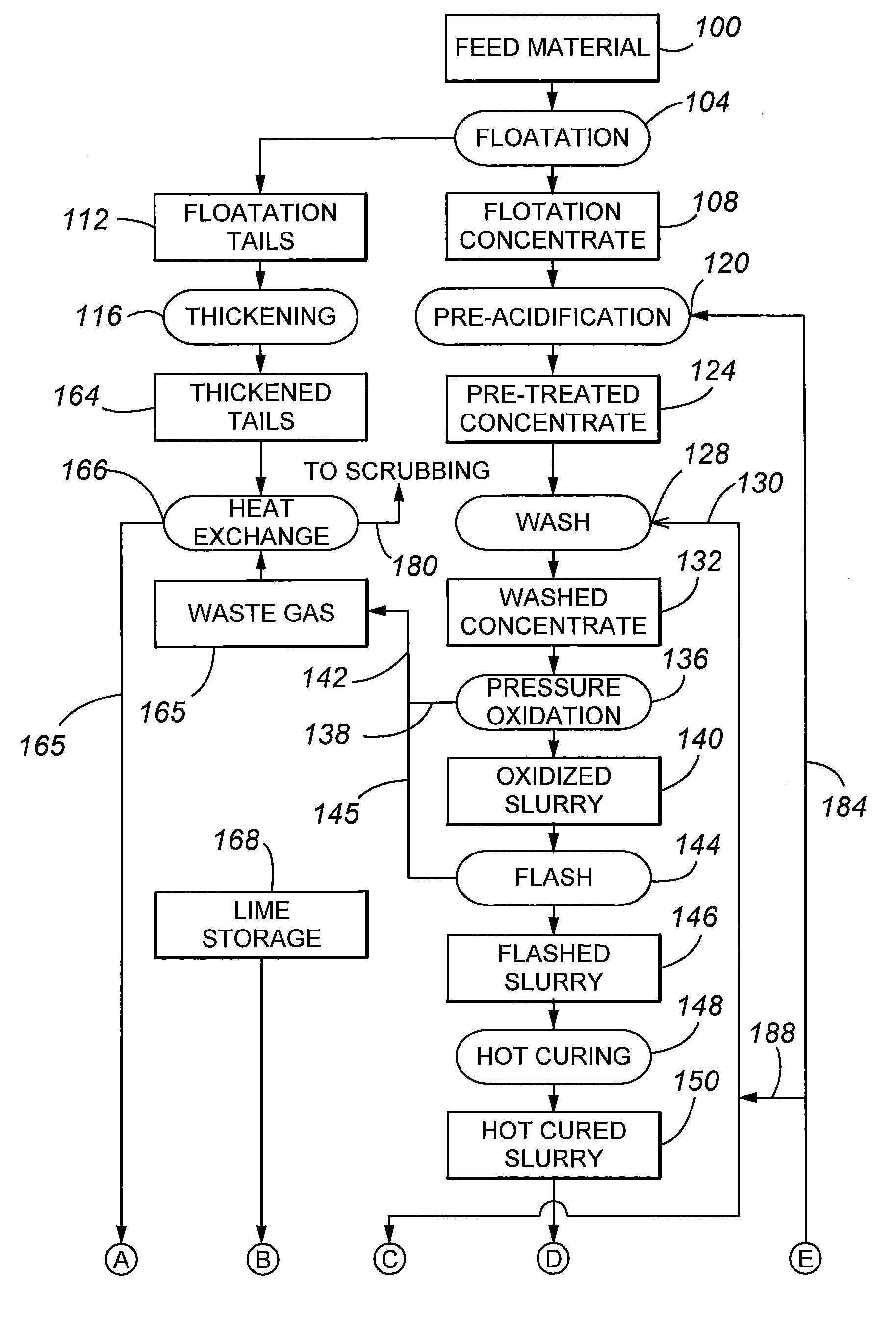
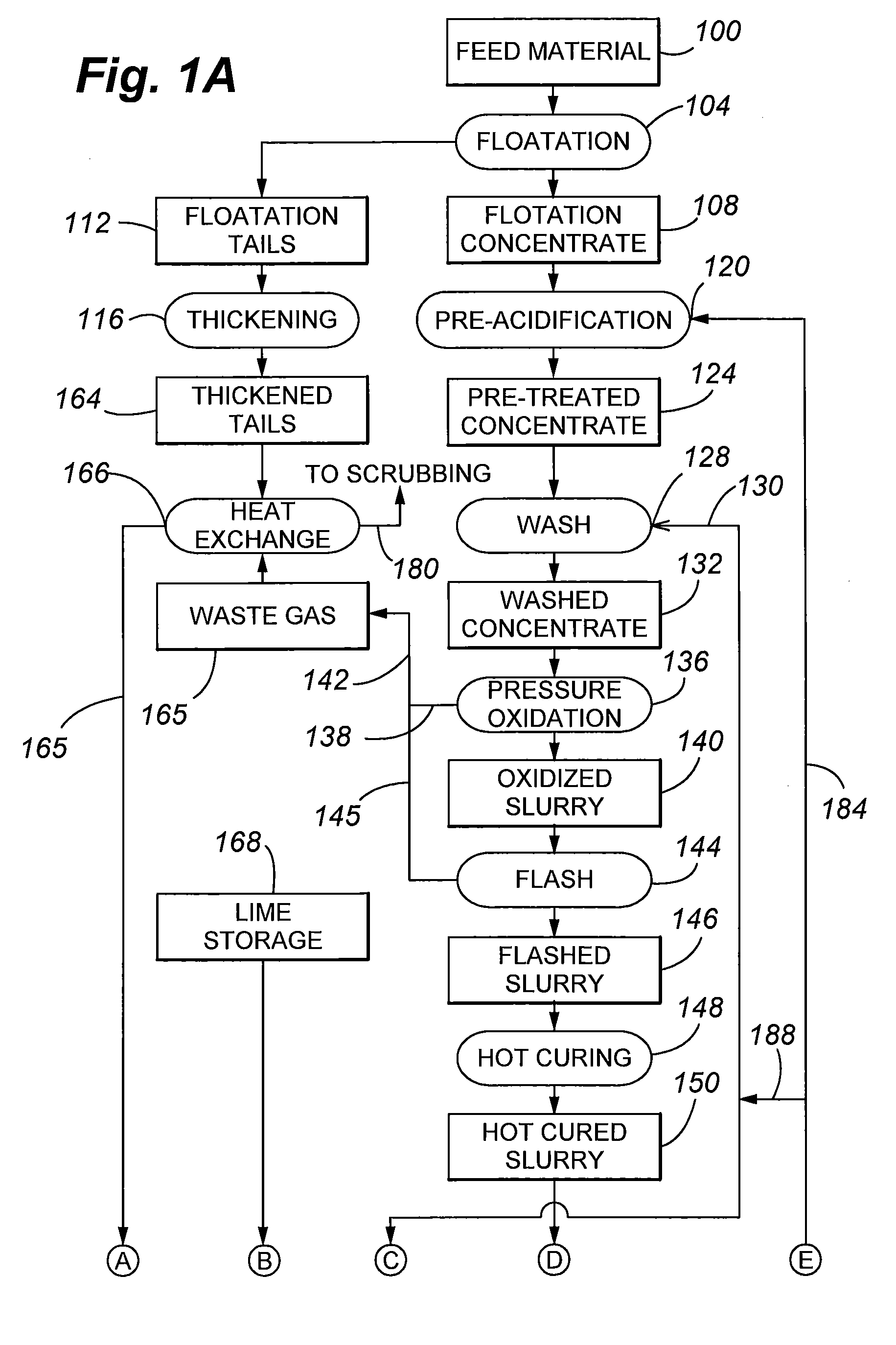
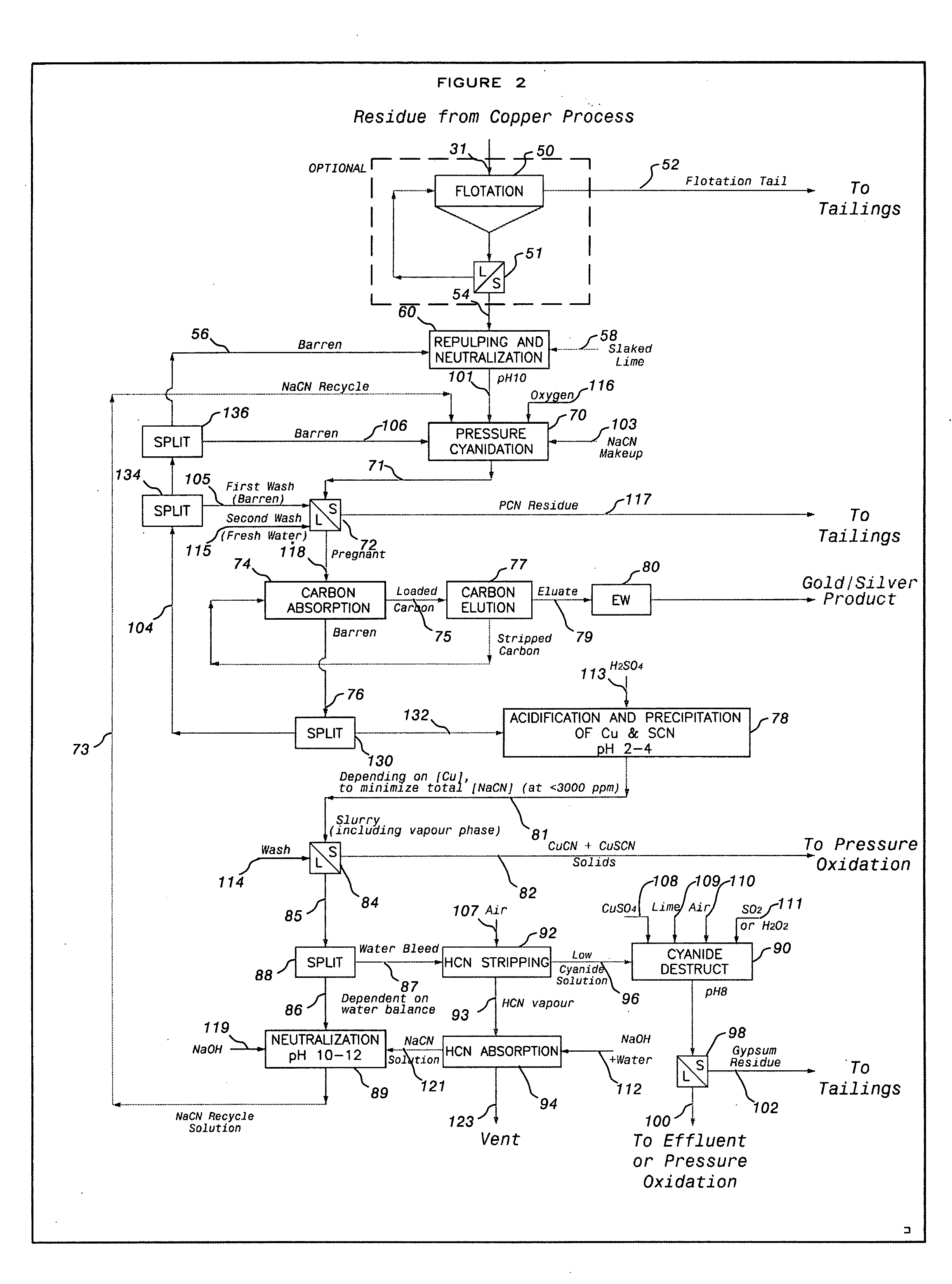
The present invention is directed to flotation of refractory gold sulfide ores and to pressure oxidized residue neutralization using flotation tailings that have been contacted with an off gas of pressure oxidation.
Owner:BARRICK GOLD
Process for gold and silver recovery from a sulphide concentrate
ActiveUS20080286180A1Simple processAcceptable precious metal recoveryPhotography auxillary processesSolvent extractionRetention timeSource material
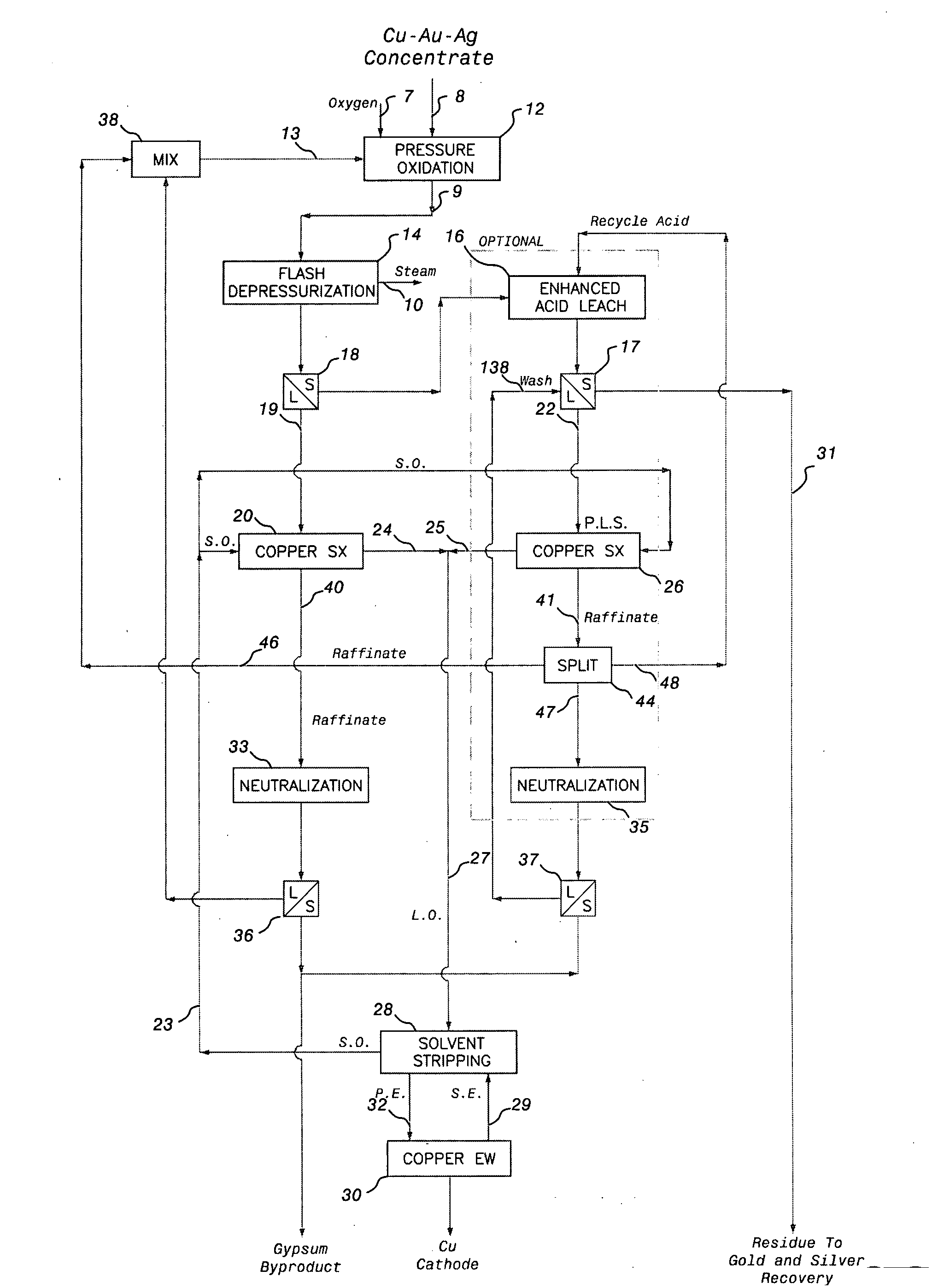
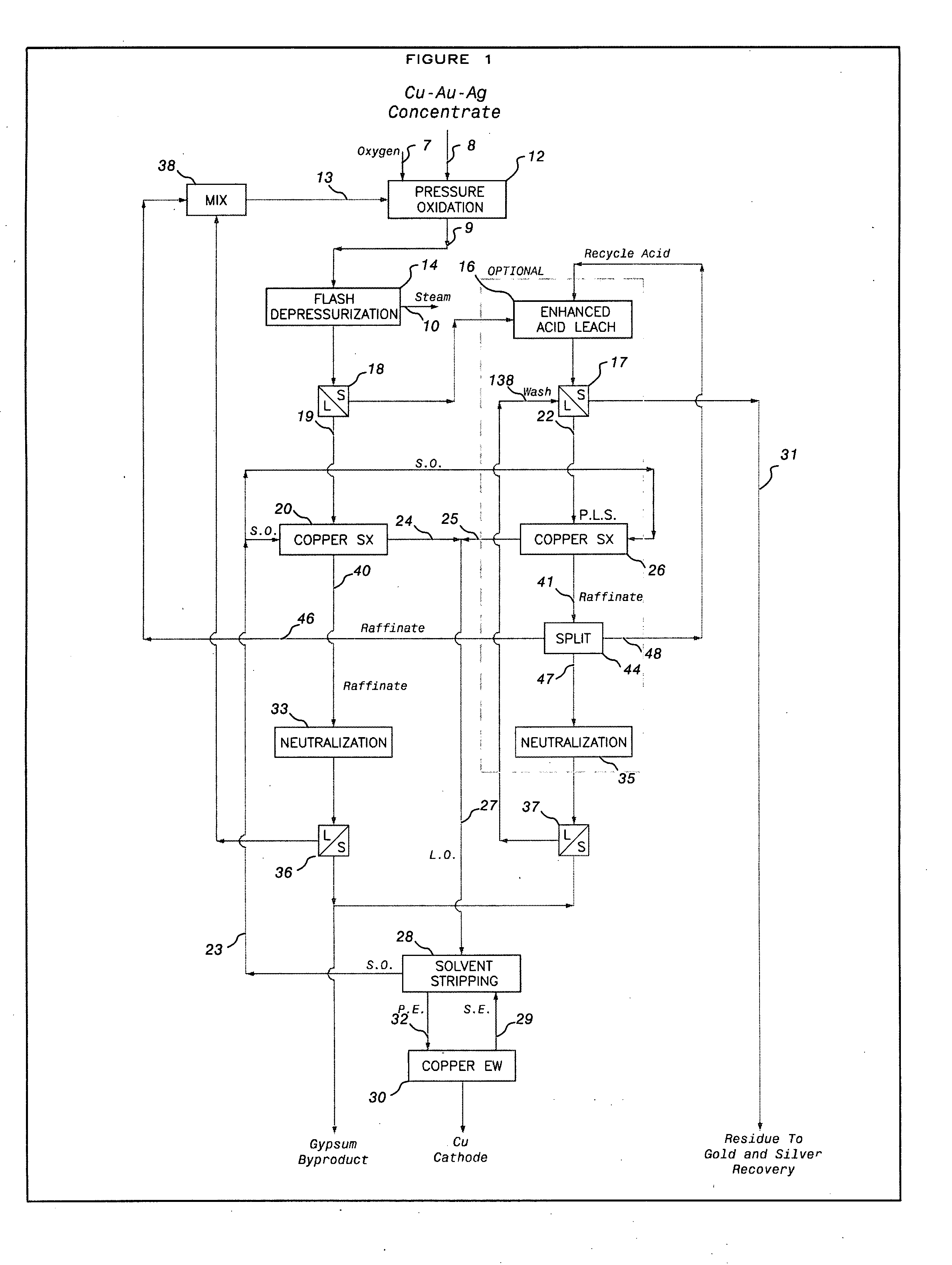
A process for the extraction of a precious metal, such as gold or silver, from a sulphide ore or concentrate or other source material comprises subjecting the source material to pressure oxidation to produce a pressure oxidation slurry. The pressure oxidation slurry is flashed down to a lower temperature and pressure and is then subjected to a liquid / solid separation to obtain a pressure oxidation solution and a solid residue containing the precious metal. The solid residue is then subjected to cyanidation to extract the precious metal. The formation of thiocyanide during cyanidation is minimized or counteracted by effecting the cyanidation at an elevated oxygen pressure and a reduced retention time, such as 30 to 90 minutes. A method for the reduction of copper cyanide formation during cyanidation leaching is also provided.
Owner:CESL LIMITED
Method for extracting molybdenum and nickel by molybdenum nickel ore whole wet method
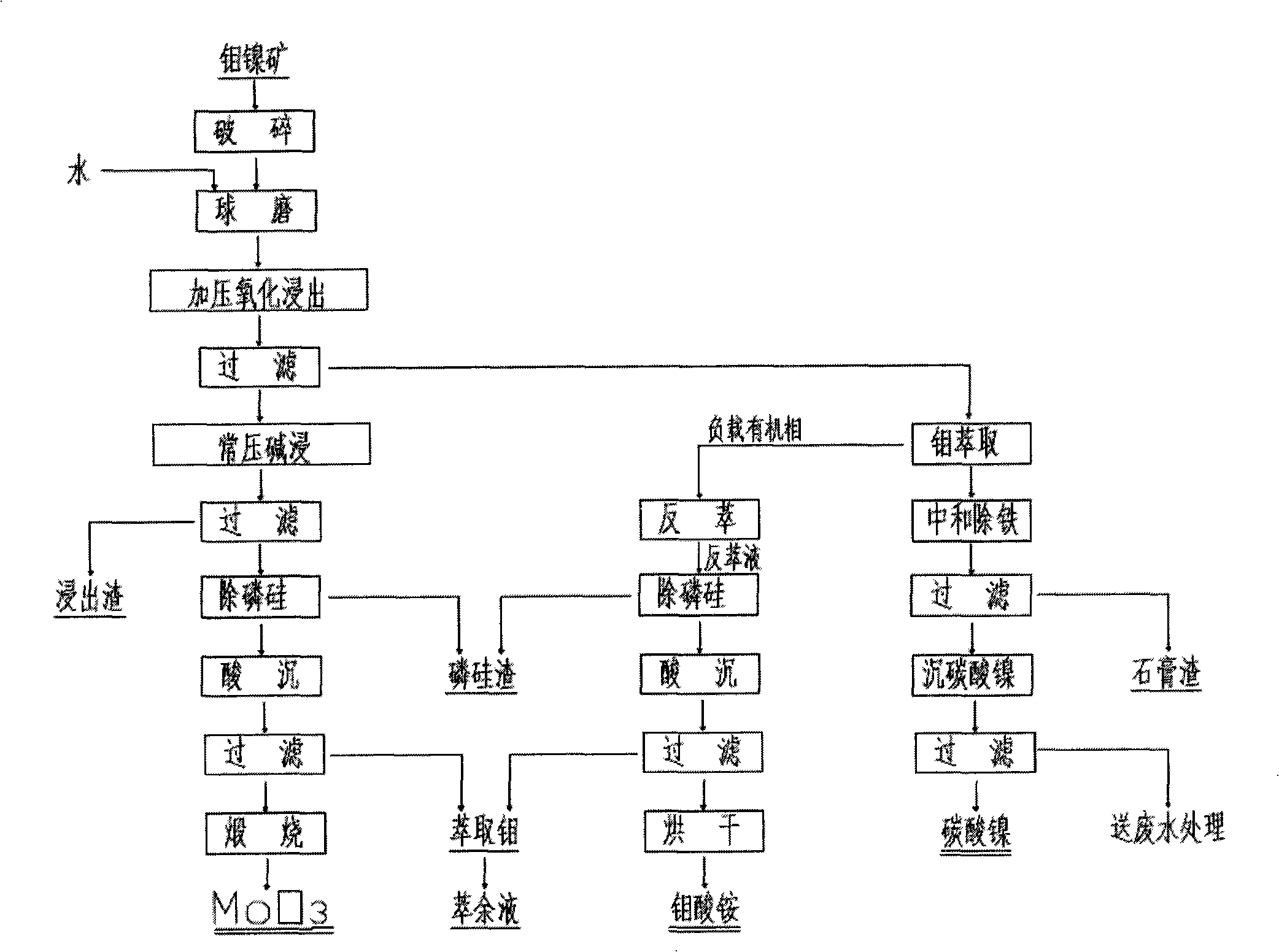
ActiveCN101323915AHigh overall yieldReduce processing costsProcess efficiency improvementNickel saltSlag
The invention discloses a method for extracting nickel and molybdenum by a nickel-molybdenum ore all-wet method, relating to the smelting of nonferrous metals by a wet method, in particular to a all-wet method for extracting nickel and molybdenum from nickel-molybdenum ores of black rock series. The method is characterized in that during extraction process, pressure oxidation leaching is carried out to the nickel-molybdenum ores milled, thus obtaining a nickel leaching solution containing nickel and molybdenum and leaching slag containing molybdenum oxides; the leaching solution undergoes extraction for separating nickel and molybdenum, thus producing nickel salt and ammonium molybdate or molybdenum trioxide; alkali steeping in a normal pressure, purification and ammonium molybdate acid deposition are carried out to molybdenum contained in the leaching slag for recycling. The method of the invention has high nickel and molybdenum recycling rate, low production cost and environmentally friendly production process.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
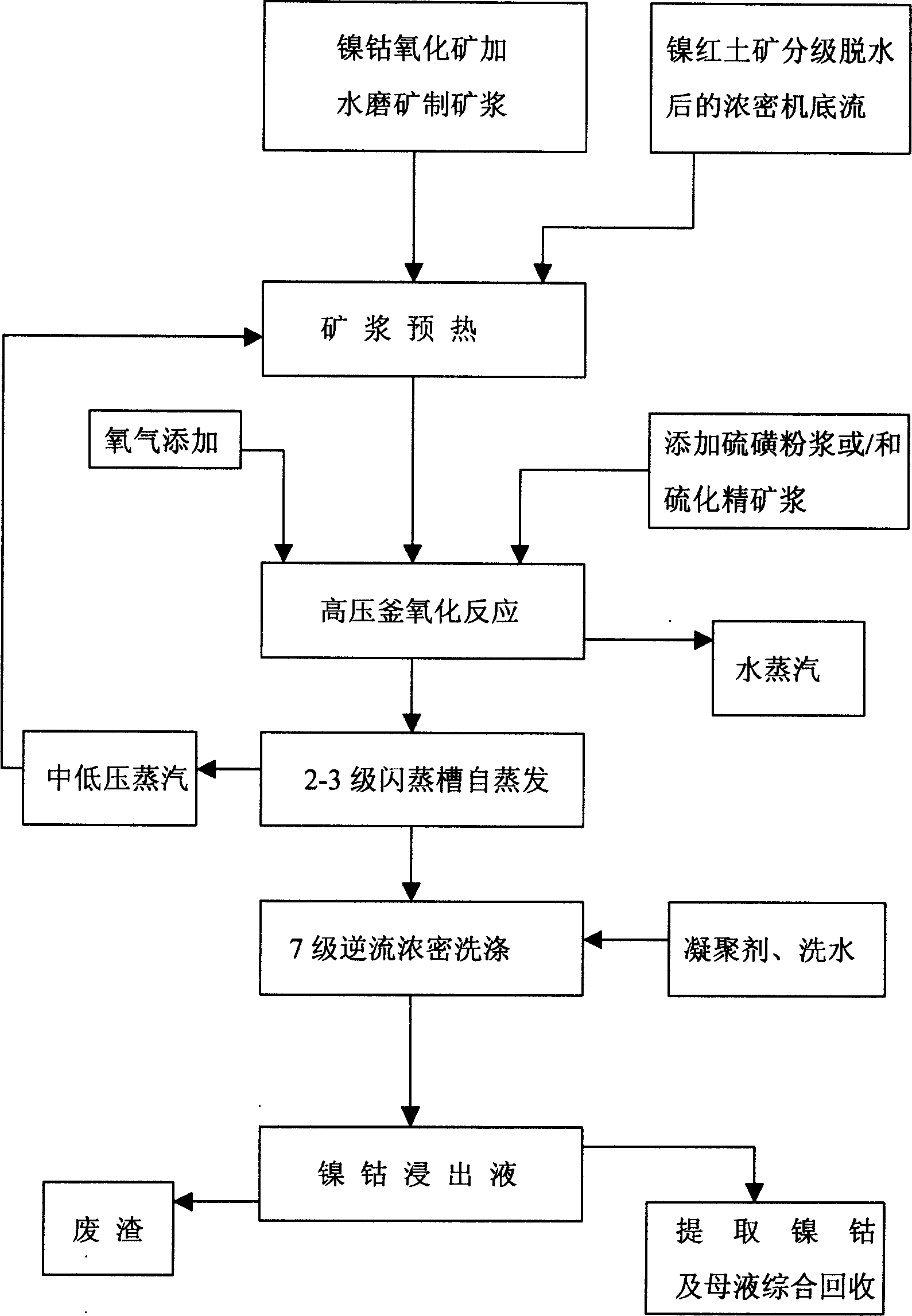
Pressure oxidation leaching-out method for nickel-cobalt oxide ore
InactiveCN1676634AReduce pollutionImprove protectionProcess efficiency improvementCobalt metalPresent method
This invention discloses a nickel cobalt oxide ore pressure ore oxygenation leaching method, which includes the technique flow of milling the nickel cobalt oxide paste, adding sulfur powder paste or sulfuration refining paste, high-pressure still oxidization, automatic steaming of flash groove, flocculating agent adding, 7-grade reflux thick cleaning, distilling nickel cobalt and comprehensively recycling bitter salt. It has high leaching ratio of leaching nickel cobalt metals and the relative components. This invention greatly improves the present method that adds pressure and acid dips nickel cobalt oxide ores and lowers the investment, reduces the operation workers, saves the energy and improve the environment, lowers the cost and expands the utilization range of this leaching method and can comprehensively uses the other components.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Process for recovery of metal values from materials containing arsenic and/or antimony
InactiveUS20090019970A1Limiting copper contentReduced cyanide consumptionProcess efficiency improvementSlurryCyanide leaching
A method for the recovery of metal values from a metal value-bearing material containing arsenic and / or antimony and a source of sulphate ions such as sulphide ore or concentrate is disclosed. In one form the method comprises the steps of: (a) providing a feed stream comprising a metal value-bearing material containing arsenic and / or antimony and a source of sulphate ions; (b) subjecting the feed stream to oxidative conditions under elevated temperature and pressure conditions in the presence of at least one component selected to decrease the effective concentration of free acid generated during the pressure oxidation step and promote the formation of pH-stable iron (III) sulphate products, thereby forming a slurry comprising a metal value-containing leach solution and a solid leach residue containing pH-stable iron (III) sulphate products and environmentally stable iron-arsenic and / or iron-antimony products; (c) separating the metal value-containing leach solution from the solid leach residue; (d) recovering the metal value (s) from the metal value-containing leach solution; and (e) recovering precious metal values, if present, in the solid leach residue by cyanide leaching.
Owner:DUNDEE PRECIOUS METALS
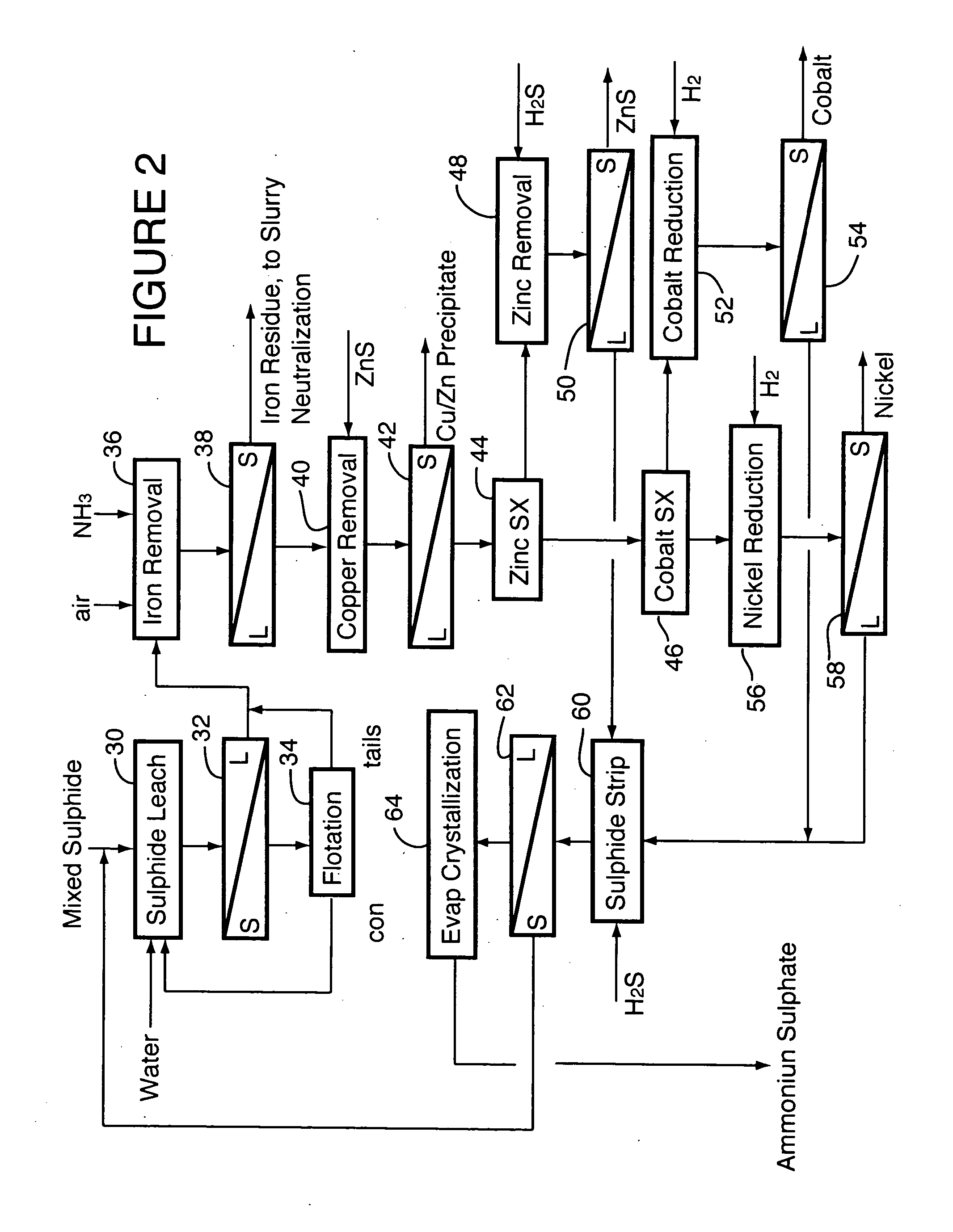
Recovery of nickel, cobalt, iron, silica, zinc and copper from laterite ore by sulfuric acid leaching
ActiveUS7387767B2Efficient separation and recoveryHigh purityCobalt sulfidesSolvent extractionFree solutionSlurry
A process for recovering nickel and cobalt values from nickel- and cobalt-containing laterite ores as an enriched mixed nickel and cobalt sulphide intermediate and for producing nickel and cobalt metal from the nickel and cobalt sulphide intermediate. The laterite ore is leached as a slurry in a pressure acid leach containing an excess of aqueous sulphuric acid at high pressure and temperature, excess free acid in the leach slurry is partially neutralized to a range of 5 to 10 g / L residual free H2SO4 and washed to yield a nickel- and cobalt-containing product liquor, the product liquor is subjected to a reductant to reduce any Cr(VI) in solution to Cr(III), the reduced product liquor is neutralized to precipitate ferric iron and silicon at a pH of about 3.5 to 4.0, and the neutralized and reduced product liquor is contacted with hydrogen sulphide gas to precipitate nickel and cobalt sulphides. The precipitated nickel and cobalt sulphides can be leached in a water slurry in a pressure oxidation leach, the leach solution subjected to iron hydrolysis and precipitation, the iron-free solution contacted with zinc sulphide to precipitate copper, the iron- and copper-free solution subjected to zinc and cobalt extraction by solvent extraction to produce a nickel raffinate, the nickel raffinate contacted with hydrogen gas to produce nickel powder and the cobalt strip solution from the solvent extraction step contacted with hydrogen gas to produce cobalt powder.
Owner:SHERRITT INC
Production of pure molybdenum oxide from low grade molybdenite concentrates
InactiveUS20050019247A1High purityValue maximizationOxide/hydroxide preparationMolybdeum compounds preparationProcess chemistryFiltration
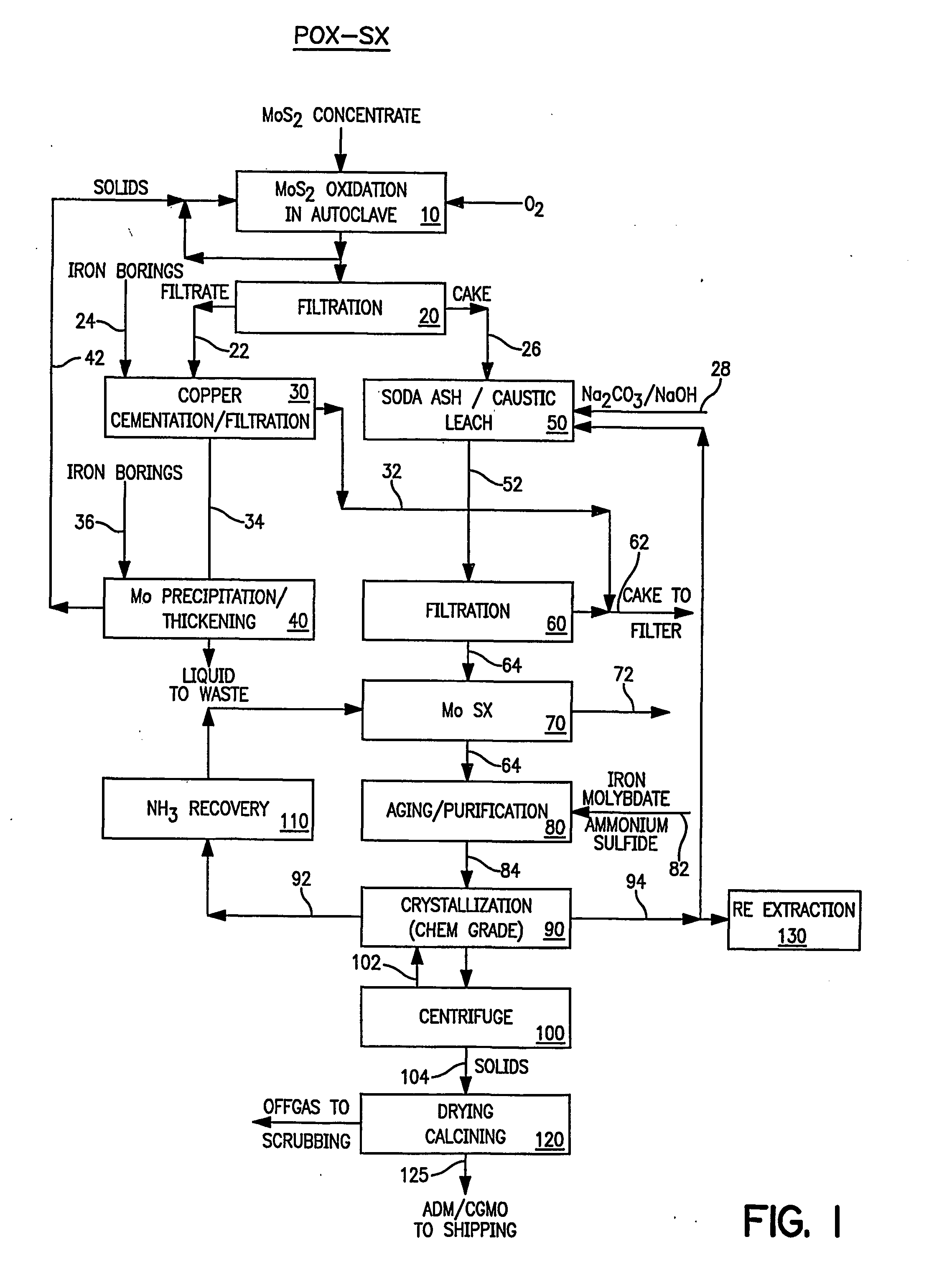
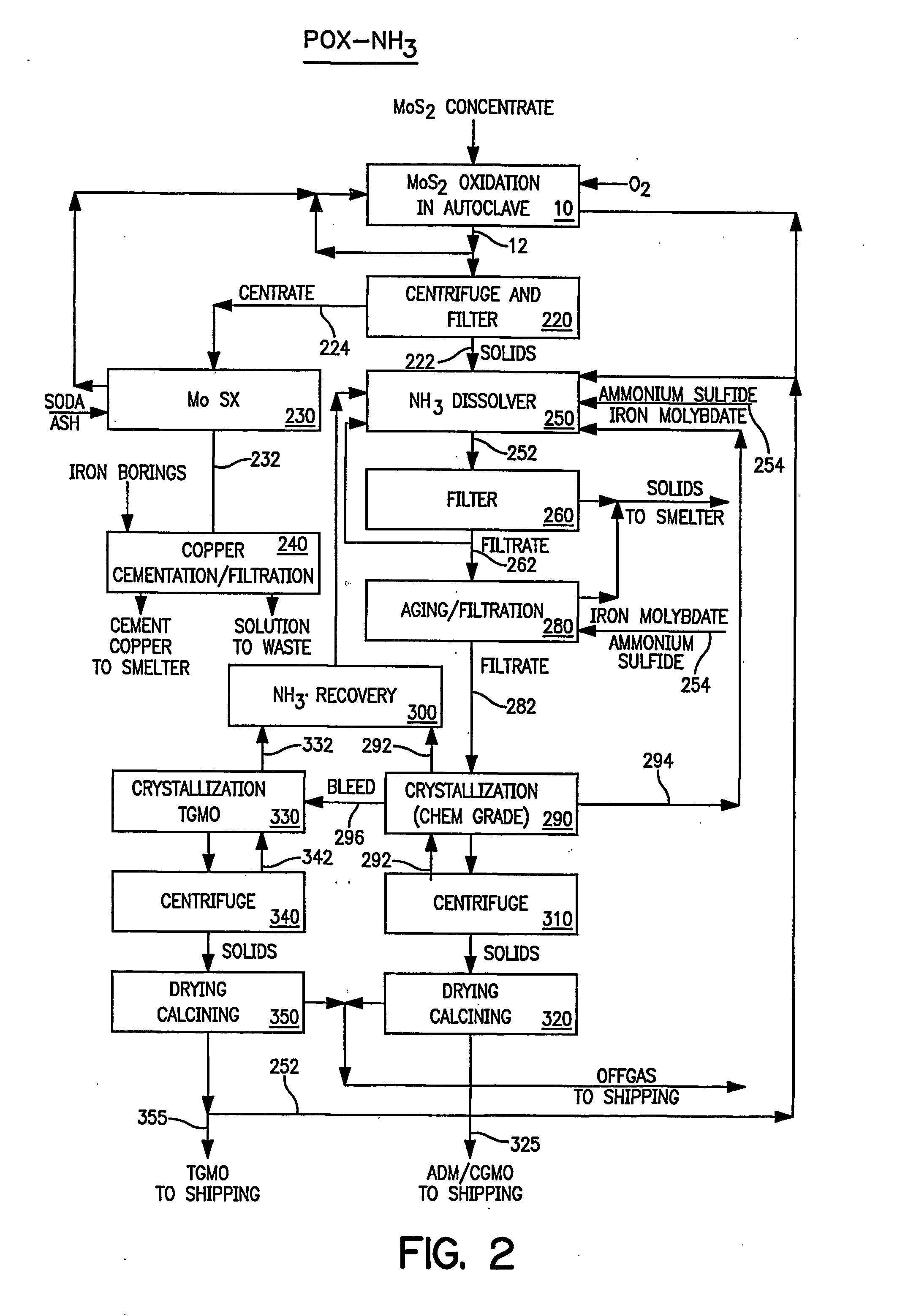
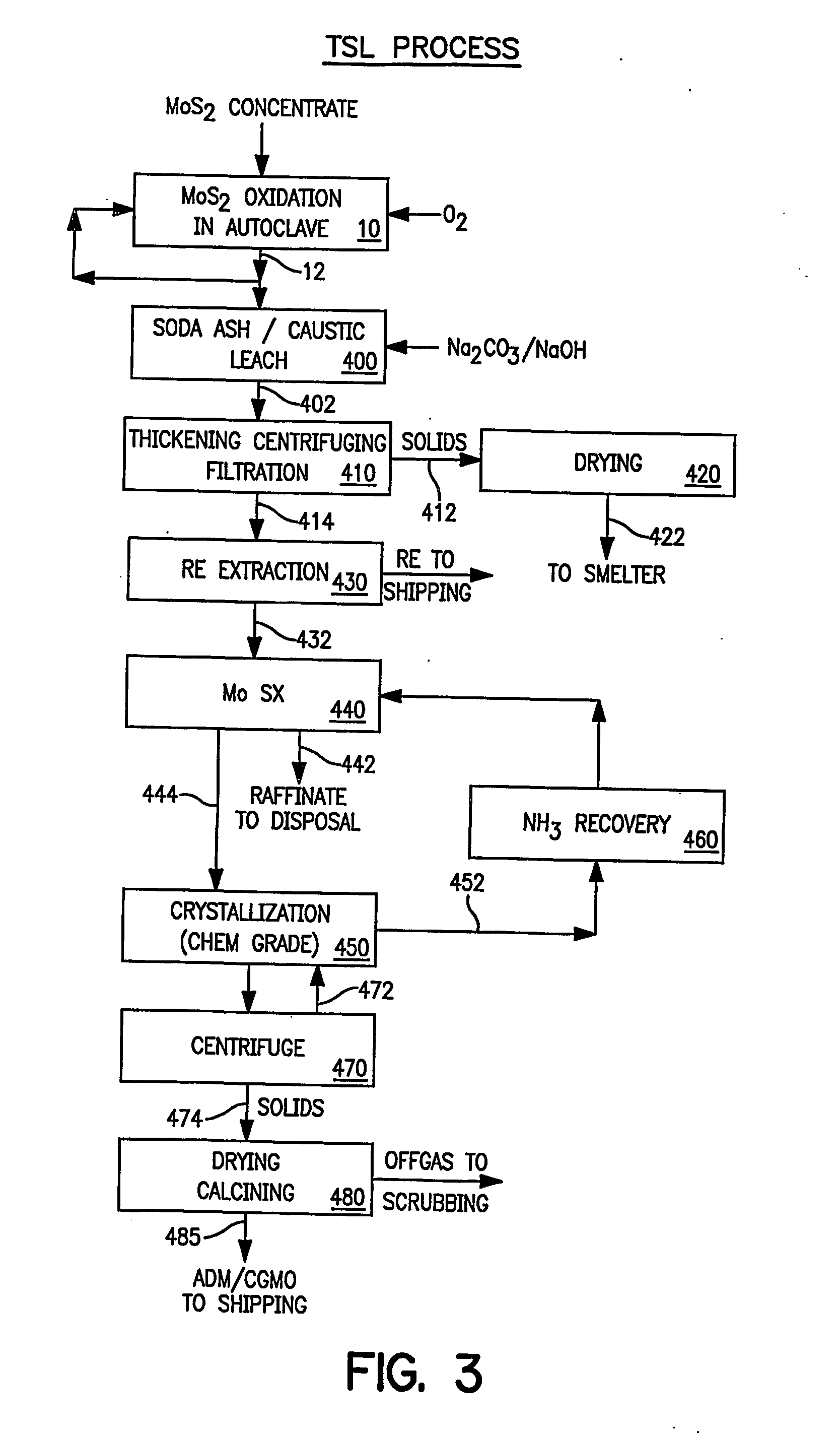
High purity ammonium dimolybdate or molybdenum oxide is produced by the pressure oxidation of low grade molybdenite concentrates or molybdenum intermediates. The process entails nearly complete oxidation of the sulfide minerals while optimizing the process chemistry and autoclave conditions to solubilize as little of the molybdenum values as possible. The autoclave discharge 12 is then subjected to a leaching step, either an alkaline leach 50, 400 or ammonium leach 250 process, before or after a liquid / solid separation step 20, 220, 410. The solution is then subjected to (a) filtration 60, 410, solvent extraction 70, 440, crystallization 90, 450, and calcination 120, 480 or (b) filtration 260, 280, crystallization 290, and calcination 320 to produce a product suitable for chemical-grade molybdenum oxide 125, 325, 485.
Owner:BALLIETT ROBERT W +6
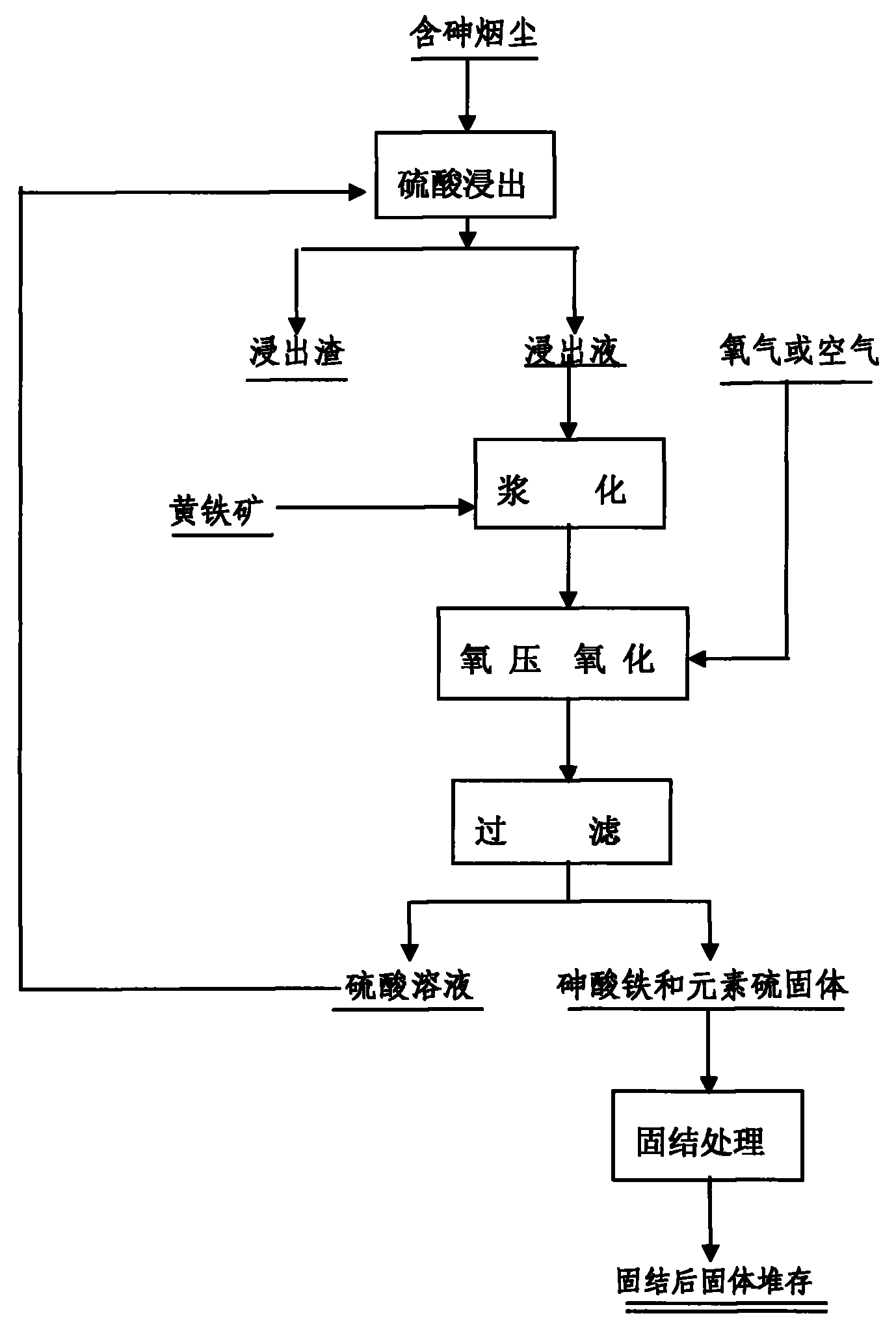
Method for treating arsenic-containing smoke dust
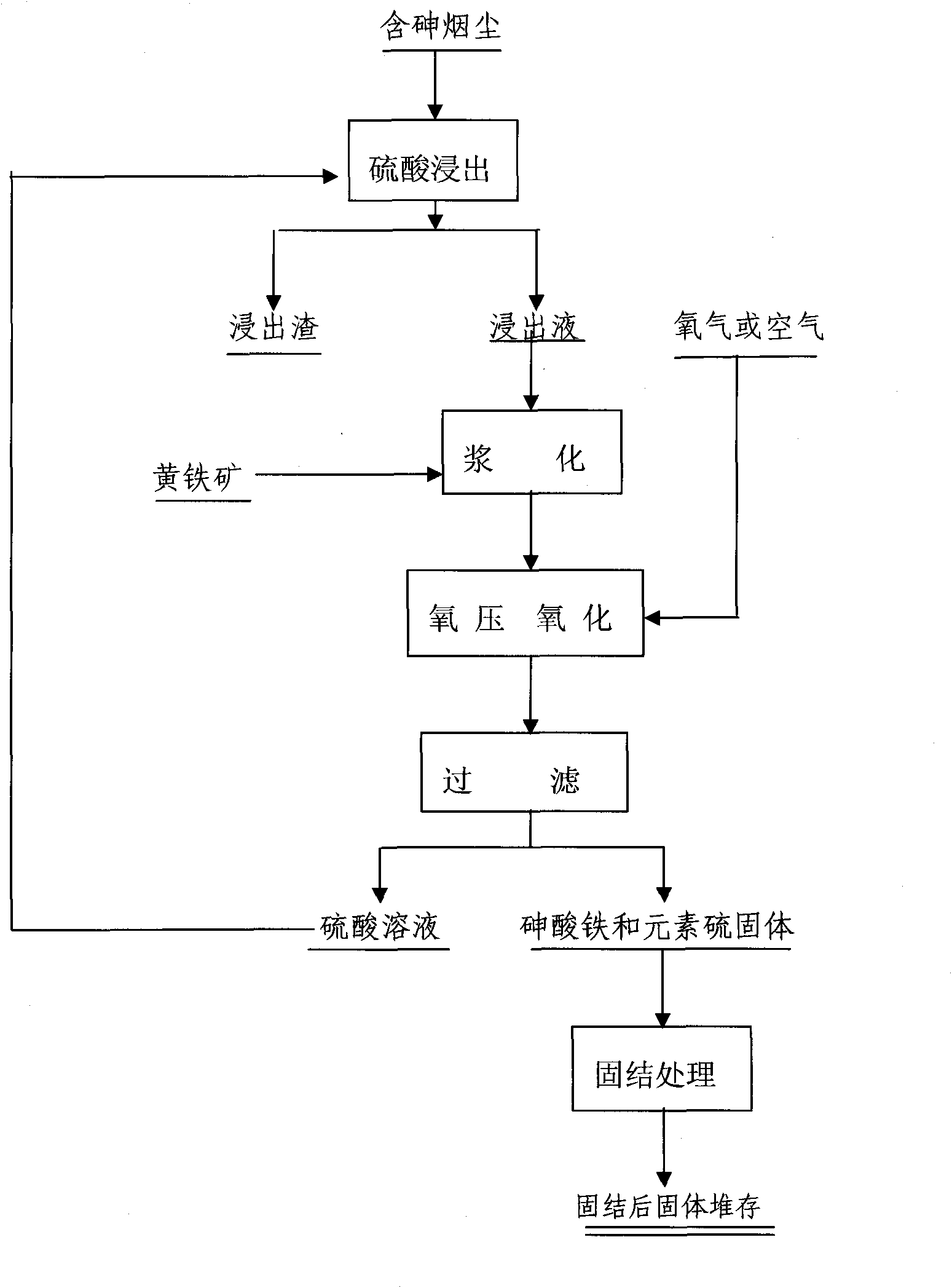
ActiveCN101817553ASolve the redissolution problemSolve the open circuit problemArsenites/arsenatesSulfur preparation/purificationPyriteWastewater
The invention provides a method for synthesizing ferricarsenate from arsenic-containing smoke dust by leaching, pressure oxidation and conversion, and consolidating the ferricarsenate. The method comprises the following steps of: leaching the arsenic-containing smoke dust by using 10 to 30g / L of dilute sulfuric acid solution; mixing and stirring the smoke dust and powdered pyrite; adding the mixture into a closed stirring reactor; introducing oxygen into the reactor until the oxygen partial pressure is between 0.6 and 1.5MPa; heating the reactor to the temperature of between 100 and 160 DEG C, stirring the mixture to perform reaction for 2 to 4 hours; filtering the reaction product to obtain mixed solid of ferricarsenate and sulphur, and 10 to 30g / L of dilute sulfuric acid solution which is returned and leached; and solidifying the mixed solid to obtain environment-friendly hydrophobic solid with high strength. The method has no emission of waste gas or waste water in the treatment process, can solve the opening problem of arsenic in various arsenic-containing smoke dusts, and eliminates pollution of the arsenic-containing smoke dust to the environment.
Owner:红河砷业有限责任公司
Process for precious metal recovery from a sulphide ore or concentrate or other feed material
A process for the extraction of a precious metal, such as gold or silver, from a sulphide ore or concentrate or other source material comprises subjecting the source material to pressure oxidation to produce a pressure oxidation slurry. The pressure oxidation slurry is flashed down to a lower temperature and pressure and is then subjected to a liquid / solid separation to obtain a pressure oxidation solution and a solid residue containing the precious metal. The solid residue is then subjected to cyanidation to extract the precious metal. The formation of thiocyanide during cyanidation is minimized or counteracted by effecting the cyanidation at an elevated oxygen pressure and a reduced retention time, such as 30 to 90 minutes. A method for the reduction of copper cyanide formation during cyanidation leaching is also provided.
Owner:CESL LIMITED
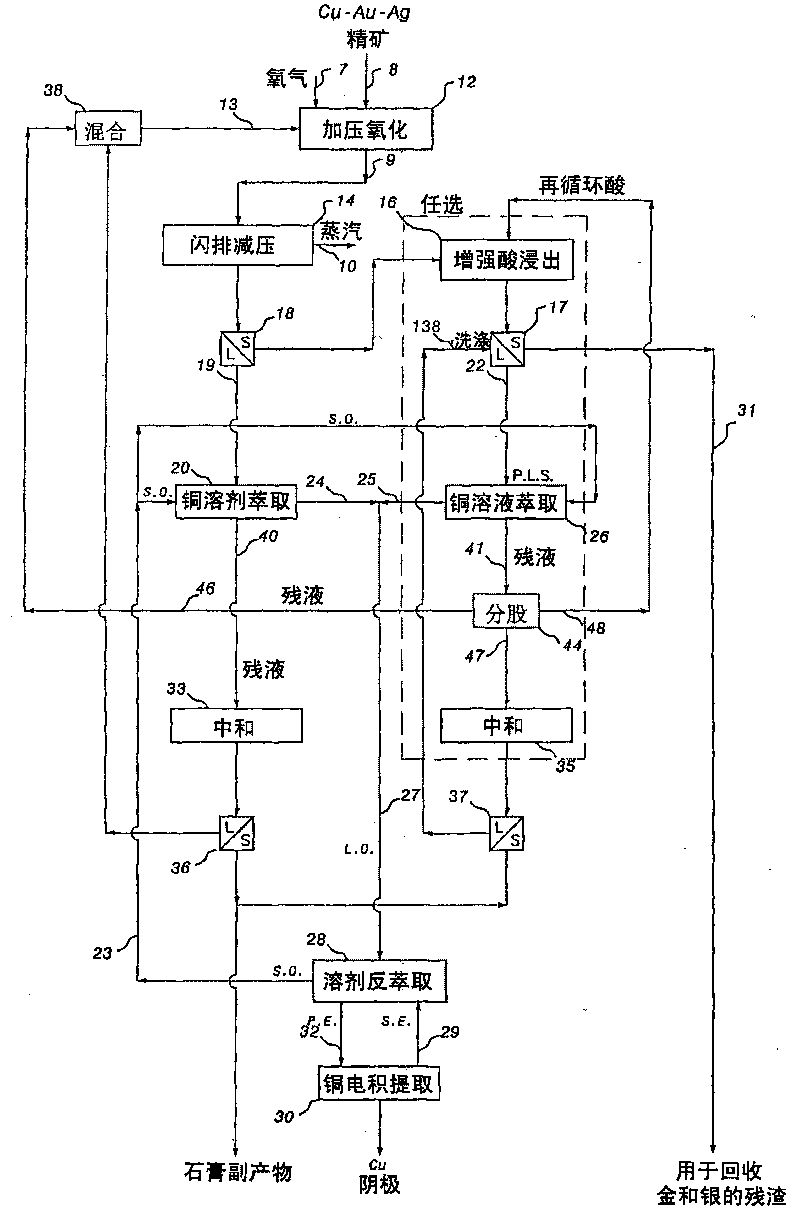
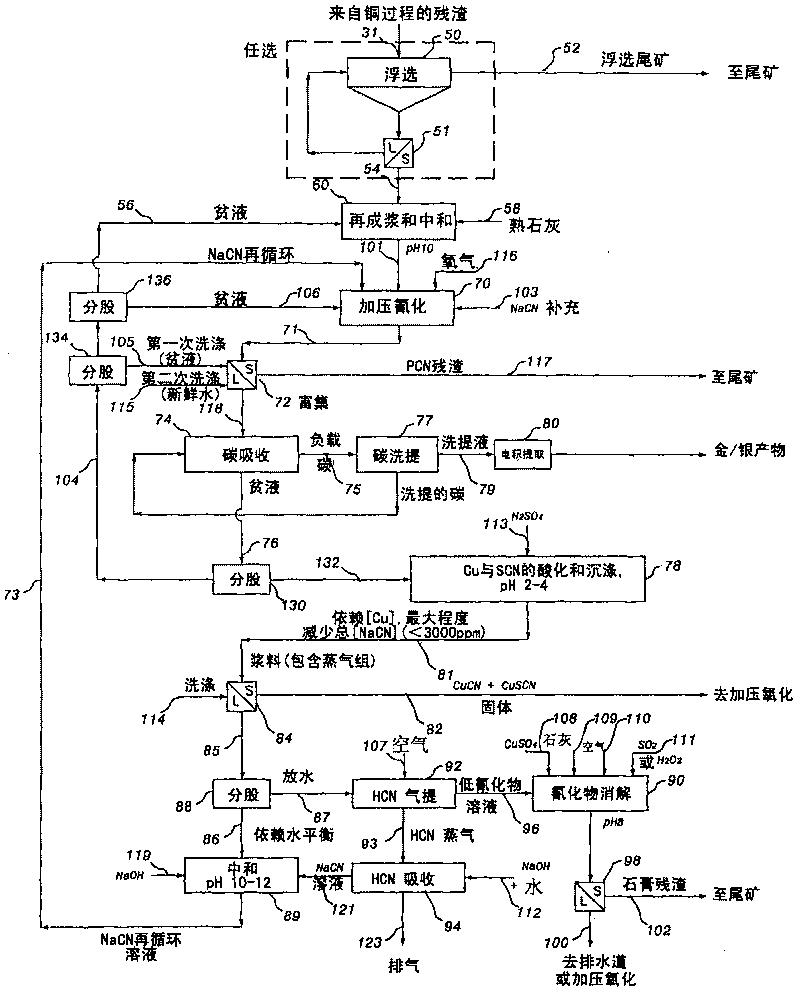
Processing of Metal Values from Concentrates
InactiveUS20090293680A1Inhibition formationEfficient separationProcess efficiency improvementImproved methodCopper
The present invention relates to an improved method for the recovery of metal values, in particular copper and gold, from a metal value-bearing material containing arsenic and / or antimony and a source of sulphate ions, by means of a high temperature pressure oxidation process followed by cyanidation of the resultant high temperature pressure oxidation residue.
Owner:DUNDEE PRECIOUS BARBADOS
Process for extracting gold by modified pressure oxidation-cyaniding
InactiveCN102127653AAvoid secondary packagingImprove leaching rateProcess efficiency improvementSulfurHigh pressure
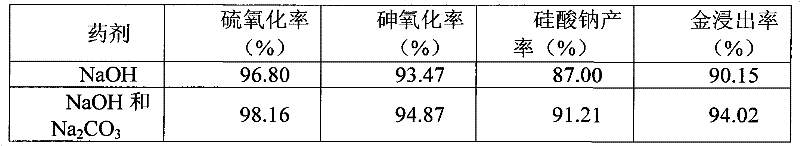
The invention discloses a process for extracting gold by modified pressure oxidation-cyaniding. The pressure oxidation technology and alkali silicon dissolving technology are organically combined and a technological scheme of mixed medicament of NaOH and Na2CO3 is adopted to process Carlin dipped-type obstinate gold-containing ore, and the pressure oxidation process is adopted, thus sulphide mineral can be fully oxidized and decomposed and gold wrapped in the ore can be fully exposed and dissociated; under the conditions of higher temperature and higher pressure, NaOH reacts with SiO2 to effectively decompose gangue, thus gold wrapped in the ore is fully exposed and dissociated; wraps of the sulphide mineral and gangue are opened, and harmful elements enter into a liquid phase in a soluble salt form, thus secondary wrapping to gold is avoided; and most harmful substances such as sulphur and arsenic are oxidized and then enter into the liquid phase to be neutralized and recycled. By applying the process disclosed by the invention, the gold leaching rate is improved to 96.5% from 5% of the conventional process, thus the gold leaching rate is obviously improved; and the pollution to the environment is greatly reduced.
Owner:CHANGCHUN GOLD RES INST +1
A method for separating tungsten, molybdenum and bismuth in bismuth sulfide concentrate
InactiveCN102296180AEfficient separationComprehensive recycling benefits are goodProcess efficiency improvementBismuth sulfideMaterials science
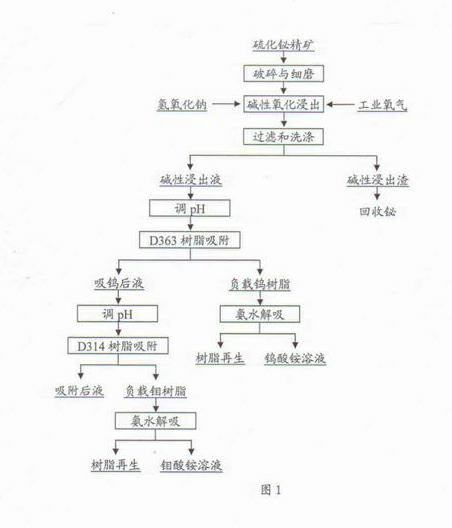
The invention discloses a method capable of effectively separating tungsten, molybdenum and bismuth in bismuth sulfide ore concentrate. The method comprises the following steps of: performing pressure oxidation leaching on the bismuth sulfide ore concentrate containing tungsten and molybdenum in sodium hydroxide solution, wherein the tungsten and the molybdenum enter the alkali leachate, and the bismuth and other heavy metals enter the alkali leached residue in an oxide form, so that effective separation of the tungsten, the molybdenum and the bismuth in the bismuth sulfide ore concentrate isrealized; adsorbing the tungsten and the molybdenum in the alkali leachate by using macroporous weak alkali acrylic series anion exchange resin D363 and D314 respectively; and finally, desorbing the tungsten and the molybdenum by using aqueous ammonia respectively, so that effective reclamation of the tungsten and the molybdenum in the leachate is realized. By the method, effective separation of the tungsten, the molybdenum and the bismuth in the bismuth sulfide ore concentrate is realized, the leaching rate of the tungsten and the molybdenum is over 99 percent, and the bismuth, copper and the like enter the alkali leached residue after being oxidized; the tungsten and the molybdenum in the alkali pressure leachate are adsorbed by adopting resin, and the recovery rate of the tungsten and the molybdenum is over 99 percent; and the method is low in labor intensity, short in treatment time and good in operating environment.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Sintering flue gas ammonia desulfurization system and process
ActiveCN102527210AReasonable structureGuaranteed qualityDispersed particle separationFiltrationSulfate
The invention relates to a sintering flue gas ammonia desulfurization system and a sintering flue gas ammonia desulfurization process. The sintering flue gas ammonia desulfurization system comprises an ammonia supply system, an absorption system, a filtration system and an oxidation system, wherein the ammonia supply system is connected with the absorption system which is connected with the filtration system; and the filtration system is connected with the oxidation system. The sintering flue gas ammonia desulfurization system can effectively remove sulfur dioxide from flue gas, and reduces the escape degree of ammonia; a generated byproduct ammonium sulfite is filtered, is subjected to impurity removal and then is subjected to low-concentration normal-pressure oxidation, so that the conversion rate of ammonia sulfate is guaranteed, and a qualified raw material solution is provided for a next-stage ammonia sulfate preparation system; the sintering flue gas ammonia desulfurization system has a reasonable structure, ensures that the flue gas reaches standard to discharge and reduces secondary pollution caused by escaped ammonia; and the qualified raw material solution is provided for the next-stage ammonia sulfate preparation system through the pretreatment process of the byproduct of filtering first and then oxidizing, so that the quality of a byproduct ammonia sulfate is ensured.
Owner:中钢集团工程设计研究院有限公司
Method for preparing super-hydrophobic film on copper surface by low-voltage oxidation process
InactiveCN101476121AEmission reductionReduce manufacturing costMetallic material coating processesMicro nanoAdhesive
The invention discloses a method for preparing a super-hydrophobic thin film on copper surface by using low pressure oxidation process method that can be used for various copper surface needing waterproof adhesive, which belongs to the material surface physical chemistry field. A prior art reaches aim of super-hydrophobic by using organic chemical reagent with low surface energy for decorating, which has high cost, complex technique and has effect to environment. The invention provides a simple low pressure oxidation process that can generate an oxidation copper thin-film with double layers micro-nano structures for reaching super-hydrophobic state, which can remove process of low surface energy organic chemical reagent for decorating, save manufacturing cost, simplify technique and reduce discharge of organic waste.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
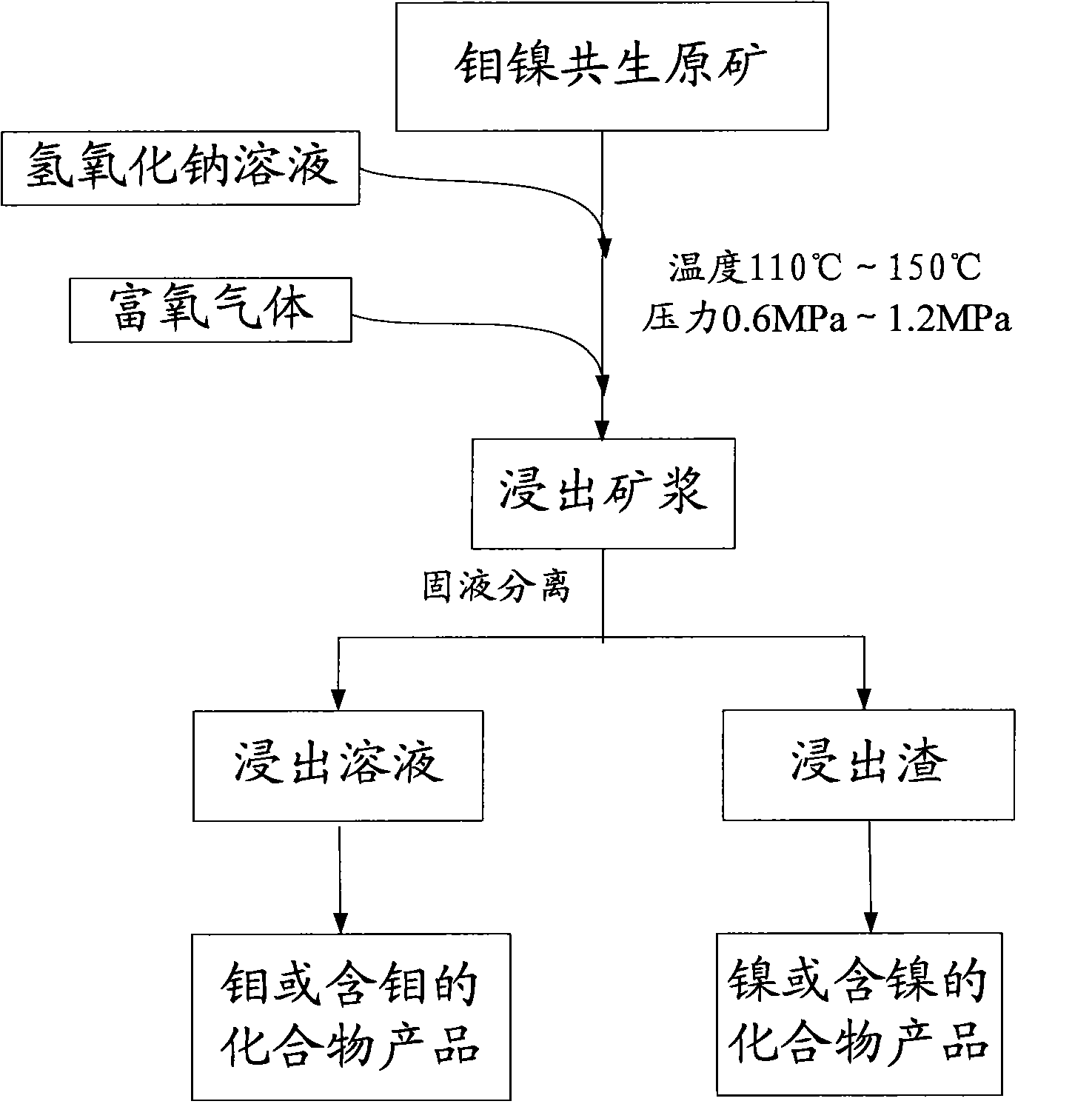
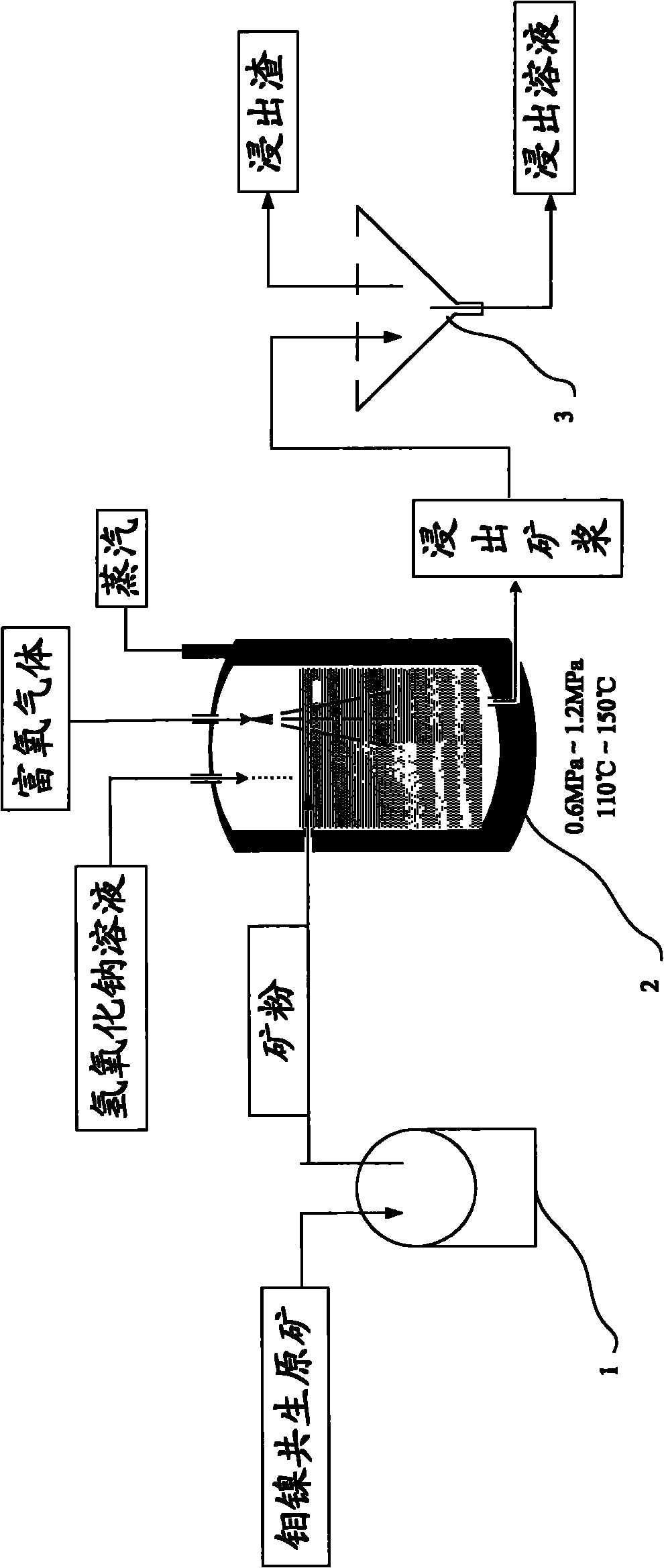
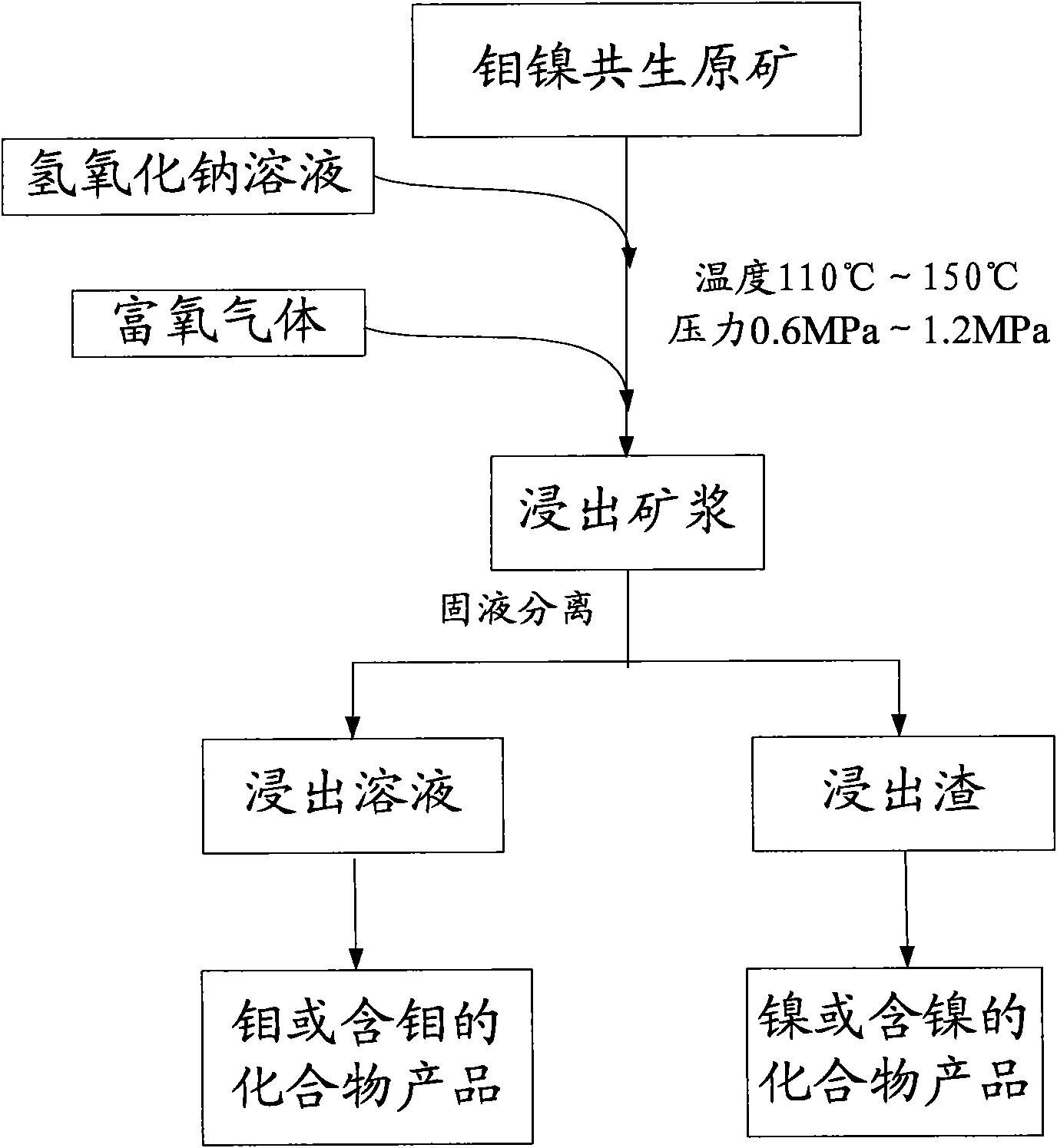
Pressure leaching method of molybdenum-nickel paragenetic raw ore
InactiveCN101899569AEfficient separationAchieve separationProcess efficiency improvementOxygenNickel sulfide
The invention provides a method for separating molybdenum and nickel from molybdenum-nickel sulfide paragenetic raw ore by pressure oxidation and alkaline leaching, comprising the following steps: adding the molybdenum-nickel paragenetic raw ore and sodium hydroxide solution into a reaction vessel; introducing oxygen-enriched gas into the reaction vessel, and controlling pressure at 0.6MPa-1.2MPa and temperature at 110-150DEG C in the reaction vessel respectively to obtain leaching pulp; carrying out liquid-solid separation on the leaching pulp to form leaching solution and leaching residue; treating the leaching solution to obtain the molybdenum or a molybdenum-containing compound; and smelting the leaching residue to obtain the nickel or a nickel-containing compound. The method can strengthen the leaching process to achieve the purpose of efficiently leaching the molybdenum in the molybdenum-nickel sulfide paragenetic raw ore, while the nickel is almost fully retained in the leaching residue, thus effectively realizing separation of the molybdenum and the nickel.
Owner:云南冶金集团股份有限公司技术中心
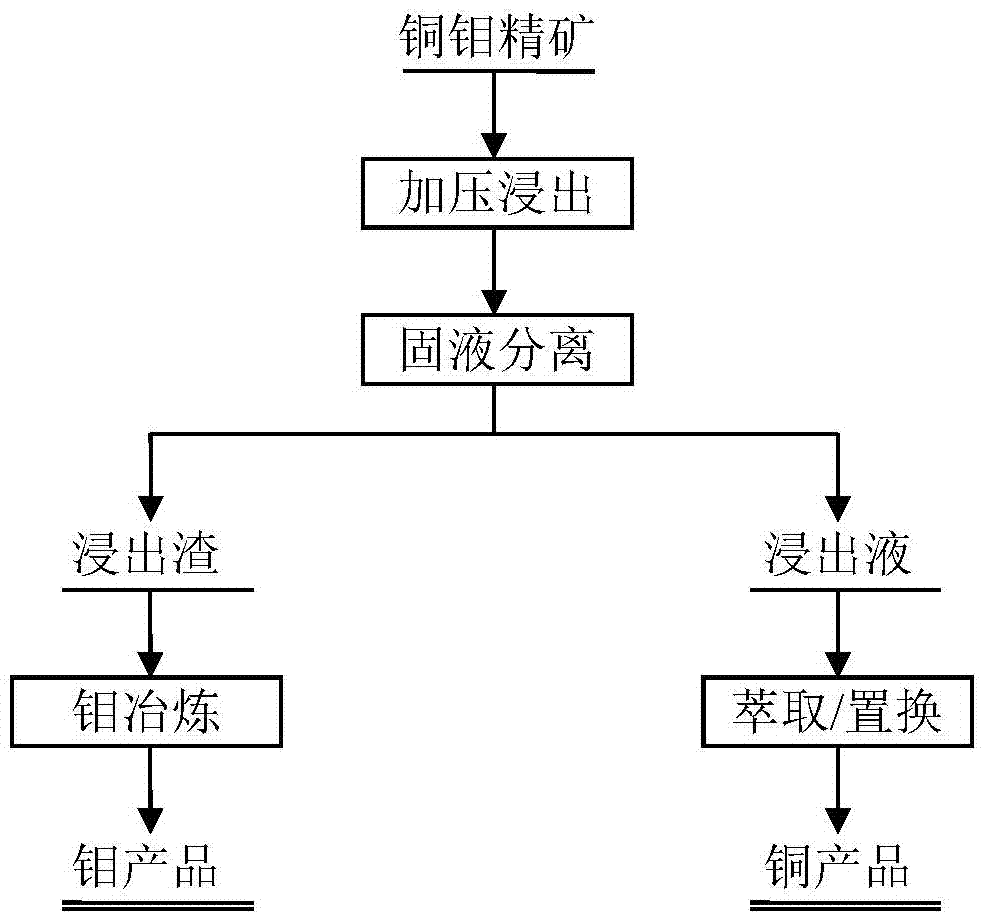
Treating method for complex copper-molybdenum deposit
ActiveCN104846216ASolving Recycling ProblemsSimple processProcess efficiency improvementIron powderHydrometallurgy
The invention discloses a treating method for a complex copper-molybdenum deposit, which belongs to the technical field of wet metallurgy. The method comprise the following steps: adding a proper amount of sulfuric acid and an additive into the copper-molybdenum deposit and carrying out pressure leaching, wherein copper and the like are leached and enter a solution and molybdenum is left in leaching residue in the form of molybdenum sulfide; and subjecting the leaching residue to roasting or pressure oxidation so as to produce products like molybdenum oxide and subjecting leachate, i.e., a copper sulphate solution, to iron powder replacement so as to produce copper sponge or extract products like copper sulphate and electrolytic copper. The treating method provided by the invention can realize convenient and fast separation of molybdenum and copper, improves the grade of molybdenum concentrate, reduces the content of impurities in products and comprehensively recovers copper.
Owner:BEIJING GENERAL RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY
Method enhancing oxidization leaching with arsenic in arsenic-cobalt-nickel containing slag
The invention relates to a method for enhancing oxidization leaching of low-valence arsenic existed as an alloy form of arsenic copper, arsenic cobalt and arsenic nickel in arsenic-cobalt-nickel containing slag by taking NaOH or KOH solution as a leaching medium and taking a copper oxide as an oxidizing agent. In the method, on one hand, an alkali medium is taken as the leaching medium, thereby the risk of generation of arsine gas with severe toxicity can be avoided during acid leaching; on the other hand, the copper oxide is taken as the oxidizing agent, by comparing with oxygen pressure leaching of the alkali medium, operation pressure of a system is reduced, copper in the copper oxide can not be dissolved in the alkali medium, and can follow with copper in the arsenic-cobalt-nickel containing slag into a copper smelting system. The method is the further improvement of a pressure oxidation leaching-out method for the alkali medium.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Production method for sodium pyroantimonate by using high-temperature high-pressure pure-oxygen oxidation
InactiveCN103318959ALower requirementExcellent and stable product qualityAntimony compoundsFiltrationHigh pressure
The invention discloses a production method for sodium pyroantimonate by using high-temperature high-pressure pure-oxygen oxidation. The method comprises the following steps: with antimony oxide powder as a raw material, leaching the powder in a highly alkaline medium to extract antimony; purifying an obtained leachate; carrying out filtration, feeding an antimony-containing filtrate into an autoclave and controlling temperature to be 110 to 150 DEG C; introducing an oxygen oxidizing medium; adjusting and maintaining pressure to be 1.0 to 2.5 MPa; directly carrying out pressure oxidation, allowing a reaction to last 1 to 6 h and carrying out discharging; carrying out solid-liquid separation so as to obtain a sodium pyroantimonate precipitate; and washing, drying and screening the precipitate so as to obtain a sodium pyroantimonate product. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of simple process flow, a small amount of needed equipment, low production cost, reinforced process, a short production period, no environmental pollution, stable product quality, etc., and has wide application prospects.
Owner:CHENZHOU CITY JINGUI SILVER IND CO LTD
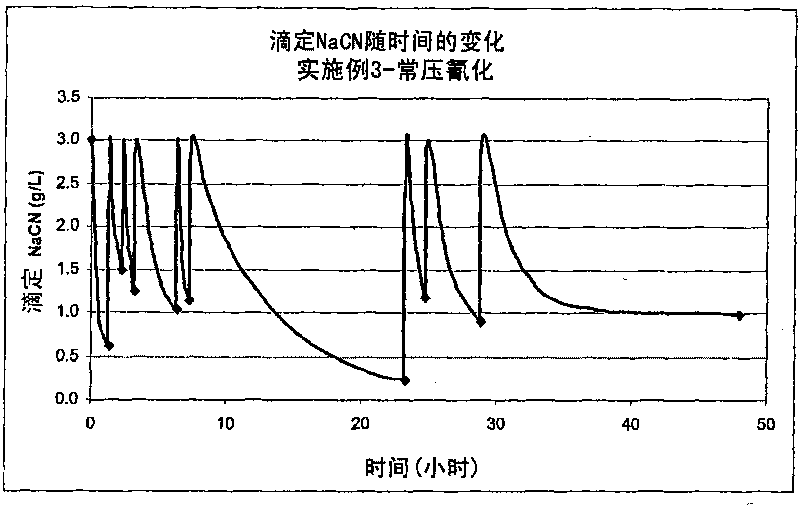
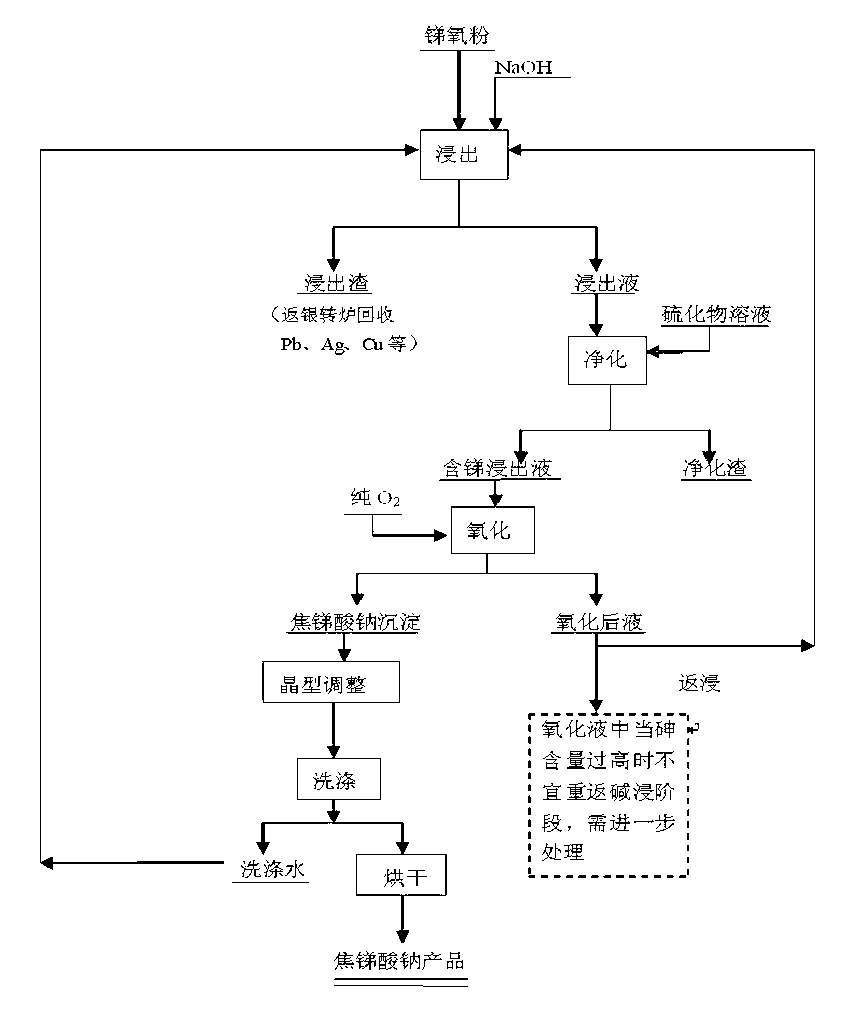
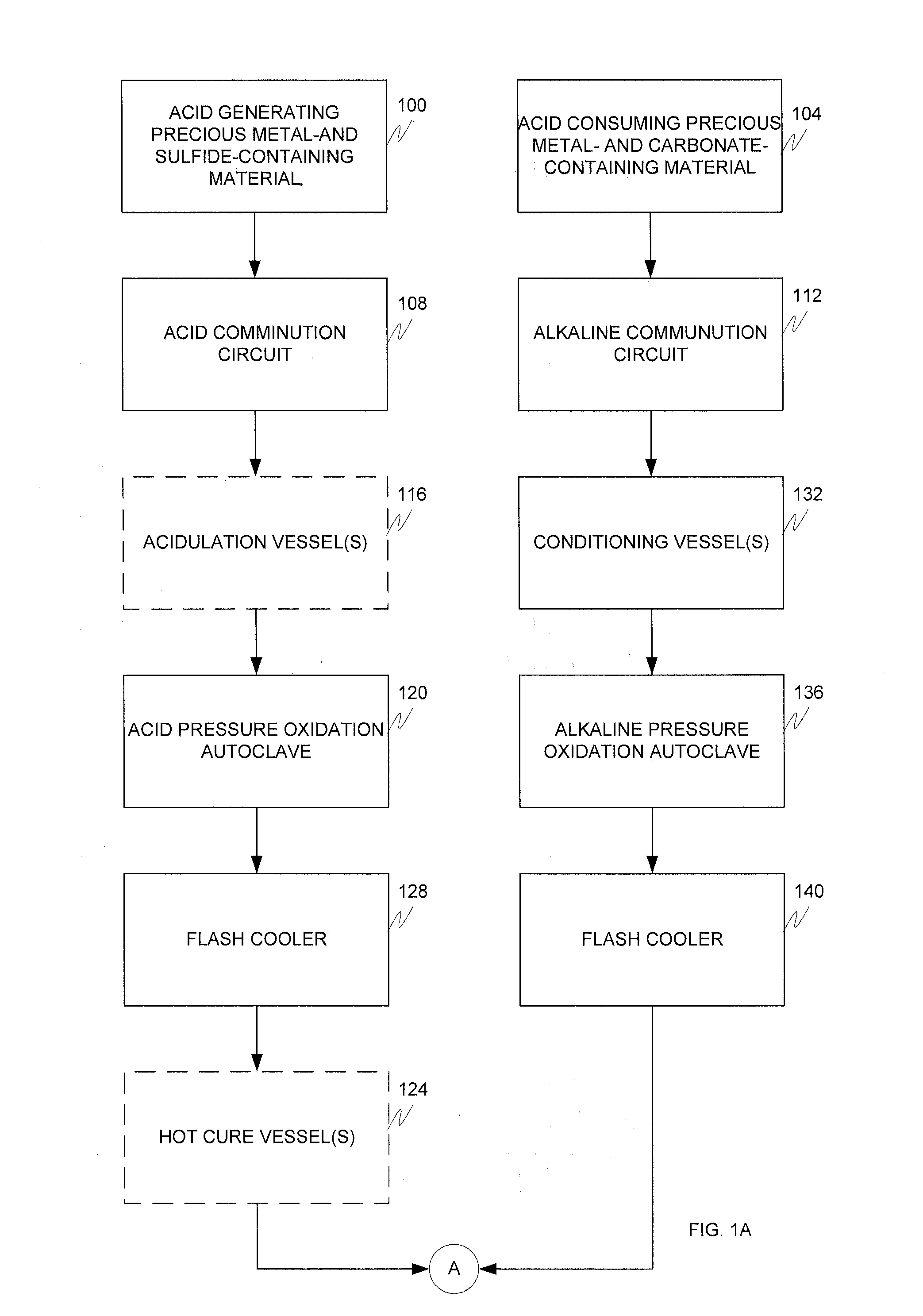
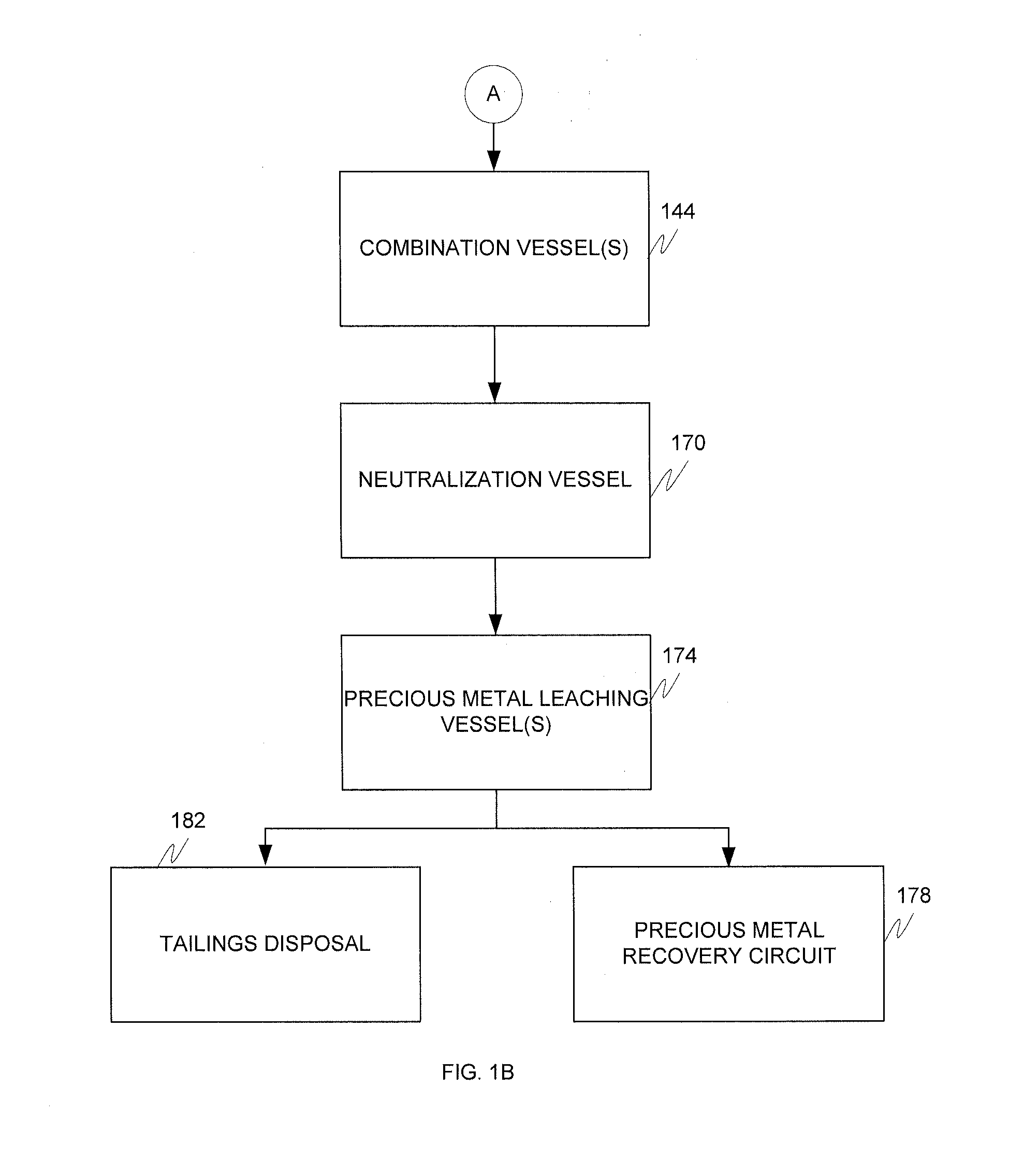
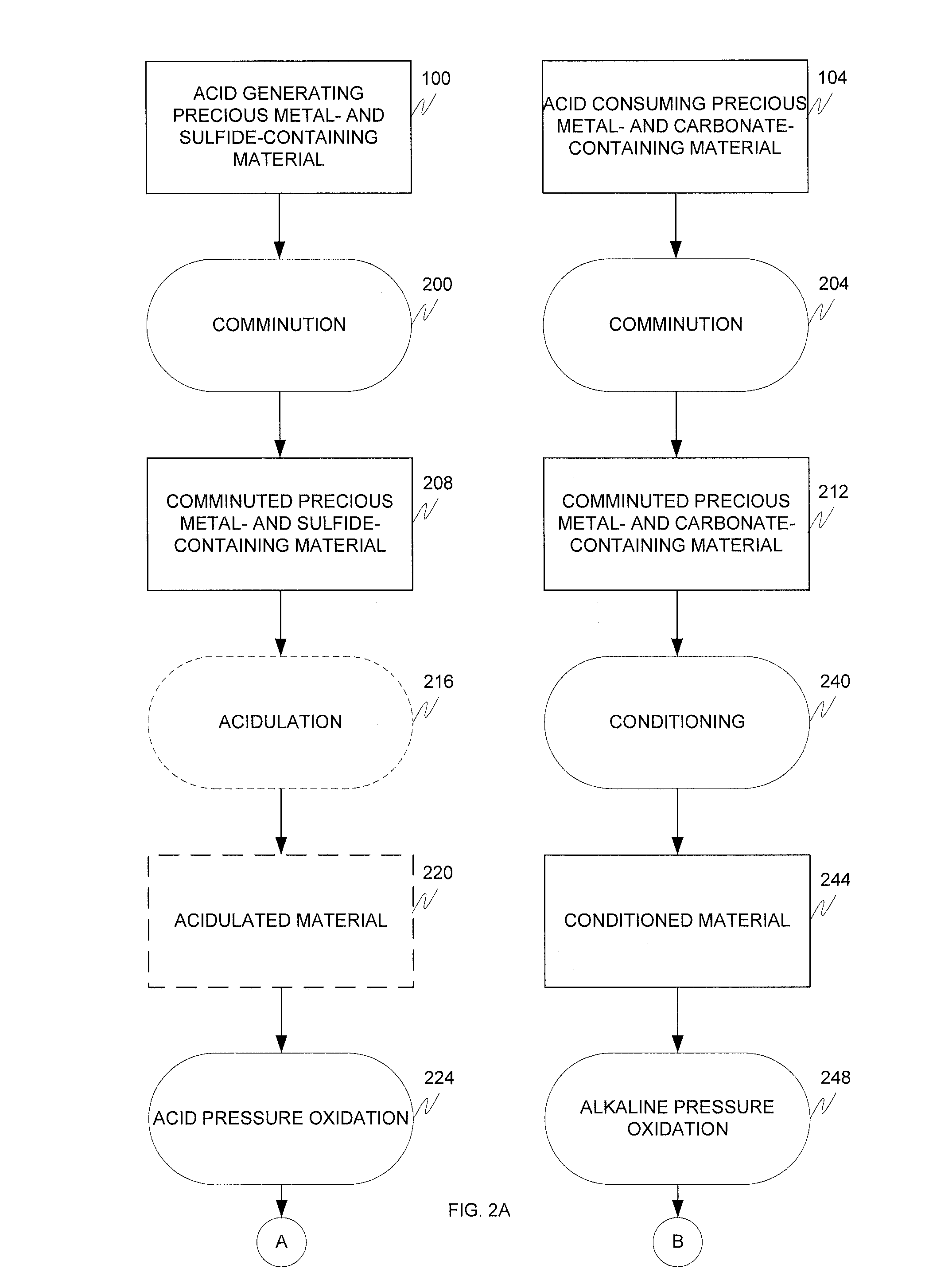
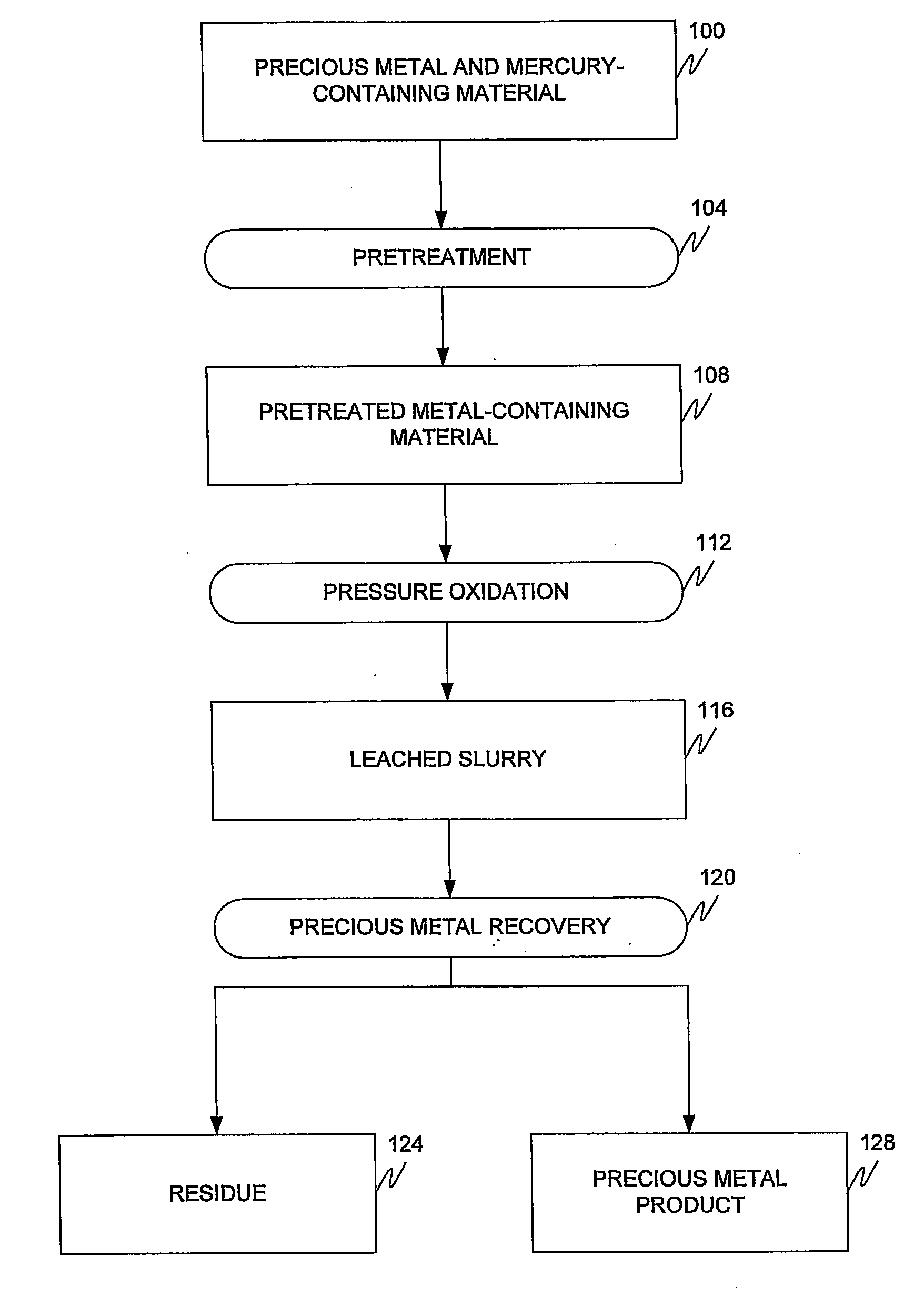
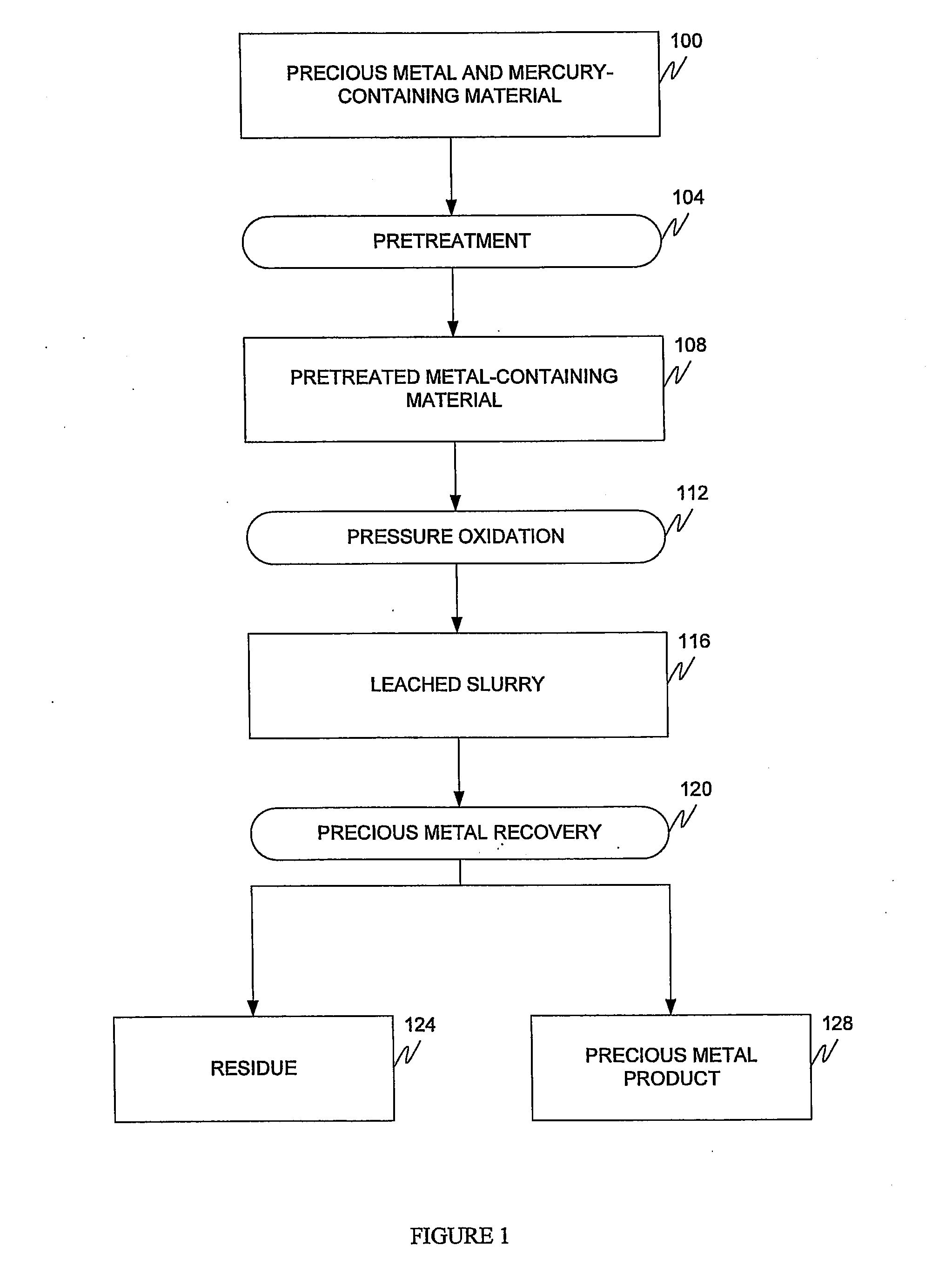
Alkaline and acid pressure oxidation of precious metal-containing materials
ActiveUS20120128528A1Reduce consumptionLow costMetal boridesRecycling and recovery technologiesSulfideSlurry
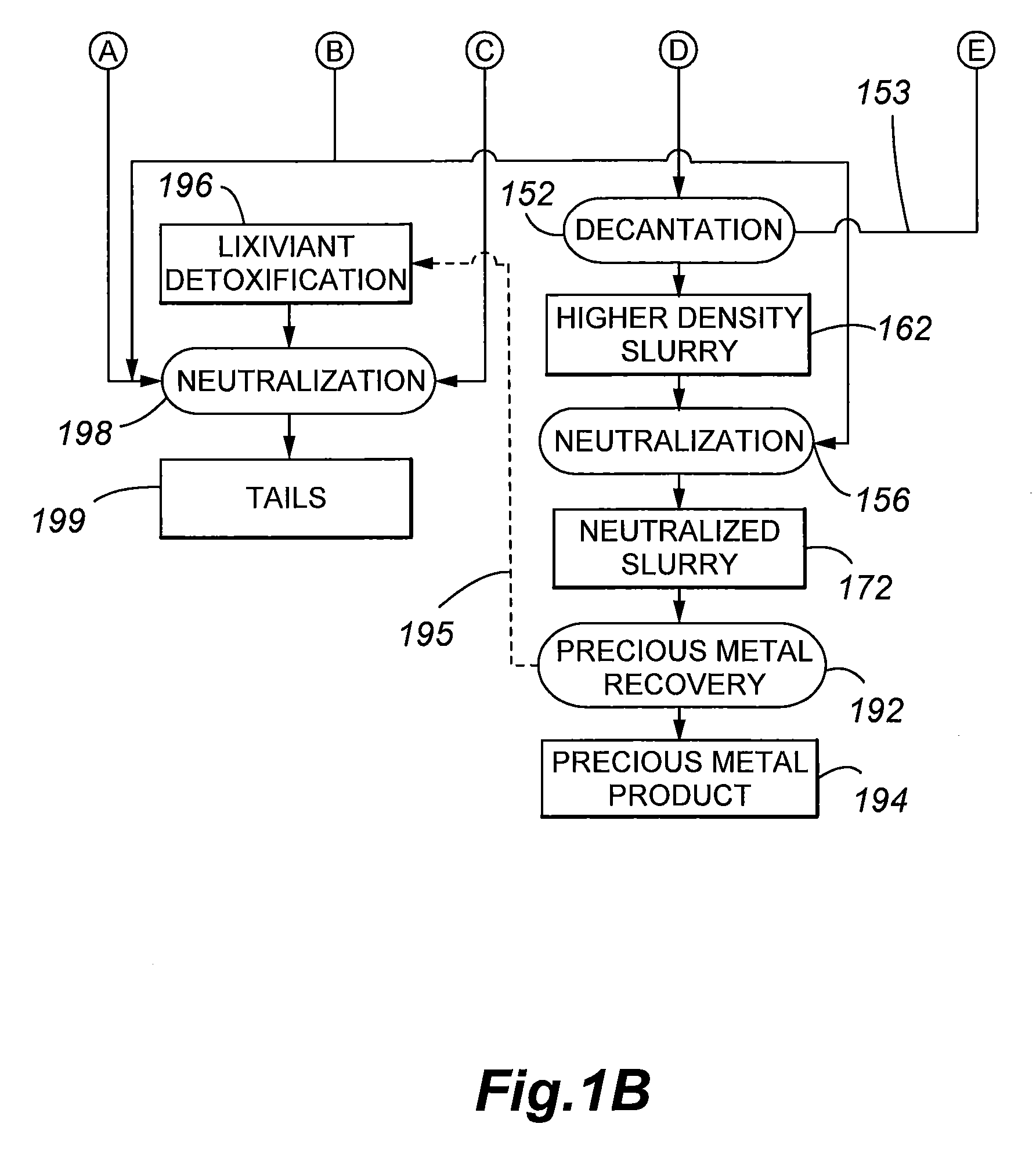
The present invention is directed to a precious metal recovery process in which an acid sulfidic feed material is subjected to acid pressure oxidation and an alkaline sulfidic feed material is subjected to alkaline pressure oxidation, with the discharge slurries from the pressure oxidation processes being combined to reduce neutralization requirements prior to precious metal recovery.
Owner:BARRICK GOLD
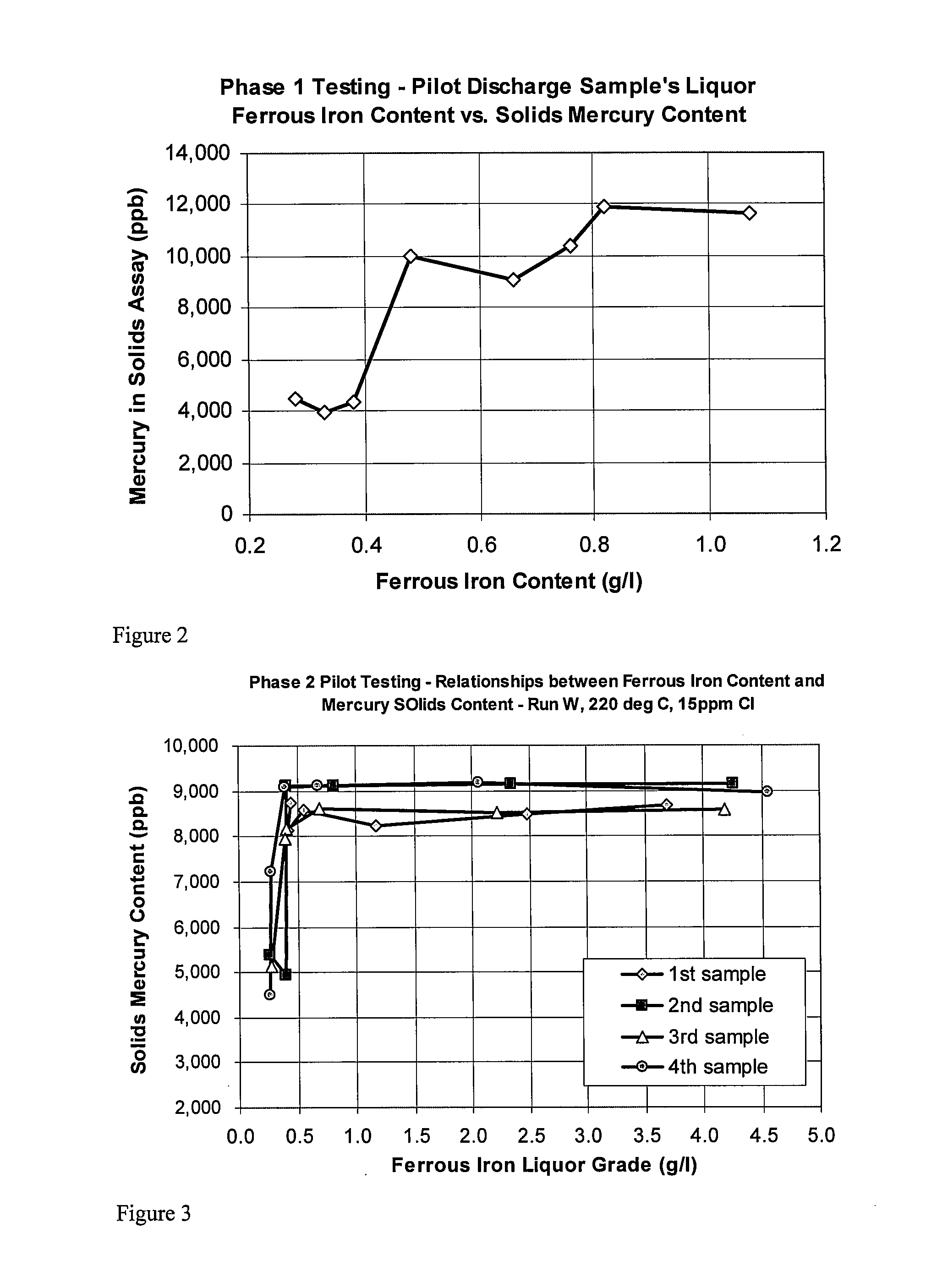
Process for mercury control during pressure oxidation
ActiveUS20090074608A1Reduce contentSimplify effluent treatmentSolvent extractionGold compoundsHalogenPressure oxidation
A method for suppressing mercury dissolution during pressure oxidation of precious metal-containing materials in the presence of halogens and halides is provided. Pressure oxidation is performed under controlled oxidative conditions to maintain the mercury predominantly in the solid residue.
Owner:BARRICK GOLD
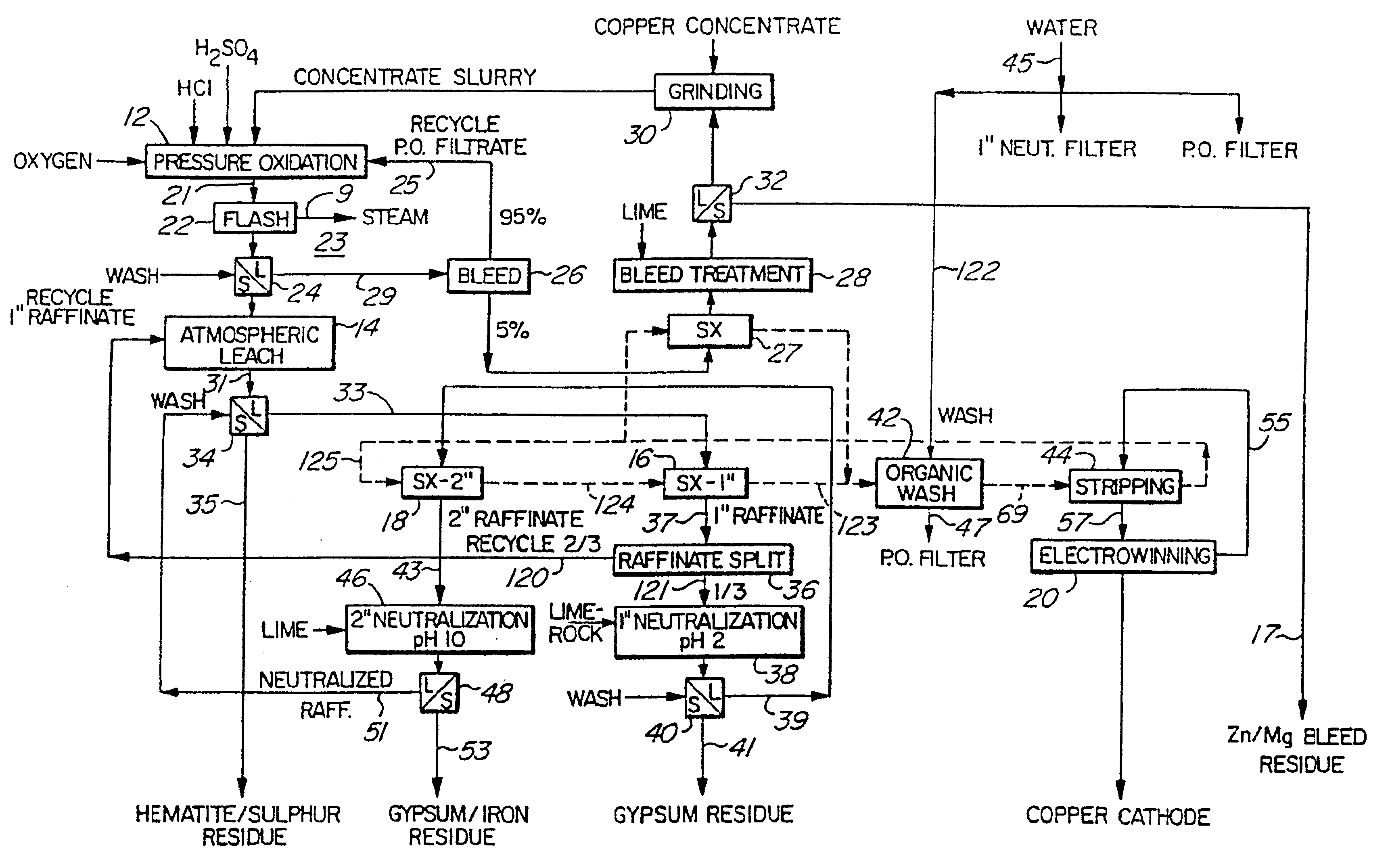
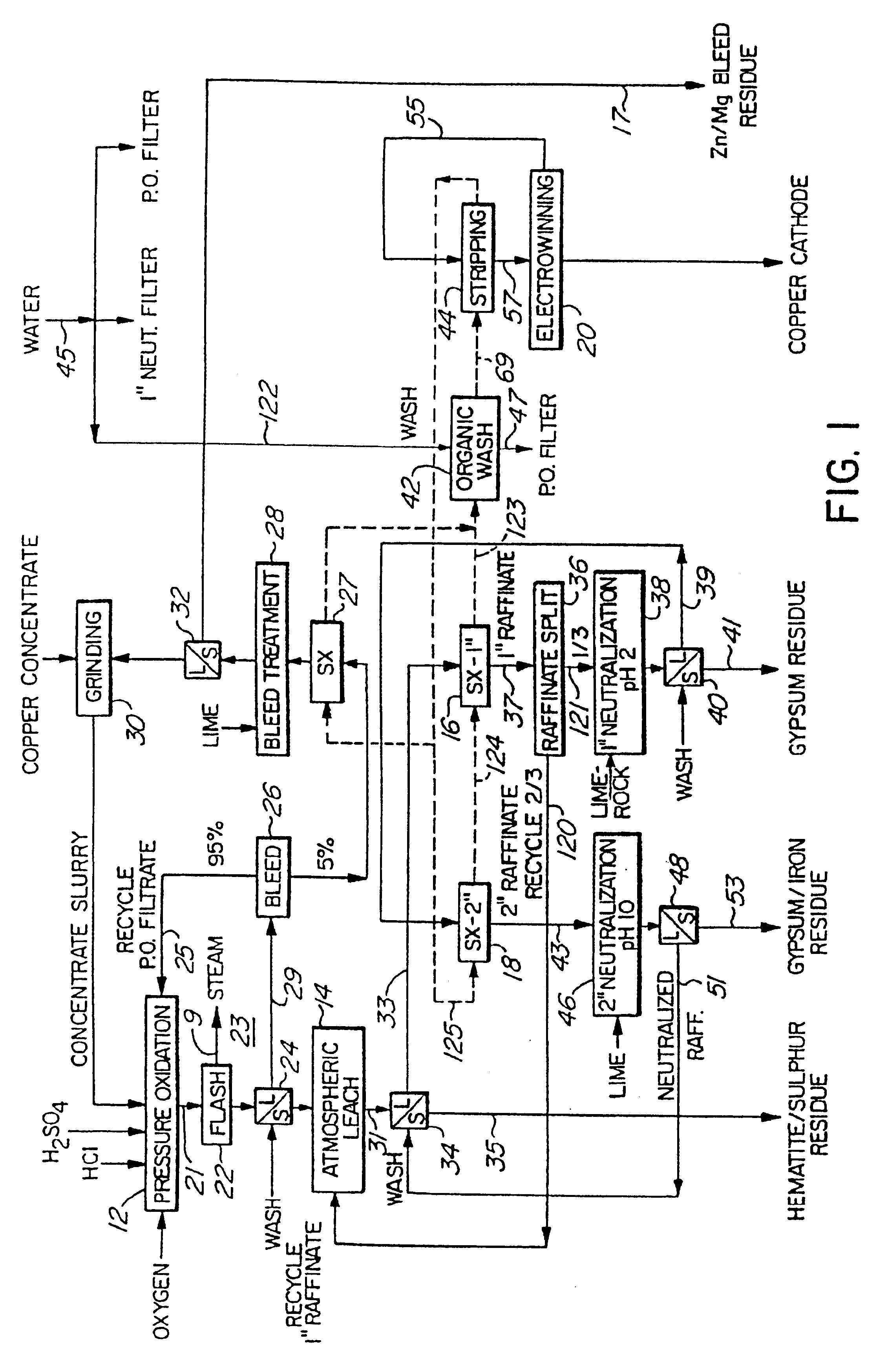
Process for the treatment of molybdenum concentrate
A method of treatment or purification of a molybdenum concentrate also containing copper, comprises the step of subjecting the molybdenum concentra te to pressure oxidation in the presence of oxygen and a feed solution containi ng copper (e.g. CuSO4) and halide (e.g. CuCl2) to produce a pressure oxidation solution containing copper and a solid residue containing molybdenum. The pressure oxidation solution may be combined with feed solution containing sulfuric acid to a second pressure oxidation in which a copper concentrate i s treated for the recovery of copper therefrom.
Owner:COMINCO ENG SERVICES
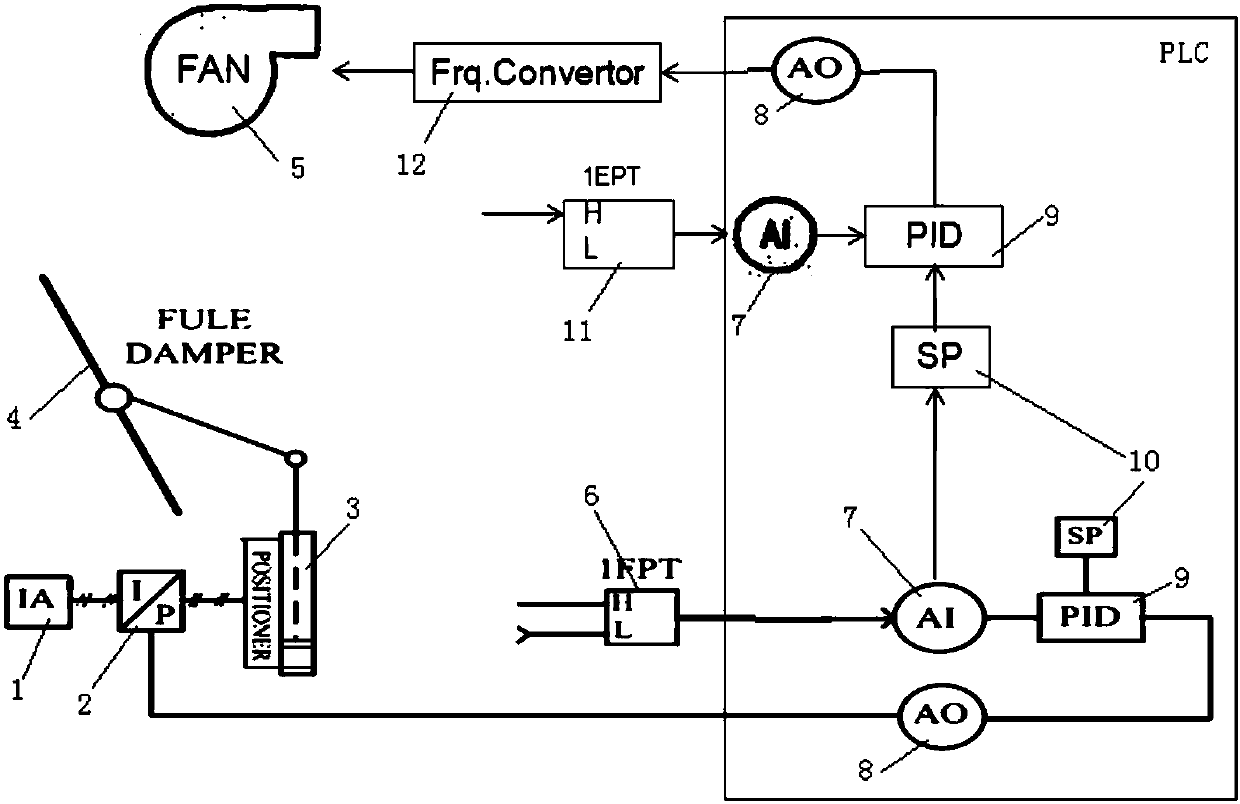
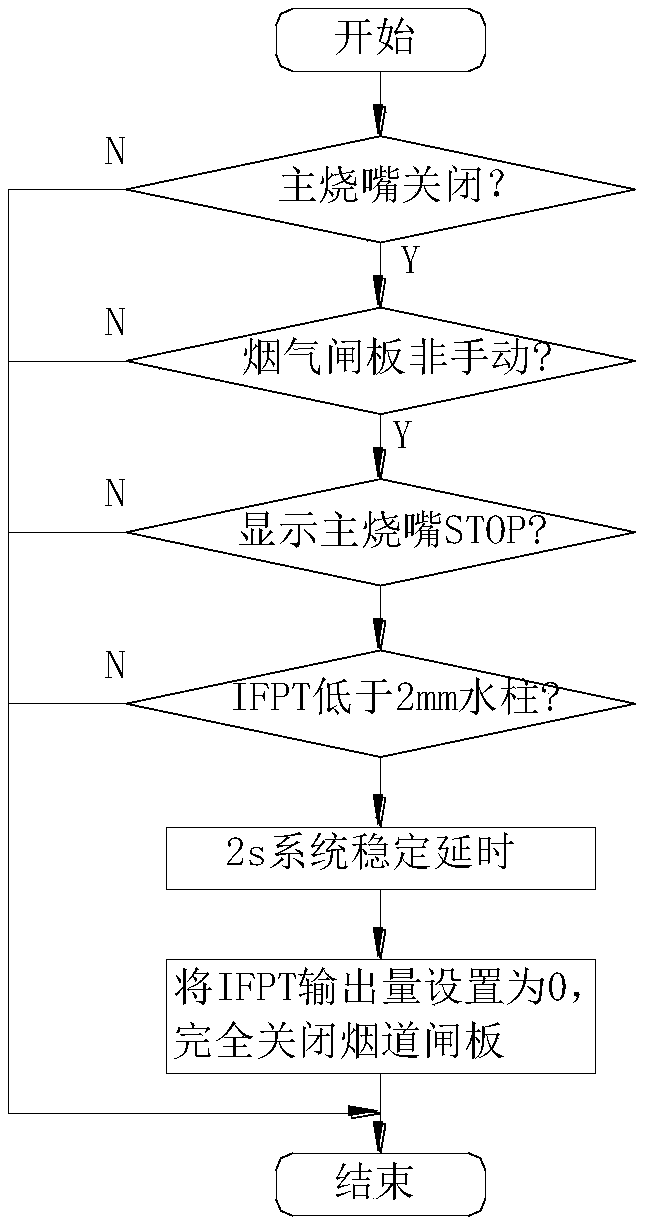
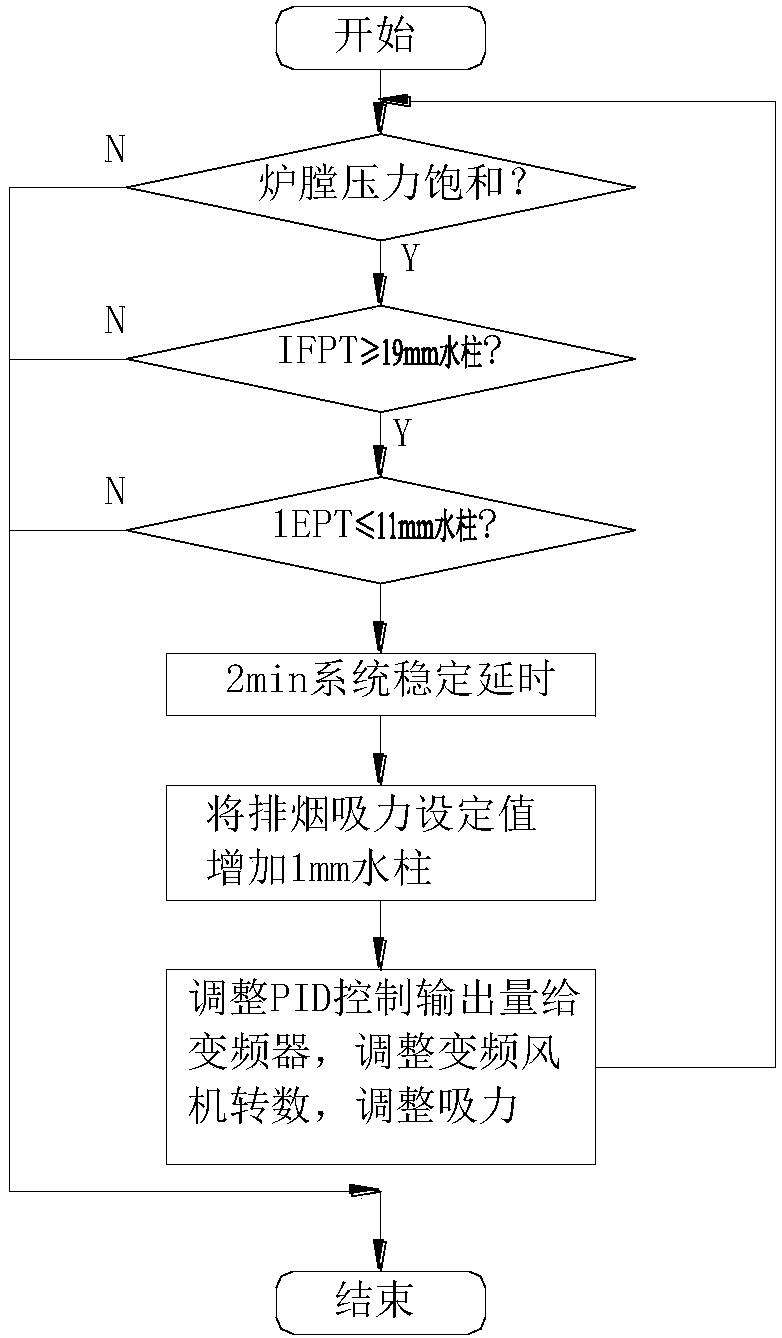
Furnace pressure control system and control method for automobile steel production by using open-flame continuous annealing furnace
InactiveCN107797512ASolve the problem of negative pressure oxidationReduce entryProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersSuction forceControl variable
The invention relates to a furnace pressure control system and control method for automobile steel production by using an open-flame continuous annealing furnace. The furnace pressure control system includes a pneumatic controller, a pneumatic valve locator, a smoke gate, a furnace pressure sensor, a smoke exhaust suction sensor, a frequency converter, a variable-frequency fan, and a PLC system. The pneumatic controller receives the pressure output by an analog output module AO of the PLC to the pneumatic valve locator, and controls the opening and closing of the smoke gate. The furnace pressure sensor converts the instantaneous furnace pressure into an input current of an analog input module AI and transmits the input current to the PLC system. The smoke exhaust suction sensor converts the instantaneous smoke exhaust suction force in the flue into an input current of the analog input module AI and transmits the input current to the PLC system. The frequency converter receives an output current from the AO of the PLC system as a control variable, and makes the rotation speed of the variable-frequency fan high enough to control the smoke exhaust suction force. The beneficial effectsare as follows: the problem of negative-pressure oxidation in the furnace under temporary stoppage and the problem of pressure fluctuation in the furnace during wide-range load adjustment in the open-flame section can be solved, the loss of refractory materials in the furnace can be reduced, and the production quality of automobile steel products can be improved.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
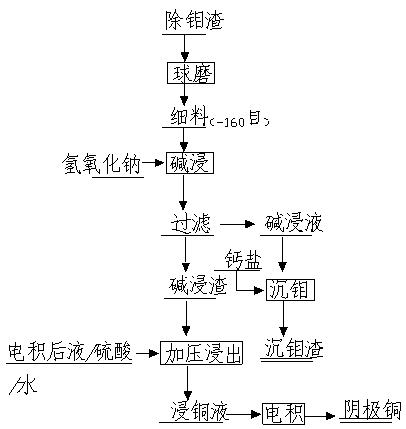
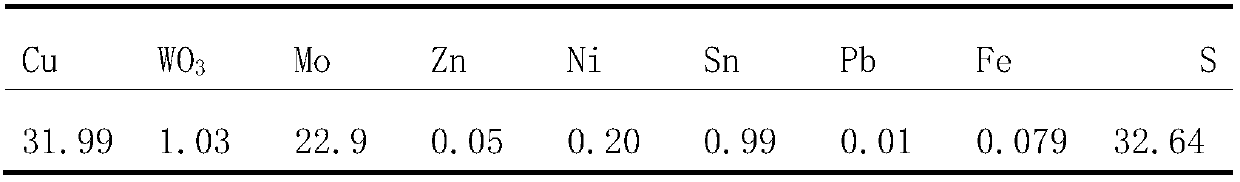
Method for recycling molybdenum and copper from tungsten smelting low grade molybdenum slag
InactiveCN108034823AAchieve separationHigh recovery ratePhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementSlagCathode
The invention relates to a method for recycling molybdenum and copper from tungsten smelting low grade molybdenum slag. The method comprises the following steps: ball milling, leaching of molybdenum,precipitating of molybdenum, leaching of copper and electrodeposition of copper. The alkaline leaching is subjected to alkaline leaching, so that molybdenum is obtained; molybdenum enters molybdenum leaching liquid, and copper is in molybdenum leaching slag, so that the separation of molybdenum and copper is realized; calcium chloride or calcium hydroxide is added into the molybdenum leaching liquid, and molybdenum is precipitated, so that a calcium molybdate product is obtained; the molybdenum leaching slag is subjected to pressure oxidation, and copper is leached, so that a copper-bearing solution is obtained; and the copper-bearing solution is subjected to electrodeposition, so that a cathode copper product is obtained. The method has the advantages of mature technology, environmental protection and high metal recovery rate.
Owner:江西自立环保科技有限公司
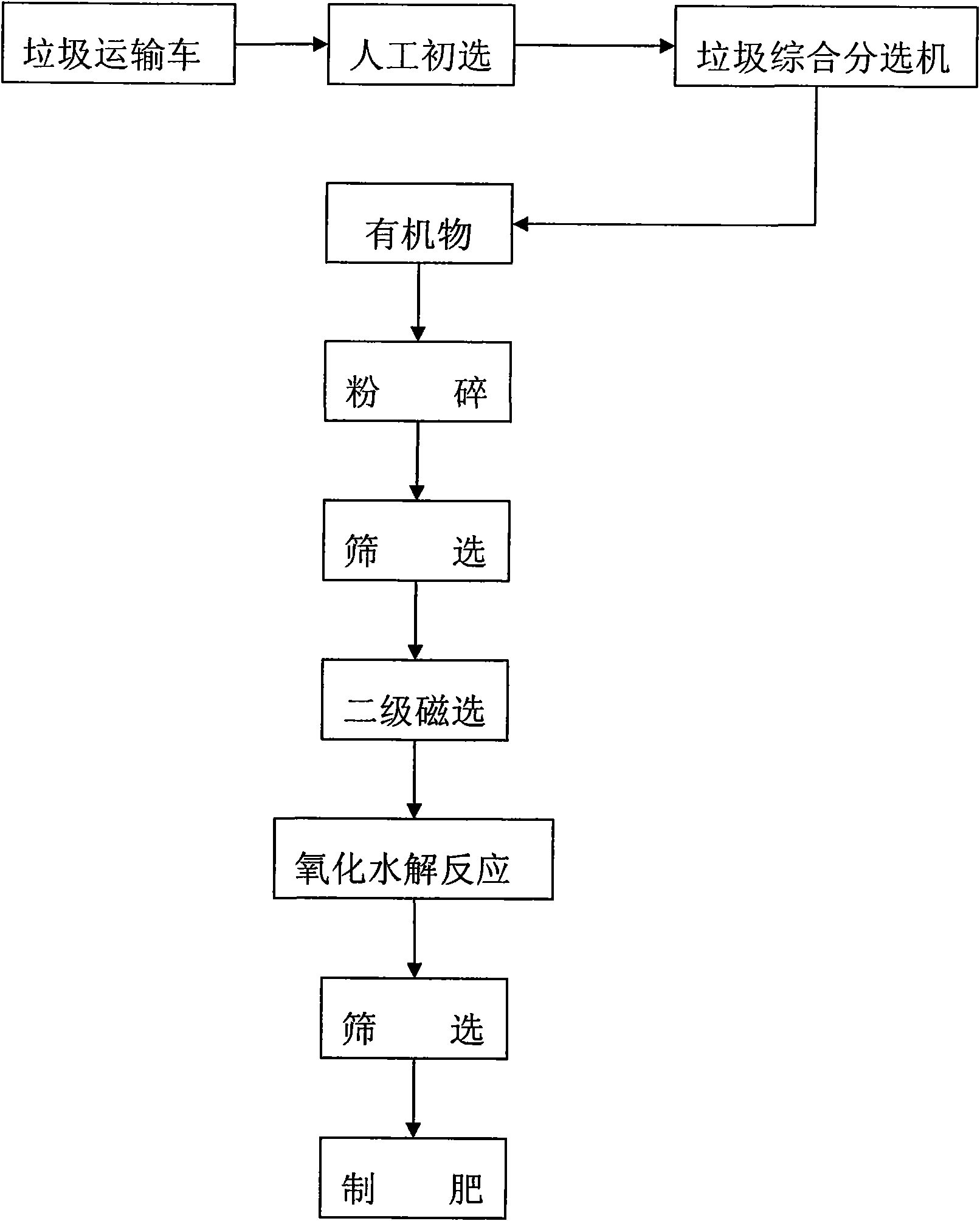
Process for treating domestic rubbish and wastes of agriculture and animal husbandry by low-pressure oxidation degradation method
InactiveCN101856662AHarm reductionCause secondary pollutionSolid waste disposalClimate change adaptationThree stageEngineering
The invention relates to a process of treating domestic rubbish and wastes of agriculture and animal husbandry by a low-pressure oxidation degradation method. Domestic rubbish, wastes of agriculture and animal husbandry, and biomass wastes are used as raw materials; after separation and crushing, the raw materials are treated in an oxidation kettle with a near critical low-pressure oxidation degradation method; and according to the three components of the raw materials, the method is divided into three stages, i.e. a low temperature stage, an intermediate temperature stage and a high temperature stage, to carry out low-pressure oxidation degradation so as to ensure that the raw materials in each temperature stage are thoroughly degraded. The production efficiency and the product quality are enhanced, the wastes are changed into resources to the largest limit, and the residue-free treatment is realized by recycling.
Owner:云南天远生态环保科技有限责任公司
Hydrometallurgical treatment process for extraction of metals from concentrates
ActiveUS9540706B2Minimize consumptionQuality improvementRecovering materialsHydrometallurgySulfide minerals
Owner:LIFEZONE
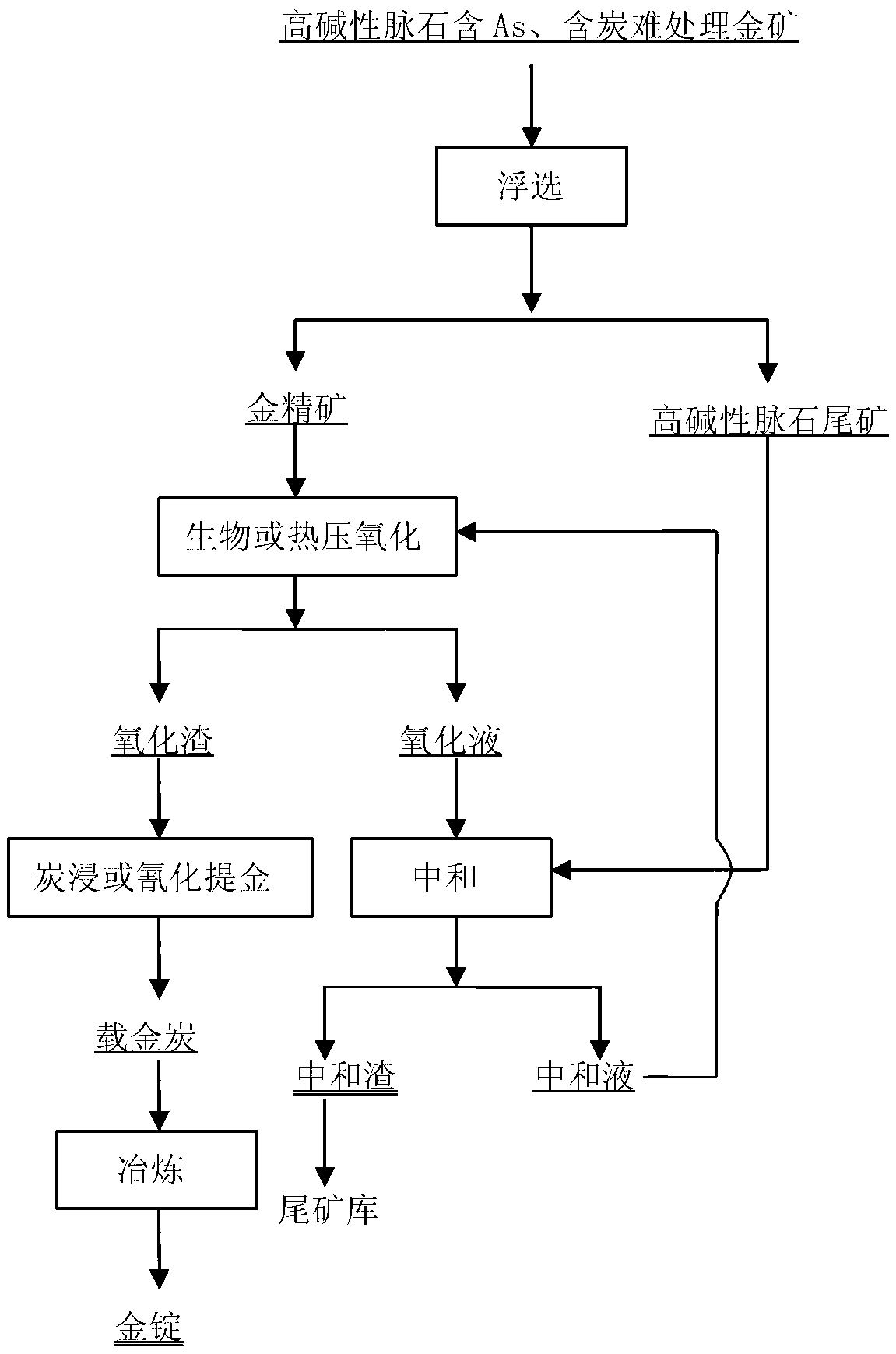
Method for extracting gold from high basic gangue containing arsenic and carbon
The invention relates to a method for extracting gold from high basic gangue containing arsenic and carbon. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: firstly performing flotation on micro-fine particles containing the As and carbon of the high basic gangue and gold ore which is difficult to treat to respectively obtain a gold concentrate and tailings of the high basic gangue, then performing gold extraction on the gold concentrate by adopting a biological oxidation-carbon leaching gold extraction process or a hot-pressure oxidation-cyanidation gold extraction process, finally adopting the tailings of the high basic gangue, obtained by flotation, to neutralize high acid, high Fe and As-containing oxidation waste liquid, which are produced by biological oxidation or hot-pressure oxidation, stacking neutralization slag in a tailing pond, and returning neutralization liquid for recycling. According to the method, high-efficient and low-cost recovery of the gold can be realized, and the following situations can be simultaneously realized: (1) harmful ingredients, namely SO4<2->, Fe, As and other harmful ions in an oxidation solution of the gold concentrate can be neutralized with CaO, MgO and other basic gangue in the tailings, and wastes can be used for treating the wastes; (2) the cost of neutralizing biological oxidation waste liquid or hot-pressure oxidation waste liquid is zero; and (3) the As, the Fe and other harmful ions exist in a stable safe state, the permeability of the neutralization tail slag is good, and the safety of the obtained neutralization slag is in line with national and related industry standards.
Owner:ZIJIN MINING GROUP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com