Patents
Literature
213 results about "Molybdenite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Molybdenite is a mineral of molybdenum disulfide, MoS₂. Similar in appearance and feel to graphite, molybdenite has a lubricating effect that is a consequence of its layered structure. The atomic structure consists of a sheet of molybdenum atoms sandwiched between sheets of sulfur atoms. The Mo-S bonds are strong, but the interaction between the sulfur atoms at the top and bottom of separate sandwich-like tri-layers is weak, resulting in easy slippage as well as cleavage planes. Molybdenite crystallizes in the hexagonal crystal system as the common polytype 2H and also in the trigonal system as the 3R polytype.
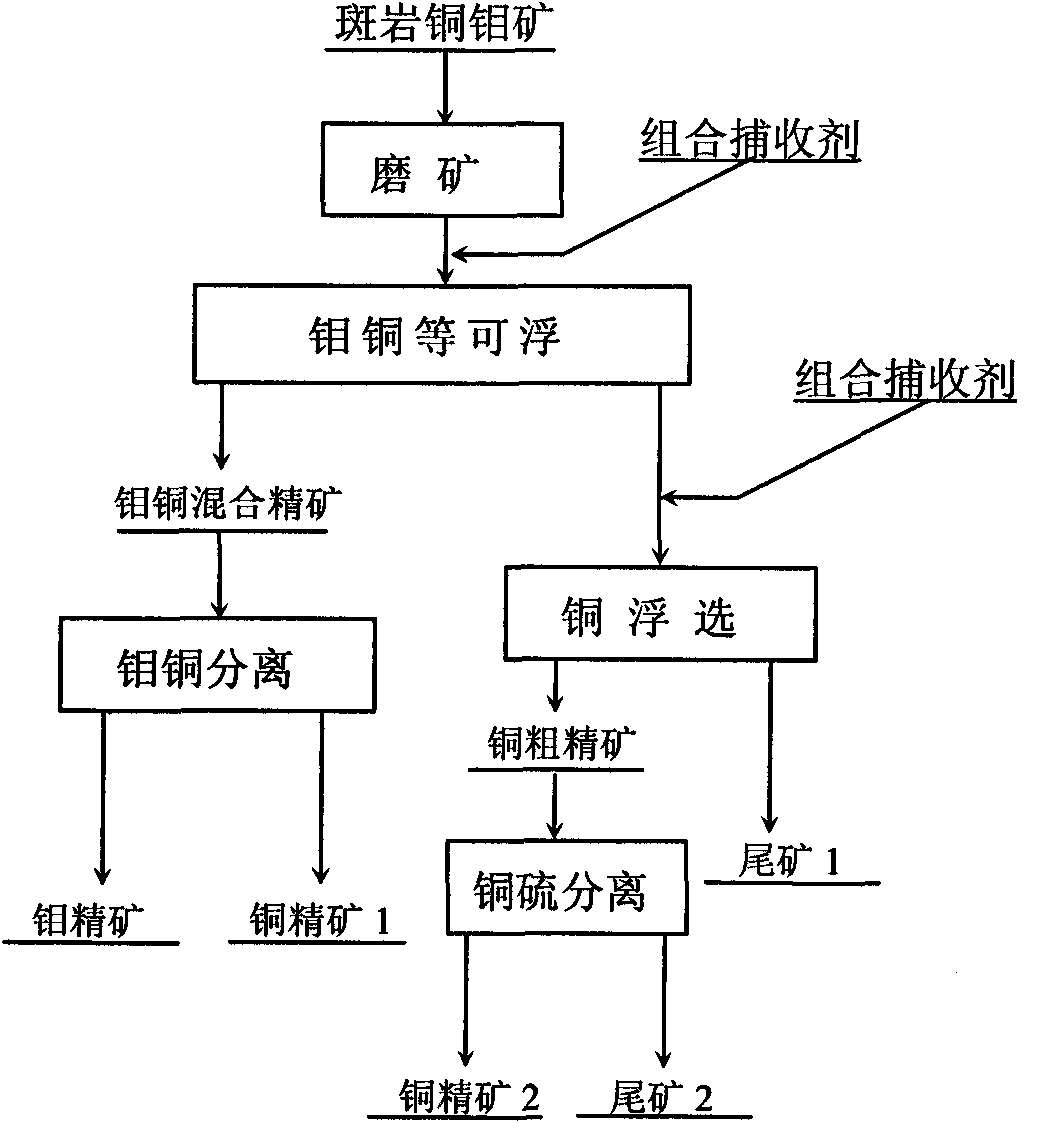
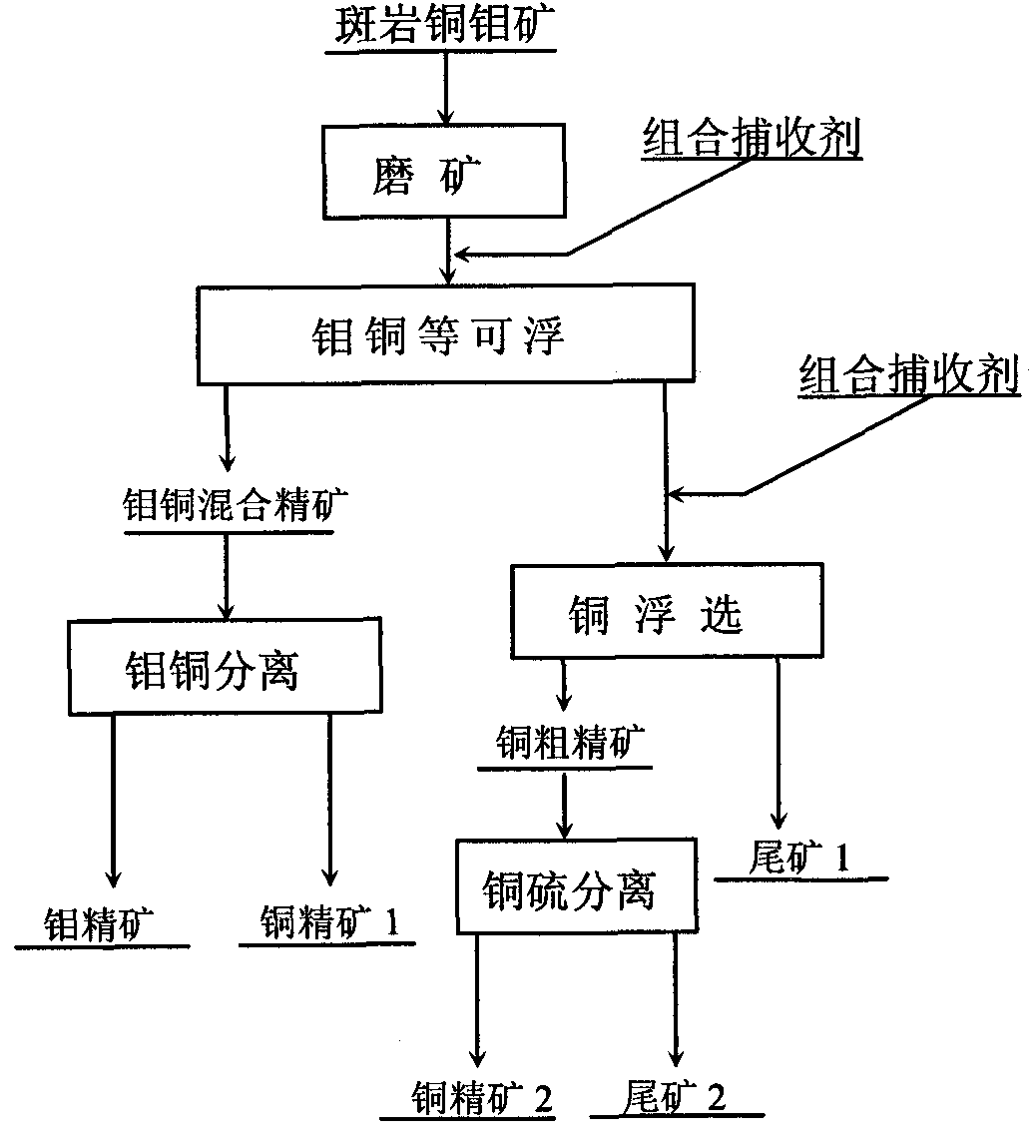
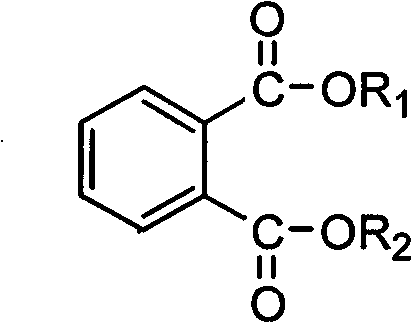
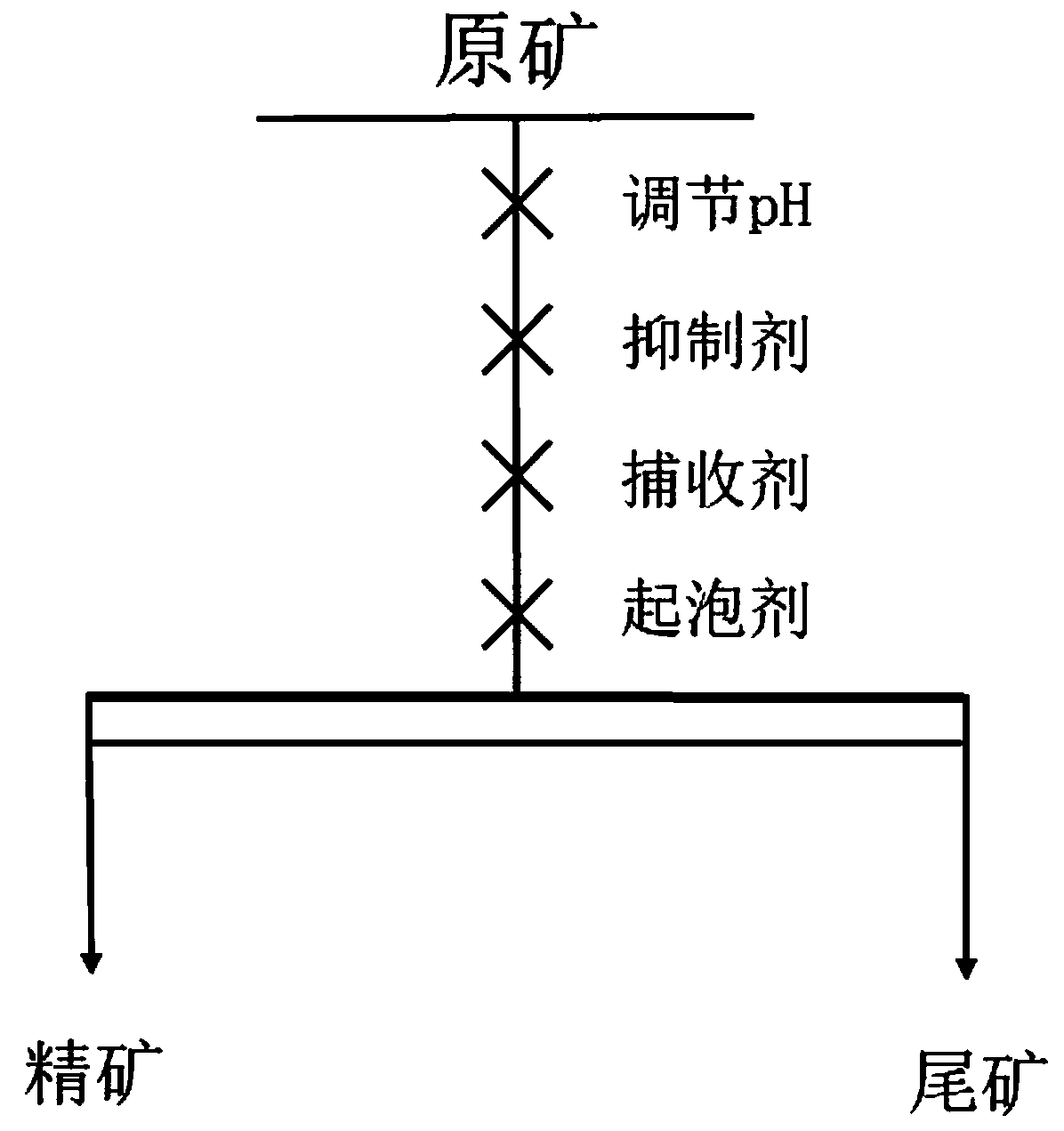
Combined collector for floatation of porphyry copper-molybdenum mine and floatation method thereof
The invention discloses a combined collector for floatation of a porphyry copper-molybdenum mine and a floatation method thereof. The combined collector is characterized by at least comprising phthalate and carboalkoxy (aryloxy)-thiourea. The combined collector is used in a process of the floatation of the porphyry copper-molybdenum mine and the method comprises the following steps of: performing the floatation on molybdenum, copper and the like in which the molybdenum is as a majority; floating molybdenite and part of copper sulfide minerals with high floatability so as to obtain a molybdenum and copper mixed concentrate with high a molybdenum recovery rate; and enhancing the recovery of the copper sulfide minerals with poor floatability. Due to the adoption of the combined collector and the method, the problem of strong inhibiting effect on the molybdenite caused by a high-alkali environment of lime in a conventional mixed floatation process of the porphyry copper-molybdenum mine is solved effectively; and the method has the characteristics of simple and reasonable flow, high molybdenum recovery rate and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Phyllosilicate mineral depressor for sulfide ore floatation and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a phyllosilicate mineral depressor for sulfide ore floatation and a preparation method thereof. The phyllosilicate mineral depressor for the sulfide ore floatation is prepared from the following components in part by weight: 0 to 20 parts of modified corn starch, 8 to 30 parts of sodium alginate, 1 to 35 parts of carboxymethyl cellulose or polyanionic cellulose or methylenenapadisilate dinaphthalene sulfonate, and 5 to 55 parts of sodium hexametaphosphate. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: selecting the reagents according to types of depressed minerals; adding the reagents in a high-speed mixing granulator in the set ratio for granulation; and drying the obtained grains to obtain the phyllosilicate mineral depressor for the sulfide ore floatation. The product has the characteristics of small dosage, good depression selectivity, low toxicity, and the like. The specific depressor is mainly applied to depressing phyllosilicate minerals such as talcs, serpentines, chlorites, kaolinites and the like during the sulfide ore floatation, thus the specific depressor is favorable for improving floatation concentrate grade and metal recovery rate, and is particularly suitable for floating talc-containing molybdenites and nickel sulfide ores.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU MINERALS COMPOSITIVE UTILIZATION RES INST CHINESE GEOLOGICAL ACAD
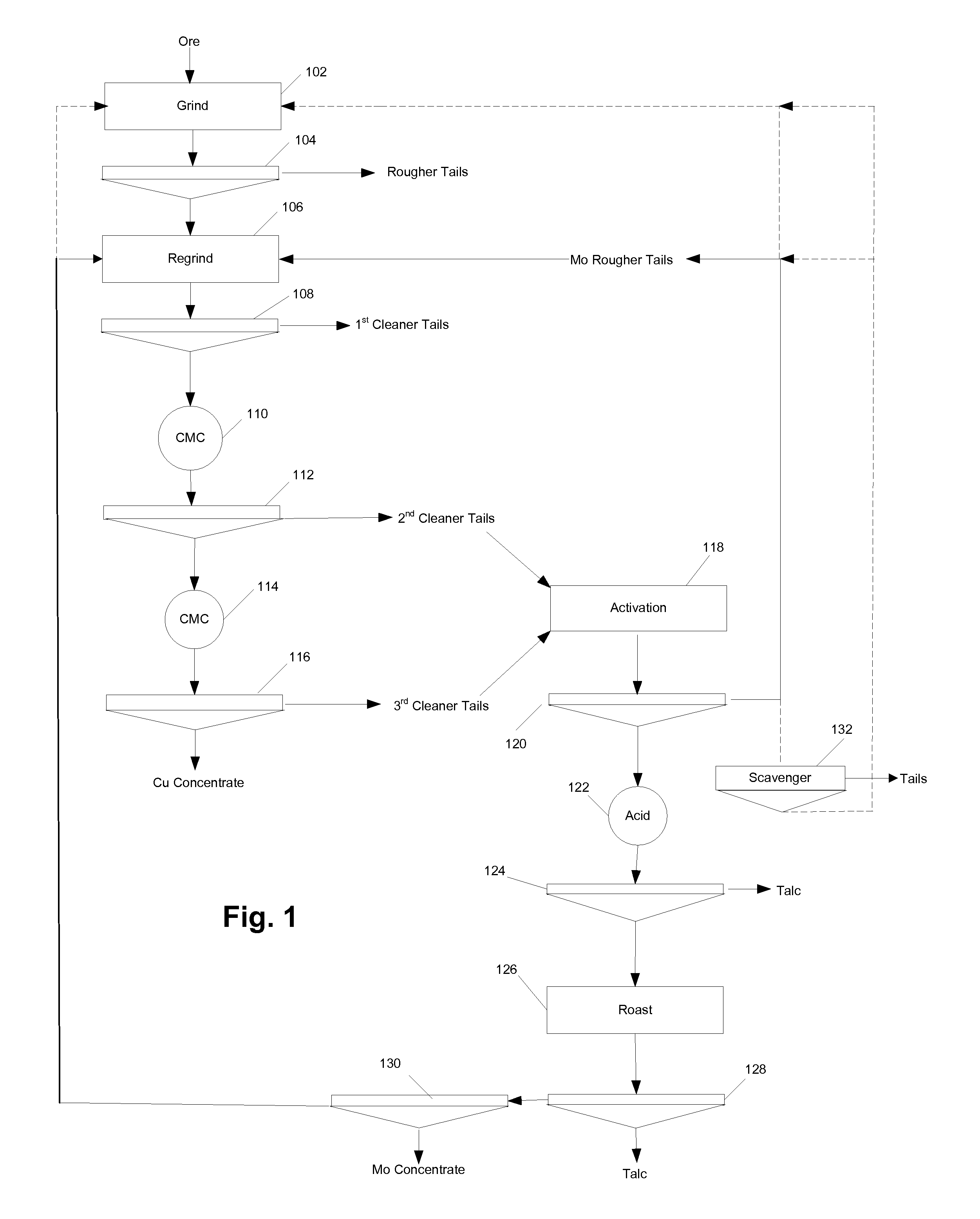
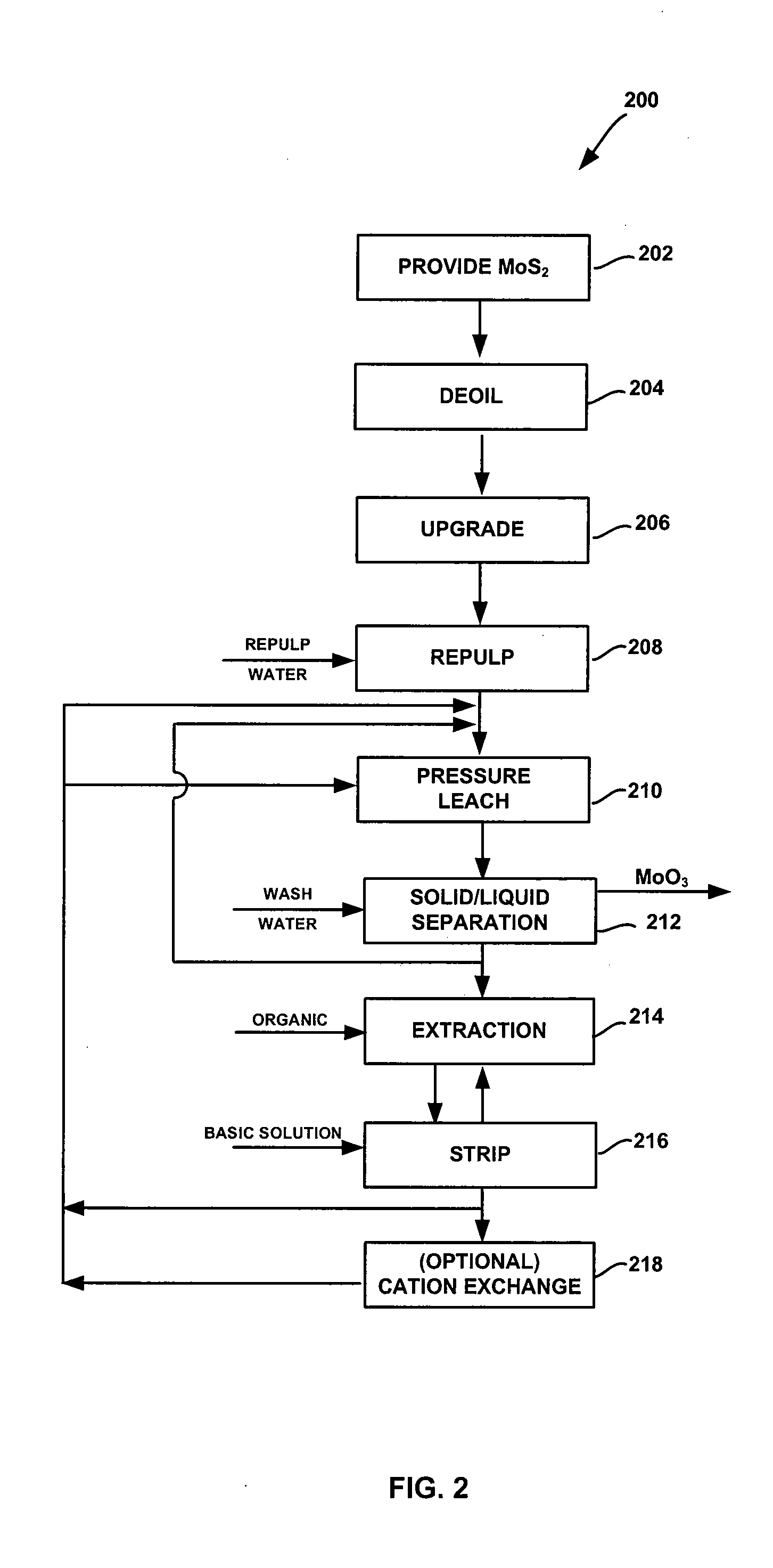
Methods for the recovery of molybdenum
A method for the recovery of molybdenum from an ore that includes a molybdenum-bearing mineral, such as molybdenite. The ore is treated to recover metal values from the ore, such as base metals, by utilizing a depressant to depress the flotation of the molybdenite. The tailings, which can include insoluble silicate minerals in addition to the molybdenite, are then activated to render the molybdenite floatable in one or more subsequent flotation steps, thereby producing a high-grade molybdenum concentrate.
Owner:KUHN MARTIN C
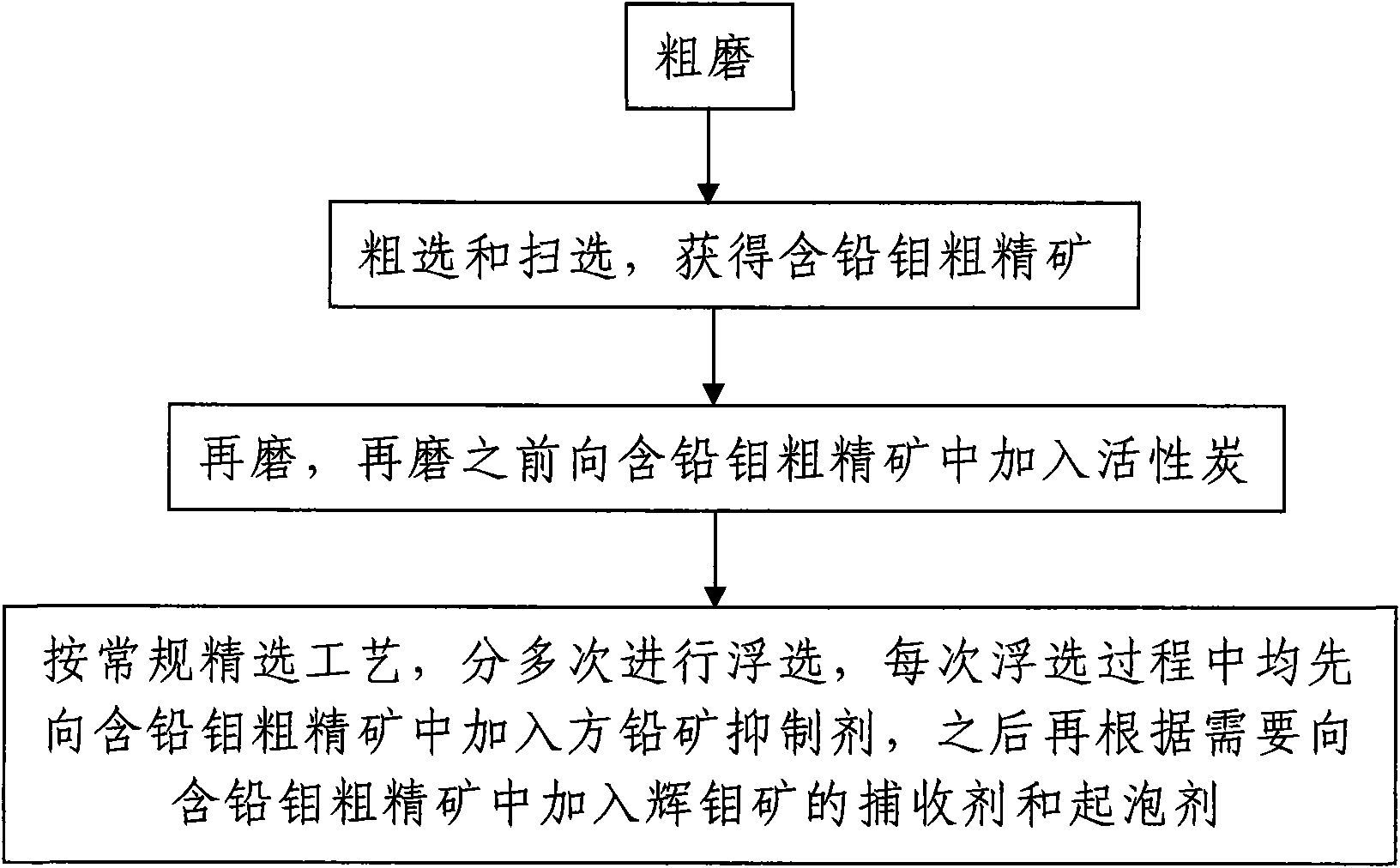
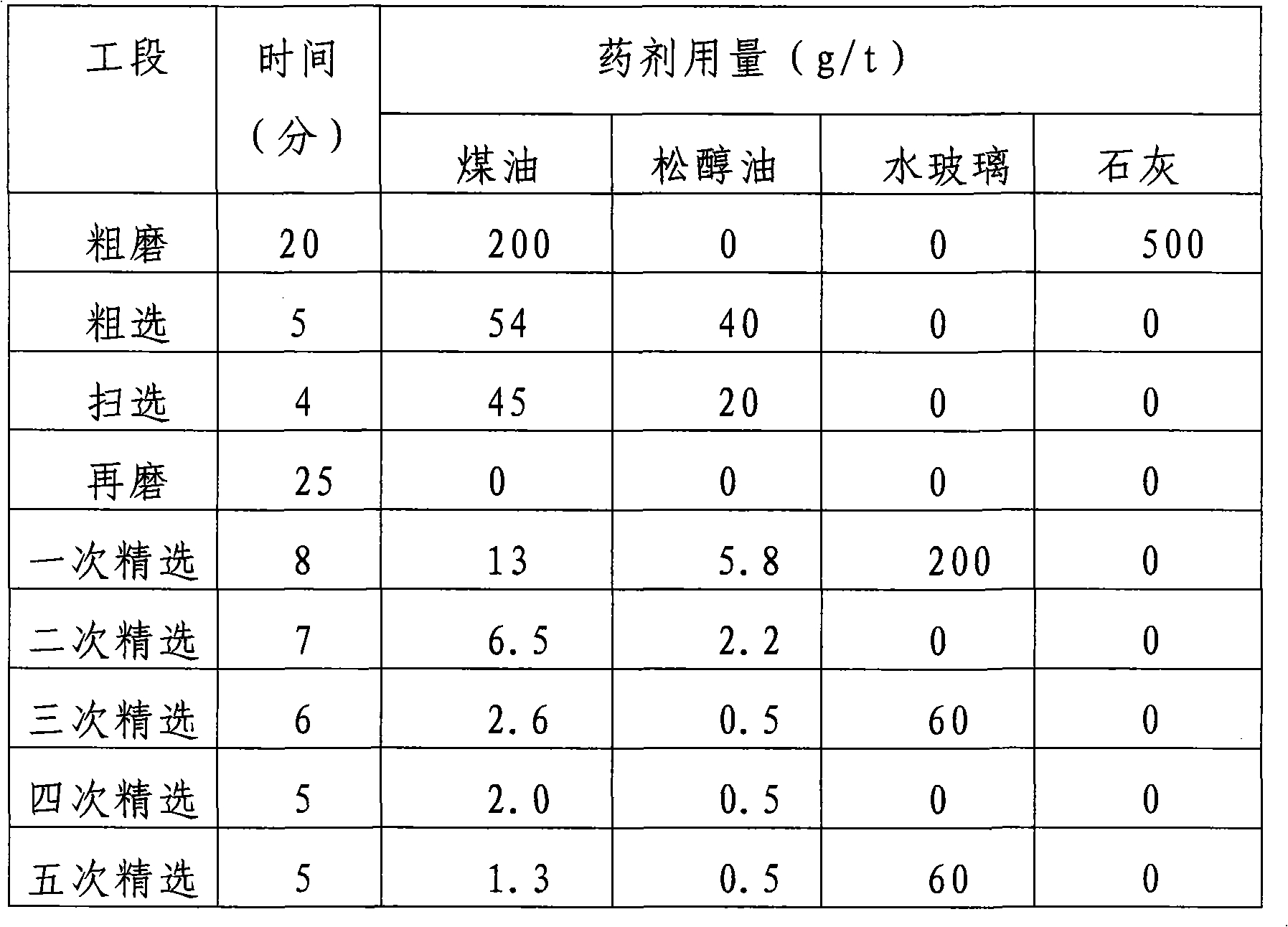
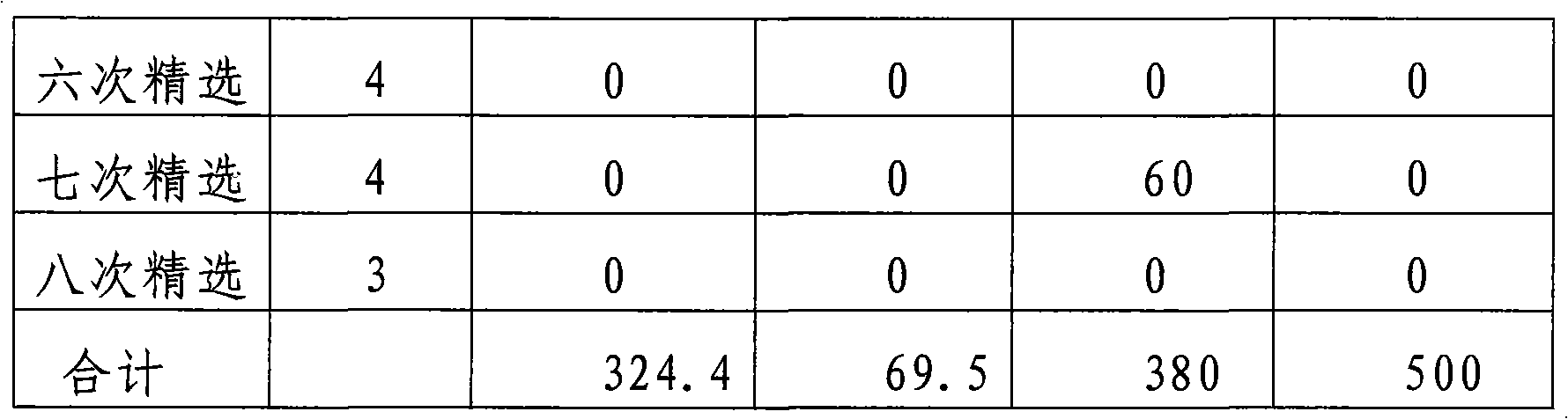
Flotation separation method for molybdenite and galena
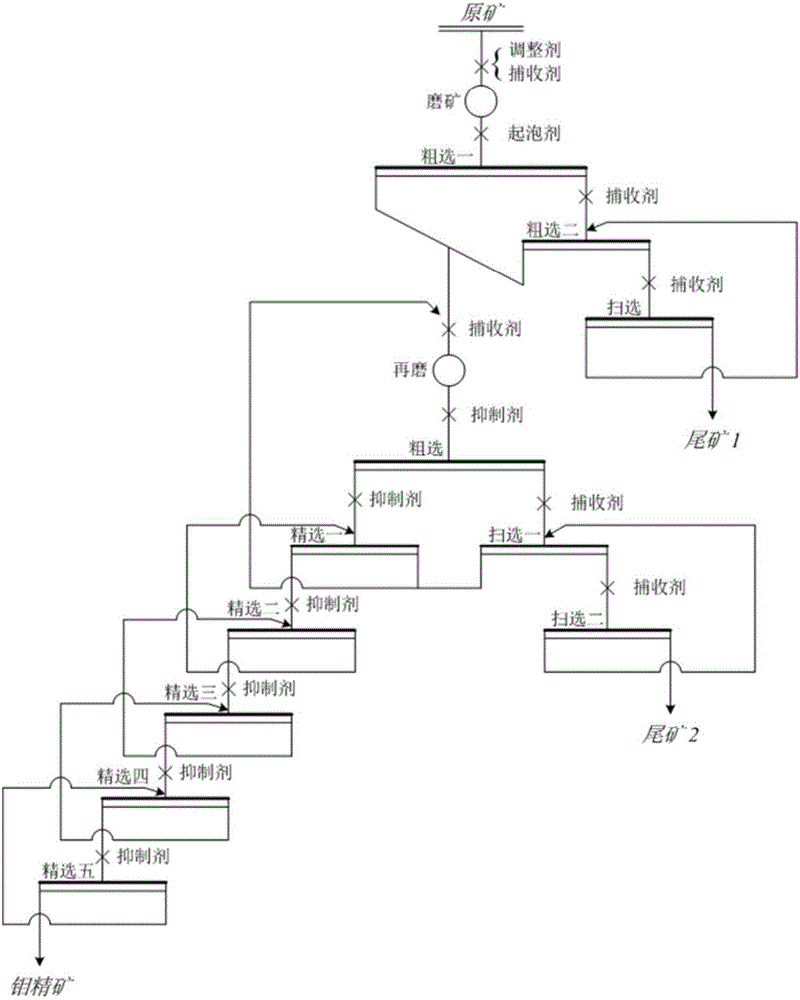
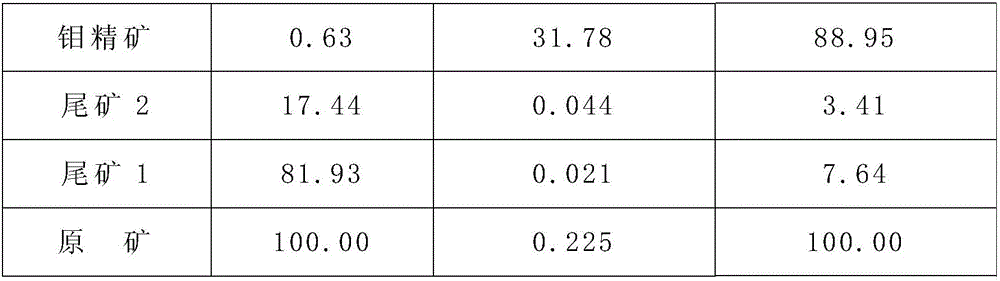
The invention discloses a flotation separation method for molybdenite and galena, which comprises the following steps of: 1, rough grinding; 2, rough selection and scavenging for obtaining lead-containing molybdenum rough concentrate; 3, regrinding after a certain amount of active carbon is added into the lead-containing molybdenum rough concentrate; and 4, multiple selection: selecting the reground lead-containing molybdenum rough concentrate for multiple times according to the conventional selection process, adding a galena inhibitor into the lead-containing molybdenum rough concentrate at each time of selection, and then adding a molybdenite collecting agent and a foaming agent into the lead-containing molybdenum rough concentrate as required. The method has the advantages of simple separation process, reasonable design, good separation effect and capabilities of reducing the lead content to be as minimum as possible in an ore dressing process of molybdenum, effectively improving the reclamation rate of the molybdenum and thoroughly reducing the pollution of the lead to the environment at the same time of reducing the molybdenum concentrate smelting production cost and simplifying the production process.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Preparation method and application of non-molybdenum sulfide mineral flotation and separation inhibitor
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a non-molybdenum sulfide mineral flotation and separation inhibitor. The preparation method for the flotation and separation inhibitor comprises the step of enabling phosphorus pentasulfide and alkaline compounds to react with water-soluble macromolecules, and thus the flotation and separation inhibitor can be obtained. According to the preparation method for the non-molybdenum sulfide mineral flotation and separation inhibitor, operation is easy, the process conditions are mild, the raw material cost is low, and the industrial production requirements are met; and moreover, the prepared product directly serves as the non-molybdenum sulfide mineral inhibitor applied to flotation and separation of molybdenum sulfide minerals and non-molybdenum sulfide minerals, the molybdenum sulfide minerals and the non-molybdenum sulfide minerals can be effectively separated, the grade of molybdenum concentrates is improved, and the flotation and separation inhibitor is particularly suitable for flotation and separation of molybdenite, copper sulfide ore, galena, pyrite, jamesonite, arsenopyrite, bismuth sulfide ore and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Beneficiation method for effectively recovering extremely-fine-particle molybdenum ore
The invention discloses a beneficiation method for effectively recovering extremely-fine-particle molybdenum ore. The beneficiation method comprises the steps that a novel separation technique combining sulfur induction with oil agglomeration flotation is adopted, the surface flotation particle sizes of extremely-fine ore particles are increased through oil agglomeration, enrichment of associated metal ore is improved through sulfur induction, and thus the effect that high-recovery-rate molybdenum crude concentrate is obtained in the rough grinding stage is ensured; and in the regrinding and concentration stage, molybdenite aggregates are disaggregated under mechanical action and then enriched again with hydrocarbon oil, molybdenite is effectively separated from the associated metal ore by optimizing a reagent system, and molybdenum concentrate meeting the beneficiation indexes that the grade is higher than 30% and the recovery rate is 87% or over can be obtained. By the adoption of the beneficiation method for effectively recovering the extremely-fine-particle molybdenum ore, the problem that it is difficult to recover and reuse molybdenite with the crystal particle sizes being smaller than 0.020 mm is effectively solved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
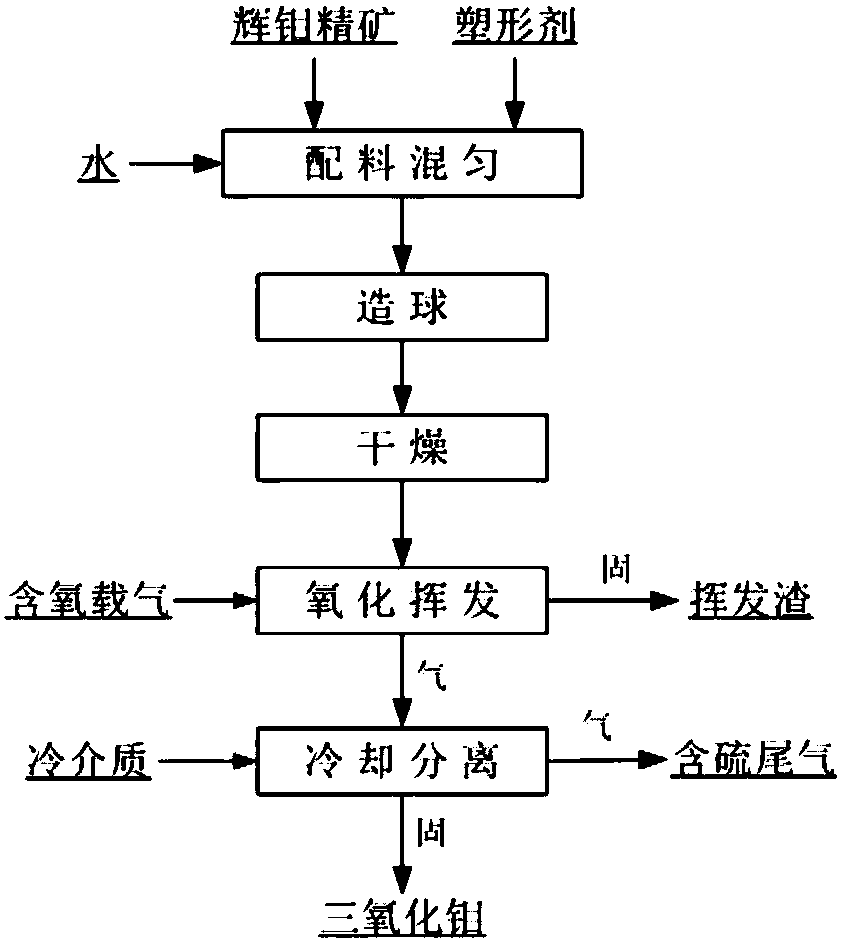
Method for microwave roasting of molybdenite concentrate to produce high-purity molybdenum oxide
ActiveCN104326509AEvenly heatedUniform compositionMolybdenum oxides/hydroxidesMicrowave cavityThermal insulation
Belonging to the technical field of molybdenum metallurgy, the invention relates to a method for microwave roasting of molybdenite concentrate to produce high-purity molybdenum oxide. The method includes: firstly conducting crushing and ball milling on molybdenite concentrate, then spreading the crushed molybdenite concentrate to a thickness of 1-4cm, and placing the product in a microwave cavity; turning on a microwave output switch, blowing in compressed air, regulating the microwave output power, and carrying out pre-oxidation on the crushed molybdenite concentrate; heating the pre-oxidized molybdenite concentrate to a sublimation temperature and performing thermal insulation for 30-60min, in the process, letting the molybdenum trioxide steam generated by oxidizing roasting overflow through a microwave reactor top, performing water-cooling and then conducting collection by a bag dust collector, thus obtaining high-purity molybdenum trioxide reaching the nonferrous metal industry grade 2 standard. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of short technological process, low energy consumption, and high product purity, etc.
Owner:徐州宇帆机电科技有限公司
Method for separating bright molybdenum and brass in refractory molybdenum copper sulphide ore
InactiveCN102824954ALow recovery rateHigh recovery rateFlotationWet separationChalcopyriteRefractory
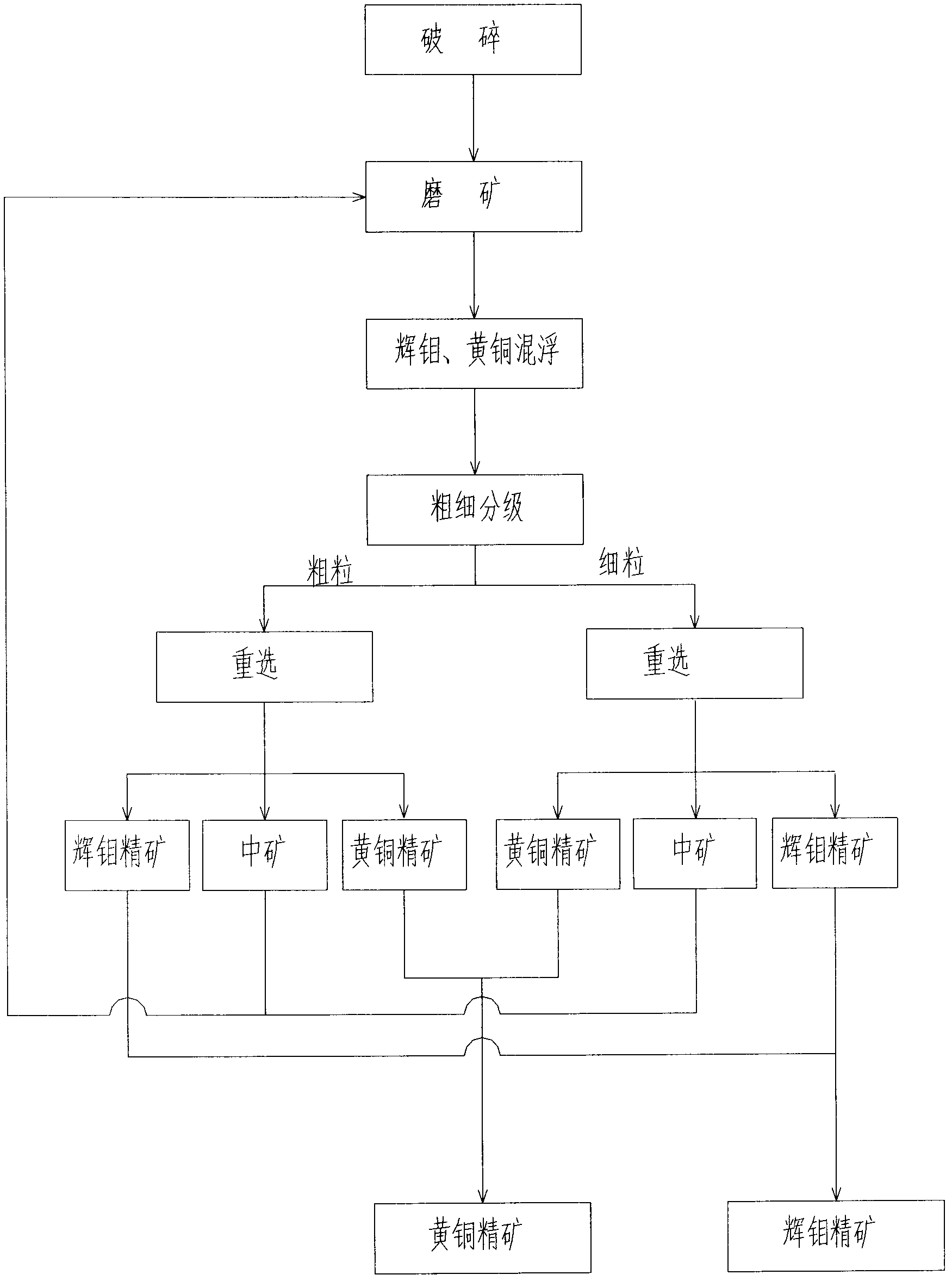
The invention discloses a method for separating bright molybdenum and brass in refractory molybdenum copper sulphide ore. According to the method, primordial bright molybdenum and brass ore are used as raw materials and are subject to general floatation after being crushed and ground, thereby enriching bright molybdenum and brass; the bright molybdenum and brass are subject to thickness grading in order to separate out coarse and fine products, the coarse particle portion and the fine particle portion are respectively subject to table re-separation in order to separate bright molybdenum and brass, thereby obtaining the qualified bright molybdenum and brass ore concentrate, mixed intermediate ore of bright molybdenum ore and brass ore, and qualified brass ore; the mixed intermediate ore is returned back to the re-grinding technique and introduced into the circulating system, thereby realizing the separation of the refractory bright molybdenum and brass. The technique has the following advantages that the disadvantages of greatly increased cost caused by the addition of a large amount of inhibitors in the common separation of bright molybdenum and brass for inhibiting the brass ore and the removing of the regents when brass is recovered from the tailings, in particular the disadvantages of the reduction of recovering ratio of the bright molybdenum particularly the brass when a large amount of brass ore inhibitors are existent in the water system, and the environmental impact due to the need of reagents in the common floating separation, are avoided.
Owner:北京华夏建龙矿业科技有限公司
Method for recovering tungsten and molybdenum from phosphor middling
The invention relates to a method for recovering tungsten and molybdenum from phosphorus middling ore, which relates to a method for recovering the tungsten and the molybdenum from the phosphorus middling ore (containing 15 to 30 percent of P2O5). Minerals to be processed are minerals which undergo primary floatation and enrichment and contain 15 to 30 percent of P2O5, wherein the content of the apatite is about 30 percent, the content of the dolomite is more than 15 to 20 percent, and scheelite and a small amount of calcium molybdate mine and molybdenite are accompanied. Moreover, the content of WO3 is between 12 and 25 percent; the content of Mo is between 2 and 6 percent; and the mass ratio of the Mo to the WO3 is between 12 and 40 percent. By application of the processing method provided by the invention, more than 50 percent of mine which is easy to be acid soluble including the apatite completely enters into a solution and simultaneously more than 60 percent of molybdenum and a small amount of tungsten enter into the solution as well; and the content of the WO3 in the tunstite left is between 50 and 70 percent, and the mass ratio of the Mo to the WO3 is reduced to 5 percent. The method has the advantages that the technololgy is simple and easy; the reagent is single; the separation effect of P-WO3 and Mo-WO3 is good; and three valuable elements including P, Mo and W can be respectively recycled.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
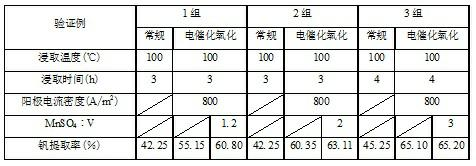
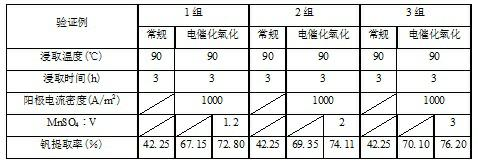
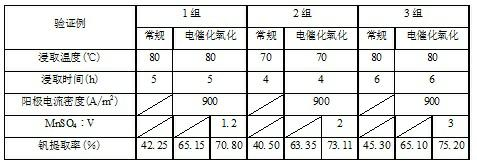
Method for leaching vanadium slag in converter by electro-catalytic oxidation
InactiveCN102134640AIncreased electrocatalytic oxidationHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementElectrodesSlagHigh energy
The method discloses a method for leaching vanadium slag in a converter by electro-catalytic oxidation. In the method, the vanadium slag in the converter is mixed with MnSO4 and H2SO4 to obtain slurry and then leaching is conducted by non-membrane electro-catalytic oxidation; and after the leached ore slurry is filtered and separated, the vanadium in the obtained leaching solution is extracted through conventional ammonium salt (ammonium sulfate) vanadium precipitation so as to prepare vanadium pentoxide. During the leaching, the low-valent vanadium which is not easily leached in the vanadium slag is oxidized into high-valent vanadium which is easily leached by an anode-generated strong oxidant Mn3+ so that the leaching rate of the vanadium is improved by using an electro-catalytic oxidation method to leaching the vanadium slag, therefore, the problems of high energy consumption and high pollution in the traditional leaching methods are avoided, otherwise, the method is also suitable for the extraction of the vanadium in the raw materials including vanadium and the selective leaching of molybdenite concentrate; meanwhile, the method has the characteristics of being good in selectivity, moderate in technological condition, free of pollution and the like, therefore, a novel environmentally friendly wet decomposition method is provided.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
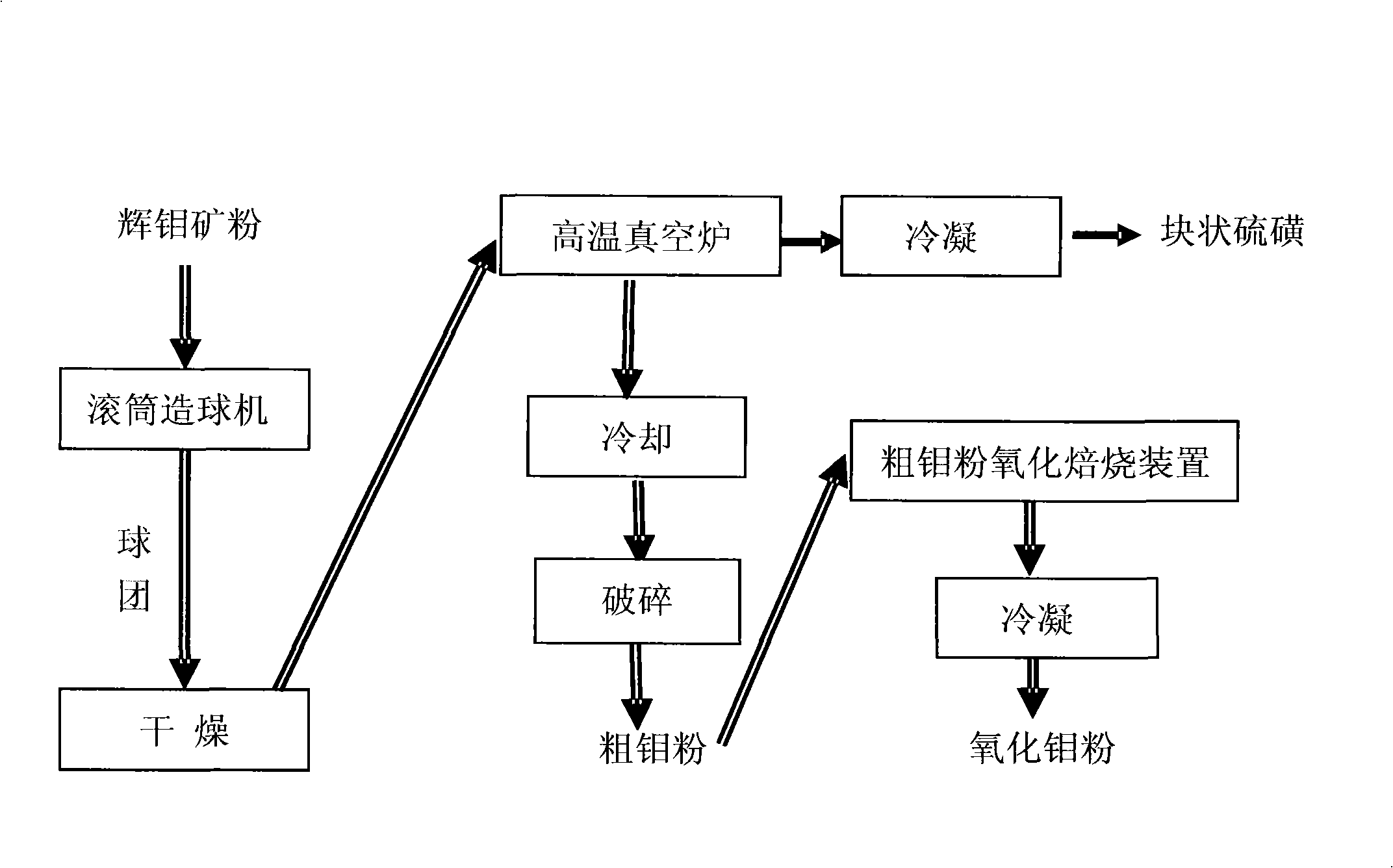
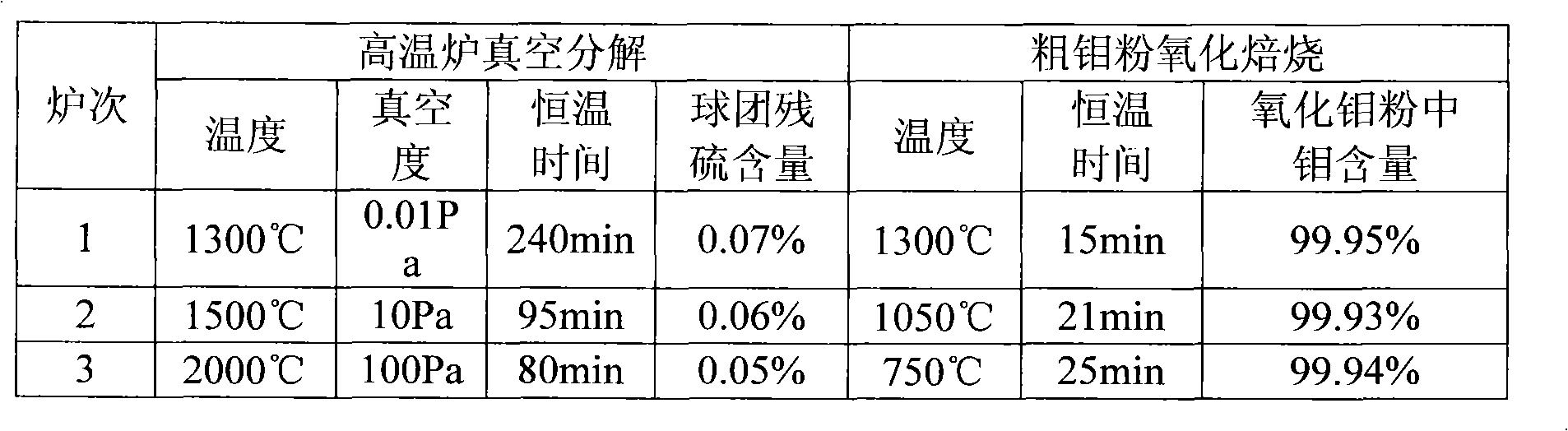
Method for preparing high-pure molybdenum oxide by vacuum decomposition of molybdenite
InactiveCN101254949AImprove efficiencyAvoid processing powerMolybdenum oxides/hydroxidesHydrogenDecomposition
The invention relates to the technology field of nonferrous metallurgy, in particularly to a method of preparing pure molybdenum trioxide by vacuum decomposing a molybdenite which is suitable for producing a metal molybdenum powder. The method takes two steps to prepare the pure molybdenum trioxide MoO3: the first step is to prepare a nonferrous impurity and a molybdenum powder with low content of sulfur; the second step is to oxidize the molybdenum powder into the pure molybdenum trioxide by the oxidation process, then the pure MoO3 powder can be produced, and at the same time the method has no SO2 exhaust emission and recovery problems, which reduces exhaust emission and enhances comprehensive efficiency of resources. The MoO3 powder can also be taken as the raw material for producing molybdenum powder by hydrogen reduction; the pure molybdenum powder can be obtained and the application field of the method is broader.
Owner:SONGXIAN EXPLOITER MOLYBDENUM
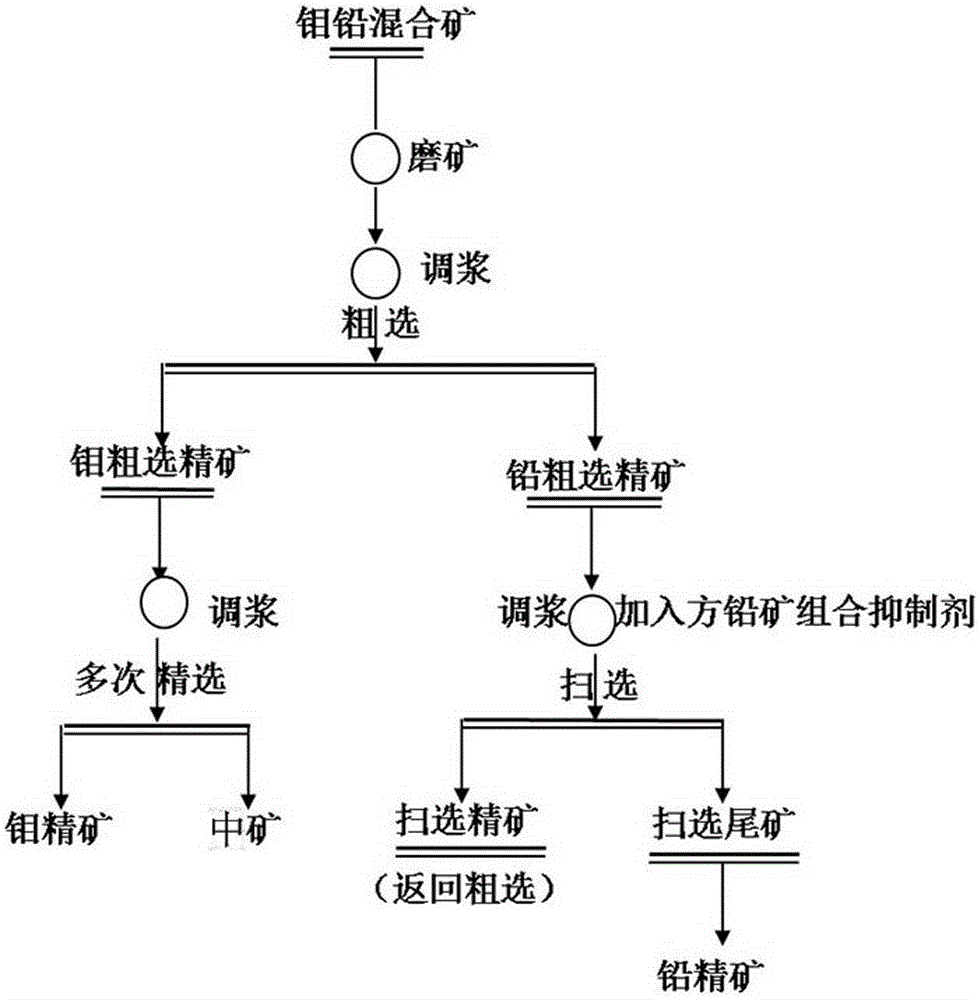
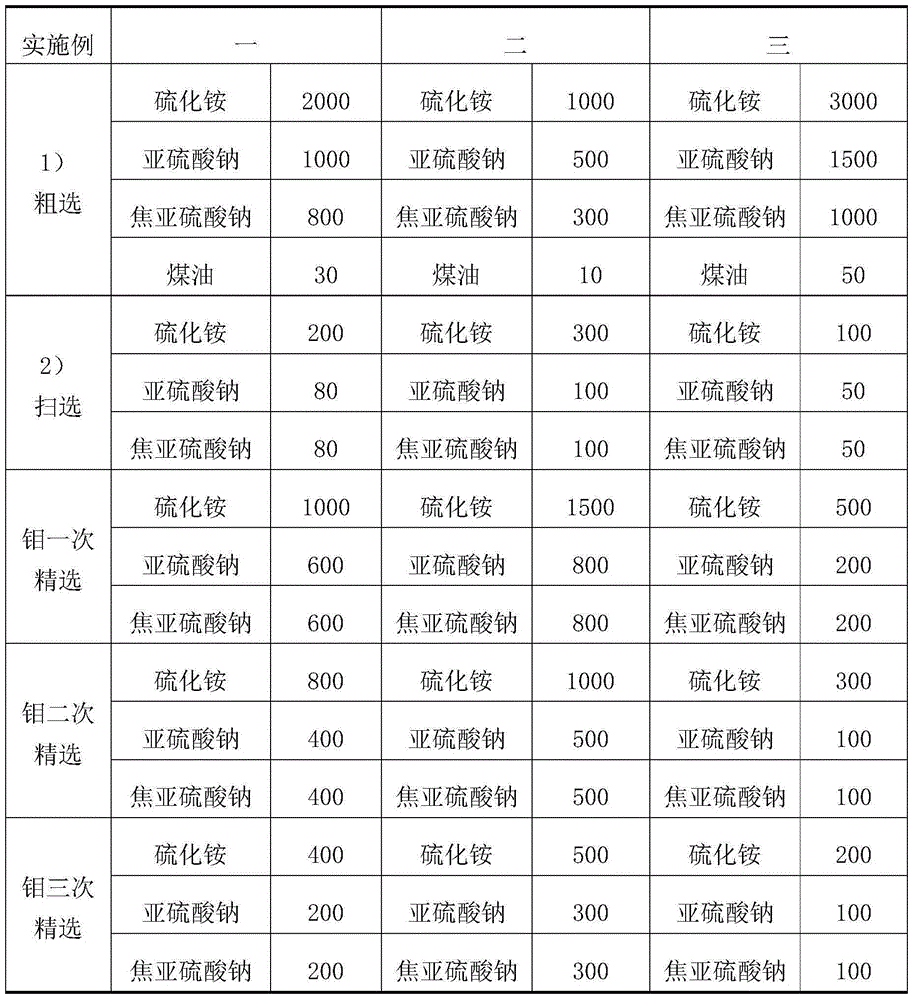
Separation mineral processing method for molybdenite and galena
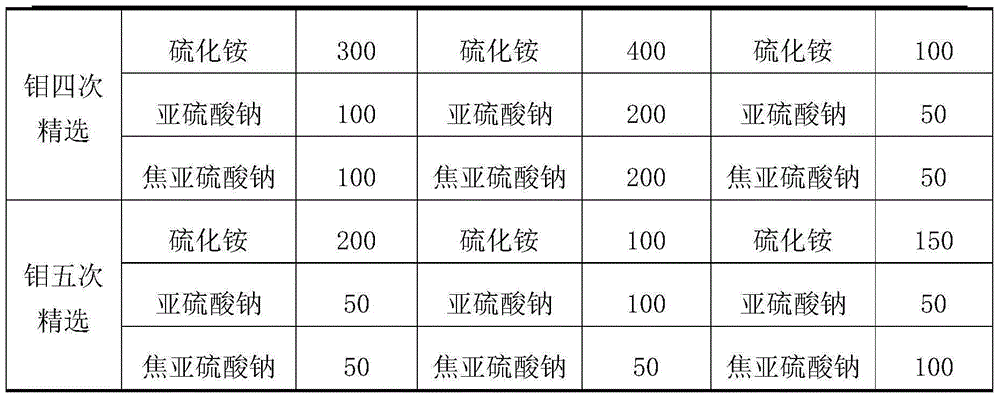
The invention provides a separation mineral processing method for molybdenite and galena. The method is characterized in that molybdenum lead mixed ore, that is, raw ore is ground to be in the certain fineness, and the concentration and the PH of the slurry are adjusted; a galena combined inhibitor is added to restrain the galena, and a molybdenite collecting agent is added to achieve separation of the molybdenite and the galena; and the galena combined inhibitor is composed of ammonium sulfide, sodium sulfite and sodium pyrosulfite. A medicine agent used in the method is environment-friendly, and finally-obtained molybdenum concentrates and lead concentrates are high in grade. The mineral processing method is simple in technology, management and operation on site are easy, and the higher economic and technical indexes can be obtained through the technology.
Owner:NORTHWEST RES INST OF MINING & METALLURGY INST
Method for leaching molybdenum and rhenium from molybdenum concentrate by mineral slurry electrolysis method
InactiveCN101353803AImprove leaching rateNo pollution in the processElectrolysis componentsProcess efficiency improvementRheniumIridium
The invention discloses a slurry electrolysis method applied to leach molybdenum and rhenium from molybdenum ore concentrate. The method comprises the following steps: molybdenum ore concentrate containing rhenium is put into an electrolysis bath, wherein, water is added in the electrolysis bath to keep the mass rate of liquid to solid in the range of 10-20: 1, and a mechanical stirring device is used for stirring the slurry obtained so as to cause the slurry to be in suspension status; sodium chloride is added into the electrolysis bath as an electrolyte, appropriate quantity of dextrin with the mass percentage concentration of 0.1 percent is added and sodium carbonate is added to control pH value of the slurry in electrolysis process at 8 to 10; after slurry mixing, a titanium plate of ruthenium-iridium-titanium coating is used as an anode, a pure titanium plate is used as a cathode, direct current is provided to carry out slurry electrolysis, simultaneously stirring is carried out, and the molybdenum and the rhenium are leached from the molybdenum ore concentrate after electrolysis. The method has the advantages of moderate reaction conditions, simple technology, high leaching rate of the molybdenum and the rhenium, and no pollution, wherein, the leaching rate of the molybdenum is not less than 99 percent, the leaching rate of the rhenium is not less than 95 percent, and the electrolysis current efficiency is not less than 92 percent, thereby being capable of effectively recycling the rhenium from the molybdenum ore concentrate and improving the utilization rate of molybdenum resource.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Recovery method of molybdenum concentrates
InactiveCN101956070AResolve recovery rateSolve environmental pollutionMolybdeum compoundsProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodSlag
The invention discloses a recovery method of molybdenum concentrates. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out a hot pressing natural reaction of materials to be processed under an alkaline condition; enriching molybdenite through flotation from natural oxide slag after natural leaching, returning for hot pressing oxidation and floating tailing slag to recover copper; producing high-purity ammonium molybdate and ammonium perrhenate from leached liquid after the natural leaching through the process of extraction, purification, acid precipitation, ammonia dissolution, concentration and crystallization; and removing sodium sulfate by evaporating or freezing and crystallizing raffinate to produce a sodium sulfate product. According to the invention, the recovery rate of the molybdenum concentrates is improved.
Owner:ZIJIN MINING GROUP
Method and apparatus for separation of molybdenite from pyrite containing copper-molybdenum ores
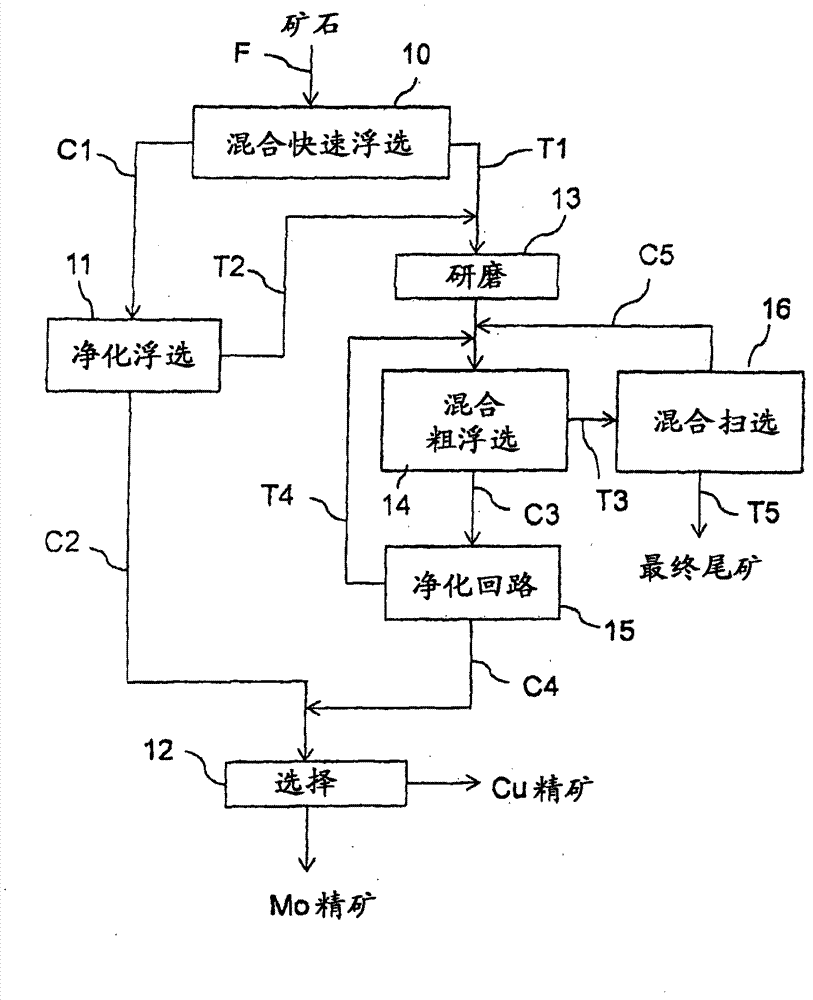
A method and an apparatus for the separation of the mineral components of a pyrite containing copper-molybdenum ore by flotation. The method comprises grinding the ore in the presence of soda ash in an open circuit to produce an aqueous ore slurry; subjecting the slurry to a collective flash flotation step (10) in the presence of soda ash and sodium sulphide to recover a first part of metal sulphides of the ore in the form of a first concentrate (C1); subjecting the tailings (T1) of the collective flash flotation step (10) to a grinding step (13) and to a collective rougher flotation step (14) to recover a second part of metal sulphides of the ore in the form of a second concentrate (C3); and subjecting the concentrate (C1) of the collective flash flotation step (10) and the concentrate (C3) of the collective rougher flotation step (14) to a selection step (12) to separate molybdenite from the other metal sulphides of the concentrate.
Owner:OUTOTEC FINDLAND OY
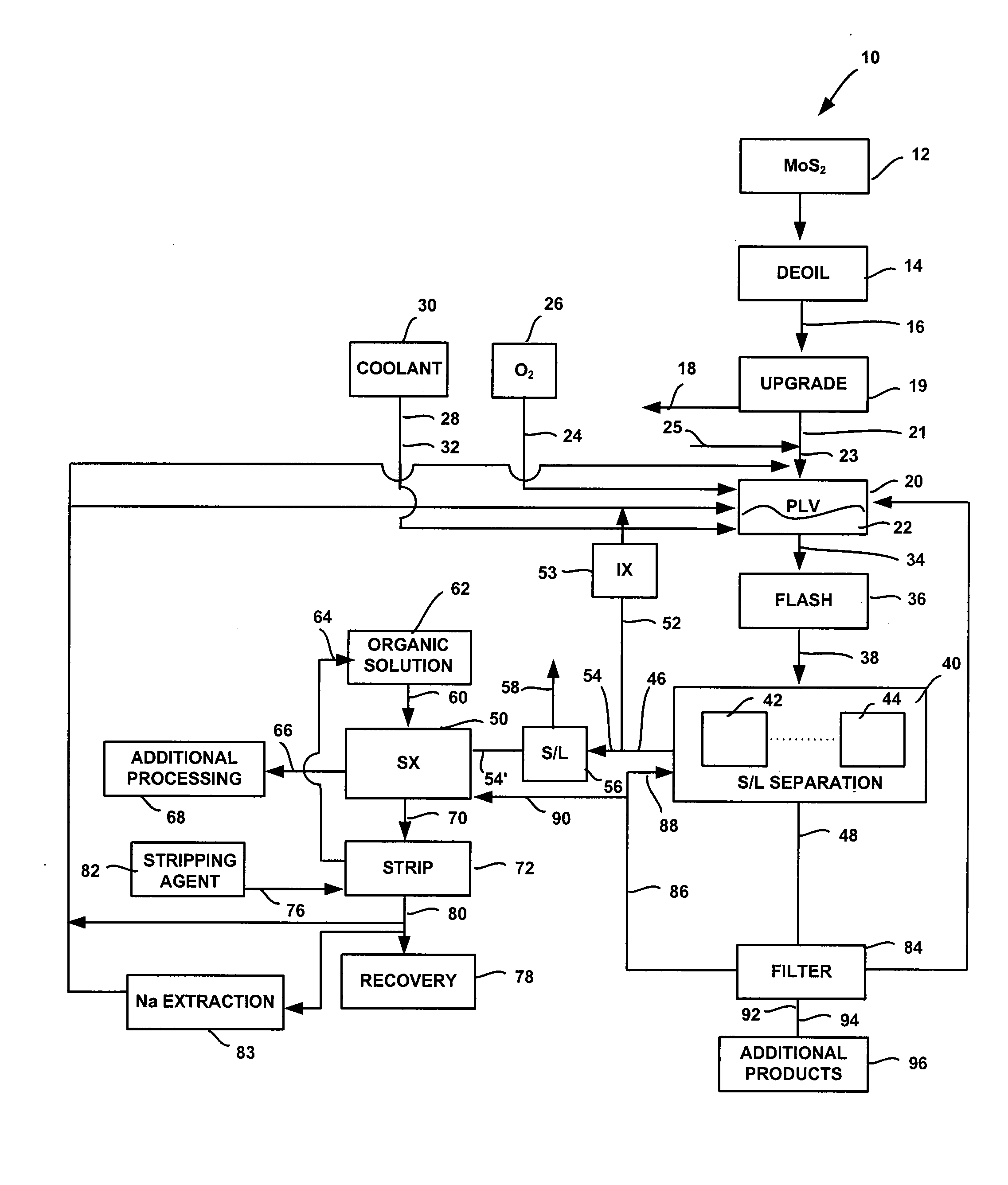
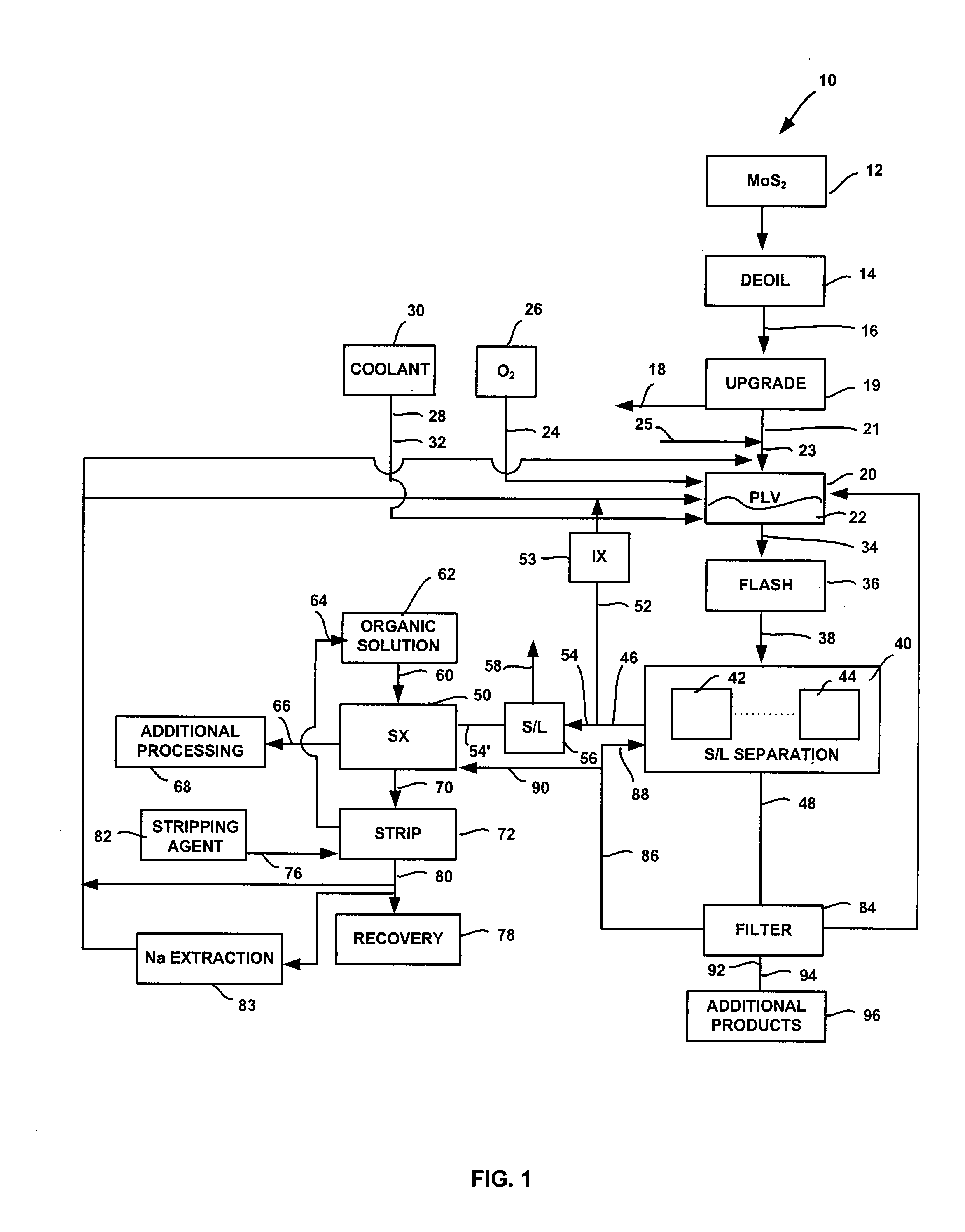
System and method for conversion of molybdenite to one or more molybdenum oxides
InactiveUS20080118422A1Promote oxidationMaintain pressurePressurized chemical processOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideSolventSolvent extraction
A system and method for producing molybdenum oxide(s) from molybdenum sulfide are disclosed. The system includes a pressure leach vessel, a solid-liquid separation stage coupled to the pressure leach vessel, a solvent-extraction stage coupled to the solid-liquid separation stage, and a base stripping stage coupled to the solvent-extraction stage. The method includes providing a molybdenum sulfide feed, subjecting the feed to a pressure leach process, subjecting pressure leach process discharge to a solid-liquid separation process to produce a discharge liquid stream and a discharge solids stream, and subjecting the discharge liquid stream to a solvent extraction and a base strip process.
Owner:FREEPORT MCMORAN COPPER & GOLD INC
Molybdenum cleaning metallurgy method
ActiveCN108396141ASolve pollutionSolve the output problem of ammonia nitrogen wastewaterProcess efficiency improvementMolybdenum oxides/hydroxidesRheniumRaffinate
The invention provides a molybdenum cleaning metallurgy method. The molybdenum cleaning metallurgy method comprises the following steps: 1) calcium molybdenum roasted sand obtained by roasting molybdenite through calcium adding is leached by using inorganic acid to obtain molybdenum-contained inorganic acid leaching liquid; 2) a positive ion extracting agent is used for extracting to obtain a molybdenum acyl positive ion-loaded organic phase and raffinate; 3) hydrogen peroxide water solution is used as a reverse extracting agent to obtain molybdenum reverse extracting liquid; and 4) the molybdenum reverse extracting liquid is heated to dissociate molybdic acid peroxide inside to form molybdic acid precipitations for calcining to obtain molybdenum trioxide products. The technical route of anon-ammonia nitrogen molybdenum cleaning metallurgy new process is provided with the calcium molybdenum roasted sand of molybdenite as raw materials by using multi-acid chemical properties of molybdenum without using traditional molybdenum metallurgy ammonia nitrogen flow. The cleaning metallurgy method greatly simplifies the molybdenum smelting flow, thoroughly solves the sulfur dioxide pollution and ammonia nitrogen waste water output problems, can enrich and recover rhenium, has the characteristics of short flow and efficient cleaning, and is easy to industrially popularize.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
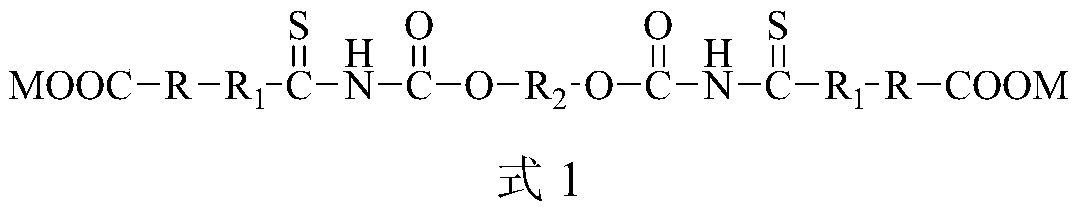
Ether-based double-sulfur amine ester derivative or ether-based bis-thiourea derivative and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105801458ASpecial molecular structureHas surfactant propertiesOrganic chemistryFlotationChloroformateNickel sulfide
The invention provides an ether-based double-sulfur amine ester derivative or an ether-based bis-thiourea derivative and a preparation method and application thereof. The molecular structure of the ether-based double-sulfur amine ester derivative or the ether-based bis-thiourea derivative contains a large quantity of thioamide or thiourea or thioacid amide ether or other lipophilic groups and carboxyl hydrophilic groups. The preparation method includes the steps that bis-chloro-carbonic ester and thiocyanate are subjected to a substitution reaction, an intermediate product containing bis-acyl bis-isothiocyanate is generated, the intermediate and an alcohol compound or an amine compound or a phenol compound are subjected to an addition reaction, and then the ether-based double-sulfur amine ester derivative or the ether-based bis-thiourea derivative is obtained. The preparation method is simple, the prepared product directly serves as a non-molybdenum sulphide ore inhibitor, and floatation separation of molybdenum sulfide ore and the non-molybdenum sulphide ore can be effectively achieved. The preparation method is especially suitable for separation of molybdenite and copper sulphide ore, galena, sphalerite, pyrite, arsenopyrite, jamesonite concentrate, nickel sulfide ore, bismuth sulfide ore and the like, and the grade of molybdenum concentrate is improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for preparing molybdenum disulfide from molybdenite
InactiveCN101898795AImprove leaching efficiencyHigh purityMolybdenum sulfidesHydrofluoric acidChloride
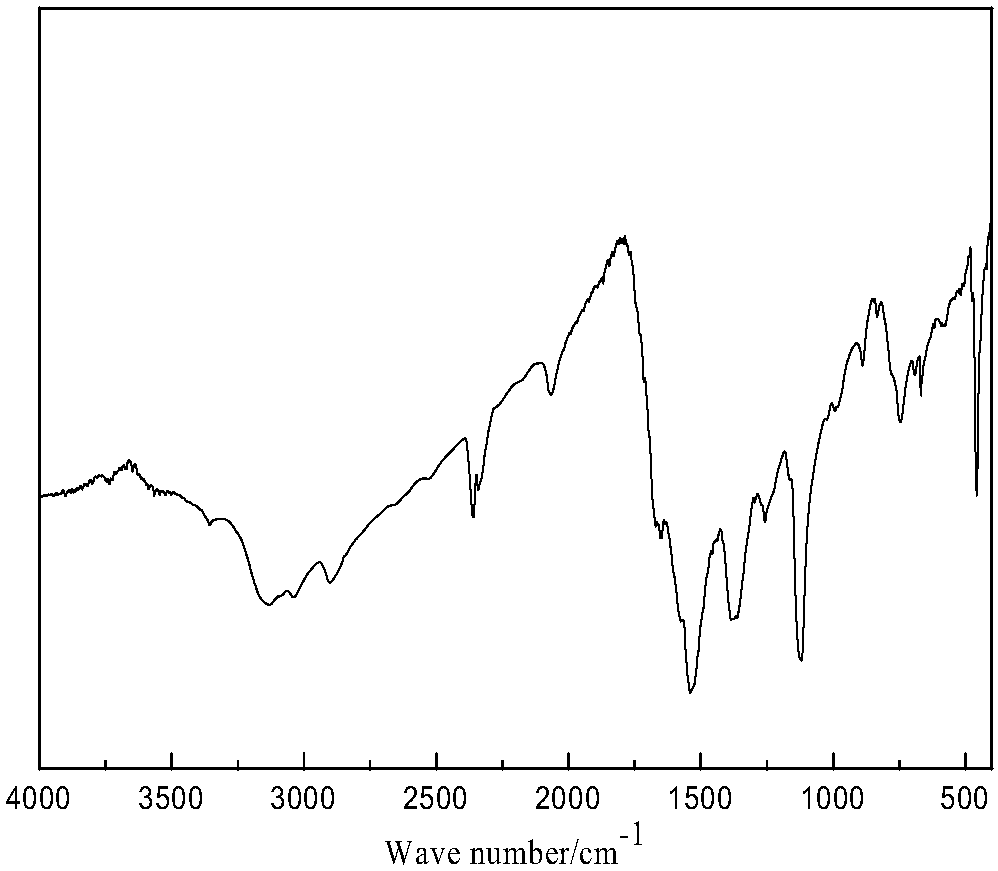
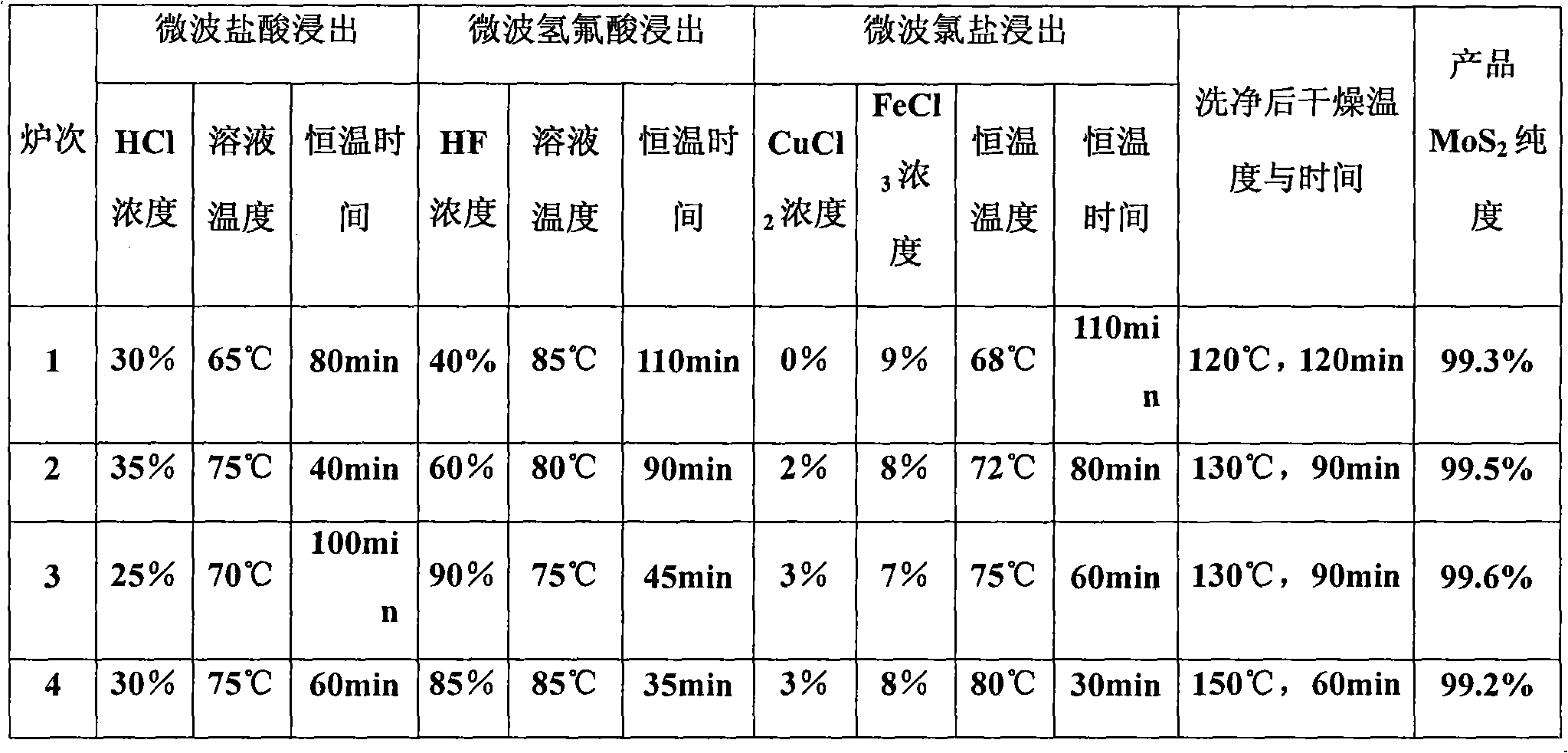
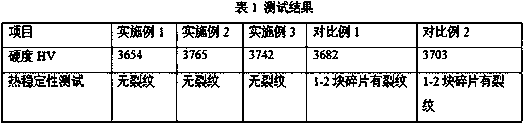
The invention provides a method for preparing molybdenum disulfide from molybdenite. The polybdenum disulfide is prepared by microwave assisted multi-stage leaching, and the molybdenum disulfide with the purity of over 99.2 percent, excellent quality and stable performance can be obtained. By adopting the polybdenite by using microwave assisted leaching, the method for preparing the molybdenum disulfide from the molybdenite comprises the following four steps of: 1, hydrochloric acid leaching by using microwaves; 2, hydrofluoric acid leaching by using microwaves; 3, chloride leaching by using microwaves; and 4, cleaning the powder with deionized water, drying the powder to obtain the polybdenum disulfide powder with the purity of over 99.2 percent. The method has the advantages of simple method and convenient operation, improvement on the working efficiency, and simultaneously improvement on the product quality and market competitive power.
Owner:洛阳开拓者投资管理有限公司
Ceramic product with high cold resistance and high heat resistance and preparation process thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of ceramic preparation, in particular to a ceramic product with high cold resistance and high heat resistance and a preparation process thereof. The ceramic product comprises a blank body, a heat insulation layer and a glaze material, wherein the blank body is prepared from 42 parts of olivinite, 8 parts of sodium lignin sulfonate, 13 parts of quartz, 15 parts of clay, 26 parts of molybdenite, 15 parts of melting aids, 20 parts of spodumene, 13 parts of mullite, 11 parts of sodium feldspar and 9 parts of calcium metasilicate; the heat insulation layer is prepared from 22 parts of glass fiber powder, 15 parts of rock wool powder, 9 parts of sodium silicate and 3 parts of sodium hexametaphosphate; the glaze material is prepared from 23 parts of mullite, 35 parts of Kaolin, 15 parts of spodumene, 17 parts of potash feldspar and 7 parts of clay. The preparation process comprises the following steps of proportioning, blank pulling, biscuiting, heat insulation layer coating, glazing and firing. The ceramic product produced by the process has the advantages of high mechanical intensity and strong thermal shock resistant performance.
Owner:福建省德化县嘉威陶瓷有限公司
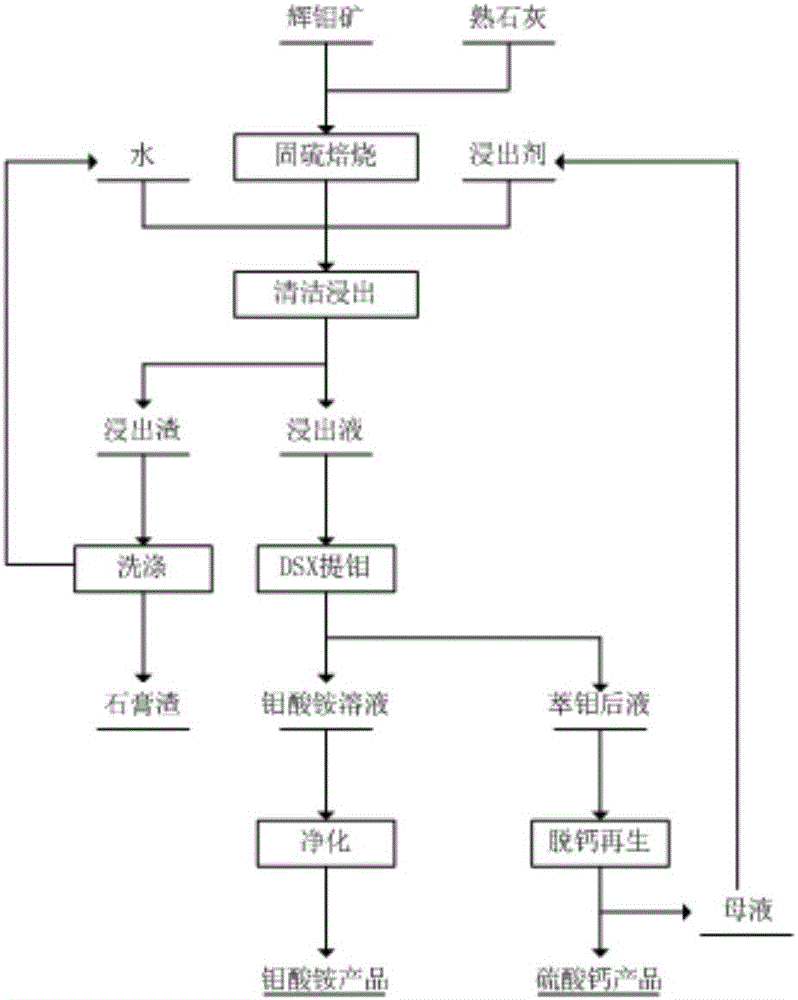
Efficient and clean molybdenum smelting method
ActiveCN105838908AHigh recovery rateSpeed up leachingProcess efficiency improvementEvaporationRaffinate
The invention provides an efficient and clean molybdenum smelting method. The method comprises the steps that lime sulphur-fixed roasting is conducted on molybdenite through a gradient heat preservation method; roasted products are leached with a leaching agent, namely roasted product, and molybdenum-contained leach liquid is obtained; the molybdenum-contained leach liquid is sequentially treated by an acid phosphorus extraction system for extracting molybdenum, and an ammonium hydroxide / ammonium salt system for back-extracting molybdenum, and molybdenum-contained strip liquid and molybdenum raffinate are obtained; impurities in the molybdenum-contained strip liquid are removed through a Mg(OH)2 one-step precipitation method, evaporation and concentration are conducted, and ammonium molybdate products are obtained; and sulfuric acid is added into the molybdenum raffinate for regeneration, calcium sulphate dihydrate products are obtained, and regenerated liquid serves as a leaching agent and is returned back to the leaching process. By the adoption of the method, molybdenum mineral raw materials can be cleaned and treated efficiently, and ammonium molybdate can be prepared, the molybdenum recovery rate reaches 99%, the sulfur fixing rate reaches 98% or over, reagent consumption is low, the production period is short, the process is easy to control, the reaching residue quantity is greatly reduced, zero emission of waste water is achieved, and industrialized application is achieved easily.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
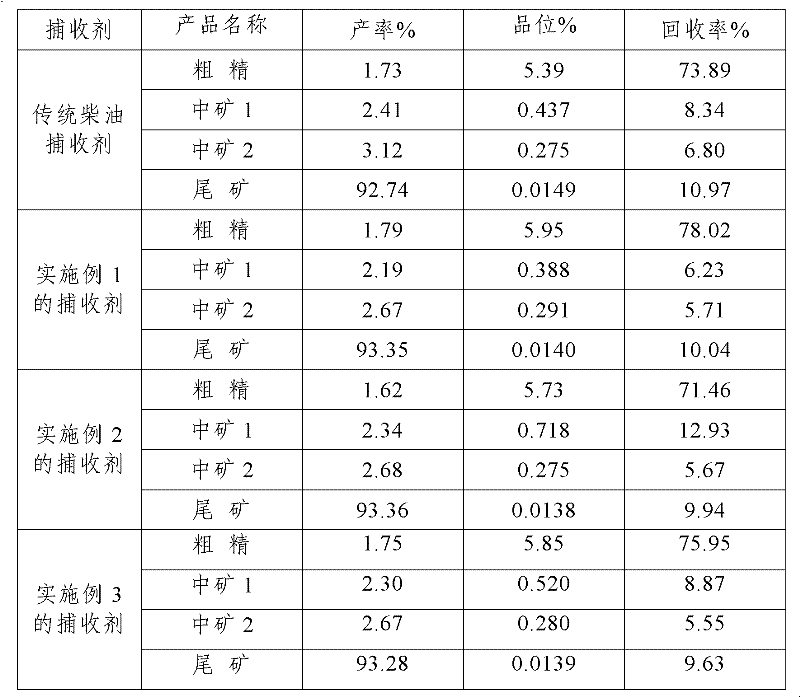
A molybdenite flotation collector
The invention discloses a molybdenite flotation collector, which is formed by mixing butyl oleate and diesel oil, and the volume percentage of butyl oleate in the collector is 10% to 20%. The manufacture method of collector of the present invention is simple, easy to operate, and the usage and consumption of this collector are all equivalent with traditional diesel oil collector, and price is also quite, adopt this collector to carry out the flotation of molybdenite according to conventional method, The recovery rate of molybdenum was significantly improved.
Owner:JINDUICHENG MOLYBDENUM CO LTD
Method for associated producing ammonium molybdate and manganese sulfate by roasting molybdenite and pyrolusite
InactiveCN101049968AReduce pollutionHigh recovery rateMolybdeum compoundsManganese sulfatesPyrolusiteSolvent
This invention discloses a method for combined production of ammonium molybdate and manganese sulfate by co-torrefication of molybdenite and pyrolusite. The method comprises: (1) mixing molybdenite and pyrolusite at a ratio of nMnO2:nMoS2 = 1.0-10.0; (2) co-torrefying the mixture at 350-950 deg.C for 60-360 min; (3) acidolyzing with an inorganic acid at 5-95 deg.C and a liquid / solid ratio of 1.0-50.0 for 5-300 min until the pH value is below 5.5; (4) extracting the leaching solution with solvent, separating to obtain an organic phase containing Mo and an aqueous phase containing Mn, and back-extracting the organic phase with ammonia to obtain ammonium molybdate; (5) processing into ammonium molybdate and manganese sulfate products by using the present metallurgical technique. The method has such advantages as short process, simple apparatus, low energy consumption, little pollution, high metal recovery rate, and high product quality.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
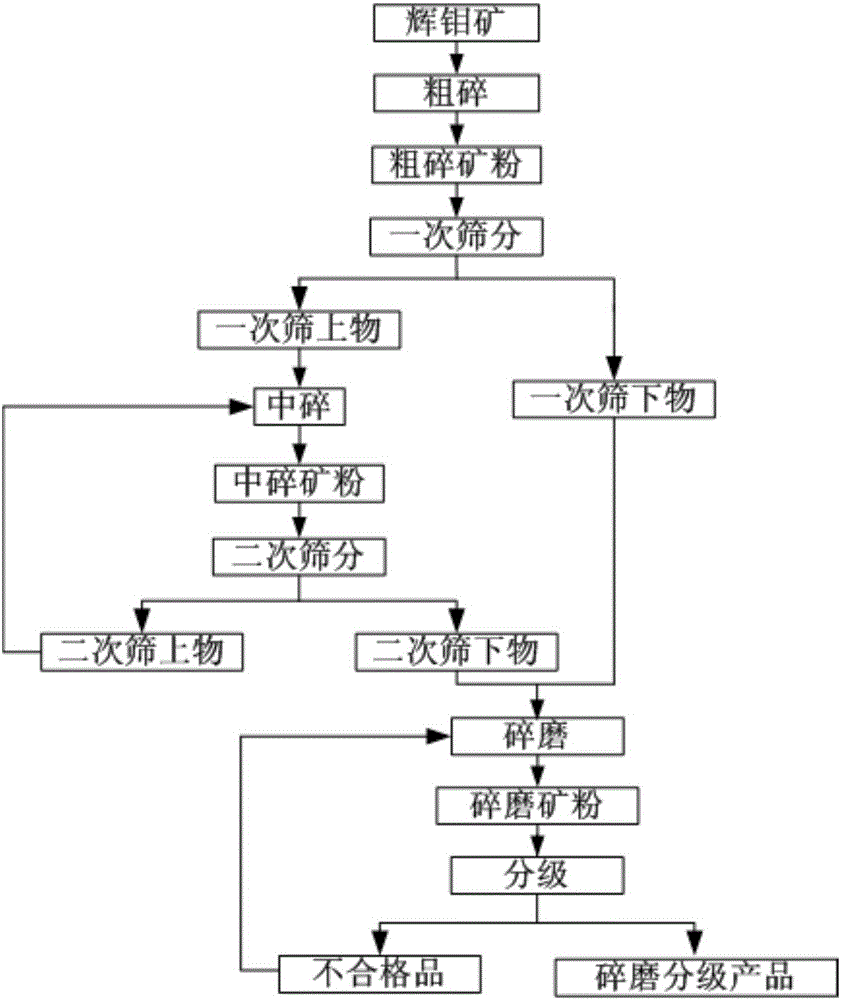
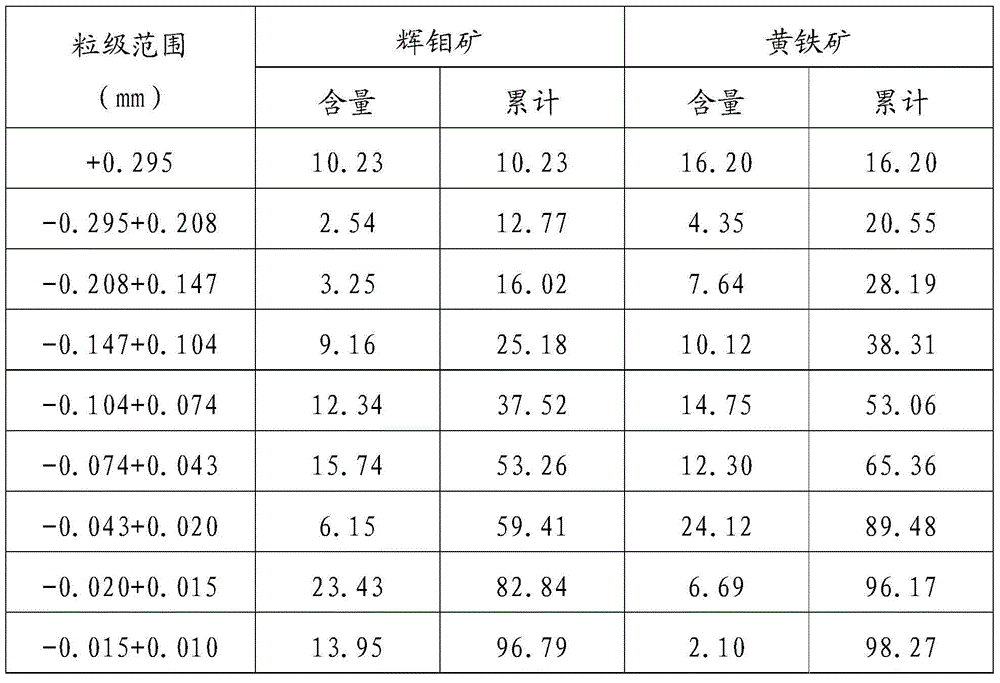
Smashing and classifying technology for molybdenite
The invention provides a smashing and classifying technology for molybdenite. The technology comprises the following steps that first, a gyratory crusher is used for conducting coarse crushing treatment on the molybdenite, so that coarsely-crushed mineral powder is obtained; then primary screening is carried out, and accordingly primary oversize products and primary screen underflow are obtained; second, a cone crusher is used for conducting intermediate crushing treatment on the primary oversize products, so that intermediately-crushed mineral powder is obtained; then secondary screening is carried out, and accordingly secondary oversize products and secondary screen underflow are obtained; third, the primary screen underflow and the secondary screen underflow are evenly mixed and then added into a high-pressure grinding roller to be smashed, so that smashed mineral powder is obtained; and fourth, the smashed mineral powder is classified, and hence smashed and classified products with the granularity D55 being smaller than or equal to 0.074 mm are obtained. By the adoption of the smashing and classifying technology, the technical problems that the process is long, the number of devices is large, smashing and classifying production cost is high, classification efficiency is low, easy-to-select size fraction content of the mineral is low, and the molybdenum selection recovery rate is affected in the prior art are effectively solved. The application prospect is broad.
Owner:JINDUICHENG MOLYBDENUM CO LTD
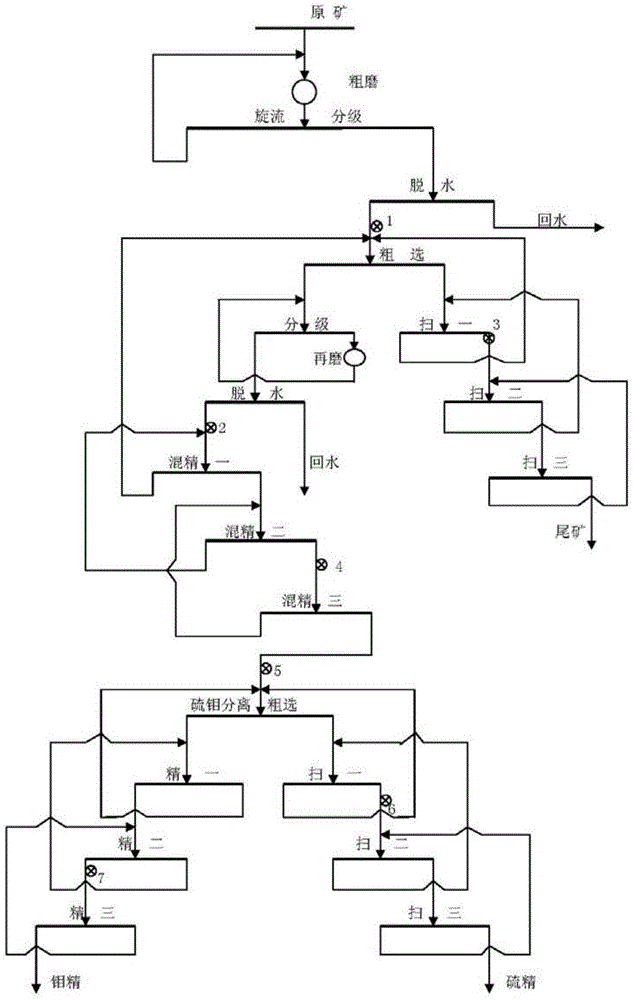
Mineral processing technology of refractory molybdenum ores with molybdenite and pyrite in close symbiotic relationship
The invention discloses a mineral processing technology of refractory molybdenum ores with molybdenite and pyrite in a close symbiotic relationship, and provides a mineral processing technology which can be used for improving the recovery rate of molybdenum and decreasing the mineral processing cost. The technology comprises the following steps of crushing ores into a crushed material till a grinding feed size of 15mm is realized through a two-stage one-closed-circuit crushing process; implementing a two-stage two-closed-circuit crushing process on the crushed material to obtain ore pulp till 85% of 200-mesh grinding fineness is realized; implementing mixing roughing and third-time scavenging on the ore pulp to obtain qualified tailings; regrinding the roughing concentrates till 85% of 325-mesh fineness, and implementing third-time concentration to obtain bulk concentrates; feeding chemicals into the ore pulp before mixing roughing; feeding chemicals after regrinding and before first concentration; feeding chemicals after first scavenging which follows mixing roughing; feeding chemicals after second concentration which follows the regrinding; implementing separation floatation on mixed concentrates; after the separation floatation, implementing one-time roughing and third-time scavenging to obtain sulfur concentrates; implementing third-time concentration to obtain molybdenum concentrates; feeding chemicals before classification flotation. By applying the technology provided by the invention, the operation is simple, and the cost is lowered.
Owner:阿鲁科尔沁旗厚德矿业开发有限责任公司
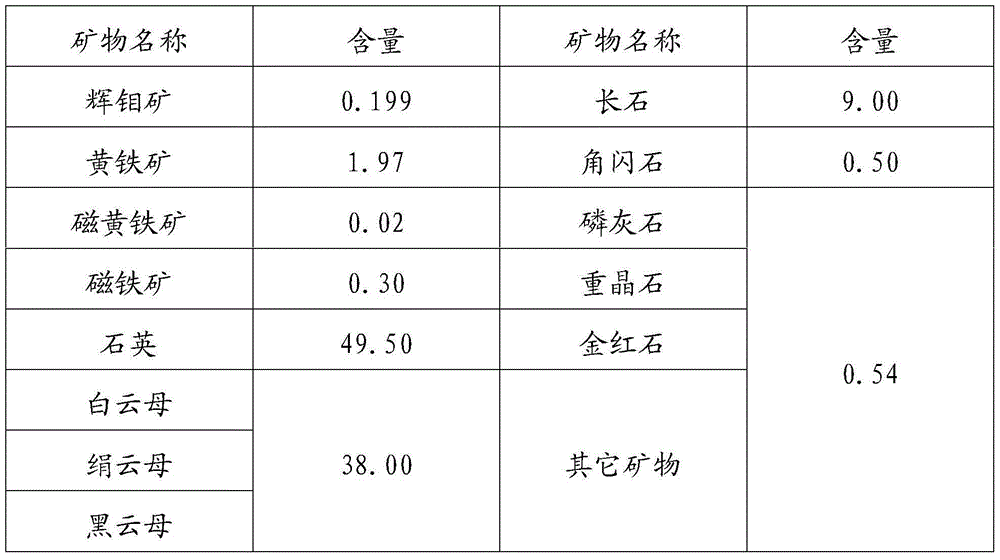
Method for preparing high purity molybdenum trioxide by one-step roasting of molybdenite concentrate
ActiveCN108383163AReduce air volumeAvoid swelling and breakingMolybdenum oxides/hydroxidesChemical productsOxygen
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Non-copper sulphide ore inhibitor and application thereof
ActiveCN110918263AEnhanced inhibitory effectEfficient flotation separationFlotationSulfide mineralsGalena
The invention relates to the technical field of non-ferrous metal beneficiation, in particular to a non-copper sulphide ore inhibitor and application thereof. The non-copper sulphide ore inhibitor isprepared from the following components in parts by mass: 1-3 parts of xanthan gum, 1-2 parts of pectin and 1-2 parts of arabic gum. The non-copper sulphide ore inhibitor is simple in preparation, lowin cost and green and environment-friendly and has a quite high inhibition effect on molybdenite, galena, sphalerite, pyrite and other sulphide ores in the copper bulk concentrate. With application ofthe inhibitor, efficient flotation separation of chalcopyrite and other sulfide minerals can be achieved.
Owner:SDIC XINJIANG LUOBUPO POTASH CO LTD
Soil remediation stabilizer prepared from high-iron tailings and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109796982ARealize resource utilizationTo achieve the purpose of using waste to control pollutionContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersApatiteSoil remediation
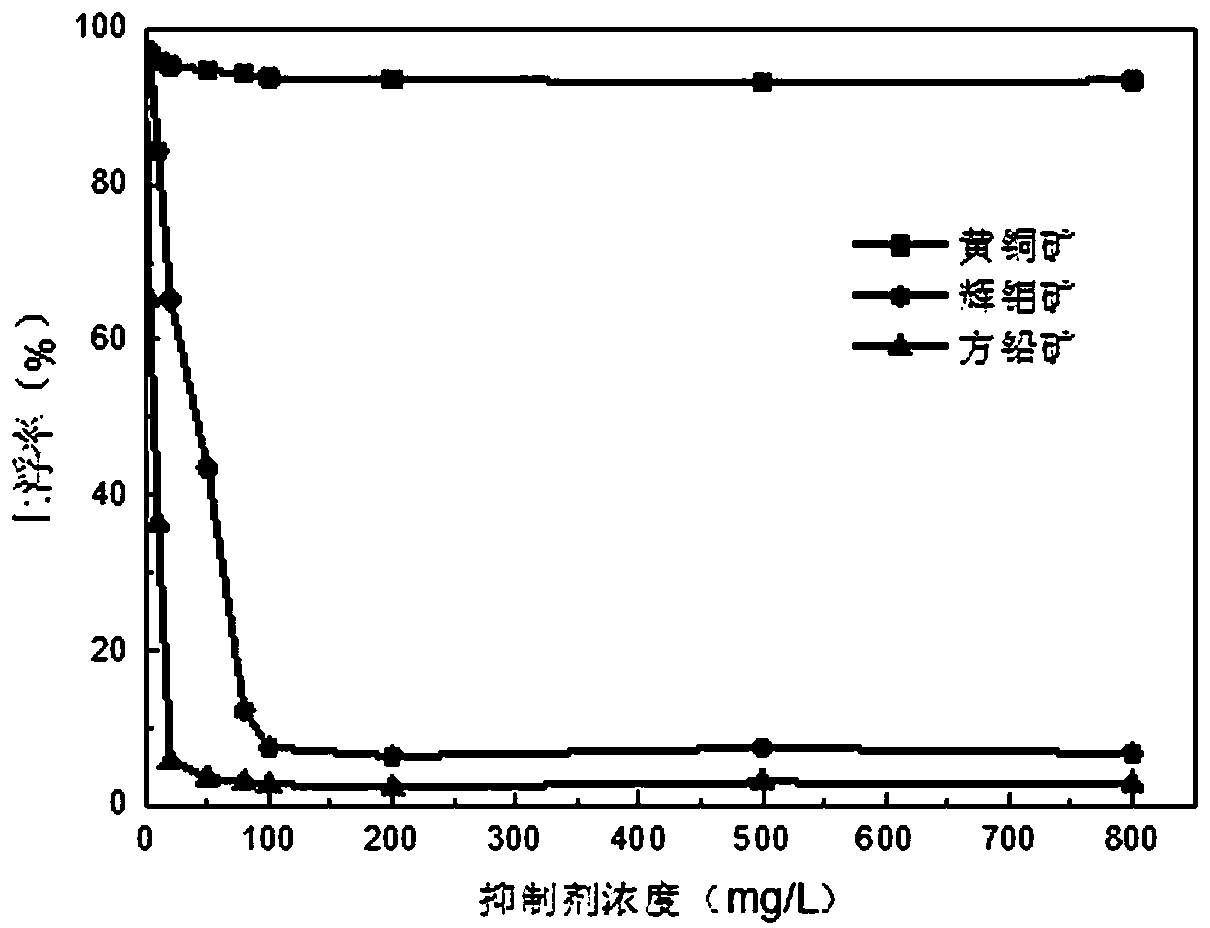
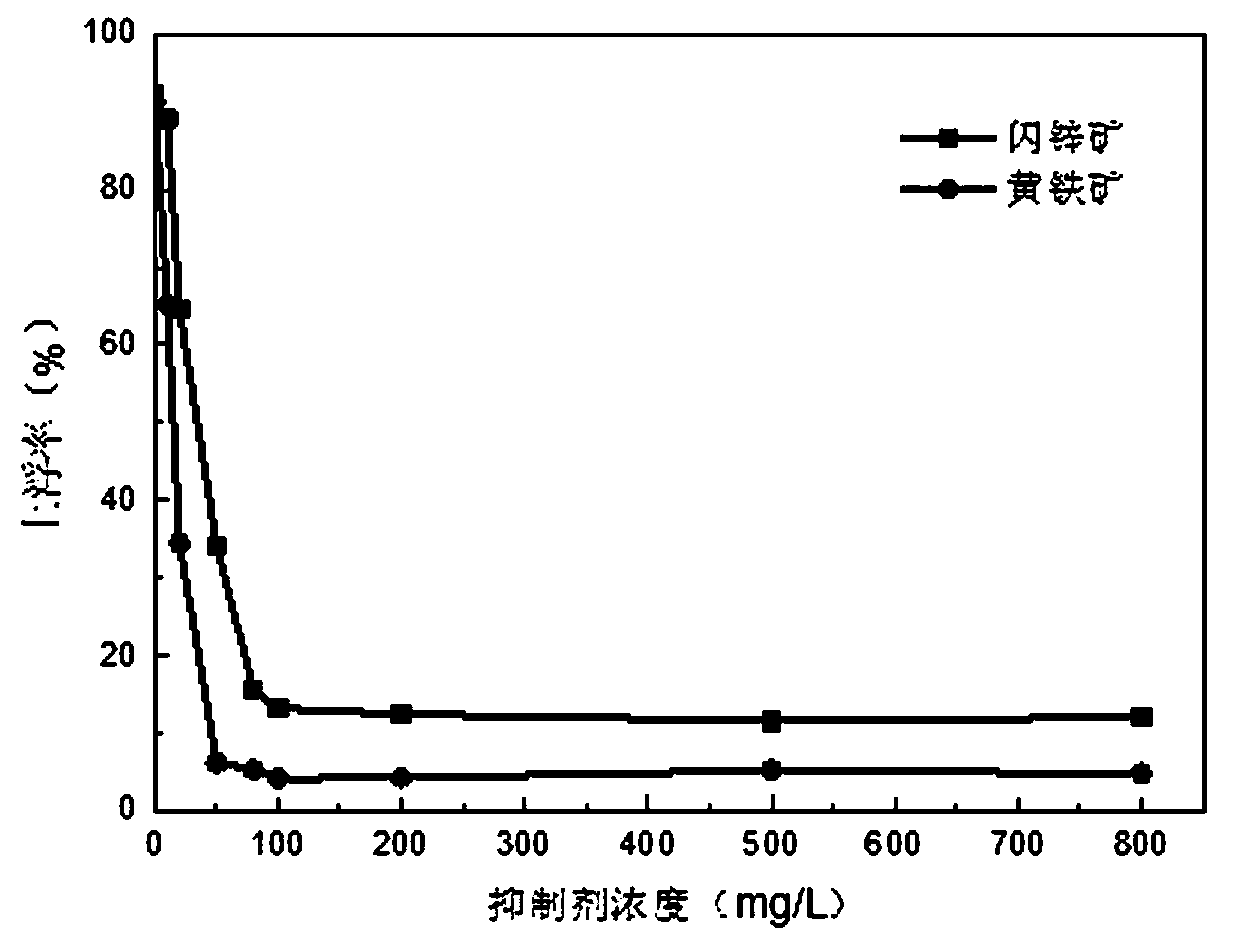
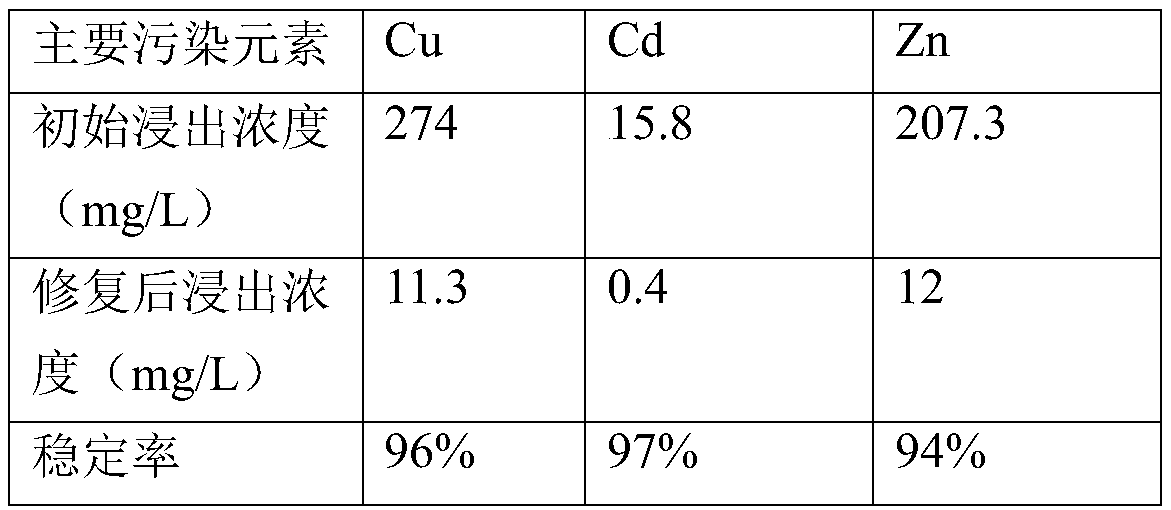
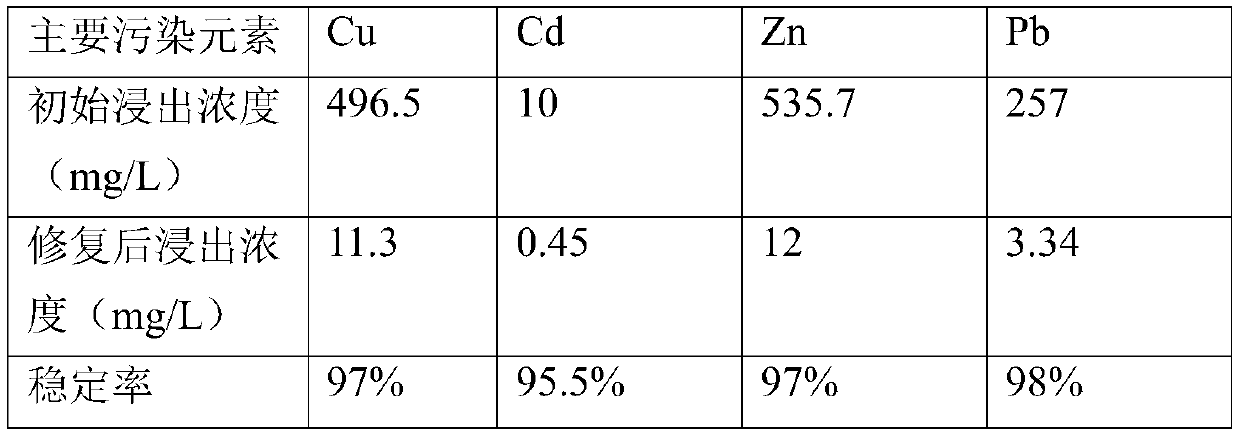
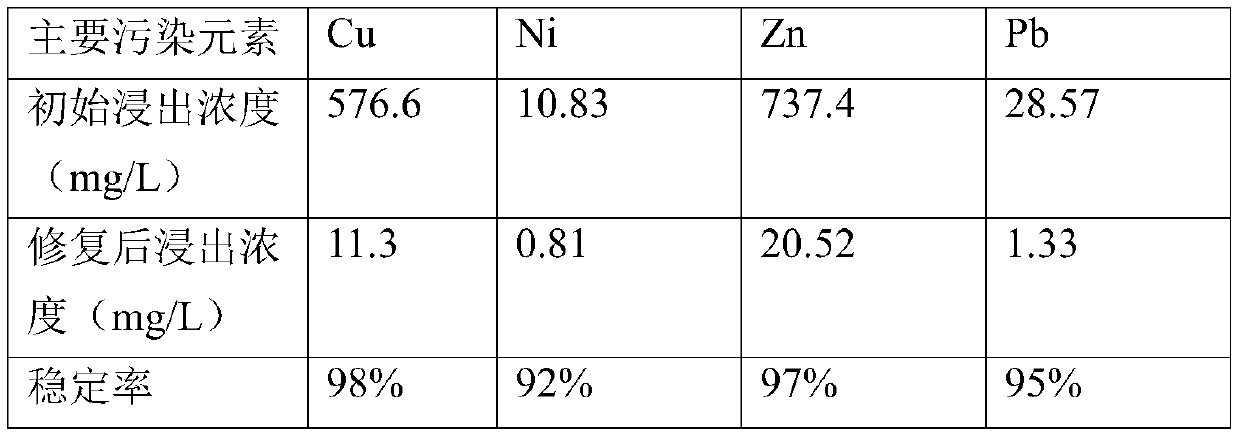
The invention relates to a soil remediation stabilizer prepared from high-iron tailings and a preparation method and application thereof. The remediation stabilizer comprises, by mass, 40-60 parts ofthe high-iron tailings, 10-30 parts of fly ash, 10-30 parts of hydroxyapatite and 10-20 parts of molybdenite. During preparation, the soil remediation stabilizer used for heavy metal contaminated soilremediation is prepared through mixing, ball milling, hydrothermal treatment and drying. The preparation method is simple, the raw materials are easy to obtain, the price and cost are low, the usingprocess is simple and easy to operate, the curing time is short, and the curing effect on common soil contamination elements Cu, Pb, Cd, Ni and Zn is achieved.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
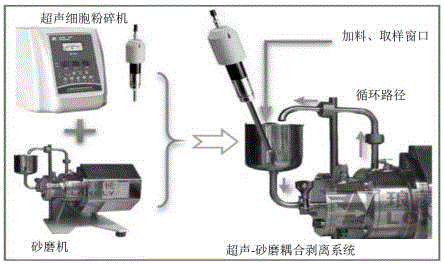
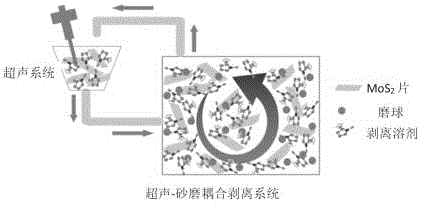
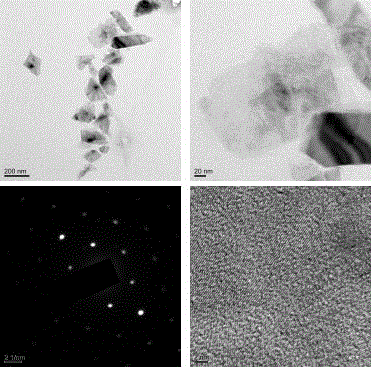
Method for preparing molybdenum disulfide nano-sheet from molybdenite through ultrasonic-sanding coupling stripping
ActiveCN106044856AGood dispersionEfficient strippingMaterial nanotechnologyMolybdenum sulfidesPerformance functionCoupling
The invention belongs to the technical field of nanometer material processing, and particularly relates to a method for preparing a molybdenum disulfide nano-sheet from molybdenite through ultrasonic-sanding coupling stripping. The method comprises following steps: 1), molybdenite micropowder is dispersed in a stripping solvent, and a suspension liquid is formed; 2), a dispersing agent and a stripping assistant are dissolved in the suspension liquid obtained in the step 1) and subjected to ultrasonic dispersion; 3), the suspension liquid after subjected to the ultrasonic dispersion in the step 2) is subjected to continuous stripping under the ultrasonic-sanding coupling action, and the molybdenum disulfide nano-sheet is obtained. According to the designed novel method for preparing the molybdenum disulfide nano-sheets in a large scale from the molybdenite micropowder through ultrasonic-sanding coupling stripping, green transformation from a natural mineral to a high-performance function material is realized, and the method has important application value and economic benefit.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Selection-smelting combined technology for treating mixed ore containing molybdenum, oxygen, sulfur and copper
InactiveCN103184334AReduce manufacturing costImprove resource utilizationFlotationProcess efficiency improvementResource utilizationSulfur
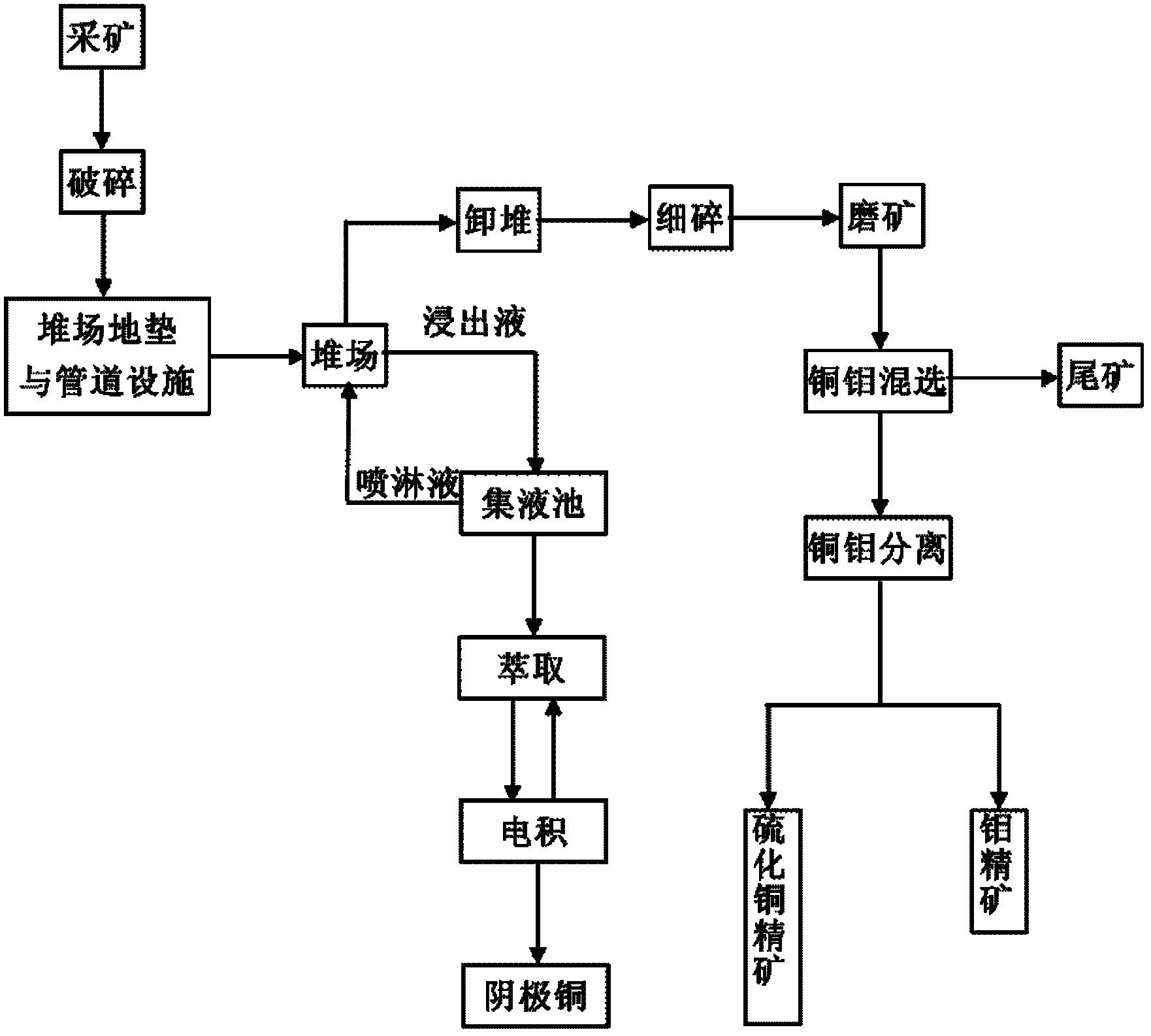
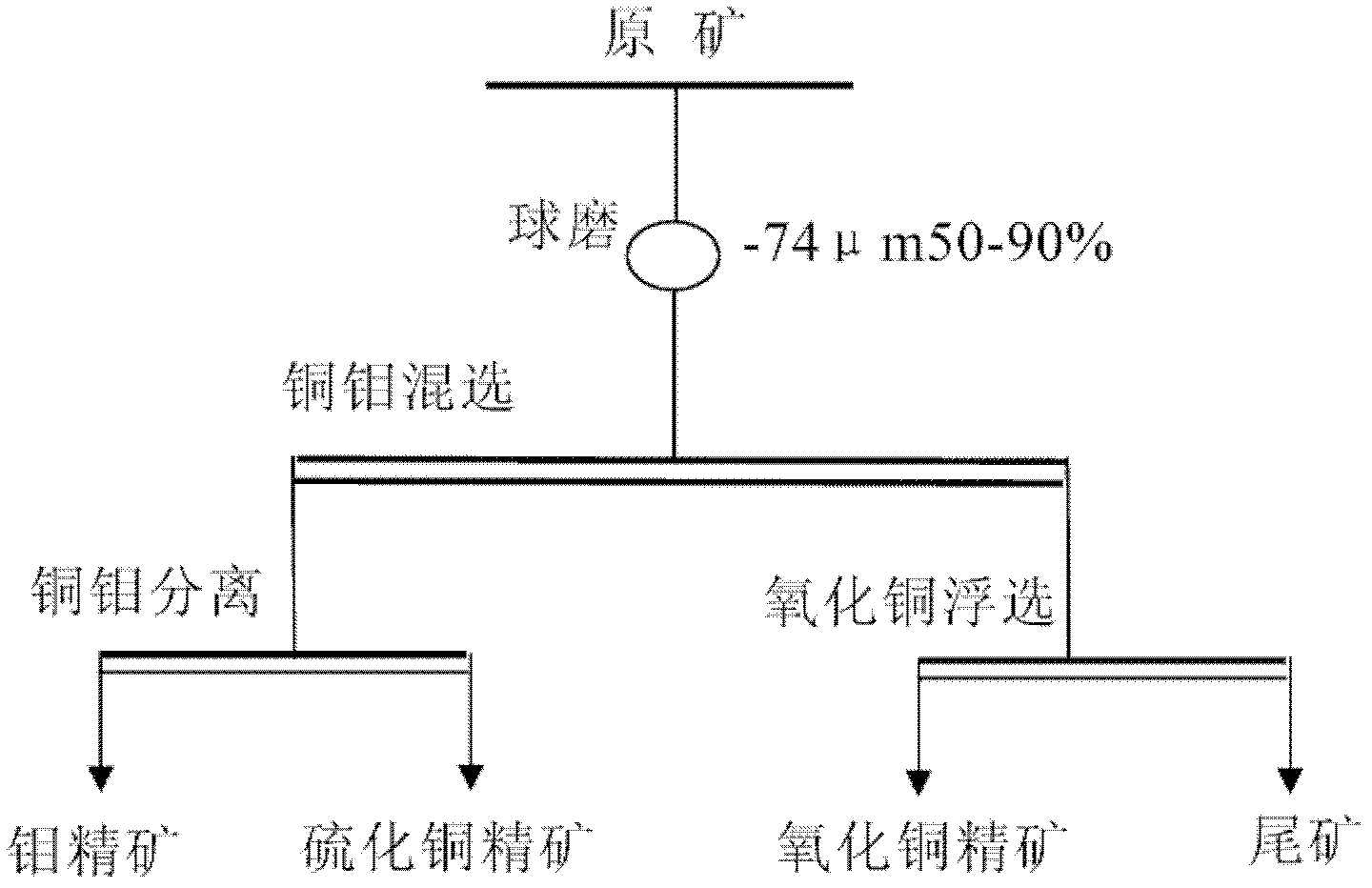
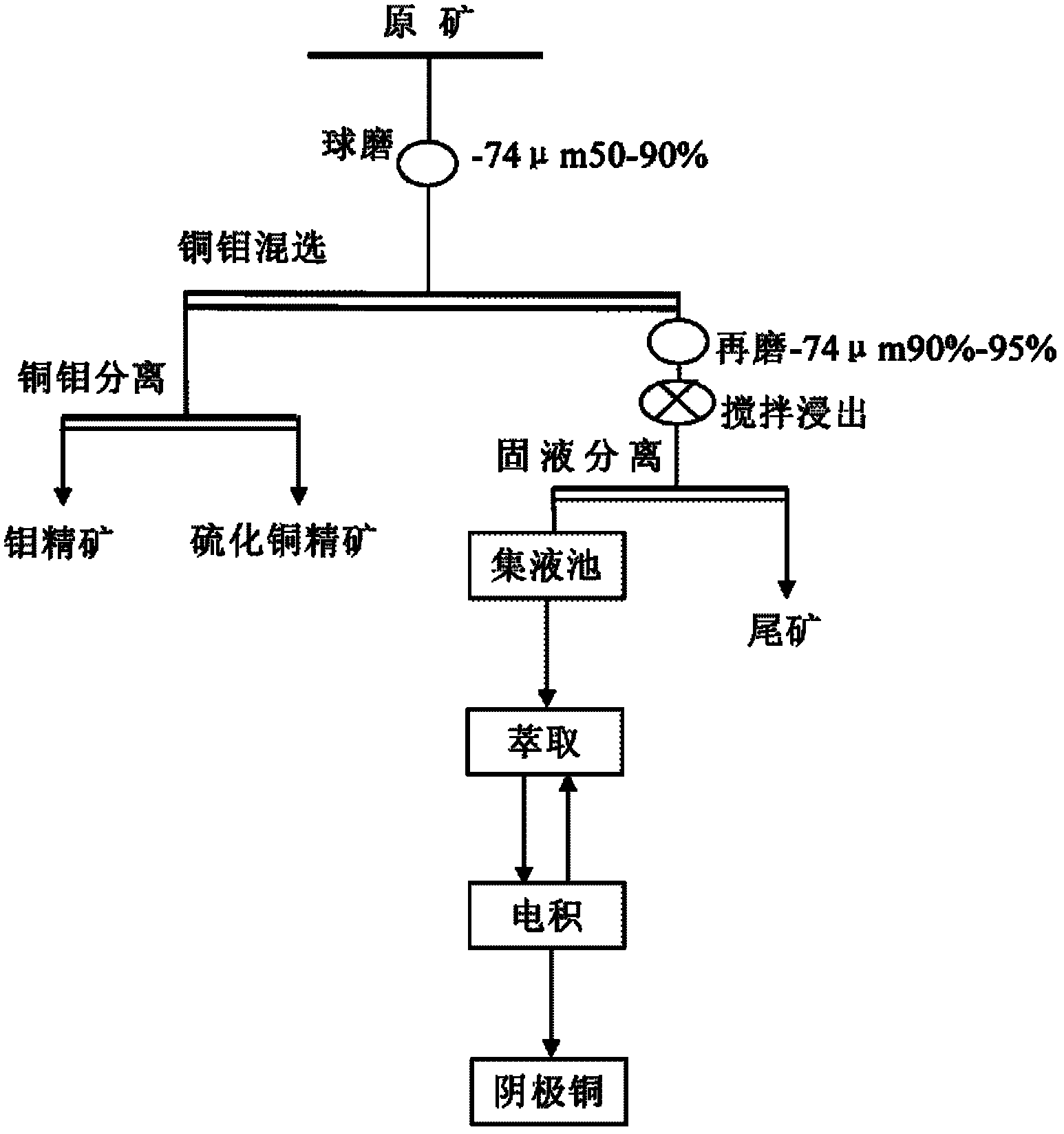
The invention relates to a selection-smelting combined technology for treating mixed ore containing molybdenum, oxygen, sulfur and copper, wherein the copper ore in the mixed ore containing molybdenum, oxygen, sulfur and copper is copper oxide ore and copper sulphide ore, molybdenum ore is molybdenite; the selection-smelting combined technology is characterized in that the copper oxide ore in raw ores can be leached through a dump leaching process, processes of unstacking and crushing can be carried out after the dump leaching process is finished, and then the copper sulphide ore and molybdenum ore can be recovered through a select flotation process. The selection-smelting combined technology is capable of reducing the production cost, increasing the resource utilization rate and bringing good economic benefit for enterprises.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com