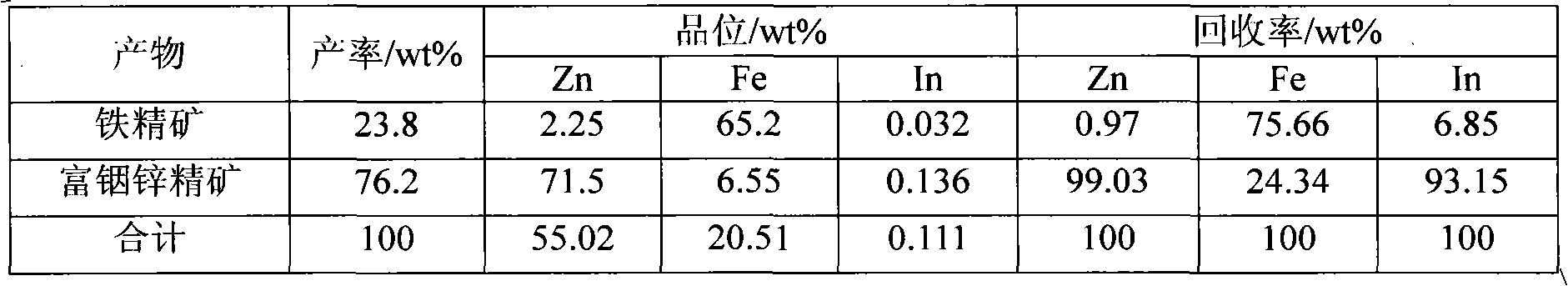Patents
Literature
1440 results about "Mineral processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In the field of extractive metallurgy, mineral processing, also known as ore dressing, is the process of separating commercially valuable minerals from their ores.
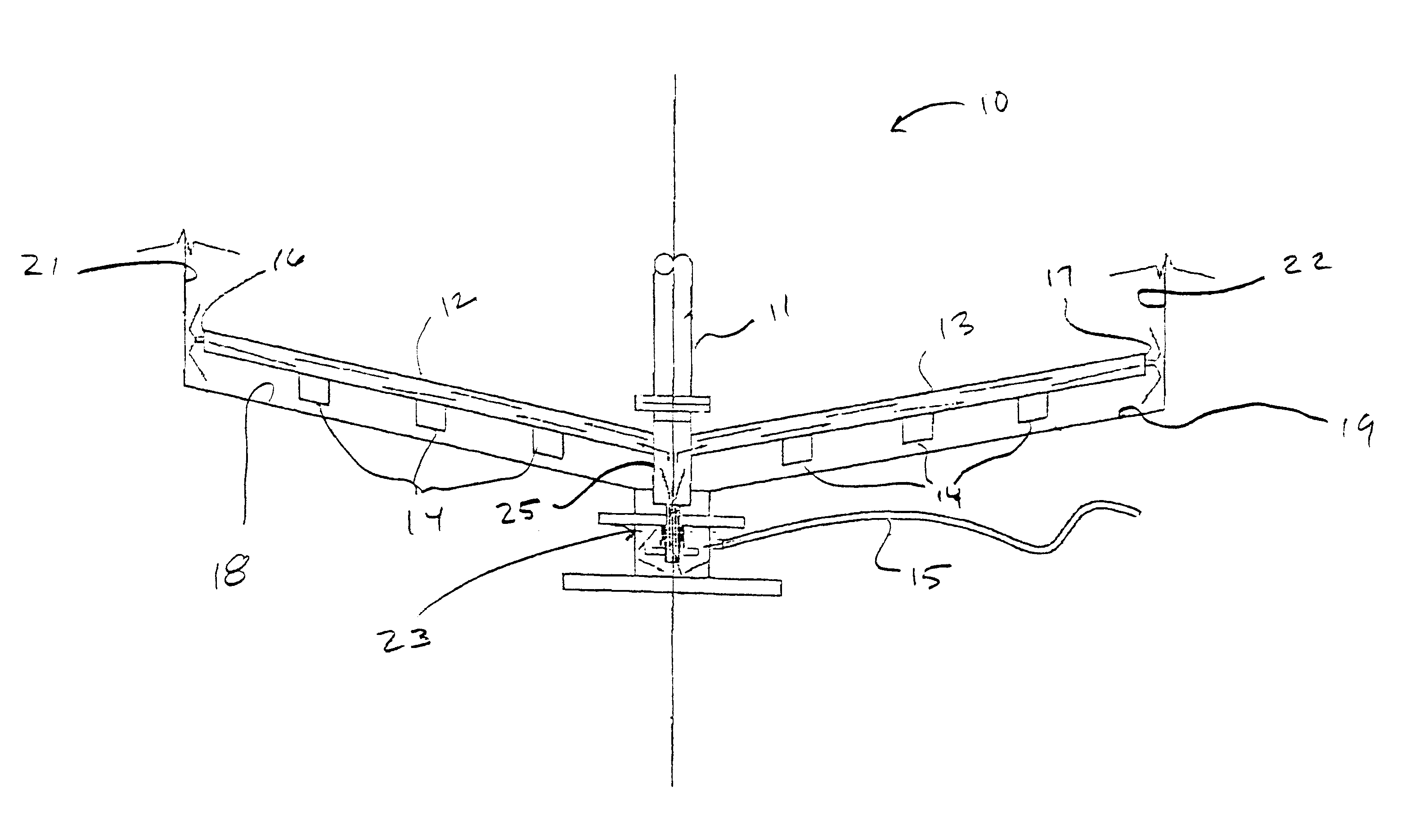
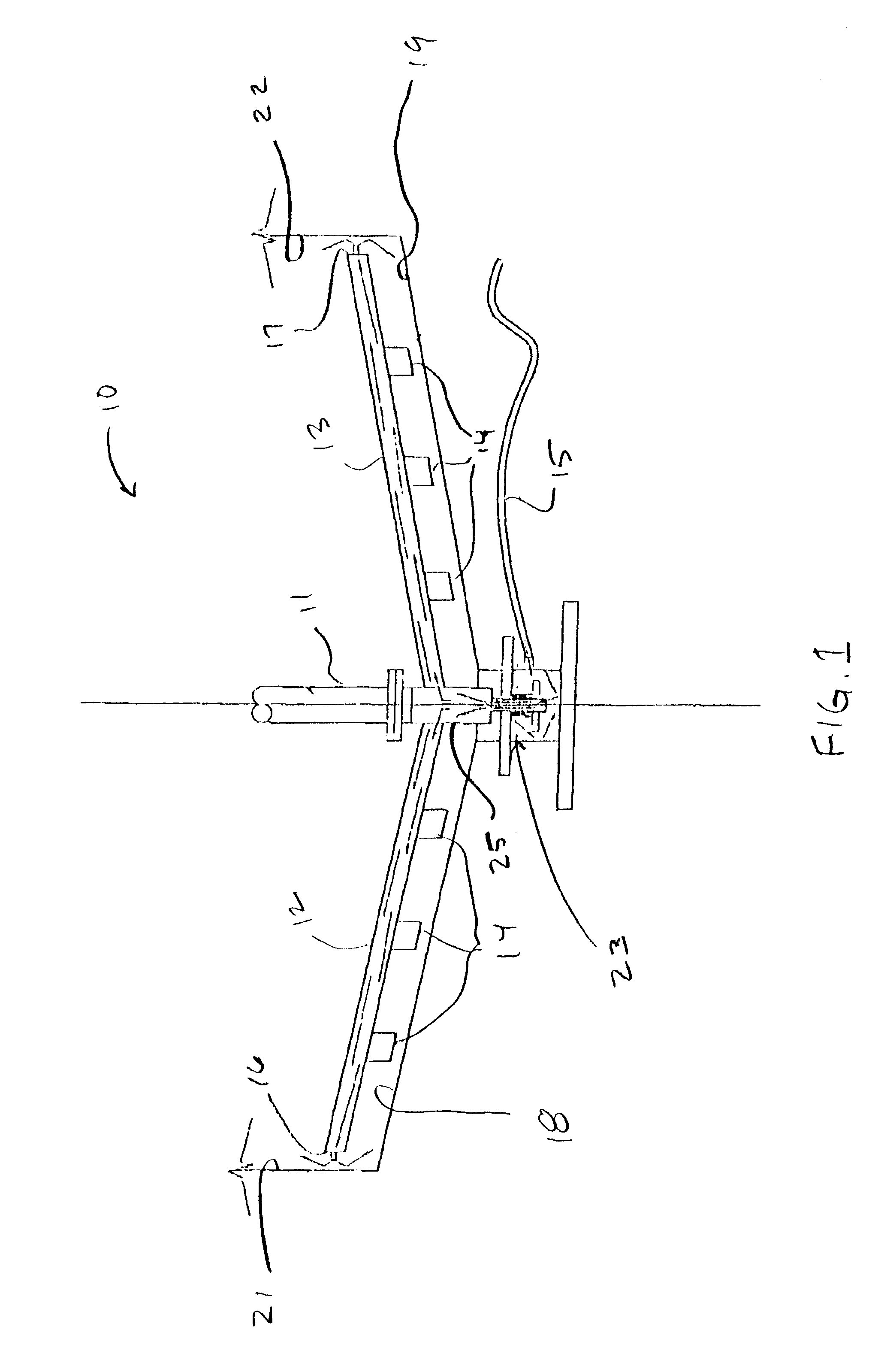
Rheology modification of settled solids in mineral processing
InactiveUS6365116B1Low viscosityIncrease speedRotary stirring mixersTransportation and packagingEngineeringSlurry
The present invention comprises a method for reducing the viscosity of the settled mud or underflow of a raked thickener thereby reducing the torque necessary to move the rake blade through the settled mud. The method includes the step of delivering a viscosity modifier to the settled mud and in front of the rake blade by pumping the viscosity modifier down the rake arm to an area in front of the rake blade. The method also includes an improved rake mechanism that includes a means for delivering viscosity modifier to the settled mud and in front of the rake blade. The present invention also includes a method for increasing the rate of consolidation of flocculated solids in a slurry.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
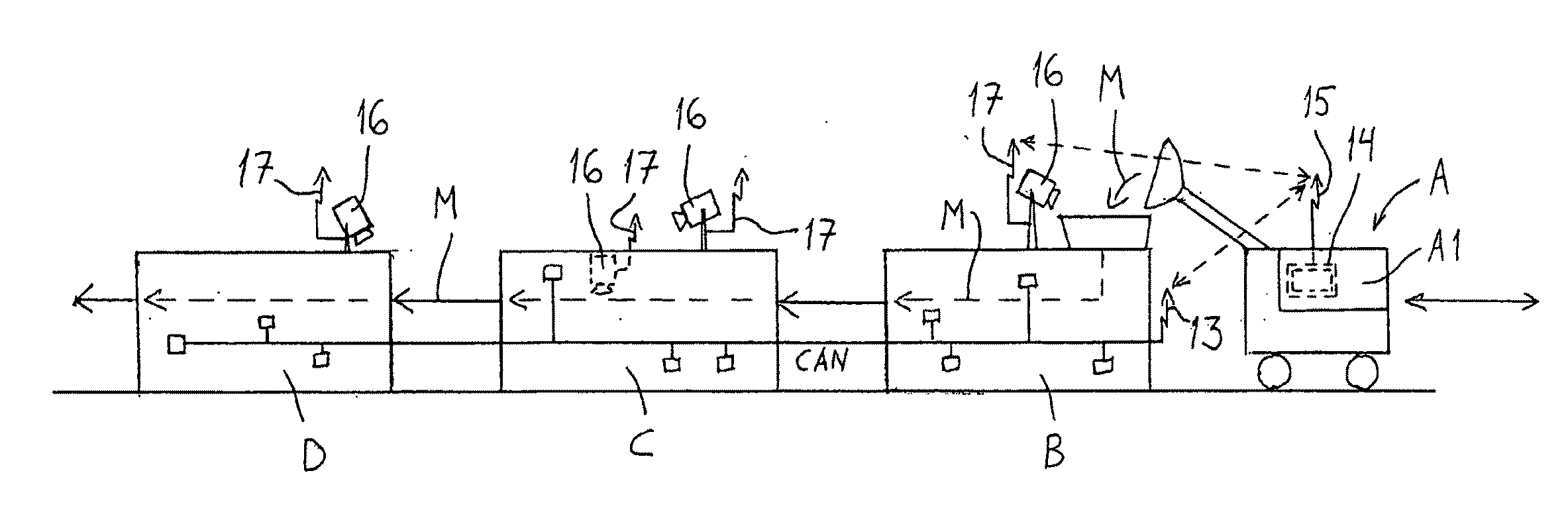
User interface of mineral material processing equipment
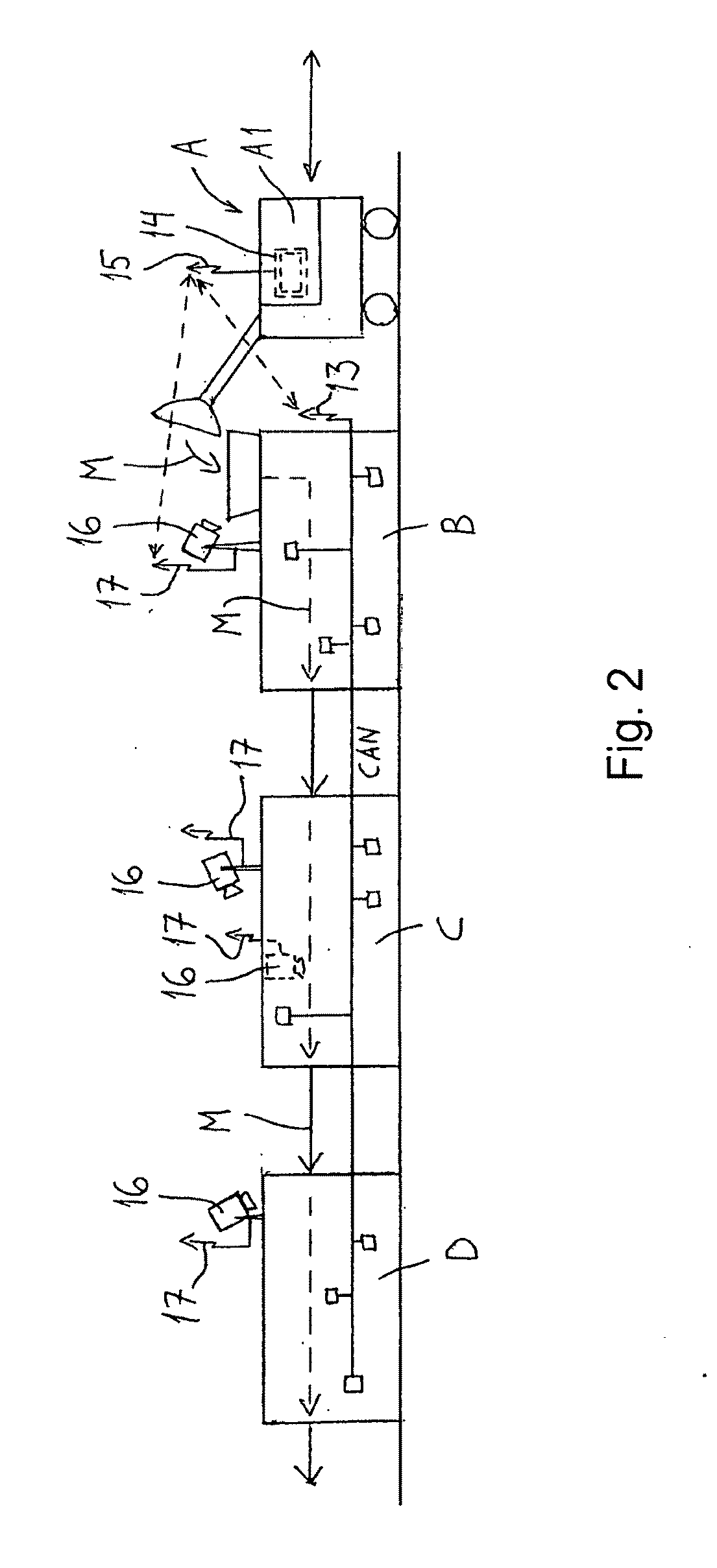
InactiveUS20100091103A1Available space is limitedSievingTelevision system detailsTraffic signalActuator
User interface of a mineral processing equipment governs a mineral processing line having several units (crushers, screens) connected in series. The user interface comprises a display screen (14) and control buttons or keys and is connected through a data transmission link to sensors and actuators of the mineral processing equipment for receiving measurement data and sending control commands. The user interface is arranged to show within the display screen (14), by choice of the userstatus of the mineral processing equipment in diagrammatic representation, ora live camera view (21) of at least one point of the equipment.The diagrammatic representations can be in form of a traffic lights (20) indicating the feeding speeds of the units.
Owner:METSO MINERALS INC
Iron tailing concrete
InactiveCN101671146AReduce pollutionNot brokenSolid waste managementMineral processingEnergy consumption
The invention provides an iron tailing concrete which comprises the following ingredients of cement, mineral processing barren rocks and detritus, admixture, water and pumping aid for the concrete determined according to performances, and the ingredients of the concrete according to the weight percentages of the concrete are respectively 4-20 percent of cement, 0-35 percent of mineral processing barren rocks and detritus, 1-8 percent of admixture, 1.5-2.5 percent of pumping aid for the concrete based on the weight sum of the cement and the admixture, and the balance of water. The invention hasthe effects that the novel concrete adopts tailing ores and detritus and is applied to the production of the concrete for partially or completely replacing natural aggregate. The concrete can reducethe pollution to the environment from mineral processing barren rocks, decrease the production volume and the production energy consumption of natural ore materials, accord with three 'green' meaningssuggested by the world environment organization: saving resources and energy; no environmental damages, and more environment friendly; and also according with the strategy of sustainable development,thereby not only satisfying requirements of the contemporary people, but also not damaging the capacity of satisfying unborn requirements.
Owner:天津港保税区航保商品砼供应有限公司
Method for comprehensively recycling valuable minerals in rare-earth tailings
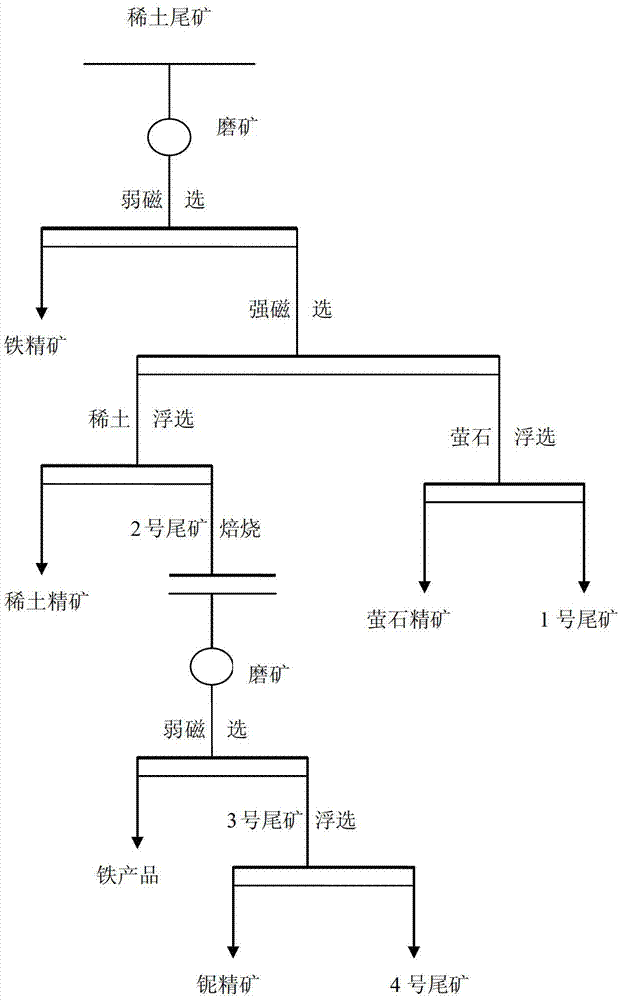
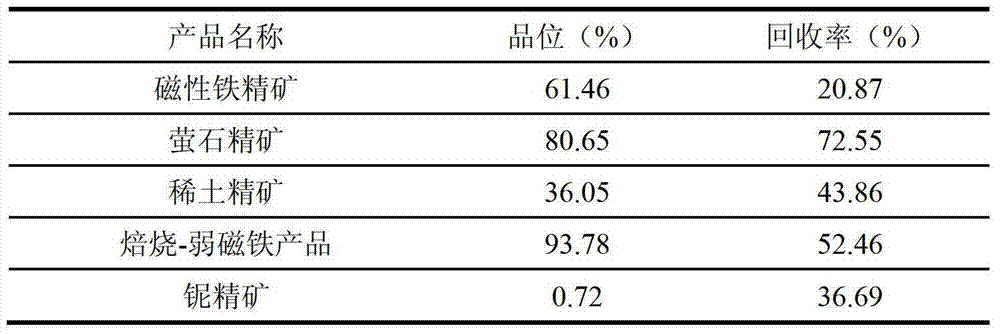
InactiveCN103394408ATake advantage ofOptimized flotation collectionFlotationWet separationResource utilizationNiobium
The invention relates to a method for comprehensively recycling valuable compositions of rare earth, iron, niobium and fluorite in rare-earth tailings, and belongs to the fields of comprehensive resource utilization technologies and mineral processing engineering. The rare earth, the iron, the niobium and the fluorite in the rare-earth tailings are efficiently and comprehensively recycled by the method including 'grinding the rare-earth tailings, performing low-intensity magnetic separation, performing high-intensity magnetic separation on weak-intensity magnetic tailings, performing flotation on high-intensity magnetic tailings to obtain fluorite in the high-intensity magnetic tailings, performing flotation separation on high-intensity magnetic concentrates to obtain rare earth, iron and niobium in the high-intensity magnetic concentrates, reducing and roasting base flows, performing low-intensity magnetic separation to obtain iron and niobium in the base flows and performing flotation on low-intensity magnetic tailings to obtain niobium in the low-intensity magnetic tailings according to characteristics that the rare-earth tailings contain the various valuable compositions. Compared with a method for singly recycling one or two valuable compositions, the method has the advantages that the purpose of comprehensively recycling the valuable compositions in the rare-earth tailings can be effectively achieved, secondary resources can be sufficiently utilized, and the method has excellent economical and social benefits.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
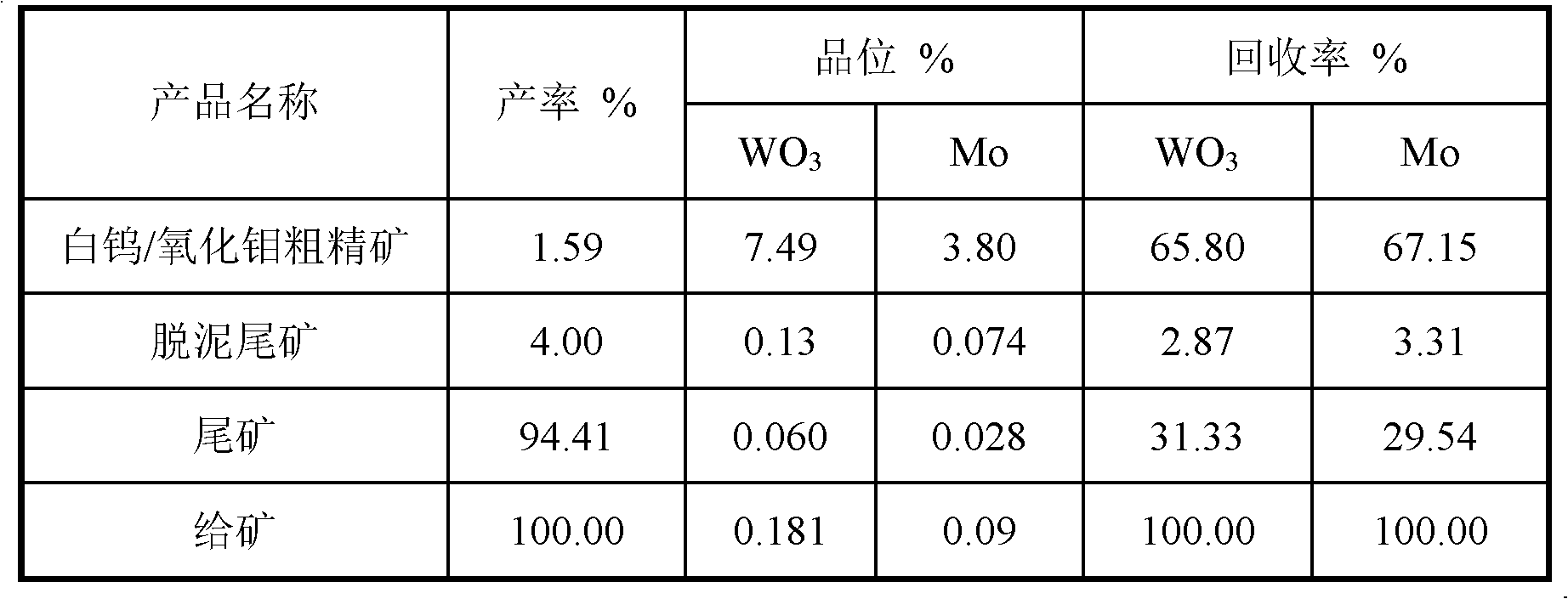
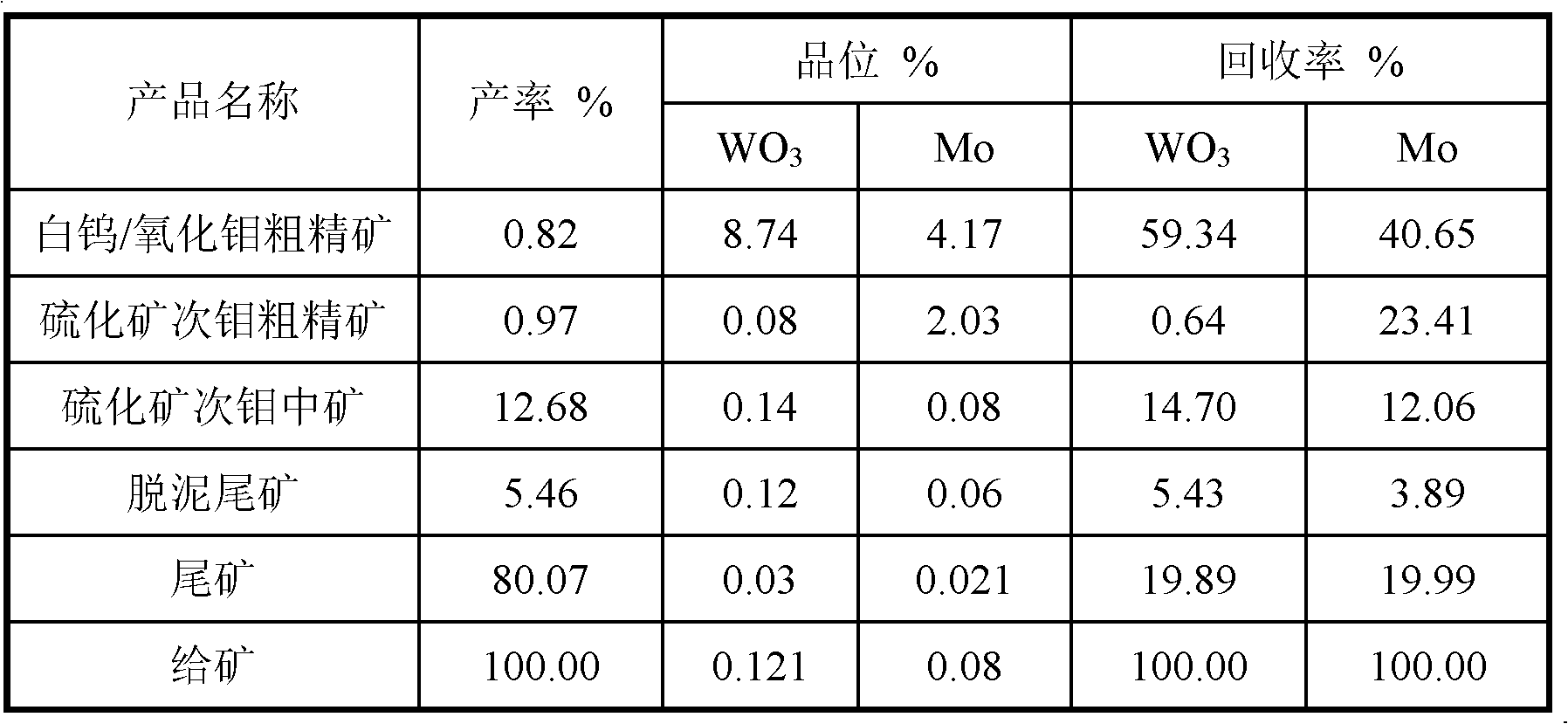
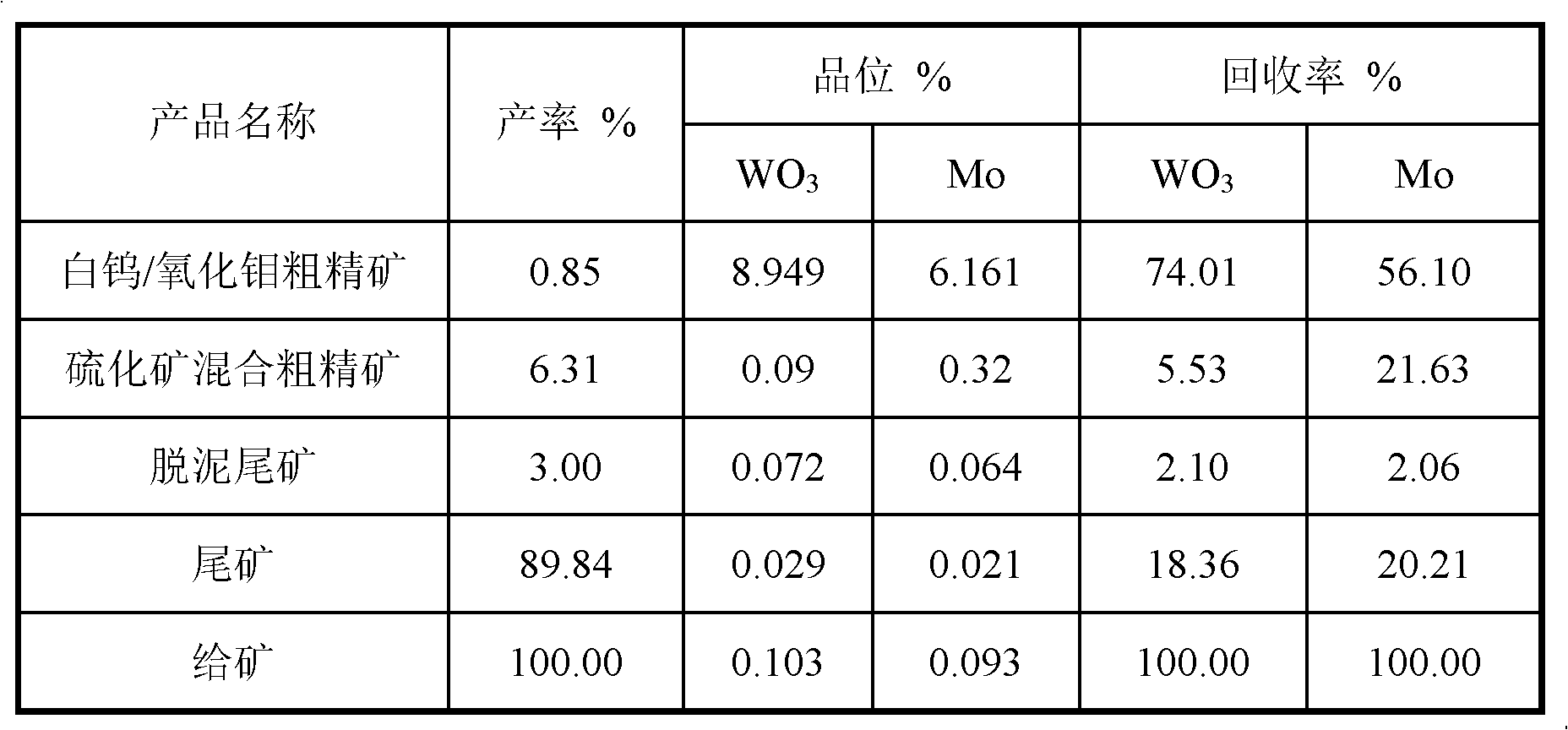
Mineral processing method for recycling scheelite/molybdenum oxide ores from molybdenum sulfide flotation tailings
The invention discloses a mineral processing method for recycling scheelite / molybdenum oxide ores from molybdenum sulfide flotation tailings. The mineral processing method comprises the following steps of: taking the molybdenum sulfide flotation tailings as raw materials and further levigating the raw materials; carrying out reselection and / or flotation and desliming on ore pulp which is levigated according to demands; adding a regulator, an auxiliary inhibitor, an inhibitor and a modified aliphatic acid collecting agent into the flotation tailing pulp; and recycling the scheelite / molybdenum oxide ores at room temperature so as to obtain scheelite / molybdenum oxide ore concentrates after roughing, scavenging and concentrating. The mineral processing method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple process flow, low production cost, resource saving, high product level and high recovery.
Owner:HUNAN SHIZHUYUAN NON FERROUS METAL
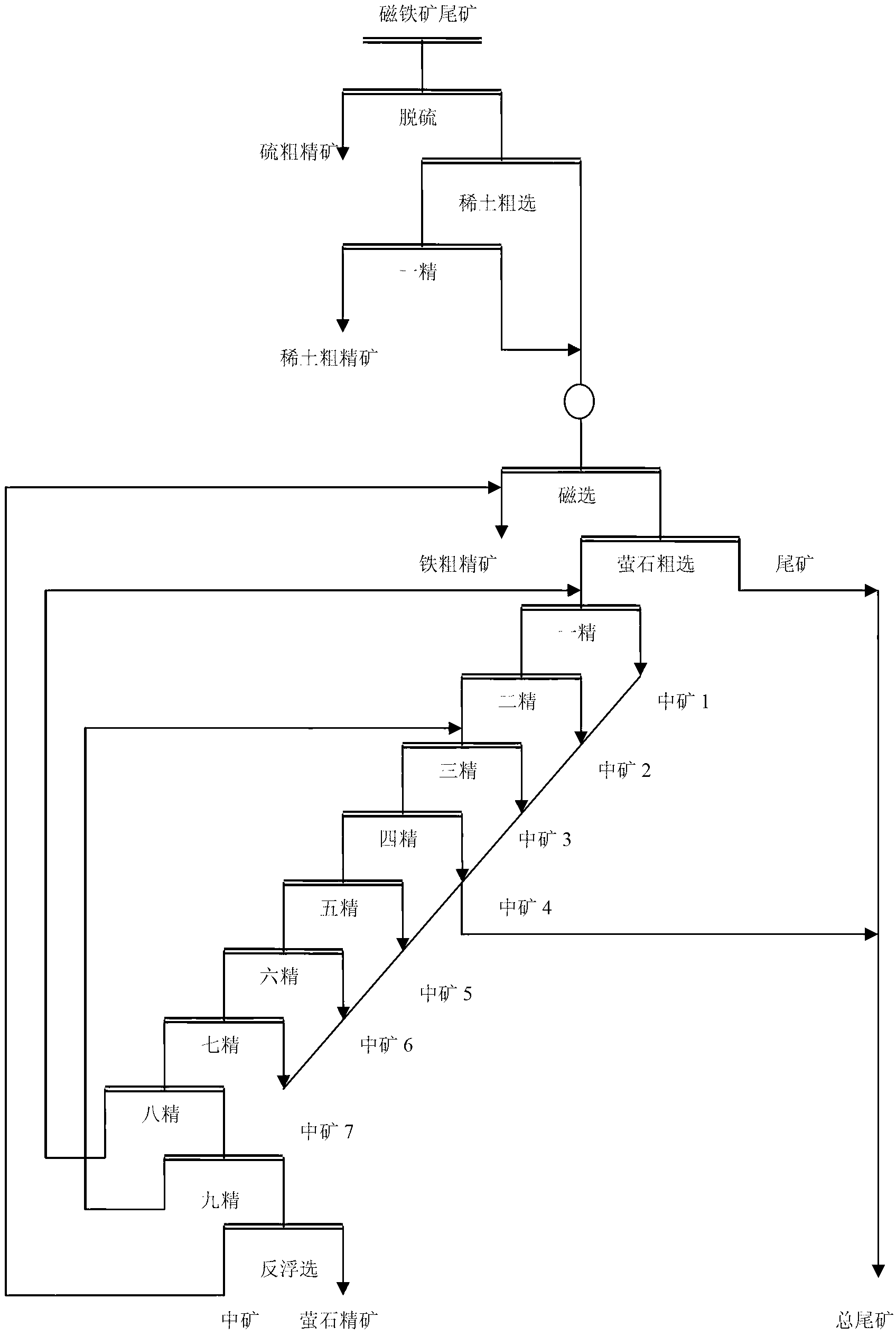
Mineral processing technology for recycling fluorite from baotite, magnetite and tailing
The invention belongs to the technical field of mineral engineering and provides a mineral processing technology for recycling fluorite from baotite, magnetite and tailing. In the tailing, mineral particle size of the fluorite is thin, iron-bearing mineral, rare-earth mineral, gangue mineral and the fluorite mineral are closely symbiotic and floatability of minerals such as rear earth, barite, apatite, calcite and dolomite is close to the fluorite mineral, so that separation of the fluorite mineral is difficult. According to the mineral processing technology for recycling the fluorite from the baotite, the magnetite and the tailing, priority desulfuration, rear earth flotation, ore grinding, iron selection through magnetic separation, fluorite selection through direct flotation and a reverse flotation sorting technology are performed on the magnetite and the tailing to enable pyrite, the rare earth, the iron-bearing mineral and the fluorite to be picked out in sections, efficient, high selective, easy-to-operate inhibitor and collecting agent combination is utilized in sorting of fluorite which is mostly performed monomer separation, so that fine fluorite of high grade and high recovery rate is obtained, a purpose of synthetically recycling valuable minerals is achieved, and effective separation of the fluorite mineral and the gangue mineral is achieved.
Owner:包钢集团矿山研究院(有限责任公司)
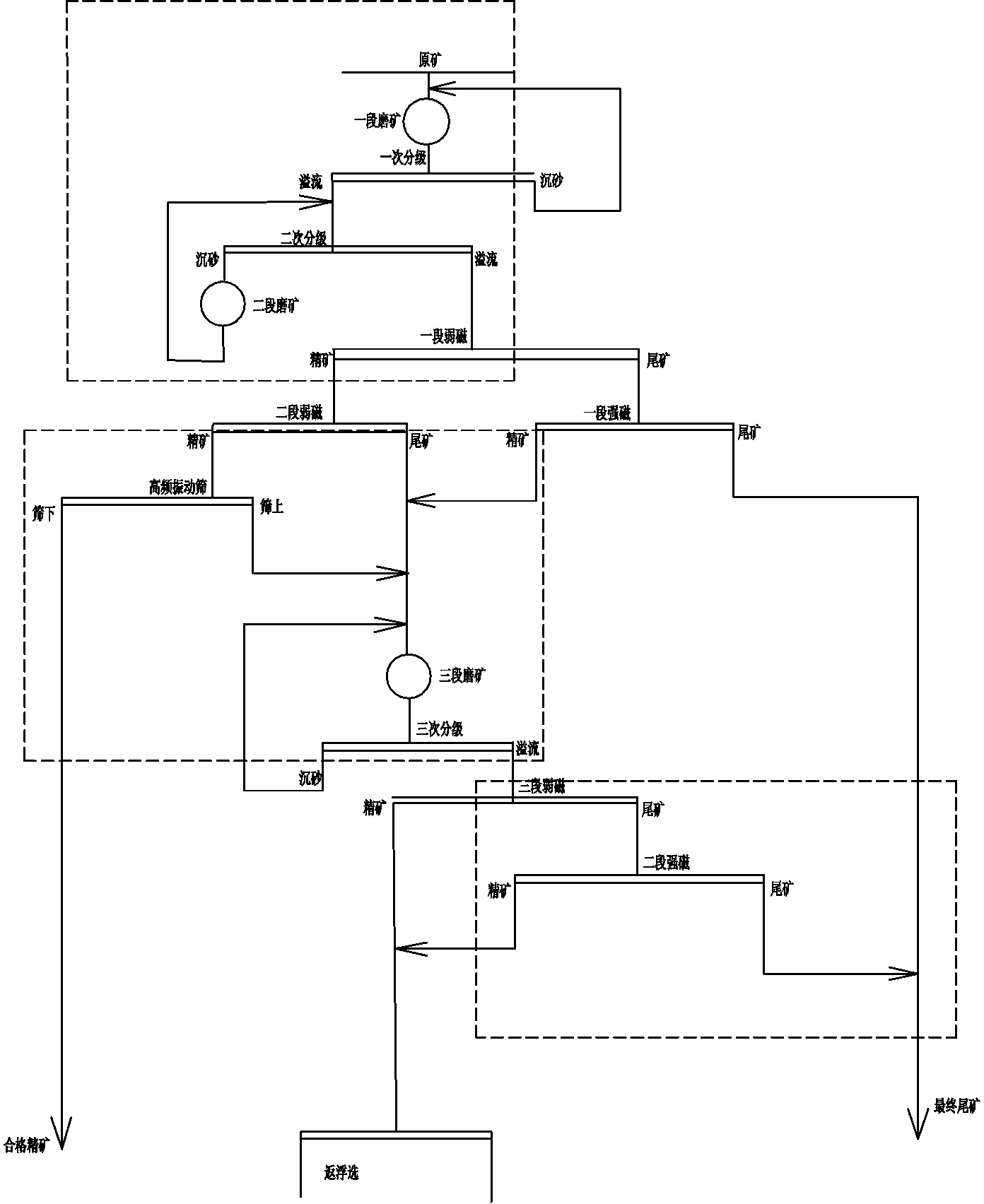
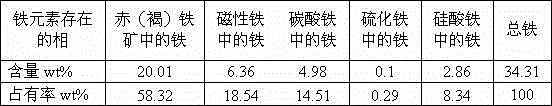
Mineral processing process for processing mixed ore of magnetic iron ore and hematite-limonite ore
The invention relates to a mineral processing process for processing mixed ore of magnetic iron ore and hematite-limonite ore. The mineral processing process comprises steps as follows: raw ore containing the mixed ore of the magnetic iron ore and the hematite-limonite ore is smashed and then subjected to two-stage continuous ore grinding; overflowing ore of a secondary classifying cyclone is subjected to two-stage low-intensity magnetic separation and one-stage fine screening and separation in combination of a single magnetic separation, fine screening and regrinding process for processing magnetic ore; under the condition of rougher ground ore particles, a part of undersize qualified magnetite concentrate products are firstly obtained, the other part of oversize products are combined with one-stage high-intensity magnetic separator concentrate and two-stage low-intensity magnetic separator tailings to serve as middlings, and the middlings are subjected to three-stage ore grinding classification operation for regrinding and separation; and overflowing ore of a tertiary classifying cyclone is subjected to three-stage low-intensity magnetic separation and high-intensity magnetic separation, fine-grain qualified tailings are thrown again, three-stage low-intensity magnetic concentrate and two-stage high-intensity magnetic concentrate are combined to obtain mixed magnetic concentrate, the mixed magnetic concentrate is subjected to a reverse flotation process for separation, and a qualified flotation concentrate product is obtained. According to the mineral processing process, the mixed ore of the magnetic iron ore and the hematite-limonite ore with different dissemination particle sizes is reasonably processed, the qualified iron ore concentrate product is obtained, and the mineral processing process is economical, energy-saving and environment-friendly.
Owner:ANSTEEL GRP MINING CO LTD
Dual zone feedwell for a thickener
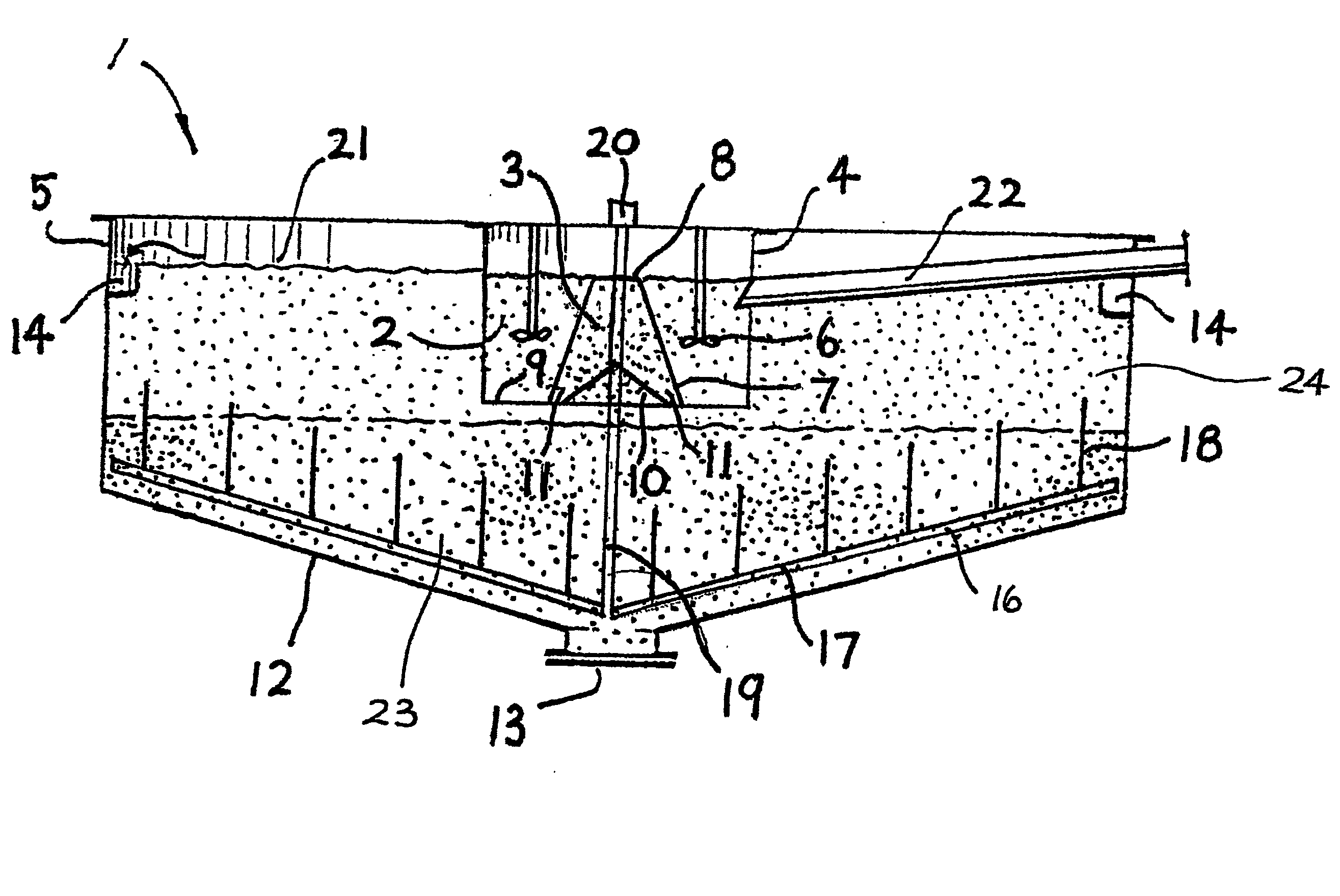
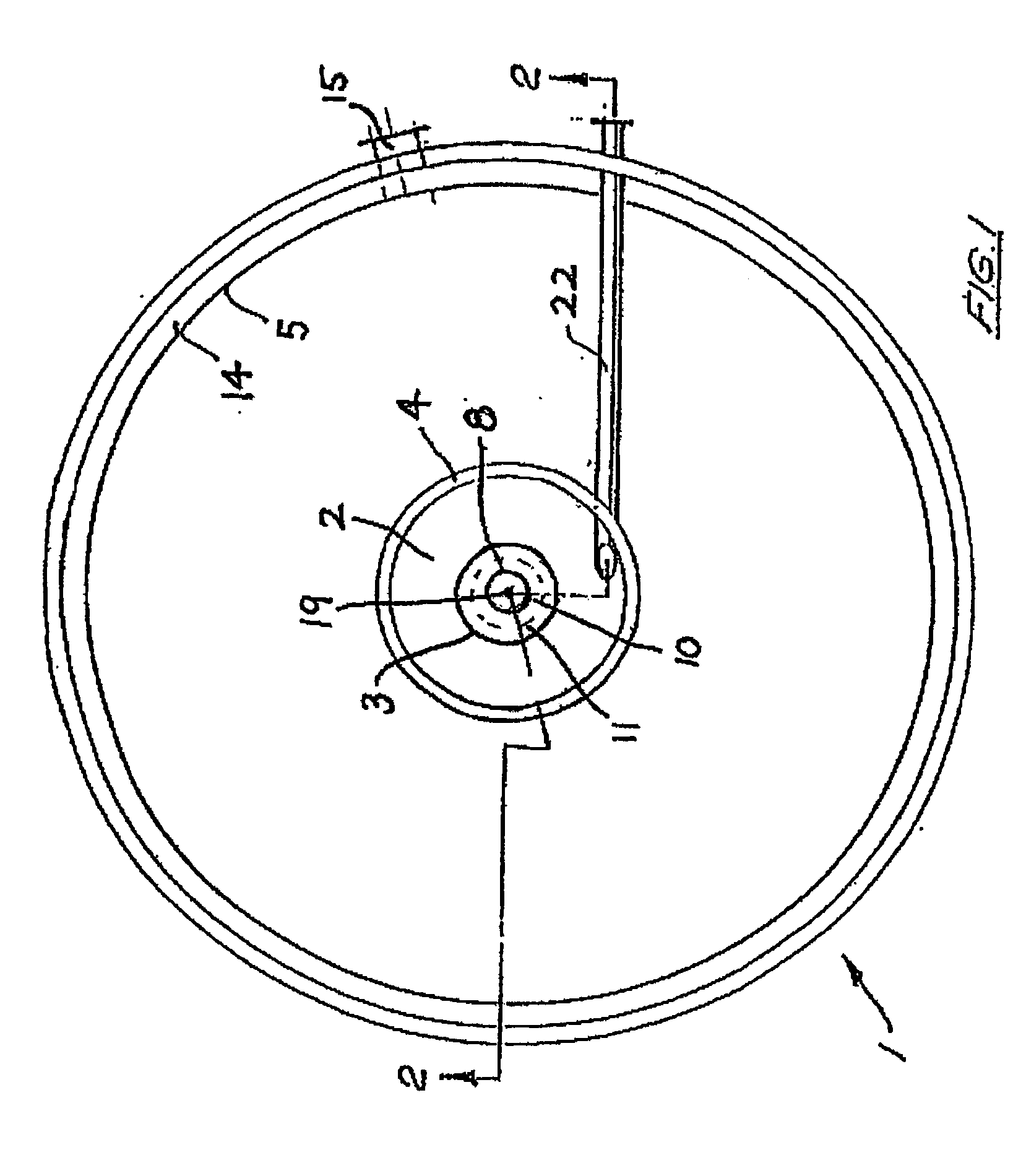
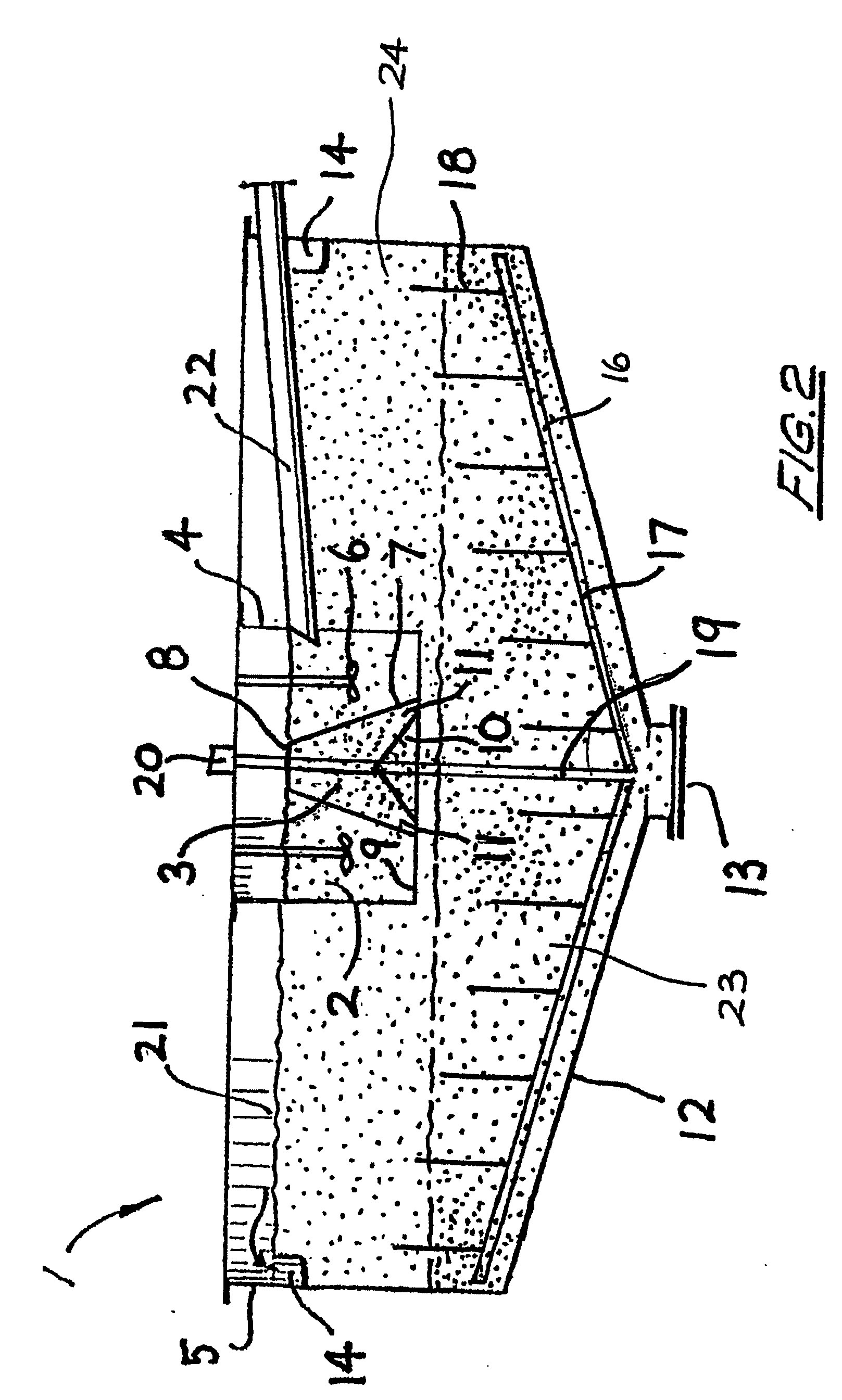
ActiveUS20050115907A1Easy to separateOther chemical processesSettling tanks feed/dischargeMineral processingLiquid suspension
The invention provides an extraction device (1) for liquid suspensions and pulps and is designed for use in the field of mineral processing. The extraction device includes two adjacent upstream and downstream concentric chambers (2) and (3) defining a feedwell (4). The feedwell is centrally located upstream of a third chamber in the form of a thickening tank (5). All three chambers are in sequential unidirectional fluid flow relationship such that feed liquid flows firstly from chamber (2) to chamber (3) and then to the tank (5).
Owner:OUTOKUMPU OY +1
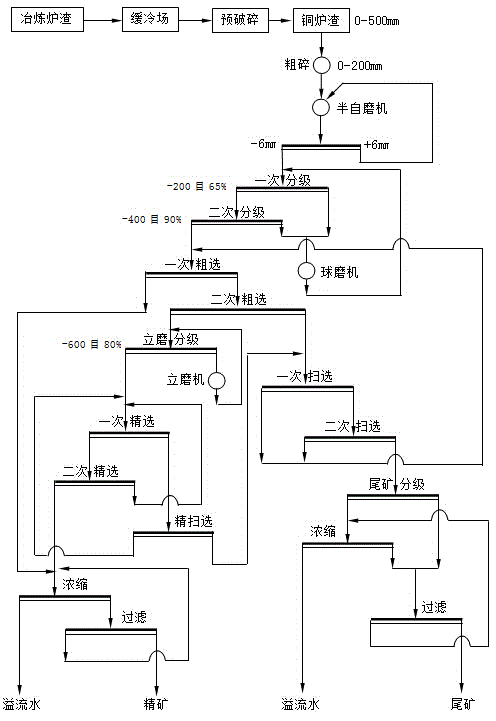
Copper furnace slag mineral processing process
InactiveCN104399573AExtend slow cooling timeIncrease collisionFlotationGrain treatmentsSlagEngineering
The present invention provides a copper furnace slag mineral processing process. According to the copper furnace slag mineral processing process, the slow cooling mode adopts centralized natural slow cooling for 12 h and spraying slow cooling for 60 h so as to prolong the slow cooling time of the slag ladle at a temperature of 1000-1250 DEG C, increase the opportunity of collision and growth of the copper matte particles, and easily achieve the crystallization development of the copper crystal, such that the recovery rate of the subsequent flotation operation is easily increased; the disseminated grain size of the copper sulfides in the furnace slag is fine, and for complete dissociation of the useful minerals, the stirring mill is adopted to carry out mineral grinding, ie., the crude concentrate is graded with a cyclone device, the setting sand after the grading is subjected to mineral grinding by adopting the stirring mill, the overflow after the grading is subjected to fine selection twice by adopting the flotation column, and the selected concentrate is directly adopted as the final concentrate, wherein the tailings being subjected to the one fine selection through the flotation column is sorted by adopting the flotation machine, and the tailings being subjected to the double fine selection through the flotation column cyclically returns. According to the present invention, the flotation machine, flotation column and vertical stirring mill combined process combining the machine, the column and the mill is adopted, such that the useful minerals with various particle sizes are easily recovered, and the metal recovery rate is efficiently increased.
Owner:广西金川有色金属有限公司
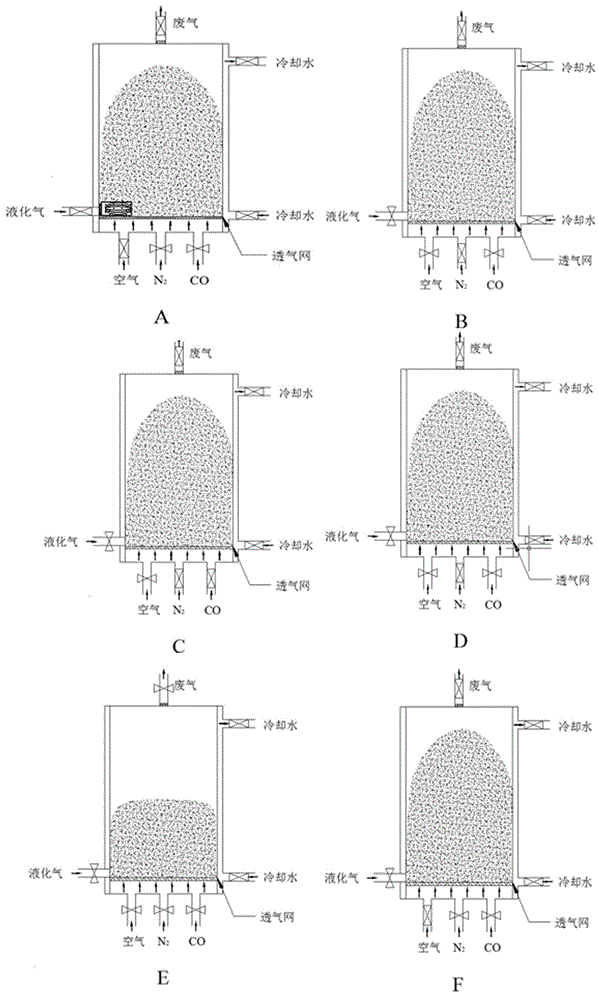
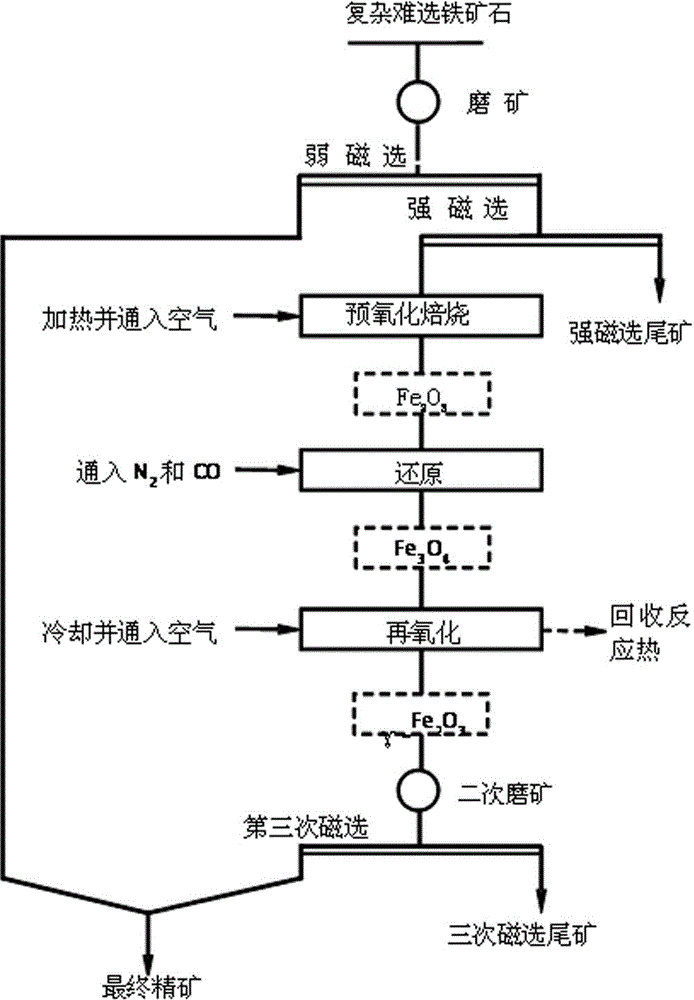
Preenrichment-three segment suspension roasting-magnetic separation treatment method of complex refractory iron ores
The invention discloses a preenrichment-three segment suspension roasting-magnetic separation treatment method of complex refractory iron ores, and belongs to the technical field of mineral processing. The method comprises the following steps: 1, levigating the complex refractory iron ores, carrying out weak magnetic separation, and carrying out strong magnetic separation on mine tailings; 2, putting concentrate obtained after strong magnetic separation in a suspension roasting furnace, and heating to 450-800DEG C in a suspension state in order to carry out pre-oxidation roasting; 3, introducing nitrogen to displace air, and introducing a reducing gas to carry out reduction in a suspension loose state; 4, introducing air when the temperature decreases to 250-400DEG C in order to oxidize, taking out the obtained material when the temperature decreases to below 100DEG C, and carrying out ore milling; and 5, carrying out third segment magnetic separation, and mixing concentrate obtained after three segment magnetic separation with concrete obtained after the weak magnetic separation to obtain finial concentrate. The method has the advantages of simple process, improvement of the recovery rate of the complex refractory iron ores, strong adaptability, safe and reliable process, uniform and stable product quality, energy saving and consumption reduction.
Owner:上海逢石科技有限公司
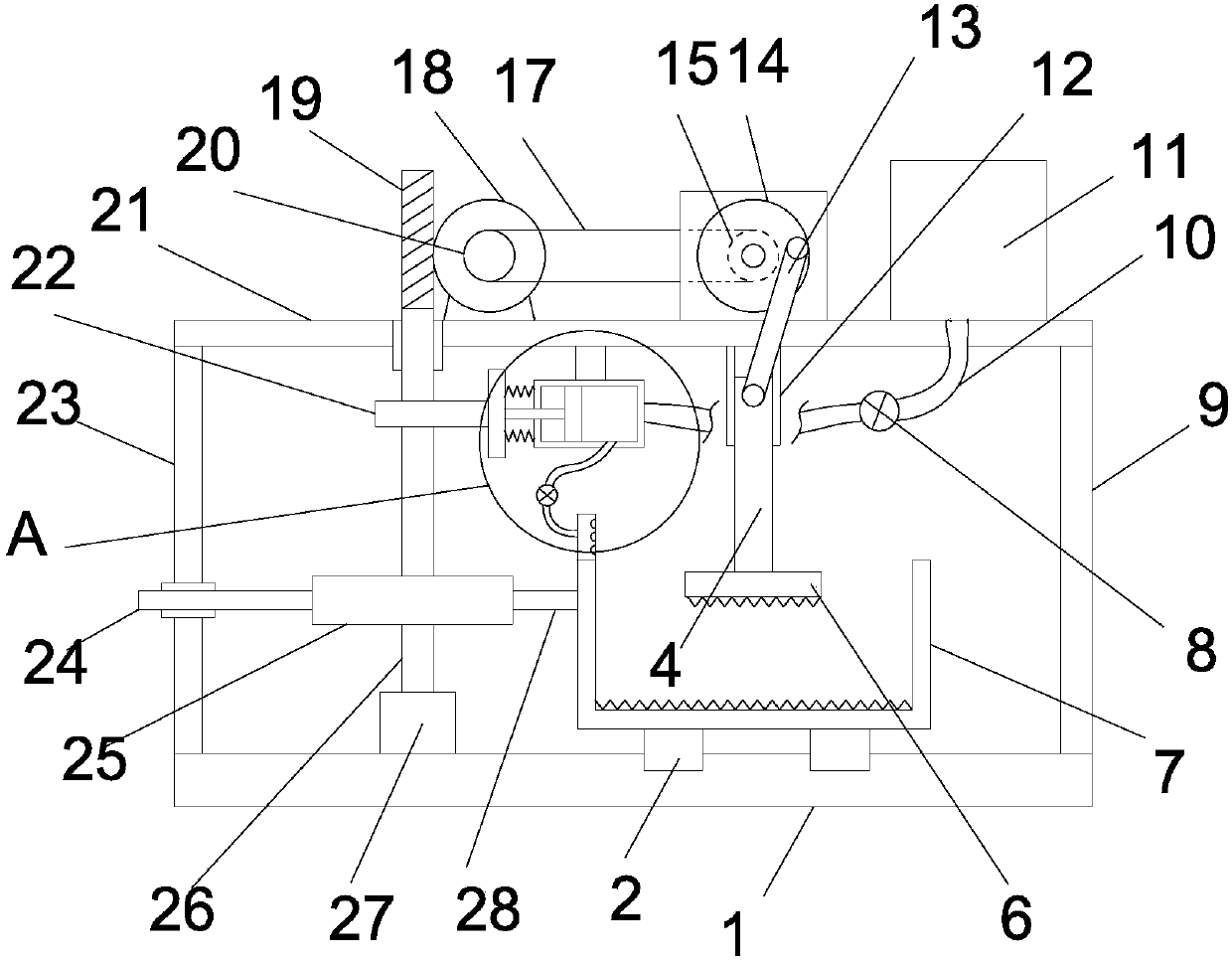
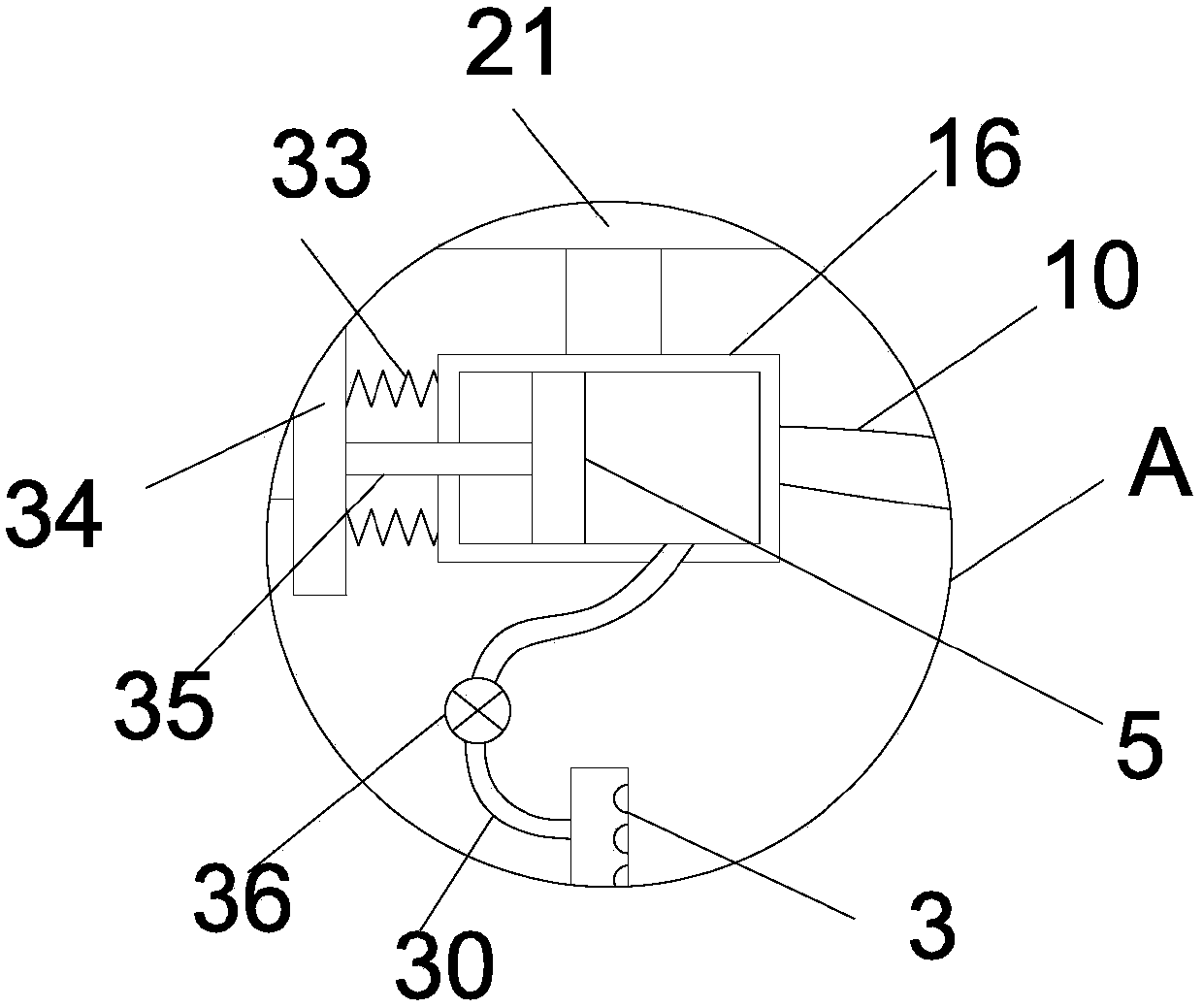
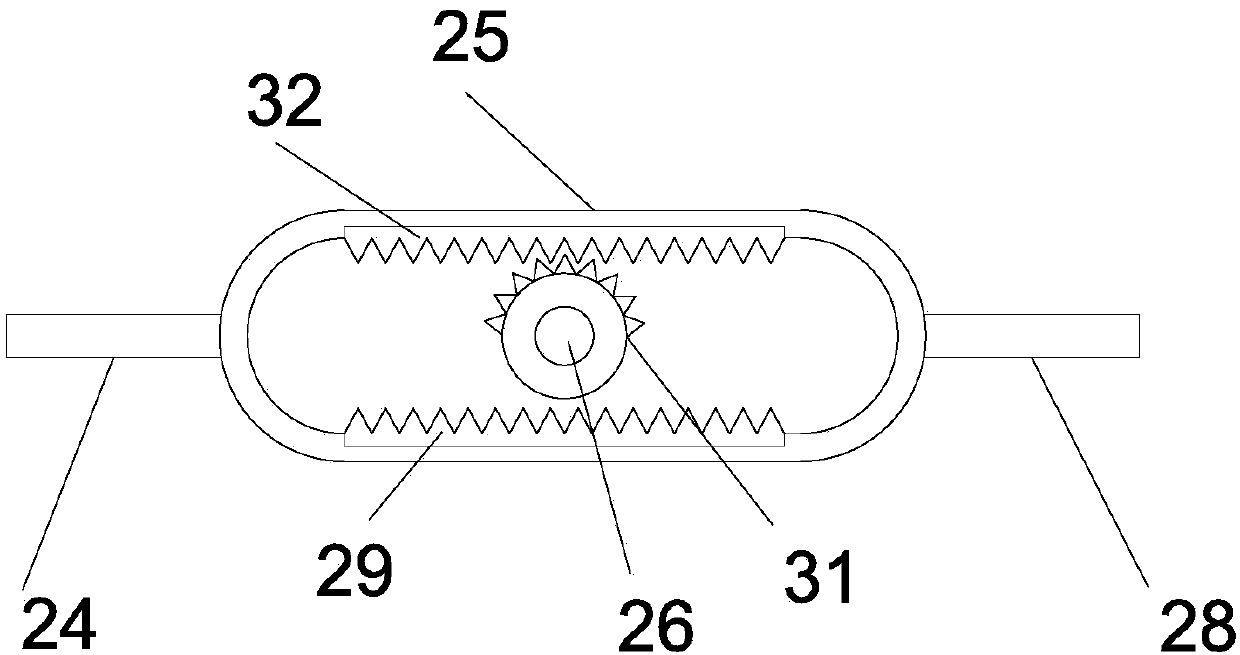
Ore coarse crushing device for mineral product processing
InactiveCN107552129AFull impact crushing actionImprove crushing efficiencyUsing liquid separation agentGrain treatmentsReciprocating motionEngineering
The invention discloses an ore coarse crushing device for mineral processing, which comprises a bottom plate, a left vertical plate and a right vertical plate are vertically and fixedly installed on the bottom plate, a limit slideway is vertically arranged on the top plate, and the vertical limit slideway is vertically The sliding type is equipped with a sliding rod, and a transmission rod is connected between the sliding rod and the runner. The piston head is connected with a piston rod extending to the left to the outside of the water-drawing sleeve. The left end of the piston rod is fixed with a push plate. There is a nozzle connected to the water-drawing sleeve through the liquid outlet pipe; the structure of the invention is ingenious and the design is reasonable, and the ore in the crushing tank is broken through the up and down reciprocating motion of the impact block, and the left and right reciprocating motion of the crushing tank makes the ore evenly spread on the ground. The bottom of the crushing tank makes the ore get a comprehensive impact crushing effect and improves the crushing efficiency of the ore; the nozzle sprays water intermittently into the crushing tank to reduce the dust generated during the crushing process of the ore, avoiding the spread of dust, and more Environmental friendly.
Owner:长沙德科投资管理咨询有限公司
Use of polyethylene glycol based fluidized polymer suspension in functional systems
ActiveUS20060018968A1Increase stickinessBiocideCosmetic preparationsPersonal carePolyethylene glycol
An aqueous based functional system contains a stable fluid polymer suspension (FPS) thickening agent of a polysaccharide, polyethylene glycol (PEG), and hydrated thickening silica. The functional systems may be formulations of personal care excluding oral care, household care, oil field servicing fluids, Civil Engineering servicing fluids, paper coatings, construction fluids, ceramic glazes, foods, firefighting retardants, mineral processing, aqueous based coatings, building materials, construction, pharmaceuticals, medical care, paper making process, and paper coating. The FPS provides to the functional system comparable or better rheology and viscosity properties as compared to when using similar thickening agents in dry, solid form. A method of preparing the aqueous based functional system is also provided by adding a sufficient amount of a stable FPS that is compatible with the functional system to the system to thicken the functional system.
Owner:HERCULES LLC
Inhibition reelection and separation method for bulk concentrate floatation of plumbum-zincium, plumbum-zincium-copper or plumbum-copper
InactiveCN101293221AKeep natural propertiesImprove the quality of metallurgical productsWet separationEconomic benefitsCopper
An inhibition gravity treatment separation method for lead-zinc, lead-zinc-copper or lead-copper floatation collective concentrates pertains to the mineral processing technical field. In gravity treatment separation of the collective concentrates, lead sulphide inhibitor is added. The method includes the following procedures: after lead sulphide inhibitor is added, the collective concentrate is sent to a table concentrator again for gravity treatment separation; after the gravity treatment separation in the table concentrator, the concentrate belt includes lead concentrate and sub-concentrate belt and the tailing zone includes sub-concentrate and gangue containing lead-zinc, lead-zinc-copper or lead-copper; the obtained sub-concentrate and the gangue undergo the gravity treatment separation in the table concentrator again or for a plurality of times, thus finally obtaining lead concentrate, zinc concentrate, zinc-copper concentrate or copper concentrate. Due to the existence of lead sulphide inhibitor, the floatability of the lead sulphide is completely inhibited so as to highlight the high specific gravity feature of the lead sulphide; therefore, the lead sulphide is easily separated from a plurality of metallic collective concentrates by the gravity treatment separation in the table concentrator. The content of the metal elements in the obtained concentrates is mutually low and the major metal concentrate and the attaching metal concentrate can both satisfy the metallurgical standards and requirements, thus having extremely remarkable economic benefits.
Owner:兰坪县矿产三废回收厂
Production and using method of environmentally-friendly noble metal mineral processing reagent
ActiveCN102321807AEasy to produceAccurate ingredientsProcess efficiency improvementMolten stateCopper oxide
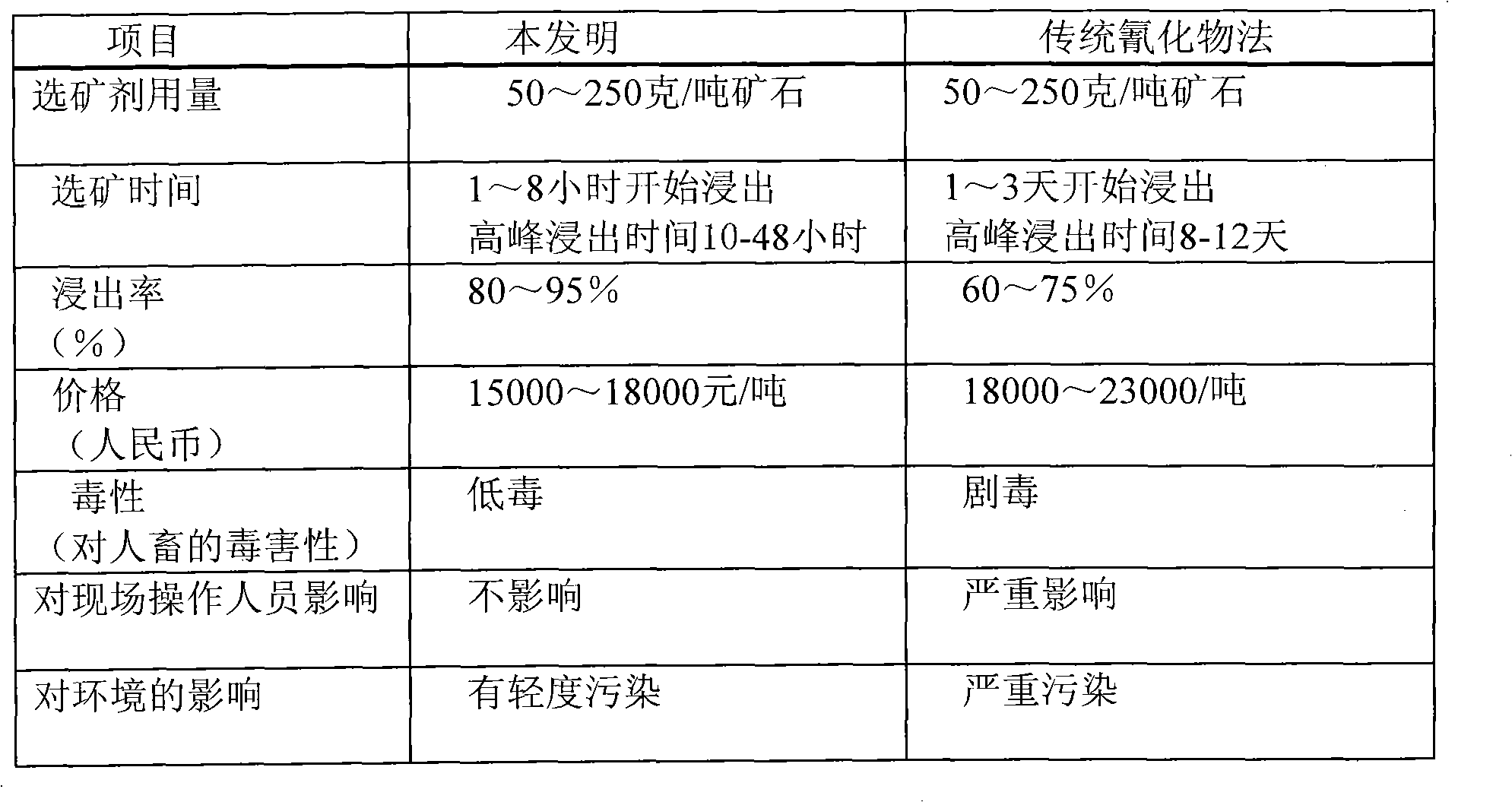
The invention discloses the production method of an environmentally-friendly noble metal mineral processing reagent. The method comprises the following steps: putting potassium ferrocyanide and urea after being mixed into a reactor; adding a pH regulator during the slow temperature rise process; heating to the molten state; taking a small amount of molten material detection samples, cooling and dissolving into water; measuring the pH value, enabling the molten material pH value to be 8-14; keeping the molten temperature for 5-60 minutes; and cooling to the normal temperature, thus the environmentally-friendly noble metal mineral processing reagent is obtained. The product obtained from the invention can be widely applied to the production of noble metal mine, such as the soaking, core spray of gold oxide ores, silver oxide ores and copper oxide ores, also can be used in industrial production industries such as electroplating, and used as medicaments for replacing toxic Cymag; and compared with all the other non-toxic or low-toxicity mineral processing reagents, the noble metal mineral processing reagent has the advantages of good effect, stable drug property, environmentally-friendly product, simple production method, low cost and the like.
Owner:广西地生金矿业科技有限公司 +2
Method for comprehensively recovering Fe, Cu and Si from copper smelting slag
InactiveCN101555551AImprove resource utilizationImprove product added valueSilicaCalcium/strontium/barium chloridesSilicon dioxideMaterials science
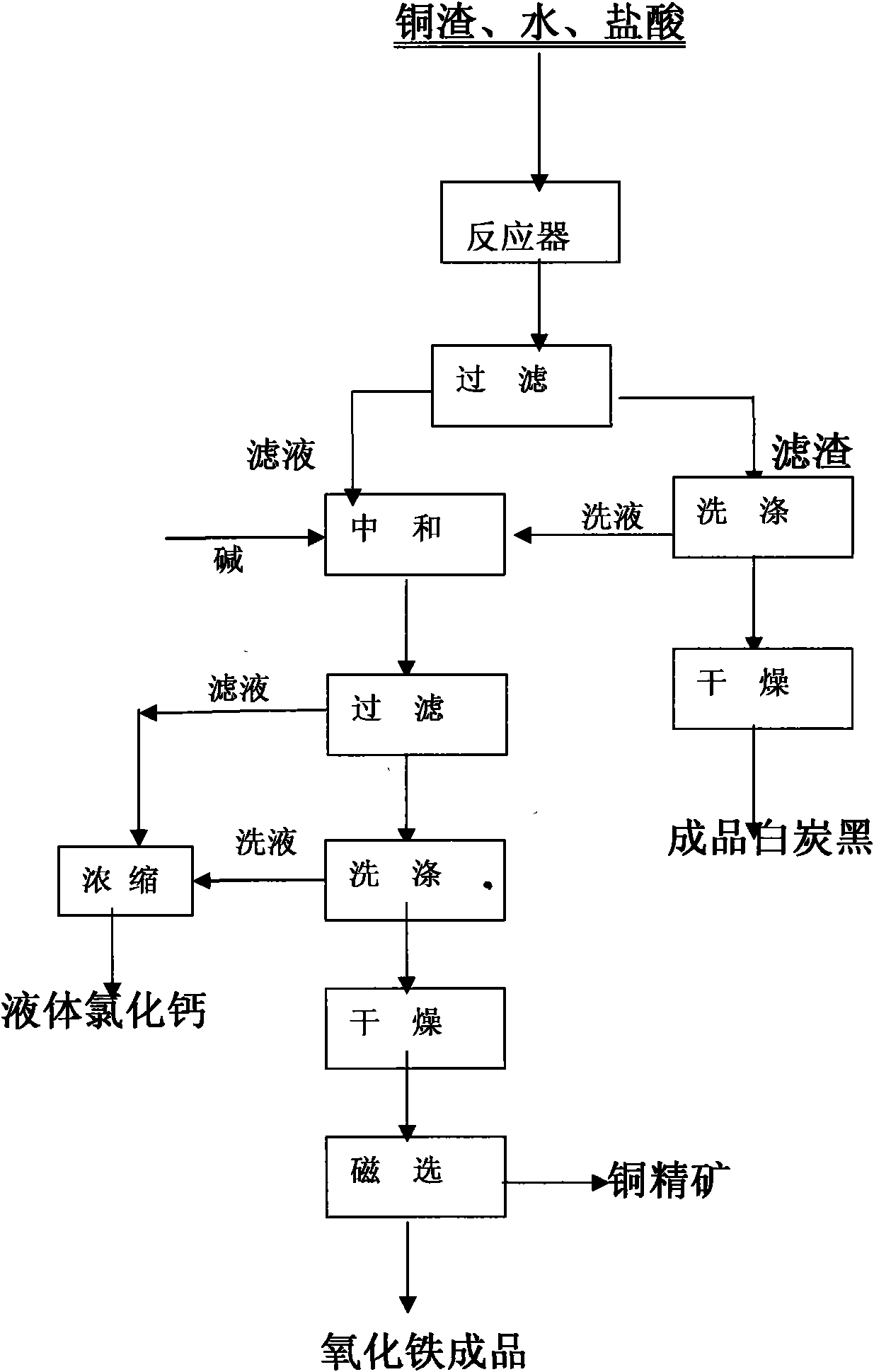
The invention discloses a method for comprehensively recovering iron, copper and silicon dioxide from copper smelting slag. The method takes copper smelting slag as a raw material, and comprehensively recovers Fe, Cu and Si in copper slag by adopting wet chemistry metallurgical technology. A muriatic acid and an inorganic acid are mainly adopted for leaching the copper smelting slag, the leaching acid concentration, the solid to liquid ratio, the leaching temperature and the leaching time are selected according to the quality requirement of silicon dioxide products under certain conditions, and silicon dioxide is firstly separated through filtering and drying to prepare silica pigment; the leaching filtered liquid is counteracted, settled, filtered, dried and ground, and ferric oxide phase and copper-bearing phase are selectively separated by adopting a conventional mineral processing method.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A method for preparing schistose nanometer magnesium hydroxide and sphericity nanometer white carbon black using zillerite gangue
InactiveCN101161591ASmall specific surface areaHigh puritySilicaMagnesium hydroxideSootSodium sulfate
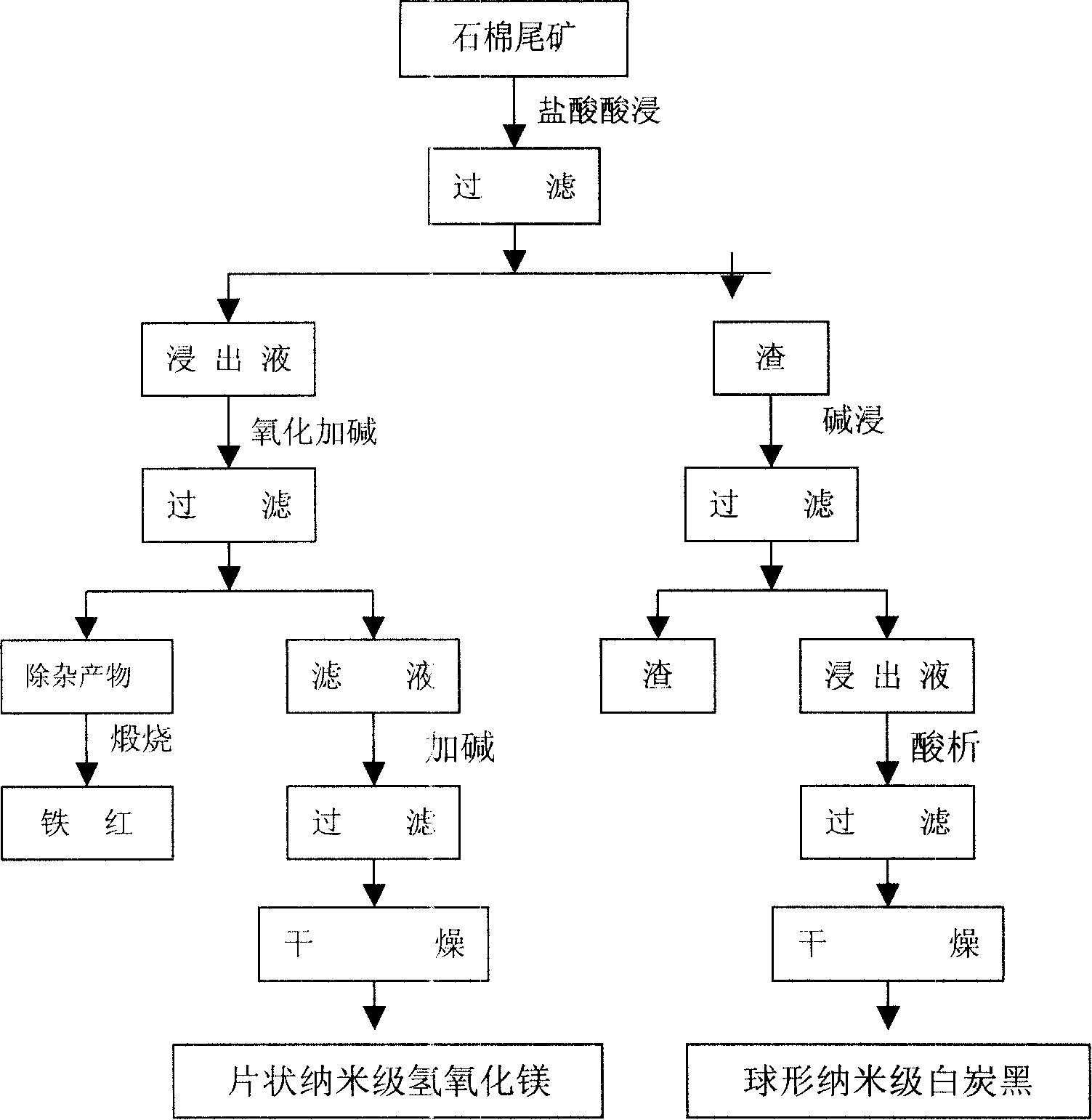
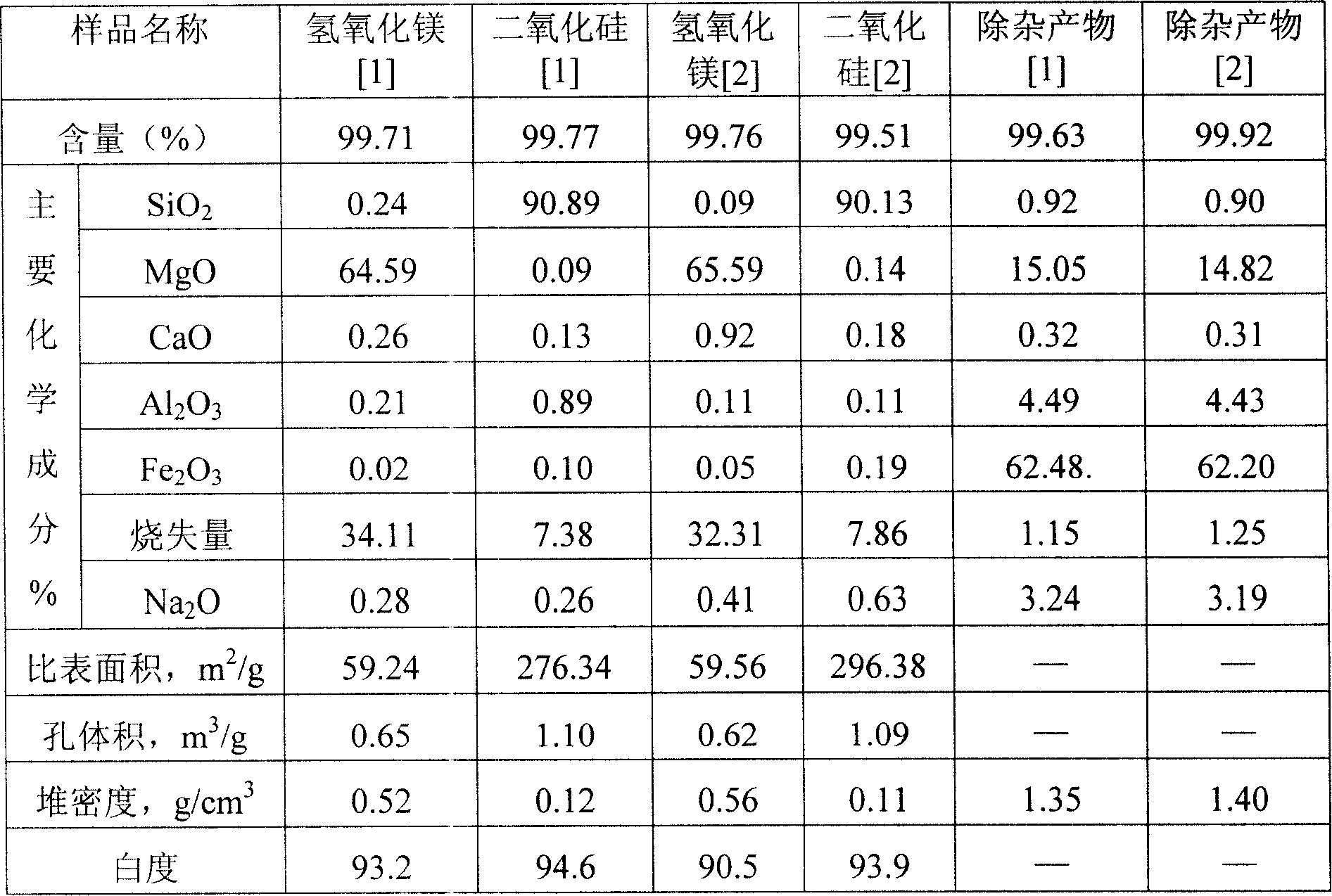
The invention relates to a method of synthesis use of asbestos gangue, belonging to the mineral processing and environment protection field. The asbestos gangue powder and hydrochloric acid solution are conducted soaking reaction and separate solid and liquid component. The filtrate is added with oxidizer to oxidize Fe<2+> and added with alkali solution precipitate iron, aluminum and calcium filtrate components in the filter solution. Deposit is removed by filter and alkali is added for reaction. Right amount of particle separating dose is added at the same time. Magnesium hydroxide of nanometer grade and sheet shape grain shape is obtained. Reacted residue of asbestos gangue powder and hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate react in heating situation. The reacted product is filtered and the filter solution is added with little sodium sulfate and water to adjust thickness. Surface modifier or particle separating dose is added and acid is used to settle out. The settled out product is aged, filtered, washed and dried to get the round-shape nanometer grade white carbon soot. The impurity of the filter is removed by acid to get precipitation. The precipitation passes through drying and calcinations to get iron oxide, alumina and calcium oxide mixture (product of removing impurity).
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
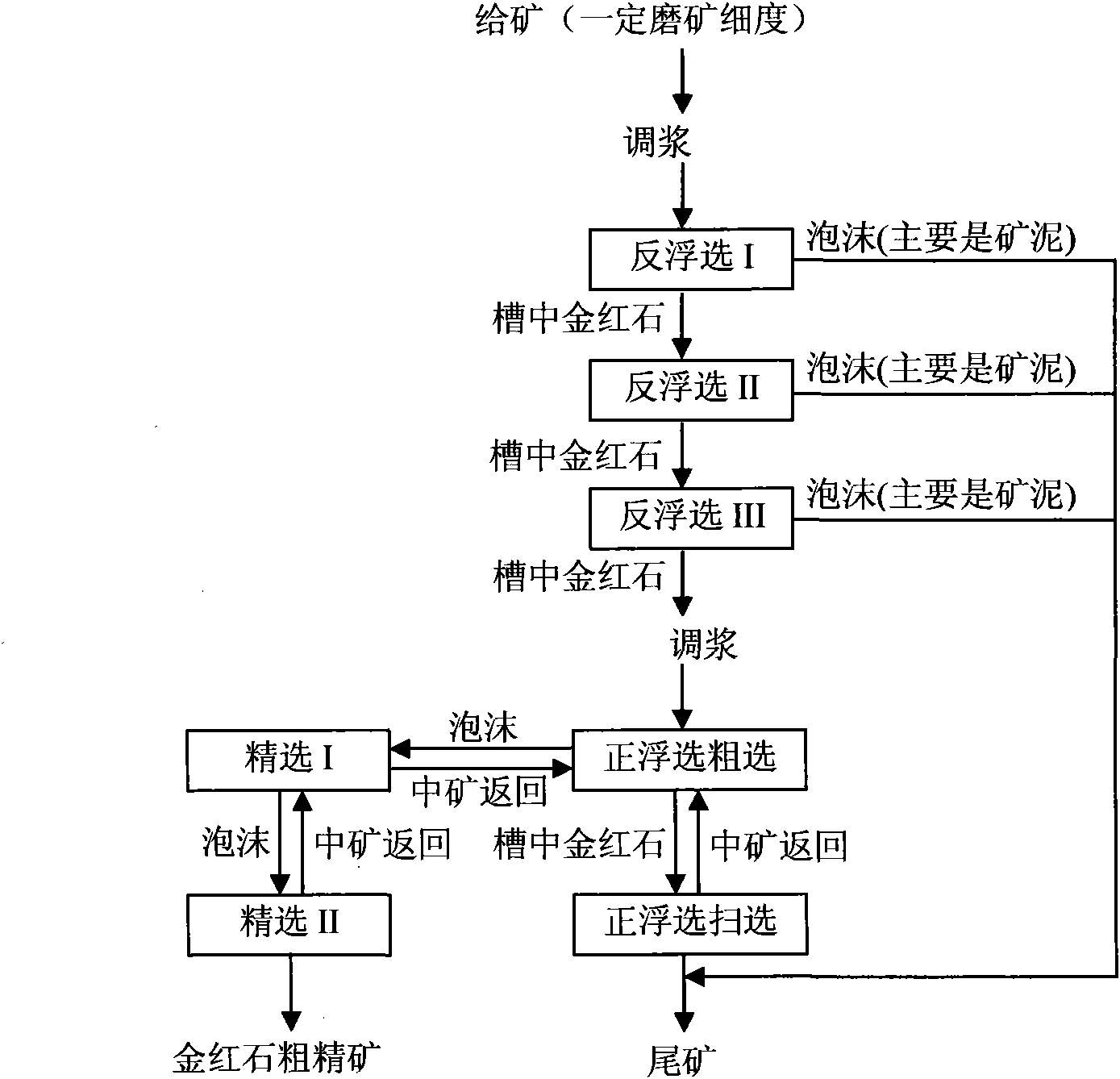
Method for roughing and tailings-discarding of fine rutile ore by multi-stage floatation
The invention provides a method for roughing and tailings-discarding of fine rutile ore by multi-stage floatation, relating to the technique for roughing and tailings-discarding of fine rutile ore by multi-stage floatation and belonging to the technical field of mineral processing engineering. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: firstly, conducting the reverse floatation of rutile by using sodium oleate as a collector according to the characteristics that aluminum sulfate can inhibit the rutile and activate silicate minerals in varying degrees, so as to effectively deslime in the process of reverse floatation; and then, conducting the forward floatation of rutile by using lead nitrate (or lead acetate) as an activator of rutile and using sodium alkyl hydroxamate and benzyl arsonic acid (or styryl phosphonic acid) as a combined collector according to the characteristic that gangue minerals can be inhibited on a combined basis under the synergistic action of sodium fluorosilicate, carboxymethylcellulose and the residual aluminum sulfate in the ore pulp, briefly, the method of the invention can realize the roughing and tailings-discarding of fine rutile by the multi-stage floatation comprising the following steps: firstly, conducting the reverse floatation by inhibiting the rutile; and then, conducting the forward floatation by activating the rutile. The method of the invention has the advantages that the enrichment ratio and recovery rate of rutile are high, the tailings of rutile ore can be discarded thoroughly and the mineral processing cost of rutile can be greatly reduced.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
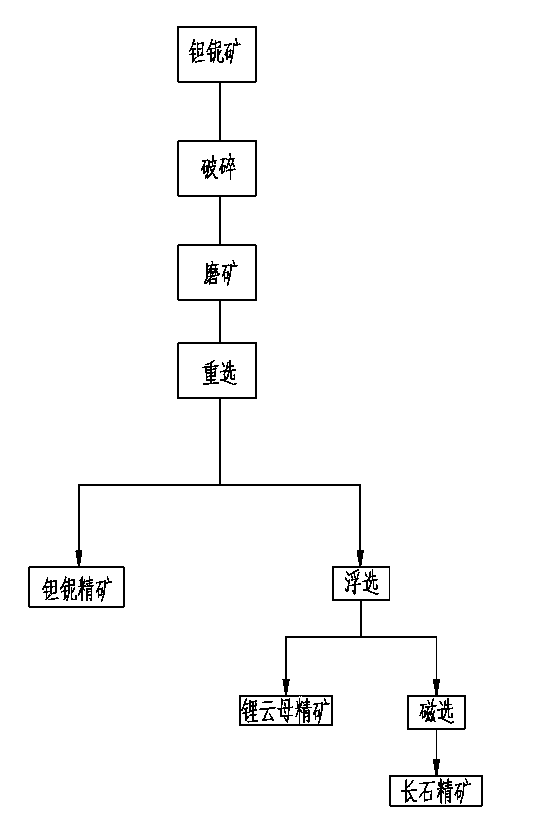
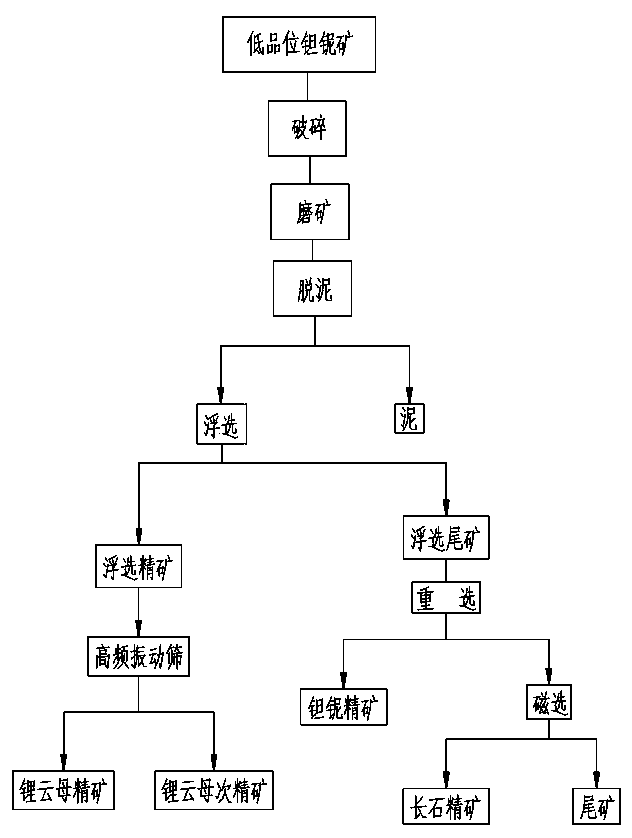
Production method for preferably selecting lepidolite from tantalum and niobium ores
The invention relates to the technical field of mineral processing, in particular to a production method for preferably selecting lepidolite from tantalum and niobium ores. The technological process comprises crushing, ore grinding, desliming and floation, the flotation concentrate is filtered by a high-frequency vibrating screen to obtain lepidolite concentrate and secondary lepidolite concentrate, the flotation tailings are re-elected to obtain tantalum and niobium concentrate, and the re-elected tailings are magnetically separated to obtain feldspar concentrate. The comprehensive recovery rate of lepidolite in the tantalum and niobium ores is greater than 70%, so that the economic efficiency of tantalum and niobium ores is greatly improved. The production method provided by the invention is particularly suitable for preferably selecting the lepidolite from the low-grade tantalum and niobium ores.
Owner:HUBEI XINYING ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
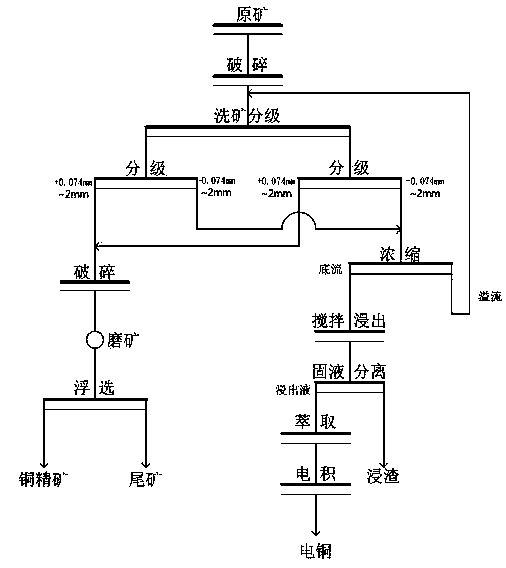
Dressing and smelting method for high-silt content copper oxide ores
InactiveCN103555938AReduce pollutionHigh recovery rateFlotationProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionFiltration
The invention relates to a dressing and smelting method for high-silt content copper oxide ores, and belongs to the technical field of mineral processing. The method comprises the following steps of crushing and washing the high-silt content copper oxide ores to obtain silt-free coarse-grain ore pulp and silt-free fine-grain ore pulp, and grinding and floating coarse grains to obtain copper concentrates with copper grade of 12-22wt% and tailings by using the prior art; concentrating the fine-grain ore pulp, returning overflow water for washing operation, adding acids to leach base flow after the base flow is concentrated to 30-60wt%, washing filter residues after filtration (solid-liquid separation), and performing extraction and electro-deposition on cleaning fluid obtained by washing and leachate obtained by filtration to prepare electrolytic copper. The method has the characteristics of high recovery rate, low production cost, high adaptability, less environmental pollution and the like.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Hydrometallurgical process and method for recovering metals
InactiveCN102939397AReduce demandAvoid demandCerium oxides/hydroxidesEnergy inputMineral processingMetal
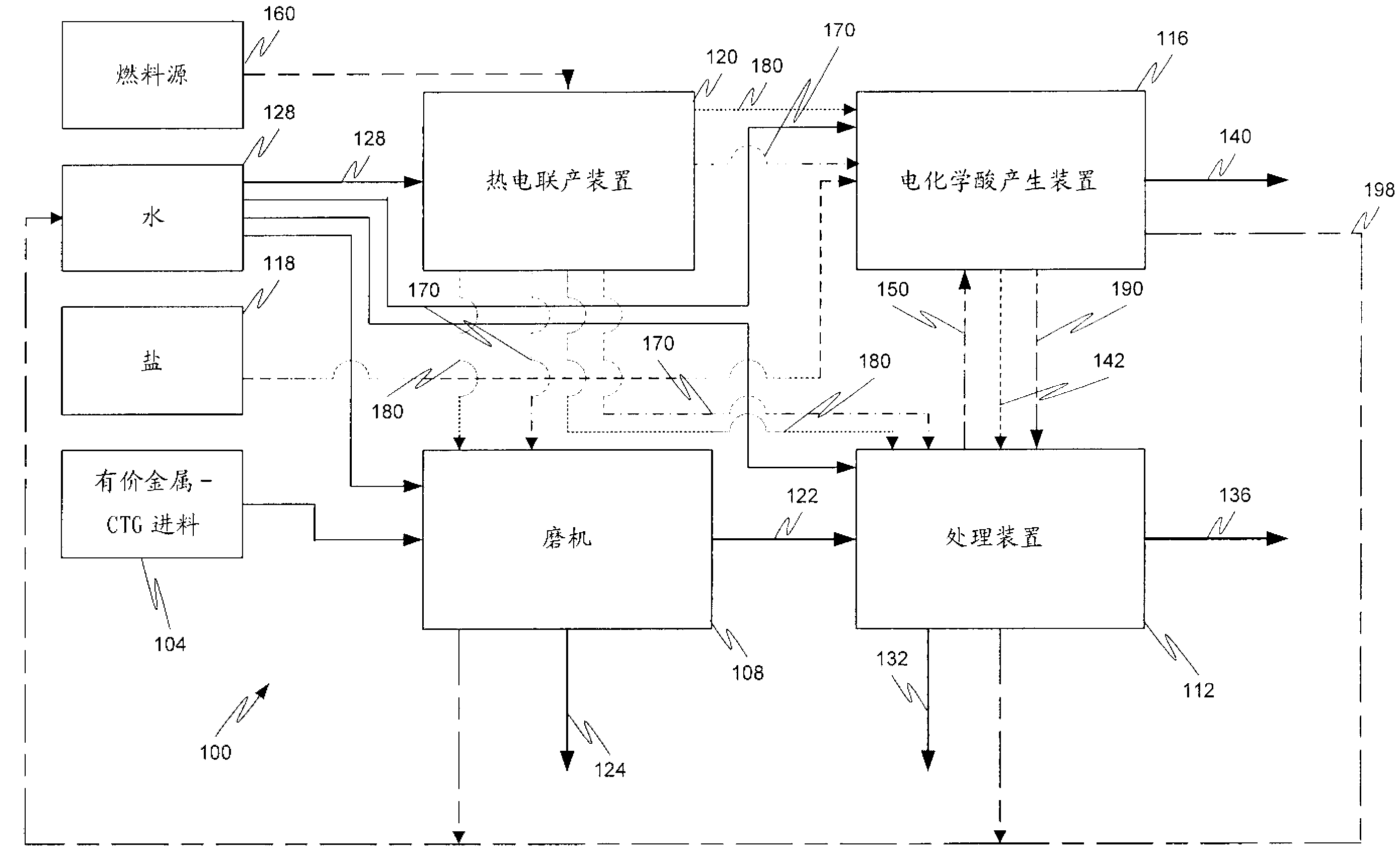
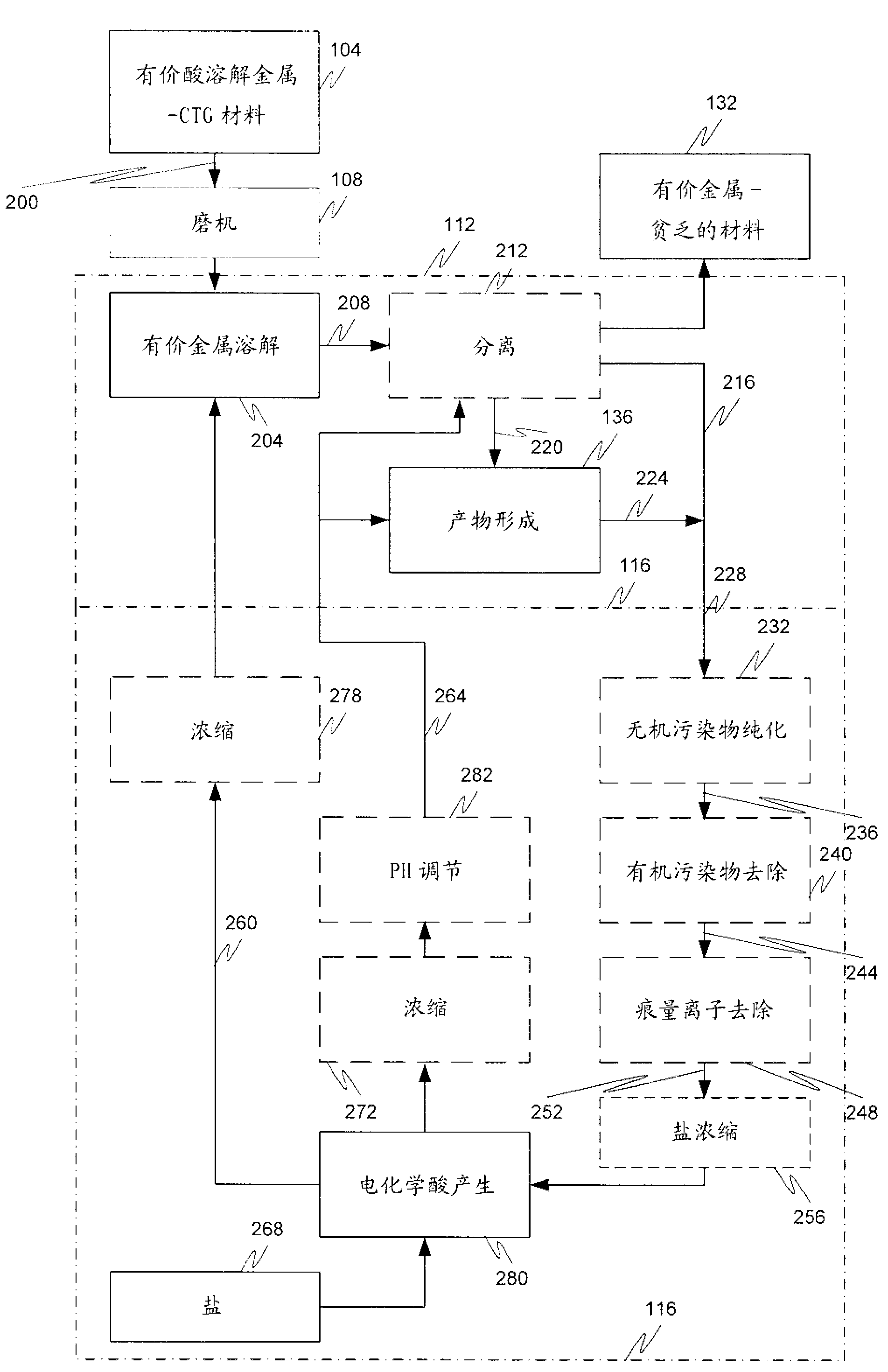
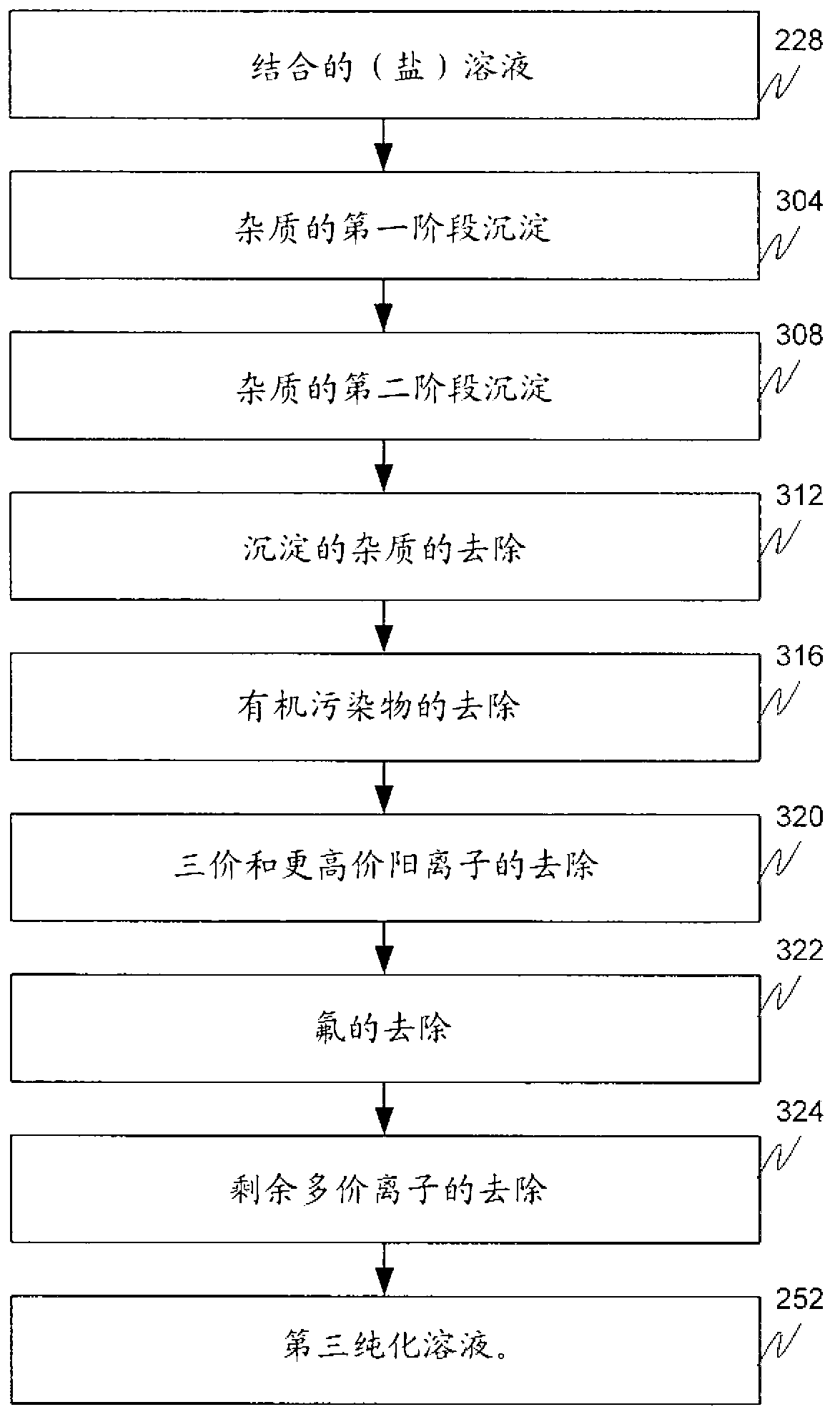
A mineral processing facility is provided that includes a cogen plant to provide electrical energy and waste heat to the facility and an electrochemical acid generation plant to generate, from a salt, a mineral acid for use in recovering valuable metals.
Owner:MOLYCORP MINERALS
Combined mineral processing technology of low-grade laterite type weathering titanium placers
The invention relates to a combined mineral processing technology of low-grade laterite type weathering titanium placers and belongs to the technical field of mineral processing. The combined mineral processing technology includes subjecting raw materials with the titanium dioxide content of below 5% to low-intensity magnetic-high-intensity magnetic pre-treatment technologies, then gravity separation-regrinding-gravity separation, gravity separation-regrinding-flotation processing and regrinding-flotation processing. According to the combined mineral processing technology of the low-grade laterite type weathering titanium placers, by means of the low-intensity magnetic-high-intensity magnetic pre-treatment technologies, a large number of slurries which are rich in kaolin minerals can be cast, technological procedures can be simplified, obtained rough titanium concentrates have few slurries, and follow-up treatment can be easily performed, for example, the interference of the slurries is avoided when technologies such as flotation and tabling gravity separation are performed; the grade and the recovery rate of the obtained titanium concentrates are high, and high intensity magnetic separation is beneficial to recovery of fine-particle grade titanium particles; and by means of the technologies of gravity separation-regrinding-gravity separation, gravity separation-regrinding-flotation processing and regrinding-flotation processing, the recovery rate of titanium is high, simultaneously, the content of iron in mineral samples is increased, and additional values of products are improved.
Owner:KUNMING METALLURGY INST
Method for sorting high-phosphorus iron ore by combining microwave reduction roasting and low intensity magnetic separation
InactiveCN102212677AReduce grinding energy consumptionShorten milling timeMagnetic separationMixed materialsQuenching
The invention relates to a method for refining iron and removing phosphorus from complex refractory high-phosphorus iron ore, in particular to a method for sorting high-phosphorus iron ore by combining microwave reduction roasting and low intensity magnetic separation, and belongs to the technical field of mineral processing, particularly iron ore beneficiation. The method comprises the following steps: crushing refractory high-phosphorus iron ore used as raw material into granules with granularity of less than 2mm; mixing the crushed raw ore with a fluxing agent and a reducing agent in a certain proportion; transferring the obtained mixed material into a microwave reaction furnace for reduction roasting; and carrying out water-quenching, cooling, ball-milling and wet-magnetic-separating on the obtained roasted ore to finally obtain iron ore concentrate. In the method, the ore is reduced by utilizing a microwave roasting technology, wherein microwave reduction roasting time is short, and the temperature of the ore is raised quickly; and meanwhile the fluxing agent is added so as to promote gangue softening and improve refractory ore structure together with microwave roasting reaction. By utilizing the method for sorting the high-phosphorus iron ore, the iron ore concentrate with grade of more than 58.39% can be obtained, and phosphorus removal rate reaches over 70.44%, thus a new technique is provided for sorting the high-phosphorus iron ore.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
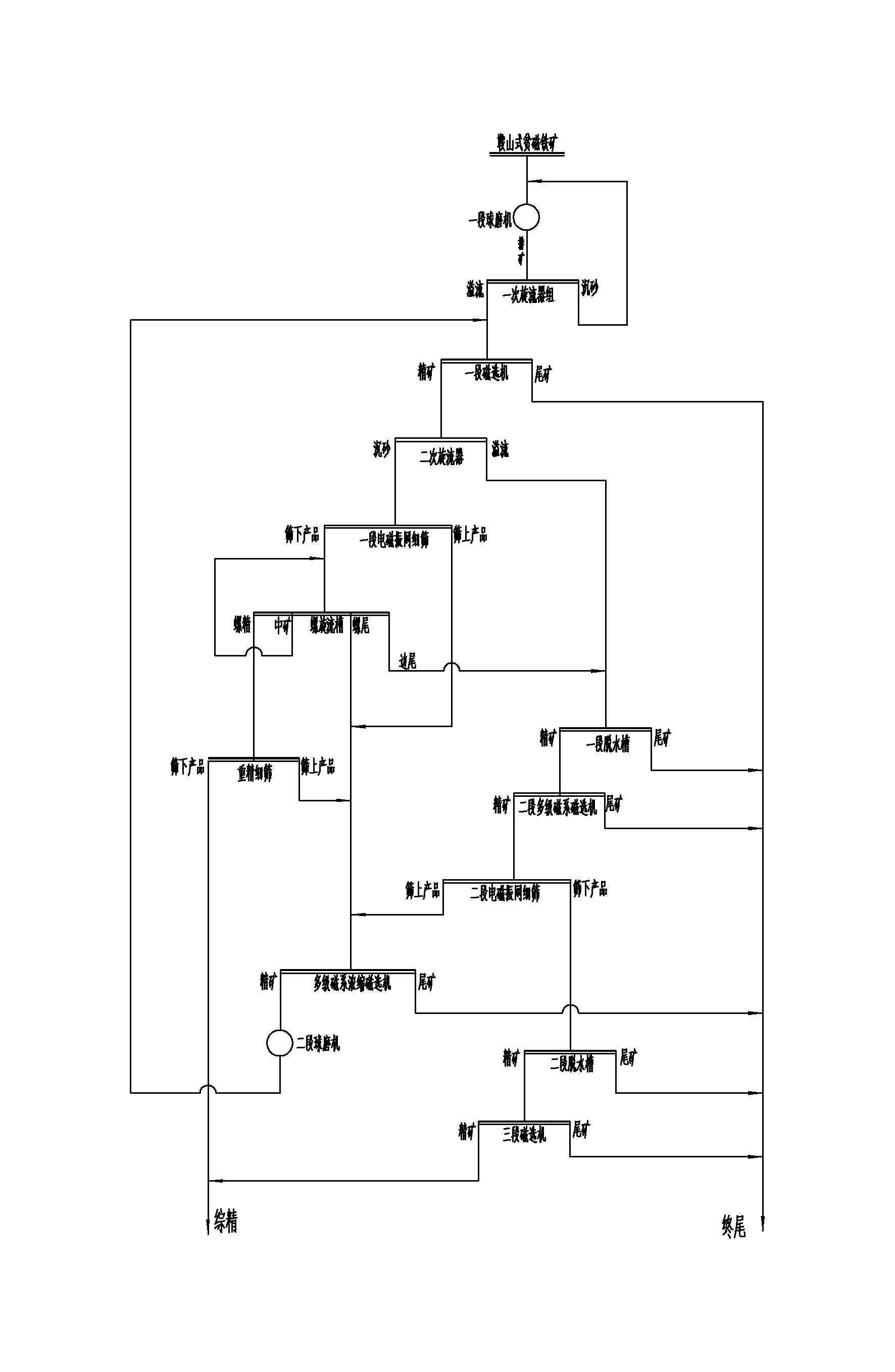
Magnetic-gravity separation technology for Anshan type lean magnetite
ActiveCN103272694AImprove mineral processing technical indicatorsGuaranteed GranularityMagnetic separationMagnetiteEngineering
The invention relates to a magnetic-gravity separation technology for Anshan type lean magnetite, which comprises the following steps: after adoption of a first-stage ball mill for ore grinding, a primary cyclone, a first-stage magnetic separator and a secondary cyclone for classification, settled sand is subjected to first-stage sieve screening, an screened product is fed into a spiral chute, concentrate in the spiral chute is fed into a gravity fine sieve, and a screened product by the gravity fine sieve is qualified concentrate; after overflow of the secondary cyclone and the edge tail of the spiral chute are merged, the concentrate is fed into a second-stage sieve after separation by a first-stage dehydration tank and a second-stage magnetic separator; products on the first-stage sieve, the second-stage sieve and the gravity fine sieve as well as mineral tailings in the spiral chute are merged and fed into a concentration magnetic separator, the mixture is fed into a second-stage ball mill for ore grinding after concentration, then the products return to the first-stage magnetic separator, and after separation by a second-stage dehydration tank and a third-stage magnetic separator, the screened product of the second-stage sieve is merged with the screened product of the gravity fine sieve into the final concentrate. The magnetic-gravity separation technology has the advantages that mineral processing technical indexes for the Anshan type lean magnetite are improved, the mineral processing efficiency is improved, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:ANSTEEL GRP MINING CO LTD
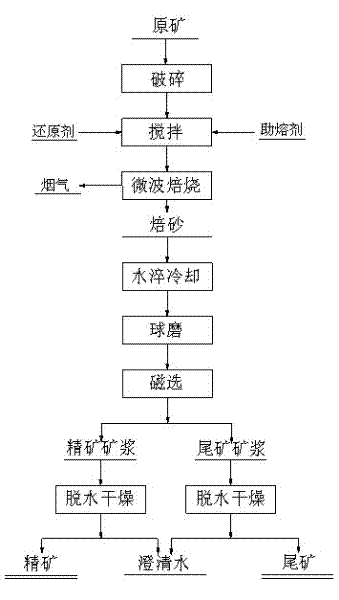
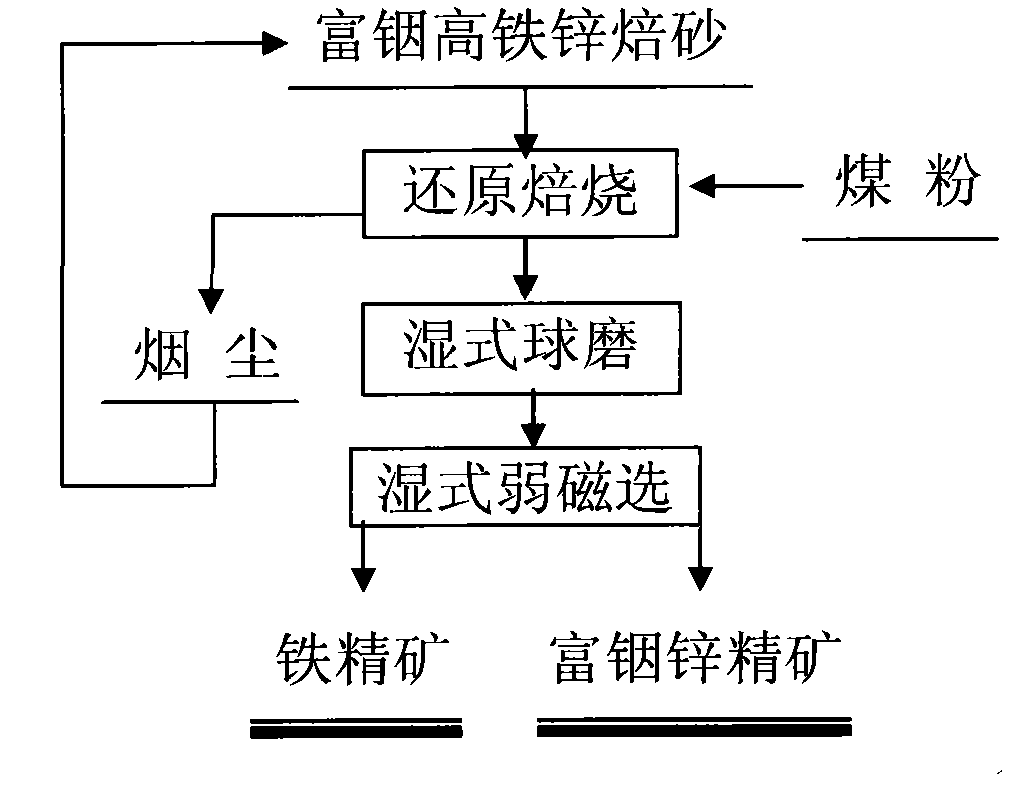
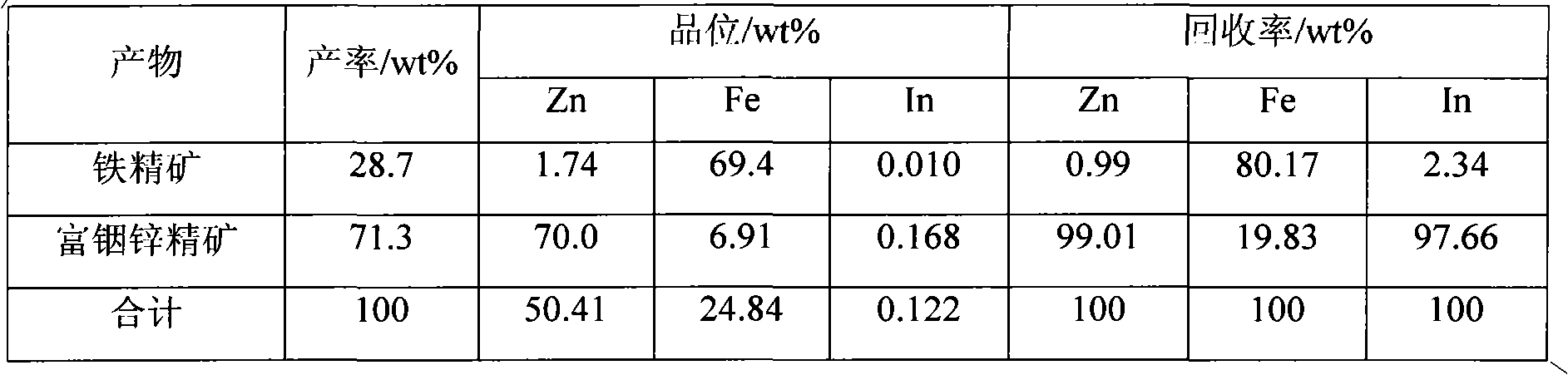
Method for separating zinc and indium and iron from indium-enriched high-iron high-zinc calcine through reduction-magnetic separation
InactiveCN102134655AReduce dosageReduce energy consumptionMagnetic separationReduction treatmentIndium
The invention relates to a method for separating zinc and indium and iron from indium-enriched high-iron high-zinc calcine through reduction-magnetic separation, belonging to the technical field of mineral processing. The invention is characterized in that the method adopts the technical means that mineral dressing is combined with smelting and performs smelting firstly and mineral dressing secondly; and the method is as follows: the waste heat of the indium-enriched high-iron zinc calcine obtained through fluidized roasting is utilized, the indium-enriched high-iron zinc calcine is introduced to perform low-temperature weak reduction treatment at below 570 DEG C and ensure that zinc ferrite is decomposed and reduced to ZnO, Fe3O4 and iron, the reduced calcine is levigated to prepare slurry, and zinc and indium and iron is separated through wet-type magnetic separation to obtain iron ore concentrates and indium-enriched zinc- enriched ore concentrates. The method has low energy consumption and low dosage of a reducing agent, is simple in operation, easy in control and high in metal recovery rate. Therefore, the indium embedded and distributed in zinc ferrite can be released, the loss caused by the high temperature volatilization of indium can be avoided, and the zinc and indium and iron of the indium-enriched high-iron high-zinc calcine can be separated in an ore dressing manner before leaching.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
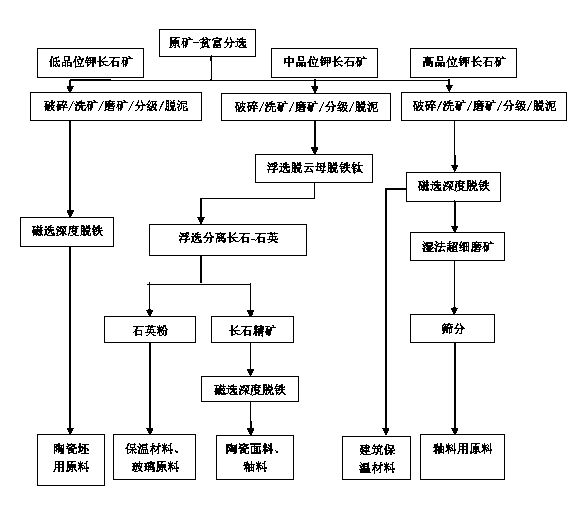
Mineral processing technology by utilizing grade difference of potassium feldspar
The invention relates to a mineral processing technology by utilizing the grade difference of potassium feldspar. The mineral processing technology comprises the following steps that (1), potassium feldspar raw ore is mined and sorted in a separated mode according to the three classes of low-grade potassium feldspar ore, medium-grade potassium feldspar ore and high-grade potassium feldspar ore; (2), the mineral processing processes of crushing, washing, grinding for grading, desliming, and magnetic separation for deep iron removal are carried out on the low-grade potassium feldspar ore; (3), the mineral processing processes of crushing, washing, grinding for grading, desliming, flotation for mica removal and iron removal, flotation for separating feldspar from quartz, and magnetic separation for deep iron removal are carried out on the medium-grade potassium feldspar ore; (4), the mineral processing processes of crushing, washing, grinding for grading, desliming, magnetic separation for deep iron removal, wet superfine grinding and screening are carried out on the high-grade potassium feldspar ore. The different mineral processing technical schemes are adopted for the potassium feldspar ore of different grades, and the purposes of being free of environmental pollution, simplifying the production processes and efficiently developing and utilizing resources are achieved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU MINERALS COMPOSITIVE UTILIZATION RES INST CHINESE GEOLOGICAL ACAD
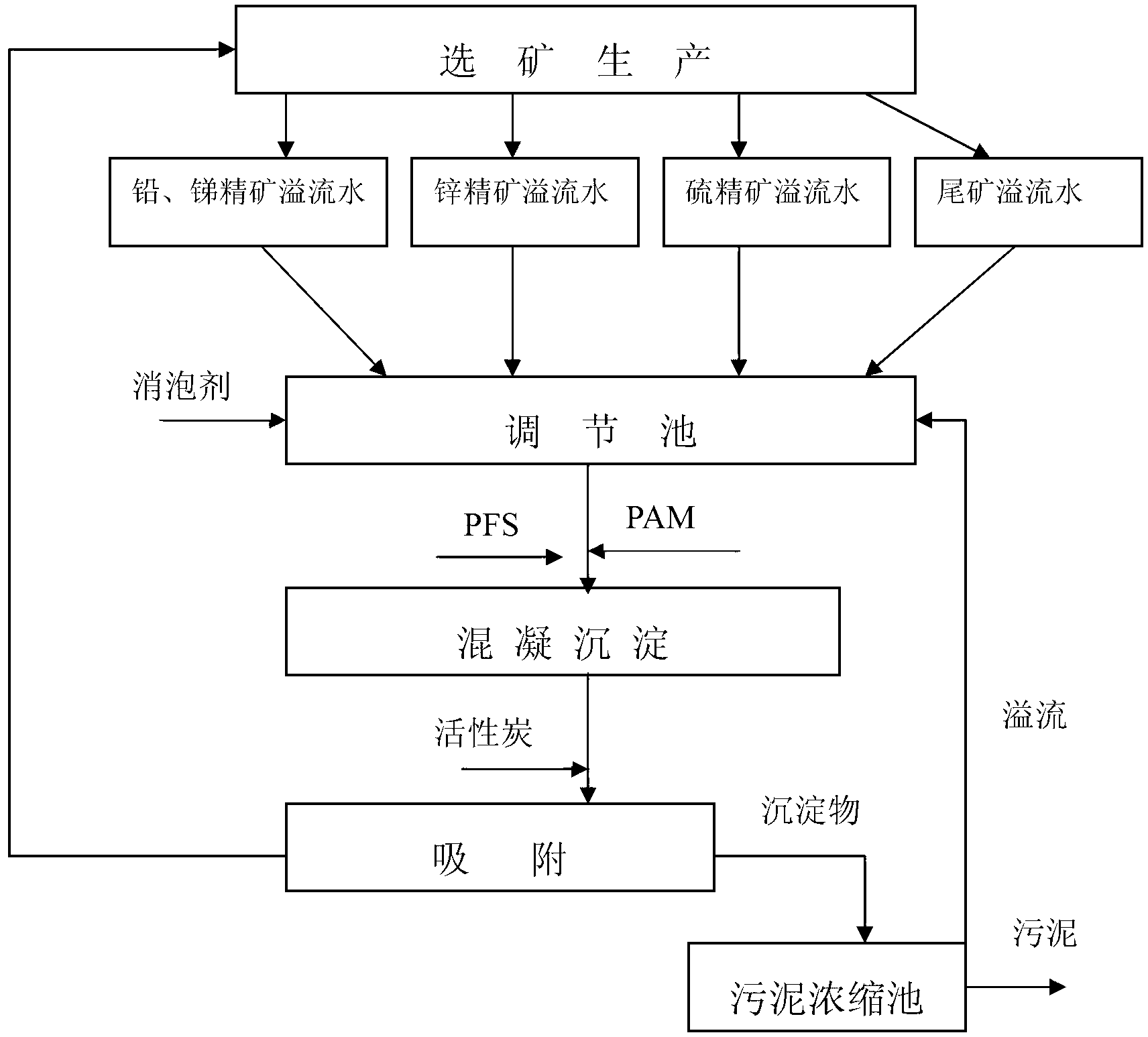
In-process circular and comprehensive recovery technology for mineral processing wastewater of tin-lead-zinc polymetallic sulphide ores
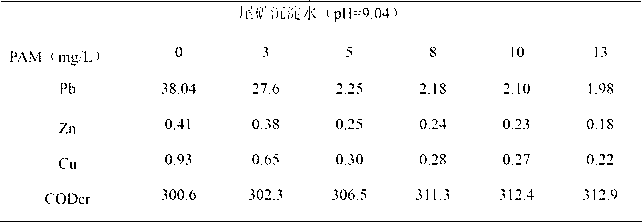
InactiveCN102936068AReduce dosageGood effectWaste water treatment from quariesMultistage water/sewage treatmentChemical oxygen demandSludge
The invention discloses an in-process circular and comprehensive recovery technology for mineral processing wastewater of tin-lead-zinc polymetallic sulphide ores. The technology includes primary treatment and secondary treatment, wherein the primary treatment is to coagulate and precipitate, comprising the step of adding a coagulant to remove suspended solid and metal ion, wherein some organic pollutants are removed at the same time; the secondary treatment is to carry out an adsorption method to remove flotation agent in the wastewater so as to further reduce the CODCr (Chemical Oxygen Demand) and foamability of the wastewater; and all water generated in the secondary treatment is recycled. The technology has the advantages of being simple in equipment, high in processing efficiency, high in adaptability, less in occupied area, and few in resulting sludge, and has higher effect of processing the mineral processing wastewater of tin-lead-zinc polymetallic sulphide ores; the polymeric ferric sulfate (PFS) and polyacrylamide (PAM) are selected and used as the compound coagulant to remove the pollutants such as the suspended solid and the metal ion during precipitating and removing the pollutants in the wastewater; and compared with single inorganic coagulant, the compound coagulant of the PFS and the PAM is low in dosage, good in effect, low in cost, and safe and nontoxic, and has no secondary pollution.
Owner:GUANGXI GAOFENG MINE IND
Process and apparatus for treating tailings
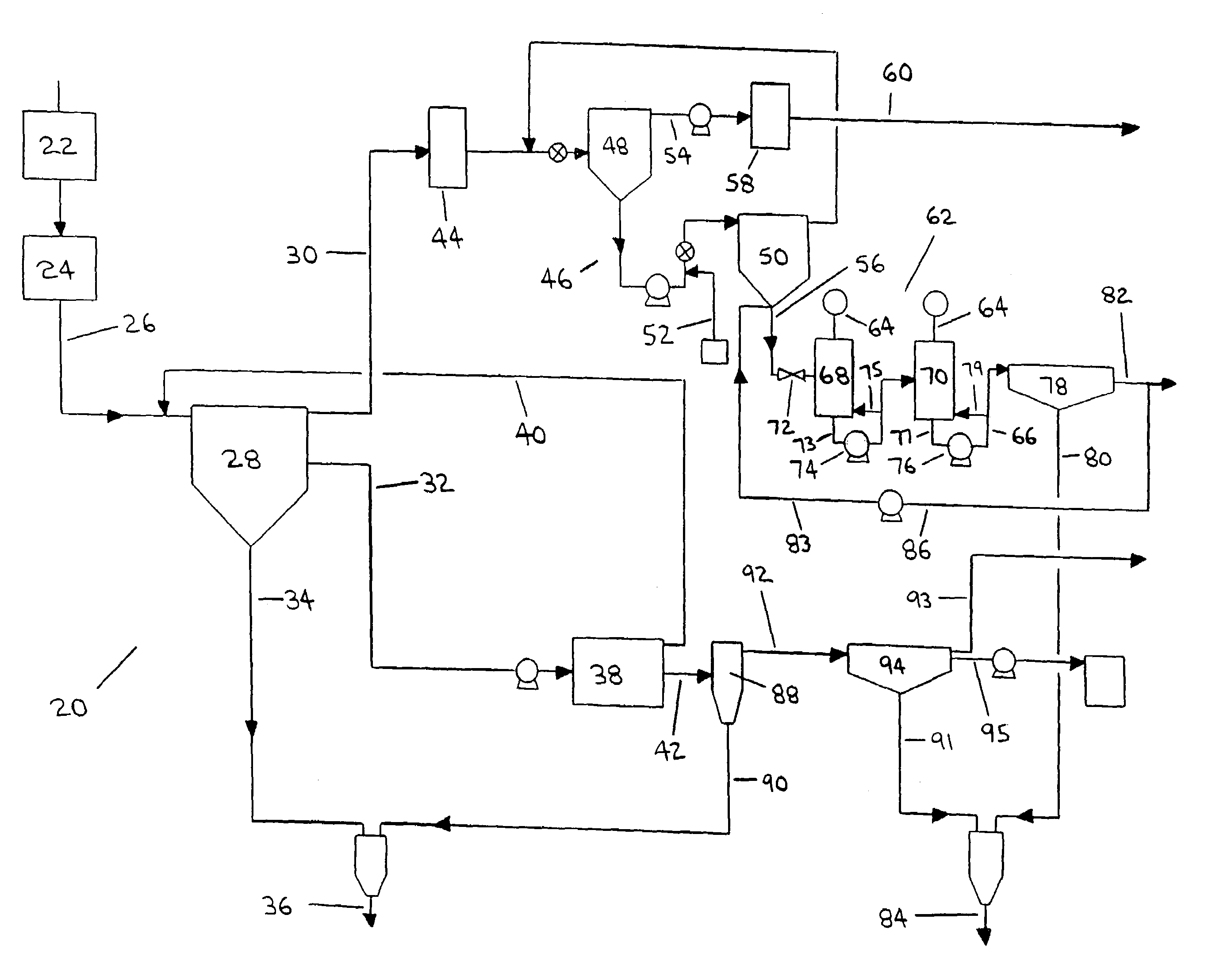
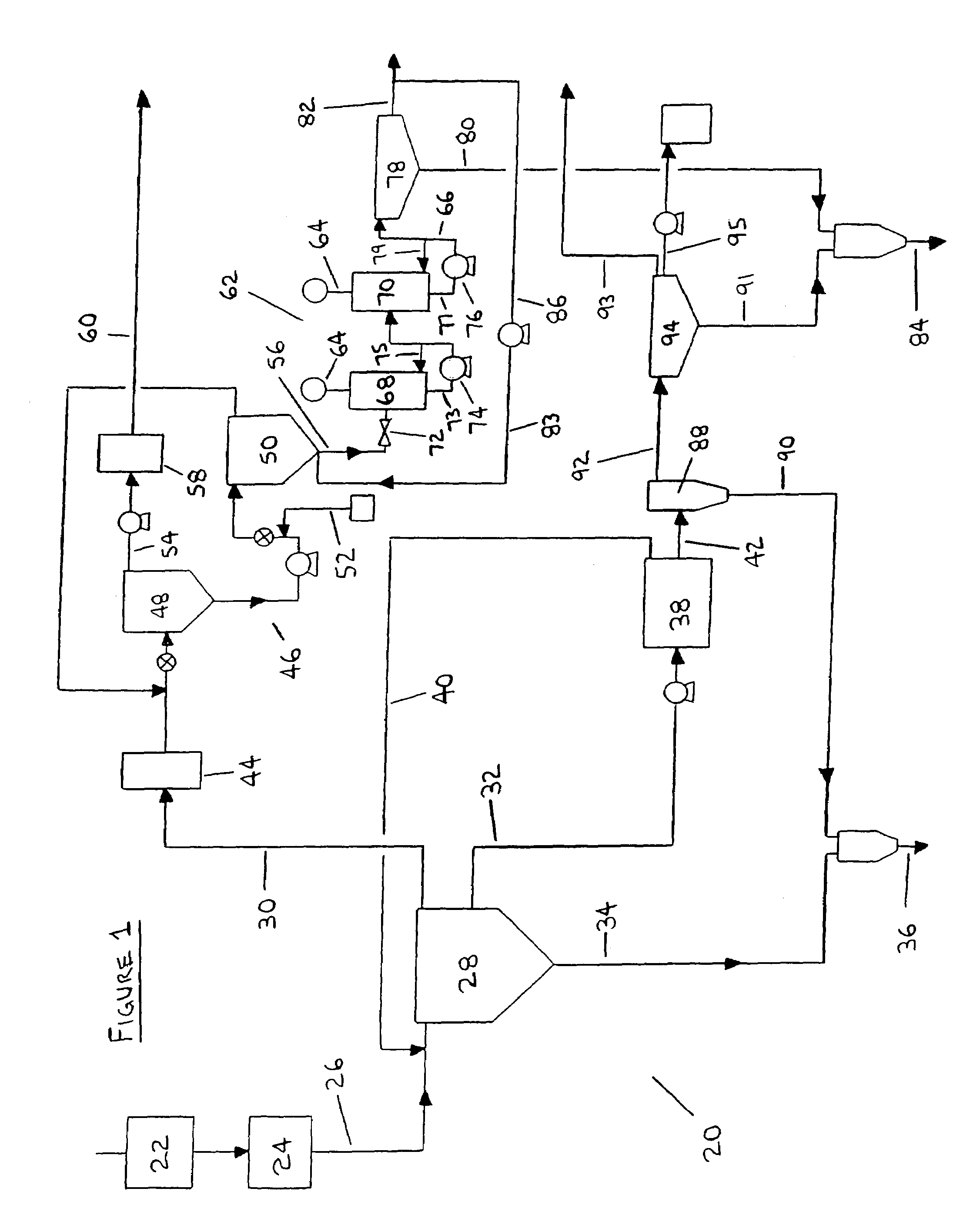
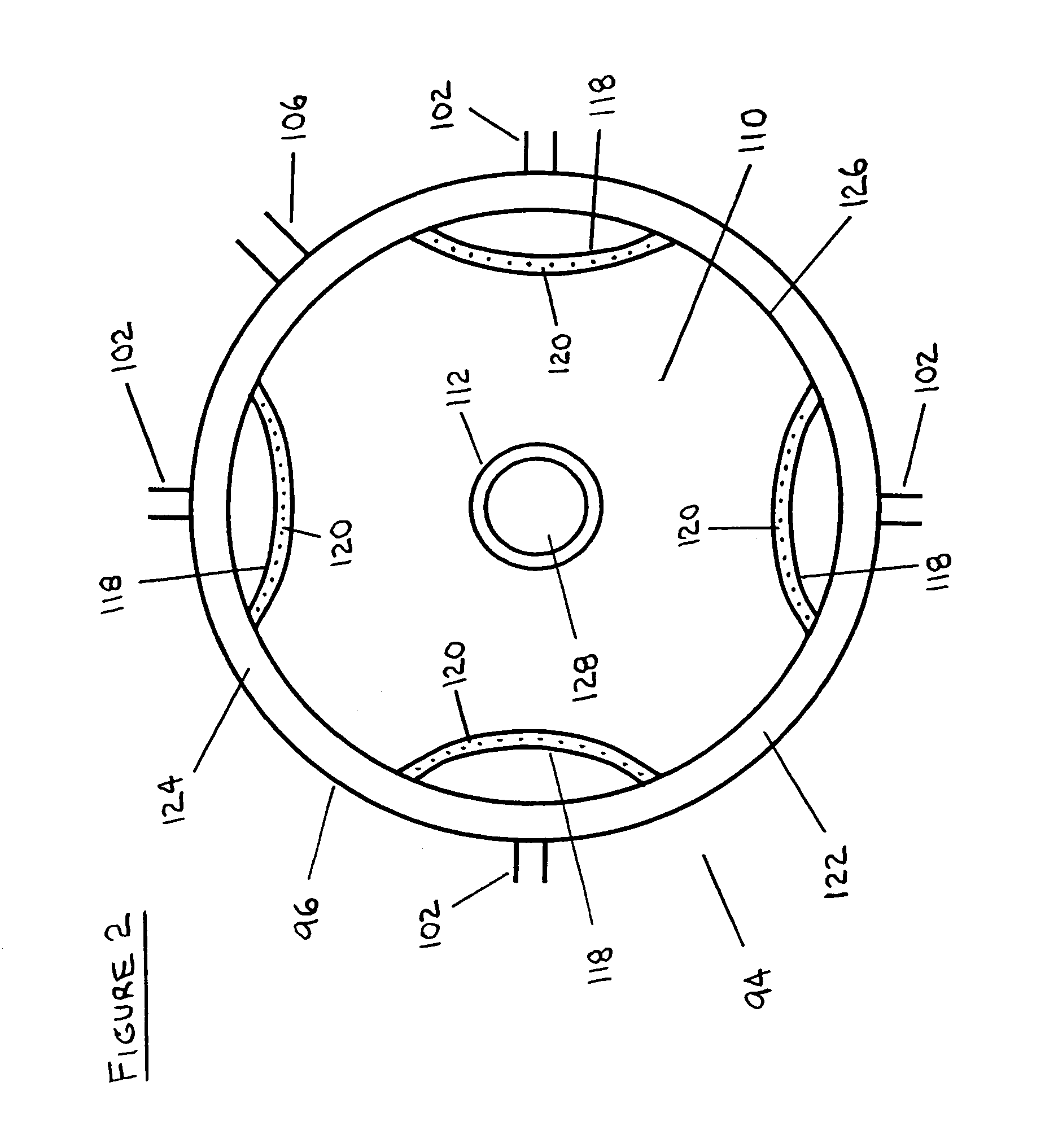
ActiveUS7569137B2High trafficAvoid accumulationWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by selective extractionSolid separationProcess efficiencySolvent
Processes and apparatus for the treatment of product streams from mineral processing operations, including the treatment of tailings which result from oil sand processing operations. The processes and apparatus relate to the recovery of a diluent solvent from bitumen froth tailings and to the thickening of tailings from a bitumen froth stream and a middlings stream resulting from an oil sand extraction process. In one aspect the processes and apparatus relate particularly to the recycling of product streams to maximize process efficiencies. In a second aspect the processes and apparatus relate particularly to the thickening of tailings to produce an underflow component, a clarified overflow component and an unclarified overflow component.
Owner:TRUENORTH ENERGY CORP
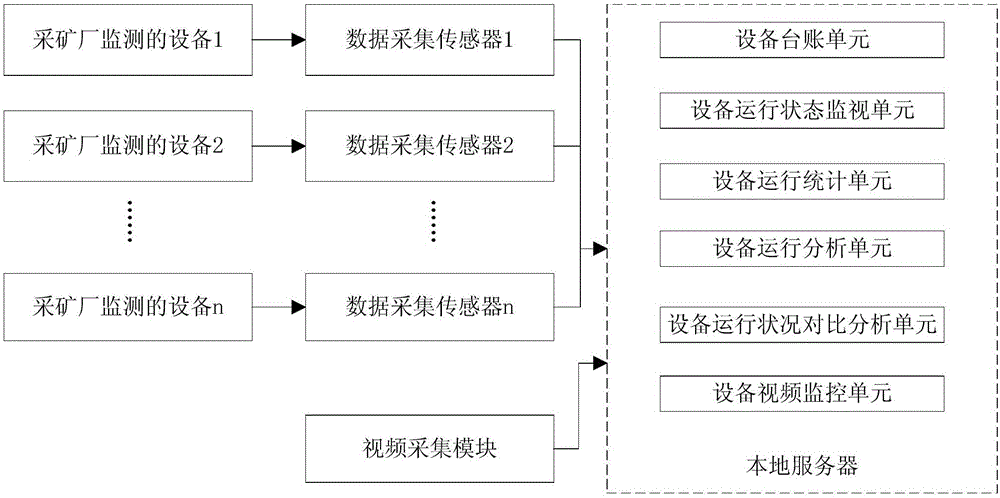
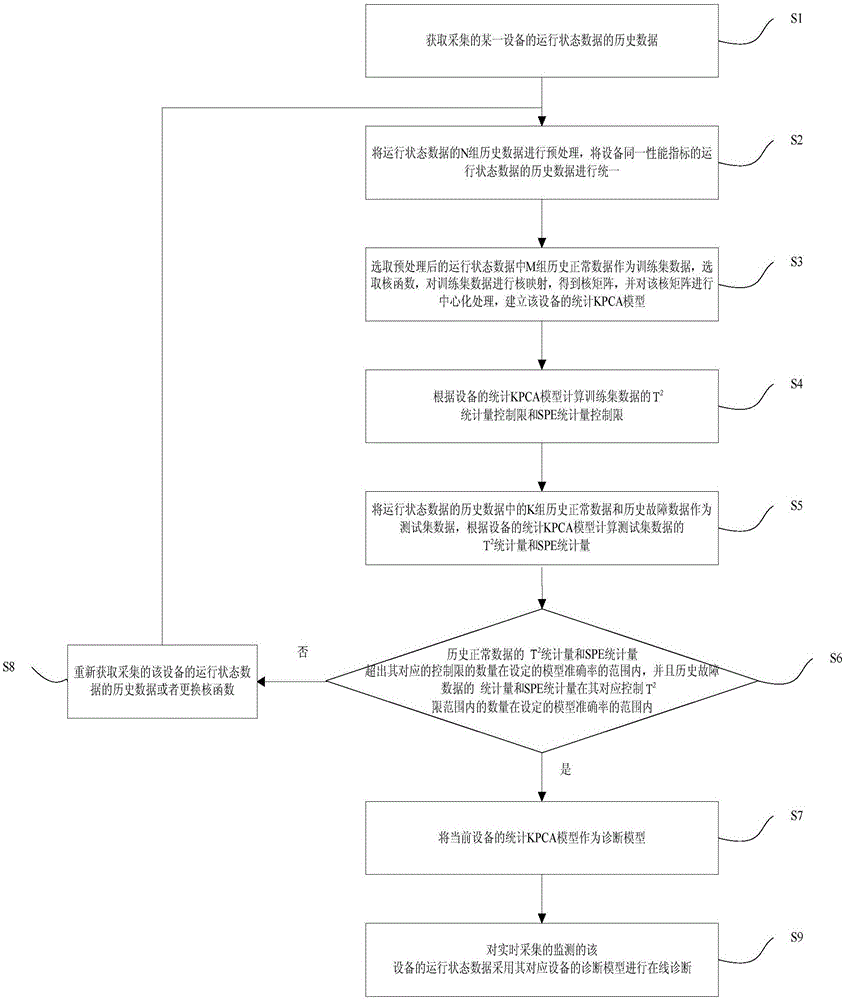
Mineral processing equipment operating state monitoring system and method
ActiveCN106408192ARealize real-time monitoringImplement diagnosticsResourcesData acquisitionMonitoring system
The invention provides a mineral processing equipment operating state monitoring system and a mineral processing equipment operating state monitoring method. The mineral processing equipment operating state monitoring system comprises a local server, a plurality of data acquisition sensors and a video acquisition module, wherein input ends of the plurality of data acquisition sensors are connected with monitored equipment in a mining plant, output ends of the plurality of data acquisition sensors are connected with the local server, and an output end of the video acquisition module is connected with the local server. Operating state data and equipment index data of the monitored equipment are acquired by means of the data acquisition sensors in real time, operation videos of the equipment are acquired by means of the video acquisition module in real time, the operating state data and the equipment index data of the equipment are monitored by means of the local server, the local server sends out early warning when the equipment index data exceeds a threshold value, calculates an equipment failure rate of the corresponding equipment and OEE analytical value of the equipment, and performs online diagnosis on the operating state data acquired in real time by utilizing a KPCA model. The mineral processing equipment operating state monitoring system and the mineral processing equipment operating state monitoring method can realize the real-time monitoring of the equipment operating state by the mineral processing production-manufacturing execution layer.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
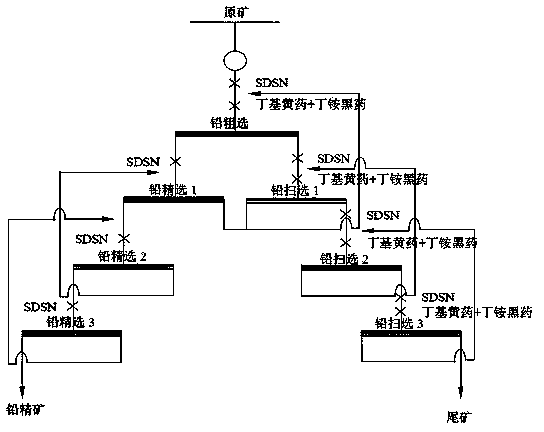
Flotation separation inhibitor and separation method of galena, pyrite and sphalerite
InactiveCN103909020AEfficient separationPlay a synergistic roleFlotationEcological environmentSeparation technology
The invention discloses a flotation separation inhibitor and separation method of galena, pyrite and sphalerite, and belongs to the technical field of mineral processing. The method includes adopting raw ores of sulfide lead-zinc mine as raw material, and adding SDSN (dimethyl dithiocarbamate : 2-(methylthio)ethylamine = 1-3:1)to serve as inhibitor of the pyrite and the sphalerite so as to perform lead and zinc sulphur flotation separation after the raw ores are grinded. Compared with an existing lead and zinc sulphur separation technology, the composite inhibitor SDSN has the advantages that selectivities of the pyrite and the sphalerite are high, inhibiting capability is high, usage is fewer, and adding is facilitated. The the pyrite and the sphalerite can be inhibited well, efficient separation of the galena and the zinc sulphur is implemented, the problems that according to the traditional lime or cyanide method, the recovery rate of associated gold, silver and other precious metals in the lead-zinc sulfide mine is low and ecological environment is seriously damaged are overcome, and an efficient and environment-friendly flotation separation method is provided for complex sulfide lead-zinc mine separation.
Owner:HUNAN RES INST FOR NONFERROUS METALS
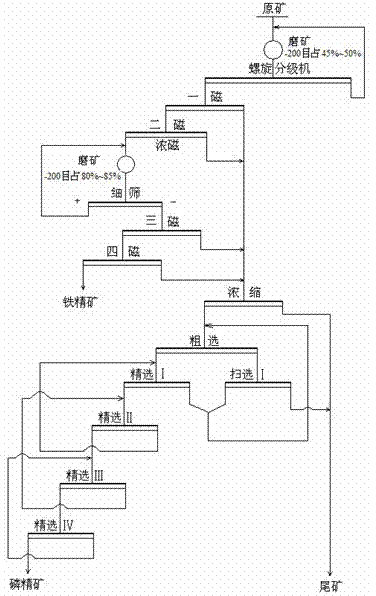
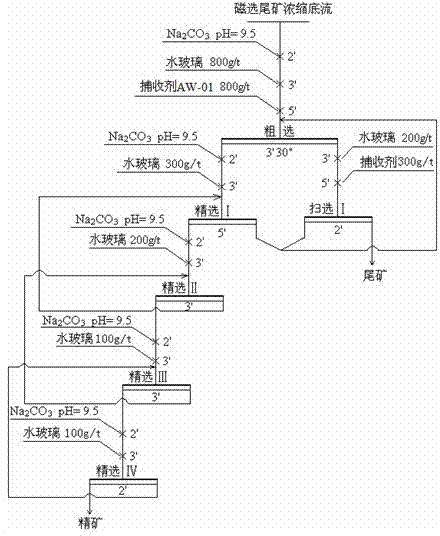
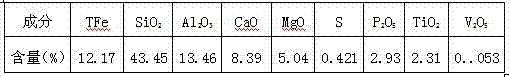
Mineral processing technology for comprehensively recycling iron phosphate from low-grade high phosphorus vanadium titanium magnetite
InactiveCN102728477AEfficient use ofIncrease the economic benefits of the dressing plantFlotationMagnetic separationPhosphateMagnetite
The invention discloses a mineral processing technology for comprehensively recycling iron phosphorus from low-grade high phosphorus vanadium titanium magnetite. The low-grade high phosphorus vanadium titanium magnetite is subjected to stage grinding and low intensity magnetic separation processes to obtain iron ore concentrate and magnetic separation tailings; the magnetic separation tailings uses low temperature flotation to recycle phosphorus after concentration, wherein the low temperature flotation is as follow: adding a slurry pH adjusting agent, an inhibitor and a collecting agent to the slurry of magnetic separation tailings, adjusting the pH of the slurry to 9-10, and performing flotation under 15-20 DEG C. The technology provided by the invention puts forward a mineral processing technology for comprehensively recycling iron phosphorus aiming at the low-grade high phosphorus vanadium titanium magnetite, which firstly adopts the low intensity magnetic separation method to recycle iron from ores and then adopts the low temperature flotation method to recycle phosphorus from tailings, thus realizing efficient utilization of such kind of mineral resources and increasing the economic benefits of concentrators. The low temperature flotation of the technology can reduce the subsequent costs of processing phosphate ores, improve the benefit of the comprehensive utilization of resources, reduce the production cost and achieve low cost and efficient recycling of phosphorus.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com