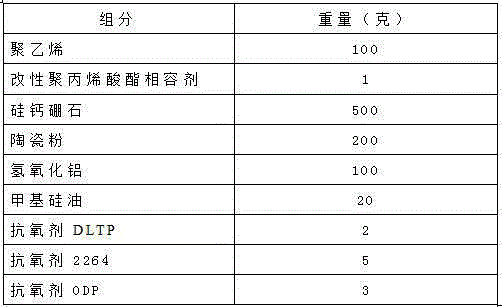
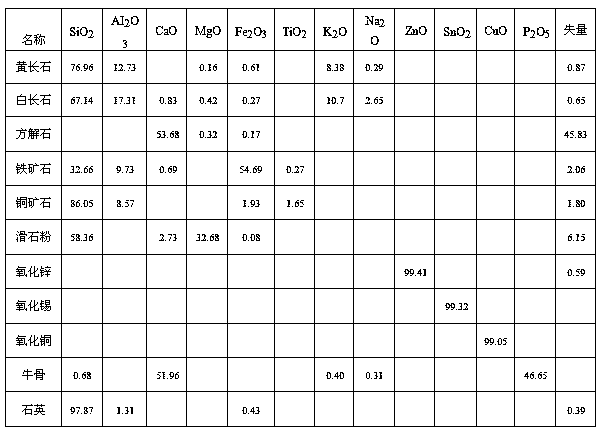
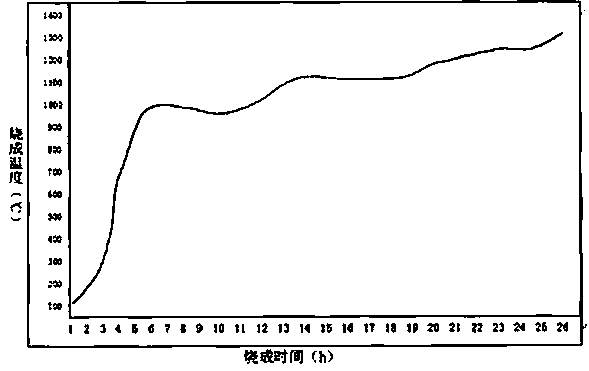
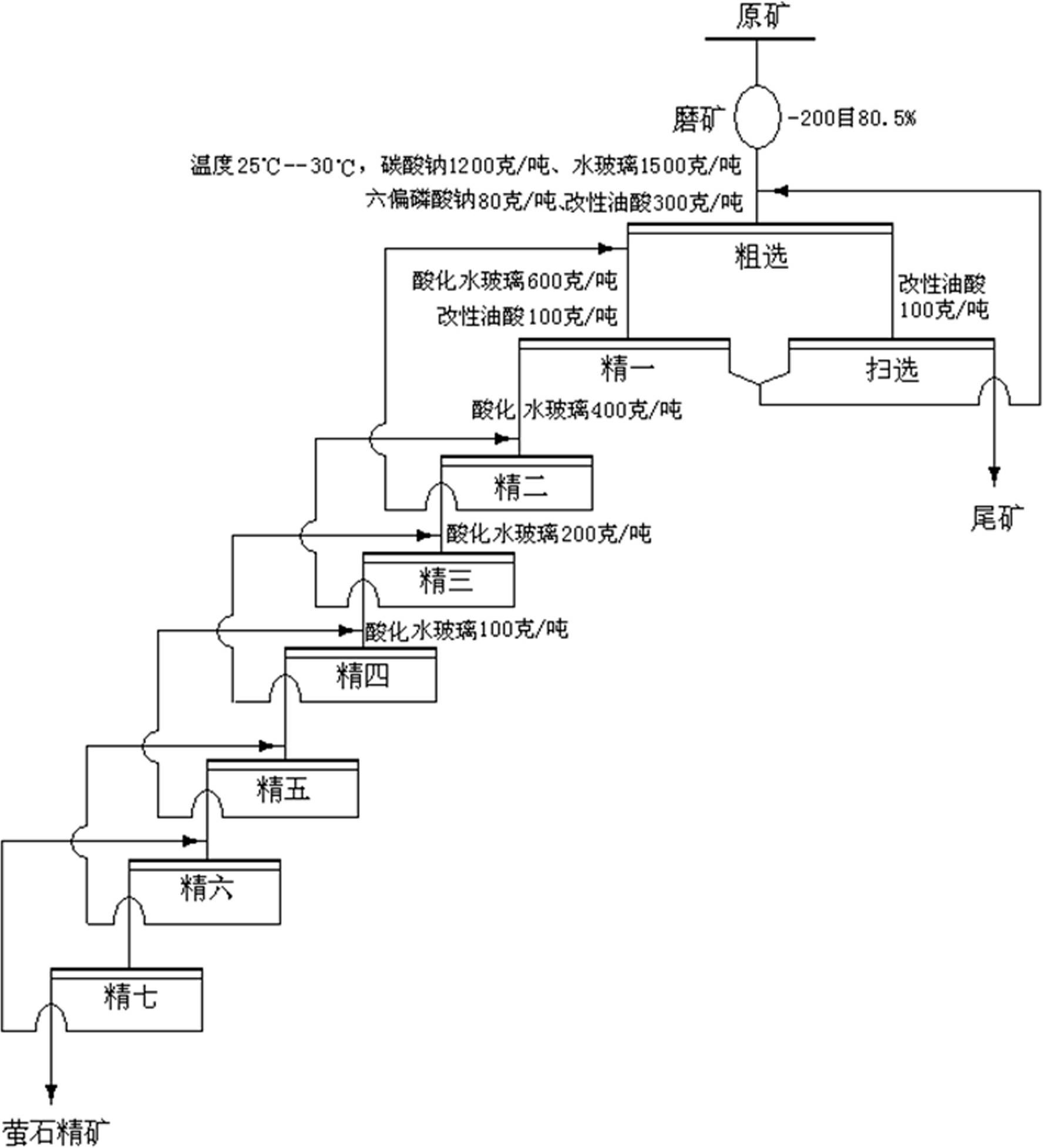
Patents
Literature
2400 results about "Calcite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Calcite is a carbonate mineral and the most stable polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO₃). The Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratch hardness comparison, defines value 3 as "calcite". Other polymorphs of calcium carbonate are the minerals aragonite and vaterite. Aragonite will change to calcite over timescales of days or less at temperatures exceeding 300 °C, and vaterite is even less stable.
Acicular calcite and aragonite calcium carbonate
InactiveUS6071336AIncrease costIncrease production costCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesPigmenting treatmentToothpasteCalcite
The present invention relates to a calcium carbonate composition having both calcite and aragonite crystalline morphology. More particularly, the present invention relates to an acicular calcite and an acicular aragonite product and a method for the production of the same and the use of such as fillers, additives and modifiers of consumer and commercial products such as toothpaste, paper, plastics and sealants. The acicular calcite / aragonite composition of the present invention provides a balance of properties such as sheet bulk, strength, stiffness, and sizing, when employed as a filler for paper. As a coating pigment, the acicular calcite / aragonite product of the present invention provides gloss characteristics suitable for dull and matte grades of low gloss coated paper. Upon further processing such as milling, grinding, or other means of comminution, the resulting product provides gloss characteristics suitable for high gloss coated paper. For paint formulations, the acicular calcite / aragonite composition of the present invention provides properties such as low sheen and high contrast ratio. As an additive in polymers, the acicular calcite / aragonite product of the present invention imparts reinforcing properties, rigidity, and impact strength, including sealant applications.
Owner:MINERALS TECH
Method of exfoliating skin
InactiveUS6294179B1Avoid excessive abrasion of and damageInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsCosmetic preparationsMean diameterViscous liquid
A viscous, liquid, skin washing composition comprising water, at least one surface active agent, abrasive particles and a viscosifier, CHARACTERISED IN THAT the viscosity of the composition is typically that of a shower gel, i.e. in the range 4000-8000 mPas measured at a shear rate of 10 s-1, the particles, preferably calcite, have a mean diameter of 40-400 micrometres and a bulk density of 1-4.
Owner:LEVER BROTHERS
Composite foaming agent and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses a composite foaming agent, a preparation method thereof and application thereof. The composite foaming agent comprises azodicarbonamide, sodium bicarbonate and an auxiliary foaming agent in a weight ratio of (0.3-0.9):(0.2-0.6):(0.1-0.8). The auxiliary foaming agent is prepared by uniformly stirring attapulgite, zeolite and calcite, soaking the mixture in diluted hydrochloric acid of which the concentration is 0.5 to 6 weight percent, drying the mixture, crushing the dried mixture into powder, blending the powder and powdery white carbon black and uniformly stirring the mixture, wherein the weight ratio of the attapulgite to the zeolite to the calcite to the white carbon black is (0.3-0.8):(0.02-0.6):(0.1-0.8):(0.01-0.8). The composite foaming agent disclosed by the invention has relatively high liquidity and dispersibility, a low decomposition temperature and a long decomposition temperature period.
Owner:常州市英特玛柯橡塑科技有限公司
Acicular calcite and aragonite calcium carbonate
InactiveUS6022517AReduce conductivityIncrease production costCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesAmmonium nitratesToothpasteCalcite
The present invention relates to a calcium carbonate composition having both calcite and aragonite crystalline morphology. More particularly, the present invention relates to an acicular calcite and an acicular aragonite product and a method for the production of the same and the use of such as fillers, additives and modifiers of consumer and commercial products such as toothpaste, paper, plastics and sealants. The acicular calcite / aragonite composition of the present invention provides a balance of properties such as sheet bulk, strength, stiffness, and sizing, when employed as a filler for paper. As a coating pigment, the acicular calcite / aragonite product of the present invention provides gloss characteristics suitable for dull and matte grades of low gloss coated paper. Upon further processing such as milling, grinding, or other means of comminution, the resulting product provides gloss characteristics suitable for high gloss coated paper. For paint formulations, the acicular calcite / aragonite composition of the present invention provides properties such as low sheen and high contrast ratio. As an additive in polymers, the acicular calcite / aragonite product of the present invention imparts reinforcing properties, rigidity, and impact strength, including sealant applications.
Owner:MINERALS TECH
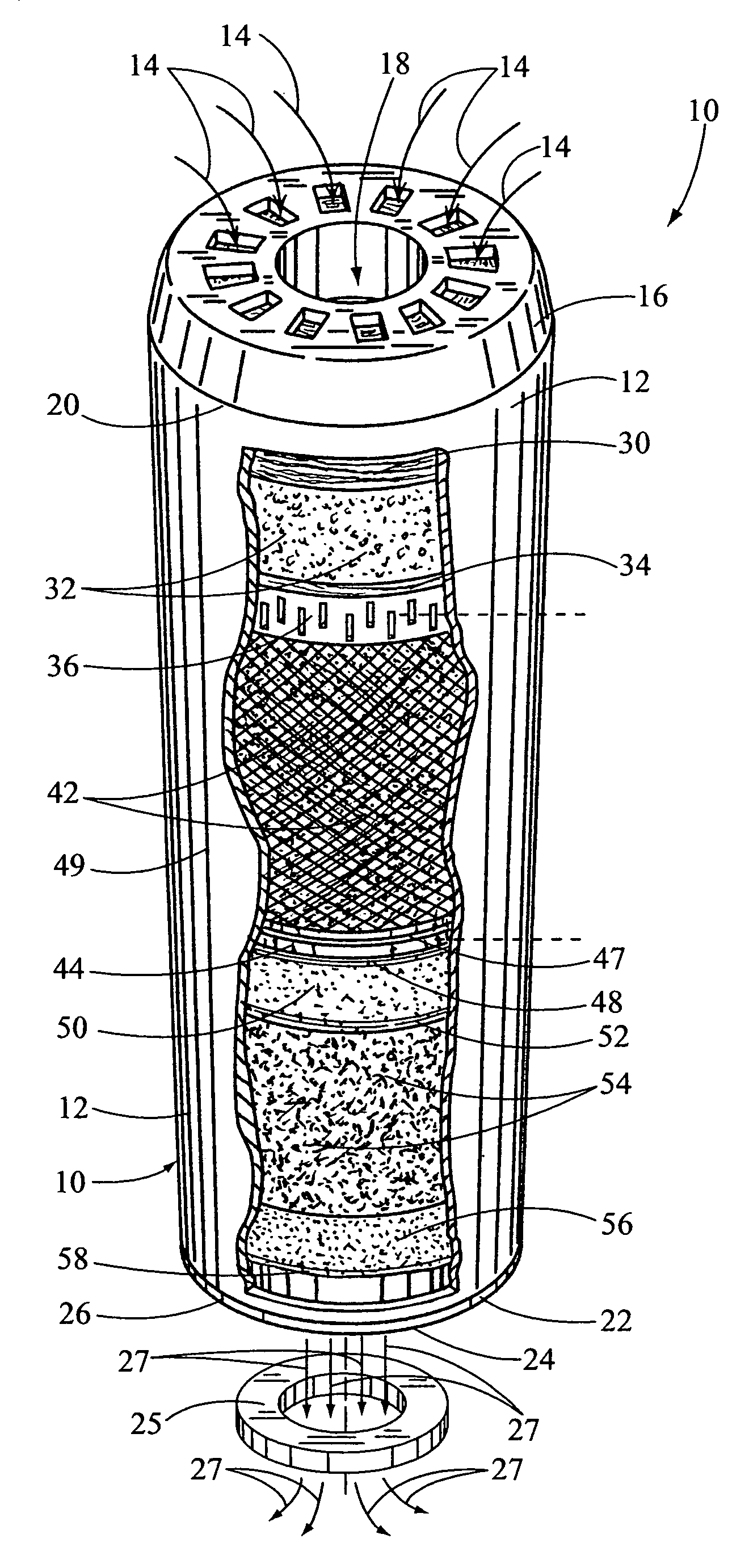
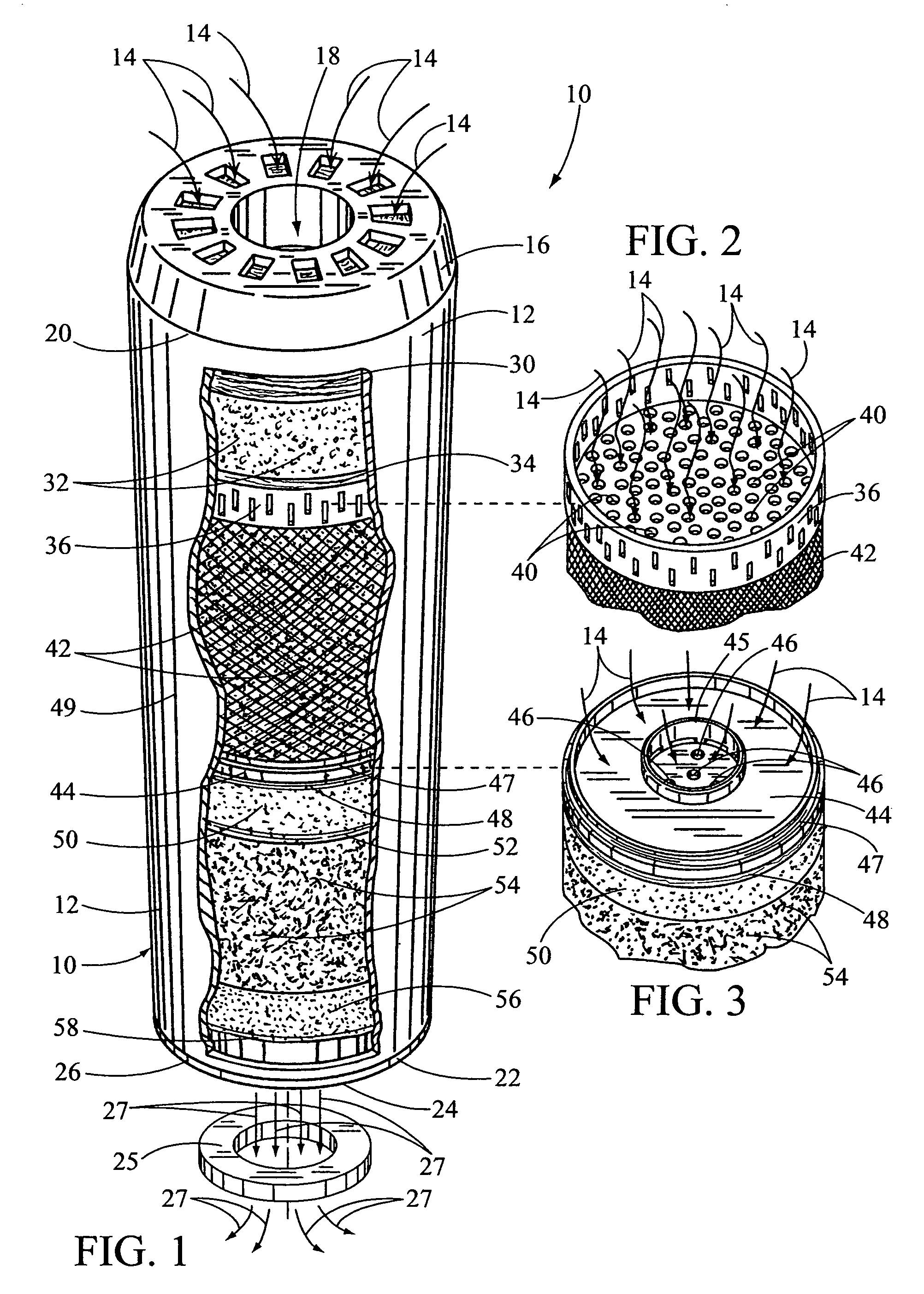
Drinking water filter used with tap water and other water sources
InactiveUS7156994B1Save spaceEliminate needTreatment involving filtrationWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeWater sourceFiltration
A drinking water filter for filtering major water contaminates from tap water and other drinking water sources. The water filter a cylindrical cartridge for receiving a plurality of sponge filters used as dividers between different layers of filtration material and along a length of the cartridge. The sponge filters are designed to remove large and small sediments in the water from 1 to 100 microns in size and greater when the water is introduced through the cartridge. The layers of filtration material includes a layer of granulated zinc and copper alloy, a fine mesh carbon block, a layer of granulated ion exchange resin, a layer of granulated activated carbon and layer of granulated activated calcite. The carbon block and the granulated carbon material is used for removing chlorine, odor, color, cysts, protozoa and organic contaminants such as pesticides, herbicides, arsenic, mercury, and trihalomnethanes. The zinc and copper alloy is used for removing chlorine and heavy metals in the water and reducing bacteria in the water. The calcite is used to raise the pH in the filtered water when the pH is below neutral.
Owner:ARCHER VIRGIL L
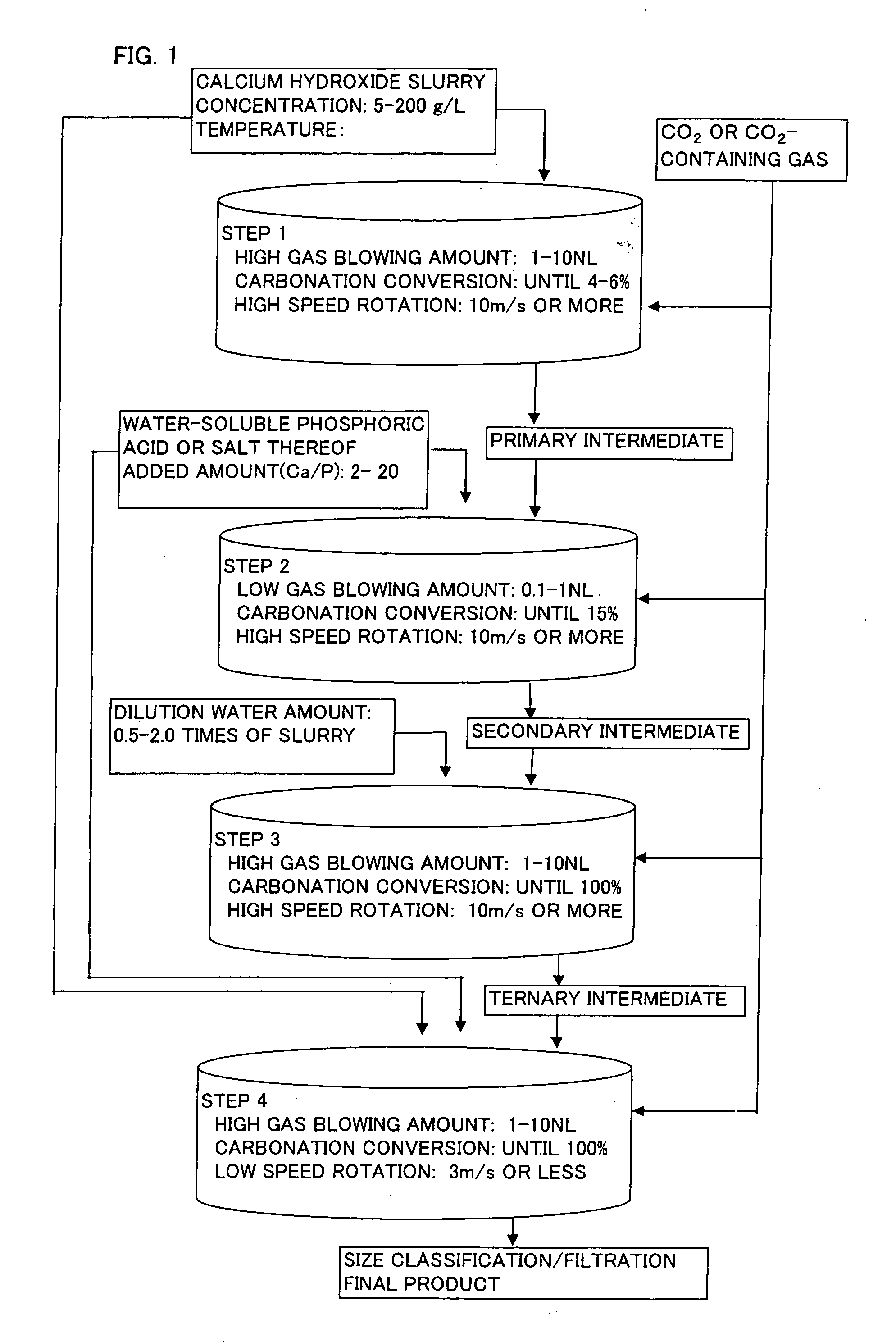
Spherical calcium carbonate and method for producing thereof
InactiveUS20060165583A1Inferior physical propertyLow blowing rateCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesCosmetic preparationsCalcium hydroxideO-Phosphoric Acid
When spherical calcium carbonate is produced by blowing a carbon dioxide gas or a carbon dioxide-containing gas into an aqueous suspension containing calcium hydroxide to react them, after start of the reaction, an aqueous solution or suspension of a water-soluble phosphoric acid compound or a water-soluble salt thereof is added to the reaction mixture when carbonation ratio reaches 2 to 10%, and the reaction is further allowed to continue at a low gas blowing rate of 1.0 NL / minute or lower (step (a)). Subsequently, an aqueous suspension containing calcium hydroxide and an aqueous solution or suspension of a water-soluble phosphoric acid compound or a water-soluble salt thereof are added to the reaction mixture, and a carbon dioxide gas or a carbon dioxide-containing gas is introduced to allow to react and thereby produce spherical calcium carbonate having a mean particle diameter of 10 μm or larger. This production method is performed under high velocity revolution from the start of the reaction to the end of the step (a) This method provides calcite type spherical calcium carbonate showing high brightness and small friction coefficient, and having a shape comparatively close to a true sphere and a mean particle diameter of 10 μm or larger.
Owner:OKUTAMA IND
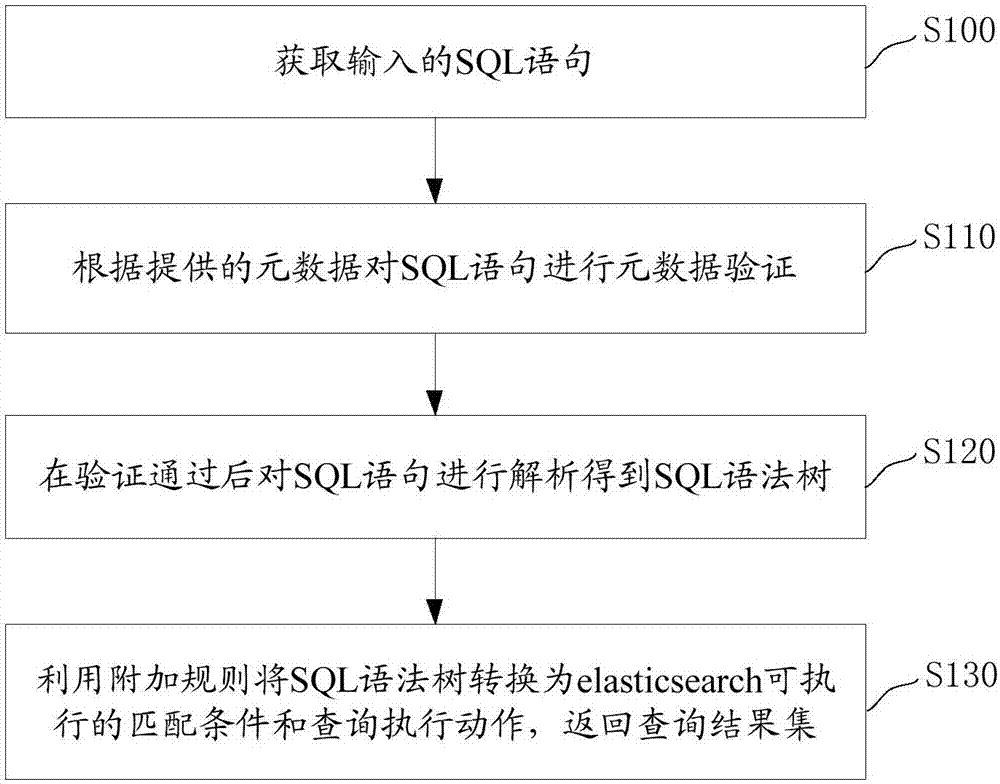
Realization method and system for querying elasticsearch
The invention discloses a calcite-based realization method for querying elasticsearch by an sql. The method comprises the steps of obtaining an input SQL statement; performing metadata verification on the SQL statement according to provided metadata; after the verification is passed, analyzing the SQL statement to obtain an SQL syntax tree; and converting the SQL syntax tree into a matching condition and a query execution action executable for the elasticsearch by utilizing an additional rule, and returning a query result set. According to the realization method, the SQL statement is analyzed, and the adaptation and optimization of the SQL to an elasticsearch java API are finished. The invention discloses a calcite-based realization system for querying the elasticsearch by the sql. The system has the abovementioned beneficial effects.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Process of preparing high purity light calcium carbonate fine powder with carbide residue
InactiveCN101020579AHigh purityReduce the difficulty of manufacturing processCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesCalciteSlurry
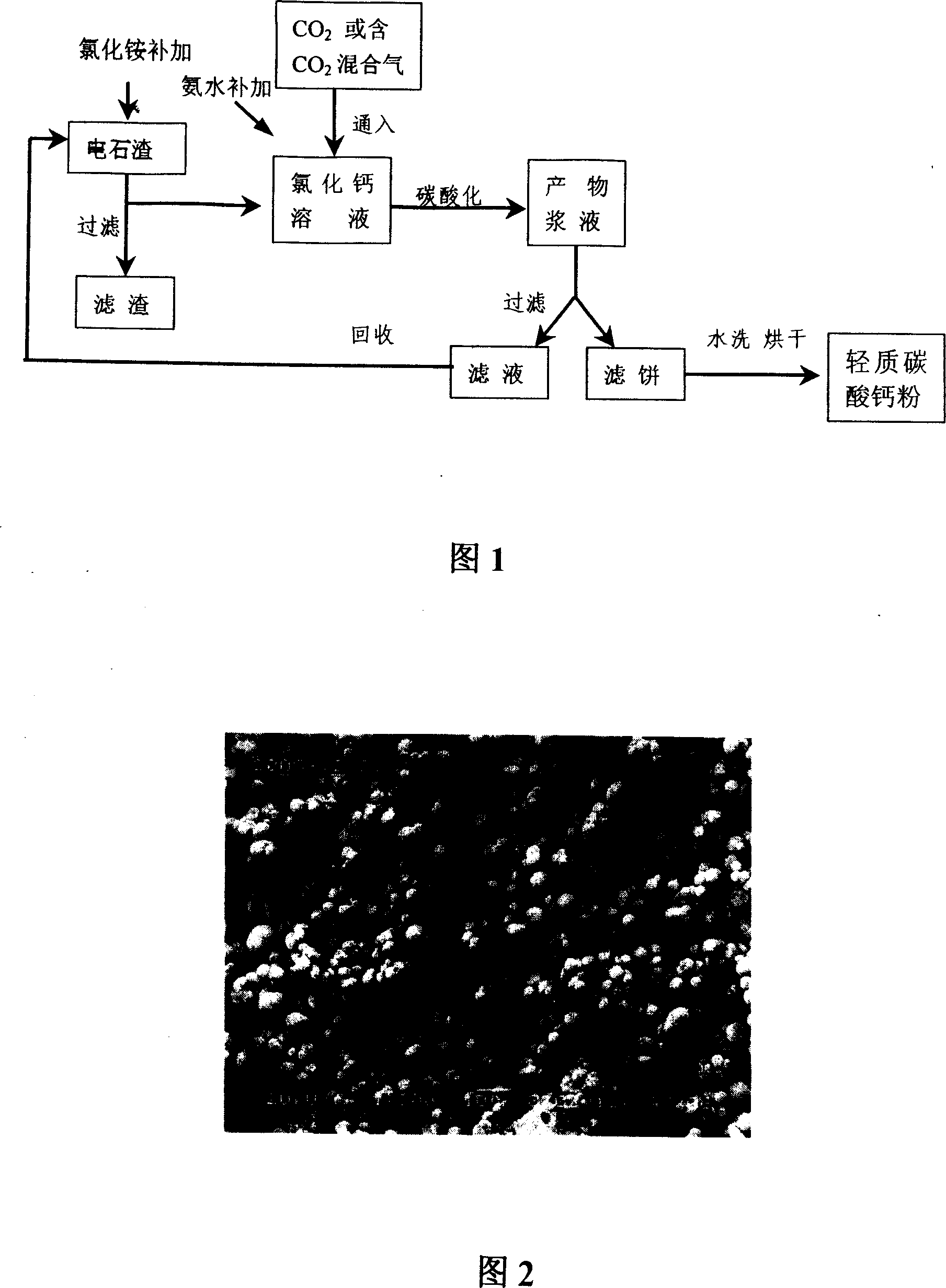
The process of preparing high purity light calcium carbonate fine powder with carbide residue includes reacting carbide residue as one kind of industrial waste directly with ammonium chloride solution to produce mixture solution of calcium chloride and ammonia water, filtering, introducing CO2 gas for carbonating reaction, filtering the produced slurry, water washing the filter cake and stoving to obtain calcite type spherical light calcium carbonate fine powder, and circulating ammonium chloride solution for reuse. The present invention has simple technological process, lowered production cost, high product purity and high product quality.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Zero-invasion acidic drilling fluid
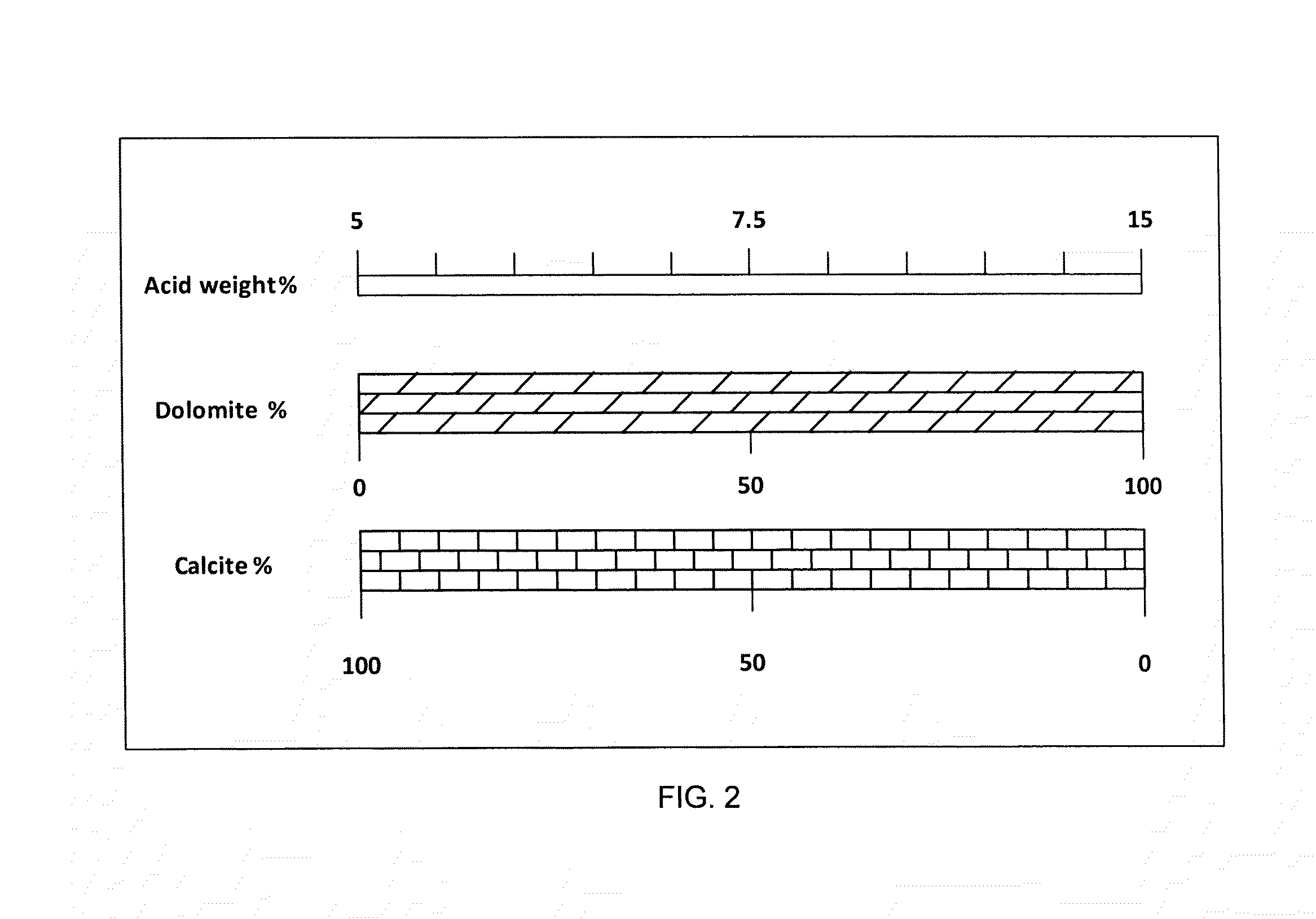
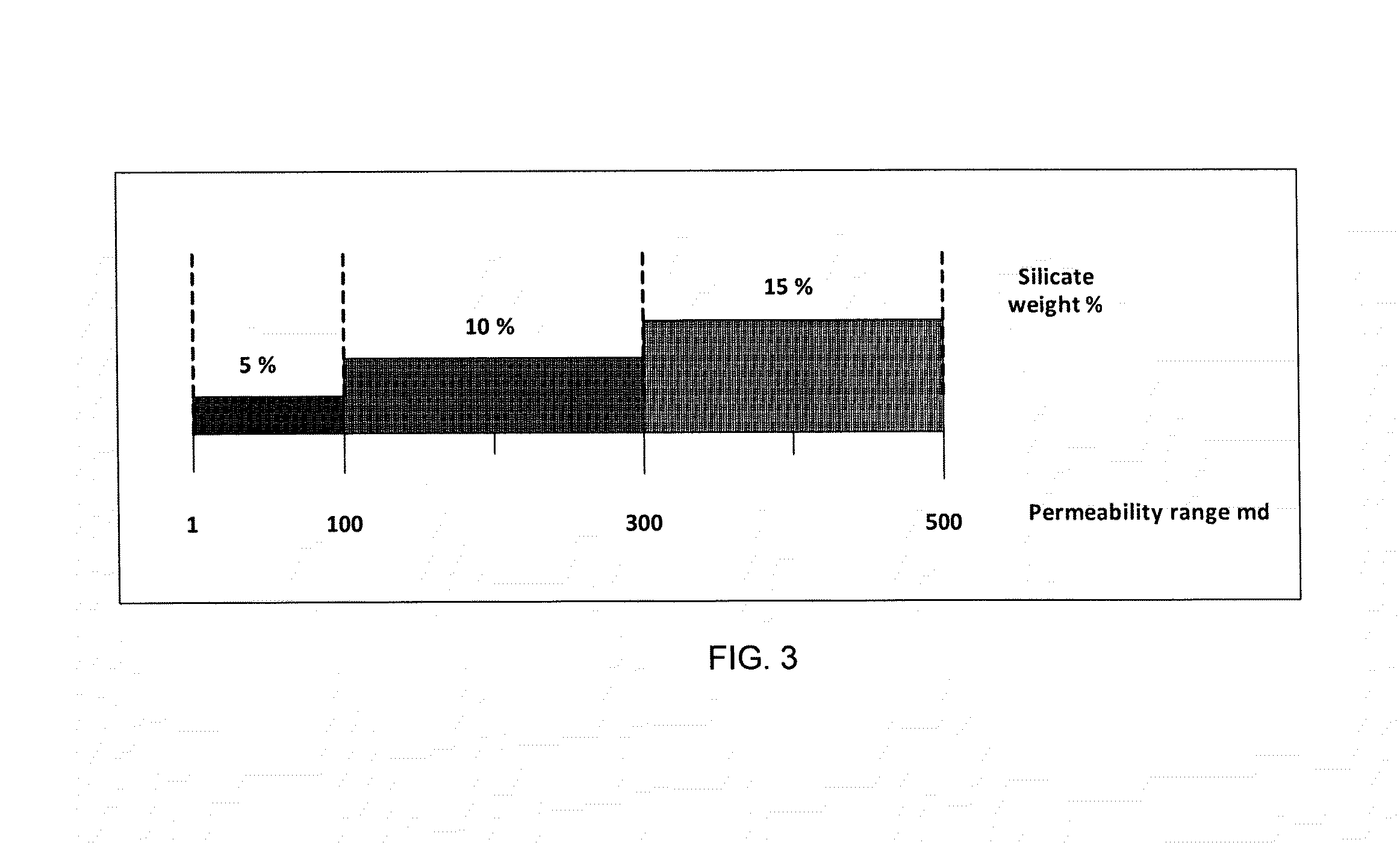
A drilling fluid system using retarded acid systems such as gelled acid (VES or polymer) and / or emulsified acid to drill carbonate formations (calcite and dolomite). Foamed acid may be used in low abnormal pressure carbonate reservoirs. The drilling fluid system permits drilling a target hydrocarbon-producing formation with zero-invasion of the drilling fluid system. A method for using the drilling fluid system for fluid loss control during drilling operations.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
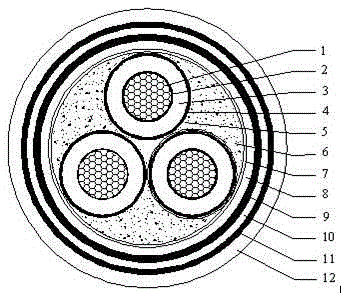
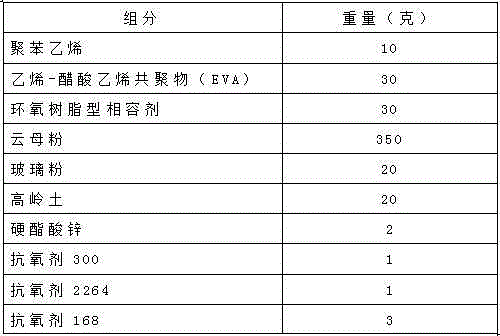
Ceramifying polyolefin fireproof cable material
InactiveCN105348627ALow priceSimple processing technologyPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsInsulated cablesElastomerPolyolefin
The invention provides a ceramifying polyolefin fireproof cable material. The material is prepared by the following components in parts by weight: 40-100 parts of polyolefin; 1-30 parts of a compatilizer; 350-450 parts of ceramifying powder; 20-200 parts of a flux; 20-90 parts of a fire retardant; 2-20 parts of a lubricant; and 1-10 parts of an anti-oxidant. Polyolefin is selected from one or more of an ethane-vinyl acetate copolymer, polypropylene, polystyrene, polyethylene and a polyolefin elastomer. The ceramifying powder is selected from one or more of pottery clay, powdered steatile, mica powder, pyrophillite, ascharite, datolite, calcite, limestone, spodumene and clay. The ceramifying polyolefin fireproof cable material has the advantages of good fireproof performance, environmental protection, low cost, easy processing and good application prospect.
Owner:SUZHOU CPLUS NEW MATERIAL
High fluidity grouting material and production method thereof
ActiveCN101798208AImprove mobilityEasy to pump over long distancesSolid waste managementNeutral phPortland cement
The invention discloses a high fluidity grouting material and a production method thereof. The high fluidity grouting material comprises the following components in percentage by weight: on the basis of 100 percent of total amount, 60 to 96 percent of conventional portland cement, 1 to 20 percent of calcite powder, 1 to 20 percent of a mineral modifying component, and 2 to 18 percent of swelling agent, wherein measuring on the basis of using the total amount of four substances as base number, 0.01 to 4 weight percent of high efficiency slushing agent and 0.0005 to 1 weight percent of plasticity swelling agent are added in the mixture of the four substances. The high fluidity grouting material can be made of raw materials mixed by adopting a dual-shaft paddle non-gravity high-efficiency mixer. The material has simple industrialized production process and stable product quality, adopts the water-cement ratio of between 0.24 and 0.28, is evenly blended by water with neutral pH value, and has the advantages of high fluidity, no bleeding, no segregation or layering, slight swelling, easy pump delivery, good durability and the like after the material is uniformly mixed by water.
Owner:HUBEI CHIDGE TECH
Novel tang-dynasty jun porcelain glaze and manufacturing process thereof
The invention discloses novel tang-dynasty jun porcelain glaze. Yellow feldspar, white feldspar, calcite, quartz, copper ore and iron core are used as glaze raw materials; the yellow feldspar, the white feldspar, the calcite, the quartz, the talcum powder, the copper ore, the zinc oxide, the tin oxide, the copper oxide and ox bone are used as ground coat raw materials; the burnt jun porcelain glaze satisfies the requirement of the tang-dynasty jun porcelain glaze technology, so that the glaze color is natural and variable.
Owner:JIA COUNTY RENSHI CERAMIC IND CO LTD
Formulation for medicinal neutral boron silicate glass
The present invention is one kind of neutral borosilicate glass for medicine production. The neutral borosilicate glass has recipe comprising quartz sand 168-178 Kg, feldspar powder 14.7-18.7 Kg, borax pentahydrate 49-51 Kg, sodium carbonate 8-12 Kg, barium carbonate 8.6-9.4 Kg, sodium nitrate 0.4-0.6 Kg, calcite 1-2 Kg, fluorite 0-4 Kg, potassium carbonate 8.5-9.5 Kg, salt 0.8-1.6 Kg, cerium oxide 0.5-0.9 Kg and cullet 120 Kg. It has high chemical stability, high hydrolysis stability, few alkali metal volatilizations, simple production process and low cost.
Owner:东营力诺玻璃制品有限责任公司
Ru agate glaze and processing method and application thereof
The invention discloses a Ru agate glaze, which contains the following components by weight parts: 6 to 26 parts of agate, 40 to 65 parts of feldspar, 10 to 23 parts of calcite, 13 to 28 parts of black limestone, 3 to 8 parts of limonite, 2 to 4 parts of talcum and 5 to 10 parts of chestnut ash. The invention also discloses a processing method for the Ru agate glaze and the application of the Ru agate glaze on Ru porcelains, and also discloses a Ru porcelain. The basic tones of the glaze of the Ru porcelain fired with the Ru agate glaze are green and blue, and therefore the glaze can present the deep colors of azure, cyan and bluish white as well as the bright, transparent colors of pea green, light green and light greenish blue; the texture of the porcelain body is fine and dense, the porcelainizing degree is high, the water absorption does not exceed 1.2 percent, and the sound is silvery when the product is knocked; the thermostability is good, and defects, such as through cracks and leakage, do not exist.
Owner:郭秀贞
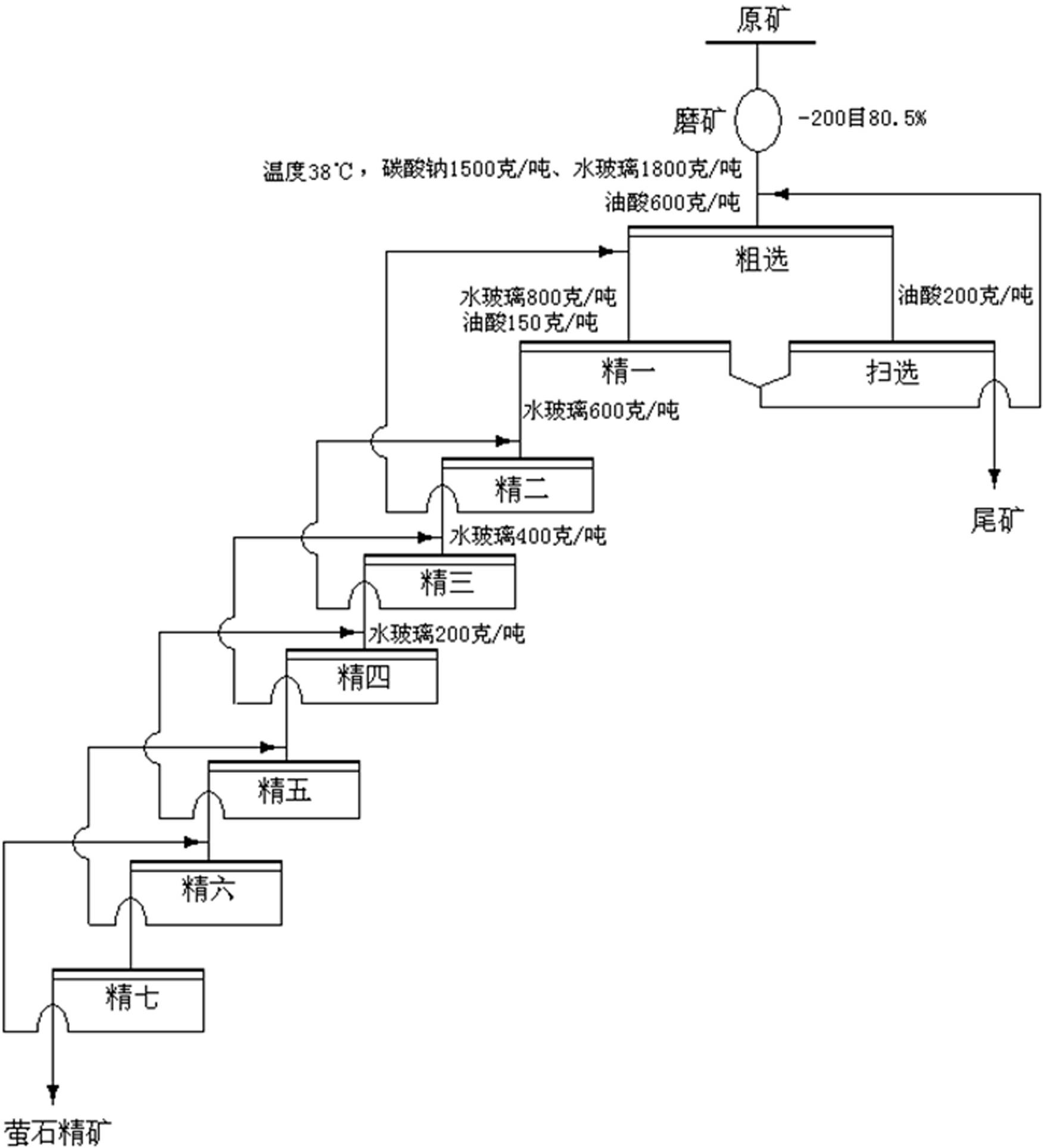
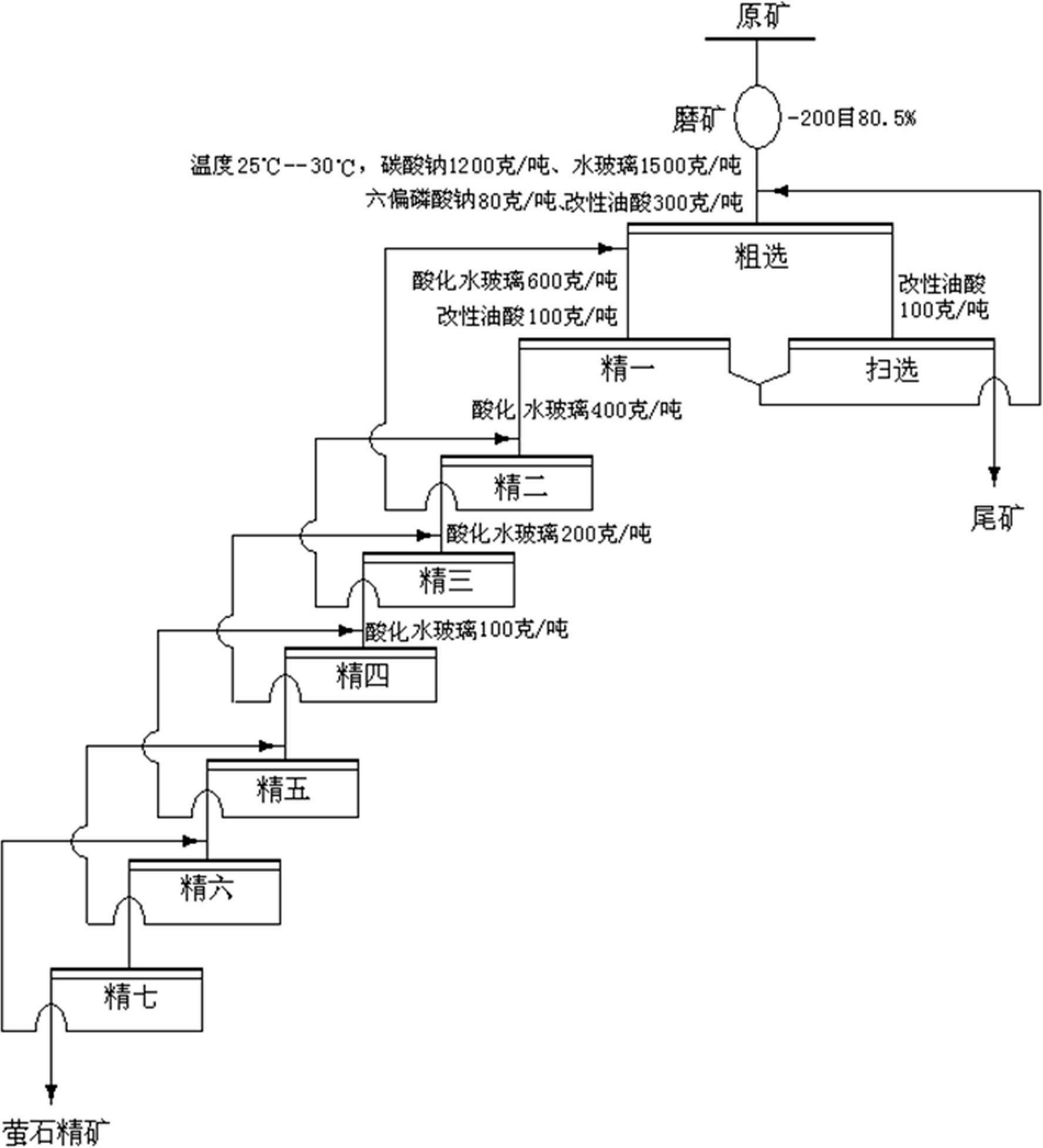
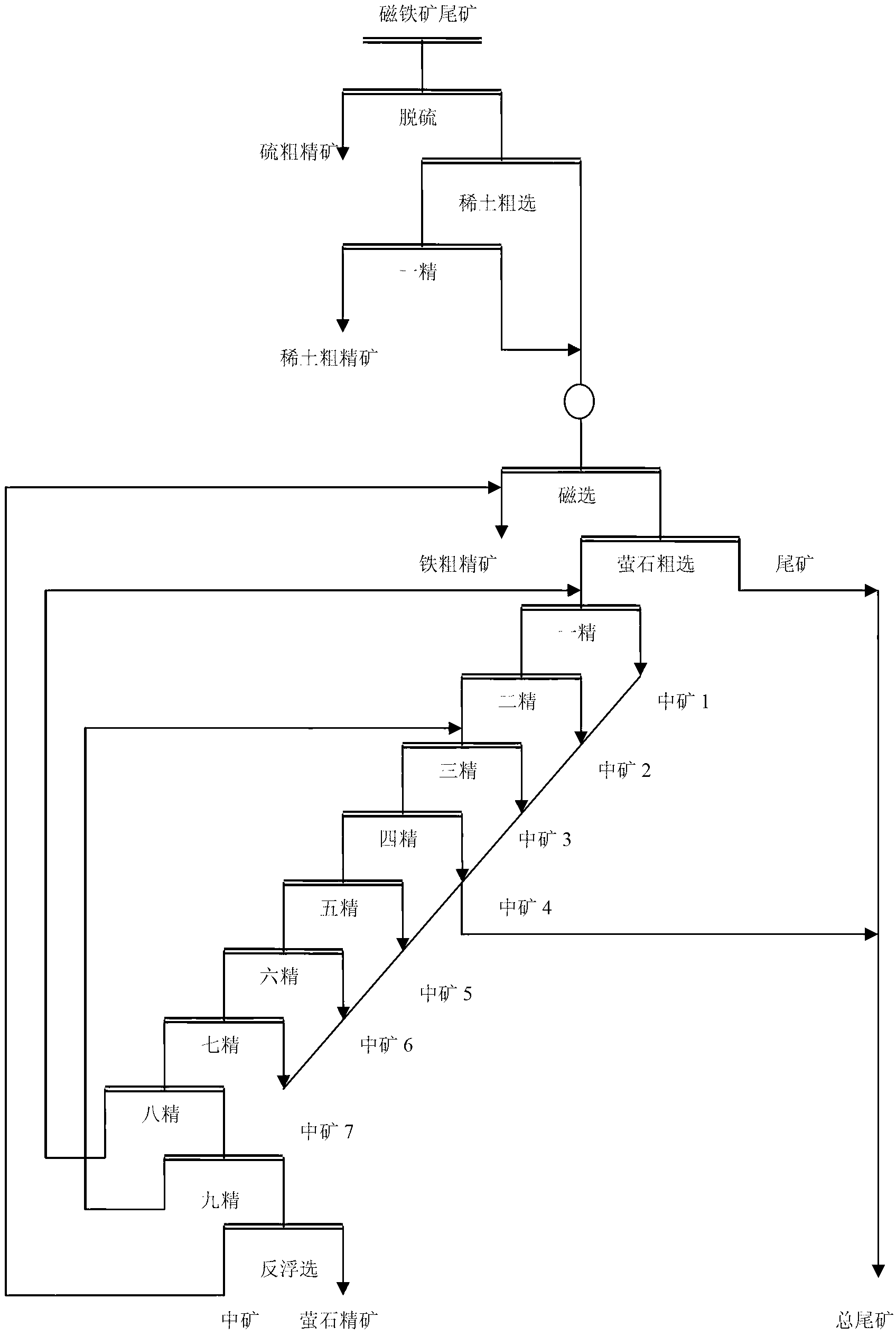
Mineral separation process of complex fluorite difficult to separate
The invention relates to a mineral separation process, in particular to a mineral separation process of complex fluorite difficult to separate. The process includes utilizing sodium hydroxide to treat oleic acid to obtain modified oleic acid, utilizing concentrated sulfuric acid to treat water glass and obtain acidized water glass, conducting ore grinding on fluorite ores according to the prior art, conducting coarse separation under the temperature of 25-30 DEG C, then conducting seven times fine separation on coarse separation foams and adding the acidized water glass into the foams in the first four times of fine separation to prepare fluorite concentrate. The process can improve separation efficiency of calcium fluoride, silica and calcite, improves quality and recycle rate of the fluorite ores, obtains high quality acid grade fluorite ores and resolves the problem of difficulty in separation of complex fluorite flotation, is remarkable in application effect in separation of the complex fluorite difficult to separate, has repeatability, simultaneously reduces requirements of fluorite mineral flotation for ore temperature, reduces energy consumption, reduces usage of collectingagent oleic acid, reduces environment pollution caused by exhaust of a large amount of waste water containing oleic acid and has better economical and social benefits.
Owner:BAIYIN NONFERROUS GROUP
Glass fiber blanket and producing method thereof
ActiveCN103103695AImprove adhesionGood peeling effectGlass making apparatusNon-woven fabricsGlass fiberFlat glass
The invention discloses a glass fiber blanket and a producing method thereof. The method comprises the steps of mixing the following components , by mass, 35-40 parts of silica flour, 5-12 parts of feldspar, 9-14 parts of borax, 1-3.5 parts of calcite, 6-8 parts of dolomite, 11-14 parts of soda ash, and 15-25 parts of sheet glass to form a mixture; melting the mixture to obtain glass metal; placing the glass metal in a centrifugal machine for spinning treatment to obtain glass fiber and spraying water and binders onto the surface of the glass fiber in a vaporific mode at the same time; placing the glass fiber coated with the binders in a cotton collecting machine to enable the glass fiber to evenly fall onto the cotton collecting machine under the action of a negative-pressure fan to form a glass cotton layer; and conveying the glass cotton layer well laid to a curing oven through a conveyer to be cured to obtain the glass fiber blanket.
Owner:CHENGDU HANJIANG NEW BUILDING MATERIAL
Composite lithium base lubricant and its preparing method
ActiveCN1616612AGood mechanical stabilityGood colloidal stabilityBase-materialsLithium soapLithium hydroxide
The composite lithium-base lubricating grease consists of the following components: high alkality calcium sulfonate with calcium carbonate existing in calcite crystal and dispersed colloid particle form in 20-60 wt%; thickener comprising composite lithium soap in 3-15 wt%; and lubricating base oil in the rest amount. The preparation process of the lubricating grease includes mixing and heating Newtonian fluid high alkality calcium sulfonate, converting agent and base oil until thickening; adding C12-C24 fatty acid and auxiliary acid and producing saponification with lithium hydroxide aqua; heating to dewater and cooling to form grease. The composite lithium-base lubricating grease of the present invention has excellent mechanical stability, colloid stability, water resistance, rust resistance and high temperature use performance.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
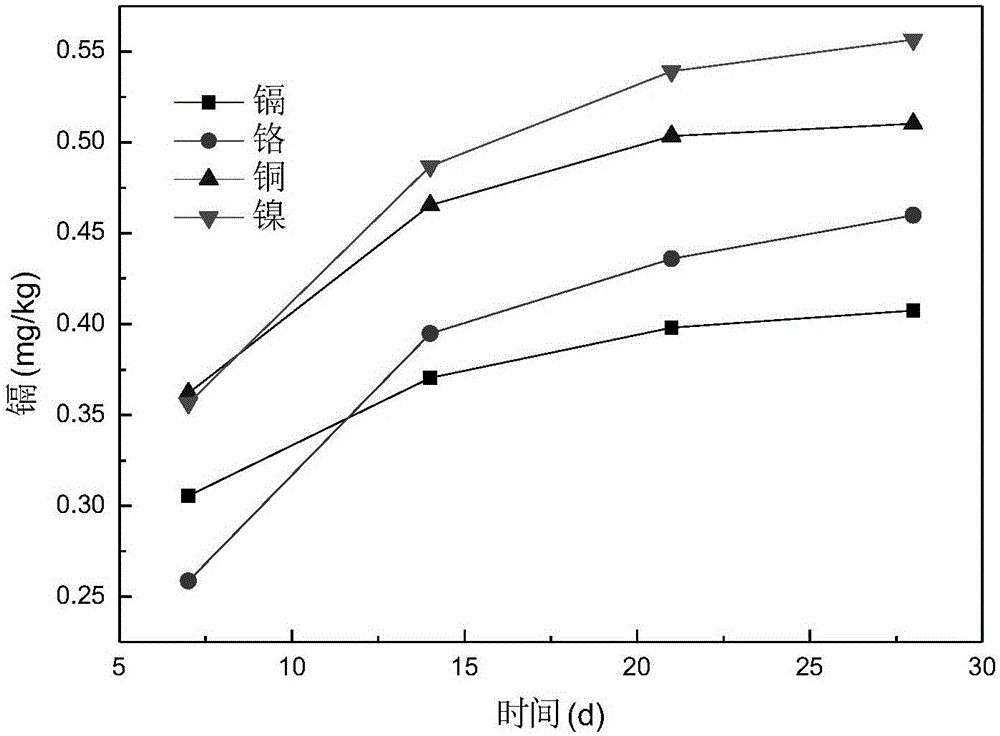
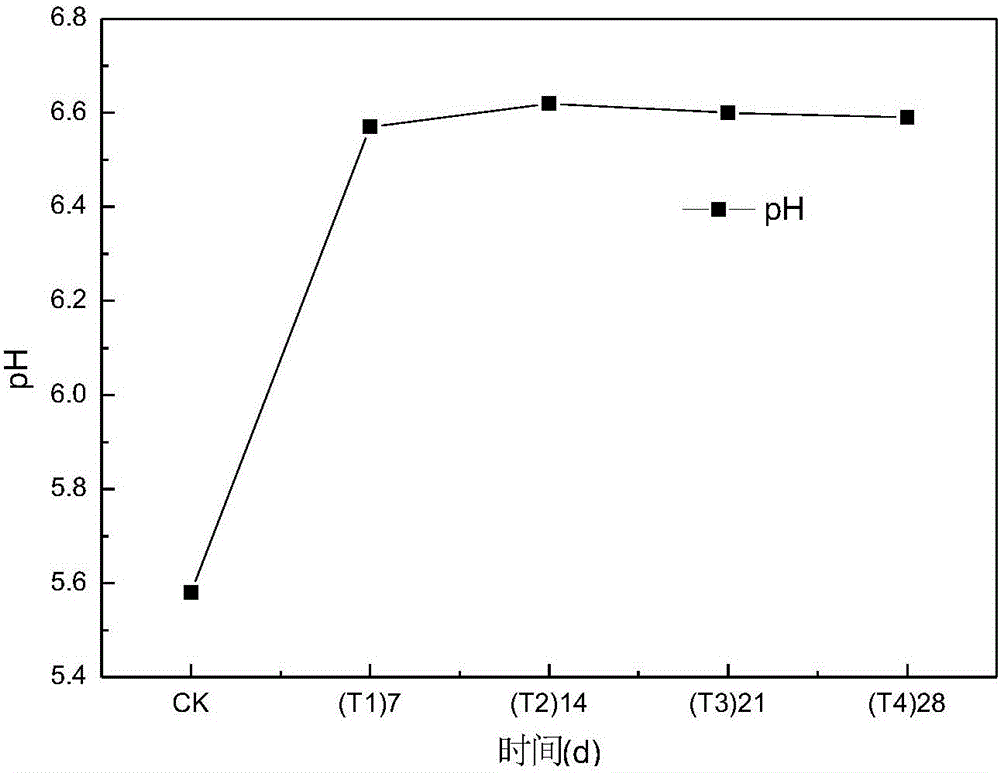
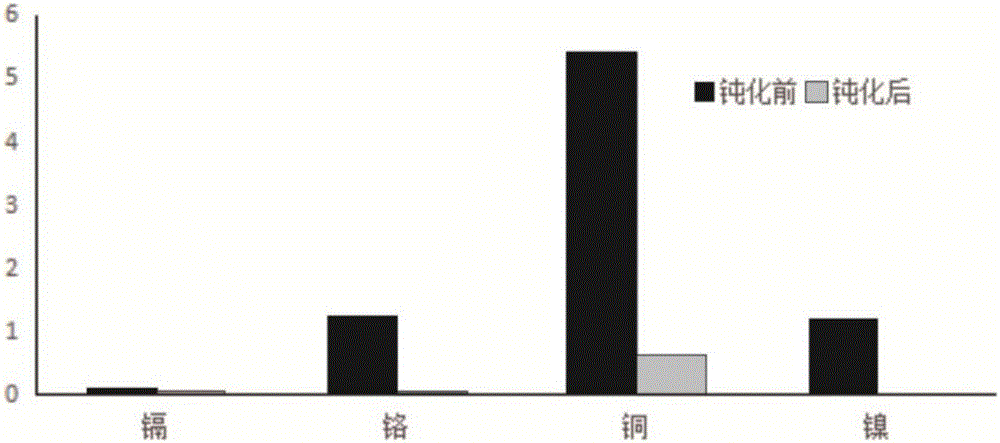
Passivator for remediation of farmland soil subjected to combined pollution of heavy metals, and preparation method and use method of passivator
InactiveCN106800933AImprove adsorption capacityImprove water retentionAgriculture tools and machinesMagnesium fertilisersIon exchangeBinding state
The invention relates to a passivator for remediation of farmland soil subjected to combined pollution of heavy metals such as cadmium, chromium, copper and nickel, and a preparation method and a use method of the passivator. The passivator is prepared from a passivator A and a passivator B, wherein the passivator A is prepared from montmorillonite, kieselguhr, sepiolite, illite and ferrous sulfate; the passivator B is prepared from periclase, calcite, calcium magnesium phosphate fertilizer, plant ash and calcium hydroxide; the passivator is suitable for the farmland soil subjected to the combined pollution of the cadmium, the chromium, the copper and the nickel, and is prepared from the multiple different porous absorption materials with specific contents and a passivation material; the components of the passivator have complementary advantages, and the principles such as absorption and stabilization are combined; the combination forms of the heavy metals are effectively enhanced by ion exchange, complexing, chelating and adsorption methods, and the combination forms are converted into more stable strong organic binding states and residue states, so that the effective state contents of the heavy metals in the farmland soil are effectively reduced, and the passivation effect is long-acting and stable; therefore, the passivator has a great repair effect for the farmland soil subjected to combined pollution of the cadmium, the chromium, the copper and the nickel.
Owner:SICHUAN YIKE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION SCI ANDTECH
Mineral processing technology for recycling fluorite from baotite, magnetite and tailing
The invention belongs to the technical field of mineral engineering and provides a mineral processing technology for recycling fluorite from baotite, magnetite and tailing. In the tailing, mineral particle size of the fluorite is thin, iron-bearing mineral, rare-earth mineral, gangue mineral and the fluorite mineral are closely symbiotic and floatability of minerals such as rear earth, barite, apatite, calcite and dolomite is close to the fluorite mineral, so that separation of the fluorite mineral is difficult. According to the mineral processing technology for recycling the fluorite from the baotite, the magnetite and the tailing, priority desulfuration, rear earth flotation, ore grinding, iron selection through magnetic separation, fluorite selection through direct flotation and a reverse flotation sorting technology are performed on the magnetite and the tailing to enable pyrite, the rare earth, the iron-bearing mineral and the fluorite to be picked out in sections, efficient, high selective, easy-to-operate inhibitor and collecting agent combination is utilized in sorting of fluorite which is mostly performed monomer separation, so that fine fluorite of high grade and high recovery rate is obtained, a purpose of synthetically recycling valuable minerals is achieved, and effective separation of the fluorite mineral and the gangue mineral is achieved.
Owner:包钢集团矿山研究院(有限责任公司)
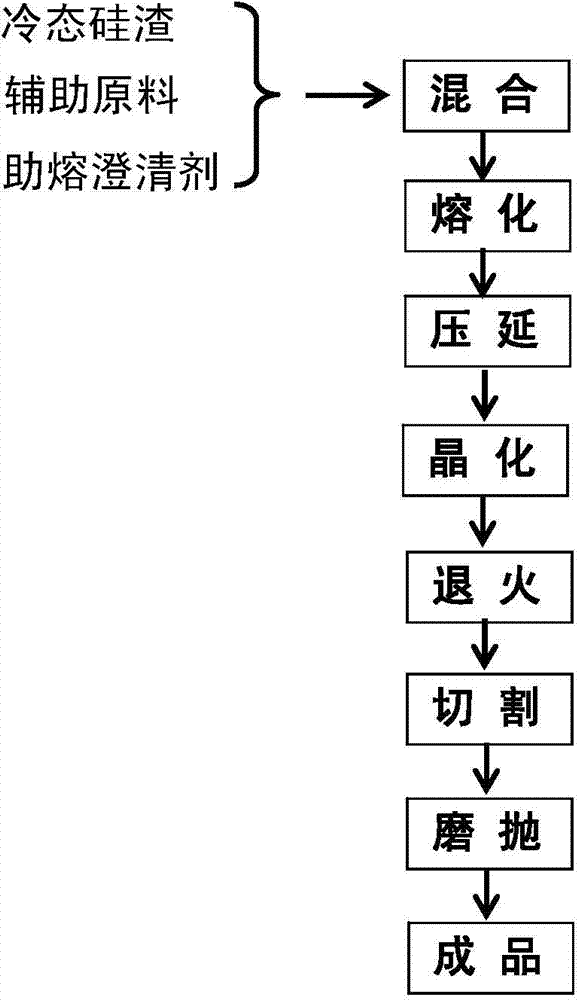
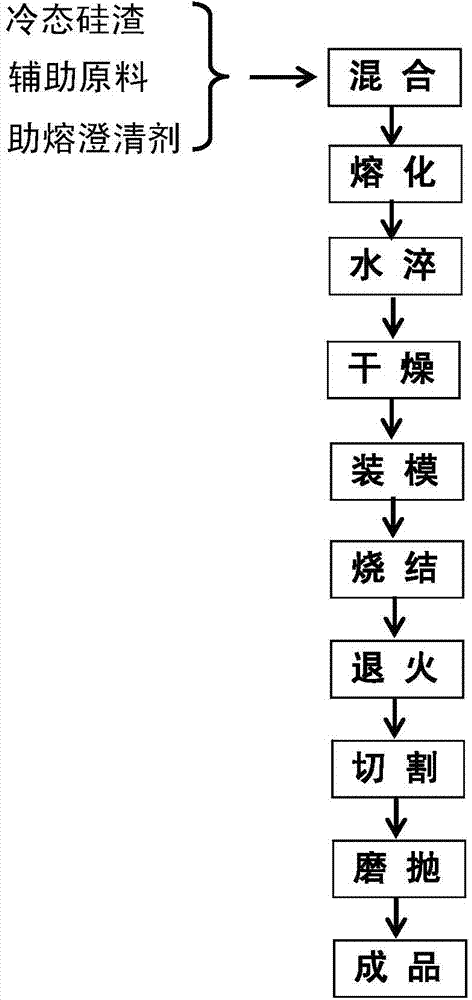
Silicon-slag microcrystalline glass and preparation method thereof
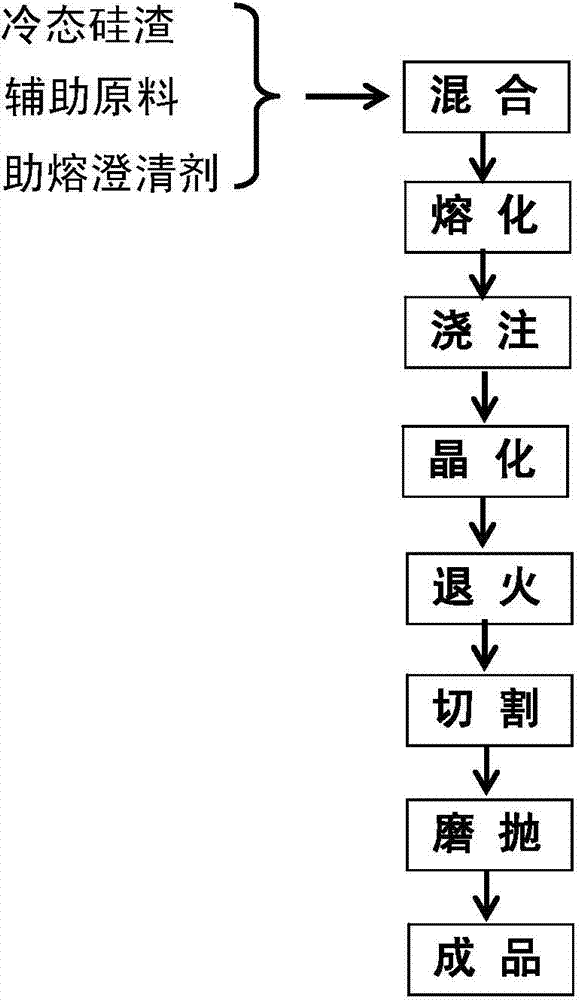
The invention relates to silicon-slag microcrystalline glass and a preparation method thereof. Silicon smelting waste slag is taken as a major raw material, and silicon dioxide or silica sand (SiO2), fluorite (CaF2), limestone or calcite (CaCO3), industrial sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), zinc oxide (ZnO) and potassium carbonate (K2CO3) are taken as auxiliary raw materials, wherein the dosage of the silicon smelting waste slag in the raw materials of the microcrystalline glass is 26.0-75.0wt%. The preparation method specifically comprises the following steps of: evenly mixing cold-state silicon slag with other auxiliary raw materials in a blender mixer to obtain a basic mixed batch, melting the basic mixed batch into qualified glass liquid in a melting furnace, and then performing calendering, casting or water quenching on the glass liquid to form a basic glass plate or granules; finally, subjecting the basic glass plate to crystallization heat treatment to obtain the microcrystalline glass. The density of the microcrystalline glass is 2.5-2.8 g / cm<3>, the rupture strength of the microcrystalline glass is 30.0-103.5 MPa, the compressive strength of the microcrystalline glass is 70.0-903.0 MPa, the Moh's hardness of the microcrystalline glass is 5-8 and the abrasive resistance of the microcrystalline glass is 0.063-0.15 g / cm<2>; the silicon-slag microcrystalline glass can be widely applied to the fields such as chemical engineering, metallurgy, architectural ornament, petroleum, mine and machinery.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Clear glaze and method for manufacturing same
InactiveCN101182238AWide firing temperatureNot prone to chromatic aberrationPotassium feldsparCalcite
The invention discloses a transparent glaze and a preparation method thereof. The weight percentages of ach component of the transparent glaze are 10 percent to 35 percent of potassium feldspar powder, 8 percent to 25 percent of calcite, 8 percent to 10 percent of kaolin, 2 percent to 5 percent of quartz, 9 percent to 15 percent of calcined kaolin, 5 percent to 8 percent of burning talc, 3 percent to 5 percent of alumina, 1 percent to 3 percent of barium carbonate, 3 percent to 10 percent of transparent of fusion cake, 0.15 percent to 0.35 percent of methyl, 0.2 percent to 0.4 percent of tripolyphosphate and 15 percent to 30 percent of water. The weight percentage of the glaze material fineness is that the 250 meshes sieve residue is less than 0.15 percent. The technical process of the manufacturing method is as follows: the raw material enters the factory for testing, proportioning, ball milling, detecting, removing iron, sieving and storing in a storehouse for using. The sintering temperature of ball milled glaze slurry is 1200 DEG C to 1210 DEG C, and the sintering period is 50min to 65min. The application range of the invention is wide; the performance of the glaze material is good; the glaze surface is smooth and is not easy for producing chromatic aberration; the cost can be reduced by about 35 percent.
Owner:霍炳祥
Antibacterial ceramic tile capable of releasing negative oxygen ions and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of ceramic materials and in particular relates to an antibacterial ceramic tile capable of releasing negative oxygen ions and a preparation method thereof. The antibacterial ceramic tile capable of releasing the negative oxygen ions comprises a green body and a glaze layer, wherein the glaze layer is prepared from the following raw materials: potassium feldspar, potassium feldspar, calcite, calcined talc, zinc oxide, barium carbonate, alumina, a frit, calcined soil and kaolin; and the antibacterial ceramic tile also comprises antibacterial ceramic glaze additives capable of releasing the negative oxygen ions. The produced ceramic tile has the effects of permanently releasing the negative oxygen ions, emitting far-infrared rays, cleaning self, resisting to bacteria and purifying the air; and meanwhile, a ceramic glaze surface contains multiple mineral substances and trace elements, such as germanium and strontium, which are beneficial to human health.
Owner:山东统一陶瓷科技有限公司
Complete polishing glaze archaizing brick overglaze and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a complete polishing glaze archaizing brick overglaze and a preparation method thereof. The complete polishing glaze archaizing brick overglaze is prepared from the following raw materials by weight percent: 4-8% of albite, 9-12% of potassium feldspar, 12-15% of calcite, 4-6% of barium carbonate, 6-10% of alumina, 12-15% of burnt talcum, 2-4% of zinc oxide, 2-5% of quartz powder, 9-13% of kaolin, 5-9% of wollastonite and the balance of impurities. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out ball milling in a ratio of weighed raw material to ballstone to ethylene glycol to squeegee oil of 1: (1.8-2): 0.25: 0.3, and simultaneously controlling the fineness degree as follows: the screenings of 325-mesh sieve is 0.3-0.4%; printing on ground glaze and fancy glaze layers through 100-mesh silk screen by using a continuous printing process; and finally, firing through a liquefied gas raceway kiln firing system. According to the invention, the purposes of improving the stability of the process and the quality of the product, reducing glaze material loss in production process, reducing cost and simultaneously avoiding the generation of a screen sticking problem in production are achieved.
Owner:霍镰泉
Production raw material of foamed glass and process for producing foamed glass
The invention relates to raw materials for producing foam glass and a method for applying the same to produce the foam glass. The compositions by weight portion of the raw materials are: 380 to 580 portions of quartz sand, 105 to 250 portions of potassium feldspar, 130 to 270 portions of albite, 115 to 200 portions of dolomite, 5 to 25 portions of calcite, 150 to 250 portions of calcined soda, 0.5 to 30 portions of glauber salt, 1.0 to 12 portions of magnesium carbonate and 1.0 to 8.5 percent of potassium carbonate. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, various raw material compositions are mixed into uniform glass mixture; secondly, the glass mixture is melted and cooled into cullet; thirdly, ball milling, foaming and annealing of the cullet are performed, and then foam glass is obtained. The method can automatically control and adjust the chemical compositions of the glass and add various functional compositions as required to meet the demand of producing the foam glass with different performances by adoption of common mineral and chemical raw materials of the natural world.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHENSHEN INSULATION TECH CORP
Glaze material for Jun red glaze and process for preparing Jun porcelain from glaze material
The invention discloses a glaze material for Jun red glaze and a process for preparing Jun porcelain from the glaze material. The glaze material consists of the raw materials of melilite, quartzite, calcite, white feldspar, copper ore, ZnO, SnO, GuO, talc, BaO, zirconium silicate and spodumene. The preparation process comprises the following steps: firstly, smashing roughcast raw materials and conducting moulding to fire a plain roughcast, then immersing the plain roughcast into slurry of the glaze material of the Jun red glaze for glazing, and when the slurry adhered on the surface of the plain roughcast is dried, putting the plain roughcast in a kiln for firing, so as to obtain the Jun red glaze Jun porcelain. According to the glaze material for the Jun red glaze and the process for preparing the Jun porcelain by utilizing the glaze material, spodumene and zirconium silicate are added in the glaze material for the Jun red glaze, so that the fired Jun red glaze Jun porcelain is bright in color, mild and smooth in glaze surface, and uniform in cracking, and breaks through the condition that the general Jun red glaze Jun porcelain is dim in color and nonuniform in cracking; the Jun porcelain is taken as the specialty of China, and represents the advanced level of the manufacture process of China, and the social value of the Jun porcelain is improved.
Owner:JIAXIAN HONGDA PORCELAIN CO LTD
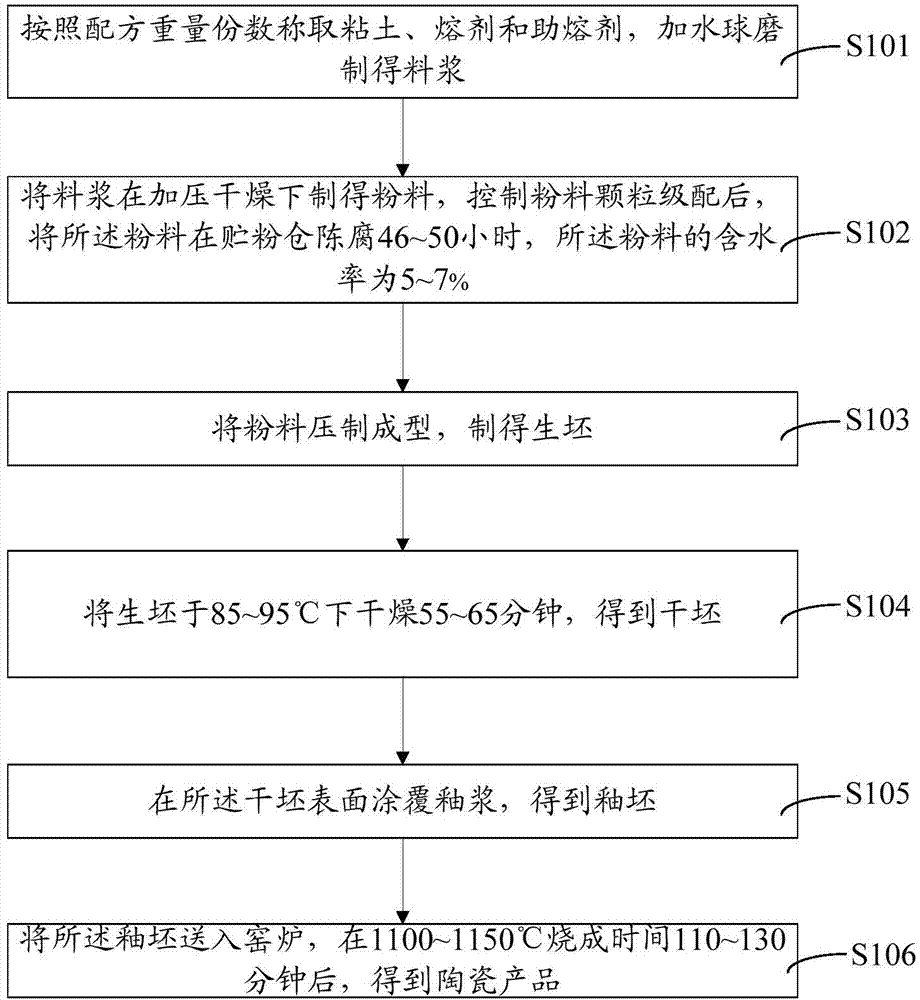
Ceramic formula and preparation method for ceramic product
The invention provides a ceramic formula, comprising, by weight, 55 to 65 parts of clay, 20 to 30 parts of a flux and 15 to 23 parts of a fluxing agent, wherein the clay is a mixture of purple sandshale and china clay mixed according to a weight ratio of 0.67 to 2.0, the flux is shale, and the fluxing agent is one or more selected from the group consisting of limestone, calcite, diopside, wollastonite, dolomite, talcum and industrial waste residue. A preparation method for a ceramic product comprises the following steps: weighing the clay, the flux and the fluxing agent according to the formula, carrying out crushing and screening with a 250-mesh sieve, wherein the weight of screen residue is 1 to 1.5%, adding water, carrying out blending to obtain slurry and then carrying out drying and granulation so as to obtain powder; grading particles and then carrying out molding so as to prepare a green body; carrying out drying so as to prepare a dry body; and carrying out firing so as to prepare a seasonal ceramic body. According to the ceramic formula and the preparation method for the ceramic product in the invention, raw materials are cheap, process is simple, firing temperature is reduced, production cost is decreased, investment for production equipment is lowered down, production efficiency is improved, and energy consumption is reduced.
Owner:怀化市亿智陶瓷有限公司
Method for comprehensively recovering tungsten and fluorine from minerals
InactiveCN102586632AHigh recovery rateImprove solubilitySilicaProcess efficiency improvementDecompositionApatite
The invention provides a method for comprehensively recovering tungsten and fluorine from minerals, namely a mixed acid of phosphoric acid and sulfuric acid is adopted for decomposing complex calcium-containing minerals containing fluorite, scheelite, apatite, and calcite, wherein the fluorite is decomposed to fluorine hydride or silicon tetrafluoride to escape, and absorption treatment is performed for preparing hydrofluoric acid or a fluoride salt; and the scheelite is transformed to phosphotungstic acid to enter into a solution, and filtrate after filtration is supplemented into the consumed sulfuric acid and the phosphoric acid after extraction of the tungsten and returned to the new-round mineral leaching. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of comprehensively recovering the fluorine and the tungsten from the minerals, reducing the requirements on the fluorite or the tungsten ore raw material, reducing the pressure on a mineral dressing link, improving the comprehensive recovery rate and simultaneously ensuring the decomposition rate of the fluorite and the scheelite, wherein the decomposition rate of the fluorite is above 98%, and WO3 contained in decomposition slag is reduced to below 0.5%; furthermore, a leaching agent can be recycled, so that leaching cost and wastewater emission are greatly reduced; and the method also has the advantages of simple leaching equipment, convenience in operation and easiness in realization of industrialization.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
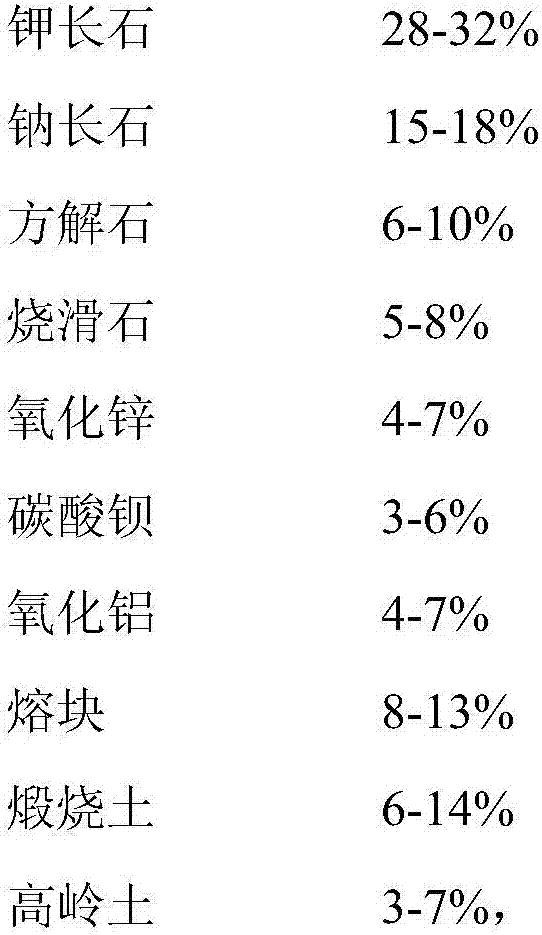
Fully glazed ceramic chip and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a fully glazed ceramic chip and a preparation method of the fully glazed ceramic chip. The fully glazed ceramic chip comprises a green body layer, a ground coat layer, an overglazed layer and a fancy glaze layer. A fully glazed layer is arranged on the surface of the fancy glaze layer. The fully glazed layer comprises 64-71% of fully glazed smelted blocks, 0-7% of clinker, 25-32% of water, and 0.1-0.5% of auxiliary materials by weight percentage, wherein materials used by the fully glazed smelted blocks comprise potash feldspar, calcite, burned talc, zinc oxide, boronic acid, barium carbonate, aluminum oxide and quartz, and the clinker is qidao clay or kaolin. The fully glazed ceramic chip provided by the invention is used for ceramic chip decoration, and the glazing effect of the ceramic chip is good, the transparency of the enamel layer and the evenness are high, and the ceramic chip polished is bright so as to represent the clear texture level and rich texture of pictures under glazes, and the brick deformation is small, the thermal shock resistance is good, the mirror finish effect is good, and the transparent texture is excellent.
Owner:FOSHAN KEJIE GLAZE
Process for separating rare-earth element by extraction
InactiveCN101781706ALow impurity contentEliminate pollutionProcess efficiency improvementRare-earth elementCalcium bicarbonate
The invention mixes and pre-extracts the mixed solution of acidic organic extractants such as P507, P204, C272, and naphthenic acid with magnesium bicarbonate and / or calcium bicarbonate solution and rare-earth solution. The rare-earth ions are extracted into the organic phase, then the loaded organic phase containing rare-earth ions are obtained through clarification, and can be used for the extract separation of the mixed rare-earth feed liquid. After a plurality of different levels of extraction, washing, stripping, single rare-earth compounds or rare-earth elements-containing enrichments can be obtained. The magnesium bicarbonate and / or calcium bicarbonate solution are prepared by roasting, digesting, carbonizing magnesite, limestone, calcite, dolomite and similar minerals, so that the content of impurities, such as silicon, iron, aluminum is lower. Ternary phase sediment is not produced in the pre-extraction and extraction separation process, so that the purity of the rare-earth products are not affected. The organic phase does not need ammonia saponification and does not produce ammonia-nitrogen wastewater. By adopting the invention, the production cost of rare-earth products is greatly lowered and the cost for three waste disposal is also greatly saved.
Owner:GRIREM ADVANCED MATERIALS CO LTD
Natural solid cleaning agent
InactiveCN101880608AEasy to cleanNo pollution in the processInorganic non-surface-active detergent compositionsDetergent powders/flakes/sheetsFiberCalcite
The invention discloses a natural solid cleaning agent for cleaning stains on hard surfaces of objects, which is prepared from the following raw material in percentage by weight: 6 to 50 percent of kaolin, 4 to 36 percent of zeolite, 7 to 45 percent of calcite powder, 3 to 40 percent of pumice powder, 4 to 55 percent of feldspar powder, 2 to 17 percent of kieselguhr, 3 to 22 percent of montmorillonite powder, 4 to 40 percent of talcpowder, 1 to 15 percent of saponin, 3 to 18 percent of white carbon black and 0 to 40 percent of water. The natural solid cleaning agent has desirable cleaning effect on various stains, such as oil stains, sweat stains, tea stains, juice stains, milk stains, blood stains, ink stains, ash stains and dust stains on hard surfaces of metal, ceramic, wood, glass, fiber plates and stone plates. The raw materials are natural powder and plant extracts. The cleaning agent has high biodegradability and is safe, environmentally-friendly, pollution-free and convenient to use.
Owner:深圳市成为生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com