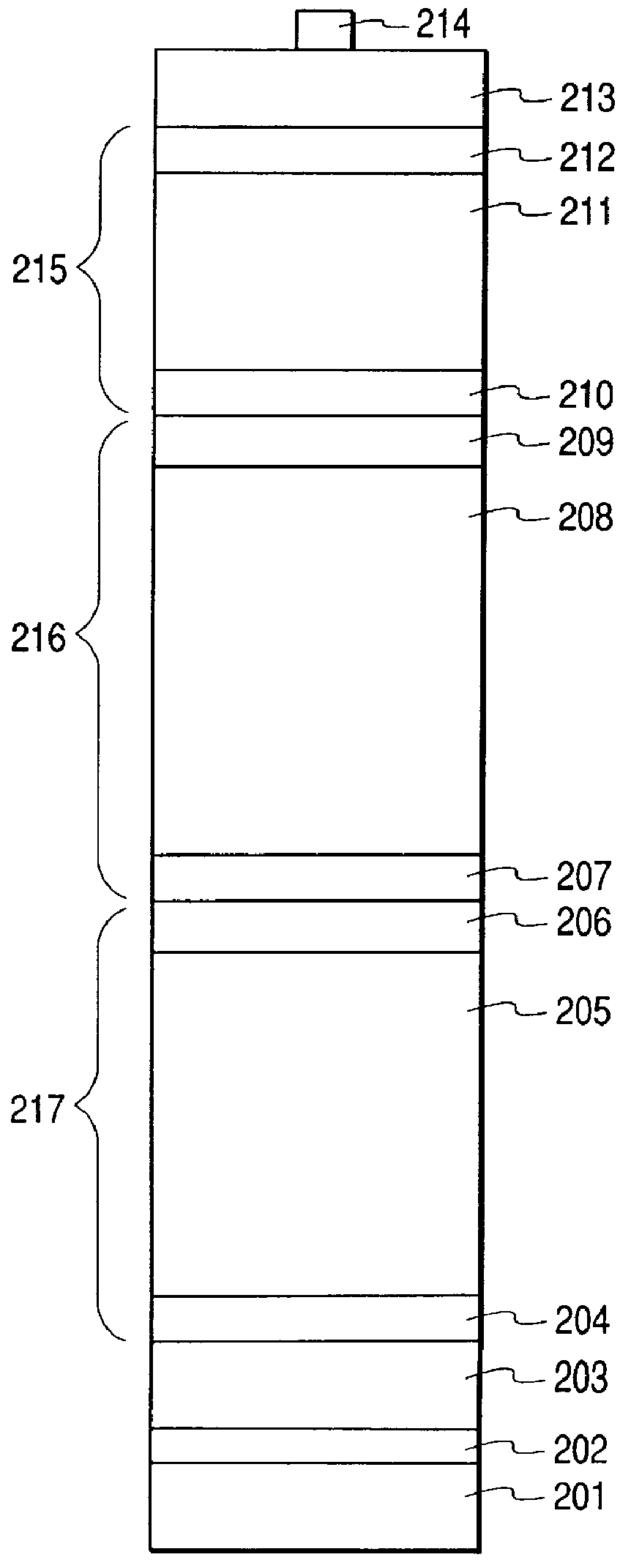
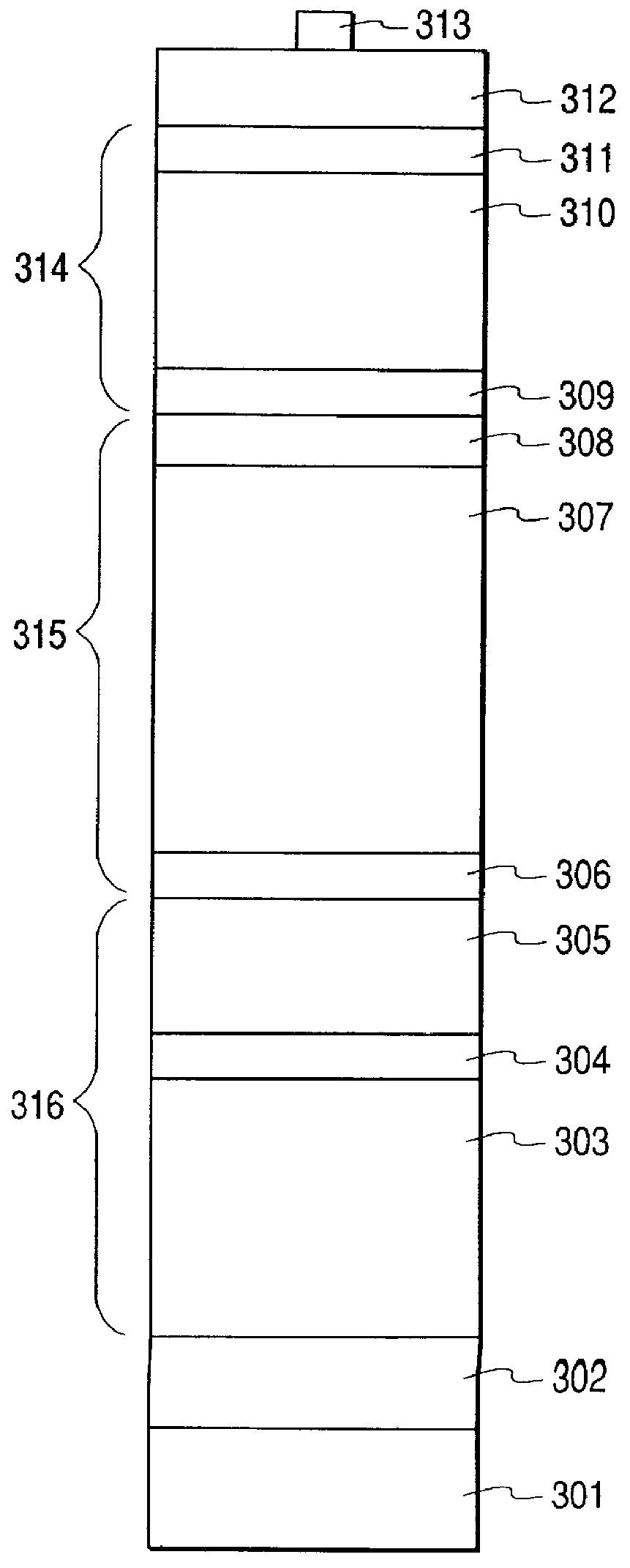
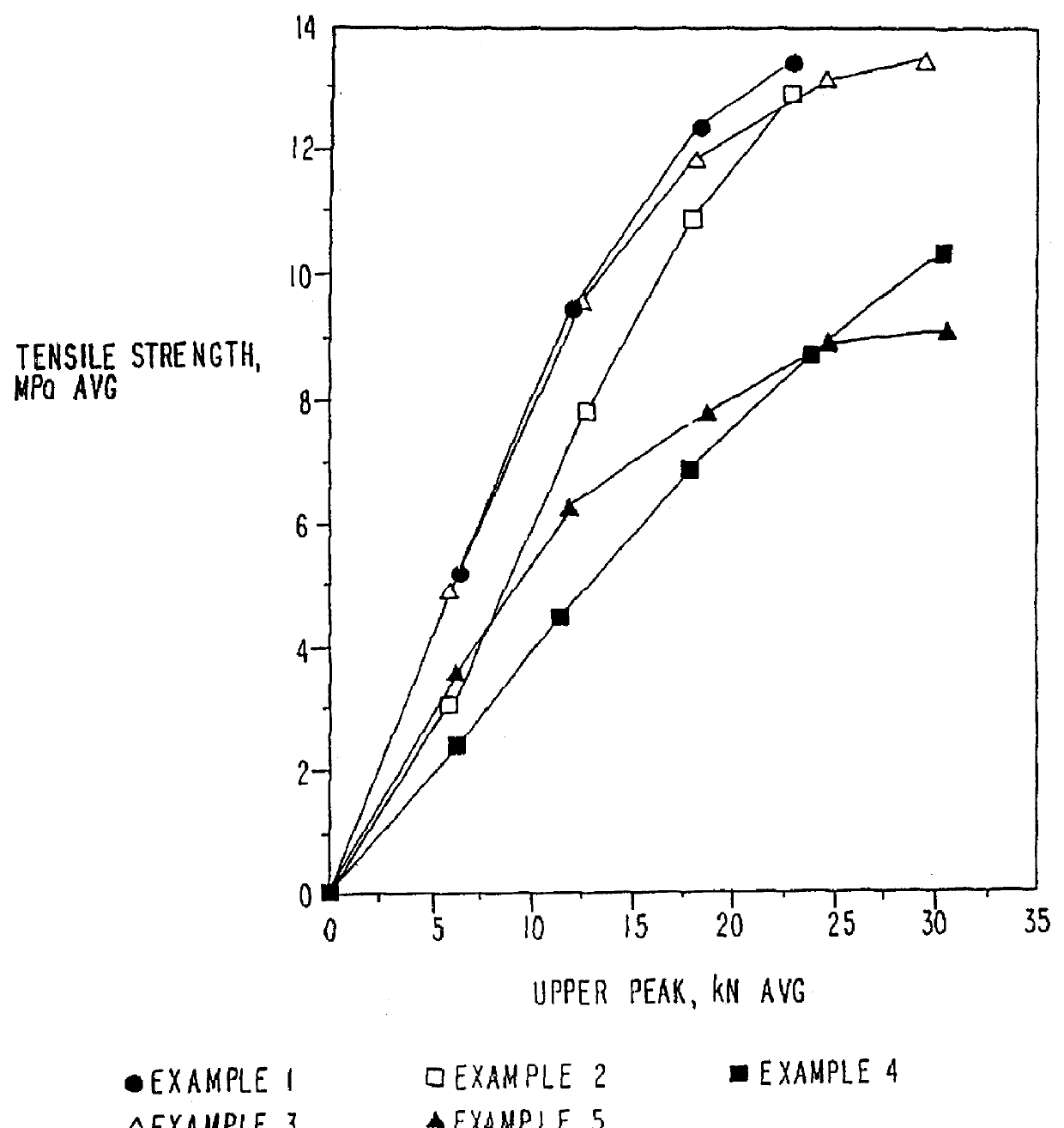
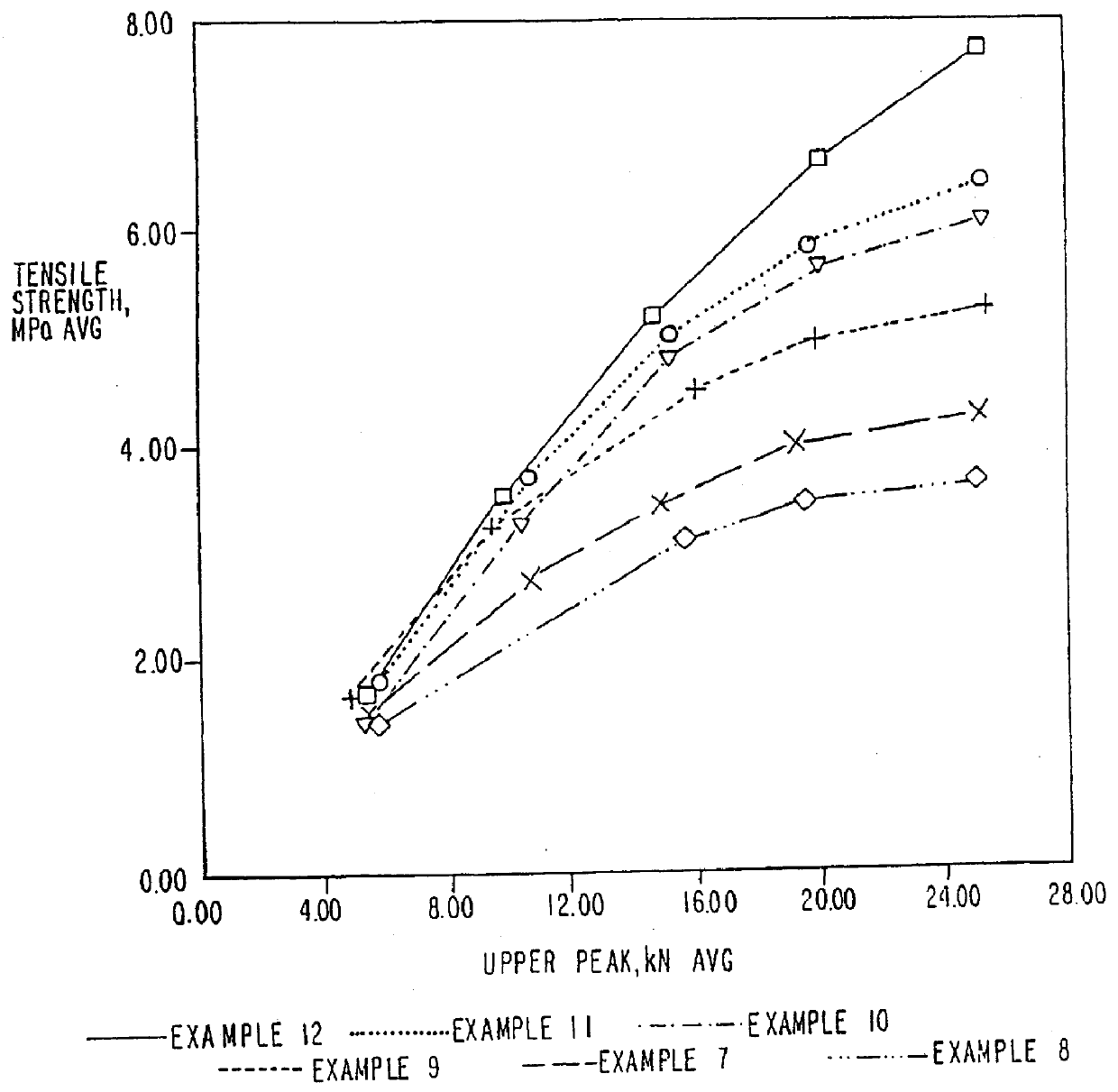
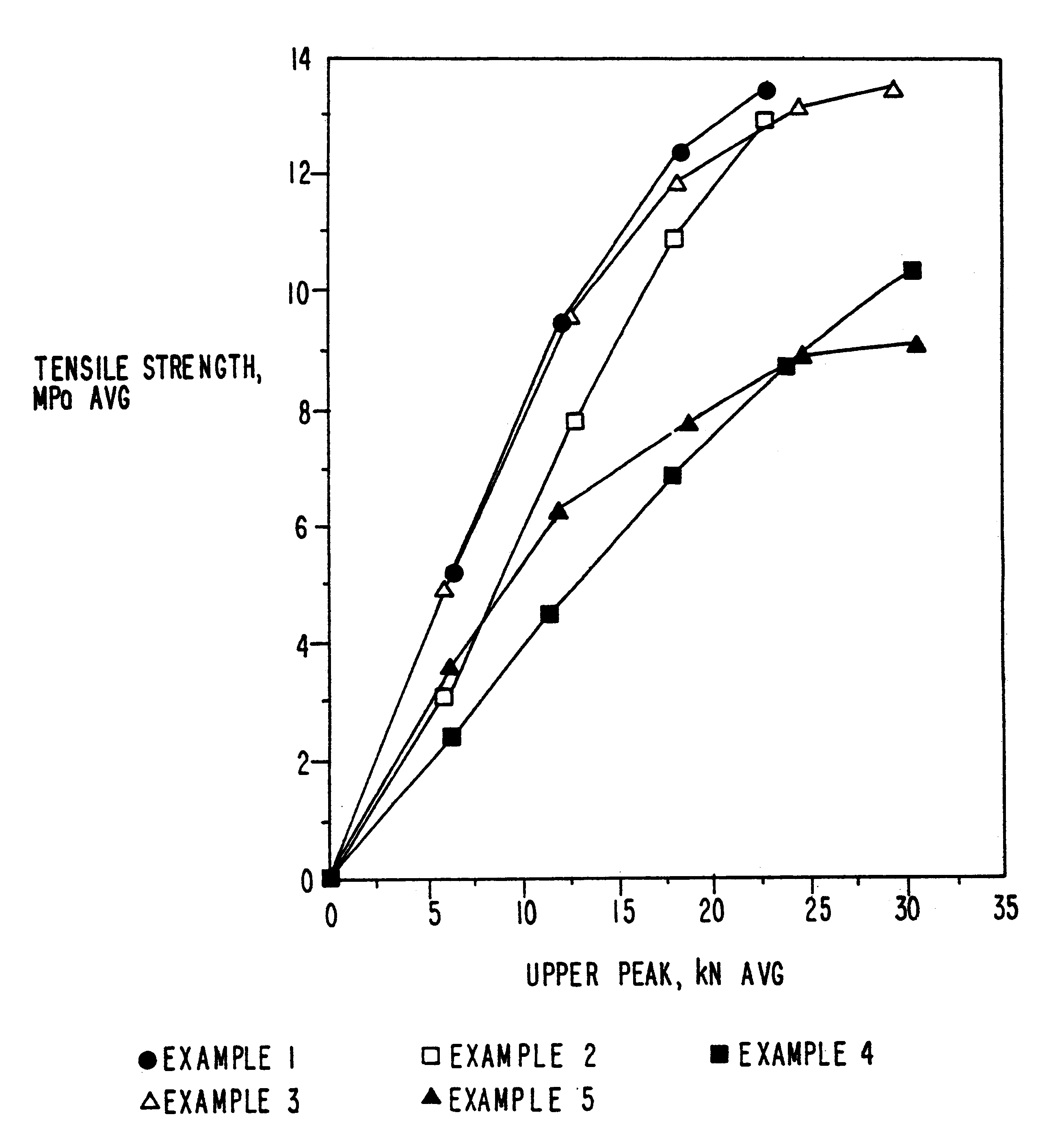
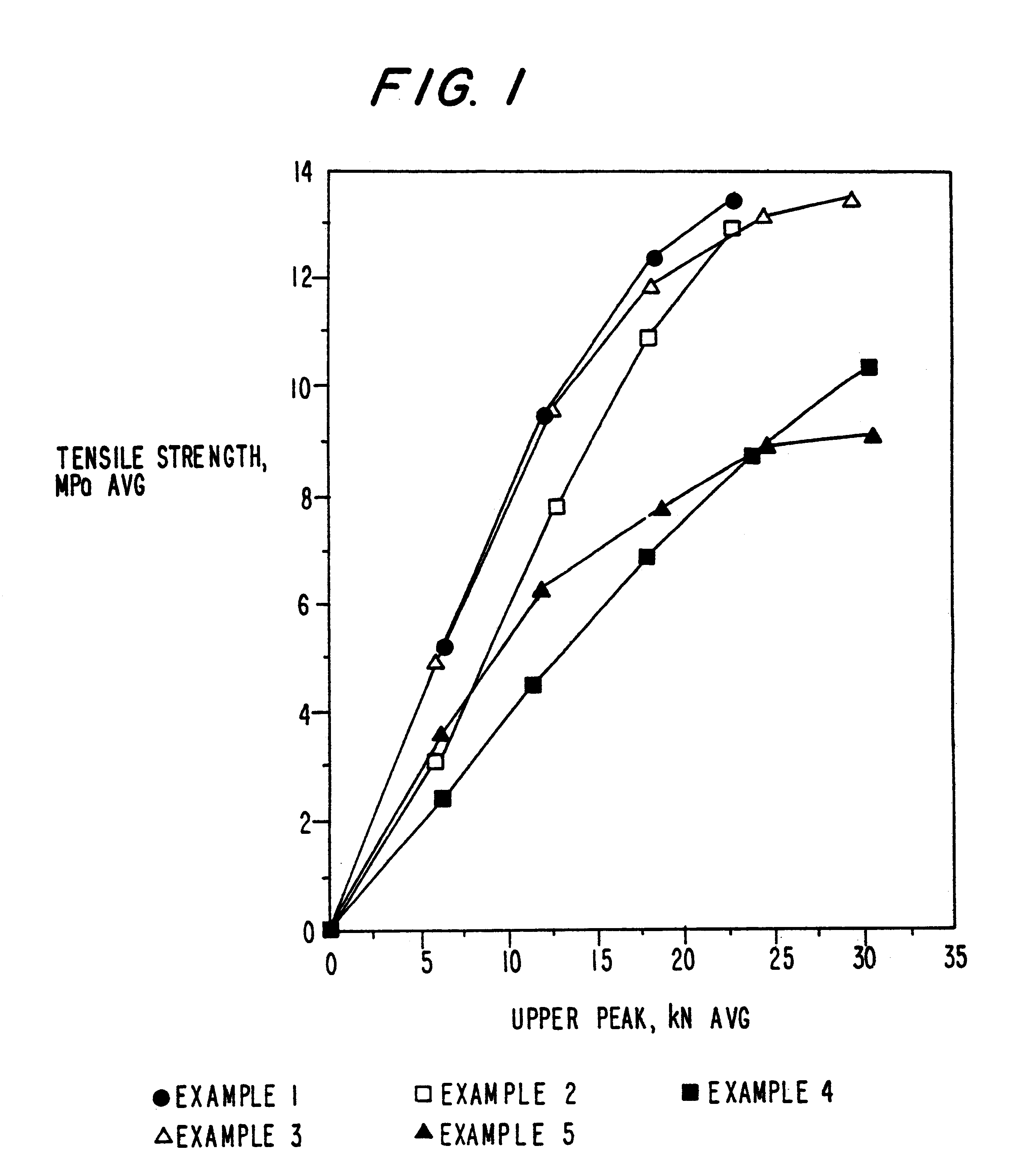
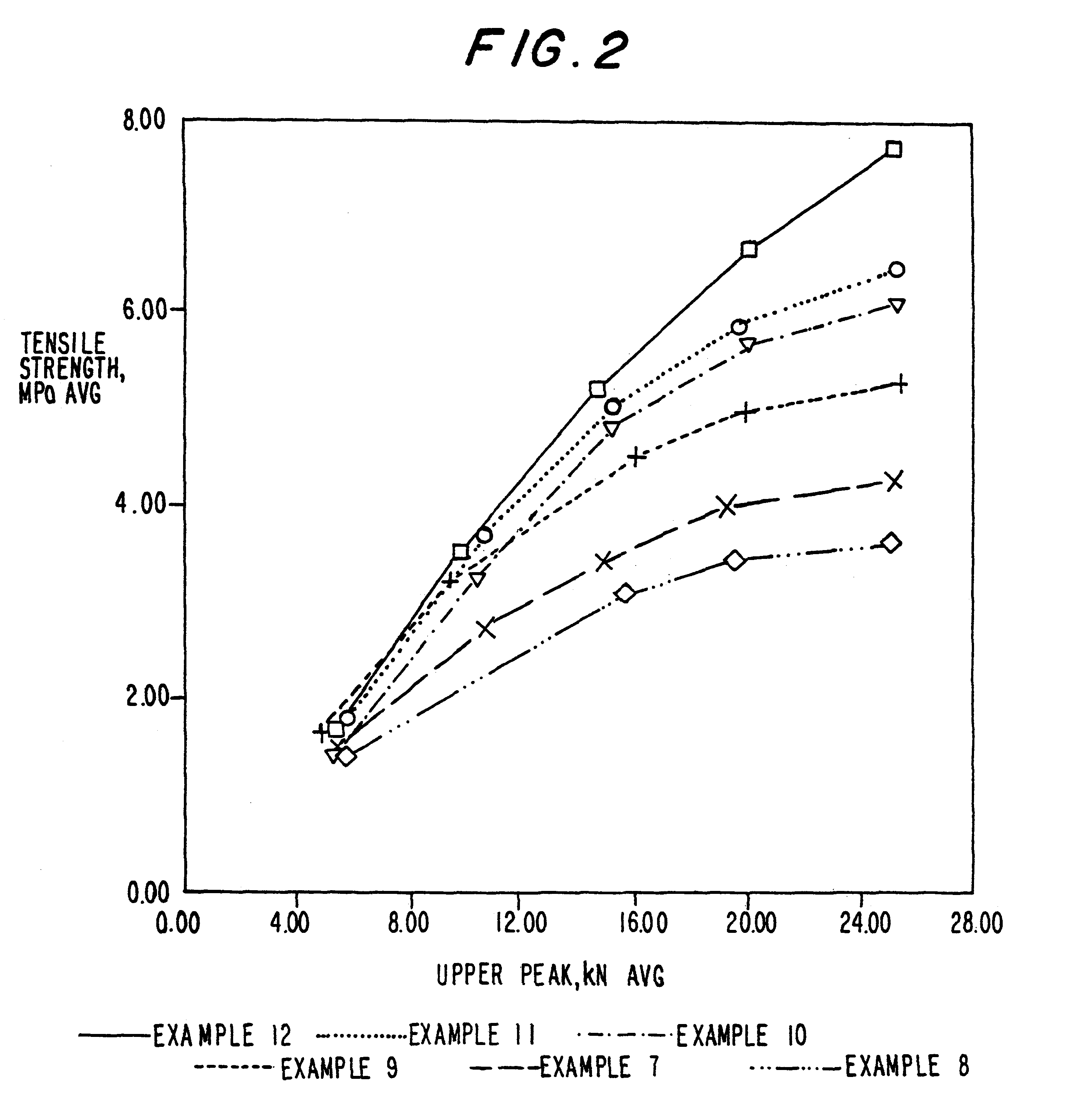
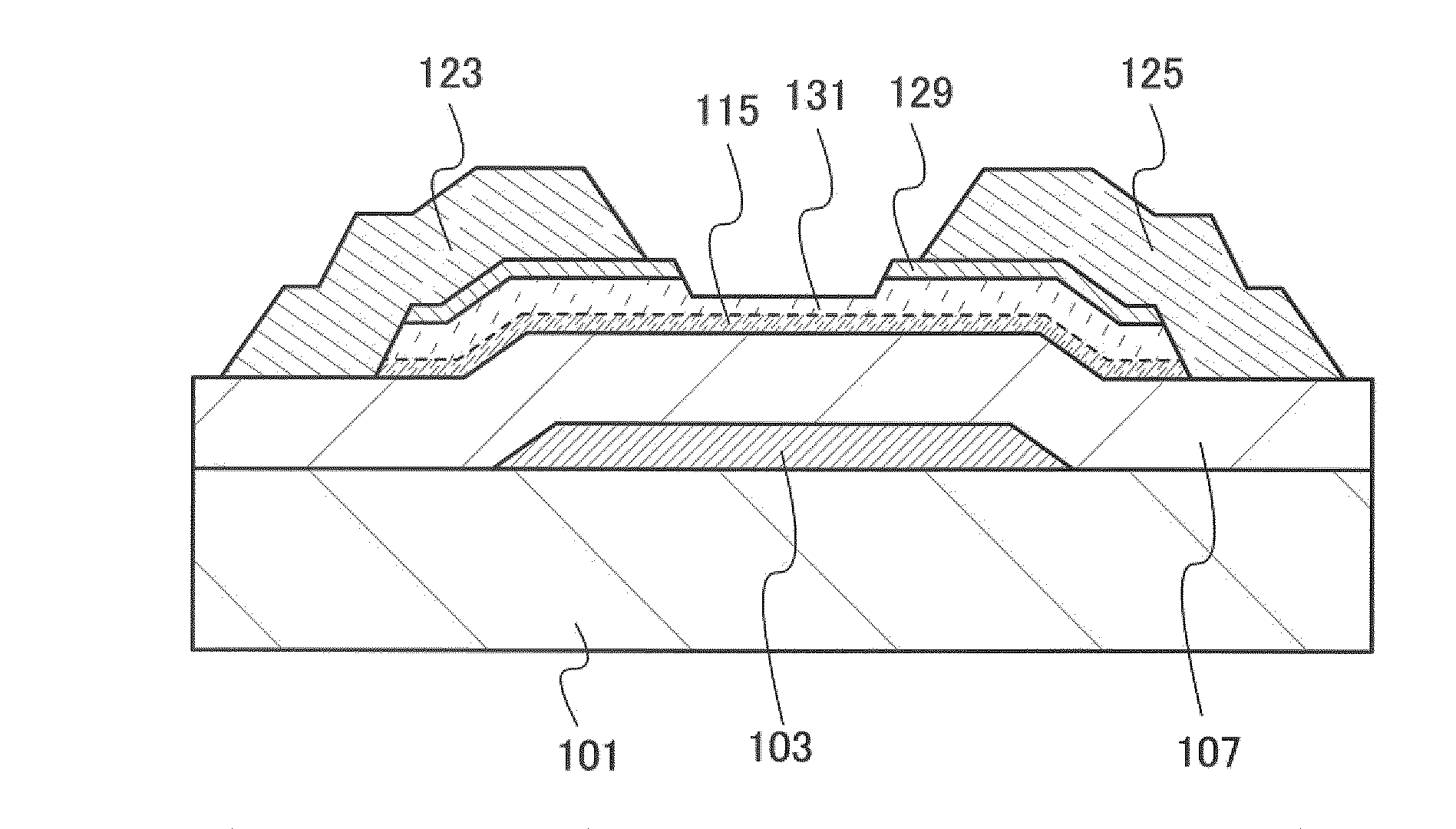
Patents
Literature
4347 results about "Microcrystalline" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A microcrystalline material is a crystallized substance or rock that contains small crystals visible only through microscopic examination.
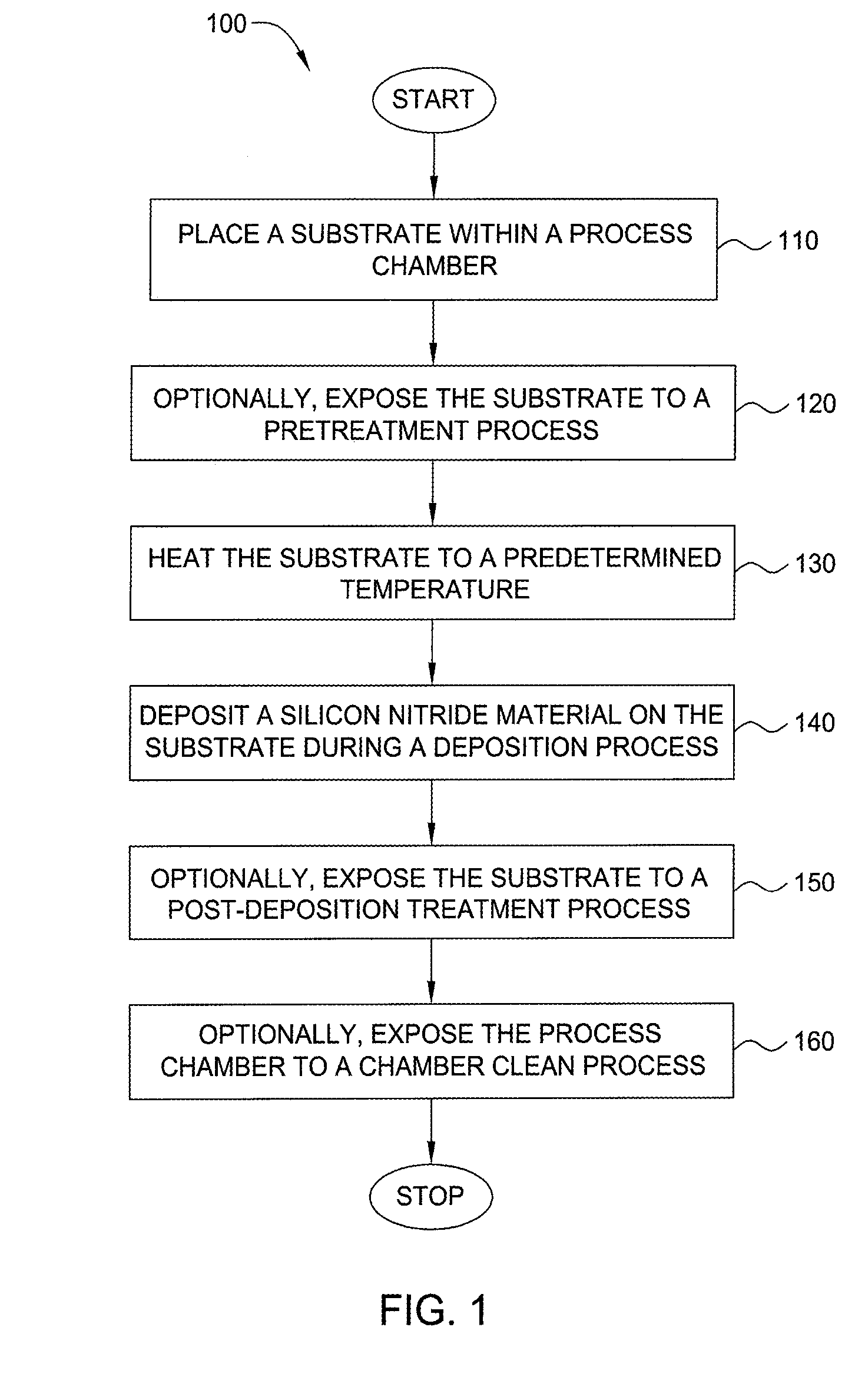
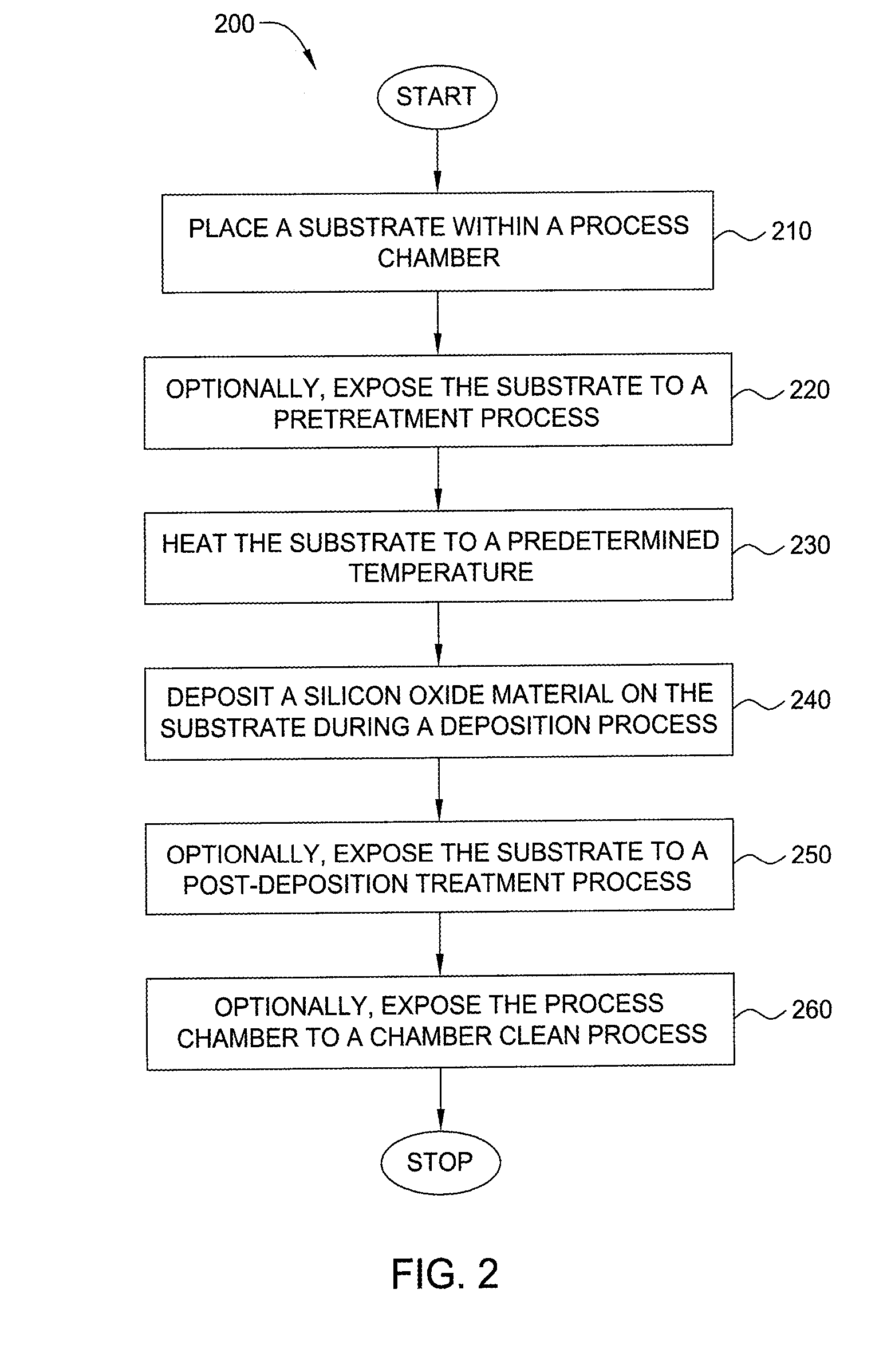
Method for forming silicon-containing materials during a photoexcitation deposition process
InactiveUS20060286774A1Enhance chamber cleaning processHigh surface energyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVolatilesSilicon oxide
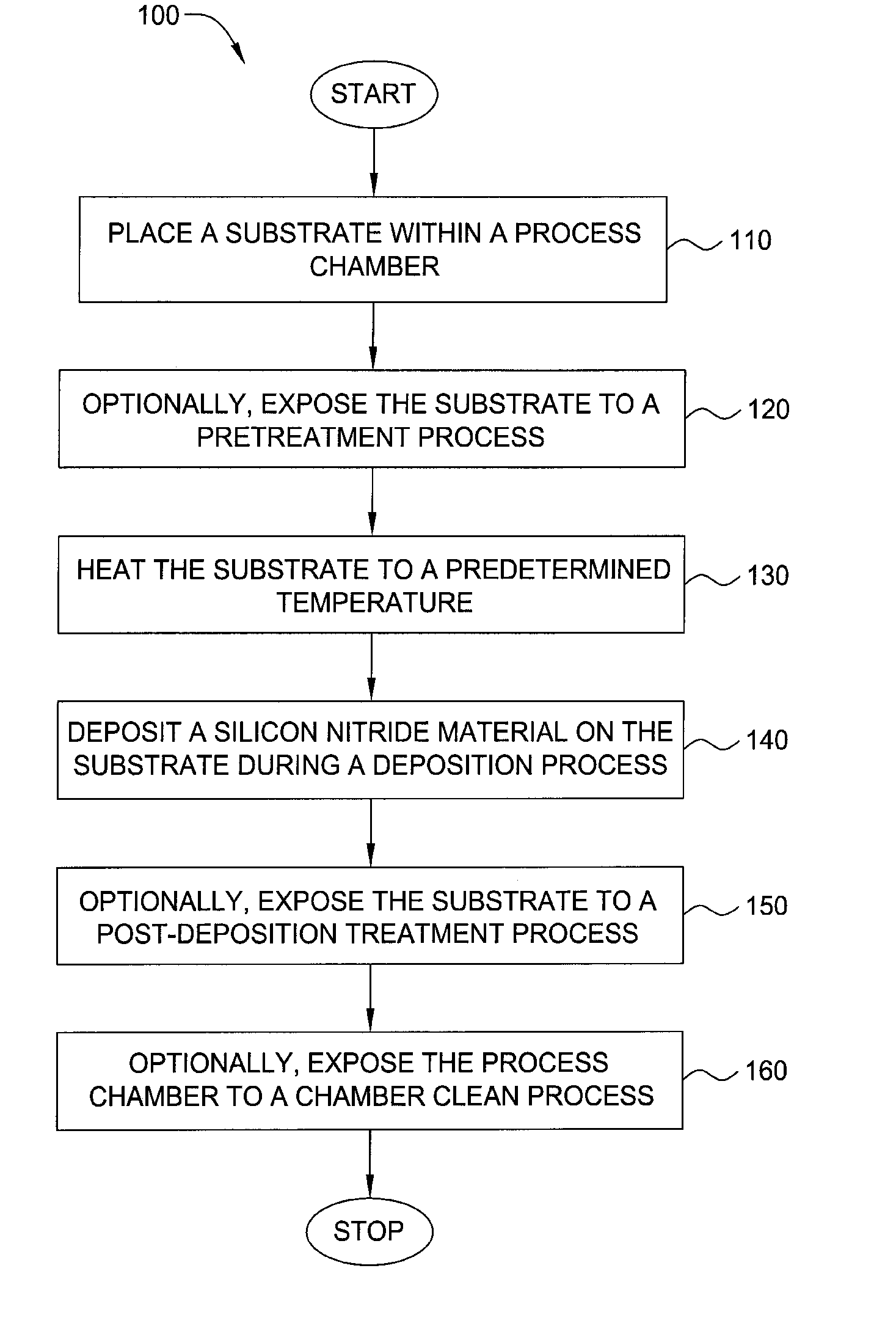
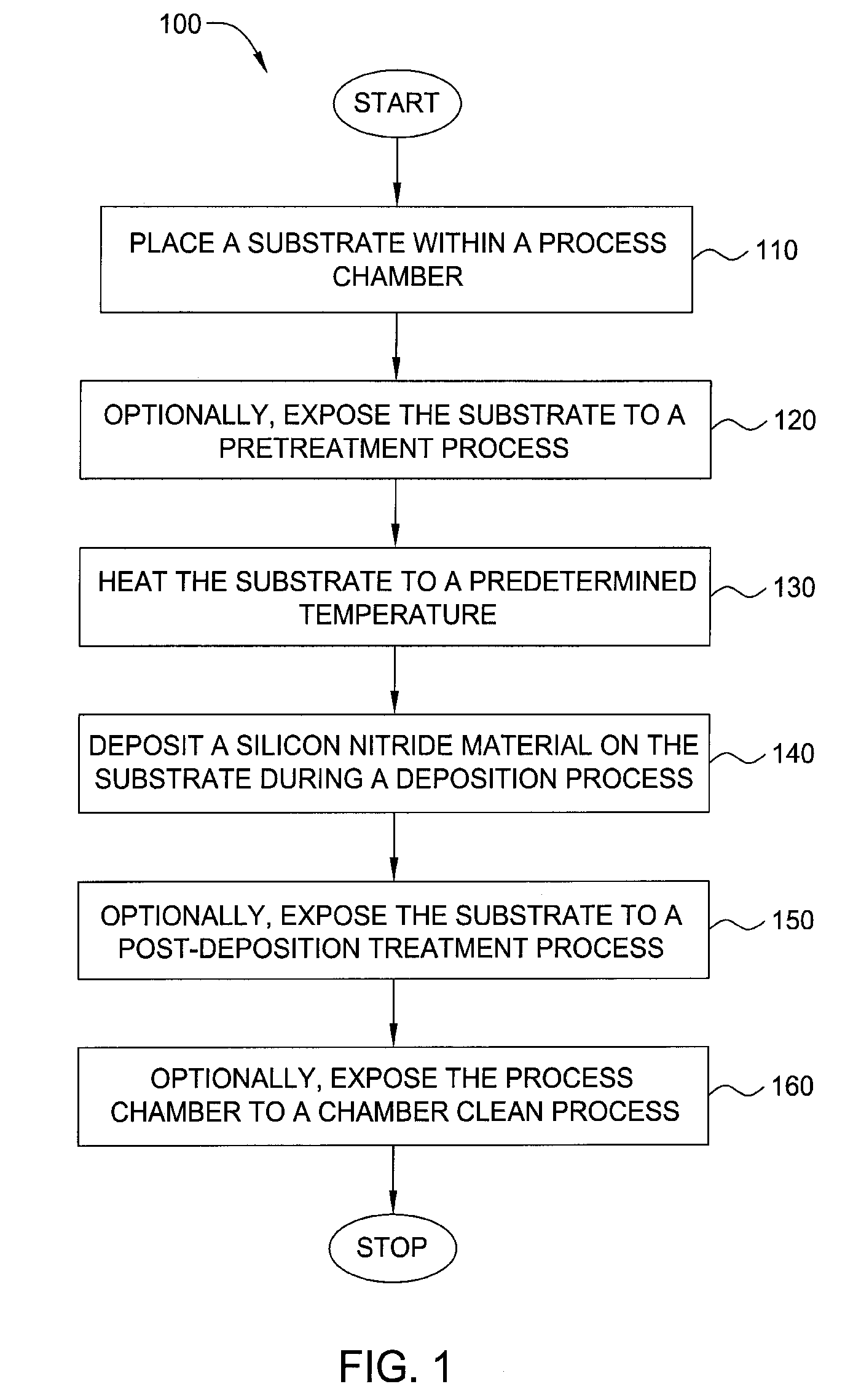
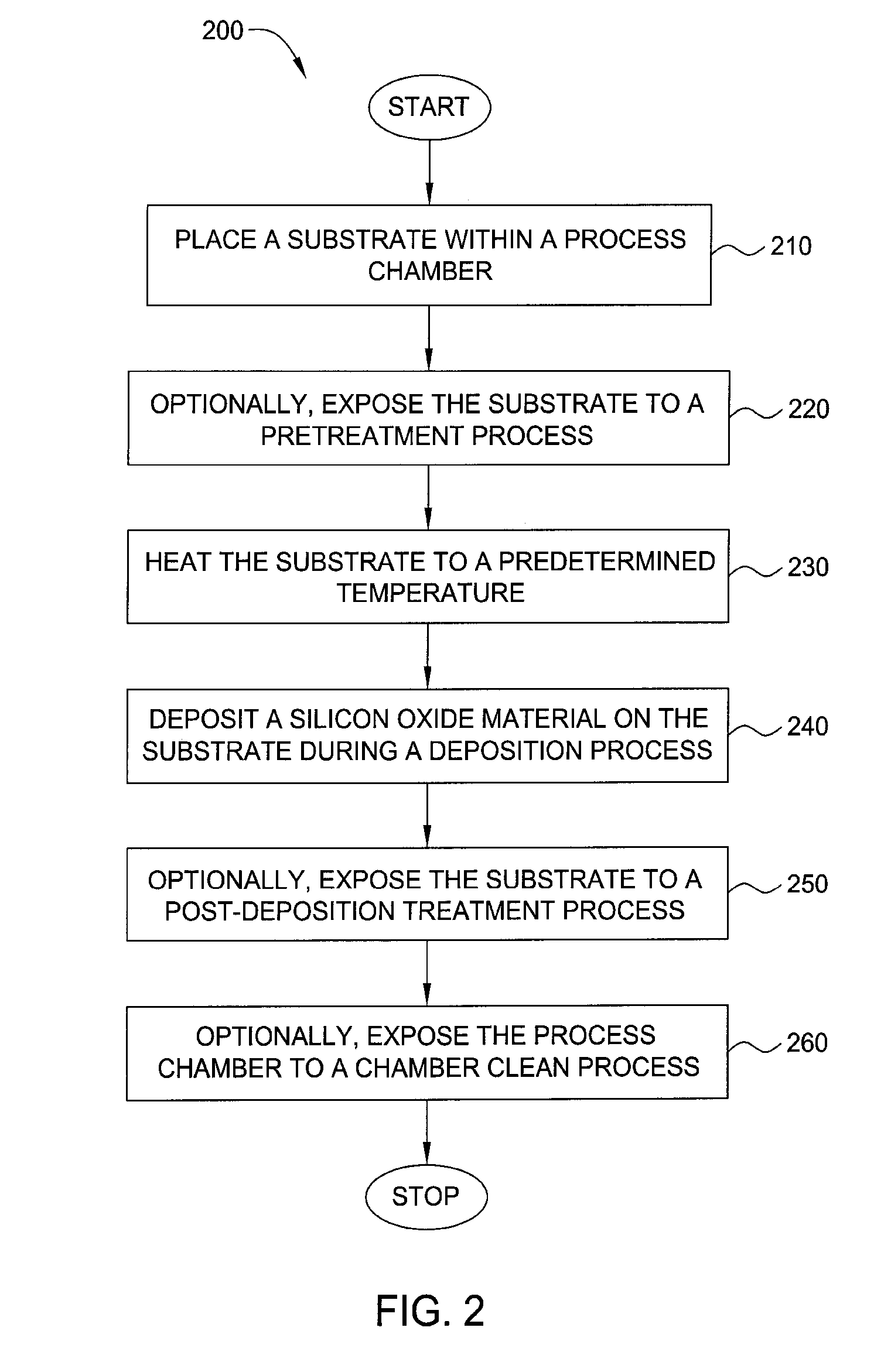
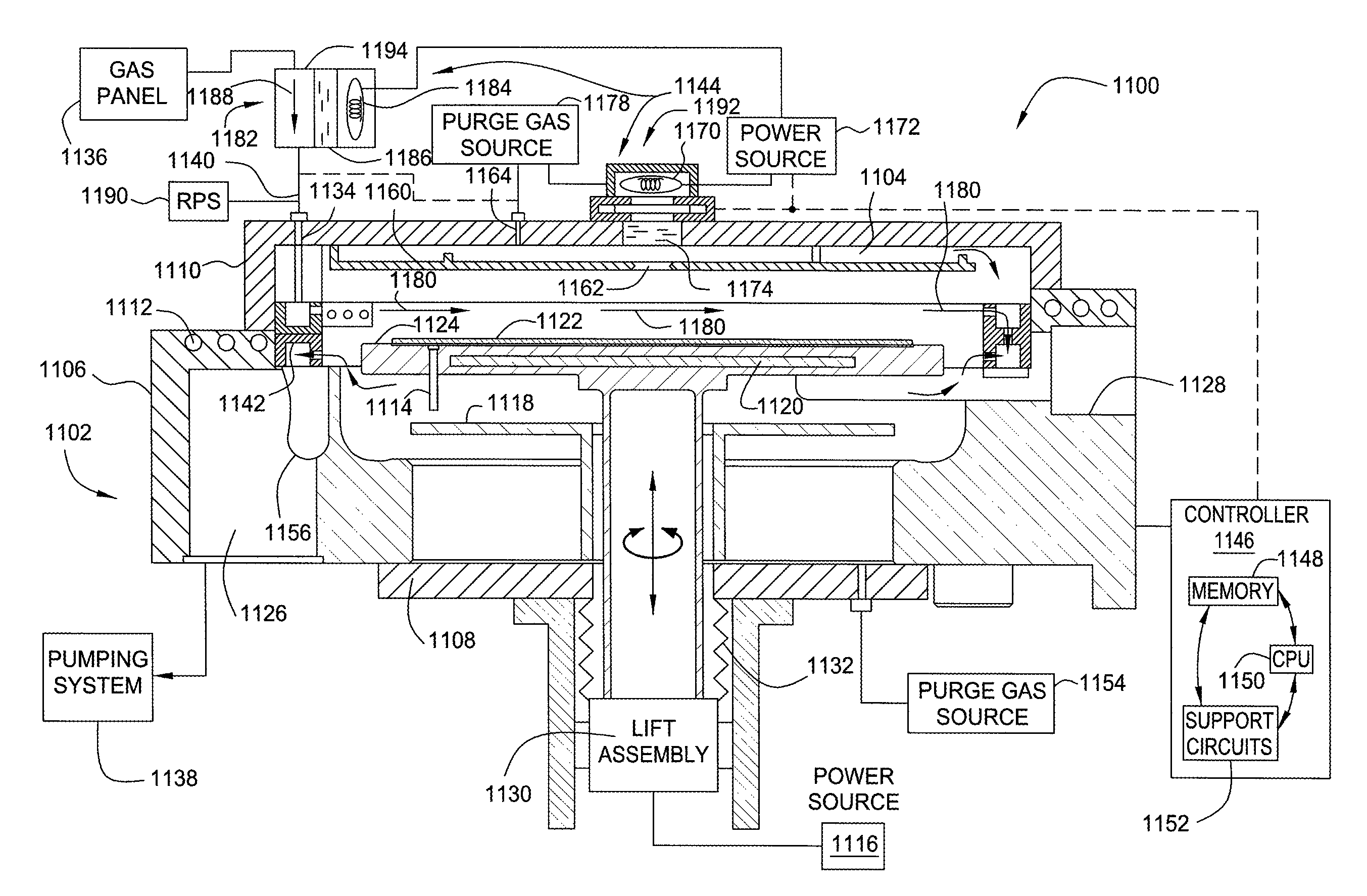
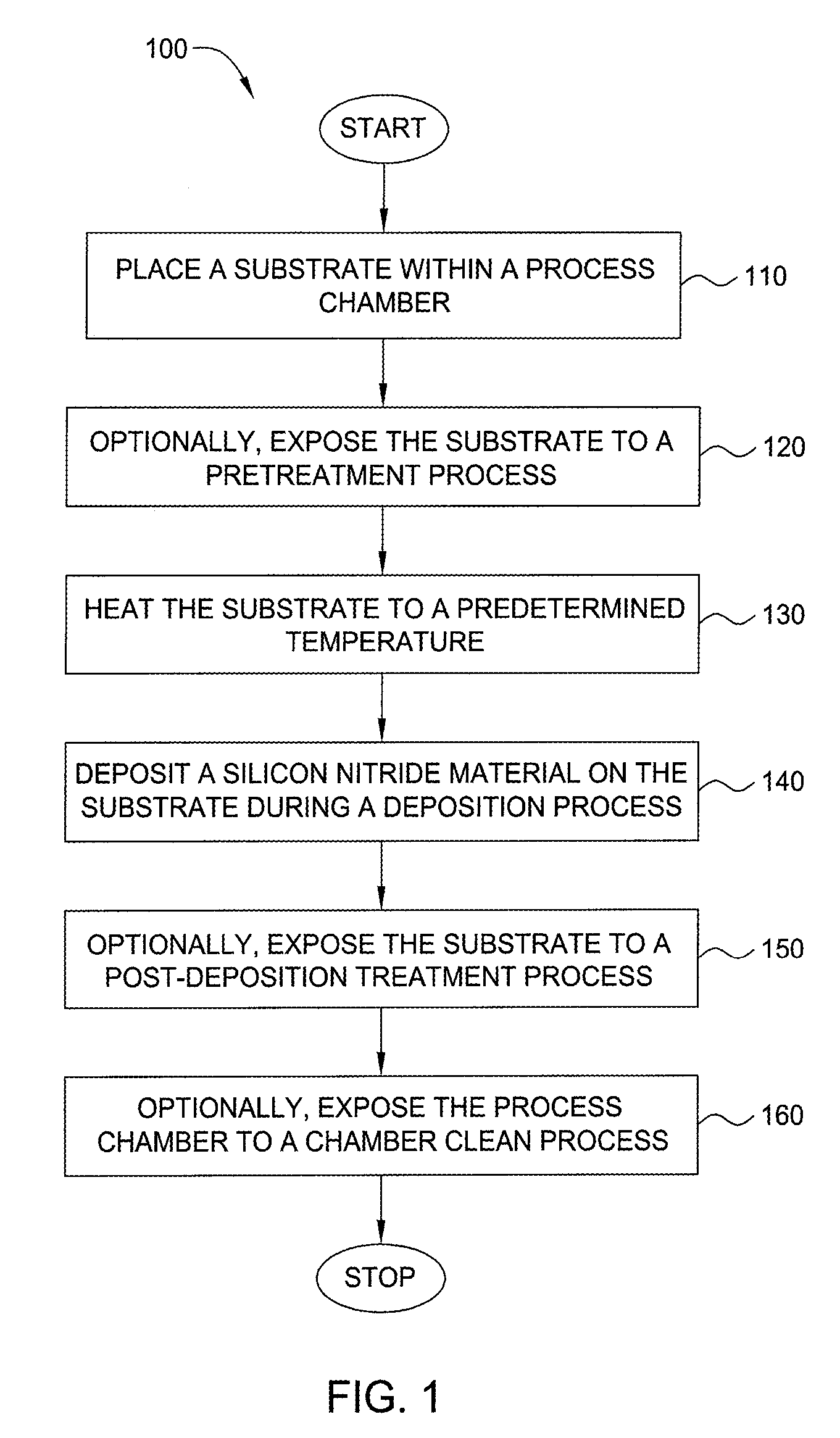
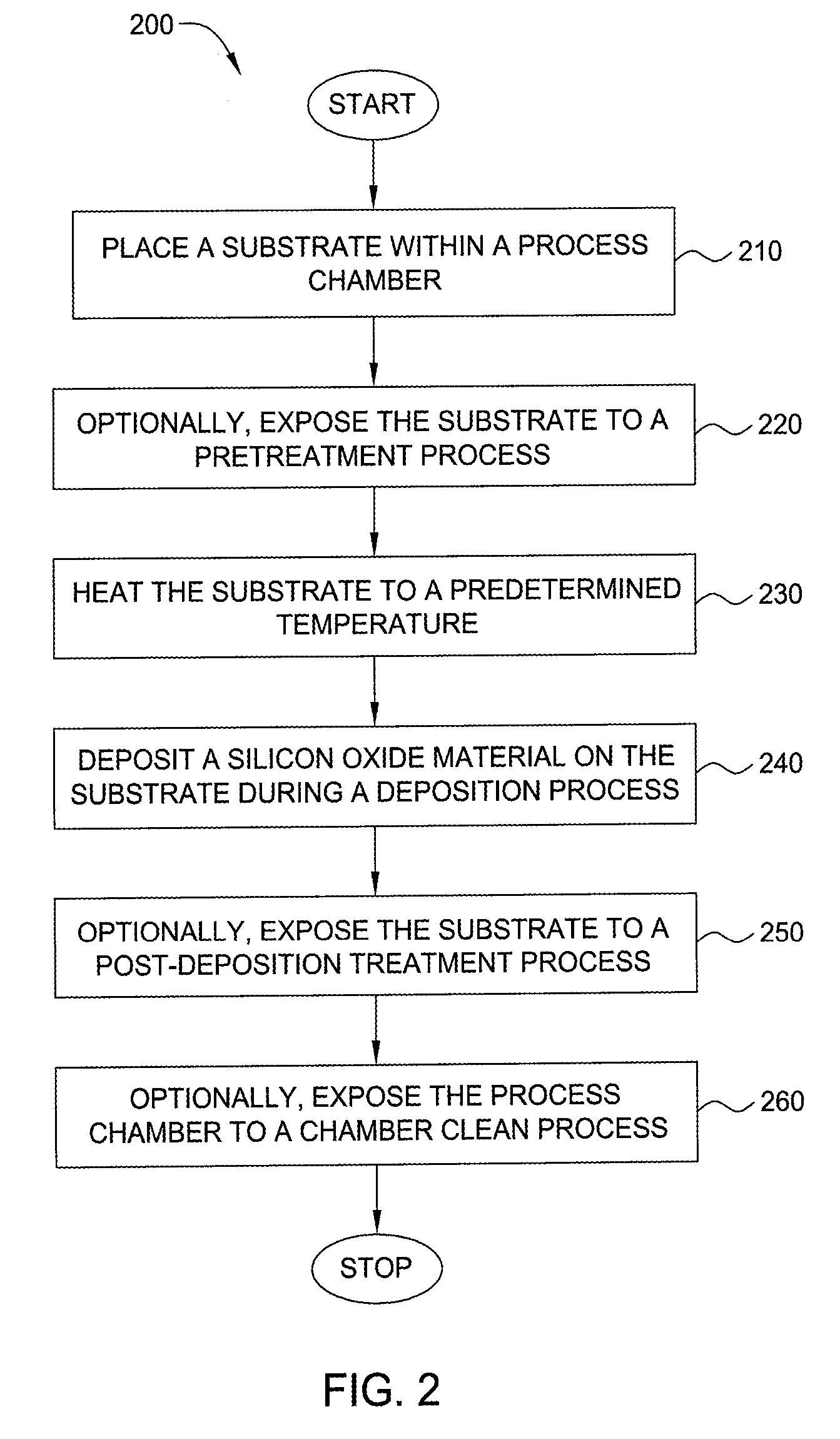
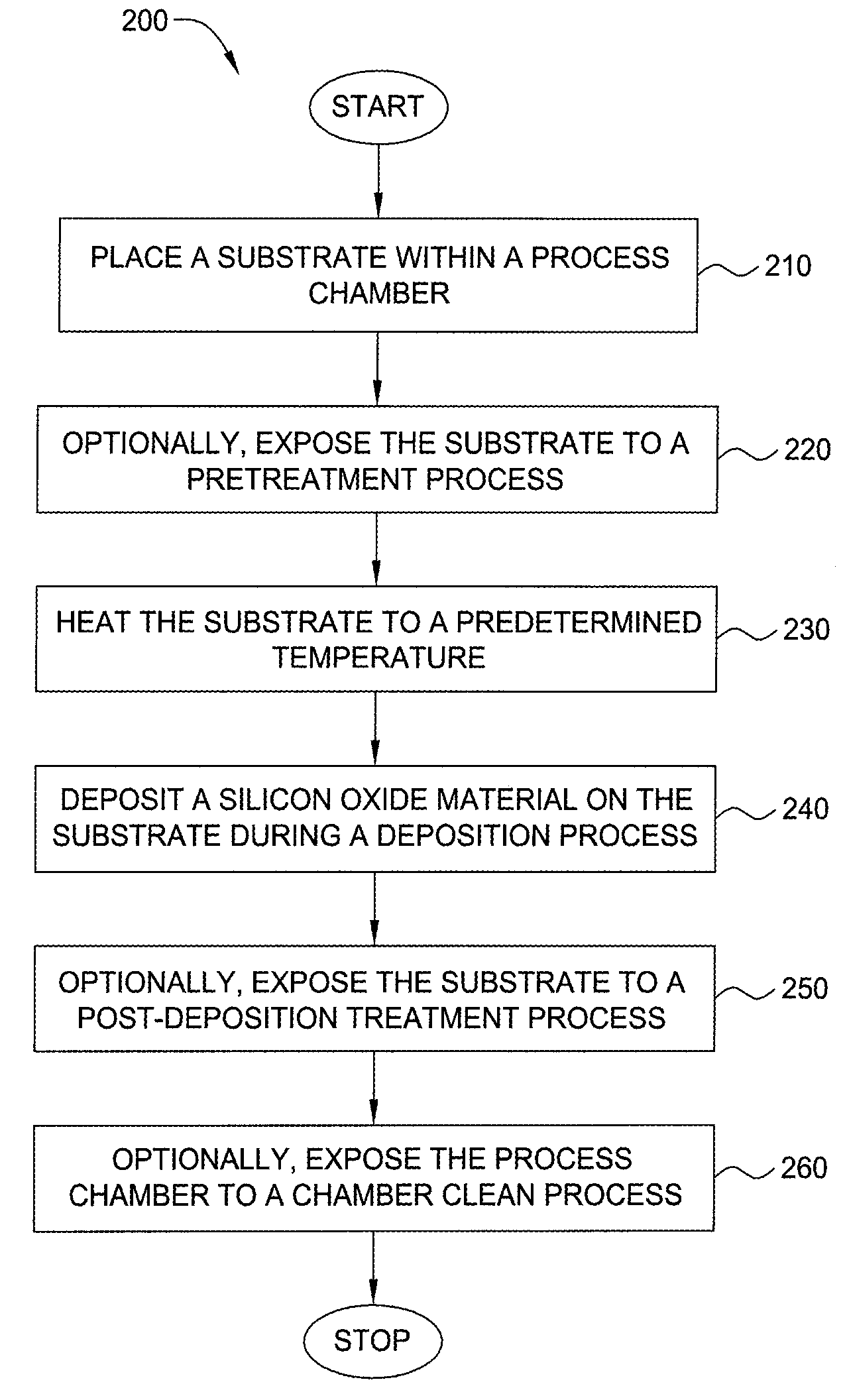
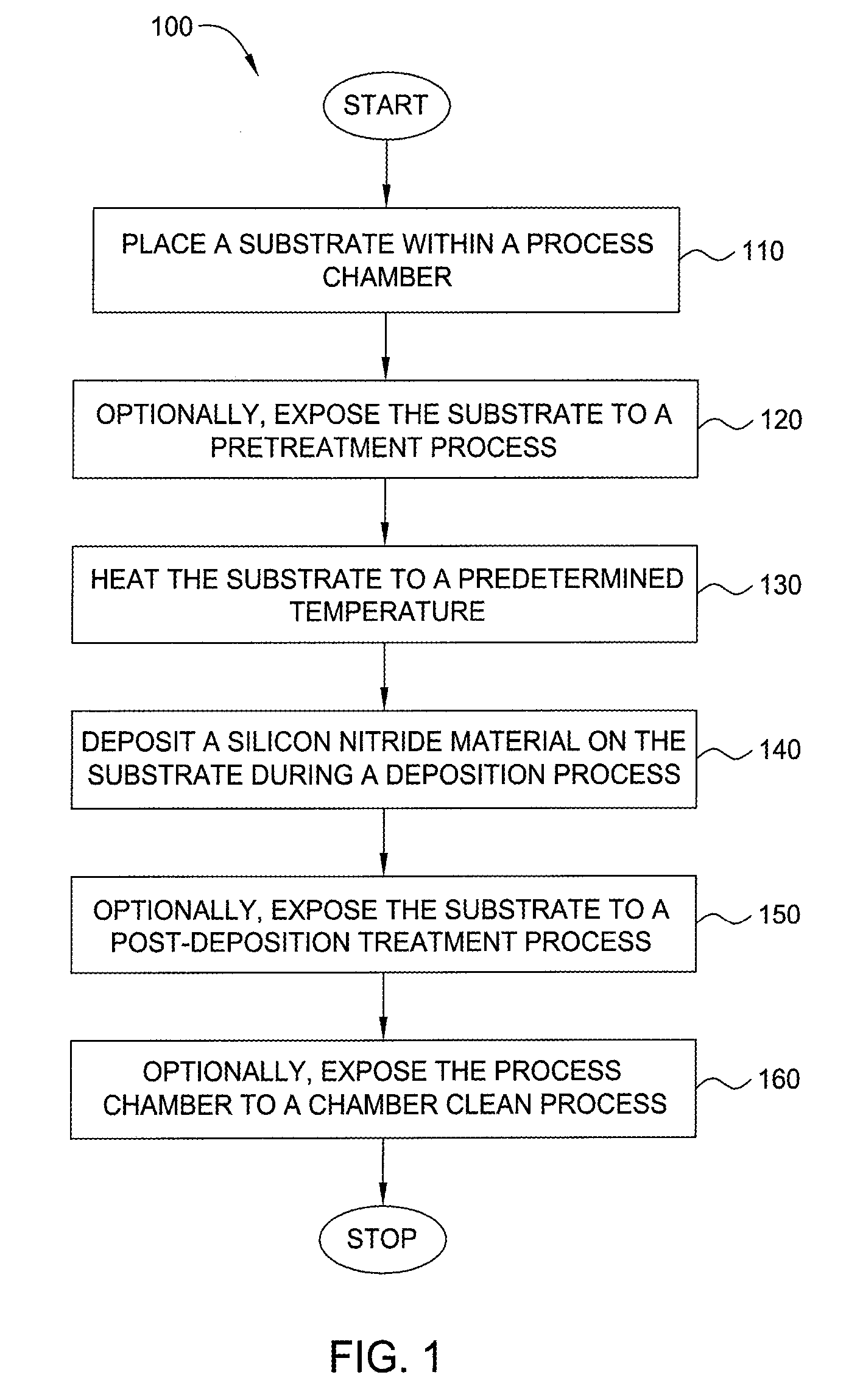
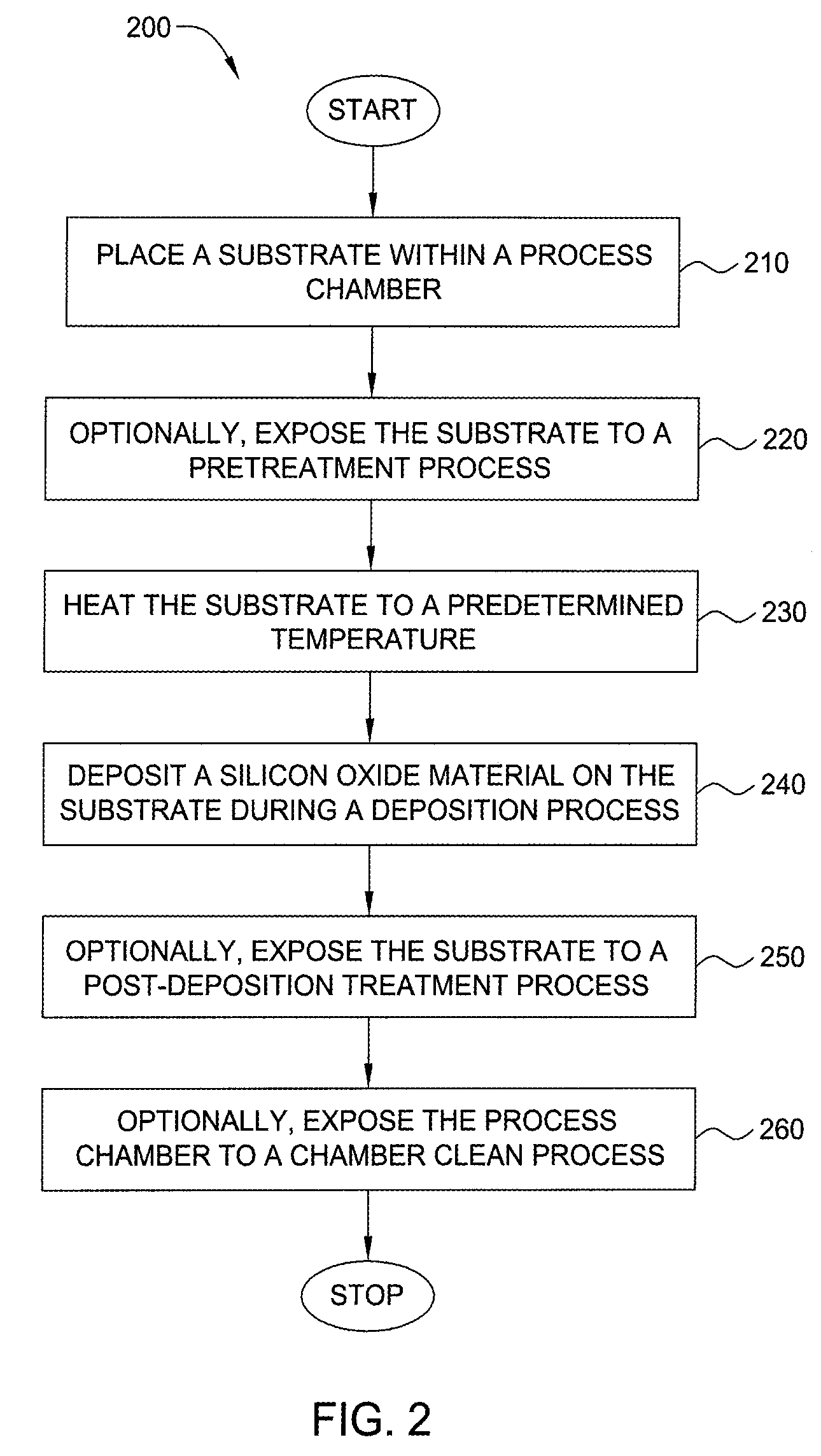
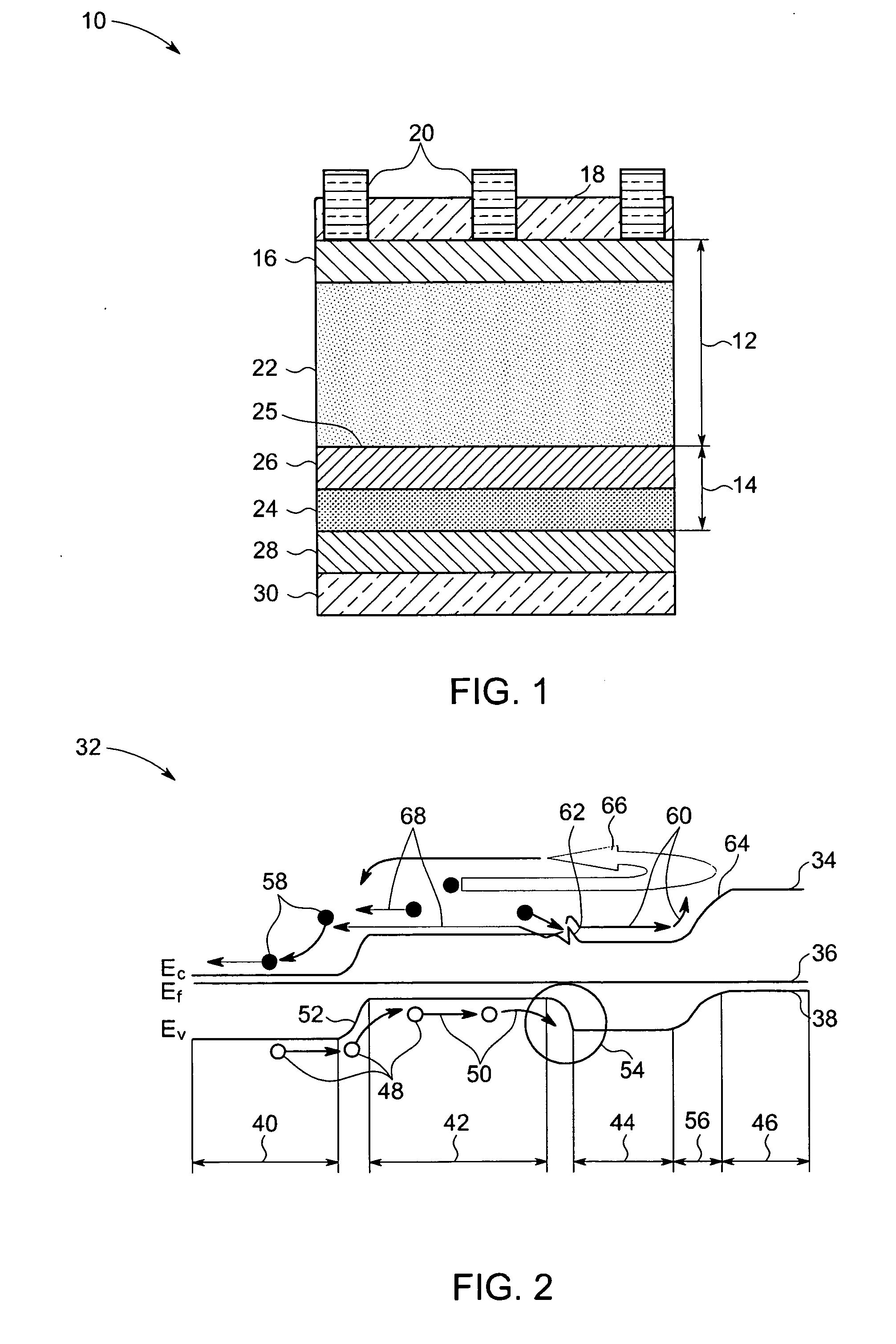
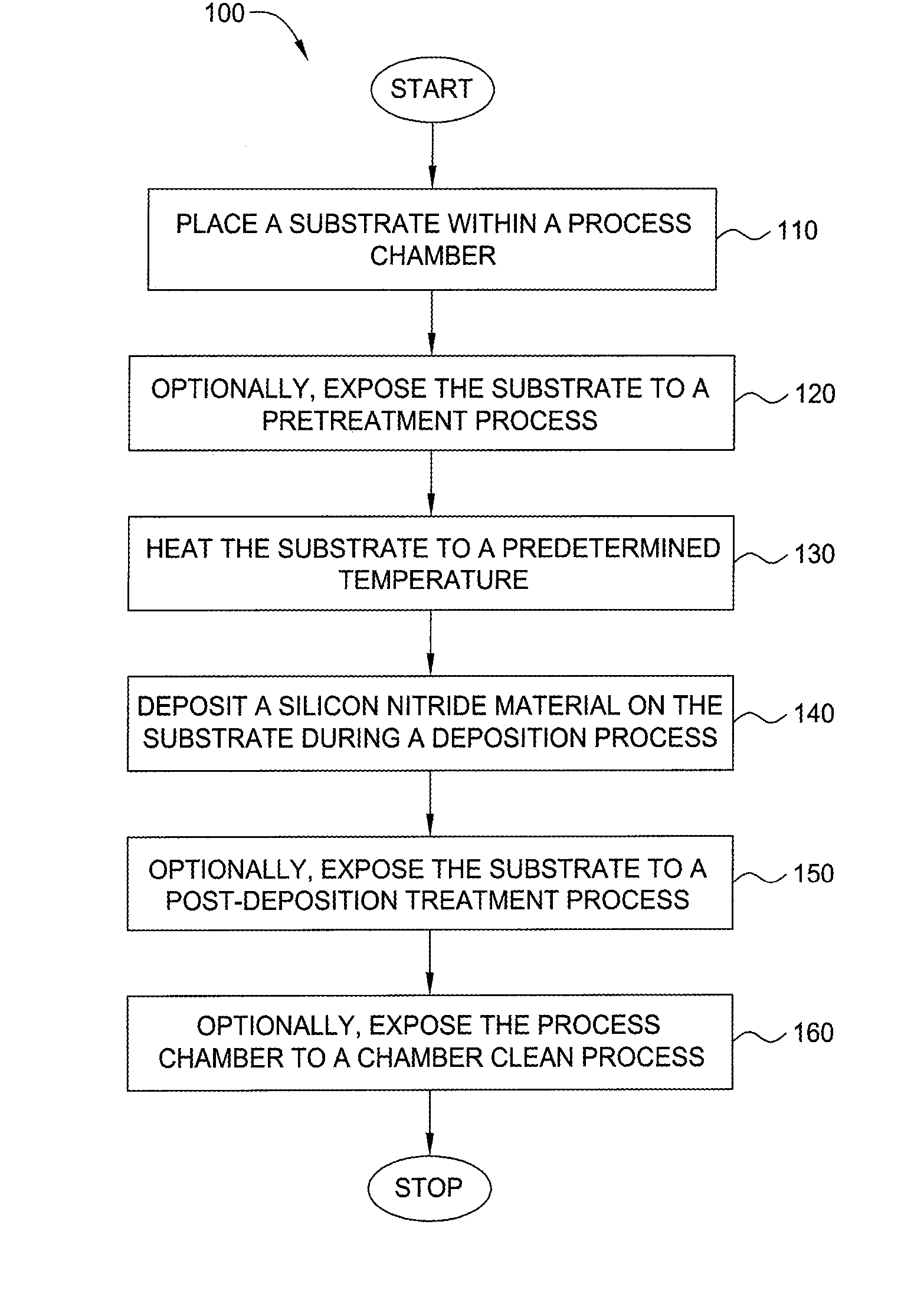
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films or layers using a UV source during a photoexcitation process. The films are deposited on a substrate and usually contain a material, such as silicon (e.g., epitaxy, crystalline, microcrystalline, polysilicon, or amorphous), silicon oxide, silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, or other silicon-containing materials. The photoexcitation process may expose the substrate and / or gases to an energy beam or flux prior to, during, or subsequent a deposition process. Therefore, the photoexcitation process may be used to pre-treat or post-treat the substrate or material, to deposit the silicon-containing material, and to enhance chamber cleaning processes. Attributes of the method that are enhanced by the UV photoexcitation process include removing native oxides prior to deposition, removing volatiles from deposited films, increasing surface energy of the deposited films, increasing the excitation energy of precursors, reducing deposition time, and reducing deposition temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for forming silicon-containing materials during a photoexcitation deposition process
InactiveUS7651955B2Easy to cleanHigh surface energyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAutoxidationDeposition temperature
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films or layers using a UV source during a photoexcitation process. The films are deposited on a substrate and usually contain a material, such as silicon (e.g., epitaxy, crystalline, microcrystalline, polysilicon, or amorphous), silicon oxide, silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, or other silicon-containing materials. The photoexcitation process may expose the substrate and / or gases to an energy beam or flux prior to, during, or subsequent a deposition process. Therefore, the photoexcitation process may be used to pre-treat or post-treat the substrate or material, to deposit the silicon-containing material, and to enhance chamber cleaning processes. Attributes of the method that are enhanced by the UV photoexcitation process include removing native oxides prior to deposition, removing volatiles from deposited films, increasing surface energy of the deposited films, increasing the excitation energy of precursors, reducing deposition time, and reducing deposition temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for forming silicon-containing materials during a photoexcitation deposition process
InactiveUS7648927B2Easy to cleanHigh surface energyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAutoxidationDeposition temperature
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films or layers using a UV source during a photoexcitation process. The films are deposited on a substrate and usually contain a material, such as silicon (e.g., epitaxy, crystalline, microcrystalline, polysilicon, or amorphous), silicon oxide, silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, or other silicon-containing materials. The photoexcitation process may expose the substrate and / or gases to an energy beam or flux prior to, during, or subsequent a deposition process. Therefore, the photoexcitation process may be used to pre-treat or post-treat the substrate or material, to deposit the silicon-containing material, and to enhance chamber cleaning processes. Attributes of the method that are enhanced by the UV photoexcitation process include removing native oxides prior to deposition, removing volatiles from deposited films, increasing surface energy of the deposited films, increasing the excitation energy of precursors, reducing deposition time, and reducing deposition temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method for manufacturing photoelectric conversion device
InactiveUS20090029503A1Quality improvementReduce deterioration rateFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProduction rateMicrowave
To form a microcrystalline semiconductor with high quality which can be directly formed at equal to or less than 500° C. over a large substrate with high productivity without decreasing a deposition rate. In addition, to provide a photoelectric conversion device which employs the microcrystalline semiconductor as a photoelectric conversion layer. A reactive gas containing helium is supplied to a treatment chamber which is surrounded by a plurality of juxtaposed waveguides and a wall, the pressure in the treatment chamber is maintained at an atmospheric pressure or a subatmospheric pressure, microwave is supplied to a space sandwiched between the juxtaposed waveguides to generate plasma, and a photoelectric conversion layer of a microcrystalline semiconductor is deposited over a substrate which is placed in the treatment chamber.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
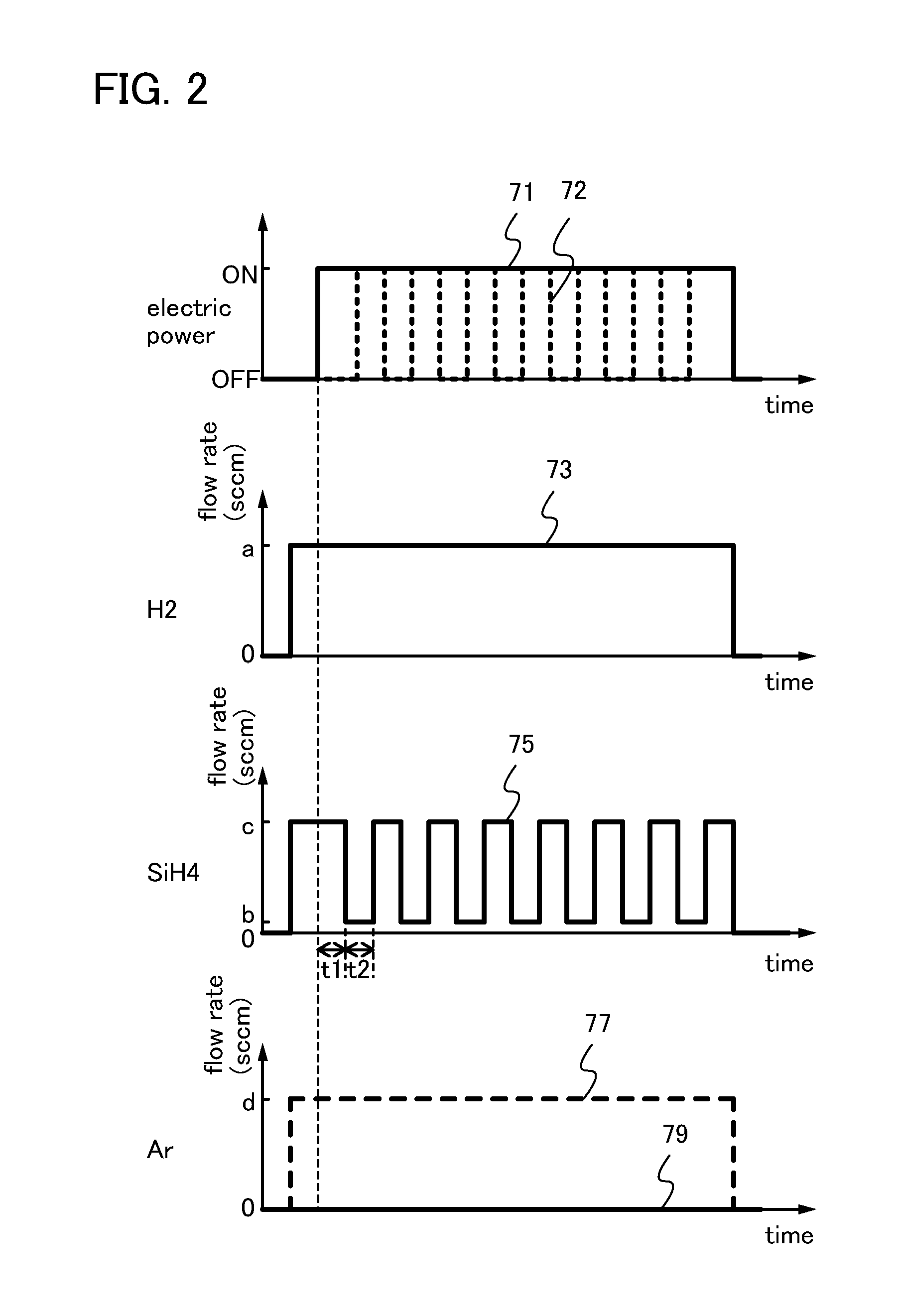
Method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20110318888A1High crystallinityExcellent electrical propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHydrogenEngineering
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device comprises the steps of forming a seed over the insulating film by introducing hydrogen and a deposition gas into a first treatment chamber under a first condition and forming a microcrystalline semiconductor film over the seed by introducing hydrogen and the deposition gas into a second treatment chamber under a second condition: a second flow rate of the deposition gas is periodically changed between a first value and a second value; and a second pressure in the second treatment chamber is higher than or equal to 1.0×102 Torr and lower than or equal to 1.0×103 Torr.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Surface passivated photovoltaic devices
InactiveUS20060255340A1Raise the level of dopingReduce potential barrierSolid-state devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor materialsBack surface field
A photovoltaic device comprising a photovoltaic cell is provided. The photovoltaic cell includes an emitter layer comprising a crystalline semiconductor material and a lightly doped crystalline substrate disposed adjacent the emitter layer. The lightly doped crystalline substrate and the emitter layer are oppositely doped. Further, the photovoltaic device includes a back surface passivated structure coupled to the photovoltaic cell. The structure includes a highly doped back surface field layer disposed adjacent the lightly doped crystalline substrate. The highly doped back surface field layer includes an amorphous or a microcrystalline semiconductor material, wherein the highly doped back surface field layer and the lightly doped crystalline substrate are similarly doped, and wherein a doping level of the highly doped back surface field layer is higher than a doping level of the lightly doped crystalline substrate. Additionally, the structure may also include an intrinsic back surface passivated layer disposed adjacent the lightly doped crystalline substrate, where the intrinsic back surface passivated layer includes an amorphous or a microcrystalline semiconductor material.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Single-source precursors for ternary chalcopyrite materials, and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS6992202B1Effective yieldFurnaces without endless coreMaterial nanotechnologyChalcopyriteQuantum dot
A single source precursor for depositing ternary I-III-VI2 chalcopyrite materials useful as semiconductors. The single source precursor has the I-III-VI2 stoichiometry “built into” a single precursor molecular structure which degrades on heating or pyrolysis to yield the desired I-III-VI2 ternary chalcopyrite. The single source precursors effectively degrade to yield the ternary chalcopyrite at low temperature, e.g. below 500° C., and are useful to deposit thin film ternary chalcopyrite layers via a spray CVD technique. The ternary single source precursors according to the invention can be used to provide nanocrystallite structures useful as quantum dots. A method of making the ternary single source precursors is also provided.
Owner:OHIO AEROSPACE INST +1
Electrode for rechargeable lithium battery and rechargeable lithium battery
InactiveUS7192673B1Improve charge and discharge cycle characteristicsInhibition formationElectrode manufacturing processesSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsAmorphous siliconMaterials science
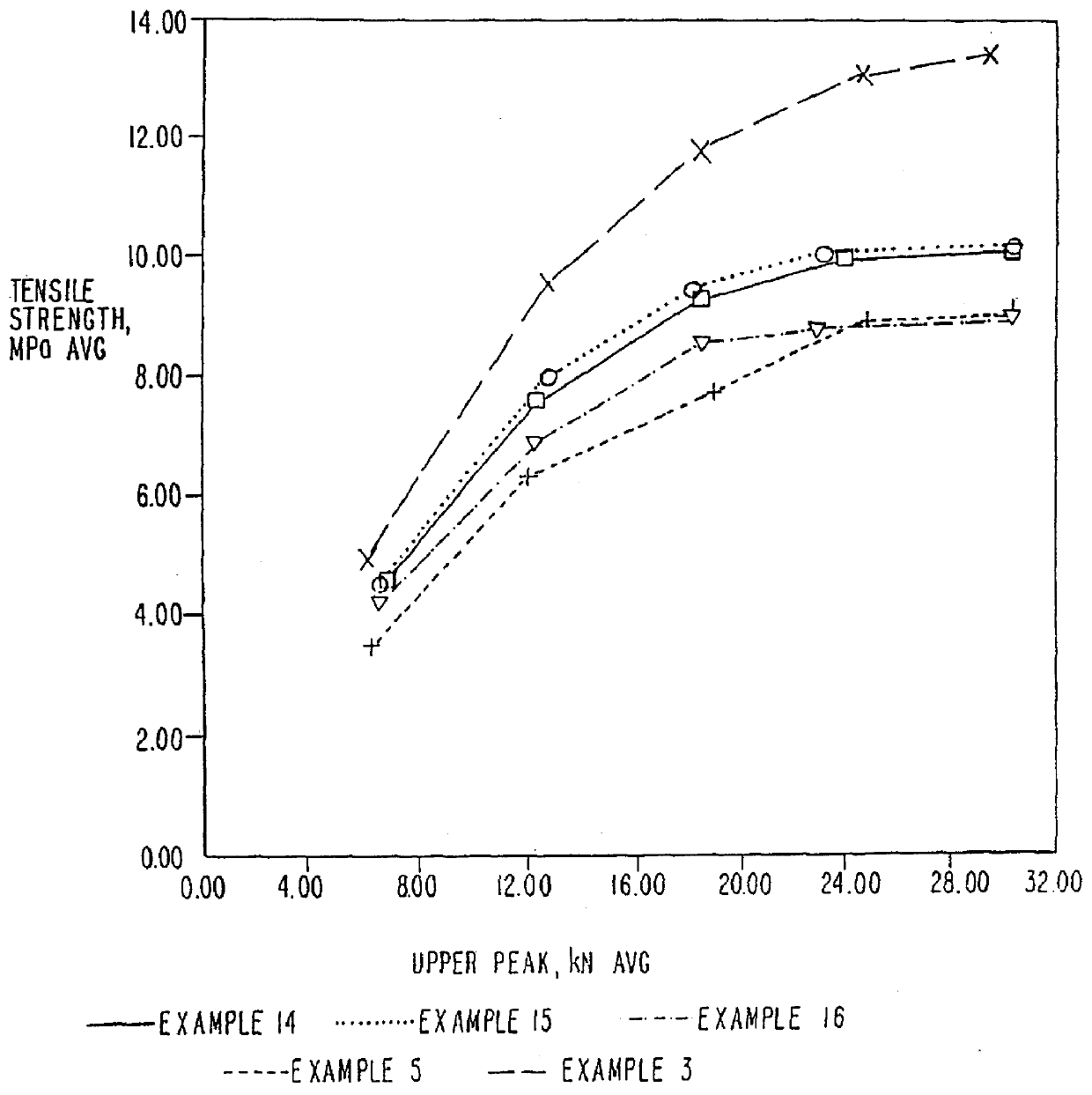
An electrode for a rechargeable lithium battery which includes a thin film composed of active material that expands and shrinks as it stores and releases lithium, e.g., a microcrystalline or amorphous silicon thin film, deposited on a current collector, characterized in that said current collector exhibits a tensile strength (=tensile strength (N / mm2) per sectional area of the current collector material×thickness (mm) of the current collector) of not less than 3.82 N / mm.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
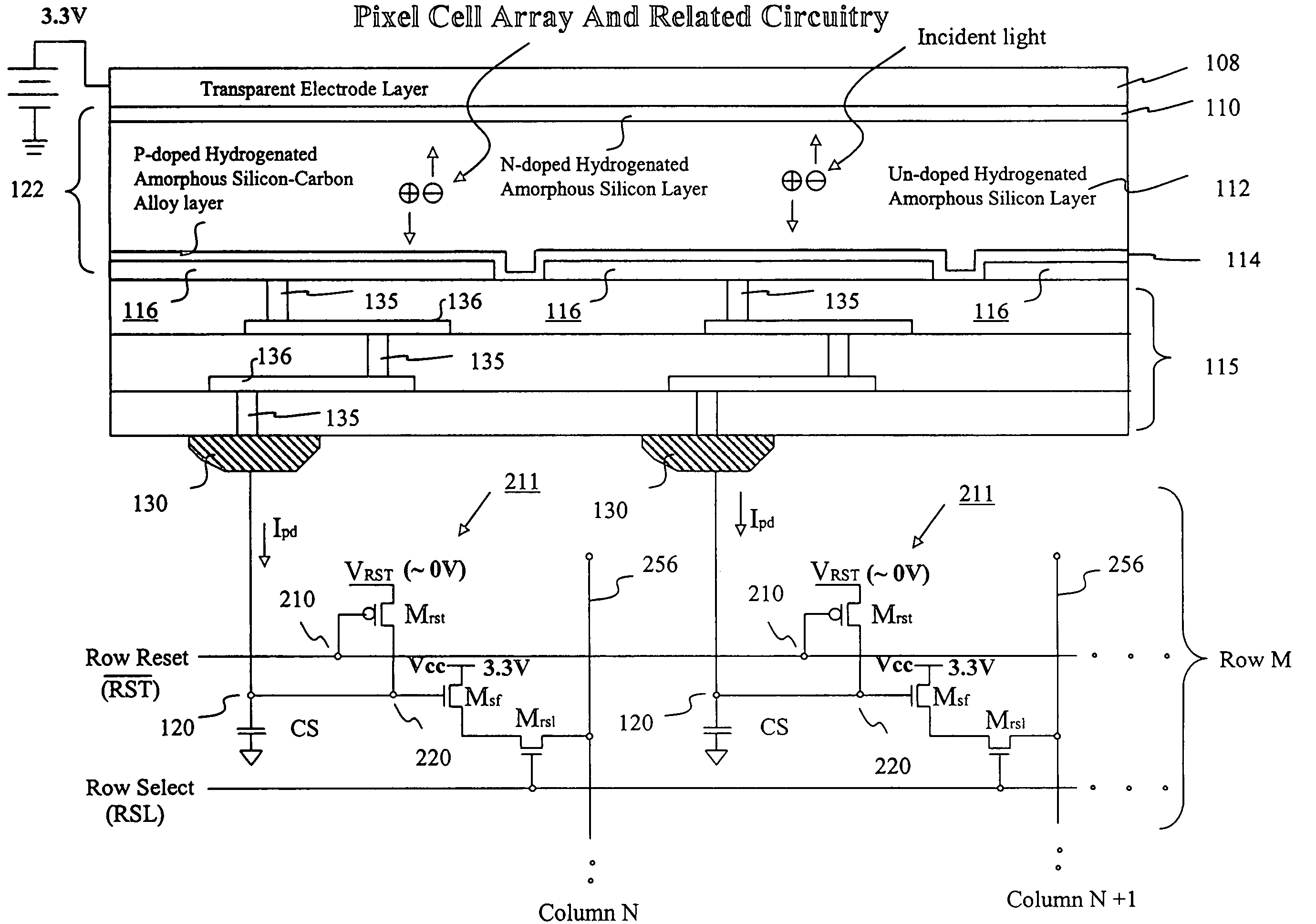
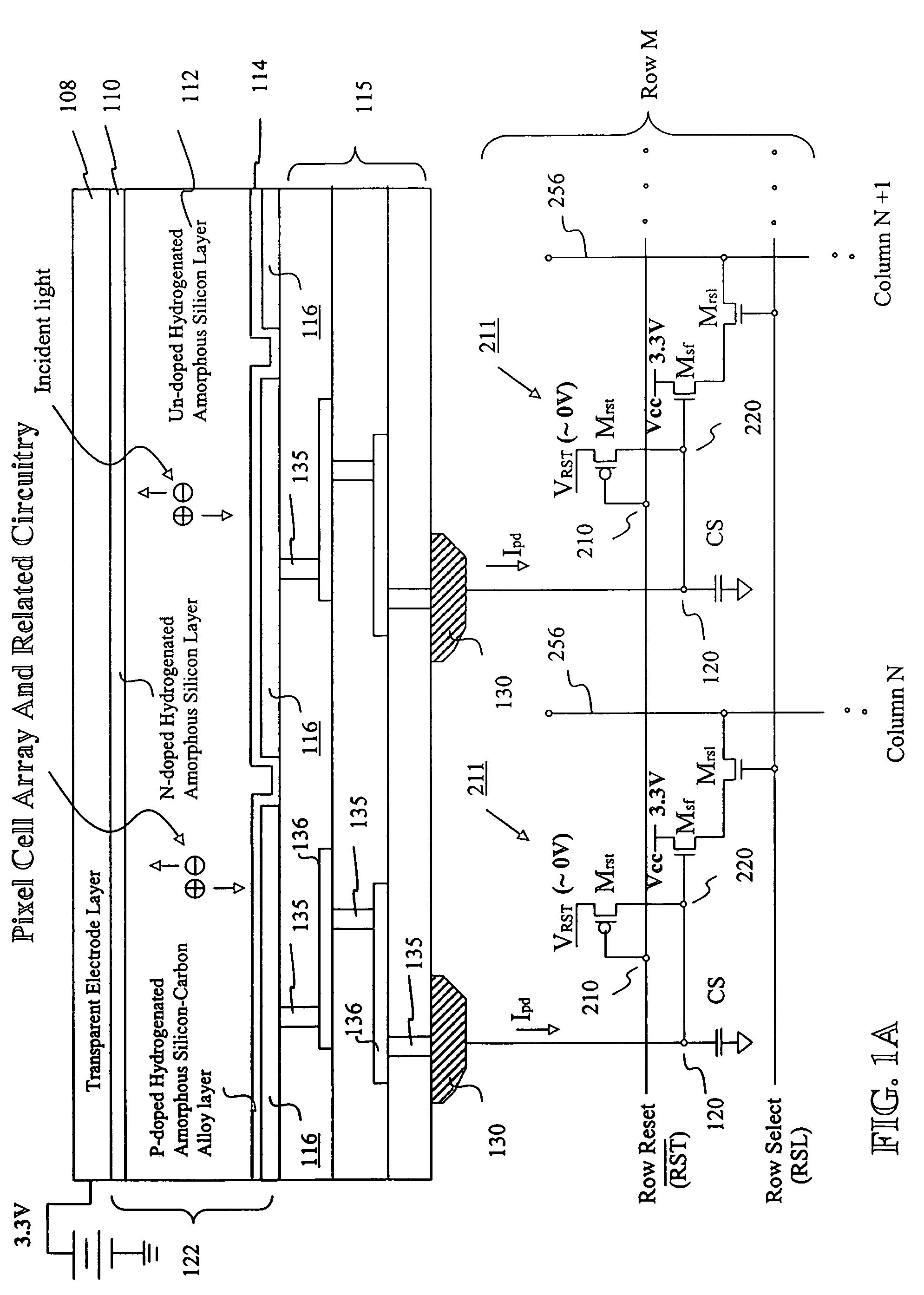
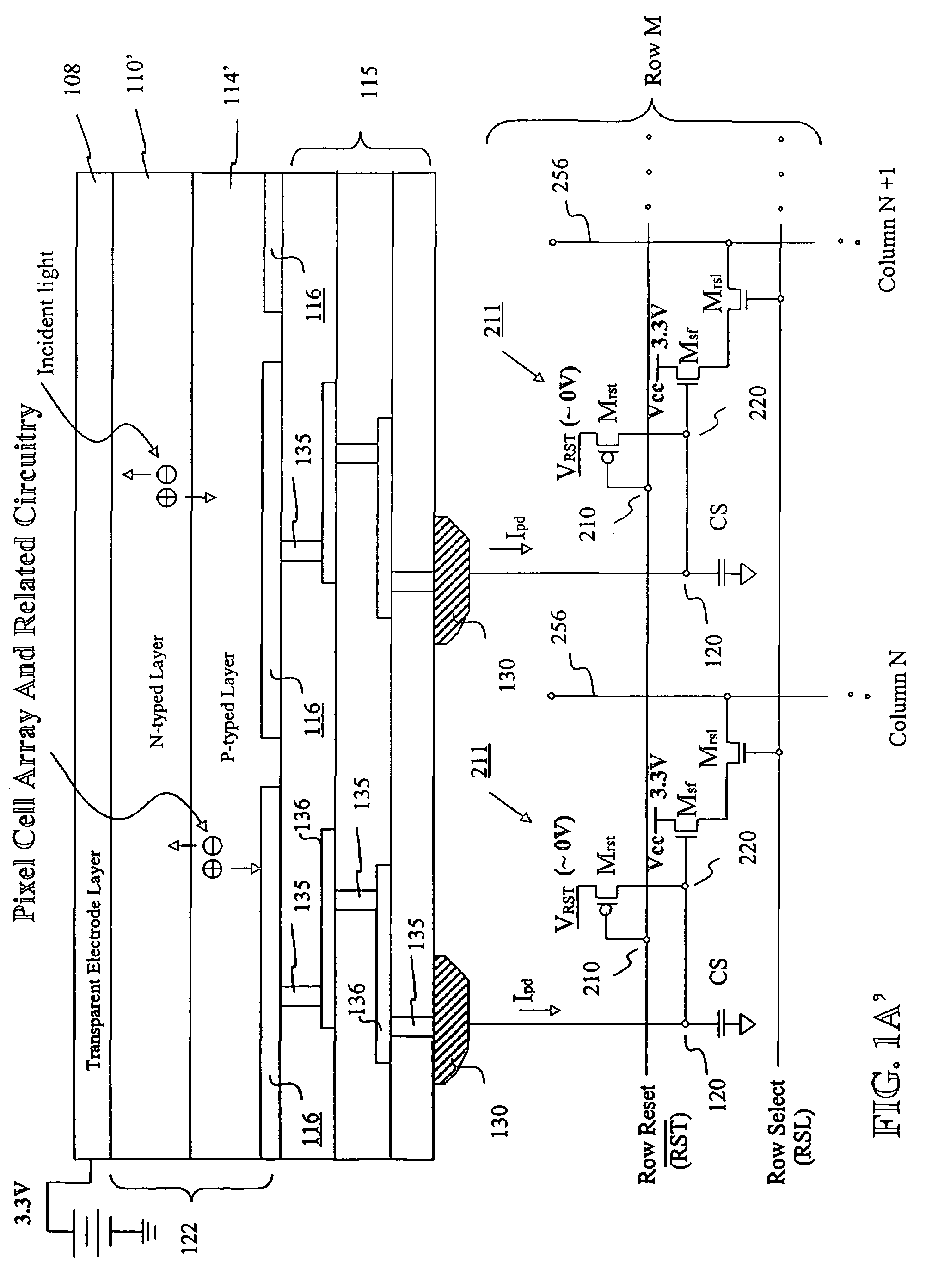
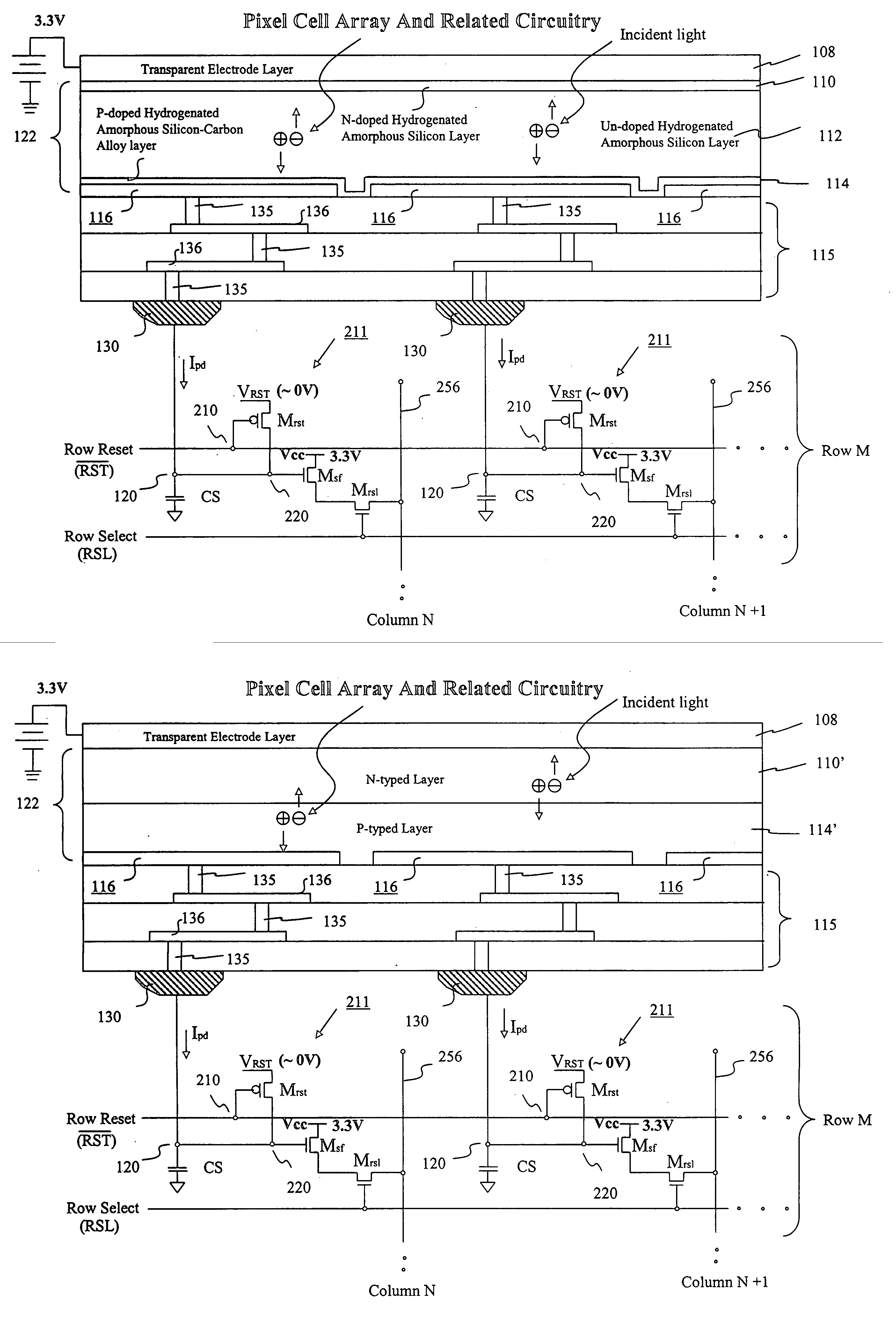
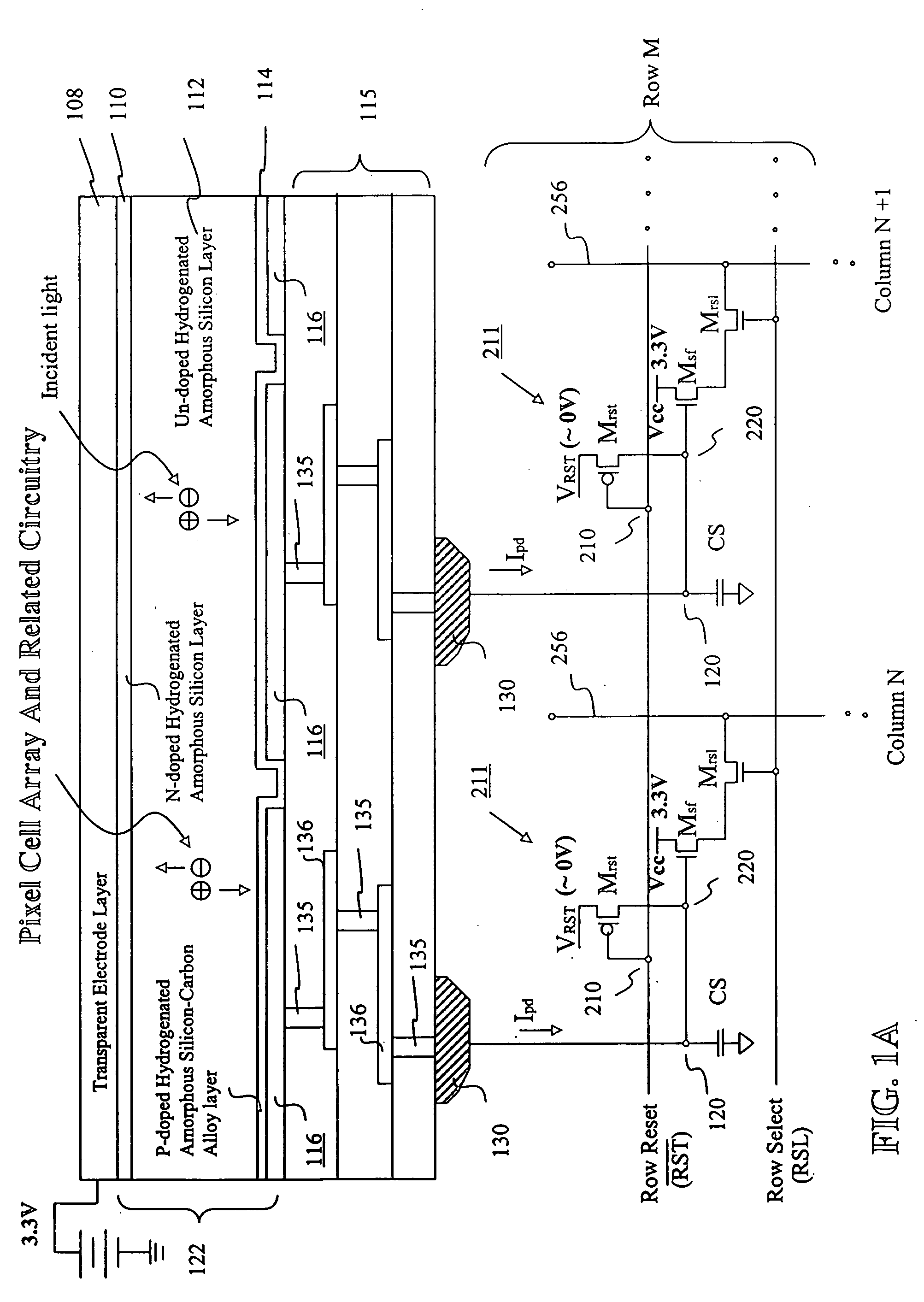
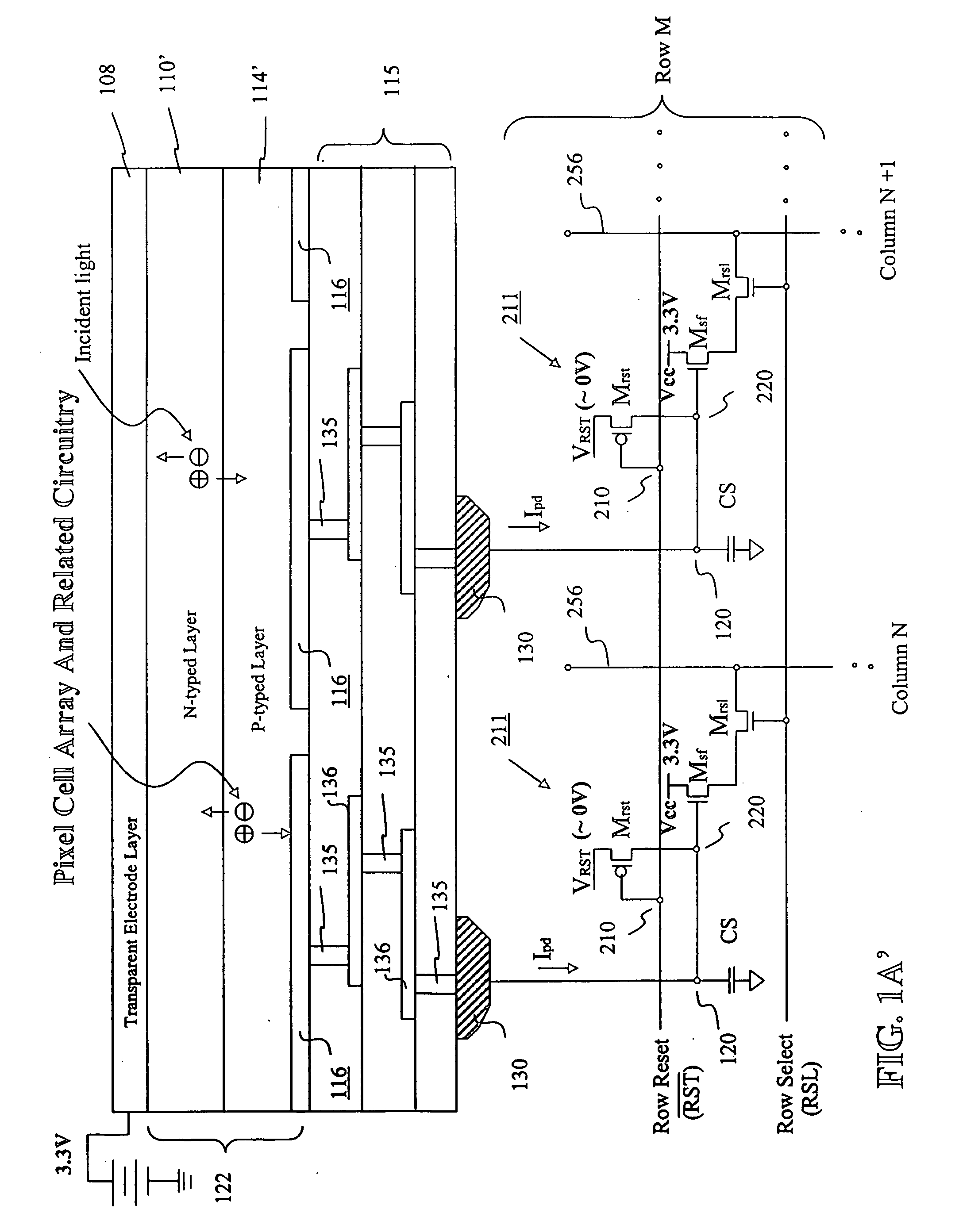
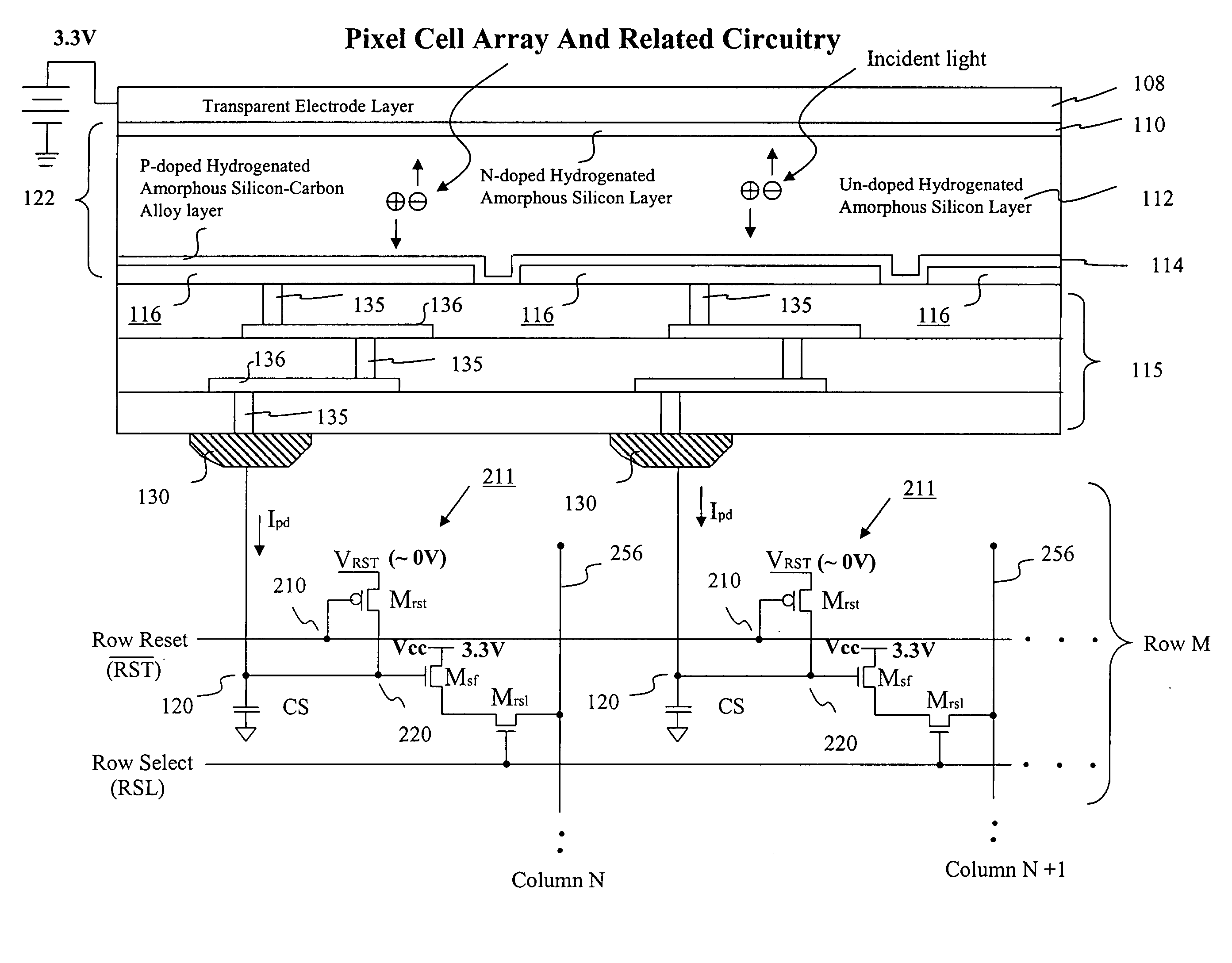
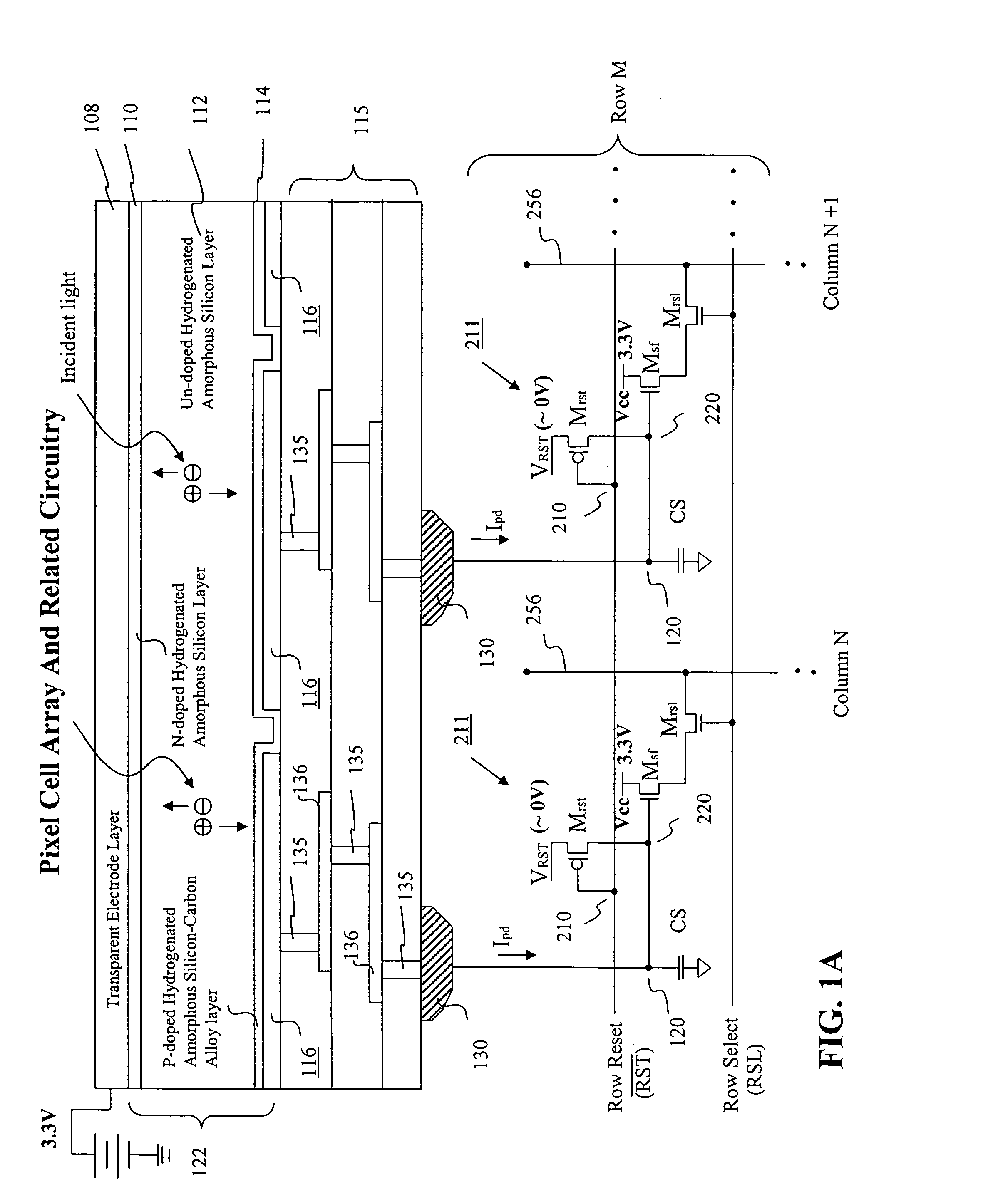
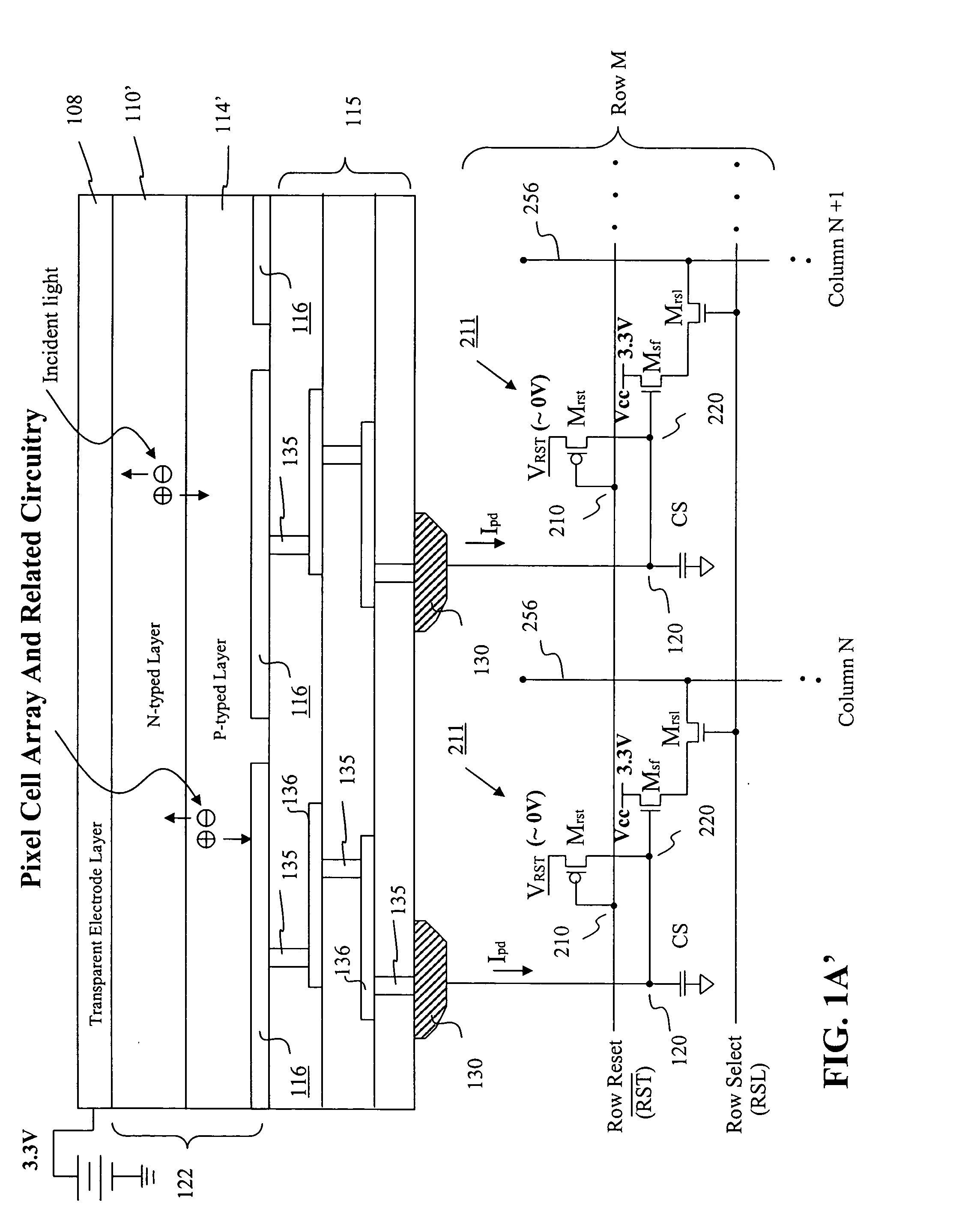
Image sensor with microcrystalline germanium photodiode layer
InactiveUS7276749B2Improve performanceRaise countTransistorSolid-state devicesSensor arrayElectromagnetic radiation
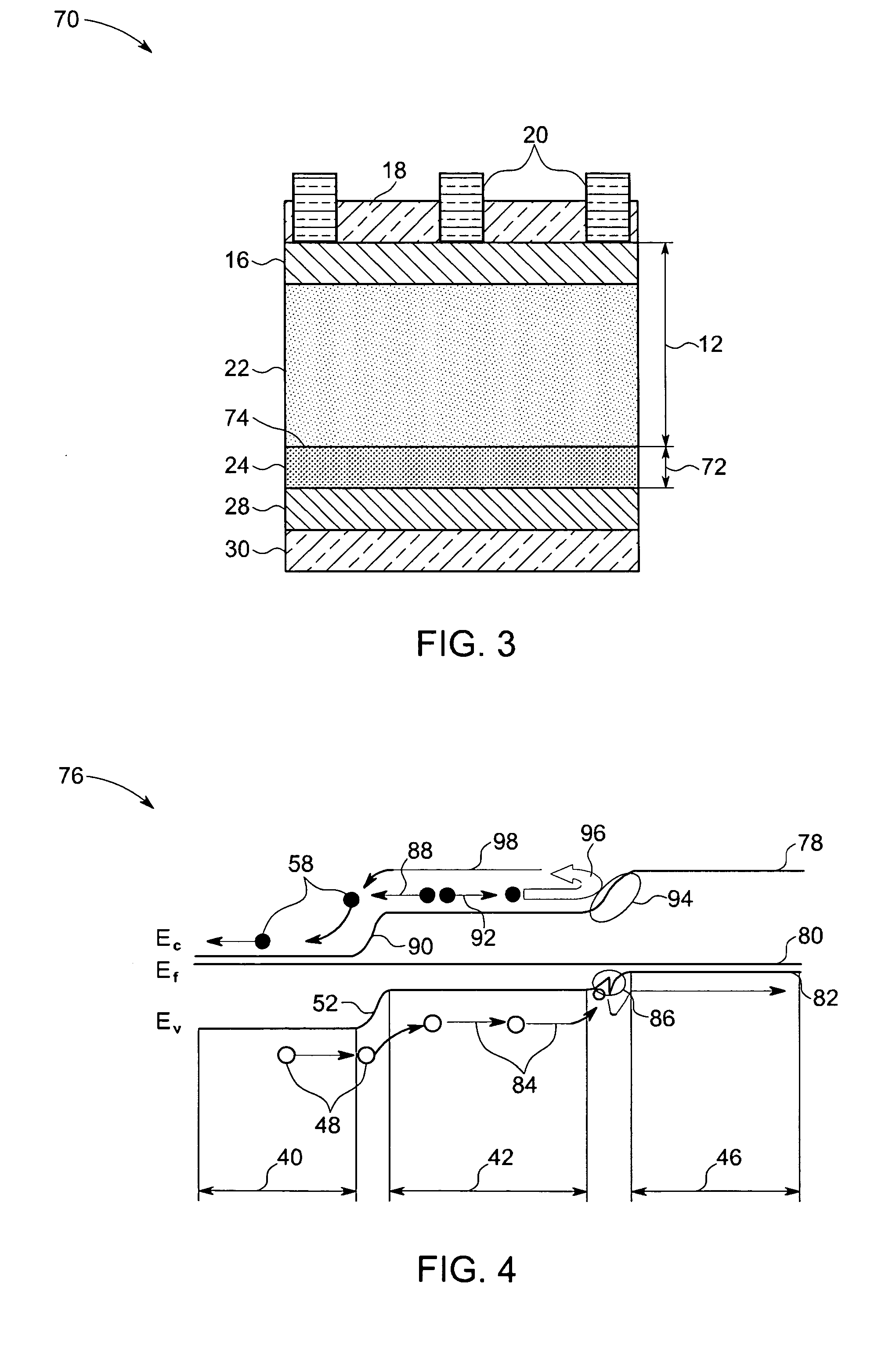
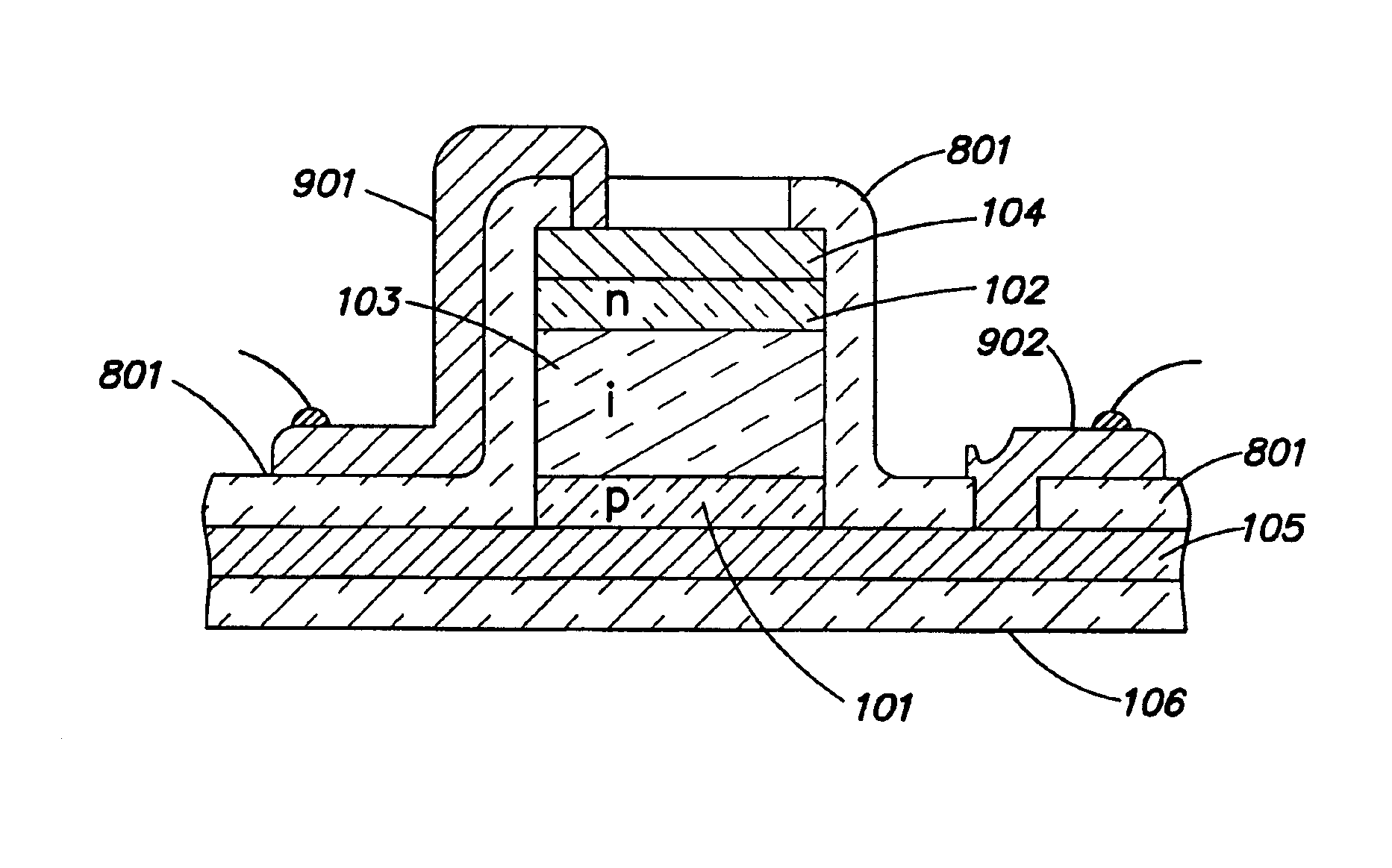
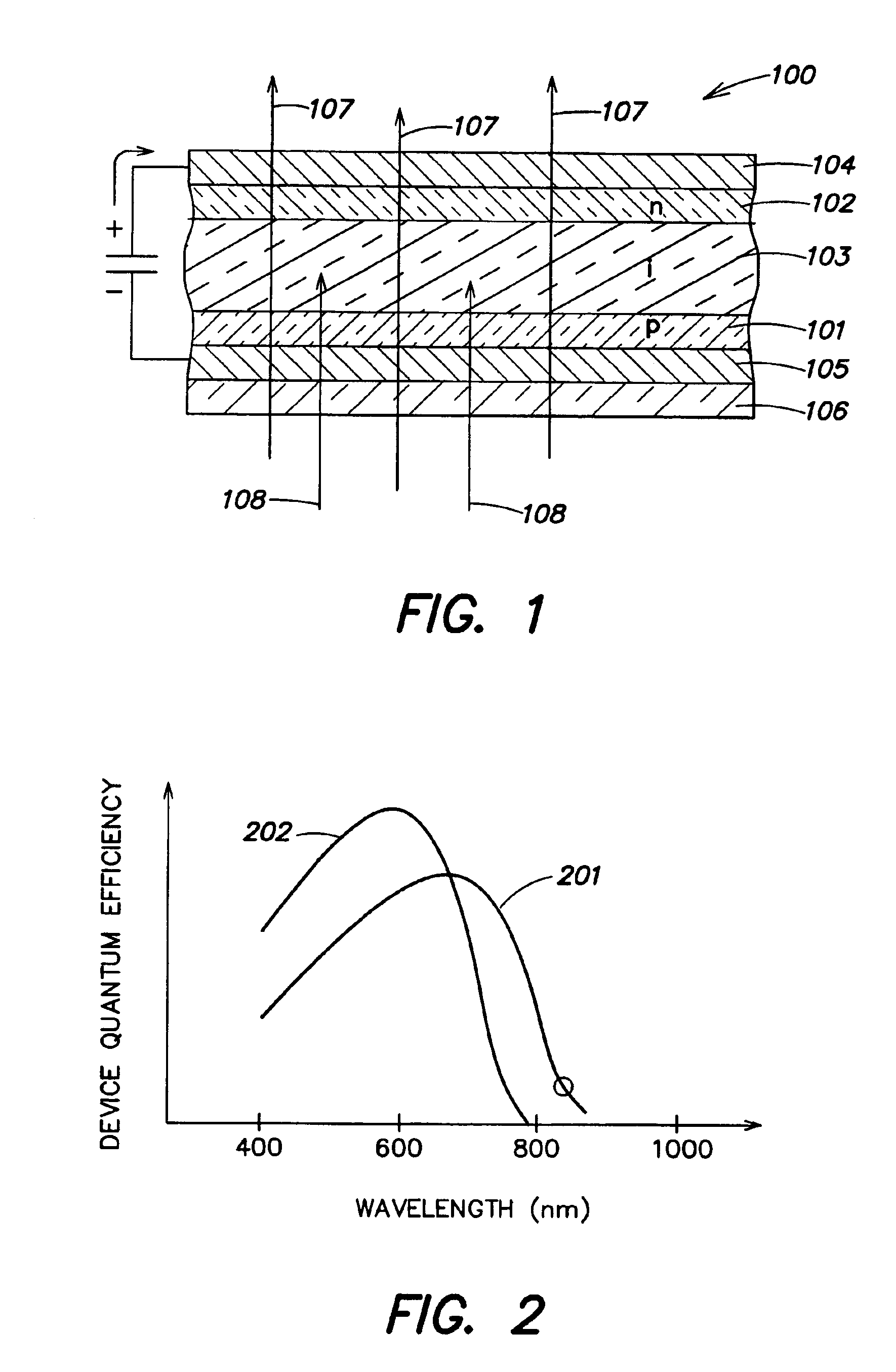
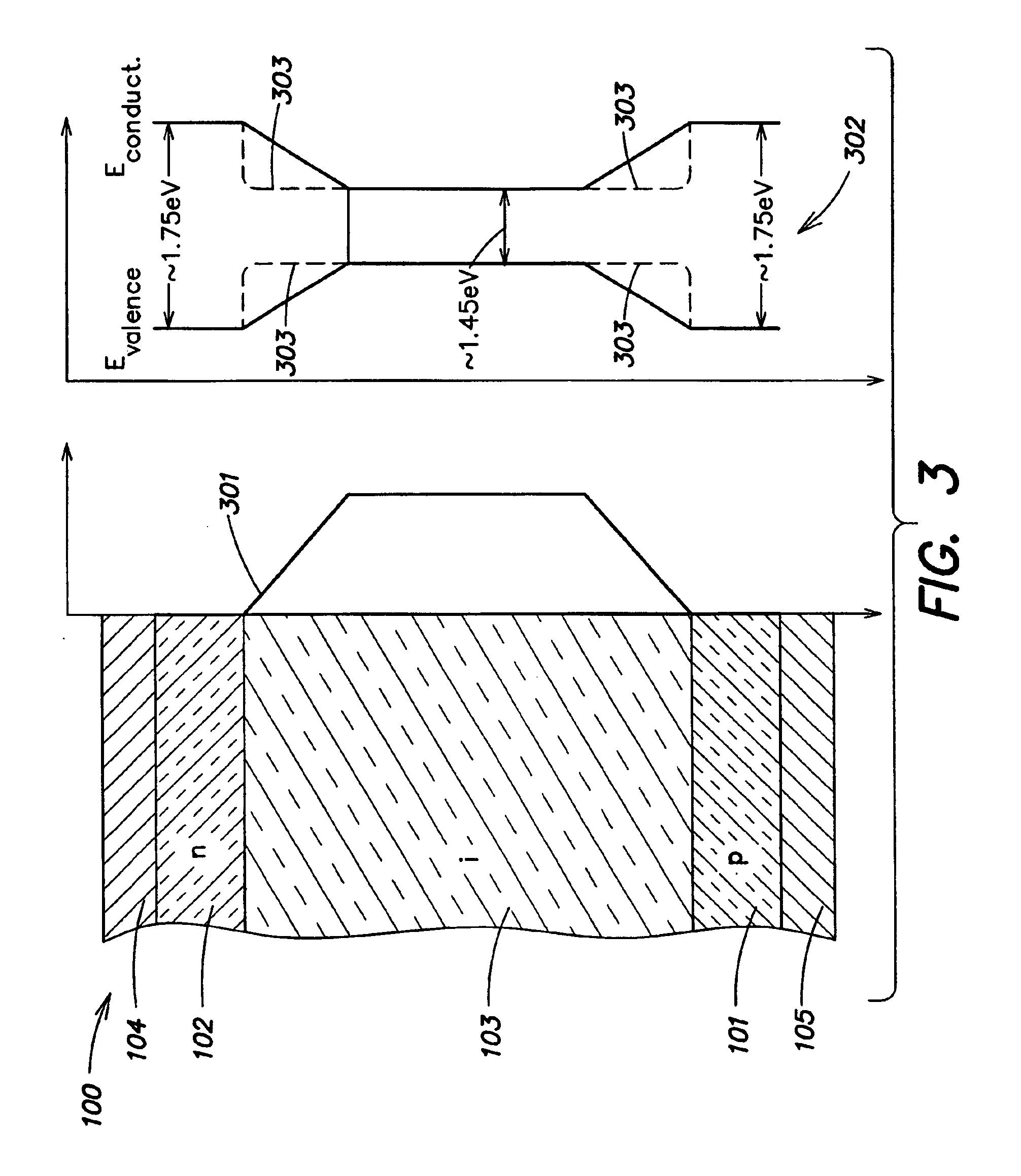
A microcrystalline germanium image sensor array. The array includes a number of pixel circuits fabricated in or on a substrate. Each pixel circuit comprises a charge collecting electrode for collecting electrical charges and a readout means for reading out the charges collected by the charge collecting electrode. A photodiode layer of charge generating material located above the pixel circuits convert electromagnetic radiation into electrical charges. This photodiode layer includes microcrystalline germanium and defines at least an n-layer, and i-layer and a p-layer. The sensor array also includes and a surface electrode in the form of a grid or thin transparent layer located above the layer of charge generating material. The sensor is especially useful for imaging in visible and near infrared spectral regions of the electromagnetic spectrum and provides imaging with starlight illumination.
Owner:E PHOCUS
Method for forming silicon-containing materials during a photoexcitation deposition process
InactiveUS20060286776A1Enhance chamber cleaning processHigh surface energyPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingVolatilesSilicon oxide
Embodiments of the invention generally provide a method for depositing films or layers using a UV source during a photoexcitation process. The films are deposited on a substrate and usually contain a material, such as silicon (e.g., epitaxy, crystalline, microcrystalline, polysilicon, or amorphous), silicon oxide, silicon nitride, silicon oxynitride, or other silicon-containing materials. The photoexcitation process may expose the substrate and / or gases to an energy beam or flux prior to, during, or subsequent a deposition process. Therefore, the photoexcitation process may be used to pre-treat or post-treat the substrate or material, to deposit the silicon-containing material, and to enhance chamber cleaning processes. Attributes of the method that are enhanced by the UV photoexcitation process include removing native oxides prior to deposition, removing volatiles from deposited films, increasing surface energy of the deposited films, increasing the excitation energy of precursors, reducing deposition time, and reducing deposition temperature.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Image sensor with microcrystalline germanium photodiode layer
InactiveUS20060267054A1High sensitivityEnhanced pixel size pixelTransistorSolid-state devicesSensor arrayElectromagnetic spectrum
A microcrystalline germanium image sensor array. The array includes a number of pixel circuits fabricated in or on a substrate. Each pixel circuit comprises a charge collecting electrode for collecting electrical charges and a readout means for reading out the charges collected by the charge collecting electrode. A photodiode layer of charge generating material located above the pixel circuits convert electromagnetic radiation into electrical charges. This photodiode layer includes microcrystalline germanium and defines at least an n-layer, and i-layer and a p-layer. The sensor array also includes and a surface electrode in the form of a grid or thin transparent layer located above the layer of charge generating material. The sensor is especially useful for imaging in visible and near infrared spectral regions of the electromagnetic spectrum and provides imaging with starlight illumination.
Owner:E PHOCUS
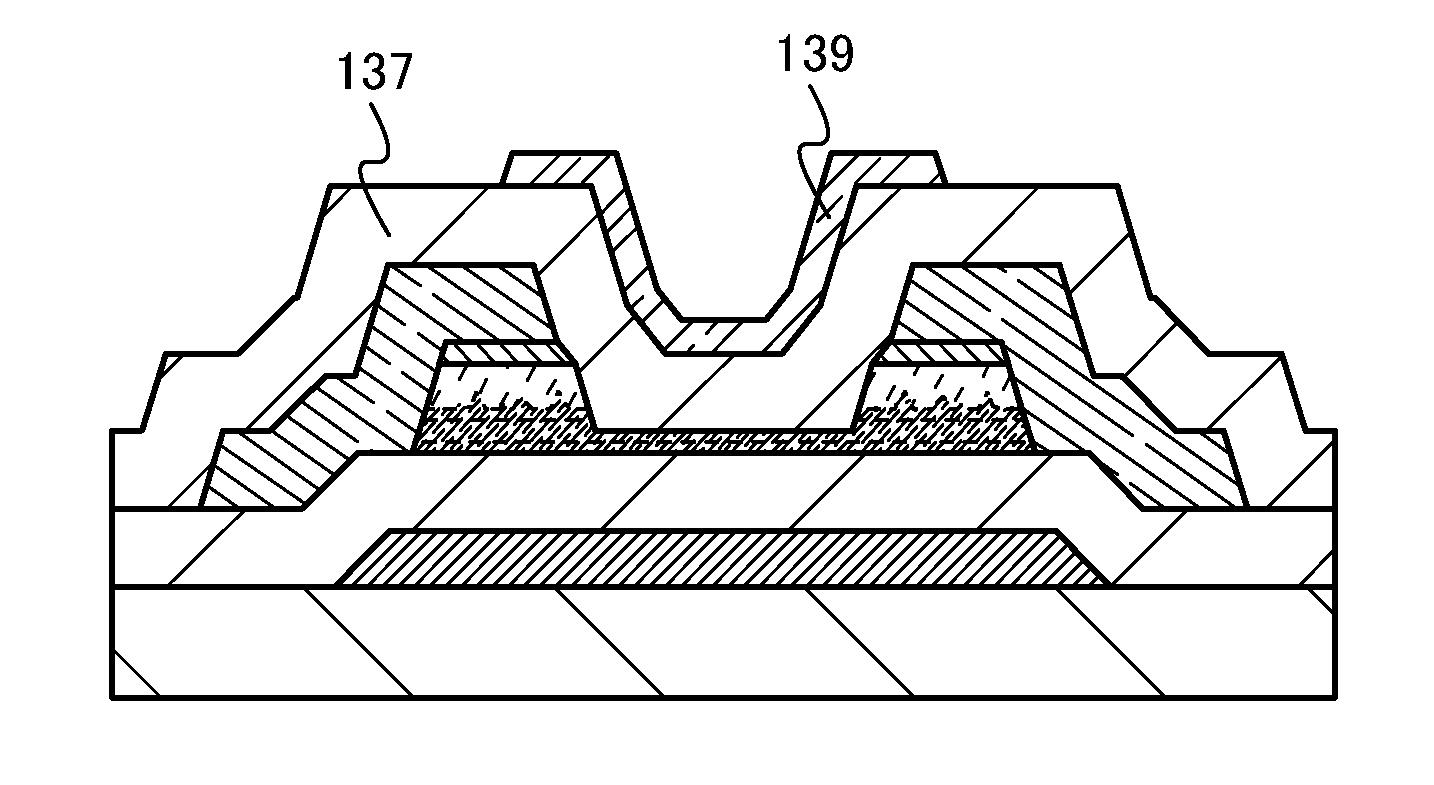
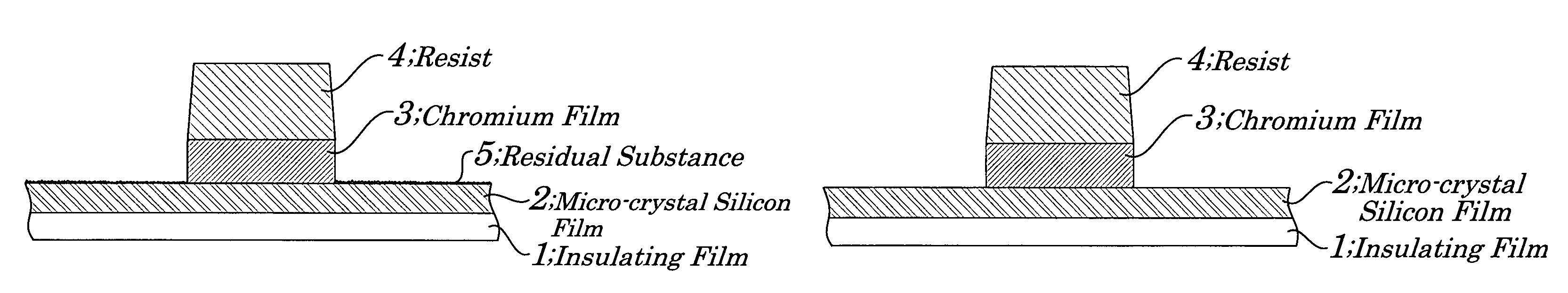
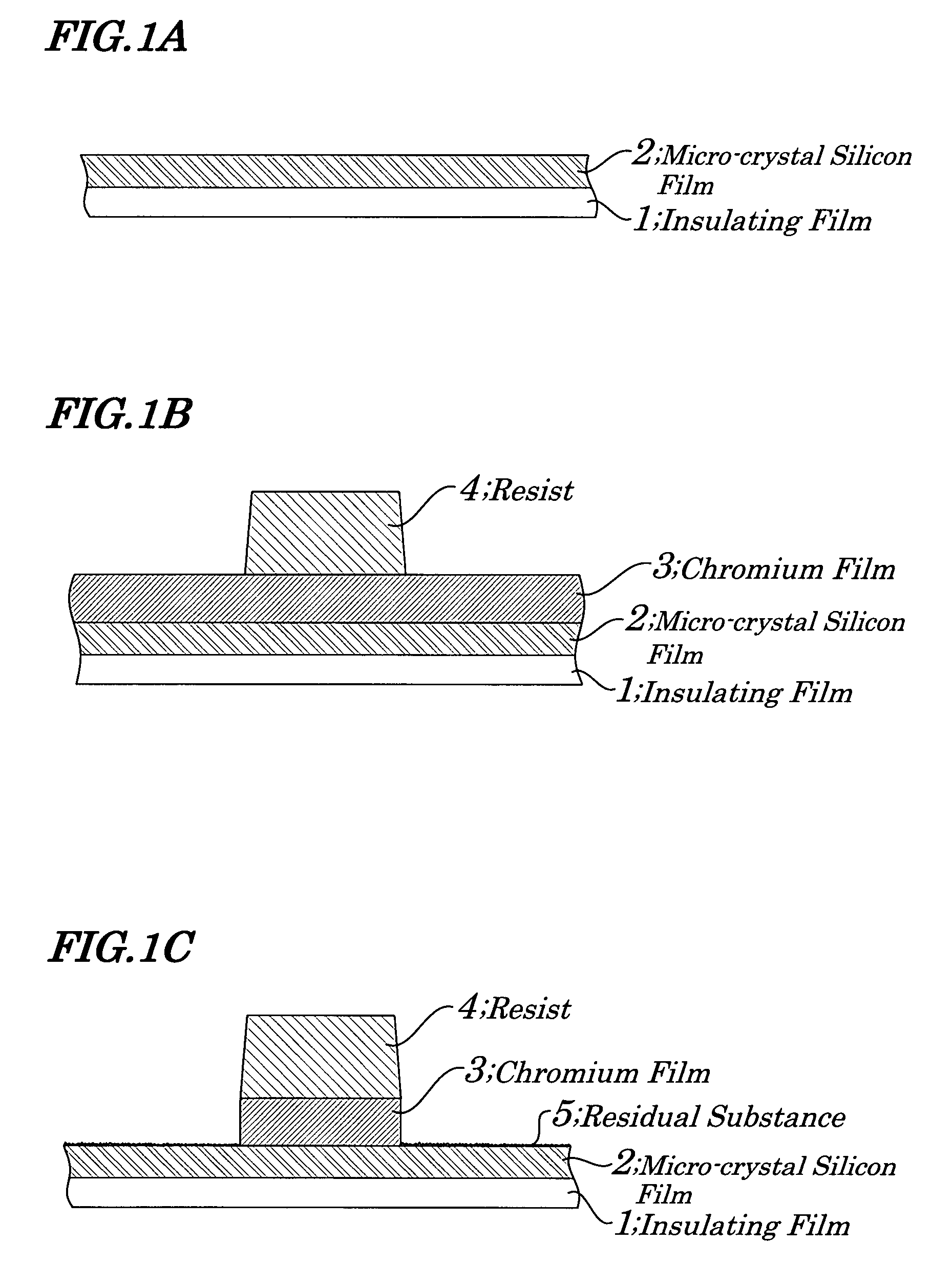
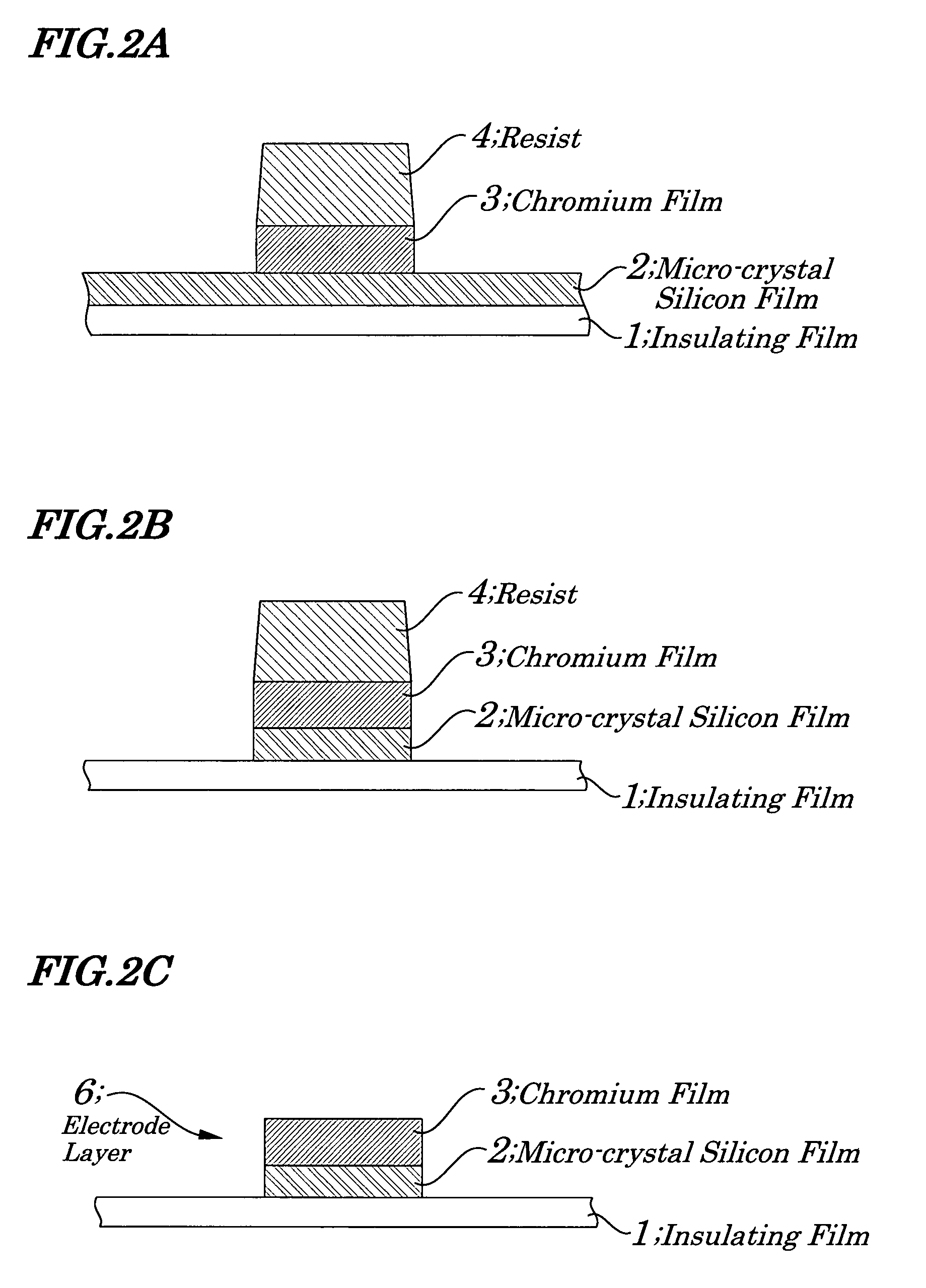
Stacked film patterning method and gate electrode forming method
InactiveUS7723221B2Improve uniformityAvoid it happening againSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesResistMixed gas
A stacked film patterning method is provided which is capable of reliably removing residual substances remaining after etching of a metal film, improving etching uniformity of a silicon film, and preventing an occurrence of etching residues. A micro-crystal film and a chromium film are sequentially formed on an insulating film serving as a front-end film and the chromium film is etched to be patterned by using a resist as a mask. Next, a micro-crystal silicon film on which the residual substances exist is exposed to plasma of a mixed gas including chlorine gas and oxygen gas to selectively etch the residual substances on a surface of the micro-crystal silicon film. After that, the micro-crystal silicon film is dry etched.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
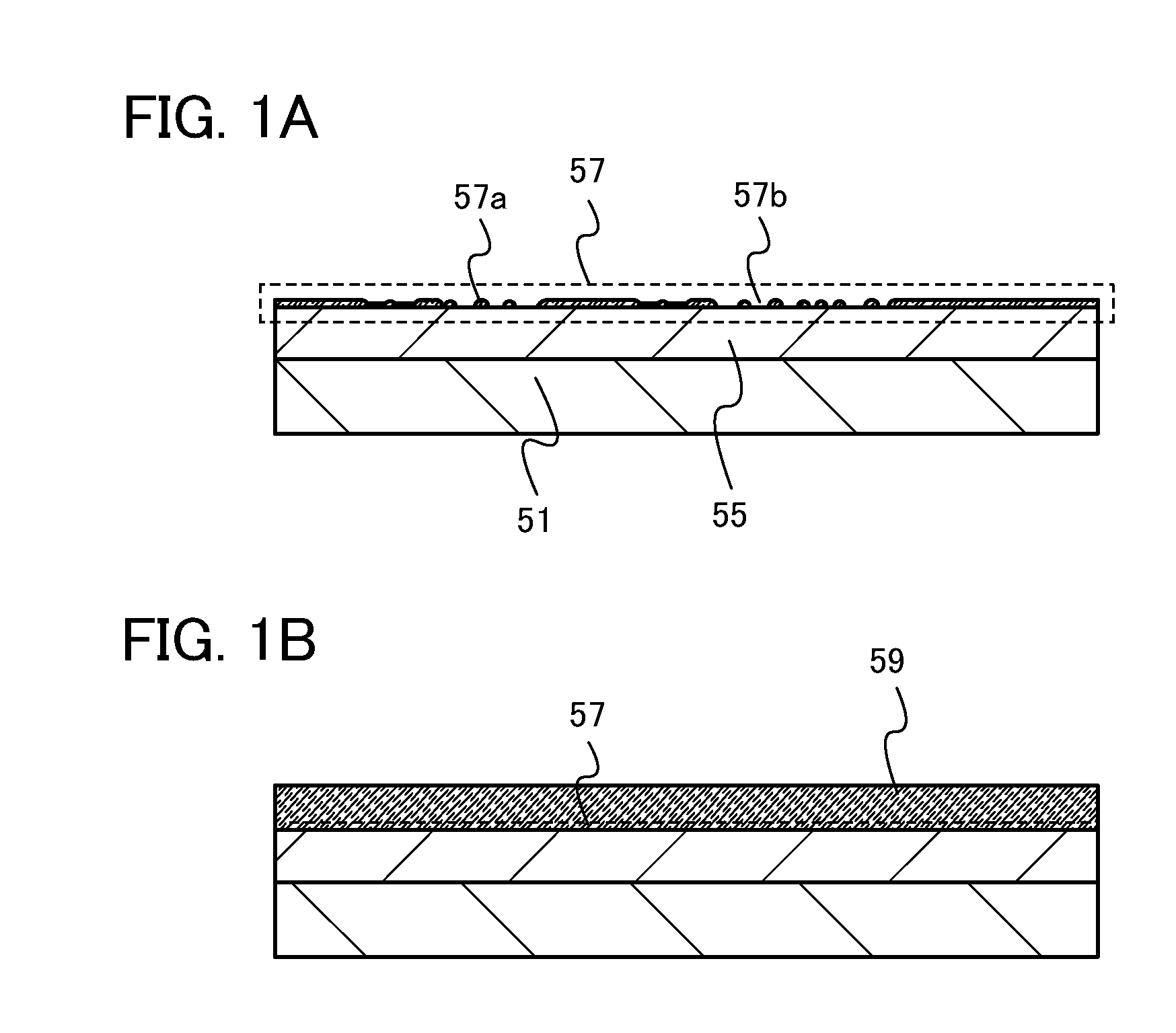
Display device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20080308807A1Inhibition of mobilityReduce oxidationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceEngineering
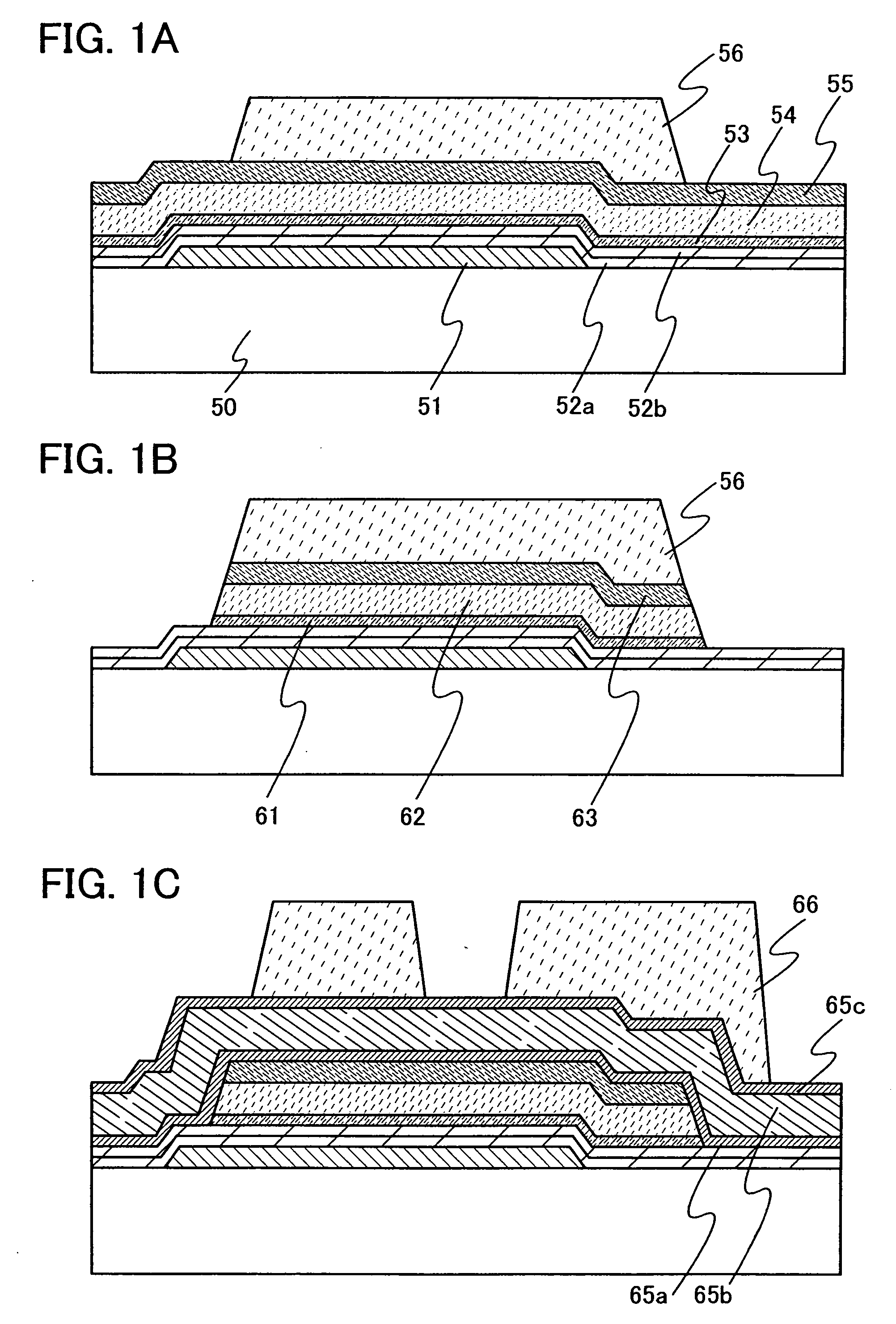
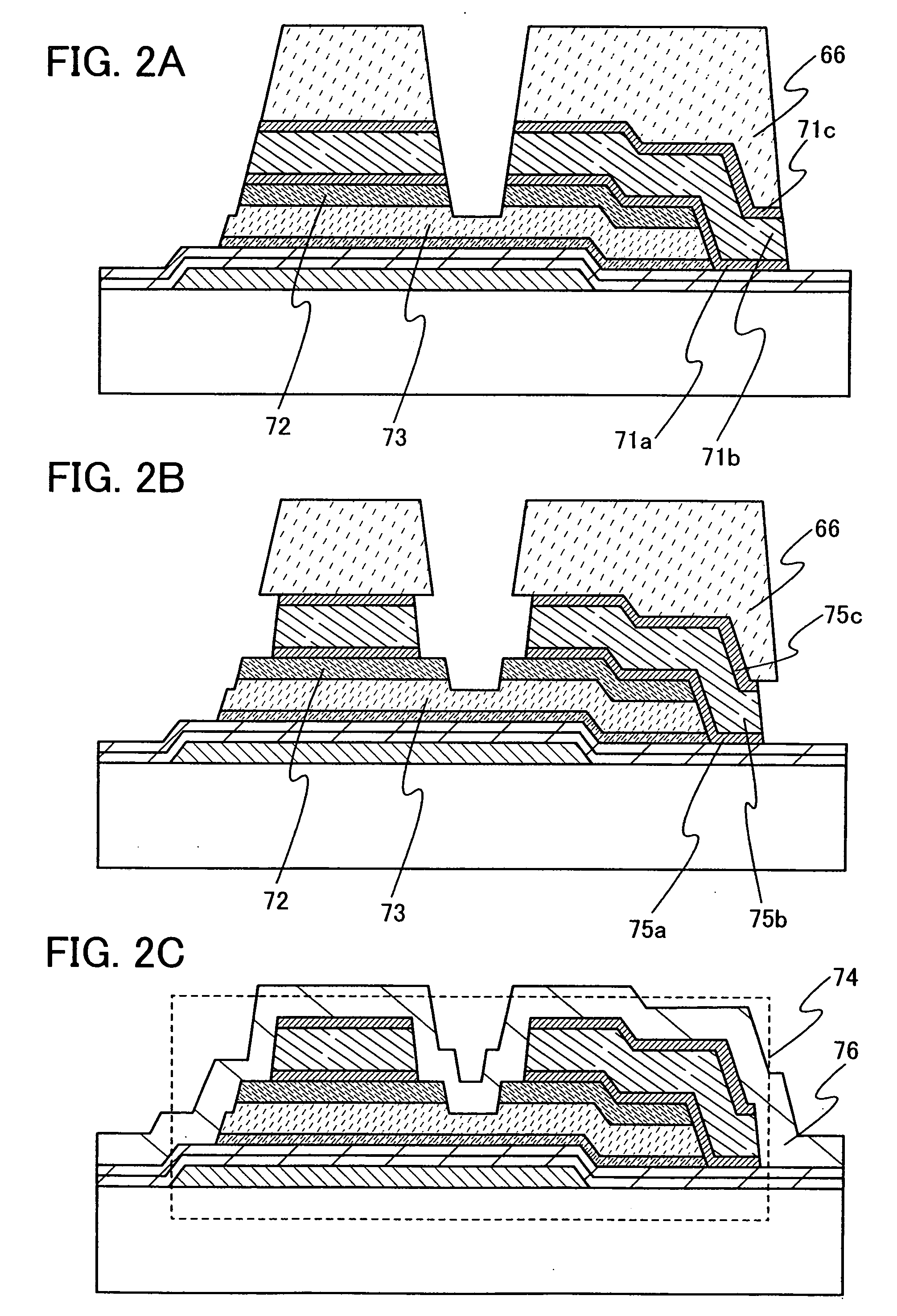
It is an object to provide a manufacturing method by which display devices can be manufactured in quantity without degrading the characteristics of thin film transistors. In a display device including a thin film transistor in which a microcrystalline semiconductor film, a gate insulating film in contact with the microcrystalline semiconductor film, and a gate electrode overlap with each other, an antioxidant film is formed on a surface of the microcrystalline semiconductor film. The antioxidant film on the surface of the microcrystalline semiconductor film can prevent a surface of a microcrystal grain from being oxidized, thereby preventing the mobility of the thin film transistor from decreasing.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Electrode for use in lithium battery and rechargeable lithium battery
InactiveUS7235330B1High charge and discharge capacityImprove featuresElectrode manufacturing processesSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsAmorphous siliconSurface roughness
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
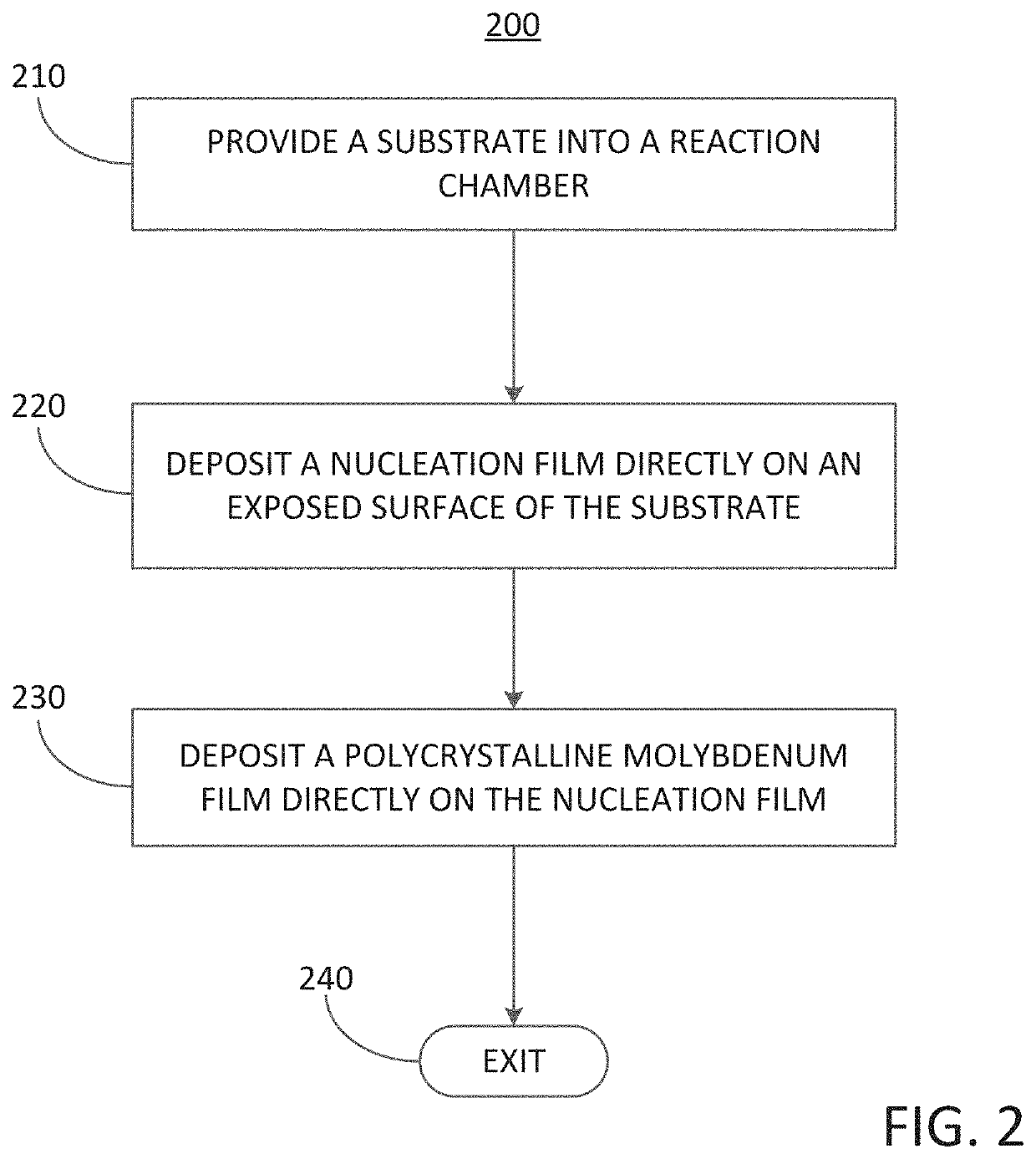
Methods for forming a polycrystalline molybdenum film over a surface of a substrate and related structures including a polycrystalline molybdenum film
Methods for forming a polycrystalline molybdenum film over a surface of a substrate are disclosed. The methods may include: providing a substrate into a reaction chamber; depositing a nucleation film directly on an exposed surface of the substrate, wherein the nucleation film comprises one of a metal oxide nucleation film or a metal nitride nucleation film; and depositing a polycrystalline molybdenum film directly on the nucleation film; wherein the polycrystalline molybdenum film comprises a plurality of molybdenum crystallites having an average crystallite size of less than 80 Å. Structures including a polycrystalline molybdenum film disposed over a surface of a substrate with an intermediate nucleation film are also disclosed.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Visible/near infrared image sensor
InactiveUS20050104089A1Improve performanceHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLow earth orbitBeam steering
A MOS or CMOS sensor for high performance imaging in broad spectral ranges including portions of the infrared spectral band. These broad spectral ranges may also include portions or all of the visible spectrum, therefore the sensor has both daylight and night vision capabilities. The sensor includes a continuous multi-layer photodiode structure on a many pixel MOS or CMOS readout array where the photodiode structure is chosen to include responses in the near infrared spectral ranges. A preferred embodiment incorporates a microcrystalline copper indium diselenide / cadmium sulfide photodiode structure on a CMOS readout array. An alternate preferred embodiment incorporates a microcrystalline silicon germanium photodiode structure on a CMOS readout array. Each of these embodiments provides night vision with image performance that greatly surpasses the GEN III night vision technology in terms of enhanced sensitivity, pixel size and pixel count. Further advantages of the invention include low electrical bias voltages, low power consumption, compact packaging, and radiation hardness. In special preferred embodiments CMOS stitching technology is used to provide multi-million pixel focal plane array sensors. One embodiments of the invention made without stitching is a two-million pixel sensor. Other preferred embodiments available using stitching techniques include sensors with 250 million (or more) pixels fabricated on a single wafer. A particular application of these very high pixel count sensors is as a focal plane array for a rapid beam steering telescope in a low earth orbit satellite useful for tracking over a 1500-meter wide track with a resolution of 0.3 meter.
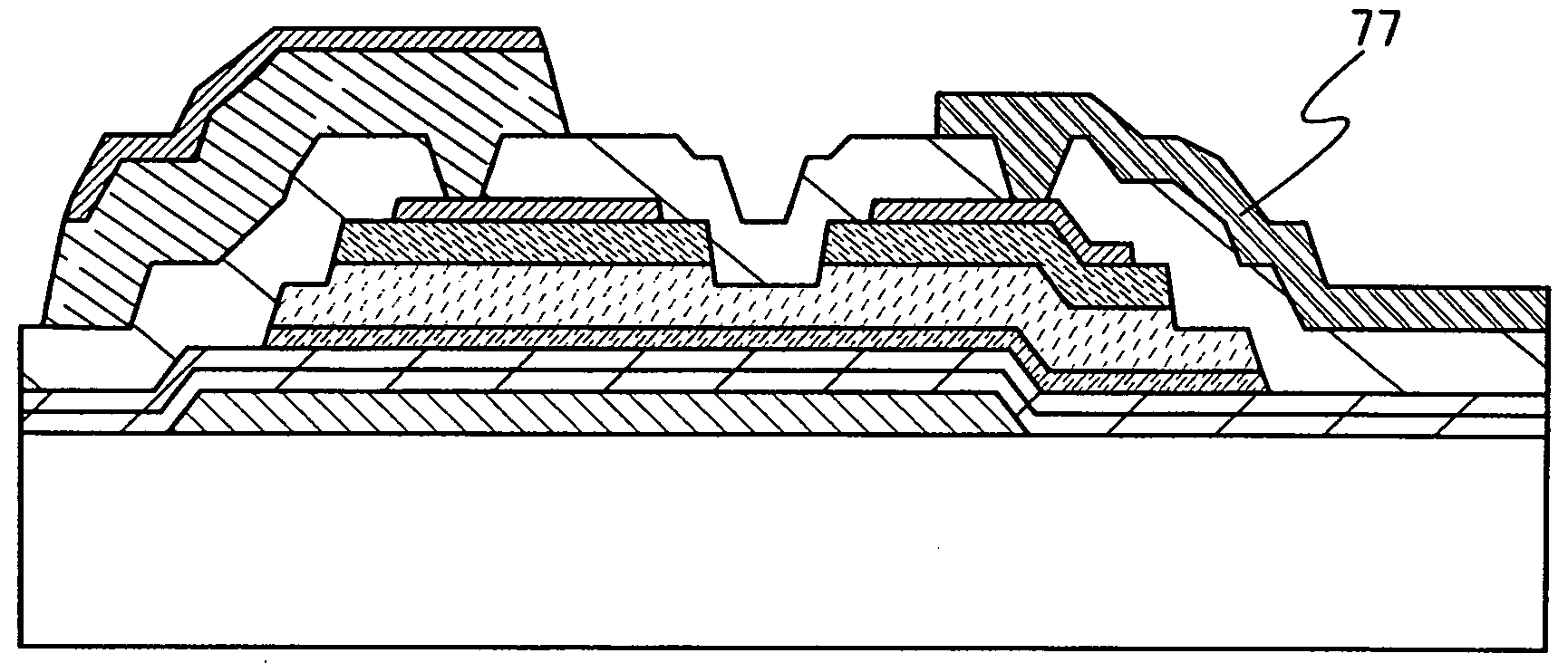
Owner:C PHOCUS
Liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20090002591A1Improve batch productivityHighly reliable electric characteristicSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
An object is to propose a method of manufacturing, with high mass productivity, liquid crystal display devices having thin film transistors with highly reliable electric characteristics. In a liquid crystal display device having an inverted staggered thin film transistor, the inverted staggered thin film transistor is formed as follows: a gate insulating film is formed over a gate electrode; a microcrystalline semiconductor film which functions as a channel formation region is formed over the gate insulating film; a buffer layer is formed over the microcrystalline semiconductor film; a pair of source and drain regions are formed over the buffer layer; and a pair of source and drain electrodes are formed in contact with the source and drain regions so as to expose a part of the source and drain regions.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
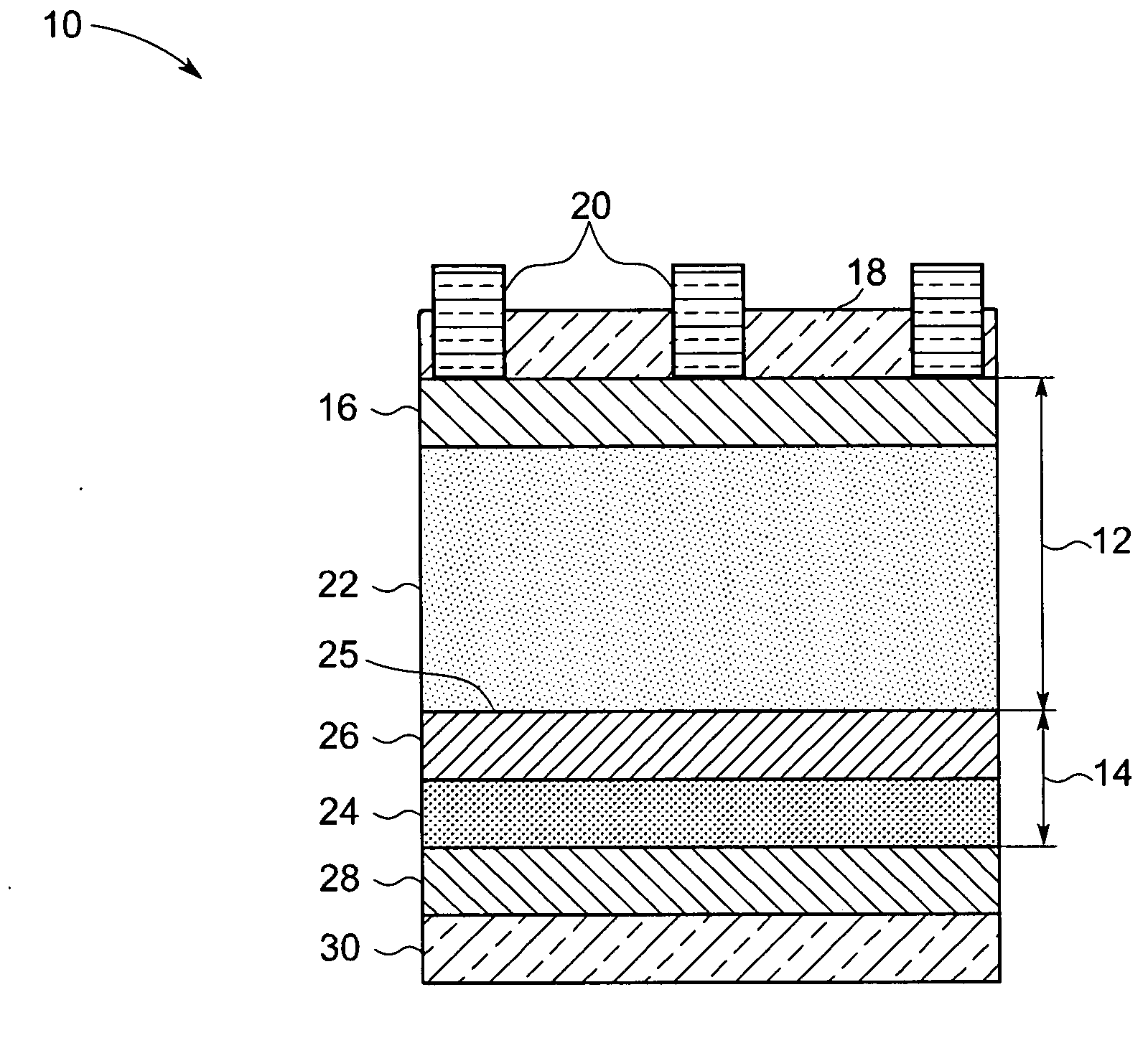
Multi-junction photovoltaic device with microcrystalline I-layer
A photovoltaic element of the present invention is a photovoltaic element having a plurality of pin junctions each formed of a p-type semiconductor layer, an i-type semiconductor layer, and an n-type semiconductor layer each comprising a non-single-crystal material comprising a Group IVA element as a principal component, the photovoltaic element having a first pin junction comprising microcrystal silicon carbide (hereinafter referred to as microcrystal SiC) as a principal component of the i-type semiconductor layer and a second pin junction comprising microcrystal silicon (hereinafter referred to as microcrystal Si) as a principal component of the i-type semiconductor layer, wherein the first pin junction is provided closer to the light incidence side than the second pin junction. Provided thereby are a low cost photovoltaic element which exhibits little photodeterioration and with a high photoelectric conversion efficiency, and production method of the photovoltaic element capable of forming i-type microcrystal silicon and microcrystal SiC at a practical deposition rate.
Owner:CANON KK
Composition for promoting healthy bone structure
InactiveUS6447809B1Increase bone densityPrevents radial bone lossBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsVitamin CRegimen
A dietary supplement for benefitting human bone health includes a calcium source, a source of vitamin D activity, and an osteoblast stimulant. A preferred calcium source is microcrystalline hydroxyapatite, which also contains protein (mostly collagen), phosphorus, fat, and other minerals. A preferred source of vitamin D activity is cholecalciferol, and a preferred osteoblast stimulant is ipriflavone. In addition to these basic ingredients, the composition can further include various other minerals known to occur in bone, vitamin C, and glucosamine sulfate, all of which exert beneficial effects on growth and maintenance of healthy bone. A method for benefitting human bone health involves administering a daily regimen of the dietary supplement.
Owner:PHOENIX DICHTUNGSTECHN +1
Pharmaceutical excipient having improved compressibility
InactiveUS6103219AImprove compression performanceReduce the amount requiredCosmetic preparationsPowder deliverySilica particleColloid
A microcrystalline cellulose-based excipient having improved compressibility, whether utilized in direct compression, dry granulation or wet granulation formulations, is disclosed. The excipient is an agglomerate of microcrystalline cellulose particles and from about 0.1% to about 20% silicon dioxide particles, by weight of the microcrystalline cellulose, wherein the microcrystalline cellulose and silicon dioxide are in intimate association with each other. The silicon dioxide utilized in the novel excipient has a particle size from about 1 nanometer to about 100 microns. Most preferably, the silicon dioxide is a grade of colloidal silicon dioxide.
Owner:J RETTENMAIER & SOEHNE GMBH CO KG ROSENBERG
Semitransparent optical detector including a polycrystalline layer and method of making
InactiveUS6879014B2Final product manufactureSolid-state devicesVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserElectrical conductor
Materials suitable for fabricating optical monitors include amorphous, polycrystalline and microcrystalline materials. Semitransparent photodetector materials may be based on silicon or silicon and germanium alloys. Conductors for connecting to and contacting the photodetector may be made from various transparent oxides, including zinc oxide, tin oxide and indium tin oxide. Optical monitor structures based on PIN diodes take advantage of the materials disclosed. Various contact, lineout, substrate and interconnect structures optimize the monitors for integration with various light sources, including vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) arrays. Complete integrated structures include a light source, optical monitor and either a package or waveguide into which light is directed.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC +1
Heat spreader and semiconductor device and package using the same
InactiveUS7067903B2Improve thermal conductivityLarge thermal conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPolymer adhesiveCeramic
A semiconductor device and package has a heat spreader directly disposed on the reverse surface of the semiconductor device. This heat spreader includes a diamond layer or a layer containing diamond and ceramics such as silicon carbide and aluminum nitride. The heat spreader is directly formed on a substrate for the semiconductor device. In particular, the heat spreader is composed of a diamond layer and one or two metal or ceramic members, which are bonded to the diamond layer with one or two polymer adhesive layers. This diamond layer has a fiber structure across the thickness or a microcrystalline structure. Cilia are formed on a surface of the diamond layer facing the one or two metal or ceramic members.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Systems and Methods of Laser Texturing of Material Surfaces and their Applications
InactiveUS20100143744A1Enhance light absorptionImprove conductivityDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAlloyElectron
The surface of a material is textured and by exposing the surface to pulses from an ultrafast laser. The laser treatment causes pillars to form on the treated surface. These pillars provide for greater light absorption. Texturing and crystallization can be carried out as a single step process. The crystallization of the material provides for higher electric conductivity and changes in optical and electronic properties of the material. The method may be performed in vacuum or a gaseous environment. The gaseous environment may aid in texturing and / or modifying physical and chemical properties of the surfaces. This method may be used on various material surfaces, such as semiconductors, metals and their alloys, ceramics, polymers, glasses, composites, as well as crystalline, nanocrystalline, polycrystalline, microcrystalline, and amorphous phases.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Surface passivated photovoltaic devices
InactiveUS7375378B2Solid-state devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor materialsBack surface field
A photovoltaic device comprising a photovoltaic cell is provided. The photovoltaic cell includes an emitter layer comprising a crystalline semiconductor material and a lightly doped crystalline substrate disposed adjacent the emitter layer. The lightly doped crystalline substrate and the emitter layer are oppositely doped. Further, the photovoltaic device includes a back surface passivated structure coupled to the photovoltaic cell. The structure includes a highly doped back surface field layer disposed adjacent the lightly doped crystalline substrate. The highly doped back surface field layer includes an amorphous or a microcrystalline semiconductor material, wherein the highly doped back surface field layer and the lightly doped crystalline substrate are similarly doped, and wherein a doping level of the highly doped back surface field layer is higher than a doping level of the lightly doped crystalline substrate. Additionally, the structure may also include an intrinsic back surface passivated layer disposed adjacent the lightly doped crystalline substrate, where the intrinsic back surface passivated layer includes an amorphous or a microcrystalline semiconductor material.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Electrode for lithium batteries and rechargeable lithium battery
InactiveUS7410728B1Improve charge and discharge cycle characteristicsImprove featuresElectrode carriers/collectorsPrinted batteriesAmorphous siliconOptoelectronics
An electrode for lithium batteries, in which a thin film of active material capable of storage and release of lithium, such as a microcrystalline or amorphous silicon thin film, is provided, through an interlayer, on a current collector, the electrode being characterized in that the interlayer comprises a material alloyable with the thin film of active material.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Pharmaceutical excipient having improved compressibility
InactiveUS6217909B1Improve compression performanceReduce the amount requiredInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsPowder deliverySilica particleSilicon dioxide
Owner:J RETTENMAIER & SOEHNE GMBH CO KG ROSENBERG
Thin film transistor
InactiveUS20090321737A1Increase the on-currentOff-current can be reducedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesNitrogenSemiconductor
A thin film transistor includes, as a buffer layer, a semiconductor layer which contains nitrogen and includes crystal regions in an amorphous structure between a gate insulating layer and source and drain regions, at least on the source and drain regions side. As compared to a thin film transistor in which an amorphous semiconductor is included in a channel formation region, on-current of a thin film transistor can be increased. In addition, as compared to a thin film transistor in which a microcrystalline semiconductor is included in a channel formation region, off-current of a thin film transistor can be reduced.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Back contact and back reflector for thin film silicon solar cells
InactiveUS20050172997A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationDielectricBack reflector
A thin film silicon solar cell for use in photovoltaic cells having a carrier substrate, a front transparent conductive oxide contact, a thin film silicon solar cell layer having at least one layer of hydrogenated microcrystalline silicon or nanocrystalline silicon, and a back contact having a transparent conductive oxide contact layer and a back reflective layer comprising a white pigmented dielectric reflective media.
Owner:UNAXIS BALZERS LTD
Light-emitting device
InactiveUS20090001375A1Improve batch productivityHighly reliable electric characteristicElectroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor devicesLight emitting deviceSemiconductor
In a light-emitting device having an inverted staggered thin film transistor, the inverted staggered thin film transistor is formed as follows: a gate insulating film is formed over a gate electrode; a microcrystalline semiconductor film which functions as a channel formation region is formed over the gate insulating film; a buffer layer is formed over the microcrystalline semiconductor film; a pair of source and drain regions are formed over the buffer layer; and a pair of source and drain electrodes are formed in contact with the source and drain regions so as to expose a part of the source and drain regions.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
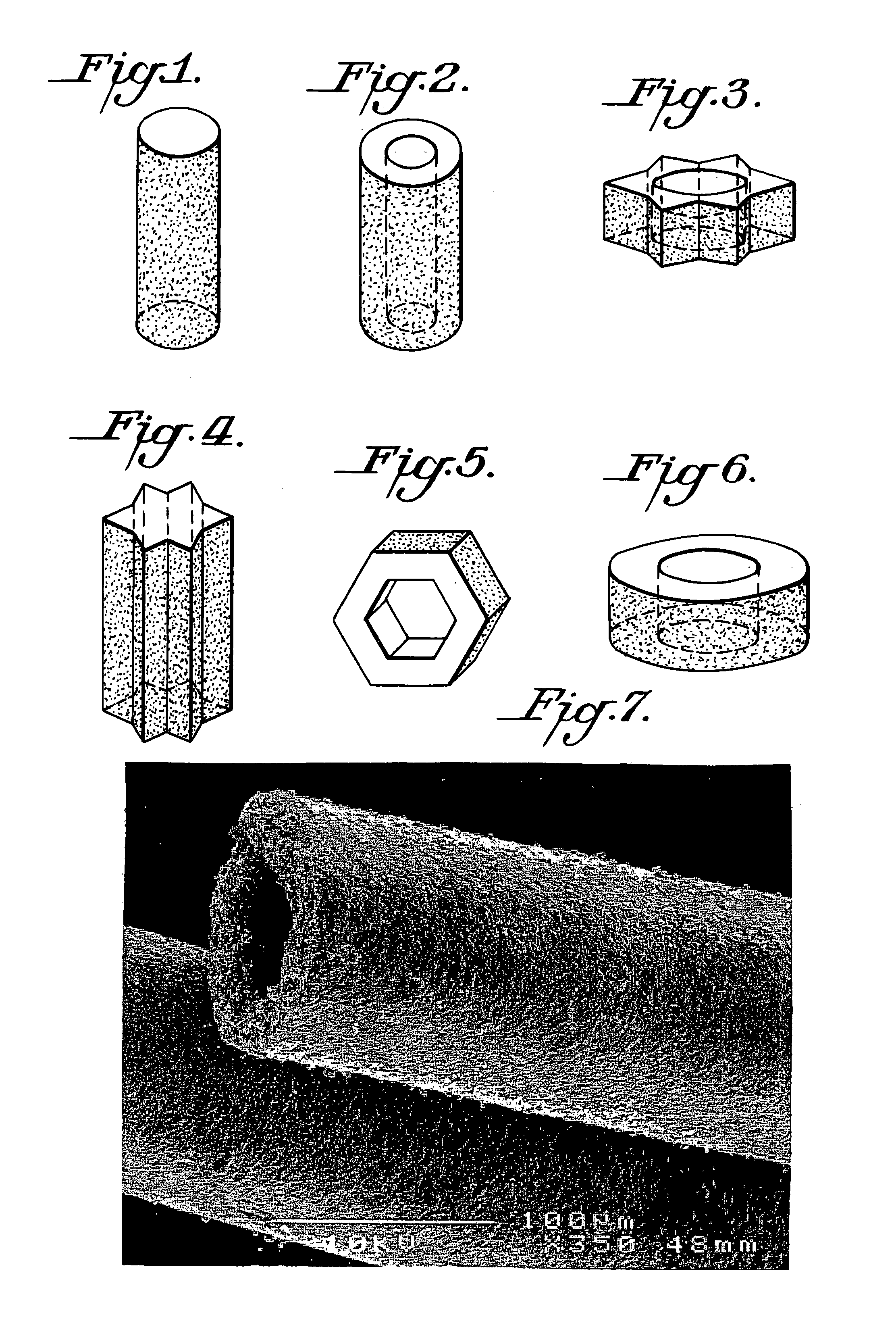
Microcrystalline alpha-Al2O3 shaped body, method for the production and use thereof
InactiveUS7169198B2Lower sintering temperatureHigh densityPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesMetallurgySolvent
The invention relates to a method for the production of a sintered, microcrystalline α-Al2O3-based shaped body, which are used, for example, as abrasive bodies, wherein an α-Al2O3 powder is used as starting material, said powder having an average particle diameter of <2 μm, and processed with at least one binder and a solvent with the purpose of obtaining an extrudable material that is subsequently extruded. The extrudate is then further processed into a shaped body that is sintered at a temperature range of between 1300° C. and 1750° C.
Owner:IMERTECH SAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com