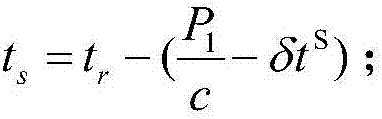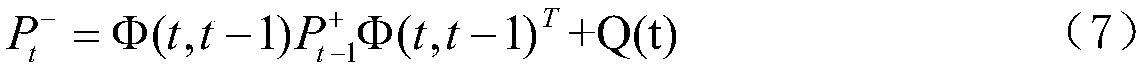Patents
Literature
524 results about "Low earth orbit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
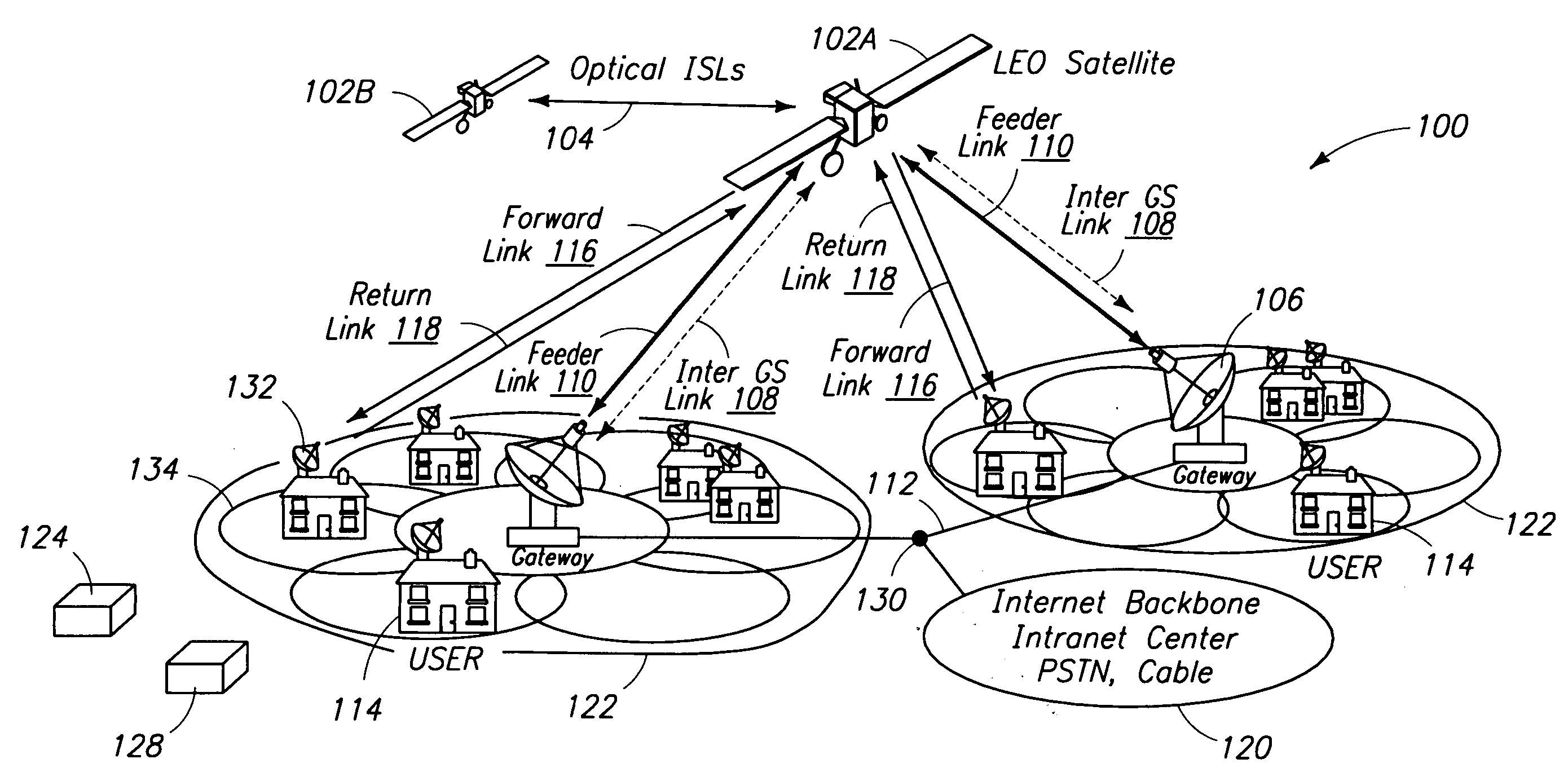
A low Earth orbit (LEO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an altitude of 2,000 km (1,200 mi) or less (approximately one-third of the radius of Earth), or with at least 11.25 periods per day (an orbital period of 128 minutes or less) and an eccentricity less than 0.25. Most of the manmade objects in outer space are in LEO.
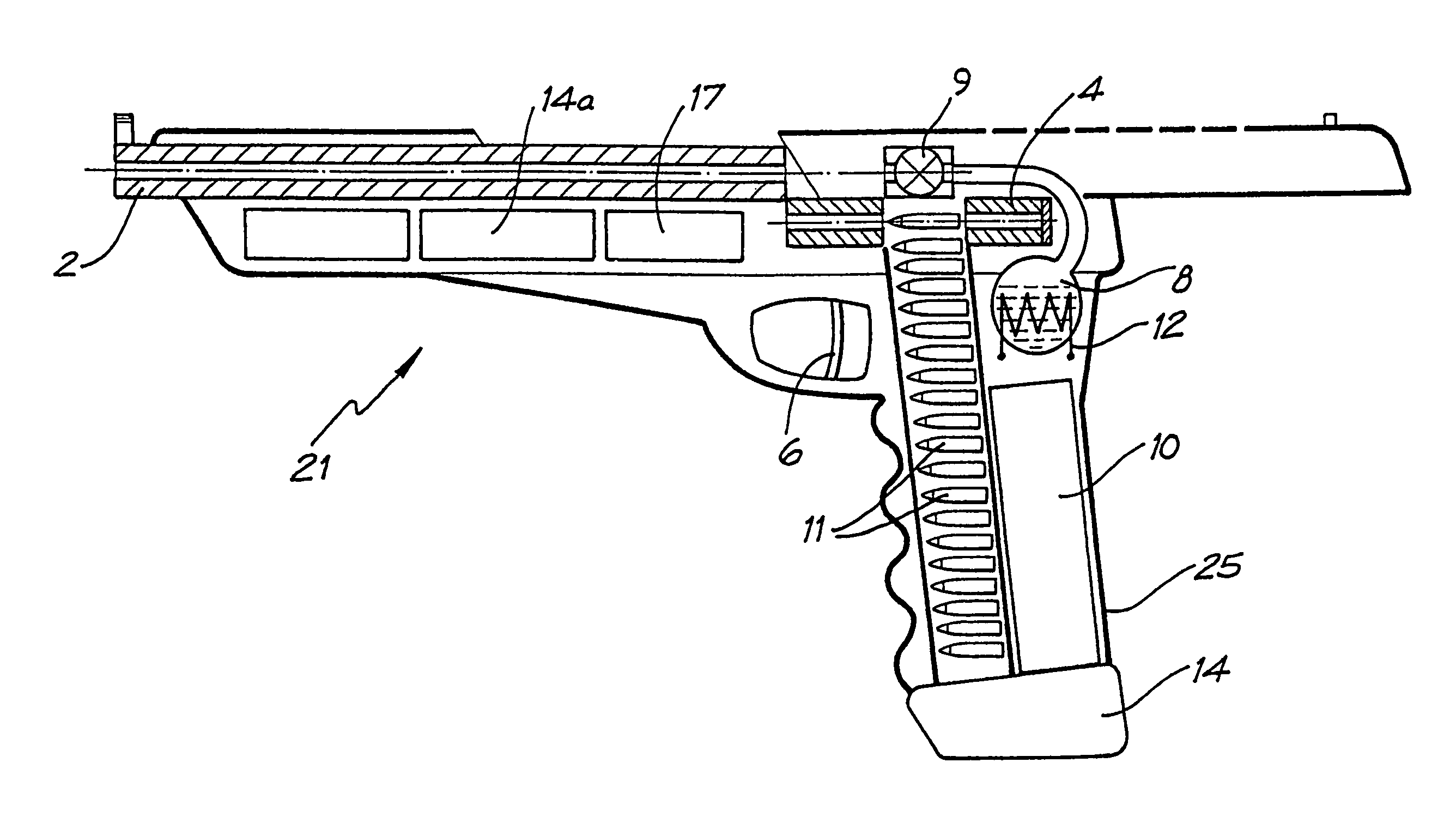
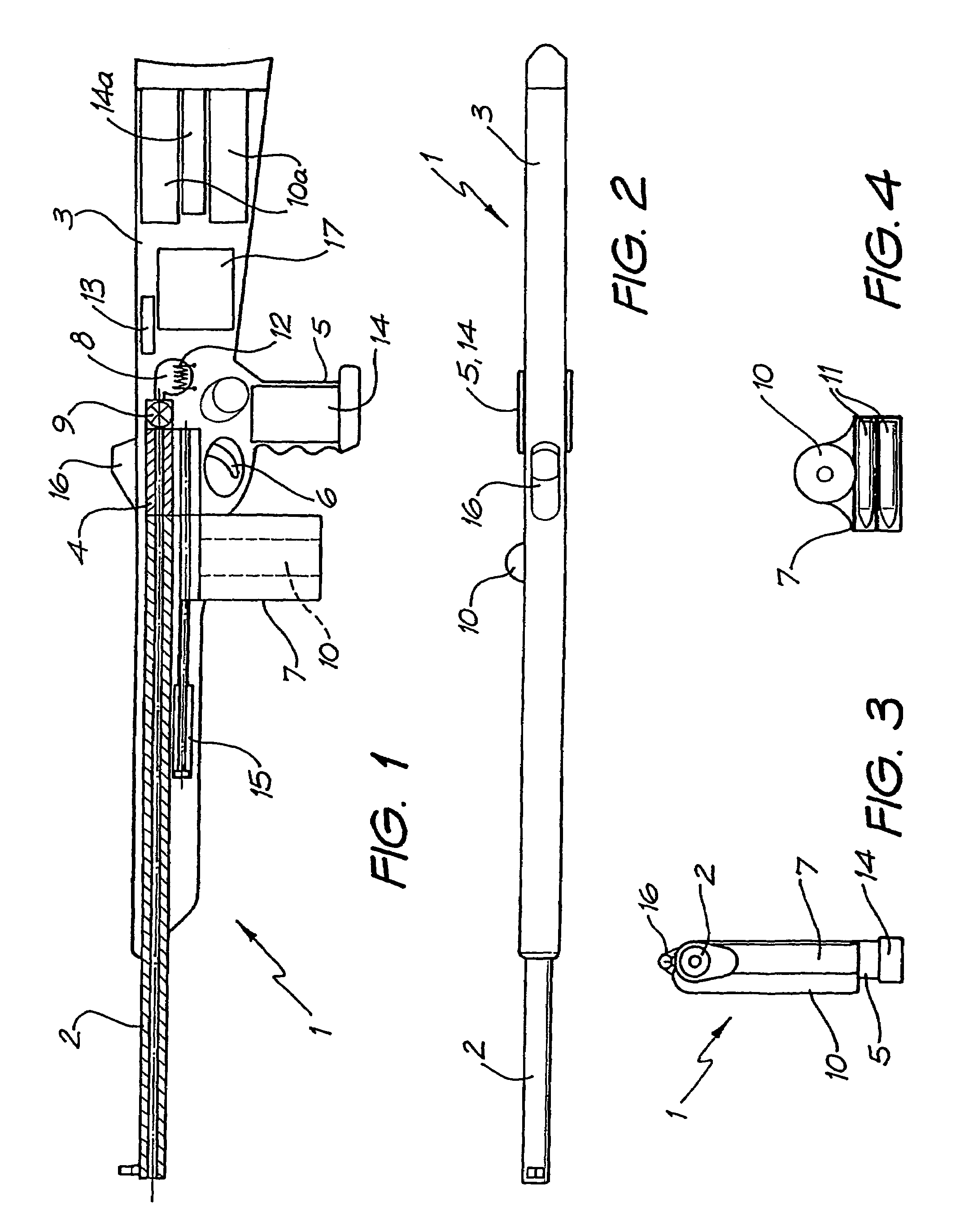
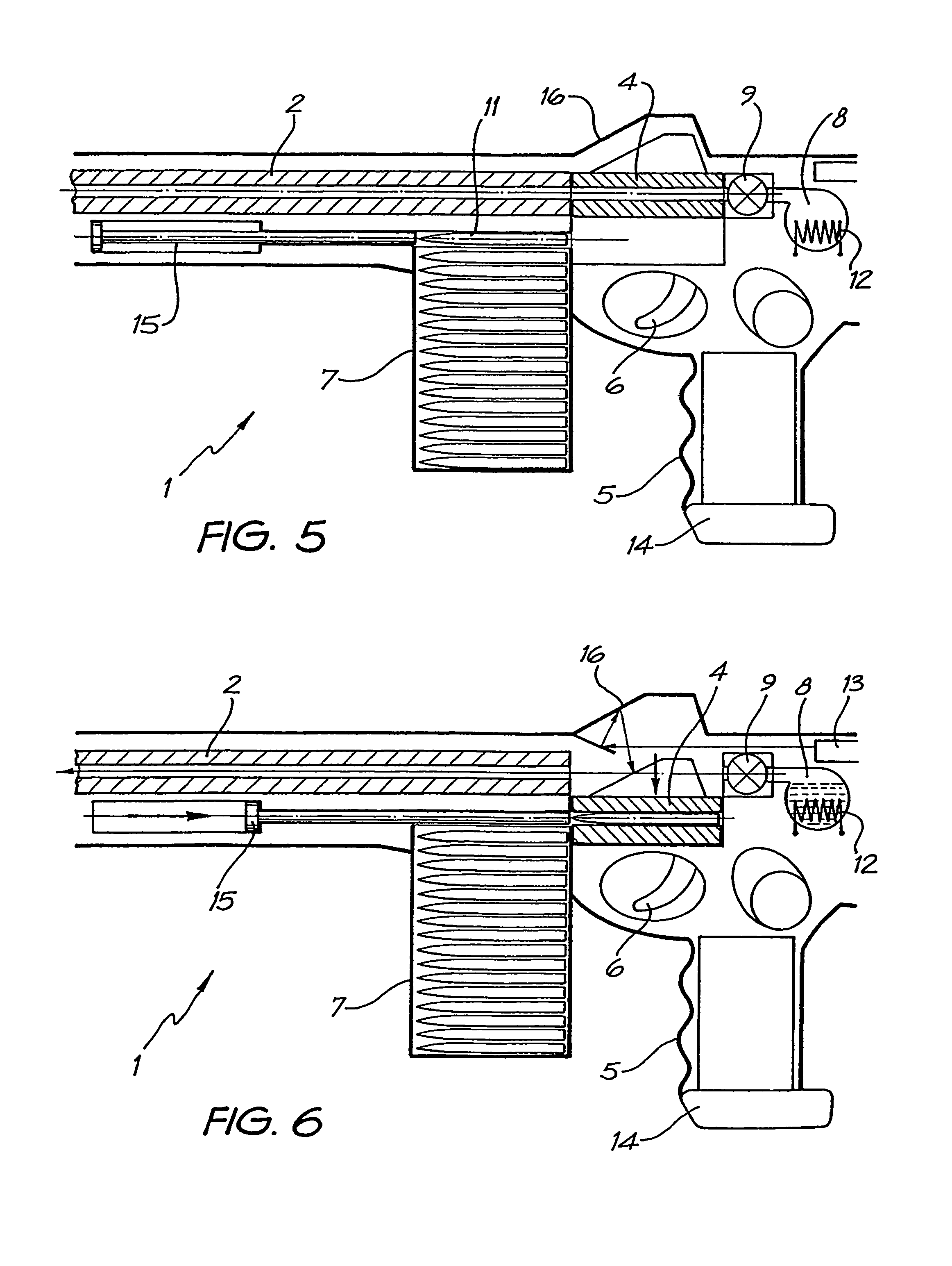
Projectile firing device using liquified gas propellant
Rifle (1) comprises barrel (2) and loading means (15) for introducing a projectile from magazine (7) into breech (4). The projectile is propelled by a compressed gas propellant initially stored as a liquid in canister (10). The liquid is heated to a super critical state in chamber (8) by heating element (12) to induce a phase change such that the liquid becomes a highly dense gas. The phase change from liquid to gas provides the energy required to expel the projectile at high velocity from rifle (1), regardless of the ambient temperature. The propellant is preferably CO2 which is heated to 31.06° C. Rifle (1) produces minimal noise and no heat signature, making it suitable for military and stealth purposes. A pistol and launchers for grenades or mortar bombs are also disclosed. Another version can launch low earth orbit satellites or payloads.
Owner:POLY SYST PTY LTD
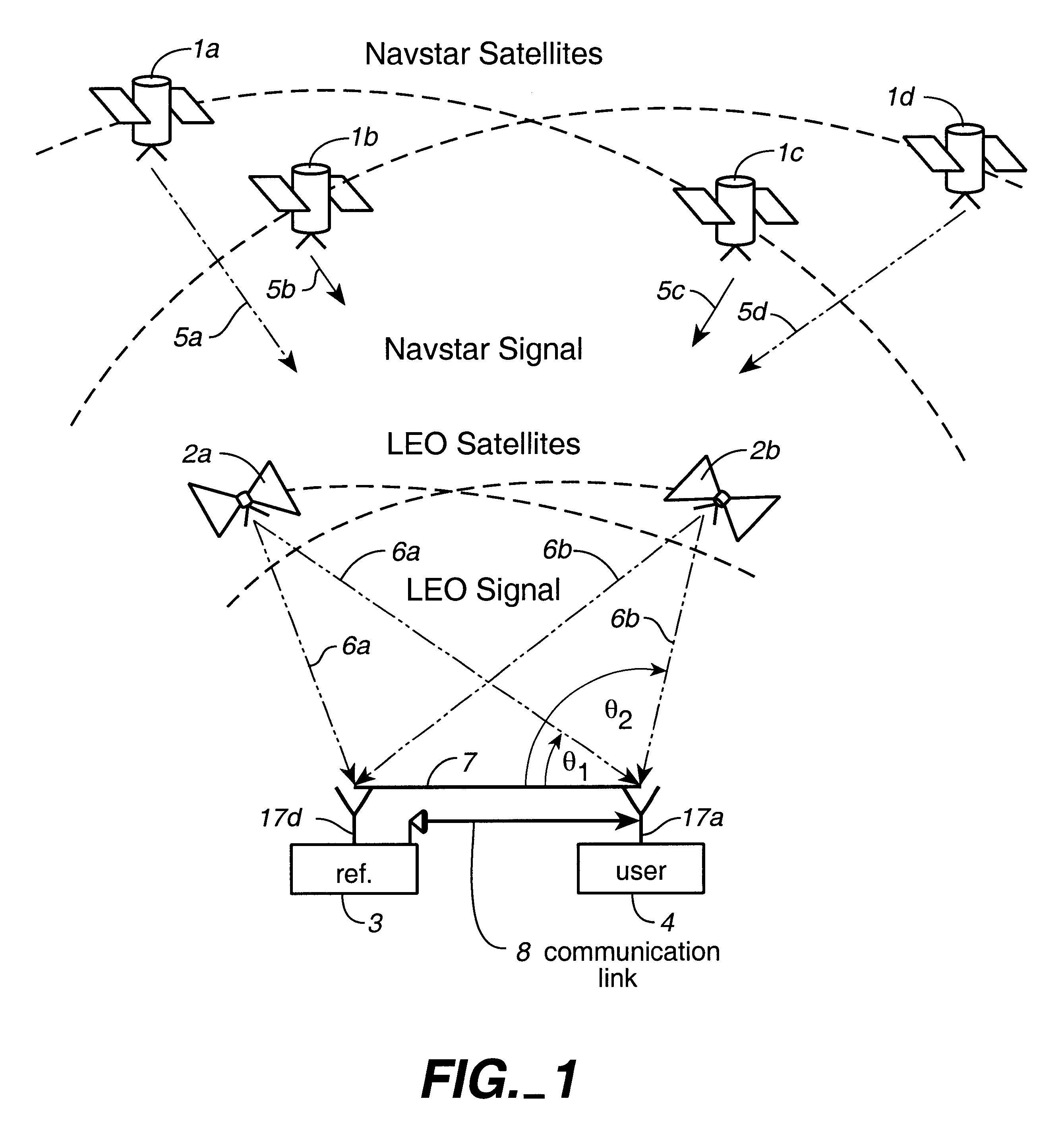
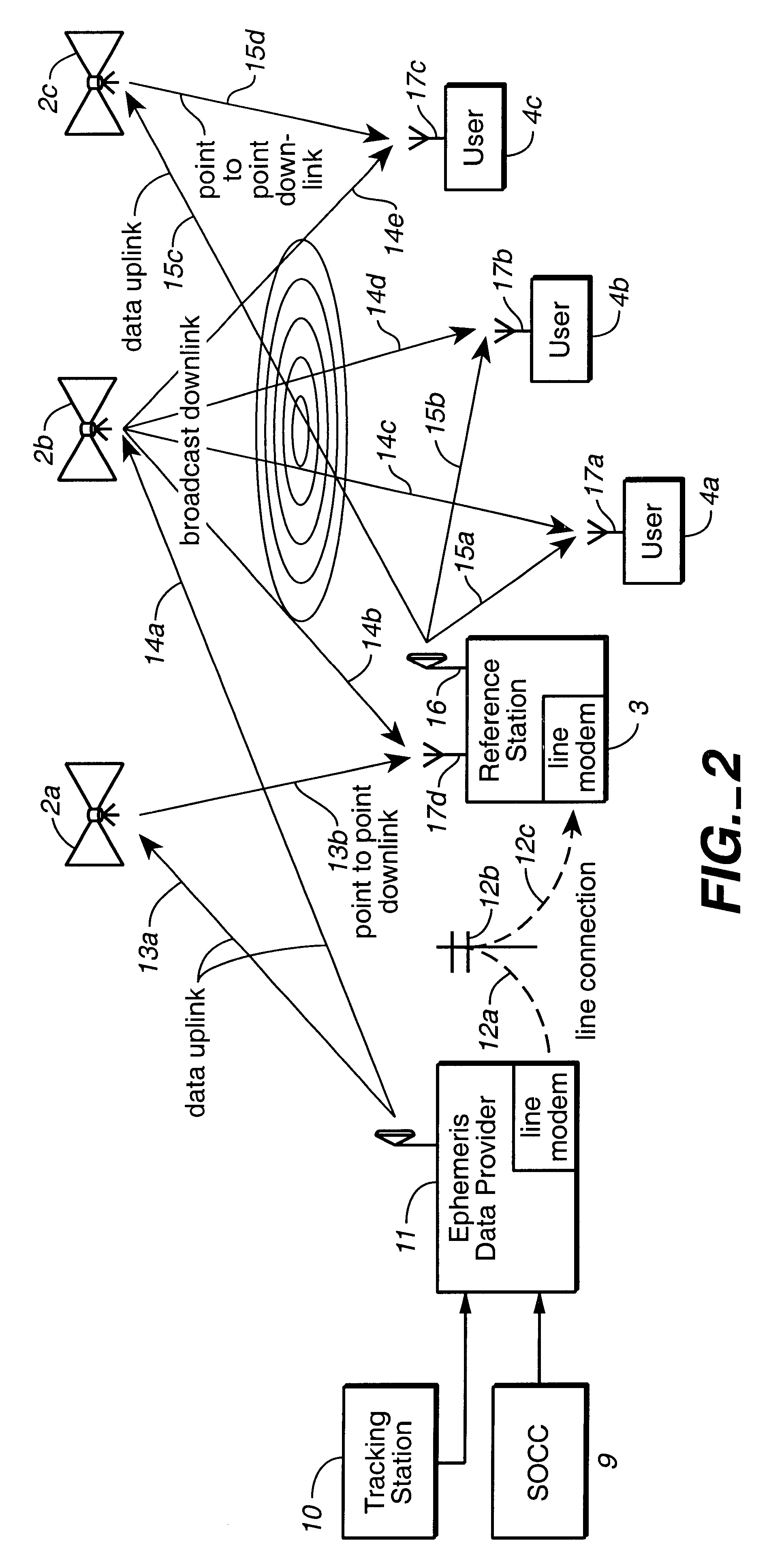
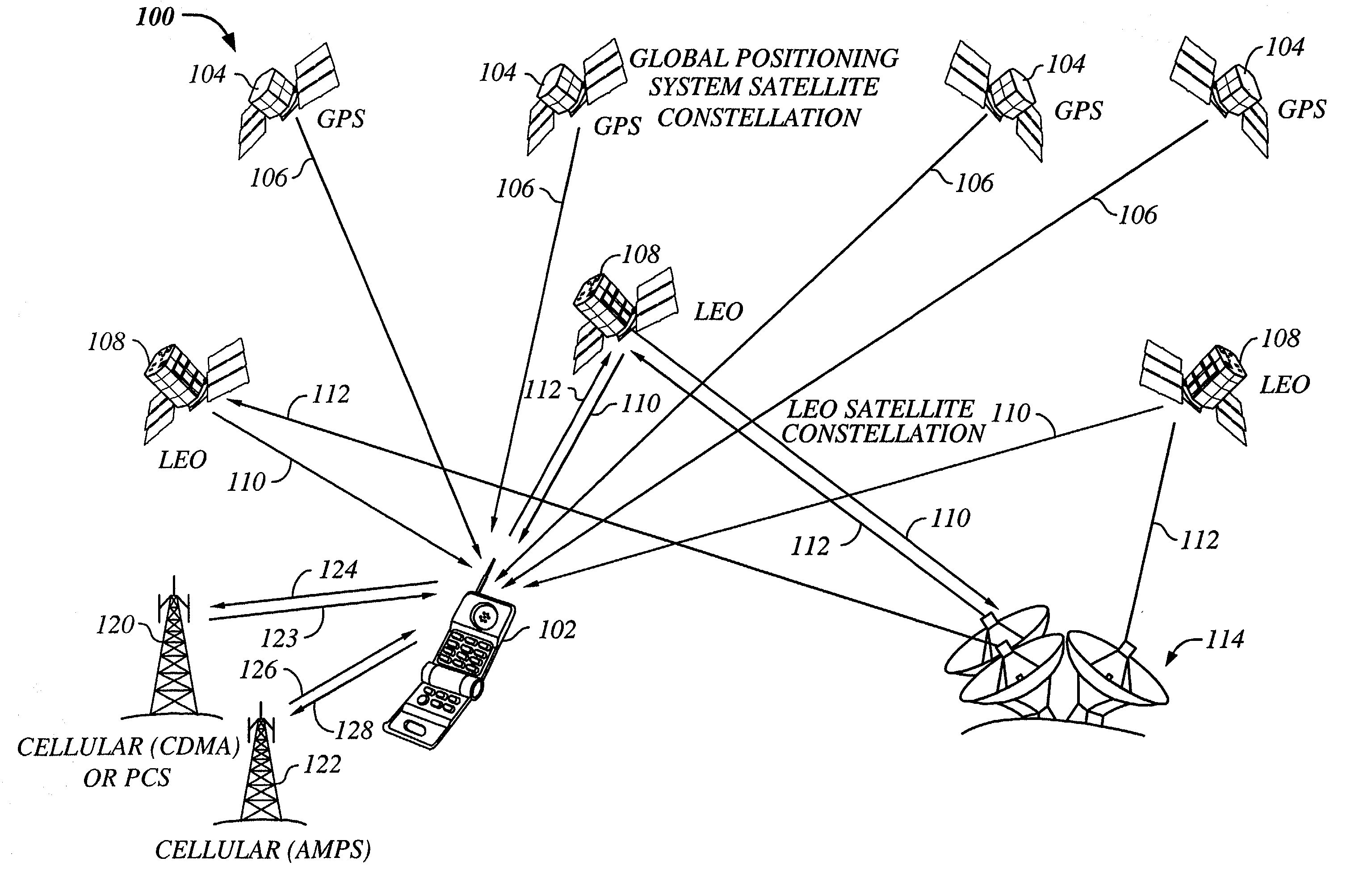
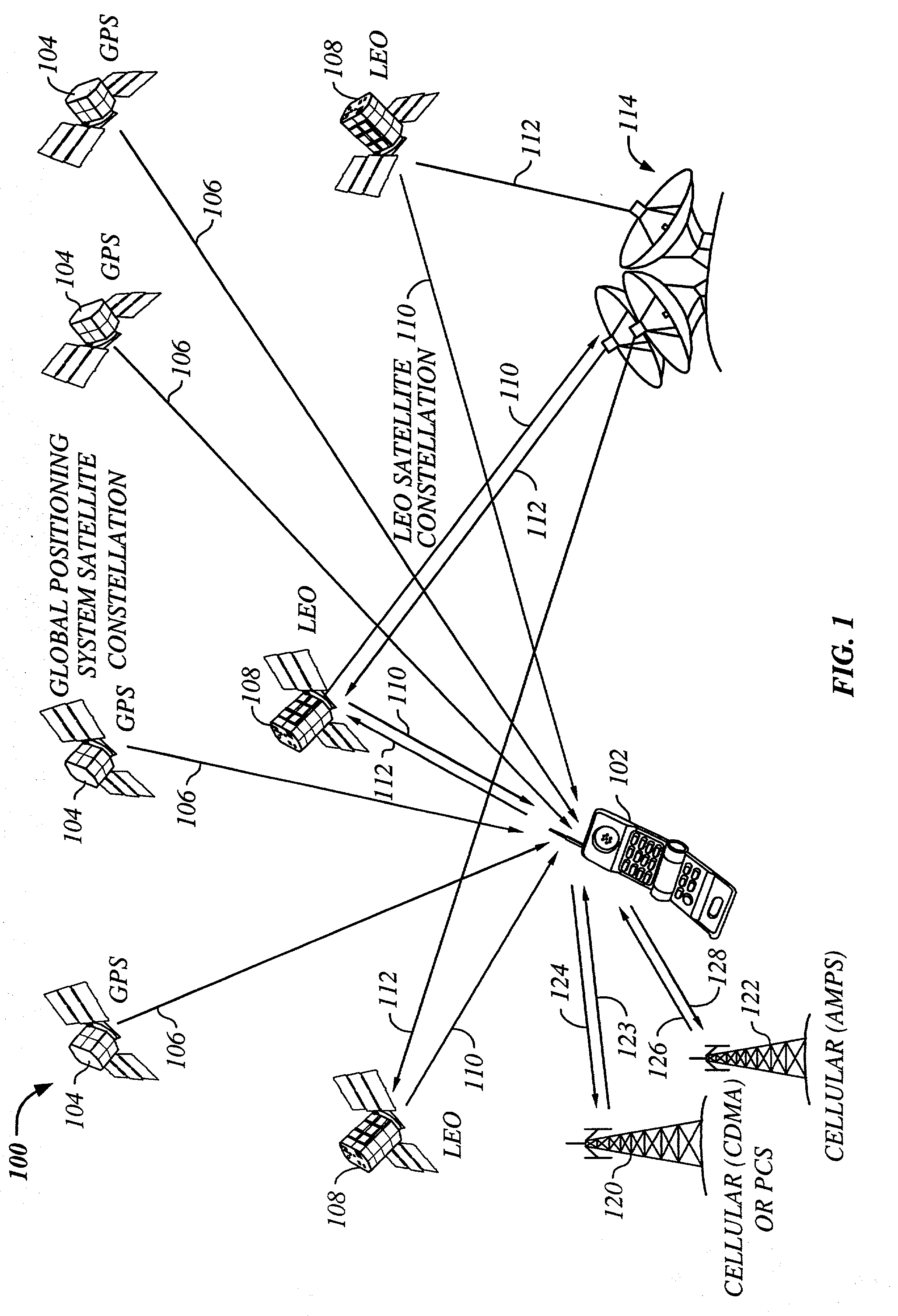
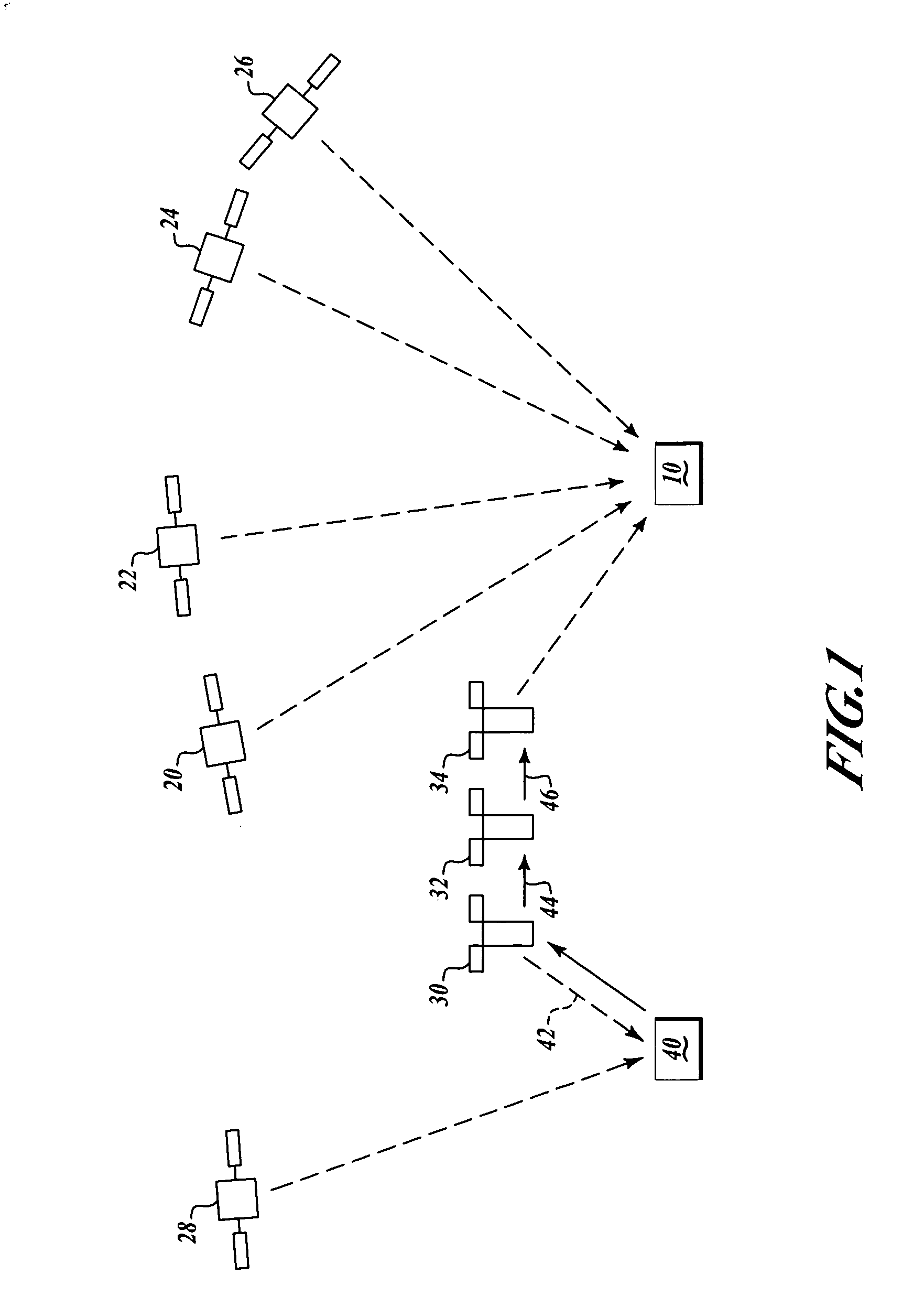
System using leo satellites for centimeter-level navigation
InactiveUS6373432B1Improve reliabilityEasy accessPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsNatural satelliteAmbiguity
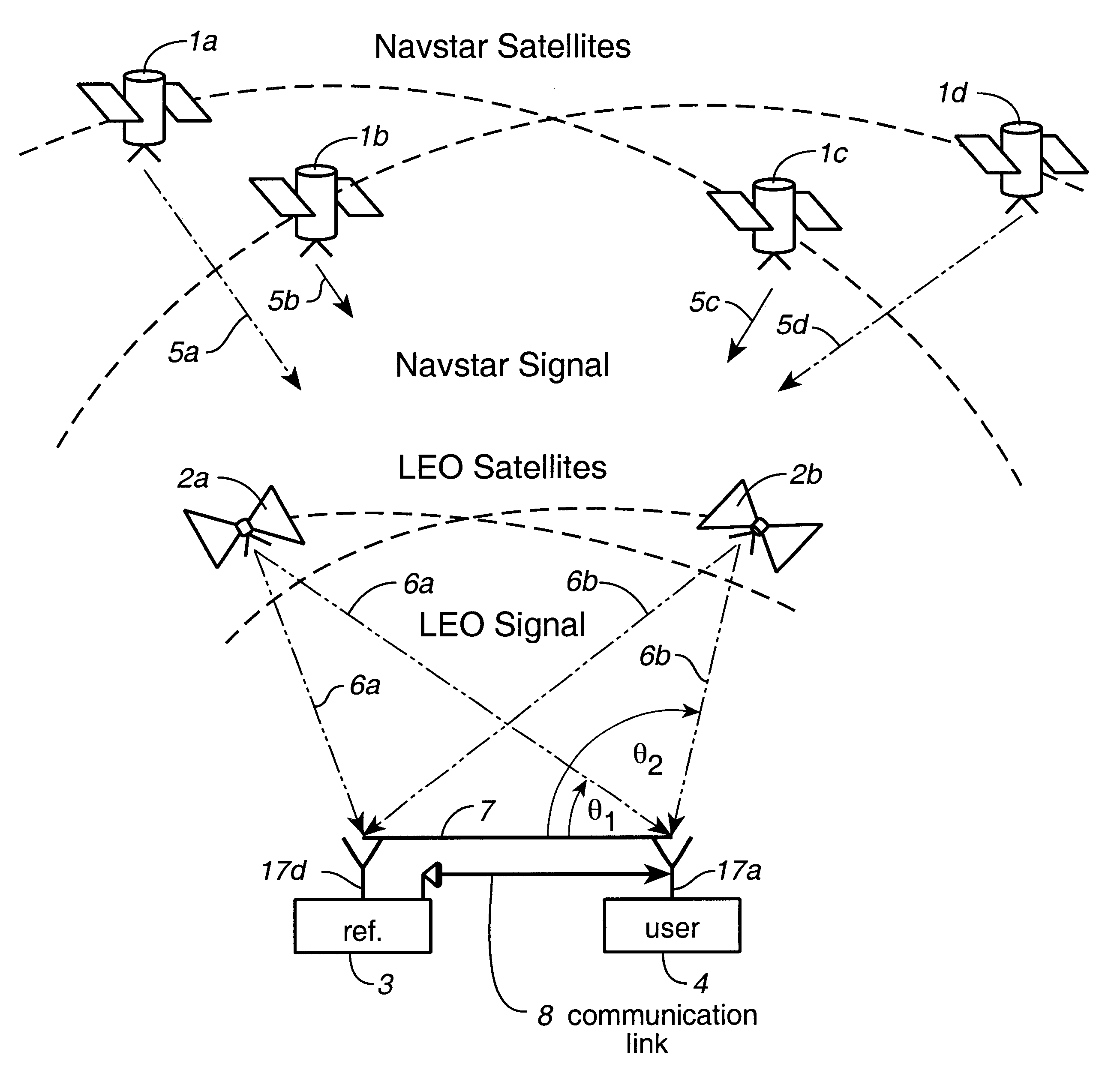
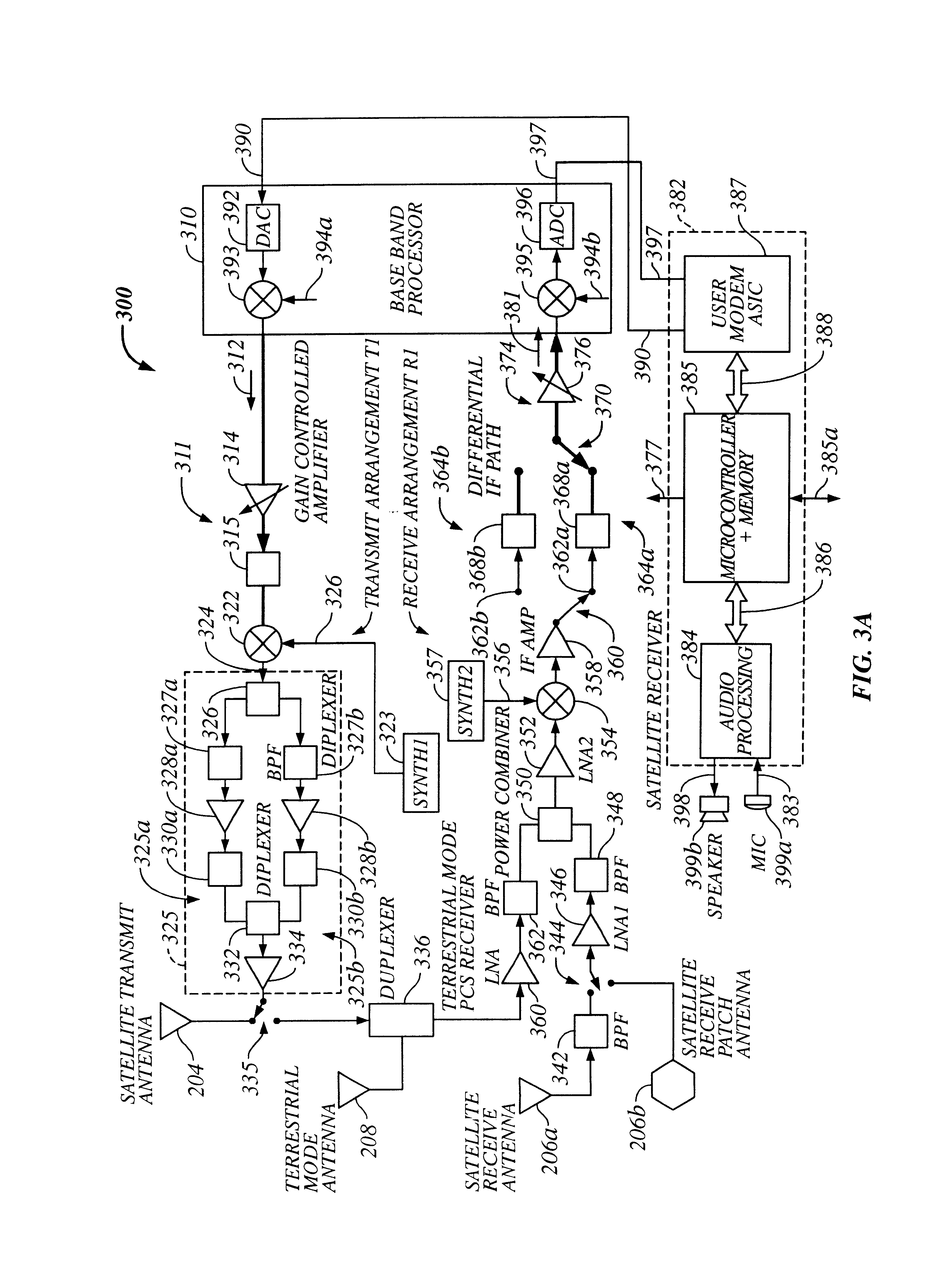
Disclosed herein is a system for rapidly resolving position with centimeter-level accuracy for a mobile or stationary receiver [4]. This is achieved by estimating a set of parameters that are related to the integer cycle ambiguities which arise in tracking the carrier phase of satellite downlinks [5,6]. In the preferred embodiment, the technique involves a navigation receiver [4] simultaneously tracking transmissions [6] from Low Earth Orbit Satellites (LEOS) [2] together with transmissions [5] from GPS navigation satellites [1]. The rapid change in the line-of-sight vectors from the receiver [4] to the LEO signal sources [2], due to the orbital motion of the LEOS, enables the resolution with integrity of the integer cycle ambiguities of the GPS signals [5] as well as parameters related to the integer cycle ambiguity on the LEOS signals [6]. These parameters, once identified, enable real-time centimeter-level positioning of the receiver [4]. In order to achieve high-precision position estimates without the use of specialized electronics such as atomic clocks, the technique accounts for instabilities in the crystal oscillators driving the satellite transmitters, as well as those in the reference [3] and user [4] receivers. In addition, the algorithm accommodates as well as to LEOS that receive signals from ground-based transmitters, then re-transmit frequency-converted signals to the ground.
Owner:INTEGRINAUTICS
Child locating and tracking apparatus
InactiveUS6278370B1Reduce manufacturing costImprove product reliabilityDirection finders using radio wavesBurglar alarmLow earth orbitTower
A child locating and tracking apparatus which provides for the location of a child that is lost, abducted or in general danger to be quickly located is disclosed. The apparatus uses a small transmitter that is always carried by the child and as such, is always present when danger arises. The transmitter is easily disguised and hidden in the child's clothing or personal adornments such as shoes, coats, watches, earrings, bracelets, rings and the like. The apparatus uses a system of world wide receivers such as those provided by local cellular telephone towers or by low earth orbiting satellites used for low power communication. When a child is lost or in danger, the child simply activates the transmitter which sends a signal to a central reporting station or stations where trained personnel will contact the respective parents and / or care givers to determine if the child could possibly be in danger. If an affirmative decision is reached, the monitoring station personnel will then assist the local law enforcement officials in the respective area anywhere in the world where the alarm was received in locating the child and removing the child from harm's path.
Owner:UNDERWOOD LOWELL
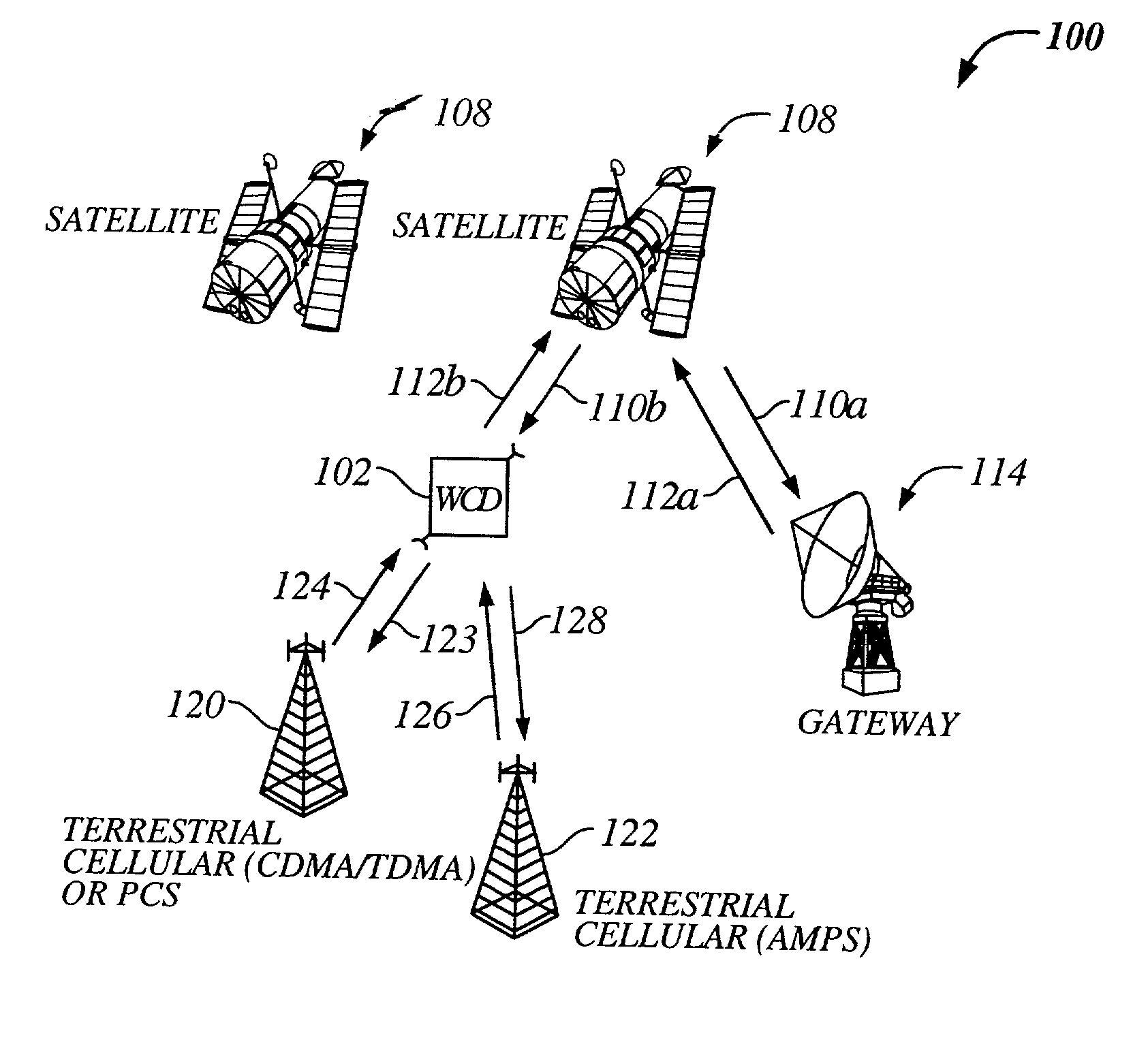
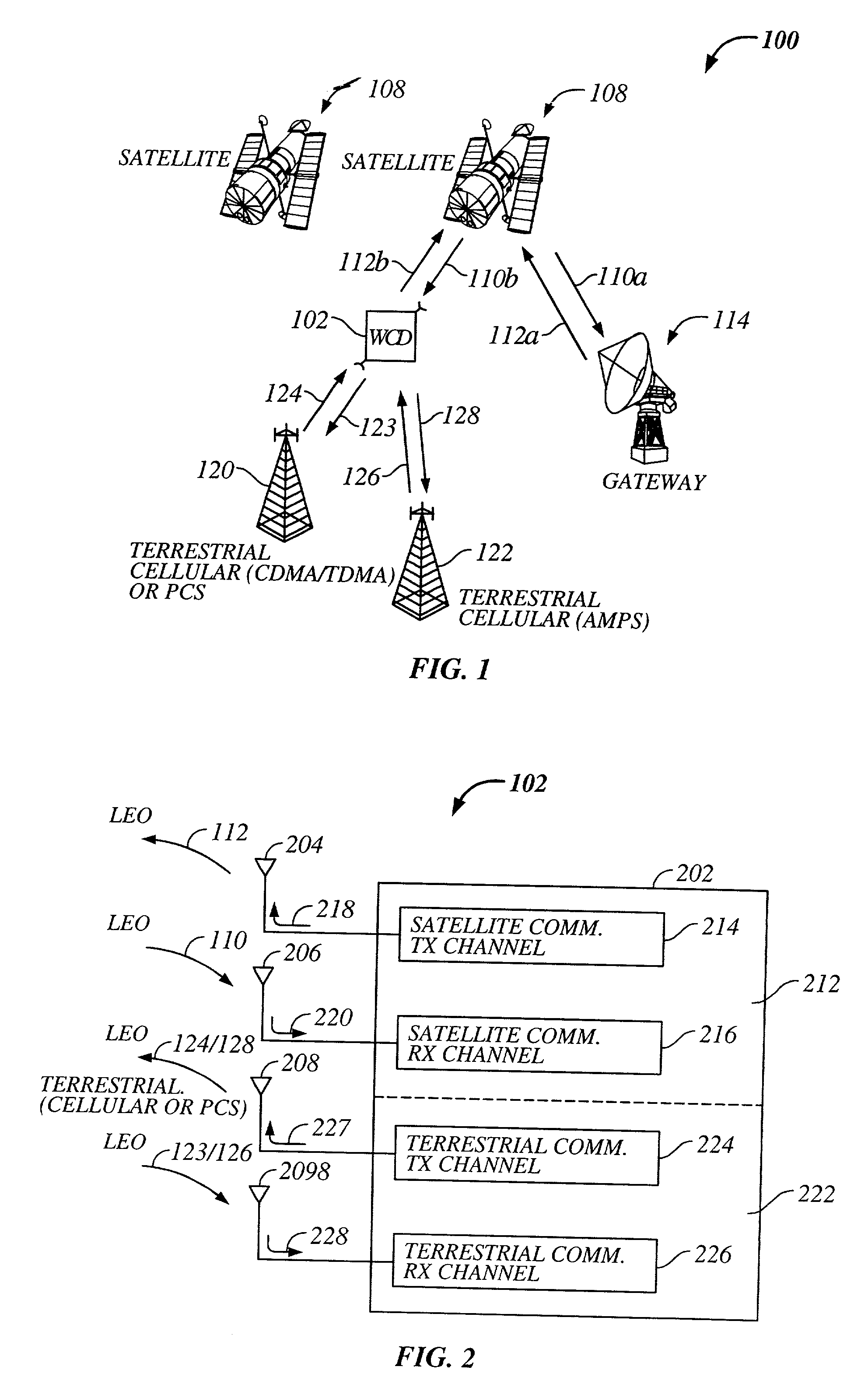
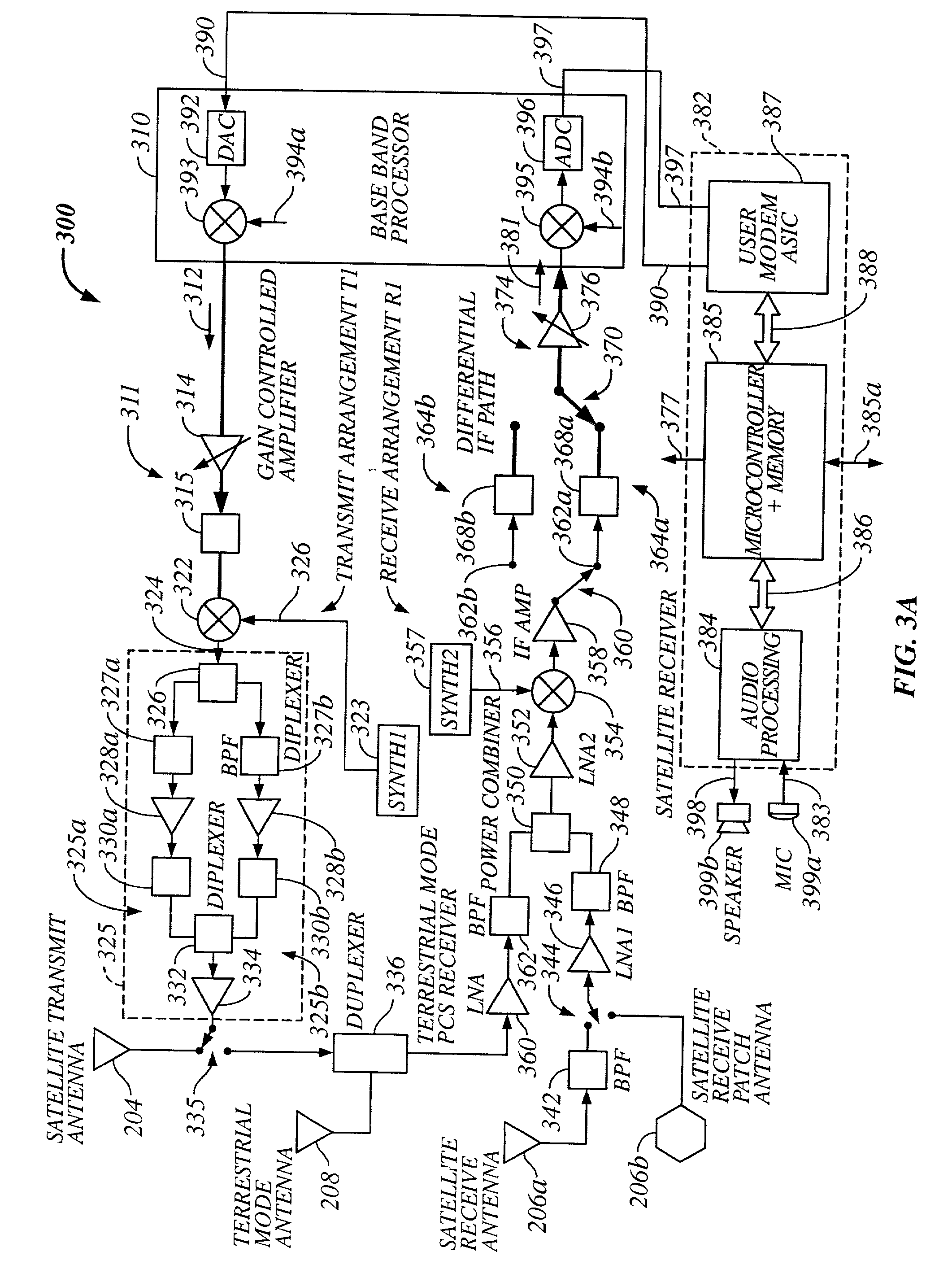
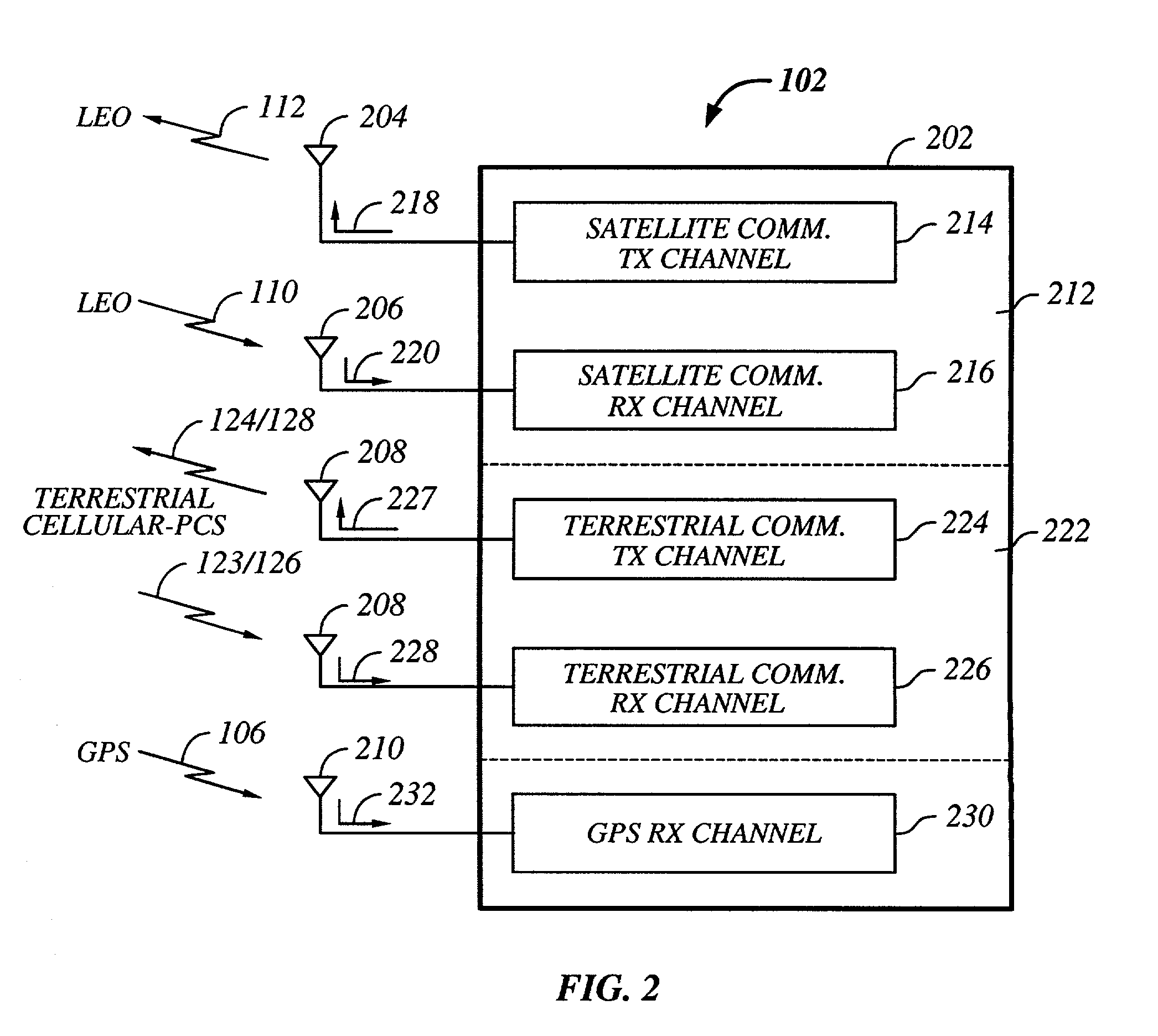
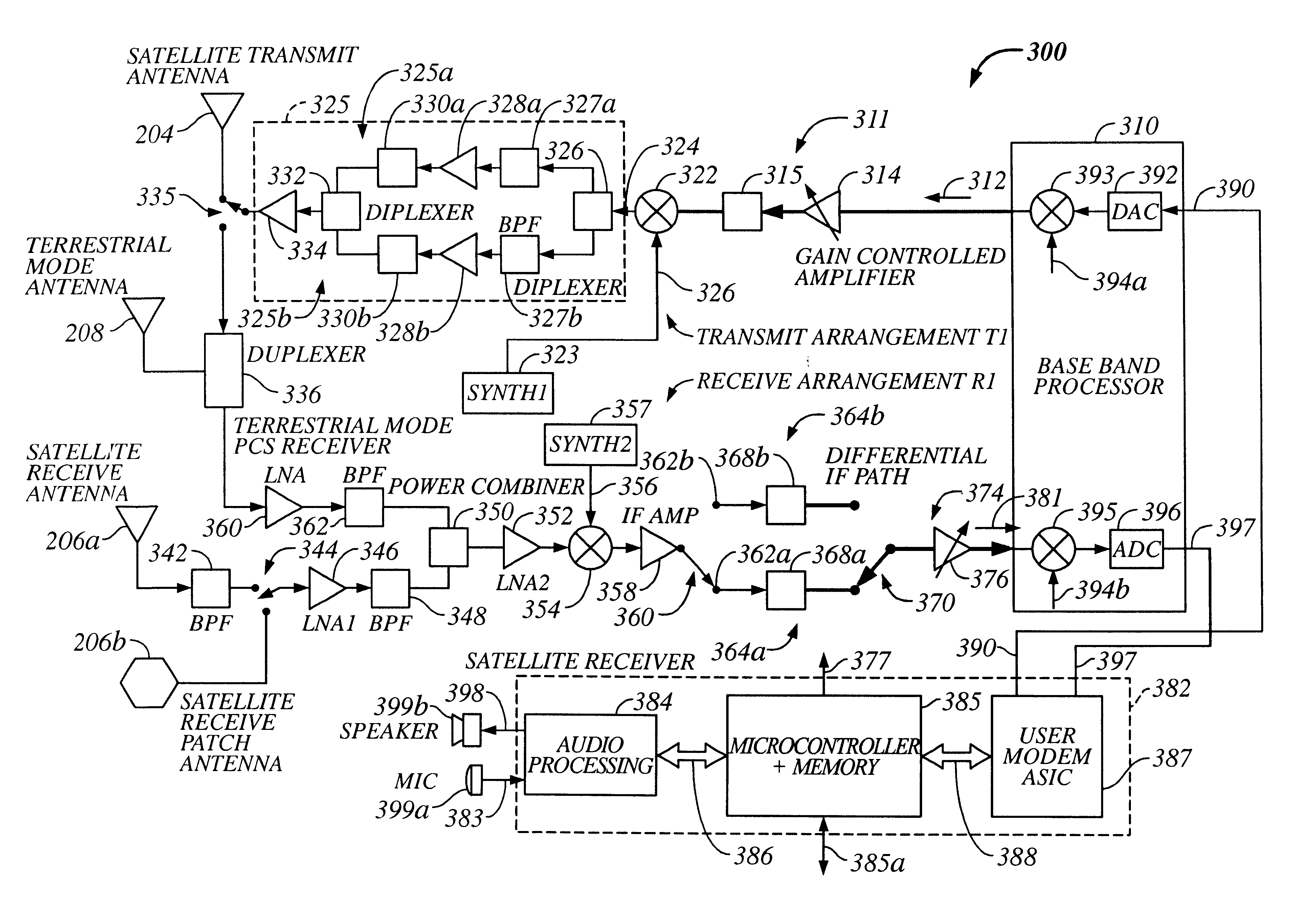
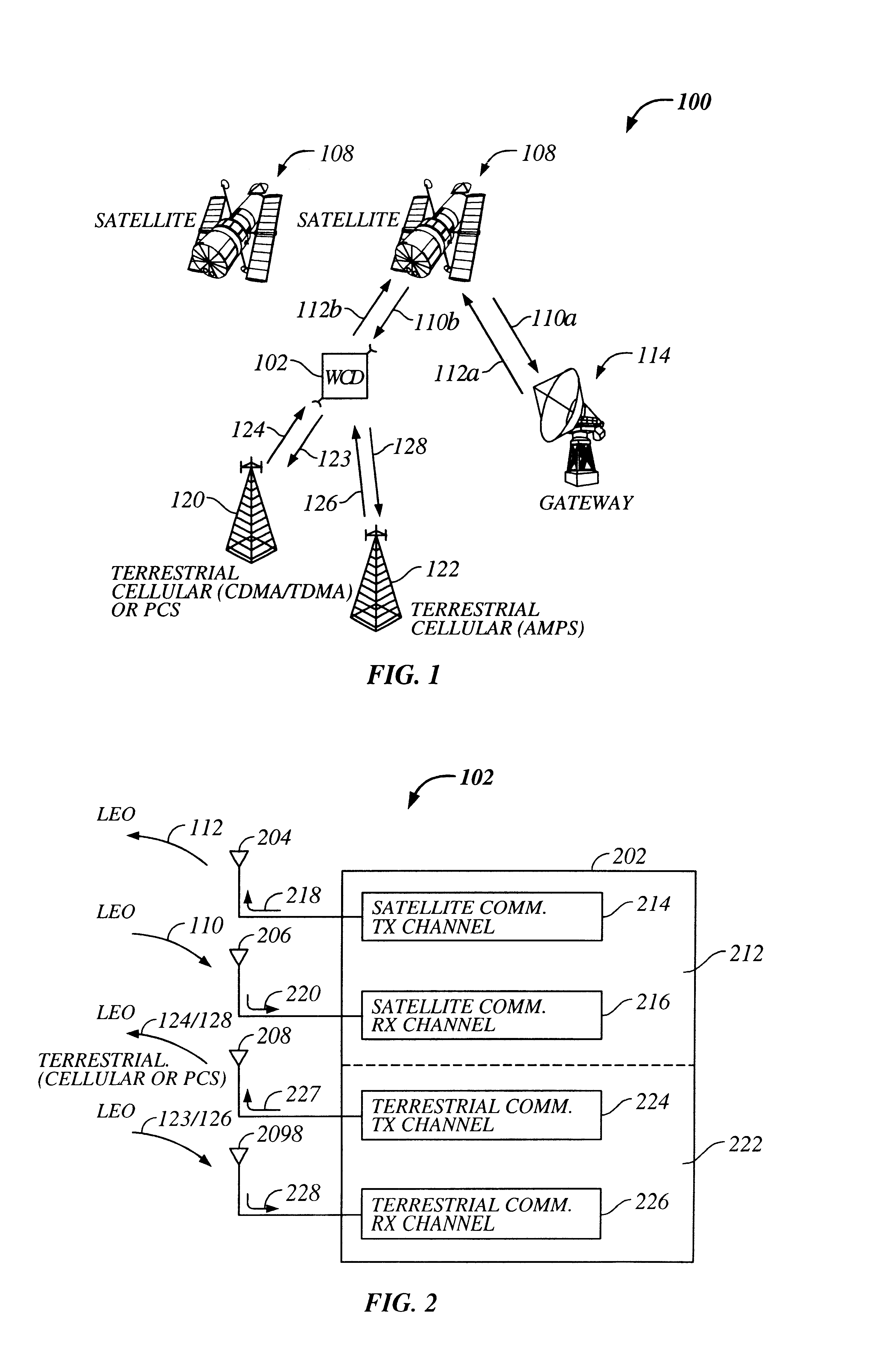
Multi-mode satellite and terrestrial communication device
InactiveUS20020177465A1Appropriate performanceSubstation equipmentRadio transmissionCommunications systemLow earth orbit
The present invention provides a multiple band mobile radio (also referred to as a Wireless Communication Device (WCD)) capable of communicating with both a satellite communication system and a terrestrial communication system. The satellite communication system can be, for example, a Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite system. The terrestrial communication system can be a Personal Communication System (PCS), or a cellular system, including either an analog or a digitally based cellular system. The cellular analog system can be AMPS. The digitally based cellular system can be a CDMA or a TDMA based communication system. The WCD can concurrently receive signals from the terrestrial communication system and the satellite communication system.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for providing wideband services using medium and low earth orbit satellites
InactiveUS6678520B1Interference minimizationMinimize interferenceActive radio relay systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsHigh elevationLow earth orbit
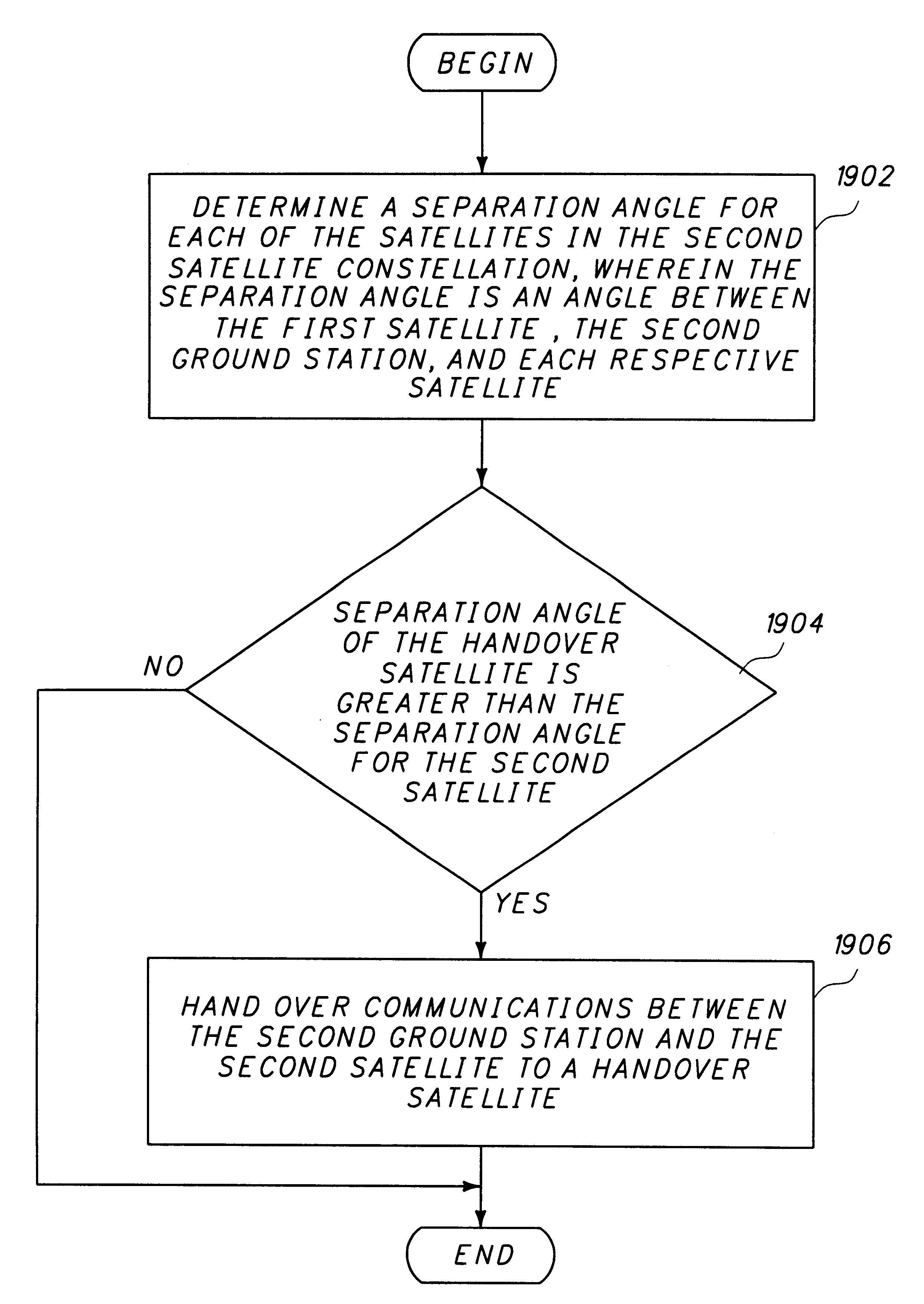
A method and apparatus for mitigating communications interference between satellite communications systems in different orbits is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of evaluating a geometrical relationship between a second ground station and the satellites in the second satellite constellation, and directing communications between the second ground station and the second satellite according to the evaluated geometrical relationship. In one embodiment communications are handed over from a first satellite to another satellite when the first satellite is no longer at the highest elevation angle of visible satellites. In another embodiment, handover occurs when the first satellite drops below a minimum elevation angle.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
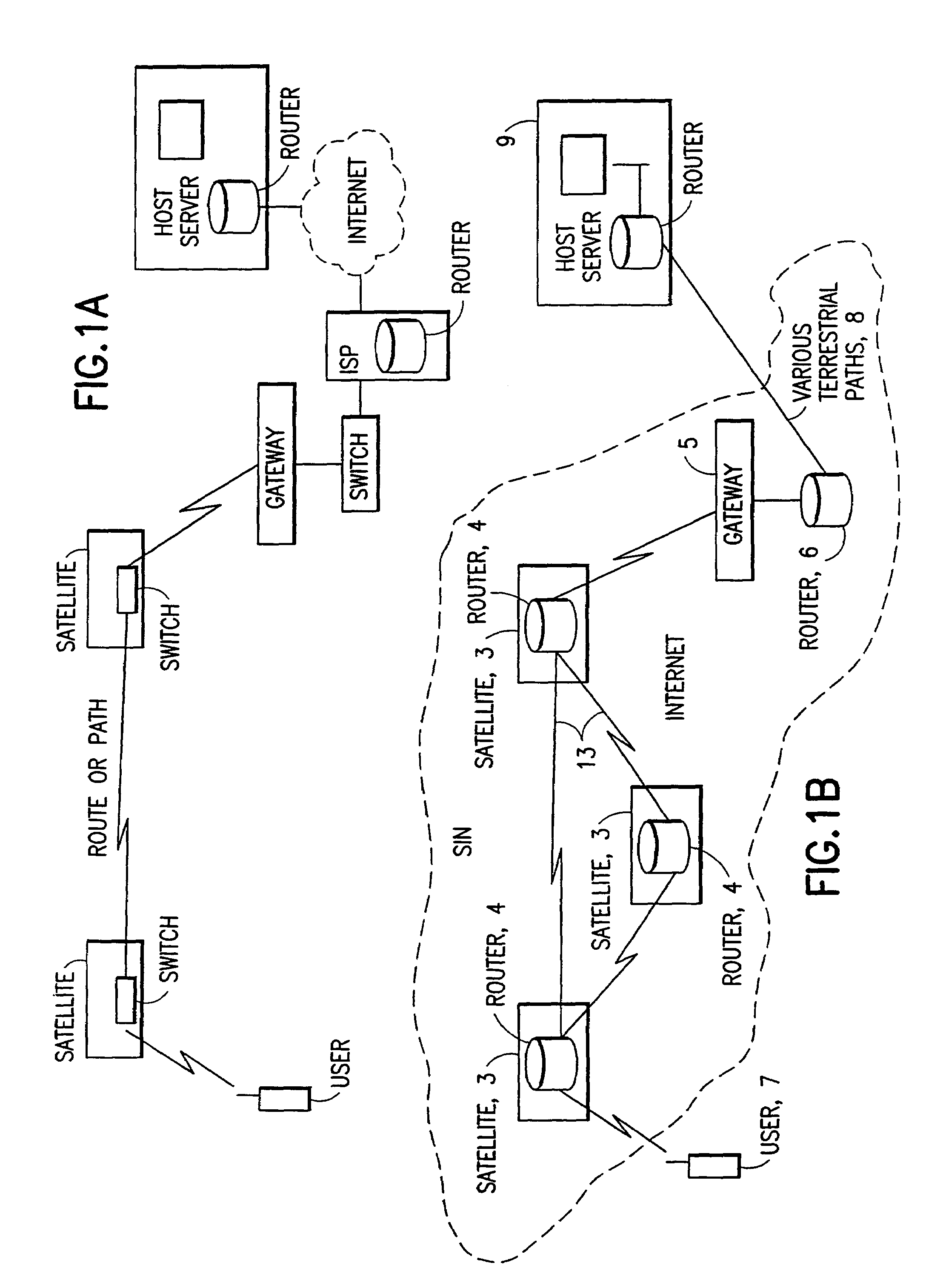
ISP system using non-geosynchronous orbit satellites
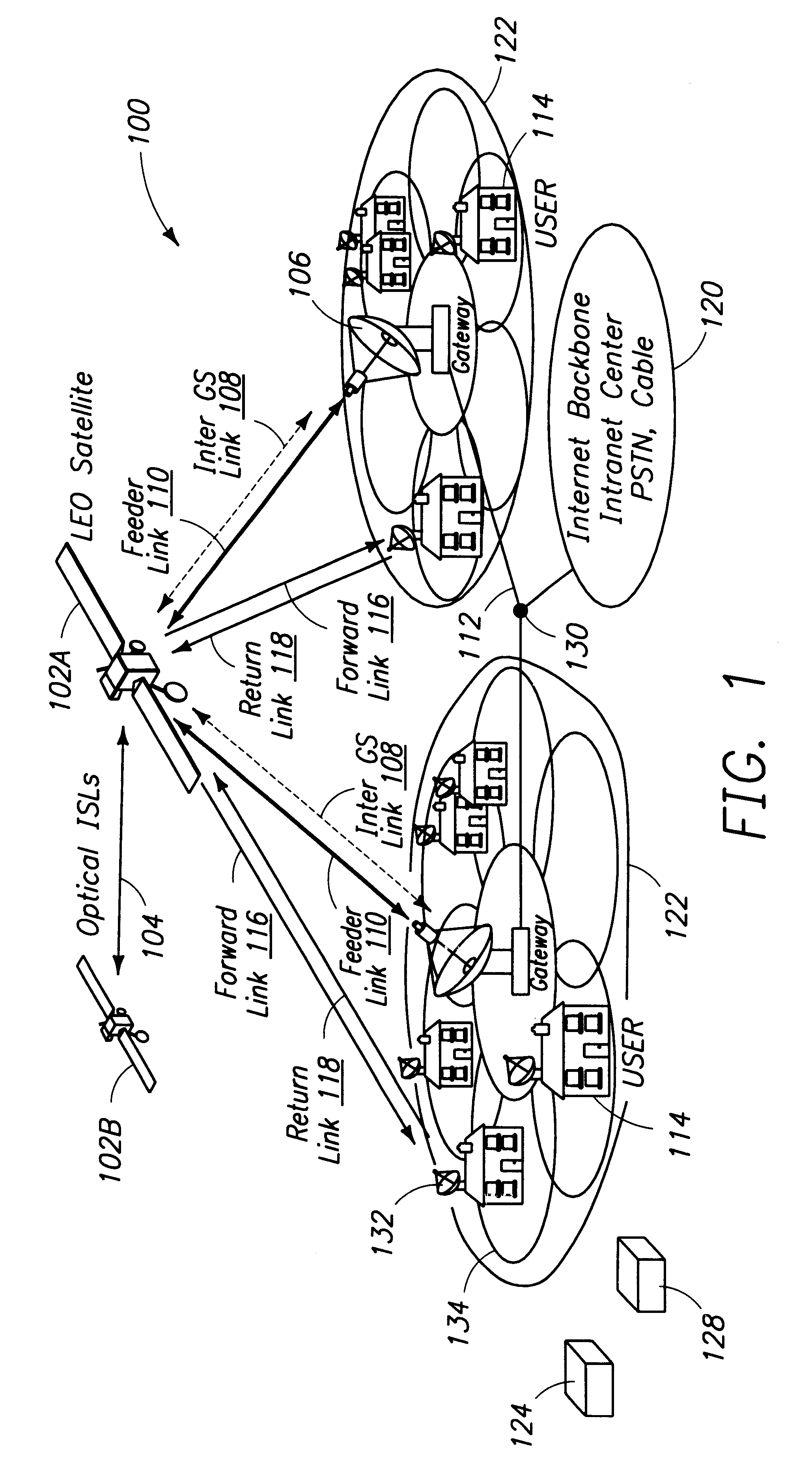
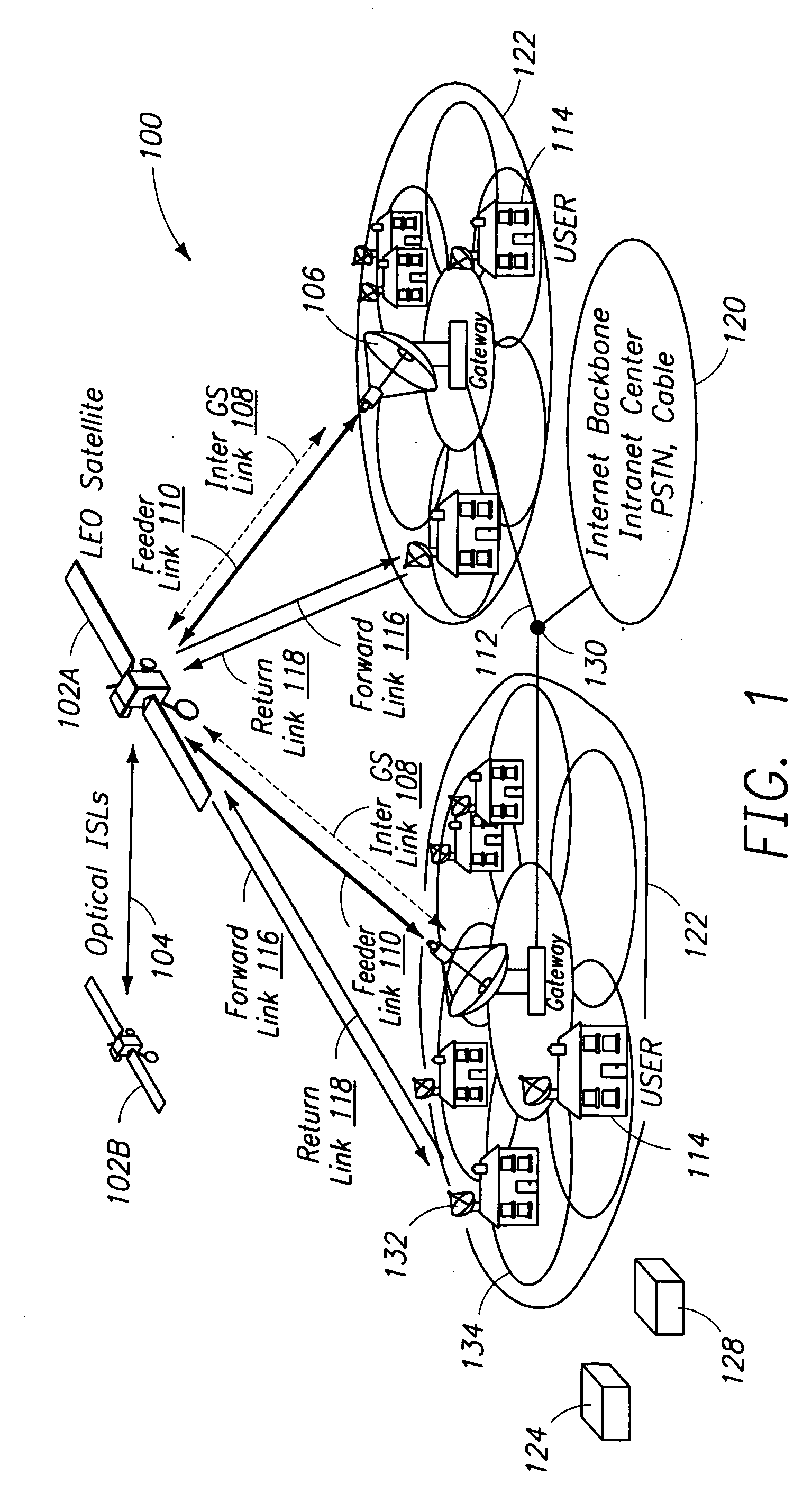
A satellite communication system includes a plurality of satellites, such as low earth orbit satellites, and a plurality of gateways. The satellite communication system is bidirectionally coupled to a terrestrial communication system through at least the plurality of gateways. The satellite communication system and the terrestrial communications system together form a data communication network having a plurality of nodes including source nodes, destination nodes and intermediate nodes. Multiple copies of a packet can coexist within the data communication network, and the packet and its one or more copies are routed, using at least in part satellite-resident routers and gateway-resident routers, over a plurality of different paths between a particular source node and a particular destination node. At least one duplicate copy of a given packet is simply not used during the execution of a packet reordering procedure in the destination node, or at an intermediate node. Certain of the paths are carried over satellite-to-satellite cross-links, while certain other ones of the paths are carried over satellite-to-gateway uplinks and downlinks, and at least one path exists between a user terminal and at least one satellite. In a preferred embodiment the packets are TCP / IP (or equivalent protocol) packets containing information for enabling the selective destruction of a duplicate packet to occur.
Owner:GLOBALSTAR INC
Multi-mode satellite and terrestrial communication device with position location
InactiveUS20020193108A1Quick buildEasy to carryNetwork topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemLow earth orbit
The present invention provides a multiple band mobile radio (also referred to as a Wireless Communication Device (WCD)) capable of communicating with both a satellite communication system and a terrestrial communication system. The satellite communication system can be a Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite communication system. The terrestrial communication system can be a Personal Communication System (PCS), or a cellular system, including either an analog or a digitally based cellular system. The WCD can concurrently receive signals from the terrestrial communication system and the satellite communication system. Also, the WCD can receive signals useful for position location, such as a GPS satellite signal alone, or both GPS and satellite communication signals, simultaneously.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
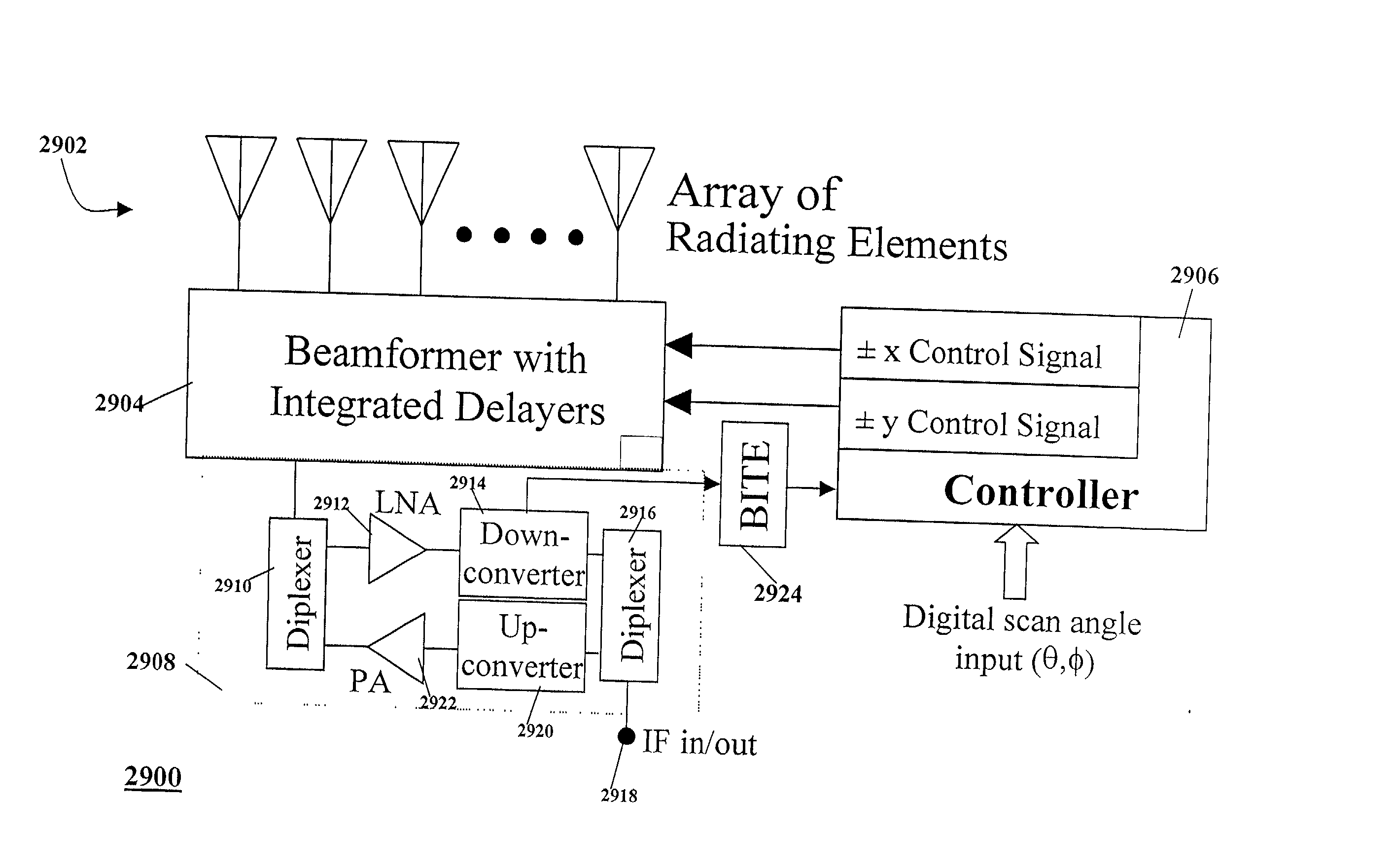
Electro-mechanical scanned array system and method
InactiveUS20030043071A1Improve signal quality indicationImprove signal qualityParticular array feeding systemsWaveguide type devicesRadar systemsBeam steering
An antenna system includes a beamformer having a feed port and a one-dimensional or two-dimensional arrangement of output ports, radiating antenna elements coupled with output ports of the beamformer, and an antenna control unit coupled with the beamformer to steer a beam of the antenna system. The antenna system forms an electrically steerable, phased array antenna having a beam steering angle which is constant over a very broad band of frequencies. Specific applications for the antenna system include satellite communications including tracking low earth orbiting satellites, radar systems and data links using a steerable antenna for self-installation, self-healing and adaptation.
Owner:E TENNA CORP
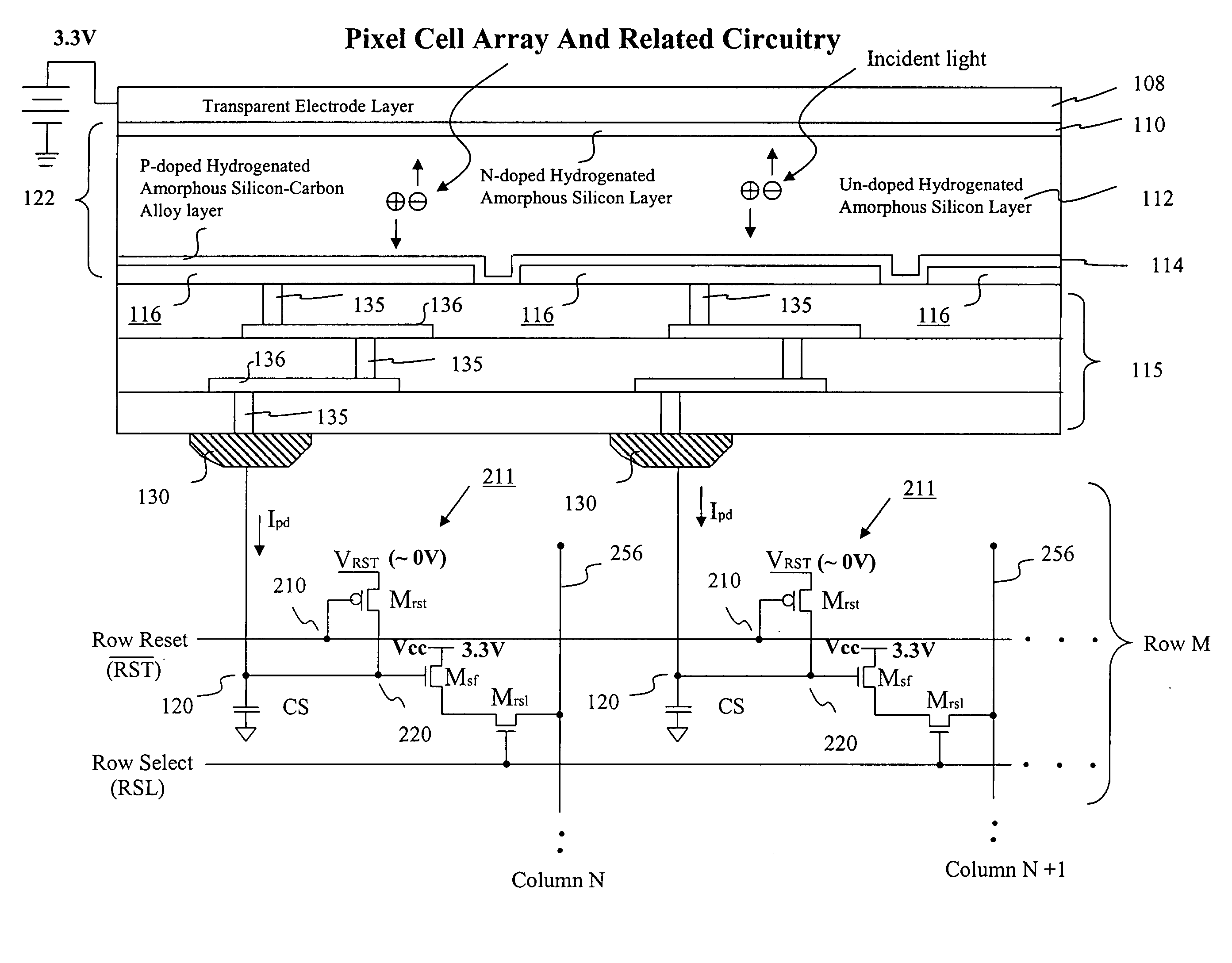
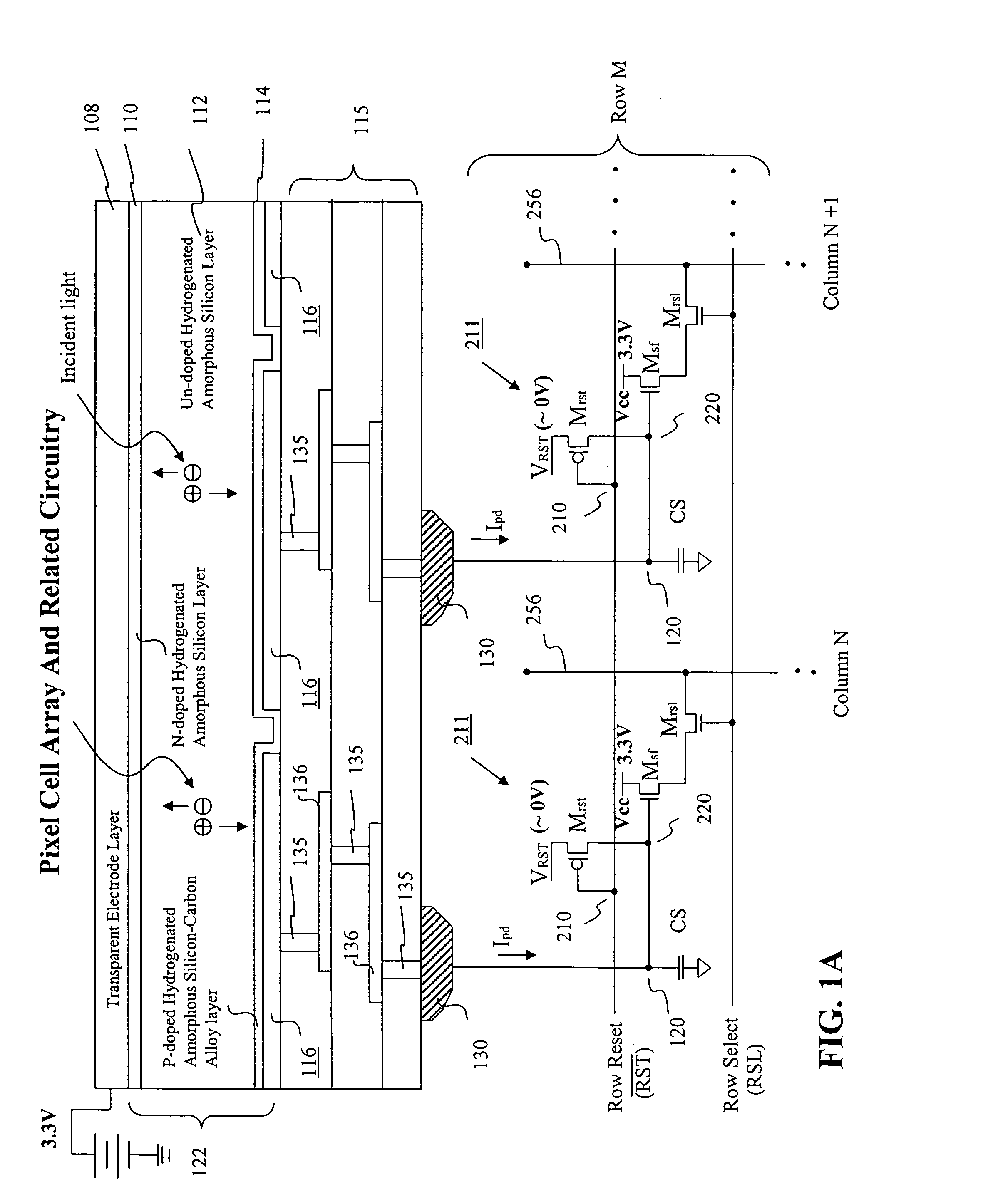
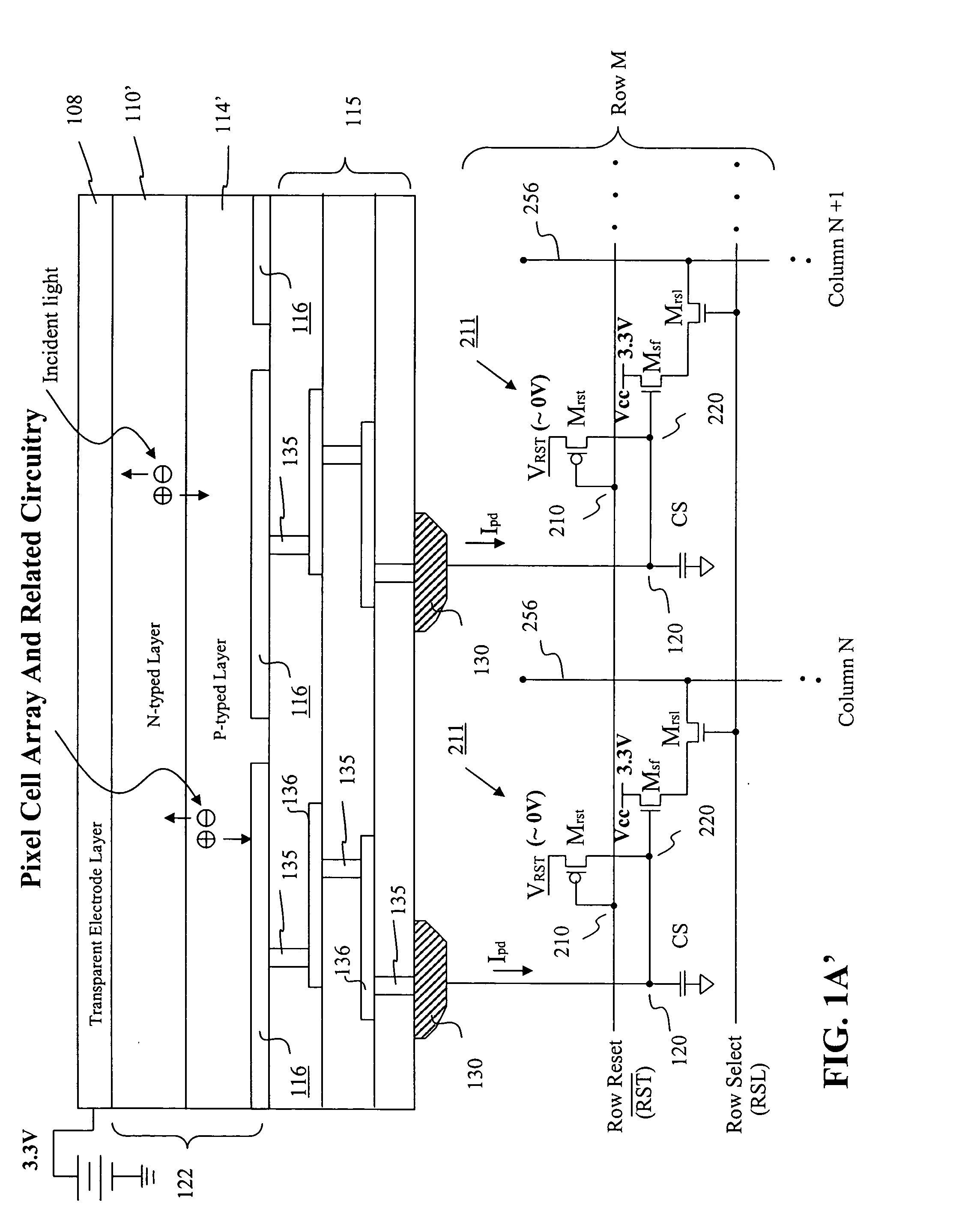
Visible/near infrared image sensor
InactiveUS20050104089A1Improve performanceHigh sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLow earth orbitBeam steering
A MOS or CMOS sensor for high performance imaging in broad spectral ranges including portions of the infrared spectral band. These broad spectral ranges may also include portions or all of the visible spectrum, therefore the sensor has both daylight and night vision capabilities. The sensor includes a continuous multi-layer photodiode structure on a many pixel MOS or CMOS readout array where the photodiode structure is chosen to include responses in the near infrared spectral ranges. A preferred embodiment incorporates a microcrystalline copper indium diselenide / cadmium sulfide photodiode structure on a CMOS readout array. An alternate preferred embodiment incorporates a microcrystalline silicon germanium photodiode structure on a CMOS readout array. Each of these embodiments provides night vision with image performance that greatly surpasses the GEN III night vision technology in terms of enhanced sensitivity, pixel size and pixel count. Further advantages of the invention include low electrical bias voltages, low power consumption, compact packaging, and radiation hardness. In special preferred embodiments CMOS stitching technology is used to provide multi-million pixel focal plane array sensors. One embodiments of the invention made without stitching is a two-million pixel sensor. Other preferred embodiments available using stitching techniques include sensors with 250 million (or more) pixels fabricated on a single wafer. A particular application of these very high pixel count sensors is as a focal plane array for a rapid beam steering telescope in a low earth orbit satellite useful for tracking over a 1500-meter wide track with a resolution of 0.3 meter.
Owner:C PHOCUS
Method and apparatus for providing wideband services using medium and low earth orbit satellites
InactiveUS20040110467A1High data rate serviceReduce distractionsActive radio relay systemsSubstation equipmentHigh elevationLow earth orbit
A method and apparatus for mitigating communications interference between satellite communications systems in different orbits is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of evaluating a geometrical relationship between a second ground station and the satellites in the second satellite constellation, and directing communications between the second ground station and the second satellite according to the evaluated geometrical relationship. In one embodiment communications are handed over from a first satellite to another satellite when the first satellite is no longer at the highest elevation angle of visible satellites. In another embodiment, handover occurs when the first satellite drops below a minimum elevation angle.
Owner:THE DIRECTV GRP INC
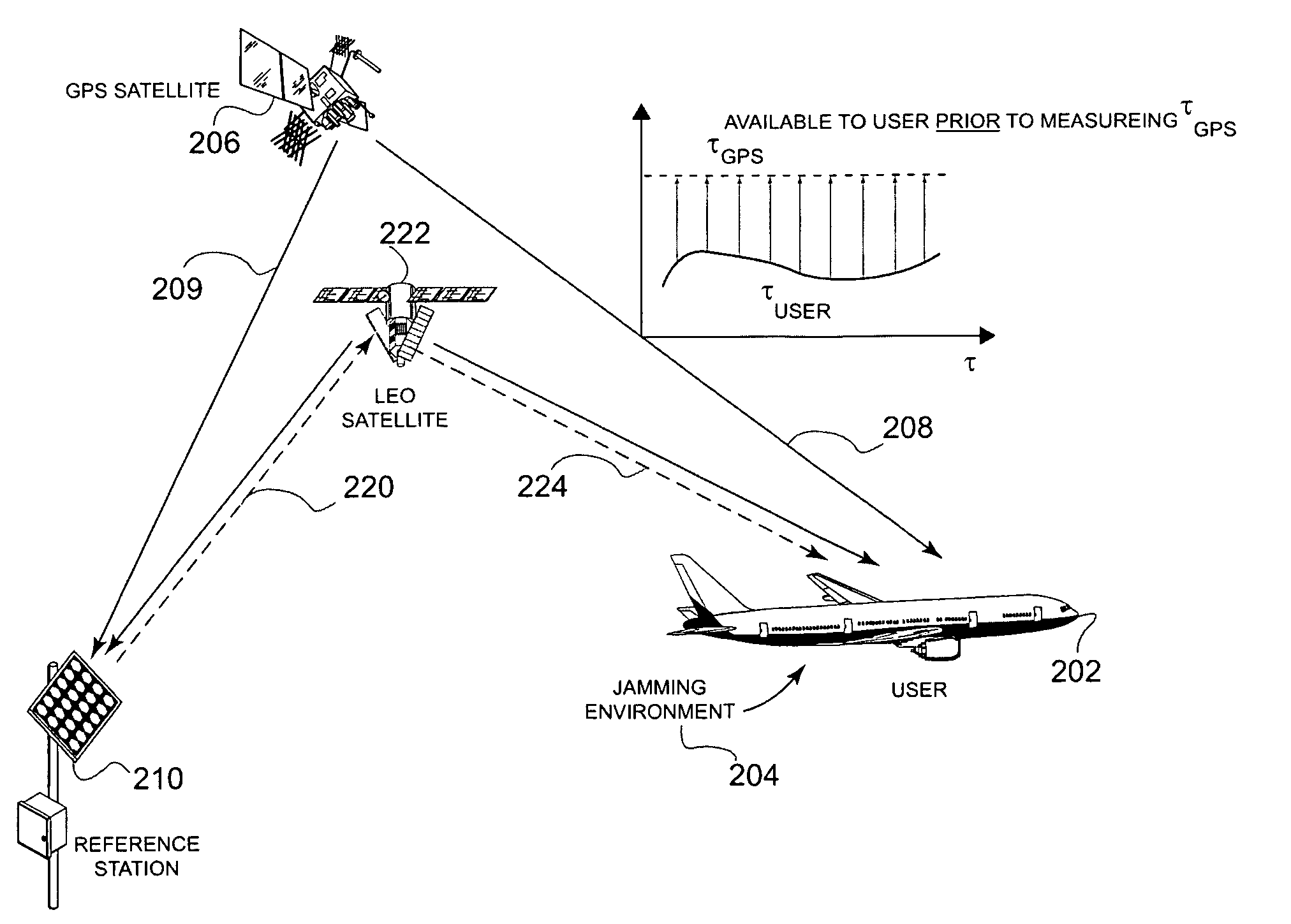
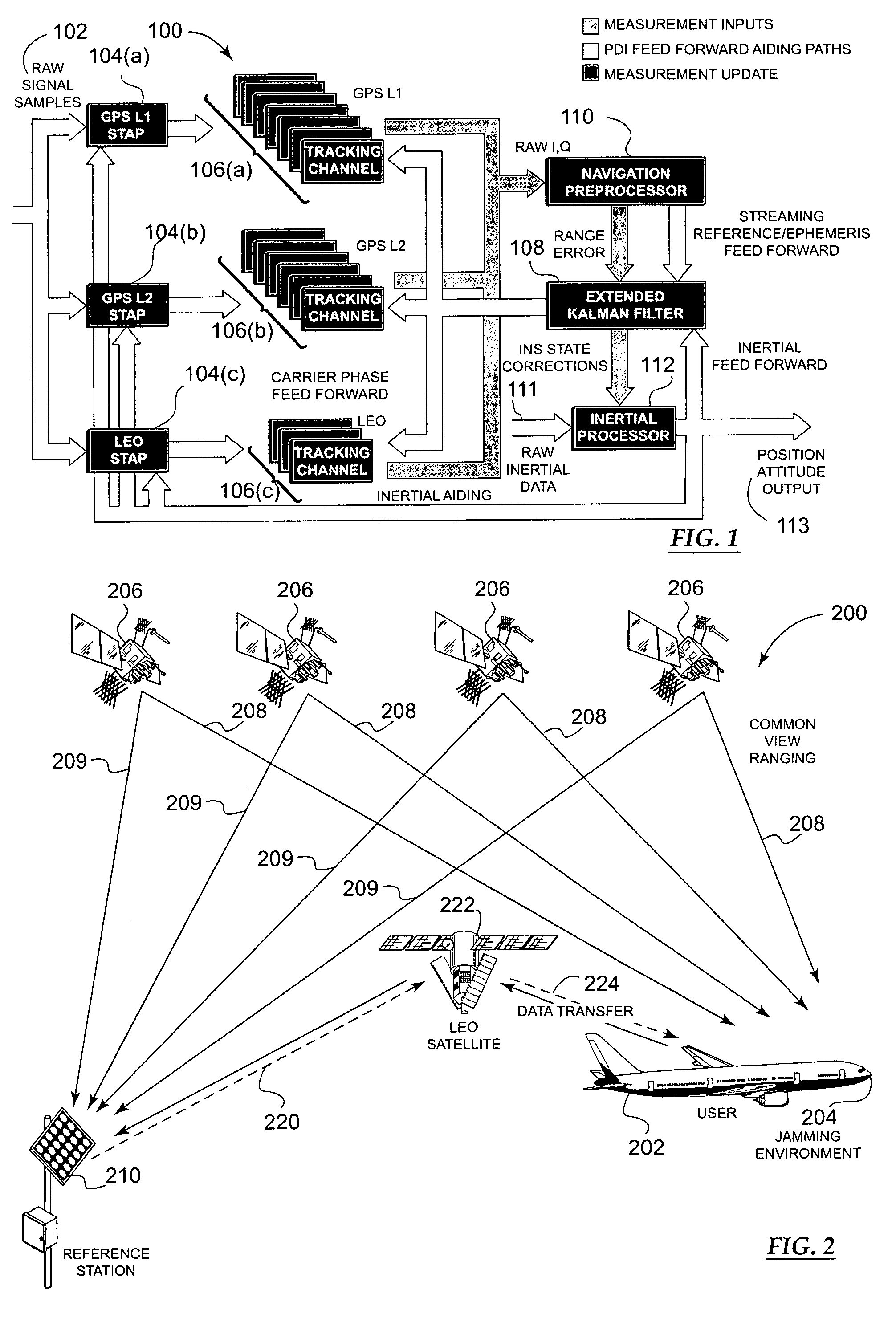
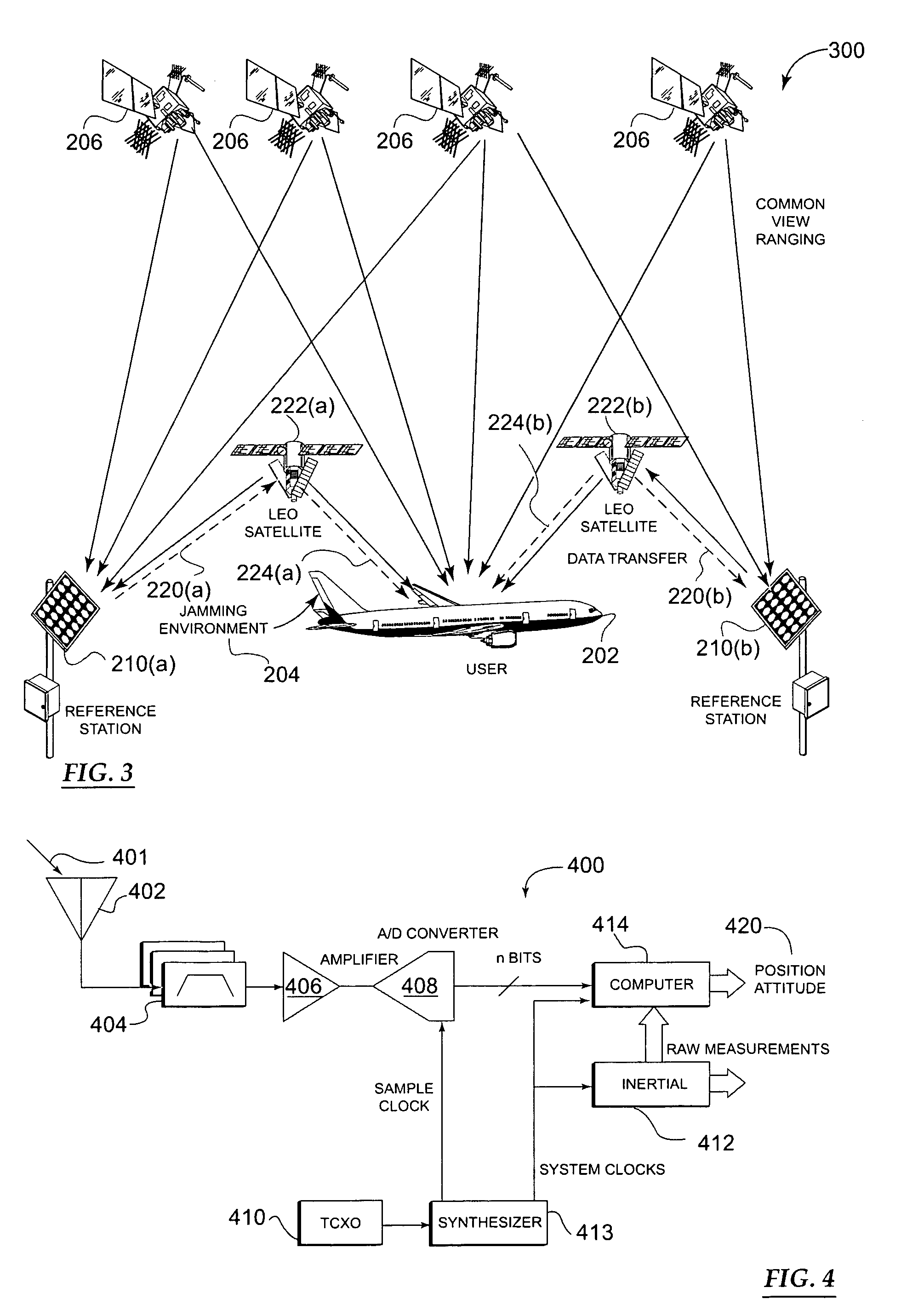
Methods and apparatus for a navigation system with reduced susceptibility to interference and jamming
ActiveUS7372400B2Improve anti-interference abilityCostPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsSide informationLow earth orbit
Owner:THE BOEING CO
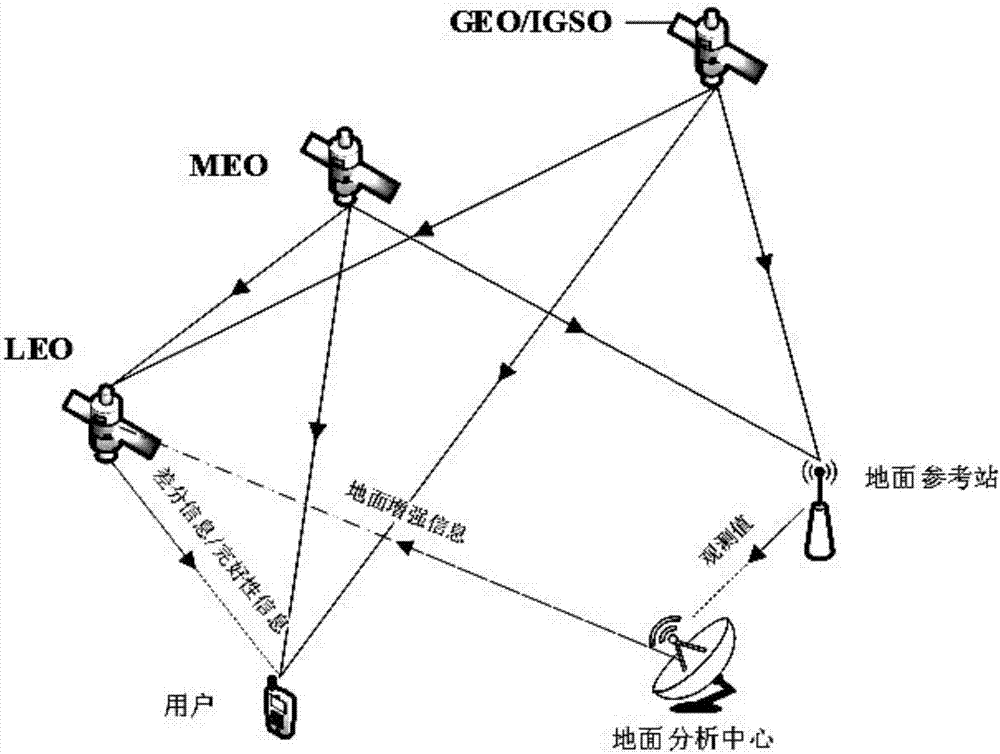
Low earth orbit satellite-based satellite-earth differential real-time precise positioning method
ActiveCN107229061ARapid positioningRealize Differential Positioning ServiceSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceNatural satellite
The invention belongs to the satellite navigation and positioning technical field and discloses a low earth orbit satellite-based satellite-earth differential real-time precise positioning method. A low earth orbit satellite is utilized to broadcast the observation data and real-time orbit data of the satellite-borne GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receiver of the low earth orbit satellite to the ground; and after receiving the differential information broadcasted by the low earth orbit satellite, a ground receiver generates a double-difference observation value consisting of the differential information and a local GNSS observation value and performs pseudorange-based moving base station DGNSS (Differential Navigation Satellite System) positioning and carrier phase-based moving base station RTK (Rea-time kinematic) positioning. According to the positioning method of the invention, the global mobile low earth orbit satellite platform is adopted as a reference station, so that real-time precision differential positioning service in the whole world can be realized, and the method does not depend on the distribution of ground reference stations; and a user can realize differential real-time precise positioning just through using a single receiver, and therefore, the method is free of operating range restrictions, and data communication links are not required to be considered.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
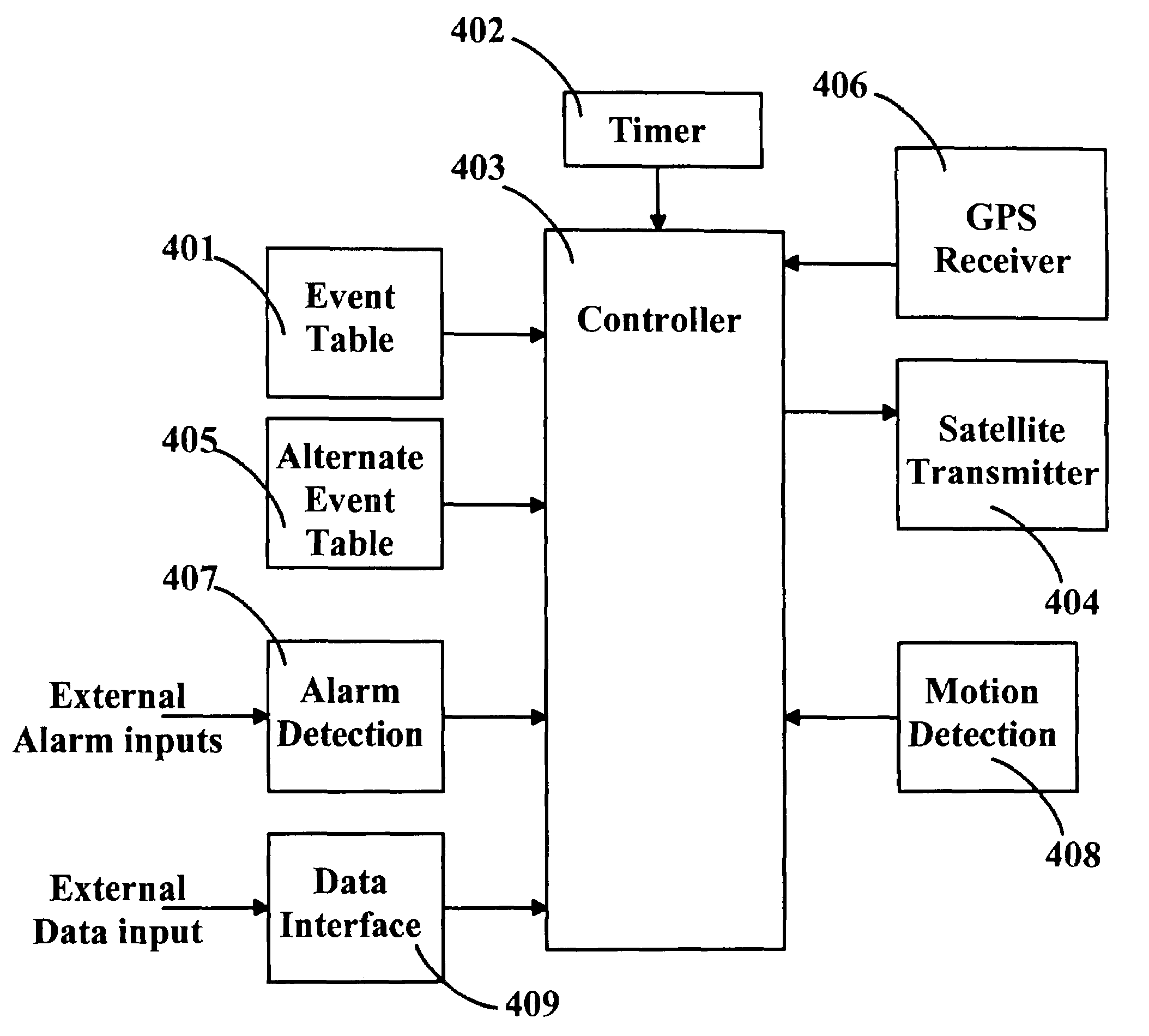
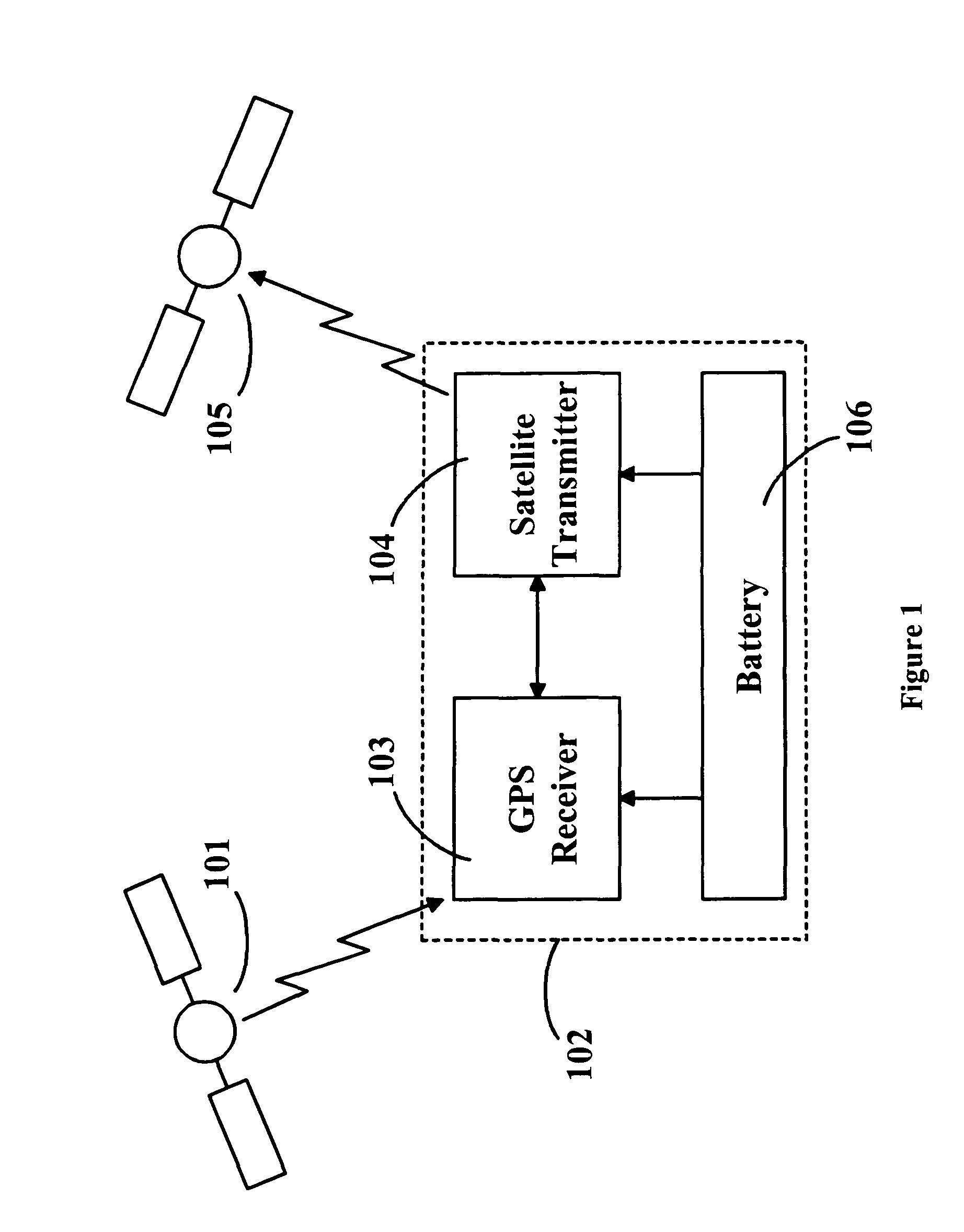
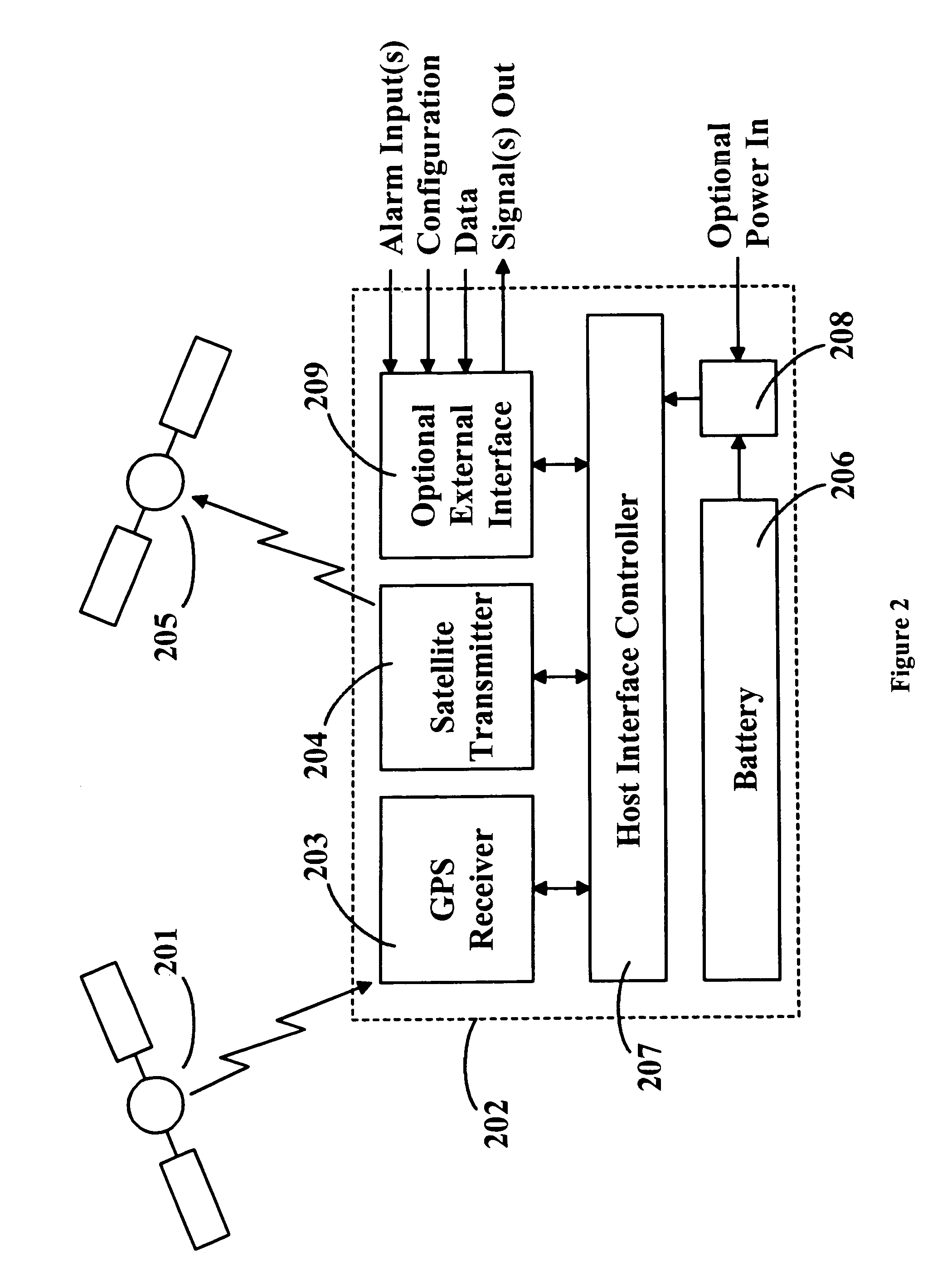
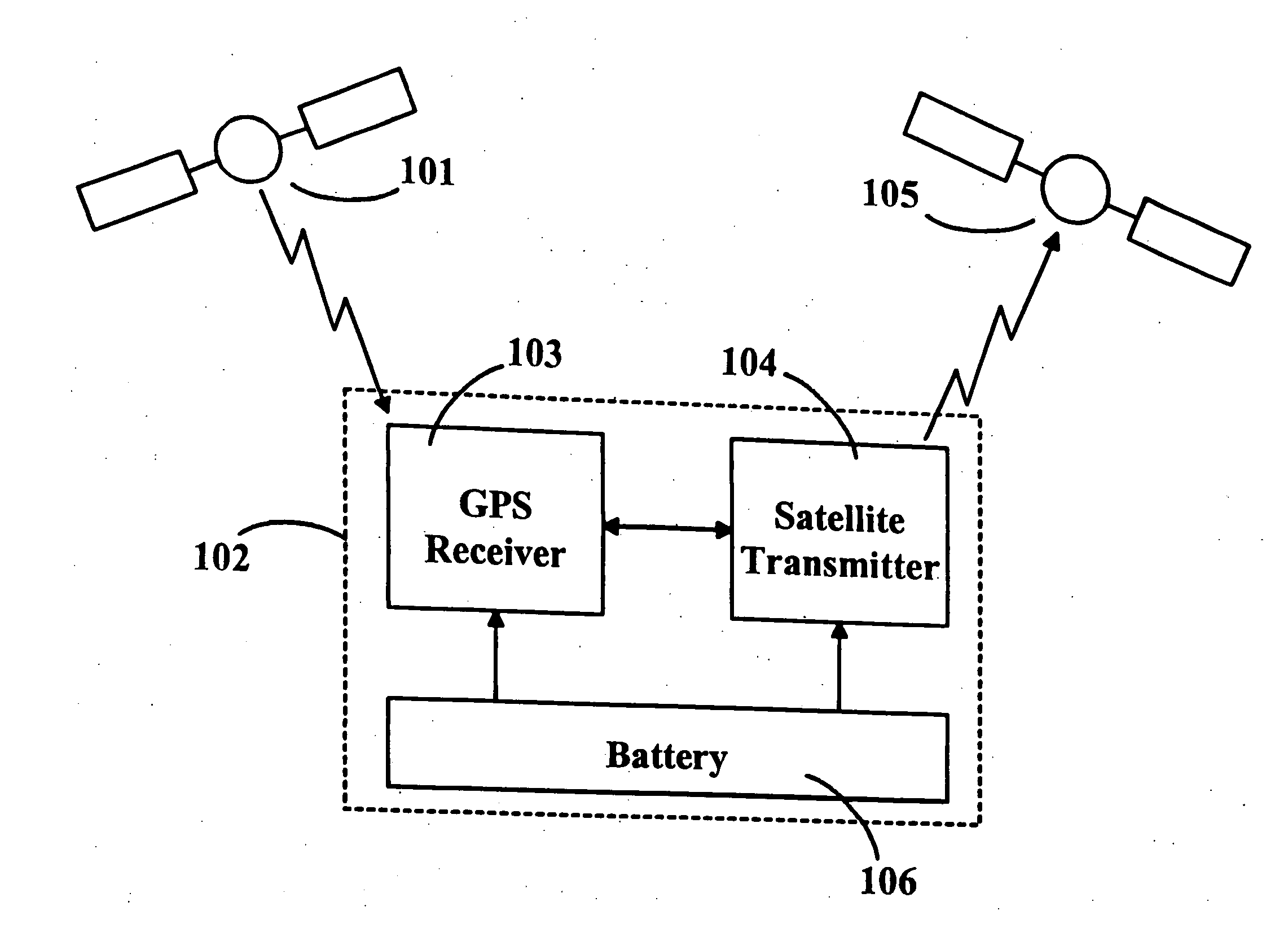
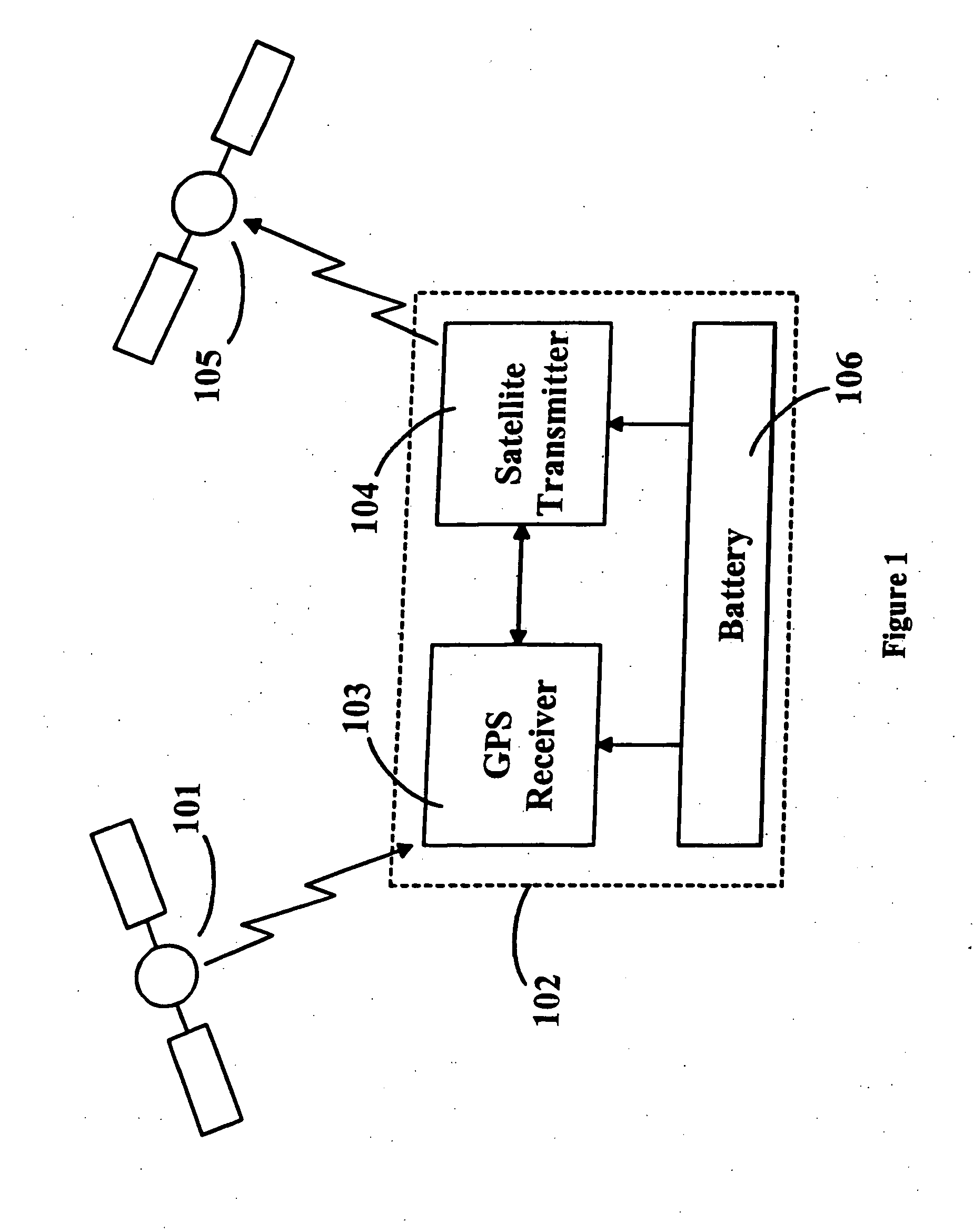
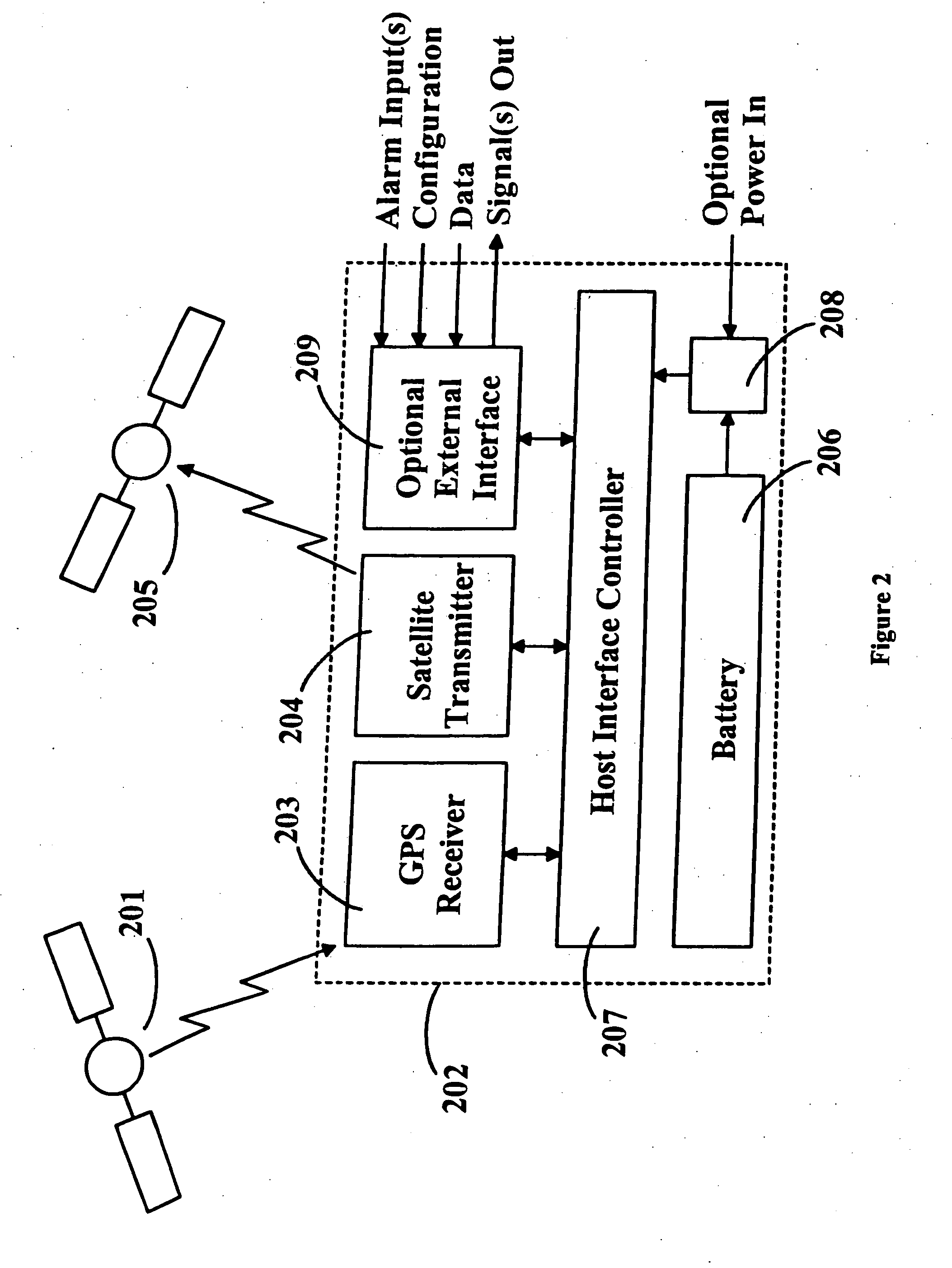
Location monitoring and transmitting device, method, and computer program product using a simplex satellite transmitter
InactiveUS7099770B2Efficient and reliable location determinationReduce power consumptionAnalogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationSatellite transmitterTelecommunications
A device, method, and computer program product for monitoring and transmitting a location and a local status of a remote device using a simplex satellite transmitter. The monitoring device includes a position location unit, a simplex satellite transmitter, a power source, and a controller. The position location unit is configured to determine a location of the remote device. The simplex satellite transmitter is configured to transmit the location to one or more satellites in low earth orbit. The controller includes a power management unit configured to control a power state of the position location unit and the simplex satellite transmitter, and to periodically enable and disable power from the power source to the position location unit and the simplex satellite transmitter.
Owner:BNP PARIBAS AS SECURITY AGENT
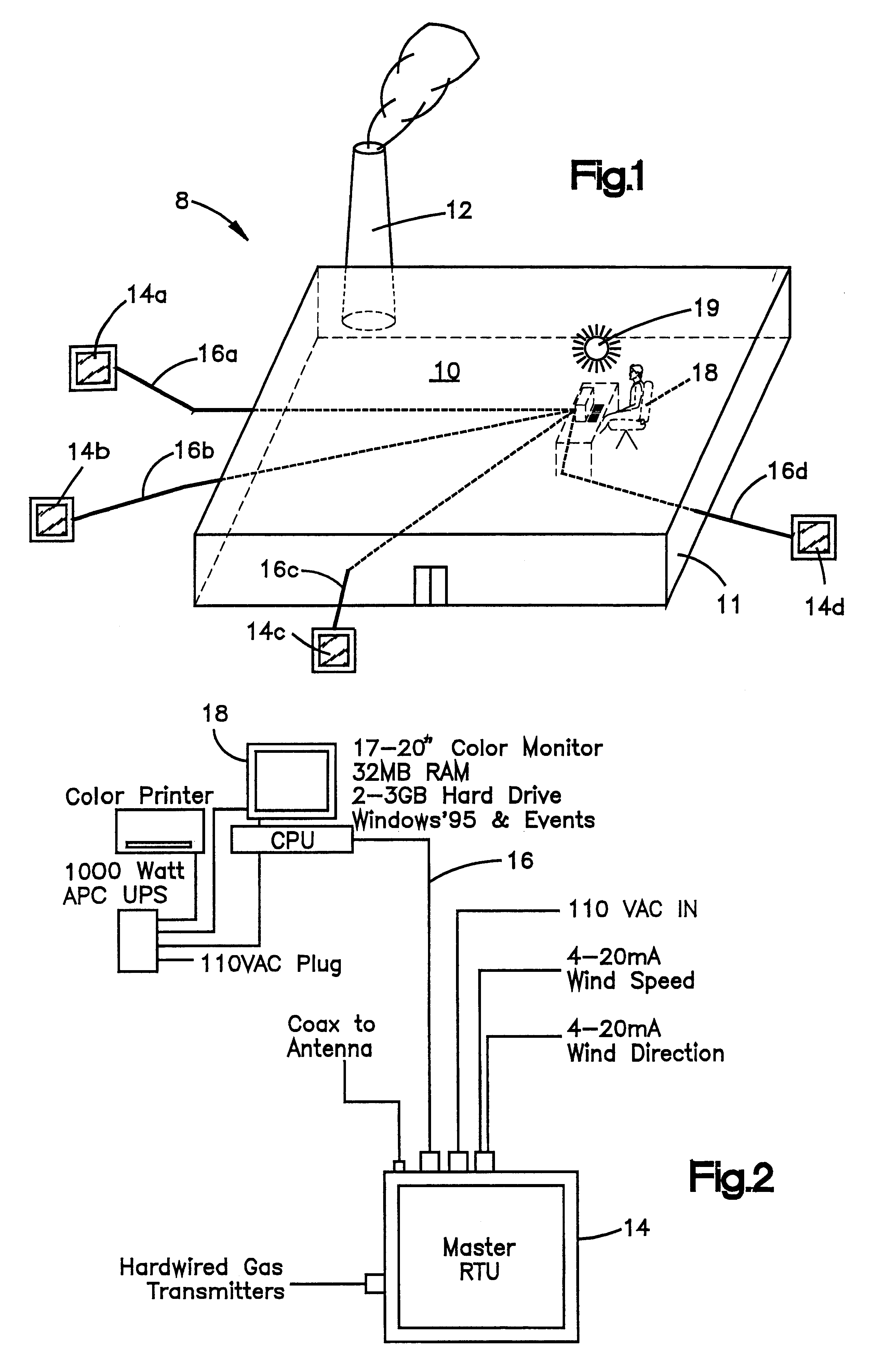
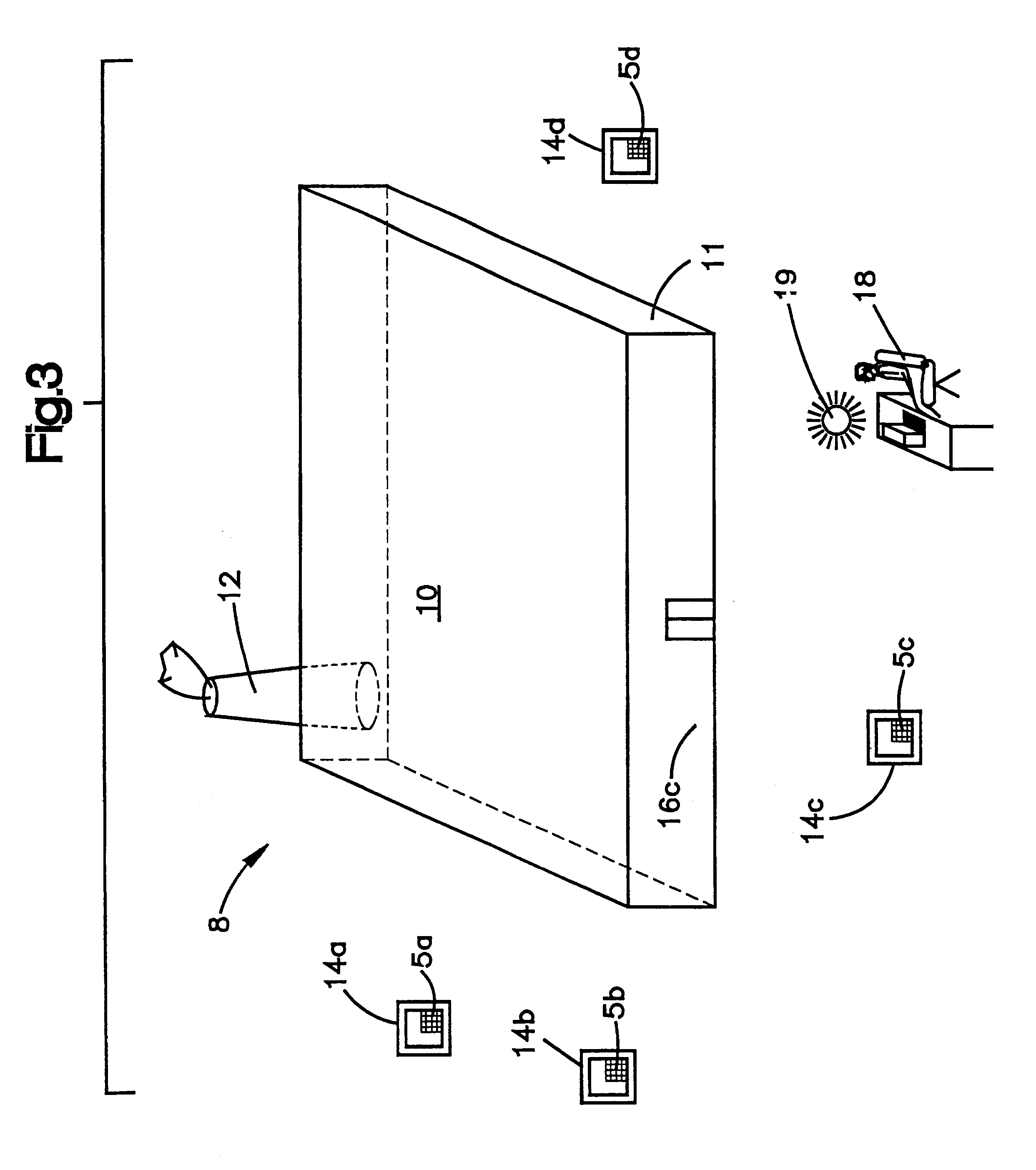
Apparatus and method for wireless gas monitoring
InactiveUS6670887B2Electric signalling detailsFire alarm smoke/gas actuationSatellite technologyTransceiver
The current invention provides a wireless monitoring system. The system has one or more monitoring devices. Each device can transmit data and receive messages from an output center or alarm system. The output center can also transmit and receive messages. Both the output center and each device preferably have a transceiver that enables both the transmission and receipt of messages. No remote terminal units hardwiring is required for the system to function. The system is truly a wireless gas monitoring system. The system may use low earth orbit satellite technology, or licensed radio frequencies or any other means to wirelessly transmit and receive messages.
Owner:GASTRONICS
Multi-mode satellite and terrestrial communication device
InactiveUS6714760B2Appropriate performanceBroadcast transmission systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemSimulation based
The present invention provides a multiple band mobile radio (also referred to as a Wireless Communication Device (WCD)) capable of communicating with both a satellite communication system and a terrestrial communication system. The satellite communication system can be, for example, a Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite system. The terrestrial communication system can be a Personal Communication System (PCS), or a cellular system, including either an analog or a digitally based cellular system. The cellular analog system can be AMPS. The digitally based cellular system can be a CDMA or a TDMA based communication system. The WCD can concurrently receive signals from the terrestrial communication system and the satellite communication system.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
LEO-based positioning system for indoor and stand-alone navigation
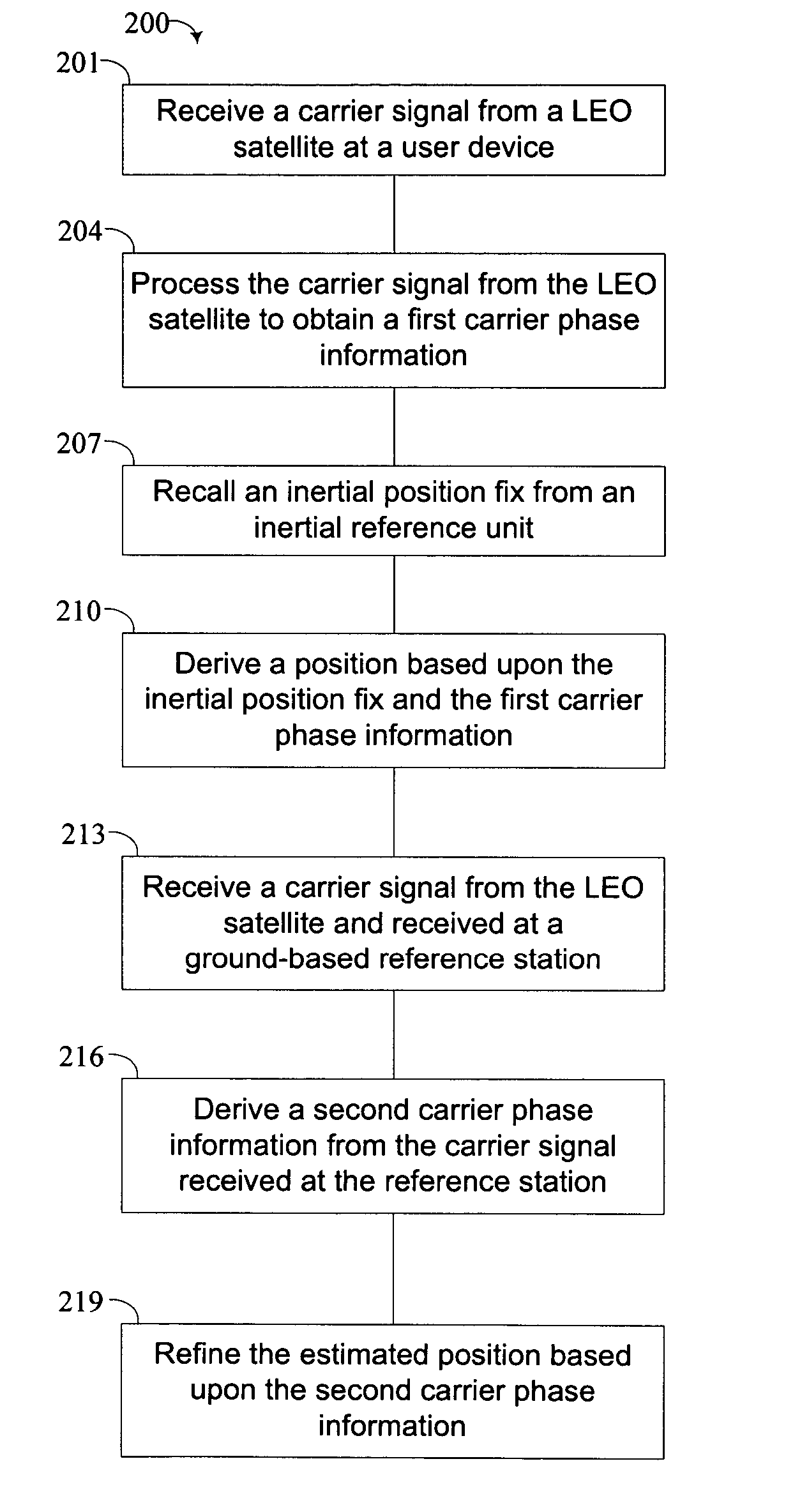
ActiveUS7489926B2Ameliorate integration loadImprove approximationPosition fixationRadio transmissionUser deviceCarrier signal
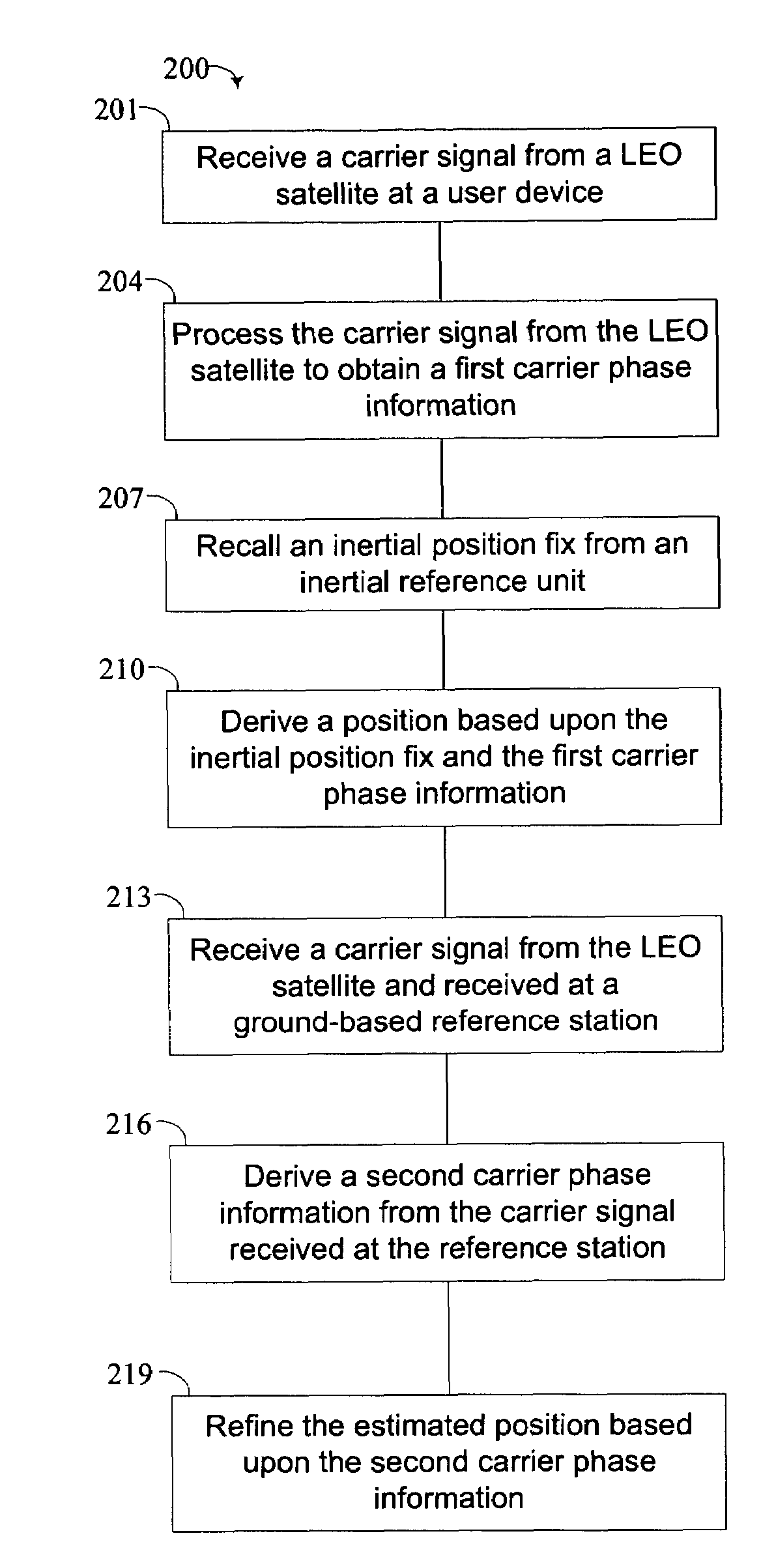
A method for estimating a precise position of a user device from signals from a low earth orbit (LEO) satellite includes receiving at least one carrier signal at a user device, each carrier signal being transmitted a distinct LEO satellite. The user device processes the carrier signals to obtain a first carrier phase information. The user device recalls an inertial position fix derived at an inertial reference unit. The user device derives a position of the user device based on the inertial position fix and the first carrier phase information.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Satellite downlink via patterns of uncollimated light
InactiveUS7925167B1Eliminate security concernsEliminating regulatory issueBroadcast transmission systemsSatellite communication transmissionLow earth orbitGround station
A satellite or spacecraft in low Earth orbit, when in eclipse and not illuminated by sunlight, represents a low-bandwidth datastream through modulation of a source of uncollimated light, such as a set of light emitting diodes. Transmission modes include generating patterns in the color, intensity or polarization of a light source, or precise timing control of a strobe signal. A ground station tracks the satellite in a telescope, stewing the telescope to follow the satellite as it moves across the sky, recording light generated by the satellite with a light sensor such as a video camera. The datastream is regenerated through analysis of recorded video. Satellite downlink is initiated by detection of eclipse, by command via radio uplink, or in response to a periodic automatic timer. In an alternative embodiment, the satellite represents the datastream through modulation of its effective albedo or reflective flux during periods of solar illumination.
Owner:KOZUBAL MAREK J +1
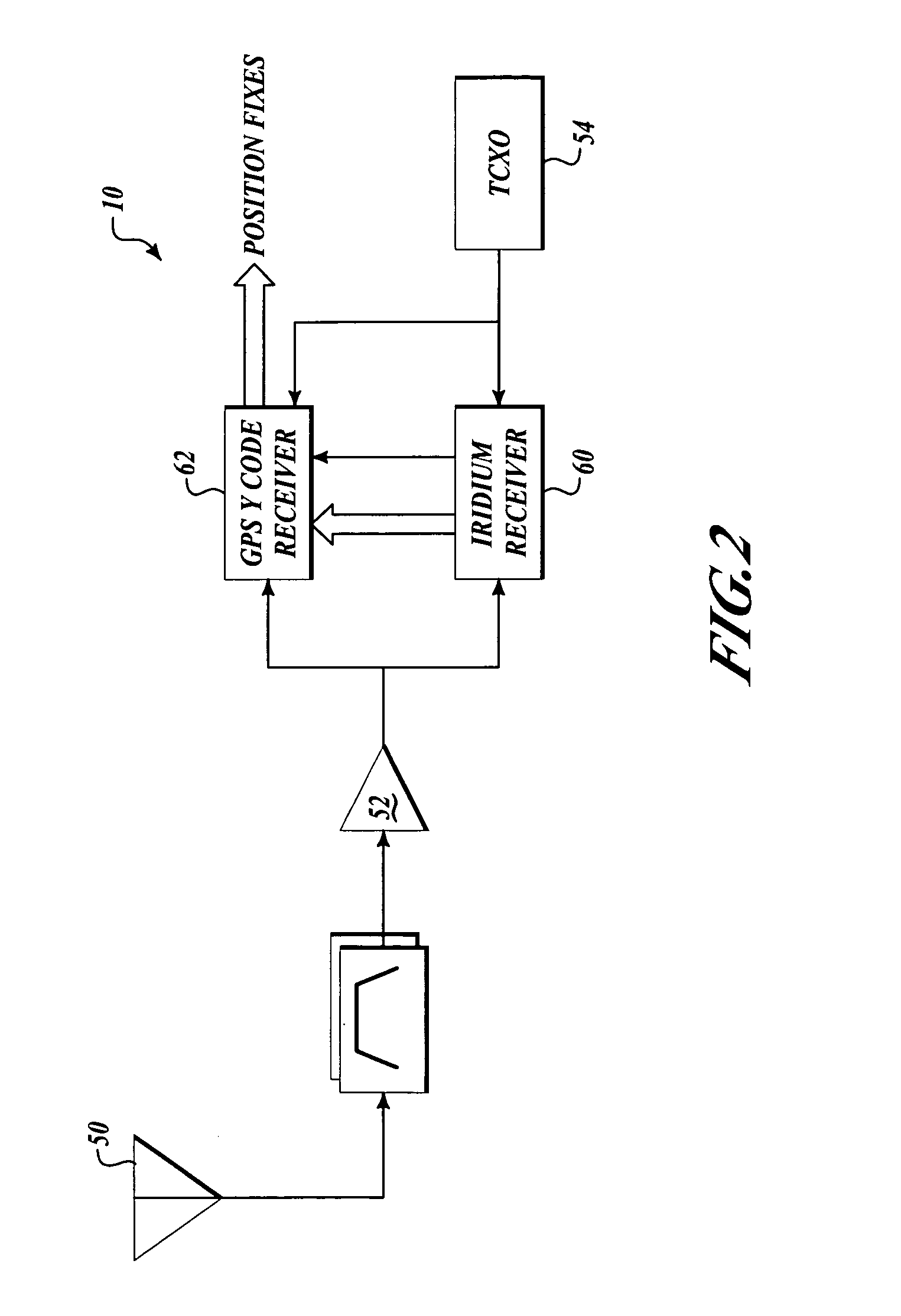
GPS access system and method
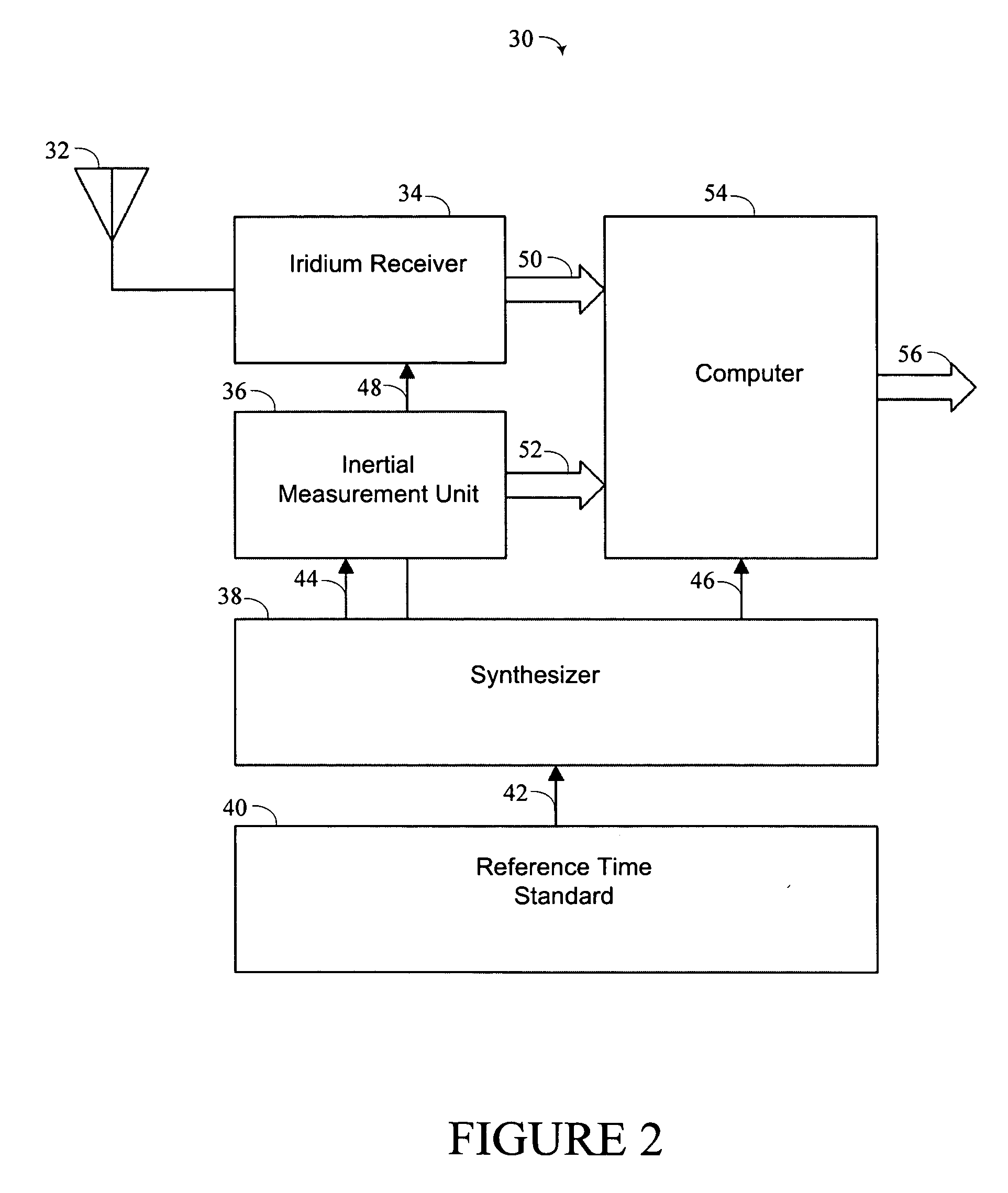
ActiveUS7042392B2Improve anti-clogging performanceInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationGps receiverLow earth orbit
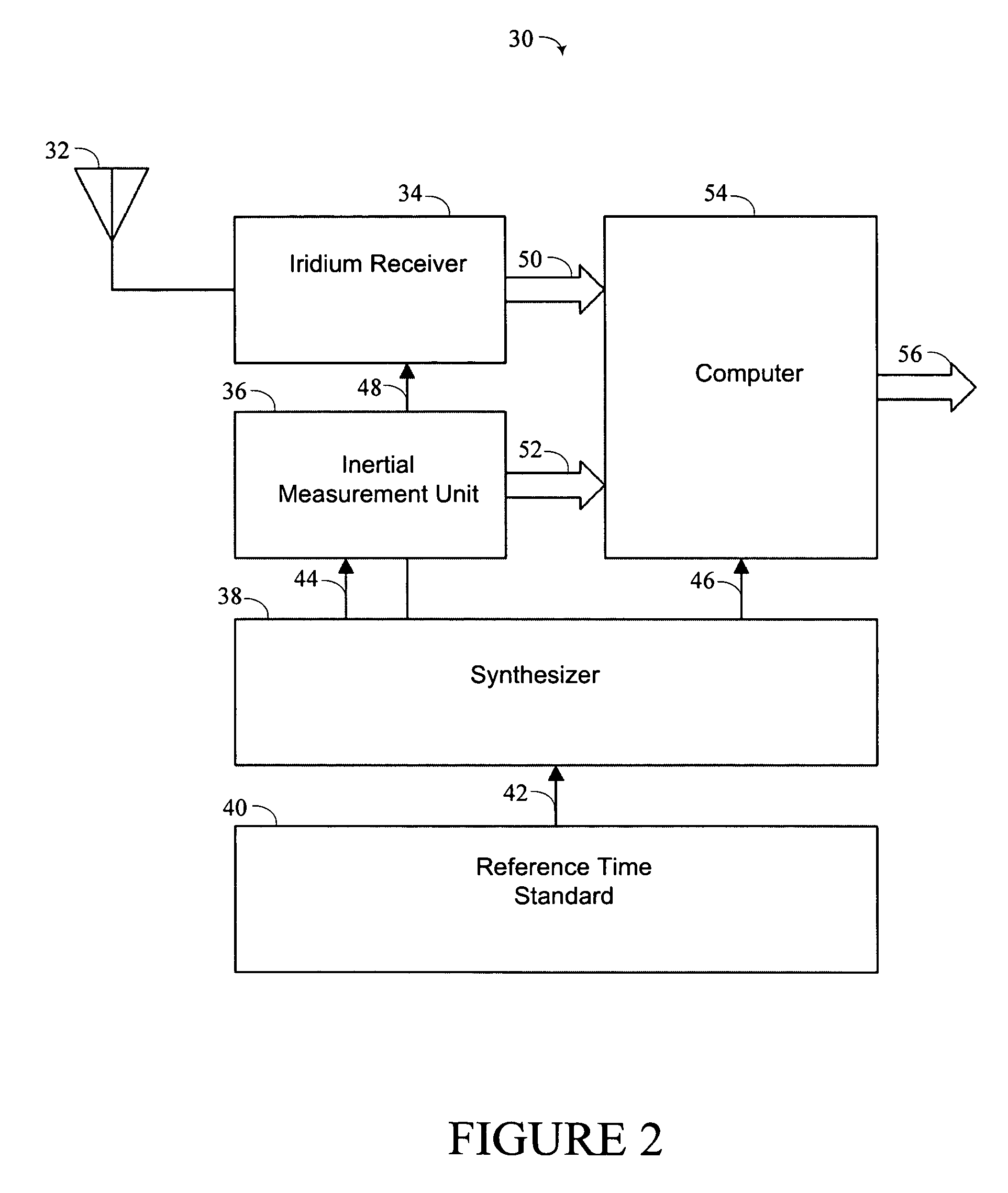
This invention describes a means for acquiring GPS P / Y code under jamming conditions. It improves jam resistance by augmenting a component of the GPS signal with one from a different satellite system, such as a low earth orbiting (LEO) satellite. The preferred embodiment of this invention employs the Iridium LEO satellite constellation broadcasting in a 10 MHz wide band about 1,621 MHz. A low-cost, integrated Iridium receiver coupled to the GPS receiver employs a single antenna that is capable of receiving both the GPS and Iridium signals together.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
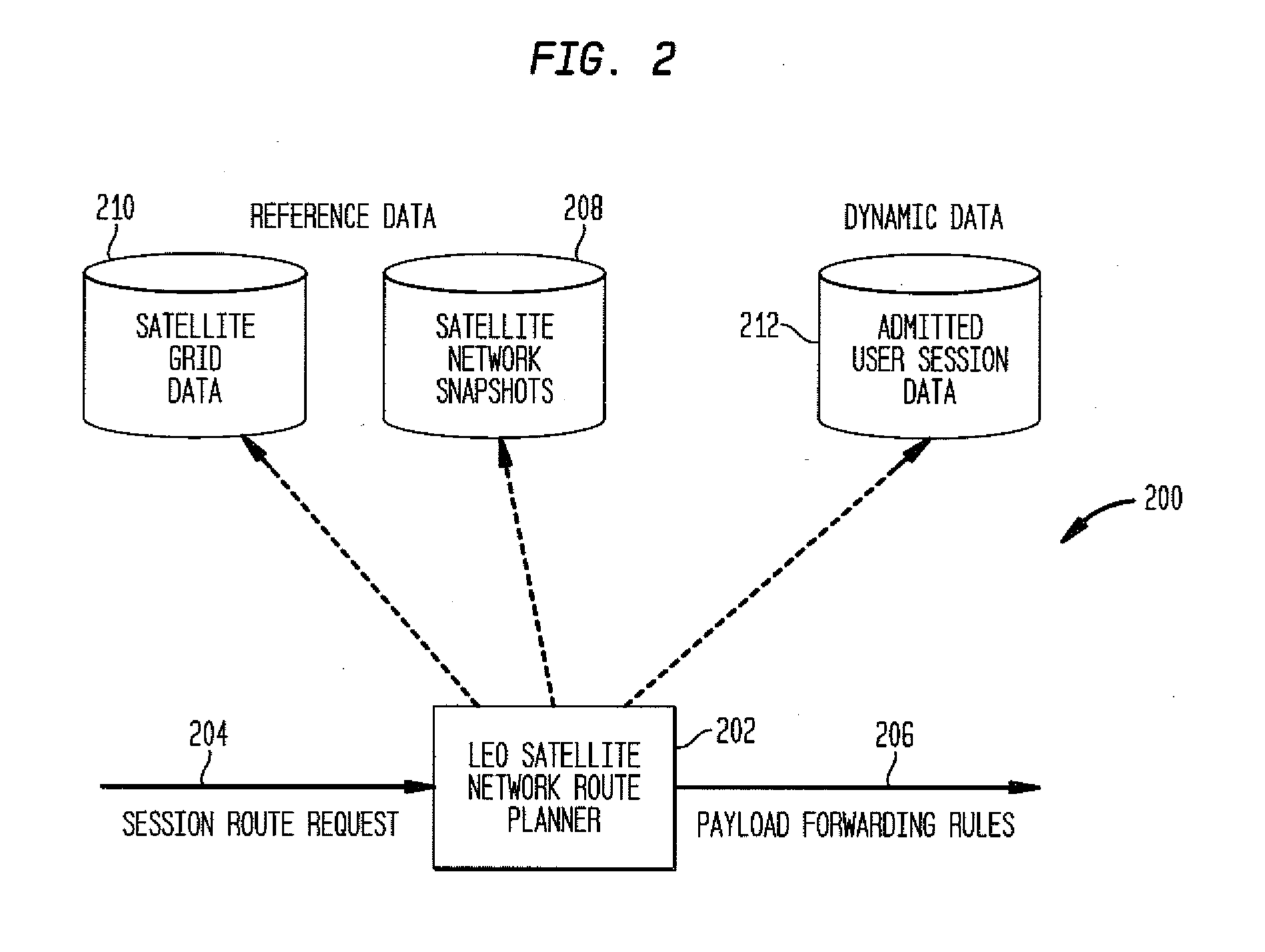
Method and system for determination of routes in leo satellite networks with bandwidth and priority awareness and adaptive rerouting
ActiveUS20120263042A1Facilitates route computationClear separationError preventionTransmission systemsLow earth orbitOrbit
In Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite networks data routes for point to point and point to multipoint communication sessions in LEO satellite networks are determined by considering session bandwidth, priority, and the constantly changing terminal-satellite and satellite-satellite connectivity. Multiple routes are computed for a session to facilitate automatic adaptive rerouting by satellite payloads when they encounter network failures or congestion conditions.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC
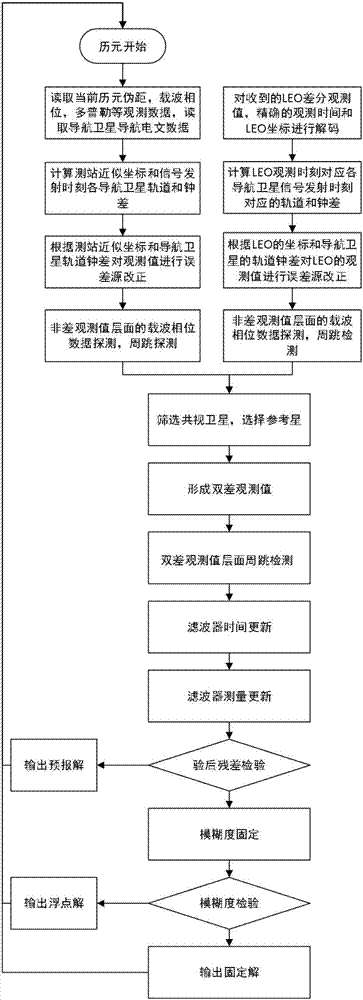
Real-time precise orbit determining method of short orbit arc low earth orbit (LEO) navigation satellite
ActiveCN107153209AError Effect CompensationLow priceSatellite radio beaconingNatural satelliteData center
The invention discloses a real-time precise orbit determining method of a short orbit arc low earth orbit (LEO) navigation satellite. The method is characterized in that four or more ground receivers are used for tracking navigation signals of a plurality of GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) navigation satellites and LEO navigation satellites, and transmitting the navigation signals to a data center in real time. The method comprises the following steps: I, acquiring and preprocessing observing data; II, performing precise time synchronization on the receivers; III, calculating tropospheric delay in an LEO gazing direction by using tropospheric delay in a vertical direction and a projection function; IV, correcting hardware delay of the receivers to build an LEO determining geometric observing equation; V, solving an LEO precise orbit and a precise clock error through a dynamical model and the geometric equation of the LEO; VI, distributing the LEO precise orbit and the precise clock error in real time. By adopting the method, the problem of need of post-processing due to incapability of calculating the precise orbit of a low earth orbit satellite can be solved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
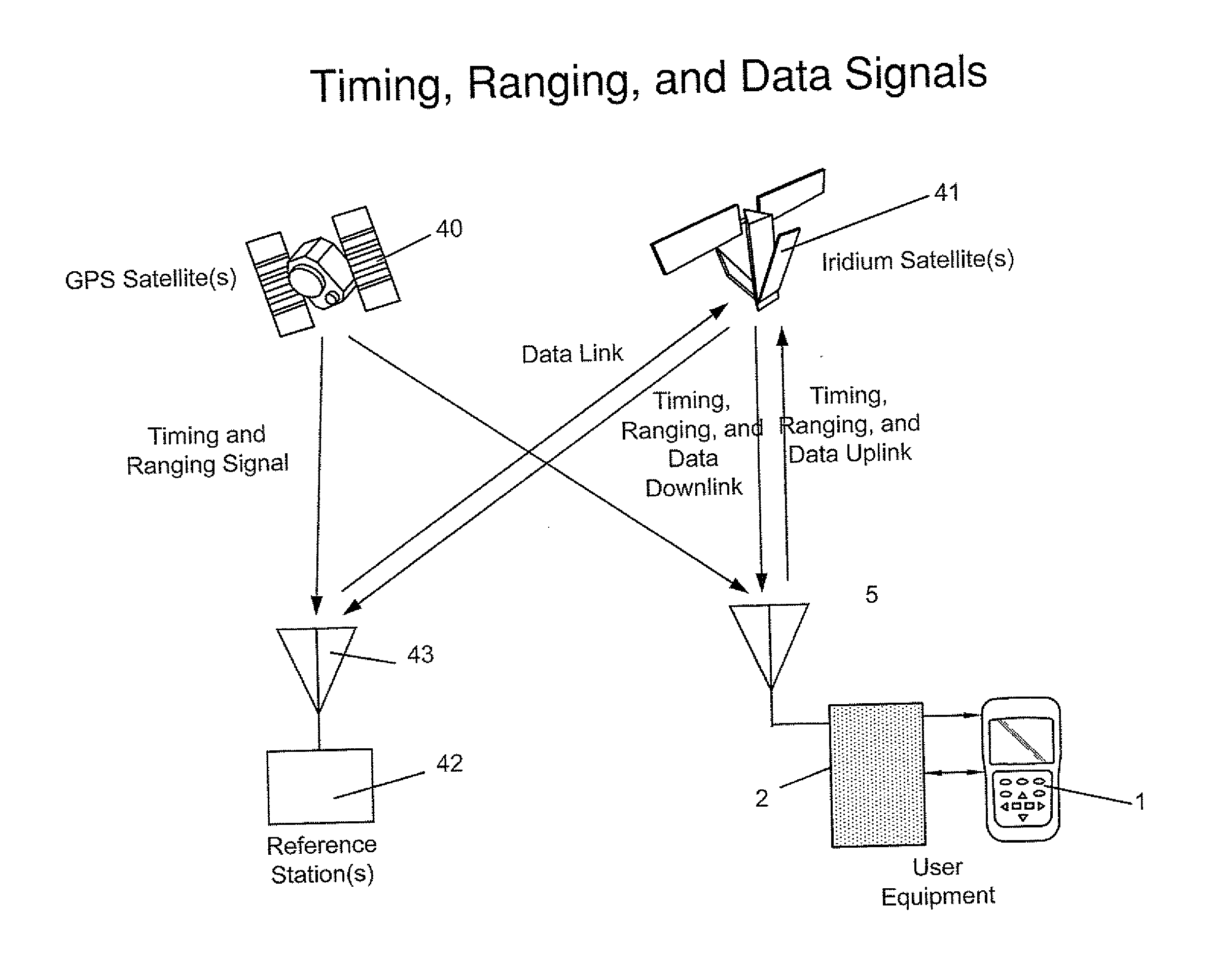
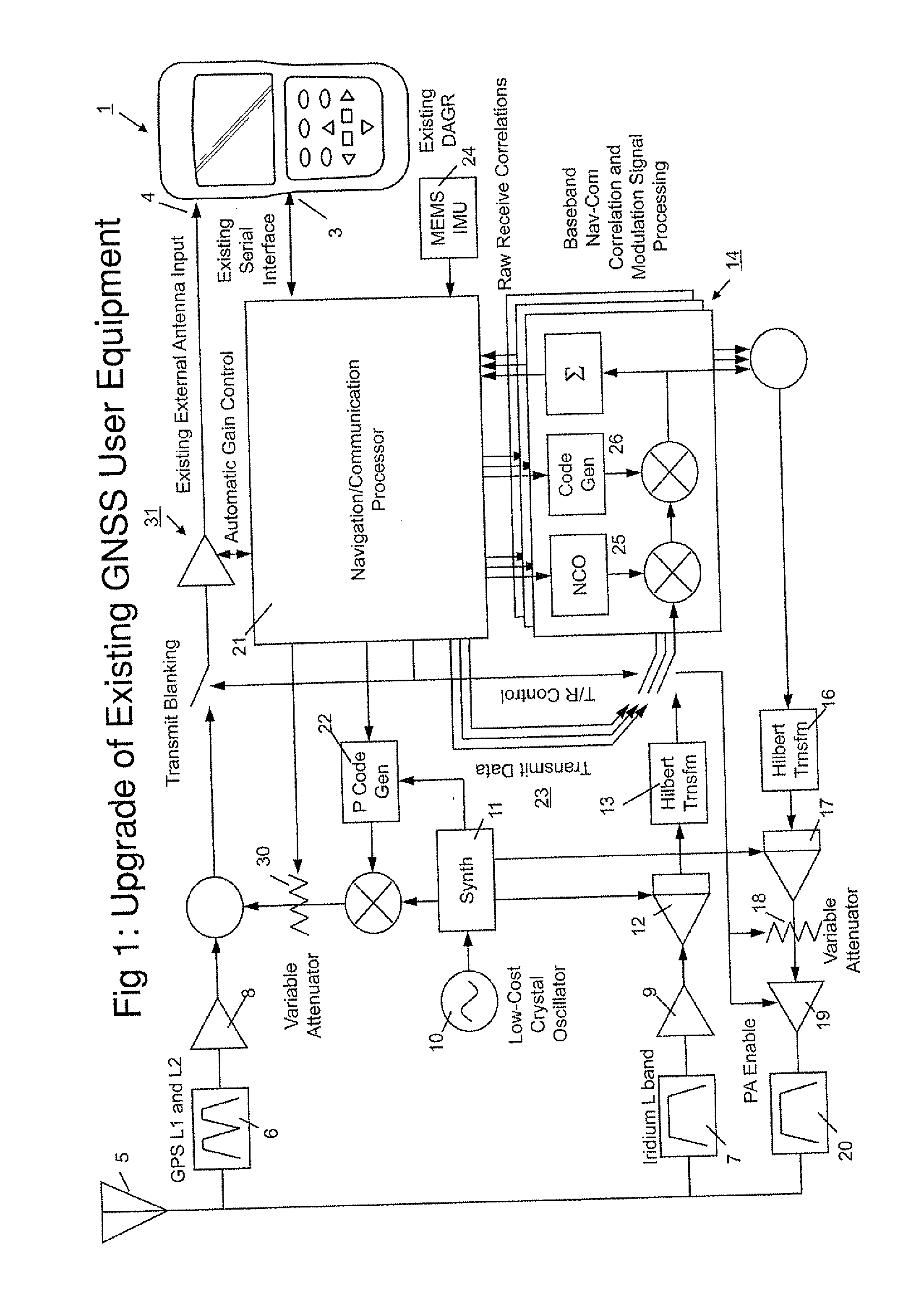
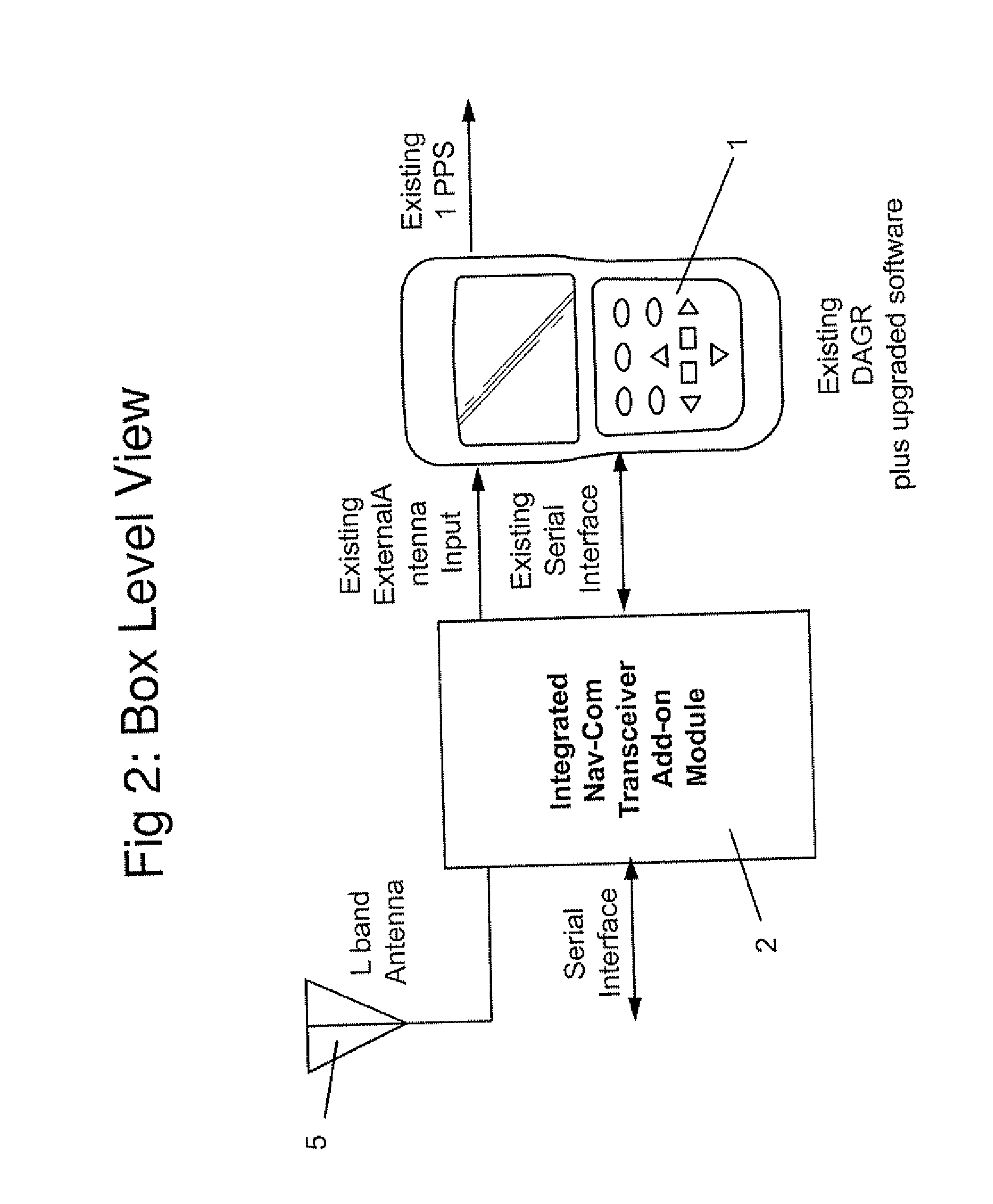
Practical Method for Upgrading Existing GNSS User Equipment with Tightly Integrated Nav-Com Capability
InactiveUS20110163913A1Improve navigation performanceCost-effectiveSatellite radio beaconingEngineeringLow earth orbit
A practical method for adding significant new high-performance, tightly integrated Nav-Com capability to any Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) user equipment, such as GPS receivers, requires no hardware modifications to the existing user equipment. In one example, the iGPS concept is applied to a Defense Advanced GPS Receiver (DAGR) and combines Low Earth Orbiting (LEO) satellites, such as Iridium, with GPS or other GNSS systems to significantly improve the accuracy, integrity, and availability of Position, Navigation, and Timing (PNT)—in some cases by three orders of magnitude, to enable high precision GNSS carrier phase observable to be more readily exploited to improve PNT availability—even under interference conditions or occluded environments, and to enable new communication enhancements made available by the synthesis of precisely coupled navigation and communication modes. To achieve time synchronization stability to the required sub-20 ps level between the existing DAGR and a plug-in iGPS enhancement module, a special-purpose wideband reference signal is generated by the iGPS module and coupled to the DAGR via the existing antenna port, so that no hardware modification of the DAGR is required.
Owner:APPLE INC +1
Apparatus and method for wireless gas monitoring
InactiveUS20040056771A1Fire alarm smoke/gas actuationMaterial analysisSatellite technologyTransceiver
The current invention discloses a wireless monitoring system. The system has one or more monitoring devices. Each device can transmit data and receive messages from an output center or alarm system. The output center can also transmit and receive messages. Both the output center and each device preferably have a transceiver that enables both the transmission and receipt of messages. No remote terminal units or hardwiring is required for the system to function. The system is truly a wireless gas monitoring system. The system may use low earth orbit satellite technology, or licensed radio frequencies or any other means to wirelessly transmit and receive messages.
Owner:GASTRONICS
LEO-based positioning system for indoor and stand-alone navigation
ActiveUS20050156782A1Ameliorate integration loadImprove approximationPosition fixationRadio transmissionUser deviceCarrier signal
A method for estimating a precise position of a user device from signals from a low earth orbit (LEO) satellite includes receiving at least one carrier signal at a user device, each carrier signal being transmitted a distinct LEO satellite. The user device processes the carrier signals to obtain a first carrier phase information. The user device recalls an inertial position fix derived at an inertial reference unit. The user device derives a position of the user device based on the inertial position fix and the first carrier phase information.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Location monitoring and transmitting device, method, and computer program product using a simplex satellite transmitter
ActiveUS20050171696A1Low-profileProvide rigidityAnalogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationSatellite transmitterPower Management Unit
A device, method, and computer program product for monitoring and transmitting a location and a local status of a remote device using a simplex satellite transmitter. The monitoring device includes a position location unit, a simplex satellite transmitter, a power source, and a controller. The position location unit is configured to determine a location of the remote device. The simplex satellite transmitter is configured to transmit the location to one or more satellites in low earth orbit. The controller includes a power management unit configured to control a power state of the position location unit and the simplex satellite transmitter, and to periodically enable and disable power from the power source to the position location unit and the simplex satellite transmitter.
Owner:BNP PARIBAS AS SECURITY AGENT
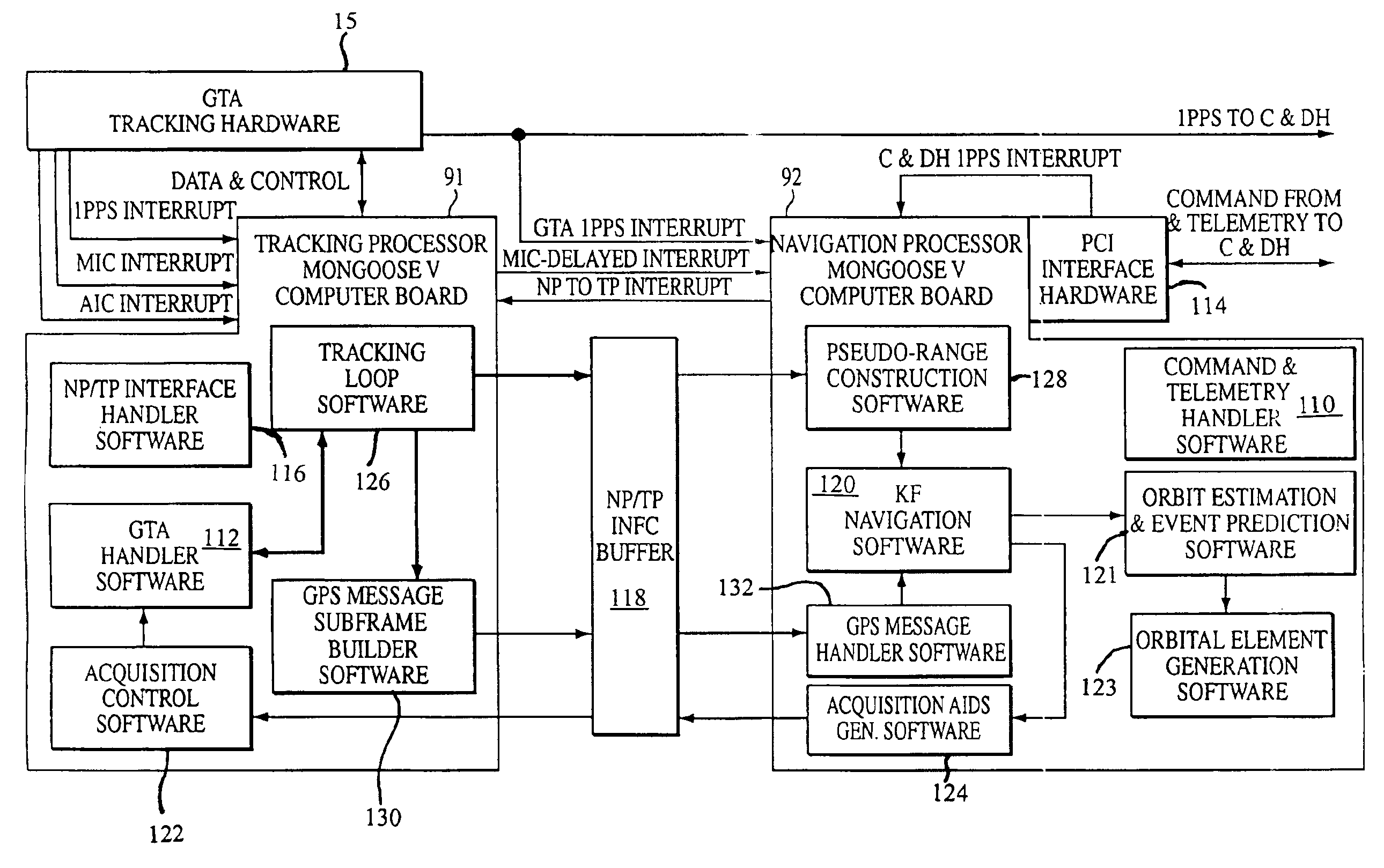
Extended kalman filter for autonomous satellite navigation system
InactiveUS6859170B2Simplify the design processMaximum capabilityInstruments for comonautical navigationArtificial satellitesLow earth orbitMedium Earth orbit
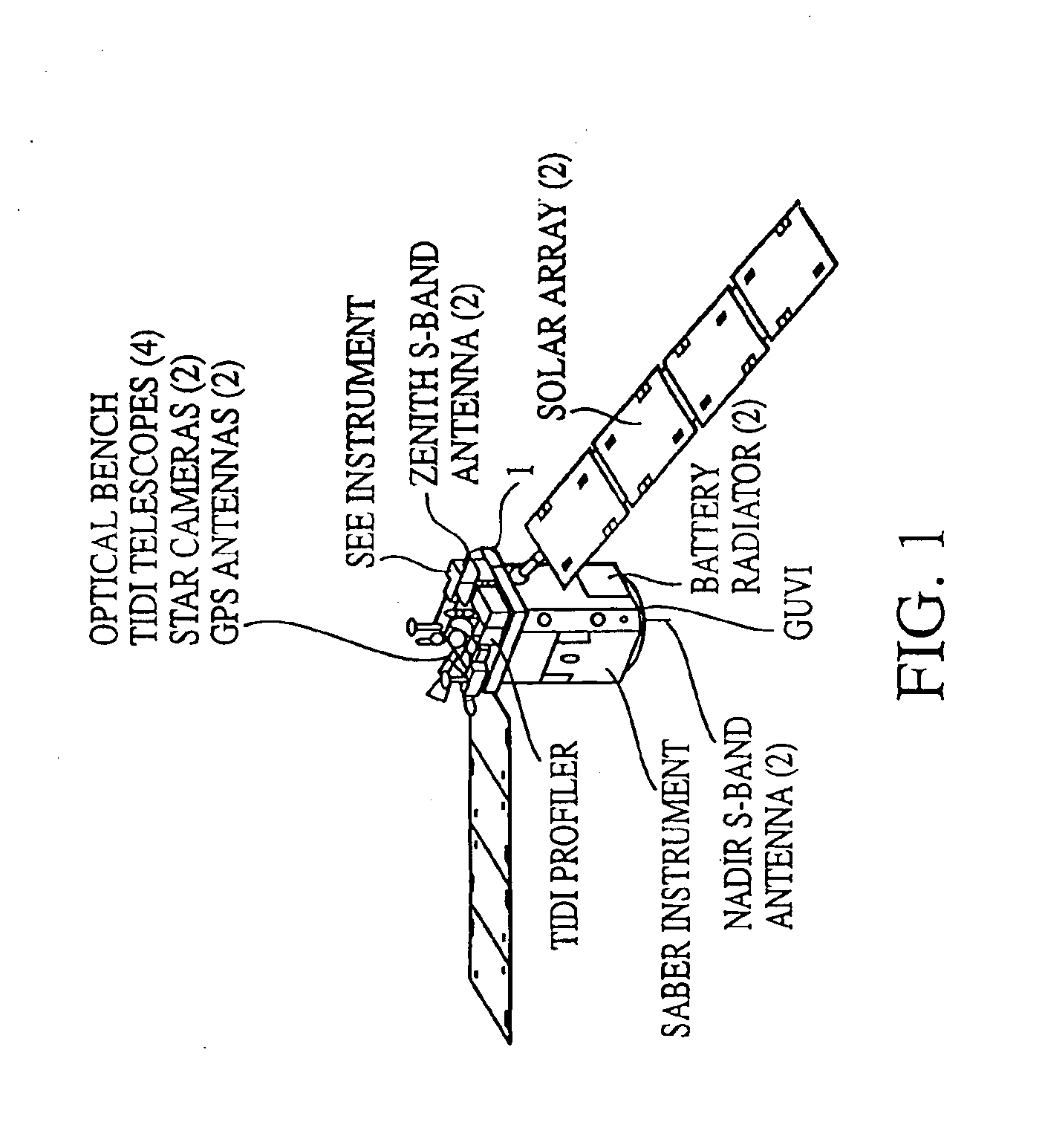
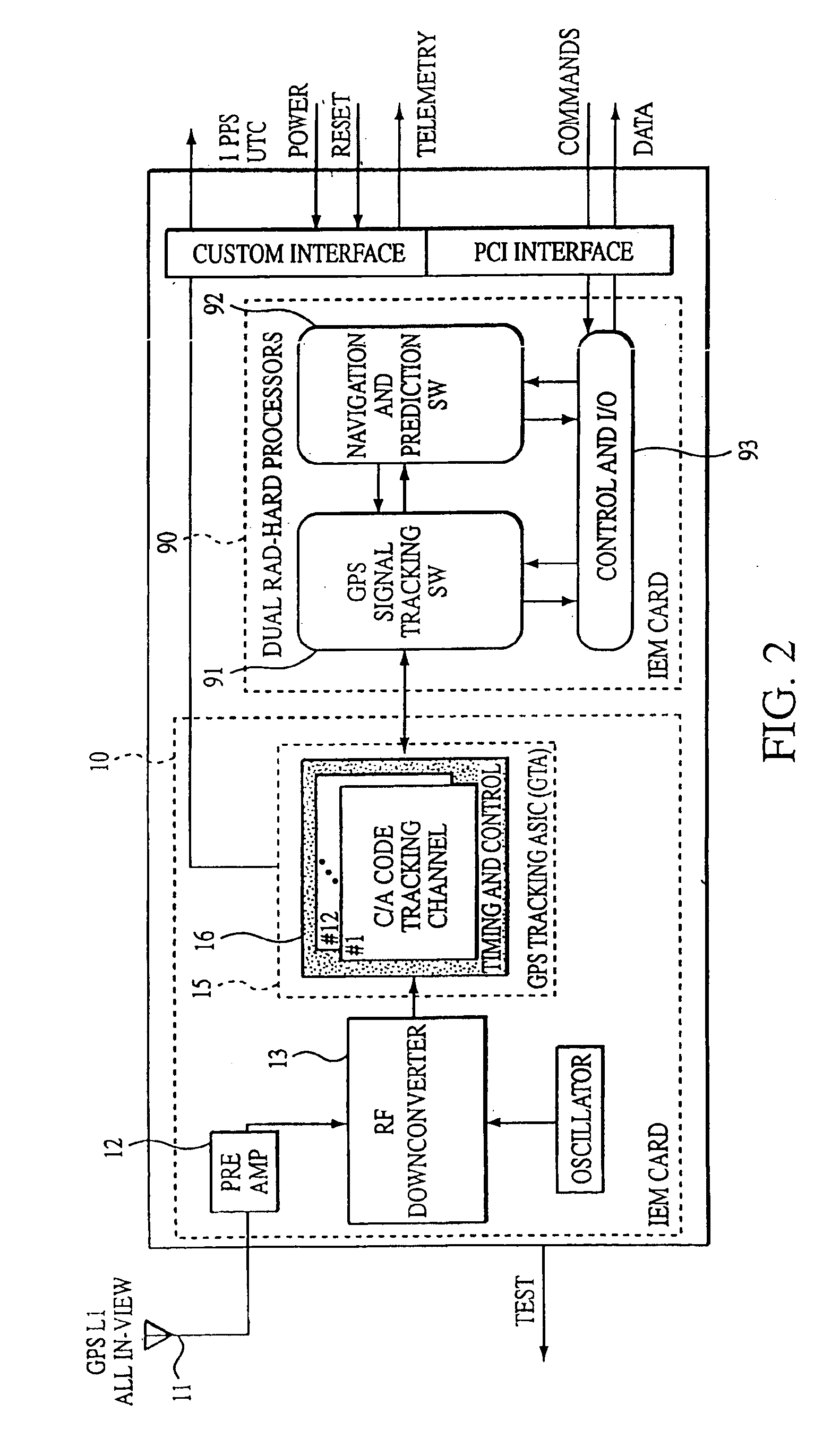
An autonomous navigation system for an orbital platform incorporating a global positioning system based navigation device optimized for low-Earth orbit and medium-Earth orbit applications including a 12 channel, GPS tracking application-specific integrated circuit (15) operating in concert with a computer system (90) implementing an extended Kalman filter and orbit propagator which autonomously generates estimates of position, velocity and time to enable planning, prediction and execution of event-based commanding of mission operations.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
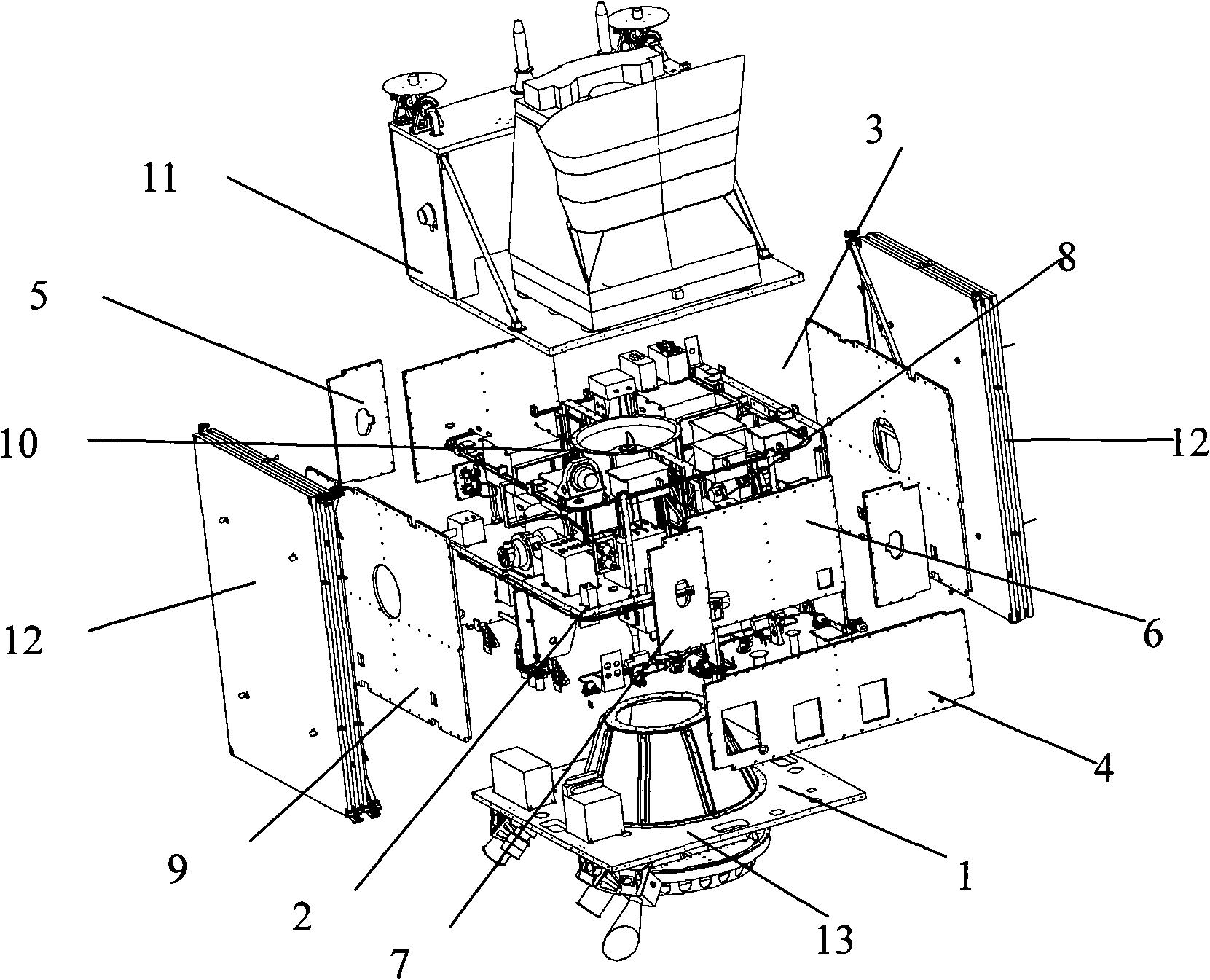
Configuration for low-earth-orbit remote sensing satellite and mounting method thereof
InactiveCN102372092AStable structureHigh precision requirementsArtificial satellitesCentral forceLow earth orbit
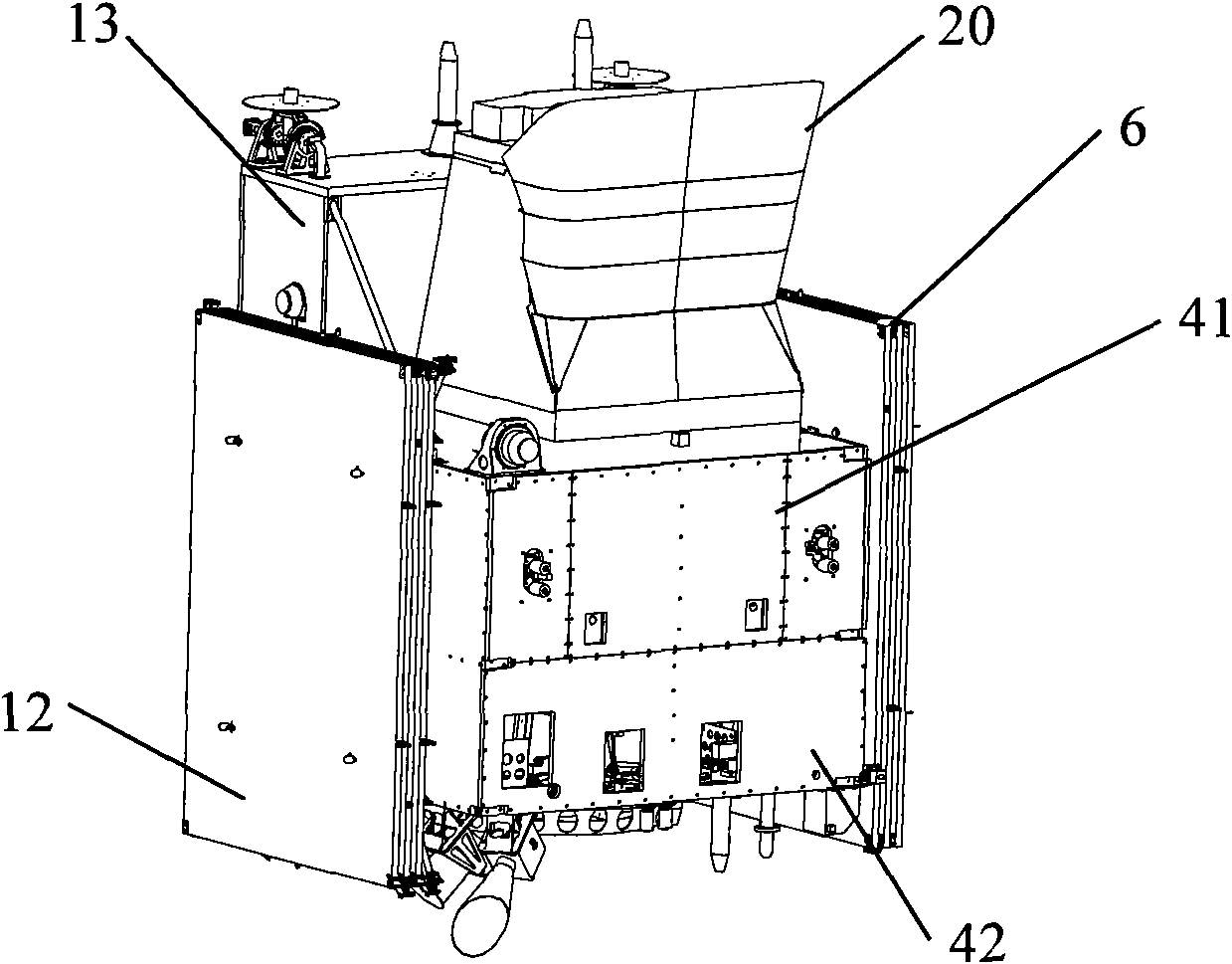
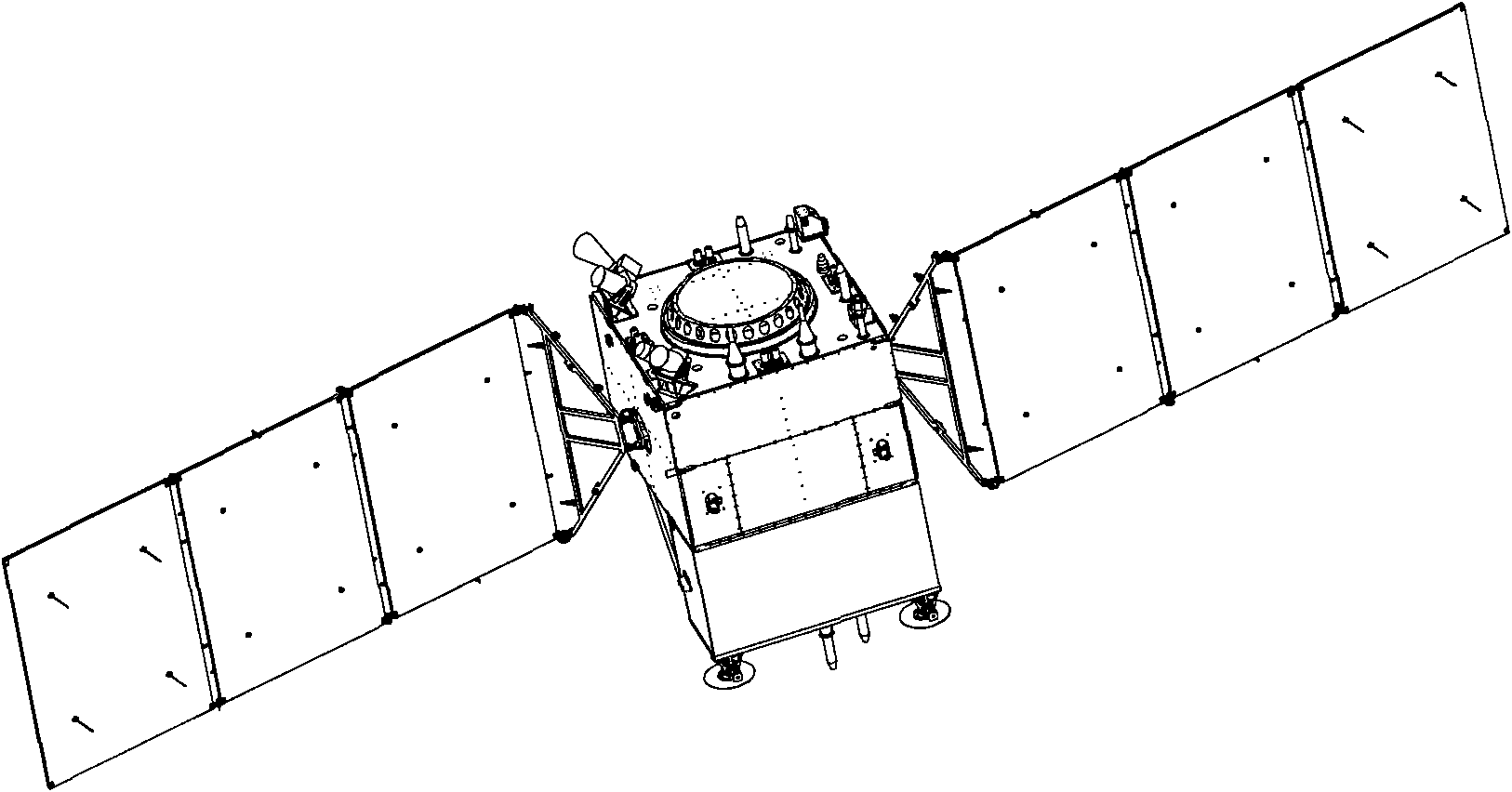
The invention provides a configuration for a low-earth-orbit remote sensing satellite, which comprises a base plate, a middle plate, a top plate, a plurality of transverse lateral plates and upright lateral plates, wherein the base plate, the middle plate and the top plate are enclosed into a sealed space by the transverse lateral plates and the upright lateral plates; a central force-bearing cylinder is arranged in the sealed space; corresponding solar cell arrays are arranged on the two sides of the sealed space; a supporting rod is connected between the base plate and the middle plate; four isolating plates are uniformly distributed and are arranged between the middle plate and the top plate; a payload bay is connected above the top plate; and an overskirt is connected to the bottom of the base plate. The configuration for the low-earth-orbit remote sensing satellite has a stable structure, is capable of carrying a large-size and large-mass load, and is high in adaptability for the characteristics of large volume, heavy weight, high precision demand and difficulty in mounting of the present payload.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
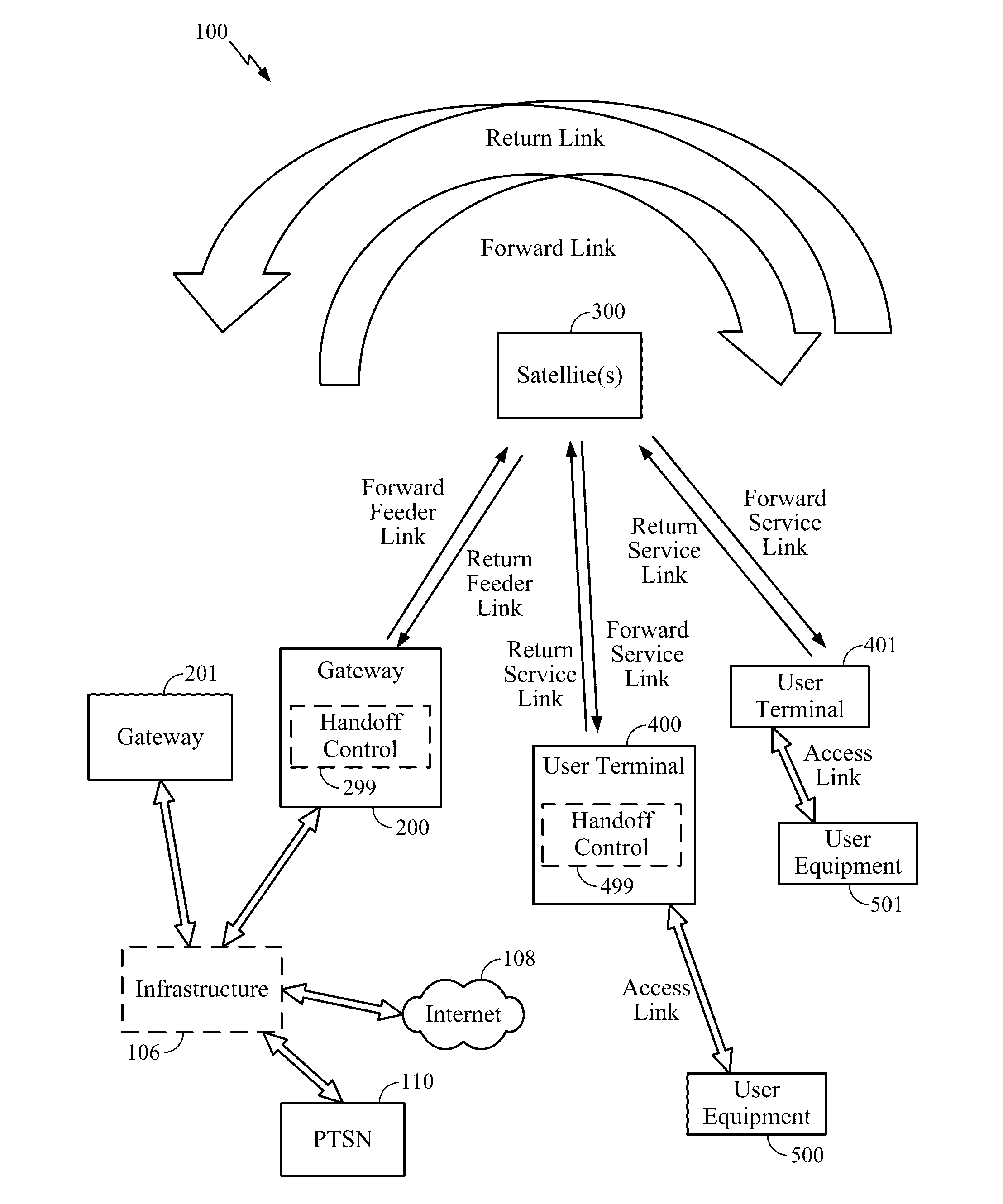
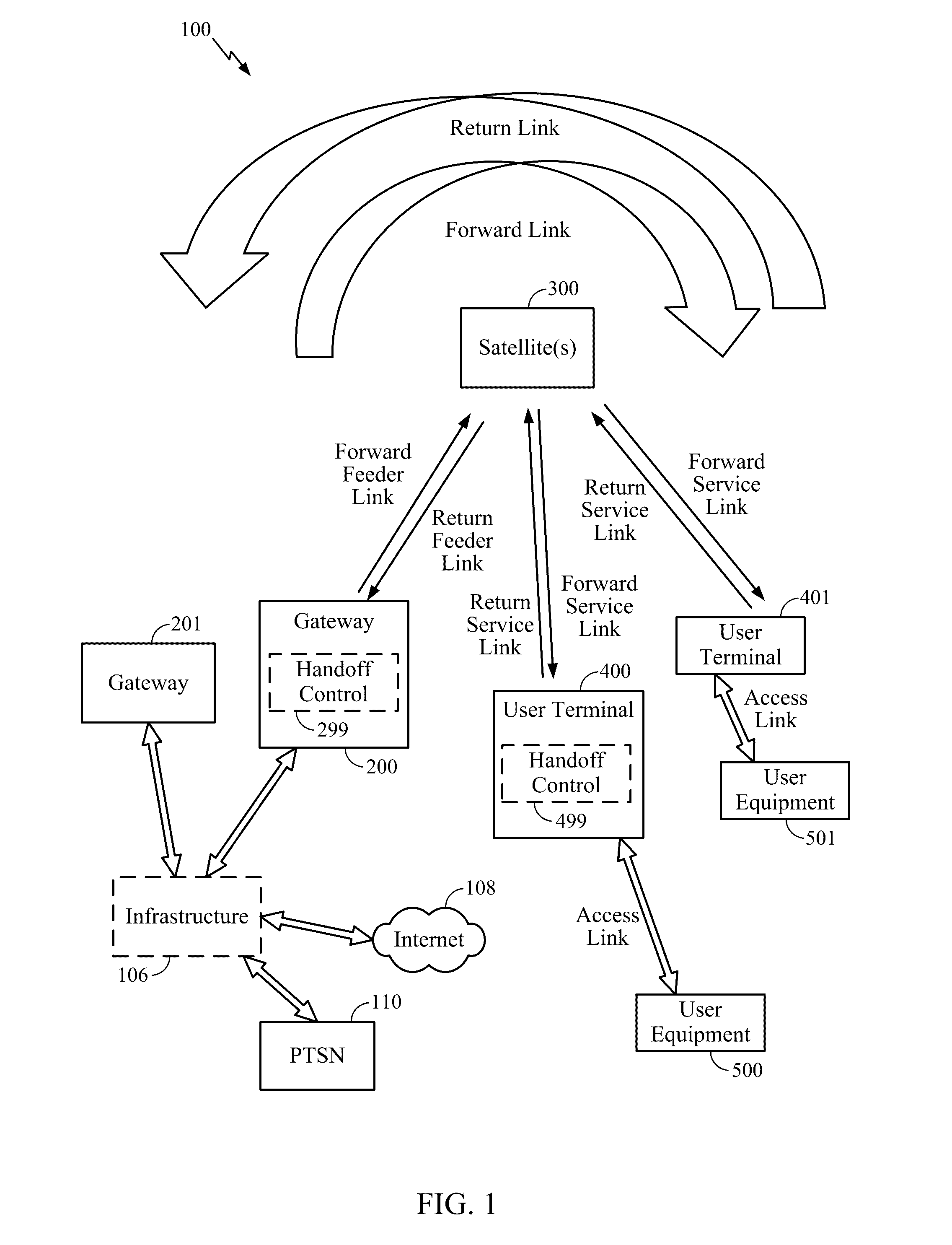
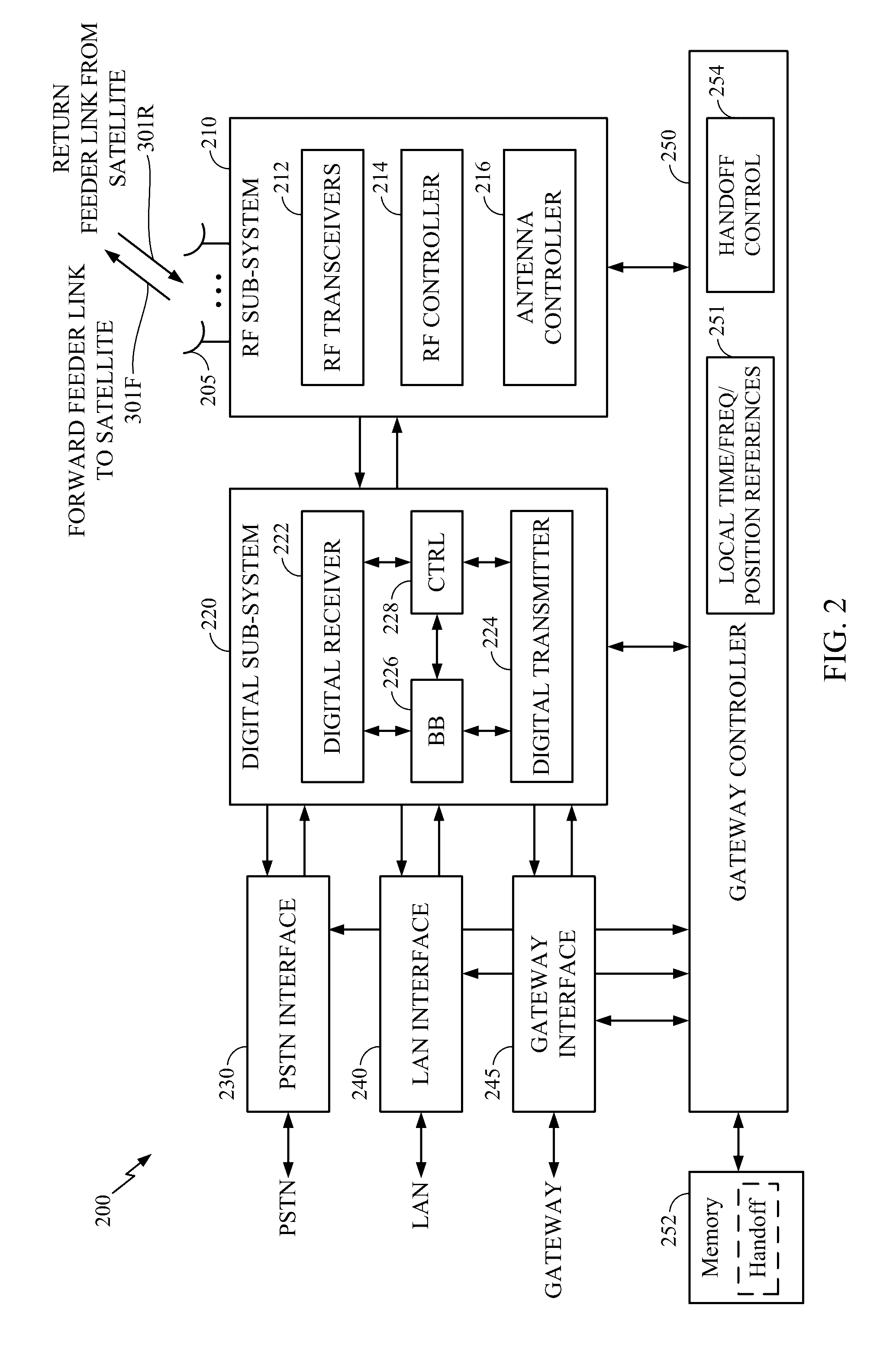
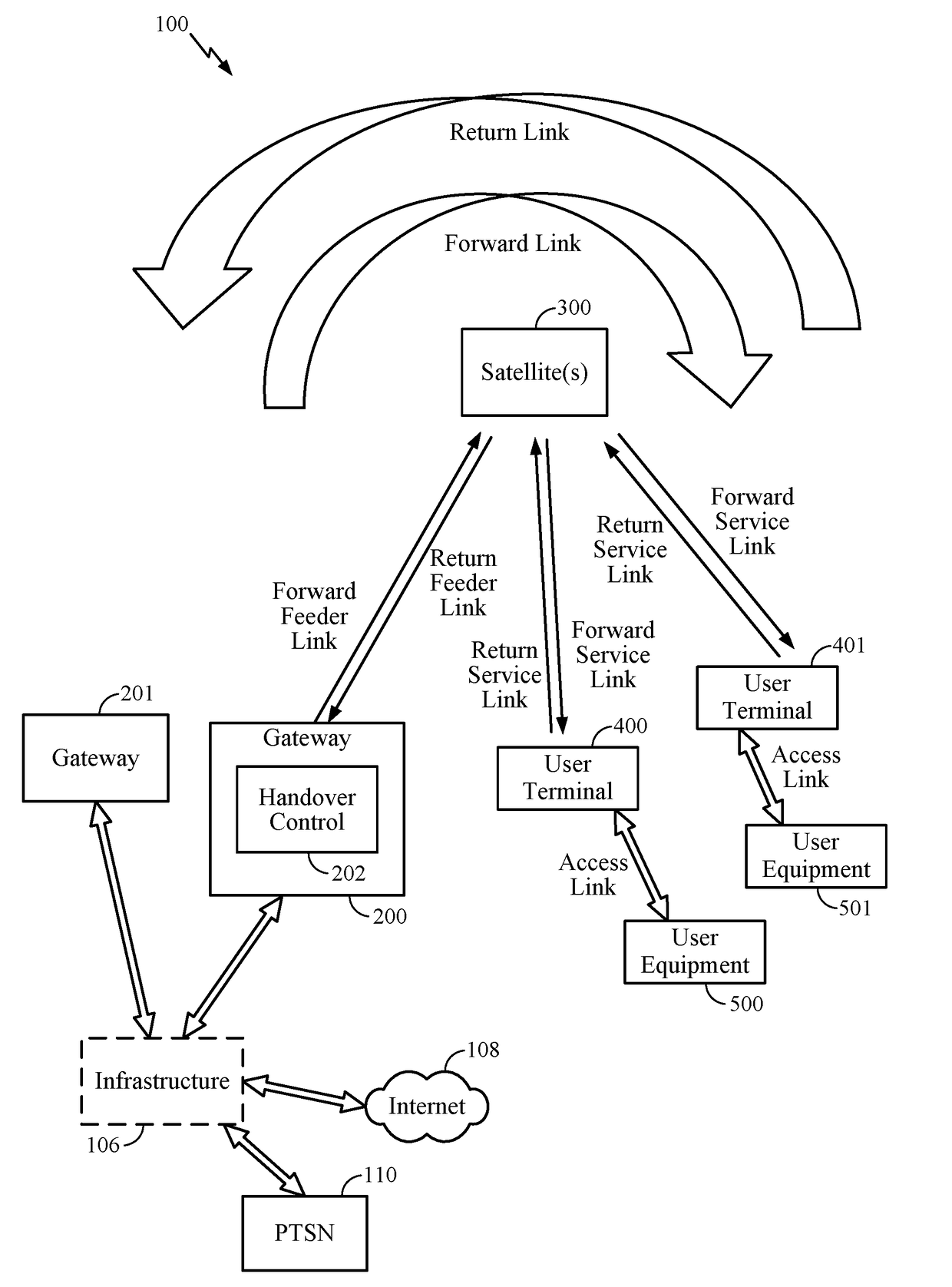
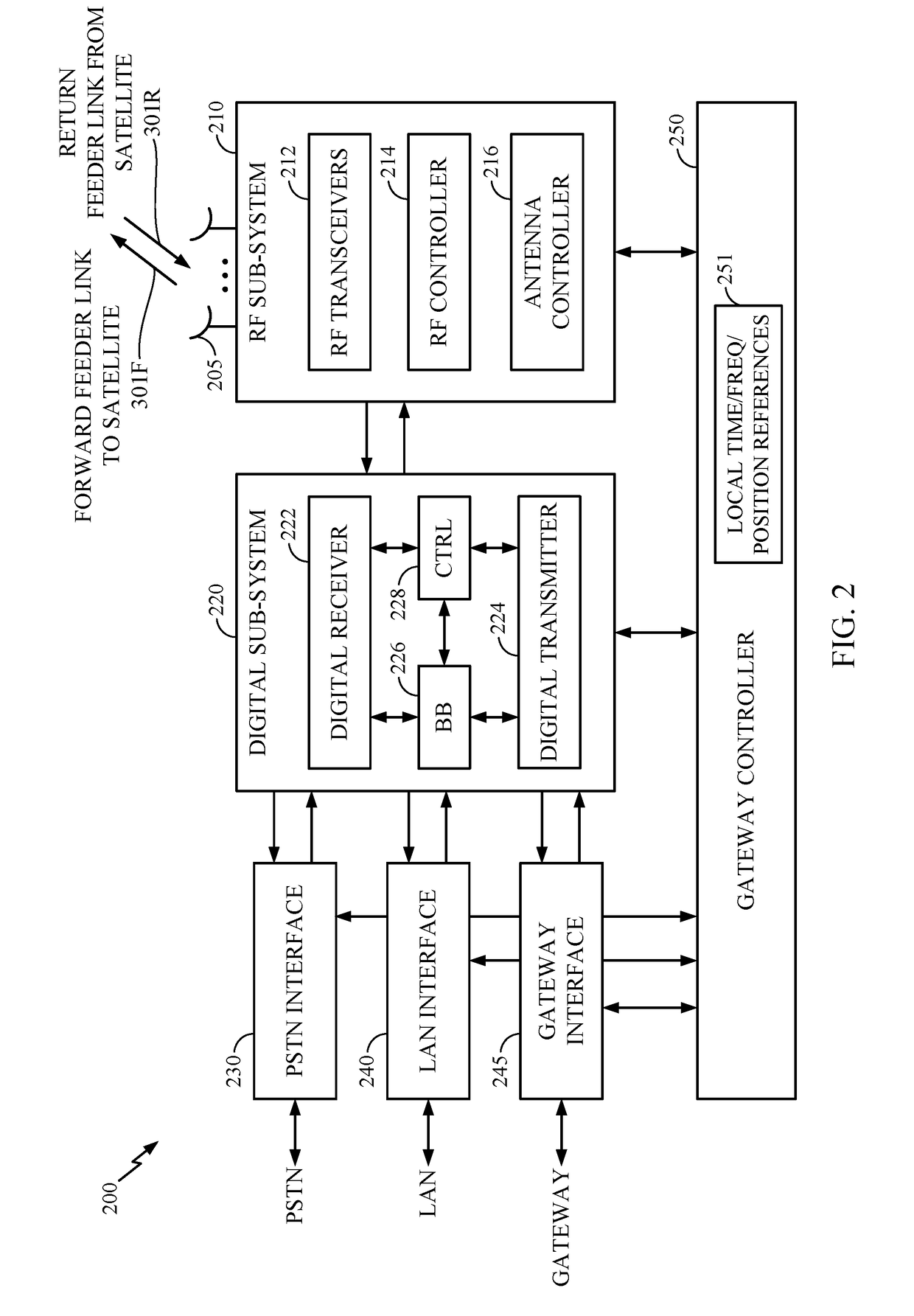
Satellite-to-satellite handoff in satellite communications system
Aspects of the disclosure provide a handoff procedure for a satellite communication system such as a broadband low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellite communication system. A gateway and a user terminal (UT) coordinate and schedule a satellite-to-satellite handoff in such a way that there are no messaging round-trip delays between the last return service link (RSL) packet transmitted from the user terminal to the source satellite and the first RSL packet transmitted from the user terminal to the target satellite. Therefore, an outage on the return link (from the user terminal to the gateway) can be limited to the actual time for moving the antenna feed from the source satellite to the target satellite. Furthermore, an outage on the forward link (from the gateway to the user terminal) can be limited to a single round-trip delay in addition to the time for moving the antenna feed.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and apparatus for inter-satellite handovers in low-earth orbit (LEO) satellite systems
ActiveUS20170105153A1Keep for a long timeNetwork topologiesTransmission monitoringSystem capacityCommunications system
Methods and apparatuses for managing inter-satellite handovers are provided to allow a user terminal to reduce the frequency of handovers while maintaining a sufficiently high system capacity in a non-geosynchronous satellite communication system. The method and apparatus for managing inter-satellite handovers may be implemented in a gateway, in infrastructure connected to a gateway, in a user terminal, or in a satellite.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Wireless tank monitoring system having satellite communications capability
ActiveUS20060111040A1Scalability of numberLow costRadio transmissionAlarmsIntrinsic safetyMonitoring system
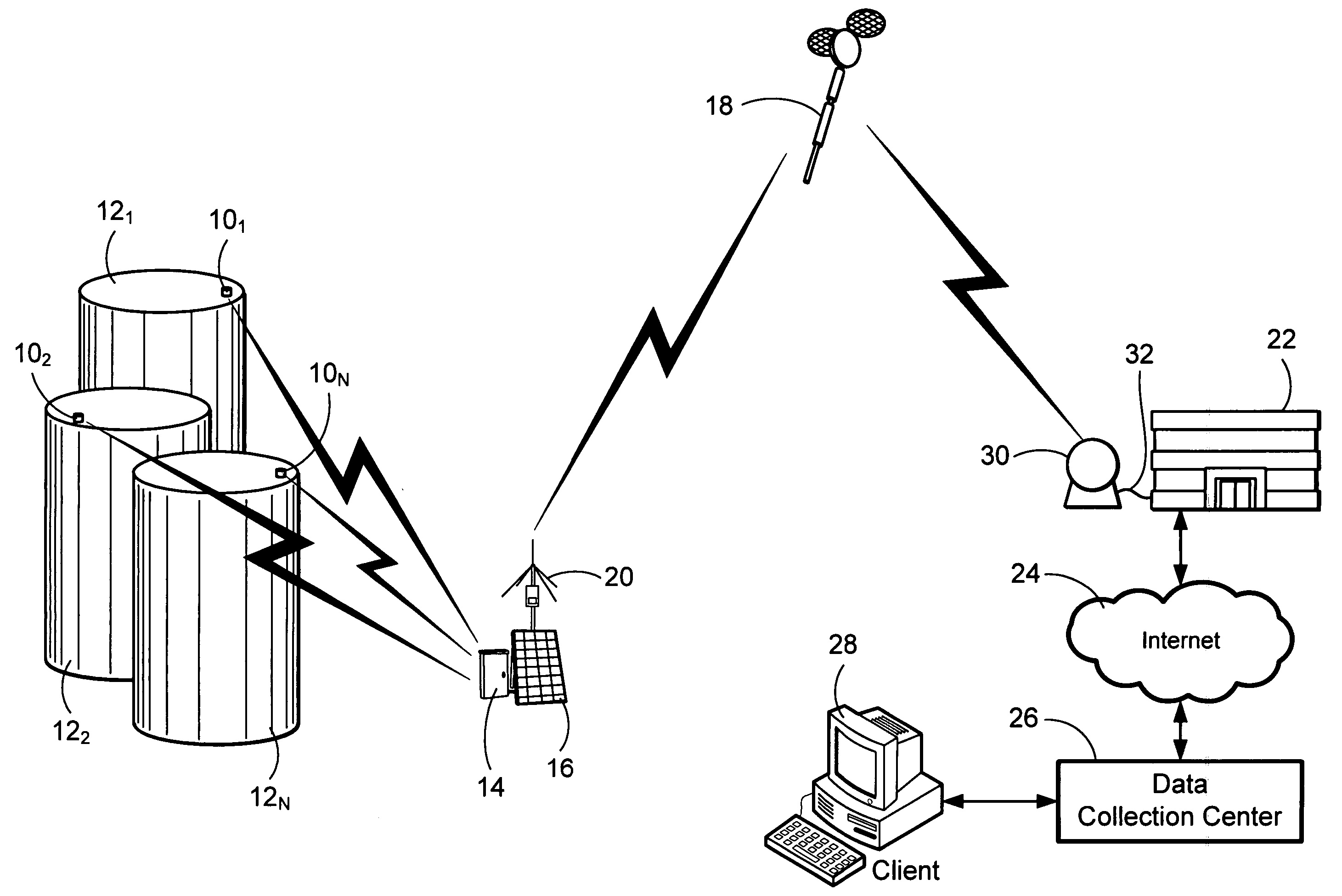
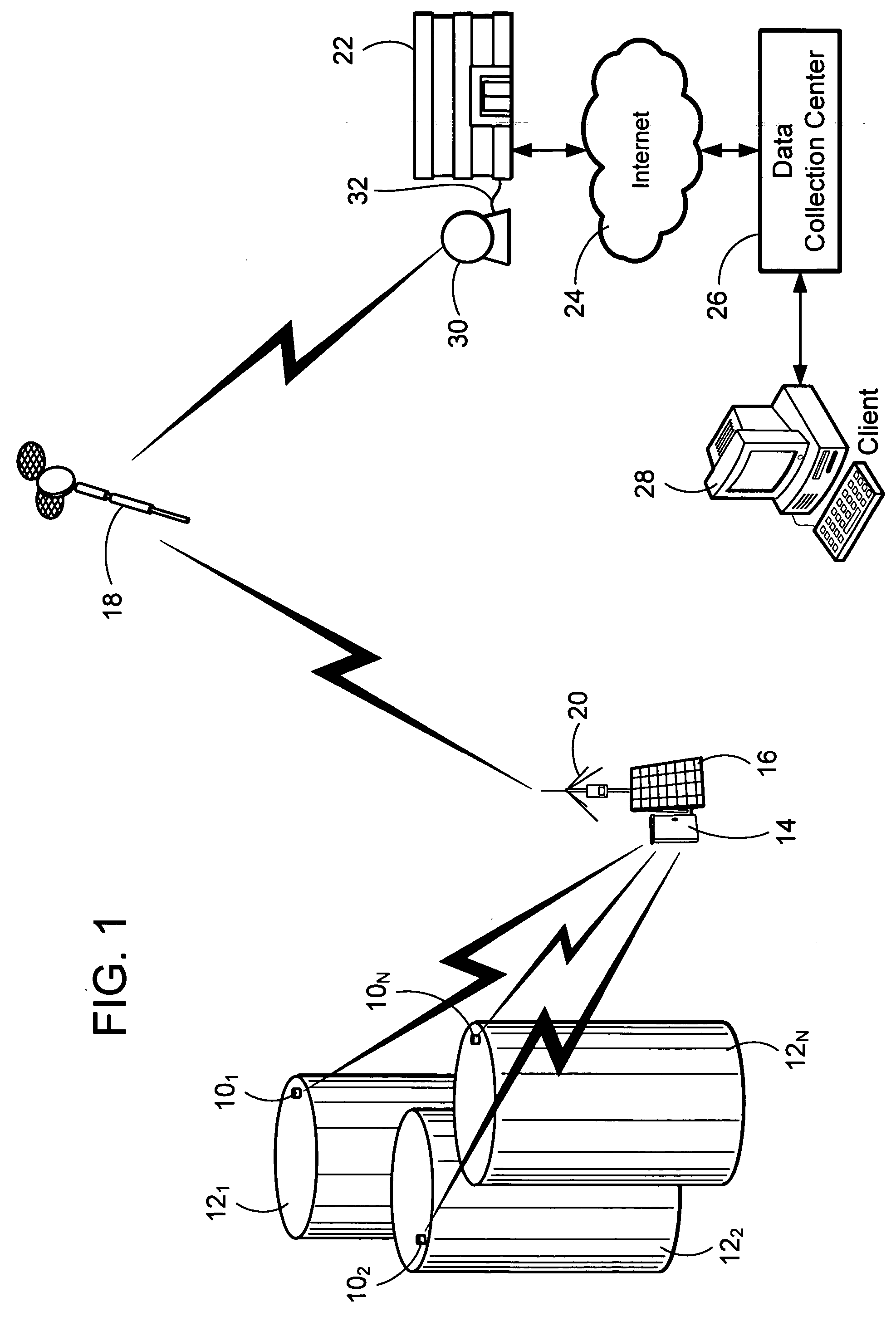
A wireless tank monitoring system for remotely monitoring a plurality of storage tanks is provided. This tank monitoring system utilizes wireless communication from individual tank level monitors to a single SatComm Gateway. The SatComm Gateway then utilizes a low-Earth Orbit satellite constellation to transmit information to a central data collection center. The data collection center then provides access to this information to clients. These clients also have the capability of controlling individual monitors via the bi-directional communications path through the satellite link to the SatComm Gateway to the individual monitors. The SatComm Gateway packages the information from each of the monitors to optimize the communications through the satellite link to decrease the cost of transmission. Intrinsic safety is provided by each of the individual tank level monitors.
Owner:INVENSYS SYST INC
Method for distributing and routing optimal services of multi-layer satellite network based on minimum time delay
ActiveCN104683016ASolve congestionImprove throughputRadio transmissionData switching networksMinimum timeLow earth orbit
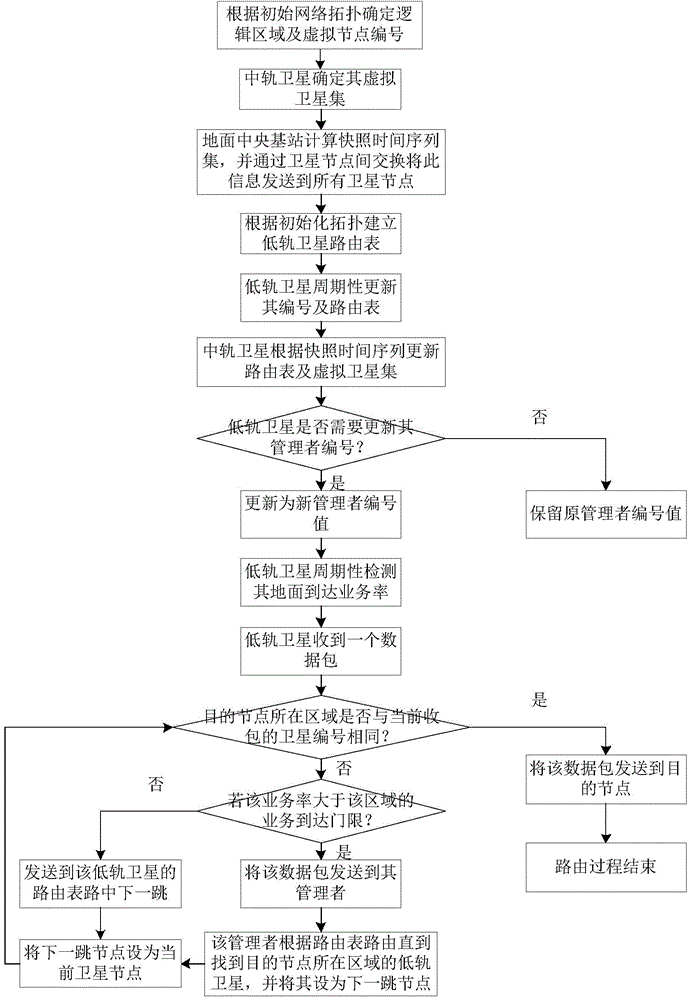
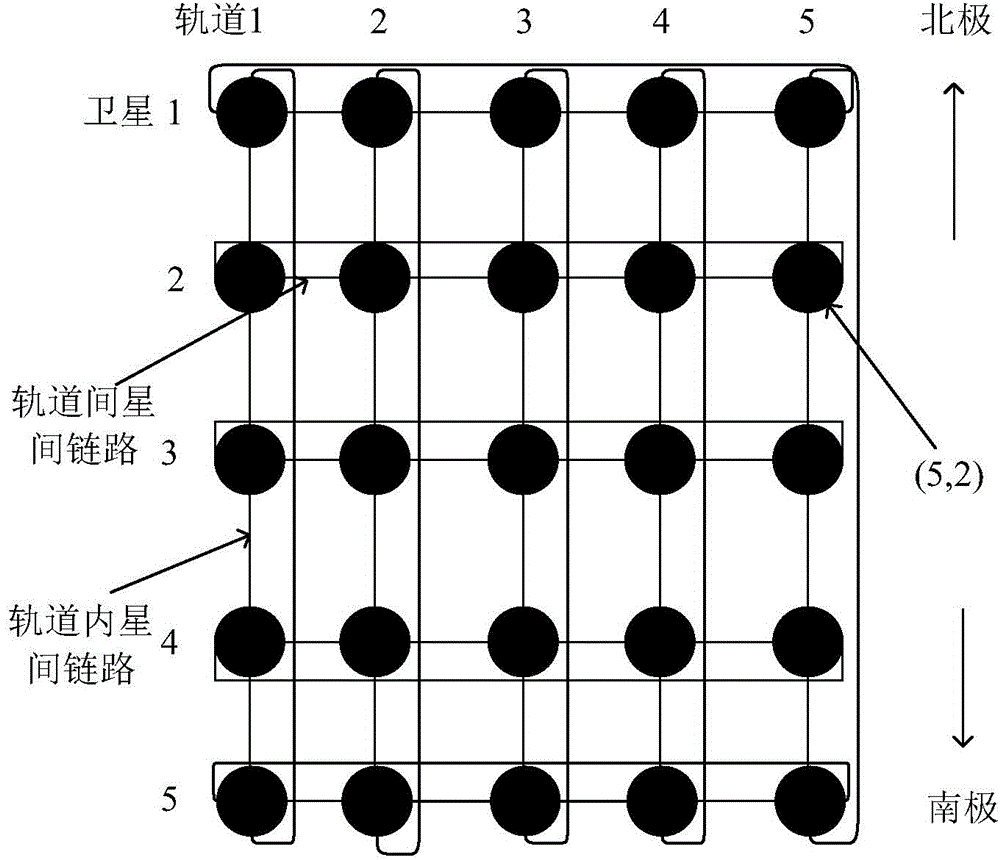
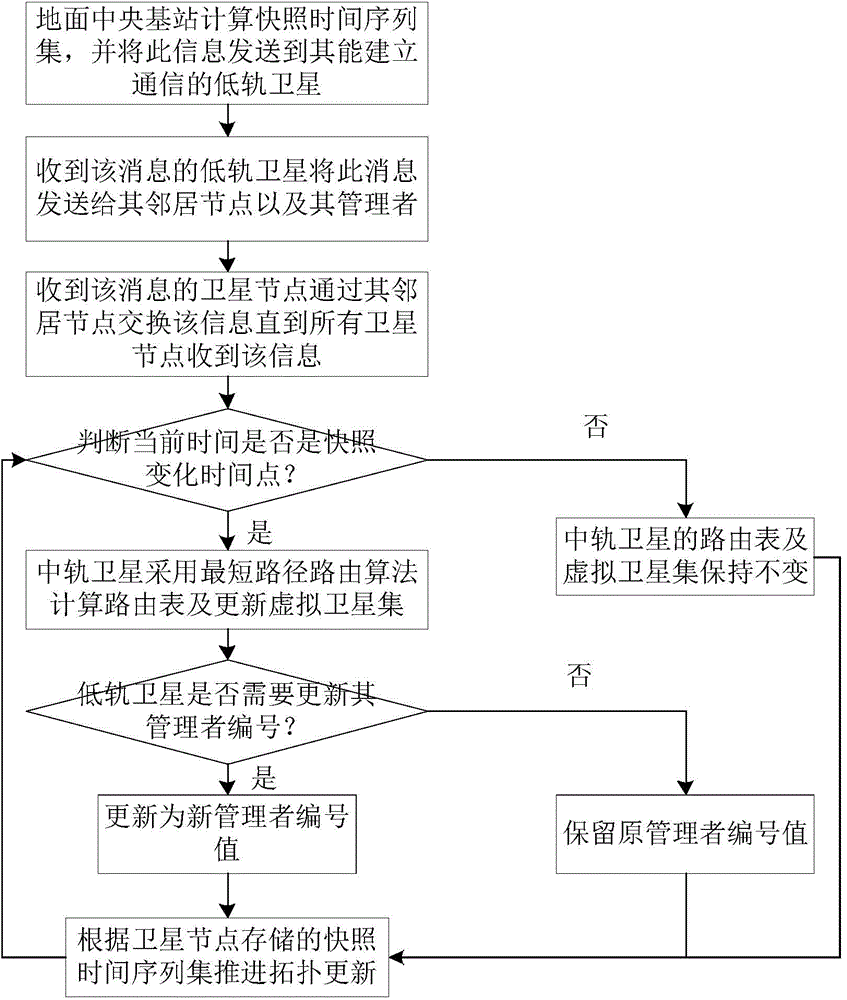
The invention discloses a method for distributing and routing optimal services of multi-layer satellite network based on minimum time delay, and aims to solve the problems of large end-to-end time delay, low handling capacity and insufficient utilization of network resource of a multi-layer satellite communication network routing method. The method comprises the following steps: determining a logic area, a virtual node number and a low-earth-orbit satellite routing list according to the initial network topology; periodically updating the node number and the routing list by a low earth orbit; updating a virtual satellite set and a member routing list according to the snapshot time sequence set by a medium earth orbit, and synchronously updating the number of an administrator by the low earth orbit; if the services arrive and the arrival rate of the current satellite area is less than the arrival rate threshold of the ground service supported by the area based on the minimum end-to-end time, transmitting the service in the low earth orbit, and otherwise, transferring the service to a high-level satellite to route, and finally sending a target node. With the adoption of the method, the performance of the multi-layer satellite communication network is improved; the method can be applied to the routing of the multi-layer satellite communication network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com