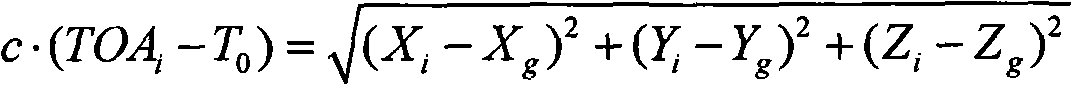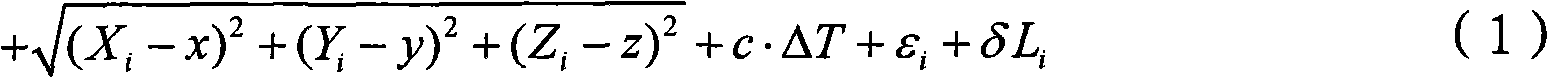Patents
Literature
79 results about "Medium Earth orbit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
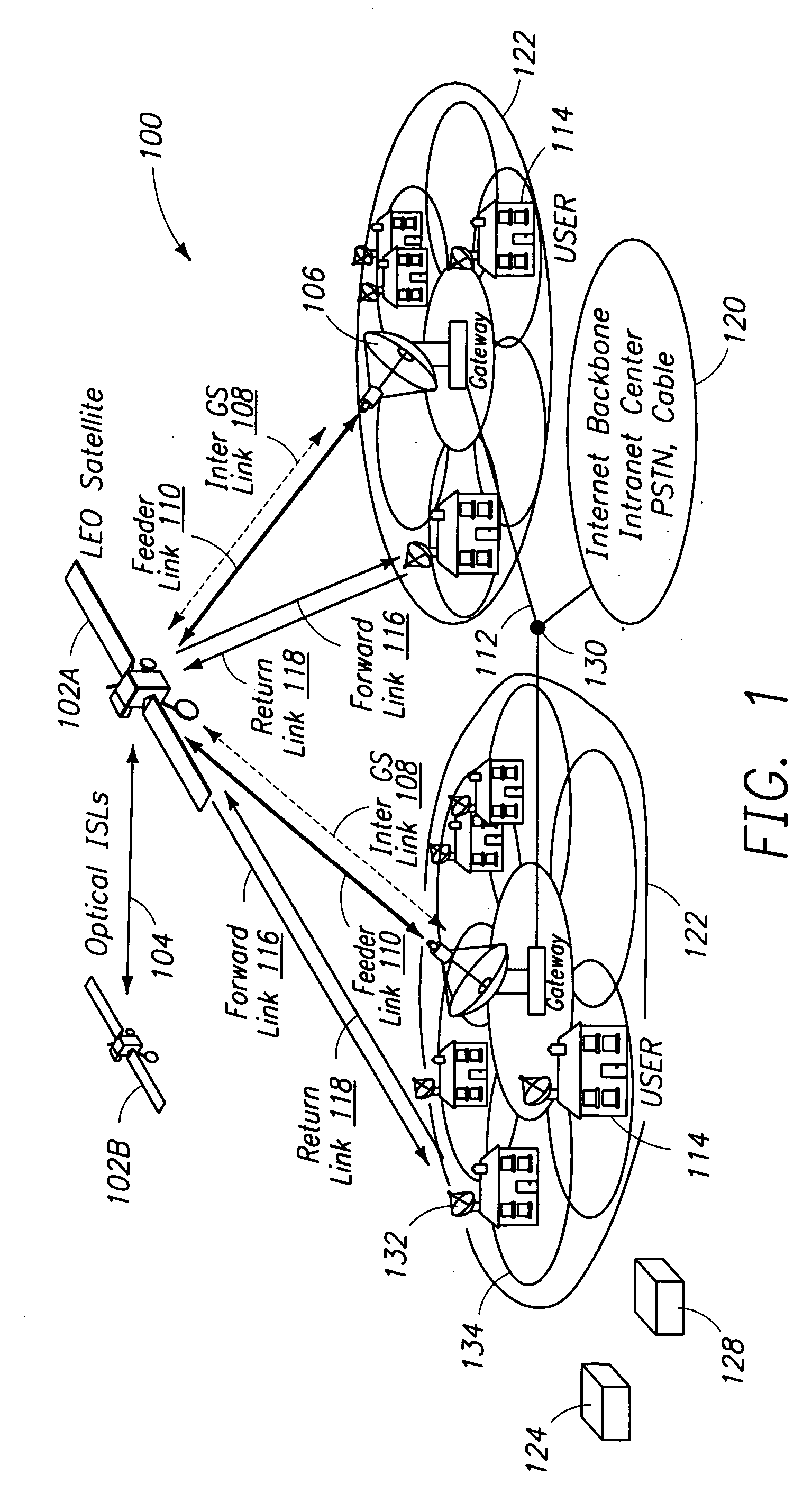
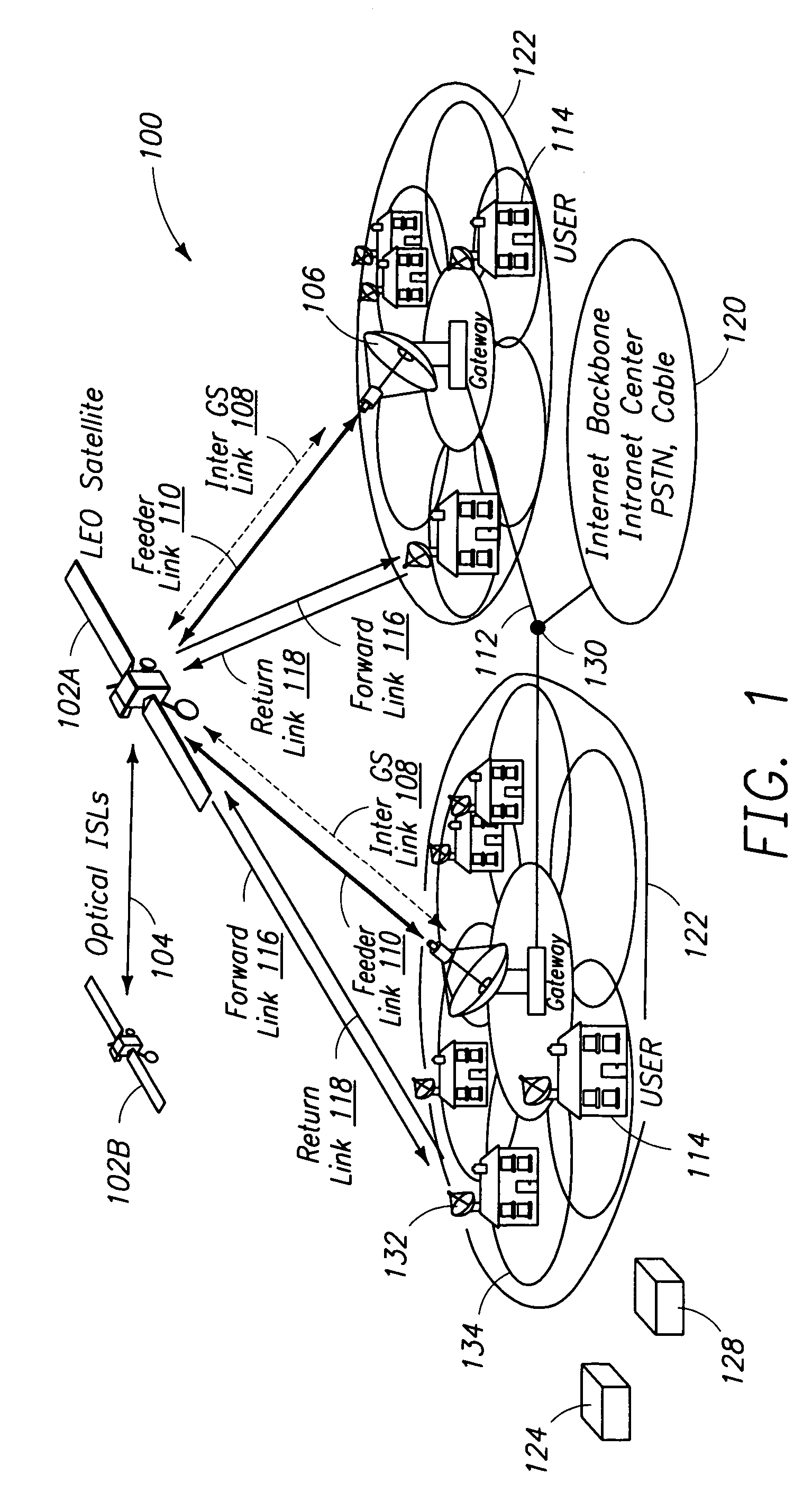
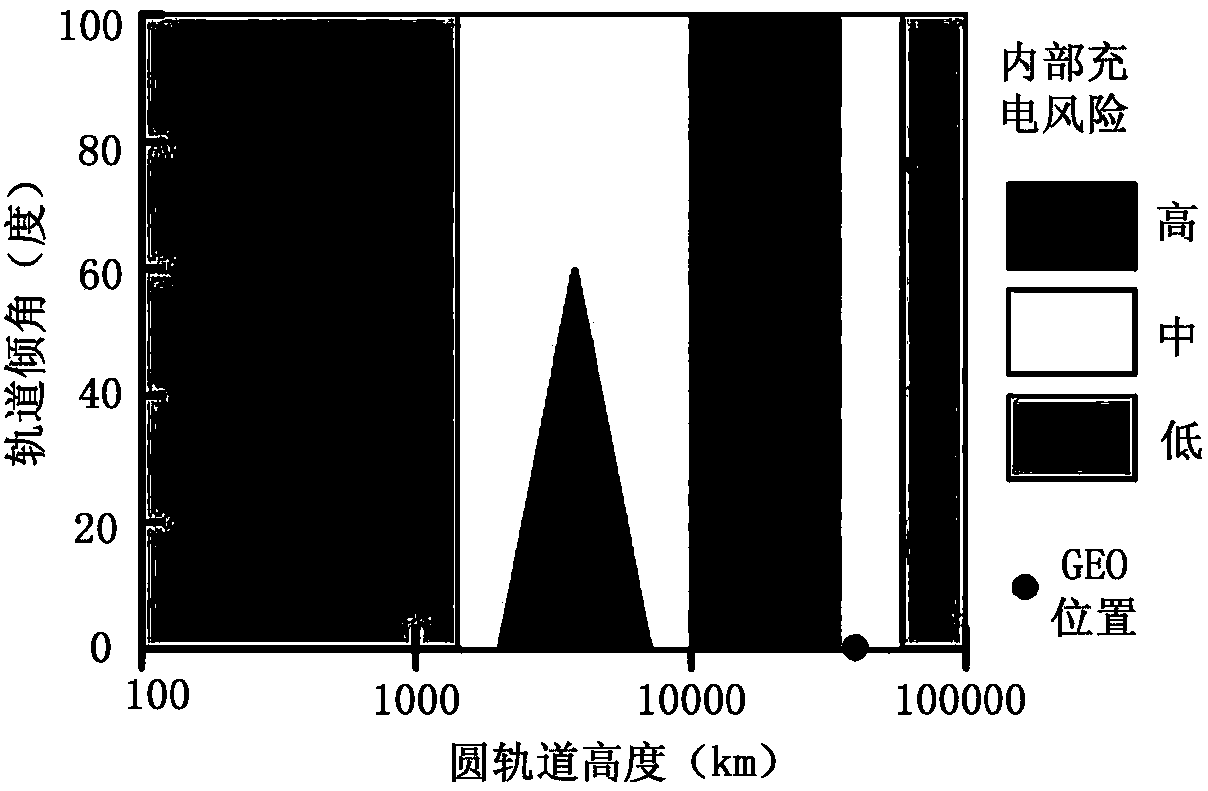
Medium Earth orbit (MEO), sometimes called intermediate circular orbit (ICO), is the region of space around Earth above low Earth orbit (altitude of 2,000 km (1,243 mi) above sea level) and below geosynchronous orbit (altitude of 35,786 km (22,236 mi) above sea level).
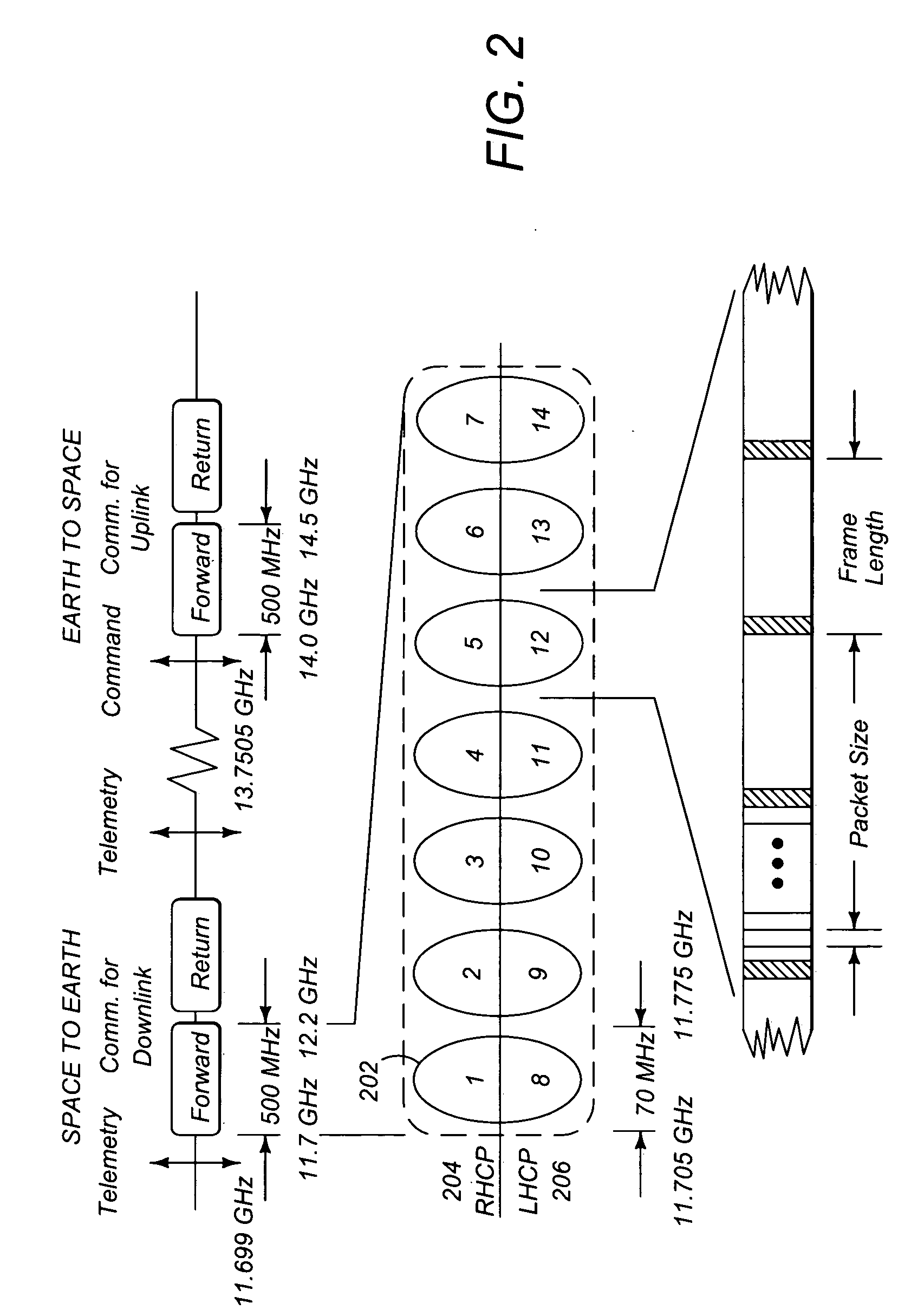
Method and apparatus for providing wideband services using medium and low earth orbit satellites
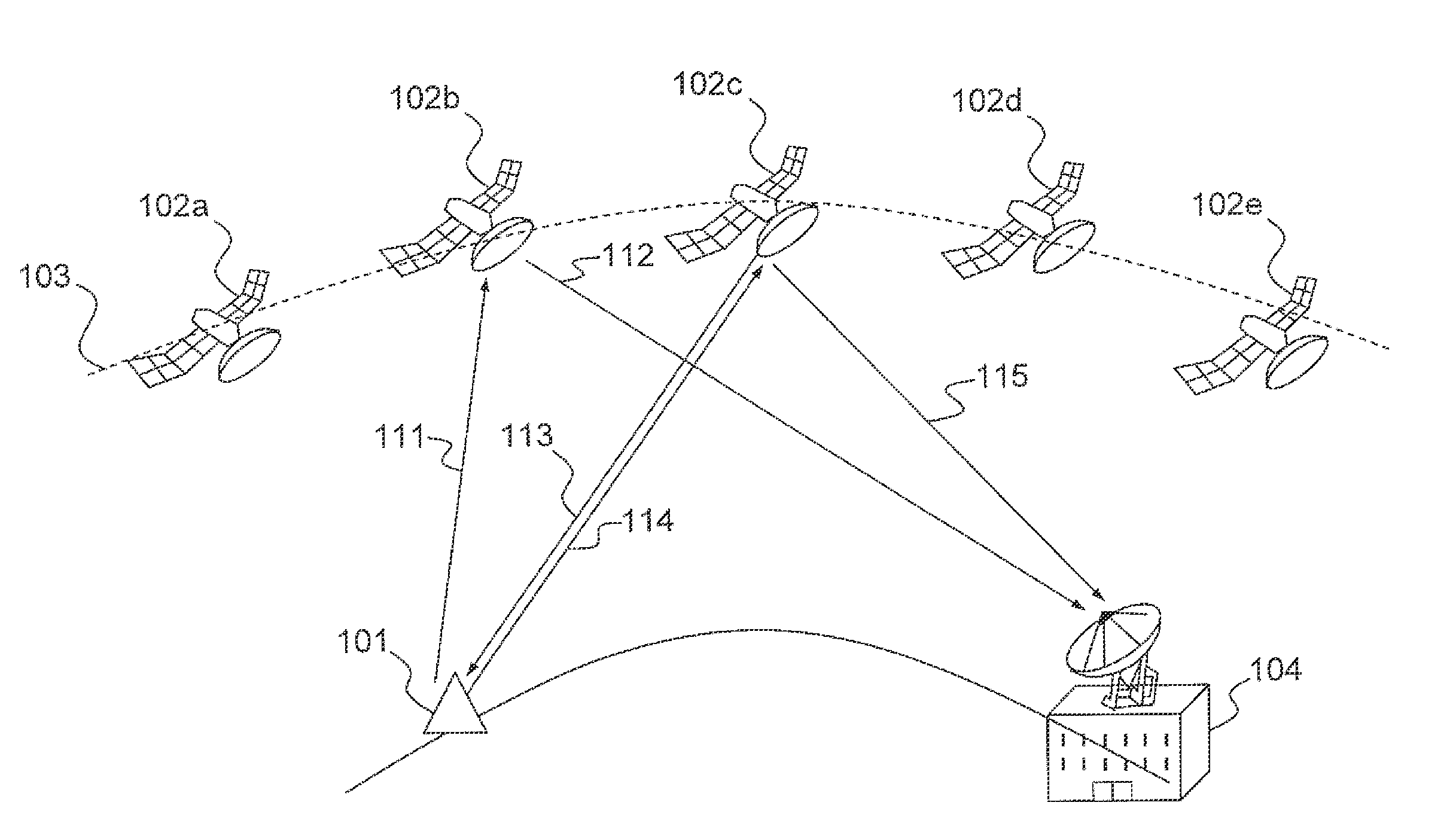
InactiveUS6678520B1Interference minimizationMinimize interferenceActive radio relay systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsHigh elevationLow earth orbit
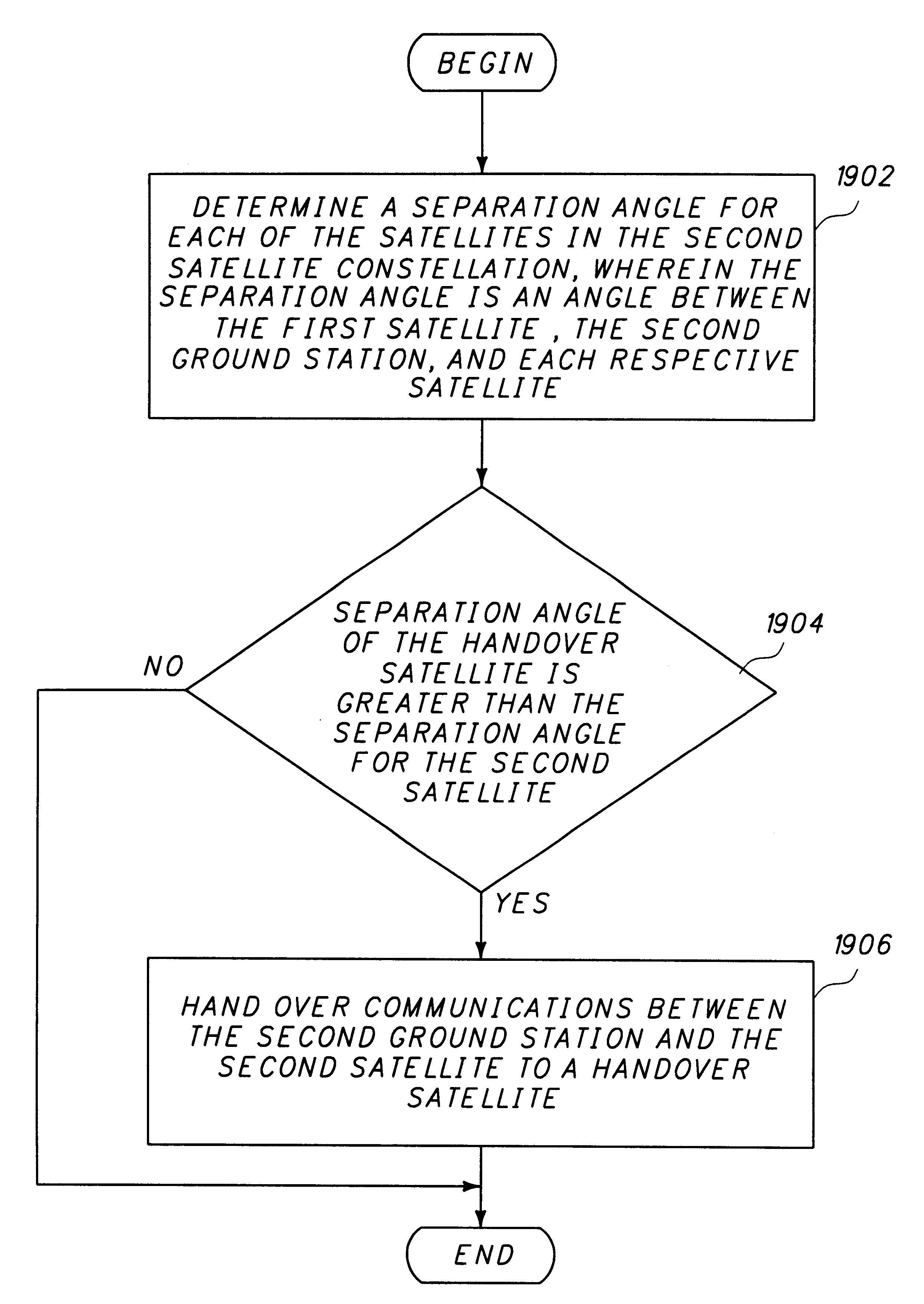
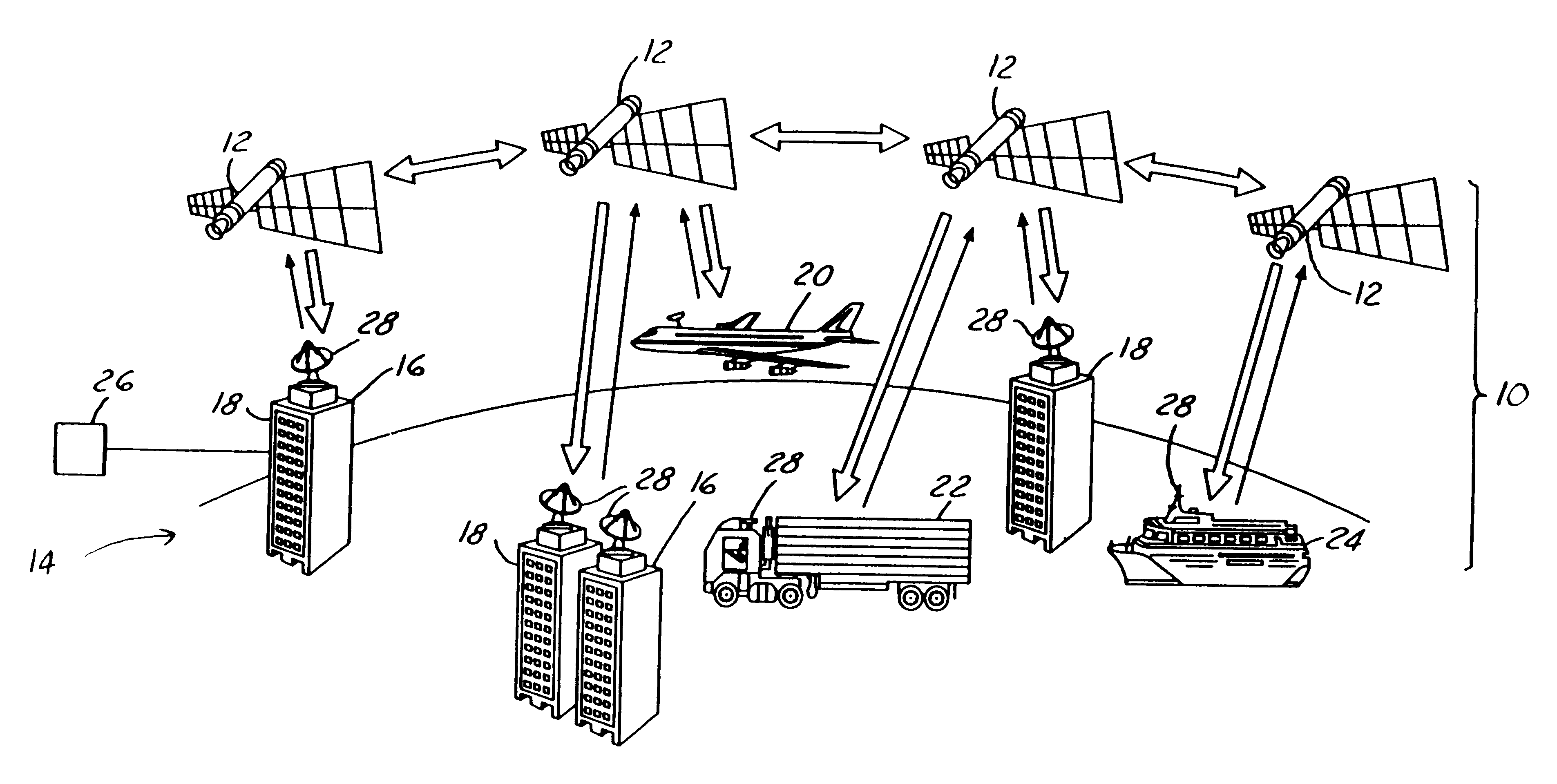
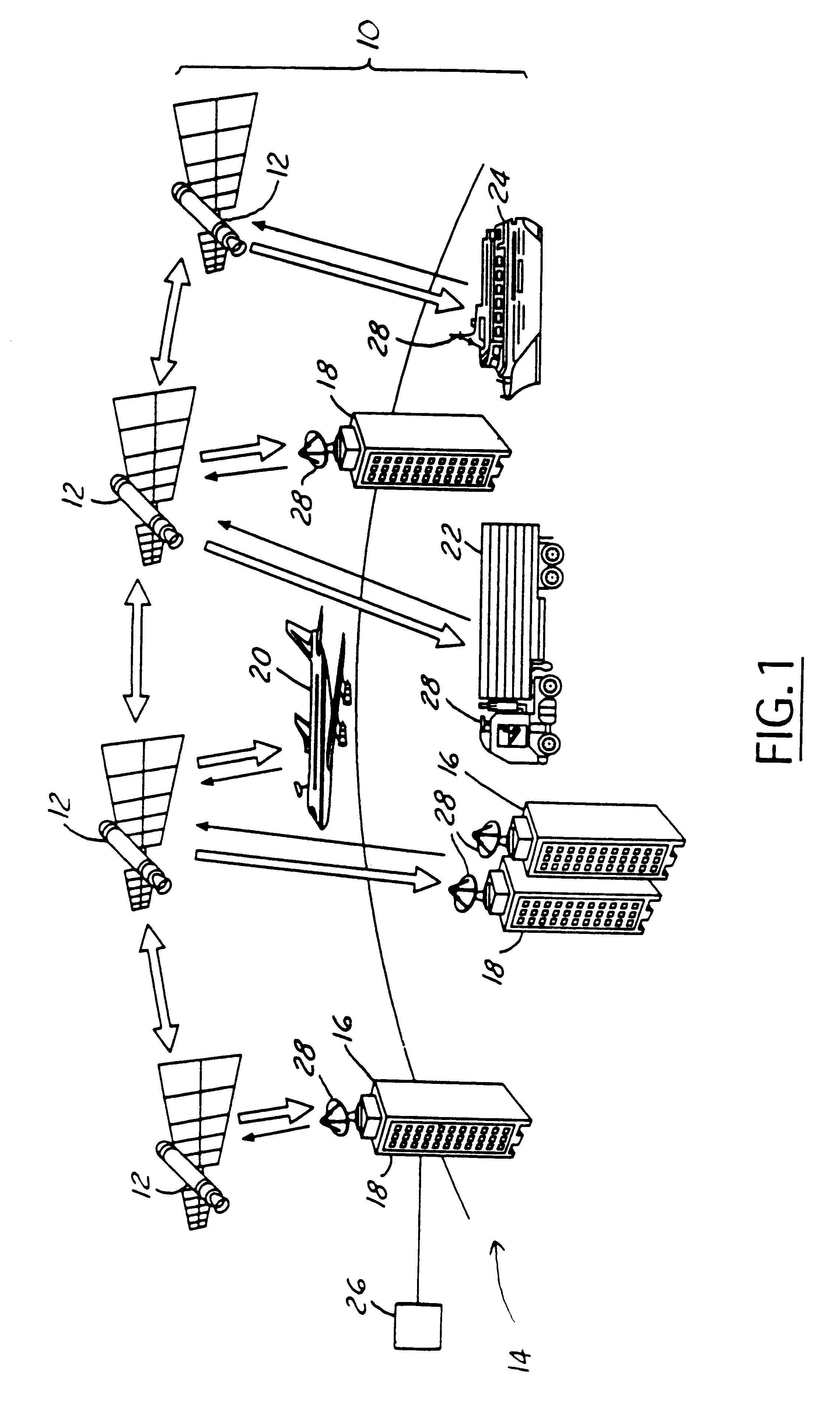
A method and apparatus for mitigating communications interference between satellite communications systems in different orbits is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of evaluating a geometrical relationship between a second ground station and the satellites in the second satellite constellation, and directing communications between the second ground station and the second satellite according to the evaluated geometrical relationship. In one embodiment communications are handed over from a first satellite to another satellite when the first satellite is no longer at the highest elevation angle of visible satellites. In another embodiment, handover occurs when the first satellite drops below a minimum elevation angle.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
Method and apparatus for providing wideband services using medium and low earth orbit satellites
InactiveUS20040110467A1High data rate serviceReduce distractionsActive radio relay systemsSubstation equipmentHigh elevationLow earth orbit
A method and apparatus for mitigating communications interference between satellite communications systems in different orbits is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of evaluating a geometrical relationship between a second ground station and the satellites in the second satellite constellation, and directing communications between the second ground station and the second satellite according to the evaluated geometrical relationship. In one embodiment communications are handed over from a first satellite to another satellite when the first satellite is no longer at the highest elevation angle of visible satellites. In another embodiment, handover occurs when the first satellite drops below a minimum elevation angle.
Owner:THE DIRECTV GRP INC
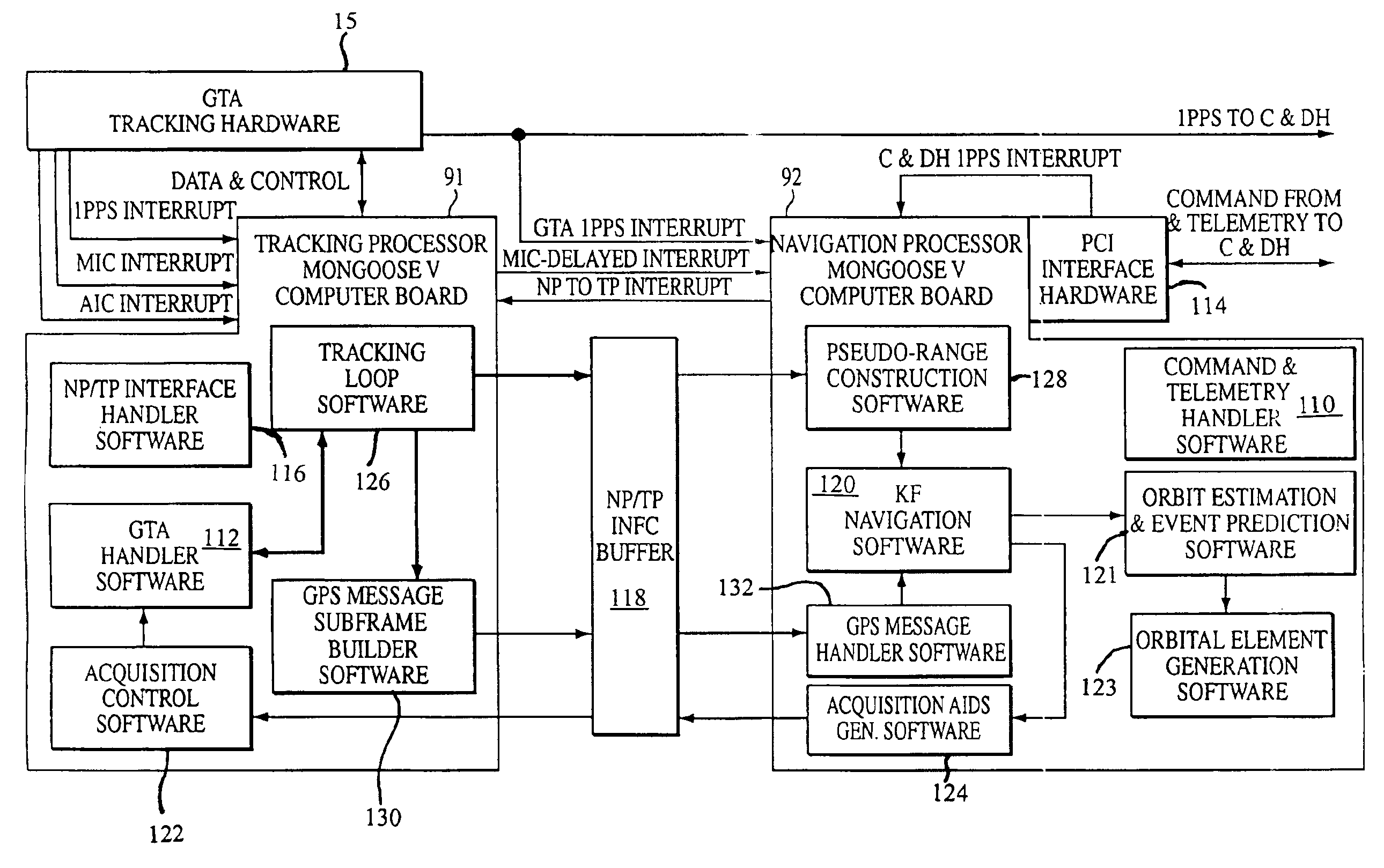
Extended kalman filter for autonomous satellite navigation system
InactiveUS6859170B2Simplify the design processMaximum capabilityInstruments for comonautical navigationArtificial satellitesLow earth orbitMedium Earth orbit
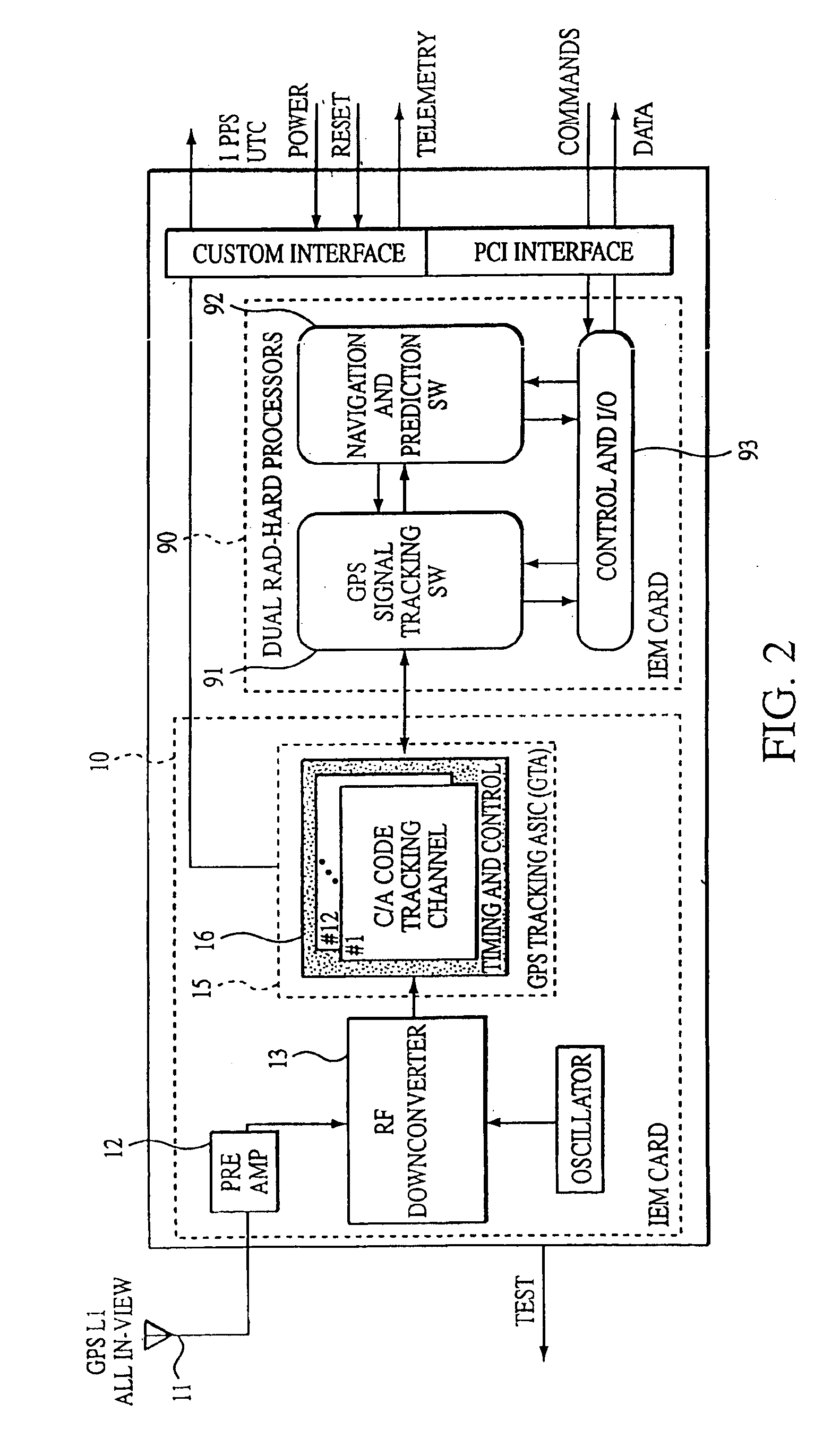
An autonomous navigation system for an orbital platform incorporating a global positioning system based navigation device optimized for low-Earth orbit and medium-Earth orbit applications including a 12 channel, GPS tracking application-specific integrated circuit (15) operating in concert with a computer system (90) implementing an extended Kalman filter and orbit propagator which autonomously generates estimates of position, velocity and time to enable planning, prediction and execution of event-based commanding of mission operations.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for distributing and routing optimal services of multi-layer satellite network based on minimum time delay
ActiveCN104683016ASolve congestionImprove throughputRadio transmissionData switching networksMinimum timeLow earth orbit
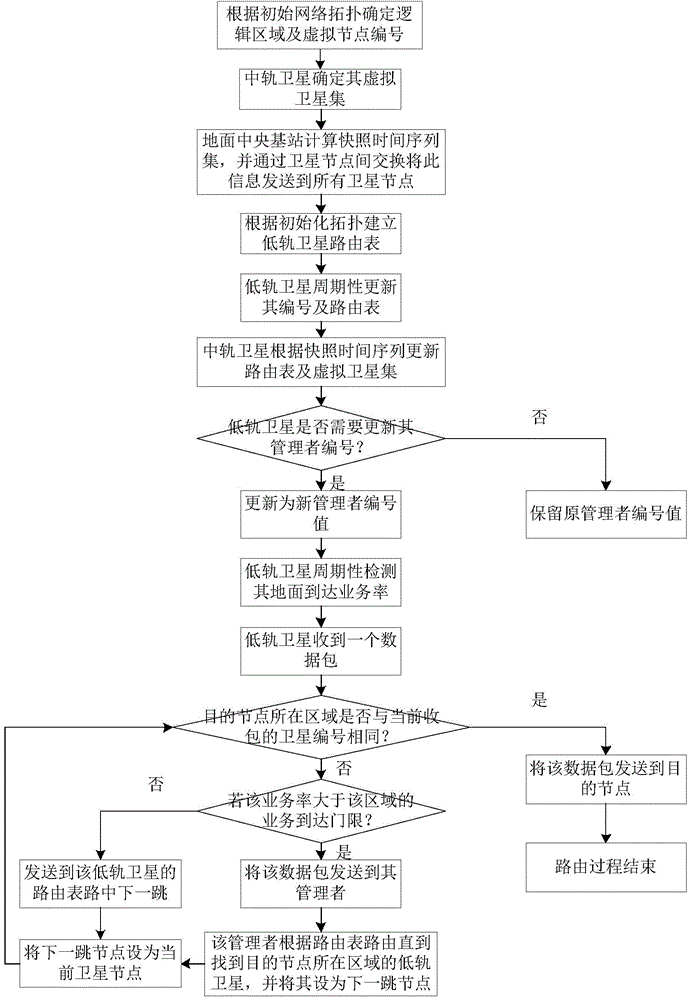
The invention discloses a method for distributing and routing optimal services of multi-layer satellite network based on minimum time delay, and aims to solve the problems of large end-to-end time delay, low handling capacity and insufficient utilization of network resource of a multi-layer satellite communication network routing method. The method comprises the following steps: determining a logic area, a virtual node number and a low-earth-orbit satellite routing list according to the initial network topology; periodically updating the node number and the routing list by a low earth orbit; updating a virtual satellite set and a member routing list according to the snapshot time sequence set by a medium earth orbit, and synchronously updating the number of an administrator by the low earth orbit; if the services arrive and the arrival rate of the current satellite area is less than the arrival rate threshold of the ground service supported by the area based on the minimum end-to-end time, transmitting the service in the low earth orbit, and otherwise, transferring the service to a high-level satellite to route, and finally sending a target node. With the adoption of the method, the performance of the multi-layer satellite communication network is improved; the method can be applied to the routing of the multi-layer satellite communication network.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
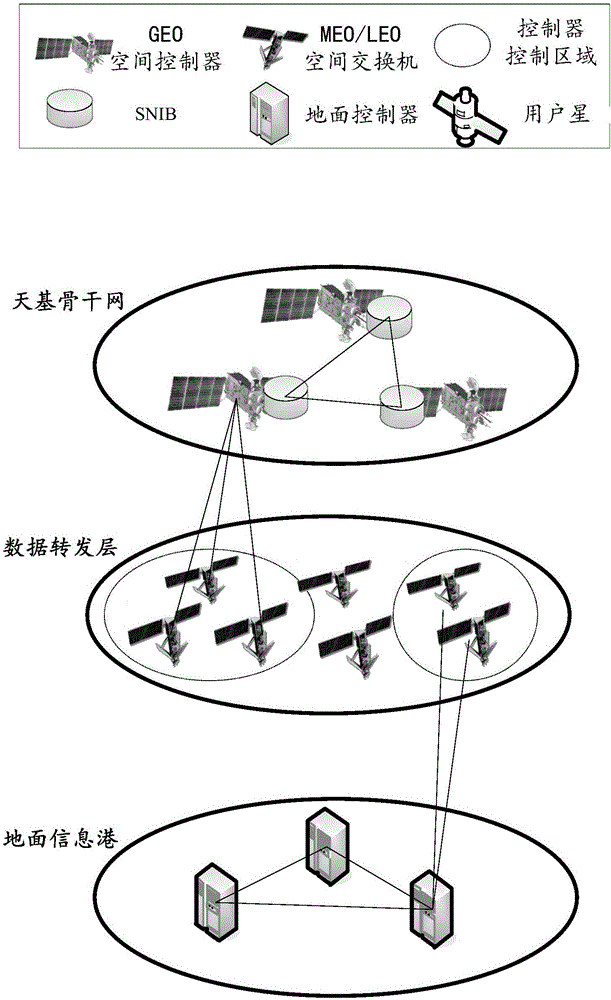
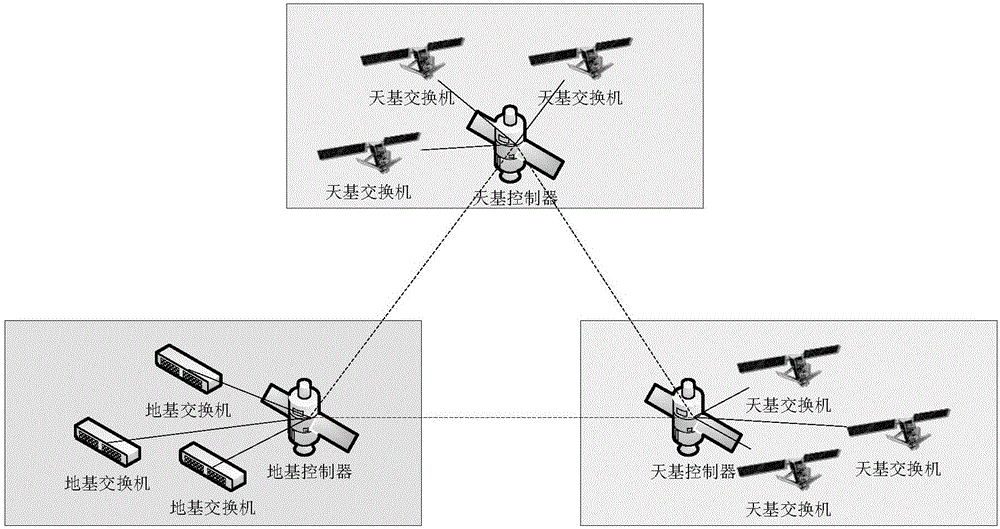
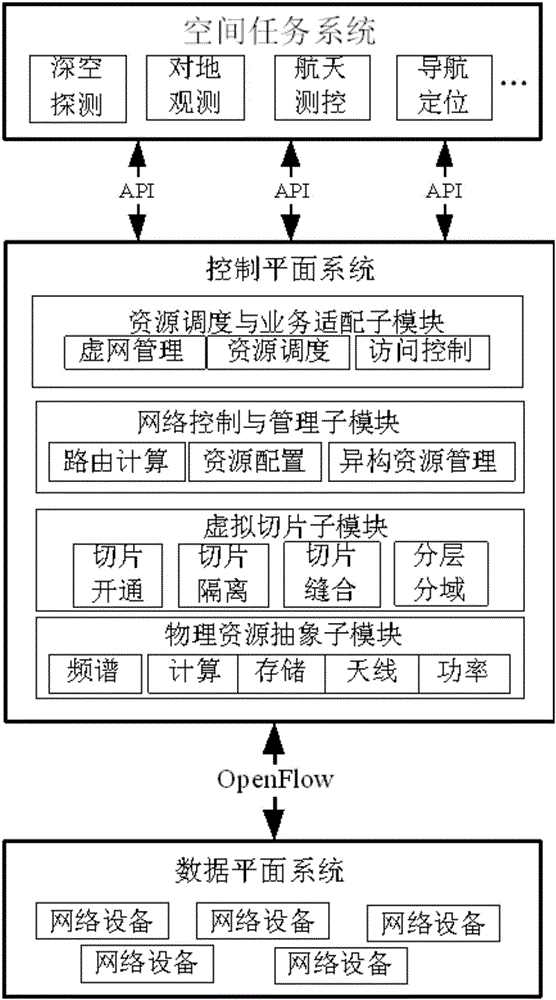
Spatial information network architecture
InactiveCN106685511AImprove collaborationReal-time accessRadio transmissionHigh level techniquesResource utilizationControl system
The invention relates to a spatial information network architecture. The spatial information network architecture comprises a ground information port, a data forwarding layer and a space-based backbone network; the ground information port is connected with the data forwarding layer, is connected with the space-based backbone network through the data forwarding layer and is used for executing a user task request according to a received flow table; the data forwarding layer is composed of at least one satellite selected from a medium earth orbit satellite and a low earth orbit satellite and is used for receiving the flow table, calling resources to execute the user task request, performing data transmission and forwarding according to the flow table; the space-based backbone network comprises at least one geostationary orbit space satellite, a controller in the geostationary orbit space satellite allocating resources for the task request and issuing the flow table; and the ground information port and the space-based backbone network together form a double-backbone control system. According to the spatial information network architecture of the invention, the global coverage characteristics of the GEO (geostationary orbit) satellite and the computing power of a ground base station are effectively combined, and the spatial information network can obtain route forwarding strategies in real time, allocate resources and nodes reasonably according to tasks and improve resource utilization rate and node cooperation ability.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method and apparatus for providing wideband services using medium and low earth orbit satellites
InactiveUS7136620B2Reduce distractionsActive radio relay systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsHigh elevationLow earth orbit
A method and apparatus for mitigating communications interference between satellite communications systems in different orbits is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of evaluating a geometrical relationship between a second ground station and the satellites in the second satellite constellation, and directing communications between the second ground station and the second satellite according to the evaluated geometrical relationship. In one embodiment communications are handed over from a first satellite to another satellite when the first satellite is no longer at the highest elevation angle of visible satellites. In another embodiment, handover occurs when the first satellite drops below a minimum elevation angle.
Owner:THE DIRECTV GRP INC
Satellite system and method of deploying same
InactiveUS6257526B1Convenient to accommodatePromotes frequency reuseLaunching/towing gearCosmonautic partsEngineeringMedium Earth orbit
A satellite communication system has a first deployment of a plurality of satellites deployed in a medium earth orbit and two later deployments of a plurality of satellites deployed in the medium earth orbit. The first deployment is spaced so that the second deployment may be easily deployed and interleaved into the first deployment. A ground terminal is used for communicating with the satellites in the first and second deployments.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
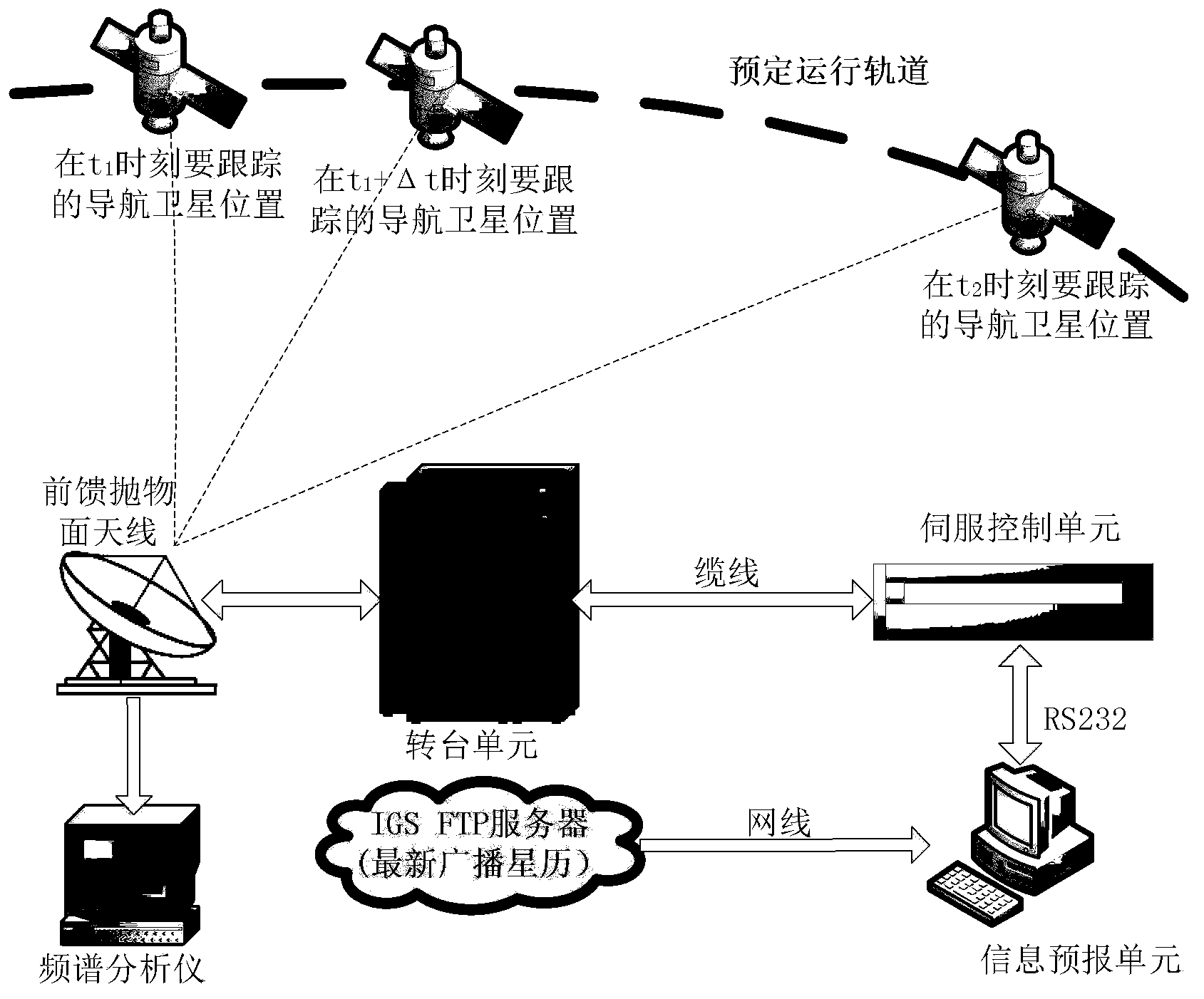
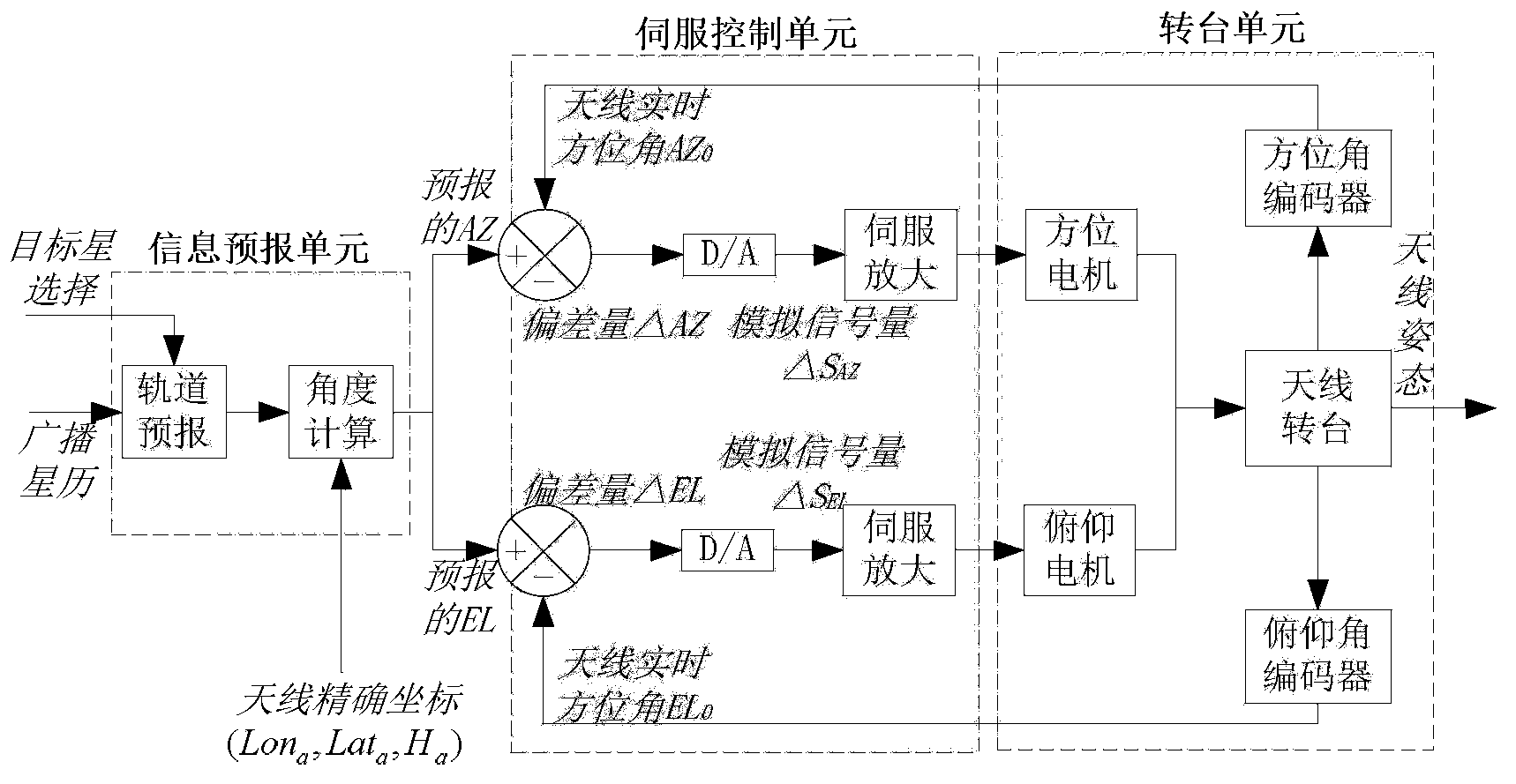
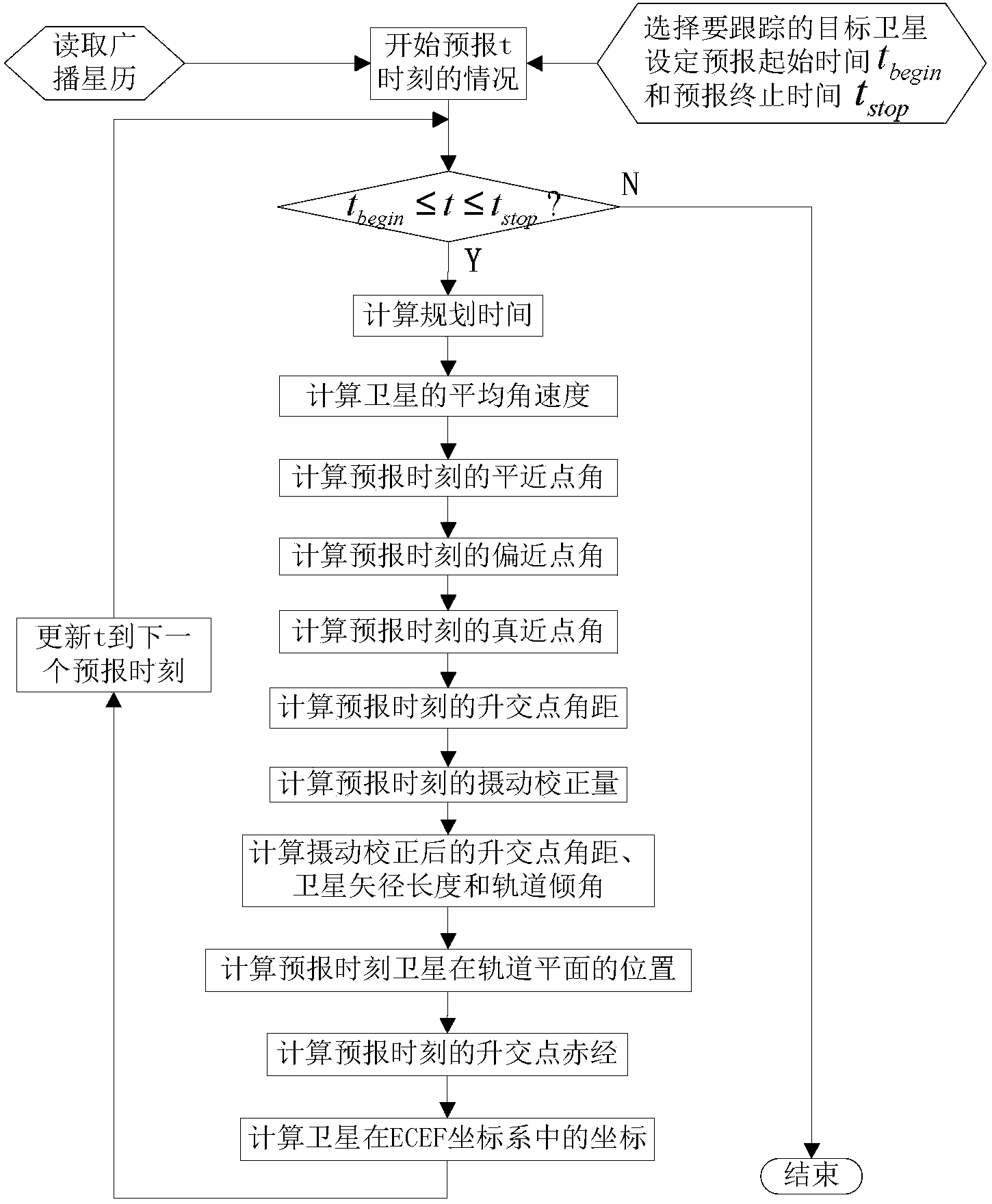
Method and system for automatically tracking medium earth orbit navigational satellite through servo antenna
ActiveCN103364805AAccurate trackingAccurate pointing trackingSatellite radio beaconingSignal qualityFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a method and system for automatically tracking a medium earth orbit navigational satellite through a servo antenna, and belongs to the technical field of satellite navigation signal quality monitoring. The system comprises an information prediction unit, a servo control unit, a rotary table unit, the feed-forward large-diameter parabolic antenna and a spectrum analyzer. The information prediction unit is used for the operation of orbit prediction and angle calculation, the servo control unit is used for adjusting antenna postures in a closed loop feedback mode, the rotary table unit is used for driving an antenna rotary table to rotate in the azimuth axial direction and in the pitch axial direction, the feed-forward large-diameter parabolic antenna is used for receiving target satellite signals, and the spectrum analyzer is used for observing quality of received signals. The method and system for automatically tracking the medium earth orbit navigational satellite can achieve an ideal tracking effect in the state of being divorced from manual monitoring.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Global satellite communication system and method
ActiveCN102413590AImprove abilitiesReduce technical complexityNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionMedium Earth orbitDirect communication
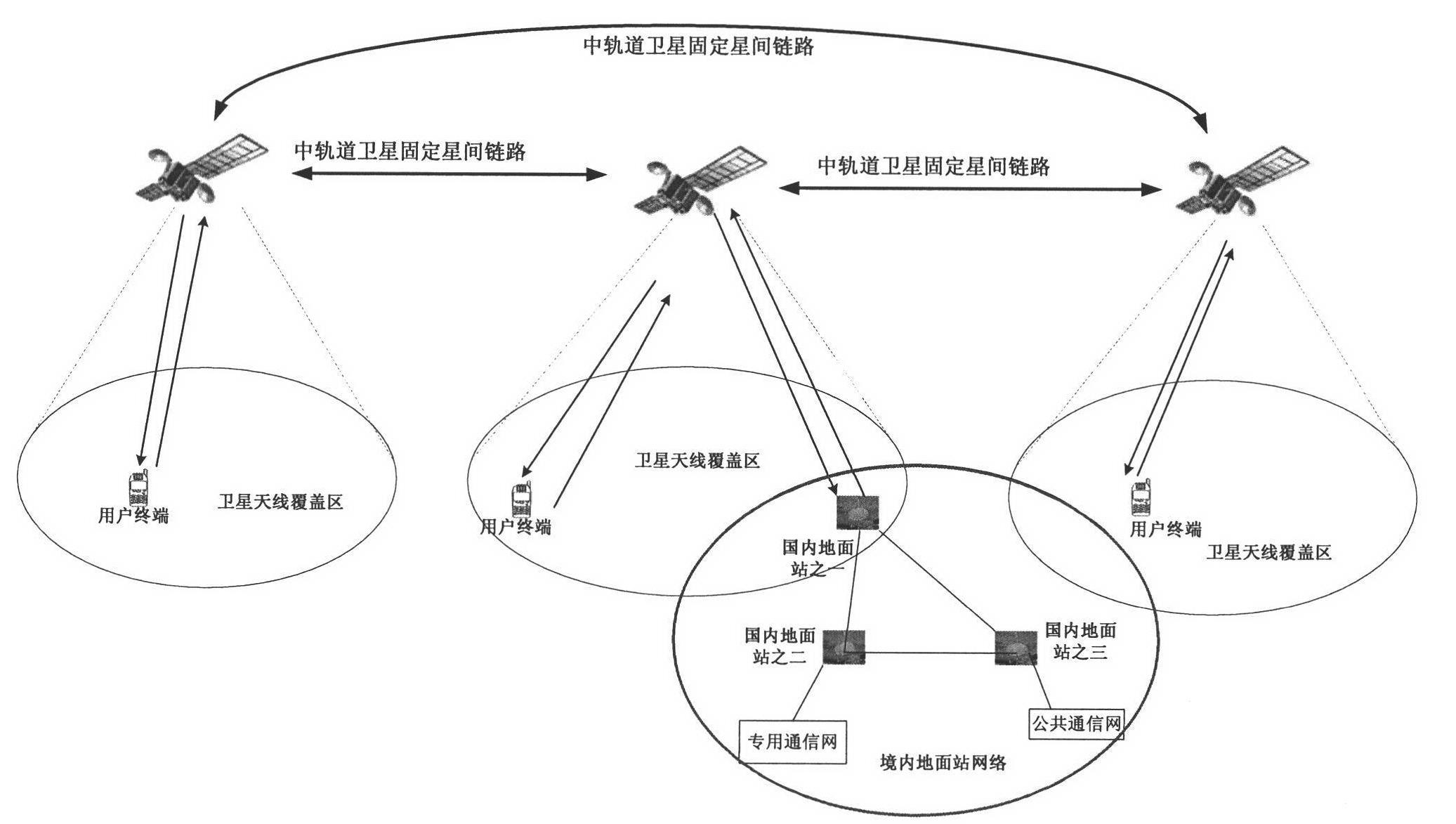
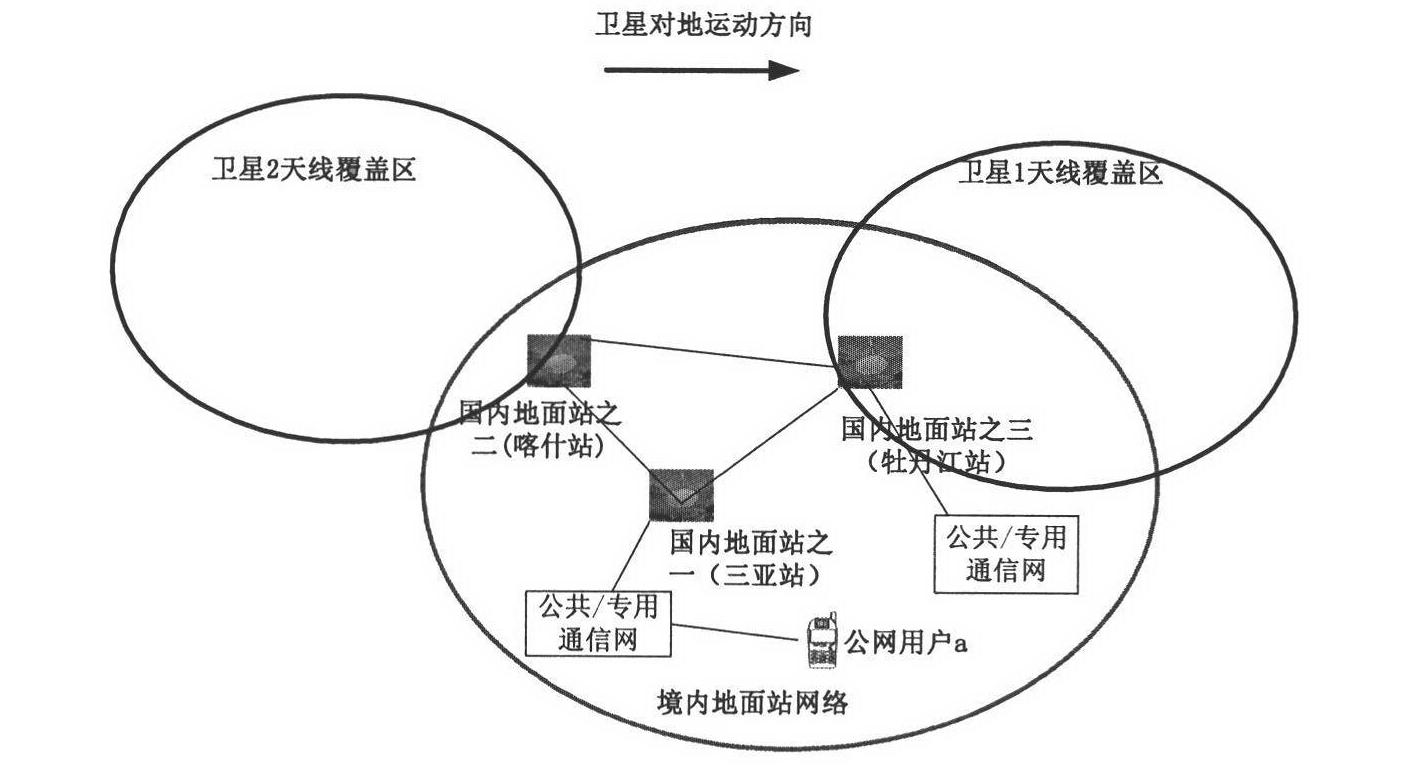
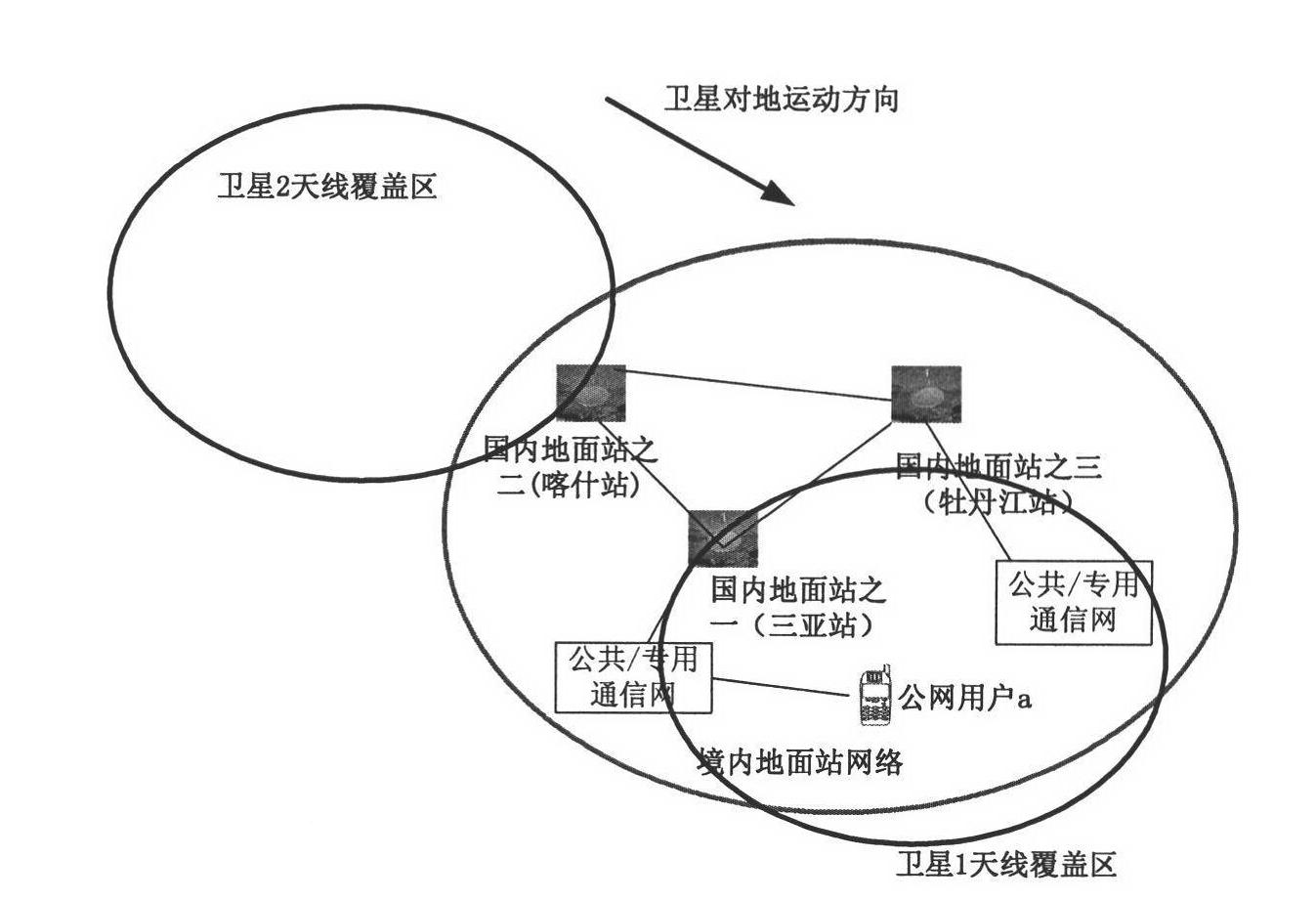
The invention discloses a global satellite communication system and method and belongs to the technical field of satellite communication. The system comprises a satellite constellation system consisting of three medium-earth orbit satellites, three ground stations and satellite user terminals used for communication, wherein the satellite user terminals in a medium-earth orbit satellite coverage area can carry out indirect / direct communication through the medium-earth orbit satellites or carry out communication by utilizing inter-satellite links among the medium-earth orbit satellites or satellite-to-ground links among the ground stations. By utilizing the system disclosed by the invention, communication among the global satellite user terminals, especially real-time communication among users in China, can be realized with lower cost.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Bistatic radar system using transmitters in mid-earth orbit
A bistatic radar system and method. In the illustrative embodiment, a receiver is positioned in a horizontal plane. A transmitter is then positioned in Middle Earth Orbit at a position that is nearly vertical to the plane of the receiver. This configuration provides significant flexibility for the radar system. As such, the radar system may engage in flight patterns, in which the transmitter and receiver have velocity vectors in opposite directions (GMTI mode), the same direction (SAR mode) and variations in between (mixed mode). Lastly, a broad beam is generated from the transmitter and illuminates an area enabling several receivers to simultaneously observe the illuminated area.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Constellation satellite system and communication method and system based on same
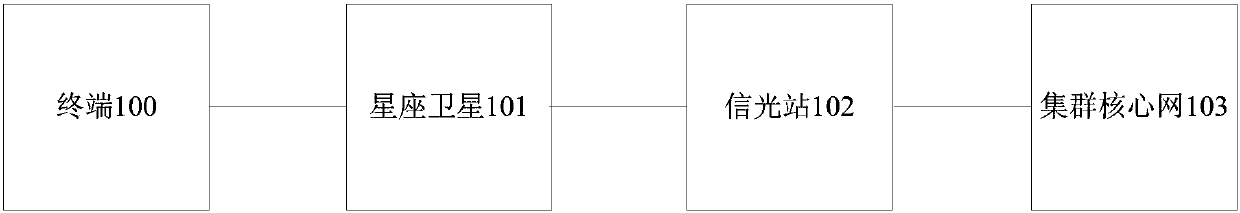
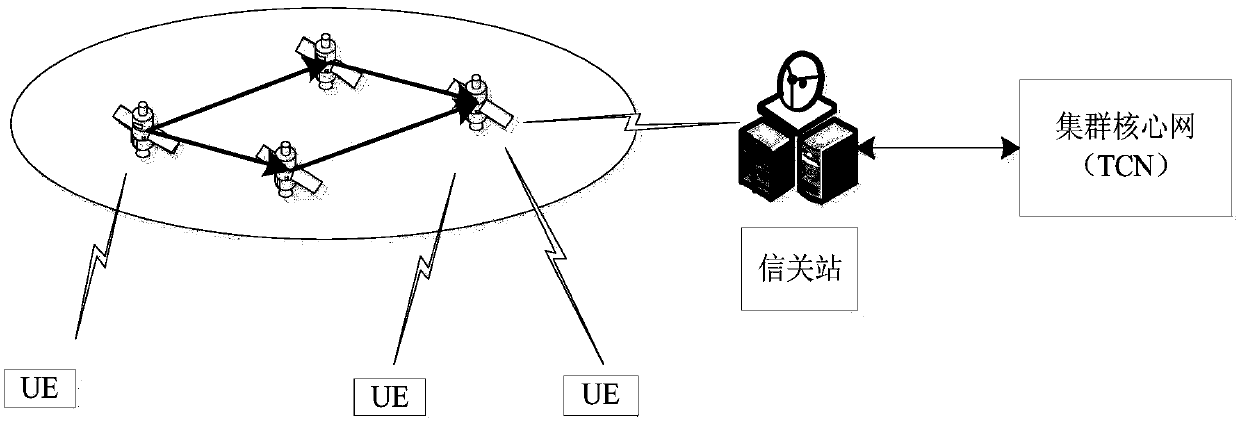
InactiveCN107592152AOvercome deficienciesExpansion of emergency command and communication capabilitiesRadio transmissionNatural satelliteNetworked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol
The invention discloses a constellation satellite system and a communication method and system based on the same. The constellation satellite system comprises terminals, constellation satellites, a gateway station, and a cluster core network. The terminals comprise various types of cluster user terminals. The constellation satellites comprise a plurality of LEO (low earth orbit) or MEO (medium earth orbit) satellites which cover the whole globe, and the constellation satellites form a constellation. The gateway station is used for completing the access of the network of the constellation satellites to the cluster core network. The cluster core network comprises a cluster user group, the registration of the group members, the discrimination of the authority of the users and business, the call processing, the charging management and the scheduling management. The cluster corn network irons out the defects of ground wireless cluster communication, and a global wireless cluster network transmission trunk line is built through a constellation satellite mobile communication network, and the emergency command communication capability of a wireless cluster is effectively extended. Meanwhile, the constellation satellite system is good in emergency adaptability, convenience and economical performances.
Owner:BEIJING XINWEI TELECOM TECH
Space-based network broadcasting method
InactiveCN102355315AEffective discardReduce congestionBroadcast transmission systemsRadio transmissionLow earth orbitMedium Earth orbit
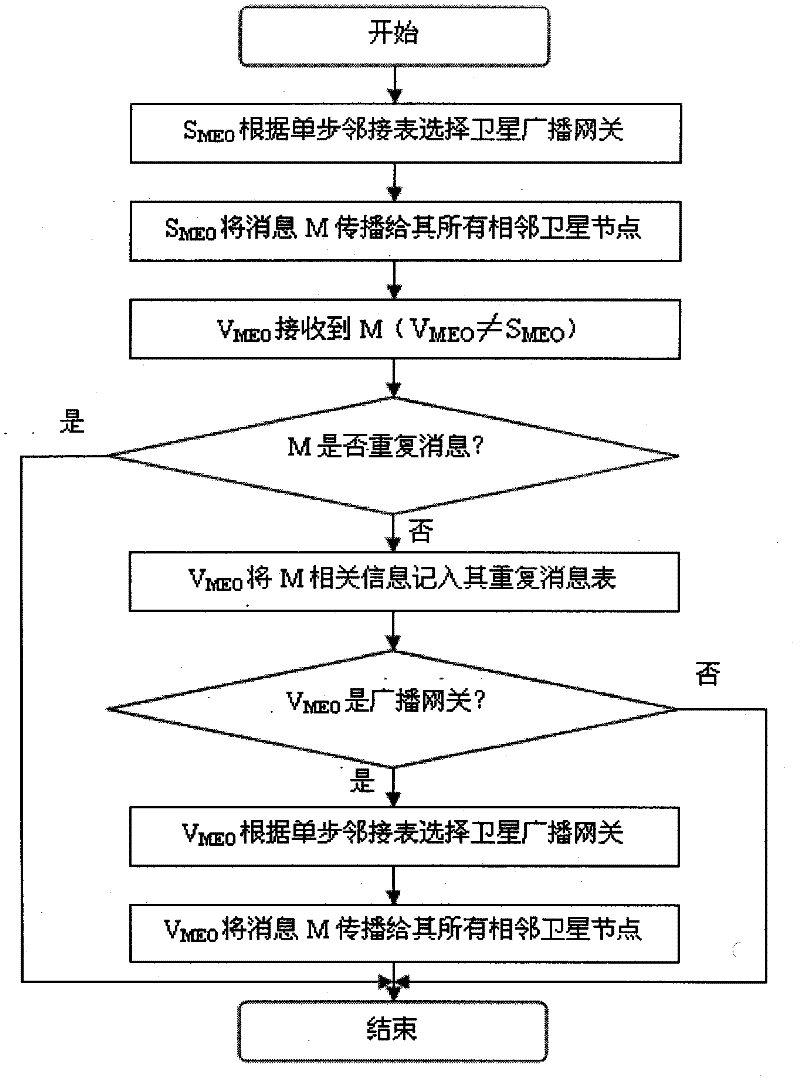
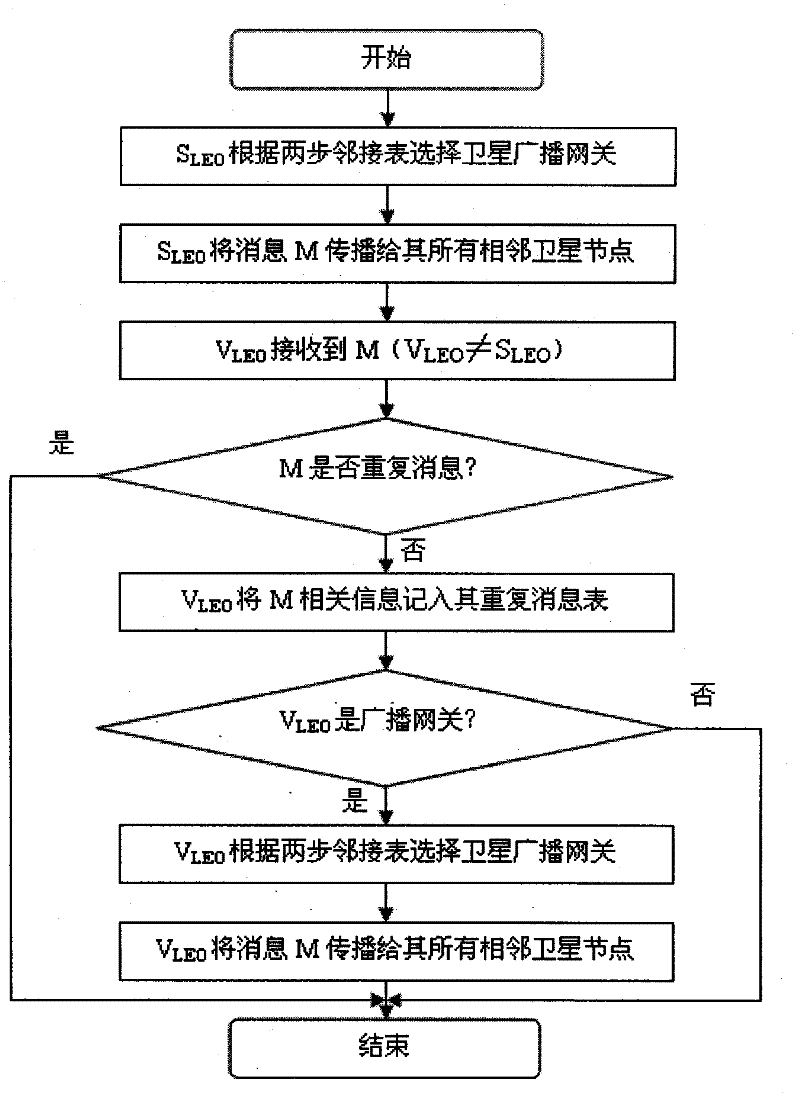
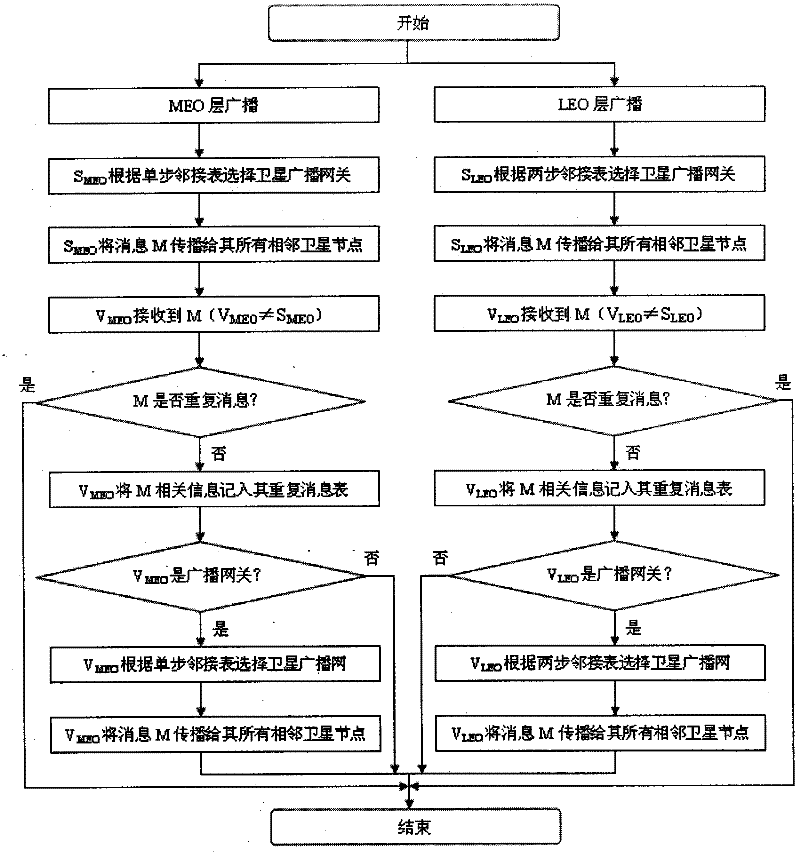
The invention discloses a space-based network broadcasting method, which solves the problem of waste of satellite network bandwidth caused by a large amount of repeated messages generated by a Flooding broadcasting mode in the existing space-based network routing protocol and the problem of a large amount of collision and crash and low success rate of message transmission caused by sharing of the transmission medium. The method comprises the following steps of: respectively setting a repetition information sheet on an MEO (Medium Earth Orbit) satellite and LEO (Low Earth Orbit) satellite to record broadcast messages received by satellite nodes; setting a single-step adjacency table on the MEO satellite, and setting a two-step adjacency table on the LEO satellite; and selecting some satellite nodes from adjacent nodes by the MEO satellite and the LEO satellite, wherein the selected satellite nodes are used as broadcasting nodes, only the broadcasting nodes broadcast and forward the messages, and the messages are finally transmitted to all the satellite nodes in the same layer through the broadcasting nodes. In the method, based on selective forwarding operation, same-layer satellite network broadcasting overhead caused by Flooding is effectively reduced. And the method can be used for the MEO layer satellite and the LEO layer satellite to execute efficient broadcasting among the networks in the same layer.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Precise satellite orbit determination technology only based on radio carrier phase observation
InactiveCN103363994AAvoiding Clock Error Estimation ProblemsInstruments for comonautical navigationNatural satelliteCarrier signal
The invention provides a technical scheme of simultaneously and precisely tracking a plurality of space objects only based on carrier observation data of ground monitoring equipment driven by an atomic frequency standard for fulfilling the purposes of high-precision orbit determination of regional navigation satellites and precise passive tracking of non-cooperative space objects. The invention designs a parameter evaluation estimation scheme of precise orbit determination only based on carrier phase data and provides a novel carrier phase cycle slip detection and repair method. The method makes full use of priori orbit and prior atomic clock speed information and is suitable for static users. The method is applied to orbit determination processing of an MEO (Medium Earth Orbit) satellite of a COMPASS system and is only based on carrier phase data of 6 regional ground stations, the mean residual of arc length orbit determination results of three days is 0.18m, and the mutual differences of one-day-arc overlap orbit are 0. 61m and 8. 09m in radial direction and three-dimensional position respectively; the mean residual of laser comparison is 0.28m; the mean residual of forecast for 24 hours and laser alignment is 1.34m. Compared with that of the prior art, the orbit determination precision is improved by 1 order.
Owner:陈刘成
Single Burst Single Satellite Beacon Localization
ActiveUS20180095156A1Low costImprove beacon localization accuracyPosition fixationBeacon systemsFrequency measurementsMedium Earth orbit
A method and devices are disclosed, for localization of a radio beacon at a remote receiver in the framework of a satellite system. Such satellite system could be Cospas-Sarsat, for Search and Rescue of people, ships and aircraft in distress, and particularly its MEOSAR (Medium Earth Orbit Search and Rescue) segments: DASS / GPS, SAR / Galileo and SAR / Glonass; said beacon is typically one of a PLB (Personal Locator Beacon) or EPIRB (Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacon) or ELT (Emergency Locator Beacon); and said remote receiver is typically a MEOLUT (Medium Earth Orbit Local User Terminal) base station.Present art MEOSAR localization is based on Time measurements and Frequency measurements on signals emitted by radio beacons, relayed by satellites and detected at a MEOLUT; however since the exact time of transmission of the beacon is unknown at the MEOLUT, Time Difference of Arrival (TDOA) equations are applied. The present invention however, discloses that by carefully configuring the time of transmission at said beacon, even without directly communicating that specific time to the MEOLUT, Time of Arrival (TOA) equations could be applied at the MEOLUT enabling enhanced localization accuracy and / or fewer satellites in view required to localize the beacon. In particular, localization is enabled even upon a single burst emitted by the beacon and relayed to the MEOLUT by a single satellite.
Owner:KATZ
Method for each of a plurality of satellites of a secondary Global Navigation Satellite System in a Low Earth orbit
ActiveUS20180210090A1Reduce system costReduce the impactSatellite radio beaconingNatural satelliteClock correction
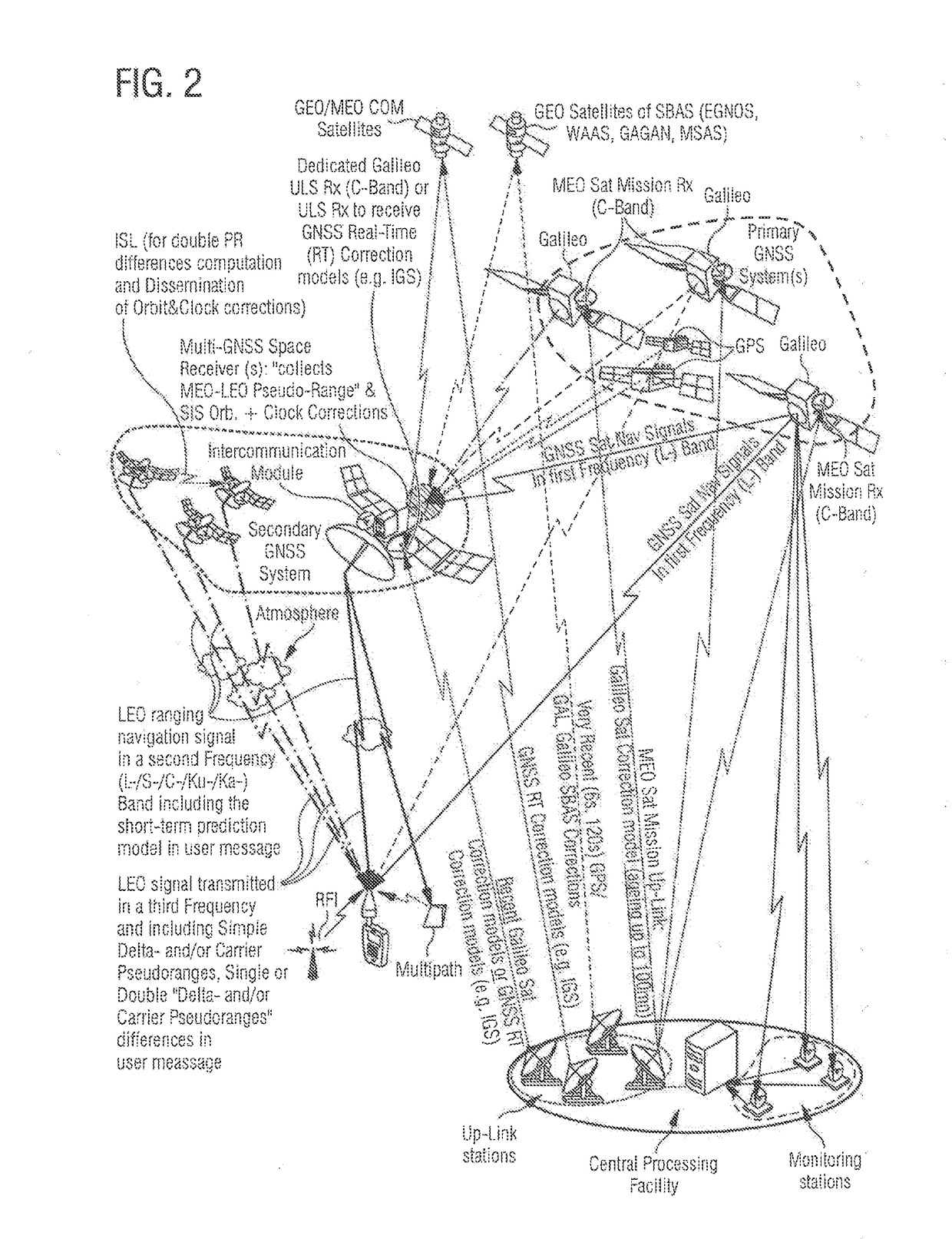
A method for each of a plurality of satellites of a secondary Global Navigation Satellite System, GNSS, in a Low Earth Orbit, LEO, comprising receiving GNSS signals, in a first frequency band, from Line-Of-Sight, LOS, satellites of at least one primary GNSS in a Medium Earth Orbit. Candidate sets of orbit and clock corrections for the LOS satellites are received. A Position-Velocity-Time, PVT, calculation is performed based on code and / or carrier pseudo-ranges between a respective satellite of the secondary GNSS and the LOS satellites. The code and / or carrier pseudo-ranges are derived from the GNSS signals and are corrected by a single set of the candidate sets. A short-term prediction model is determined for an orbit and clock of the respective satellite based on the PVT and is included in a navigation message, transmitted in a second frequency band, modulated onto a LEO navigation signal intended for terrestrial user equipment.
Owner:AIRBUS DEFENCE & SPACE
Method and system for the geolocation of a radio beacon in a search and rescue system
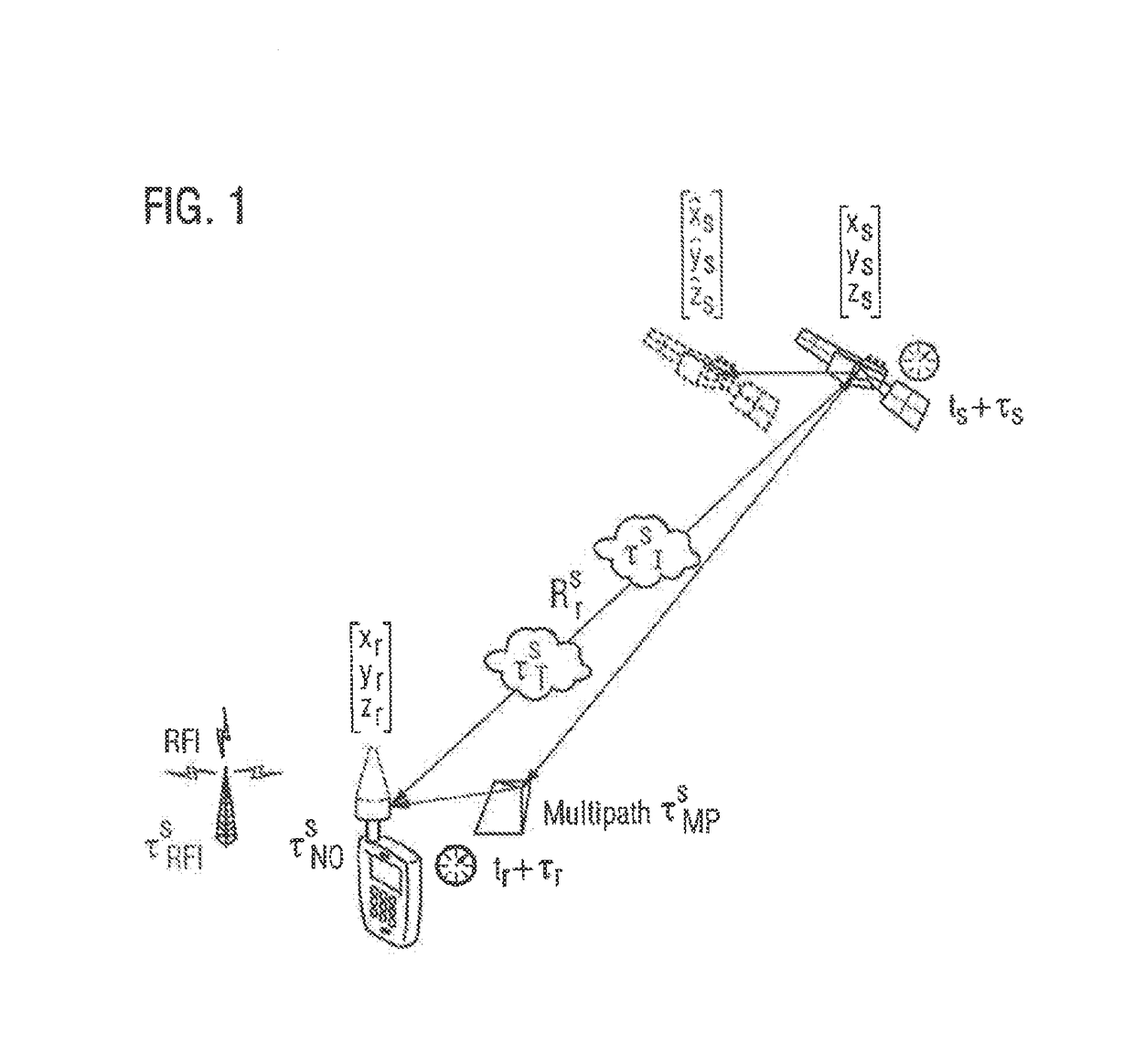
A method for the geolocation of a device transmitting a signal containing at least one message to a plurality of relay satellites in a medium earth orbit, visible from said device, receiving said message and transmitting it to processing means, comprises at least the following steps: determination of the times of reception of the message by the relay satellites; determination of the pseudo-distances between the device and the relay satellites; searching for and acquiring a minimum number N of satellite radio navigation signals; determination of the time lags between the transmission of the radio navigation signals and their reception by the said device; broadcasting by the device of these time lags in the message; and, determination of the position of the device from at least the pseudo-distances, from the time lags and from the positioning coordinates of the relay satellites and of the radio navigation satellites.
Owner:THALES SA
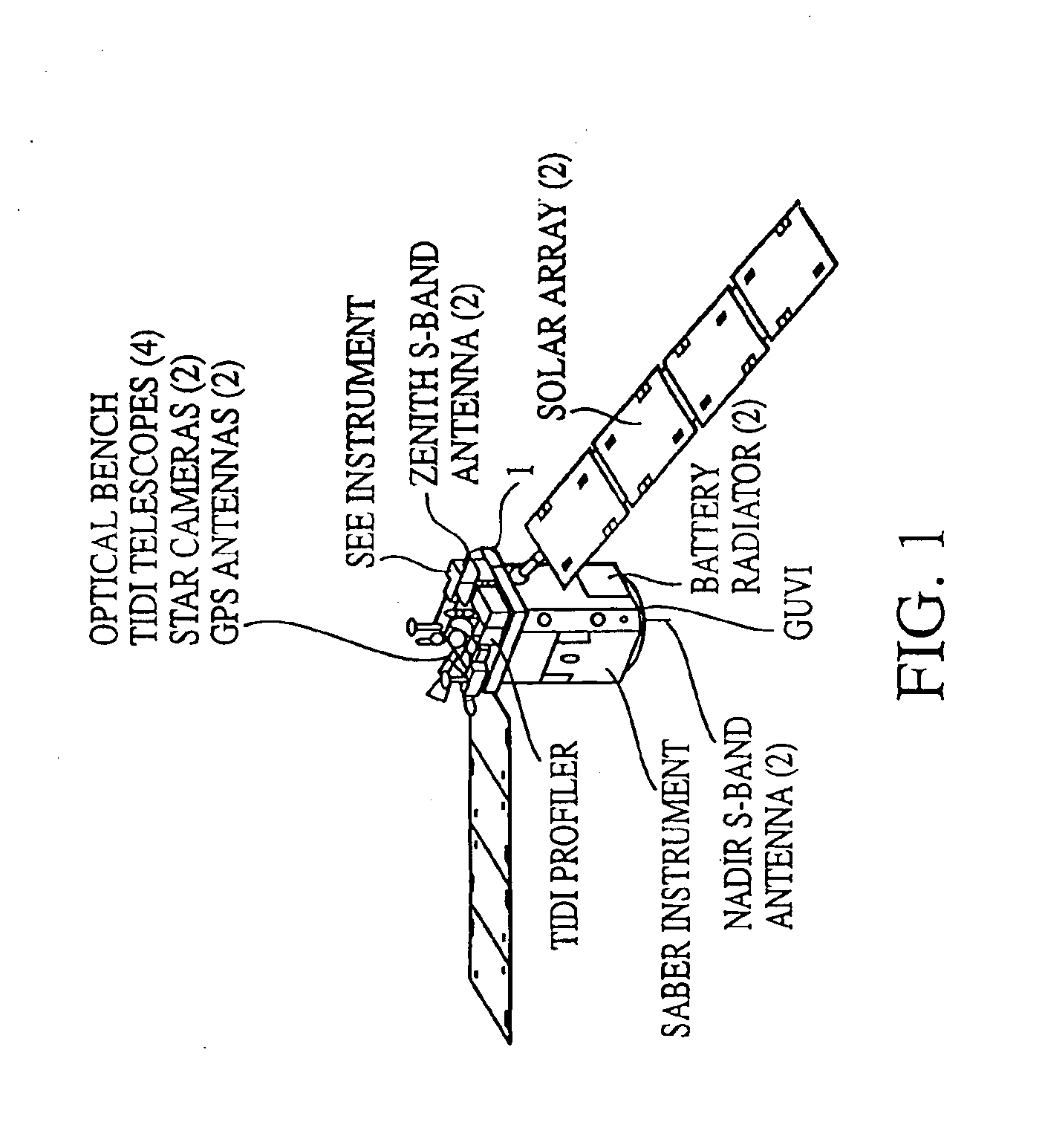
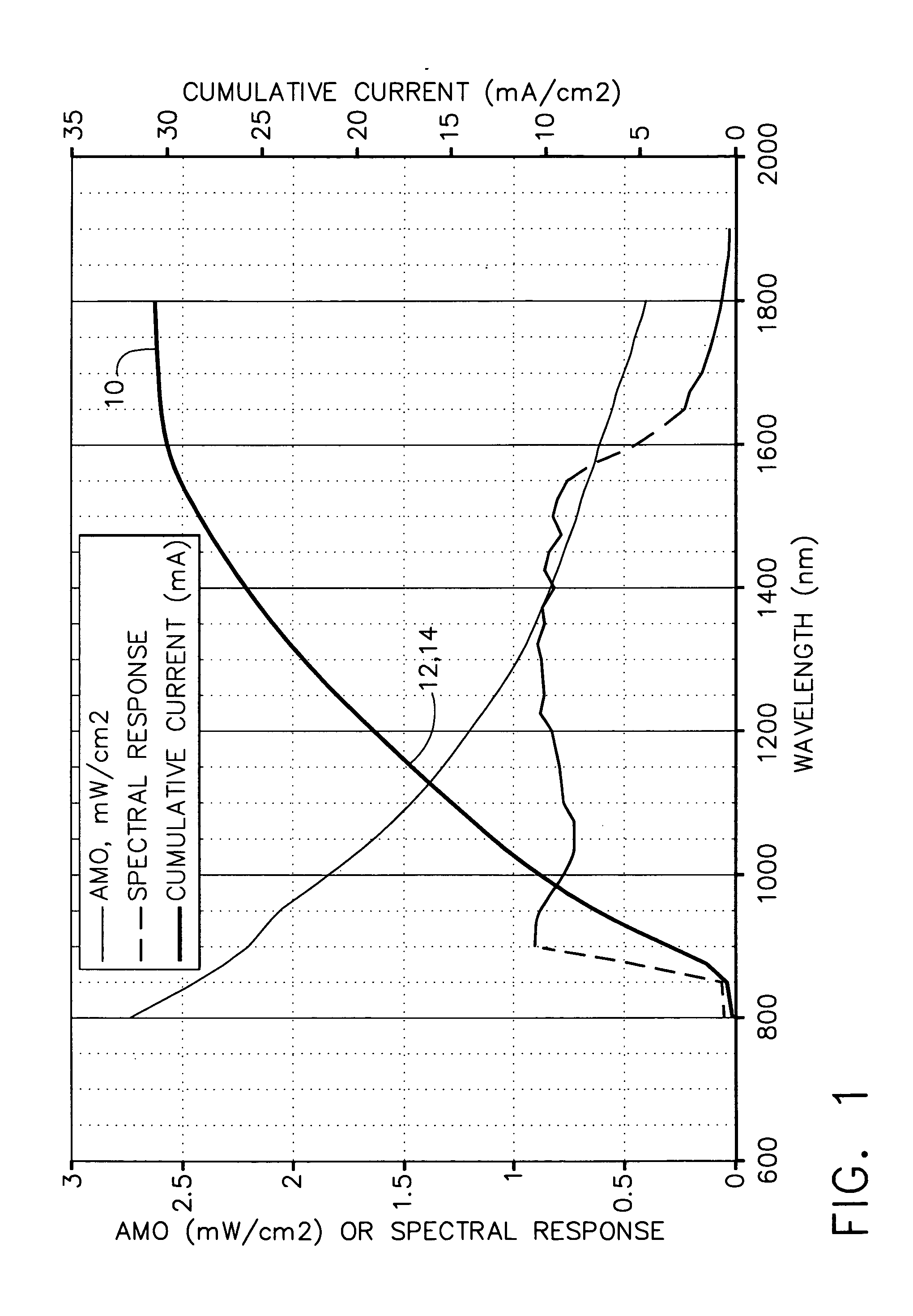
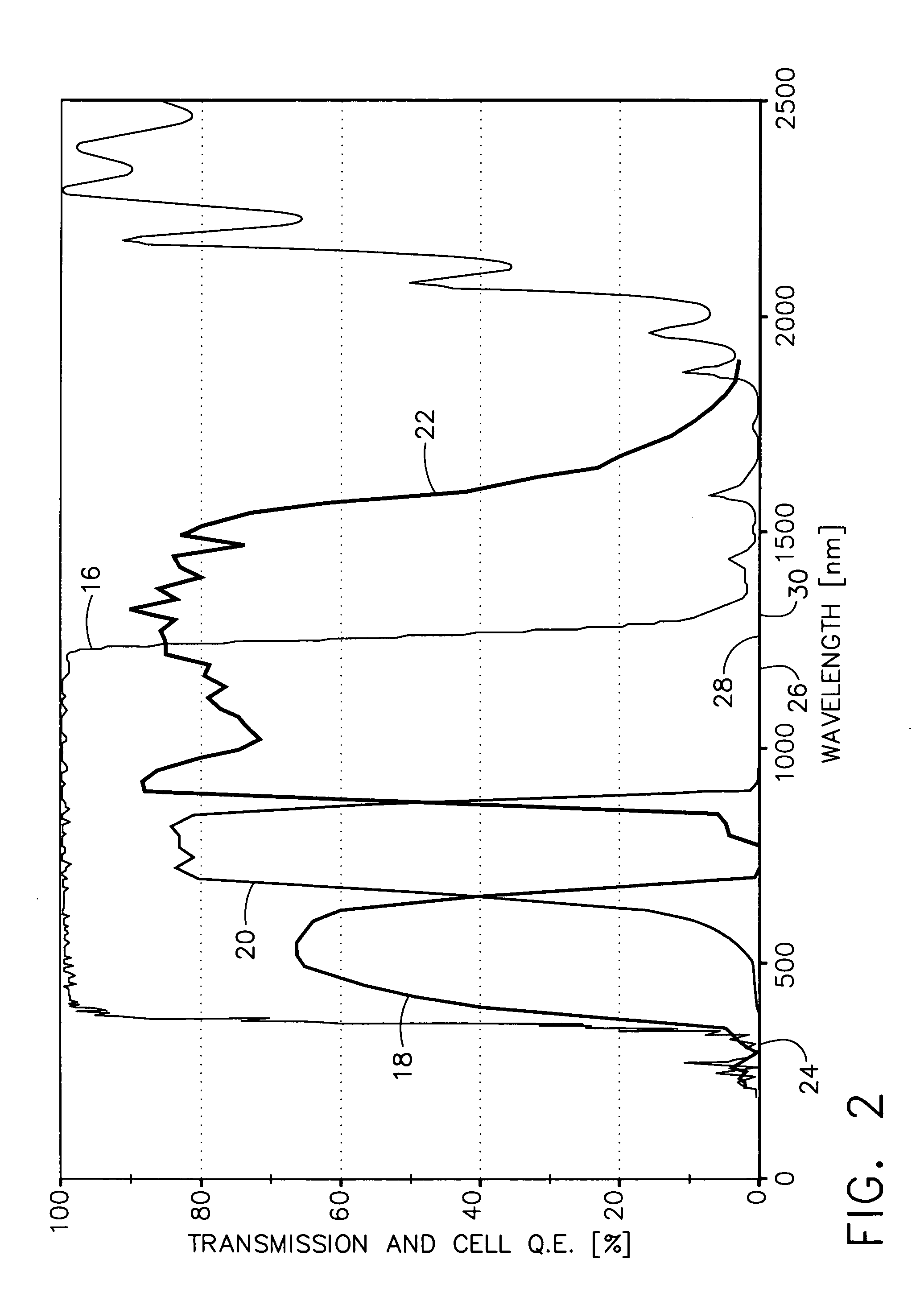
Solar power collection with near infrared wideband reflector coating
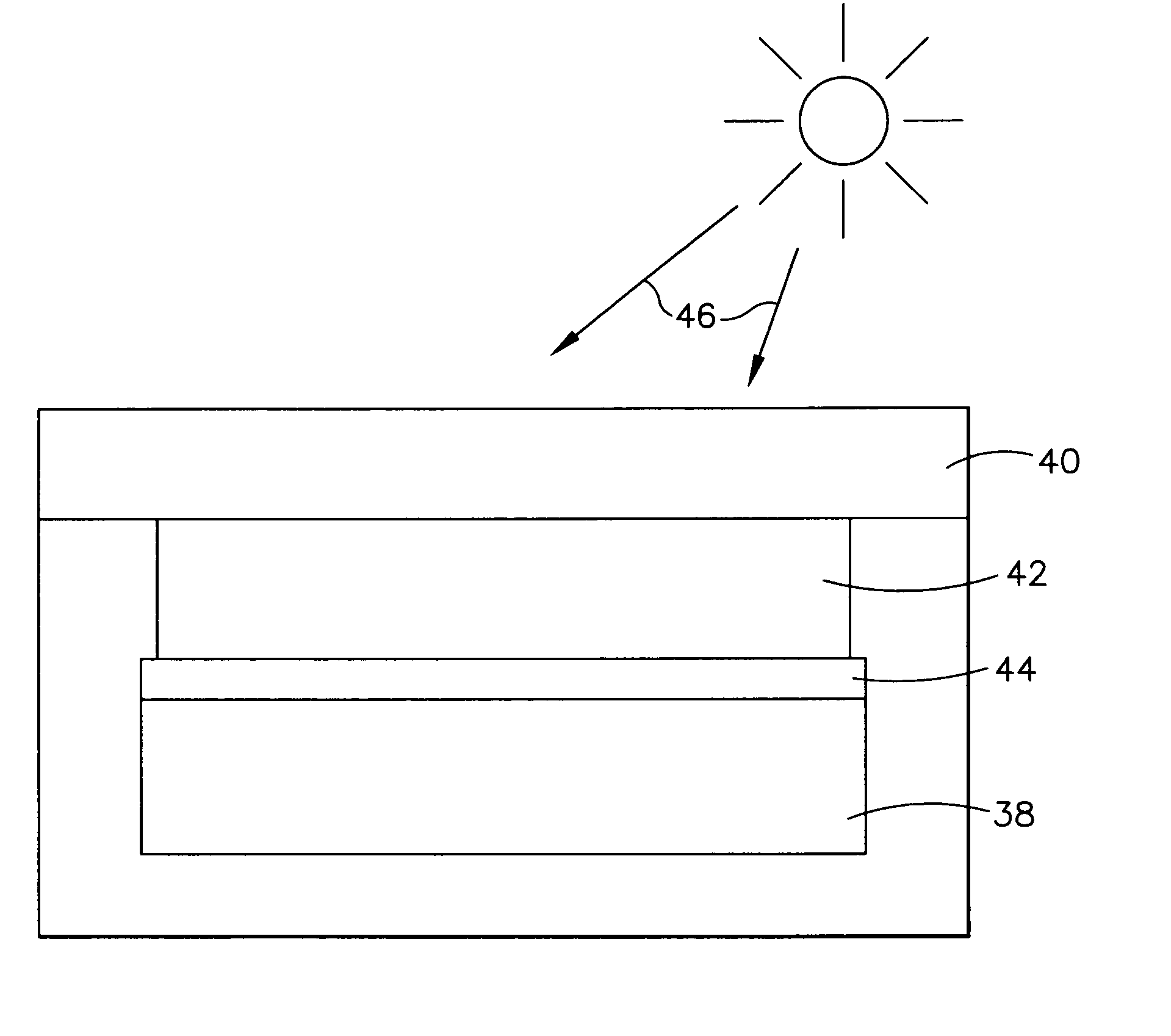
InactiveUS20050103374A1Lower operating temperatureImprove conversion efficiencyPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationSolar angleLow earth orbit
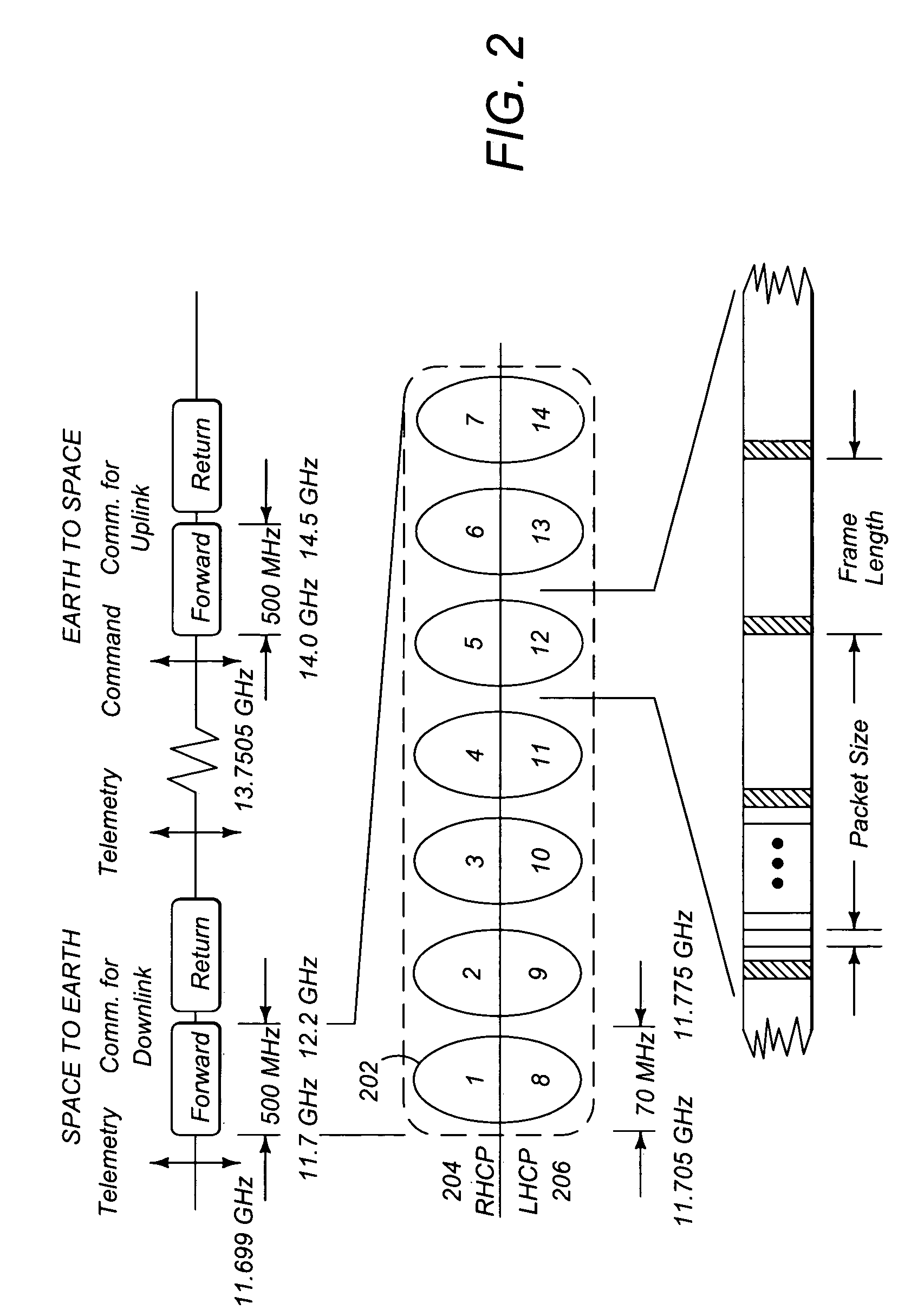
A near infrared (NIR) wideband reflector coating designed to start reflecting solar energy wavelengths from at least 1.2 microns in a typical geosynchronous earth orbit or medium earth orbit satellite and from at least 1.3 microns in a typical low earth orbit satellite. Also, the (NIR) wideband reflector coating reflects solar energy wavelengths below 0.35 microns in all three applications. This invention works on triple junction (TJ) solar cells. The performance of at least 1.2-microns is on solar panels with near-normal incident solar angle, typical of Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO) and Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) satellites. The performance of at least 1.3-microns is on solar panels with wide range of incident solar angles, a design requirement for Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
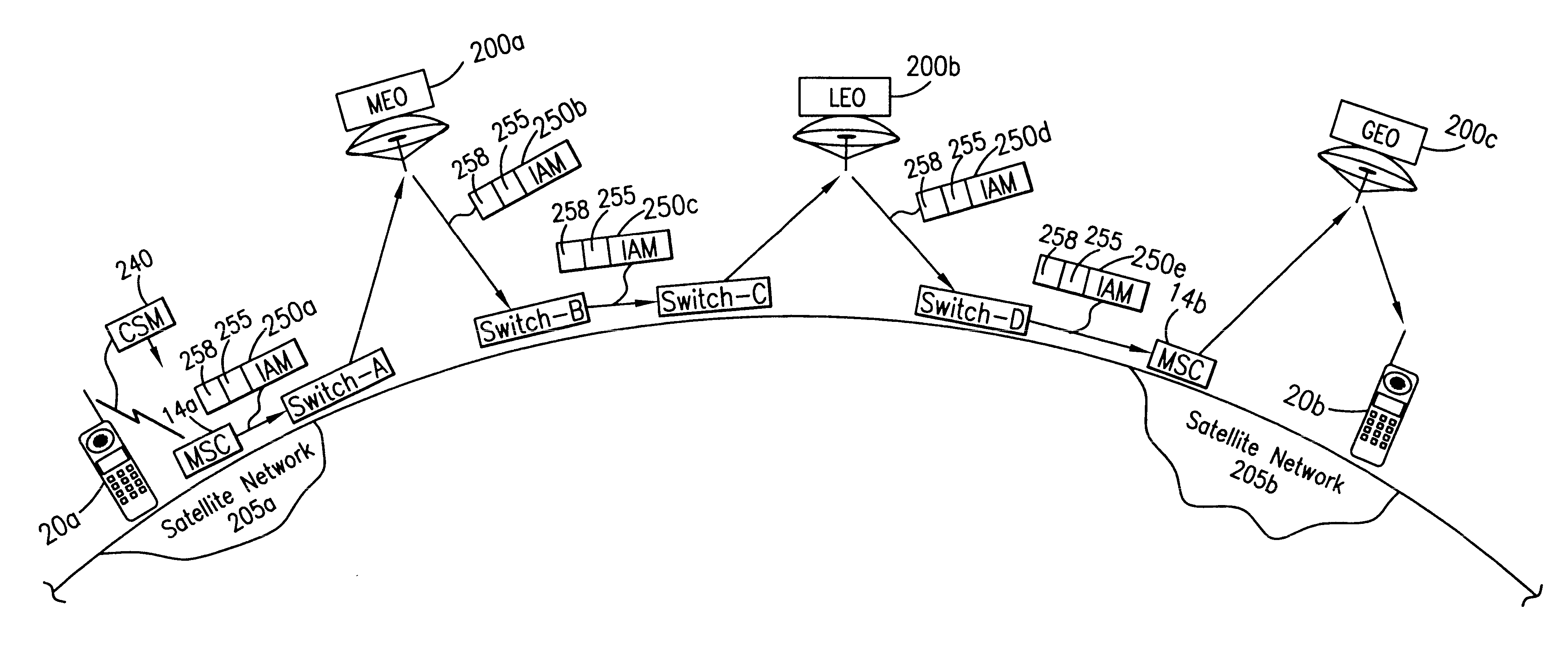
System and method for modification of satellite hop counter to reflect orbit type
InactiveUS6449478B1Accurate measurementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionNatural satelliteIntegrated Services Digital Network
A telecommunications system and method is disclosed for providing a more accurate measurement of the cumulative path delay present in a call to enable switches to make an informed decision as to the routing method to use. In one embodiment, the Integrated Services Digital Network User Part (ISUP) satellite hop counter field is expanded to include three fields, one for each type of delay: geostationary satellite hops, mid-earth orbit satellite hops and low-earth orbit satellite hops. In an alternative embodiment, a cumulative delay value in milliseconds or centiseconds, instead of the number of satellite hops, can be included in the expanded ISUP satellite hop counter field.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
Integrated antenna and RF payload for low-cost inter-satellite links using super-elliptical antenna aperture with single axis gimbal
A dual-reflector inter-satellite link (ISL) subsystem, for a communications satellite in a constellation of satellites in low earth orbit or medium earth orbit. The ISL subsystem includes a main antenna reflector which uses a single-axis gimbal to steer the main reflector only in the elevation plane. An antenna subreflector, a horn and RF feed circuitry are stationary with respect to the host satellite. The main reflector has a super-elliptical design which provides a beam shape which requires no steering in the azimuth plane, while meeting ISL signal strength requirements. By steering the main reflector only, and only in the elevation plane, the disclosed ISL subsystem delivers significantly lower size, mass, complexity and cost, and significantly greater reliability, than traditional ISL systems.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Providing Continuous Two-Way High-Speed Data Transfer for Leo Based Satellites
Various embodiments may provide a system for continuous two-way high-speed data transfer for satellites, such as Low Earth Orbit (LEO) based satellites and / or Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) based satellites.
Owner:U S A AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR OF NASA
Method and System for the Geolocation of a Radio Beacon in a Search and Rescue System
A method for the geolocation of a device transmitting a signal containing at least one message to a plurality of relay satellites in a medium earth orbit, visible from said device, receiving said message and transmitting it to processing means, comprises at least the following steps: determination of the times of reception of the message by the relay satellites; determination of the pseudo-distances between the device and the relay satellites; searching for and acquiring a minimum number N of satellite radio navigation signals; determination of the time lags between the transmission of the radio navigation signals and their reception by the said device; broadcasting by the device of these time lags in the message; and, determination of the position of the device from at least the pseudo-distances, from the time lags and from the positioning coordinates of the relay satellites and of the radio navigation satellites.
Owner:THALES SA
Motion compensation and imaging method of medium earth orbit satellite SAR
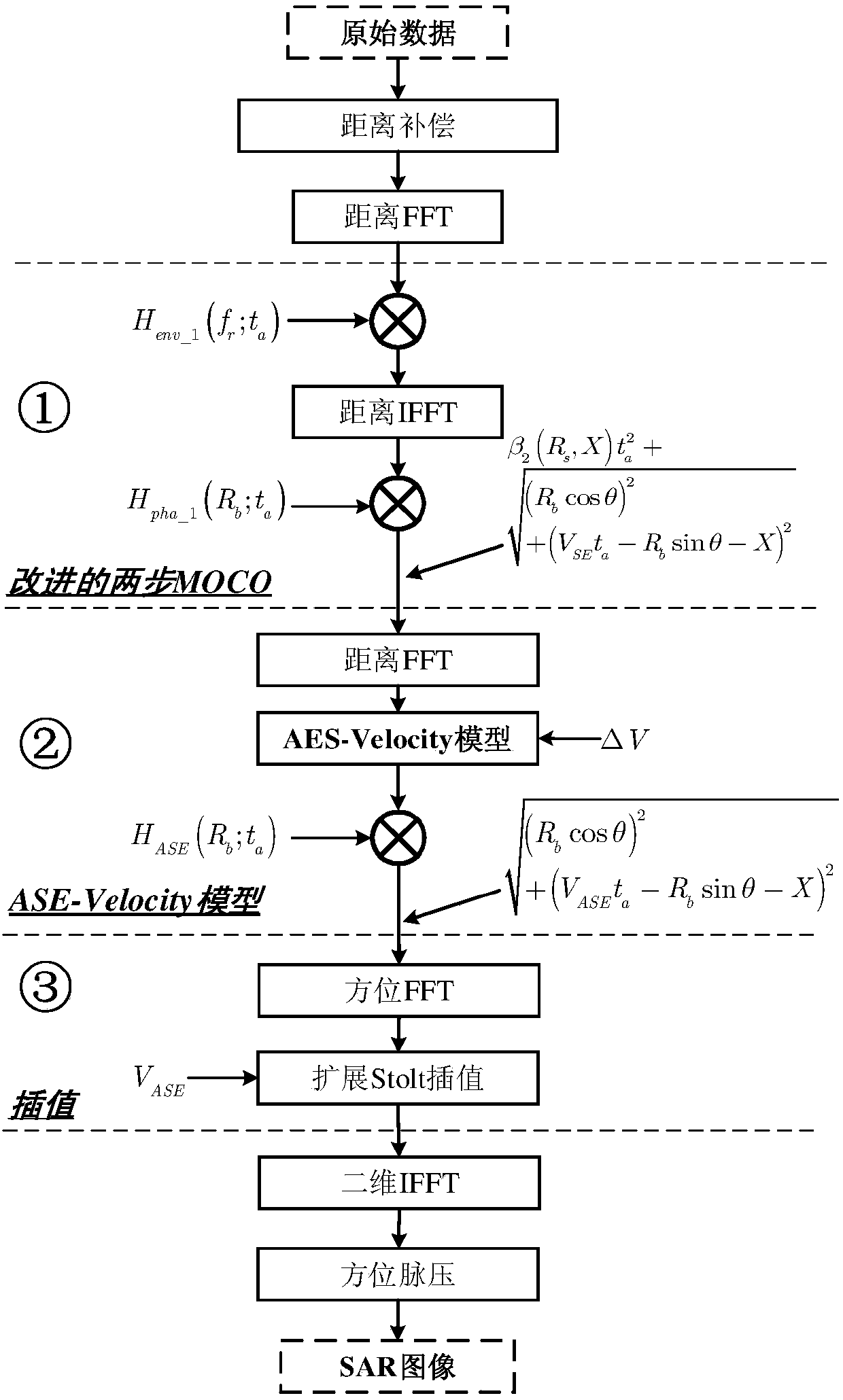
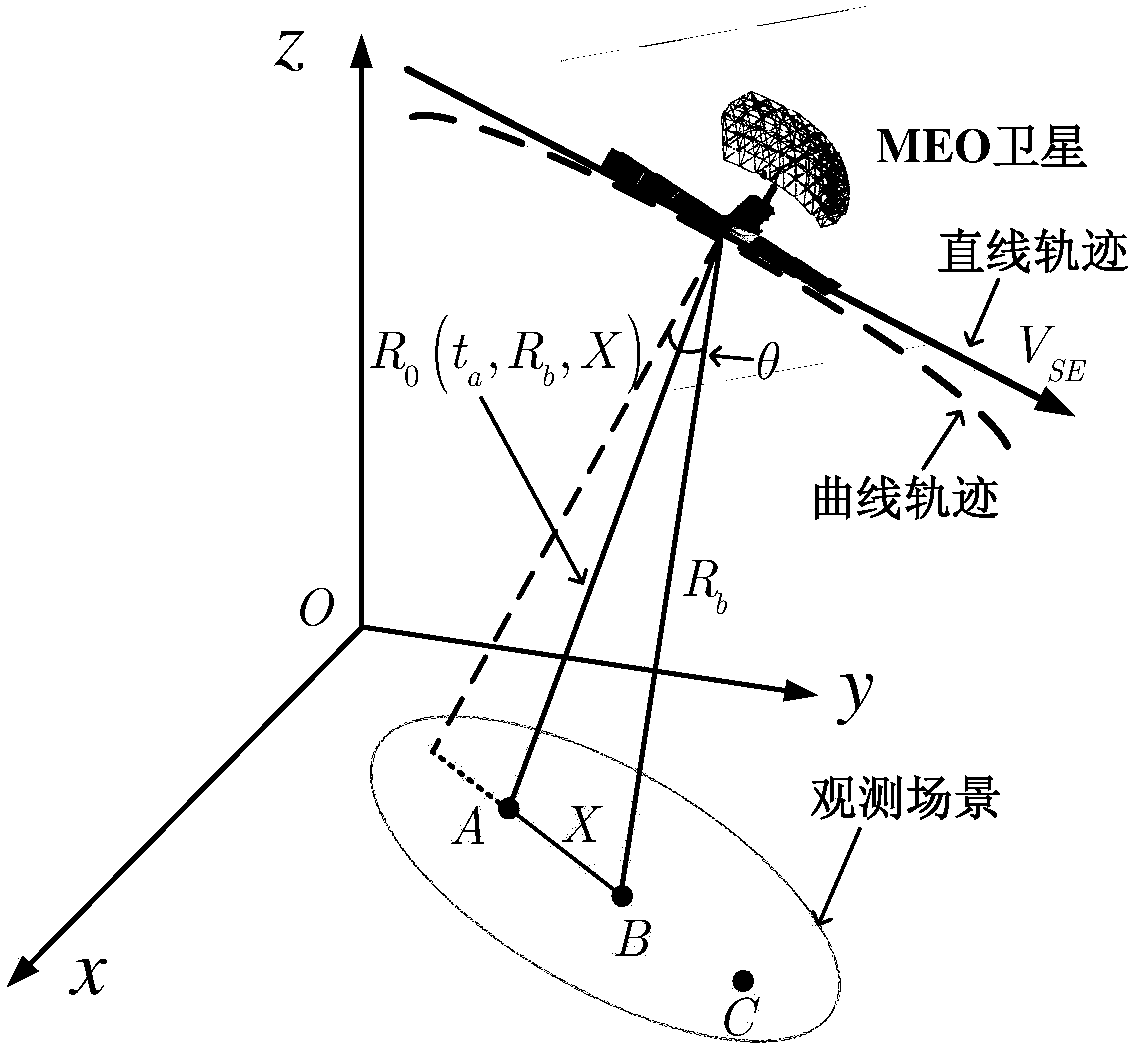
ActiveCN107607948AImprove image qualityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAmbiguityRadar signal processing
The invention belongs to the field of radar signal processing and discloses a motion compensation and imaging method of a medium earth orbit satellite SAR. The method comprises the steps that: an MEO-SAR transmits a linear frequency modulation signal, receives a corresponding echo signal and obtains a distance frequency domain signal; a two-step motion compensation method is used to obtain a compensated echo signal; an ASE velocity model is used for carrying out modeling of the compensated echo signal again; the echo signal which is subjected to modeling again is subjected to equivalent errorcompensation; the echo signal which is subjected to the equivalent error compensation is subjected to extended Stolt interpolation based on the ASE velocity model and an SAR focused image is obtained.A problem of ambiguity of an azimuth spectrum in the motion compensation of MEO-SAR imaging can be solved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Methods, systems, and apparatus for global multiple-access optical communications
ActiveUS20170302377A1Utility less-flexibleIncrease data rateWavelength-division multiplex systemsActive radio relay systemsBurst transmissionLow earth orbit
A wide-field telescope and focal plane array (FPA) that look at Earth and satellites in low- and medium-Earth orbit (LEO and MEO) from a satellite in higher orbit, such as geostationary Earth orbit (GEO), can serve as a node in an on-demand, optical multiple access (OMA) communications network. The FPA receives asynchronous low-rate signals from LEO and MEO satellites and ground stations at a signal rate determined in part by the FPA frame rate (e.g., kHz to MHz). A controller tracks the low-rate signals across the FPA as the signal sources orbit Earth. The node also includes one or more transmitters that relay the received information to other nodes via wavelength-division multiplexed (WDM) free-space optical signals. These other signals may include low-rate telemetry communications, burst transmissions, and continuous data relay links.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Satellite search and rescue signal frequency estimation method
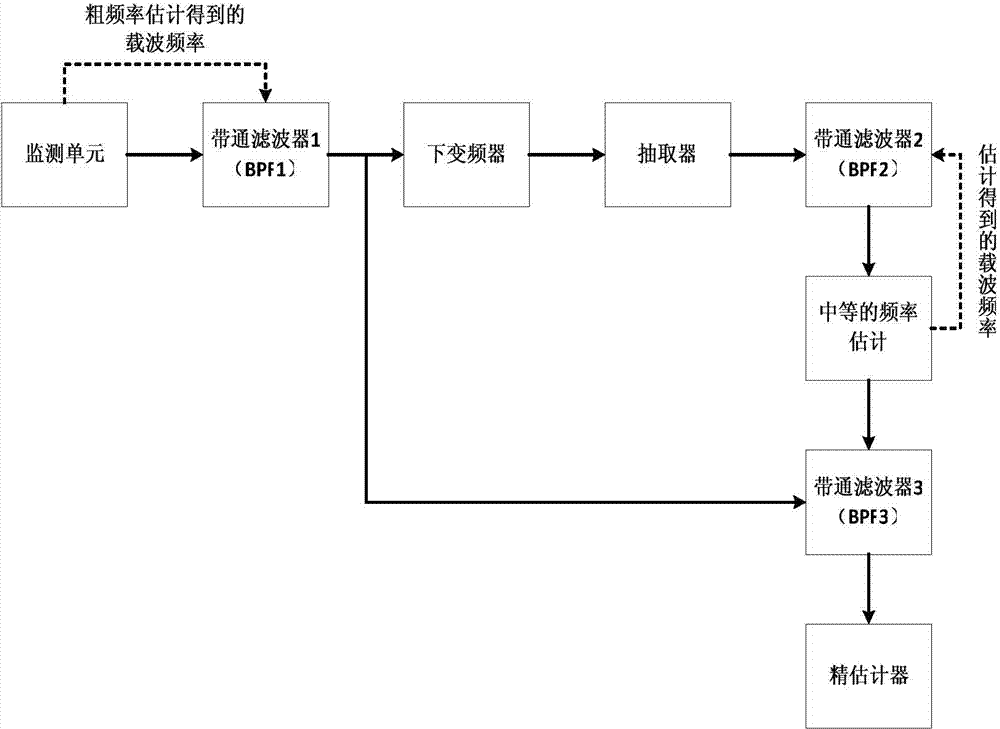
InactiveCN103576170AReduce the sampling frequencyReduce computationSatellite radio beaconingBandpass filteringEngineering
Provided is a satellite search and rescue signal frequency estimation method. By the adoption of a loop iteration processing structure, a narrow-band filter is used for meeting the requirement of a Kay fast frequency estimator for simple-frequency signals. The satellite search and rescue signal frequency estimation method comprises the following implementation steps that satellite search and rescue signals are received through a medium earth orbit local user terminal, coarse frequency estimation is conducted on the satellite search and rescue signals, and the band width of a BPF1 is designed; the signals pass through the BPF1, and signals s1 are obtained and divided into two channels; down-conversion is conducted on one channel of the s1, the sampling frequency is reduced further through an extractor, and output signals s2 of the extractor are used for iterative estimation; the s2 pass through a BPF2, medium frequency estimation is conducted so as to obtain omega2, the omega2 is used as the center frequency of the BPF2 to conduct filtering on the s2, loop iteration is conducted in this way, and omega3 is obtained and used as the center frequency of a BPF3; the other channel of the s1 passes through the BPF3, and signals s3 are obtained; fast frequency estimation is conducted on the s3.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
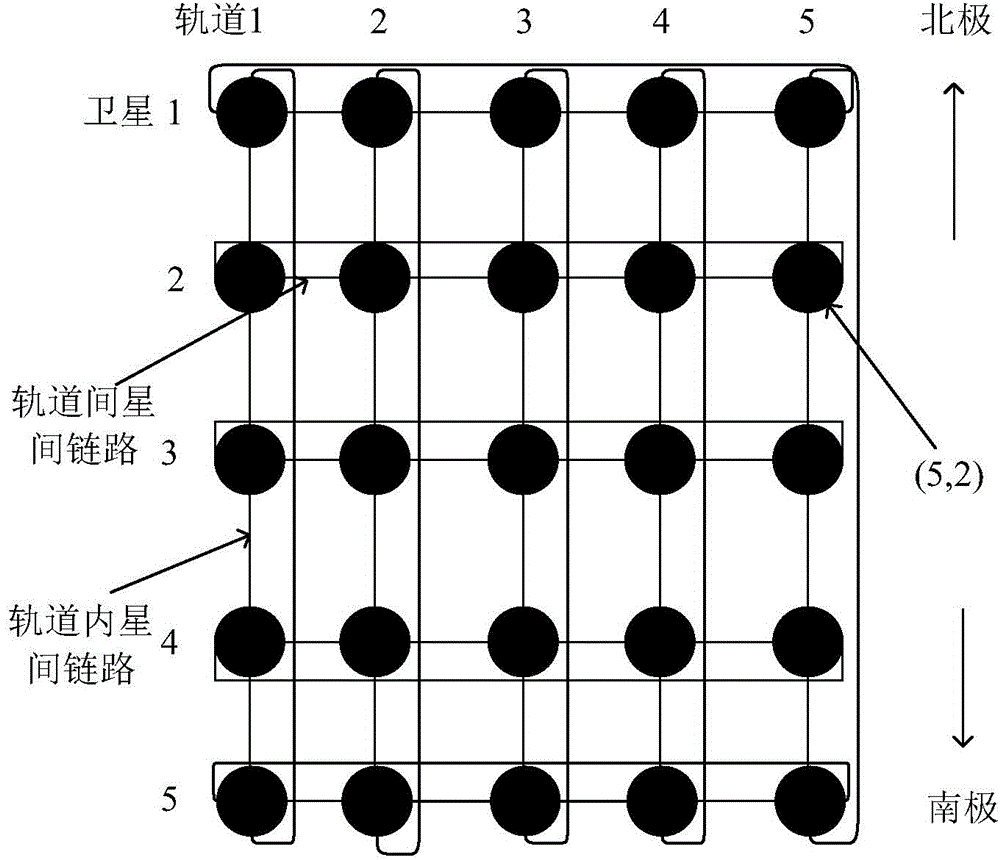
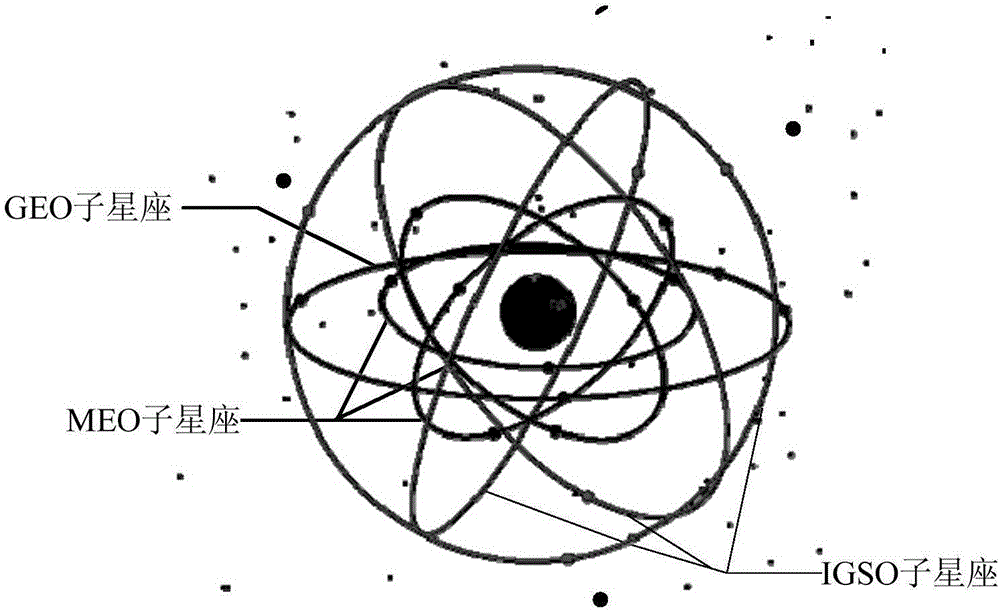
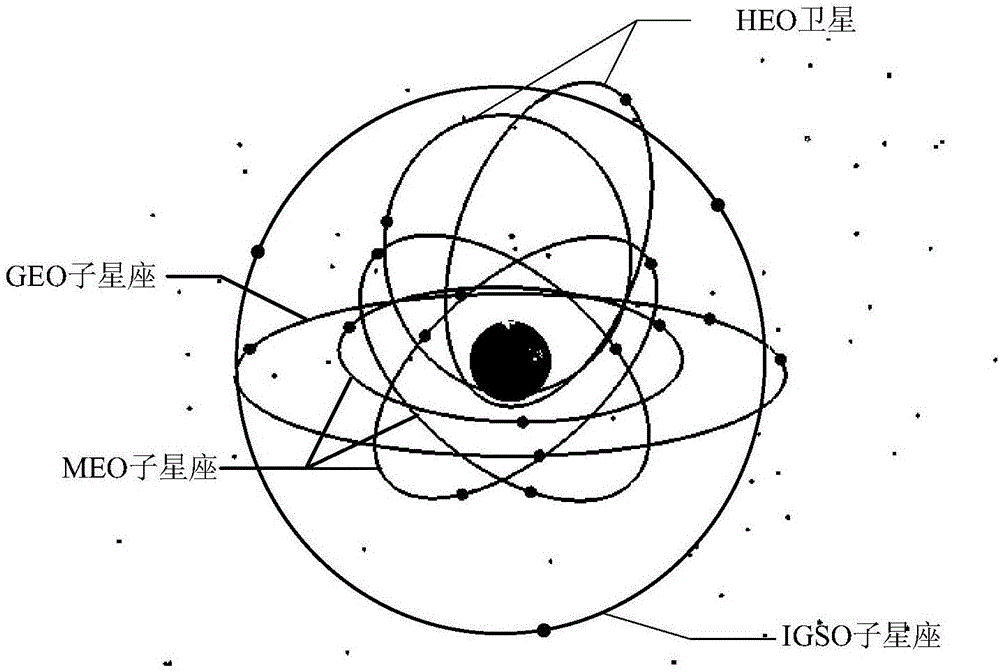
Structure variable mixed-orbit satellite constellation
ActiveCN106788671AIncreased global coverage multiplicityImprove self-management abilityNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionNatural satelliteLow latitude
The invention discloses a structure variable mixed-orbit satellite constellation, comprising a GEO (Geosynchronous Orbit) sub constellation, an IGSO (Inclined Geo Stationary Earth Orbit) sub constellation and an MEO (Medium Earth Orbit) sub constellation. The GEO sub constellation comprises n GEO satellites distributed on n orbit positions of a geosynchronous orbit, and coverage areas between the adjacent satellites are connected and cover medium and low latitude areas in a full longitude manner. The IGSO sub constellation comprises five IGSO satellites, wherein the IGSO1, IGSO2 and IGSO3 satellites are located in the same orbit plane, and the phase difference between the adjacent satellites is 120 degrees; and simultaneously, the IGSO3, IGSO4 and IGSO5 satellites have the same ground track. The MEO sub constellation comprises m*k satellites distributed on k orbit planes, m satellites are on each orbit plane, and the MEO sub constellation has global coverage capability. When the structure of the constellation is reconstructed, the IGSO4 and IGSO5 satellites flexibly enter an HEO (High-altitude Earth Orbit) and run. The constellation has excellent global coverage capability, self management capability and flexible and variable structure.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
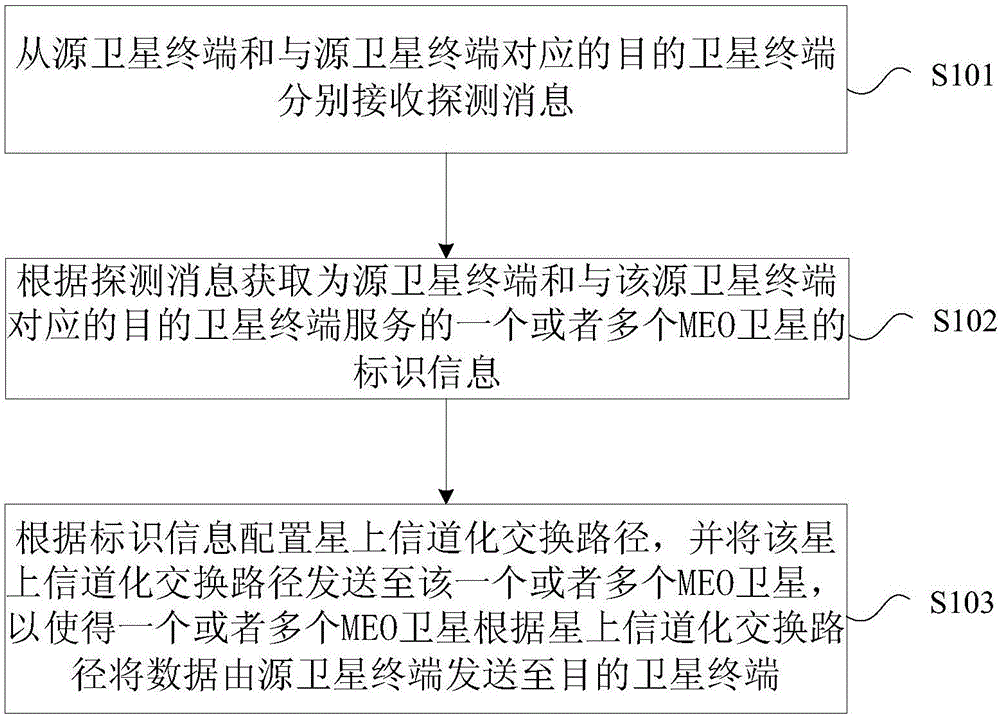
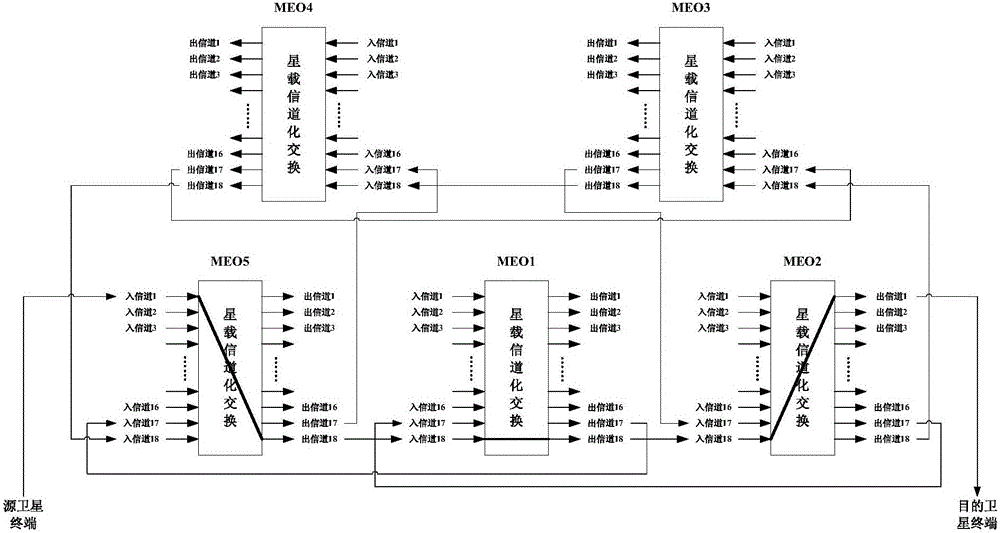
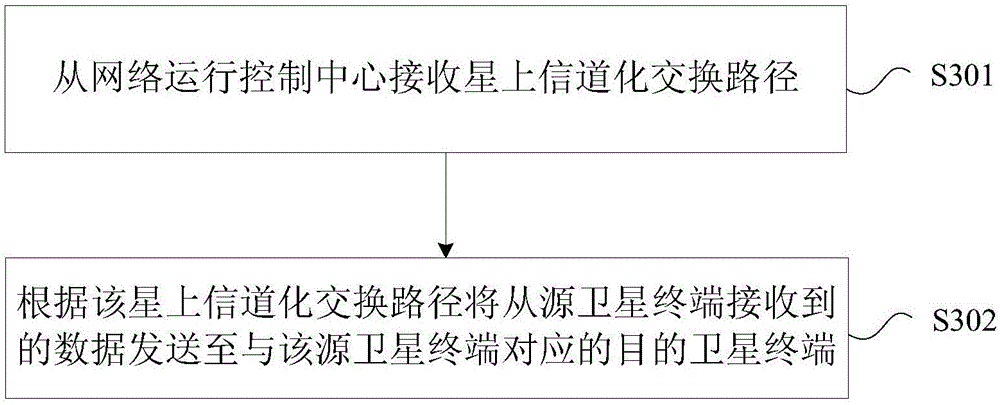
Satellite communication method, device and satellite communication system
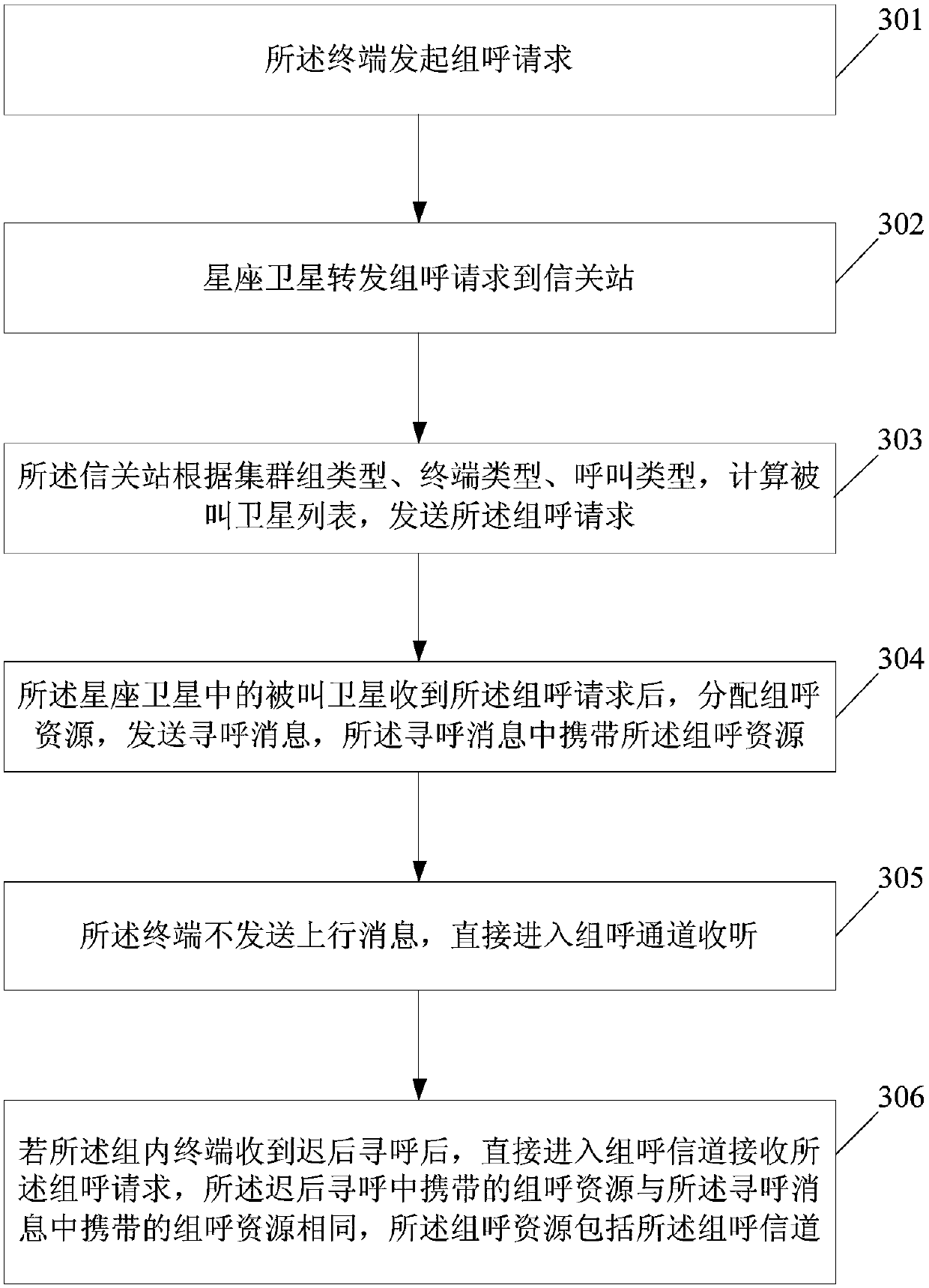
ActiveCN106850048AReduce complexityAchieve heads-up communicationRadio transmissionCommunications systemMedium Earth orbit
The invention provides a satellite communication method, a satellite communication device and a satellite communication system. The method comprises the steps of: receiving a detection message from a source satellite terminal and a destination satellite terminal corresponding to the source satellite terminal respectively, wherein the detection messages comprise information for identifying the source satellite terminal and the destination satellite terminal; acquiring identification information of one or more MEO (Medium Earth Orbit) satellites serving the source satellite terminal and the destination satellite terminal corresponding to the source satellite terminal according to the detection messages; and configuring a channel-on-satellite switching path according to the identification information, and sending the channel-on-satellite switching path to the one or more MEO satellites, so that the one or more MEO satellites send data from the source satellite terminal to the destination satellite terminal according to the channel-on-satellite switching path. The method, the device and the system solve the problem that the MEO constellation bandwidth satellite communication system in the prior art cannot complete satellite communication by adopting a channel-on-satellite switching system.
Owner:GLOBAL ENERGY INTERCONNECTION RES INST CO LTD +3
MEO (medium Earth orbit) space environment and effect integrated detection device
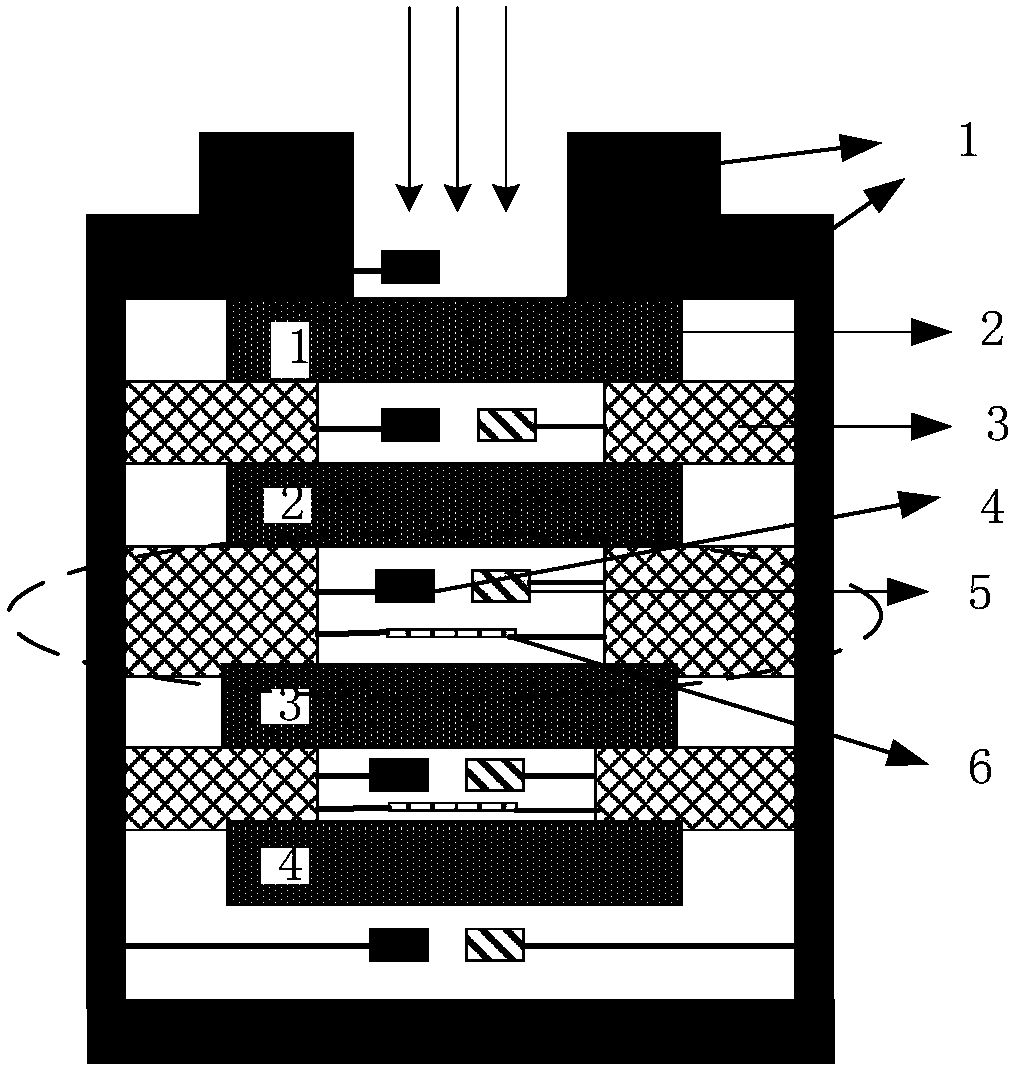
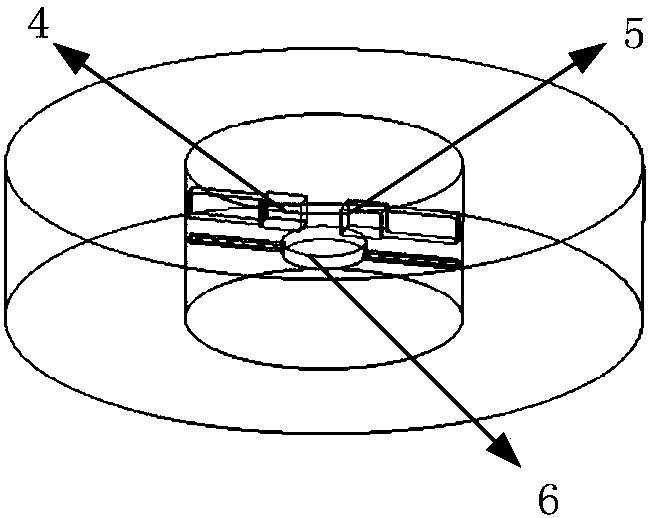
ActiveCN108072888ASimple structureVersatileCurrent/voltage measurementDosimetersInterior spaceSpace environment
The invention discloses an MEO (medium Earth orbit) space environment and effect integrated detection device, and the device comprises a cylindrical detector housing, a collimation blocking layer covering the housing, and all detection units and function layers in the cylindrical interior. The collimation blocking layer is provided with an opening which is used for receiving the emergent space environment particles. The interior of the housing is alternately provided with a metal layer and an insulating layer, wherein the insulating layer forms an internal space, and the internal space is usedfor storing a dosage sensitive element, a single-particle turnover detection element and an internal charging potential monitoring piece. The device is simple in structure, has many functions, is light in weight, and is low in power consumption.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
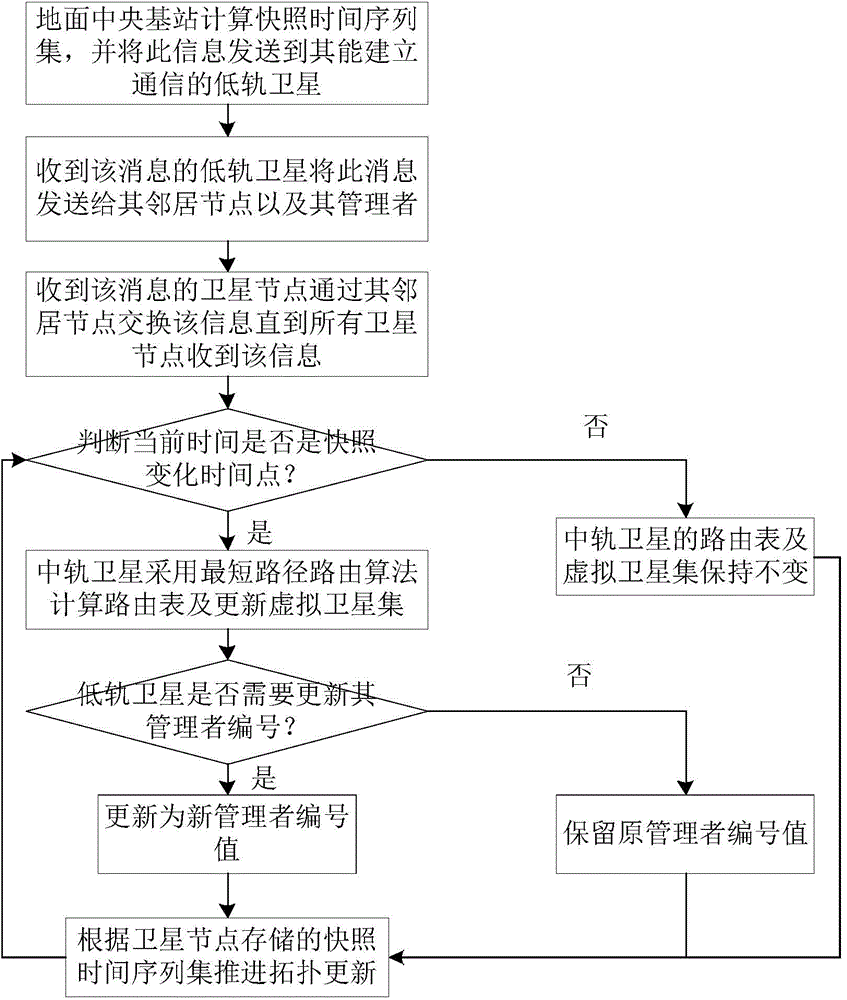
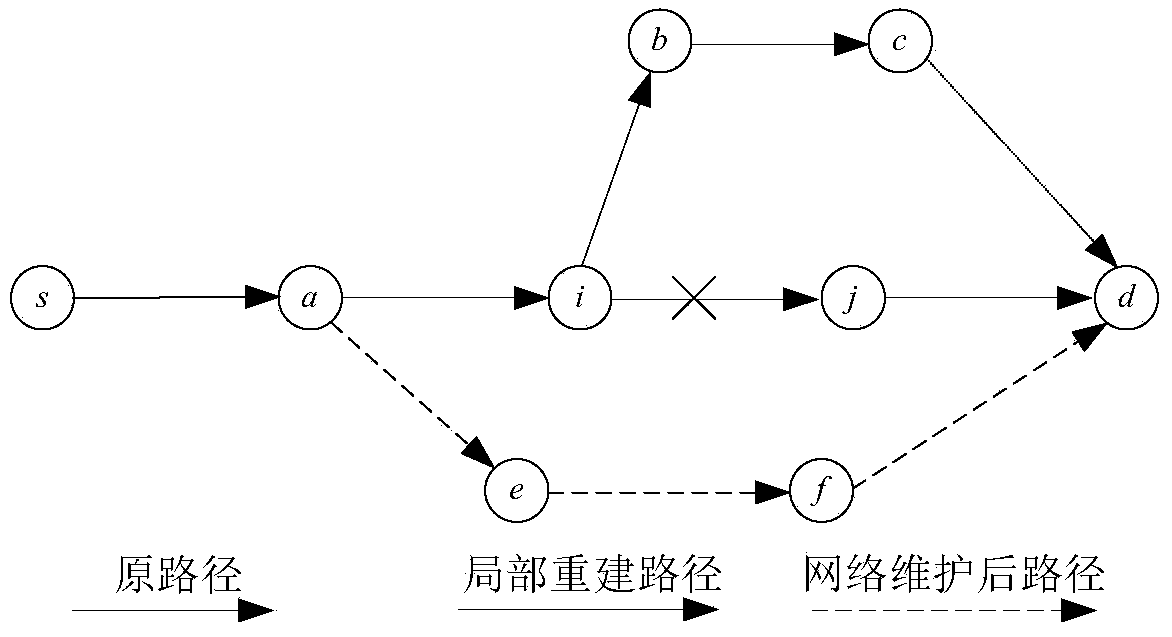
Network maintenance method for space-sky information network
The invention relates to the field of space-sky information networks, in particular to a network maintenance method for a space-sky information network. When a common node is damaged, local routing reconstruction and overall routing reconstruction are combined to guarantee the continuity of data transmission, and the optimal path is quickly restored; when a management satellite is damaged, a plurality of satellites in a medium-earth orbit satellite layer undertake tasks of the management satellite to guarantee reliable transmission of control information; when node congestion possibly happens, an additional cost is set to prevent a congested node from forwarding more data, and the transmission path of original services is kept through forced routing to avoid node congestion and frequent change of the service path. By means of the method, certain data transmission capacity of the network can be kept in an emergency, and the reliability and damage resistance of the space-sky information network are improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
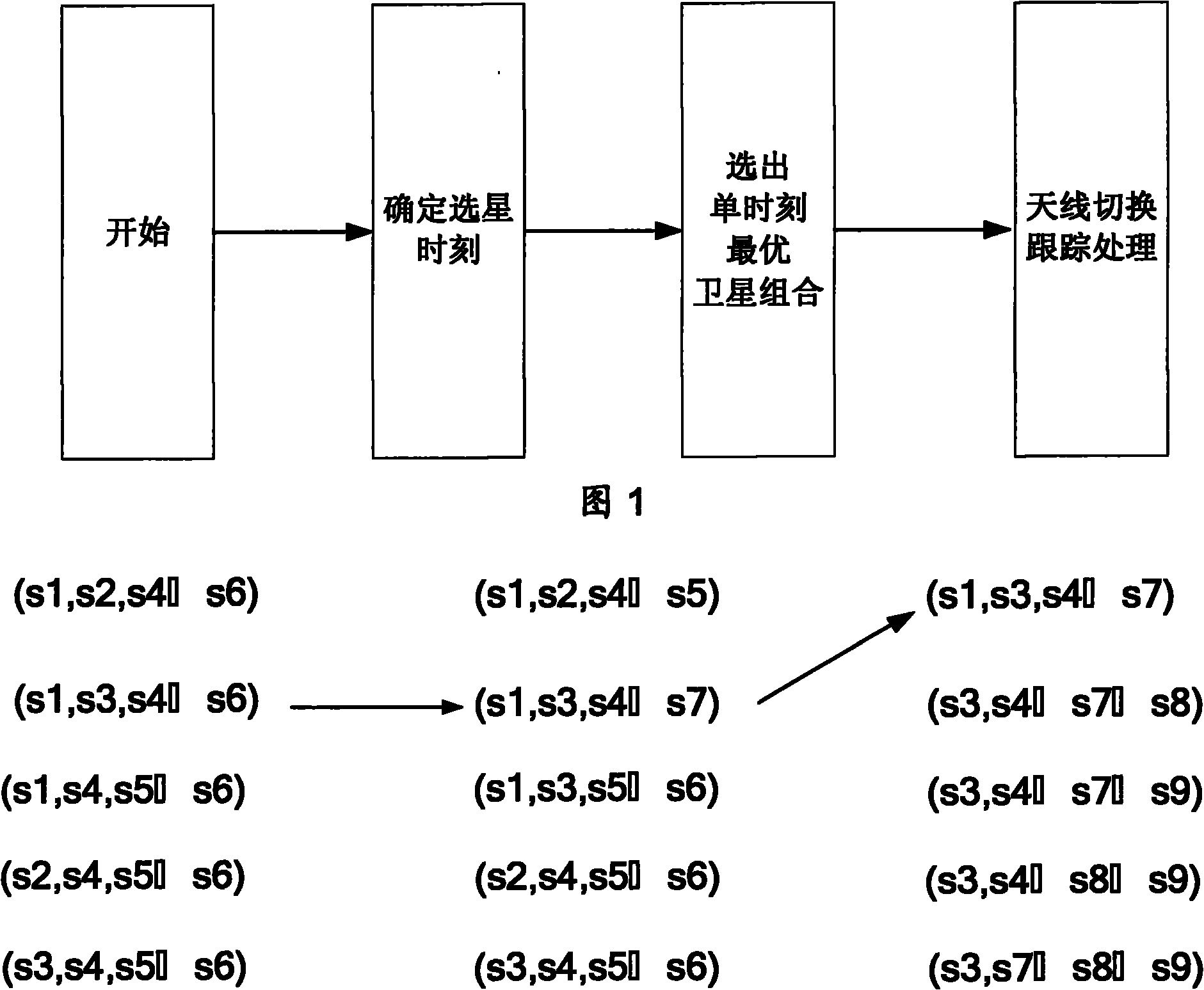
Satellite selection method for medium earth orbit satellite search and rescue system
ActiveCN102023301AReduce complexityCalculation speedSatellite radio beaconingMedium Earth orbitSearch and rescue
The invention relates to a satellite selection method for a medium earth orbit satellite search and rescue system, which comprises the single-time satellite selection step and the antenna switching and tracking processing step. The single-time satellite selection step can select the best satellite combination at the satellite selection time; and the antenna switching and tracking processing step can realize optimal switching strategy of an antenna. By adopting the method, the satellite selection problems at a ground terminal of the medium earth orbit satellite search and rescue system can be solved, the implementation speed is fast, the satellite selection precision is high, the switching times of the antenna can be reduced, and the continuity of tracking satellites of the antenna can be further ensured.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
Mobile satellite modem for combined geostationary, medium and low earth orbit satellite operation
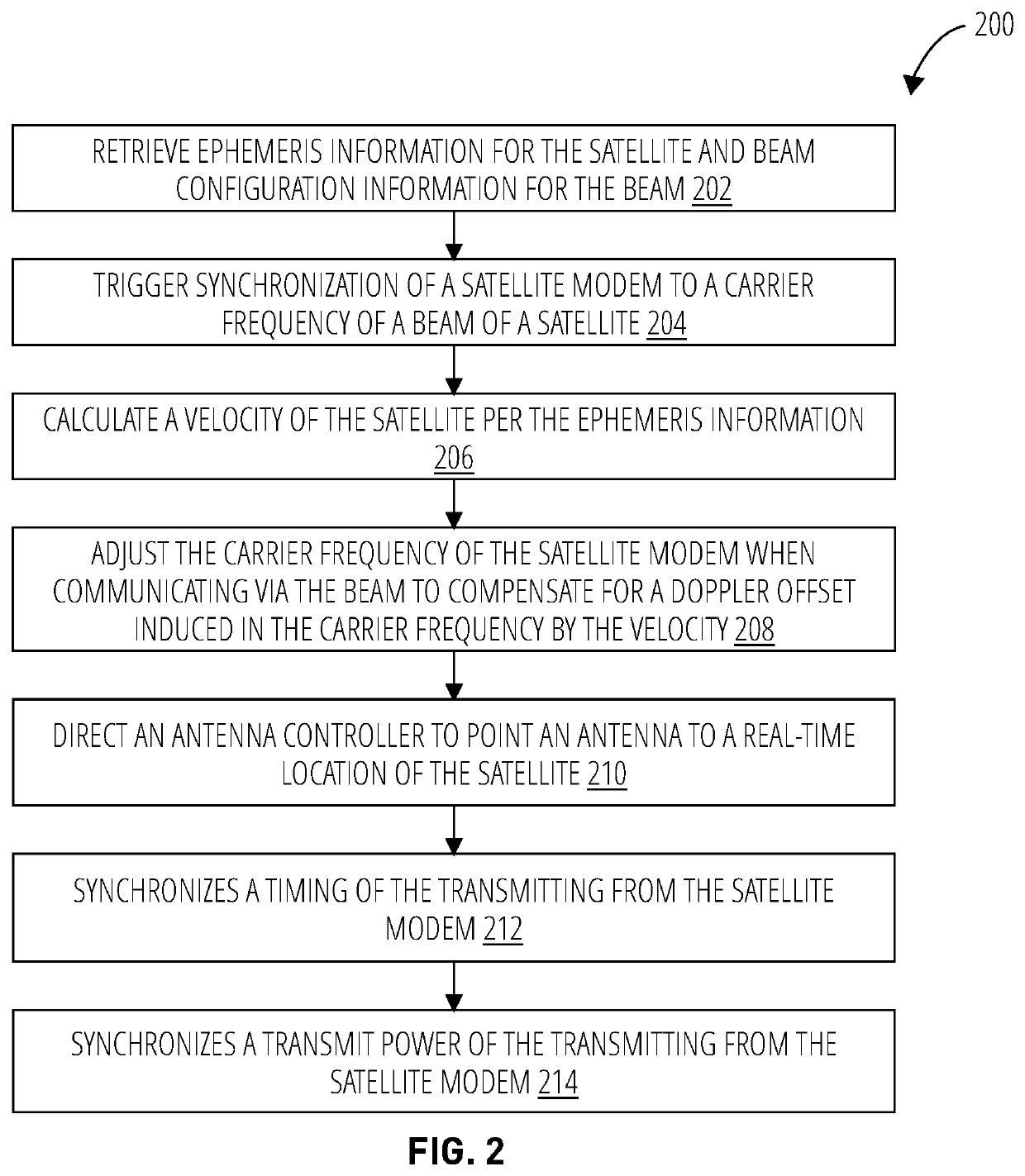
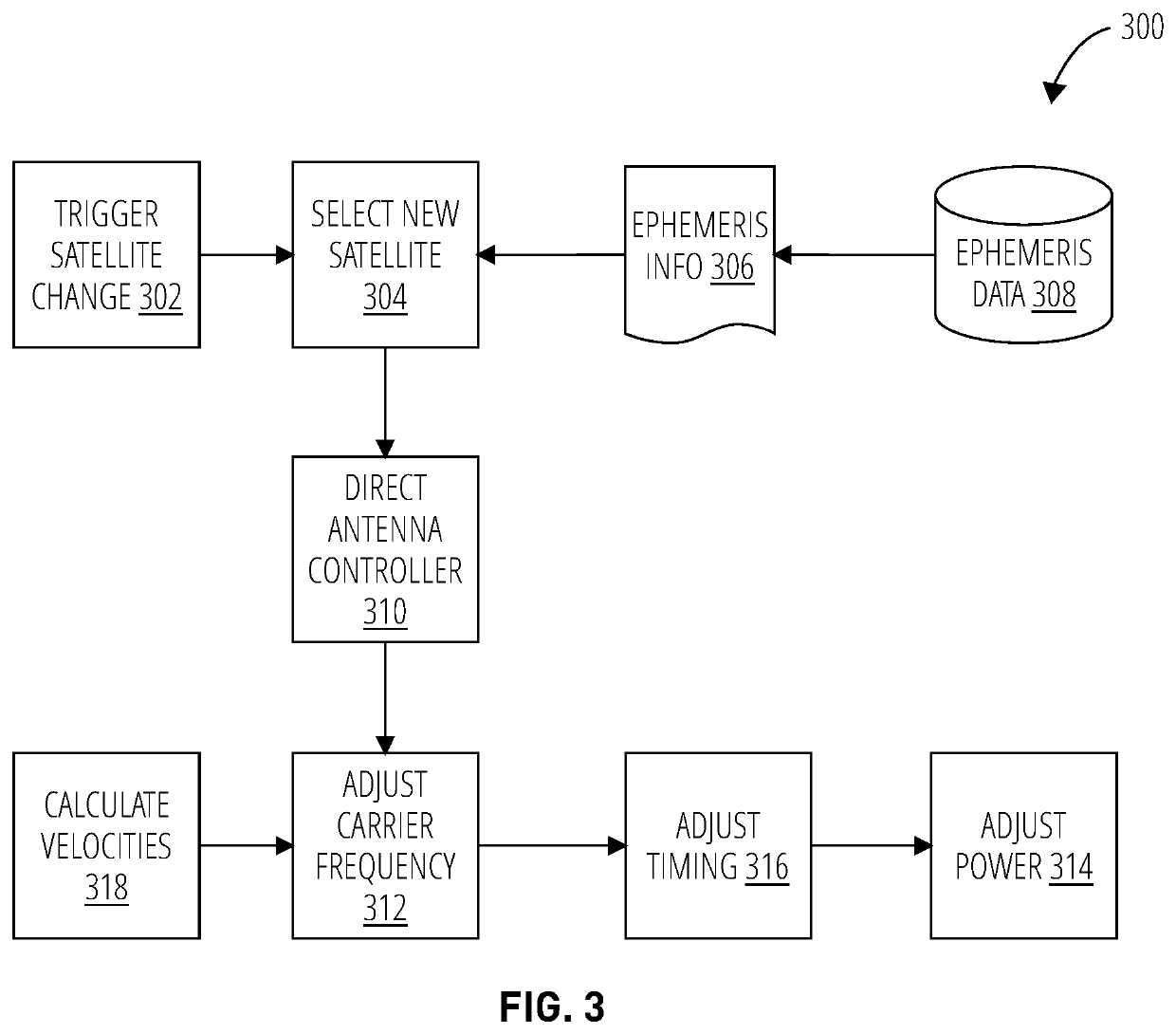
ActiveUS11233562B1Readily apparentRadio transmission for post communicationModem deviceSatellite modem
The present teachings include a method and computing apparatus for triggering synchronization of a satellite modem to a carrier frequency of a beam of a satellite, retrieving ephemeris information for the satellite and beam configuration information for the beam, calculating a velocity of the satellite per the ephemeris information, and adjusting the carrier frequency of the satellite modem when communicating via the beam to compensate for a doppler offset induced in the carrier frequency by the velocity. In the method, the satellite has a satellite type selected from a Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO), Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) or Low Earth Orbit (LEO) type of satellite, and the satellite type is different than a satellite type of an immediately preceding synchronization.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com