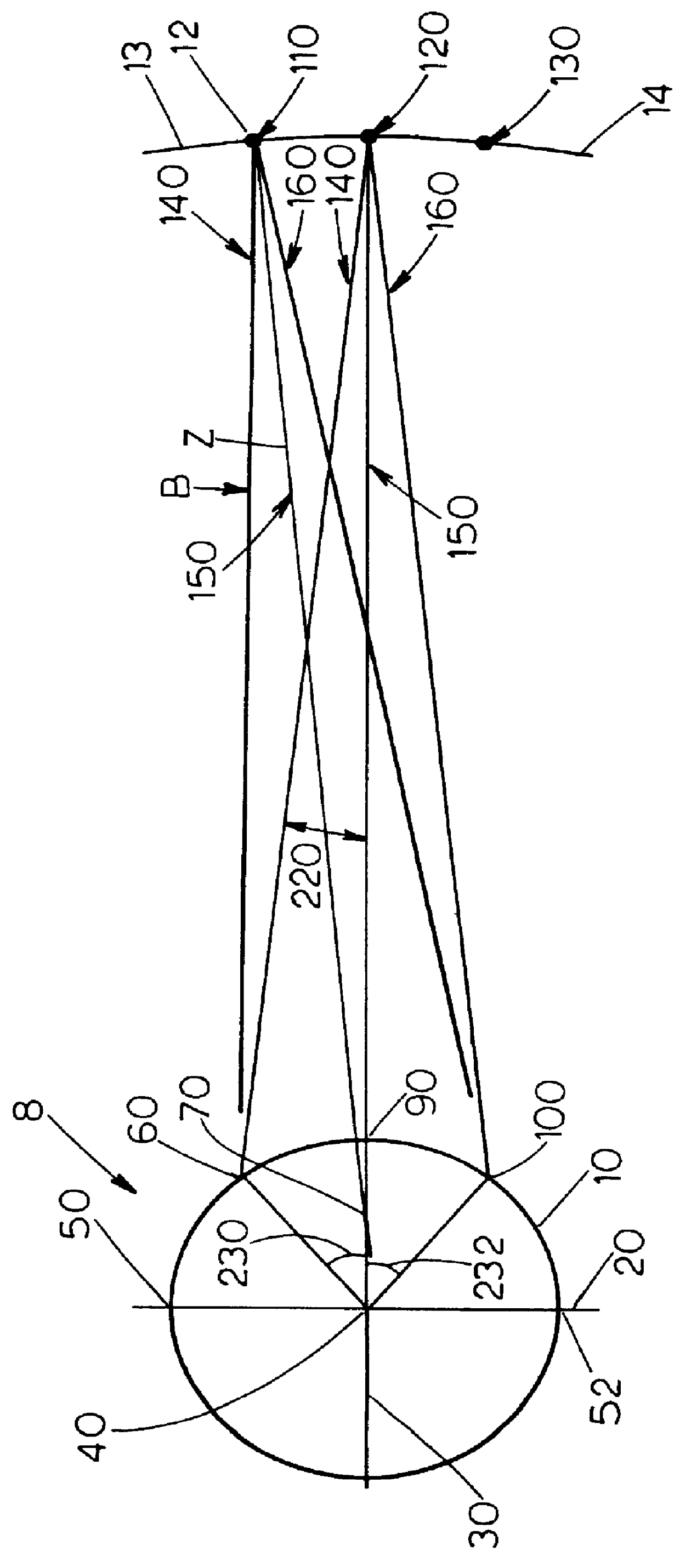
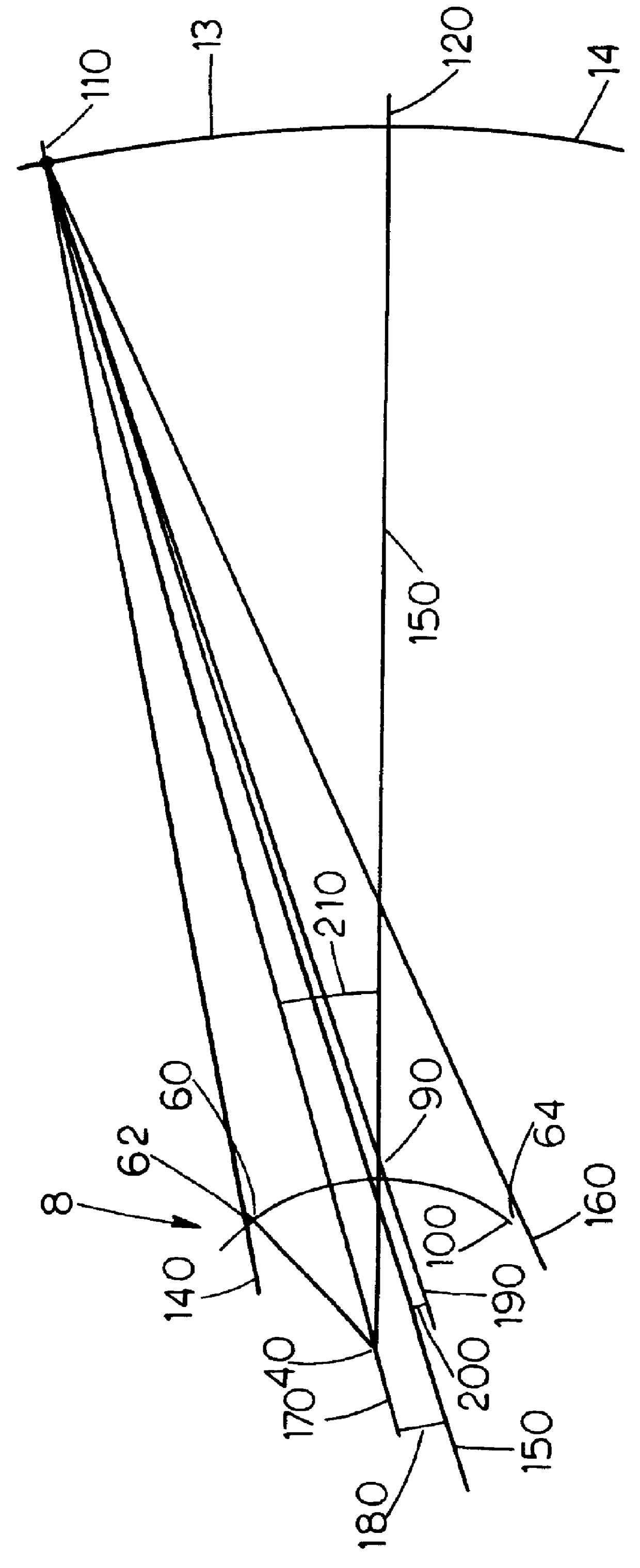
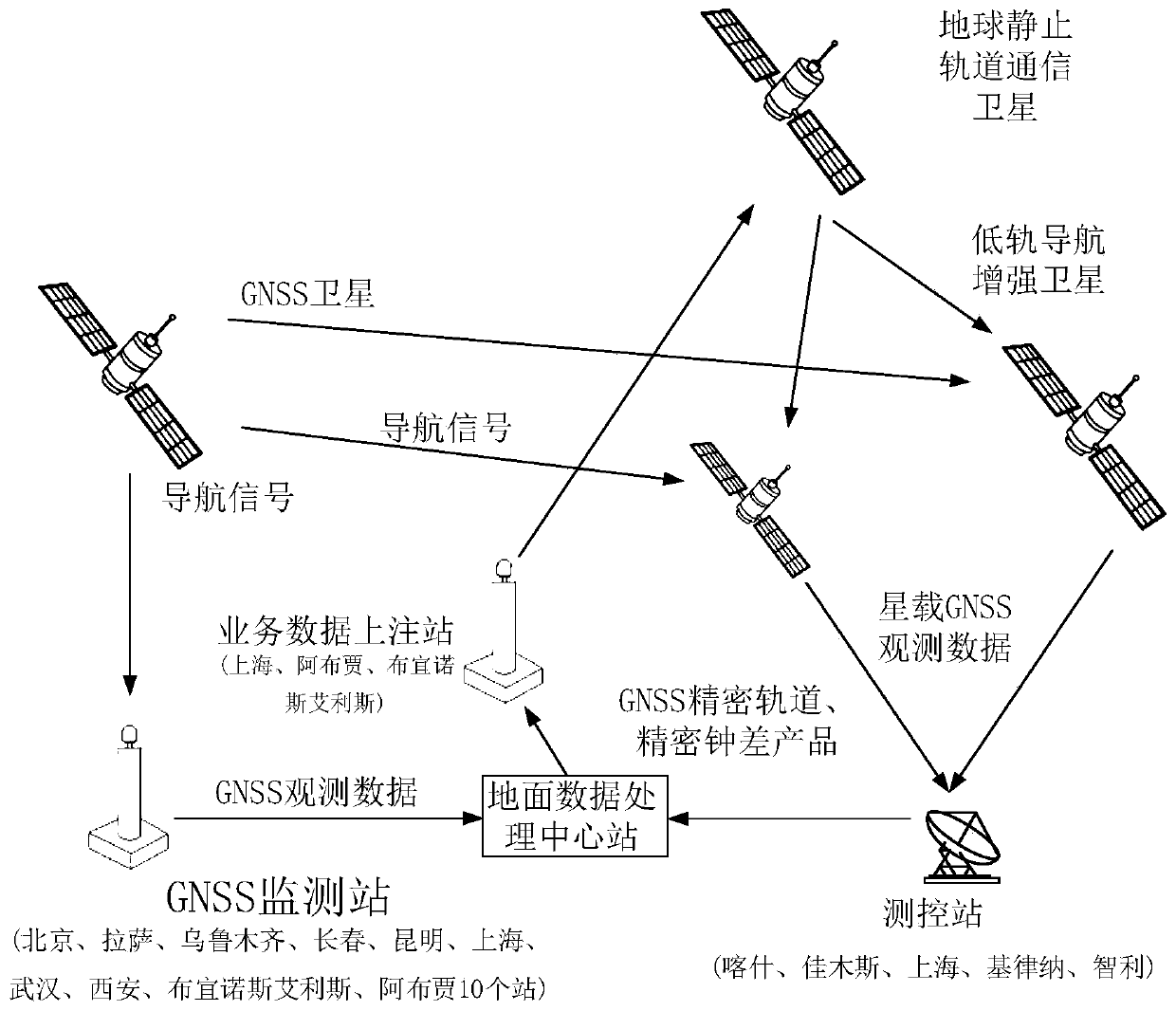
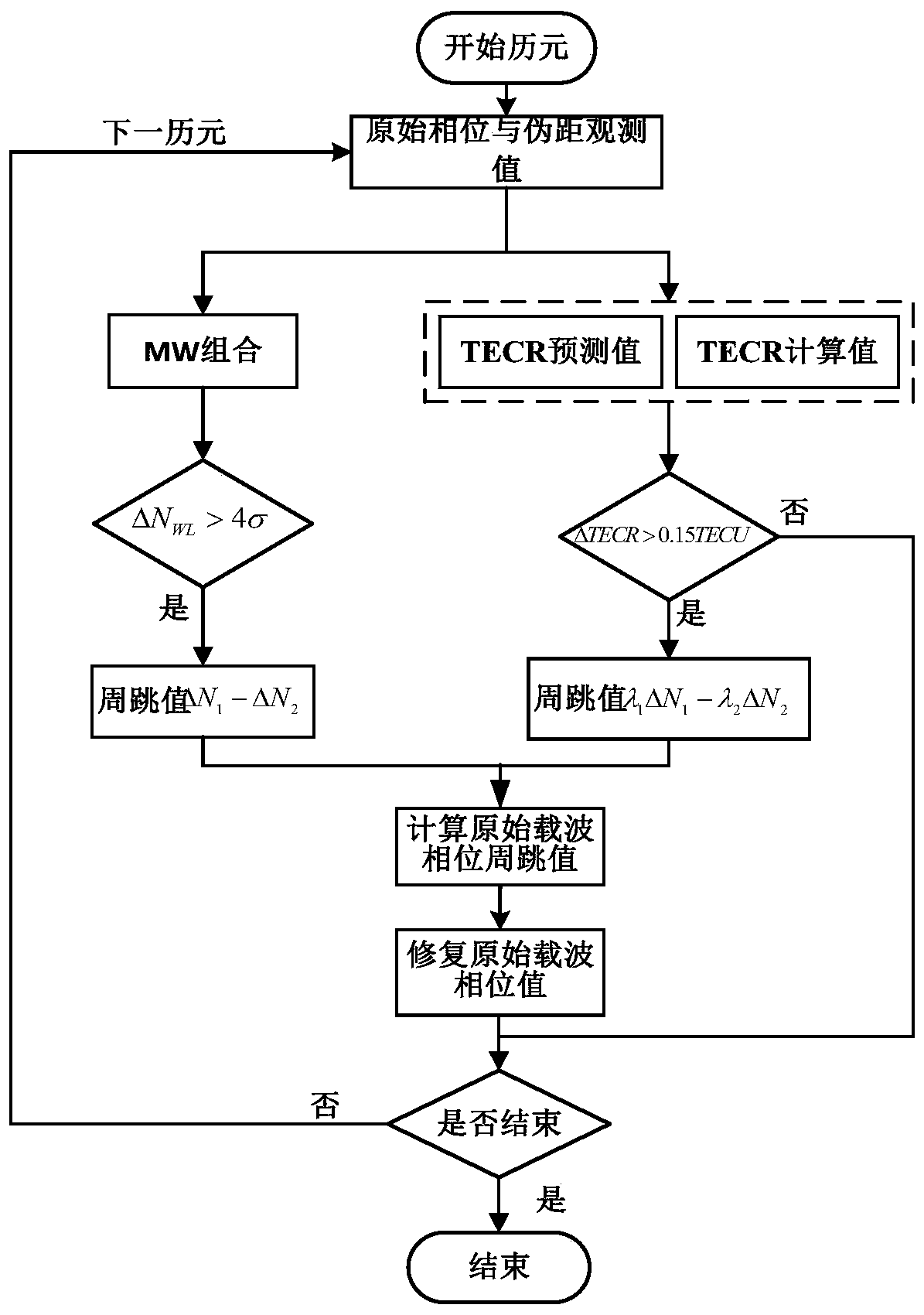
Patents
Literature
236 results about "Geostationary orbit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
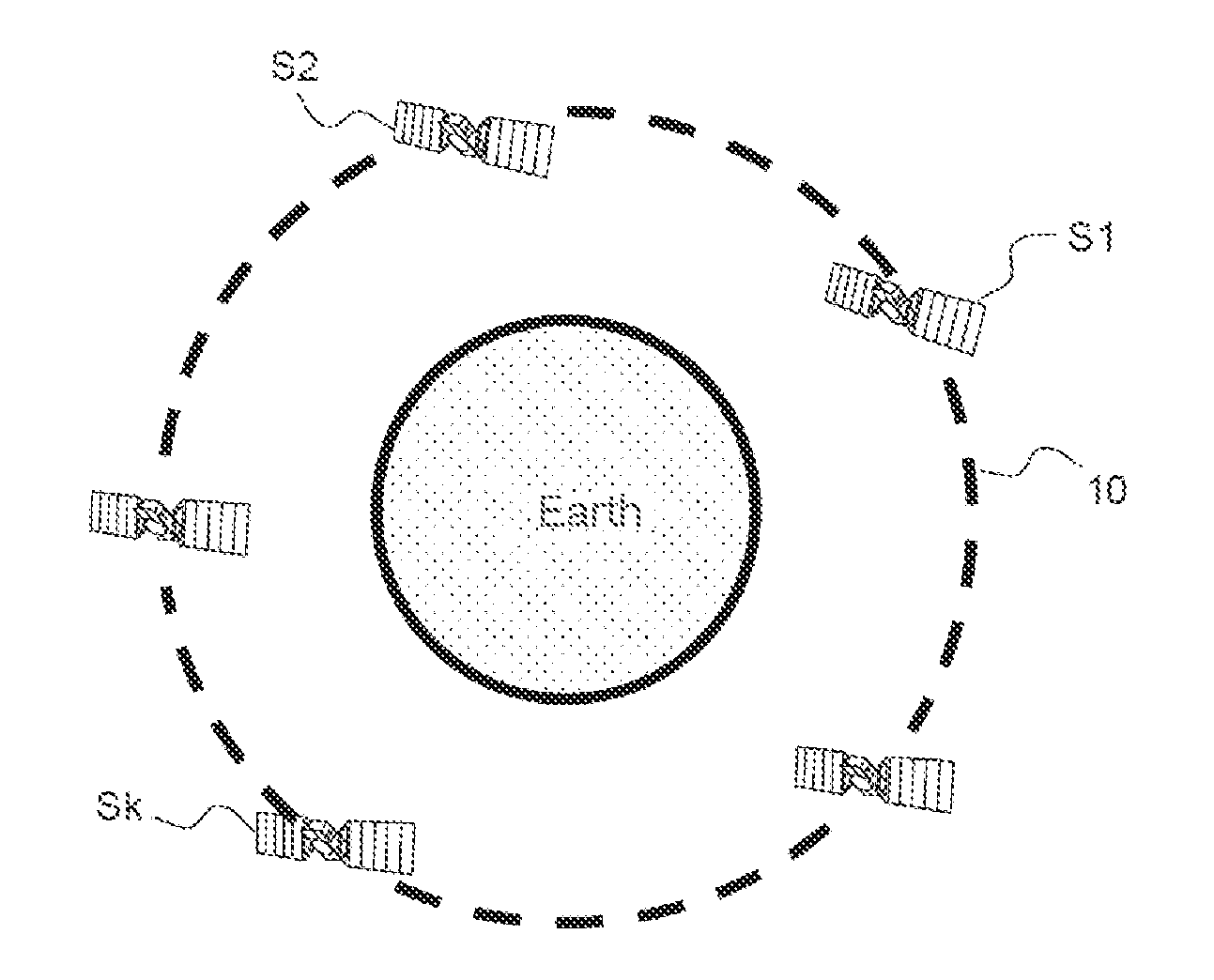
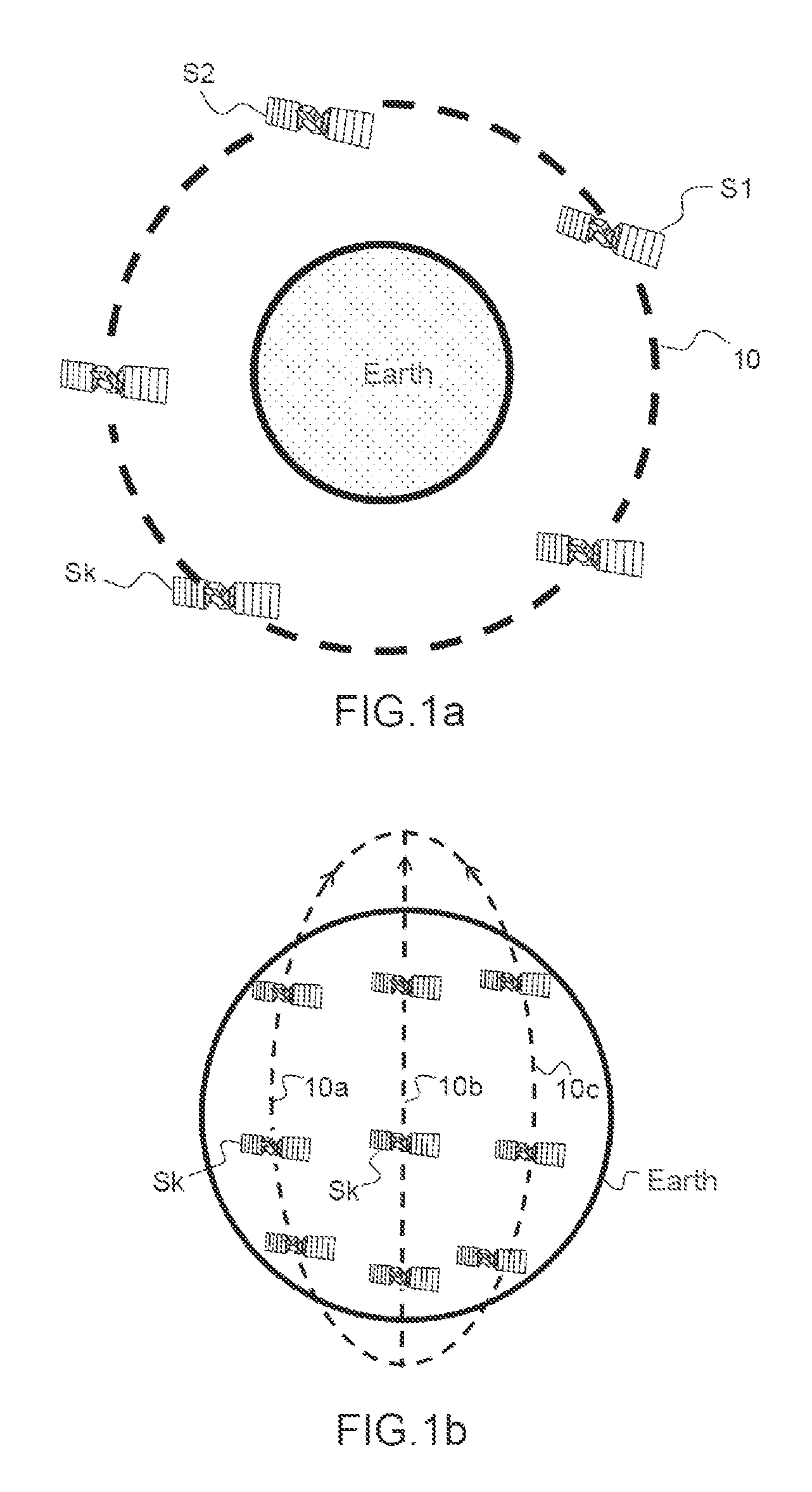
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit 35,786 kilometres (22,236 miles) above Earth's equator and following the direction of Earth's rotation.
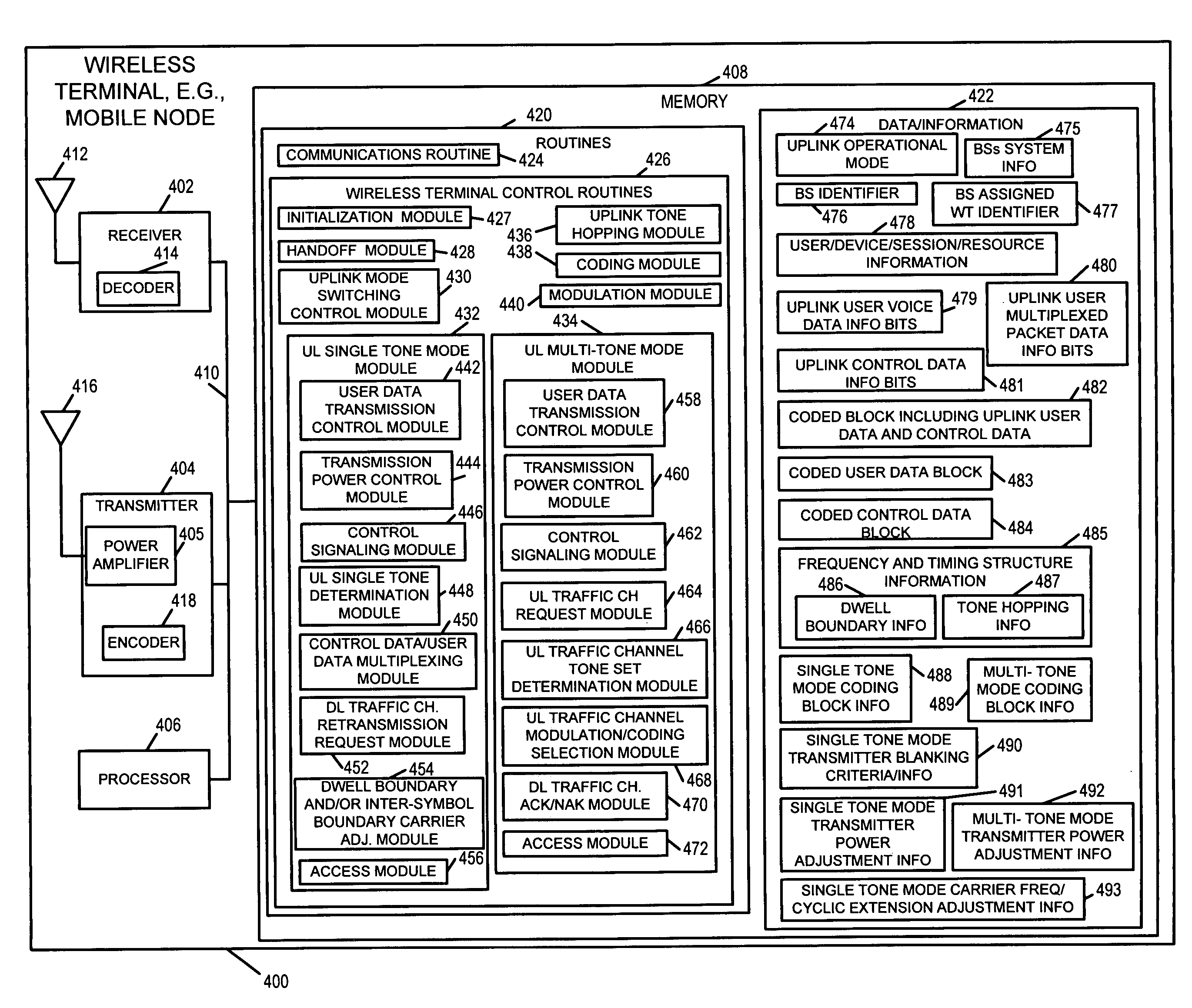
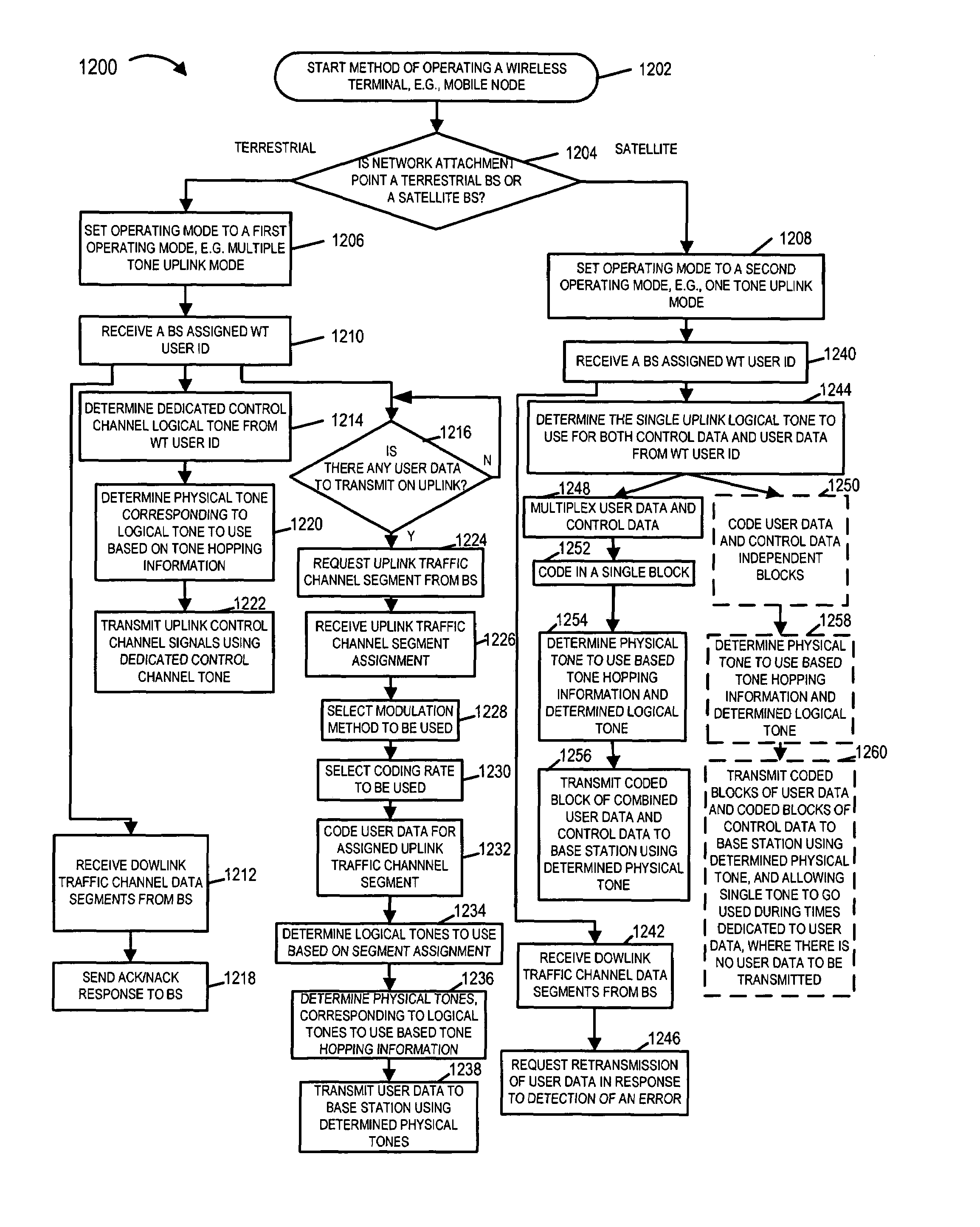
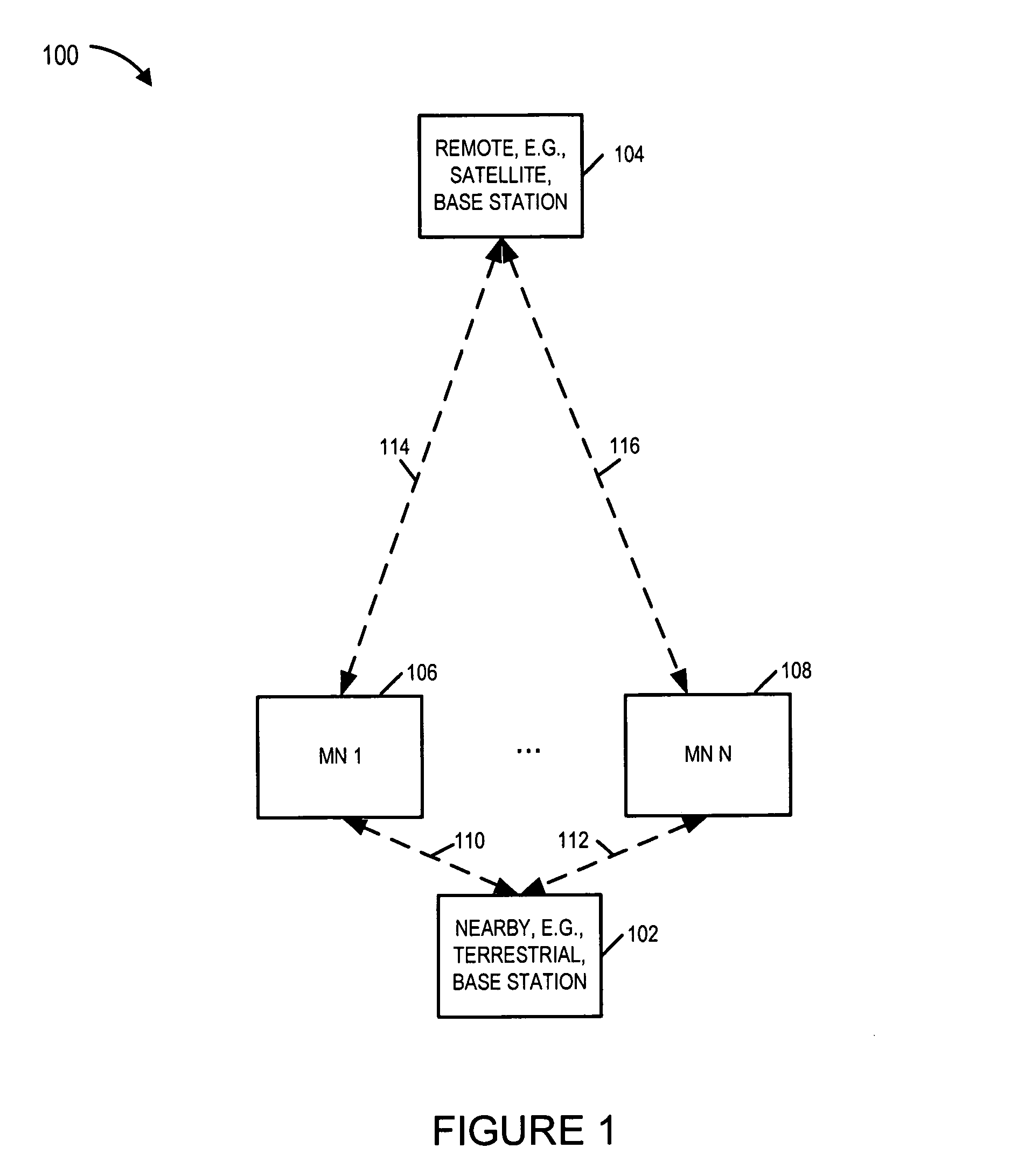
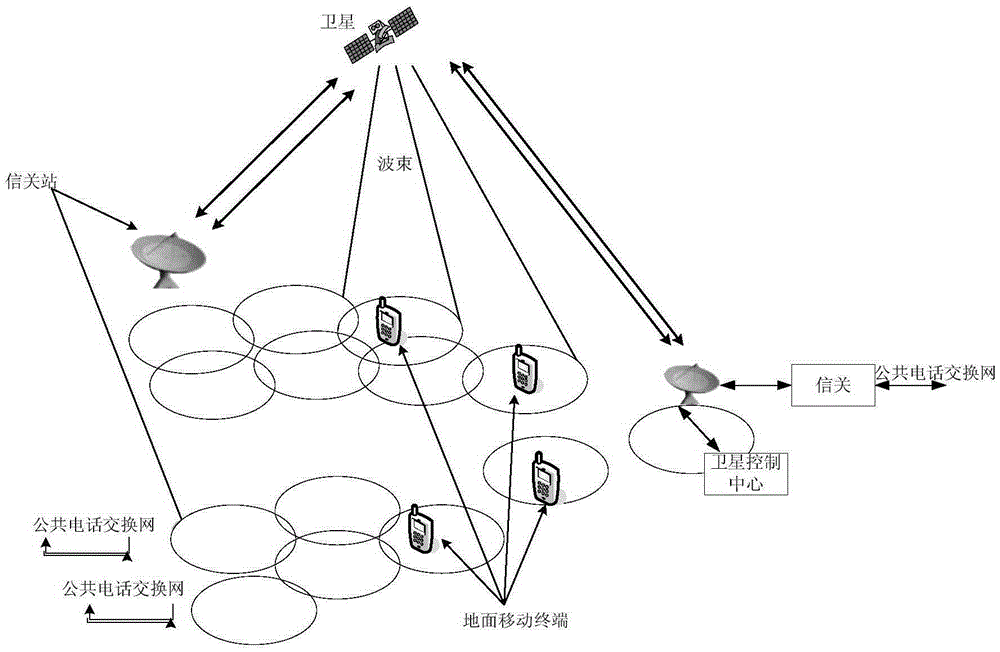
Communications system, methods and apparatus
ActiveUS20060285481A1Benefit in transmitted powerIncrease transmit powerEnergy efficient ICTError prevention/detection by using return channelCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
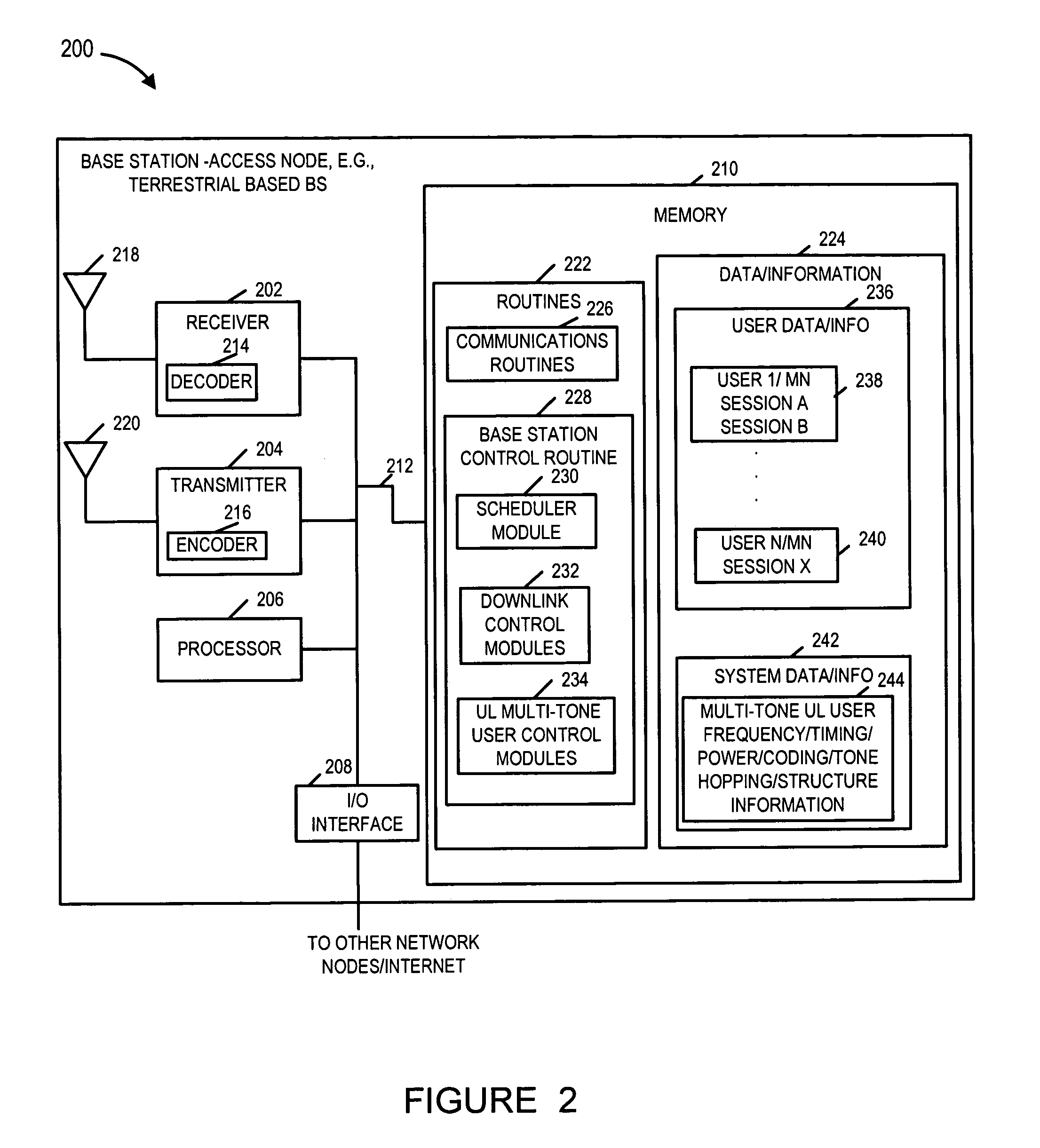
An OFDM wireless communications system includes terrestrial and satellite based base stations. Mobile nodes support two uplink modes of operation, multi-tone mode for terrestrial station interaction and single tone mode for satellite base station interaction. In single tone mode the peak to average power ratio is lower than in the multi-tone mode allowing the same power amplifier to transmit higher average power signals and thus extend range and reach a satellite in geostationary orbit. In multi-tone mode, the mobile node: is temporarily assigned a multi-tone uplink traffic channel segment for user data, is assigned a dedicated control channel for uplink control signals, and supports slaved Ack / Nak for traffic channels. In single tone mode, the mobile node: is assigned a single logical uplink dedicated tone to use for transmitting both user data and control data, and does not use a slaved Ack / Nak mechanism for traffic channels.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
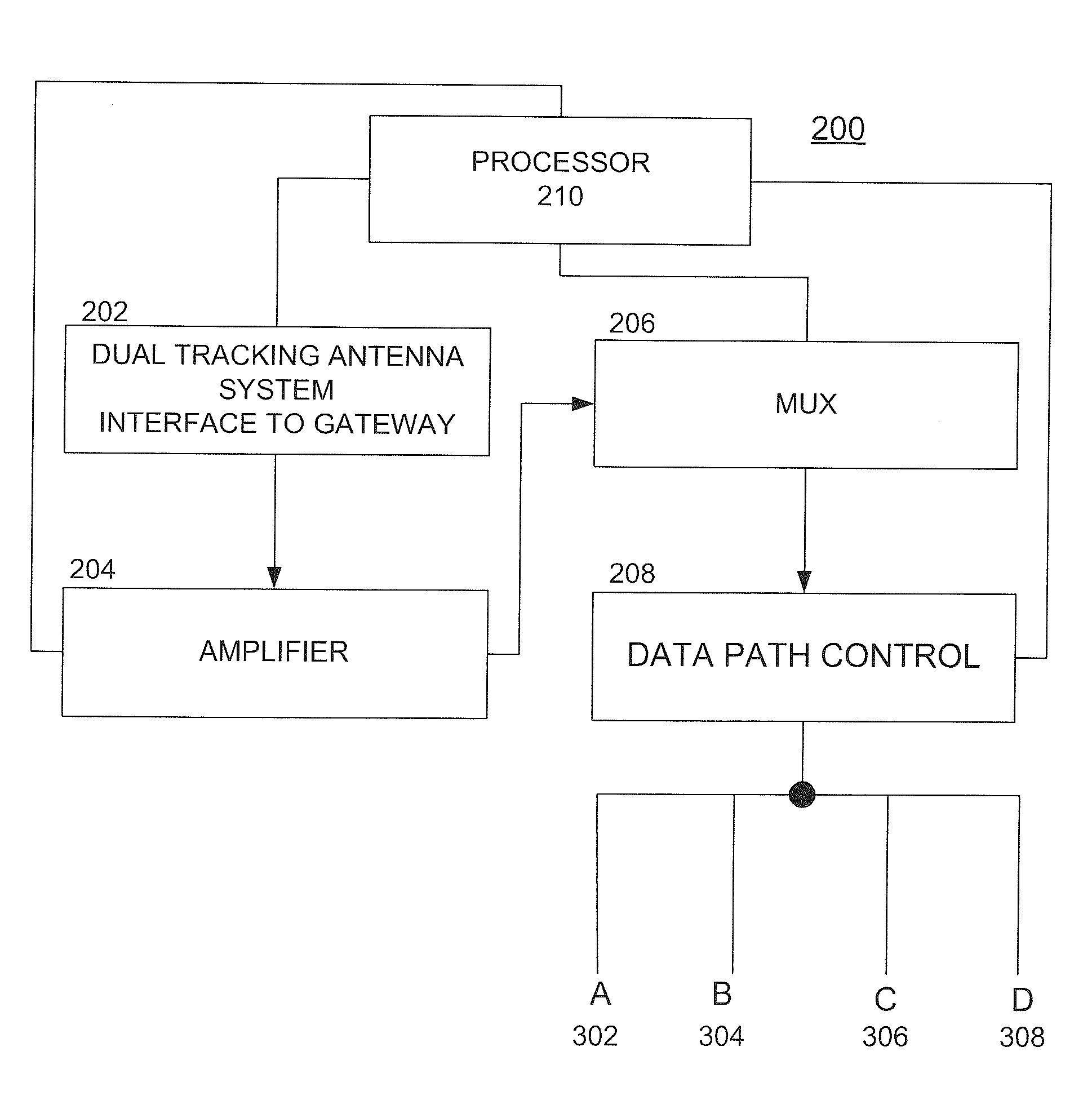
Apparatus and methods for satelite communication
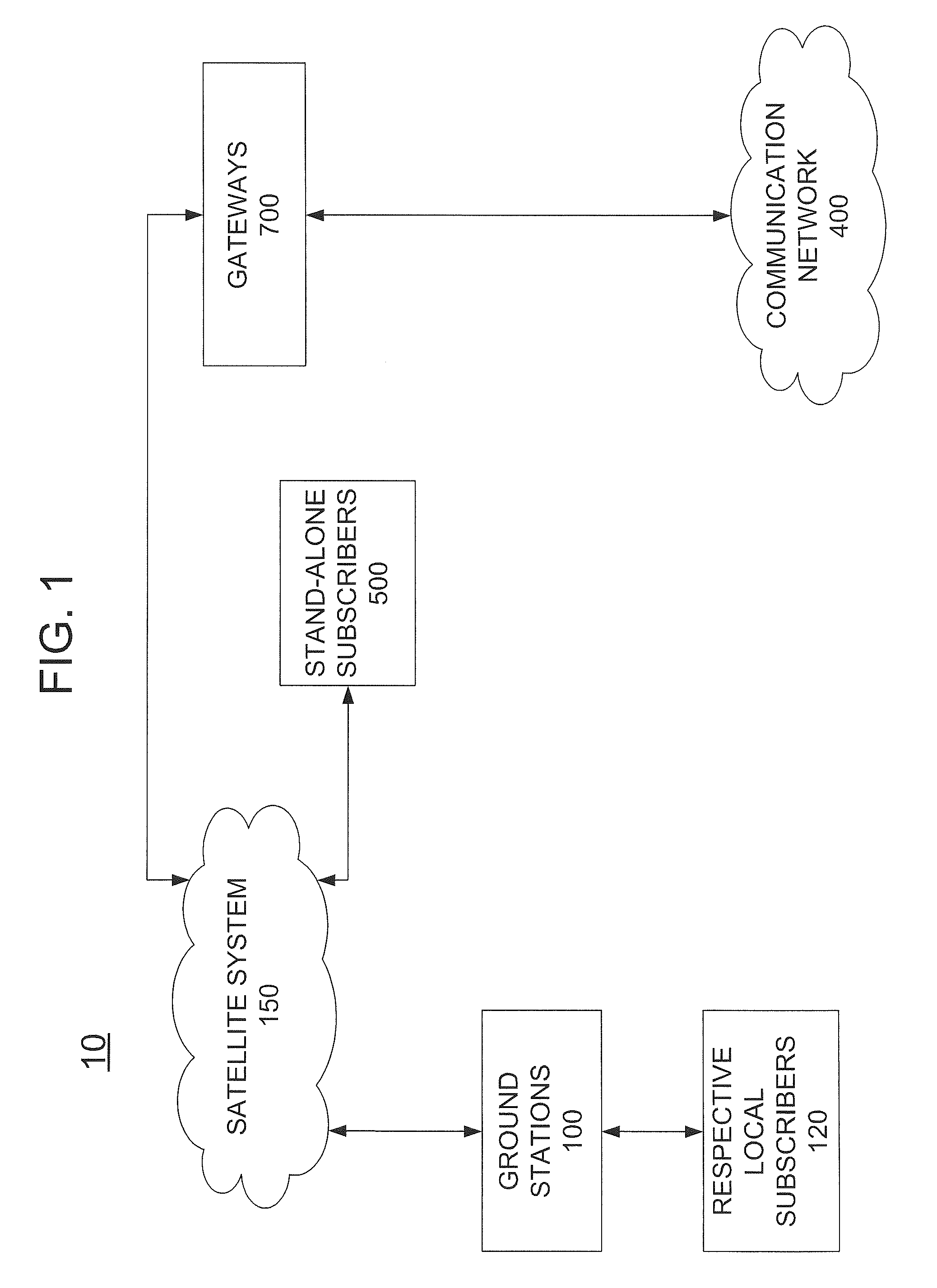
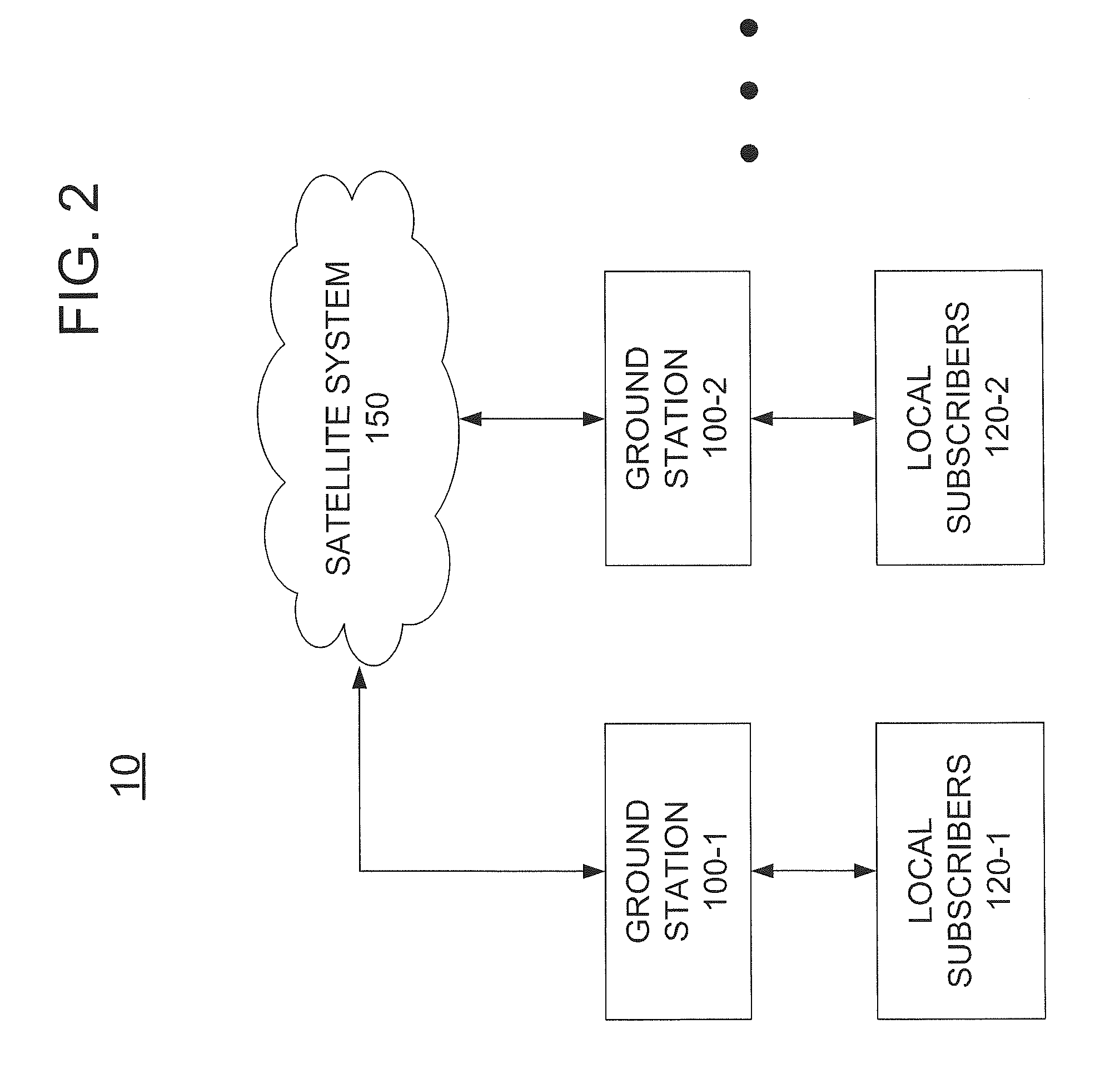
A communications system and method are disclosed that may include a constellation of satellites operating in a substantially equatorial, non-geostationary orbit; a plurality of ground stations configured to communicate with the satellites, at least one given ground station of the ground stations lacking a wired connection to any global communications network; and at least one gateway station coupled to a global communications network and to at least one said satellite, wherein each satellite includes at least one antenna having a steerable beam, the antenna being controllable to continuously direct a concentrated spot beam toward the given ground station.
Owner:WYLER GREGORY THANE
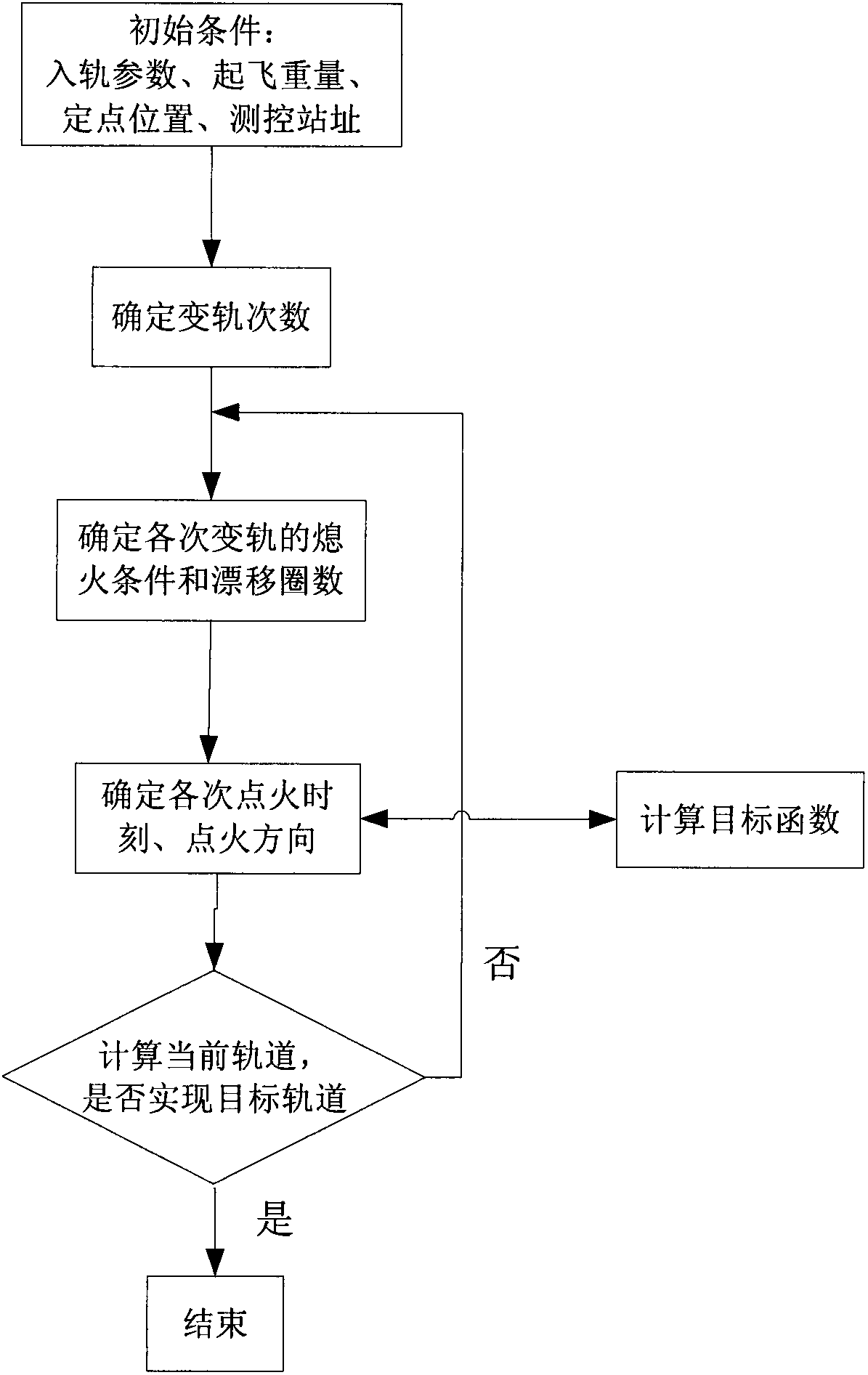
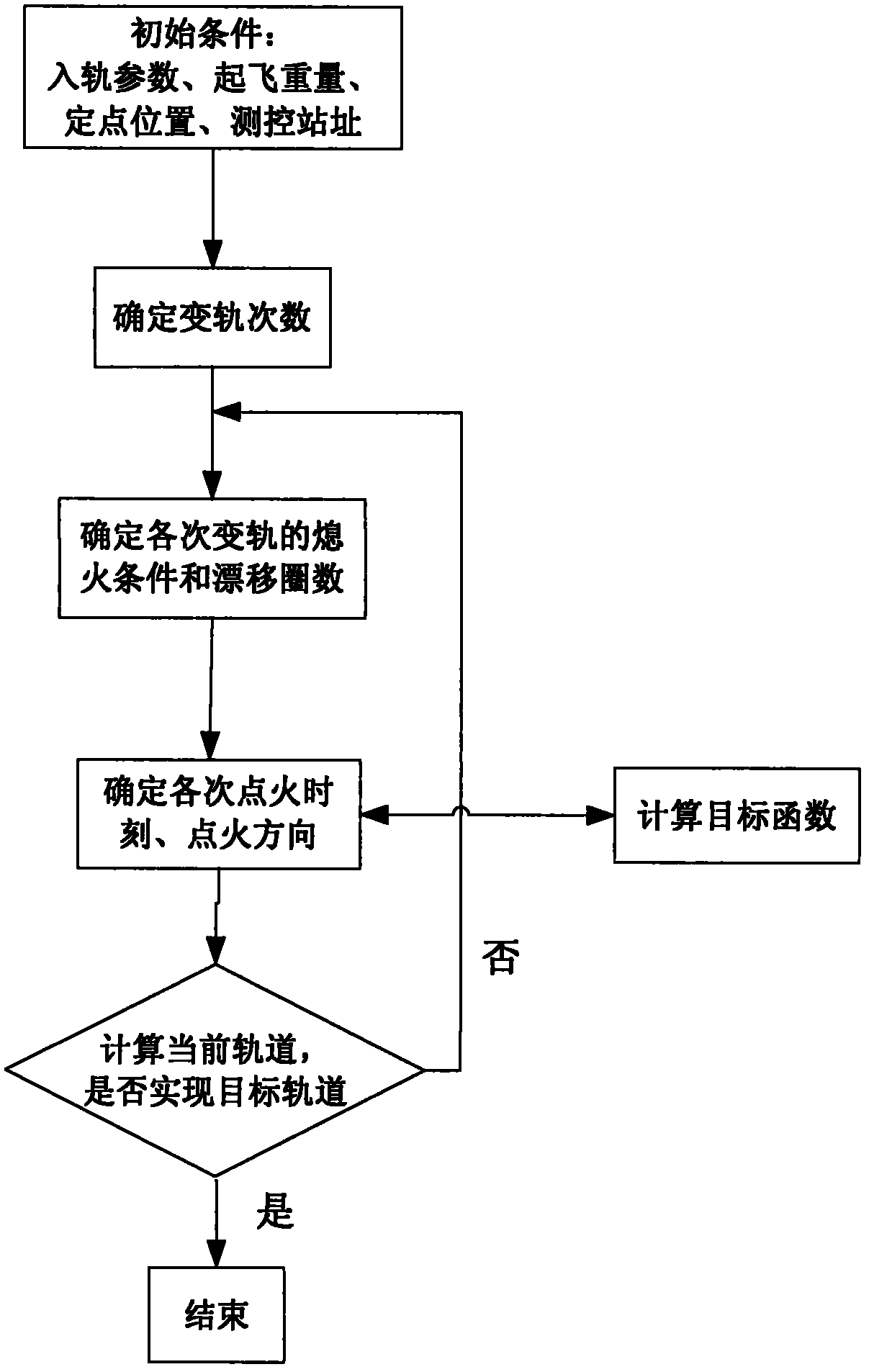
Method for optimizing orbital transfer strategy of geostationary orbit satellite
ActiveCN102424116ASmall amount of calculationShort calculation timeArtificial satellitesGeostationary orbitGeosynchronous orbit
The invention relates to a method for optimizing an orbital transfer strategy of a geostationary orbit satellite, which comprises the following steps of: 1, determining orbital transfer times, orbital transfer circle times and the controlled variable of each-time orbital transfer; and 2, determining time and a thrust direction in each-time orbital transfer. The process of launching the geostationary orbit satellite at present generally comprises the following steps of: launching the satellite into a highly elliptic transfer orbit with an inclination angle by using a carrier rocket; performing apogee / perigee orbital transfer for several times by using a self-contained liquid engine of the satellite, and transferring to a geosynchronous orbit; and correcting and rounding the inclination angle of the orbit to realize a geostationary orbit. For the satellite, operation for changing the transfer orbit into the geostationary orbit by performing apogee / perigee orbital transfer for several times is complex, so too many orbital transfer times is not suitable, and orbital transfer complexity and risk are prevented from being increased; in addition, factors such as the capacity of the liquid engine of the satellite, arc segment loss in an orbital transfer period, and the like are considered, so too few orbital transfer times is not suitable.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Solar Powered Charging Of An Electronic Device
InactiveUS20110080135A1Maximum energy transmissionBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemElectronBattery charger
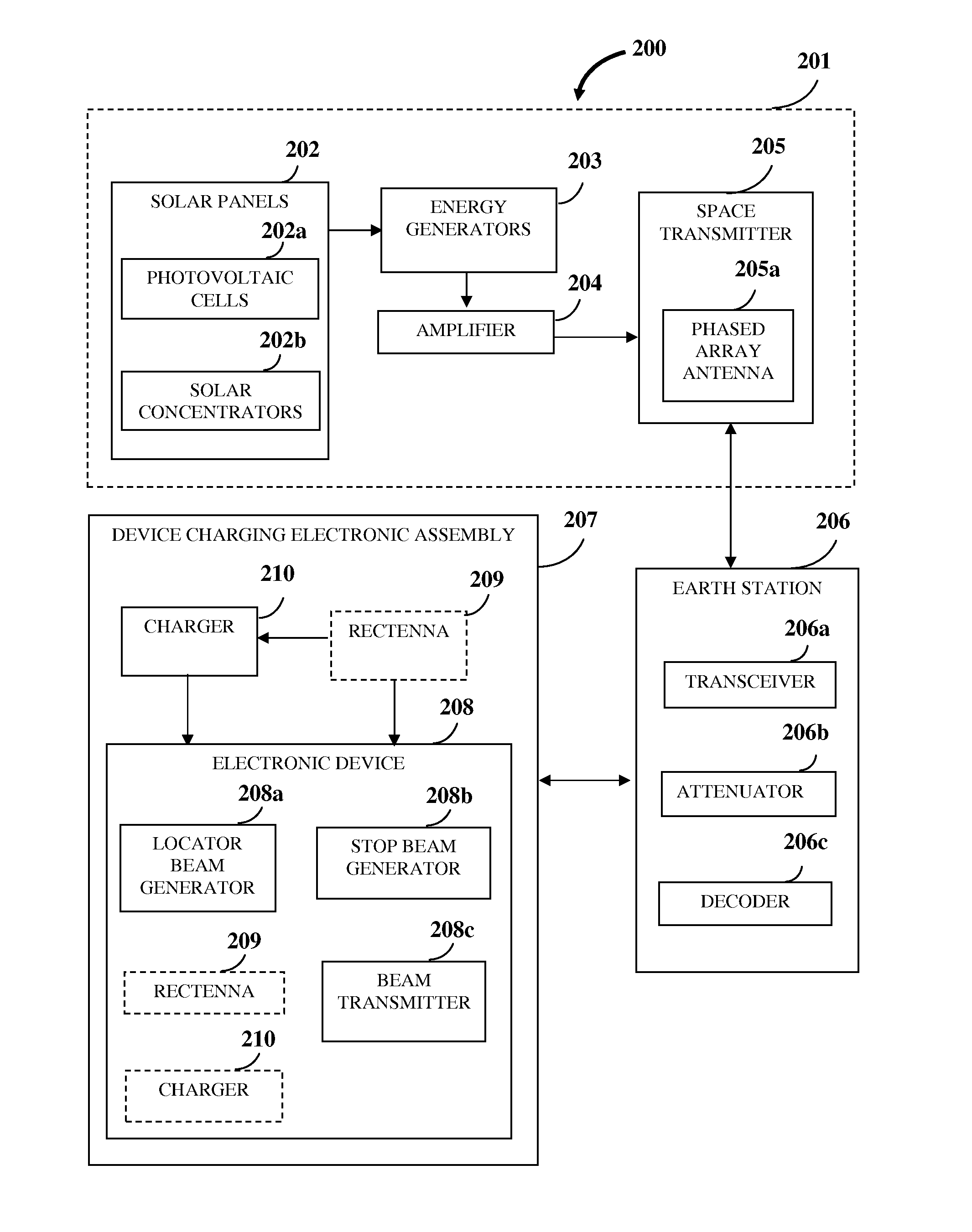
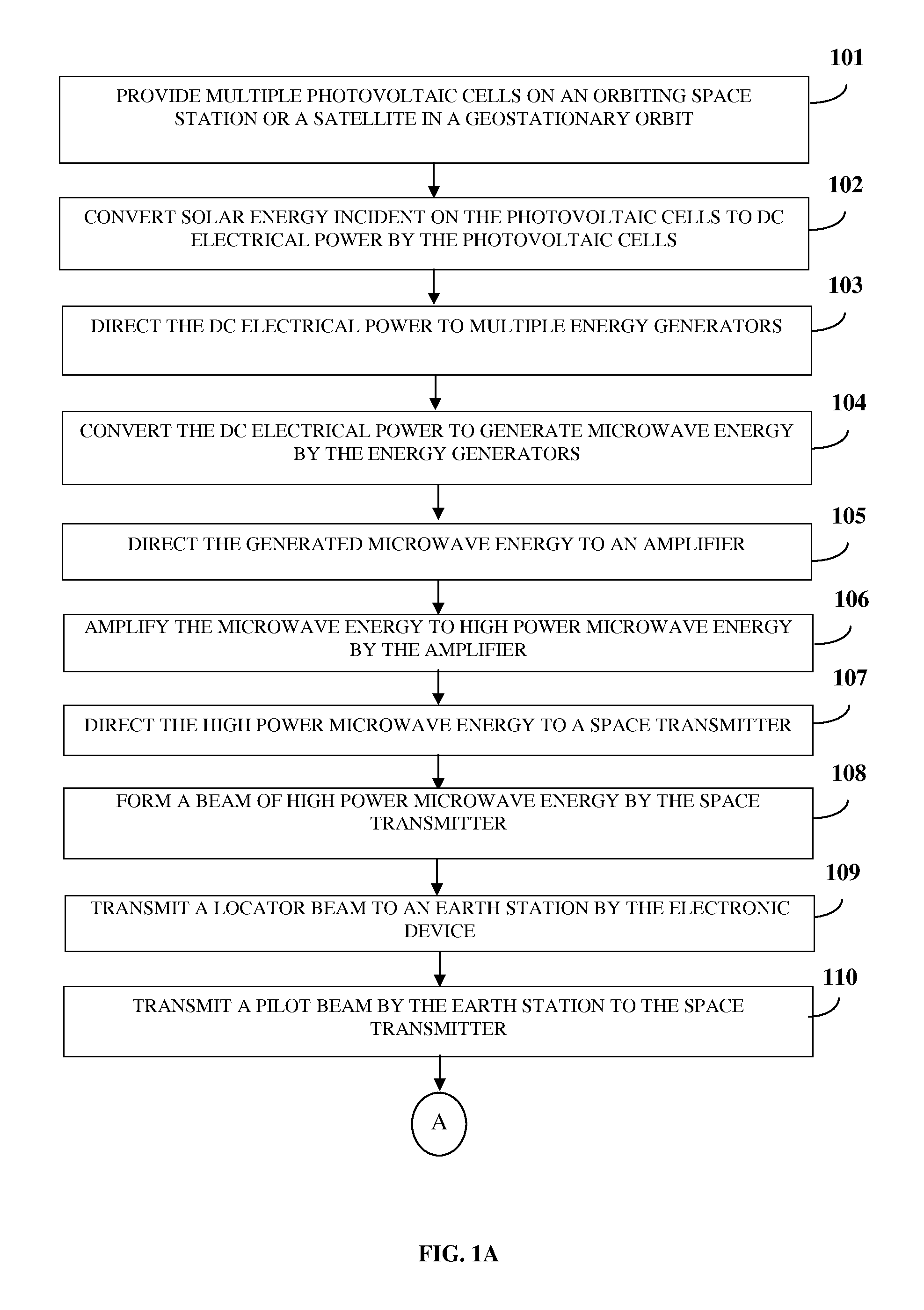
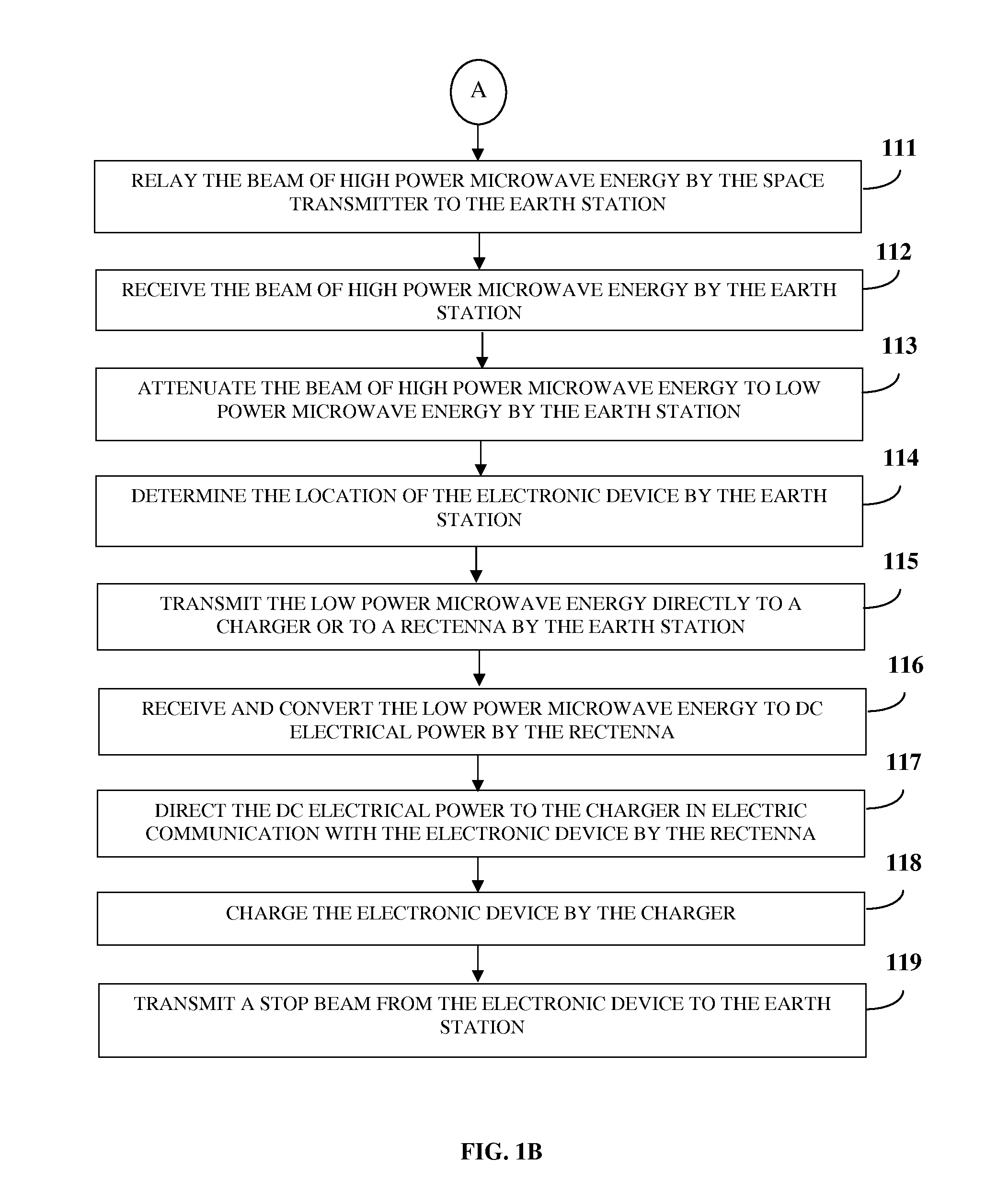
A method and system for solar powered charging of an electronic device is provided. Solar concentrators direct solar energy onto photovoltaic cells on an orbiting space station or a satellite in a geostationary orbit. The photovoltaic cells convert the solar energy to direct current (DC) electrical power. Energy generators convert the DC electrical power to generate energy waves, for example, microwaves. A space transmitter relays the energy waves to one or more earth stations. The electronic device transmits a locator beam indicating its current location. On receiving the locator beam, an earth station transmits the energy waves to the electronic device. A rectenna, in electronic communication with the electronic device, converts the energy waves to DC electrical power and directs the DC electrical power to a charger in electric communication with the electronic device. The charger receives the energy waves or the DC electrical power and charges the electronic device.
Owner:BLAND TODD ALLEN
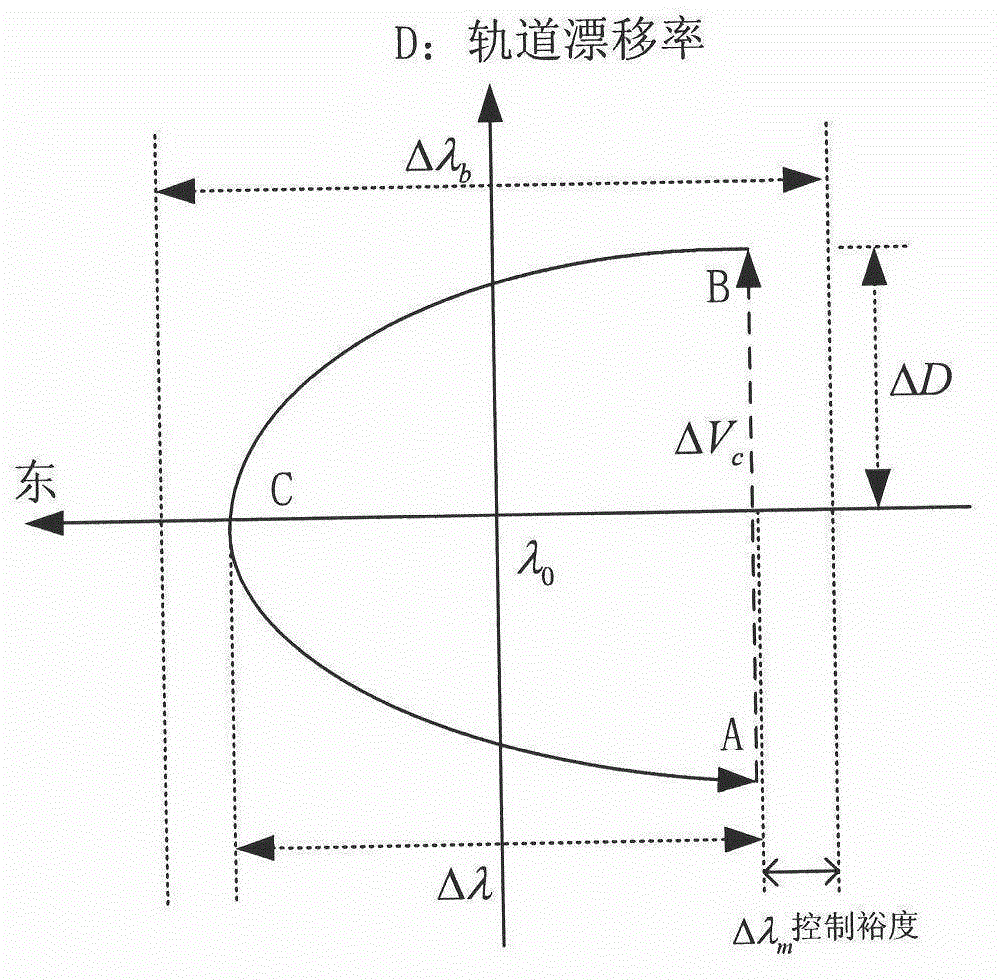
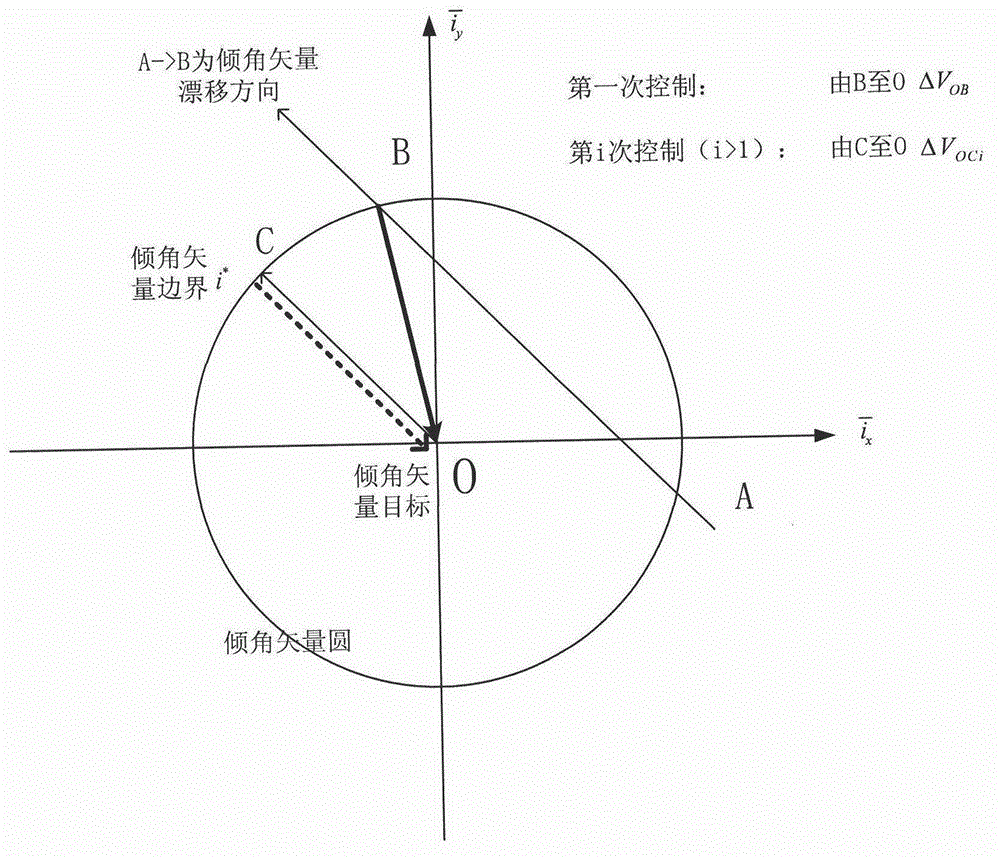
Autonomous orbit control method for stationary orbit satellite
ActiveCN102880184AStable controlReduce mistakesAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsNatural satelliteGeostationary orbit
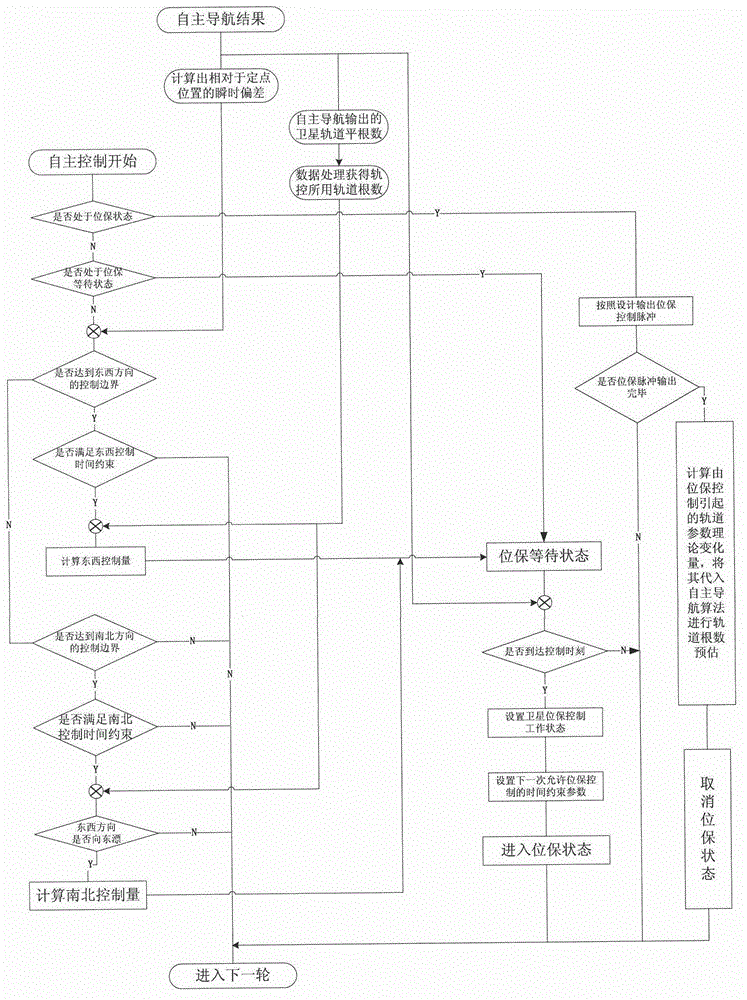
The invention relates to an autonomous orbit control method for a stationary orbit satellite, belonging to the technical field of autonomous orbit control of the satellite. The autonomous orbit control method can be applied to a long-term operation management task of the stationary orbit satellite. After the satellite goes beyond a specified error box in east-west direction or south-north direction, corresponding autonomous orbit maintenance is required to be performed; and meanwhile, by considering the regularity for drift of the satellite along a stationary orbit and error of an autonomous navigation result, the effectiveness of control quantity and the rationality of time interval between every two control processes are required to be judged at each time when the orbit control quantity of the autonomous orbit, i.e., control impulses in the south-north direction and the east-west direction which are delta VNS and delta VEW respectively, are calculated. The method has been successfully applied to china satellites; a remote sensing result shows that the autonomous control strategy of the satellite is correct; and the method can be widely applied to all geostationary orbit satellites required to have the autonomous function.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Communications system, methods and apparatus
ActiveUS7403470B2Increase data rateLow powerEnergy efficient ICTError prevention/detection by using return channelCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
An OFDM wireless communications system includes terrestrial and satellite based base stations. Mobile nodes support two uplink modes of operation, multi-tone mode for terrestrial station interaction and single tone mode for satellite base station interaction. In single tone mode the peak to average power ratio is lower than in the multi-tone mode allowing the same power amplifier to transmit higher average power signals and thus extend range and reach a satellite in geostationary orbit. In multi-tone mode, the mobile node: is temporarily assigned a multi-tone uplink traffic channel segment for user data, is assigned a dedicated control channel for uplink control signals, and supports slaved Ack / Nak for traffic channels. In single tone mode, the mobile node: is assigned a single logical uplink dedicated tone to use for transmitting both user data and control data, and does not use a slaved Ack / Nak mechanism for traffic channels.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Satellite mobile voice communication system with extra-low speed
InactiveCN102769490ALess investmentShort construction periodRadio transmissionSatellite technologyVoice communication
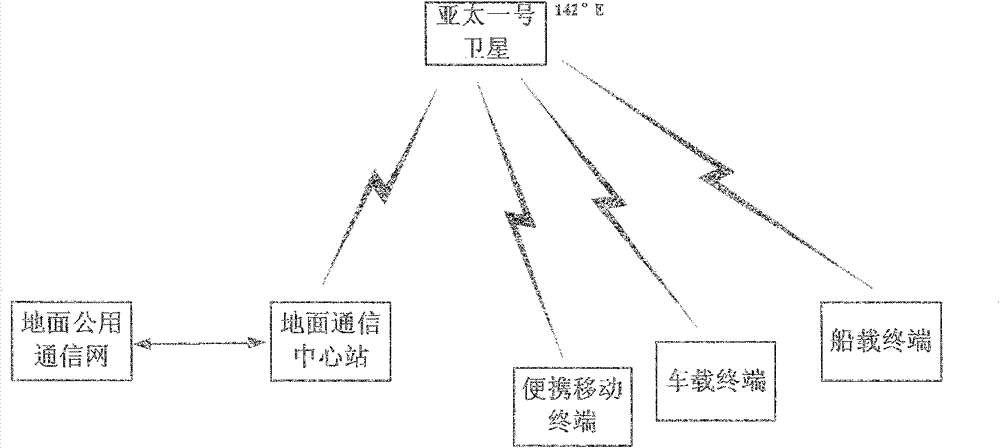
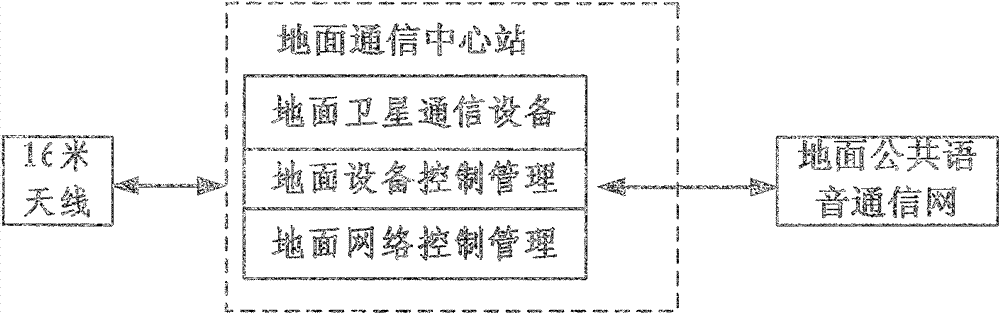
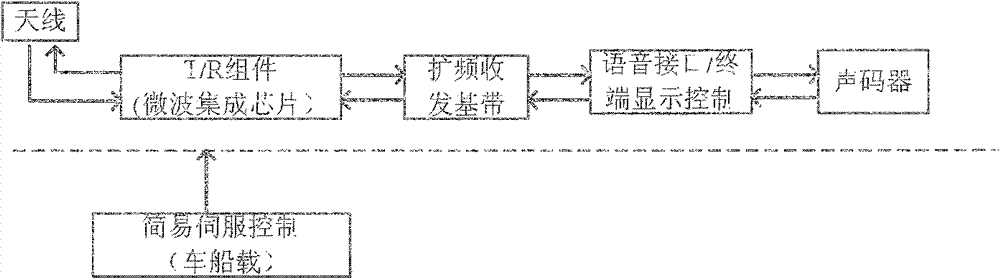
The invention discloses a satellite mobile voice communication system with an extra-low speed, and relates to the satellite technology. The satellite mobile voice communication system with the extra-low speed based on a forwarding type satellite navigation system can be built by taking advantages of GEO (geostationary orbit) communication satellite resources (or other satellite resources) in the current forwarding type satellite navigation system, adopting a speech compression coding with the extra-low speed and a ground mobile voice communication network technology, and determining a communication system, signal characteristic and a system composition of the satellite mobile voice communication through an optimized design of satellite channel, a microminiature satellite terminal and an optimized design of ground network control technology. The system provided by the invention has the advantages of system resource sharing, flexible and effective network and combined navigation and communication capability, and can provide a low-cost voice communication application service and can be applied to an air-ground emergency communication system and a measurement system with small data volume demand.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
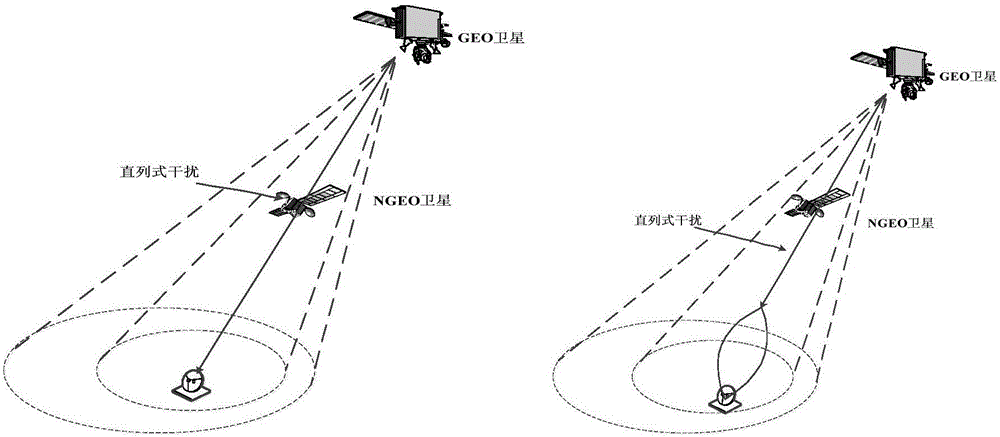
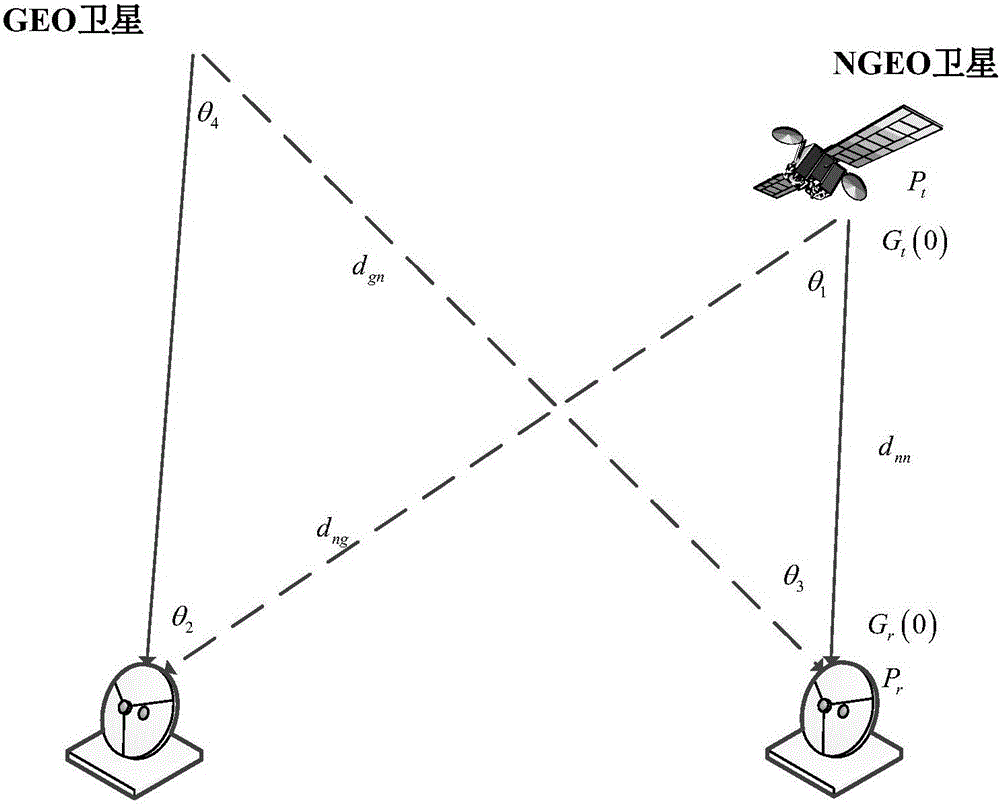
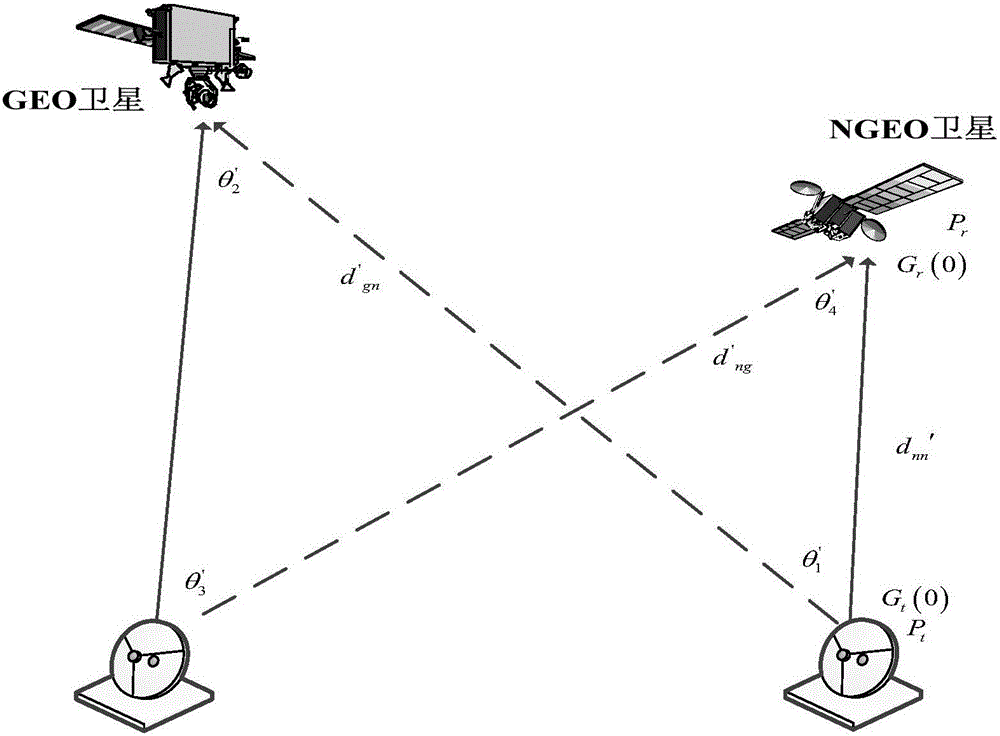
Inline interference suppression based geostationary orbit (GEO) and non-geostationary orbit (NGEO) communication satellite spectrum sharing method
ActiveCN105744531AImprove Spectrum Utilization EfficiencySolving the problem of not being able to work simultaneouslyNetwork planningPower controlGeostationary orbit
The present invention relates to an inline interference suppression based geostationary orbit (GEO) and non-geostationary orbit (NGEO) communication satellite spectrum sharing method. In the method, interference analysis is performed on GEO and NGEO satellite communication systems using the same frequency band, so as to determine inline interference constraints of the communication satellite systems in a downlink sharing frequency scene and an uplink sharing frequency scene; mathematical models of the GEO and NGEO satellites in the downlink sharing frequency scene and the uplink sharing frequency scene are established according to a power control method; and a carrier to noise ratio of an NGEO ground station and total interference of the NGEO satellite to a GEO ground station in the downlink sharing frequency scene and the uplink sharing frequency scene are calculated, and a transmitting power range of the NGEO satellite is obtained. Through adoption of the method, the spectrum use efficiency of the two satellite systems is improved, and the problem that the satellite systems cannot work simultaneously due to inline interference is solved.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Geosynchronous satellite constellation
ActiveUS20060240767A1Avoid interferenceCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsFrequency spectrumCommunications system
A satellite communications system is described for increasing capacity through spectrum reuse by multiple satellites. The system includes a constellation of satellites traveling in a geosynchronous orbit, where the geosynchronous orbit defines a satellite track. The satellite track of the constellation overlaps a geostationary orbital location occupied by a legacy satellite traveling in a geostationary orbit. To prevent interference between the co-located constellation and legacy satellite, each of the constellation satellites operates in a silent mode when traveling within an interference beam width of a ground terminal in communication with the legacy satellite. Once outside of the interference beam width, the constellation satellites return to an active mode of operation.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
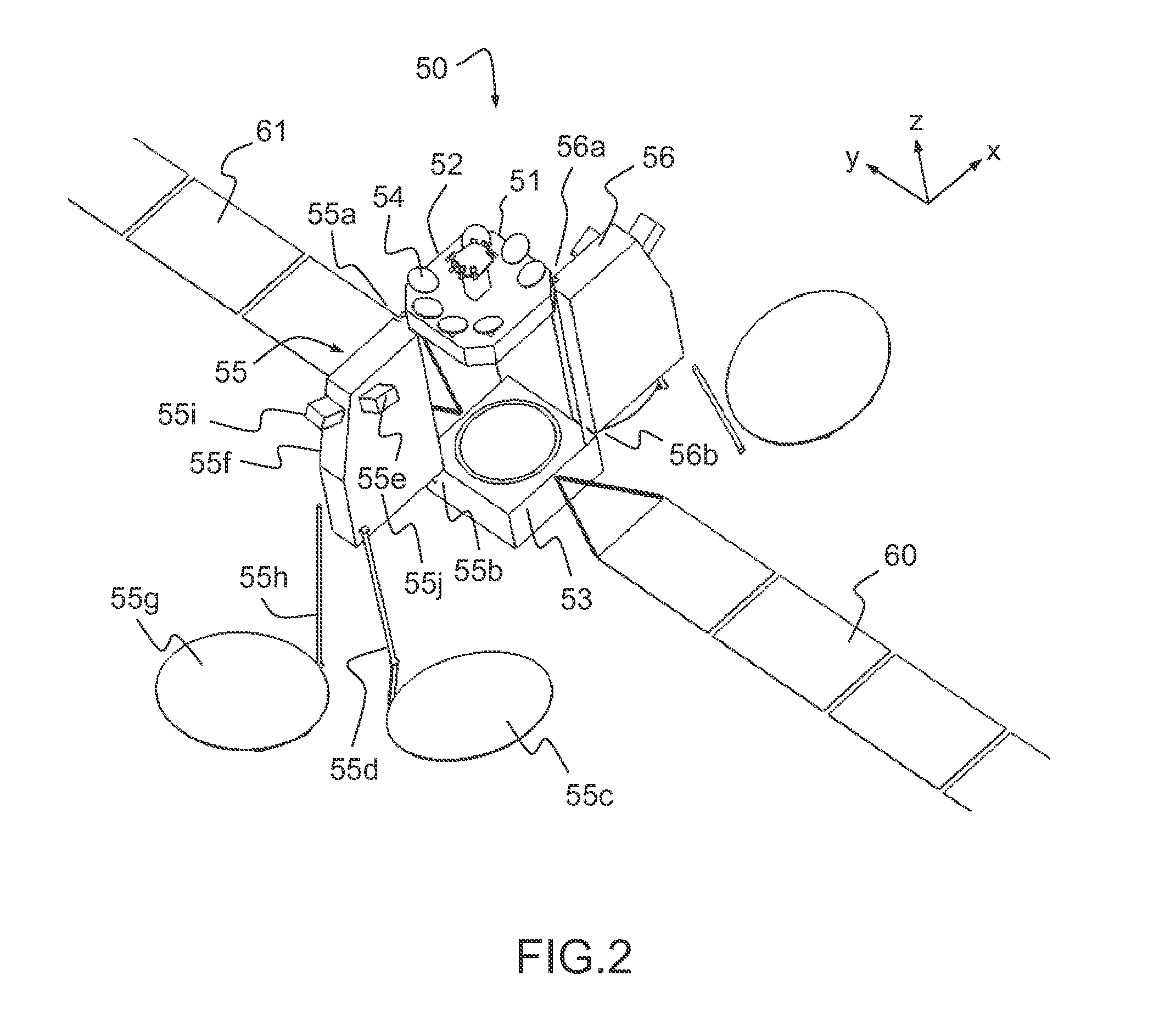
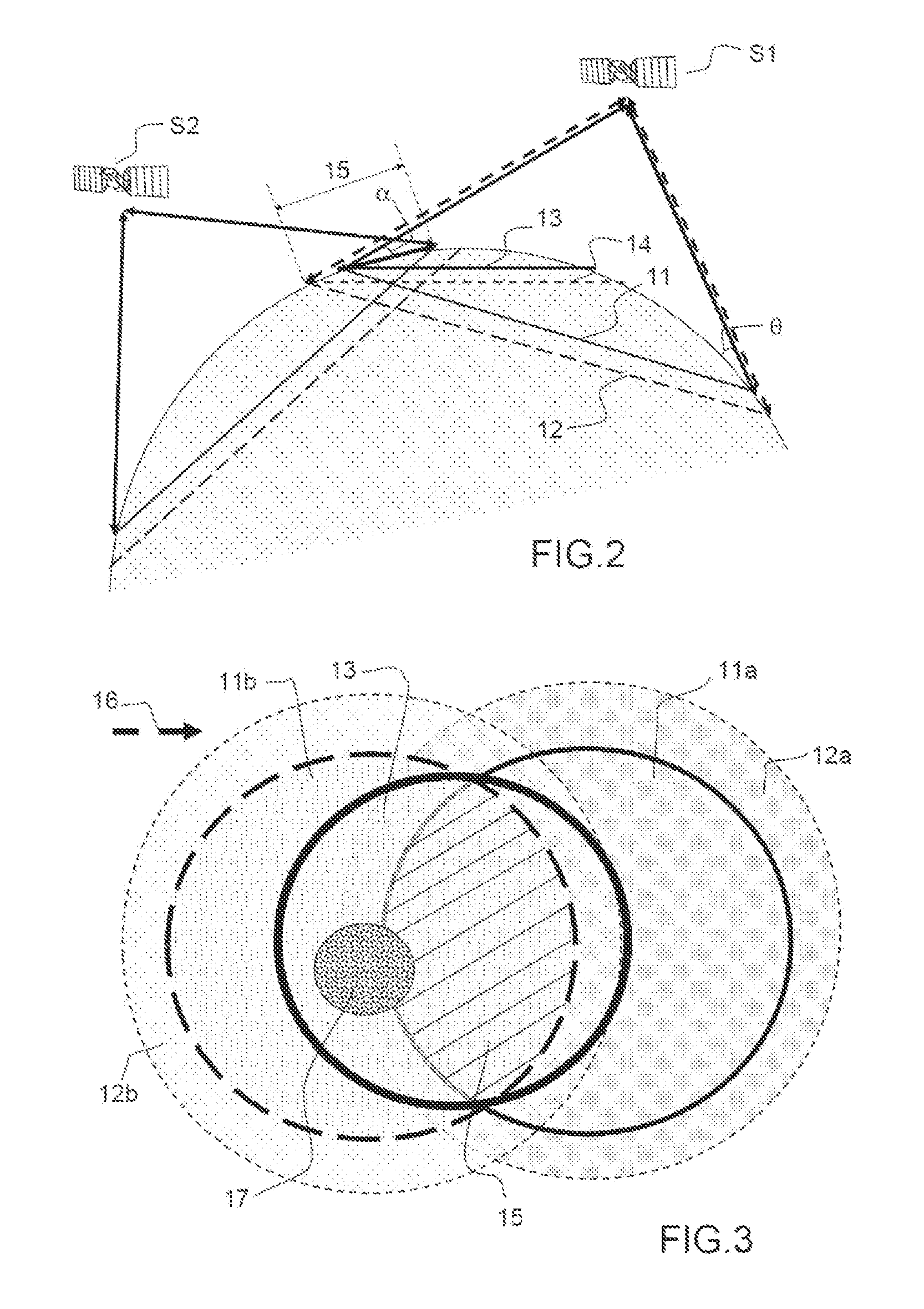
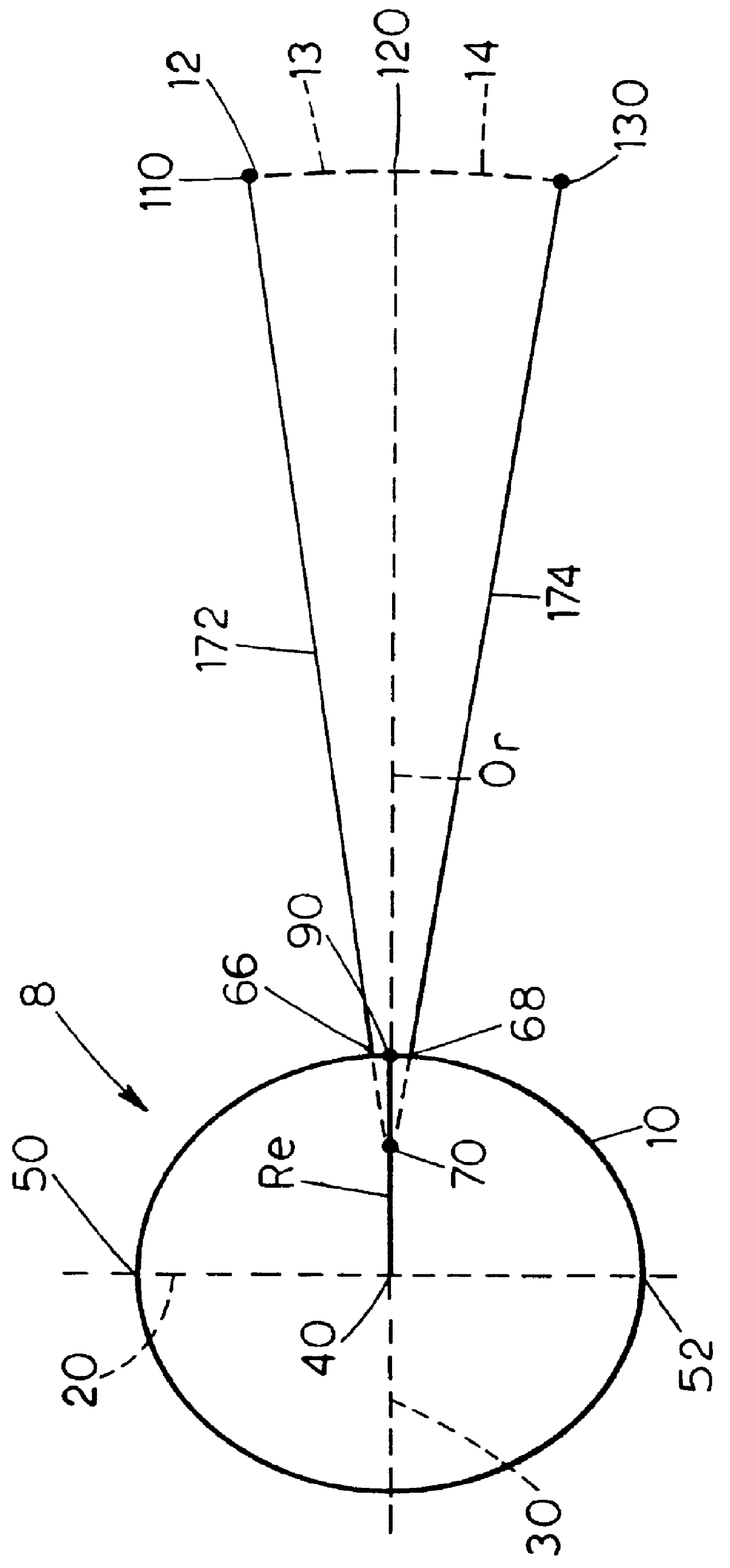
Determination method of satellite antenna pointing accuracy
A determination method of satellite antenna pointing accuracy comprises the following steps: firstly, with respect to a satellite large-scale system, determining various error sources that influence the satellite antenna pointing accuracy, wherein the error sources mainly comprise antenna characteristics, installation errors of satellite general assembly and parts, attitude control errors of a satellite system system, and satellite orbit drift; secondly, performing effect characteristic analysis of the determined various error source items, wherein the error source items are divided into constant errors, daily variable errors, short-period errors, and long-term errors; finally, calculating the rolling, pitching, yaw pointing errors of the satellite antenna on a satellite shaft, the pointing errors in the north-south and west-east directions, and the antenna pointing half cone angle errors. The method of the invention comprehensively considers various error sources and their characteristics that influence the satellite antenna pointing accuracy, can accurately provide the satellite antenna pointing accuracy, is simple in calculation, and is applicable to the engineering calculation of earth stationary orbit satellite antenna pointing accuracy.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Deployable radiator having an increased view factor
ActiveUS20130200221A1Improving thermal rejectionSimple processCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic power supply systemsGeostationary orbitView factor
A geostationary earth orbit (GEO) spacecraft is disclosed that includes a body with north, east, south, and west sides and a north-south axis. The spacecraft has at least one deployable radiator rotatably coupled to the body. The deployable radiator has a stowed position proximate to one of the east and west sides and a deployed position that is greater than 90 degrees from the north-south axis in a direction away from the respective one of the east and west sides.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
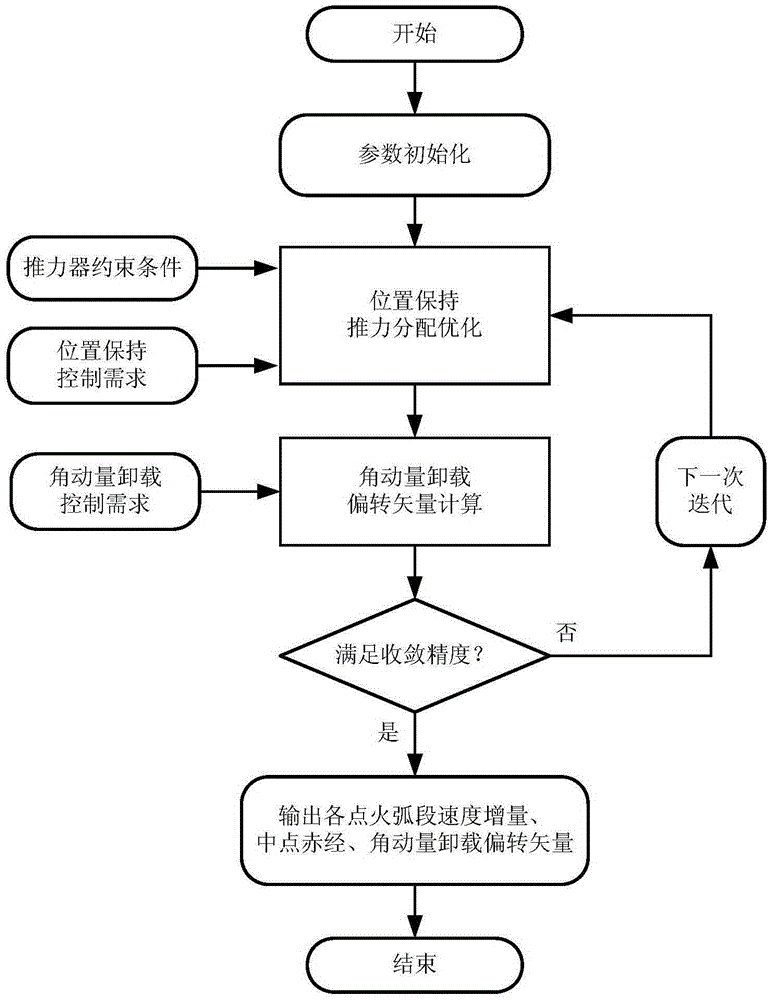
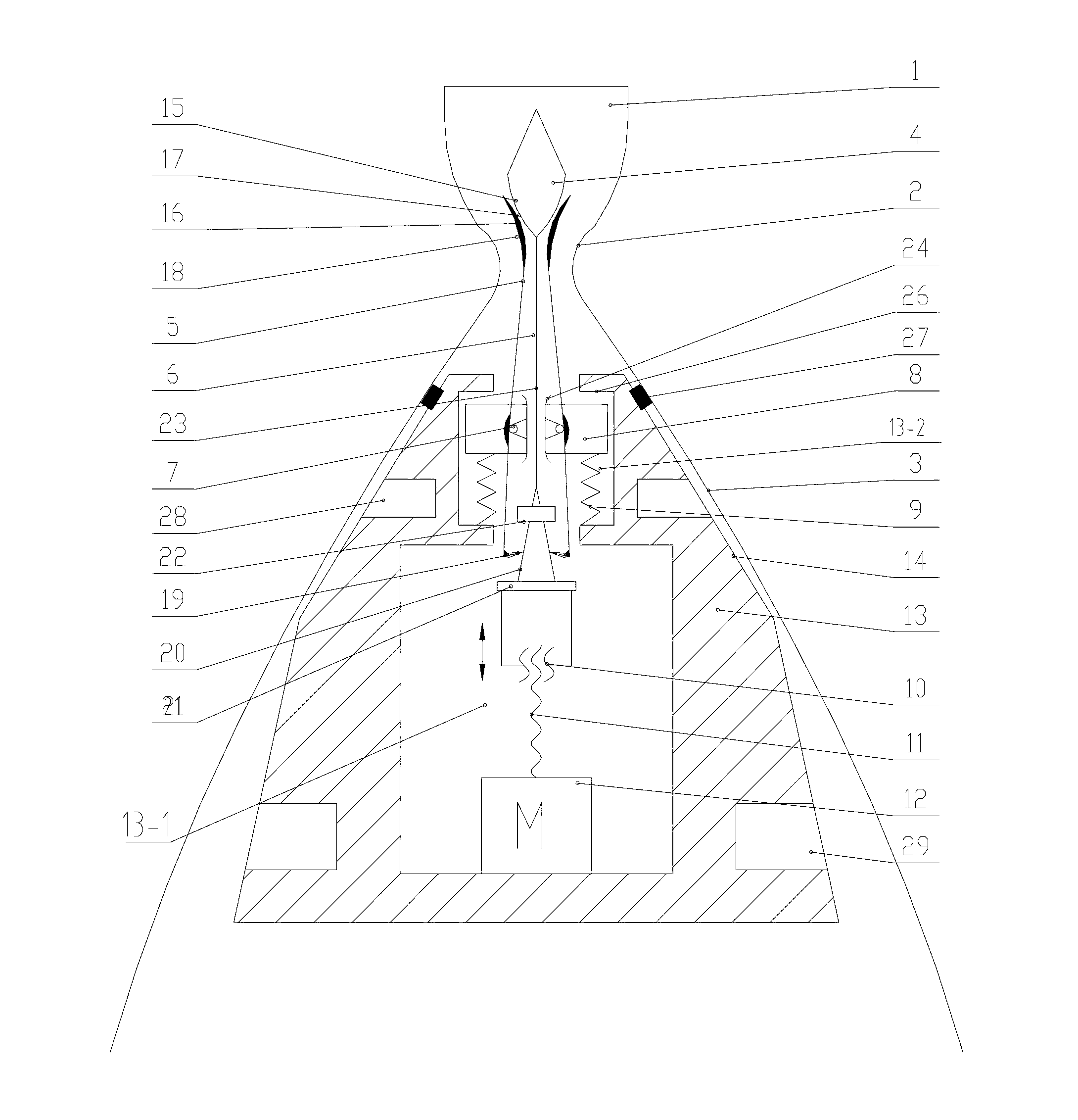
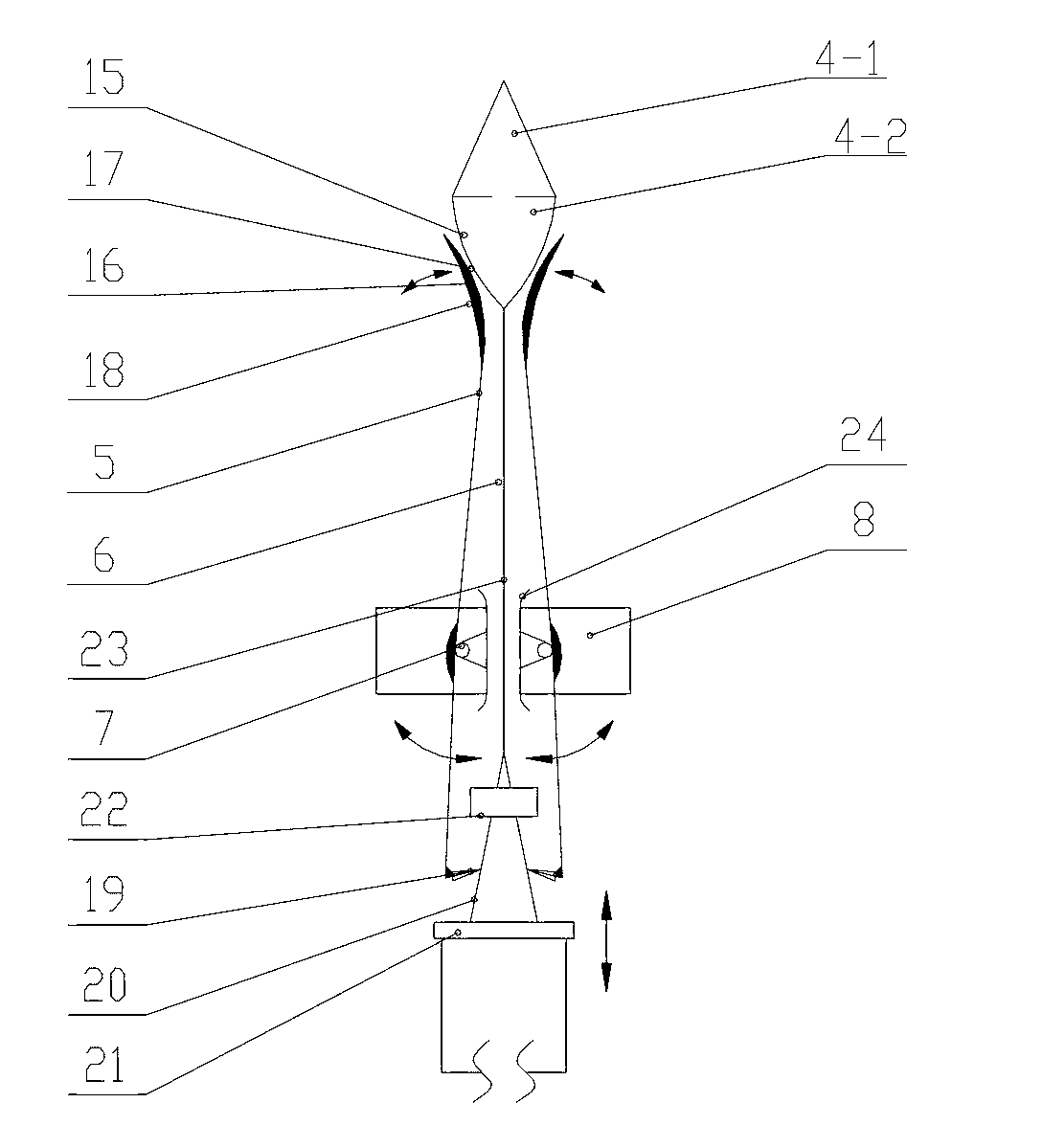
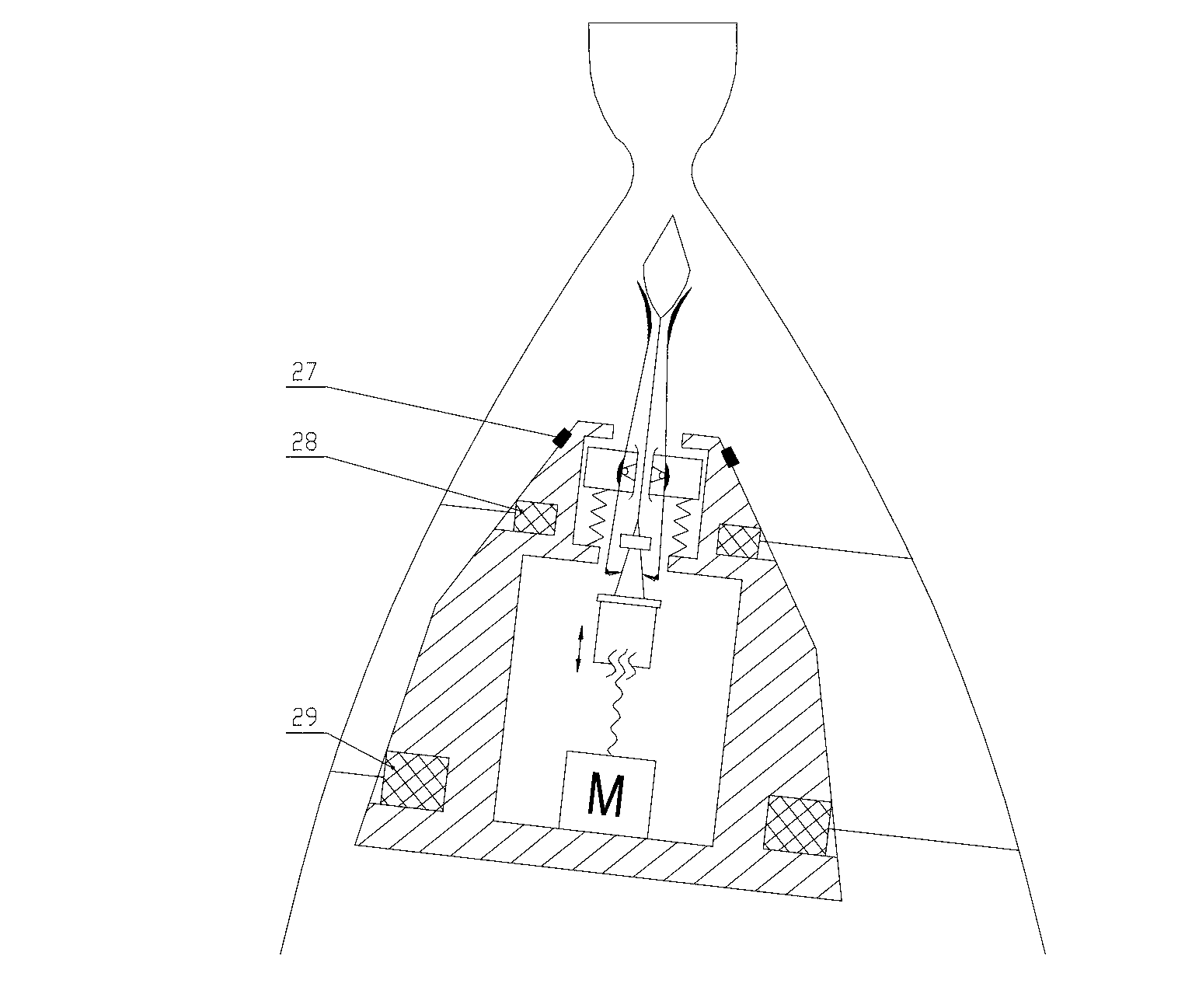
Fault mode thrust allocation method for geostationary orbit satellite electric thruster
ActiveCN105353621AOptimal satisfactionQuick and autonomous implementationAdaptive controlElectricityMomentum
The invention belongs to the field of spacecraft control, and relates to a fault mode thrust allocation method for a geostationary orbit satellite electric thruster. The method comprises the steps of firstly, determining a thrust allocation input condition, including ignition position constraint, ignition velocity increment constraint and orbit control demand; secondly, allocating and optimizing position keeping thrust, establishing an electric thruster pointing model, selecting a thruster, defining ignition parameters, and optimizing and calculating the ignition parameters; and finally, calculating an angular momentum unloading deflecting vector. Aiming at the problem of high fuel consumption in a traditional definitive solution mode, a nonlinear hybrid constraint optimization model is established, and key parameters such as time length of each thrust ignition arc, ignition position and the like are solved by taking fuel optimization as a target, so that the method can realize fuel optimization under engineering constraints.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Non-cooperative target docking mechanism with peripheral swing-rod-type expansion joint
InactiveCN102849228ASmall form factorCompact structureCosmonautic component separationGeostationary orbitMovement control
The invention relates to a non-cooperative target docking mechanism with a peripheral swing-rod-type expansion joint, which aims to solve the problems of the complex structure, large size, heavy weight, and limitation on the application in the missions of 'GEO (geostationary orbit) protection' and 'in-orbit maintenance' of the present non-cooperative target docking mechanism. The mechanism realizes the rotation around a rotary shaft via the contact and the interaction of a swing rod, a slide surface and a conical inclined surface to finish the expansion and folding functions of a swing rod and realize docking and docking unlocking. An expansion mechanism is used for docking a throat structure of the inner surface of a spray tube, and after the swing rod is expanded, the docking rigidity is ensured by virtue of the compression surfaces of a locking slider and a shell, thereby realizing a docking function. The mechanism performs stepping by virtue of the expansion of the swing rod caused by a return spring and the locking movement of the locking slider, so that the control on the locking movement is simple. The mechanism disclosed by the invention is used for the field of aeronautics and astronautics.
Owner:黄刚
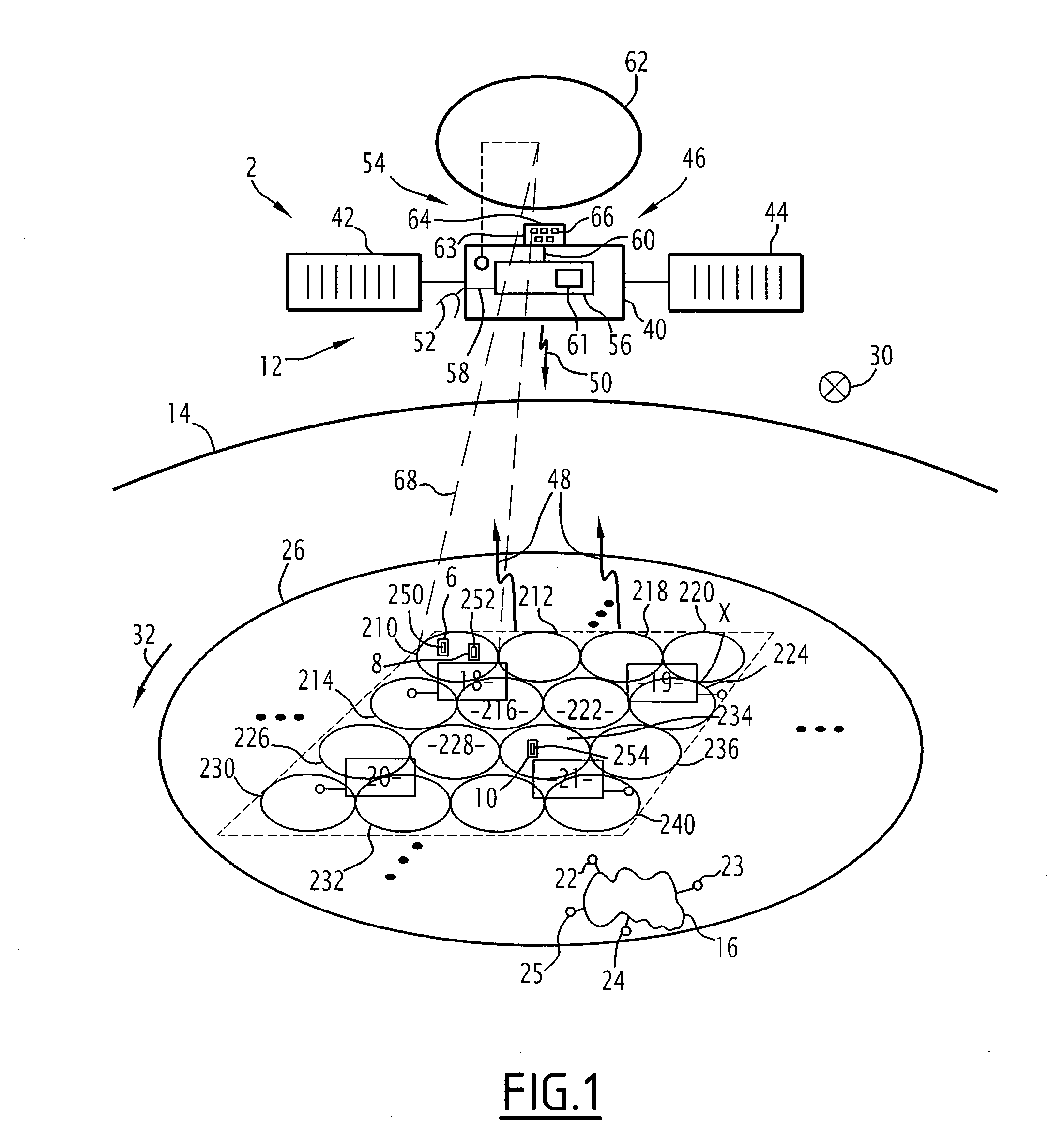
Direct broadcast satellite imaging system and method providing real-time, continuous monitoring of earth from grostationary earth orbit
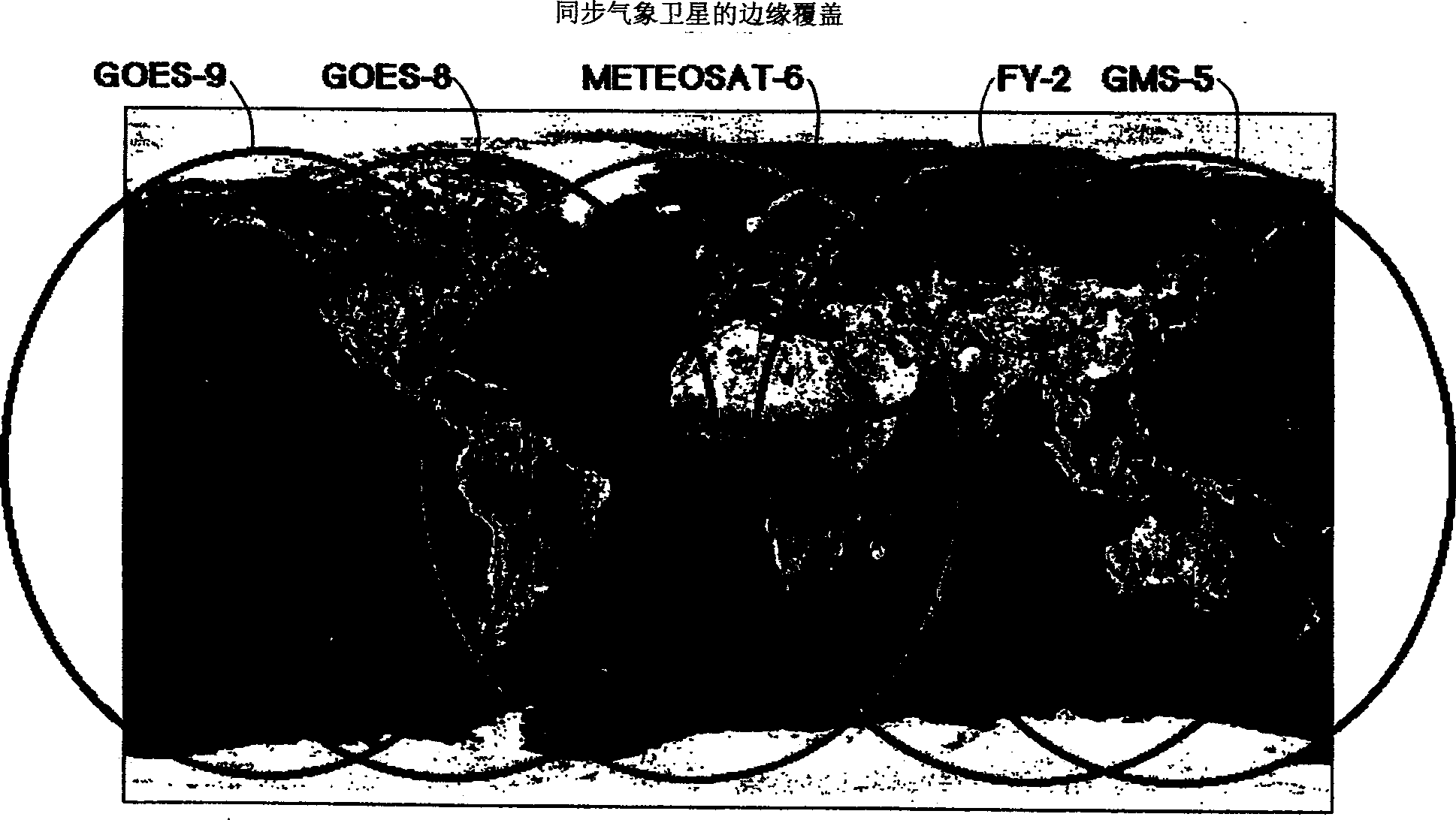
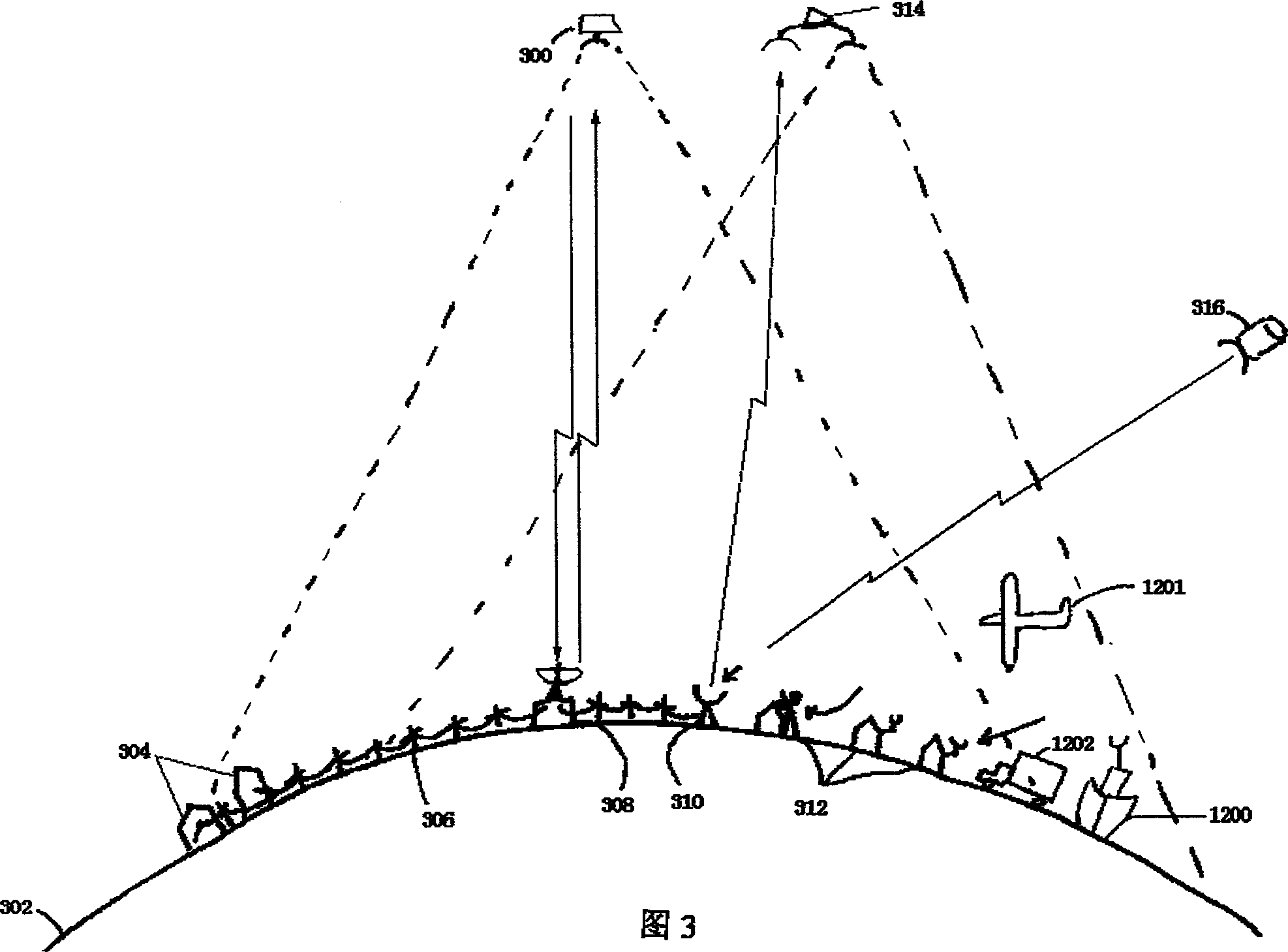
A system, method and apparatus for collecting and distributing real-time, high resolution images of the Earth (302) from GEO include an electro-optical sensor based on multimegapixel two-dimensional charge coupled device (CCD) arrays mounted on a geostationary platform. At least four, three-axis stabilized satellites (300, 314) in Geostationary Earth orbit (GEO) provide worldwide coverage, excluding the poles. Image data that is collected at approximately 1 frame / sec, is broadcast over high-capacity communication links (306) (roughly 15 MHz bandwidth) providing real-time global coverage of the Earth at sub-kilometer resolutions directly to end users. This data may be distributed globally from each satellite through a system of space and ground telecommunication links. Each satellite carries at least two electro-optical imaging systems that operate at visible wavelengths so as to provide uninterrupted views of the Earth's full disk and coverage at sub-kilometer spatial resolutions of most or selected portions of the Earth's surface.
Owner:ASTROVISION INT
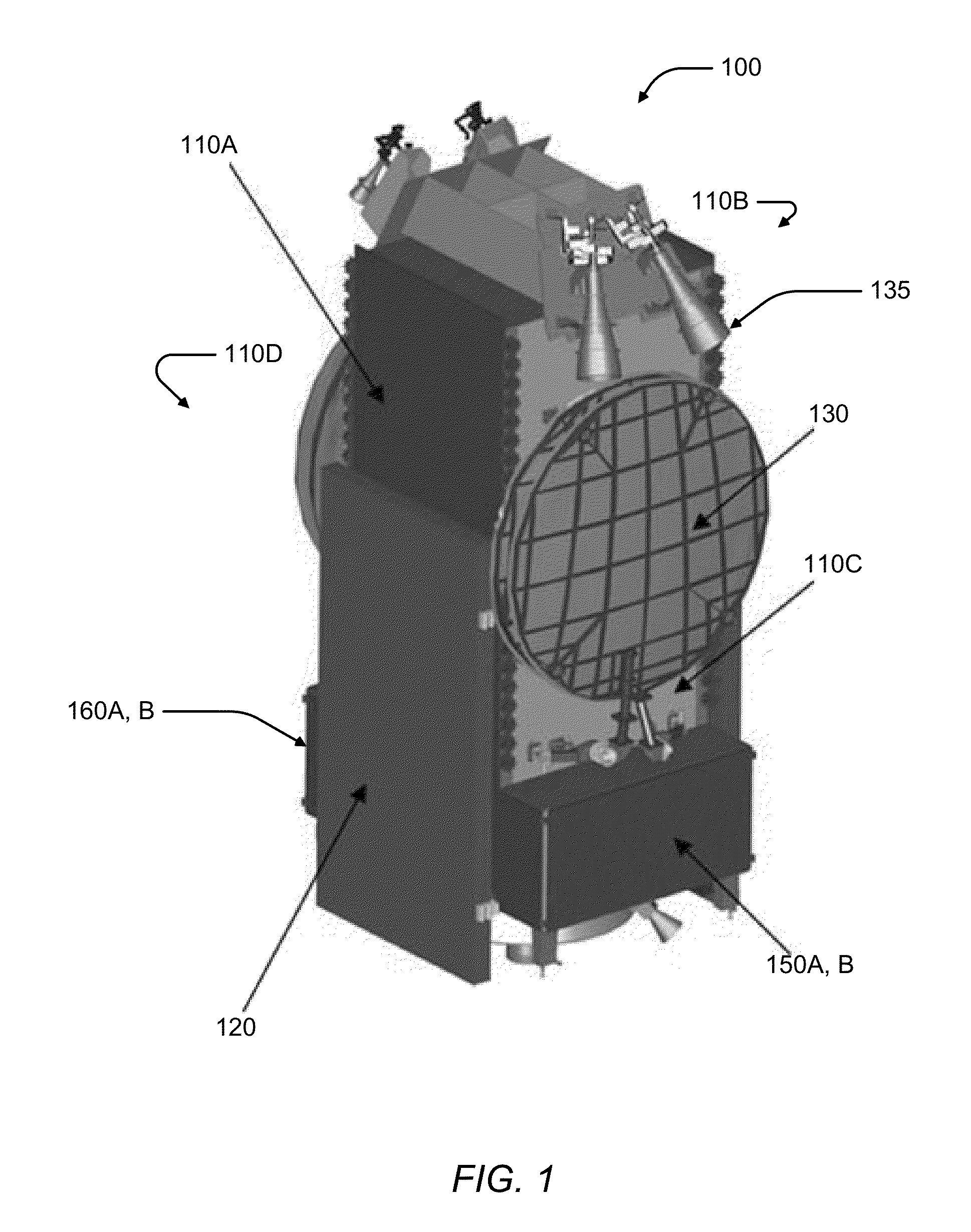
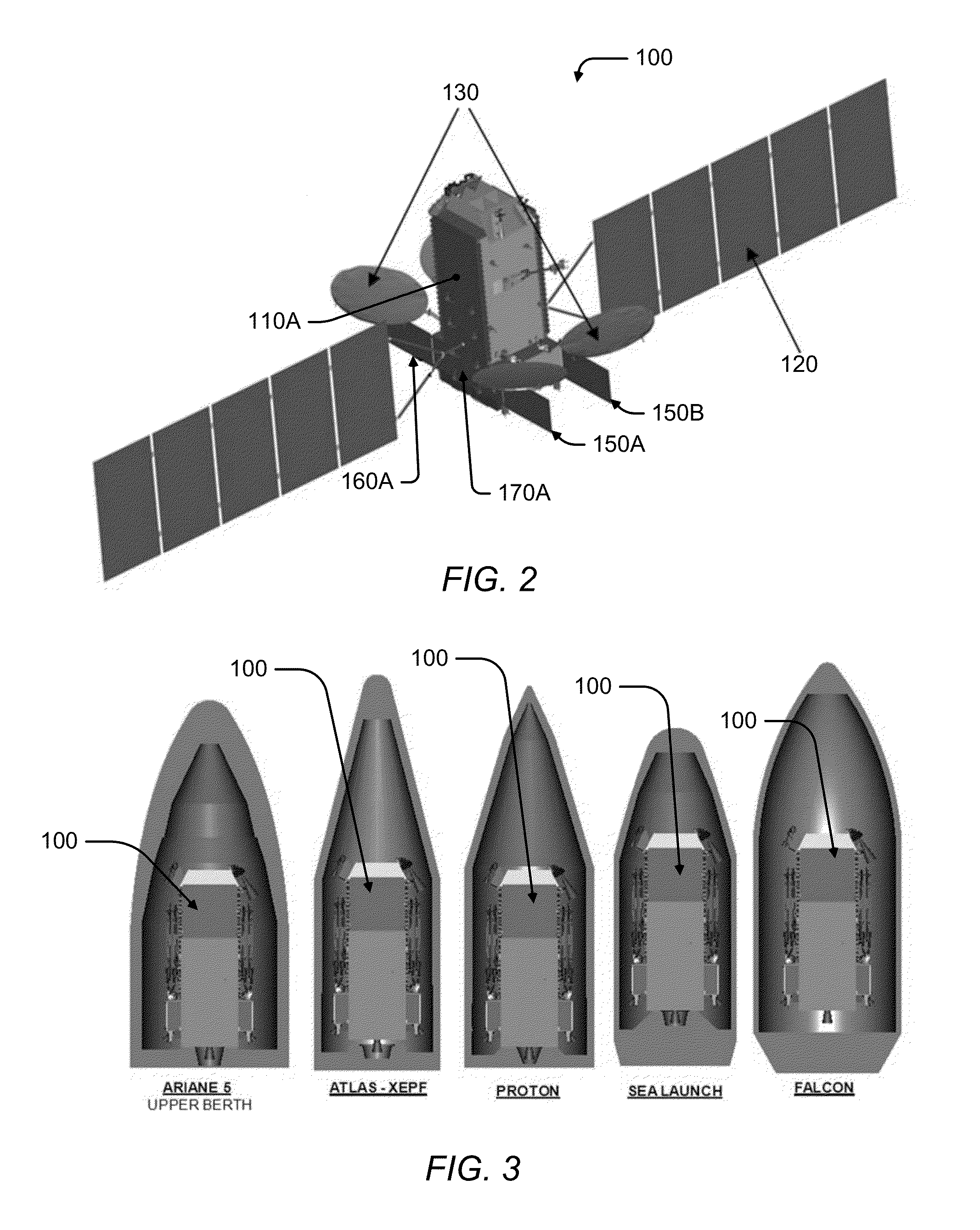
Satellite with deployable payload modules
ActiveUS20140097981A1Increase capacityIncrease heatCosmonautic radiation protectionCosmonautic power supply systemsGeostationary orbitEngineering
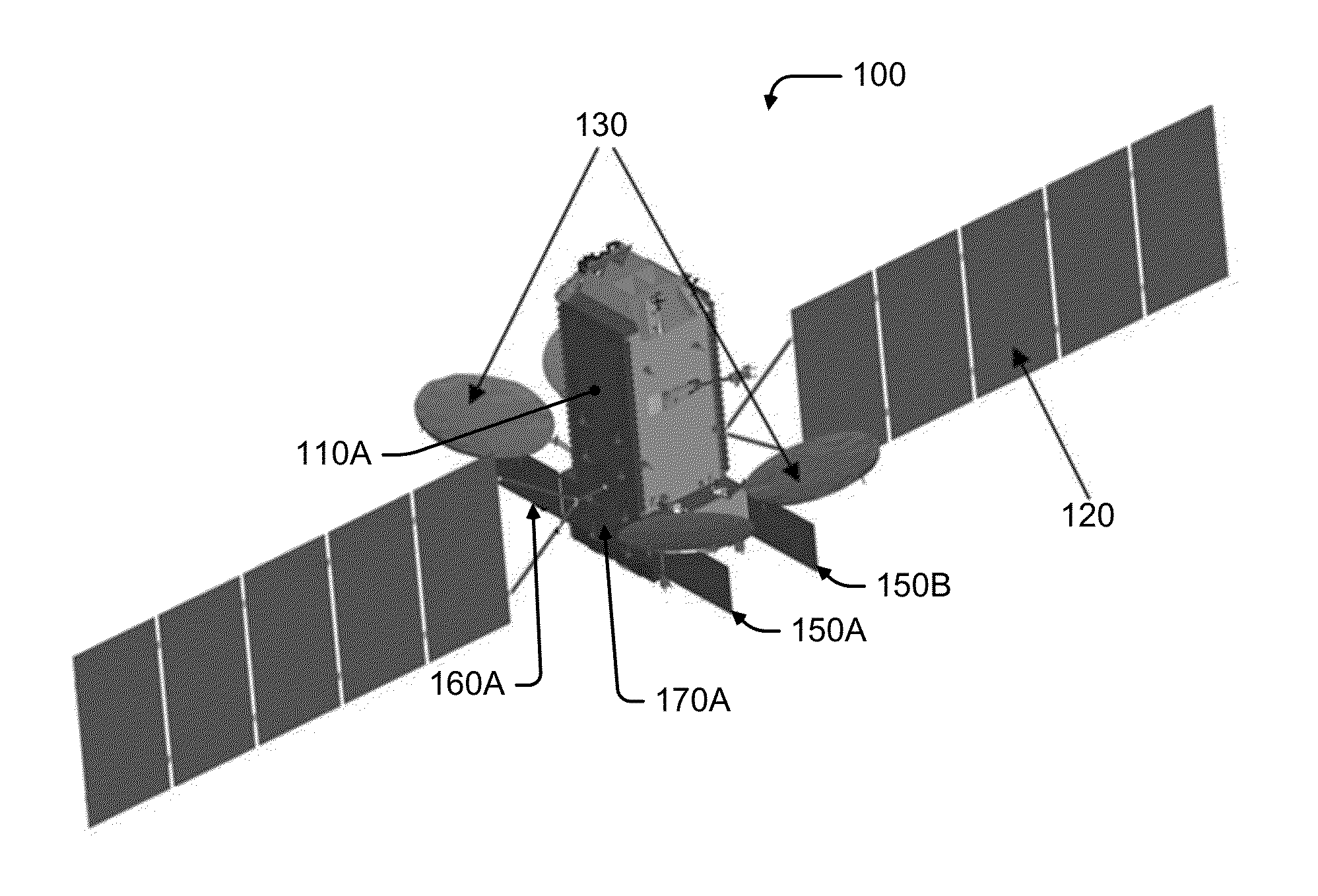
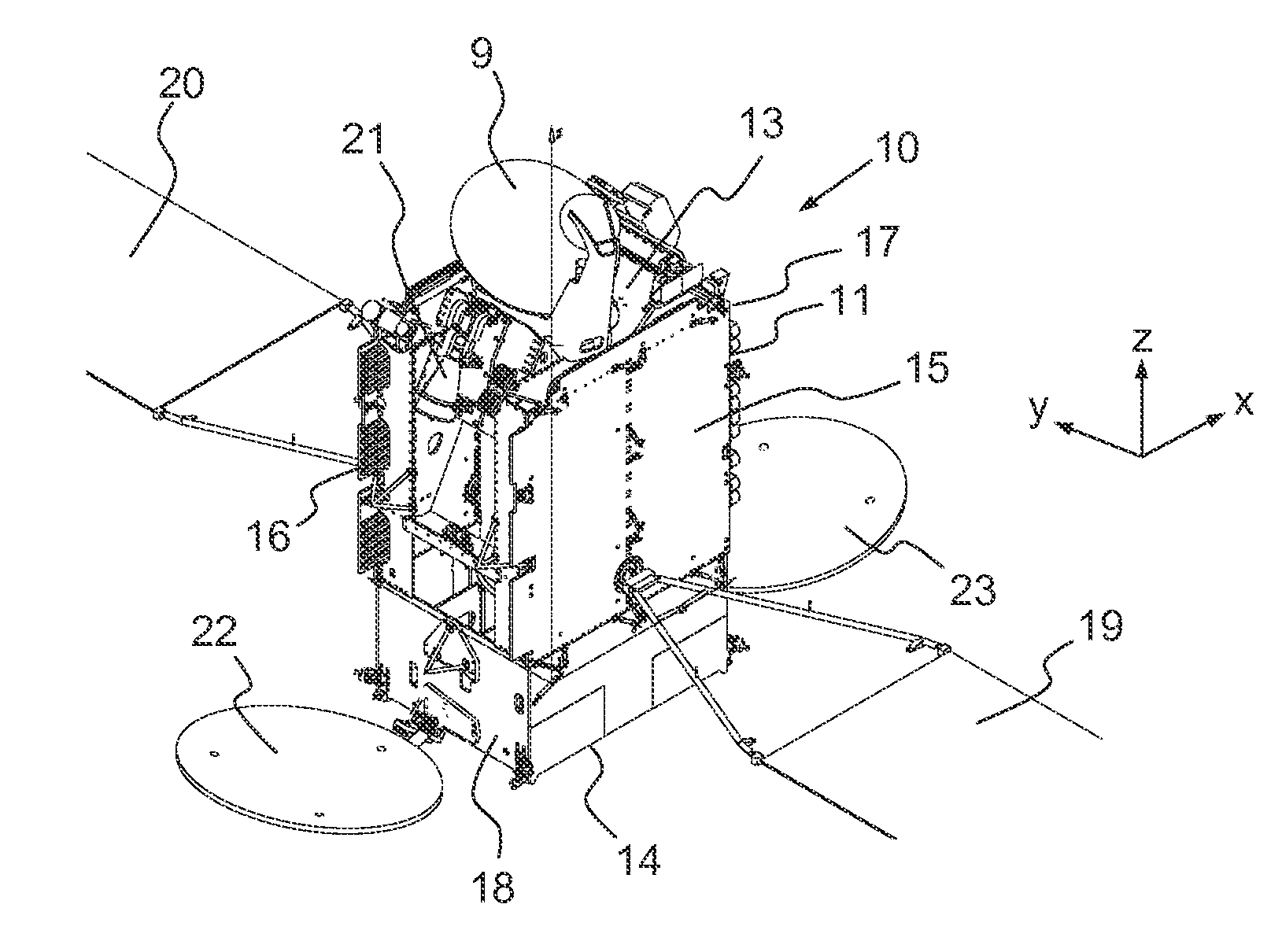
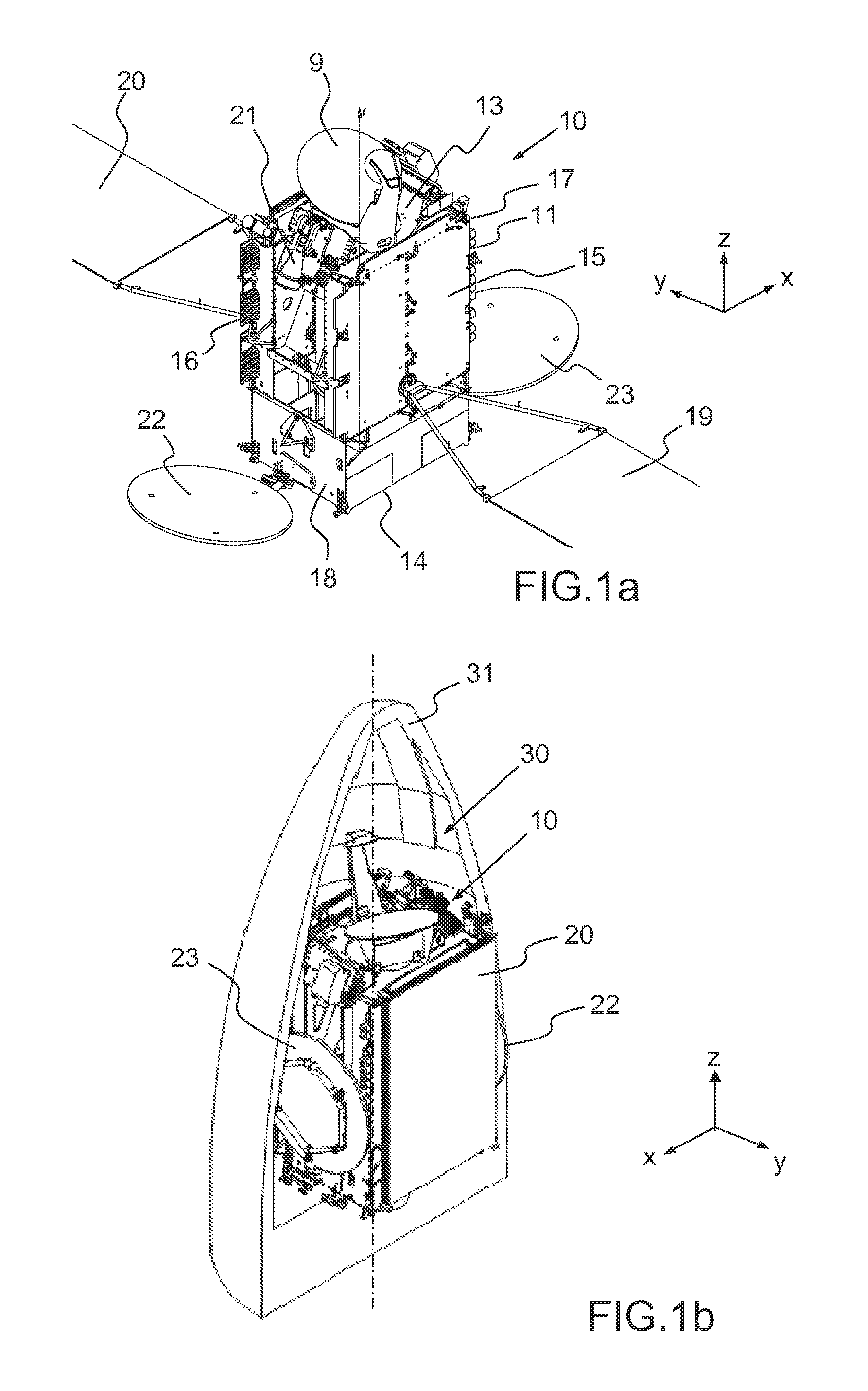
A telecommunication satellite with geostationary orbit comprises an upper module, a lower module, and a lateral module, disposed in a storage configuration between the upper module and the lower module, and deployed to an operational configuration of the satellite in the orbit by a rotation in relation to an axis Z oriented towards the earth in the operational configuration. The lateral module comprises two substantially plane and mutually parallel main surfaces, termed dissipative surfaces, able to dissipate by radiation a quantity of heat generated by facilities of the satellite; the dissipative surfaces being, in the operational configuration, held in a manner substantially parallel to the plane of the orbit, making it possible to limit the solar flux received by the dissipative surfaces and to optimize the quantity of heat dissipated by the lateral module.
Owner:THALES SA
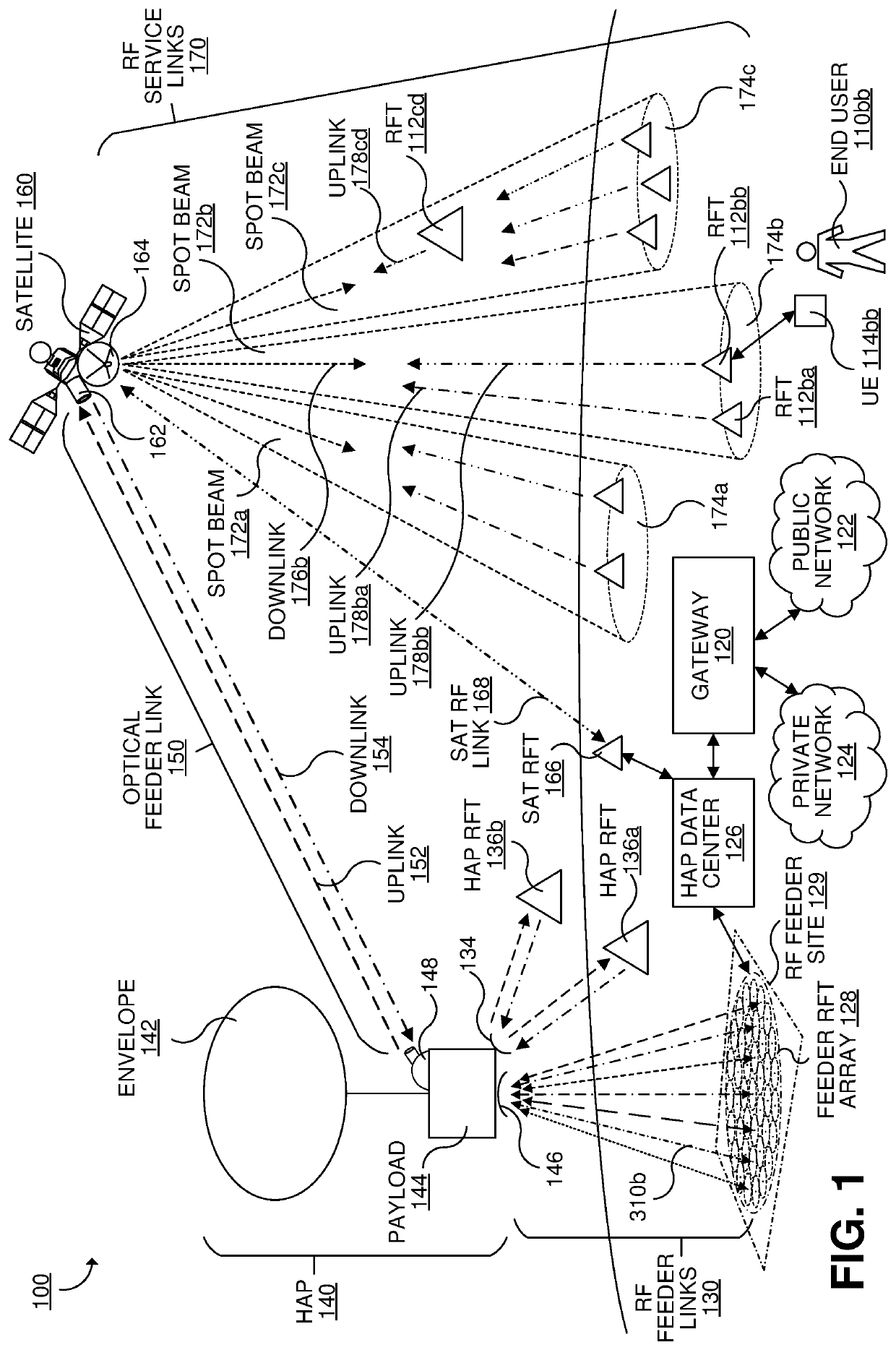
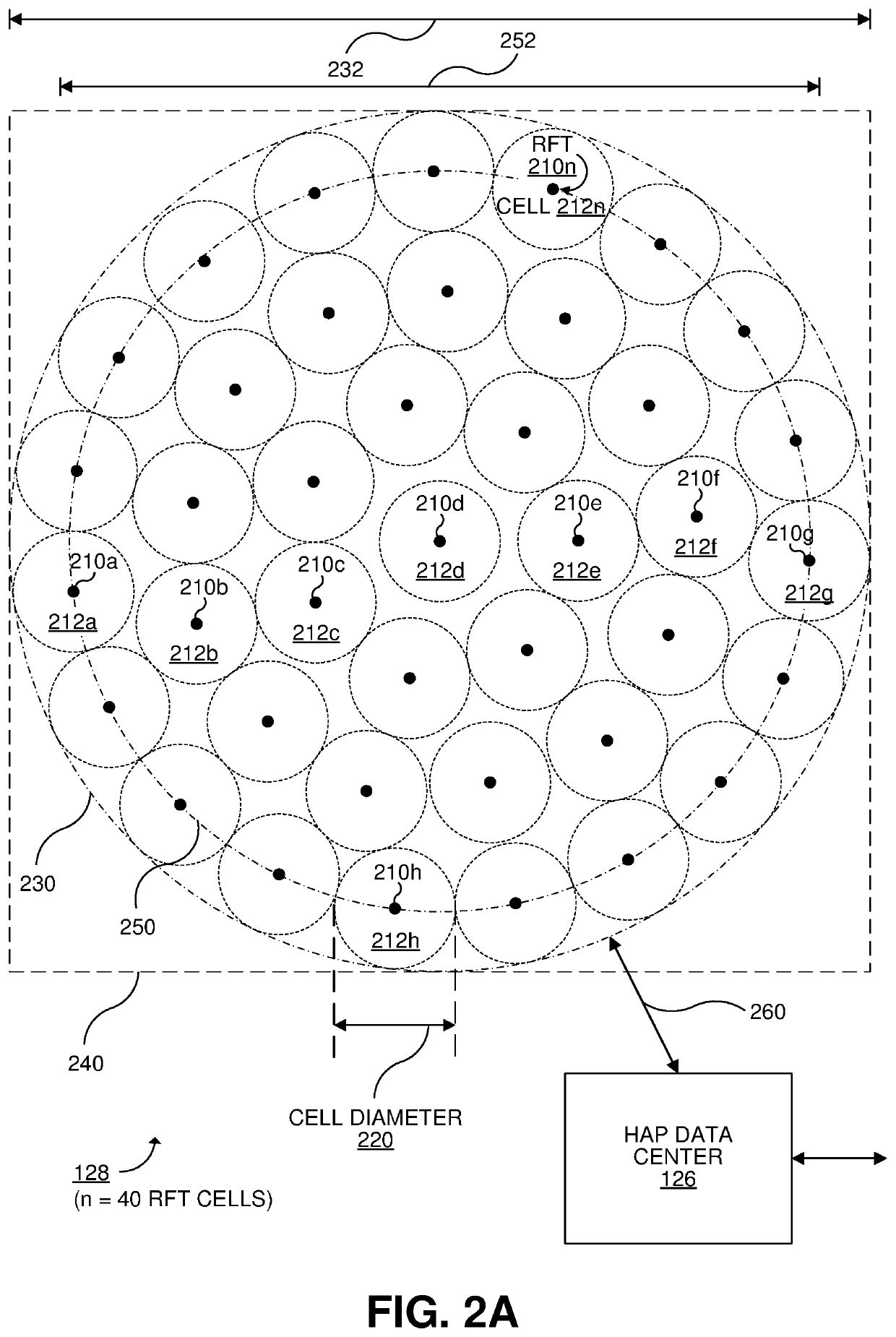
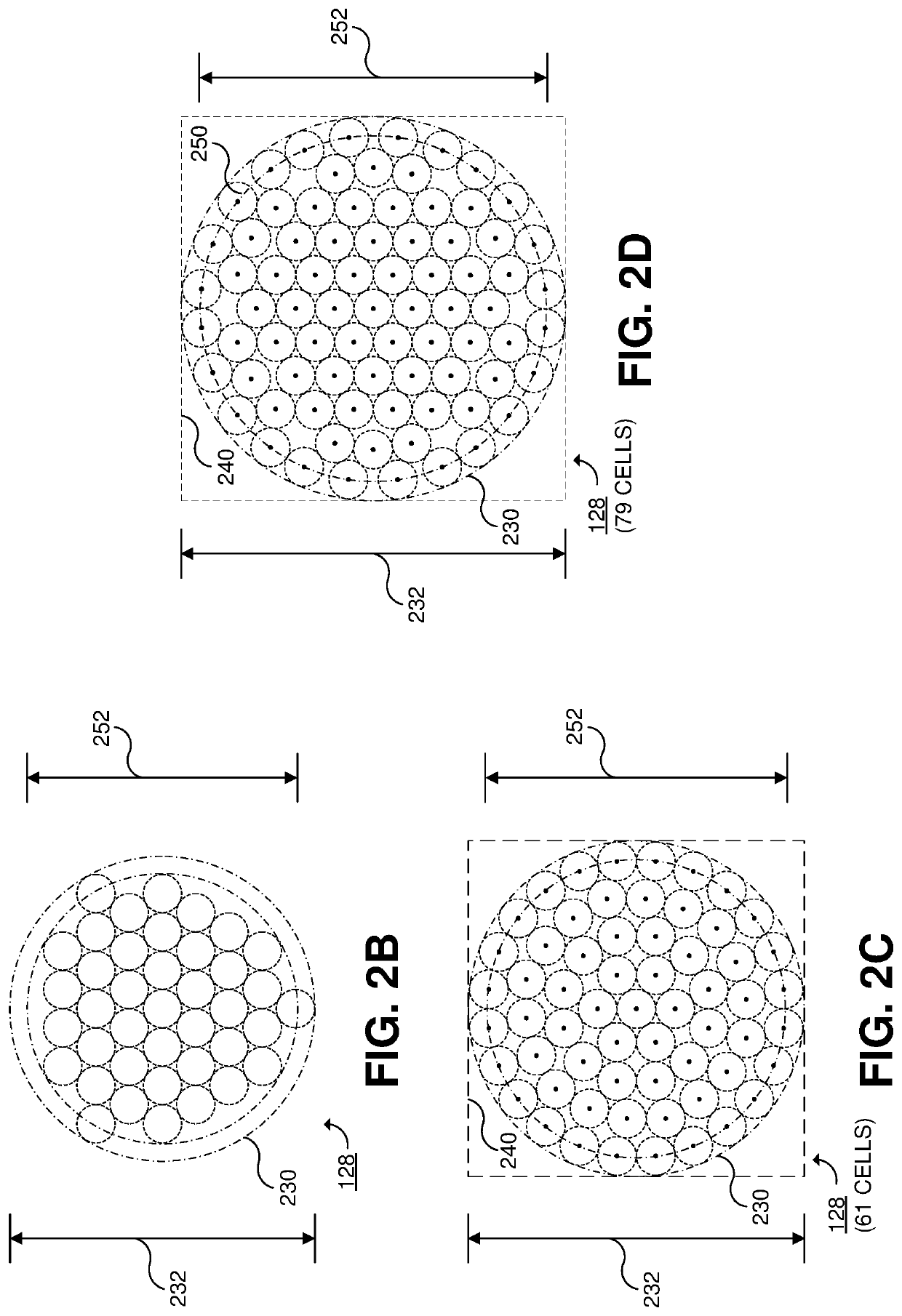
Systems and methods for high-altitude radio/optical hybrid platform
ActiveUS20200119811A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsActive radio relay systemsGeostationary orbitRadio frequency
Techniques for data transmission including receiving, at a geostationary earth orbiting satellite, forward-direction user data via a forward optical link; transmitting, by the geostationary earth orbiting satellite via multiple radio frequency (RF) spot beams, the forward-direction user data received via the forward optical link; receiving, at a stratospheric high-altitude communication device, forward-direction user data via multiple concurrent forward RF feeder links; transmitting, by the stratospheric high-altitude communication device via the forward optical link, the forward-direction user data received via the forward RF feeder links; transmitting, by each of multiple ground-based feeder RF terminals at a same RF feeder site, a respective one of the forward RF feeder links. At least 95% of forward feeder data throughput for all of the forward RF service link transmissions by the satellite is carried via the forward optical link and the forward RF feeder links.
Owner:HUGHES NETWORK SYST
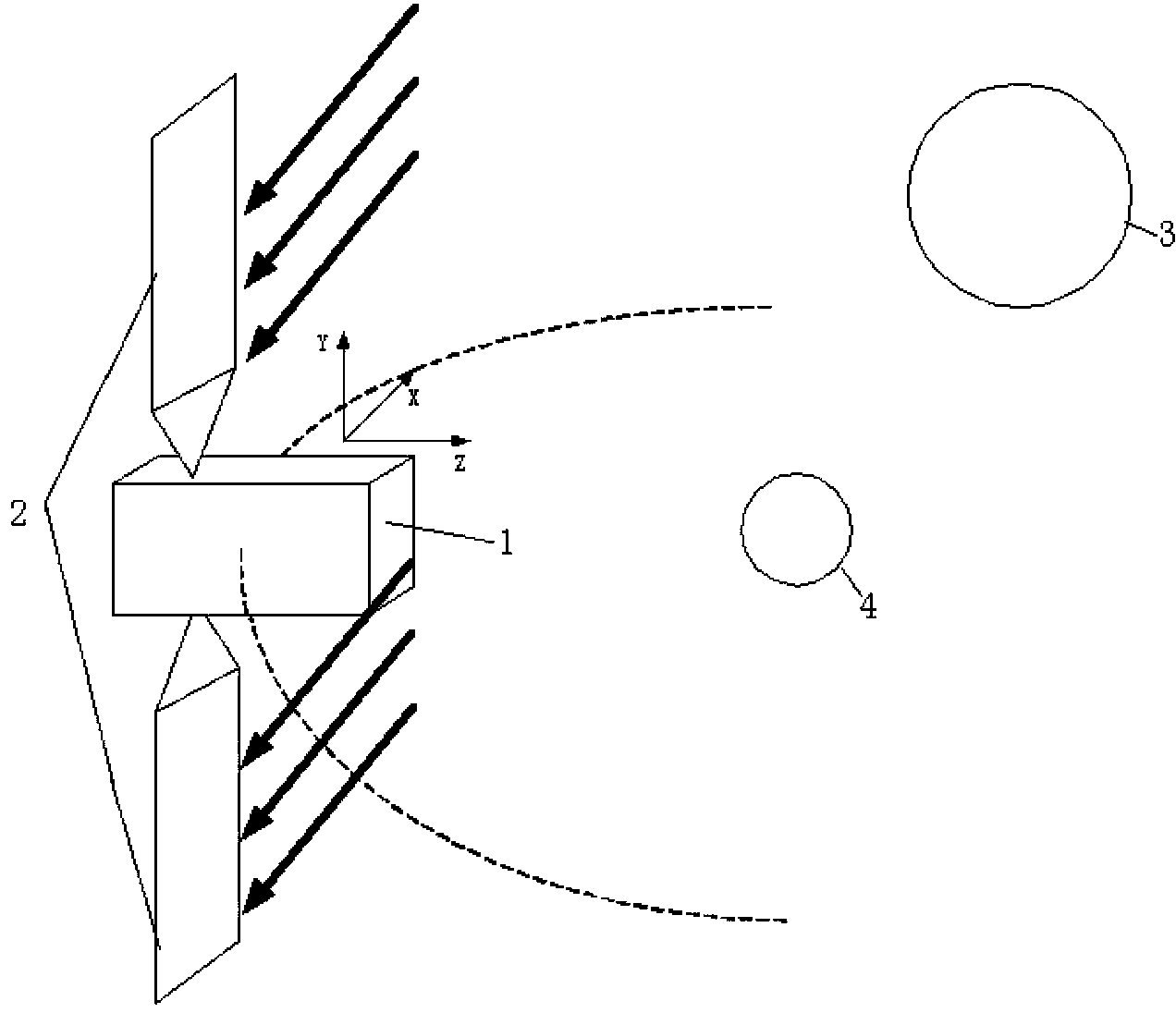
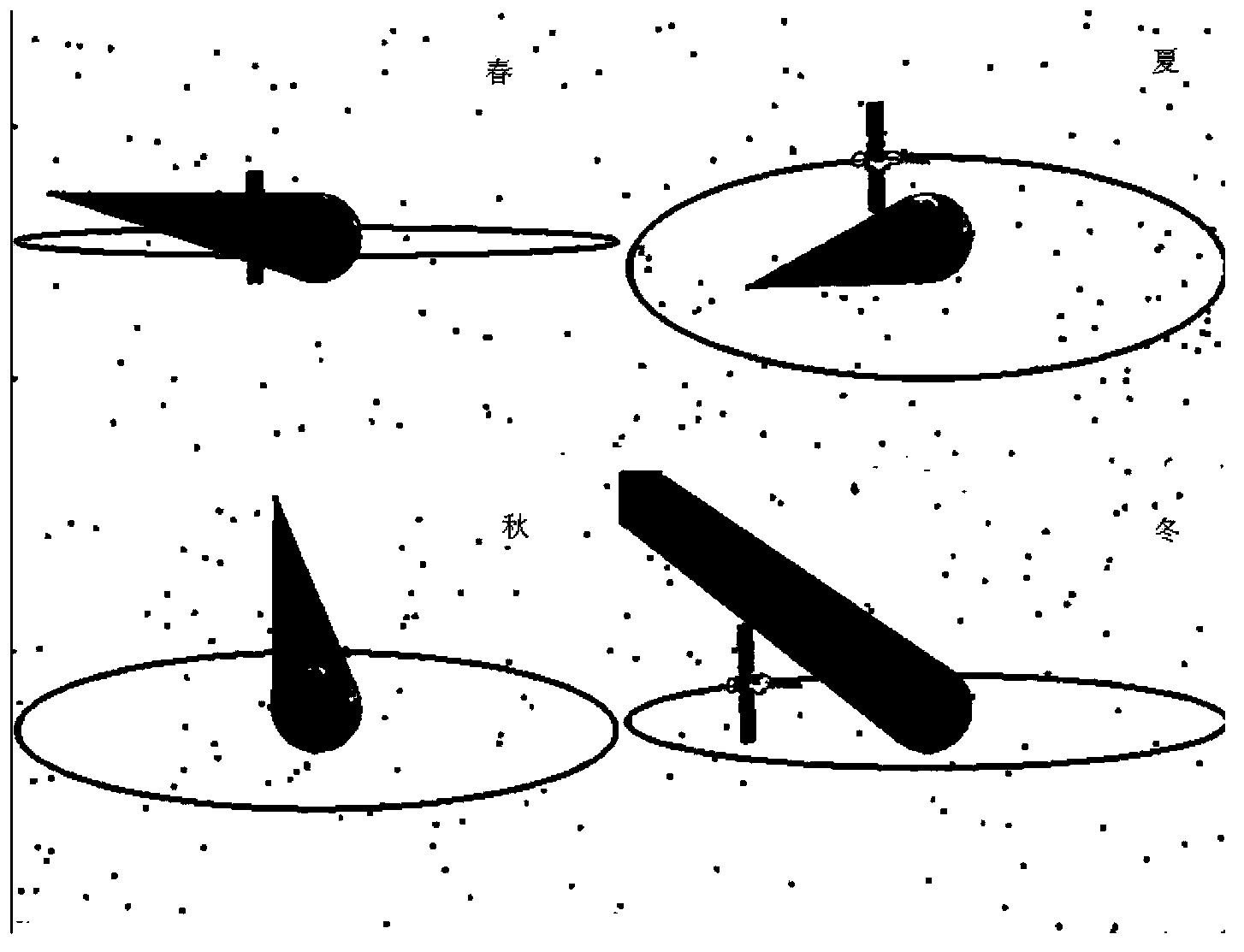
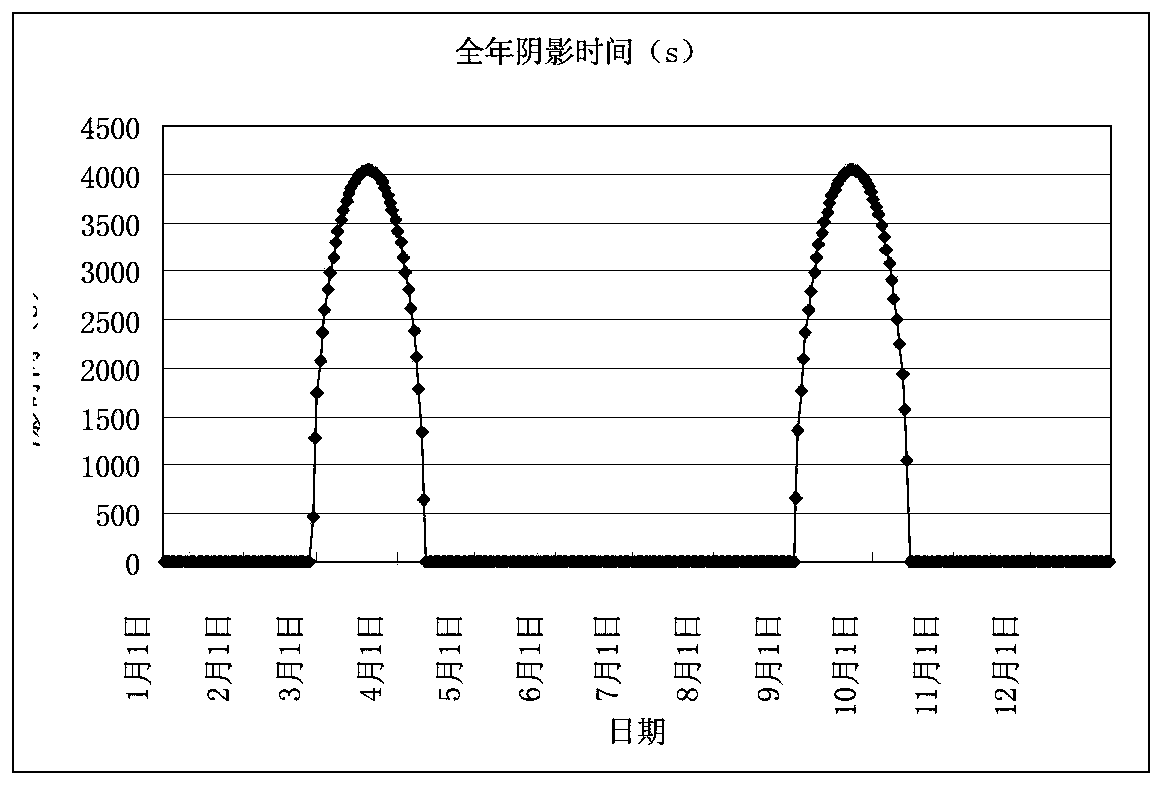
Analysis and calculation method for orbital shading of geostationary orbit satellite solar cell array
The invention discloses an analysis and calculation method for orbital shading of a geostationary orbit satellite solar cell array and relates to the field of the space technology. The method includes the steps of 1, analyzing annual average change rules of solar illumination angle of a geostationary orbit satellite; 2, analyzing change rules of orbital shading of the satellite solar cell array by stars; 3, calculating and simulating orbital shade area of the cell array according to the analysis results. The analysis and calculation method has the advantage that the basis for the design of solar cell array substrate configuration is provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI SATELLITE ENG INST
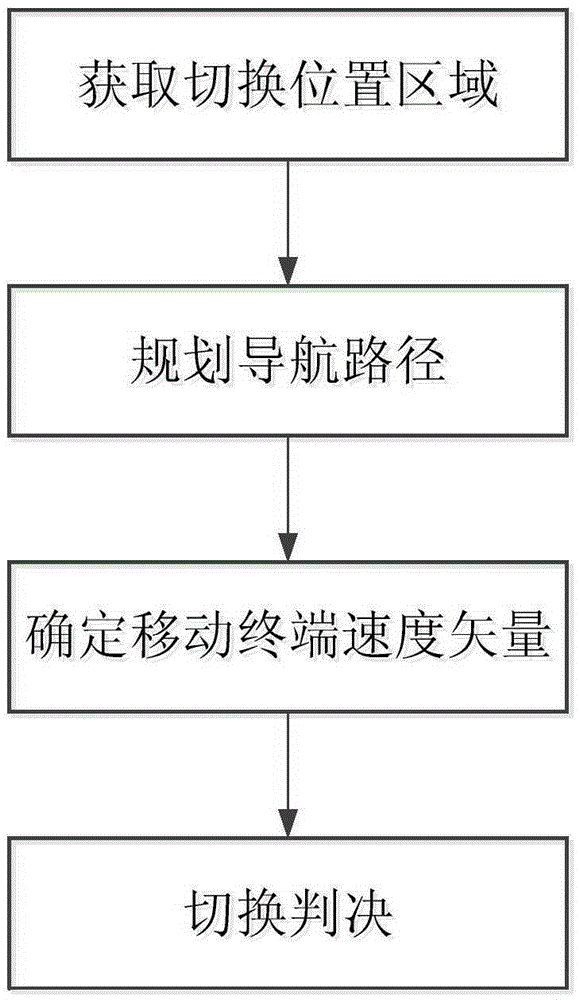
Method for reducing satellite communication system switching delay
ActiveCN105357725AReduce latencyReduce the ping-pong effectRadio transmissionWireless communicationGeostationary orbitGeosynchronous orbit
The invention relates to a method for reducing satellite communication system switching delay, in particular to a switching method for spot beams in the same gateway station of a geostationary orbit satellite. In the method, a switching position area is acquired by using the position information of a mobile terminal of a satellite communication system and combining historical measurement information; the possibly-spanned switching position area is pre-judged according to a navigation path; a velocity vector of the current mobile terminal is acquired by combining a digital map, if the time when the mobile terminal travels to the switching position area from the current position is less than a certain threshold value, pre-switching is completed and finally, switching confirmation is carried out through measurement. Through the adoption of the method, the satellite beam switching delay can be reduced greatly, and in addition, the switching ping-pong effect can be reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
System and method for satellite communication
A system and method are disclosed which may include providing at least one satellite having a plurality of beamformers configured to provide a plurality of respective beams having a plurality of different respective fixed pitch angles about an axis of the satellite; causing the at least one satellite to move around the earth along a non-geostationary orbit; establishing a data communication path between a first of the beamformers on the satellite and a communication target, the data communication path having a satellite end at the first beamformer and an target end at the communication target; shifting the satellite end of the data communication path through a succession of the beamformers as the satellite moves along its orbit; and at least substantially reducing an amount of RF wave energy directed to beamformers of the plurality of beamformers not forming part of the data communication path.
Owner:O3B NETWORKS
GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System)-based signal aided time frequency difference comprehensive correction method
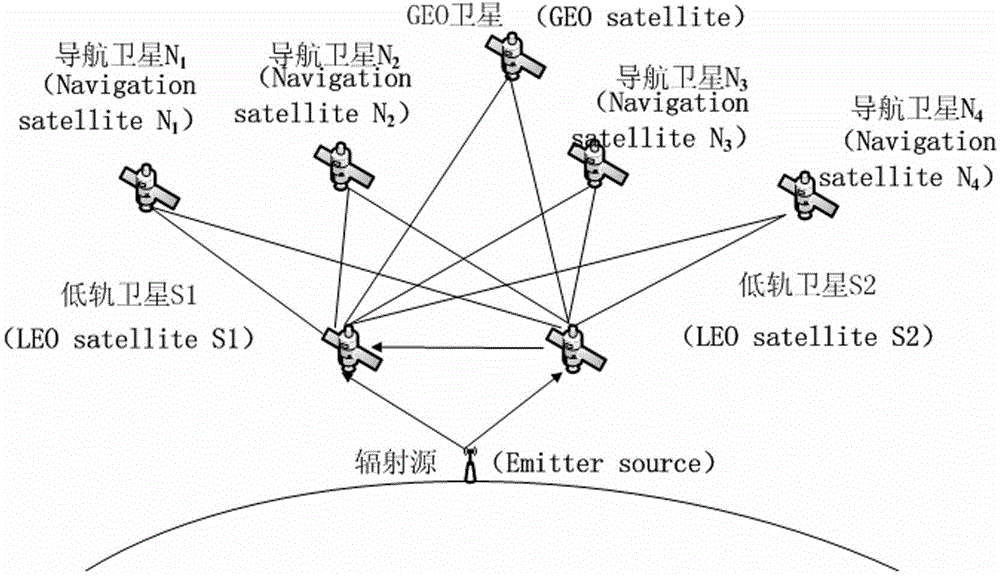
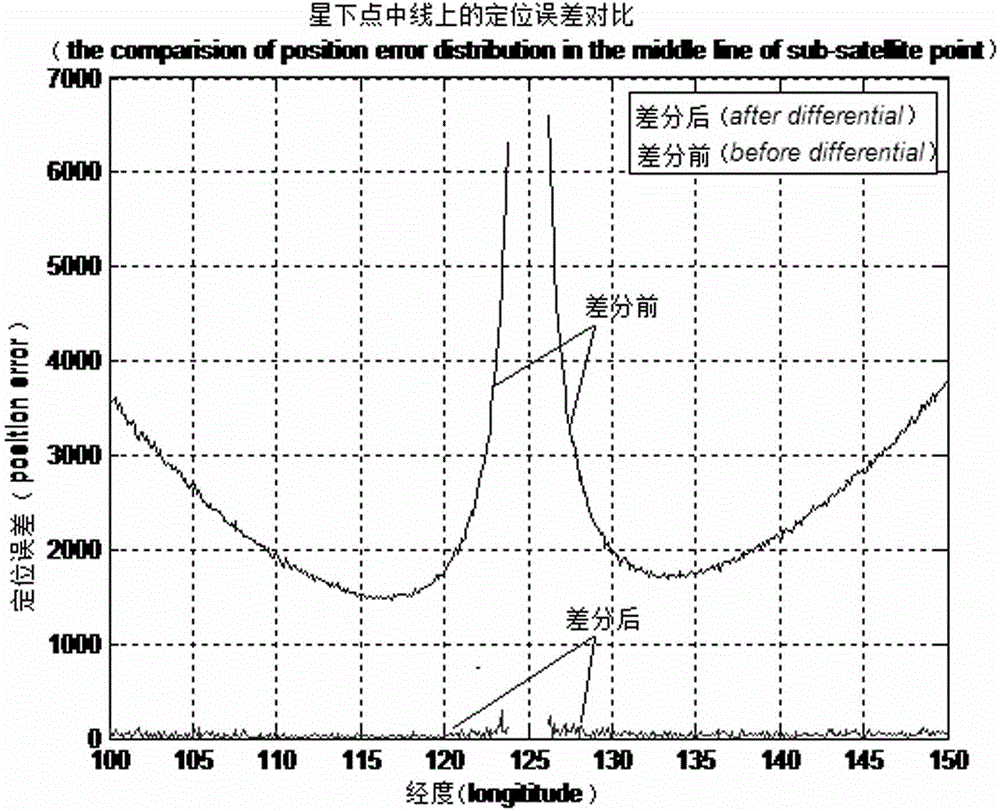
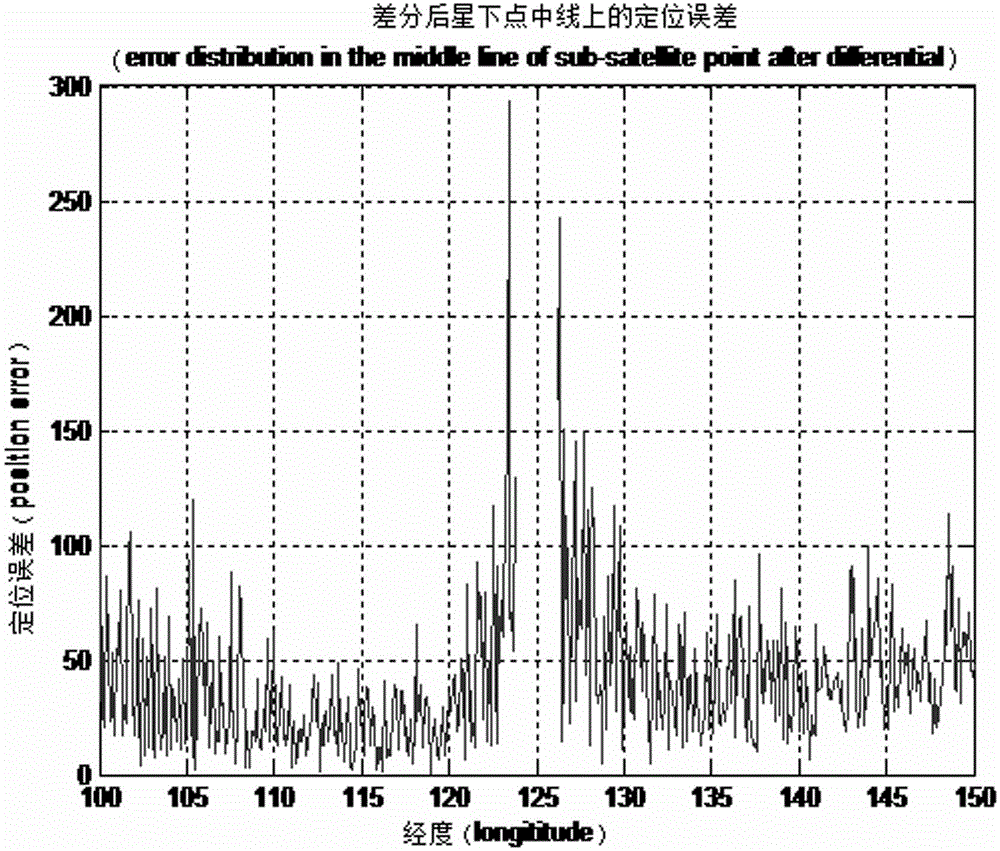
The invention discloses a GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System)-based signal aided time frequency difference comprehensive correction method, which specifically comprises the following steps of: (1) calculating orbit coordinates and movement velocity of two low earth orbit satellites in current epoch, respective distances from the two low earth orbit satellites to the GEO satellite and the distance between the two earth orbit satellites by using position coordinates of a low earth orbit satellite on-board navigation receiver and a GEO (Geostationary Orbit) satellite; and (2) calculating correction quantity of time difference of arrival and correction quantity of frequency difference of arrival of the low earth orbit satellites according to the GEO satellite coordinates and the calculated orbit coordinates and the velocity parameter of the two low earth orbit satellites in the current epoch, and correcting the time difference of arrival and the frequency difference of arrival before correction of a radiation source obtained by the low earth orbit navigation receiver according to the correction quantities to obtain the corrected time difference of arrival and frequency difference of arrival. By using the method, the fixed deviation of the time difference of arrival of the radiation source can be excellently corrected, so that the positioning accuracy of the radiation source of a space passive positioning system is obviously improved.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Satellite communication system for a continuous high-bitrate access service over a coverage area including at least one polar region
ActiveUS20150358861A1Quality improvementLow costNetwork topologiesActive radio relay systemsInternet networkGeostationary orbit
A system comprises a constellation of satellites placed in non-geostationary orbit, user terminals located in a coverage area, and N anchor stations able to ensure bidirectional communications with the user terminals by way of at least one satellite. The system furthermore comprises a network of routers interconnected with one another and to the Worldwide Internet Network, each anchor station is connected to the Worldwide Internet Network by way of a router, and each anchor station comprises a management device for managing the handovers to ensure service continuity for the communications. This management device is able to control the handovers between the successive orbiting satellites progressing over the coverage area, the handovers between anchor stations, or the handovers between simultaneously successive satellites and anchor stations.
Owner:THALES SA
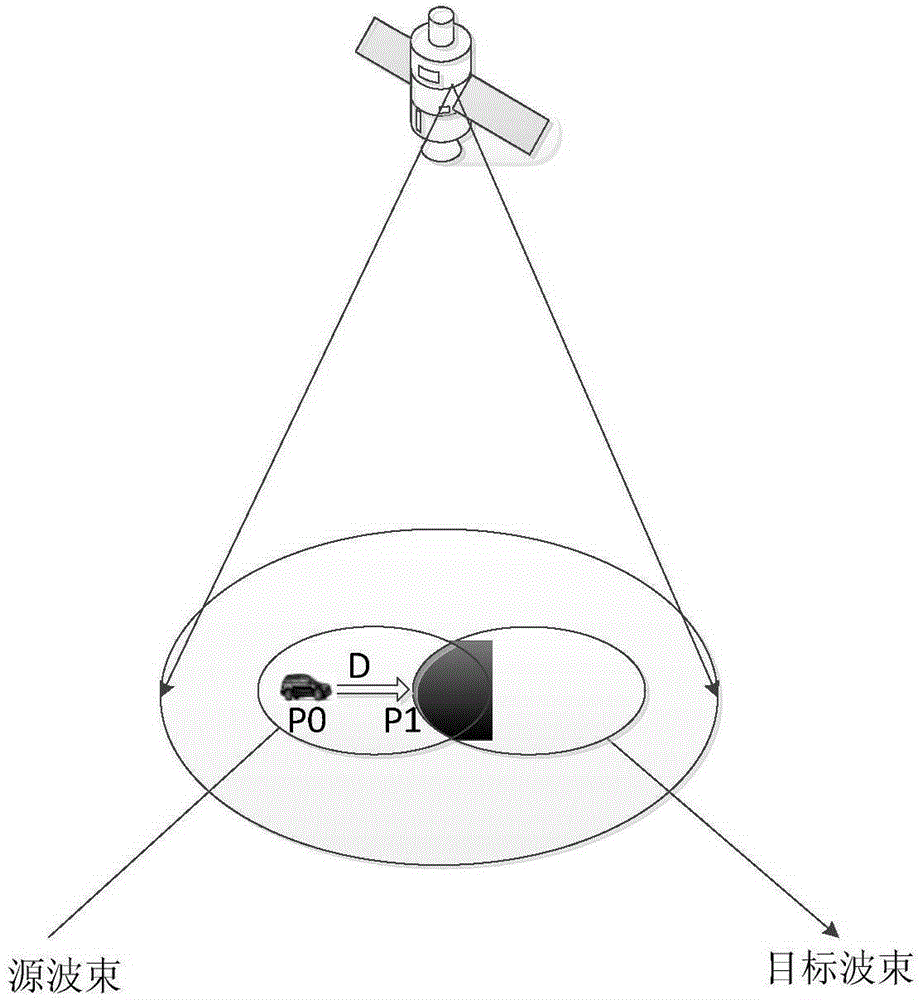
Subterranean target steering strategy
A method for steering the payload beam of a satellite in a non-geostationary orbit toward an intended service area having known geographical dimensions in order to obtain improved pointing performance with a corresponding reduction in the demand on onboard hardware and software systems. The method comprises the steps of determining a subterranean target point and a direction fixed in the payload beam, calculating the orientation that points the payload beam direction through the subterranean target point, and maintaining this payload beam orientation using an on-board attitude control system.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
Low-orbit navigation enhancement precision correction data generation and uploading system and method
ActiveCN110187364AReduce in quantityReduce construction costsSatellite radio beaconingRadio transmissionGeostationary orbitDependability
The invention relates to a low-orbit navigation enhancement precision correction data generation and uploading system and method. A ground data processing central station combines monitoring data acquired by a GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) monitoring station and low-orbit satellite monitoring data acquired by a satellite measurement and control station for processing to generate SSR (State Space Representation) data; the generated SSR data is evaluated and then transmitted to three service data uploading stations, the three service data uploading stations respectively transmit theSSR data to three geostationary orbit communication satellites as high elliptical orbit satellites through an uploading channel, a low-orbit navigation enhancement satellite receives the SSR data broadcasted by the geostationary orbit communication satellites, and processes the uploaded SSR data by adopting a navigation enhancement load t generate enhanced navigation signals so as to complete high-precision orbit determination and low-orbit navigation enhancement information generation. Compared to the prior art, the method for generating and uploading the SSR correction data of the navigationsystem required by the low-orbit navigation enhancement system is achieved without depending on low-orbit inter-satellite links, so that the complexity of the low-orbit system is reduced, the reliability of the low-orbit constellation system is improved, and the service life of the low-orbit constellation system is prolonged.
Owner:火眼位置数智科技服务有限公司
Satellite communication system for a continuous high-bitrate access service over a coverage area including at least one polar region
ActiveUS9363712B2Quality improvementLow costNetwork topologiesActive radio relay systemsInternet networkGeostationary orbit
A system comprises a constellation of satellites placed in non-geostationary orbit, user terminals located in a coverage area, and N anchor stations able to ensure bidirectional communications with the user terminals by way of at least one satellite. The system furthermore comprises a network of routers interconnected with one another and to the Worldwide Internet Network, each anchor station is connected to the Worldwide Internet Network by way of a router, and each anchor station comprises a management device for managing the handovers to ensure service continuity for the communications. This management device is able to control the handovers between the successive orbiting satellites progressing over the coverage area, the handovers between anchor stations, or the handovers between simultaneously successive satellites and anchor stations.
Owner:THALES SA
Multi-beam telecommunication antenna onboard a high-capacity satellite and related telecommunication system
ActiveUS20120075149A1Waveguide hornsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesGeostationary orbitEngineering
A high-throughput multi-beam telecommunication antenna is configured to cover a geographical area from a geostationary orbit.It comprises a single reflector and a feed block configured so that each elementary feed is able to generate a different unique beam, the angular separation of any two adjacent primary beams is substantially equal to the angular separation of any two adjacent secondary beams, and the spillover energy losses associated with each source are between 3 and 10 dB, preferably between 3 and 7.5 dB.
Owner:CENT NAT DETUD SPATIALES C N E S
Satellite constellation implementation method for implementing communication by utilizing recursive orbit
ActiveCN107980210AReduce co-channel interferenceRealize coexistence at the same frequencyCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsGeostationary orbitIntersection of a polyhedron with a line
The invention relates to a satellite constellation implementation method for implementing communication by utilizing a recursive orbit, and the method comprises the steps: a regression period, an orbital semi-major axis, an inclination of an orbit, an eccentricity ratio and an argument of perigee of the orbit are determined; the number of satellites and orbital planes are determined as n; right ascension of ascending node and a mean anomaly of a first satellite are determined, and according to service needs of the satellite, right ascension of ascending node and mean anomaly of following satellites are determined in sequence; a geostationary orbiting satellite network set that needs to be coordinated and the width of a non-geostationary satellite to geostationary satellite interference protection band are determined; all set satellites successively passes the top in the air along a same fixed orbit are seen at any position of the ground, and when multi-coverage is formed, users on theground can see a plurality of satellites; and if satellite trails pass the interference protection band for the geostationary satellite, when present accessed satellite enters the protection band, theusers on the ground switch to another satellite that does not in the protection band to continuously implement communication.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Shipborne satellite communication system and method for shipborne antenna to track satellite
InactiveCN106602261AAccurate trackingAttitude control extensionAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesCommunications systemGeostationary orbit
Owner:中云卫星通信有限公司
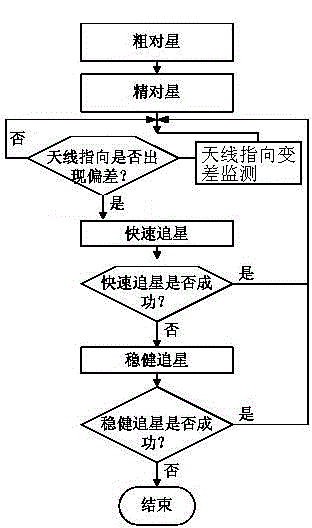
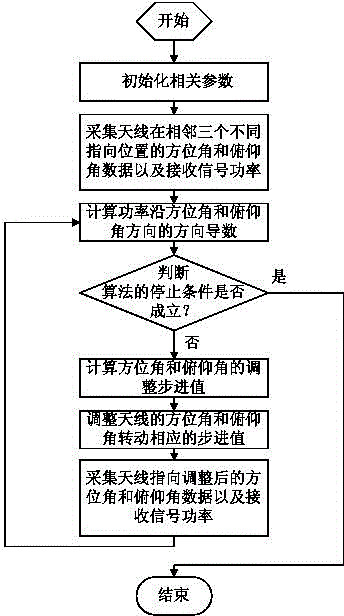
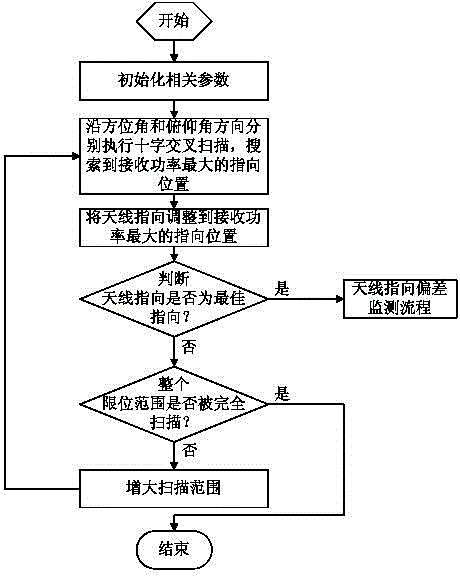
Automatic aligning method for satellite antenna
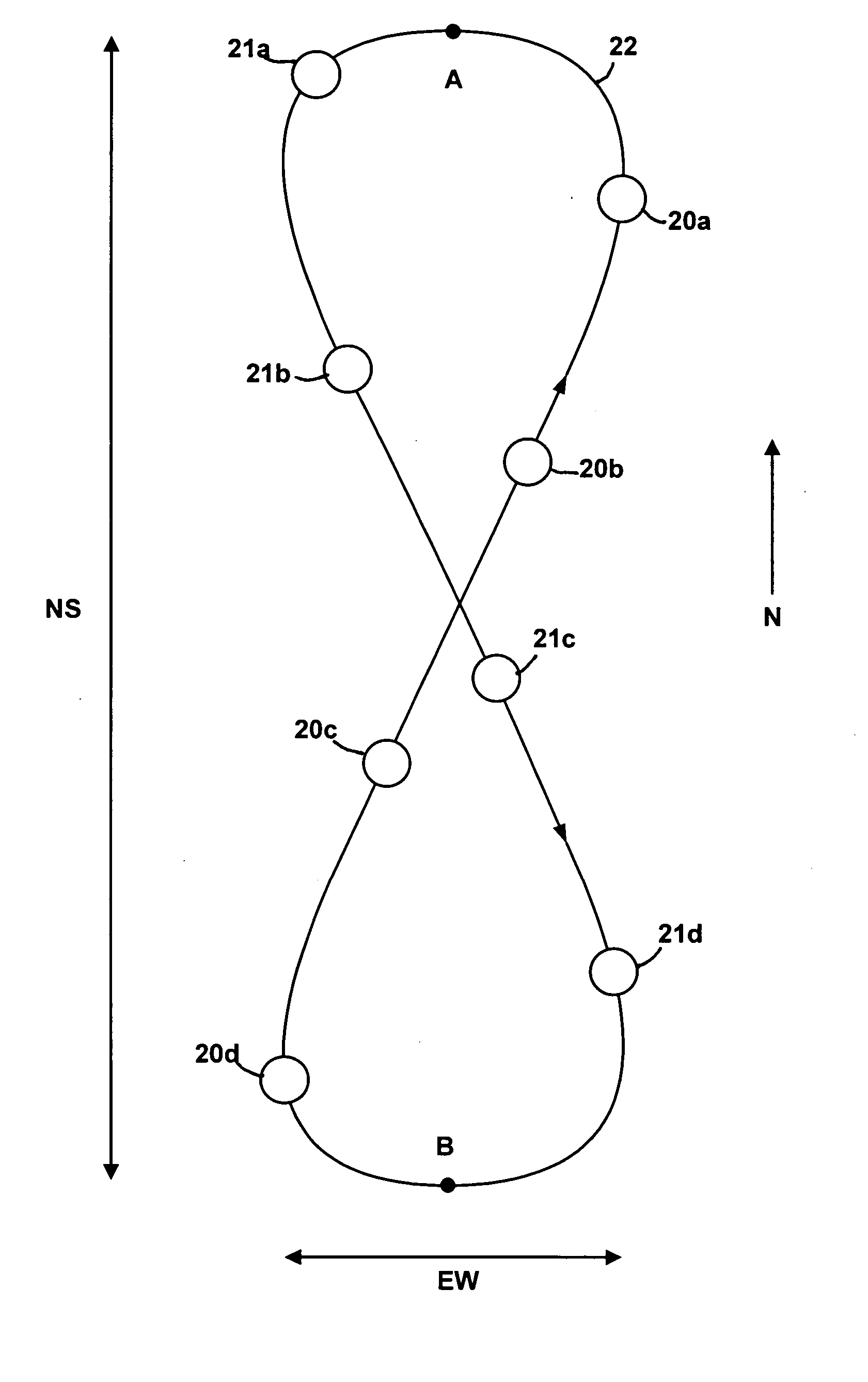
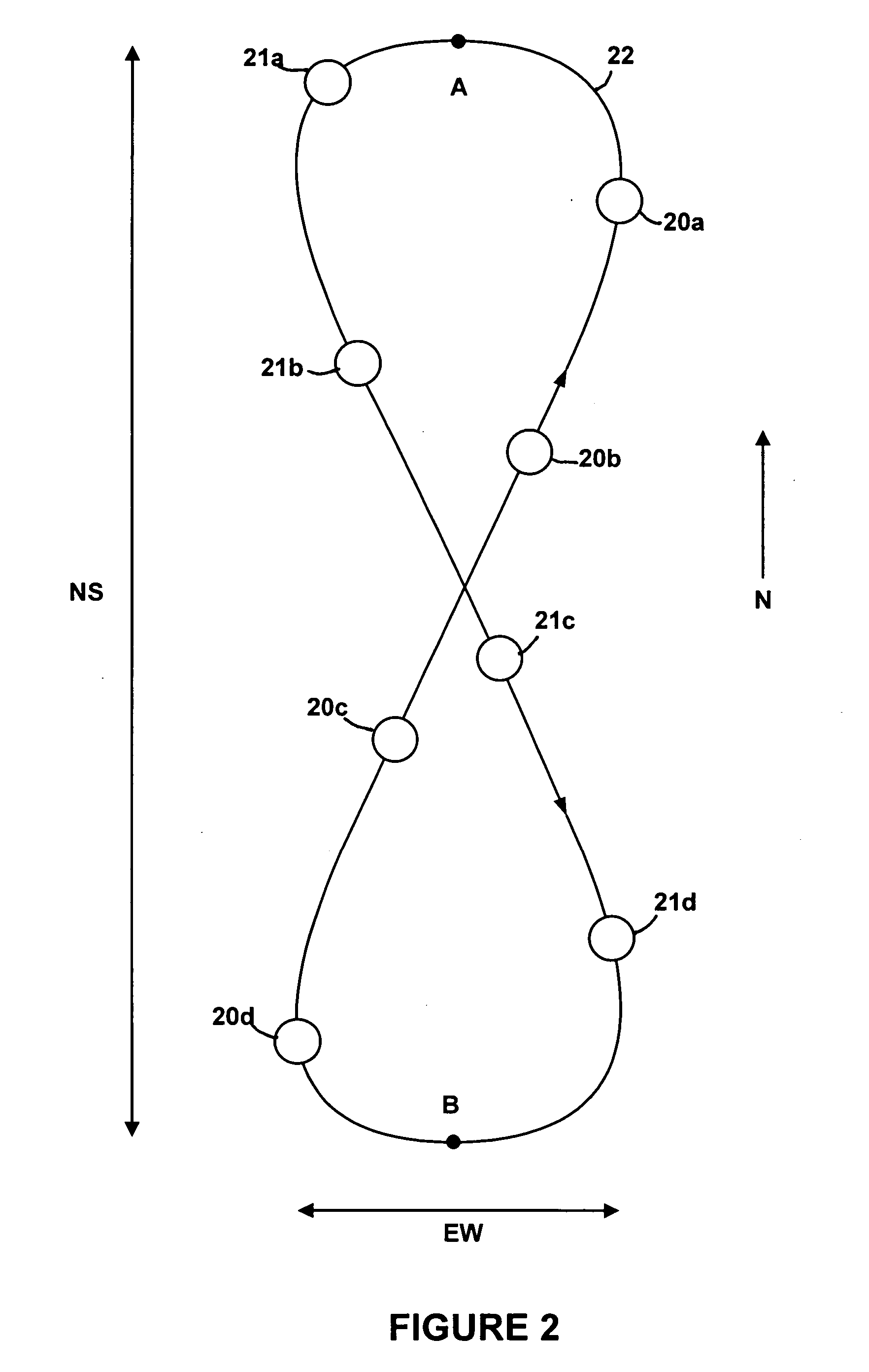
The invention relates to an automatic aligning method for a satellite antenna. The automatic aligning method is characterized in that the aligning method comprises the following processes: coarse alignment, precision alignment, antenna pointing deviation monitoring and automatic satellite tracking, wherein the automatic satellite tracking process comprises quick satellite tracking and stable satellite tracking. According to the automatic aligning method for the satellite antenna, the steps of quick tracking and stable satellite tracking are additionally added in the conventional satellite antenna aligning method, so that the antenna pointing can be corrected to the optimal position through realization of automatic satellite tracking under the situation that longitude and latitude of the satellite are changed due to the fact that a geostationary orbit satellite shifts periodically by following a 8-shaped path or relative antenna pointing deviation occurs due to physical cause.
Owner:四川安迪科技实业有限公司
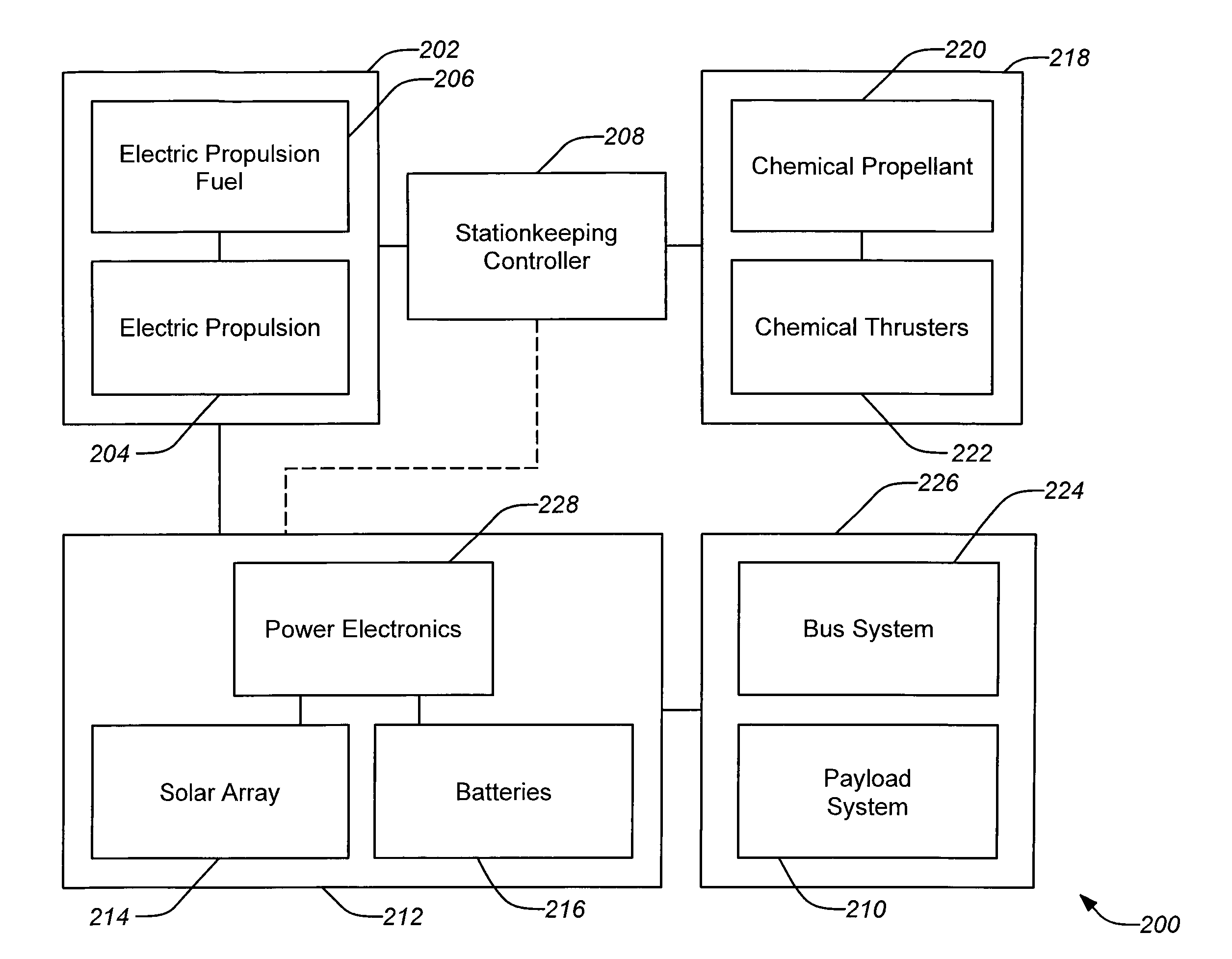
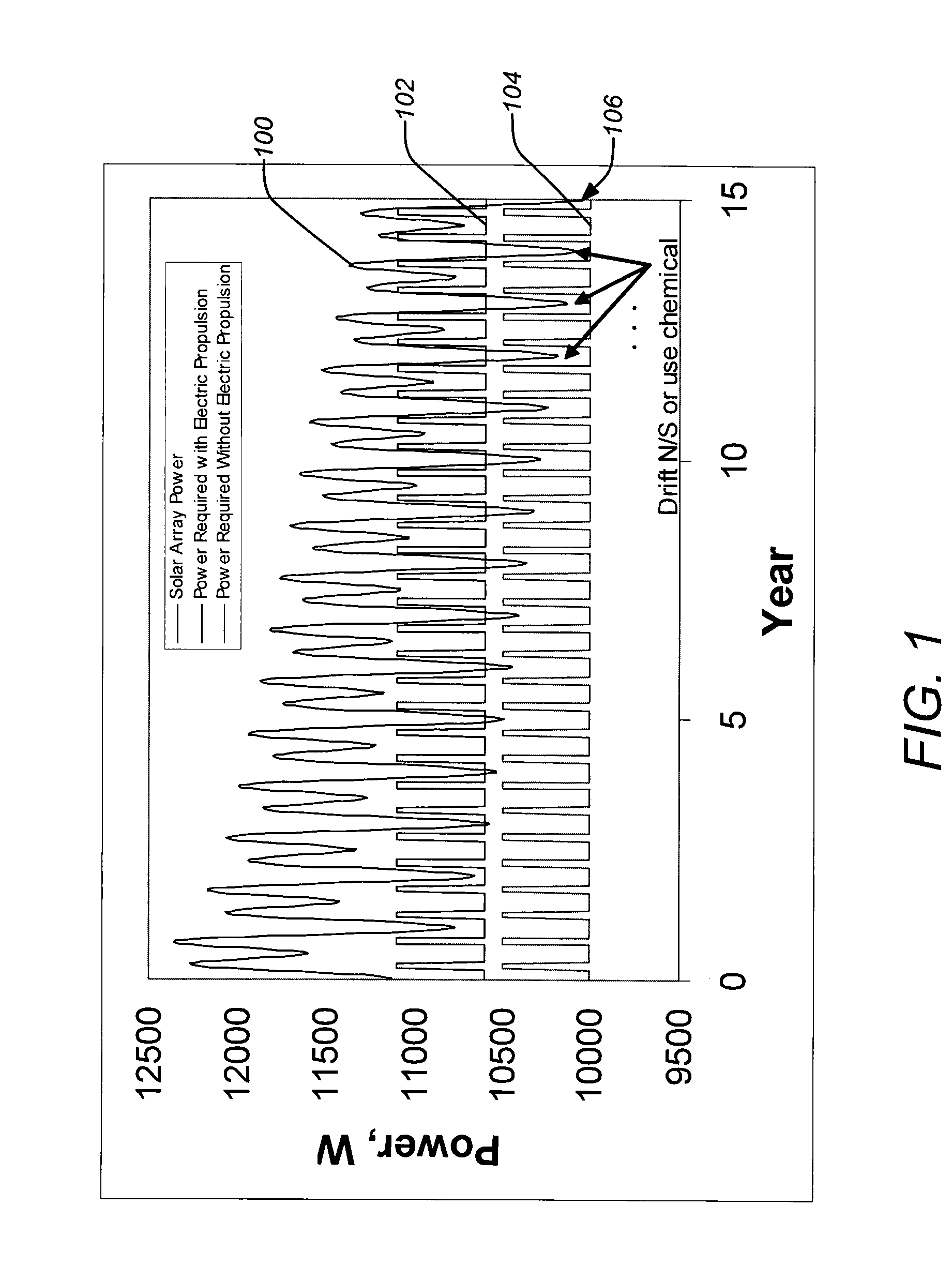
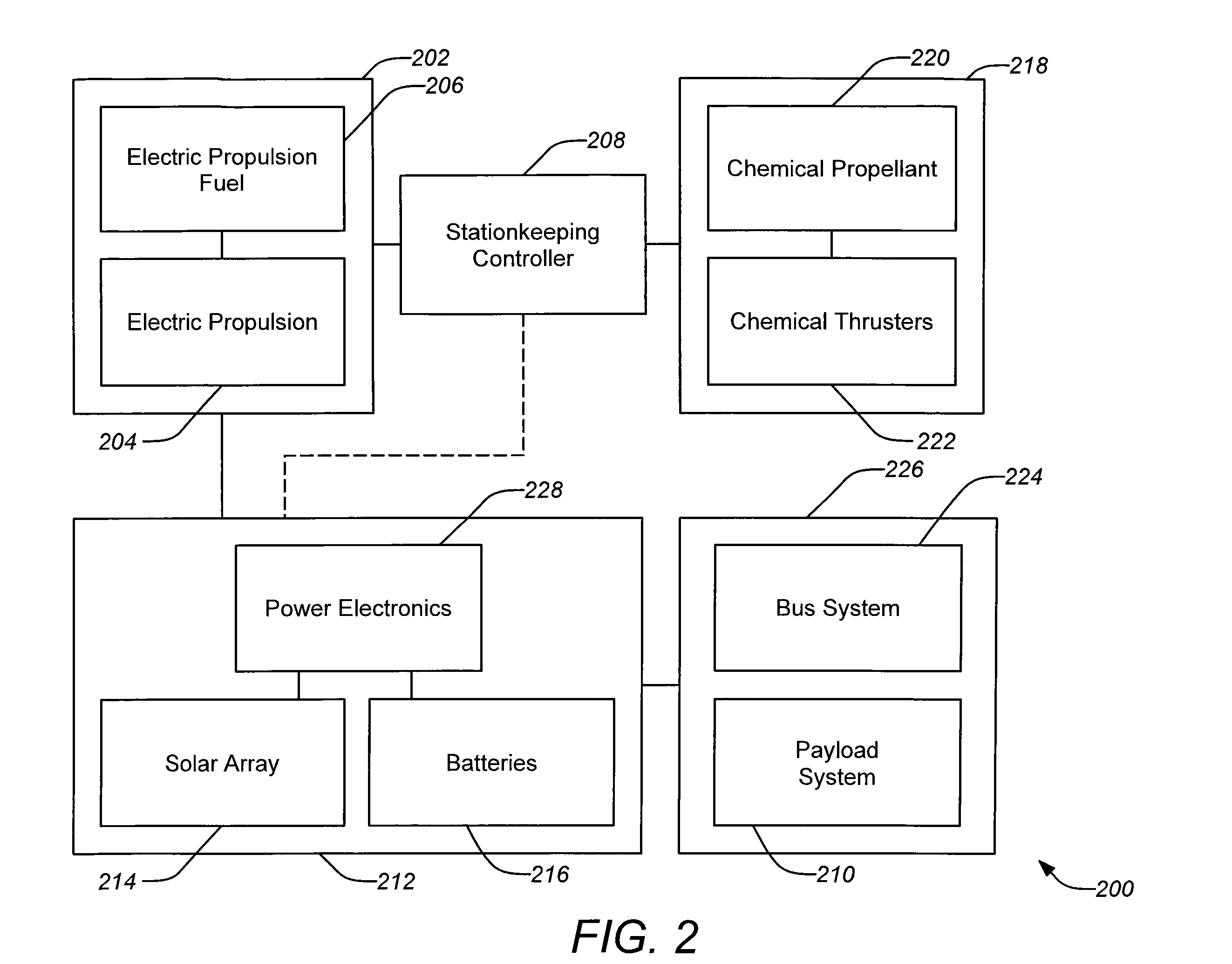
Power optimized system for electric propulsion stationkeeping geosynchronous spacecraft
ActiveUS20080135685A1Reduction in required solar powerReduce power marginsCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusCosmonautic power supply systemsElectricitySystems design
Systems and methods are disclosed employing electric propulsion stationkeeping in a cyclical manner to better match the cyclical pattern of power generated by the solar array system. For a typical orbit design, e.g. a geostationary orbit, North-South stationkeeping can be intermittently suspended, tolerating some additional drift but yielding in a very significant reduction in the required solar power system. If necessary, stationkeeping can be supplemented with a chemical thrusters during off periods for the electric propulsion. Because of this, the overall electrical power margin for the solar array system design can be reduced without compromising the mission performance.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
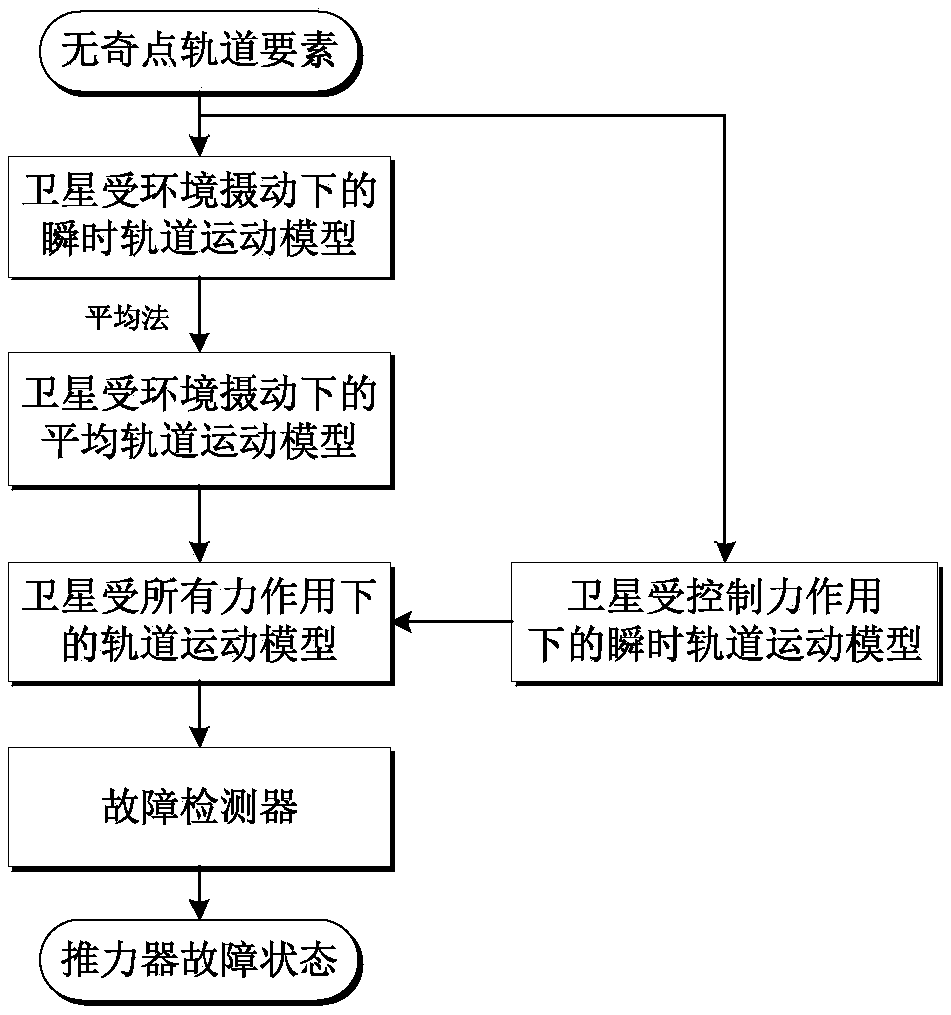
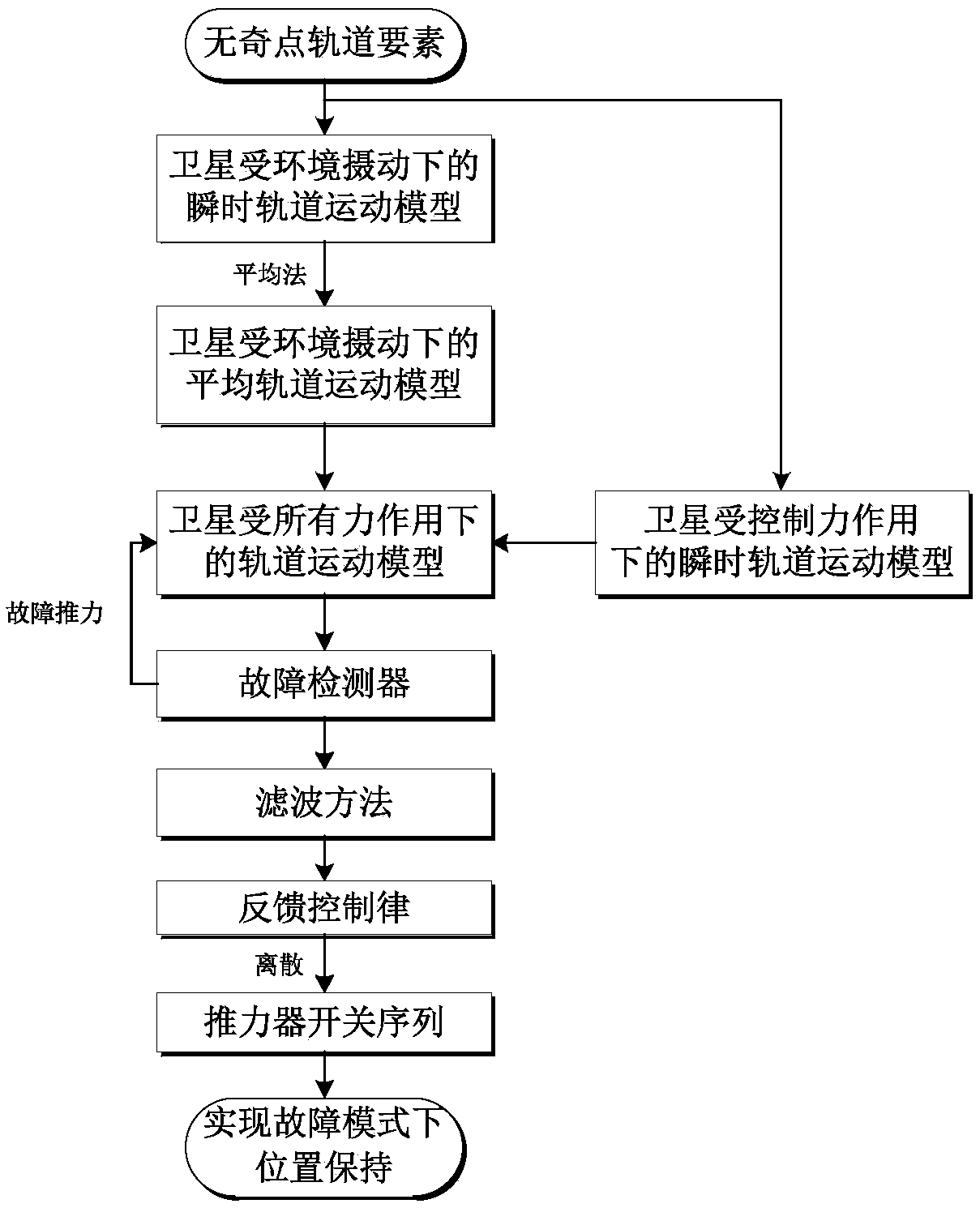
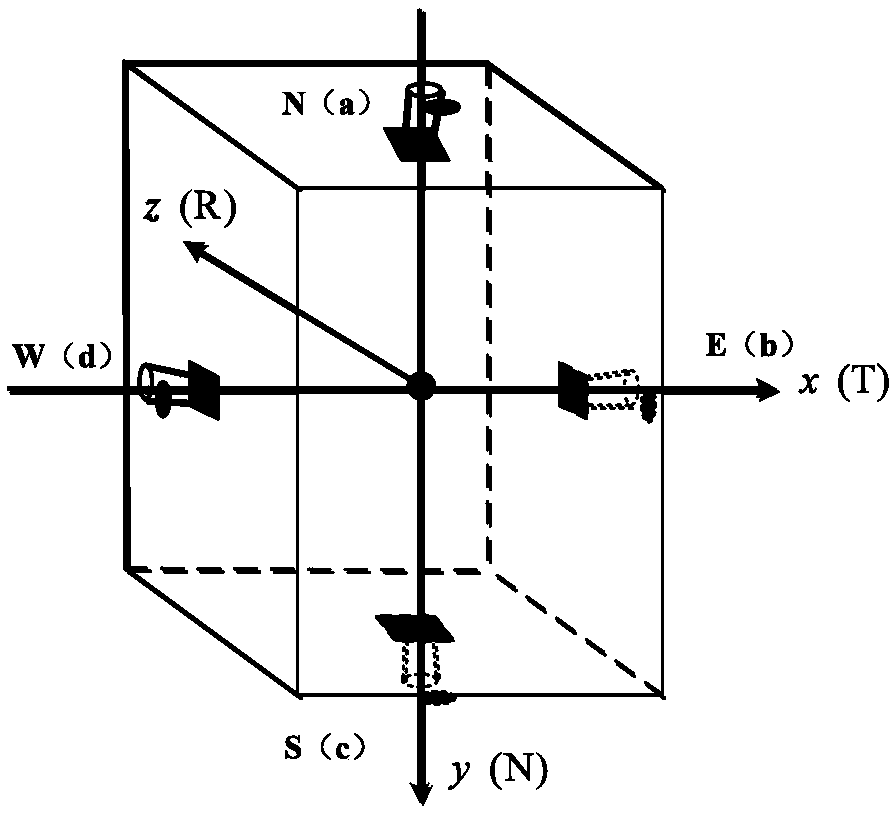
Method for detecting fault of electric propulsion satellite in geostationary orbit and position maintaining method thereof
ActiveCN109063380AImprove computing efficiencyEffective response to thrust failure situationsDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElectricityDesign control
The invention belongs to the field of spacecraft orbit dynamics and control. The invention discloses a fault detection method of a geostationary orbit electric propulsion satellite, which is realizedby establishing an instantaneous orbit motion model of the geostationary orbit satellite under environmental perturbation. the average orbital motion model is established; the orbital motion model under the action of the controlled force is established. The orbital motion model under all forces is deduced. The fault detector is designed and the convergence of the designed fault detector is verified. The invention also discloses a position maintaining method of a failure mode of a geostationary orbit electric propulsion satellite. On the basis of the satellite failure detecting method, the orbit drift caused by the failure of a thruster is calculated. A control law is designed to correct the orbital drift caused by thruster failure. The discrete control law is used to obtain the switching sequence of the electric thruster. By using the switching sequence, the position maintenance of the GEO electric propulsion satellite in the failure mode is realized. The invention is universally applicable to high-orbit and geostationary orbit electric propulsion satellites.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com