Patents
Literature
216 results about "Transfer orbit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
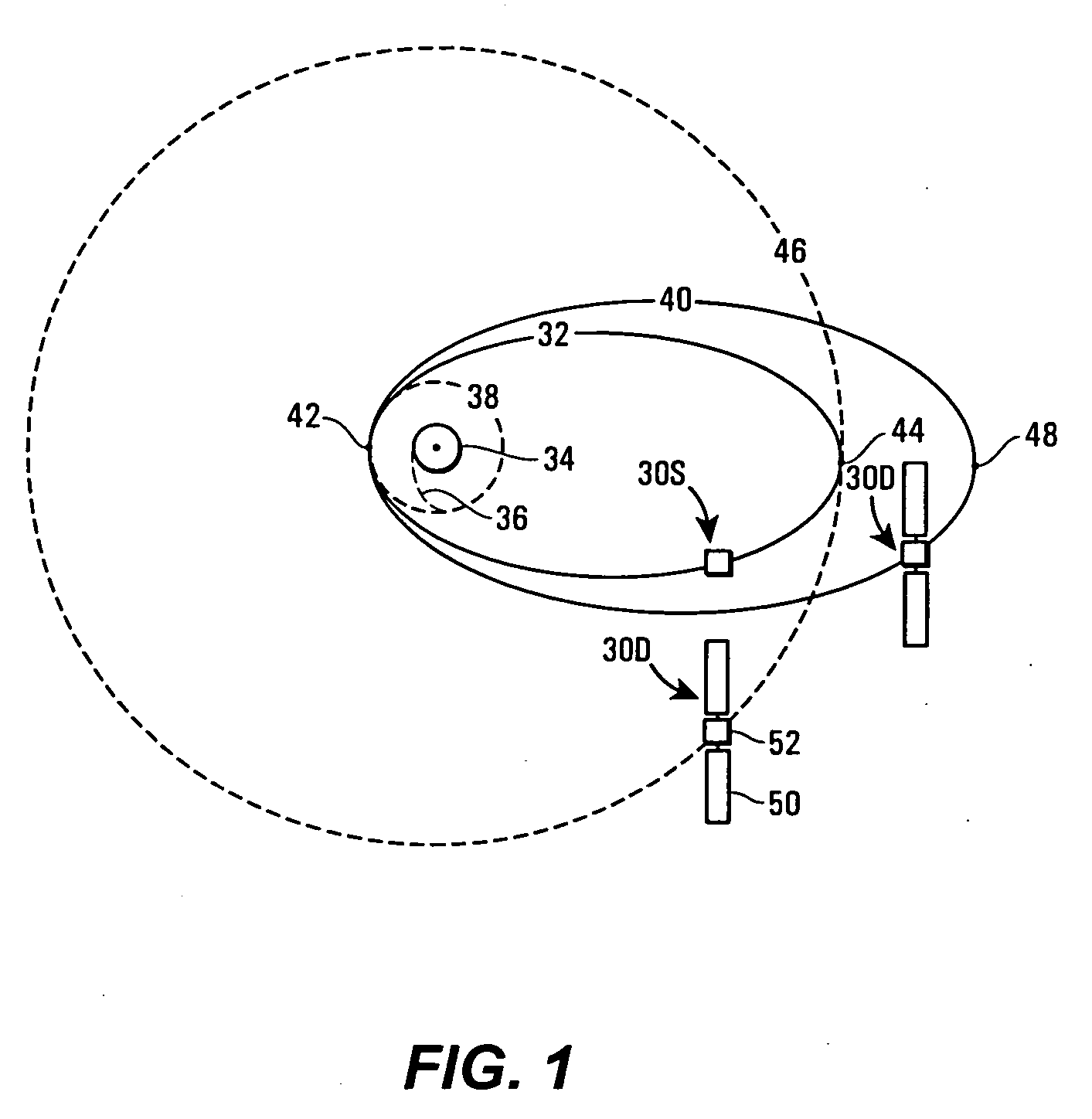
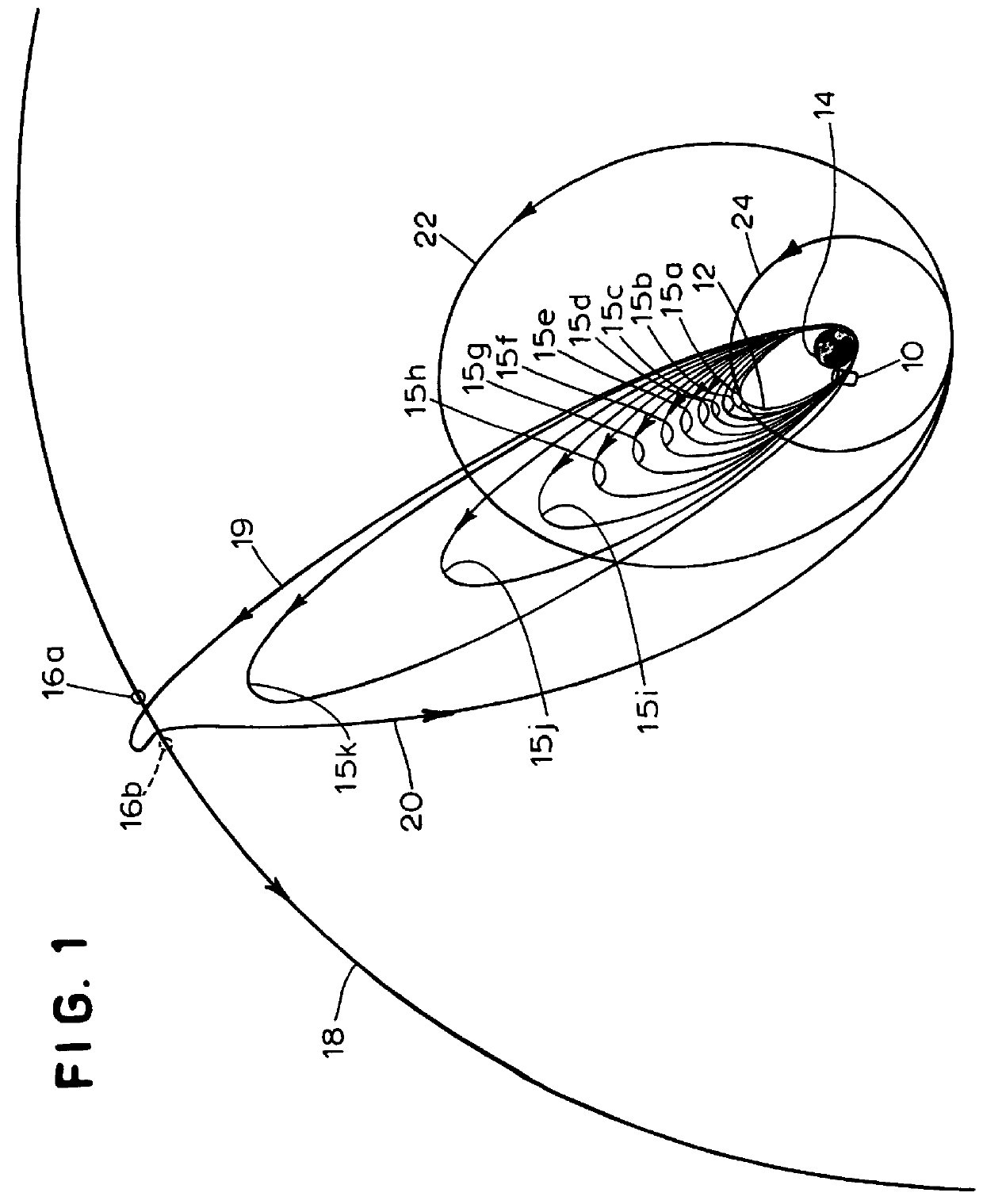
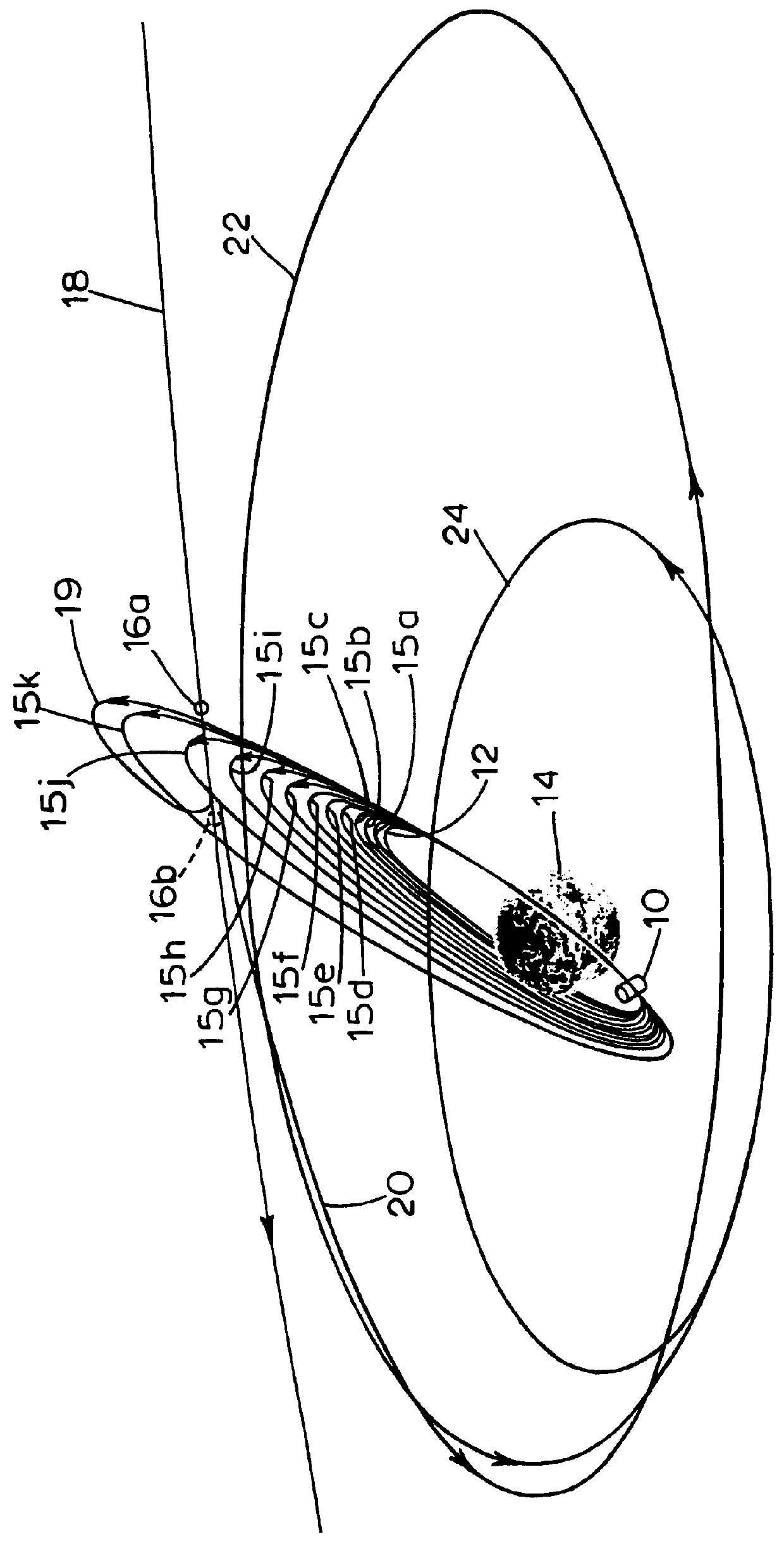
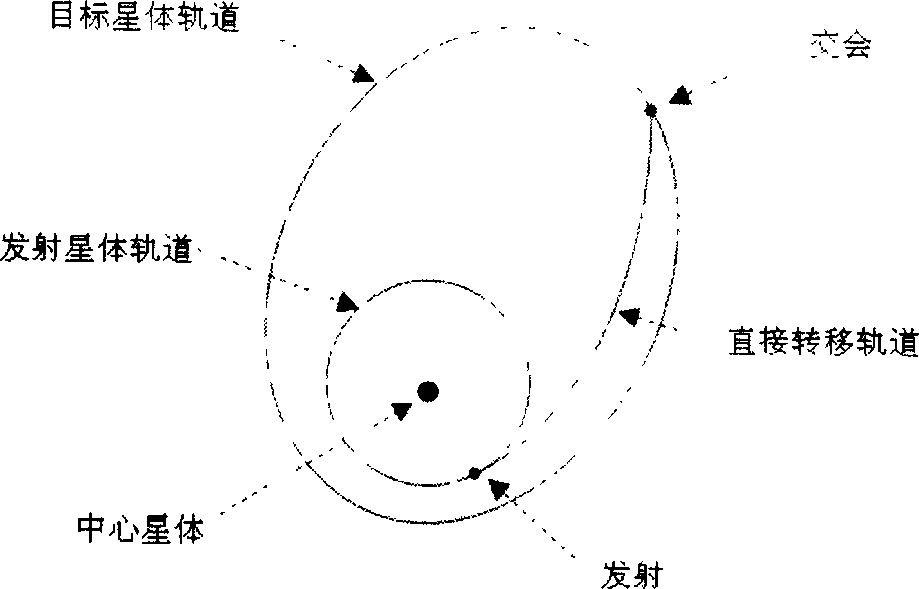
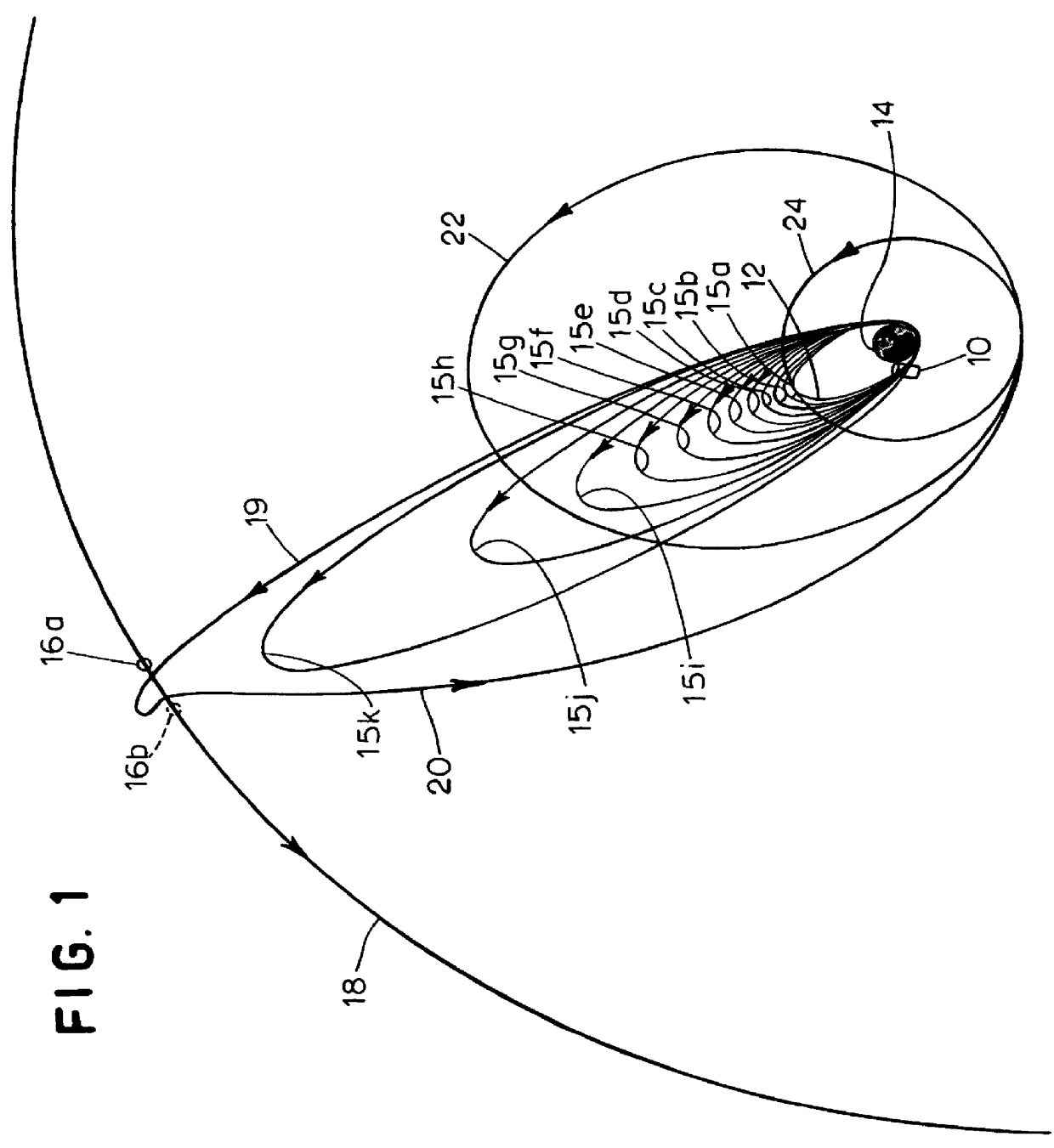
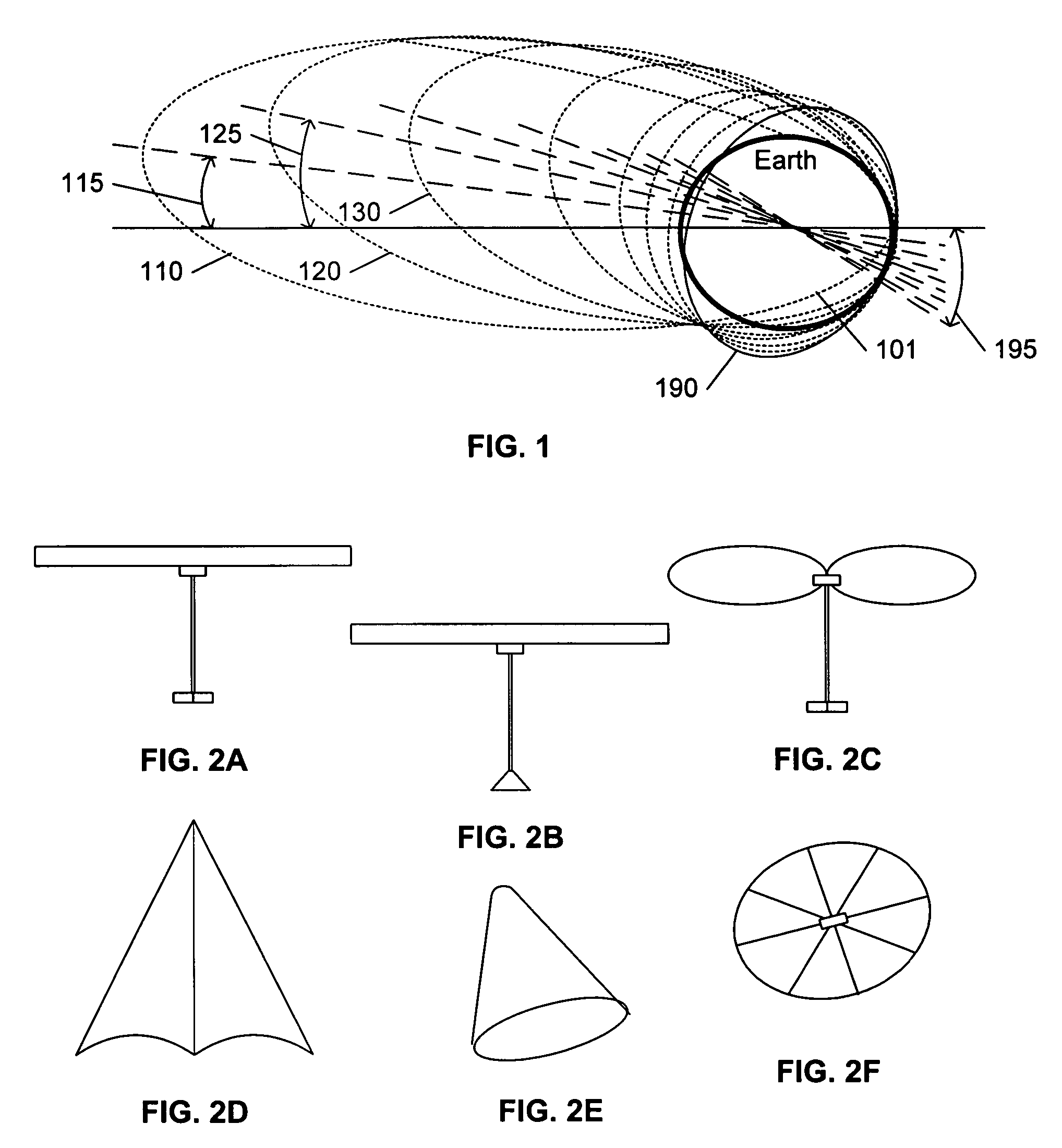
In orbital mechanics a transfer orbit is an intermediate elliptical orbit that is used to move a satellite or other object from one circular, or largely circular, orbit to another. There are several types of transfer orbits, which vary in their energy efficiency and speed of transfer.
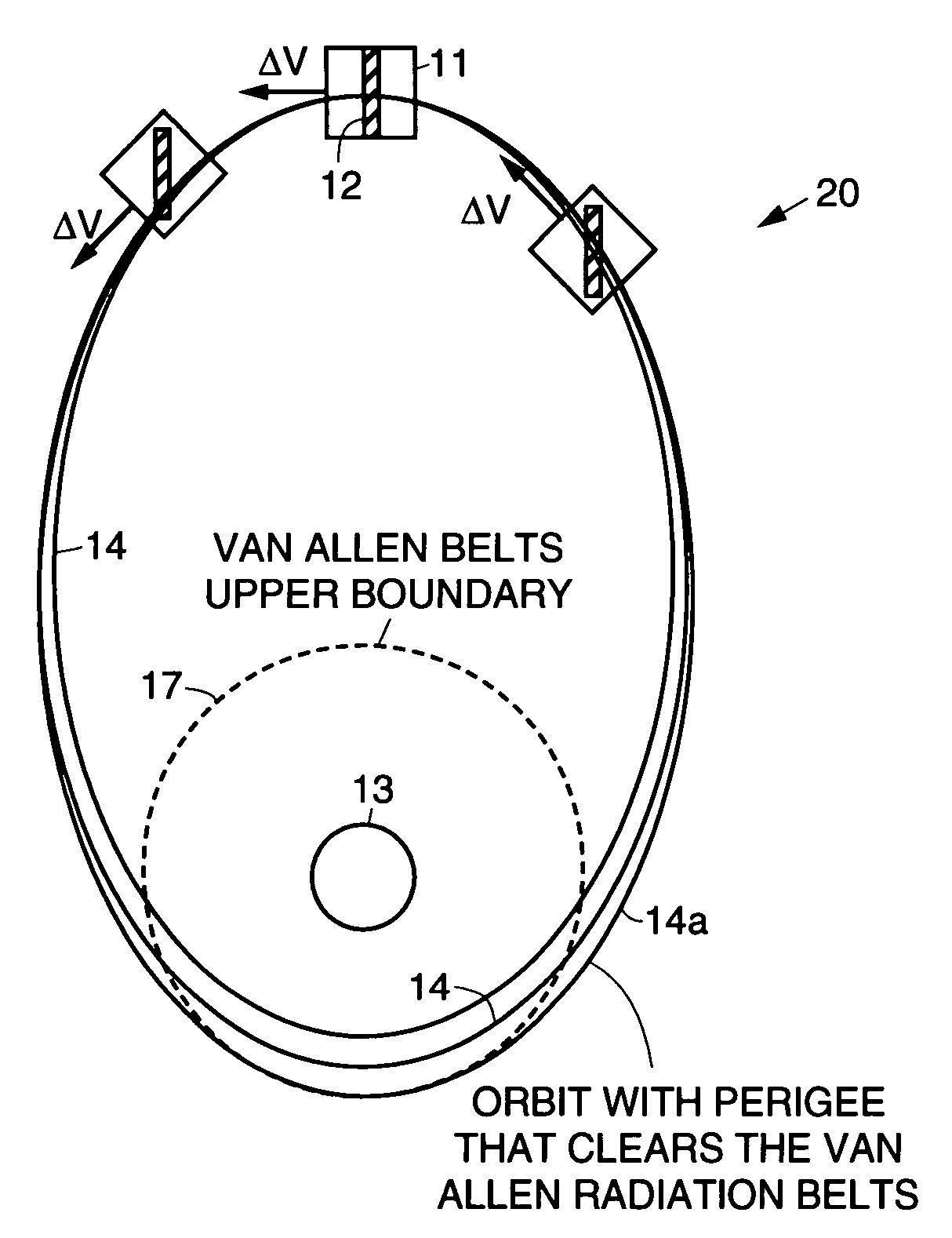
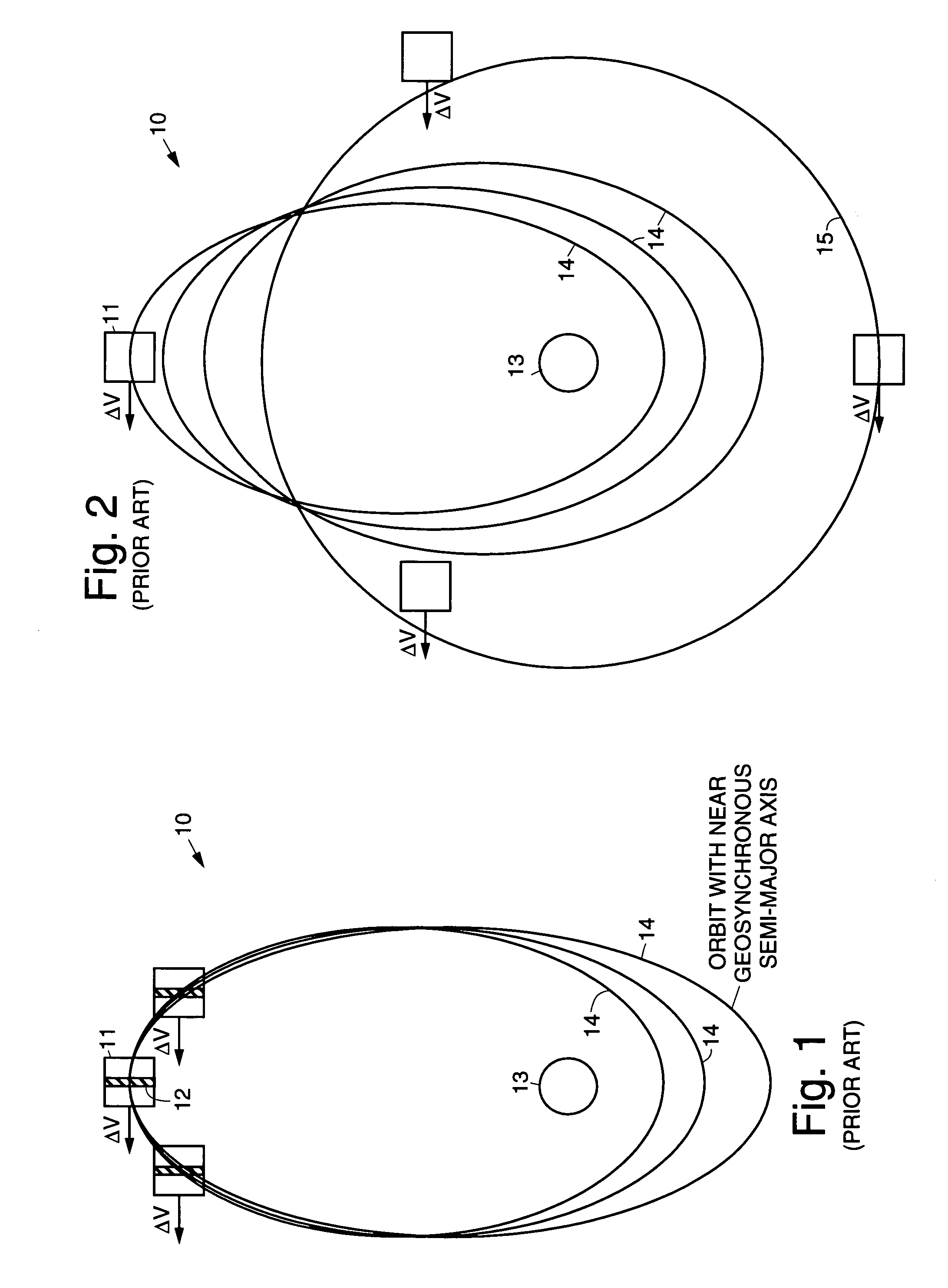
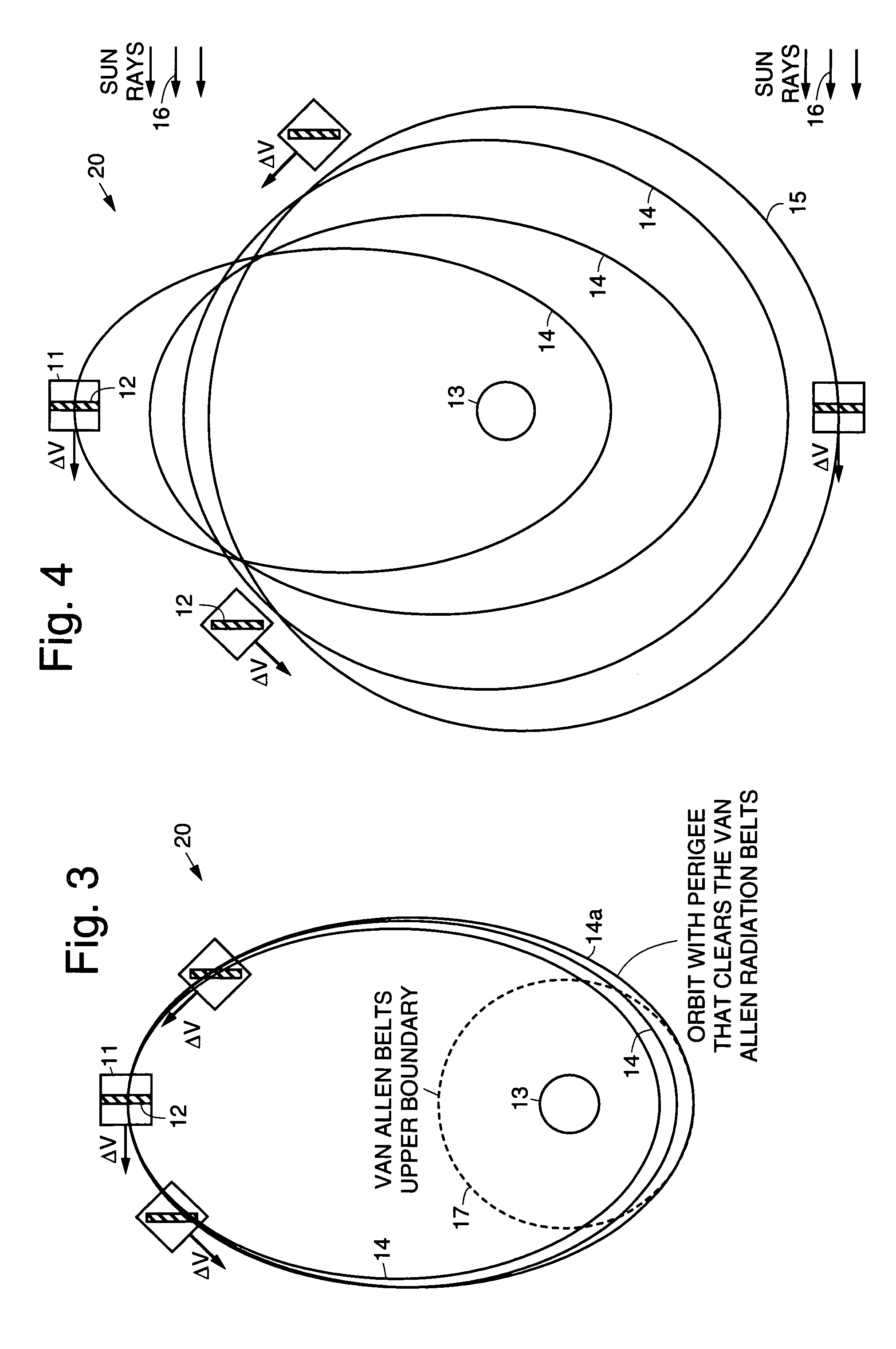
Practical orbit raising system and method for geosynchronous satellites
InactiveUS7113851B1Maximizing payload massMaximizing mission lifeLaunch systemsCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusElectricitySynchronous orbit
A practical orbit raising method and system wherein a satellite quickly escapes the Van Allen radiation belts and payload mass and mission life are maximized. A satellite is launched that contains high thrust chemical propulsion thrusters, high specific impulse electric propulsion thrusters and a solar array. The satellite quickly escapes the Van Allen radiation belts by firing the high thrust chemical propulsion thrusters at apogees of intermediate orbits, starting from the transfer orbit initiated by a launch vehicle, to successively raise the perigees until the perigee clears the Van Allen radiation belts. The payload mass and mission life are maximized by firing high specific impulse electric propulsion thrusters to raise the satellite to near synchronous orbit, while steering the thrust vector and solar array to maintain the sun's illumination on the solar array. The chemical and / or electric propulsion thrusters are then fired to achieve geosynchronous orbit.
Owner:SPACE SYST LORAL INC
Method and a system for launching satellites on non-coplanar orbits, making the use of gravitational assistance from the moon
InactiveUS6059233AMinimize energy usageAccurate acquisitionLaunch systemsArtificial satellitesEllipseAerogravity assist
A first satellite is placed practically directly by a launcher on a first final orbit. A second satellite is placed on the same launcher is initially transferred to a highly elliptical waiting orbit whose semi-major axis points to intercept the torus formed by the sphere of influence of the moon on its orbit, and then during a maneuver at the perigee of the highly elliptical orbit, the second satellite is transferred to lunar transfer orbit. Changes in the perigee altitude and the inclination of an intermediate orbit on which the second satellite is to be found are obtained mainly by gravitational reaction in the sphere of influence of the moon, and during a last maneuver, the second satellite is placed on a final orbit having orbital parameter values that are quite different from those of the orbital parameters of the first final orbit.
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
Satellitic self-determination orbital transfer method
ActiveCN101219713AAccurate track changeImprove reliabilitySpacecraft guiding apparatusStable stateAccelerometer
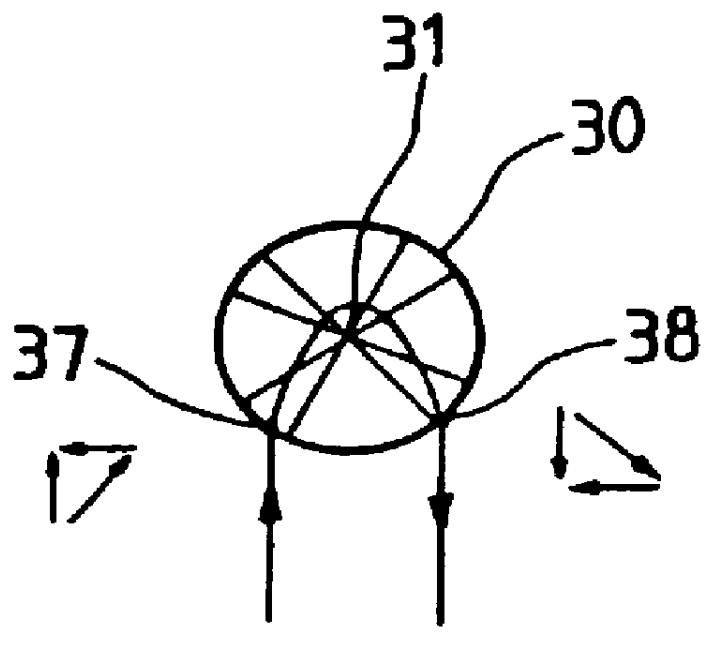
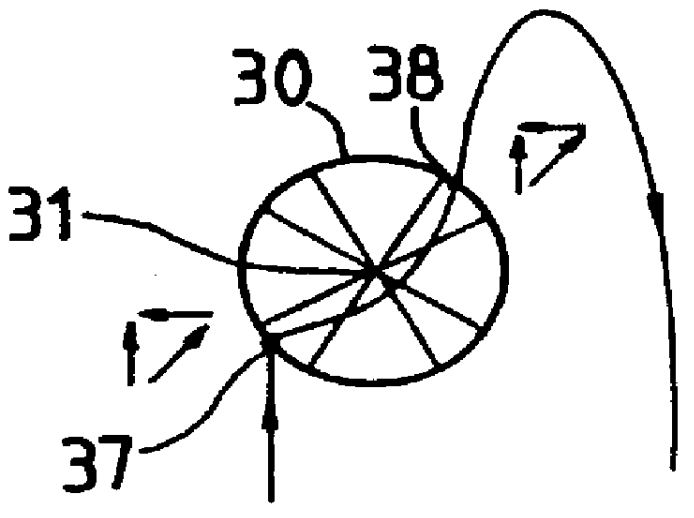
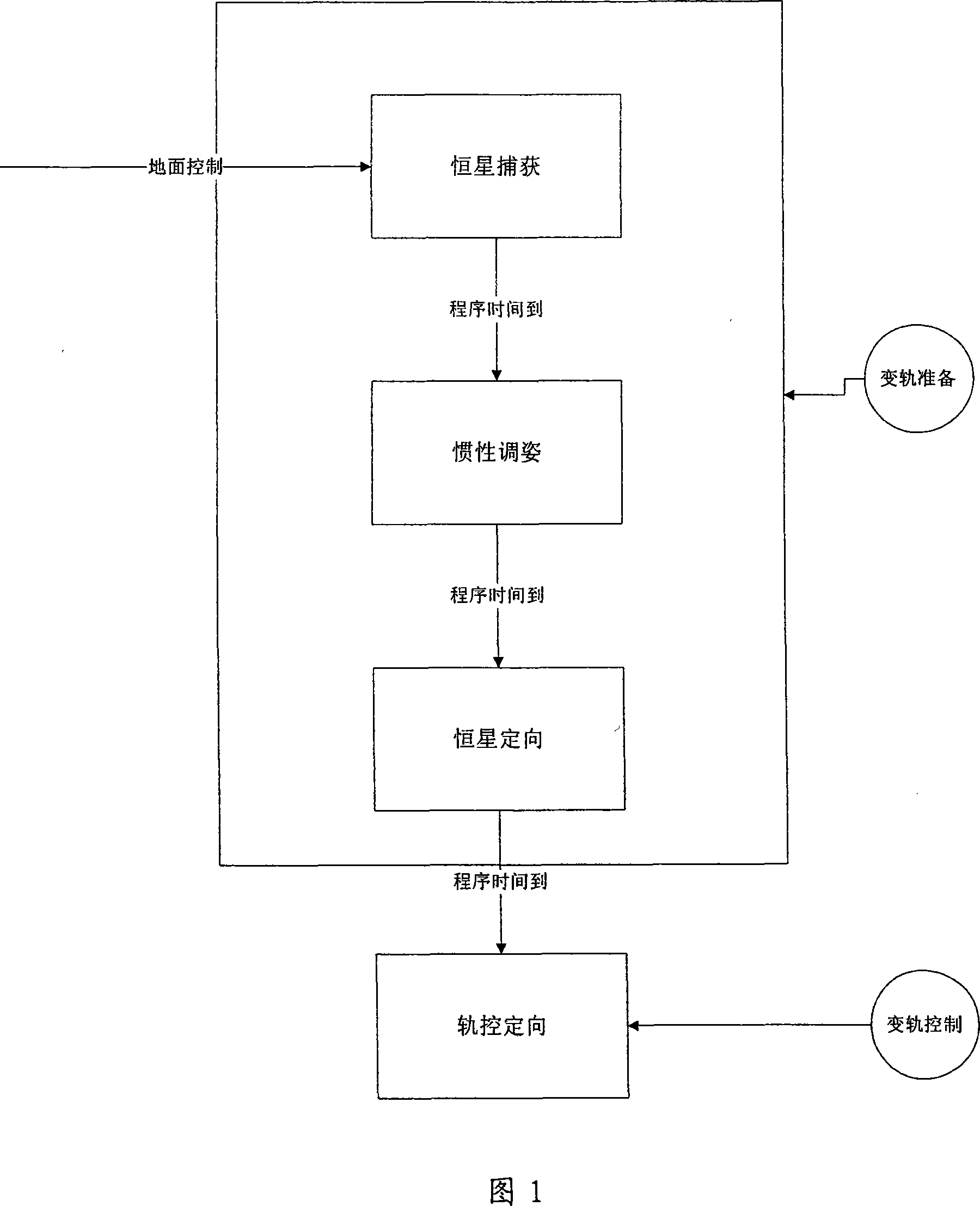
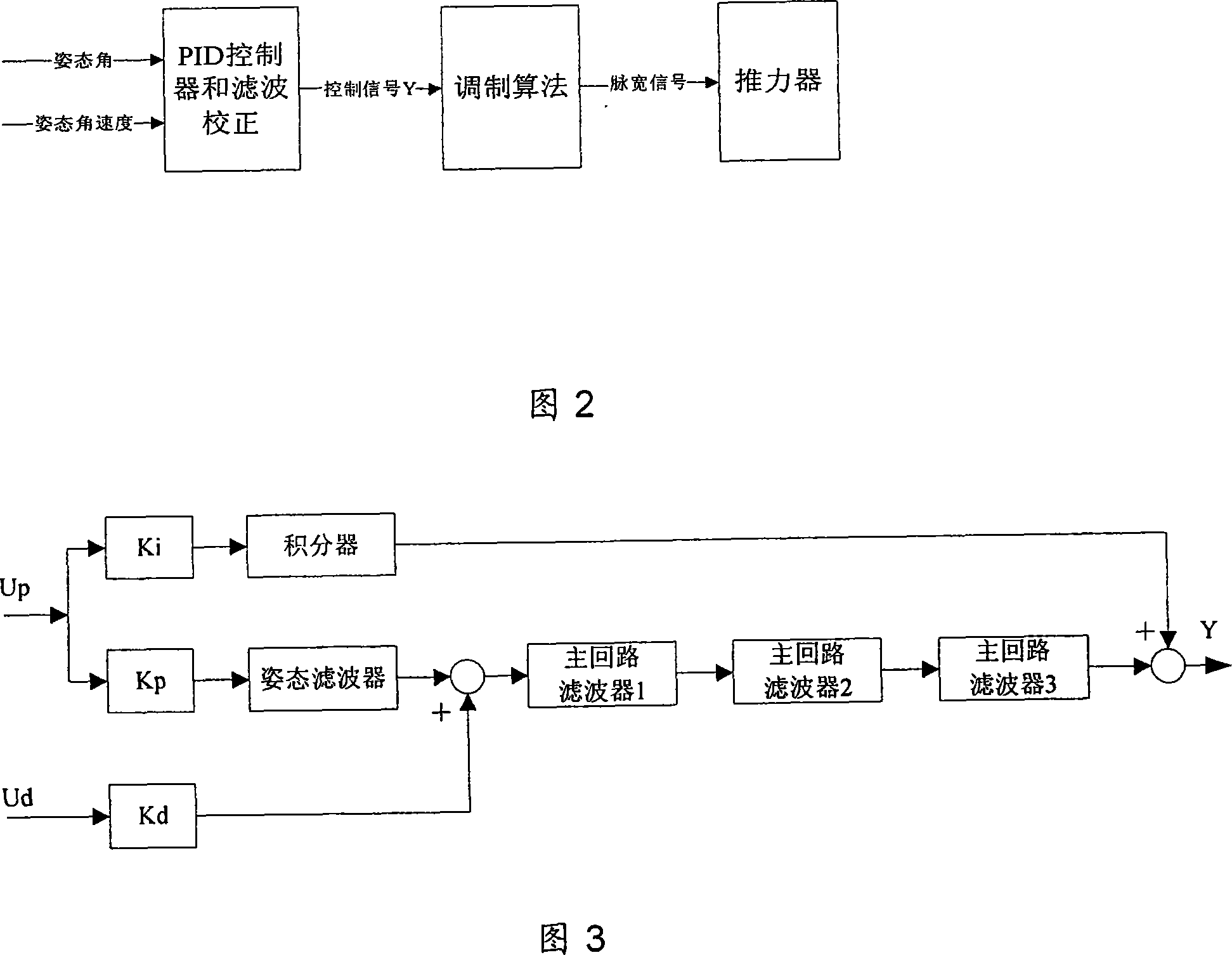
The invention relates to an independent orbital transfer of a satellite, comprising (1) star capture step, in which before the satellite establishes orbit-controlled ignition attitude, inertia attitude of the satellite is pre-estimated and satellite attitude is controlled; zero offset of gyro drift and an accelerometer is marked; (2) inertia attitude regulation step, used for establishing the orbit-controlled ignition attitude of the satellite, realizing maneuver of the satellite attitude, pre-estimating the inertia attitude of the satellite and a jet control is used for controlling the satellite attitude; (3) star orientation step, in which after the satellite establishes the orbit-controlled ignition attitude, a stable state control is carried out and a star sensor is used for filtering and correcting the satellite attitude; and (4) orbit-controlled orientation step, in which starting and shutdown control is carried out for a rail-controlled engine; the ignition attitude of the satellite is determined and attitude stable control is carried out in the period of the ignition. The invention solves the problem that spacecraft such as a deep space exploitation satellite transfers orbit, and ensures that the orbital transfer can be completed accurately and reliably.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Method for optimizing orbital transfer strategy of geostationary orbit satellite
ActiveCN102424116ASmall amount of calculationShort calculation timeArtificial satellitesGeostationary orbitGeosynchronous orbit
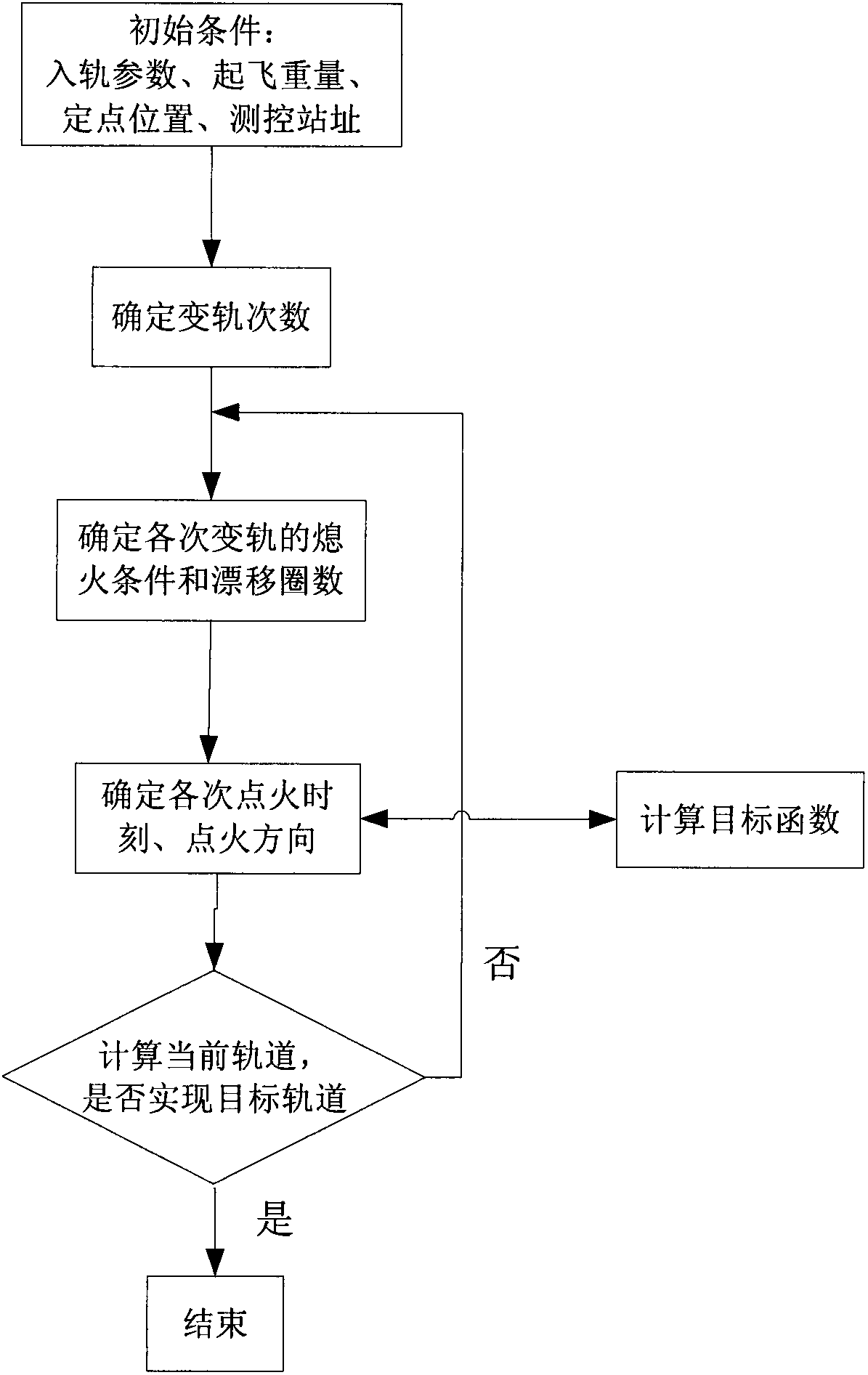
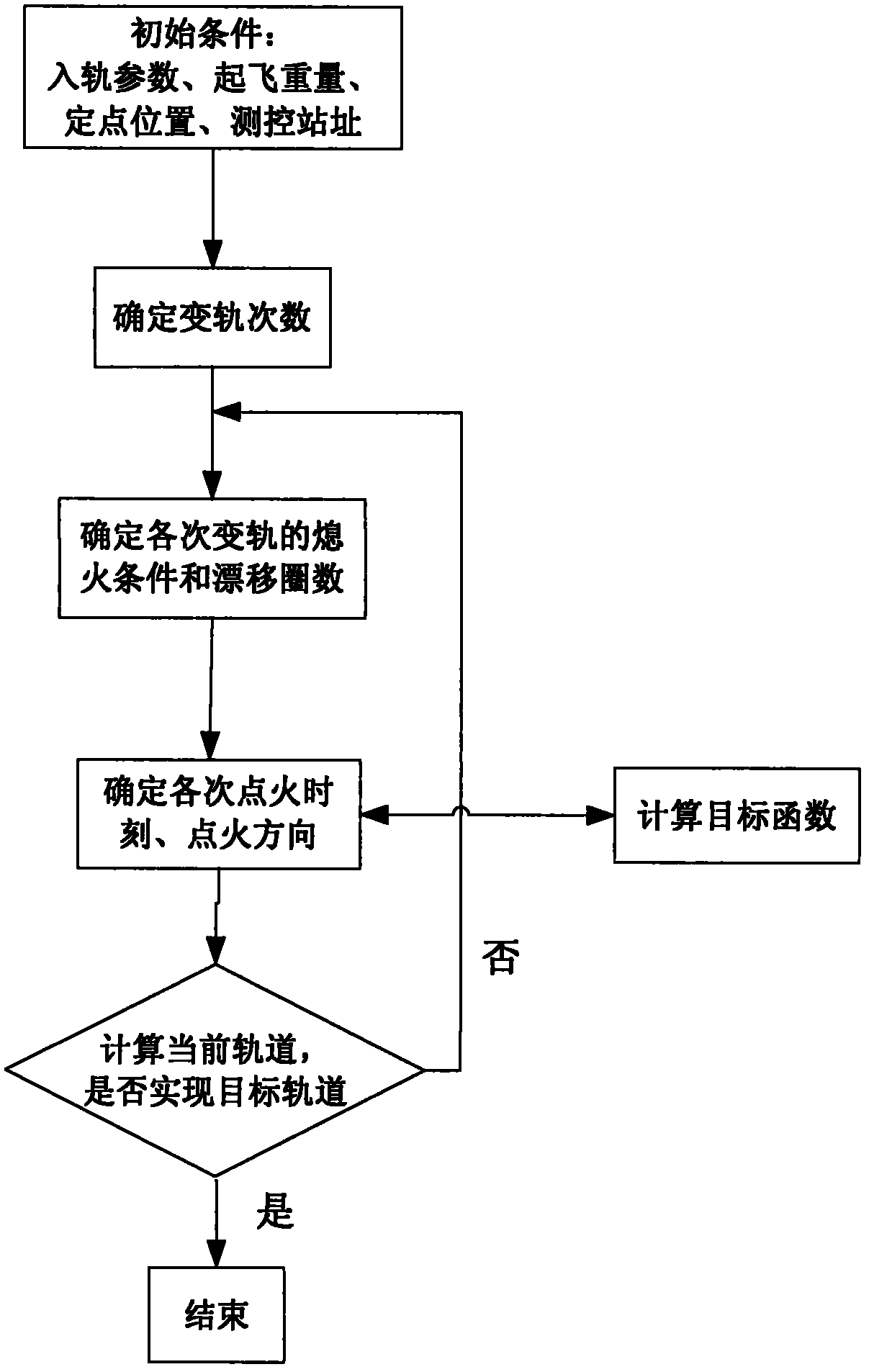
The invention relates to a method for optimizing an orbital transfer strategy of a geostationary orbit satellite, which comprises the following steps of: 1, determining orbital transfer times, orbital transfer circle times and the controlled variable of each-time orbital transfer; and 2, determining time and a thrust direction in each-time orbital transfer. The process of launching the geostationary orbit satellite at present generally comprises the following steps of: launching the satellite into a highly elliptic transfer orbit with an inclination angle by using a carrier rocket; performing apogee / perigee orbital transfer for several times by using a self-contained liquid engine of the satellite, and transferring to a geosynchronous orbit; and correcting and rounding the inclination angle of the orbit to realize a geostationary orbit. For the satellite, operation for changing the transfer orbit into the geostationary orbit by performing apogee / perigee orbital transfer for several times is complex, so too many orbital transfer times is not suitable, and orbital transfer complexity and risk are prevented from being increased; in addition, factors such as the capacity of the liquid engine of the satellite, arc segment loss in an orbital transfer period, and the like are considered, so too few orbital transfer times is not suitable.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
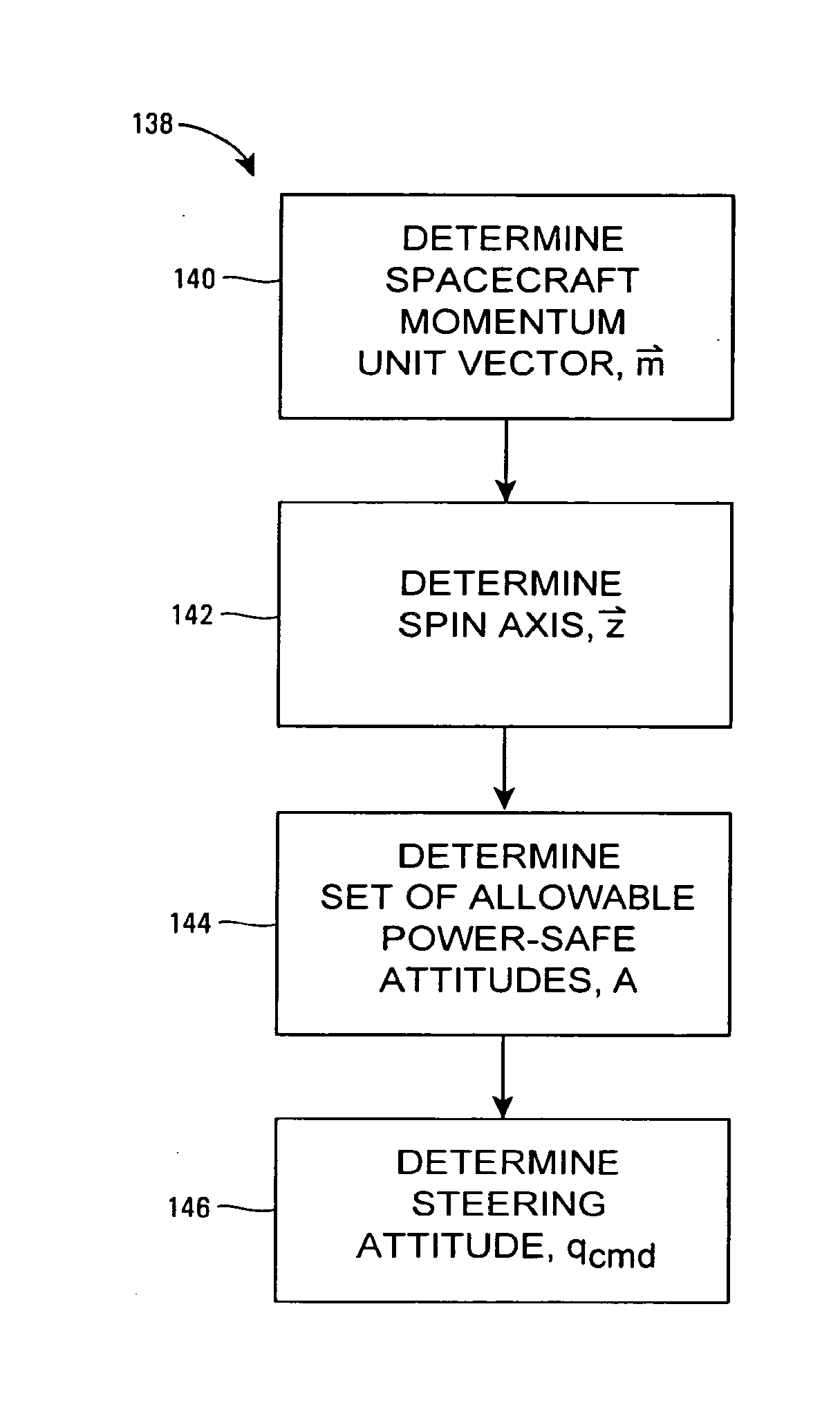
Unified attitude control for spacecraft transfer orbit operations
ActiveUS20070023579A1Launch systemsCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusAttitude controlEngineering
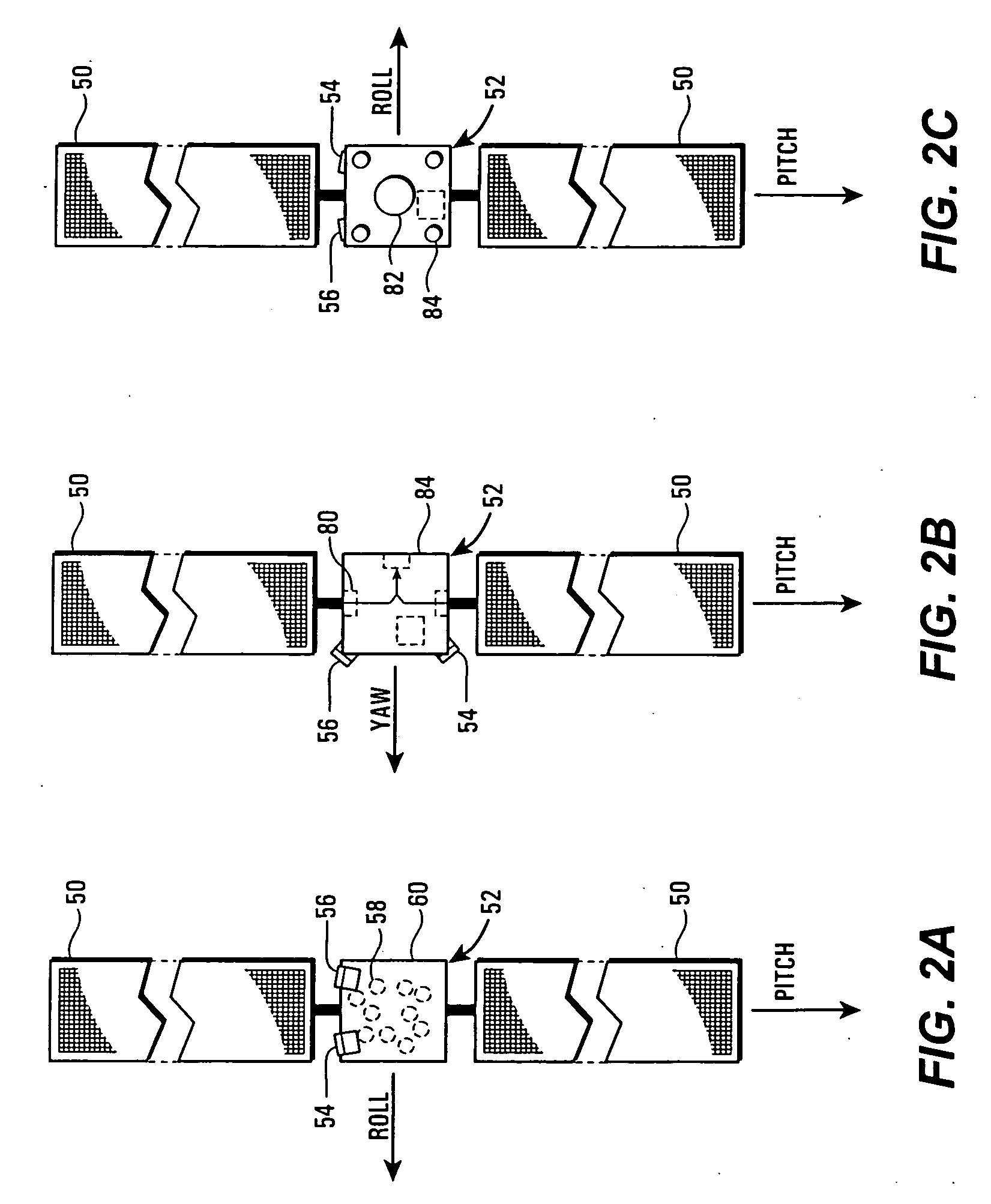
A method of controlling attitude of a spacecraft during a transfer orbit operation is provided. The method includes providing a slow spin rate, determining the attitude of the spacecraft using a unified sensor set, and controlling the attitude of the spacecraft using a unified control law. The use of a unified set of sensors and a unified control law reduces spacecraft complexity, cost, and weight.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Lightweight composite wall panel moulding apparatus and product line
ActiveCN101244581ASignificant progressFix fixMouldsCeramic shaping plantsProduction lineVehicle frame
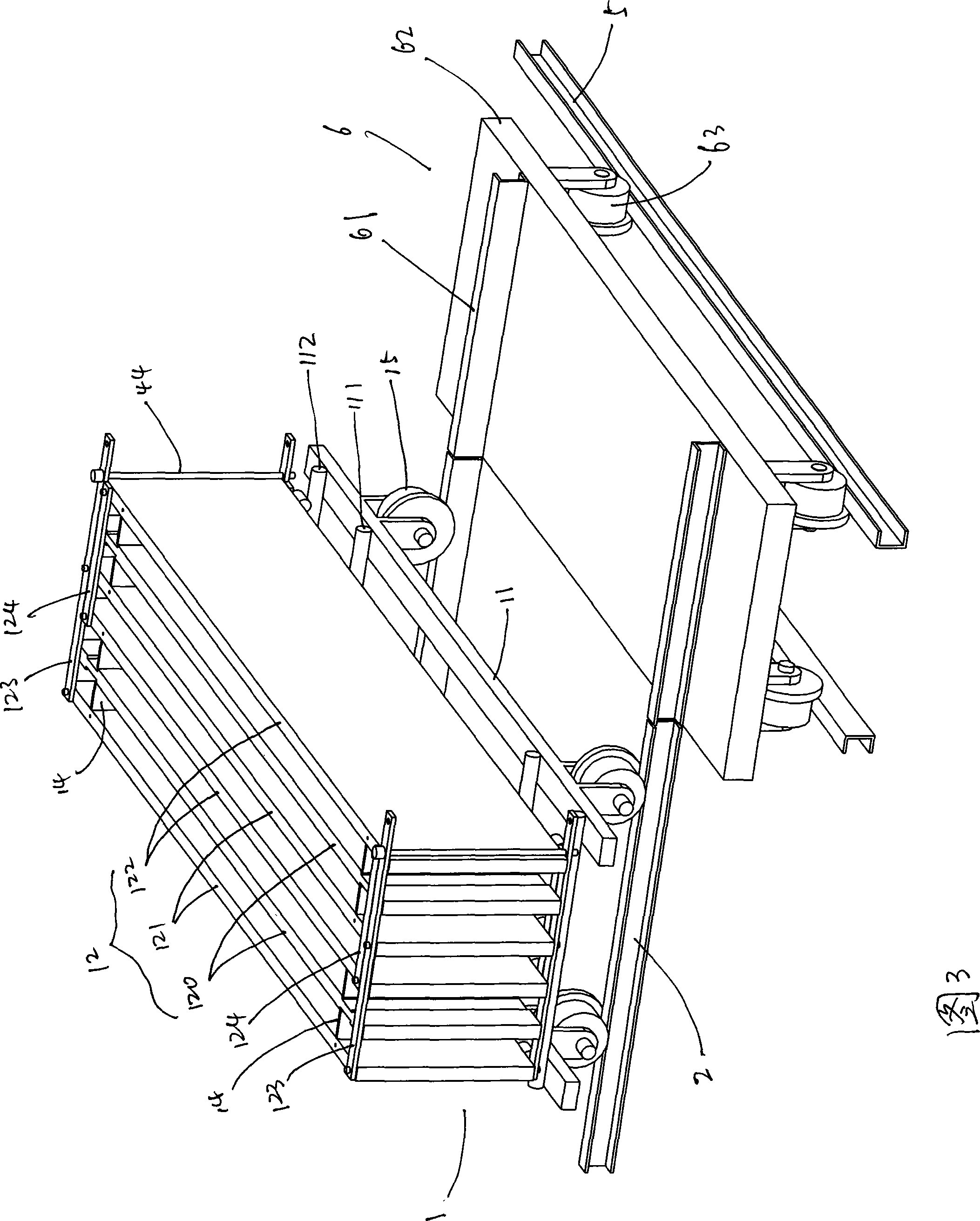
The invention provides a forming machine for a lightweight composite wallboard, which is characterized in that three side vertical templates are classified as a group; one template in the center of each group is the fixed template; two templates at two sides of each group are respectively the left moving template and right moving template; the fixed template is fixed at a frame; the left moving template, the right moving template, a left bed die band and a right bed die band are flexibly connected with the beams of the frame; each left moving template, right moving template, left bed die band and right die band are respectively connected with a plurality of link bars. The invention still provides a production line for lightweight composite wallboard. The production line is provided with a die car track and a sinking transfer orbit; a transfer wheelbarrow is arranged at the orbit; the forming machine can be arranged at the transfer wheelbarrow through a connection orbit or can enter into a die car orbit from the transfer wheelbarrow. The forming machine for a lightweight composite wallboard has the advantages of simple equipment and light weight, overcoming the defect that traditional wallboard forming machine is so big that the machine can not be moved; the side vertical template and bed die band adopt the grouping connection design, solving the problem of the heeling and opening of the side vertical template and the fixation of the bed die band; the open die facility is classified and the operation becomes very convenient; the wallboard production line uses flow shop and the forming machine is handled movably according to the working procedure, improving work efficiency.
Owner:广州市建筑材料工业研究所有限公司
Deployable spacecraft mount for electric propulsion
InactiveUS7059571B2Deleterious effectImprove cooling effectCosmonautic environmental control arrangementLaunch systemsElectricityTransfer orbit
An apparatus and method including a deployable spacecraft mount for electric propulsion is disclosed. A typical apparatus includes a spacecraft body, a deployable element having at least two basic positions including a compact stowed position and a deployed position of the element and an electric thruster disposed on the deployable element where the electric thruster is disposed to mitigate negative plume effects in the deployed position that would be present in stowed position. The deployable element can be a radiator and can optionally be disposed on a second deployable payload module. Further, deployable elements can be selective deployed such that some electric thrusters can be used to assist in transfer orbit while undeployed elements help retain heat.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Interplanetary transfer orbit design method
InactiveCN103112600ASmall amount of calculationRapid designCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsAviationDelta-v
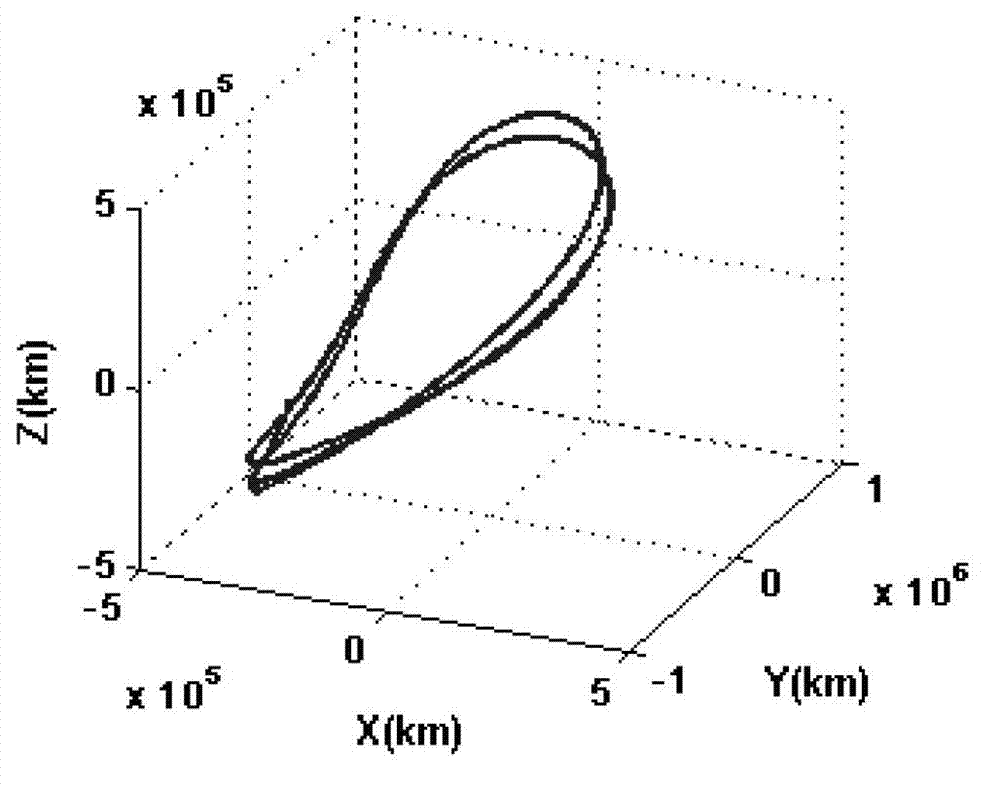
The invention relates to an interplanetary transfer orbit design method, in particular to a transfer orbit design method from a periodical orbit which is near dynamic balance points of a three-body system to a small celestial body and belongs to the technical field of aerospace. Firstly, based on the periodical orbit which is near the dynamic balance points of the three-body system where a detector is located, an initial state of the detector x0=[ r0, v0] is assumed. Secondly, a speed increment delta v is exerted along a tangential direction so that the detector sets off from the periodical orbit near the dynamic balance points. Based on a multiple-body model, relations between the detector and a distance df of the detector and the target small celestial body, a flying period tf and the tangential direction speed increment delta v are built up when the detector flies across the target small celestial body is built. Through an optimizing algorithm, an initial value of the transfer orbit is obtained when the fight distance df is minimum. Finally, a secondary-level differential correction method is used based on the initial value to obtain orbit parameters which can meet two point boundary values. The interplanetary transfer orbit design method can achieve rapid design of flight from the periodical orbit which is near the dynamic balance points of the three-body system to the small celestial body, calculation amount is small and efficiency is high.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Staircase portal frame assembling fixture and assembling method thereof
ActiveCN102166715AScientific and reasonable designEasy to useMetal working apparatusEngineeringPortal frame
The invention relates to a staircase portal frame assembling fixture and an assembling method thereof. The staircase portal frame assembling fixture comprises a portal frame guide rail (7), a portal frame location dolly (10), a station transfer orbit (17), a station transfer dolly (28), a clamping location dolly guide rail (6), an upper clamping location dolly (4) and a lower clamping location dolly (8), and further comprises an upper fixture location base (10), a lower precise hoisting fixture (9), a lower fixture location base (11), a lower portal frame location dolly (10) and a middle portal frame location dolly. The invention further provides an assembling method of the staircase portal frame assembling fixture. The invention fills in a gap in the prior art, solves the bottleneck of assembling the portal frame station, and has the advantages of high degree of automation, high efficiency, high precision and simple and power-saving operation.
Owner:HANGZHOU XO ELEVATOR
Geostationary orbit spacecraft electrical propulsion transfer track control method
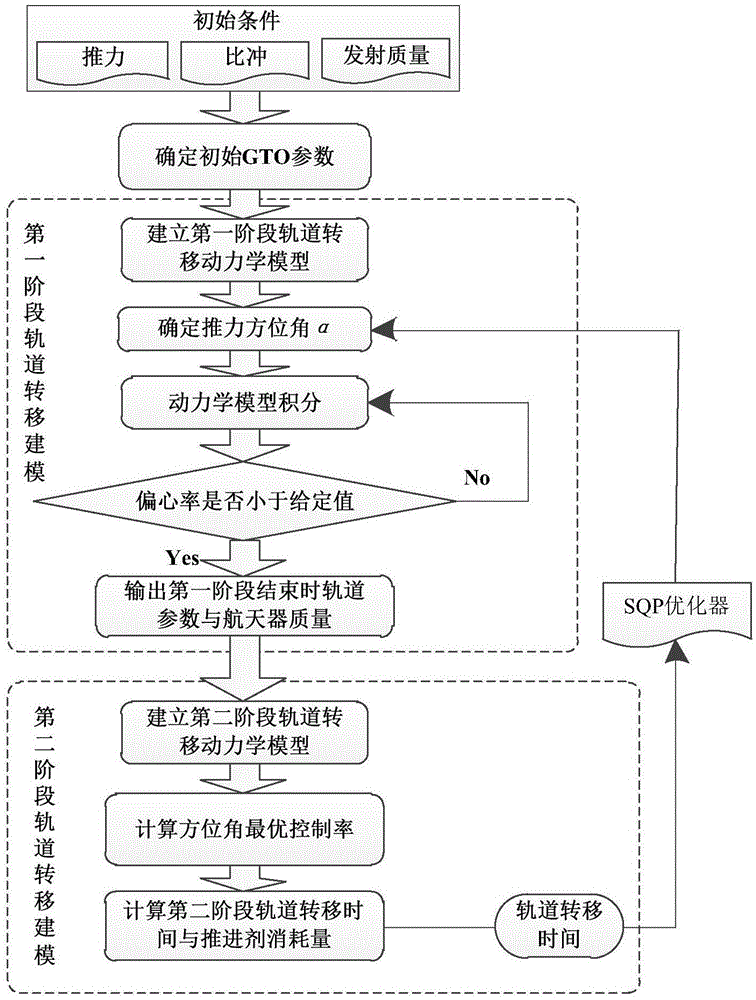
The invention relates to a geostationary orbit spacecraft electrical propulsion transfer track control method. The method comprises the following steps: determining initial conditions, a carrier rocket transmitting a geostationary orbit spacecraft to a first initial orbit, and determining a Kepler radical of the first initial orbit; establishing a first initial orbit kinetic equation by means of the Kepler radical, reducing the orbit inclination angle of the first initial orbit through a thrust azimuth alpha and performing rounding to obtain a second initial orbit, and obtaining transfer time tf1 and a propellant consumption amount mfuel1; fixing a thrust accelerated speed in a second preset plane, transferring the second initial orbit through a thrust azimuth beta to a geostationary orbit, and obtaining transfer time tf2 and a propellant consumption amount mfuel2; calculating total time tf=tf1+tf2 of a geostationary orbit transfer process and a propellant consumption amount of the transfer process; and by taking minimization of the geostationary orbit total time tf as a design object, optimizing the thrust azimuth alpha at a first initial orbit phase to obtain an optimal geostationary orbit transferring scheme.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Packaged food packaging system
InactiveCN104554910AReduce labor intensityReduce security risksPackage sterilisationWrapper twisting/gatheringFood safetyEngineering
The invention discloses a packaged food packaging system and belongs to the technical field of mechanical equipment for food. The packaged food packaging system solves the problem of low production efficiency of the prior art. The packaged food packaging system comprises a charging orbit, a packaging bag opening / closing mechanism, a bag discharge orbit, a plate filling mechanism, a plate stacking mechanism, a plate transfer orbit, a bag discharging mechanism, a sterilizing mechanism, a drying mechanism, a bag arranging mechanism, a binning mechanism and an automatic bin sealing mechanism connected in sequence. The packaged food packaging system integrates automatic feeding, automatic sealing, automatic bag discharge, automatic plate filling, automatic plate stacking, automatic plate transfer, automatic bag discharging, automatic sterilizing, automatic drying, automatic bag arranging, automatic binning and automatic bin sealing, the production staff number in a workshop is greatly reduced, the labor intensity is lowered, and the production efficiency is improved; because the packaged food packaging system rarely depends on manpower, the probability of carrying bacteria and impurities into food packaging bags by operators is less, and the potential safety hazard of food is lowered; the system is compact and centralized, and accordingly the space is saved.
Owner:HANGZHOU FUYANG FUSHIDE FOOD CO LTD
Pulse and pneumatic assistance combination-based low-orbit orbit plane transfer method
InactiveCN106383994AGreat changeabilityIncrease flexibilitySpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsAviationDynamic equation
The invention discloses a pulse and pneumatic assistance combination-based low-orbit orbit plane transfer method, relates to a large-range orbit plane transfer method for an earth low-orbit spacecraft, and belongs to the field of aerospace. The method comprises the steps of firstly establishing the number of orbits and a dynamic equation of a flight process in atmosphere; changing an orbit of the spacecraft to a highly elliptic orbit in a maneuvering manner by applying a pulse, and enabling the spacecraft to enter the atmosphere by applying an de-orbit pulse at an apogee; selecting an optimization target as a maximum change amount of an orbit plane, giving constraints and obtaining an optimal control rate and a terminal state variable meeting aerodynamic requirements, thereby finishing pneumatic assisted orbit plane transfer; and enabling the spacecraft to fly out of the atmosphere and run to a target orbit height along a transfer orbit, and enabling the spacecraft to enter a target orbit by applying an orbit determination pulse. According to the method, the orbit plane transfer of the low-orbit spacecraft can be finished with relatively low fuel consumption; and the method is good in robustness, high in repeatability, small in influence of spacecraft orbit orientation, high in flexibility of a pneumatic assistance process, and wide in application range for the target orbit.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Interplanetary low-thrust transfer orbit design method based on polynomial approximation
InactiveCN102424119ARapid designReduce design difficultyCosmonautic componentsPerformance indexEngineering
The invention relates to an interplanetary low-thrust transfer orbit design method based on polynomial approximation. Firstly, variable initial value guess is designed, the initial value guess of the transfer orbit design is given, then, the beginning and tail end boundary conditions of a detector are calculated, next, a second type Chebyshev polynomial is adopted for fitting the transfer orbit of the detector, the performance indexes and the constrained conditions are calculated, finally, whether the feasibility conditions are met or not is judged according to the calculated thrust restriction in accordance with whether the calculated performance indexes meet the optimum conditions or not, if all requirements are met, the optimization is successful, the optimum transfer orbit is obtained, and if one requirement is not met, the initial value guess of the design variable in the first step is regulated until the optimization is successful. The method utilizes the Chebyshev polynomial for approximating the low-thrust transfer orbit shape, the time is used as the independent variable, and the flight time restriction is avoided. The polynomial factor is determined through the beginning and tail end orbit state restriction of the detector, and the method has the advantage that the fast design on the low-thrust transfer orbits in different task types can be realized according to the given beginning and tail end boundary conditions.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Glass pipe cutting device
InactiveCN101234849AUnbreakableIncrease productivityGlass severing apparatusDrive wheelBreak the glass
The invention relates to a device for cutting a glass tube, which is characterized by comprising a glass tube transferring device, a glass tube positioning device, a glass tube cutting device and a controlling device on a chassis, wherein, the glass tube transferring device consists of a transferring orbit and a glass tube clamping and transferring device on the transferring orbit; the glass tube clamping and transferring device consists of a cramp and a power device driving the cramp to move forward and backward; the glass tube positioning device consists of a pair of driving wheels arranged on ends of the transferring orbit, a power mechanism of the driving wheels which drives the driving wheels to rotate, a pressing wheel above the driving wheels, and a positioning baffle in front of the driving wheels; the glass tube cutting device consists of a cutting flywheel knife mechanism arranged on the chassis in the manner of swinging, a flywheel knife power mechanism which is arranged on the chassis and drives the flywheel knife on the cutting flywheel knife mechanism to rotate, and a power swinging mechanism which drives the cutting flywheel knife mechanism to swing. Compared with the prior art, the device for cutting the glass tube has the advantages of high production efficiency, stable production quality, and little possibility of breaking the glass tube.
Owner:李家凌
Free return lunar flyby transfer method for geosynchronous satellites havint multiple perilune stages
InactiveUS6149103ALaunch systemsInstruments for comonautical navigationLeading edgeGeosynchronous satellite
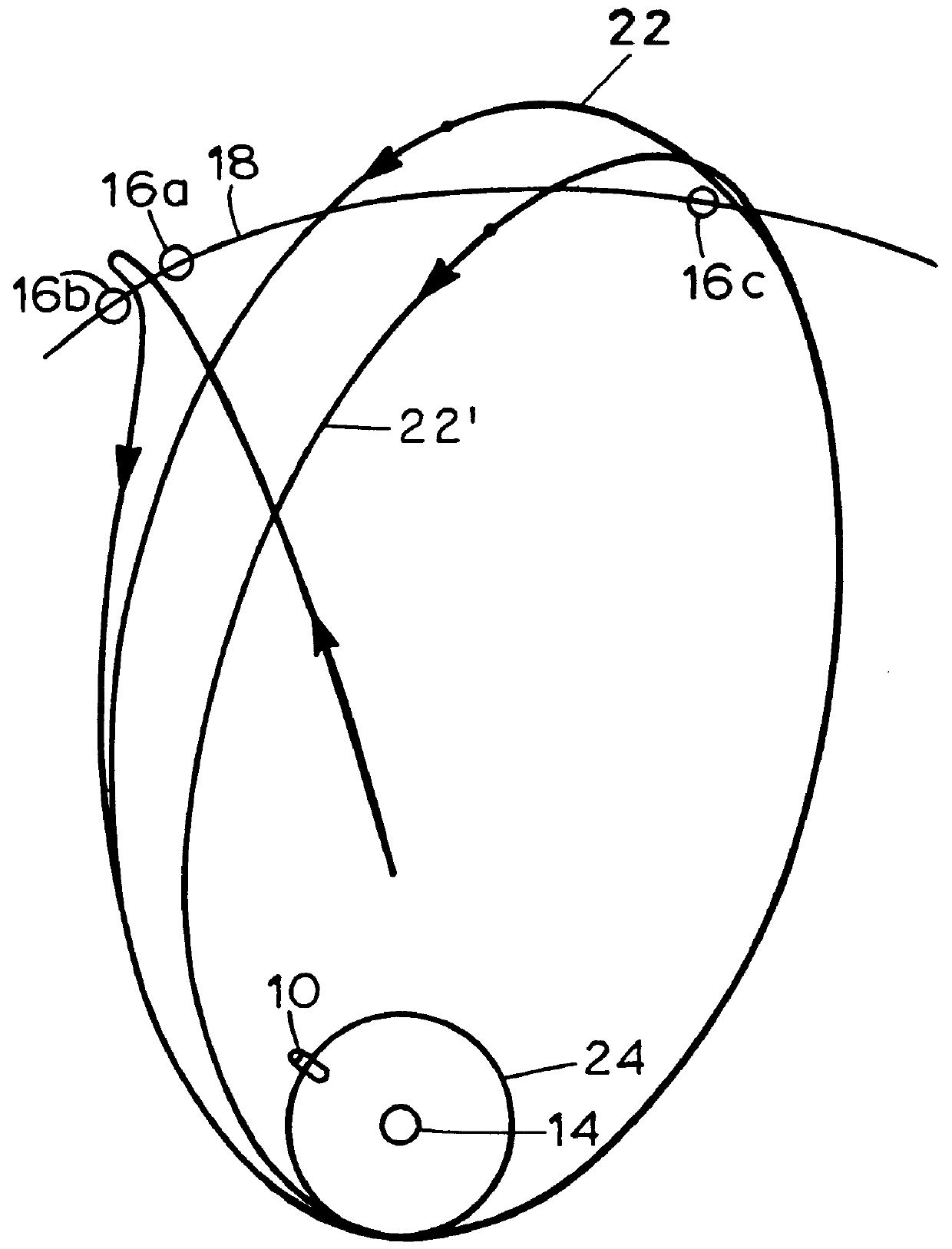
A method is provided for using at least two lunar flyby maneuvers to transfer a satellite from a quasi-geosynchronous transfer orbit having a high inclination to a final geosynchronous orbit having a low inclination. The invention may be used to take the inclination of a final geosynchronous orbit of a satellite to zero, through the use of a first leading-edge lunar flyby and subsequent successive leading or trailing edge lunar flybys resulting in a geostationary orbit.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
Detector emission method employing force-borrow mechanism to select space detection target
The invention relates to a method for emitting detector which can select the detected target via swing-by mechanism, belonging to the technique of deep space detecting rail transfer. It can solve the problems of approachability evaluation of detected target with long semi long axis or large eccentric rate. The inventive method comprises: calculating optimized dual impulse transfer track; selecting swing-by track type; and assembling the swing-by tracks. First calculating the optimized dual impulse transfer track from the target star to emitting star; using the emitting star as swing-by star; using the parameter of dual impulse transfer at the emitting star as the match parameter in swing-by flying; using the heliocentric large-ellipse orbit whose period is several times of the revolution period of emitting star and the deep space device at aphelion, to search for the emitting parameter of said match condition. The invention guides in the swing-by mechanism to realize the expansion of former dual impulse transfer, to improve the approachability of the target with long semi long axis or large eccentric rate.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
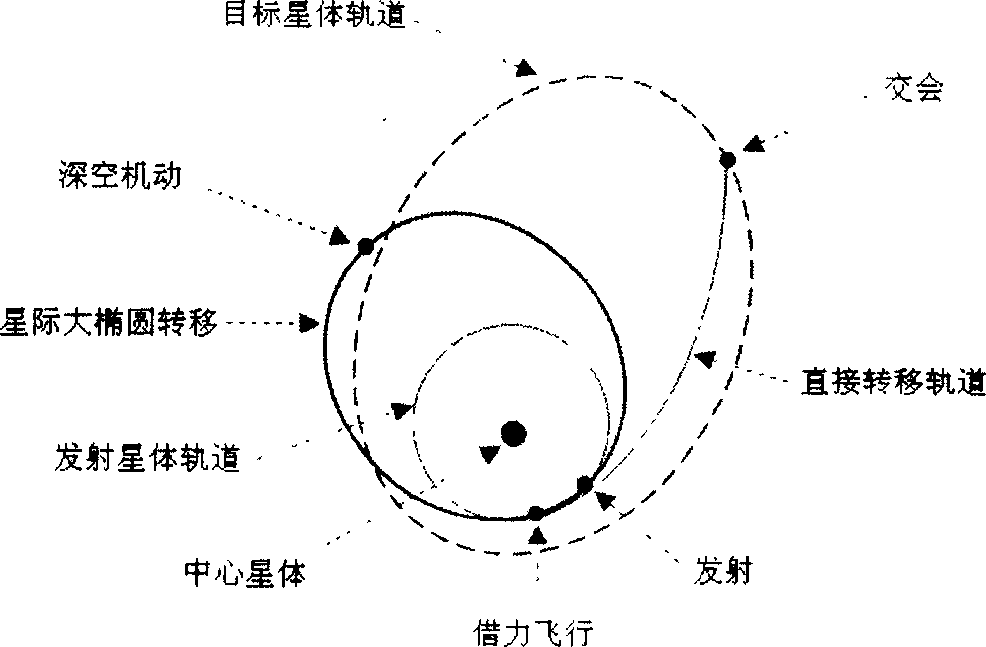
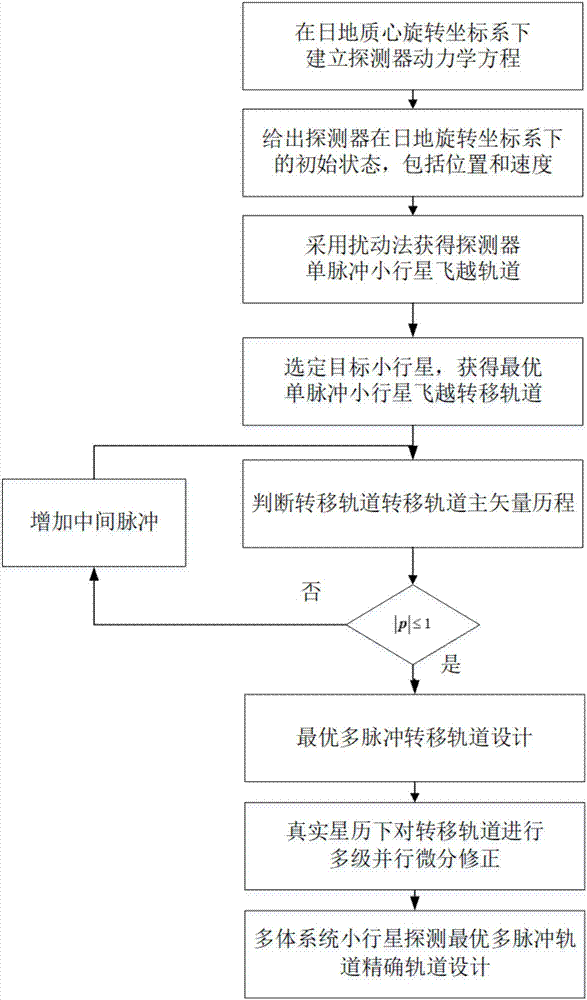
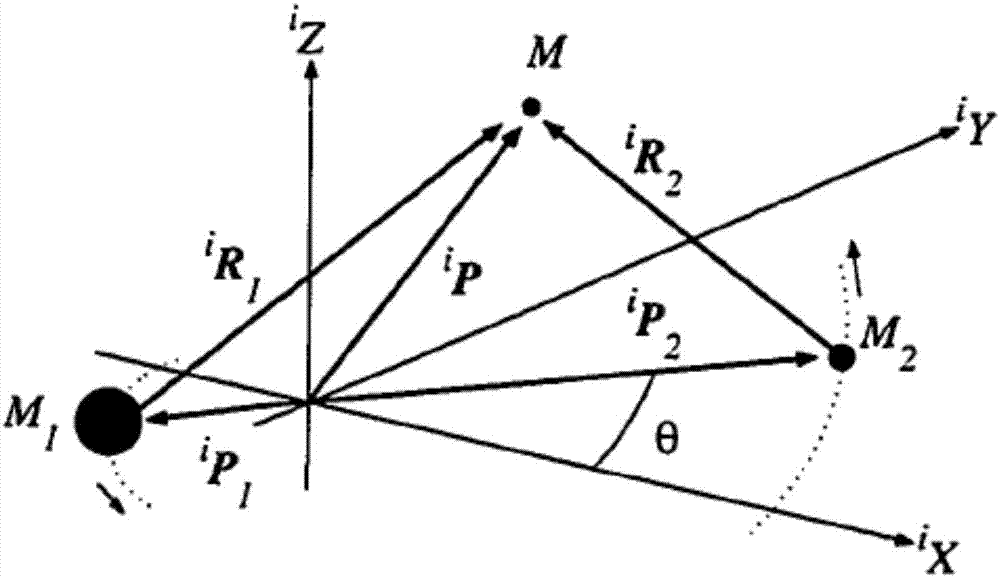
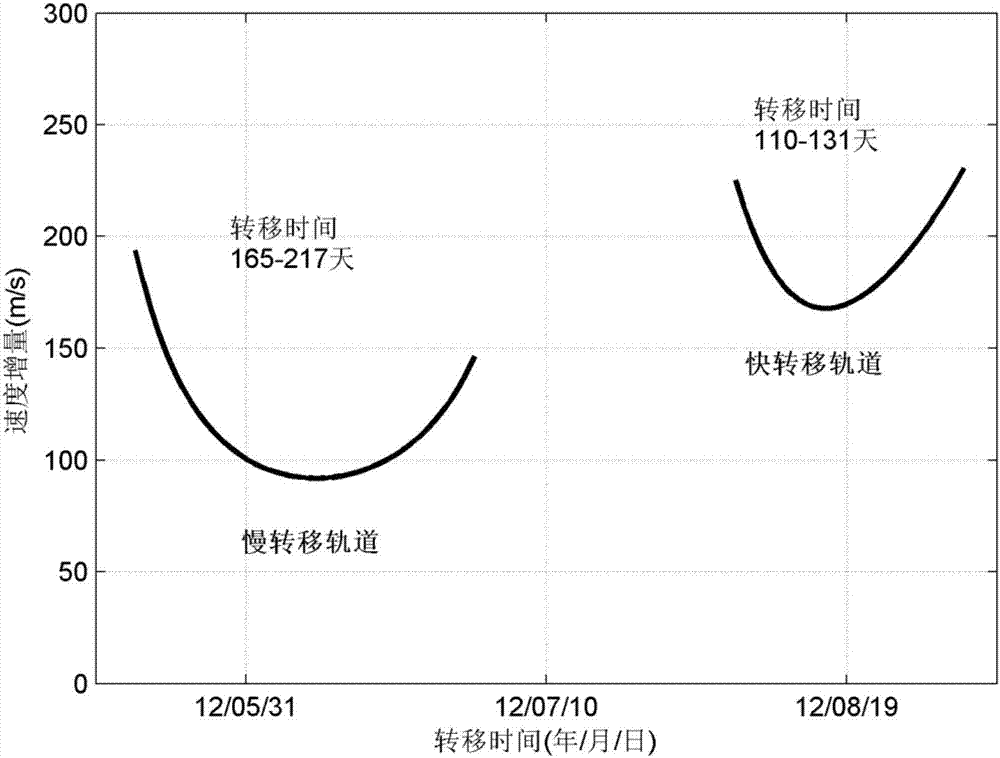
Minor planet detection optimal multi-impulse transfer method of interplanetary multibody system
InactiveCN107992682ASmall speed incrementOptimal velocity increment for asteroid detectionCosmonautic vehiclesDesign optimisation/simulationAviationVector theory
The invention discloses a minor planet detection optimal multi-impulse transfer method of an interplanetary multibody system, and belongs to the technical field of aerospace engineering. The method includes steps of firstly, building a detector kinetic equation under a geological core rotating system, namely, a high-precision kinetic model; selecting a target minor planet according to task restriction and providing an initial state of the detector under the geological core rotating coordinate system; applying a disturbance method to obtain a detector single-impulse minor planet flyover track;applying an optimization algorithm to obtain a single-impulse minor planet flyover transfer track with the minimum flyover distance; based on a main vector theory, performing a multi-impulse transfertrack design, and acquiring an optimal multi-impulse transfer track which meets the main vector condition; bringing the acquired optimal multi-impulse transfer track to the high-precision kinetic model to progressively induce; amending the transfer track by a multi-grade parallel differential amending method, and realizing the accurate track transfer of minor planet detection under a multi-celestial-body strong disturbance nonlinear environment. The minor planet detection optimal multi-impulse transfer method has the advantages of small speed increment, good applicability, and good astringency.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Fault photo-detection method for earth synchronous transfer orbit satellite in orbit
InactiveCN101450716AHigh sensitivityHigh precisionCosmonautic vehicle trackingAttitude controlTransfer orbit
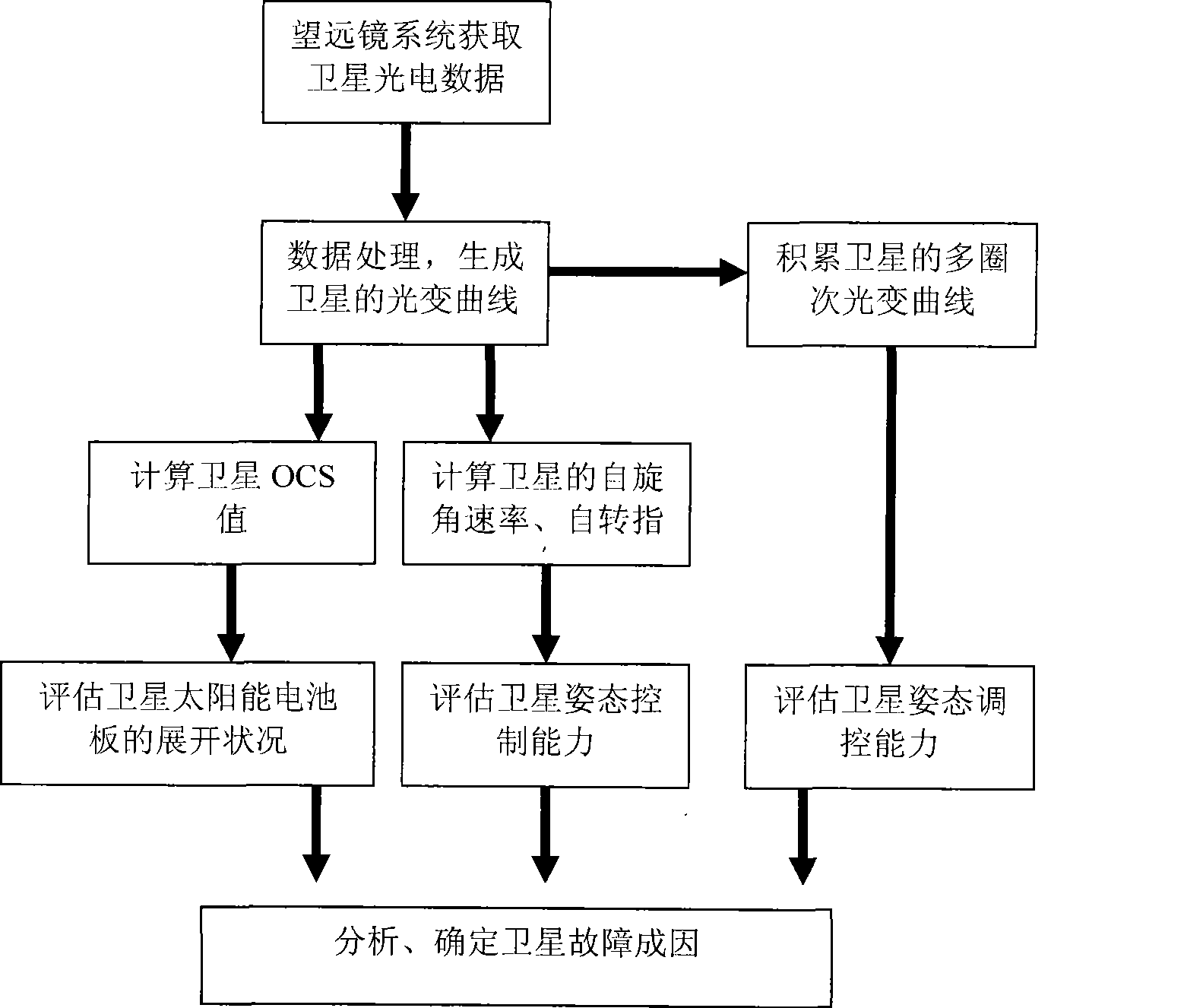
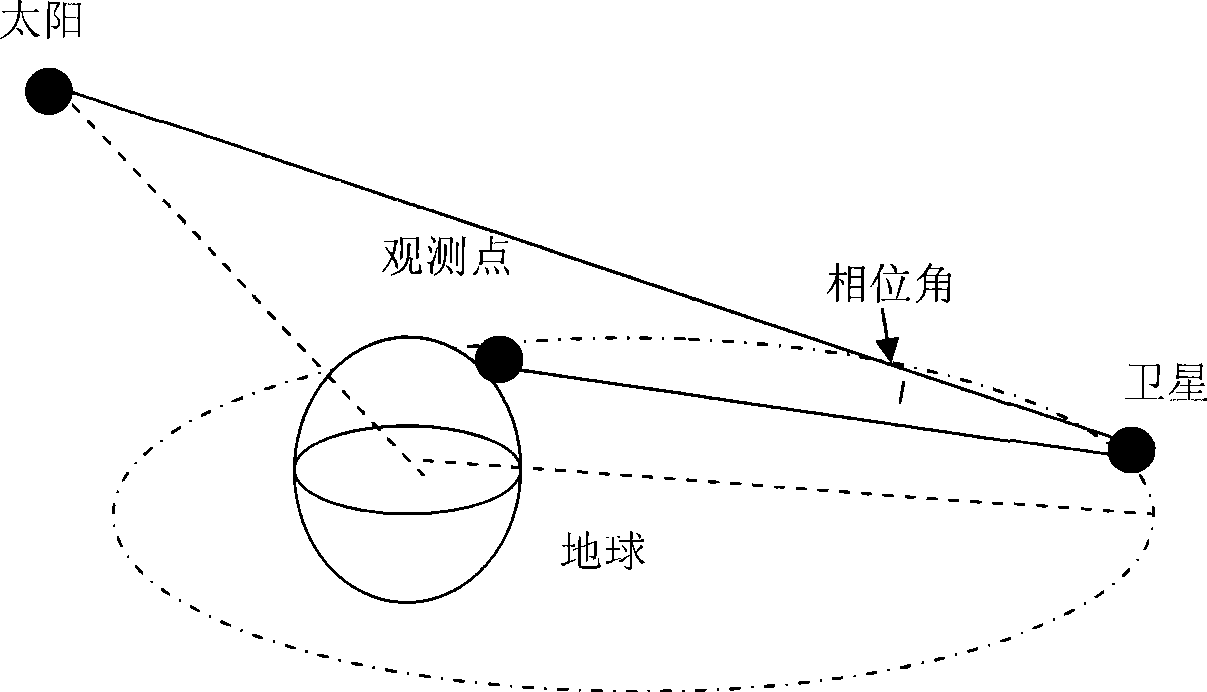
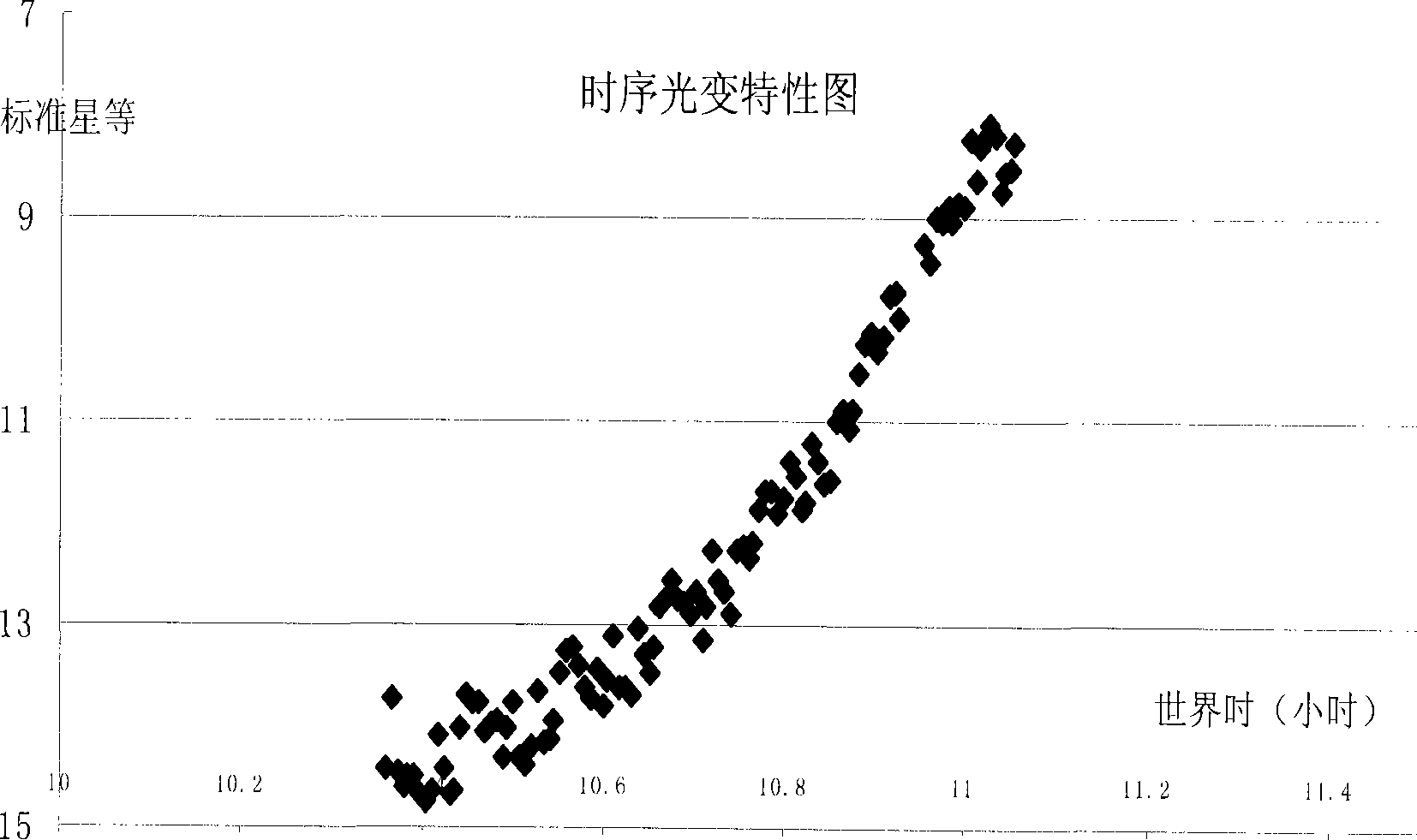
The invention is a photoelectric detection method for a satellite fault in a geostationary transfer orbit. The method comprises: acquiring a light curve of the satellite in the geostationary transfer orbit by an optical telescope detection system; obtaining an OCS value of a target through analyzing a phase angle sequence light characteristic curve, to evaluate the unfolding state of a solar panel of the satellite; obtaining an angular spin rate of the target through analyzing a time sequence light characteristic curve, to evaluate satellite platform attitude control capacity; and evaluating satellite platform attitude regulation and control capacity through accumulating multi-circle satellite phase angle sequence light characteristic curve, so as to evaluate satellite fault state and provide possibility of rescuing the satellite in time. The method does not depend on a sensor and downlink communication data of the satellite system, and has the property of passive receiving, and characteristics of high sensitivity, high precision, long detection distance, capability of observing in real time, quick data processing and so on.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
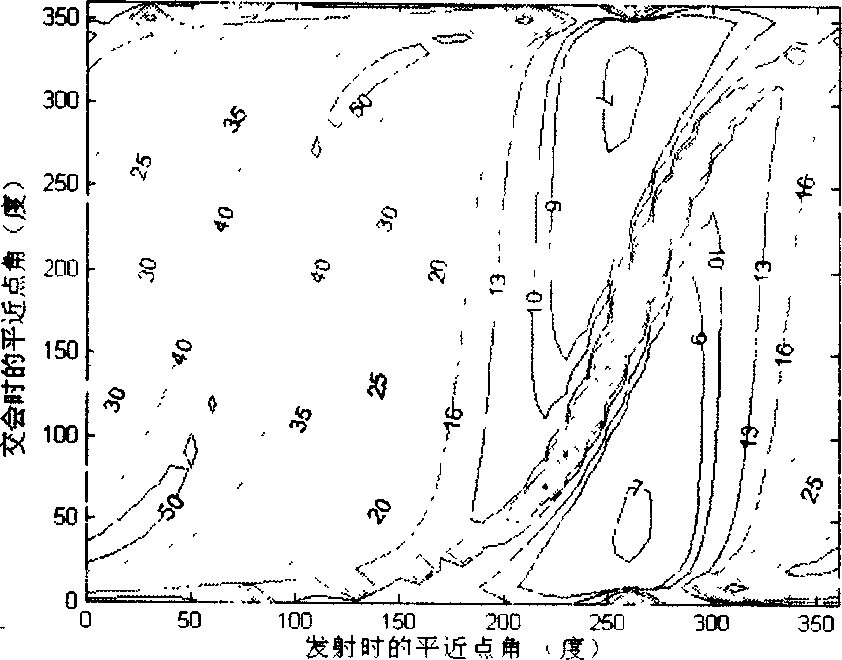
Search method for multi-constrained earth-moon transfer orbit cluster with equal launch intervals
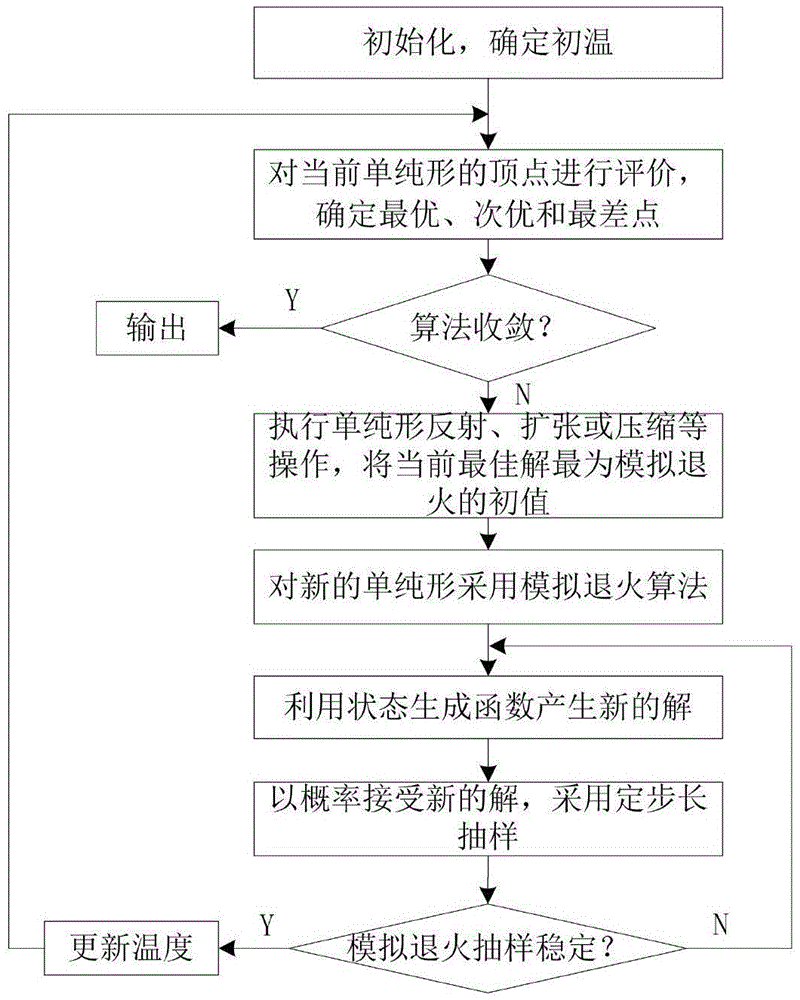
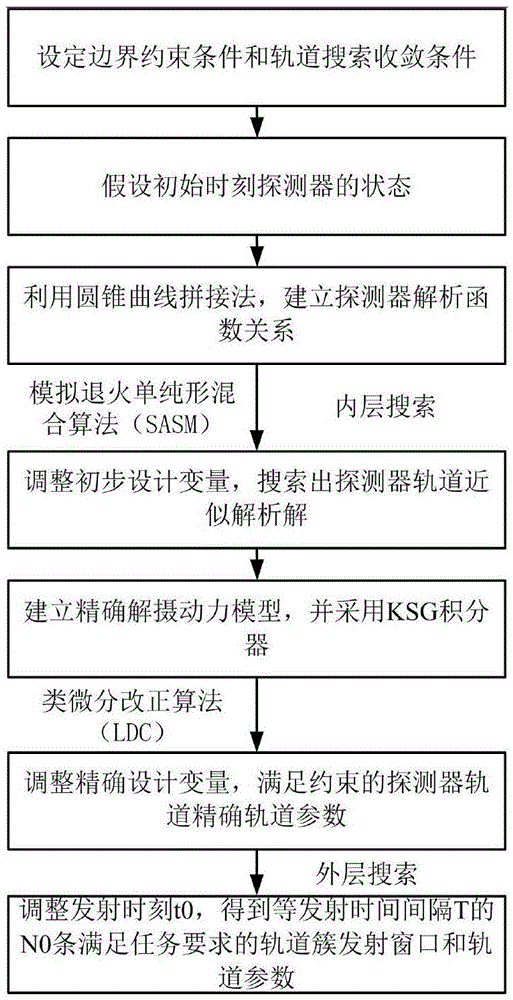
InactiveCN105631095AGuaranteed normal launchSpecial data processing applicationsRocket launchDifferential correction
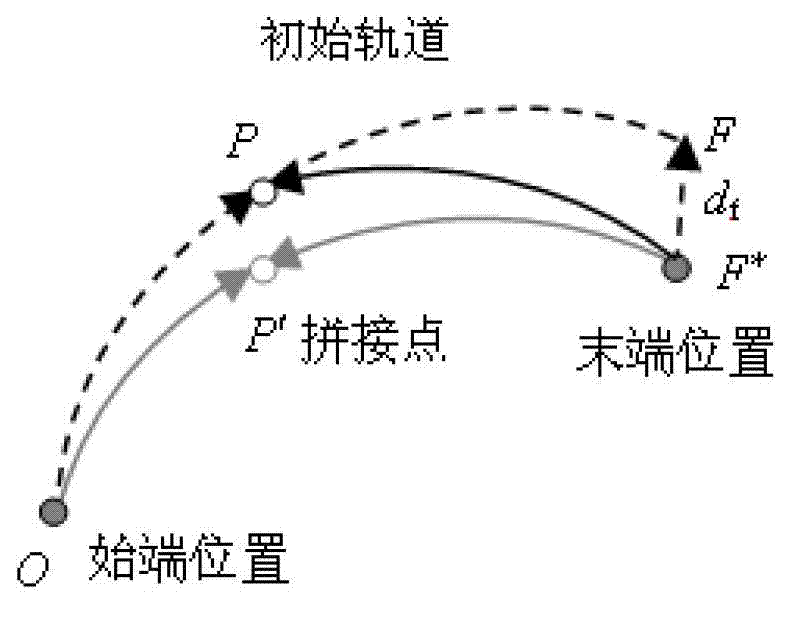
The present invention provides a search method for a multi-constrained earth-moon transfer orbit cluster with equal launch intervals. The method is used for designing n earth-moon transfer orbit clusters meeting multiple constraints and with equal launch intervals within a launch day, and the method takes full advantage of a feature that rocket launch parameters can be adjusted. The method is completed through outer-layer and inner-layer search, and the inner-layer search comprises preliminary search and refine search of a single orbit. A preliminary orbit search algorithm adopts a simulated annealing simplex hybrid algorithm, and a refine orbit search algorithm adopts a class differential correction algorithm. Firstly, preliminary design and search of the orbit are carried out based on an improved conic curve splicing method, an initial orbit parameter value is rapidly calculated, the refine orbit search algorithm is used to carry out refine design on the orbit, and an earth-moon orbit meeting the constrained condition is obtained. The outer-layer search completes continuous multi-orbit search with equal launch intervals, so that n earth-moon transfer orbits meeting the multiple constrained conditions with equal launch intervals are finally obtained.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method for designing earth-moon libration point transfer orbit via moon leveraging constraint
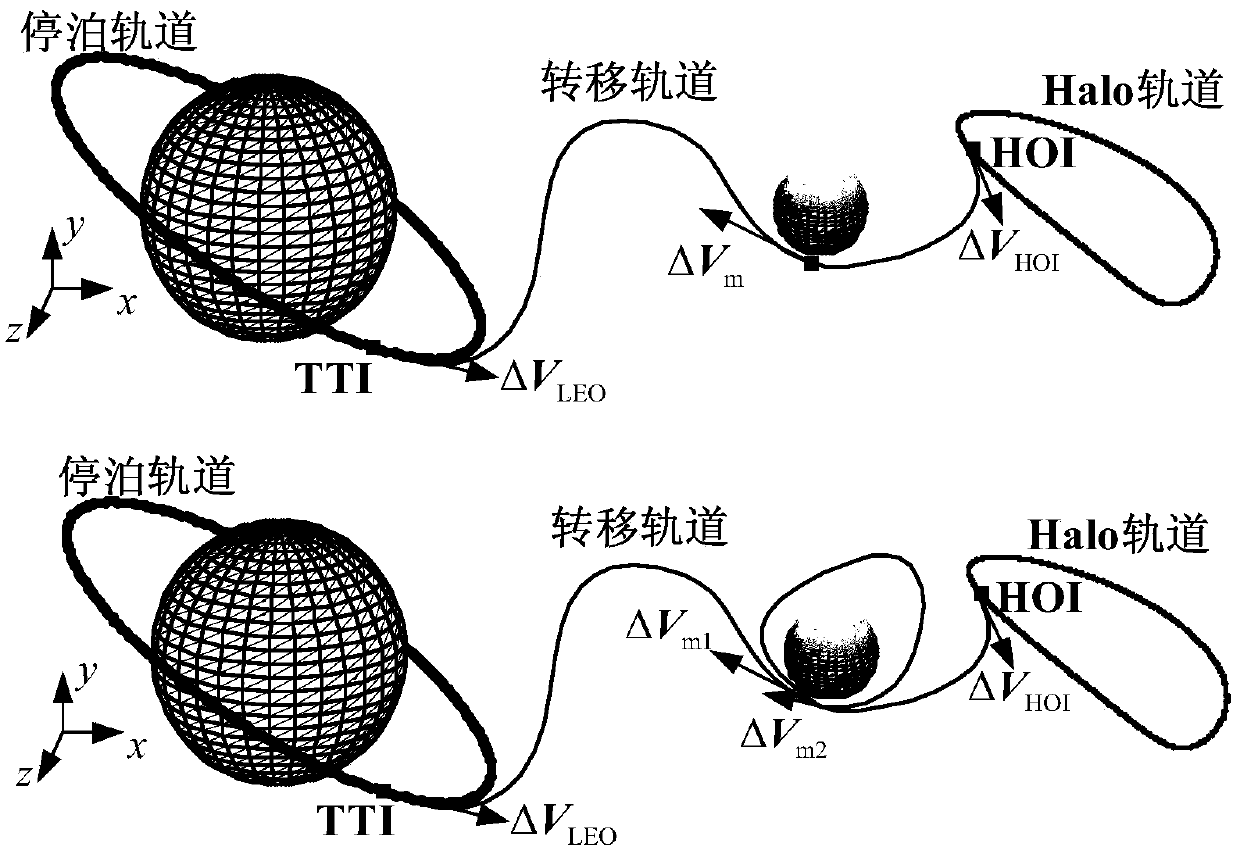
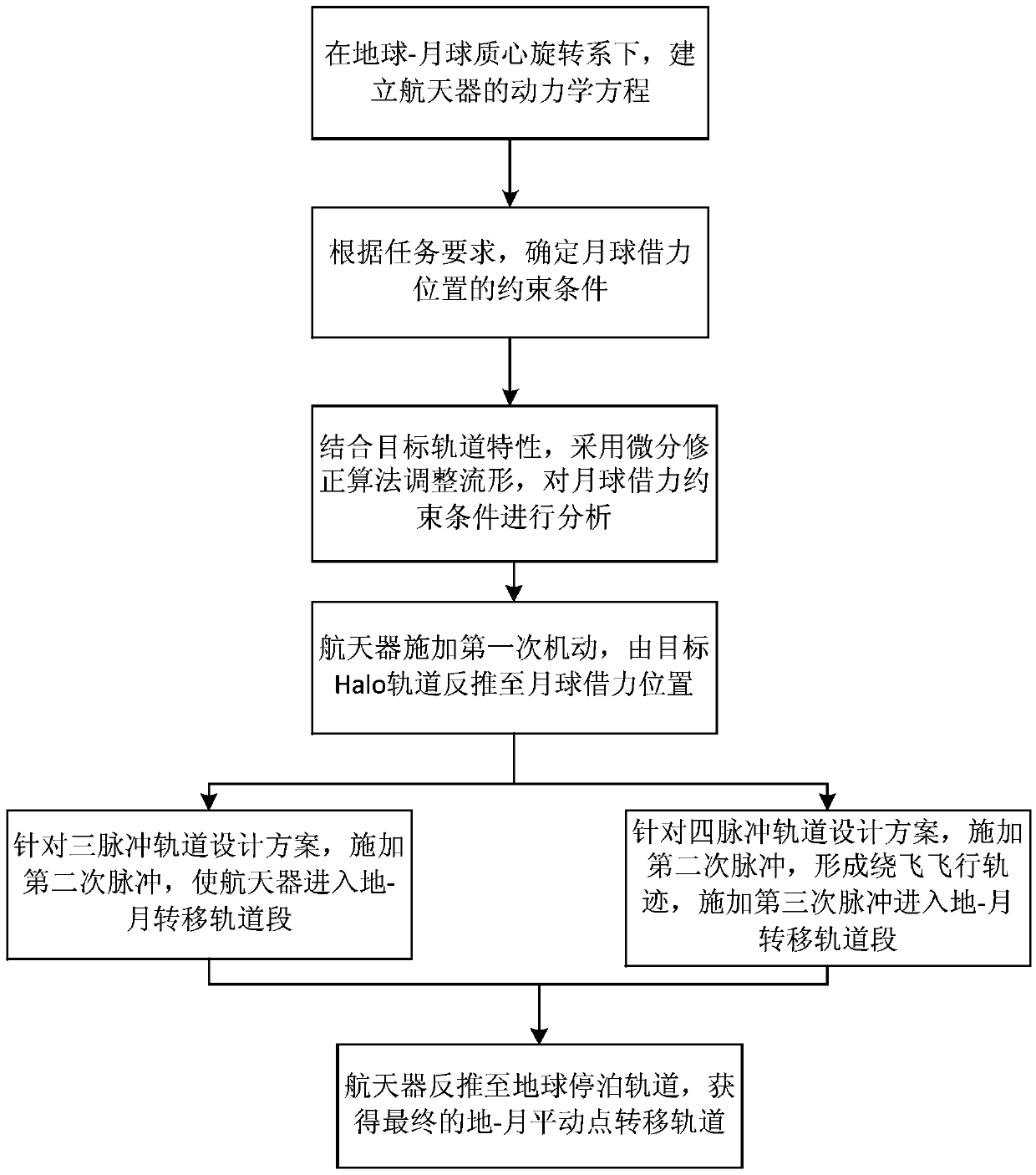
ActiveCN105574261AReduce consumptionSmall speed incrementGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsState parameterInjection point
The invention relates to a method for designing an earth-moon libration point transfer orbit via moon leveraging constraint, and belongs to the field of design and optimization of spacecraft orbits. The method comprises the following steps: selecting an injection point position of a target Halo orbit and an expected moon leveraging constraint size, and integrating the state parameter of an injection point via an equation (1) until a spacecraft arrives at an expected moon leveraging position. The state parameter of the injection point is corrected and regulated by a related optimization algorithm, so that the state of a leveraging position satisfies the constraint condition of an equation (3), and then the increment size of a maneuvering speed necessary for the spacecraft for entering the Halo orbit is determined. Since the moon leveraging constraint condition and the Halo orbit injection point and other parameters are selected, a transfer orbit with low energy consumption and capable of satisfying task requirements can be effectively designed.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Spacecraft optimal Lambert orbit rendezvous method based on multi-objective optimization algorithm
InactiveCN111090941AGood selectionPromotes even distributionDesign optimisation/simulationAdaptive controlMulti objective optimization algorithmPerformance index
The invention discloses a spacecraft optimal Lambert orbit rendezvous method based on a multi-objective optimization algorithm, and belongs to the technical field of spacecraft orbit rendezvous. The invention aims to solve the problem that the fuel consumption and the time consumption of the existing spacecraft optimal Lambert orbital rendezvous method cannot be optimal at the same time. The method comprises the following steps: determining a Lagrange representation form of a Lambert problem corresponding to pulse thrust Lambert intersection according to a spacecraft, and calculating transferorbit parameters of different-plane Lambert intersection to obtain performance indexes of fuel consumption and intersection time of the Lambert intersection; and optimizing through an optimization algorithm to obtain a comprehensively optimal motion trail of the fuel consumption and the rendezvous time. The method is mainly used for spacecraft optimal Lambert orbital intersection design and control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
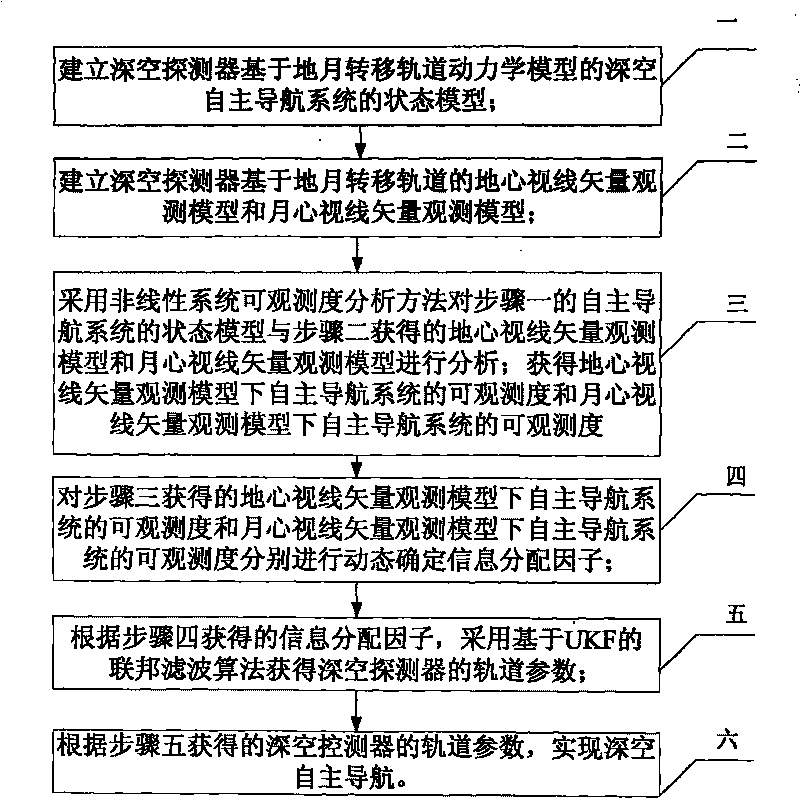
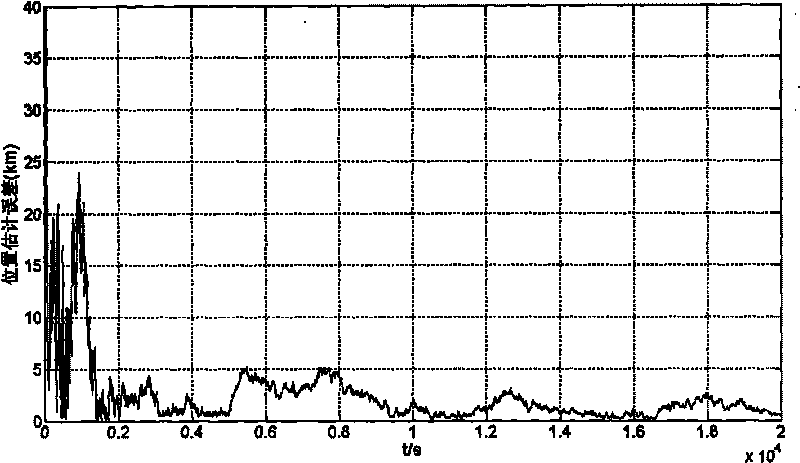
Deep space autonomous navigation method based on observability degree analysis
InactiveCN101762272AImprove adaptabilityImprove reliabilityInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDynamic modelsFilter algorithm
The invention discloses a deep space autonomous navigation method based on observability degree analysis, which relates to the field of aerospace. The invention solves the problems that when the current autonomous navigation systems comprehensively use different observing models to provide measuring information, different types of measuring information of different sensors need to be processed, thereby reducing the utilization ratio of the observed information and simultaneously reducing the adaptive ability and reliability of the autonomous navigation systems. The method of the invention is established on the basis of a dynamic model of an earth-moon transfer orbit deep space probe, obtains the observability degree of the deep space autonomous navigation system under two observing models of a geocentric sight line vector and a selenocentric sight line vector by a nonlinear system observability degree analyzing method, and acquires the orbit parameters of the deep space probe by a UKF based federal filtering algorithm. The invention is suitable for determining the orbit parameters of deep space separated section and transfer section probes. The invention can be used for improving the accuracy and reliability of the deep space autonomous navigation system, and is especially suitable for the information fusion autonomous navigation technologies under various observing models.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for rapidly designing and optimizing low-thrust transfer orbit
InactiveCN103226631AReduce in quantityHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsPolynomial methodSolar sail
The invention discloses a method for rapidly designing and optimizing a low-thrust transfer orbit. The method comprises the steps as follows: an inverse sextic polynomial method is introduced as an initial design, a high-performance optimal parameter initial value is provided for follow-up accurate optimization, and the calculating time of an entire optimizing process is reduced; a Radau legendre pseudospectral method is adopted to parameterize a low-thrust transfer orbit optimization problem into a nonlinear programming problem, not only is the number of the optimization parameters reduced, but also the accuracy of an optimization result is improved; and tedious first-order optimal necessary conditions are not needed to be deduced, even though the low-thrust transfer orbit containing various complicated constrains are processed, the operation is also convenient and simple. The method for rapidly designing and optimizing the low-thrust transfer orbit has an extremely important application value in the field of the design and optimization of transfer orbits of low-thrust propulsion spacecraft such as solar sail propulsion, solar energy electric propulsion, and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
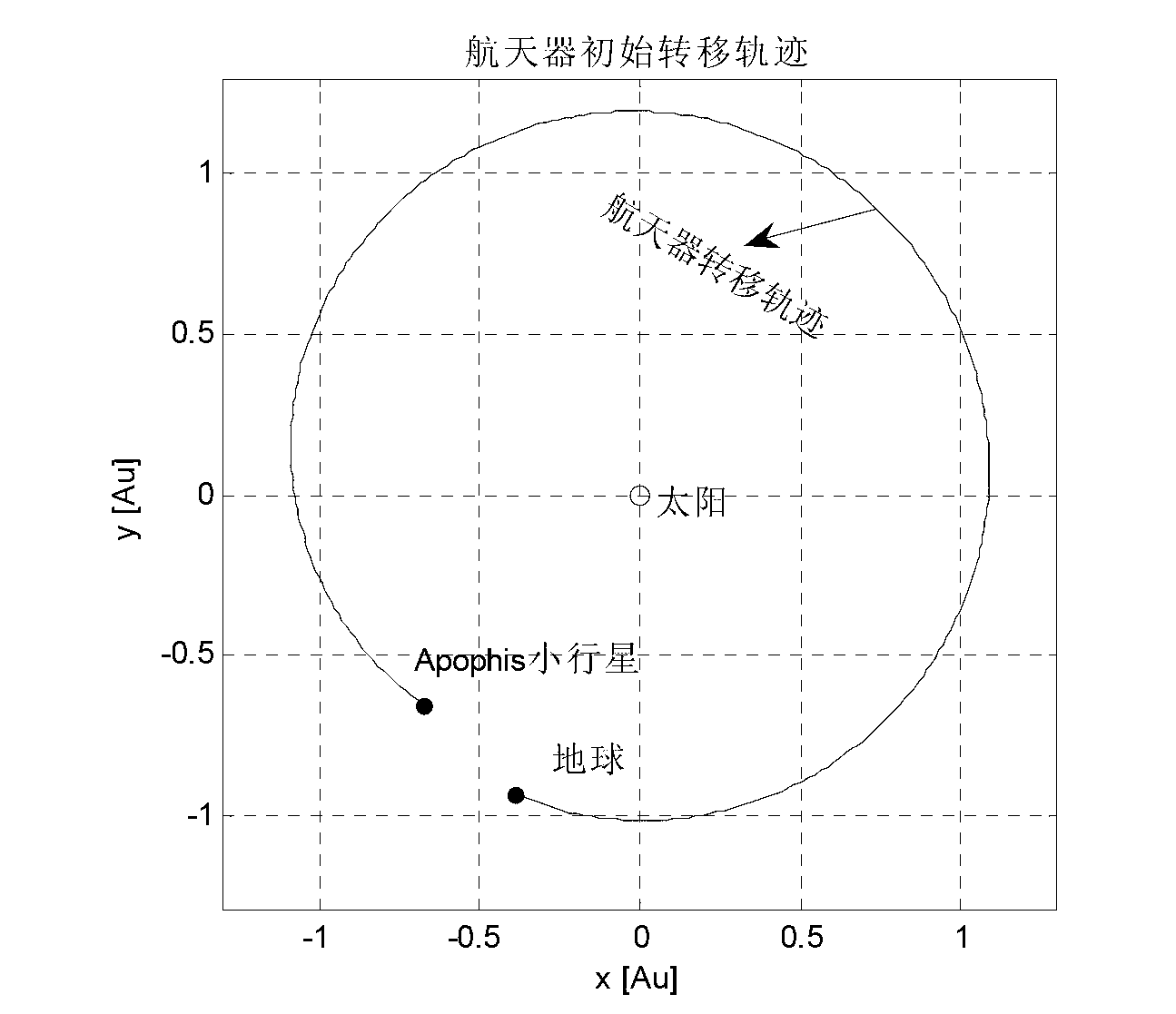
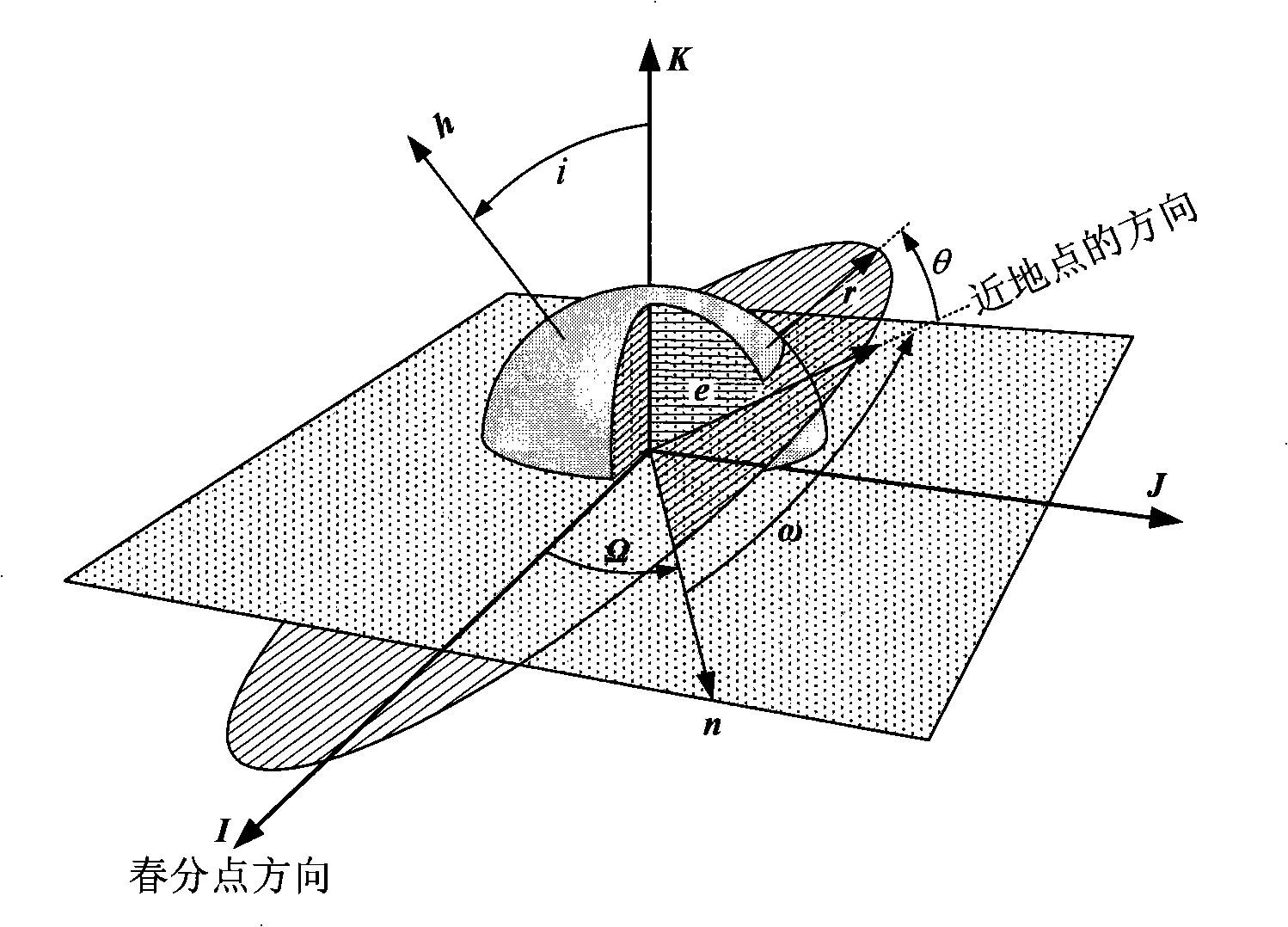
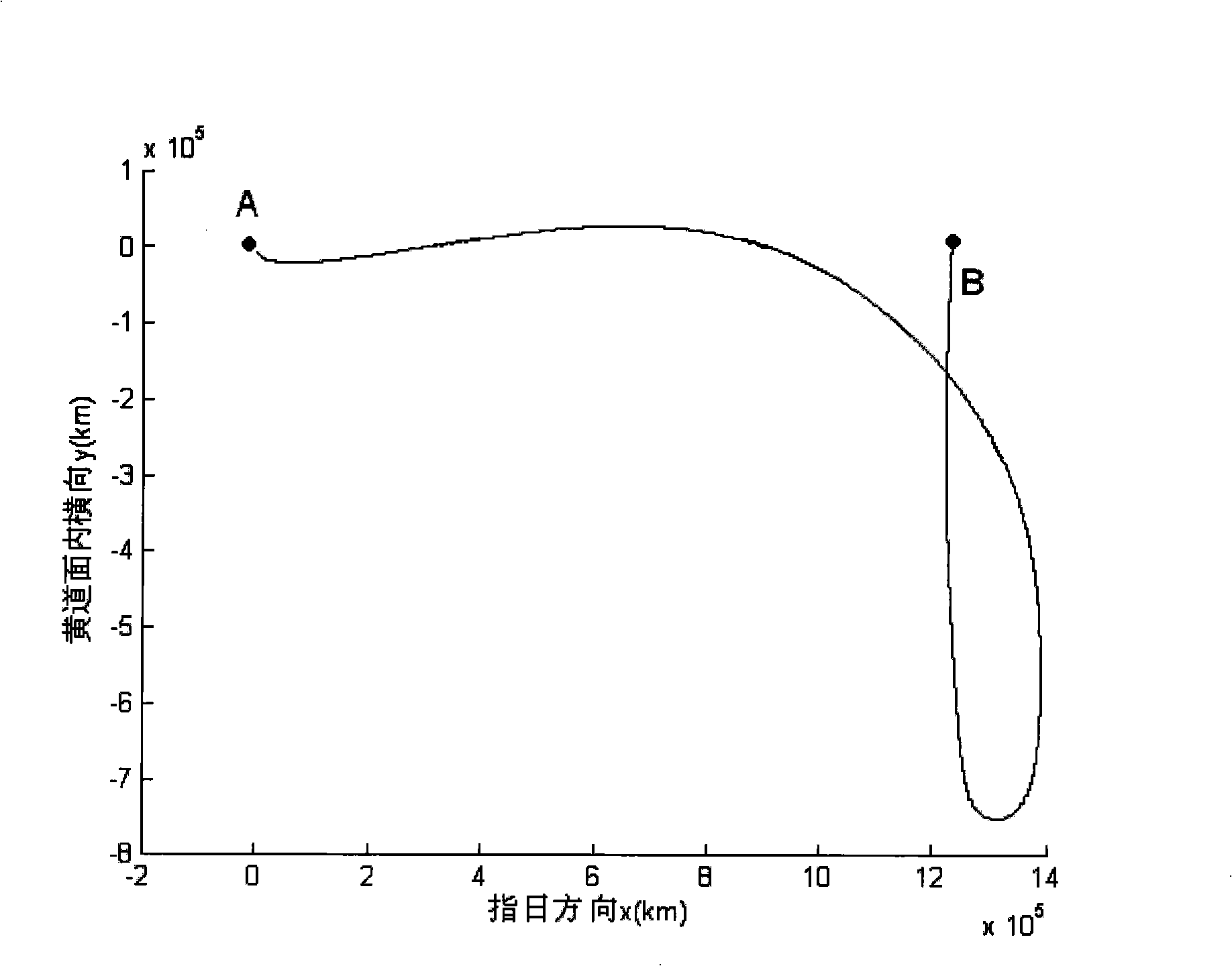
Method for determining deep space detector equivalent transfer orbit
The invention discloses a method for determining an equivalent transfer orbit of a deep space probe, which comprises the steps: (1) the equivalent transfer orbit of the deep space probe is designed according to an orbit dynamic model, and the orbit parameter of the designed transfer orbit is extracted; (2) the near-earth equivalent parameter of the transfer orbit of the deep space probe is solved according to the orbit parameter extracted in the step (1) and the spatial geometric relationship. By the method of the invention, when a carrier rocket directly sends a probe into the transfer orbit, the carrying party does not need to establish a complex dynamic model for the deep space probe, and the existing model used for estimating the launching precision can estimate the transmission precision more correctly, thereby solving the problem that the current carrier rocket in China does not have an upper stage and can not send the probe into the transfer orbit by using the upper stage for firing. The method of the invention adopts the concept of equivalence to solve the problem and is simple and reliable.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
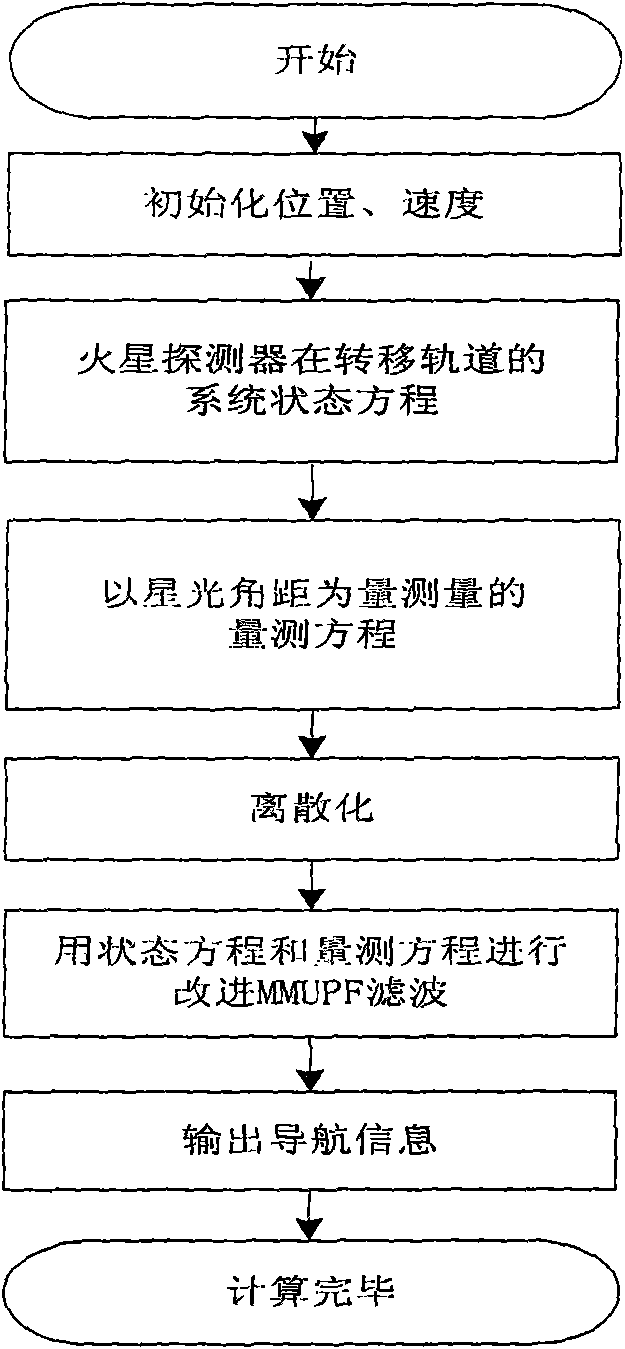
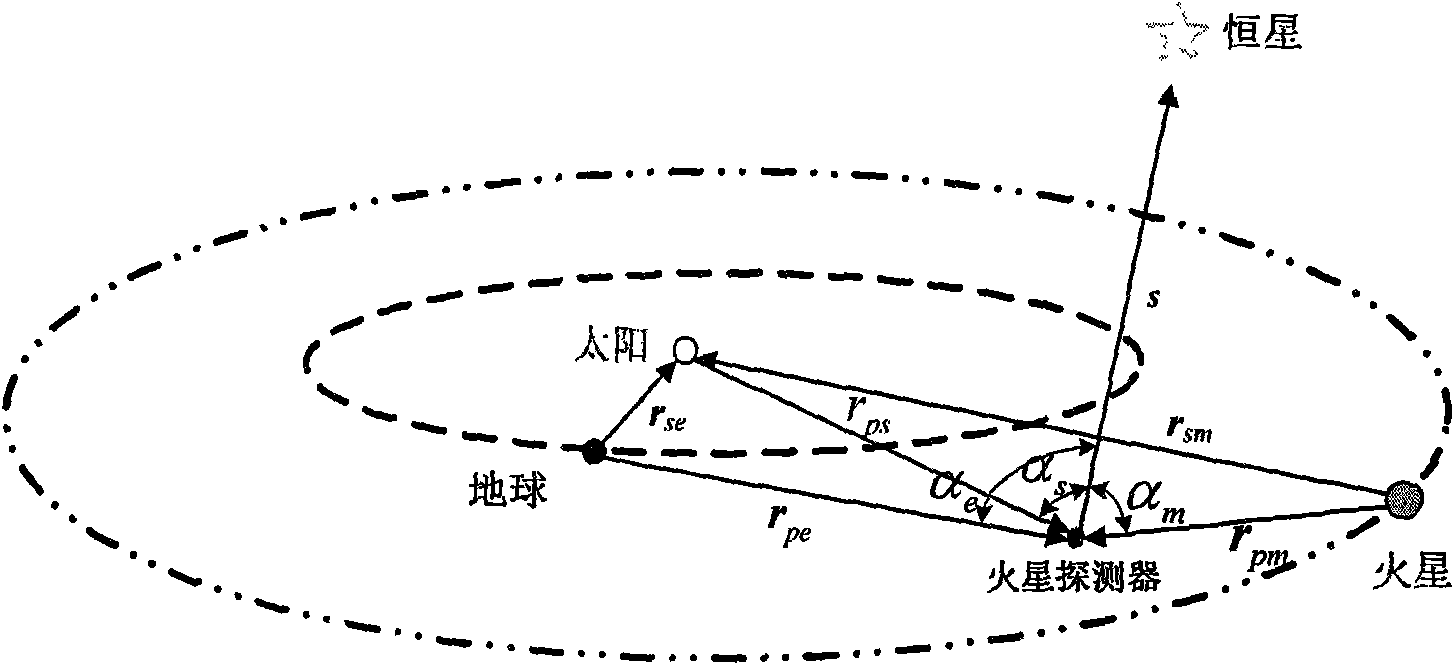
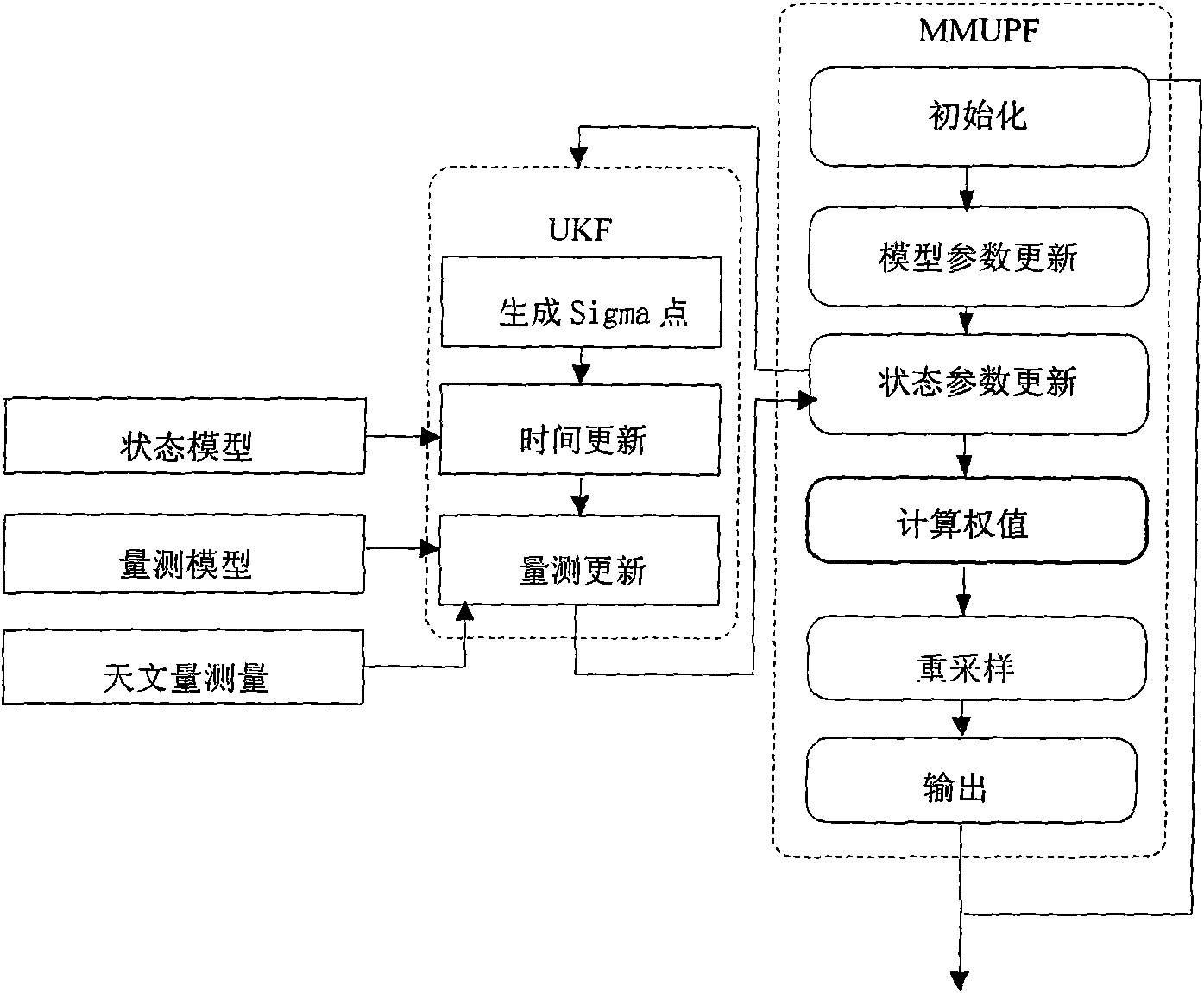
Autonomous astronomical navigation method of spark detector based on improved MMUPF filtering method
ActiveCN101672651APrecise positioningImprove navigation accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsMassive gravityAngular distance
An autonomous astronomical navigation method of a spark detector based on an improved MMUPF filtering method relates to an autonomous navigation method of a spark detector. The method comprises the following steps: accurately modeling a deep space detector positioned on a transfer orbit; then measuring with starlight angular distances as quantities; and finally, carrying out optimal estimation ofnavigation parameters by adopting the improved MMUPF filtering method, thereby solving the problem that the planet gravitation size and an orbit dynamics model are changed continuously when the distances are different, and obviously improving the navigation precision. The autonomous astronomical navigation method can be used for determining the navigation parameters of the spark detector or a planet detector positioned on the transfer orbit.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Free return lunar flyby transfer method for geosynchronous satellites
A method is provided for using a lunar flyby maneuver to transfer a satellite from a quasi-geosynchronous transfer orbit having a high inclination to a final geosynchronous orbit having a low inclination. The invention may be used to take the inclination of a final geosynchronous orbit of a satellite to zero, resulting in a geostationary orbit, provided that the satellite is launched in March or September.
Owner:HUGHES ELECTRONICS
Orbit-injection-type trajectory design method of solid rocket based on elliptical transfer orbit
ActiveCN109398762AAchieve regulationChange properties and shapeCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusThree degrees of freedomEllipse
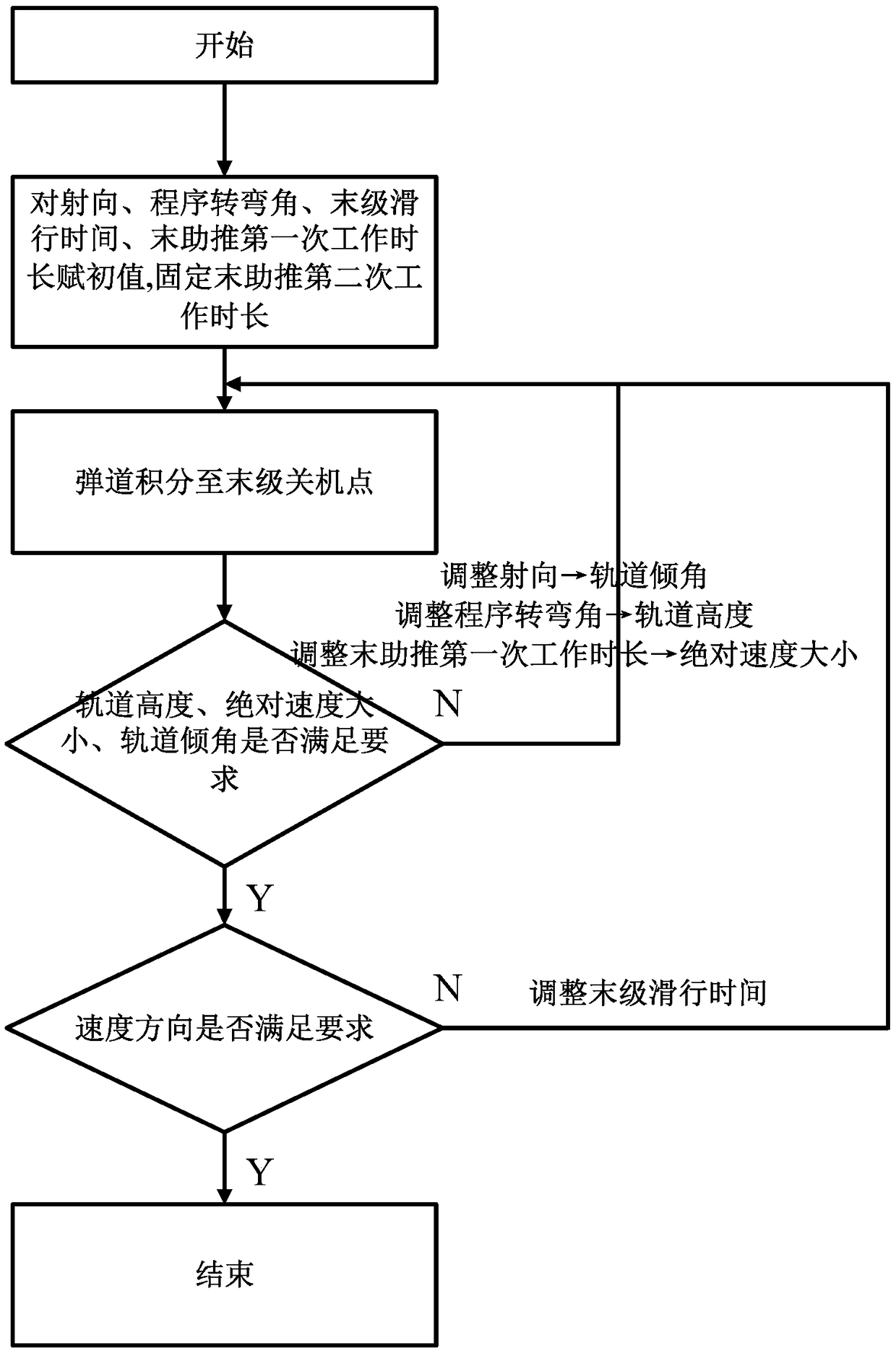
The invention discloses an orbit-injection-type trajectory design method of a solid rocket based on an elliptical transfer orbit, and relates to the field of carrier rocket trajectory design. The orbit-injection-type trajectory design method comprises the steps that a control variable is initialized; the perigee altitude of the elliptical transfer orbit is fixed by fixing the final-stage second working hour; according to the set carrier rocket fight time sequence, the force-bearing condition in the rock flight process is modeled, the speed and the position are subjected to numerical integration, and three-degree-of-freedom particle trajectory calculation is conducted; the calculated speed and position are converted through a coordinate system, whether the geocentric radius vector magnitude, the absolute speed magnitude, the orbit inclination angle and the current trajectory inclination angle meet the requirements or not is judged, if yes, related trajectory parameters such as the speed, the position, the flight program angle and the height are output, and a launch trajectory is designed; and otherwise, the control variable is adjusted according to the difference between a current value and a target value, and iterative calculation is conducted until the requirements are met. By adopting the orbit-injection-type trajectory design method, the orbit-injection-type trajectory scheme design of the elliptical transfer orbit of the solid rocket can be quickly achieved.
Owner:THE GENERAL DESIGNING INST OF HUBEI SPACE TECH ACAD
Unified attitude control for spacecraft transfer orbit operations
InactiveUS20100059631A1Launch systemsCosmonautic propulsion system apparatusAttitude controlLaws of thermodynamics
A method of controlling attitude of a spacecraft during a transfer orbit operation is provided. The method includes providing a slow spin rate, determining the attitude of the spacecraft using a unified sensor set, and controlling the attitude of the spacecraft using a unified control law. The use of a unified set of sensors and a unified control law reduces spacecraft complexity, cost, and weight.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Aerodynamic orbit inclination control
InactiveUS20050211828A1Reduce the amount requiredDifferent inclination angleAircraft navigation controlLaunch systemsHigh energyFlight vehicle
A method and system for deploying a spacecraft into a target orbit includes the use of controllable aerodynamic surfaces that can be deployed to facilitate a change in the inclination angle of the trajectory of the spacecraft. In a typical embodiment, the spacecraft includes an orbit transfer vehicle containing the aerodynamic structure, and a satellite that is to be placed into the target orbit. The spacecraft is launched to a higher-energy orbit than the target orbit, and the energy released by traveling to the target orbit is used to change the inclination angle. After entering a transfer orbit that includes a passage through the upper limits of the earth's atmosphere, the orbit transfer vehicle deploys the aerodynamic structure, and controls the aerodynamic surfaces of the structure to induce lift forces that alter its inclination angle each time the vehicle enters the atmosphere.
Owner:AEROASTRO
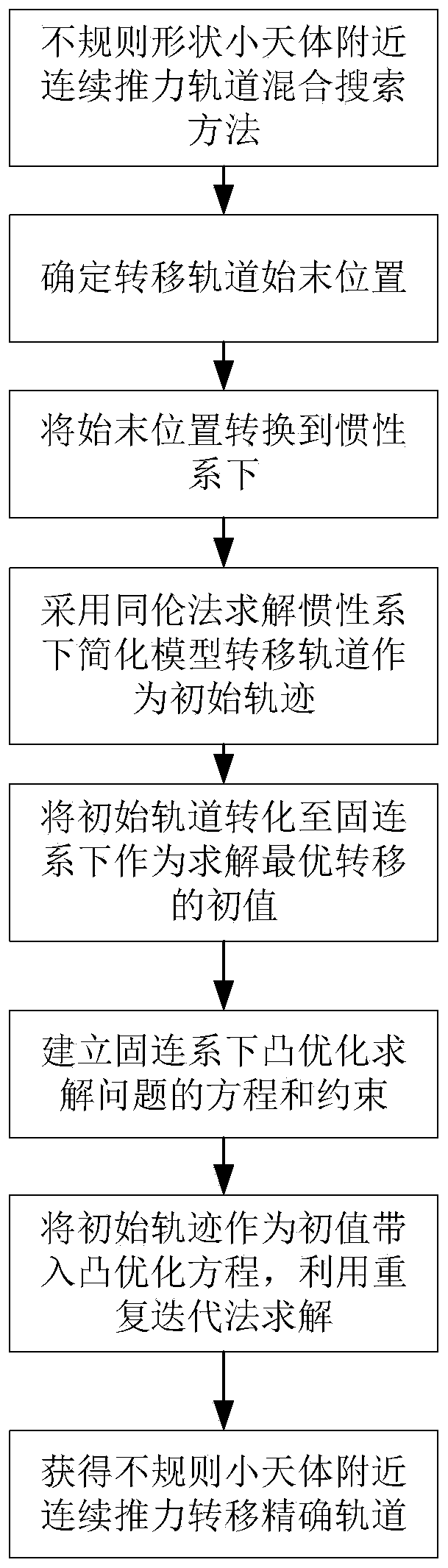
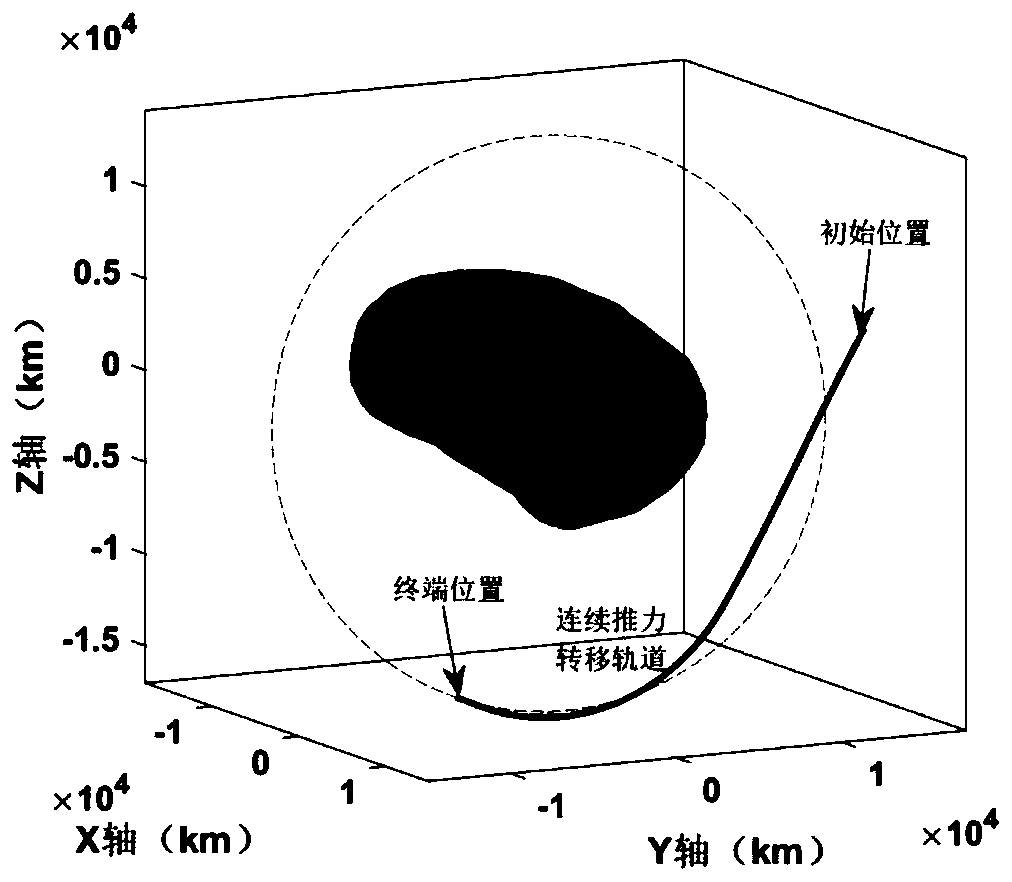
Hybrid search method for continuous thrust orbit near irregular-shaped small celestial body
ActiveCN110736470AHigh precisionSolved the inability to account for perturbations of irregular shapesInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsCelestial bodyComputational physics
The invention discloses a hybrid search method for a continuous thrust orbit near an irregular-shaped small celestial body, and belongs to the technical field of aerospace. The implementation method comprises the following steps: converting the initial state of an orbit from a small celestial body fixed connection system to an inertial system; obtaining an initial value of the continuous thrust transfer orbit by utilizing a homotopic method under the inertial system; establishing a continuous thrust equation under the fixed connection system by taking irregular-shaped perturbation of the of the small celestial body into consideration; transferring the initial orbit from the inertial system to the fixed connection system to serve as an initial value of the continuous thrust orbit; and solving an optimal transfer opportunity near the irregular small celestial body by adopting a convex optimization method by taking collision constraint into consideration. According to the invention, the problems that irregular-shaped perturbation cannot be considered in the homotopic method and that initial value searching is difficult in the convex optimization method are solved, searching for the continuous thrust transfer orbit near the irregular-shaped small celestial body is achieved, the searching convergence and precision of transfer orbit near the irregular-shaped small celestial body areimproved, and the method also has the advantages of high precision and convergence.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com