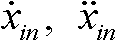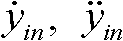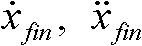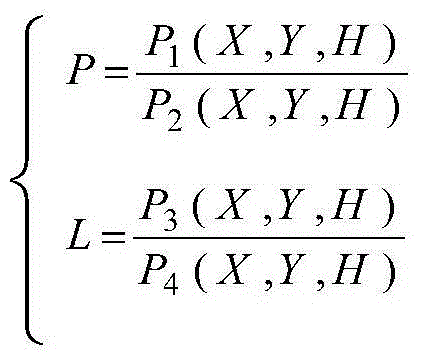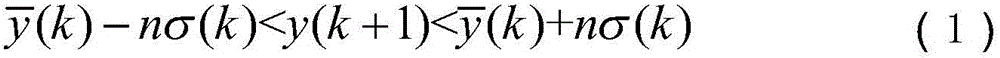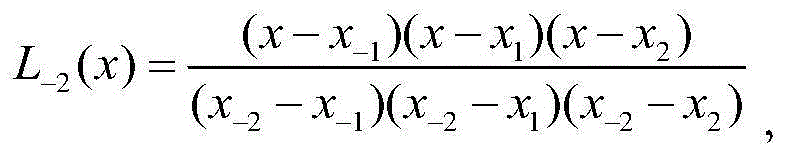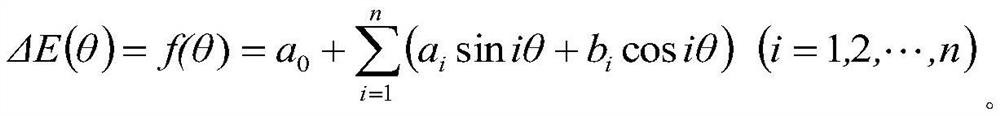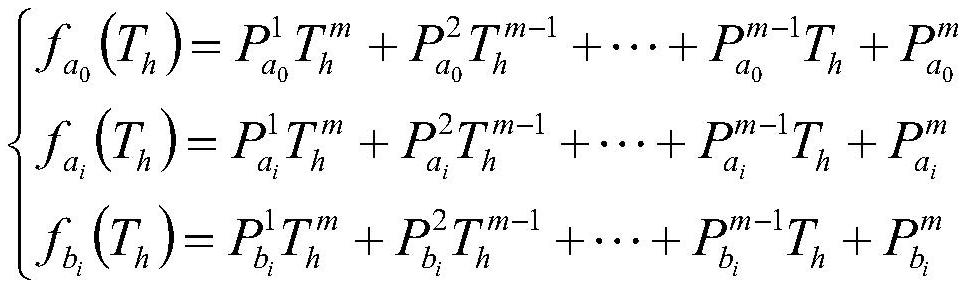Patents
Literature
34 results about "Polynomial method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The polynomial method was based on ideas from computer science. For example, suppose we have a fairly low degree polynomial over a finite field. Suppose we write a table of the values of the polynomial, and then the table gets corrupted, so that one third of the entries are replaced by errors.
Intelligent vehicle lane change path planning method based on polynomial and radial basis function (RBF) neural network
InactiveCN102609765ASimplify processing difficultyDifficulty of SimplificationAnti-collision systemsForecastingPolynomial methodSimulation
The invention relates to an intelligent vehicle lane change path planning method based on a polynomial and radial basis function (RBF) neural network. The intelligent vehicle lane change path planning method comprises the following steps that: the state information of obstacles and lane change vehicles in lanes are detected and determined according to a vehicle-mounted sensor, and the state information comprises positions, speed, acceleration and shapes; the lane change vehicles and the obstacles are geometrically covered, and in addition, a lane change path model using the time as the independent variable is built; boundary conditions of the lane change vehicles are obtained by the dynamic RBF neural network; the lane change path parameter is subjected to traversing in a certain range according to a certain step length, and the calculation of a polynomial method is combined to obtain the lane change path set under the specific boundary conditions; index functions for evaluating the merits of the lane change patch performance are defined, the optimal path in generated lance change paths is screened according to the index functions and is applied to the practical lane change process of vehicles; and whether the RBF neural network is updated or not is determined according to the merits of the boundary conditions of the generated lane change paths. The neural network has good self-adaption capability, so that the problem that the RBF neural network structure is oversize or undersize is solved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
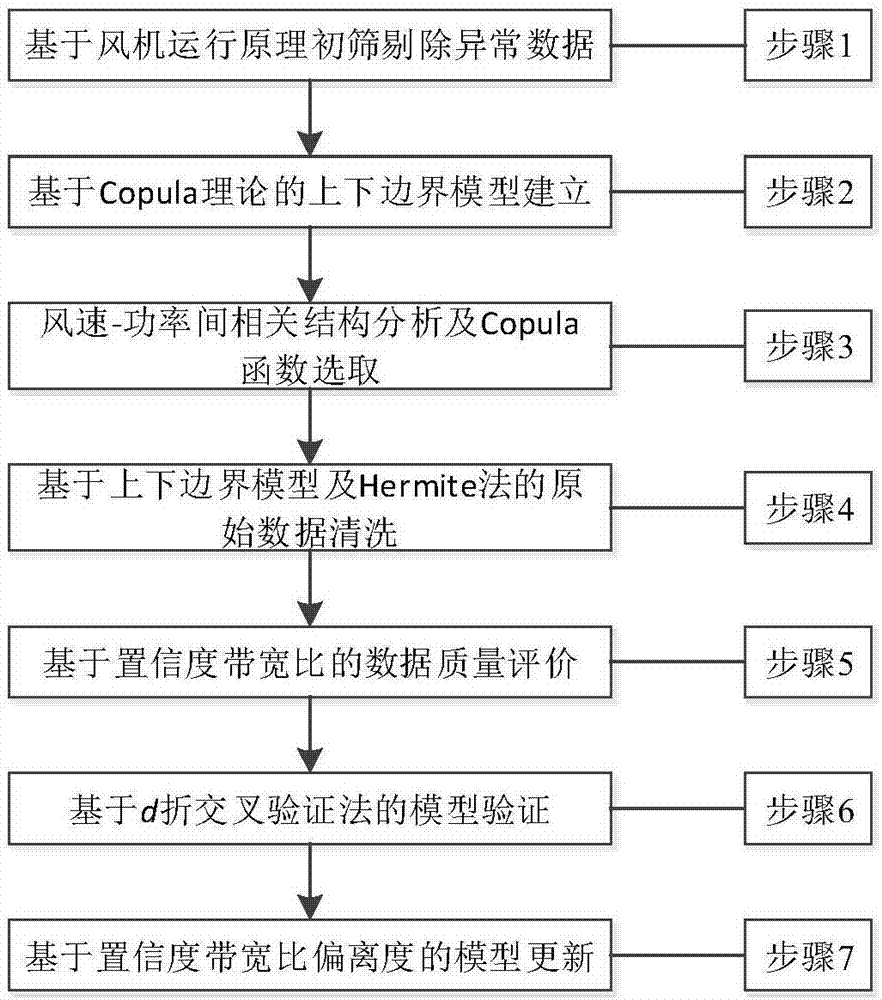
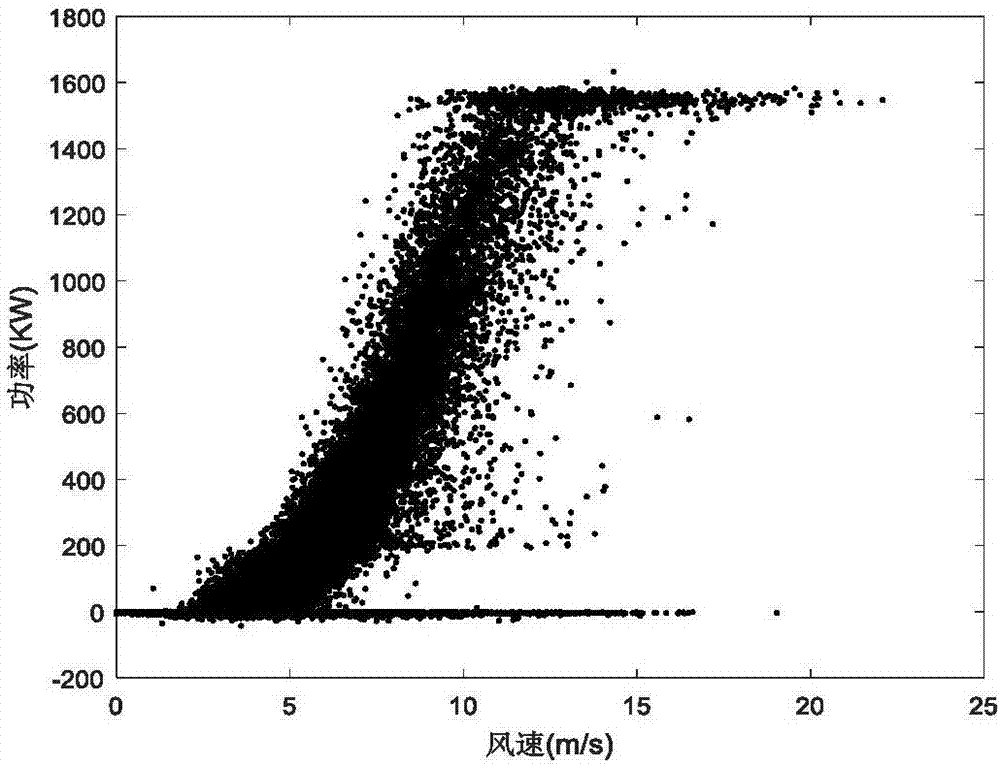
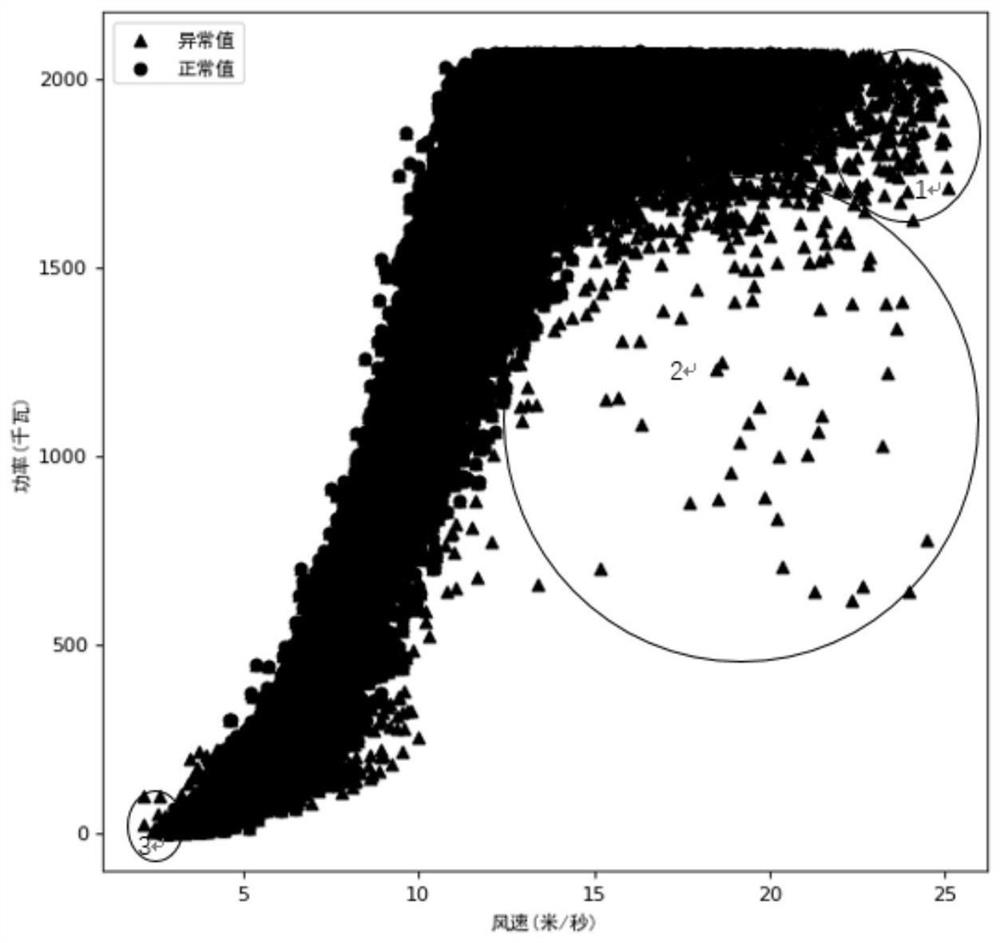
Wind power modeling and performance evaluating method based on confidence equivalent power curve band
ActiveCN107885959ARealize identification and rejectionImprove accuracyData processing applicationsDesign optimisation/simulationSliding time windowMissing data
The invention relates to the field of data processing, in particular to a wind power modeling and performance evaluating method based on a confidence equivalent power curve band. The wind power modeling and performance evaluating method includes the steps that preliminary screening and rejection are conducted on an abnormal data sample; wind speed is divided into three regions, and a kernel density estimation method is used for obtaining wind speed and power probability distributions in each region through statistics to obtain the Copula function in each region; the maximum likelihood estimation method is adopted to obtain confidence equivalent power boundary model in the corresponding region; a piecewise cubic Hermite interpolating polynomial method is used for reconstructing missing datato complete original data sample cleaning; the average value of the confidence bandwidth ratio is used as the model performance evaluation index, a d-fold cross validation method is used for validating the upper and lower boundary models in different regions, when the index is basically stabilized at a certain constant value, the up and lower boundary models of the different regions are determined; a sliding time window method is adopted to updating data, the deviation degree of the confidence bandwidth ratio is used as a triggering condition, and the up and lower boundary models are updatedwhen the deviation degree exceeds a certain threshold value.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
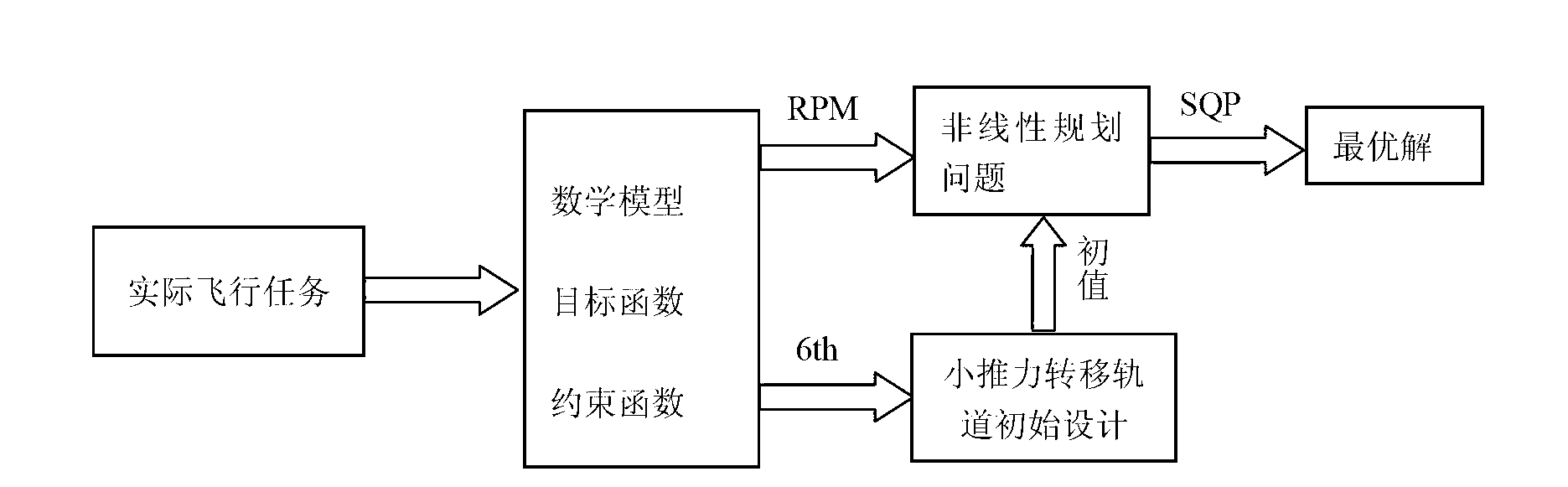
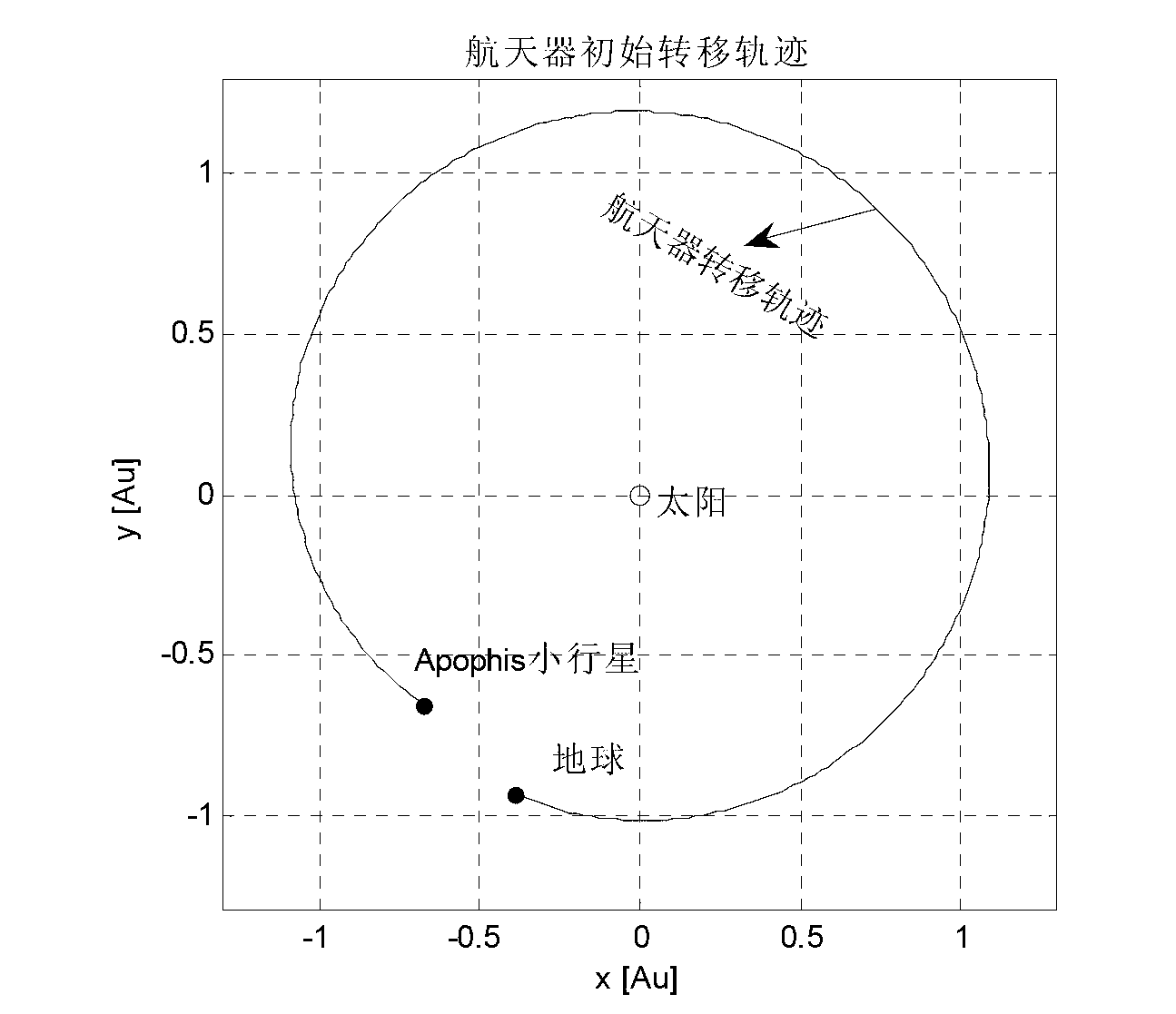
Method for rapidly designing and optimizing low-thrust transfer orbit
InactiveCN103226631AReduce in quantityHigh precisionSpecial data processing applicationsPolynomial methodSolar sail
The invention discloses a method for rapidly designing and optimizing a low-thrust transfer orbit. The method comprises the steps as follows: an inverse sextic polynomial method is introduced as an initial design, a high-performance optimal parameter initial value is provided for follow-up accurate optimization, and the calculating time of an entire optimizing process is reduced; a Radau legendre pseudospectral method is adopted to parameterize a low-thrust transfer orbit optimization problem into a nonlinear programming problem, not only is the number of the optimization parameters reduced, but also the accuracy of an optimization result is improved; and tedious first-order optimal necessary conditions are not needed to be deduced, even though the low-thrust transfer orbit containing various complicated constrains are processed, the operation is also convenient and simple. The method for rapidly designing and optimizing the low-thrust transfer orbit has an extremely important application value in the field of the design and optimization of transfer orbits of low-thrust propulsion spacecraft such as solar sail propulsion, solar energy electric propulsion, and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
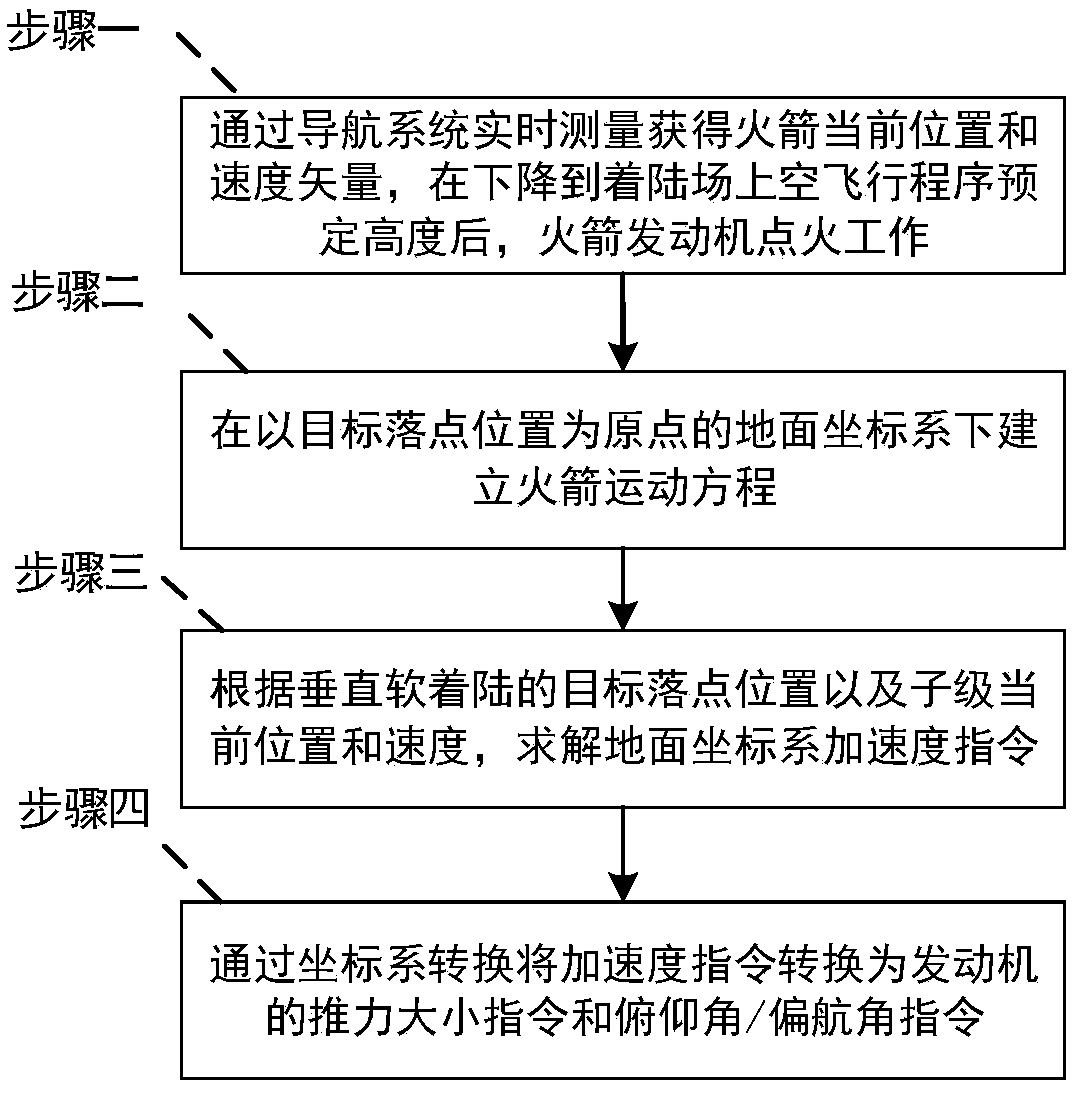
Quartic polynomial guidance method for accurate vertical soft landing of VTOL carrier rocket substage landing phase
The invention brings forward a quartic polynomial guidance method for accurate vertical soft landing of VTOL carrier rocket substage landing phase, belonging to technical field of guidance and control. A fourth-order polynomial guidance method for accurate vertical soft landing of a substage landing section of a vertical take-off and landing carrier rocket belongs to the technical field of guidance and control. In this method, the vector rocket motor is used as the actuator, and the guidance commands of high precision vertical soft landing in the rocket landing phase are obtained by using thequartic polynomial method, which is based on the substage states output from the on-board navigation system and the preset landing point positions of the target landing field. The accurate vertical soft landing guidance method for VTOL carrier rocket substage landing section can realize the accurate vertical soft landing of rocket substage.
Owner:黑龙江省工研院资产经营管理有限公司
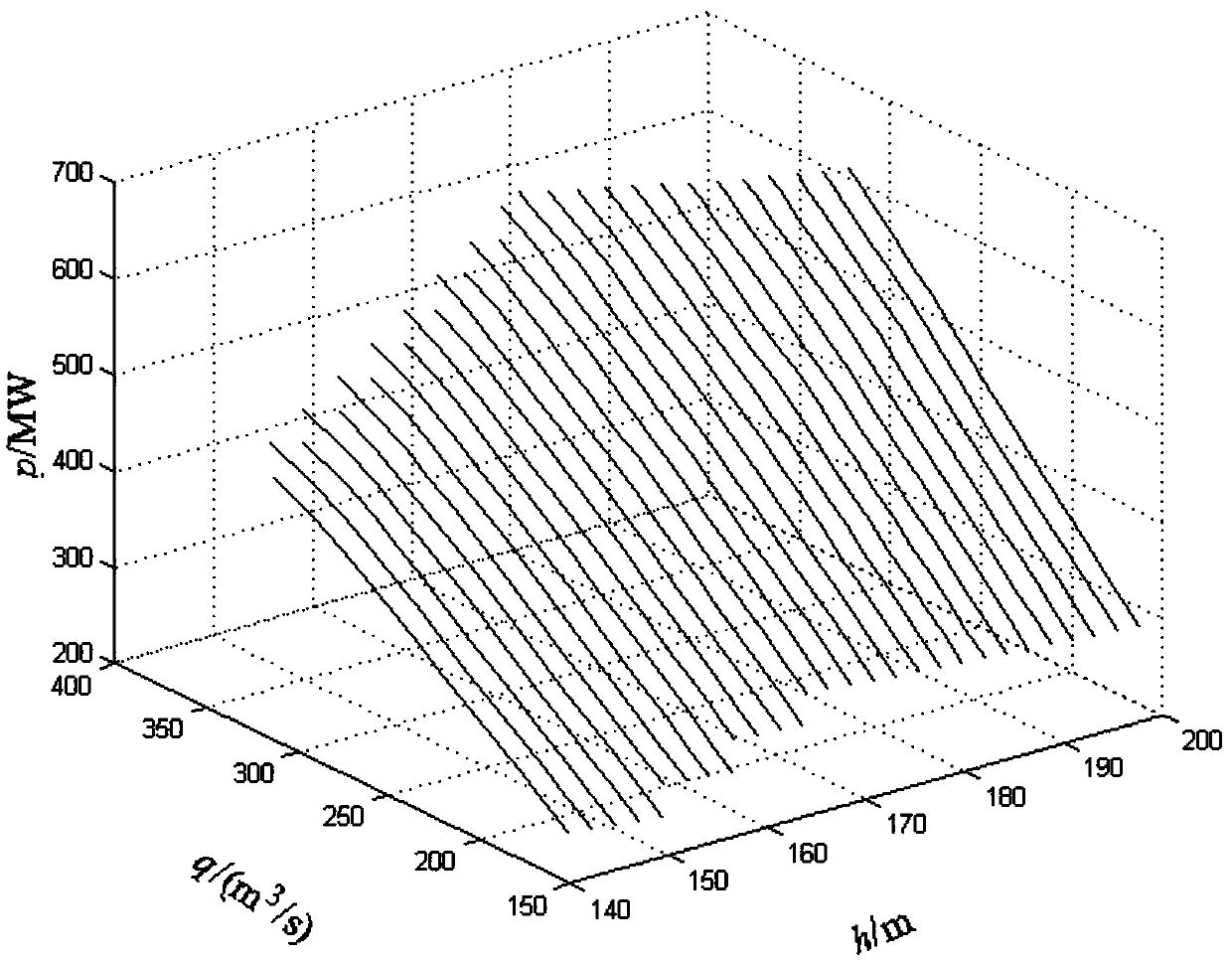
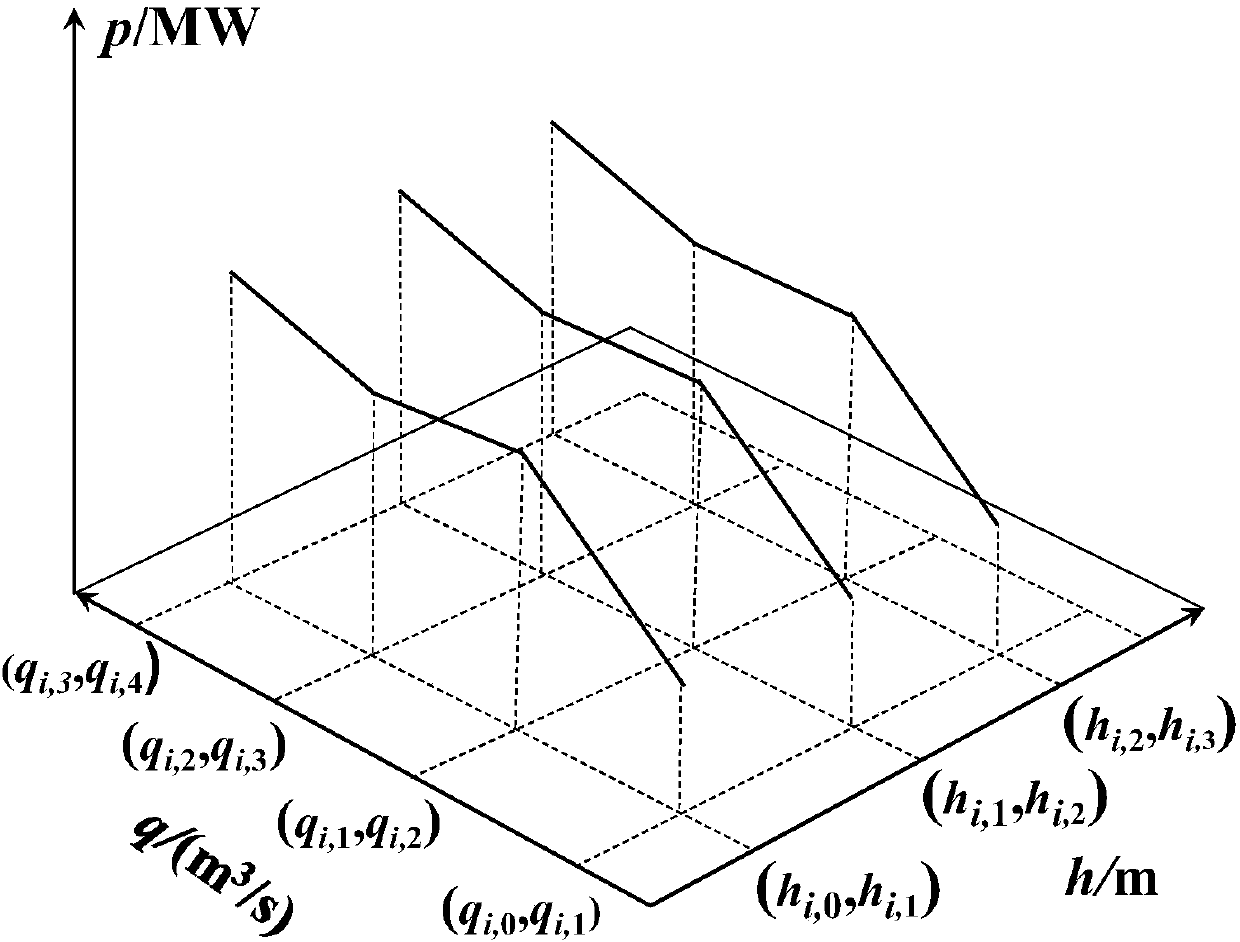
Mixed integer nonlinear programming model for solving combination problem of hydroelectric generating set
InactiveCN107844864APreserve the actual engineering characteristicsHigh precisionForecastingPower stationPolynomial method
The invention provides a mixed integer nonlinear programming model for solving the combination problem of a hydroelectric generating set, and belongs to the field of hydroelectric scheduling operation. The mixed integer nonlinear programming model for solving the combination problem of a hydroelectric generating set is characterized by utilizing a polynomial fitting technology to process the complicated power station nonlinear relation, providing a quartic equation polynomial fitting method of water level-capacity of reservoir-tailwater level-out flow, and based on a quadratic polynomial of head loss of the hydroelectric generating set, describing the generating head of the hydroelectric generating set as a multivariate quartic function of capacity of reservoir and flow; considering aboutthe influence of the head on the output, providing a binary quadratic polynomial method of accurately representing the output head and the generating flow of the hydroelectric generating set, introducing 0-1 variable, solving the startup-shutdown problem of the hydroelectric generating set, obtaining the head-flow-output relation three-dimensional fitting surface of the hydroelectric generating set, and satisfying the fine calculation demand of the output of the hydroelectric generating set under the variation head; and realizing calculation with high efficiency by means of a mature MINLP solver. The mixed integer nonlinear programming model for solving the combination problem of the hydroelectric generating set fully considers the complicated nonlinear relation of the hydroelectric systemand has the advantages of reducing the linear error and significantly improving the solution accuracy, compared with a classic MILP model. Besides, the obtained set combination and load distributionresult can preferably reflect the practical operation situation of the hydropower station.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Automobile tyre pattern recognition method based on machine vision
ActiveCN107367241AAutomatic realization of recognitionImprove accuracyUsing optical meansPattern recognitionPolynomial method
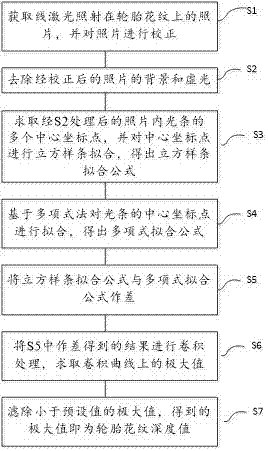
The invention discloses an automobile tyre pattern recognition method based on machine vision, and the method specifically comprises the following steps: S1, obtaining an image of linear laser on a tyre pattern, and correcting the image; S2, removing the background and vignette of the corrected image; S3, solving a plurality of central coordinate points of a light bar on the processed image at step S2, carrying out the cubic spline fitting of the central coordinate points, and obtaining a cubic spline fitting formula; S4, carrying out the fitting of the central coordinate points of the light bar based on a polynomial method, and obtaining a polynomial fitting formula; S5, solving the difference between the cubic spline fitting formula and the polynomial fitting formula; S6, carrying out the convolution of the difference result at step S5, and solving the maximum values of a convolution curve; S7, filtering the maximum value less than a preset value, wherein the obtained maximum value is the depth value of the tyre pattern. The method can achieve the accurate and efficient recognition of the tyre pattern and the measurement of the depth of the tyre pattern, and is very high in precision and robustness.
Owner:SHANDONG JIAOTONG UNIV
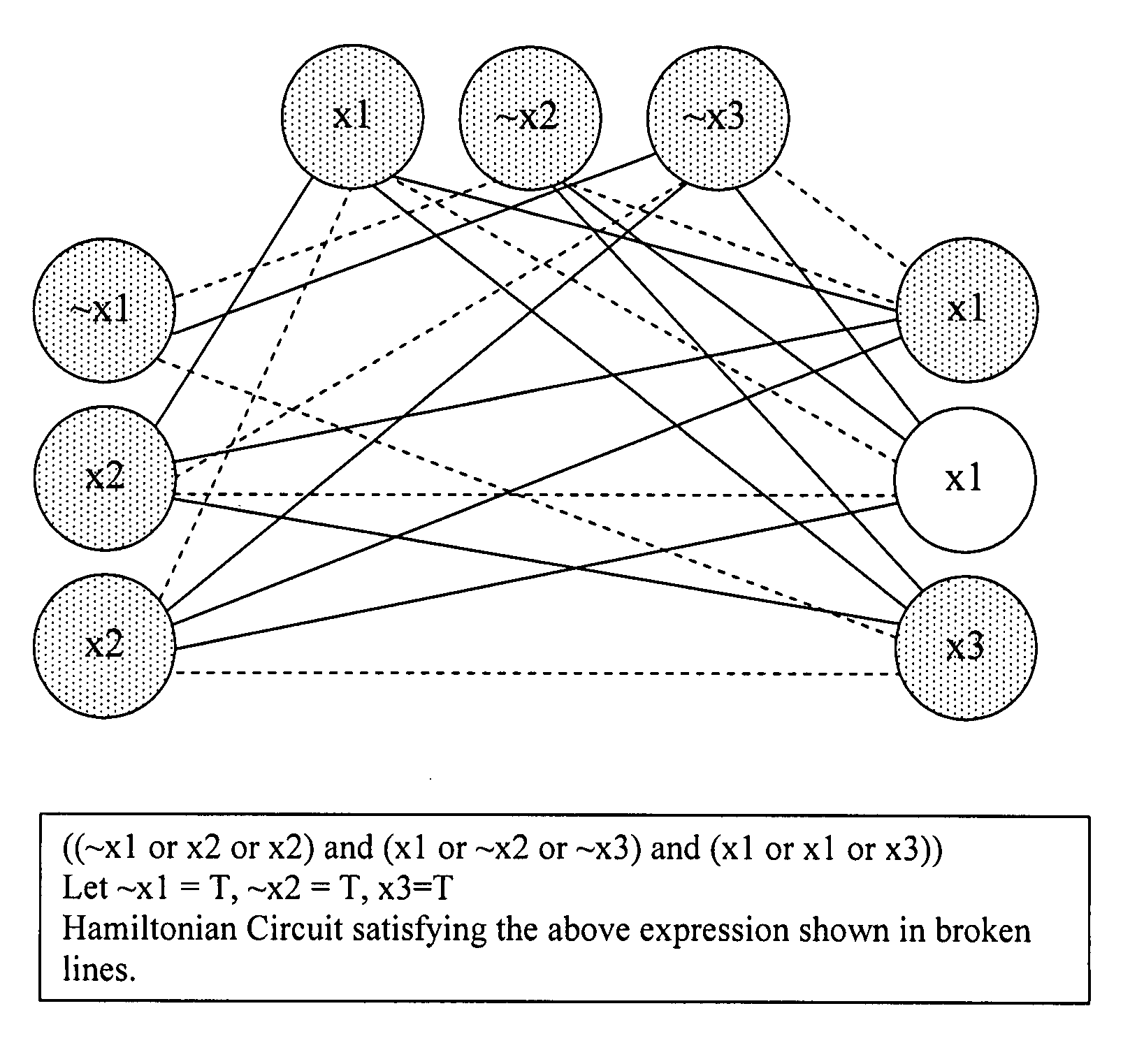
Polynomial method for detecting a Hamiltonian circuit
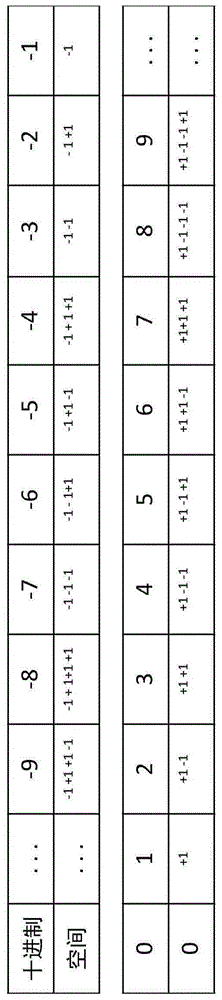
An NP-complete problem can be transformed in polynomial time into any known NP problem. The Hamiltonian circuit problem may be transformed into any other known NP problem (such as the Traveling Salesman problem) and has applications in any context that can be represented by a graph, map, or network structure. The reverse calculation of this transformation from any NP problem into the NP-complete Hamiltonian circuit problem also has a polynomial running time. The composition of this reverse calculation from any known NP problem to the Hamiltonian circuit problem with the polynomial running time of the given algorithm together form a polynomial running time algorithm. Therefore, with this polynomial running time calculation result given for detecting the presence of a Hamiltonian circuit in an undirected graph, it has been shown that P equals any known NP problem or NP. Hence the existence of this Hamiltonian circuit detection algorithm proves P=NP.
Owner:KRIEGER CYNTHIA ANN HARLAN
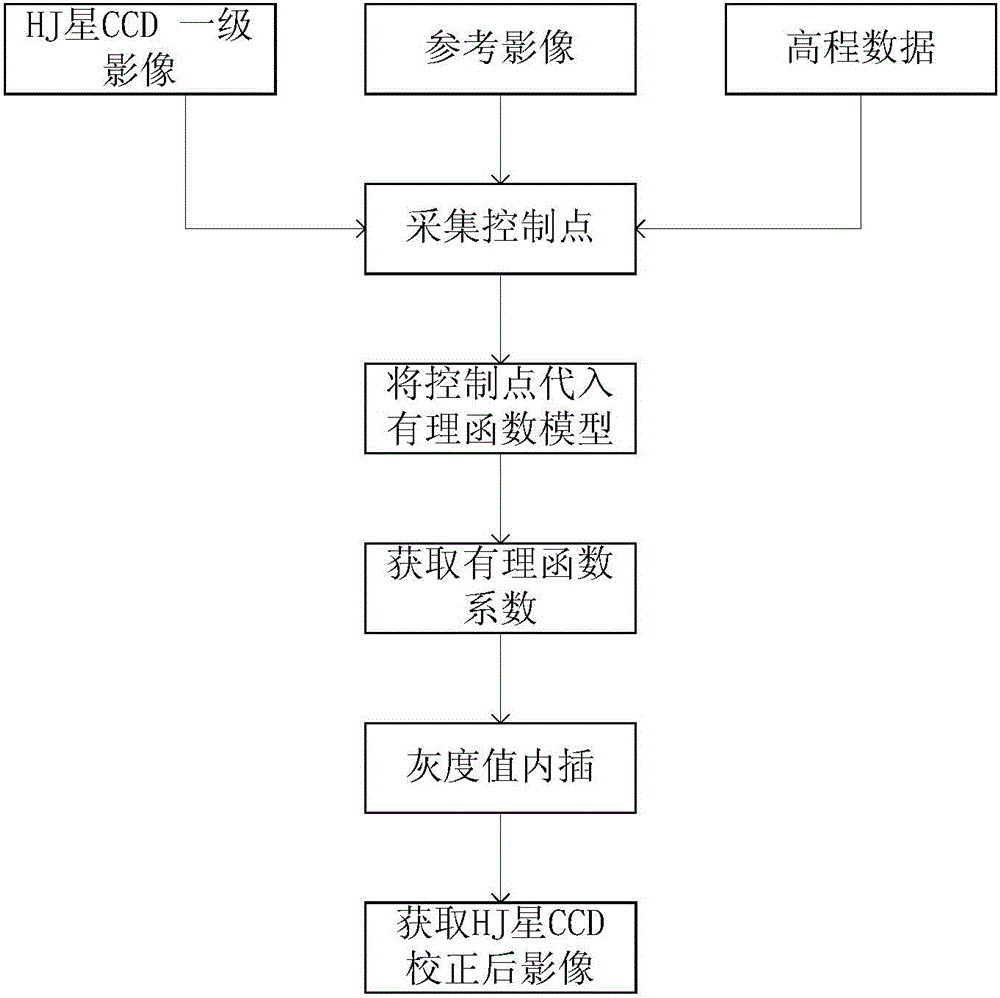
Orthographic correction method of CCD image of HJ-1 satellite
ActiveCN104537614AHigh positioning accuracyMultiple lossesImage enhancementPolynomial methodElevation data
The invention relates to an orthographic correction method of a CCD image of an HJ-1 satellite. A first-stage image of a CCD of an HJ satellite as well as corresponding altitude data and reference data are introduced; ground control points are collectedly uniformly at the first-stage image of the CCD of the HJ satellite; coordinates of the collected control points are introduced into a cubic rational function model and calculation is carried out to obtain a rational polynomial coefficient (RPC), so that a corresponding rational function model is obtained; pixel coordinates of all points of the first-stage image of the CCD of the HJ-1 satellite are inputted into the rational function model to obtain coordinates corresponding to all points of an image after orthographic correction; and with a bilinear interpolation method, interpolation of gray values of all points of the image after correction is carried out on points with pixel coordinates in an entire row or column mode, thereby obtaining an orthographic correction image. According to the invention, compared with the traditional polynomial method, the provided orthographic correction method enables the precision to be improved.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
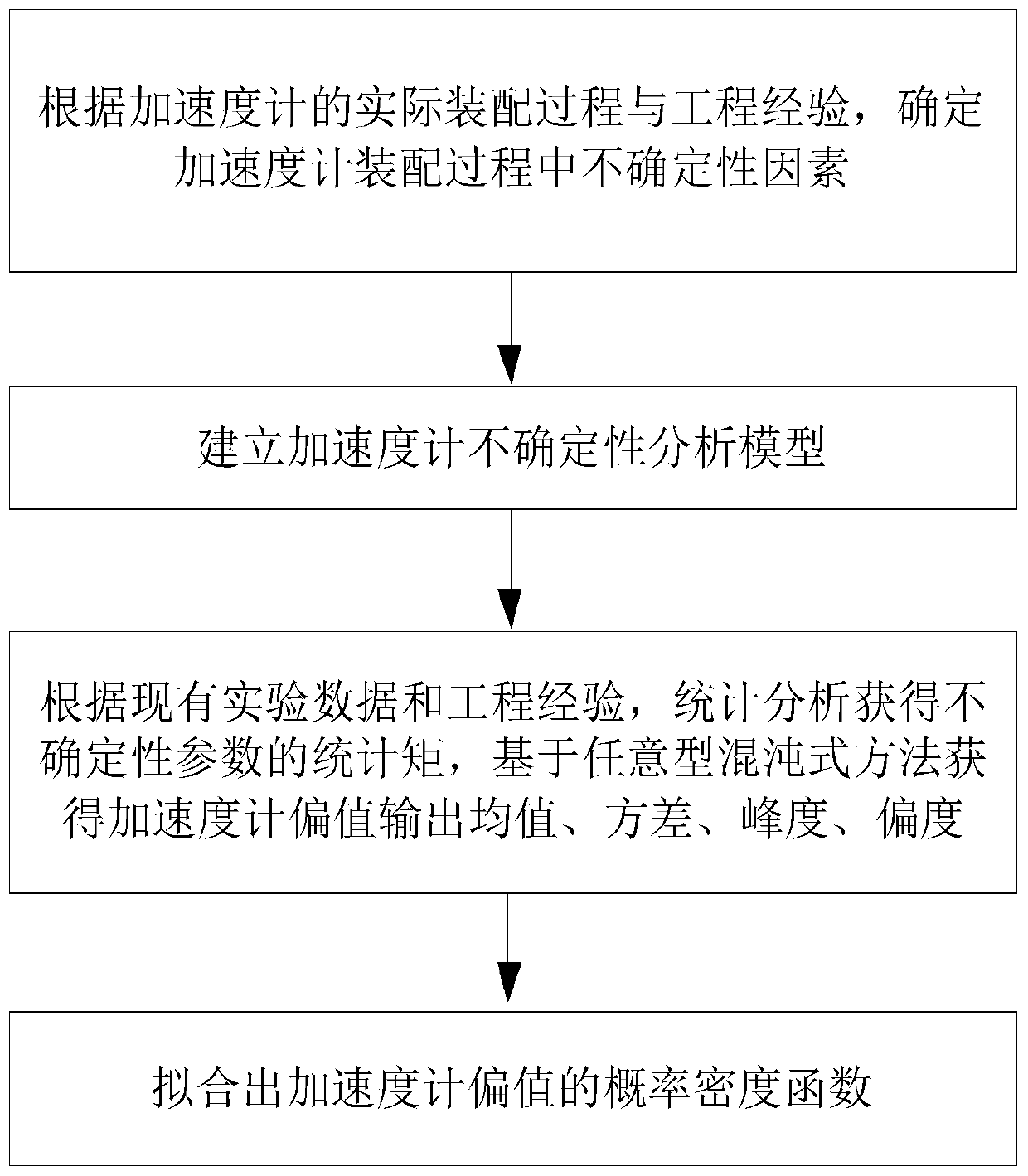
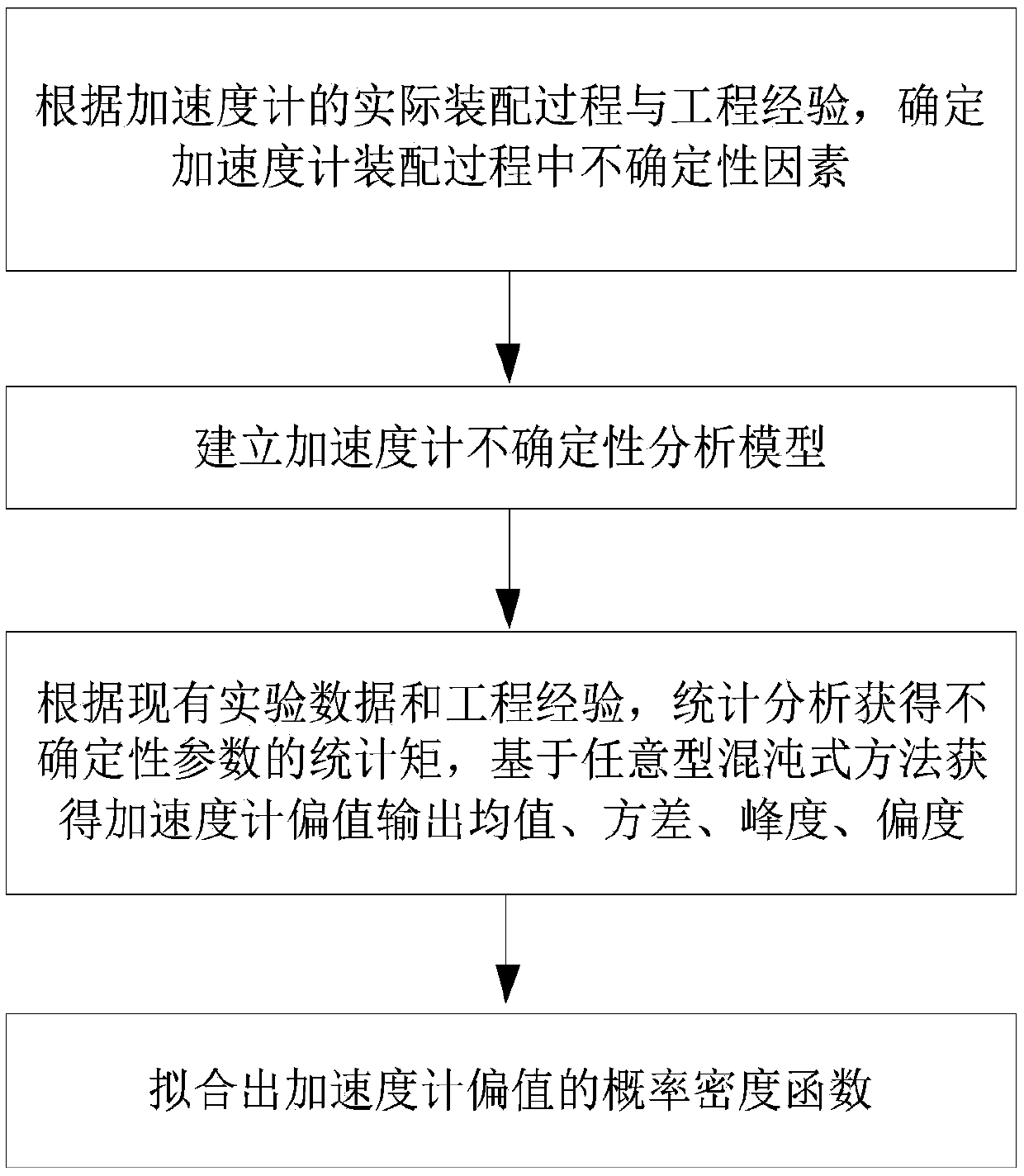
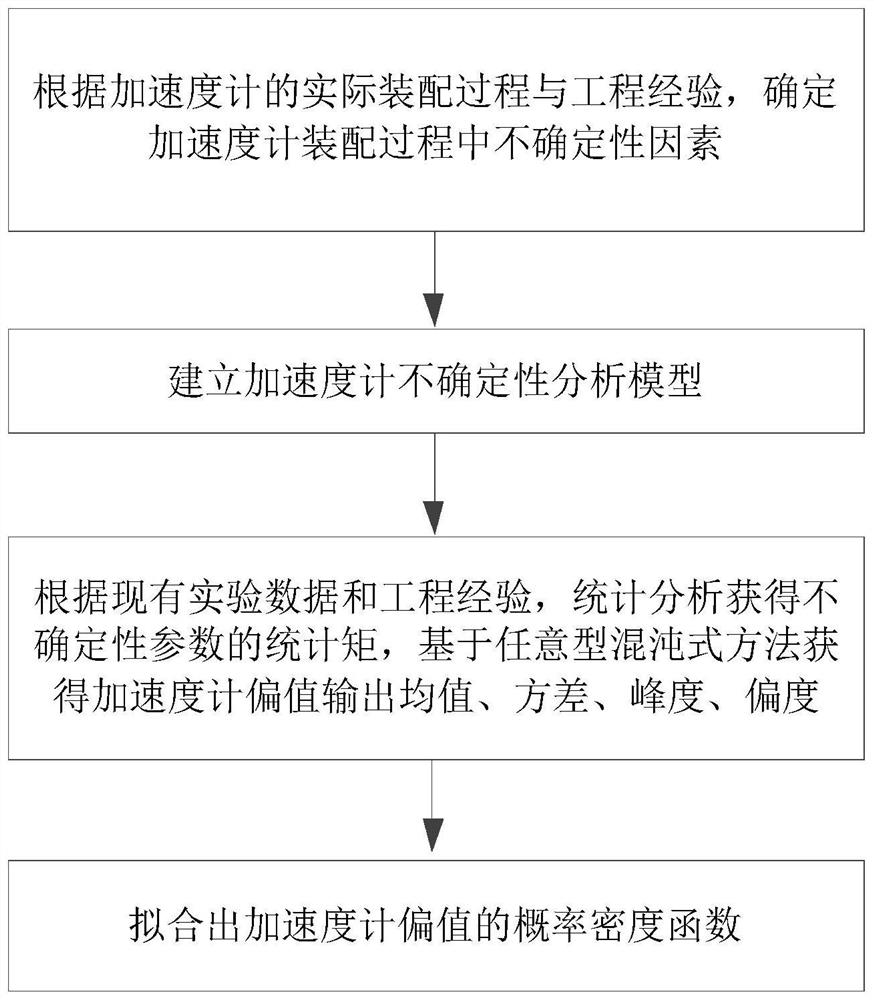
Accelerometer uncertainty analysis method based on arbitrary chaotic polynomial
ActiveCN110175391AUncertainty representationImprove pass rateDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPolynomial methodAccelerometer
The invention belongs to the technical field of inertial navigation, and discloses an accelerometer uncertainty analysis method based on an arbitrary chaotic polynomial. The method comprises the stepsof analyzing the uncertain factors existing in the accelerometer assembling process, establishing an accelerometer uncertainty analysis model, obtaining the statistical moment information of the uncertain parameters through statistical analysis according to the existing experimental data and the engineering experience, and solving the output mean value, variance, kurtosis and skewness of the biasvalue of the accelerometer based on an arbitrary chaotic polynomial method, and fitting the probability distribution outputted by the bias value of the accelerometer by adopting a maximum entropy principle. According to the method, the influence of the uncertain factors during the accelerometer assembling process on the offset output of the accelerometer is quantitatively evaluated, and the theoretical guidance is provided for the subsequent optimization of the accelerometer assembling process and structure so as to improve the accelerometer percent of pass.
Owner:XIAN FLIGHT SELF CONTROL INST OF AVIC +1
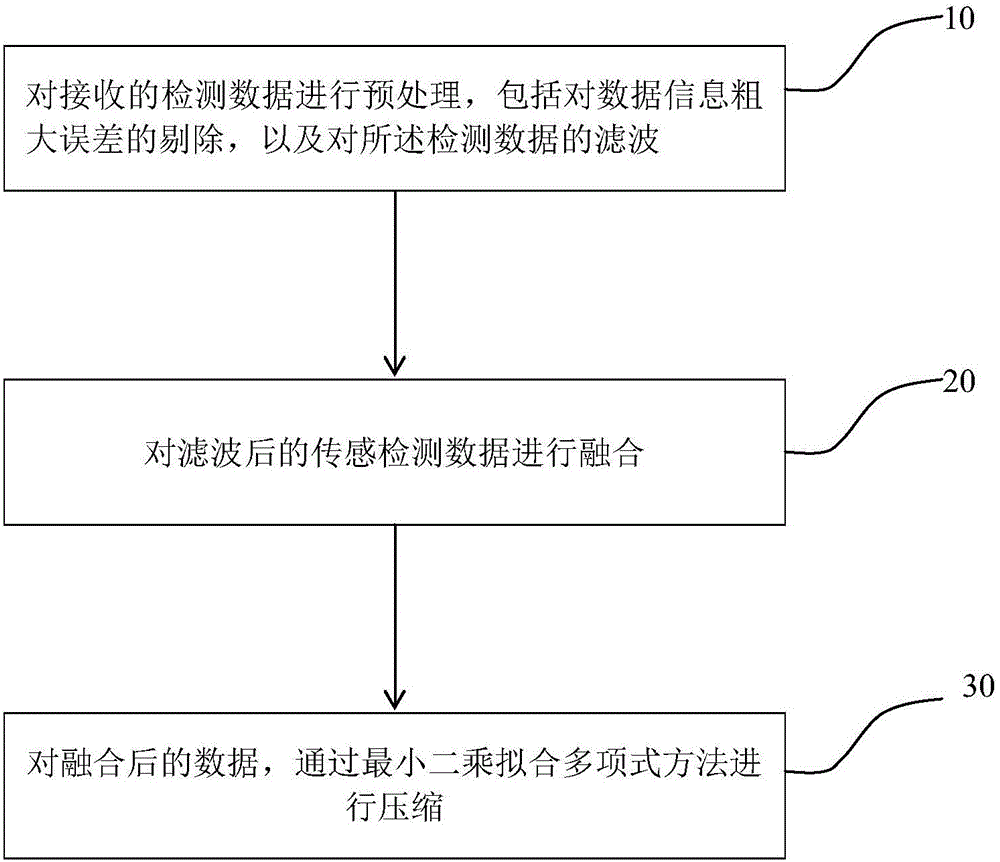
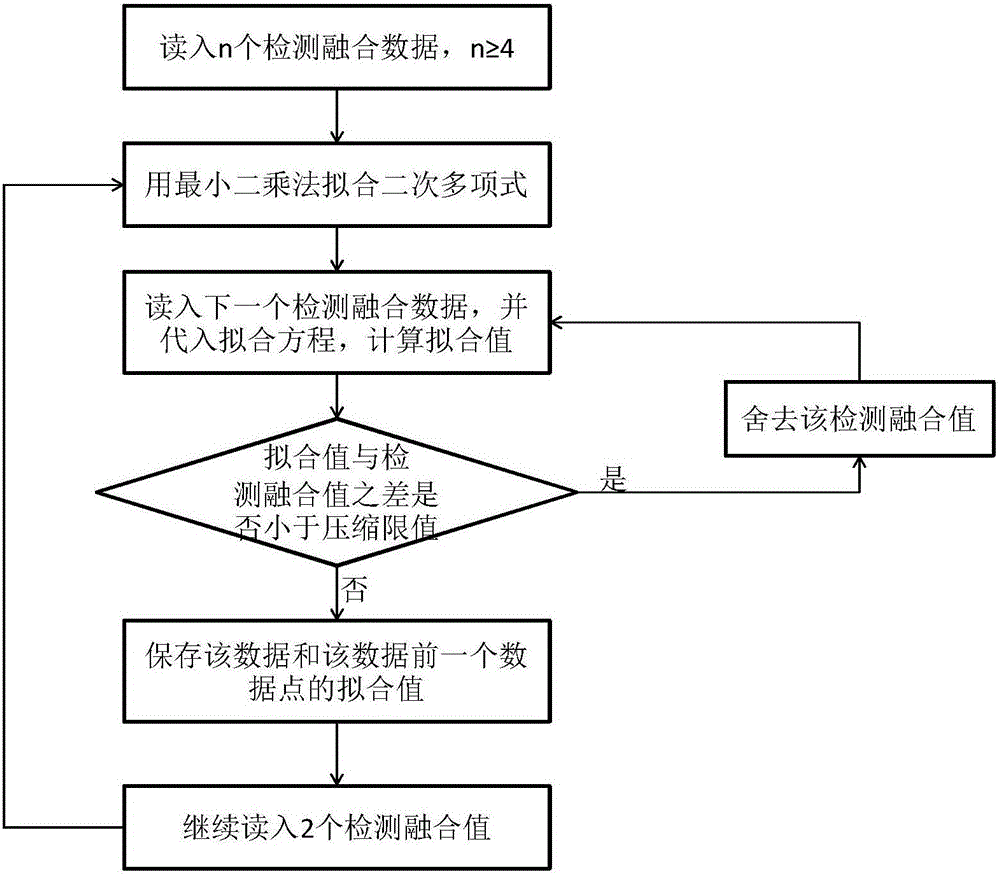
Quick data compression method
InactiveCN105808708ASave storage spacePreserve Curve FeaturesSpecial data processing applicationsData compressionPolynomial method
The invention discloses a quick data compression method, which comprises the following steps: preprocessing received detection data: ejecting the gross error of data information, and filtering the detection data; measuring the filtered detection data through a sensor, and carrying out fusion on the measured data; and compressing the fused data through a least square fit polynomial method. The method provided by the invention greatly compresses a data storage space, simultaneously improves data reliability, keeps the curve characteristics of the data and has a good use value through data preprocessing, data fusion and data compression.
Owner:GUANGDONG IND TECHN COLLEGE
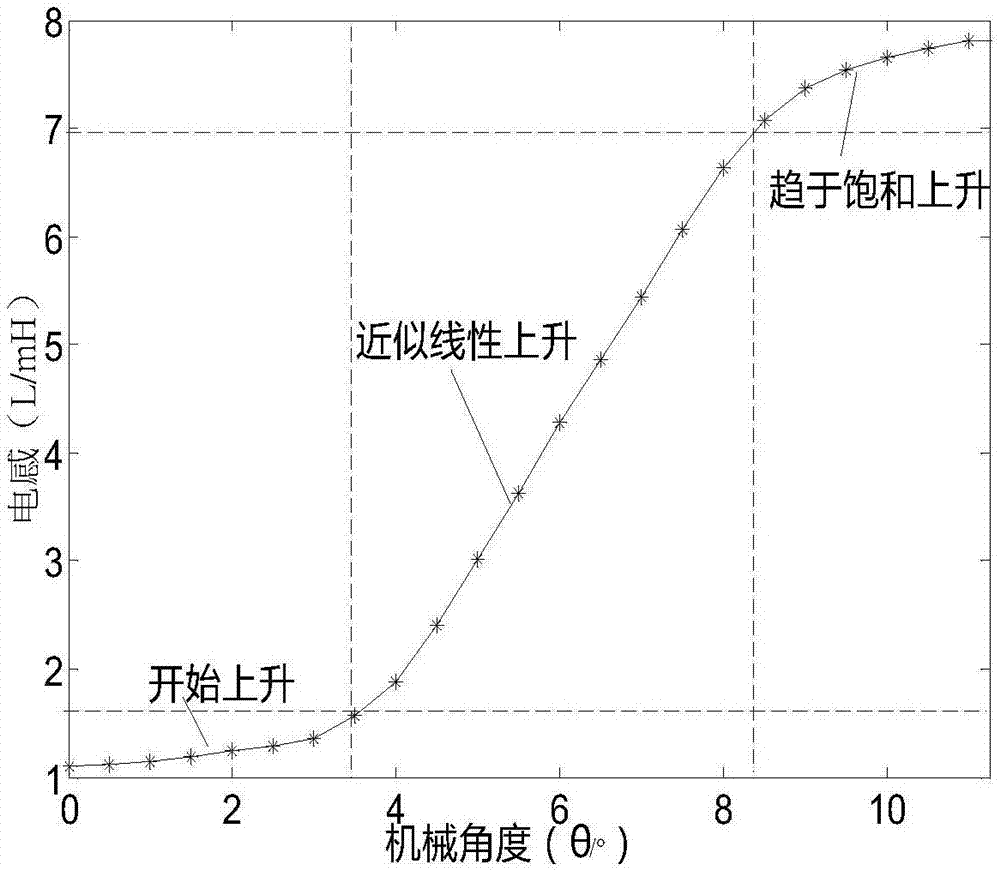
Rotor position measurement method of transverse flux switch reluctance motor without position sensor
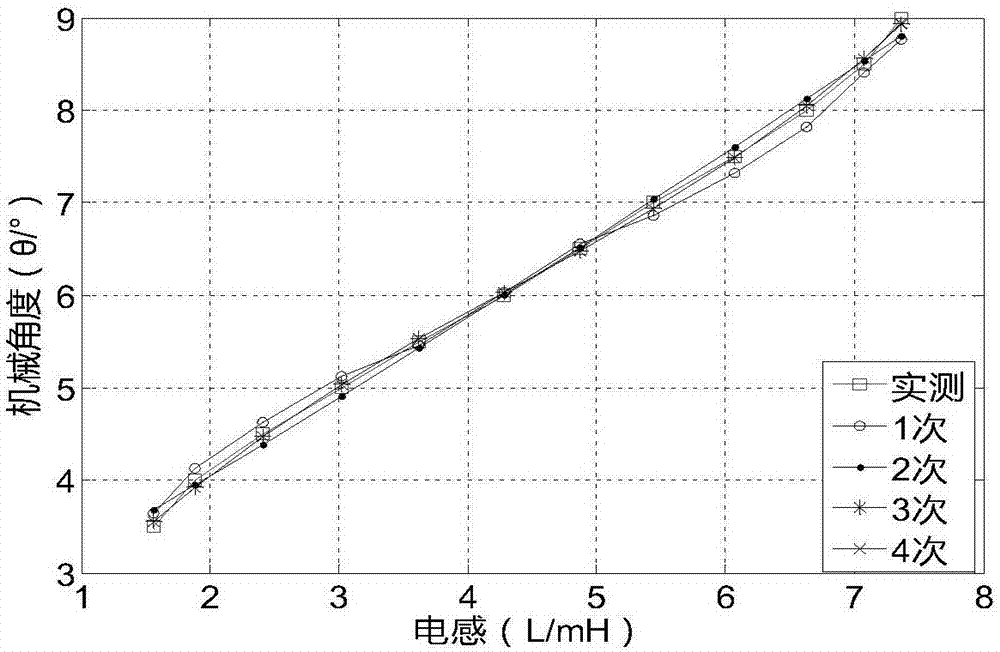
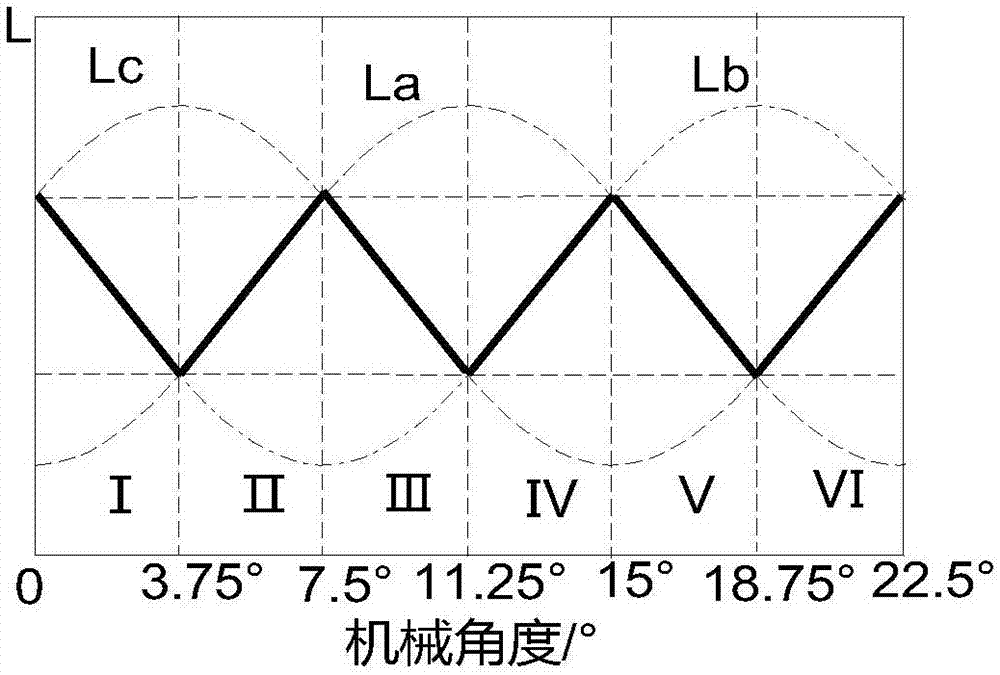
ActiveCN107979311AEasy to implementHigh precisionElectronic commutation motor controlPosition angleLower threshold
The invention discloses a rotor position measurement method of a transverse flux switch reluctance motor without a position sensor. The rotor position measurement method comprises the steps of settingan initial position angle of the motor, and applying a high-frequency pulse voltage to an A phase; adding a step to the initial position angle of the motor, and sequentially calculating an inductancevalue corresponding to each angle to obtain an A phase angle-inductance relation curve; dividing the inductance curve in a mechanical angle period into six regions, performing fitting by employing aquadratic polynomial method to obtain an ideal inductance curve, analyzing the ideal inductance curve, selecting appropriate low-threshold inductance TL, and obtaining a starting phase logic in the mechanical angle period according to a relation between three-phase inductance and the TL in each region; simultaneously calculating a three-phase inductance value from a three-phase injection high-frequency pulse voltage, comparing the three-phase inductance value with the starting phase logic, and determining a starting phase; and injecting a next conduction phase of the starting phase into the high-frequency pulse voltage, switching off the starting phase after a commutation threshold is reached, and conducting the next phase to achieve commutation running. The rotor position measurement method is easy to implement and is relatively high in accuracy.
Owner:南通大学技术转移中心有限公司
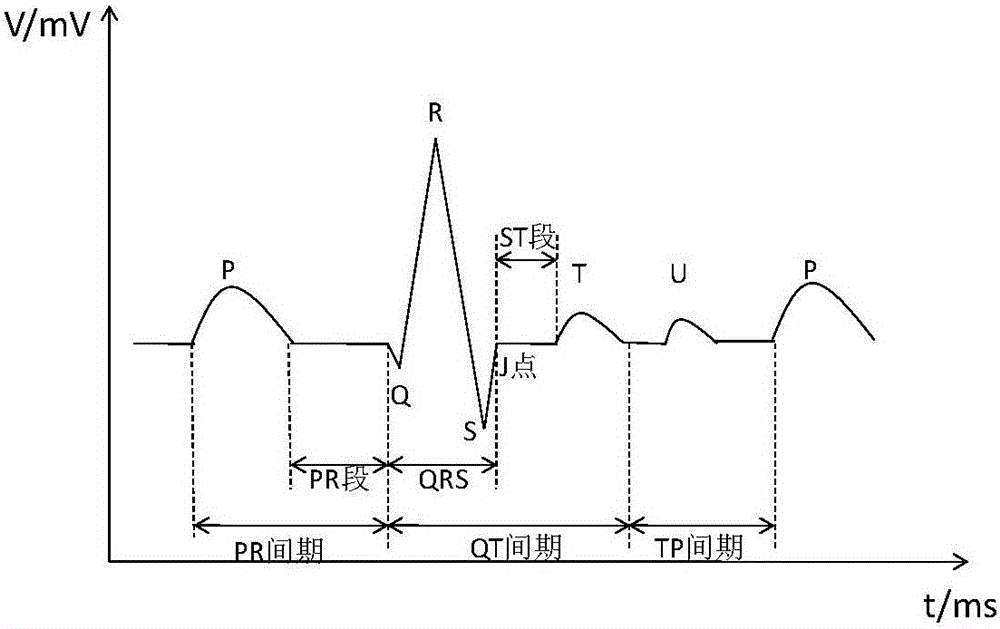
Electrocardiogram signal R wave positioning method
ActiveCN105078447APrecise positioningSimple calculationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalPolynomial method
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Self-acceptance technology debt detection and classification method based on multi-method ensemble learning
PendingCN111782807ADetectableAchieve classification effectCharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsPolynomial methodClassification methods
The invention relates to a self-acceptance technology detection and classification method based on multi-method ensemble learning. The method comprises the following five steps: preprocessing featurewords; selecting the first k most useful features to train a classifier; training corresponding sub-classifiers by using a naive Bayes polynomial method and a linear Logistic regression method; and performing integrated prediction on the prediction result through a sub-classifier voting rule to obtain accuracy, a recall rate, comprehensive accuracy and a recall rate, and finally calculating an F1value as a subsequent evaluation standard. And finally, the features which frequently appear in the experiment process and have high information gain values are clustered through a clustering method,so that the detected technical debts are classified.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
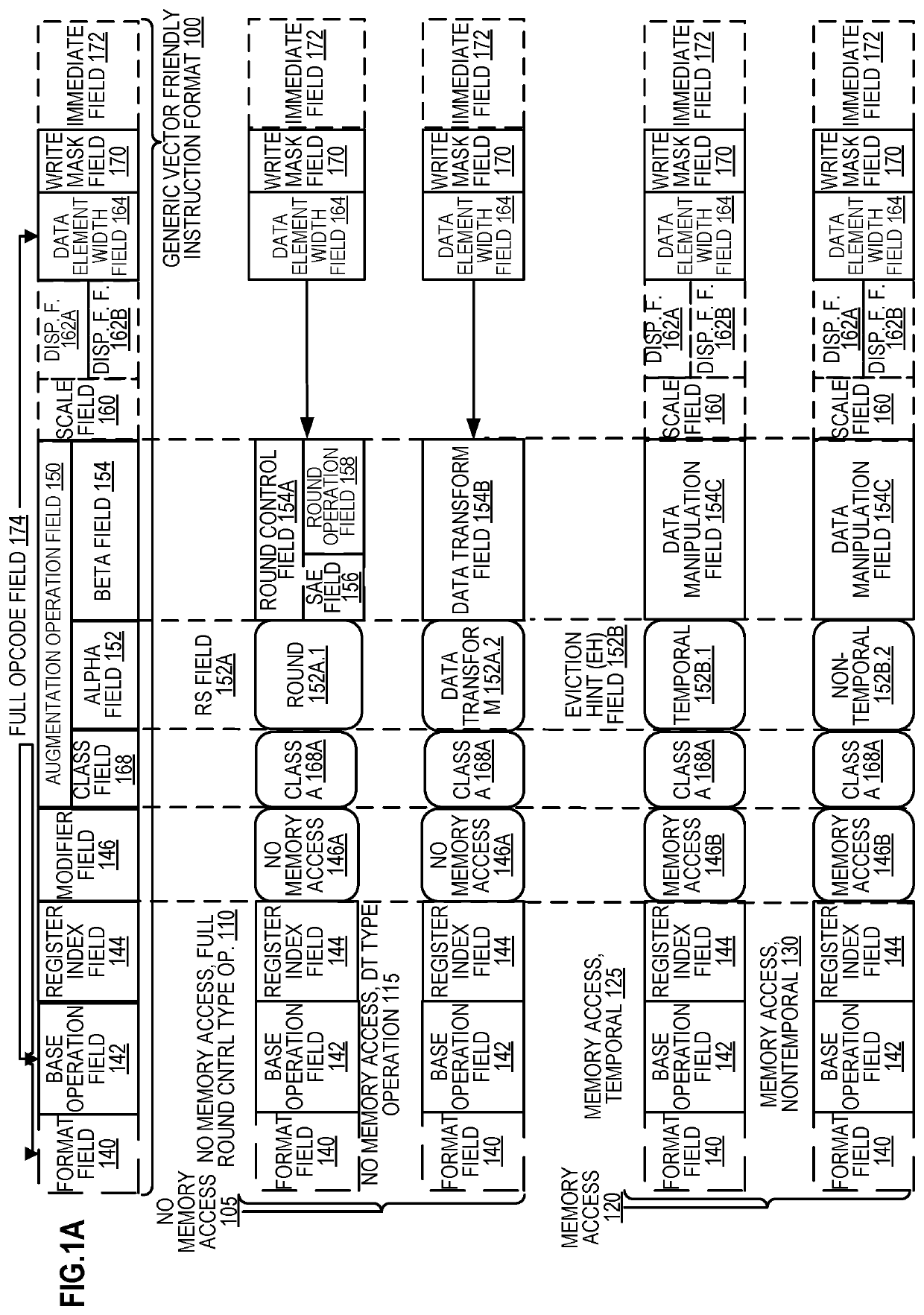
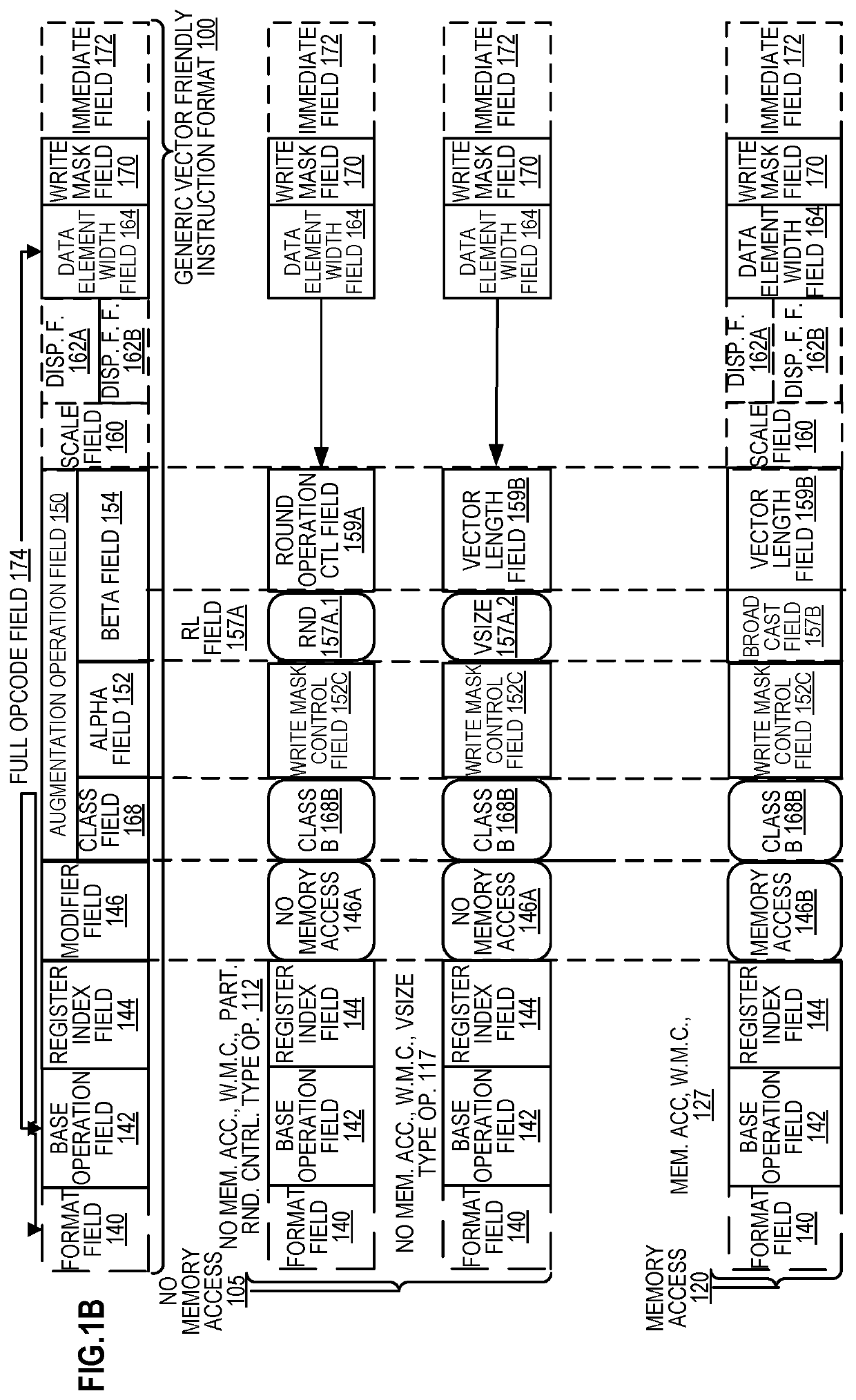
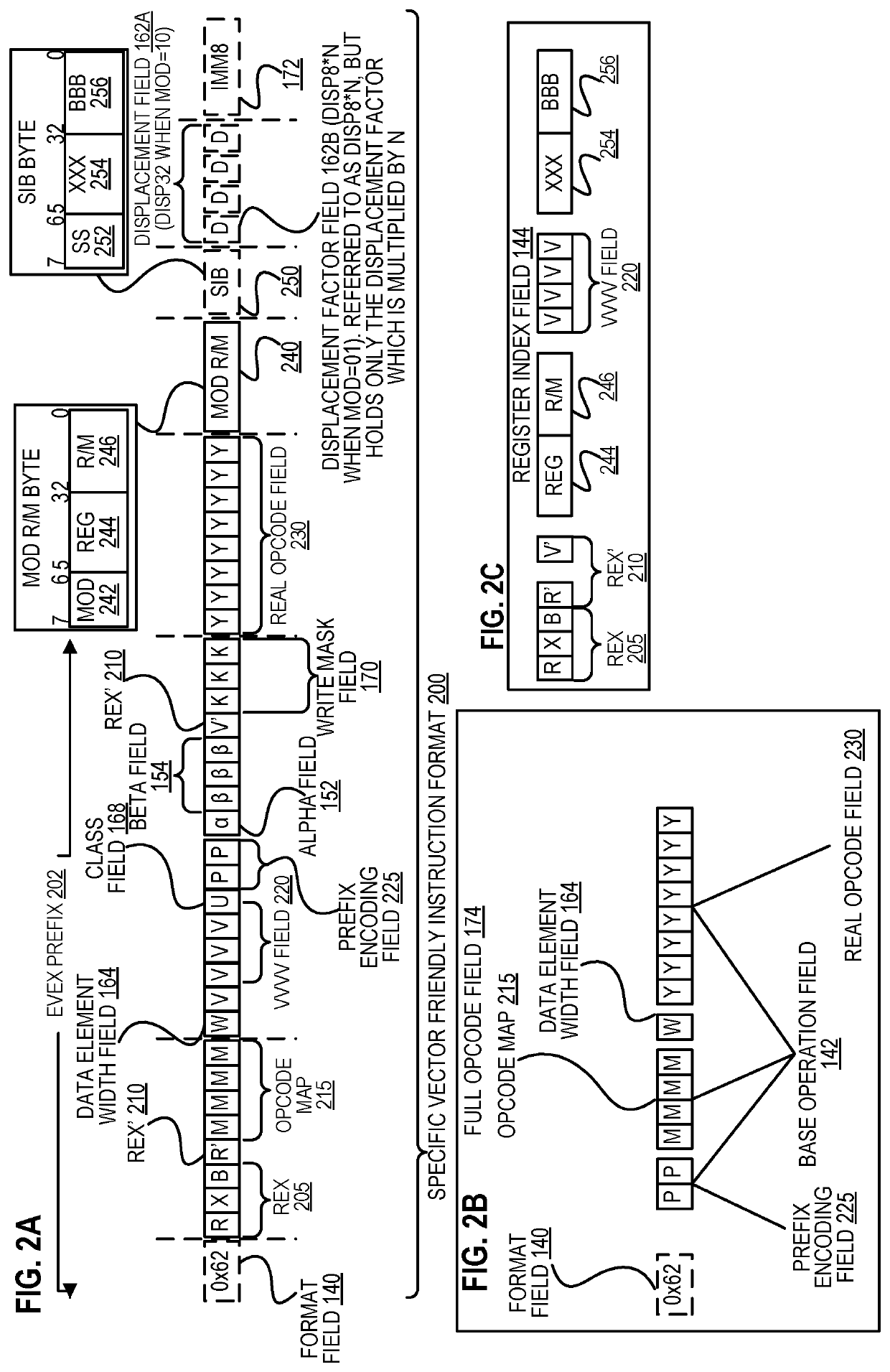
Method and apparatus for approximation using polynomials
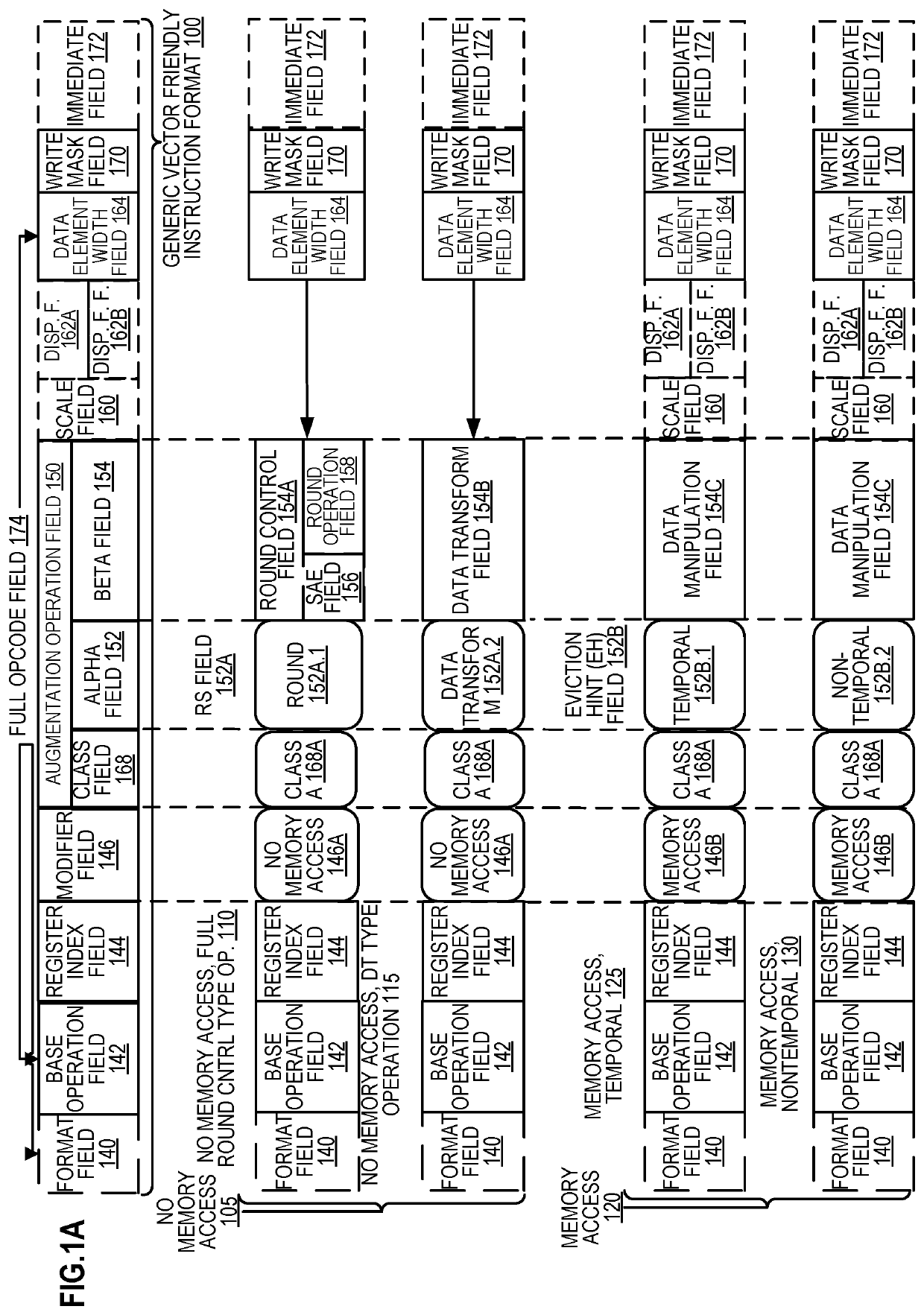
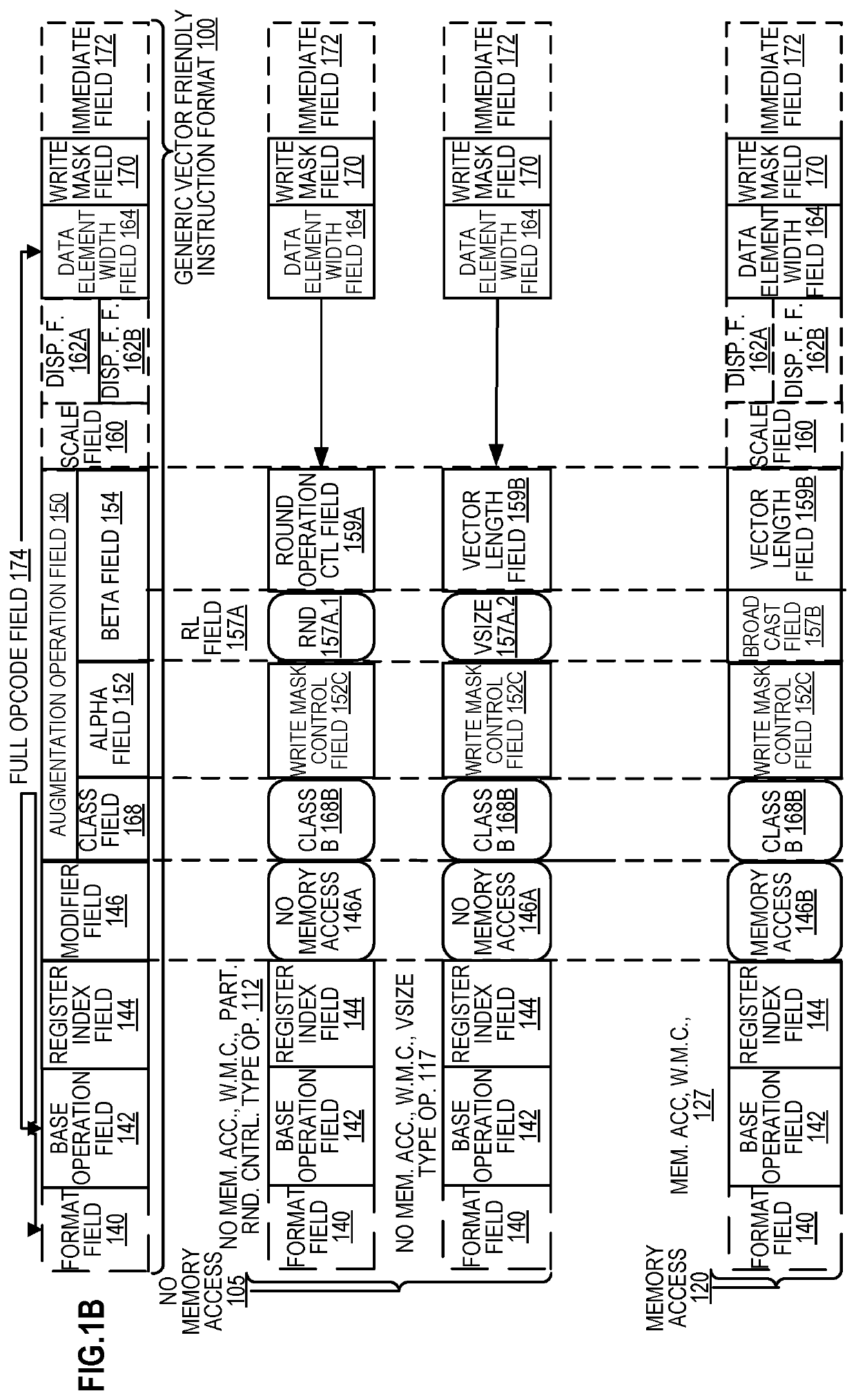
Methods and apparatus for approximation using polynomial functions are disclosed. In one embodiment, a processor comprises decoding and execution circuitry. The decoding circuitry is to decode an instruction, where the instruction comprises a first operand specifying an output location and a second operand specifying a plurality of data element values to be computed. The execution circuitry is to execute the decoded instruction. The execution includes to compute a result for each of the plurality of data element values using a polynomial function to approximate a complex function, where the computation uses coefficients stored in a lookup location for the complex function, and where data element values within different data element value ranges use different sets of coefficients. The execution further includes to store results of the computation in the output location.
Owner:INTEL CORP
An accelerometer uncertainty analysis method based on an arbitrary chaotic polynomial
InactiveCN109583111AUncertainty representationImprove pass rateDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPolynomial methodAccelerometer
The invention belongs to the technical field of inertial navigation, and discloses an accelerometer uncertainty analysis method based on an arbitrary chaotic polynomial. The method comprises the stepsthat uncertain factors existing in the accelerometer assembling process are analyzed; Establishing an accelerometer uncertainty analysis model; Statistical moment information of the uncertain parameters is obtained through statistical analysis according to existing experimental data and engineering experience, and the output mean value, variance, kurtosis and skewness of the bias value of the accelerometer are obtained based on an arbitrary chaotic polynomial method; And fitting probability distribution output by the bias value of the accelerometer by adopting a maximum entropy principle. According to the method, the influence of uncertain factors in the accelerometer assembling process on the offset output of the accelerometer is quantitatively evaluated, and theoretical guidance is provided for subsequent optimization of the accelerometer assembling process and structure so as to improve the accelerometer percent of pass.
Owner:XIAN FLIGHT SELF CONTROL INST OF AVIC +1
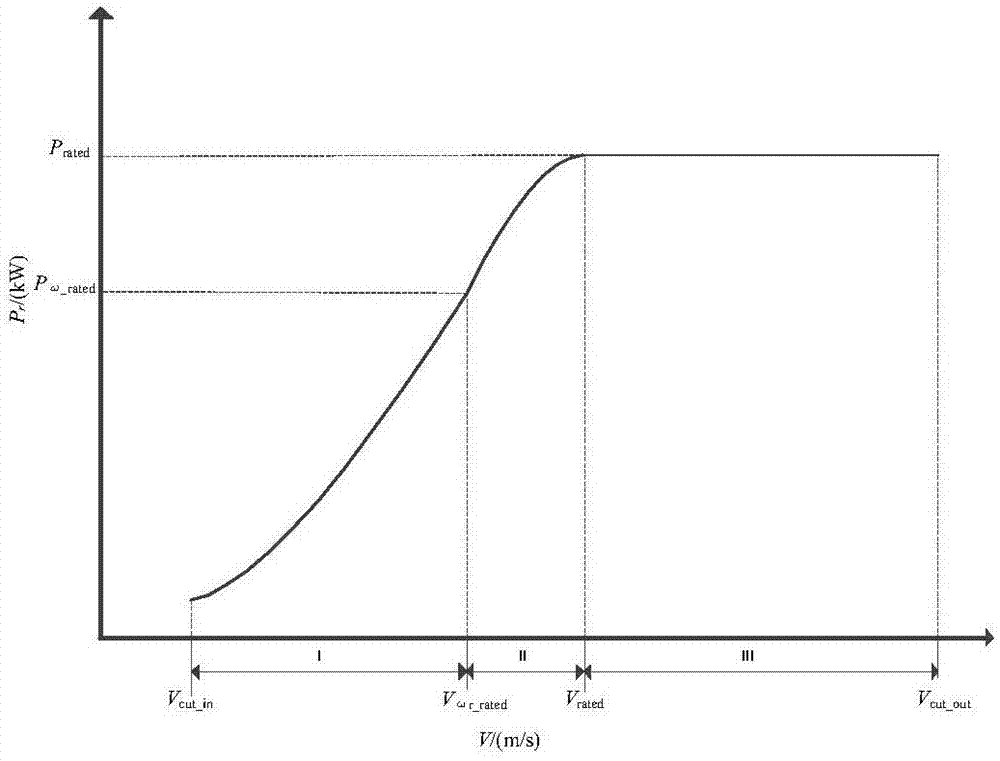
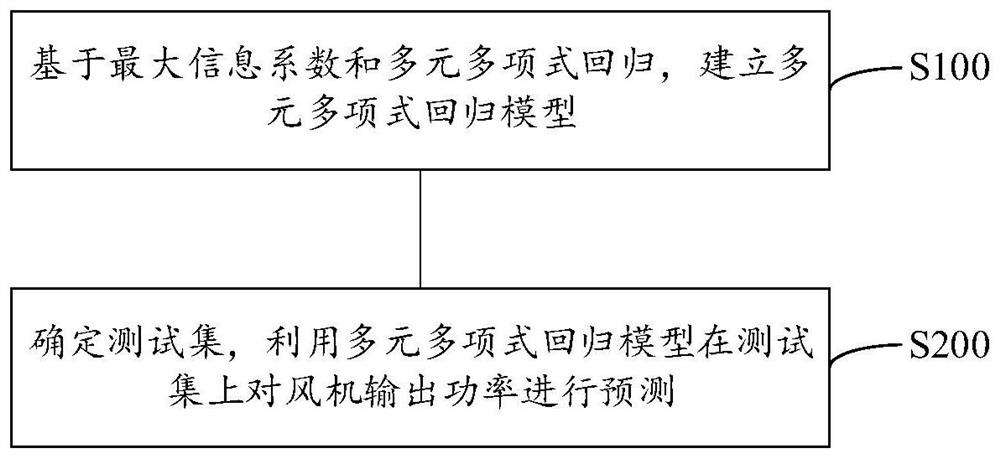
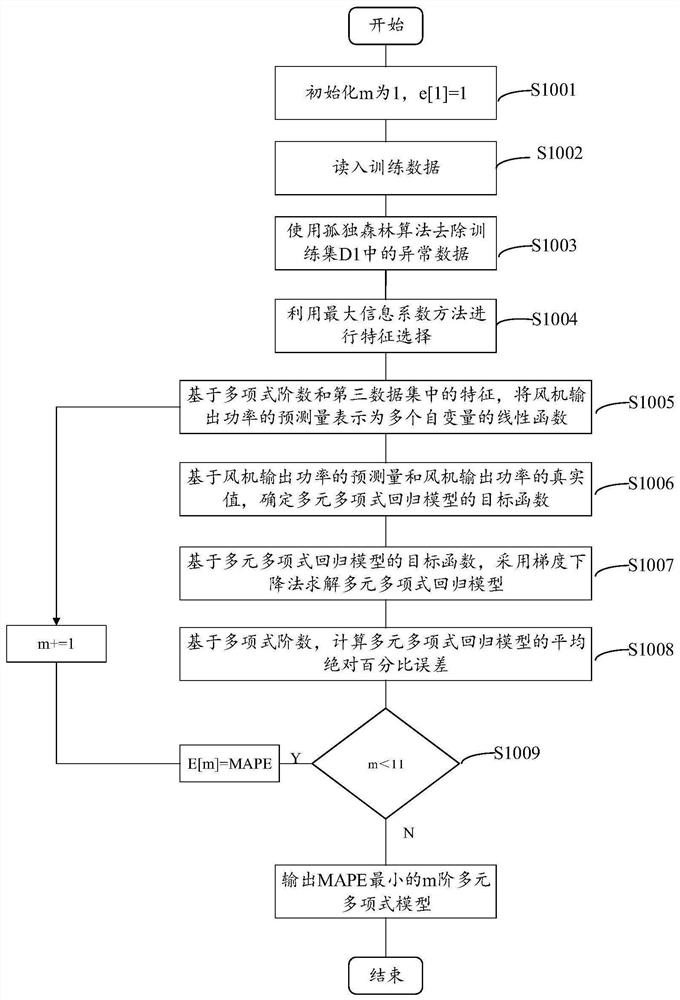
Fan output power prediction method and system
PendingCN113821931ASolve the problem of insufficient analysisImprove accuracyForecastingDesign optimisation/simulationPolynomial methodPolynomial regression model
The invention discloses a fan output power prediction method, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, establishing a multivariate polynomial regression model based on a maximum information coefficient and multivariate polynomial regression; and then, determining a test set, and predicting the output power of the fan on the test set by using the multivariate polynomial regression model. In addition, the invention further provides a fan output power prediction system. According to the method and system, the maximum information coefficient is used for selecting the important variables influencing the output power of the fan in the process of establishing the multivariate polynomial regression model, multiple important variables are comprehensively considered, the problem that analysis is not comprehensive enough due to the fact that influence factors of the output power of the fan are analyzed manually is solved, and further, the relation between multivariable and the fan output power is modeled through a polynomial method, so that prediction of the fan output power has high accuracy and low model complexity.
Owner:SHANGHAI MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Aircraft posture coupling rapid and stable control method based on mechanical arm driving
ActiveCN109270955AExtended service lifeGuaranteed convergenceAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsEngineeringAngular acceleration
The invention relates to an aircraft posture coupling rapid and stable control method based on mechanical arm driving. According to the aircraft posture coupling rapid and stable control method, a mechanical-arm-driven aircraft posture coupling kinematics model considering joint mass center bias factors is established, and the influences of initial linear momentum and angular momentum are considered and serve as the model basis for the design of a control law; and a reference posture limited time convergence trajectory is determined based on a polynomial method according to initial posture errors of an aircraft, and the determined polynomial coefficients need to satisfy joint angle, joint angular velocity and joint angular acceleration constraints. The aircraft posture coupling rapid and stable control method based on mechanical arm driving does not need to consume a chemical propellant, and can prolong the service life of an on-orbit aircraft; and the aircraft posture coupling rapid and stable control method based on mechanical arm driving can ensure that aircraft posture errors converge within reasonable given time, has good dynamic performance, and can ensure that the mechanicaljoint motion satisfies the angle constraint, angular velocity constraint and angular acceleration constraints.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF LAUNCH VEHICLE TECH
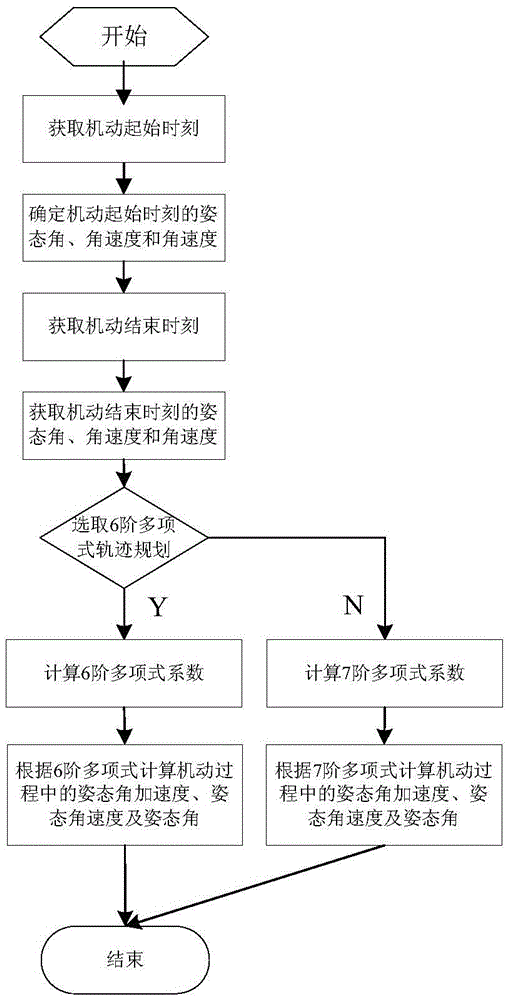
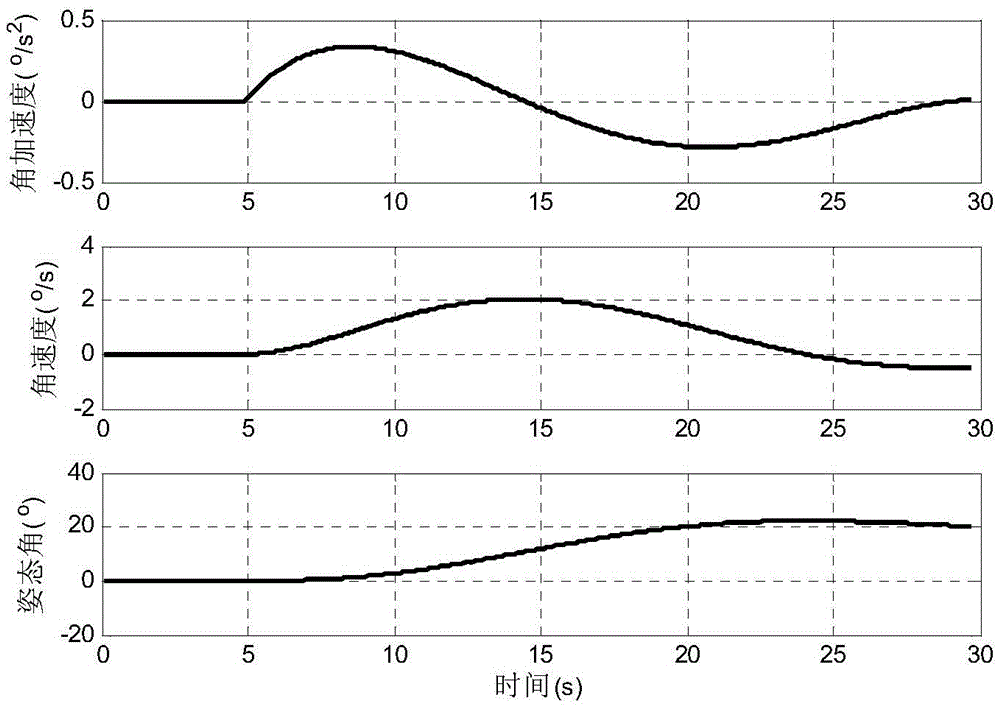
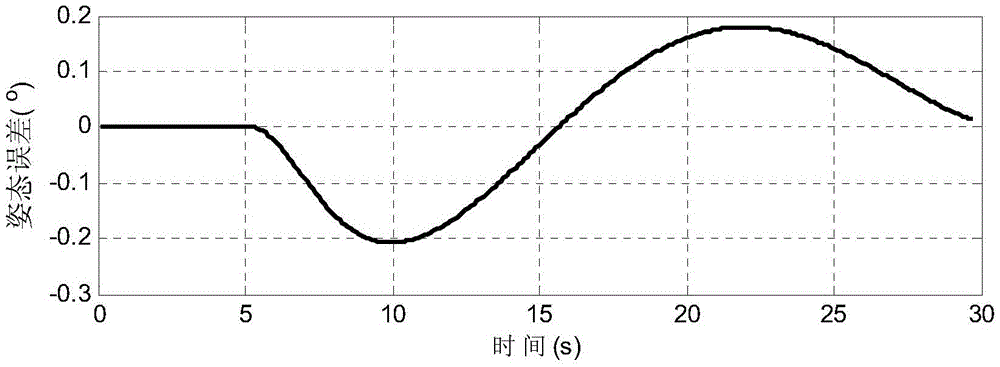
A Method of Satellite Attitude Maneuvering Based on Polynomials
ActiveCN103941739BGuaranteed seamless connectionGuaranteed smoothnessAttitude controlNatural satellitePolynomial method
Disclosed is a satellite attitude maneuvering method based on polynomial. The attitude angle, the angular speed and the angular acceleration at the start moment of the satellite attitude can be appointed at will, and meanwhile the attitude angle, the angular speed and the angular acceleration at the end moment of satellite maneuvering can also be appointed at will. The method can ensure that the satellite attitude is guided to a target value at the appointed moment and can also ensure the stability of the whole maneuvering path. Meanwhile, due to the utilization of the smoothing technology at the tail end, smooth transition of the attitude angle, the angular speed and the angular acceleration at the end moment of satellite maneuvering can be ensured, the control error of the satellite attitude at the end moment of satellite maneuvering is small, and consequently the performance is ensured when maneuvering is finished. The satellite attitude maneuvering method based on polynomial is particularly suitable for the state establishment stage of maneuvering tasks such as movement imaging observation and target tracking of an agile satellite, and can easily meet the requirement that maneuvering is stable the moment when in place.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
A polynomial method of constructing a non-deterministic (NP) turing machine
ActiveCN105190632AObvious featuresObvious advantagesKnowledge representationInference methodsPolynomial methodNon-deterministic Turing machine
A nondeterministic Turning machine (NTM) performs computations using a spatial binary enumeration system, a three-dimensional relation system, a simulated-human logic system, and a bijective-set memory system. The NTM may be used to perform a variety of computational tasks, such as multiple sequence alignment, factorization, and other nondeterministic polynomial algorithms in polynomial time. The NTM may be constructed by a deterministic Turing machine (DTM) using the four systems listed above.
Owner:BEIJING BOSI BIOINTELLIGENCE TECH
Method and apparatus for approximation using polynomials
ActiveUS11327754B2Digital data processing detailsConcurrent instruction executionPolynomial methodAlgorithm
Methods and apparatus for approximation using polynomial functions are disclosed. In one embodiment, a processor comprises decoding and execution circuitry. The decoding circuitry is to decode an instruction, where the instruction comprises a first operand specifying an output location and a second operand specifying a plurality of data element values to be computed. The execution circuitry is to execute the decoded instruction. The execution includes to compute a result for each of the plurality of data element values using a polynomial function to approximate a complex function, where the computation uses coefficients stored in a lookup location for the complex function, and where data element values within different data element value ranges use different sets of coefficients. The execution further includes to store results of the computation in the output location.
Owner:INTEL CORP
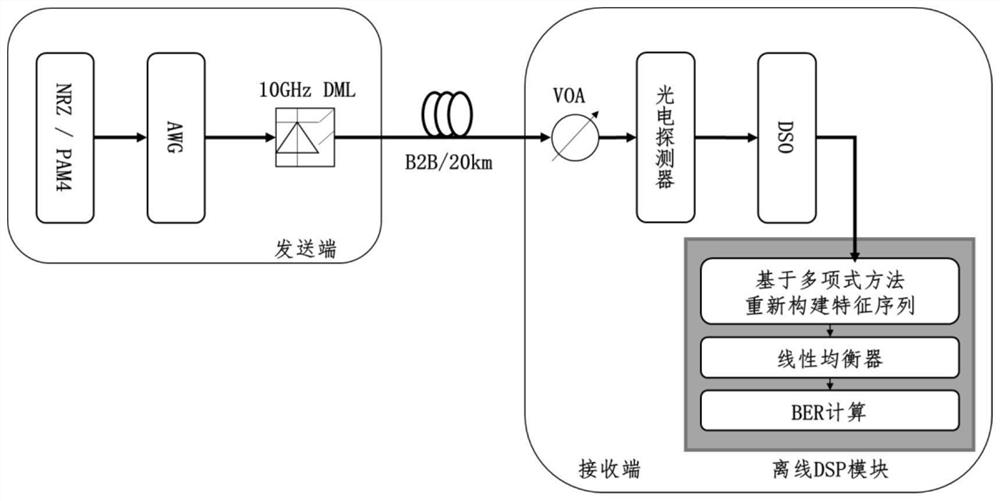
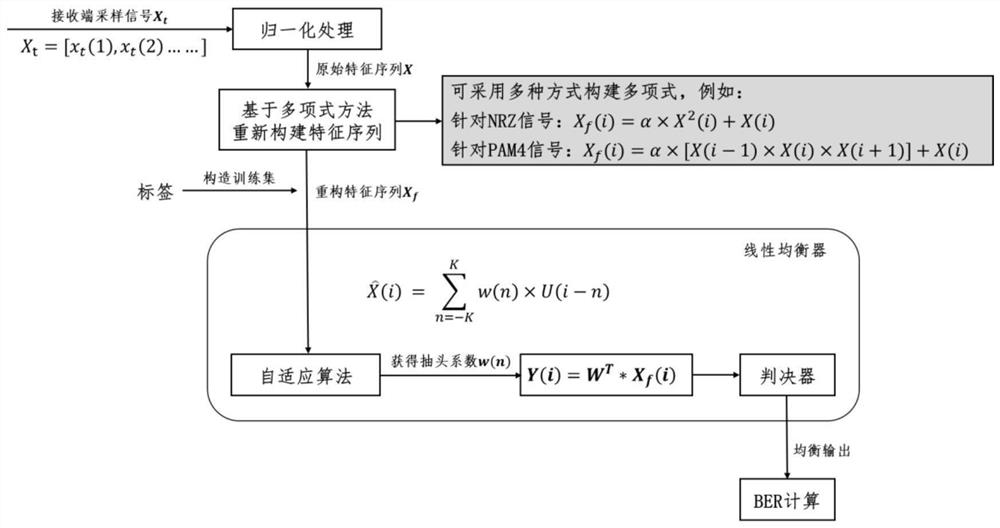
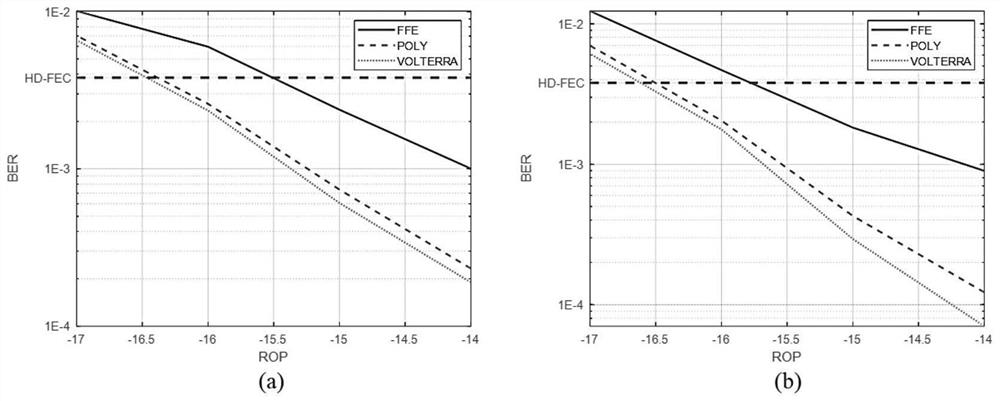
Nonlinear equalization method and system based on feature construction of polynomial mapping
ActiveCN114204993ASolve the problem of not being able to deal with signal nonlinear impairmentsReduce the number of featuresElectromagnetic transmissionHigh level techniquesPolynomial methodEqualization
The invention discloses a nonlinear equalization method and system based on polynomial mapping feature construction. The method comprises the following specific steps: S1, carrying out normalization processing on a receiving end sampling signal Xt to obtain a receiving end sampling signal X normalized by an equalizer; s2, nonlinear features of signals are introduced according to a polynomial method, and a feature sequence Xf is reconstructed; and S3, adjusting the tap coefficient of the linear equalizer on the training set by using an adaptive algorithm to obtain a trained linear equalizer, inputting a signal needing to be equalized into the equalizer, and judging the output of the equalizer to realize channel equalization. Compared with a traditional nonlinear equalizer, the linear equalizer has the advantages that the huge calculated amount in the process of adaptively adjusting the weight of each tap of the equalizer is greatly relieved through feature construction, and the performance of the same order of magnitude as that of the nonlinear equalizer can be obtained.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
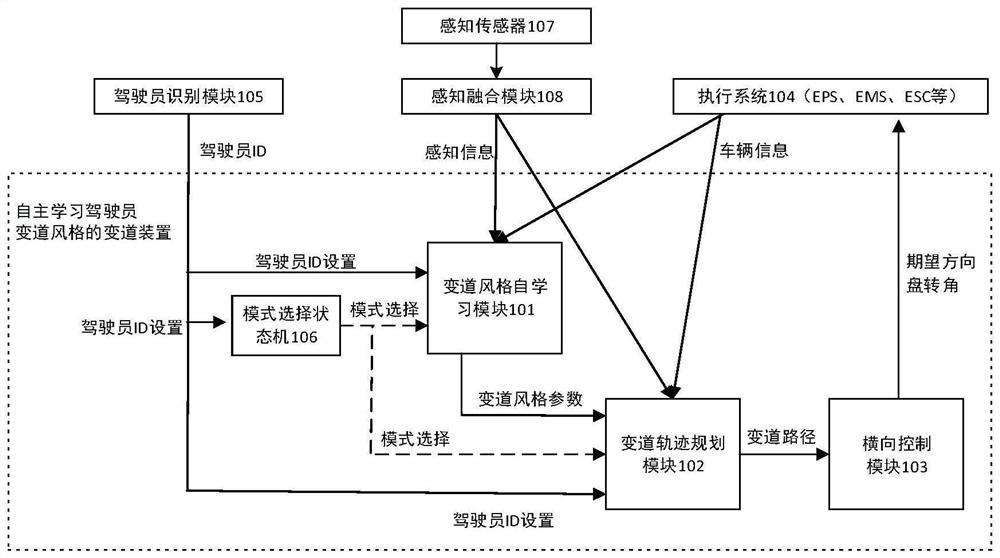
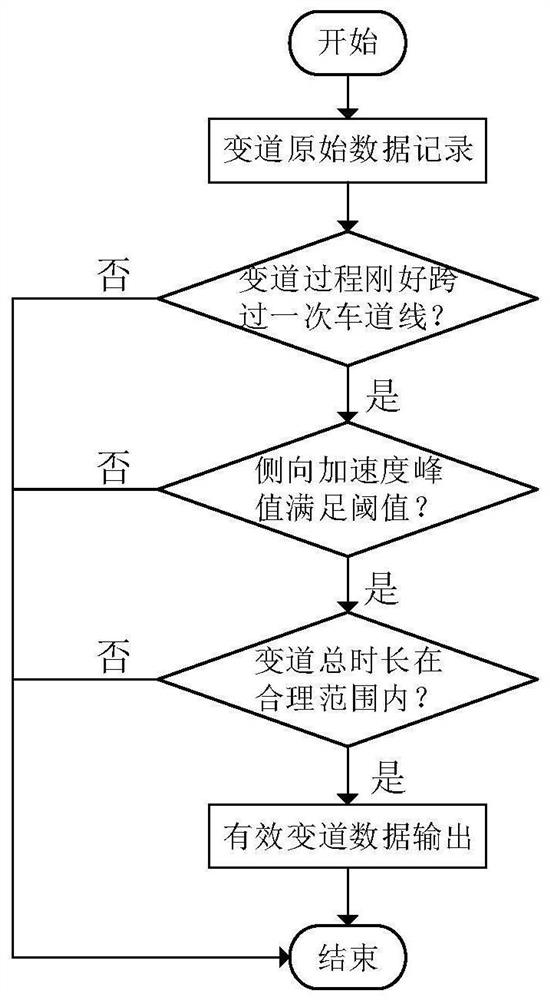
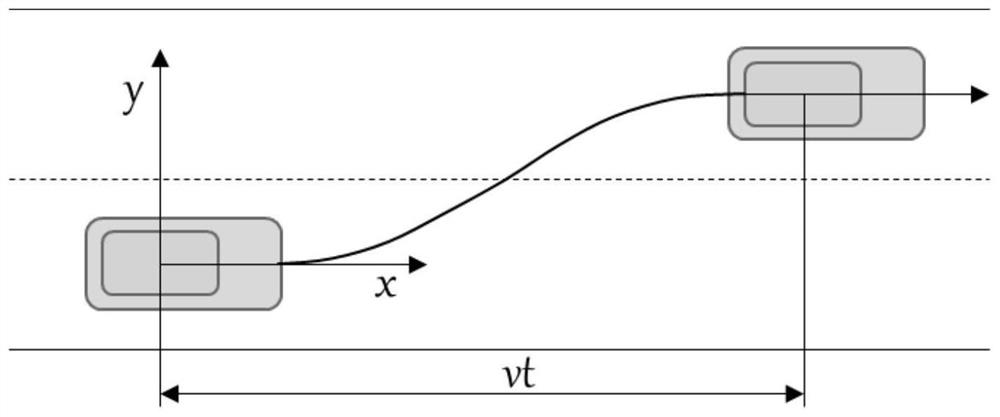
Lane-changing device and method for autonomously learning driver's lane-changing style
The invention discloses a lane-changing device and method for autonomously learning the driver's lane-changing style, which can learn the driver's lane-changing style parameters-lane-changing time autonomously, and then use a polynomial method to plan the lane-changing path, according to the planned lane-changing Based on the path and vehicle dynamics control principles, the control parameters when the vehicle changes lanes are calculated; finally, the vehicle is controlled to change lanes according to the calculated control parameters when the vehicle changes lanes. The lane changing device and method for autonomously learning a driver's lane changing style of the present invention can adapt to the driving habits of different drivers.
Owner:DONGFENG MOTOR CORP HUBEI
An Accelerometer Uncertainty Analysis Method Based on Arbitrary Chaotic Polynomials
ActiveCN110175391BUncertainty representationImprove pass rateDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAnalytic modelAccelerometer
The invention belongs to the technical field of inertial navigation, and discloses an accelerometer uncertainty analysis method based on arbitrary chaotic polynomials. The invention includes analyzing the uncertainty factors existing in the assembly process of the accelerometer; establishing the uncertainty analysis model of the accelerometer; according to the existing experimental data and engineering experience, statistical analysis to obtain the statistical moment information of the uncertainty parameters, based on arbitrary chaos The mean value, variance, kurtosis and skewness of accelerometer bias output are obtained by polynomial method; the probability distribution of accelerometer bias output is fitted by the principle of maximum entropy. The invention quantitatively evaluates the influence of uncertainty factors in the accelerometer assembly process on its bias output, provides theoretical guidance for subsequent optimization of the accelerometer assembly process and structure, and improves the pass rate of the accelerometer.
Owner:XIAN FLIGHT SELF CONTROL INST OF AVIC +1
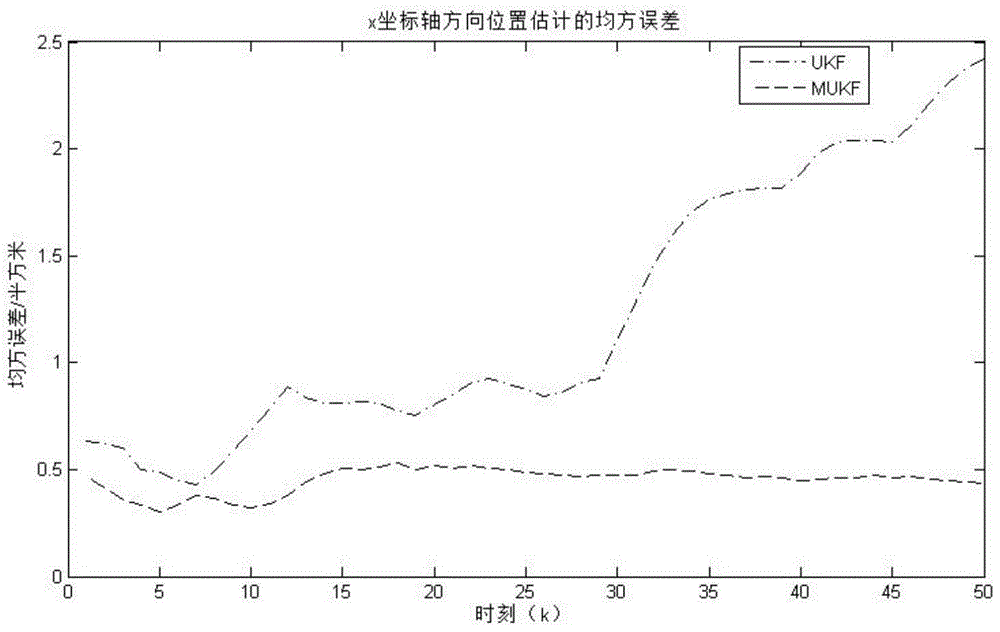
Polynomial Method of Unscented Kalman Filter Based on Higher Order Moment Matching
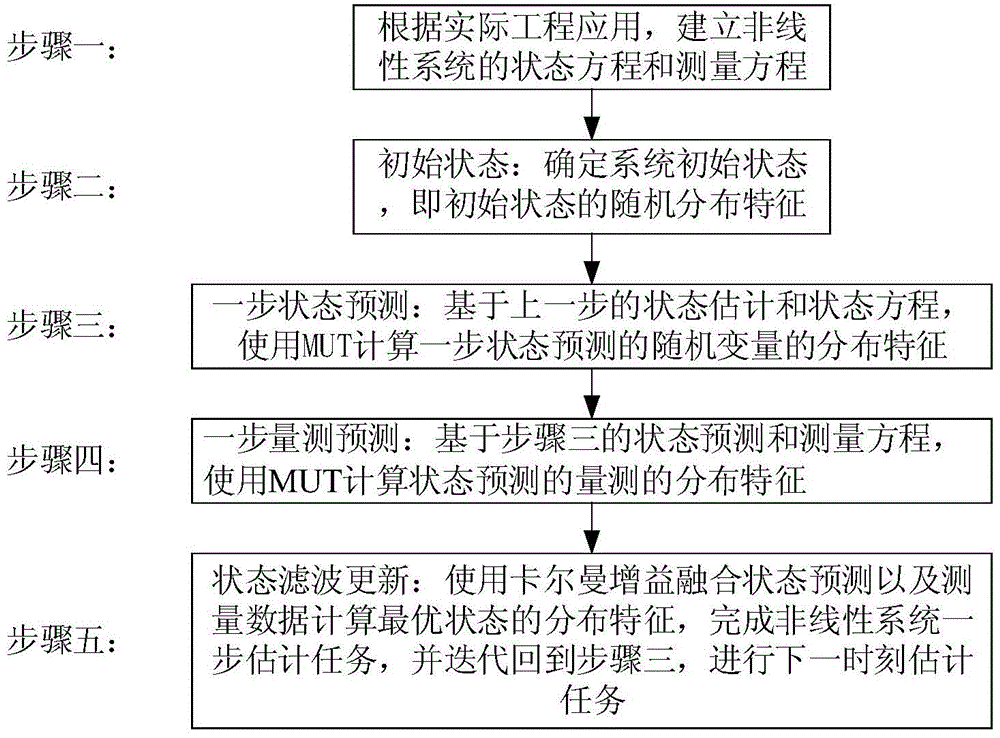
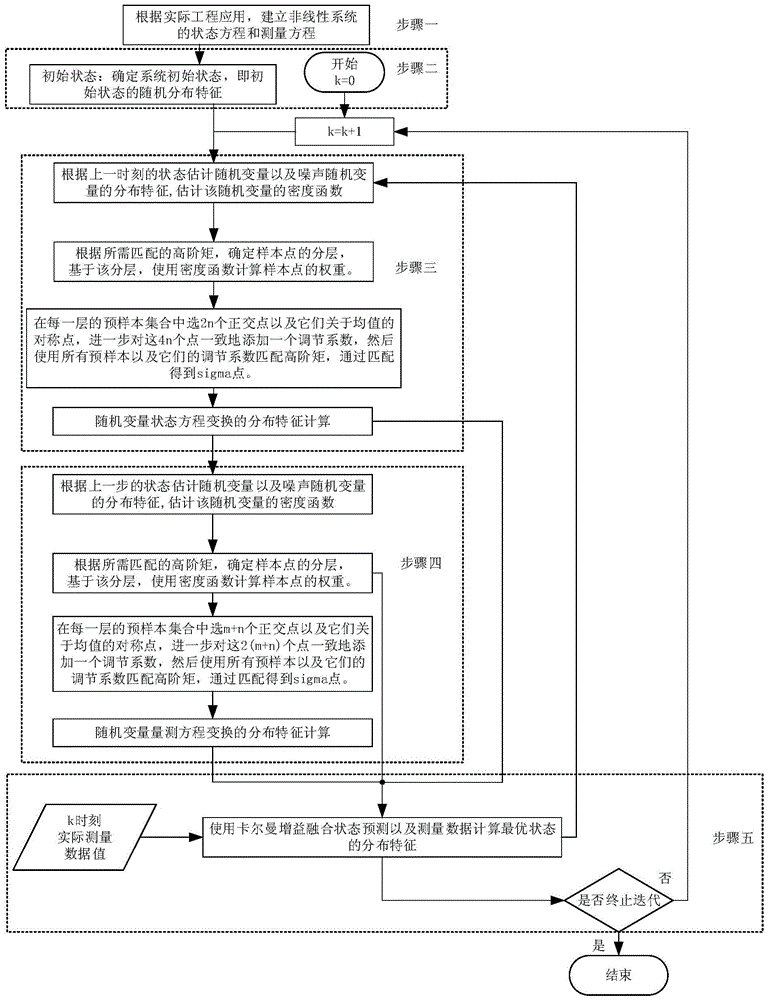
InactiveCN104038180BImprove stabilityImproved Approximation AccuracyDigital technique networkNonlinear filterState prediction
The invention discloses a polynomial method of an unscented Kalman filter based on high-order moment matching, and belongs to the technical field of nonlinear filtering. It includes the following steps: establish the state equation and measurement equation of the nonlinear system; determine the random distribution characteristics of the initial state, including its mean, covariance and higher-order moments, the distribution characteristics of noise, and the initial measurement value; based on the state of the previous moment Estimation and state equations, using multi-layer unscented transformation to calculate the distribution characteristics of random variables for one-step state prediction; based on the state prediction and measurement equations of step 3, using MUT to calculate the distribution characteristics of state prediction measurements; using Kalman gain to fuse states Predict and measure the data to calculate the distribution characteristics of the optimal state, and complete the one-step estimation task of the nonlinear system. This method is used to solve the accuracy and calculation stability problems of nonlinear filters in the actual application process. Combining with the existing sampling strategy, high-order moments and multiple symmetric sampling are used to improve the accuracy.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
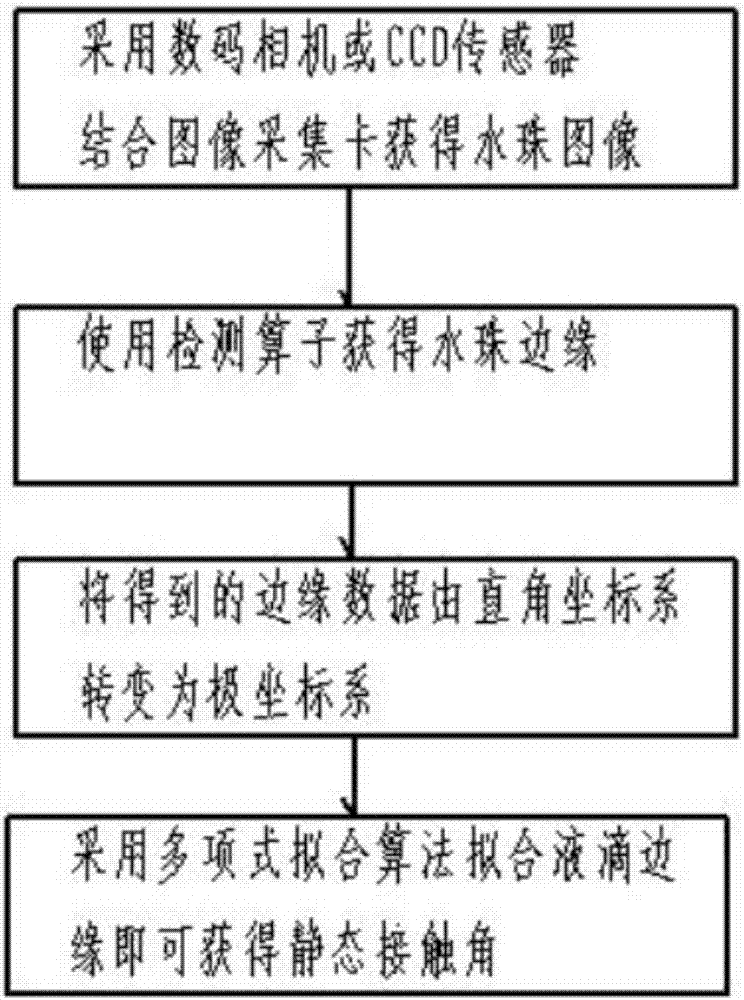
A method for measuring the static contact angle of liquid droplets
InactiveCN104458505BImprove calculation accuracyImprove anti-interference abilitySurface/boundary effectDigital imagingOrthogonal coordinates
A method for measuring the static contact angle of a droplet. First, drip water on the surface of a material, and then use a digital imaging device to take pictures of the droplet on a plane perpendicular to the surface of the material to obtain an image of the droplet, and use an edge detection operator to measure the droplet. The droplet image is processed to obtain the droplet edge; then the droplet edge point data is transformed from the Cartesian coordinate system to the polar coordinate system, and then the polynomial fitting method is used to fit the droplet edge, and then the droplet edge is transformed from the polar coordinate system to Cartesian coordinate system, and finally calculate the slope of the droplet edge at the solid, liquid, and gas three-phase junction point, and obtain the static contact angle from the slope. In the present invention, the rectangular coordinate system is converted into the polar coordinate system first, and then the edge of the droplet is fitted. Since the edge of the droplet is closer to a polynomial in the polar coordinate system, the calculation accuracy of the contact angle is higher, and it is converted into polar coordinates. The number of points involved in fitting the edge after the system is more, and the anti-interference ability is stronger.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
A Compensation Method for Angle Measuring Error of Circular Grating
ActiveCN110030953BImprove angle measurement accuracyImprove Angle Measurement ReliabilityUsing optical meansGratingPolynomial method
The invention discloses a circular grating angle measurement error compensation method, which comprises the following steps: obtaining an angle measurement error of a circular grating at different temperatures with a temperature gradient of 5 in a given temperature; establishing a circular grating angle measurement error compensation model at a certain temperature by using a harmonic method; then,establishing a functional relation between the harmonic coefficient and the ambient temperature by using a polynomial method; substituting the function relational expression obtained by polynomial fitting into a harmonic error compensation model to obtain a circular grating angle measurement error compensation model containing a temperature influence factor; and under different temperature gradients, the experiment is repeated to obtain a new angle measurement error, and the compensation effect of the novel circular grating angle measurement error compensation method is verified. The circulargrating angle measurement error compensation method can save cost, improve the angle measuring precision of the rotary joint, and further improve the measuring precision of the portable joint type coordinate measuring device and the reliability of products.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
SAR image target identification method based on feature construction
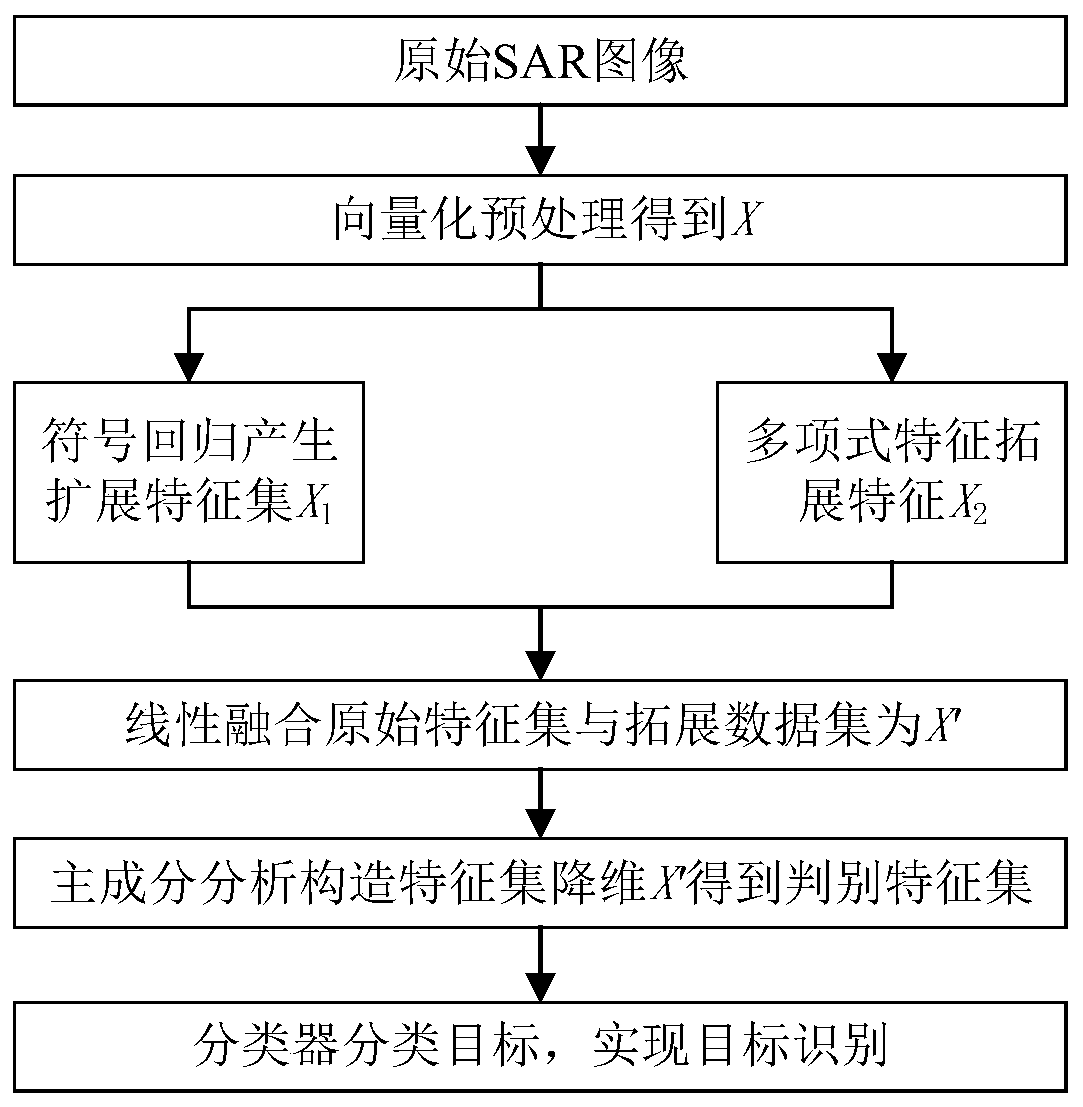
The invention belongs to the field of radar automatic target recognition, and particularly provides an SAR target recognition method based on feature construction. According to the invention, the characteristics of the original image are not damaged; the method comprises the following steps of: constructing SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image features by utilizing a Symbolic Regression method anda polynomial method; linearly fusing the original features and the constructed features, using a global feature dimension reduction method for achieving high-discrimination-capability feature extraction, and finally conducting classification through a classifier. According to the method, the spatial structure relationship between pixels of the original images is fully utilized to construct features with stronger identification capability, and then the features are fused with the features of original SAR images, so that target identification performance of SAR images are effectively improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
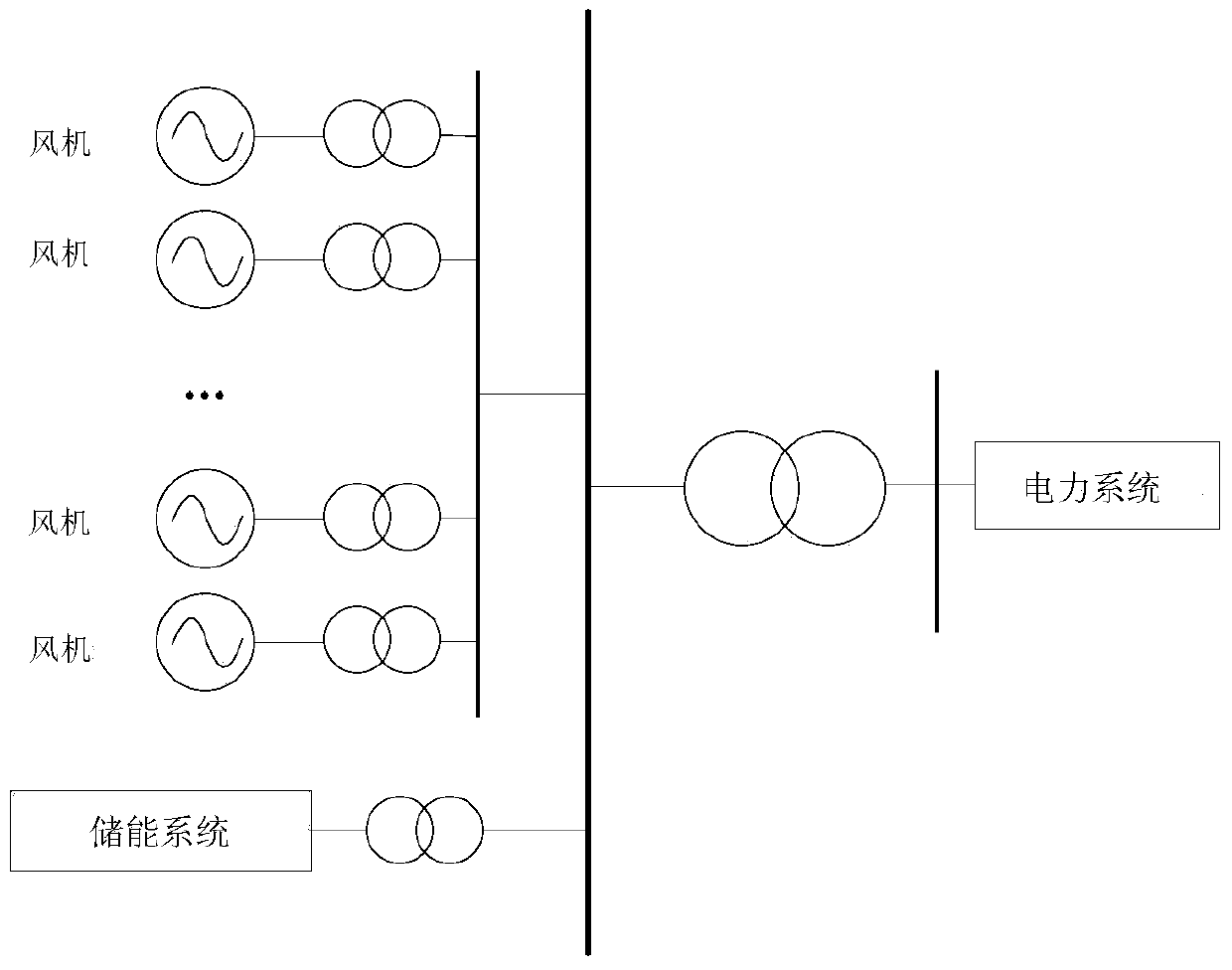
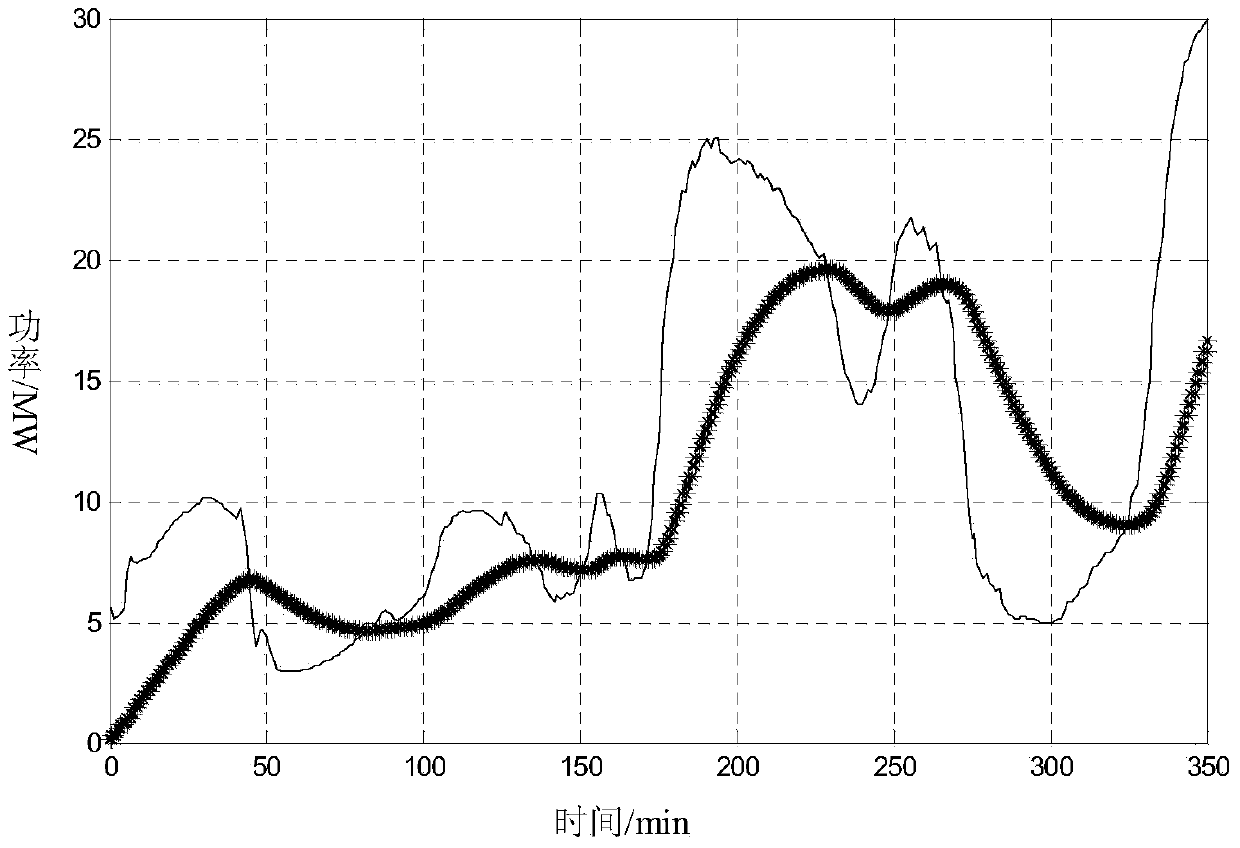
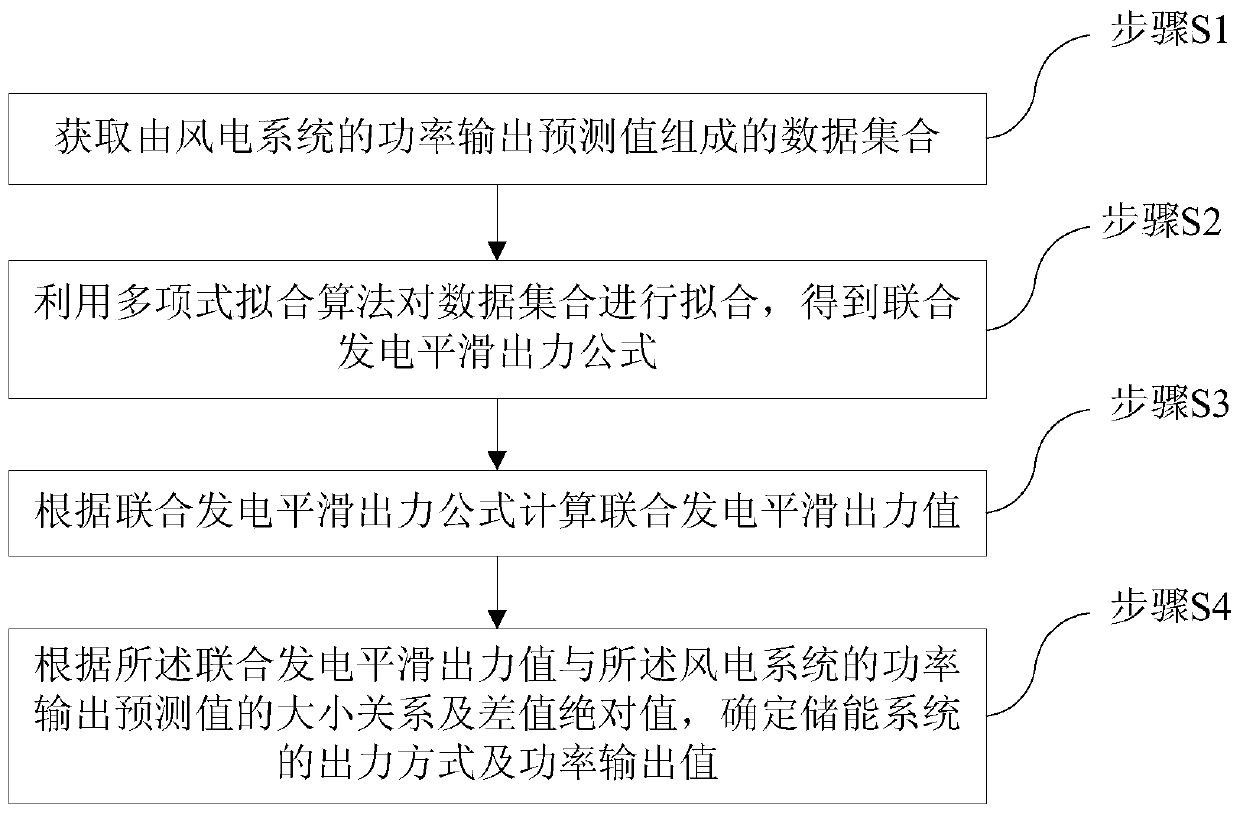
A method for smoothing output of joint power generation of wind power system and energy storage system
ActiveCN105680459BReduce inertia timeOptimize smooth output effectPower oscillations reduction/preventionData setCogeneration
The present invention provides a method for smoothing joint power generation of a wind power system and an energy storage system, comprising: obtaining a data set composed of power prediction values of the wind power system; using a polynomial fitting algorithm to fit the data set to obtain a smooth joint power generation Output formula; calculate the smoothed output value of the combined power generation according to the smoothed power output formula of the combined power generation; determine the energy storage system according to the relationship between the smoothed output value of the combined power generation and the predicted power value of the wind power system and the absolute value of the difference The output mode and power output value. The present invention uses a polynomial fitting method to determine the output value of smooth wind power fluctuations, taking into account the entire planned output range, making the optimized output value more moderate, and reducing the inertia time of the first-order low-pass filtering method. Compared with the prior art, The embodiment of the present invention has a more optimized smooth output effect.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
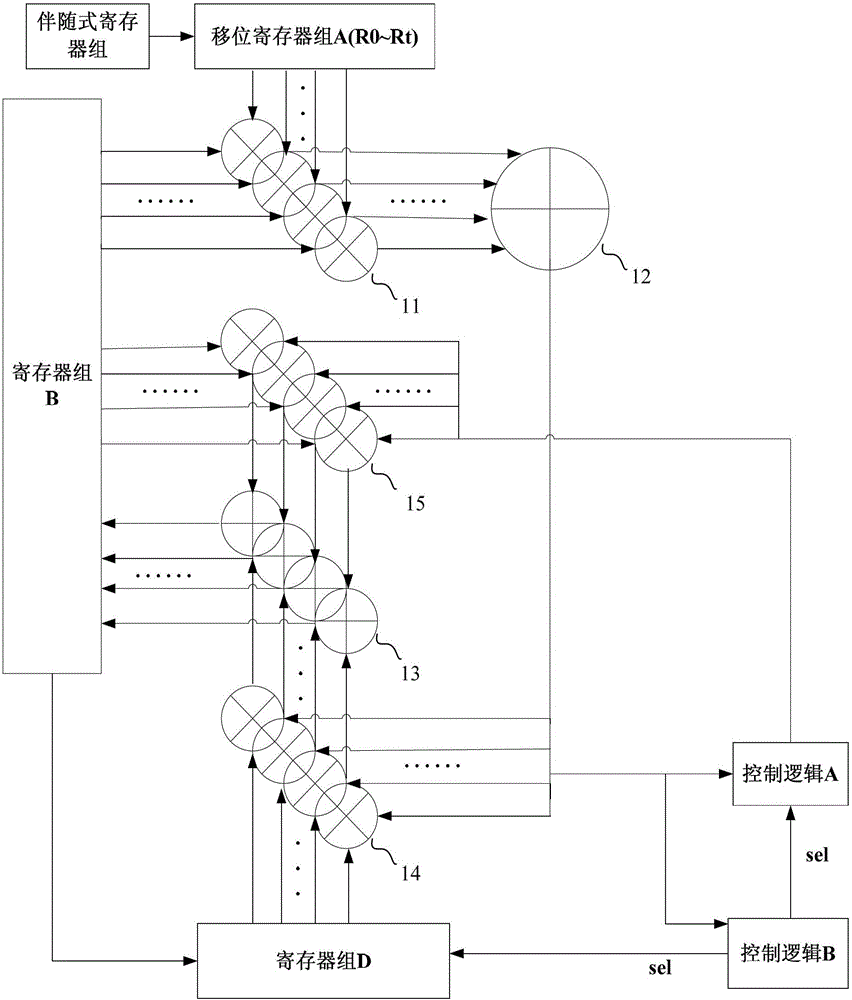
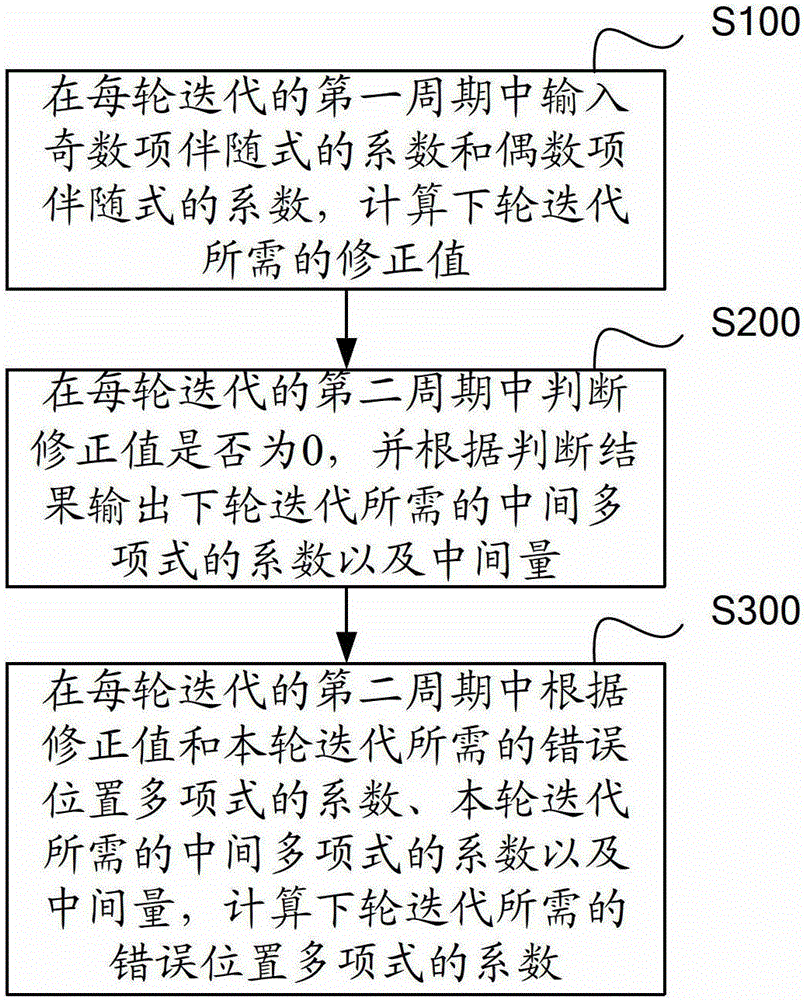
Method and device for solving polynomial error position
Owner:SHENZHEN STATE MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
A Polynomial Method for Constructing Nondeterministic (np) Turing Machines
Owner:BEIJING BOSI BIOINTELLIGENCE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com