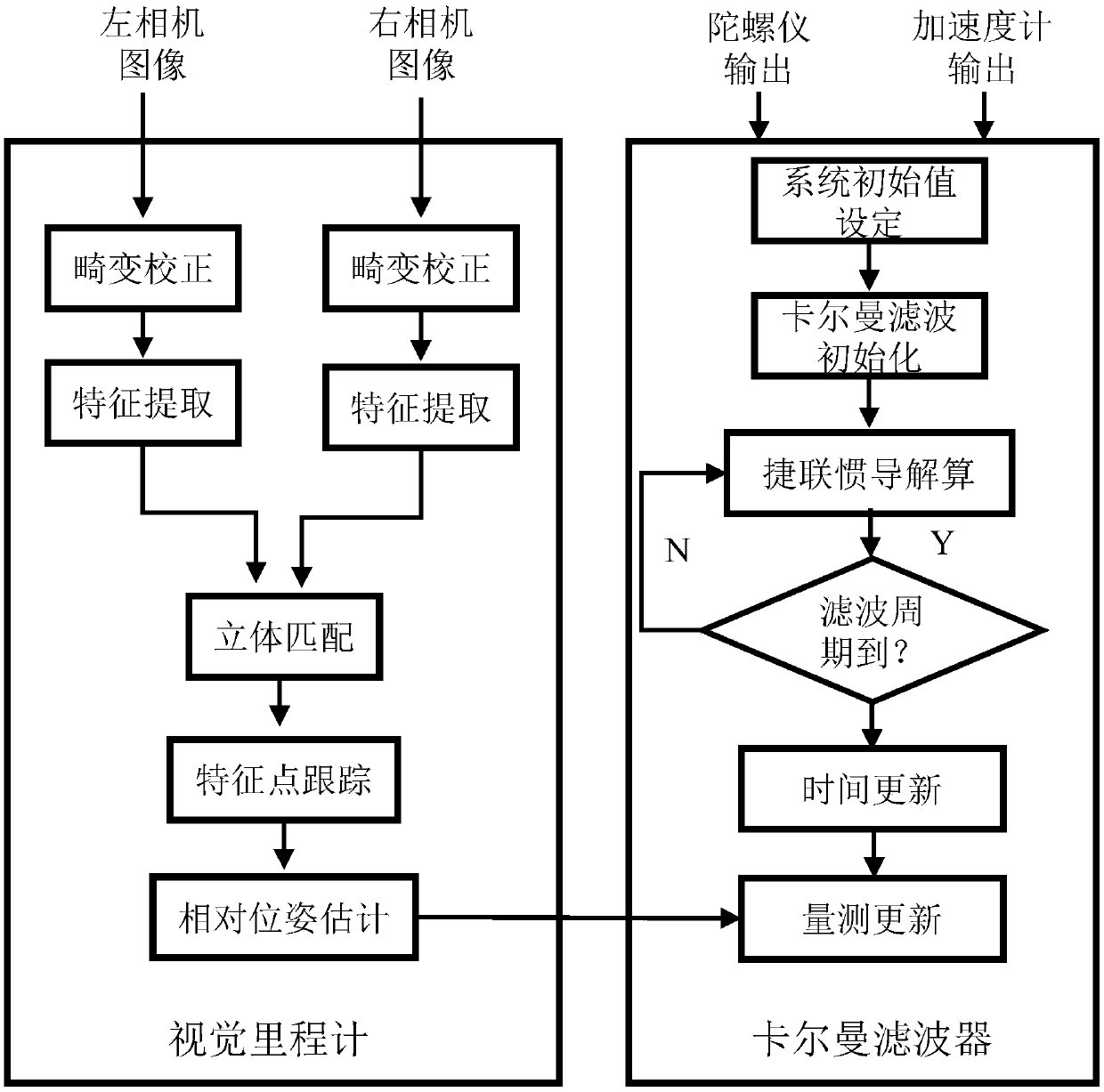
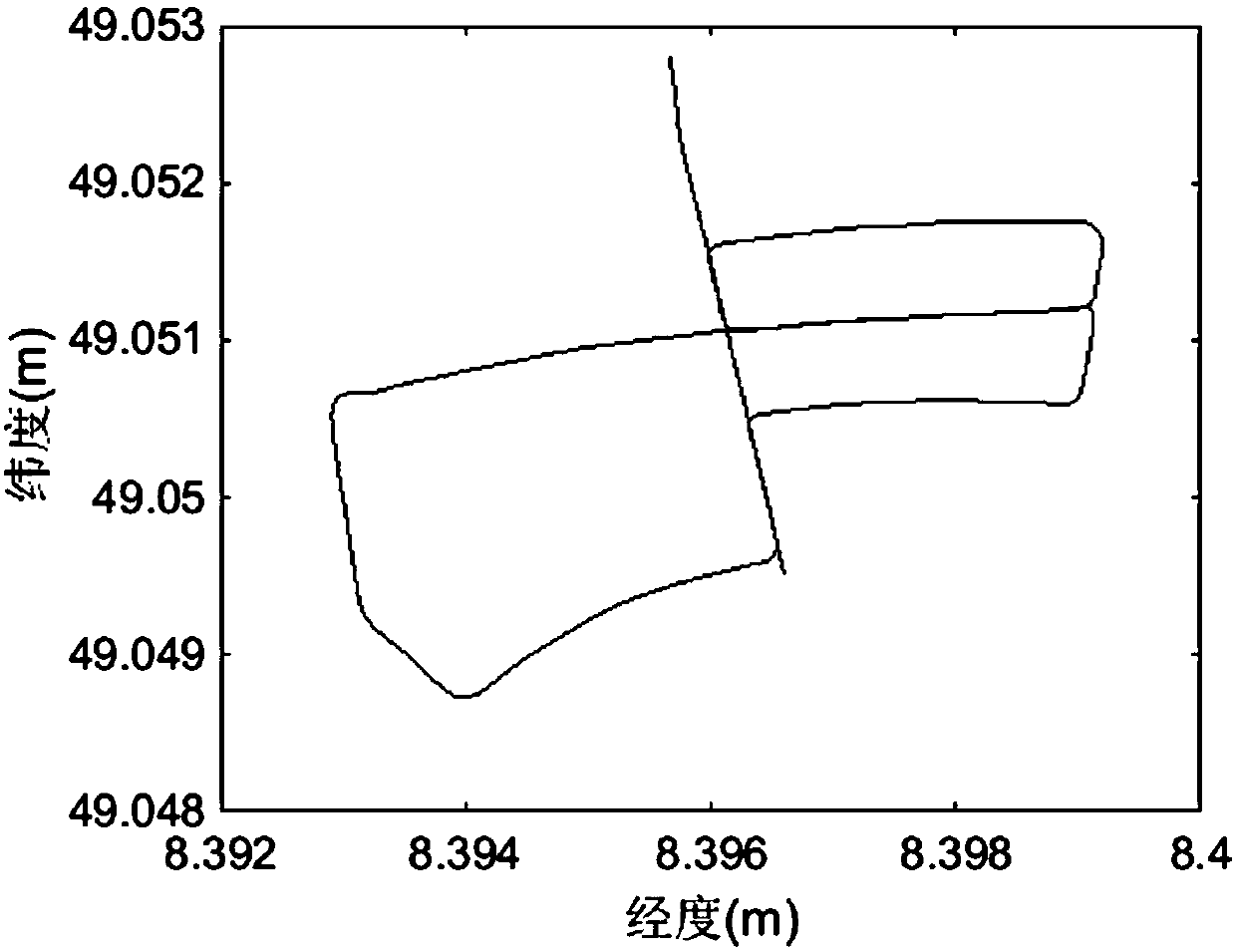
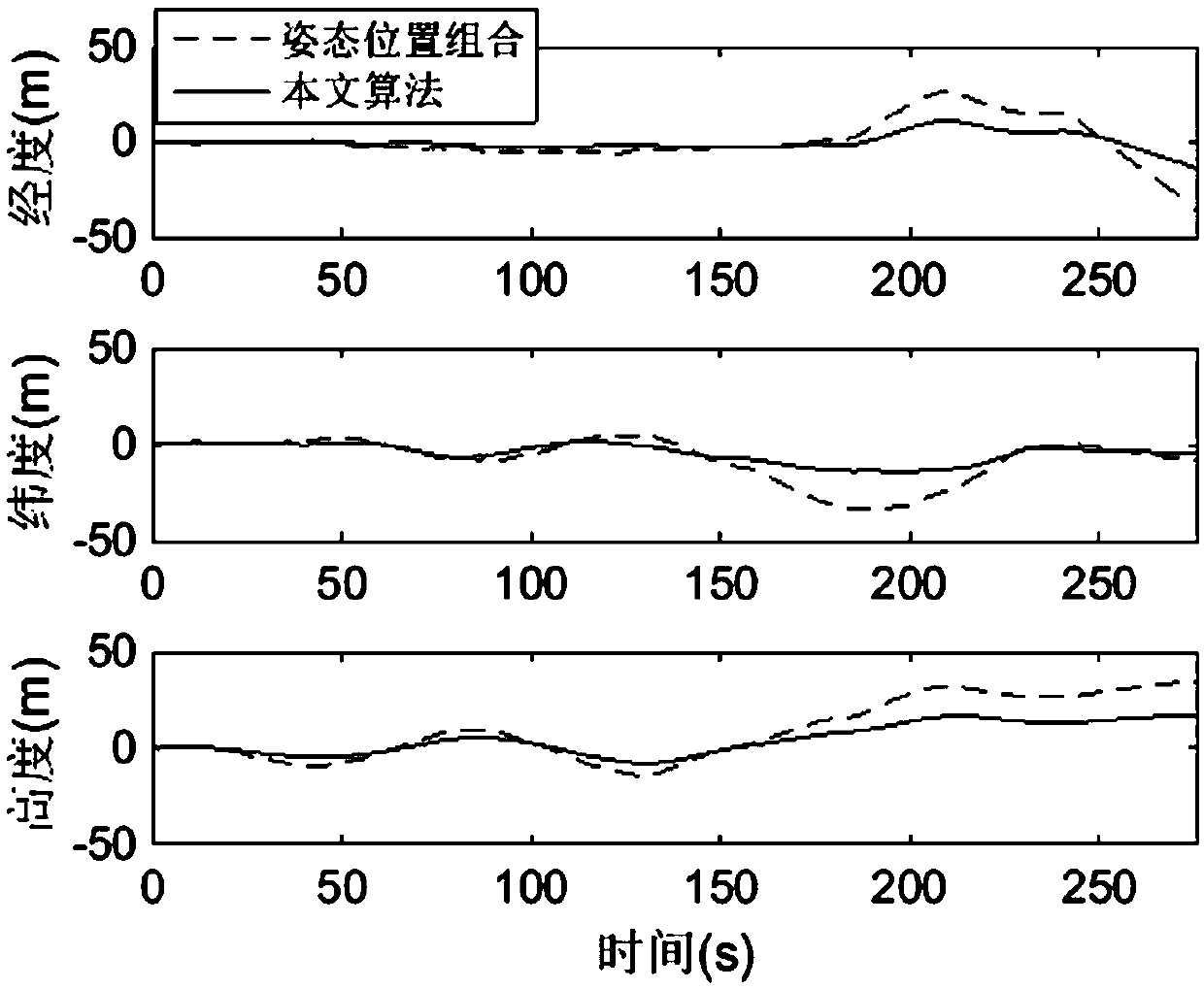
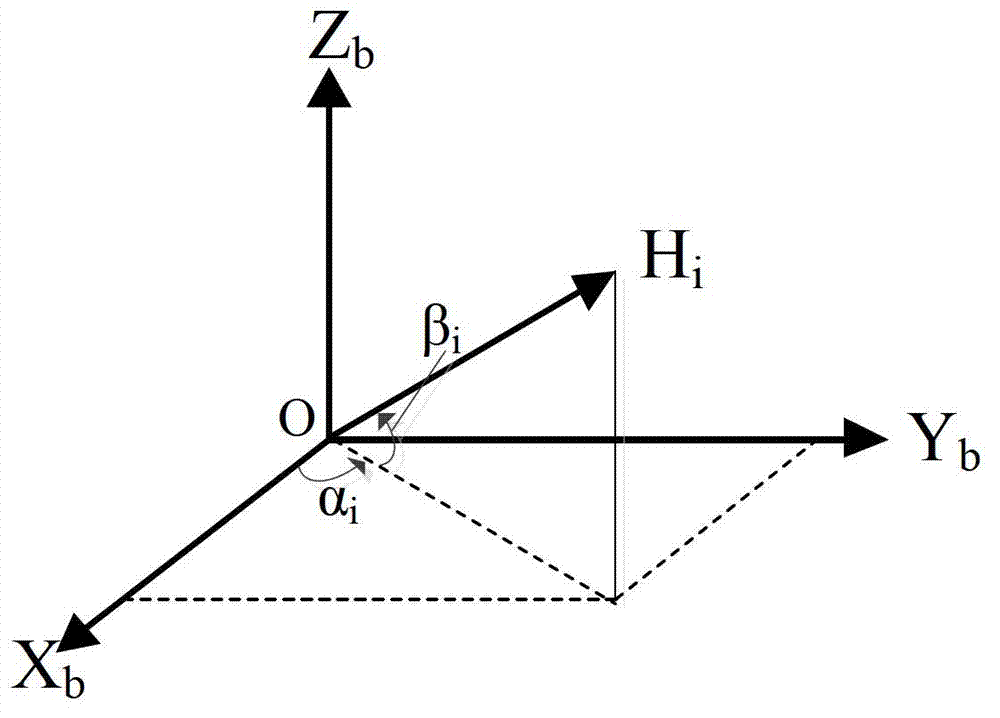
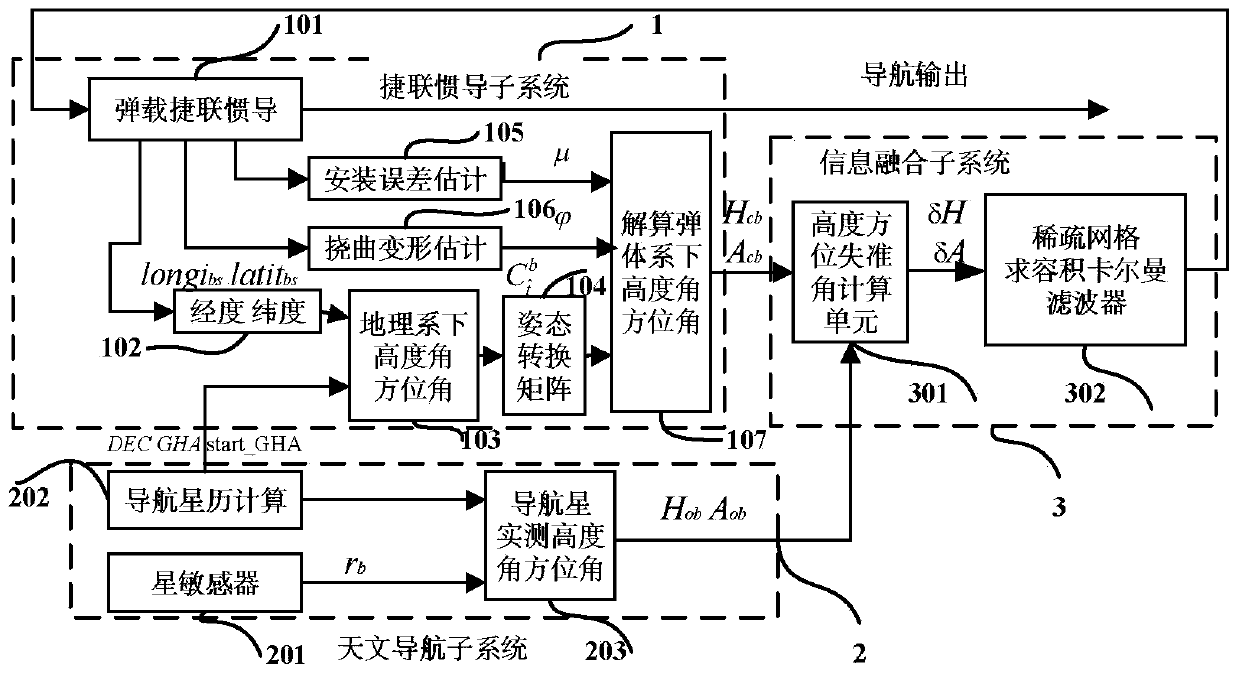
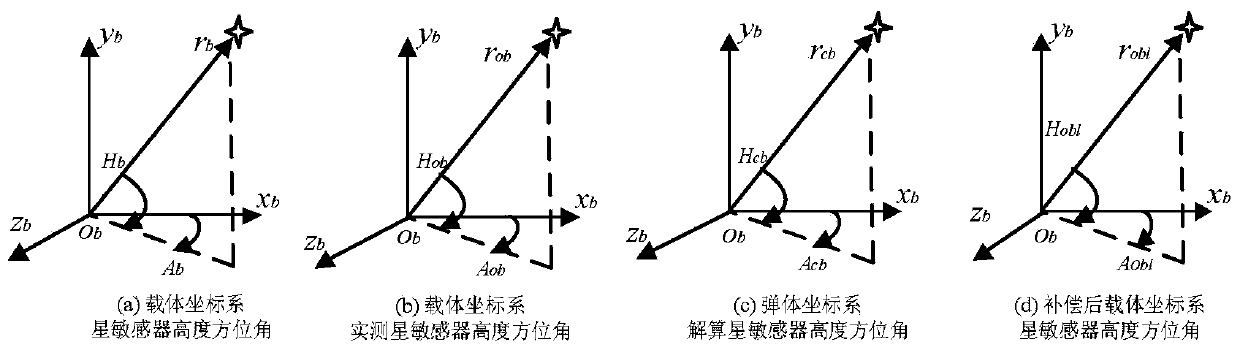
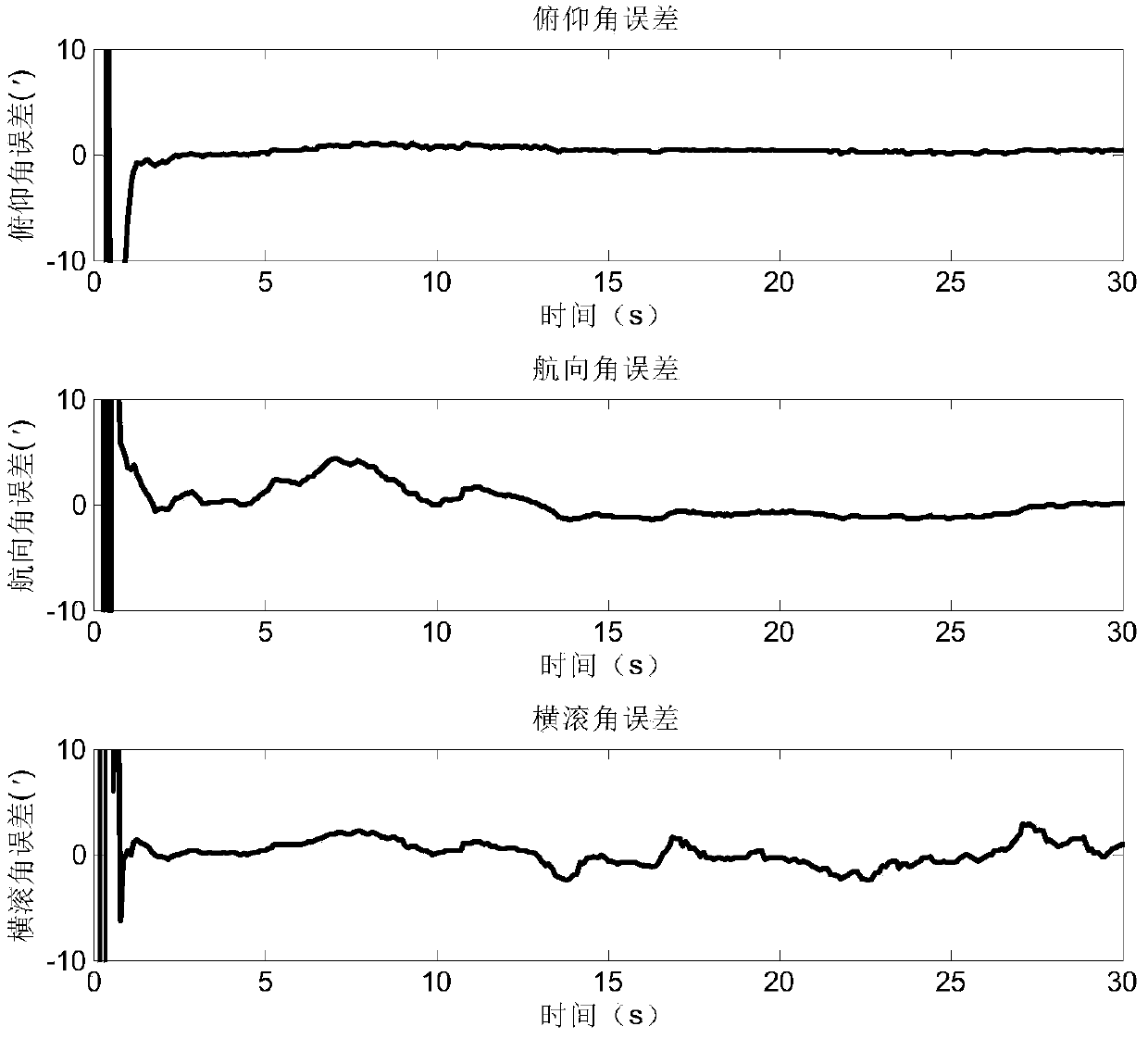
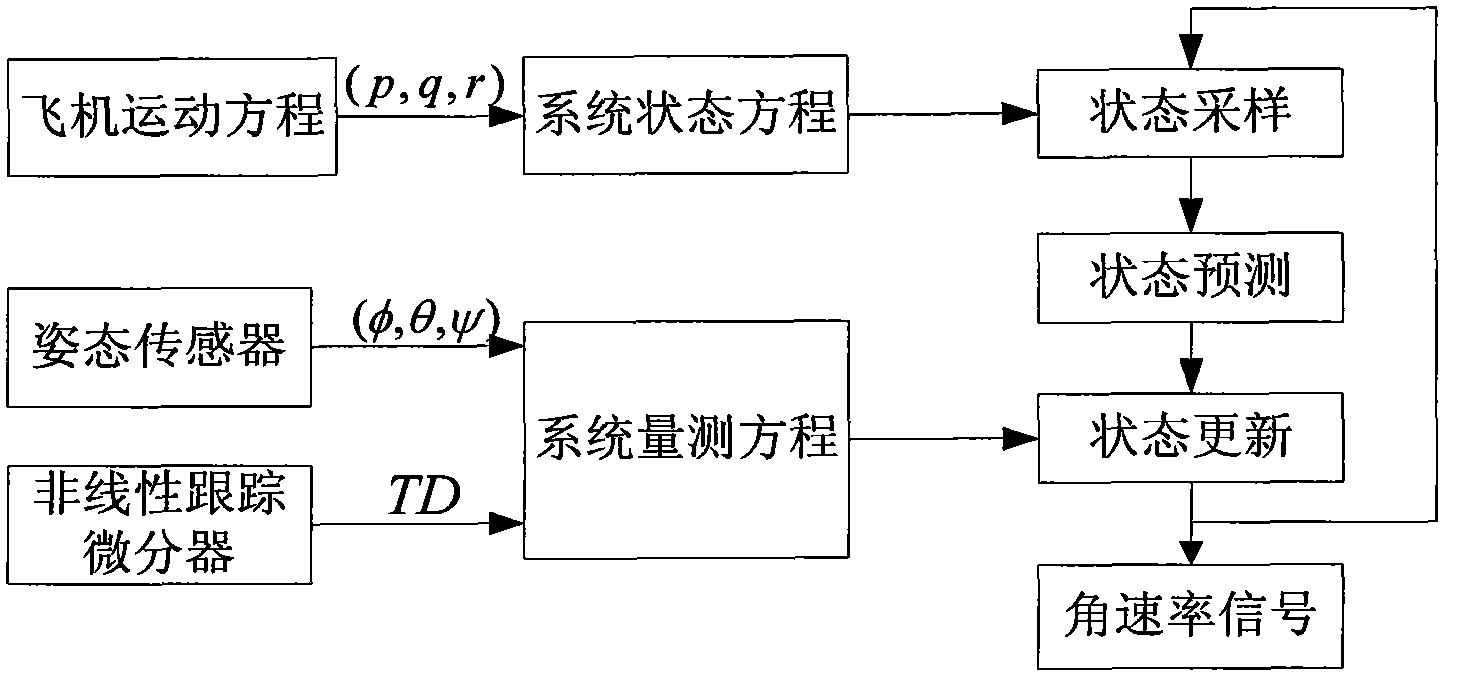
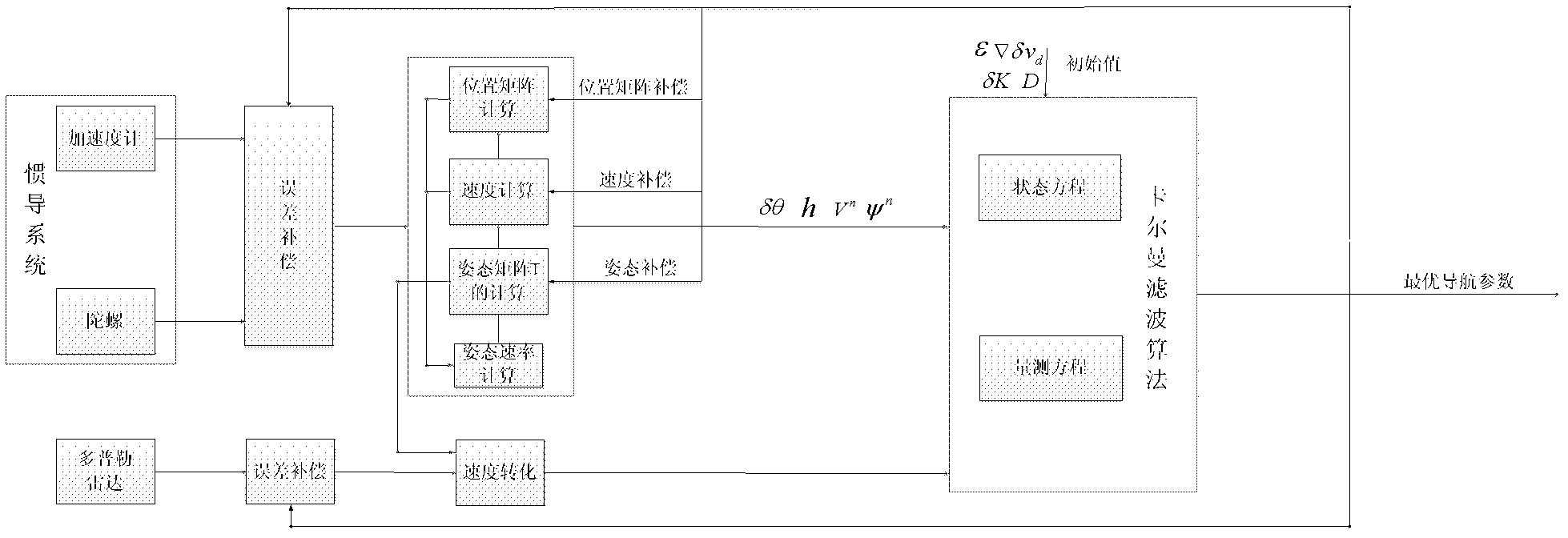
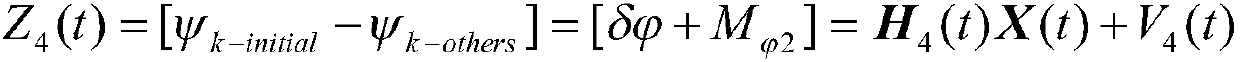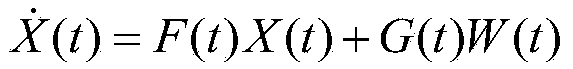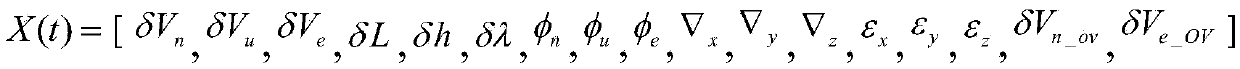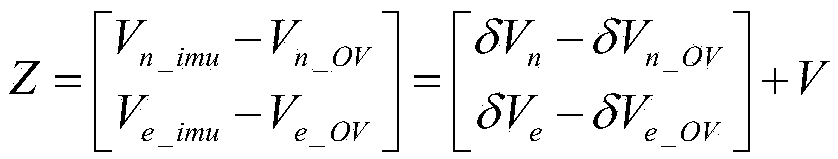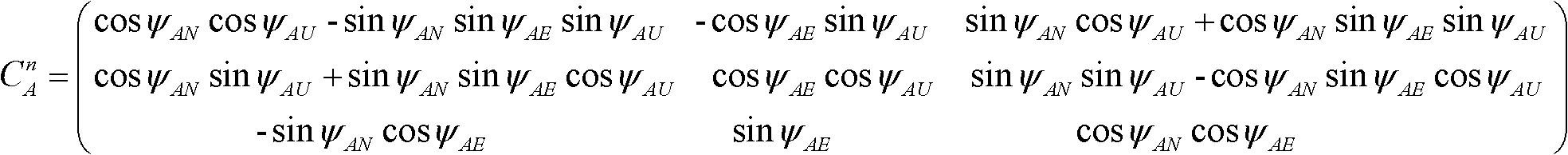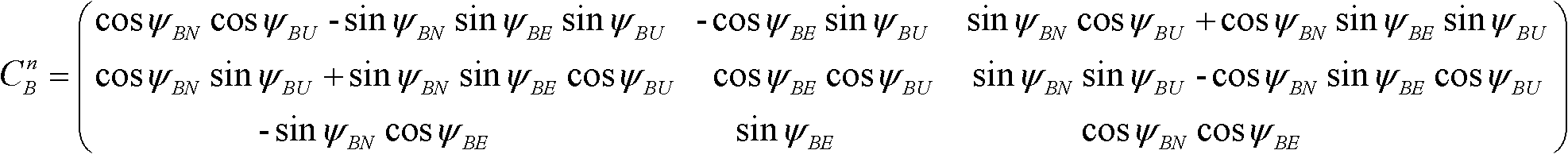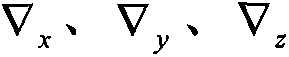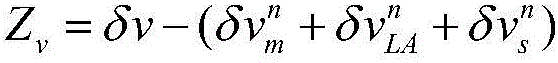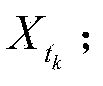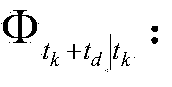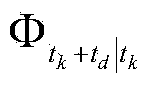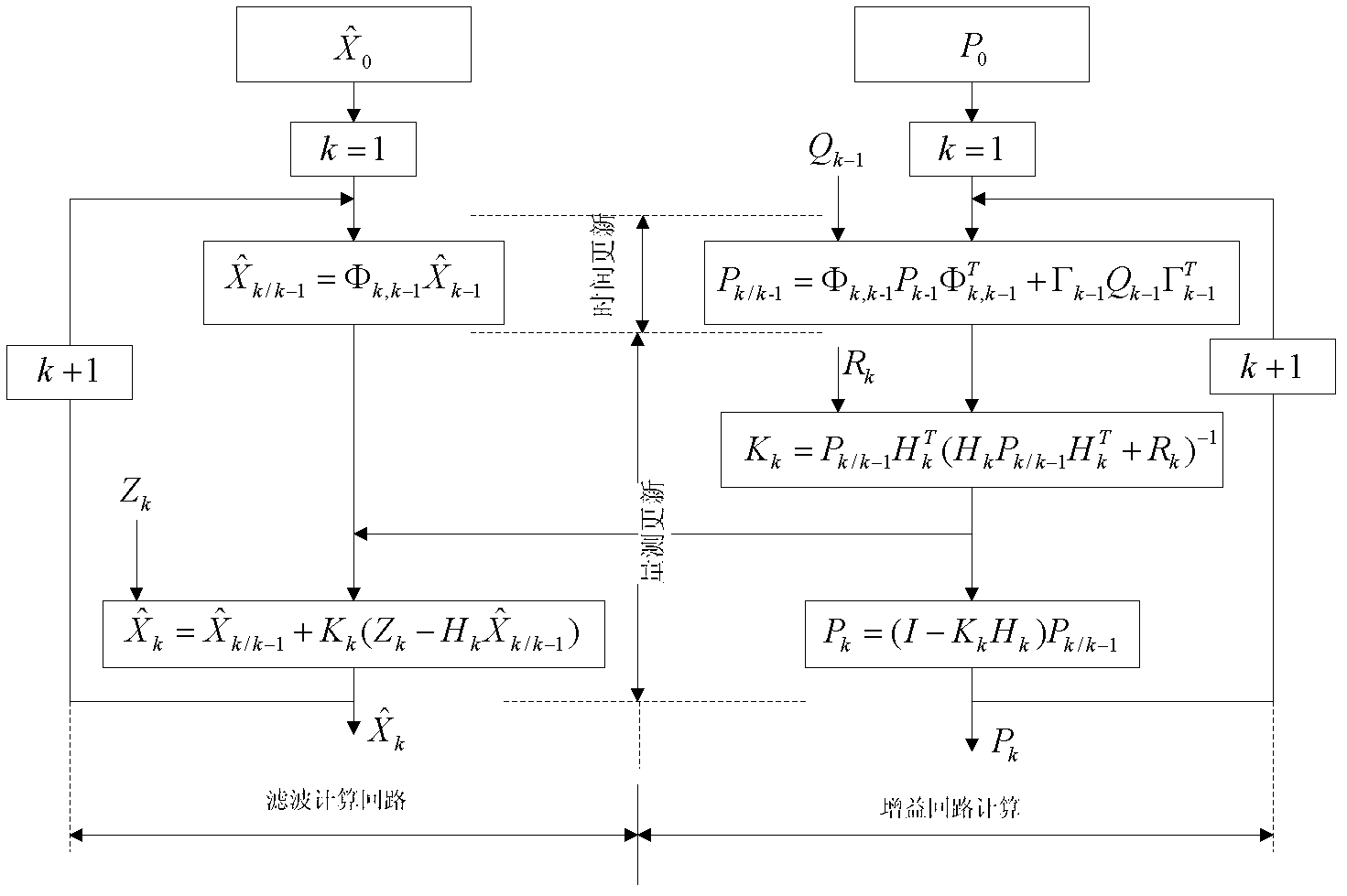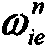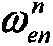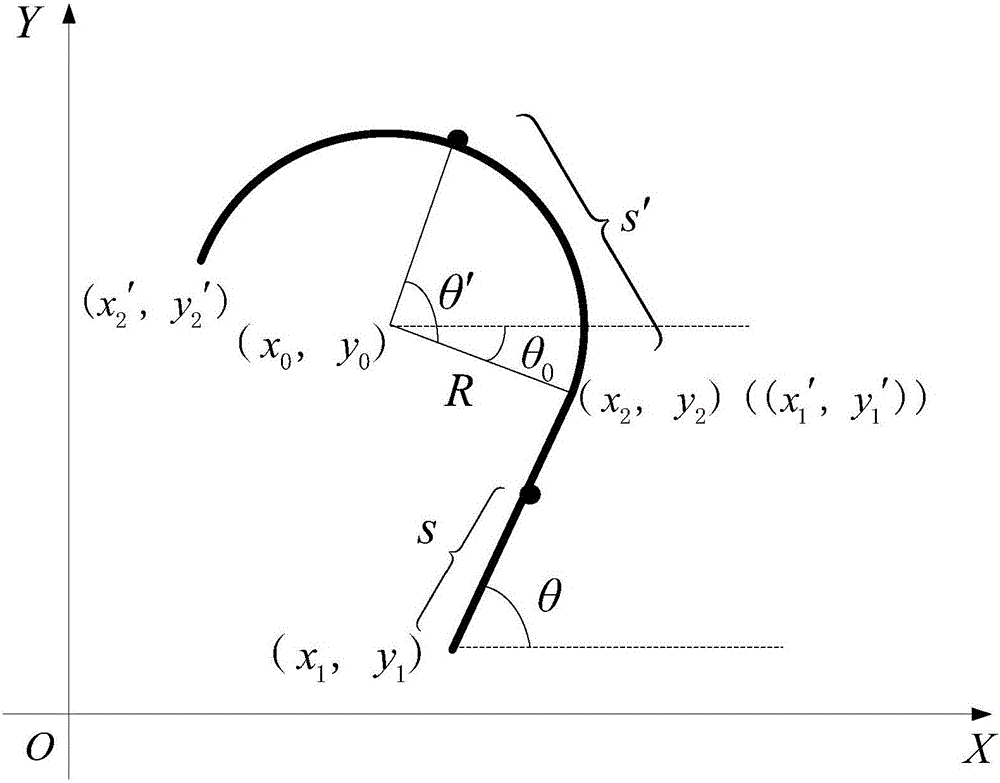Patents
Literature
823 results about "Measurement equations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Vehicle-mounted SINS/GPS combined navigation system performance reinforcement method
InactiveCN101476894AHigh precisionImprove reliabilityInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationNavigation systemMarine navigation
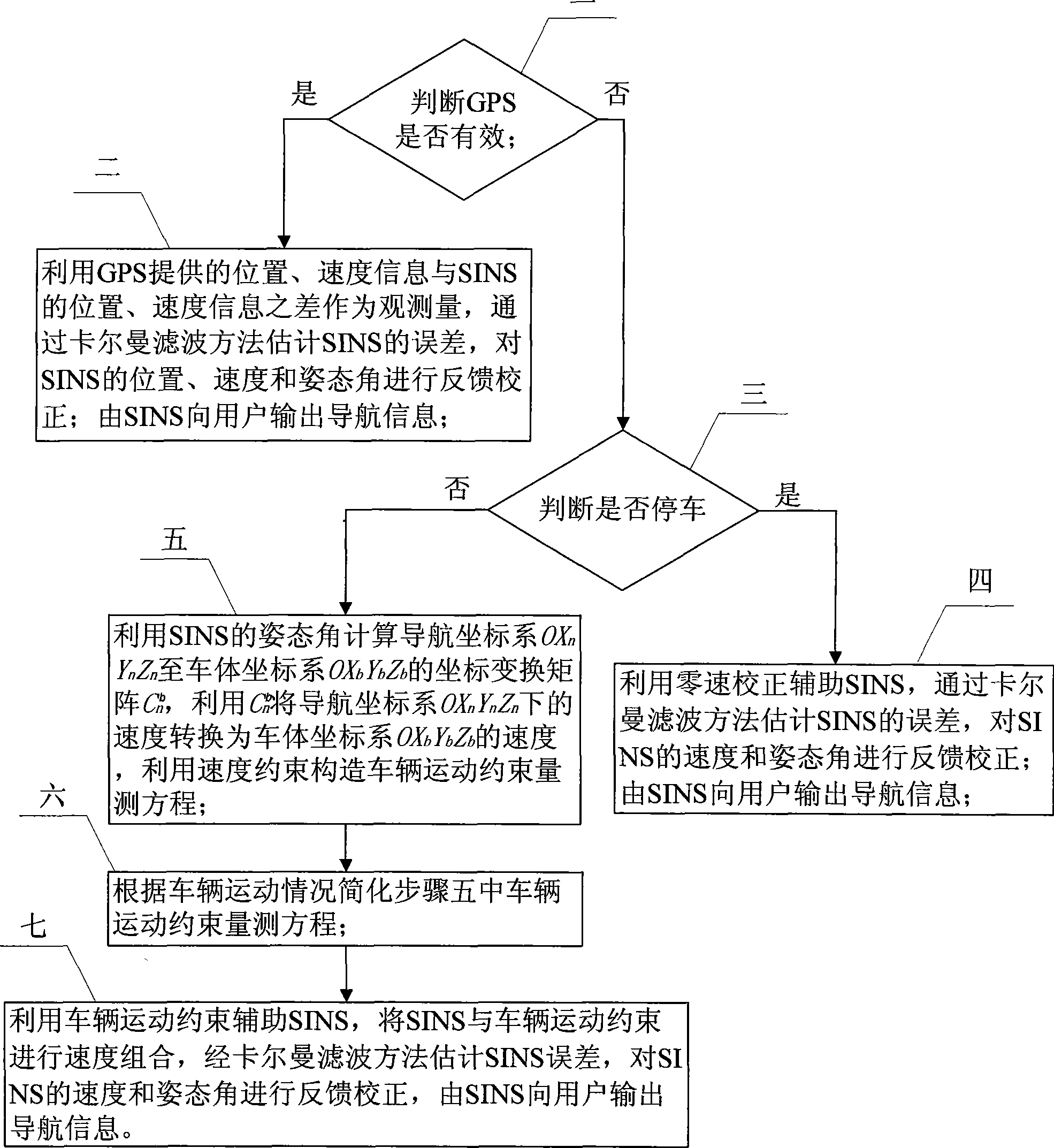
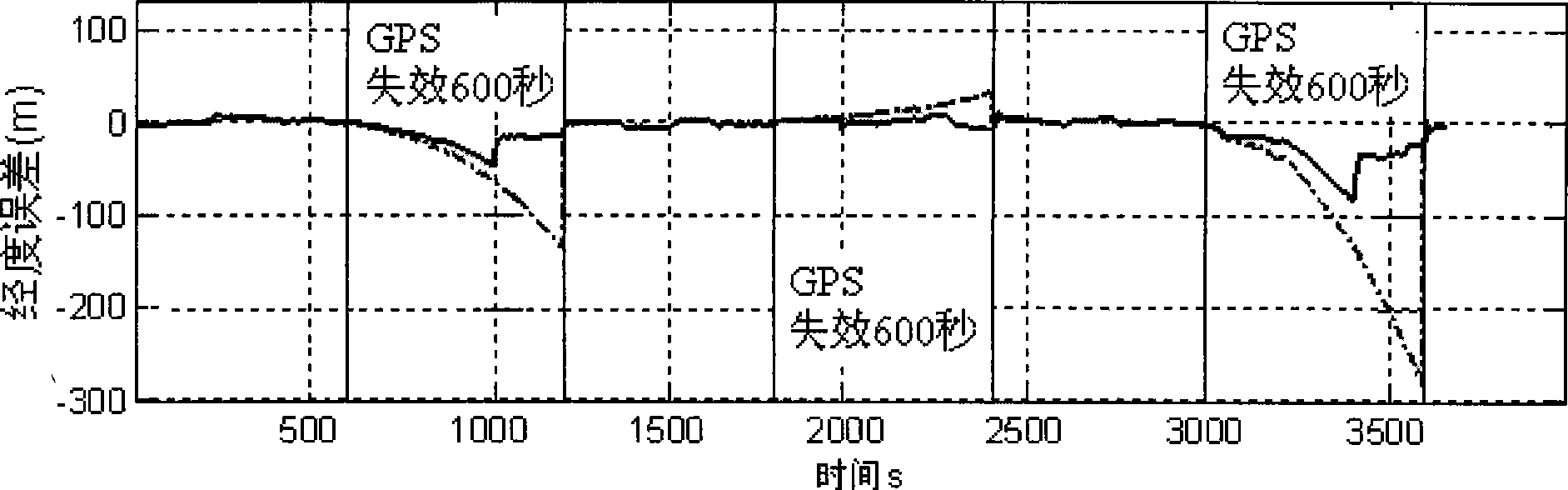
The invention discloses a method for enhancing the performance of a vehicle-mounted SINS / GPS combined navigation system. The invention relates to the technical field of navigation and solves the problems of the prior vehicle-mounted SINS / GPS combined navigation system of low precision and low reliability of the system due to the temporary failure of the GPS. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, judging whether or not the GPS is effective; if the GPS is effective, evaluating and correcting an SINS error by a Kalman filtering method and by using the difference between position and velocity information provided by the GPS and the position and velocity information of the SINS as an observed quantity; if the GPS is noneffective, judging whether or not to stop; if to stop, correcting the SINS error by using a zero velocity update auxiliary SINS; if not to stop, calculating coordinate transformation matrix Cn from a navigation coordinate system to a vehicle body coordinate system by using the attitude angle of the SINS, converting the velocity under the navigation coordinate system into a velocity under the vehicle body coordinate system by using the Cn and creating a vehicle motion constraint measurement equation by using velocity constraint; simplifying the equation according to vehicle motion; and carrying out the velocity composition of the SINS and the vehicle motion constraint and correction by using a vehicle motion constraint auxiliary SINS. The method is used for improving the precision and reliability of the vehicle-mounted SINS / GPS combined navigation system.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
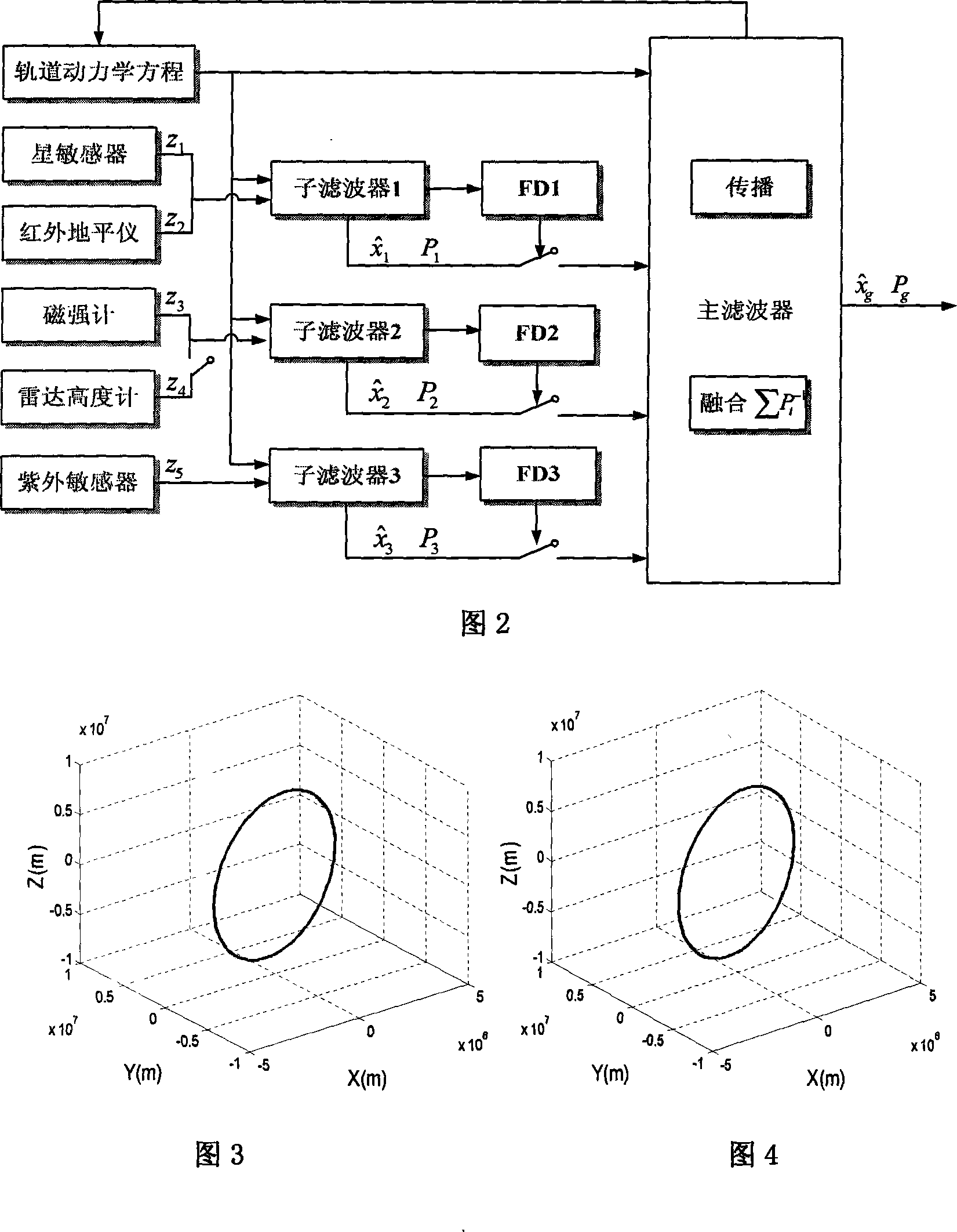
Low orbit satellite multi-sensor fault tolerance autonomous navigation method based on federal UKF algorithm
InactiveCN101216319AGuaranteed continuityGuaranteed stabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsInstruments for comonautical navigationEarth satelliteFault tolerance
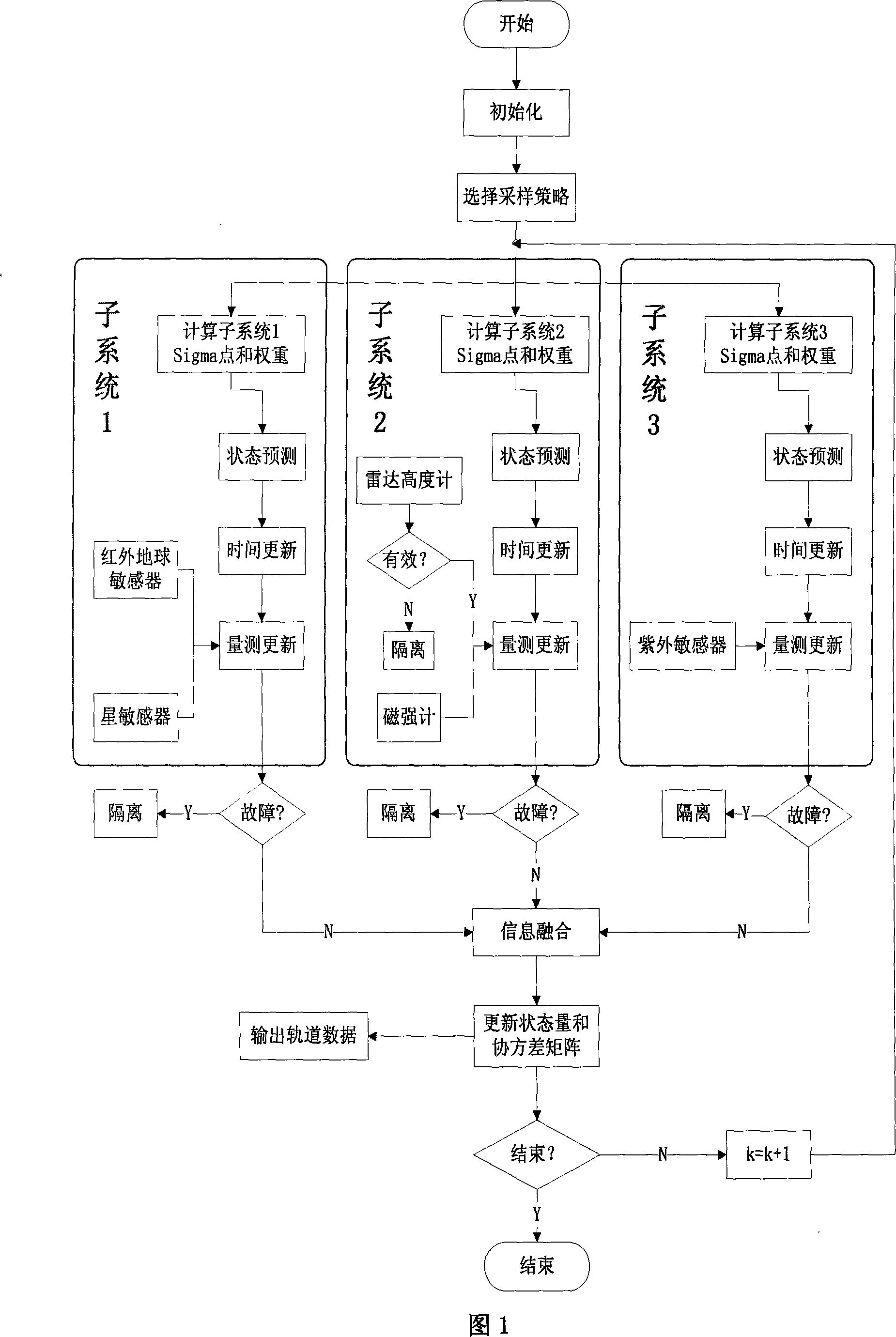
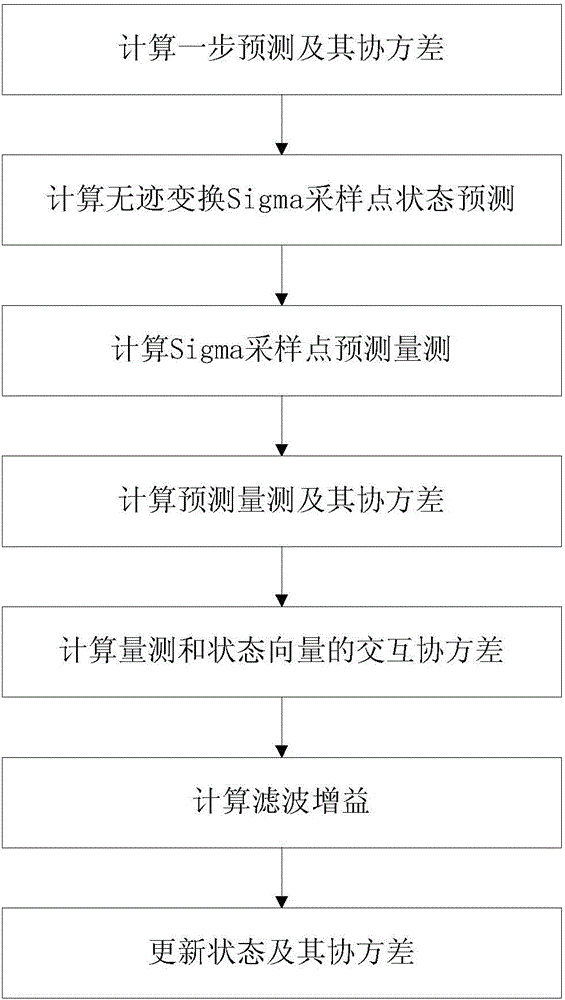
The invention relates to a multi-sensor autonomous navigation method for the low-orbiting satellite with fault-tolerance function and based on federated UKF algorithm, belonging to satellite autonomous navigation method. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing an orbital dynamics equation of earth satellite in a rectangular coordinate system; constructing a subsystem measurement equation with the output values of a star sensor and an infrared earth sensor as measurement quantities; constructing a subsystem measurement equation with the output values of magnetometer and a radar altimeter as measurement quantities; constructing a subsystem measurement equation with the output value of an ultraviolet sensor as measurement quantity; selecting a Sigma sampling point; constructing a predictive equation and an update equation of discrete UKF algorithm; respectively and independently performing Sigma sampling point calculation of each subsystem, and performing predictive update and measurement update; determining whether the output of each sub-filter is valid according to the predicted filter residual, isolating in case of malfunction, otherwise, inputting the filter result to a main filter for information fusion; constructing a non-reset federated UKF filter equation based on the UKF algorithm; and outputting earth satellite state estimated value X and variance matrix P thereof according to the steps.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
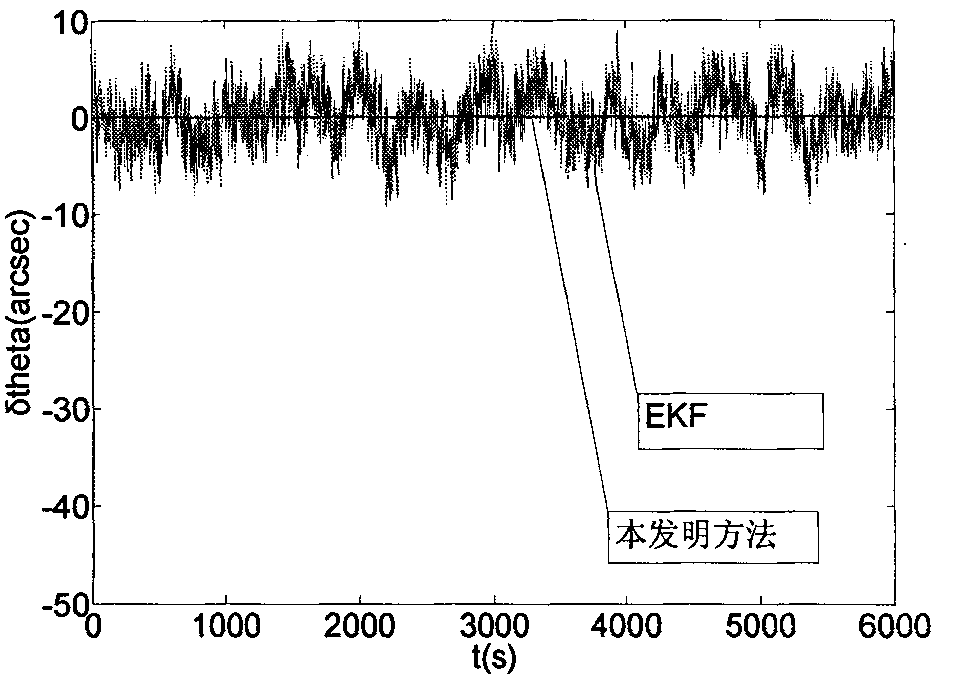
High-precision satellite attitude determination method based on star sensor and gyroscope
InactiveCN101846510AOvercome the disadvantage of error processing as zero-mean white noiseHigh precisionAngle measurementNavigation instrumentsGyroscopeZero mean
The present invention discloses a high-precision satellite attitude determination method based on star sensor and gyroscope, which comprises the following steps: step 1. establishing a status equation of a satellite attitude determination system; step 2. establishing a measurement equation of the satellite attitude determination system; step 3. performing an online real-time model error estimation through predictive filtering; and step 4. performing a status estimation on a compensated model through 2-order interpolation filtering to obtain the attitude of a satellite. By applying predictive filtering to performing an online real-time model error estimation and correcting the system model, the invention overcomes the shortcoming existing in the conventional estimation process that error is processed into zero-mean white noise; and in addition, the invention can process any nonlinear system and noise conditions to obtain an estimation result of higher precision and is applicable to thefield of high-precision attitude determination.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Estimation for accumulator loading state of electric vehicle and carrying out method thereof
InactiveCN1601295ACorrection of SOC changesFast convergenceElectrical testingBattery chargeState of charge
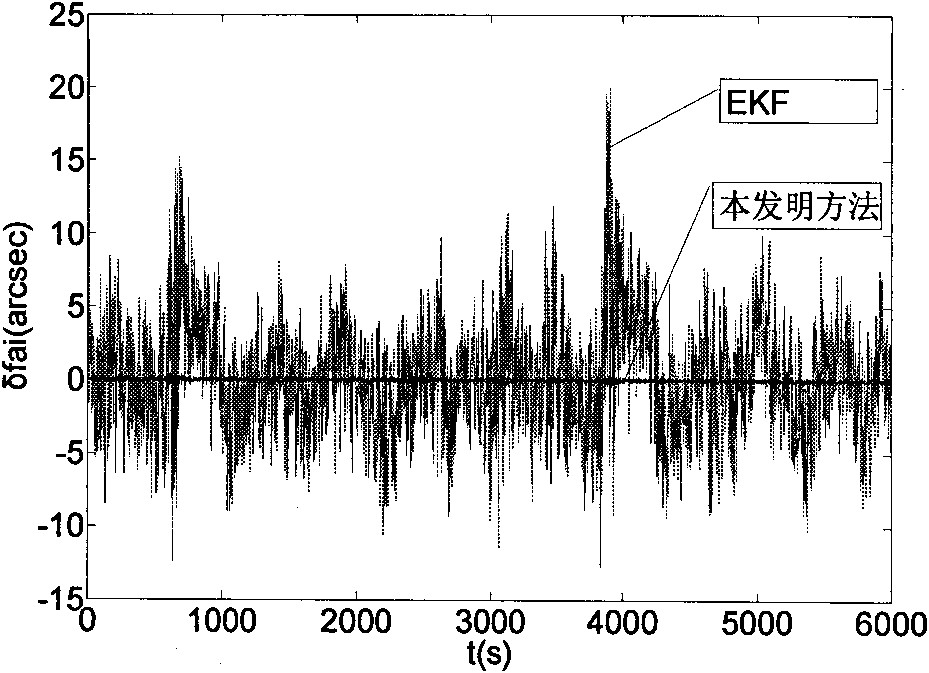
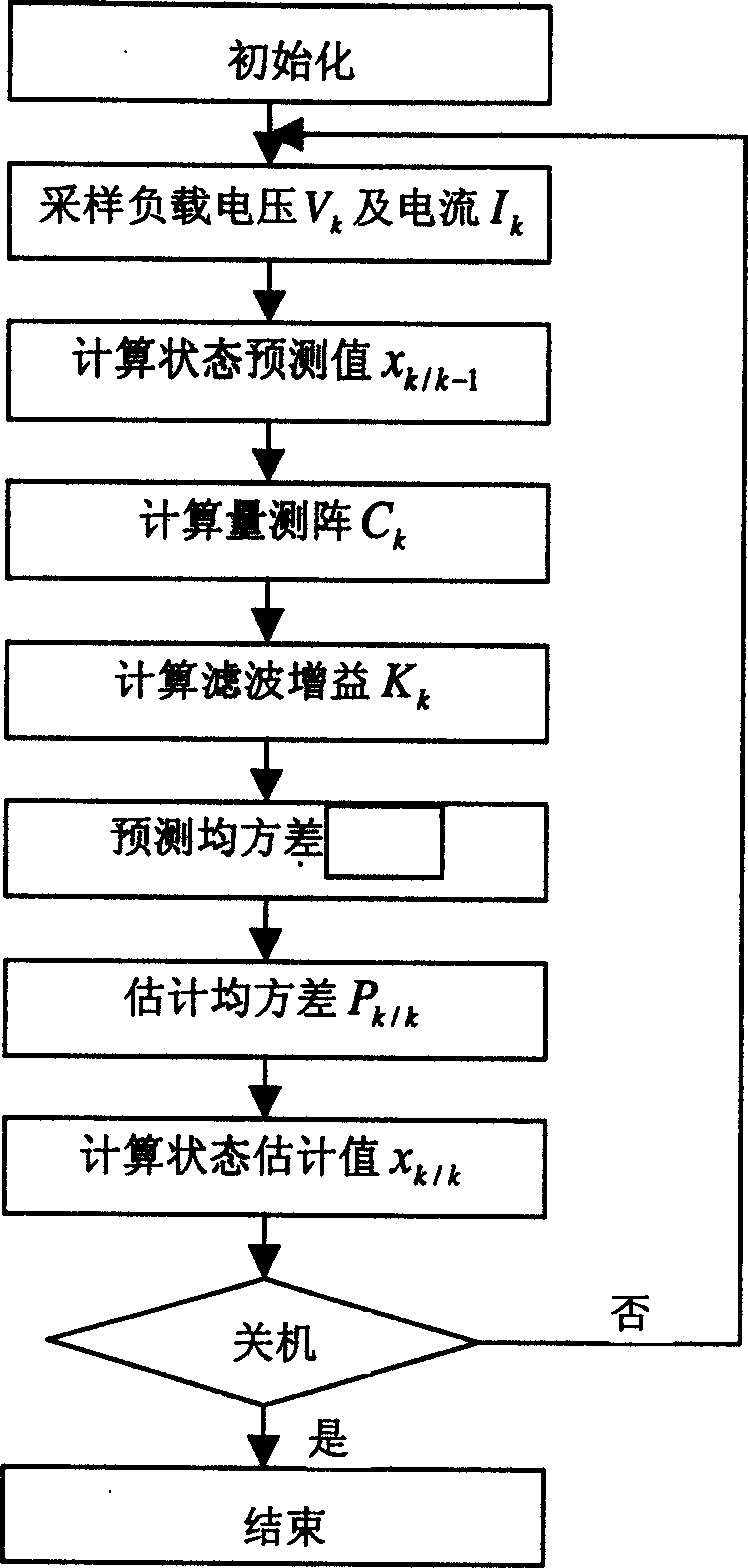
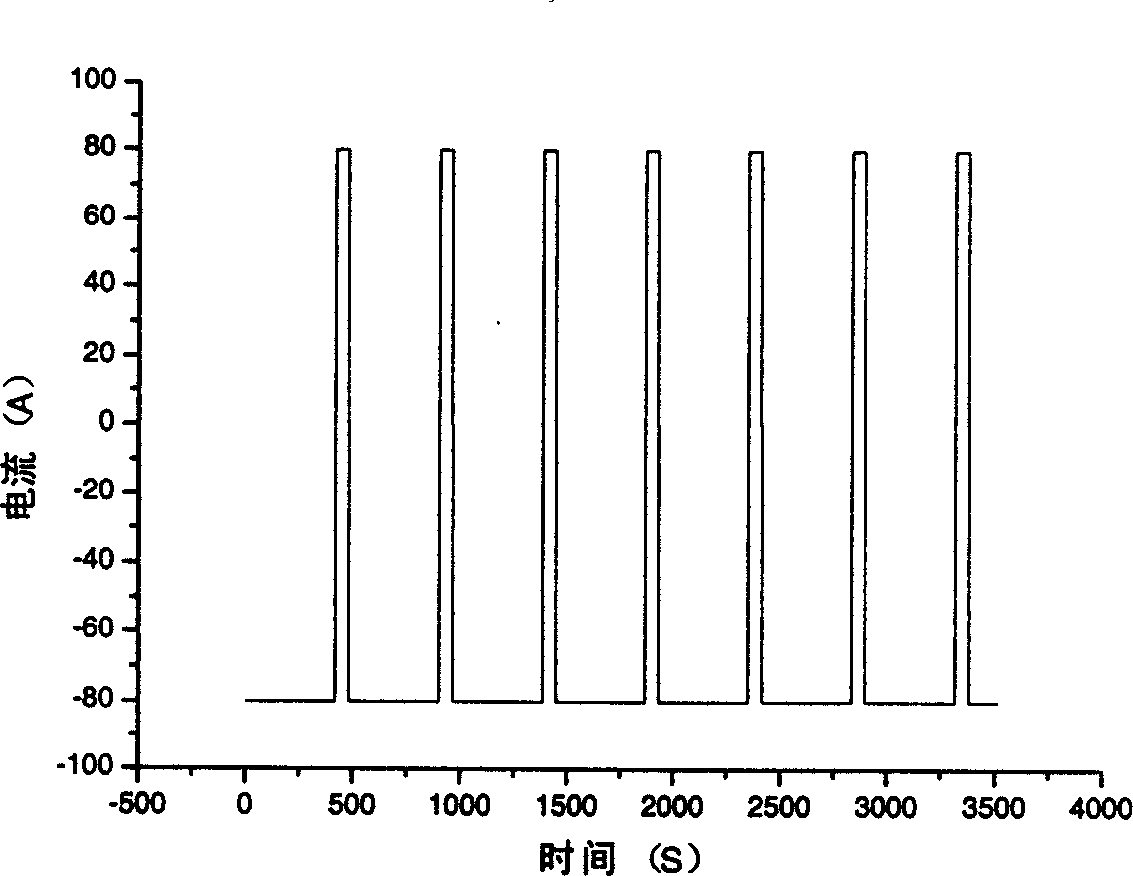
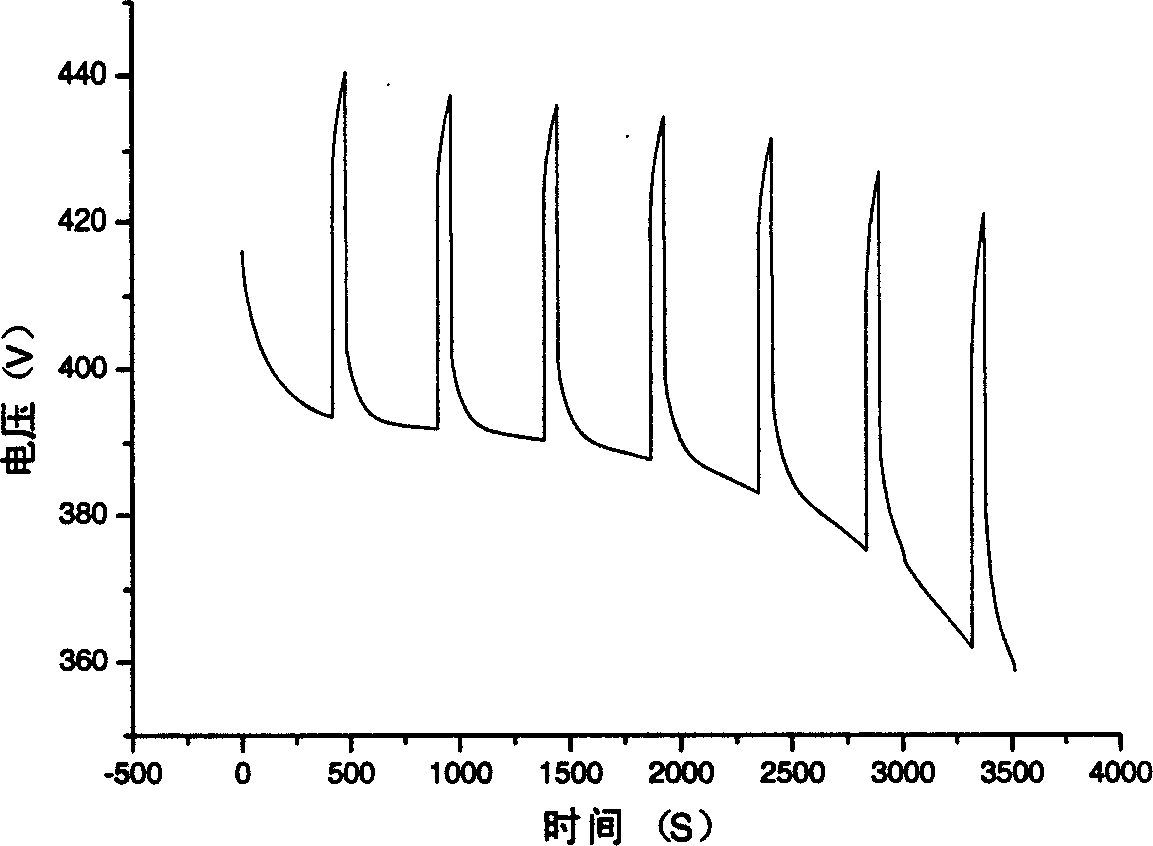
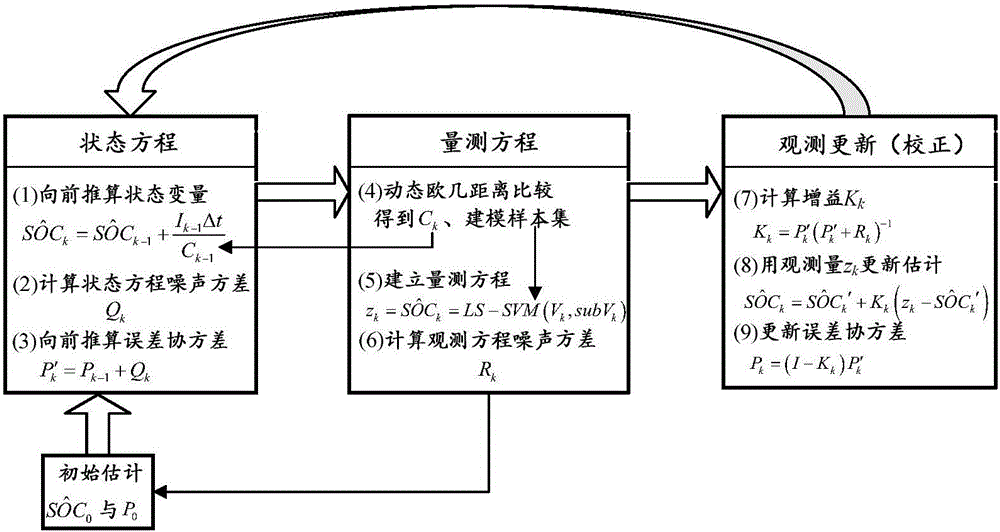
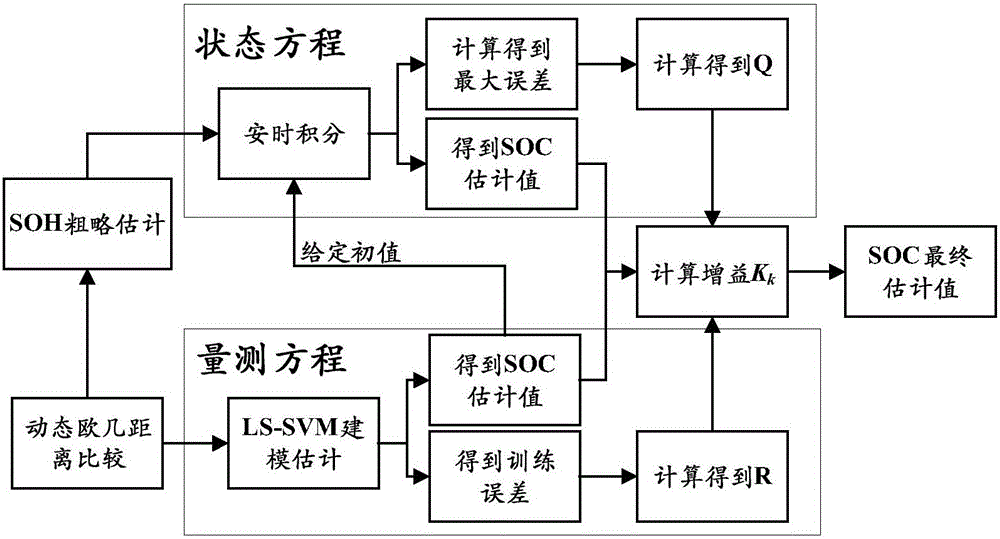
The invention relates to an estimation and implement method of state of charge (SOC) of battery for electric car, belonging to the field of electric car intelligent niformation processing technology. Said method utilizes the state space equation of battery which is formed from battery charge state equation based on ampere-hour metering method and measurement equation of battery load votlage, and uses the improved extended Kalman filtering equation to calculate and obtain the stale of charge of battery. Said invented advantage lies in that it has stronger adaptability, can eliminate initial error of SOC, and can raise the convergence of error or reduce speed, at the same time it can modify the change of SOC resulted frmo self-discharge of battery. Said invention is applicable to SOC estimation of cell monomer, module and battery.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
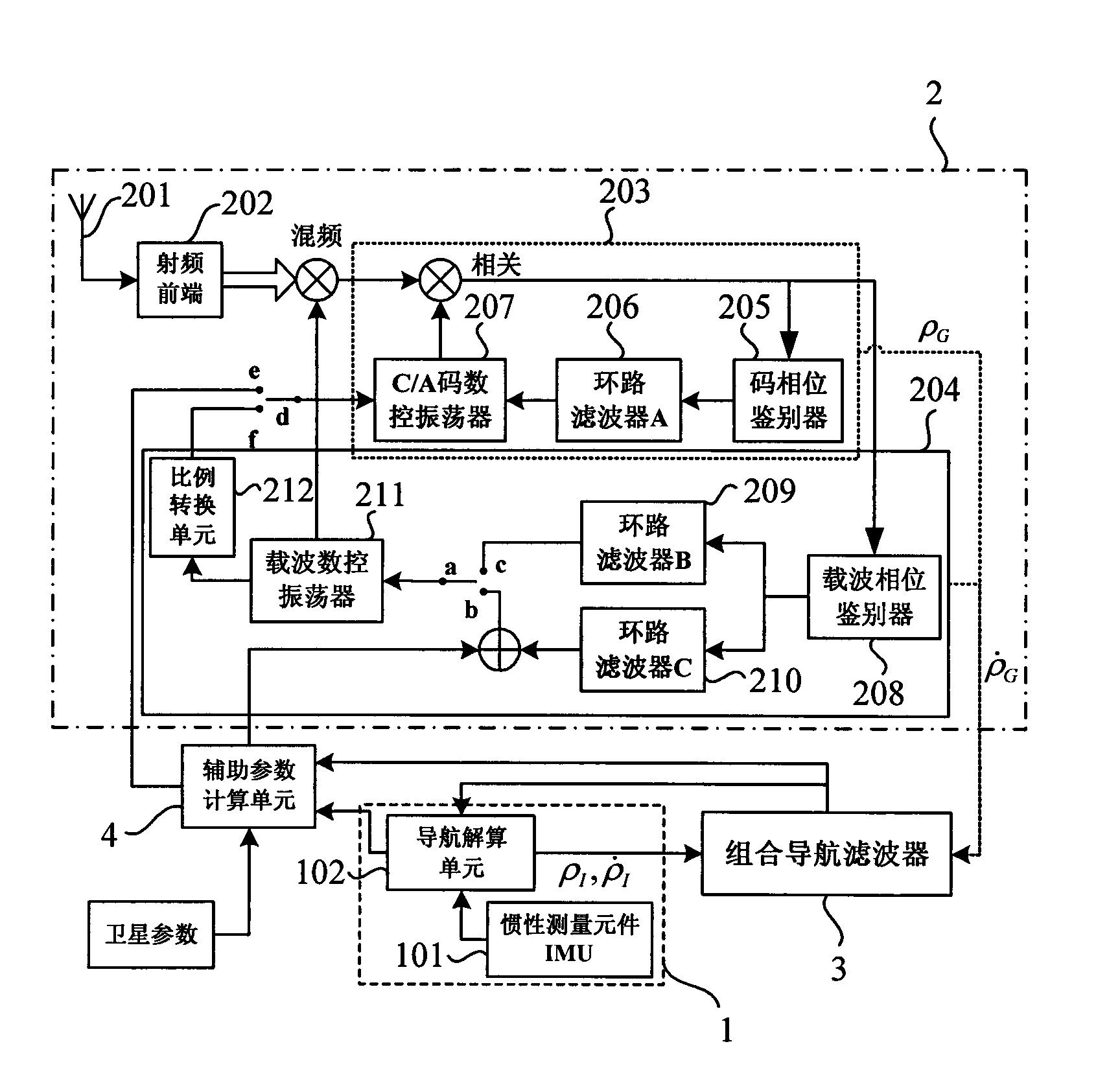
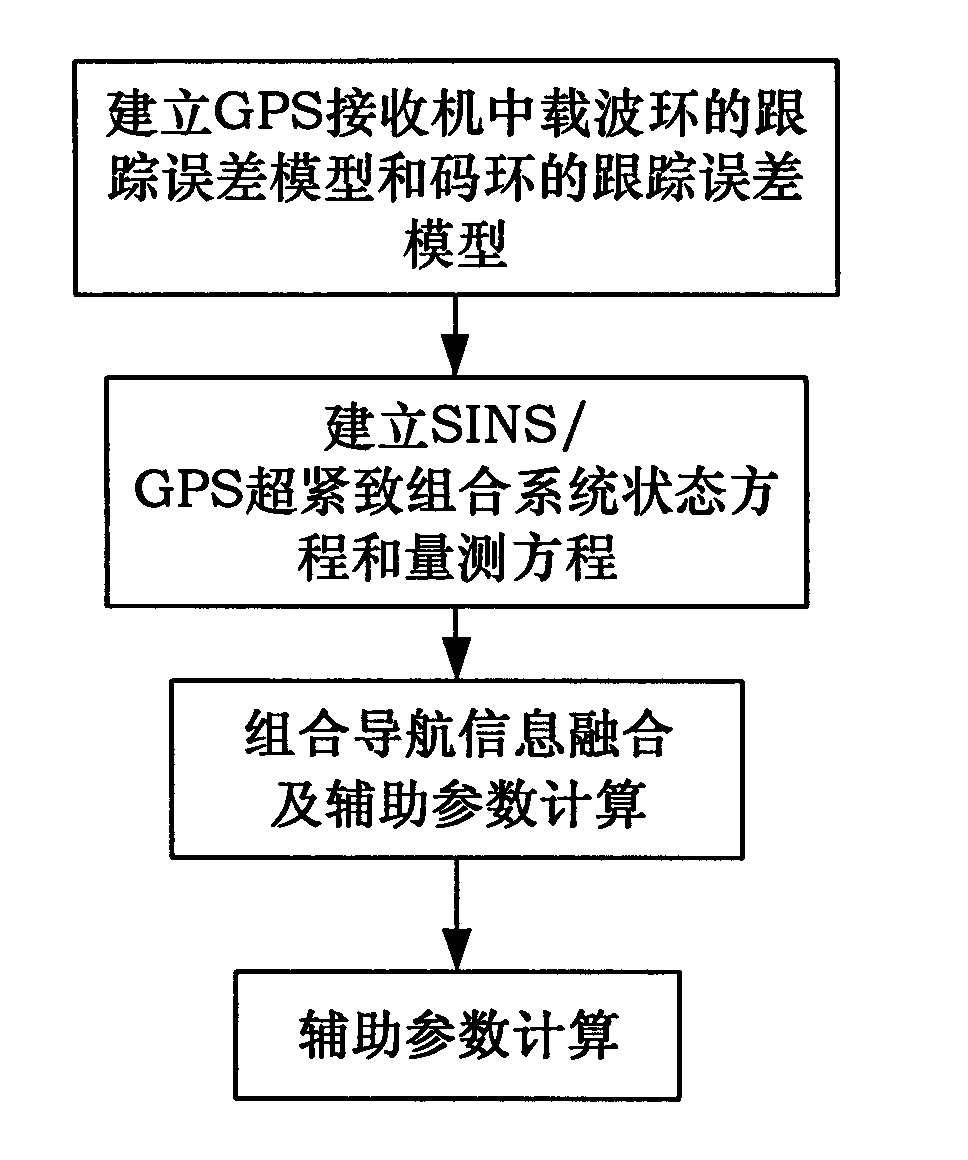
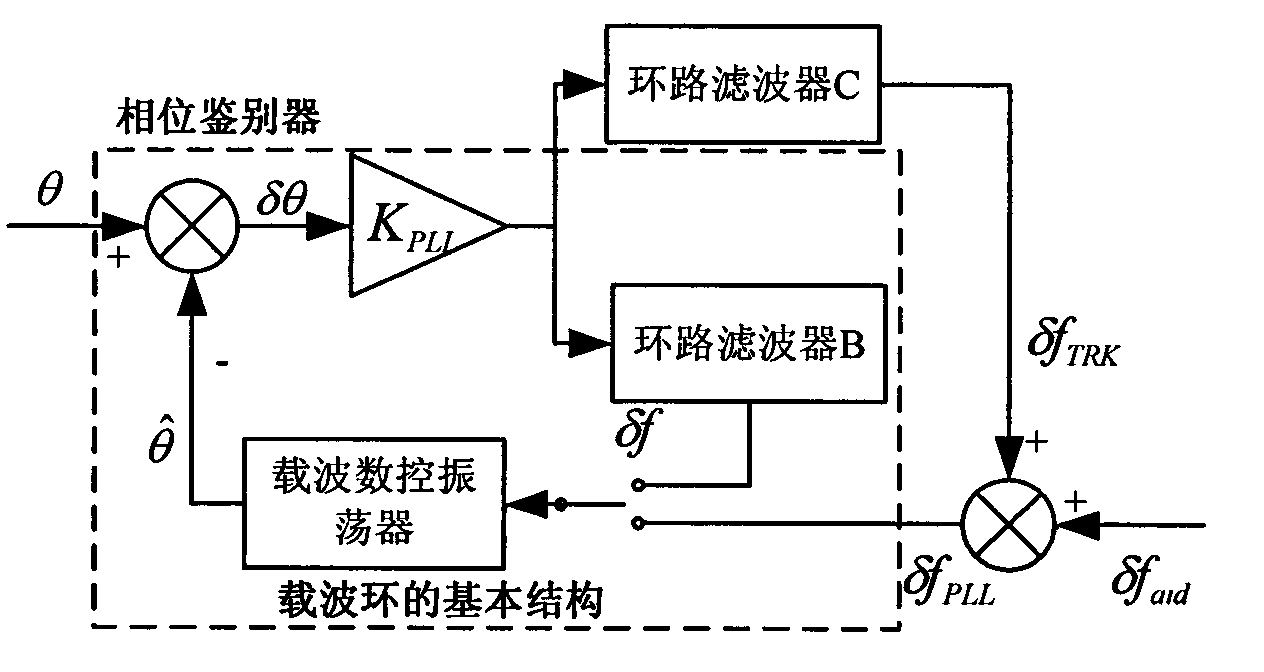
SINS/GPS super-compact integrated navigation system and implementing method thereof
InactiveCN101666650AIncrease equivalent bandwidthReduce dynamic tracking rangeBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationCarrier signalGps receiver
The invention discloses an SINS / GPS super-compact integrated navigation system and an implementing method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: the doppler frequency assistance is provided for a GPS carrier loop by using the velocity information of a strapdown inertial navigation system, therefore, the loop equivalent bandwidth is increased, the influence of the carrier dynamic stateon the carrier loop is lowered, and the noise suppression capability is improved by reducing the bandwidth of a filter; meanwhile, in order to eliminate the correlation between the pseudo-range rate error and the inertial navigation error, a carrier loop tracking error model is obtained by establishing the relationship between the carrier tracking error and the inertial navigation speed error, andthe influence of the carrier tracking error is subduced in the measurement equation; and in addition, the carrier frequency is adjusted according to the output error estimation information, and the tracking accuracy of the carrier loop is enhanced. The invention can effectively enhance the noise suppression capability and the dynamic tracking performance of the tracking loop and enhance the tracking accuracy of a GPS receiver and the navigation accuracy of the integrated navigation system under strong interference and high dynamic circumstance.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
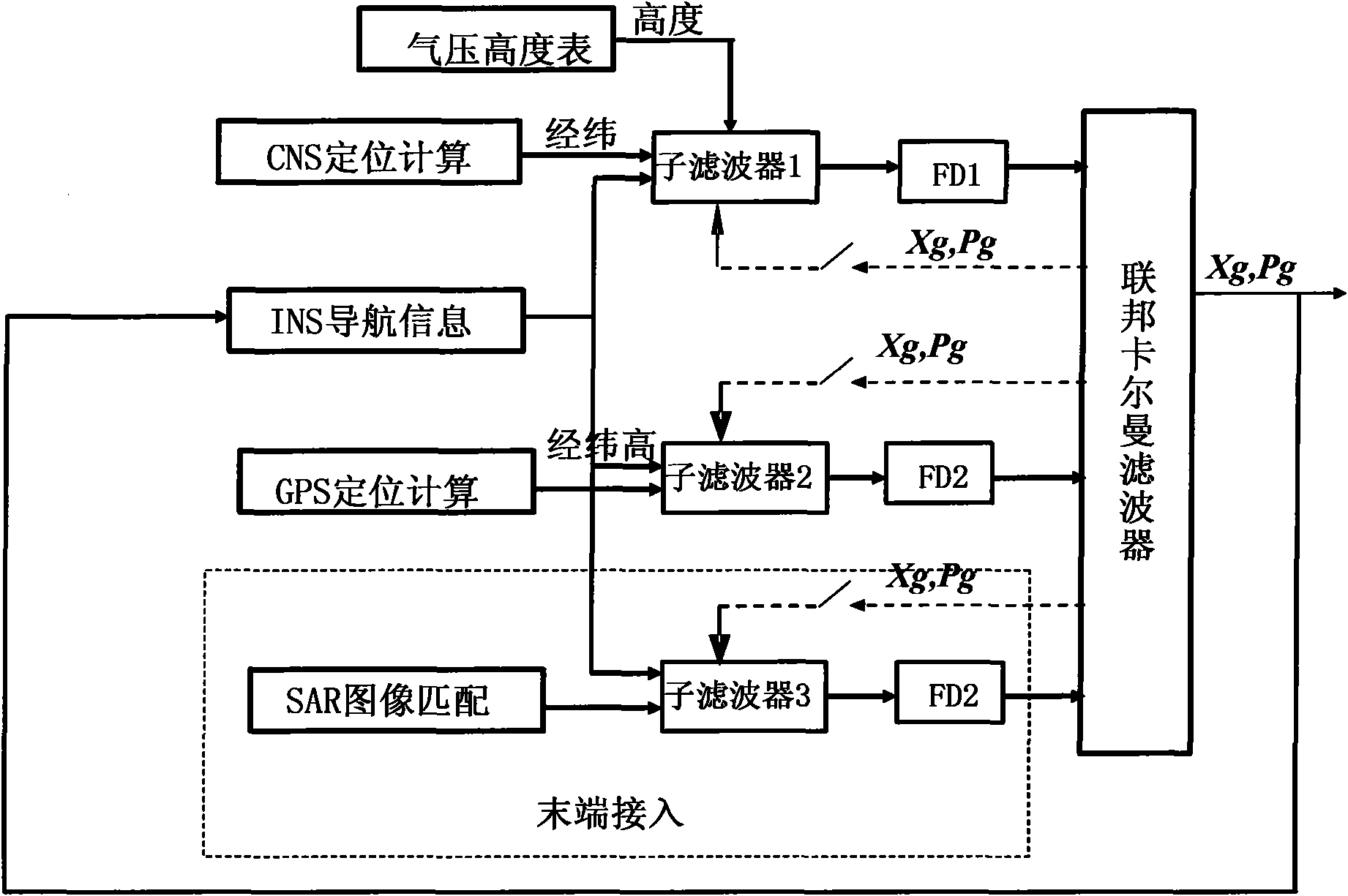
Fault-tolerance autonomous navigation method of multi-sensor of high-altitude long-endurance unmanned plane
InactiveCN101858748AOvercoming the lack of navigation stabilityDoes not affect workInstruments for comonautical navigationFault toleranceFault detection algorithm
The invention discloses a fault-tolerance autonomous navigation method of a multi-sensor of a high-altitude long-endurance unmanned plane. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, carrying out theory analysis on work environment and work characteristics of three navigation sensors including GPS (Global Position System), CNS (astronomy) and SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar), and establishing an observation linearity measurement equation by combining a geography system based on a position combined observation principle of inertia / GPS, inertia / astronomy and inertia / SAR under an airborne geography system; then analyzing error characteristics of a navigation sensor and simulating the output during the fault of GPS, and establishing a corresponding fault detection algorithm unit to carry out fault detection and isolation on a filter; and finally, designing and completing an inertia / GPS combined navigation system mathematic model based on the assistance of astronomy and SAR, and optimally evaluating the error state of the inertia navigation by means of federated filtering. The invention has high navigation precision, and can fully play the role of evaluating the error state quantity of an airborne inertia navigation system by the combined navigation of the multi-sensor under the geography system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
High-precision pedestrian foot navigation algorithm based on multi-information fusion compensation
ActiveCN107655476ASolve the positioning problemSolve the heading divergence problemNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerGyroscope
The invention discloses a high-precision pedestrian foot navigation algorithm based on multi-information fusion compensation. The high-precision pedestrian foot navigation algorithm is characterized in that the original measuring data of a gyroscope and an accelerometer is collected in real time, the error compensation of the initial gyroscope is zero, the error compensation of the accelerometer is also zero, and a strapdown inertial navigation calculating algorithm is used to perform strapdown calculation; on the basis above, a Kalman filter correction model is built to perform filter correction, state equation consistency is achieved while measurement equations are dynamically adjusted along with multi-dimensional measurement information, a corresponding algorithm is built under different multi-dimensional information detections, the measurement equation is transformed in real time, navigation positioning result errors and sensor errors are estimated and corrected, and the errors arereturned to the error compensation of the gyroscope and the error compensation of the accelerometer; a navigation positioning result which includes the position, speed and posture of a pedestrian isoutput. The high-precision pedestrian foot navigation algorithm has the advantages that a low-precision consumer-grade sensor chip and a magnetic sensor are used, the high-precision pedestrian positioning problem under an environment without a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) is solved, and the long-hour course divergence problem is solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Status estimating method for dynamic process of electrical power system
ActiveCN101291061AStable and reliableRealize dynamic monitoringElectrical testingSystems intergating technologiesPower stationLoad model
The invention provides a method for estimating a state of dynamic process of a power system. The method takes an estimated result of the static state before the electric grid disturbance as a basic section and introduces a load model and a motor model to perform the equivalent treatment to the electric grid; in the process of the electric grid disturbance, a synchronous phasor measuring unit(PMU) is used to measure and obtain data of a motor, and according to the active power and the reactive power zero injection pseudo-measurement equations of all nodes of the original electric grid, states of all nodes of the electric grid are estimated, and the state of dynamic process of the electric grid is acquired only by the PMU measurement of a power plant. Because the state of the electric grid before disturbance is taken as a basis and only the PMU distribution of the power plant is required, the method effectively resolves the problem of state monitoring under the condition of the electric grid disturbance; on the same disturbance, for continuous PMU measurement sections, PMU measurement data can be directly put in iterative computations, thereby the continuous sections in the process of electric grid disturbance are provided for stable control and analysis; moreover, the method is fast in speed, so that the method meets the requirement for monitoring the dynamic process in real time.
Owner:NR ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
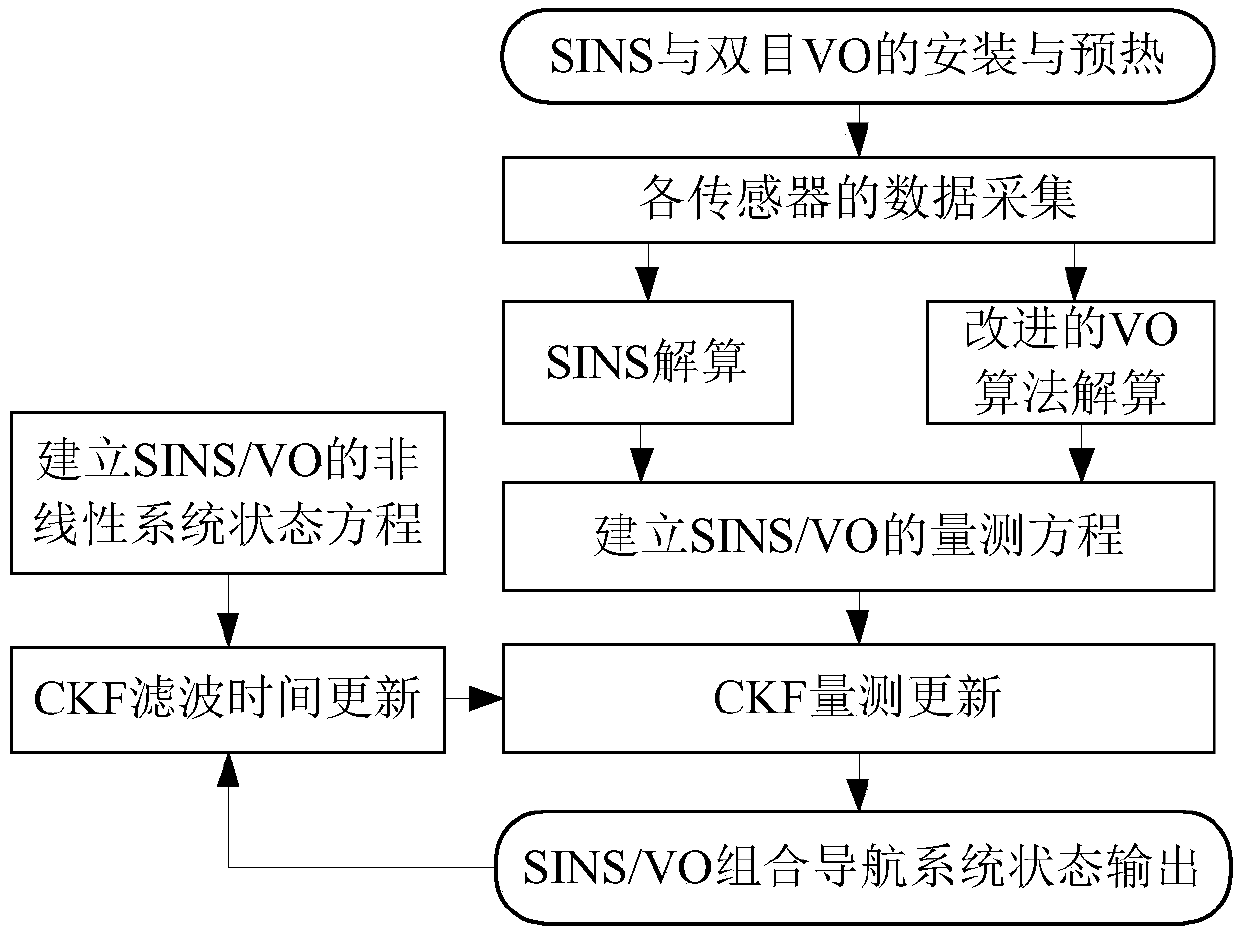
Inertia/visual odometer combined navigation and positioning method based on measurement model optimization
ActiveCN108731670AEfficient use ofHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerGyroscope
The invention discloses an inertia / visual odometer combined navigation and positioning method based on measurement model optimization. A state equation of a combined navigation system is established,errors of an inertial sensor are expanded into system state variables including random constant drifting of a gyroscope, one-order markoff process drifting of the gyroscope and one-order markoff process drifting of an accelerometer; then, a visual odometer is taken as an angular velocity, linear velocity and position sensor to acquire measurement data, and a measurement equation is established; finally, in the carrier motion process, the navigation errors are fed back and corrected in real time, and a navigation result of an inertial navigation system after errors are corrected is obtained. According to the method, angular velocity, linear velocity and position information of the visual odometer can be effectively utilized in the carrier motion process, effective fusion with inertial navigation is realized, the accuracy and the reliability of the combined navigation system are improved, and the method is applicable to engineering applications.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
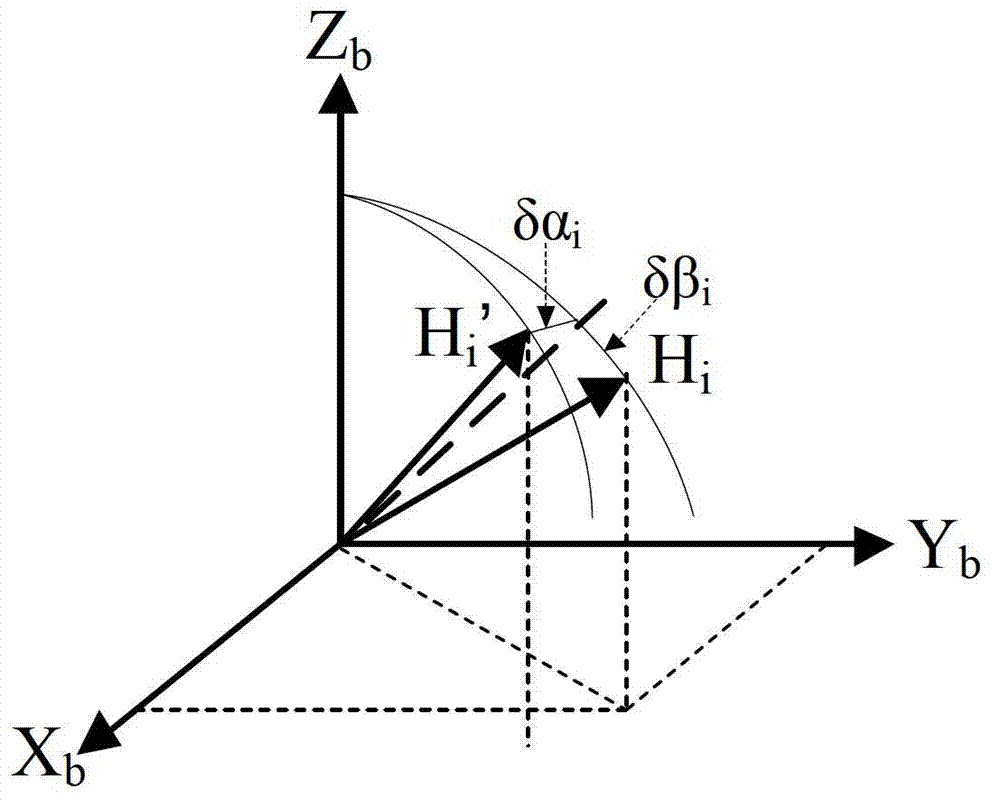
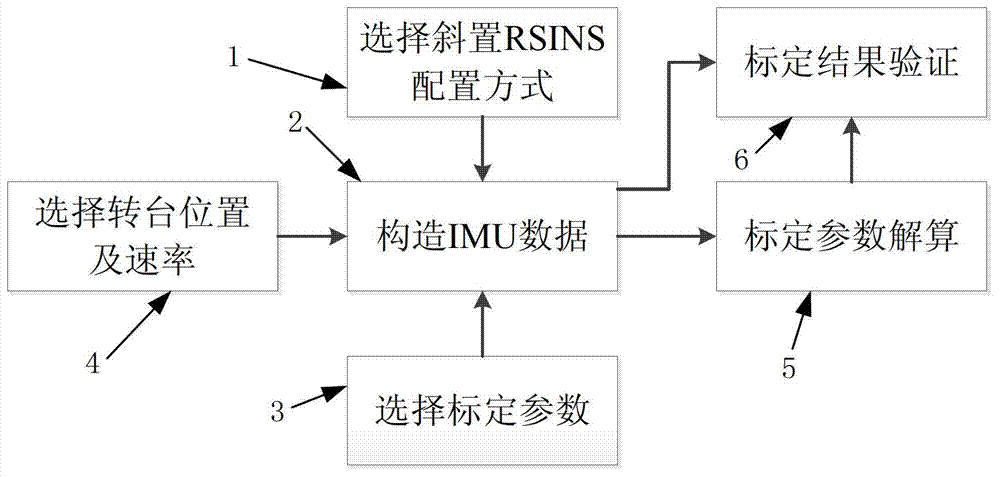
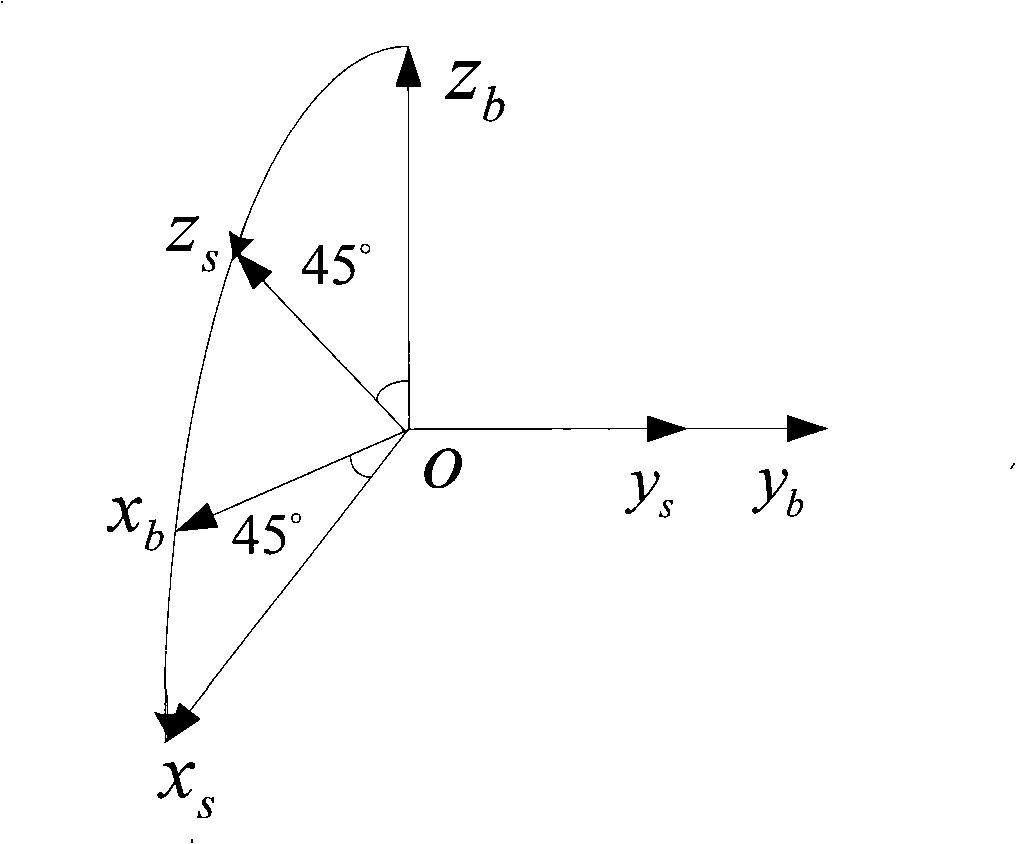
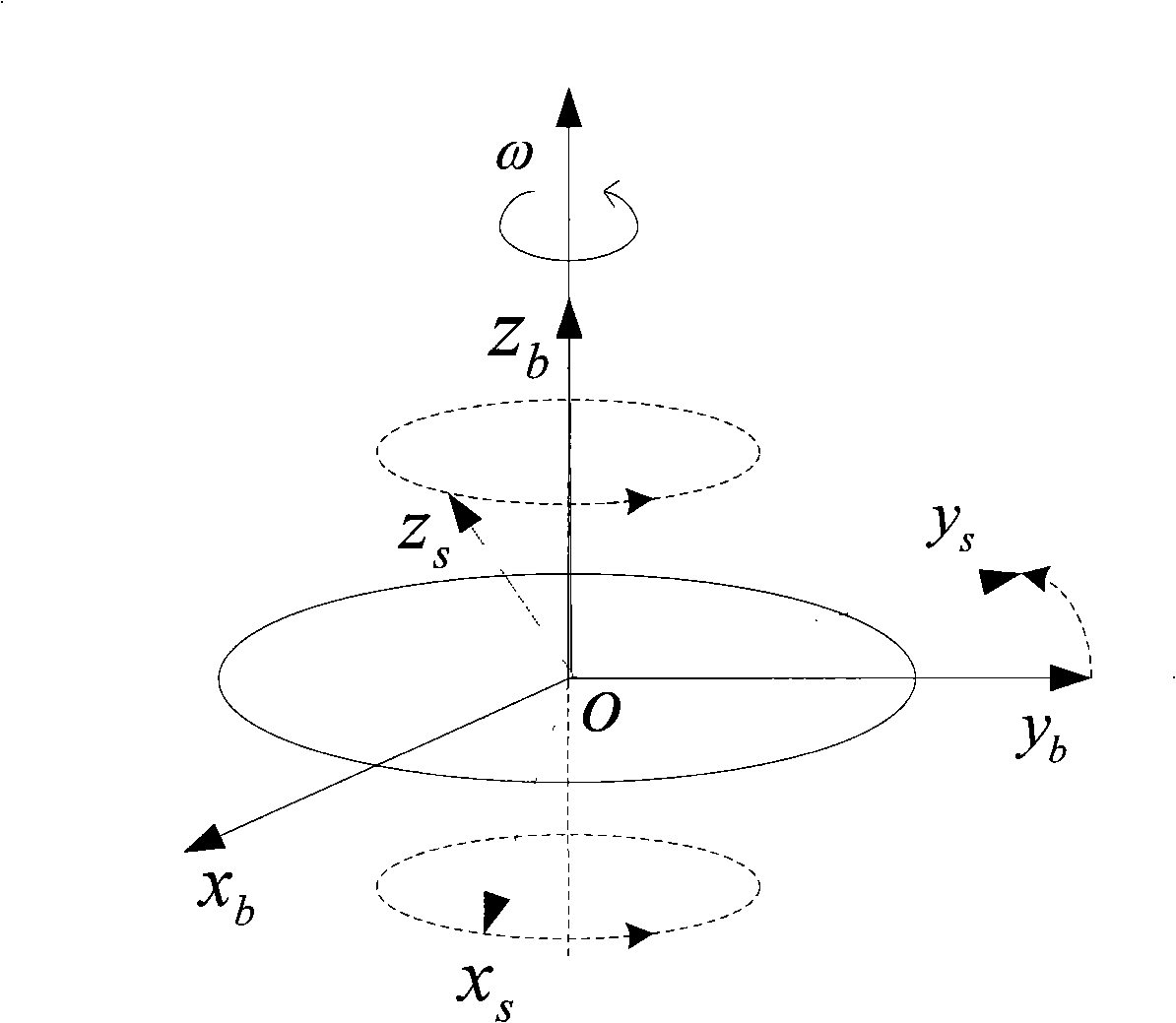
Method of quickly calibrating oblique redundant strapdown inertial navigation system
The invention discloses a method of quickly calibrating an oblique redundant strapdown inertial navigation system. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, describing a mounting misalignment angle of the oblique RSINS (Redundant Strapdown Inertial Navigation System), and giving a calibrating measurement equation; 2, designing a calibrating scheme of the oblique RSINS; and 3, constructing a calibrating simulation platform of the oblique RSINS, and verifying accuracy of the calibrating method by utilizing the simulation platform. The method, provided by the invention, is capable of quickly calibrating the oblique RSINS on the basis of a tri-axial position / speed turntable, calibrating parameters, such as zero offsets, scale factors and mounting misalignment angles of a redundant accelerometer and a gyro, are calibrated by utilizing a four-position method and a three-position rotating method, and accuracy of the calibrating method can be verified by utilizing the simulation platform. The method, provided by the invention, has the advantages of high calibration precision, simple operation, capability of meeting quick calibration requirements of the oblique RSINS at low and middle precisions, and better engineering application value.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
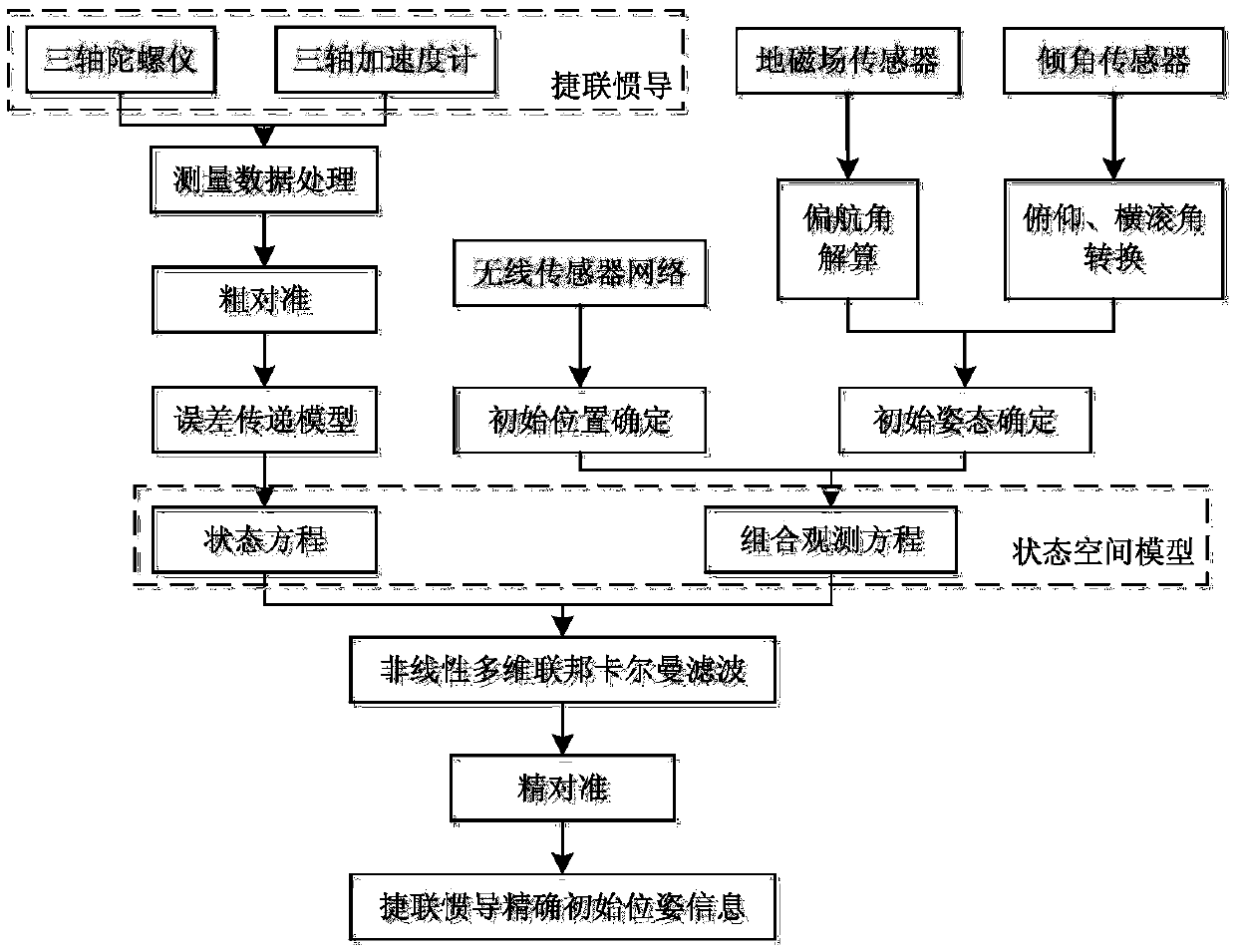
Combined initial alignment system and alignment method for strapdown inertial navigation system of underground coal mining machine
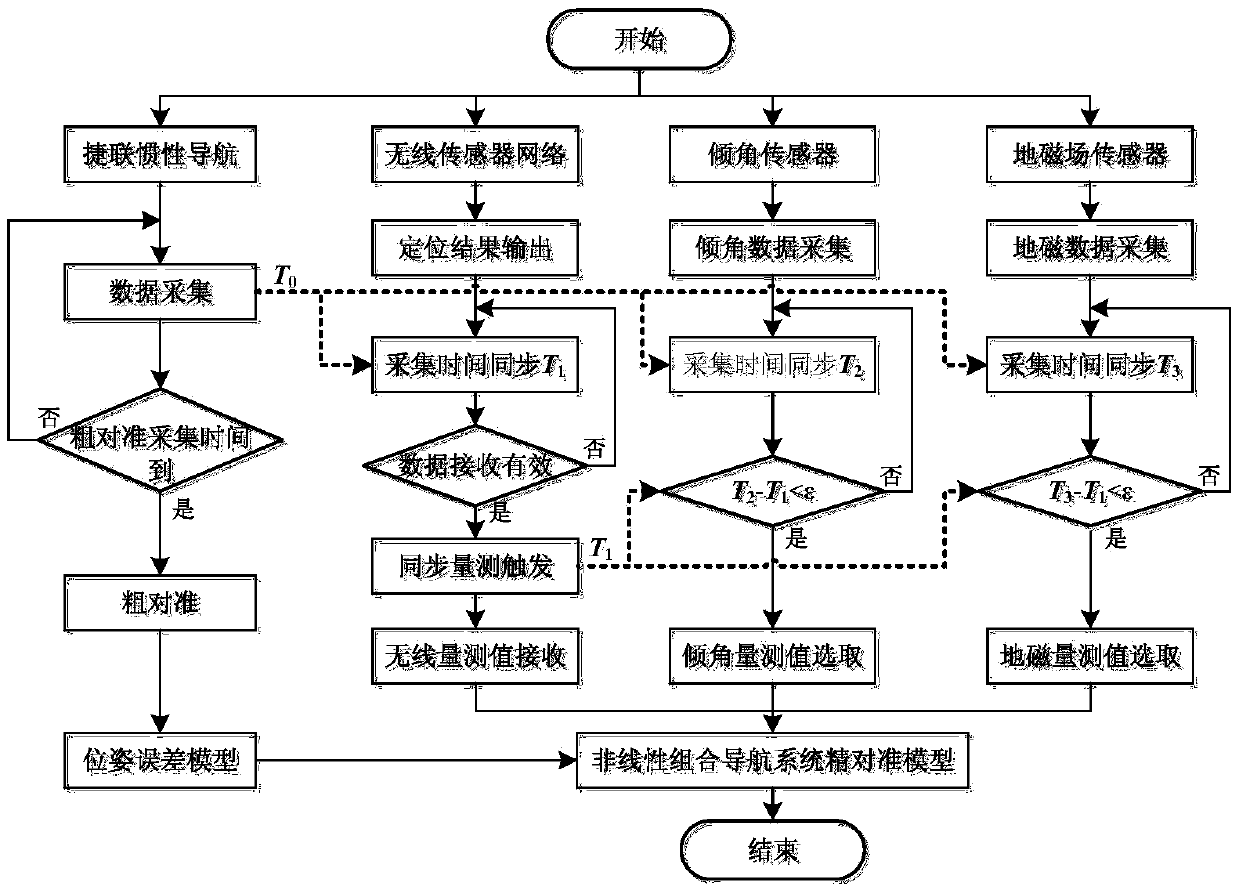
ActiveCN105371871AHigh positioning accuracyAddresses difficulty relying on external positioning systems for initial alignment of SINSNavigation by terrestrial meansNetwork topologiesWireless sensor networkingEngineering
A combined initial alignment system and alignment method for a strapdown inertial navigation system of an underground coal mining machine belong to initial alignment system and alignment method for positioning navigation of underground coal mining machines. The system is composed of a strapdown inertial navigation system installed on the coal mining machine, a wireless sensor network mobile node, an inclination sensor, a geomagnetic field sensor and anchor nodes installed on a hydraulic support. After coarse alignment of the strapdown inertial navigation system, the wireless sensor network is used to detect the location information of the underground coal mining machine, the inclination sensor measures the roll and pitch angle, and the geomagnetic field sensor measures the yaw angle. A pose measurement equation of the coal mining machine is constructed, and the pose measurement equation is combined with an error model after the coarse alignment of the strapdown inertial navigation system to establish a state equation; fusion smoothing is carried out to obtain the accurate location information of the coal mining machine; and the precise alignment of the strapdown inertial navigation system is conducted to complete the initial alignment. The invention realizes precise initial alignment of strapdown inertial navigation combination under the severe closed condition in coal mine, and greatly improves the precision of the integrated positioning under large misalignment angle of the strapdown inertial navigation system of the coal mining machine.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Method for combined navigation of inertia/visual odometer/laser radar
ActiveCN105371840AAccurate distance measurementAccurate measurement of speedNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsElectromagnetic wave reradiationOdometerVisual perception
The invention belongs to navigation methods and particularly relates to a method for combined navigation of an inertia / visual odometer / laser radar. The method comprises (1) state model establishment, (2) visual odometer speed measurement based on characteristic information, (3) establishment of a measurement equation and obtaining of a measurement value, (4) Kalman filtering and (5) system error correction. The method has the advantages that a machine vision autonomous navigation technology is used, a monocular camera can measure a vector speed under the conditions of a known distance through the difference of a front frame image and a rear frame image, the laser radar can accurately measure the distance of an observation point and then measure a vector speed, navigation is performed by utilizing combination of the speed obtained through measurement and an inertial reference speed, and high-accuracy navigation is performed finally under the conditions of no outside reference information.
Owner:BEIJING AUTOMATION CONTROL EQUIP INST
Near-space missile-borne strap-down inertial navigation system transfer alignment method based on star sensor
ActiveCN104165640AAttitude Error Estimation High AccuracyComply with flight altitudeMeasurement devicesInertial coordinate systemInstallation Error
The invention discloses a near-space missile-borne strap-down inertial navigation system transfer alignment method based on a star sensor. The method comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a missile-borne strap-down inertial navigation system transfer alignment state equation by taking an inertial coordinate system (launching point coordinate system for short) on a carrier launching point as a navigation coordinate system and a strap-down inertial navigation system (SINS) on a missile to be launched as sub-inertial navigation; 2) calculating navigation information and observed quantity of the missile-borne strap-down inertial navigation system; 3) establishing a measurement equation; 4) by depending on the state equation and the measurement equation established, estimating a mathematics platform misalignment angle, a speed error, a position error and an installation error of the missile as well as flexural deflection of the carrier through a sparse grid integral kalman filter, and correcting a sub-inertial navigation system, thus finishing a transfer alignment process.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Airplane angular rate signal reconstruction method based on unscented kalman filter
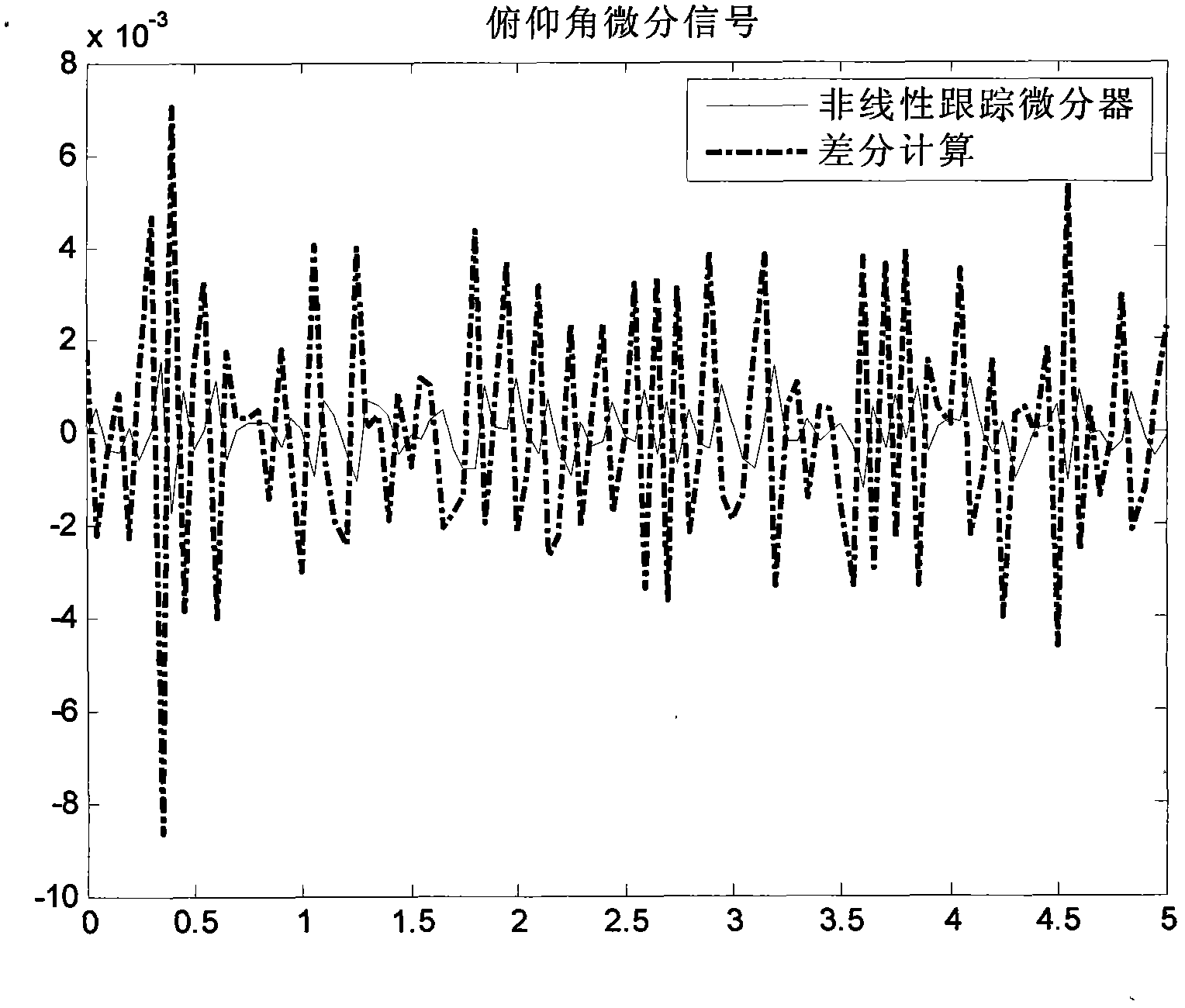
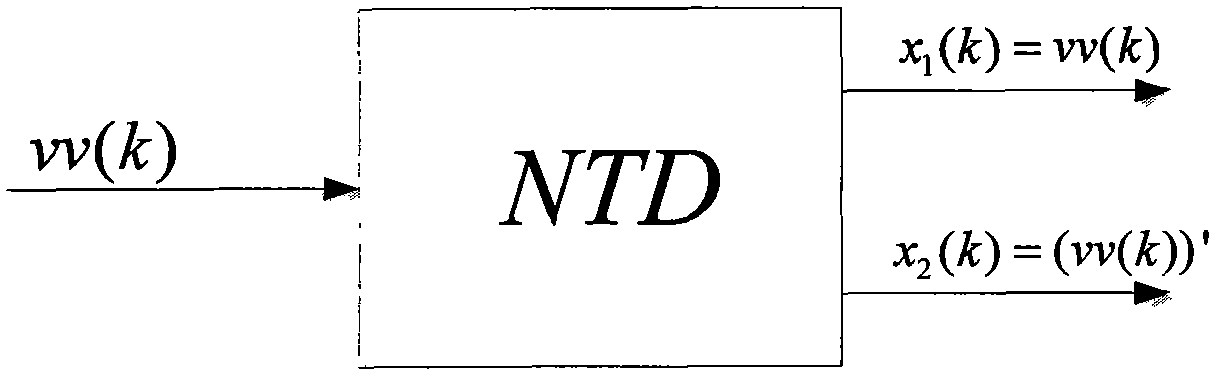
InactiveCN103363993AThe result is accurateNavigational calculation instrumentsJet aeroplaneDifferentiator
The invention discloses an airplane angular rate signal reconstruction method based on unscented kalman filter. The method comprises the following steps of: (1), denoising an attitude angle measurement signal containing measurement noise through a nonlinear tracking differentiator to obtain a differential signal of an attitude angle, and constructing a virtual measurement equation; (2), constructing a state equation of a system on the basis of natural characteristics of an airplane and according to tri-axial angular rate signals and torque characteristics of the airplane; and (3), reconstructing an angular rate signal of the system by selecting the unscented kalman filter technology as the processing manner because both the state equation and the measurement equation are nonlinear and the estimation precision can be influenced by traditional operation for linearizing a nonlinear equation.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Asynchronous sensor space alignment algorithm
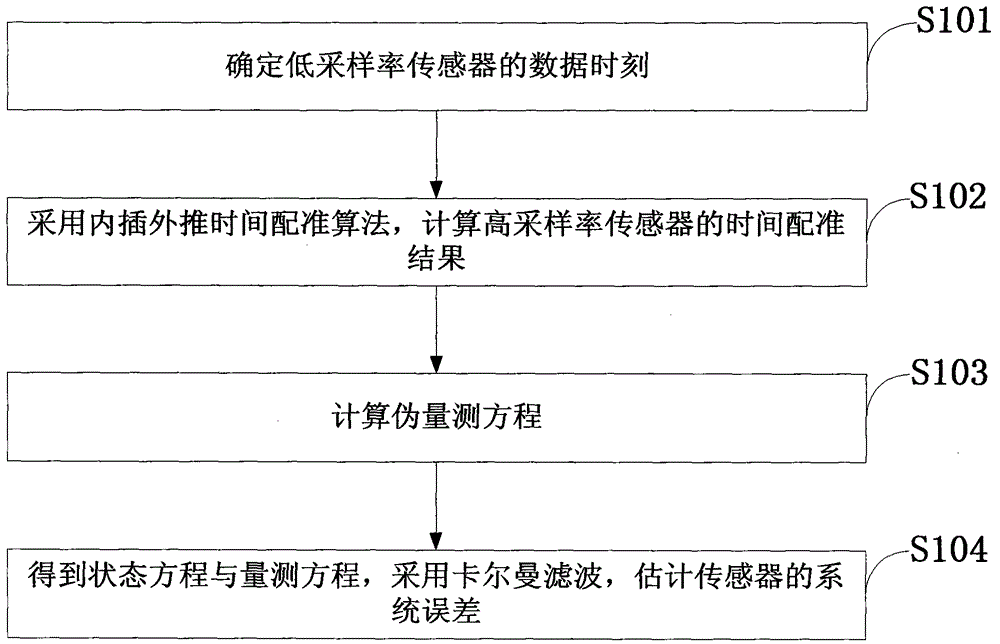
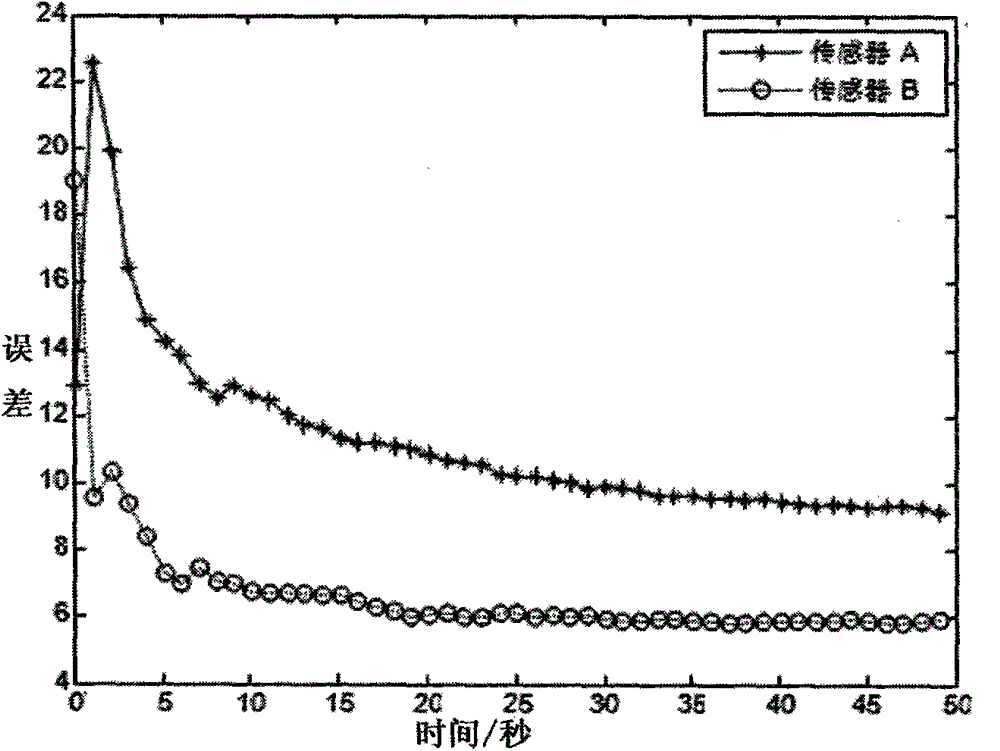
InactiveCN104809326ASolving Spatial Registration ProblemsMeasurement devicesSpecial data processing applicationsState vectorMeasurement equations
The invention discloses an asynchronous sensor space alignment algorithm. Data of two sensors are synchronized by the aid of an interpolation and extrapolation time alignment algorithm, a pseudo measurement equation is built according to time alignment results, and the asynchronous sensor space alignment algorithm based on the interpolation and extrapolation time alignment algorithm and a geocentric earth fixed coordinate system is provided to solve the problem of space alignment under target maneuvering conditions. The building process of the pseudo measurement equation is unrelated to a target state vector, and pseudo measurement built by the time alignment results can be proved to be unrelated to the target state vector, so that the algorithm can effectively solve the problem of asynchronous sensor space alignment under the target maneuvering conditions. Simulation experiments confirm that the algorithm can still accurately estimate system errors of the sensors under the condition of snakelike maneuvering of a target, and the influence of the sampling period ratio of the sensors and random errors on system error estimation precision is analyzed by simulation.
Owner:方洋旺 +1
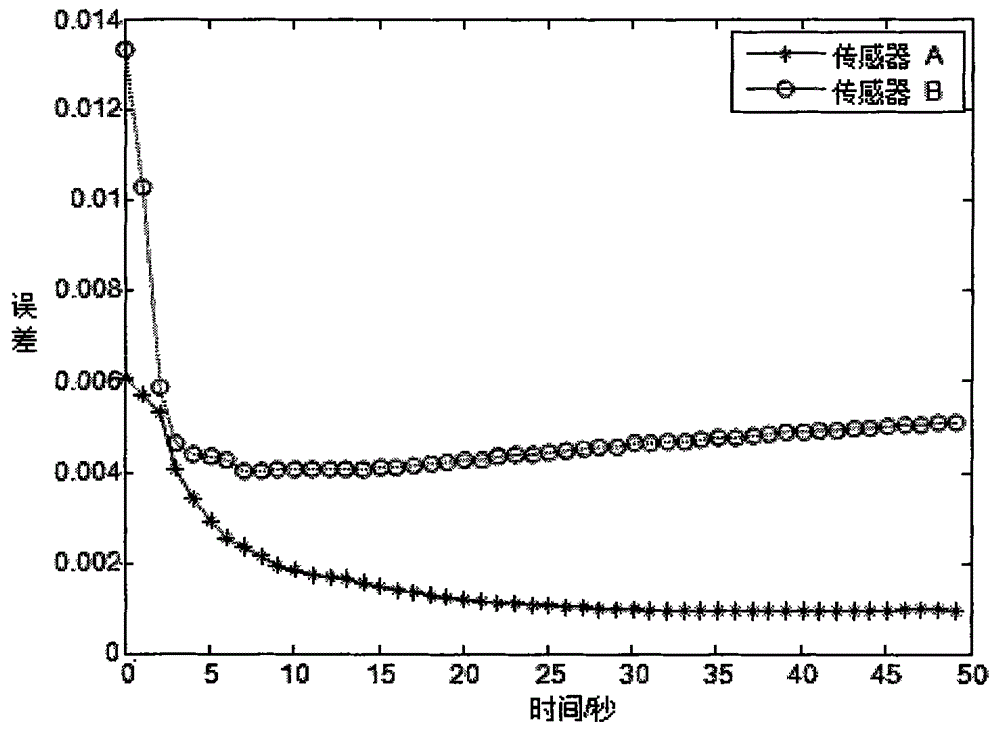
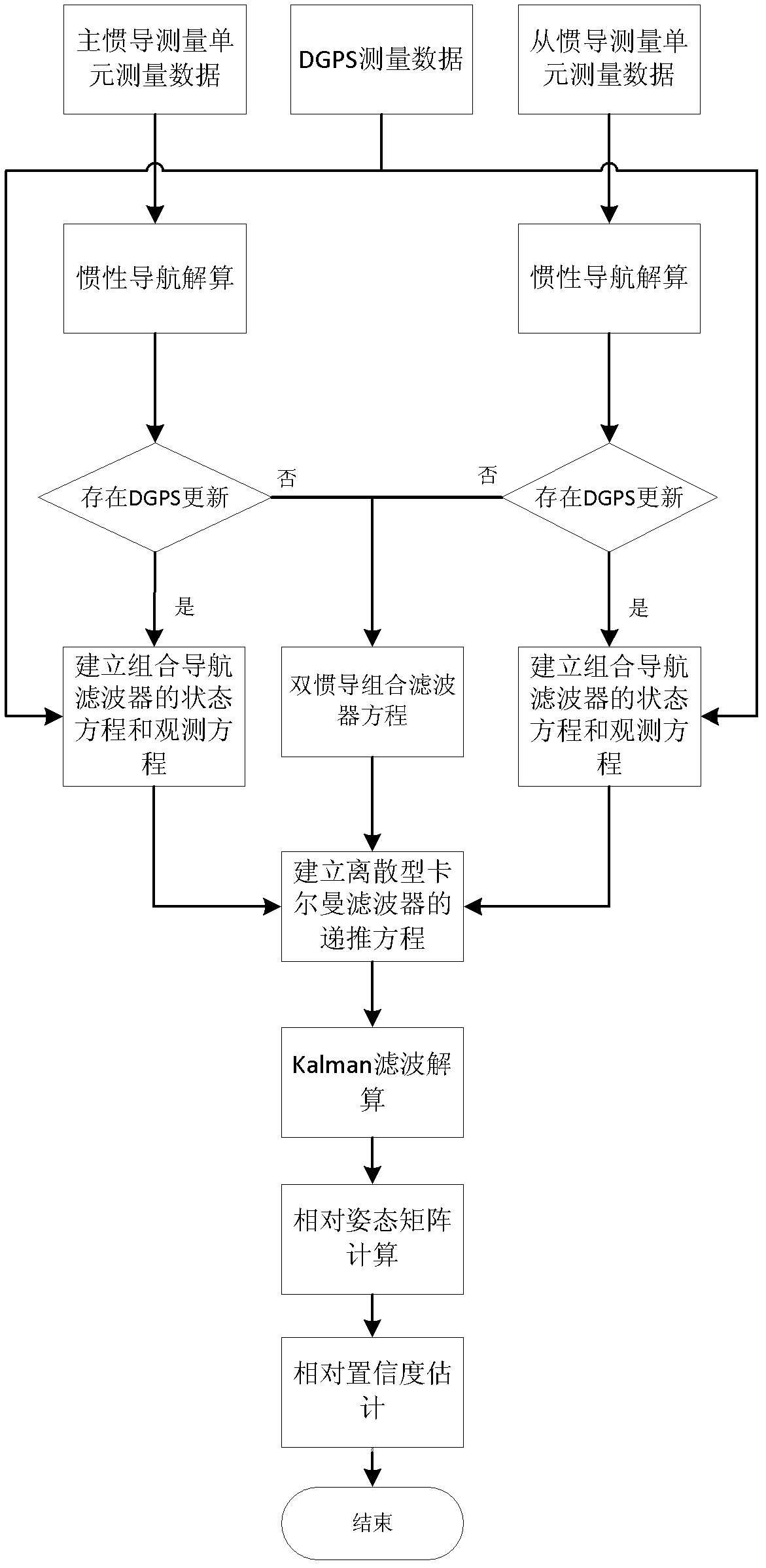
Relative attitude measurement real-time dynamic filter method based on dual-inertial measurement unit/differential global positioning system (IMU/DGPS) combination
InactiveCN102506857ASolve solving problemsImprove stabilityNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingNavigation systemGlobal Positioning System
The invention discloses a relative attitude measurement real-time dynamic filter method based on a dual-inertial measurement unit / differential global positioning system (IMU / DGPS) combination. The method comprises the following steps of: resolving through strapdown inertial navigation in real time by adopting a dual optical fiber strapdown inertial navigation system to obtain navigation information of a master inertial navigation system and a slave inertial navigation system; judging whether information of a differential global positioning system (DGPS) is updated, and generating two situations: when the information of the DGPS is updated, the master inertial navigation system and the slave inertial navigation system perform filter correction to construct a measurement equation of a combined navigation filter, when the information of the DGPS is not updated, the master inertial navigation system is used for performing the filter correction on the slave inertial navigation system to construct a measurement equation of the combined navigation filter; discretizing the combined filter measurement equations obtained according to the two situations, constructing a recurrence equation of a discrete kalman filter, and resolving to obtain a pitching angle, a transversely rolling angle and a heading angle of each of the master inertial navigation system and the slave inertial navigation system; and then resolving a relative attitude matrix to obtain main values of relative attitude angles of the master inertial navigation system and the slave inertial navigation system. According to the method, the stability of a navigation system is improved; the speed information, the position information and the attitude information of the navigation system during measurement can be output in real time; and the measurement range is large.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
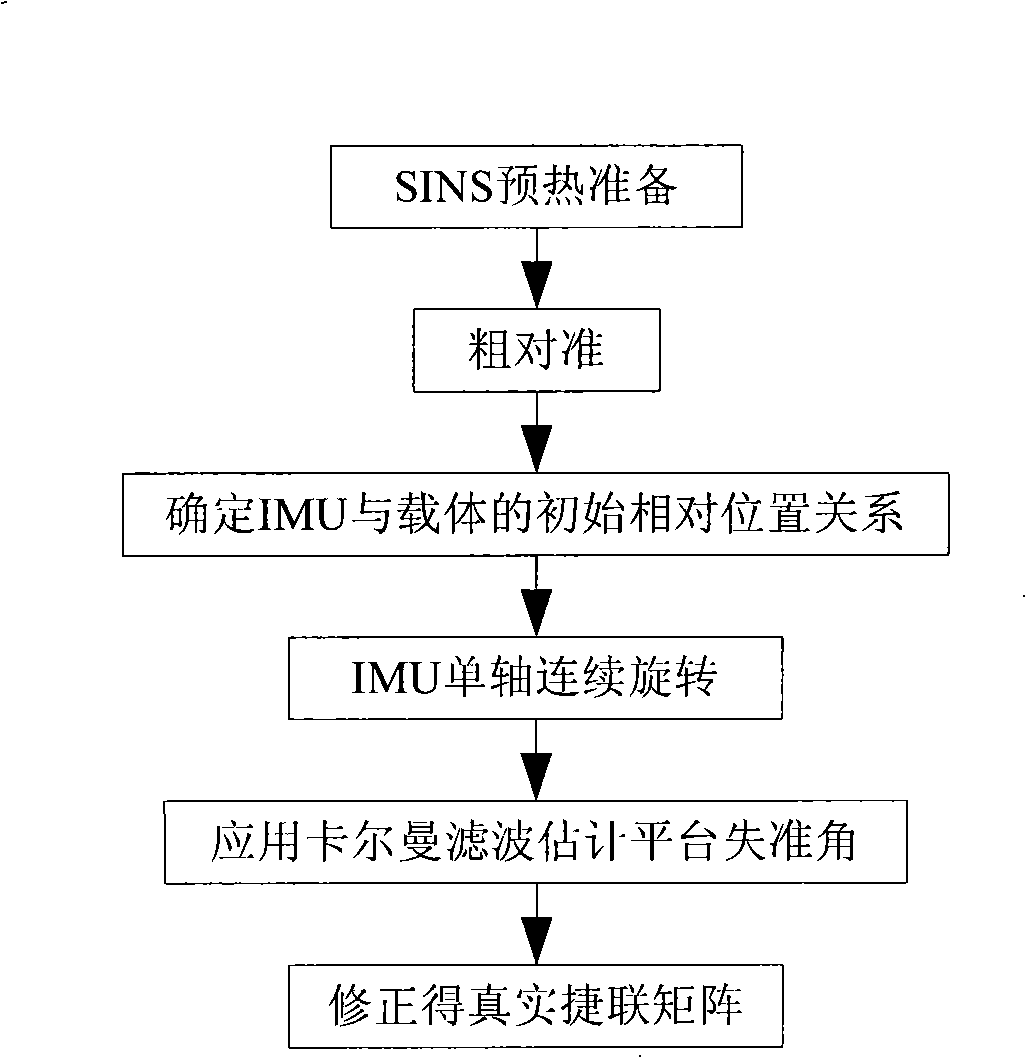
Method for initial alignment of a single-axis rotation strap-down inertial navigation system (SINS)
The invention provides a method for initial alignment of a single-axis rotation strap-down inertial navigation system (SINS). The method comprises the following steps: building a carrier coordinate system and computing a transfer matrix between geographic coordinate systems on the basis of coarse alignment completed by collecting the information output by gyroscopes and accelerometers in the SINS with the carrier being in a static state; establishing Kalman filtering state equations with speed errors as the state variables and measurement equations with the speed errors as the measurement variables; and estimating the misalignment angles of the carrier by the Kalman filtering technique and feeding back to the SINS to complete the initial alignment of the SINS. The invention can overcome the influence on the estimation precision of the azimuth misalignment angles caused by the equivalent gyroscope drift of the geographic coordinate systems and improve the alignment precision.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
SINS/GPS/polarized light combination navigation system modeling and dynamic pedestal initial aligning method
ActiveCN103217159AImprove estimation accuracyHigh degree of autonomyNavigational calculation instrumentsAviationSimulation
The invention provides a SINS / GPS / polarized light combination navigation system modeling and a dynamic pedestal initial aligning method, which relates to the dynamic pedestal initial aligning method for vehicle, ship and aviation aircraft. The invention concretely comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a SINS error equation as an initial aligning state equation; (2) according to a polarization azimuth, a GPS outputted speed and a position, establishing an initial aligning measurement equation base on the polarization azimuth error, a speed error and a position error; (3) estimating an attitude error, a speed error and a position error using a Kalman filtering; (4) correcting the feedbacks of the attitude, the speed and the position of SINS. The SINS outputs the attitude, the speed and the position information of the carrier to users. The invention has the advantages of high precision, small computational complexity and good anti-interference capability, and is used for improving the aligning precisions of vehicle, ship and aviation aircraft, with reduced initial aligning time.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
GPS accumulated delta range processing for navigation applications
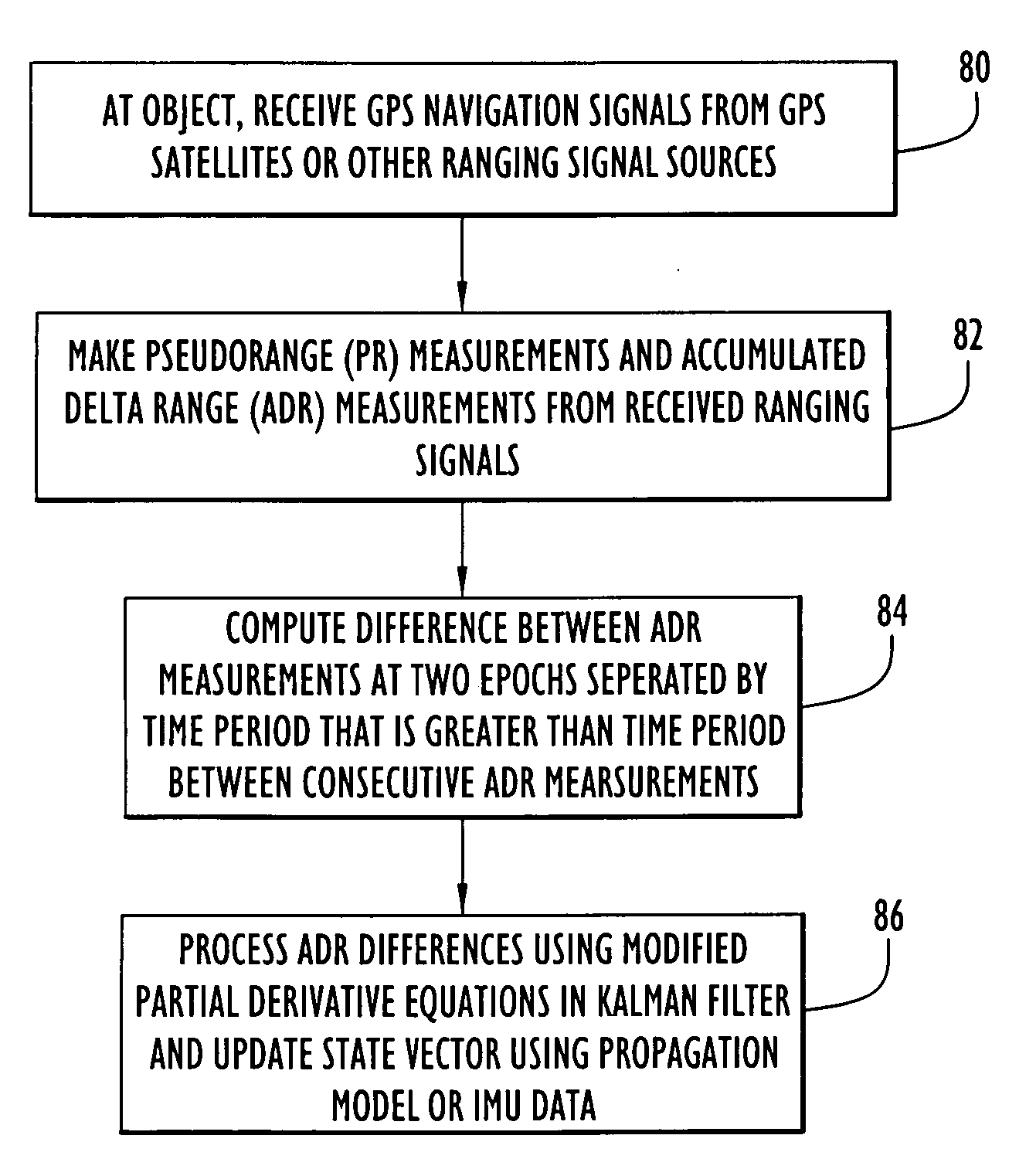
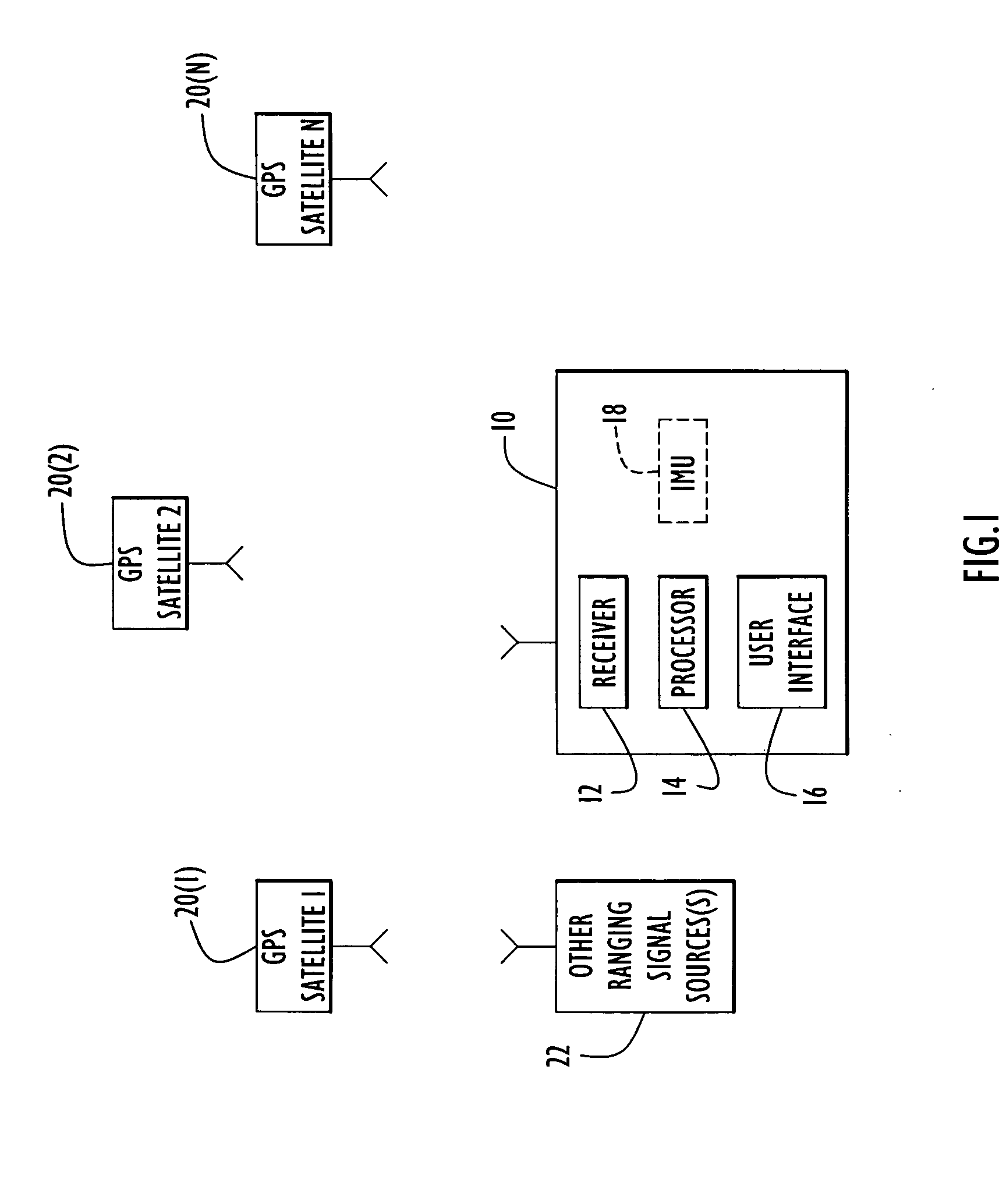
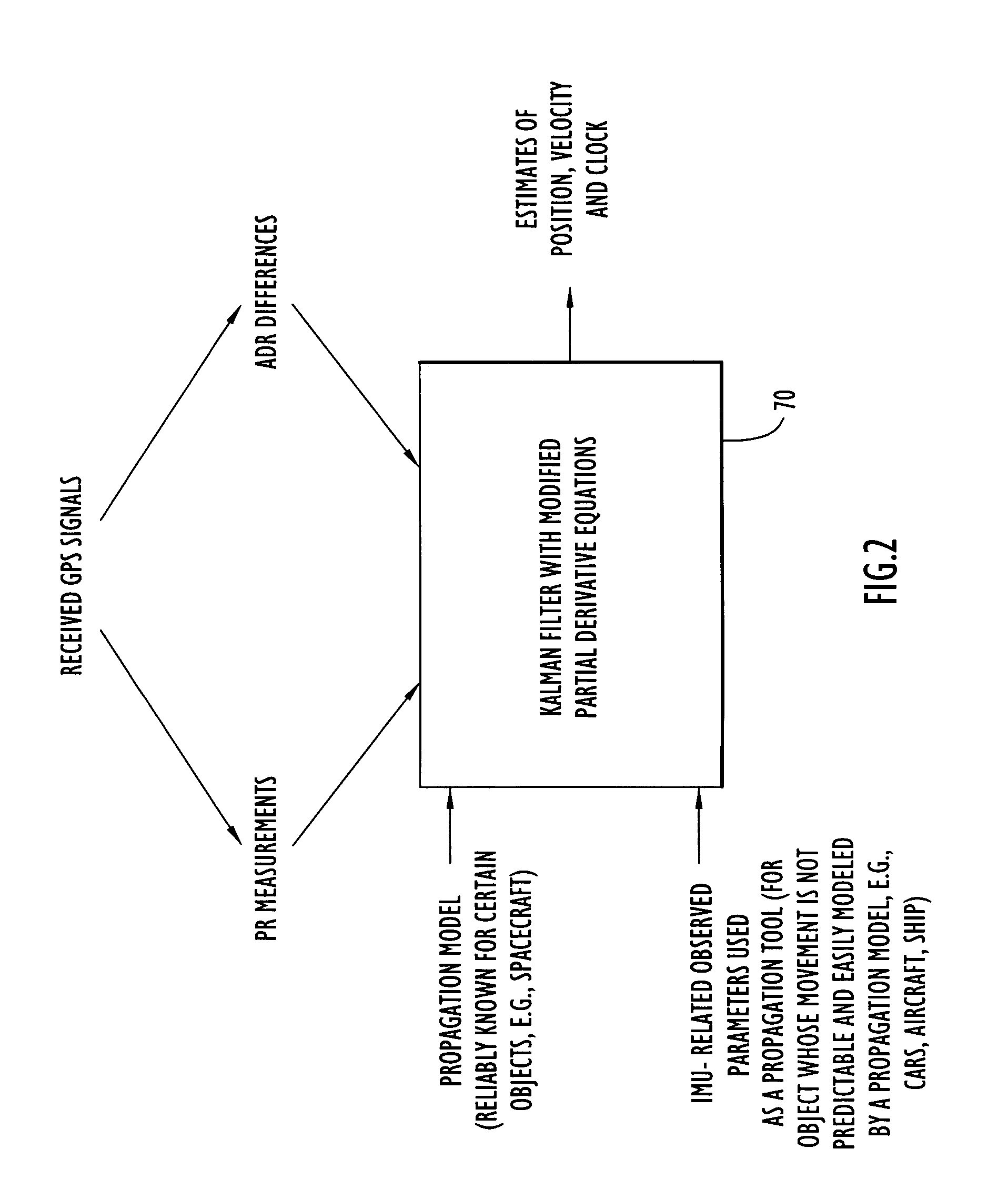
ActiveUS20060195262A1Accurate mappingShorten convergence timeInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationContinuous measurementGps navigation
Techniques for GPS navigation used to determine the position and velocity of a moving object. Pseudorange (PR) measurements and accumulated delta range (ADR) measurements are made at the object from received GPS signals. Differences are computed between ADR measurements that are separated by a time interval that is greater than a time interval between consecutive ADR measurements. Navigational parameters (e.g., position, velocity and clock) are estimated from the PR measurements and the ADR differences. The ADR measurement equations set for herein are formulated in a much more accurate way so that the time interval between the ADR measurements used to compute an ADR difference can be much larger than that used for current ADR differencing techniques in GPS navigation applications. Consequently, the ADR differences are more accurate, which translates into a much more accurate navigation solution. In addition, the ADR differencing technique contributes to shorten convergence times of the Kalman filter processing, and thereby improve the accuracy of spacecraft navigation. Techniques are also provided to extend these highly accurate ADR processing algorithms to integrated GPS / IMU navigation applications, where IMU data is used as an accurate propagation model to propagate the state vector.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
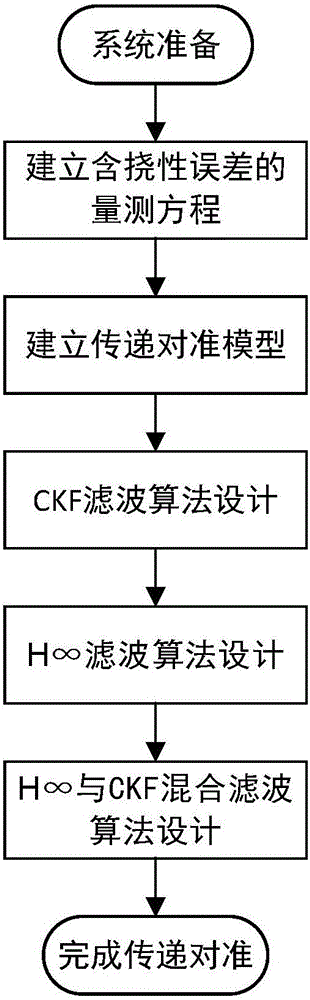
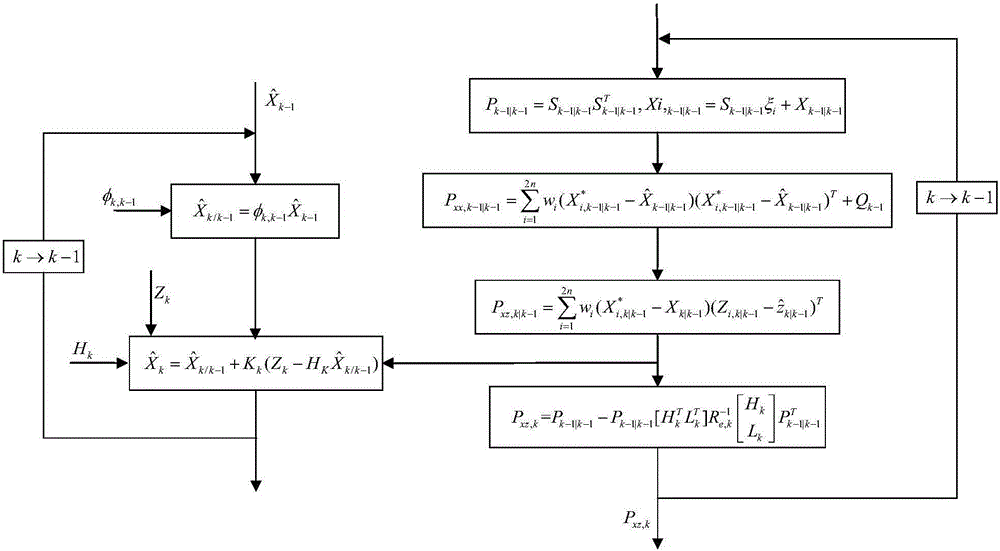
Airborne distributed POS transfer alignment method based on H infinity and CKF hybrid filtering
ActiveCN106352876AReduce precisionReduced stabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsFilter algorithmSelf adaptive
The invention relates to an airborne distributed POS transfer alignment method based on H infinity and CKF (Capacity Kalman Filtering) hybrid filtering. The method comprises the following steps: first, incorporating a deflection deformation error into measurement noise, determining a speed match measurement equation and an attitude match measurement equation, and primarily establishing a transfer alignment model of a system; designing nonlinear filtering, namely a CKF algorithm with high precision based on Kalman filtering; finally, achieving the purposes of weakening and eliminating the deflection deformation and a dynamic lever arm by utilizing good robust adaptive ability of H infinity filtering, designing an H infinity filtering algorithm, combining an H infinity filtering module and the CKF filtering, and designing a new H infinity and CKF hybrid filtering algorithm so as to estimate more accurate position, speed and attitude information of a slave inertial navigation system to complete transfer alignment. According to the airborne distributed POS transfer alignment method based on the H infinity and CKF hybrid filtering, the problem that the position, speed and attitude information of the slave inertial navigation system cannot be estimated accurately under the situation that the deflection deformation is difficult to model is solved, so that the airborne distributed POS transfer alignment method based on the H infinity and CKF hybrid filtering has the characteristics of high precision and strong anti-interference capacity.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Kalman filtering and data driving fusion battery SOC estimation method
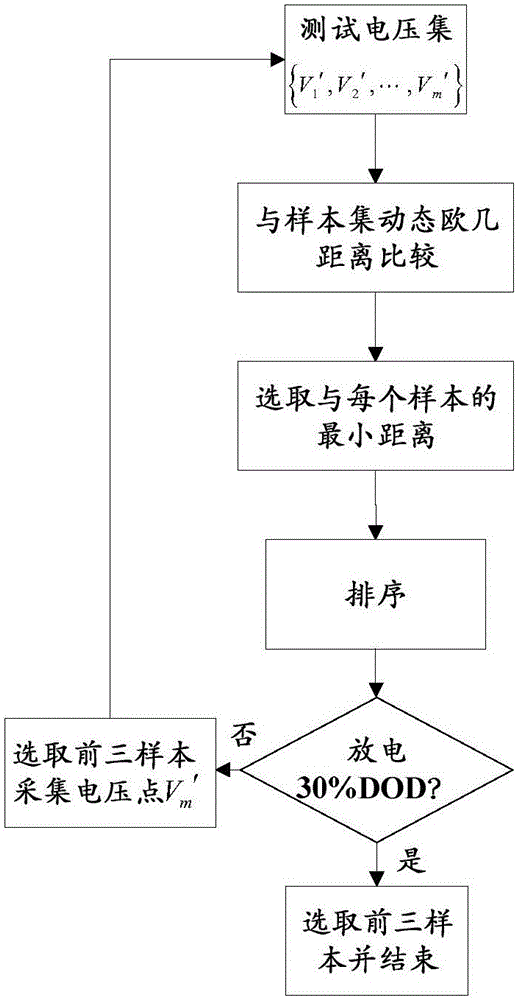
InactiveCN106093783AImprove estimation accuracyHigh precisionElectrical testingData setSimple sample
The invention discloses a Kalman filtering and data driving fusion battery SOC estimation method belonging to the battery SOC estimation method technology field. The invention provides a varied variance Kalman filter least square support vector machine (VVKF LSSVM) fusion method. Based on two equations of a KF, a noise variance, which is adapted to a current system state to the greatest extent, is set during every iteration, and a problem of declined precision caused by Kalman filtering noise variance initial value relied on artificial experience setting is solved. A least square support vector machine (LS SVM) is selected as the measurement equation of the KF, and by starting from a data angle, the SOC estimation method suitable for various batteries is completed by establishing a simple sample library, and the estimation precision is improved by dynamic modeling. A part of data in an NASA lithium battery data set and a CACLE lithium battery data set is used for experimenting to prove the superiority of the VVKF by comparing with the KF, and the validity of the whole method on the lithium battery SOC estimation.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Missile-borne inertia/ satellite tight combination navigation method
ActiveCN104181572AWith independent operating status discriminationWith independent fault diagnosisNavigation instrumentsSatellite radio beaconingMarine navigationMeasurement equations
The invention discloses a missile-borne inertia / satellite tight combination navigation method. The method utilizes pseudo-range, pseudo-range rate information and inertial navigation output by a GNSS to calculate relative pseudo-range and pseudo-range rate difference of a satellite, filtering is carried out and the current system is corrected according to the filtering results. The method mainly comprises the following steps: carrying out SINS initialization; carrying out SINS navigation calculation; carrying out satellite altitude angle and azimuth angle calculation; carrying out navigational satellite selection; carrying out pseudorange measuring error compensation of the navigational satellite; carrying out calculation on pseudo-range and pseudo-range rate of a carrier with respect to each navigational satellite; carrying out system state judgment and navigation strategy selection; carrying out system state equation construction and system measurement equation construction; and carrying out filtering calculation, and for hysteresis error due to communication delay, correcting the system through an error compensation method based on state transition according to the filtering results. The method can realize inertia / satellite-based pseudo-range and pseudo-range rate seamless combination navigation; navigation accuracy and adaptability to complex environment are improved; and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
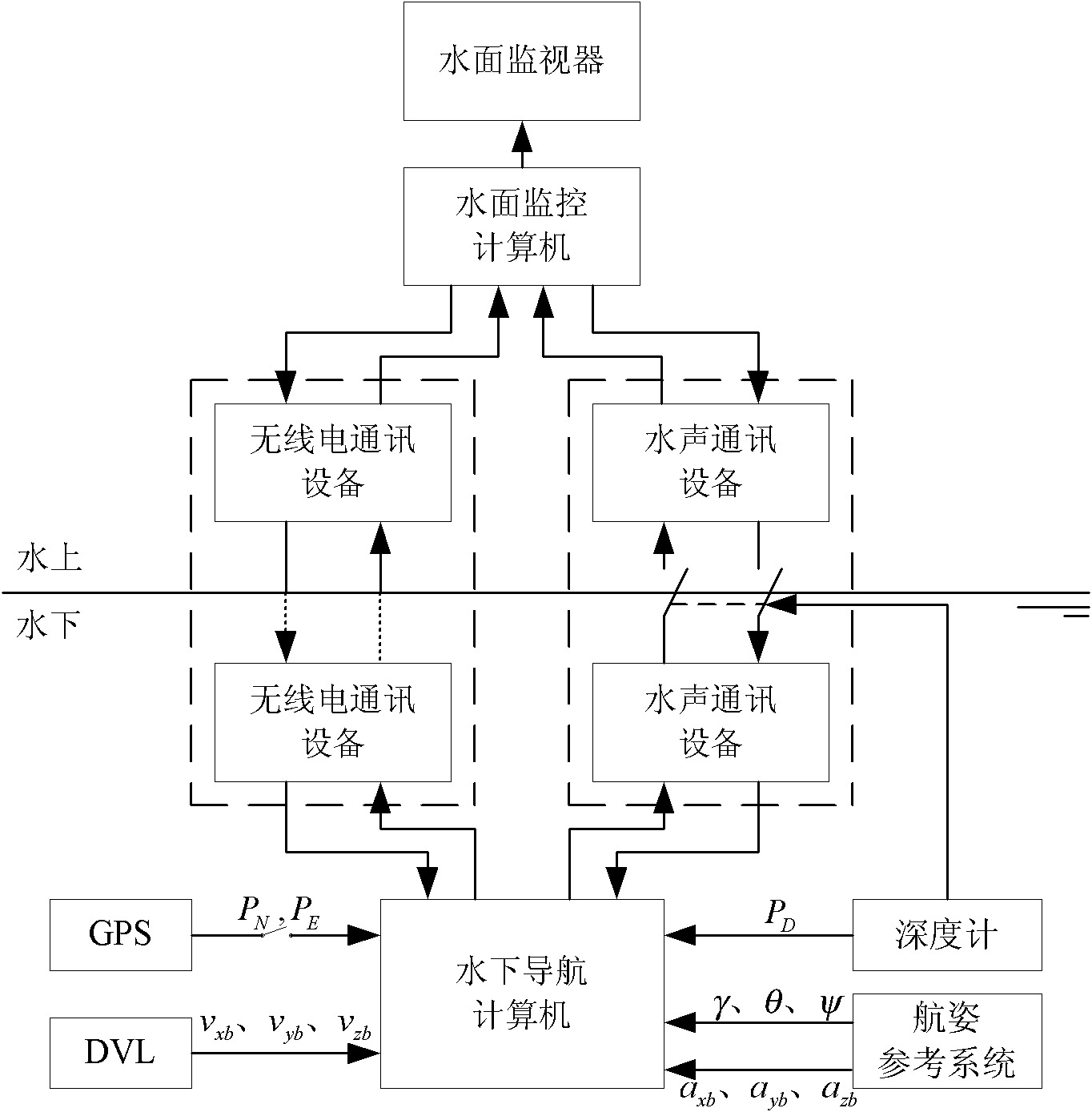
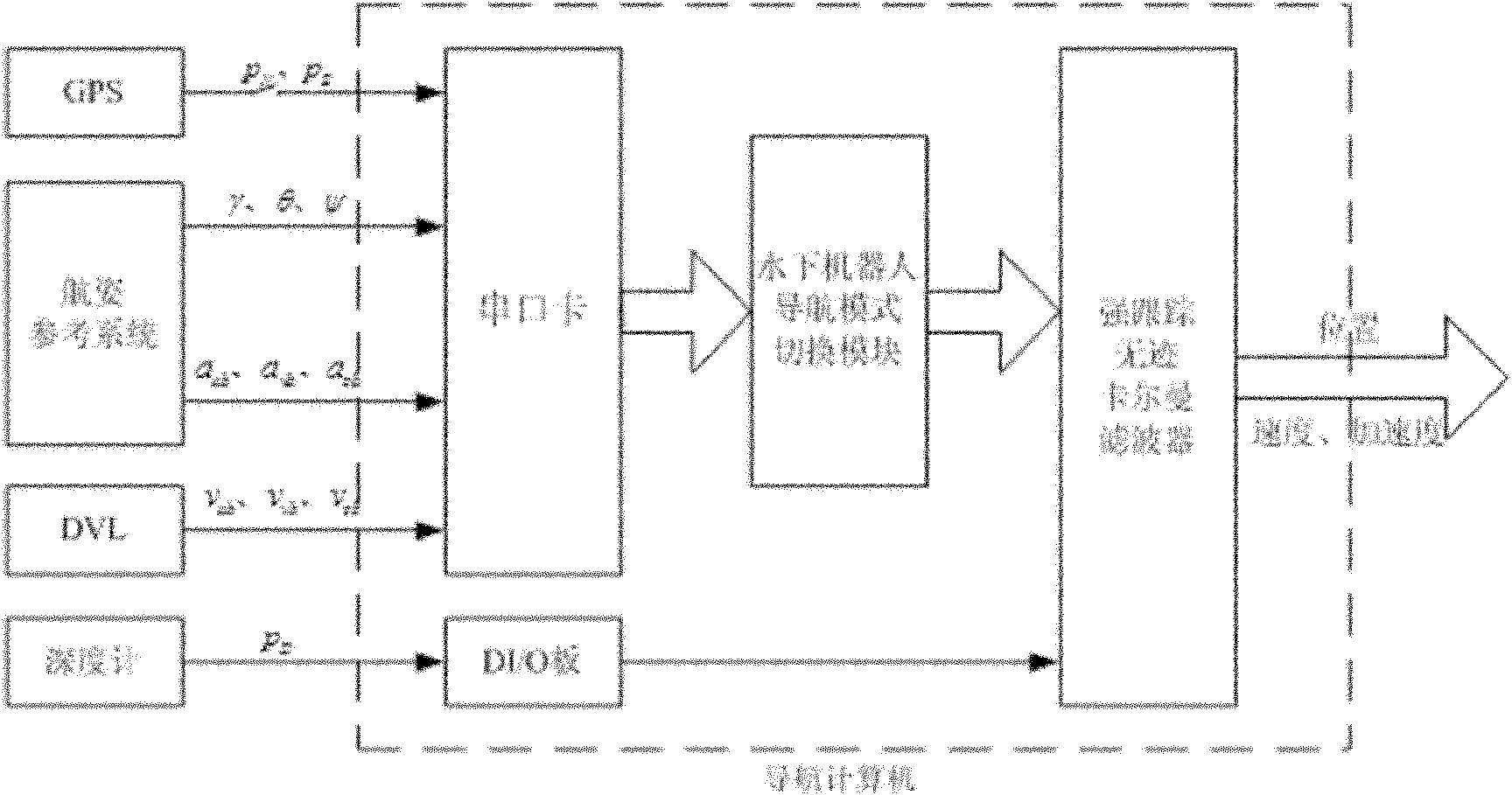
Combined navigation and positioning method of small underwater robot
InactiveCN102052924AAvoid mismatchNavigation data is continuous and stableNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSea wavesNavigation system
The invention provides a combined navigation and positioning method of a small underwater robot, which comprises the following steps: fusing measurement data of various navigation facilities by means of a strong tracking unscented Kalman filter; using position vectors and heading angles under a navigation system as well as speed vectors and acceleration vectors under a vector system as state vectors of the filter; using the strong tracking unscented Kalman filter to implement autonomous navigation and data filtering of the underwater robot; based on horizontal position information output by a GPS (global positioning system) receiver, using the strong tracking unscented Kalman filter to implement autonomous correction and data filtering of the underwater robot; and implementing the switching between two different measurement equations (i.e. overwater and underwater measurement equations) based on the significance bit of the output signal of the GPS receiver. The invention can fuse the position, depth and attitude information of the small underwater robot measured by various navigation facilities, and can implement the autonomous navigation and autonomous correction of the small underwater robot under the interference of sea current or sea wave.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Attitude standard deviation estimation and correction method of star sensor and payload
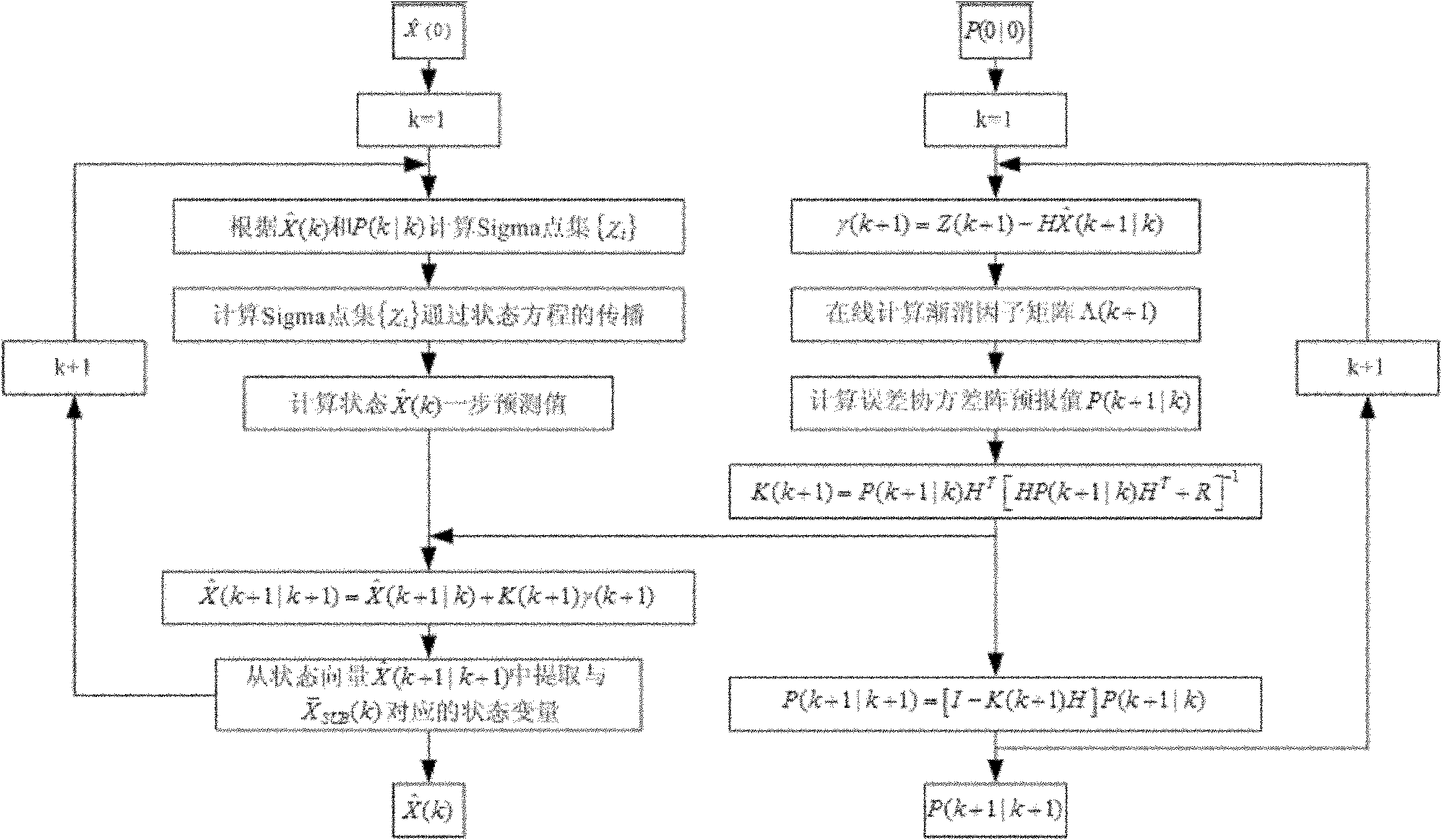
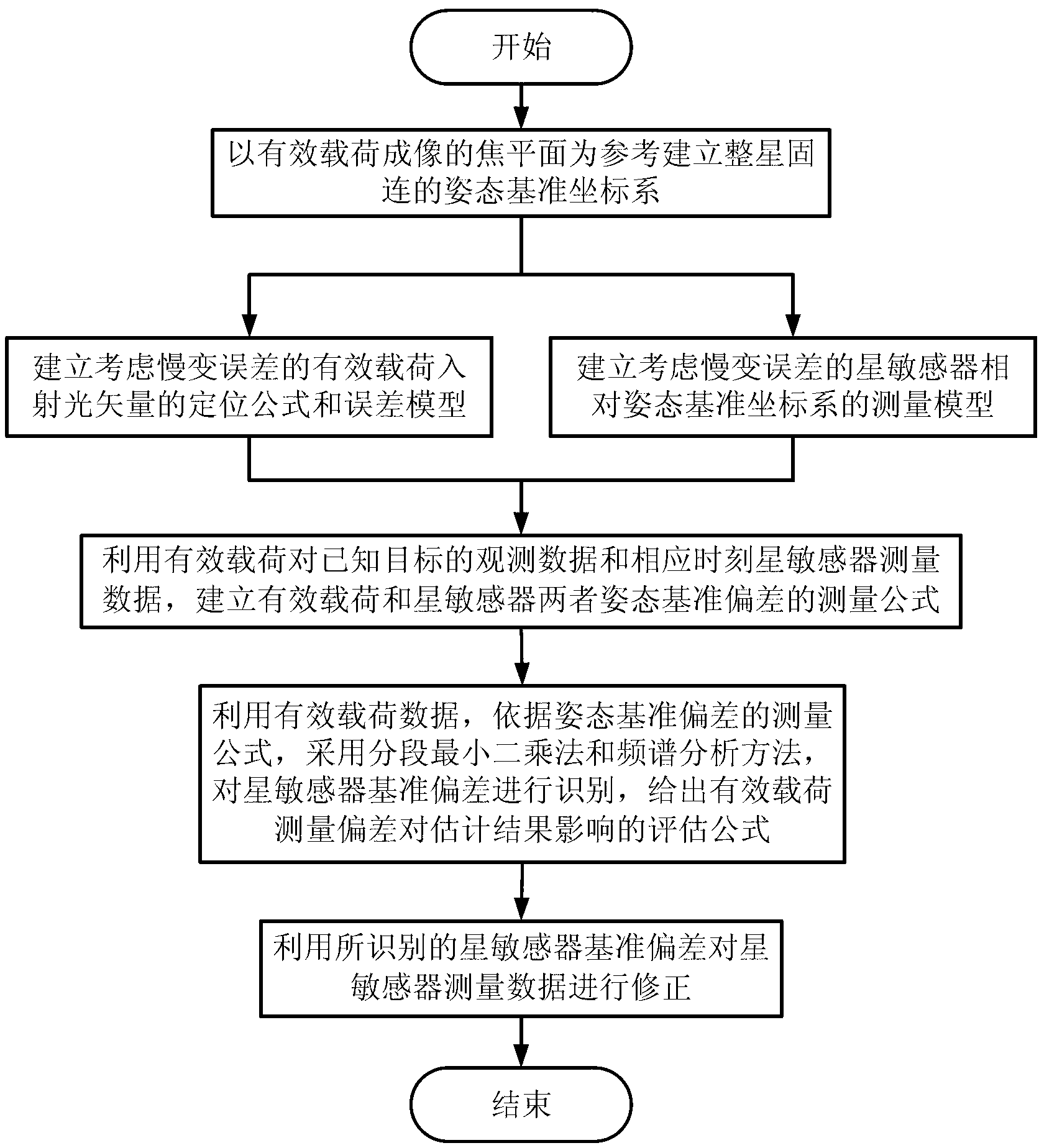
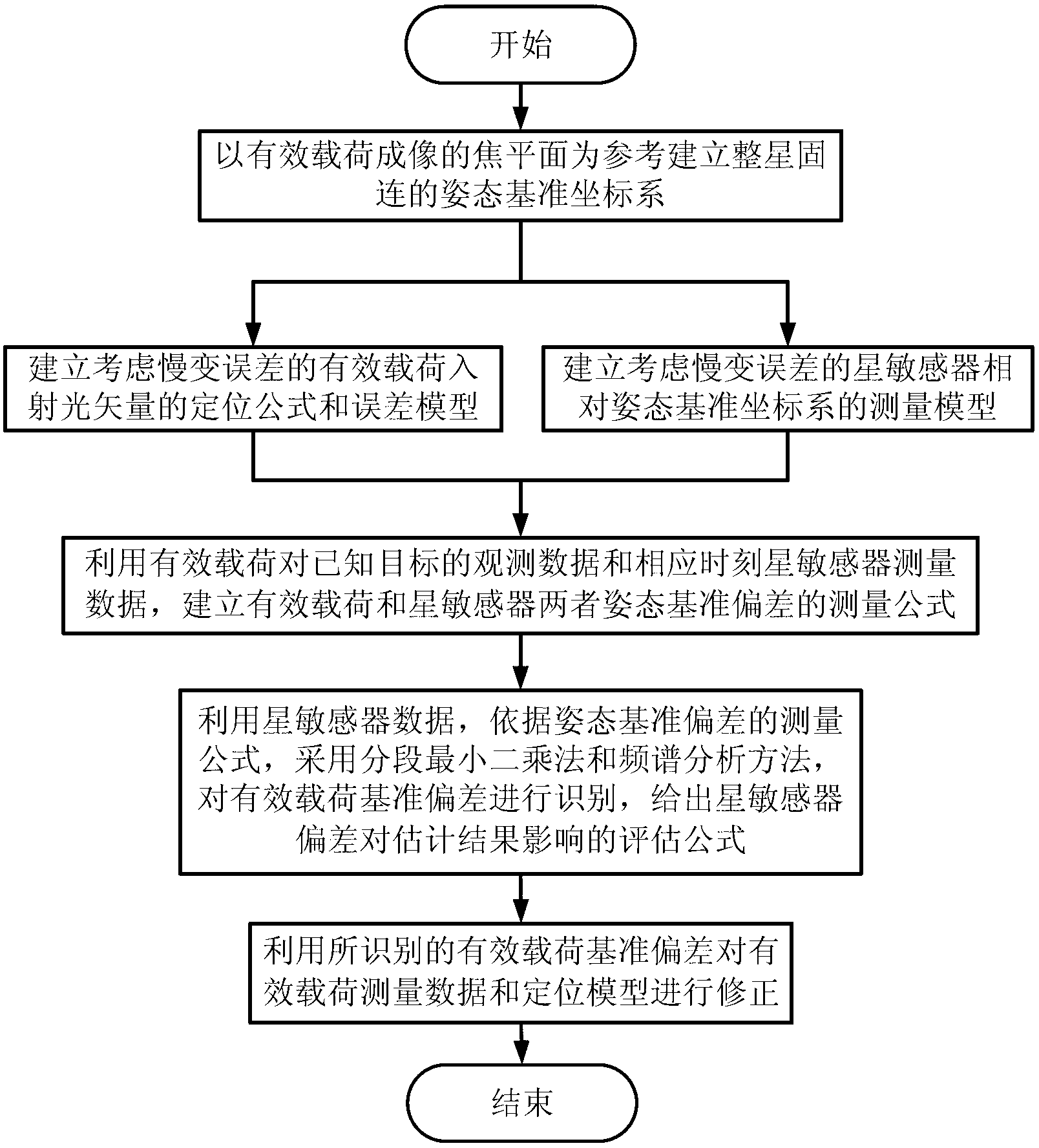
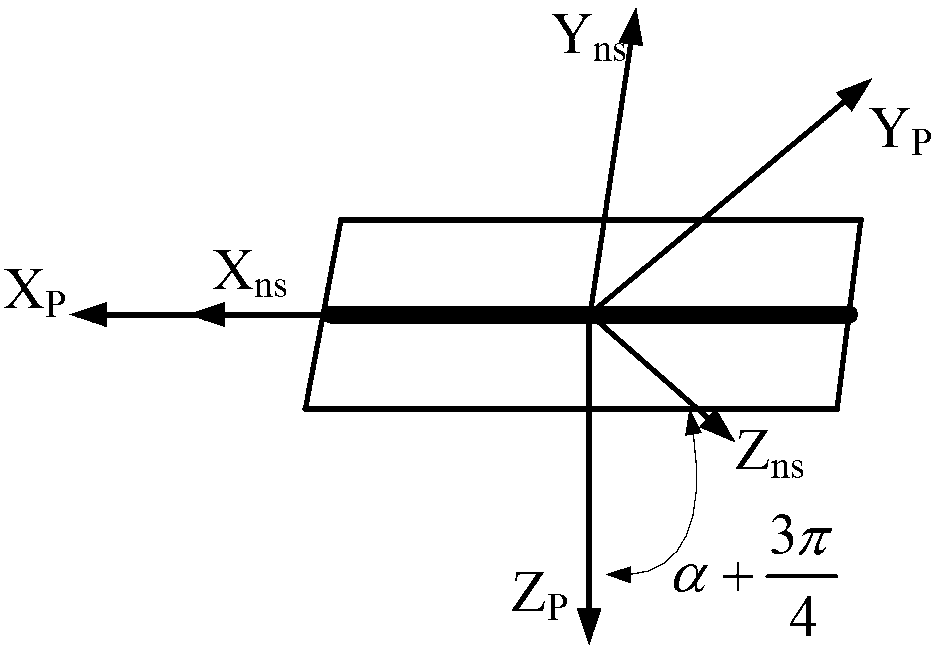
ActiveCN103323026AHigh precisionThe installation structure is stableMeasurement devicesImaging qualityObservation data
The invention discloses an attitude standard deviation estimation and correction method of a star sensor and a payload. The attitude standard deviation estimation and correction method comprises the following steps of 1, according to payload characteristics, determining a location formula of an incident light vector of a payload and building a payload error model with payload standard deviation, 2, according to star sensor characteristics, building a star sensor error model with star sensor standard deviation, 3, through the payload, determining measured deviation by observation data of a known target and corresponding star sensor measured data, and building a payload and star sensor standard deviation measurement equation according to the measured deviation, the payload standard deviation and the star sensor standard deviation, 4, carrying out estimation of the star sensor or payload standard deviation according to the payload and star sensor standard deviation measurement equation, and 5, correcting the star sensor or payload measured data by the estimated standard deviation. The attitude standard deviation estimation and correction method can reduce star sensor and imaging payload attitude standard deviation and improve imaging quality and an image positioning precision.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Information fusion method for airborne inertia/Doppler radar integrated navigation system
InactiveCN102608596ATroubleshoot navigation errorsHigh precisionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionClosed loop feedbackState variable
The invention discloses an information fusion method for an airborne inertia / Doppler radar integrated navigation system. The method comprises the following six major steps of: I, establishing an error model of an inertia device and a Doppler radar; II, determining a state variable based on the application of inertia / Doppler integrated navigation on an airborne fixed-wing aircraft; III, establishing an inertia / Doppler radar integrated navigation state equation; IV, establishing an inertia / Doppler radar integrated navigation measurement equation; V, discretizing a Kalman filtering continuous system; and VI, performing Kalman filtering data fusion resolving, obtaining the sub-optimal estimation related to navigation parameters through state estimation, and correcting the inertial navigation and Doppler radar in a closed-loop feedback mode at the same time. The method disclosed by the invention makes full use of the Doppler information and inertial navigation information, puts forward a data fusion scheme for airborne inertia / Doppler radar integrated navigation, effectively solves the problem of a navigation error caused by an imperfect error model, and improves the system precision.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Nonlinear-model-based SINS/DVL (strapdown inertial navigation system/doppler velocity log) integrated navigation method
InactiveCN103278163AHigh precisionStrong reliabilityNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNonlinear modelSigma point
The invention discloses a nonlinear-model-based SINS / DVL (strapdown inertial navigation system / doppler velocity log) integrated navigation method. The method comprises the following steps of: building a quaternion-based SINS nonlinear speed, posture and position error model according to the working principles of an SINS and a DVL, and confirming an error model of the DVL; building a state equation of the systems according to the error models of the two systems, measuring by taking the difference between the actually-measured speeds of the SINS and the DVL as the quantity, and building a measurement equation of the system; discretizing an actual continuous system to obtain a discrete nonlinear model which is convenient to compute; initializing the system, and computing sampling points and corresponding weight numbers by the discrete nonlinear model and unscented conversion; and sequentially carrying out time update and measurement update on unscented kalman filter on the basis of the discrete nonlinear model according to the constructed Sigma point. After the SINS / DVL integrated navigation system is used, information of each subsystem can be effectively used, and the best of each subsystem can be taken, so that the overall positioning accuracy can be greatly improved; the UKF (unscented kalman filter) estimation can be carried out by the nonlinear model of the SINS / DVL integrated navigation system, so that the positioning error of the system can be effectively reduced and the accurate positioning of the navigation system can be realized better.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
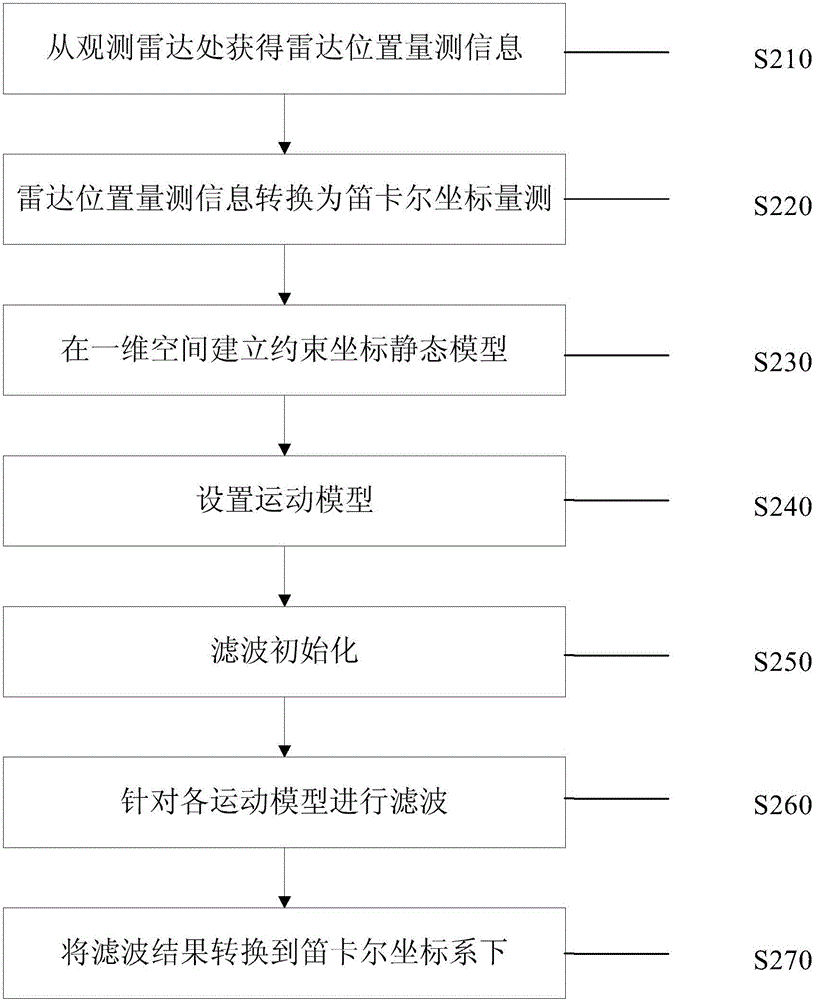
Maneuvering target tracking method under constraint conditions
ActiveCN106054170AImprove tracking performanceRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEquation of stateComputer science
The invention discloses a maneuvering target tracking method under constraint conditions, comprising the steps of: A, obtaining the position measurement information of a maneuvering target; B, converting the position measurement information into Cartesian coordinate measurement; C, establishing a constrained coordinate static model in a one-dimensional space, i.e., building the mileage S expression of the position of the maneuvering target in road x, y directions; D, setting motion models according to motion characteristics of the maneuvering target, and establishing a state equation and a measurement equation according to the established expression; and E, for each motion model, filtering converted Cartesian coordinate measurement to obtain a one-dimensional variable mileage S and speed filtering result. According to the embodiment, the tracking performance of a maneuvering target can be improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
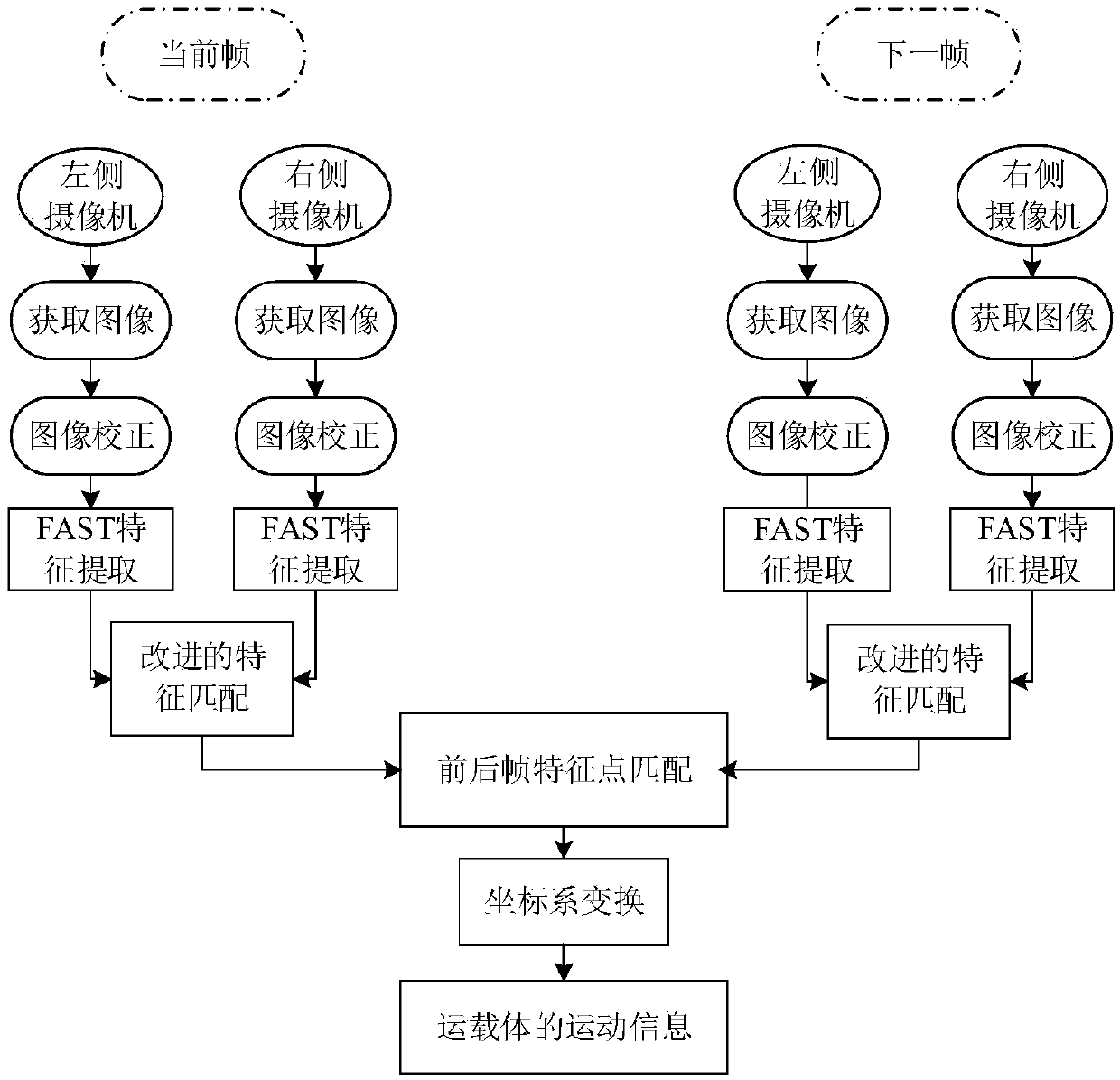
Strap-down inertial navigation system/visual odometer integrated navigation method
PendingCN107796391AHigh precisionImprove positioning accuracy and robustnessNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNonlinear filterCelestial navigation
The invention provides a strap-down inertial navigation system / visual odometer integrated navigation method which comprises the following steps: mounting a binocular visual odometer and a fiber-opticgyroscope inertial navigation system on a transporter and collecting data of all sensors; extracting features in an image sequence with an FAST method, completing feature matching with a feature matching method based on random sample consensus and calculating movement information of the transporter; establishing a nonlinear state equation and a measurement equation of a strap-down inertial navigation system / visual odometer integrated navigation system; and completing time update and measurement update of the strap-down inertial navigation system / visual odometer integrated navigation system with a volume Kalman filter of a nonlinear filter, and estimating the state of the system, so as to realize the navigation and location of the strap-down inertial navigation system / visual odometer integrated navigation system. According to the strap-down inertial navigation system / visual odometer integrated navigation method, a feature matching algorithm is optimized, and a nonlinear volume Kalman filter algorithm is utilized, so that the location accuracy and the robustness of the integrated navigation system are improved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for dynamically measuring attitude of star sensor based on top accurate angle relevance
ActiveCN103674023ASuppression errorSuppress noiseNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPosition fixationFixed starsComputer science
The invention discloses a method for dynamically measuring attitude of a star sensor based on top accurate angle relevance and belongs to the field of navigation and positioning. Based on the prior art that dynamic compensation is performed on each measurement exposure frame of the star sensor and a vector matrix matched with a fixed star containing dynamic error and noise effect is obtained, transformation matrixes between every two adjacent measurement frames of the star sensor are accurately measured through an assembly of three tops fixedly linked with the star sensor, the vector matrixes matched with adjacent measurement frames of the star sensor are correlated via the transformation matrixes, and finally, a correlated measurement equation is established by using a series of correlated measurement frames, that is a series of measurement frames are processed as a single measurement frame, and an attitude matrix is solved by using the least square method. With the adoption of the method, dynamic error and noise effect can be effectively restrained, high-accuracy dynamic attitude and change information of a carrier in motion can be obtained.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Strap-down inertial navigation air initial alignment method for floating aircraft
ActiveCN103557871AReduce coarse alignment timeImprove universalityNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsLinear motionGlobal Positioning System
The invention discloses a strap-down inertial navigation air initial alignment method for a floating aircraft, belonging to the technical field of inertia. According to the method, air coarse alignment of a floating aircraft inertial navigation system is realized by using a global positioning system (GPS)-assisted initial concretion analysis type coarse alignment method, inertial navigation attitude information is roughly acquired, and position information and speed information are directly acquired by a GPS; on the basis of coarse alignment, the condition of a large-orientation out-of-alignment angle is considered, a Kalman filtering state equation comprising a coarse alignment out-of-alignment angle error and a Kalman filtering measurement equation for measuring by taking navigation solving and speed difference measured by the GPS as the quantity are established, and an out-of-alignment angle is estimated through Kalman filtering. The attitude of a carrier can be tracked in real time through the GPS-assisted initial concretion analysis type coarse alignment method, the interference of an angular motion and a linear motion is shielded, and coarse alignment time is shortened greatly. The method provided by the invention is applicable to the motion conditions of the horizontal motion and rotation of the carrier, is high in universality and is feasible; expensive equipment does not need to be added.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com