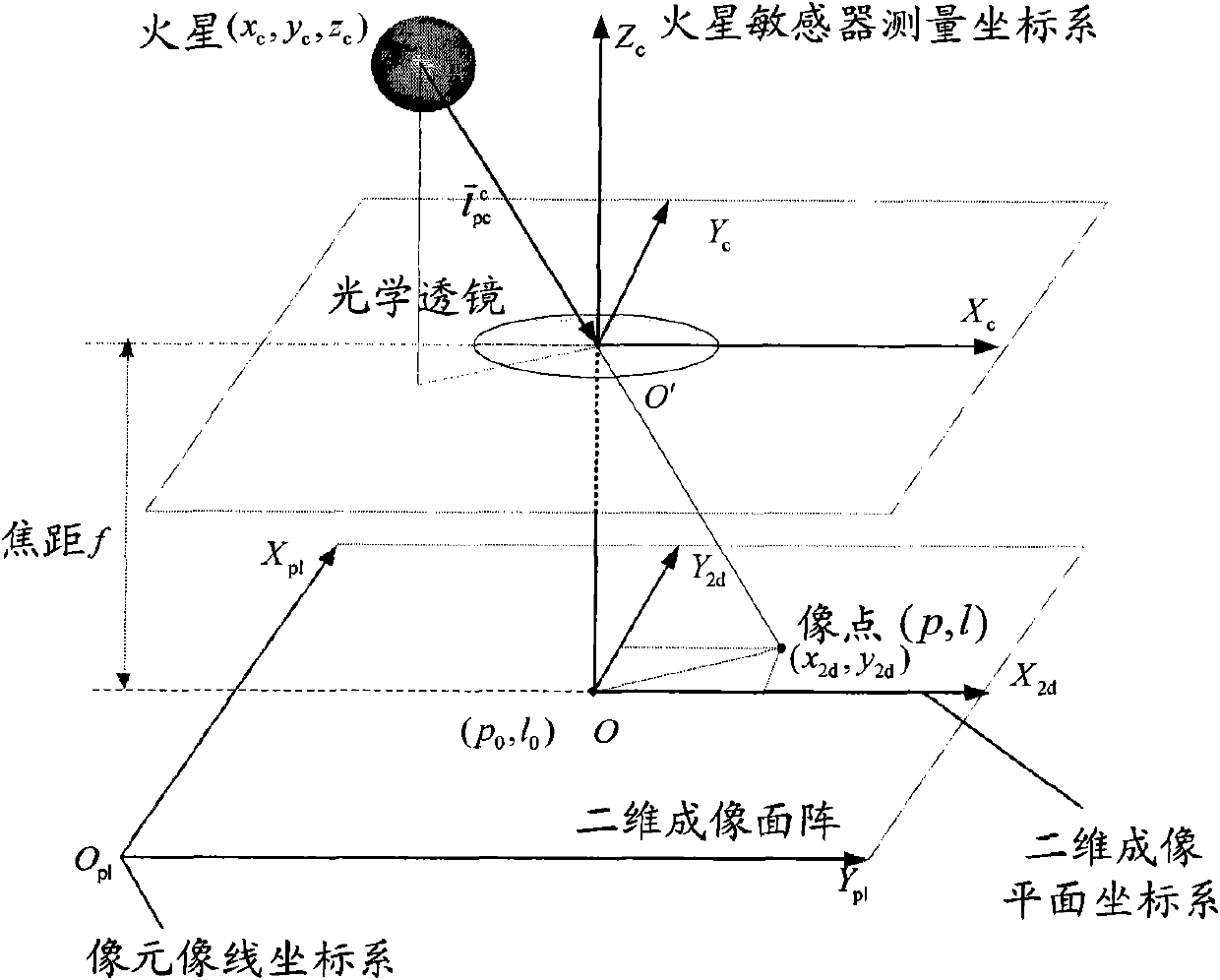
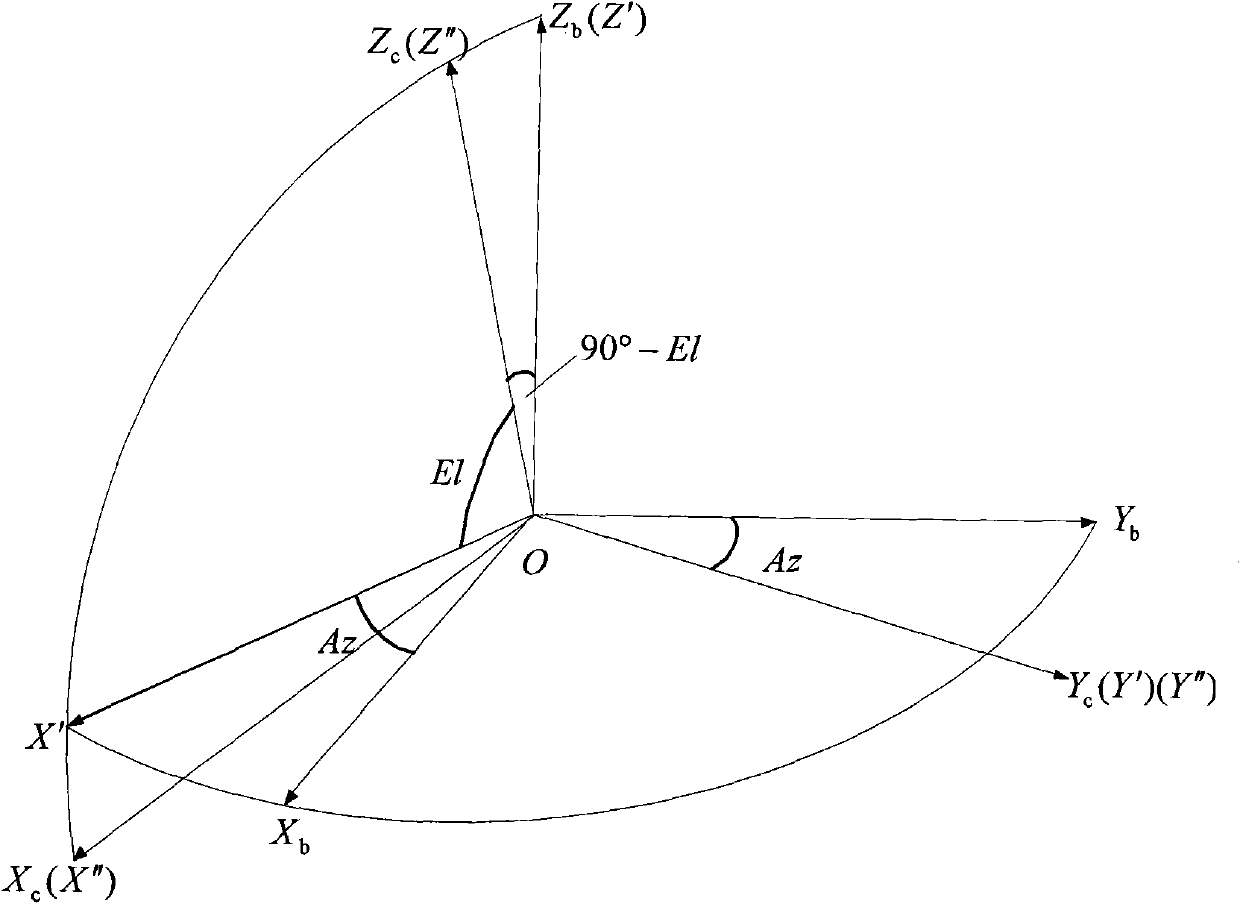
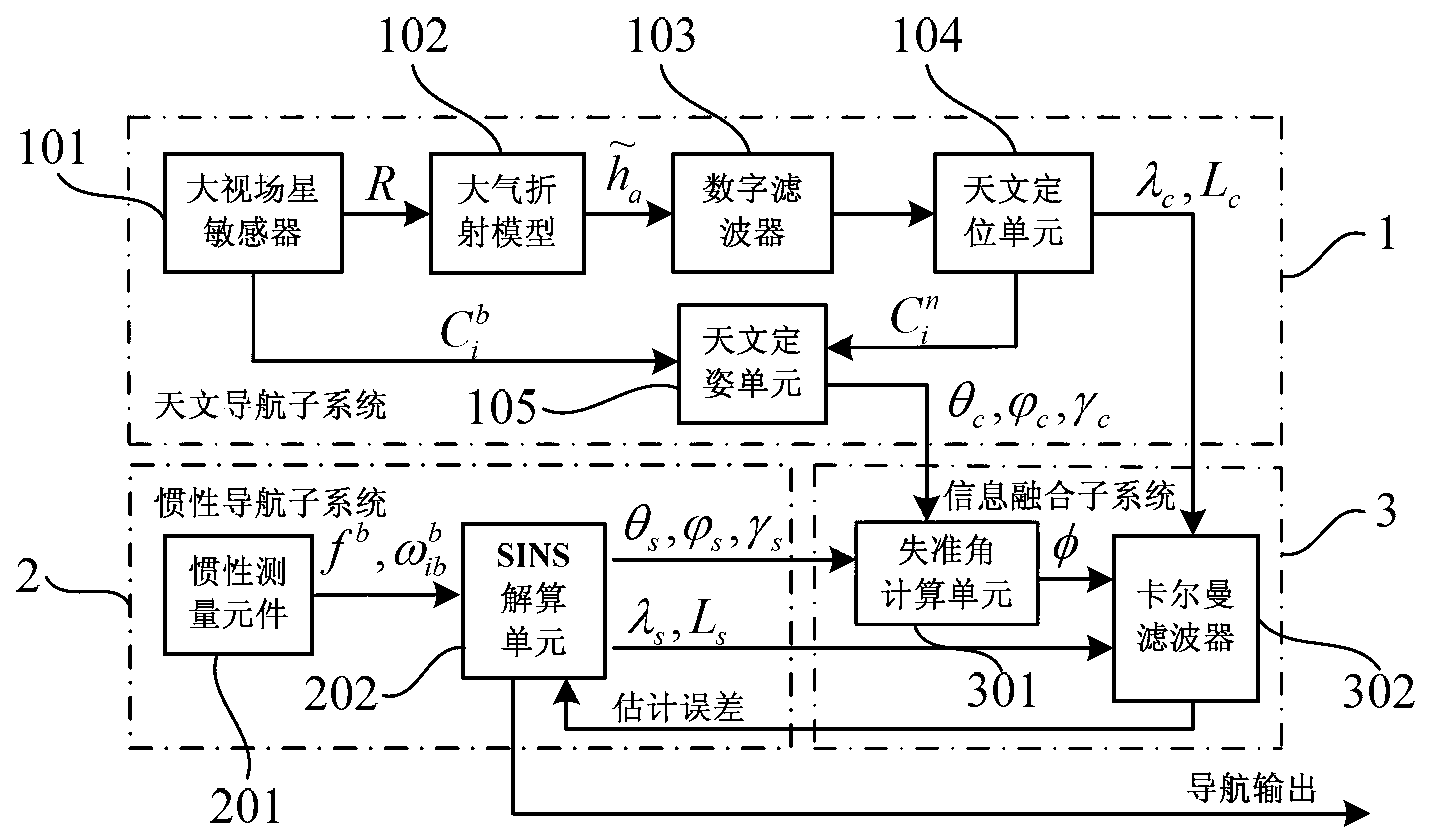
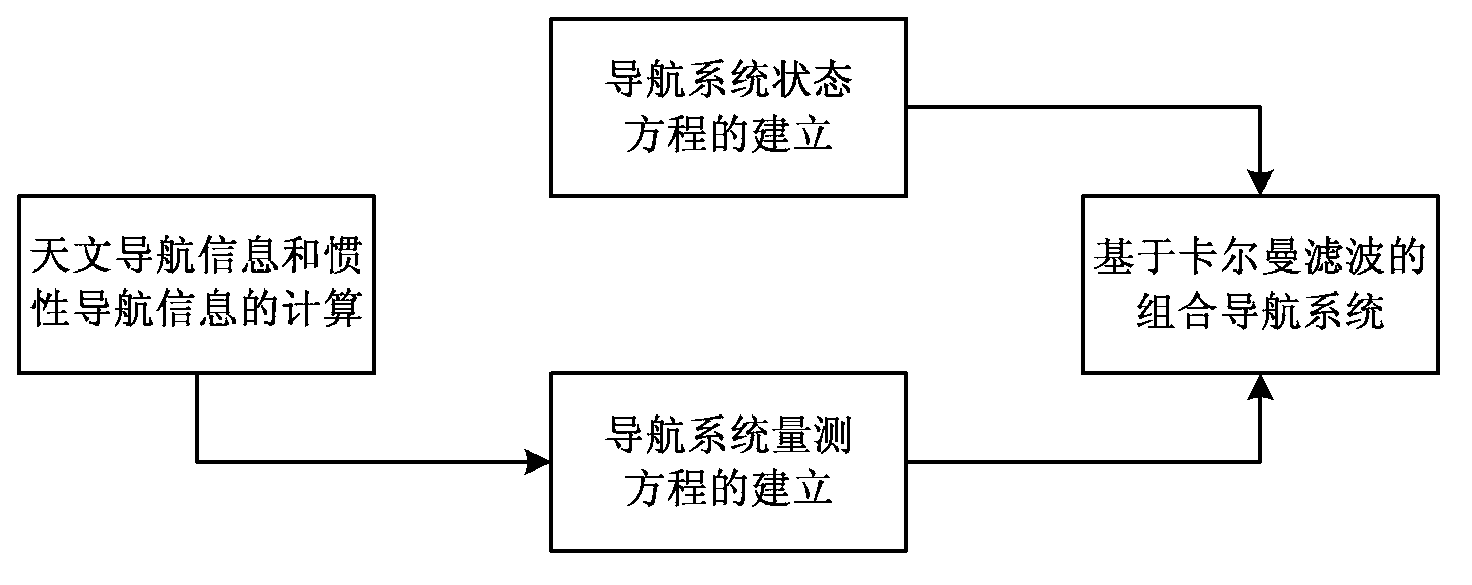
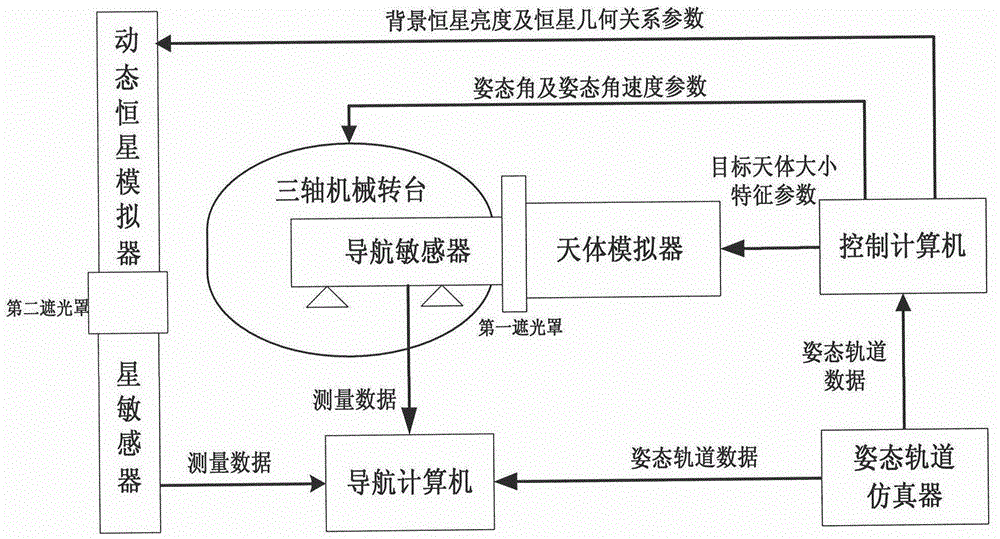
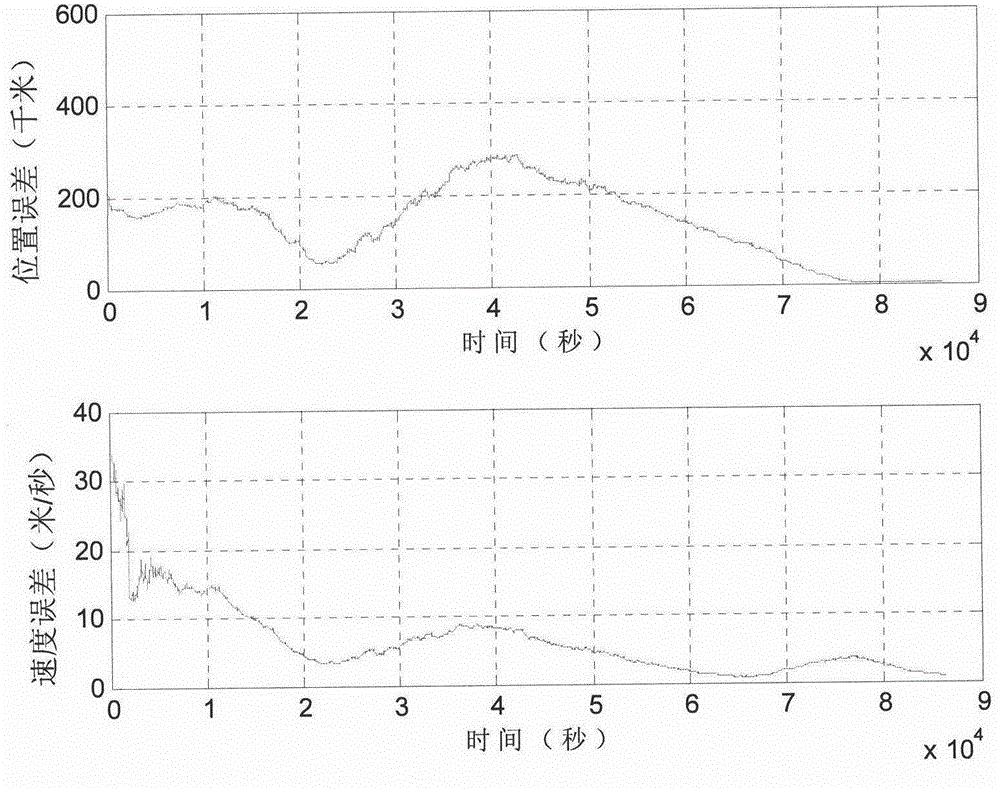
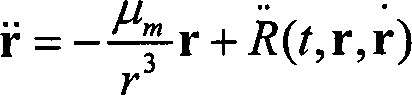Patents
Literature
362 results about "Fixed stars" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The fixed stars (Latin: stellae fixae) comprise the background of astronomical objects that appear to not move relative to each other in the night sky compared to the foreground of Solar System objects that do. Generally, the fixed stars are taken to include all stars other than the Sun. Nebulae and other deep-sky objects may also be counted among the fixed stars.
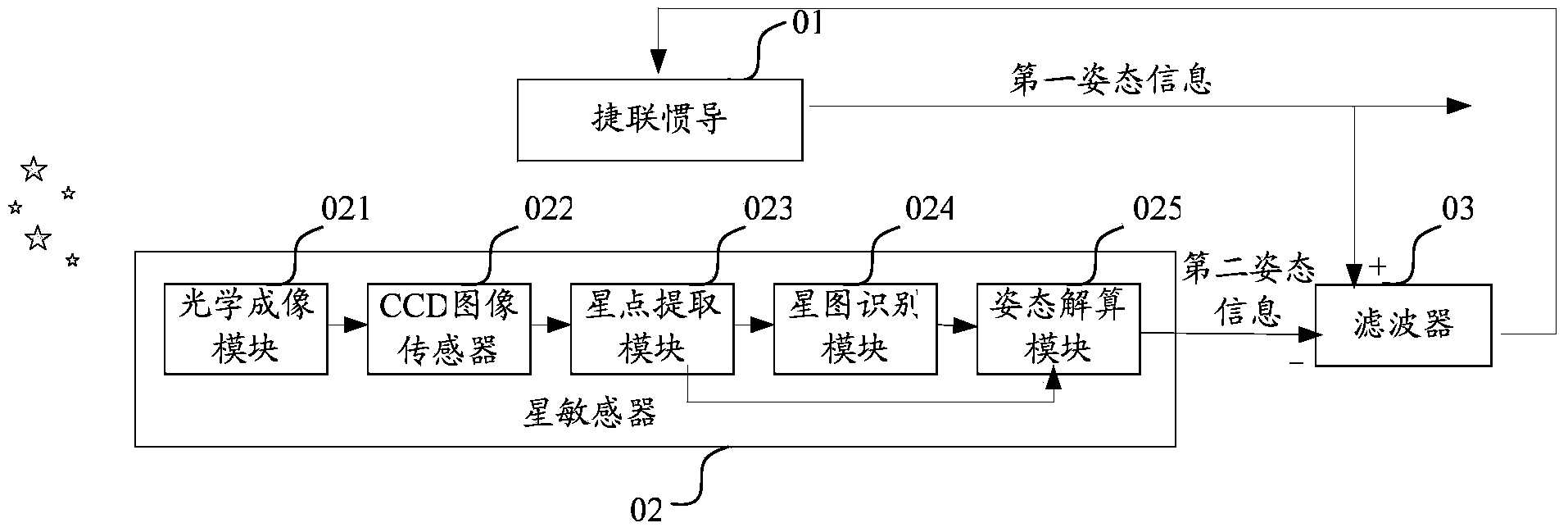
Correction method for on-track aberration of star sensor
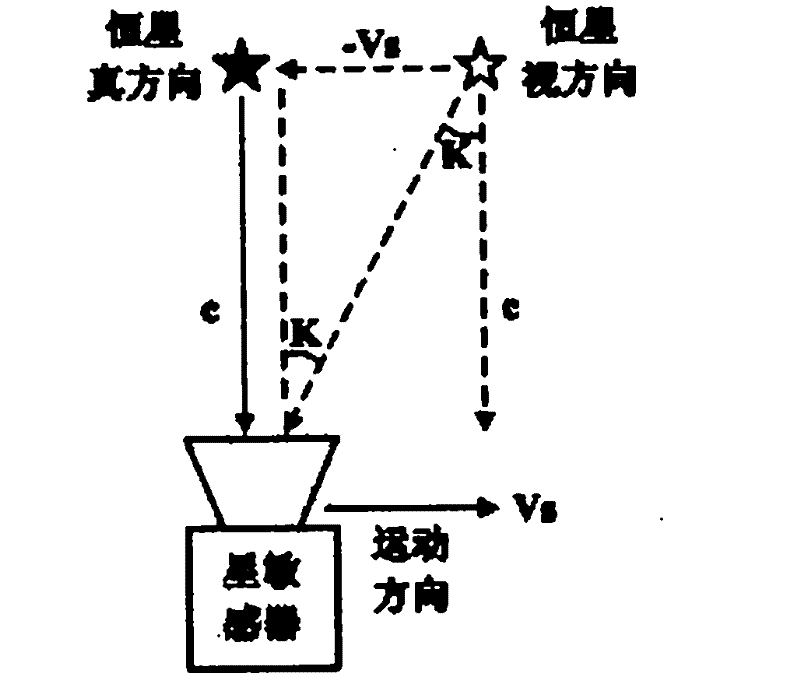
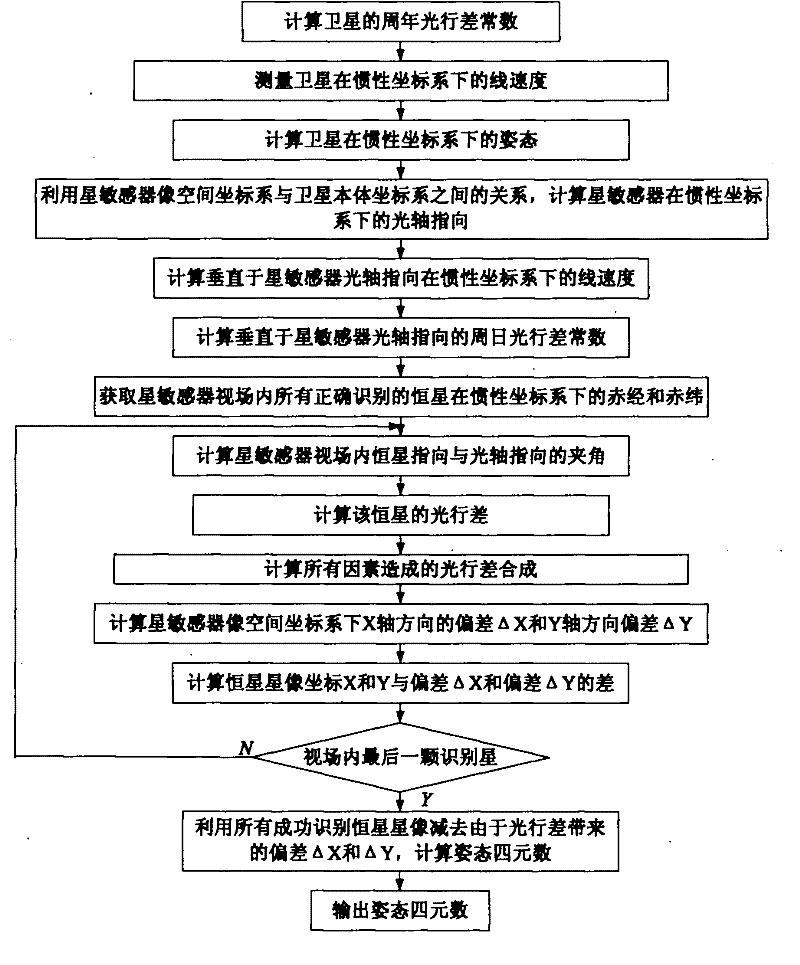
InactiveCN102252673AEliminate diurnal aberrationHigh precisionNavigation by astronomical meansFixed starsQuaternion
The invention provides a correction method for on-track aberration of a star sensor. The method comprises the following steps of: calculating the annual aberration constant of a satellite according to a formula; measuring the linear velocity of the satellite in an inertial coordinate system by using a satellite borne device; calculating the altitude of the satellite in the inertial coordinate system; calculating the optical axis direction of the star sensor in the inertial coordinate system; calculating the linear velocity vertical to the optical axis direction of the star sensor in the inertial coordinate system; calculating the diurnal aberration constant vertical to the optical axis direction of the star sensor; calculating the included angle between a fixed star direction and the optical axis direction in the view filed of the star sensor; calculating aberration synthesis caused by all factors; and calculating an altitude quaternion. In the invention, a mathematical model for eliminating the diurnal aberration and annual aberration of the star sensor and the peculiar motion aberration of the sun is induced; after the model is used to eliminate aberration, altitude information with high accuracy can be further provided for an aircraft, the angular speed of a non-gyro aircraft can be calculated by using altitude, and the accuracy of angular speed calculation can be further improved.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Independent celestial navigation method for Mars capturing section of deep space probe
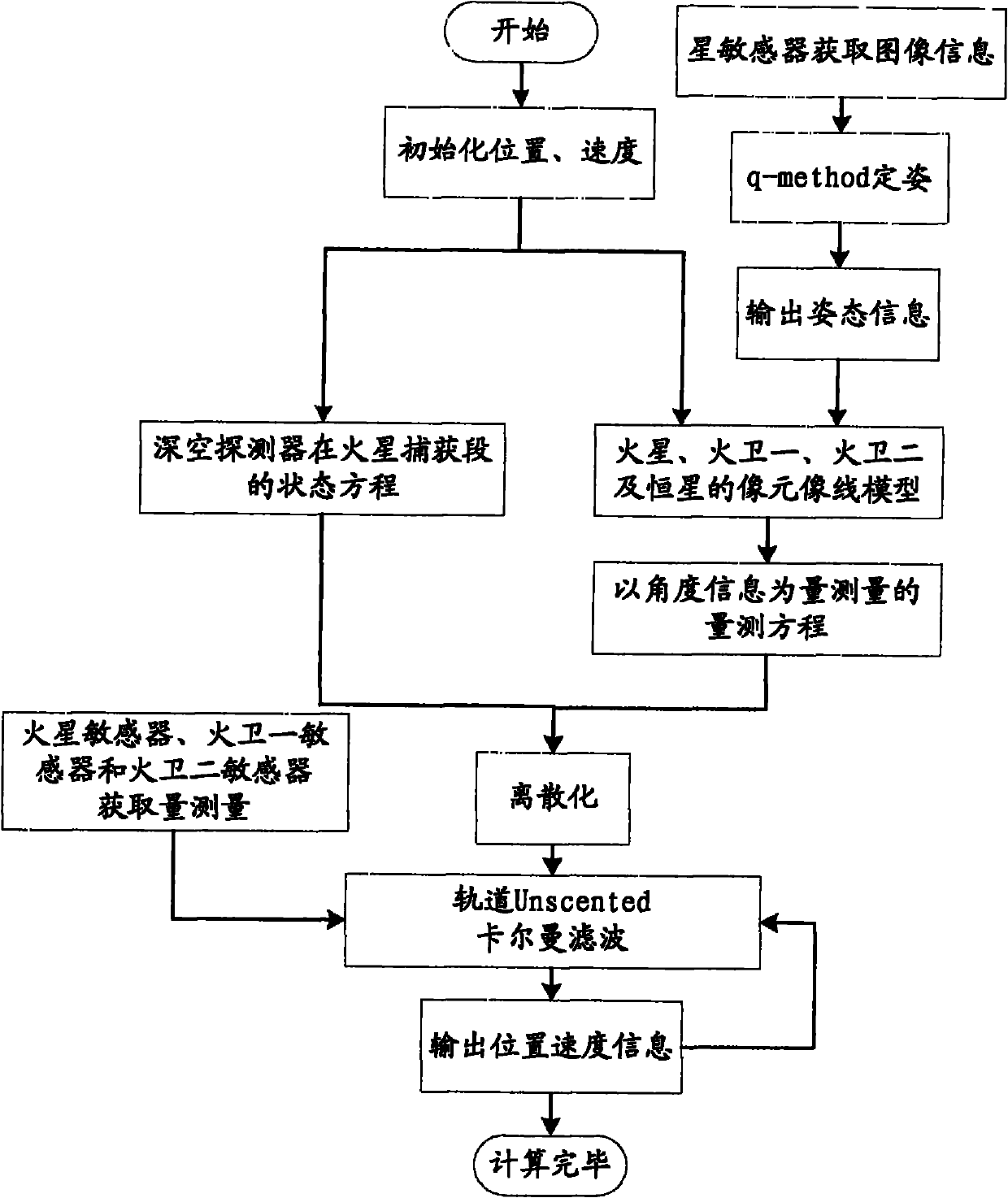
ActiveCN102168981AAvoid Accuracy ImpactImprove navigation accuracyInstruments for comonautical navigationFixed starsDynamic models
The invention relates to an independent celestial navigation method for a Mars capturing section of a deep space probe. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a state model of the deep space probe according to a circular restrictive four-body track dynamics model; acquiring picture element and picture line information of Mars, Martian satellites and a background fixed star, converting the acquired picture element and picture line information into angle information of the Mars, the Martian satellites and the background fixed star and establishing an angle measuring model of the Mars, a Martian satellite I and a Martian satellite II; and estimating the attitude information of the probe by adopting a q-method and estimating the position and speed of the deep space probe in combination with Unscented Kallman filtering. The method has high estimation accuracy, and is very suitable for independent navigation of Mars capturing. The method belongs to the technical field of aerospace navigation. By adopting the method, high-accuracy navigation parameters can be provided for Mars capturing of the deep space probe, and references can be provided for the design of an independent navigation system of the deep space probe.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
SINS/CNS integrated navigation system based on comprehensive optimal correction and navigation method thereof
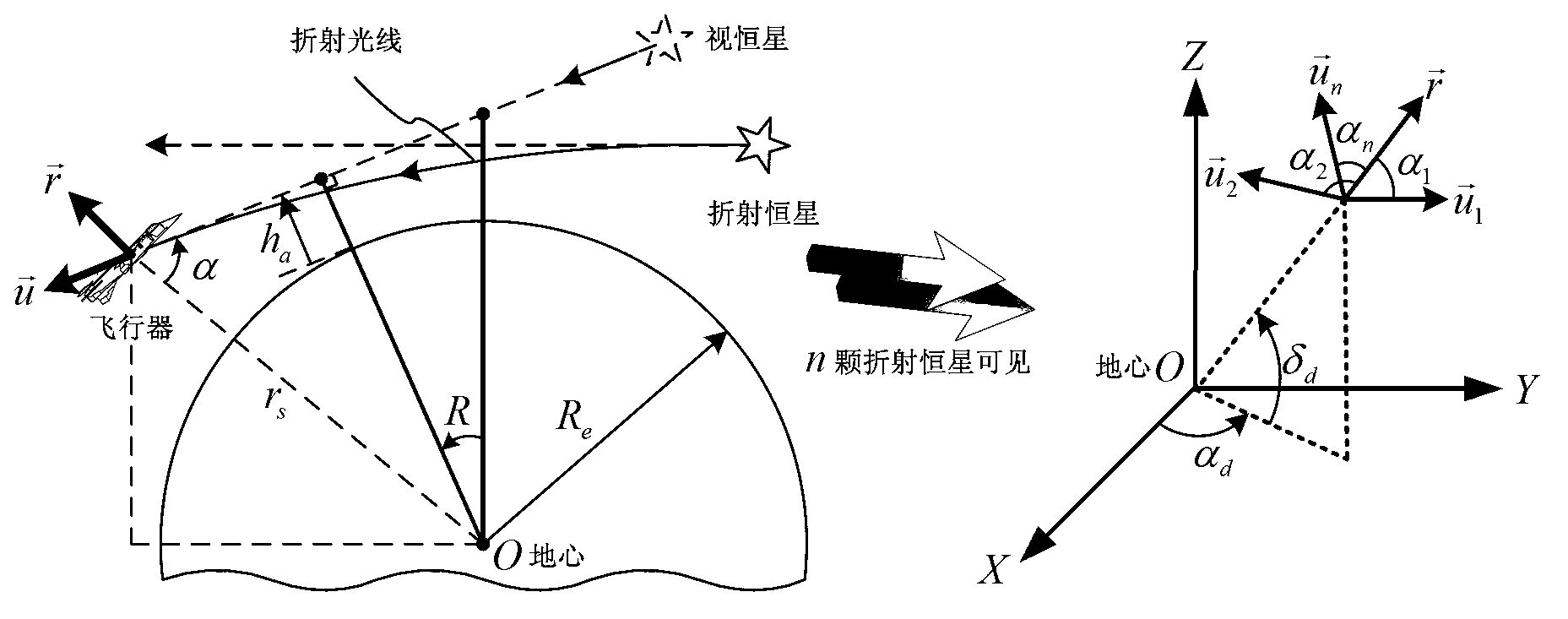
InactiveCN103076015ARealize analytical astronomical positioningHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation by astronomical meansFixed starsHorizon
The invention provides an SINS / CNS integrated navigation system based on comprehensive optimal correction and a navigation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of integrated navigation. The integrated navigation system comprises an astronavigation subsystem, an inertia navigation subsystem and an information fusion subsystem. The navigation method comprises the following steps: analyzing celestial fix based on starlight refraction, building up navigation system state equations, building up navigation system measuring equations and performing information fusion of an integrated navigation system based on Kalman filtering. According to the invention, by utilizing the basic principle of starlight refraction indirection sensitive horizon and a large viewing field star sensor, the characteristics of a plurality of fixed stars can be observed at the same time, and the starlight refraction indirection sensitive horizon method is applied to aircrafts that do not fulfill track kinetics, so that the problem of high-precision autonomous horizon of the celestial navigation system is solved. According to the invention, position and posture information of the celestial navigation system are fully utilized to perform comprehensive optimal correction on the SINS deviation, so that the integrated navigation accuracy is significantly improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for dynamically measuring attitude of star sensor based on top accurate angle relevance
ActiveCN103674023ASuppression errorSuppress noiseNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPosition fixationFixed starsComputer science
The invention discloses a method for dynamically measuring attitude of a star sensor based on top accurate angle relevance and belongs to the field of navigation and positioning. Based on the prior art that dynamic compensation is performed on each measurement exposure frame of the star sensor and a vector matrix matched with a fixed star containing dynamic error and noise effect is obtained, transformation matrixes between every two adjacent measurement frames of the star sensor are accurately measured through an assembly of three tops fixedly linked with the star sensor, the vector matrixes matched with adjacent measurement frames of the star sensor are correlated via the transformation matrixes, and finally, a correlated measurement equation is established by using a series of correlated measurement frames, that is a series of measurement frames are processed as a single measurement frame, and an attitude matrix is solved by using the least square method. With the adoption of the method, dynamic error and noise effect can be effectively restrained, high-accuracy dynamic attitude and change information of a carrier in motion can be obtained.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Satellite Gravity Retrieval Method Based on 3D Interpolation Principle of Double Star Space
InactiveCN102262248ALower performance requirementsSmall amount of calculationGravitational wave measurementNatural satelliteFixed stars
The invention relates to a method for precisely measuring an earth gravitational field, in particular to a satellite gravity inversion method based on a double-satellite spatial three-dimensional interpolation principle. An earth disturbing potential (obtained by computing an inter-satellite speed of a GRACE satellite K wave band measuring instrument, a satellite orbit position and a satellite orbit speed of a global positioning system (GPS) receiver, a satellite nonconservative force of an accelerometer and a satellite three-dimensional attitude data of a fixed star sensitive device) which is positioned on a gravity double-satellite orbit with a relatively irregular spatial position is interpolated three-dimensionally onto a reference spherical surface with a relatively regular spatial position and uniform grid division, so that the earth gravitational field is precisely and quickly inversed. By the method, satellite gravity inversion precision is high, physical meaning in the resolving process is clear, the computing speed is high, requirements on performance of a computer are low, and the method is sensitive to high-frequency signals in the gravitational field, so that the double-satellite spatial three-dimensional interpolation method is an effective method for resolving the earth gravitational field with high precision and high spatial resolution.
Owner:INST OF GEODESY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
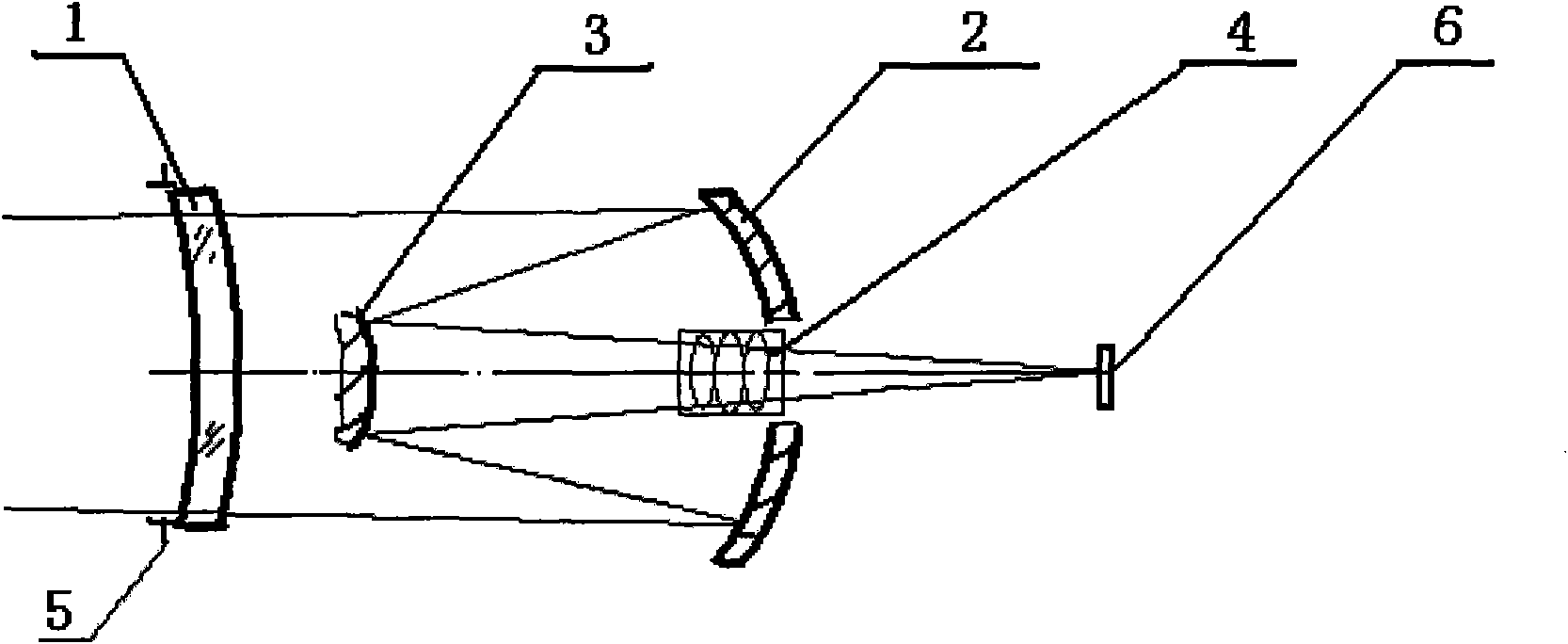
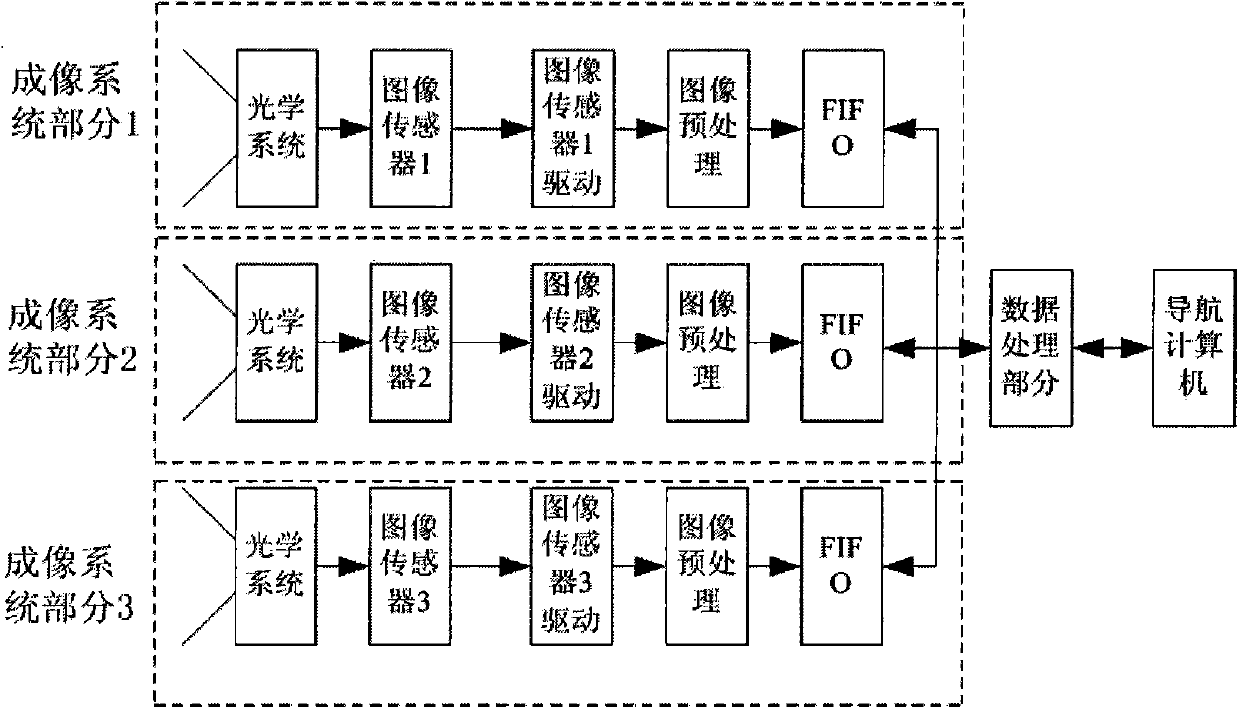
Imaging structure of fixed star sensor
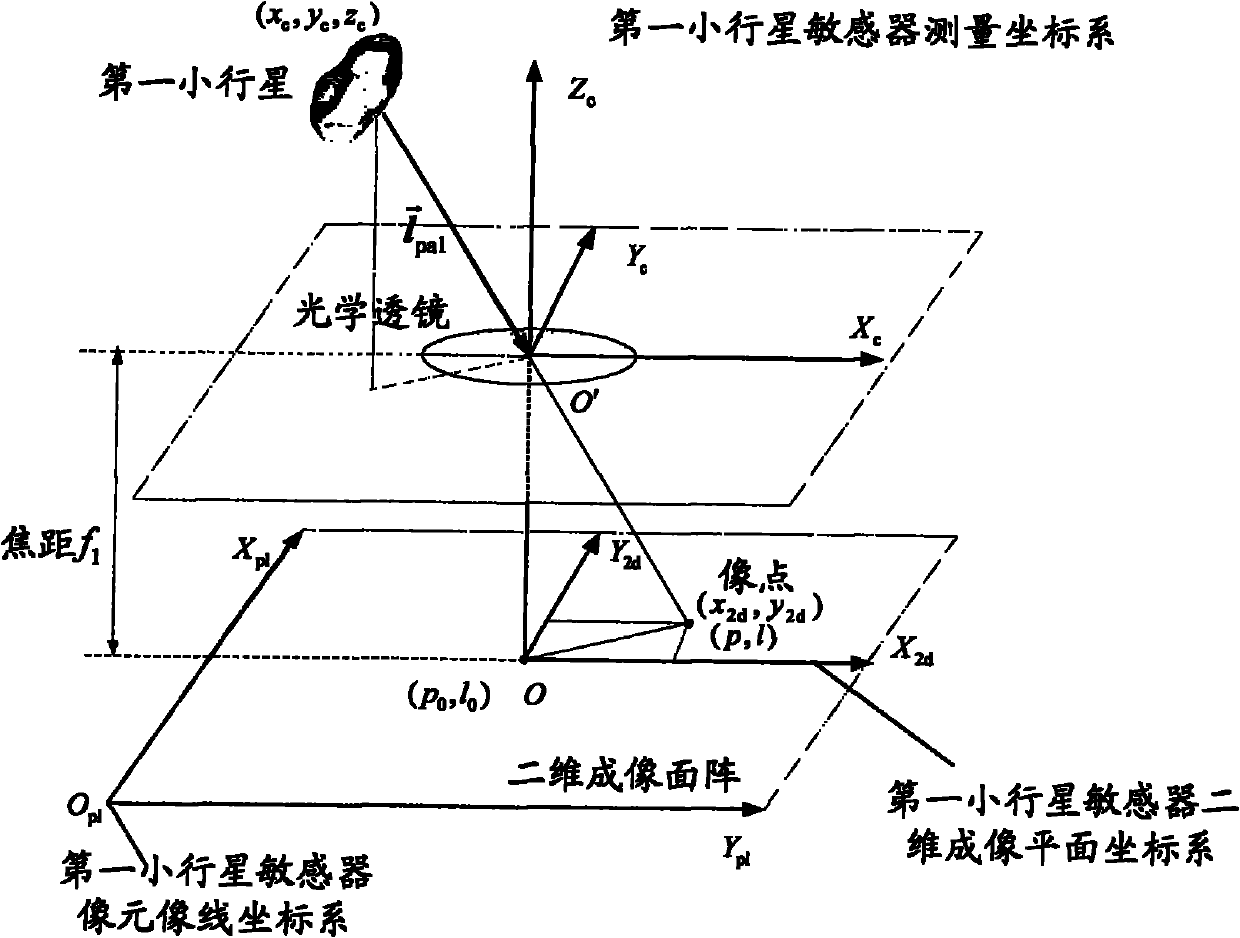
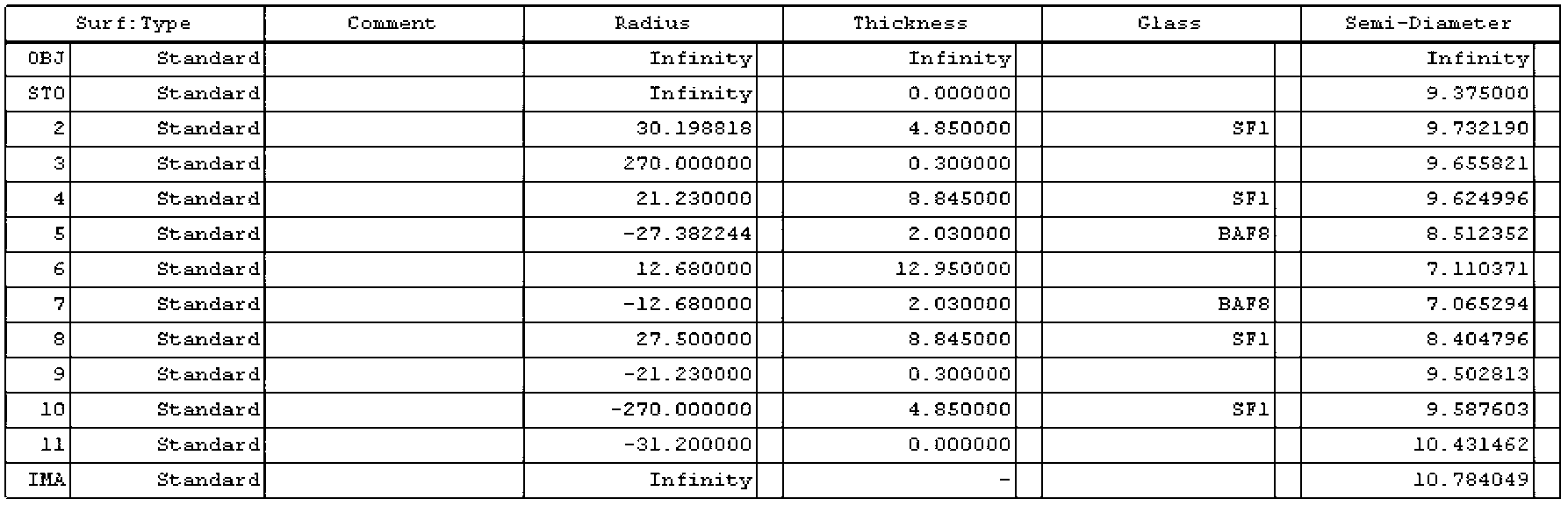
ActiveCN102116926APlay the role of correcting aberrationsReduce processing difficultyNavigation by astronomical meansOptical elementsFixed starsSpace environment
The present invention belongs to the technical field of deep space navigation sensor, specifically discloses an imaging structure of a fixed star sensor, wherein a secondary aspheric surface is applied to an optical surface of an aberration correction lens, which not only can correct the aberration to make system imaging reach a level of near diffraction limit, but can also reduce difficulties ofsystem processing and resetting, and save cost; simultaneously the aberration correction lens can play a part in protecting a window, so as to prevent the system from the damage of space environment,such as irradiation, temperature difference, etc.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
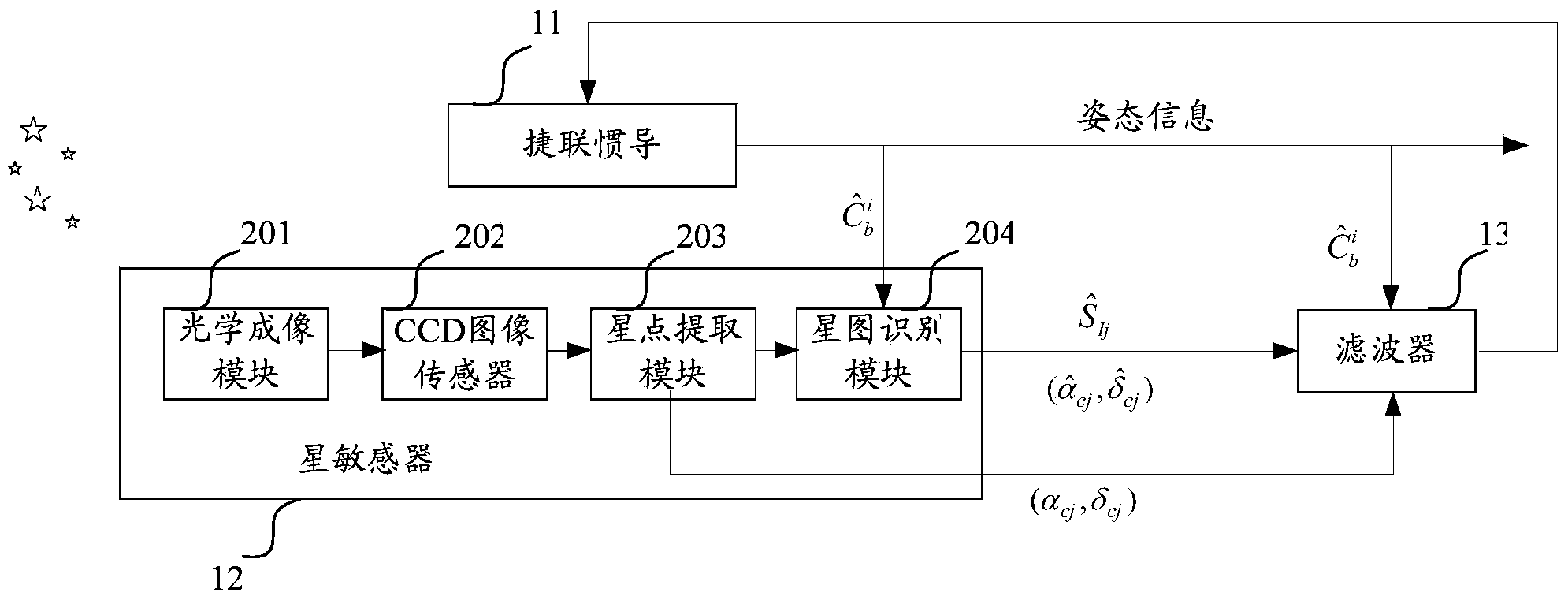
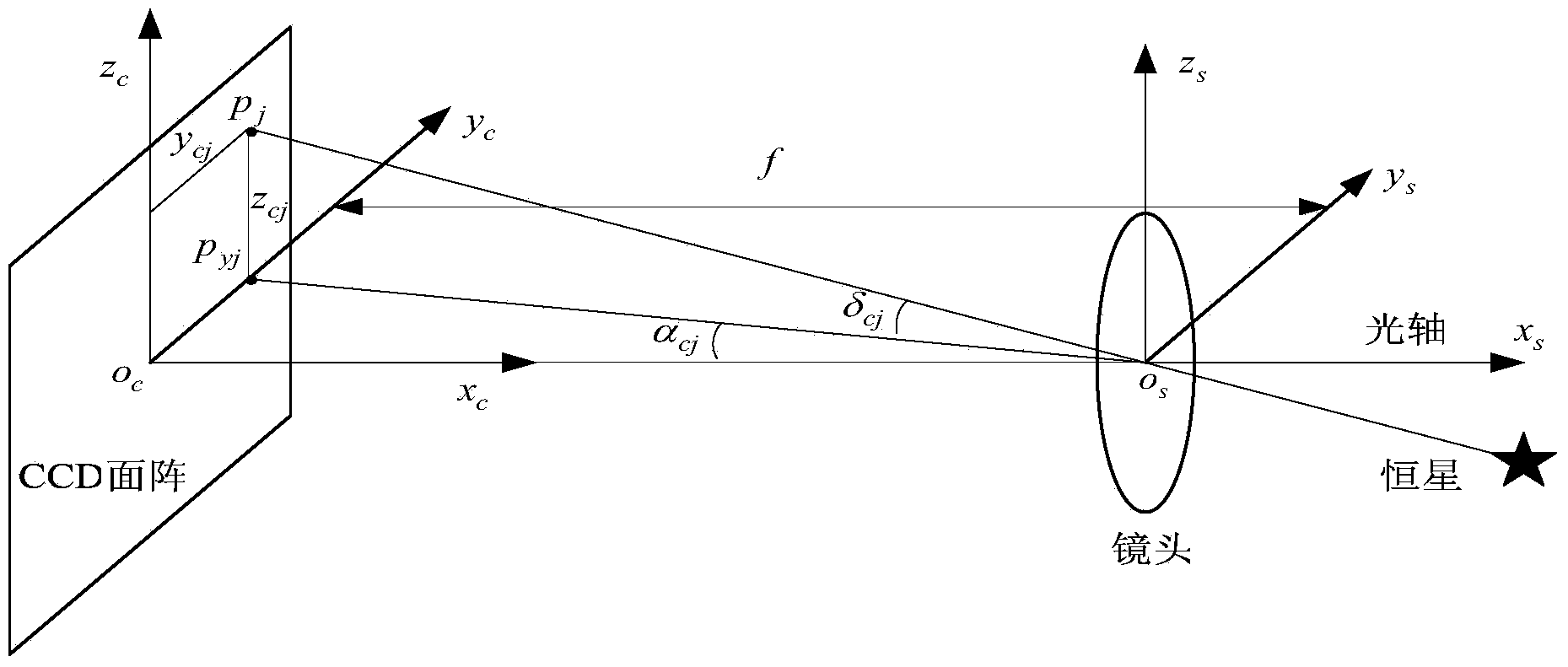
Integrated navigation system and method based on SINS (Strapdown Inertial Navigation System) and star sensor
ActiveCN103674021AHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation by astronomical meansFixed starsLongitude
The invention discloses an integrated navigation system and method based on an SINS and a star sensor. The integrated navigation system comprises the SINS, the star sensor and a filter, wherein the SINS is used for detecting the attitude information of a carrier, and amending the attitude information according to the optimum estimate of a state error term; the star sensor is used for acquiring the longitude and latitude, in a star sensor coordinate system, of an imaged fixed star, the direction unit vector, in a geocentric inertial coordinate system, of a reference fixed star matched with the imaged fixed star, and the longitude and latitude, in the star sensor coordinate system, of the reference fixed star; when the number of fixed stars observed by the star sensor is one or two, the filter is used for acquiring the optimum estimate of the state error term of the SINS according to an observation equation, wherein the observation equation is established by taking a longitude and latitude difference as a state quantity and by taking the pre-established error equation of the SINS as a state equation, and the longitude and latitude difference is composed of the longitude difference and latitude difference, in the star sensor coordinate system, between the reference fixed star and the imaged fixed star. According to the invention, the application range of the integrated navigation system can be widened.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
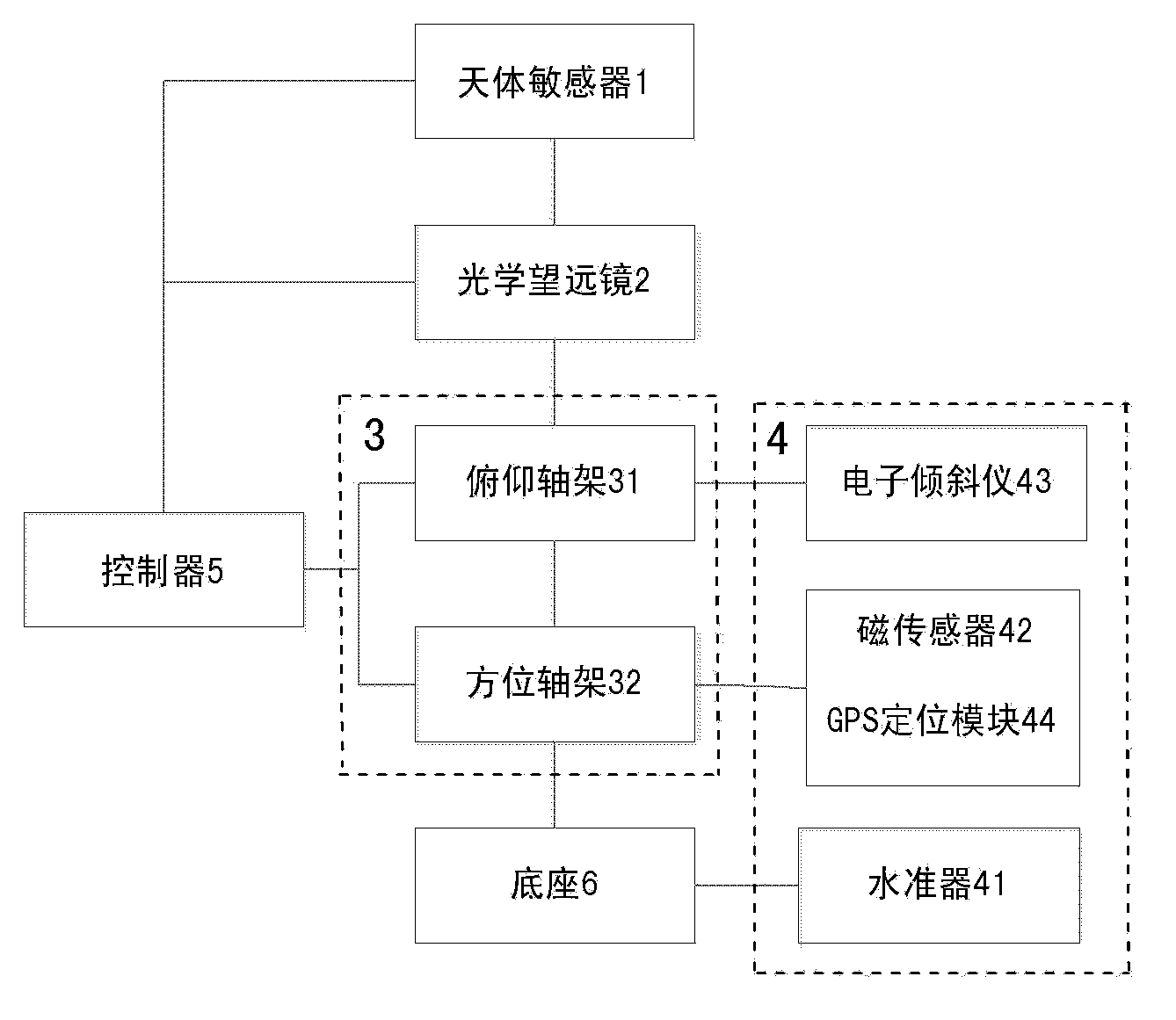
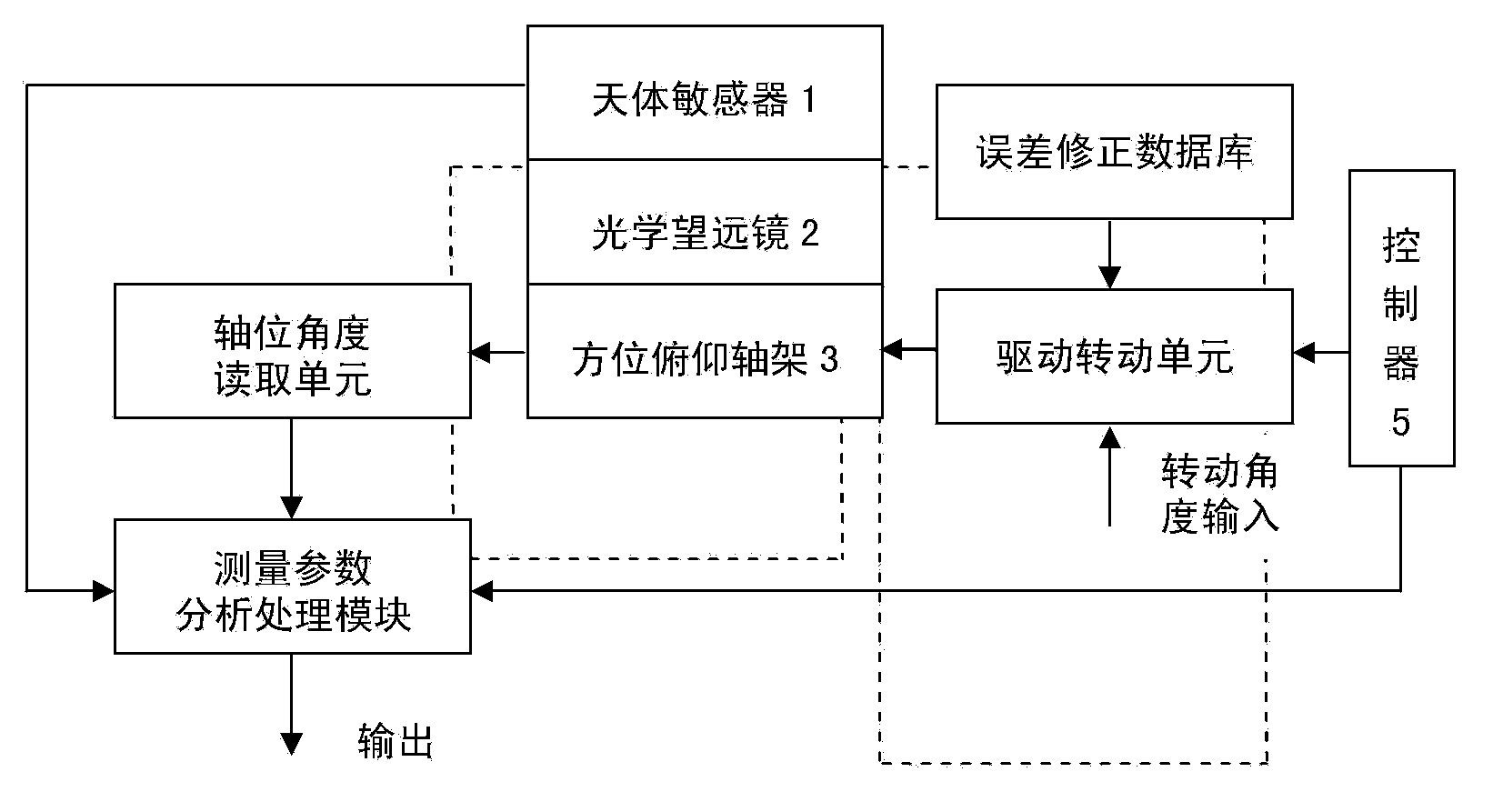
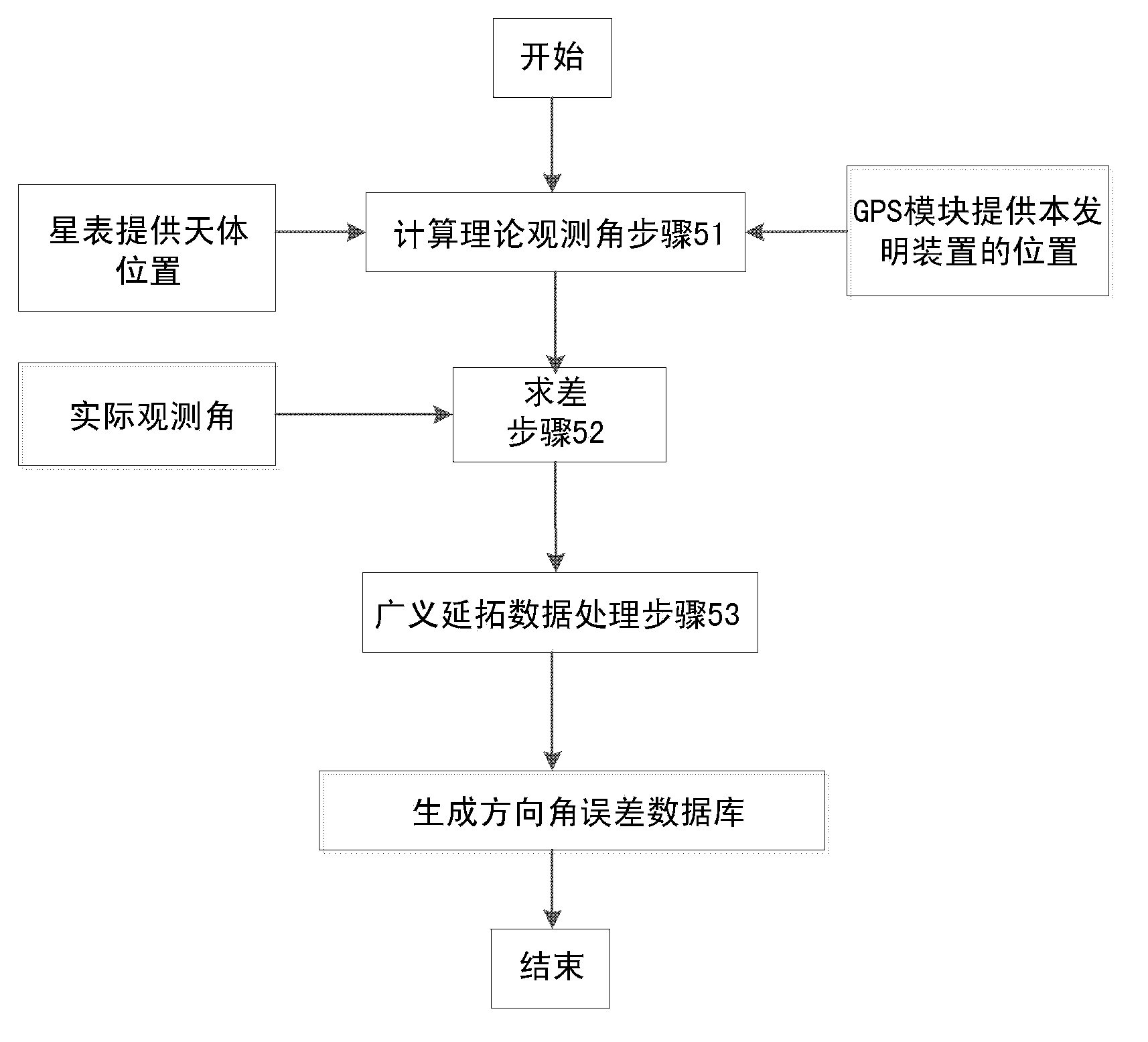
Three-dimensional direction angle measuring device and method using celestial body position as alignment calibration reference
InactiveCN103837126ARealize direction findingAchieving Pointing CorrectionAngle measurementCompassesFixed starsMeasurement device
The invention discloses a three-dimensional direction angle measuring device and method using celestial body position as alignment calibration reference. The device is composed of a celestial body sensor, an optical telescope, an azimuth pitch axis frame, a plurality of sensors, a controller and a base. The optical telescope is arranged on the pitch axis of the azimuth pitch axis frame; the celestial body sensor is installed above the lens cone of the optical telescope or on the spindle nose of the pitch axis; and the principal optic axis of the celestial body sensor is parallel to that of the lens cone of the optical telescope. Because the celestial body sensor can sense the positions of fixed stars and planets in the sky, the positions of fixed stars and planets can be used as the calibration reference for spatial measurement to provide three-dimensional high precision angle of direction, so as to further improve the accuracy of the space angle of direction of three-dimensional directional instrument. At the same time, high precision directing of horizontal reference surface, tilt datum plane, due east, due south, due west, due north and vertical direction, and the accuracy of the angle of direction reaches the level of arc second even sub arc second.
Owner:施浒立
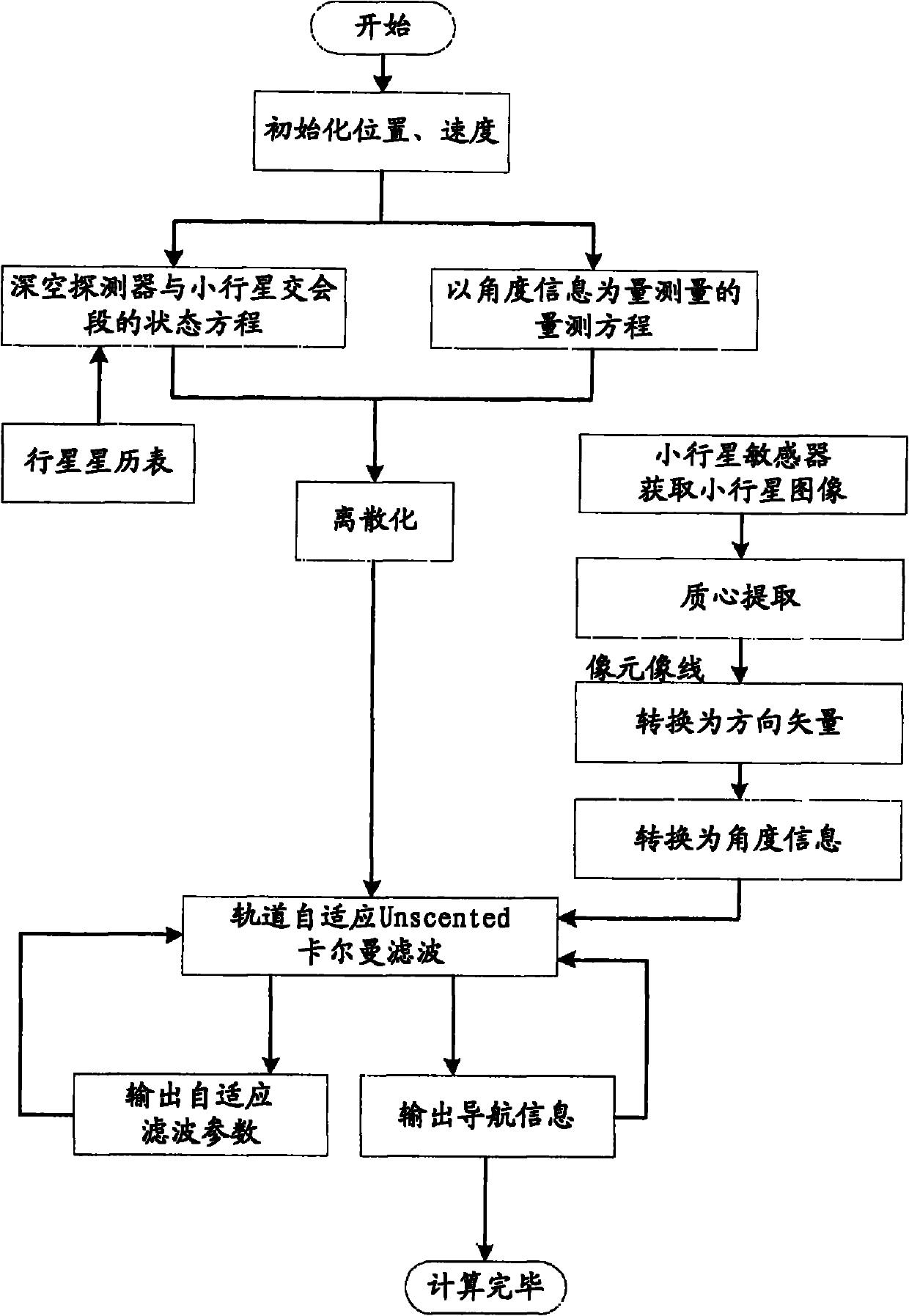
Independent celestial navigation method of deep space probe based on minor planet intersection
ActiveCN102168980AHigh precisionRealize high-precision navigationInstruments for comonautical navigationFixed starsAutonomous Navigation System
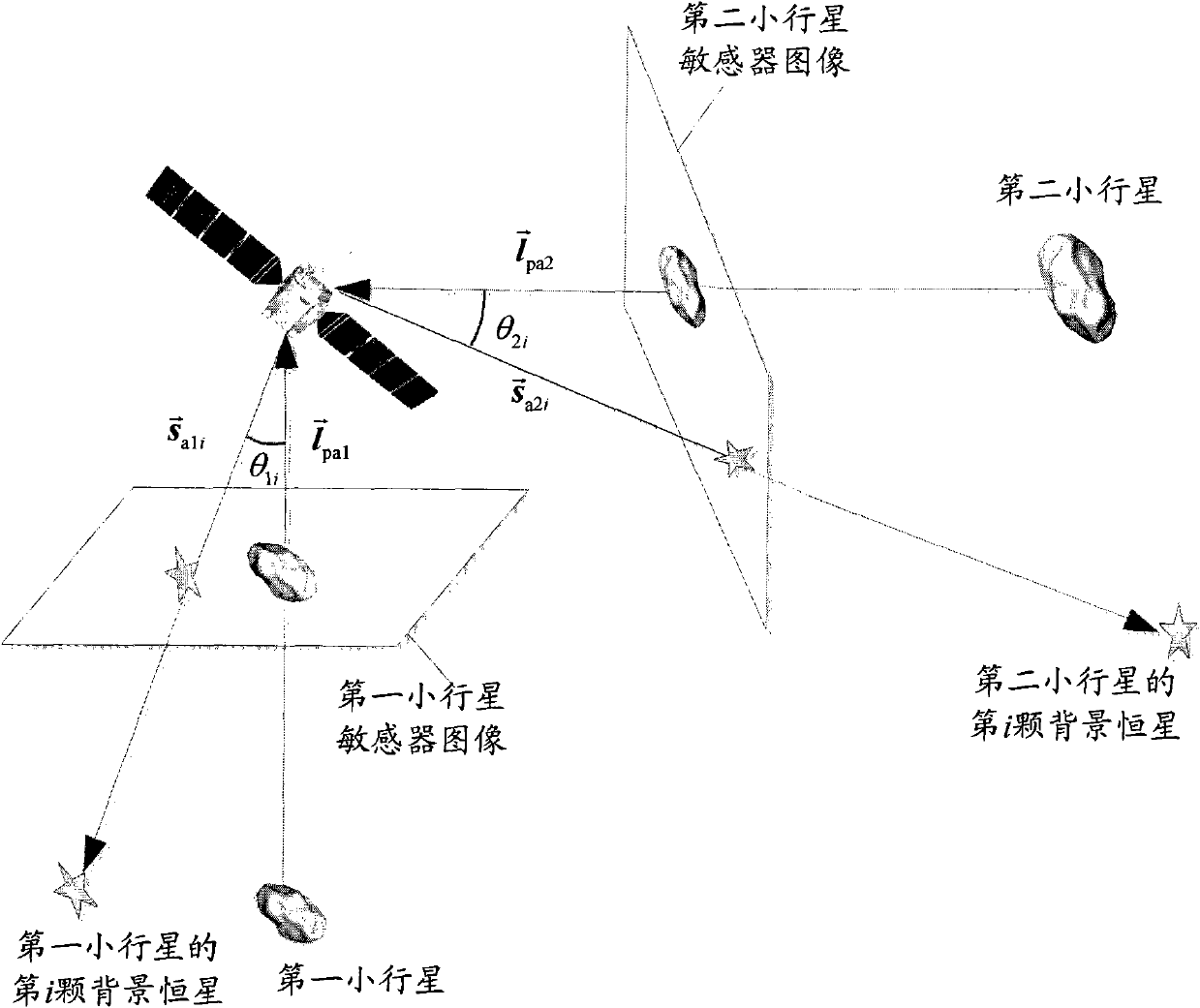
The invention relates to an independent celestial navigation method of a deep space probe based on minor planet intersection. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a state model of the deep space probe according to a circular restrictive track dynamics model; acquiring picture element and picture line information of minor planets and a background fixed star by using a sensor, converting the acquired picture element and picture line information into angle information of the minor planets and the background fixed star and establishing an angle measuring model of the minor planets; and estimating the position and speed of the deep space probe in combination with self-adaptive Unscented Kallman filtering. The method has high estimation accuracy, and is very suitable for independent navigation during minor planet intersection. The method belongs to the technical field of aerospace navigation. By adopting the method, high-accuracy navigation parameters can be provided for the deep space probe, and references can be provided for the design of an independent navigation system of the deep space probe.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Rapid autonomous all-sky map fixed star identification method
ActiveCN103868510ASave storage spaceThe number of angular distances is reducedNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by astronomical meansFixed starsVisual field loss
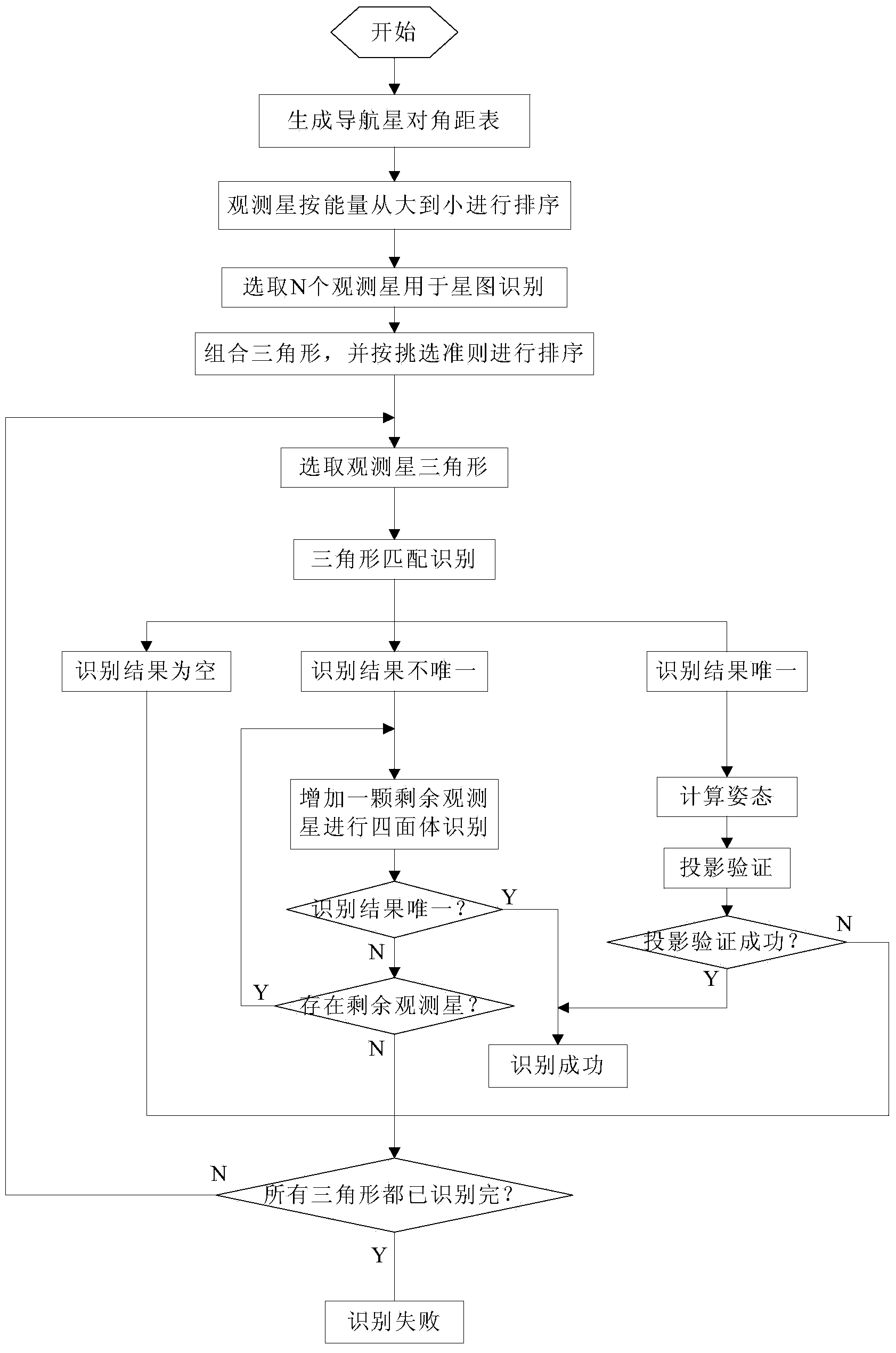
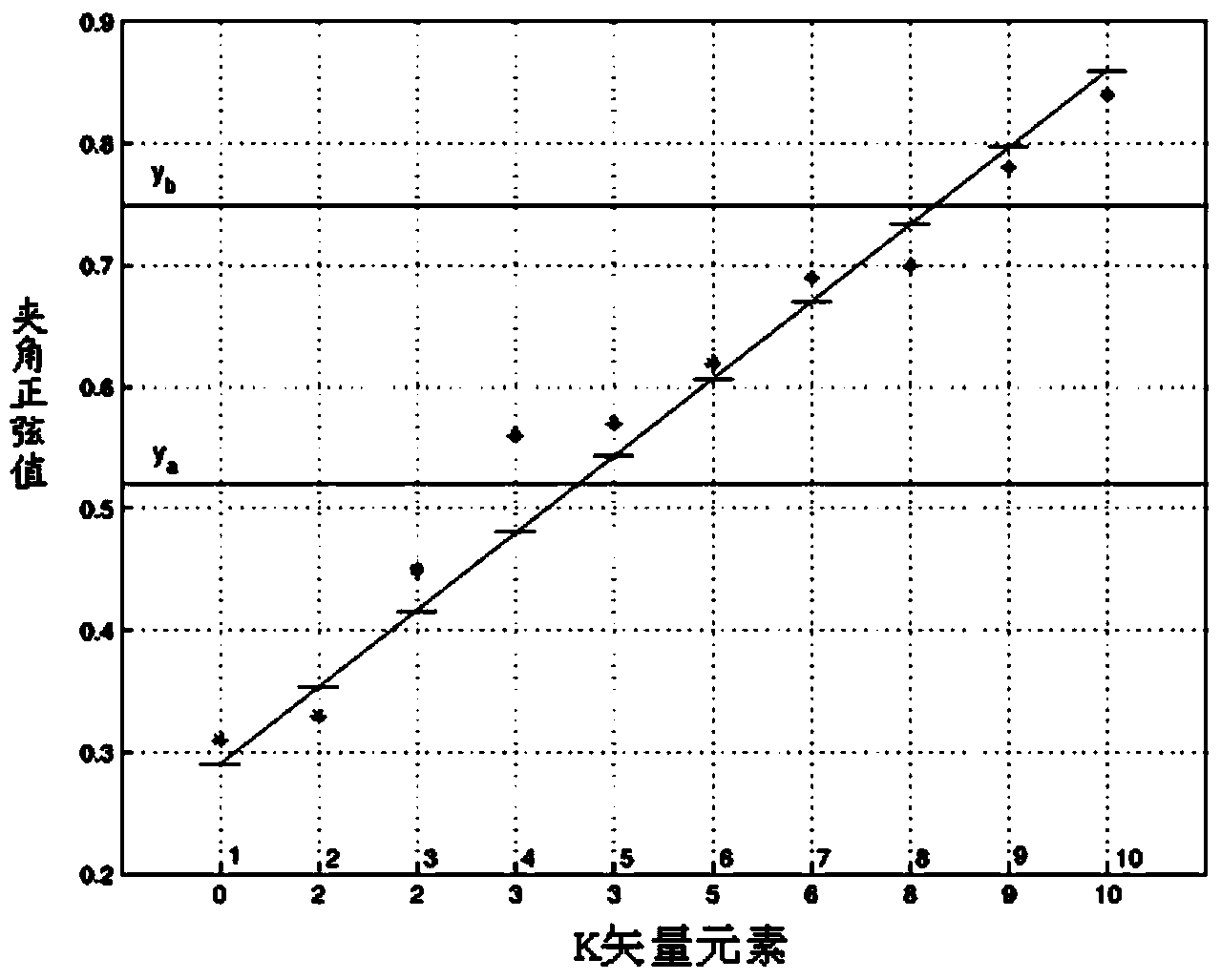
The invention discloses a rapid autonomous all-sky map fixed star identification method which comprises the following steps: (1), generating a navigation star diagonal pitch table according to a visual field of a star sensor; (2), sequencing all observation stars according to energy; (3), constructing an observation star triangle by using a novel triangle selection method; (4), performing triangle matching identification on the observation star triangle based on an improved K vector method; (5), if a triangle matching identification result is unique, calculating a current gesture and carrying out projection verification, if the result is not unique, performing tetrahedron identification, if a tetrahedron identification result is unique, calculating a gesture and carrying out projection verification, and if the result is not unique, re-selecting observation stars to form a tetrahedron for performing matching identification; and (6), performing projection verification on the identified unique result according to the calculated gesture, and if the projection verification is passed, indicating that the identification is successful. The rapid autonomous all-sky map fixed star identification method has the advantages of saving storage space, reducing star map identification time and increasing identification accuracy, and is great in practical value.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Layout design method of multi-star sensor configuration layout
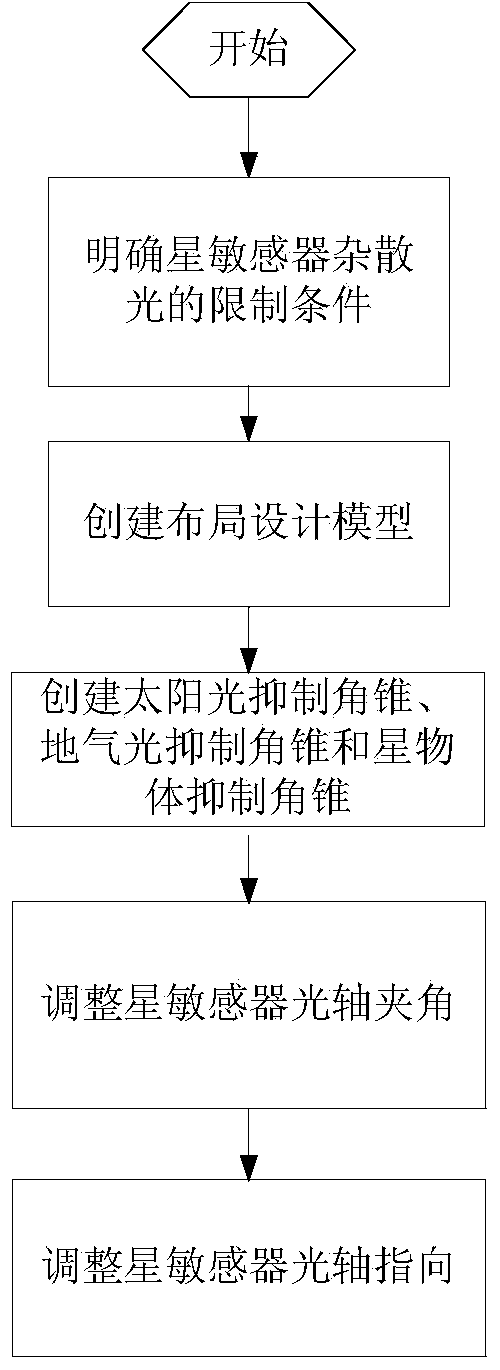
ActiveCN104296751APrecise Control of Angular RelationshipsPrecise control relationshipNavigational calculation instrumentsFixed starsOptical axis
The invention discloses a layout design method of a multi-star sensor configuration layout. The layout design method comprises the steps of (1) defining minimum included angles between an optical axis of a star sensor and sunlight, ground gas light and a star object; (2) creating a layout design model; (3) creating a sunlight inhibition pyramid, a ground gas light inhibition pyramid and a star object inhibition pyramid of each star sensor in a satellite stereo model; (4) adjusting the layout of each star sensor in real time on the satellite model; (5) adjusting the included angle between the optical axes of two star sensors from 20 theta s to 180 degrees, so that the included angle is greater than twice of a sunlight inhibition angle; and (6) rotating the star sensors, so that the relative movement of fixed stars is uniformly distributed on two coordinate axes which are perpendicular to the optical axis of each star sensor. By using the layout design method, the best attitude measuring precision of multi-star sensor attitude combined determination can be obtained, and the layout design efficiency of multiple star sensors is improved.
Owner:AEROSPACE DONGFANGHONG SATELLITE
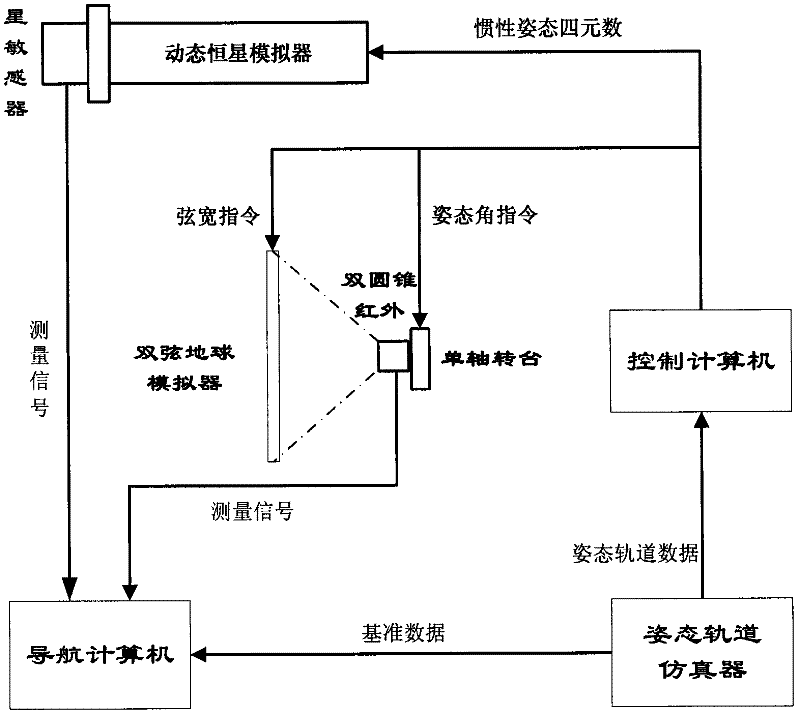
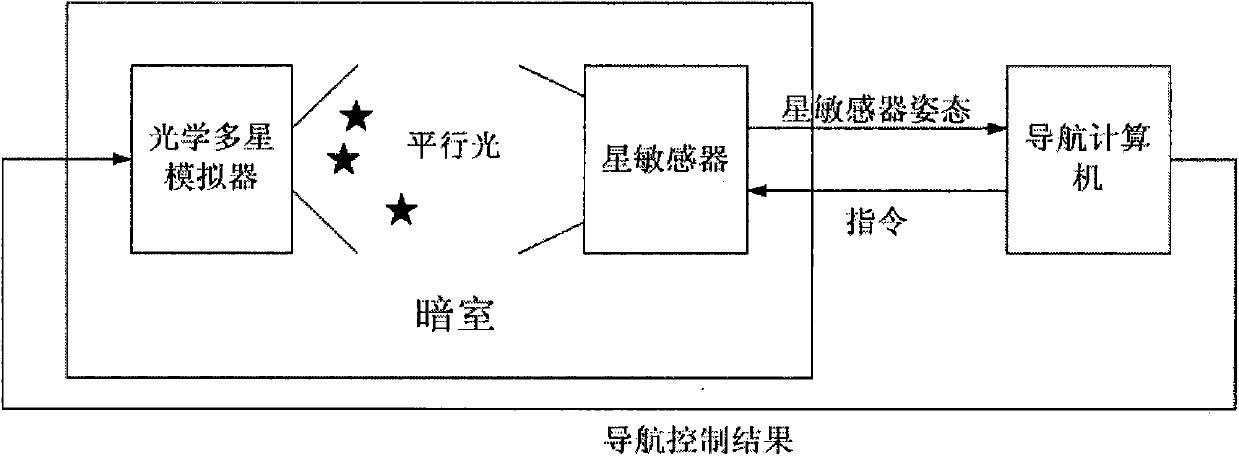
Autonomous navigation semi-physical simulation test system based on biconical infrared and star sensors
ActiveCN102538819AVerify performanceNavigation Accuracy VerificationMeasurement devicesFixed starsAutonomous Navigation System
The invention relates to an autonomous navigation semi-physical simulation test system based on biconical infrared and star sensors. The biconical infrared earth sensor is used for observing a dual-string-width earth simulator, the star sensor is used for observing a dynamic fixed star simulator, and a measurement signal is sent to a navigation computer; an attitude orbit simulator is used for calculating a satellite attitude orbit and sending the satellite reference orbit attitude data to a control computer; the control computer, according to the reference attitude orbit data, generates a string-width control instruction to control the string width of the earth simulator and an inertial quaternion instruction to control a star map of the dynamic fixed star simulator to change; and the navigation computer, according to the measurement signal, performs navigation filtering calculation to obtain a satellite position estimation value and a speed estimation value, and compares the satellite position estimation value and the speed estimation value with the reference data to obtain navigation accuracy. According to the autonomous navigation semi-physical simulation test system based on the biconical infrared and star sensors provided by the invention, the semi-physical simulation verification test for real measurement data of a hardware in a loop based on the biconical infrared and star sensors is realized, and the performance of the full-autonomous navigation system for a satellite can be effectively verified on the ground.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
3D visualization system for web survey
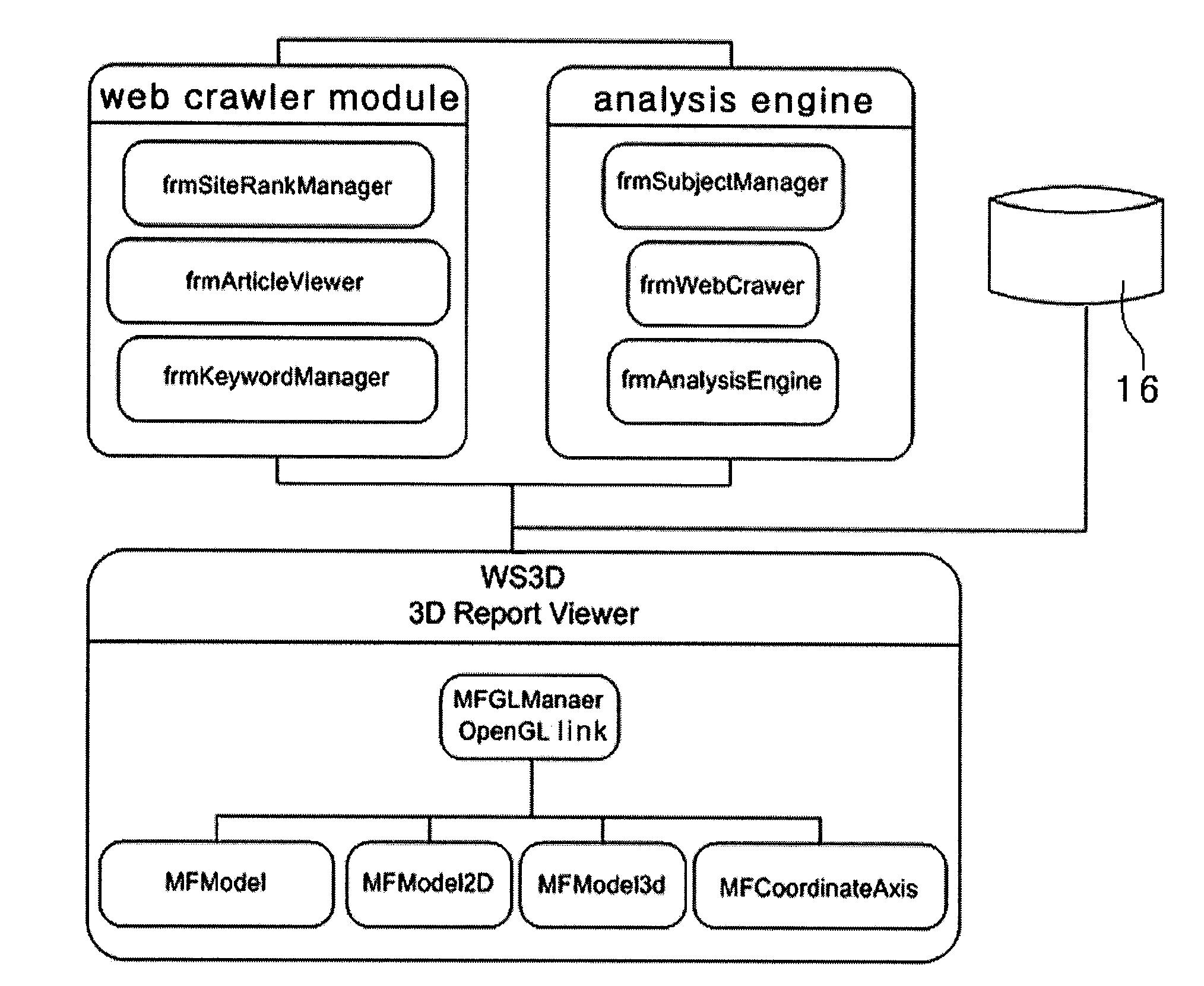
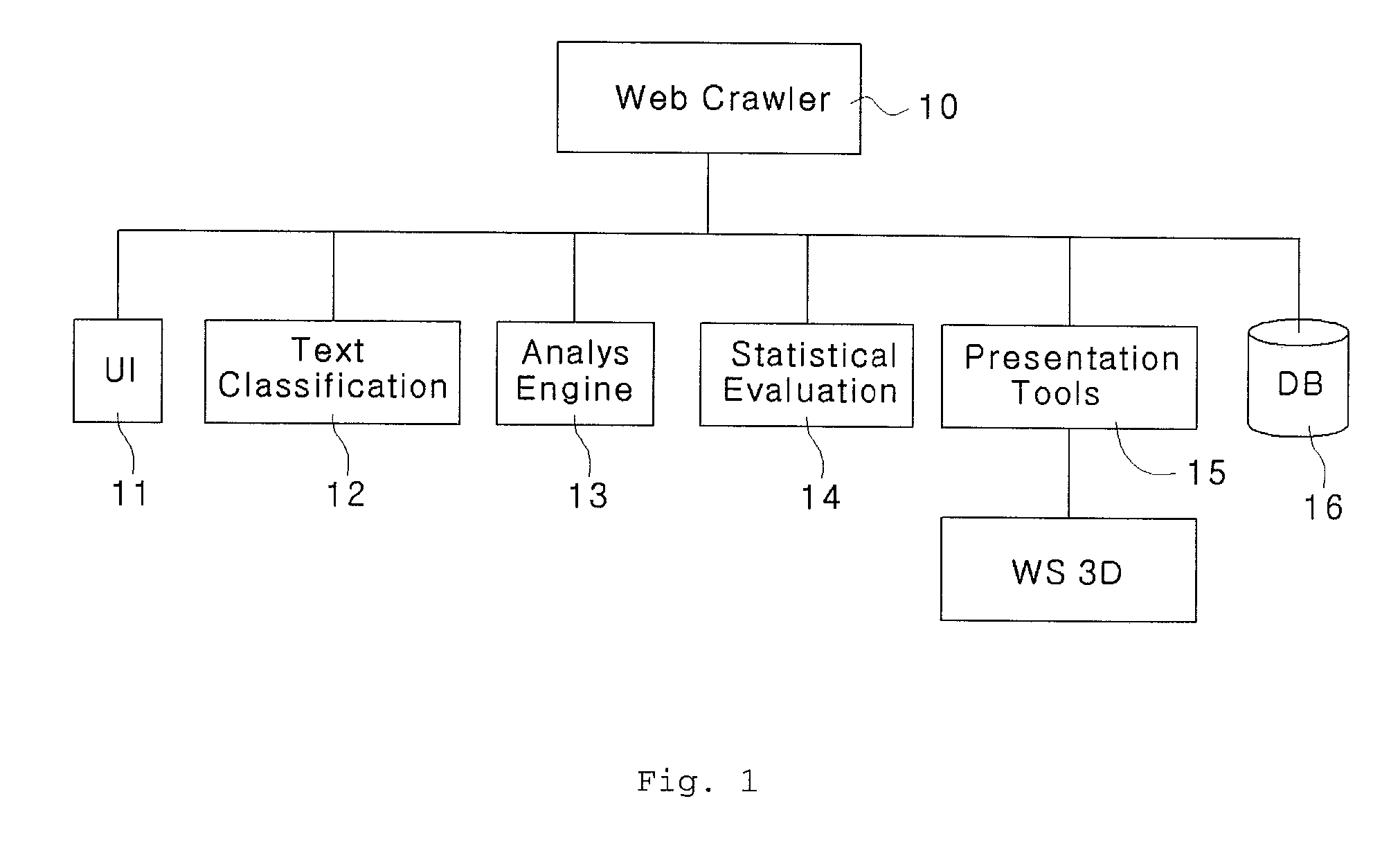
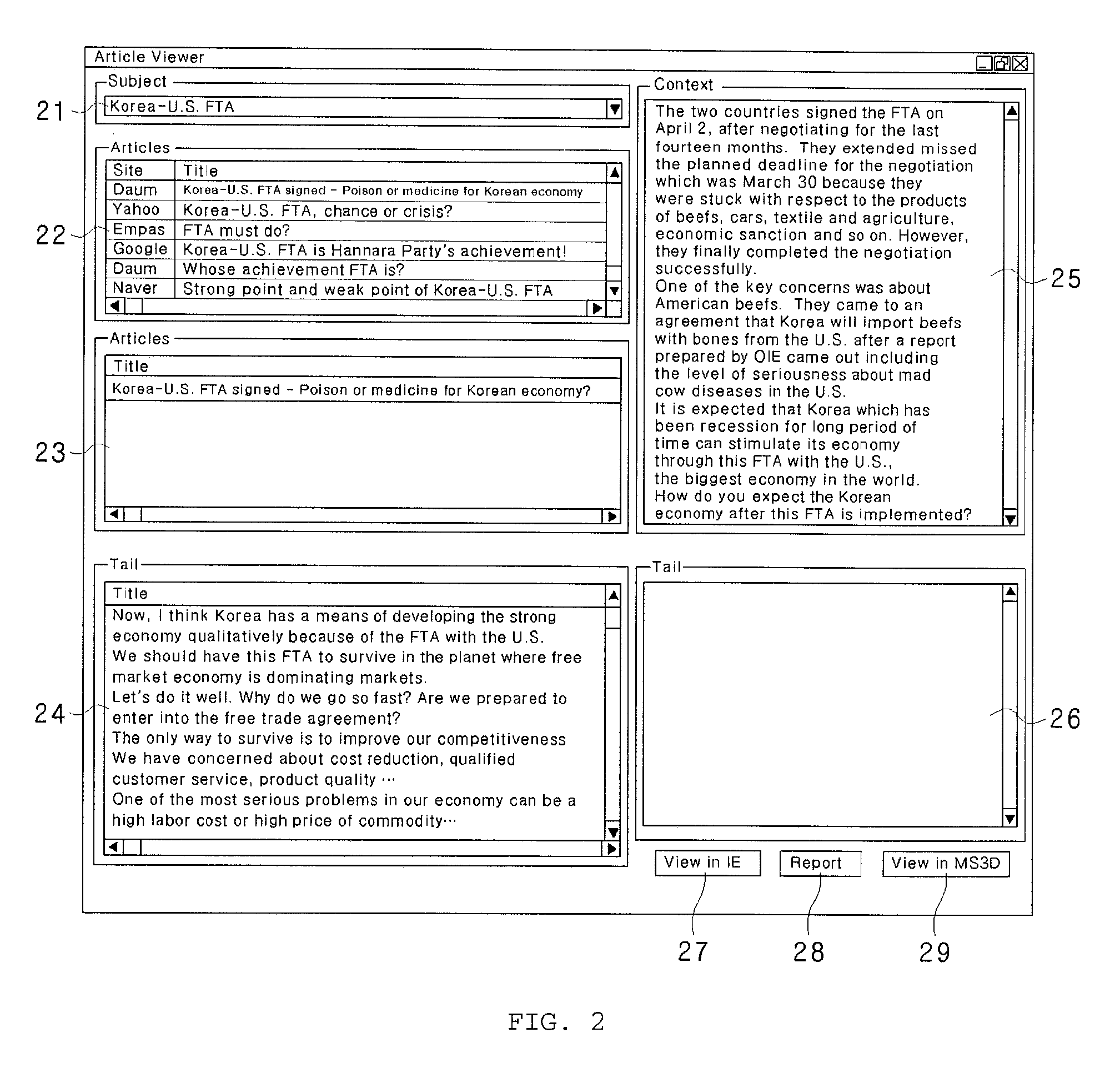
InactiveUS20100153372A1Easy to understandImprove abilitiesWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsFixed starsReal-time web
The present disclosure relates to a three-dimensional visualization system for internet-based web surveys which can collect in real time web articles about specific companies, products or public figures from specific websites, blogs or knowledge-search web pages, process and analyze collected articles and display survey results with a planetary system having a three-dimensional fixed star and planets such that the user can understand easily and accurately the survey results. The system can include a user interface, a database server configured to store collection conditions, a web crawler module a text classification module, an analysis engine module, a statistical evaluation module, and store rate values of the web articles and a presentation tool configured to display three-dimensional graphics of the rate values of the web articles stored in the statistical evaluation module symbolizing a planetary system having a fixed star and planets.
Owner:KIM SEA WOO
High precision low cost starlight simulator
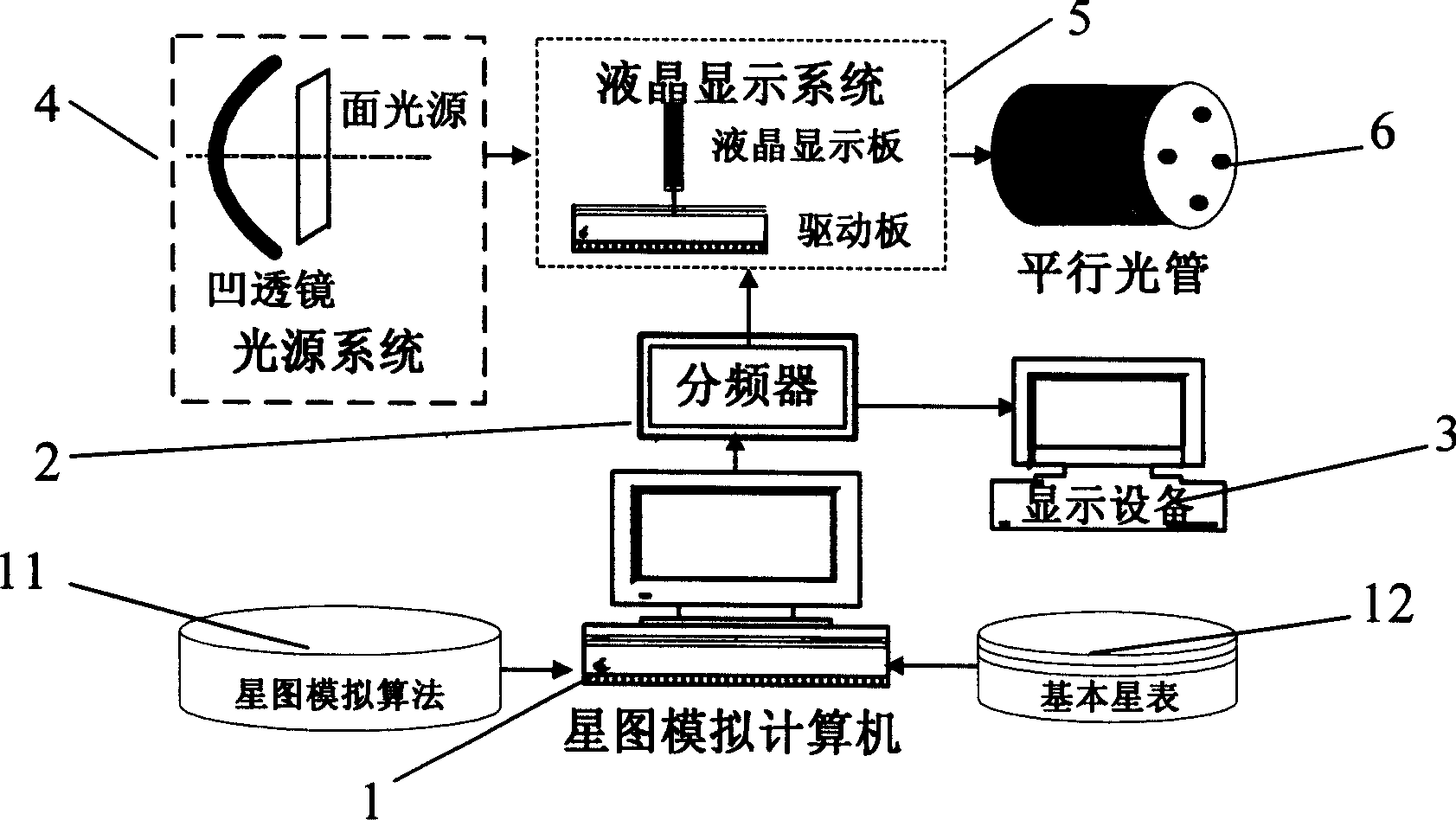
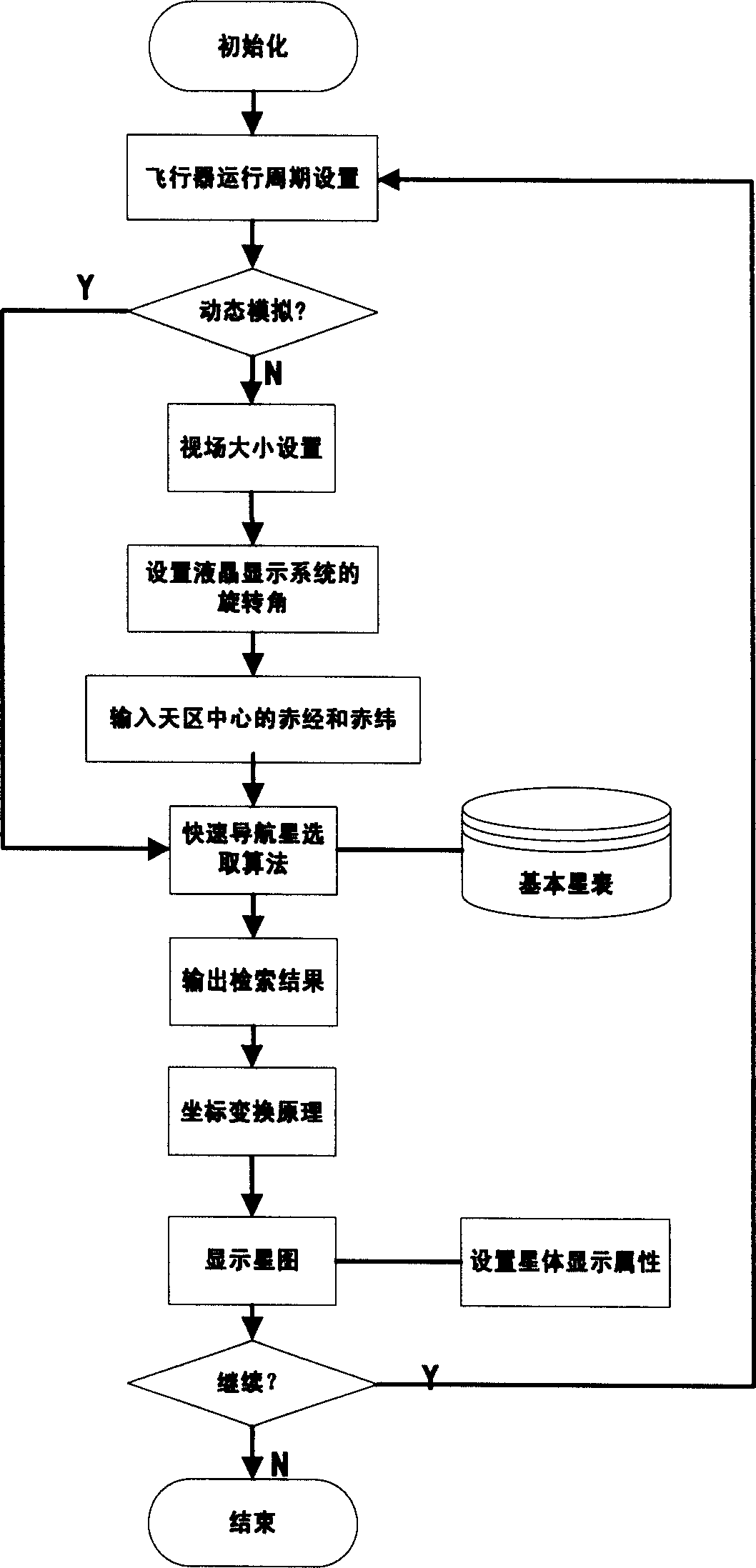
ActiveCN1912547AOvercome precisionOvercome speedInstruments for comonautical navigationCosmonautic vehicle trackingVisual field lossFixed stars
A starlight simulator with high accuracy consists of light source system formed by concave lens and surface light source, star atlas analog computer being set with star atlas analog algorithm and basic star table for calculating out mapping positions of each navigation star on liquid crystal display system, frequency divider for dividing said mapping positions to different units, display unit for carrying out directly viewing display, liquid crystal display system for displaying distribution of fixed star, parallel light tube being used to set liquid crystal display system on its focal plane and being used to simulate parallel star light of infinite truly under specific visual field and shaft.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
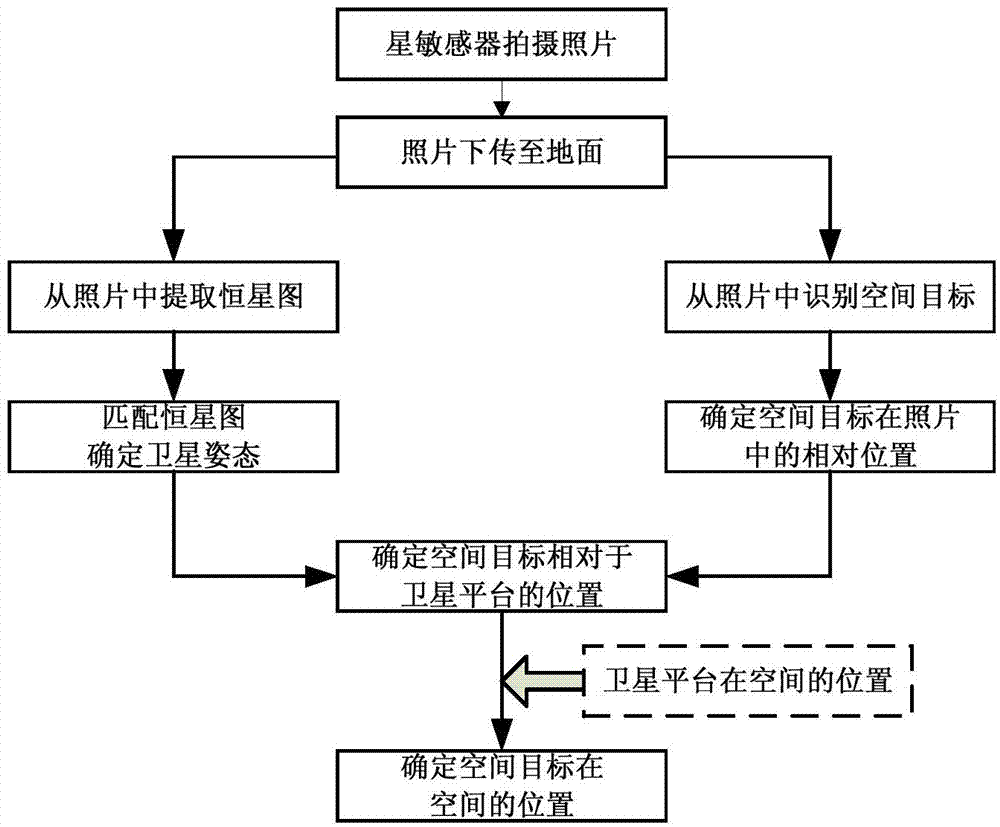
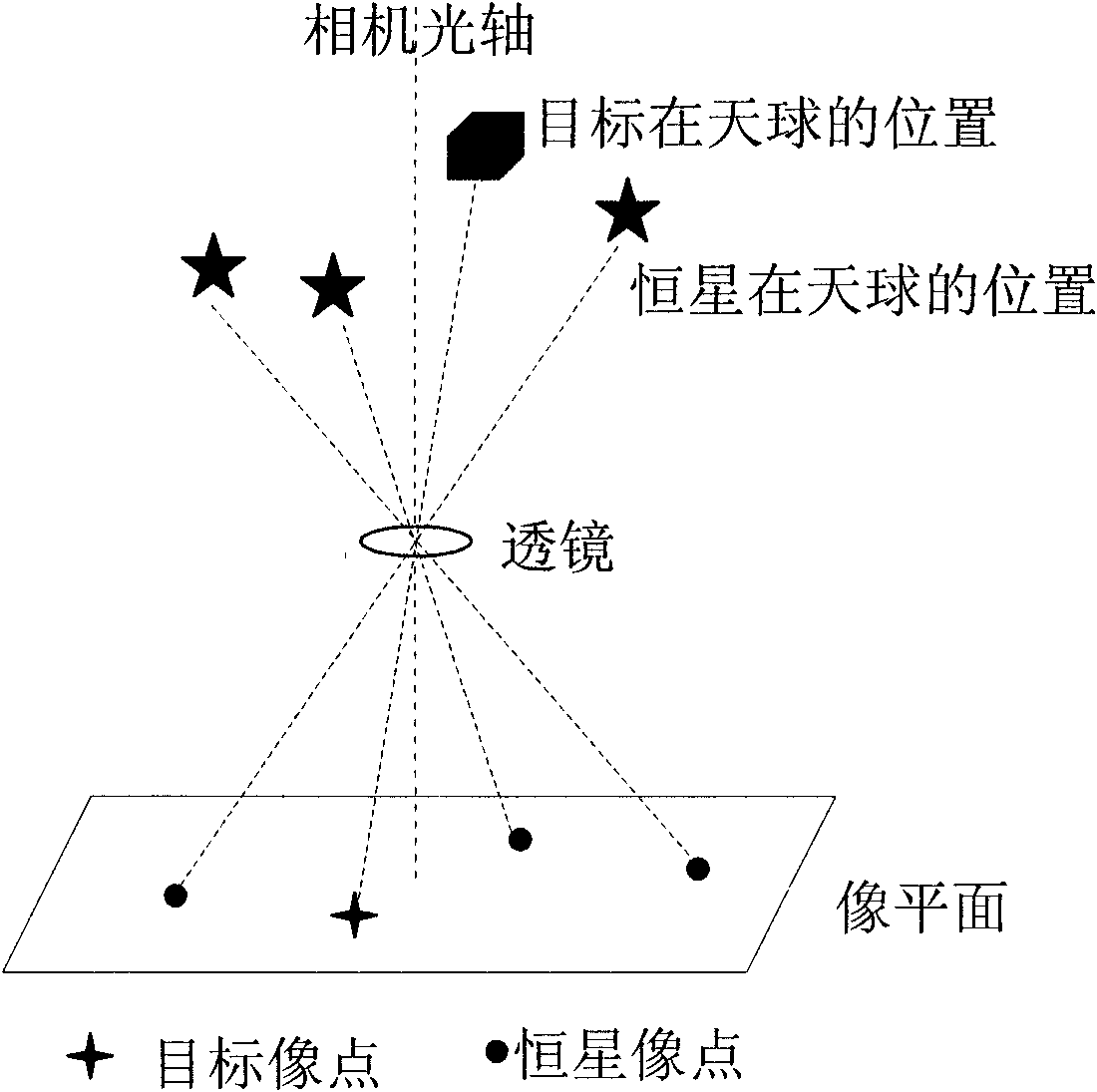
Space target identifying, positioning and tracking method
InactiveCN104776848AMake up for the weakness of few and weak load monitoring capabilitiesIncrease the amount of information collectedInstruments for comonautical navigationPicture interpretationFixed starsFeature extraction
The invention provides a space target identifying, positioning and tracking method which comprises the following steps: shooting the starry sky by star sensors on a satellite-in-orbit platform; transmitting photos to a ground information receiving device; transferring the photos to a data processing computer by the ground information receiving device for feature extraction, to obtain a fixed star map and identify the space target in the map at the same time; determining the space pointing of the star sensors loaded on the satellite platform when shooting, determining the position of the space target relative to the satellite platform; and determining the position of the space target in the photos in the space finally. On the basis of not affecting the initial tasks of the satellite, the satellite acts as the space target monitoring satellite; a general survey space target monitoring is realized by the unconscious information acquired by each satellite, the weaknesses of less special monitoring satellites and weak load monitoring capacity in our country are compensated on the advantages of amount and system, so as to construct a space-based space target monitoring system of China.
Owner:李智
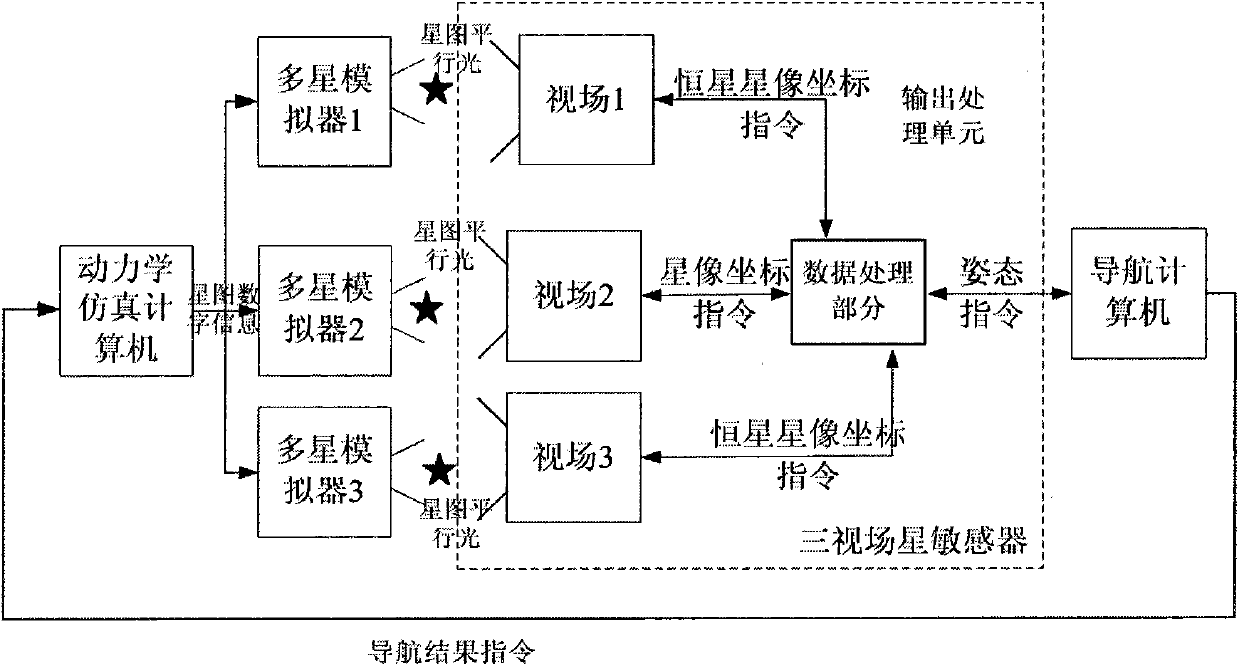
Laboratory testing method for multi-field-of-view star sensor
ActiveCN103344256AMeet the requirements of debuggingSolve the influence of time and spaceMeasurement devicesFixed starsLab test method
The invention relates to a laboratory testing method for a multi-field-of-view star sensor. The method comprises the steps that: a dynamics simulation computer respectively generates fixed star maps of a first field of view, a second field of view and a third field of view according to the initial track parameter set by a user, track dynamics, installation direction between the first field of view and an aircraft, installation direction between the second field of view and the sircraft and installation direction the third field of view and the aircraft, and concurrently sends the generated fixed star maps to a first multi-star simulator, a second multi-star simulator and a third multi-star simulator through a VGA (Video Graphics Array), all the fields of view of the multi-field-of-view star sensor respectively shoot the star maps and conduct integration calculation. The practical testing environment of an external field can be entirely simulated through using the testing method, and therefore, the reliability, robustness and the like of the multi-field-of-view star sensor can be tested. The accuracy of the rolling angles of the multi-field-of-view star sensor can be improved by adopting the data integration method, in addition, the method can be used for testing a single-field-of-view star sensor, and therefore, the university of testing equipment can be improved, and the equipment testing cost can be lowered.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
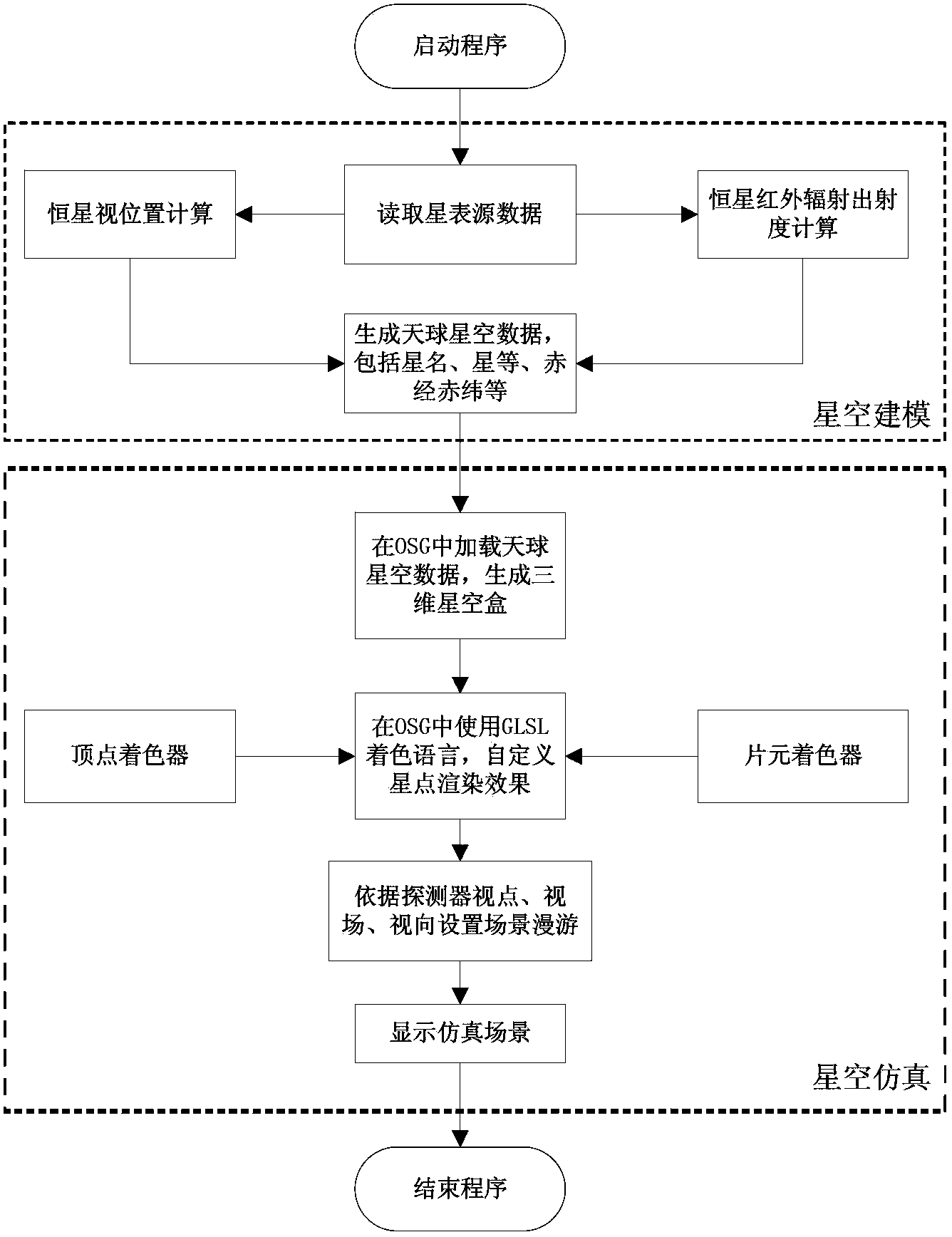
A method for fast generating an optical starry sky background
InactiveCN103679799APrevent size changeIncrease generation speedPlanetaria/globes3D modellingFixed starsNutation
The invention belongs to optical technical field and specifically relates to a method for fast generating an optical starry sky background. The method comprises following steps including: a step 1, modeling a sky background in which star catalogue data of fixed stars is used as a source, by means of transformation of time and a coordinate system and correction of the apparent positions of heavenly bodies, starry sky background models at any observation point any time are constructed and a calculating result is inputted into a base in order to be used for simulation, wherein the calculating result comprises star names, star magnitudes, right ascension, and declination; and a step 2, simulating the established starry sky background model. The step 1 uses Hipparcos Catalogue as a data source of a visible light band. According to the selected Hipparcos Catalogue, the apparent positions of the fixed stars are calculated. Considered factors comprise annual parallax and proper motion caused by revolution of the earth, aberration caused by the self motion of an observer, annual aberration, precession, and nutation caused by earth revolution about the sun. The speed for generating a starry sky background by using the method may reach 50Hz.
Owner:中国航天科工集团第二研究院二〇七所
Low-frequency error measuring method for star sensor
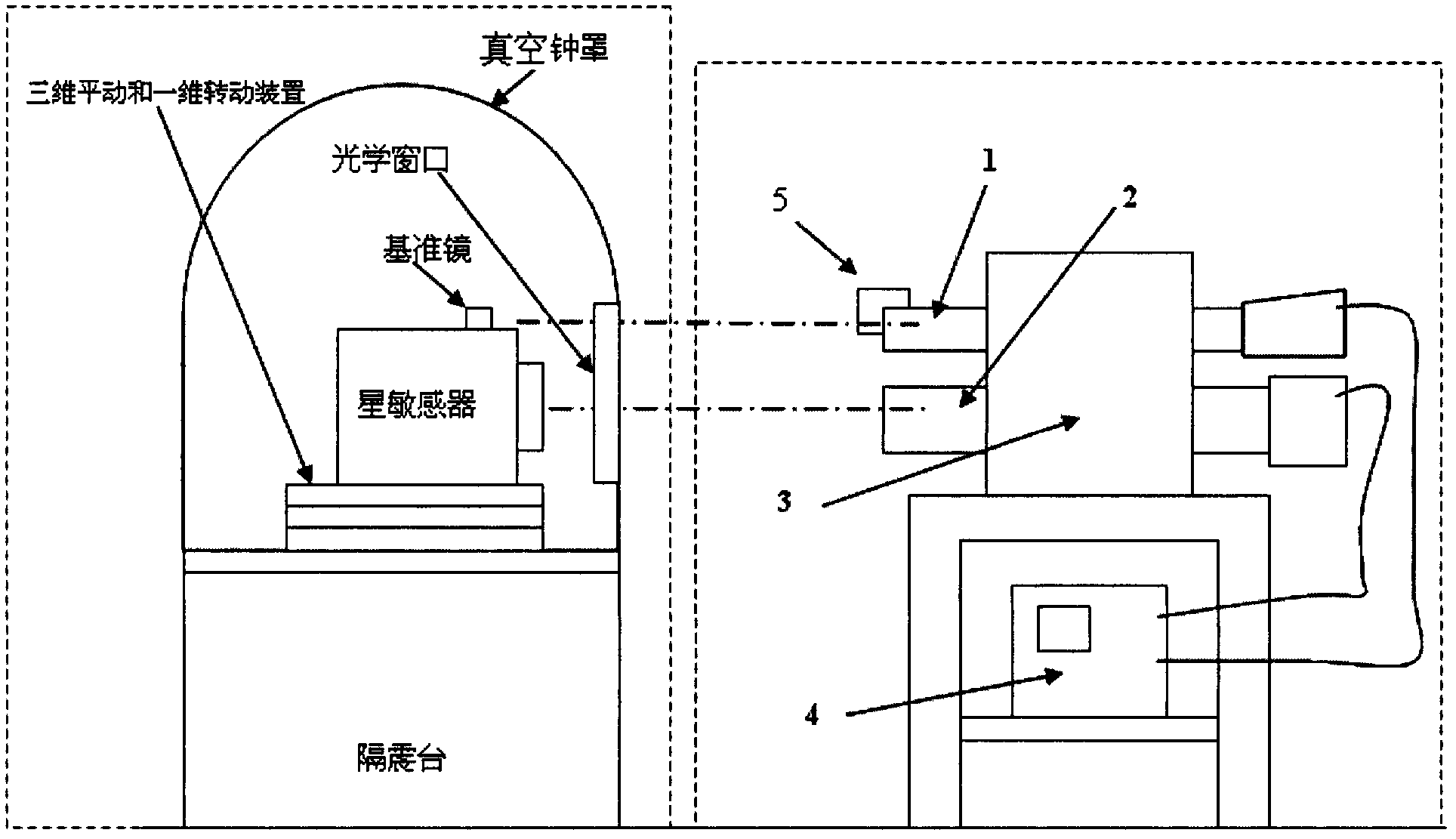
ActiveCN102564458ARealize measurementHigh measurement accuracyMeasurement devicesFixed starsVibration isolation
The invention discloses a low-frequency error measuring method for a star sensor, and builds a low-frequency error measuring system comprising an auto-collimating collimator, a static multi-optical path star simulator, an adjusting bracket, a measuring system and a laser sight, wherein the star sensor is mounted on a vibration isolation table; a vacuum bell jar is used for providing a vacuum environment for the star sensor; a glass window is arranged on the vacuum bell jar; the transmittivity of the glass window is not less than 95 percent; and the star point imaging positions of the star sensor and the auto-collimating imaging positions of an optical datum mirror are monitored and measured at different temperatures under vacuum conditions, so as to fulfill the measuring of the low-frequency error of the star sensor. The invention further provides a measuring system to analog fixed stars of different spectra independently or simultaneously while measuring the auto-collimating angle of the optical datum mirror, and monitor and measure the star point imaging positions of the star sensor and the auto-collimating imaging positions of the optical datum mirror, so as to improve the measuring accuracy.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Method for identifying long-distance space motion target based on stellar map matching
InactiveCN102254147AImprove anti-interference abilityEfficient acquisitionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFixed starsStar catalogue
The invention provides a method for identifying a long-distance space motion target based on stellar map matching. The method comprises the following steps: extracting coordinates of image points of all original images photographed by a visible light camera of a miniature space detector; composing the arranged image points into triangles in a combination mode; reading a star catalogue in the memory of the visible light camera of the miniature space detector, and identifying all triangles formed by the image points by adopting a triangle identification algorithm; and deleting all the identified image points, and remaining the unidentified image points which are image points of the motion target. In the method, the characteristics of relative motion of the visible light camera of the miniature space detector and the motion target is not required to know in advance, the image points of a fixed star are deleted by adopting a star catalogue identification method, and the star catalogue contains all fixed stars in the starry sky, so that the image points of the target can be effectively acquired by adopting the method, and the star catalogue identification method has the advantage of higher interference resistance.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
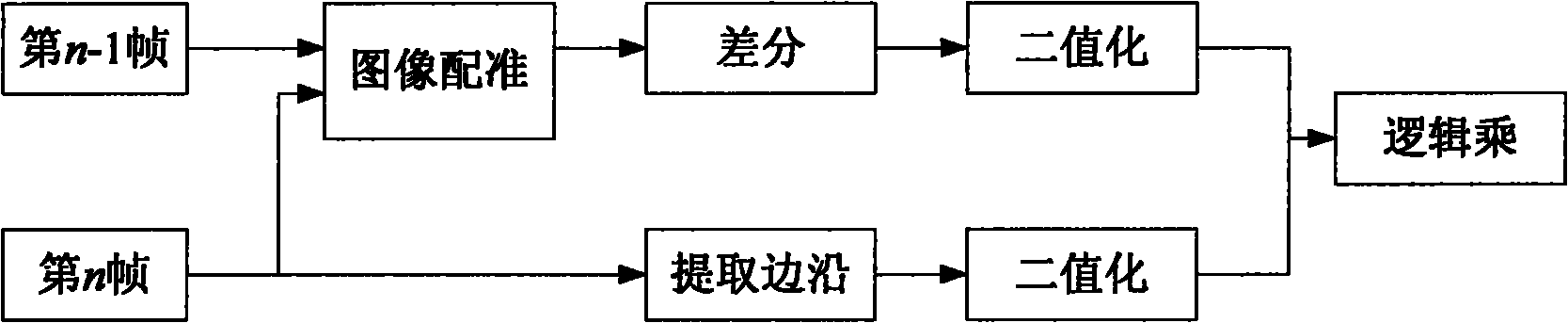
Method for detecting and tracking space target in space-based optical sequential image
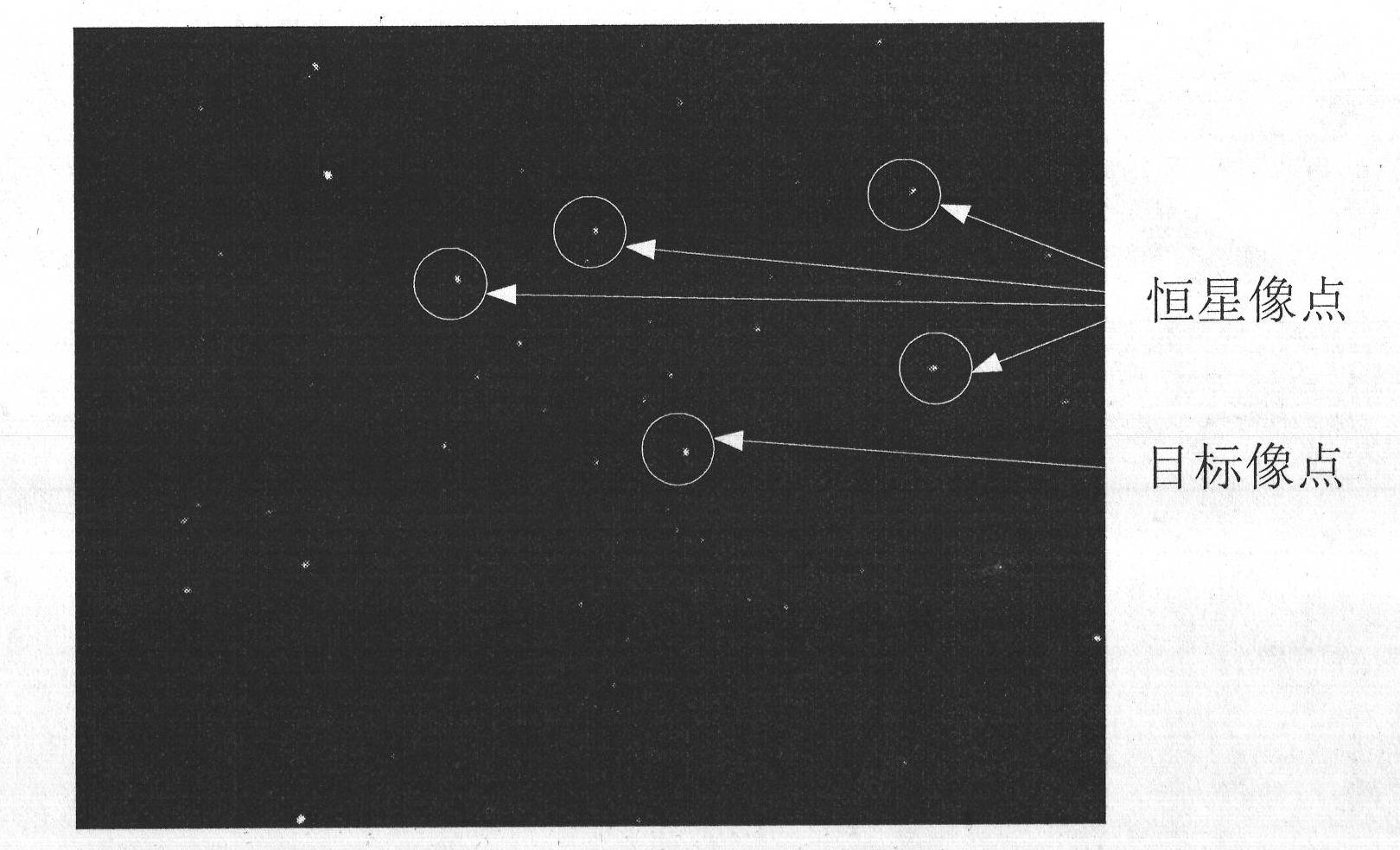
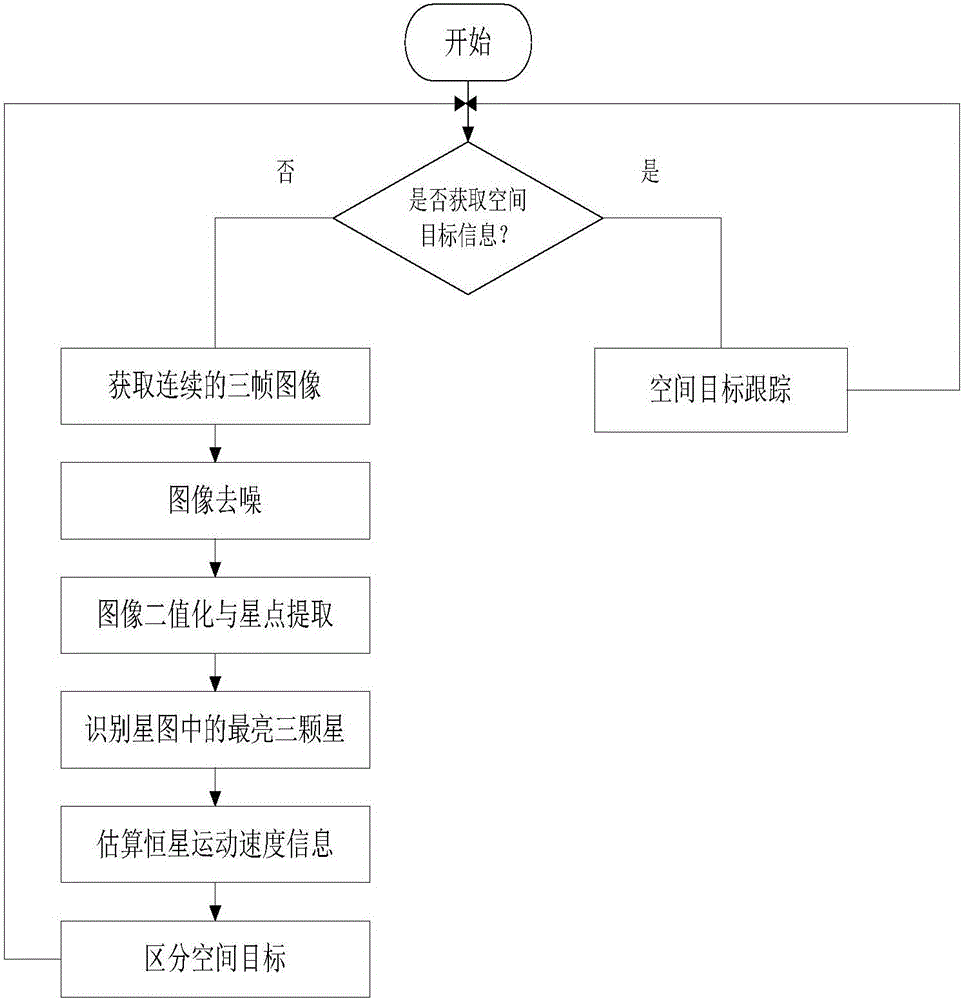
The invention discloses a method for detecting and tracking a space target in a space-based optical sequential image. The method comprises the steps of (1) acquiring continuous N framesof star charts, carrying out image de-noising on the N frames of star charts, and then extracting star point targets in each frame of star chart; (2) ranking the star point targets in each frame of star chart according to brightness, identifying three fixed stars in each frame of star chart in order by using a triangle matching method, and taking all of the fixed stars which appear in each frame of star chart as reference fixed stars; (3) calculating displacement pixel distances of the reference fixed stars in the N frames of star charts on the star charts, as movement speeds of all fixed star backgrounds in the star charts; (4) detecting the space target in the star chart according to the movement speed information; and (5) acquiring the movement information of the space target. According to the method, on the basis of space target detection, the space target is tracked in combination with Kalman filtering, and the method provides a technical support for calculation and continuous updating of position information of the space target in the deep space.
Owner:AIR FORCE EARLY WARNING ACADEMY
Attitude parameter calibration method and attitude parameter calibration device of airborne inertial navigation system
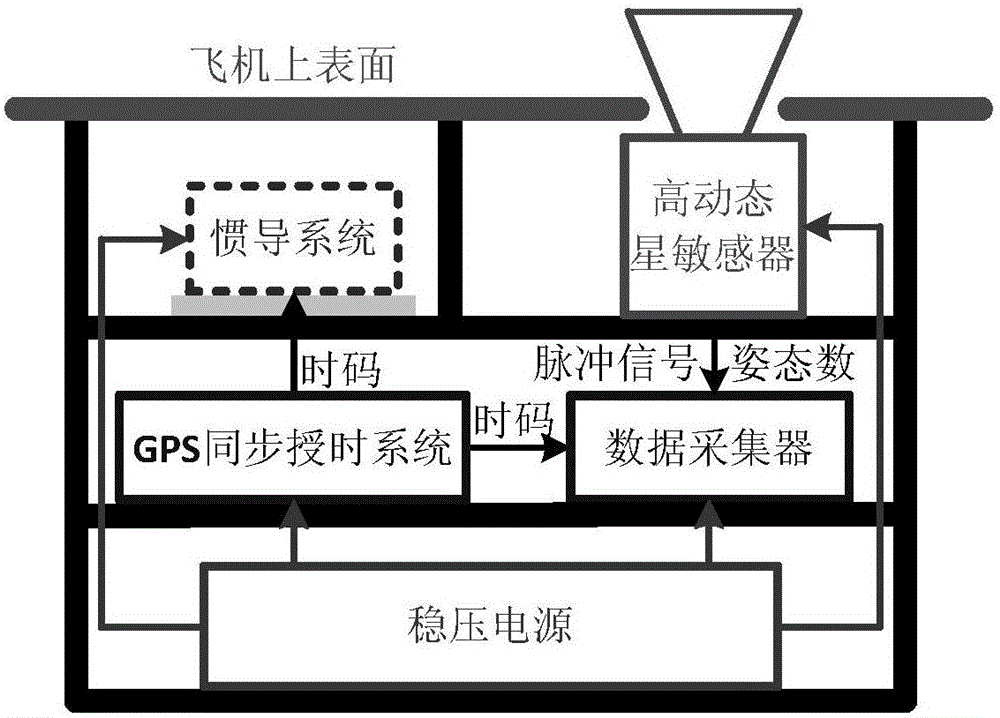
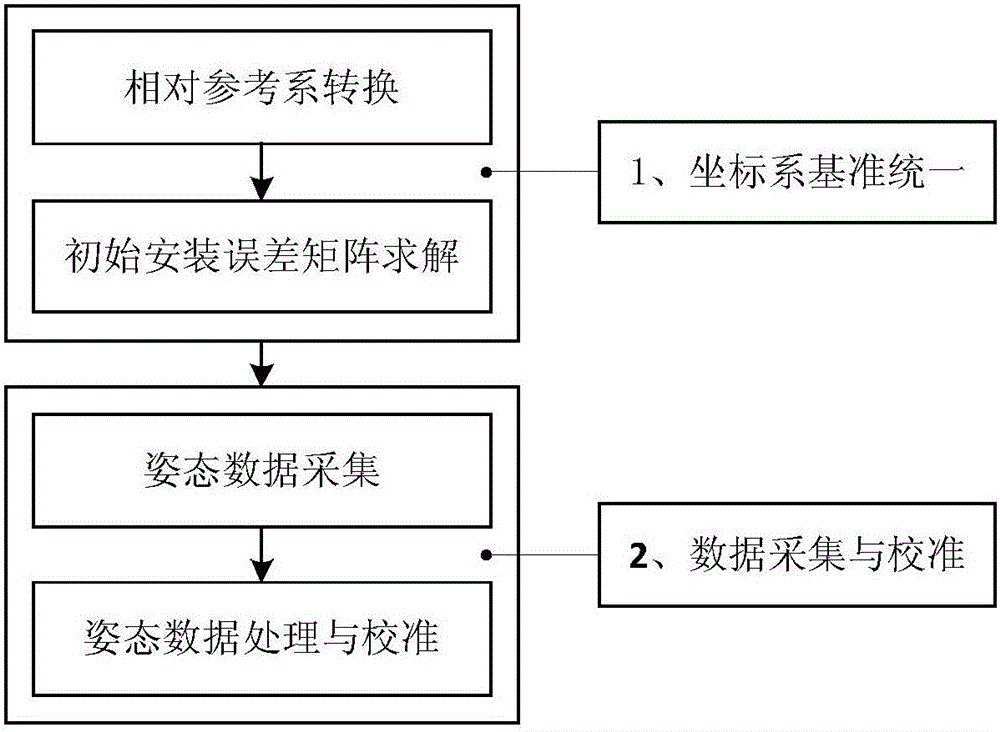
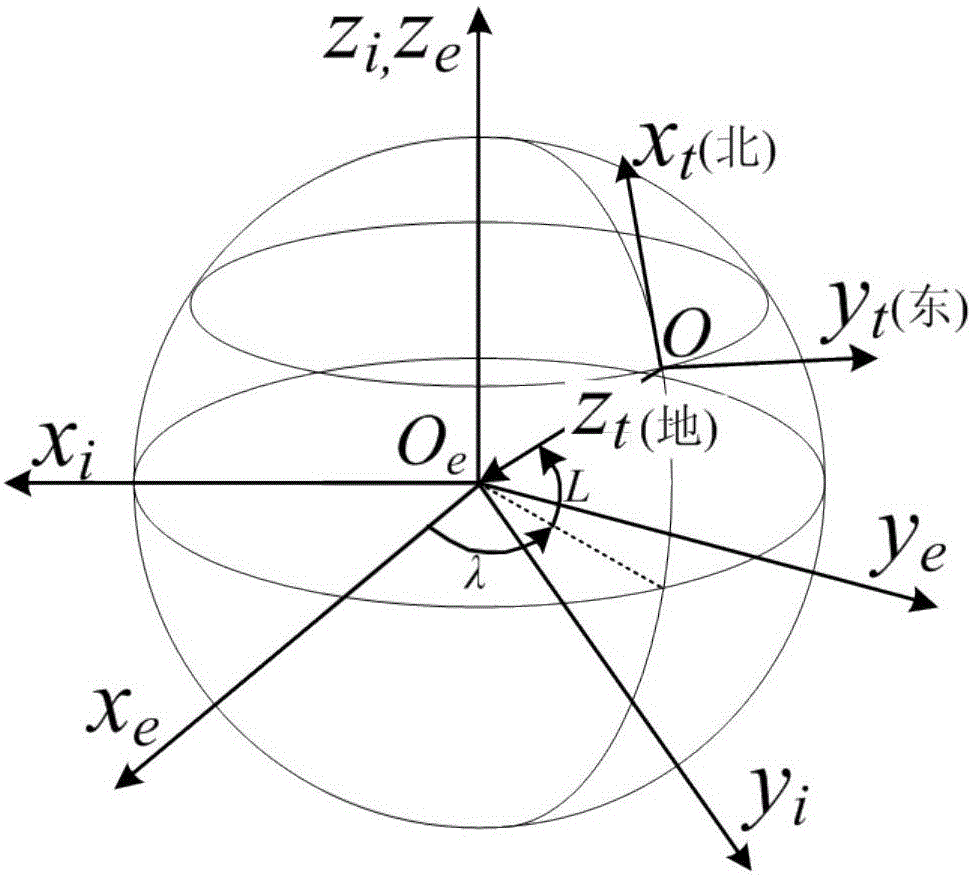
ActiveCN105737858ARealize dynamic online calibrationImprove reliabilityMeasurement devicesBaseline dataFixed stars
The invention discloses an attitude parameter calibration method and an attitude parameter calibration device of an airborne inertial navigation system. A high-dynamic star sensor is used as a data acquisition method and fixed stars are used as measuring objects; the plurality of fixed stars on a celestial sphere are detected, and start point positioning, star map identification and attitude calculation are carried out to provide attitudes of the star sensor relative to an inertial reference system; then, airplane attitude standard data under an inertial navigation coordinate system is obtained according to a conversion relation between a star sensor coordinate system and the inertial navigation coordinate system; finally, the standard data is used as reference and is compared with the attitude data of the inertial navigation system, so that the dynamic online calibration of the attitude precision of the inertial navigation system is realized under an airborne environment.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for making guide star database based on output accuracy of star sensors
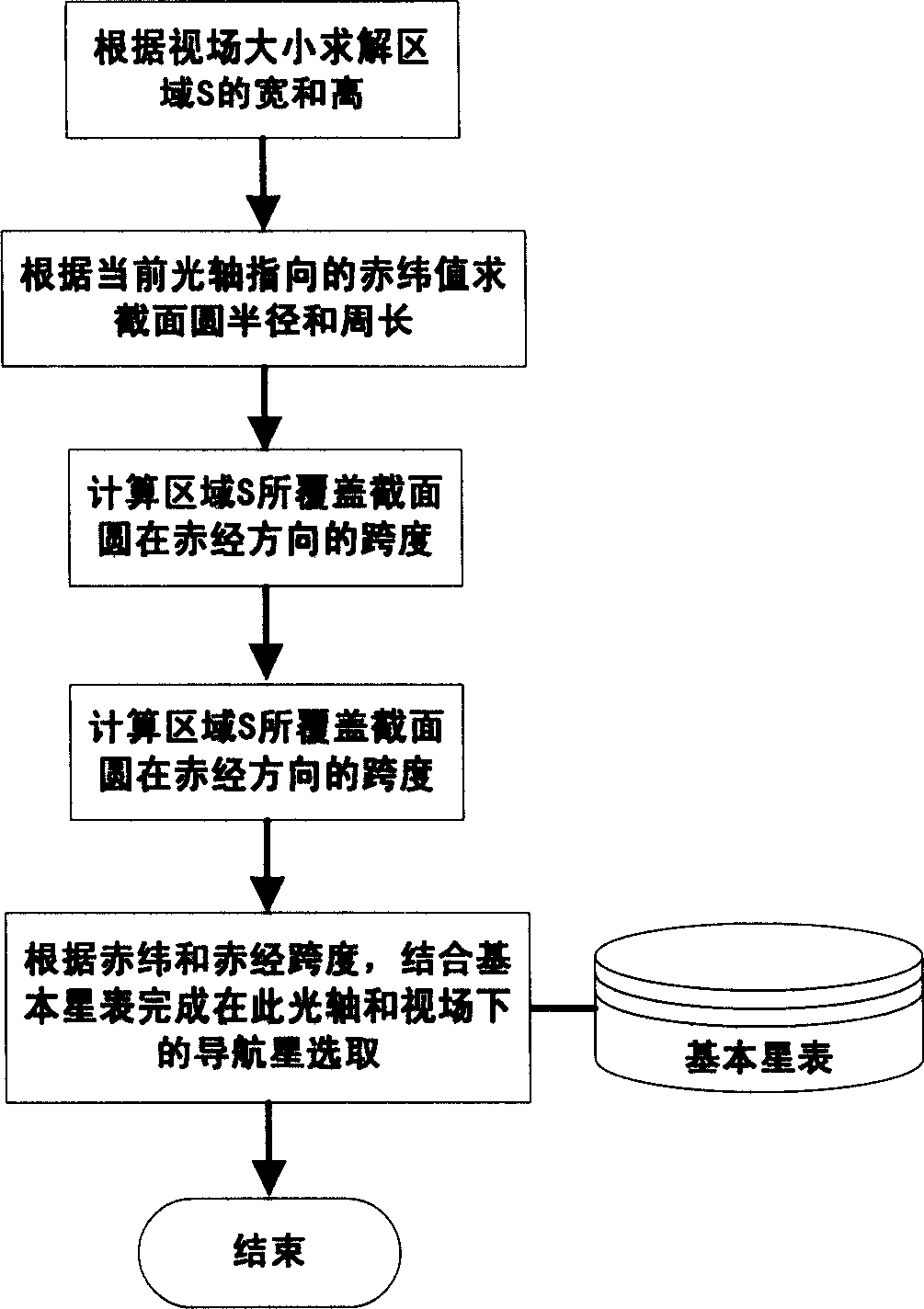
InactiveCN106595645AGuaranteed completenessGuaranteed even distributionNavigation by astronomical meansFixed starsSky
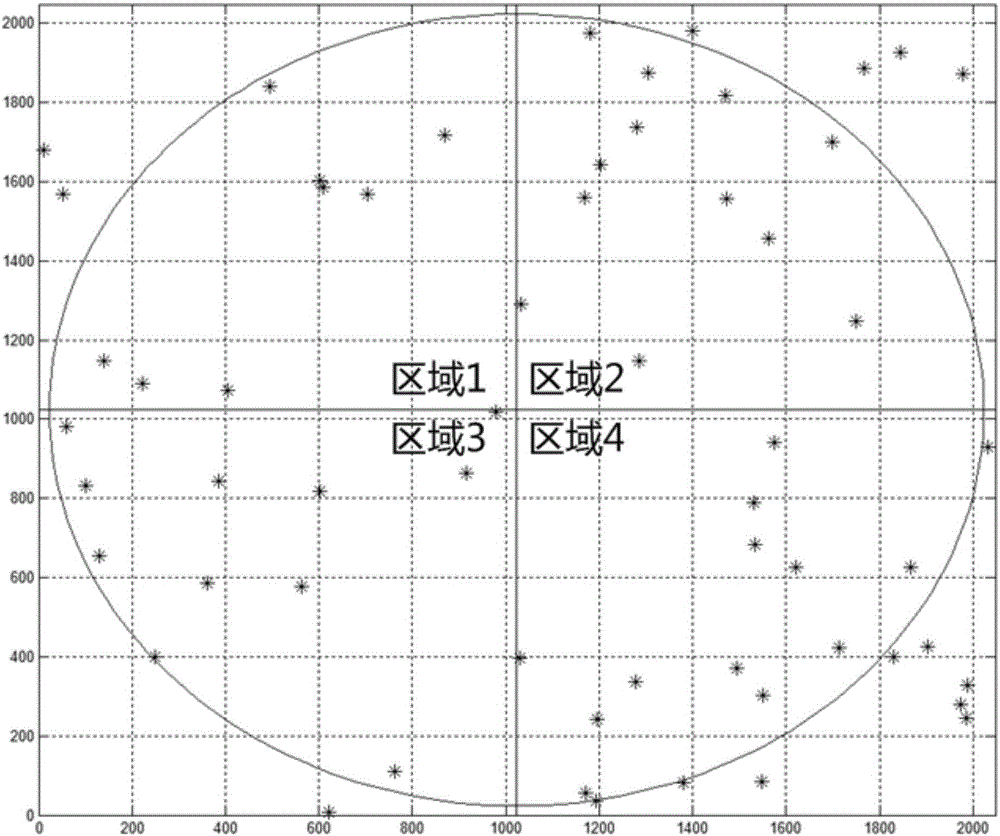
The invention provides a method for making a guide star database based on output accuracy of star sensors. The method comprises the following steps: S1, subjecting a basic star database to screening of fixed stars; S2, generating the direction of an optical axis of a test sky area covering the whole celestial sphere; S3, converting the celestial system of coordinates of all the fixed stars in a field of view under the direction of the optical axis into a planar system of image plane projection; S4, dividing an image plane into n regions and arraying fixed stars in each region according to m combination modes; S5, carrying out attitude solution on each combination mode of the fixed stars and removing combination modes with great errors in an accuracy index; S6, searching for fixed stars in the whole view field of the image plane and combination modes of the fixed stars forming polygons with great errors in a mismatching accuracy index; and S7, carrying out steps S2 to S6 on each optical axis direction and combining overlapped fixed star points in each sky area so as to obtain the guide star database. According to the invention, the selection process of guide stars in each field range is optimized, so a fixed star combination eventually chosen is guaranteed to meet requirements of average distribution, and attitude calculation precision is guaranteed to be optimal.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE CONTROL TECH INST
On-line calibrating method of inertia/astronomy combination system error
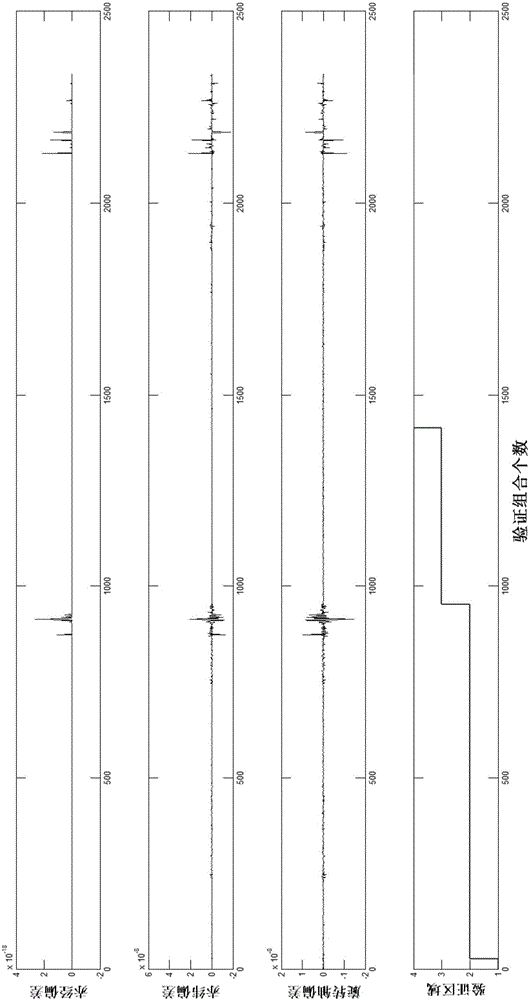
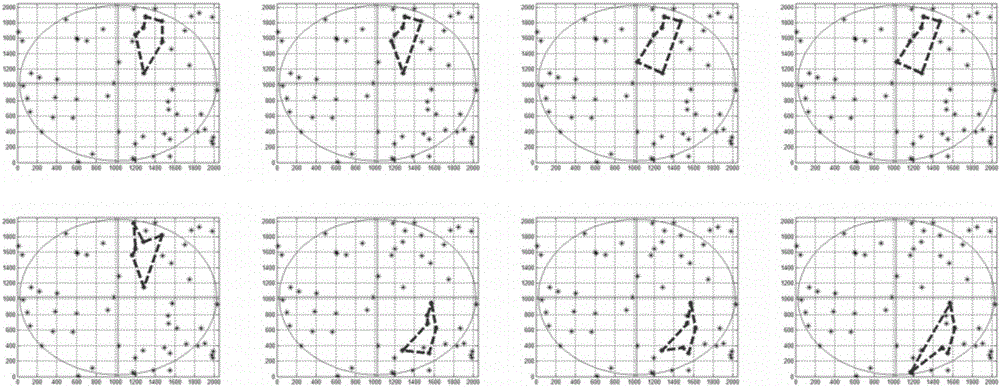
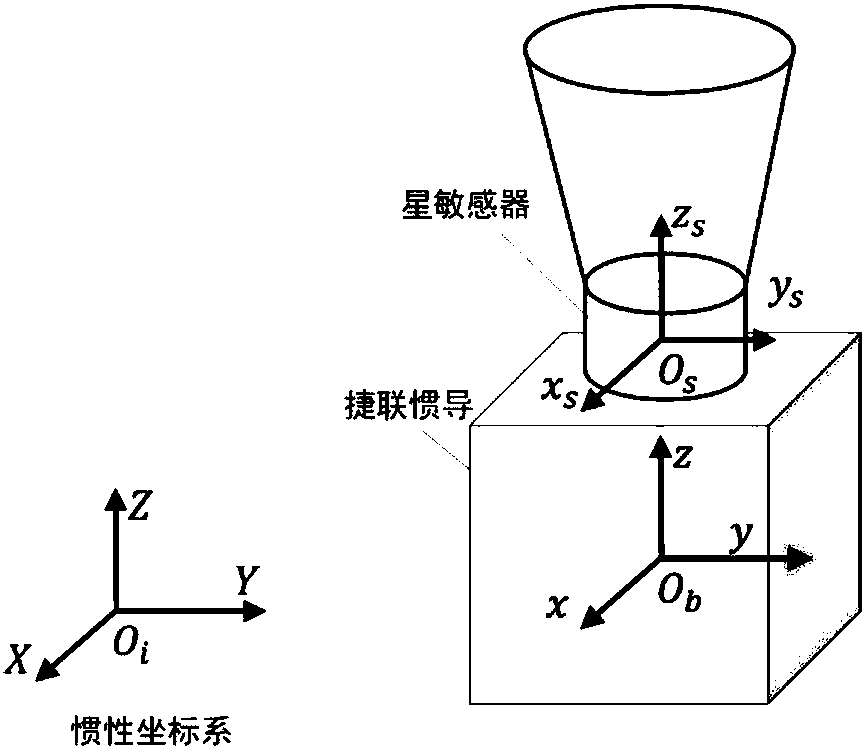
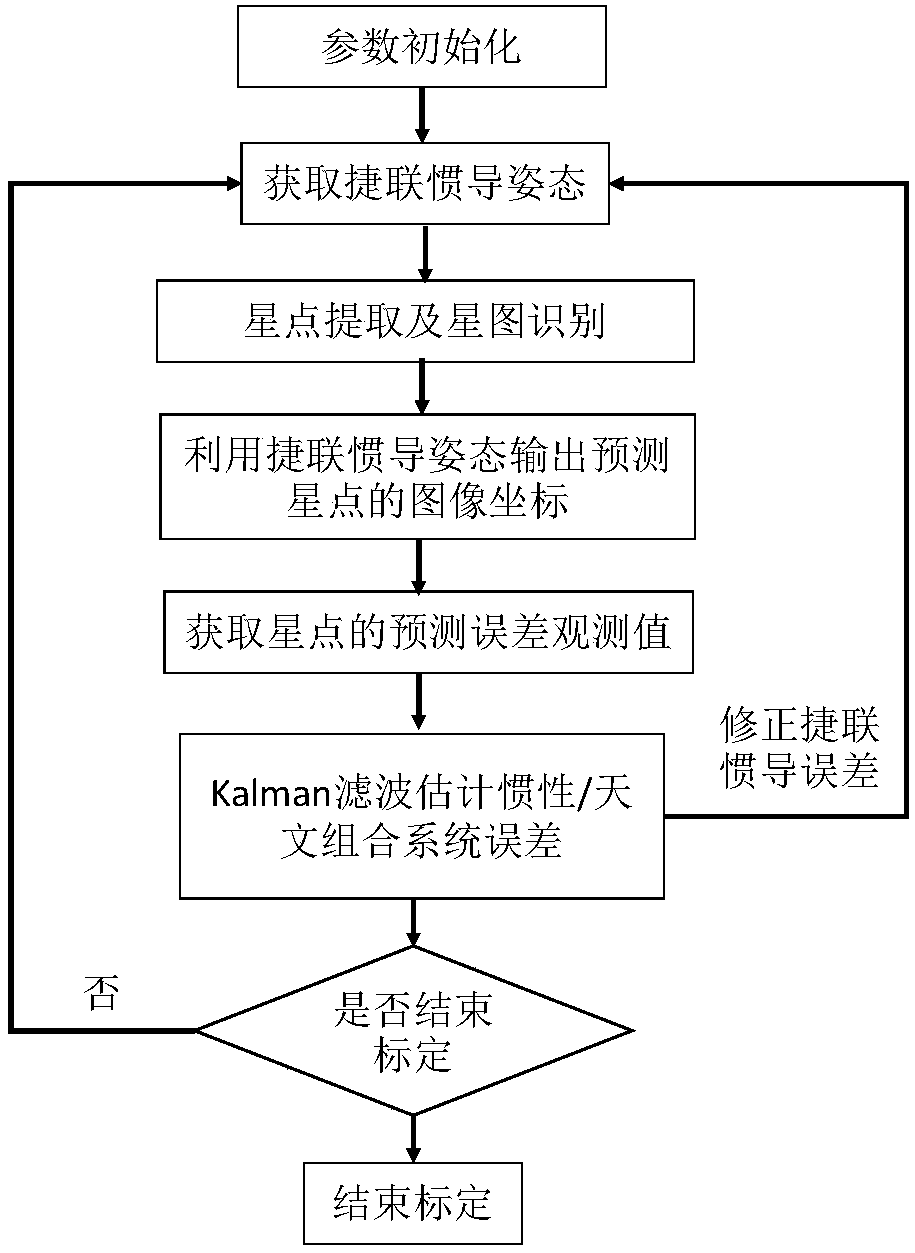
ActiveCN108592945AAvoid Pose Solving ProcessImprove performanceMeasurement devicesFixed starsCoupling
The invention discloses an on-line calibrating method of inertia / astronomy combination system error. According to the method, prior attitude information provided by strapdown inertial navitation is used to obtain a prediction coordinate of a fixed star coordinate at a star sensor image, a star atlas identification algorithm is used for realizing coupling of star point position through practical shooting and the predicted coordinate, accurate connection of deviation of a star point prediction image position coordinate and the practical star point image coordinate as well as error with inertialnavitation attitude, error with the star sensor internal and external parameters and the amount of dispersion with the star point coordinate can be established, and the estimation and compensation ofthe inertial navitation and the star sensor error can be realized by using a Kalman filtering algorithm. The method can realize global calibration on all error factors, increases the comprehensive performance of an inertia / astronomy combination navigation system, and can reach optimum combination. The method can avoid an attitude solving method of the star sensor, normal work of a filter in a viewfiled under less available star numbers (if the star number is less than 3), the effective rate of the observation information is increased, and the algorithm reliability is increased.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Iterative optimization distance categorization-based space weak and small target detection method
InactiveCN102096829AReduce computational complexityImprove target detection efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionFixed starsComputation complexity
The invention discloses an iterative optimization distance categorization-based space weak and small target detection method, which is used for solving the technical problem that the existing space weak motion target detection method is low in detection efficiency. The technical scheme of the method comprises the steps: extracting a plurality of candidate targets by a method based on the iterative optimization distance categorization; constructing an error square and a criterion function; categorizing all star points into fixed stars and non-fixed stars; iteratively computing a class mean andan error square function to obtain an optimization distance categorization threshold value; and filtering out the great mass of fixed star backgrounds and noise points, so that the complexity of the successor operation is reduced. A correlation method of a target track is used in the process of filtering the candidate targets, so that the computing complexity of the algorithm is reduced, and the detection efficiency of the space weak motion target is improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Optical detection method of verticality error of longitudinal axis and latitudinal axis of horizontal type telescope
InactiveCN101650165AThe principle of the method is simpleEasy to operateUsing optical meansFixed starsTheodolite
The invention relates to an optical detection method of the verticality error of a longitudinal axis and a latitudinal axis of a horizontal type telescope, comprising the following steps: respectivelyinstalling an optical planar mirrors on axis heads of the longitudinal axis and the latitudinal axis of the horizontal type telescope; also correspondingly installing a theodolites on the outer sideof each optical planar mirror, and enabling optical axes of the two theodolites to respectively coincide with turning axes of the longitudinal axis and the latitudinal axis of the horizontal type telescope; rotating azimuth axes and pitch axes of the two theodolites, enabling the optical axes of the two theodolites to be aligned, and recording rotating azimuth angles (A1 and A2) of the two theodolites so that the verticality error of the longitudinal axis and the latitudinal axis of the horizontal type telescope is that delta=90 DEG-(A1+A2). The detection method has simple principle, is easy to operate compared with a star comparison method, does not need to know the position of a fixed star, is not limited by weather and fields, does not need to carry out complicated mathematical calculation and is easy to realize.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical imaging autonomous navigation semi-physical simulation testing system for deep space exploration proximity process
An optical imaging autonomous navigation semi-physical simulation testing system for a deep space exploration proximity process is characterized in that a navigation sensor is mounted on a rotary table to be docked with a celestial simulator, a star sensor is docked with a dynamic fixed star simulator, an attitude and orbit simulator generates deep space probe reference attitude and orbit data and transmits the data to a control computer and a navigation computer, the control computer drives the celestial simulator, the dynamic fixed star simulator and the rotary table to move, the celestial simulator simulates position changes of a deep space probe and a target celestial body, the dynamic fixed star simulator simulates inertial attitude changes of the deep space probe, the rotary table simulates attitude disturbance of the deep space probe, and the navigation computer acquires measurement data of the navigation sensor and the star sensor, performs navigation filtering computation and compares a computed result with the reference data so that autonomous navigation precision is obtained. The optical imaging autonomous navigation semi-physical simulation testing system for the deep space exploration proximity process achieves hardware-in-the-loop semi-physical simulation testing on the basis of real measurement data of the sensors and can effectively test and verify the performances of an optical imaging autonomous navigation system for the deep space exploration proximity process on the ground.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
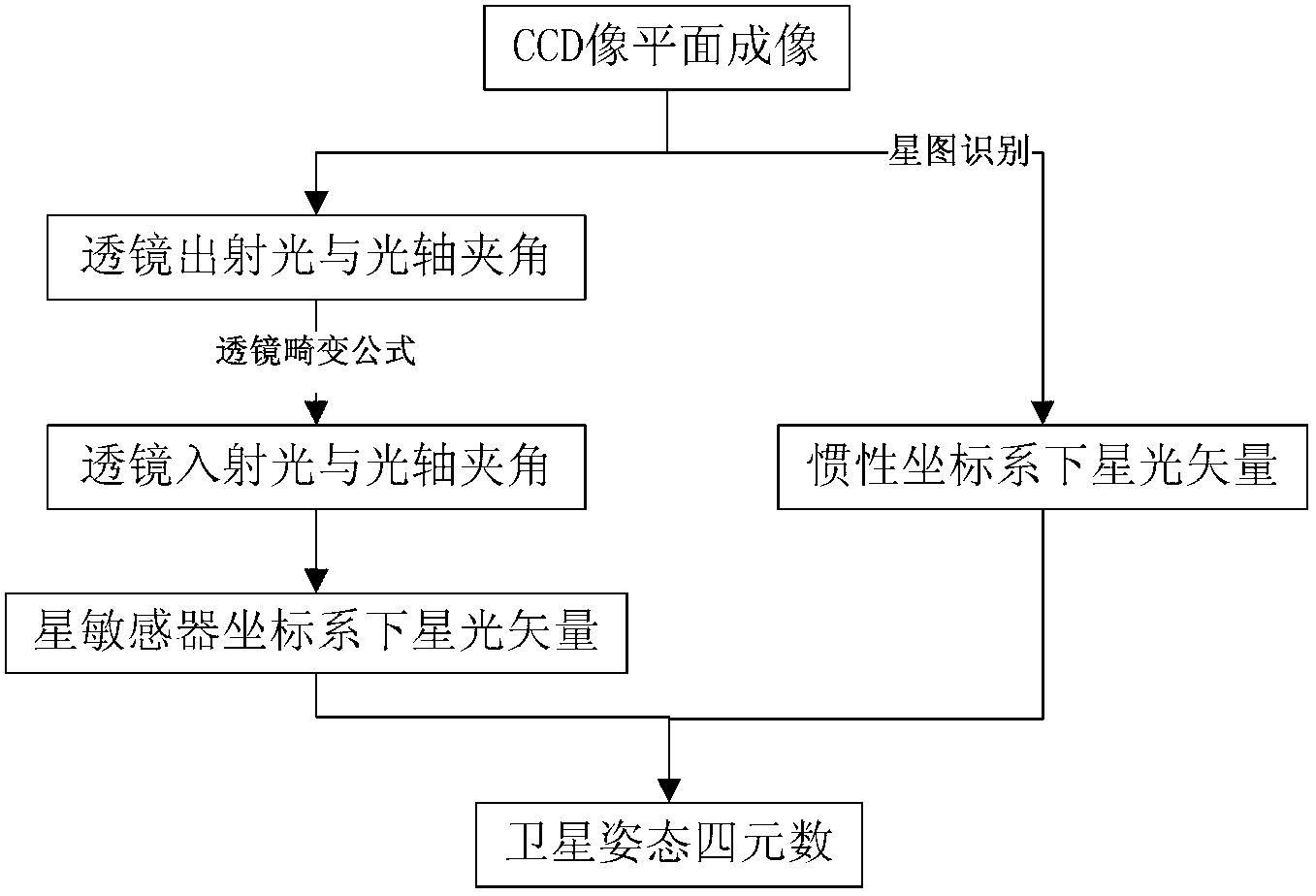
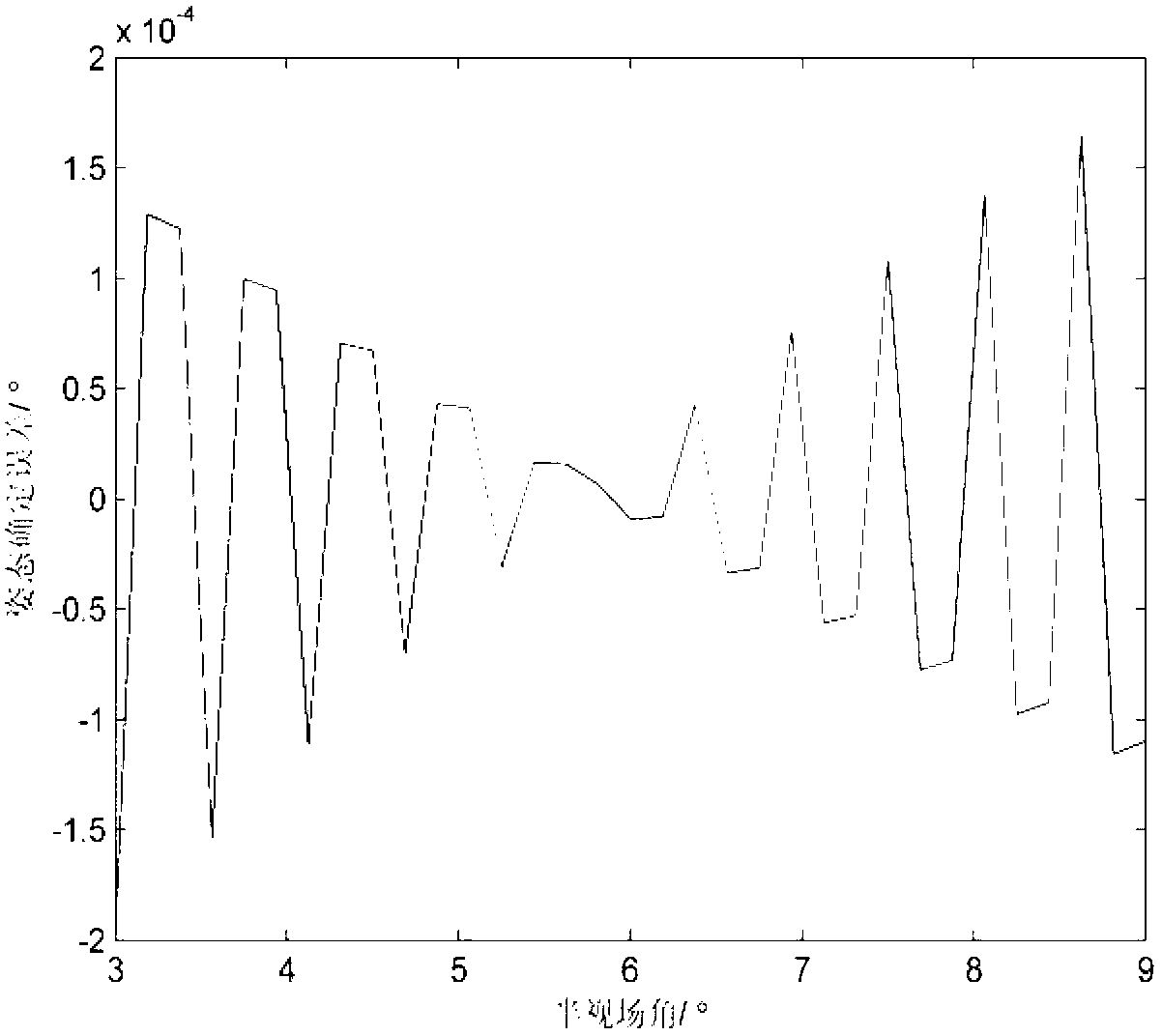
In-orbit calibration method of star sensor lens distortion and satellite attitude determination method based on starlight vector correction
InactiveCN103234556ARealize CalibrationEliminate errors in satellite attitude determinationMeasurement devicesFixed starsOptical axis
The invention relates to an in-orbit calibration method of star sensor lens distortion and a satellite attitude determination method based on starlight vector correction. The invention relates to an in-orbit calibration method of star sensor lens distortion and a satellite attitude determination method. The invention aims at solving a problem of incapability of calibrating a temperature distortion term of an existing calibration method, and a problem of low precision of an existing satellite attitude determination. The star sensor lens distortion in-orbit calibration method comprises the steps that: an included angle between fixed star incident light and a lens optical axis is obtained by calculation according to target fixed star imaging point coordinates and a star sensor lens distortion formula; a light vector direction of the target fixed light is obtained according to the included angle of the incident light and the lens optical axis; and in-orbit calibration of star sensor lens distortion is carried out according to a principle that the included angles of light vector directions of a plurality of target fixed stars are fixed. The attitude determination method comprises the steps that: a target fixed star starlight vector is obtained by calculation according to the target fixed star imaging point coordinates and the star sensor lens distortion formula obtained by calibration; and satellite attitude is determined through star map matching. The methods provided by the invention are applied in the technical field of satellite attitude determination.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
GNSS-CCD-integrated zenith telescope high-precision vertical deflection fast measurement method
ActiveCN104913780AShorten the timeMeasurement accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsInformaticsFixed starsStar catalogue
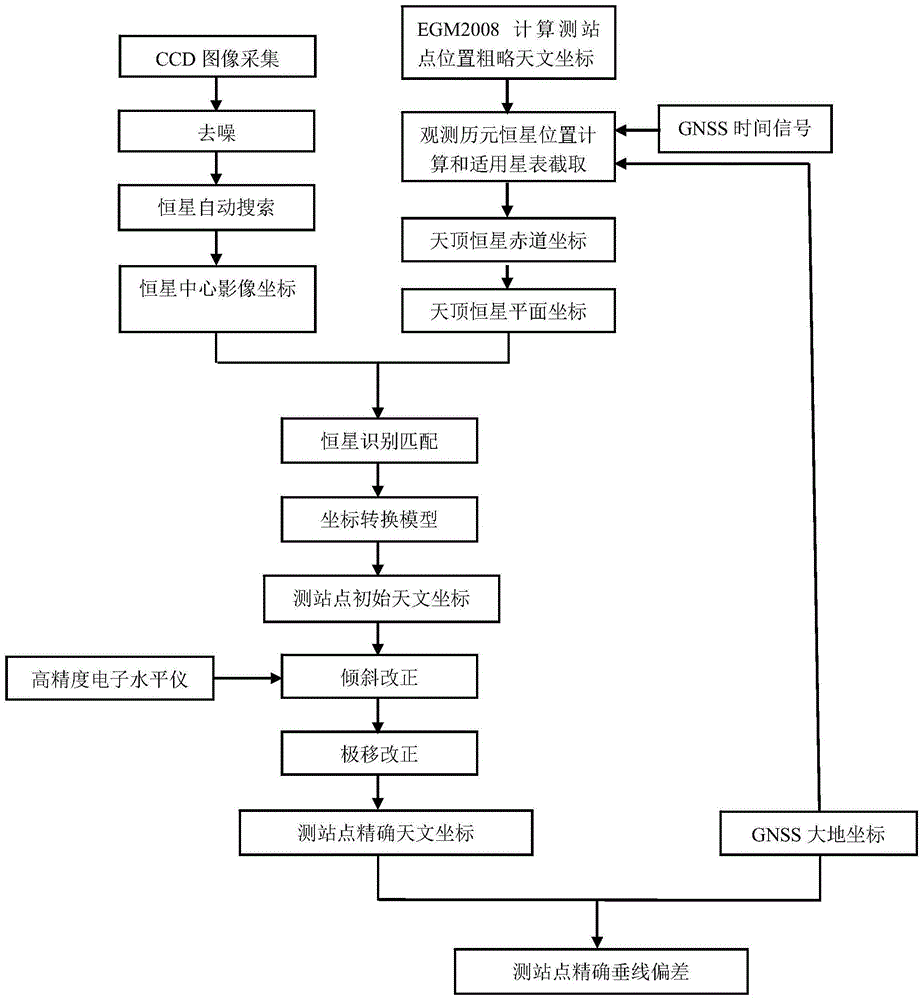
The invention discloses a GNSS-CCD-integrated zenith telescope high-precision vertical deflection fast measurement method. At a measurement station, the optical axis of a zenith telescope faces to the zenith and takes a picture of a zenith zone so that a CCD fixed star image is obtained, fixed star image coordinates are calculated, exposure epoch is controlled by geodetic coordinates and a GNSS time signal measured by GNSS, fixed star information in the zenith zone is acquired in an appropriate star catalogue according to the measurement station vertical deflection calculated by an EGM2008 geopotential model, coupling identification of fixed stars in a zenith tangent plane zone of a celestial sphere in the star catalogue and in the CCD fixed star image is realized, zenith astronomical coordinates are calculated by least spuare iterative computation, and vertical deflection of the observed point is calculated according to geodetic coordinates. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention has the characteristics of simple operation, time and labor saving and high measurement precision and is suitable for high-precision vertical deflection fast measurement.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ship-borne high-precision star sensor setting angle calibrating method
InactiveCN105387874AHigh measurement accuracyAutomate calculationMeasurement devicesFixed starsReference vector
The invention discloses a ship-borne high-precision star sensor setting angle calibrating method, and relates to the field of spacecraft attitude control ground application to solve the problem of unable reaction of accurate calibration of the setting angle of a ship-borne star sensor in the prior art. A ship-borne radar equipment pedestal is provided with a star sensor; when a ship docks, a ship-borne alignment calibration theodolite determines the course angle of a measurement ship through a star measurement or azimuth vane tracking technology, and the horizontal reference pitching angle and rolling angle of a whole ship are calibrated to obtain an inertial navigation horizontal system to deck coordinate system transformation matrix; and the star sensor shoots a star atlas, the observation vectors and the reference vectors of i fixed stars are obtained, the azimuths and the pitching angles of the i fixed stars in a view field are calculated, the pitching angles undergo atmospheric refraction correction one by one, the inertial navigation horizontal system reference vectors of the i fixed stars are reconstructed, and star sensor attitude matrix and the ship-borne star sensor setting matrix under the inertial navigation horizontal system are calculated to resolve the setting angle. The method improves the measurement precision of the attitude of the body of a spaceflight measurement ship.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A star sensor autonomous navigation method based on satellite identification
ActiveCN106382927AWeak perturbationOrbital parameters are accurateNavigation by astronomical meansFixed starsAngular distance
The invention provides a star sensor autonomous navigation method based on satellite identification, and belongs to the technical field of star sensor autonomous navigation methods. The method achieves star-sensor-based fully-autonomous navigation, and provides a carrier with attitude and position information that is high in precision and not emanative along with time. The method includes creating a satellite star map and an integrated star map, and acquires all information and attitude information of fixed stars and satellites according to match of all heavenly bodies with the star maps. According to the acquired fixed star and planet information, high-precision positioning is performed by an improved starlight angular distance process, thus completing transformation into carrier attitude information, and achieving the star-sensor-based fully-autonomous navigation method base in its true sense. The method is advantageous in that 1) the satellite information is adopted in the method so that adaptability and flexibility are good, 2) satellite positioning is adopted in the method so that stability and precision are good, 3) redundancy multi-star resolving is adopted in the method and is anti-interference, and 4) integrated star map matching is adopted in the method, thus increasing information reliability.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com