Independent celestial navigation method of deep space probe based on minor planet intersection
A technology for deep space probes and astronomical navigation, which can be used in integrated navigators and other directions to solve problems such as high requirements for probe orbit design, small number of navigation pulsars, and long distances from the sun, planets and their satellites to the probe.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
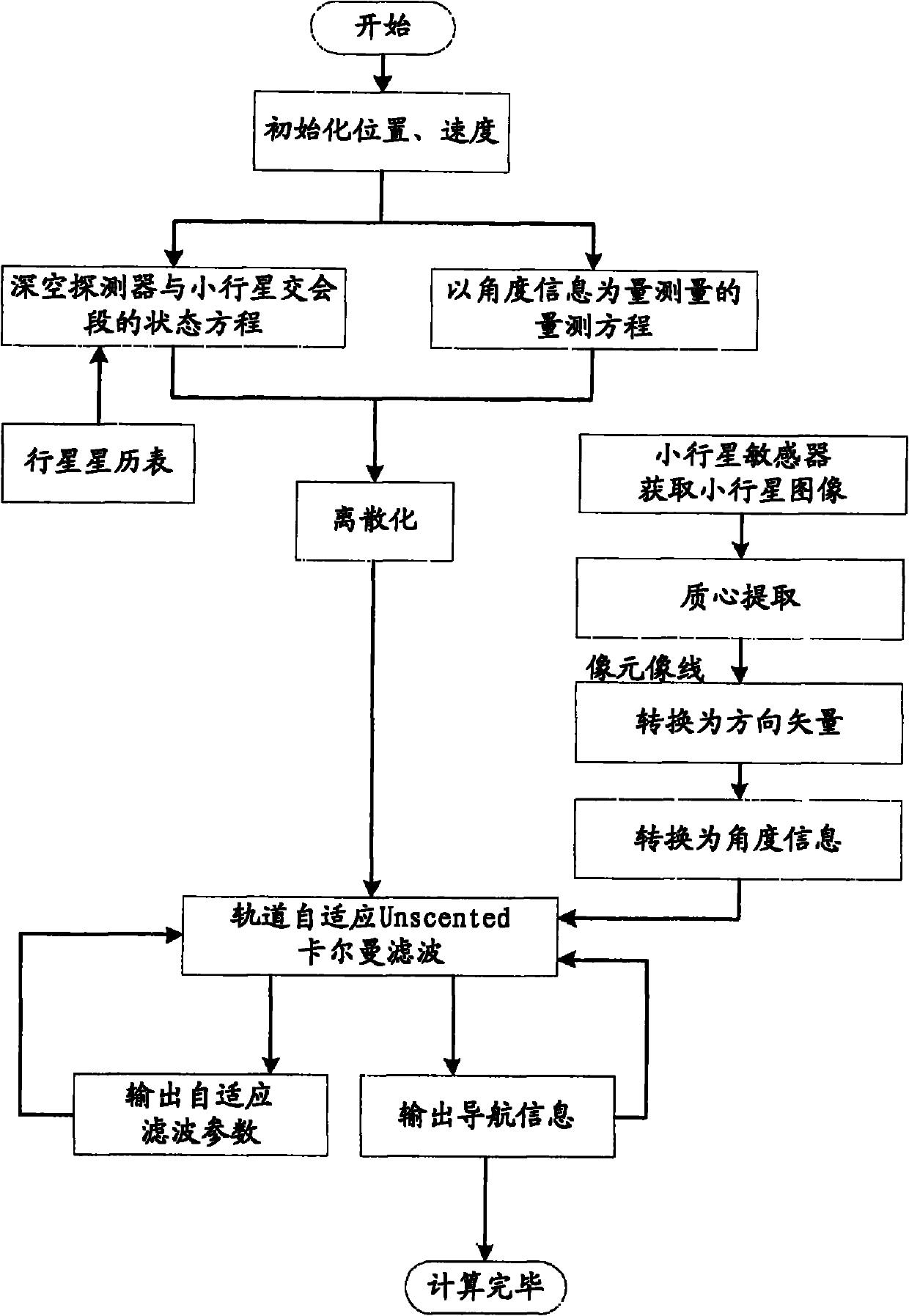
[0070] Such as figure 1 Shown, the concrete implementation method of the present invention is as follows:
[0071] 1. Establish a state model of deep space probes in the asteroid rendezvous based on orbital dynamics;
[0072] First initialize the position and speed of the detector, set the state quantity X=[x, y, z, v x , v y , v z ] T ,x,y,z,v x , v y , v z are the three-axis position and velocity of the detector in the heliocentric inertial coordinate system, respectively. According to the orbit design of the detector, the initial values of the position and velocity of the detector are selected as
[0073] X=[-1.853×10 11 m-1.168×10 11 m-5.032×10 10 m
[0074] -9.213×10 3 m / s-1.855×10 4 m / s-8.065×10 3 m / s] T
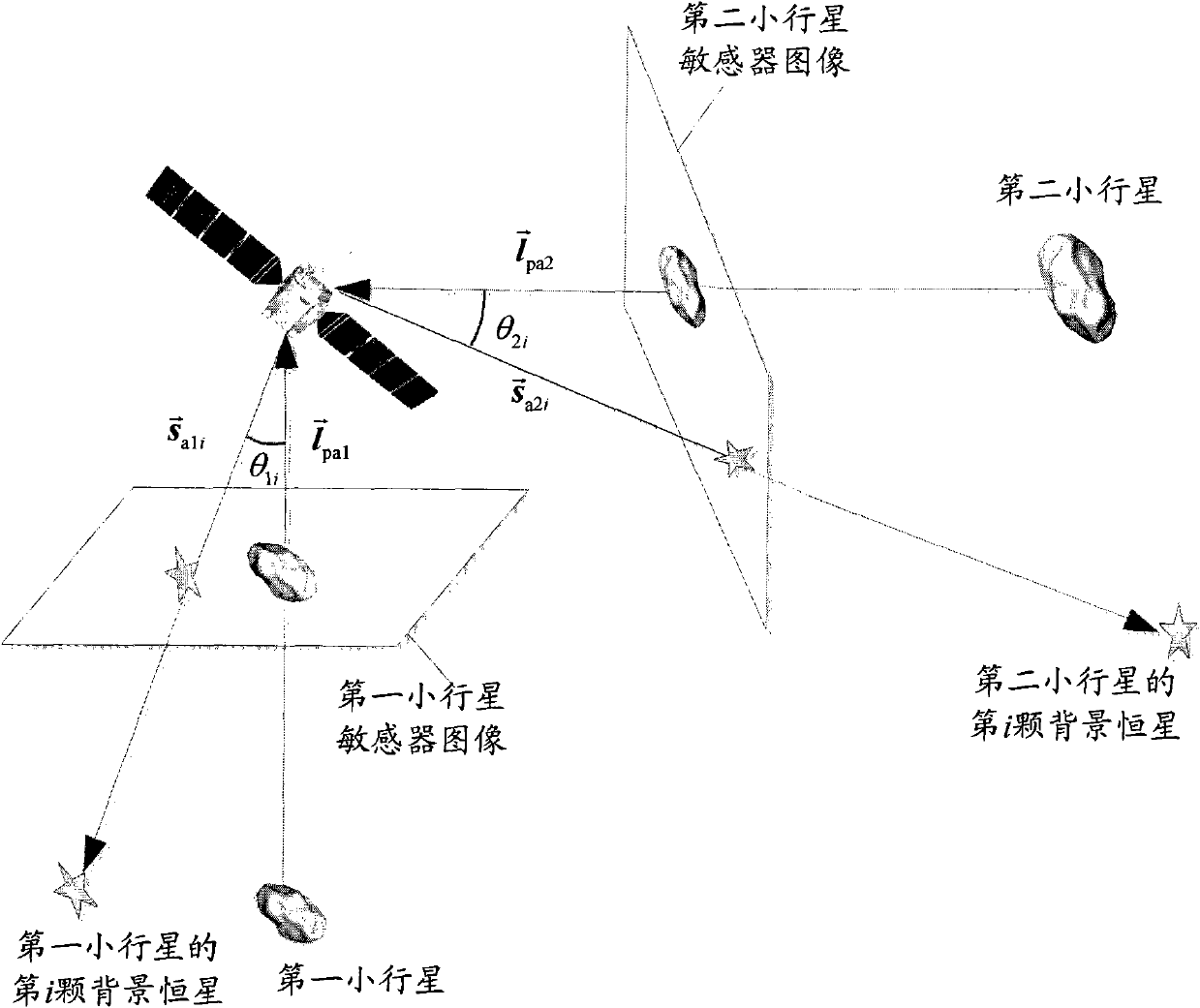
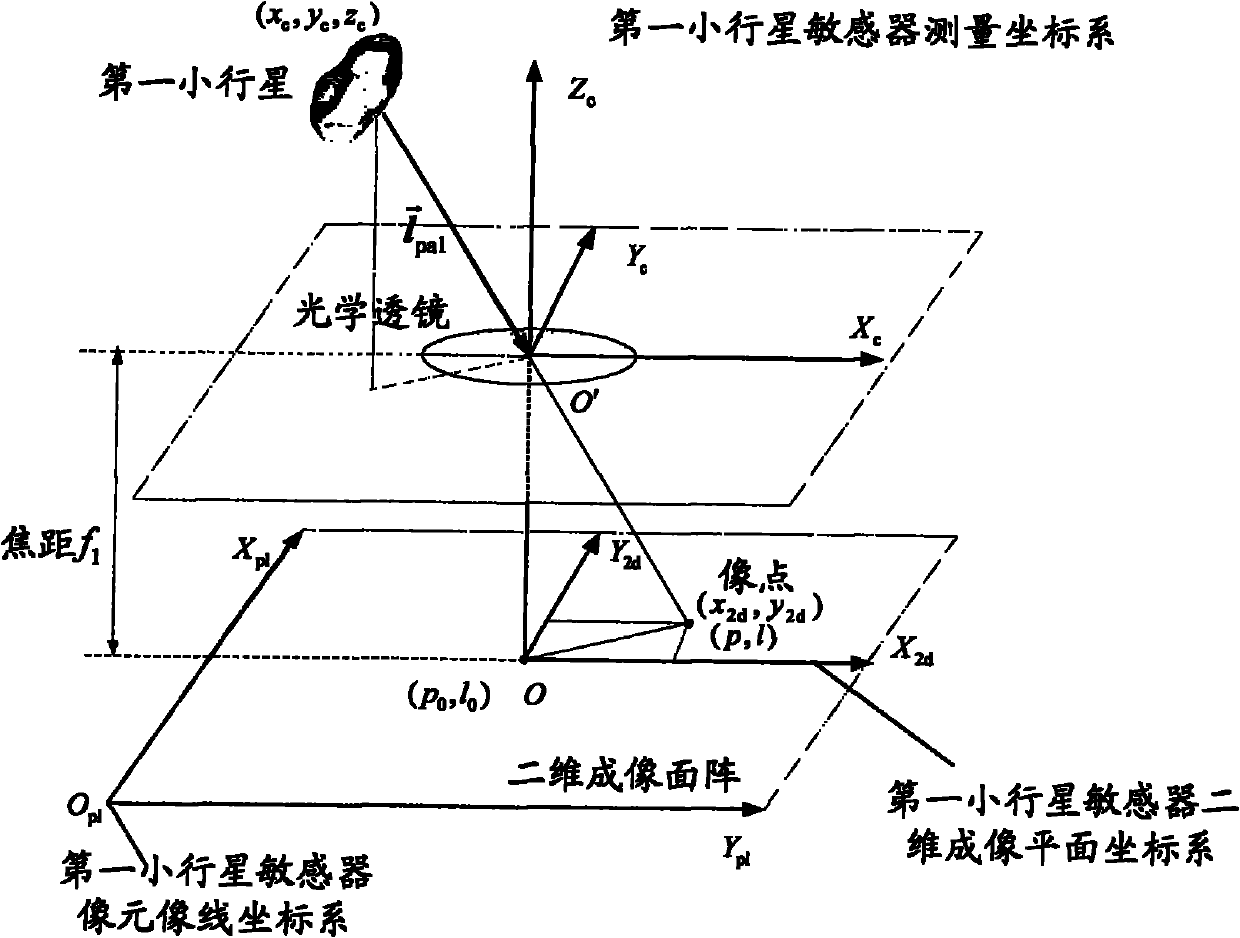
[0075] Considering the effects of the central gravity of the sun, the central gravity of Mars, the central gravity of the earth and the central gravity of Jupiter on the probe, and selecting the heliocentric ecliptic inertial coordinate system, the st...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com