Rapid autonomous all-sky map fixed star identification method
A star recognition and fast technology, applied in the field of star map recognition, can solve the problems of low recognition rate, long recognition time, poor real-time performance, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the number of redundant angular distances, improving the recognition success rate, and reducing the recognition time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0078] Specific embodiments of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
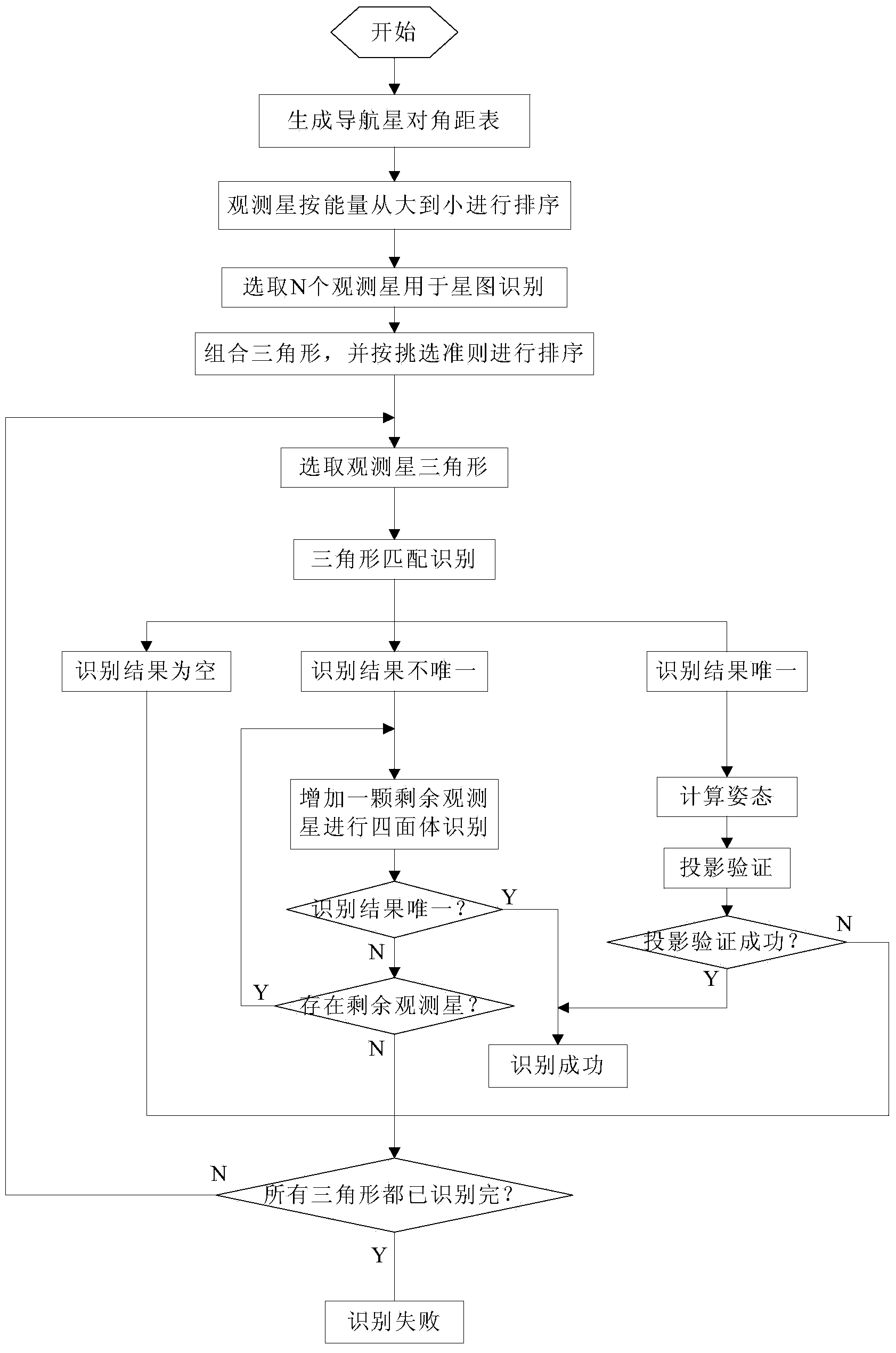
[0079] figure 1 It is a flow chart of the present invention, assume that the full field of view of the star sensor is ω, and the threshold of the number of navigation stars is Thr_Nstar. Taking a certain star sensor product as an example, its field of view is 20°×20°, that is, ω is 20° , set Thr_Nstar to 15, star map matching angular distance threshold Thr_angle1 to 60″, projection verification meets the angular distance threshold Thr_Nangle to 5, and projection verification angular distance threshold Thr_angle2 to 35″.
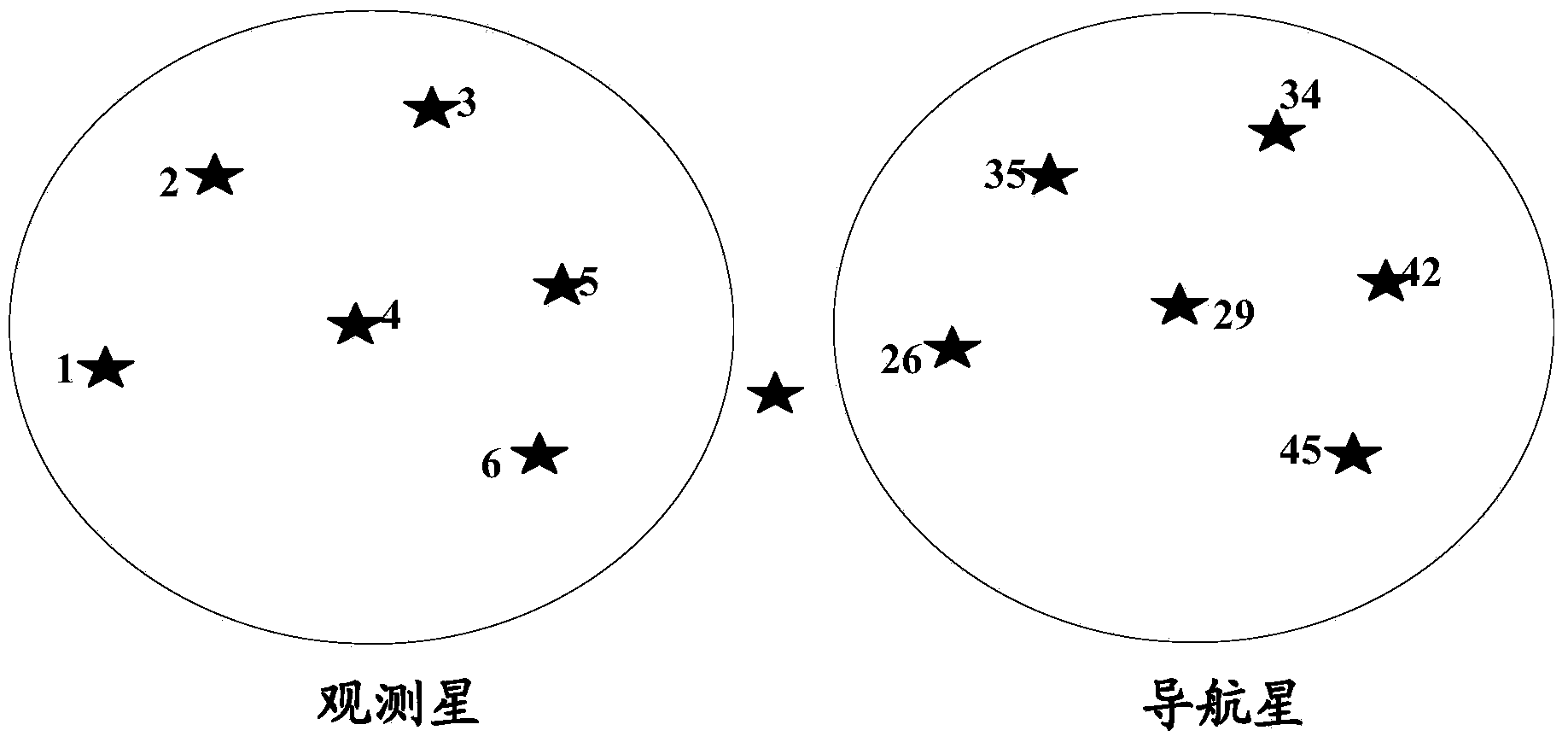
[0080] by image 3 Take the observation star and navigation star in the example as an example to illustrate the whole autonomous star map identification process. Such as image 3 As shown, the selected observation stars are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6, and the corresponding navigation star numbers are 26, 35, 34, 29, 42, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com