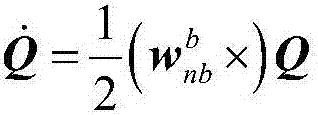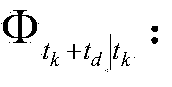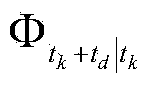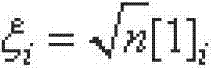Patents
Literature
714results about How to "Improve navigation accuracy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
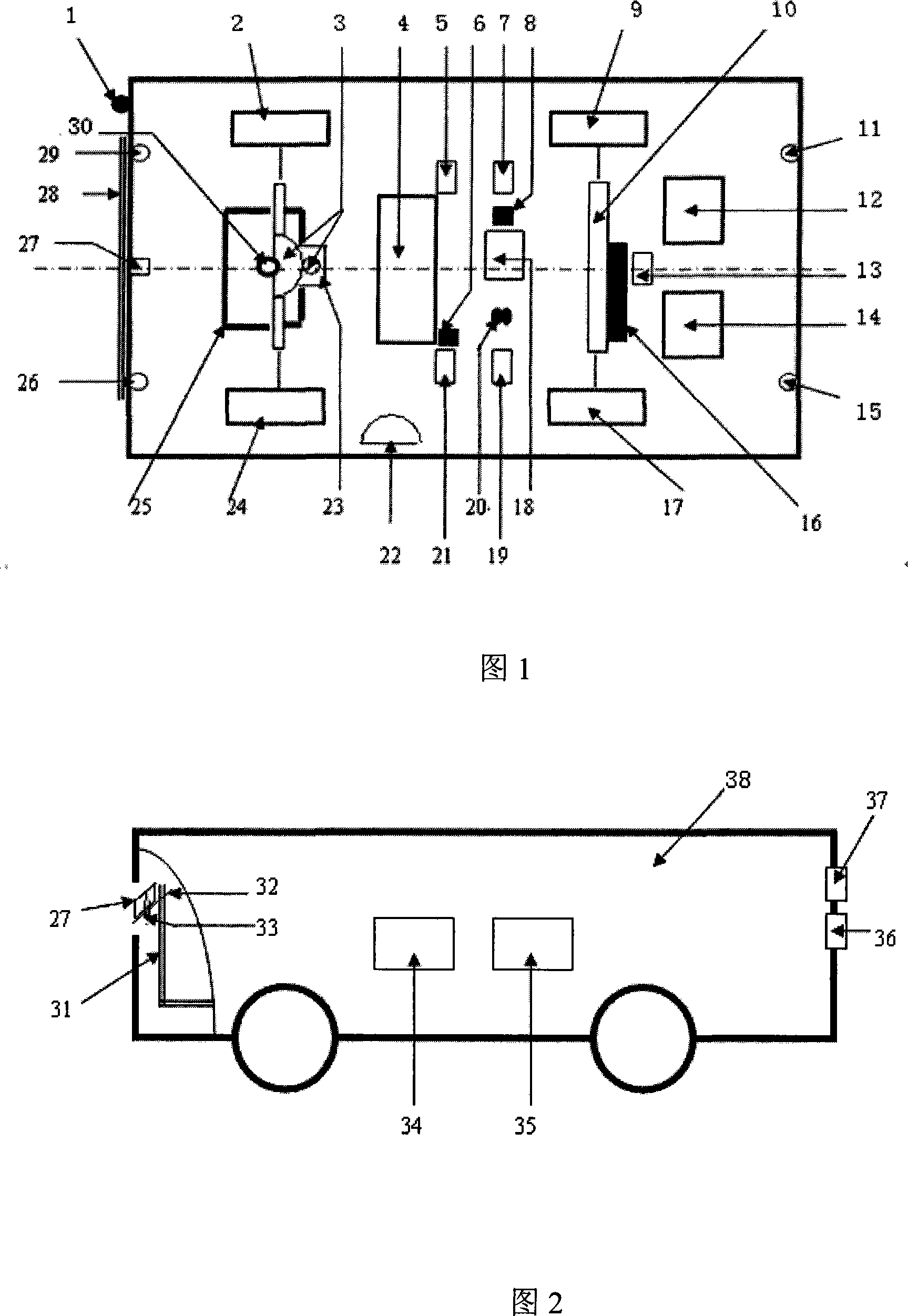
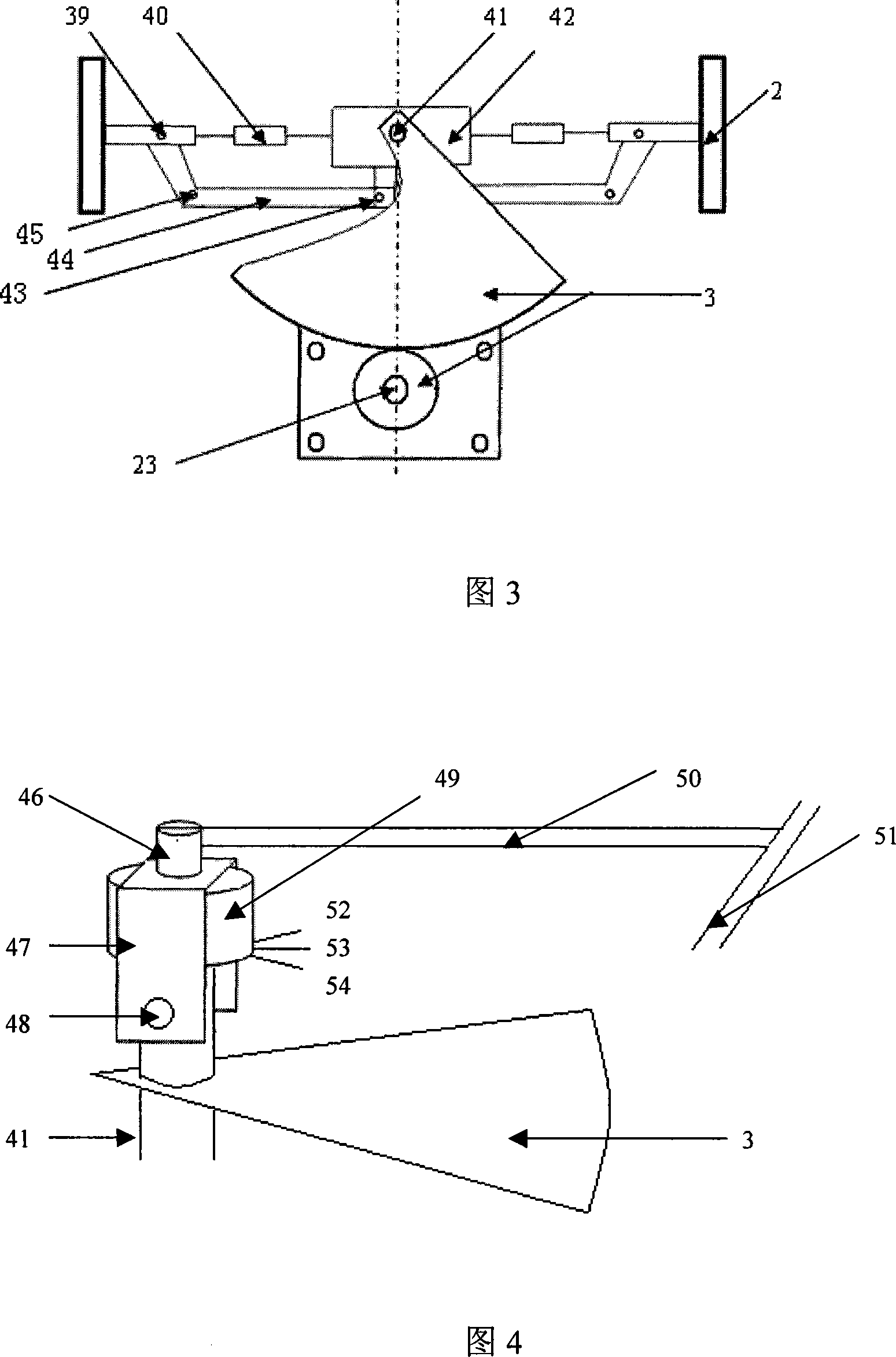
Wheel type mobile fruit picking robot and fruit picking method
InactiveCN102124866AReduce energy consumptionShorten speedProgramme-controlled manipulatorPicking devicesUltrasonic sensorData acquisition
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Automatic-navigation crawler-type mobile fruit picking robot and fruit picking method
InactiveCN102165880AFully automated pickingSimple structureProgramme-controlled manipulatorPicking devicesSimulationActuator
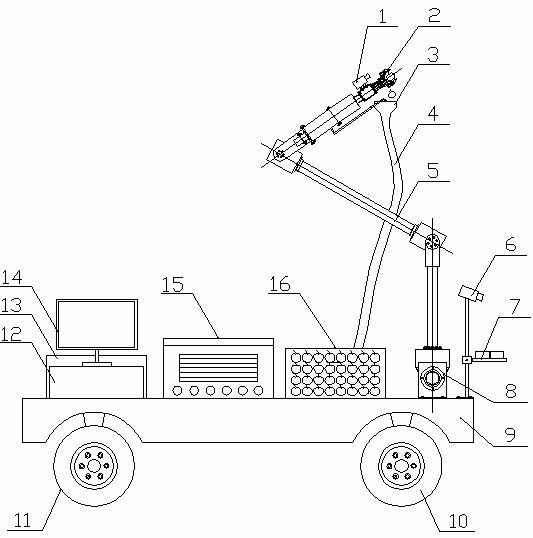
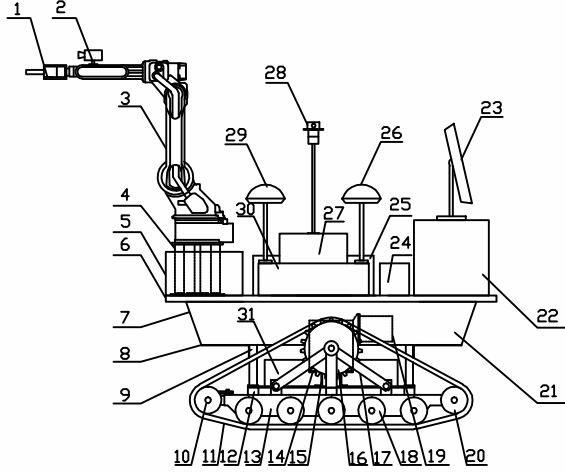
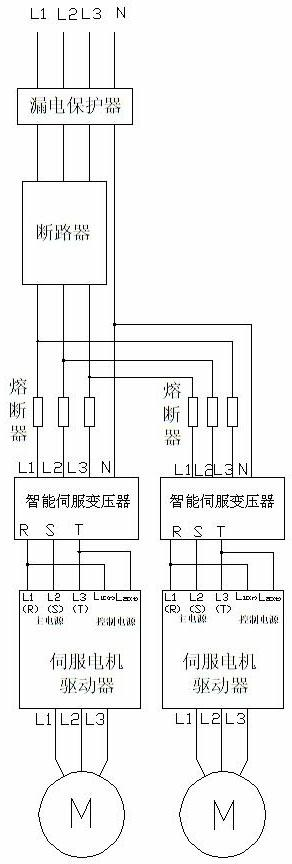
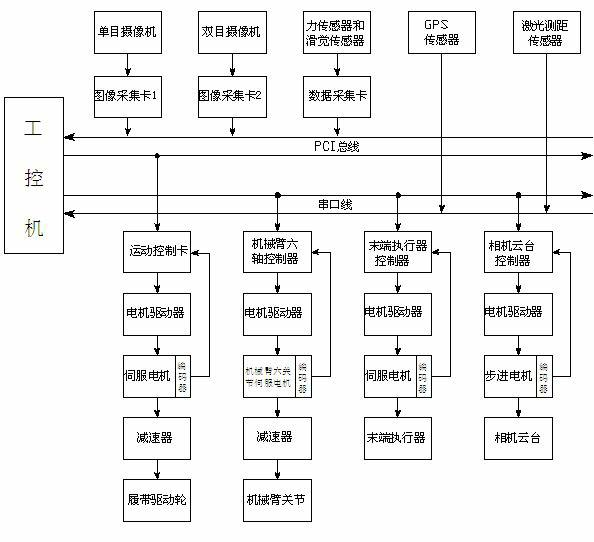
The invention discloses an automatic-navigation crawler-type mobile fruit picking robot which comprises a mechanical execution system and a control system and is characterized in that the mechanical execution system comprises an intelligent movable platform, a fruit picking mechanical arm and a two-finger type manipulator, wherein the intelligent movable platform comprises two crawler assemblies, an experimental facility fixing rack, a supporting stand column, a cross beam, a speed reducer and the like; and the control system comprises an industrial personal computer, a motion control card, a data collecting card, an image collecting card, an encoder, a GPS (global position system), a monocular zooming camera assembly, a binocular camera, a laser ranging sensor, a control circuit and the like. The automatic-navigation crawler-type mobile fruit picking robot integrates the fruit picking mechanical arm, the two-finger type manipulator, the intelligent movable platform and the sensor system, integrates multiple key technologies such as fruit identification, motion of the picking mechanical arm, grabbing of a tail-end executer, automatic navigation and obstacle avoidance of the movable platform, and the like, and really realizes automatic and humanized fruit picking.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Unmanned aerial vehicle vision/inertia integrated navigation method in unknown environment
InactiveCN101598556AWide adaptabilityImprove concealmentInstruments for comonautical navigationImaging processingCanyon
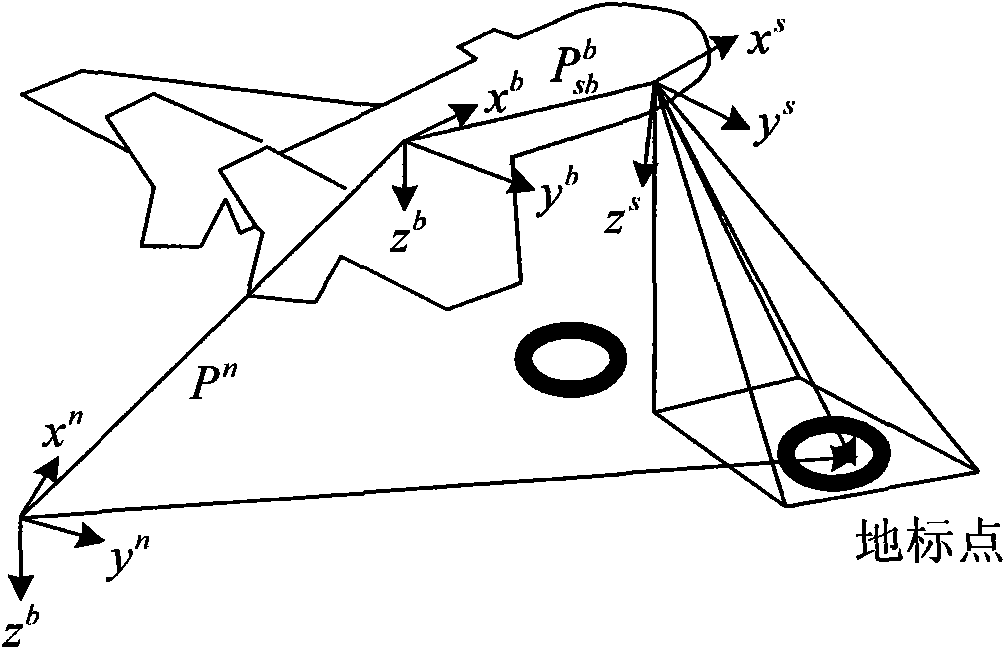
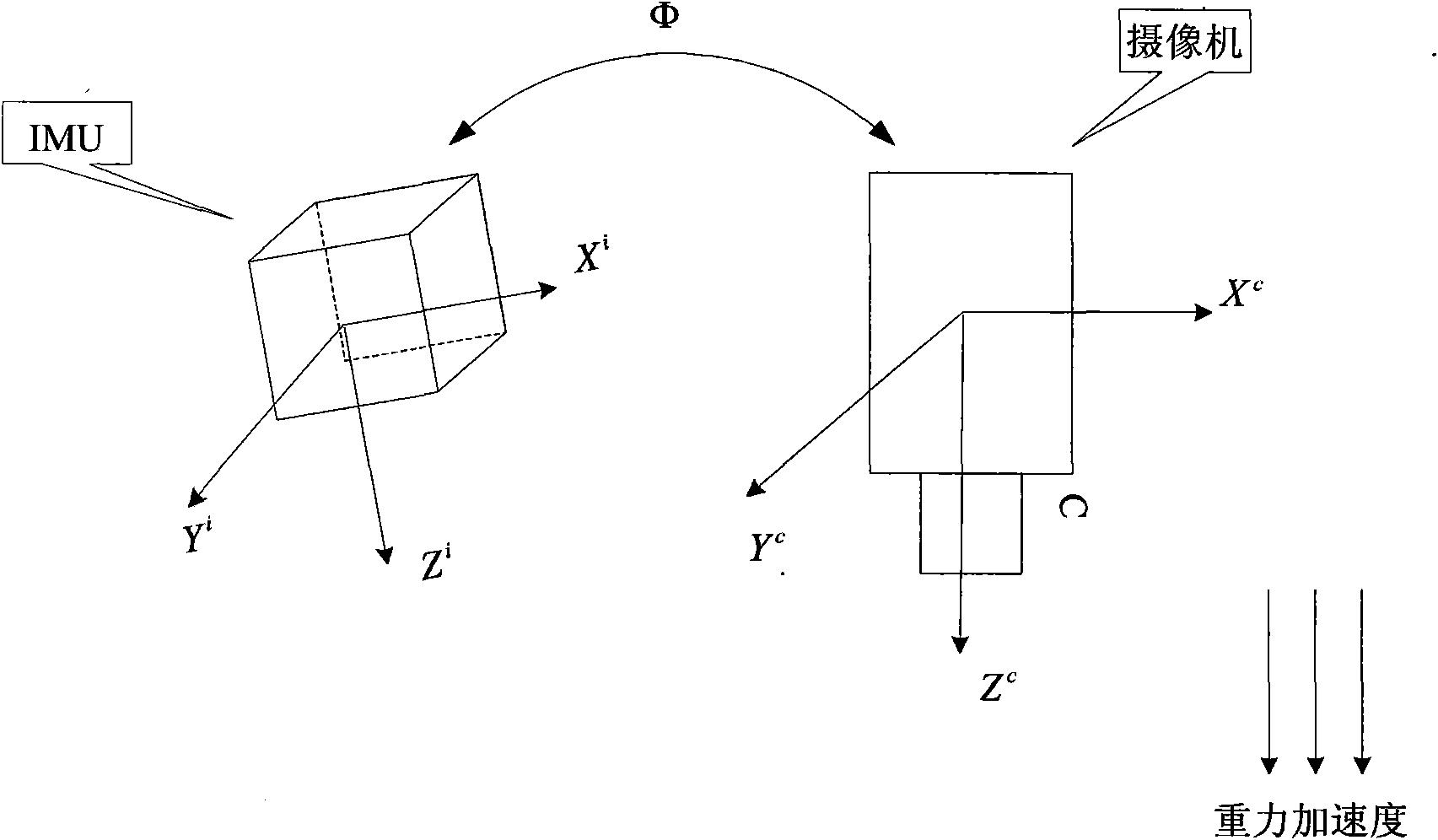
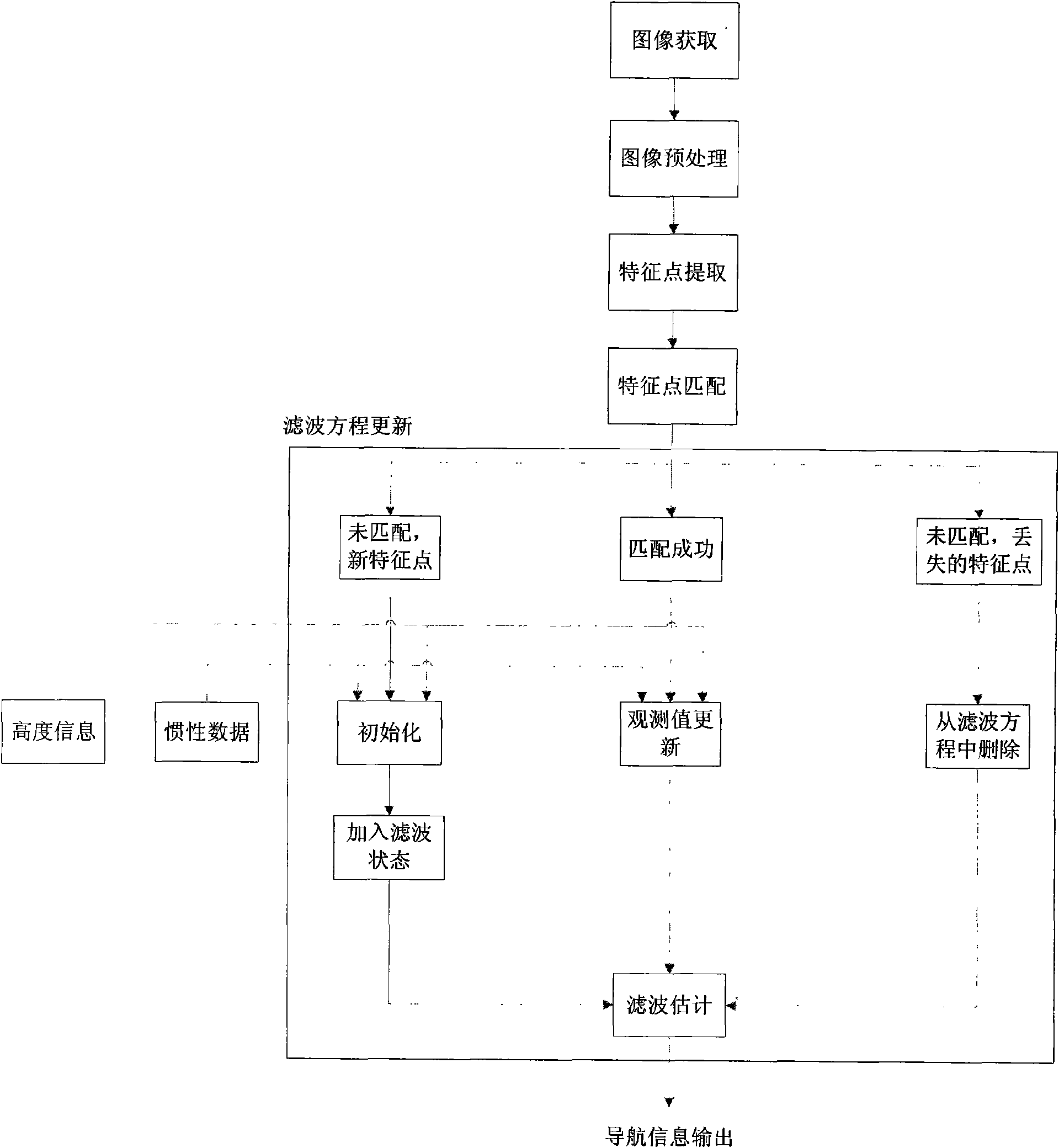
The invention relates to an unmanned aerial vehicle vision / inertia integrated navigation method in the unknown environment. The method relates to image processing, inertial navigation calculation and filtering estimation, so that the steps of defining coordinate system, aligning the coordinate system, setting up filter equation and the like are firstly carried out before the main navigation method is implemented. The navigation process of the method comprises five steps: acquiring and pretreating image; extracting feature points by a SIFT method; matching the feature points; updating the filter equation; and carrying out the filtering estimation on the updated filter equation. The method only needs the current ground image instead of specific external information for matching, so as to be used in any environment (including underwater, shelter, canyon, underground and the like) in theory; furthermore, the method has the advantages of good sheltered property and high accuracy.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Vision-based combined navigation robot and navigation method
ActiveCN102789233AImplement combined navigationImprove reliabilityNavigation instrumentsPosition/course control in two dimensionsVisual navigationDigital camera
The invention relates to a vision-based combined navigation robot and a navigation method. The robot comprises a four-wheel drive trolley and a color digital camera arranged on the body of the trolley; a plurality of ultrasonic sensors which are arranged at the front and the rear ends of the trolley body and used for detecting the distance information of obstacles around the robot; a gyroscope mounted inside the trolley body and used for detecting the attitude information of the robot; four photoelectric encoders which are arranged on four sets of servo drive motors respectively and used as speedometers; a motor controller; and a robot trolley body control system computer used for ensuring the real time performance of image processing and control. The navigation method provided by the invention mainly works based on the visual navigation in combination with the related information of the speedometer, the gyroscope and the ultrasonic sensors, resulting in combined navigation, so as to improve the reliability and navigation precision of the system to the greatest extent.
Owner:HUBEI SANJIANG AEROSPACE HONGFENG CONTROL
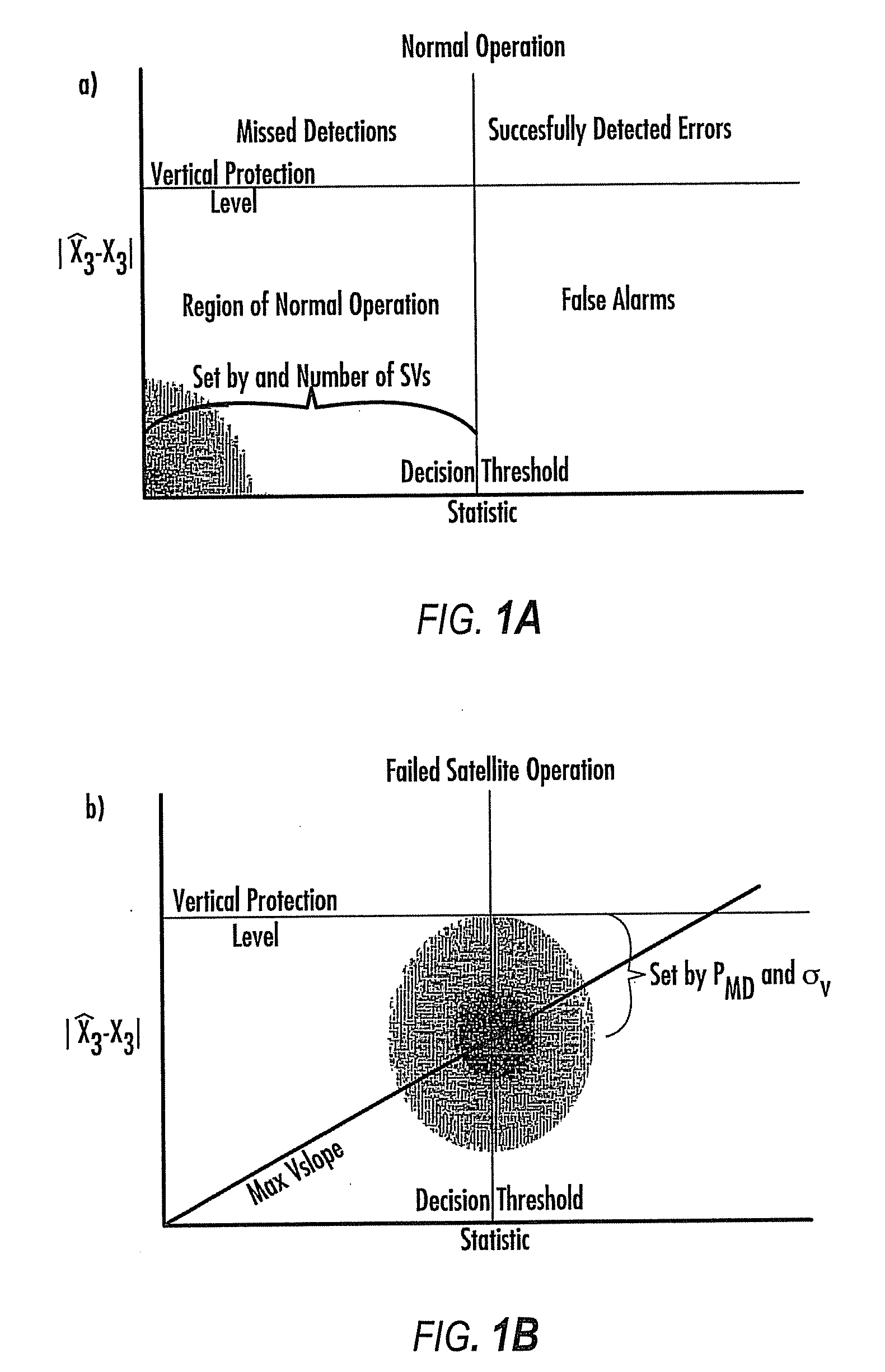
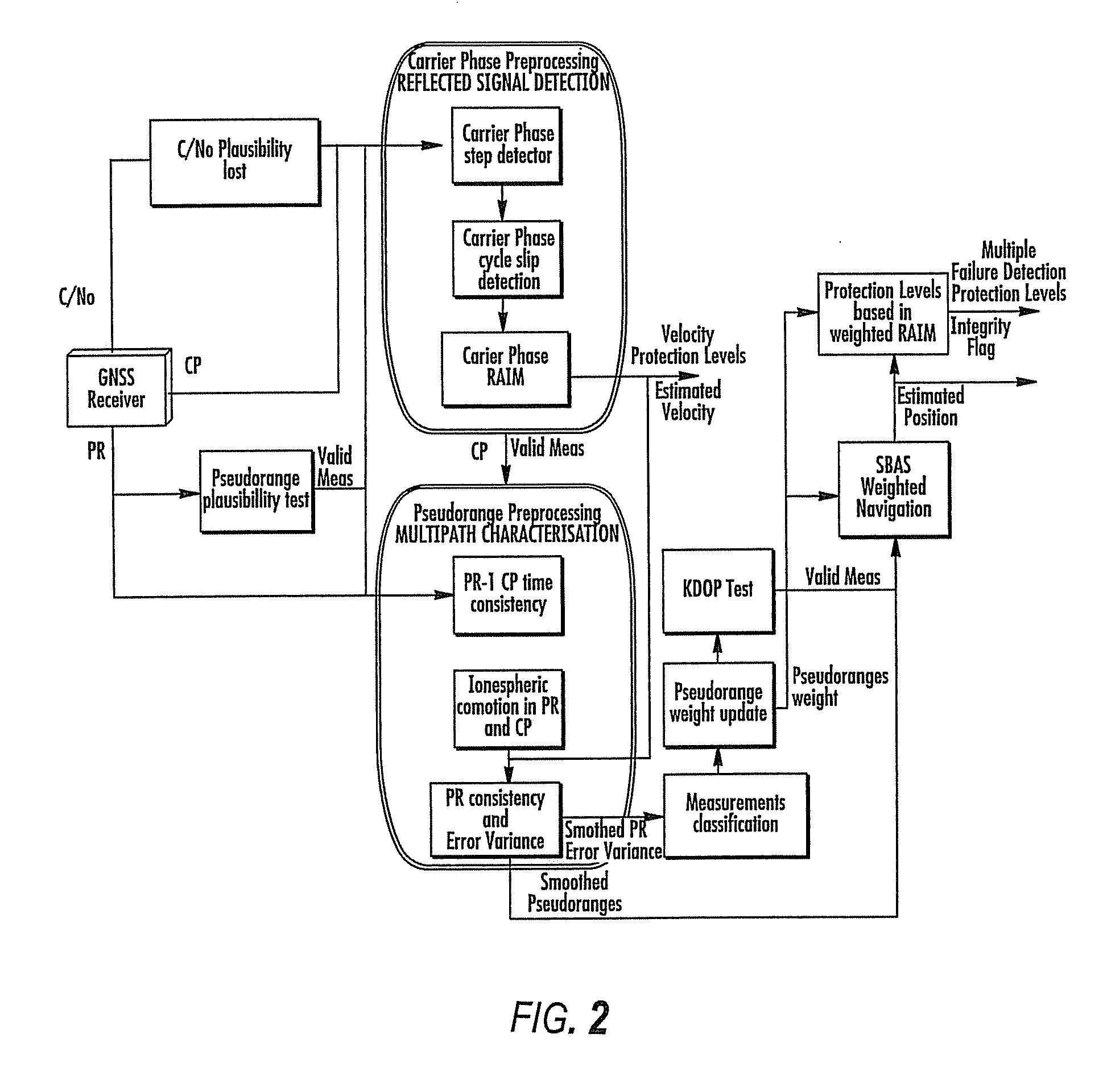
GNSS navigation solution integrity in non-controlled environments
ActiveUS20100033370A1Efficient methodImprove navigation accuracyPosition fixationNavigation instrumentsNoise levelMarine navigation
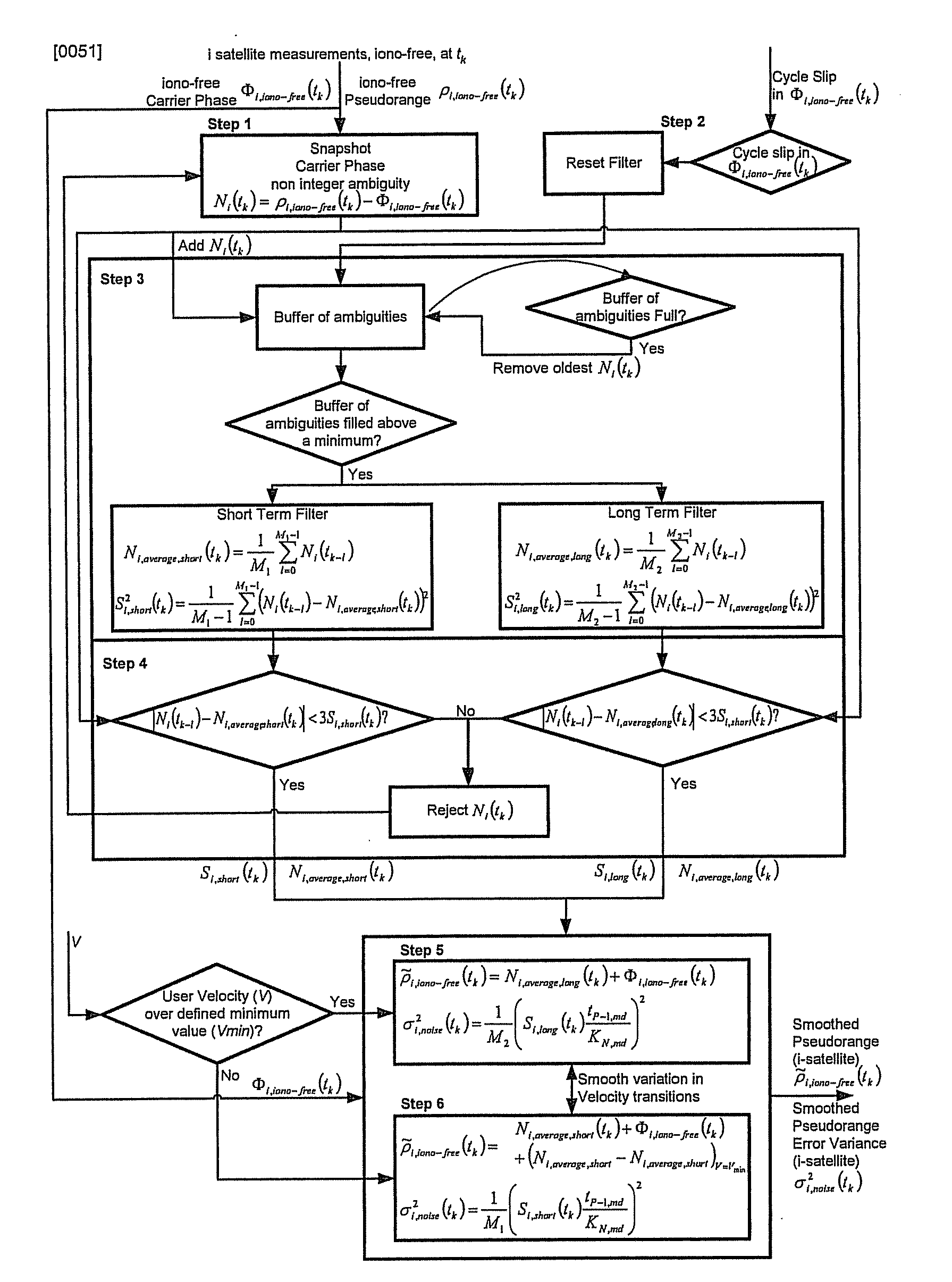
Disclosed is a method for providing a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) navigation position solution with guaranteed integrity in non-controlled environments, the method including processing a (GNSS) signal including multiple satellites generating at least one signal to obtain carrier phase and pseudorange measurements; pre-processing the measurements to detect and characterize local errors in the measurements, wherein the local errors cannot be ascertained a priori, the characterization including providing error bounds estimated by measuring the carrier phase and pseudoranges measurements, thereby providing a set of measurements rejections when the characterization is not possible; and using the estimated error bounds, together with error bounds provided by the GNSS signal concerning satellite and ionospheric errors, to build in each measurement an estimated noise level in the measurements as input to a weighted Receiver Autonomous Integrity Monitoring (RAIM) algorithm in order to compute position coordinates and associated protection levels in the non-controlled environments.
Owner:GMV AEROSPACE & DEFENCE
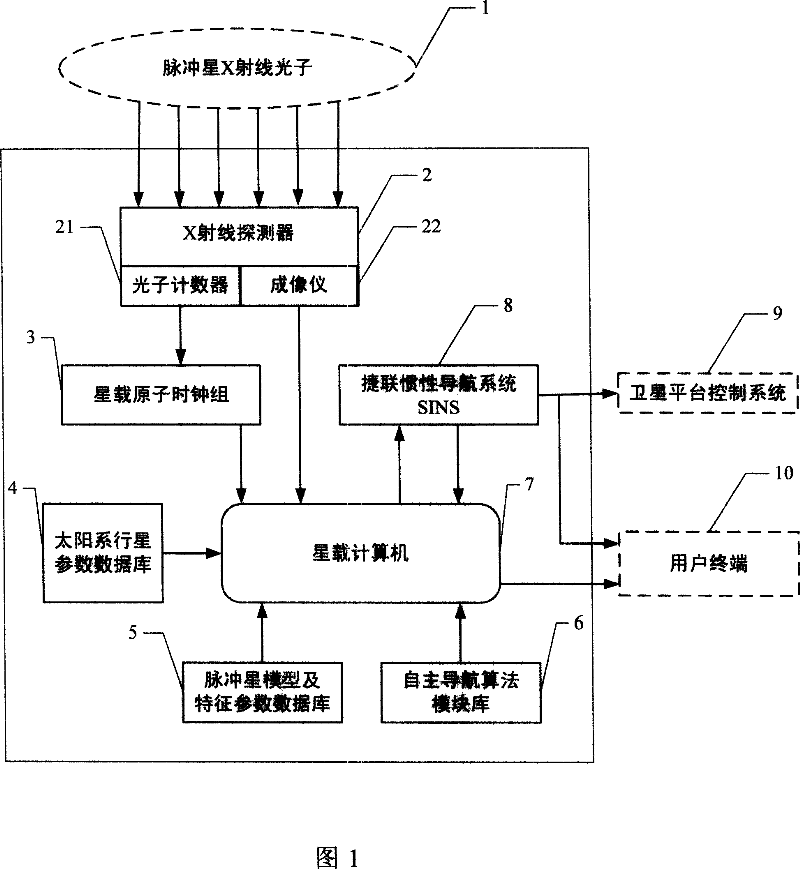
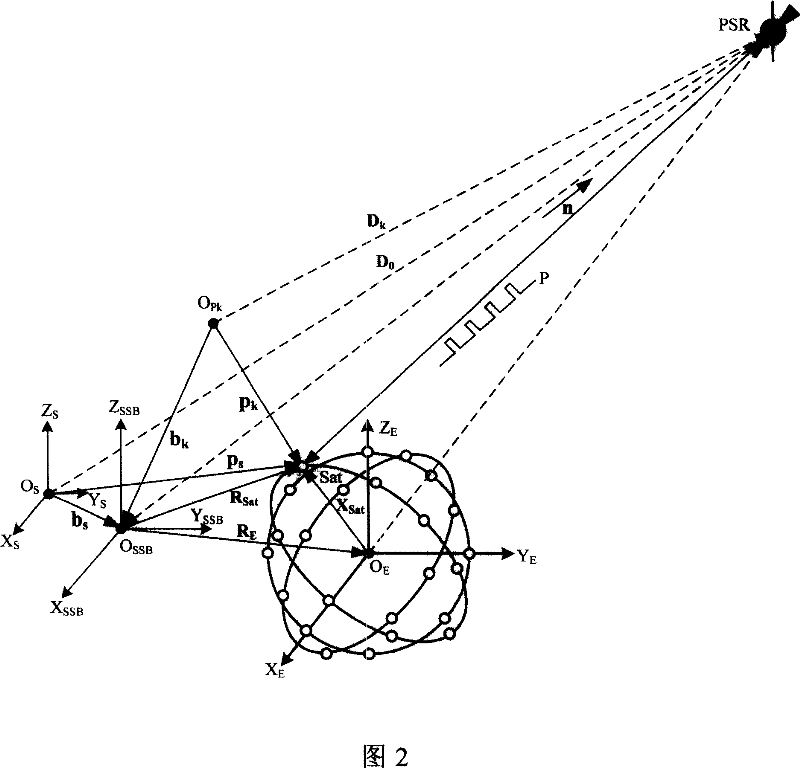
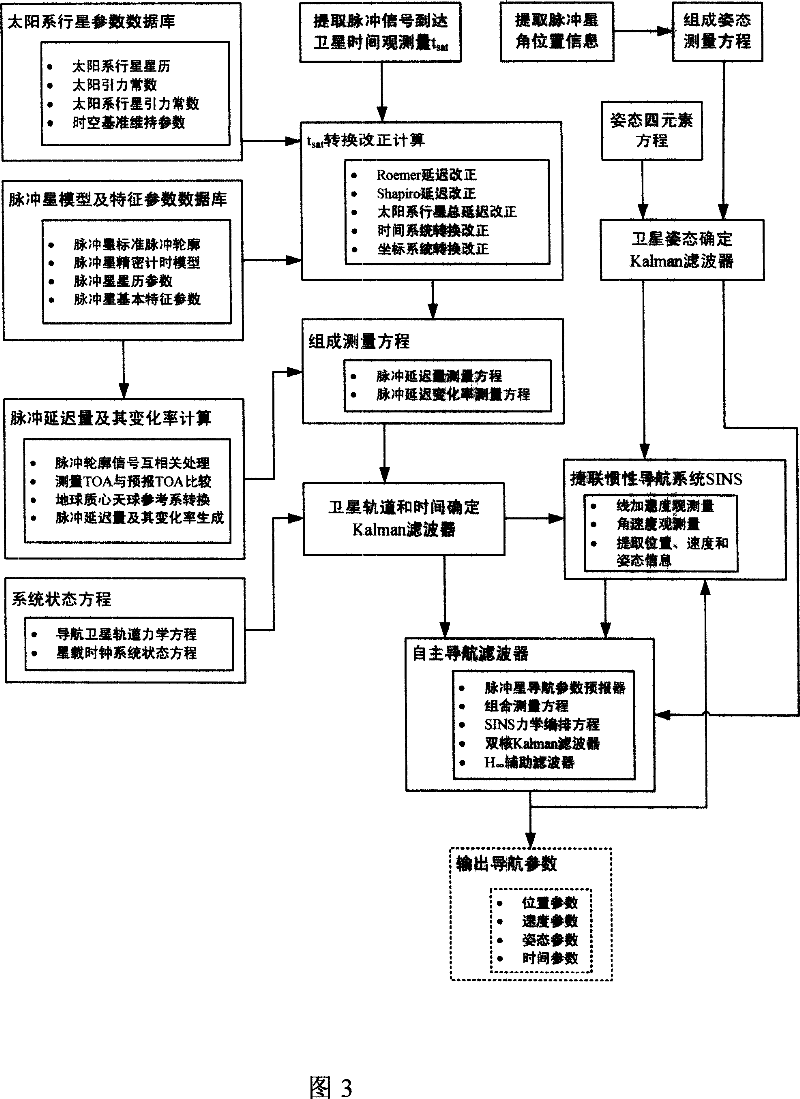
Navigation satellite autonomous navigation system and method based on X-ray pulsar
InactiveCN101038169AHigh precision autonomous navigationStable periodicityInstruments for comonautical navigationNavigation by astronomical meansFault toleranceInformation processing
A autonomous navigation system of a navigational satellite based on X radial pulse satellite includes: an X radial detector, an atomic clock group on the satellite, a planet of our solar system parameter database, an X radial pulsar module and a characteristic parameter database, a computer on the satellite, a strap-down inertial navigation system SINS and an autonomous navigation algorithm module library; in the autonomous navigation method, the X radial photons radiated from the pulsar are used as the input of the external information; the pulse arrival time TOA and the angular position information are obtained; data is processed through a autonomous navigation filter; and the navigational parameters such as the position, the speed, the time and the pose of the navigational satellite; the navigational telegraph text and the control command are generated independently, and the independent running of the navigational satellite is realized. The present invention has the advantages of providing a long time and a high degree of accuracy autonomous navigation, and providing the fault-tolerance capacity of the autonomous navigation information processing. The autonomous navigation system is also be adequate for the high degree of accuracy autonomous navigation of the near earth orbit, the deep space, the interplanetary flight space vehicle, the a celestial body lander without thickset atmosphere and the surface peripatetic machine.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT SYST ENG
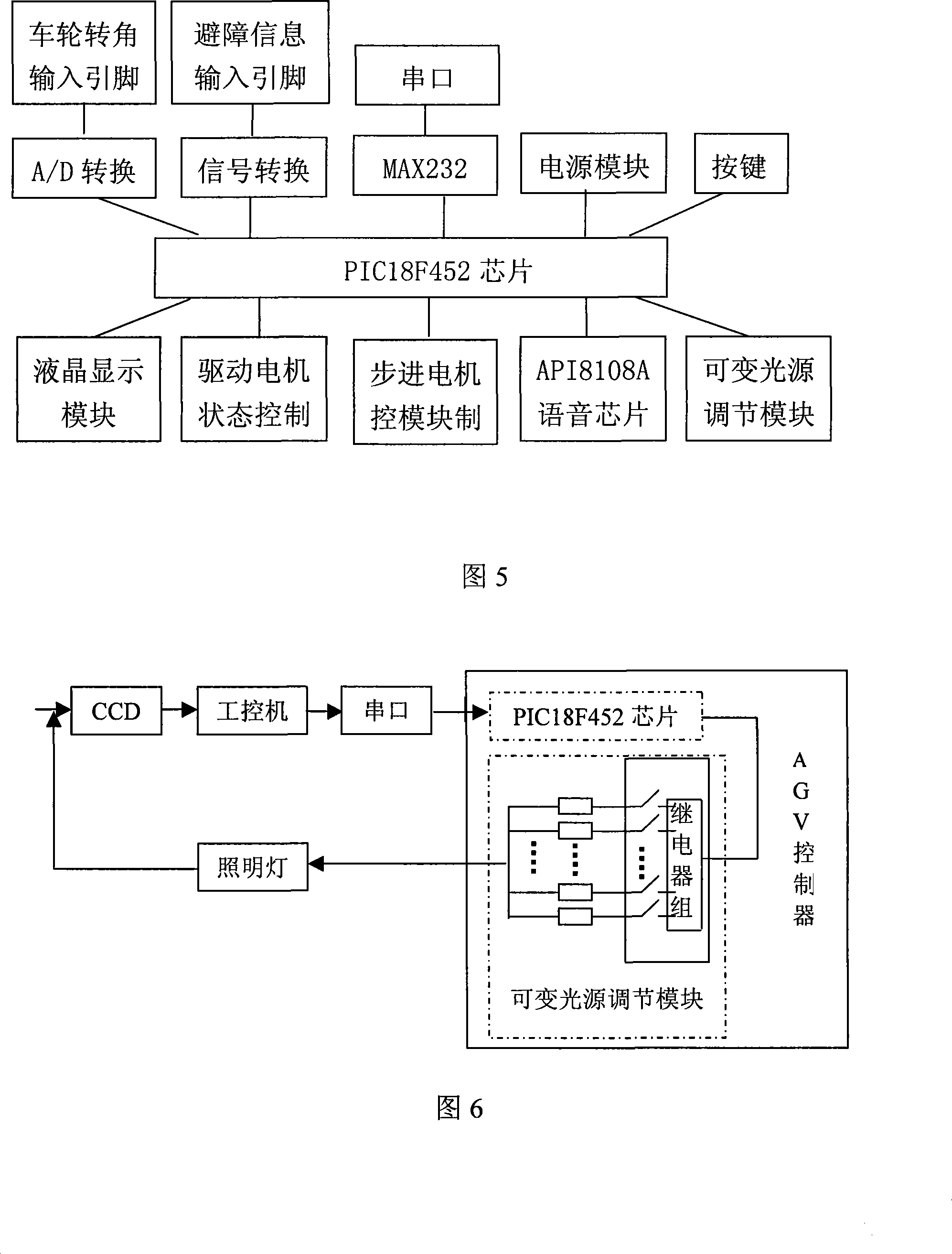
Automatic guidance system based on radio frequency identification tag and vision and method thereof
InactiveCN101183265AImprove stabilityLarge information capacityCo-operative working arrangementsCharacter and pattern recognitionWireless transceiverControl signal
The invention discloses an automatic guidance system based on radio frequency identification labels and vision, and the method of the automatic guidance system. The invention is characterized in adopting a four-wheel structure, wherein two front wheels are used for steering and two rear wheels are used for driving; a direct current motor is used as the travelling and driving device, which is driven to steer by a stepping motor; the invention is provided with a wheel steering angle positioning device, so the invention has relatively high dynamic response ability; a black and white parallel guide belt is adopted as a guide path, with the radio frequency identification labels discontinuously laid below, and red work station characters arranged at both sides; CCD collects road surface information, and the brightness of light source adaptive controls according to image gray information; characters are extracted by utilizing color differences; straight lines are rapidly HOUGH transformed and identified; a control signal is sent to AGV controller after processed by an industrial control computer, and the direct current motor and the stepping motor are controlled. In order to effectively realize the communication dispatch between AGVS in real time, radio frequency identification labels are adopted for positioning, and a wireless transceiver module is adopted for communication between AGVS and a host. The invention has the advantages of good environmental adaptability and navigation precision, and lower cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
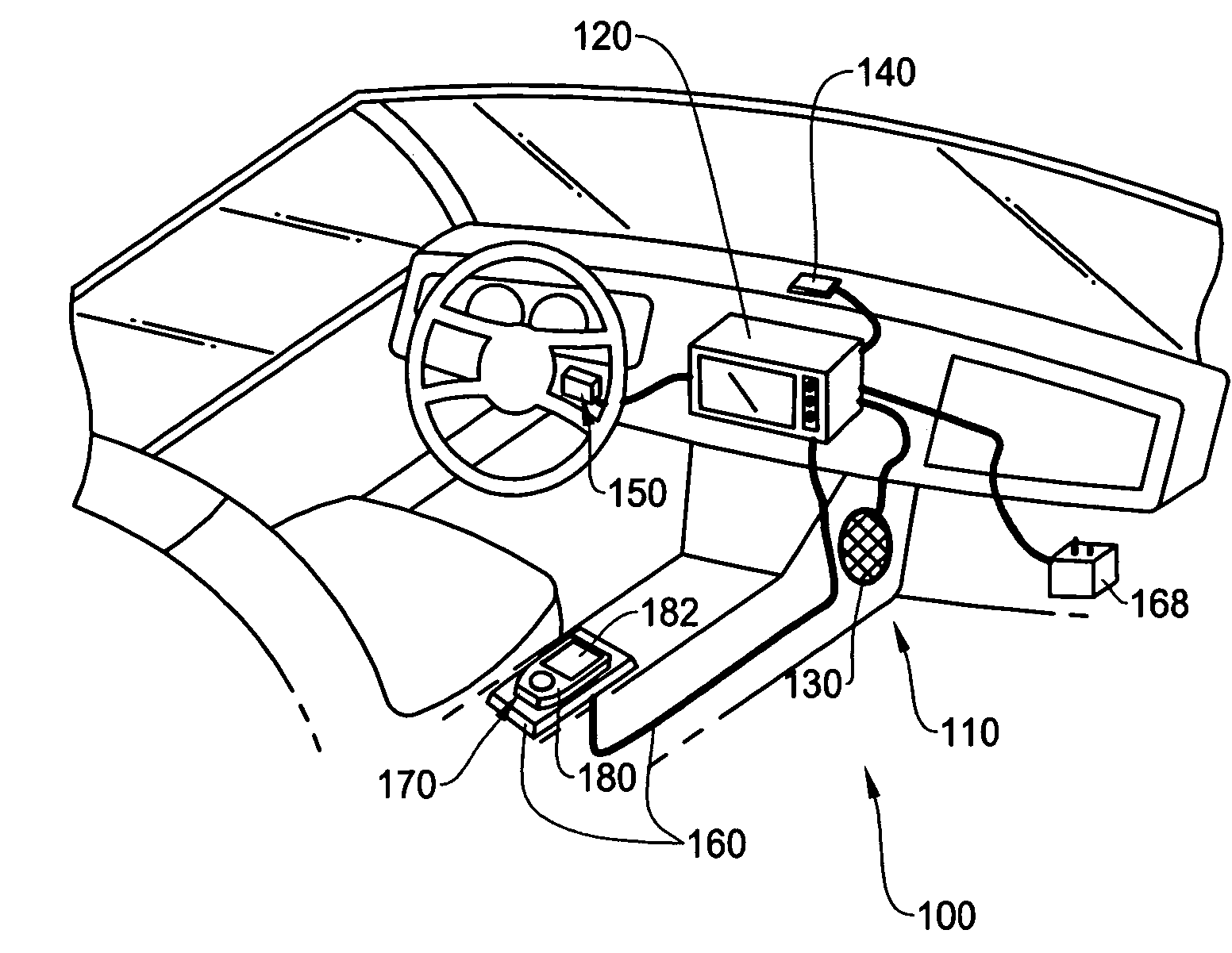
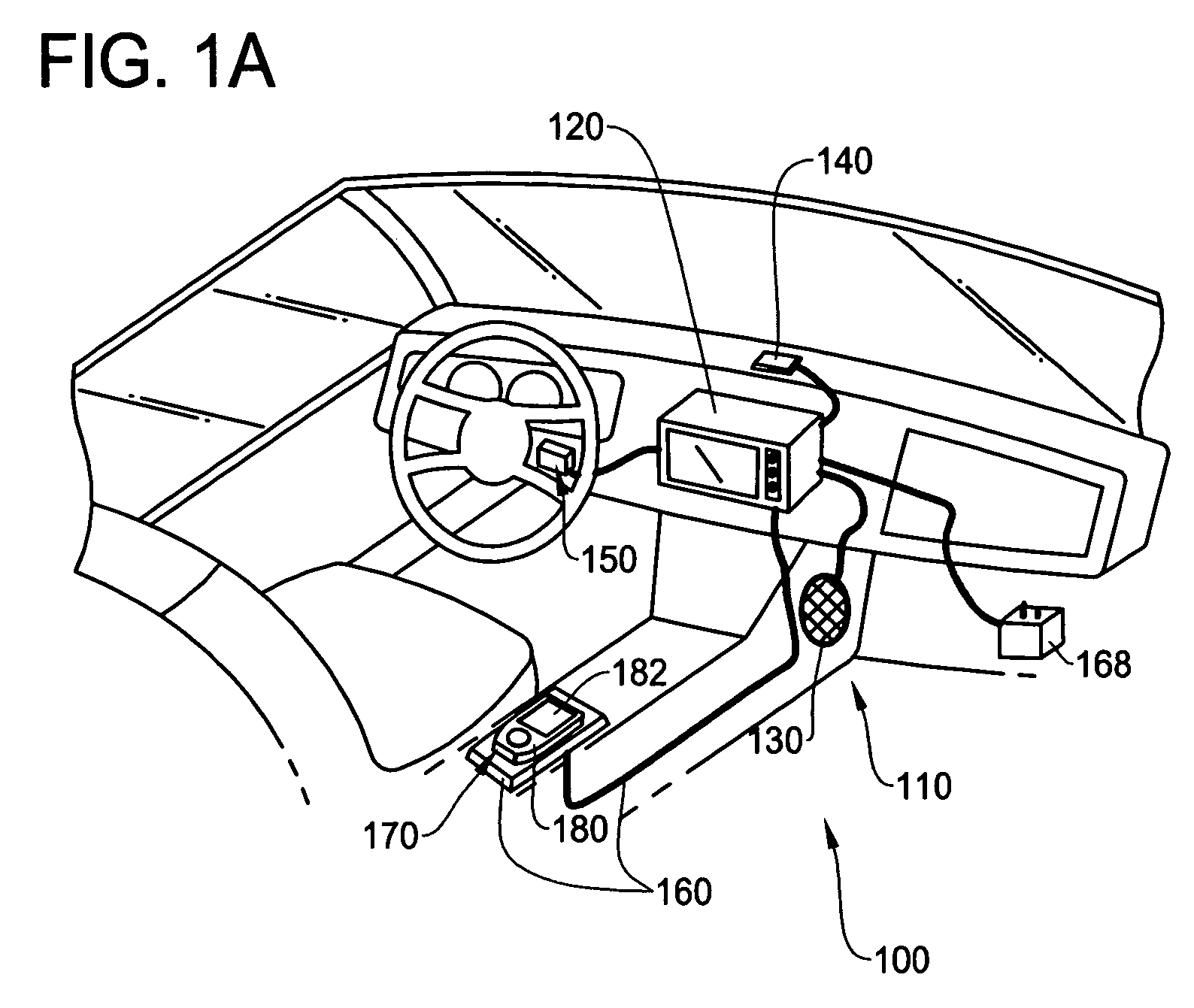
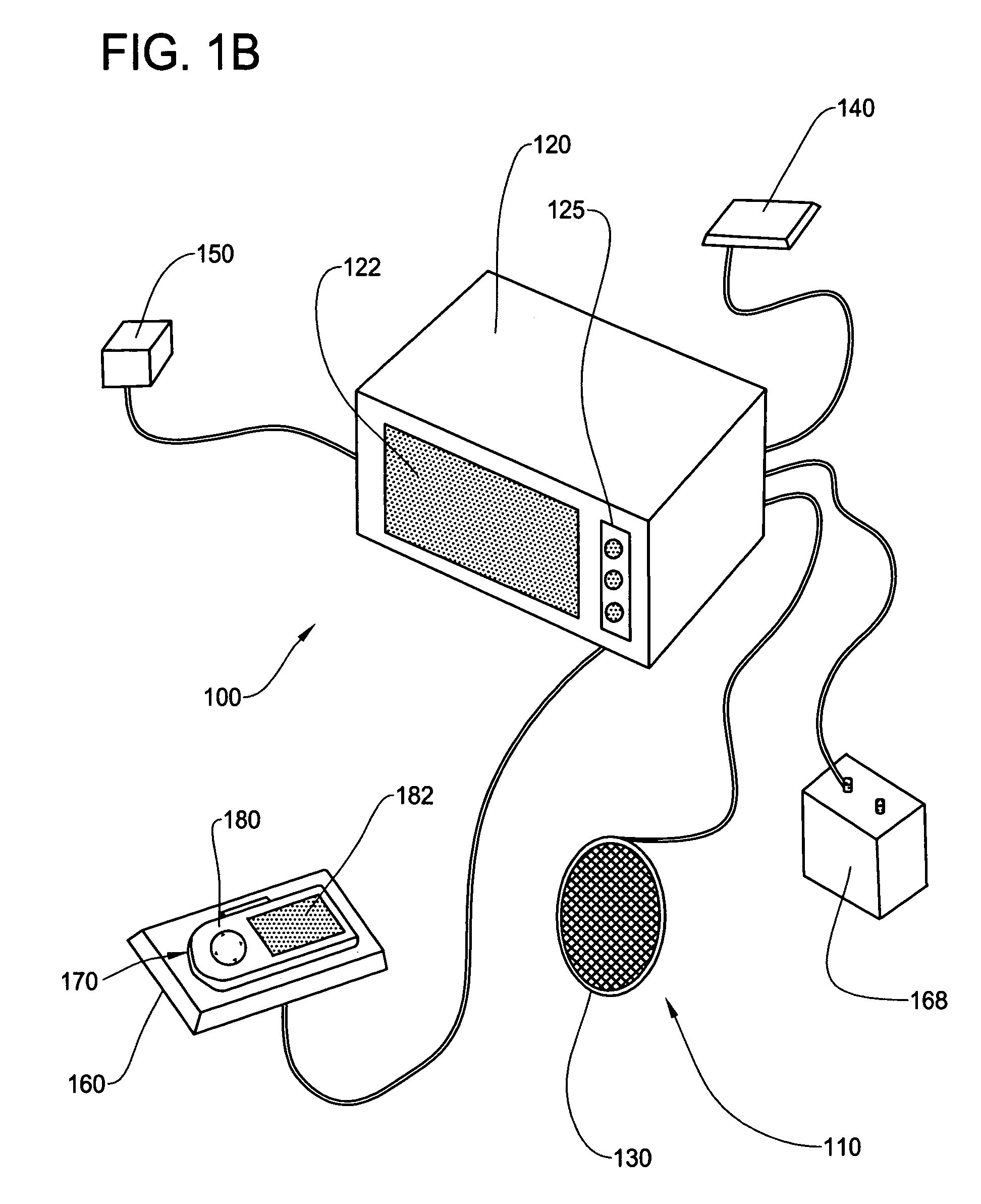
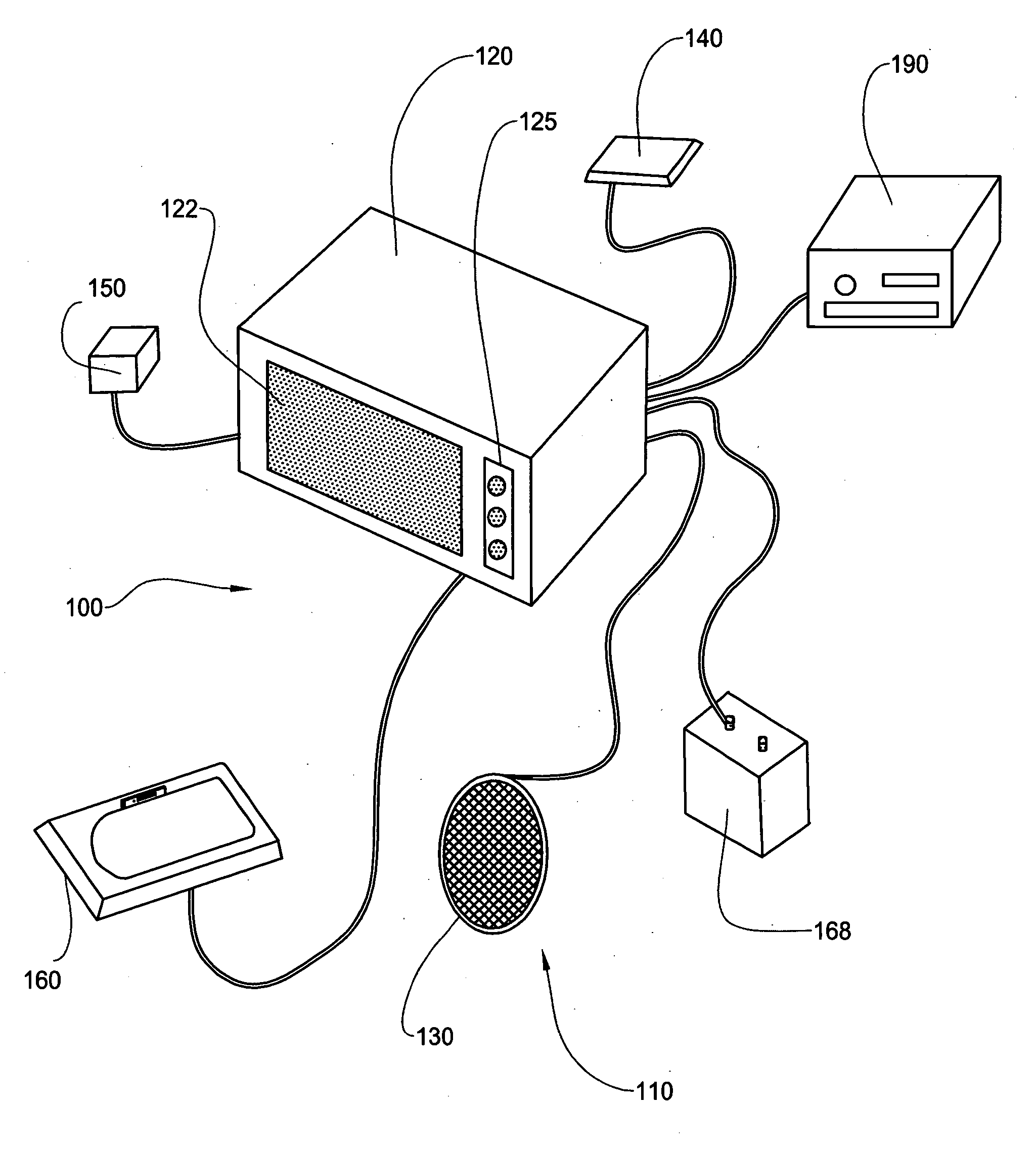
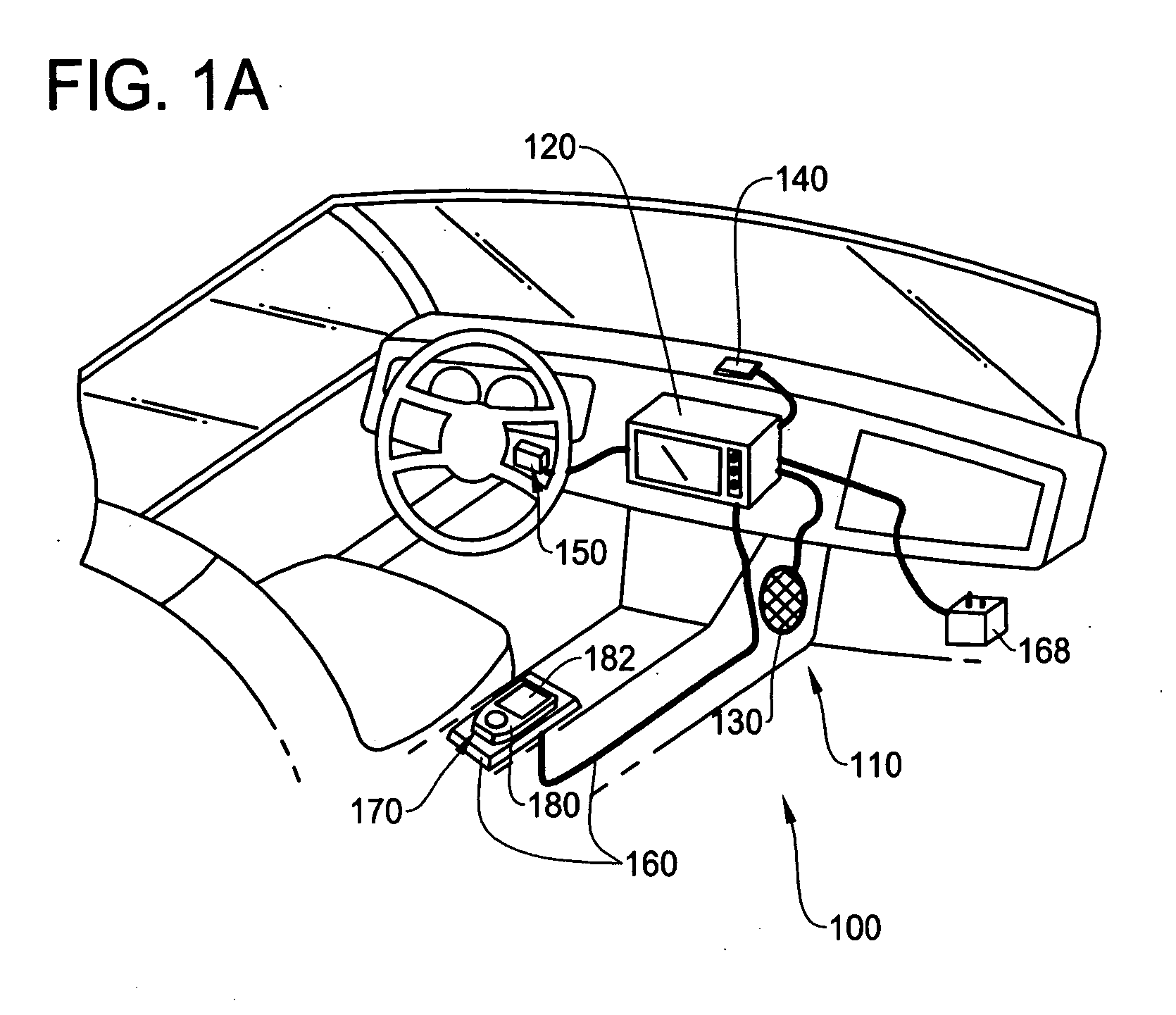
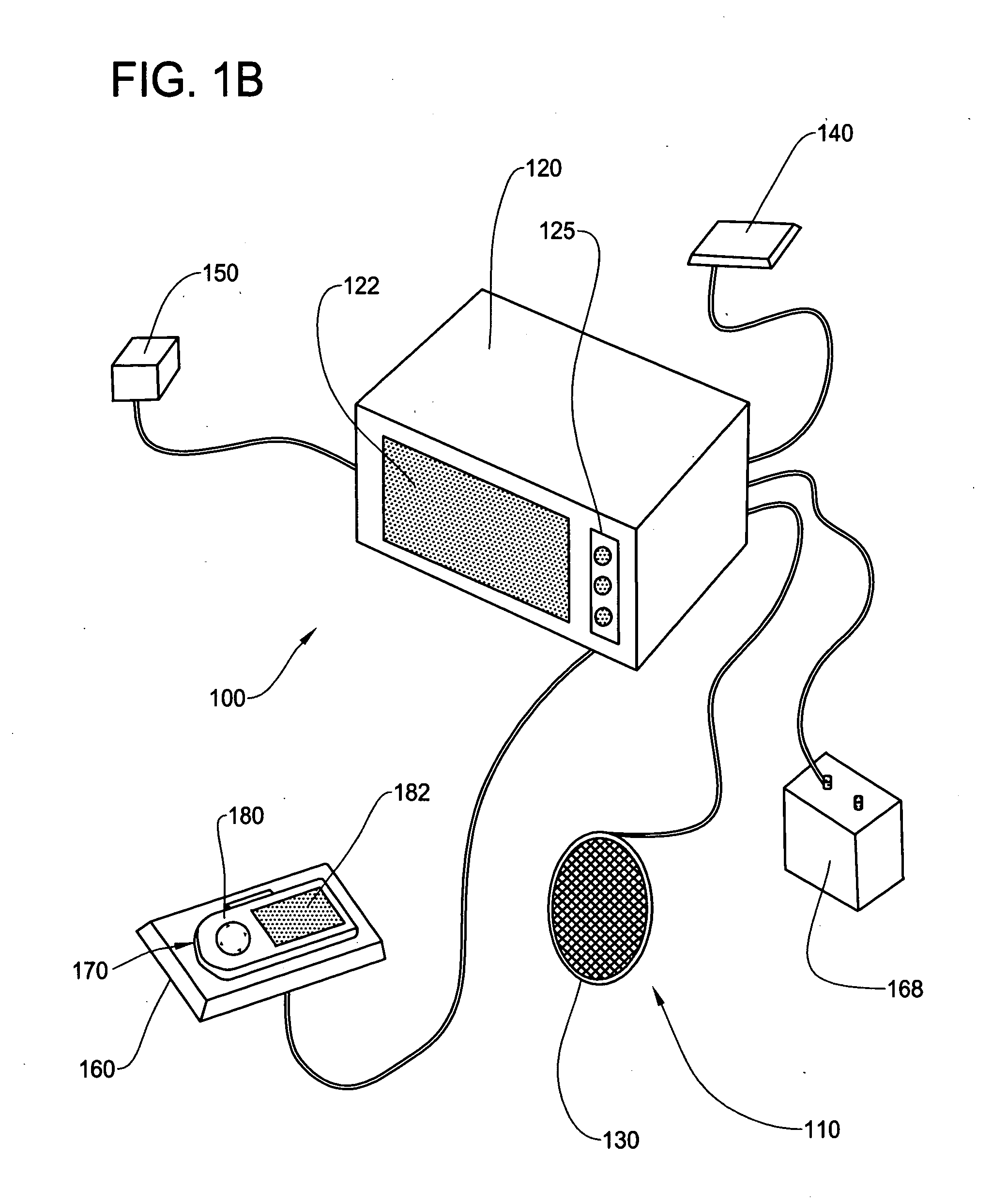
In-vehicle navigation system with removable navigation unit
ActiveUS7606660B2Promote generationEasy to useInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlIn vehicleCombined use
A navigation system includes an in-vehicle portion and a removable navigational unit, where the removable navigation unit is a portable device with navigation capability on its own. The removable navigation unit is capable of being connected to the in-vehicle portion through an navigation interface to perform the navigation function in combination with the in-vehicle portion. The removable navigation unit seamlessly integrates with the in-vehicle portion of the vehicle to provide portability of navigation function when used independently from the in-vehicle portion, and taking advantage of the components of in-vehicle portion when used in conjunction with the in-vehicle portion.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
In-vehicle navigation system with removable navigation unit
ActiveUS20070203641A1Promote generationEasy to useInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlIn vehicleCombined use
A navigation system includes an in-vehicle portion and a removable navigational unit, where the removable navigation unit is a portable device with navigation capability on its own. The removable navigation unit is capable of being connected to the in-vehicle portion through an navigation interface to perform the navigation function in combination with the in-vehicle portion. The removable navigation unit seamlessly integrates with the in-vehicle portion of the vehicle to provide portability of navigation function when used independently from the in-vehicle portion, and taking advantage of the components of in-vehicle portion when used in conjunction with the in-vehicle portion.
Owner:ALPINE ELECTRONICS INC
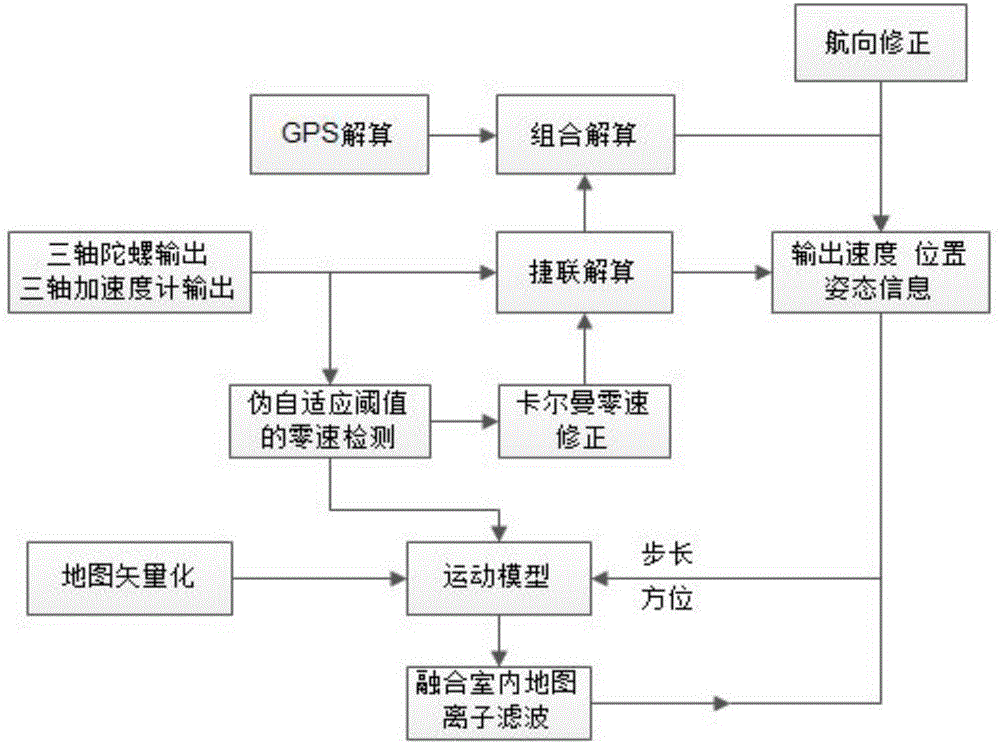
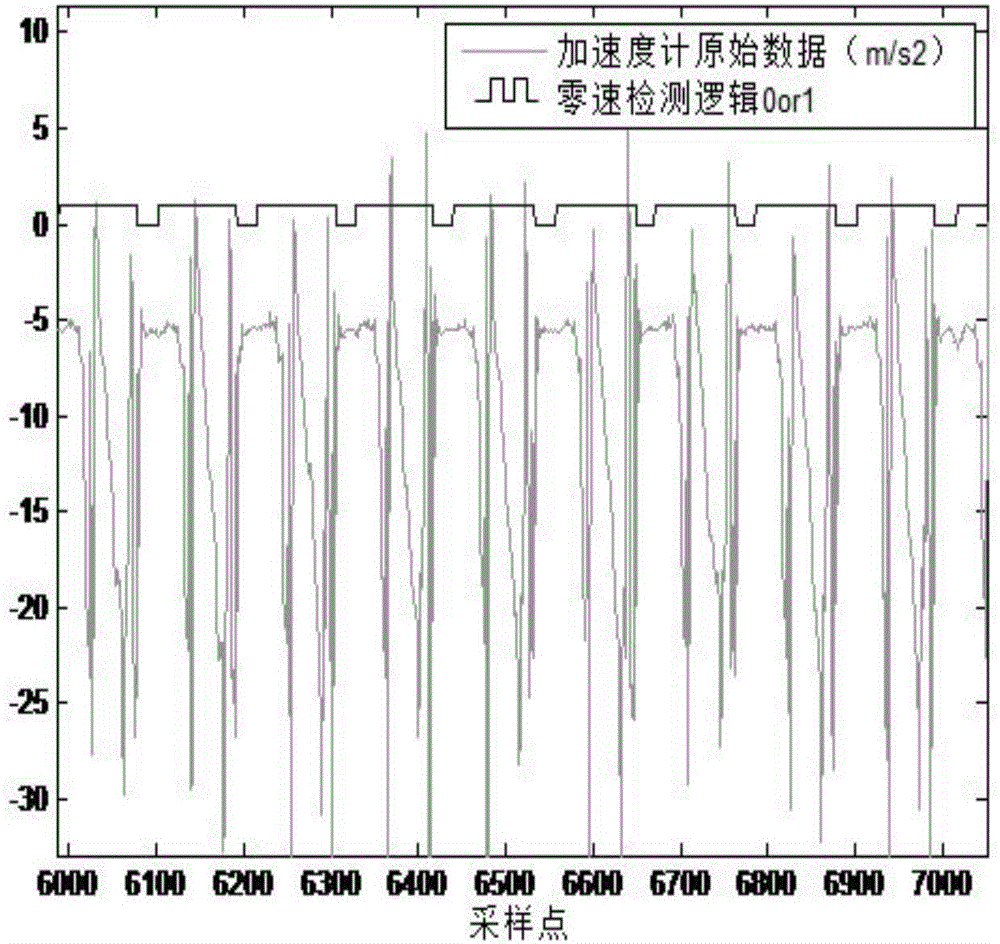
Indoor and outdoor personal navigation algorithm based on INS/GPS (inertial navigation system/global position system) integration of MEMS (micro-electromechanical system)
InactiveCN104819716AHigh precisionAccurate timingNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingSatelliteMarine navigation
Disclosed is an indoor and outdoor personal navigation algorithm based on INS / GPS integration of MEMS. The method is implemented through the following steps of, in an INS / GPS loosely-coupled integrated navigation error model, selecting the attitude error, the speed error and the position error of INS and the constant drift errors of a gyroscope and an accelerometer as the state variables of an integrated navigation system. Achieving personal position purely through inertial devices can lead to increase of navigation errors over time. The indoor and outdoor personal navigation algorithm based on INS / GPS integration of the MEMS determines whether the system enters an integrated mode through the accuracy of adjacent effective information detected by GPS to GPS measured positions. On the traditional basis of determining through the number of receiving satellites and precision estimation factors, the indoor and outdoor personal navigation algorithm based on INS / GPS integration of the MEMS adds a determining identification window. By fusing the particle filter algorithm of indoor maps and determining whether particle calculation results meet objective facts, the indoor and outdoor personal navigation algorithm based on INS / GPS integration of the MEMS can correct the course errors of an original algorithm and accordingly optimize pedestrian tracks, thereby well providing long-time and high-precision indoor autonomous navigation.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
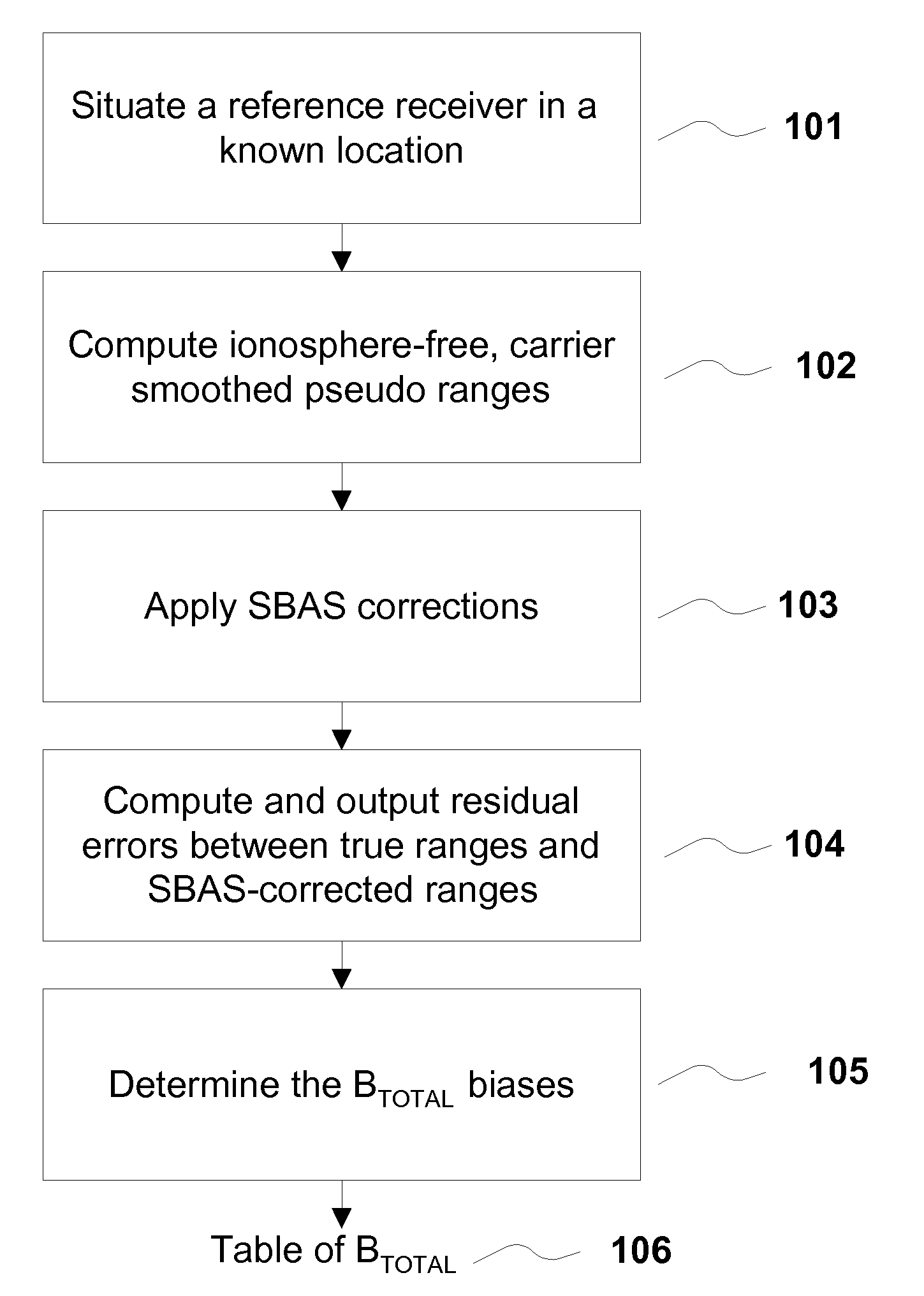
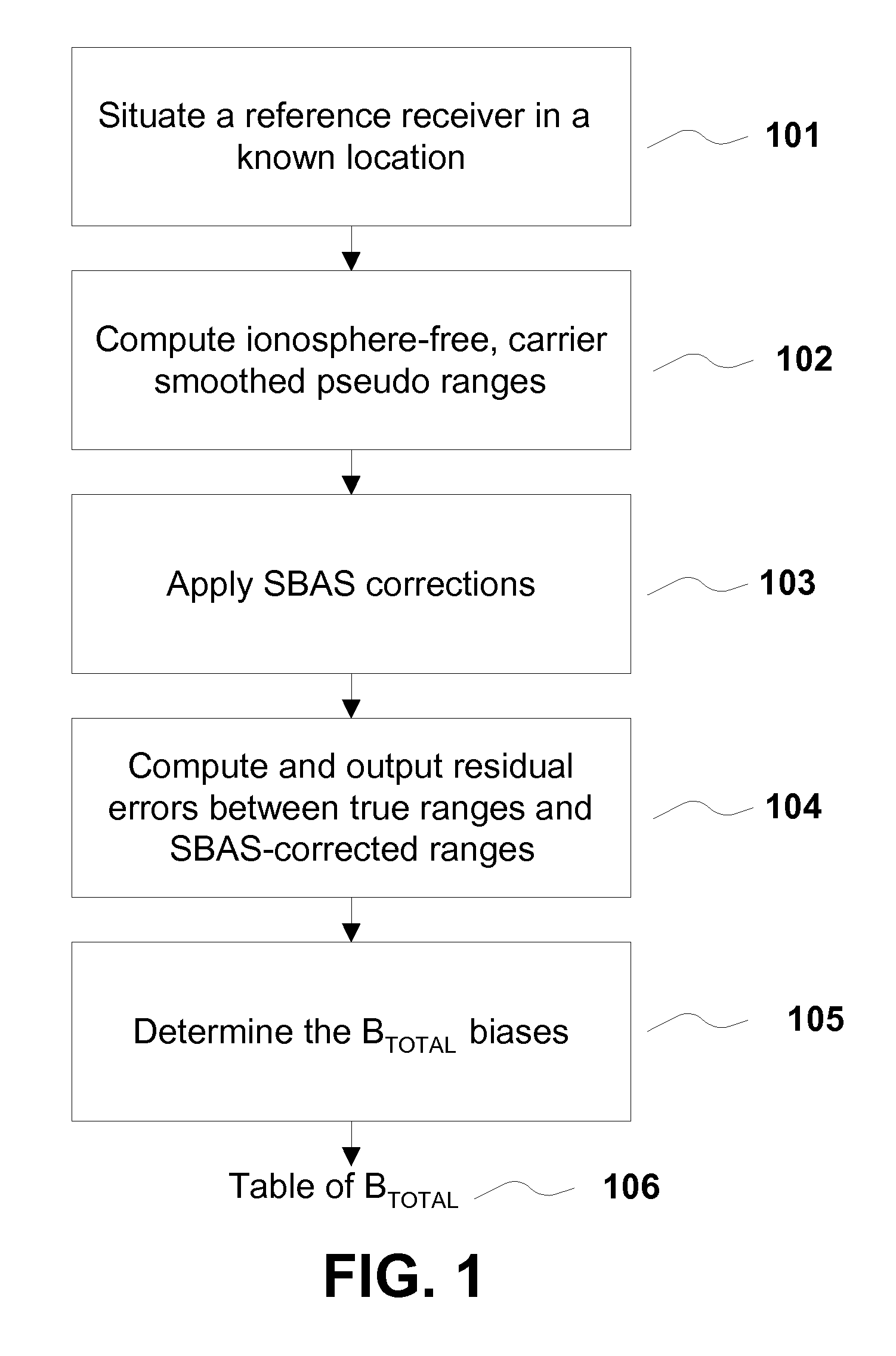
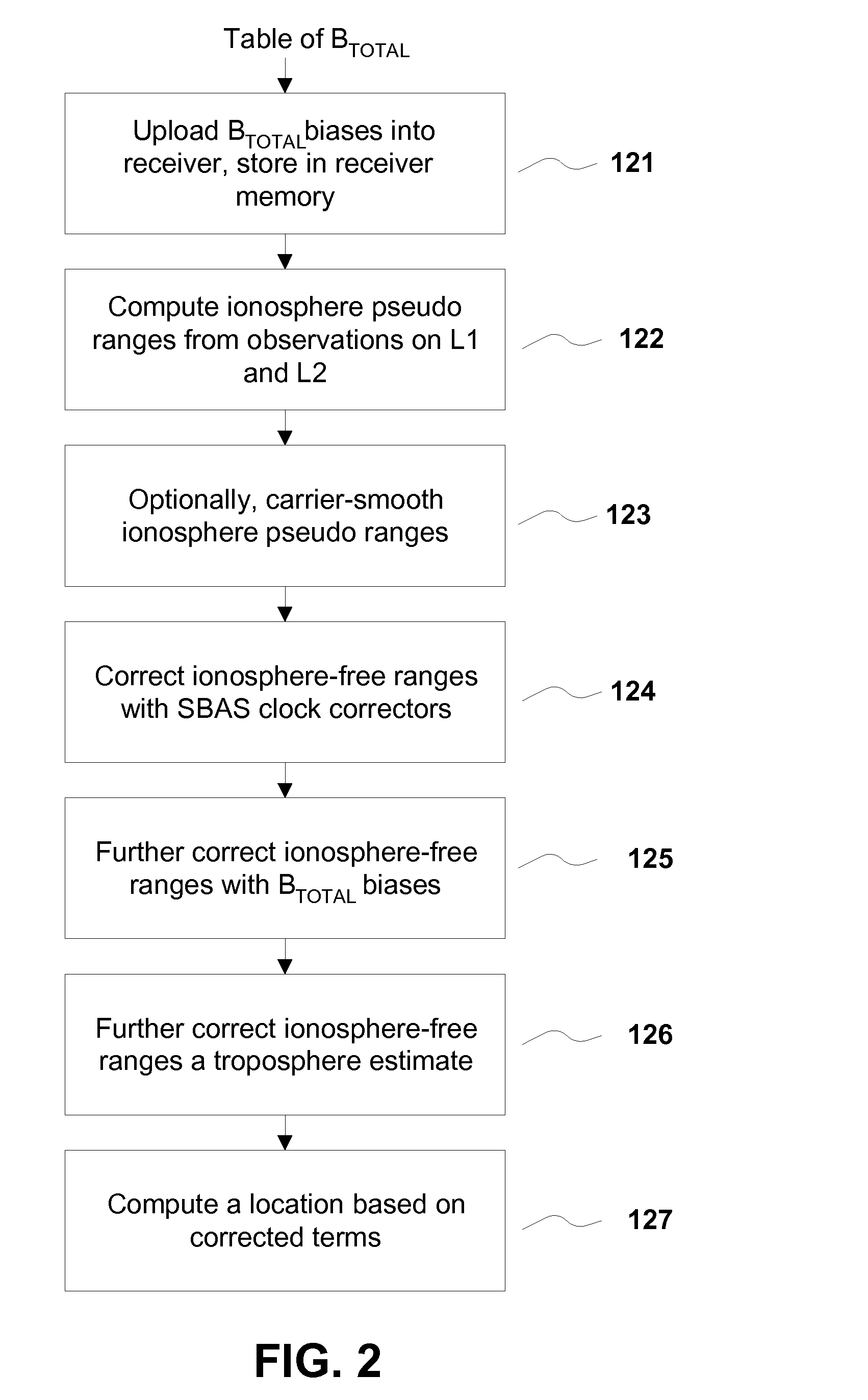
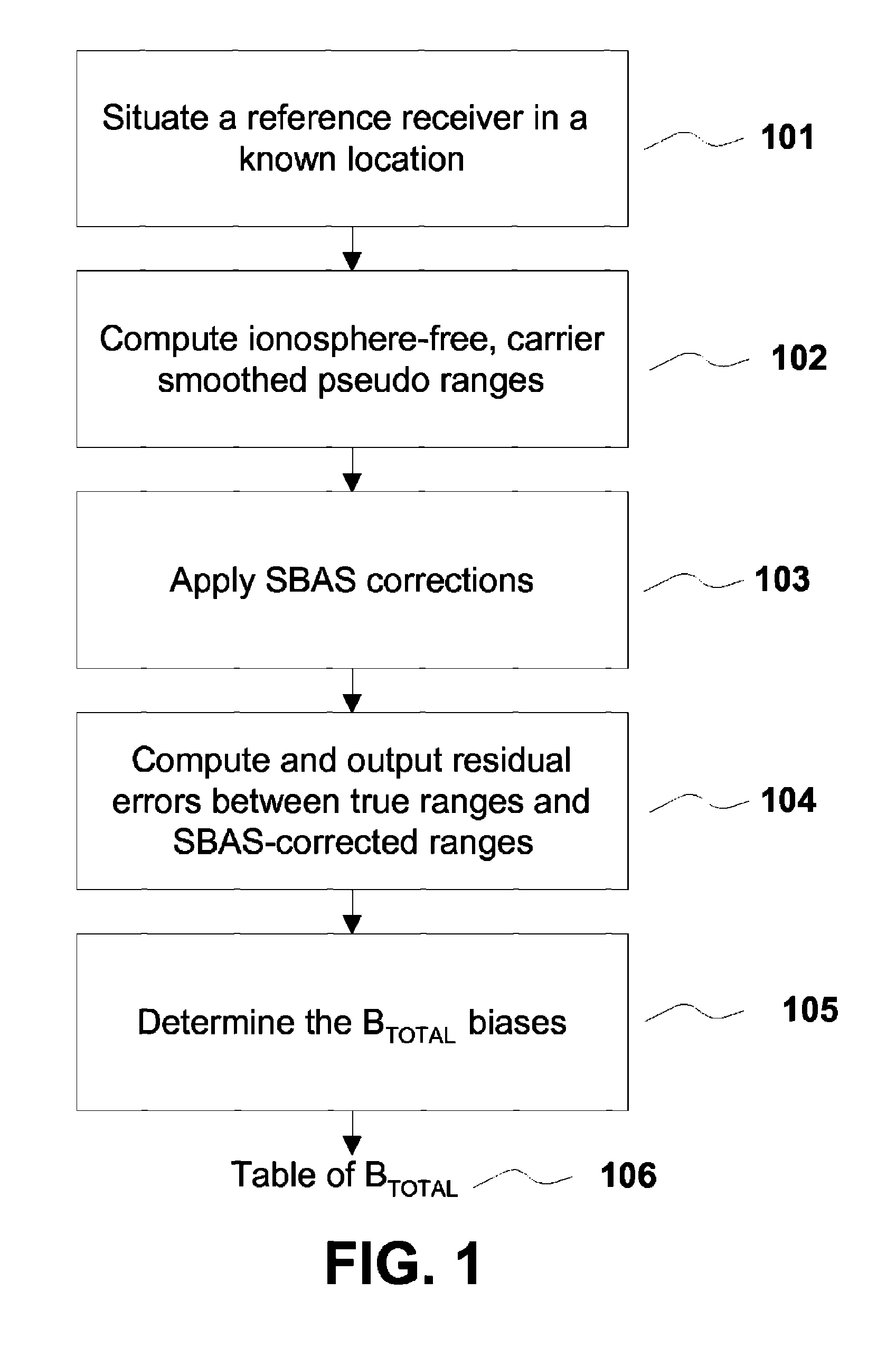
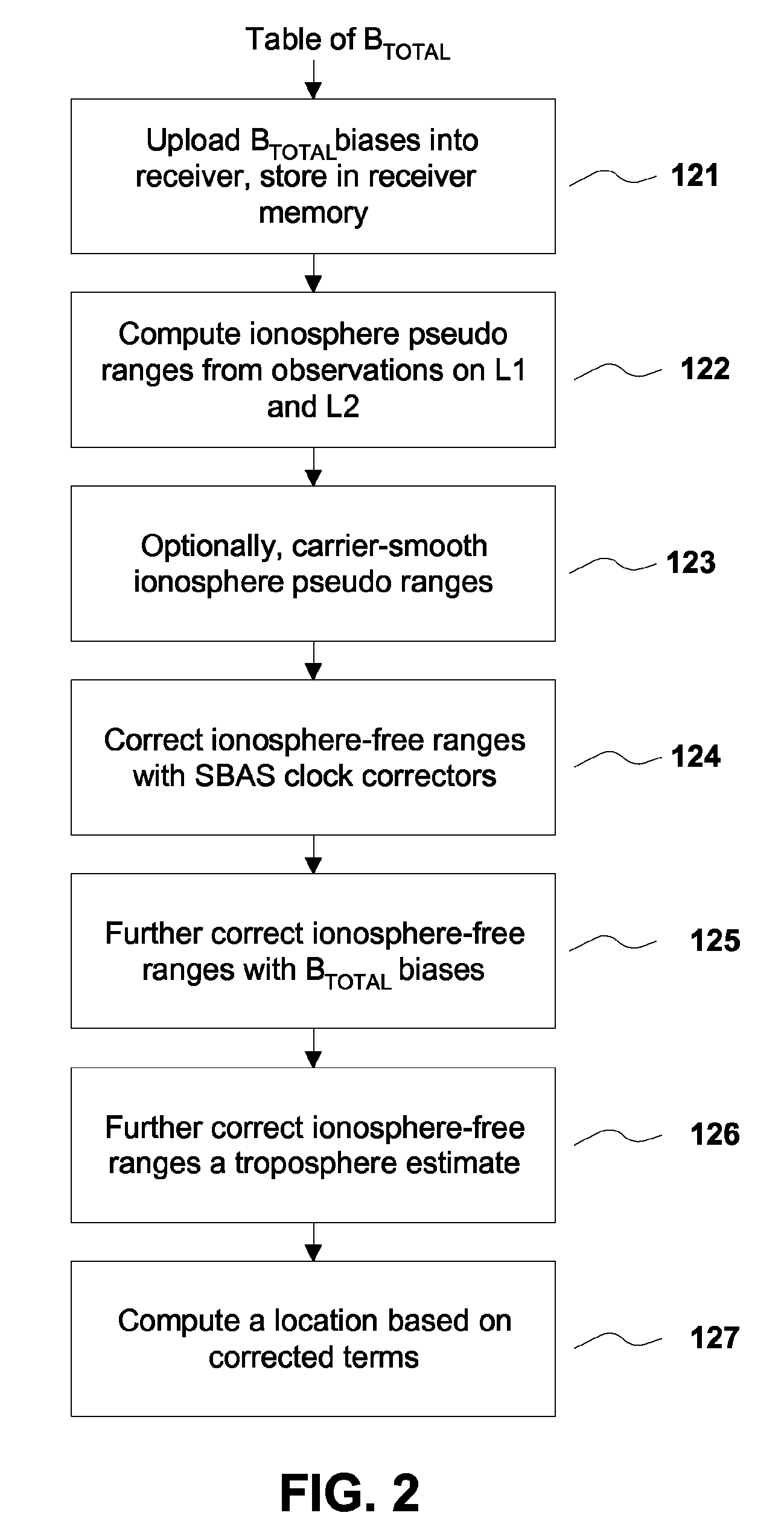
Removing biases in dual frequency GNSS receivers using sbas
ActiveUS20100231443A1Improve performanceImprove navigation accuracySatellite radio beaconingDual frequencyIonosphere
A method for removing biases in dual frequency GNSS receivers circumvents the need for ionosphere corrections by using L2(P) in combination with either L1(P) or L1(C / A) to form ionosphere-free ranges. A table of biases is stored in microprocessor controller memory and utilized for computing a location using corrected ionosphere-free pseudo ranges. A system for removing biases in dual frequency GNSS receivers includes a dual frequency GNSS receiver and a controller microprocessor adapted to store a table of bias values for correcting pseudo ranges determined using L2(P) in combination with either L1(P) or L1(C / A).
Owner:HEMISPHERE GNSS
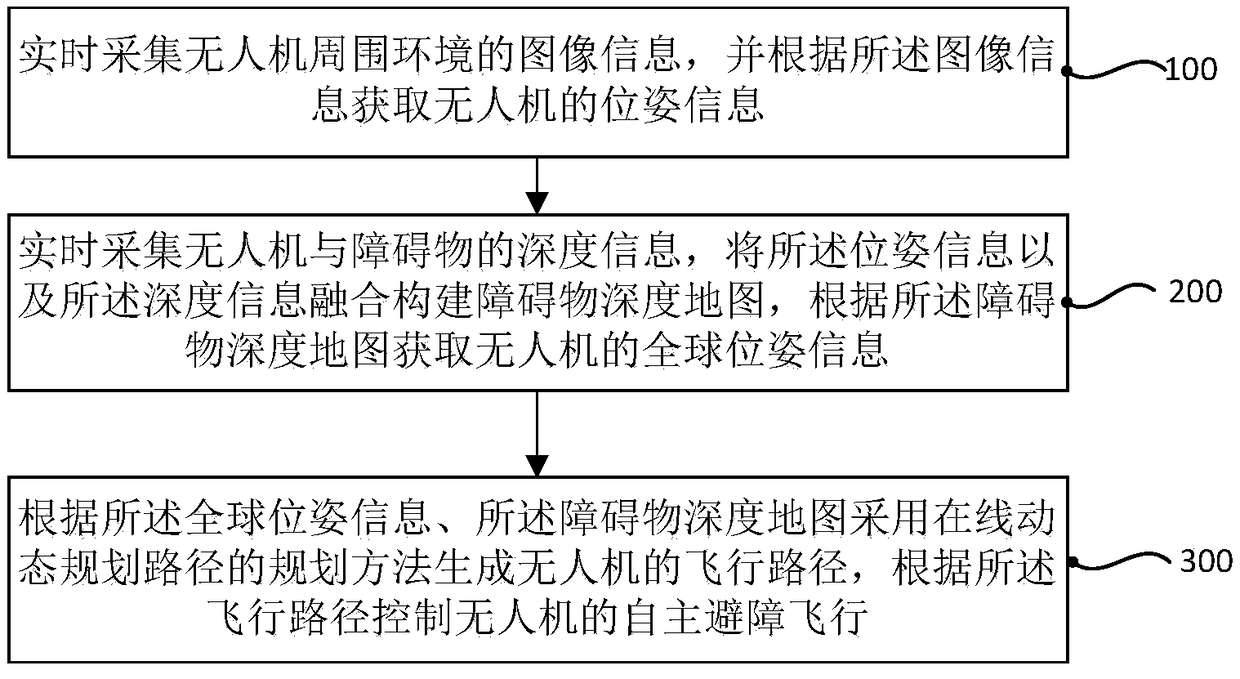
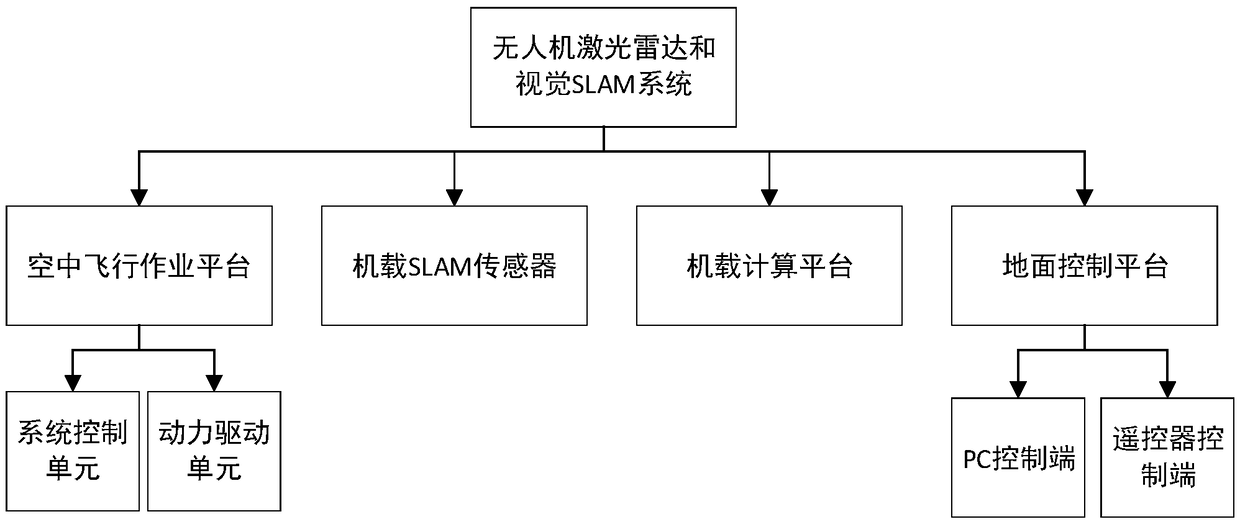
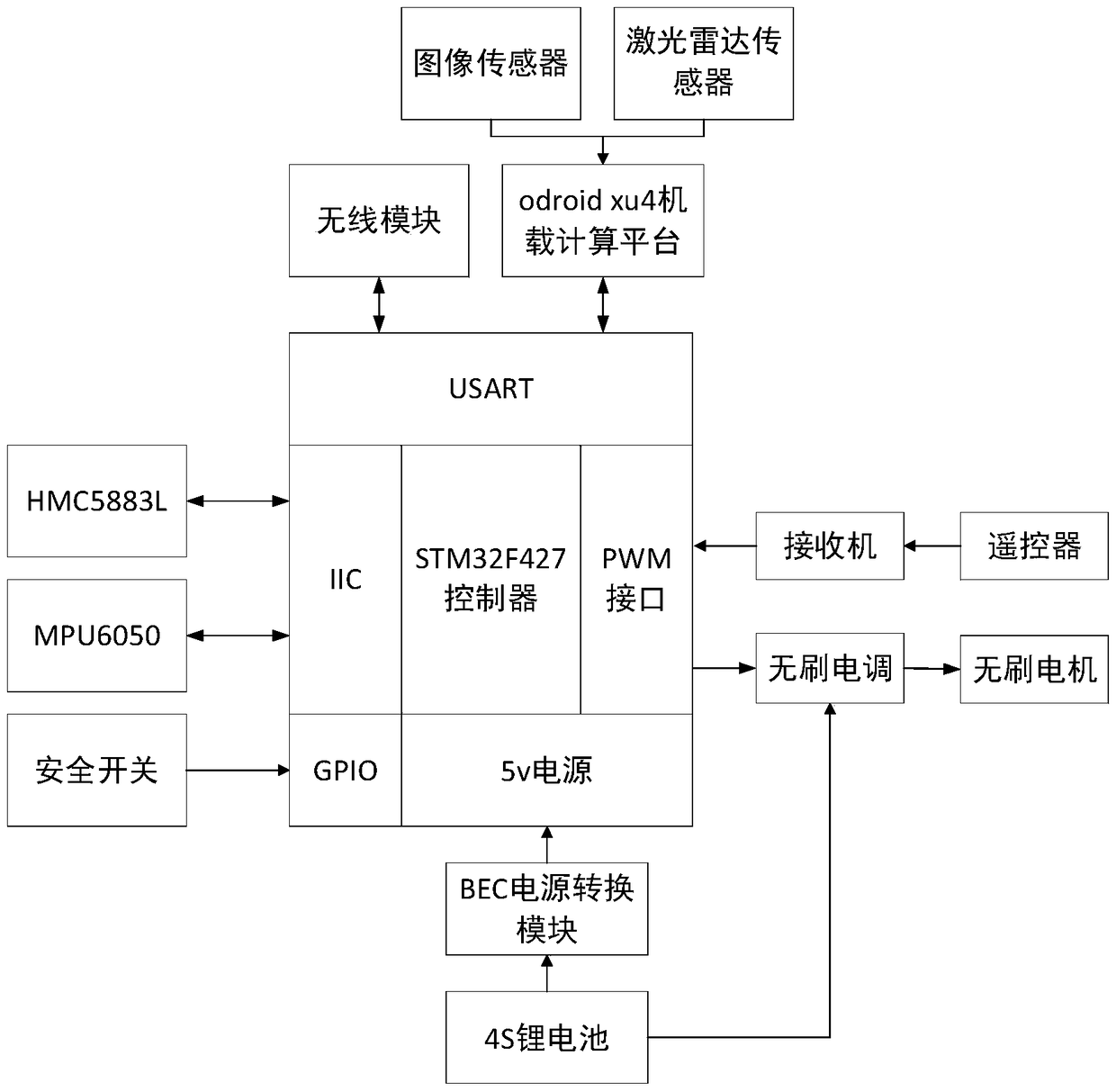
Multisensor fusion-based nmanned aerial vehicle SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping) navigation method and system
ActiveCN108827306AImprove completenessImprove navigation accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsSimultaneous localization and mappingUncrewed vehicle
The invention discloses a multisensor fusion-based unmanned aerial vehicle SLAM (simultaneous localization and mapping) navigation method and a multisensor fusion-based unmanned aerial vehicle SLAM navigation system. The multisensor fusion-based unmanned aerial vehicle SLAM navigation method comprises the following steps: acquiring image information of the surrounding environment of an unmanned aerial vehicle in real time, and acquiring pose information of the unmanned aerial vehicle according to the image information; acquiring depth information of the unmanned aerial vehicle and an obstaclein real time, fusing the pose information and the depth information to construct an obstacle depth map, and acquiring global position information of the unmanned aerial vehicle according to the obstacle depth map; according to the global pose information and the obstacle depth map, generating a flight path of the unmanned aerial vehicle by an online dynamic path planning method, and controlling autonomous obstacle-avoiding flight of the unmanned aerial vehicle according to the flight path. Through the multisensor fusion-based unmanned aerial vehicle SLAM navigation method and the multisensor fusion-based unmanned aerial vehicle SLAM navigation system, real-time localization and mapping of the unmanned aerial vehicle in a complex environment can be achieved; compared with the conventional unmanned aerial vehicle navigation technology, the navigation technology adopted by the invention has the advantages as follows: real-time localization and mapping and autonomous navigation are achieved, and the intelligence degree and the navigation accuracy of the unmanned aerial vehicle are improved.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Gasture estimation and interfusion method based on strapdown inertial nevigation system
InactiveCN1851406ALow costDoes not change the installation structureNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDisplay deviceInformation integration
The invention discloses a state estimating and interfusion method based on strap down inertial navigation system that includes the following steps: using the sensor in IMU to induce the kinetic characteristic; taking strap down inertial computing; using the state signal of acceleration estimating system; judging the reliability of state estimating value; taking state information interfusion; outputting navigation parameter. The invention has the following advantages: no additional hardware cost, fully autonomy; effectively improving the navigation accuracy of the system; and supplying 50 navigation signals per second to control display device.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Inertial measuring system error model demonstration test method
InactiveCN101021879AHigh precisionImprove navigation accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsObservational errorPrimary standard
This invention relates to a test method for error model verification of an inertial measurement system, which sets up a multifunction software platform to simulate and argue the airliner load test plan directly including: designing specific flying trails based on the error model of an inertial sensor, in which, an aircraft flies along the designed flying trail and collects inertial sensor data of specific flight path points and transmits them to a master navigation computer, then the collected data are compared with the data output by a measurement primary standard device to get the measurement error of the sensor to compute and get the error parameters in the inertial navigation error model with an airborne inertial navigation space multi-position online demarcating method to understand the inertial navigation performance and is convenient for the compensation in navigation computation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
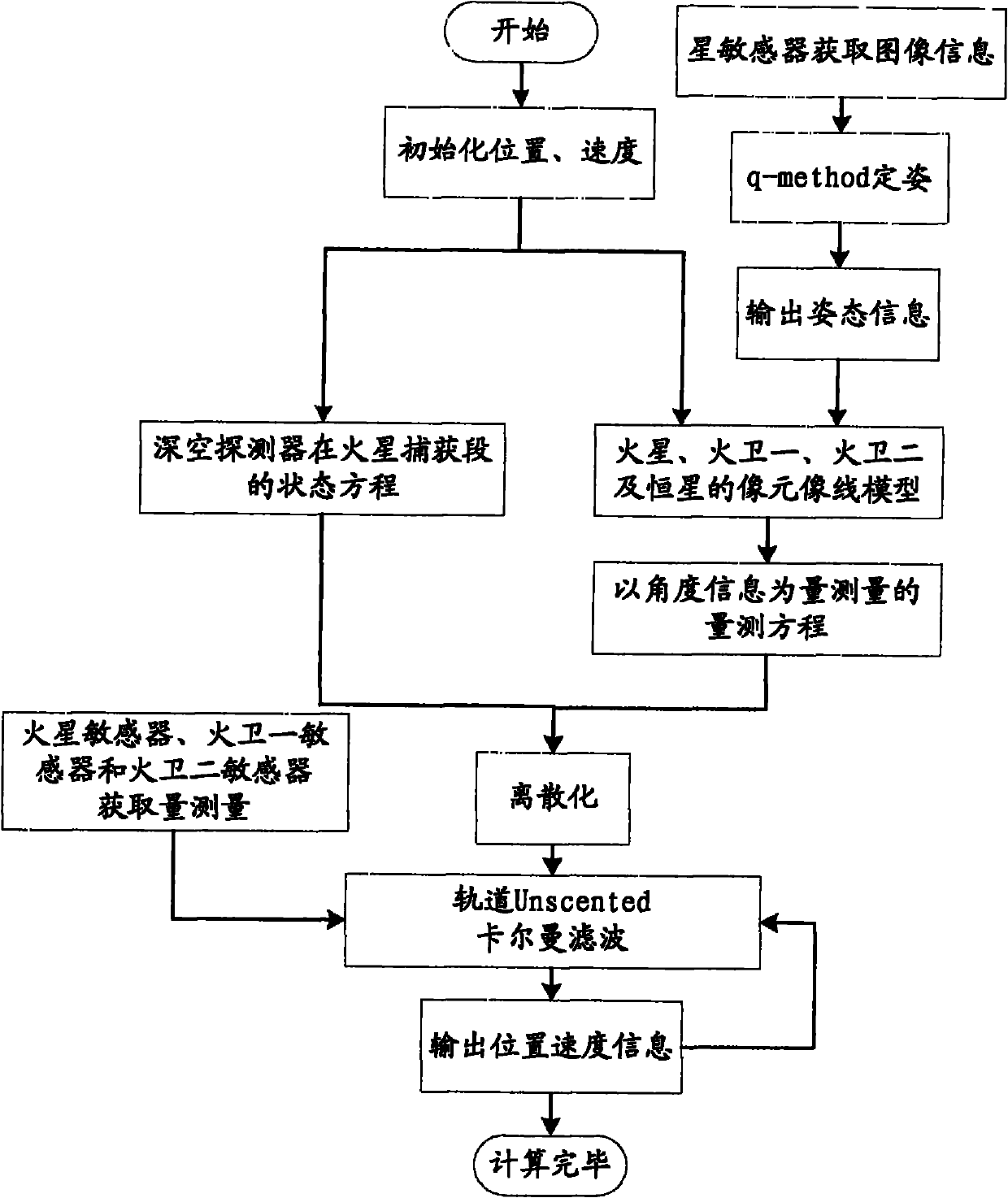
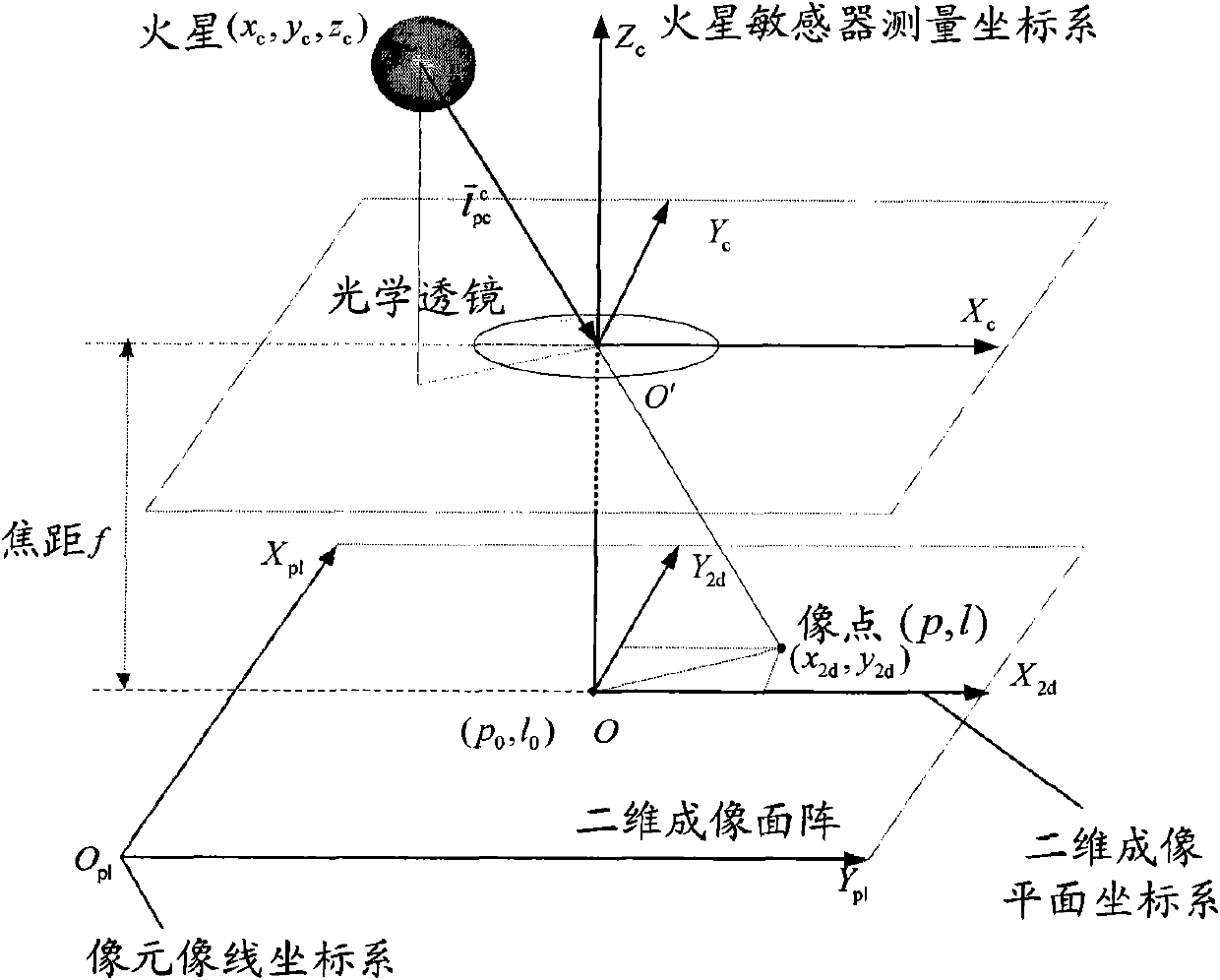
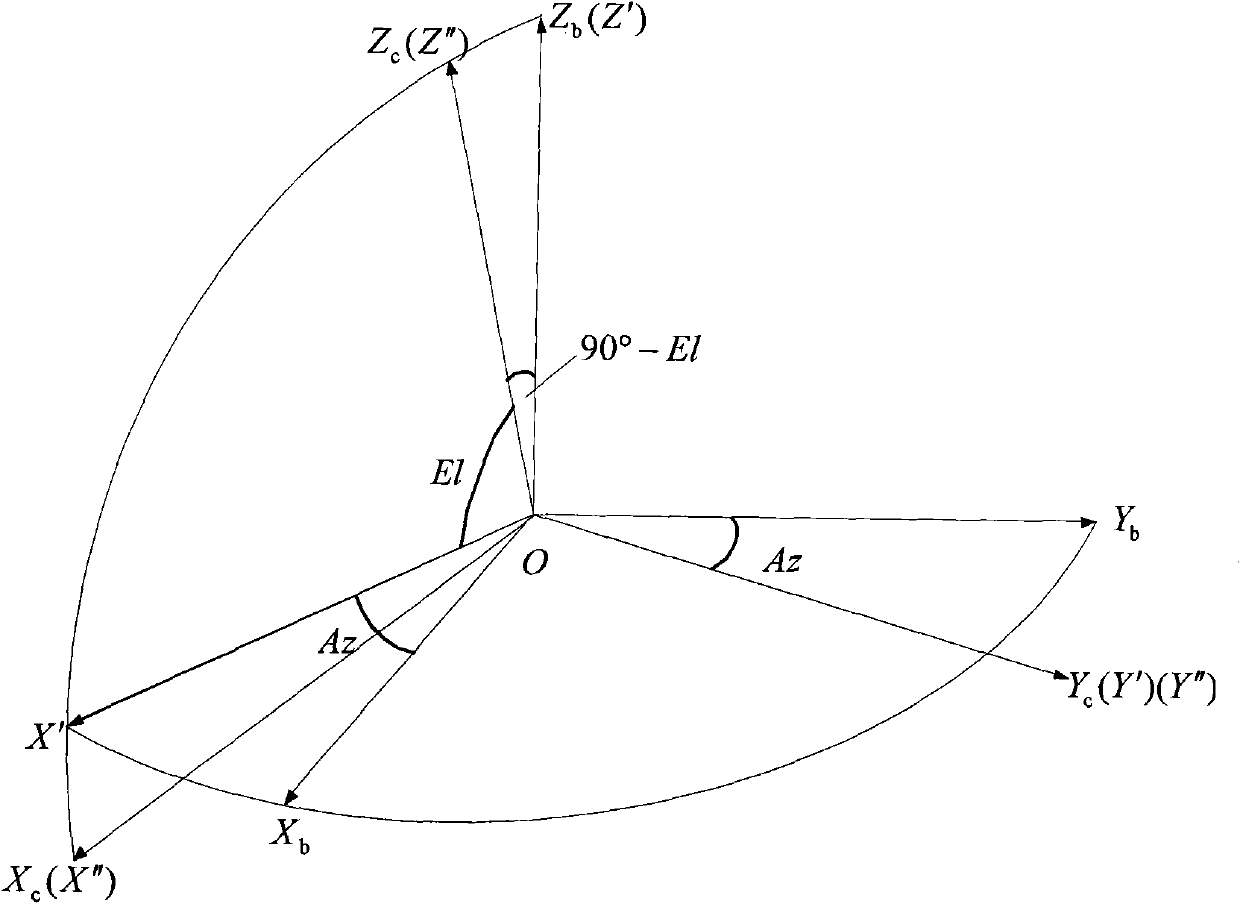
Independent celestial navigation method for Mars capturing section of deep space probe
ActiveCN102168981AAvoid Accuracy ImpactImprove navigation accuracyInstruments for comonautical navigationFixed starsDynamic models
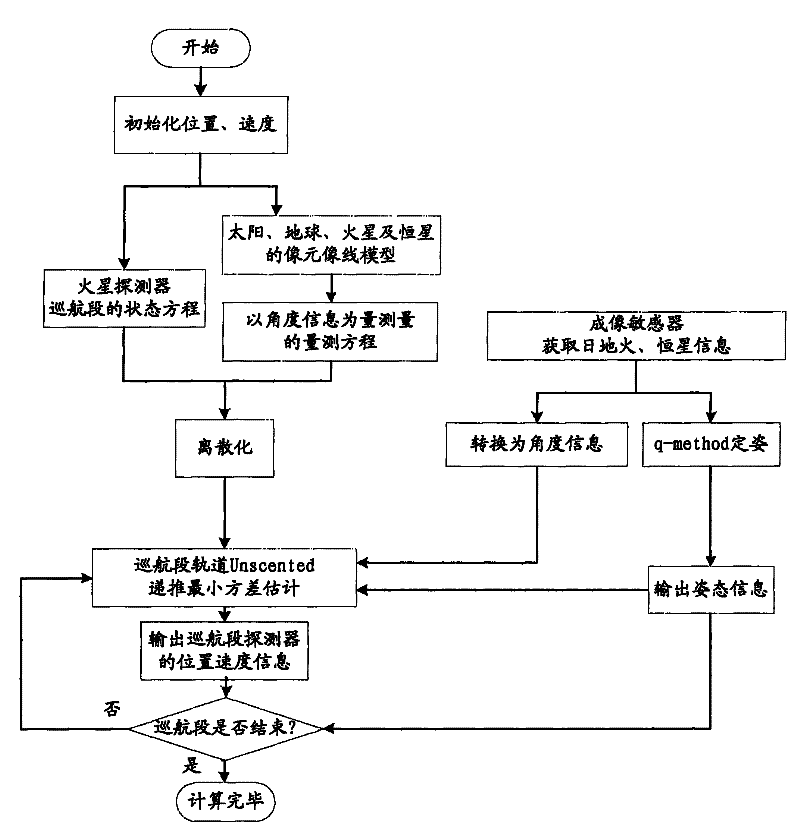
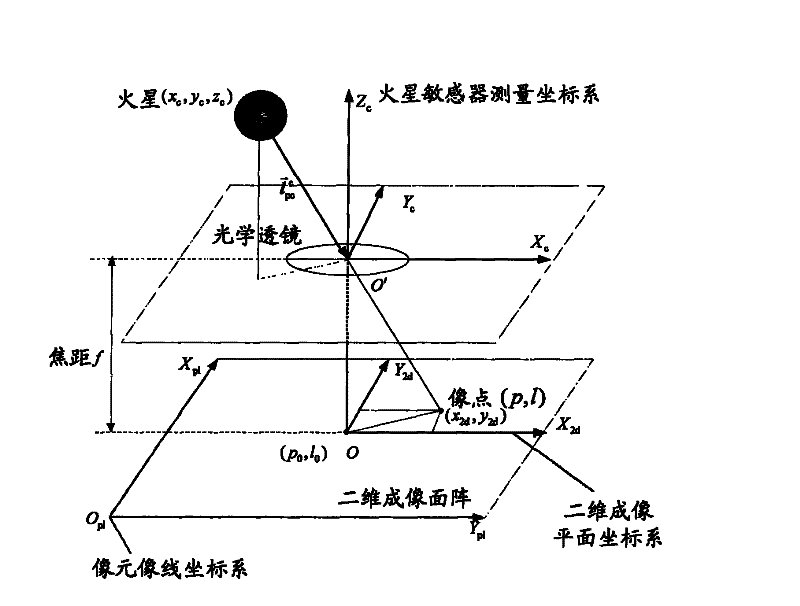
The invention relates to an independent celestial navigation method for a Mars capturing section of a deep space probe. The method comprises the following steps of: establishing a state model of the deep space probe according to a circular restrictive four-body track dynamics model; acquiring picture element and picture line information of Mars, Martian satellites and a background fixed star, converting the acquired picture element and picture line information into angle information of the Mars, the Martian satellites and the background fixed star and establishing an angle measuring model of the Mars, a Martian satellite I and a Martian satellite II; and estimating the attitude information of the probe by adopting a q-method and estimating the position and speed of the deep space probe in combination with Unscented Kallman filtering. The method has high estimation accuracy, and is very suitable for independent navigation of Mars capturing. The method belongs to the technical field of aerospace navigation. By adopting the method, high-accuracy navigation parameters can be provided for Mars capturing of the deep space probe, and references can be provided for the design of an independent navigation system of the deep space probe.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
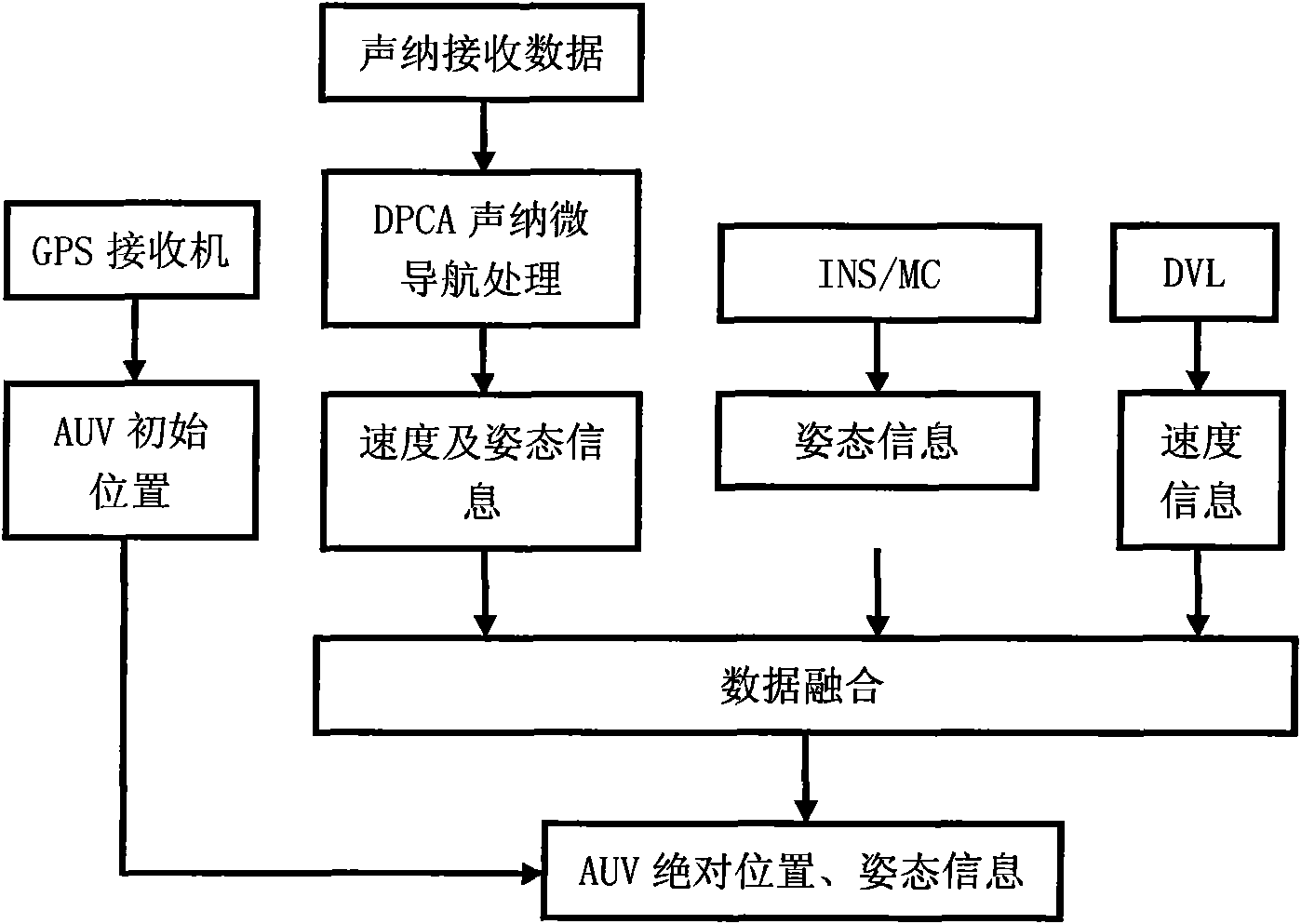
Combined navigation method of integrated sonar micro navigation autonomous underwater robot
InactiveCN101900558AImprove navigation accuracyNavigation instrumentsAcoustic wave reradiationMarine engineeringComputer vision
The invention discloses a combined navigation method of an integrated sonar micro navigation autonomous underwater robot, mainly comprising the following steps of: (1) acquiring initial absolute position information of the autonomous underwater robot by using a global positioning system, acquiring speed information and posture information of the autonomous underwater robot by using a sensor and estimating the speed information and / or posture information of the autonomous underwater robot by using a sonar system; and (2) fusing the speed information and the posture information which are acquired by the sensor and the speed information and / or posture information estimated by the sonar system by using a data fuse method and acquiring absolute position information and posture information of the autonomous underwater robot by combing the initial absolute position information of the autonomous underwater robot. The invention has the advantages that the absolute position of an AUV (Autonomous Underwater Vehicle) can be estimated and the navigation precision of the AUV can be improved by fusing the speed and / or posture information estimated by AUV-boarded sonar and the speed and posture information acquired by the sensor.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
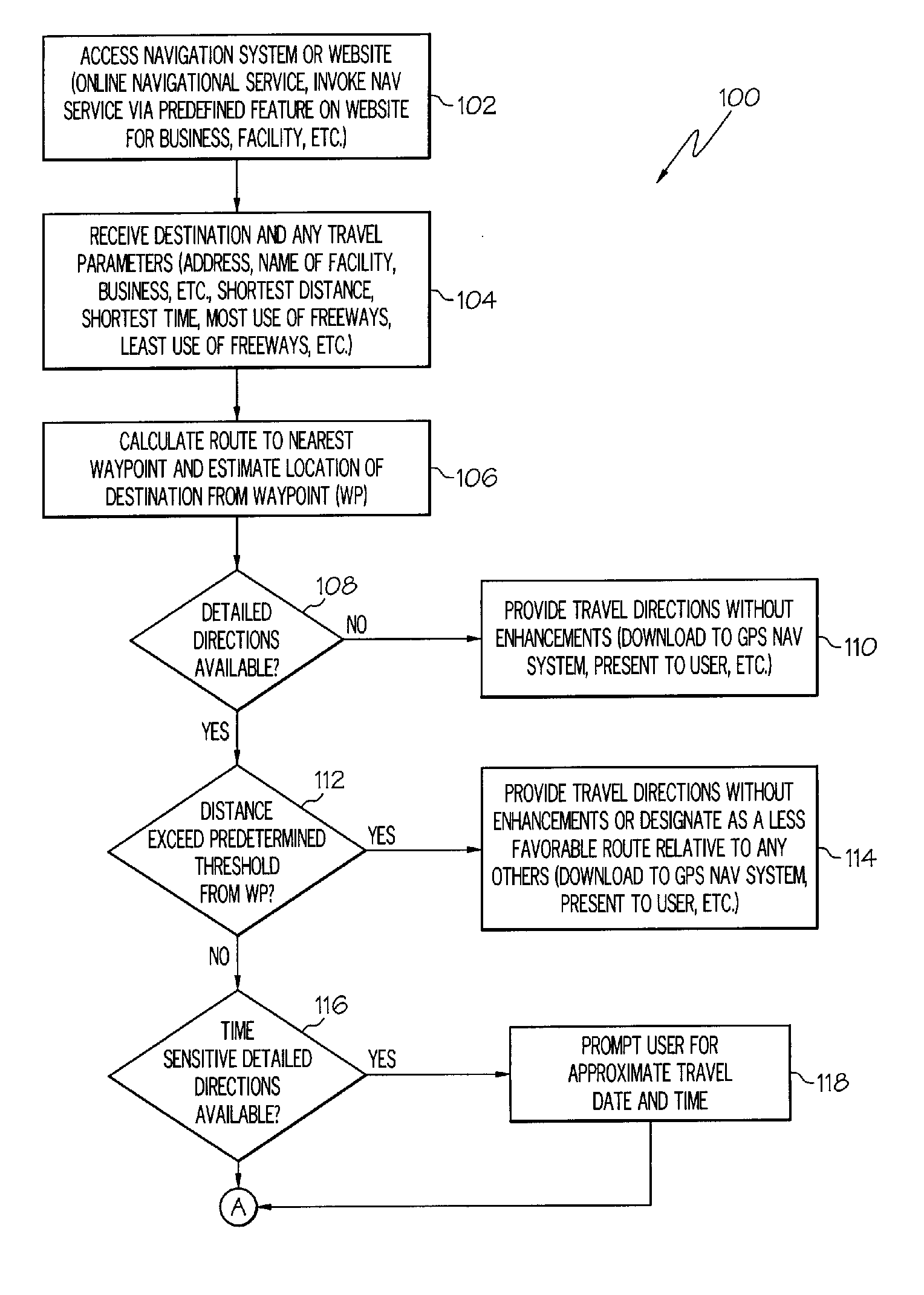
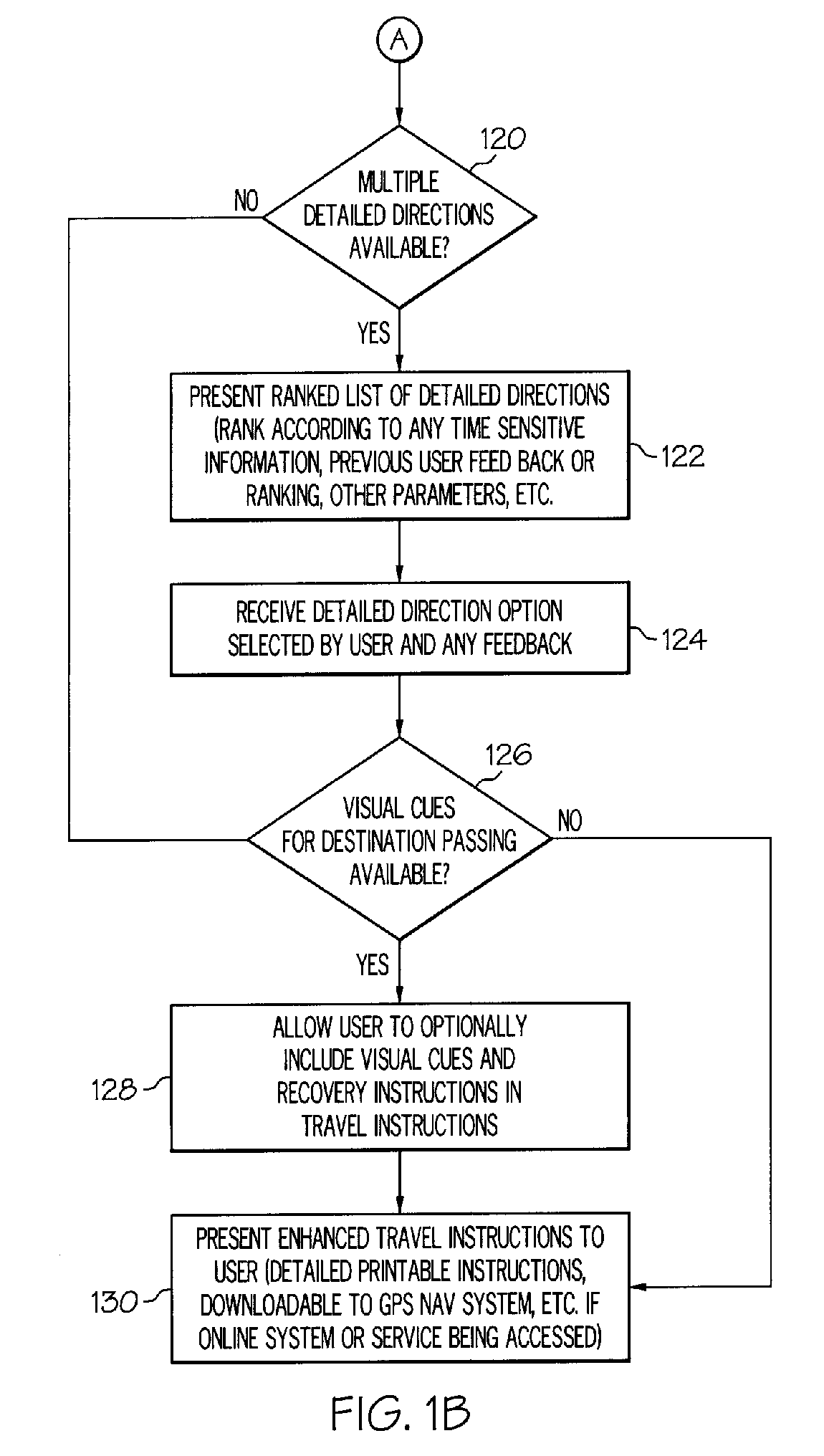
Navigation method, system or service and computer program product
InactiveUS20060265119A1Improve navigation accuracyInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlComputer scienceMarine navigation
A navigation method, system, service and computer program product may include providing enhanced travel instructions in response to receiving a destination and detailed travel directions from at least one waypoint to the destination being available.
Owner:IBM CORP
Removing biases in dual frequency GNSS receivers using SBAS
ActiveUS8085196B2Improve performanceImprove navigation accuracySatellite radio beaconingDual frequencyIonosphere
A method for removing biases in dual frequency GNSS receivers circumvents the need for ionosphere corrections by using L2(P) in combination with either L1(P) or L1(C / A) to form ionosphere-free ranges. A table of biases is stored in microprocessor controller memory and utilized for computing a location using corrected ionosphere-free pseudo ranges. A system for removing biases in dual frequency GNSS receivers includes a dual frequency GNSS receiver and a controller microprocessor adapted to store a table of bias values for correcting pseudo ranges determined using L2(P) in combination with either L1(P) or L1(C / A).
Owner:HEMISPHERE GNSS
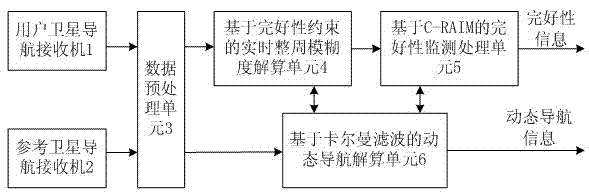
Satellite navigation integrity monitoring device based on carrier phase and application method of device
InactiveCN102819027AImprove navigation accuracyImprove integritySatellite radio beaconingCarrier signalInteger ambiguity
The invention discloses a satellite navigation integrity monitoring device based on a carrier phase and an application method of the device and belongs to the technical field of satellite navigation positioning. The device comprises a user satellite navigation receiver, a reference satellite navigation receiver, a data preprocessing unit, a real-time integer ambiguity revolving unit based on integrity constraint, an integrity monitoring processing unit based on C-RAIM (Carrier Phase-Receiver Automatic Integrity Monitoring) and a dynamic navigation resolving unit based on Kallman filtering. At present, home and abroad satellite navigation integrity monitoring technologies are mostly based on pseudo range observation, carrier phase observation is necessary in the field of high-precision satellite navigation, while the research on a satellite navigation integrity monitoring technology based on the carrier phase is rare. Compared with the prior art, the device disclosed by the invention can be used for obviously improving the navigation accuracy and integrity at the same time and has great significance in the field of high-performance navigation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
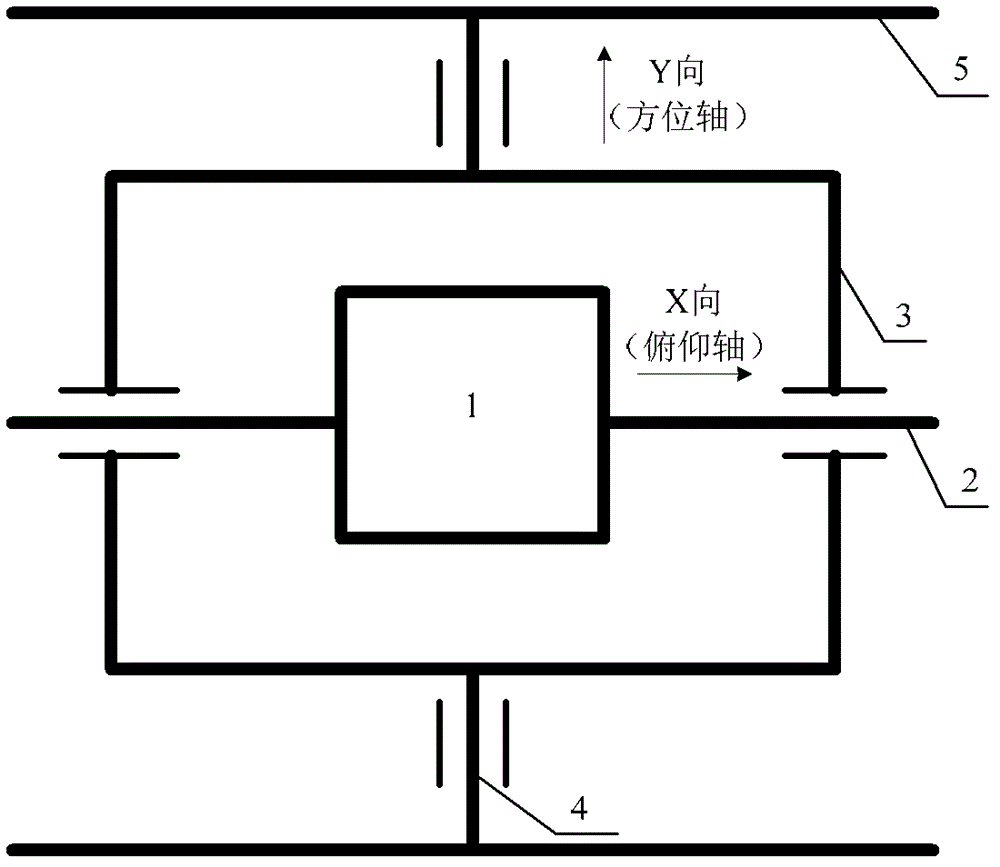
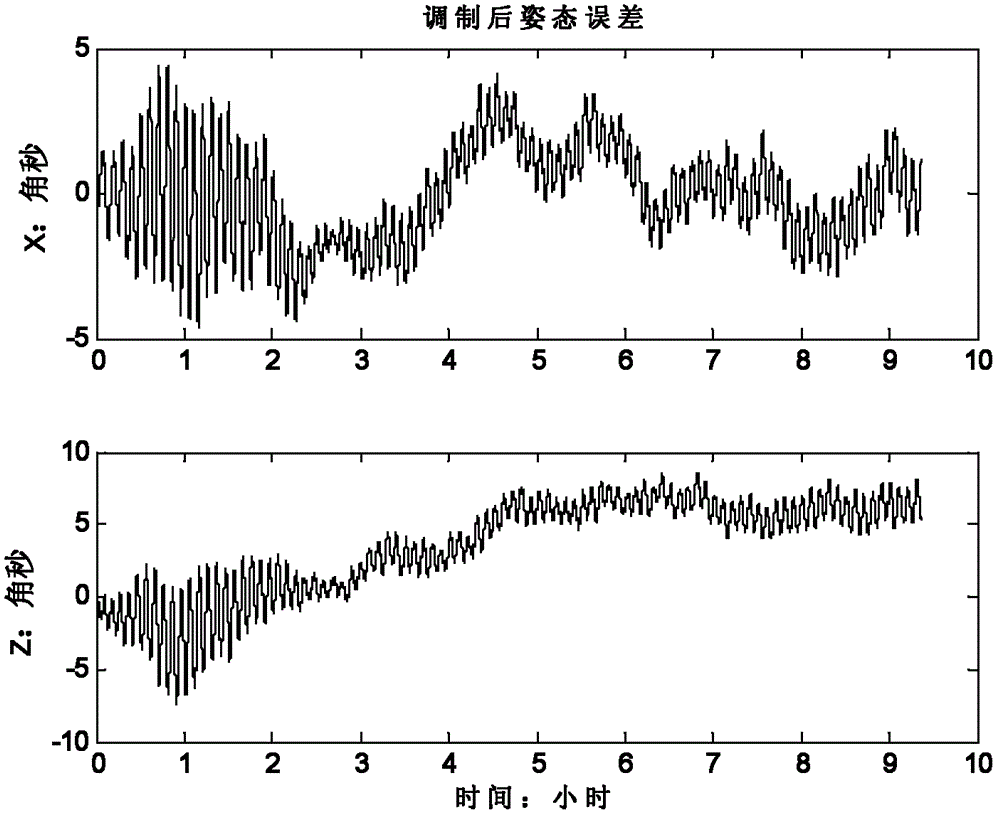
Optical fiber strapdown inertial navigation double-shaft rotation modulation method and double-shaft rotation mechanism
ActiveCN102749079AModulation errorAccurate Motion ParametersNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsDual axisContinuous rotation
The present invention belongs to the technical field of inertial navigation, and specifically relates to an optical fiber strapdown inertial navigation double-shaft rotation modulation method and a double-shaft rotation mechanism. A purpose of the present invention is to improve alignment accuracy of an inertial navigation system and navigation accuracy during long-distance navigation. The method comprises: S1, establishing a double-shaft rotation mechanism, such that any two axial directions of an inertial measurement unit are parallel to two rotation shafts of the double-shaft rotation mechanism, and rotations of the rotation shafts are continuous; S2, controlling rotation of the rotation mechanism, and carrying out initial alignment to obtain an error of an initial attitude matrix; and S3, carrying out concurrent rotation on the two shafts of the rotation mechanism, and carrying out inertial navigation to obtain an attitude matrix in a transporter coordinate system. According to the present invention, with establishment of the continuously-rotating double-shaft rotation mechanism, an error of an inertial device can be modulated well, and navigation accuracy can be improved; with double shaft rotation modulation and attitude matrix change, an attitude matrix in a transporter coordinate system can be obtained so as to obtain accurate transporter movement parameters.
Owner:BEIJING AUTOMATION CONTROL EQUIP INST
CKF filtering-based vehicle dynamic model auxiliary inertial navigation combined navigation method
InactiveCN107144284AImprove navigation accuracyImprove reliabilityInstruments for road network navigationVehicle dynamicsSteering wheel
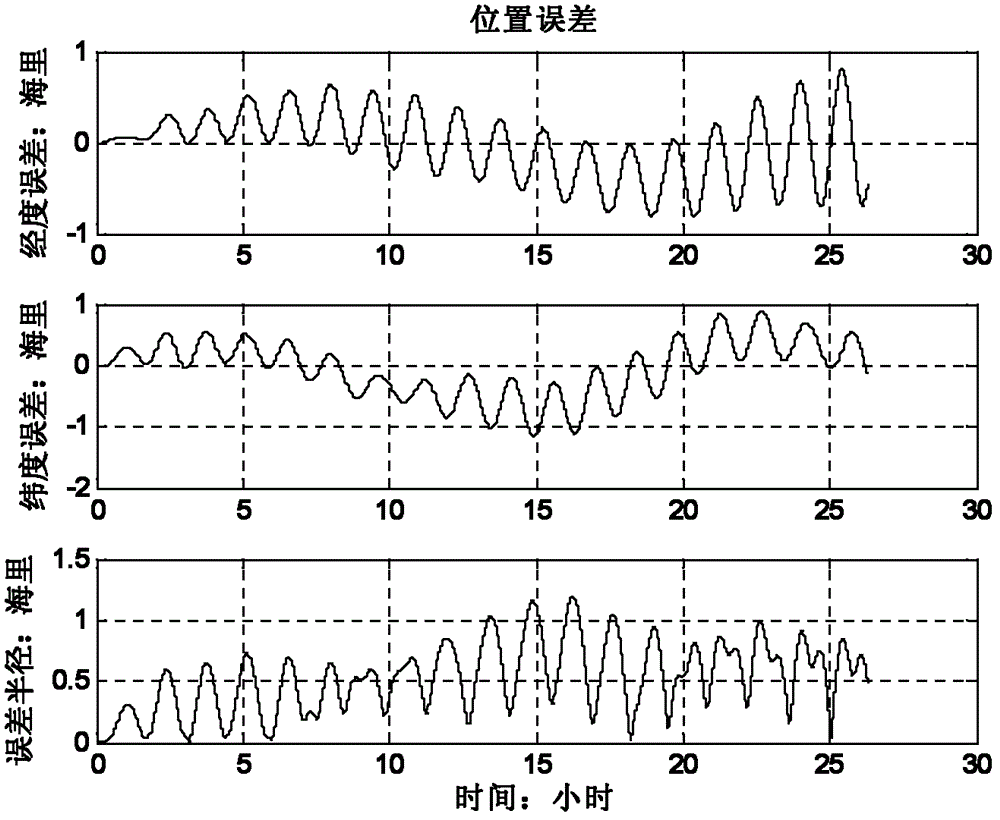
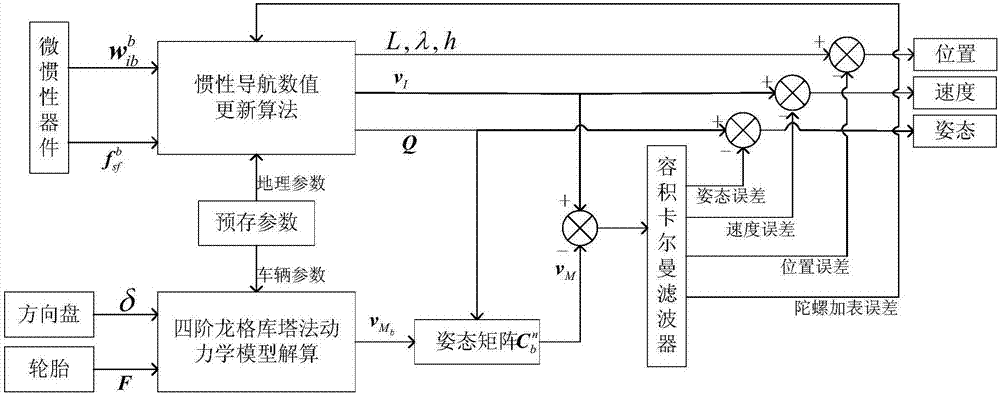
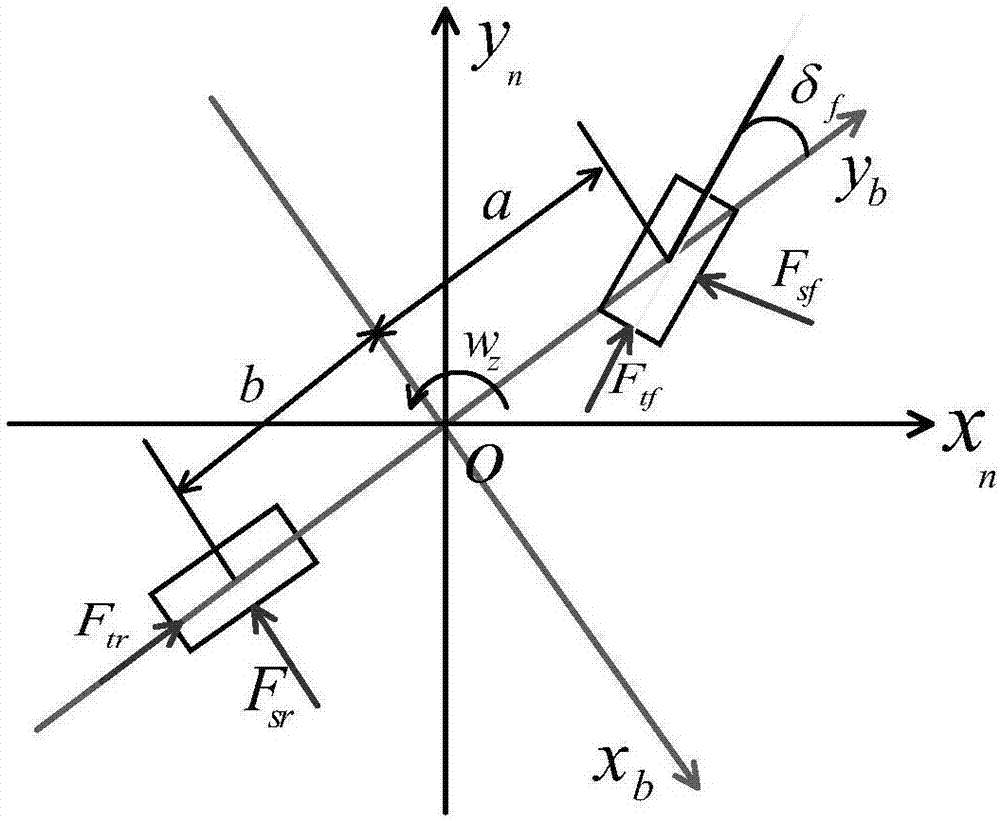
The invention discloses a CKF filtering-based vehicle dynamic model auxiliary inertial navigation combined navigation method. The CKF filtering-based vehicle dynamic model auxiliary inertial navigation combined navigation method comprises the following steps: calculating posture, speed and position of a vehicle according to angle increment and specific force output by a micro-inertia device and by an inertial navigation numerical value updating algorithm; establishing a three-degree-of-freedom vehicle dynamic model, and calculating the speed of a carrier by taking a steering wheel angle and a longitudinal force as control input quantity and by a fourth order Ronge-Kutta method in real time; designing a CKF filter by taking an inertial navigation equation as a state equation and speed difference between a dynamical model and inertial navigation calculation to perform state estimation on a combined navigation system; performing output correction on strapdown inertial navigation calculation result by the position the speed and the posture error obtained by CKF estimation, and performing feedback correction on the inertial navigation through peg-top and adding error. The method aims at the problems that the inertial navigation error is accumulated along with time and navigation precision cannot be maintained for a long time, and the accuracy and the reliability of a vehicle navigation system can be improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
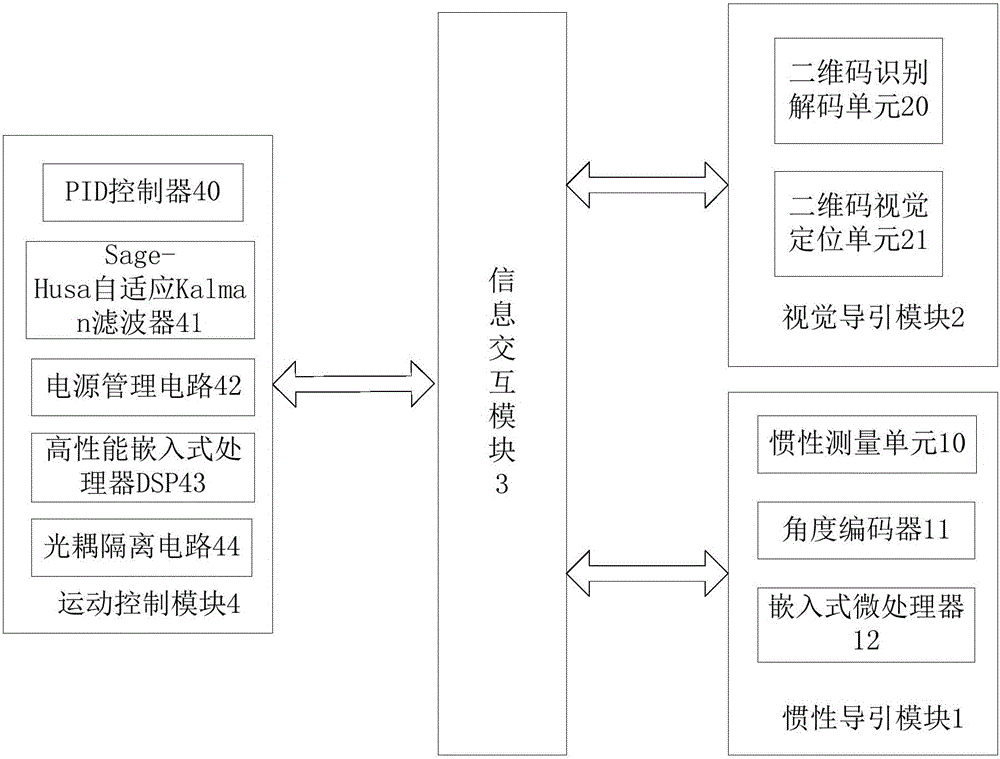
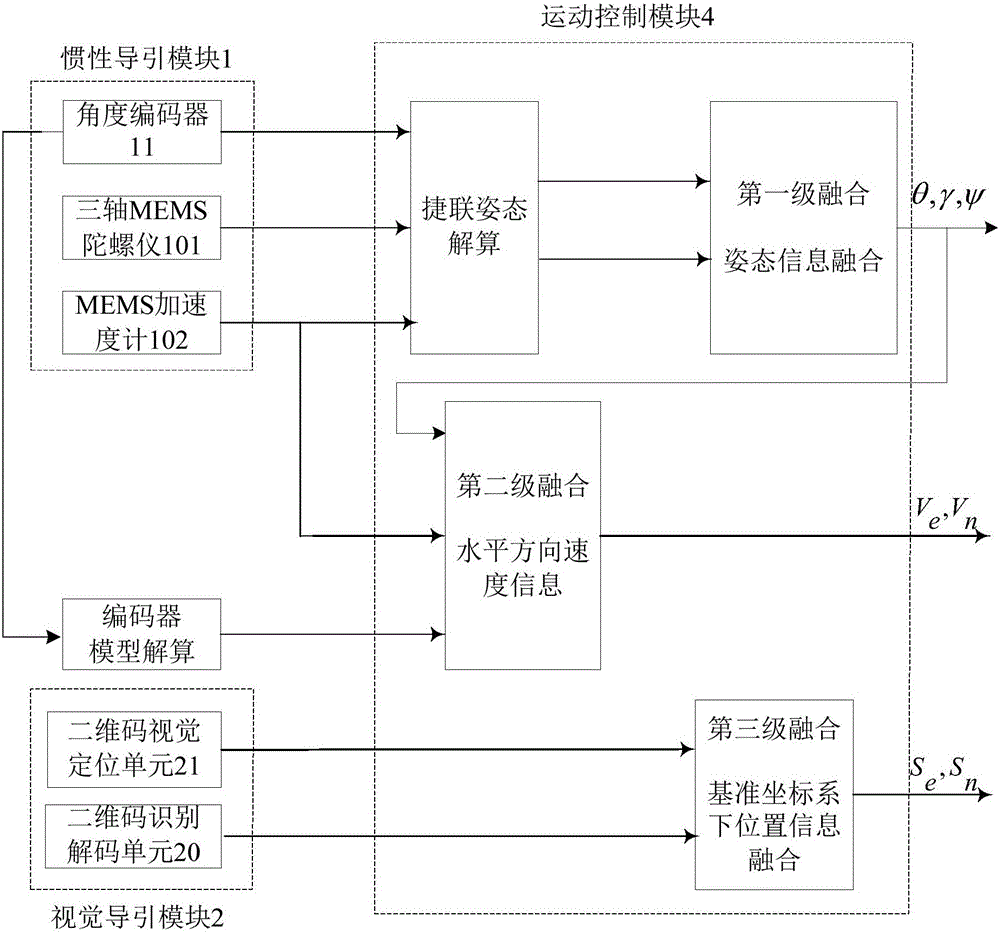
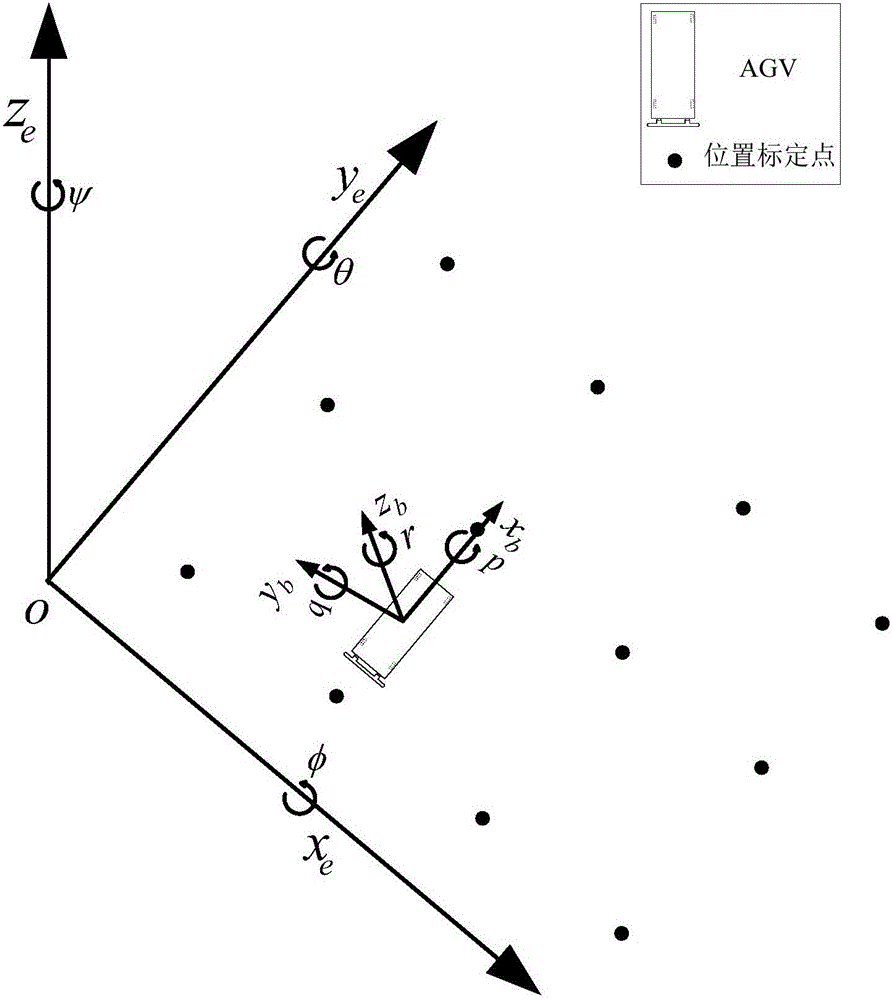
AGV composite guiding system based on image and inertia technology
InactiveCN105928514AWith redundancyImprove navigation accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPosition/course control in two dimensionsMovement controlVision sensor
The invention discloses an AGV composite guiding system based on an image and inertia technology. The system comprises an inertia guiding module, which can intelligently sense the positions and moving information of AGV in a vehicle coordinate system in every moment through a plurality of inertia sensors; a visual guiding module, which can intelligently sense the position and environment information of AGV through a visual sensor, when AGV move to a preset position in a reference coordinate system; an information interaction module, which efficiently passing information among the inertia guiding module, the visual guiding module, and a movement control module, and the movement control module, wherein the movement control module obtains the data of the sensors of the inertia guiding module and the visual guiding module, then the data of each sensor are fused by a Sage-Husa self-adaption Kalman filtering algorithm, according to the obtained fused data, AGV is controlled, and the accumulated errors of the inertia guiding module are corrected. Based on visual guiding and inertia guiding technologies, multiple information sources supplement each other, and an AGV composite guiding system, which has redundancy and higher navigation accuracy, is constructed.
Owner:广州智能装备研究院有限公司
Missile-borne inertia/ satellite tight combination navigation method
ActiveCN104181572AWith independent operating status discriminationWith independent fault diagnosisNavigation instrumentsSatellite radio beaconingMarine navigationMeasurement equations
The invention discloses a missile-borne inertia / satellite tight combination navigation method. The method utilizes pseudo-range, pseudo-range rate information and inertial navigation output by a GNSS to calculate relative pseudo-range and pseudo-range rate difference of a satellite, filtering is carried out and the current system is corrected according to the filtering results. The method mainly comprises the following steps: carrying out SINS initialization; carrying out SINS navigation calculation; carrying out satellite altitude angle and azimuth angle calculation; carrying out navigational satellite selection; carrying out pseudorange measuring error compensation of the navigational satellite; carrying out calculation on pseudo-range and pseudo-range rate of a carrier with respect to each navigational satellite; carrying out system state judgment and navigation strategy selection; carrying out system state equation construction and system measurement equation construction; and carrying out filtering calculation, and for hysteresis error due to communication delay, correcting the system through an error compensation method based on state transition according to the filtering results. The method can realize inertia / satellite-based pseudo-range and pseudo-range rate seamless combination navigation; navigation accuracy and adaptability to complex environment are improved; and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Autonomous astronomical navigation method of Mars probe in cruise section
ActiveCN102175241AImprove navigation accuracyAccurate Navigation PerformanceNavigation by astronomical meansStar sensorExploration of Mars
The invention relates to an autonomous astronomical navigation method of a Mars probe in a cruise section. The method comprises the following steps: building a state model of the Mars probe according to a round limited four-body track kinetic model; obtaining pixel wire information of the sun, the earth, the Mars and the fixed stars by a solar sensor, an earth sensor, a Mars sensor and a star sensor, converting the obtained pixel wire information into angle information of the sun, the earth and the Mars, and building angle information measurement models of the sun, the earth and the Mars; andestimating gesture information of the probe by a q-method method, and estimating the position and speed of the Mars probe by combining with Unscented recurrence minimum variance estimation. The method in the invention is high in estimation precision, and suitable for autonomous navigation of the Mars probe at the cruise section. The method belongs to the technical field of aerospace navigation, not only can provide a high-precision navigation parameter for the Mars probe, but also can provide reference for an autonomous navigation system design.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Error restraining method for fiber-optic gyroscope strapdown inertial navigation system rotating relative to geocentric inertial system
InactiveCN103090867AReduce divergent positioning errorsImprove navigation accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsGyroscopeAngular velocity
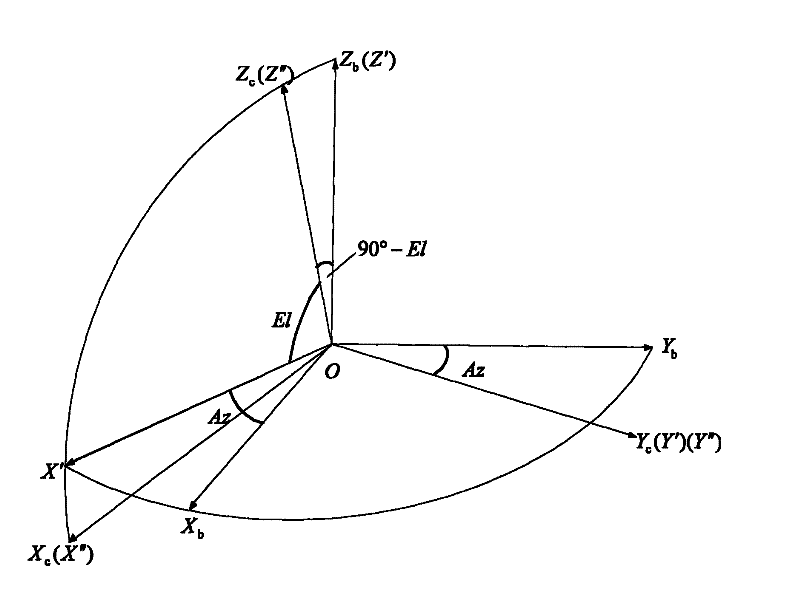
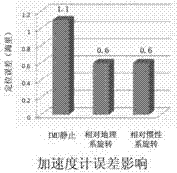
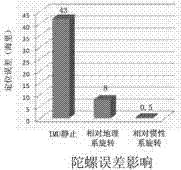
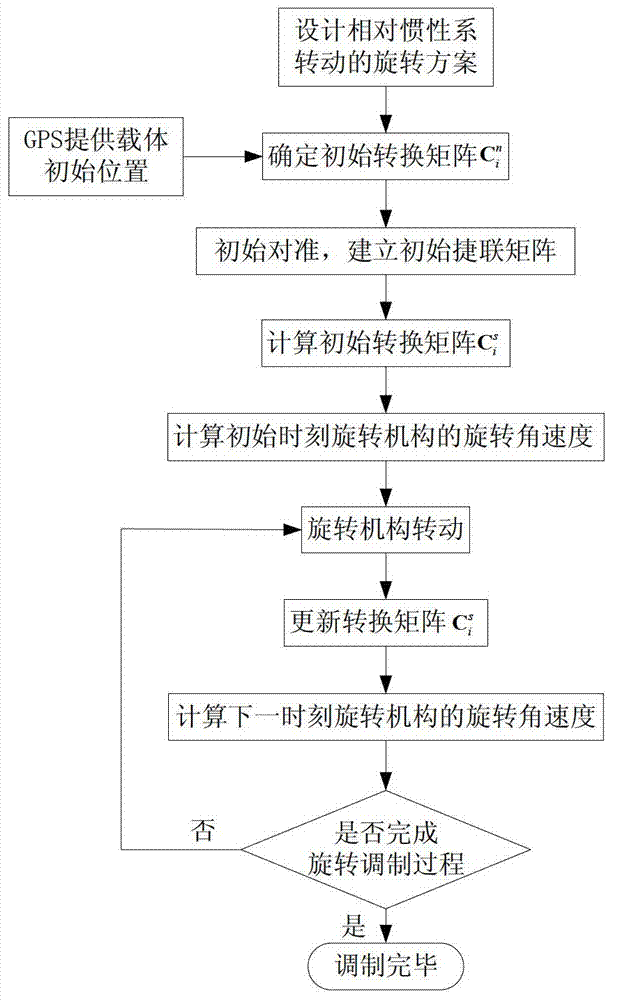
The invention discloses an error restraining method for a fiber-optic gyroscope strapdown inertial navigation system rotating relative to a geocentric inertial system. The method comprises the specific steps of firstly, determining a rotating scheme, then, establishing an initial strapdown transfer matrix according to initial position parameters of a carrier, and then calculating to obtain an initial transfer matrix of the inertial navigation system; and then, resolving position information of the carrier and the transfer matrix in real time according to the strapdown inertial navigation system in a rotating process of a rotating mechanism, and updating a rotating angular speed of the rotating mechanism at next time until finishing a modulating process of the rotating of the modulation type strapdown inertial navigation system relative to the inertial system. According to the error restraining method, the influence of each constant error item of inertial devices on the navigation precision of the system can be completely eliminated, particularly a gyroscope scale factor error, an installation error and an earth rotation speed coupling item error are eliminated, and the navigation precision of the inertial navigation system is improved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Online calibrating method of ship-based rotary strapdown inertial navigation system
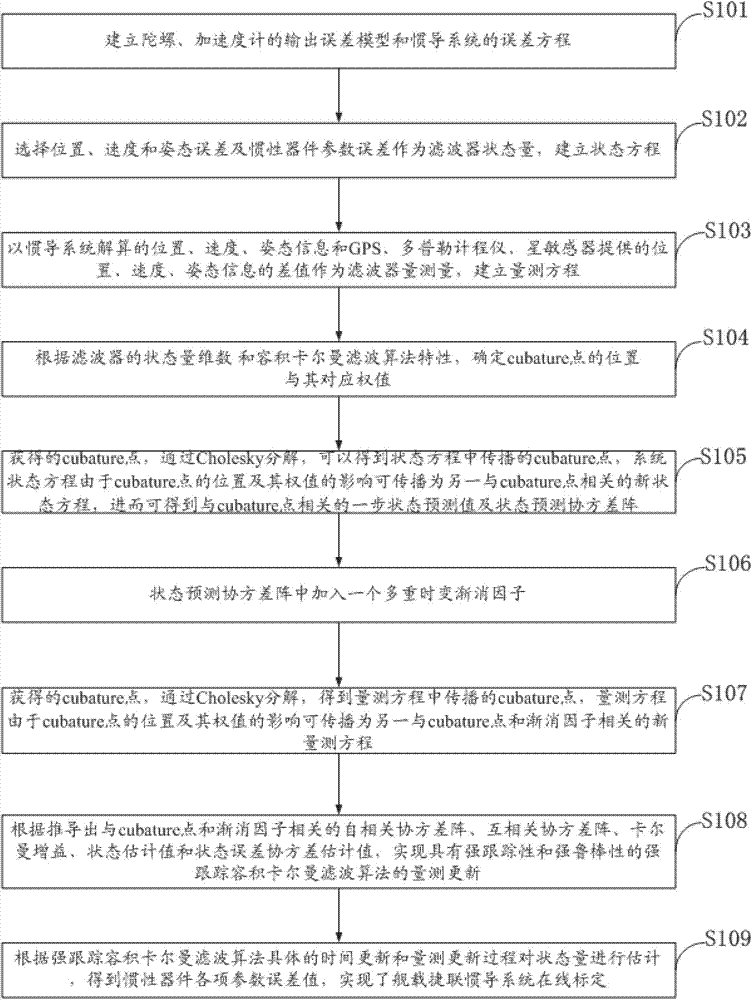
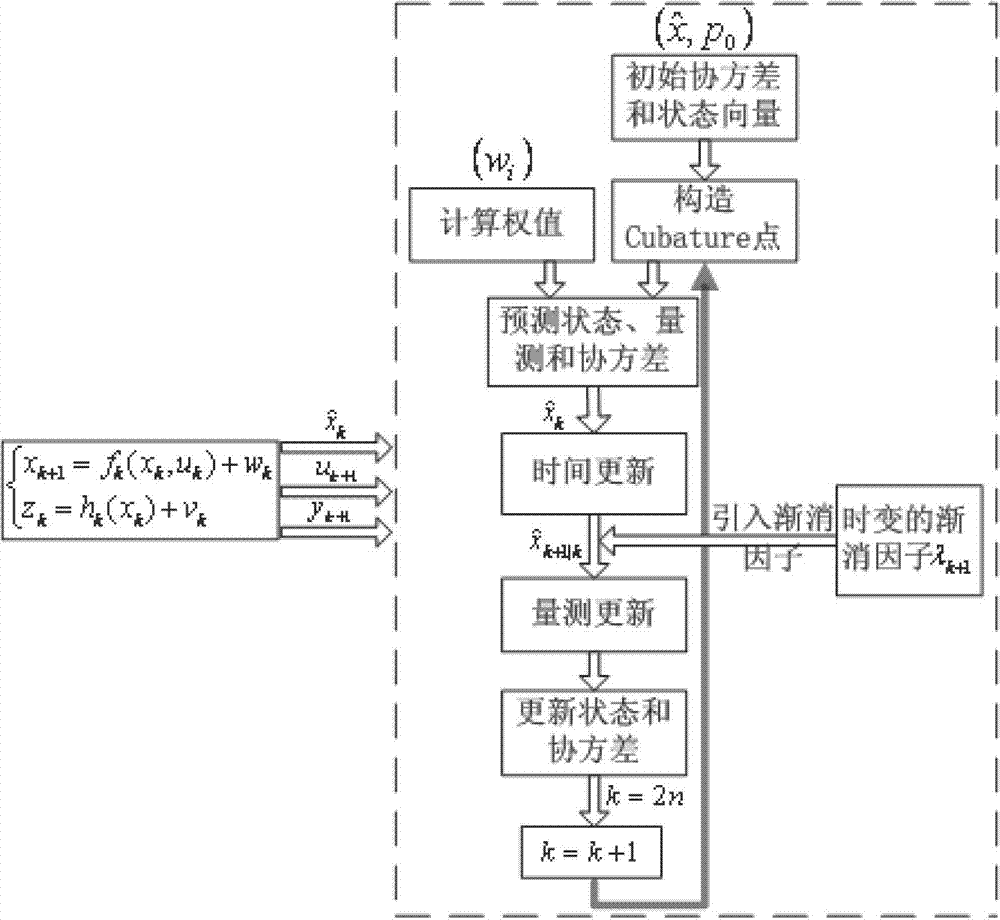
InactiveCN103591965AImprove navigation accuracyEasy to handle calculationsMeasurement devicesState predictionFilter algorithm
The invention discloses an online calibrating method of a ship-based rotary strapdown inertial navigation system. The method comprises the following steps: establishing an inertial component output error model and an inertial navigation system error equation, and researching the calibration of inertial component parameter errors and determining the quantity of state and the quantity of measuration; determining the position and weight of a cubature point according to dimension of the quantity of state, deducing a state equation and a one-step state prediction and state prediction covariance matrix related to the cubature point, and introducing a multiple time-varying fading factor modified state prediction covariance matrix; and deducing a measuring equation related to the cubature point and the fading factors, a self-correlated covariance matrix, a cross-correlated covariance matrix, a gain matrix, a state estimated value and a state error covariance estimated value, and designing a strong tracking volume Kalman filtering method with strong tracking performance and strong robustness. The method disclosed by the invention estimates the inertial component parameter errors by a filtering algorithm and carries out online calibration and compensates the inertial component parameter errors, so that the navigation precision is effectively improved. The method has strong parameter-varying robustness.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
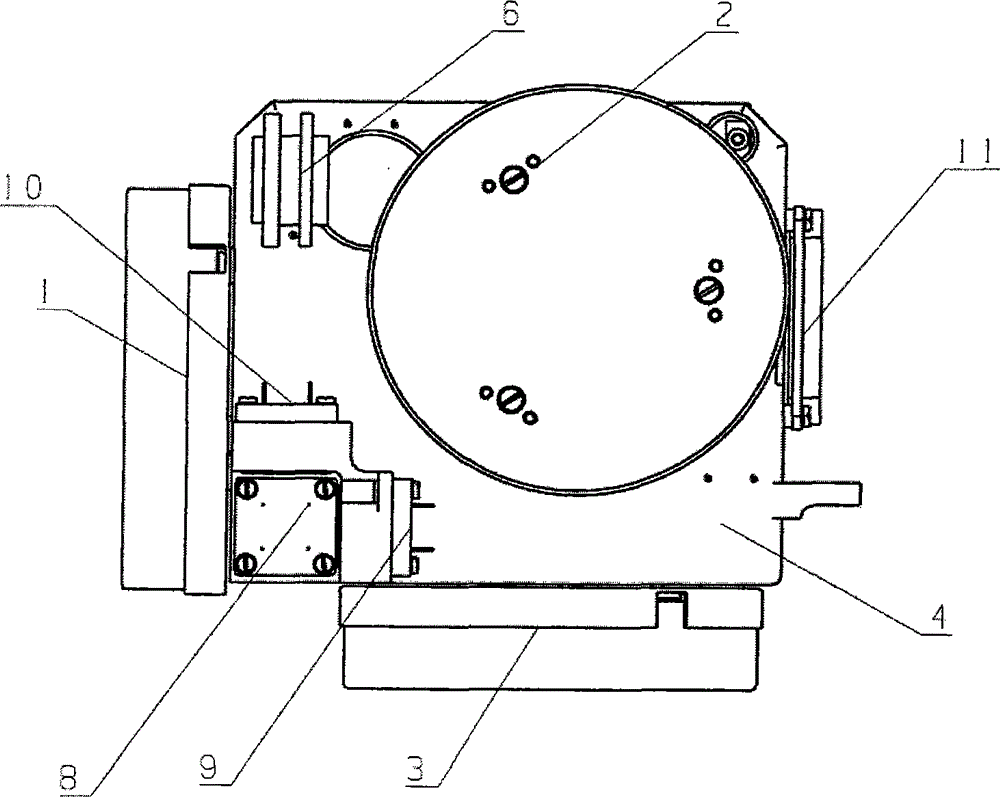
Double-shaft rotation optical fiber strapdown inertia navigation device
ActiveCN102980578AGuaranteed autonomyImprove navigation accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsMarine navigationQuartz
Owner:BEIJING AUTOMATION CONTROL EQUIP INST
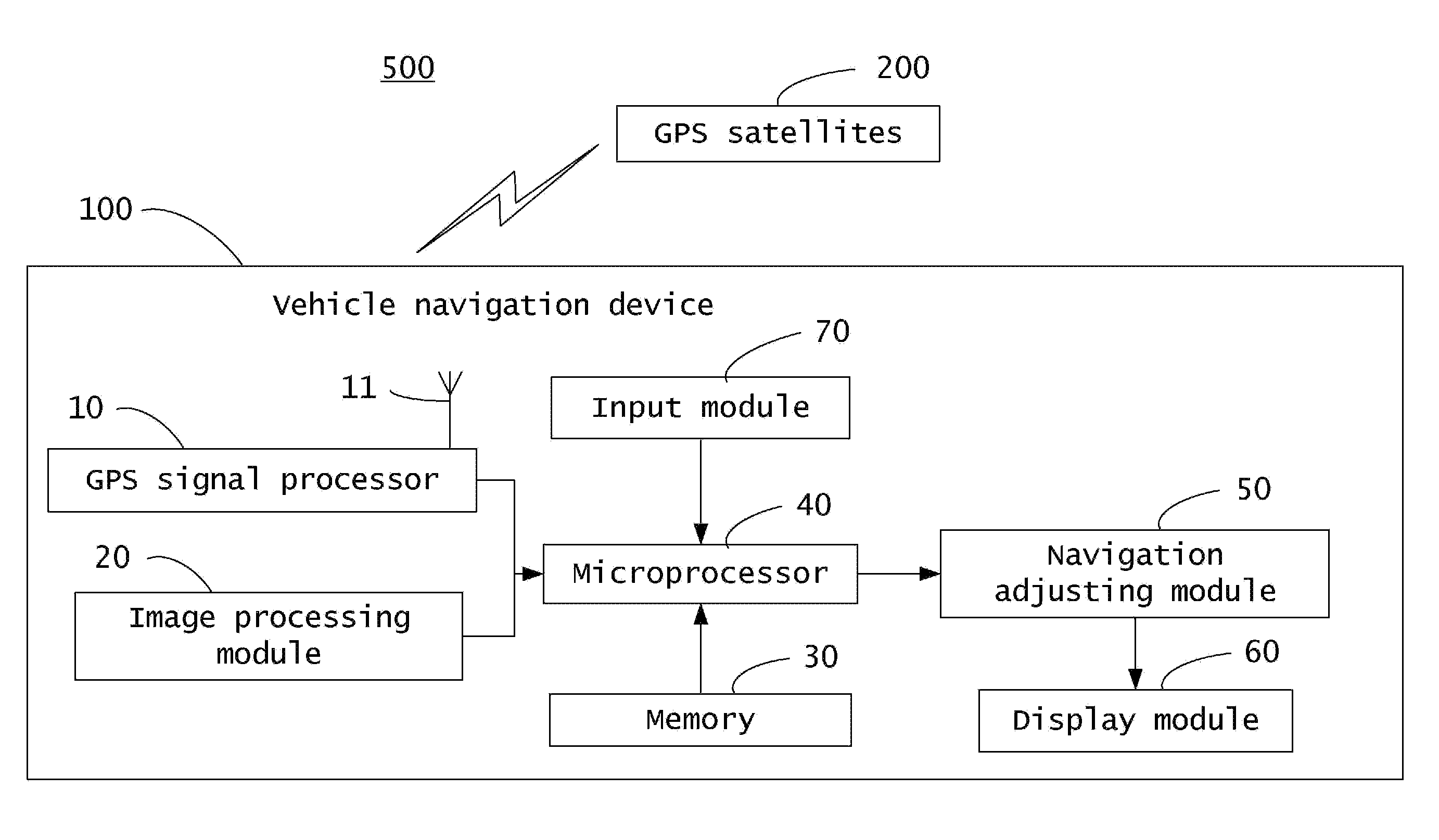
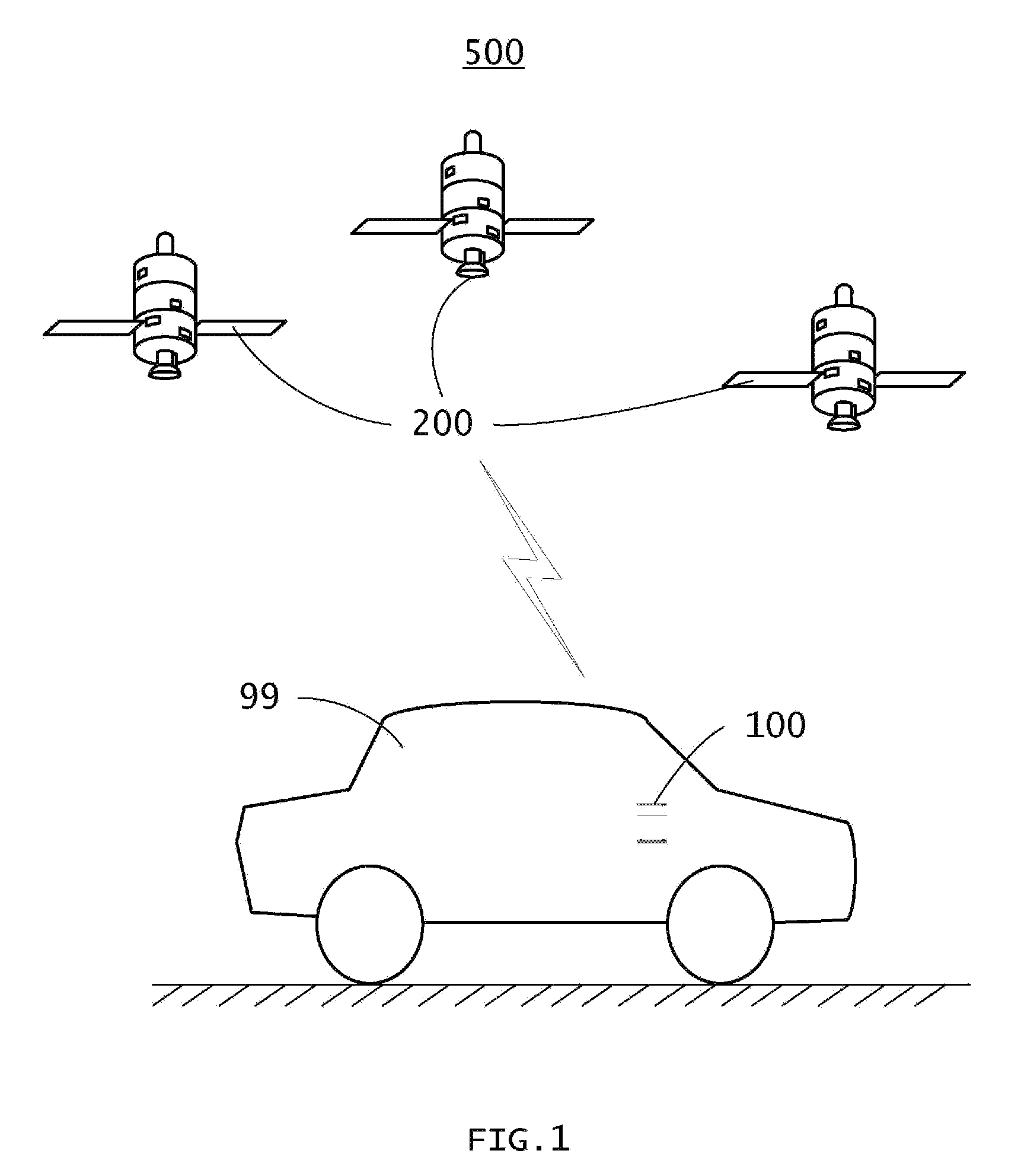
Vehicle navigation systems and methods
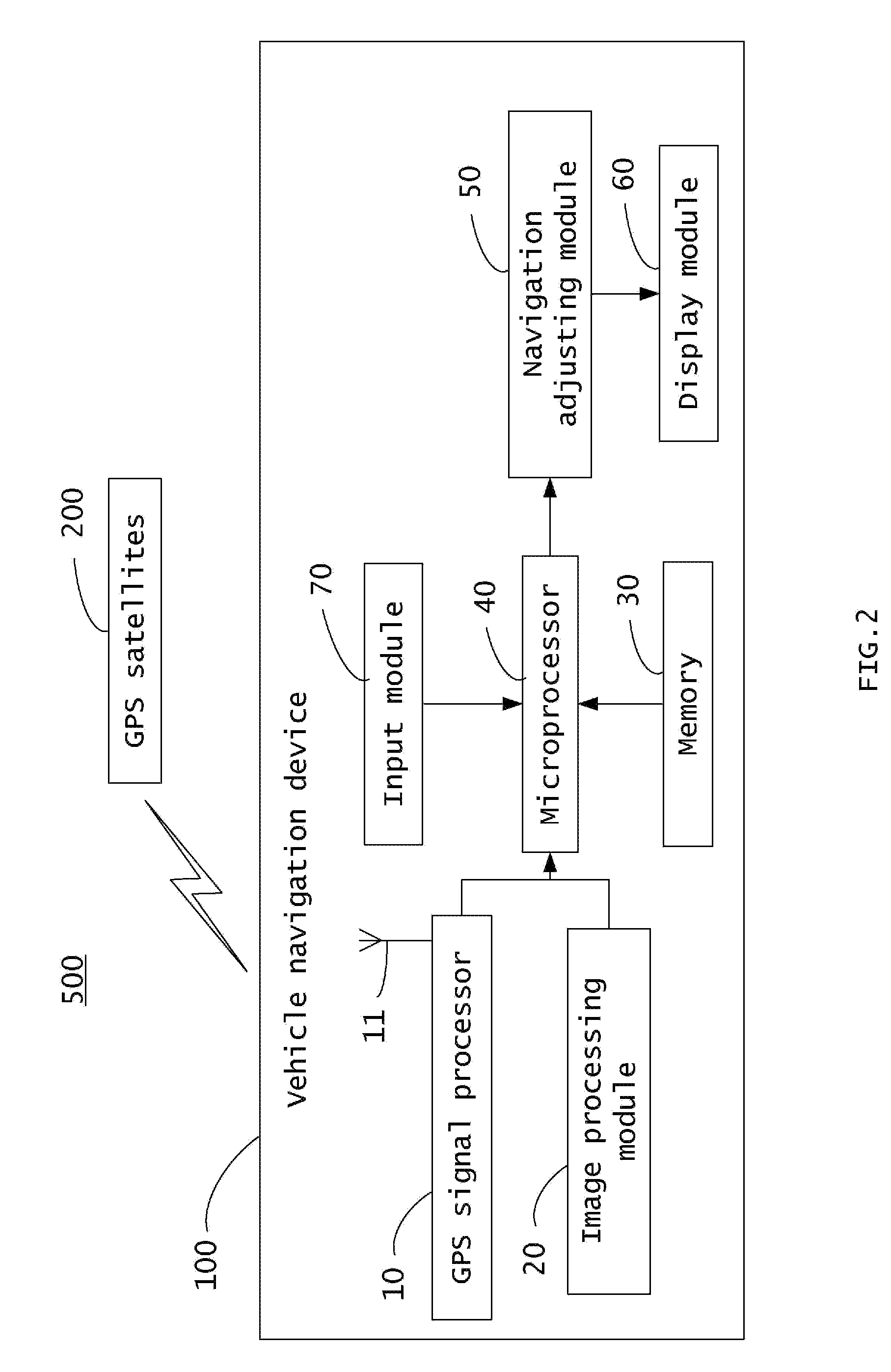
InactiveUS20090005977A1Improve navigation accuracyInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlImaging processingNavigation system
A vehicle navigation system includes a GPS signal processor, an image processing module, a memory, a microprocessor, a navigation adjusting module, and a display module. The GPS signal processor receives GPS signals and obtains an unadjusted navigation position according to the GPS signals. The image processing module captures pictures of surrounding areas and acquires a reference position according to the pictures. The microprocessor calculates an offset between the reference position and the unadjusted navigation position and compares the offset with a predetermined offset. The navigation adjusting module adjusts the unadjusted navigation position according to the reference position and the offset comparison and displays a result on the display module.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Full-digital simulation method and device for global positioning system (GPS)/strapdown inertial navigation system (SINS) combined navigation
InactiveCN102508954AImprove navigation accuracyLow costSpecial data processing applicationsGyroscopeNavigation system
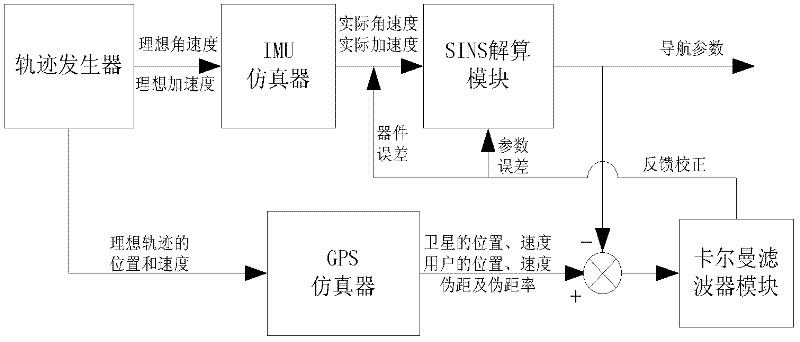
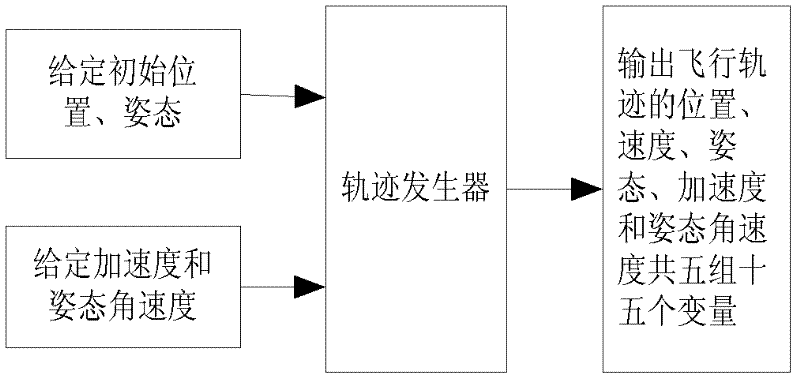
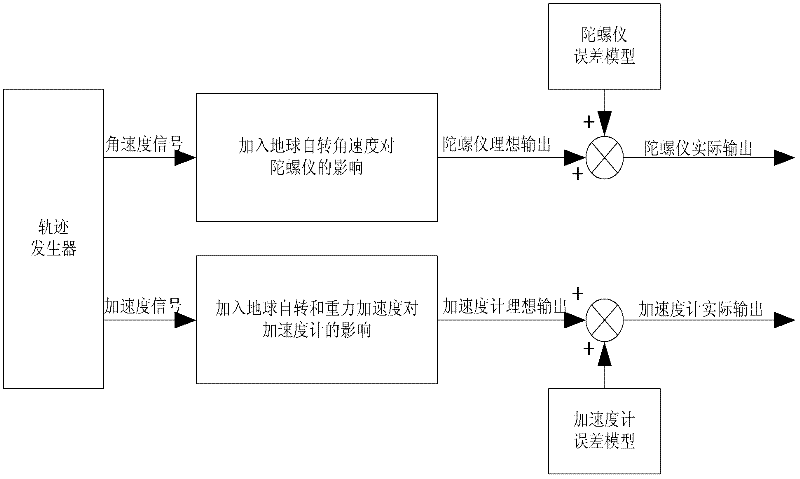
The invention belongs to the field of combined navigation. In order to provide a low-cost and high-precision navigation device and a low-cost and high-precision navigation method, the technical scheme adopted by the invention is as follows: a full-digital simulation device for global positioning system (GPS) / strapdown inertia navigation system (SINS) combined navigation is composed of a trace generator module, an inertial measurement unit (IMU) simulator, a GPS simulator, an SINS calculation module and a Kalman filter module, wherein the trace generator module is used for generating flying trace data; the IMU simulator is used for simulating the actual situations of a gyroscope and an accelerator; the GPS simulator is used for simulating a GPS receiver and outputting the pseudorange, pseudorange rate, position and speed information of a carrier; the SINS calculation module is used for calculating the outputs of the IMU simulator to acquire the position, speed and attitude information of the carrier; and the Kalman filter module is used for performing data fusion on a GPS and an SINS by adopting a Kalman filter method according to two different combination modes, namely loose combination and compact combination. The device and the method are mainly applied to navigation.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Navigation system and method backing up several modes
ActiveCN101019771APrecise Navigation EffectGuaranteed navigation accuracyDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsSurgical operationDisease
The present invention is navigation system and method backing up several modes. The navigation system includes fixed imaging equipment, tracking system, surgical operation equipment, sick bed, calibrating pin, calibrating mold and navigation software. It has at least one tracer constituting the world coordinate system, one surgical operation equipment tracer as the surgical operation equipment coordinate system, one sick bed tracer constituting the sick bed coordinate system, one characteristic point set I and one characteristic point set II set inside and outside the calibrating mold separately. After calibration, the disease focus image and the surgical operation equipment are shown in the same coordinate system. The present invention may be used widely in the navigation course of different surgical operations.
Owner:SYMBOW MEDICAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com