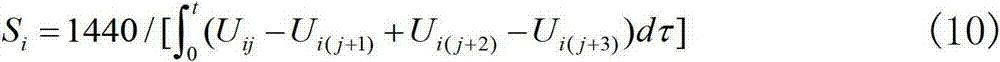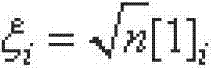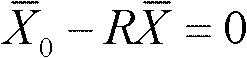Patents
Literature
273 results about "Error equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
How to find percent error: To correctly put together the percent error equation, take the difference from accepted value which is also your result minus the accepted value, divide by accepted value and multiply this result by 100. Calculation result is always in percentages.
Mixed measurement analysis method for satellite antenna
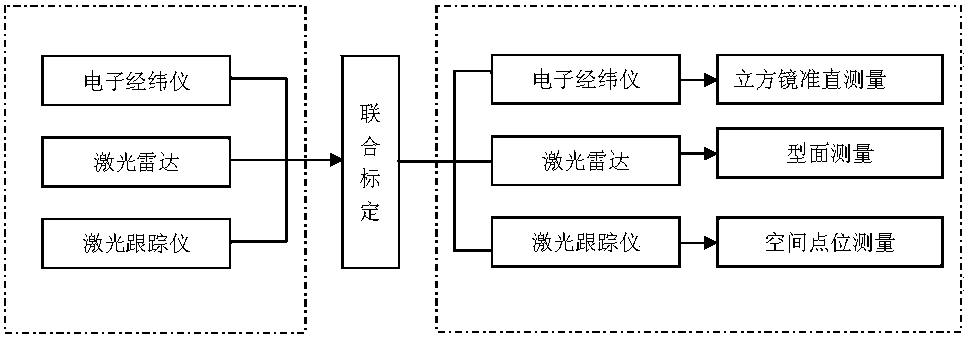
The invention relates to a mixed measurement analysis method for a satellite antenna. The method effectively solves the problems that various measurement devices are used for co-measurement to reduce detection difficulty and improve detection efficiency during a measurement process of the satellite antenna. The method comprises the steps: cubic mirror collimating measurement is carried out by electronic theodolites during antenna installation and detection processes, scanning measurement of an antenna shaped surface is carried out by a laser radar, a space point position is measured by a laser tracker, and thus the measurement of the satellite antenna is jointly completed by the various measurement devices; union calibration algorithm of 'six freedom degree measurement station three-dimensional network' is employed, a conversion relationship between measurement station coordinates and measurement coordinates is utilized, various observed value error equations are directly listed, so as to overcome shortcomings of a traditional algorithm and improve adaptability of the algorithm. The method provided by the invention is simple, is easy to operate, enables an initial value to be fast acquired, has low requirements for precise degree of the initial value, has a few iteration times, is quick in convergence speed, theoretically is an optimal solution, and has strong algorithm adaptability, high measuring efficiency, fast speed and high precision.
Owner:BEIJING SATELLITE MFG FACTORY +1
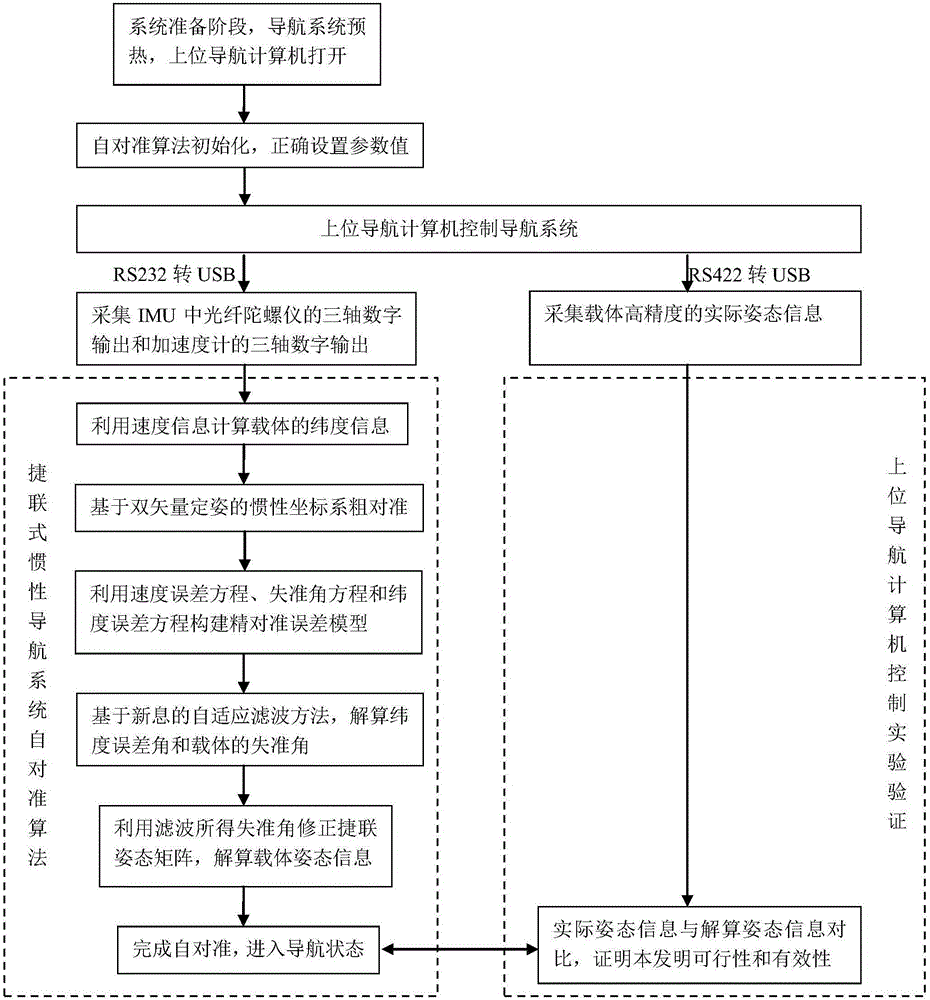
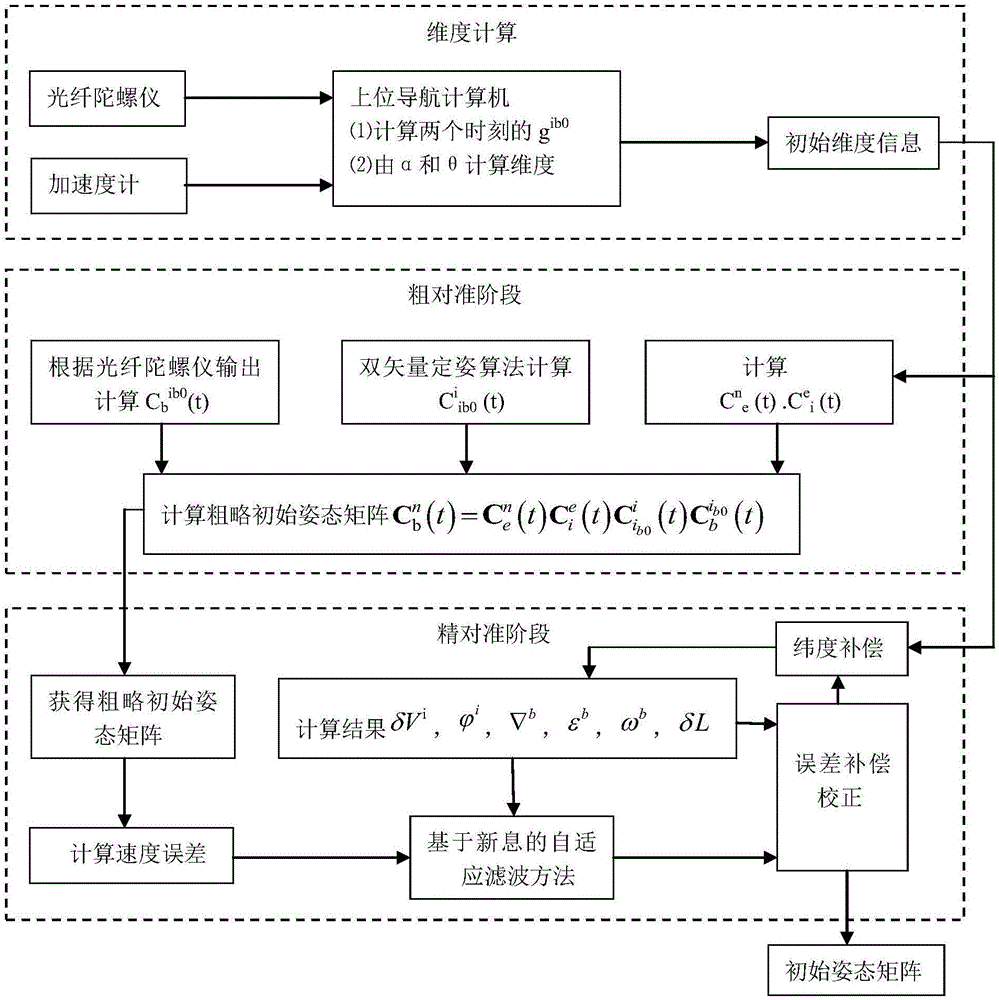
Optical fiber gyroscope strap-down inertial navigation system initial posture determination method
InactiveCN101187567AReduce divergenceReduce system dimensionalityDigital technique networkNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAccelerometerFiltering theory
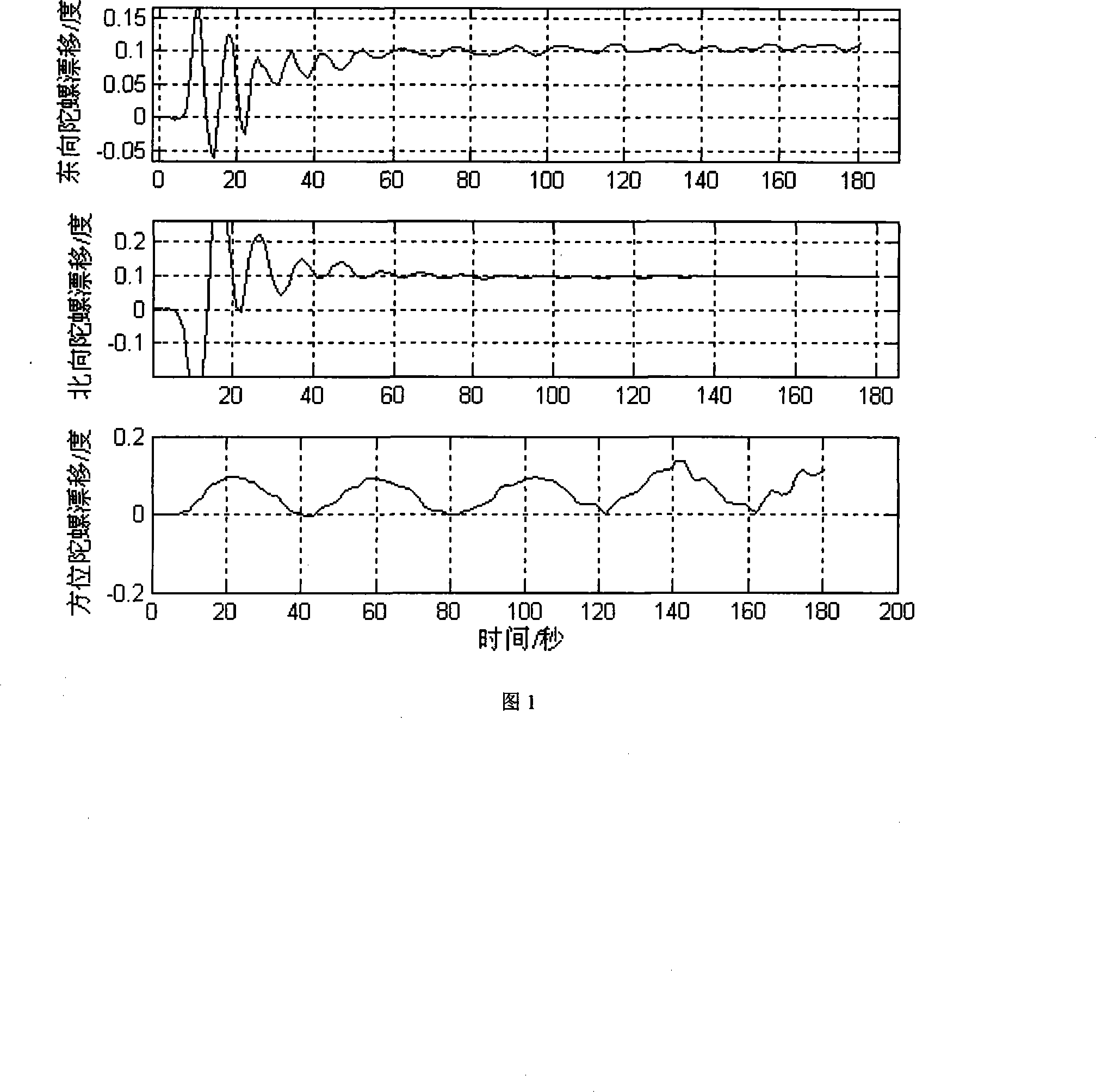
The invention discloses a determined method for an initial gesture on the basis of Doppler optical fiber gyro strapdown inertial navigation system, which comprises continuously collecting data which is output by an optical fiber gyro and a quartz flexible accelerometer after being preheated, processing the data of the gyroscope and the accelerometer which are collected, finishing a rough alignment of the strapdown inertial navigation system, entering into an extractive alignment after the rough alignment is finished, establishing a dynamic base error equation of a marine strapdown inertial navigation system, employing an optimal control filtering theory to design an electric filter, and doing a filtering estimation, extracting information of ship hull gesture misalignment angle to correct the ship hull gesture when a combined extractive alignment is finished, finishing extractive initial alignment, simultaneously obtaining shift estimated value of the gyroscope, and realizing a drift course of the initial alignment. The method of the invention can realize accurate estimation to a zero drift of the optical fiber gyro when the requirement of accuracy and rapidity is guaranteed.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for calibrating in-orbit exterior orientation parameters of push-broom optical cameras of remote sensing satellite linear arrays
ActiveCN103679711AMeet the needs of on-orbit geometry calibrationImprove accuracyImage analysisMathematical modelOrbit
The invention discloses a method for calibrating in-orbit exterior orientation parameters of push-broom optical cameras of remote sensing satellite linear arrays. The method includes steps of (1), acquiring information of high-precision control points; (2), acquiring interior orientation elements of the cameras at the control points, acquiring auxiliary data of orbits and the like and building rigorous imaging geometric models of various control points; (3), computing positioning errors of the various control points, eliminating coarse and poor control points and acquiring information of preliminarily calibrated control points; (4), building geometric calibration mathematical models of exterior orientation elements of the cameras, and computing theoretical pointing vectors and actual pointing vectors of the various control points; (5), creating three-axis rotation error equations among the theoretical pointing vectors and the actual pointing vectors and linearly processing the equations; (6), solving parameters of the error equations by a least square process to acquire calibration exterior parameters. The method has the advantage that after errors of a system are compensated by the aid of the calibration exterior parameters, the cameras are stable in non-control positioning precision.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
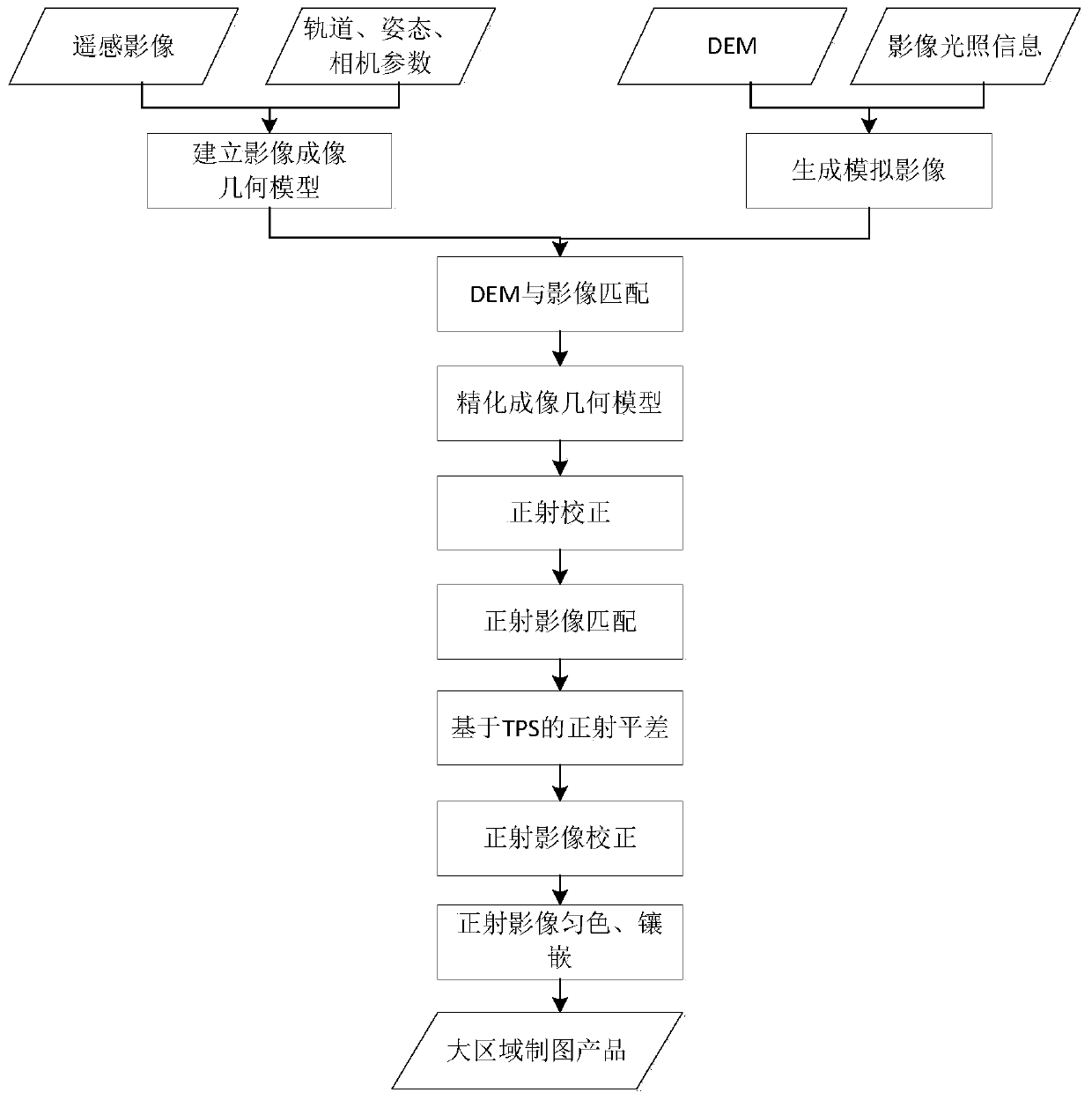
A satellite remote sensing image large-area seamless orthographic image manufacturing method
ActiveCN109903352ASolve the problem that the geometric accuracy does not meet the requirementsReduce in quantityImage analysis2D-image generationComputer scienceImaging data
The invention relates to a satellite remote sensing image large-area seamless orthographic image manufacturing method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) constructing a remote sensing imageimaging geometric model; 2) reading a to-be-matched remote sensing image and DEM data, and matching the DEM data with the to-be-registered remote sensing image data; 3) carrying out remote sensing image ortho-rectification to obtain a corresponding DOM product; 4) according to the position relation between the orthographic images obtained in the step 3), determining an overlapping region between the images, performing matching in the overlapping region to obtain homonymous points, establishing an error equation based on a TPS model for each group of homonymous points, and performing iterativesolution to obtain a correction amount of geometric deviation between the images; And 5) carrying out dodging and inlaying on all the corrected ortho-images to obtain large-area ortho-image map products, and introducing a thin plate spline model in the ortho-image adjustment process to solve the problem of low precision of a traditional geometric correction model caused by a small overlapping range between the images.
Owner:INST OF REMOTE SENSING & DIGITAL EARTH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Latitude unknown self-aligning method of strapdown inertial navigation system under dynamic interference condition
ActiveCN106123921AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed validityNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsInertial coordinate systemSelf adaptive
A latitude unknown self-aligning method of a strapdown inertial navigation system under the dynamic interference condition includes the steps that firstly, a geometrical analytic formula is built by means of the characteristic that the projection of gravity acceleration is unchanged in an inertial coordinate system, the gravity acceleration is subjected to integration to obtain speed information, and the latitude value of the position where a carrier is located is calculated according to the speed information; secondly, on the basis of the double-vector altitude determination principle and by means of the characteristic that the gravity acceleration of an inertial system includes north orientation information, rough solution of an initial attitude matrix under the inertial system is achieved; finally, on the basis that coarse alignment is finished, a precise alignment error model under the latitude unknown dynamic interference condition is built according to a speed error equation, a misalignment angle equation and a latitude error equation, the latitude error angle and the misalignment angle of the carrier are calculated by means of the self-adaptive filtering method based on information, the latitude value is compensated with the latitude error angle, the strapdown altitude matrix is corrected according to the misalignment angle, and high-precision quick self-aligning of the strapdown inertial navigation system is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
SINS/GPS/polarized light combination navigation system modeling and dynamic pedestal initial aligning method
ActiveCN103217159AImprove estimation accuracyHigh degree of autonomyNavigational calculation instrumentsAviationSimulation
The invention provides a SINS / GPS / polarized light combination navigation system modeling and a dynamic pedestal initial aligning method, which relates to the dynamic pedestal initial aligning method for vehicle, ship and aviation aircraft. The invention concretely comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a SINS error equation as an initial aligning state equation; (2) according to a polarization azimuth, a GPS outputted speed and a position, establishing an initial aligning measurement equation base on the polarization azimuth error, a speed error and a position error; (3) estimating an attitude error, a speed error and a position error using a Kalman filtering; (4) correcting the feedbacks of the attitude, the speed and the position of SINS. The SINS outputs the attitude, the speed and the position information of the carrier to users. The invention has the advantages of high precision, small computational complexity and good anti-interference capability, and is used for improving the aligning precisions of vehicle, ship and aviation aircraft, with reduced initial aligning time.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
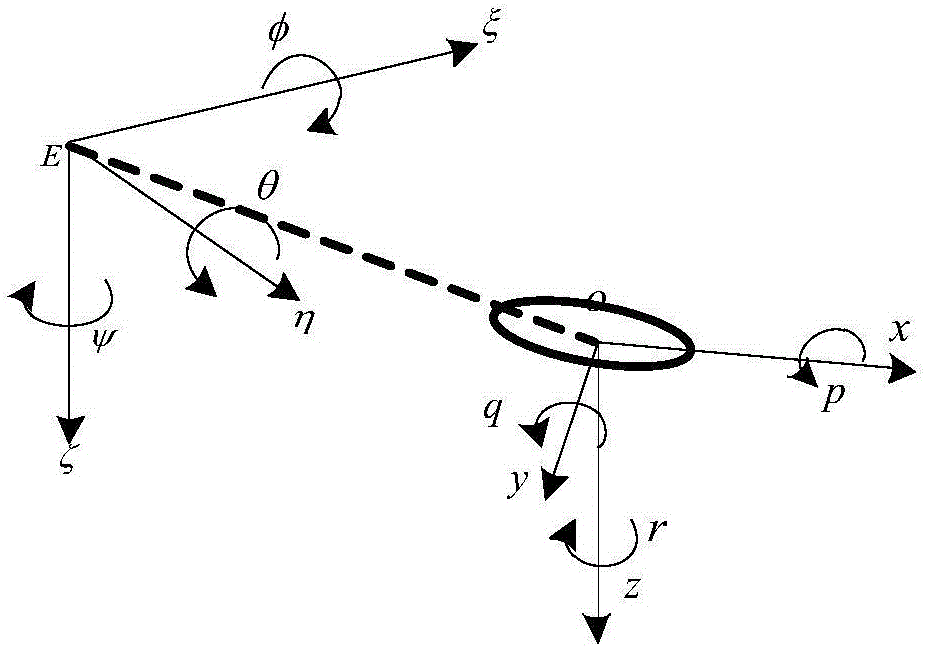
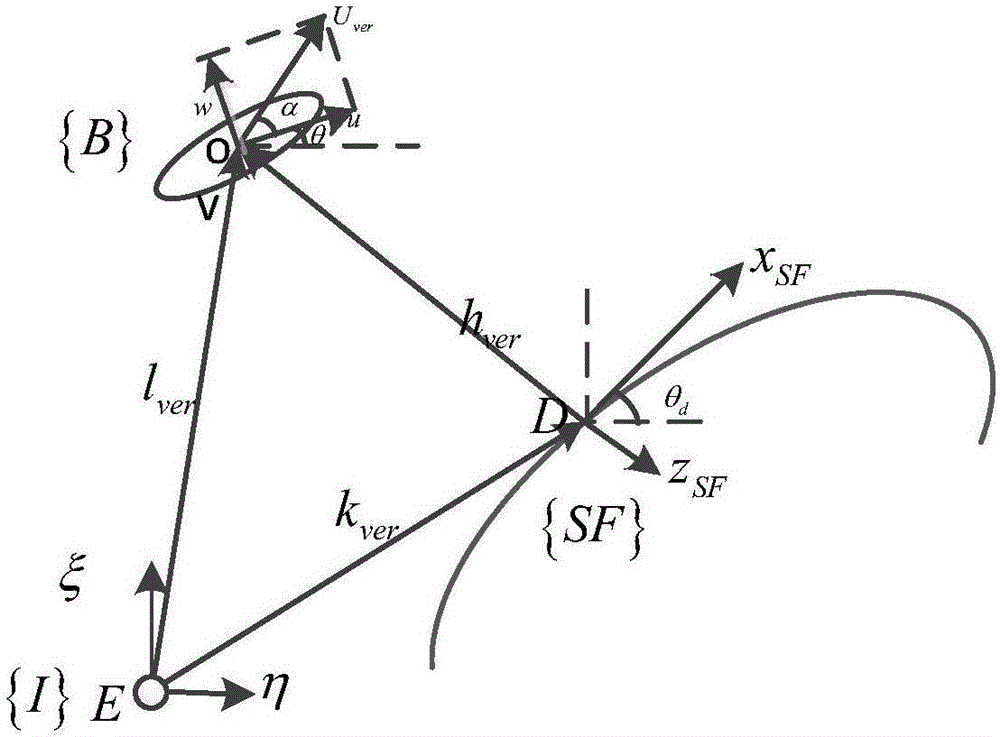
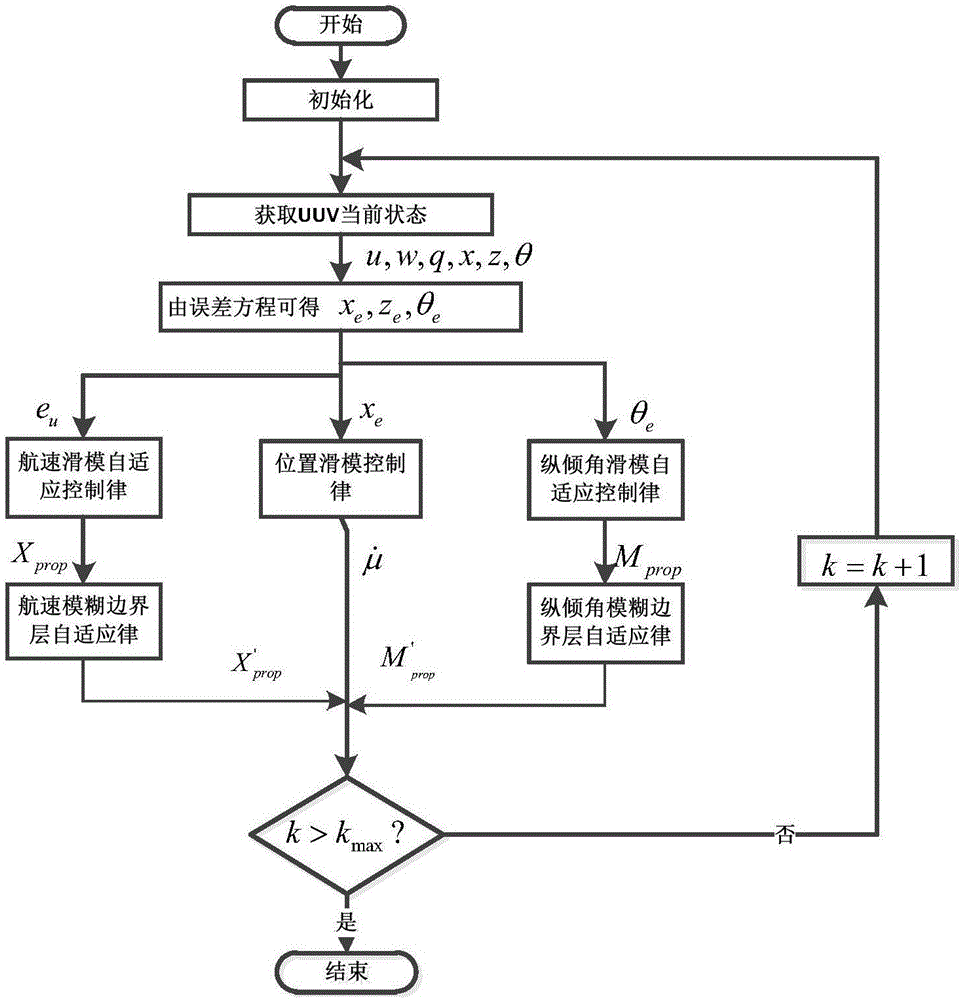
Sliding-mode control method for parameter-free driving-insufficient UUV (Unmanned Underwater Vehicle) vertical plane route tracking
ActiveCN106444794AGet rid of dependenceImprove speed tracking accuracyAltitude or depth controlVertical planeControl system
The invention provides a sliding-mode control method for parameter-free driving-insufficient UUV (Unmanned Underwater Vehicle) vertical plane route tracking. The sliding-mode control method comprises the following steps: I, performing initialization; II, acquiring a current state of a UUV; III, establishing an error equation of the horizontal plane of the driving-free UUV so as to obtain position deviation values xe and ze and course deviation value theta e; IV, according to a sliding-mode control method, respectively designing traveling speed sliding-mode self-adaptive control rules, position sliding-mode control rules and trimming angle sliding-mode self-adaptive control rules, controlling propelling force Xprop, an excepted traveling speed U and a torque Mprop, wherein eu is 0, xe is 0 and theta e is 0; V, designing fuzzy control rules for a boundary layer, setting k to be equal to k+1, turning to step II, and updating control rules and self-adaptive rules of a next time. By adopting the sliding-mode control method, a controller for stabilizing a system can be designed only according to a vertical surface kinetic model, self-adaptive rules can be designed for water kinetic parameters with uncertainties, furthermore a control system can be relieved from dependency on parameters, the system has robustness, and the influence of the uncertainties on the sliding-mode control approaching process can be reduced.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
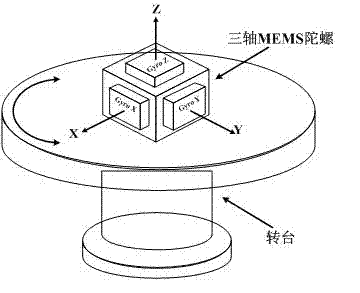
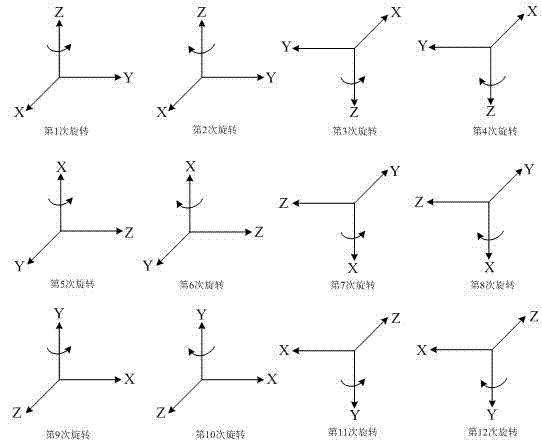
Triaxial MEMS gyroscope rotation integral calibration method based on uniaxial turntable
The invention discloses a triaxial MEMS gyroscope rotation integral calibration method based on a uniaxial turntable. According to the invention, first, a triaxial MEMS gyroscope error model is established; the triaxial MEMS gyroscope is fixed on the uniaxial turntable; MEMS gyroscope six-position rotary calibration is carried out; test data and sampling time of 12 times of rotation of the MEMS gyroscope at the 6 positions are tested and recorded; through the 12 times of rotation of the MEMS gyroscope at the 6 positions, a MEMS gyroscope error model is simplified, and an error model after gyroscope rotation is obtained; integral calculations are carried out upon two sides of the equation of the error model after gyroscope rotation, an error equation set is established, and MEMS gyroscope error coefficient is obtained by calculation. With the method provided by the invention, calibration precision is ensured; and fixed zero bias, scale factor, cross-coupling error coefficient, and acceleration sensitivity coefficient of the MEMS gyroscope can be solved rapidly, such that calibration efficiency is improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA INST OF OPTOELECTRONICS INTEGRATEDDEVICE
Online calibrating method of ship-based rotary strapdown inertial navigation system
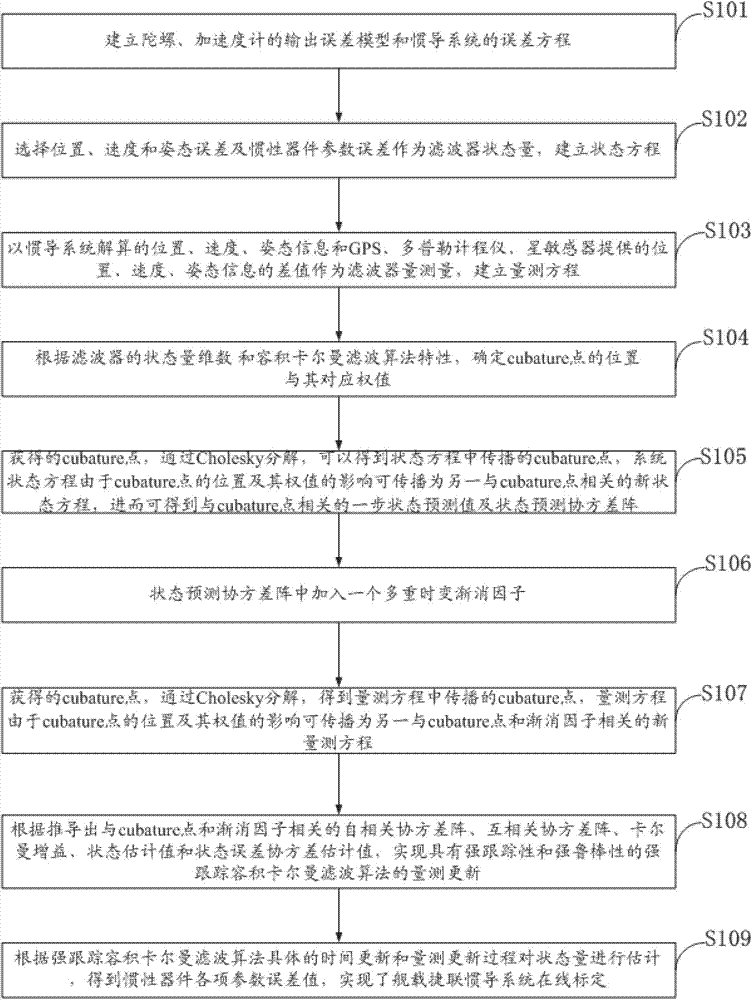
InactiveCN103591965AImprove navigation accuracyEasy to handle calculationsMeasurement devicesState predictionFilter algorithm
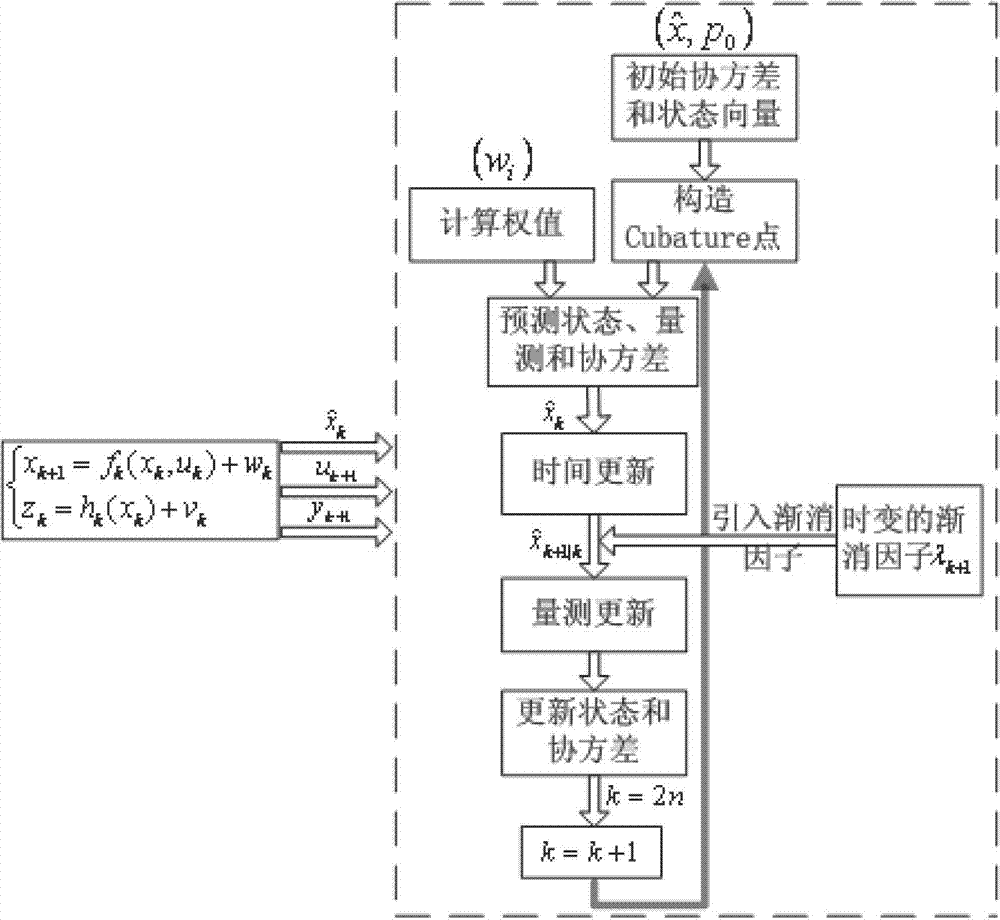
The invention discloses an online calibrating method of a ship-based rotary strapdown inertial navigation system. The method comprises the following steps: establishing an inertial component output error model and an inertial navigation system error equation, and researching the calibration of inertial component parameter errors and determining the quantity of state and the quantity of measuration; determining the position and weight of a cubature point according to dimension of the quantity of state, deducing a state equation and a one-step state prediction and state prediction covariance matrix related to the cubature point, and introducing a multiple time-varying fading factor modified state prediction covariance matrix; and deducing a measuring equation related to the cubature point and the fading factors, a self-correlated covariance matrix, a cross-correlated covariance matrix, a gain matrix, a state estimated value and a state error covariance estimated value, and designing a strong tracking volume Kalman filtering method with strong tracking performance and strong robustness. The method disclosed by the invention estimates the inertial component parameter errors by a filtering algorithm and carries out online calibration and compensates the inertial component parameter errors, so that the navigation precision is effectively improved. The method has strong parameter-varying robustness.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
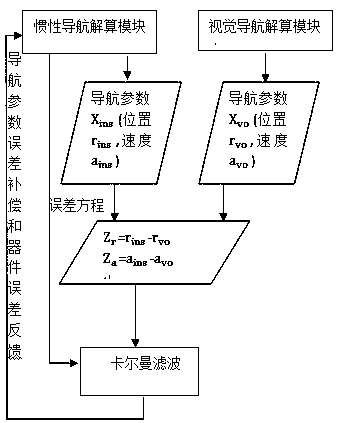
Navigation method realized by means of loose combination of visual navigation/inertial navigation
PendingCN107063246AHigh precisionAccuracy impactNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSimulationEquation of state
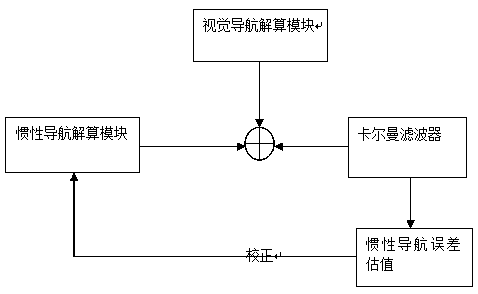
The invention relates to a navigation method realized by means of loose combination of visual navigation / inertial navigation. The main research content is to periodically correct inertial navigation parameters by using the position of the visual navigation and velocity information. The navigation method solves the problem that inertial navigation error accumulates over time. According to the navigation method, an error equation of an inertial navigation system is used as a state equation of a filter, the difference between the position calculated by means of the visual navigation and the position solved by using the inertial navigation system is used as measurement of Kalman filtering, and the parameters of the inertial navigation system and the error of a sensor are estimated, so that the inertial navigation parameters are corrected. Compared with the prior art, by adopting the scheme, the navigation method can enable the inertial navigation system to be maintained to have high accuracy for a long time, and the accuracy of the inertial navigation system is not affected due to failure of visual navigation calculation.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
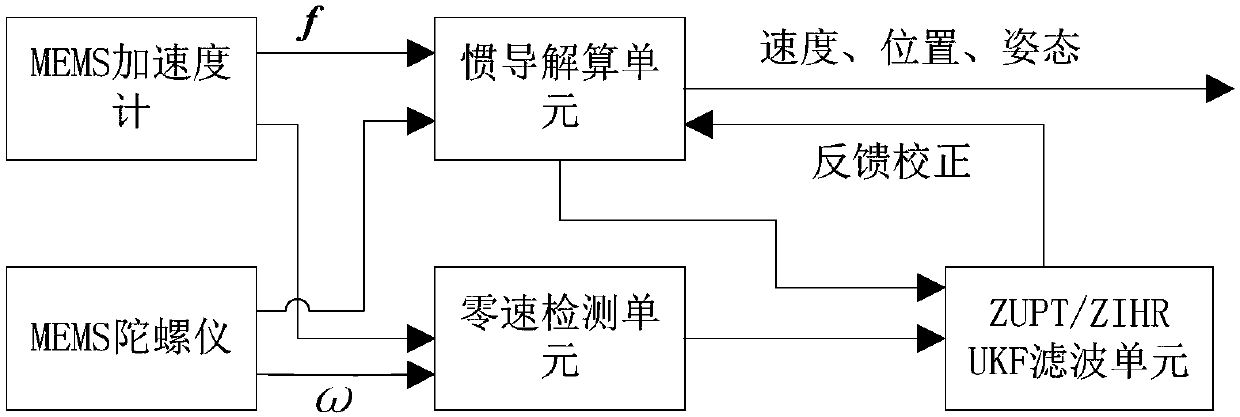
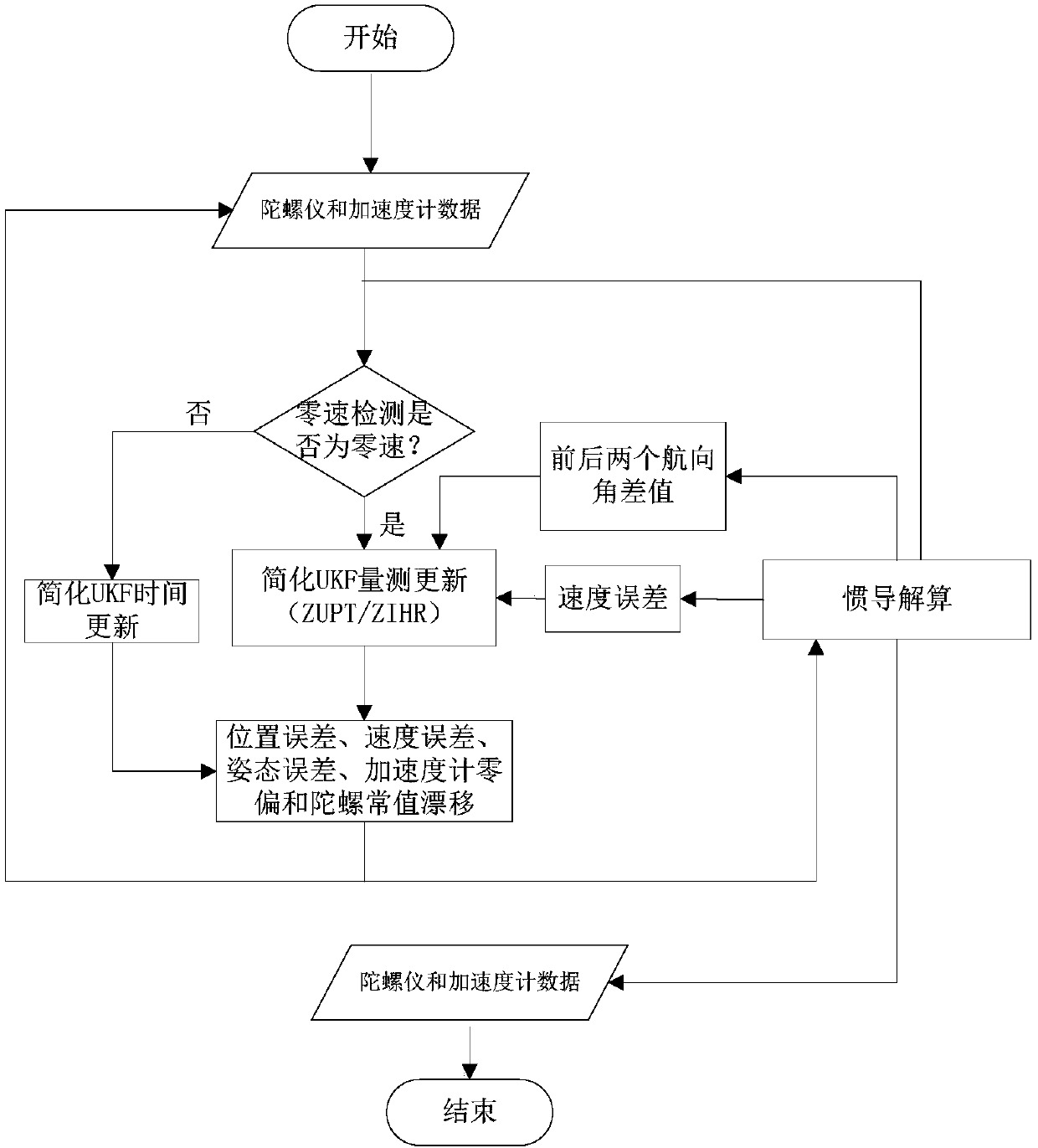
MEMS pedestrian navigation method based on ZIHR heading angle correction algorithm
InactiveCN108426574AAvoid divergenceExtended 1D measurementNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsCorrection algorithmAccelerometer
The invention provides an MEMS pedestrian navigation method based on ZIHR heading angle correction algorithm. The method includes: 1. conducting initial alignment on an MEMS pedestrian navigation system with an accelerometer and a magnetometer at a static moment; 2. working out an inertial navigation calculation equation and an error equation of the MEMS pedestrian navigation system; 3. conductingzero velocity state detection with the output values of a gyroscope and the accelerometer; 4. working out the relationship between the heading angle difference of adjacent moments under a zero velocity state, gyroscopic drift and a heading error angle in ZIHR (zero integrated heading rate) correction algorithm; and 5. establishing a simplified MEMS pedestrian navigation UKF filter model, and performing UKF filtering. The method provided by the invention maximumly utilizes the information of static moment, has uncomplicated calculation amount, and can well inhibit the divergence of the headingerror angle. Use of the UKF filter for real-time feedback correction at a zero velocity moment can well inhibit the problem of navigation parameter error divergence after long-time operation of a low-precision MEMS sensor, and improve the positioning precision of a pedestrian navigation system.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
SINS dynamic base transfer alignment method based on satellite positioning
ActiveCN101750066AThe difficulty of avoiding ambiguityHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsKaiman filterFault tolerance
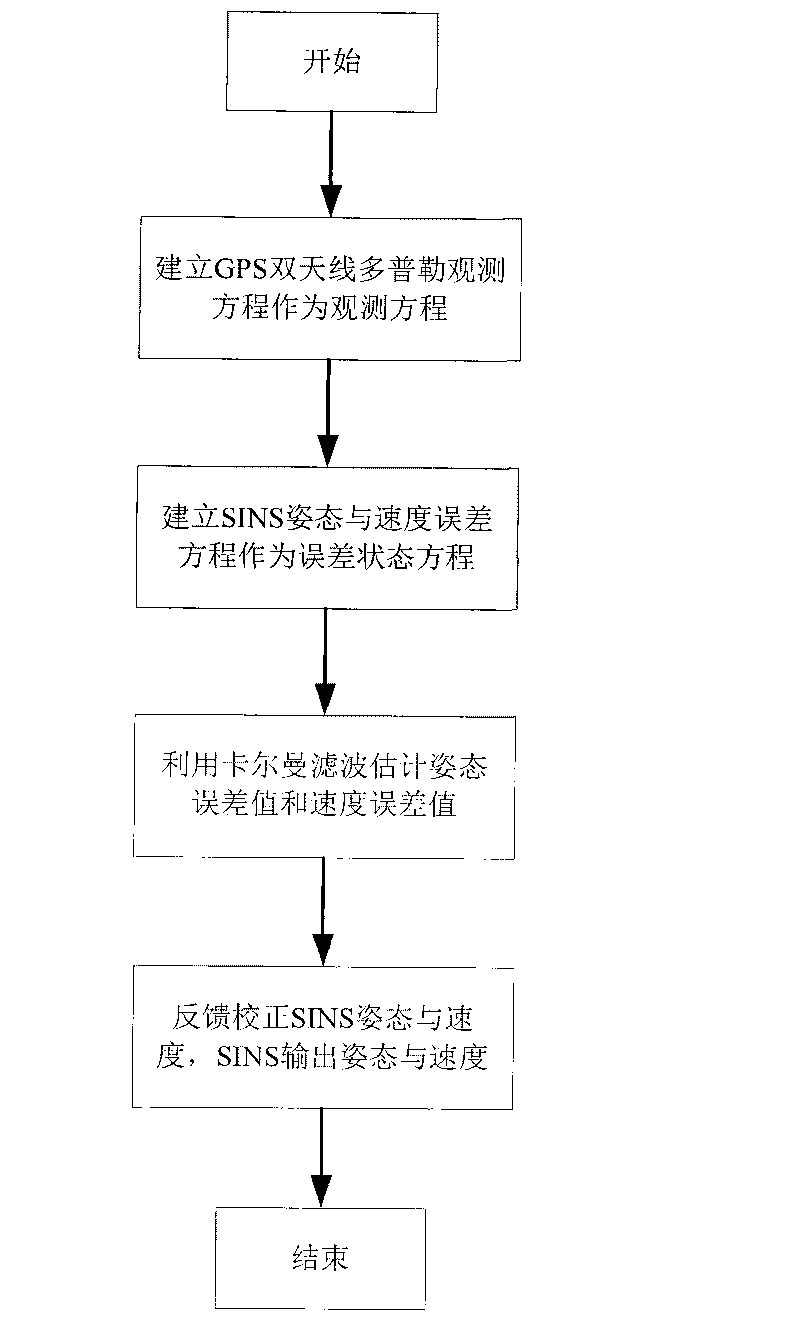
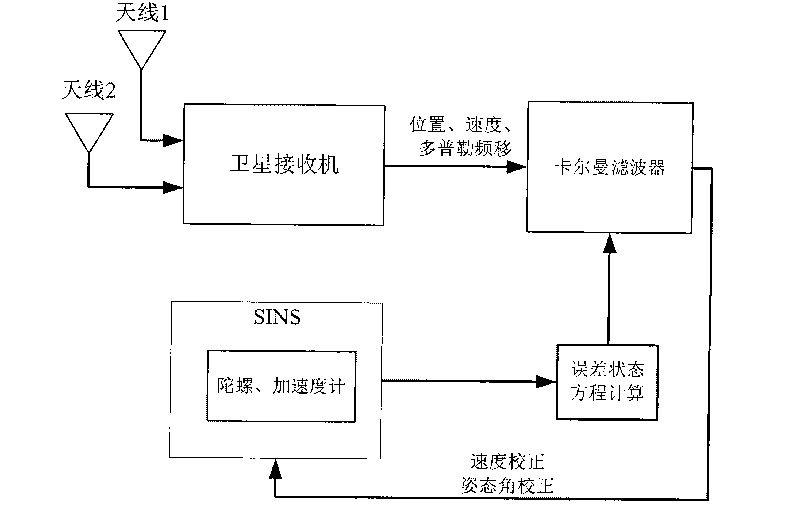
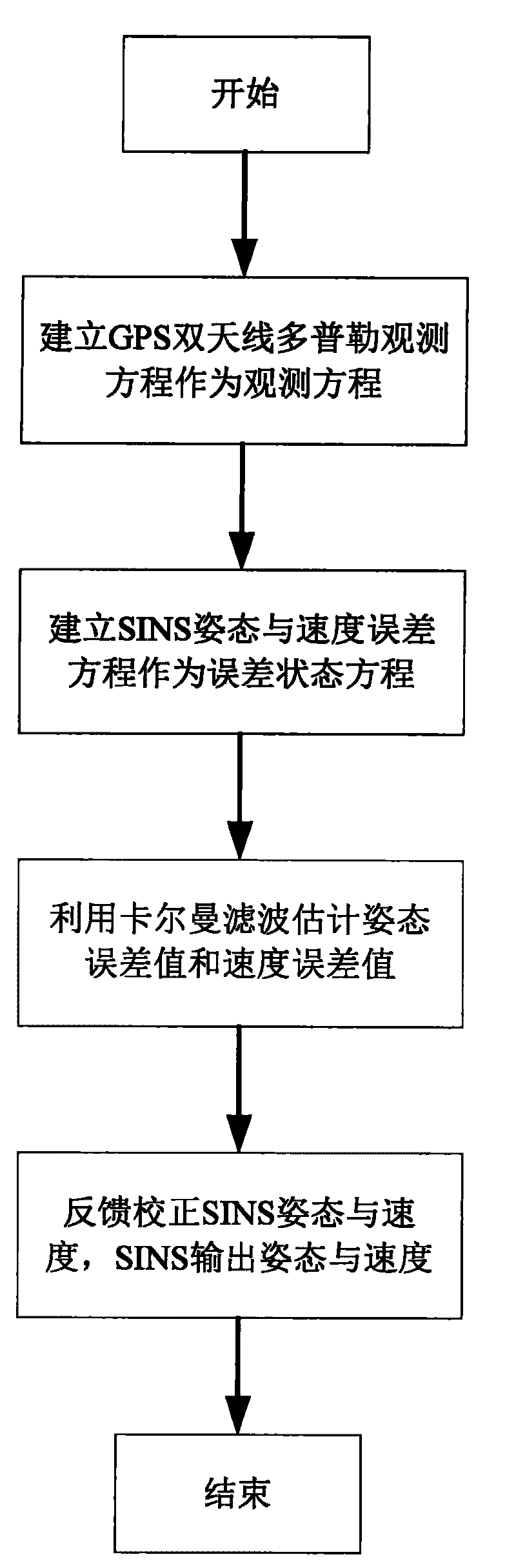
A SINS dynamic base transfer alignment method based on satellite positioning includes the following steps: (1) the baseline vector direction of the GPS dual-antenna is in accordance with the navigation direction of the SINS, wherein one antenna is positioned at a carrier and the other antenna is positioned at the sub-carrier of the SINS, a GPS dual-antenna Doppler observational equation is used to establish the observational equation of SINS dynamic base transfer alignment method, and the position and speed information received by the GPS receiver are used as the position and speed of the initial state SINS; (2) an attitude error equation and an speed error equation of the SINS are established and used as the error state equation of the alignment method; (3) a kalman filter is adopted for attitude error and speed error estimation; (4) the feedback correction on attitude and speed are carried out for the SINS, and the SINS output the attitude and speed information of the carrier to the user. The SINS dynamic base transfer alignment method based on satellite positioning has high processing speed, high accuracy, small computation quantity, strong fault tolerance and is not affected by the deflection deformation of the carrier.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
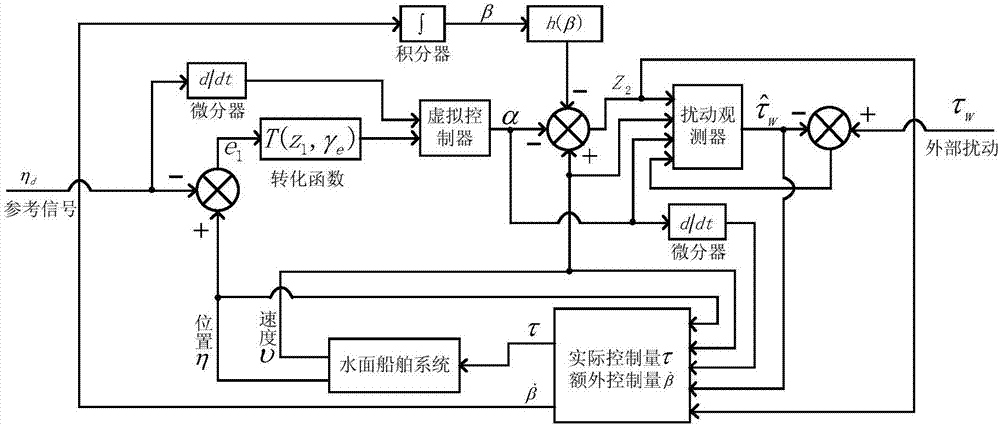
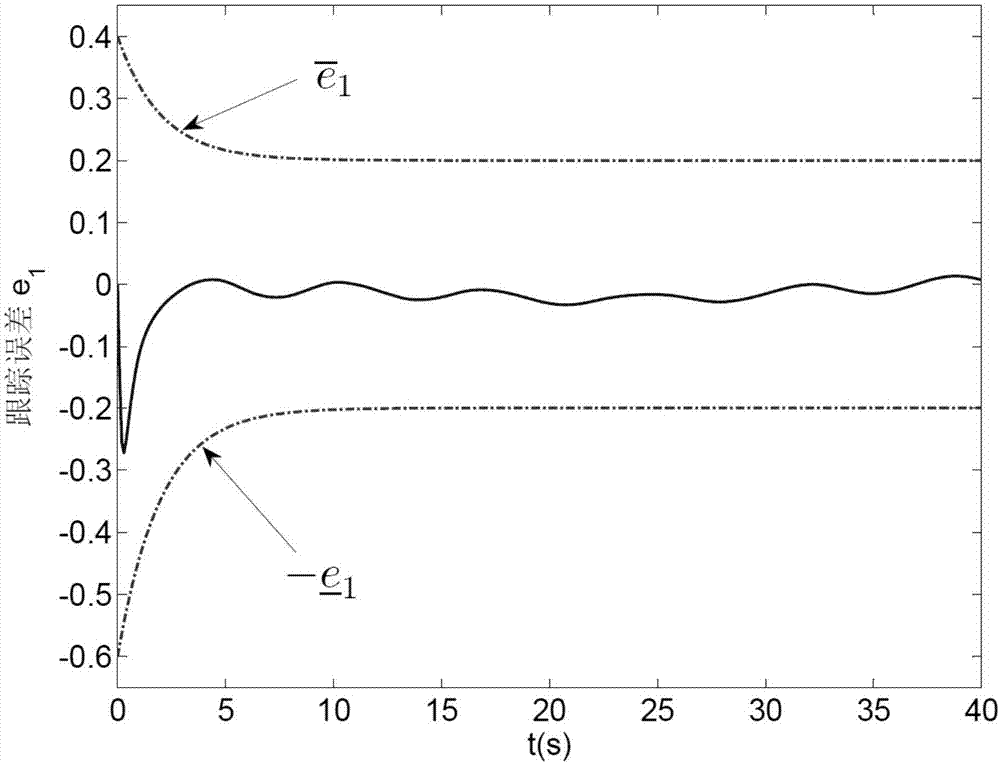
Under-actuated water surface ship control method satisfying preset tracking performance
ActiveCN107015562AEasy to troubleshoot system stability issuesImprove performancePosition/course control in two dimensionsDynamic modelsNon linear dynamic
The invention discloses an under-actuated water surface ship control method satisfying preset tracking performance. Aiming at an under-actuated water surface ship nonlinear dynamic model, tracking error steady state precision and a transient state performance index are designed, a transverse function is built to introduce extra control input, and design of a tracking controller is completed, thereby ensuring that a tracking error of a closed-loop control system converges to a preset arbitrarily small area, and ensuring that the convergence rate and overshoot satisfy preset requirements. The method specifically includes the following steps: establishing an under-actuated water surface ship dynamic model; designing steady state performance and transient state performance requirements of a control system; designing a speed error equation to introduce extra control; designing a disturbance observer to compensate external time-varying disturbance; and designing a state feedback tracking controller. The control method designed by the invention can solve the problem of under-actuated water surface ship motion control, realize tracking control of any smooth reference trajectory, and improve tracking error steady state performance and transient state performance of the control system.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
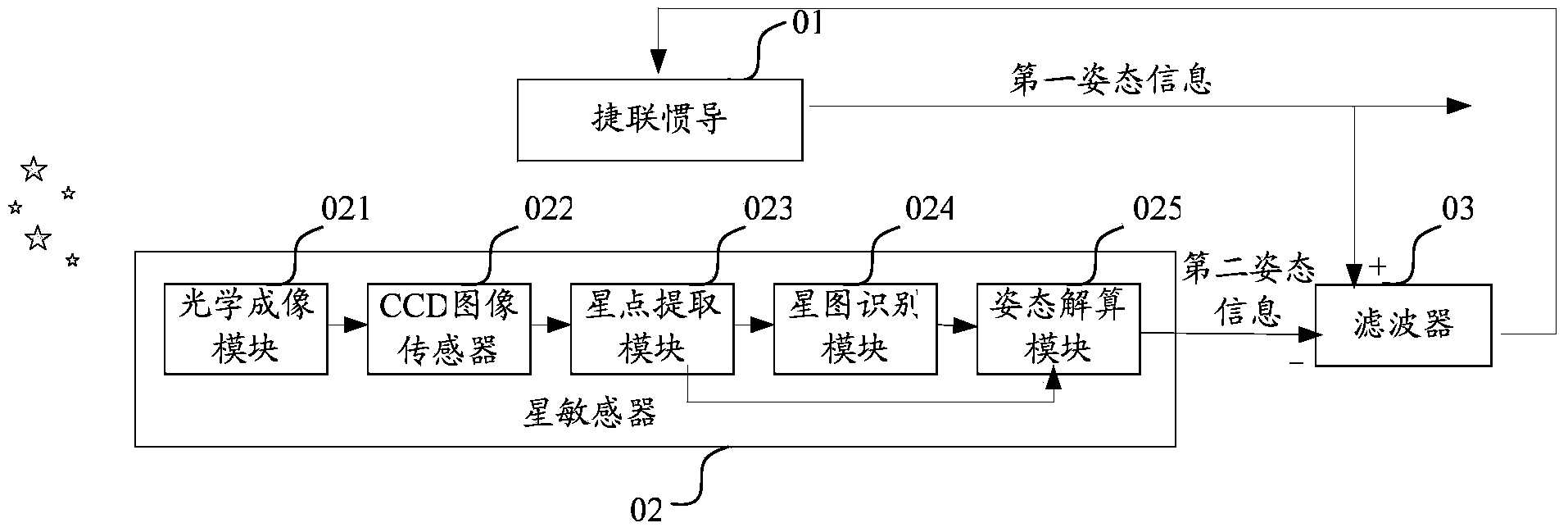
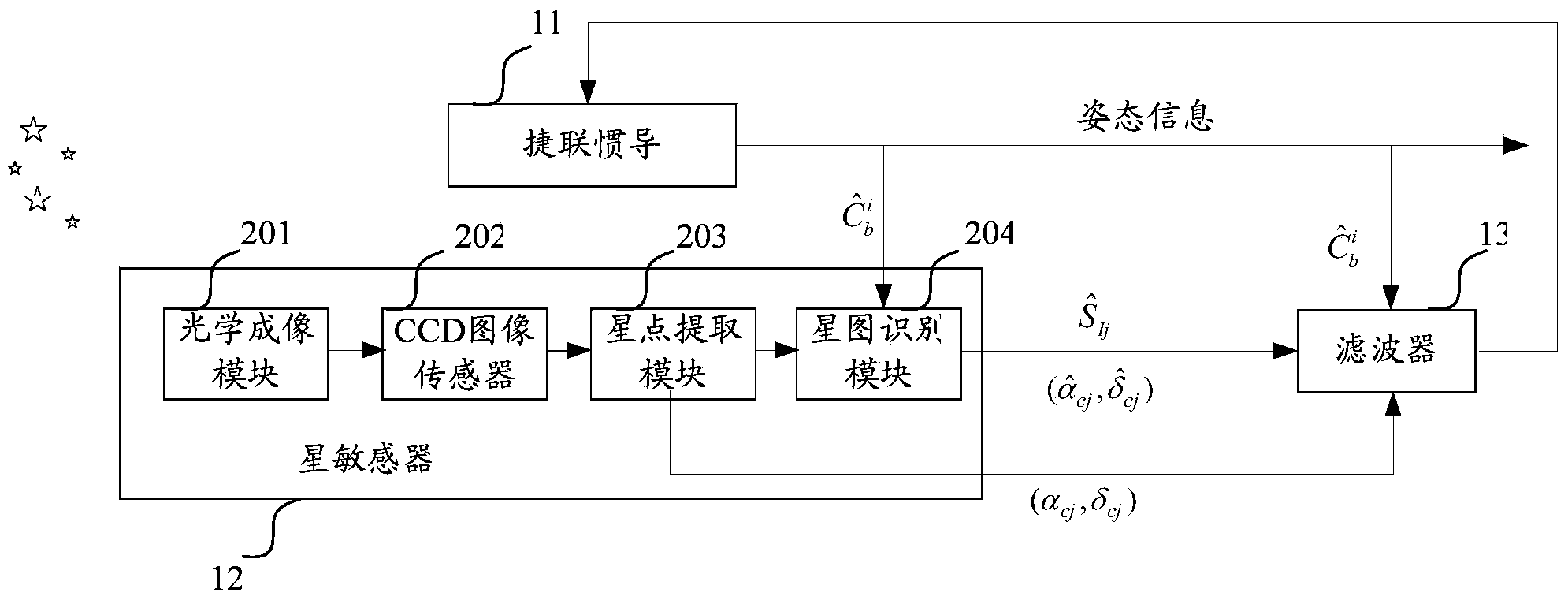
Integrated navigation system and method based on SINS (Strapdown Inertial Navigation System) and star sensor
ActiveCN103674021AHigh precisionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation by astronomical meansFixed starsLongitude
The invention discloses an integrated navigation system and method based on an SINS and a star sensor. The integrated navigation system comprises the SINS, the star sensor and a filter, wherein the SINS is used for detecting the attitude information of a carrier, and amending the attitude information according to the optimum estimate of a state error term; the star sensor is used for acquiring the longitude and latitude, in a star sensor coordinate system, of an imaged fixed star, the direction unit vector, in a geocentric inertial coordinate system, of a reference fixed star matched with the imaged fixed star, and the longitude and latitude, in the star sensor coordinate system, of the reference fixed star; when the number of fixed stars observed by the star sensor is one or two, the filter is used for acquiring the optimum estimate of the state error term of the SINS according to an observation equation, wherein the observation equation is established by taking a longitude and latitude difference as a state quantity and by taking the pre-established error equation of the SINS as a state equation, and the longitude and latitude difference is composed of the longitude difference and latitude difference, in the star sensor coordinate system, between the reference fixed star and the imaged fixed star. According to the invention, the application range of the integrated navigation system can be widened.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
INS/GNSS/polarization/geomagnetism combined navigation alignment method based on Kalman filtering
ActiveCN109556632AGood autonomyReduce power consumptionNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation systemInertial navigation system
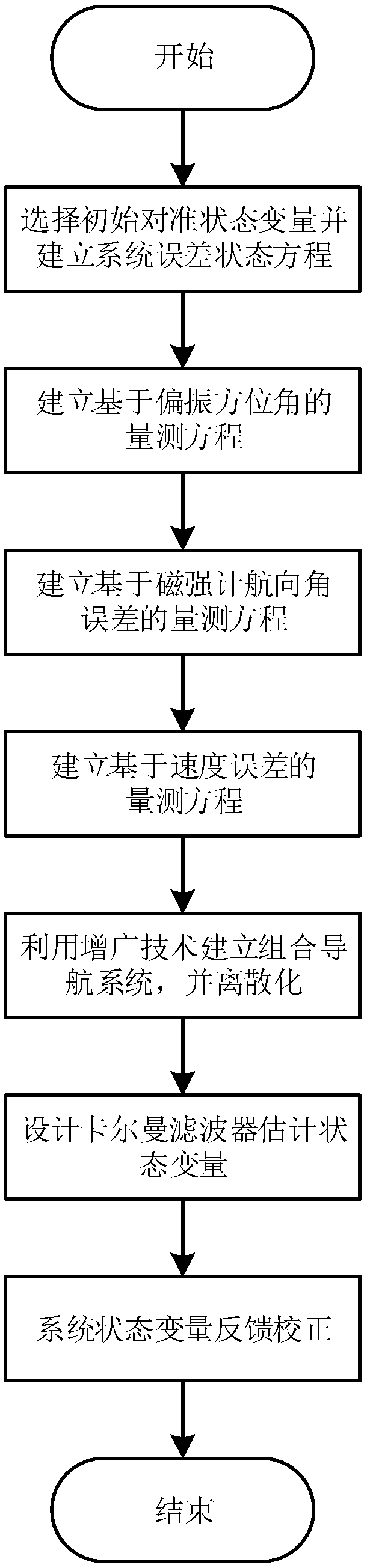
The invention relates to an INS (Inertial Navigation System) / GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) / polarization / geomagnetism combined navigation alignment method based on Kalman filtering. The method comprises the following steps: selecting an initial aligned state variable, and establishing an error equation of a combined navigation system; performing matching and fusing to establish a polarization measuring equation according to a polarization azimuth angle output by a polarization sensor and an azimuth angle output by the INS; establishing a geomagnetism measuring equation according toa heading angle output by a magnetometer and the heading angle output by the INS; performing matching and fusing to establish an error measuring equation according to a speed and position informationoutput by the GNSS, the speed and the position information output by the INS; establishing a unified measuring equation for the combined navigation system by utilizing an augmented reality technology;designing a Kalman filter to estimate physical quantities such as a misalignment angle, a speed error, a position error, etc., of the combined navigation system; and performing feedback correction onan attitude, the speed and the position of the combined navigation system to improve the initial alignment estimation precision. The method has the advantages of being high in precision, small in calculation amount and high in compatibility, and the initial alignment time is reduced.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
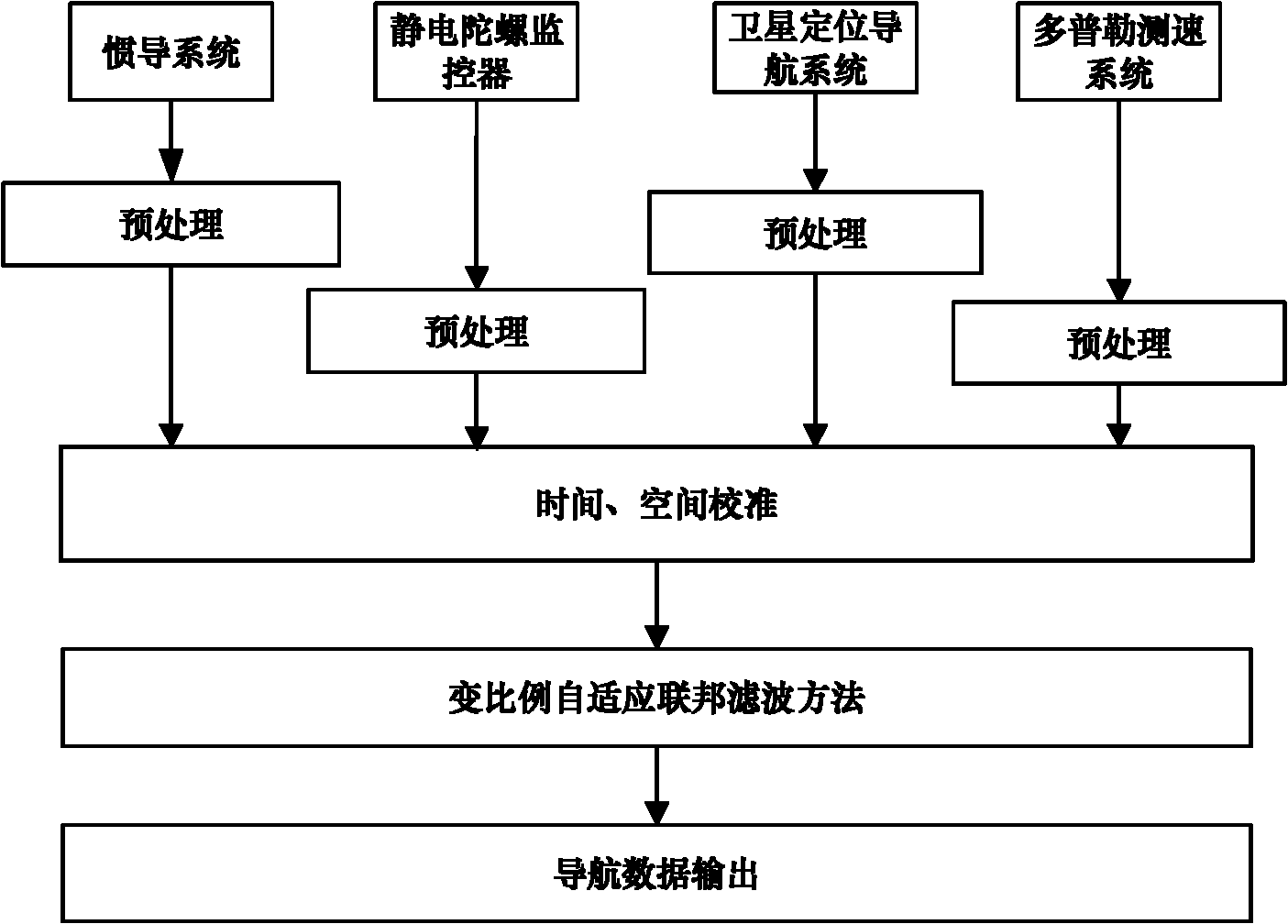
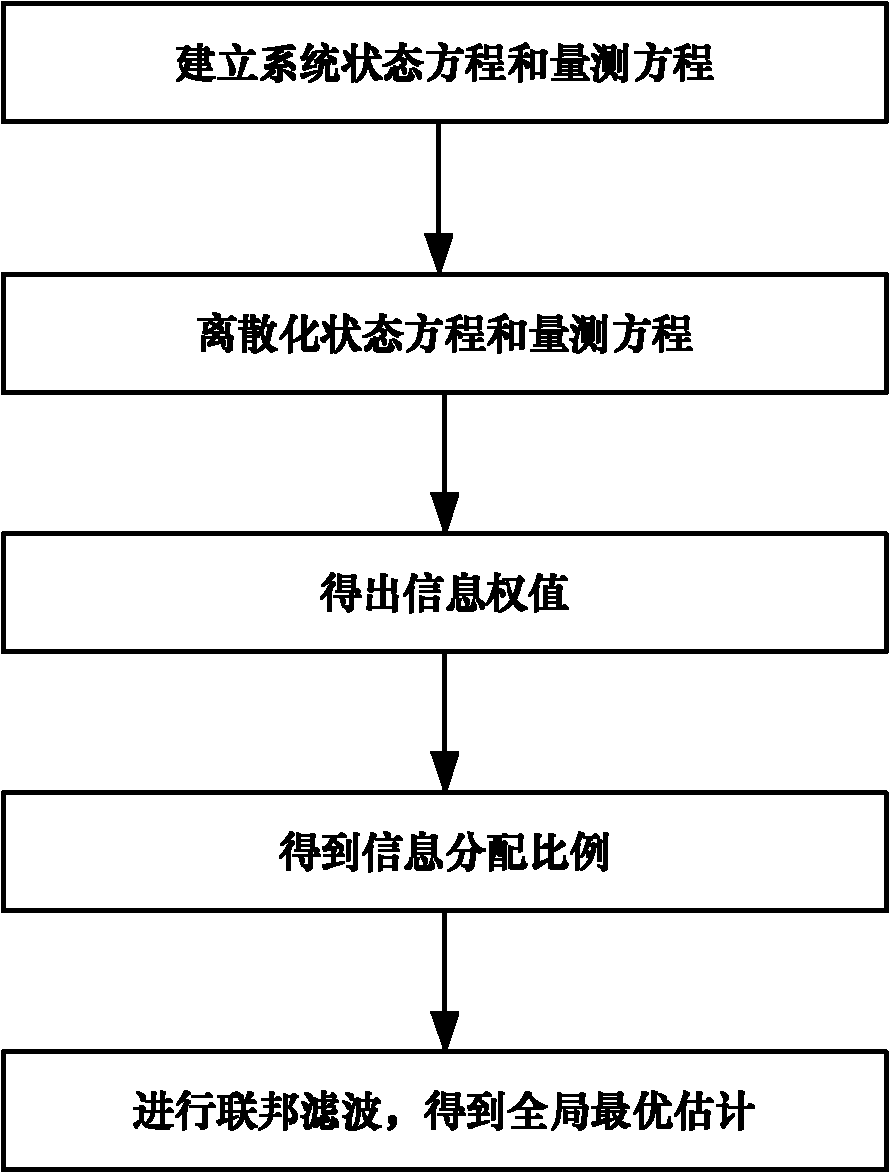
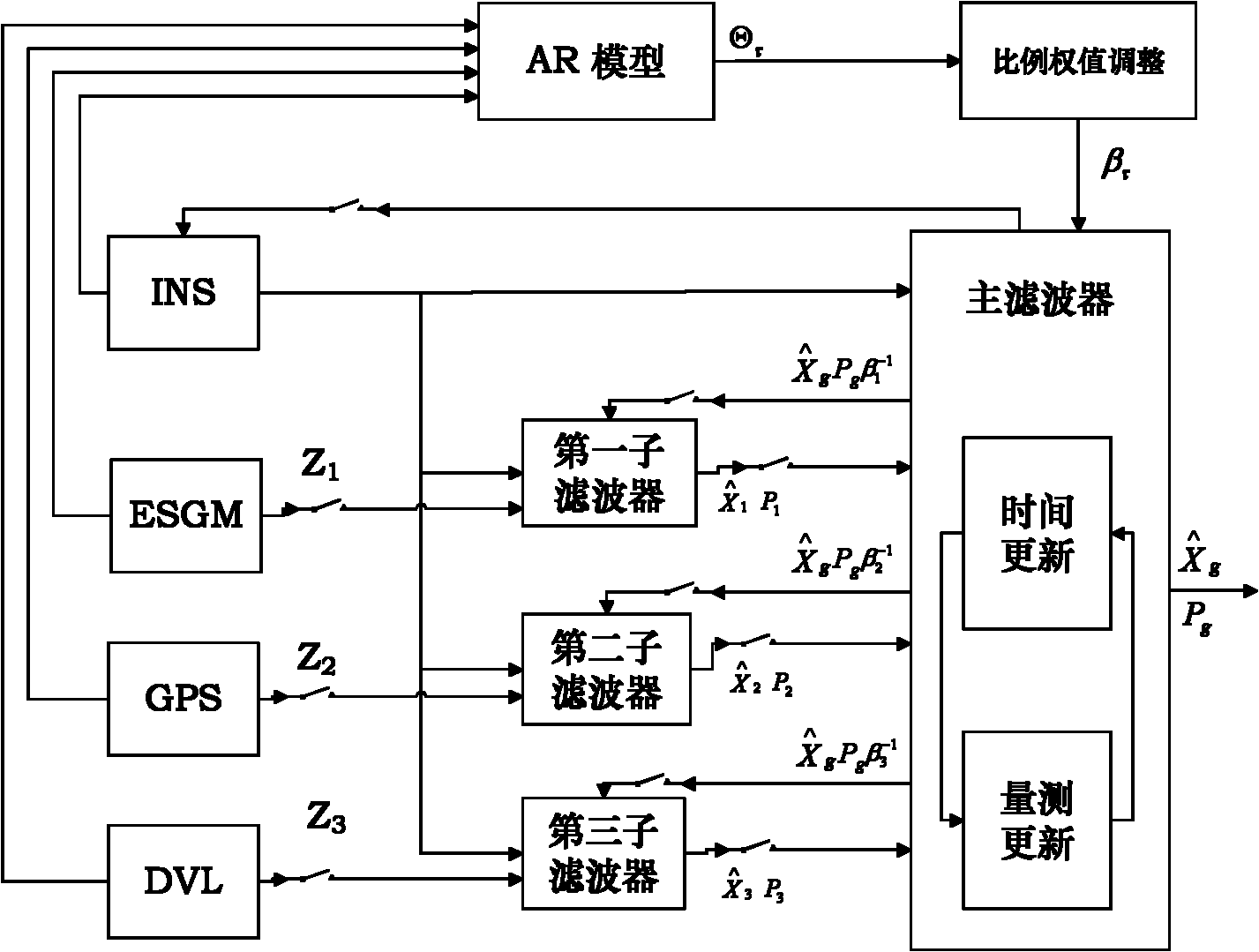
Time series analysis-based variable proportion self-adaptive federal filtering method
InactiveCN102252677AIncrease profitAvoid errorsNavigational calculation instrumentsFault toleranceNavigation system
The invention discloses a time series analysis-based variable proportion self-adaptive federal filtering method, and the method is utilized for underwater multi-sensor integrated navigation systems. The time series analysis-based variable proportion self-adaptive federal filtering method is characterized by establishing system state equations and measurement equations according to error equations belonging to all navigation sensor systems, carrying out discretization processing of the established equations, creating discrete state-space models respectively corresponding to the all navigation sensor systems, acquiring information weight of the navigation sensor systems through an autoregressive model according to historical data of the navigation sensor systems, acquiring an information distribution ratio according to the obtained information weight and a law of information conservation, realizing global optimal estimates, and resetting a filtering value and an evaluated error covariance matrix by the global optimal estimates. The time series analysis-based variable proportion self-adaptive federal filtering method improves system navigation precision, system stability and fault tolerance, and can satisfy requirements which belong to underwater navigation devices and comprise high precision and high reliability requirements.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
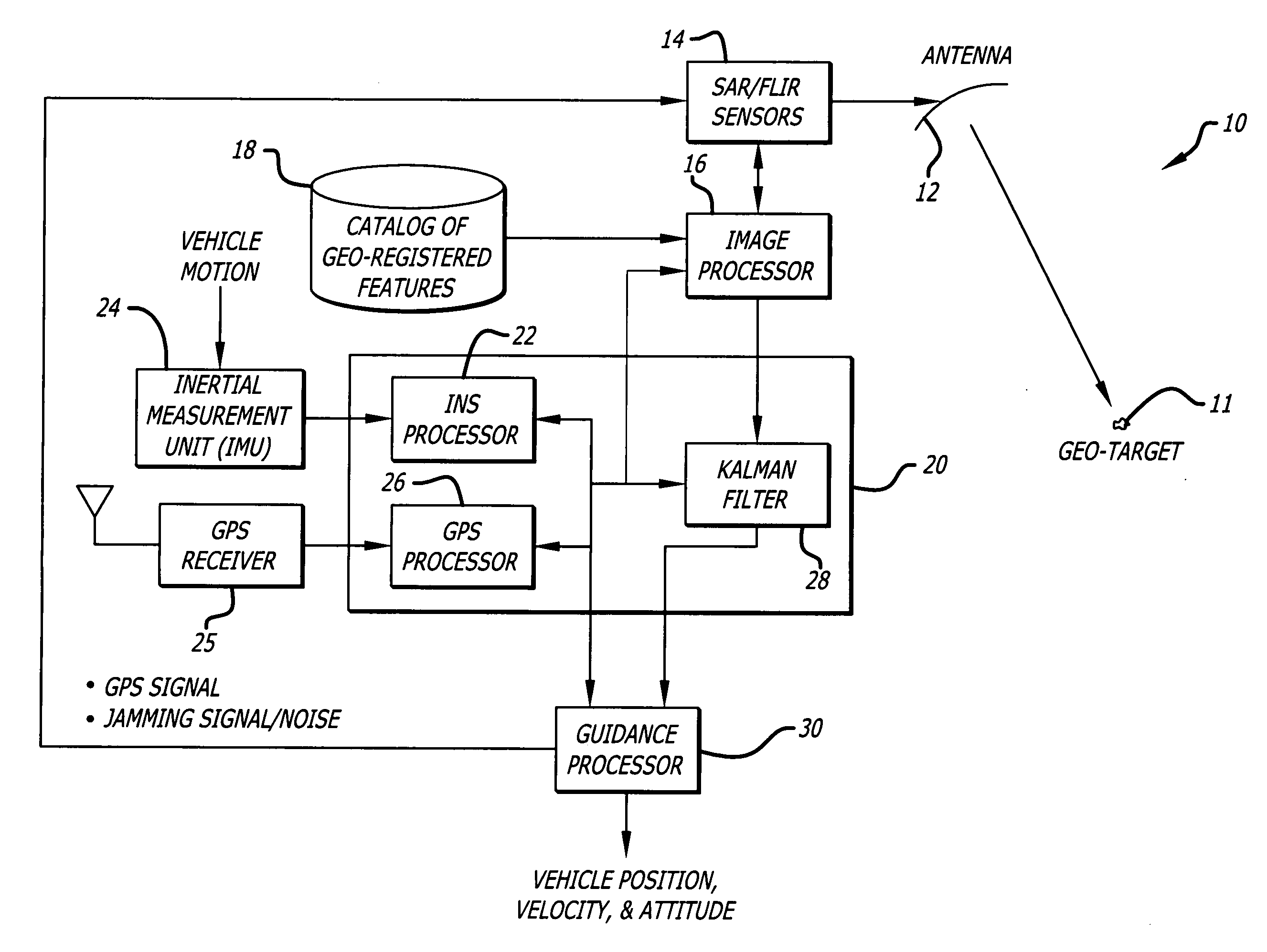
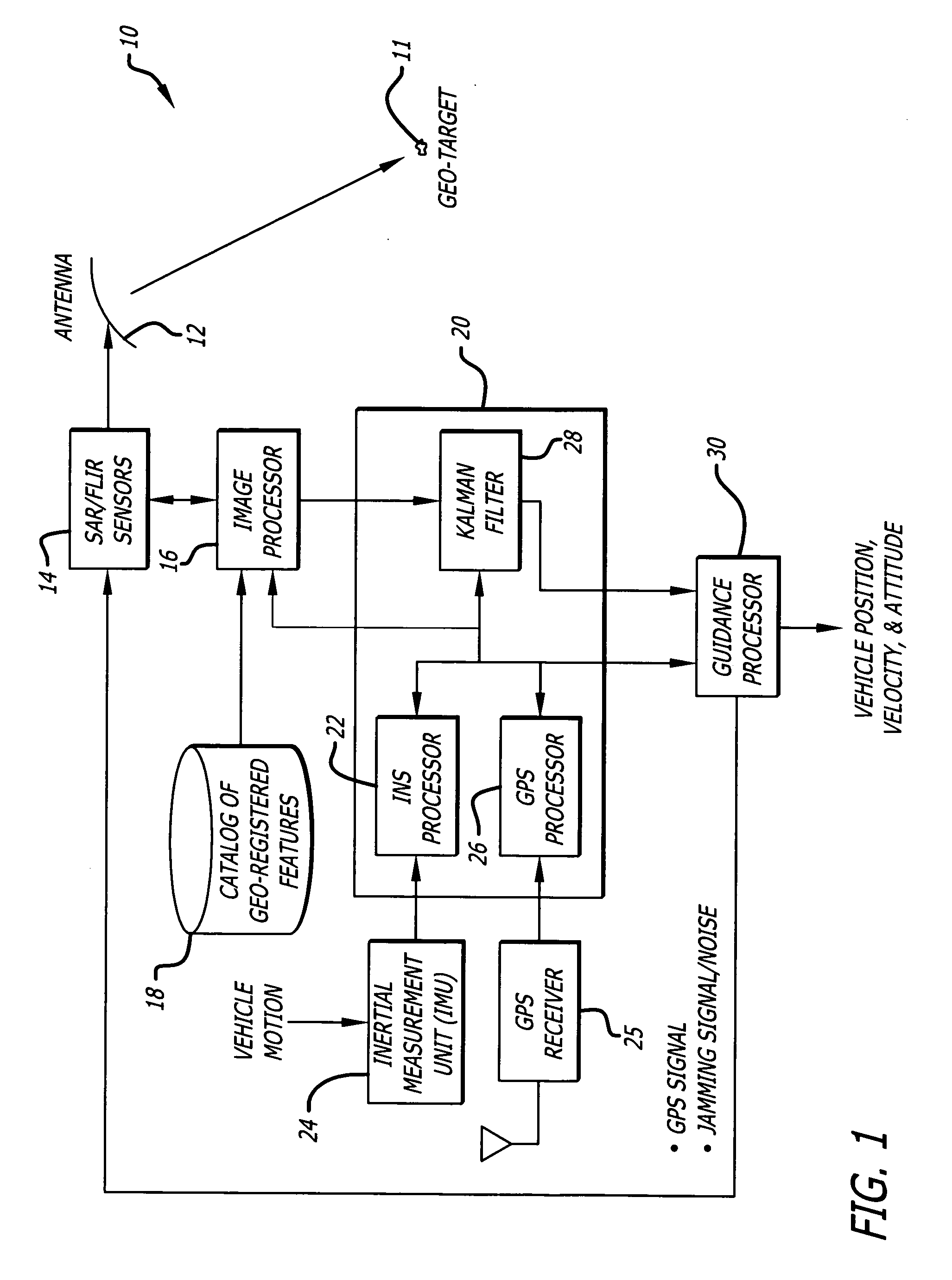
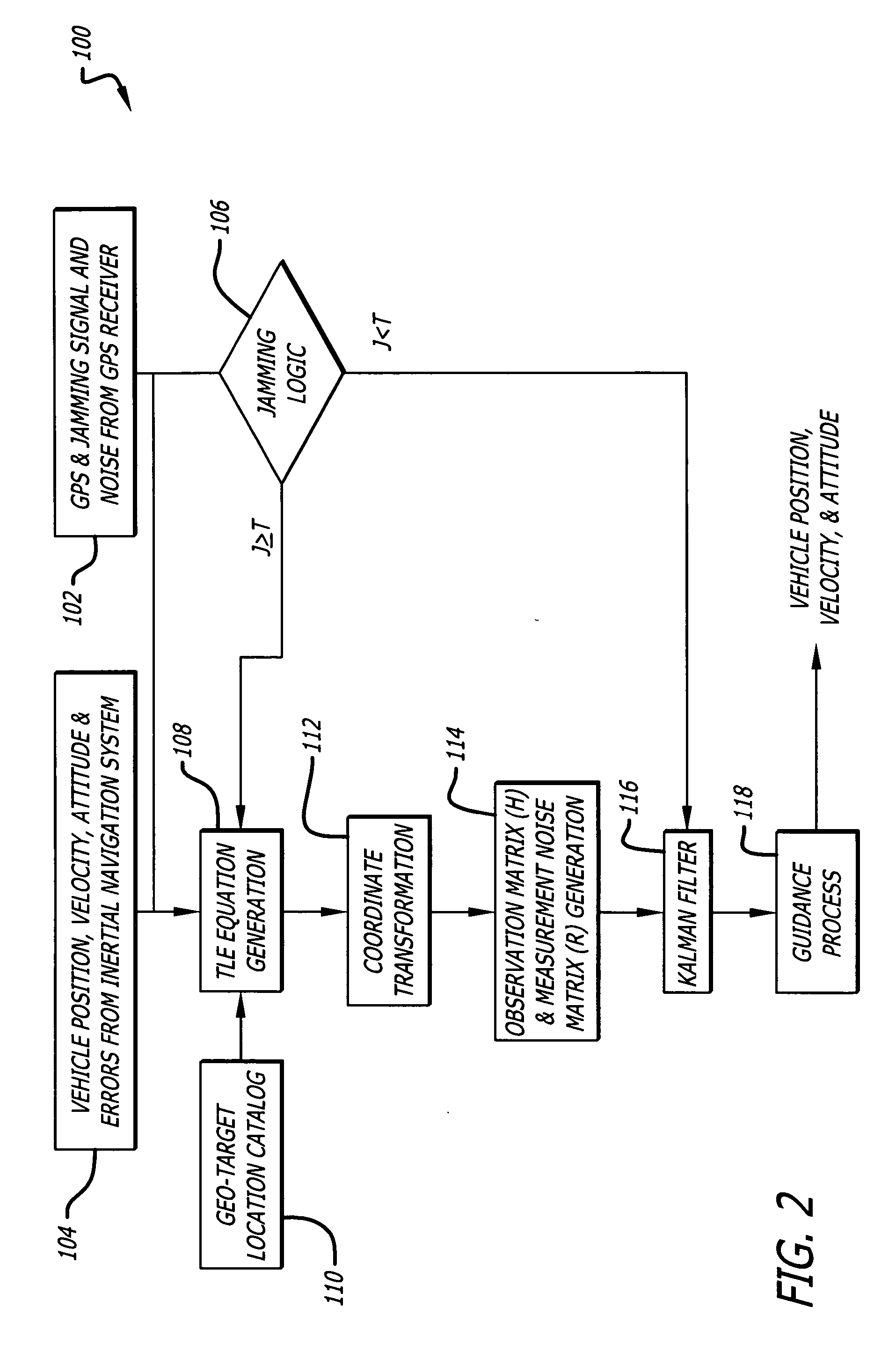
System and method for geo-registration with global positioning and inertial navigation
ActiveUS20060293854A1Improve navigation accuracyAnti-collision systemsPosition fixationSynthetic aperture radarForward looking
A position estimation system including a first arrangement for providing an image with a known target in a known reference frame. A second arrangement correlates the image with a stored image. The correlation is used to compute an error with respect to a position estimate. In a specific embodiment, the error is referenced with respect to first (x), second (y) and third (z) directions. A target location error is computed with respect to a stored image provided by a target image catalog. The target image catalog includes target geo-locations and digital terrain elevation data. In an illustrative application, the image data is provided by synthetic aperture radar and forward-looking infrared systems. An observation model and a measure noise matrix are Kalman filtered to ascertain a position error in navigation data generated by an integrated inertial navigation and Global Positioning system. In the illustrative application, geo-registered SAR / FLIR imagery is used to track targets and to determine a target location error (TLE). This TLE information is a set of error equations that describe the relationship between vehicle navigation information and target data. In accordance with the invention, this relationship is used to form an observation model for vehicle navigation with respect to target locations. Using Kalman filtering and the observation model, vehicle navigation errors can be bound and the navigation accuracy of the vehicle can be improved.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
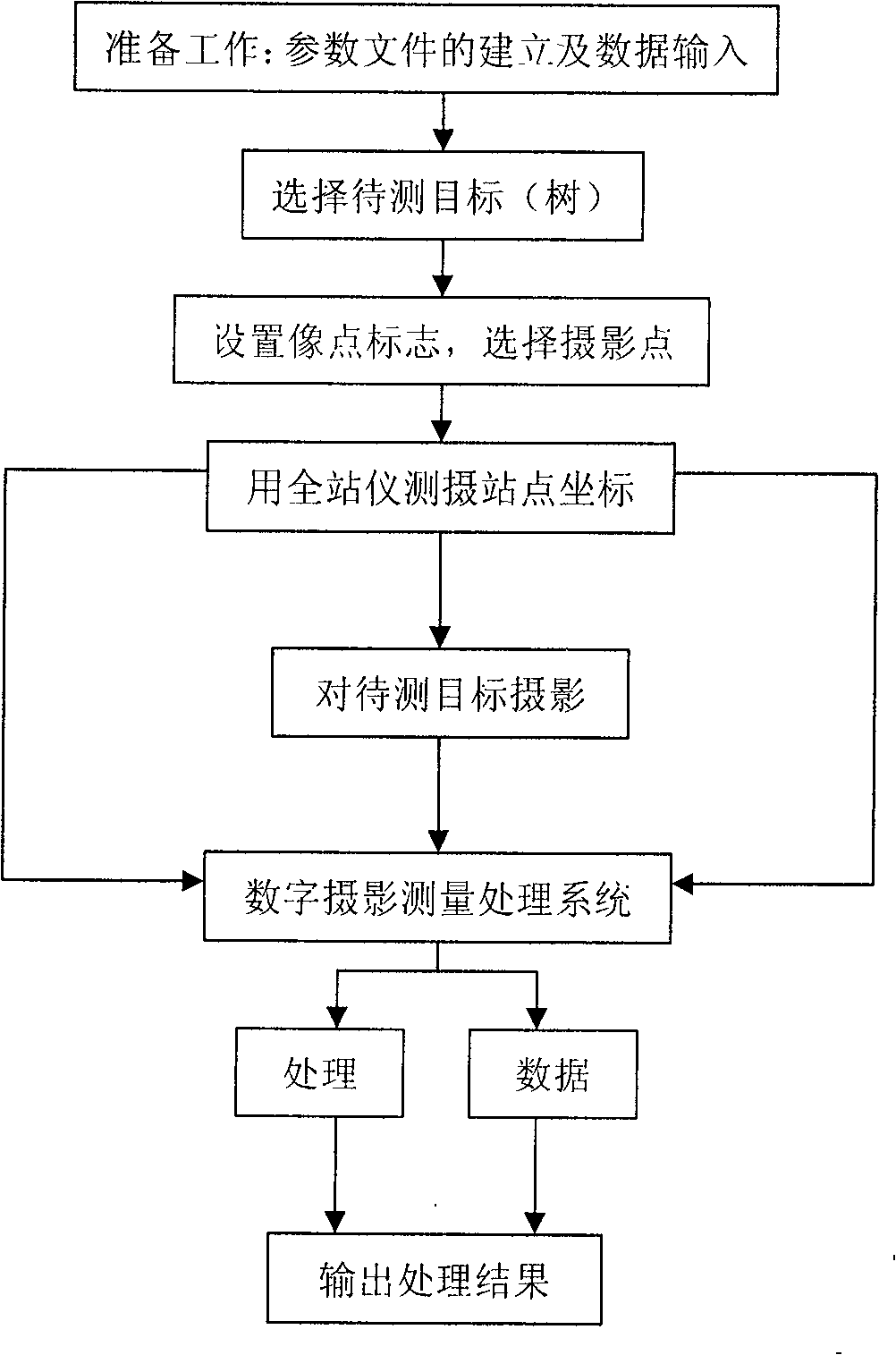
Estimate survey technique using metric camera cooperating with theodolite
InactiveCN101298979ARigorous theoryHigh precisionUsing optical meansPicture interpretationTheodoliteLight beam
The invention discloses a technology for measuring the camera cooperation theodolite double image estimate survey, which uses the measurement camera, the electronical theodolite as the tool, wherein the inner orientation element is unknown and the outer orientation element is known to realize to measure the height of the stumpage by measuring the camera cooperation theodolite double image estimate surve. First, the axiallateral method of the space front is used to obtain the coordinate of the control point, then, the measurement camera is adopted to obtain the two imaged in the area to be measured, and the homologous image point of the two images are used to list the error equation, thereby resolving the outer orientation element of the two images, finally the light beam method is used to process the error compensation. The measurement method can simply and fast measure the tree height of the stumpage, overcomes the defect in the traditional technology.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Finite time robust fault diagnosis design method for leader-follower multi-agent system
ActiveCN106444701AImprove transient performanceEnhanced inhibitory effectProgramme controlElectric testing/monitoringDiagnosis designEngineering
The invention discloses a finite time robust fault diagnosis design method for a leader-follower multi-agent system. The method includes the steps: firstly, building a multi-agent system connection diagram with a leader and showing the multi-agent system connection diagram by a directed graph to obtain a Laplacian matrix L of a follower and an adjacent matrix G of the leader; building a state equation and an output equation of each node flight control system and augmenting a state vector and a fault vector into new vectors; constructing a distributed error equation and a global error equation based on the directed graph for each node according to the built directed graph, constructing a finite time fault diagnosis observer of a flight control system based on finite time robust control, and performing finite time fault diagnosis for faults of a multi-agent executor based on the directed graph. Faults of an optional node of the control system or simultaneously occurring faults of a plurality of nodes are effectively and accurately diagnosed and estimated on line in finite time.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
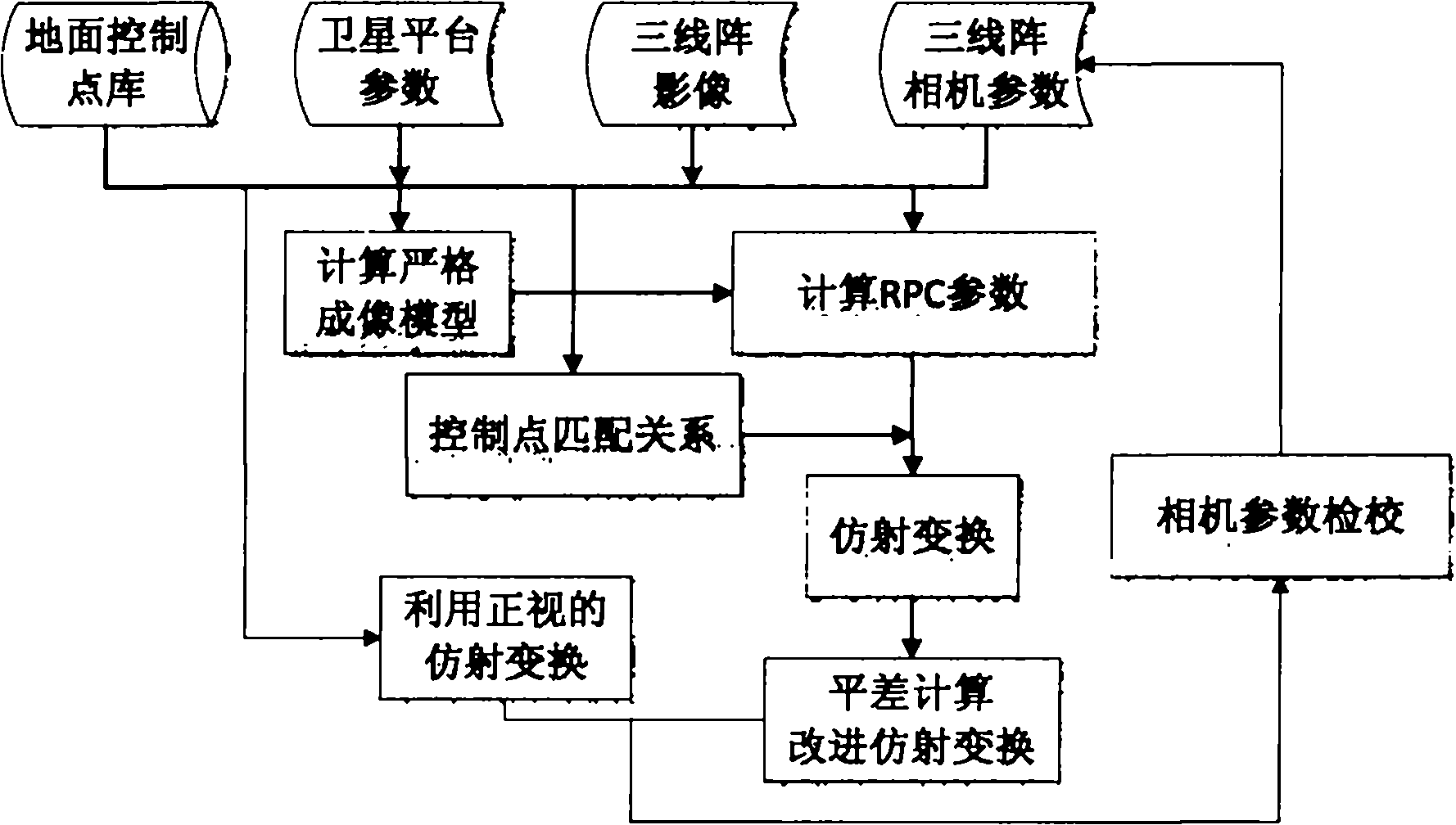
RPC-based method for improving and calibrating block adjustment of three-linear array three-dimensional satellite
ActiveCN102168972ASolve computational difficultiesImprove compatibilityPicture interpretationArea networkImage matching
The invention relates to a rational-polynomial-coefficients (RPC)-based method for improving and calibrating the block adjustment of a three-linear array three-dimensional satellite, which comprises the following steps of: (1) determining the mapping relationship between ground points and image points, namely a strict imaging model; (2) solving RPC parameters of each image in three linear arrays according to the strict imaging model, and searching for connection points among the three linear arrays by image matching; (3) listing three affine transformation formulas of fore sight, front sight and back sight of the three-linear array images; (4) establishing an error equation and solving to acquire corrections of affine transformation parameters, and revising the affine transformation formulas by utilizing the corrections; (5) listing the affine transformation formulas of the fore sight and the back sight again by utilizing camera parameters and the revised affine transformation formula of the front sight; and (6) solving the revised affine transformation formulas of the fore sight and the back sight in the step (4) and the listed affine transformation formulas of the fore sight and the back sight in the step (5) simultaneously to acquire the corrections of the camera parameters, and revising the camera parameters to improve and calibrate the block adjustment of the three-linear array three-dimensional satellite.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
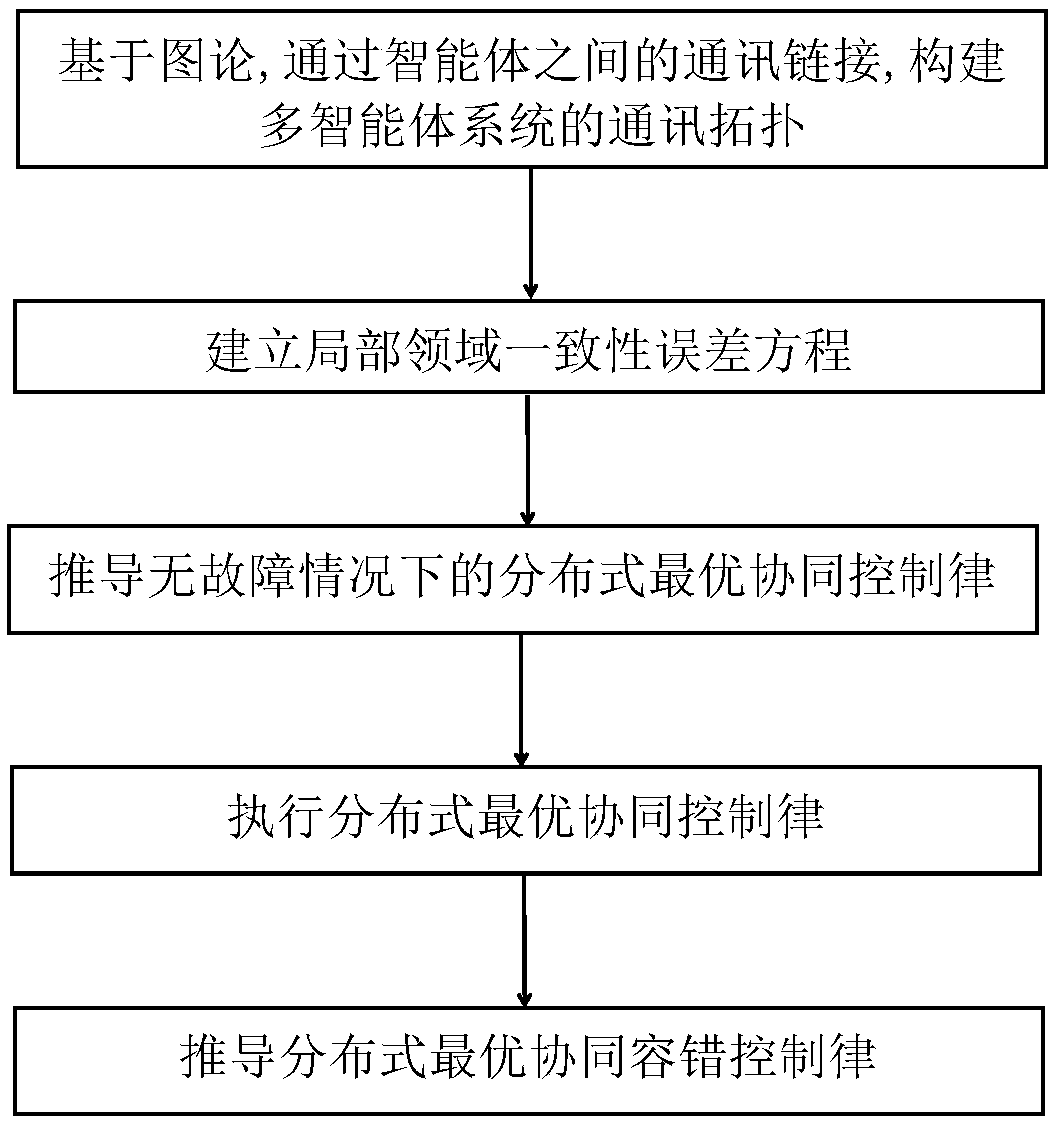
Distributed optimal cooperative fault-tolerant control method based on self-adaptive dynamic planning
ActiveCN108828949AGuaranteed to minimizeSolve problemsAdaptive controlDynamic planningMulti-agent system
The invention discloses a distributed optimal cooperative fault-tolerant control method based on self-adaptive dynamic planning. The distributed optimal cooperative fault-tolerant control method comprises the steps of: firstly, constructing a communication topology of a multi-agent system by means of communication links among agents, and representing the communication topology by a directed graphG=(V, E, A); secondly, establishing a local domain consistency error equation, and defining a failure-free cooperative control input quantity of the agent vi as ui based on an optimal control theory and a minimum value principle, so as to obtain a distributed optimal cooperative control law; thirdly, executing the distributed optimal cooperative control law; and finally, designing a distributed optimal cooperative fault-tolerant control law of the agents. The distributed optimal cooperative fault-tolerant control method can overcome the shortcomings of the existing nonlinear multi-agent systemfault-tolerant control method, and has a good application prospect in the fault-tolerant control of UAV formation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
GPS/SINS/CNS integrated navigation method based on five-order CKF
ActiveCN105737823AHigh precisionGood filter efficiencyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingKaiman filterCubature kalman filter
The invention discloses a GPS / SINS / CNS integrated navigation method based on a five-order cubature kalman filter (CKF).The method is characterized by comprising the steps of 1, establishing an integrated navigation system non-linear error equation and a linear measurement equation based on a SINS error equation; 2, establishing the five-order CKF by means of the five-order spherical surface radial cubature rule; 3, filtering and fusing information output by a SINS, a GPS and a CNS by means of the five-order CKF to obtain the optimal estimation of navigation parameters.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
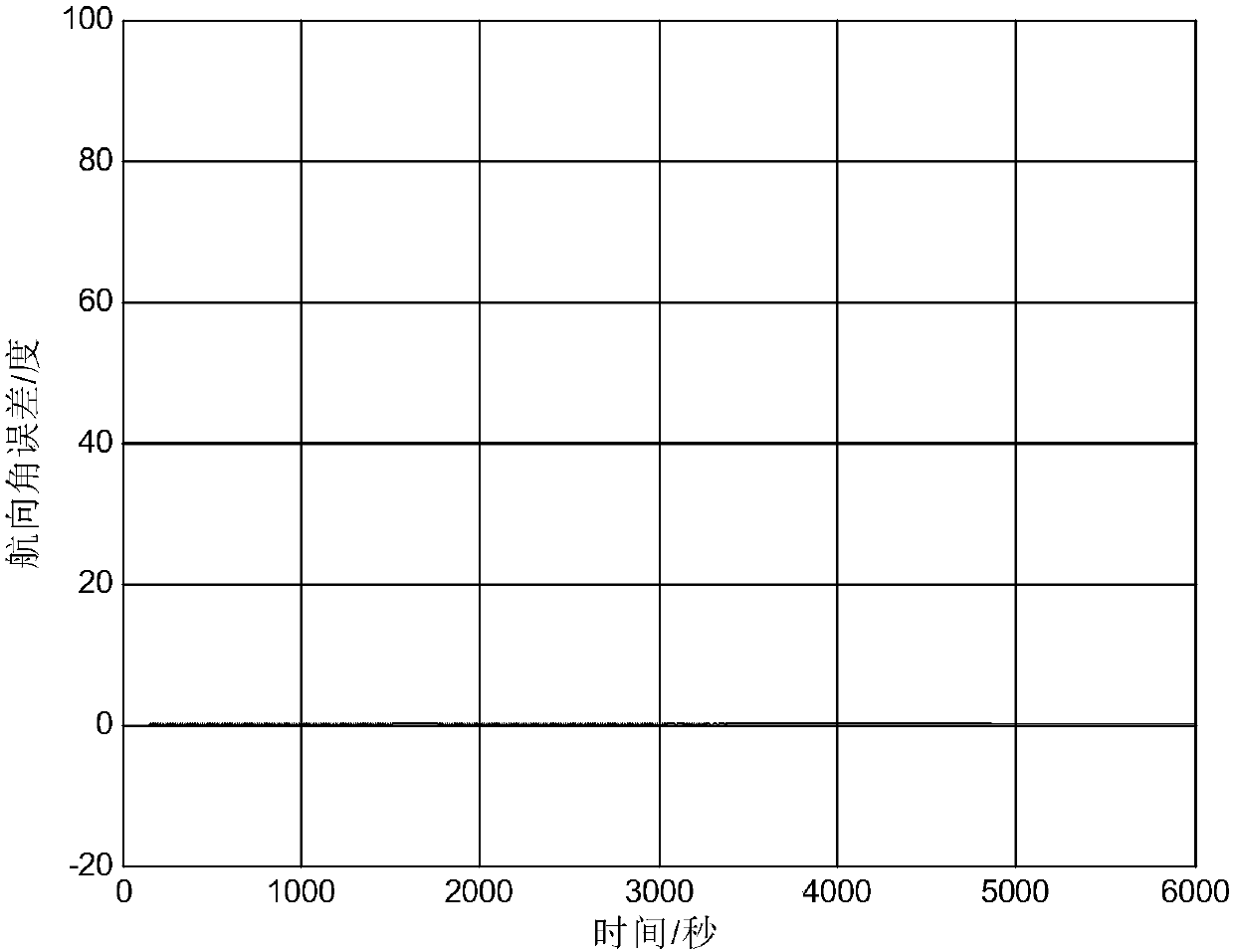
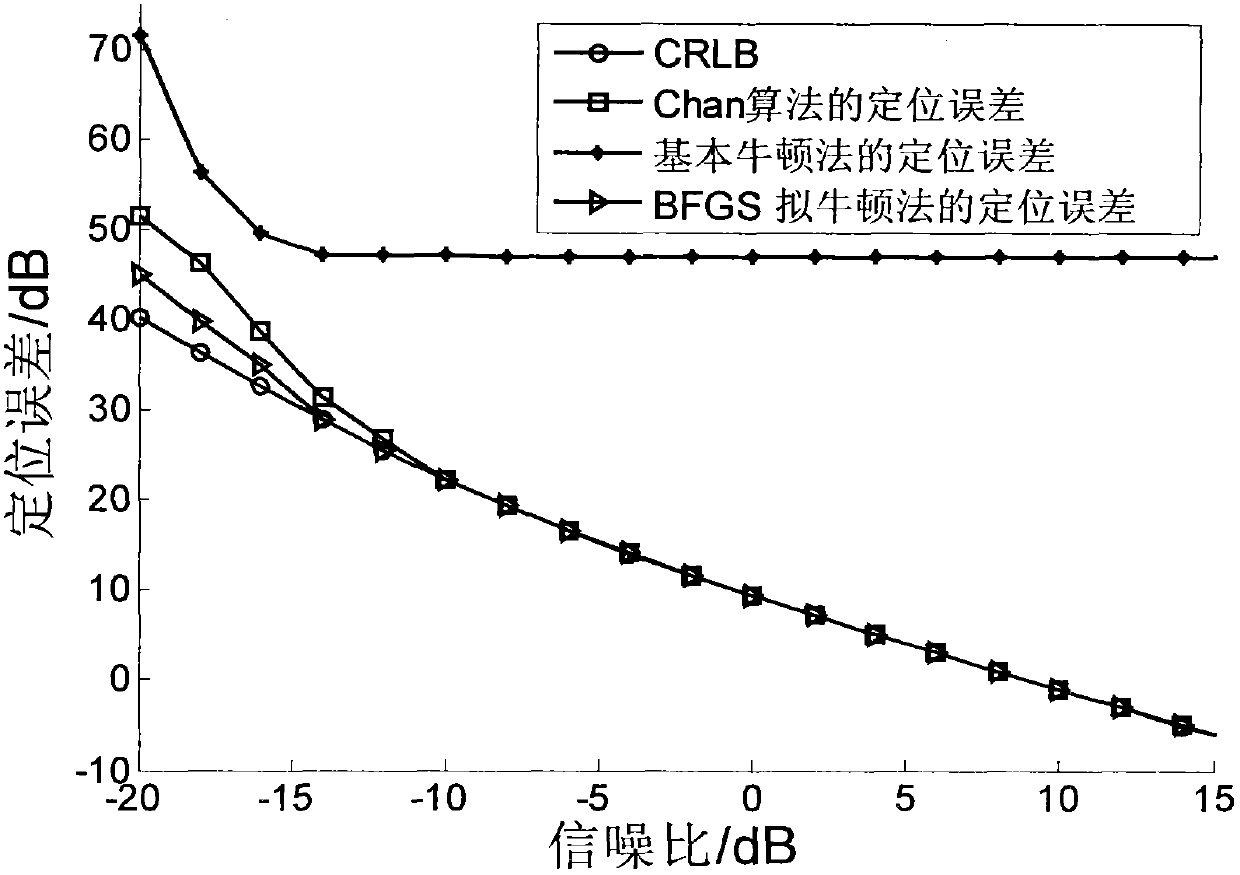
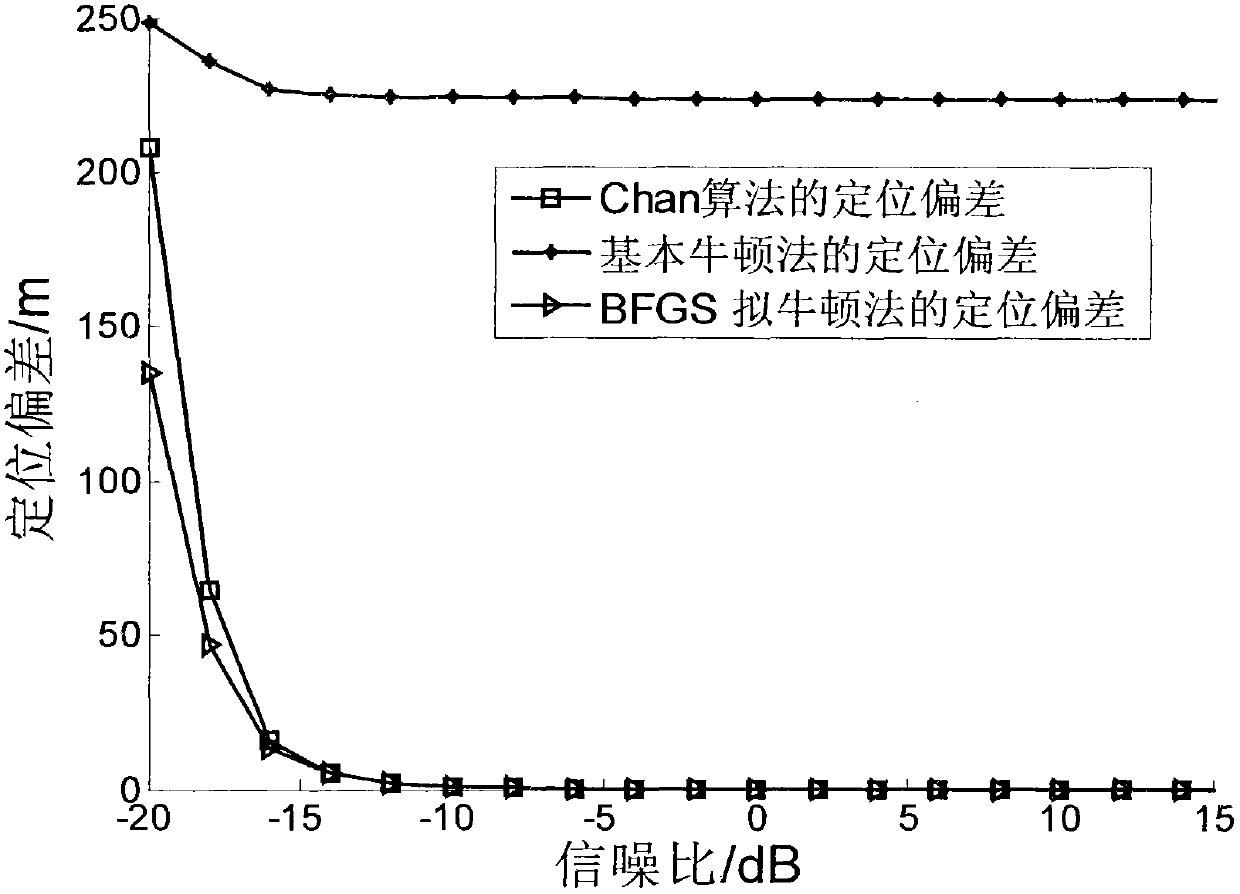
Signal source positioning method based on BFGS quasi-Newton method
InactiveCN103135094AOvercome errorHigh positioning accuracyPosition fixationObservational errorMultilateration
The invention discloses a signal source positioning method based on a BFGS quasi-Newton method and mainly aims to solve the problems that median error is introduced in an existing positioning method, positioning results are fuzzy, practicality is not strong, calculation amount is large, positioning results are not stable and the like. The signal source positioning method based on the BFGS quasi-Newton method comprises the following steps of obtaining a measured value reaching time difference and a measured value reaching gain ratio; setting joint positioning error equations through the relationship that the measured valve minus measured error is a real value; obtaining solution of the positioning error equations through the BFGS quasi-Newton method; and obtaining position coordinate values of a target source through the fact that the solution of the positioning error equations plus position coordinate values of a reference monitor node. According to the signal source positioning method based on the BFGS quasi-Newton method, stable and high precision positioning is achieved. The signal source positioning method based on the BFGS quasi-Newton method is suitable for the environment with low signal-noise rate and strong in practicability.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Airspace coordinate correction method for three-coordinate measuring machine based on multi-station measurement of laser tracking instrument
The invention discloses an airspace coordinate correction method for a three-coordinate measuring machine based on multi-station measurement of a laser tracking instrument. The method comprises the steps of firstly, dividing measuring point grids within the measuring space range of the three-coordinate measuring machine, determining measuring point coordinates, moving a target mirror to each measuring point during measuring, and performing, by the laser tracking instrument, station transfer measurement beyond the grid space range to acquire a relative interference length measurement value from each measuring point to a first measuring point under different stations; secondly, solving the coordinates of each station and the distance between the corresponding station and the first measuring point by using a two-point distance formula and the principle of least square method; thirdly, solving the correction value of each measuring point via an interference length measurement error equation by using the coordinates of each station, the measuring point coordinates and the distance between each station and the first measuring point; fourthly, acquiring more accurate measuring point correction values by adopting an iteration method for improving the station coordinate precision and the distance precision from the stations to the first measuring point; and finally, acquiring the correction value of any measuring point within the grid space by using a trilinear interpolation method, thereby improving the measuring precision of the three-coordinate measuring machine.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
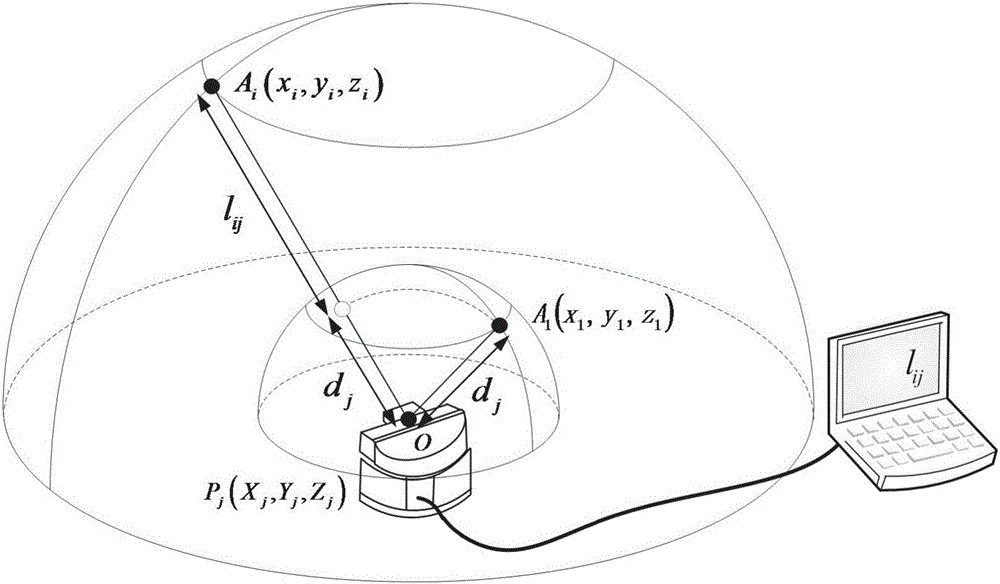
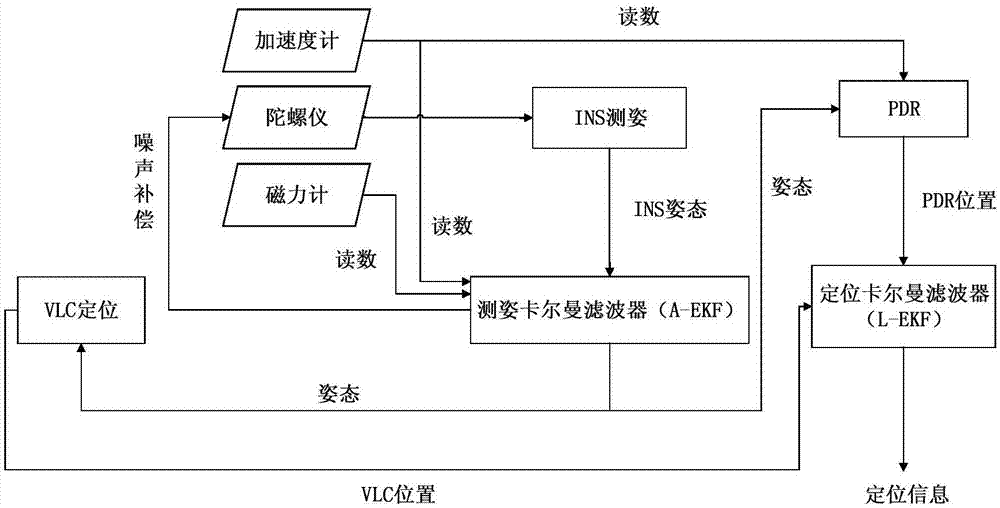
Fused dual-Kalman filter navigation device based on MEMS sensor and VLC positioning, and navigation method
ActiveCN107289933ASimple structureEliminate positioning effectsNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsKaiman filterAccelerometer
The invention discloses a fused dual-Kalman filter navigation device based on an MEMS sensor and VLC positioning, and a navigation method. The navigation device comprises an MEMS sensor, an inertial navigation system (INS) module, a pedestrian dead reckoning (PDR) positioning module, a visible light communication (VLC) positioning module, an attitude extended Kalman filter (A-EKF), and a location extended Kalman filter (L-EKF); for the A-EKF, an error equation edited mechanically based on the INS is used as a system equation, an observation equation comprises update of observation of an accelerometer and a magnetometer, and attitude information is output to the VLC positioning module and the PDR positioning module so as to correct attitude impact; and for the L-EKF, position information of a two-dimensional plane is used as a system state vector, a pedestrian dead reckoned error equation is used as a system equation, and a VLC positioning result is an observation equation. The navigation device and navigation method solve a problem that VLC positioning is easy to be affected by device attitude and cannot keep positioning continuously if an optical signal is blocked, and eliminate the influence of attitude on VLC positioning.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
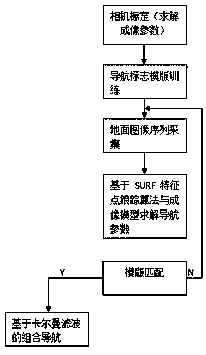
Calibration method of on-orbit optical distortion parameters of linear array push-broom camera
ActiveCN103673995AMeet the needs of on-orbit geometric internal calibrationRemove image distortionPicture taking arrangementsPhotographySatellite imageGeometric modeling
The invention discloses a calibration method of on-orbit optical distortion parameters of a linear array push-broom camera. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, collecting and obtaining dense high precision control point information by adopting an automatch algorithm based on control points, secondly, establishing strict imaging geometric models of all the control points, thirdly, computing the theoretical steering vector and the practical steering vector of each control point, and establishing an internal orientation element geometric calibration mathematical model of the camera, fourthly, establishing a distortion polynomial model, in which the theoretical steering vectors correspond to image column numbers, and fifthly, solving an error equation through a least square method, and performing iteration solving, so as to obtain internal optical distortion calibration parameters of the camera. The method calibrates internal optical system distortion of the satellite on-orbit camera by selecting a large number of high-precision ground control points, calibration results can be used for improving the uncontrolled positioning precision and the controlled positioning precision of satellite images, after internal orientation elements of the camera are corrected through internal distortion parameters, internal distortion of the images is basically eliminated.
Owner:SPACE STAR TECH CO LTD
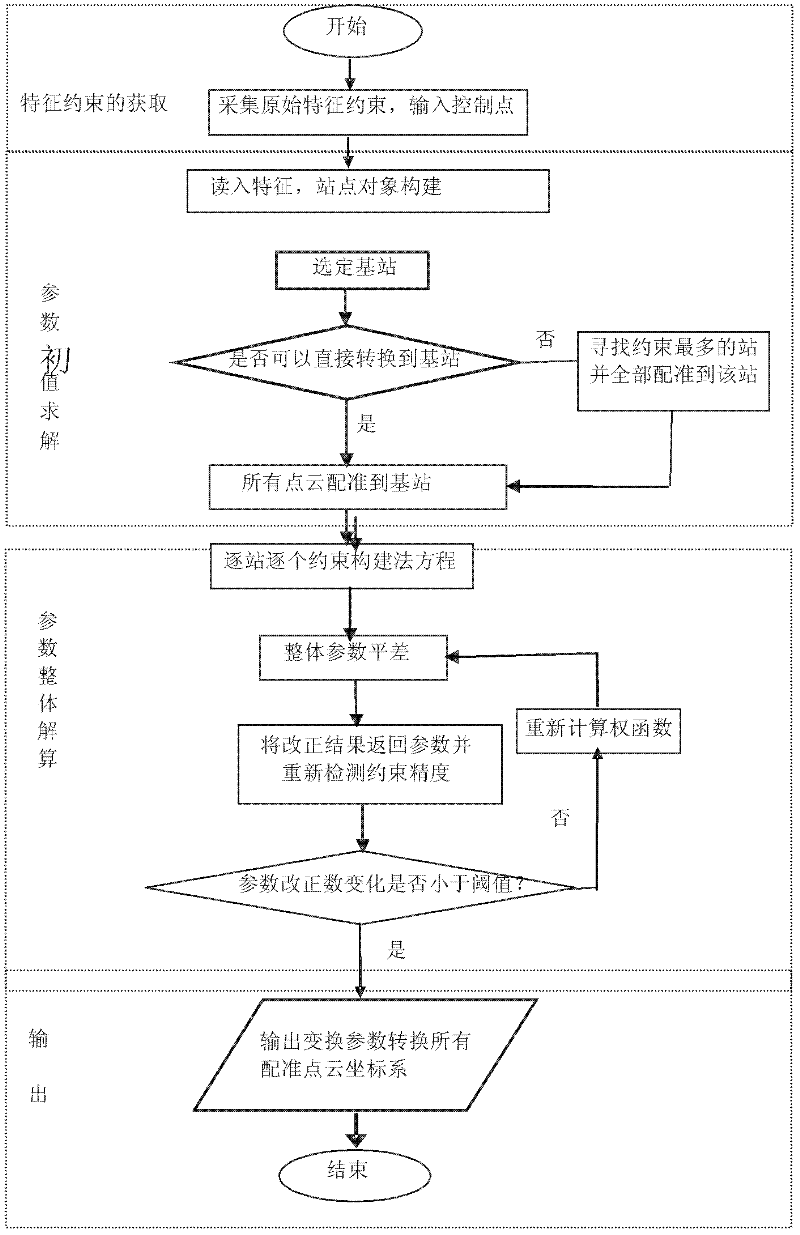
Integral registration method of high-precision multisource ground laser point clouds
InactiveCN102446354AAchieve registrationImage analysisUsing optical meansPoint cloudComputer science
The invention discloses an integral registration method of high-precision multisource ground laser point clouds, which comprises the following steps: acquiring a primitive feature constraint, inputting a control point, and using the control point as a first ground laser station; selecting a homonymous feature constraint corresponding to the primary feature constraint from all ground laser stations adjacent to the first ground laser station; determining a registration base station; establishing a vertical error equation for the feature constraint of each ground laser station, and solving the registration parameter initial value of each scanning station under control coordinates; carrying out overall adjustment on the registration parameter initial value, carrying out gross error reject until the variation of the two adjacent parameter corrected values is smaller than the threshold, and outputting a registration parameter exact value; and transforming the coordinate systems of all the ground laser station point clouds according to the registration parameter exact value to register all the ground laser station point clouds. The method disclosed by the invention can implement precise registration of multistation ground laser point clouds in a complex scene.
Owner:北京建筑工程学院
Packet consistent method for heterogeneous networked multi-agent systems with time-varying delays
ActiveCN110376889AGroup Consistency Control OvercomesFast convergenceAdaptive controlState predictionLinear matrix
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of networked multi-agent systems, provides a packet consistent method for heterogeneous networked multi-agent systems with time-varying delays. A discrete time dynamic model of a heterogeneous networked multi-agent system with the time-varying delay is established; a state observer is constructed and state prediction is performed; a packet consistency control protocol is designed; on the basis of the designed packet consistency control protocol, compact expression forms of a packet state error equation and an estimation error equation are obtained; a state feedback matrix is obtained based on a linear matrix inequation; and then the obtained state feedback matrix is substituted into the designed packet consistency protocol to realize packet consistency of the heterogeneous networked multi-agent system with time-varying delay. Therefore, a problem that the system convergence speed is affected by using the outdated information to realize the system consistency in the existing heterogeneous networked multi-agent systems with the time-varying delay is solved. The method is suitable for the packet consistency design of the high-order heterogeneous system.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multi-site point cloud integral orientation method based on laser beam process block adjustment
InactiveCN104019765AInhibition effectFast automatic orientation processingUsing optical meansMulti sitePoint cloud
The invention relates to a multi-site point cloud integral orientation method based on a laser beam process block adjustment. The multi-site point cloud integral orientation method comprises the steps: 1, distributing a target in each scanning site, determining coordinates of each target center in an engineering surveying coordinate system, and forming a block; 2, performing coarse scanning on a ground feature on each scanning site, performing fine scanning on a spherical orientation target, forming an original point cloud of each scanning site, and establishing a space index of the original point cloud; 3, figuring out coordinates of the target in a scanner coordinate system of each scanning site by using a spherical fitting method; 4, making up block adjustment information; 5, firstly setting one group of error equations of laser beams for each target, if the target is a public target of N scanning sites, setting N-1 groups of constraint equations, forming an all-regional method equation by the equations, and resolving orientation parameters of all scanning sites by using a surveying adjustment summary model; 6, evaluating the point cloud orientation precision; and 7, converting point cloud coordinates of all sites into the engineering surveying coordinate system to realize multi-site point cloud integral orientation.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Detecting method of rotor position and rotating speed of permanent magnet synchronous motor
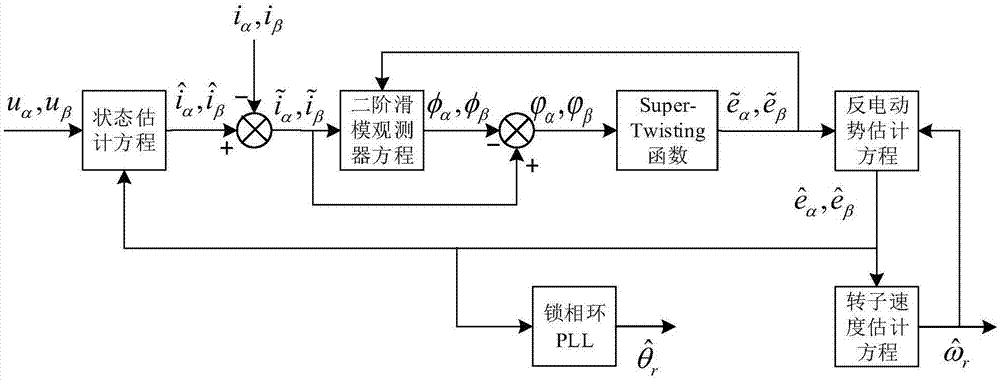
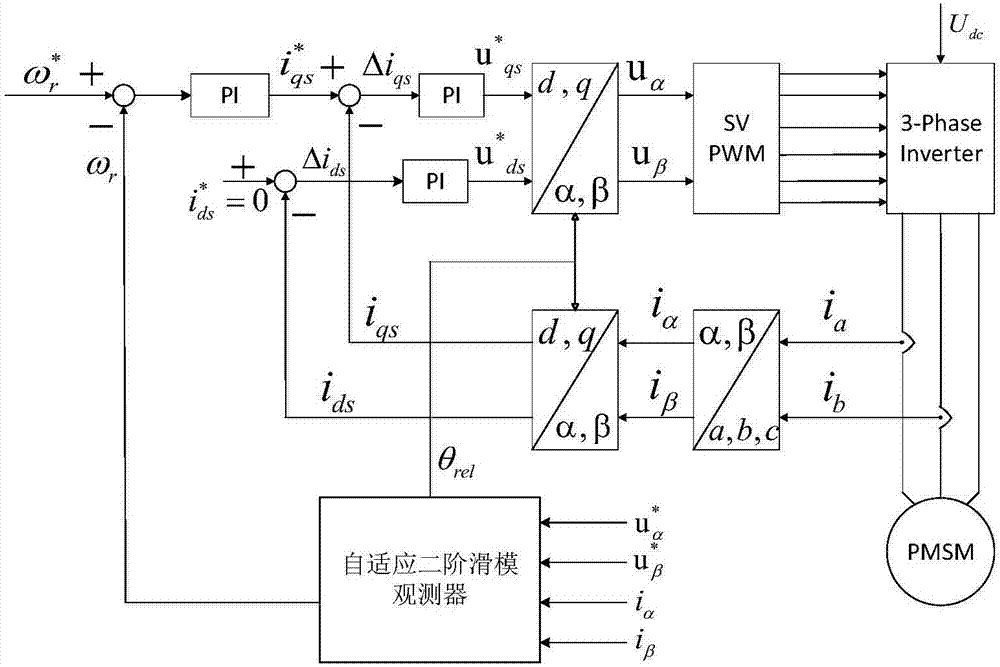
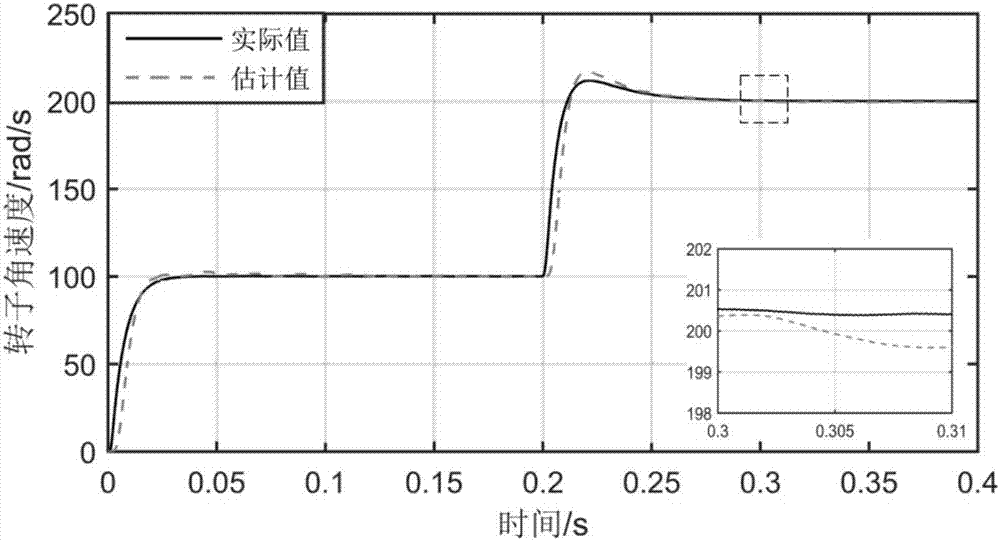
InactiveCN107482977ASuppress chatterAccurate estimateElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPermanent magnet synchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous generator
The invention relates to a detecting method of the rotor position and rotating speed of a permanent magnet synchronous motor, and belongs to the field of permanent magnet synchronous motor control. The detecting method includes the following steps that a counter electromotive force equation and a state equation of the permanent magnet synchronous motor are set up; matrix-vector arrangement is carried out on the state equation set up, and a state estimating equation is set up according to the state equation obtained after arrangement to obtain a state error equation; a second-order sliding-mode observer equation is set up according to the state error equation to obtain a counter electromotive force error equation; the sigmoid function is used for replacing the control function signum to correct the counter electromotive force error equation; a counter electromotive force estimating equation is set up according to the counter electromotive force error equation obtained after correction; the counter electromotive force estimating equation is subtracted from the counter electromotive force equation, the Lyapunov equation is used for analyzing stability to obtain and correct a rotor rotating speed estimating equation; rotor position information is extracted through the phase-locked loop technology. A model reference adaption and second-order sliding-mode combined observer is used for estimating counter electromotive force and rotor speed of the permanent magnet synchronous motor and replacing a traditional sliding-mode observer to obtain the rotor speed through counter electromotive force numerical calculation.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com