Patents
Literature
444 results about "Consistency control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
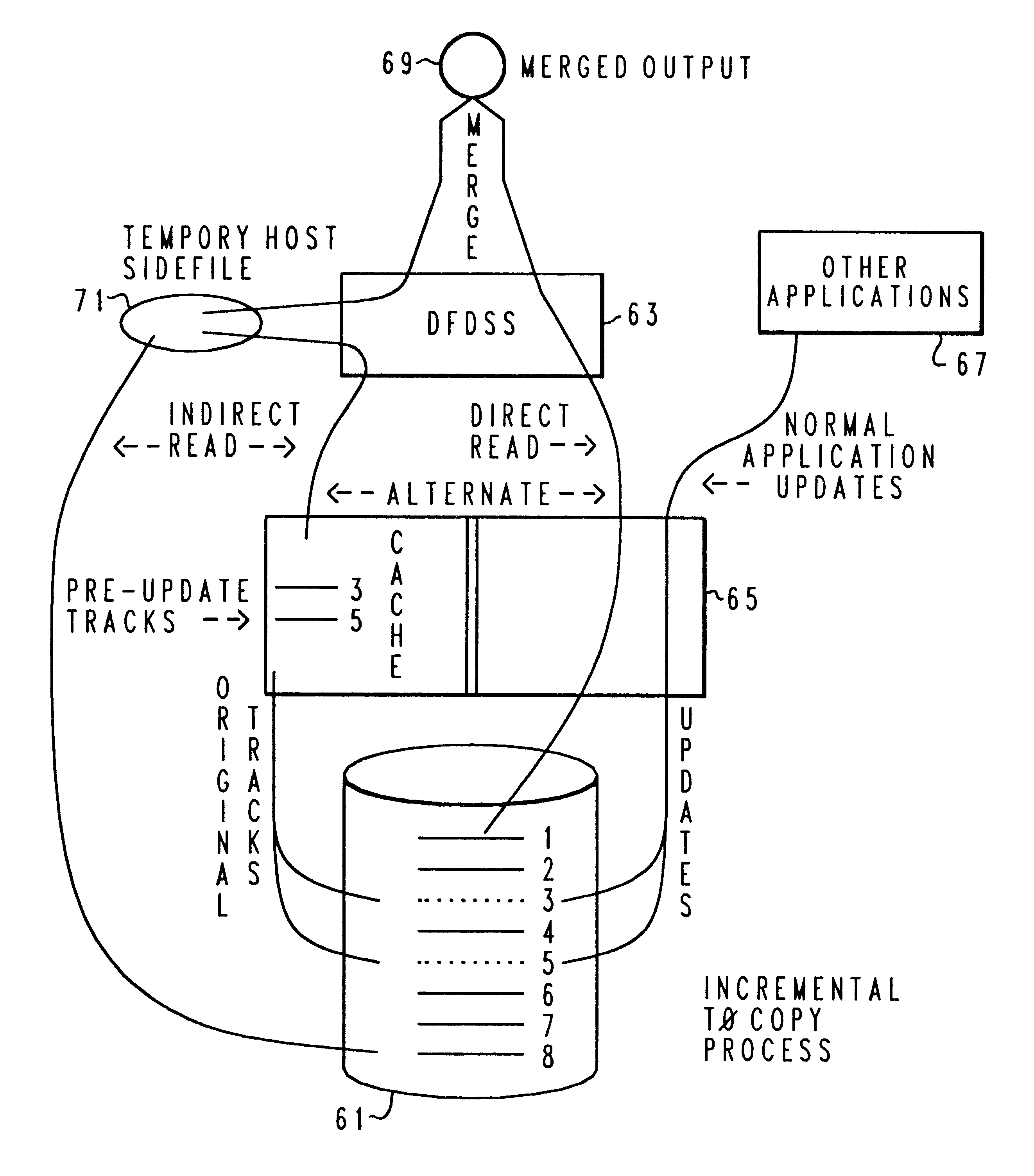
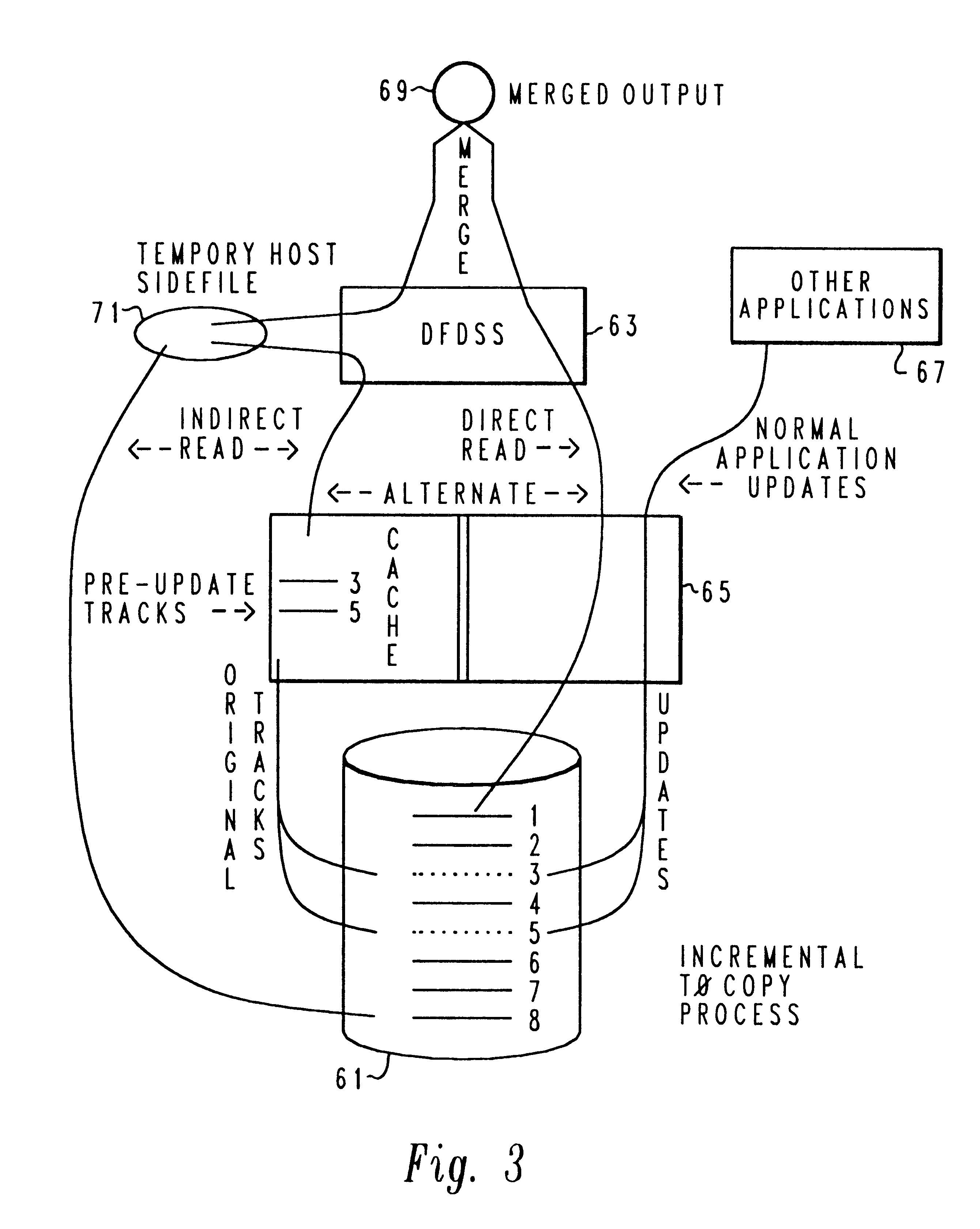
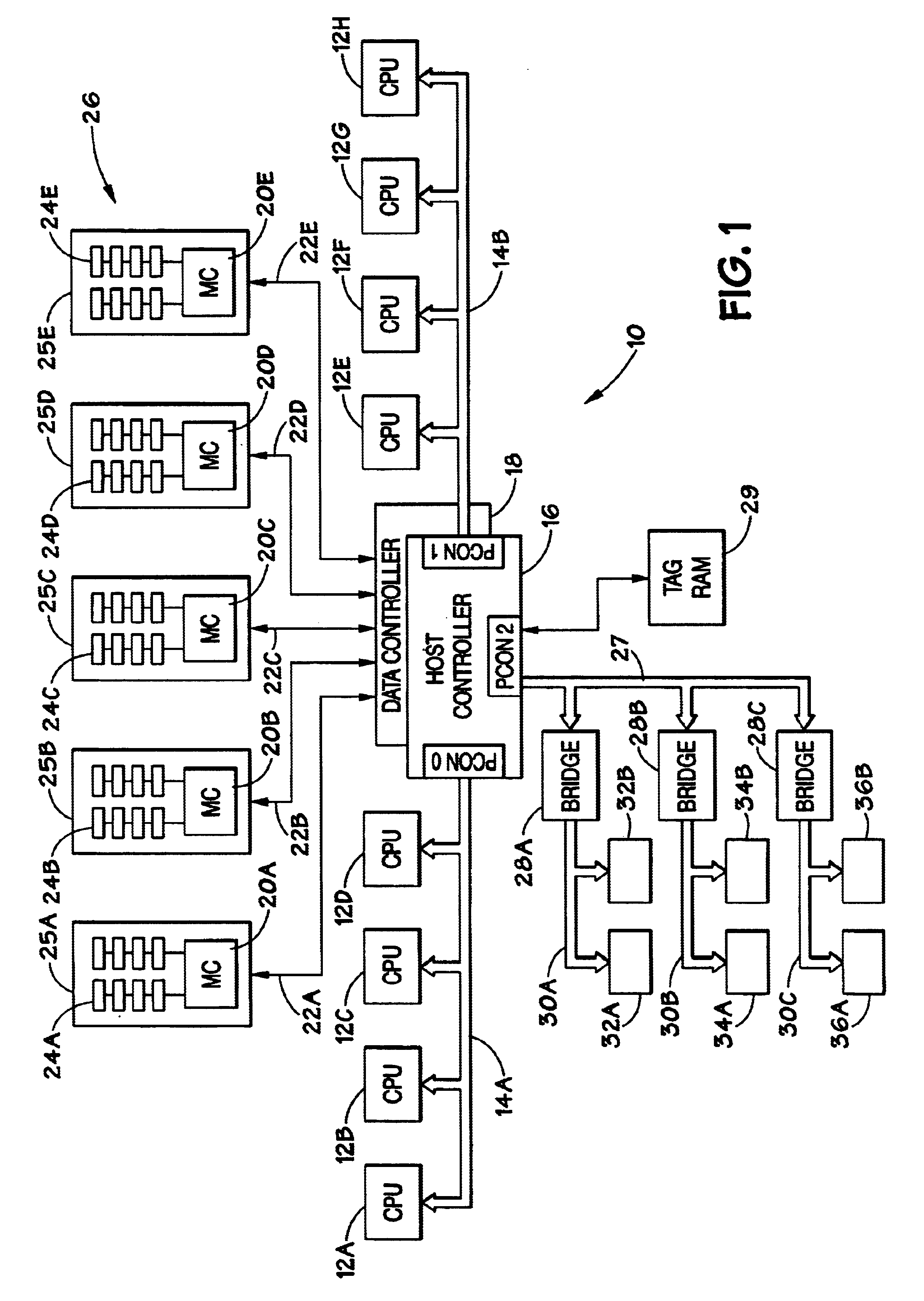
Method and system for incremental time zero backup copying of data
InactiveUSRE37601E1Maintaining continued availability of datasetsReduce suspensionRedundant operation error correctionMemory systemsData processing systemData set
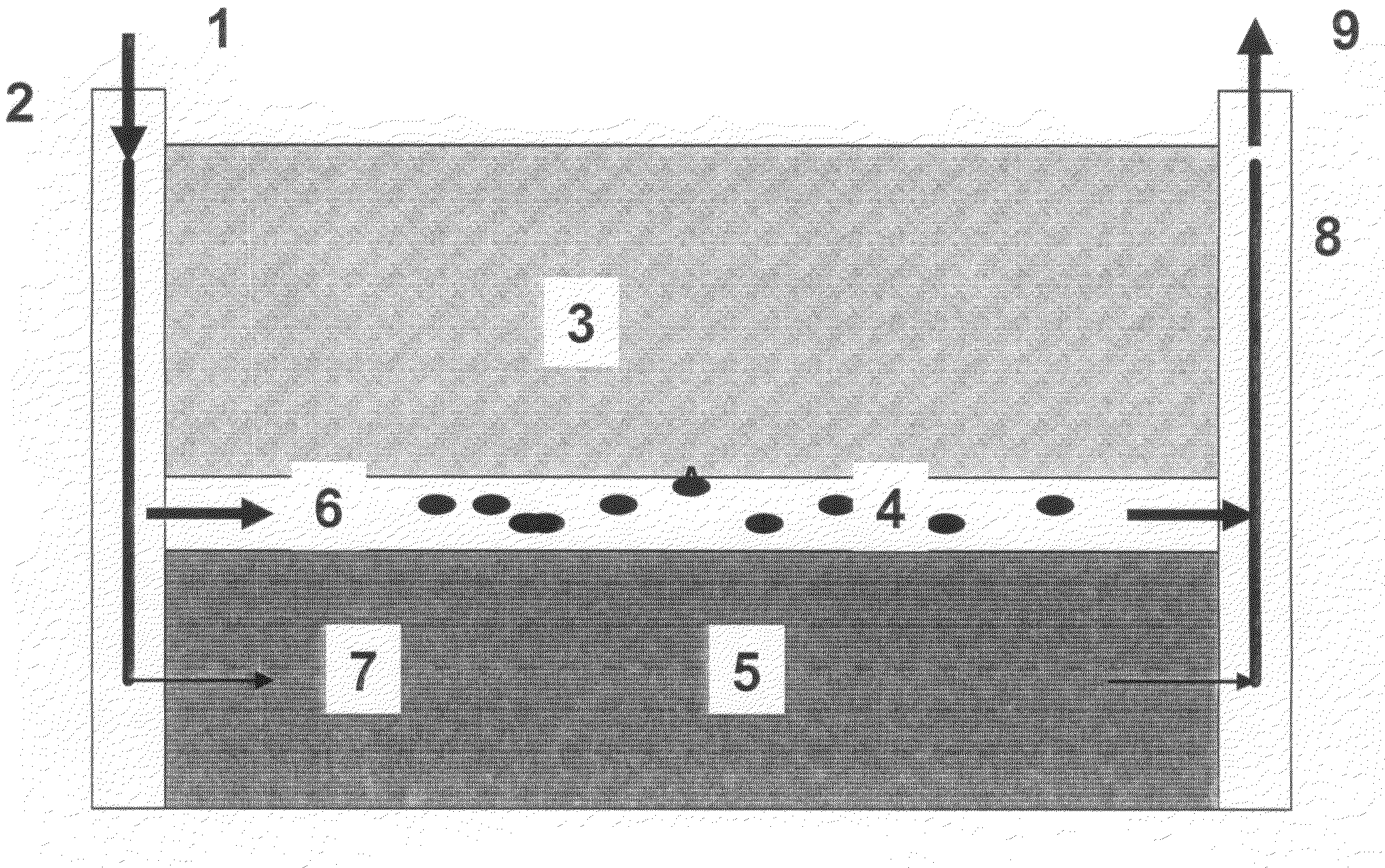
Backup copying of designated datasets representing a first selected point in time consistency may be performed in a data processing system on an attached storage subsystem concurrent with data processing system application execution by first suspending application execution only long enough to form a logical-to-physical address concordance, and thereafter physically backing up the datasets on the storage subsystem on a scheduled or opportunistic basis. An indication of each update to a selected portion of the designated datasets which occurs after the first selected point in time is stored and application initiated updates to uncopied designated datasets are first buffered. Thereafter, sidefiles are made of the affected datasets, or portions thereof, the updates are then written through to the storage subsystem, and the sidefiles written to an alternate storage location in backup copy order, as controlled by the address concordance. At a subsequent point in time only those portions of the designated datasets which have been updated after the first selected period and time are copied, utilizing an identical technique.
Owner:IBM CORP
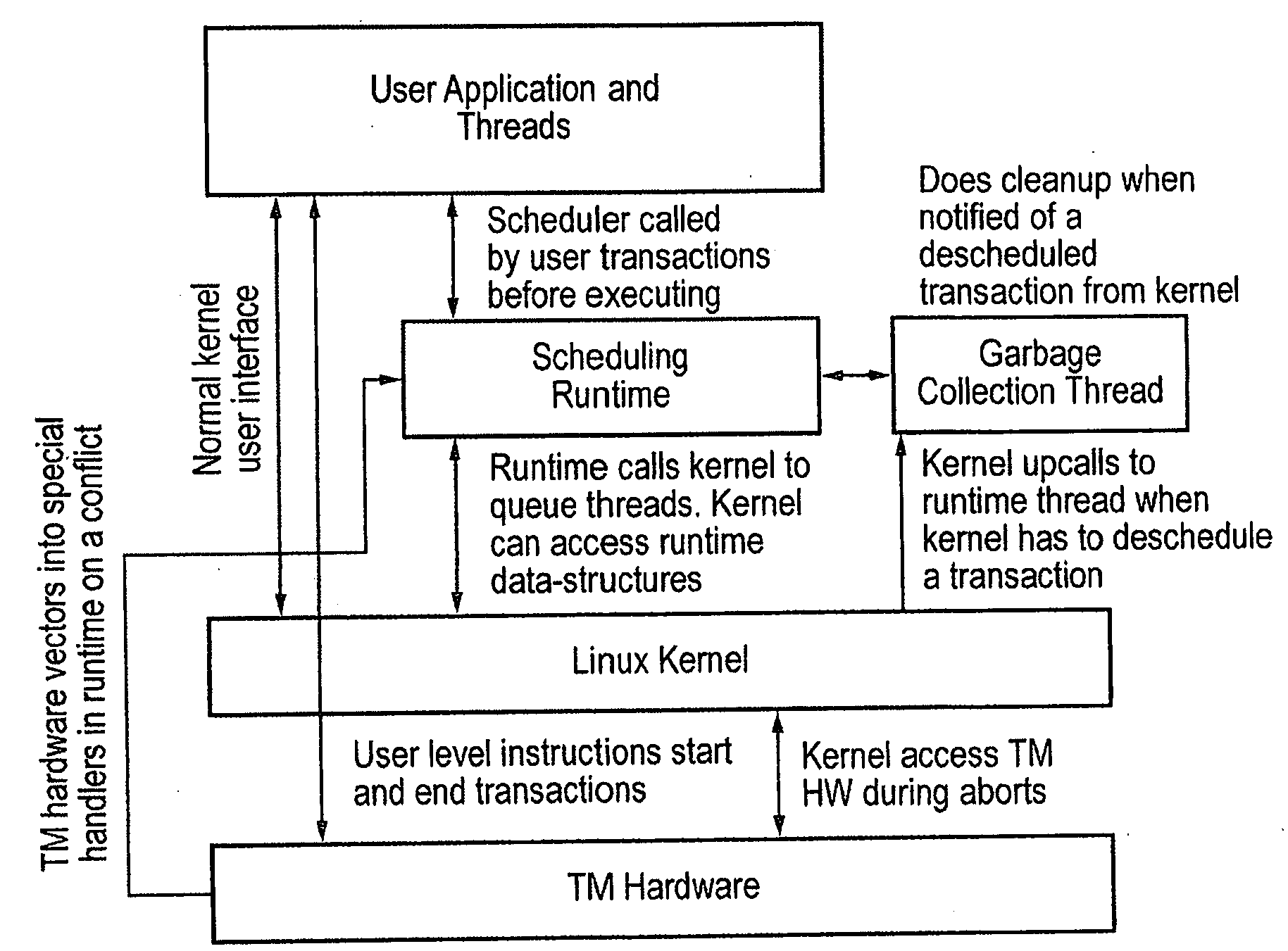
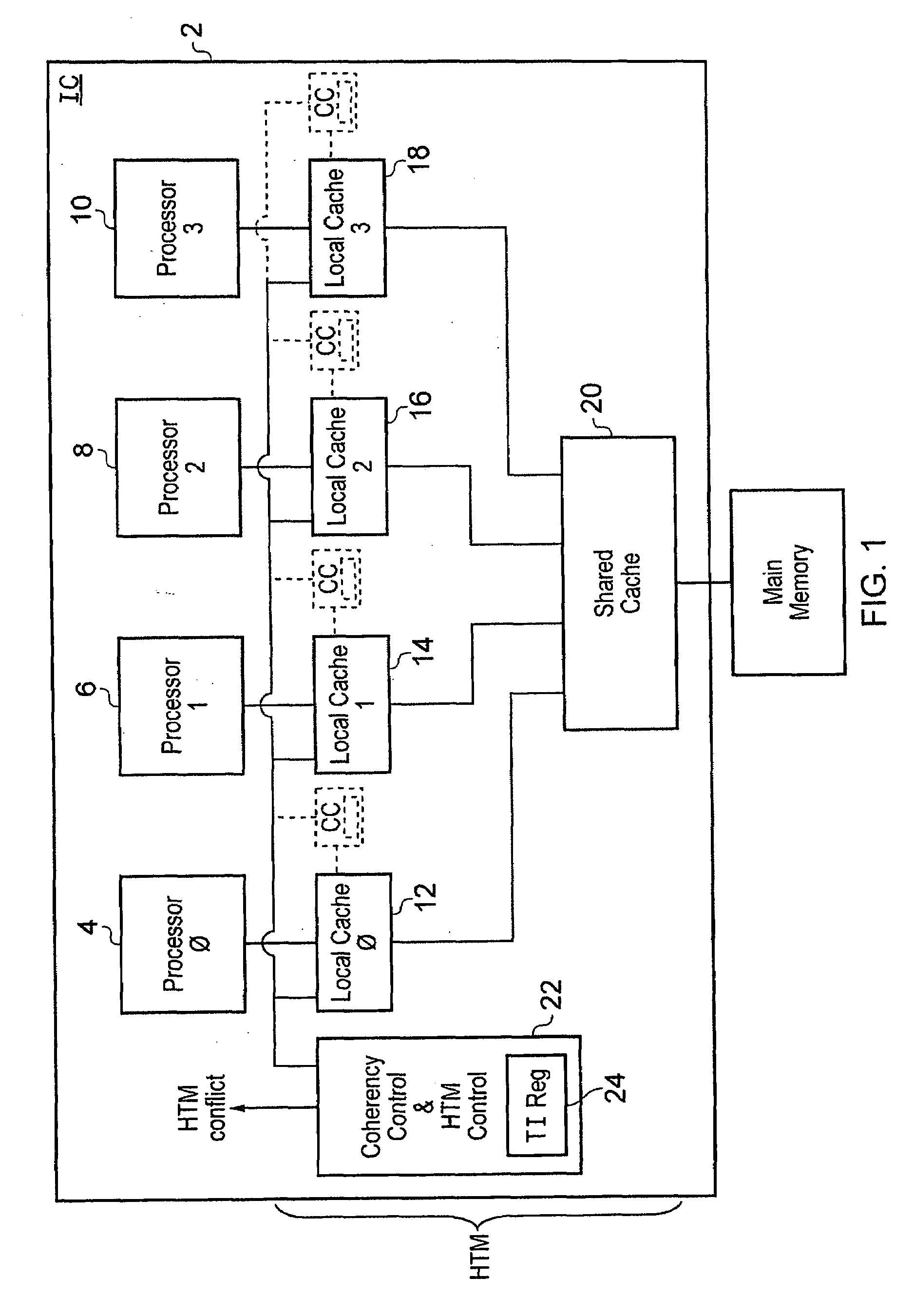
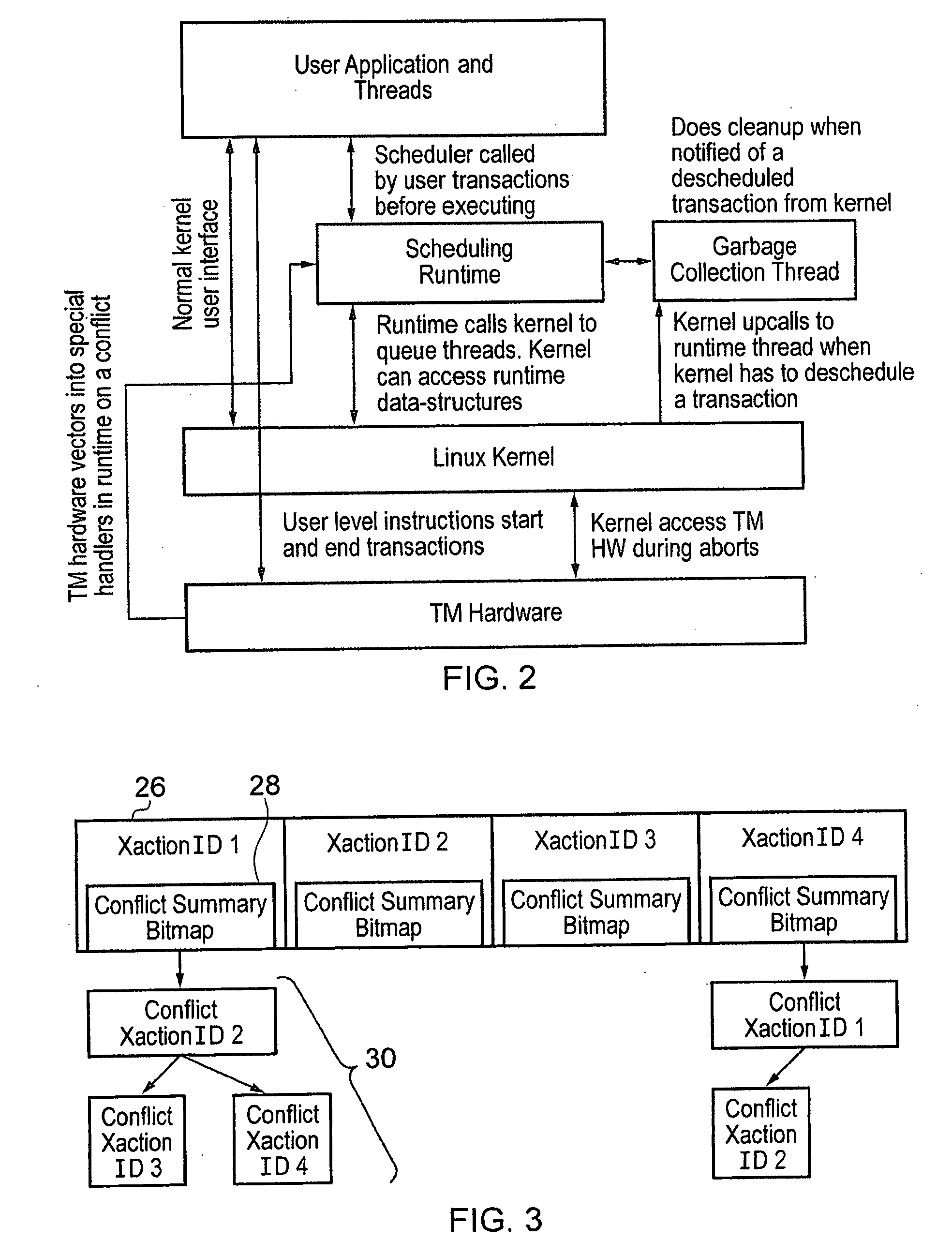
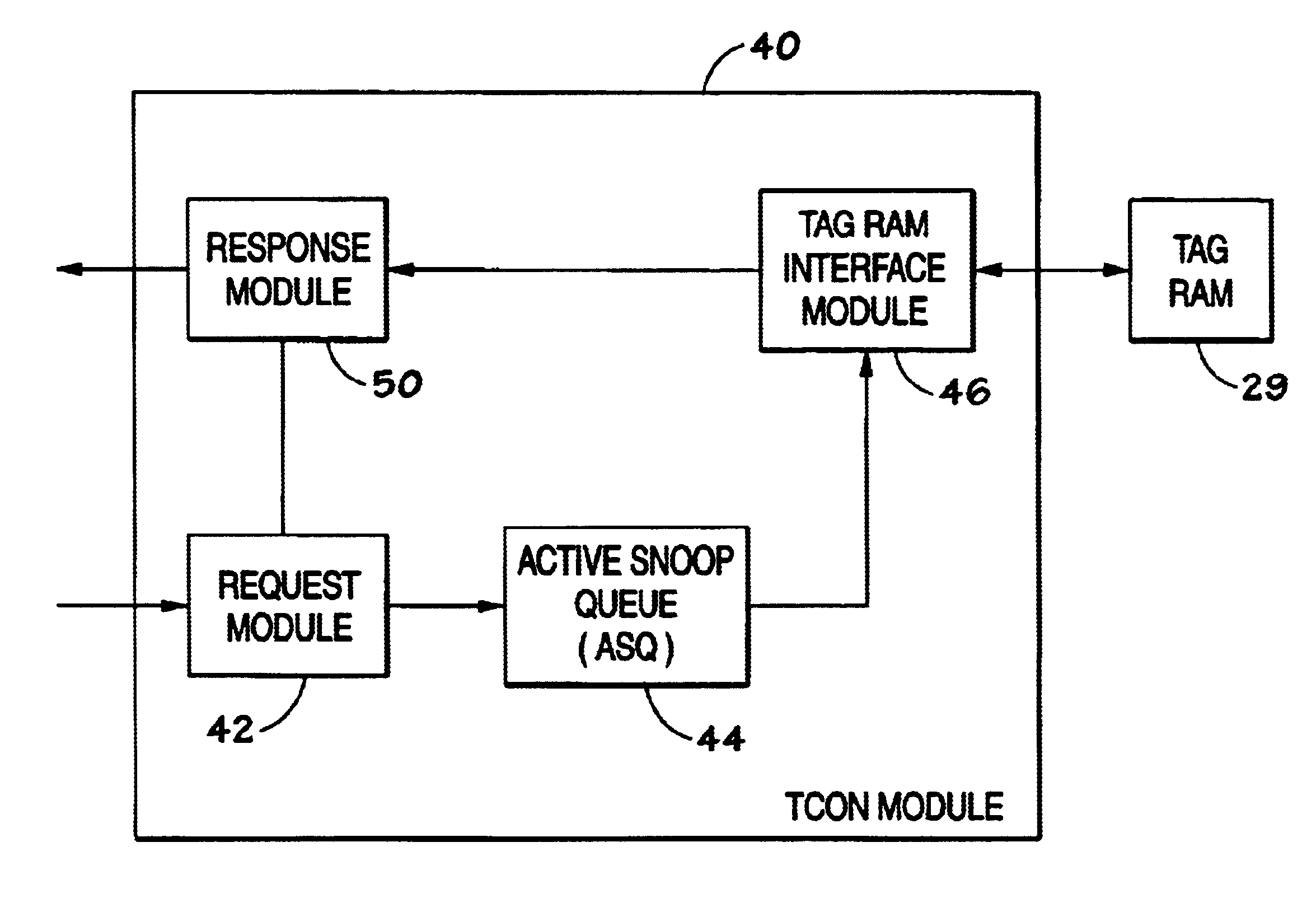
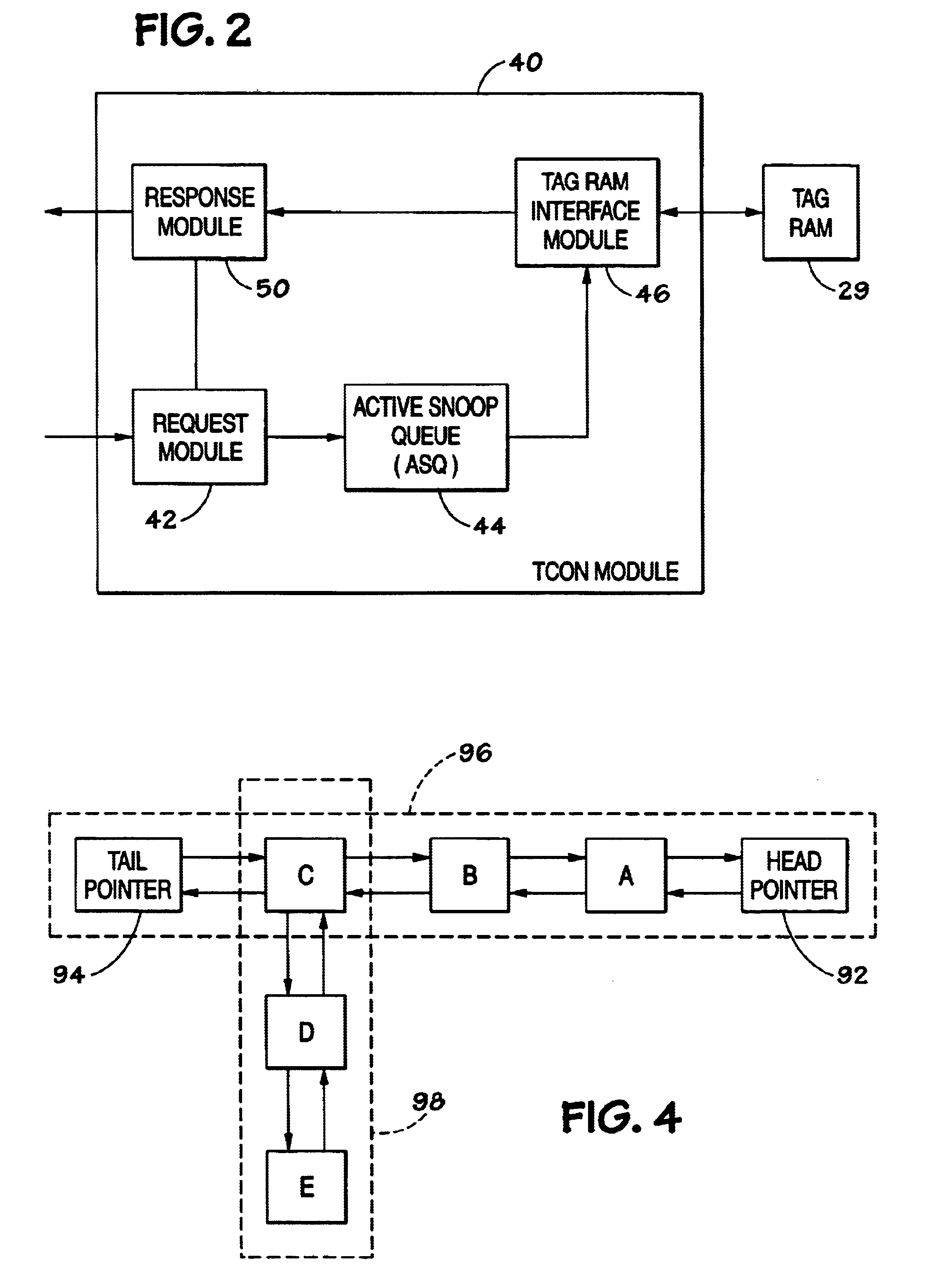
Contention management for a hardware transactional memory
InactiveUS20090138890A1Reduce storage overheadImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsConsistency controlComputer science
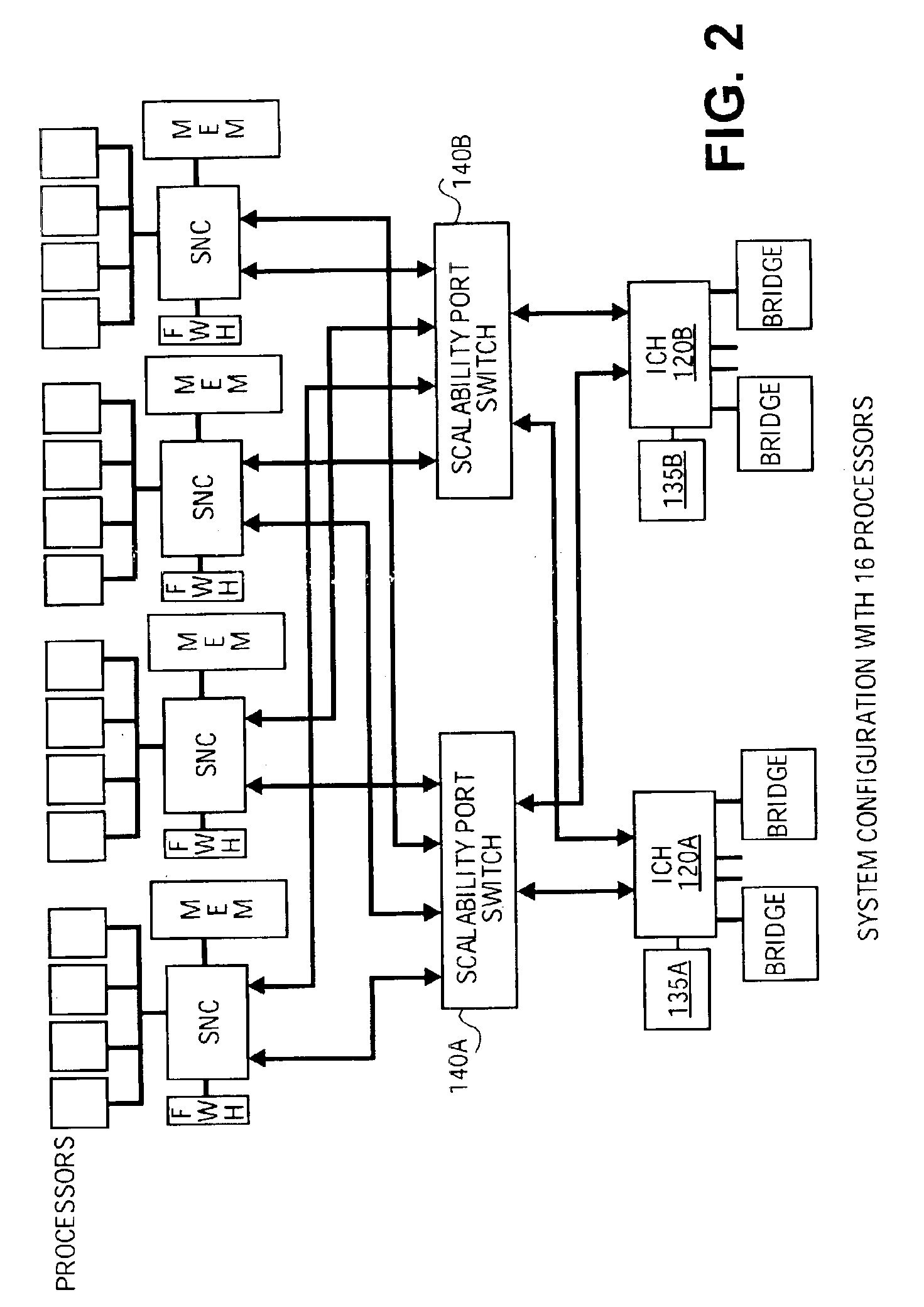
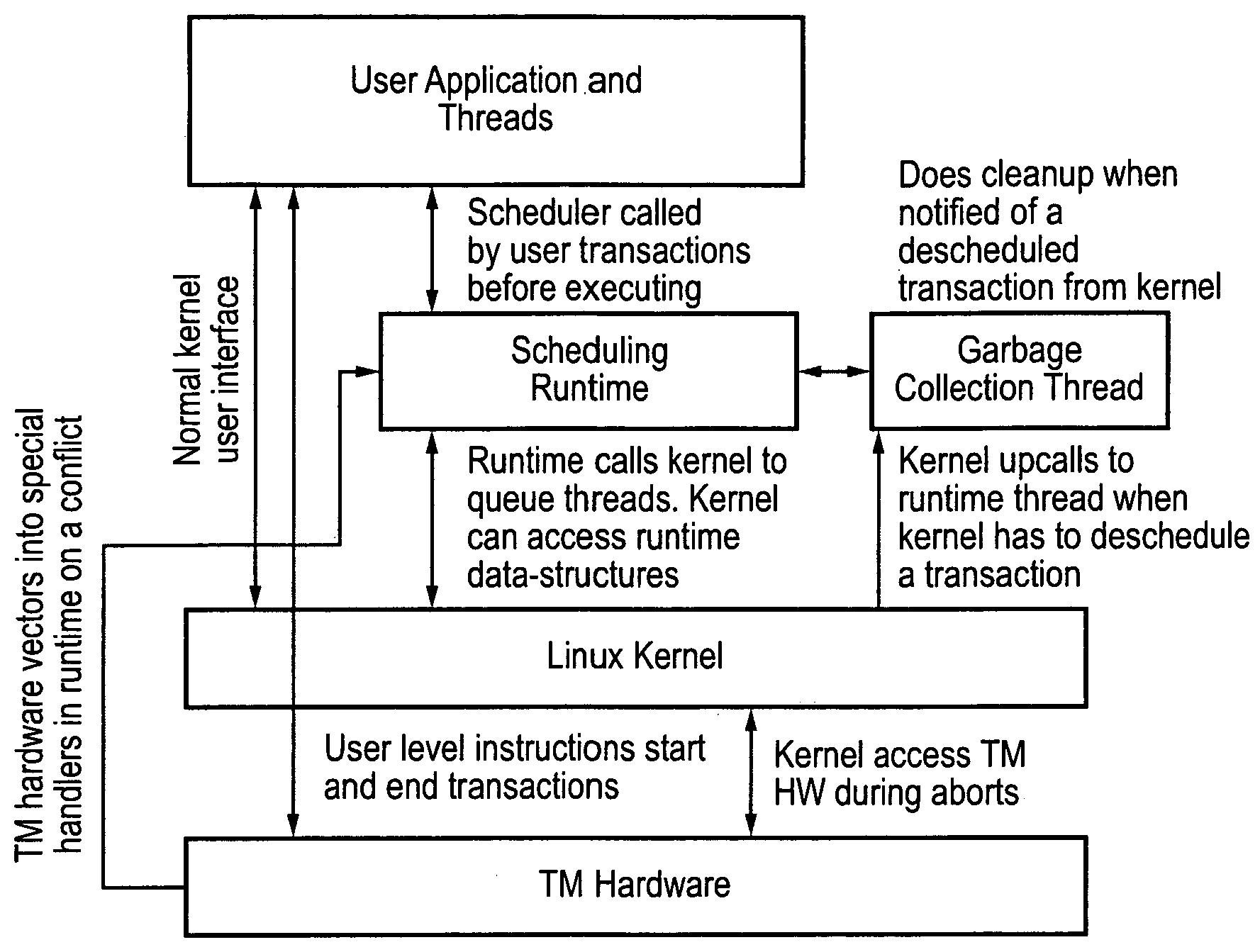
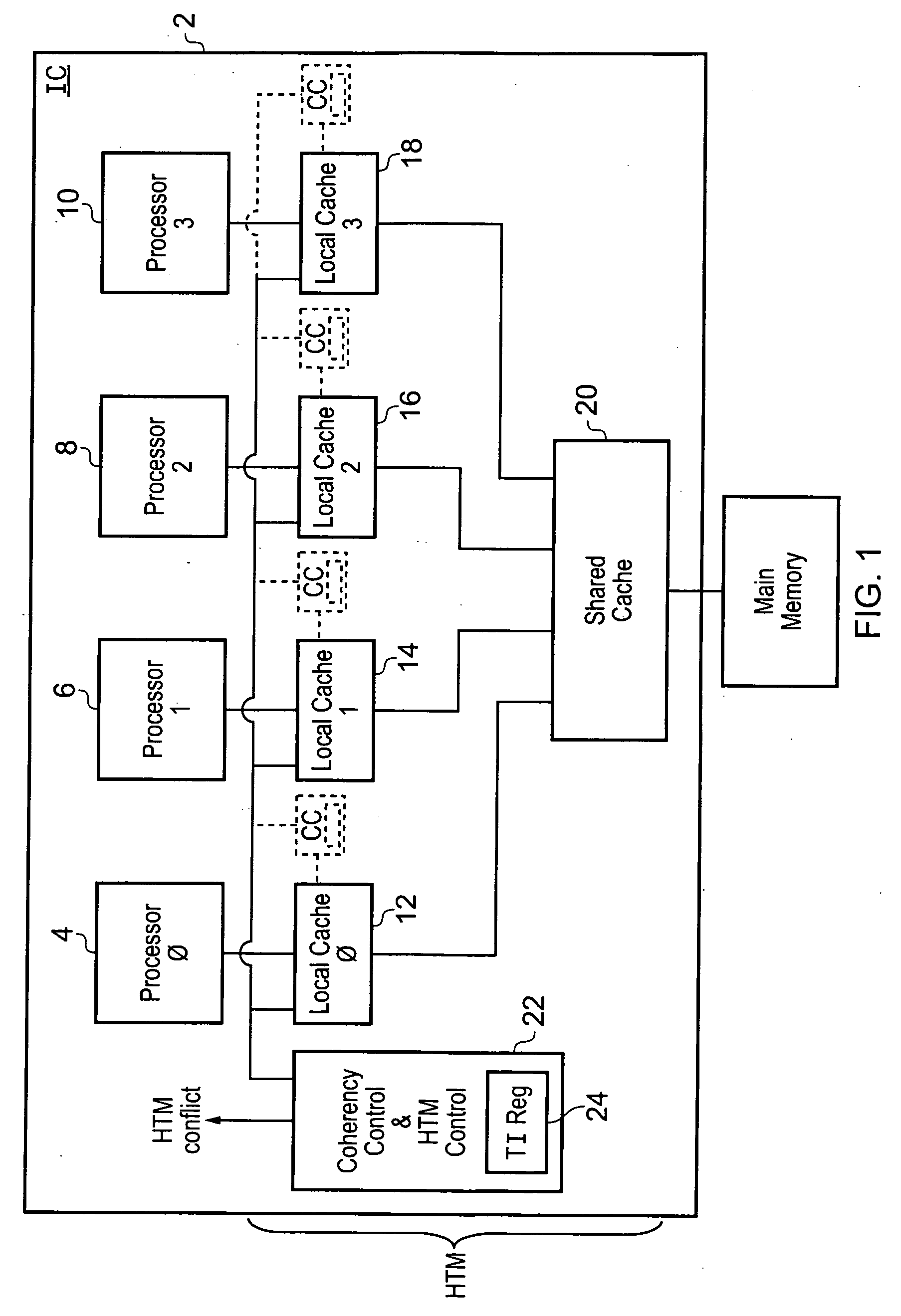
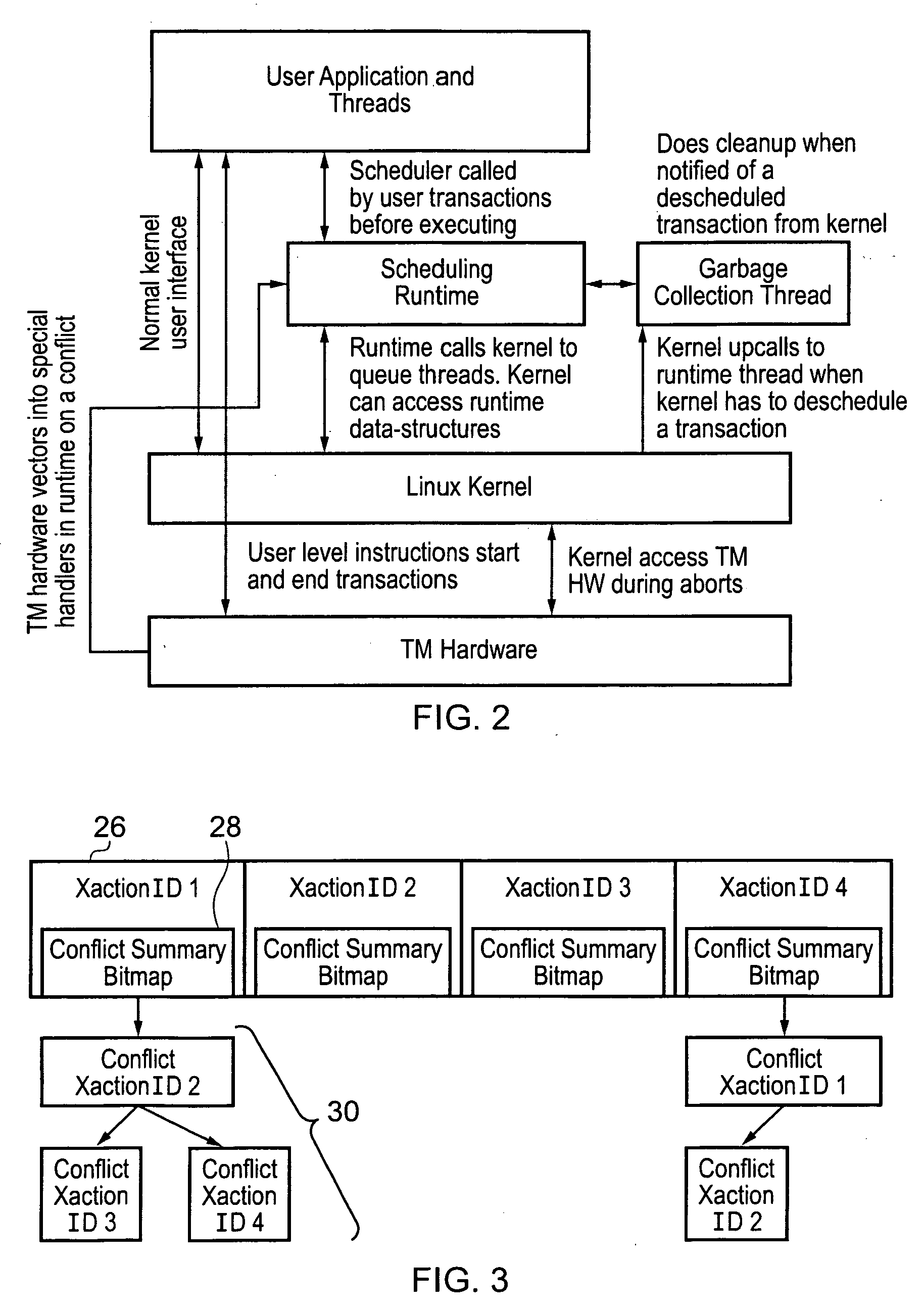
A hardware transactional memory 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 is provided within a multiprocessor 4, 6, 8, 10 system with coherency control and hardware transaction memory control circuitry 22 that serves to at least partially manage the scheduling of processing transactions in dependence upon conflict data 26, 28, 30. The conflict data characterises previously encountered conflicts between processing transactions. The scheduling is performed such that a candidate processing transaction will not be scheduled if the conflict data indicates that one of the already running processing transactions has previously conflicted with the candidate processing transaction.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
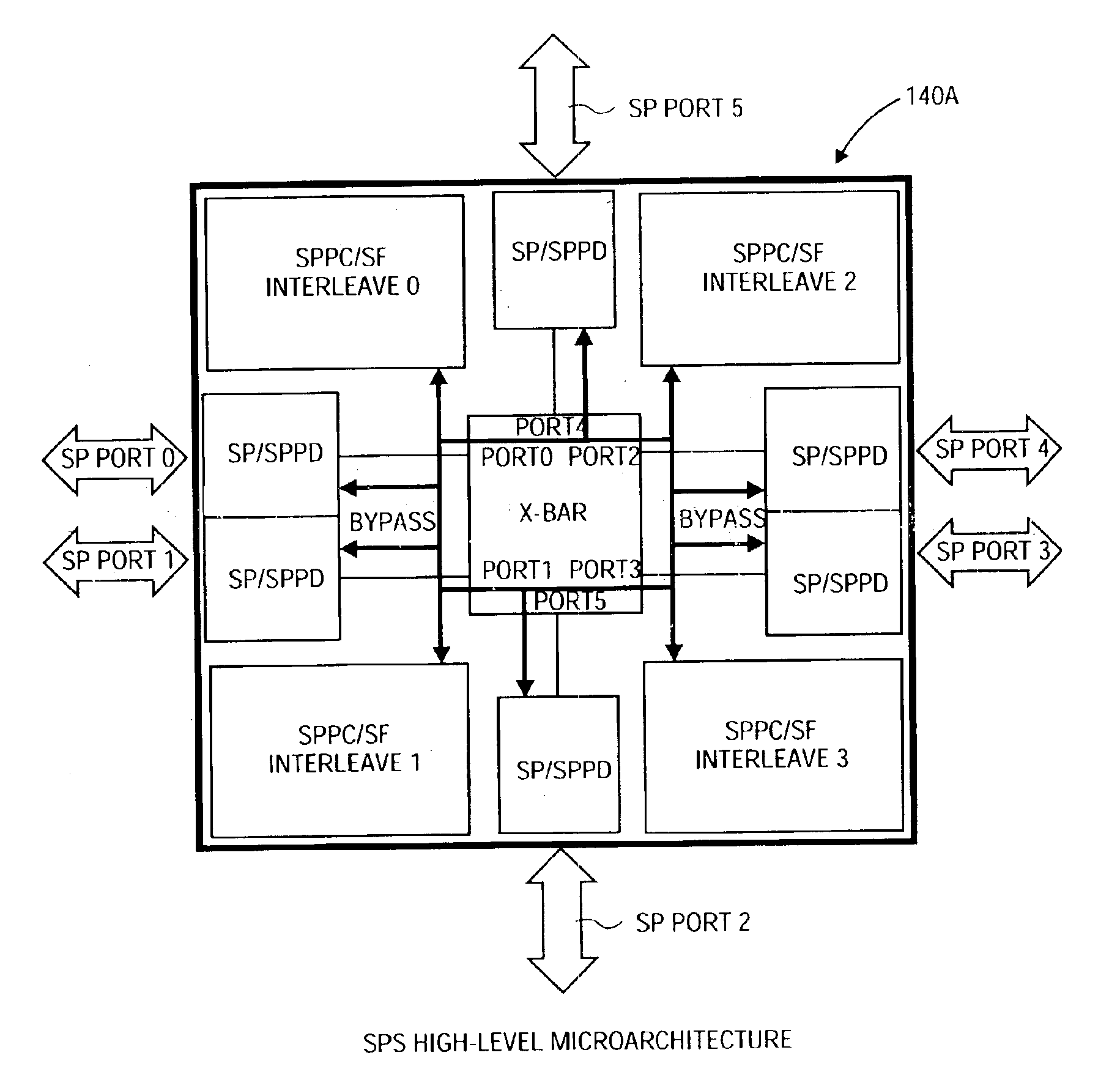
Shared bypass bus structure
InactiveUS6912612B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCrossbar switchLatency (engineering)
A shared bypass bus structure for low-latency coherency controller access in a coherent scalable switch. In a coherent scalable switch with multiple coherent interconnect ports, distributed coherency control structures, and a crossbar interface between them, a shared bypass bus permits data transfer between the coherent interconnect ports and the coherency control structures while bypassing the crossbar interface. Some embodiments may comprise scalable switches to support one or more sets of processors with substantially independent snoop or cache coherency paths or arrangements.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Contention management for a hardware transactional memory
ActiveUS20090133032A1Easy to shapeSimple taskMemory systemsTransaction processingConsistency controlOperating system
A hardware transactional memory 12, 14, 16, 18, 20 is provided within a multiprocessor 4, 6, 8, 10 system with coherency control and hardware transaction memory control circuitry 22 that serves to at least partially manage the scheduling of processing transactions in dependence upon conflict data 26, 28, 30. The conflict data characterises previously encountered conflicts between processing transactions. The scheduling is performed such that a candidate processing transaction will not be scheduled if the conflict data indicates that one of the already running processing transactions has previously conflicted with the candidate processing transaction.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
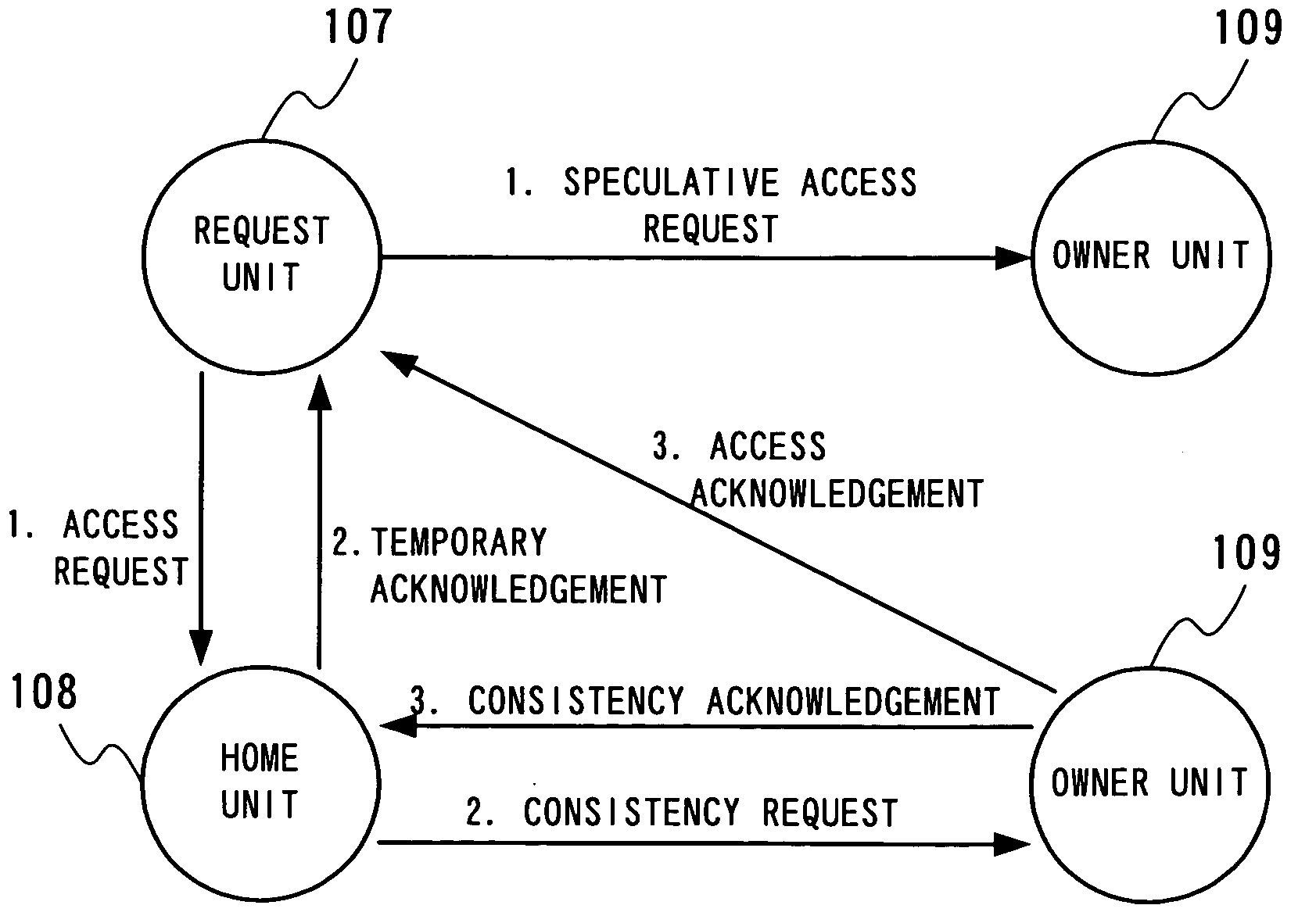
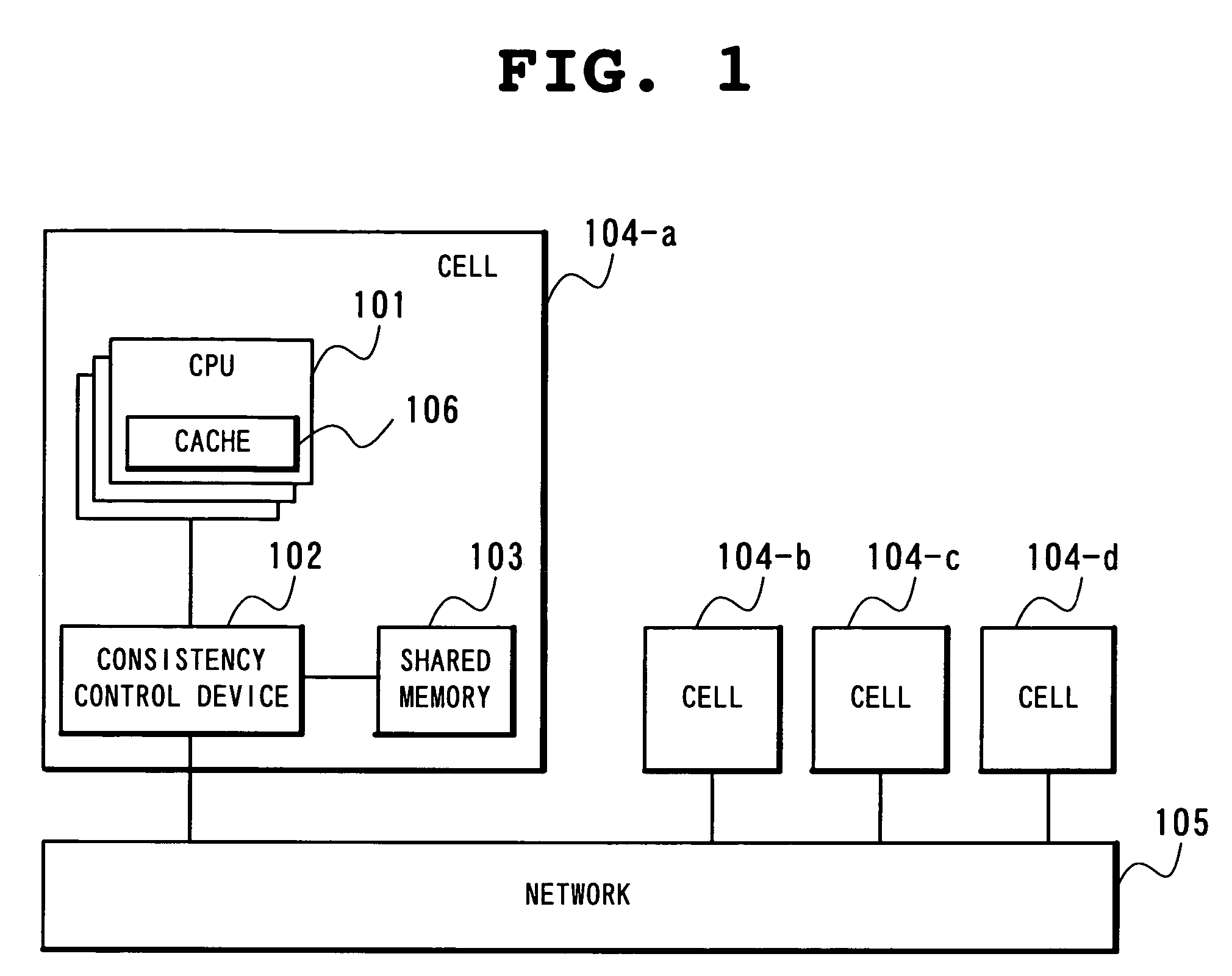
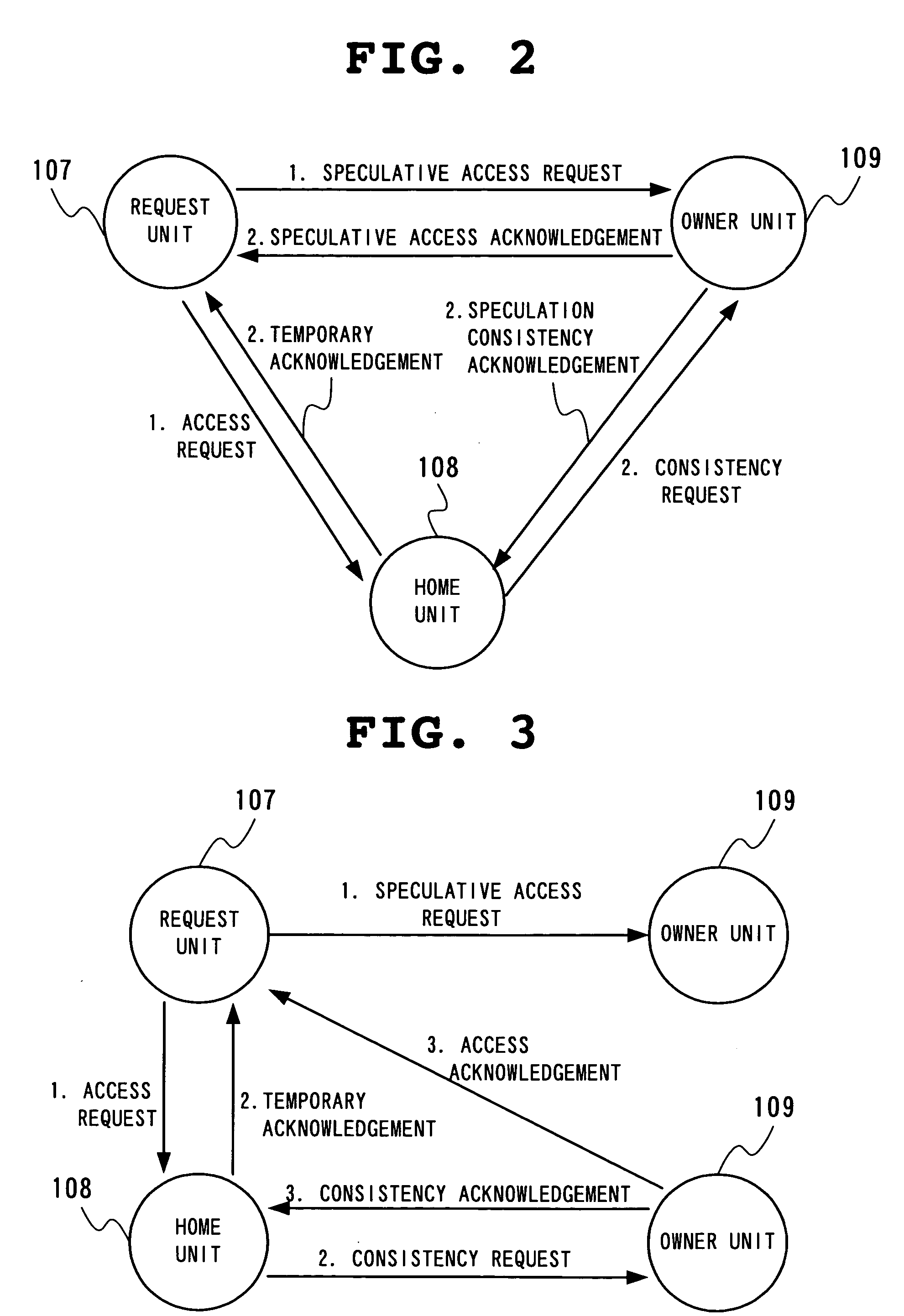
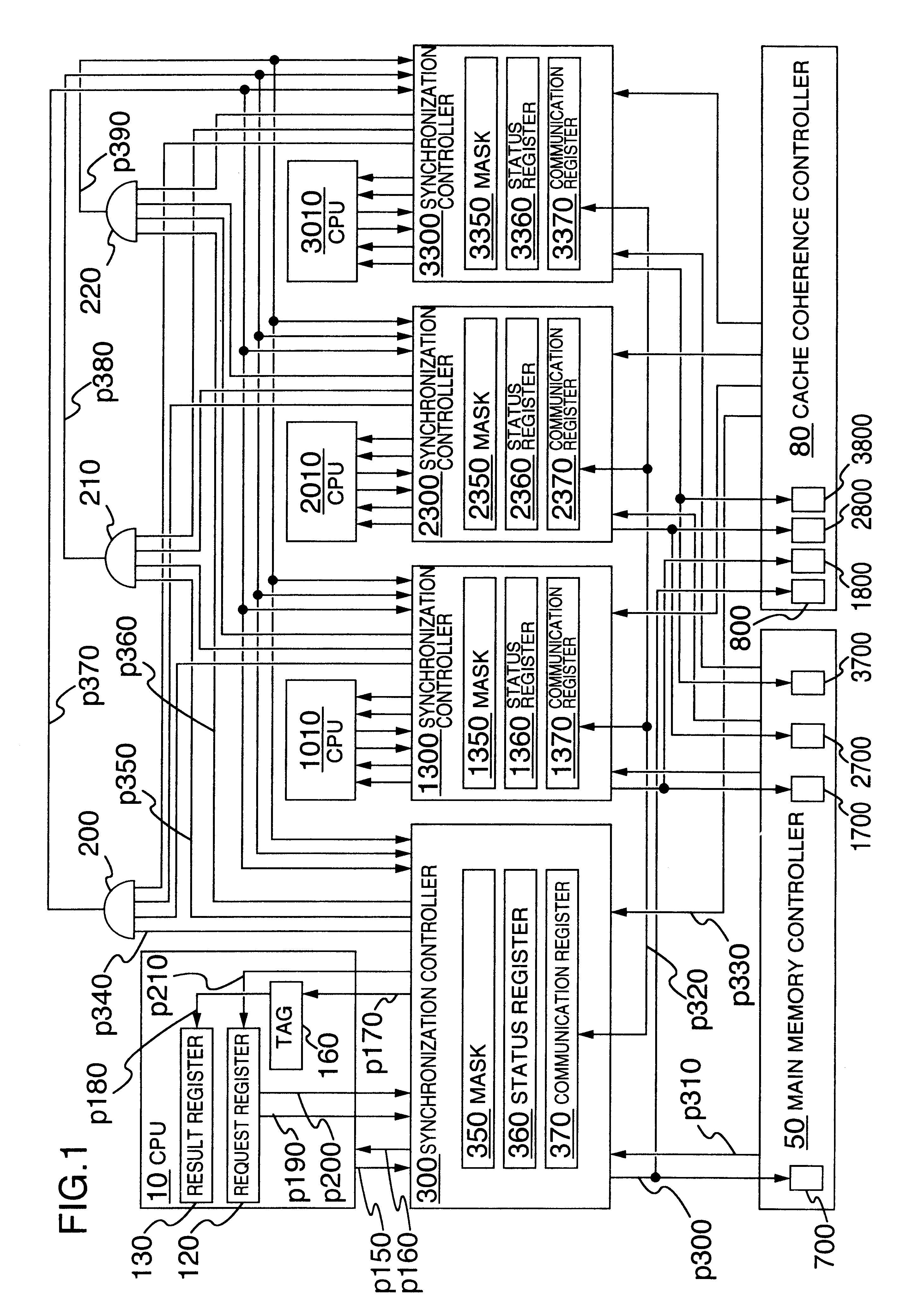
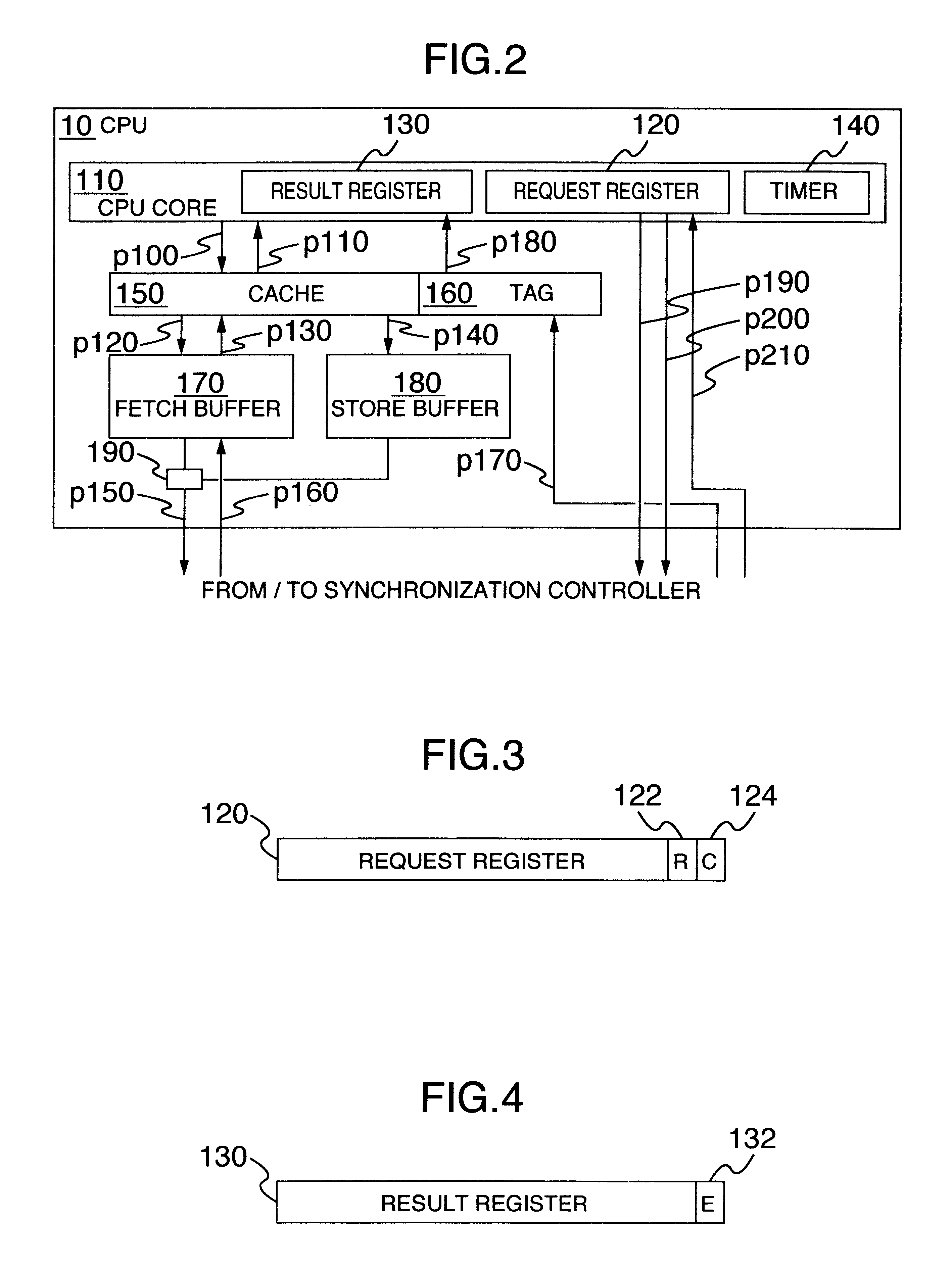
Multiprocessor system, and consistency control device and consistency control method in multiprocessor system
InactiveUS20050144399A1Improve memory access performanceAmount of hardware necessaryMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMulti processorNetwork connection
A multiprocessor system with cells having a plurality of CPUs sharing a memory and a consistency control device connected through a network, in which the consistency control device includes a request unit which issues an access request and a speculative access request, a home unit which receives an access request from the request unit of each cell, and an owner unit which receives a speculative access request from the request unit of each cell, the request unit further including an owner decision unit which predicts a cell holding requested data and a determination unit which determines whether processing based on prediction is to be conducted or not.
Owner:NEC CORP
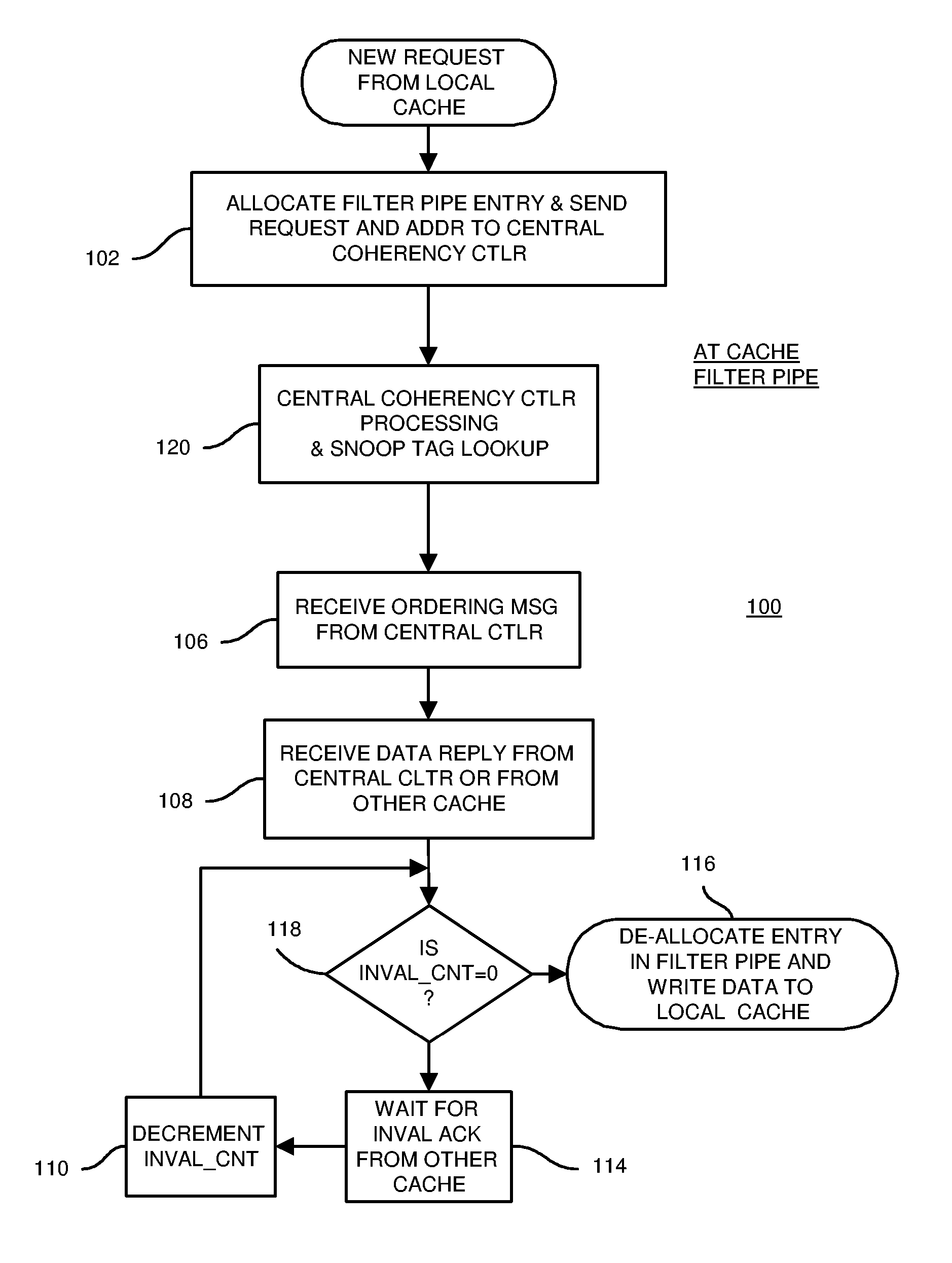
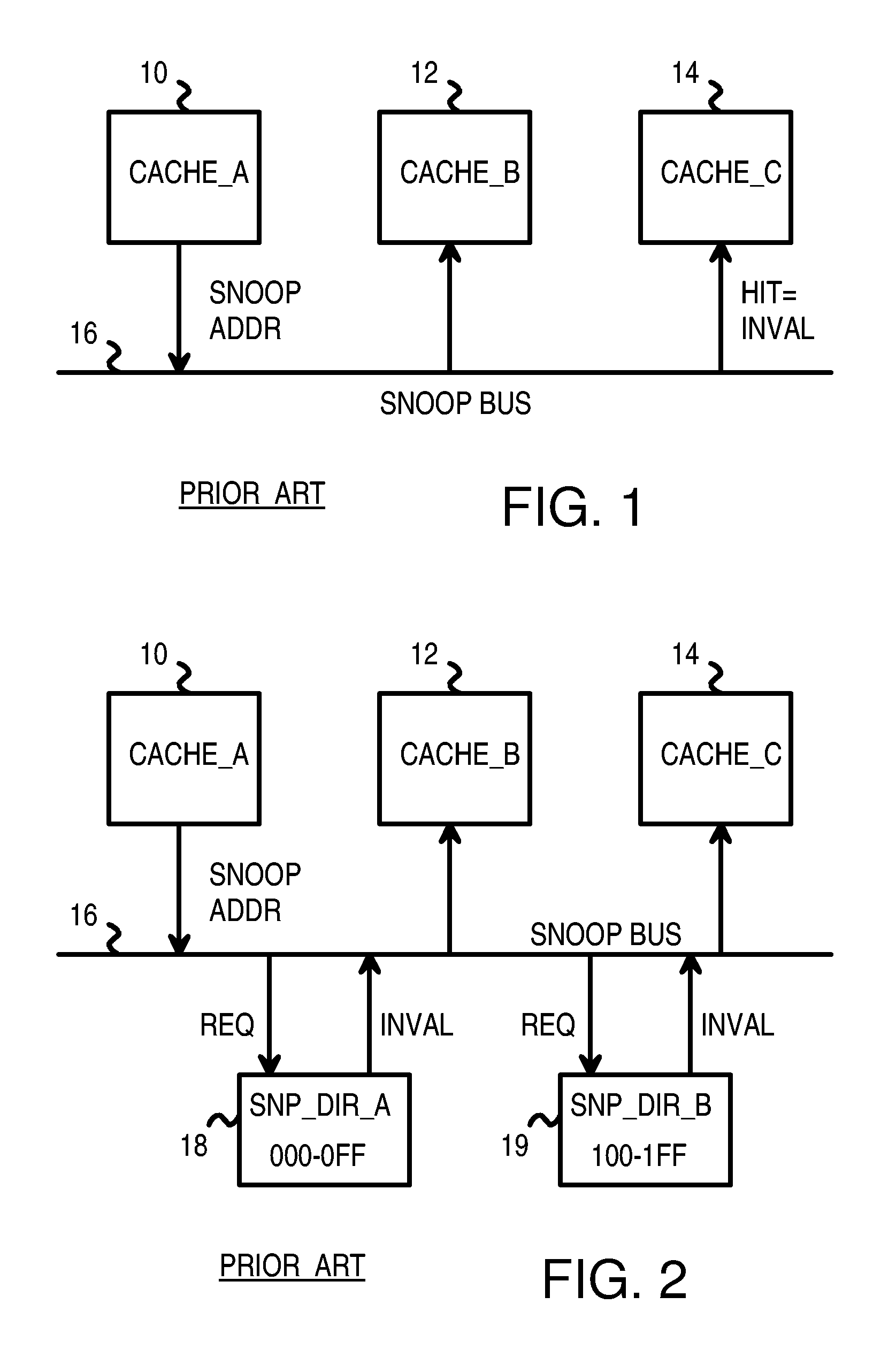
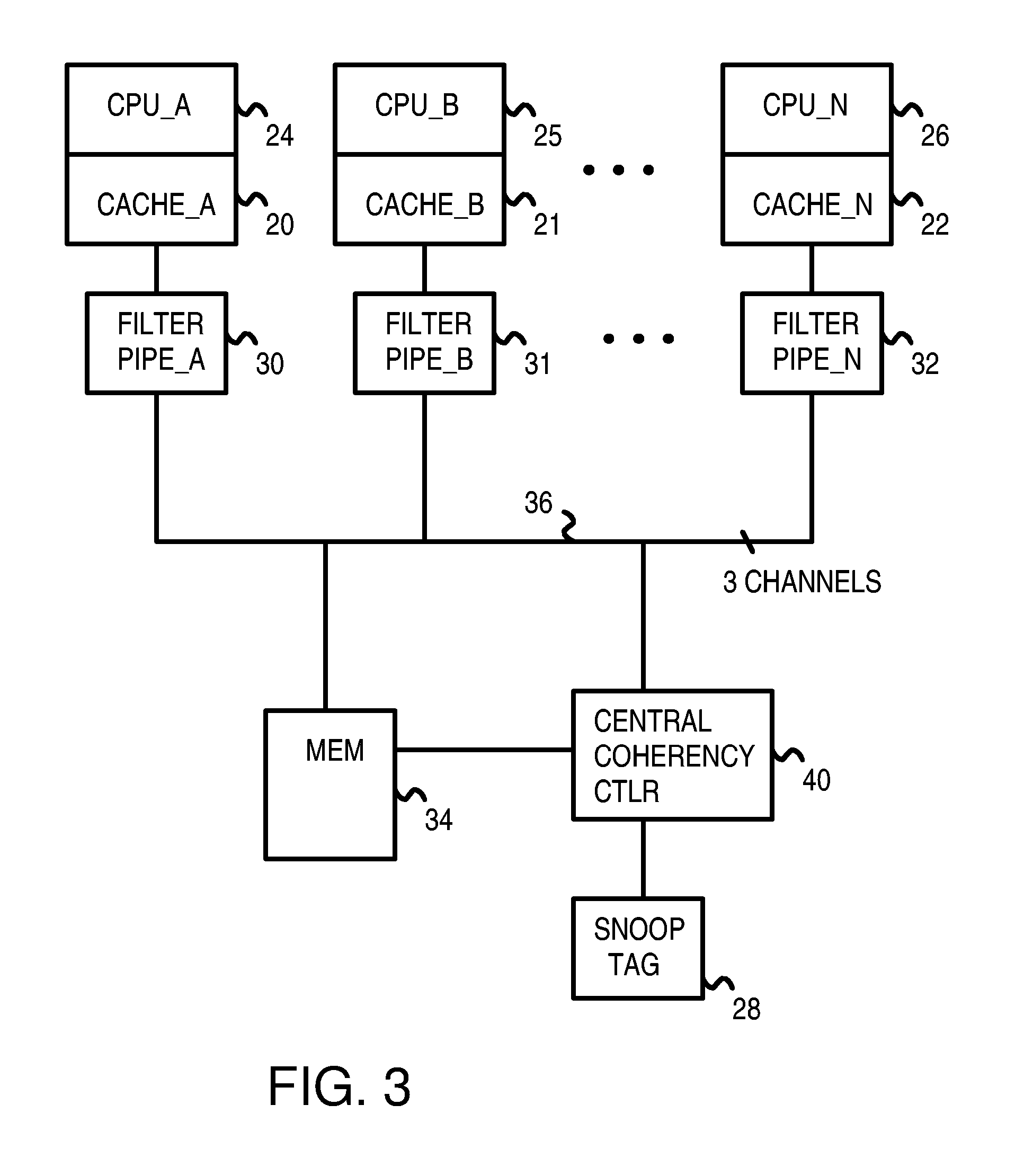
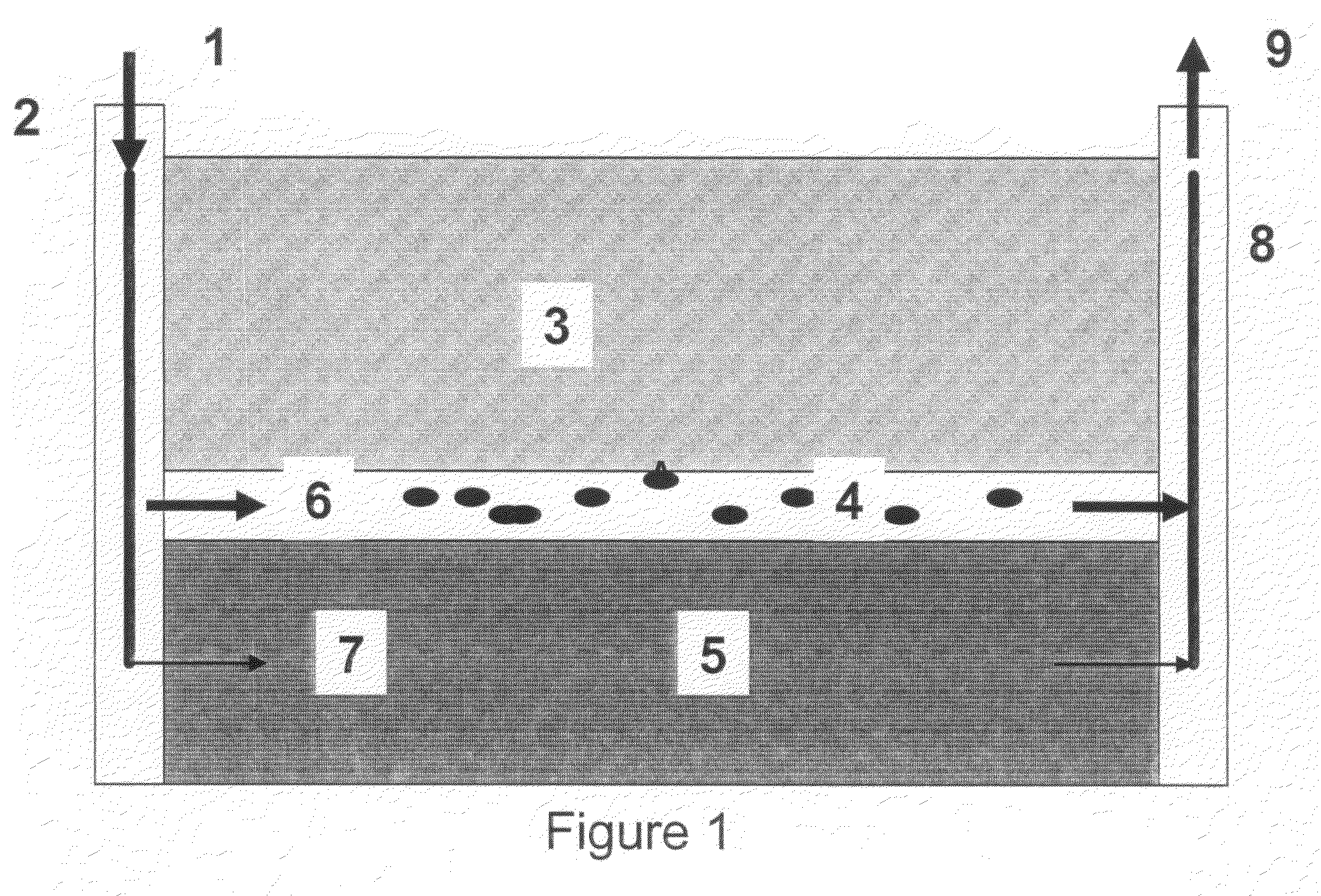
Distributed Cache Coherence at Scalable Requestor Filter Pipes that Accumulate Invalidation Acknowledgements from other Requestor Filter Pipes Using Ordering Messages from Central Snoop Tag
A multi-processor, multi-cache system has filter pipes that store entries for request messages sent to a central coherency controller. The central coherency controller orders requests from filter pipes using coherency rules but does not track completion of invalidations. The central coherency controller reads snoop tags to identify sharing caches having a copy of a requested cache line. The central coherency controller sends an ordering message to the requesting filter pipe. The ordering message has an invalidate count indicating the number of sharing caches. Each sharing cache receives an invalidation message from the central coherency controller, invalidates its copy of the cache line, and sends an invalidation acknowledgement message to the requesting filter pipe. The requesting filter pipe decrements the invalidate count until all sharing caches have acknowledged invalidation. All ordering, data, and invalidation acknowledgement messages must be received by the requesting filter pipe before loading the data into its cache.
Owner:AZUL SYSTEMS
Preformed particle gel for conformance control in an oil reservoir
Expandable and hydrophilic polymeric particles may be made in a non-emulsion system, and with controllable hardness and delay in their time to swell in a fresh or salt water environment. These particles are prepared from combining monomers, controlled monomers, stable cross-linkers, initiators, and other agents, in aqueous solution. The controlled monomers induce kinetically controllable decomposition, degrading over time, thus inducing a desired time delay in particle swelling. The delay and degree of the swelling of the particles is controlled by selection of controlled monomer, stable cross-linking agents, monomers, and process conditions. These preformed particle gels are made to an initial particle size of 0.1 micron in diameter or larger via different grinding techniques. This composition is used for modifying the permeability of subterranean formations and thereby increasing the recovery rate of hydrocarbon fluids present in the formation.
Owner:CHEMEOR
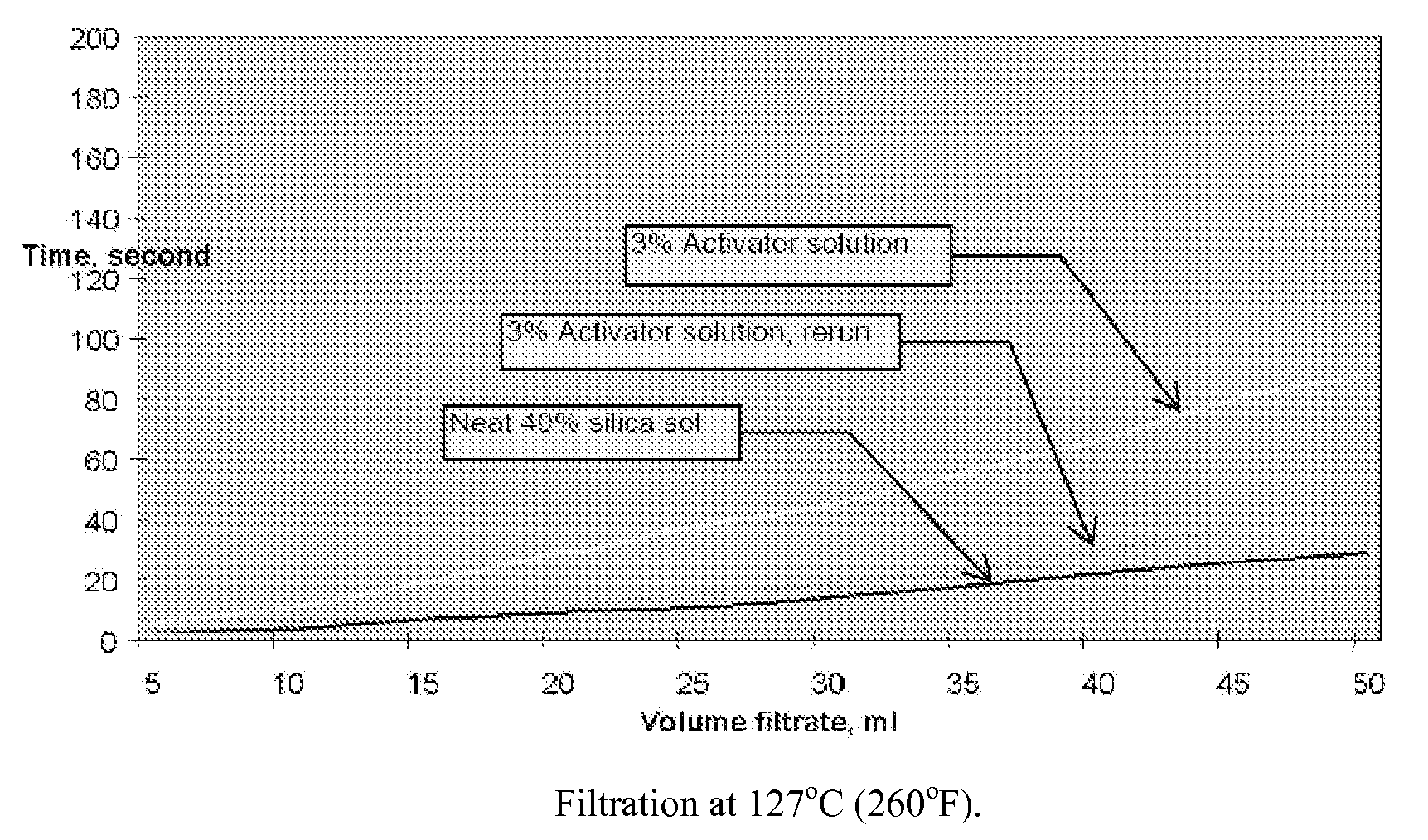
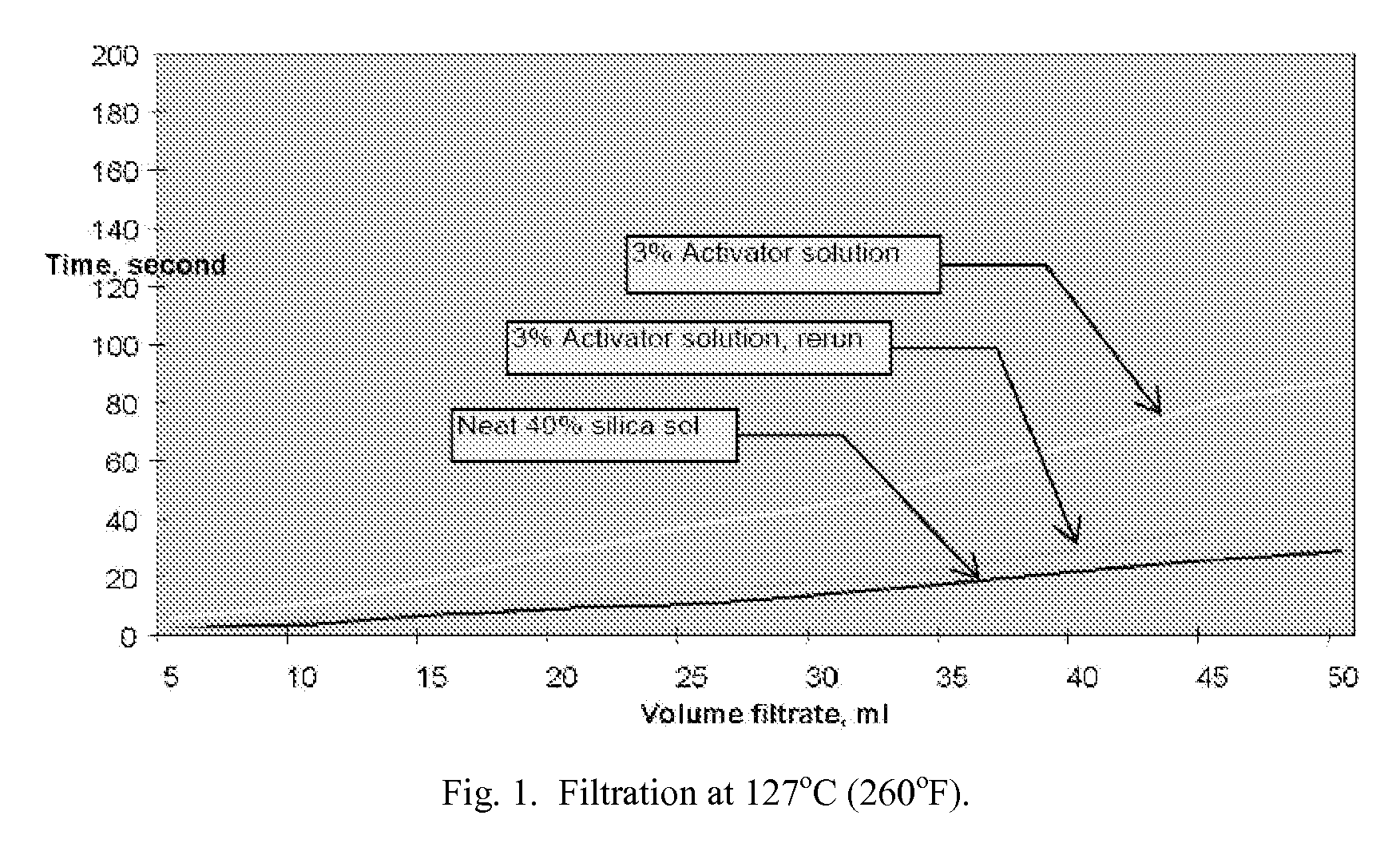
Tight formation water shut off method with silica gel
A delayed gelling system useful in conformance control in the production of petroleum from subterranean formations, especially low permeability formations, is disclosed. The gelling system comprises a basic silica sol, an activator comprising a hydroxyl donor, and an optional syneresis inhibitor. In the disclosed method of using the gelling system, the gelling system may be pumped into formations with excessive water and / or gas production and thermally activated in the formation at downhole conditions to form a hard gel to reduce water and / or gas production.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Coherence controller for a multiprocessor system, module, and multiprocessor system with a multimodule architecture incorporating such a controller
InactiveUS7017011B2Improve performanceDrawback can be obviatedMemory systemsMulti processorParallel computing
A coherence controller is included in a module which includes a plurality of multiprocessor units, each of which contains a main memory and processors equipped with respective cache memories. The module may be one of a plurality of similarly constructed modules connected by a router or other type of switching device. The coherence controller in each module includes a cache filter directory having a first filter directory for guaranteeing coherence between the local main memory and the cache memory in each of the processors of the module, and an external port connected to at least one of the other modules. The cache filter directory also includes a complementary filter directory, which tracks locations of lines or blocks of the local main memory copied from the module into other modules, and for guaranteeing coherence between the local main memory and the cache in each of the processors of the module and the other modules.
Owner:BULL SA
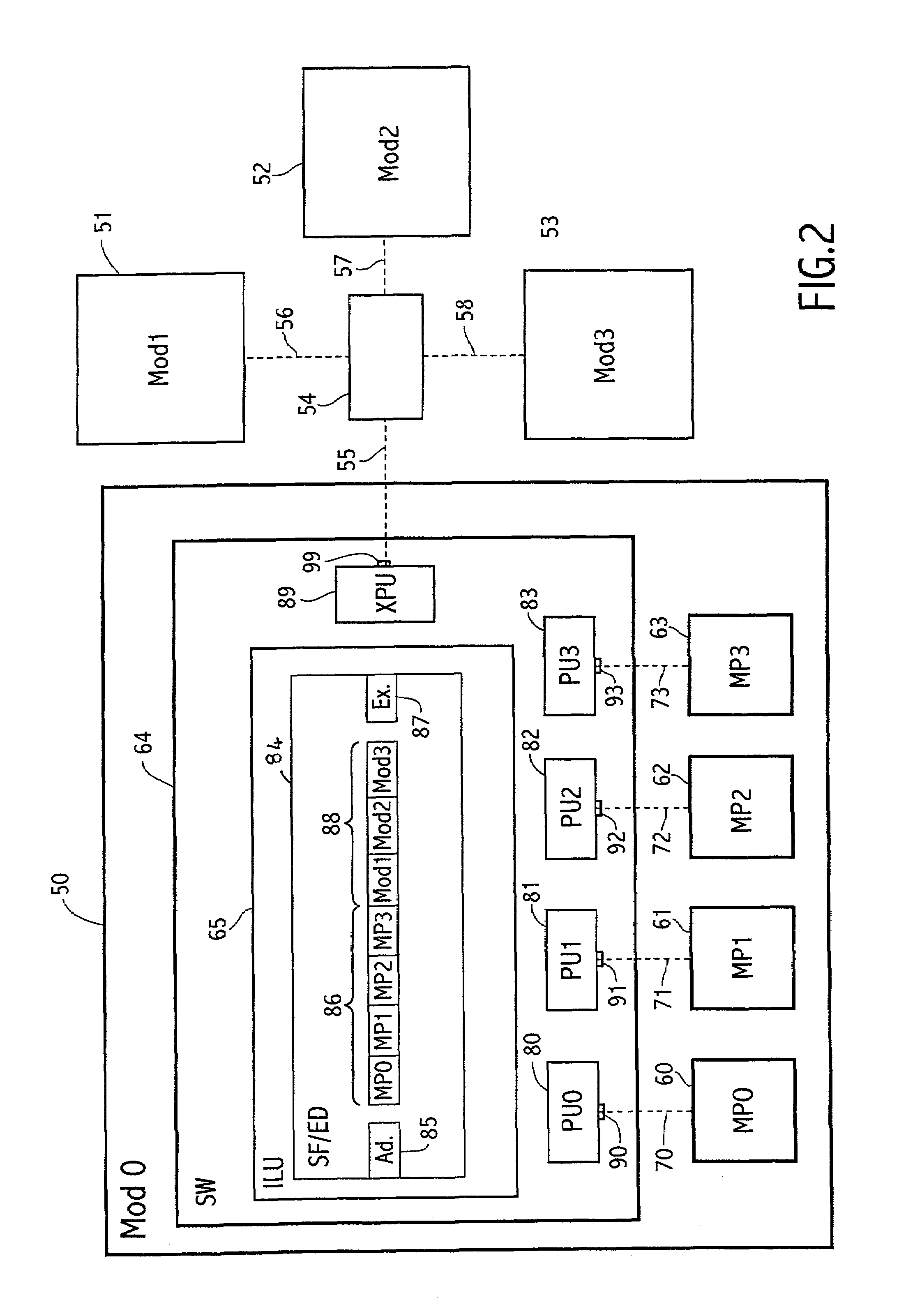
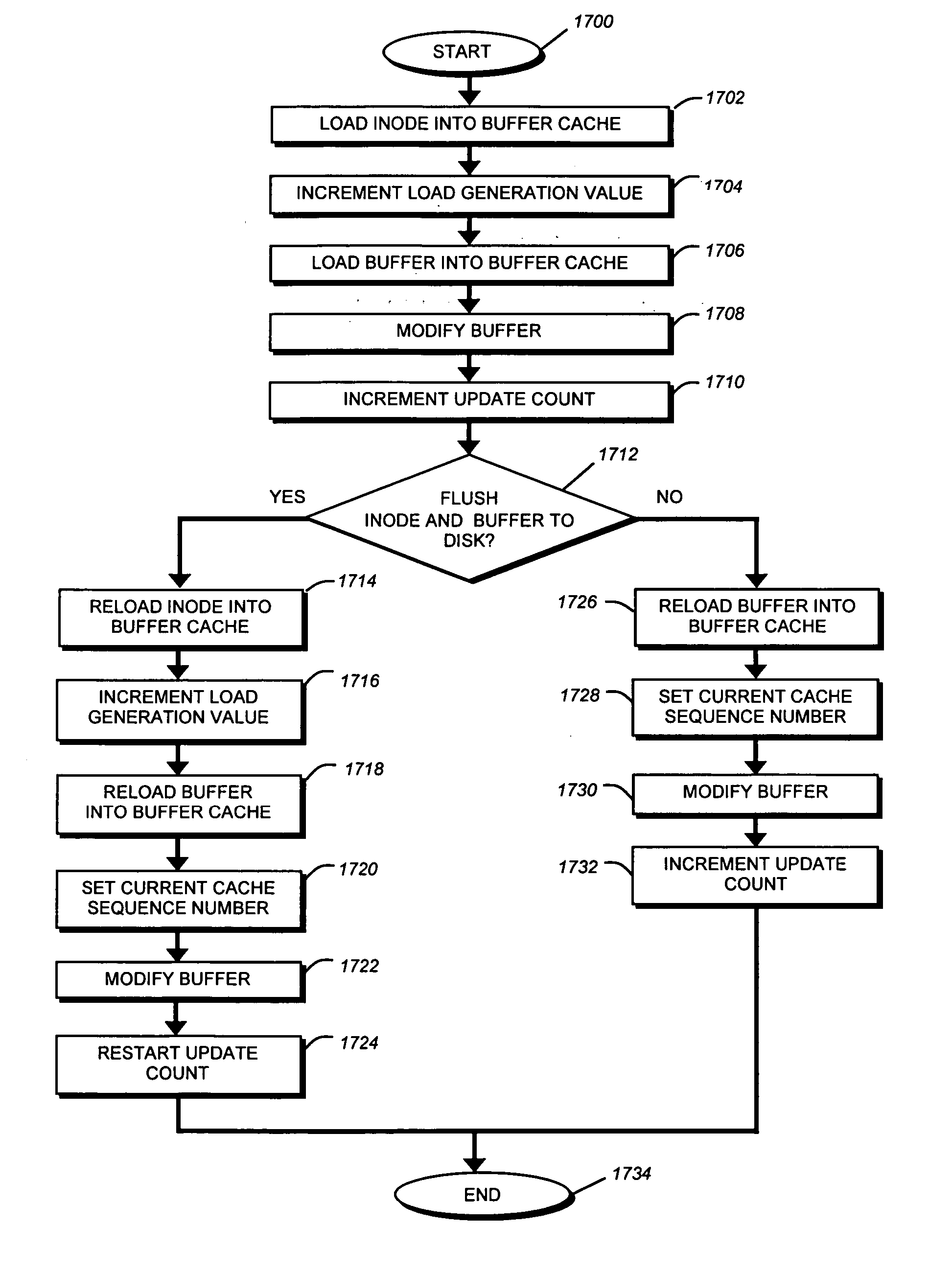
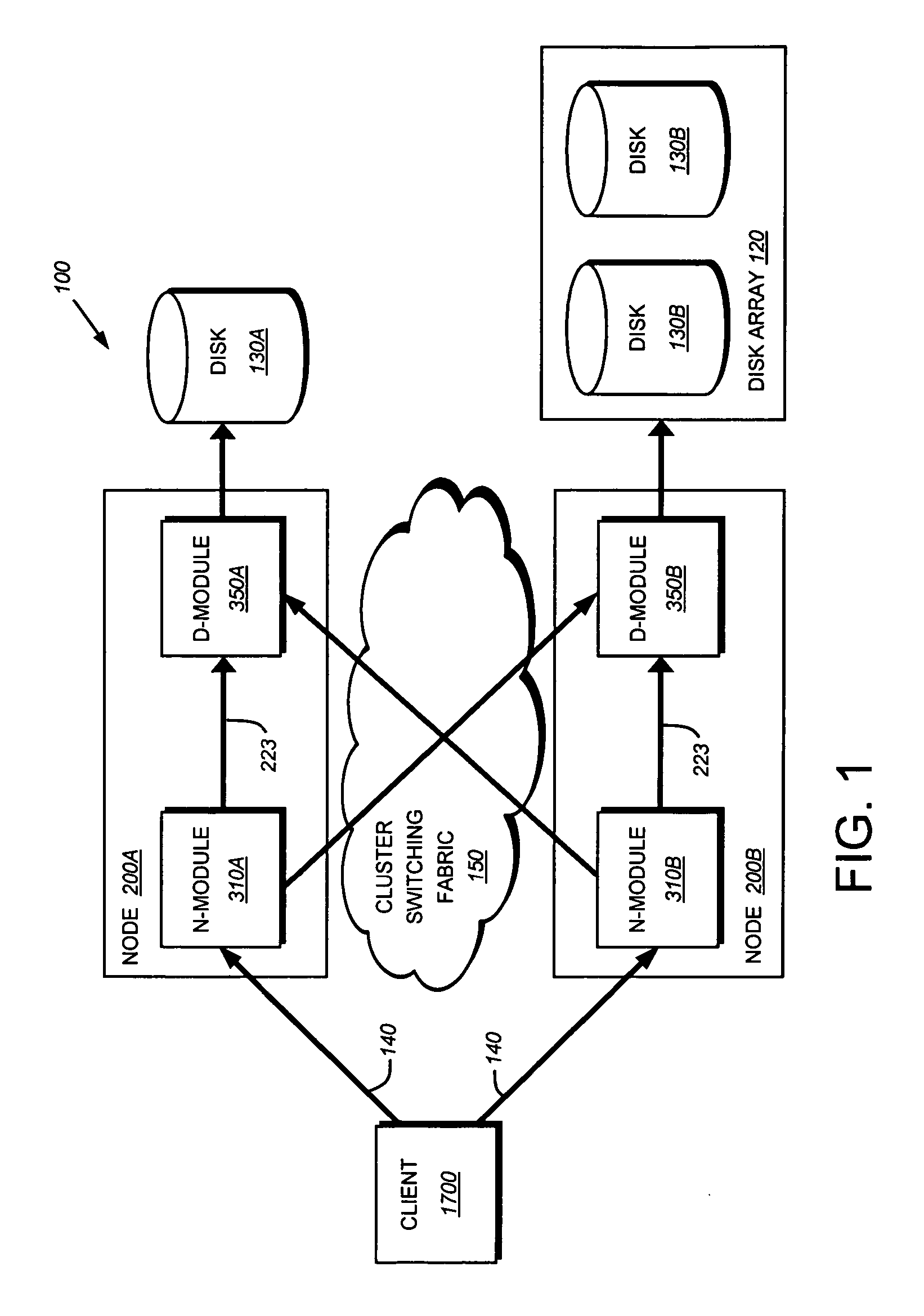
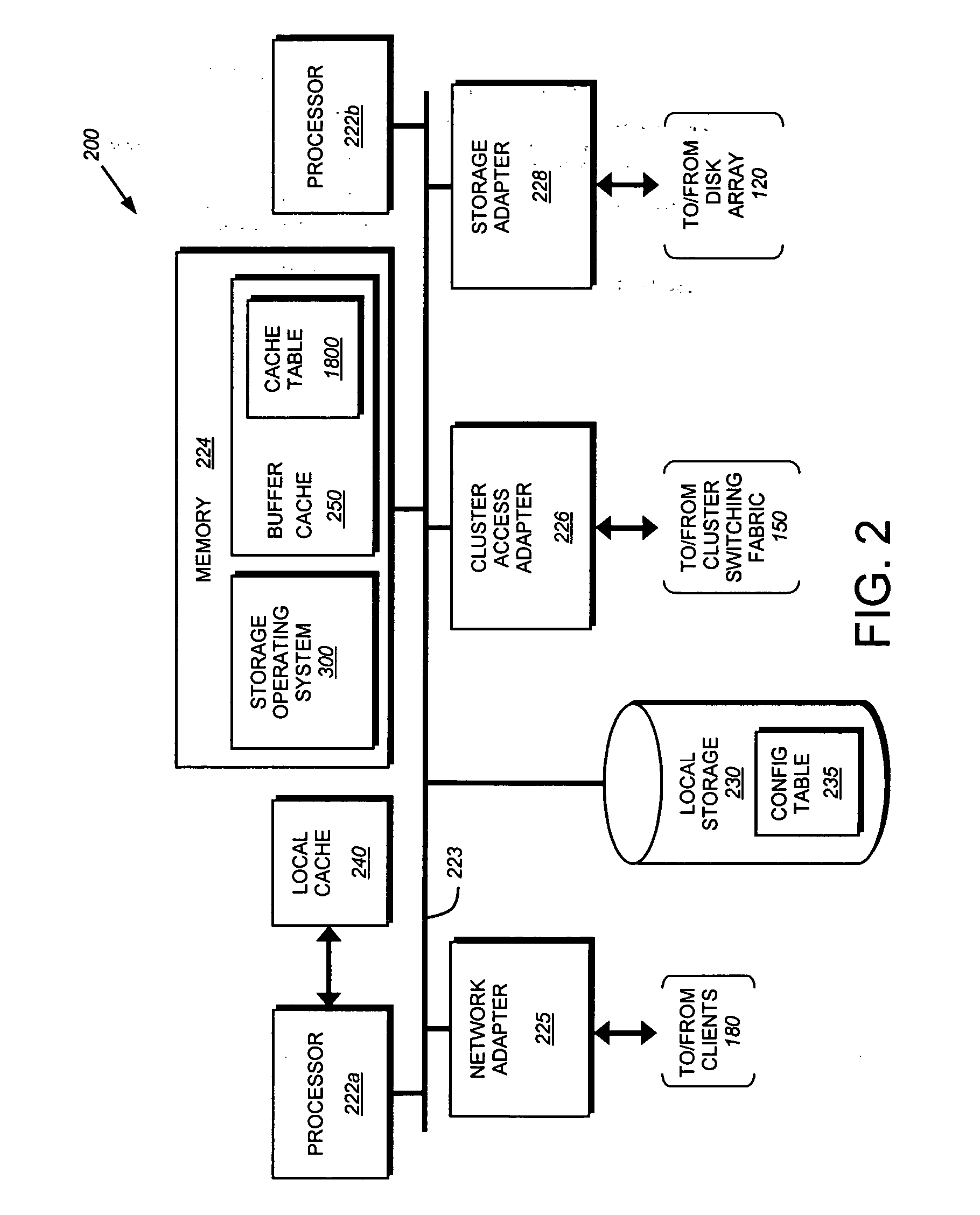
Lightweight coherency control protocol for clustered storage system
ActiveUS20070101069A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsLoad generationParallel computing
A lightweight coherency control protocol ensures consistency of data containers, such as a file, and associated data buffers stored on one or more volumes served by a plurality of nodes, e.g., storage systems, connected as a cluster. Each data buffer is associated with a current cache sequence number comprising a load generation value and an update count value. The load generation value is incremented every time an inode of a file is loaded into a memory of the storage system. Once the inode is loaded and its load generation value is set, then the appropriate buffer of a buffer tree for the file is loaded into the memory. The update count value is incremented each time the buffer is updated with a write request / operation. Therefore, each buffer loaded into memory is tagged with the load generation value and an update count from the time that buffer is loaded.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
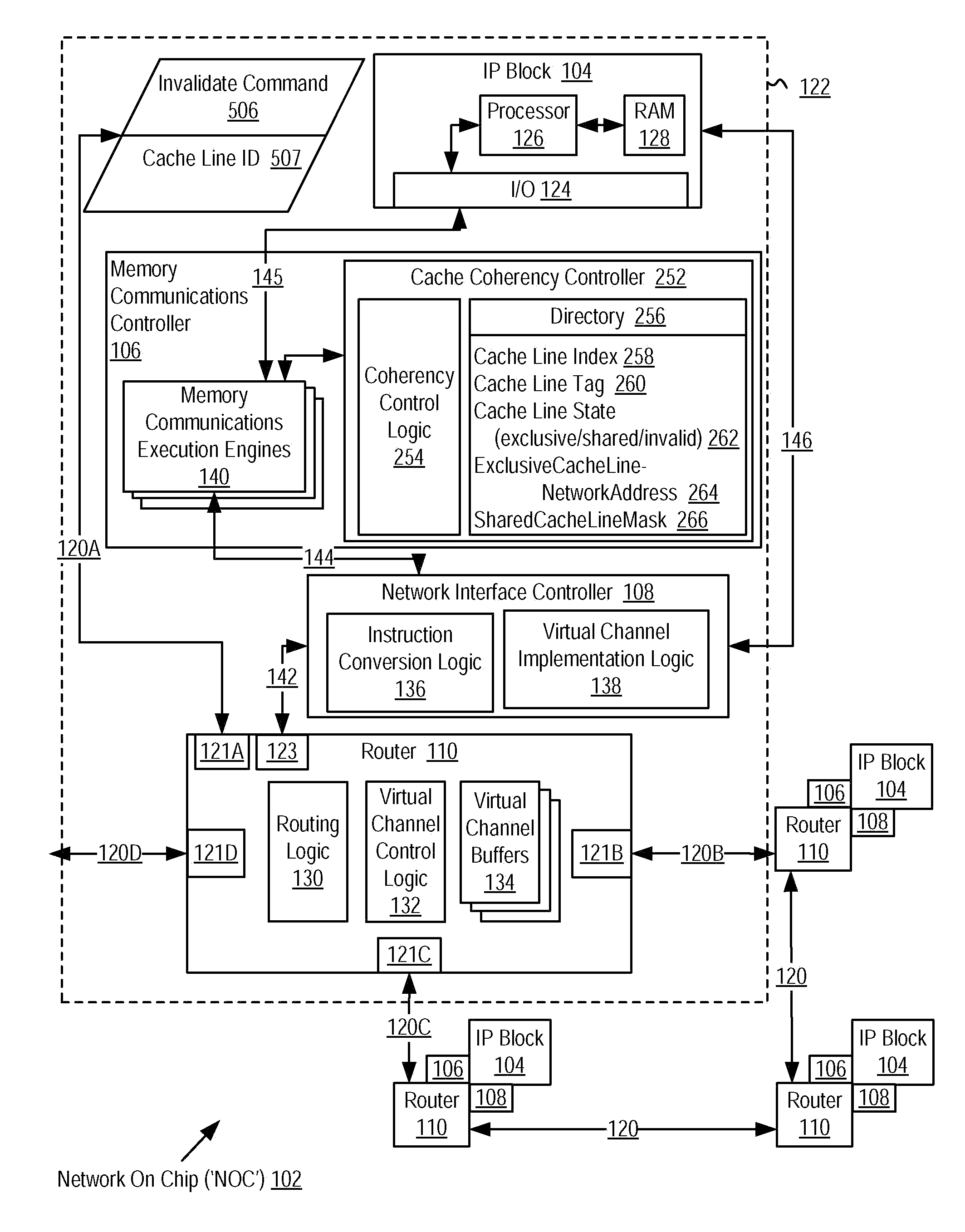
Network On Chip that Maintains Cache Coherency with Invalidate Commands
A network on chip (‘NOC’) that maintains cache coherency, the NOC including integrated processor (‘IP’) blocks, routers, memory communications controllers, and network interface controller, each IP block adapted to a router through a memory communications controller and a network interface controller, at least one memory communications controller further comprising a cache coherency controller each memory communications controller controlling communication between an IP block and memory, and each network interface controller controlling inter-IP block communications through routers, wherein the memory communications controller configured to execute a memory access instruction and configured to determine a state of a cache line addressed by the memory access instruction, the state of the cache line being one of shared, exclusive, or invalid; the memory communications controller configured to broadcast an invalidate command to a plurality of IP blocks of the NOC if the state of the cache line is shared; and the memory communications controller configured to transmit an invalidate command only to an IP block that controls a cache where the cache line is stored if the state of the cache line is exclusive.
Owner:IBM CORP
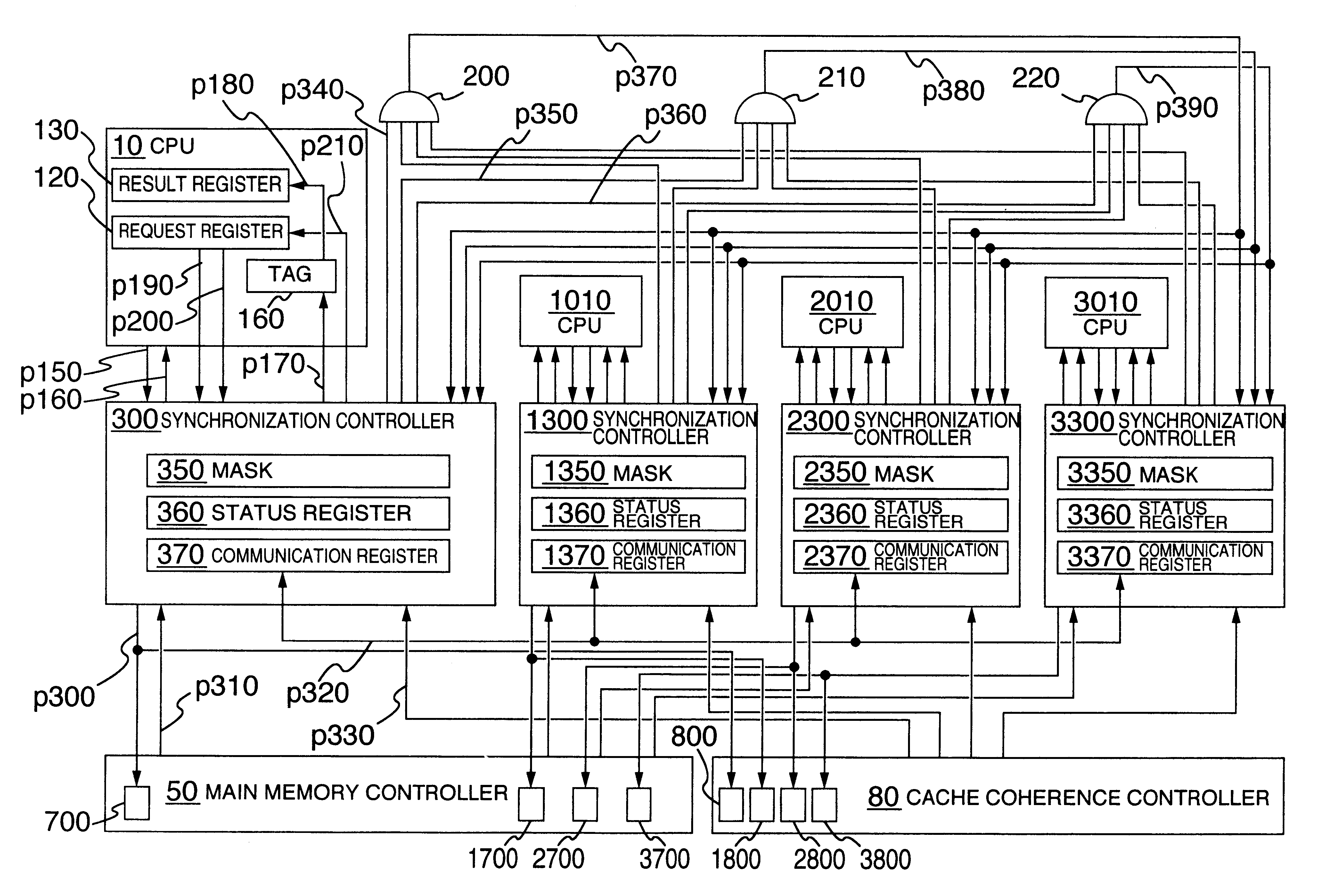
Multiprocessor synchronization and coherency control system
InactiveUS6466988B1Program synchronisationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory typeConnection type
A shared main memory type multiprocessor is arranged to have a switch connection type. The multiprocessor prepares an instruction for outputting a synchronization transaction. When each CPU executes this instruction, after all the transactions of the preceding instructions are output, the synchronization transaction is output to the main memory and the coherence controller. By the synchronization transaction, the main memory serializes the memory accesses and the coherence controller guarantees the completion of the cache coherence control. This makes it possible to serialize the memory accesses and guarantee the completion of the cache coherence control at the same time.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Compositions and methods including formate brines for conformance control
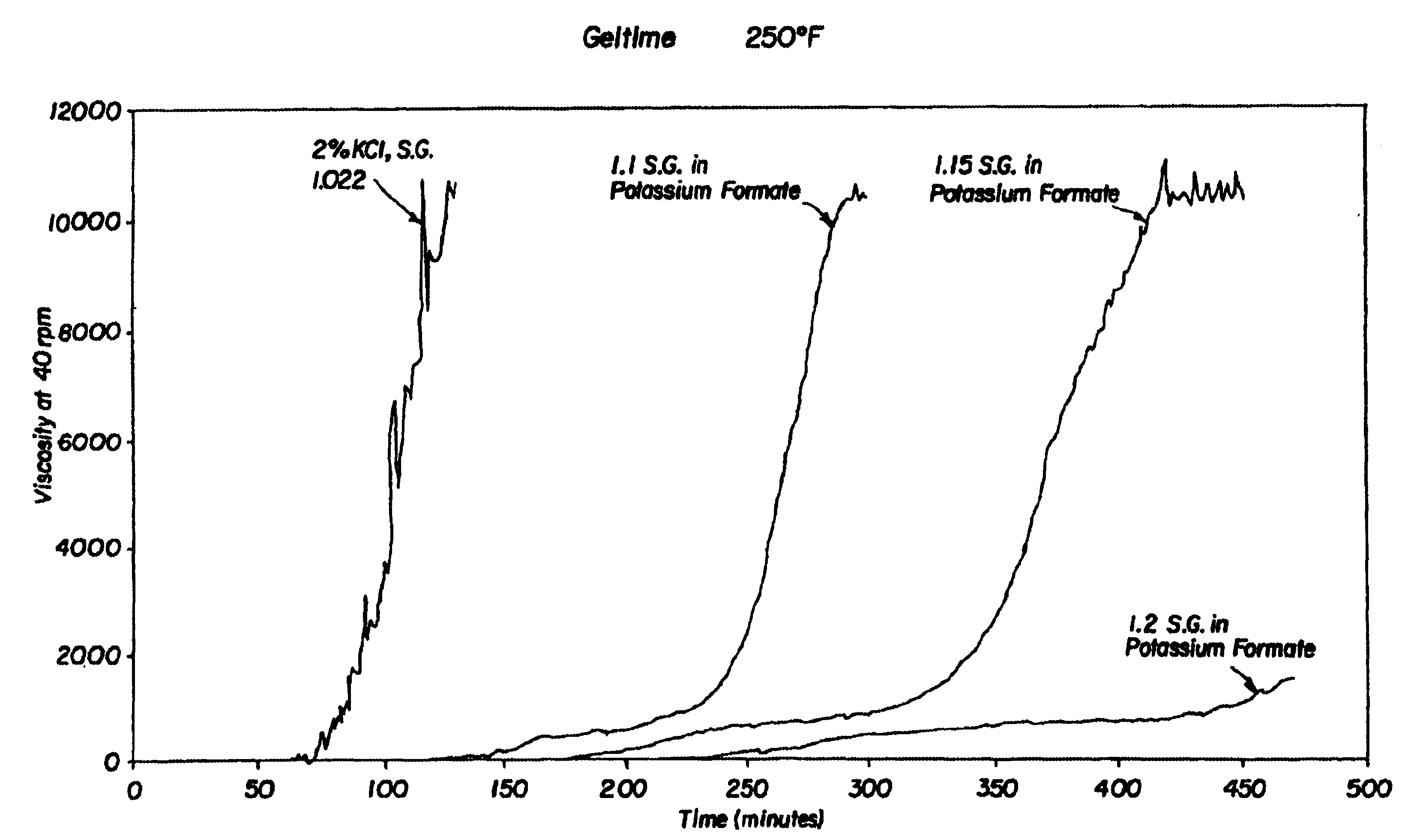
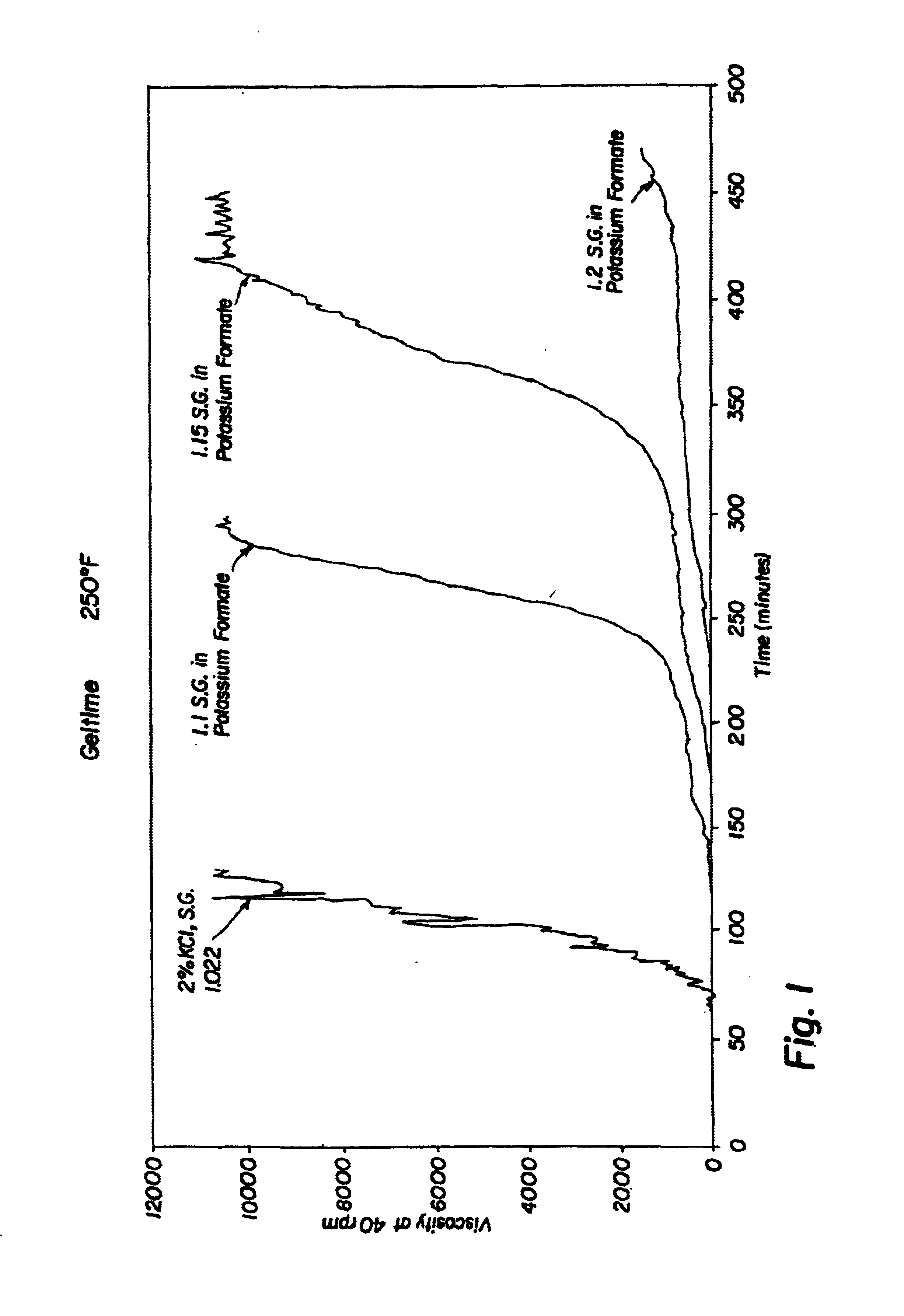
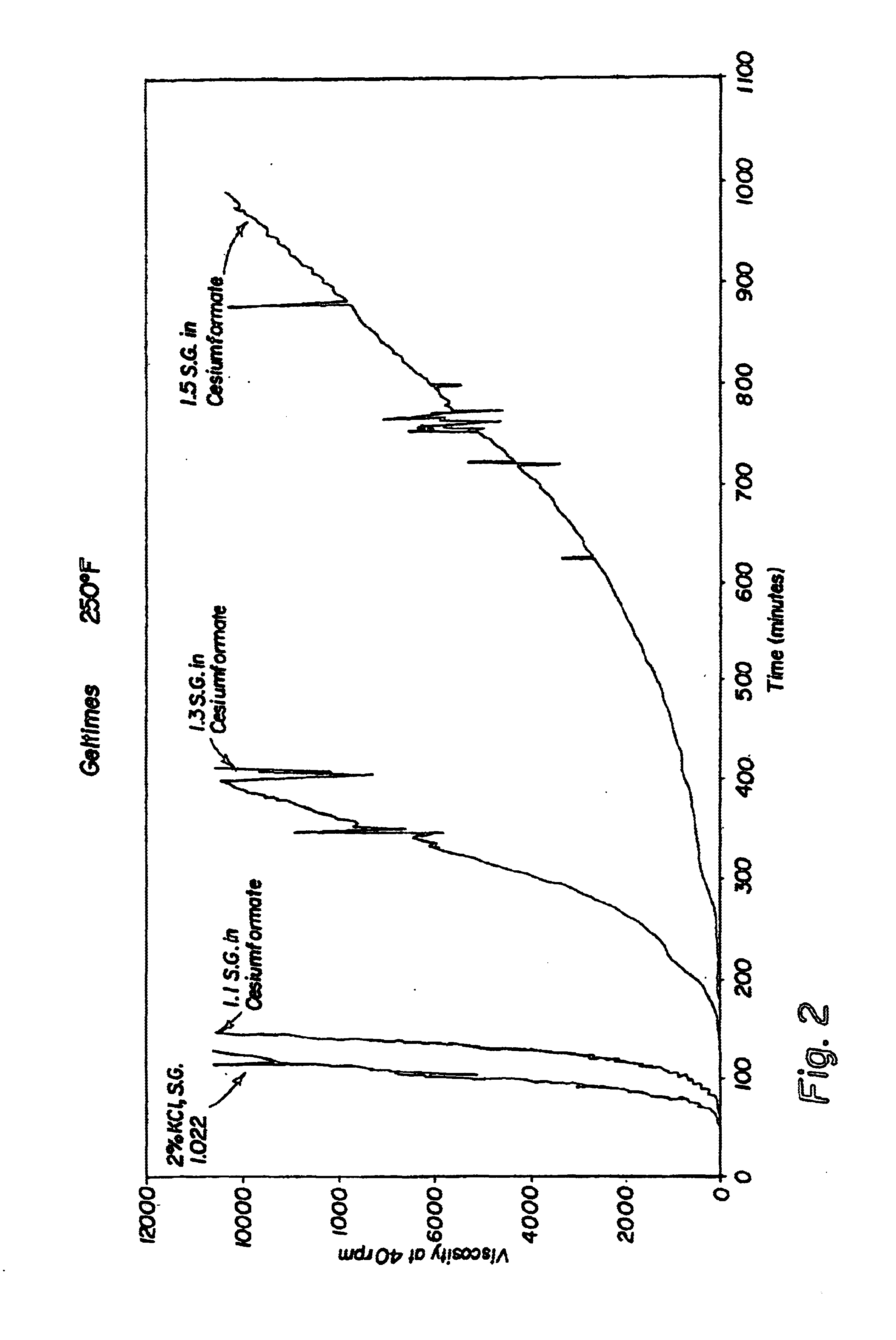
Compositions and methods are provided for reducing the permeability of subterranean zones. More particularly, water-soluble polymeric compositions which form cross-linked gels in the zones. In general, the composition comprises (a) at least one water-soluble polymer; (b) at least one organic gelling agent capable of cross-linking the water-soluble polymer; and (c) at least one water-soluble formate. More preferably, the water-soluble polymer is a copolymer of (i) at least one non-acidic ethylenically unsaturated polar monomer, and (ii) at least one copolymerisable ethylenically unsaturated ester. The gelling agent is preferably selected from the group consisting of a polyalkyleneimine, polyfunctional aliphatic amine, an aralkylamine, and a heteroaralkylamine. The preferred water-soluble formate is selected from the group consisting of ammonium formate, lithium formate, sodium formate, potassium formate, rubidium formate, cesium formate, and francium formate. Water is used to make an aqueous composition prior to use in a subterranean formation. The methods of this invention for reducing the permeability of a subterranean zone are comprised of the steps of introducing an aqueous composition according to the invention into a subterranean zone, and then allowing the aqueous composition to form a cross-linked gel in the zone. Preferably, the method includes the step of subsequently producing hydrocarbons from the subterranean formation.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Methods and compositions for conformance control using temperature-triggered polymer gel with magnetic nanoparticles
InactiveUS20150159079A1Low viscosityEnhanced overall recoveryElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyProduction rateMedicine
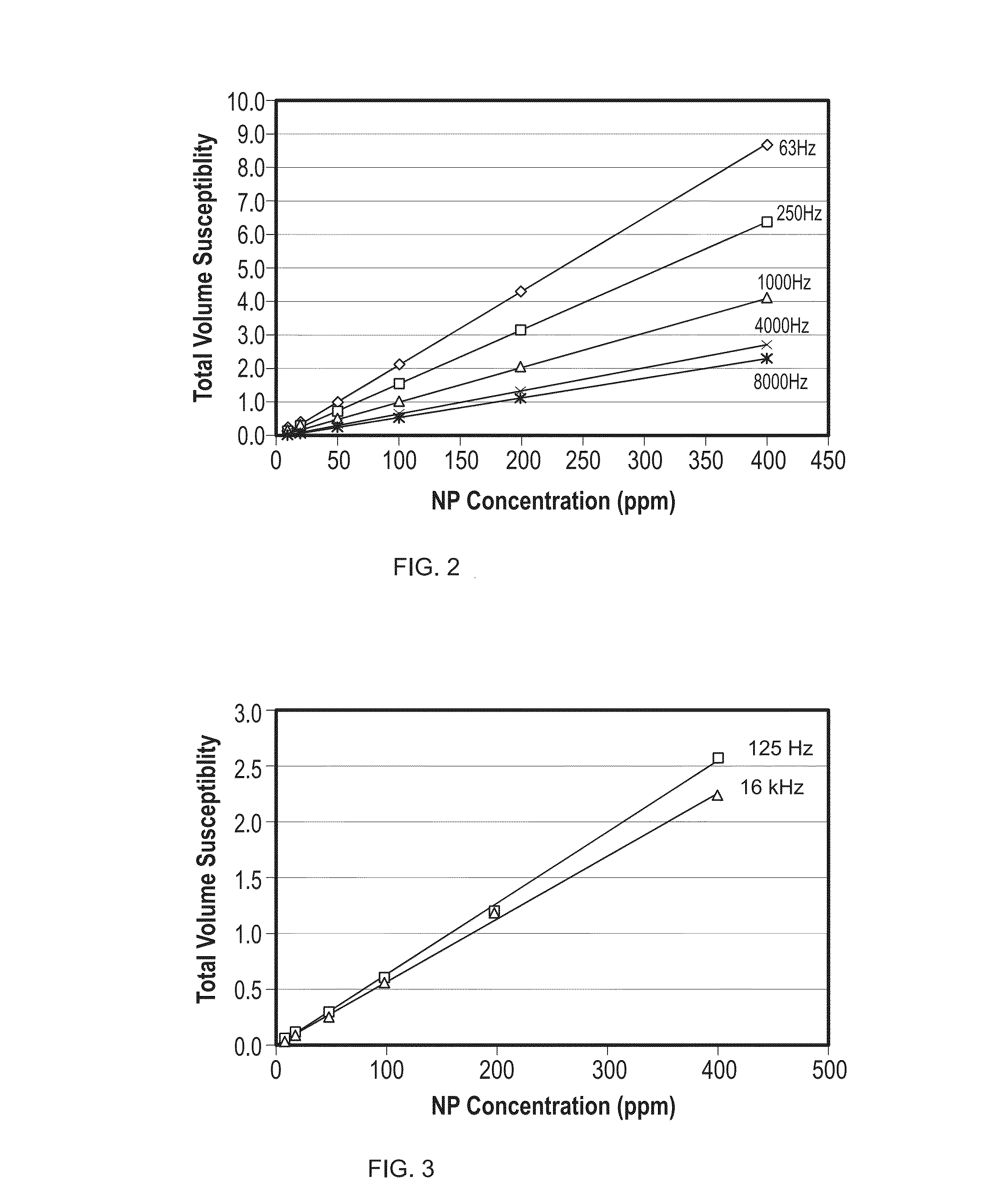
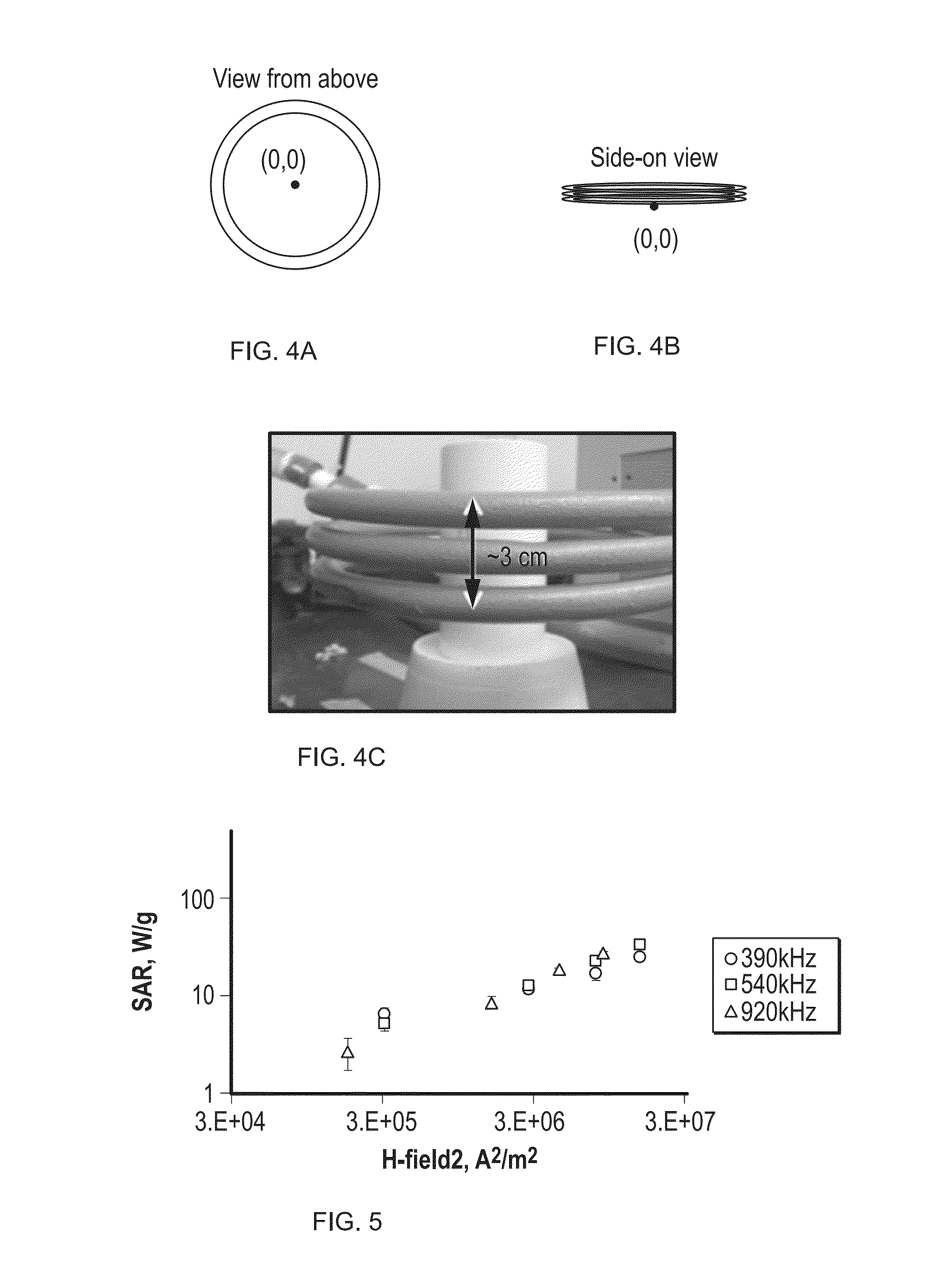
The present disclosure provides a polymer gel and method of making and using the same for use in high-permeability layers. This precision conformance control is accomplished by using paramagnetic nanoparticles and the application of the magnetic oscillation of prescribed frequency at the wellbore. If the polymer gel were created unintentionally at a certain layer, or there is a need to remove the gel blockage at the later stage of oil production, the gel could be broken and removed to restore the productivity from the layer.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
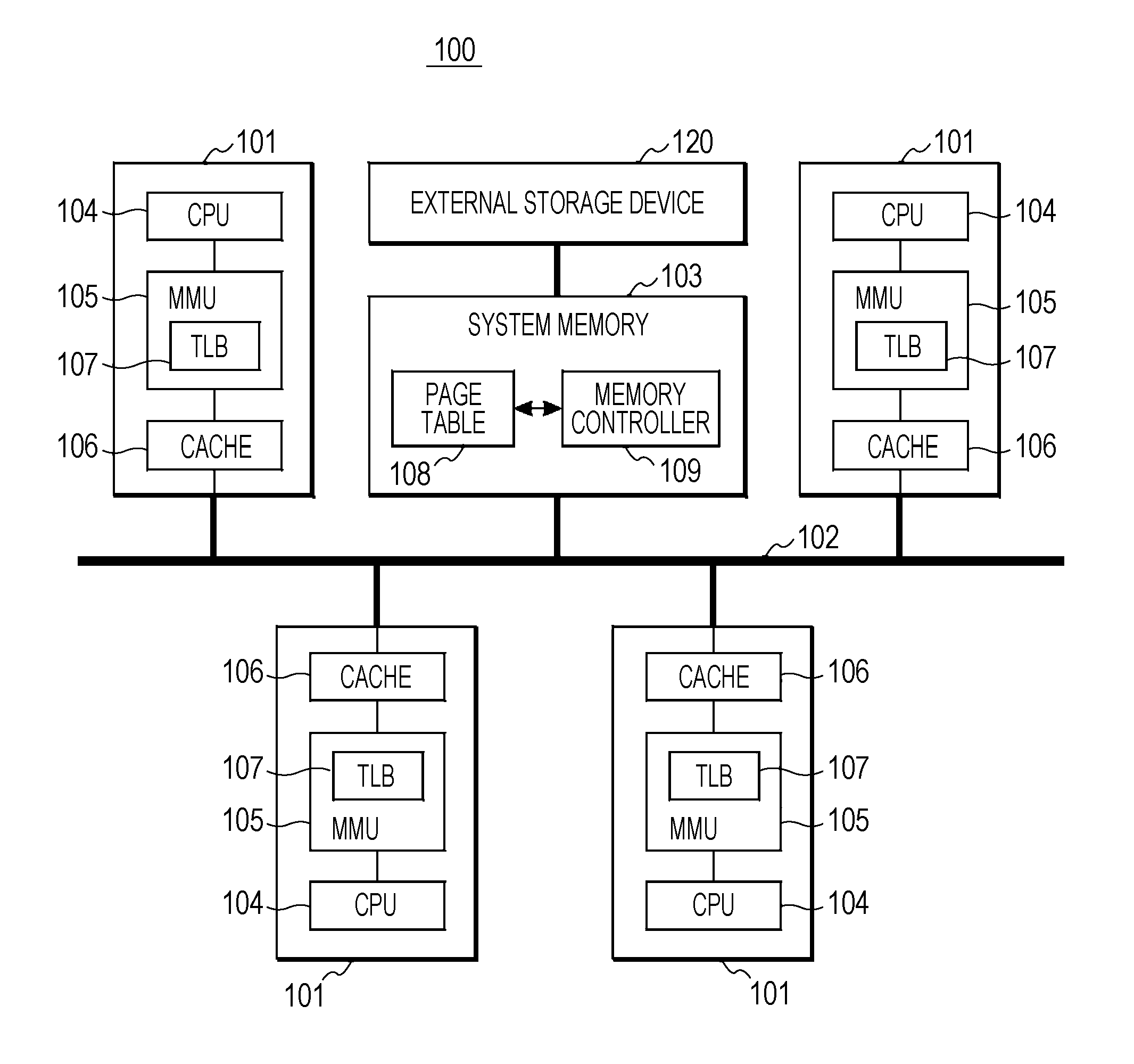
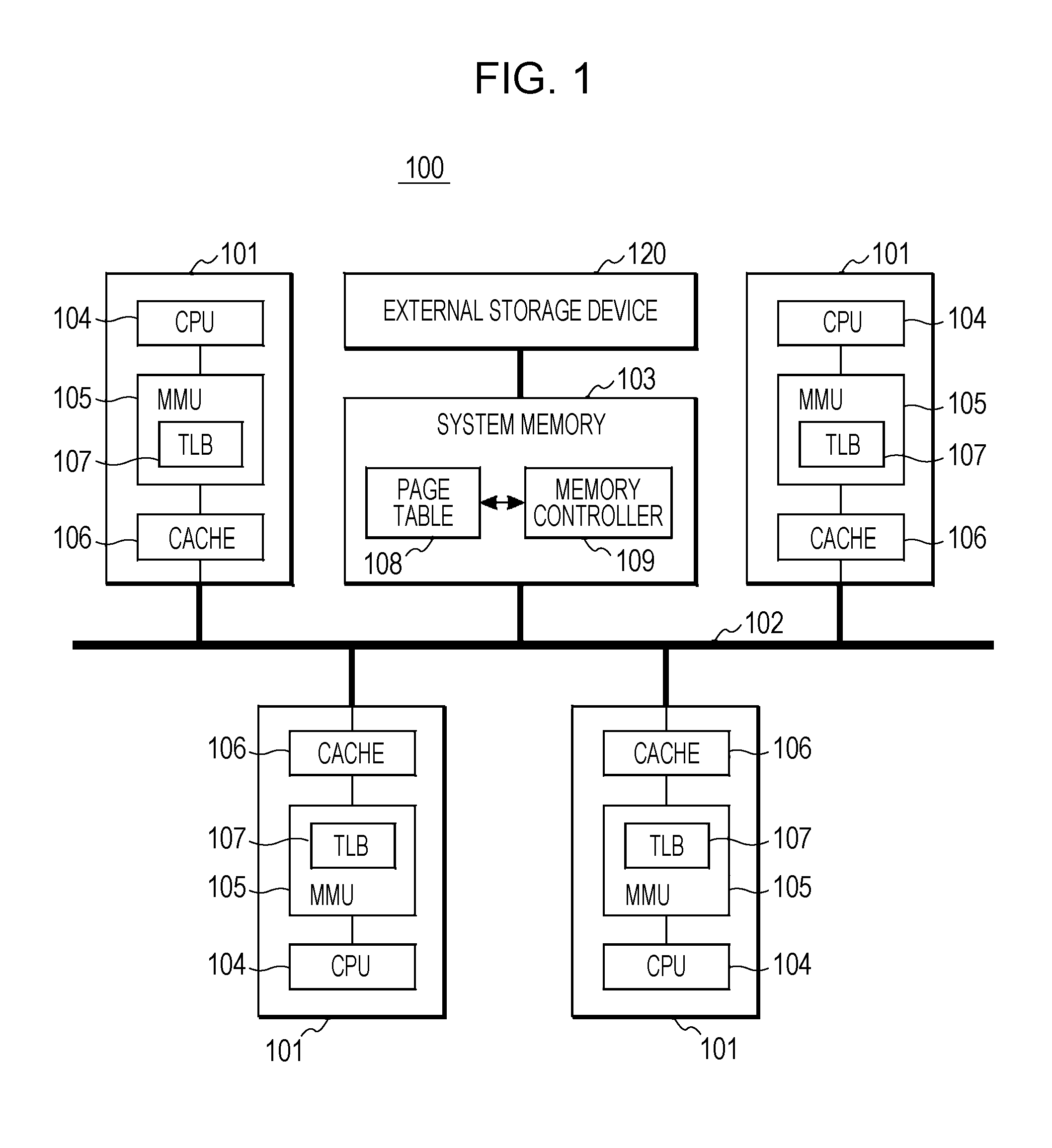
Non-uniform memory access (NUMA) data processing system having a page table including node-specific data storage and coherency control
InactiveUS6658538B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMultiple digital computer combinationsData processing systemPhysical address
A non-uniform memory access (NUMA) data processing system includes a plurality of nodes coupled to a node interconnect. The plurality of nodes contain a plurality of processing units and at least one system memory having a table (e.g., a page table) resident therein. The table includes at least one entry for translating a group of non-physical addresses to physical addresses that individually specifies control information pertaining to the group of non-physical addresses for each of the plurality of nodes. The control information may include one or more data storage control fields, which may include a plurality of write through indicators that are each associated with a respective one of the plurality of nodes. When a write through indicator is set, processing units in the associated node write modified data back to system memory in a home node rather than caching the data. The control information may further include a data storage control field comprising a plurality of non-cacheable indicators that are each associated with a respective one of the plurality of nodes. When a non-cacheable indicator is set, processing units in the associated node are instructed to not cache data associated with non-physical addresses within the group translated by reference to the table entry. The control information may also include coherency control information that individually indicates for each node whether or not inter-node coherency for data associated with the table entry will be maintained with software support.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
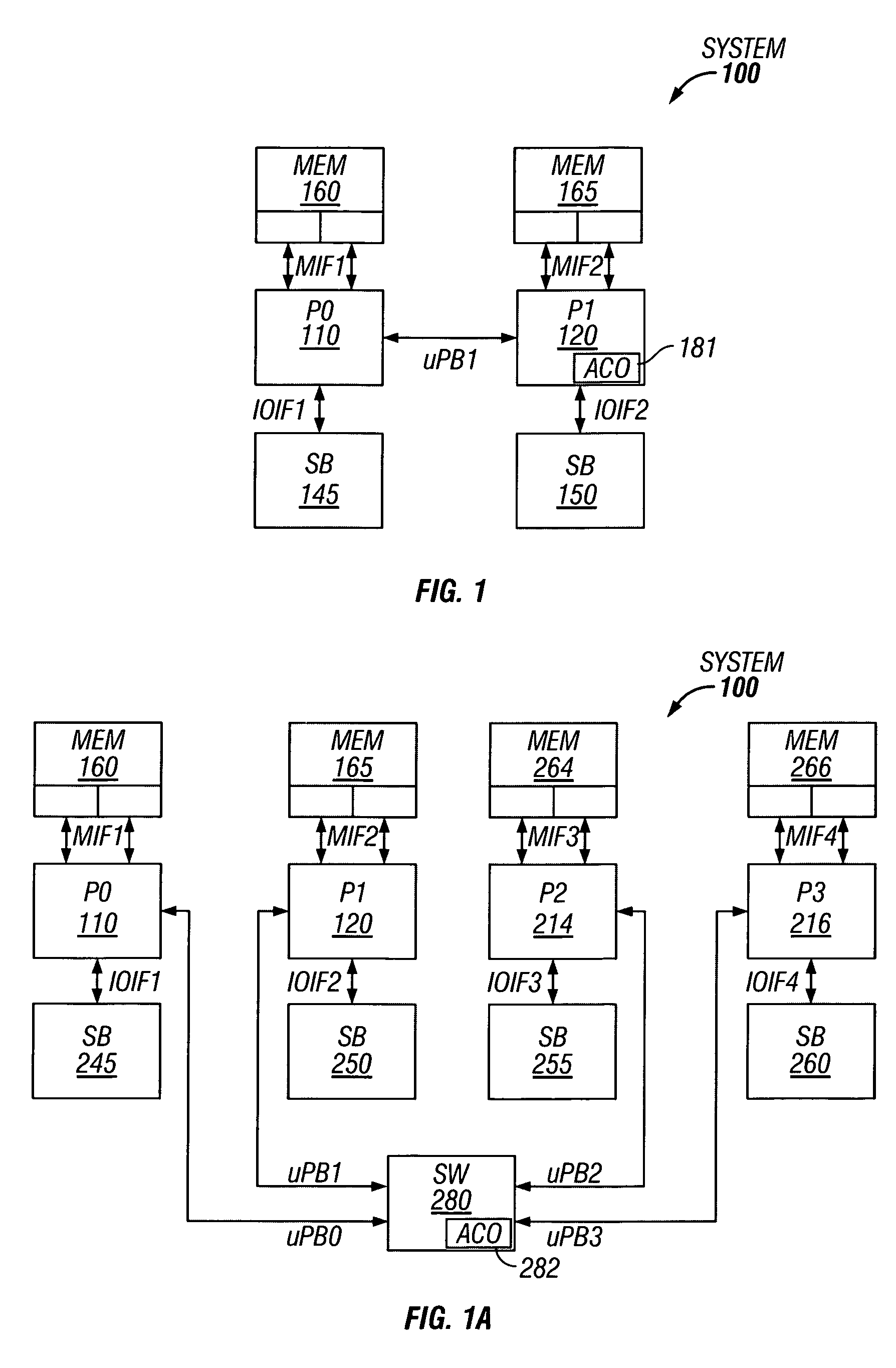
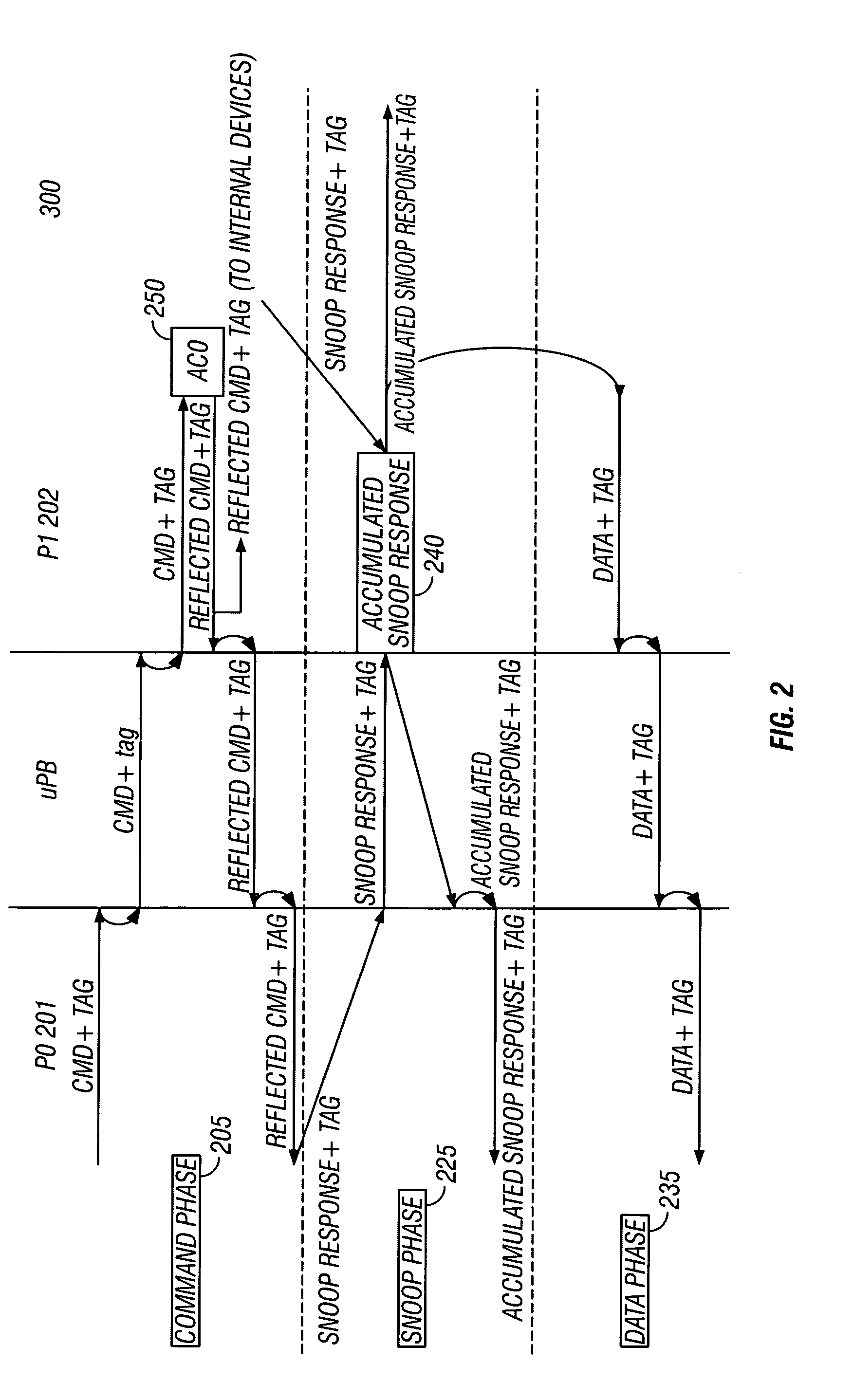
Method for supporting improved burst transfers on a coherent bus
In a multiprocessor system, comprising master and slave processors, a cache coherency controller, and address concentration devices; a method for improving coherent data transfers is described. A command transaction is generated, and a subsequent command from an initiator. Tags added to the responses or further request responses, stream on high-speed busses. Snoops and accumulated snoops expand on cacheline requests as each processor separates burst commands into multiple cacheline requests. Address concentrators containing a cacheline queue function, funnel transaction requests to a global serialization device, where a queuing process prioritizes indicia and coordinates the results among the processors. The cache issues a single burst command for each affected line. System coherency, performance, and latency improvements occur. Additional support for burst transfers between coherent processors is provided.
Owner:INTEL CORP
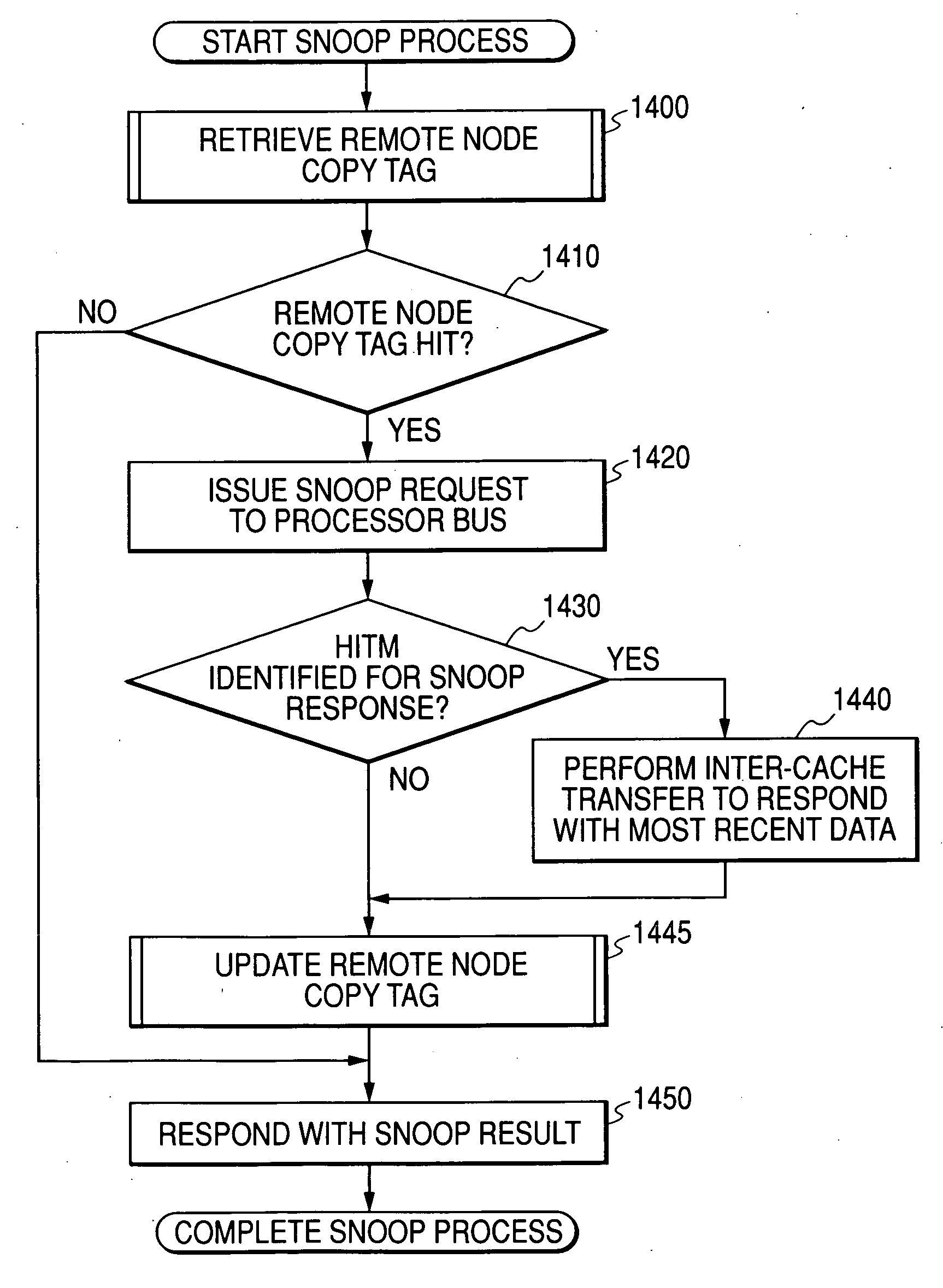
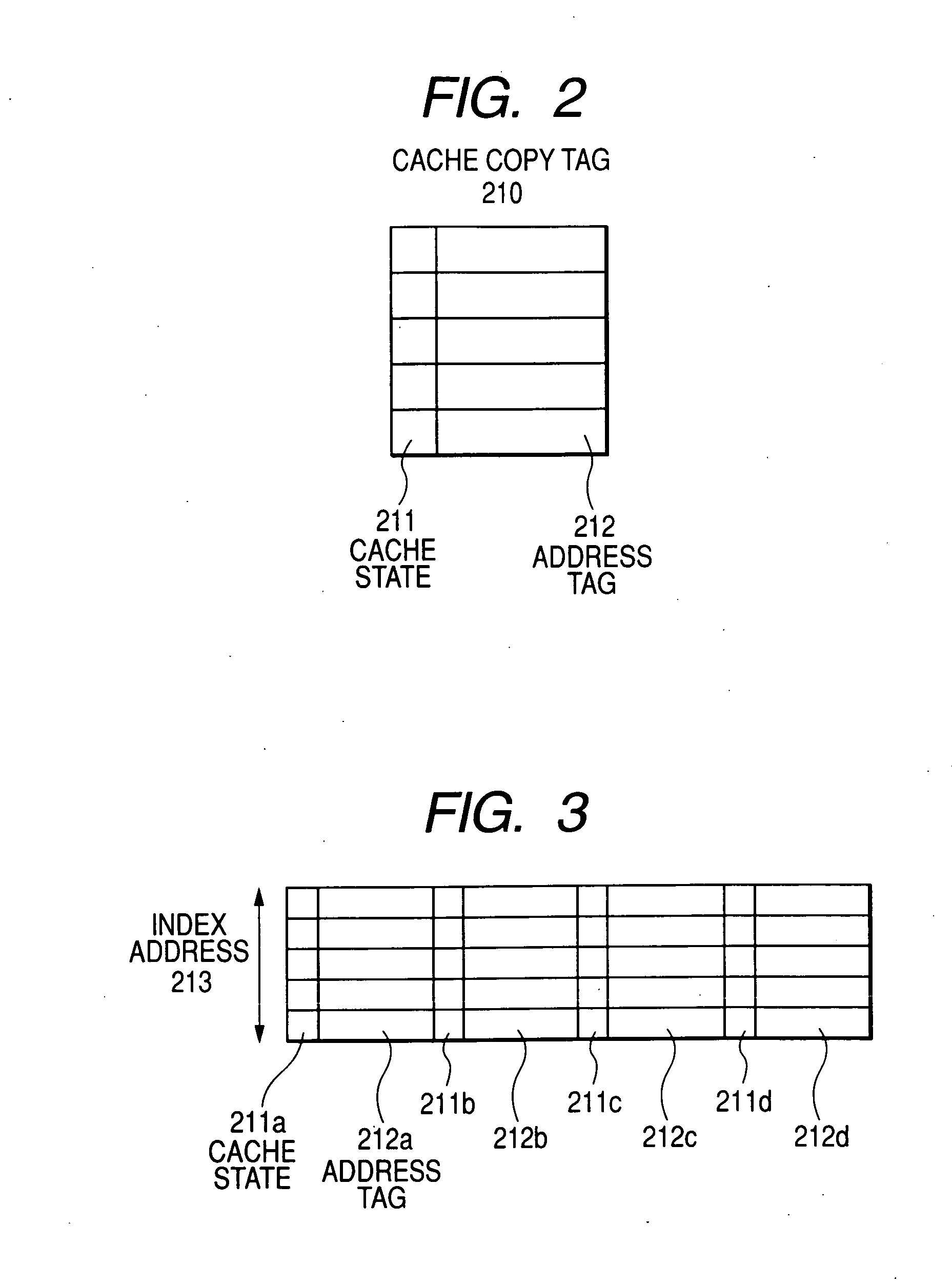
Cache coherency control method, chipset, and multi-processor system
In a multi-processor system, counting snoop results bottlenecks the broadcast-based snoop protocol. The directory-based protocol delays the latency when remote node caches data. There is a need for shortening the memory access latency using a snoop and cache copy tag information. When the local node's cache copy tag information is available, the memory access latency can be shortened by omitting a process to count snoop results. When memory position information is used to update the cache copy tag during cache replacement, it is possible to increase a ratio to hit a copy tag during reaccess from the local node.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
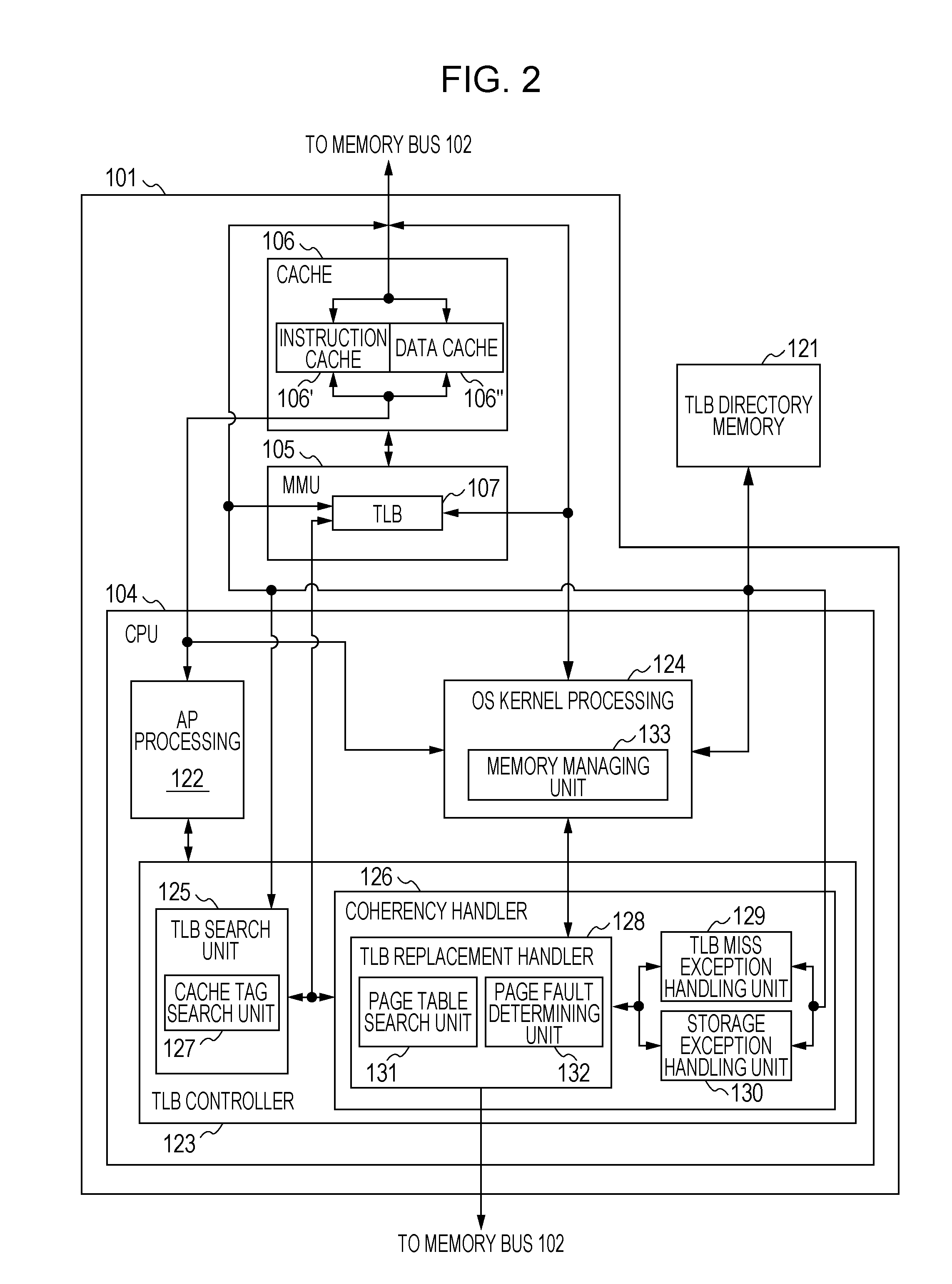
Cache coherency control method, system, and program
InactiveUS20120137079A1Improve scalabilityMeet cost performance requirementsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInformation processingMulti processor
In a system for controlling cache coherency of a multiprocessor system in which a plurality of processors share a system memory, each of the plurality of processors including a cache and a TLB, the processor includes a TLB controller including a TLB search unit that performs a TLB search and a coherency handler that performs TLB registration information processing when no hit occurs in the TLB search and a TLB interrupt occurs. The coherency handler includes a TLB replacement handler that searches a page table in the system memory and that replaces the TLB registration information, a TLB miss exception handling unit, and a storage exception handling unit.
Owner:IBM CORP
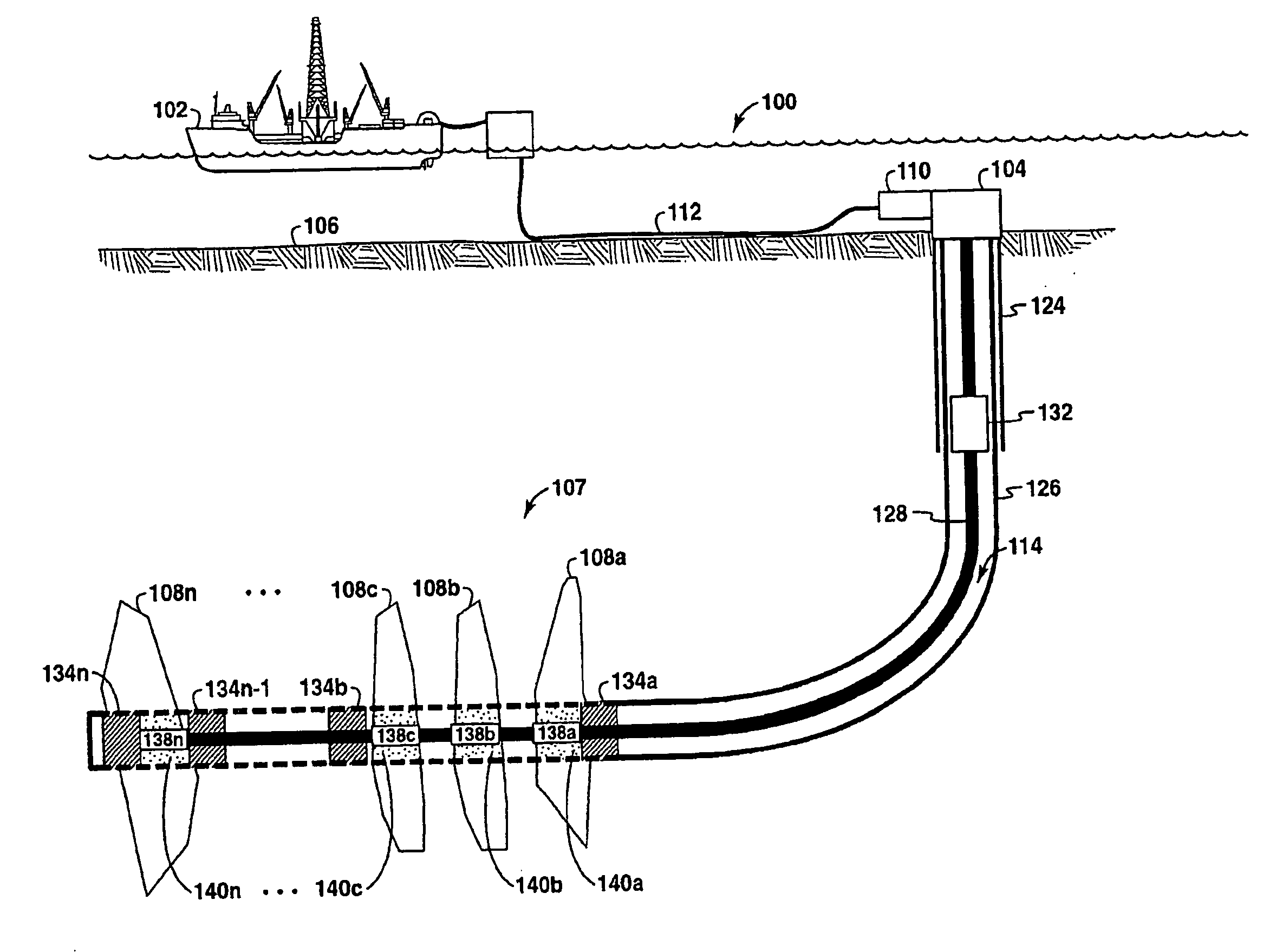
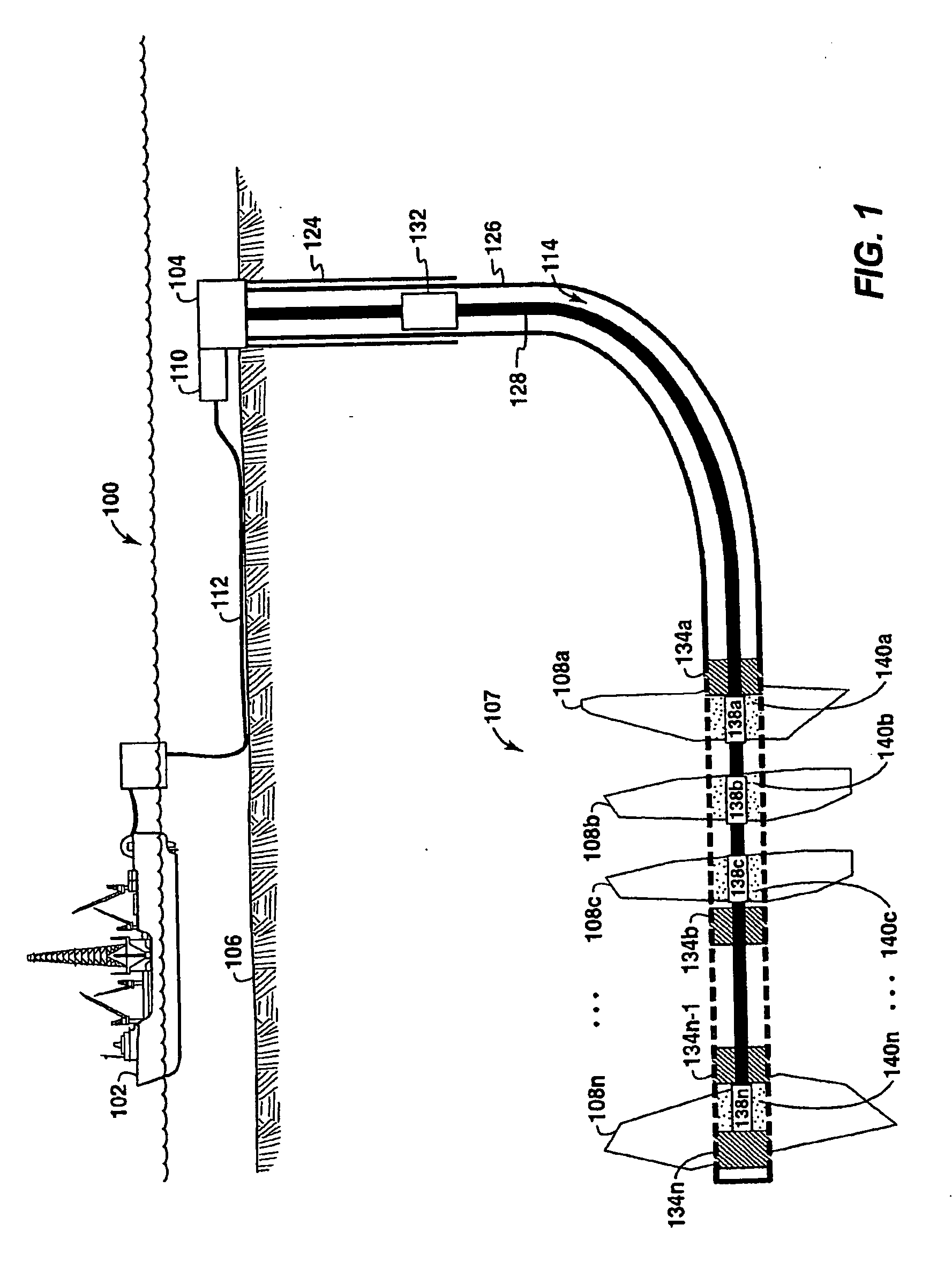
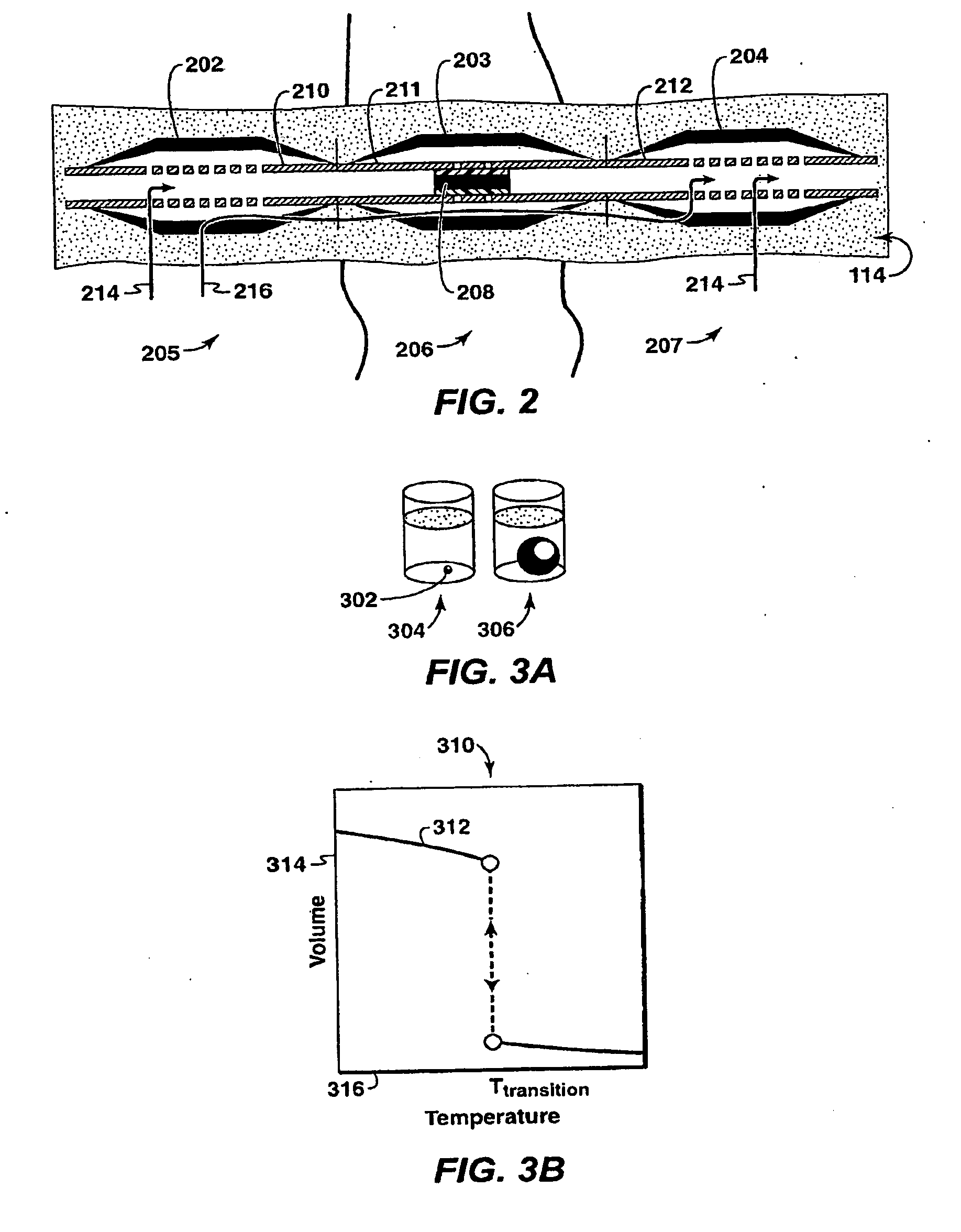
Conformance Control Through Stimulus-Responsive Materials
A method, apparatus and production well system that utilize stimulus-responsive materials for “conformance control” and profile control along the fluid flow path in a well as part of a gravel pack or a coating on a well tool. The stimulus-responsive materials are also known as intelligent or smart polymers and are typically polymeric materials that reversibly or irreversibly swell or collapse in the presence of stimulus such as changes in concentration of a fluid media in contact with the stimulus-responsive material, pH or polarity of the media the stimulus-responsive material is in contact with, salinity, current; or temperature. The stimulus-responsive materials may swell upon contact with a rust stimulus and shrink or collapse upon contact with a second stimulus or vice-versa The changes between production and injection profiles may be automatic with the application of the stimulus-responsive materials and may occur without user intervention.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
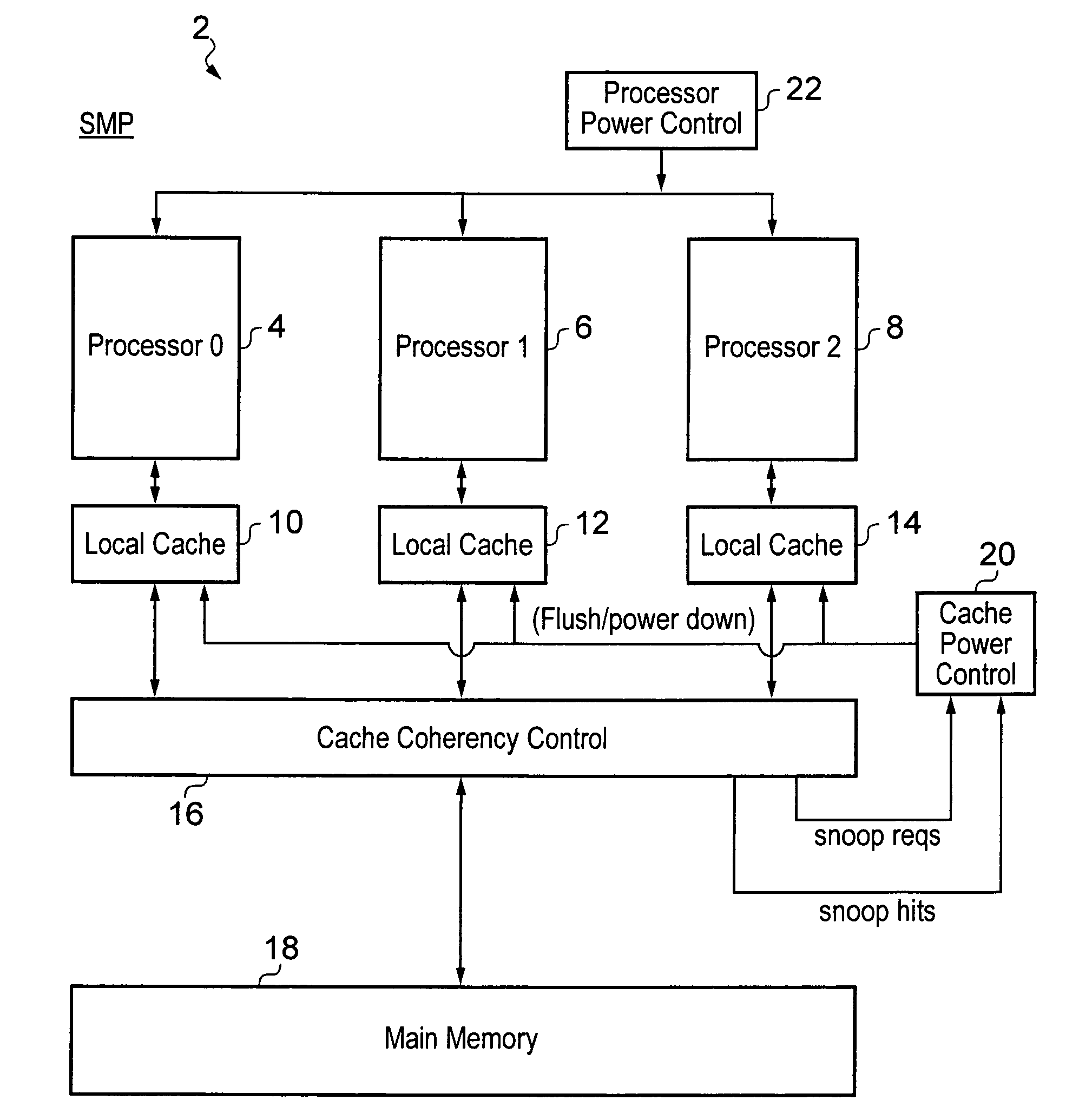
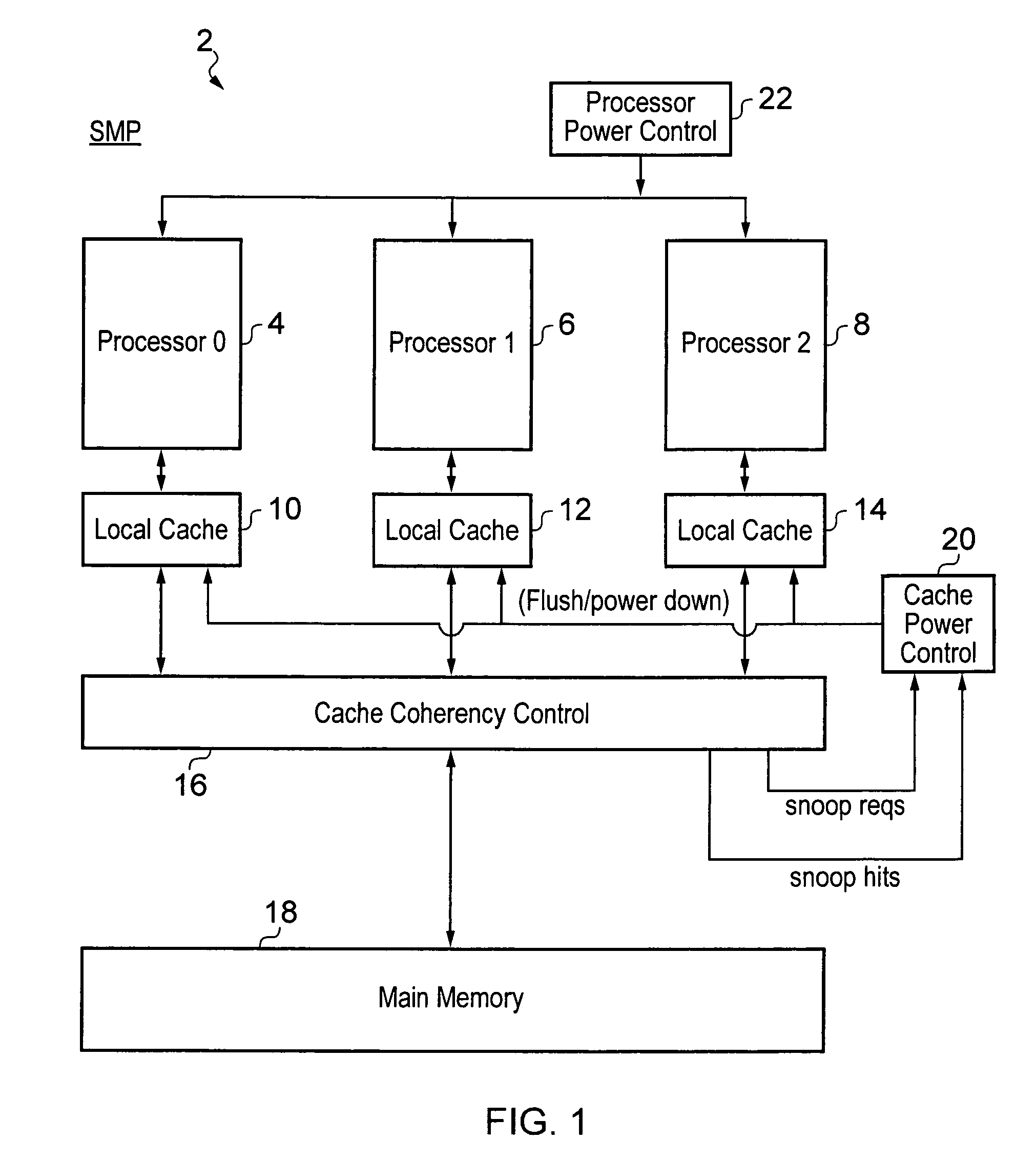
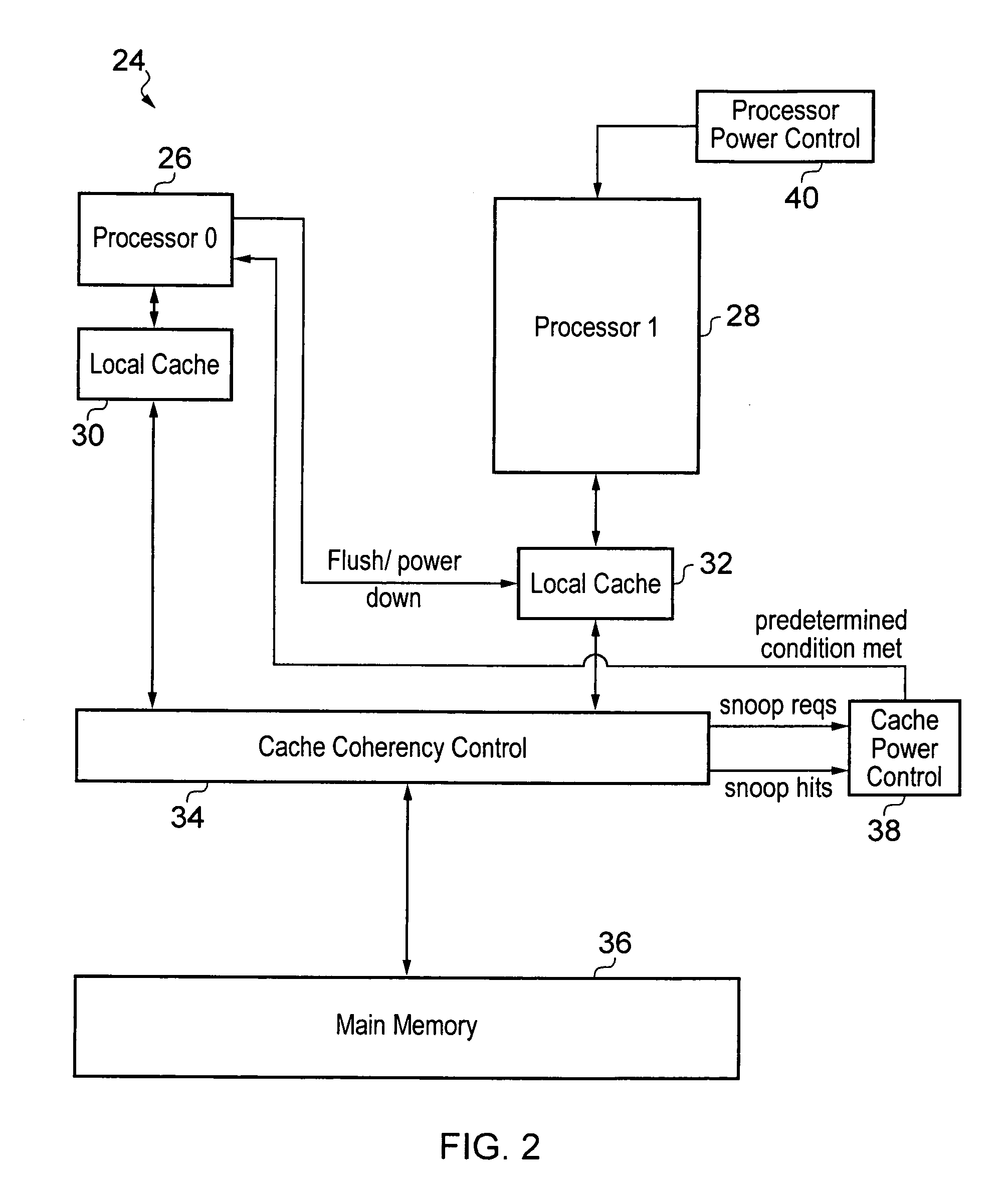
Local cache power control within a multiprocessor system
ActiveUS20100185821A1Great degreeMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData processing systemMulti processor
A data processing system including a plurality of processors 4, 6, 8 each having a local cache memory 10, 12, 14 is provided. A cache coherency controller 16 serves to maintain cache coherency between the local cache memories 10, 12, 14. When one of the processors 4, 6, 8 is placed into a low power state its associated local cache memory 10, 12, 14 is maintained in a state in which the data it is holding is accessible to the cache coherency controller 16 until a predetermined condition has been met whereupon the local cache memory 10, 12, 14 concerned is placed into a low power state. The predetermined condition can take a variety of different forms such as the rate of snoop hits falling below a threshold value, the ratio of snooping hits to snoop requests falling below a threshold value, a predetermined number of clock cycles passing since the associated processor for that local cache memory was powered down as well as other possibilities.
Owner:ARM LTD
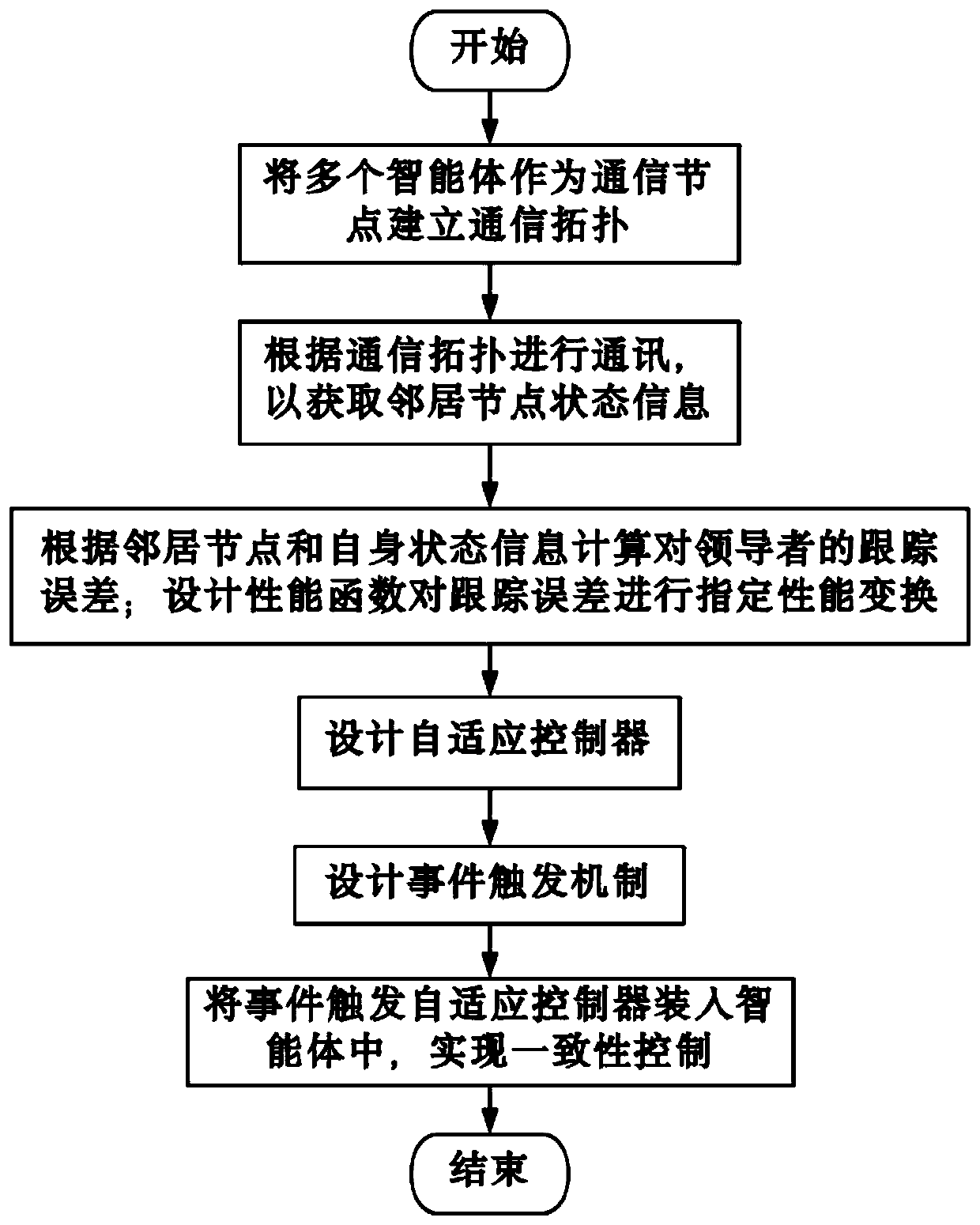
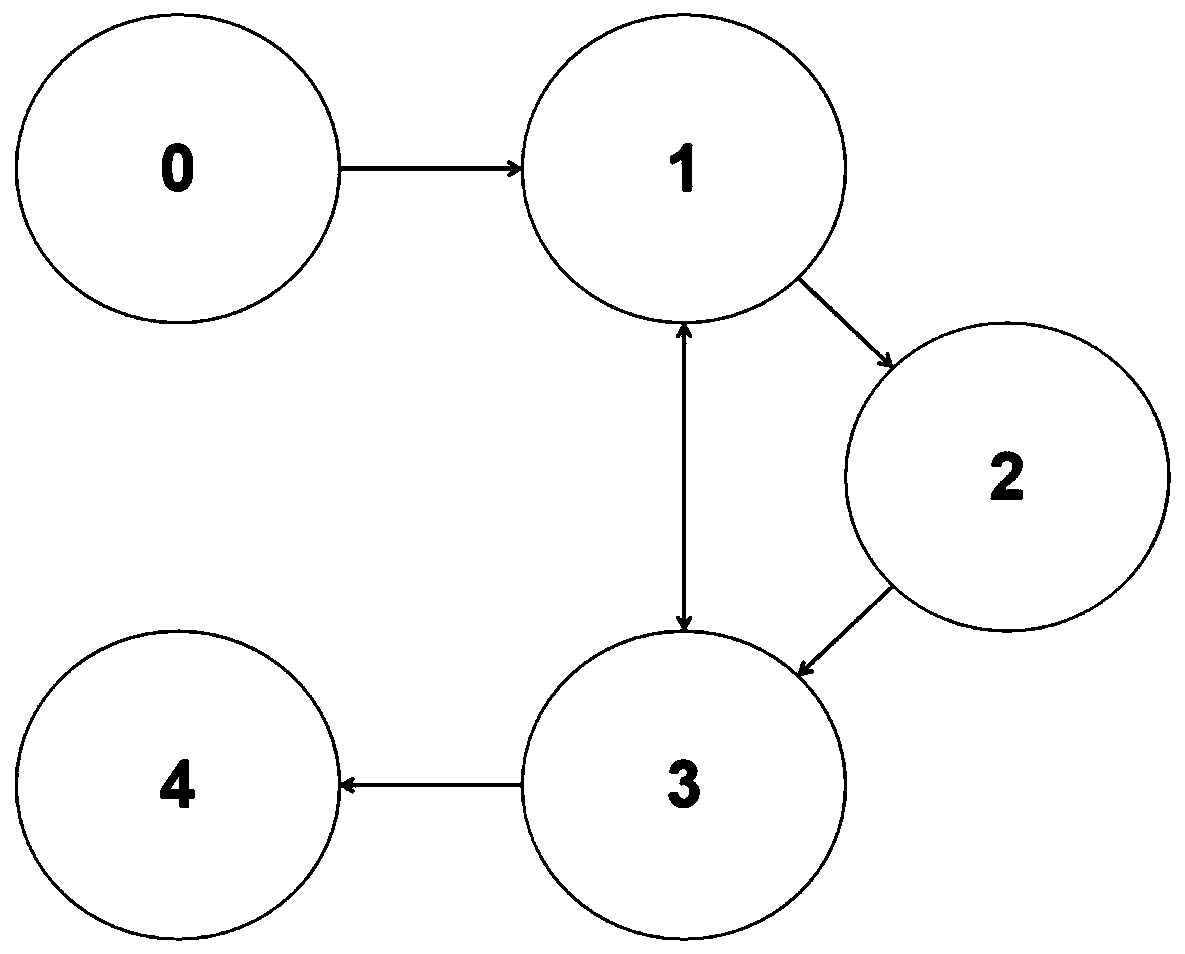
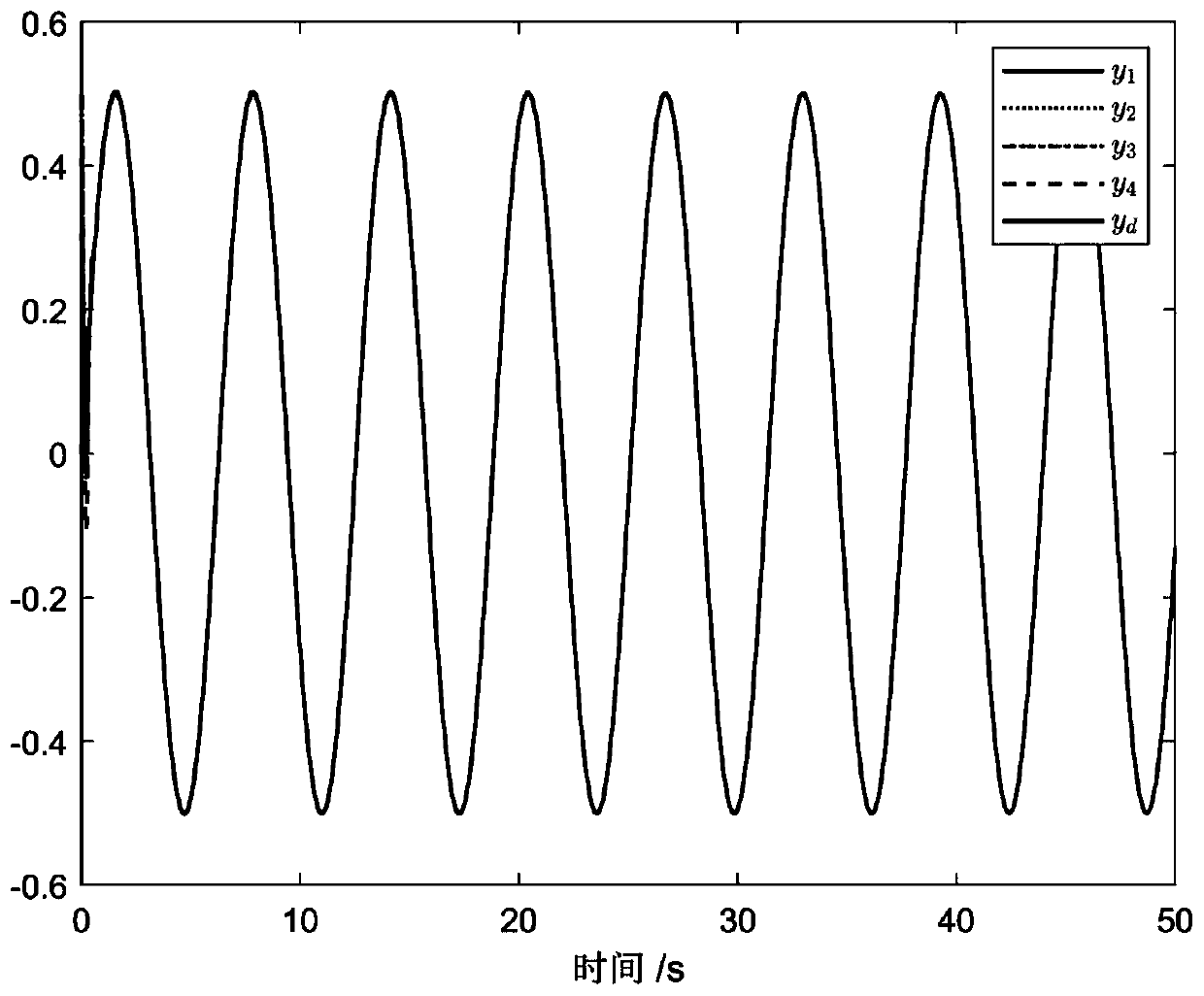
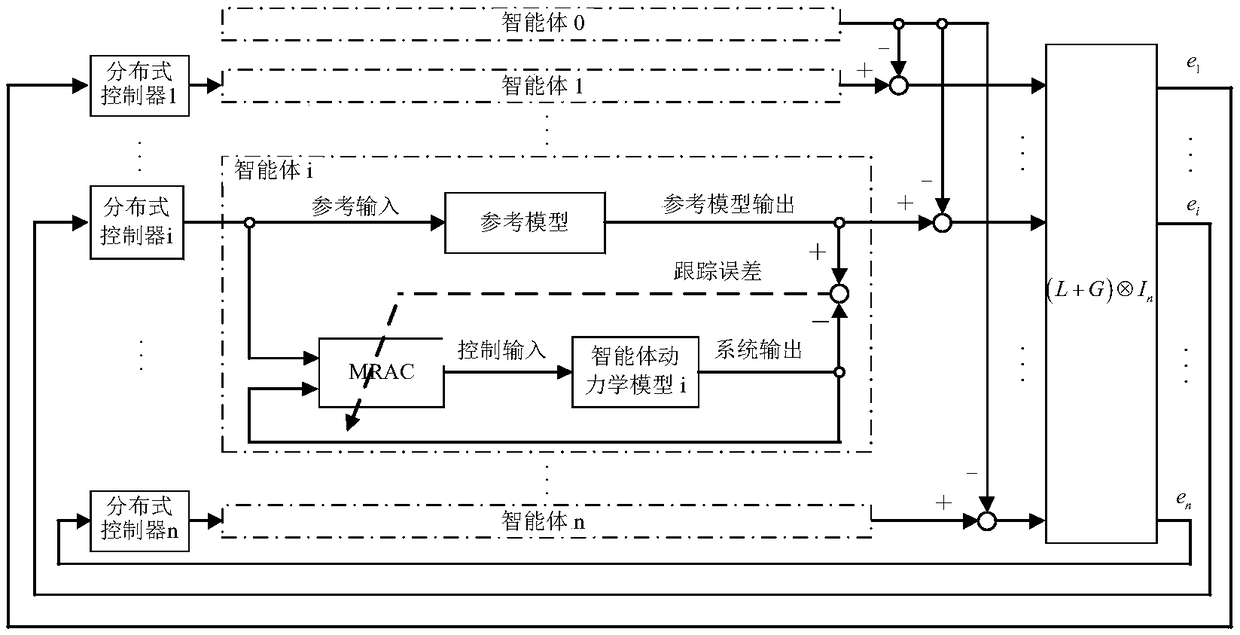
Specific performance based consistency control method for multiple intelligent agents
ActiveCN110109351AReduce economic costsImprove control effectAdaptive controlChannel state informationPerformance function
The invention discloses a specific performance based consistency control method for multiple intelligent agents. The control method comprises that the intelligent agents as communication nodes establish a communication topology; neighbor node and self state information is obtained according to the communication topology; the state information includes the position and speed; a tracking error of aleader is calculated according to the state information; the specific performance of the tracking error is transformed via a design performance function, and a transformed error model is obtained; andaccording to the transformed error model, an event triggering adaptive controller of a follower is designed via a backstepping method and a dynamic surface technology, an event triggering mechanism is designed, and specific performance based consistency control for the intelligent agents is realized. A system can obtain expected transient performance and stable error in the control process rapidly and precisely, the communication cost among the intelligent agents can be reduced, the application range is wide, and the application value is high.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
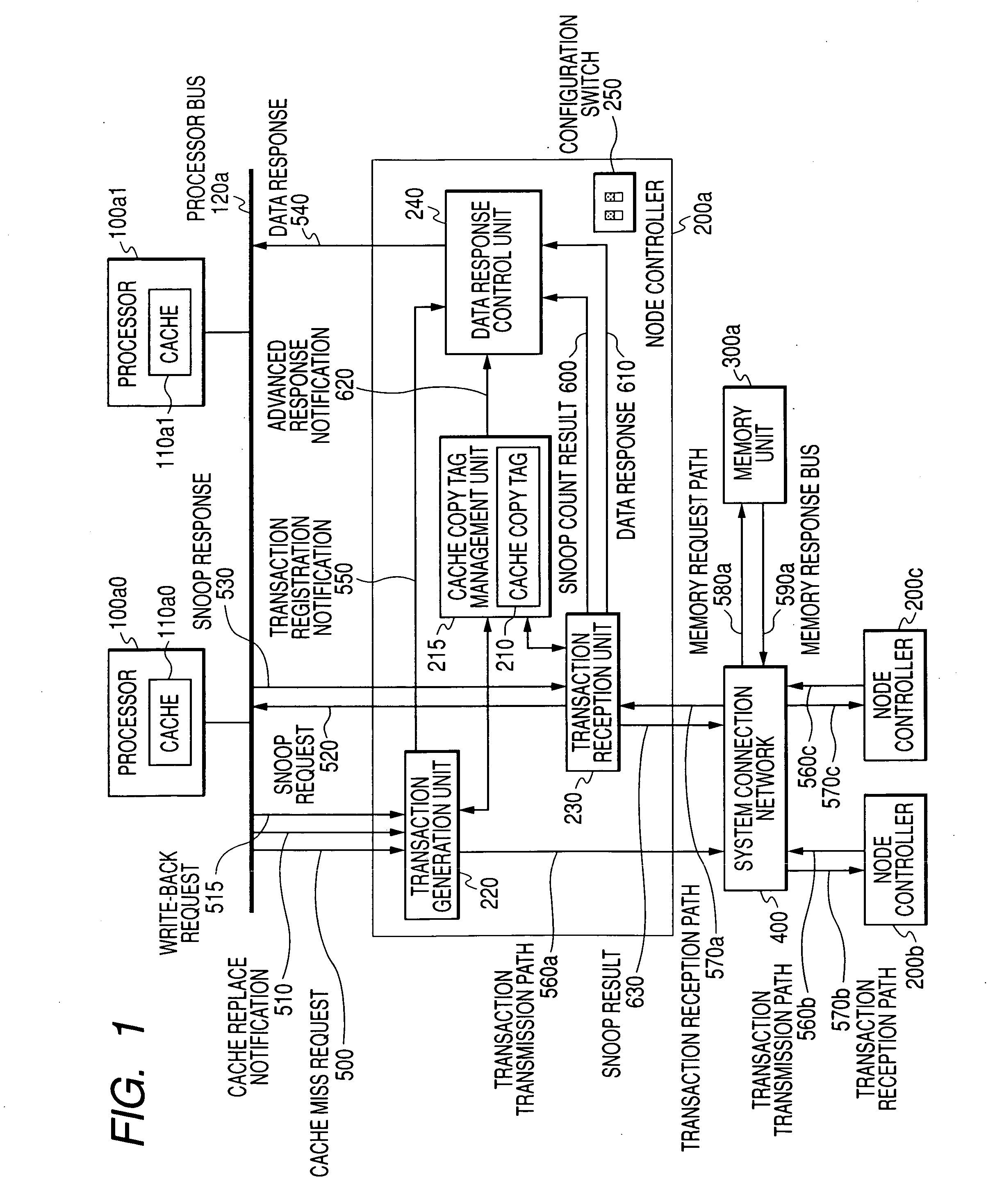
Coherency control module for maintaining cache coherency in a multi-processor-bus system
InactiveUS6823409B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationInput/output processes for data processingMulti processorConsistency control
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD +1
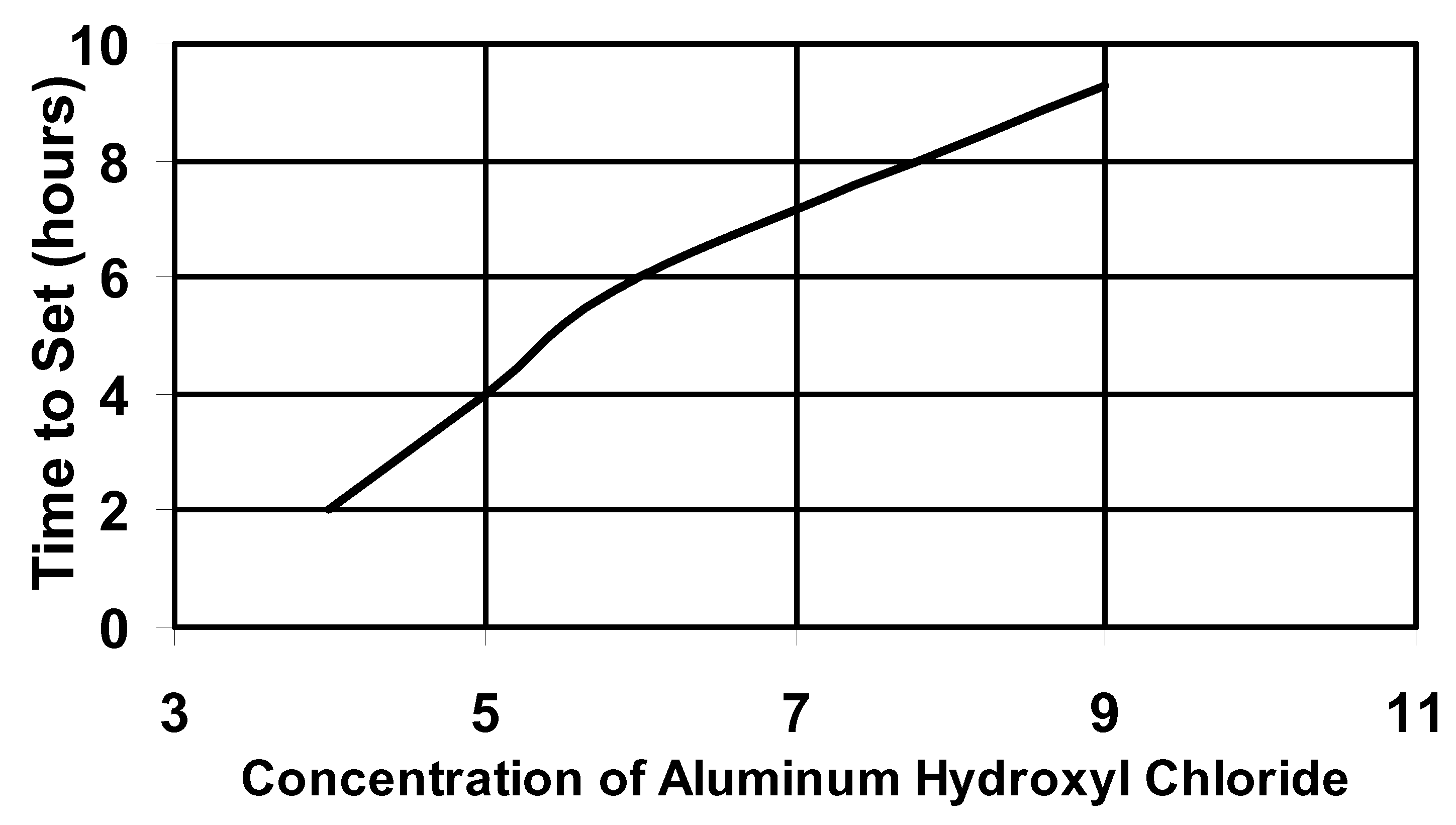
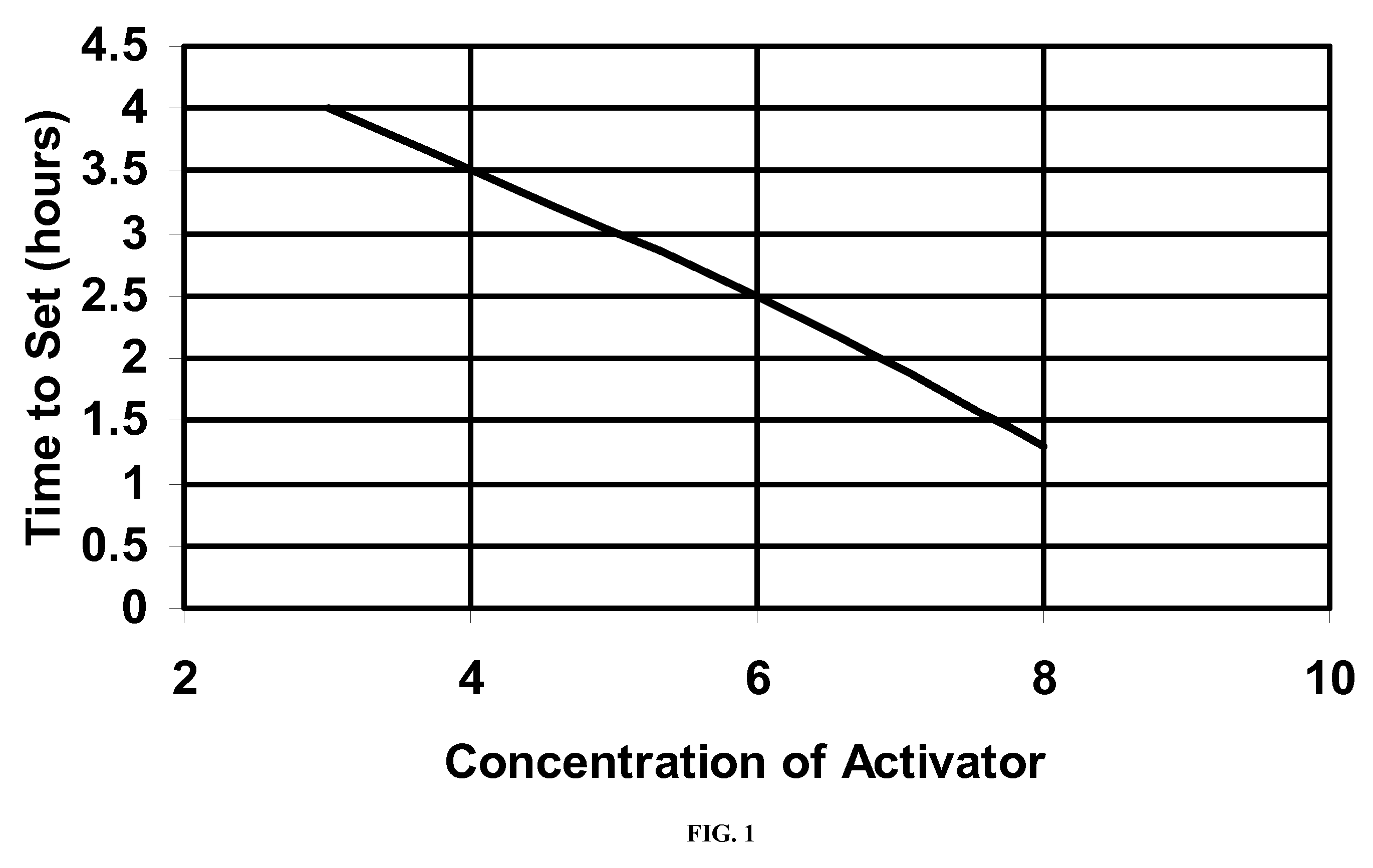
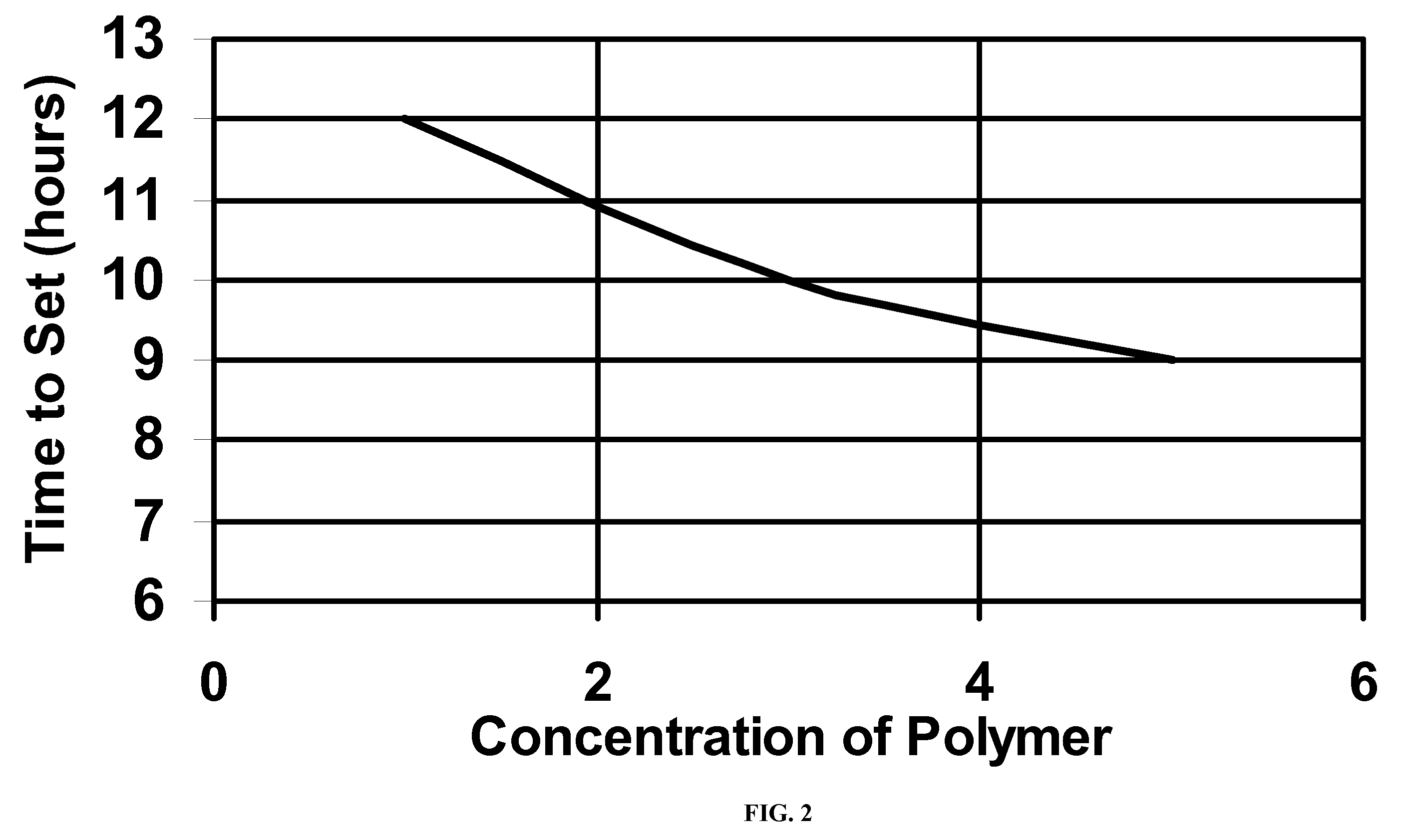
Delayed polyacrylamide-co-aluminum hydroxyl chloride gel
InactiveUS20080035344A1Improve latencyImprove solubilityFluid removalFlushingWater productionConsistency control
A delayed gelling system useful in conformance control in the production of petroleum from subterranean formations is disclosed. The gelling system comprises an acidic aqueous solution of acid-soluble or cationic polyacrylamide, an at least partially neutralized acid aluminum salt, an activator comprising a hydroxyl donor, and an optional gel modifier. The gelling system may be pumped into formations with excessive water production and thermally activated in the formation at downhole conditions to form a co-gel of polyacrylamide interspersed in an inorganic gel network to reduce water production.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
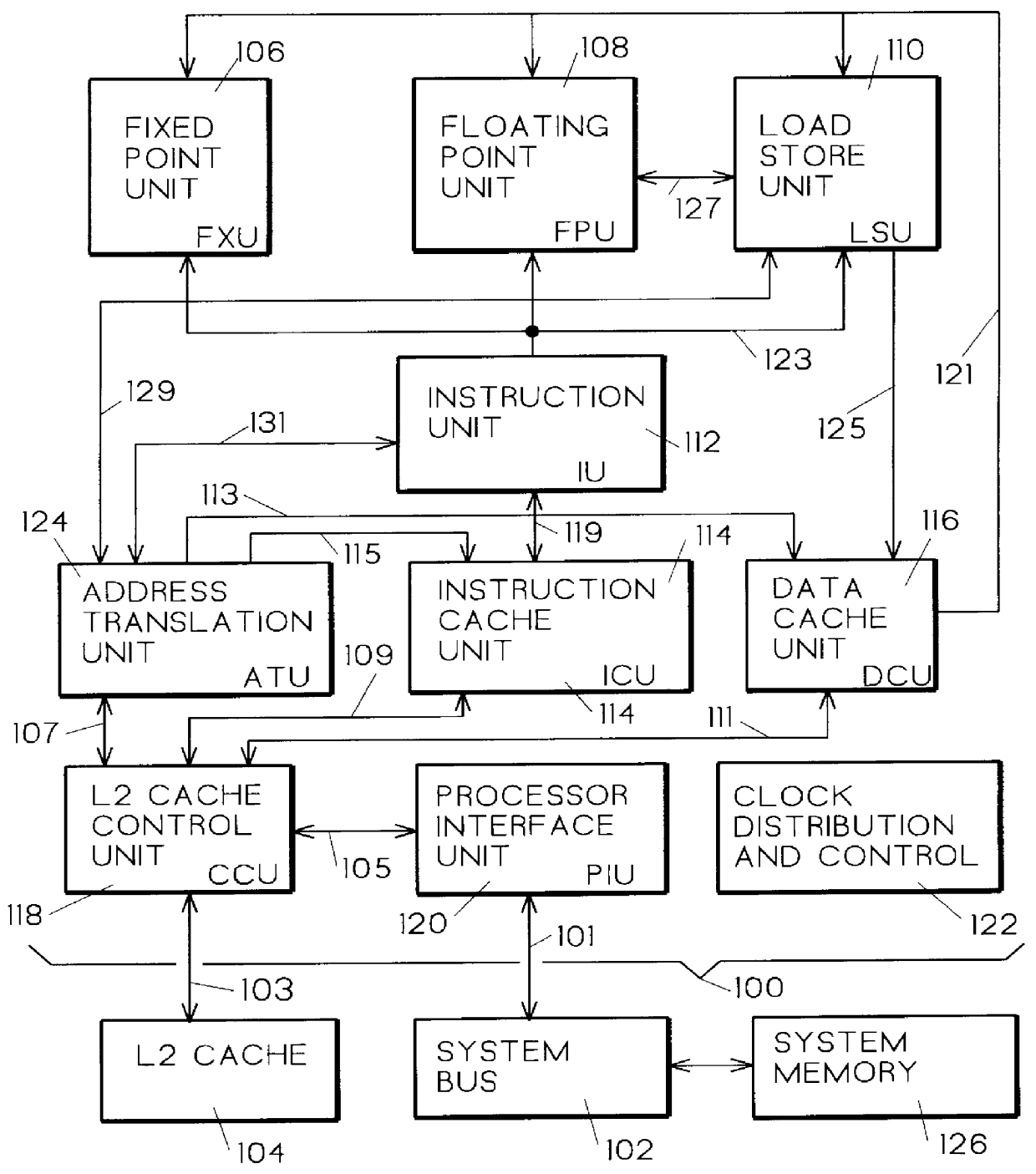
Method and apparatus for configurable multiple level cache with coherency in a multiprocessor system
A coherency controller for configurable caches. A base microprocessor design accommodates system configurations both with and without L2 cache tag and data arrays installed. Second level cache control logic exists within the microprocessor chip, and when the external second level cache tag and data arrays are removed their inputs to the microprocessor are tied to an inactive state. A configuration switch is set in the second level cache controller that causes snoop requests from a system bus to get reflected onto a first level cache snooping path. The first level cache status is then fed back to the second level cache controller, in a manner consistent with the timing required for support of a second level cache search, and fed into the second level cache status signal generation logic, effectively making the second level cache controller believe that the second level cache still exists for snooping. All other actions remain the same in the second level cache controller providing an effective and simple method for supporting snooping bus protocols. A result is that now every bus request snoops the first level cache without knowledge of presence of an L2 cache. This environment is provided to support entry level single processor configurations where the snooping requests only amount to input / output traffic.
Owner:IBM CORP
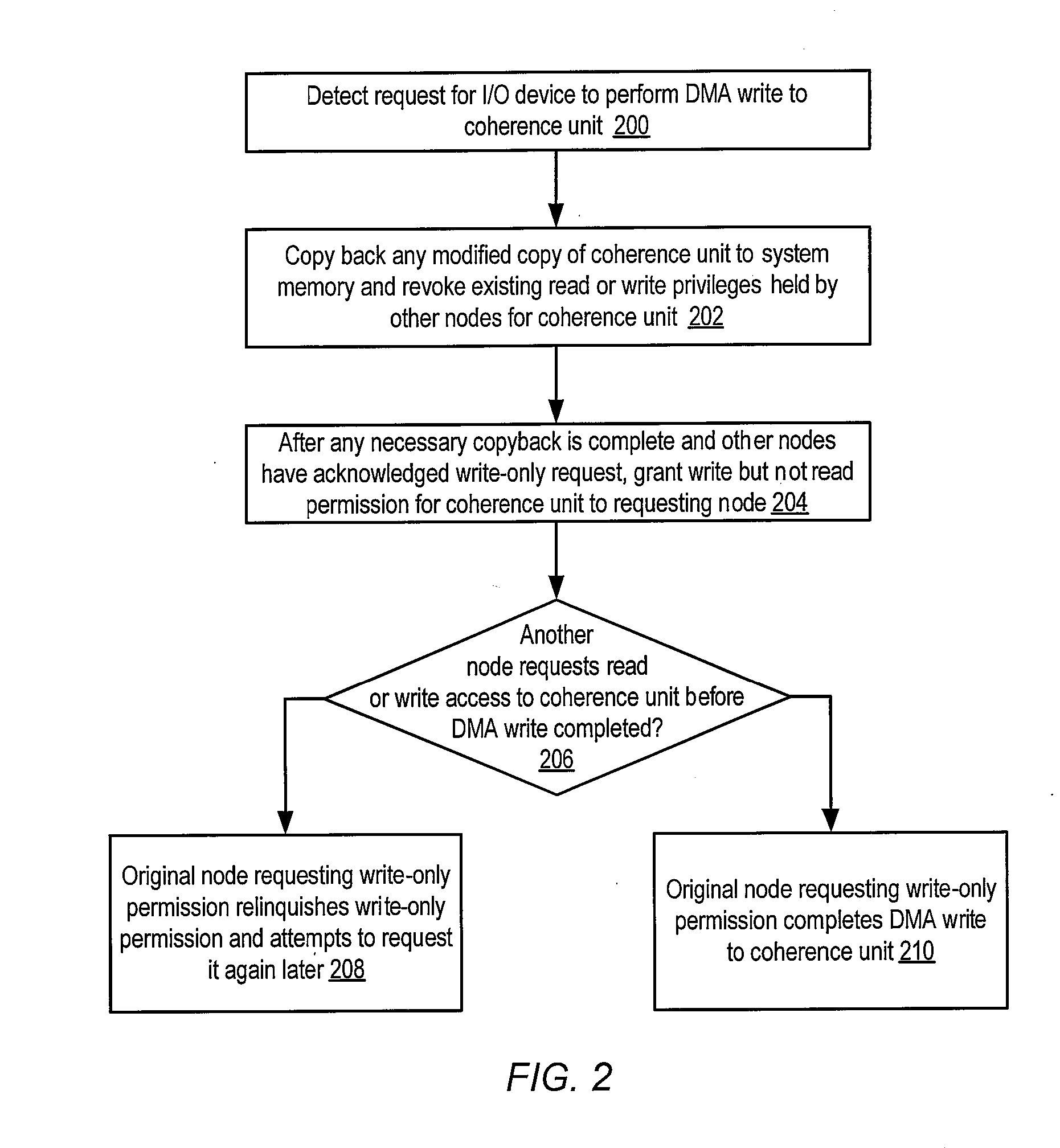
Cache coherence protocol with write-only permission
ActiveUS20080120441A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationProcessor nodeConsistency control
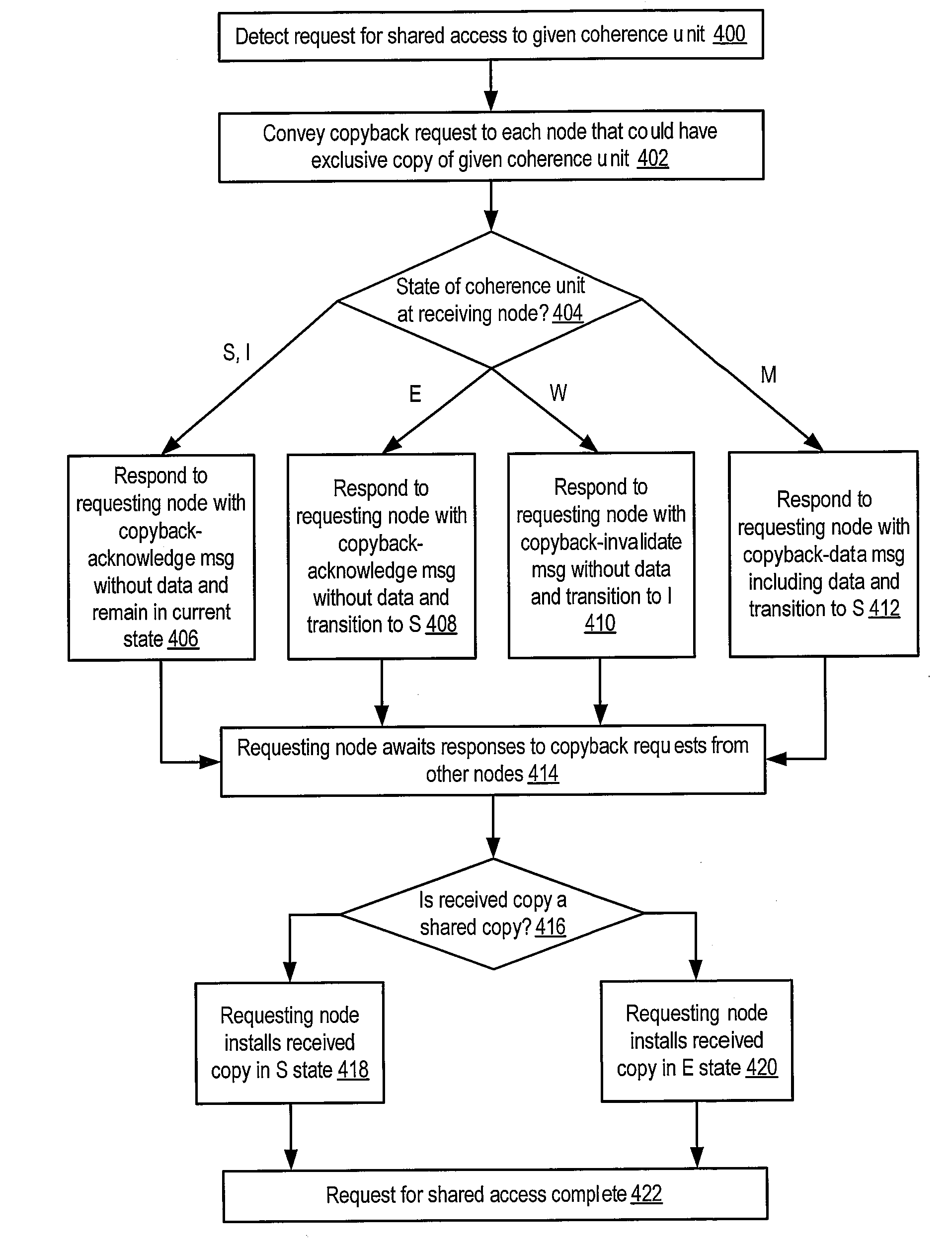
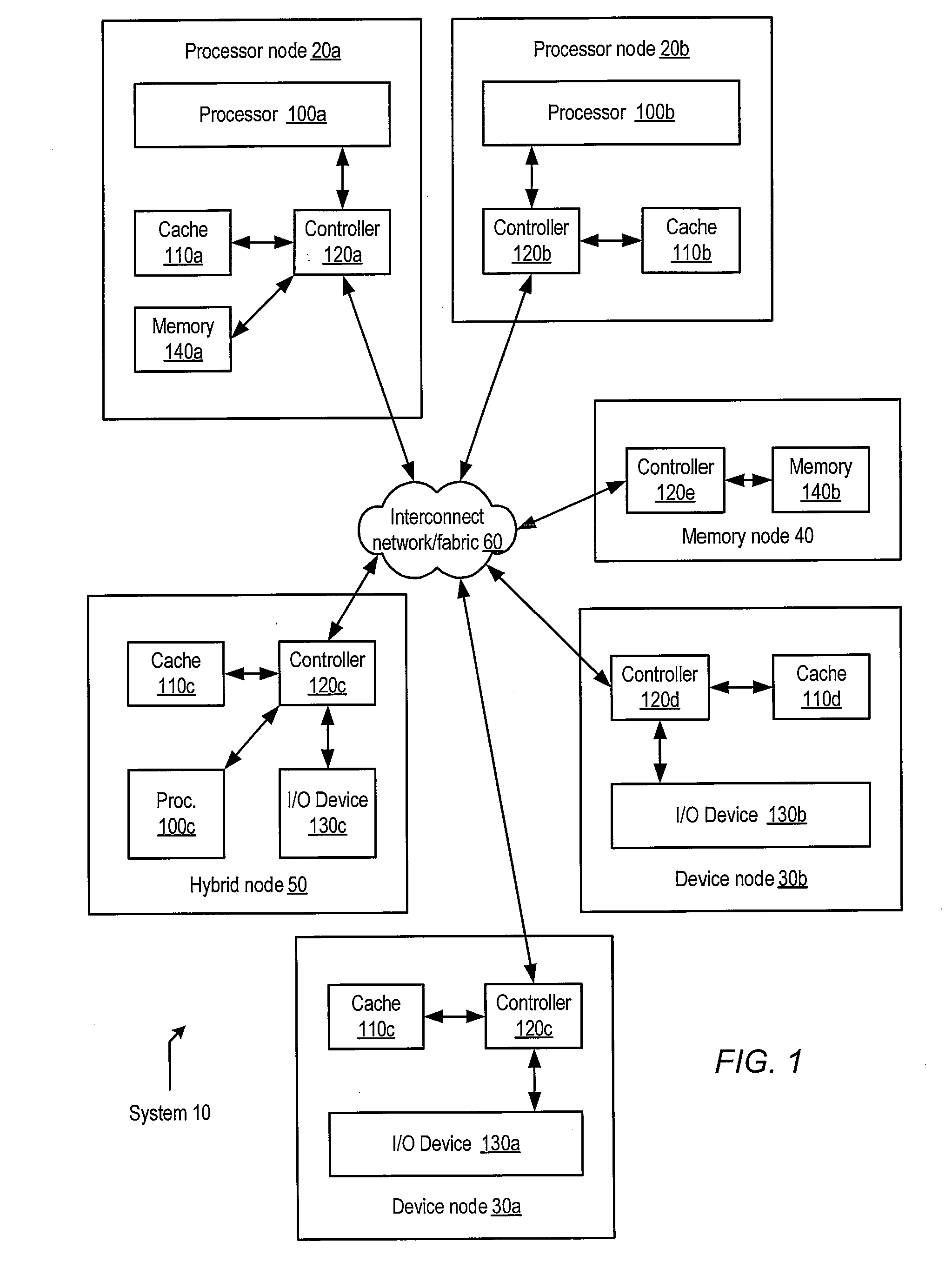
A system may include a processor node, and may also include an input / output (I / O) node including a processor and an I / O device. The processor and I / O nodes may each include a respective cache memory configured to cache a system memory and a respective cache coherence controller. The system may further include interconnect through which the nodes may communicate. In response to detecting a request for the I / O device to perform a DMA write operation to a coherence unit of the I / O node's respective cache memory, and in response to determining that the coherence unit is not modified with respect to the system memory and no other cache memory within the system has read or write permission corresponding to a copy of the coherence unit, the I / O node's respective cache coherence controller may grant write permission but not read permission for the coherence unit to the I / O node's respective cache memory.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
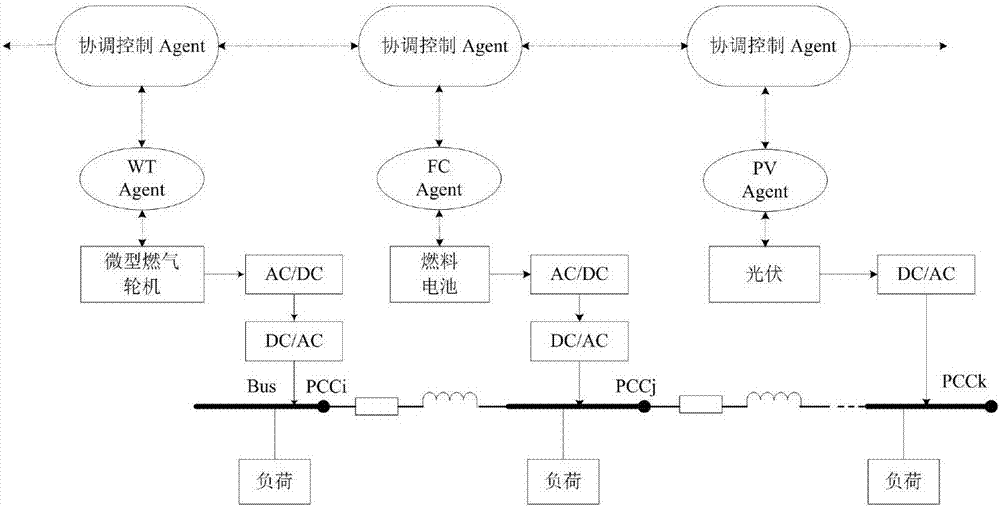
Multi-agent-based micro power supply decentralized coordination control method
ActiveCN106877398APower sharingImprove dynamic performanceSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsReaction layerMicrogrid
The invention relates to a multi-agent-based micro power supply decentralized coordination control method, which comprises the steps of building a two-layer multi-agent distributed coordination control scheme; designing the internal structure of two-layer multiple agents, wherein each lower-layer unit agent is designed to be a hybrid agent comprising a reaction layer and a negotiation layer; each upper-layer agent is designed to comprise a learning and evaluation module, a database, a knowledge base, a secondary control module and an action executing module; putting forward a micro power supply decentralized control scheme, wherein decentralized control for a distributed power supply is double closed-loop control, and a fractional order PID controller is designed; setting parameter optimization of the fractional order PID controller by using a particle swarm optimization algorithm; designing a distributed coordination controller based on a consistency control theory; and verifying the effectiveness of the scheme by using a simulation test. According to the method, a control strategy, which is economically feasible, safe and reliable, is provided for the distributed power supply of the microgrid, and the microgrid is ensured to operate safely and stably in an island mode.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
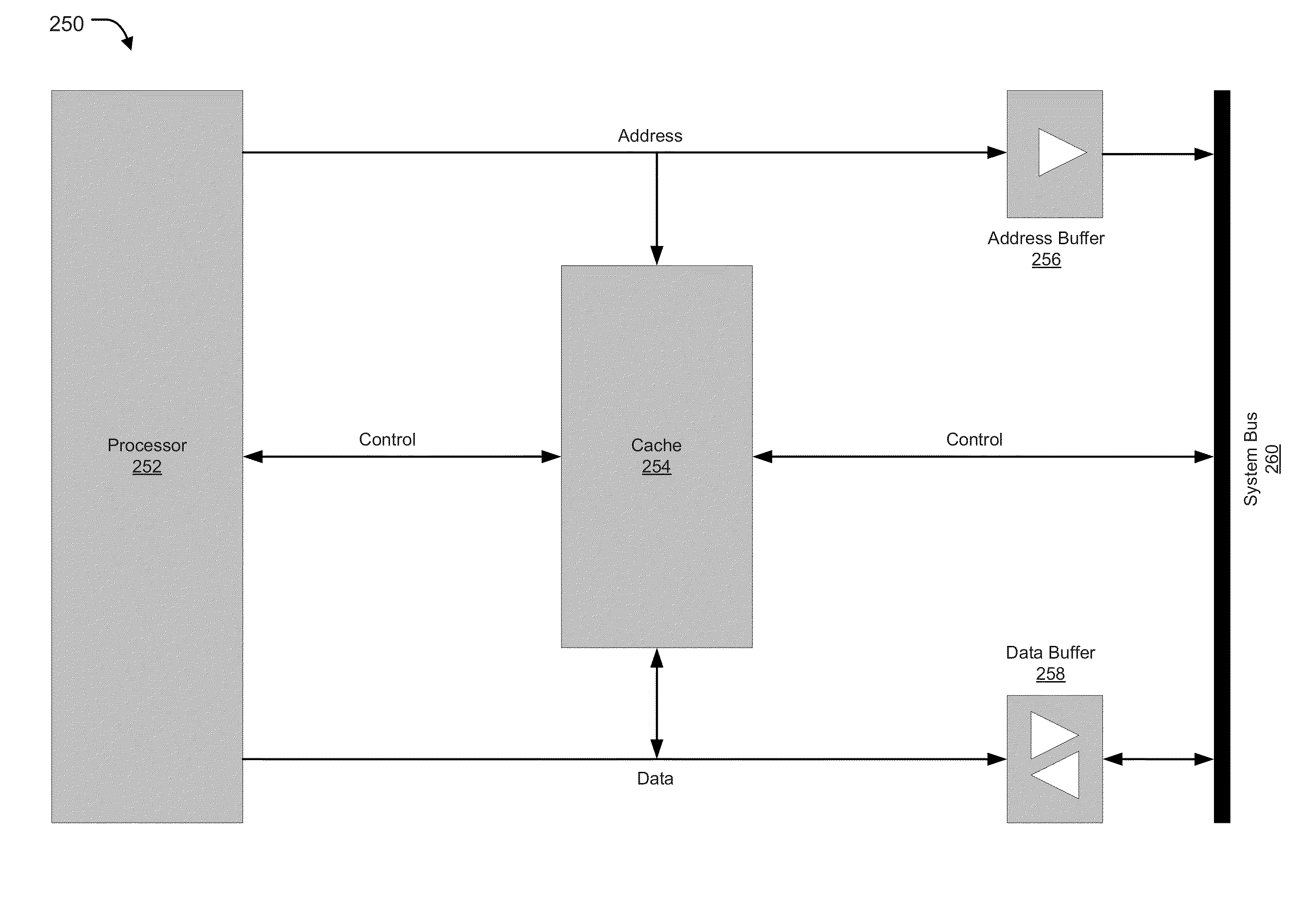
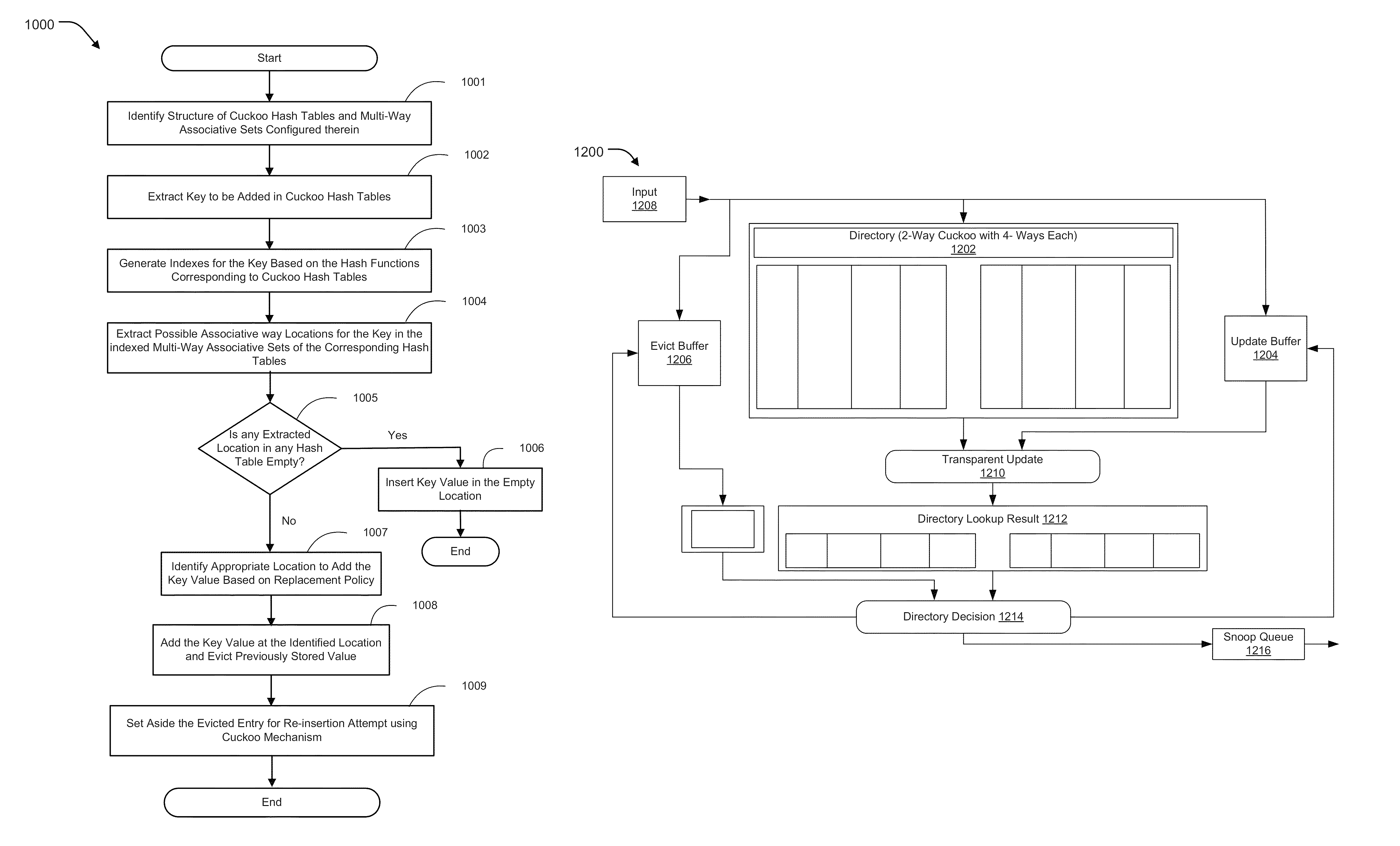
Combining associativity and cuckoo hashing
ActiveUS20150052309A1Improve performanceEfficient designMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingConsistency control
Addition, search, and performance of other allied activities relating to keys are performed in a hardware hash table. Further, high performance and efficient design may be provided for a hash table applicable to CPU caches and cache coherence directories. Set-associative tables and cuckoo hashing are combined for construction of a directory table of a directory based cache coherence controller. A method may allow configuration of C cuckoo ways, where C is an integer greater than or equal to 2, wherein each cuckoo way Ci is a set-associative table with N sets, where each set has an associativity of A, where A is an integer greater than or equal to 2.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Combining associativity and cuckoo hashing
ActiveUS9223711B2Improve performanceEfficient designMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingConsistency control
Addition, search, and performance of other allied activities relating to keys are performed in a hardware hash table. Further, high performance and efficient design may be provided for a hash table applicable to CPU caches and cache coherence directories. Set-associative tables and cuckoo hashing are combined for construction of a directory table of a directory based cache coherence controller. A method may allow configuration of C cuckoo ways, where C is an integer greater than or equal to 2, wherein each cuckoo way Ci is a set-associative table with N sets, where each set has an associativity of A, where A is an integer greater than or equal to 2.
Owner:INTEL CORP
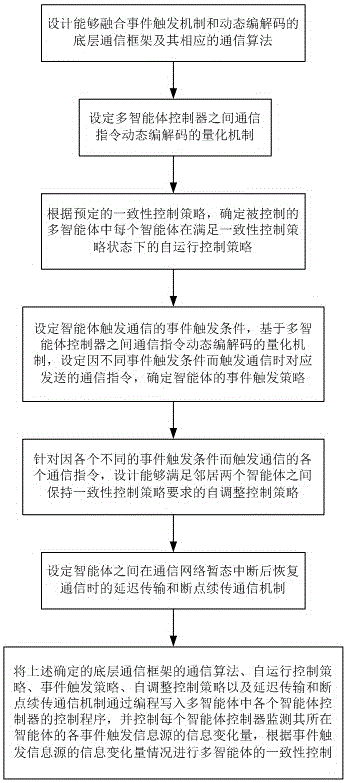
Event trigger based multi-agent consistency control method
ActiveCN105847438AReduce communication frequencyReduce computational processing loadTransmissionEvent triggerConsistency control
The invention provides an event trigger based multi-agent consistency control method, which enables information communication to be conducted among multiple agents only when an event trigger occurs, thereby reducing the calculation processing load of an agent processor and the communication frequency among the multiple agents. Meanwhile, digital channel communication is adopted among the agents, and a dynamic coding and decoding quantization mechanism, which reduces network bandwidth occupation, is set for a communication instruction, thereby enabling the data communication amount in each time to be also reduced, and greatly alleviating the network transmission load. In addition, a consistency control scheduling scheme which combines a self-operation control strategy and an event trigger based self-regulation control strategy is further adopted, thereby being capable of realizing effective multi-agent consistency control, and thus effectively solving a problem in the prior art that a multi-agent consistency control mode relying on real-time continuous information exchange is difficult to be implemented or disordered in multi-agent cooperative control in realistic network application conditions.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Optimal consistency control method and system of nonlinear multi-agent system
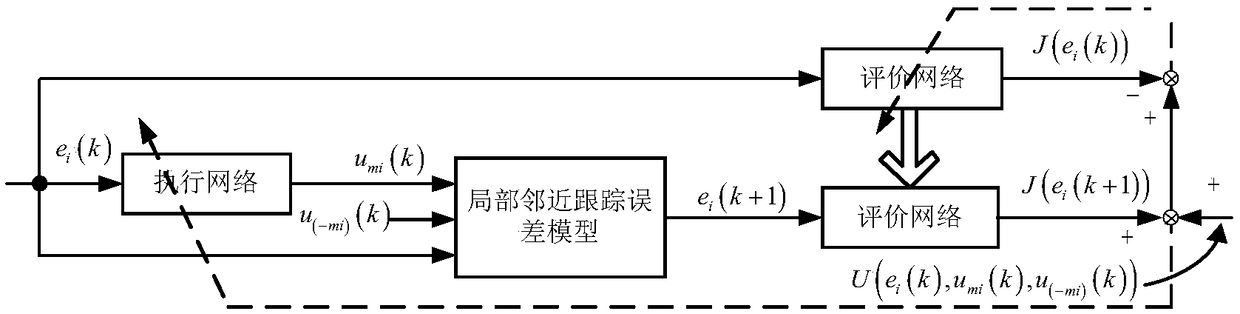
ActiveCN108803349AClose to realizationGuaranteed reliabilityAdaptive controlOptimal controlPerformance index
The invention discloses the optimal consistency control method and system of a nonlinear multi-agent system. The method is characterized by establishing a reference behavior model according to the individual dynamic characteristic of a heterogeneous multi-agent system, and using a leader-follower control model to form a multi-agent system formed by reference behavior models; then, constructing a dynamic graph game global error dynamical model according to the network topology structure of multiple agents, defining a multi-agent local performance index function, and according to the global Nashequilibrium, acquiring a Bellman optimal equation; and then, under the condition of only using local agent information, using an execution-evaluation execution network framework mode based on value function approximation to carry out online iterative learning, and acquiring an optimal consistency protocol to achieve the consistency of each reference model behavior. Compared with the prior art, byusing the method and the system of the invention, under the condition of guaranteeing optimal control performance, the consistency problem of the complex multi-agent system can be high-efficiently solved, and an actual application value and high scalability are achieved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com