Patents
Literature
513 results about "Inode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
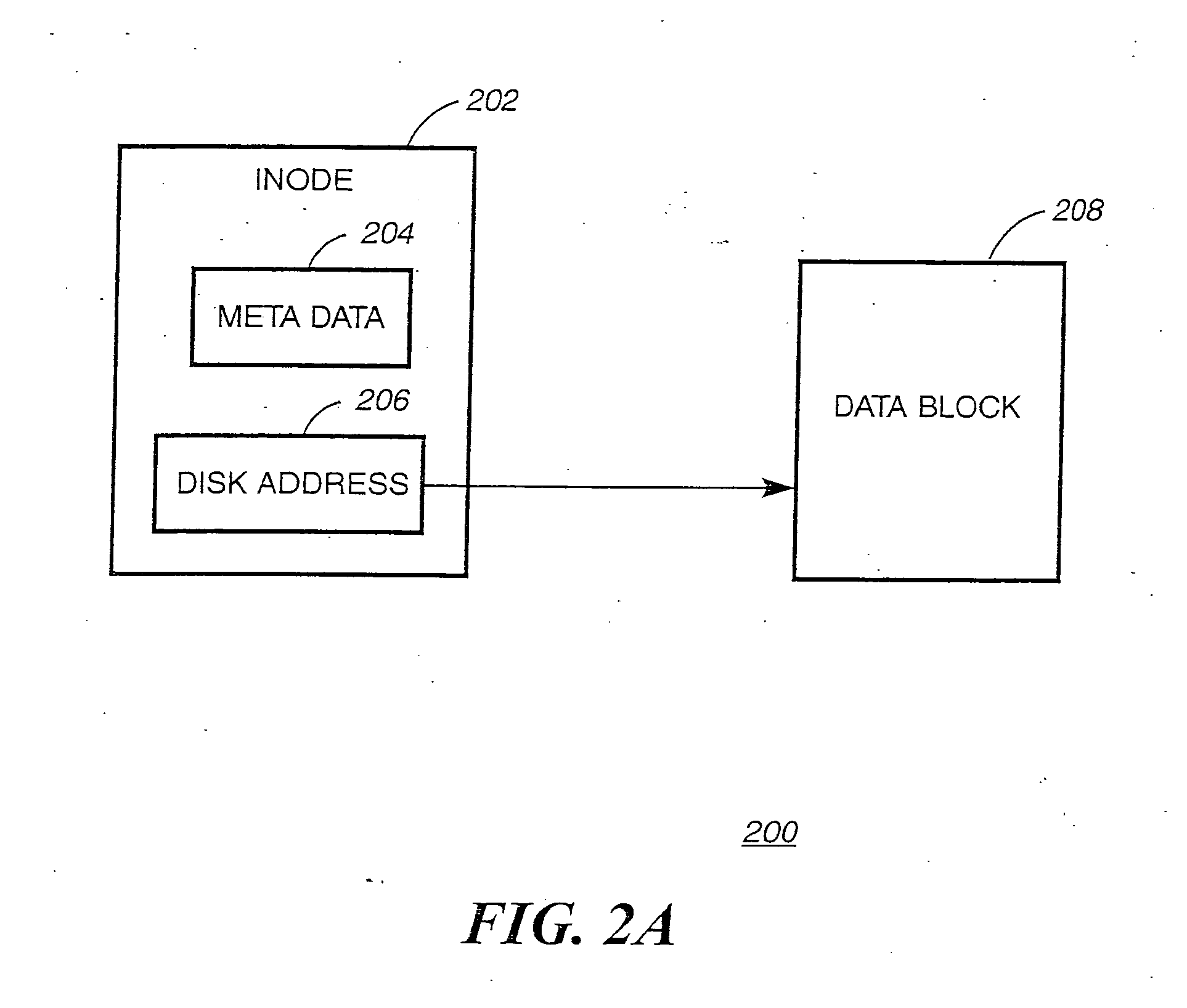
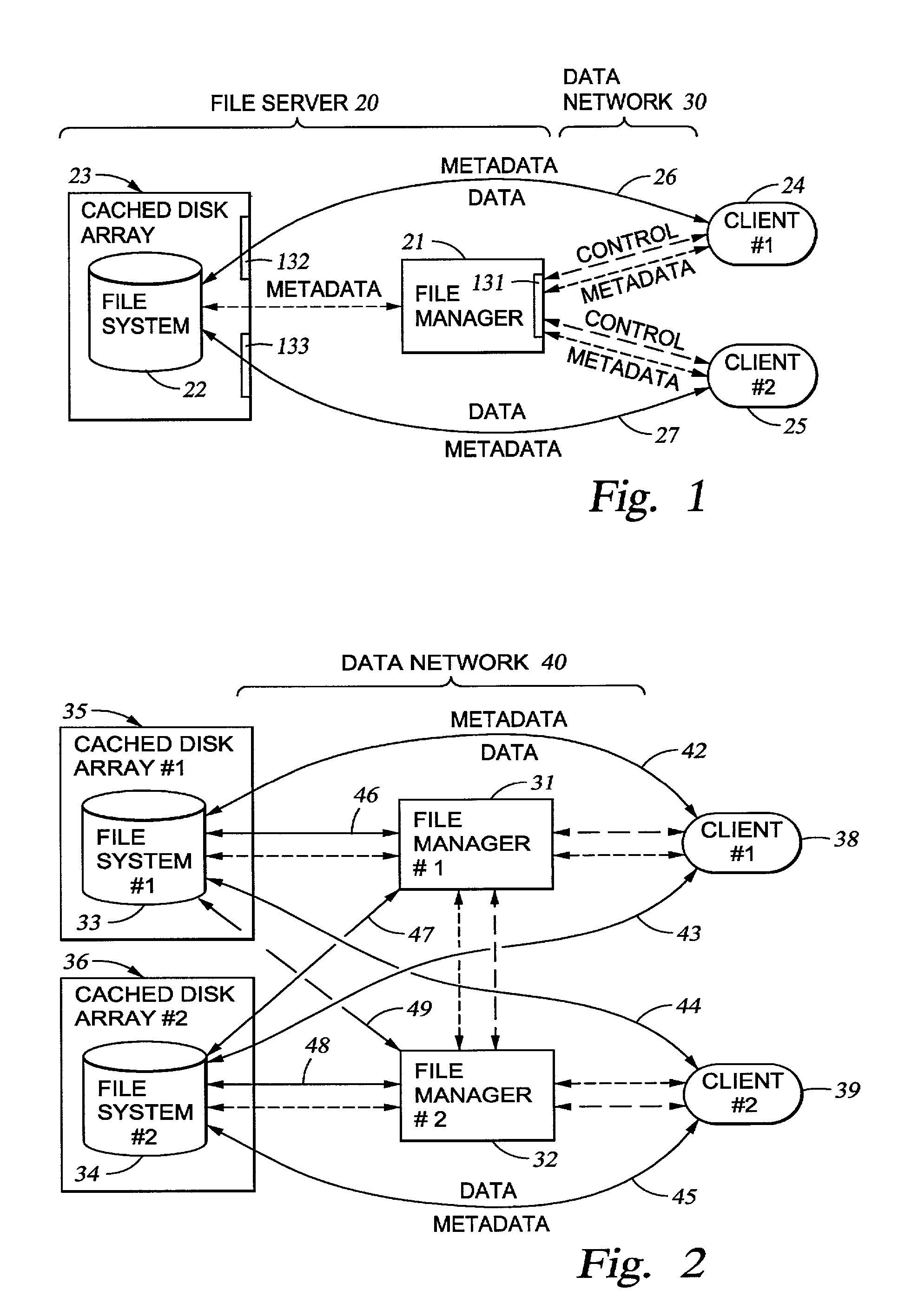
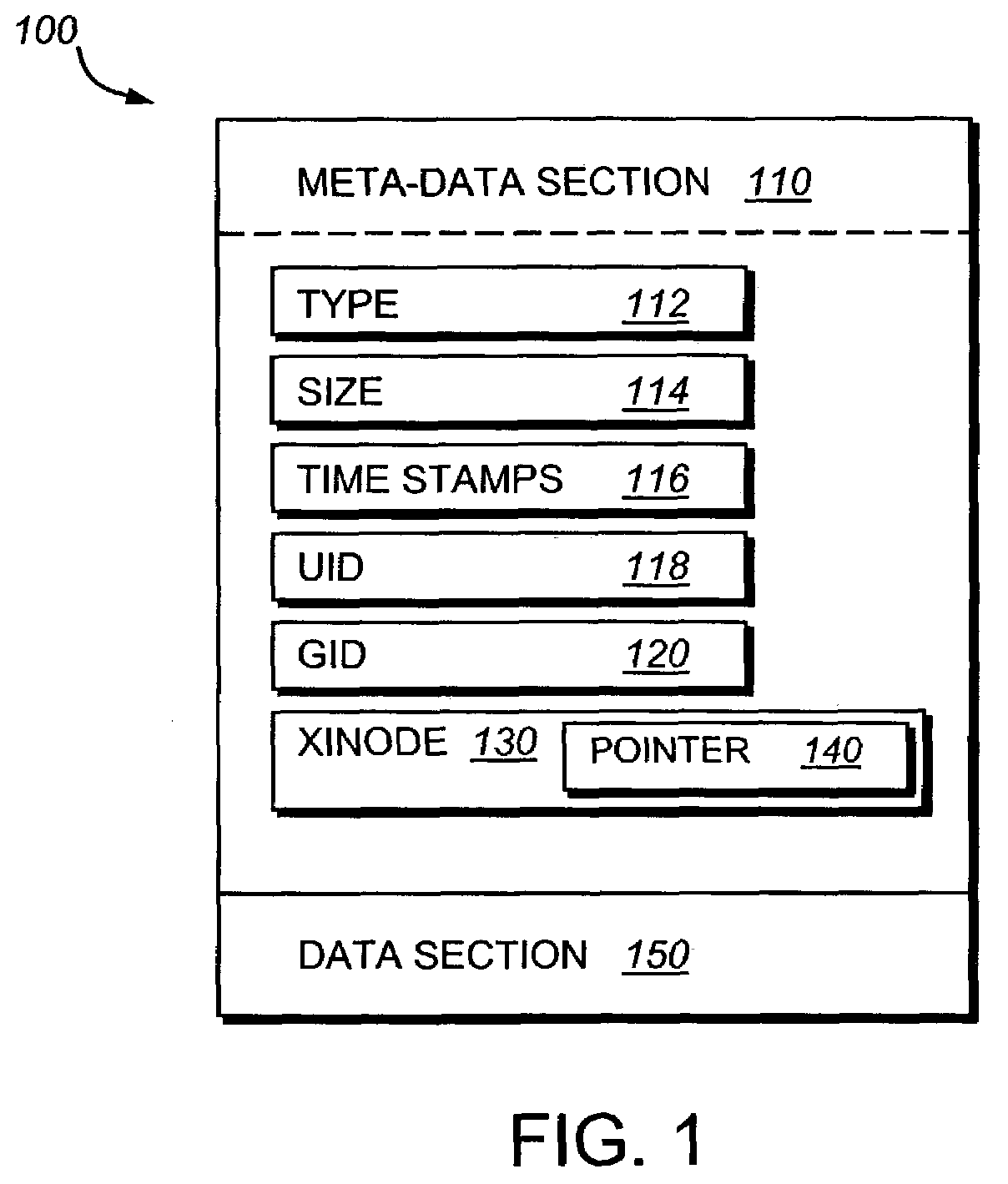
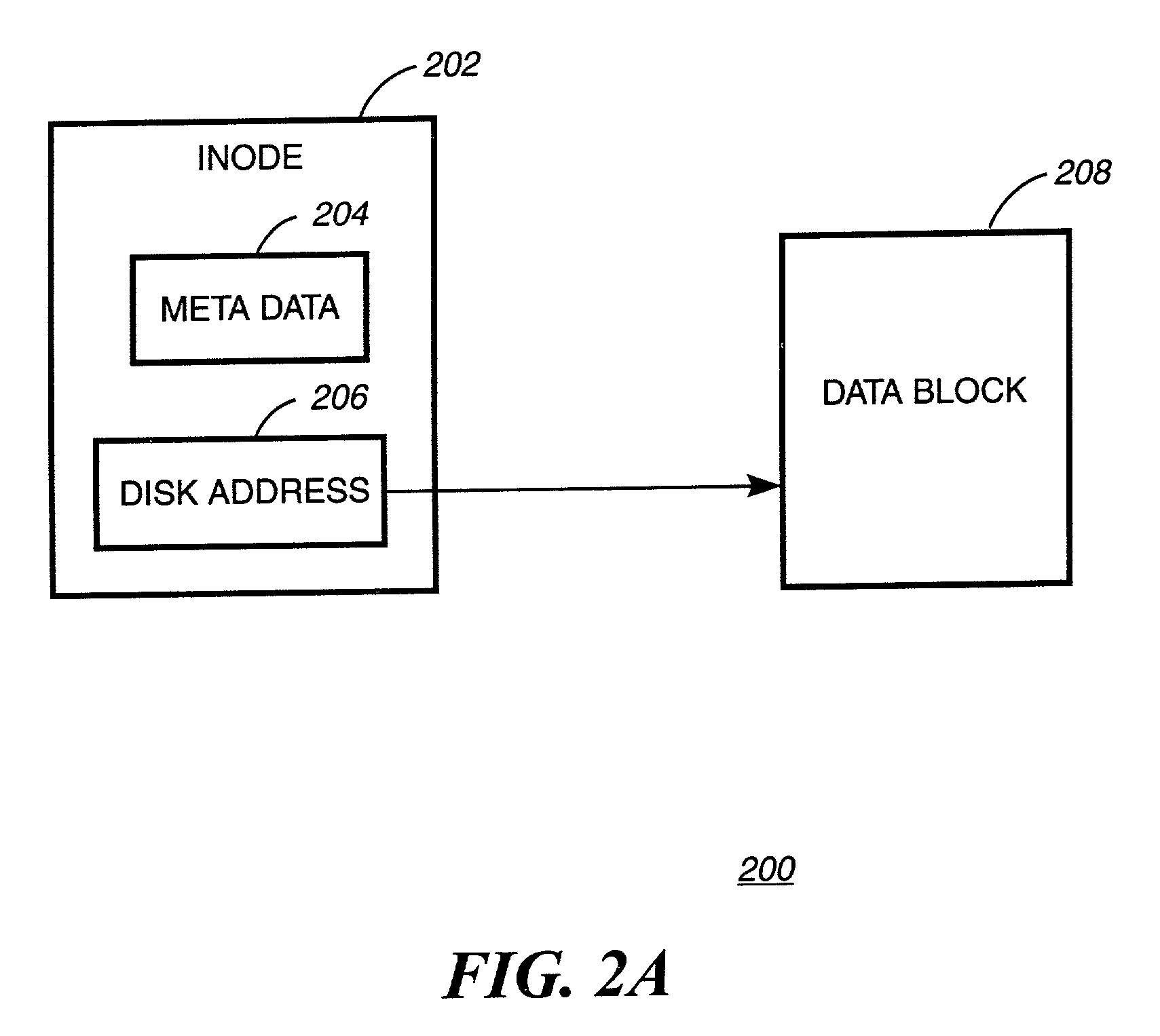
The inode (index node) is a data structure in a Unix-style file system that describes a file-system object such as a file or a directory. Each inode stores the attributes and disk block location(s) of the object's data. File-system object attributes may include metadata (times of last change, access, modification), as well as owner and permission data.
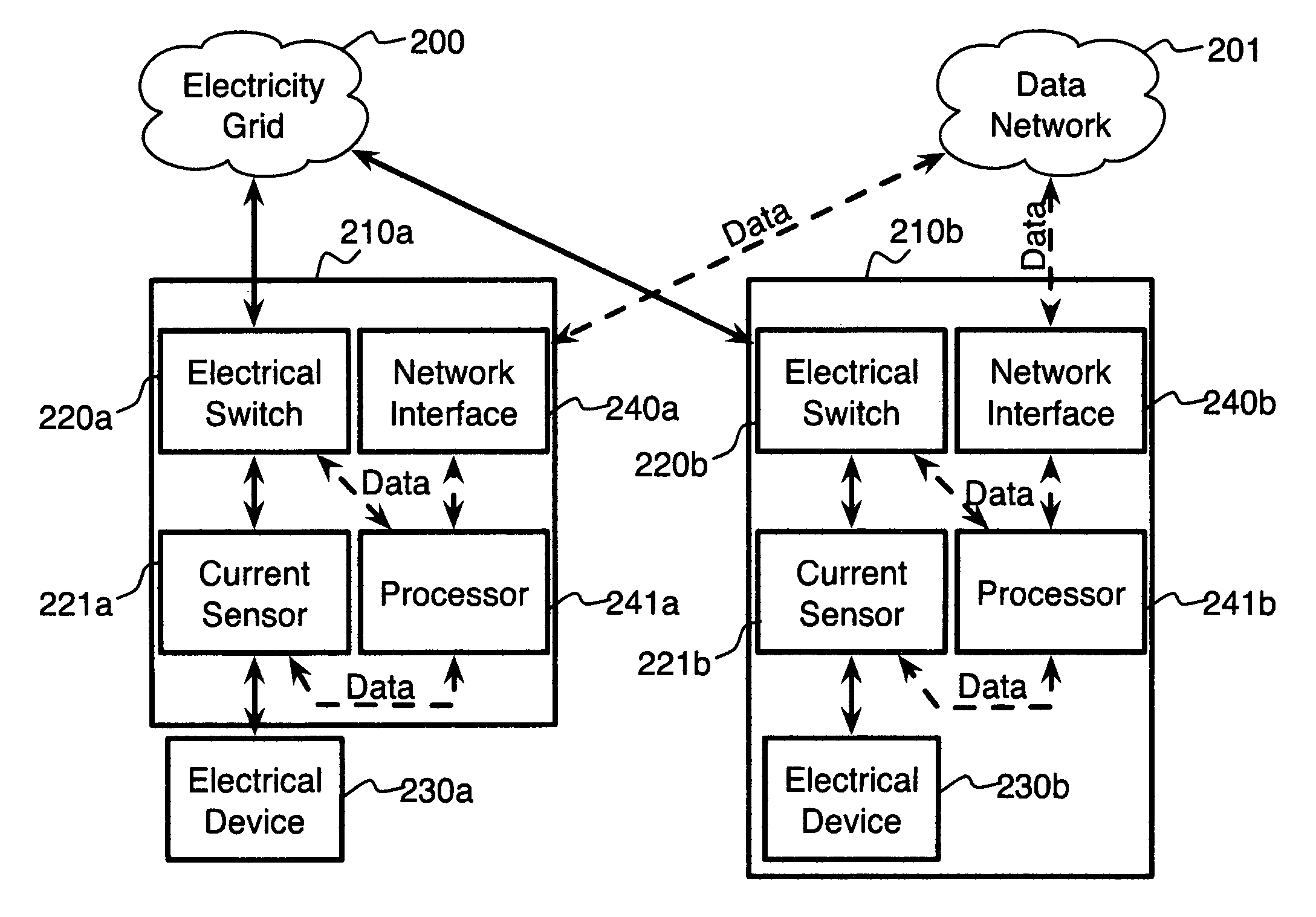
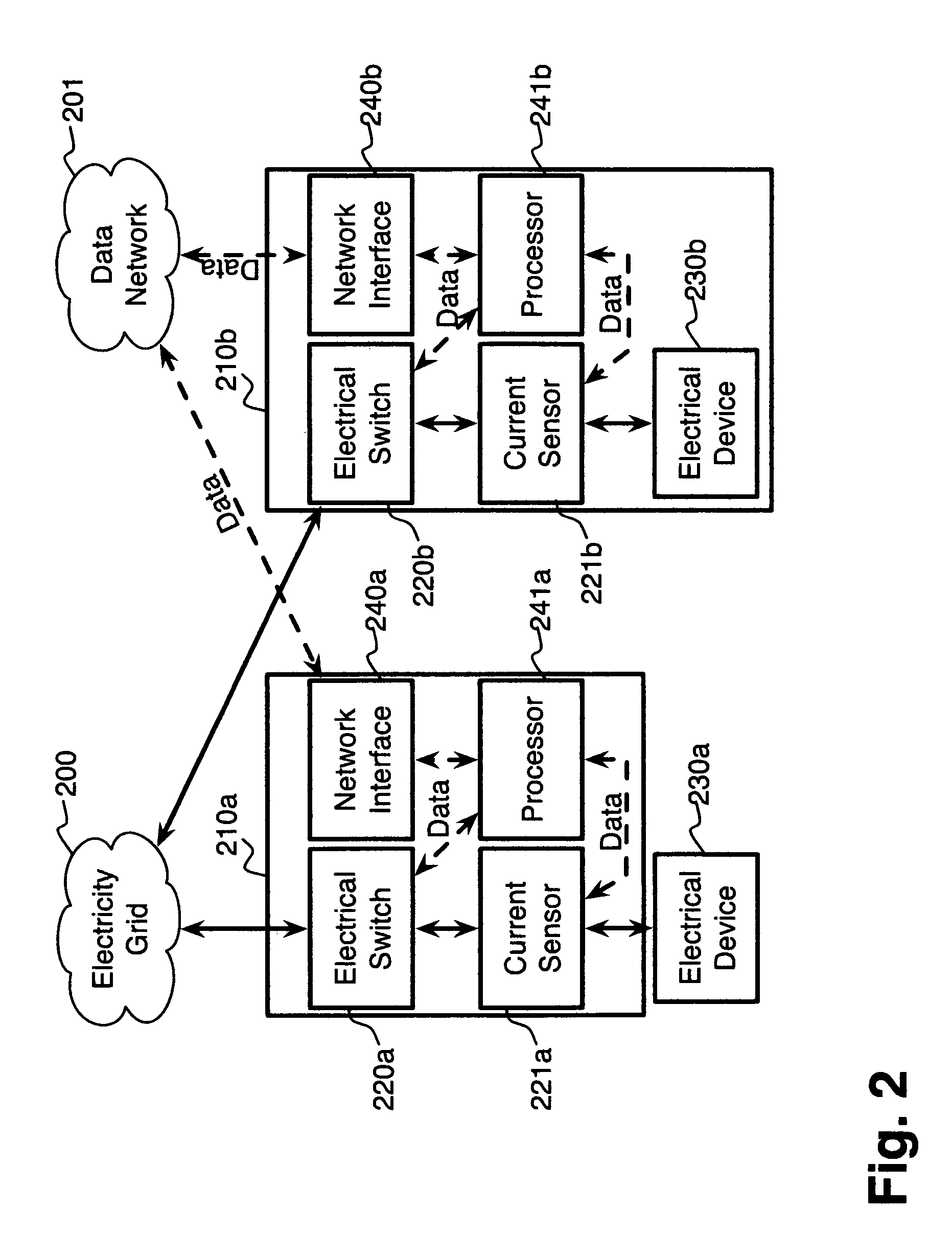
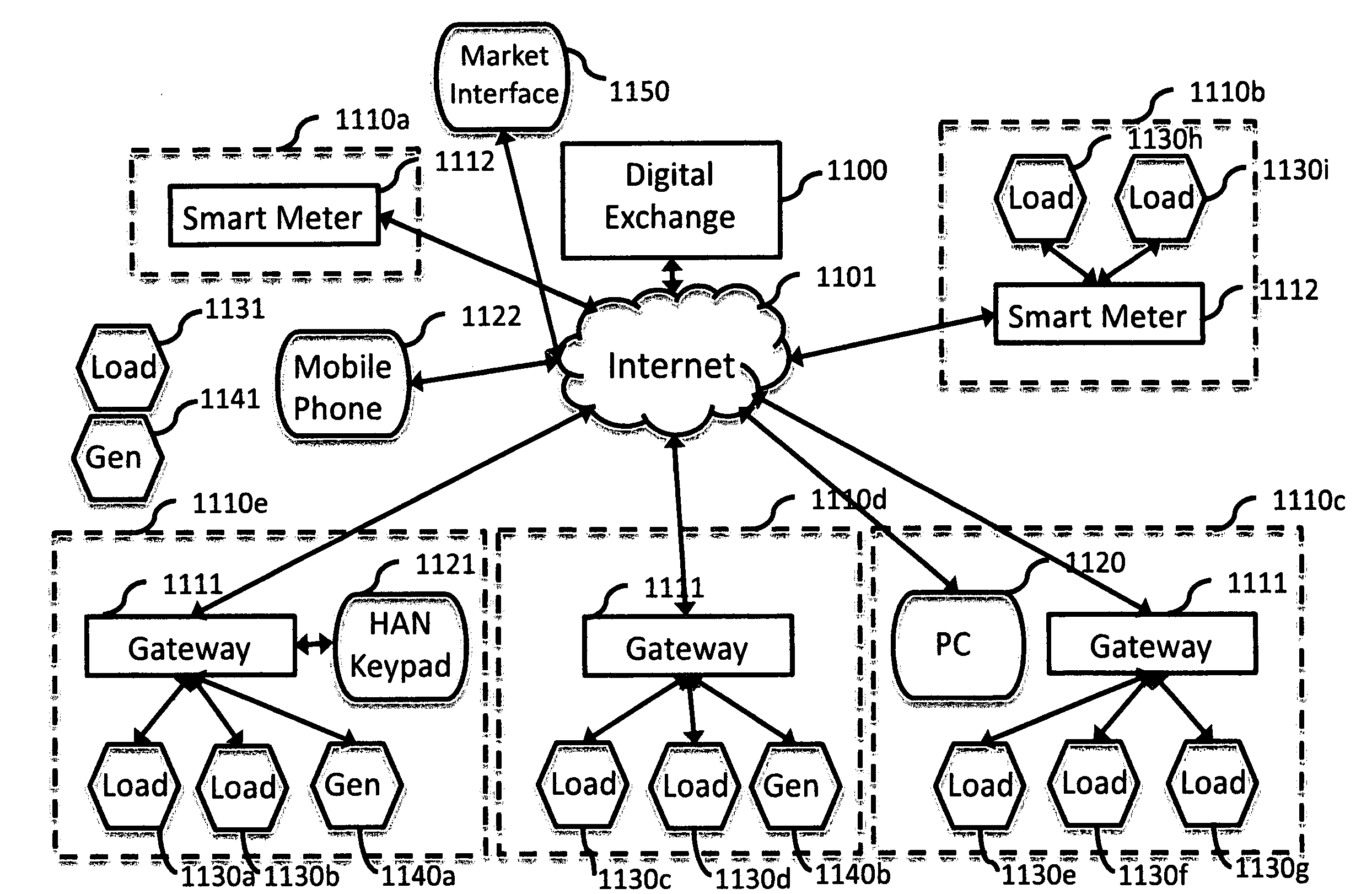
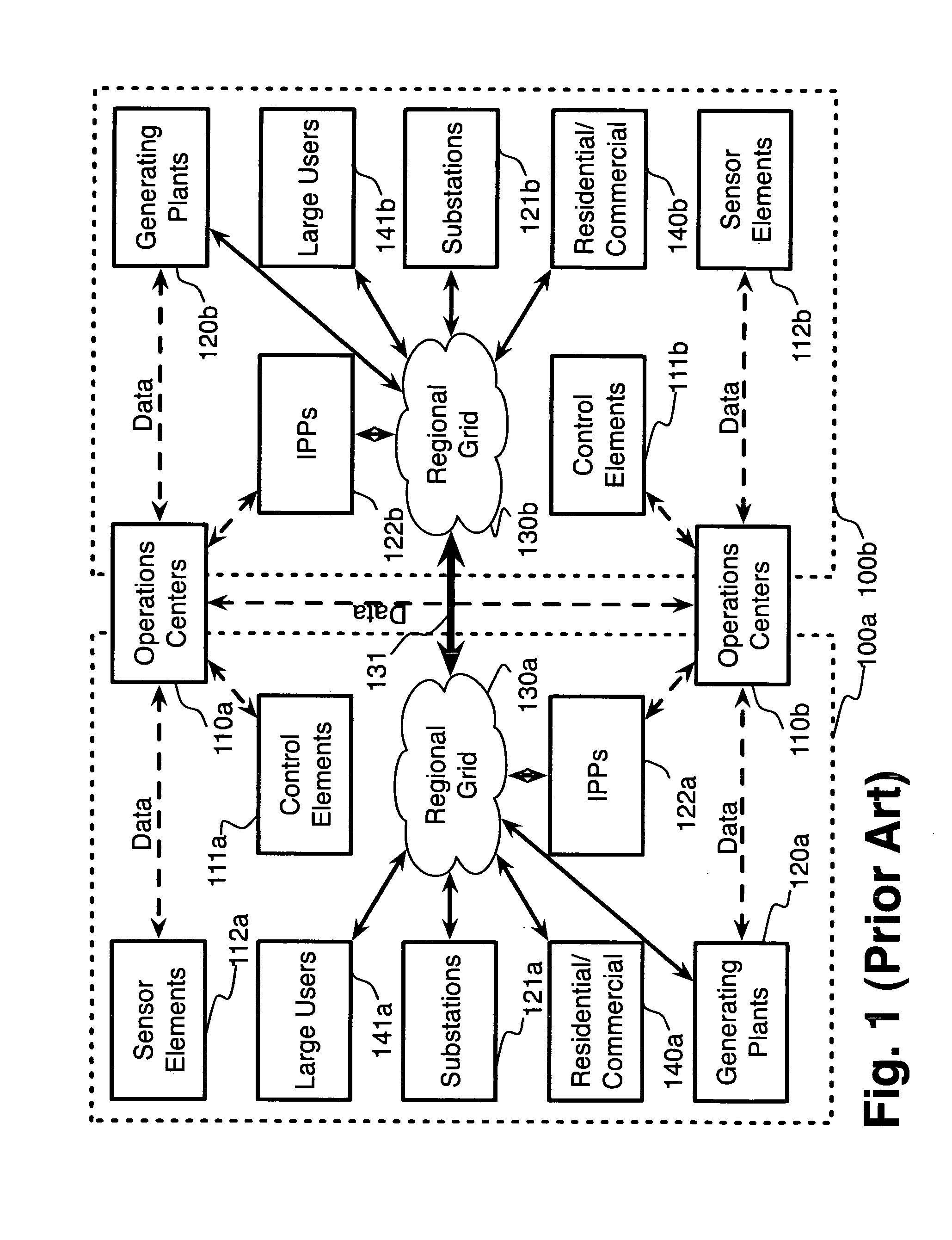
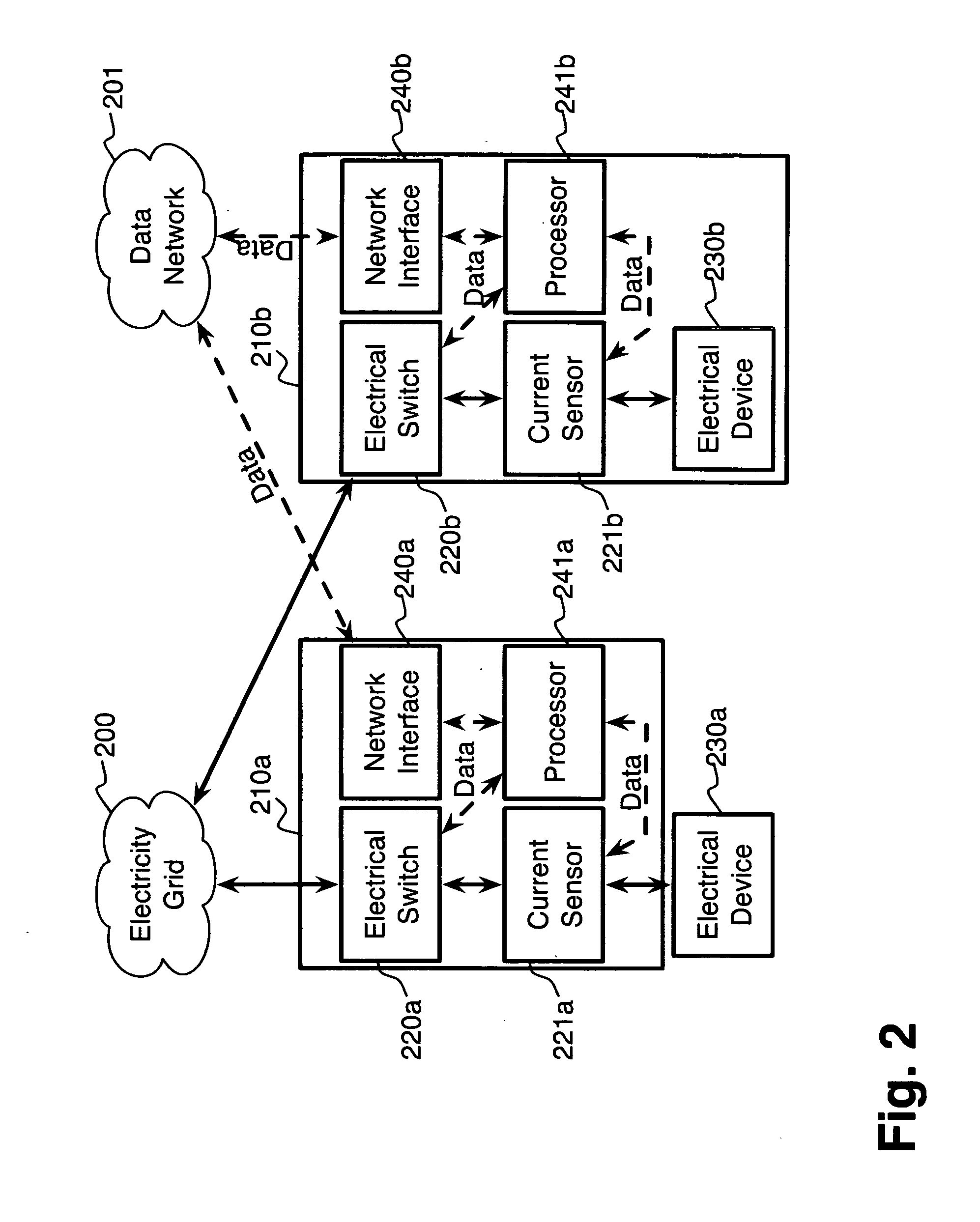
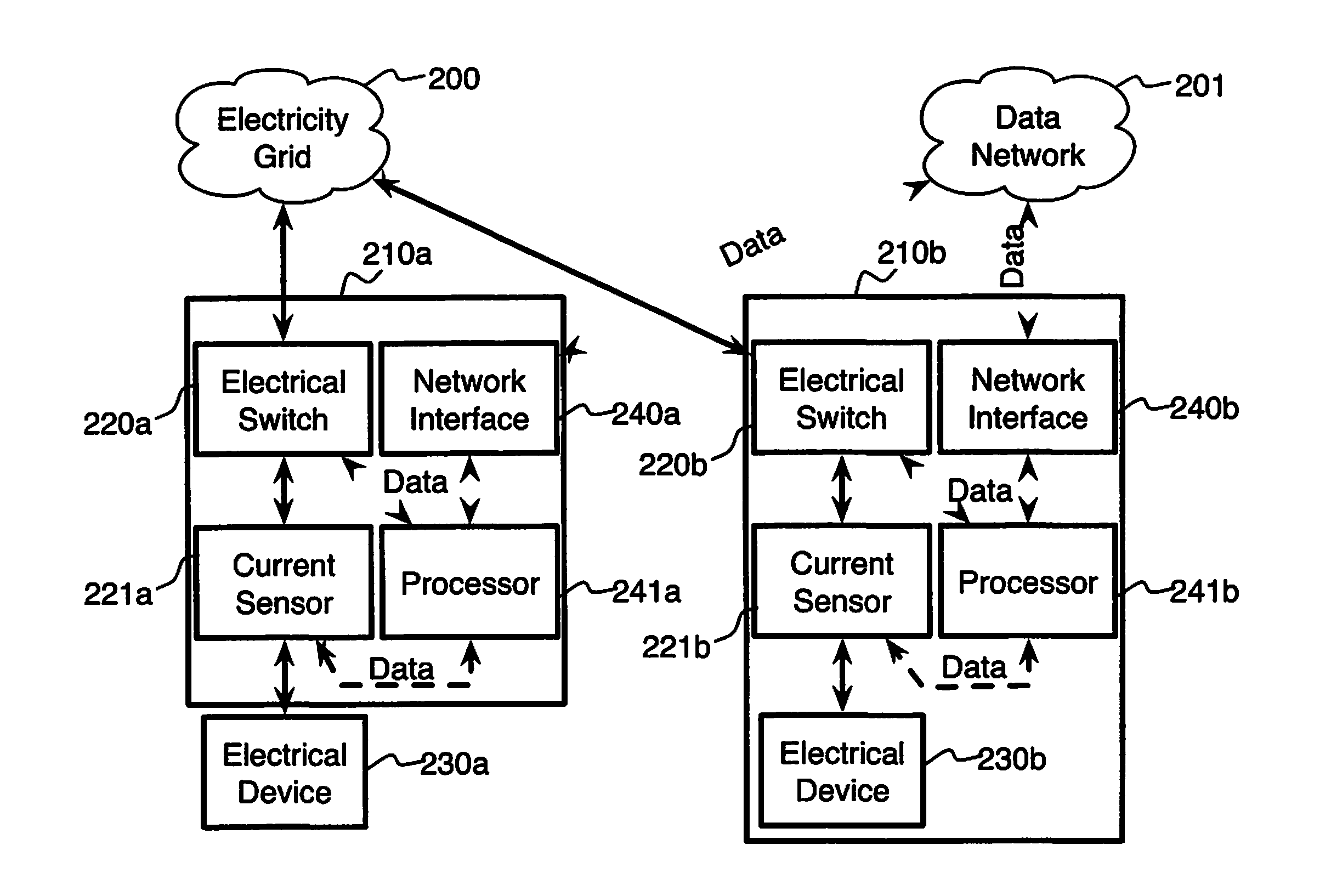
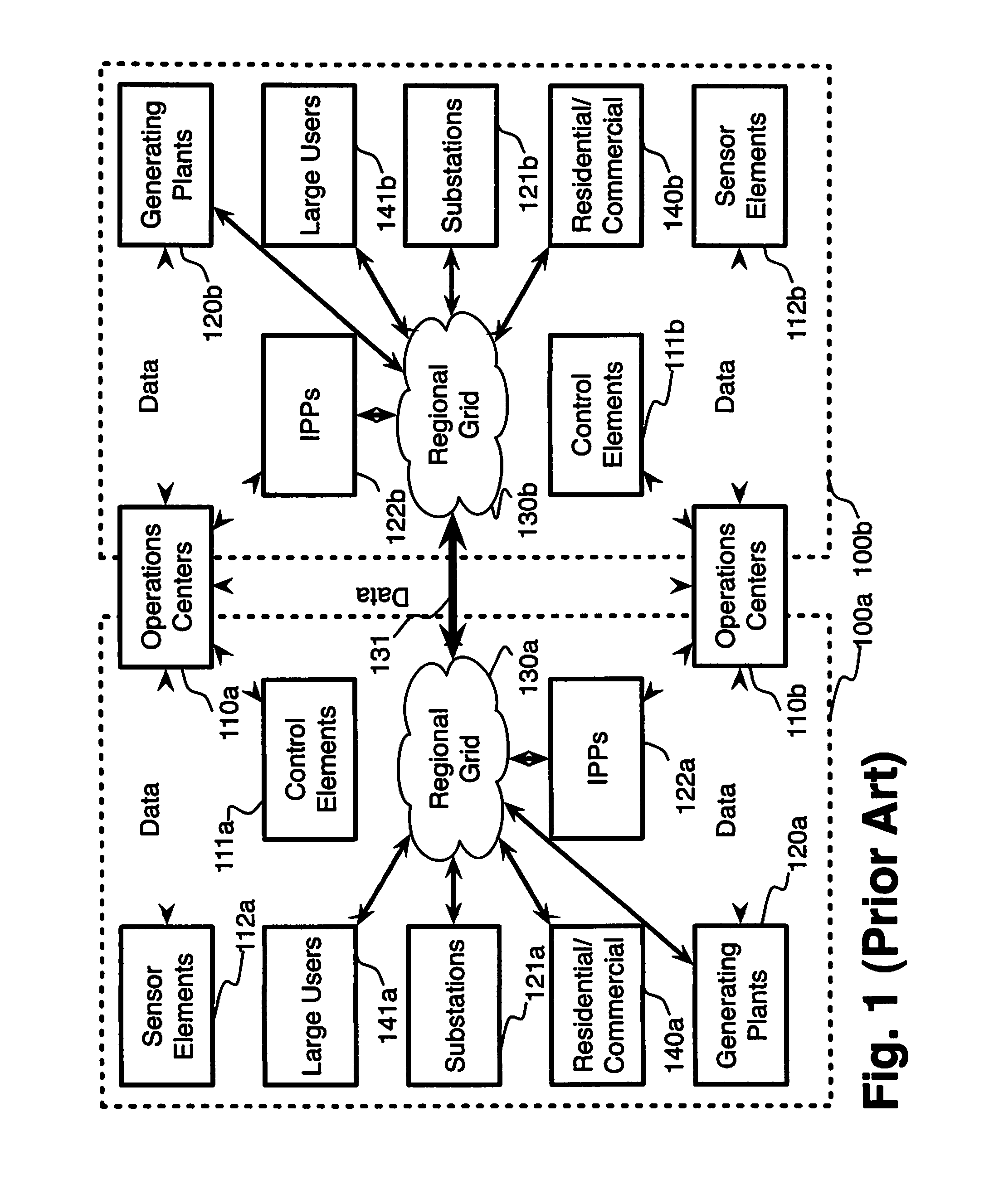
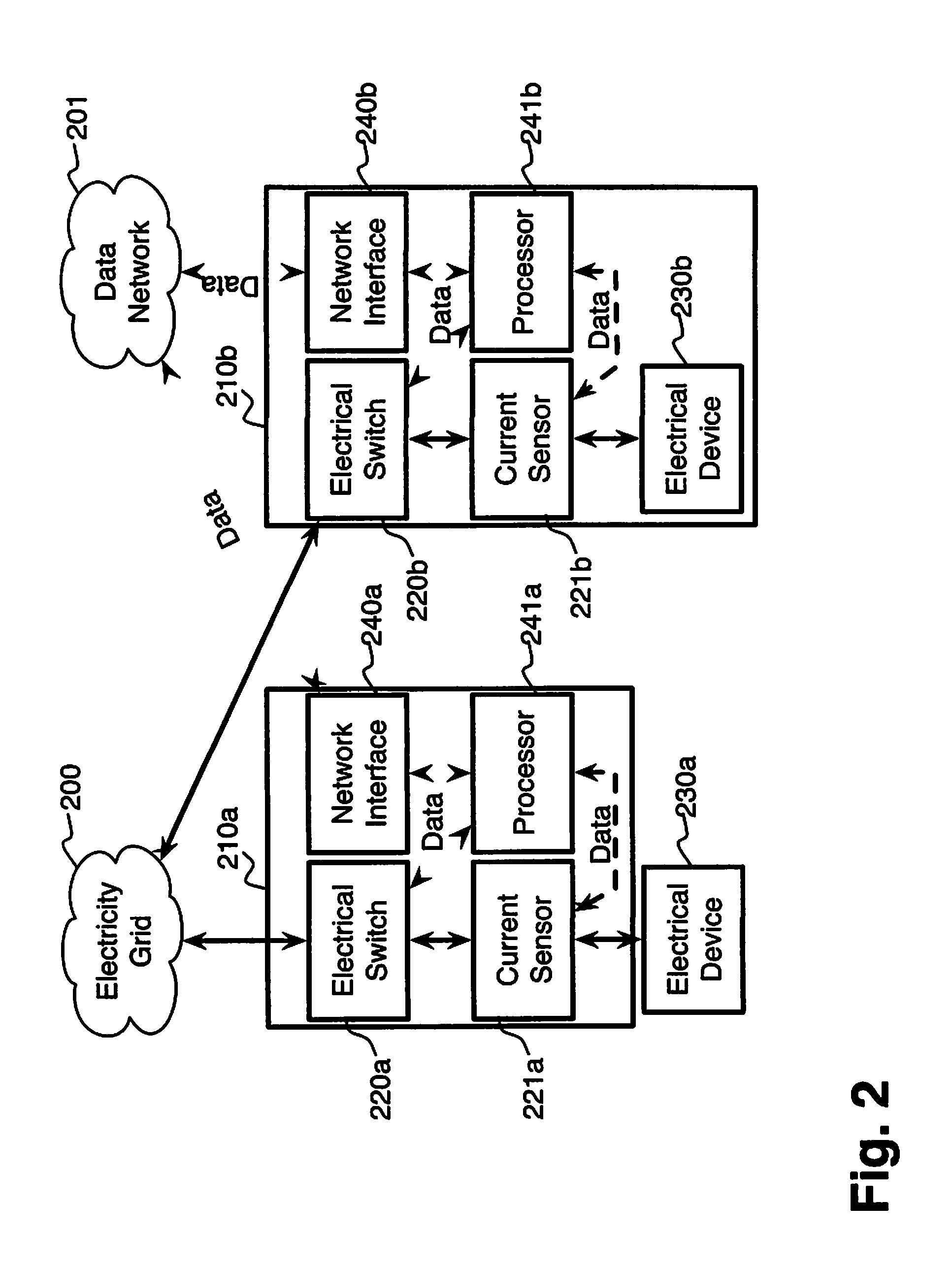
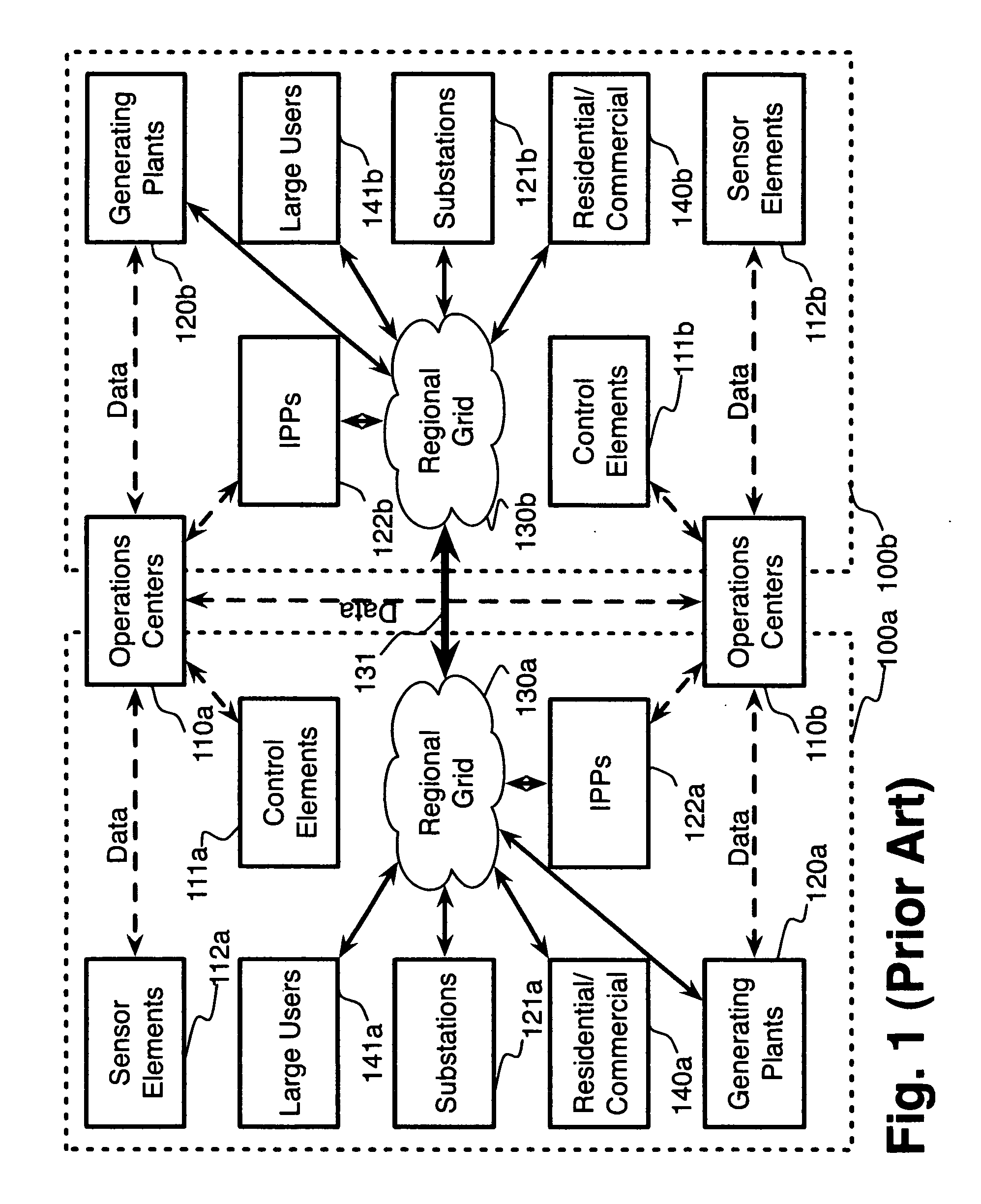
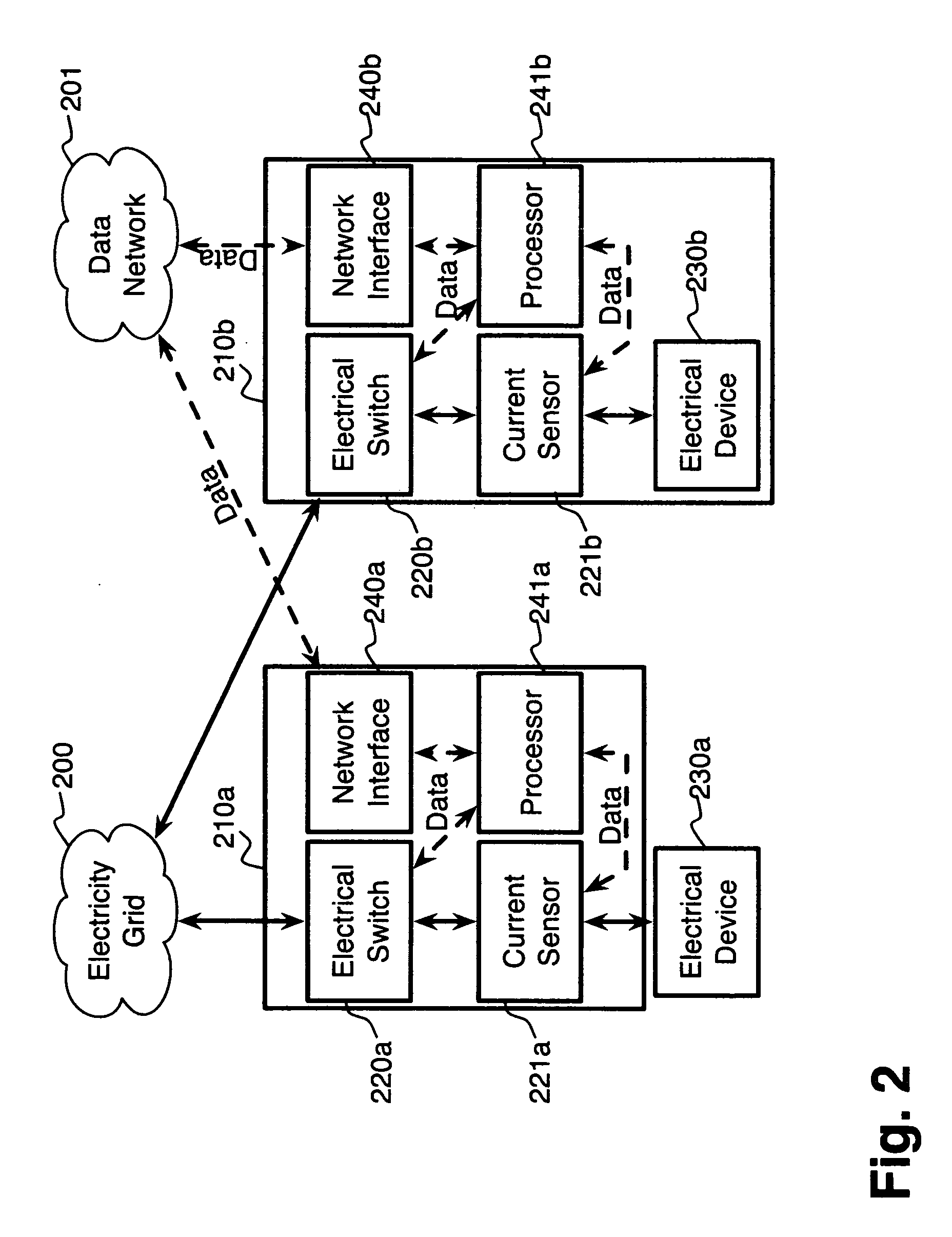
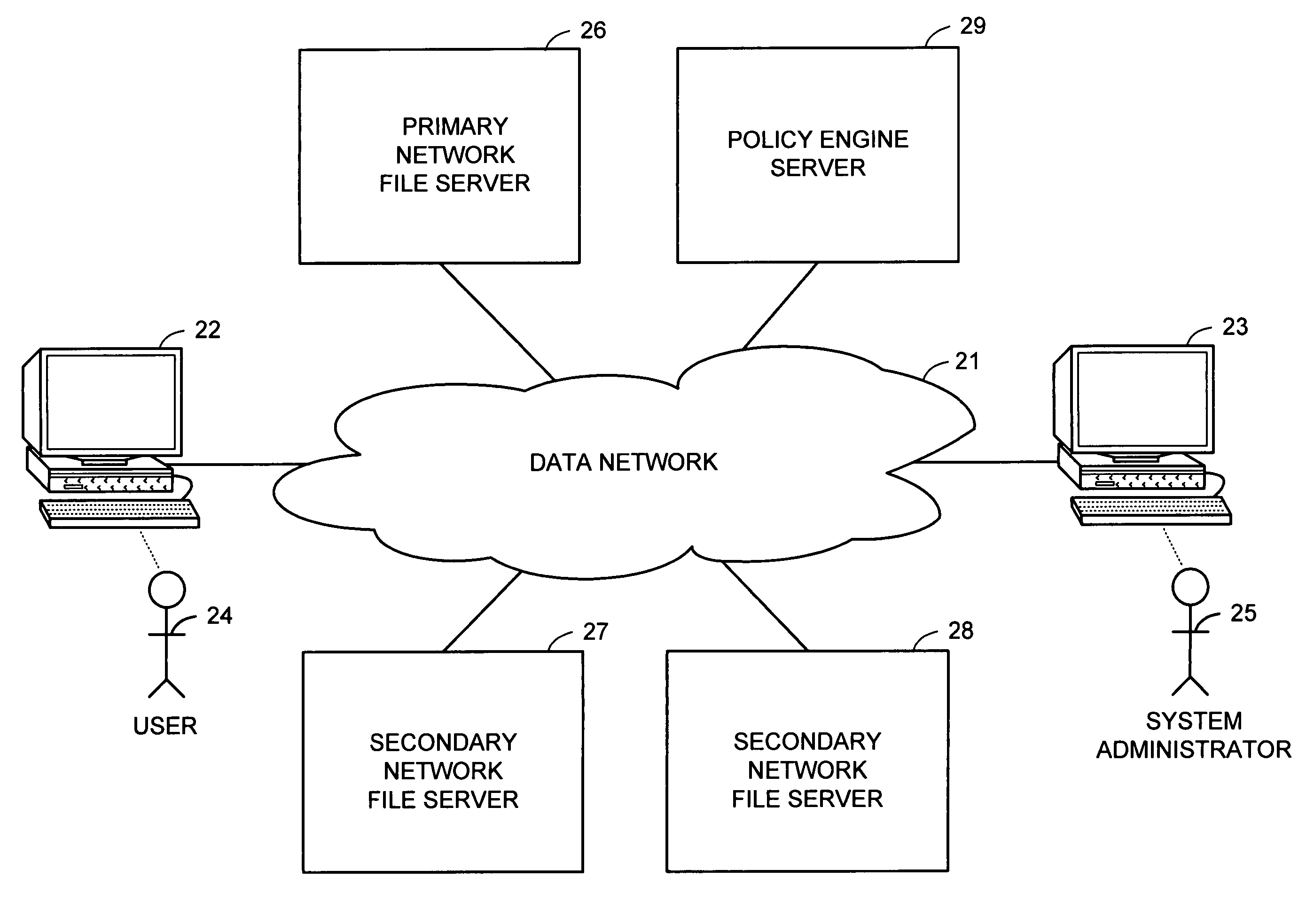
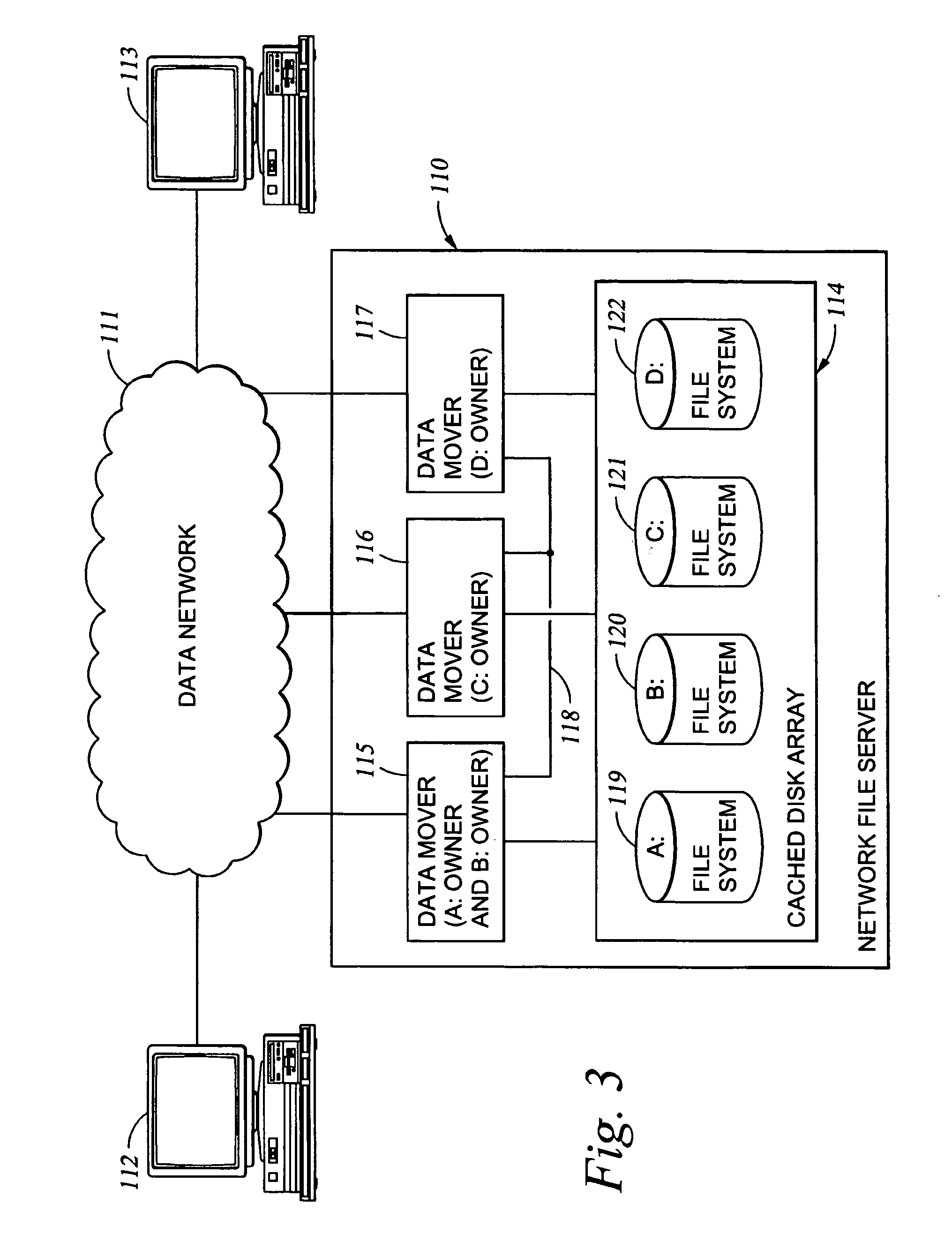
System and method for electric grid utilization and optimization
InactiveUS20100217550A1Selective ac load connection arrangementsElectric devicesSimulationTransmission loss
A system for electric grid utilization and optimization, comprising a communications interface executing on a network-connected server and adapted to receive information from a plurality of iNodes, the plurality of iNodes comprising a source iNode, a sink iNode, and a plurality of transmission or distribution iNodes, an event database coupled to the communications interface and adapted to receive events from a plurality of iNodes via the communications interface, a modeling server coupled to the communications interface, and a statistics server coupled to the event database and the modeling server, wherein the modeling server, on receiving a request to establish an allocation of at least one of transmission losses, distribution losses, and ancillary services to a specific sink iNode, computes at least one virtual path for flow of electricity between a source iNode and the specific sink iNode and wherein the modeling server further computes, for each transmission or distribution iNode included in the computed virtual path, at least one energy loss and allocates a portion thereof to the specific sink iNode, is disclosed.
Owner:CRABTREE JASON +4
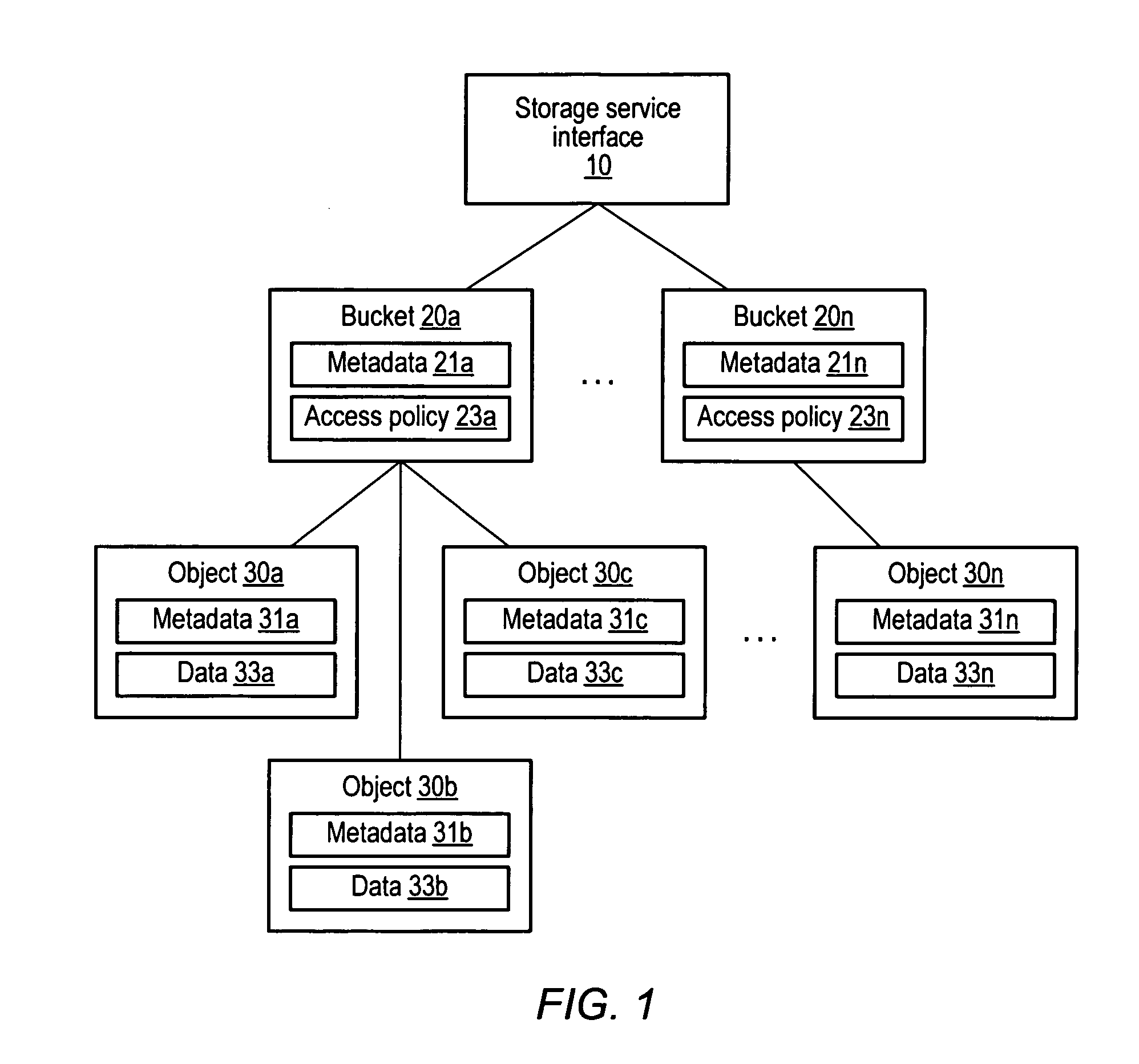
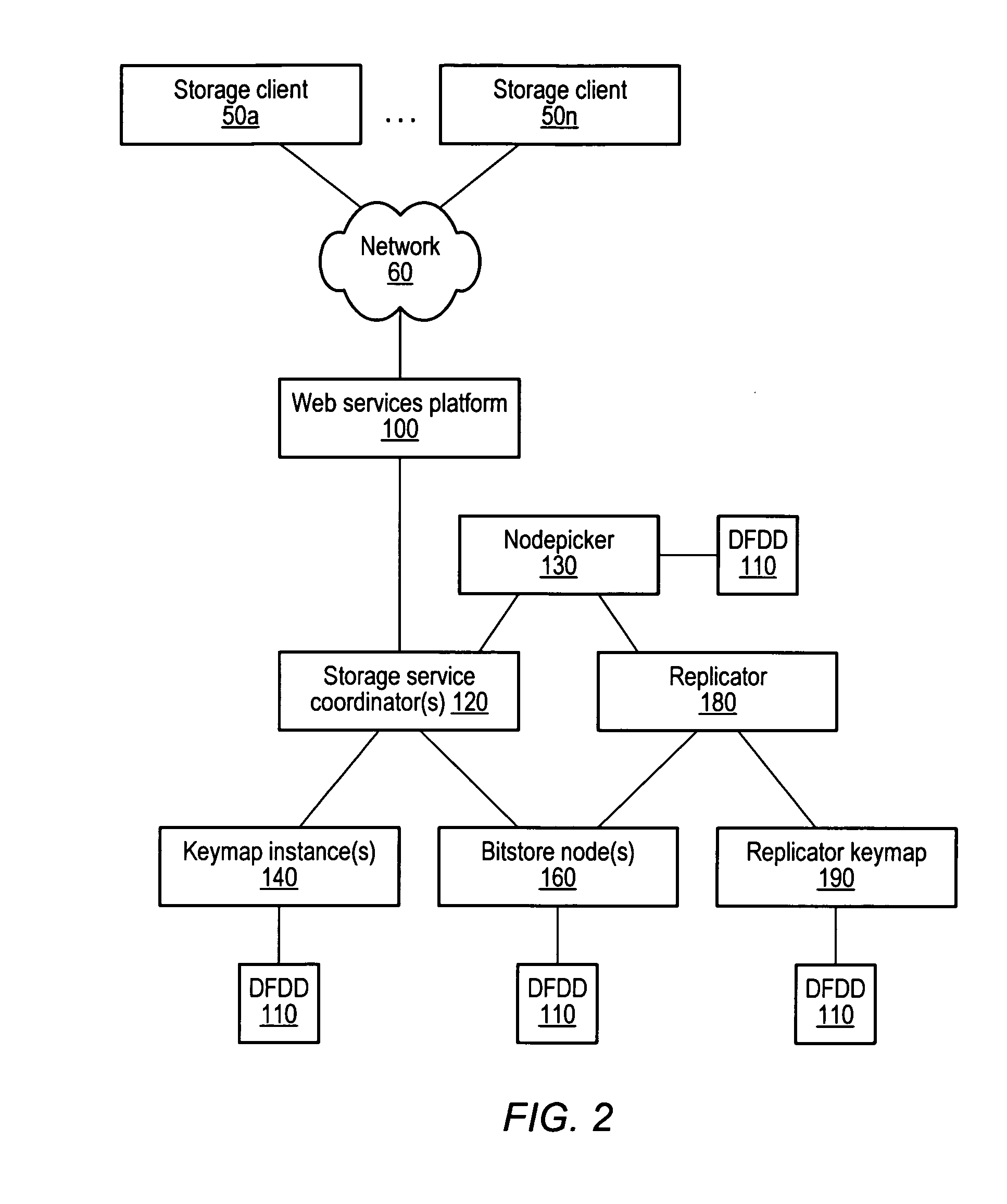
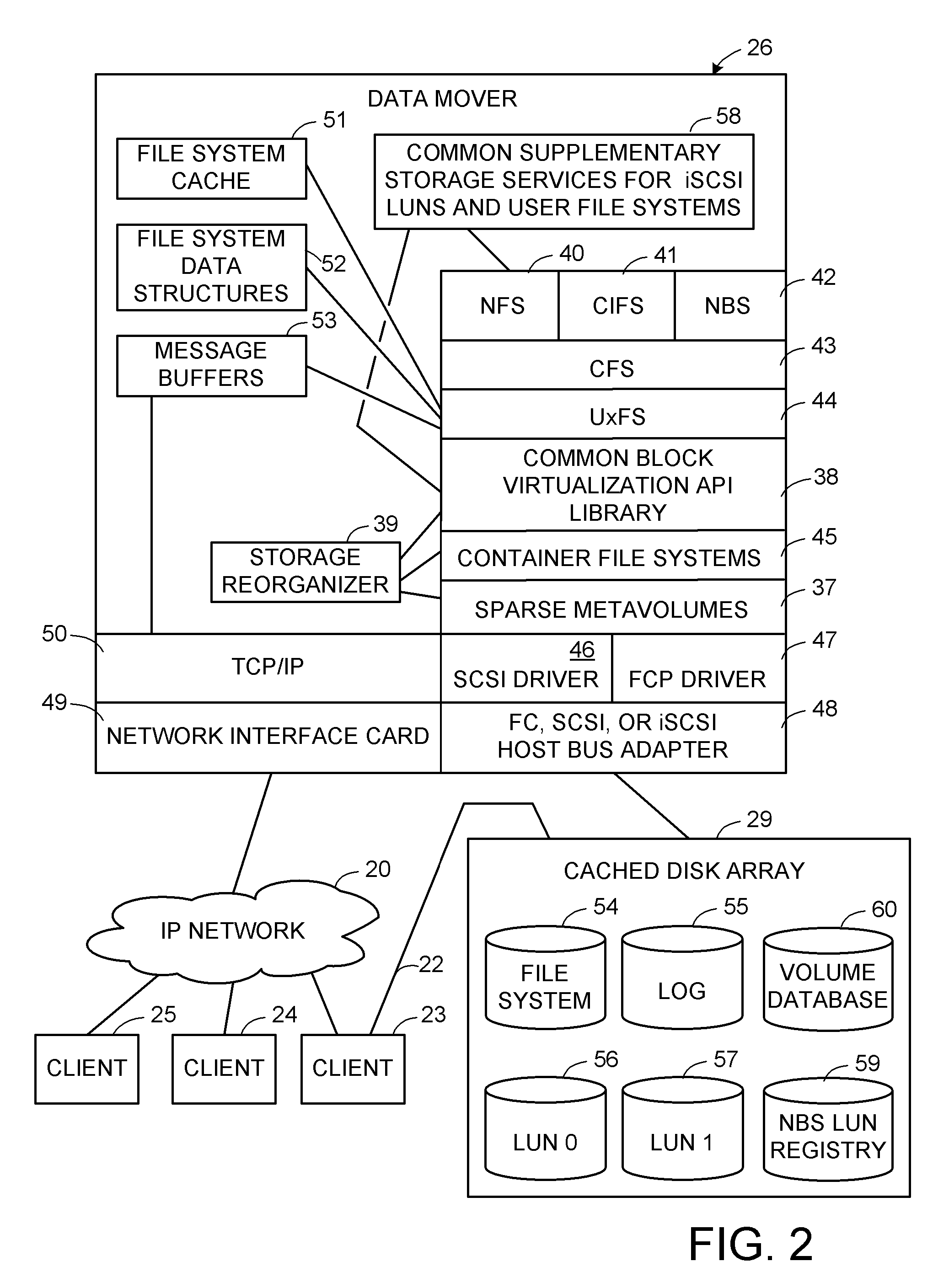
Keymap service architecture for a distributed storage system
A keymap service architecture for a distributed storage system. A system may implement storage nodes configured to store replicas of data objects, where each of the replicas is accessible via a respective locator value, and keymap instances each configured to store keymap entries corresponding respectively to the data objects. A given keymap entry may indicate a mapping from a given key value corresponding to a given data object to each respective locator value of its replicas. Each of the keymap instances may store a replica of the given keymap entry and may index its respective stored keymap entries within a respective index data structure including hierarchically arranged index nodes corresponding to keymap entries. For a given keymap entry having a given corresponding index node, each tag value associated with each ancestor of the given corresponding index node may be a prefix of the given key value.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
System and method for managing energy resources based on a scoring system
Owner:CRABTREE JASON +3
Comfort-driven optimization of electric grid utilization
InactiveUS20150094968A1Improve comfortUtilize and optimizeElectric devicesFinanceCommunication interfaceElectricity
A system for electric grid utilization and optimization comprising a communications interface executing on a network-connected server and adapted to receive information from a plurality of iNodes, the plurality of iNodes comprising a source iNode, a sink iNode, a plurality of transmission or distribution iNodes, an event database coupled to the communications interface and adapted to receive events from a plurality of iNodes via the communications interface, a modeling server coupled to the communications interface, and a statistics server coupled to the event database and the modeling server, wherein the modeling server, receives a request to establish an allocation of at least one of transmission losses, distribution losses, and ancillary services to a specific sink iNode, computes at least one virtual path for electricity flow between a source iNode and the specific sink iNode, the computed path being determined based on optimization of perceived comfort of users in affected areas.
Owner:DISTRIBUTED ENERGY MANAGEMENT
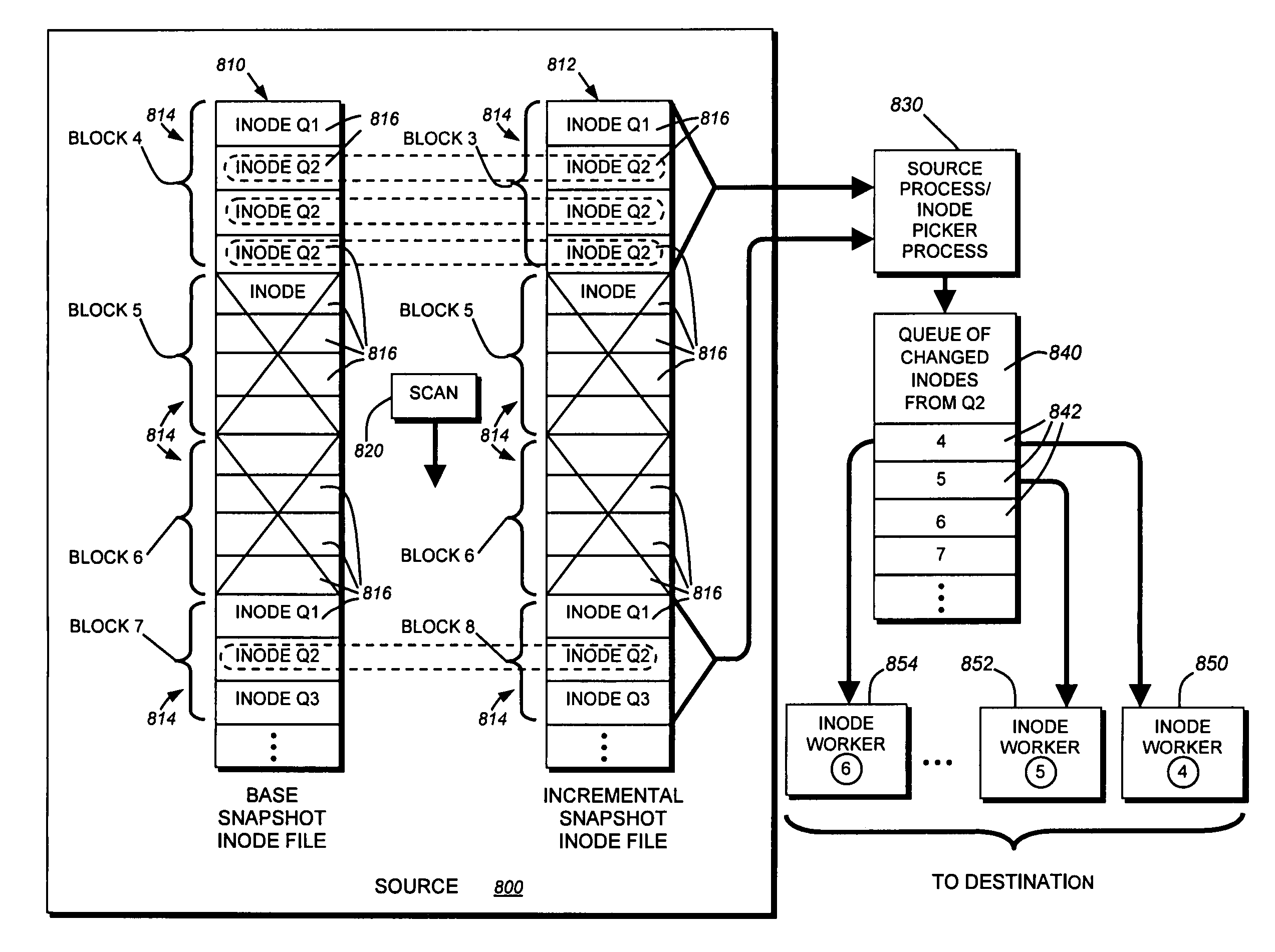
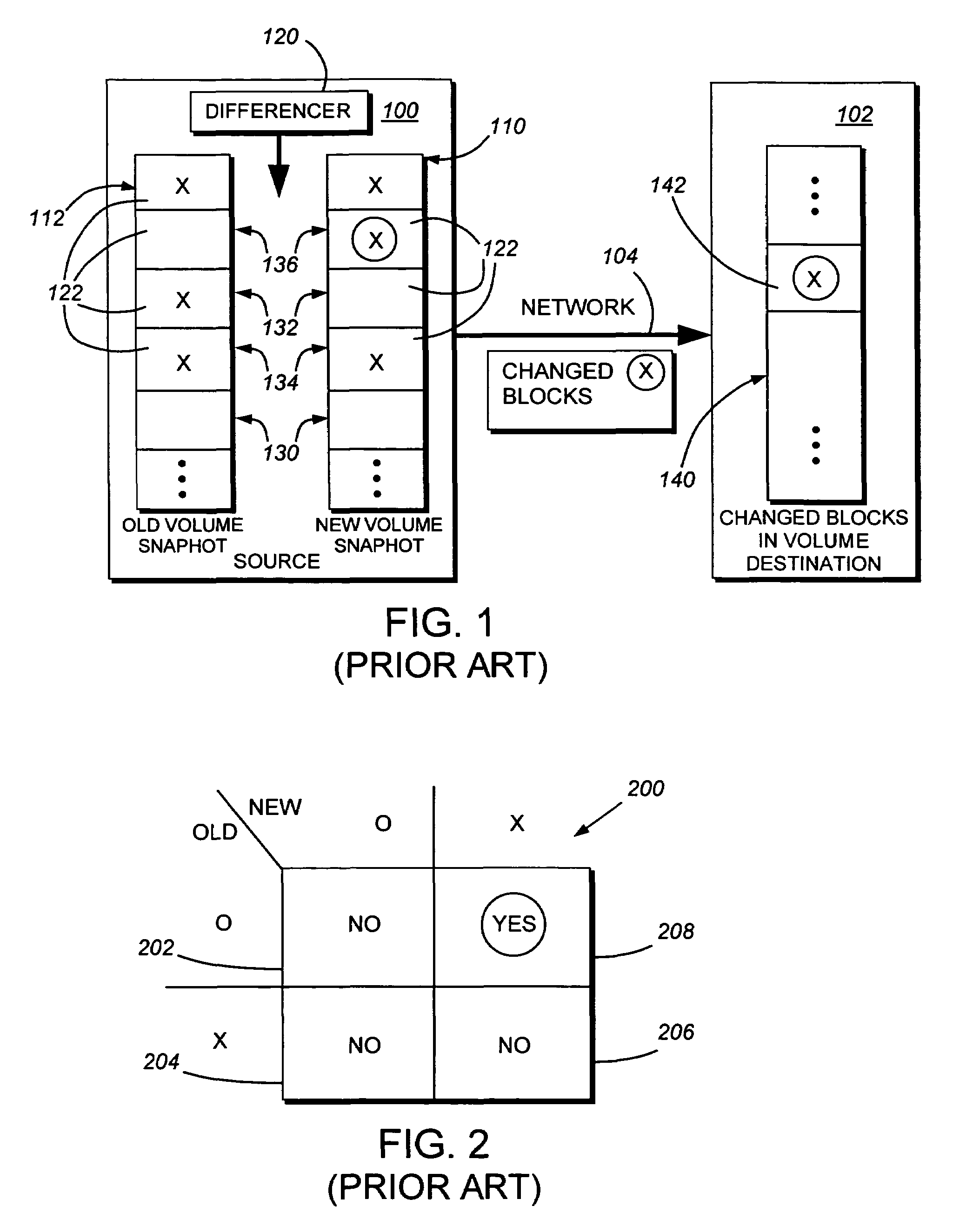
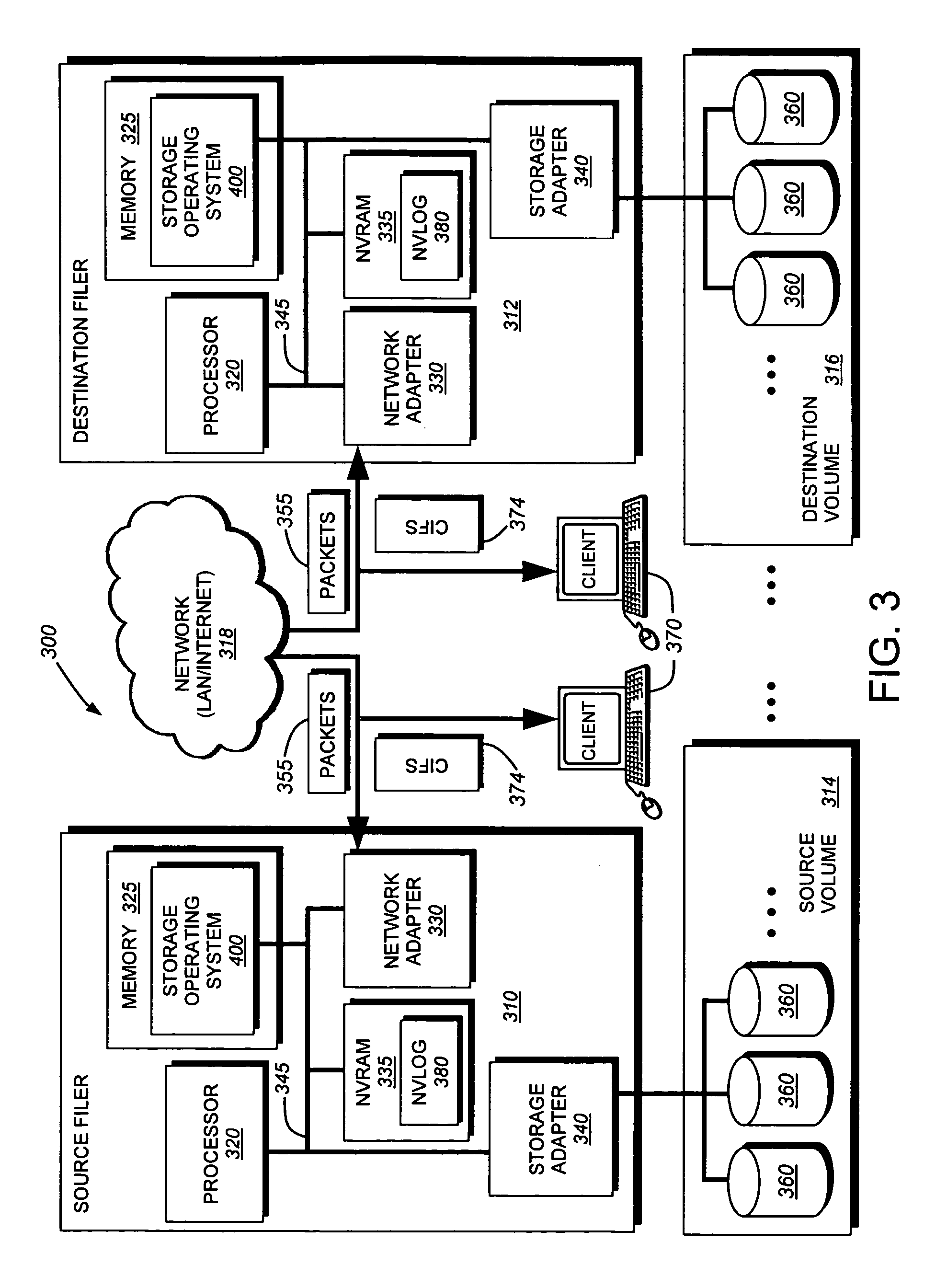
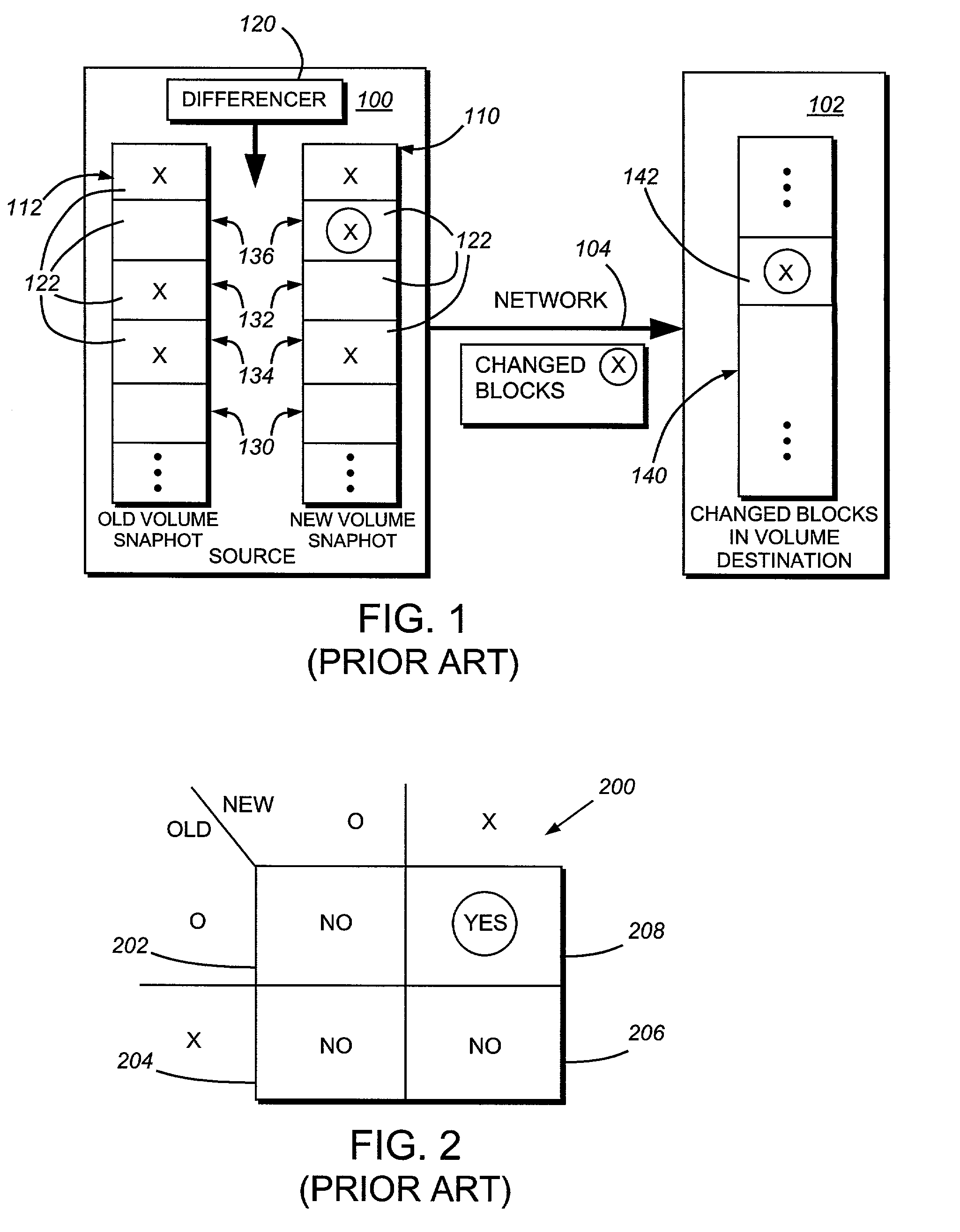
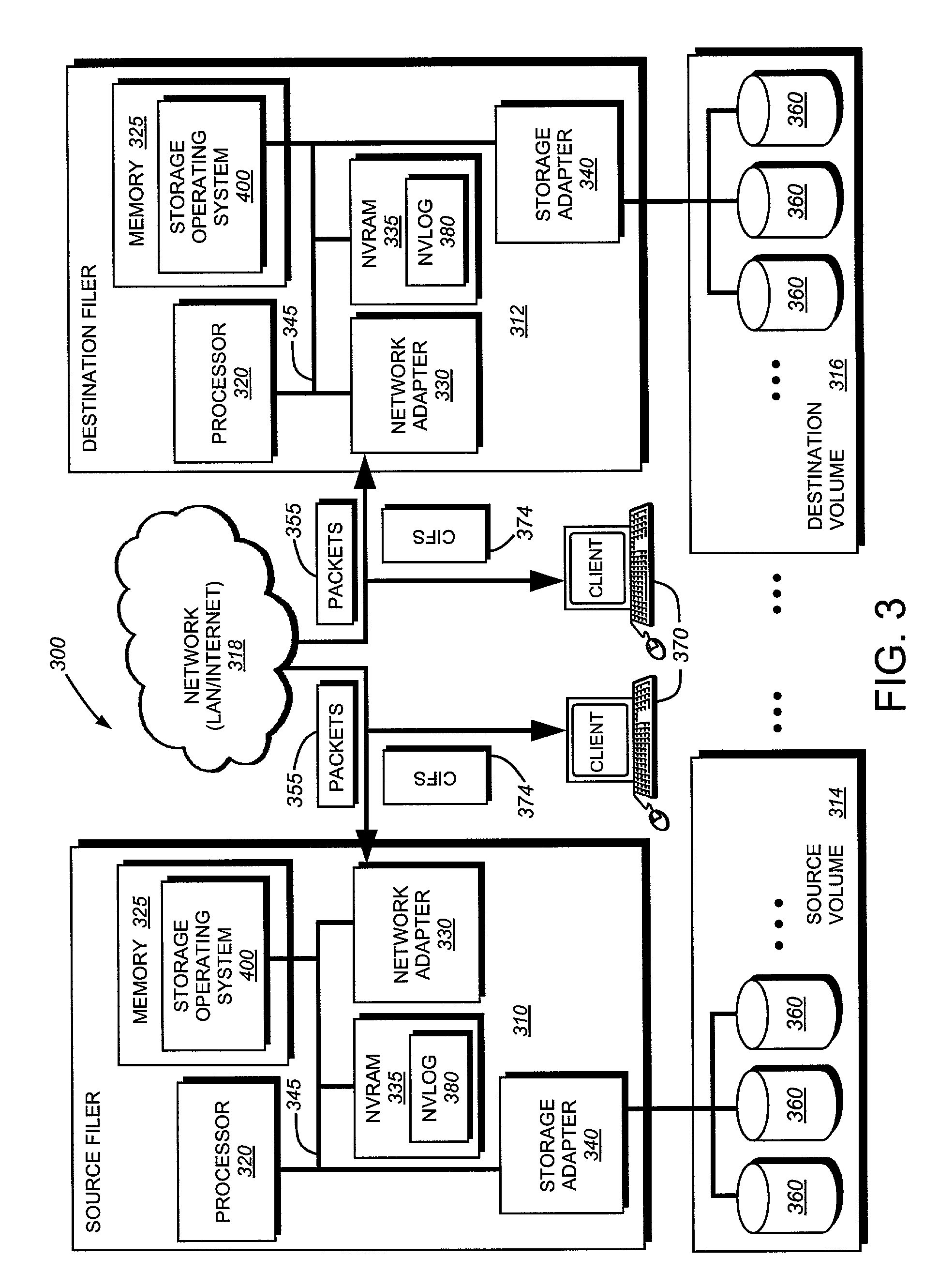
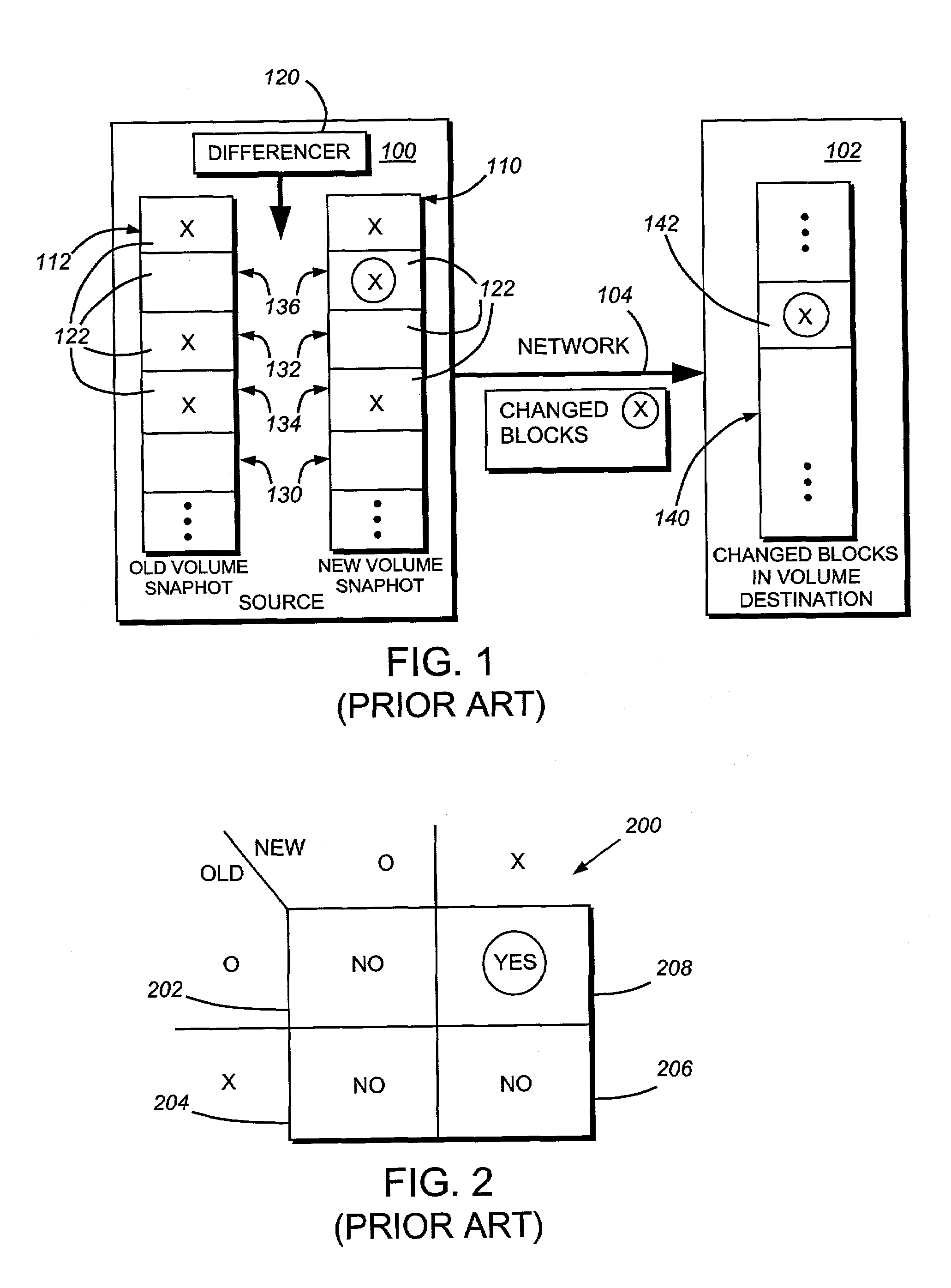
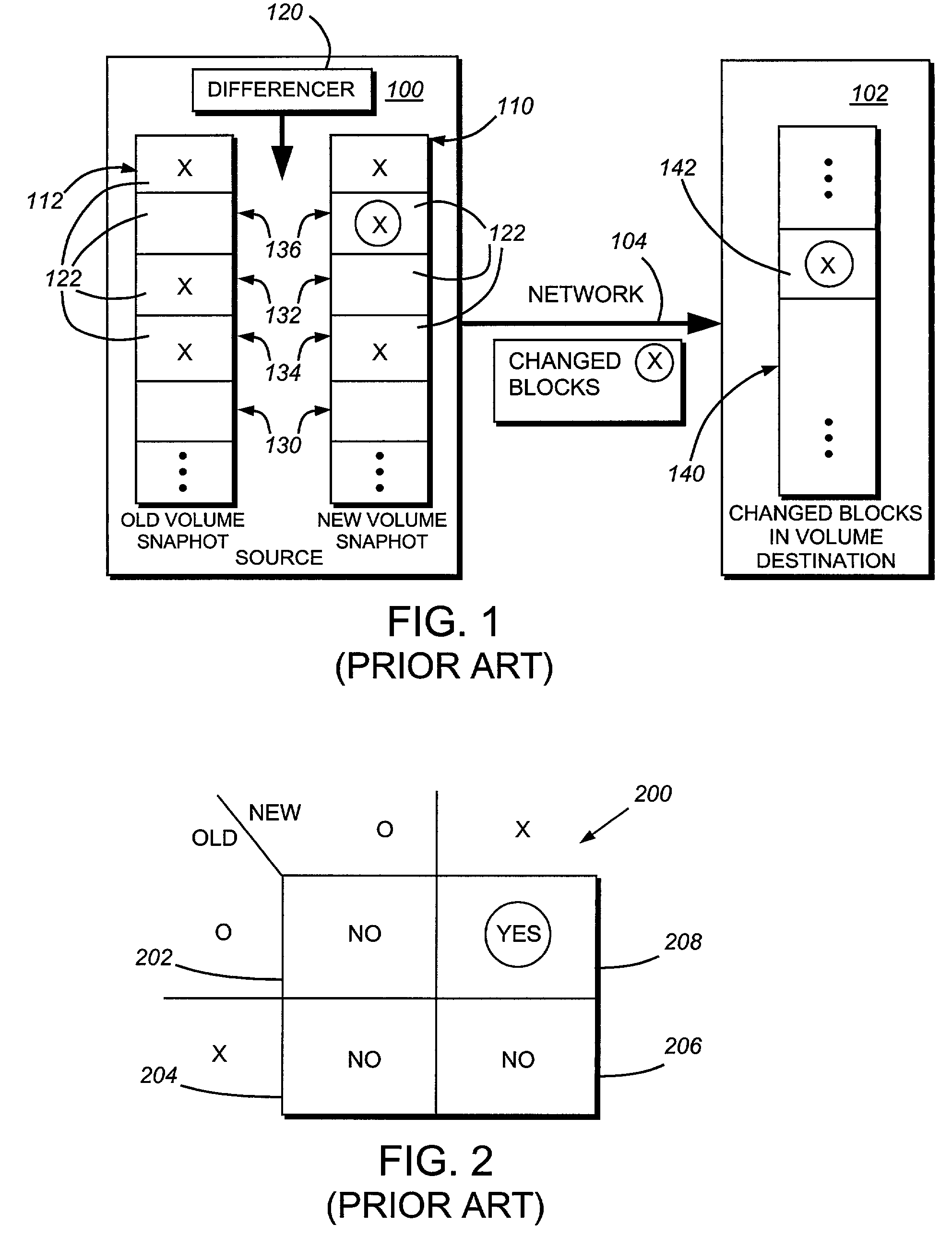
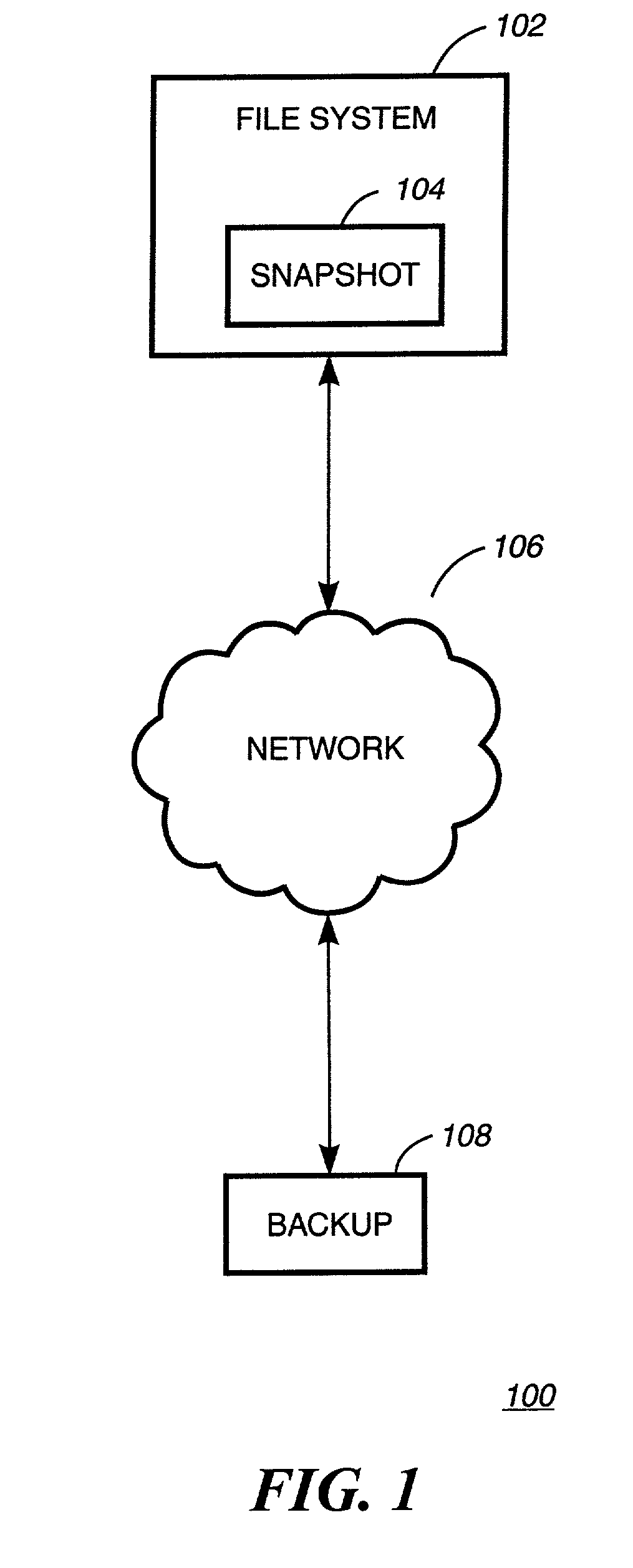
System and method for determining changes in two snapshots and for transmitting changes to destination snapshot
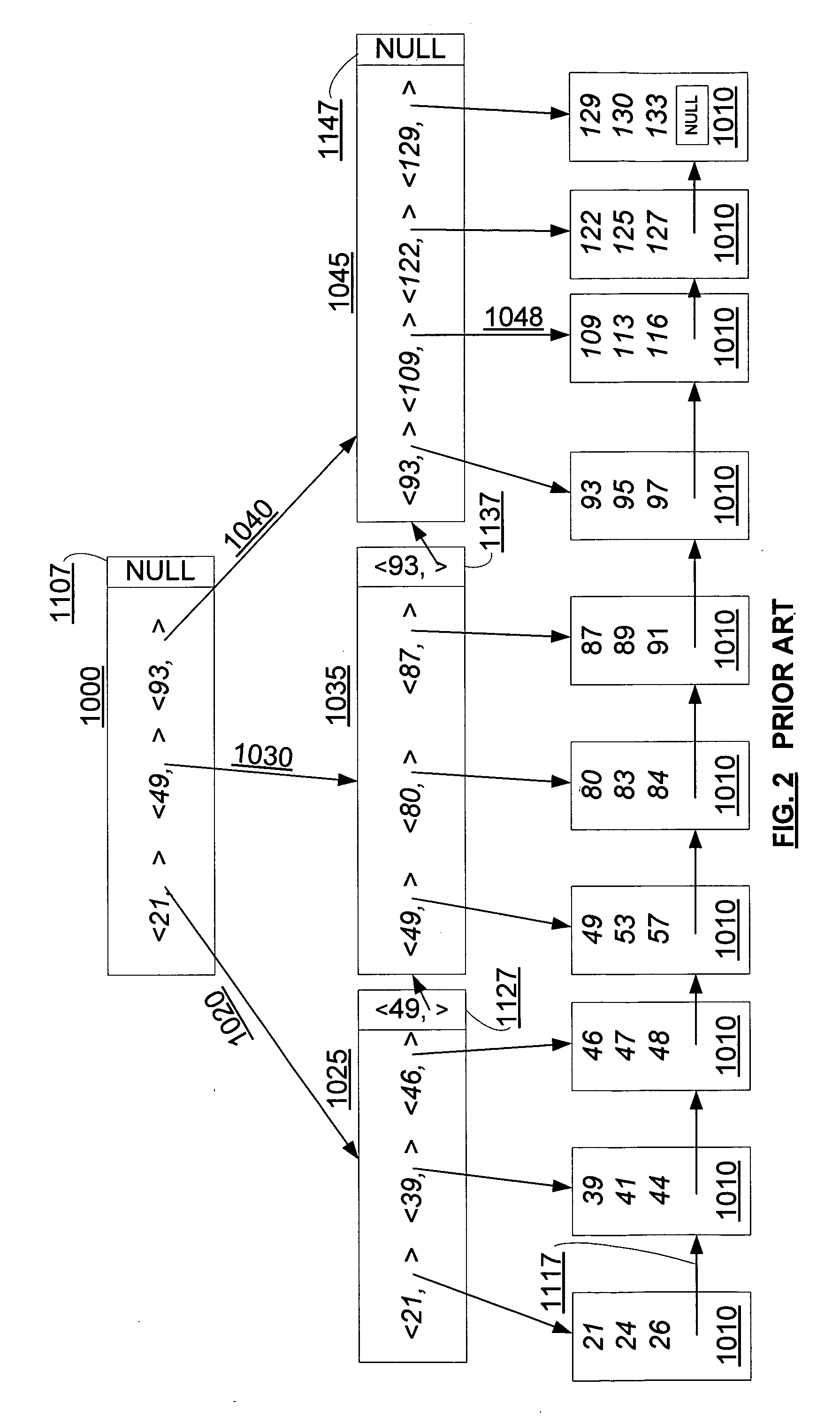
InactiveUS6993539B2Efficient scanningOvercome disadvantagesData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsData streamInode
A system and method for remote asynchronous replication or mirroring of changes in a source file system snapshot in a destination replica file system using a scan (via a scanner) of the blocks that make up two versions of a snapshot of the source file system, which identifies changed blocks in the respective snapshot files based upon differences in volume block numbers identified in a scan of the logical file block index of each snapshot. Trees of blocks associated with the files are traversed, bypassing unchanged pointers between versions and walking down to identify the changes in the hierarchy of the tree. These changes are transmitted to the destination mirror or replicated snapshot. This technique allows regular files, directories, inodes and any other hierarchical structure to be efficiently scanned to determine differences between versions thereof. The changes in the files and directories are transmitted over the network for update of the replicated destination snapshot in an asynchronous (lazy write) manner. The changes are described in an extensible, system-independent data stream format layered under a network transport protocol. At the destination, source changes are used to update the destination snapshot. Any deleted or modified inodes already on the destination are moved to a temporary or “purgatory” directory and, if reused, are relinked to the rebuilt replicated snapshot directory. The source file system snapshots can be representative of a volume sub-organization, such as a qtree.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Dynamic pricing system and method for complex energy securities
A dynamic pricing system for complex energy securities, comprising a communications interface executing on a network-connected server and adapted to receive information from a plurality of iNodes, an event database coupled to the communications interface and adapted to receive events from a plurality of iNodes via the communications interface, a pricing server coupled to the communications interface, and a statistics server coupled to the event database and the pricing server, is disclosed. According to the invention, the pricing server, on receiving a request to establish a price for an energy security, requests at least one statistical indicia of risk from the statistics server, the statistical indicia of risk being computed by the statistics server based on a plurality of historical data obtained from the event database, and the pricing server computes a price for the security based at least in part on the statistical indicia of risk.
Owner:CRABTREE JASON +3
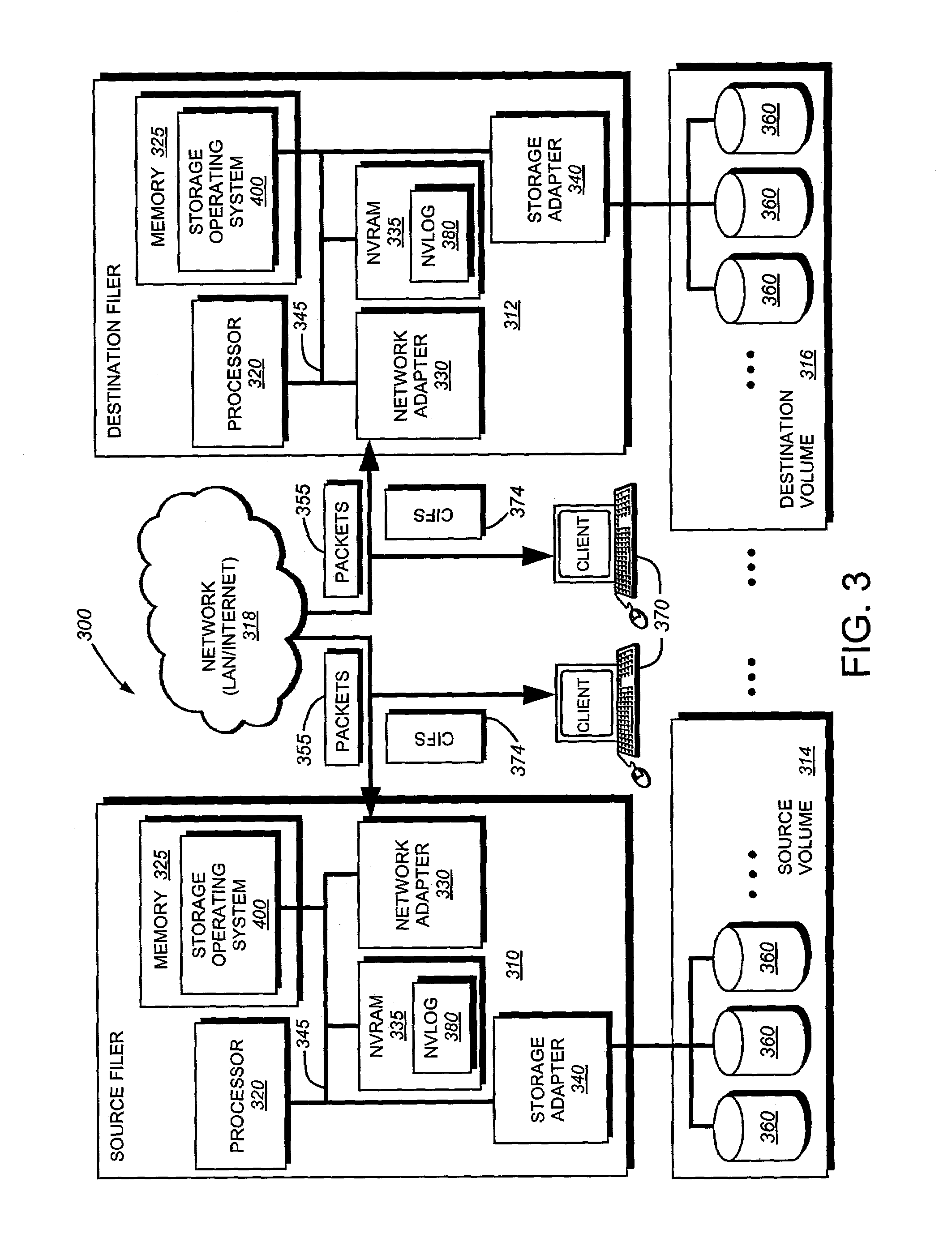
System and method for asynchronous mirroring of snapshots at a destination using a purgatory directory and inode mapping
ActiveUS7225204B2Improve versatilityImprove utilizationData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsInodeComputer science
A system and method for updating a replicated destination file system snapshot with changes in a source file system snapshot, facilitates construction of a new directory tree on the destination from source update information using a temporary or “purgatory” directory that allows any modified and deleted files on the destination active file system to be associated with (e.g. moved to) the purgatory directory if and until they are reused. In addition, an inode map is established on the destination that maps source inode numbers to destination inode numbers so as to facilitate building of the destination tree using inode / generation number tuples. The inode map allows resynchronization of the source file system to the destination. The inode map also allows association of two or more destination snapshots to each other based upon their respective maps with the source.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Maintenance of a file version set including read-only and read-write snapshot copies of a production file
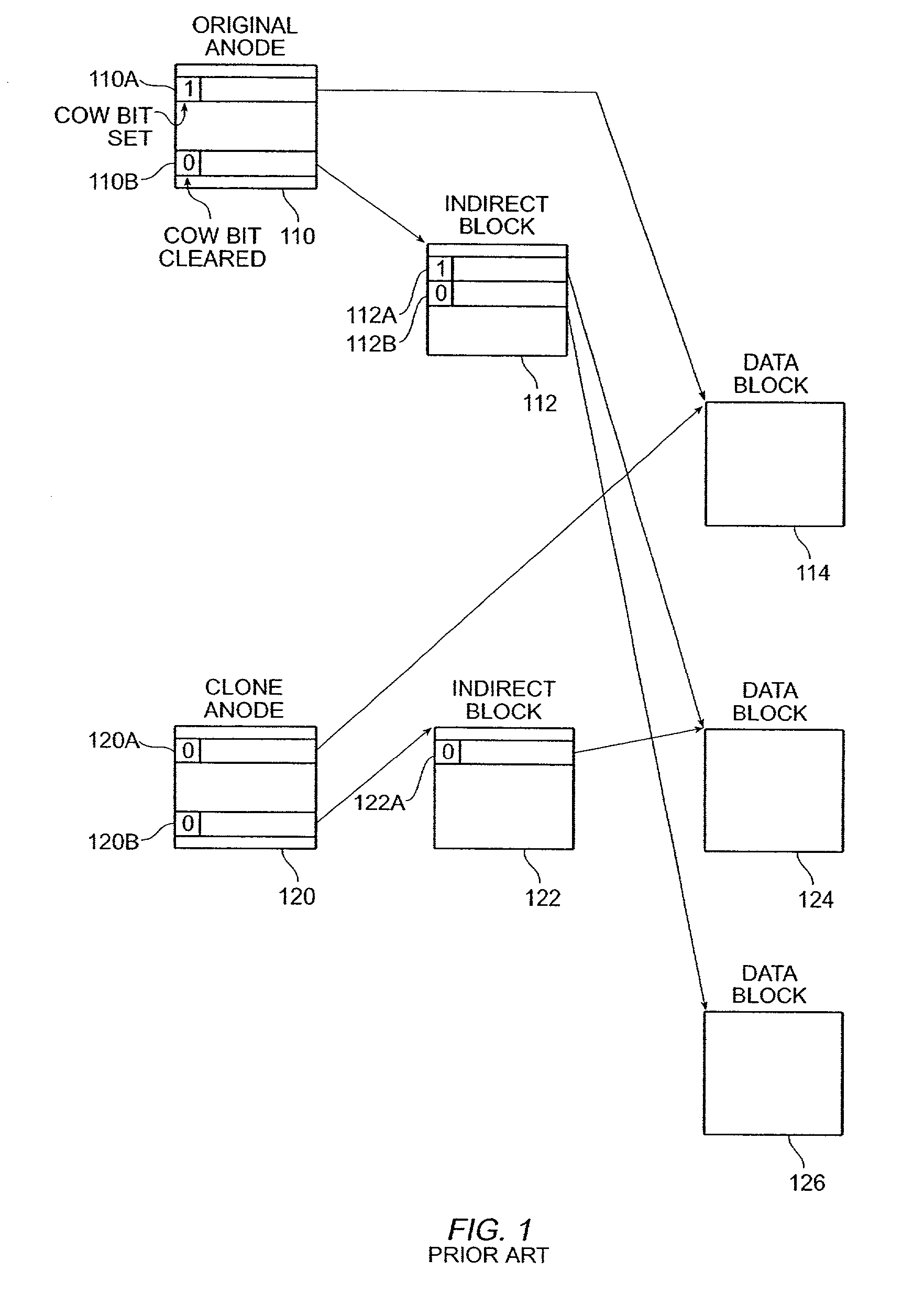
Read-only and read-write snapshot copies of a production file in a Unix-based file system are organized as a version set of file inodes and shared file blocks. Version pointers and branch pointers link the inodes. Initially the production file can have all its blocks preallocated or it can be a sparse file having only an inode and its last data block. A protocol is provided for creating read-only and read-write snapshots, deleting snapshots, restoring the production file with a specified snapshot, refreshing a specified snapshot, and naming the snapshots. Block pointers are marked with a flag indicating whether or not the pointed-to block is owned by the parent inode. A non-owner marking is inherited by all of the block's descendants. The block ownership controls the copying of indirect blocks when writing to the production file, and also controls deallocation and passing of blocks when deleting a read-only snapshot.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
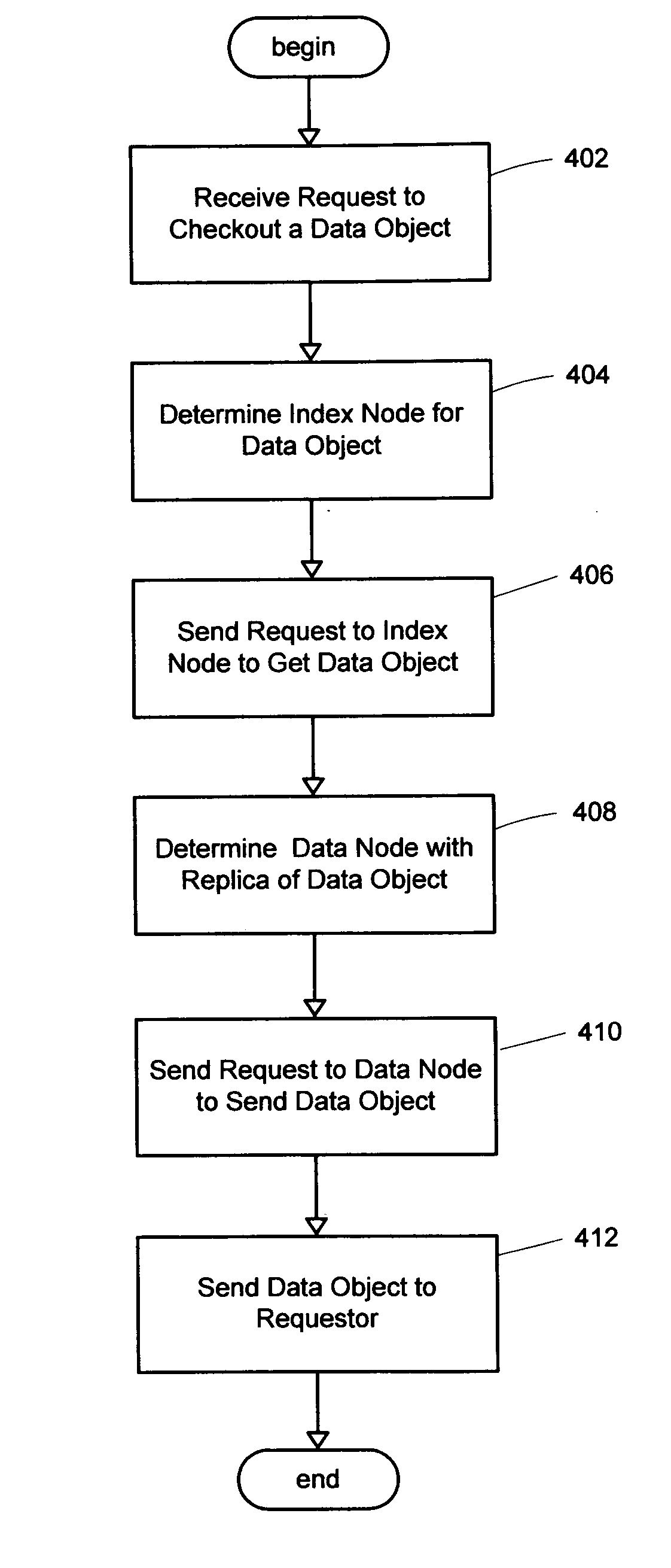
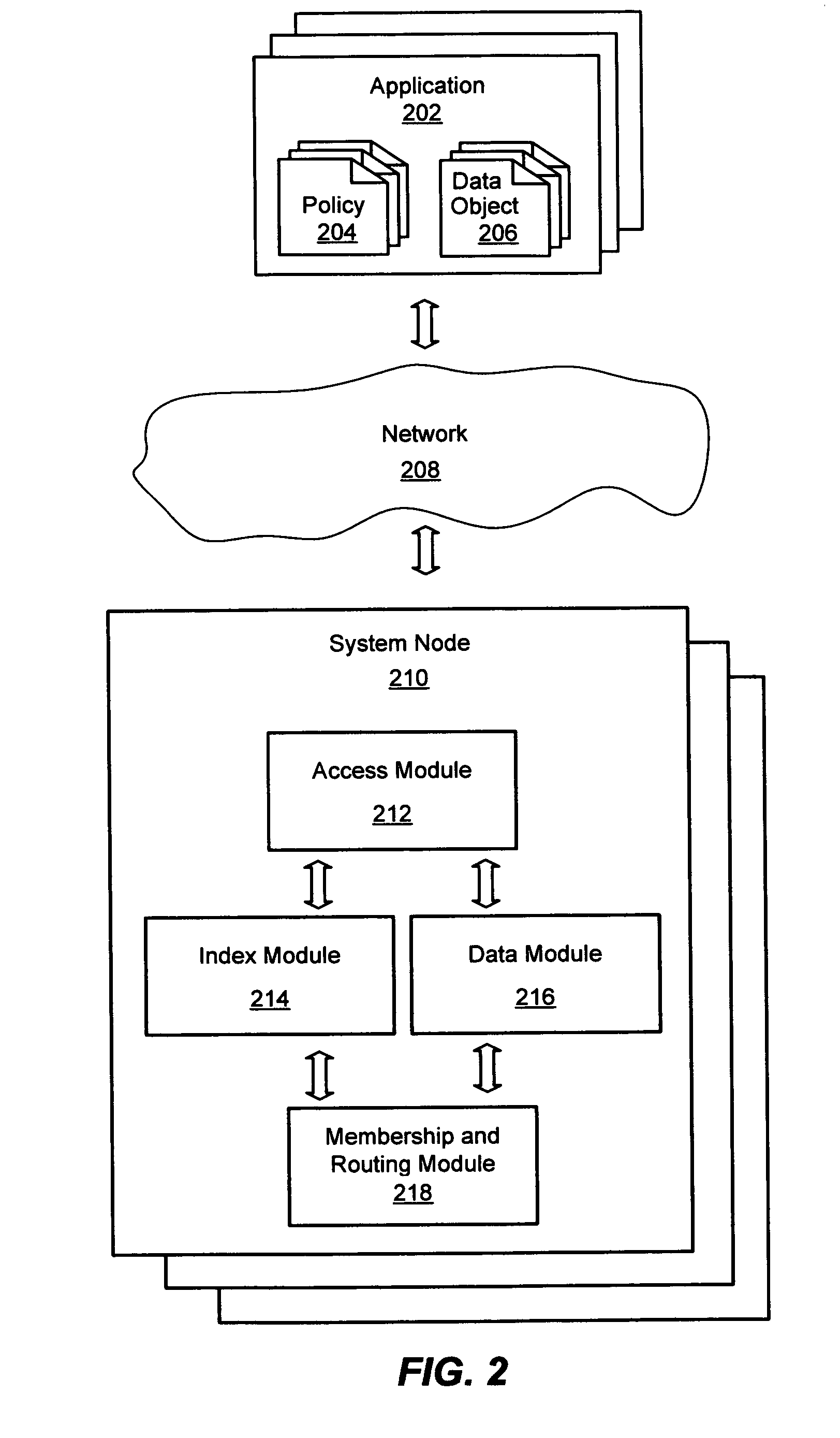
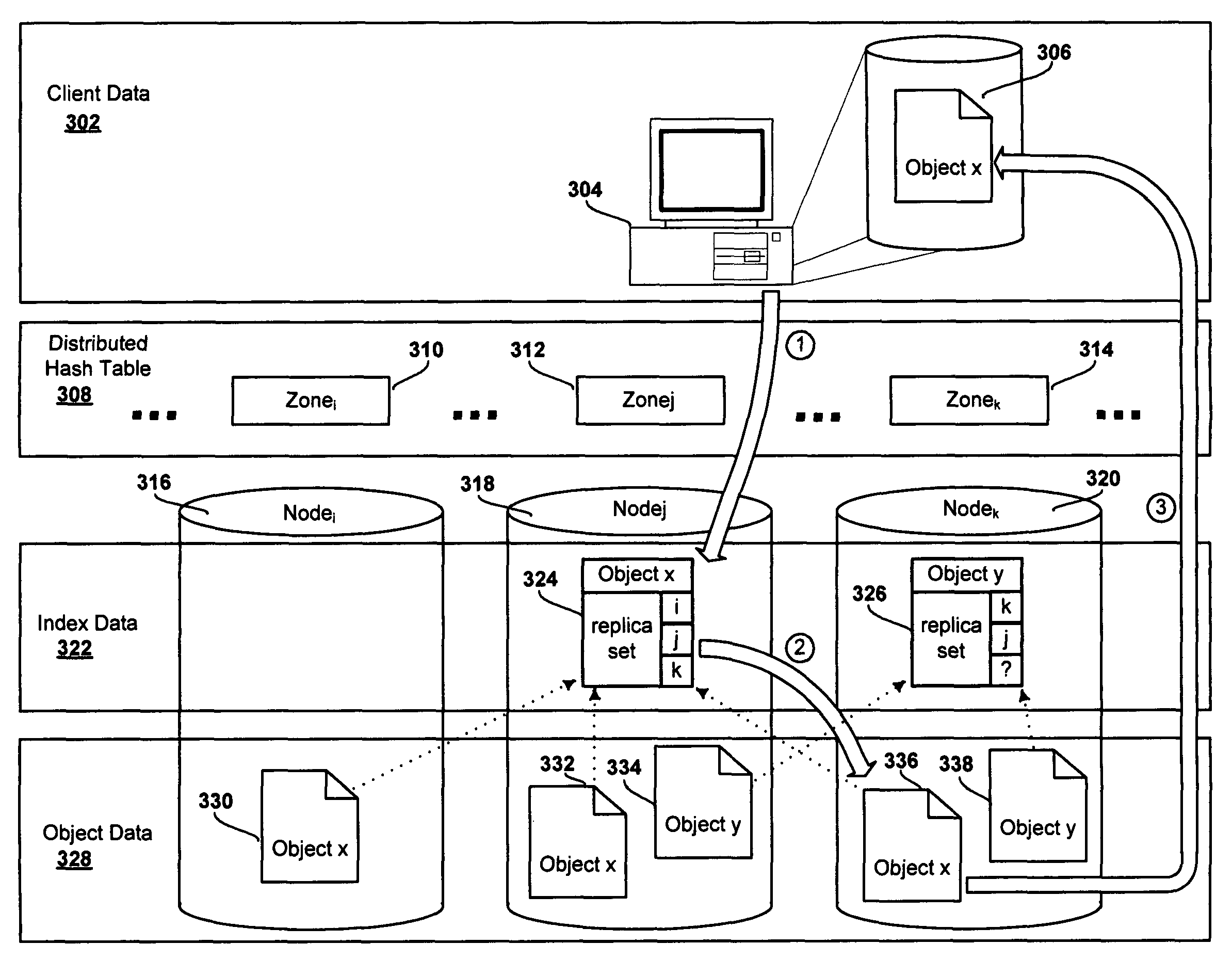
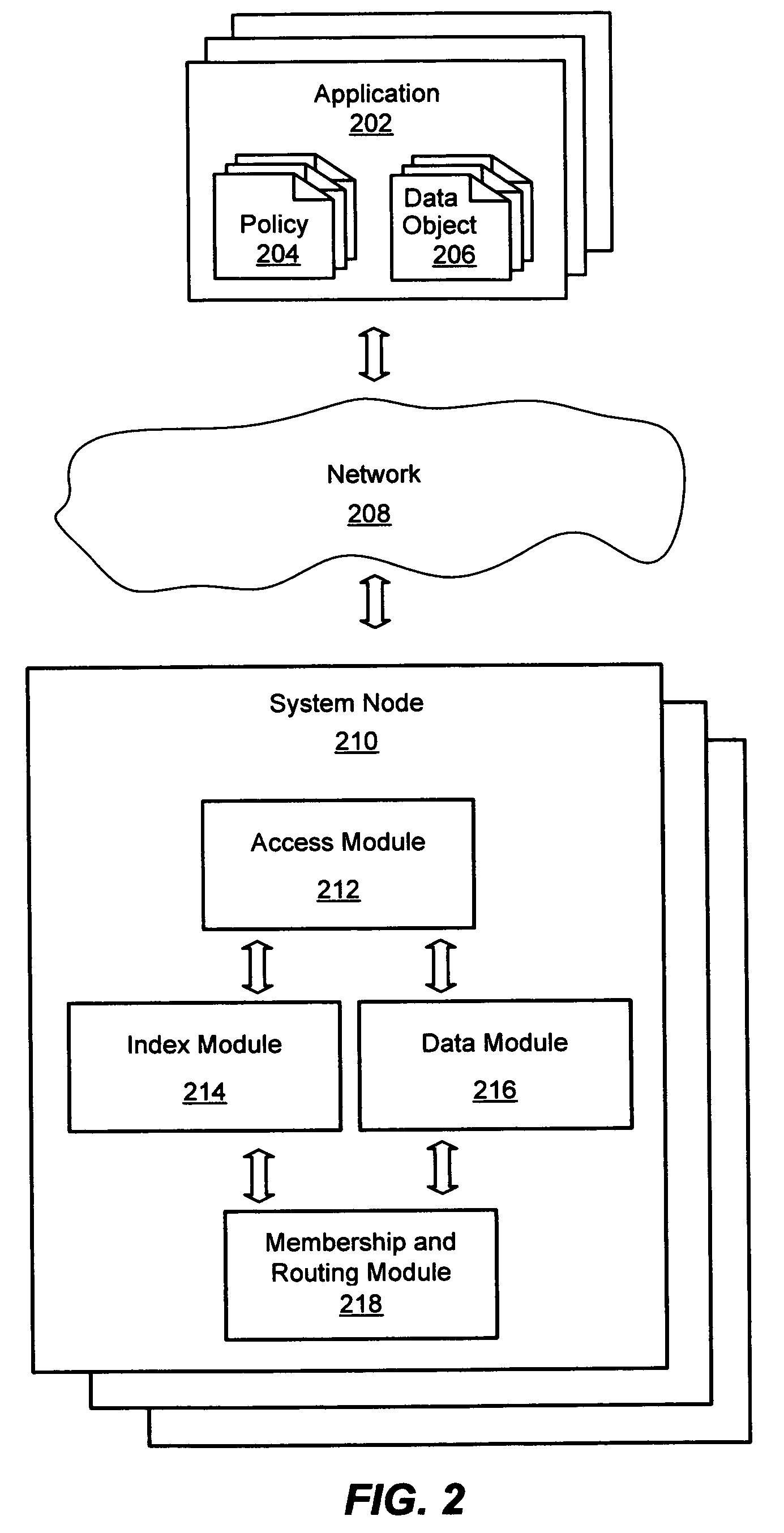
System and method for a distributed object store
InactiveUS20060168154A1Restore numberDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionDistributed objectInode
An improved system and method for flexible object placement and soft-state indexing of objects in a distributed object store is provided. A distributed object store may be provided by a large number of system nodes operably coupled to a network. A system node provided may include an access module for communicating with a client, an index module for building an index of a replicated data object, a data module for storing a data object on a computer readable medium, and a membership and routing module for detecting the configuration of operable nodes in the distributed system. Upon failure of an index node, the failure may be detected at other nodes, including those nodes that store the replicas of the object. These nodes may then send new index rebuilding requests to a different node that may rebuild the index for servicing any access request to the object.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
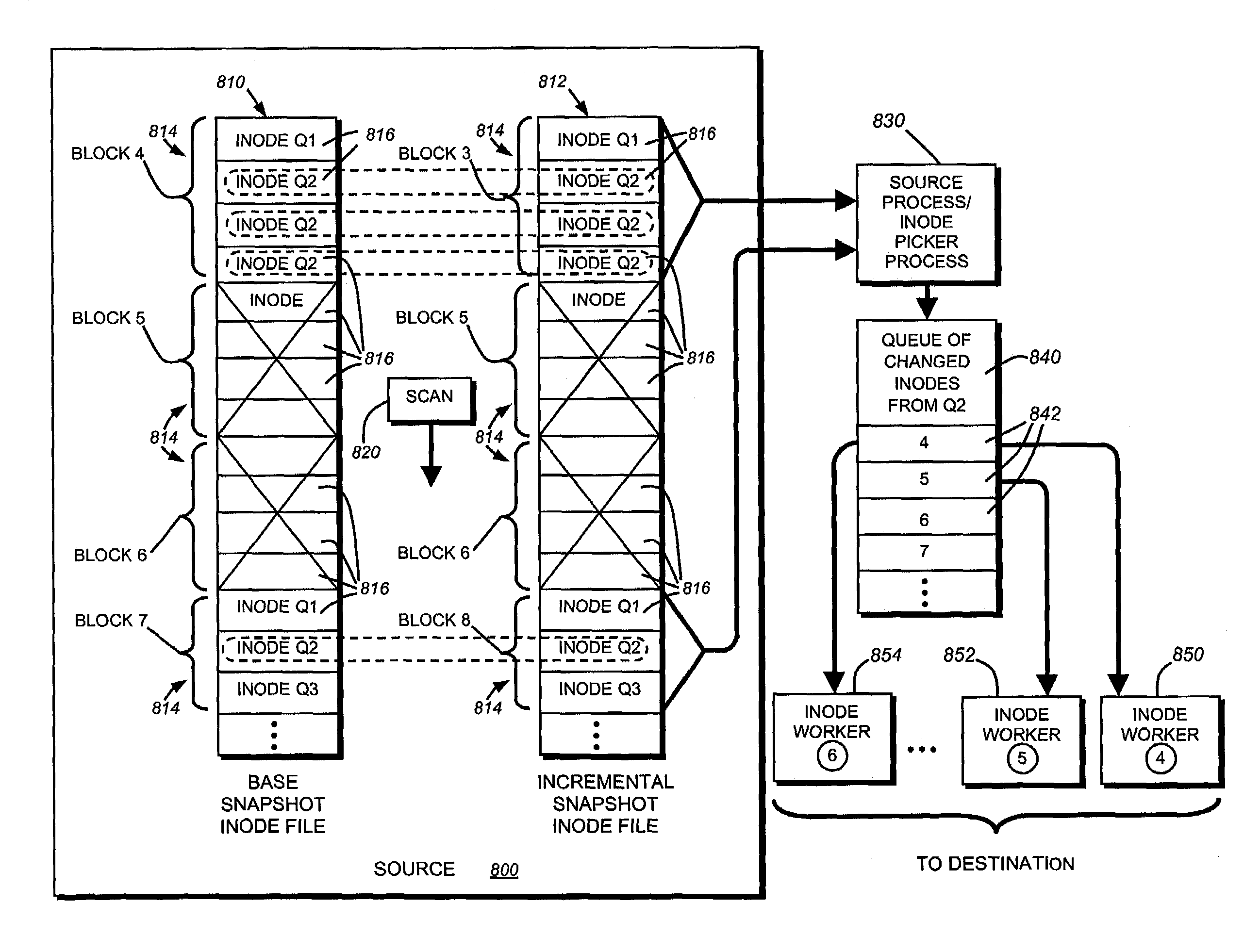
System and method for checkpointing and restarting an asynchronous transfer of data between a source and destination snapshot
InactiveUS7039663B1Significant processing timeSignificant processor overheadDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsData streamInode
A system and method for inserting checkpoints into a data stream and for restarting an asynchronous transmission of a data stream from a source file system to a destination file system is provided. The data stream can be a set of changes between a base snapshot and incremental snapshot of the source file system for update of a replicated file system on the destination. State information relating to the progress of the source in processing and transmitting the data stream is stored at regular intervals, and a checkpoint number associated with each stored segment of the state information is inserted into the data stream. The destination tracks the fall commitment of each segment of the data stream to persistent storage on the replicated file system. If an error or communication loss requires the data transfer to be restarted, the destination sends the checkpoint number associated with the last fully committed segment of the data stream. The source reinitializes its data gathering processes using the state information associated with the particular checkpoint number. The changes sent from the source file system to the destination file system relate to a sub-organization of a volume on the source such as a qtree, identified by a qtree identifier (ID) in the associated inodes and data stream.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
System and method for a distributed object store
InactiveUS7778984B2Error detection/correctionDigital data processing detailsDistributed objectClient-side
An improved system and method for flexible object placement and soft-state indexing of objects in a distributed object store is provided. A distributed object store may be provided by a large number of system nodes operably coupled to a network. A system node provided may include an access module for communicating with a client, an index module for building an index of a replicated data object, a data module for storing a data object on a computer readable medium, and a membership and routing module for detecting the configuration of operable nodes in the distributed system. Upon failure of an index node, the failure may be detected at other nodes, including those nodes that store the replicas of the object. These nodes may then send new index rebuilding requests to a different node that may rebuild the index for servicing any access request to the object.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
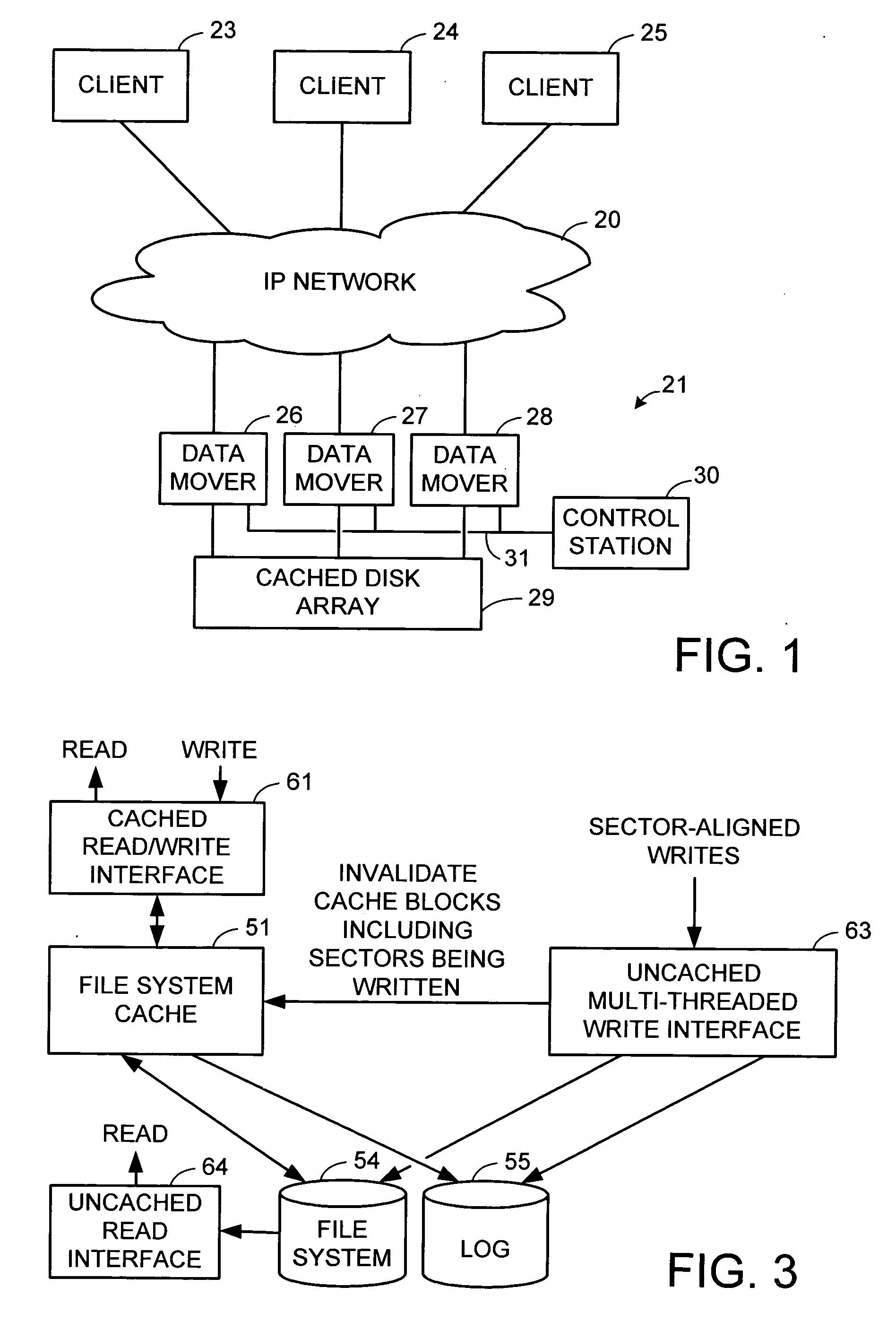
Instant snapshot
InactiveUS7072916B1Lower performance requirementsReduce performance overheadData processing applicationsRedundant operation error correctionImproved methodInode
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
System and method for redirecting access to a remote mirrored snapshot
ActiveUS7010553B2Significant processing timeSignificant processor overheadDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsInodeIndirection
In a system and method for updating a remote replicated destination file system snapshot with changes in a source file system snapshot, users and processes are redirected to a local exported snapshot of the replicated snapshot on the active file system on the destination before beginning the next update of the active file system's replicated snapshot. In this manner, an unstable replicated snapshot is not accessed. Indirection is introduced into inode lookup at the destination as the destination's active file system is being updated. The indirection can be based upon a snapshot ID that conforms to a latest exported snapshot ID.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
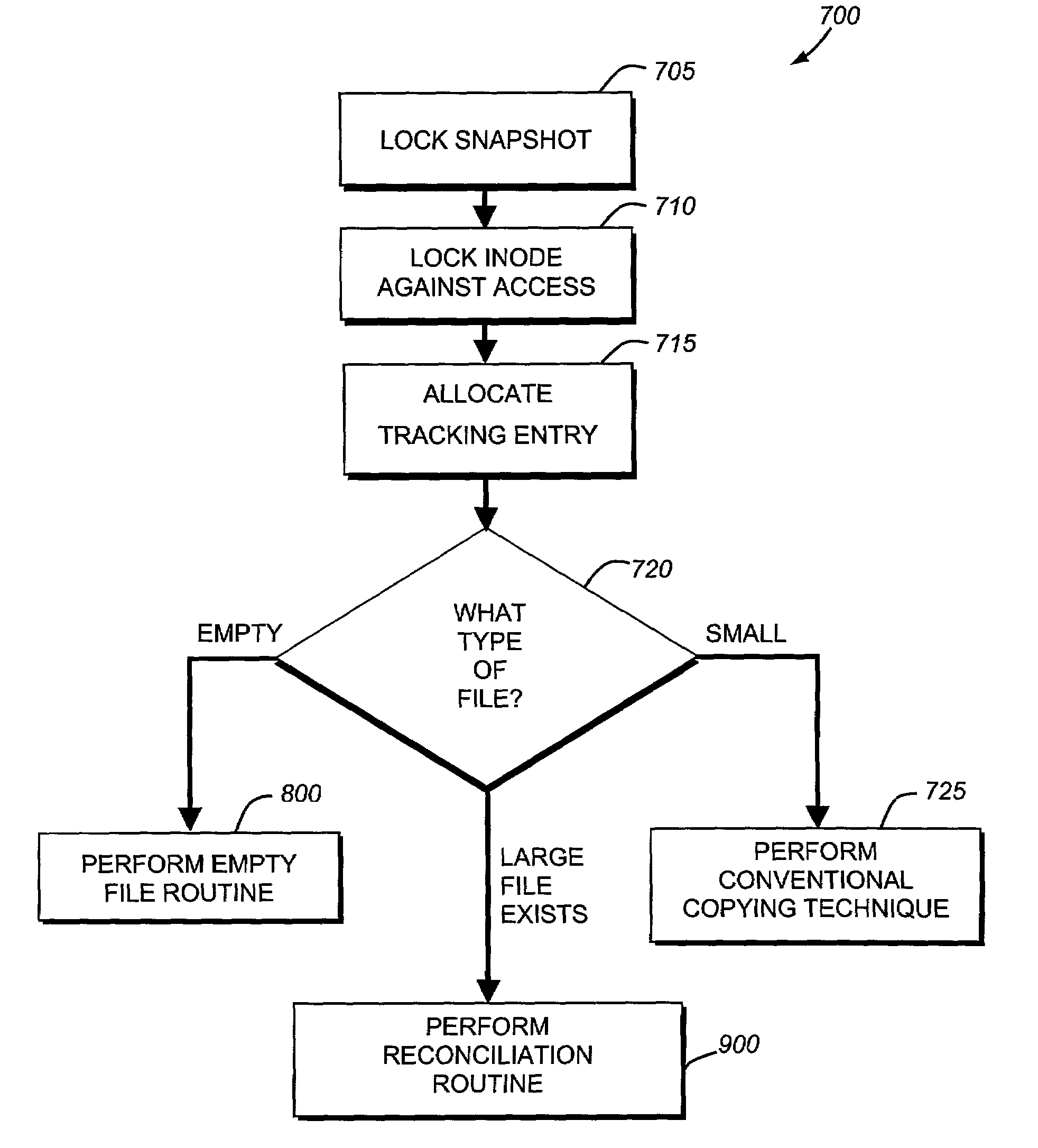
System and method for restoring a single file from a snapshot
InactiveUS7051050B2Quickly restoring a fileSubstantial overheadDigital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsInode
The present invention provides a system and method for restoring a single file from a snapshot without the need to copy every individual block or inode from the snapshot. A file restore process duplicates the inode of a file within the active file system and performs a reconciliation process between the blocks of the twin inode and the snapshot inode. If the file does not exist within the active file system, a new buffer tree is created that points to the data blocks stored in the snapshot.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
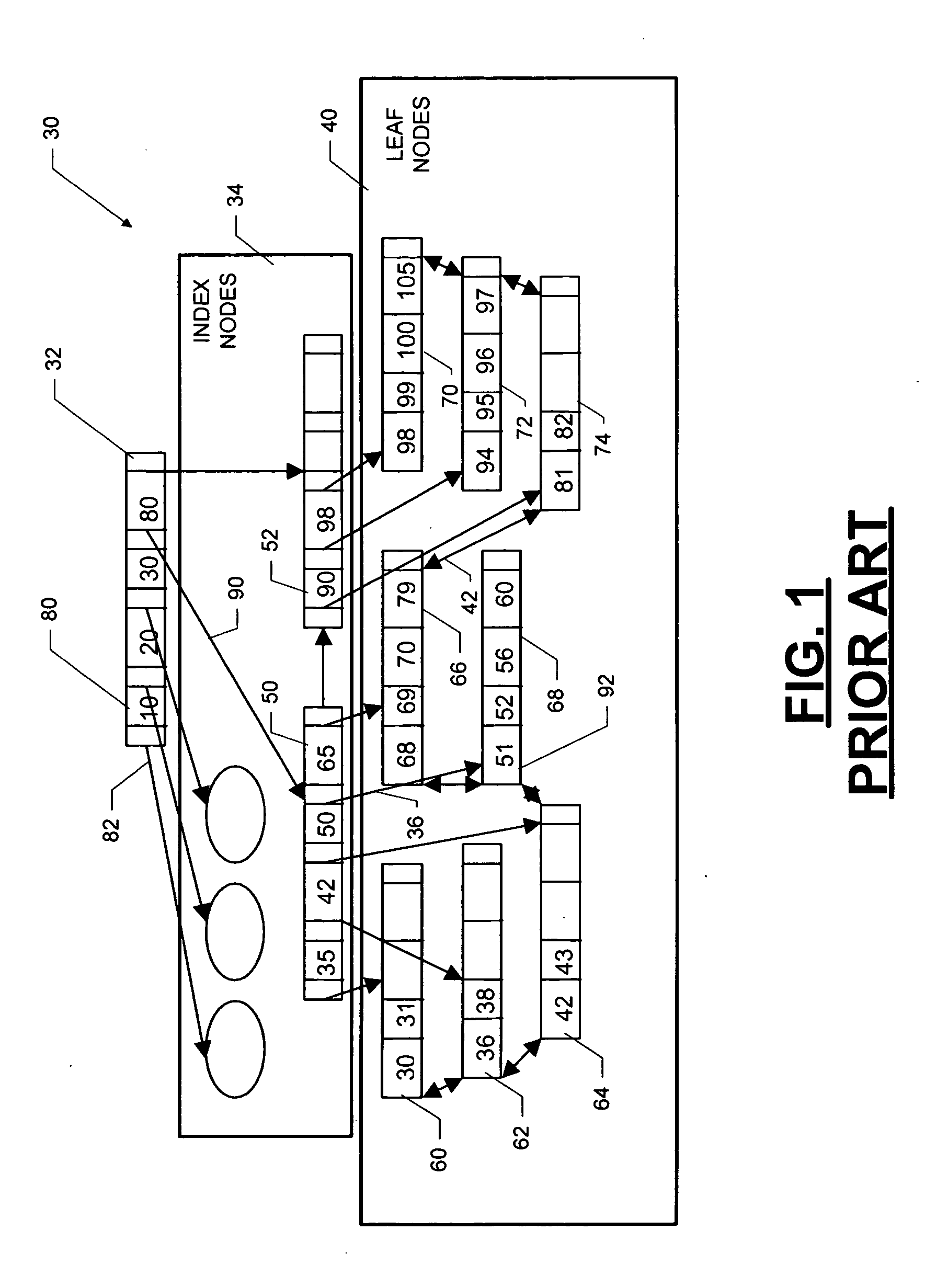
Concurrency control for B-trees with node deletion
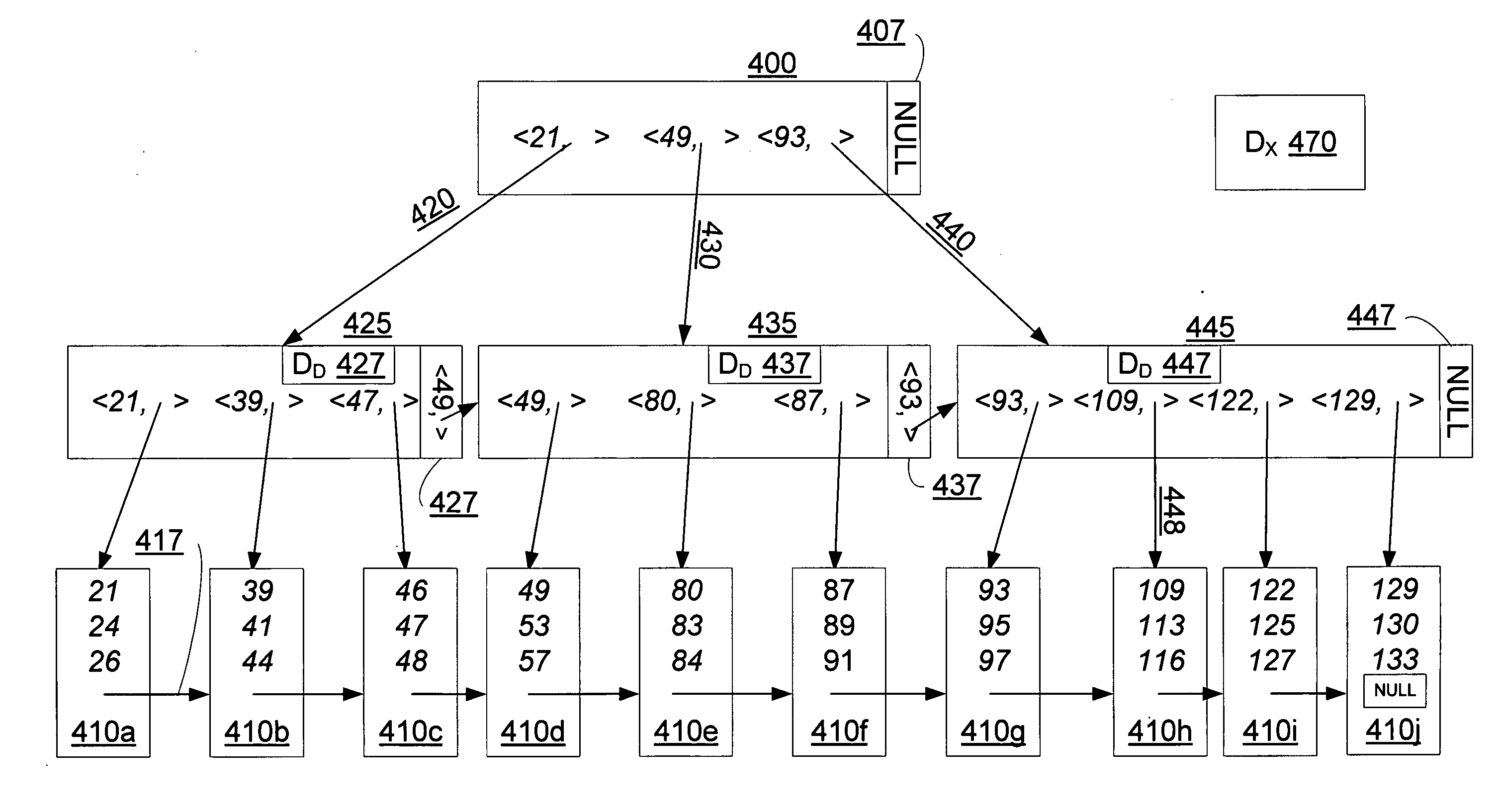
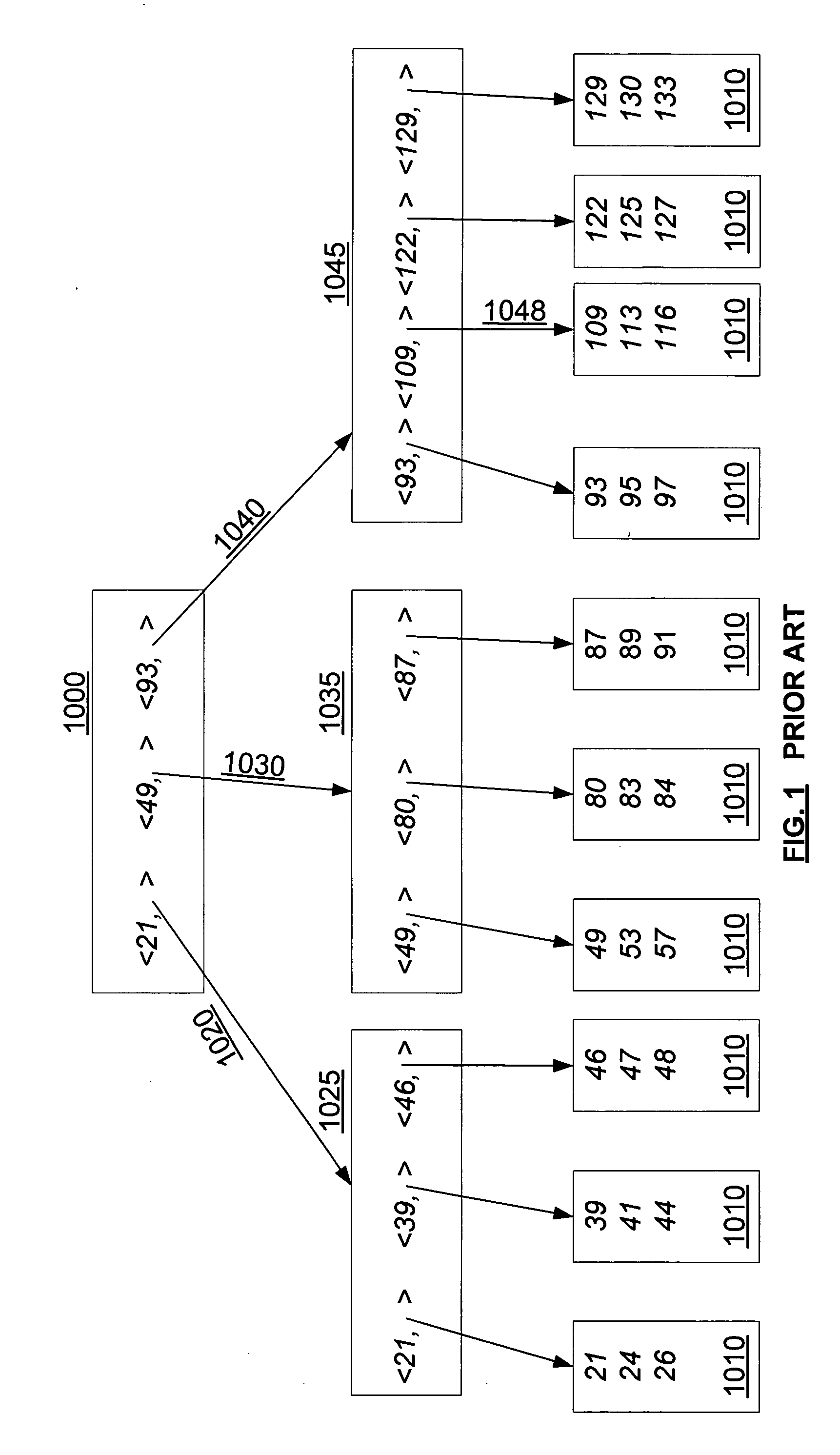
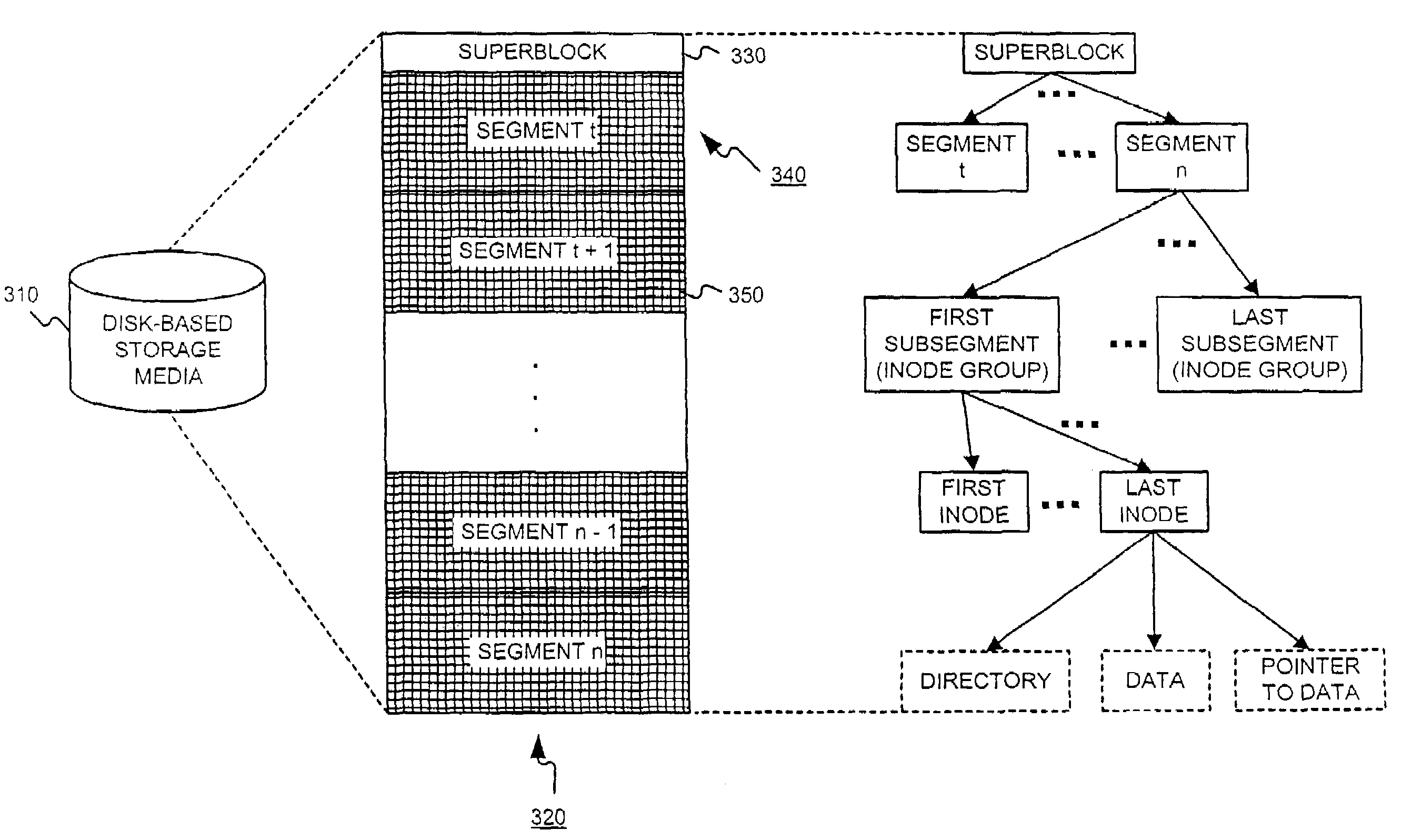
InactiveUS20050171960A1Highly concurrent access of dataEasy to solveData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalConcurrency controlTree (data structure)
A data structure, added to a modified form of the Blink-tree data structure, tracks delete states for nodes. The index delete state (DX) indicates whether it is safe to directly access an index node without re-traversing the B-tree. The DX state is maintained globally, outside of the tree structure. The data delete state (DD) indicates whether it is safe to post an index term for a new leaf node. A DD state is maintained in each level 1 node for its leaf nodes. Delete states indicate whether a specific node has not been deleted, or whether it may have been deleted. Delete states are used to remove the necessity for atomic node splits and chains of latches for deletes, while not requiring retraversal. This property of not requiring a retraversal is exploited to simplify the tree modification operations.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
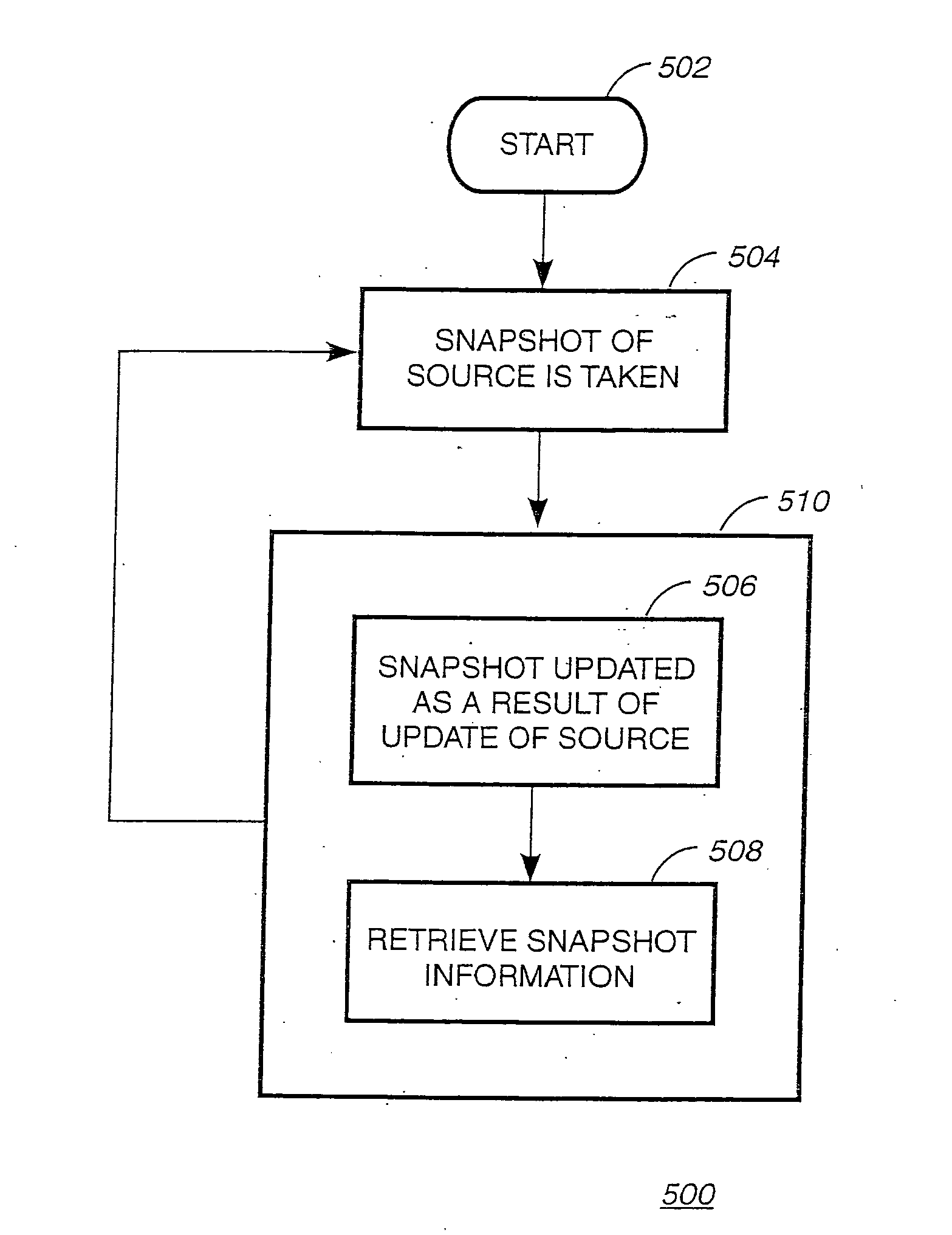
Providing a snapshot of a subset of a file system
InactiveUS20060206536A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalInodeSystems approaches
A system, method and computer readable medium for providing a snapshot of a subset of a file system. A first snapshot of a first set of source files in a file system is generated. The first snapshot includes an inode corresponding to each source file in the first set of files. Stored in each inode is a first identifier associated with the first set of files and a second identifier associated with the time of the first snapshot. Next, a second snapshot of a second set of source files is taken. The second snapshot includes an inode corresponding to each source file in the second set of files. Stored in each inode are a first identifier and a second identifier. Subsequent snapshots are taken every first period and every second period for the first set of files and the second set of files, respectively.
Owner:SAP AG
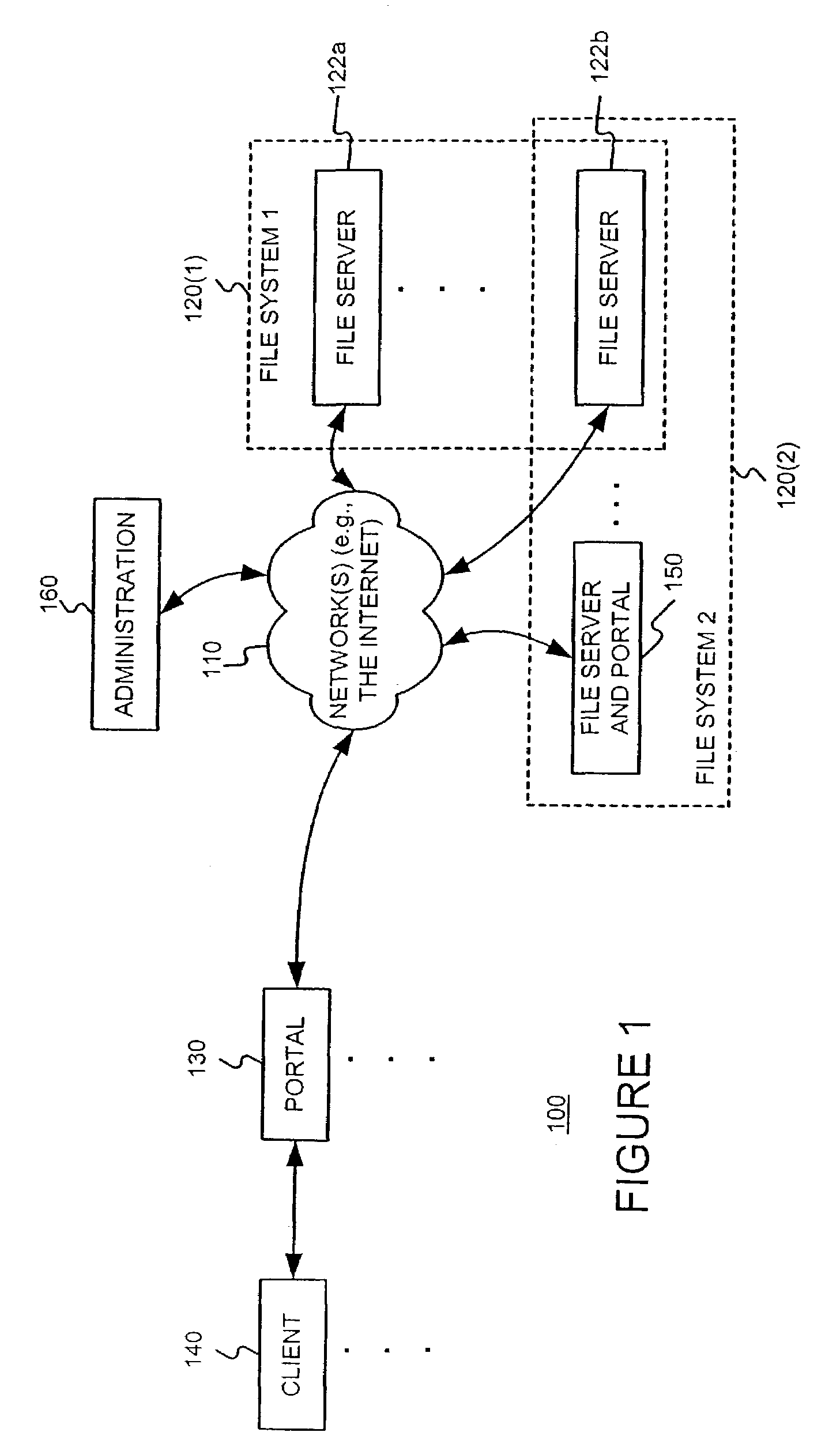
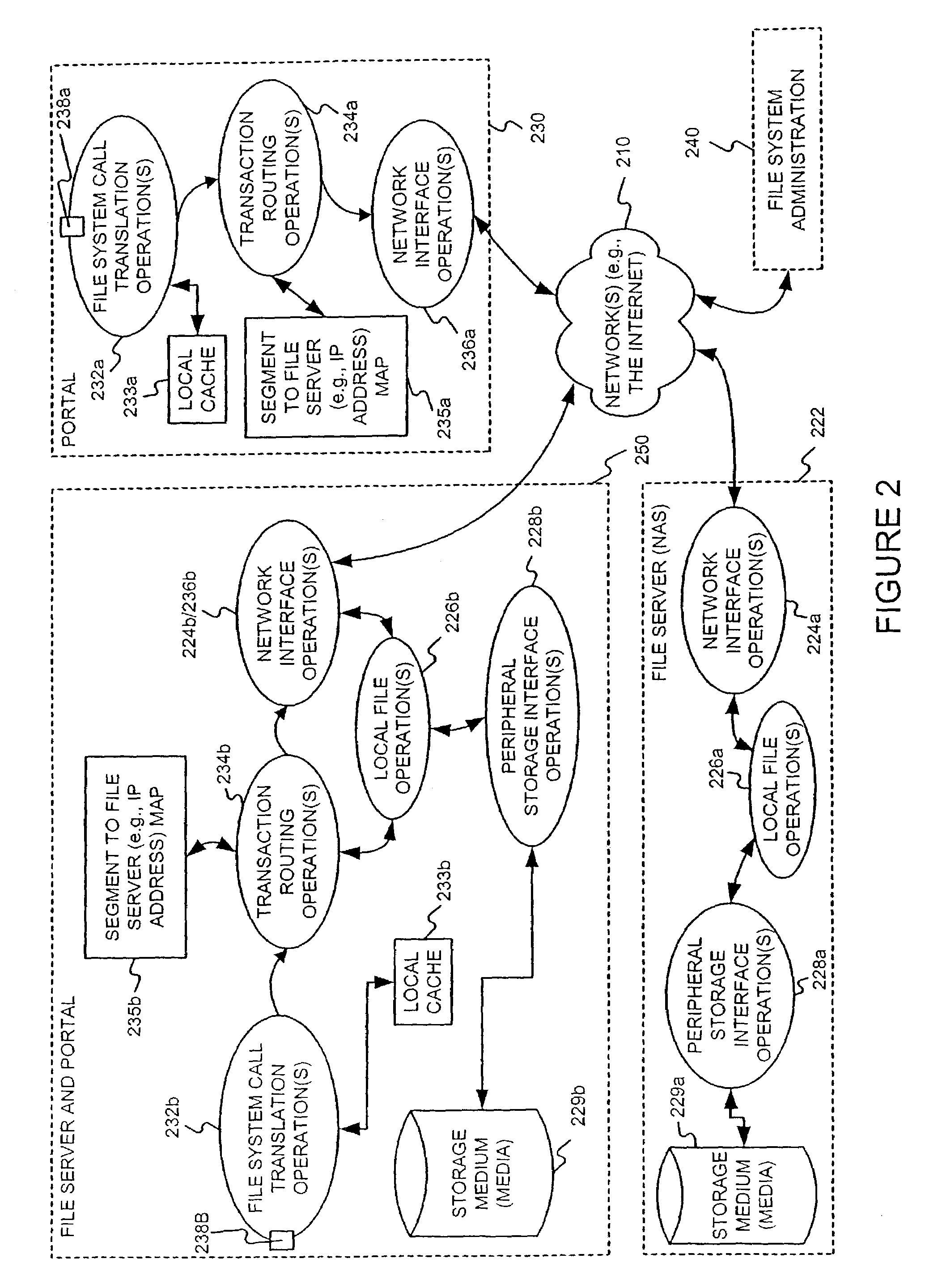
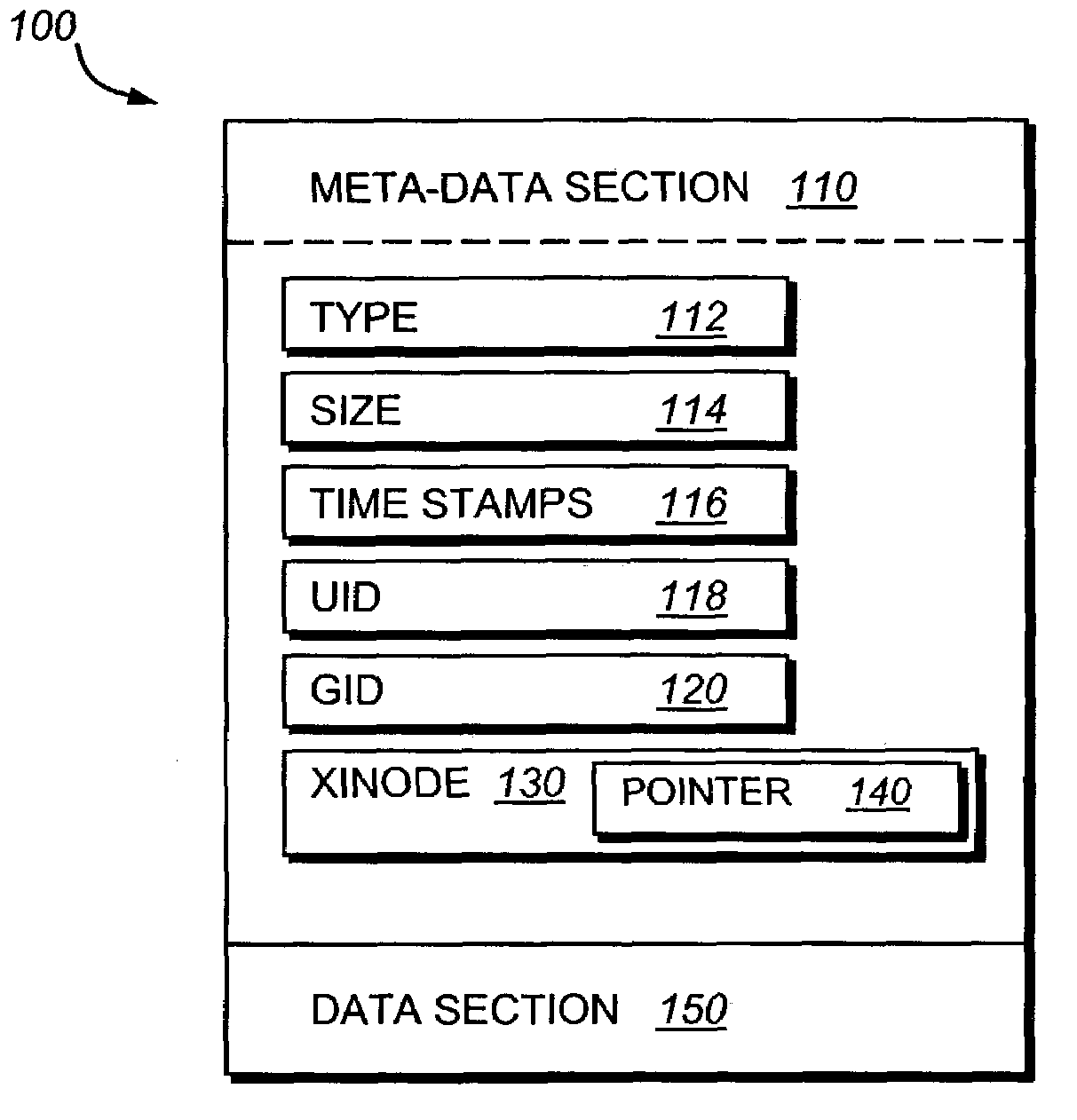
Distributing files across multiple, permissibly heterogeneous, storage devices
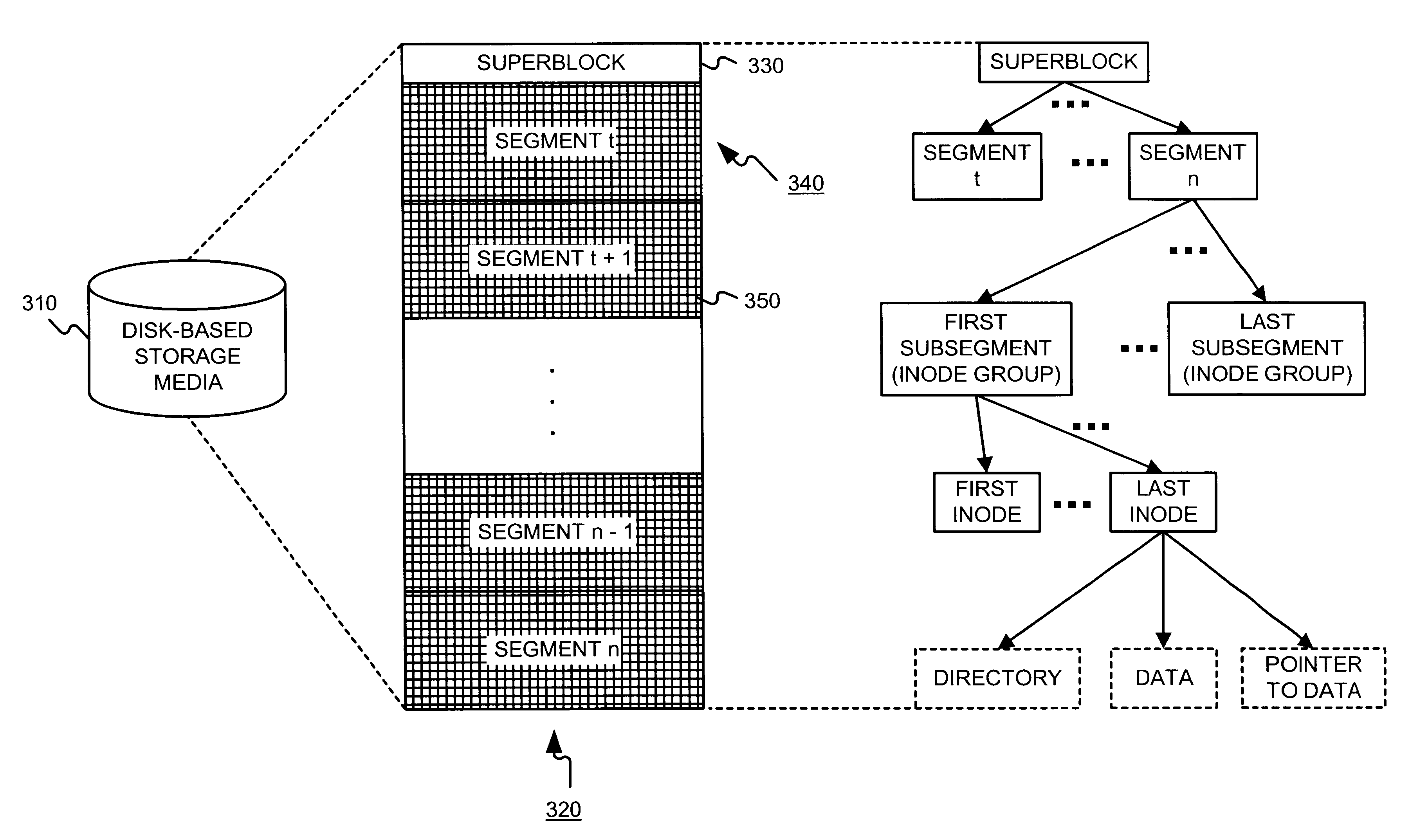
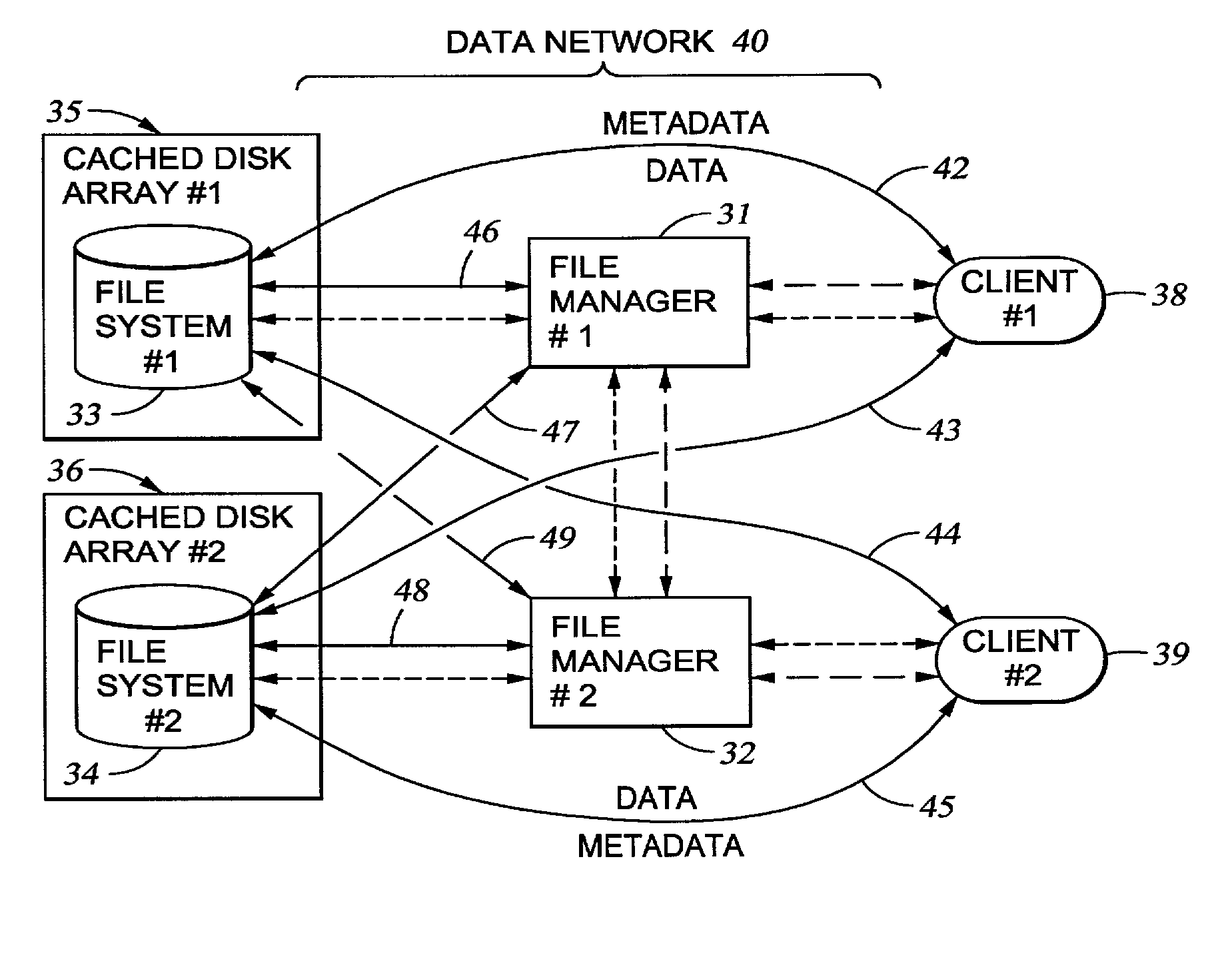
A file system (i) permits storage capacity to be added easily, (ii) can be expanded beyond a given unit, (iii) is easy to administer and manage, (iv) permits data sharing, and (v) is able to perform effectively with very large storage capacity and client loads. State information from a newly added unit is communicated (e.g., automatically and transparently) to central administration and management operations. Configuration and control information from such operations is communicated (e.g., automatically) back down to the newly added units, as well as existing units. In this way, a file system can span both local storage devices (like disk drives) and networked computational devices transparently to clients. Such state and configuration and control information can include globally managed segments as the building blocks of the file system, and a fixed mapping of globally unique file identifiers (e.g., Inode numbers) and / or ranges thereof, to such segments.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Pass-through write policies of files in distributed storage management
ActiveUS20070266056A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalAccess methodStorage management
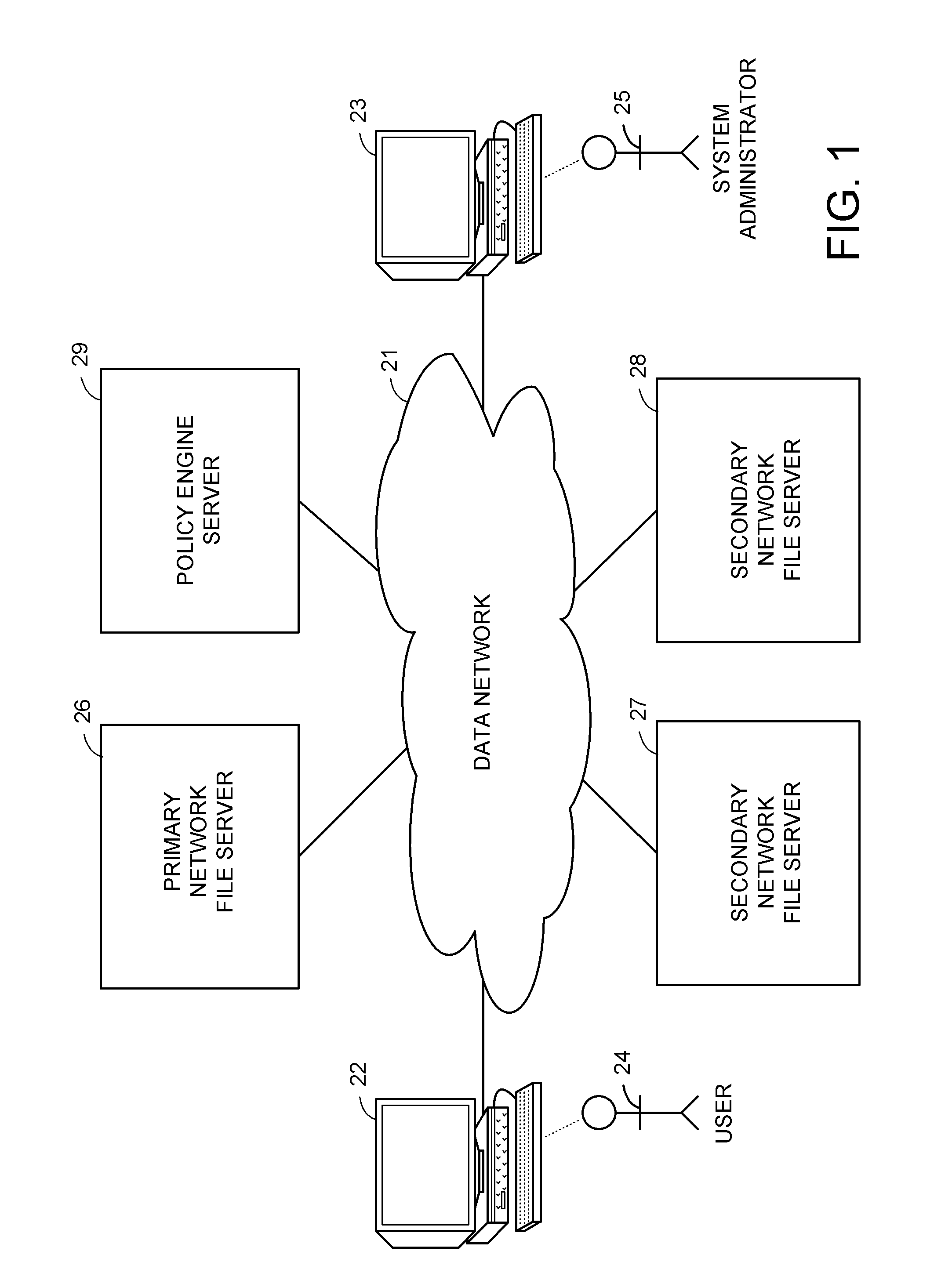
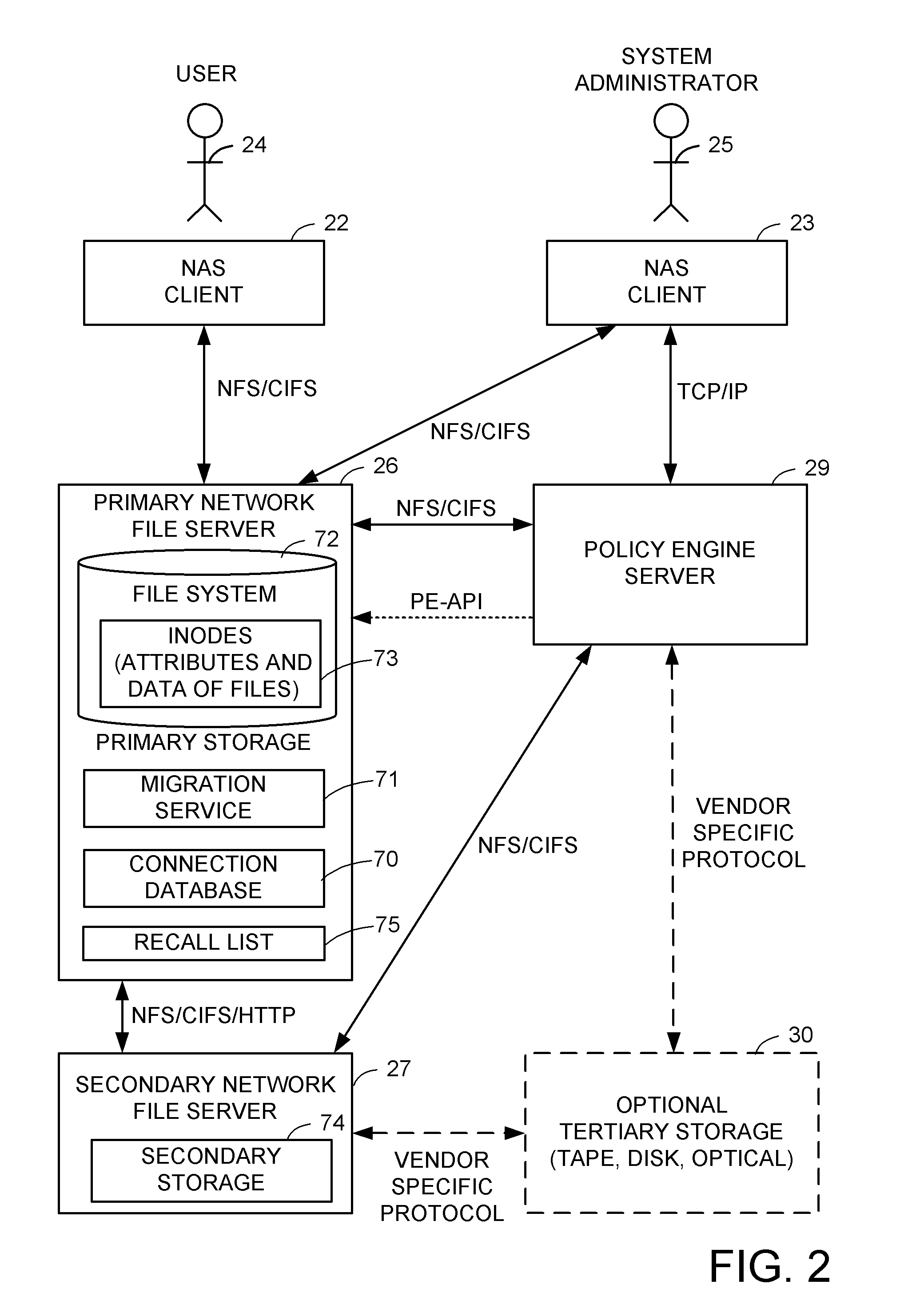
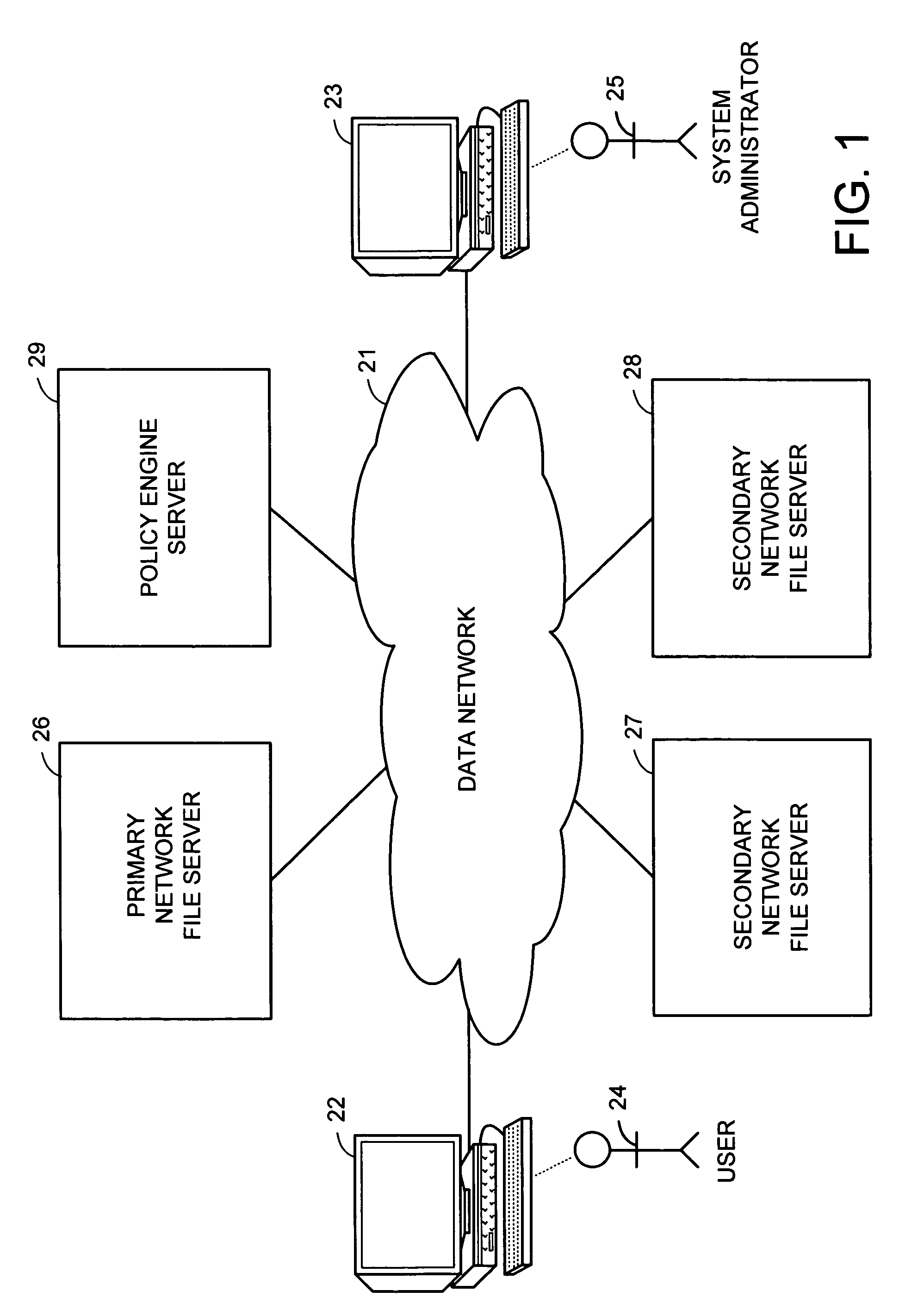
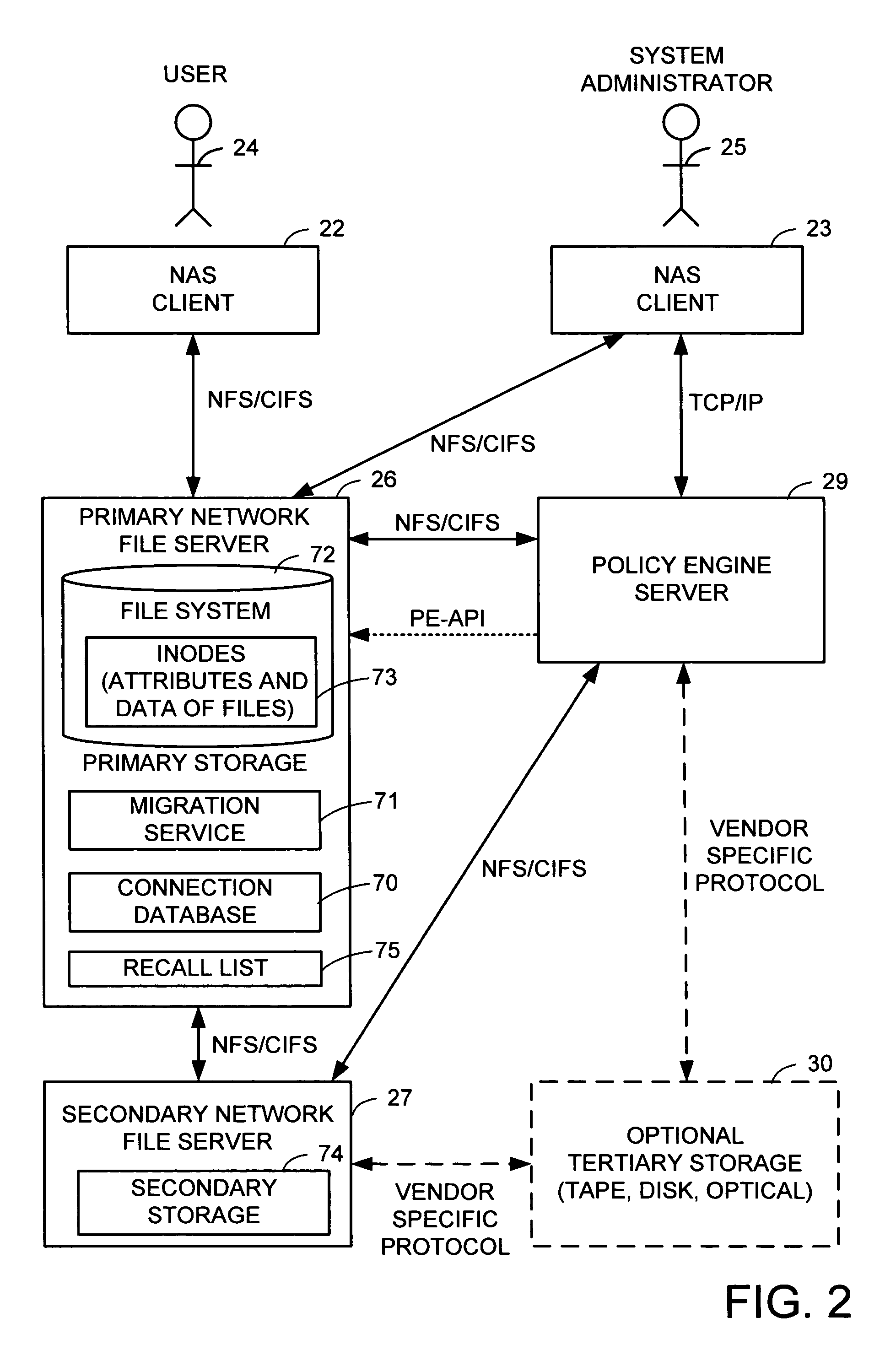
A hierarchical storage system includes file servers and a policy engine server. Offline attributes are added to file system inodes in a primary file server, file system parameters are added in the primary server, offline read and write access method fields are added to a connection database, and the primary file server uses these attributes and parameters for selecting a particular read method or write method for access to an offline file or section of an offline file. The write methods follow a “write recall full” policy, a “pass-through write” policy, a “pass-through multi-version” policy, or a “directory write pass-through” policy. The pass-through multi-version policy results in a new offline version of a file each time that a client opens and writes to a multi-version file. The directory write pass-through policy results in a new offline file when a file is created within a write pass-through directory.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
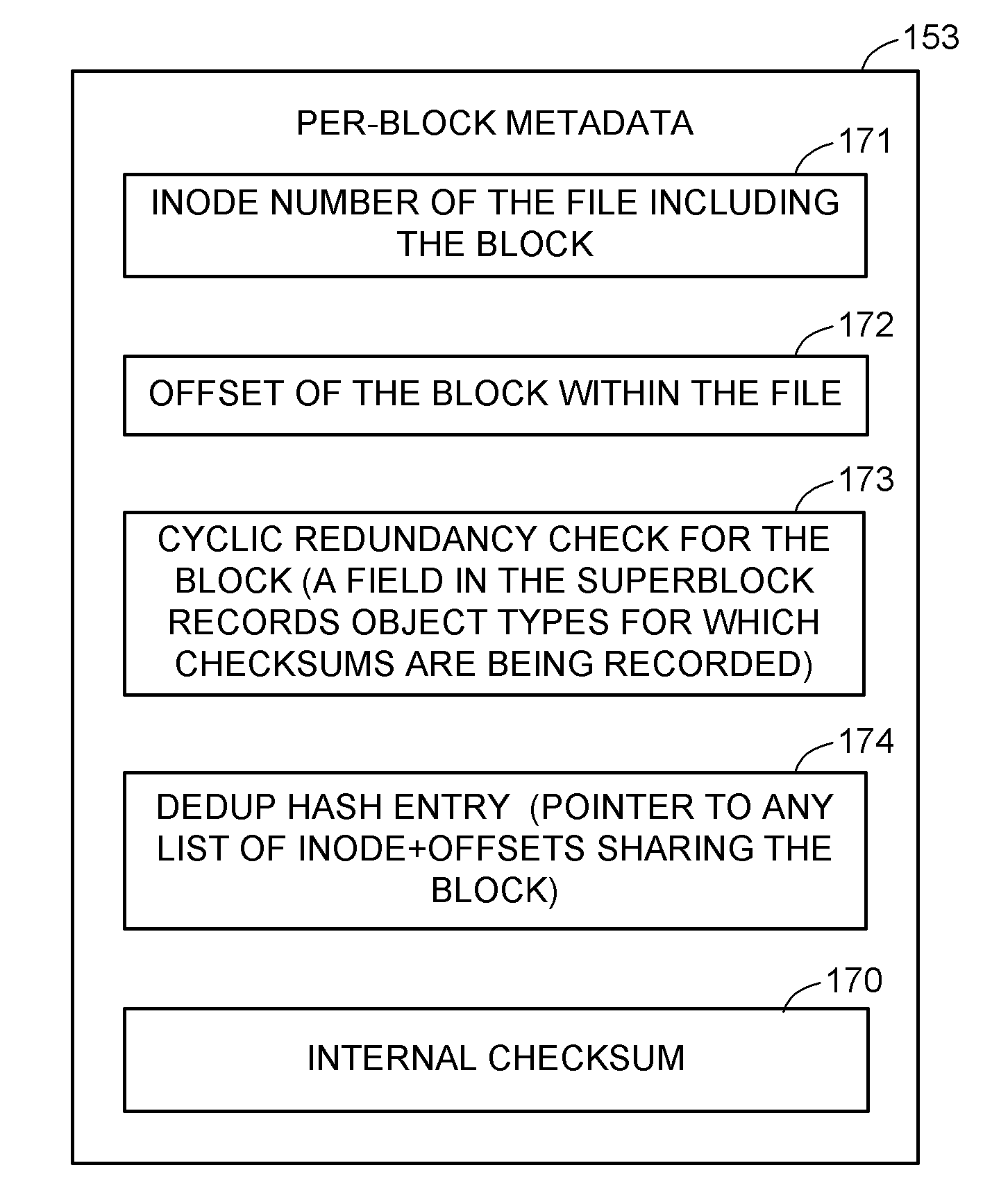
Self healing file system
A self healing file system is designed for proactive detection and containment of faults, errors, and corruptions, in order to enable in place (online) and non-intrusive recovery. For proactive fault detection, the file system maintains certain per-block metadata of each file system block. The per-block metadata includes a redundancy check, and for file system data blocks, an inode identifier, and an offset of the file system data block in the file including the file system data block. The redundancy check is used to detect and mark bad file system blocks. The inode identifier and offset is used for validating connectivity of the file system blocks to the inodes, and for tracing bad blocks to files that contain the bad blocks.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Storage allocation in a distributed segmented file system
InactiveUS7406484B1Efficient executionStorage capacity can be easilyData processing applicationsTransmissionInodeData sharing
A file system (i) permits storage capacity to be added easily, (ii) can be expanded beyond a given unit, (iii) is easy to administer and manage, (iv) permits data sharing, and (v) is able to perform effectively with very large storage capacity and client loads. State information from a newly added unit is communicated (e.g., automatically and transparently) to central administration and management operations. Configuration and control information from such operations is communicated (e.g., automatically) back down to the newly added units, as well as existing units. In this way, a file system can span both local storage devices (like disk drives) and networked computational devices transparently to clients. Such state and configuration and control information can include globally managed segments as the building blocks of the file system, and a fixed mapping of globally unique file identifiers (e.g., Inode numbers) and / or ranges thereof, to such segments.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Selection of migration methods including partial read restore in distributed storage management
ActiveUS20060212746A1Increase heightIncrease flexibilityDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsAccess methodStorage management
A hierarchical storage system is constructed from file servers and a policy engine server by building upon a file migration service. Offline attributes are added to file system inodes in a primary file server, file system parameters are added in the primary server, an offline read access method field is added to a connection database, and the primary file server is programmed to use these attributes and parameters for selecting a particular method (such as a partial read migration or a pass through read method) for read access to an offline file. In this fashion, the primary file server is provided with flexibility for selecting a particular one of a number of migration methods depending on various conditions, in order to improve the trade-off between the cost of storage and delay in file access.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
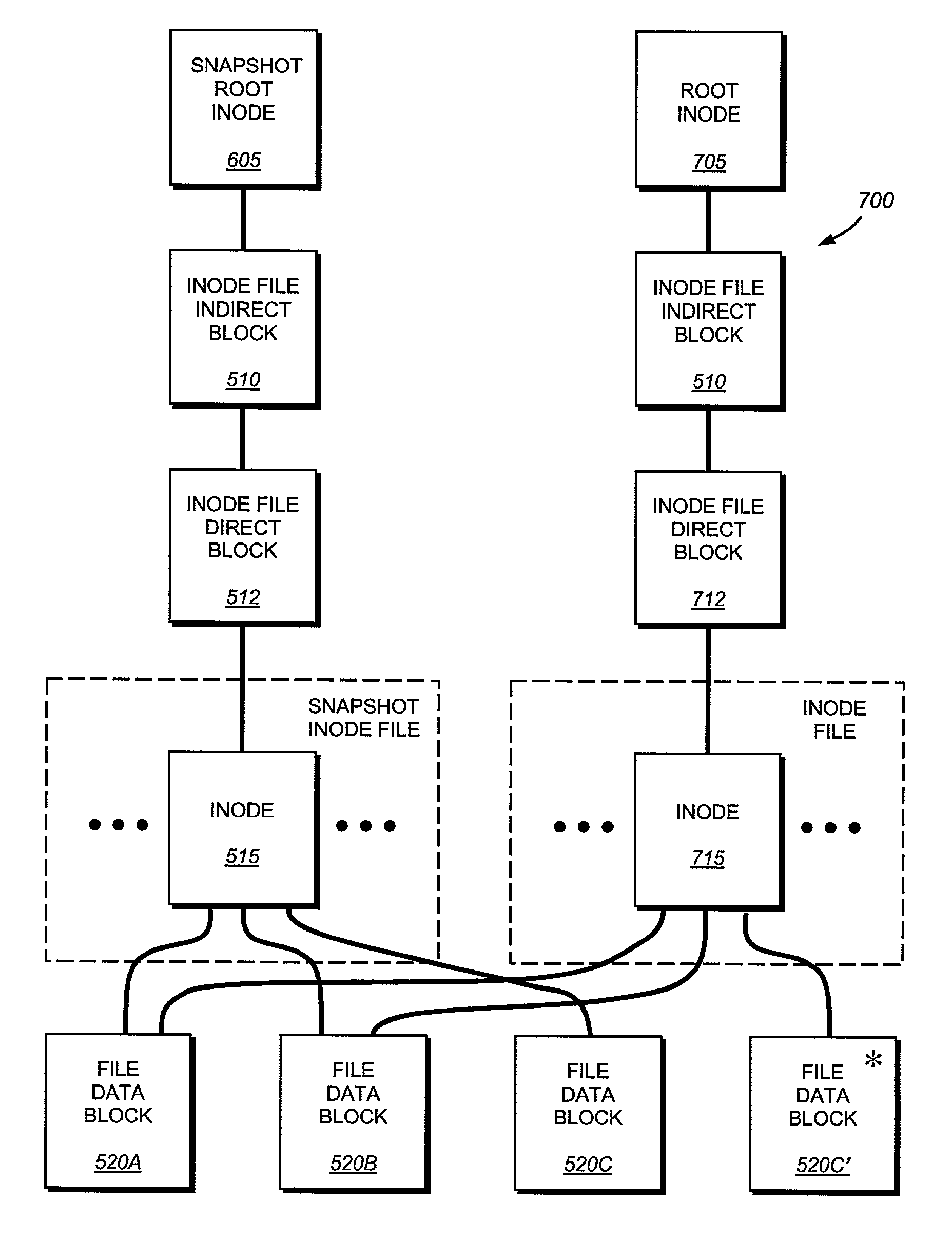
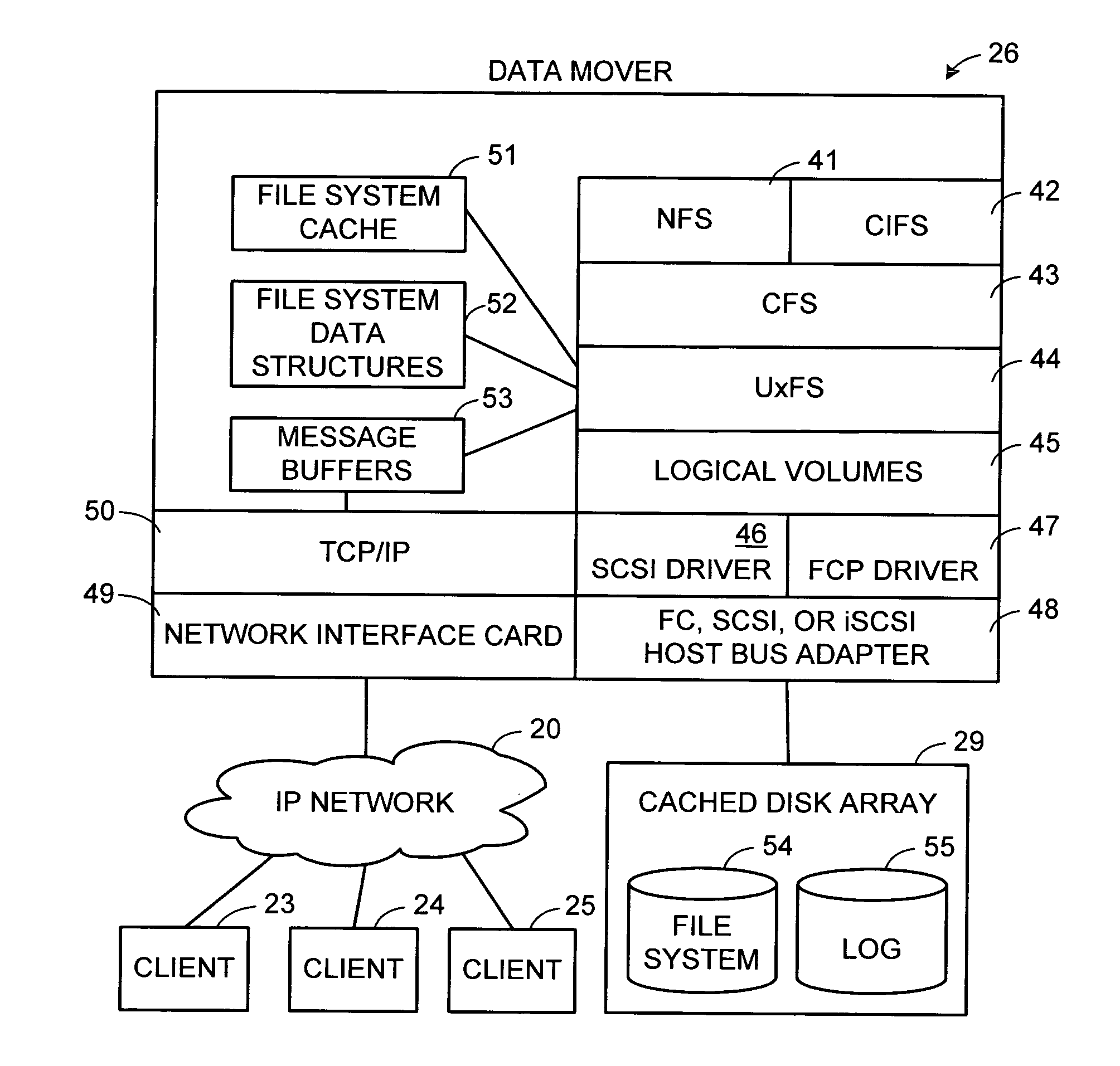
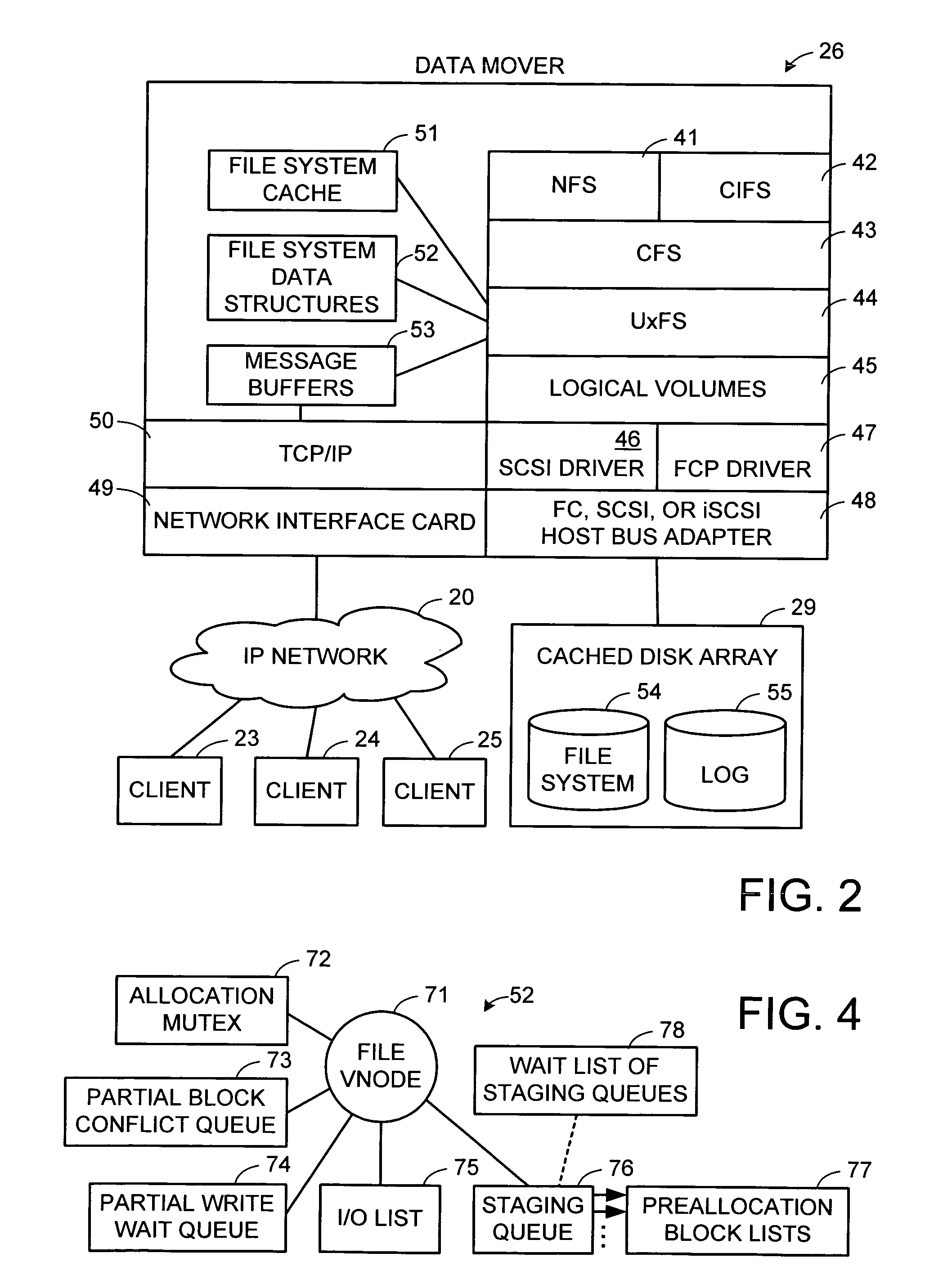
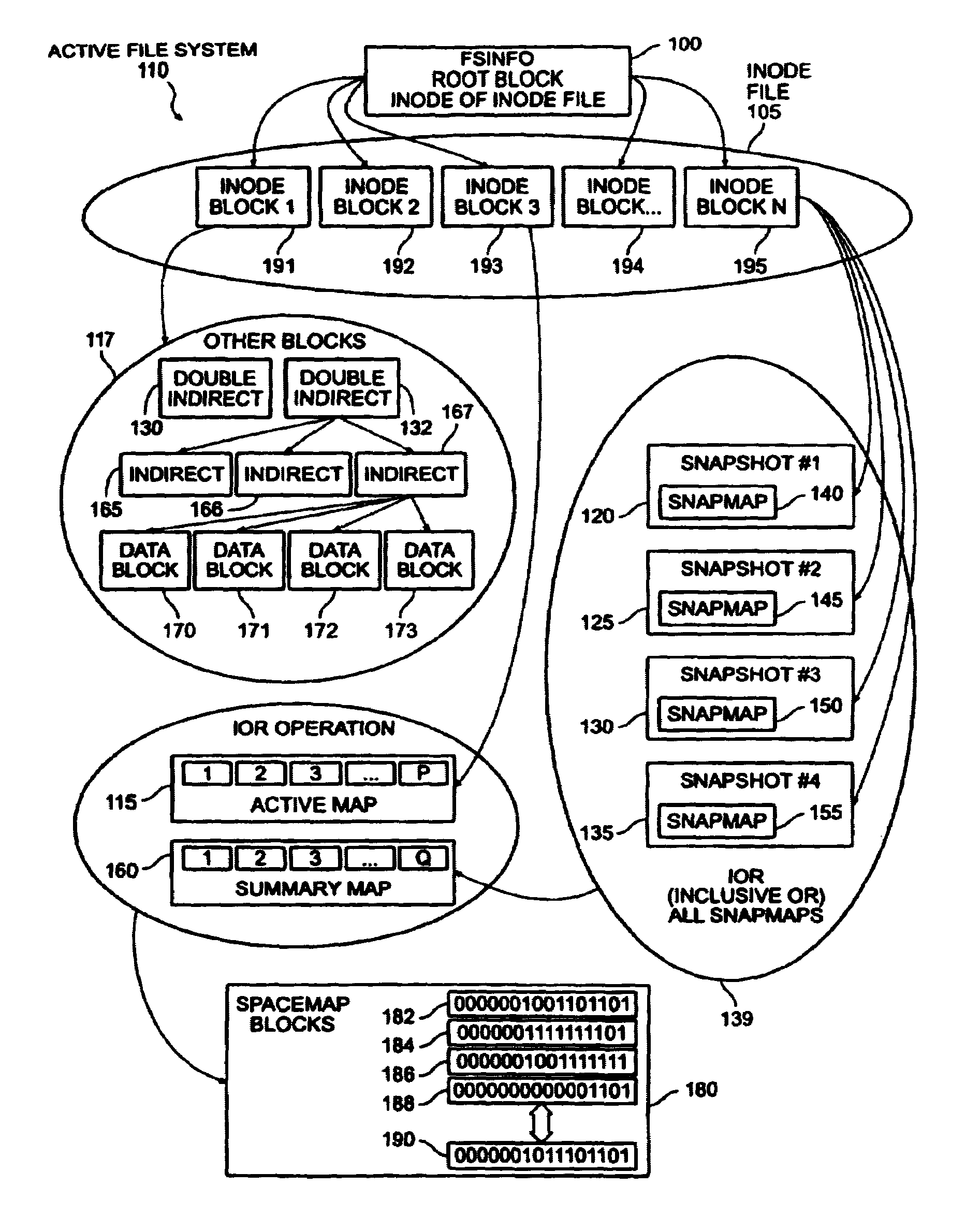
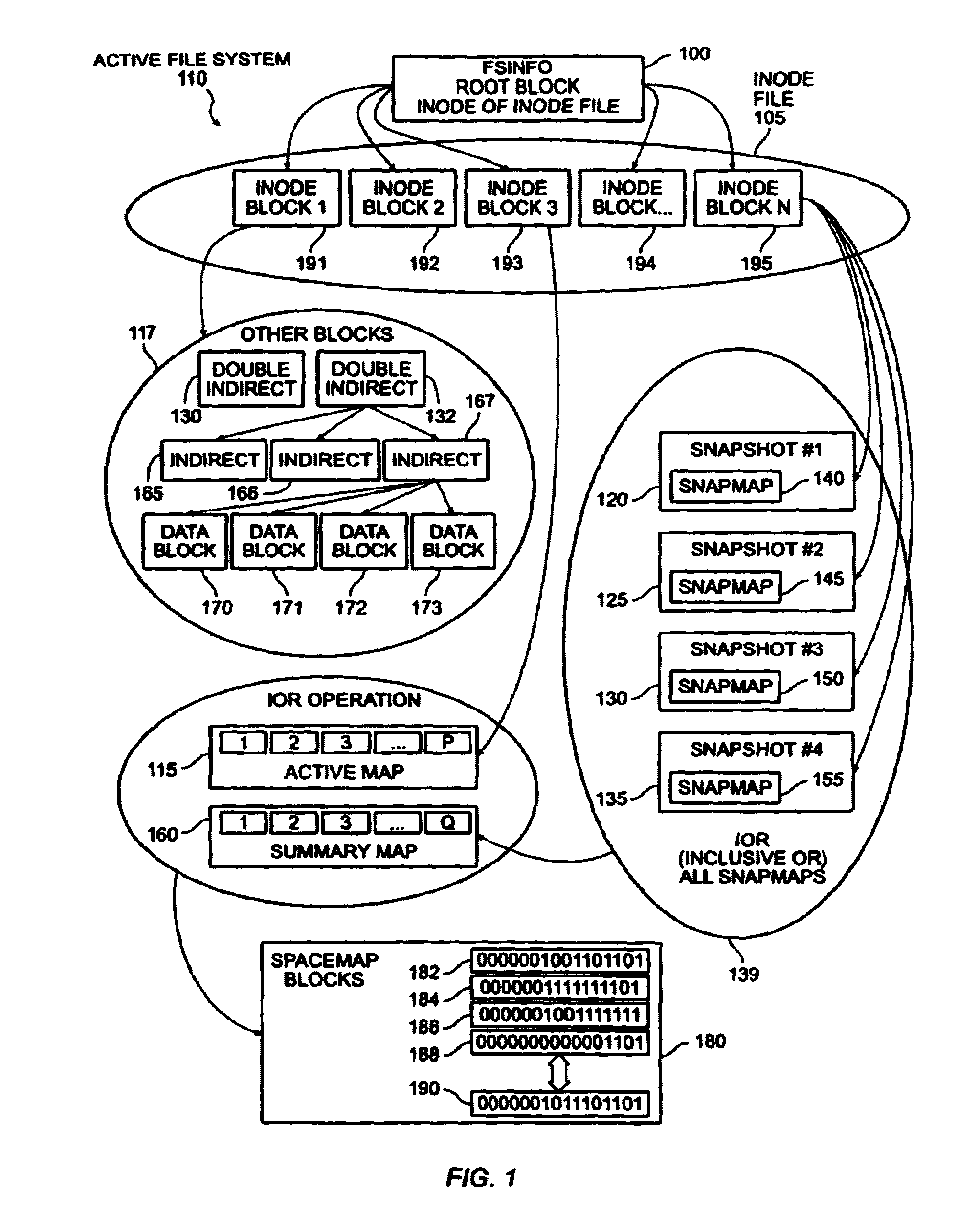
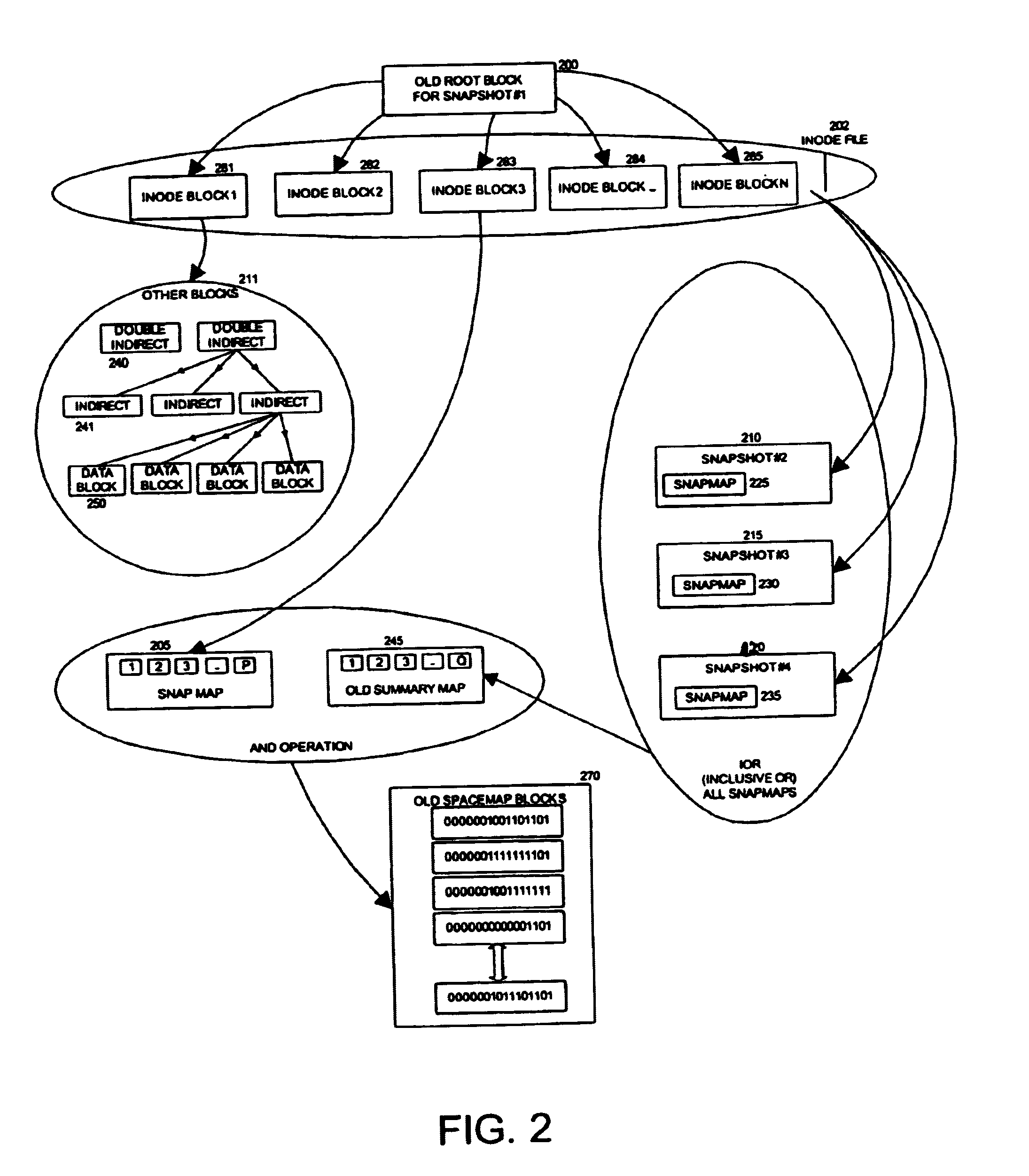
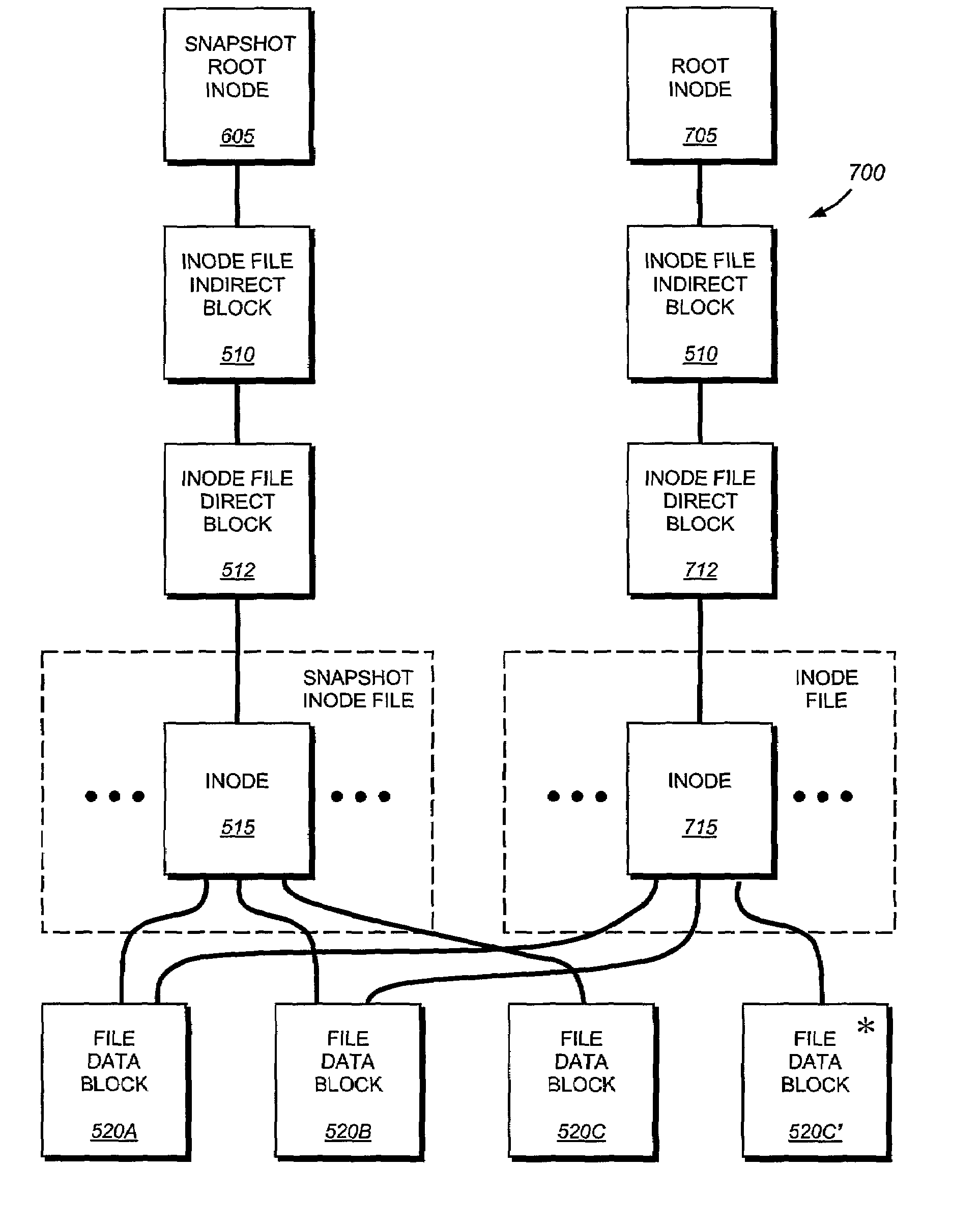
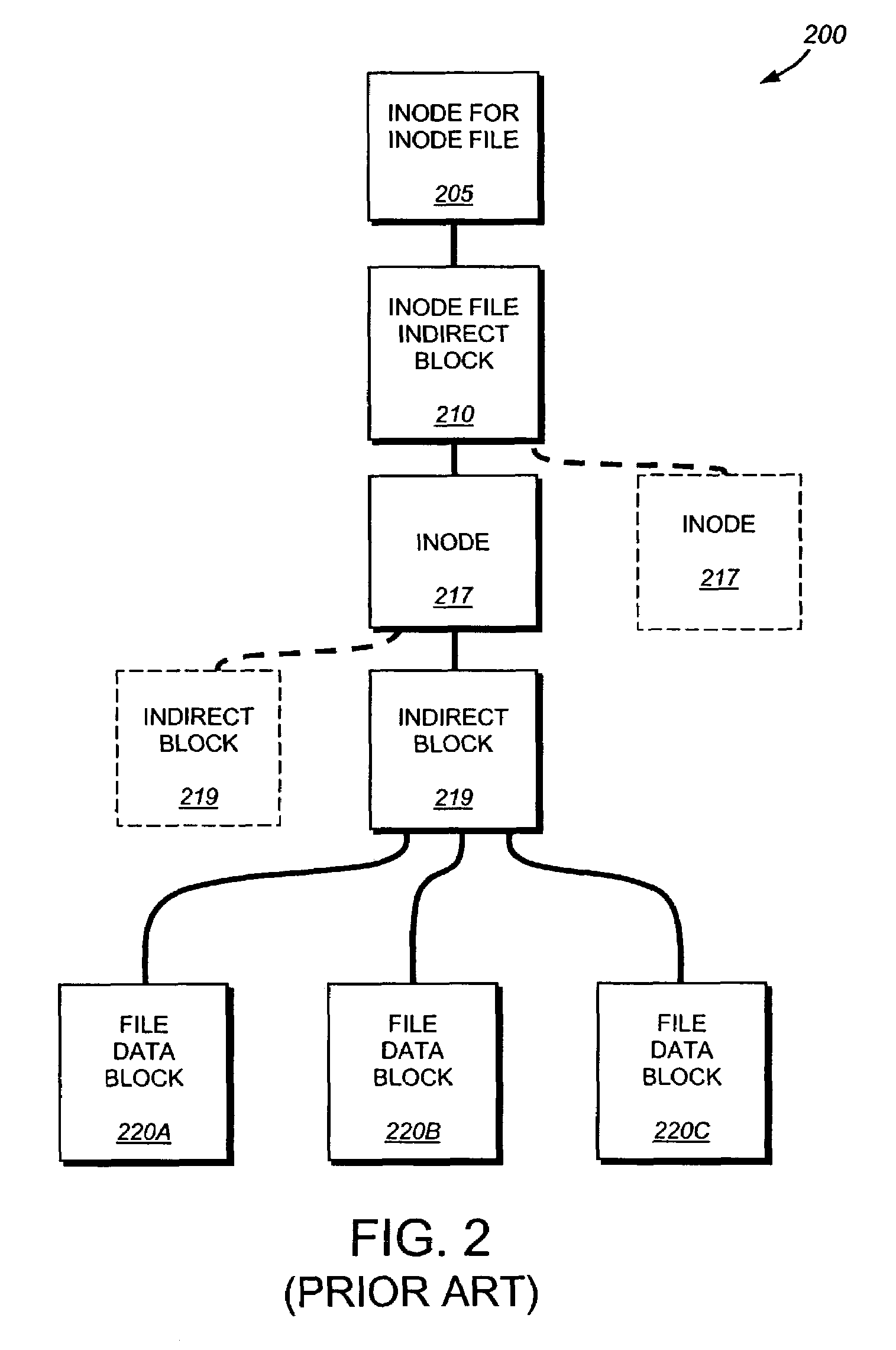
Write anywhere file-system layout
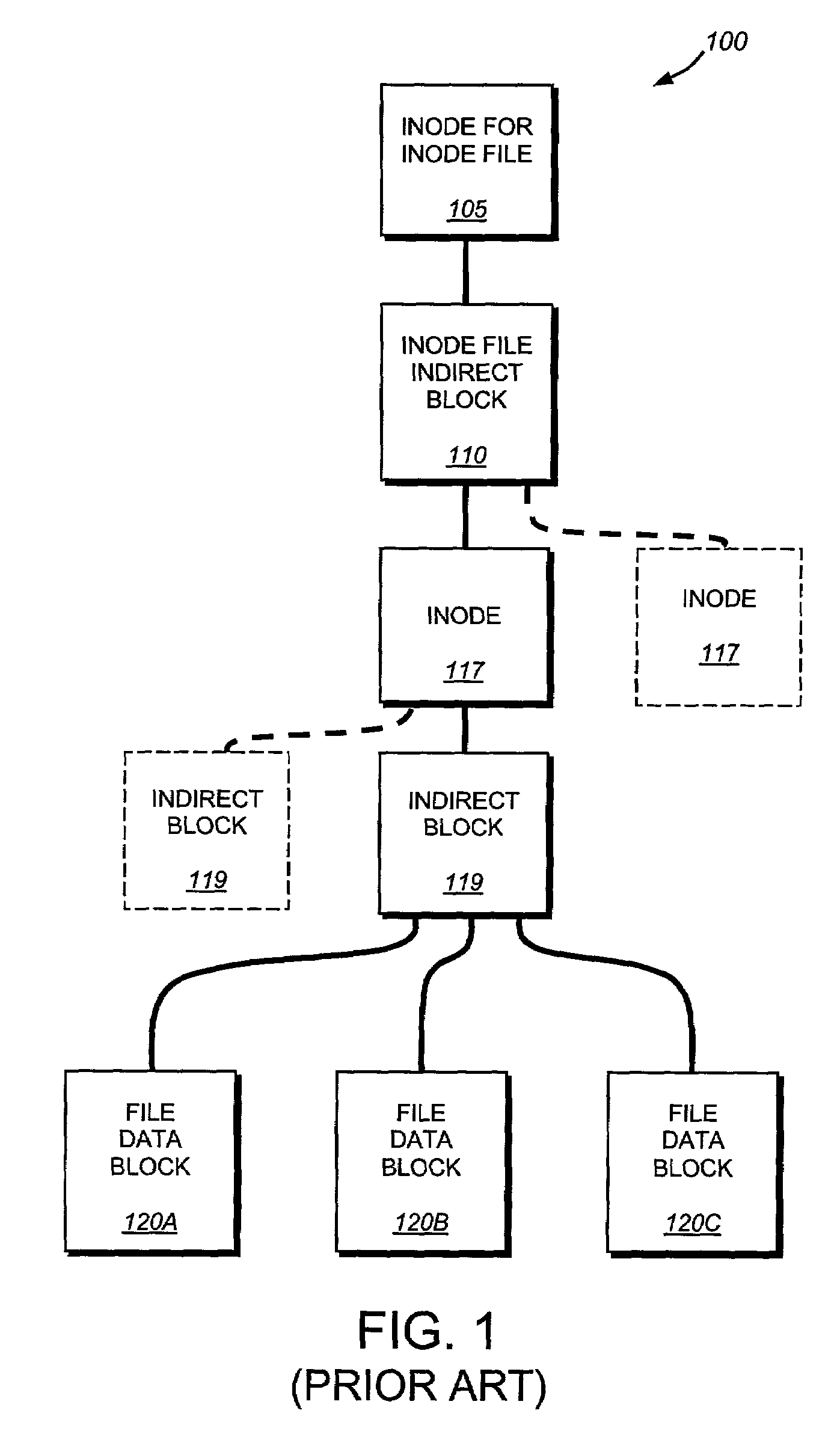
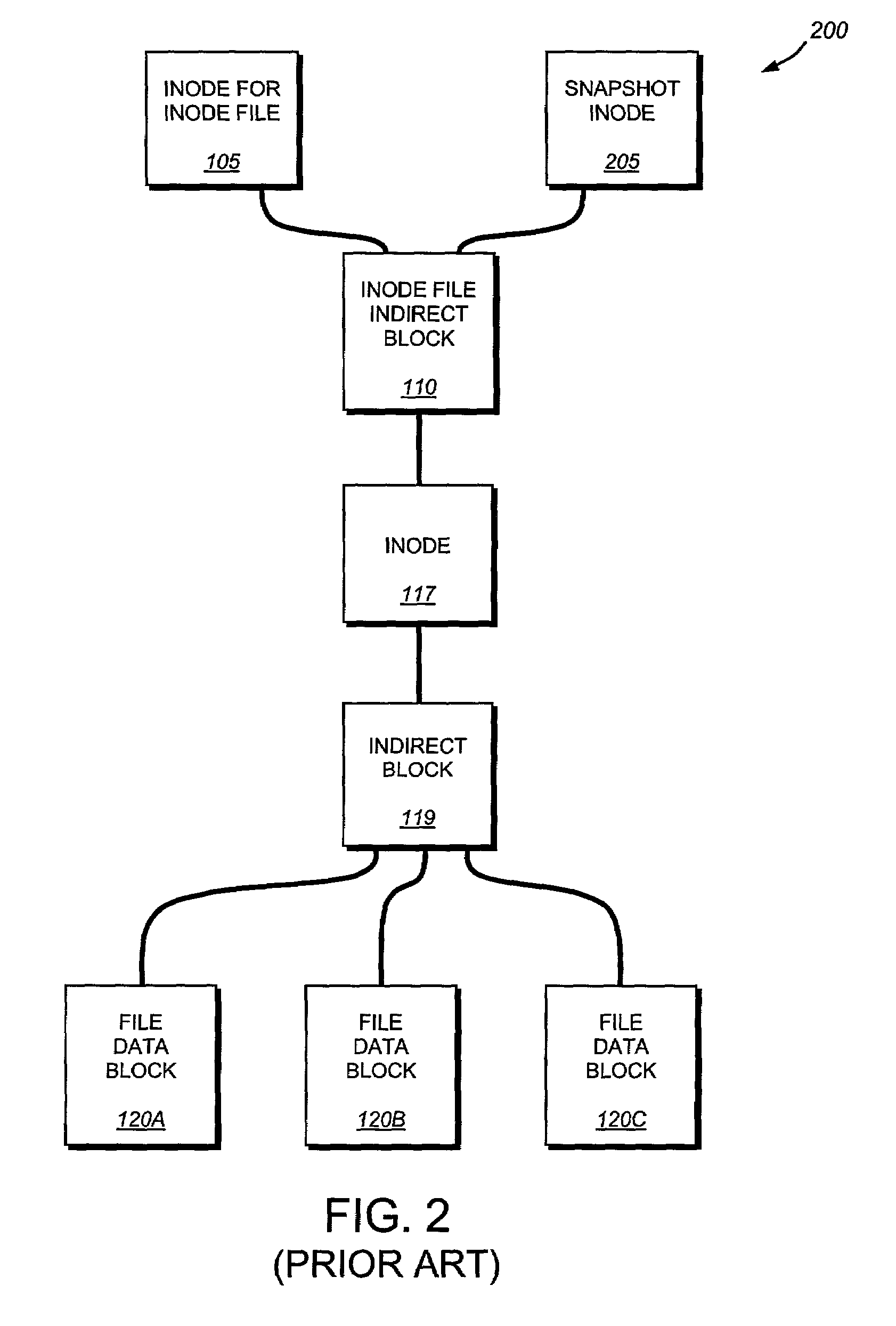
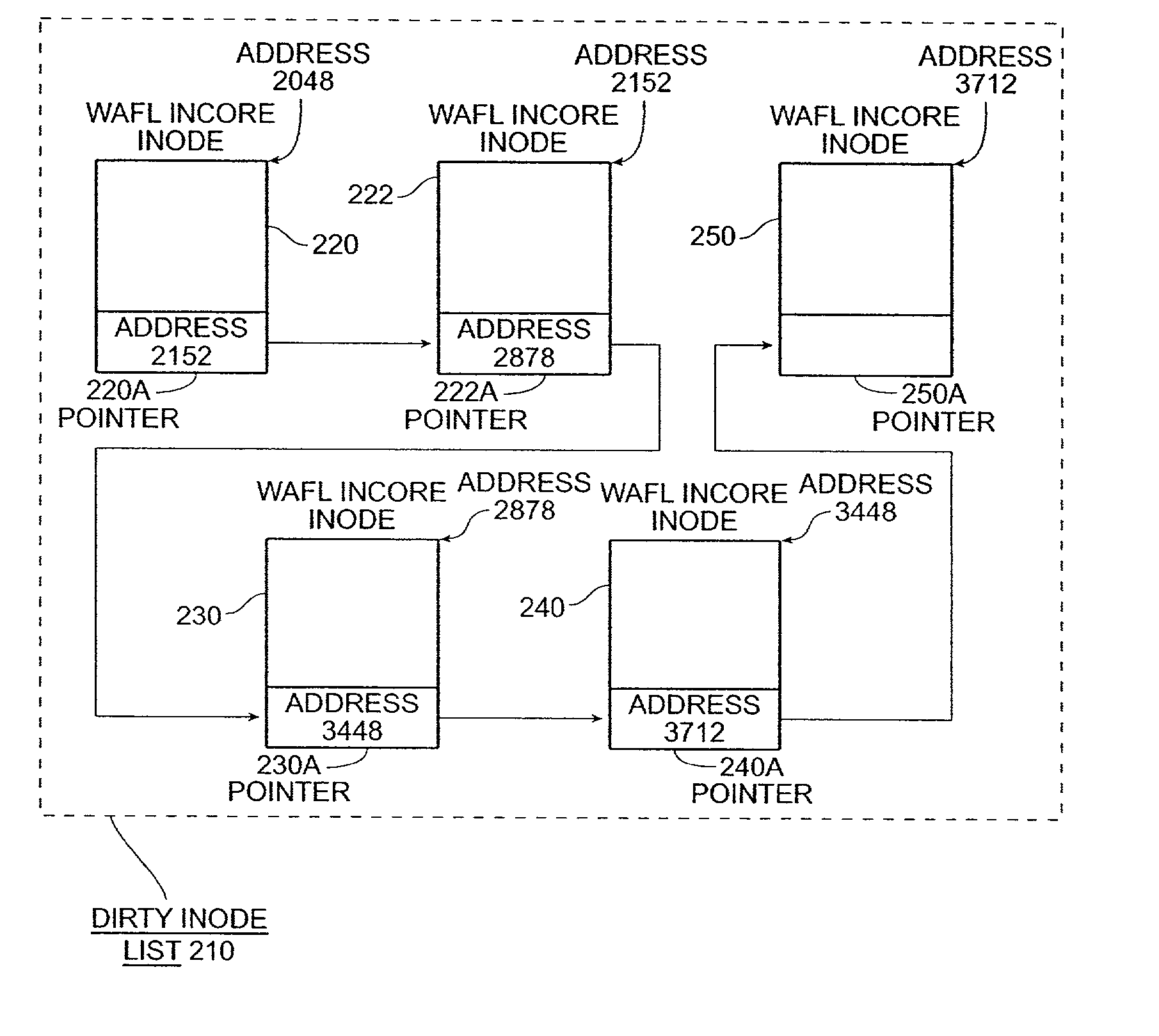
The present invention provides a method for keeping a file system in a consistent state and for creating read-only copies of a file system. Changes to the file system are tightly controlled. The file system progresses from one self-consistent state to another self-consistent state. The set of self-consistent blocks on disk that is rooted by the root inode is referred to as a consistency point. To implement consistency points, new data is written to unallocated blocks on disk. A new consistency point occurs when the fsinfo block is updated by writing a new root inode for the inode file into it. Thus, as long as the root inode is not updated, the state of the file system represented on disk does not change. The present invention also creates snapshots that are read-only copies of the file system. A snapshot uses no disk space when it is initially created. It is designed so that many different snapshots can be created for the same file system. Unlike prior art file systems that create a clone by duplicating the entire inode file and all of the indirect blocks, the present invention duplicates only the inode that describes the inode file. A multi-bit free-block map file is used to prevent data from being overwritten on disk.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
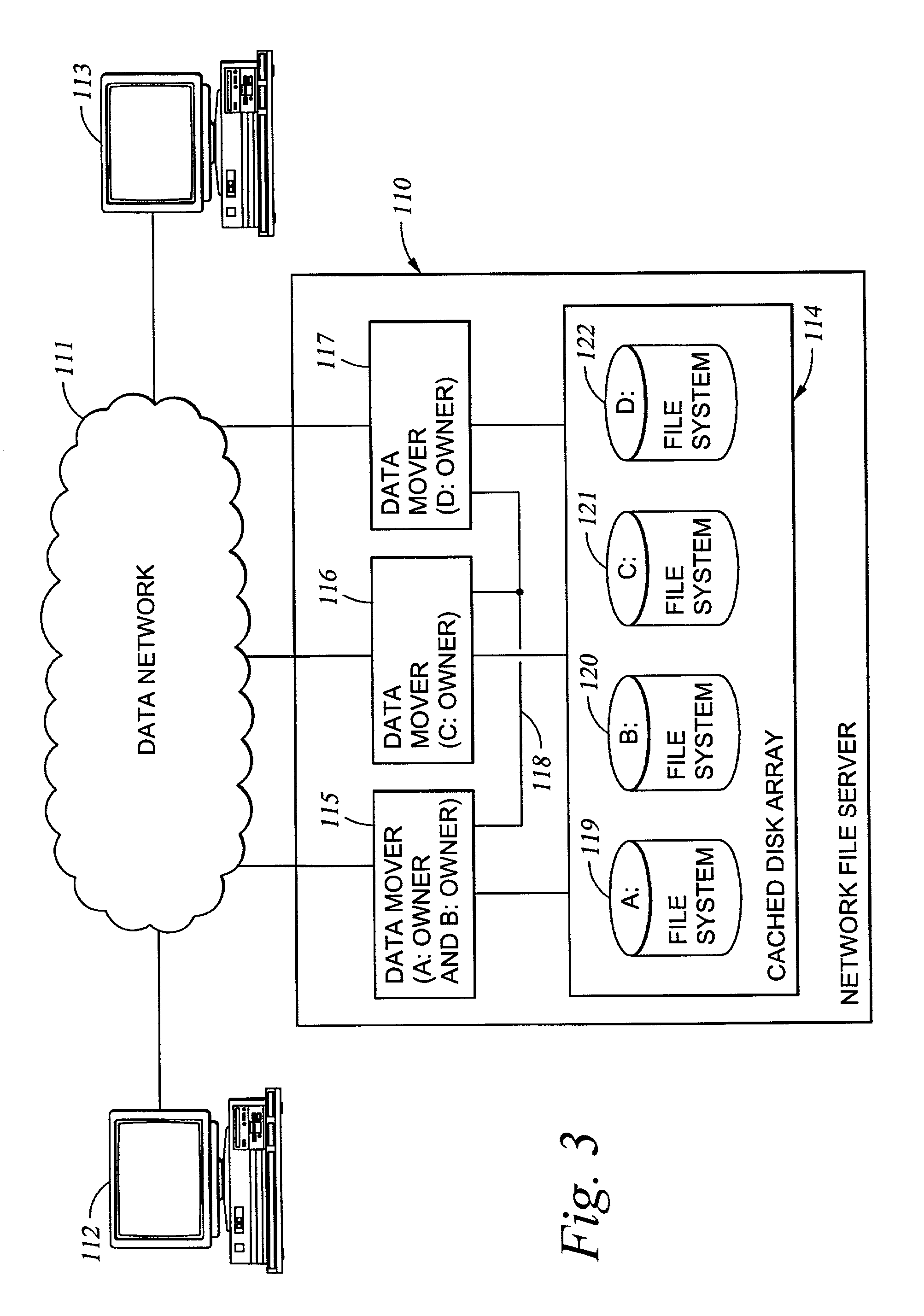
Delegation of metadata management in a storage system by leasing of free file system blocks from a file system owner
InactiveUS20050240628A1Reduce amountAvoid adjustmentData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsMetadata managementData management
Metadata management in a file server or storage network is delegated from a primary data processor to a secondary data processor in order to reduce data traffic between the primary data processor and the secondary data processor. The primary data processor retains responsibility for managing locks upon objects in the file system that it owns, and also retains responsibility for allocation of free blocks and inodes of the file system. By leasing free blocks and inodes to the secondary and granting locks to the secondary, the secondary can perform the other metadata management tasks such as appending blocks to a file, truncating a file, creating a file, and deleting a file.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
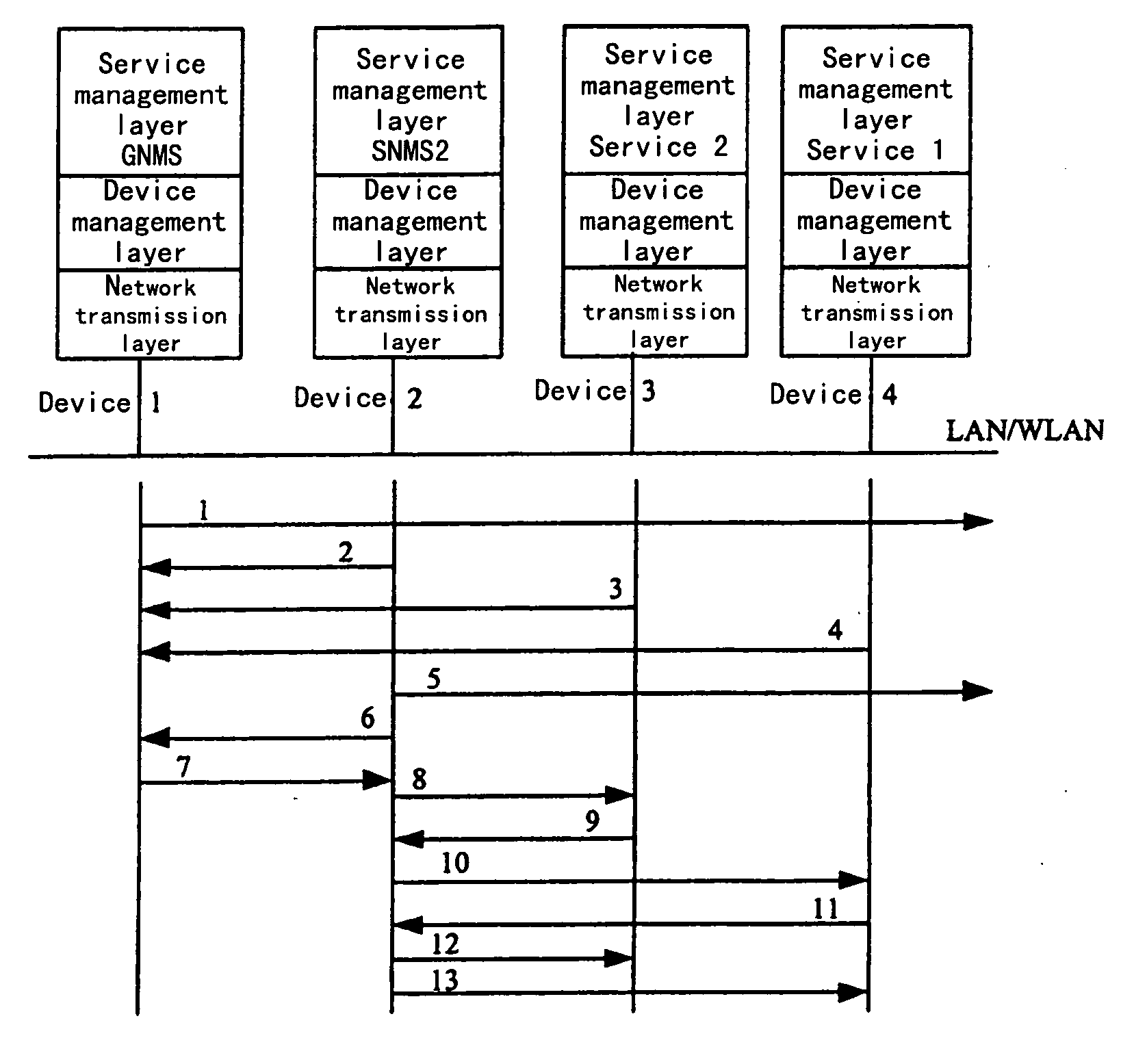
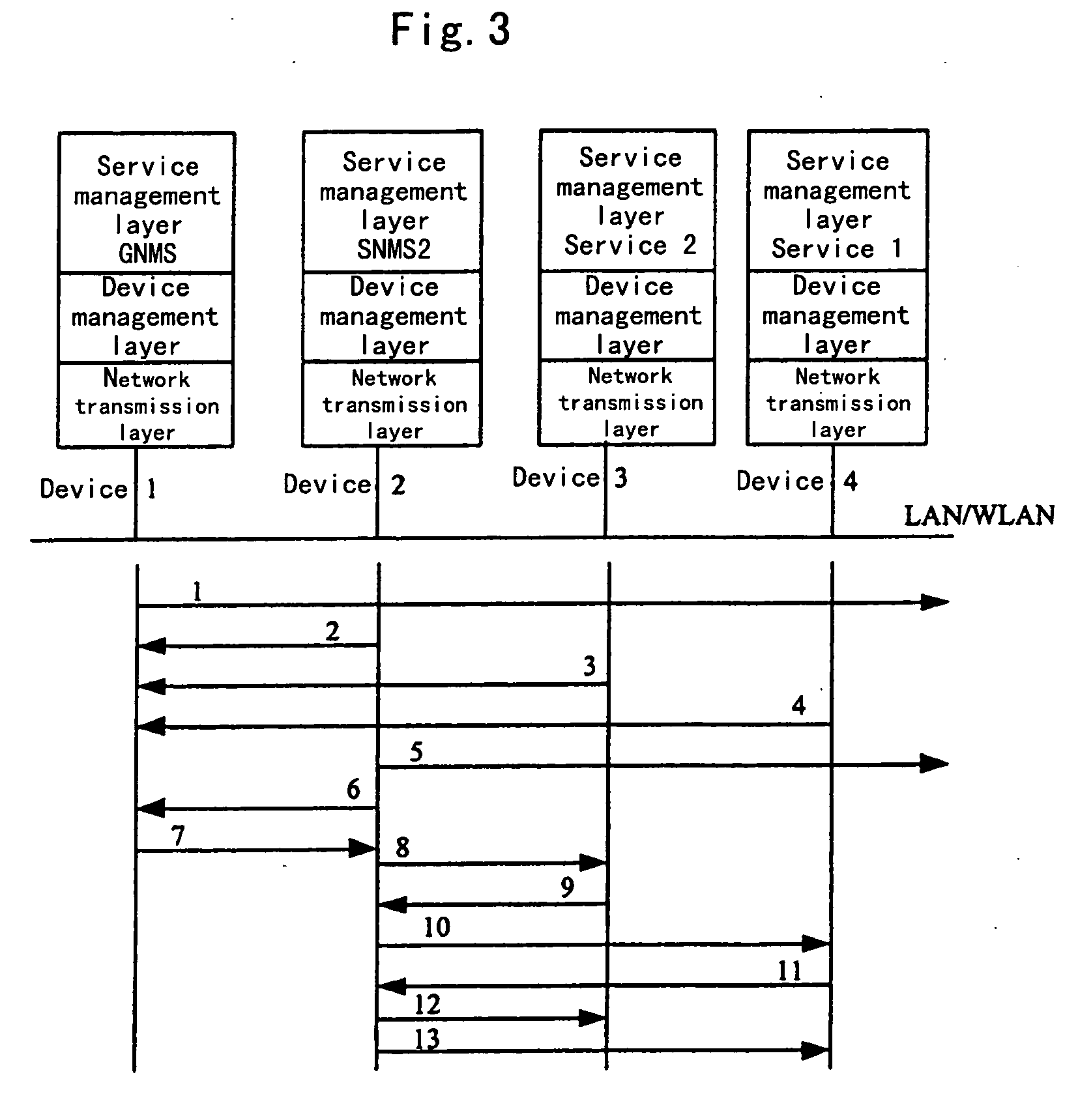
Method to realize dynamic networking and resource sharing among equipments
InactiveUS20060155802A1Implement resourcesEasy to useResource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsDevice registerInode
The invention relates to a method allowing dynamically networking among a plurality of devices to share resource. It includes: installing a software of dynamic networking and resource sharing on each of devices to realize dynamic networking and resource sharing. These devices periodically announce information with multicasting. A device serves as node control device, and announces the message of the existence of the device through multicasting, creates a node. A device can find the node by monitoring announcement message from the node. The device which requests to join into the node device registers its service information that can be provided by the device to the node control device. The device which has joined into the node finds the device providing service by indexing the nodal control device, and obtains desired service from the device by sending a service calling information. The method is applied to home backbone network for performing networking in home network. Then a topology connection structure with master / slave and peer-to-peer modes can be realized. The dynamic networking and resource sharing between the service providing device and the service utilizing device in the home backbone network can be realized.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) LTD
File system level integrity verification and validation
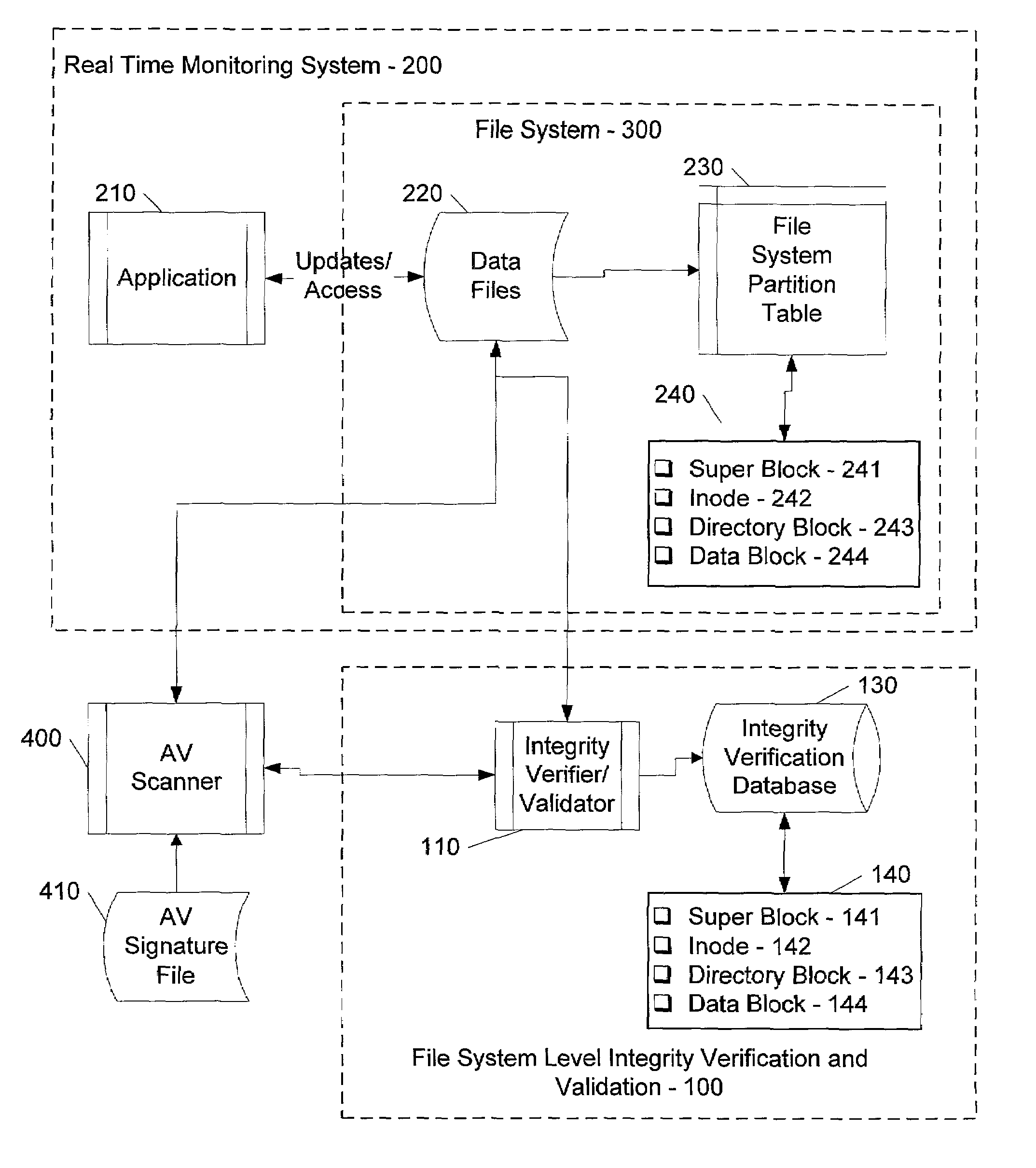
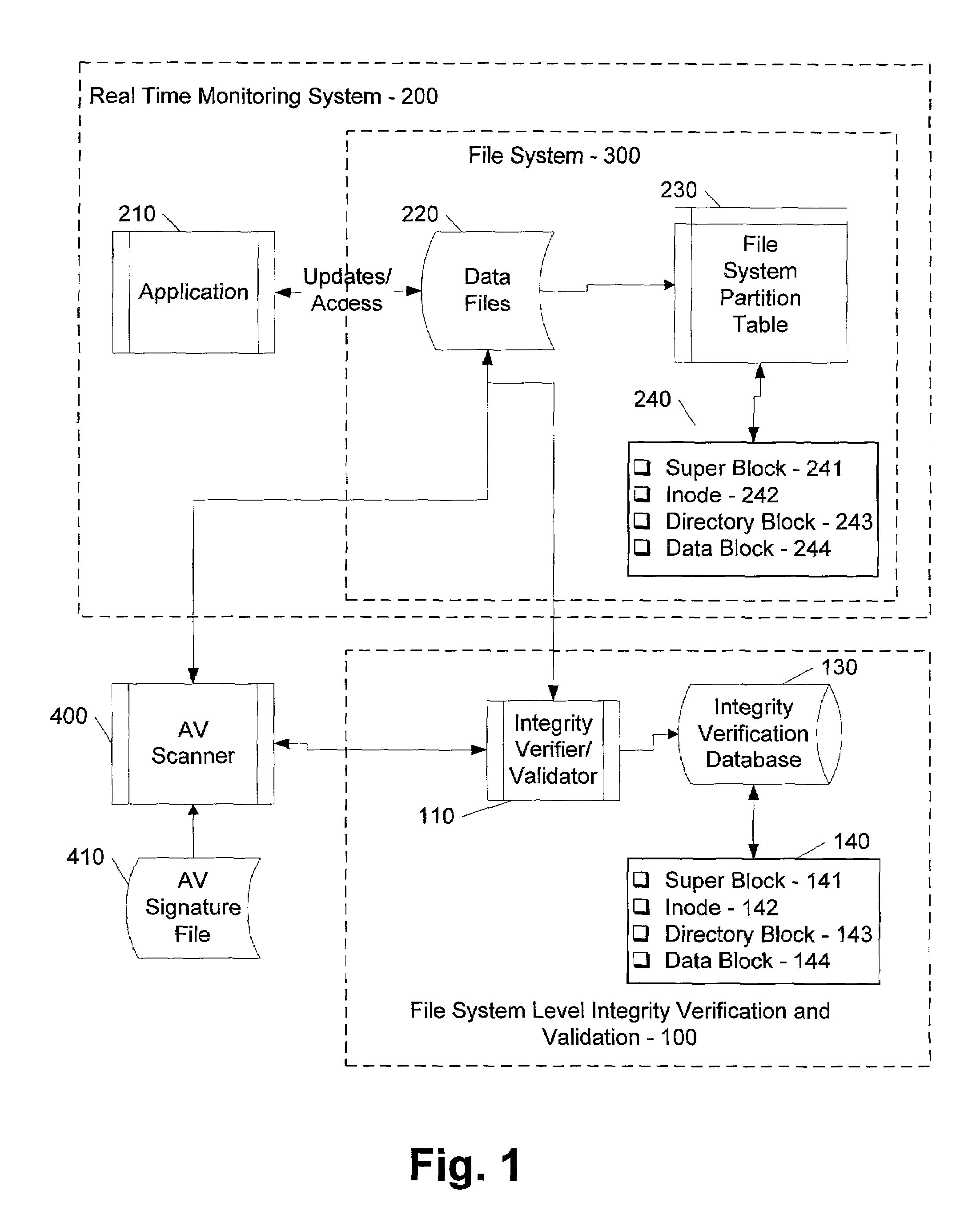
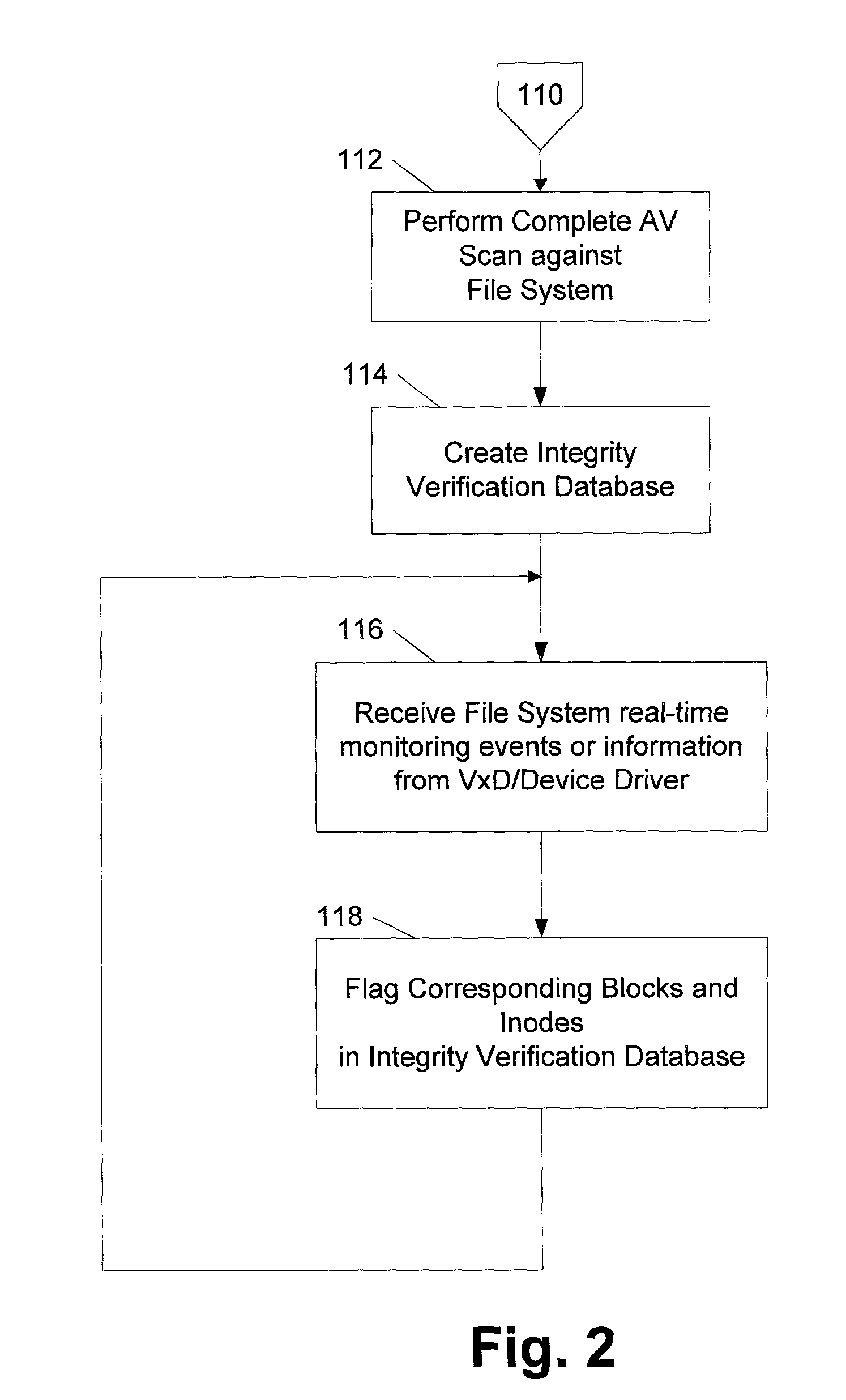
ActiveUS7069594B1Preventing rescanningGood level of efficiencyMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionAnti virusInode
An integrity verifier and validator is provided in which an initial anti-virus scan is performed against an entire file system to verify the integrity of the file system and create a corresponding file system level integrity verification database of known scanned regions of the file system. The database contains a copy of the file system's partition table referencing the range of occupied inodes and directory blocks. When new or updated content is written to the file system the integrity of the corresponding occupied inodes and directory blocks is no longer assured, and the integrity verifier flags them on the database for rescanning. Subsequent attempts to rescan any portion of the file system triggers the integrity validator to scan the database to validate whether that portion of the file system falls within any of the occupied inodes or directory blocks that have been flagged for rescanning. If they are not flagged, then rescanning of that portion of the file system is unnecessary as the integrity of at least that portion is assured. However, if they are flagged, then the anti-virus software rescans that portion of the file system for the presence of viruses.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
Delegation of metadata management in a storage system by leasing of free file system blocks and i-nodes from a file system owner
ActiveUS20030191745A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsMetadata managementInode
Metadata management in a file server or storage network is delegated from a primary data processor to a secondary data processor in order to reduce data traffic between the primary data processor and the secondary data processor. The primary data processor retains responsibility for managing locks upon objects in the file system that it owns, and also retains responsibility for allocation of free blocks and inodes of the file system. By leasing free blocks and inodes to the secondary and granting locks to the secondary, the secondary can perform the other metadata management tasks such as appending blocks to a file, truncating a file, creating a file, and deleting a file.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
System and method for restoring a virtual disk from a snapshot
ActiveUS7076509B1Substantial overheadBig spaceInput/output to record carriersData processing applicationsInode
The present invention provides a system and method for restoring a vdisk from a snapshot without the need to copy every individual block or inode from the snapshot. A vdisk restore process duplicates the inode of a vdisk within the active file system and performs a reconciliation process between the blocks of the twin inode and the snapshot inode. If the vdisk does not exist within the active file system, a new buffer tree is created that points to the data blocks stored in the snapshot.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Computer-implemented system and method for handling stored data
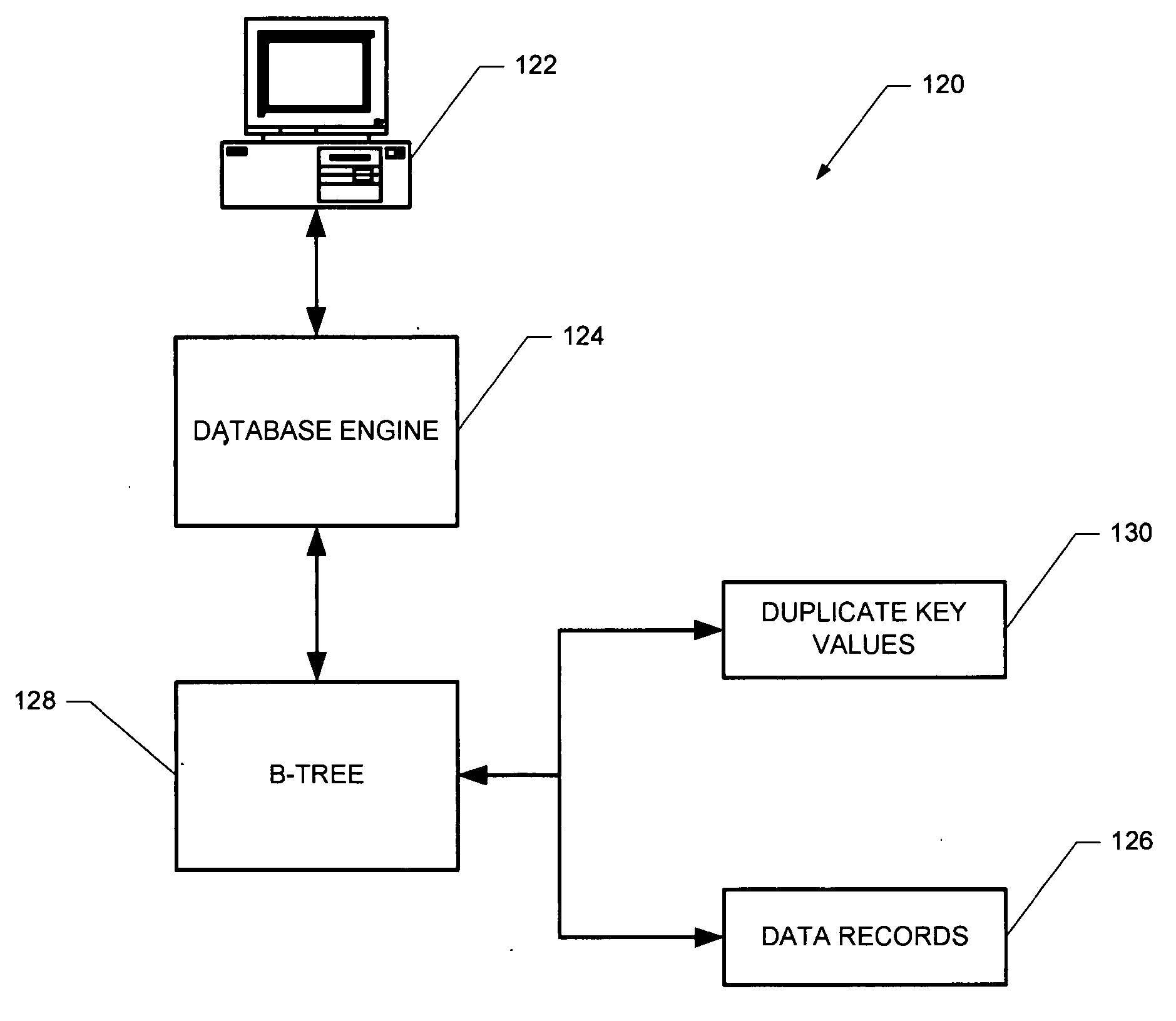
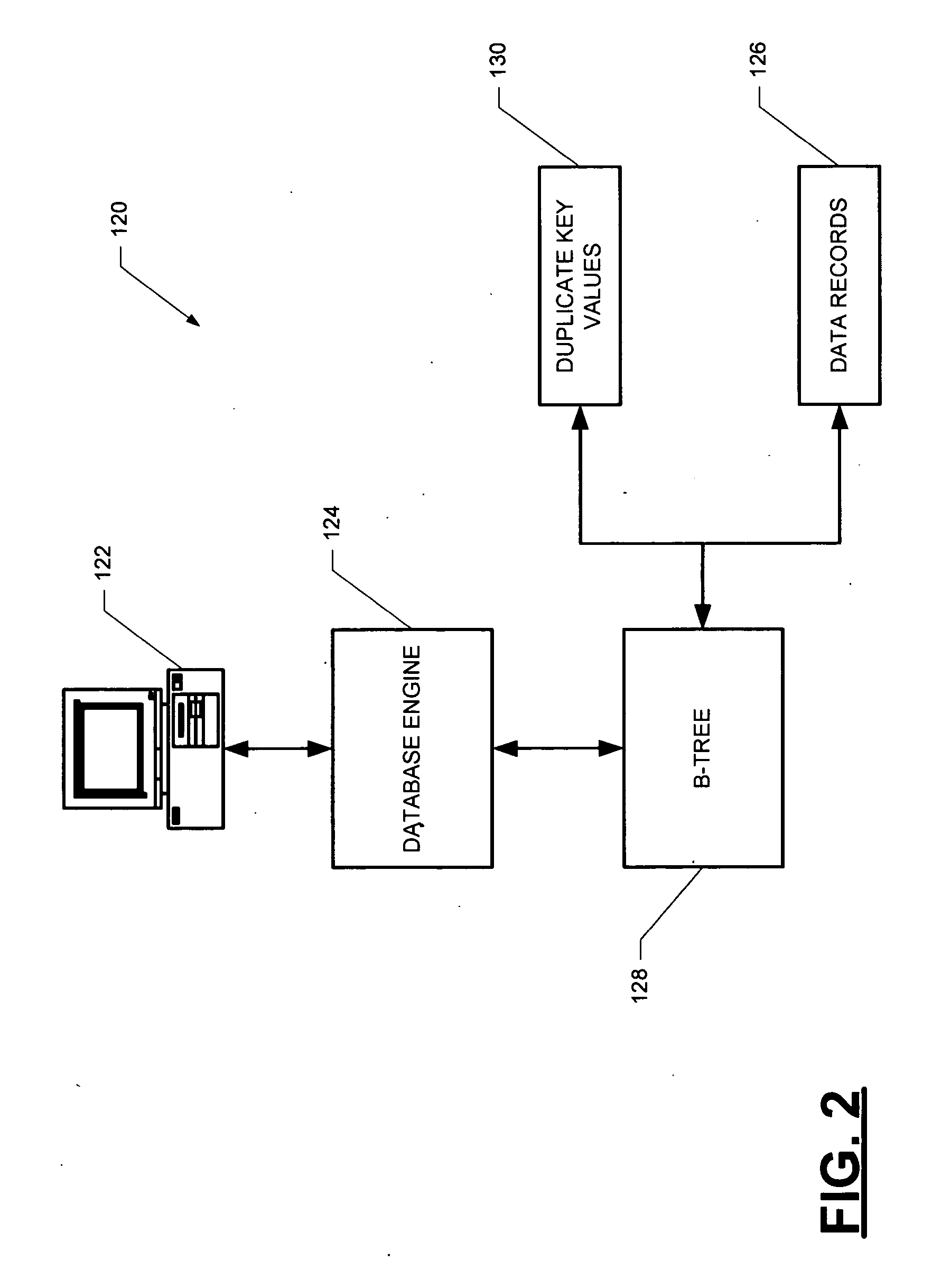
InactiveUS20050102255A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsInformation processingTheoretical computer science
A computer-implemented B-tree structure for information processing. The B-tree structure is used with any storage mechanism that can hold a plurality of data records. The B-tree includes interconnected nodes having a root node, index nodes and leaf nodes. The B-tree structure allows for the data records to be associated with duplicate keys that are stored separate from the leaf nodes.
Owner:SAS INSTITUTE
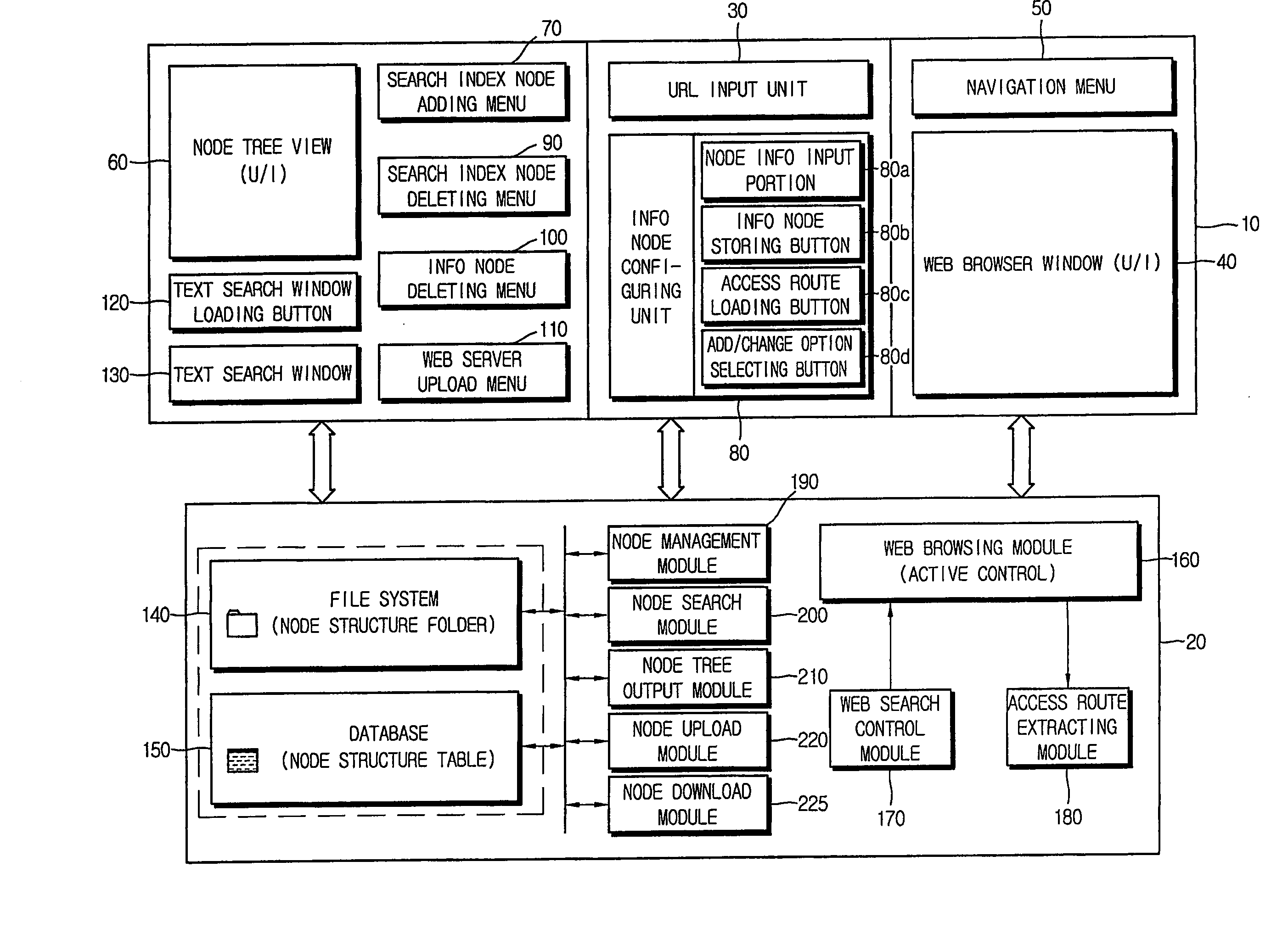
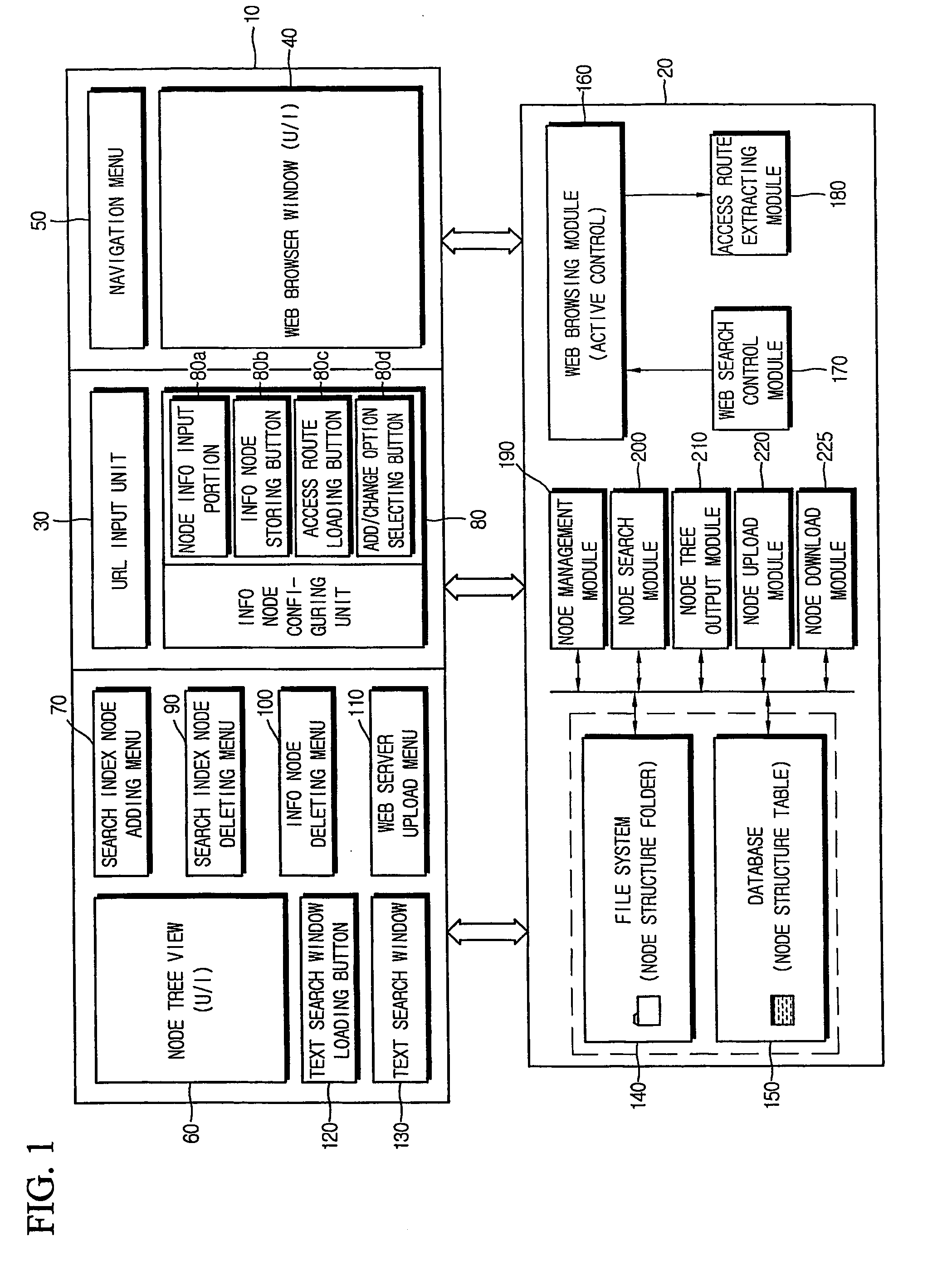
Method of collecting and searching for access route of information resource on internet and computer readable medium stored thereon program for implementing the same
InactiveUS20070110047A1Rapidly and efficiently searchEasy accessData switching by path configurationWeb data navigationAccess routeWeb browser
Disclosed is a method for systematically collecting and searching for access routes of information resources. Search index node is formed in hierarchical tree structure in the computer. Basic search information including access route and name of resource loaded on web browser is input with selection of search index node. Information node is configured and stored in linkage with the selected search index node based on the basic search information. Text search window is provided to the user to receive hierarchical information node access route distinguished by identifier, output node name list in the hierarchy corresponding to the identifier, receive user selection of node name from the list, and adds the selected node name to the identifier to hierarchically extend the access route step by step. When settled, the access route is extracted, and target information resource is obtained through Internet to be output to the user.
Owner:KIM SUN KWON
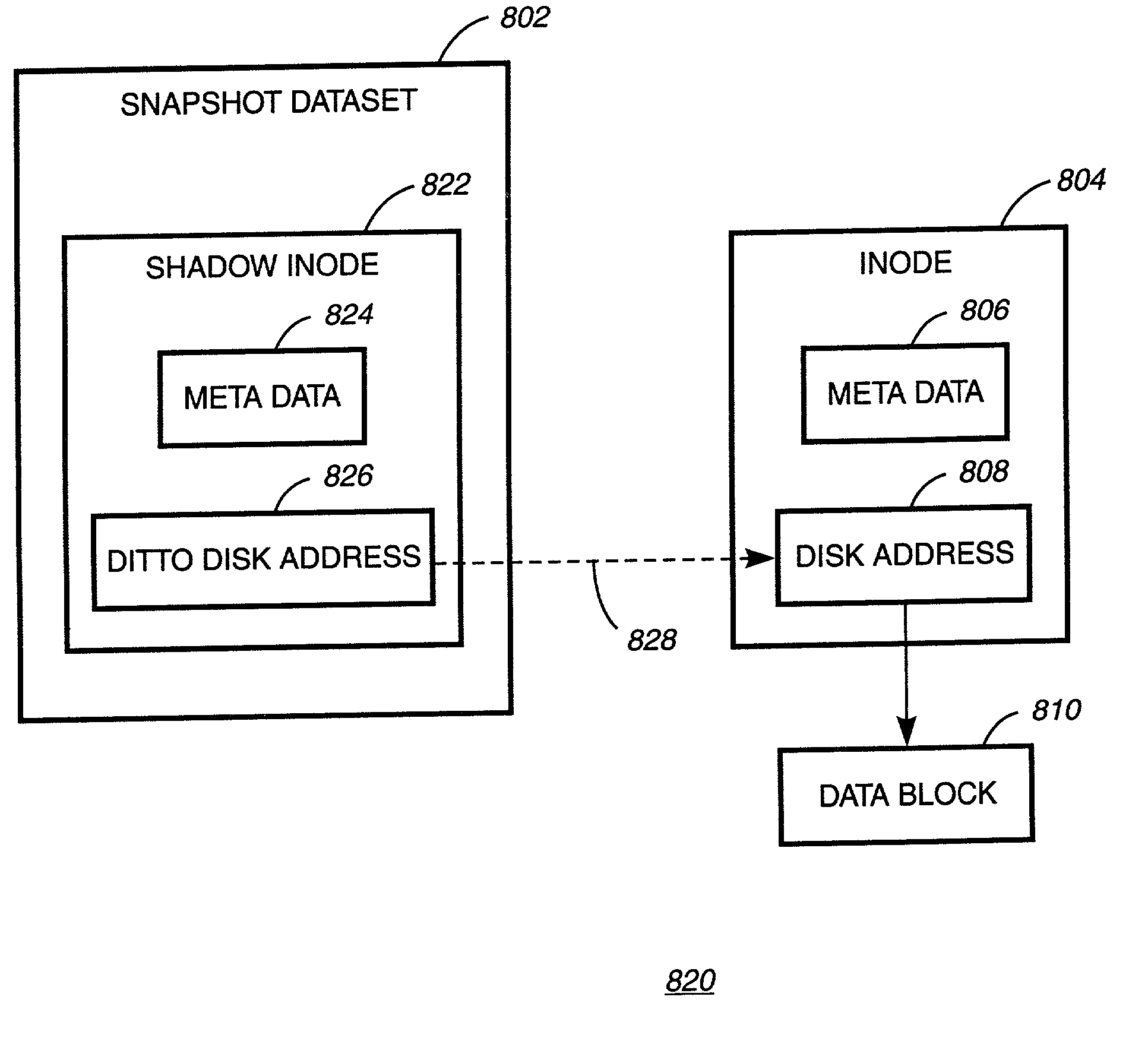
Writable file system snapshot with ditto address feature
InactiveUS7085785B2Data processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsData contentInode
A system, method and computer readable medium for providing a writable file system snapshot with ditto address feature is disclosed. In an embodiment of the present invention, the method includes accessing a first file system snapshot in a set of file system snapshots. A snapshot includes data contents comprising at least one shadow inode or at least one shadow inode and at least one data block corresponding to the shadow inode. The data contents of the first snapshot are copied and written to the next oldest file system snapshot. Subsequently, the data contents of the first snapshot are modified in accordance with modifications to at least one source file corresponding to the first snapshot. Then, a next most recent file system snapshot is accessed. The data contents of the next most recent snapshot are copied and written to the first file system snapshot.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com