Patents
Literature
186 results about "Asynchronous replication" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
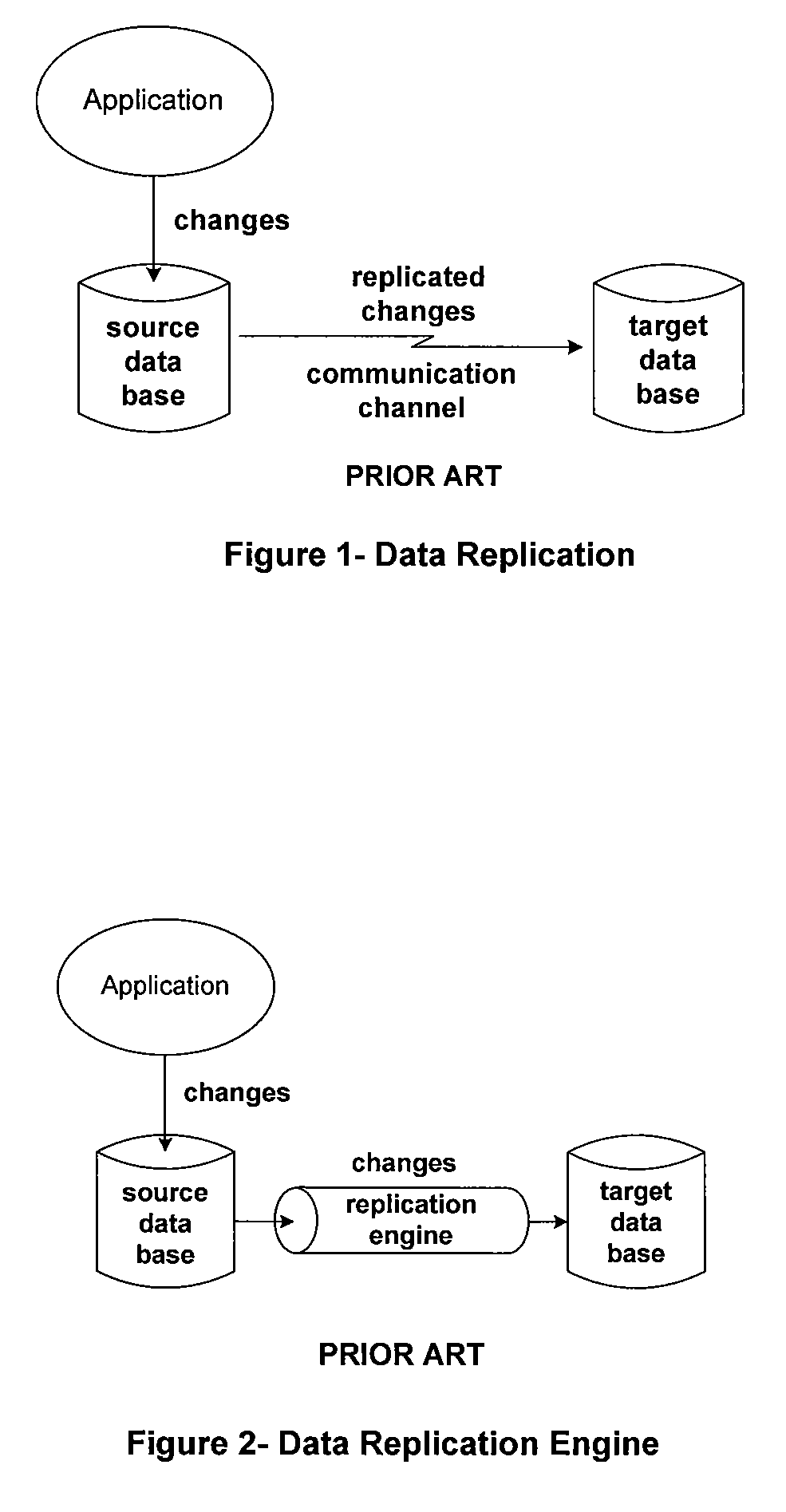
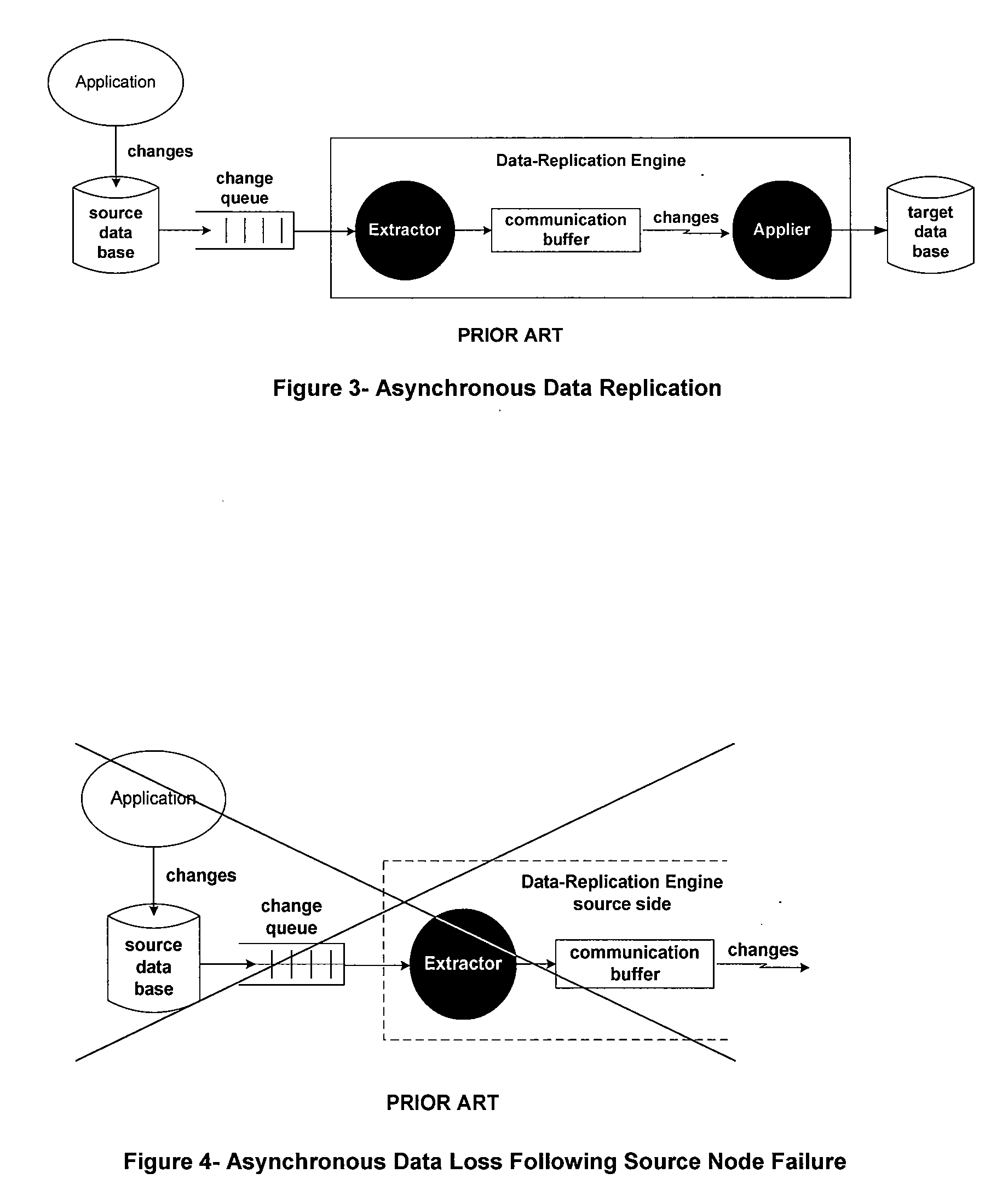
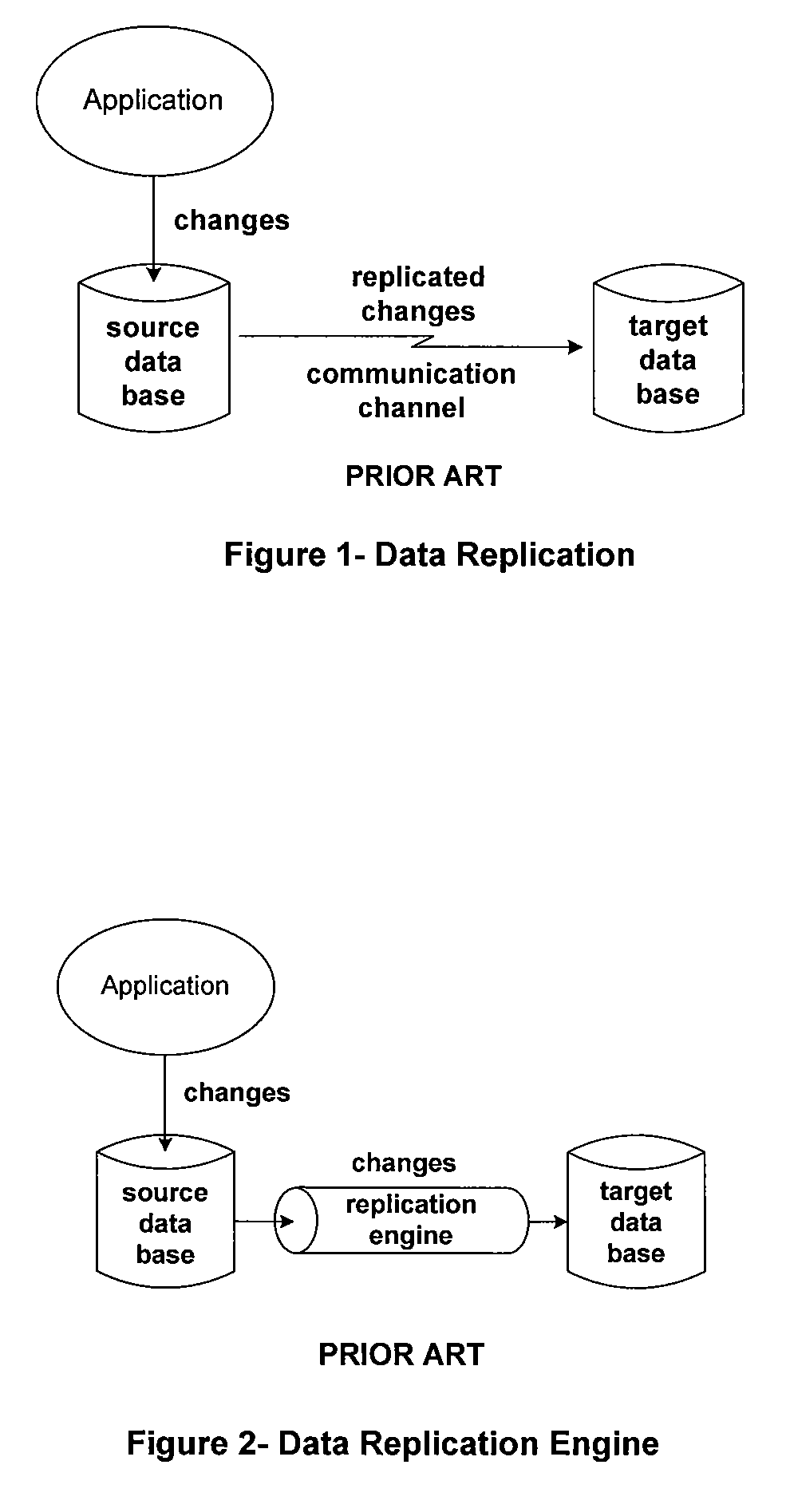
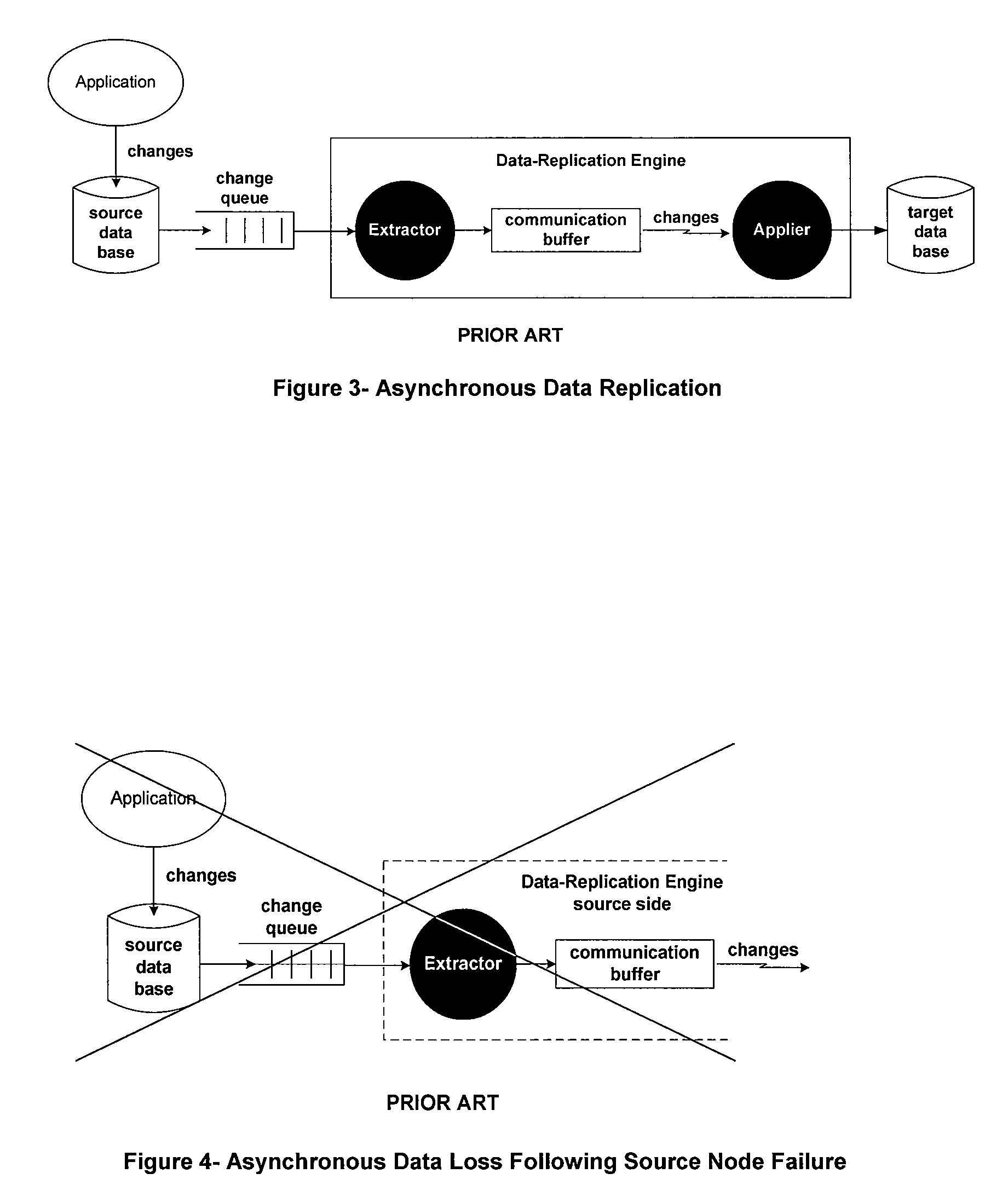
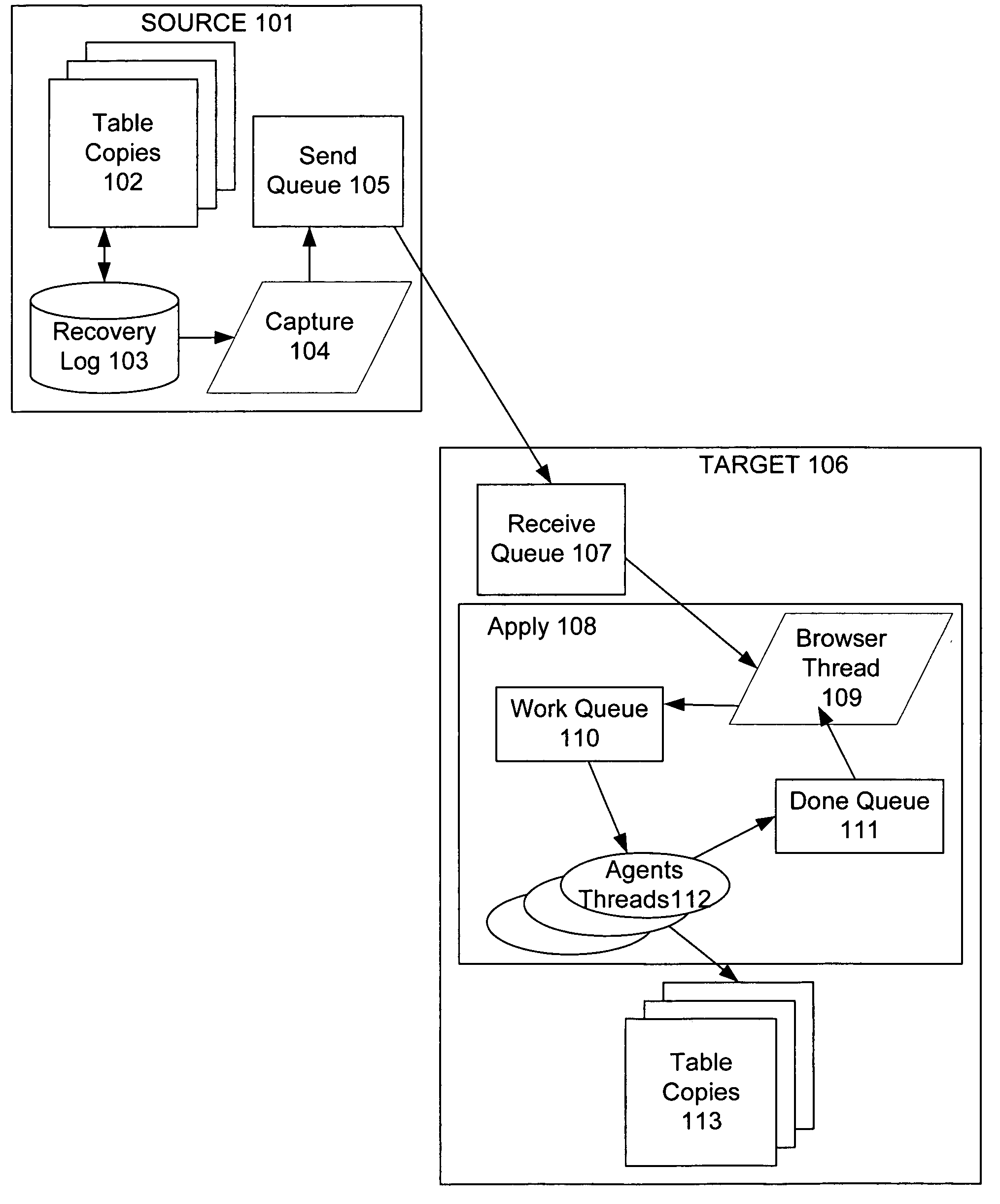
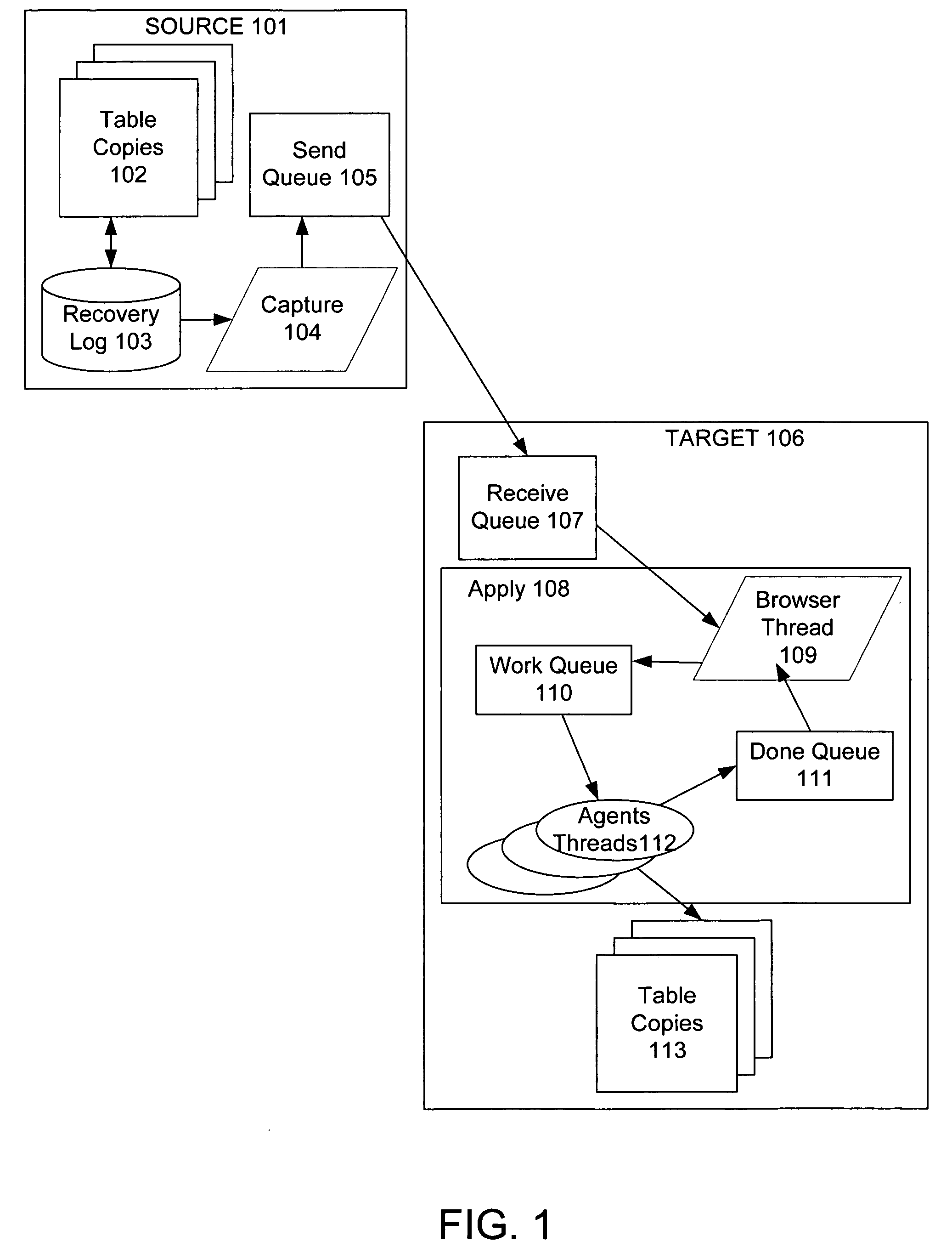
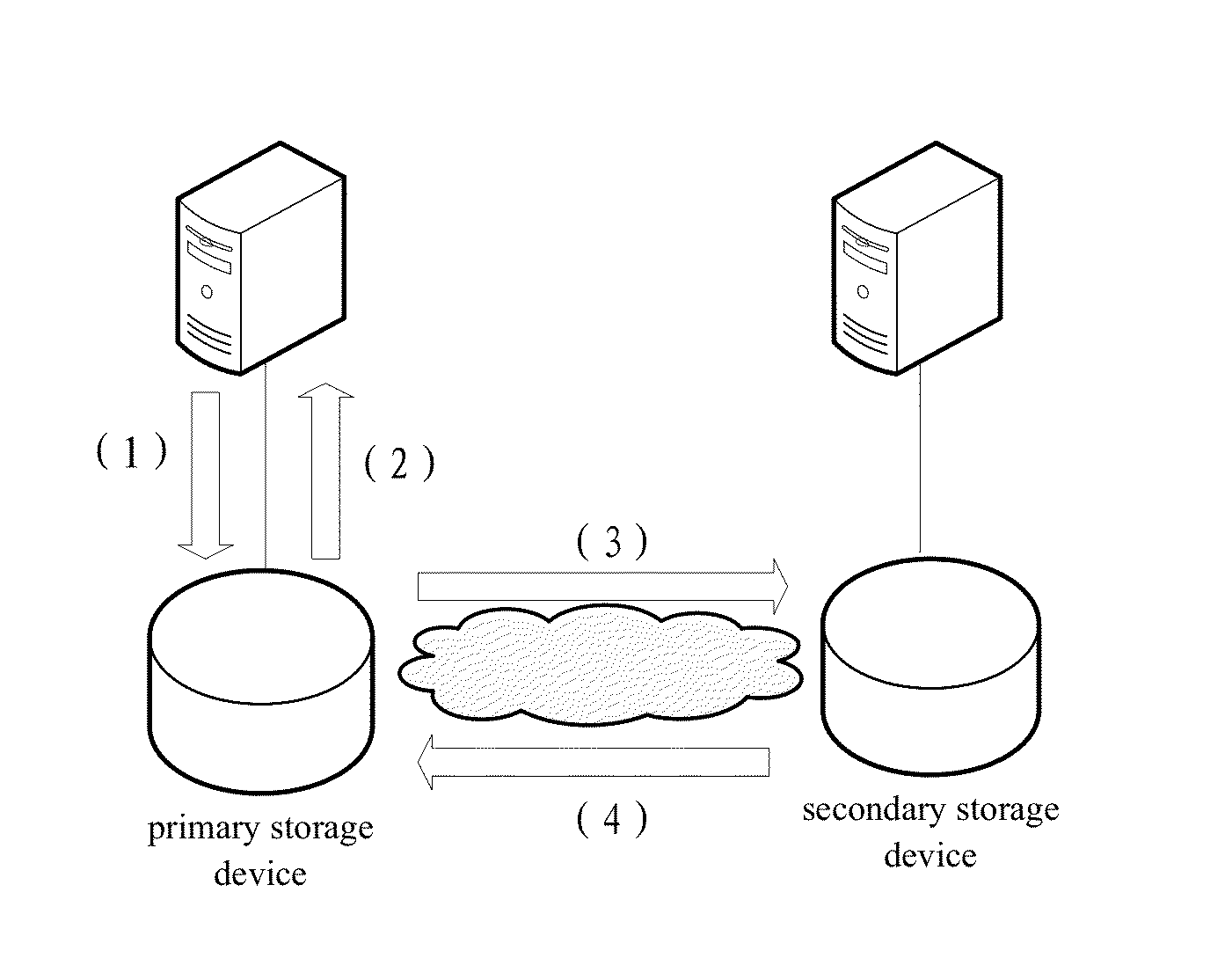
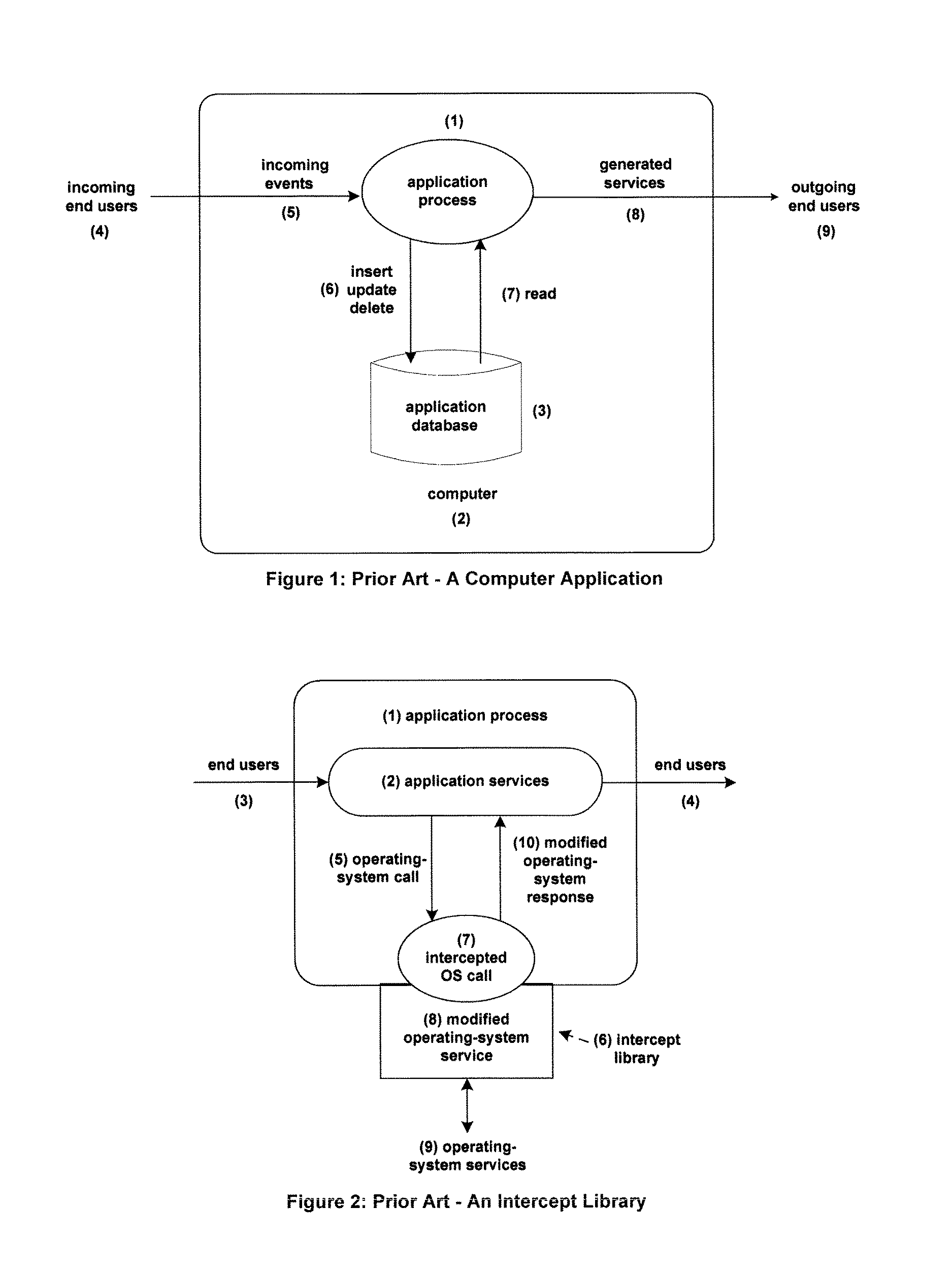
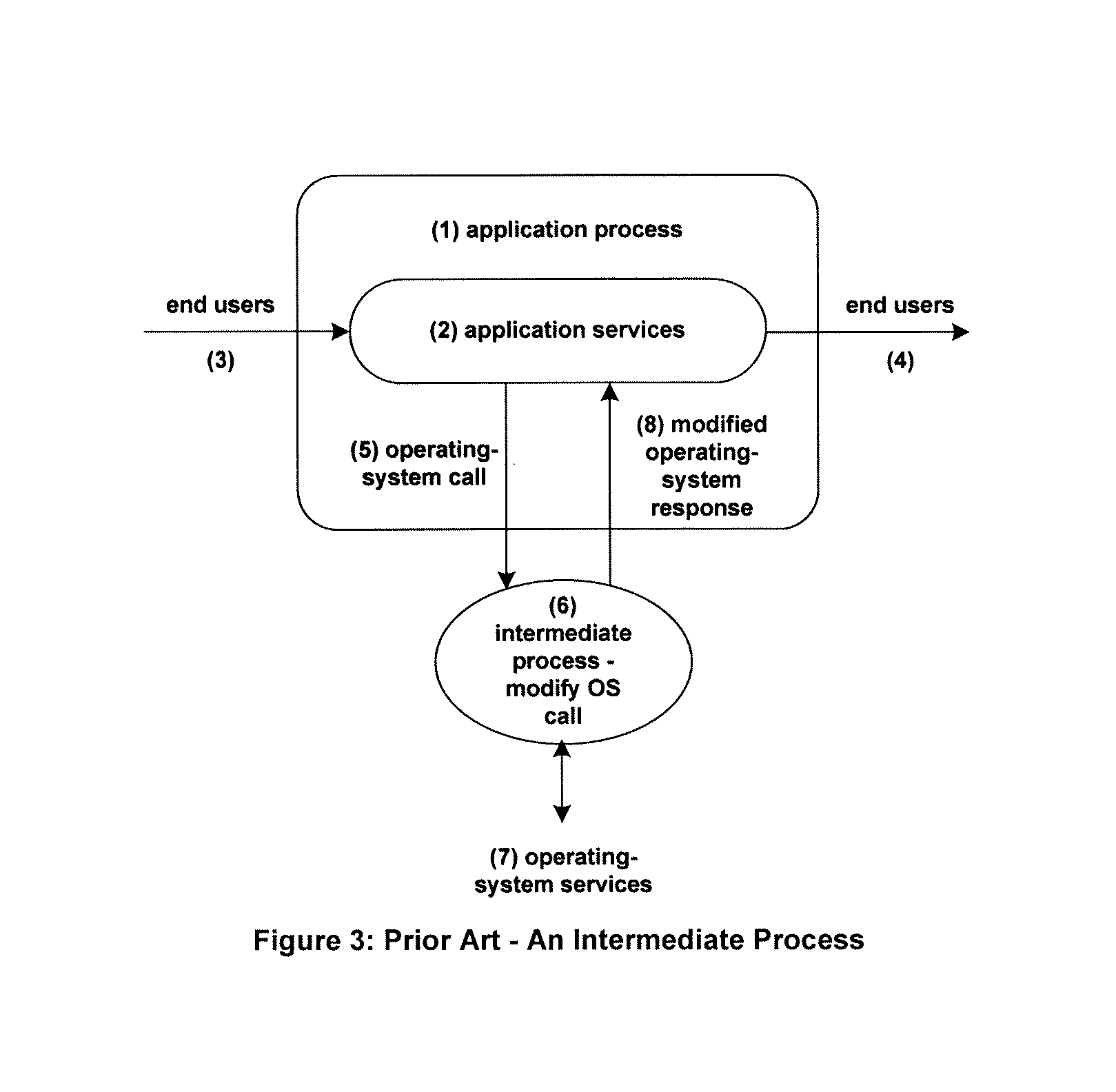
Asynchronous replication is a store and forward approach to data backup or data protection. Asynchronous replication writes data to the primary storage array first and then, depending on the implementation approach, commits data to be replicated to memory or a disk-based journal.
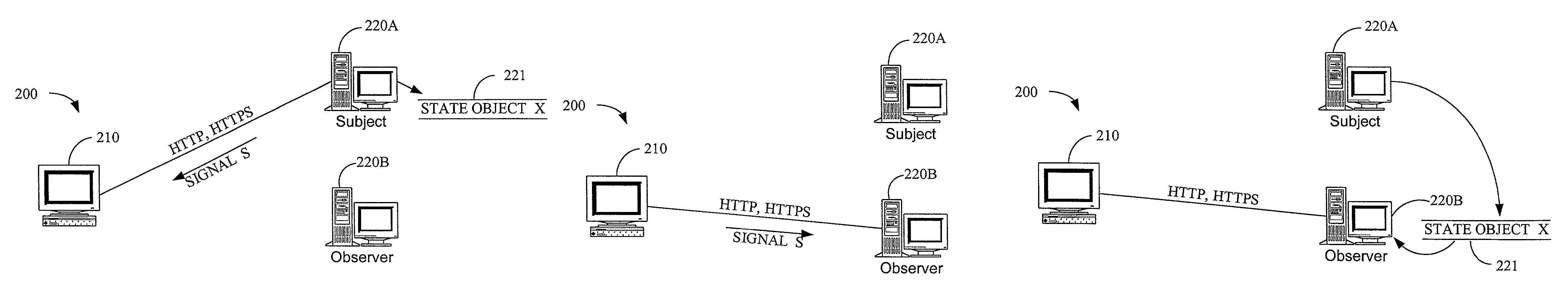
System and method for maintaining consistent independent server-side state among collaborating servers
ActiveUS7024451B2Less couplingWork lessMultiple digital computer combinationsSecuring communicationClient-sideServer-side
A system and method are provided for maintaining consistent server-side state across a pool of collaborating servers with independent state repositories. When a client performs an event on a collaborating server which affects such state on the server, it publishes notification of the event into a queue maintained in client-side state which is shared by all of the collaborating servers in the pool. As the client makes requests to servers within the pool, the queue is thus included in each request. When a collaborating server needs to access its server-side state in question, it first discerns events new to it from the queue and replicates their effects into such server-side state. As a result, the effects of events upon server-side state are replicated asynchronously across the servers in the pool, as the client navigates among them.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
Mixed mode synchronous and asynchronous replication system
ActiveUS20090313311A1Avoid data lossFast response timeMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsMixed modeMultiple applications
A replication system that includes an asynchronous replication mode and a synchronous replication mode replicates data associated with a plurality of transactions. The replication system includes one or more target nodes connected via communication media in a topology. Each target node includes a database and a plurality of appliers allocated thereto. Each transaction has one or more transaction steps or operations. A first set of transaction steps or operations are allocated to the plurality of appliers on an object-by-object basis when the replication system operates in asynchronous replication mode. A second set of transaction steps or operations are allocated to the plurality of appliers on a transaction-by-transaction basis when the replication system operates in synchronous replication mode. The replication system further includes one or more originating nodes, and the requests for the first and second sets of transaction steps or operations to execute on an originating node can be initiated during the same time period.
Owner:RPX CORP
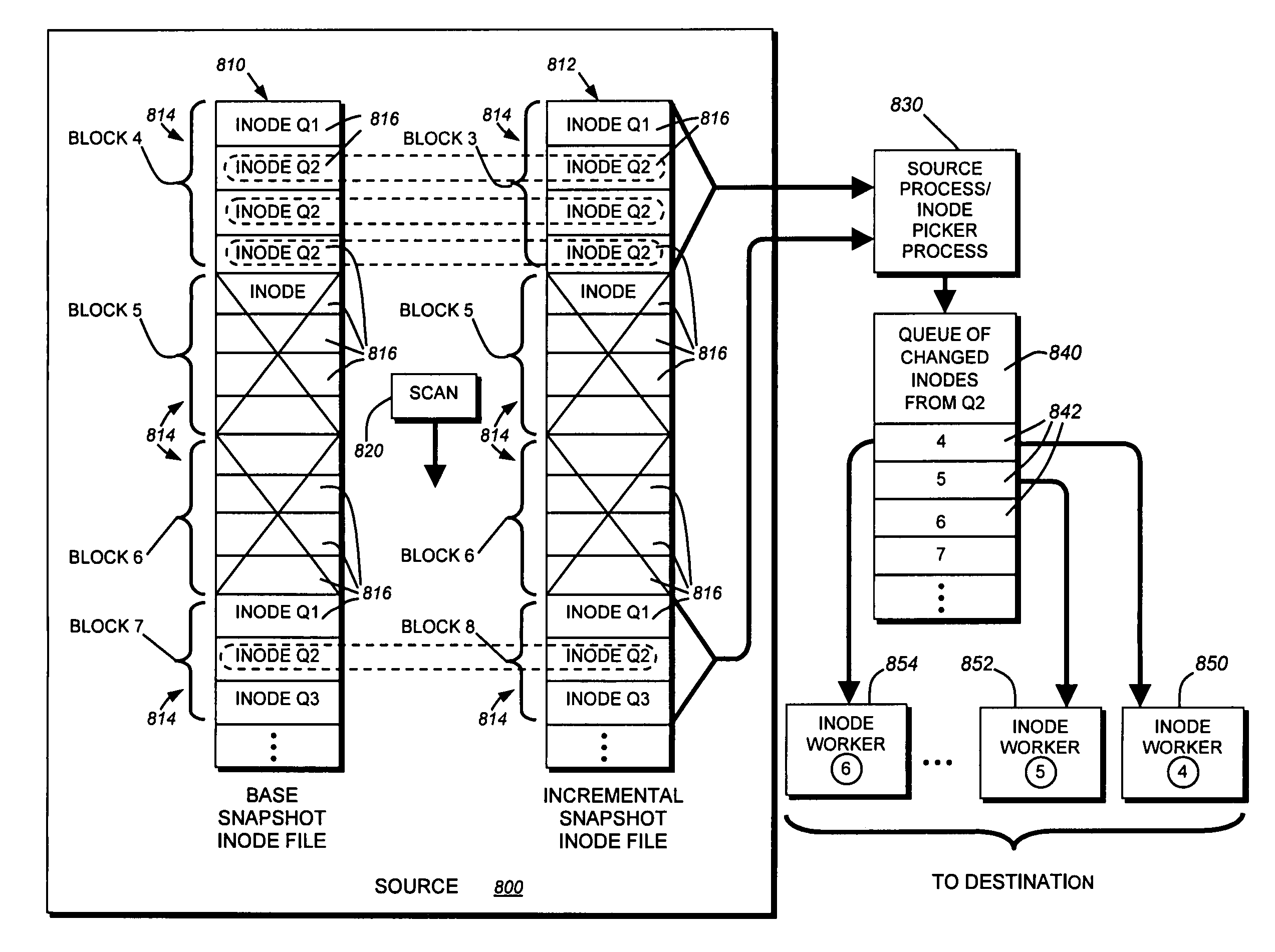
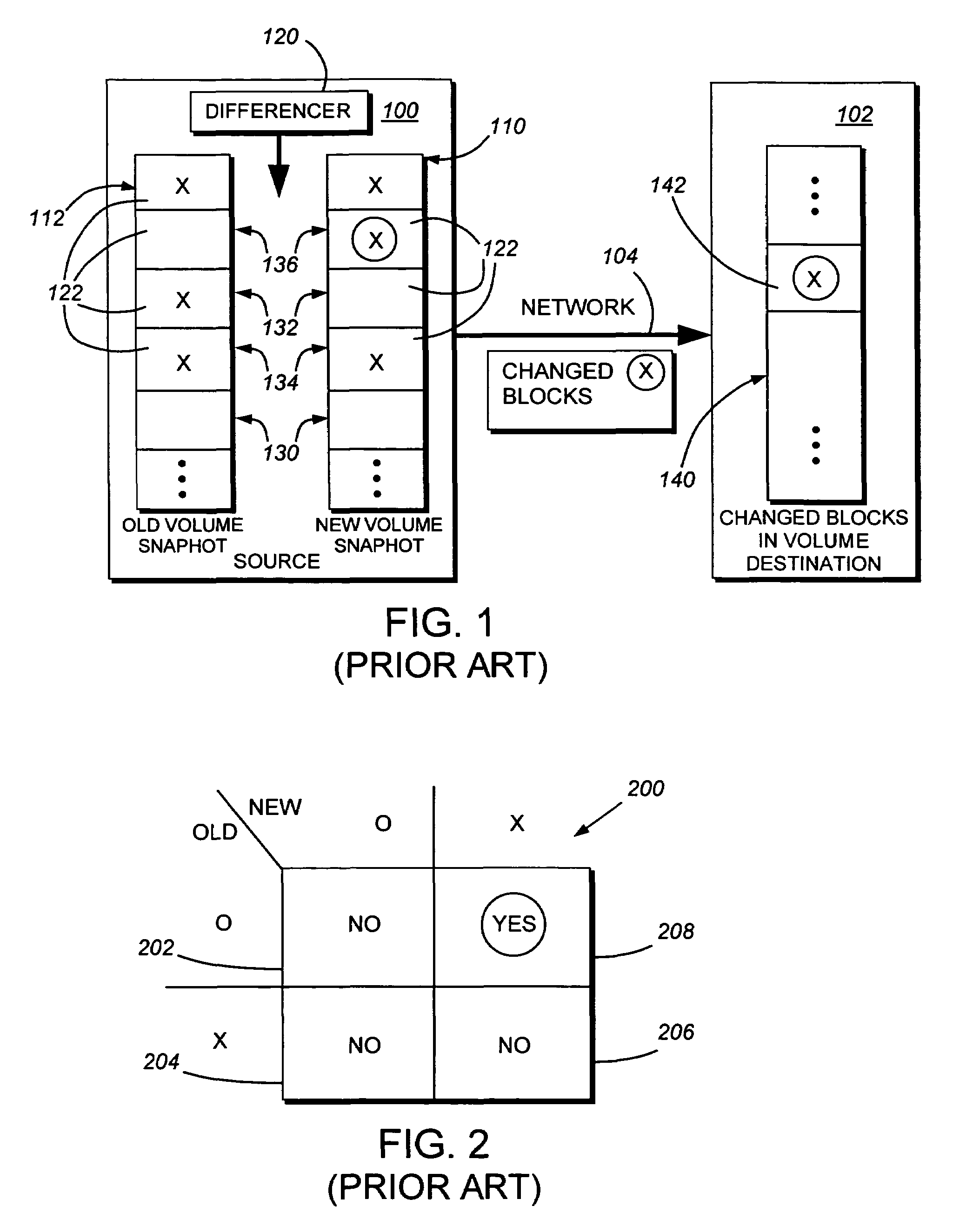
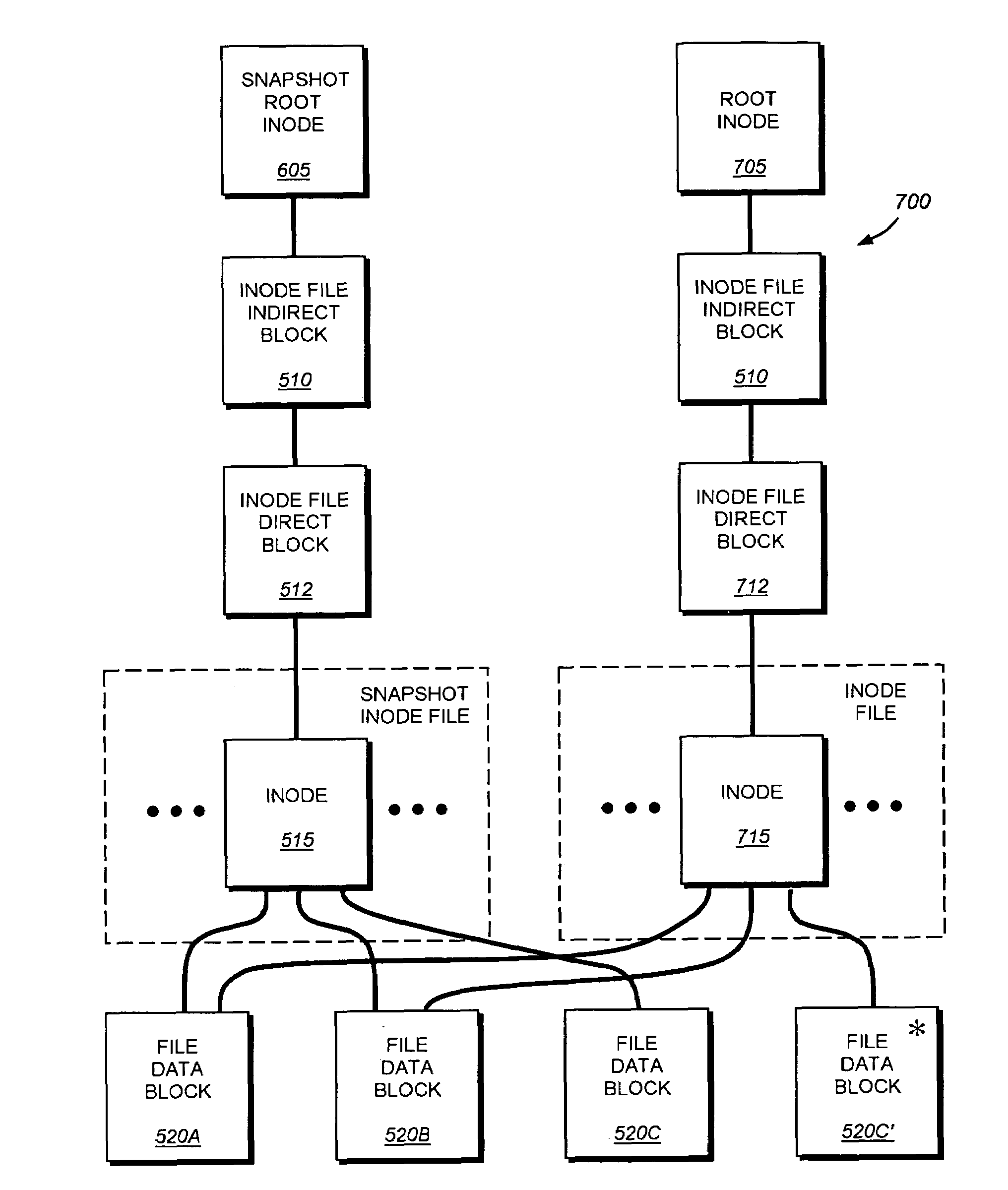
System and method for determining changes in two snapshots and for transmitting changes to destination snapshot
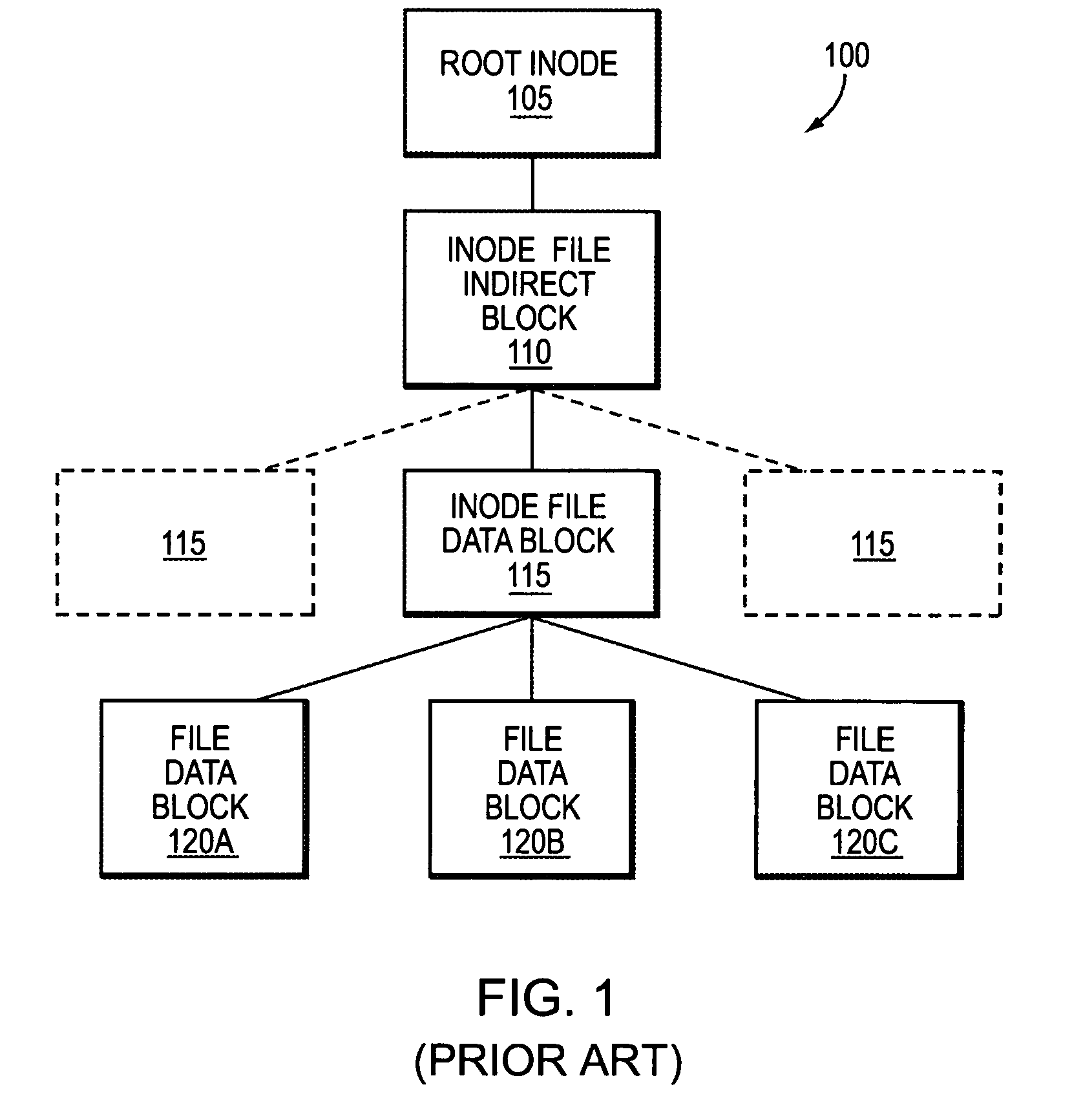
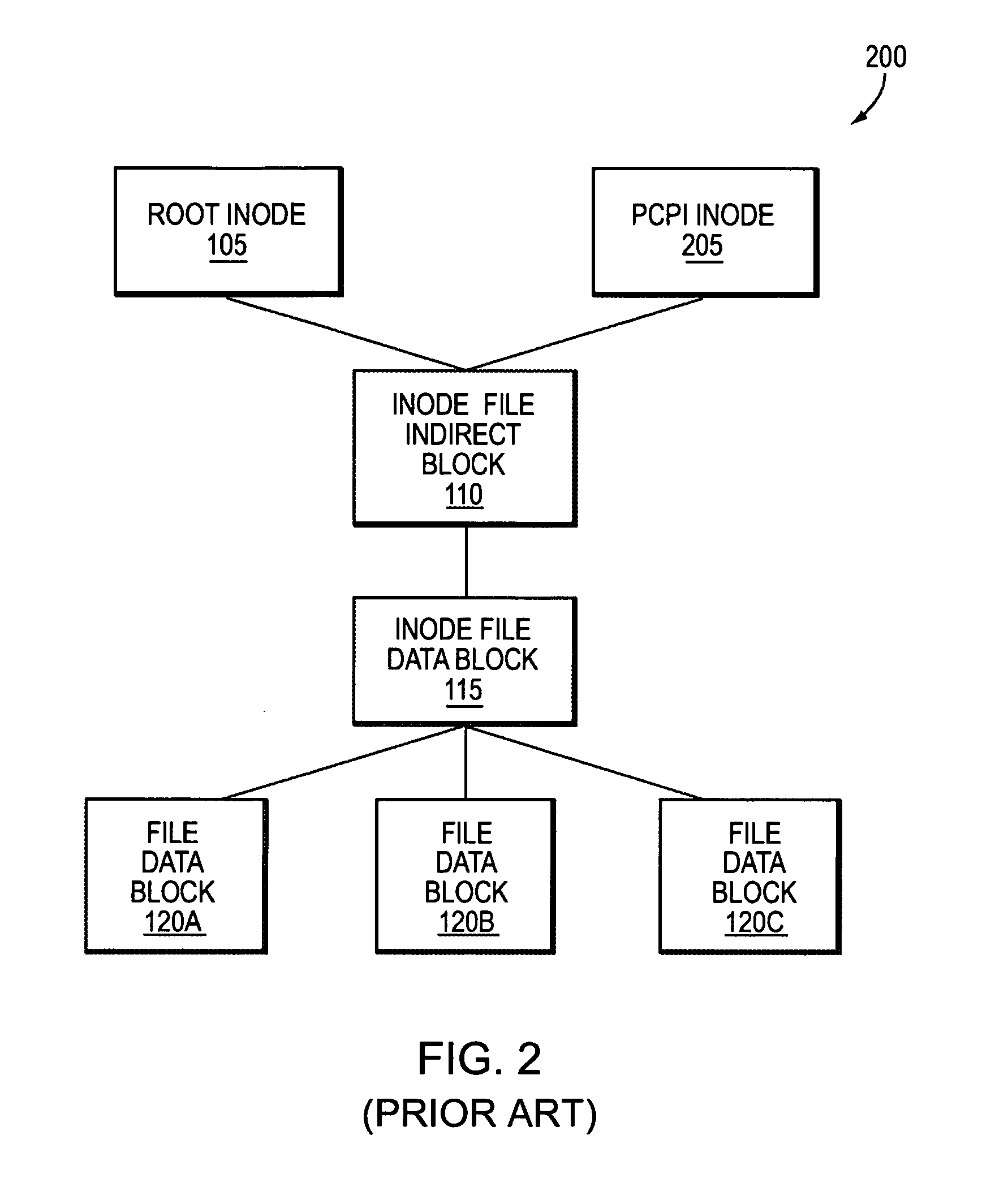
InactiveUS6993539B2Efficient scanningOvercome disadvantagesData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsData streamInode
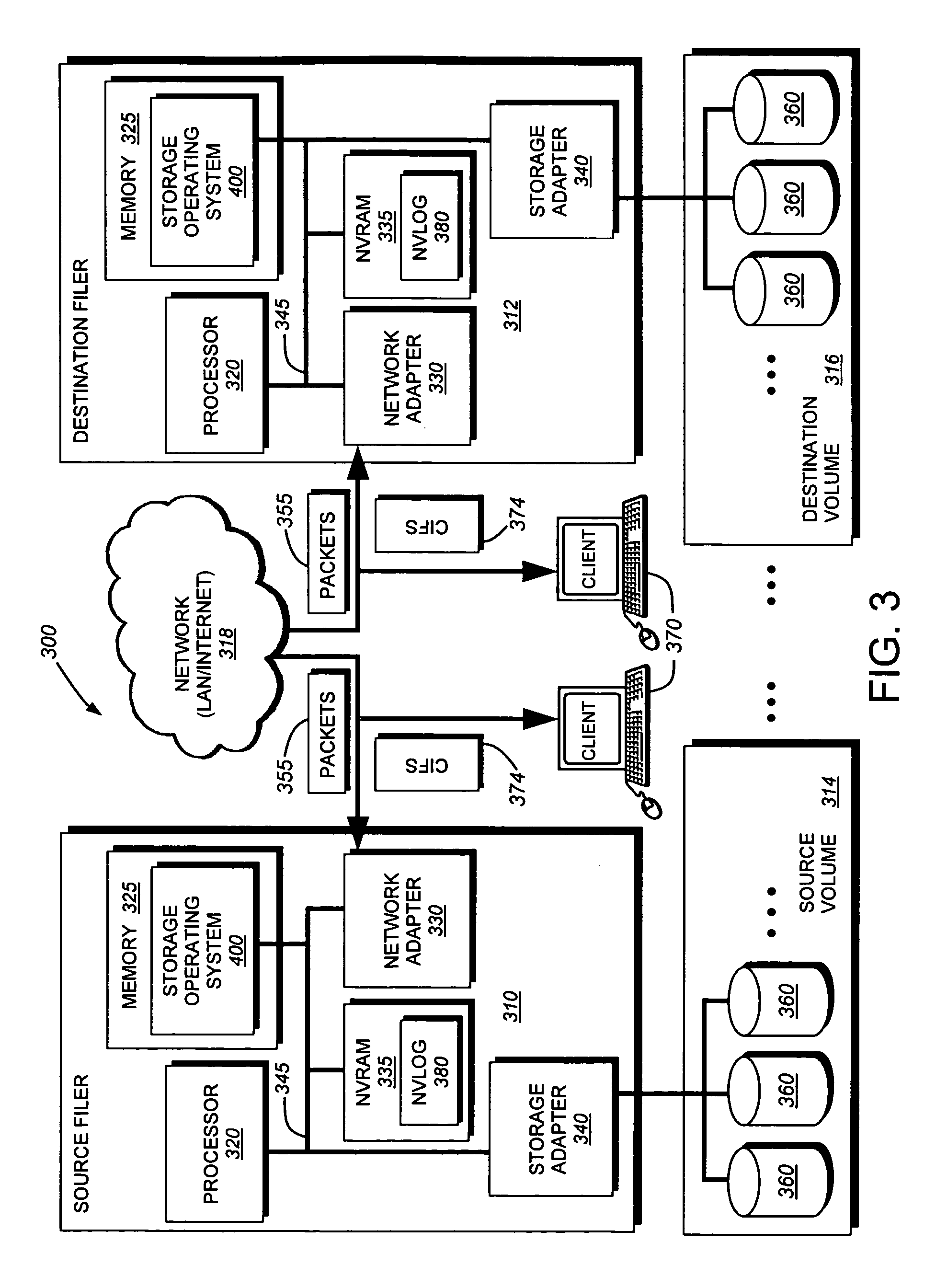
A system and method for remote asynchronous replication or mirroring of changes in a source file system snapshot in a destination replica file system using a scan (via a scanner) of the blocks that make up two versions of a snapshot of the source file system, which identifies changed blocks in the respective snapshot files based upon differences in volume block numbers identified in a scan of the logical file block index of each snapshot. Trees of blocks associated with the files are traversed, bypassing unchanged pointers between versions and walking down to identify the changes in the hierarchy of the tree. These changes are transmitted to the destination mirror or replicated snapshot. This technique allows regular files, directories, inodes and any other hierarchical structure to be efficiently scanned to determine differences between versions thereof. The changes in the files and directories are transmitted over the network for update of the replicated destination snapshot in an asynchronous (lazy write) manner. The changes are described in an extensible, system-independent data stream format layered under a network transport protocol. At the destination, source changes are used to update the destination snapshot. Any deleted or modified inodes already on the destination are moved to a temporary or “purgatory” directory and, if reused, are relinked to the rebuilt replicated snapshot directory. The source file system snapshots can be representative of a volume sub-organization, such as a qtree.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Efficient Logging for Asynchronously Replicating Volume Groups
ActiveUS20110099342A1The process is compact and efficientReduce memoryMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionAuxiliary memoryData store
A system and method for logging for asynchronously replicating volume groups. A write request to write data to a location in a volume may be received. Metadata associated with the write request may be stored. It may be determined if the write request possibly overlaps with one or more earlier write requests to the volume that have not yet been replicated to a secondary storage. The data may be stored in a replication log only if the write request possibly overlaps with one or more earlier write requests to the volume. The data may not be stored in the replication log if the write request does not overlap with one or more earlier write requests to the volume. The data may be written to the location in the volume. Changes to the volume may periodically be replicated to the secondary storage using the replication log.
Owner:VERITAS TECH
Mixed mode synchronous and asynchronous replication system
ActiveUS8301593B2Reduce stepsAvoid data lossDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionAsynchronous communicationApplication software
A replication system that includes an asynchronous replication mode and a synchronous replication mode replicates data associated with a plurality of transactions. The replication system includes one or more target nodes connected via communication media in a topology. Each target node includes a database and a plurality of appliers allocated thereto. Each transaction has one or more transaction steps or operations. A first set of transaction steps or operations are allocated to the plurality of appliers on an object-by-object basis when the replication system operates in asynchronous replication mode. A second set of transaction steps or operations are allocated to the plurality of appliers on a transaction-by-transaction basis when the replication system operates in synchronous replication mode. The replication system further includes one or more originating nodes, and the requests for the first and second sets of transaction steps or operations to execute on an originating node can be initiated during the same time period.
Owner:RPX CORP
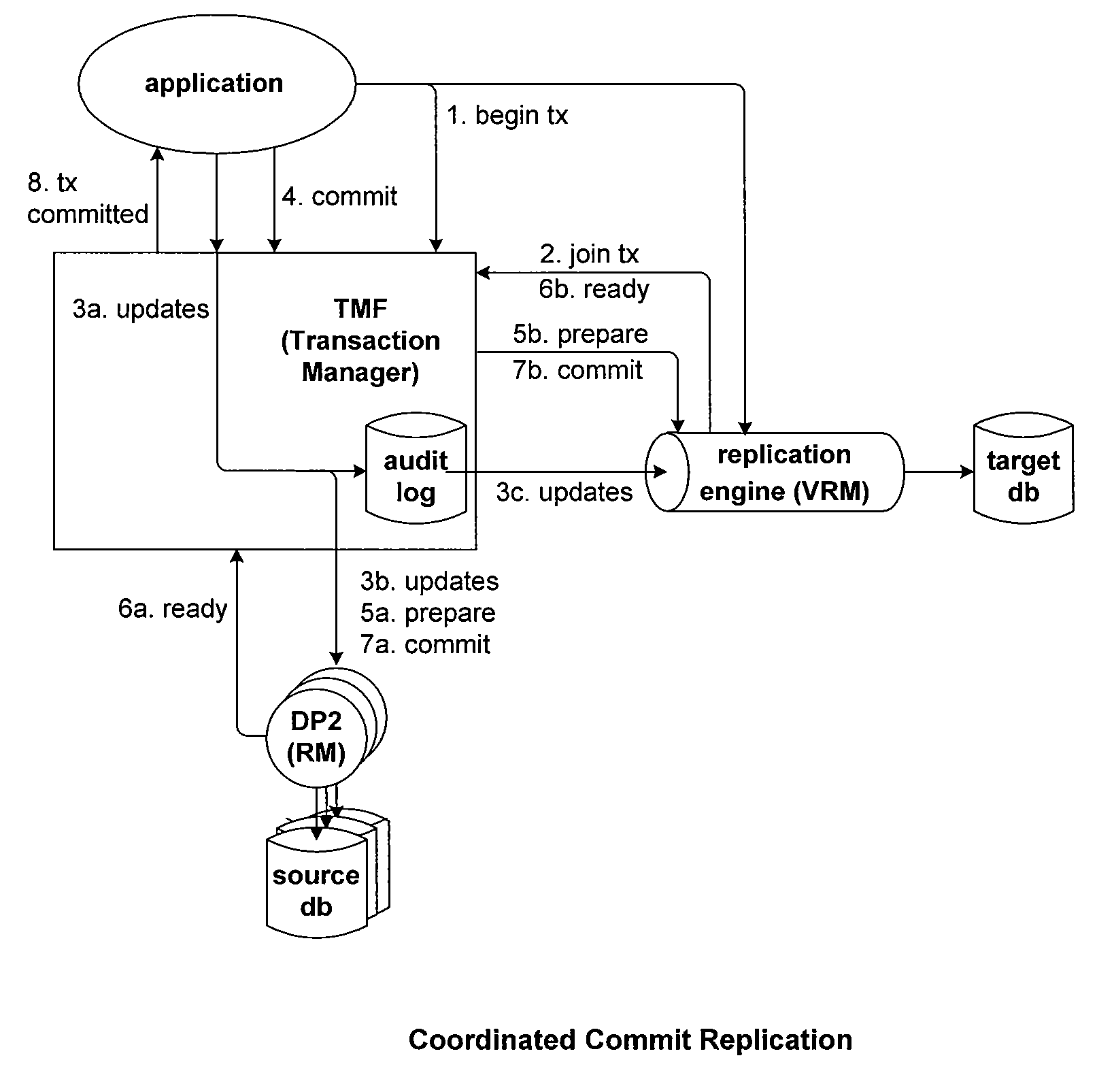
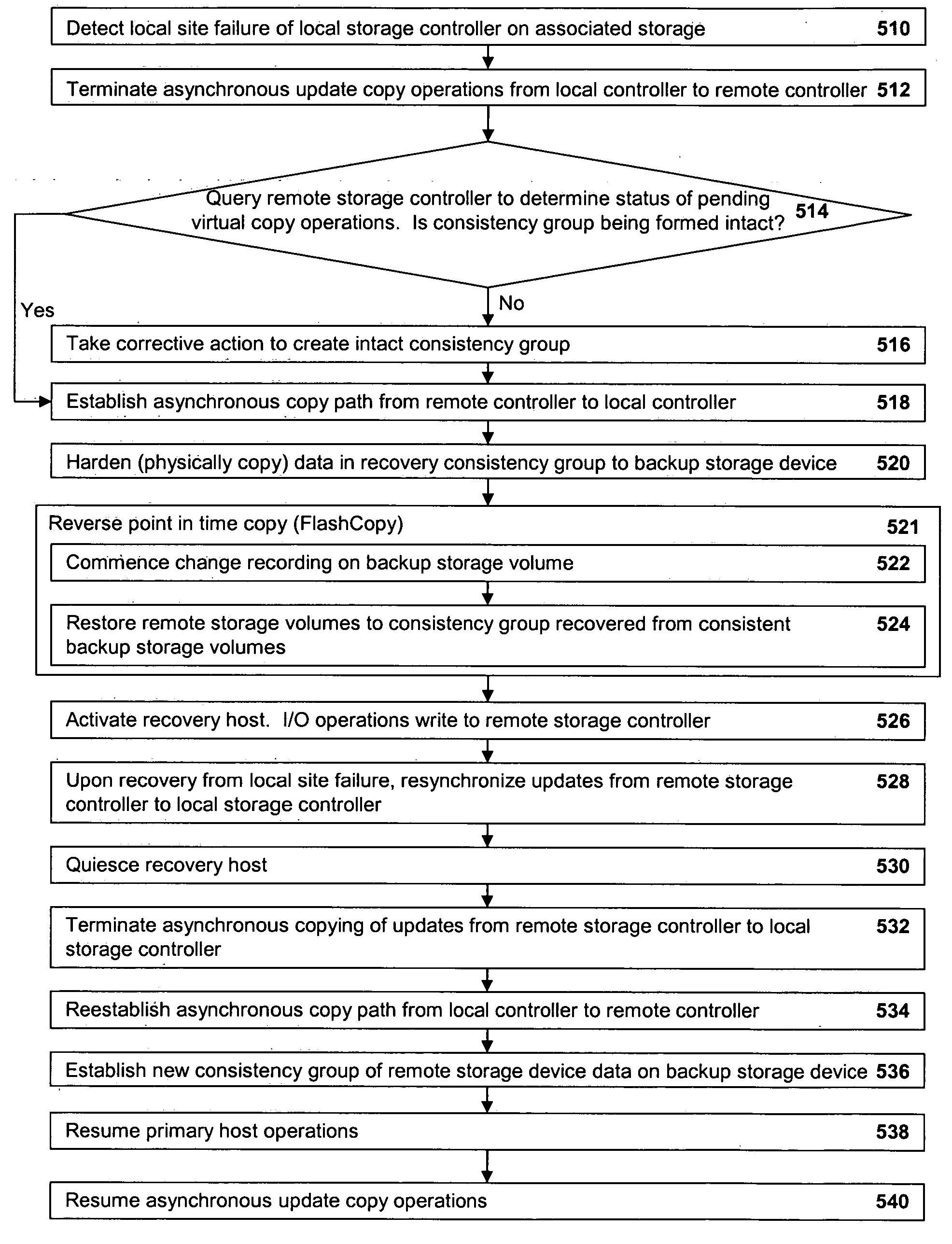
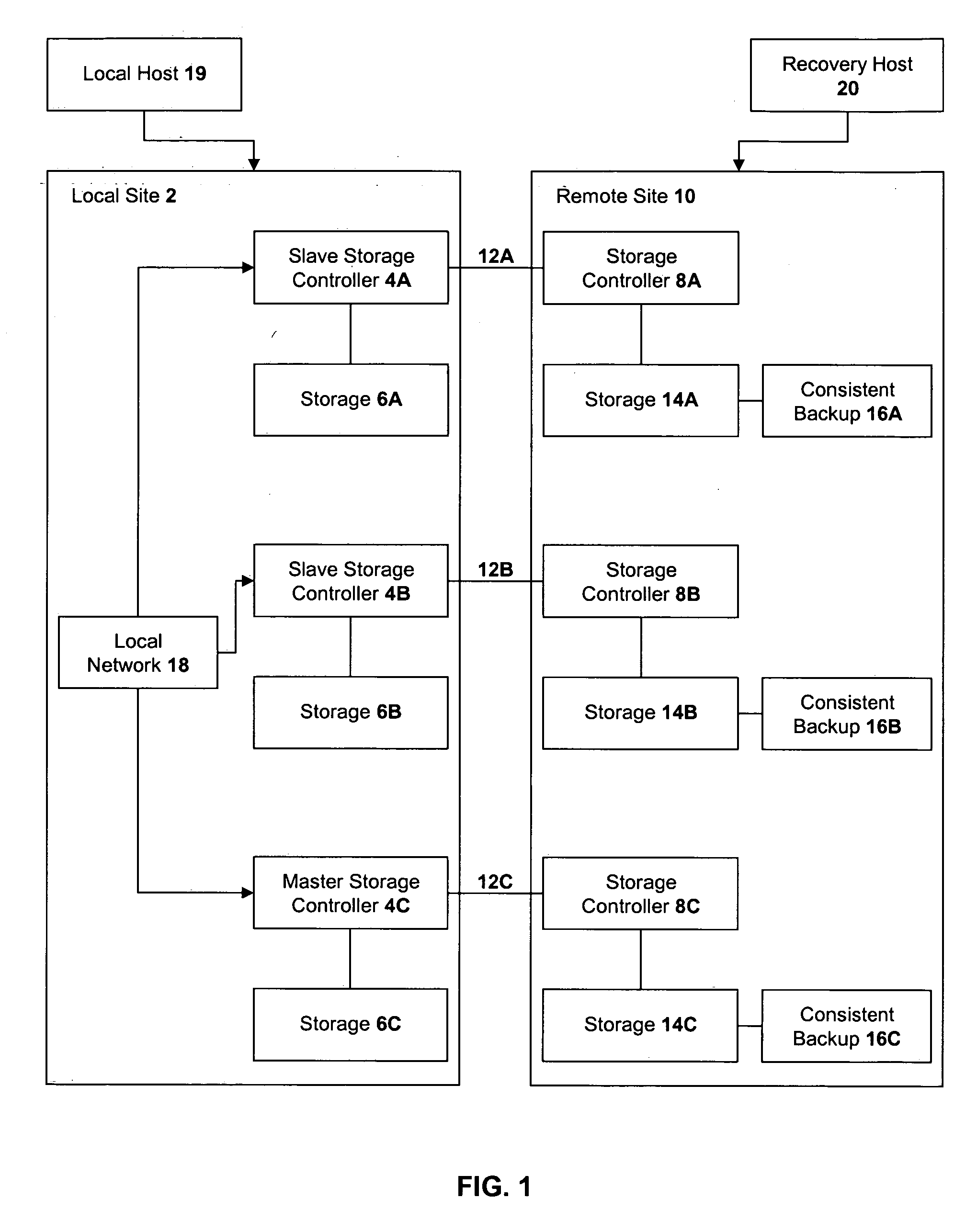
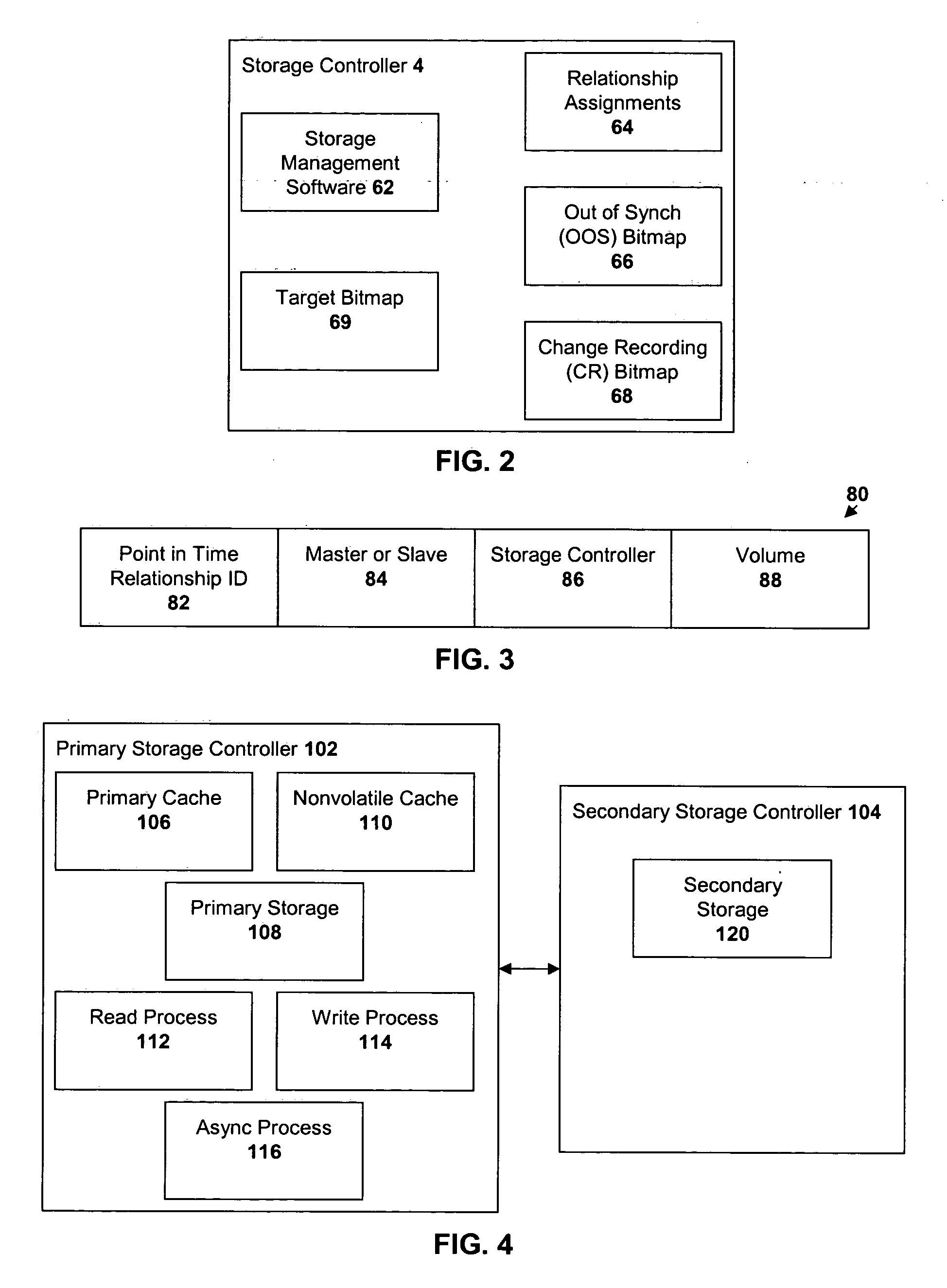
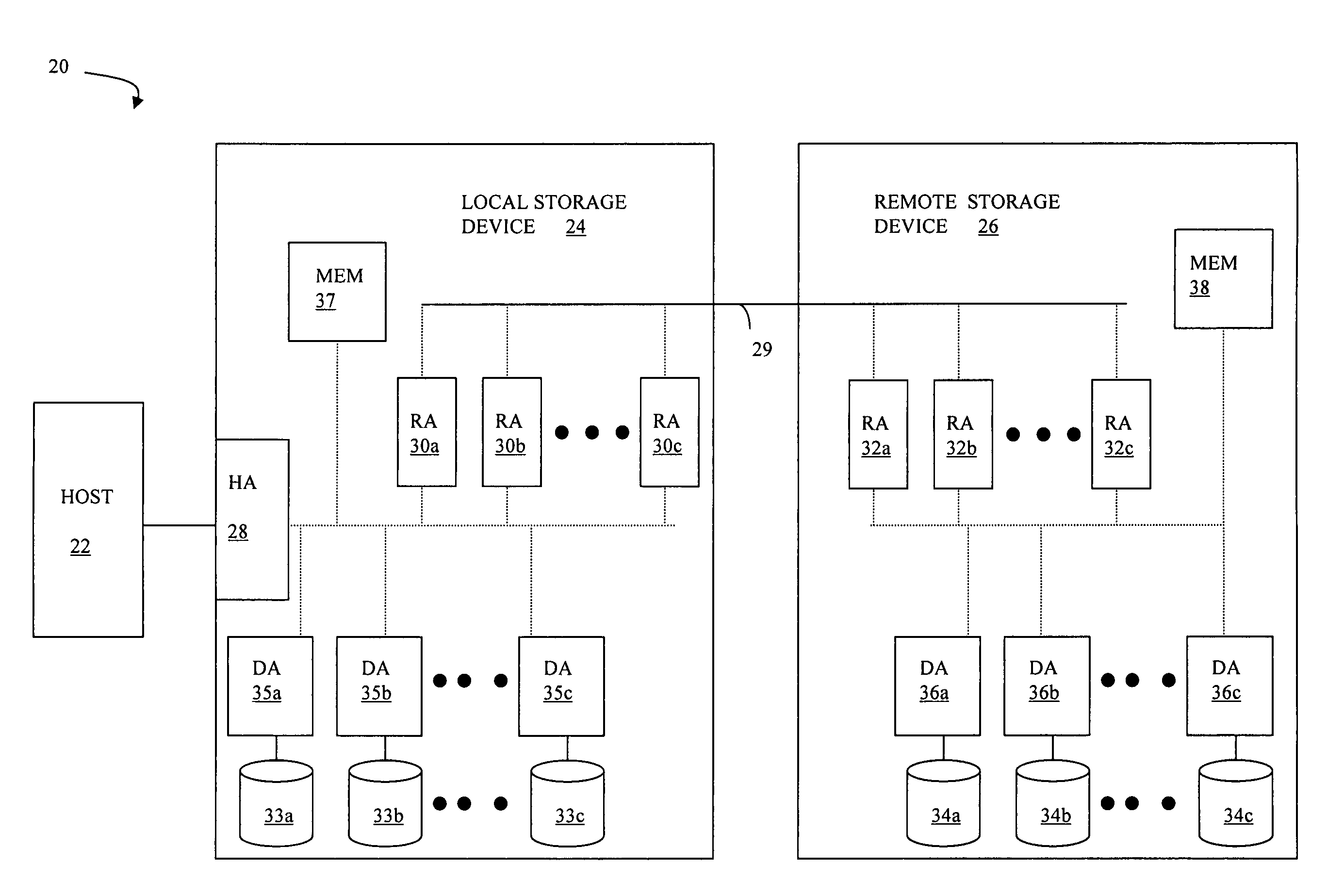
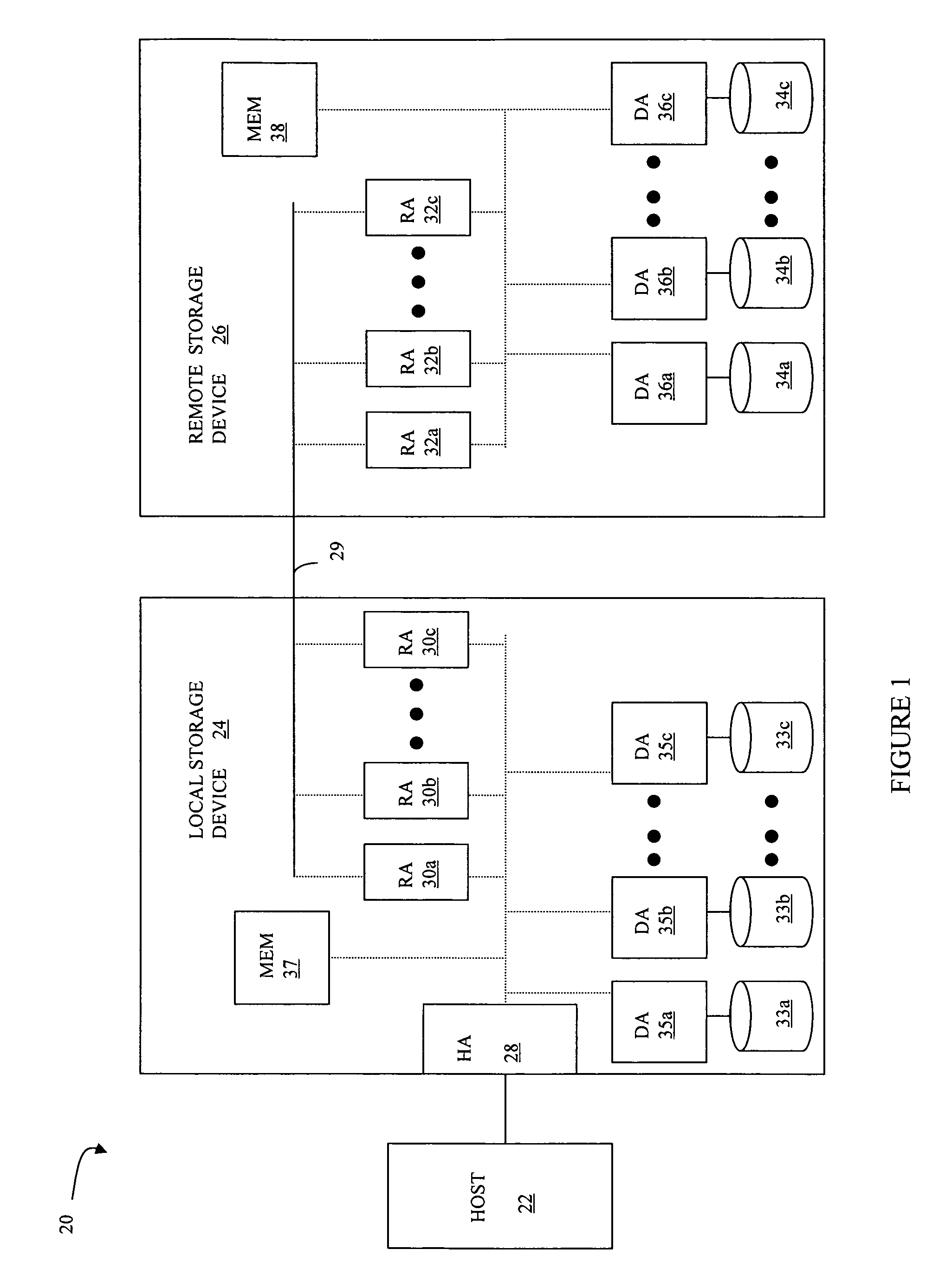
Method, system, and program for recovery from a failure in an asynchronous data copying system
InactiveUS20050071708A1Application downtime is minimizedMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionRecovery methodDevice form
A method of recovery from a data storage system failure in a data storage system having a host computer writing data updates to a local storage controller at a local site. The local controller is associated with a local storage device. The local storage controller is also configured to asynchronously copy the updates to a remote storage controller associated with a remote storage device at a remote site. In addition, the remote storage controller is configured to store a consistent point in time copy of the updates on a backup storage device. The consistent point in time copy is known as a consistency group. Upon detection of a failure associated with the local site, a determination is made whether a group of updates pending for storage on the backup storage device form an intact consistency group. If an intact consistency group has not formed, corrective action may be taken to create an intact consistency group. The recovery method further consists of synchronizing the remote storage device, initiating recovery operations and, upon recovery of the local site, resynchronization of the local storage device and the backup storage device to recovery consistency group without the need for full volume storage copies and while minimizing application downtime.
Owner:IBM CORP
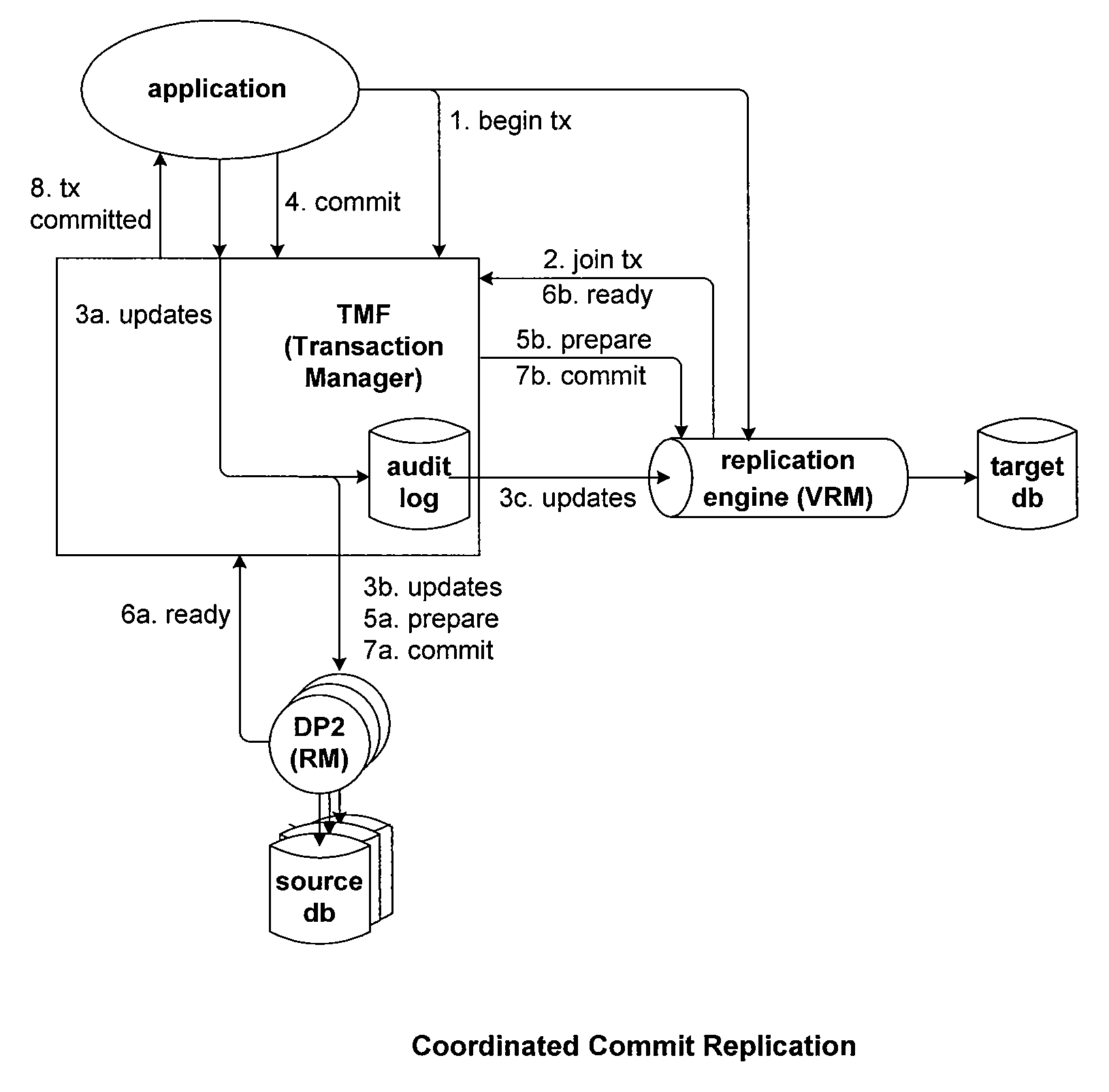
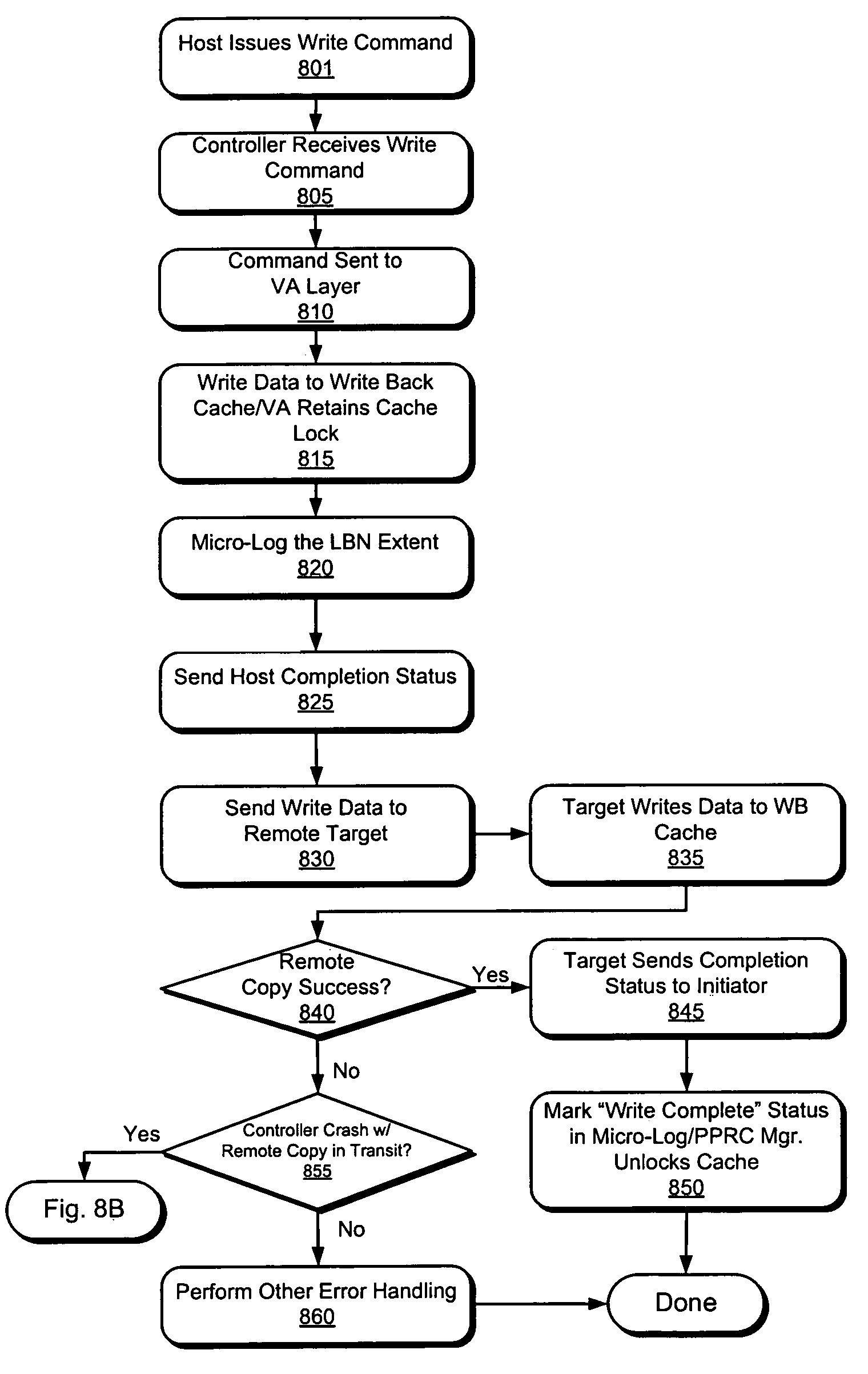
Method for transaction log failover merging during asynchronous operations in a data storage network
InactiveUS7111189B1Easily exposedPromote recoveryError detection/correctionLogic cellAsynchronous operation
A disaster-tolerant data backup and remote copy system which is implemented as a controller-based replication of one or more LUNs (logical units) between two remotely separated pairs of array controllers connected by redundant links. In the situation wherein an array controller fails during an asynchronous copy operation, the partner array controller uses a ‘micro log’ stored in mirrored cache memory to recover transactions, in order, which were ‘missed’ by the backup storage array when the array controller failure occurred.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
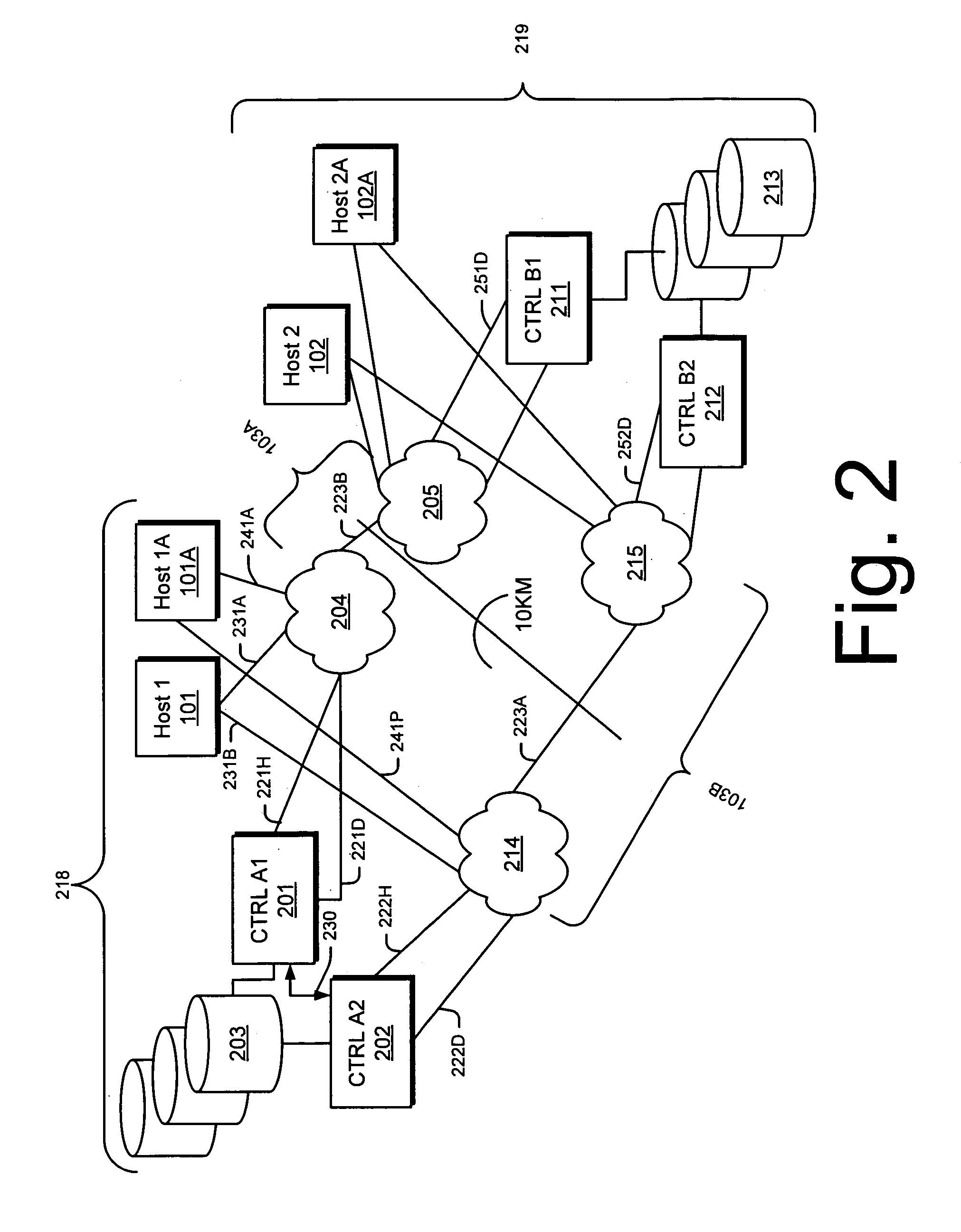
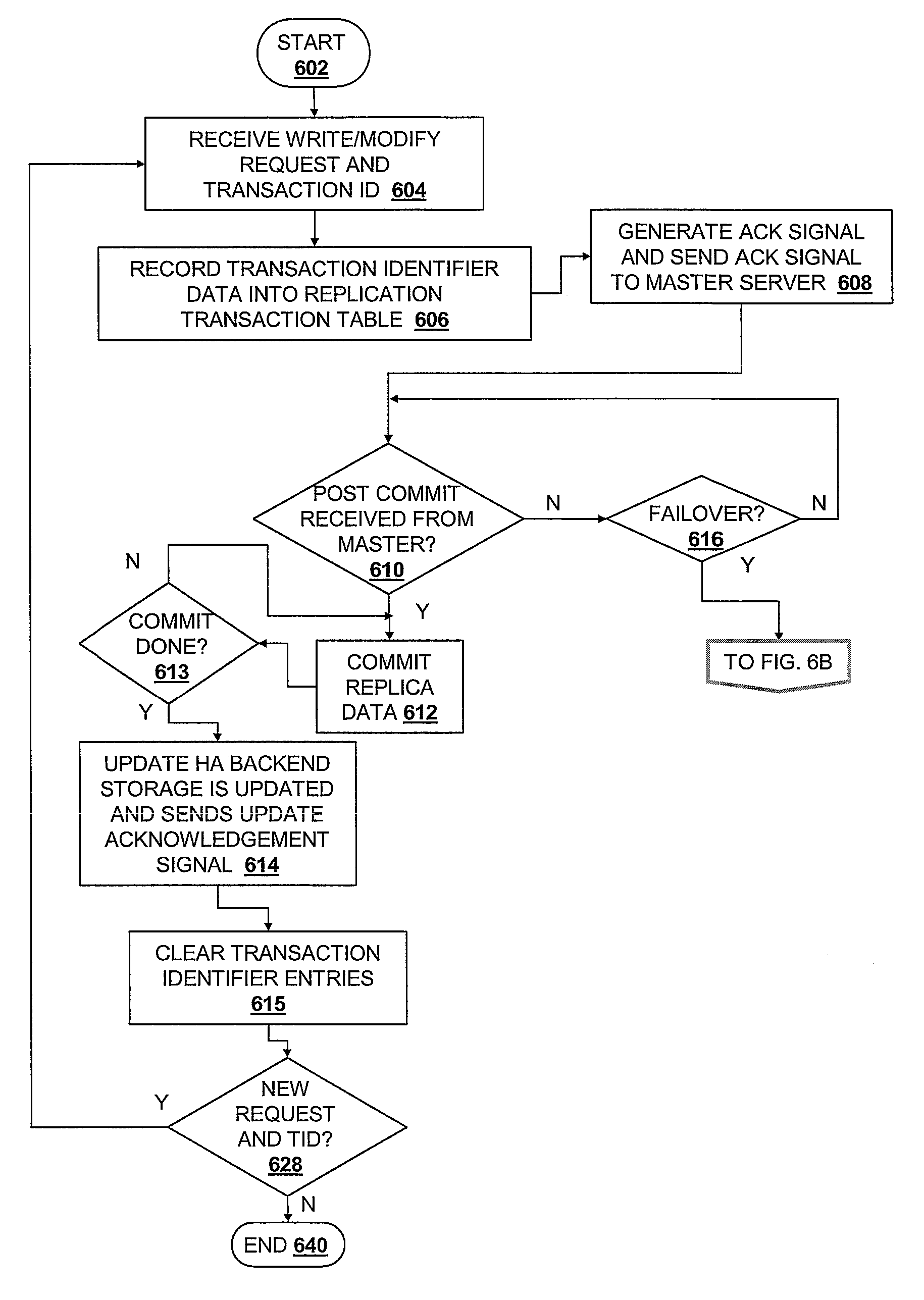
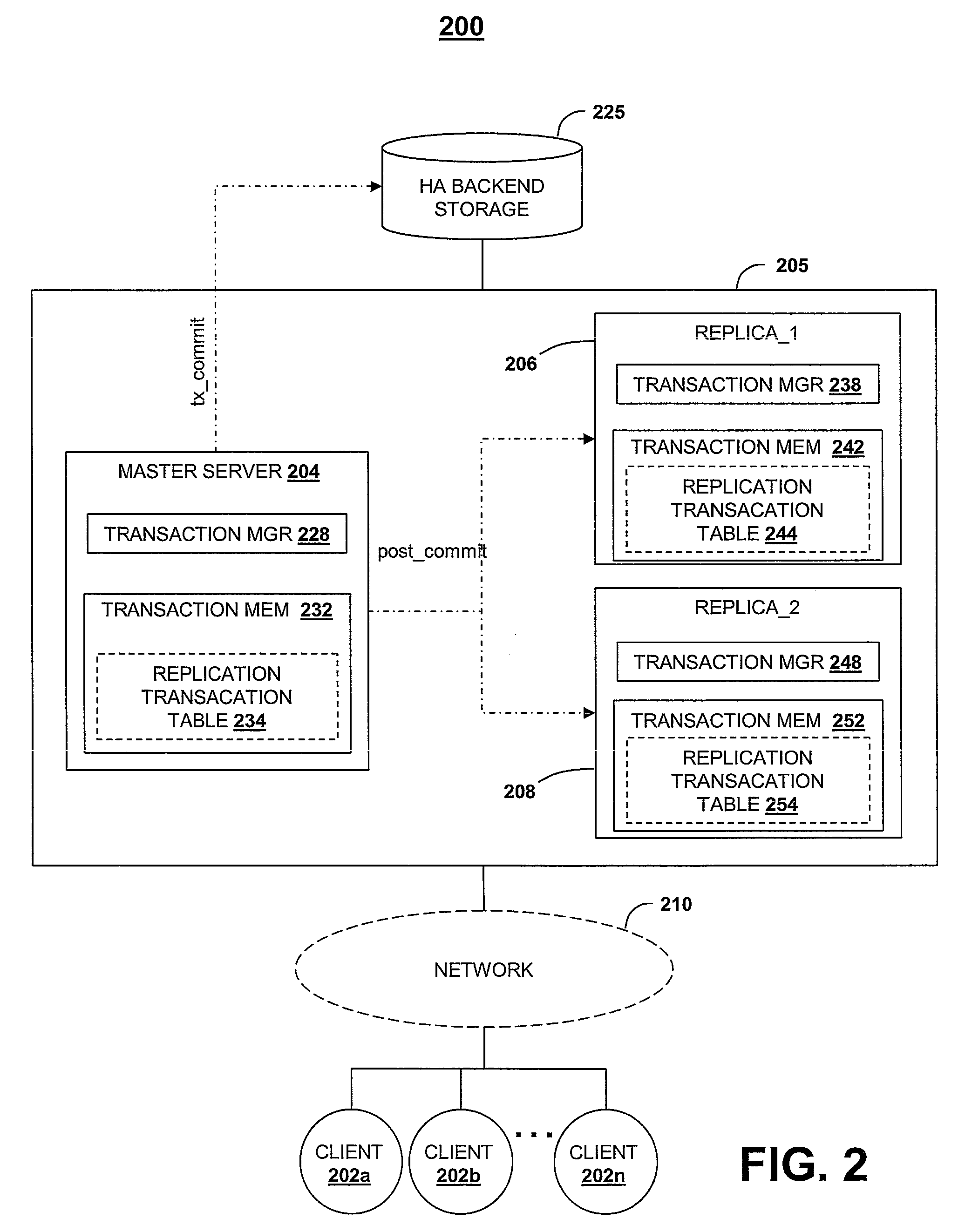
Method, System, and Computer Program Product for Ensuring Data Consistency of Asynchronously Replicated Data Following a Master Transaction Server Failover Event
InactiveUS20090157766A1Ensure consistencyDigital data information retrievalError detection/correctionFailoverData operations
A method, system, and computer program product for ensuring data consistency during asynchronous replication of data from a master server to a plurality of replica servers. Responsive to receiving a transaction request at the master server, recording in the plurality of replica servers a set of transaction identifiers within a replication transaction table stored in local memory of the plurality of replica servers. Responsive to receiving an acknowledgement signal from the plurality of replica servers, committing data resulting from the identified data operation within local memory of the master server. Responsive to a failover event that prevents the master server from sending a post commit signal to the at least one replica server, designating a new master server from among the plurality of replica servers. The selected replica server is associated with the replication transaction table having a fewest number of pending transaction requests.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for determining changes in two snapshots and for transmitting changes to a destination snapshot
InactiveUS7603391B1Efficient scanningOvercome disadvantagesData processing applicationsRedundant operation error correctionData streamInode
A system and method for remote asynchronous replication or mirroring of changes in a source file system snapshot in a destination replica file system using a scan (via a scanner) of the blocks that make up two versions of a snapshot of the source file system, which identifies changed blocks in the respective snapshot files based upon differences in volume block numbers identified in a scan of the logical file block index of each snapshot. Trees of blocks associated with the files are traversed, bypassing unchanged pointers between versions and walking down to identify the changes in the hierarchy of the tree. These changes are transmitted to the destination mirror or replicated snapshot. This technique allows regular files, directories, inodes and any other hierarchical structure to be efficiently scanned to determine differences between versions thereof. The changes in the files and directories are transmitted over the network for update of the replicated destination snapshot in an asynchronous (lazy write) manner. The changes are described in an extensible, system-independent data stream format layered under a network transport protocol. At the destination, source changes are used to update the destination snapshot. Any deleted or modified inodes already on the destination are moved to a temporary or “purgatory” directory and, if reused, are relinked to the rebuilt replicated snapshot directory. The source file system snapshots can be representative of a volume sub-organization, such as a qtree.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
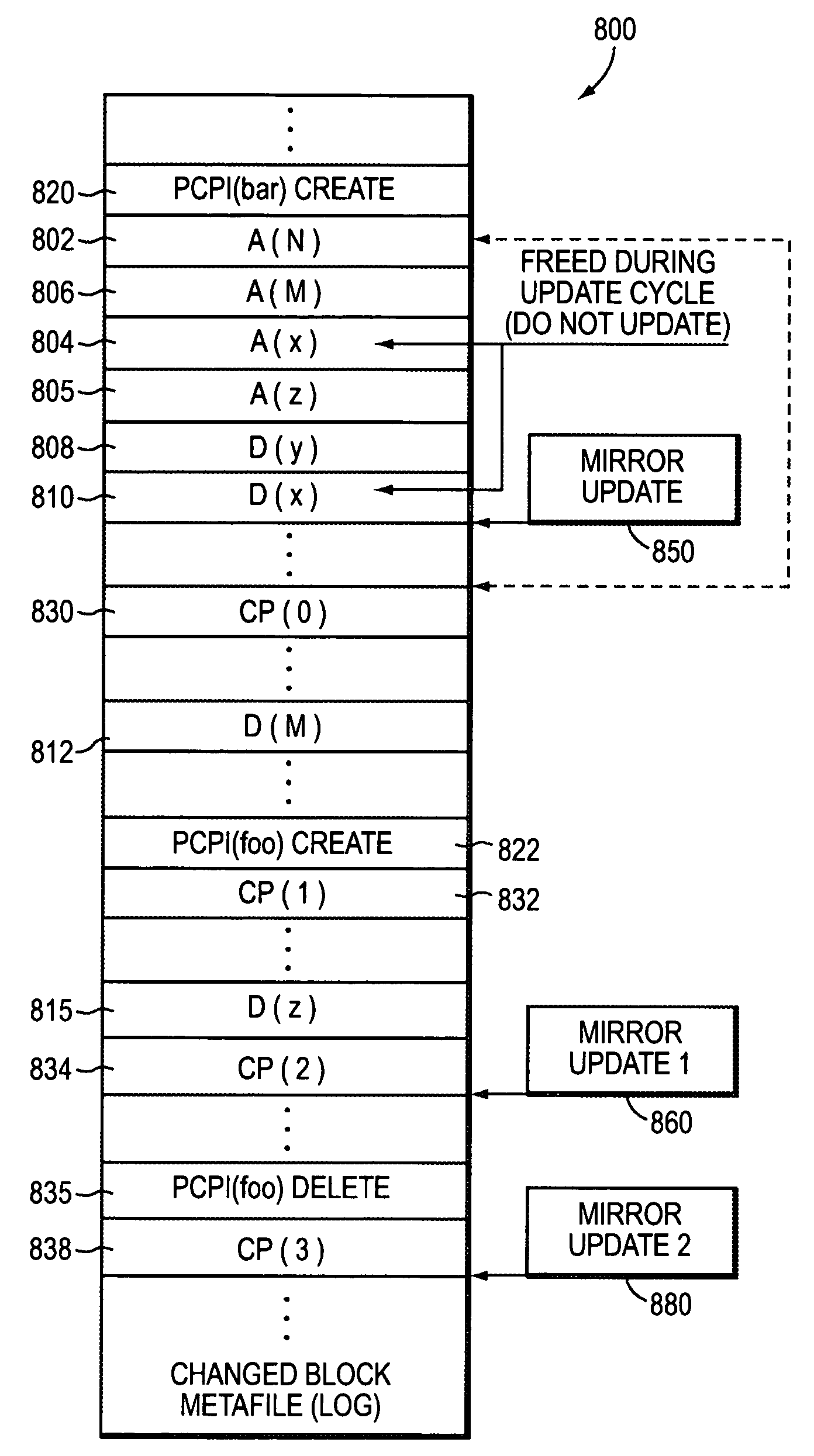
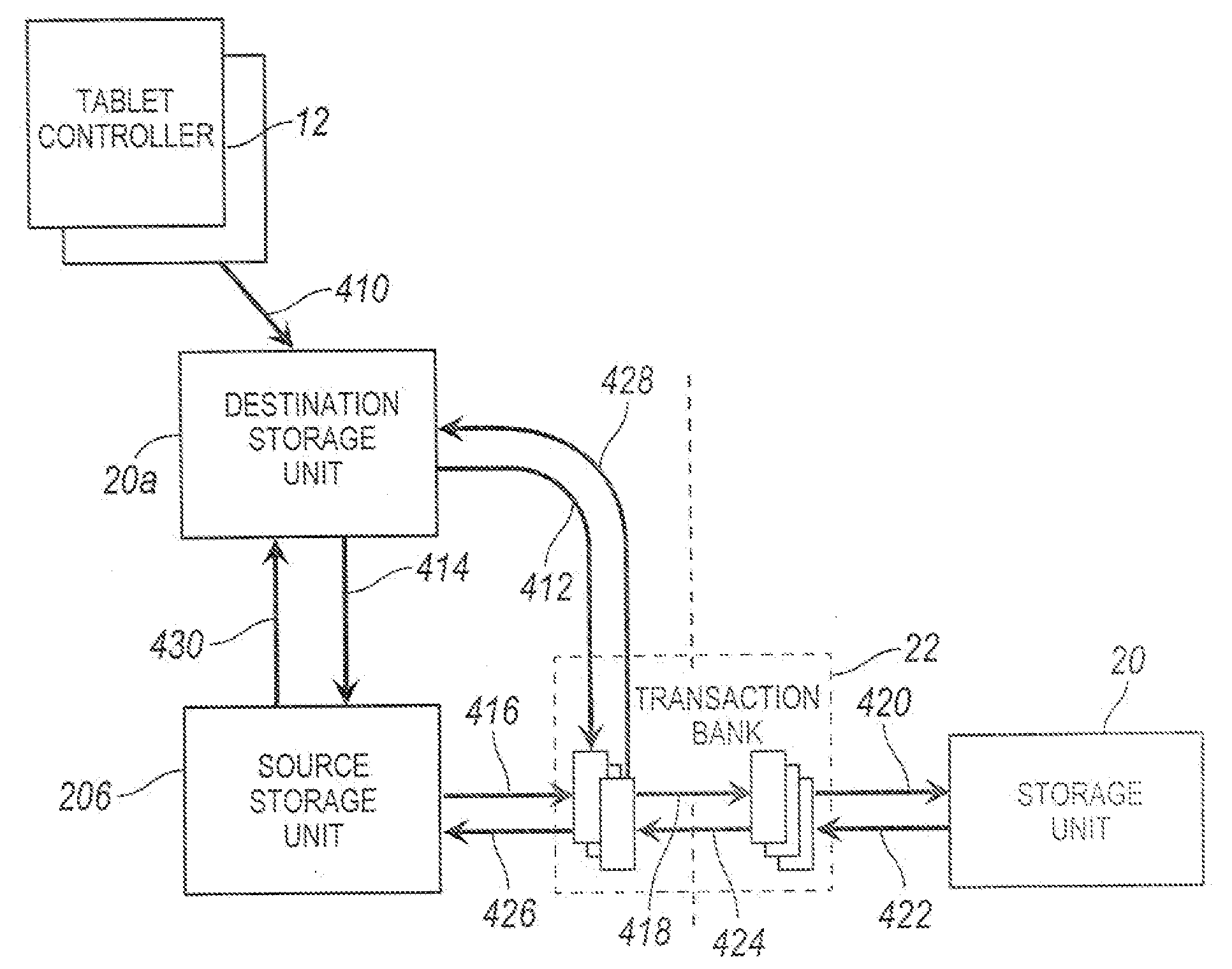
System and method for supporting asynchronous data replication with very short update intervals
ActiveUS7720801B2Avoid efficiencyReduce in quantityDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsOperational systemFile system
A system and method for improving the efficiency of the transmission of updated blocks generated by logging all the block allocations and deletes as well as CPs and PCPI creation and deletion in a persistent log. The log is scanned during each update cycle (in which changes are transmitted to a destination mirror) by the storage operating system, and only changed blocks that are referenced by the file system as it existed at the end of the update cycle or referenced by PCPIs that existed at the end of the update cycle are actually sent in the transmission. This reduces the number of changes being transmitted.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
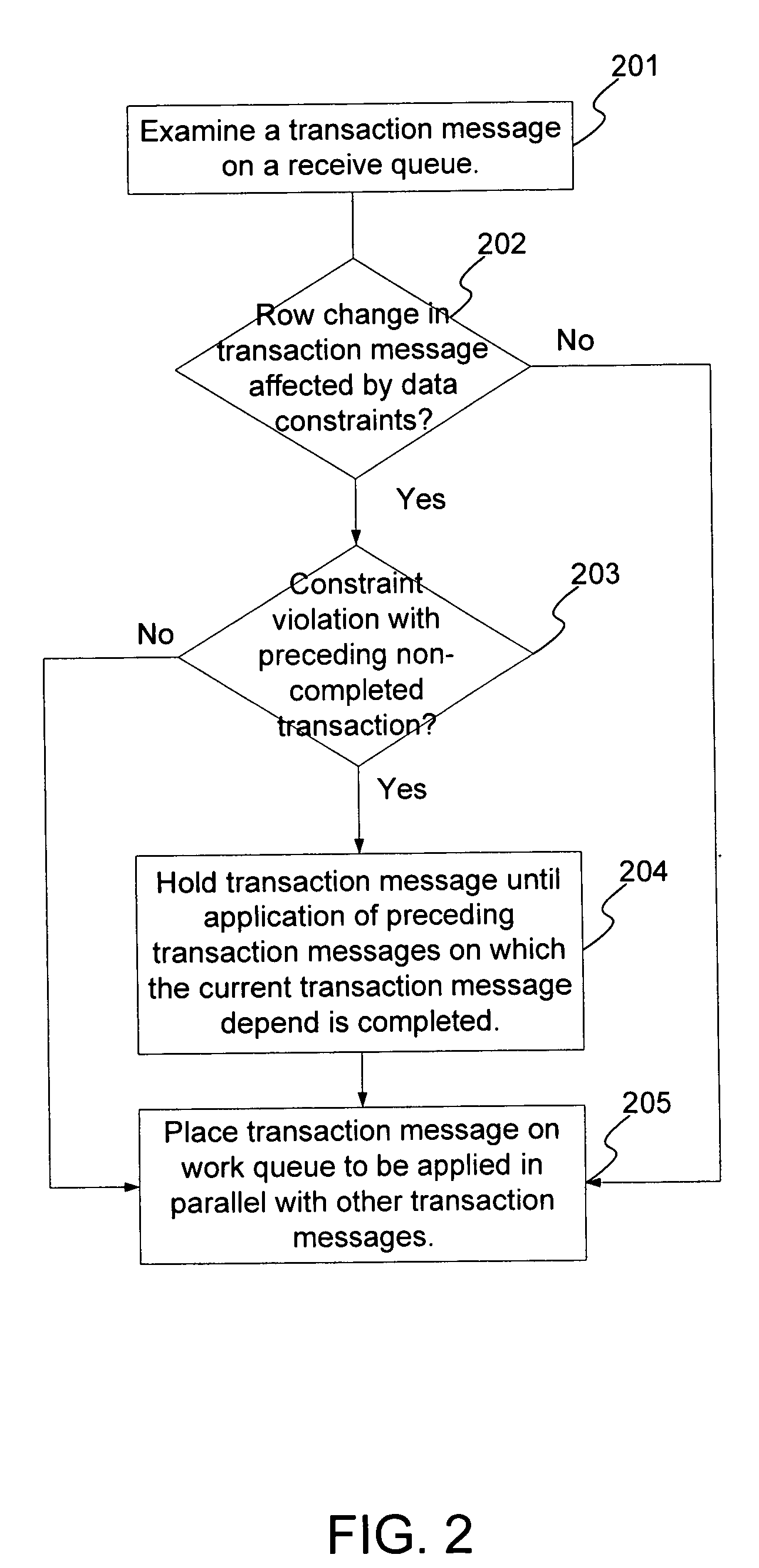
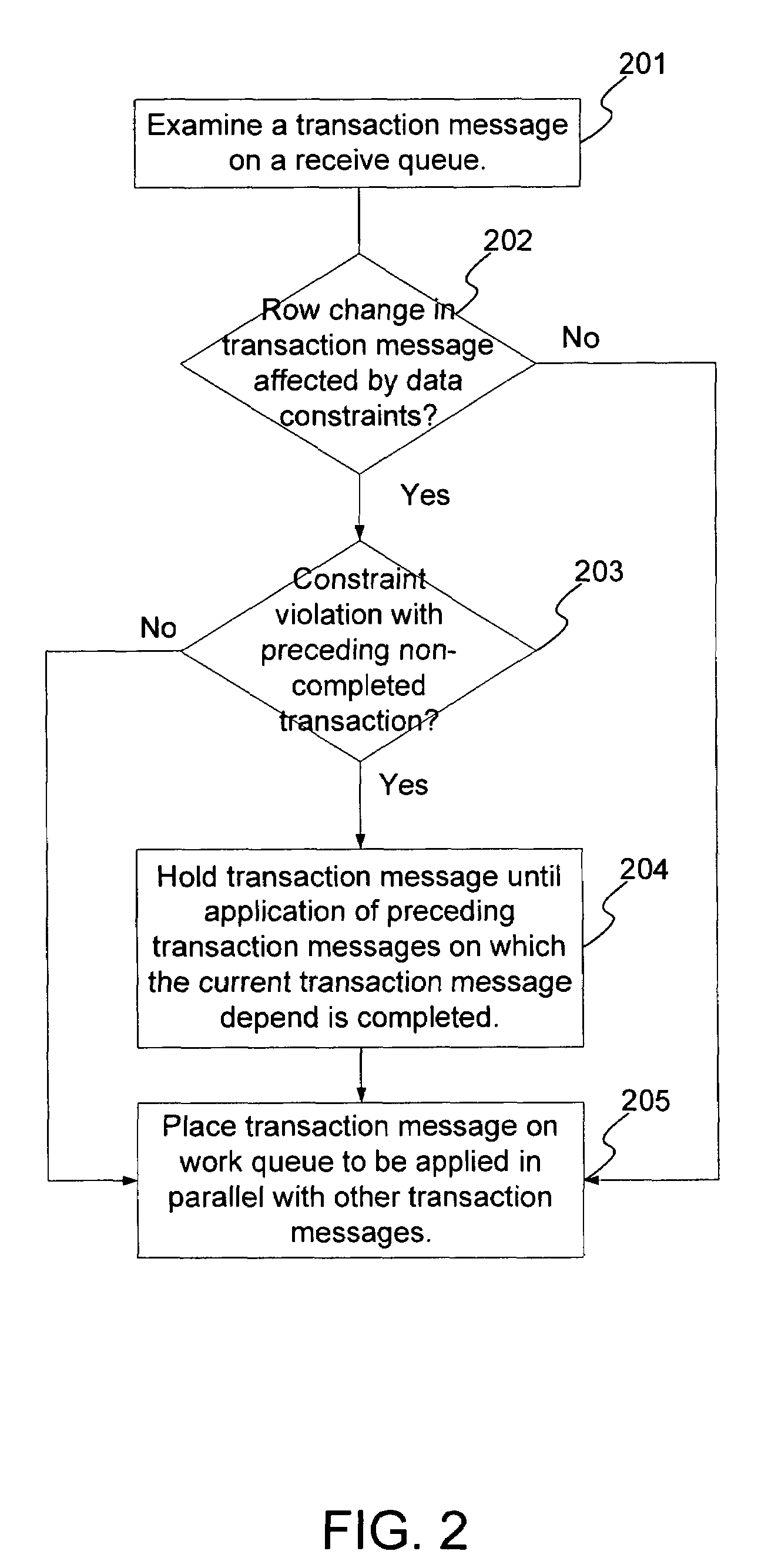
Techniques to preserve data constraints and referential integrity in asynchronous transactional replication of relational tables
InactiveUS20050192989A1High degree of parallelismData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalComputer hardwareImproved method
An improved method and system for preserving data constraints during parallel apply in asynchronous transaction replication in a database system have been disclosed. The method and system preserves secondary unique constraints and referential integrity constraints, while also allowing a high degree of parallelism in the application of asynchronous replication transactions. The method and system also detects and resolves ordering problems introduced by referential integrity cascade deletes, and allows the parallel initial loading of parent and child tables of a referential integrity constraint.
Owner:IBM CORP
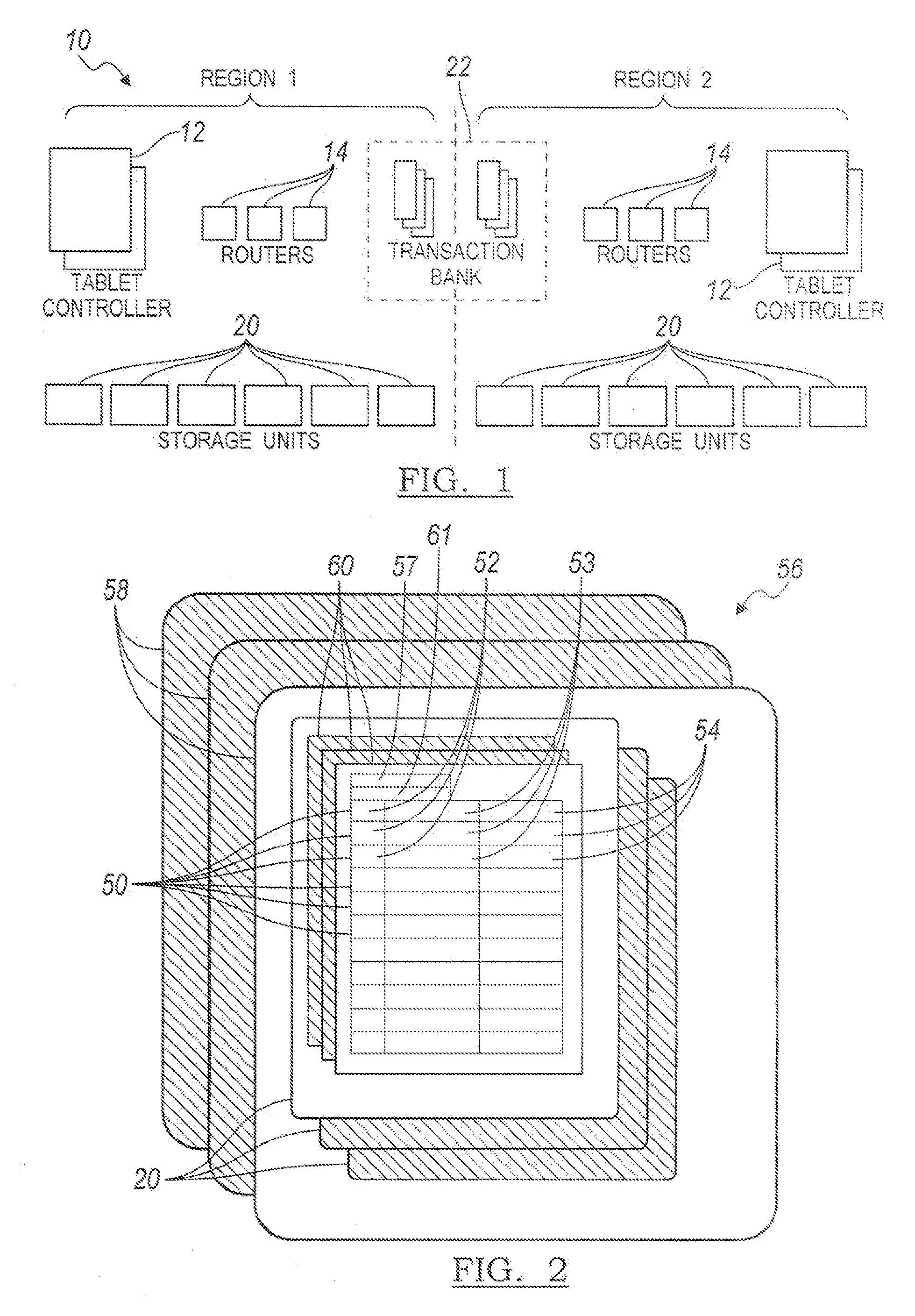
Collision avoidance in database replication systems
InactiveUS7103586B2Data processing applicationsDatabase distribution/replicationSystem usageAsynchronous replication
Database replication systems replicate blocks of transaction steps or operations with synchronous replication, and perform dual writes with queuing and blocking of transactions. Tokens are used to prepare a target database for replication from a source database and to confirm the preparation. Database replication systems switch between a synchronous replication mode and an asynchronous replication mode, and then back to a synchronous replication mode, based on detection of selected events.
Owner:RPX CORP
Asynchronously replicated database system using dynamic mastership
InactiveUS20090144338A1Efficient editingImprove performanceDigital data information retrievalMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGeographic regionsRecordset
A system for a distributed database implementing a dynamic mastership strategy. The system includes a multiple data centers, each having a storage unit to store a set of records. Each data center stores its own replica of the set of records and each record includes a field that indicates which data center is assigned to be the master for that record. Since each of the data centers can he geographically distributed, one record may be more efficiently edited with the master being one geographic region while another record, possibly belonging to a different user, may be more efficiently edited with the master being located in another geographic region.
Owner:OATH INC
System for live-migration and automated recovery of applications in a distributed system
ActiveUS20140129521A1Digital data information retrievalError detection/correctionApplication softwareProtocol processing
A method and apparatus for distribution of applications amongst a number of servers, ensuring that changes to application data on a master for that application are asynchronously replicated to a number of slaves for that application. Servers may be located in geographically diverse locations; the invention permits data replication over high-latency and lossy network connections and failure-tolerance under hardware and network failure conditions. Access to applications is mediated by a distributed protocol handler which allows any request for any application to be addressed to any server, and which, when working in tandem with the replication system, pauses connections momentarily to allow seamless, consistent live-migration of applications and their state between servers. Additionally, a system which controls the aforementioned live-migration based on dynamic measurement of load generated by each application and the topological preferences of each application, in order to automatically keep servers at an optimum utilisation level.
Owner:OPEN INVENTION NEWTORK LLC
Techniques to preserve data constraints and referential integrity in asynchronous transactional replication of relational tables
InactiveUS7240054B2High degree of parallelismData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalComputer hardwareImproved method
An improved method and system for preserving data constraints during parallel apply in asynchronous transaction replication in a database system have been disclosed. The method and system preserves secondary unique constraints and referential integrity constraints, while also allowing a high degree of parallelism in the application of asynchronous replication transactions. The method and system also detects and resolves ordering problems introduced by referential integrity cascade deletes, and allows the parallel initial loading of parent and child tables of a referential integrity constraint.
Owner:IBM CORP
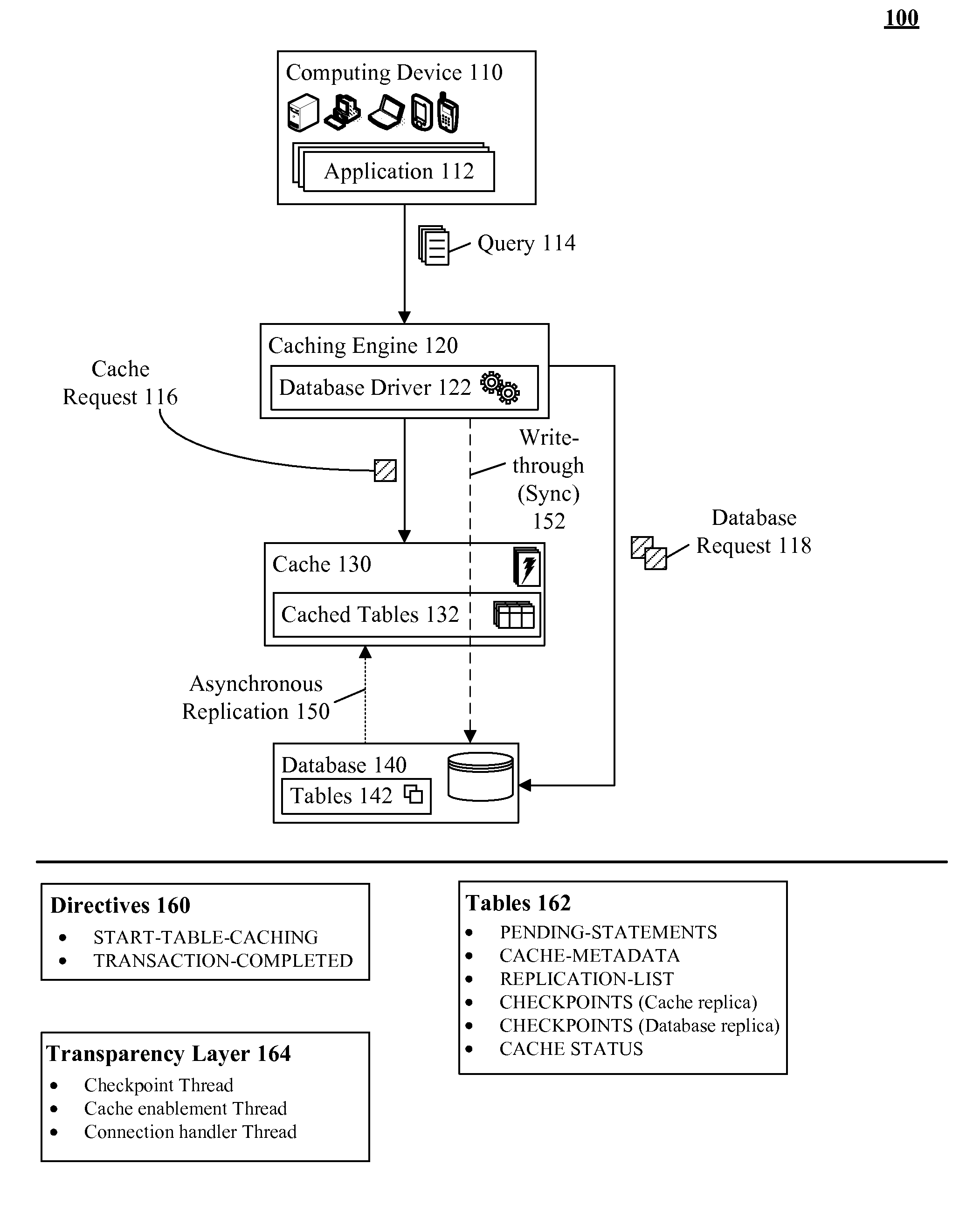
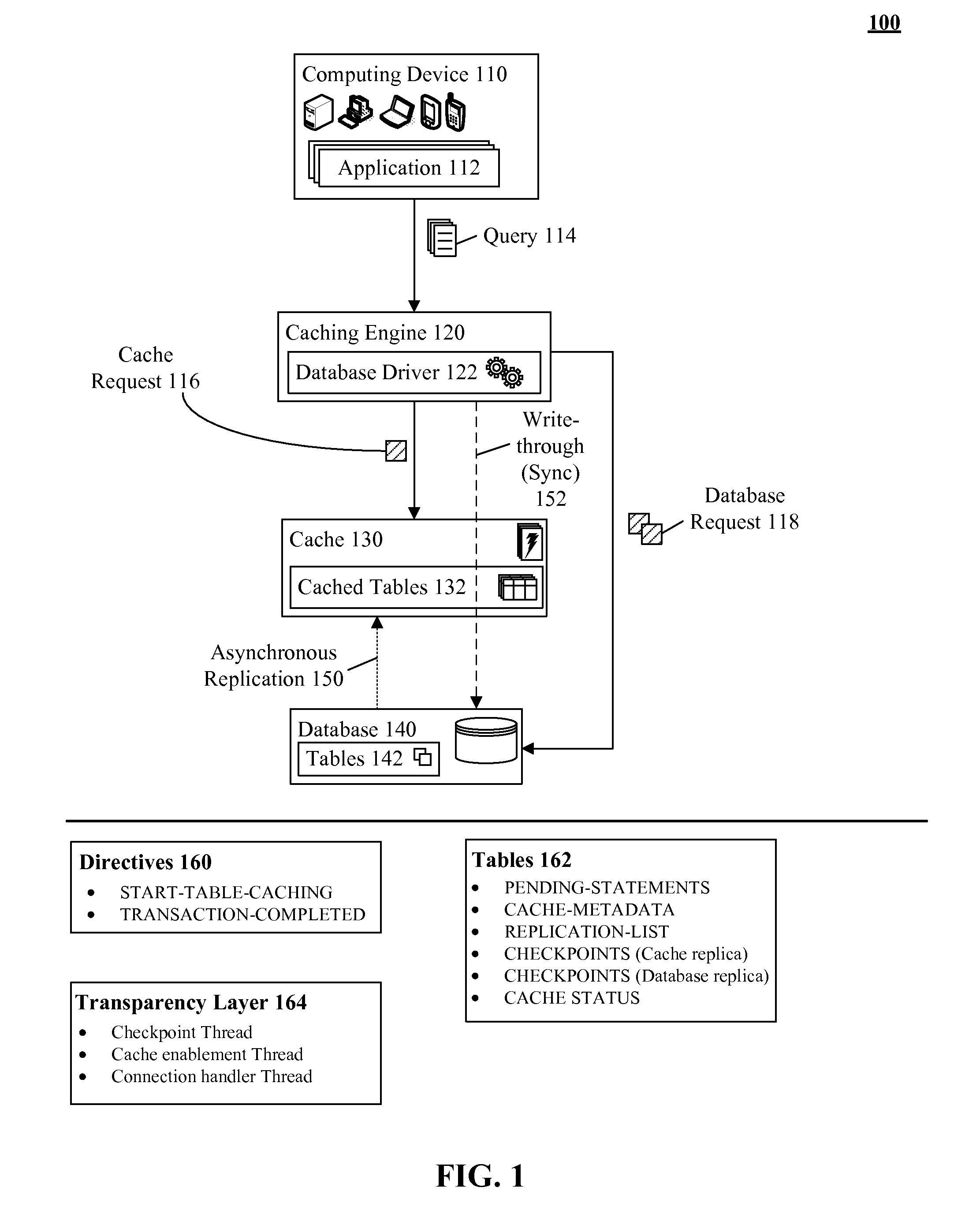
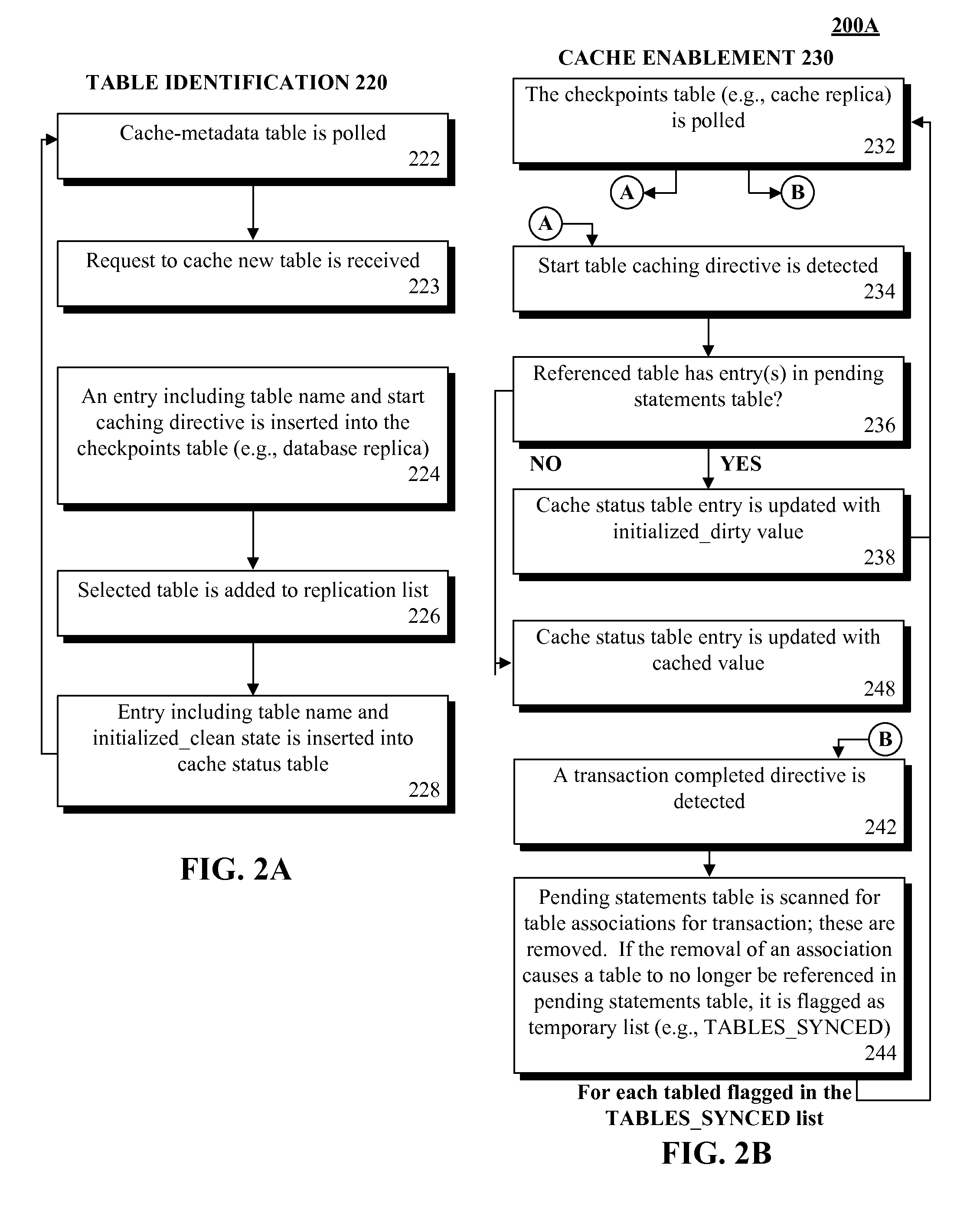
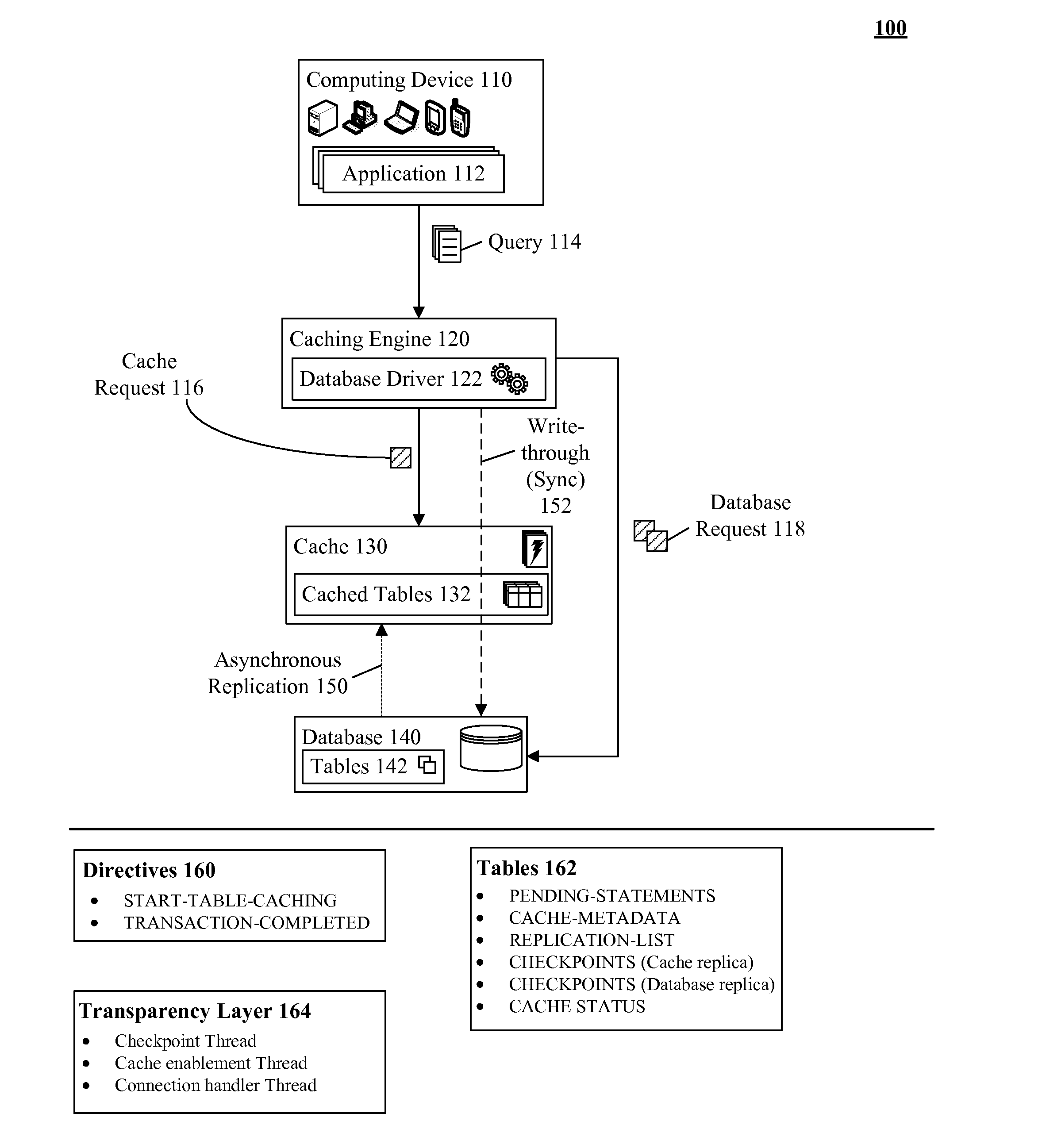
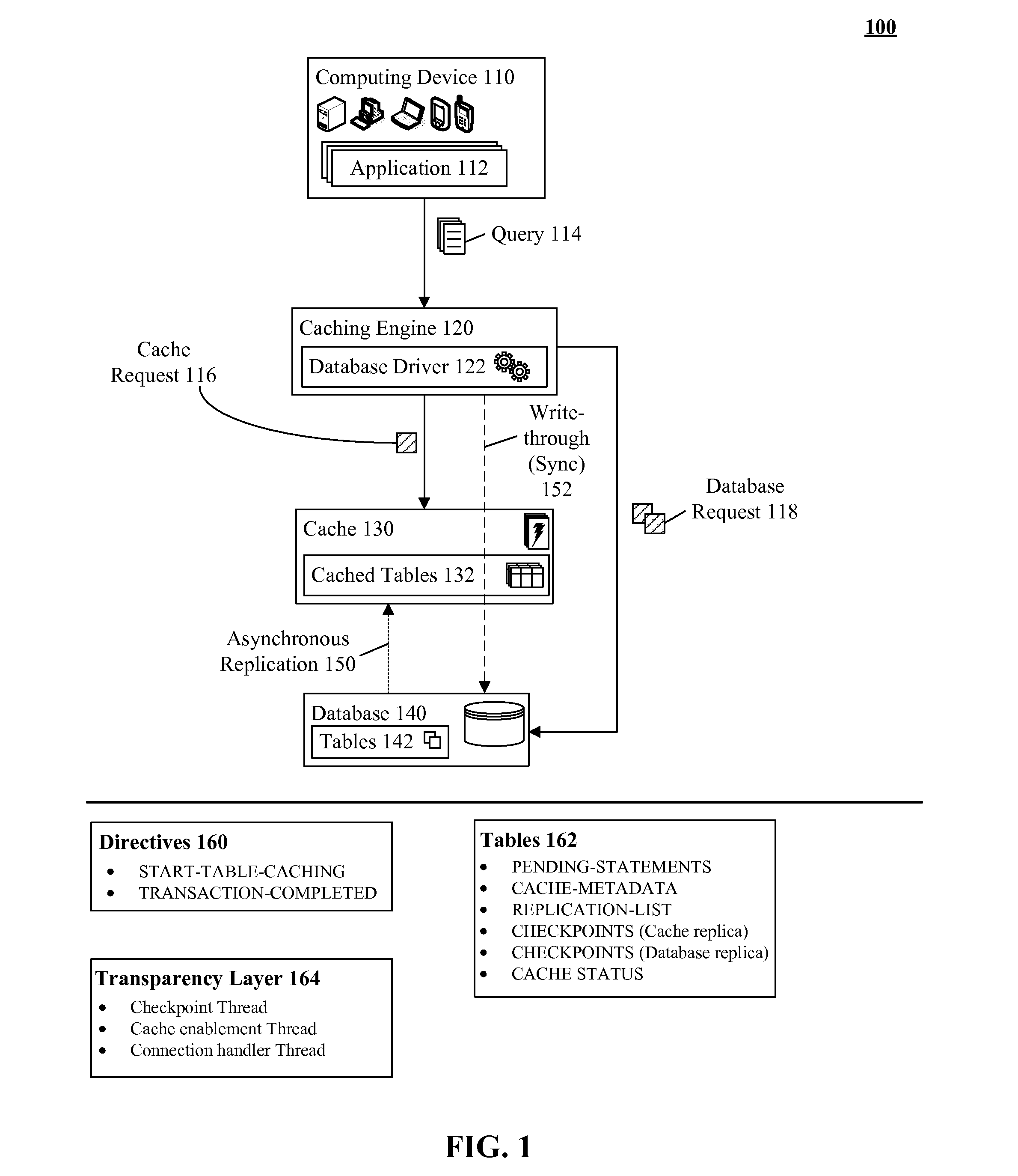
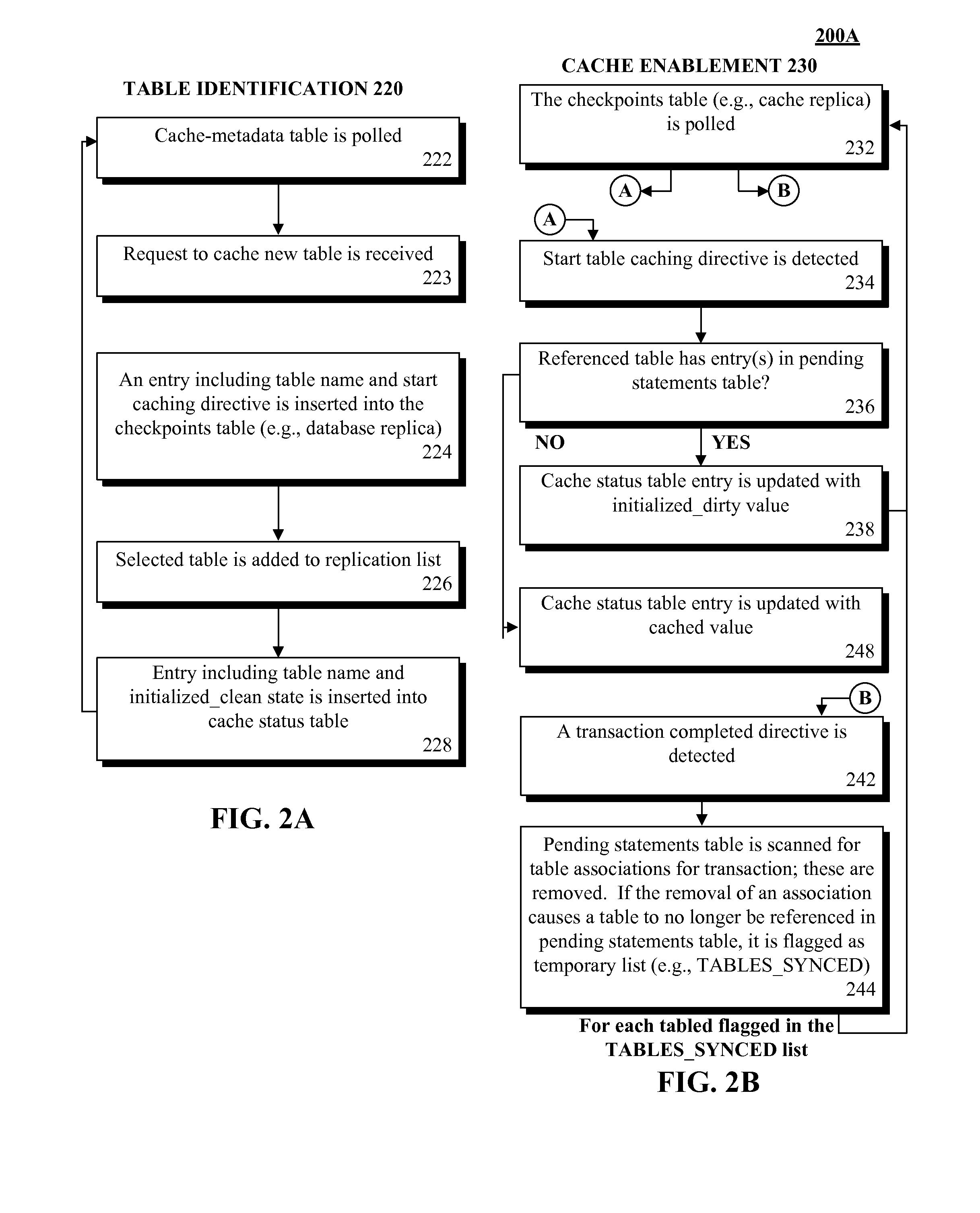
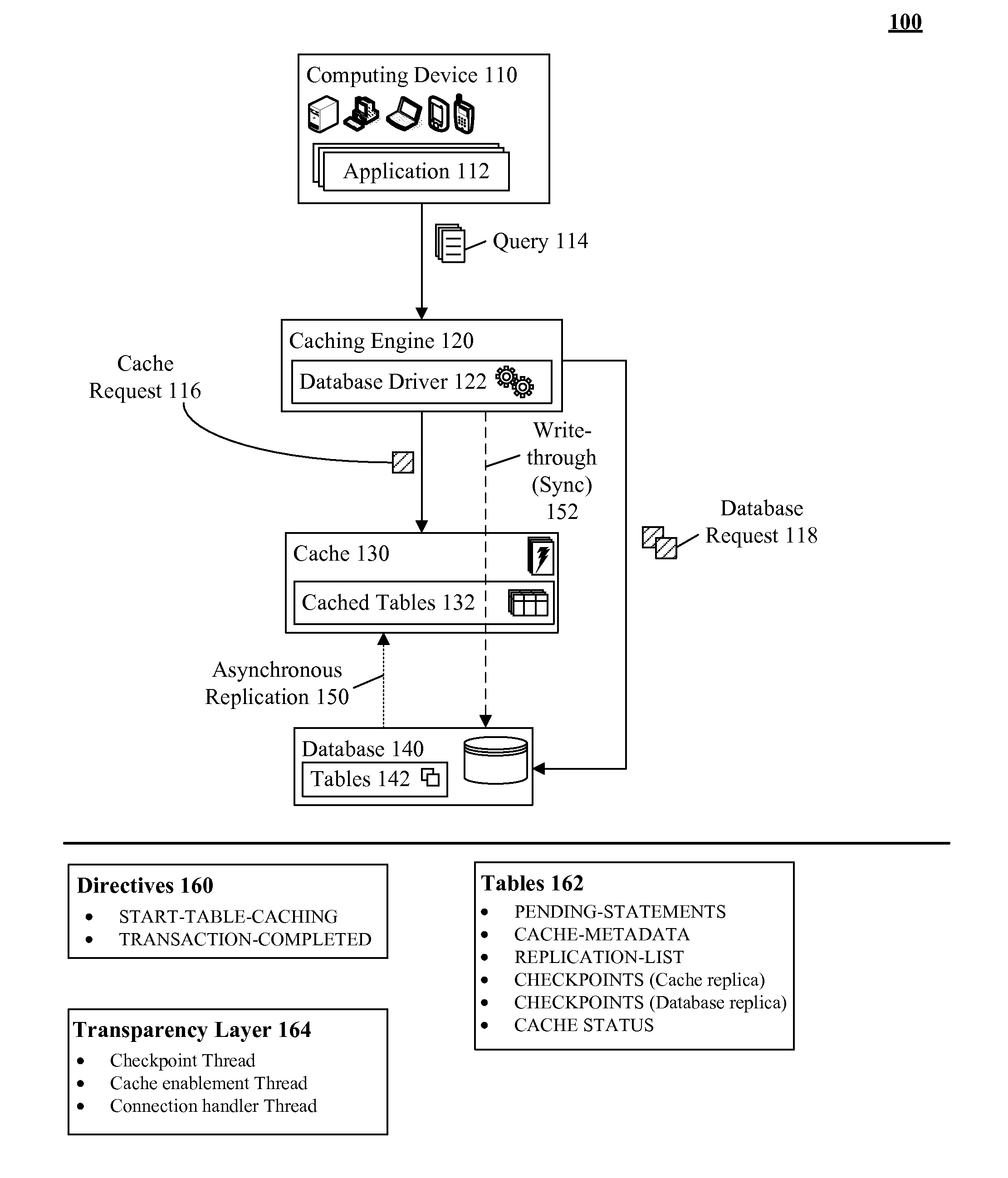
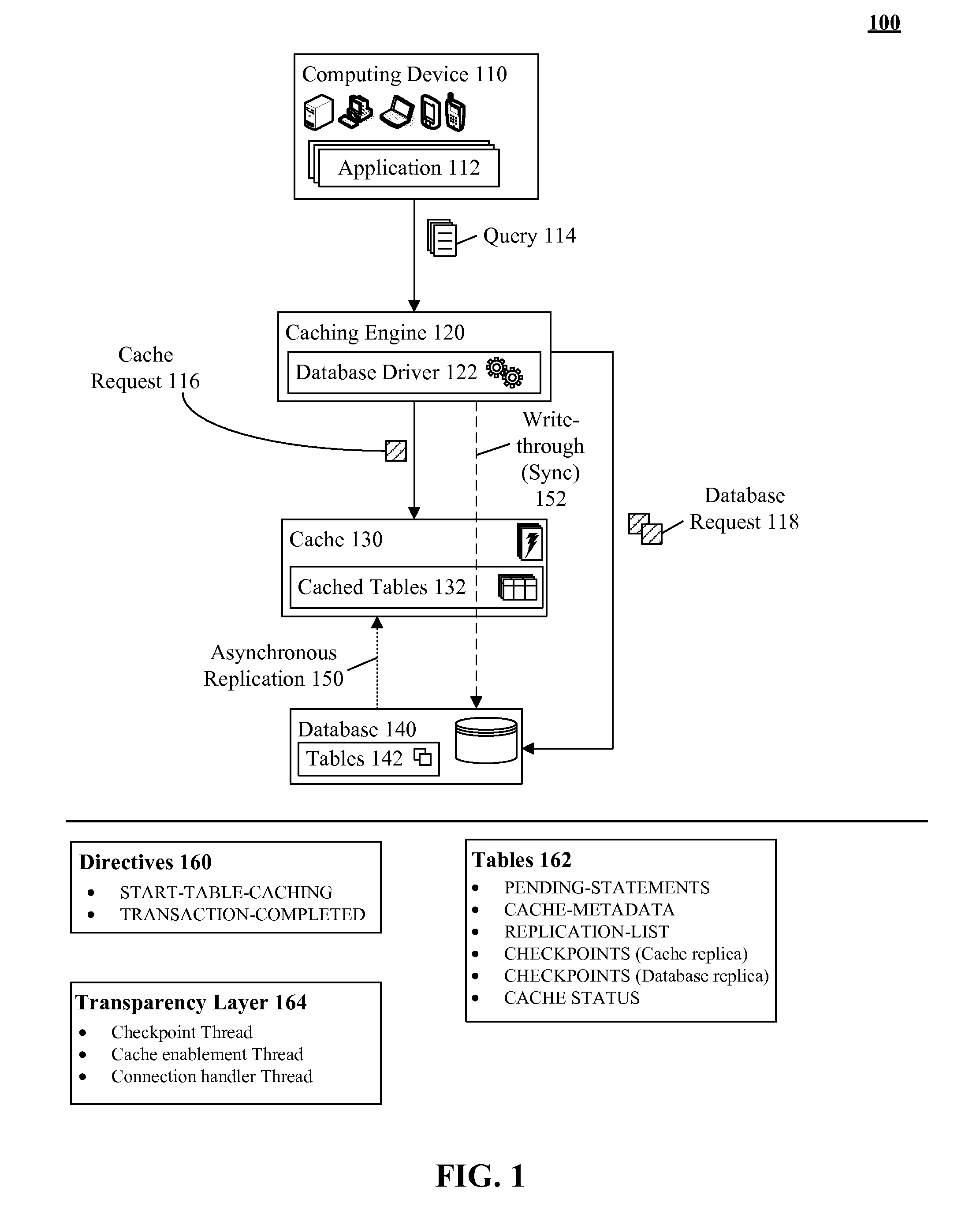
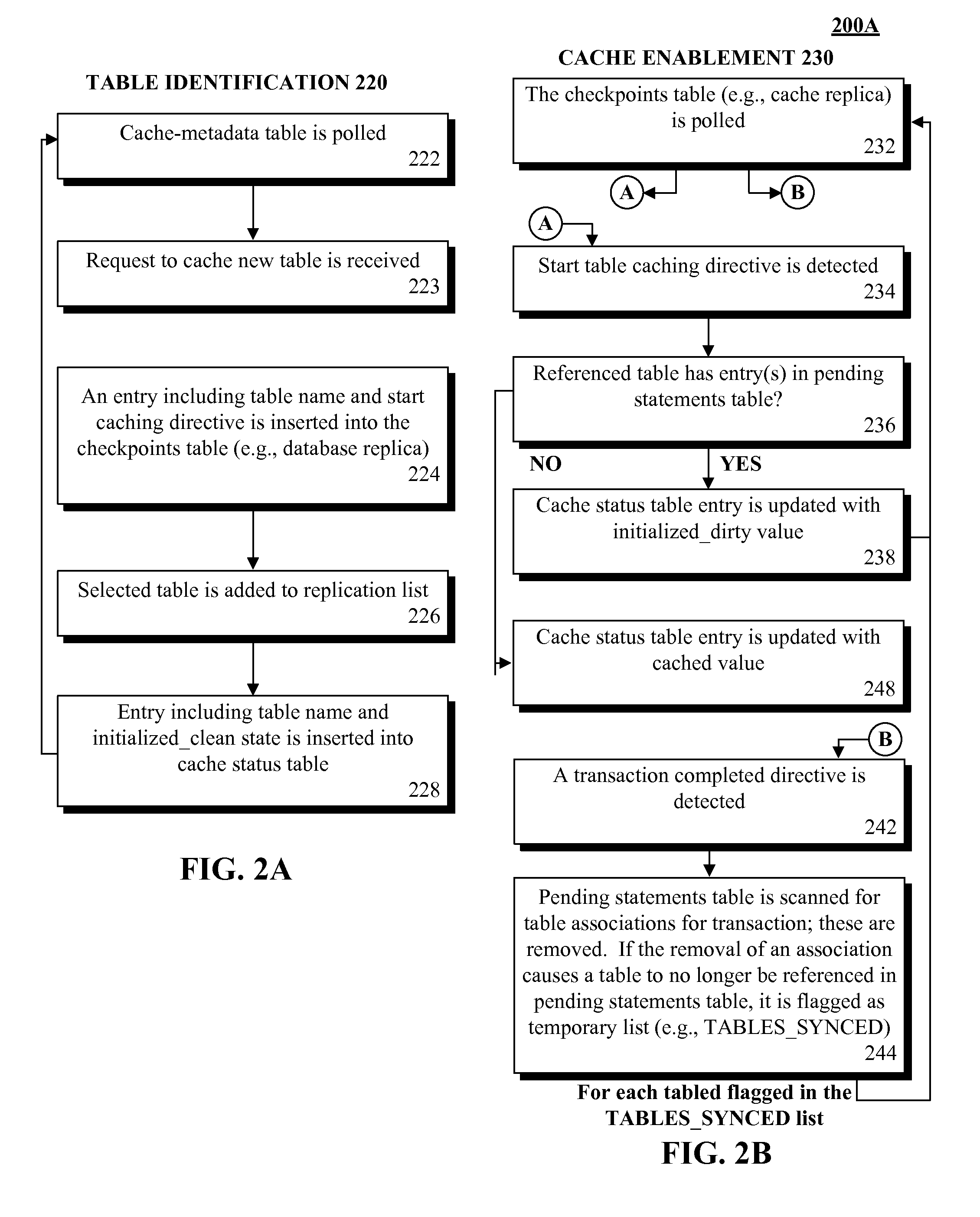
Database caching utilizing asynchronous log-based replication
ActiveUS8548945B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsRelational database management systemDatabase caching
A database table within a database to persist within a cache as a cached table can be identified. The database can be a relational database management system (RDBMS) or an object oriented database management system (OODBMS). The cache can be a database cache. Database transactions within can be logged within a log table and the cached table within the cache can be flagged as not cached during runtime. An asynchronous replication of the database table to the cached table can be performed. The replication can execute the database transactions within the log table upon the cached table. The cached table can be flagged as cached when the replication is completed.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
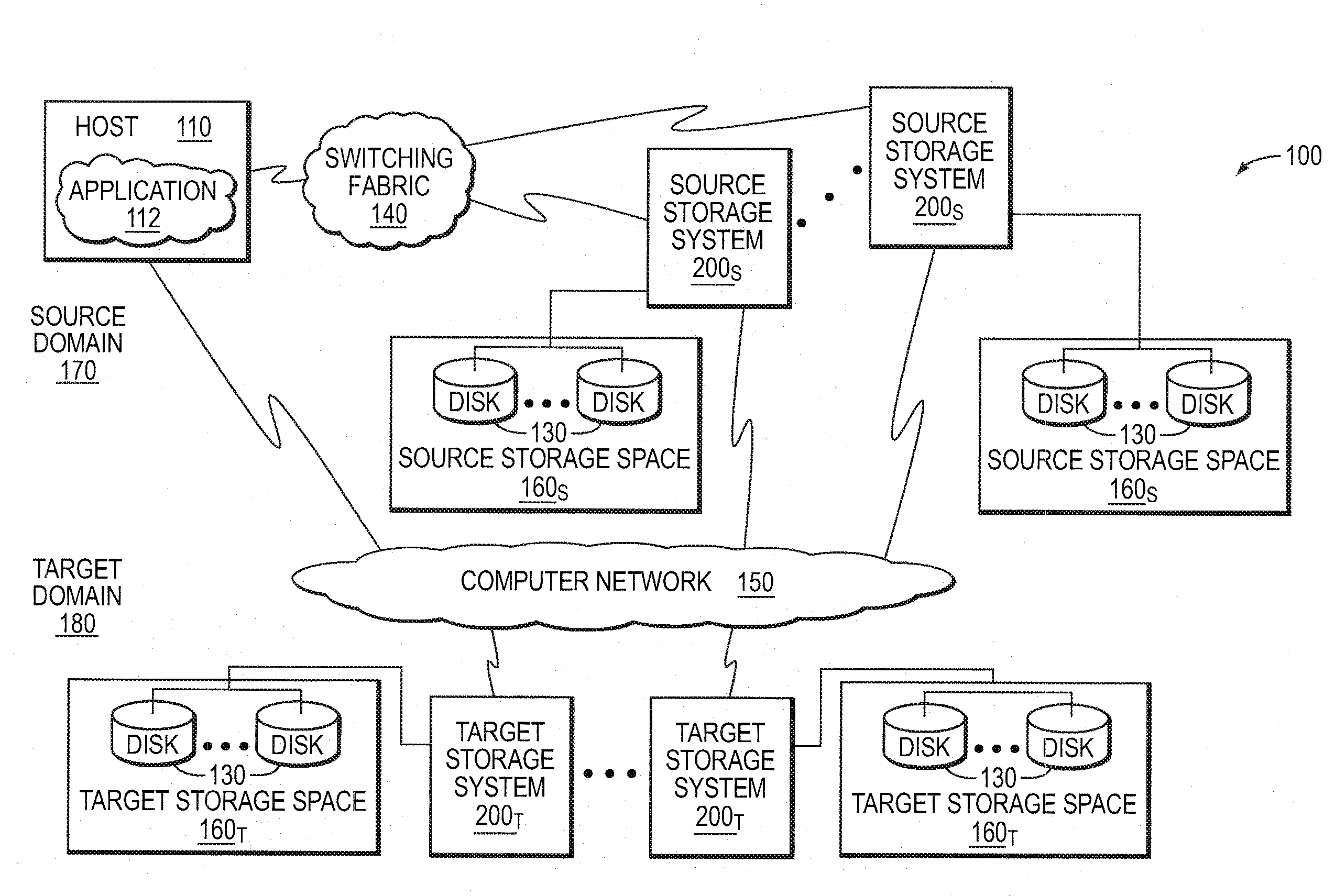
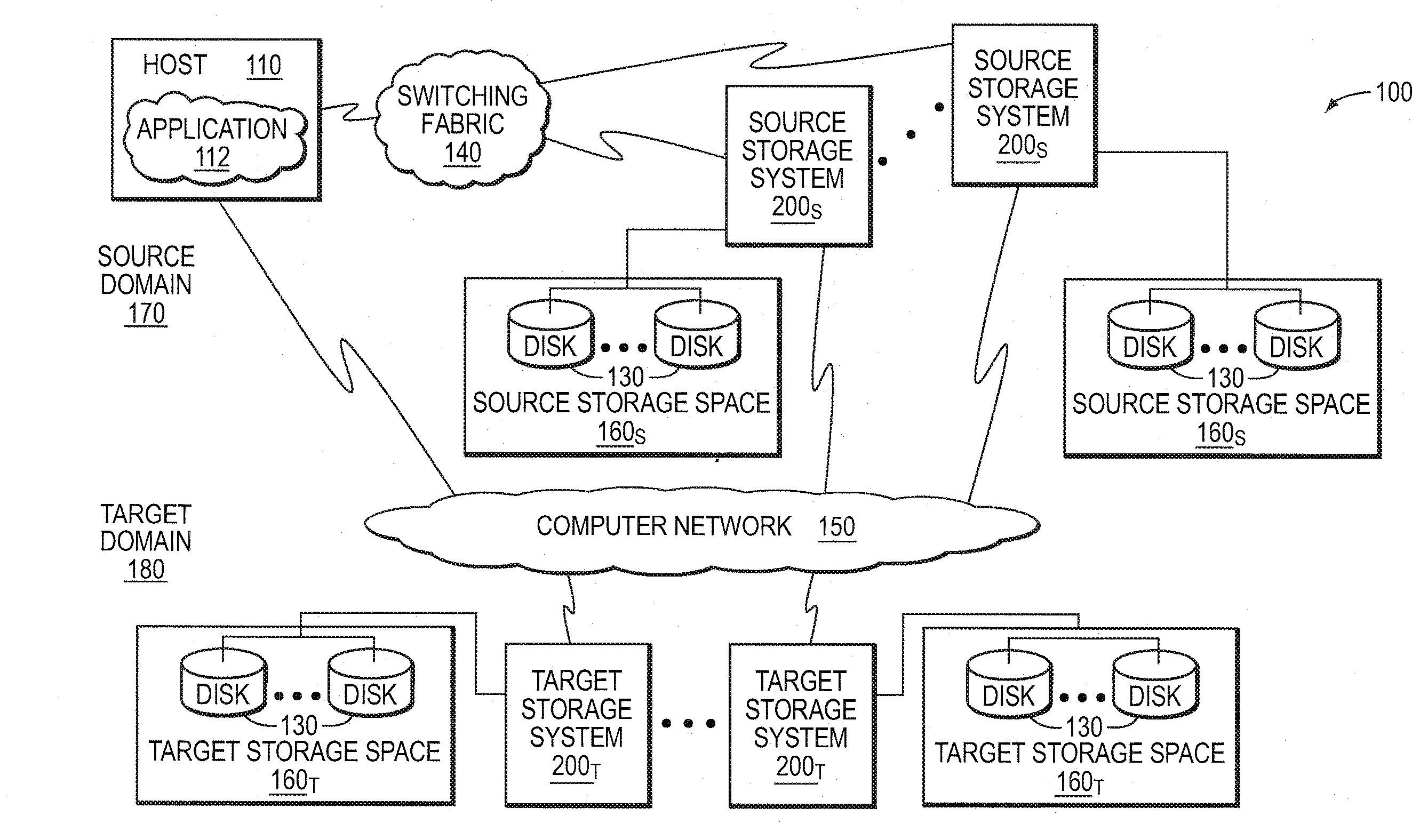
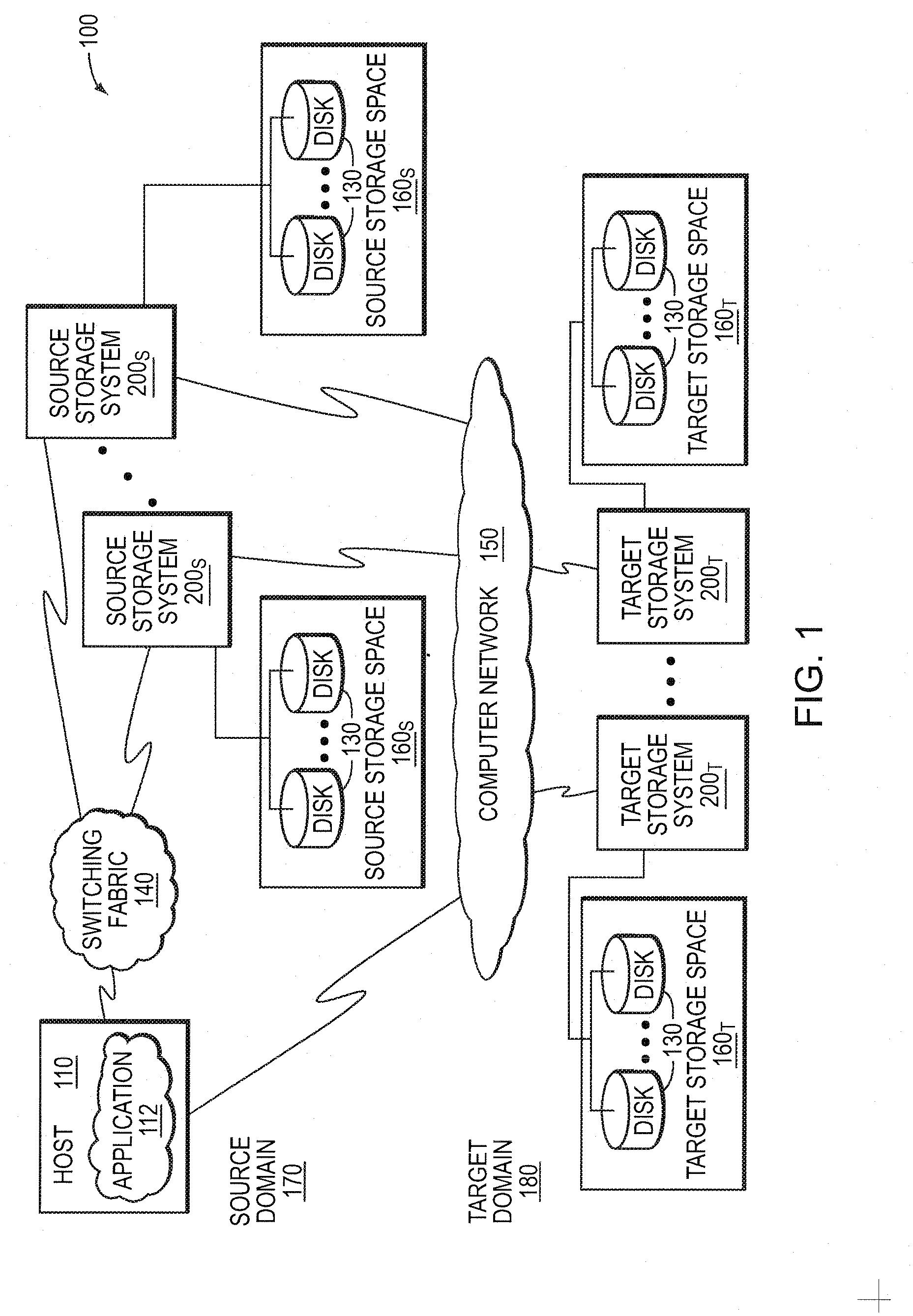
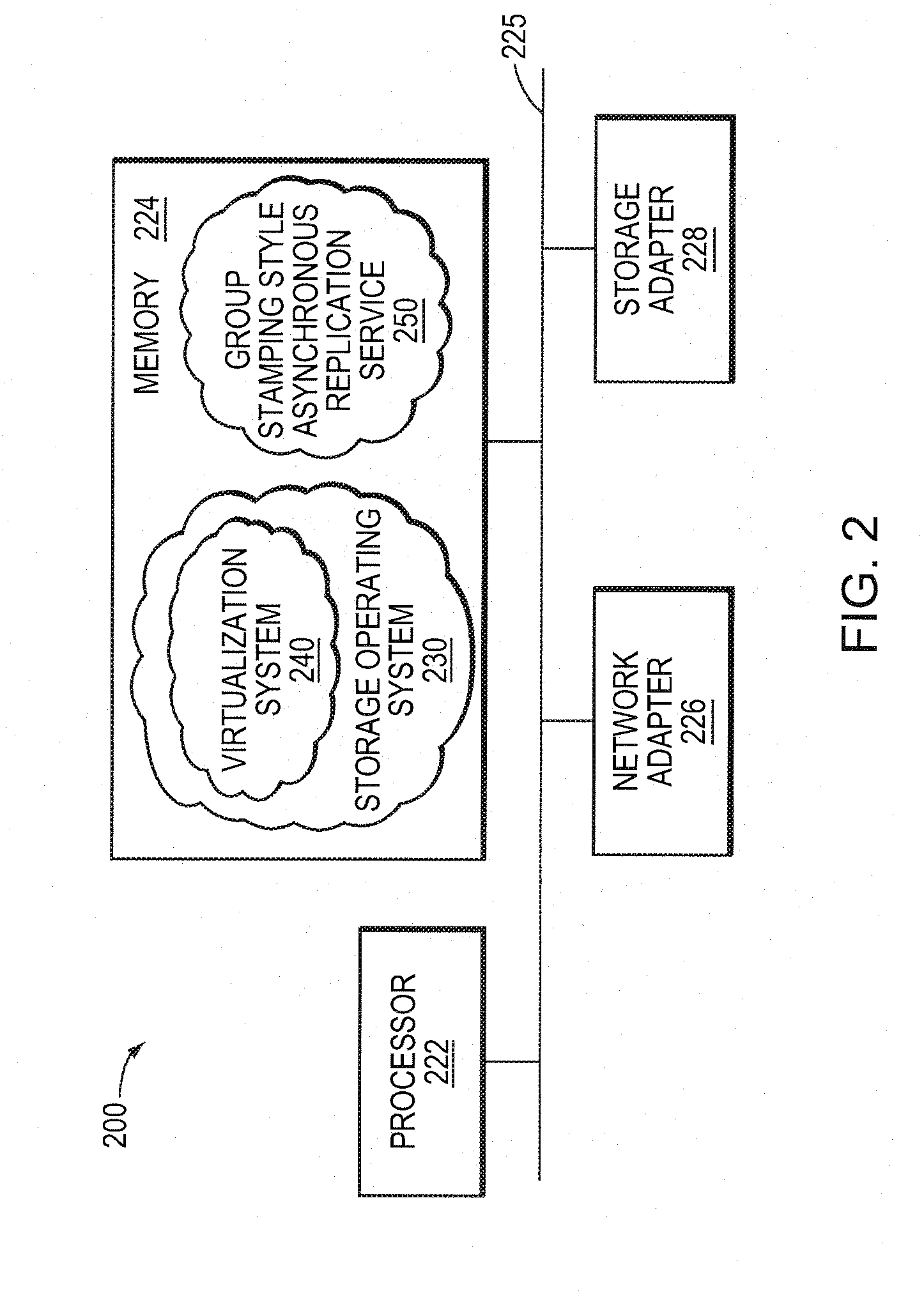
Write ordering style asynchronous replication utilizing a loosely-accurate global clock
ActiveUS20080243951A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsAsynchronous replicationBackup
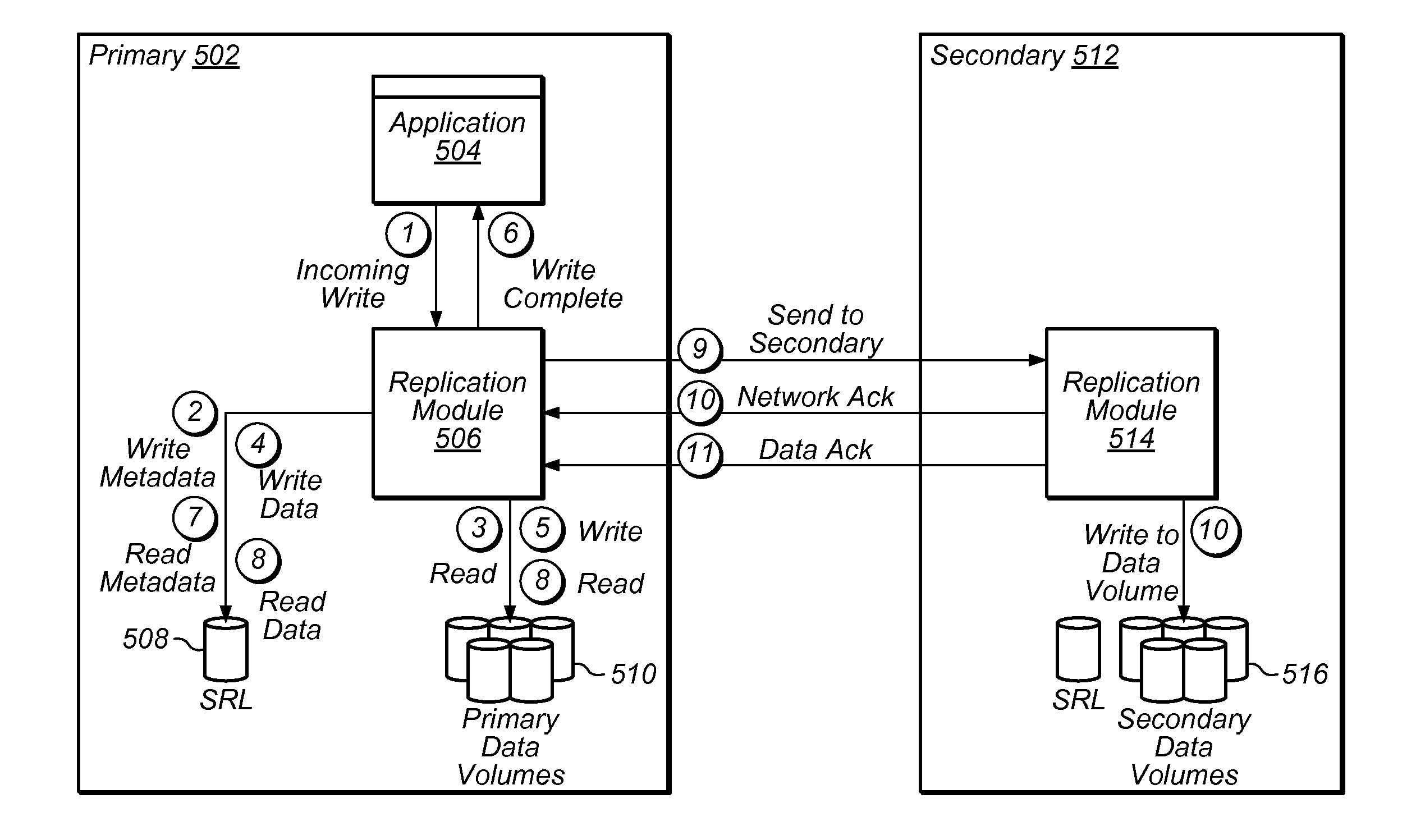
A write ordering style asynchronous replication service utilizes a loosely-accurate global clock in a data backup and recovery storage environment. The storage environment includes a set of source storage systems illustratively embodied as source replication nodes that cooperate to maintain a consistency group that may span multiple geographical sites. The storage environment also includes one or more target storage systems illustratively embodied as target replication nodes configured to service the consistency group. The write ordering style service utilizes the loosely-accurate global clock to provide consistent replication of a storage space of the consistency group.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Group Stamping Style Asynchronous Replication Utilizing A Loosely-Accurate Global Clock
ActiveUS20080243952A1Digital data information retrievalMemory loss protectionAsynchronous replicationBackup
A group stamping style asynchronous replication service utilizes a loosely-accurate global clock in a data backup and recovery storage environment. The storage environment includes a set of source storage systems illustratively embodied as source replication nodes that cooperate to maintain a consistency group that may span multiple geographical sites. The storage environment also includes one or more target storage systems illustratively embodied as target replication nodes configured to service the consistency group. The group stamping style service utilizes the loosely-accurate global clock to provide consistent replication of a storage space, e.g., a target storage space, of the consistency group.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
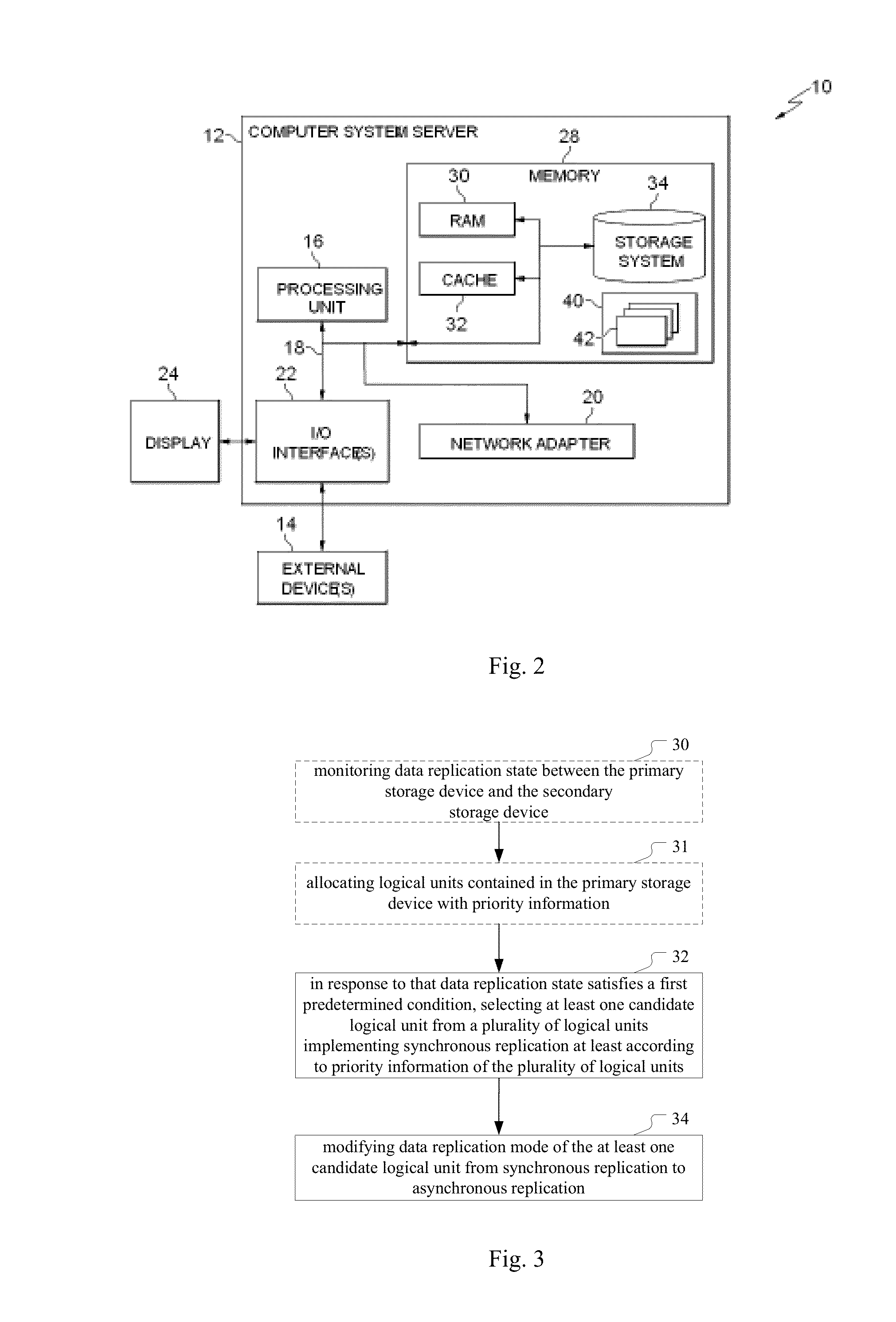
Techniques for managing a data replication mode
InactiveUS20140324774A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsAsynchronous replication
A technique for managing a data replication mode between a primary storage device and a secondary storage device includes in response to a data replication state between the primary storage device and the secondary storage device satisfying a first predetermined condition, selecting at least one candidate logical unit from a plurality of logical units implementing synchronous replication in the primary storage device at least according to priority information of the plurality of logical units. A data replication mode of the at least one candidate logical unit is then modified from synchronous replication to asynchronous replication.
Owner:IBM CORP
Database caching utilizing asynchronous log-based replication
ActiveUS20130080388A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsRelational database management systemDatabase caching
A database table within a database to persist within a cache as a cached table can be identified. The database can be a relational database management system (RDBMS) or an object oriented database management system (OODBMS). The cache can be a database cache. Database transactions within can be logged within a log table and the cached table within the cache can be flagged as not cached during runtime. An asynchronous replication of the database table to the cached table can be performed. The replication can execute the database transactions within the log table upon the cached table. The cached table can be flagged as cached when the replication is completed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for Remote Asynchronous Replication of Volumes and Apparatus Therefor
ActiveUS20100205392A1Enhanced data transmissionGuaranteed uptimeMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionOriginal dataRemote data transmission
A method for remote asynchronous volume replication and apparatus therefore are disclosed. Asynchronous replication is applied to deal with data changes on the source volume on the local site incurred by Host IO requests. In coordination with the “point-in-time differential backup” technology, the data is subjected to be backuped to Source BAS on the local site (backup-on-write operation) only when the original data being written into the block of the source volume is different from the data of the corresponding block of the destination volume on the remote site. As a result, once a new data is written into the source volume completely, the host will be responded that its Host IO request is completed. Therefore, the data necessarily transmitted to the destination volume on the remote site can be minimized, and the problem of remote data transmission limited by network bandwidth can be prevented effectively, thereby keeping the operation performance of the storage system at a better level.
Owner:INFORTREND TECH INC
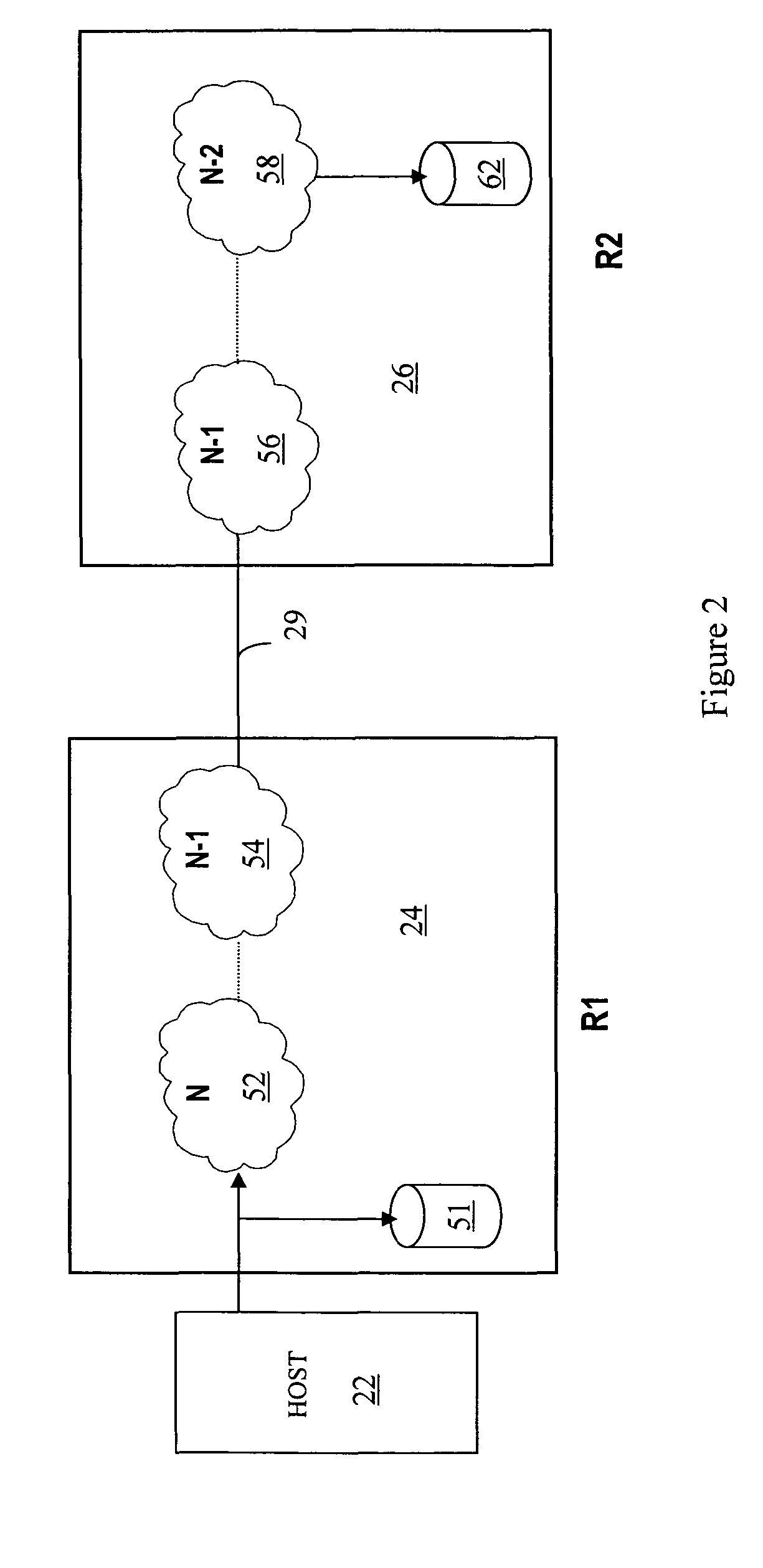
Failover to synchronous backup site in connection with triangular asynchronous replication
Handling failure of a primary group at a first data center that is part of plurality of data centers providing triangular asynchronous replication, includes creating a data mirroring relationship between at least one storage volume at a second data center having a synchronous backup group that is part of the plurality of data centers and at least one storage volume at a third data center having an asynchronous backup group that is part of the plurality of data centers and resuming work at the second data center. Handling failure of a primary group at a first data center may also include synchronizing the at least one storage volume at the second data center with the at least one storage volume at the third data center prior to resuming work at the second data center.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
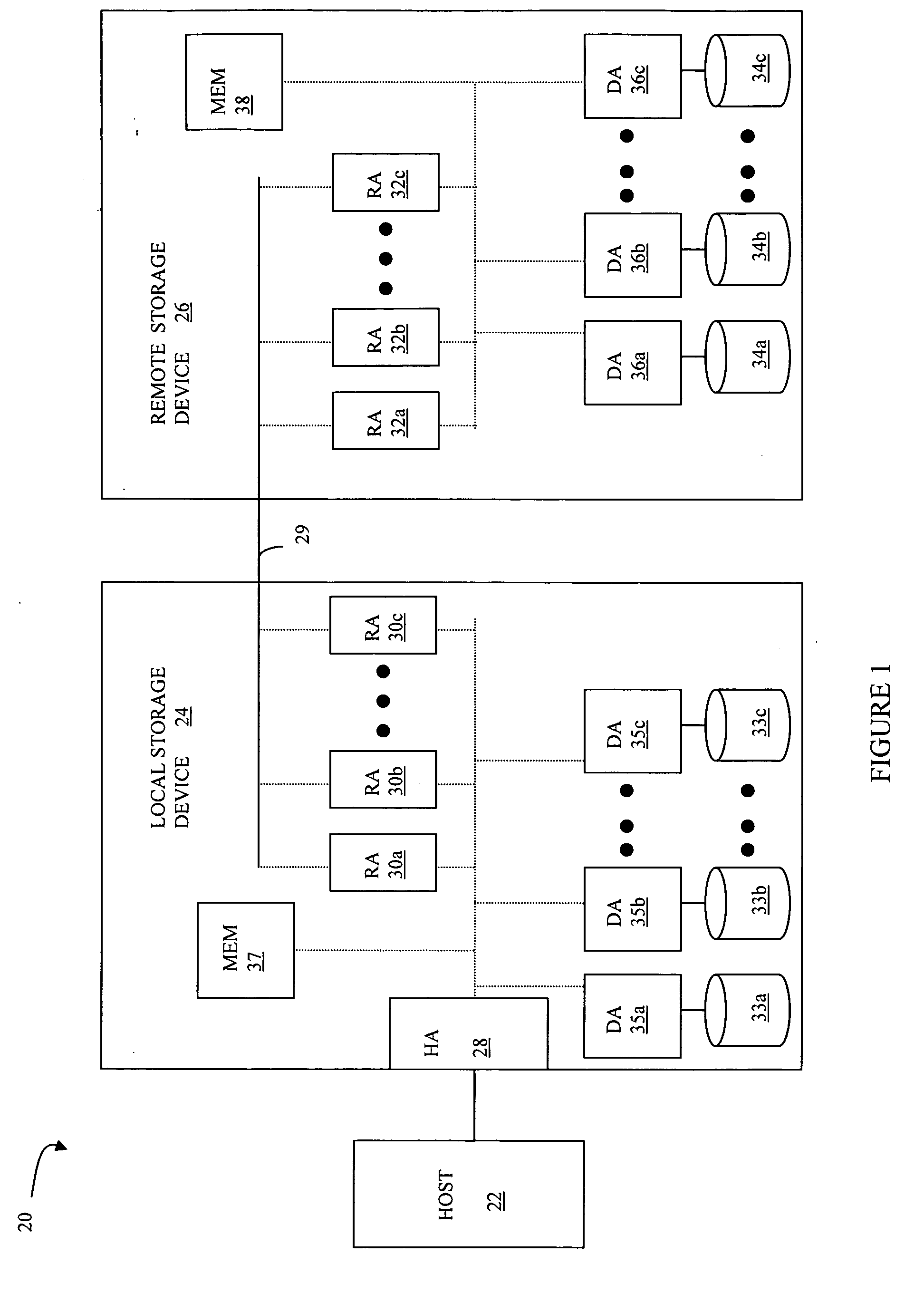
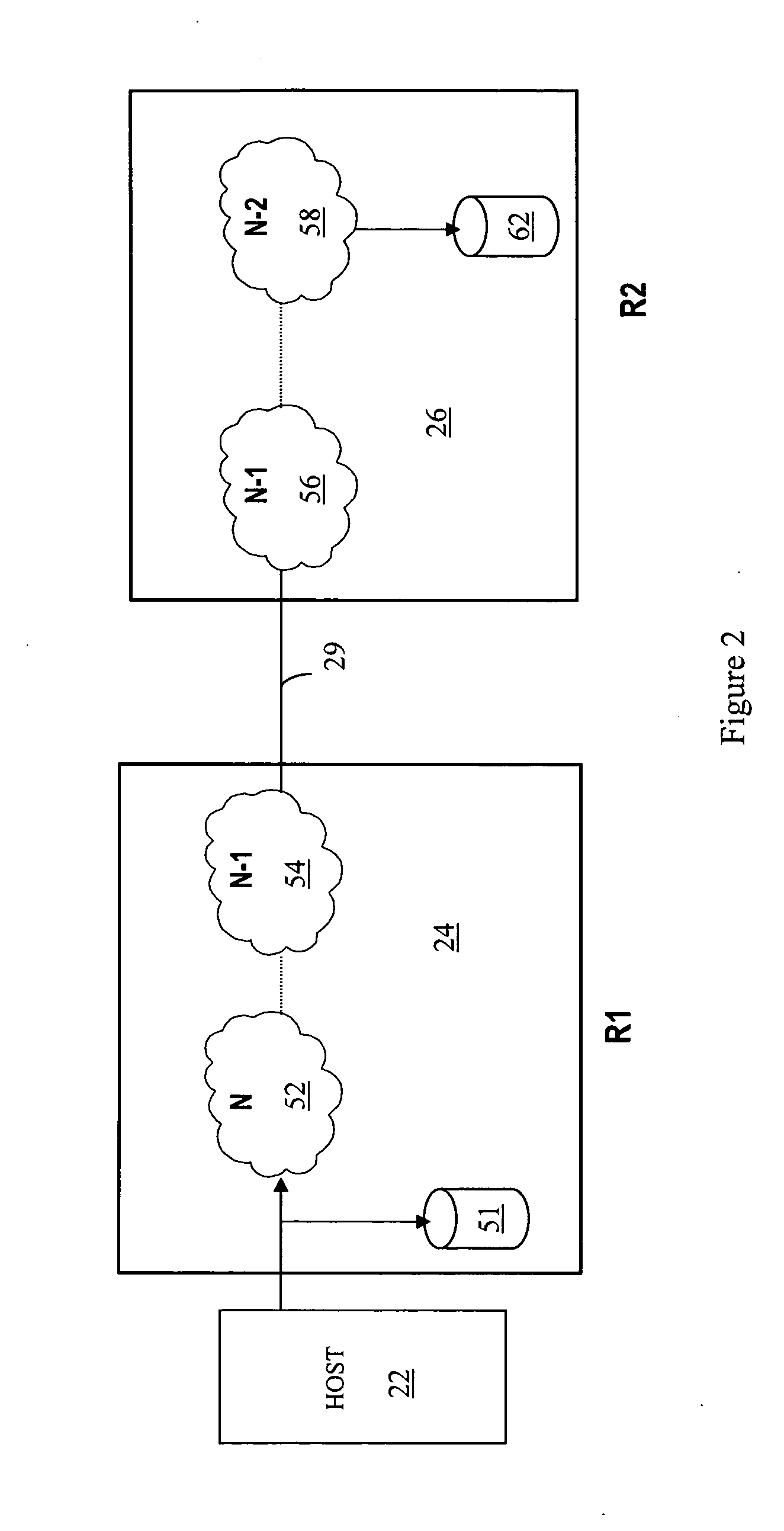
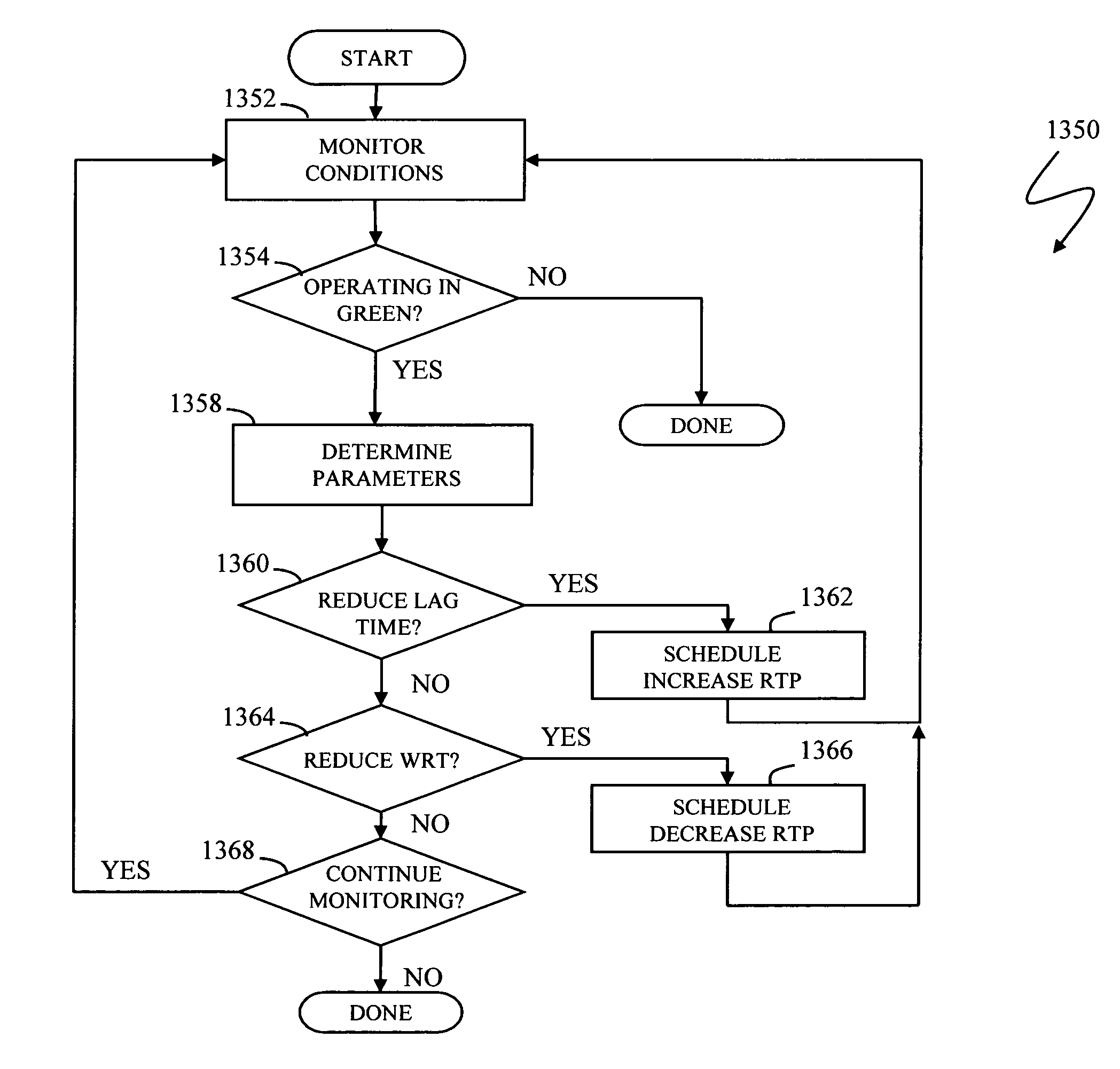
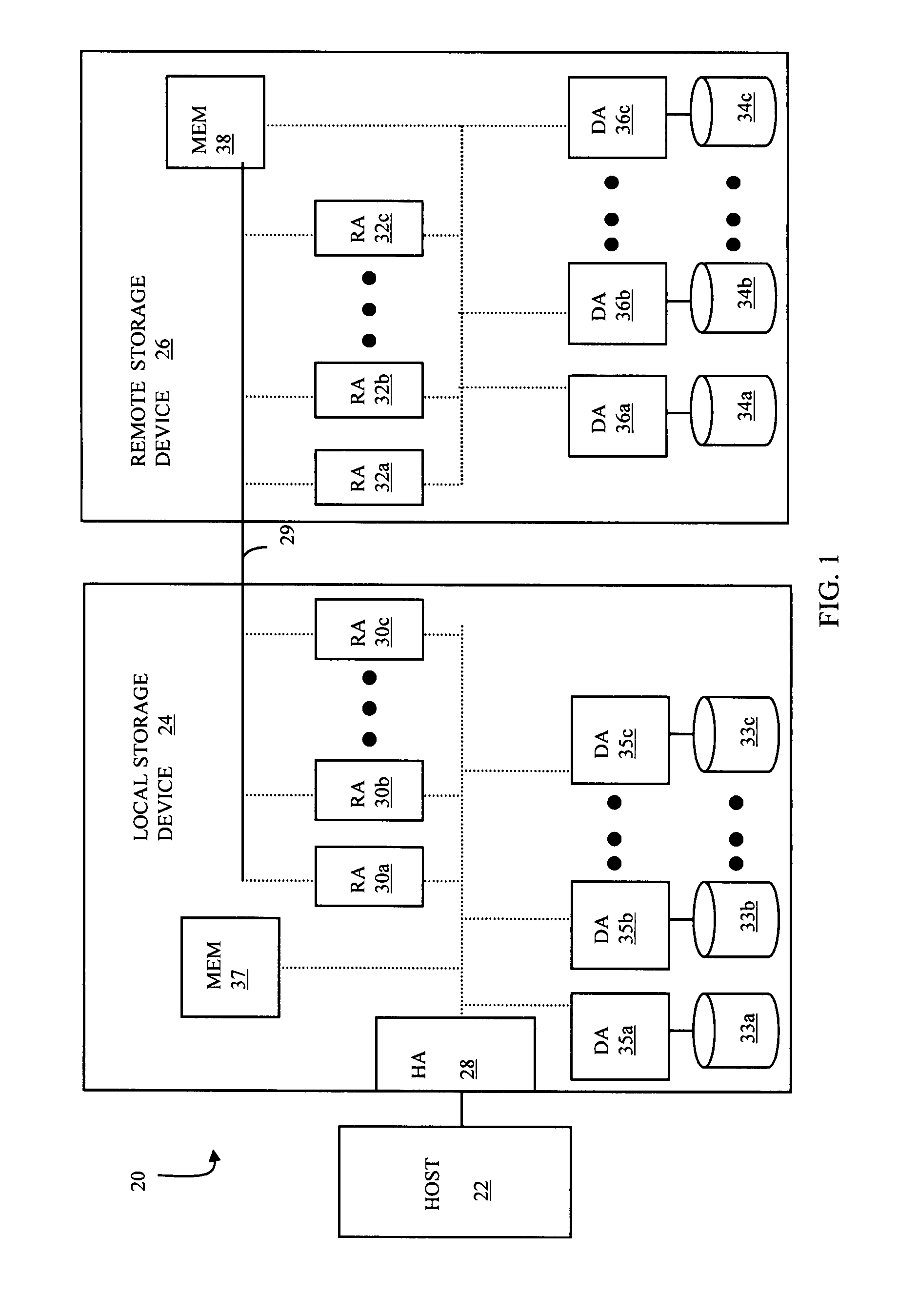
Write pacing
A system for controlling the pacing of host data writes in response to changing system conditions allows for the use of variably controlled delays that facilitate asynchronous replication with bounded lag and smooth steady-state performance. Adding delay to the writes slows down the host and dampens activity spikes. A first storage device receives a write request, transmits data to a second storage device, and acknowledges the write request. An amount of additional write response time is controlled between when the write request is received and when the write request is acknowledged by the first storage device, where the amount of additional write response time is controlled according to system parameters including an amount of lag time between when the write request is received and when the write request is committed at the second storage device.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Database caching utilizing asynchronous log-based replication
ActiveUS20130080386A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsRelational database management systemDatabase caching
A database table within a database to persist within a cache as a cached table can be identified. The database can be a relational database management system (RDBMS) or an object oriented database management system (OODBMS). The cache can be a database cache. Database transactions within can be logged within a log table and the cached table within the cache can be flagged as not cached during runtime. An asynchronous replication of the database table to the cached table can be performed. The replication can execute the database transactions within the log table upon the cached table. The cached table can be flagged as cached when the replication is completed.
Owner:IBM CORP
Resumption of operations following failover in connection with triangular asynchronous replication
Handling failure of a primary group at a first data center that is part of plurality of data centers providing triangular asynchronous replication includes creating a data mirroring relationship between at least one storage volume at a second data center having a synchronous backup group that is part of the plurality of data centers and at least one storage volume at a third data center having an asynchronous backup group that is part of the plurality of data centers and resuming work at the third data center. Handling failure of a primary group at a first data center may also include synchronizing the at least one storage volume at the second data center with the at least one storage volume at the third data center prior to resuming work at the third data center.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
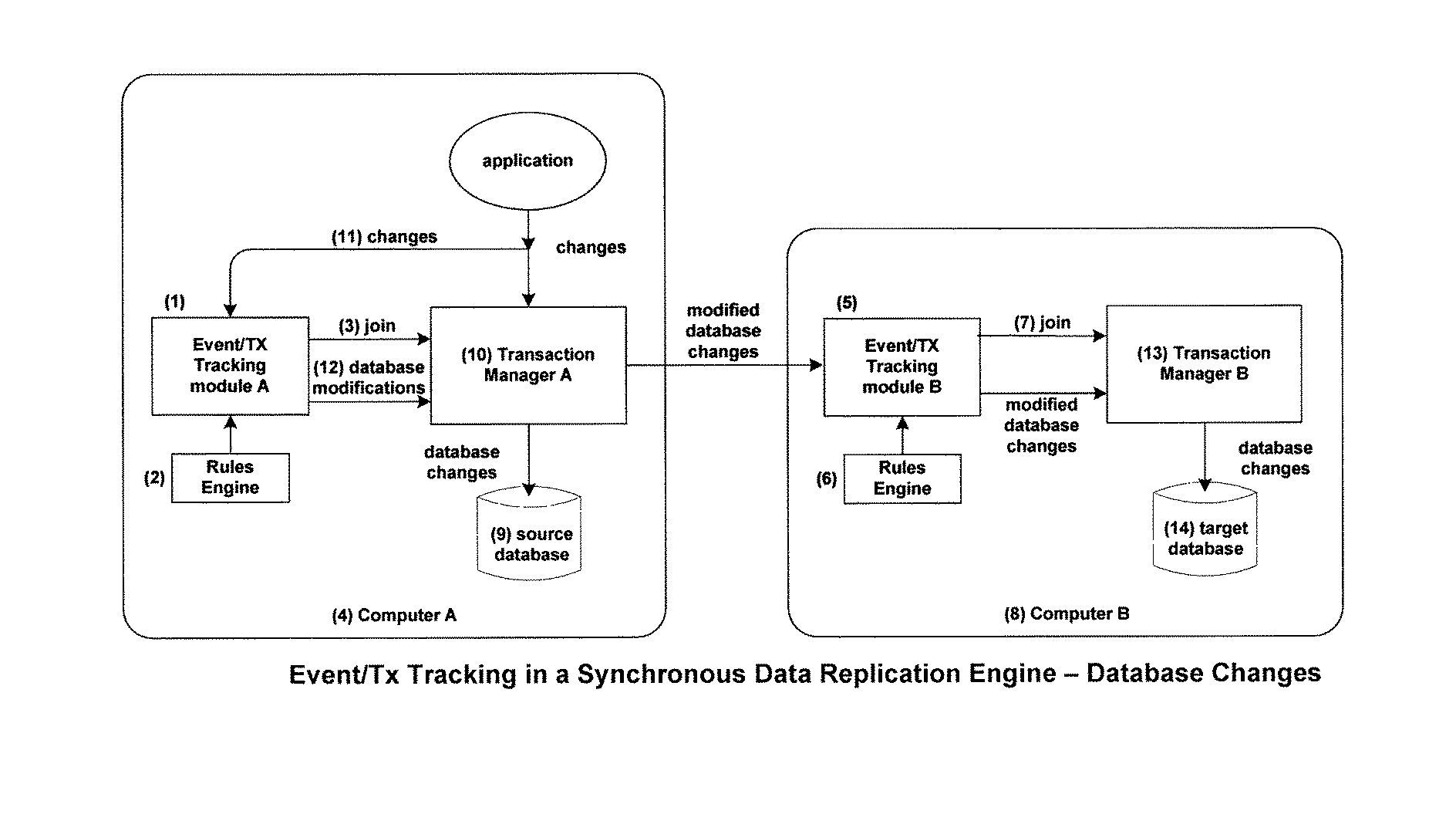
Method of controlling whether an uncompleted transaction applied against a database goes forward using either synchronous or asynchronous replication, or using either encrypted replication or unencrypted replication
ActiveUS9569473B1Increase the lengthImprove practicalityDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsProgramming languageAsynchronous communication
Transactions are applied against a database on a transaction processing system. A tracking engine identifies an uncompleted transaction to be joined, joins the uncompleted transaction, and collects one or more non-durable attributes of the joined uncompleted transaction. Collected attributes of the joined uncompleted transaction are compared against rules in a rules engine that are applicable to the transaction to determine whether an applicable rule in the rules engine is met. The joined uncompleted transaction is allowed to go forward and be applied against the database of the transaction processing system using a synchronous replication engine when the applicable rule is met, and an asynchronous replication engine when the applicable rule is not met. Alternatively, the joined uncompleted transaction is allowed to go forward using a replication engine that replicates using encryption when the applicable rule is met, or replicates unencrypted when the applicable rule is not met.
Owner:RPX CORP
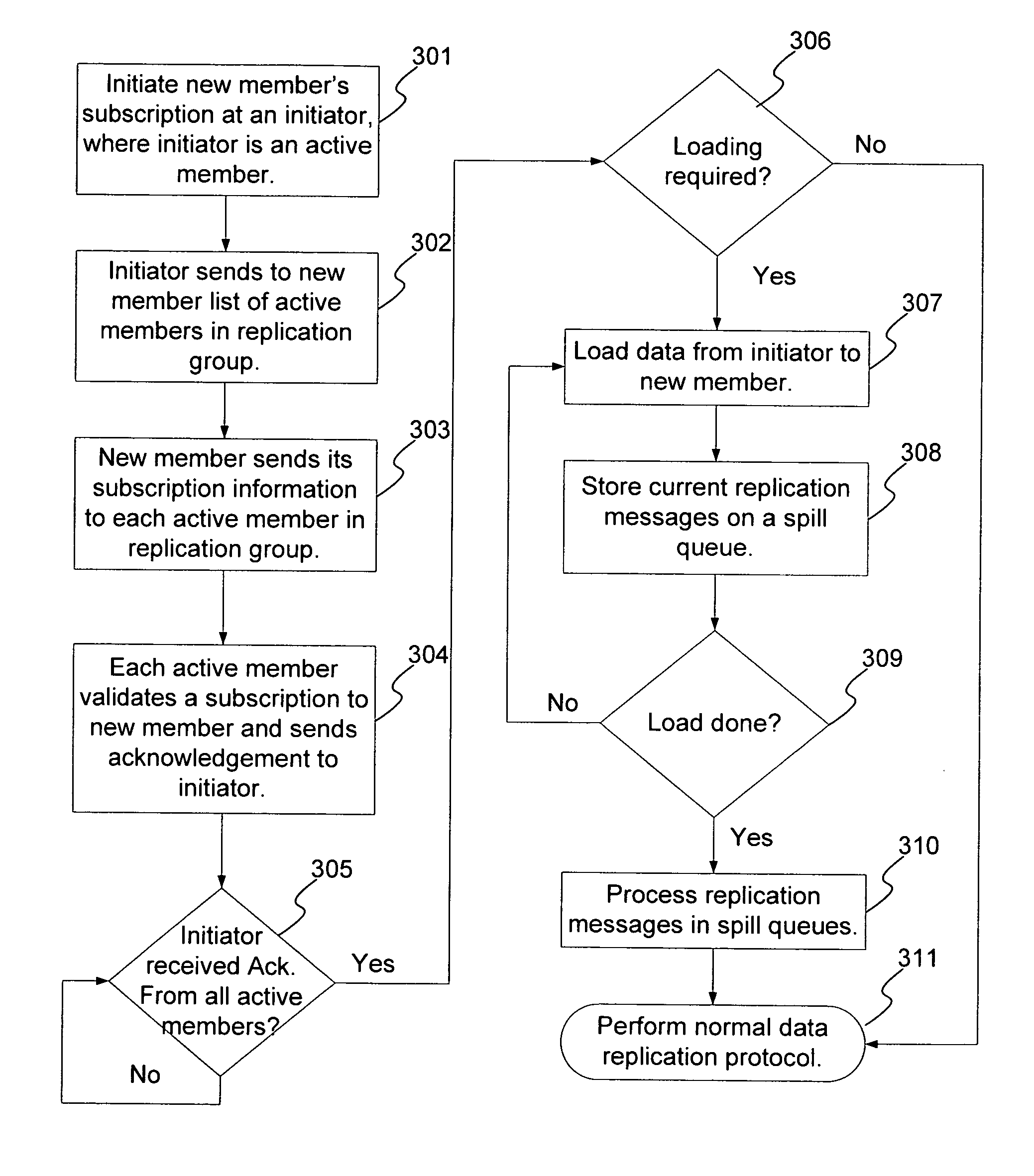
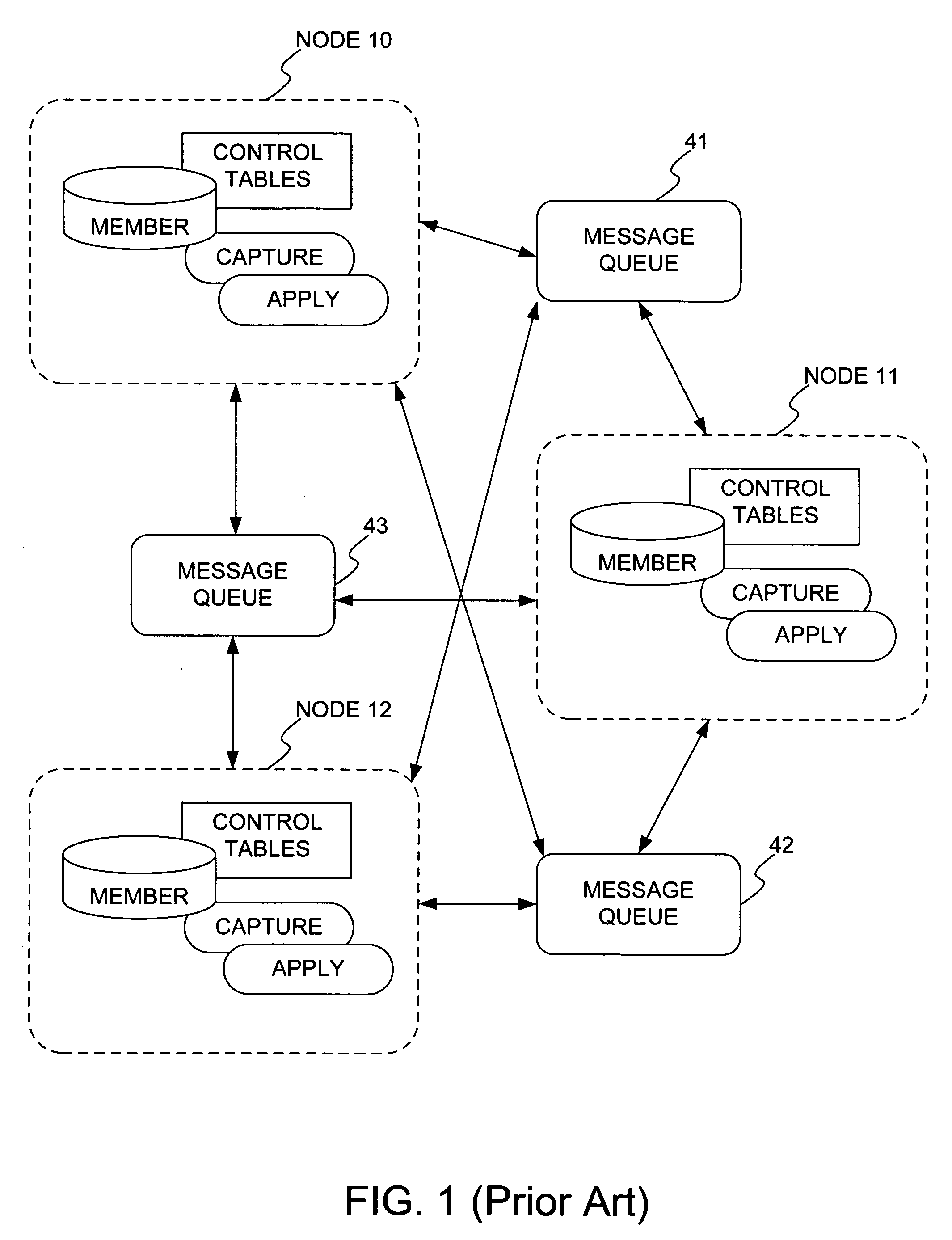
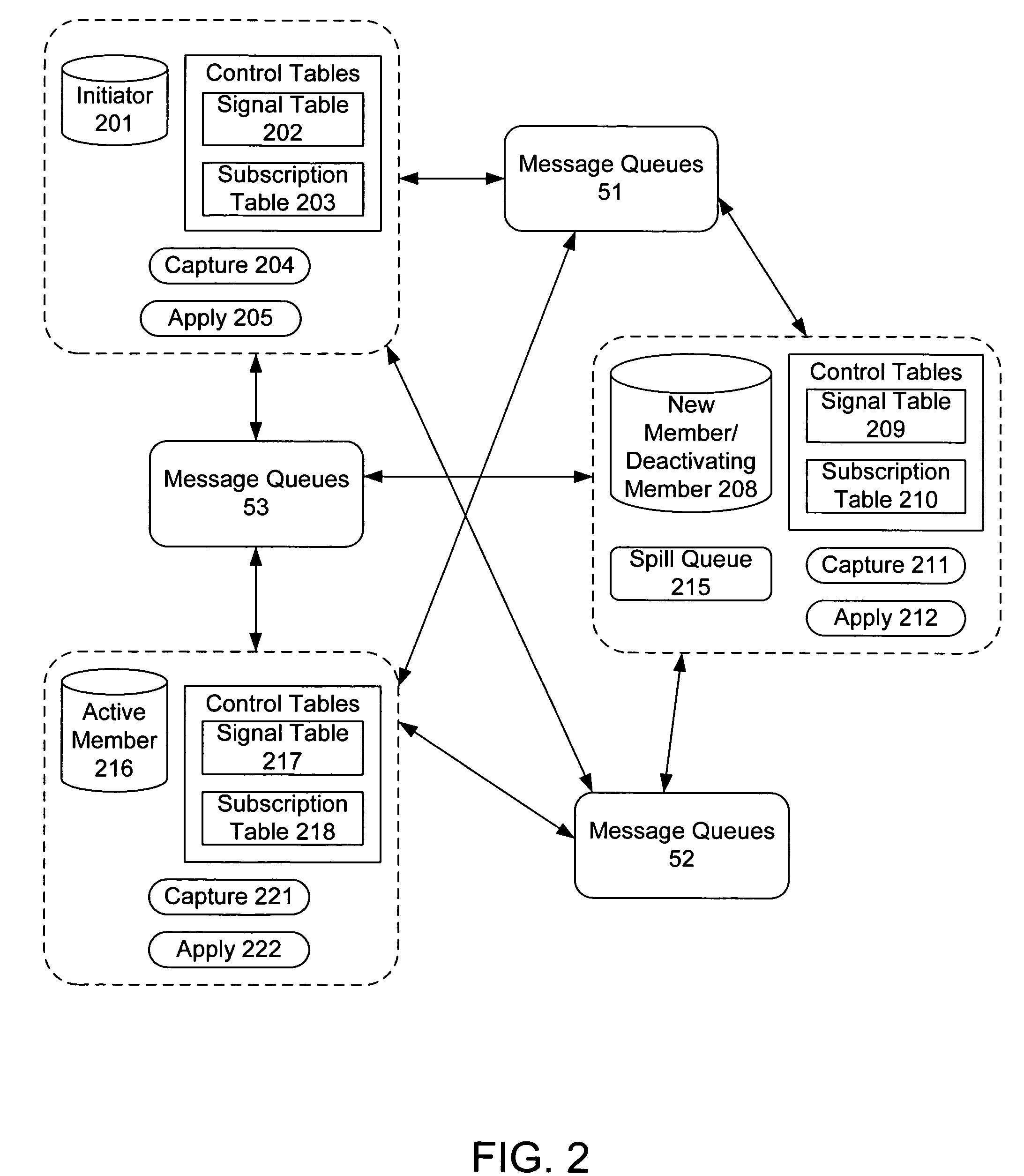
Peer-to-peer replication member initialization and deactivation
InactiveUS7203687B2Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsAsynchronous dataAsynchronous replication
A method and system for member initialization to and deactivation from an asynchronous data replication group in a database system is disclosed. The method and system allows new members to be added to the replication group or existing members to be removed from the replication group, without requiring the halting of the asynchronous replication of data. The performance advantages of asynchronous replication are still realized during member initialization or deactivation.
Owner:IBM CORP
Triangular asynchronous replication
ActiveUS8078813B2Error detection/correctionMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer scienceAsynchronous replication
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Asynchronous replication method, device and system
ActiveCN103875229ASync fastSolve the problem of uncontrollable object access timeError detection/correctionSynchronising arrangementAccess timeData center
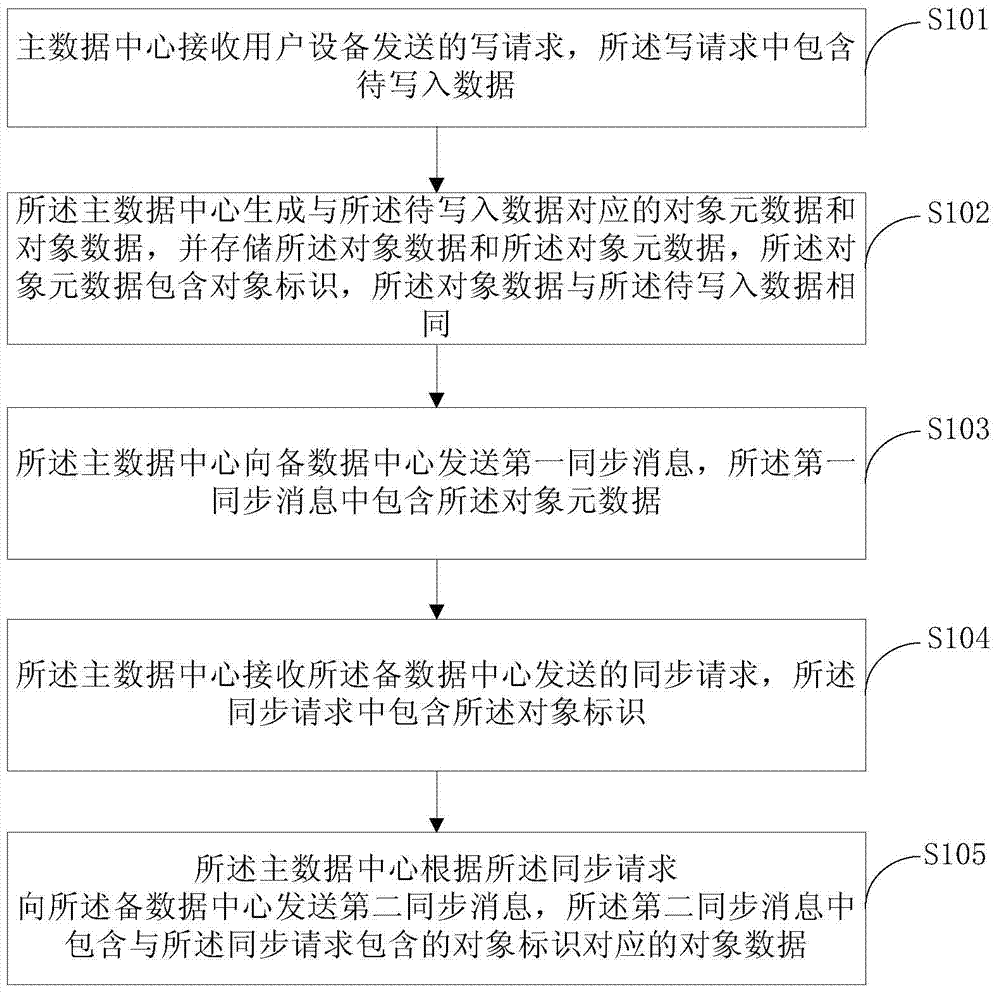
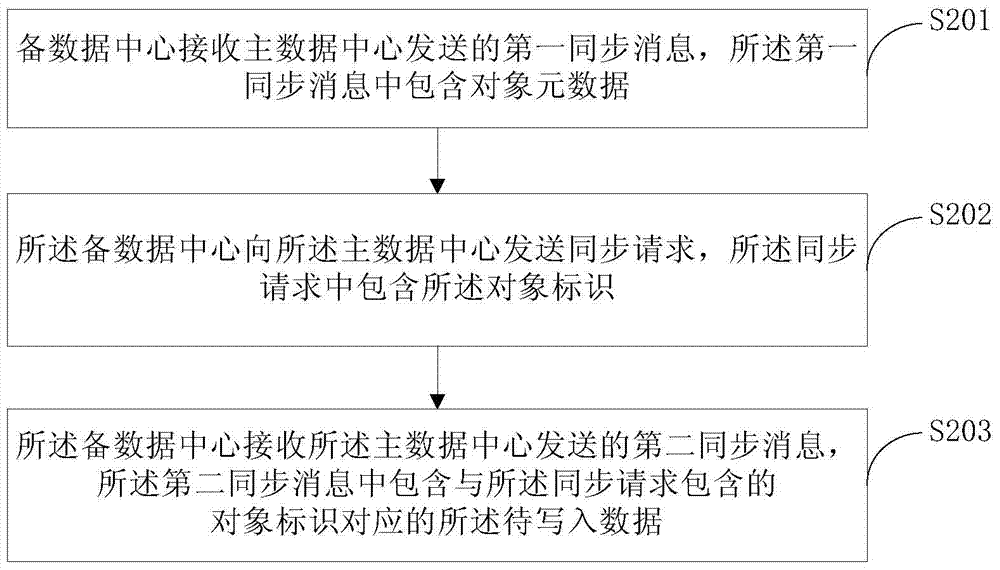
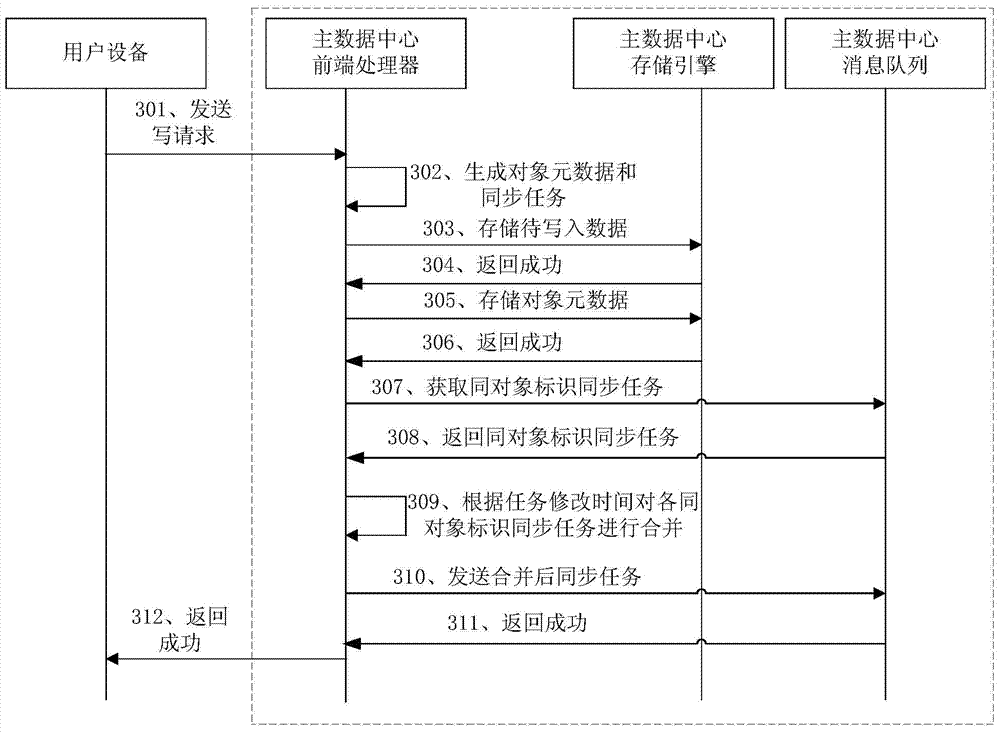
The embodiment of the invention provides an asynchronous replication method, a device and a system. The method comprises that a main data center receives a write request that is emitted by a user device and comprises to-be-written data; object metadata and object data corresponding to the to-be-written data are generated and stored, wherein the object metadata comprises an object identity and the object data is equal to the to-be-written data; a first synchronous message is sent to a backup data center and comprises the object metadata; a synchronous request emitted by the backup data center is received and comprises the object identity; and a second synchronous message is sent to the backup data center according to the synchronous message and comprises the object data corresponding to the object identity contained in the synchronous message. The method overcomes the problem that time of object access in the backup data center by a user is uncontrollable.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
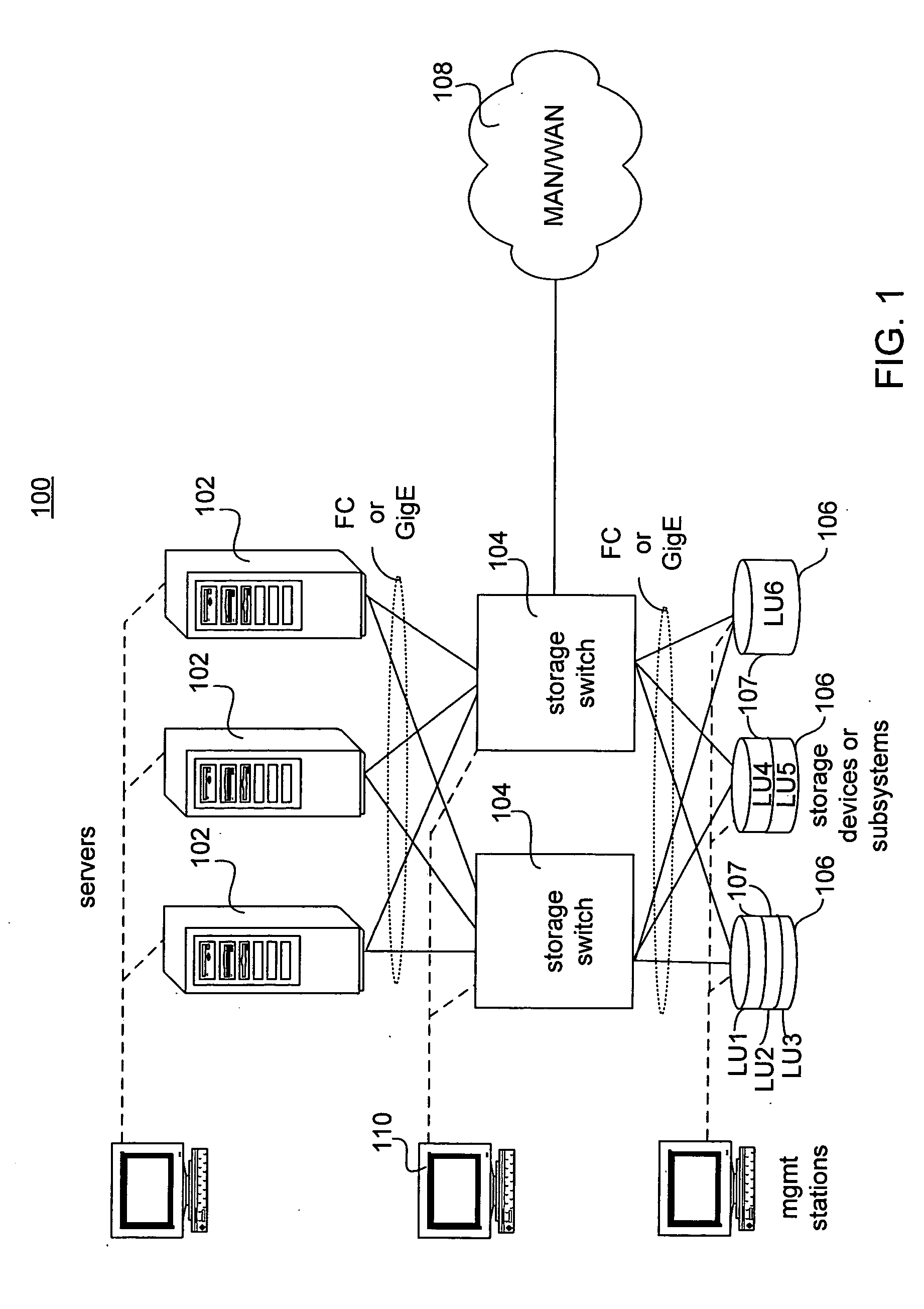
Storage switch asynchronous replication
ActiveUS20060047928A1Improve availabilityHigh data reliabilityMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionLogic cellAsynchronous replication
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com