Patents
Literature
33 results about "Sparse file" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
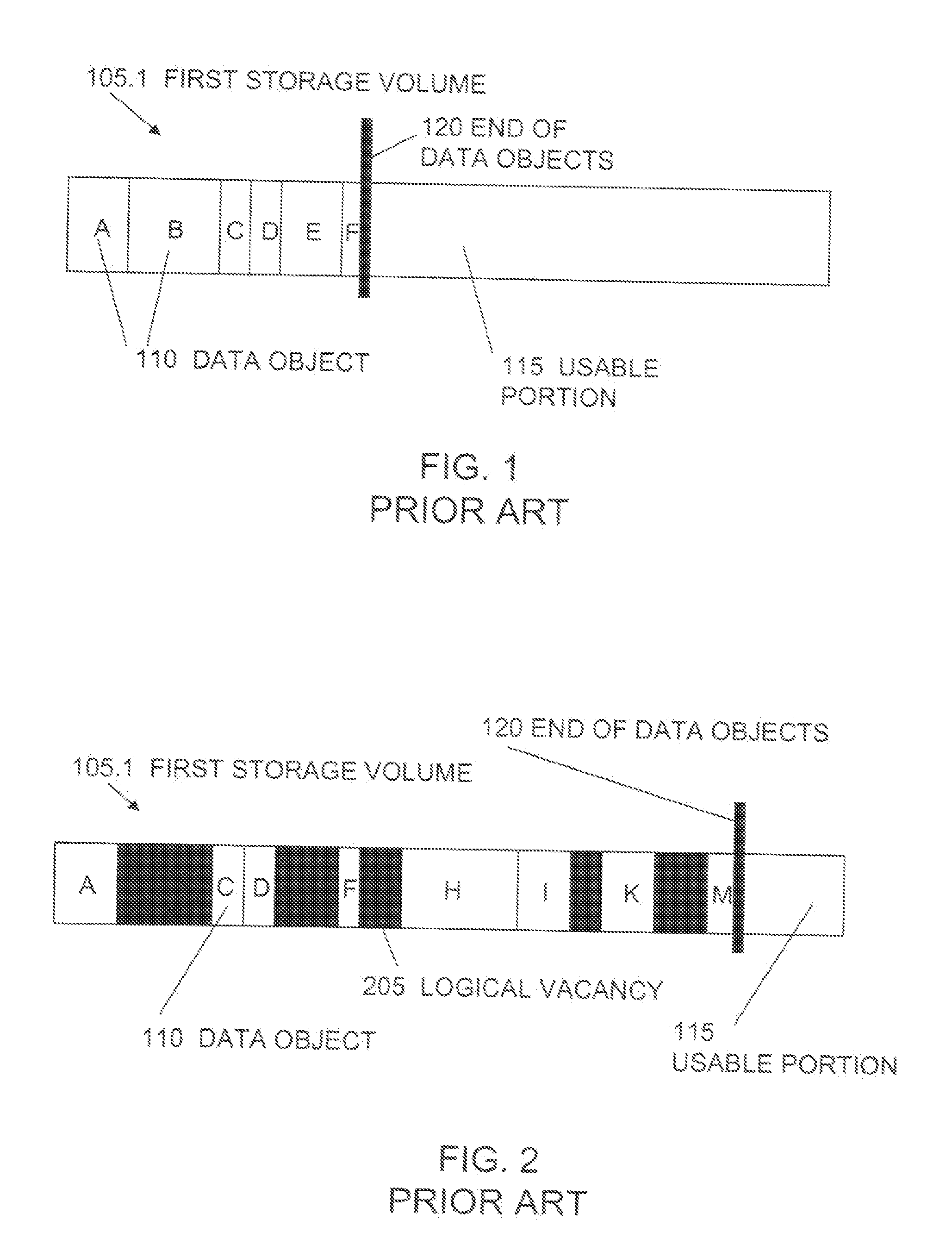
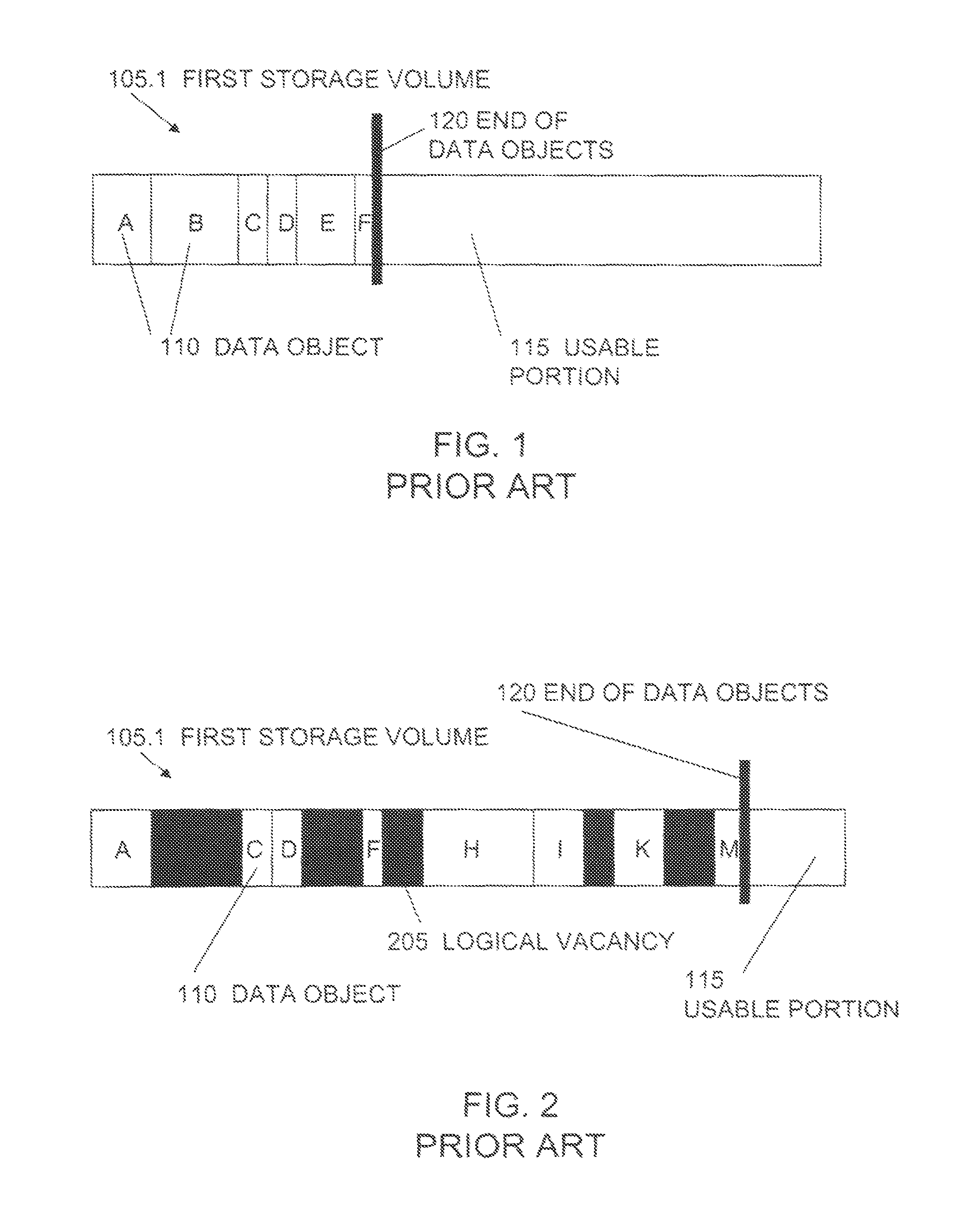
In computer science, a sparse file is a type of computer file that attempts to use file system space more efficiently when the file itself is partially empty. This is achieved by writing brief information (metadata) representing the empty blocks to disk instead of the actual "empty" space which makes up the block, using less disk space. The full block size is written to disk as the actual size only when the block contains "real" (non-empty) data.
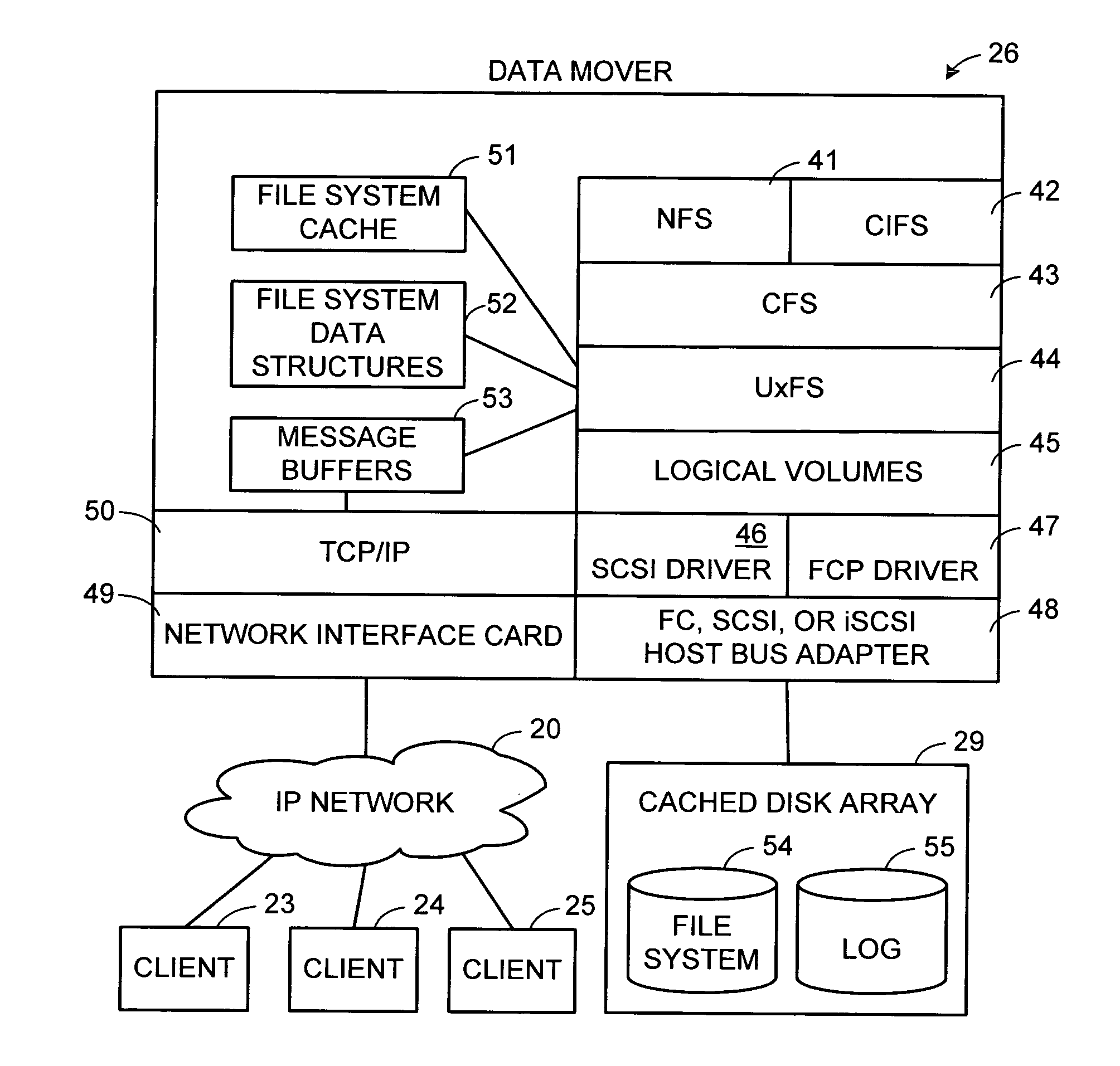
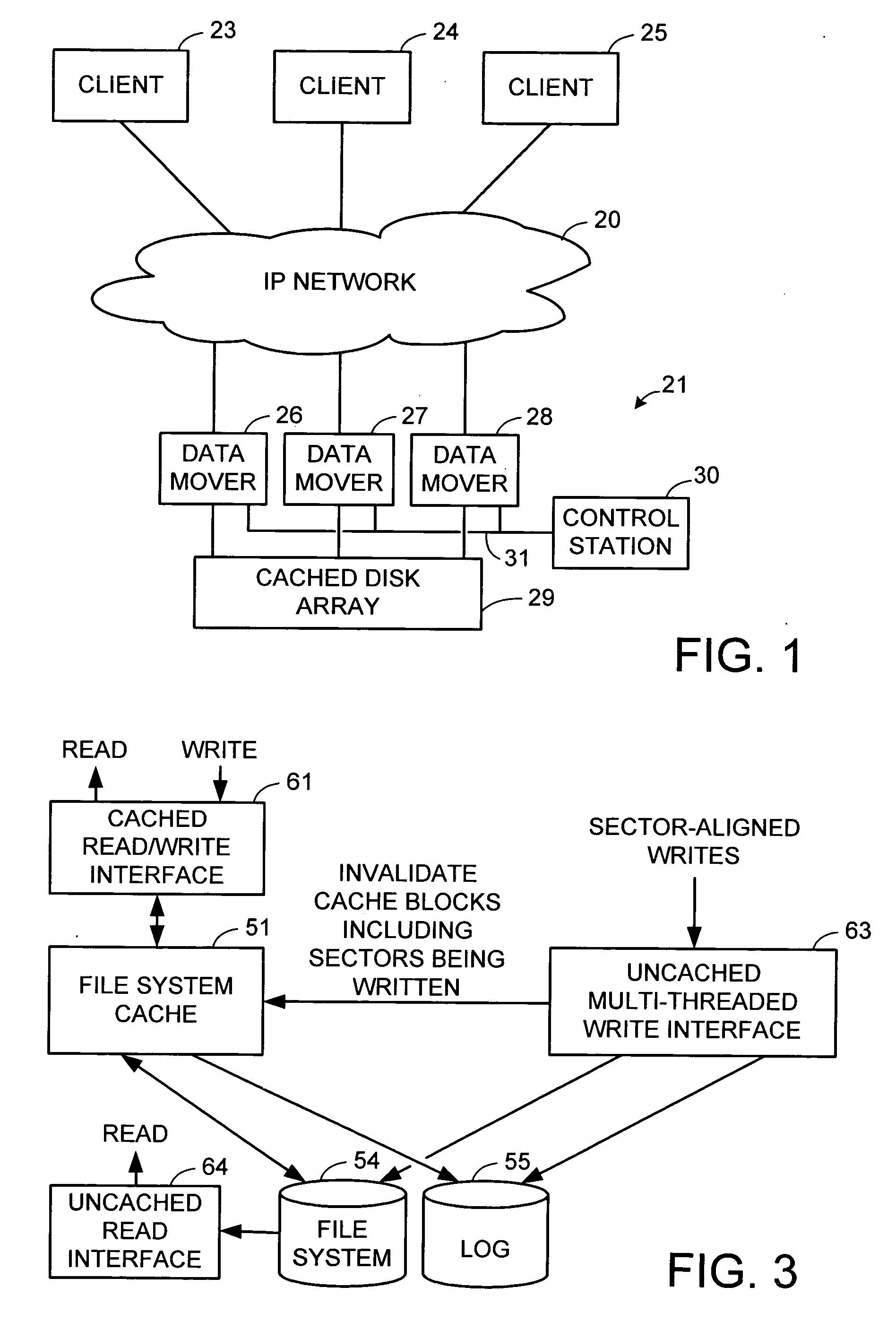
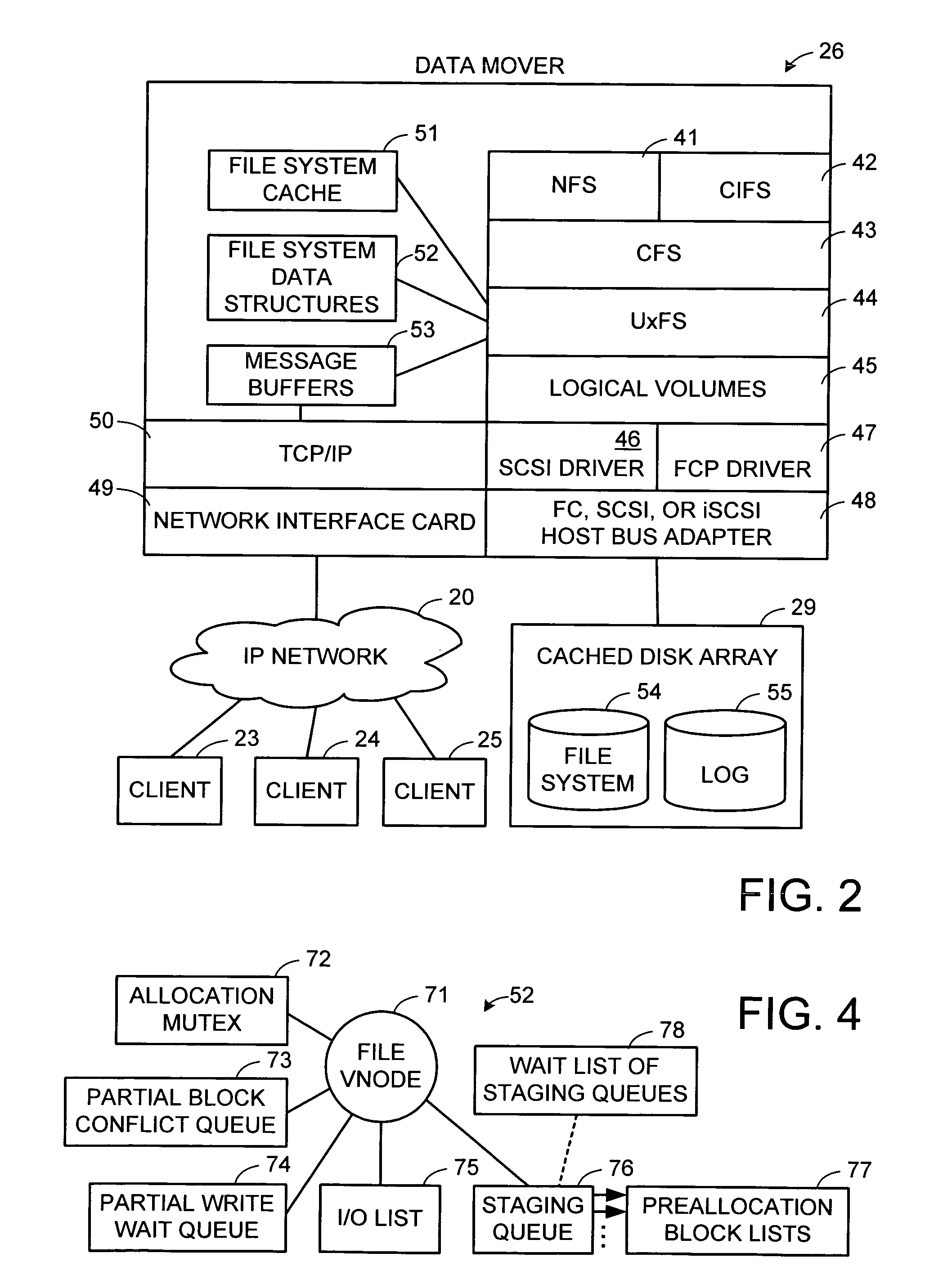
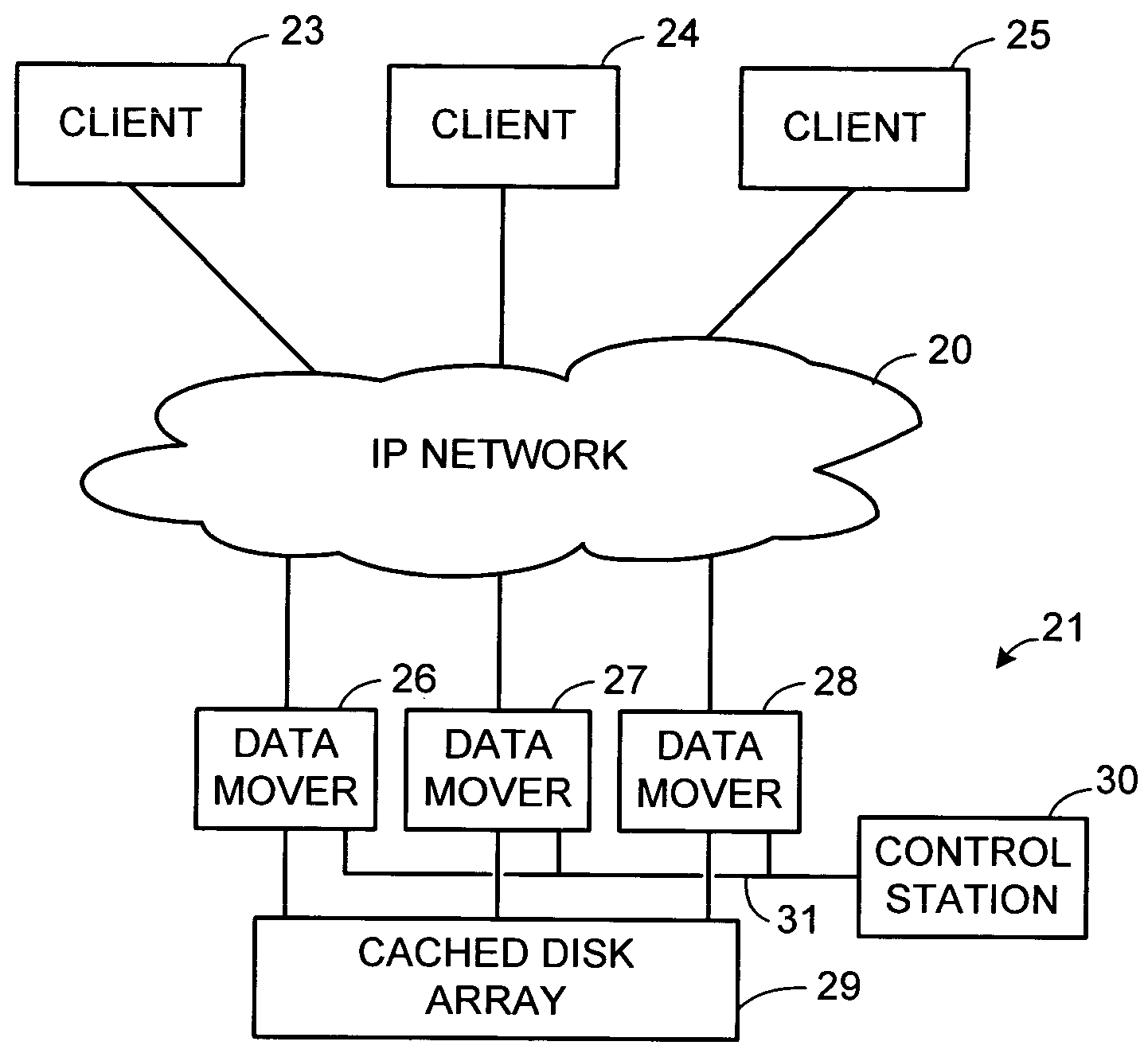
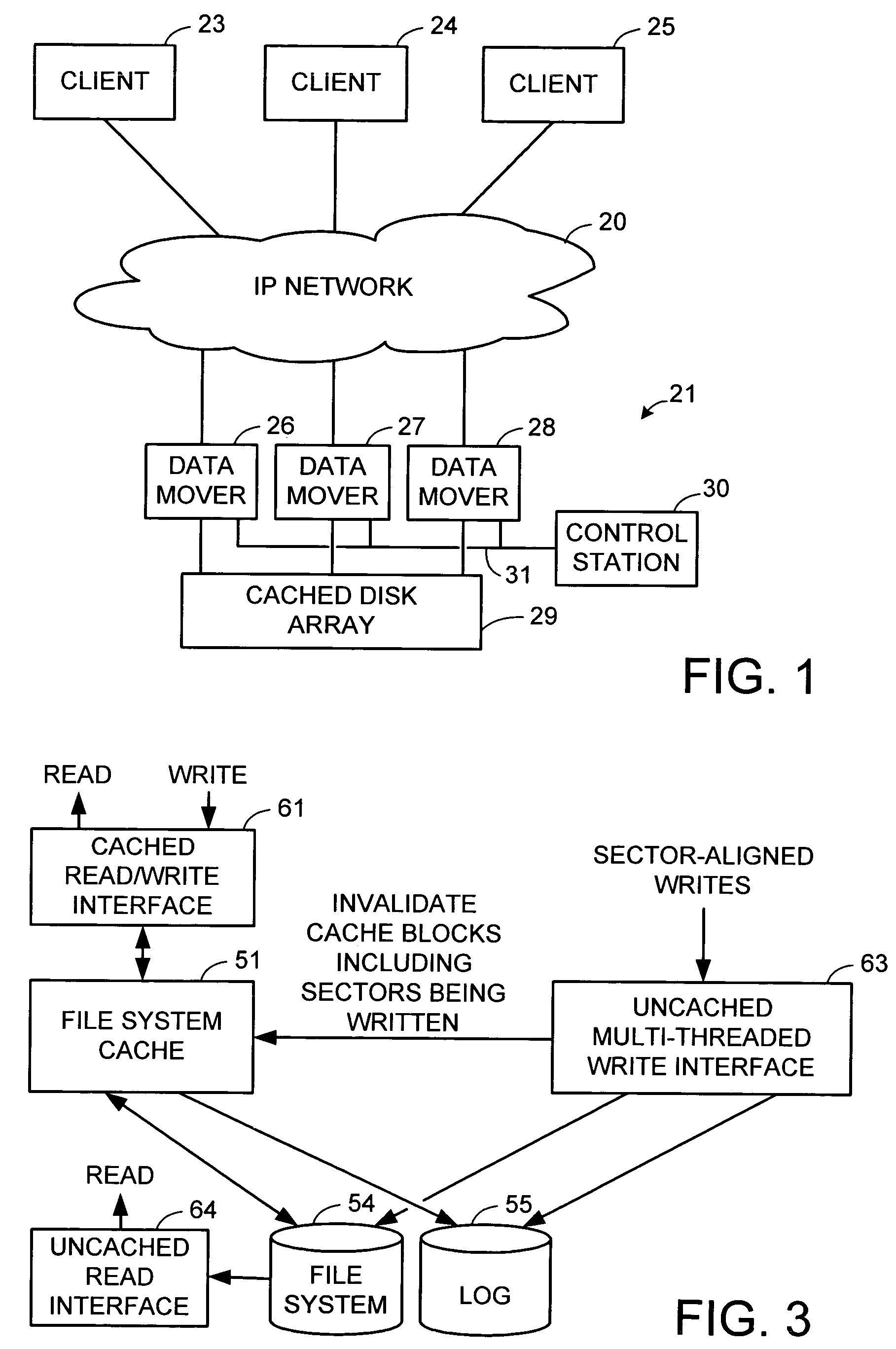
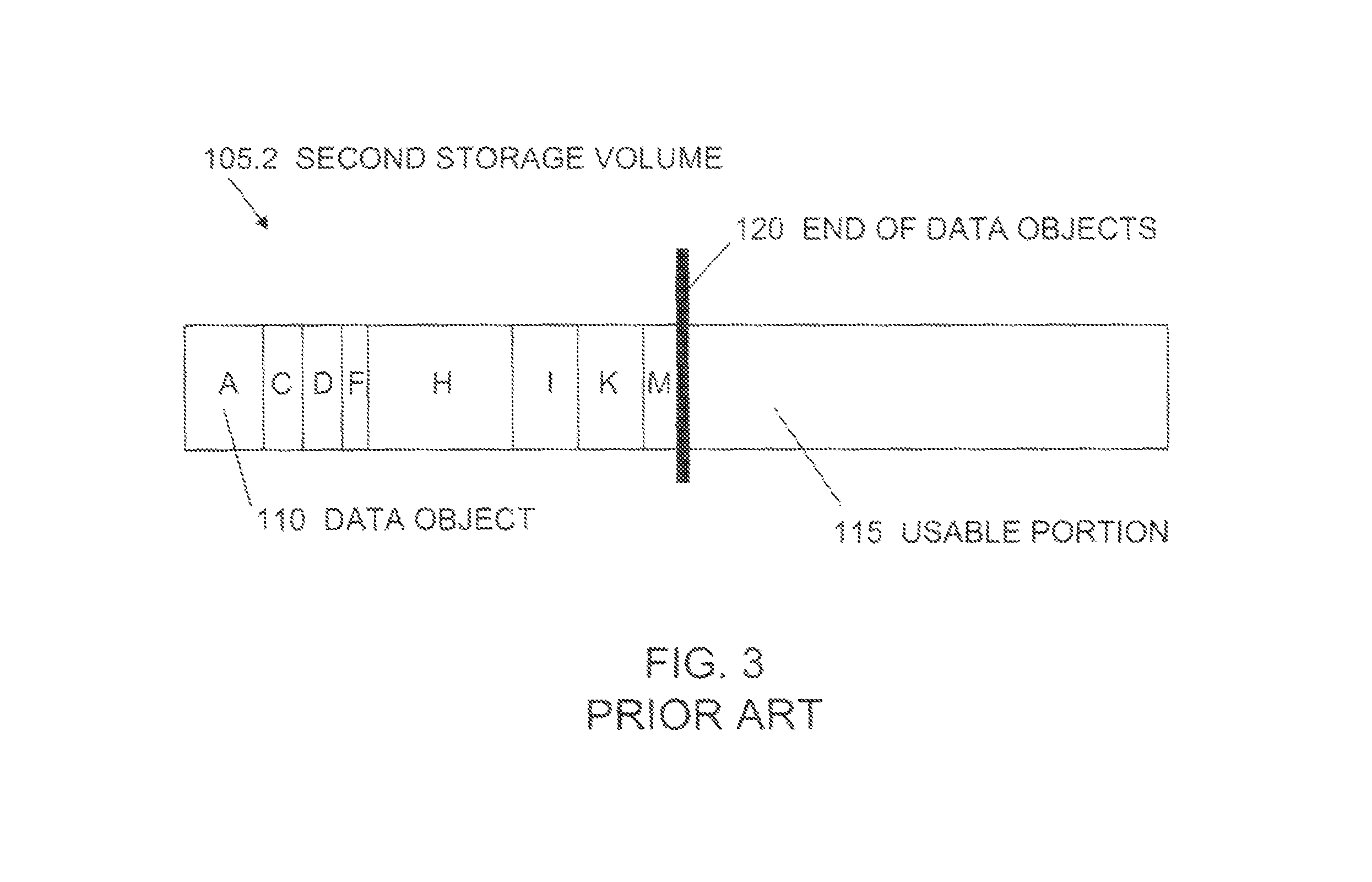
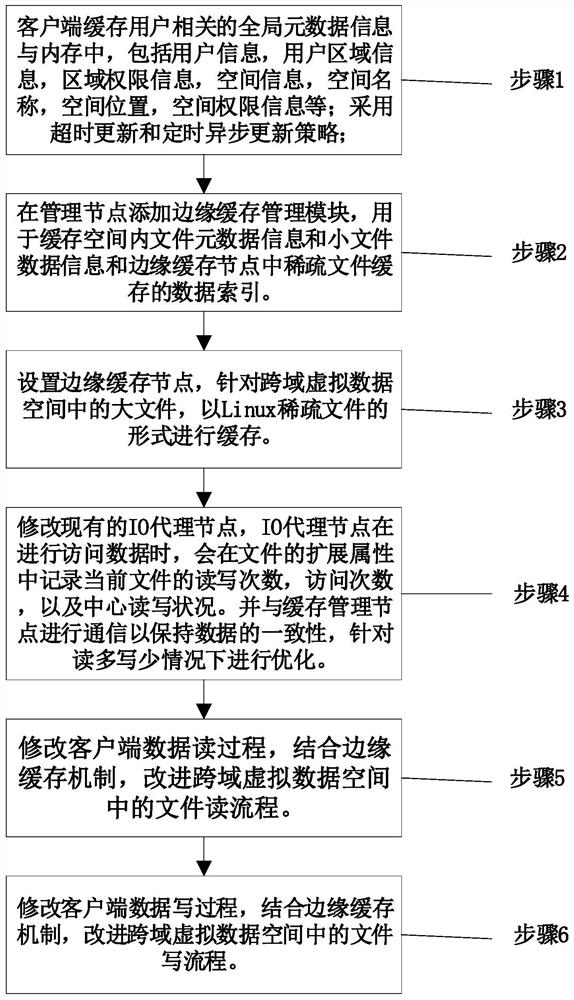
Maintenance of a file version set including read-only and read-write snapshot copies of a production file
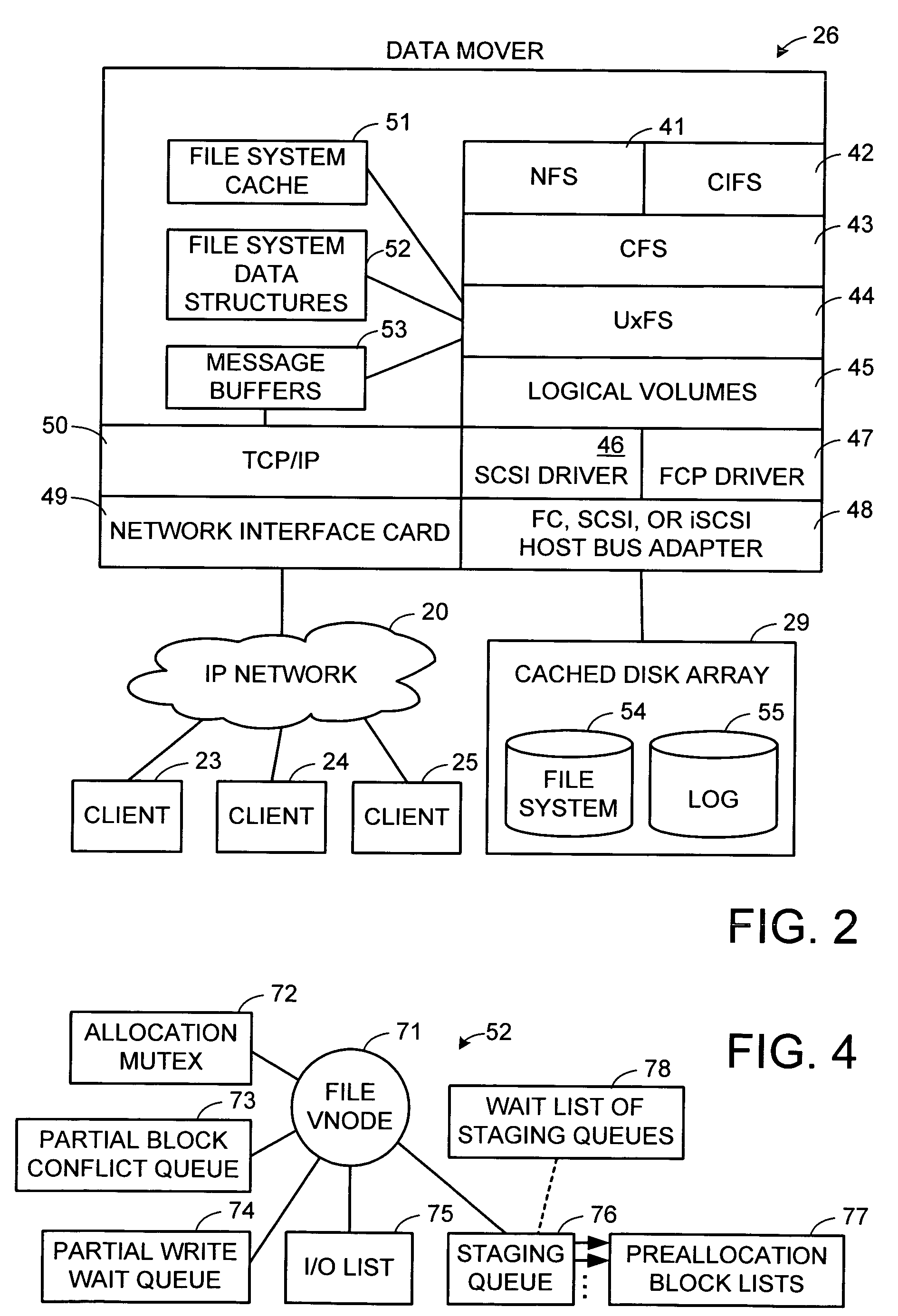
Read-only and read-write snapshot copies of a production file in a Unix-based file system are organized as a version set of file inodes and shared file blocks. Version pointers and branch pointers link the inodes. Initially the production file can have all its blocks preallocated or it can be a sparse file having only an inode and its last data block. A protocol is provided for creating read-only and read-write snapshots, deleting snapshots, restoring the production file with a specified snapshot, refreshing a specified snapshot, and naming the snapshots. Block pointers are marked with a flag indicating whether or not the pointed-to block is owned by the parent inode. A non-owner marking is inherited by all of the block's descendants. The block ownership controls the copying of indirect blocks when writing to the production file, and also controls deallocation and passing of blocks when deleting a read-only snapshot.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Maintenance of a file version set including read-only and read-write snapshot copies of a production file
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
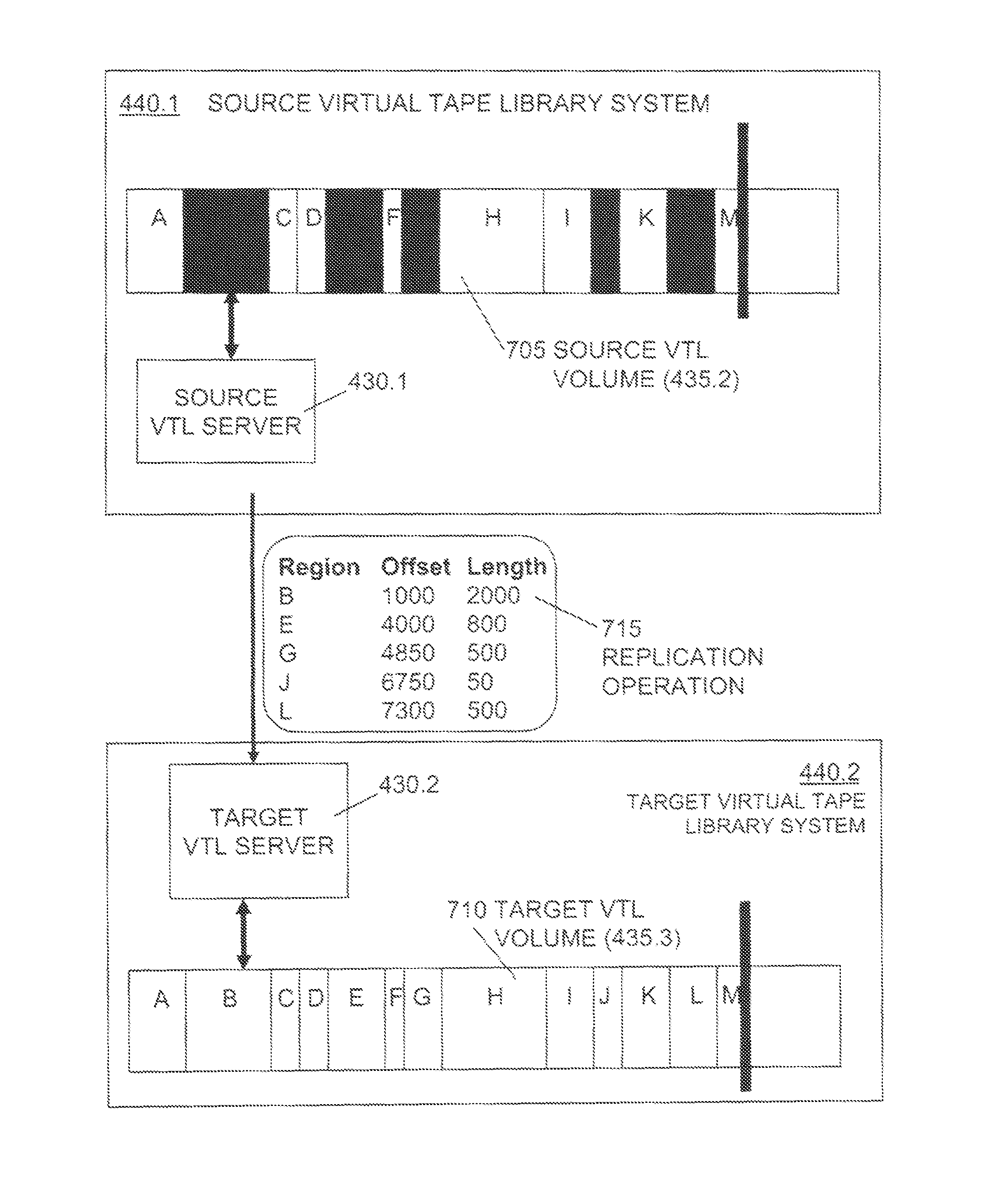
Sequential Media Reclamation and Replication
InactiveUS20080243860A1Input/output to record carriersDigital data processing detailsReplication methodParallel computing
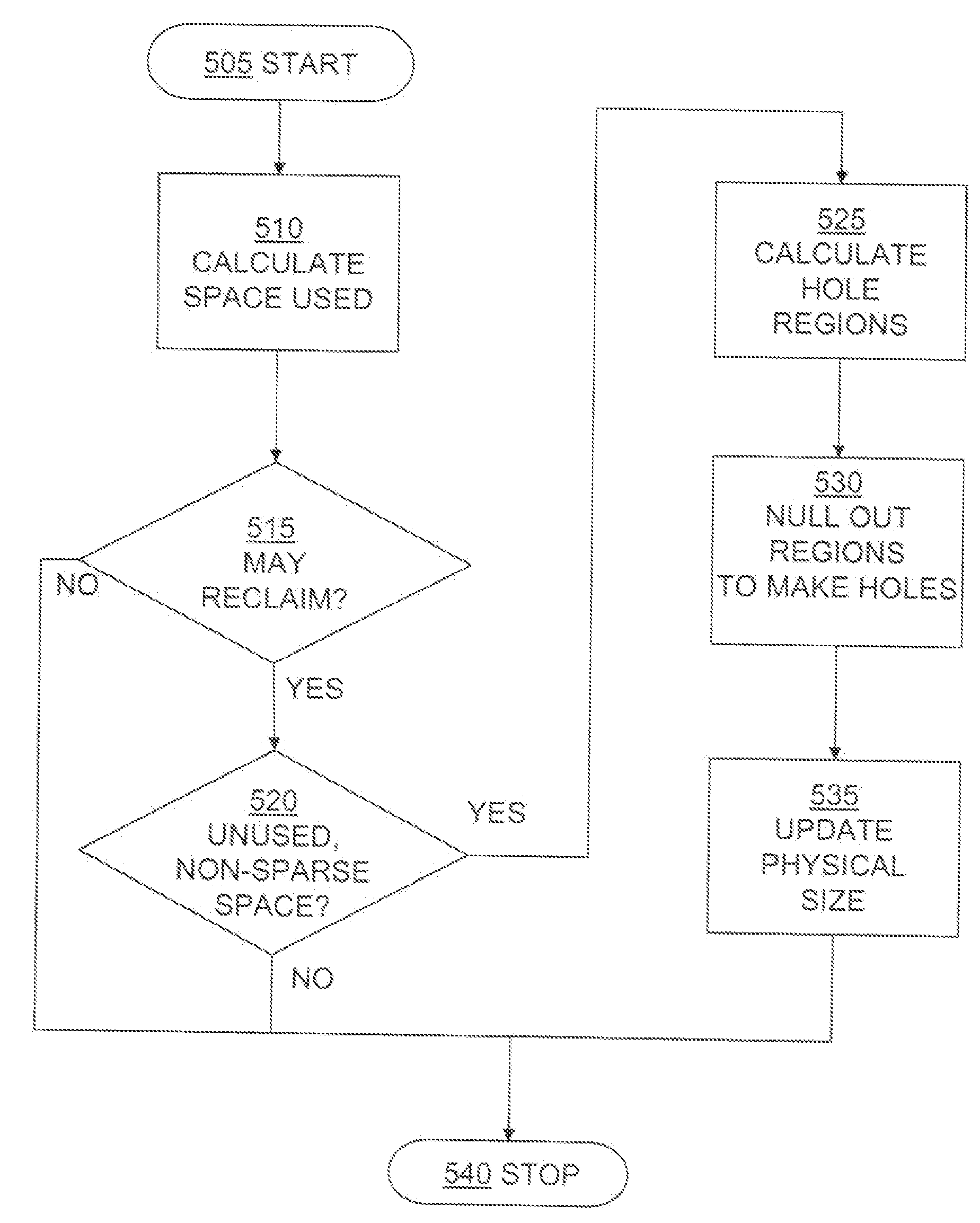
Sequential media reclamation is usually performed after portions of a sequential access volume's data are no longer needed and the unused portion of the volume exceeds a threshold. Improved sequential media reclamation is provided by using a sequential access disk volume (for example, a volume of a virtual tape library (VTL)) embodied as a sparse file. Reclamation of objects stored in the volume is accomplished by nulling out regions of the sparse file that contain the objects that are no longer needed. A replication method is also provided in which information about the objects stored in the sparse file (such as offset and length) is used during replication to enable the correct portions of a target volume (embodied as a sparse file) to be nulled out to match a source volume (also embodied as a sparse file).
Owner:IBM CORP
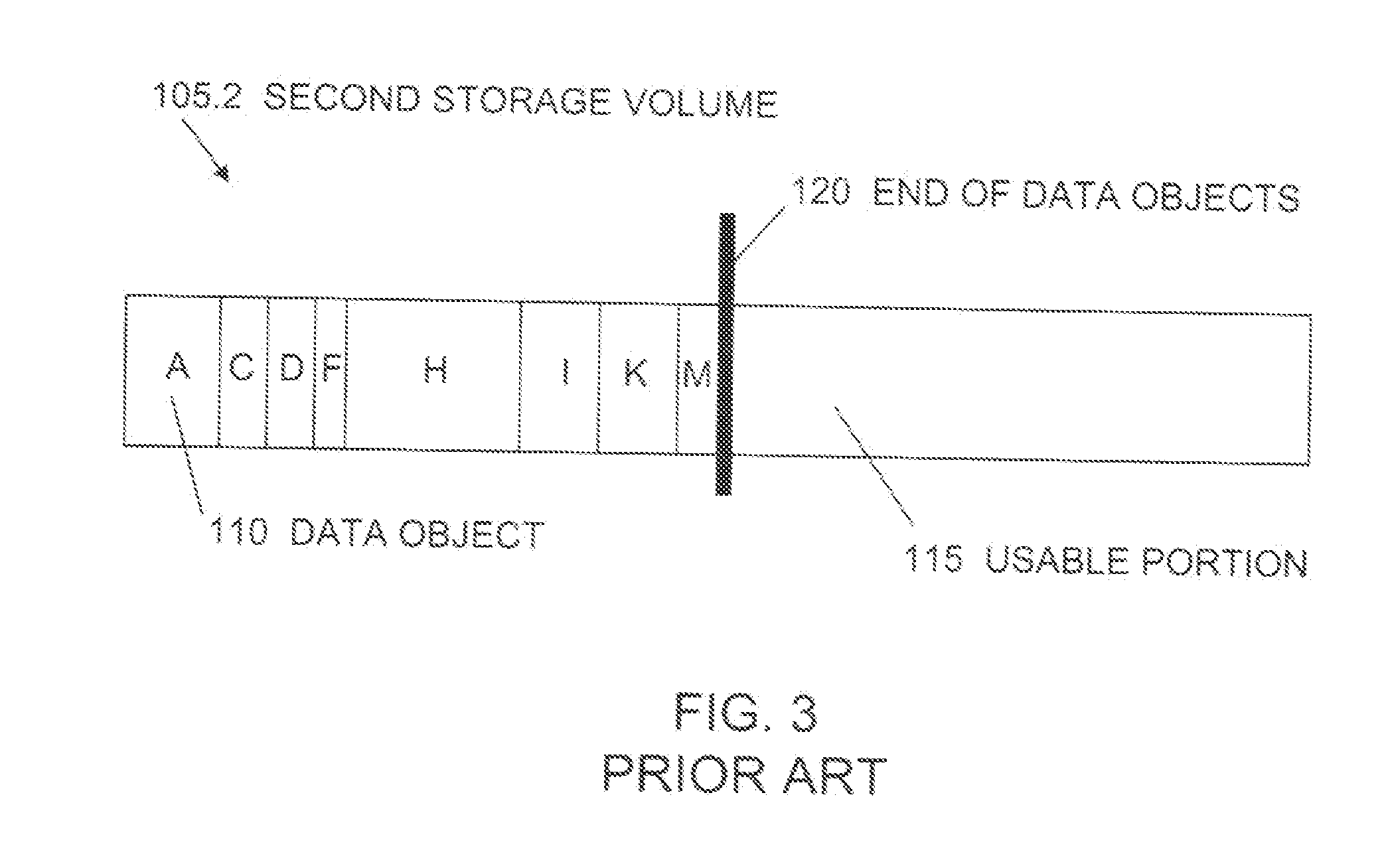
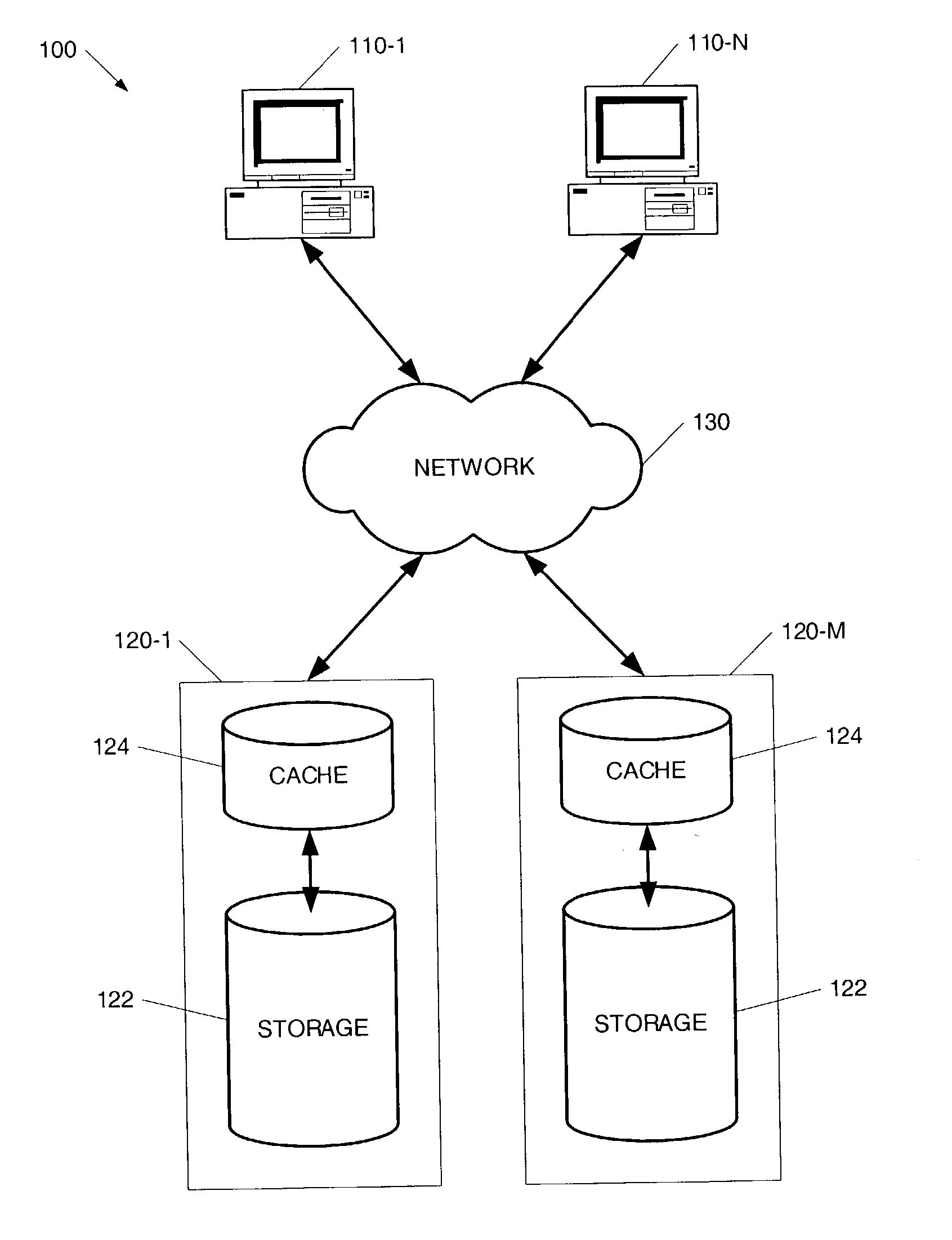
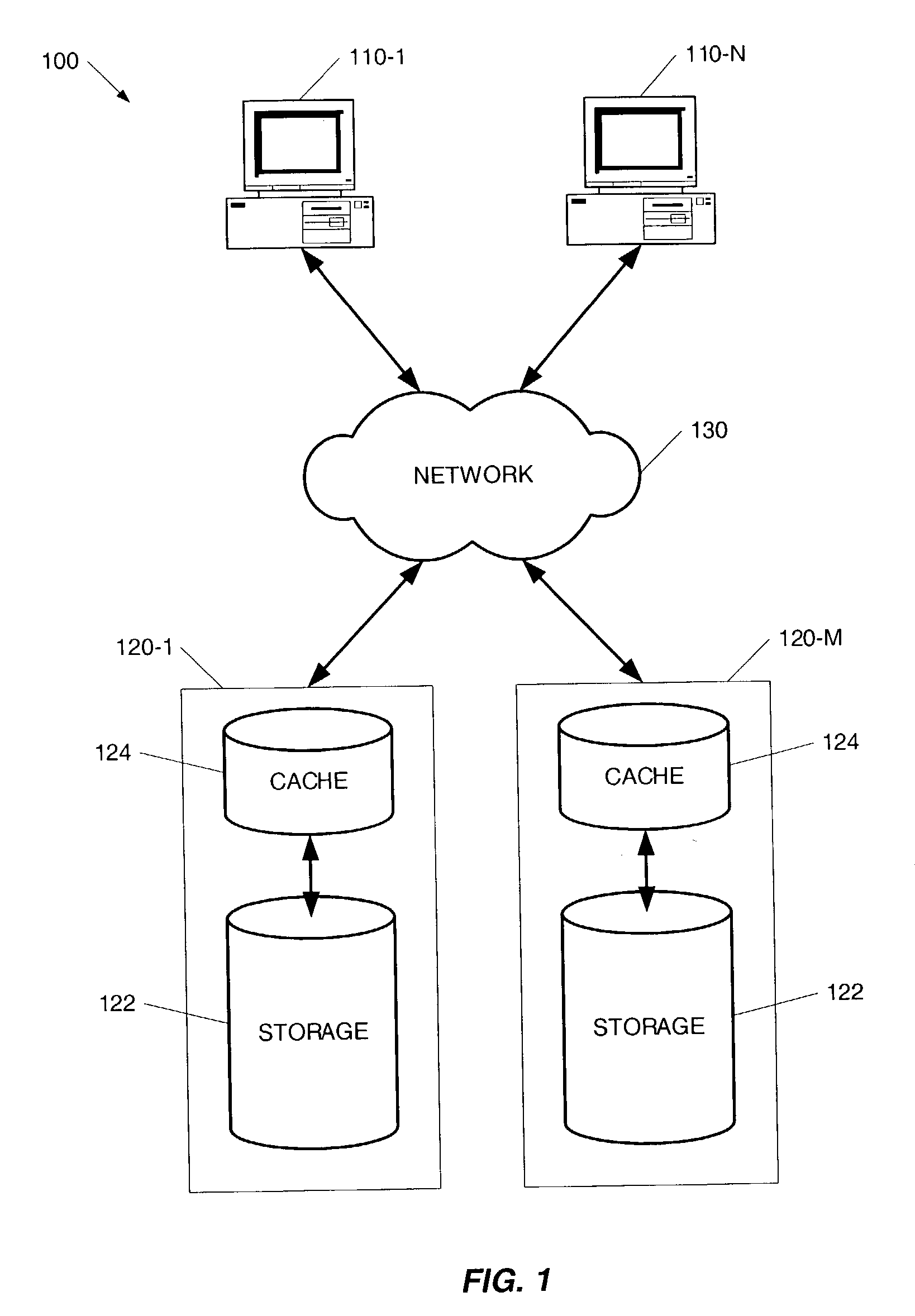
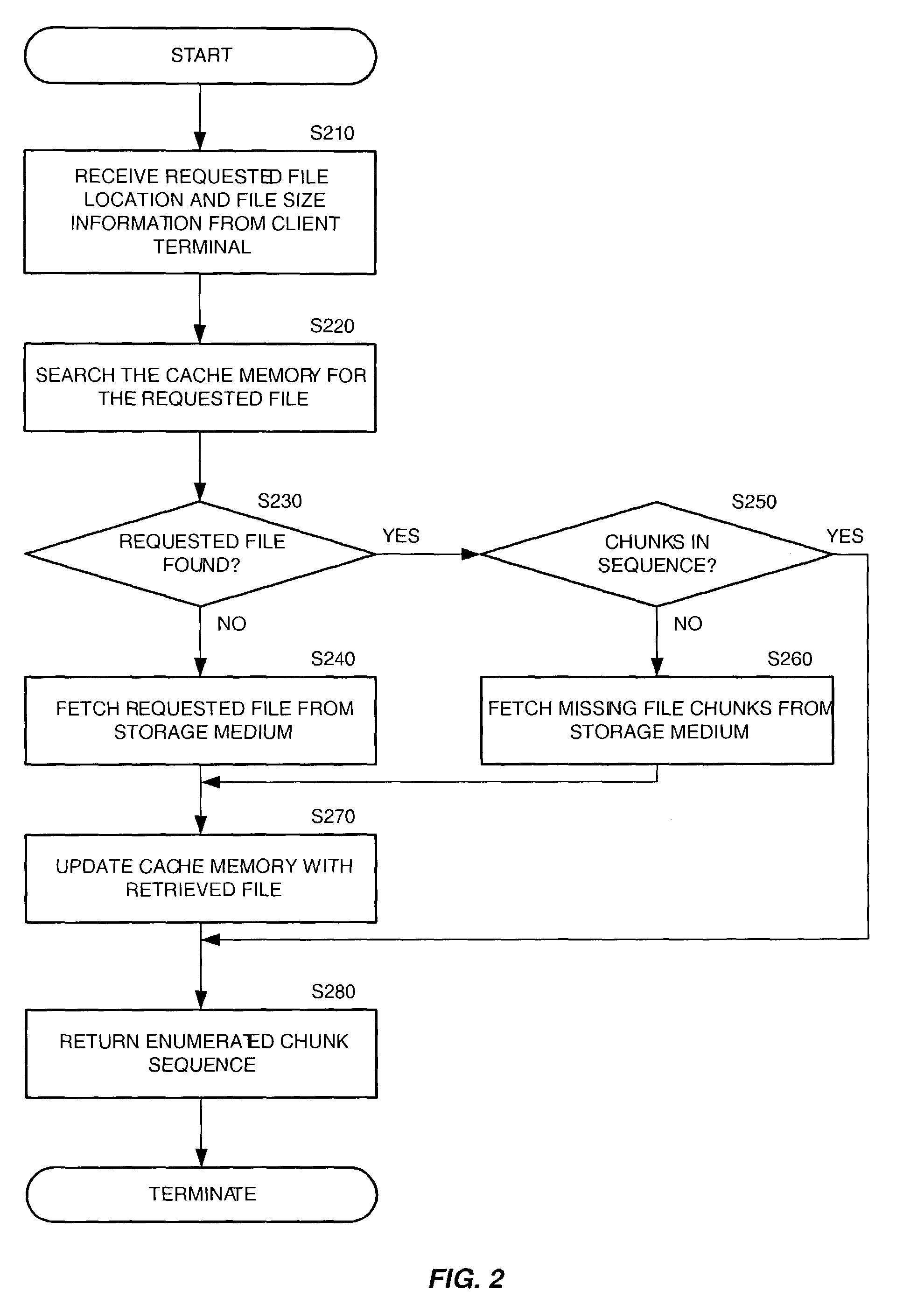
Method for efficient storing of sparse files in a distributed cache
InactiveUS20040117437A1Effective cachingMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionDistributed cacheDatabase
A method for performing efficient caching of sparse files in a distributed cache by use of an enumeration process is provided. According to the disclosed invention, the storage's objects are cached in the order that these objects are kept in the storage's directory. As a result, the directory content is enumerated in the cache, resulting in the cache not having to be associated with the server layout.
Owner:EXANET
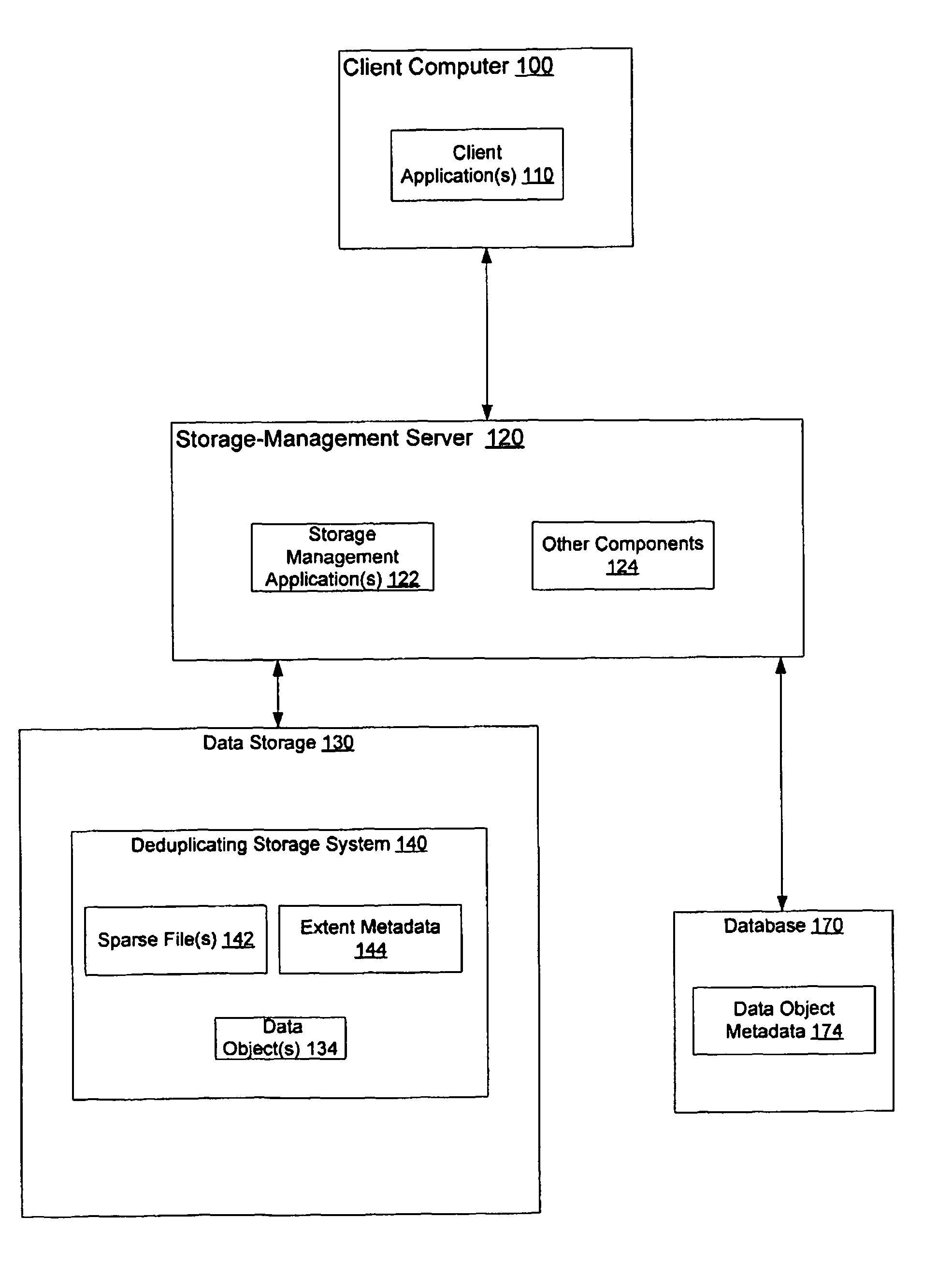
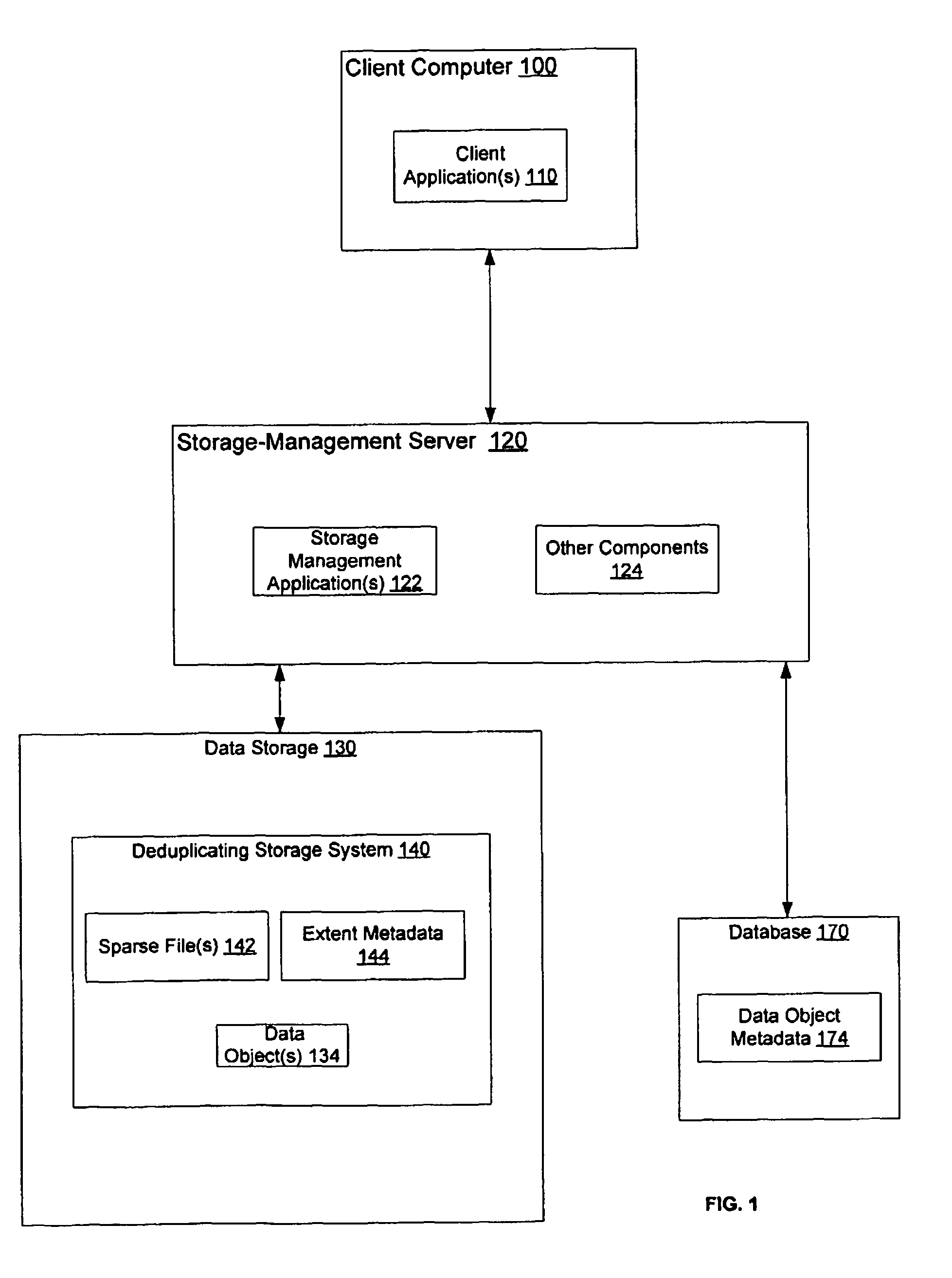
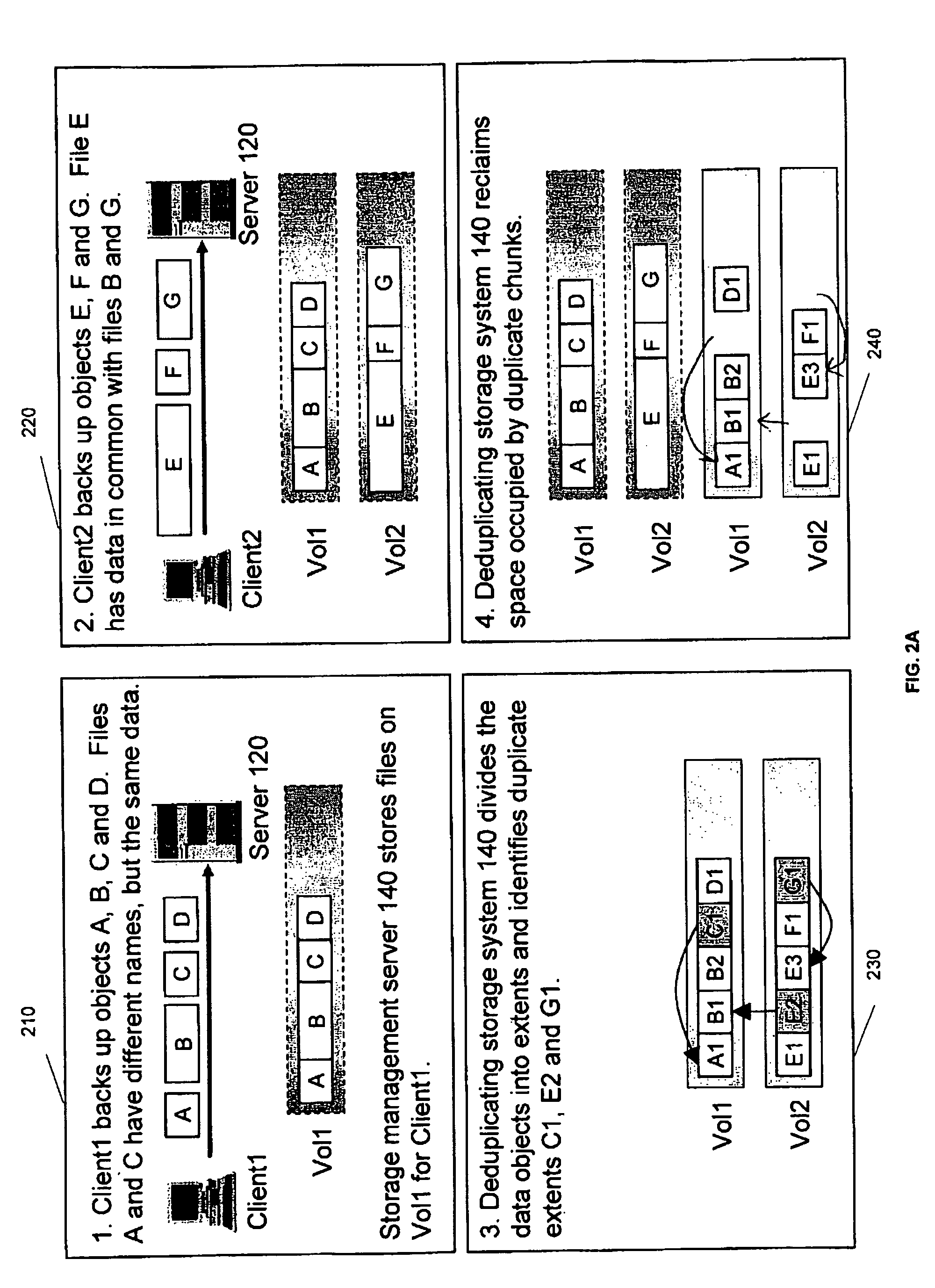
Space recovery with storage management coupled with a deduplicating storage system
InactiveUS7984022B2Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsPhysical spaceStorage management
Provided are techniques for space recovery with storage management coupled with a deduplicating storage system. A notification is received that one or more data objects have been logically deleted by deleting metadata about the one or more data objects, wherein the notification provides storage locations within one or more logical storage volumes corresponding to the deleted one or more data objects, wherein each of the one or more data objects are divided into one or more extents. In response to determining that a sparse file represents the one or more logical storage volumes, physical space is deallocated by nulling out space in the sparse file corresponding to each of the one or more extents.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
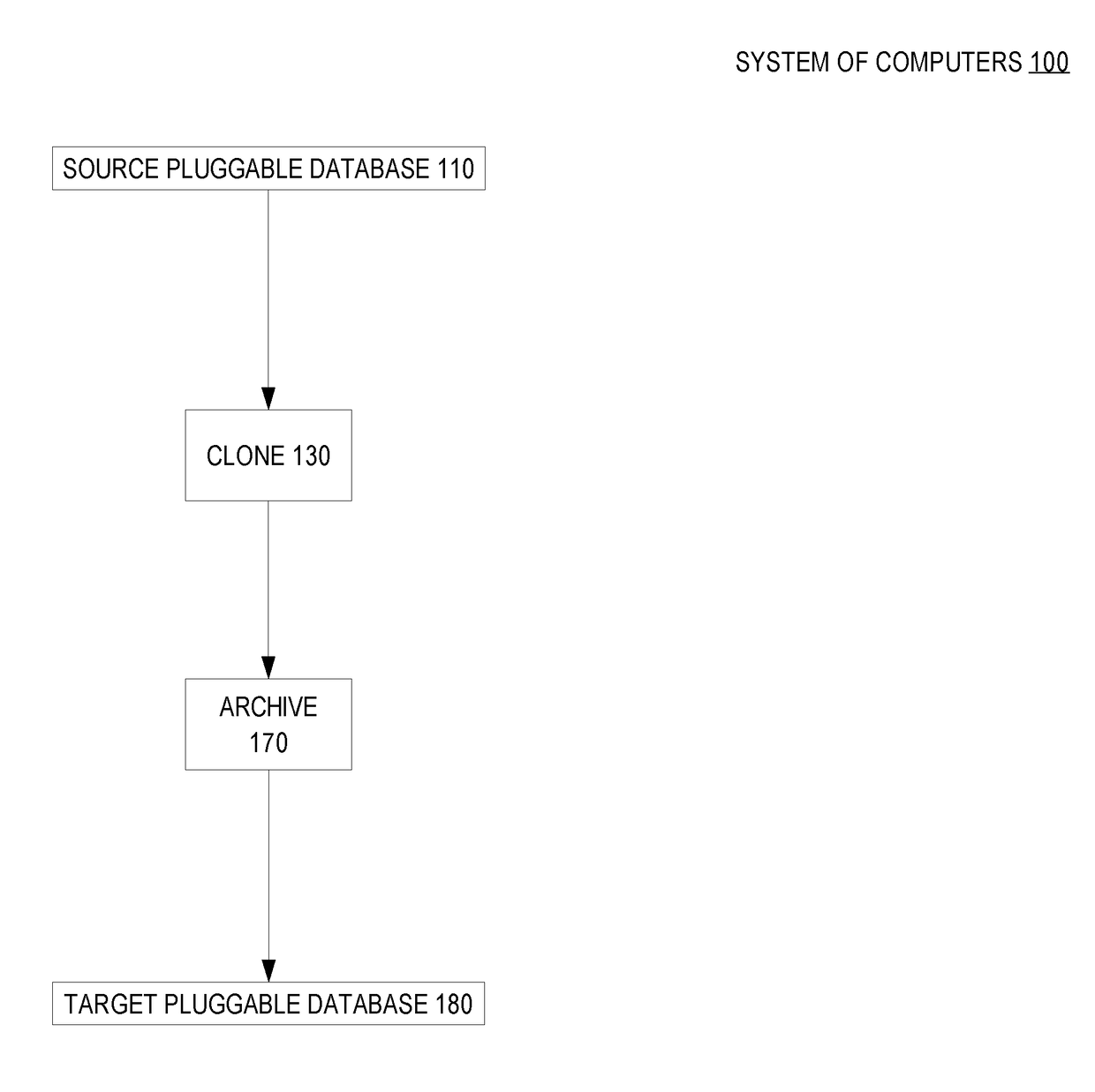
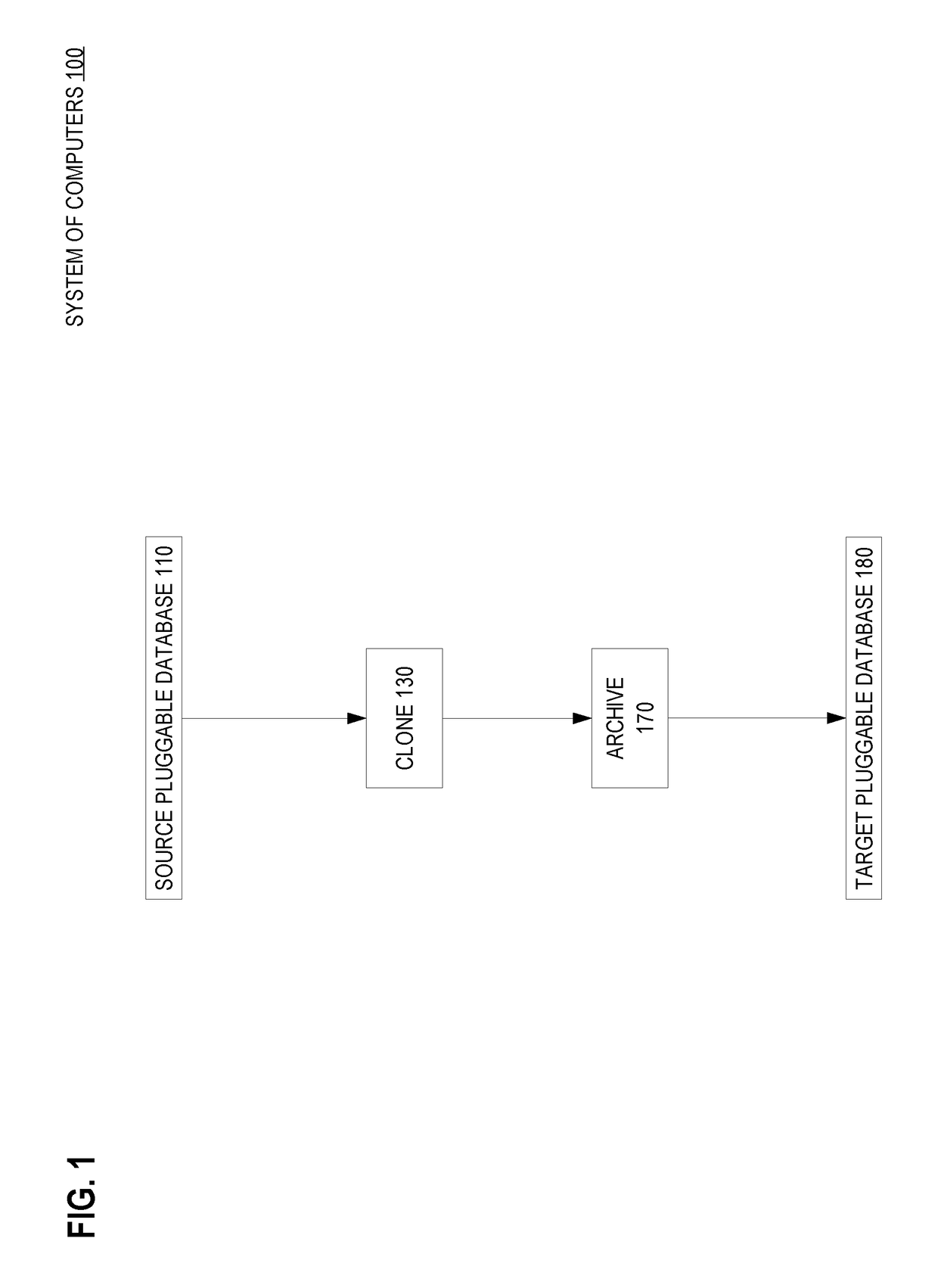
Periodic snapshots of a pluggable database in a container database
ActiveUS20180075041A1Less storageCreate additionalDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsDatabase serverTarget database
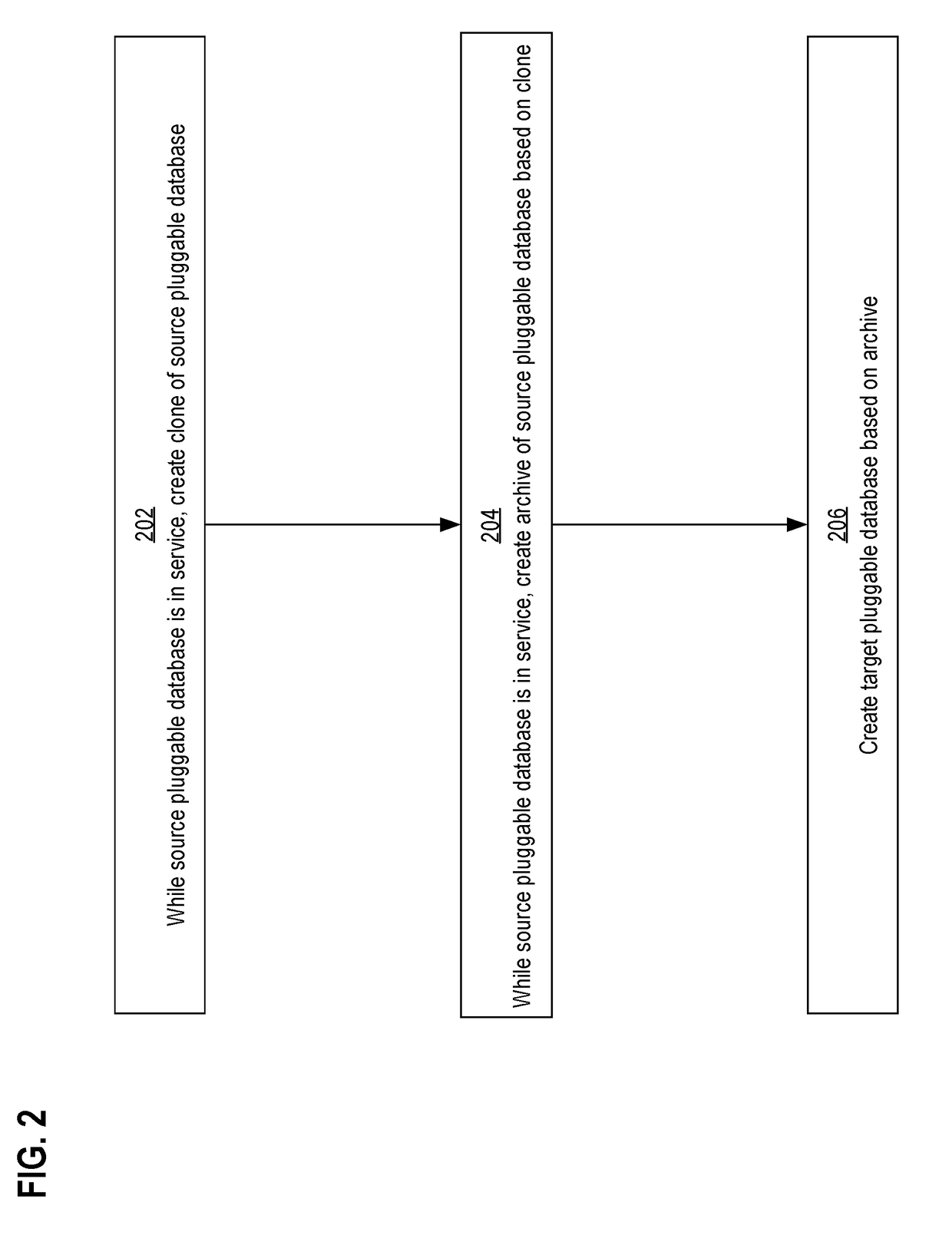
Techniques are provided for using a sparse file to create a hot archive of a pluggable database of a container database. In an embodiment and while a source pluggable database is in service, a source database server creates a clone of the source pluggable database. Also while the source pluggable database is in service, the source database server creates an archive of the source pluggable database that is based on the clone. Eventually, a need arises to consume the archive. A target database server (which may also be the source database server) creates a target pluggable database based on the archive.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
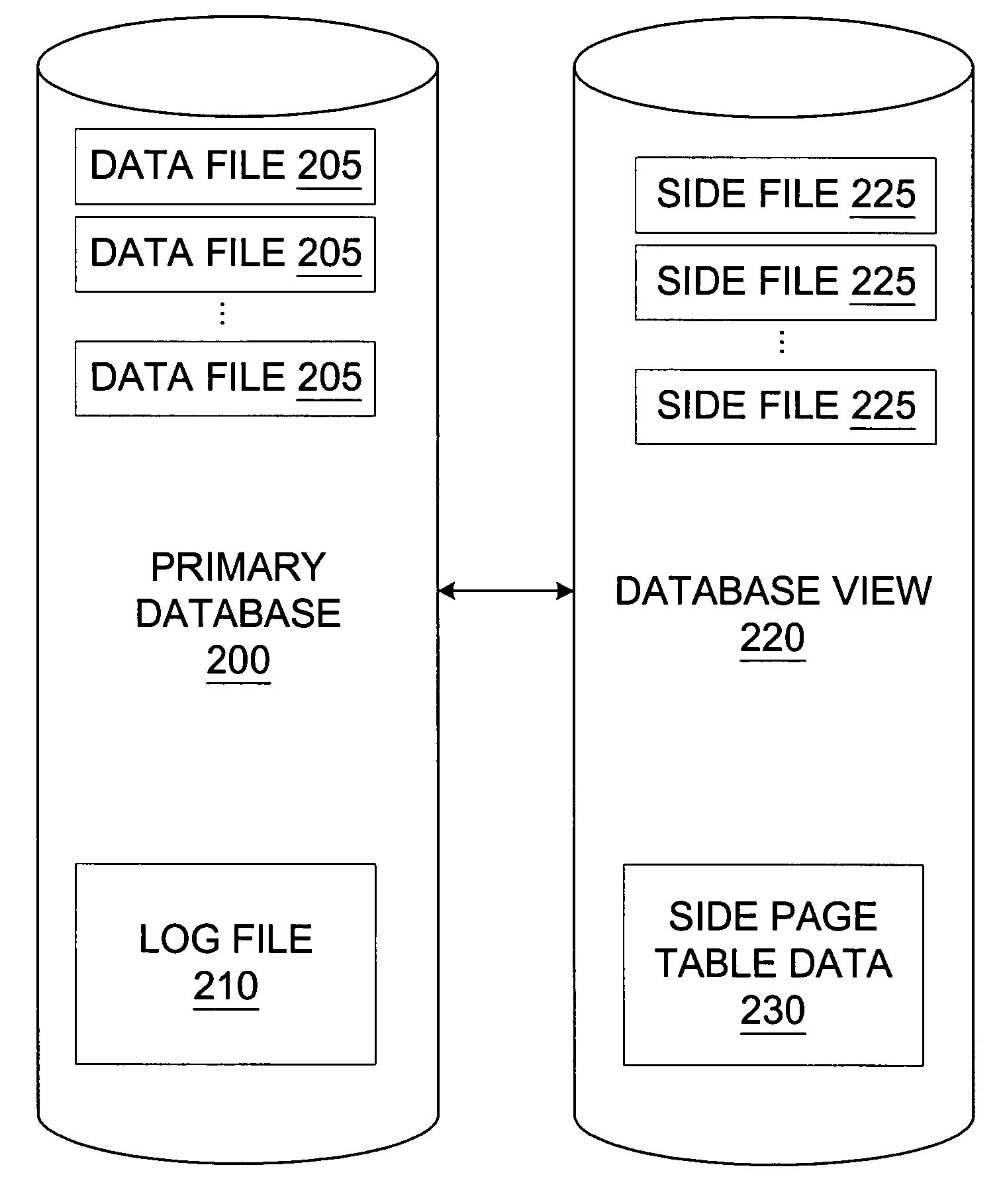
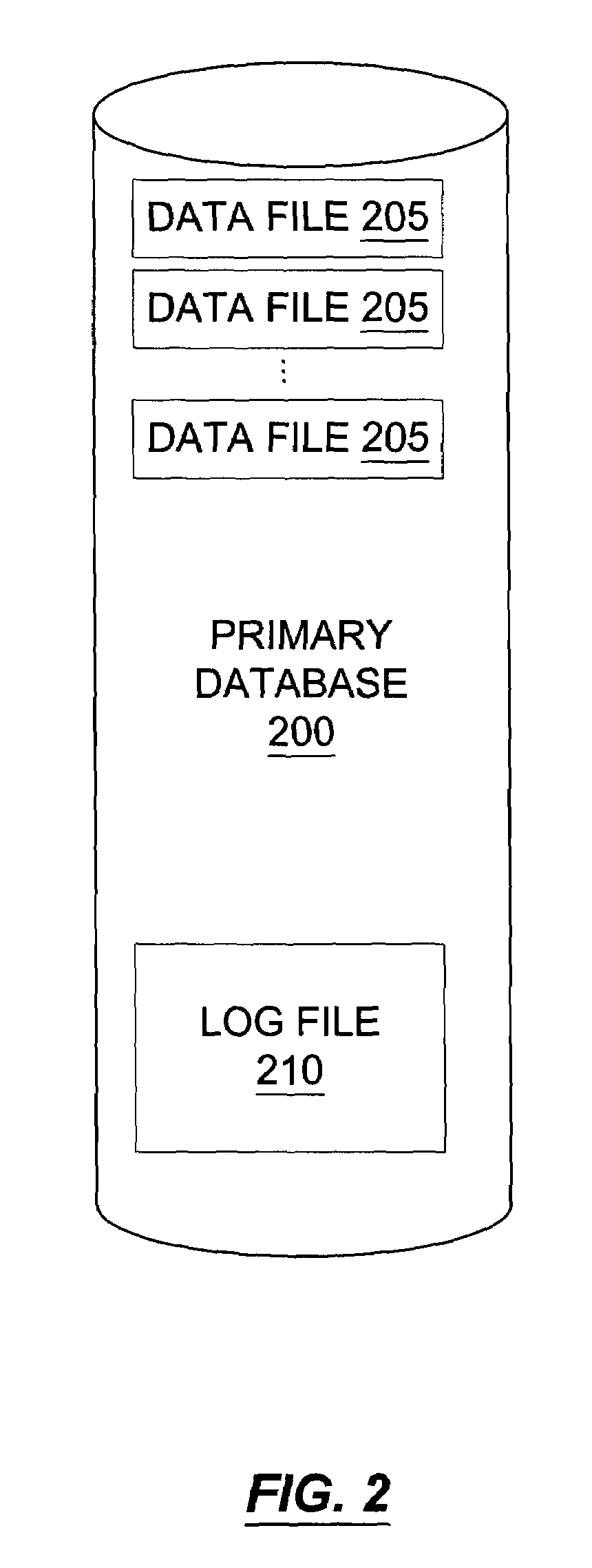
Transaction consistent copy-on-write database
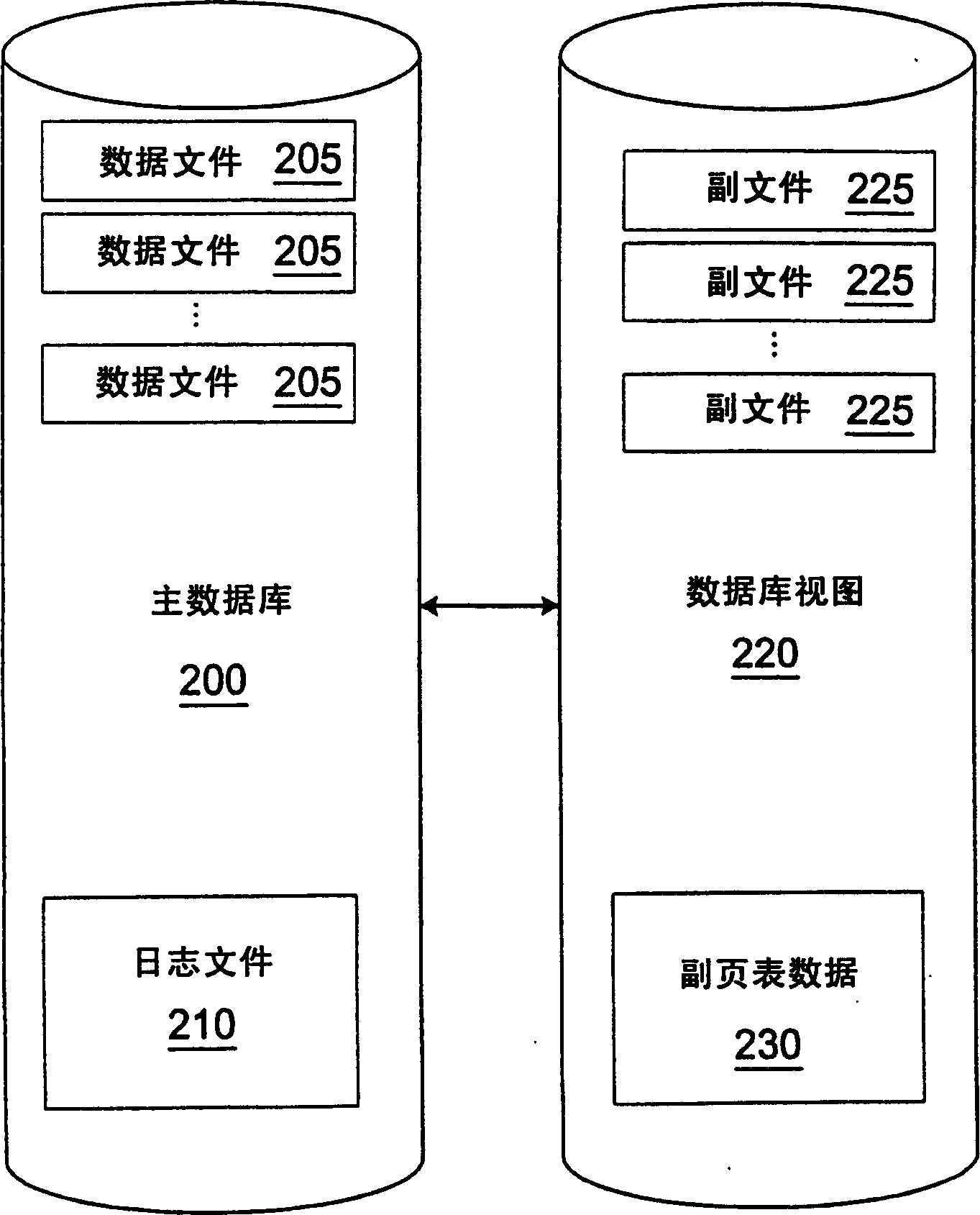
A database view of a database is created which provides a transaction-consistent view of an existing database at a previous time. Each database view contains all the information needed to, along with the primary database, determine the contents of the primary database at a previous time. The database view consists of a side file corresponding to each data file in the primary database. The side files contain a copy of all data from the corresponding data file which has been changed since the database view was created. Sparse files may be used for the side files in order to conserve space. Page table data is kept in order to allow a quick determination as to whether the page from the primary database has been modified and the old version stored in the database view side file.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and device for quickly verifying consistency of multi-duplicate storage
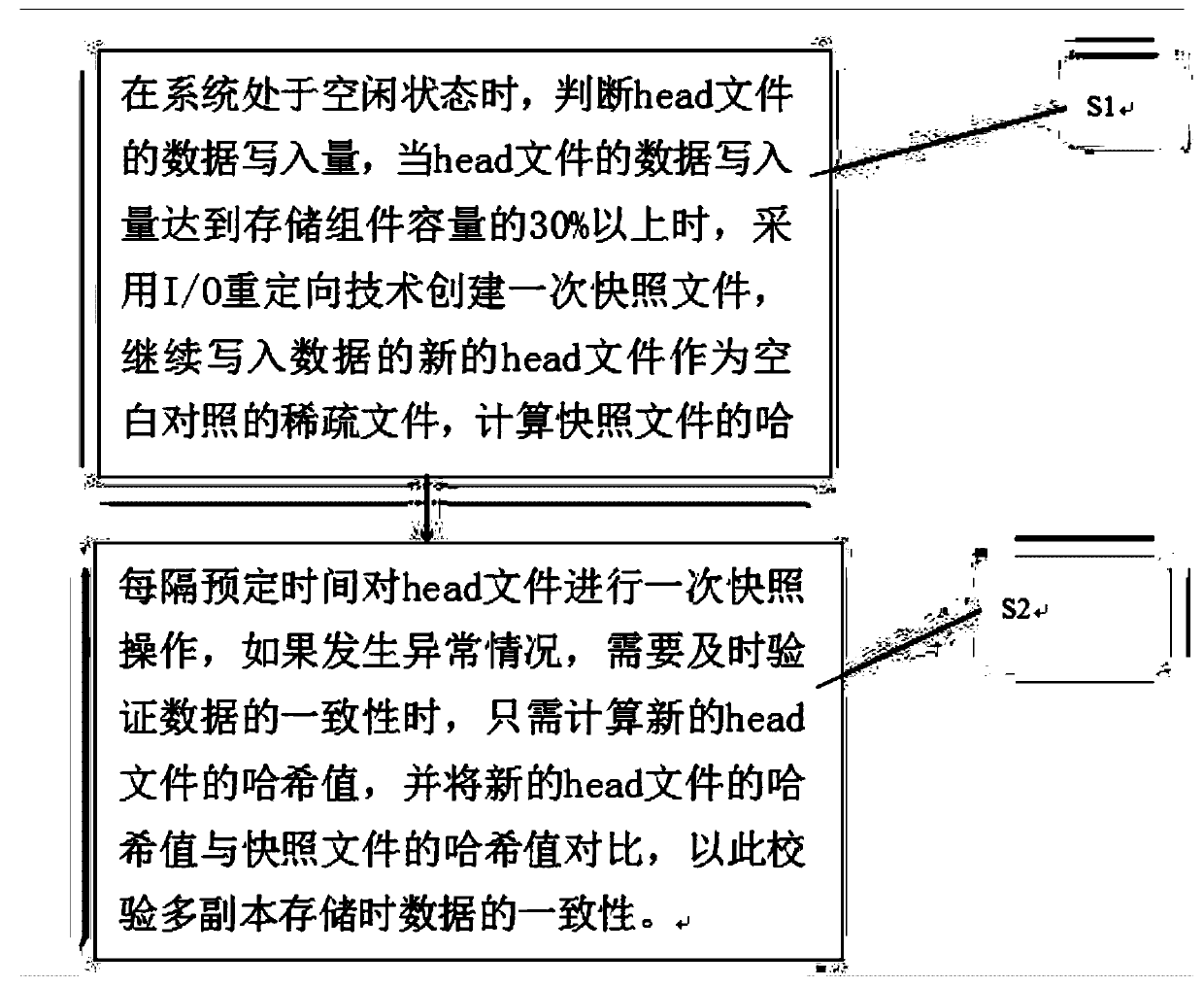
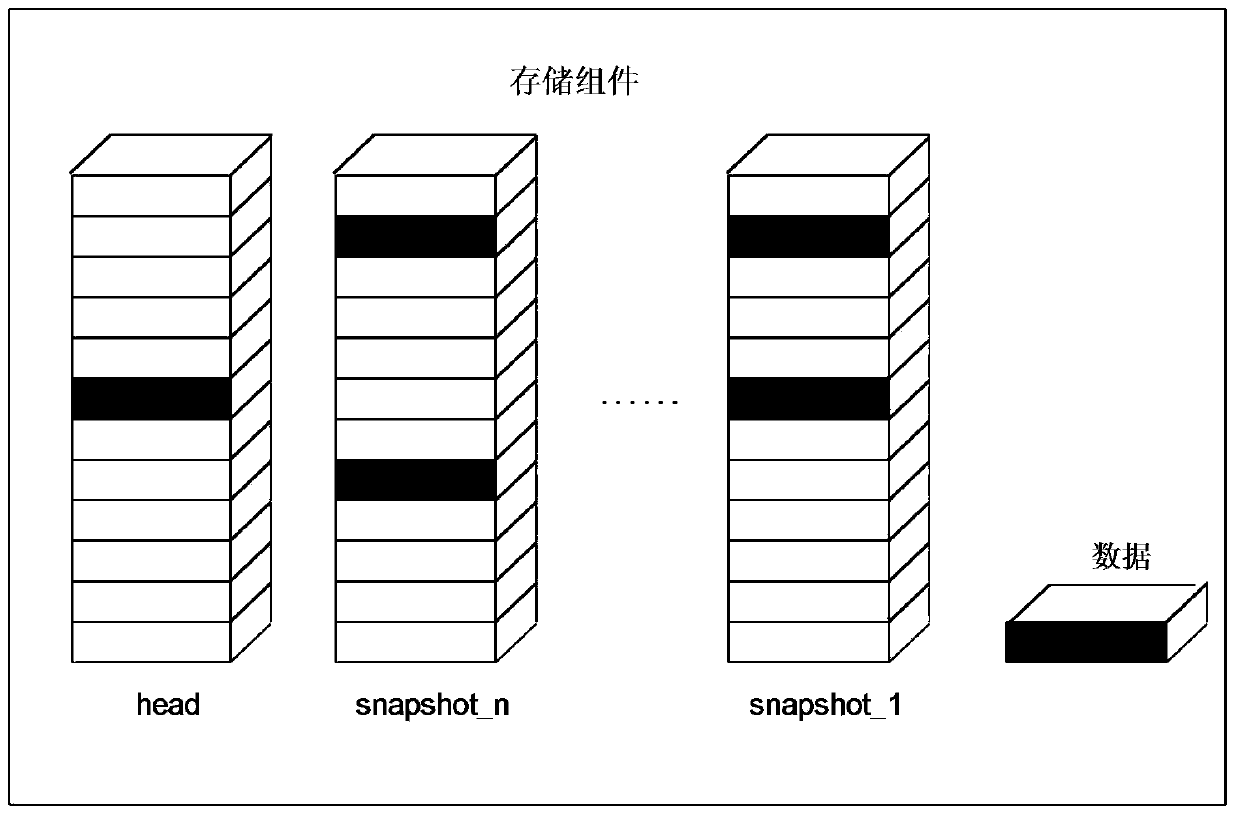
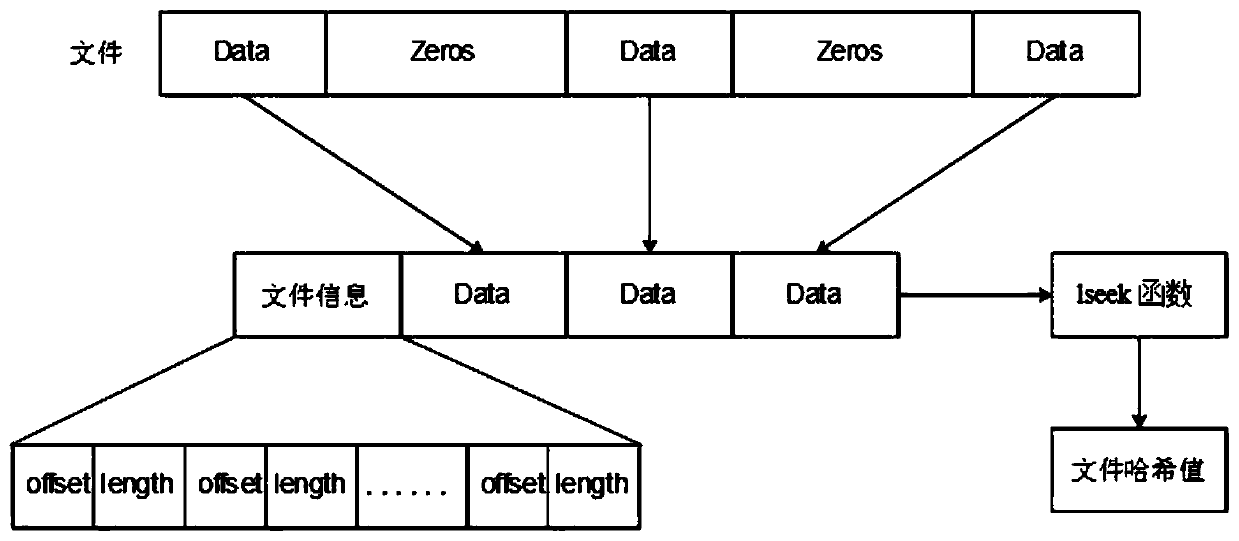
InactiveCN107203345AAvoid affecting the reading and writing businessInput/output to record carriersFault responseData needsSparse file
The invention provides a method and a device for quickly verifying the consistency of multi-duplicate storage. The method includes S1, judging data writing volumes of head files when systems are in idle states, creating snapshot files by the aid of I / O (input / output) redirection technologies when the volumes of data written into the head files reach 30% of the volumes of integral spare files at least, utilizing new head files with continuously written data as null comparison sparse files, computing hash values of the snapshot files and storing the hash values of the snapshot files as extended attributes; S2, carrying out snapshot operation on the head files once at intervals of preset time and comparing hash values of the new head files to the hash values of the snapshot files when the consistency of multi-duplicate data need to be timely verified. The method and the device have the advantages that characteristics of distributed block storage are combined with one another, the method for quickly detecting the consistency of multiple duplicates on the basis of snapshot technologies is proposed, hash value computation tasks are divided to be carried out in multiple time slots, accordingly, influence on normal reading and writing tasks of the systems can be prevented, and the multi-duplicate storage consistency verification speeds can be increased.
Owner:深圳市联云港科技有限公司
Sequential media reclamation and replication
InactiveUS8738588B2Input/output to record carriersDigital data processing detailsReplication methodParallel computing
Sequential media reclamation is usually performed after portions of a sequential access volume's data are no longer needed and the unused portion of the volume exceeds a threshold. Improved sequential media reclamation is provided by using a sequential access disk volume (for example, a volume of a virtual tape library (VTL)) embodied as a sparse file. Reclamation of objects stored in the volume is accomplished by nulling out regions of the sparse file that contain the objects that are no longer needed. A replication method is also provided in which information about the objects stored in the sparse file (such as offset and length) is used during replication to enable the correct portions of a target volume (embodied as a sparse file) to be nulled out to match a source volume (also embodied as a sparse file).
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
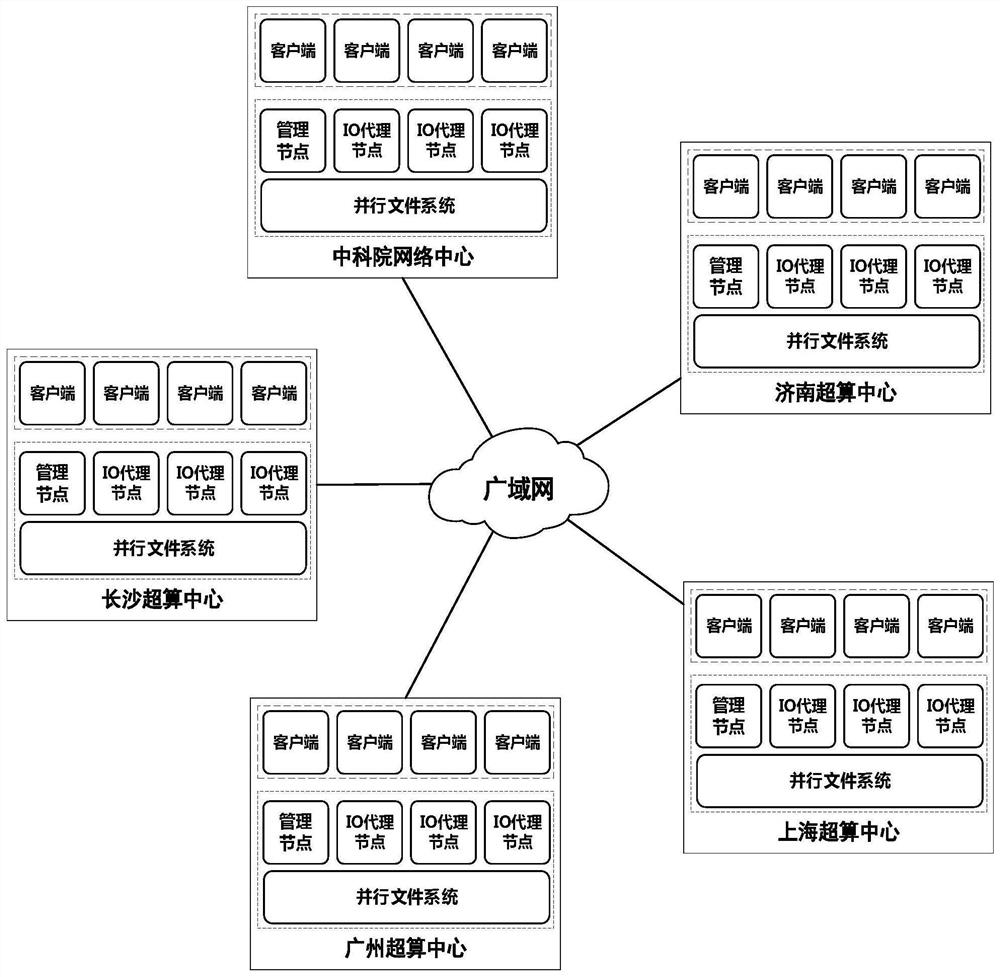
File data edge caching method in cross-domain virtual data space
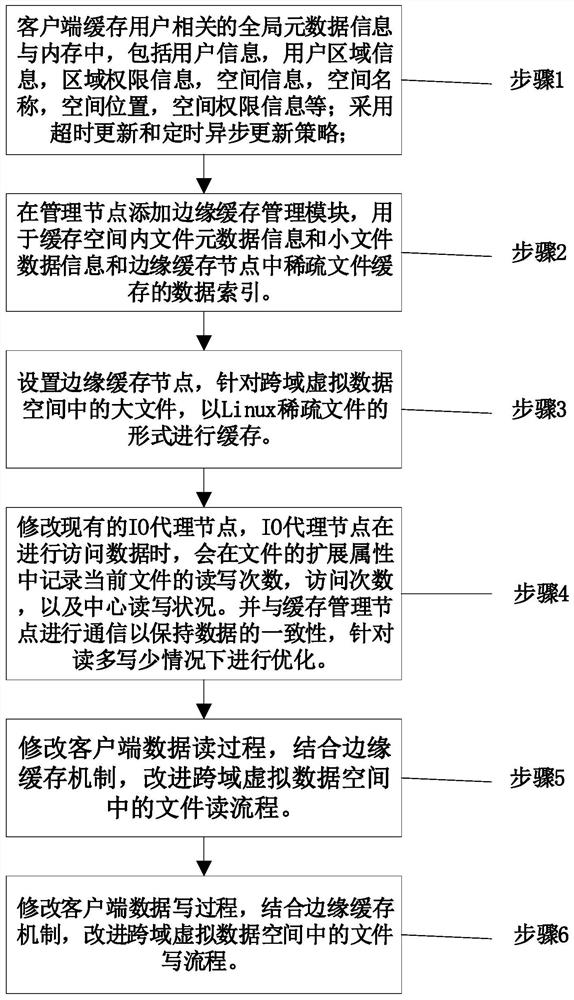
ActiveCN111782612AImprove consistencyReduce transfer volumeDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemParallel computing
The invention provides a file data edge caching method in a cross-domain virtual data space, and provides an edge caching mechanism for the file data in allusion to the requirement of efficient accessof remote data in the cross-domain virtual data space and the IO bottleneck problem brought to an upper-layer application by a wide-area environment. The method comprises the following steps: cachingremote data in a place close to a client, establishing an edge cache to improve the overall performance of accessing the remote data by an upper application, and further reducing data redundancy through cache sharing; the edge cache establishes a memory-based file cache for the small file, and establishes a sparse file-based file system cache for the large file; the consistency of data in the virtual data space is improved by adopting a caching strategy of a central read-write mark based on file extension attributes; and through a cache replacement strategy based on the file popularity, the cache performance and efficiency are ensured.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
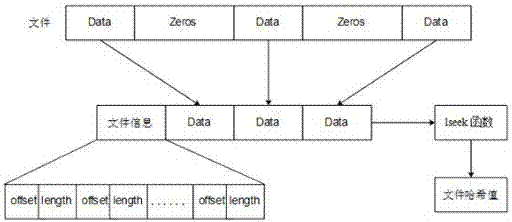
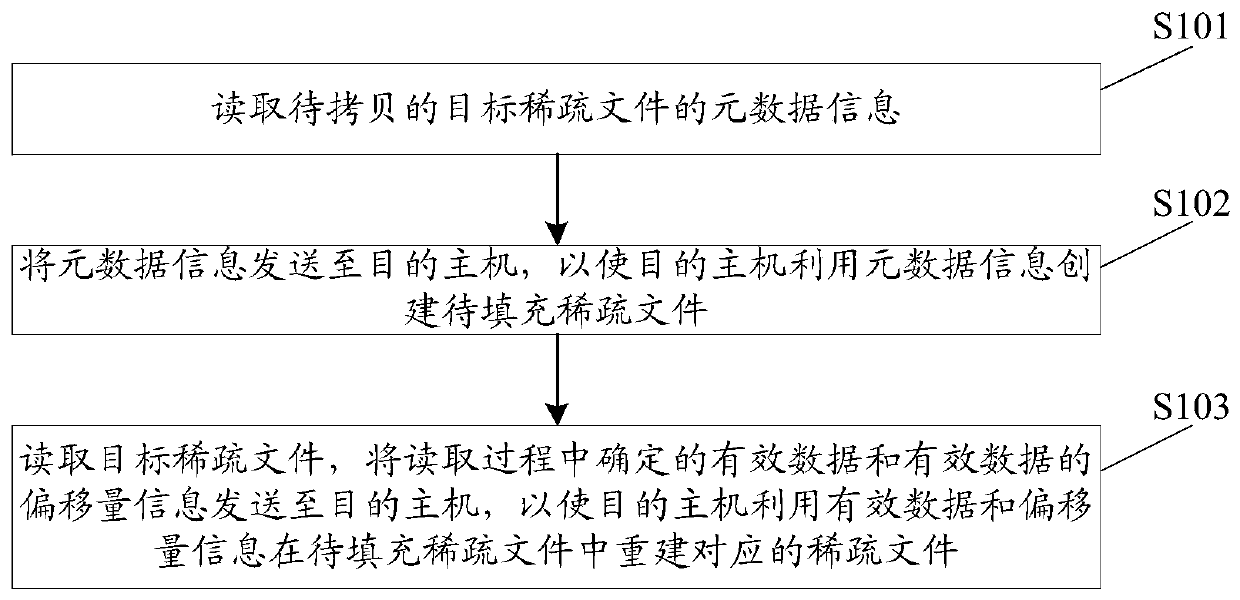
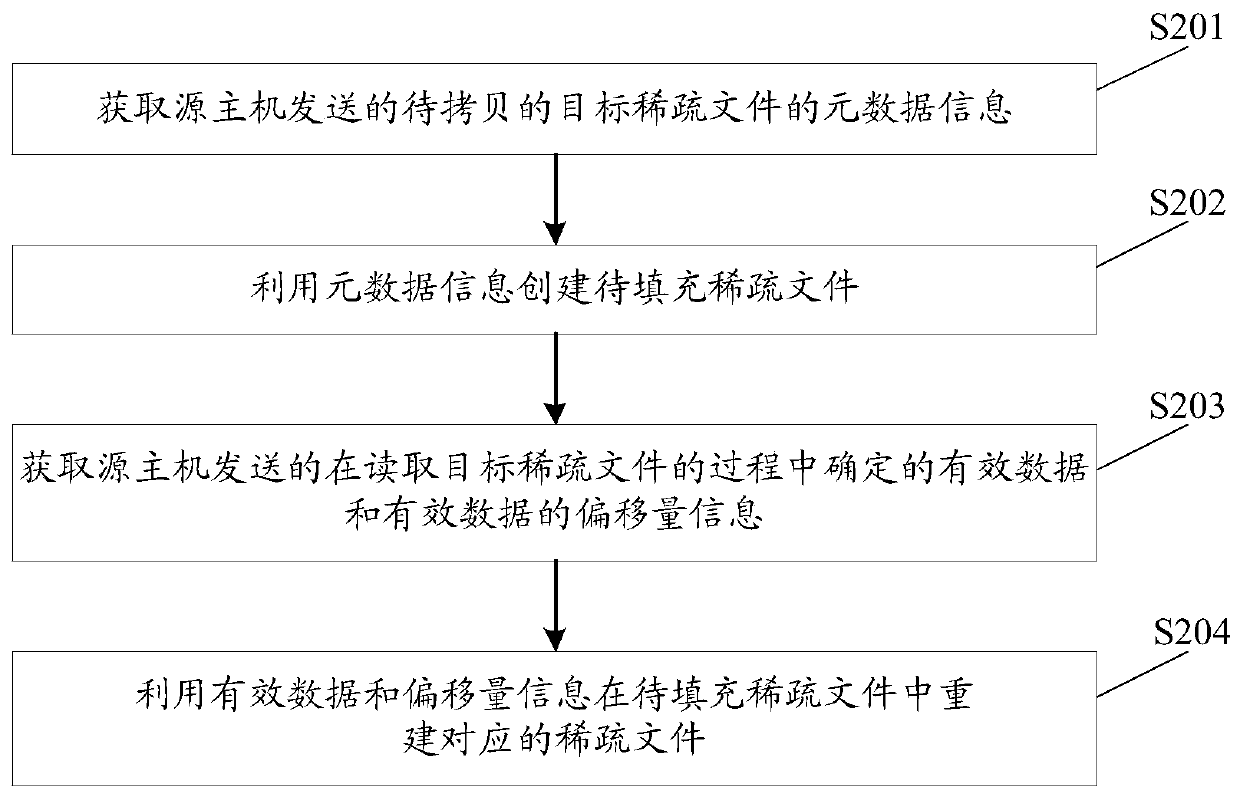
Cross-host sparse file copying method and device, equipment and storage medium
InactiveCN110888843ACopy implementationIncrease copy rateInput/output to record carriersFile/folder operationsComputer hardwareEngineering
The invention discloses a cross-host sparse file copying method, device and equipment and a computer storage medium. In the scheme, a source host reads metadata information of a to-be-copied target sparse file and then sends the metadata information to a target host, and the target host creates the to-be-filled sparse file by utilizing the metadata information; and the source host reads the targetsparse file, and sends the valid data determined in the reading process and the offset information of the valid data to the destination host, so that the destination host reconstructs the corresponding sparse file in the to-be-filled sparse file by using the valid data and the offset information. It can be seen that after the source host sends the effective data and the offset information of thesparse file to the target host, the target host can reconstruct the corresponding sparse file through the effective data and the offset information, and therefore cross-host copying of the sparse fileis achieved; moreover, only effective data is copied when the sparse file is copied, so that the file copying rate can be increased.
Owner:北京浪潮数据技术有限公司
Achieving method of high-performance elastic-capacity virtual machine disk
InactiveCN103324446ASave storage spaceLow costInput/output to record carriersSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemCloud computing
The invention relates to an achieving method of a high-performance elastic-capacity virtual machine disk. The achieving method is characterized by being achieved according to a sparse file mechanism, a logical volume management mechanism and a virtual machine disk aligning principle. The achieving method comprises the steps of (1) adopting the sparse file mechanism to achieve the elastic-capacity virtual machine disk, (2) adopting the logical volume management (LVM) mechanism to achieve on-line capacity expansion of a disk space, (3) adopting the virtual machine disk aligning principle. By means of the achieving method, at least more than 50% of memory space can be greatly saved in a cloud computing environment. In addition, the input-output (IO) performance of the virtual machine disk reaches to more than 90% of the IO performance of a physical file system.
Owner:DAWNING INFORMATION IND BEIJING
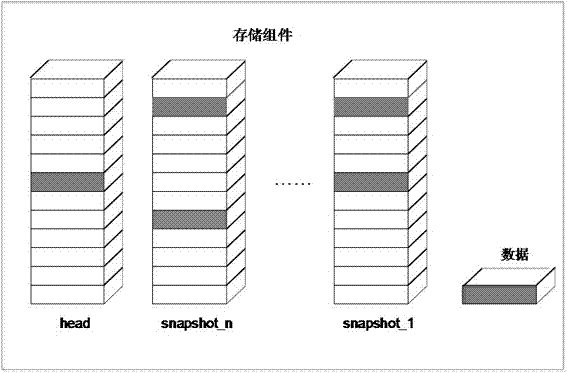
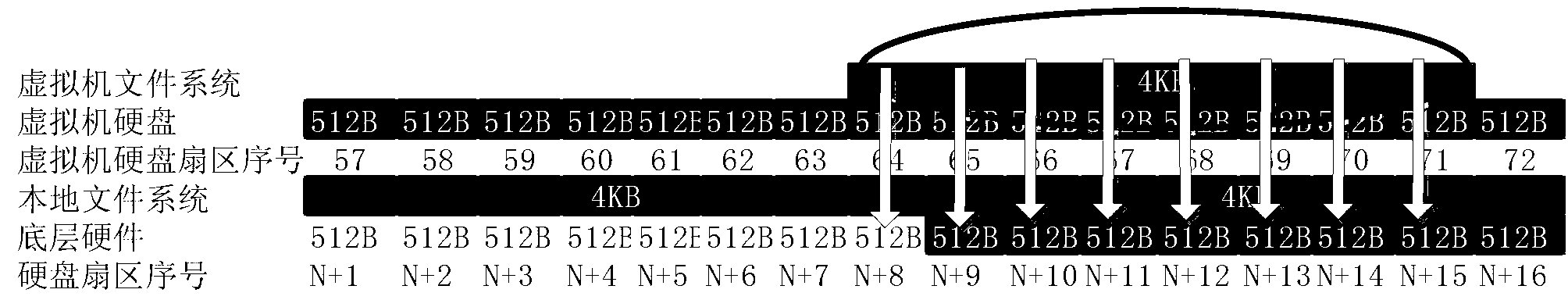
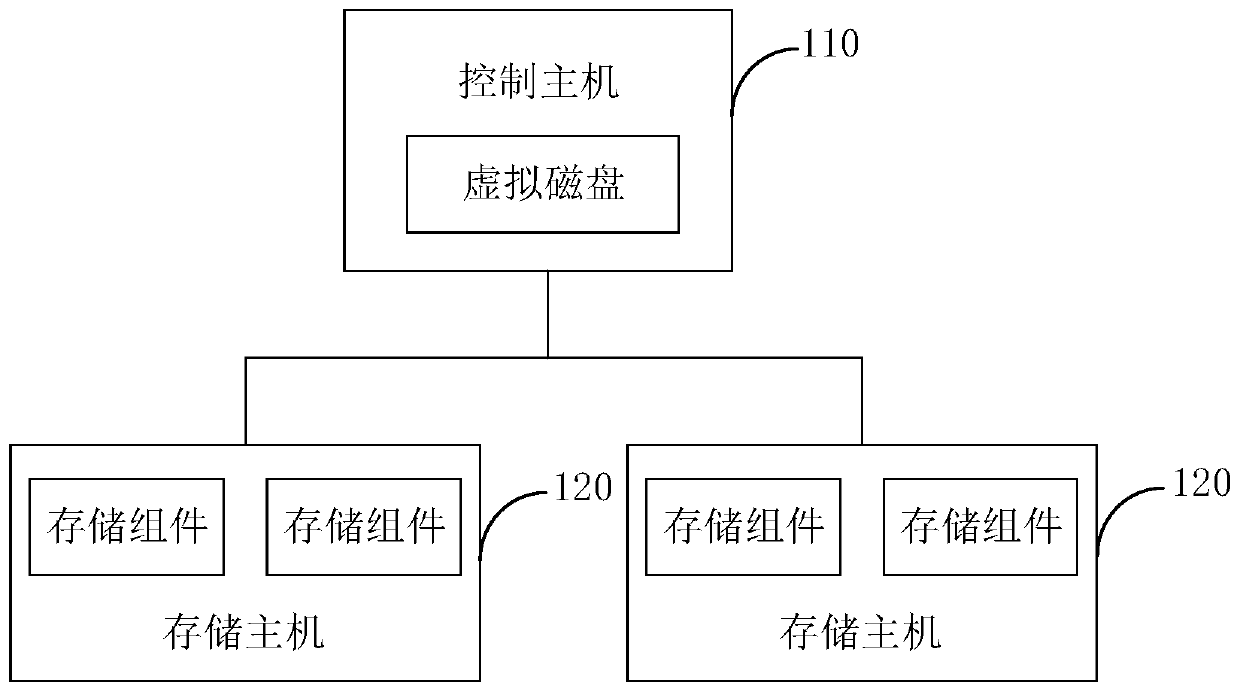
Data hierarchical storage method, reading method, storage host and storage system
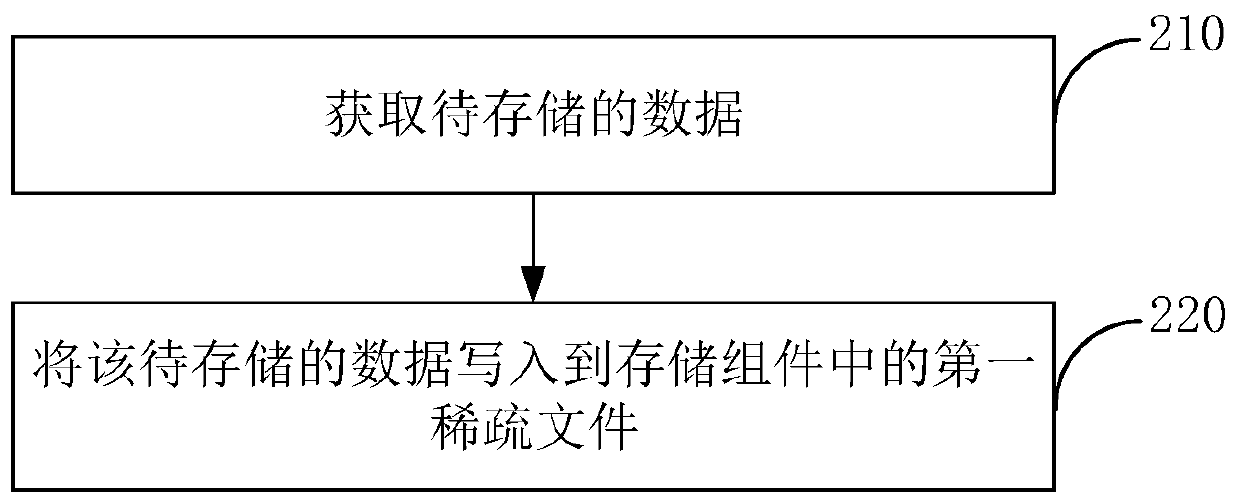
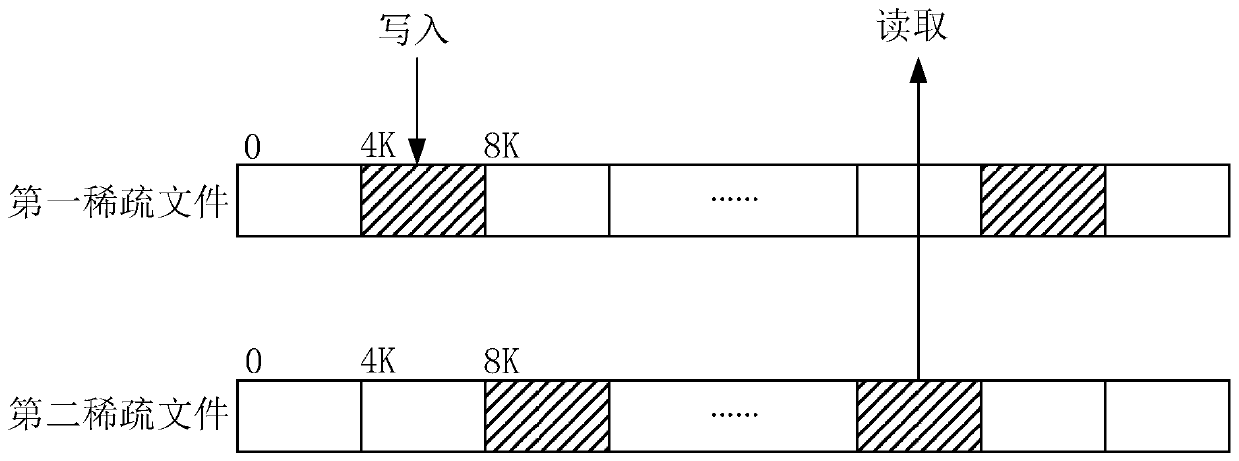
PendingCN111158602AImprove write performanceInput/output to record carriersComputer hardwareMetadata
The invention provides a data hierarchical storage method, a reading method, a storage host and a storage system, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining to-be-stored data; writing the to-be-stored data into a first sparse file in a storage component, wherein the storage component is formed by superposing the first sparse file and a second sparse file which are the same in size, and the read-write performance of a first hard disk stored in the first sparse file is superior to the read-write performance of a second hard disk stored in the second sparse file. According to the method and the device, the two sparse files falling into the first hard disk and the second hard disk respectively are superposed to form the storage component, so the data can be directly written into the sparsefiles of the first hard disk during data writing, additional metadata does not need to be written, and the writing performance is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING TOPSEC NETWORK SECURITY TECH +2
System and Method for an Efficient Database Storage Model Based on Sparse Files
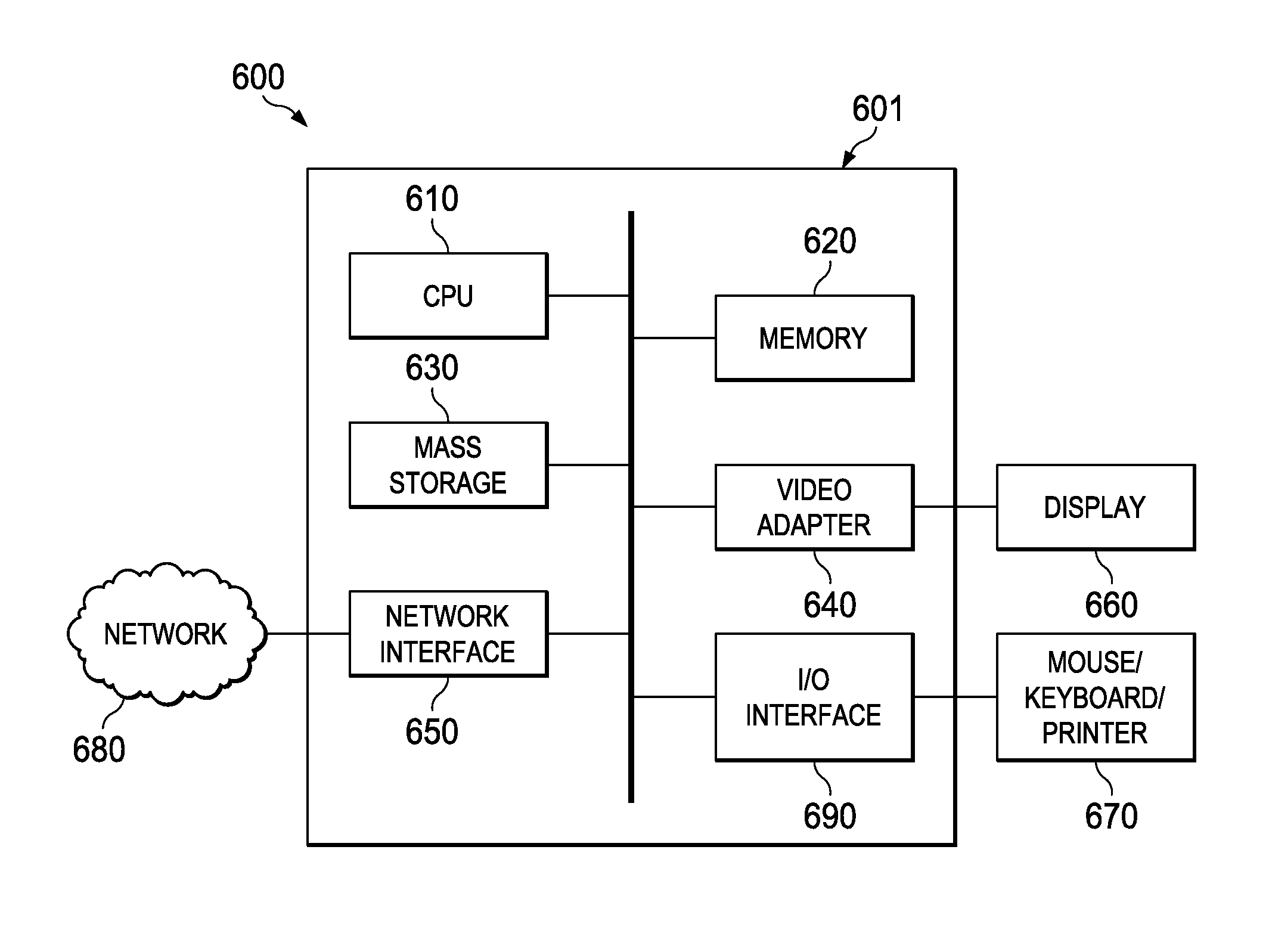
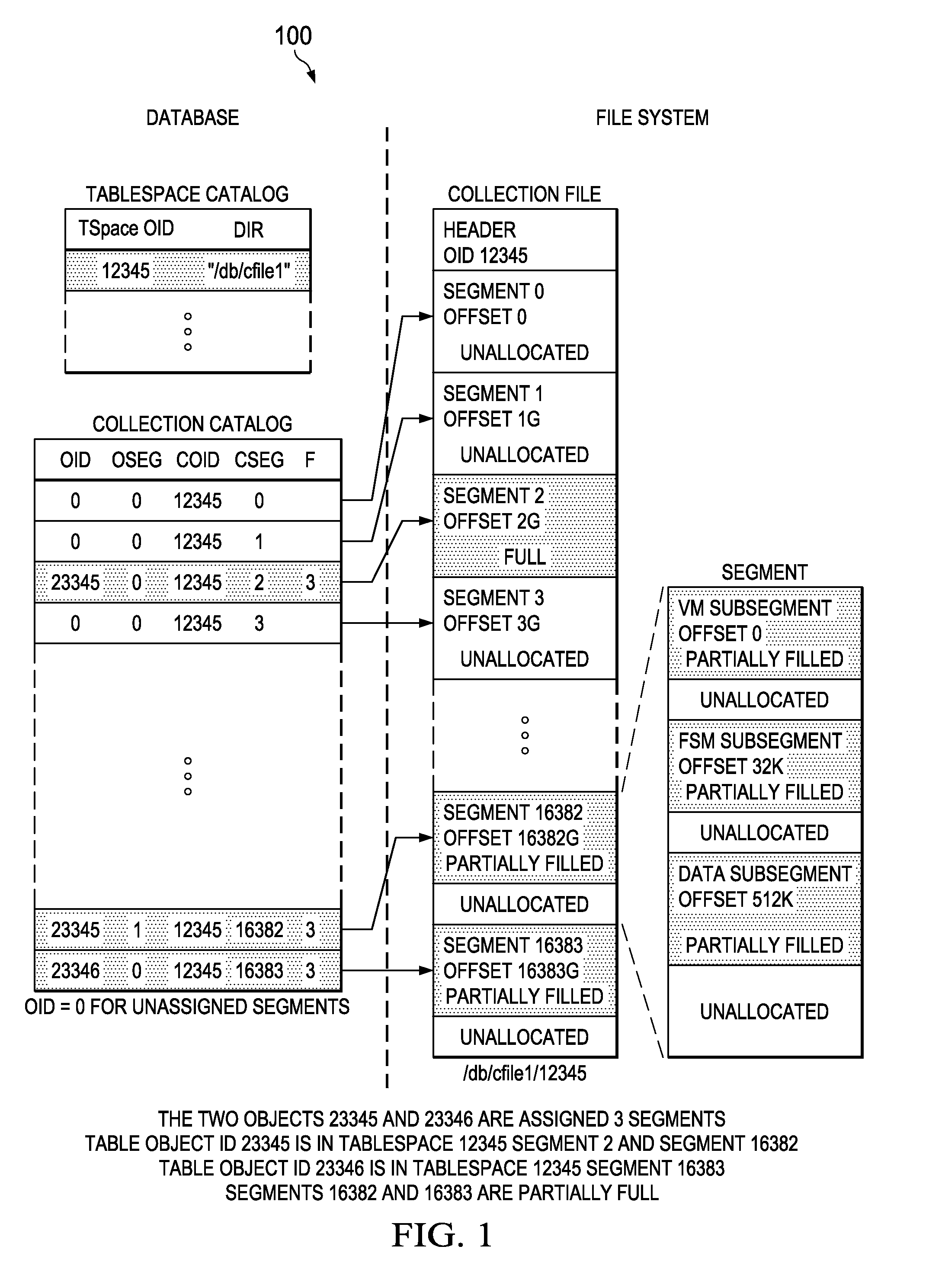
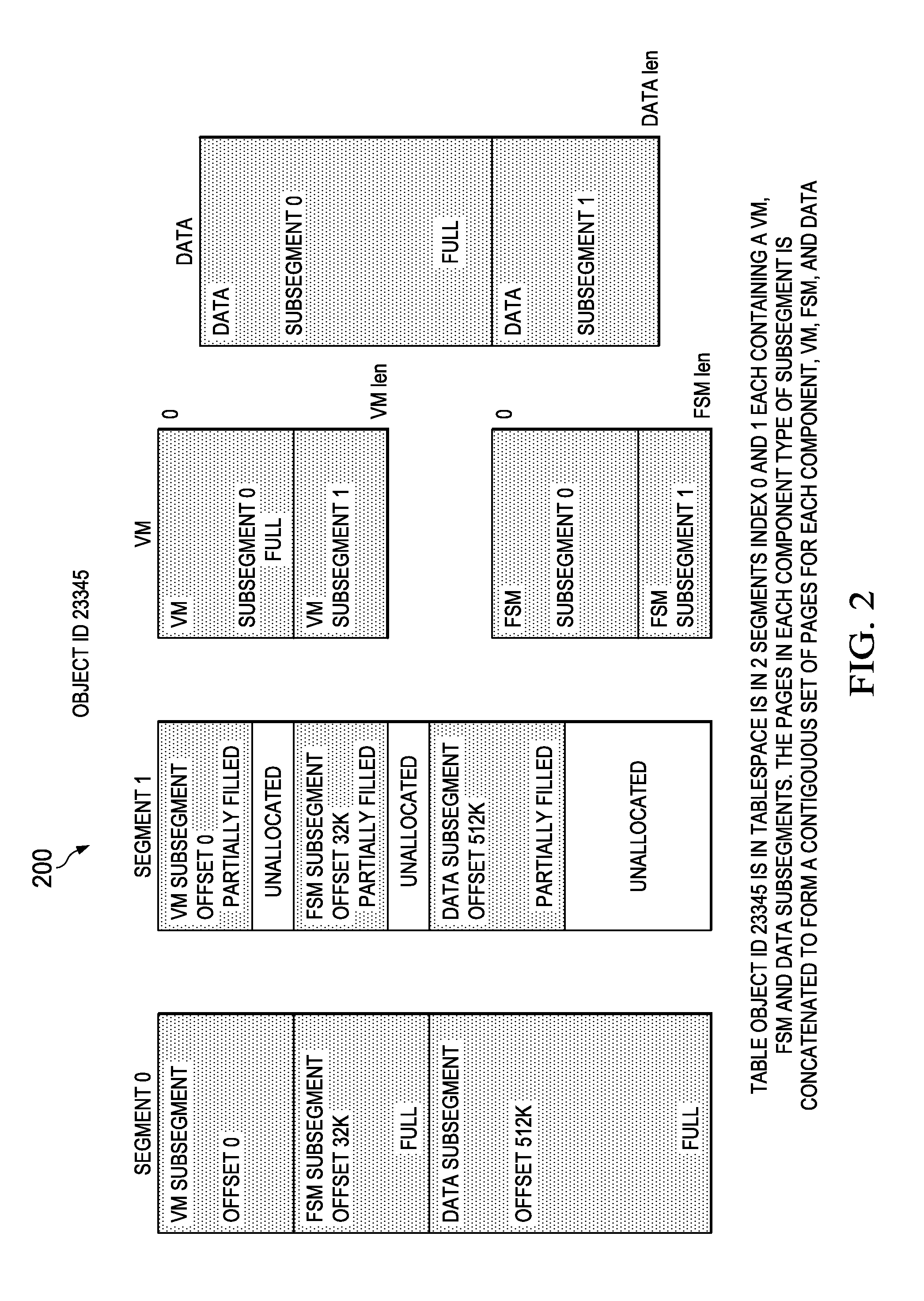
InactiveUS20150234841A1Easy to useDigital data processing detailsFile access structuresAbstraction layerFile system
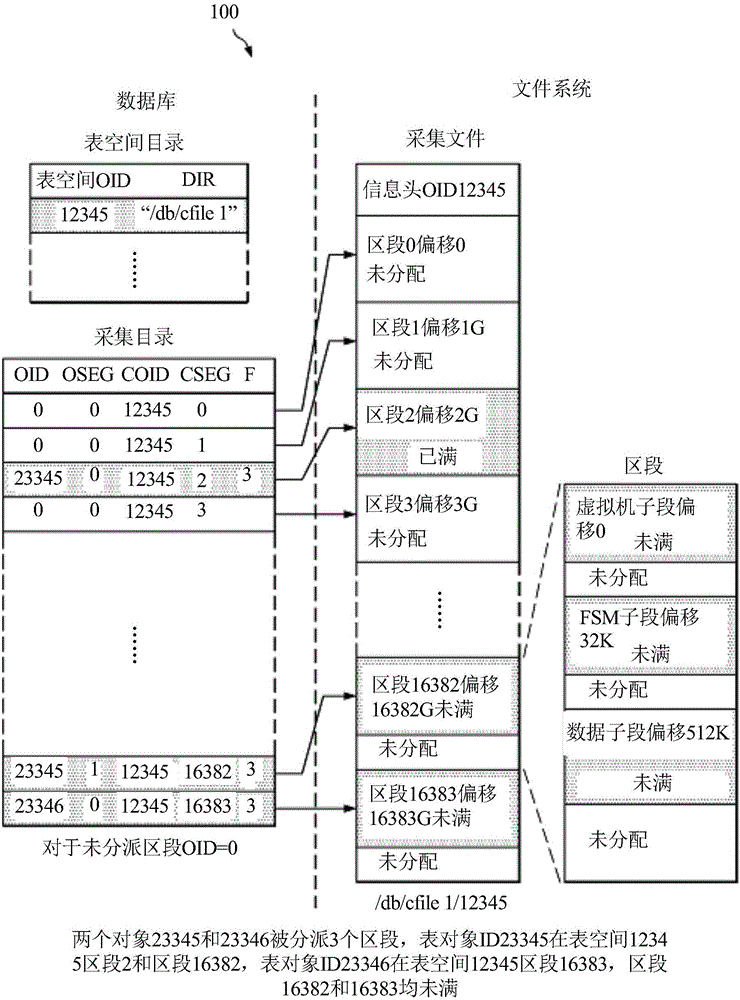
Embodiments are provided herein for an efficient database storage model, which utilizes sparse file features to efficiently store and retrieve data. The embodiments provide database algorithms that utilize the file system abstraction layer to hide the complexity of managing disk space while providing the database a linear and contiguous logical address space for holding multiple database objects. An embodiment method includes pre-allocating, in a logical sparse file, a plurality of segments fixed in size and contiguous at fixed offsets. Upon receiving a command to write database objects to the segments, the database objects are mapped to the segments in a database catalog. The method further includes interfacing with a file system to initialize storage medium space for writing the data objects to the segments at the fixed offsets.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
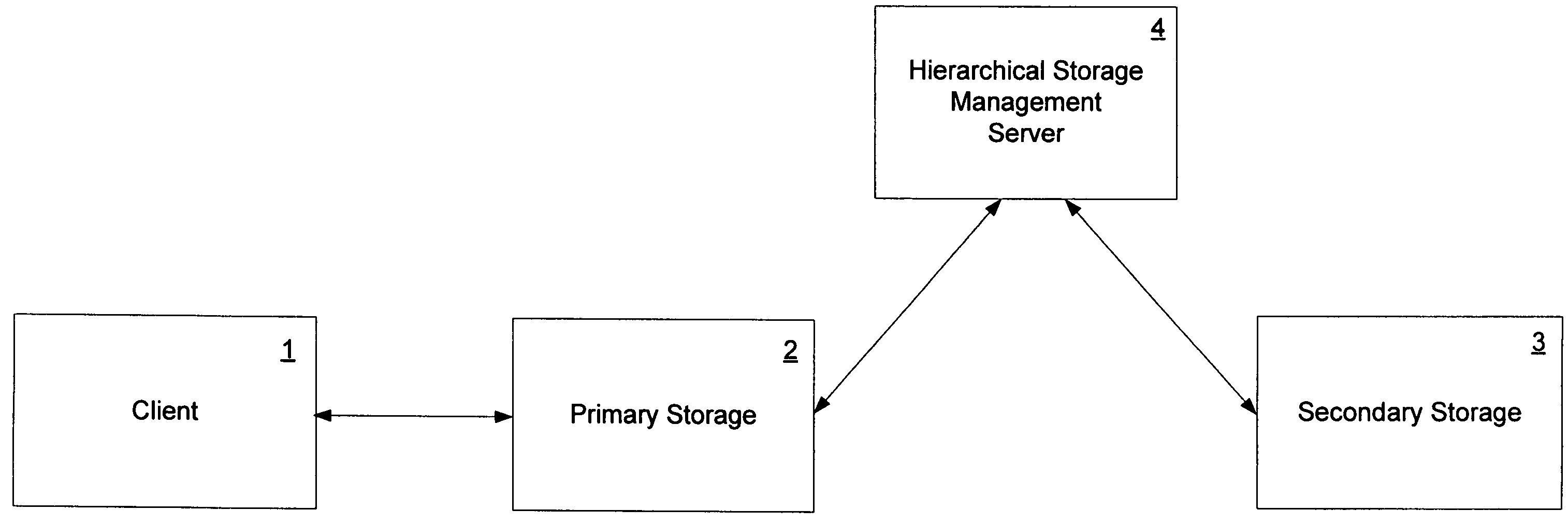
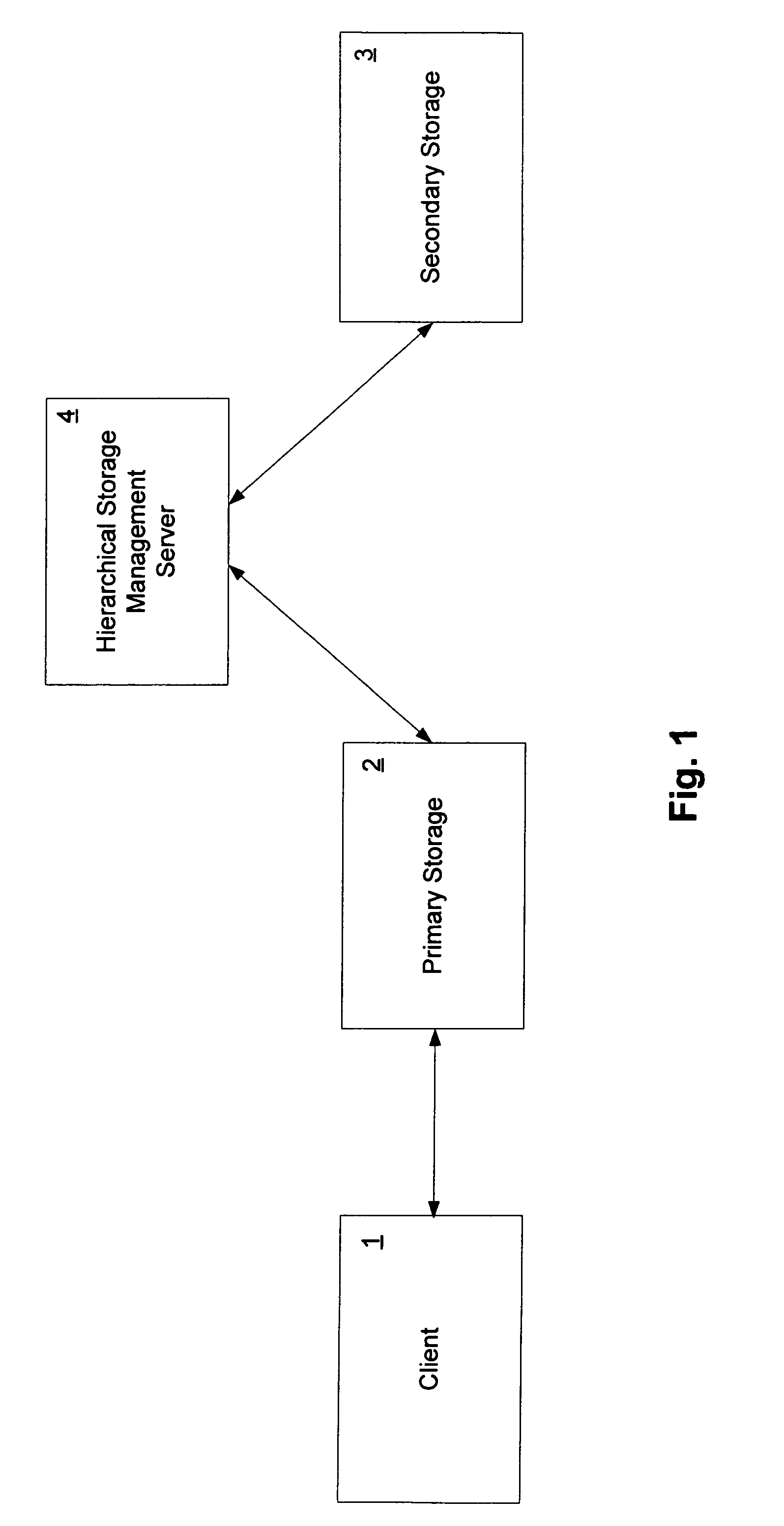
Emulation of transparent recall in a hierarchical storage management system
ActiveUS7853667B1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsClient-sideDatabase
In at least one embodiment of the invention, a primary storage facility is managed in an HSM system. Data is relocated from the primary storage facility to a secondary storage facility. A request is received from a client for only a portion of the relocated data. In response to the request, the requested portion of the data is obtained from the secondary storage facility and stored in the primary storage facility as a sparse file. The requested portion of the data is then provided to the client from the sparse file.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
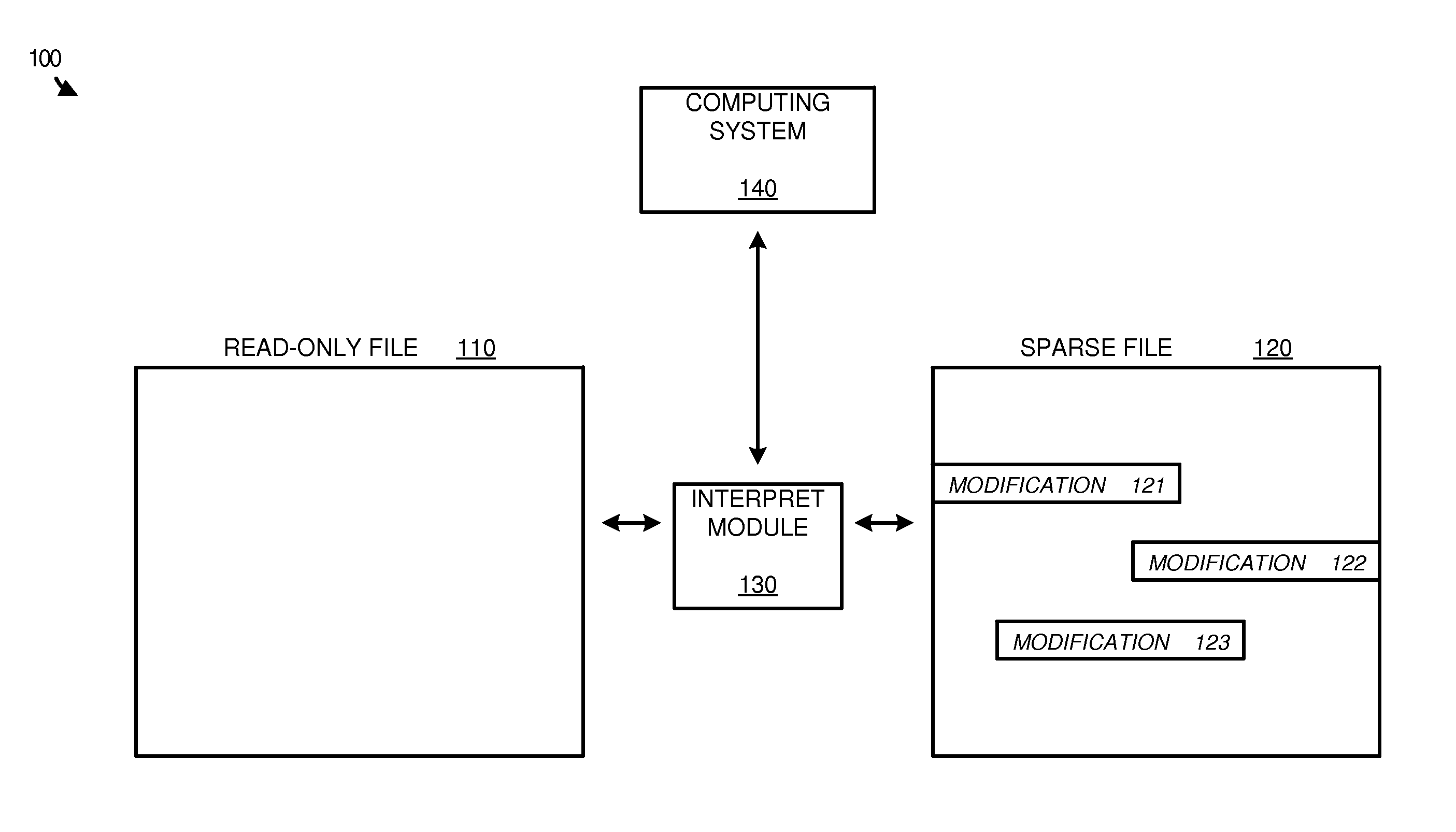
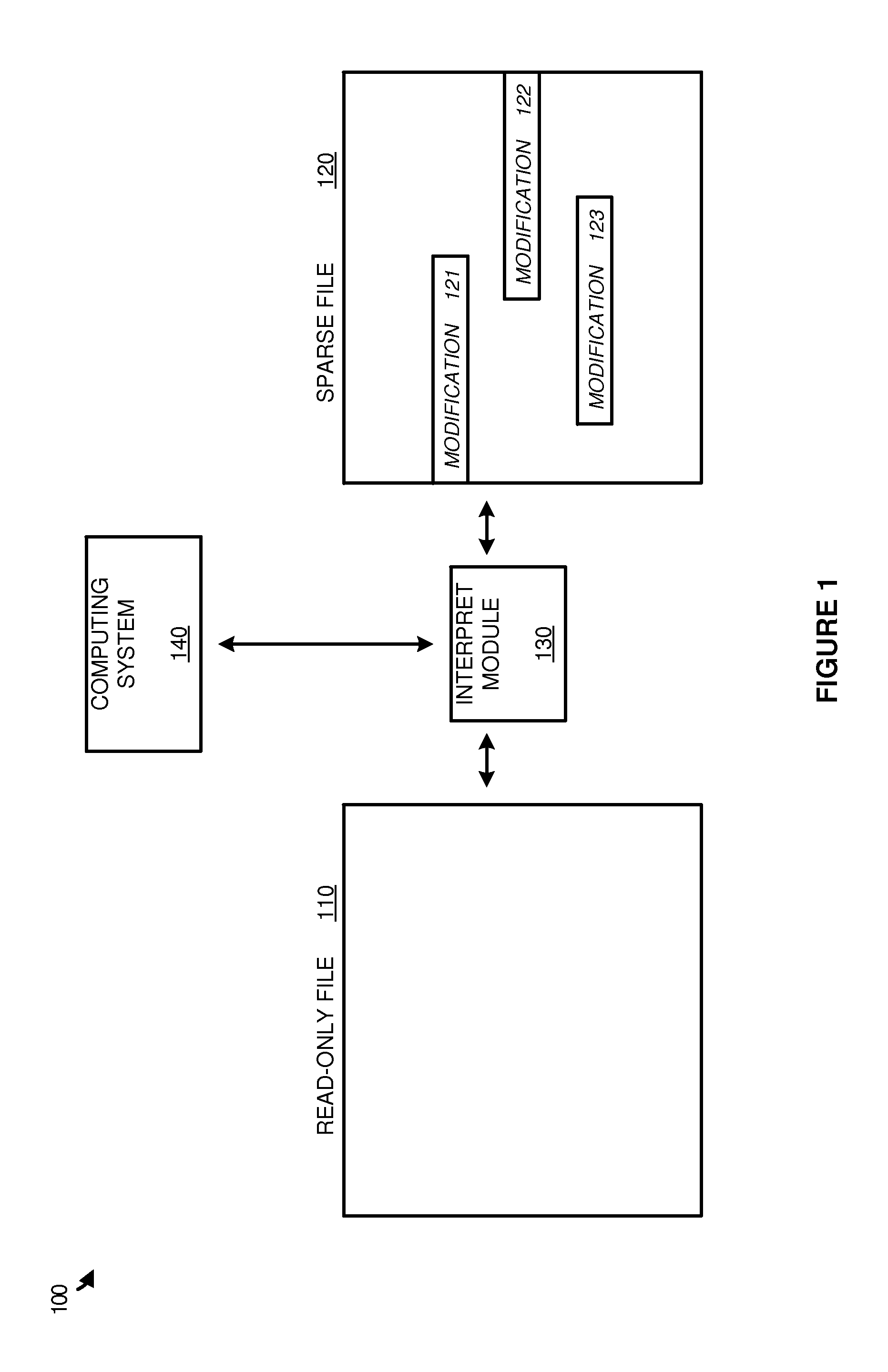
Avoiding full file replication using sparse files
ActiveUS20150339317A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFile replicationComputing systems
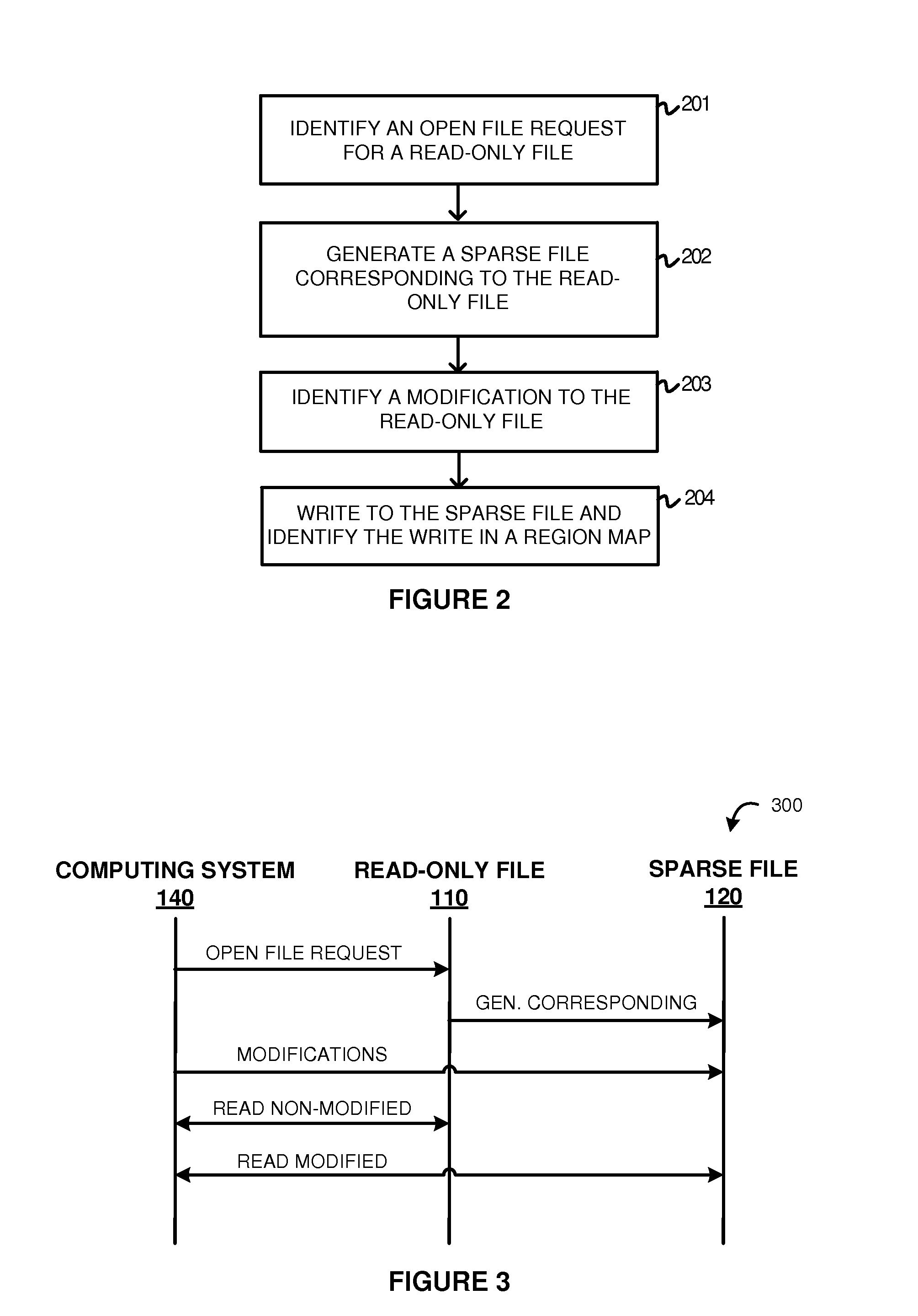
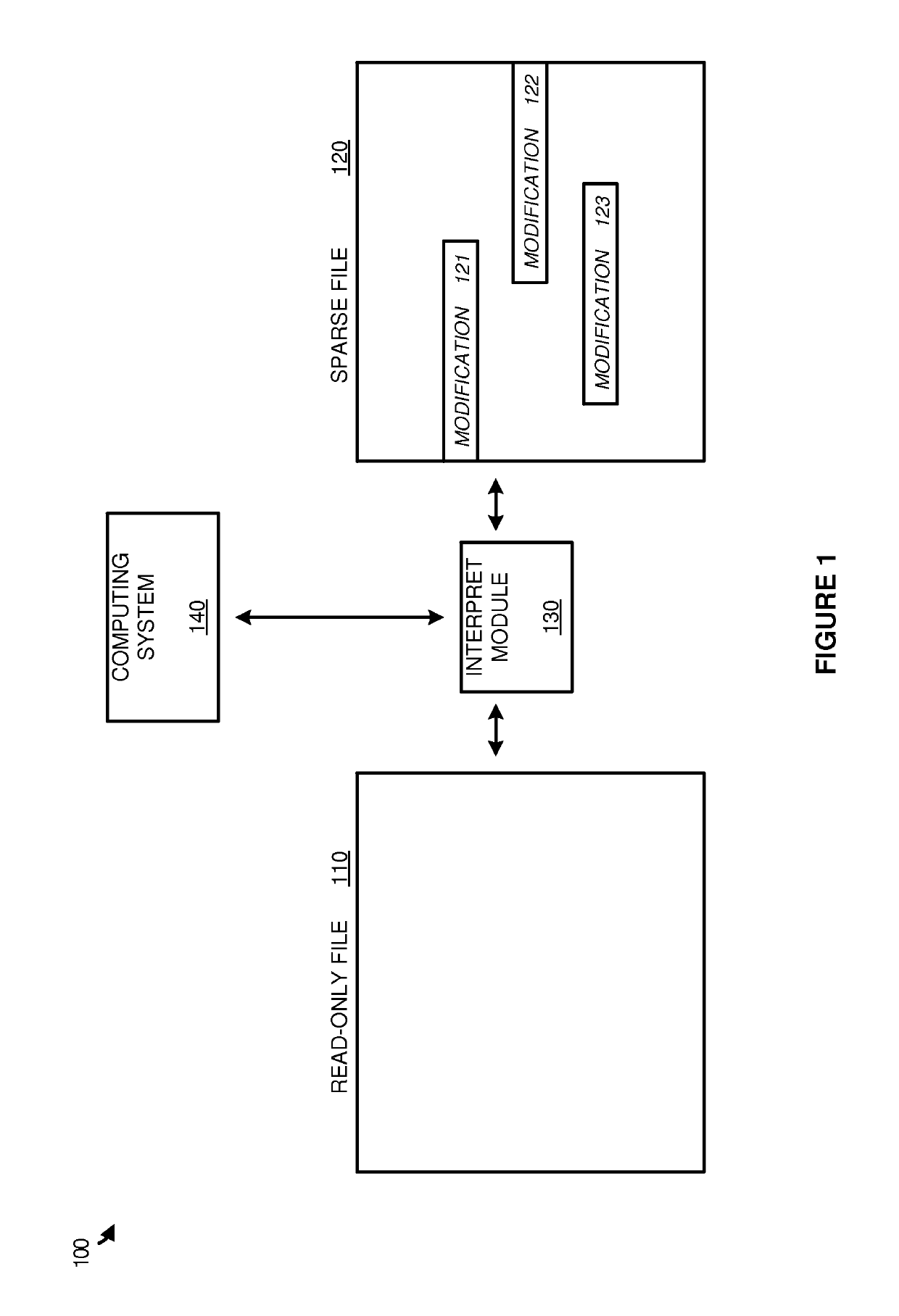
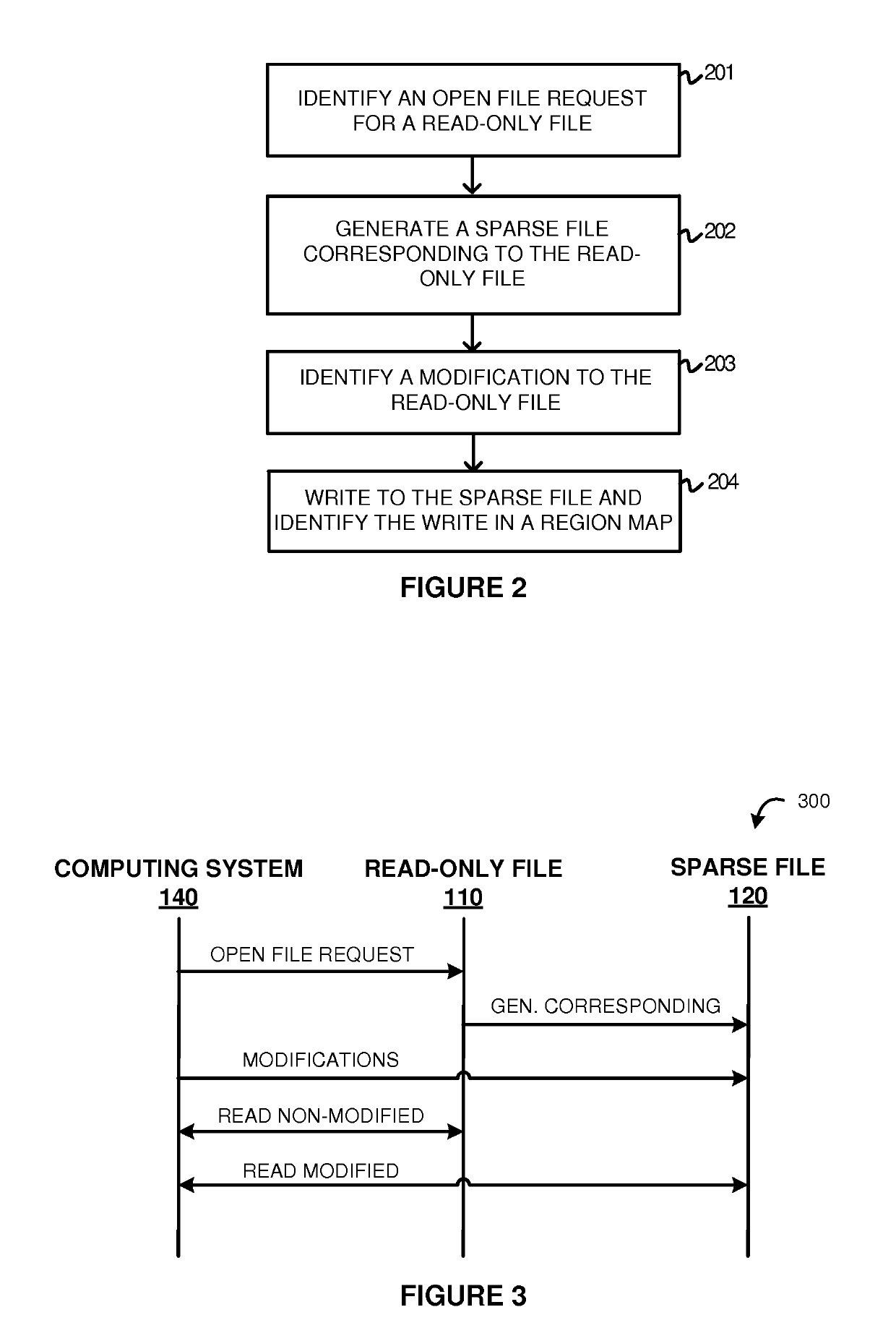
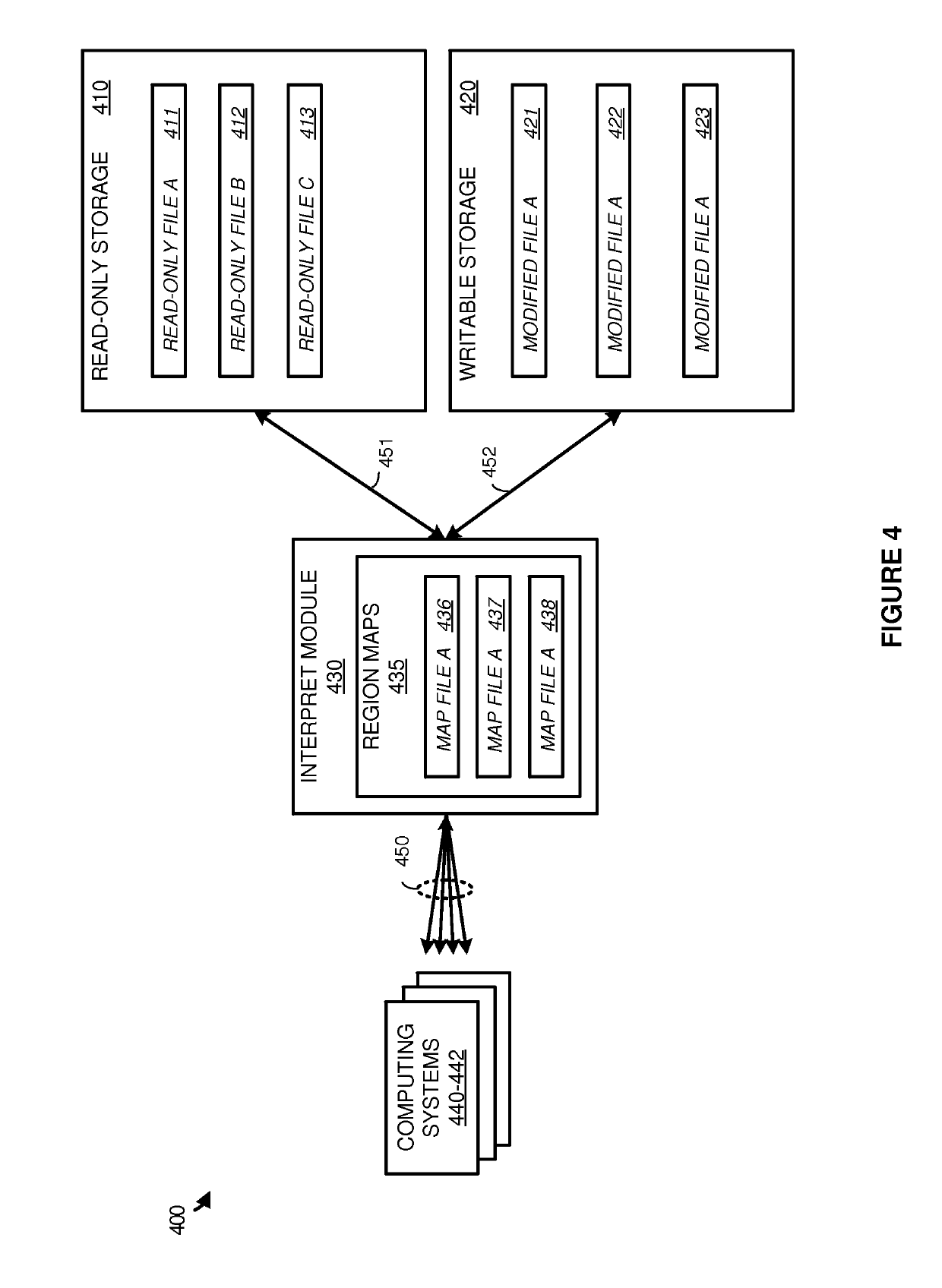
Examples disclosed herein provide systems, methods, and software for avoiding data replication using sparse files. In one example, a method of using a sparse file to manage modifications to read-only files includes identifying an open file request on a computing system for a read-only file, and generating the sparse file corresponding to the read-only file. The method further includes identifying a modification to the read-only file and, responsive to identifying the modification, initiate a write to the sparse file based on the modification and identifying the write in a region map.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Transaction consistent copy-on-write database
A database view of a database is created which provides a transaction-consistent view of an existing database at a previous time. Each database view contains all the information needed to, along with the primary database, determine the contents of the primary database at a previous time. The database view consists of a side file corresponding to each data file in the primary database. The side files contain a copy of all data from the corresponding data file which has been changed since the database view was created. Sparse files may be used for the side files in order to conserve space. Page table data is kept in order to allow a quick determination as to whether the page from the primary database has been modified and the old version stored in the database view side file.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for an efficient database storage model based on sparse files
ActiveCN105981013AEasy to modifySimple designSpecial data processing applicationsAbstraction layerFile system
Embodiments are provided herein for an efficient database storage model, which utilizes sparse file features to efficiently store and retrieve data. The embodiments provide database algorithms that utilize the file system abstraction layer to hide the complexity of managing disk space while providing the database a linear and contiguous logical address space for holding multiple database objects. An embodiment method includes pre-allocating, in a logical sparse file, a plurality of segments fixed in size and contiguous at fixed offsets. Upon receiving a command to write database objects to the segments, the database objects are mapped to the segments in a database catalog. The method further includes interfacing with a file system to initialize storage medium space for writing the data objects to the segments at the fixed offsets.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
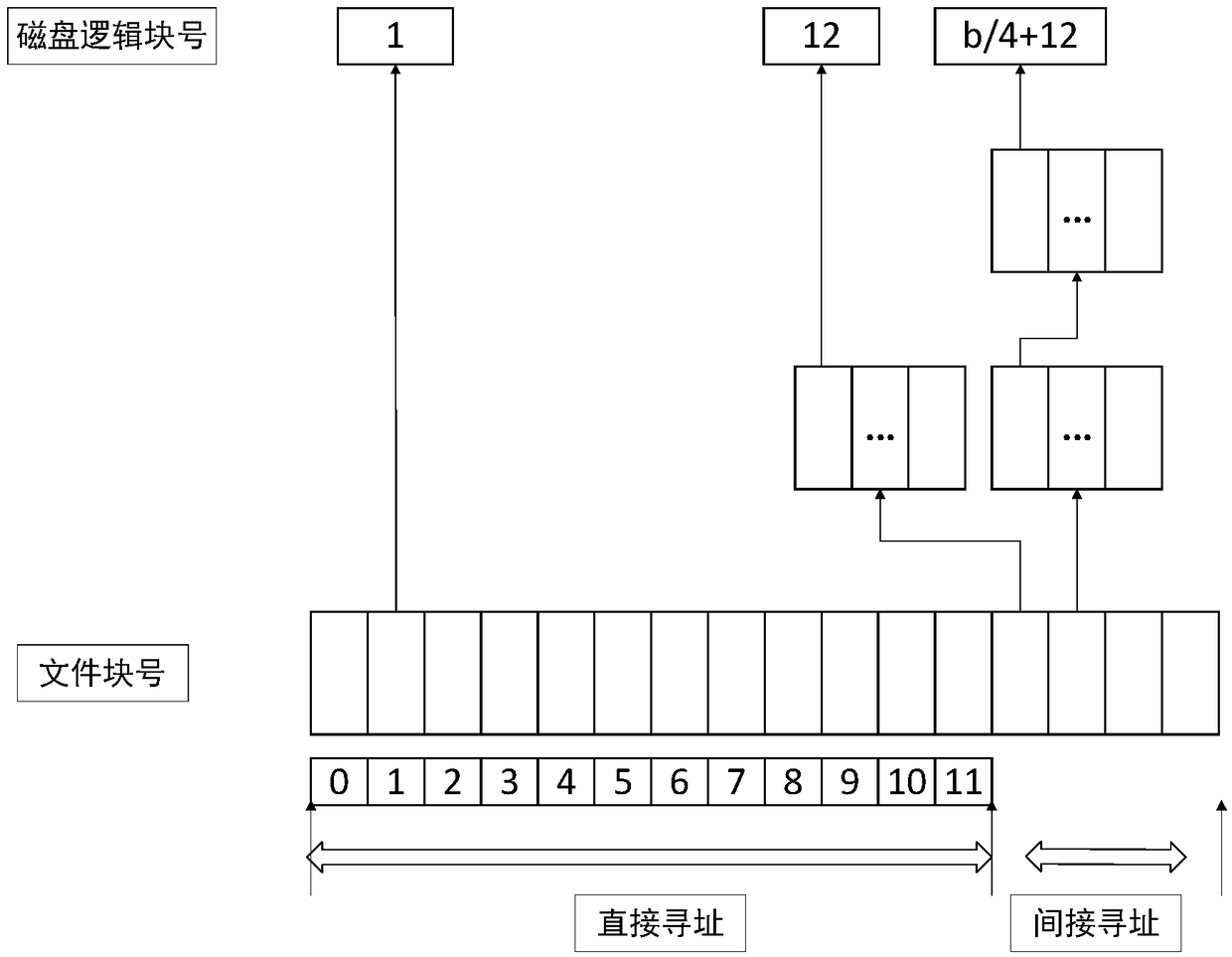
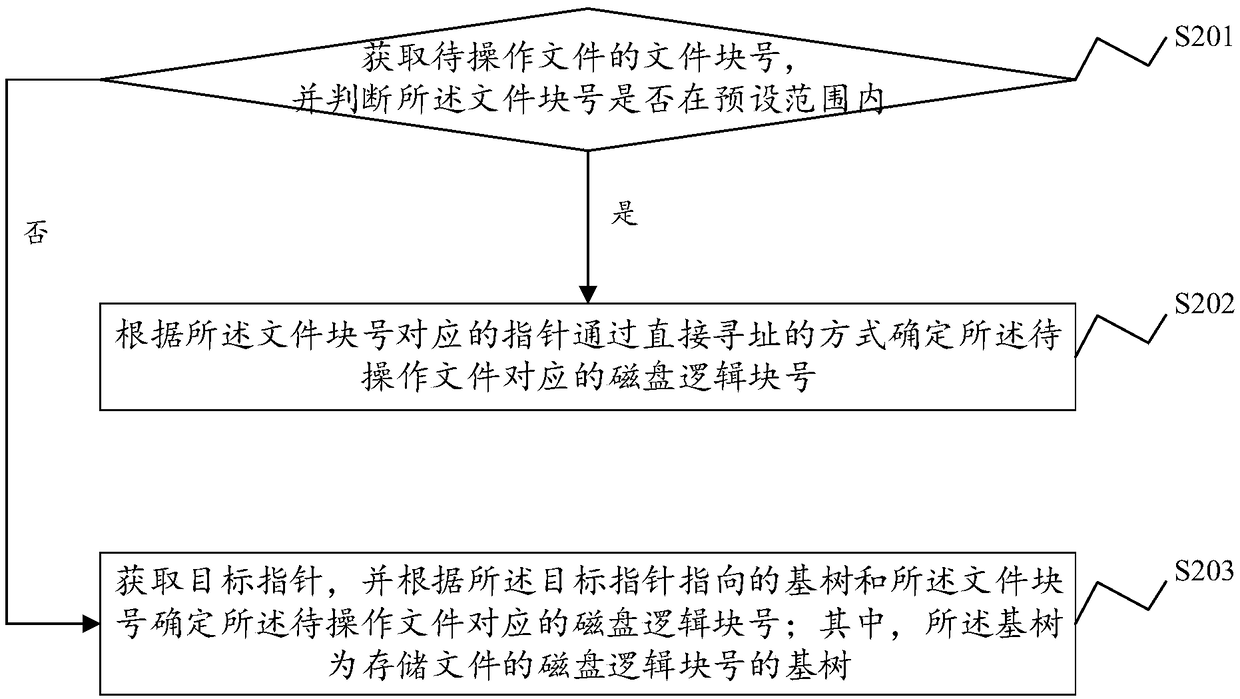
File data block addressing method, system, device and storage medium
ActiveCN108897698AReduce the number of operationsReduce occupancyMemory systemsSmall filesTree mapping
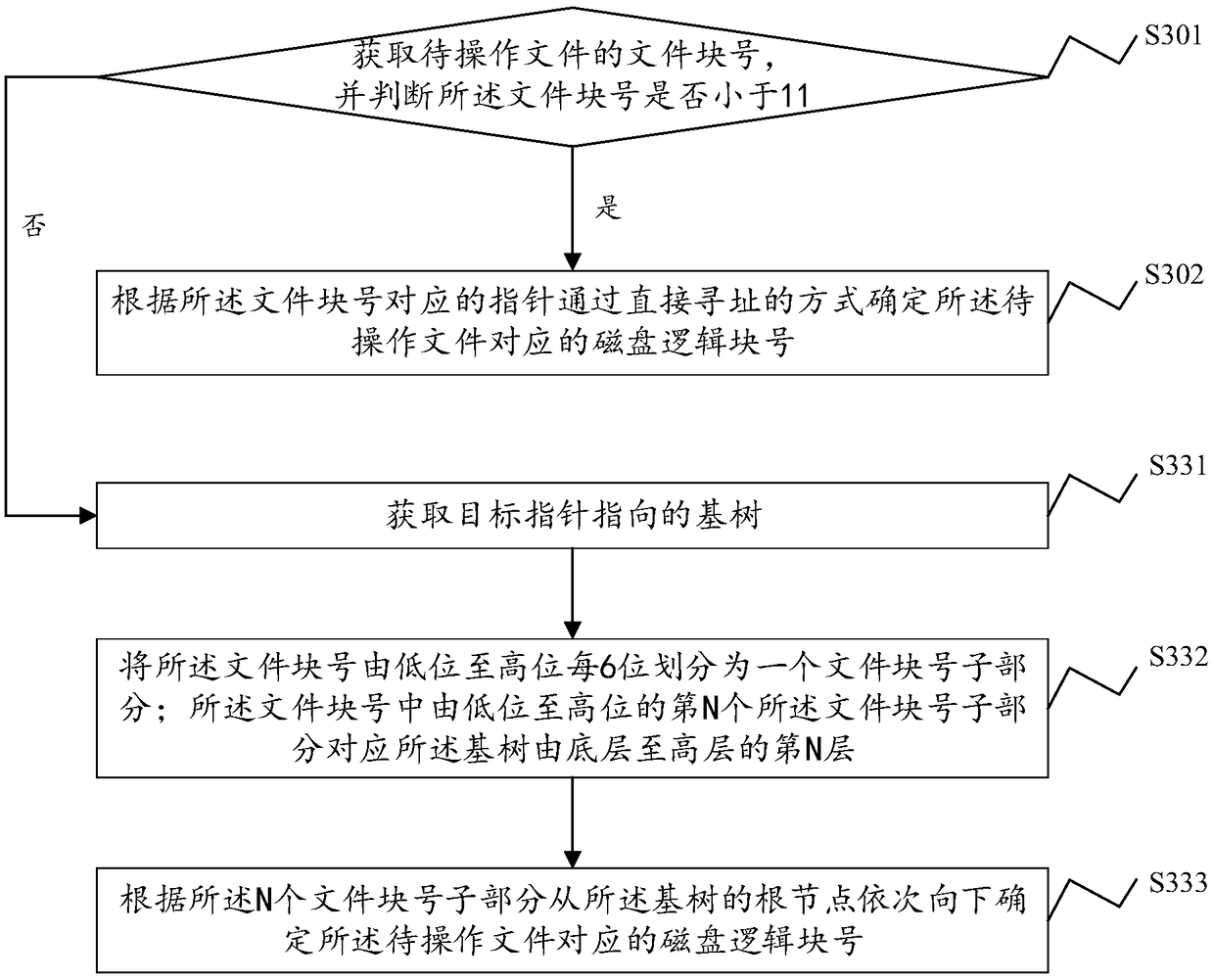
The present application discloses a file data block addressing method, system, and device and computer readable storage medium. The file data block addressing method comprises obtaining a file block number of a file to be operated, and determining whether the file block number is within a preset range; if yes, according to a pointer corresponding to the file block number, a disk logical block number corresponding to the file to be operated is determined by directly addressing; if not, a target pointer is acquired, and according to the base tree pointed by the target pointer and the file blocknumber, a disk logical block number corresponding to the file to be operated is determined; the base tree is a base tree of a disk logical block number storing the file. The file data block addressingmethod uses a direct mapping and a base tree mapping to map a file block number to a disk logical block number. Through a direct index of a preset range of the file block number, small files can complete the disk request by accessing the disk twice, and the base tree mapping is adopted for sparse files and large files, thereby effectively reducing the disk occupation of the index block.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Avoiding full file replication using sparse files
Examples disclosed herein provide systems, methods, and software for avoiding data replication using sparse files. In one example, a method of using a sparse file to manage modifications to read-only files includes identifying an open file request on a computing system for a read-only file, and generating the sparse file corresponding to the read-only file. The method further includes identifying a modification to the read-only file and, responsive to identifying the modification, initiate a write to the sparse file based on the modification and identifying the write in a region map.
Owner:VMWARE INC
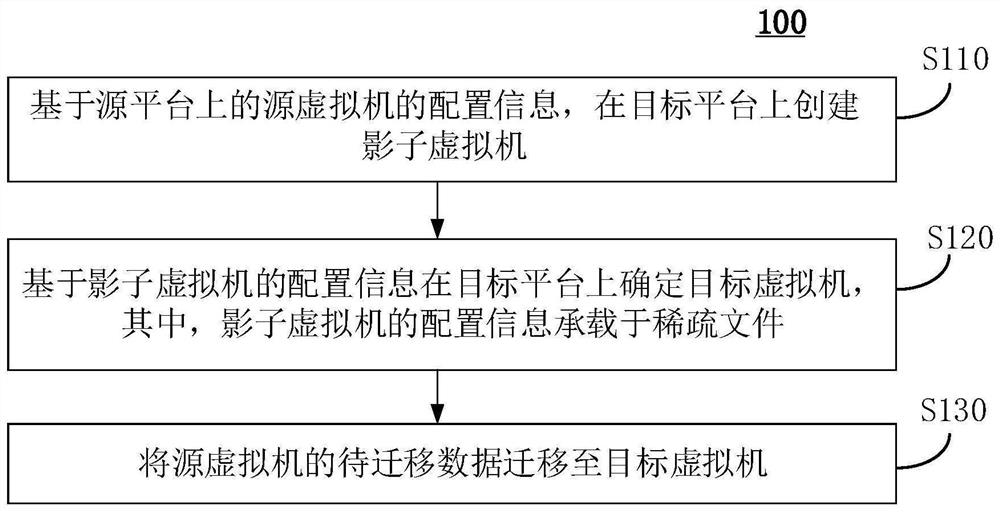
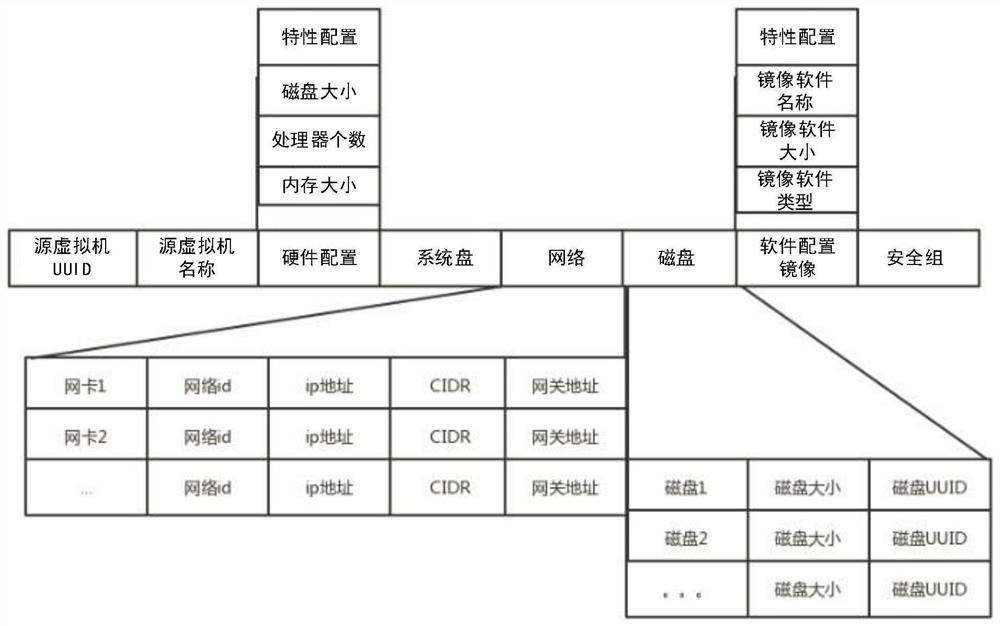
Cross-platform virtual machine live migration method and device, equipment and medium
PendingCN113127133AImprove thermal migration rateReduce data volumeProgram initiation/switchingSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationData packCross-platform
The invention discloses a cross-platform virtual machine live migration method and device, equipment and a medium. The method comprises the following steps: creating a shadow virtual machine on a target platform based on configuration information of a source virtual machine on a source platform; determining a target virtual machine on a target platform based on configuration information of the shadow virtual machine, wherein the configuration information of the shadow virtual machine is carried in a sparse file; and migrating to-be-migrated data of the source virtual machine to the target virtual machine, wherein the to-be-migrated data comprises the configuration information of the shadow virtual machine. According to the cross-platform virtual machine thermal migration method and device, the equipment and the medium provided by the embodiment of the invention, the thermal migration rate of the virtual machine can be improved.
Owner:SHANXI CHINA MOBILE COMM CORP +1
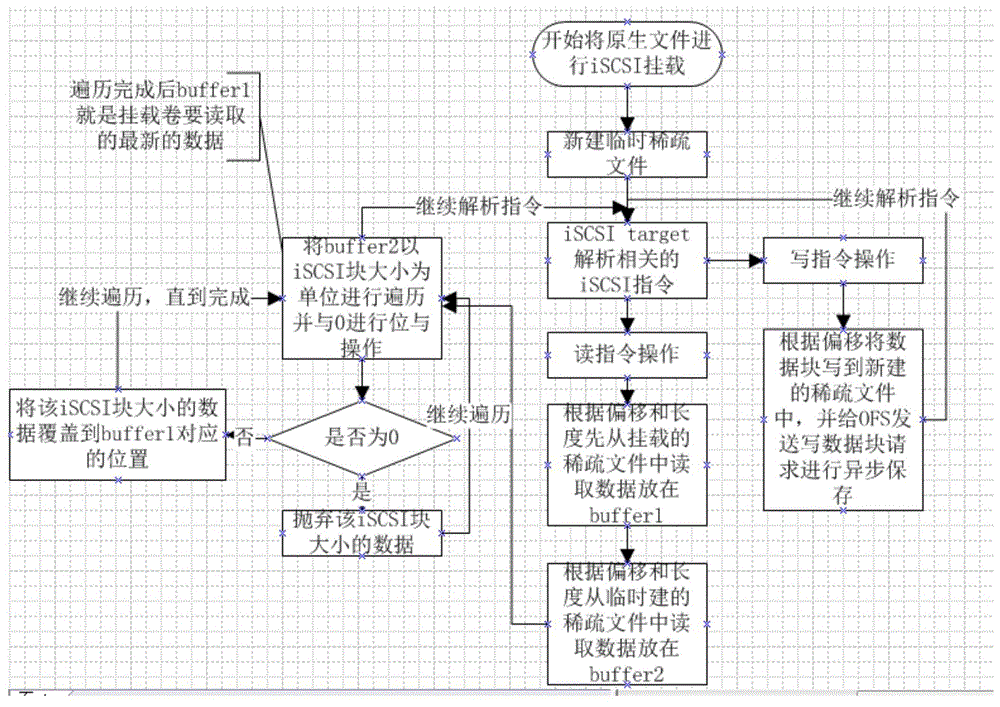
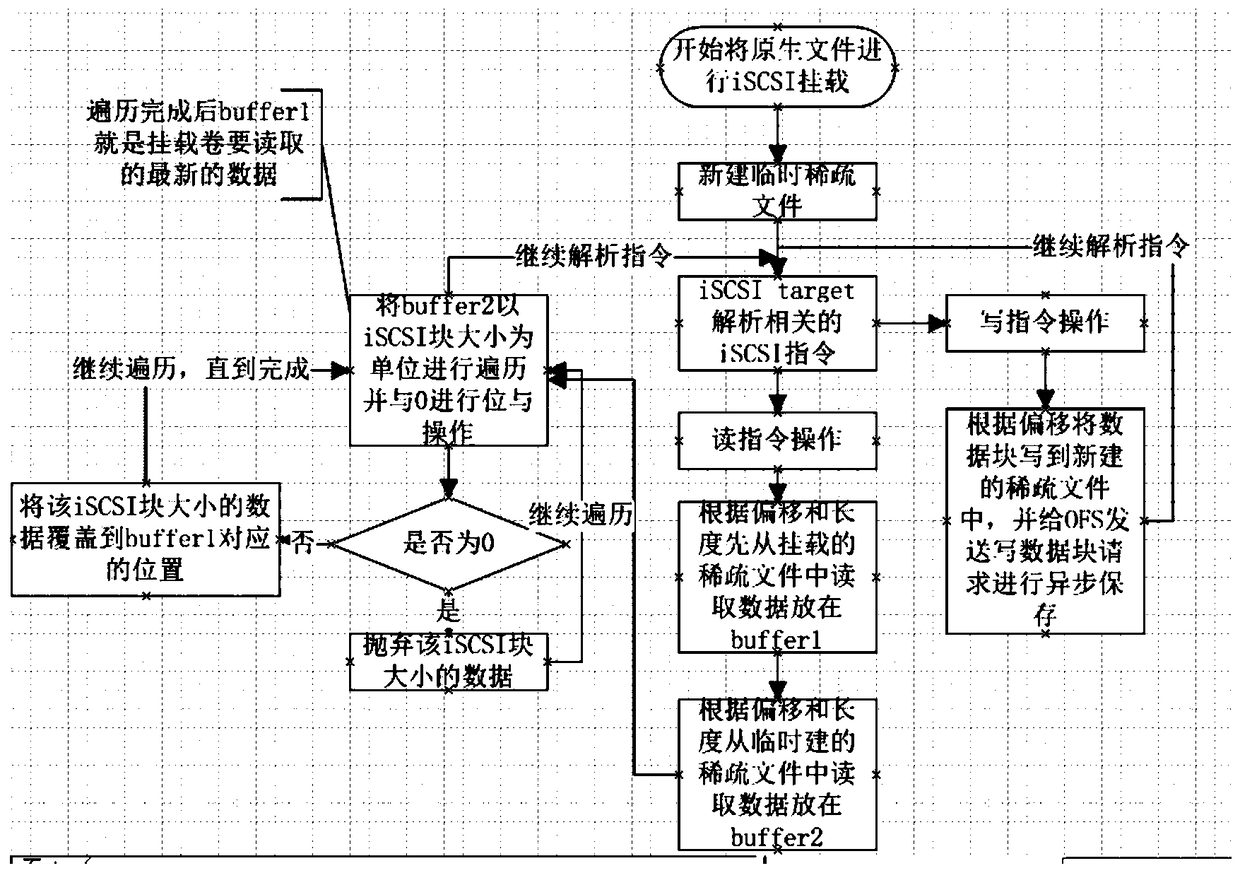
Method for redirecting read-write data of iSCSI mounting volume and backup and recovery system thereof
ActiveCN104461782AAchieve protectionImprove usabilityRedundant operation error correctionSCSIFile system
The invention relates to a method for redirecting read-write data of an iSCSI (Internet Small Computer System Interface) mounting volume and a backup and recovery system thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) creating a temporary sparse file with the same size as an original sparse file; (2) when write operation of the original sparse file is captured, directly writing the data into the temporary sparse file in the step (1); (3) when read operation of the original sparse file is captured, reading the data from the original sparse file and merging data changed read from the temporary sparse file to obtain a newest data block. The backup and recovery system comprises a storage module and an SCSI protocol analysis module of a native file system. Compared with the prior art, the read-write performance of the mounting volume is improved, so that the storage performance required by application on a production system can be met well, and the availability of the iSCSI mounting volume is improved.
Owner:EISOO SOFTWARE
Computer-implemented methods and system for preventing unauthorized file modification by malicious software and the like
In some embodiments, a cyber security method for preventing unauthorized file modification by malicious software and the like, the file accessible to an authorized handler may include: receiving a first access request from a program, the first access request having a first instruction set for modifying data of the file; determining if the file is associated with the authorized handler; processing the first instruction set to produce first modification data; and generating an initial virtual file object comprising the first modification data. In further embodiments, a cyber security method for preventing unauthorized file modification by malicious software and the like, the file accessible to an authorized handler may include: processing an instruction set for modifying a file to produce modification data; generating a virtual file object comprising the modification data; and associating the virtual file object with the file by identifying the file as a sparse file.
Owner:NEUSHIELD INC
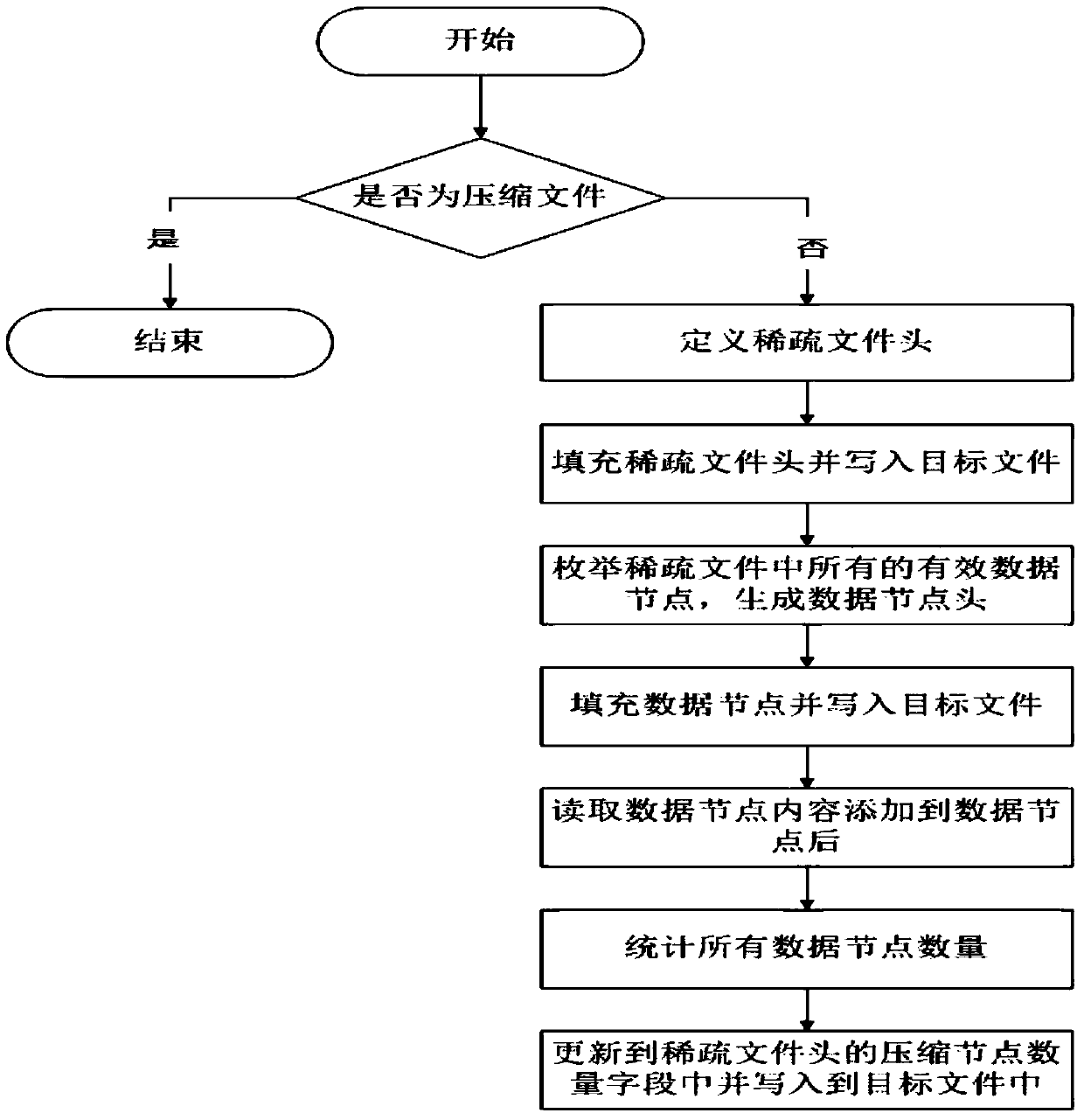
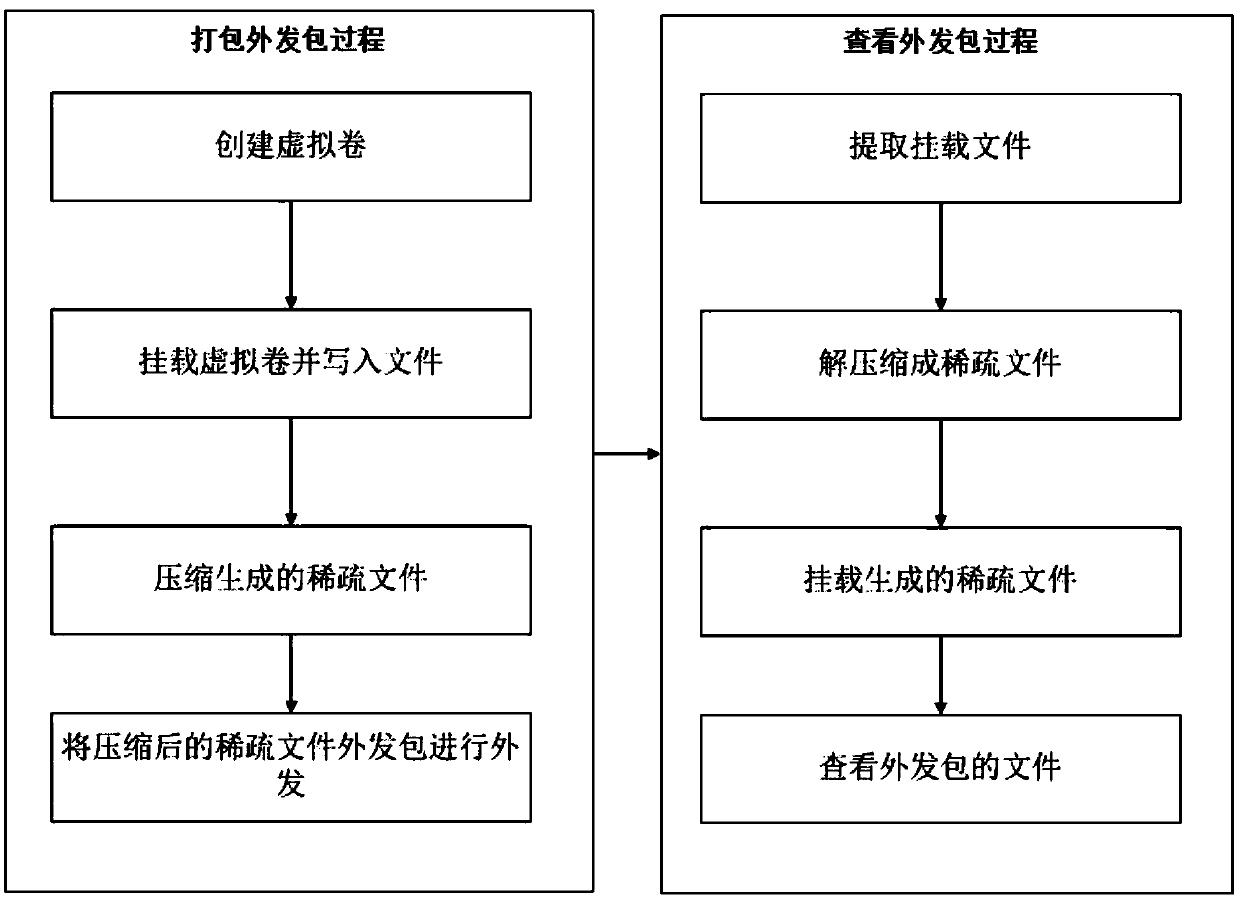
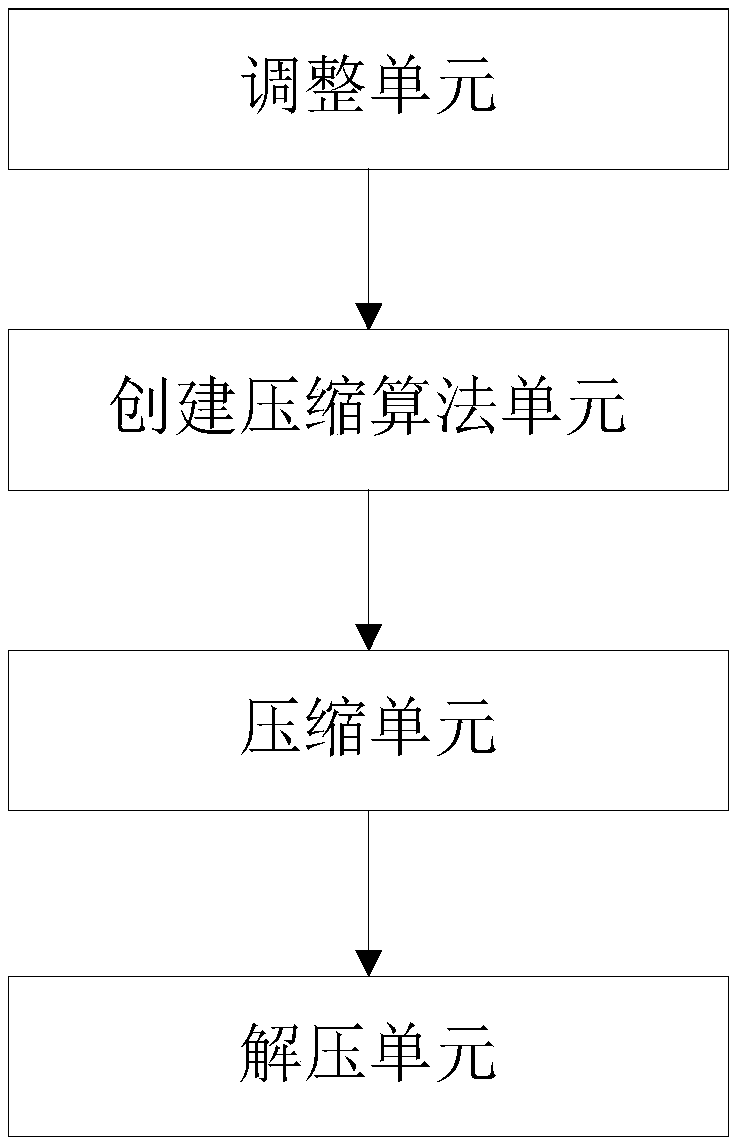
Device and method for compressing file outgoing packet
PendingCN110955381AReduce occupancyInput/output to record carriersFile/folder operationsComputer hardwareEngineering
The invention discloses a device and method for compressing a file outgoing packet, and the device comprises a packaging module and a viewing module, and the packaging module is provided with an adjustment unit, a compression model creation unit, and a compression unit; the viewing module is provided with a decompression unit. The method for compressing the file outgoing packet comprises an outgoing packet packaging process and an outgoing packet viewing process. The package outgoing process comprises the steps of firstly creating a virtual volume, then mounting the virtual volume and writingthe virtual volume into a file to generate a virtual volume mounting file, compressing the virtual volume mounting file into a compressed file through a compressed sparse file algorithm, and then outgoing a compressed file outgoing package. The outgoing package viewing process includes that the compressed file is extracted, then the compressed file is decompressed through a decompression algorithm, the decompressed file is mounted to generate a sparse file, the file of the outgoing package is viewed. The problem that the outgoing package file is large in size and not easy to carry is solved.
Owner:山东华软金盾软件股份有限公司
Distributed storage file recovery method and device
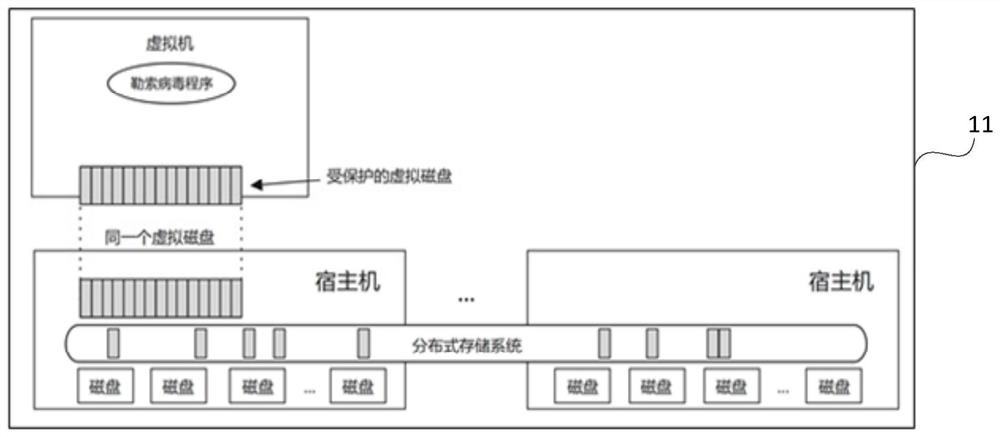
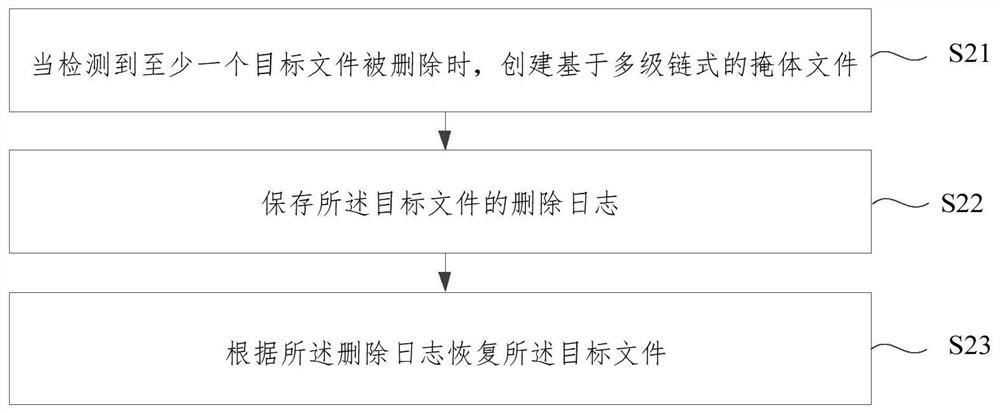
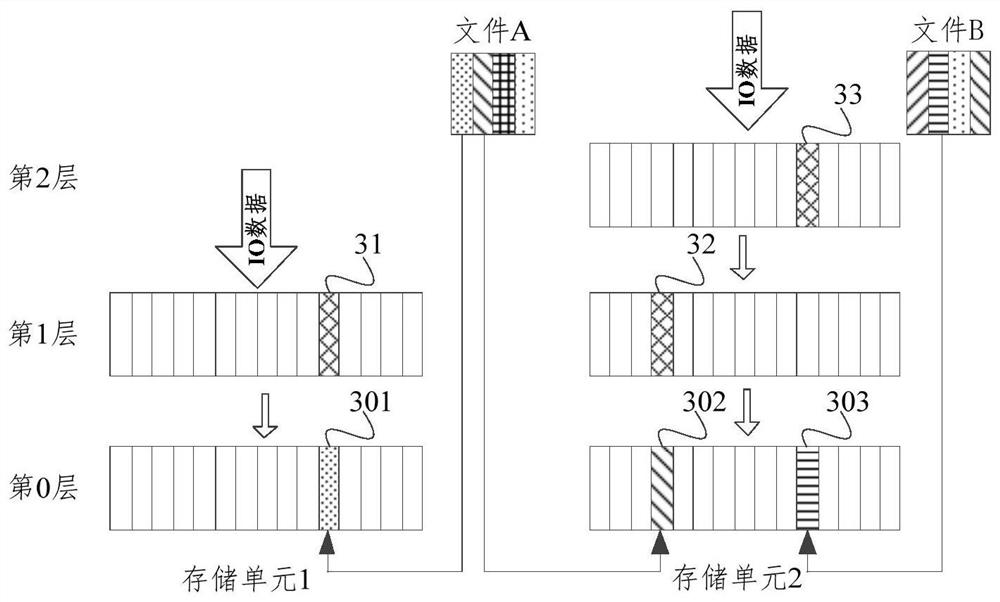
ActiveCN114564456AEnsure safetyNot lostPlatform integrity maintainanceFile/folder operationsComputer performanceDirectory
The invention provides a distributed storage file recovery method, which is applied to a hyper-fusion system, and comprises the following steps: when detecting that at least one target file is deleted, creating a multi-level chain-based blindage file; the blindage file is a sparse file generated by performing zero-write filling on a storage cell where each data block of the target file is located; storing a deletion log of the target file; the deletion log comprises a file path and position information of a target file; the file path comprises a directory where the target file is located and a file name; the position information comprises a unique number of a storage unit where each data block of the target file is located, the number of layers where the built shelter file is located and a unique number of a storage cell where the built shelter file is located; and recovering the target file according to the deletion log. By adopting the method, the problem that the computer performance is reduced due to independent detection of massive files can be avoided.
Owner:BEIJING TOPSEC NETWORK SECURITY TECH +2
Edge caching method for file data in cross-domain virtual data space
ActiveCN111782612BImprove consistencyReduce transfer volumeDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemParallel computing
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method and device for quickly verifying consistency of multi-copy storage
InactiveCN107203345BAvoid affecting the reading and writing businessInput/output to record carriersFault responseComputer hardwareData needs
The invention provides a method and a device for quickly verifying the consistency of multi-duplicate storage. The method includes S1, judging data writing volumes of head files when systems are in idle states, creating snapshot files by the aid of I / O (input / output) redirection technologies when the volumes of data written into the head files reach 30% of the volumes of integral spare files at least, utilizing new head files with continuously written data as null comparison sparse files, computing hash values of the snapshot files and storing the hash values of the snapshot files as extended attributes; S2, carrying out snapshot operation on the head files once at intervals of preset time and comparing hash values of the new head files to the hash values of the snapshot files when the consistency of multi-duplicate data need to be timely verified. The method and the device have the advantages that characteristics of distributed block storage are combined with one another, the method for quickly detecting the consistency of multiple duplicates on the basis of snapshot technologies is proposed, hash value computation tasks are divided to be carried out in multiple time slots, accordingly, influence on normal reading and writing tasks of the systems can be prevented, and the multi-duplicate storage consistency verification speeds can be increased.
Owner:深圳市联云港科技有限公司
Security for Data at Rest in a Remote Network Management Platform
ActiveUS20220164319A1Effective distributionDigital data protectionFile system functionsVirtual file systemFile system
An embodiment may involve persistent storage including a parent filesystem and a pre-configured amount of free space within the parent filesystem that is dedicated for shared use. The embodiment may also involve one or more processors configured to, for each of a plurality of child filesystems: create a sparse file with an apparent size equivalent to the pre-configured amount of free space; create a virtual mapped device associated with the sparse file; establish one or more cryptographic keys for the virtual mapped device; create an encrypted virtual filesystem for the virtual mapped device and within the sparse file, wherein the encrypted virtual filesystem uses the cryptographic keys for application-transparent encryption and decryption of data stored by way of the encrypted virtual filesystem; and mount the encrypted virtual filesystem within the parent filesystem as one of the child filesystems.
Owner:SERVICENOW INC
Computer-implemented methods and system for preventing unauthorized file modification by malicious software and the like
ActiveUS20200349269A1Avoid modificationDigital data protectionDigital data authenticationSoftware engineeringMalware
In some embodiments, a cyber security method for preventing unauthorized file modification by malicious software and the like, the file accessible to an authorized handler may include: receiving a first access request from a program, the first access request having a first instruction set for modifying data of the file; determining if the file is associated with the authorized handler; processing the first instruction set to produce first modification data; and generating an initial virtual file object comprising the first modification data. In further embodiments, a cyber security method for preventing unauthorized file modification by malicious software and the like, the file accessible to an authorized handler may include: processing an instruction set for modifying a file to produce modification data; generating a virtual file object comprising the modification data; and associating the virtual file object with the file by identifying the file as a sparse file.
Owner:NEUSHIELD INC
Method of redirecting iscsi mounted volume to read and write data and its backup recovery system
ActiveCN104461782BAchieve protectionImprove usabilityRedundant operation error correctionSCSIFile system
The invention relates to a method for redirecting iSCSI mounted volume to read and write data and a backup recovery system thereof, wherein the method includes 1) creating a temporary sparse file with the same size as the original sparse file; During the write operation, directly write the data to the temporary sparse file described in step 1); 3) when the read operation to the original sparse file is captured, read the data from the original sparse file and merge the data from the temporary sparse file The changed data is read out to obtain the latest data block; the backup recovery system includes a storage module of the native file system and a SCSI protocol analysis module. Compared with the prior art, the invention improves the reading and writing performance of the mounted volume, thereby better meeting the storage performance required by the application on the production system and improving the availability of the iSCSI mounted volume.
Owner:EISOO SOFTWARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com