Patents
Literature
493results about How to "Improve write performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
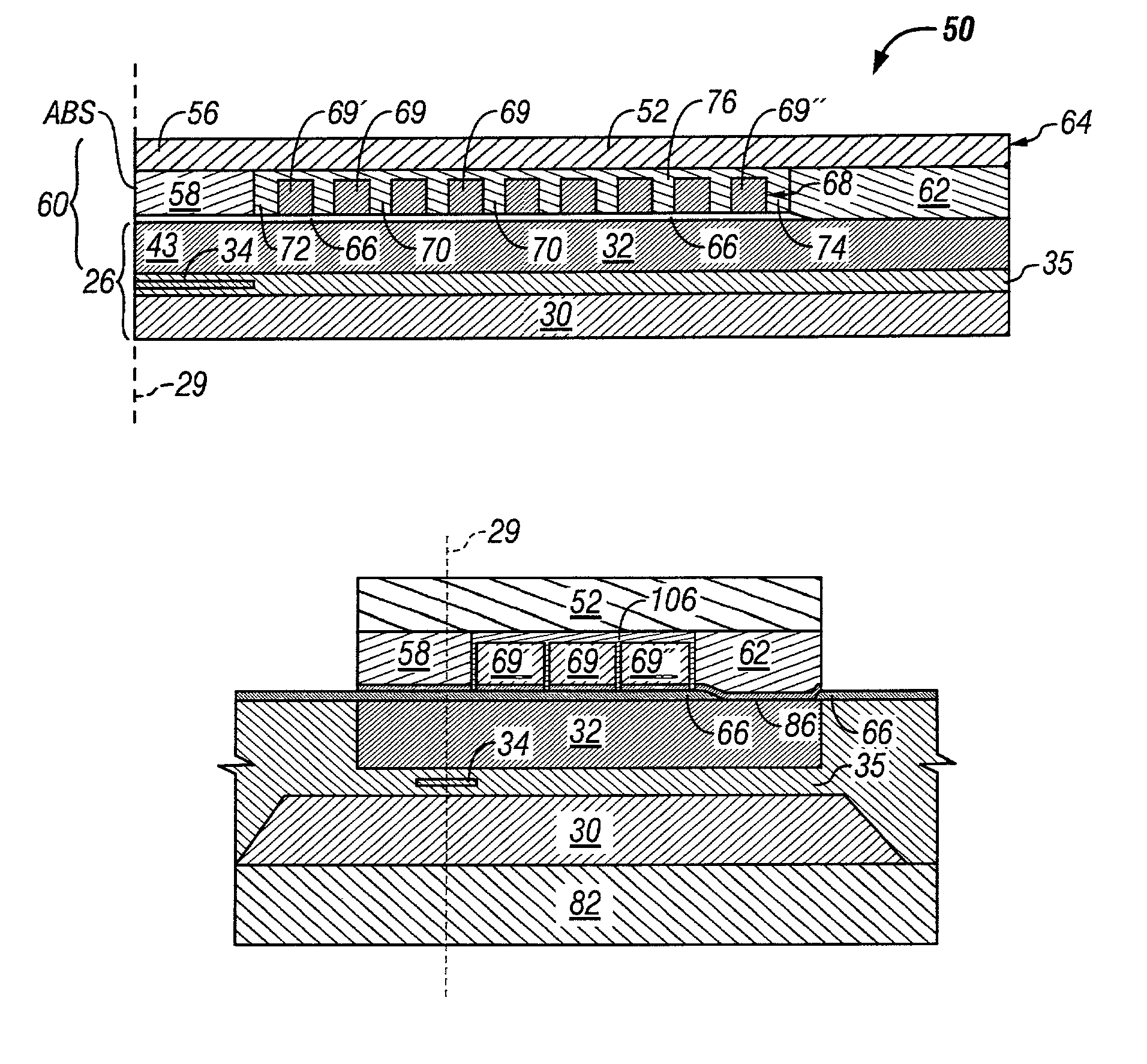
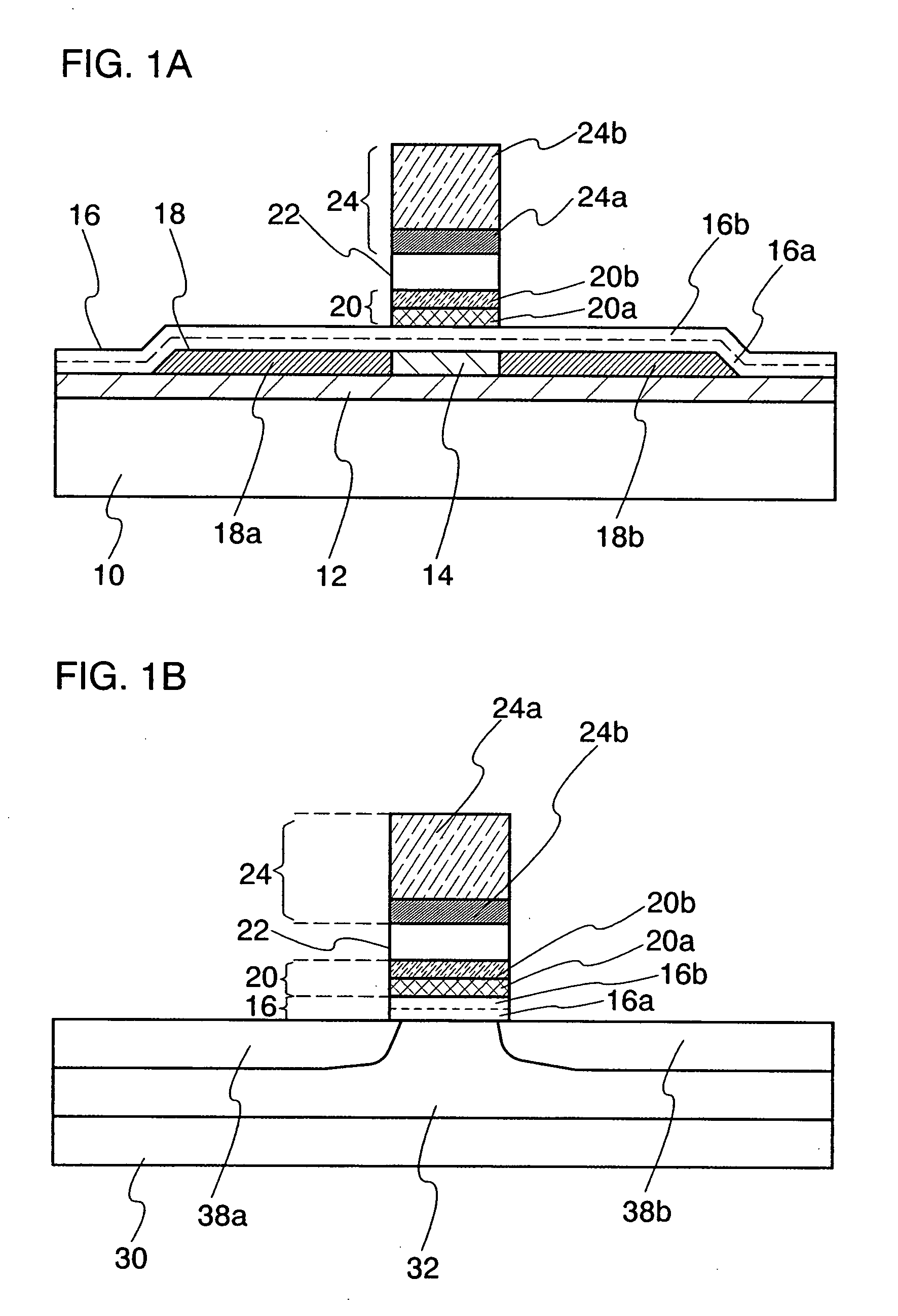
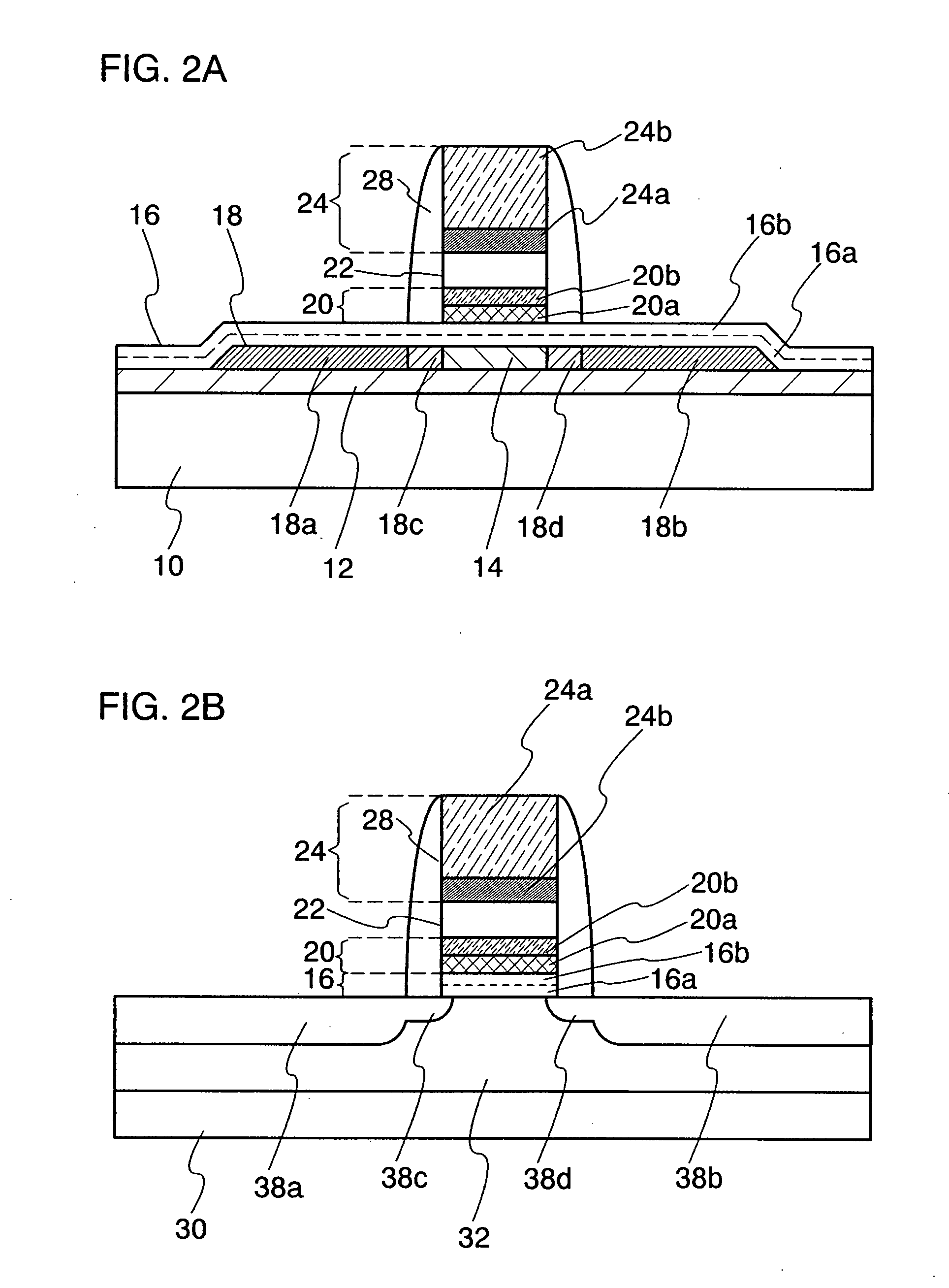
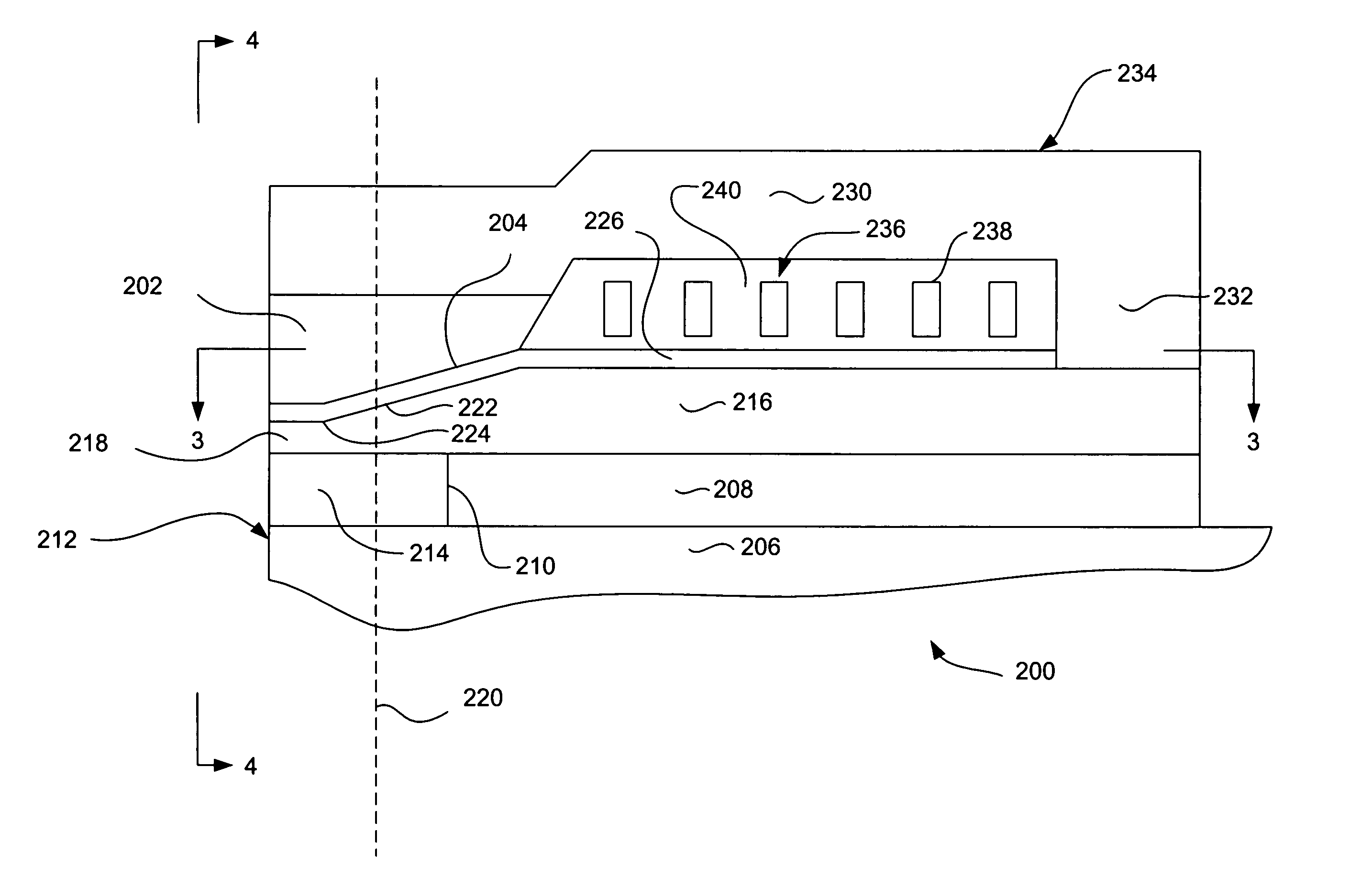
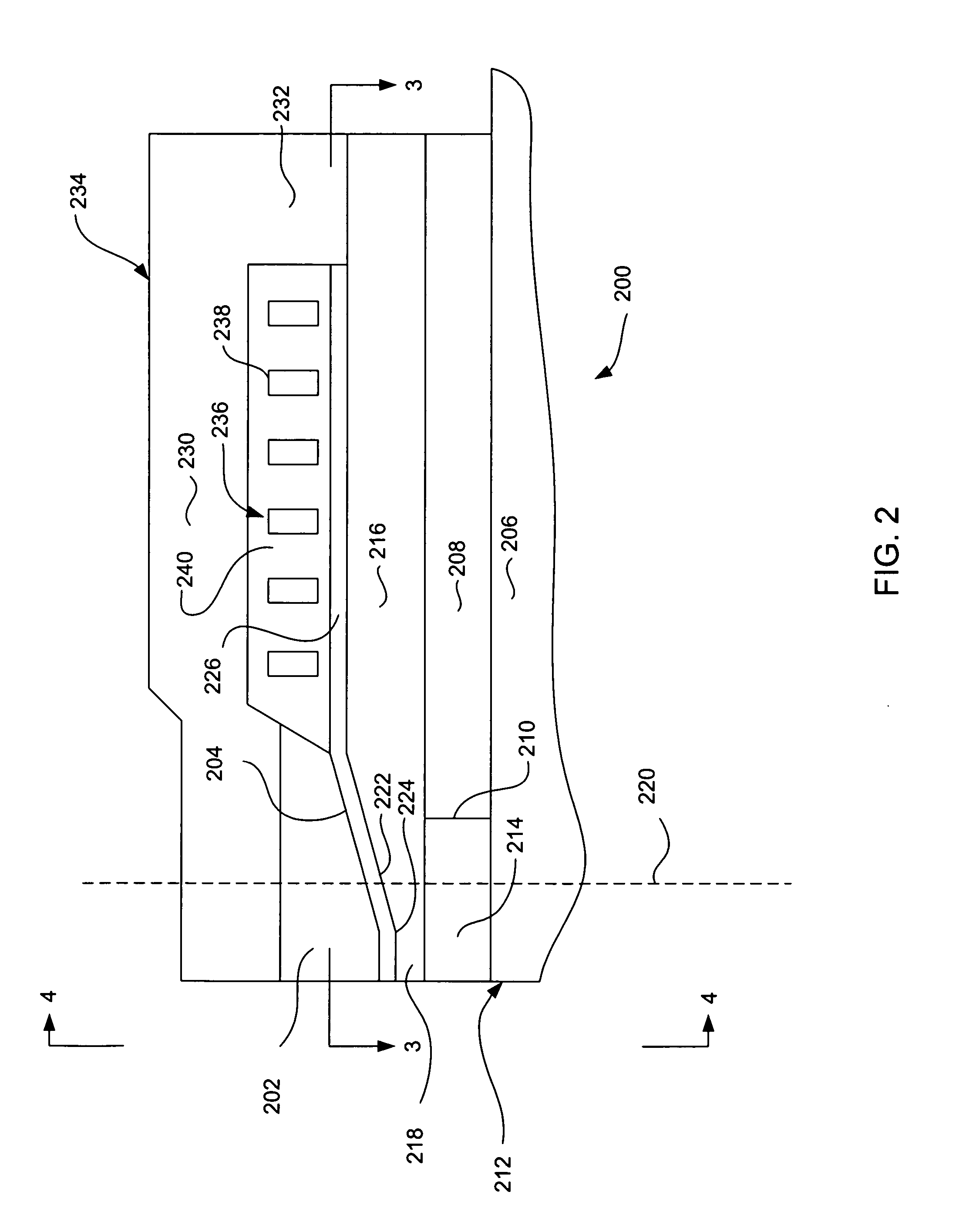
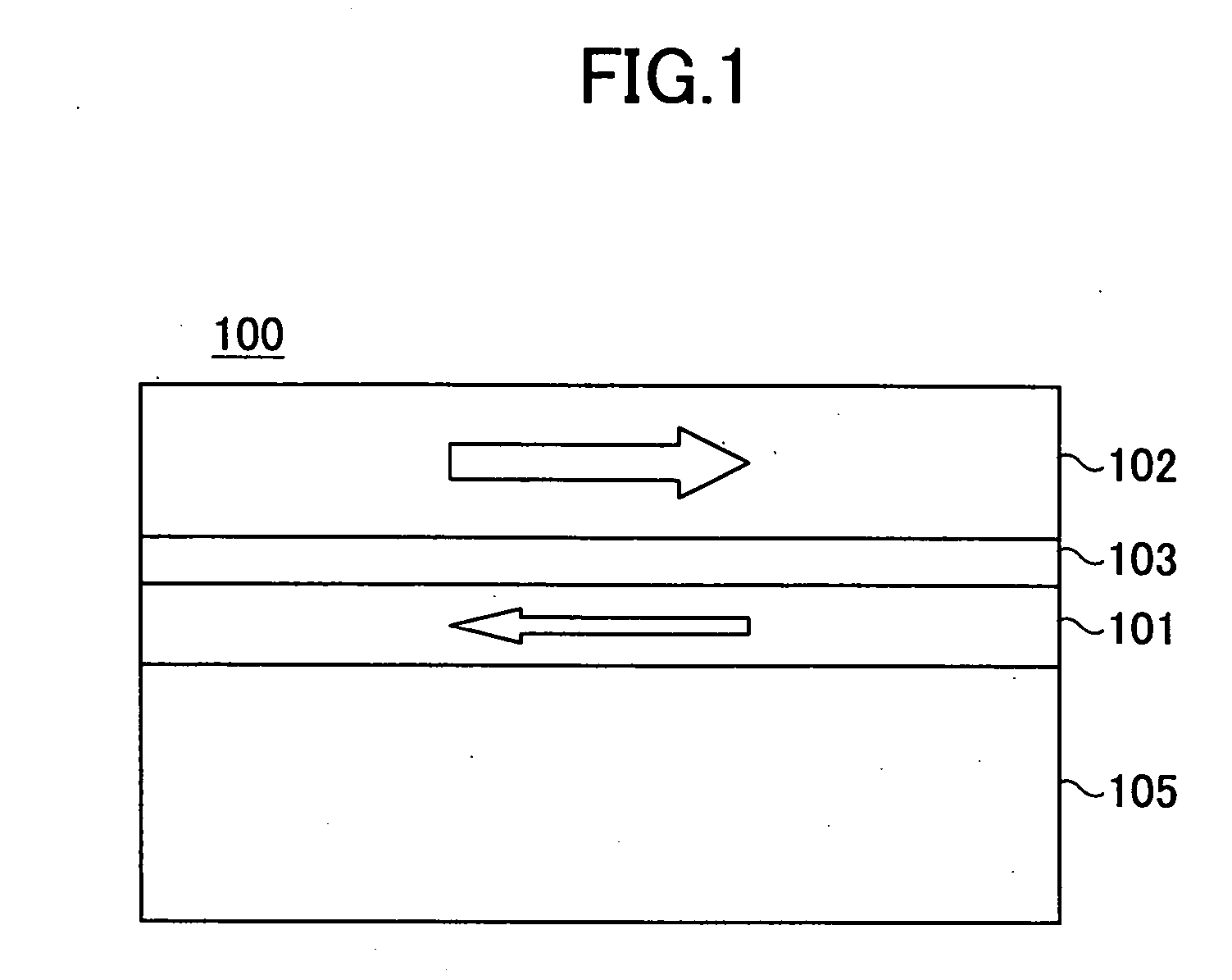
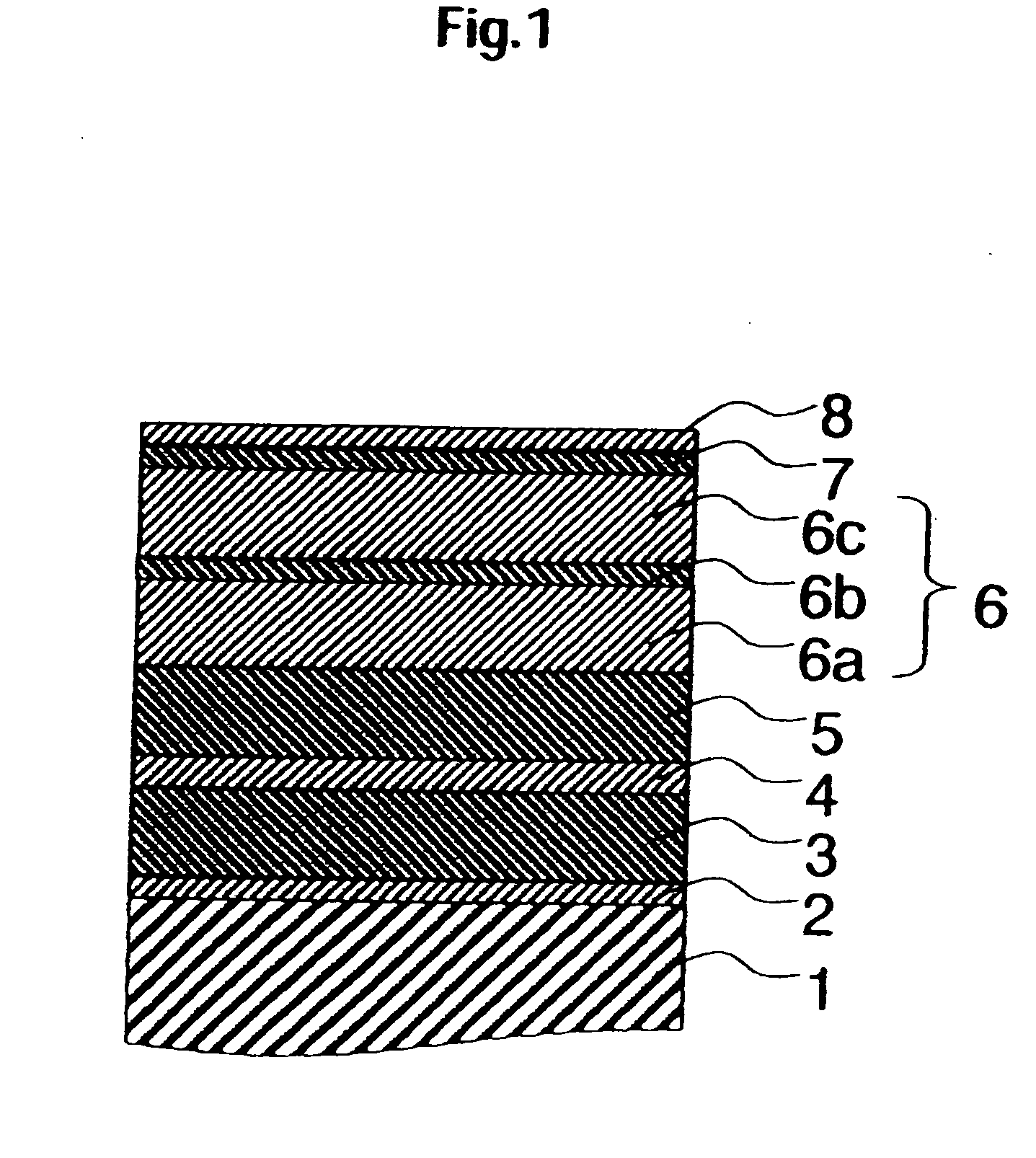
Compact MR write structure
InactiveUS6894877B1Less spaceCompact structureConstruction of head windingsManufacture head surfaceEngineeringBackplane
A compact write element includes a conductive shield layer, an insulating write gap layer, a pole pedestal, a coil, and a conductive pole layer, and, in some embodiments also includes a backgap. The pole pedestal and the coil, and, in some embodiments the backgap, constitute a self-aligned array of components that may be formed in a single masking operation to allow for very tight tolerances between the components for a shorter yoke length. The pole layer is substantially flat and parallel to the conductive shield layer, providing for a shorter stack height. Also, a compact MR read / write head includes such a write element and a magnetic data storage and retrieval system includes the compact MR read / write head having such a write element.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
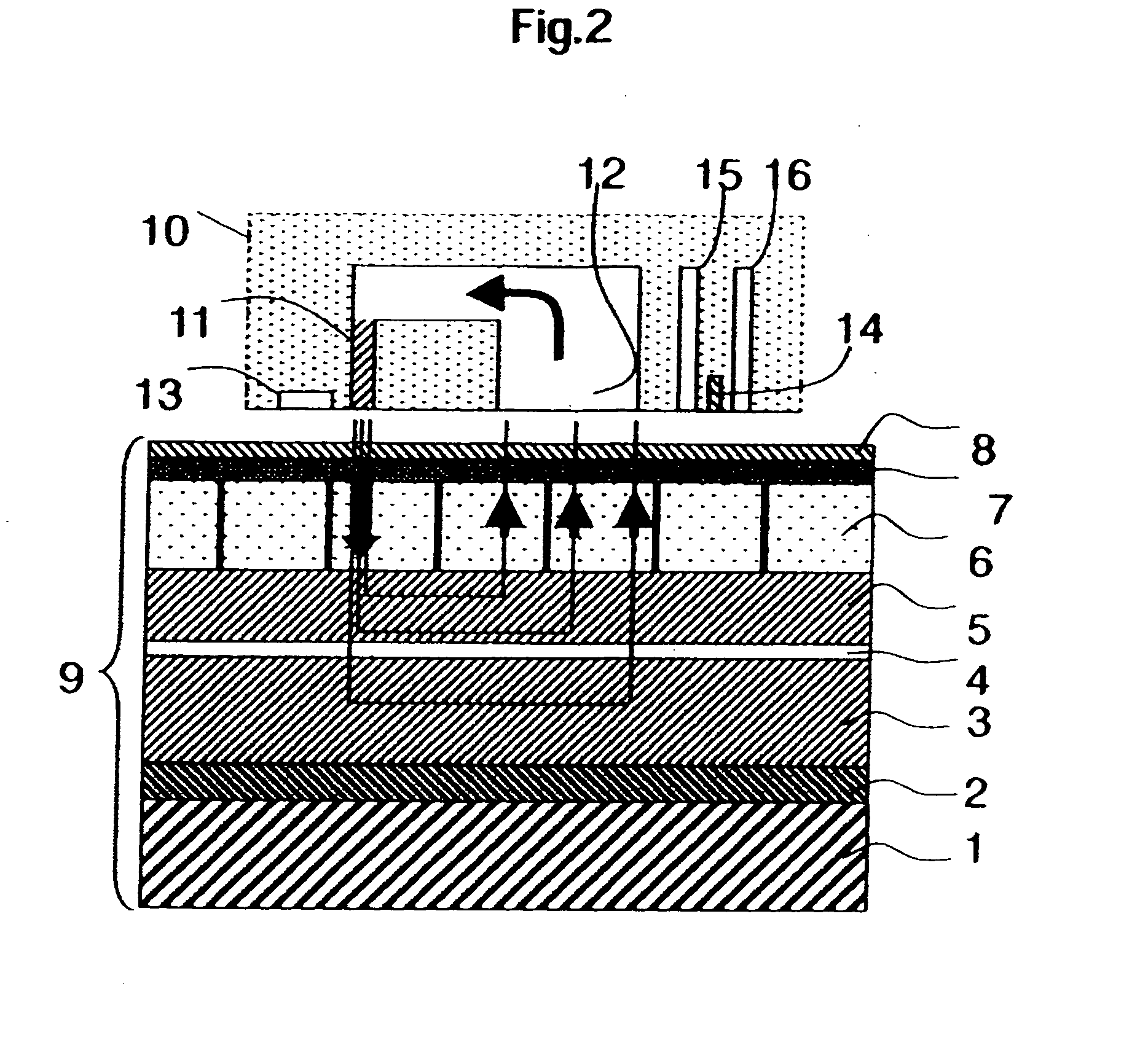
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20070278563A1Easy to keepReduce charge leakageSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCharge retentionSemiconductor package
An object is to provide a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device which is excellent in a writing property and a charge retention property. In addition, another object is to provide a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device capable of reducing writing voltage. A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device includes a semiconductor layer or a semiconductor substrate including a channel formation region between a pair of impurity regions that are formed apart from each other, and a first insulating layer, a plurality of layers formed of different nitride compounds, a second insulating layer, and a control gate that are formed in a position which is over the semiconductor layer or the semiconductor substrate and overlaps with the channel formation region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
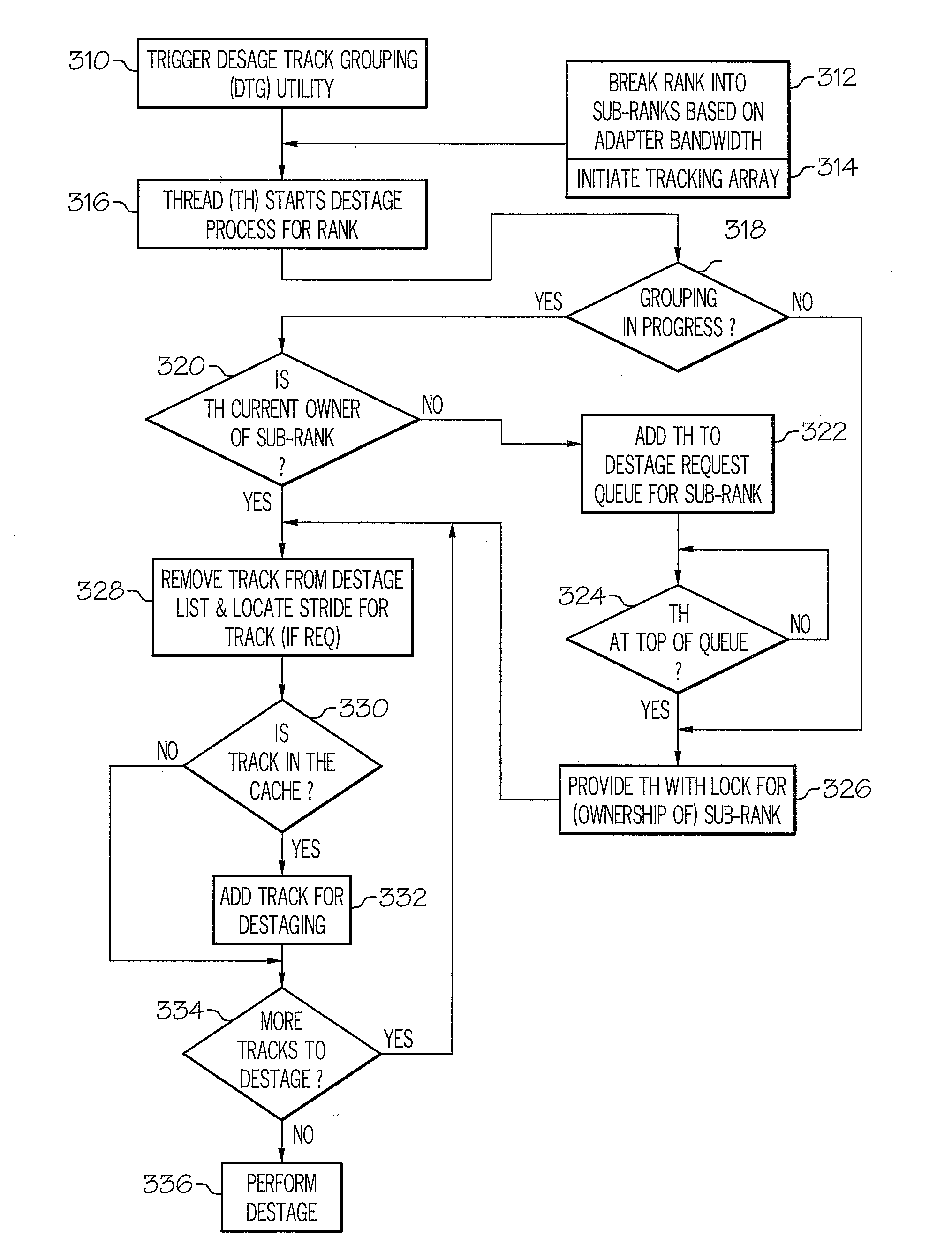
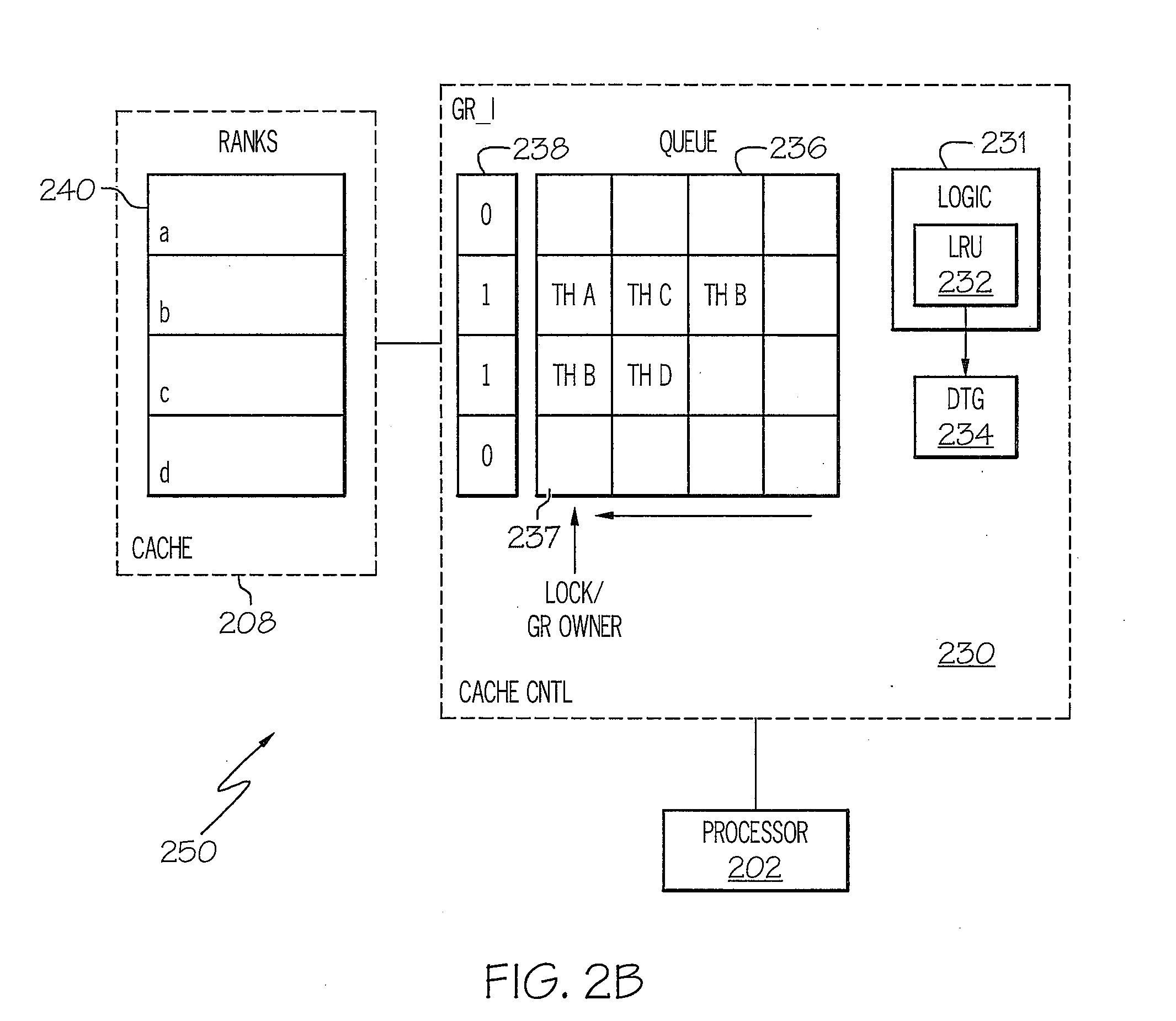
Method and system for grouping tracks for destaging on raid arrays
InactiveUS20080040553A1Maximize full stripe writesLower latencyError detection/correctionMemory systemsRAIDData selection
A method, system and processor for substantially reducing the write penalty (or latency) associated with writes and / or destaging operations within a RAID 5 array and / or RAID 6 array. When a write or destaging operation is initiated, i.e., when modified data is to be evicted from the cache, an existing data selection mechanism first selects the track of data to be evicted from the cache. The data selection mechanism then triggers a data track grouping (DTG) utility, which executes a thread to group data tracks, in order to maximize full stripe writes. Once the DTG algorithm completes the grouping of data tracks to complete a full stripe, a fall-stripe write is performed, and parity is generated without requiring a read from the disk(s). In this manner, the write penalty is substantially reduced, and the overall write performance of the processor is significantly improved.
Owner:IBM CORP
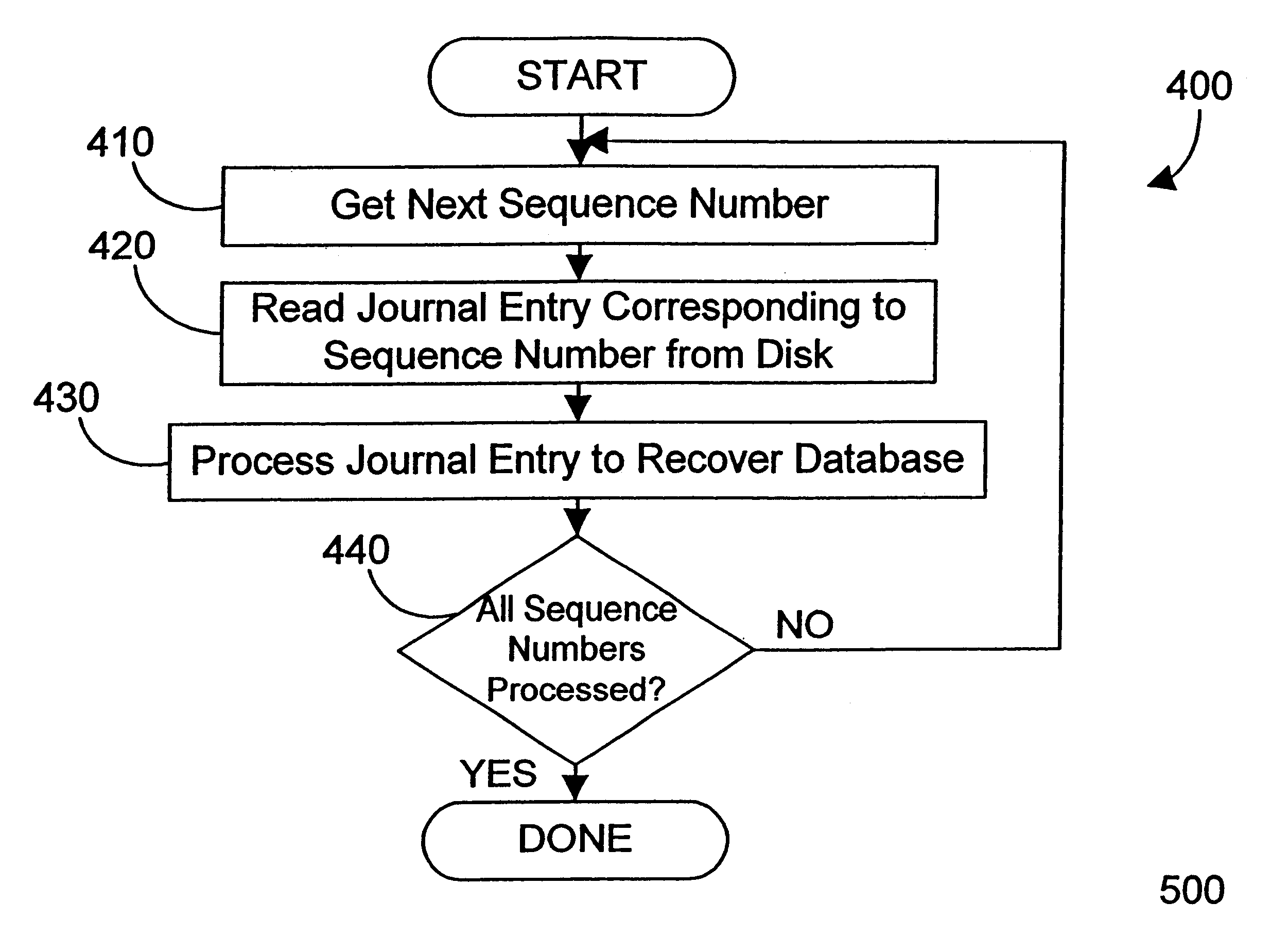
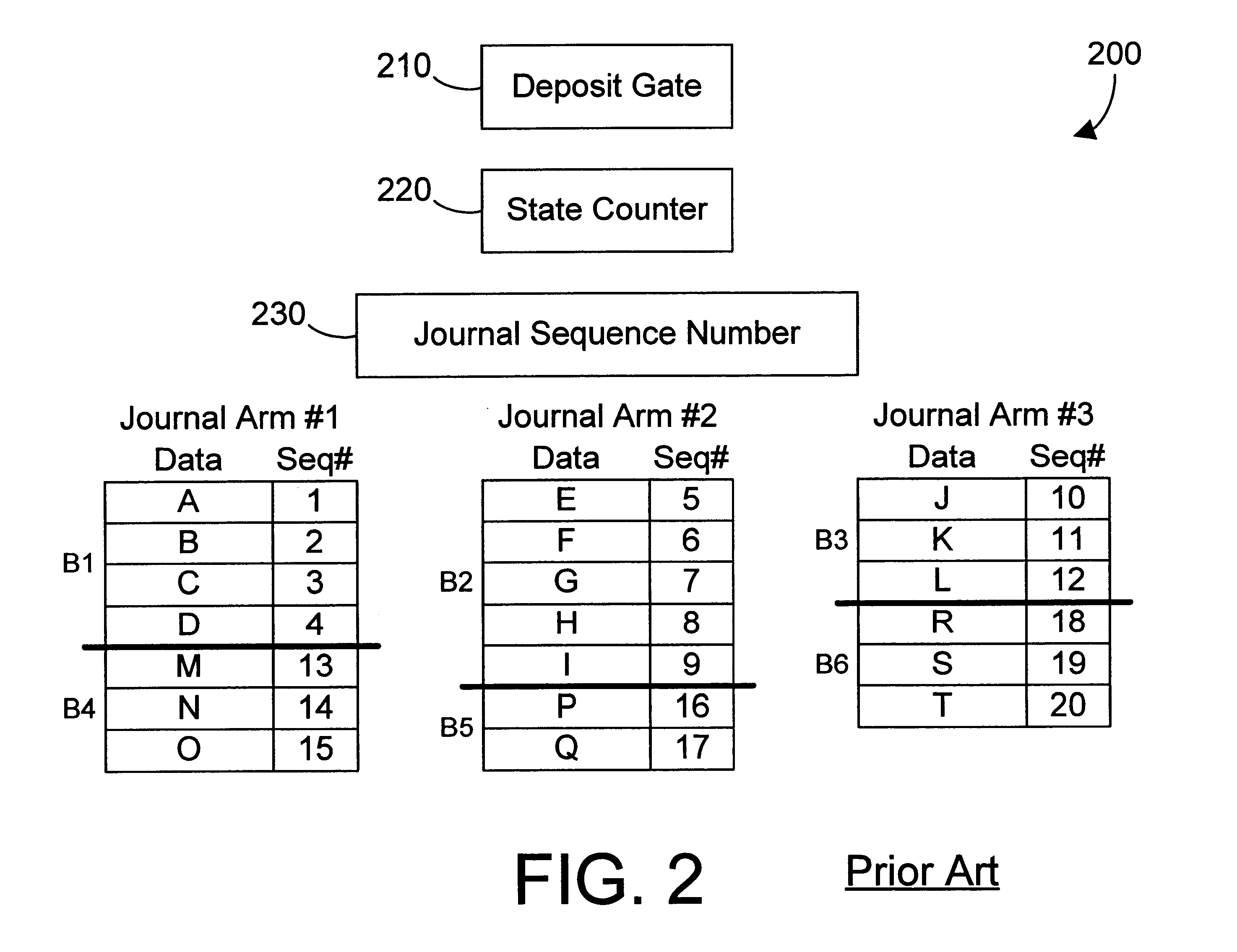
Database journal mechanism and method that supports multiple simultaneous deposits
InactiveUS6298345B1Easy to scaleContentionData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsDatabase machineData mining
A journal mechanism for a database allows simultaneous deposits on multiple journal arms. According to a first embodiment, a journaling system maintains the time-order of interdependent deposits on the journal, but does not necessarily maintain the time-order of deposits that are independent of each other, thereby providing multiple simultaneous deposit points on the journal. The first embodiment provides excellent scaling of journal functions as processors are added to a database computer system. According to a second embodiment, a journaling system maintains the time-order of deposits on the journal, but allows a group of deposits known as a "bundle" to span multiple journal arms, thereby providing multiple simultaneous deposit points on the journal. The second embodiment provides good scaling while providing compatibility with known database systems. The present invention thus relieves contention for the journal that exists as the number of processors increases in a database system.
Owner:IBM CORP
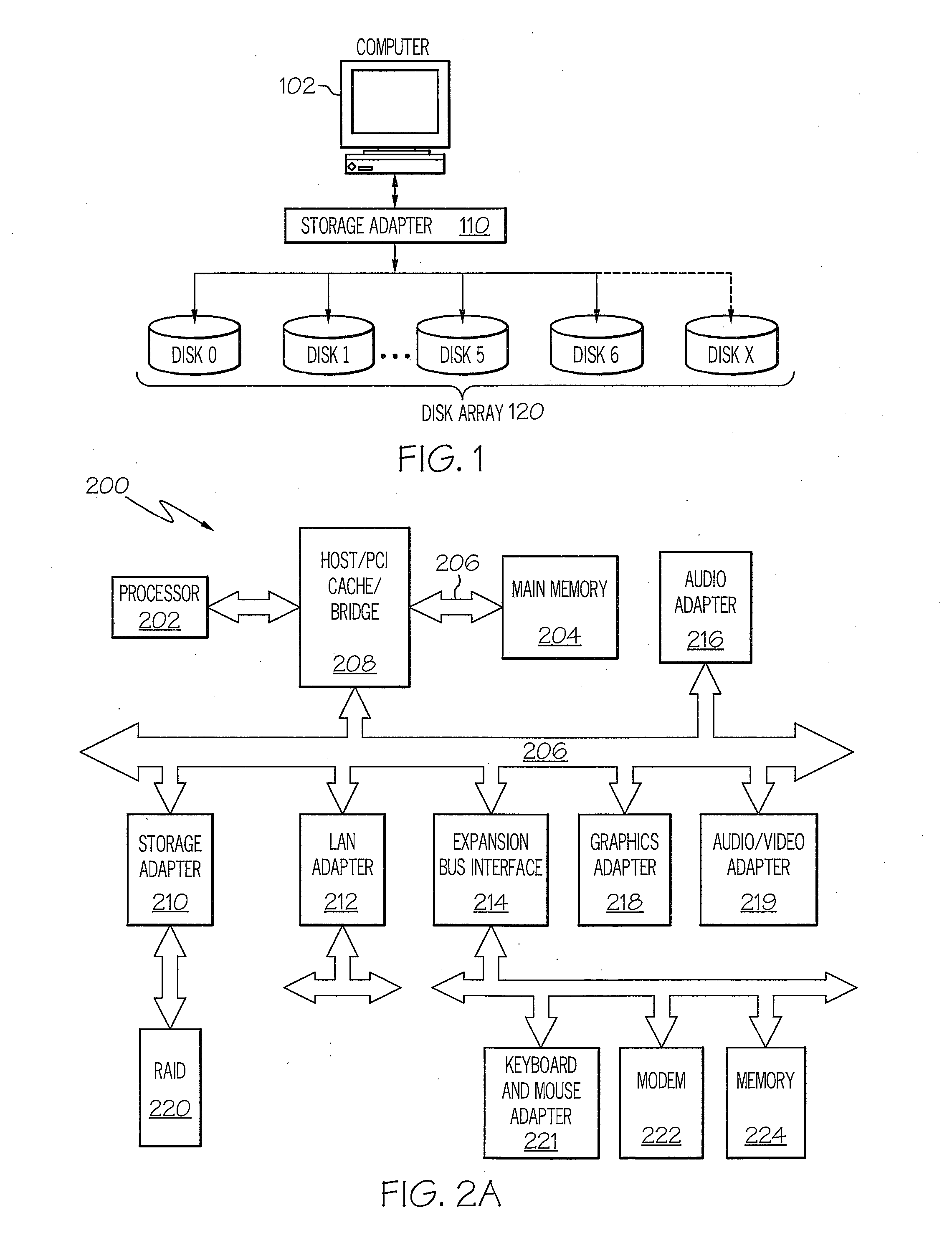
Method, system, apparatus, and computer-readable medium for improving disk array performance
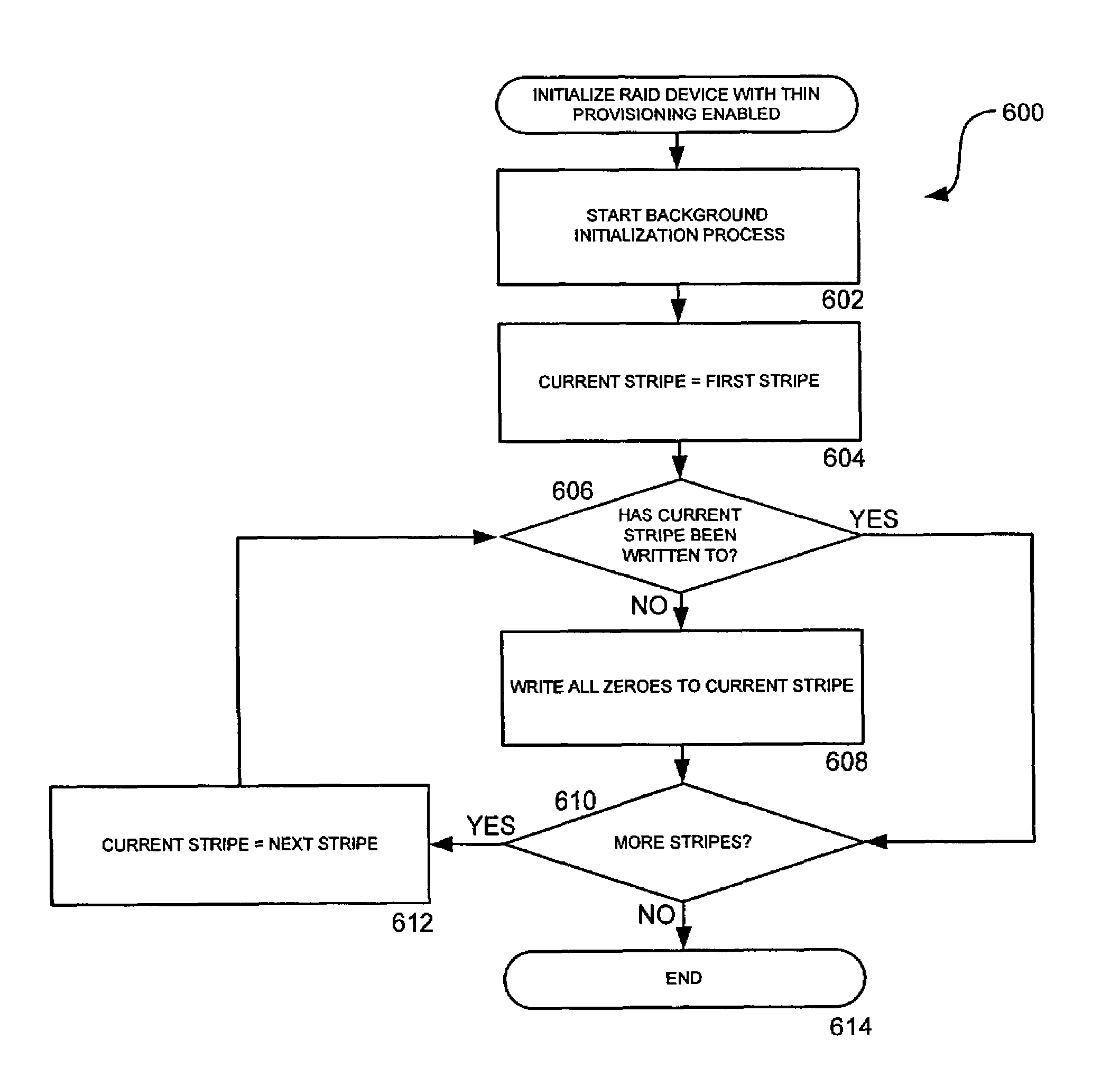
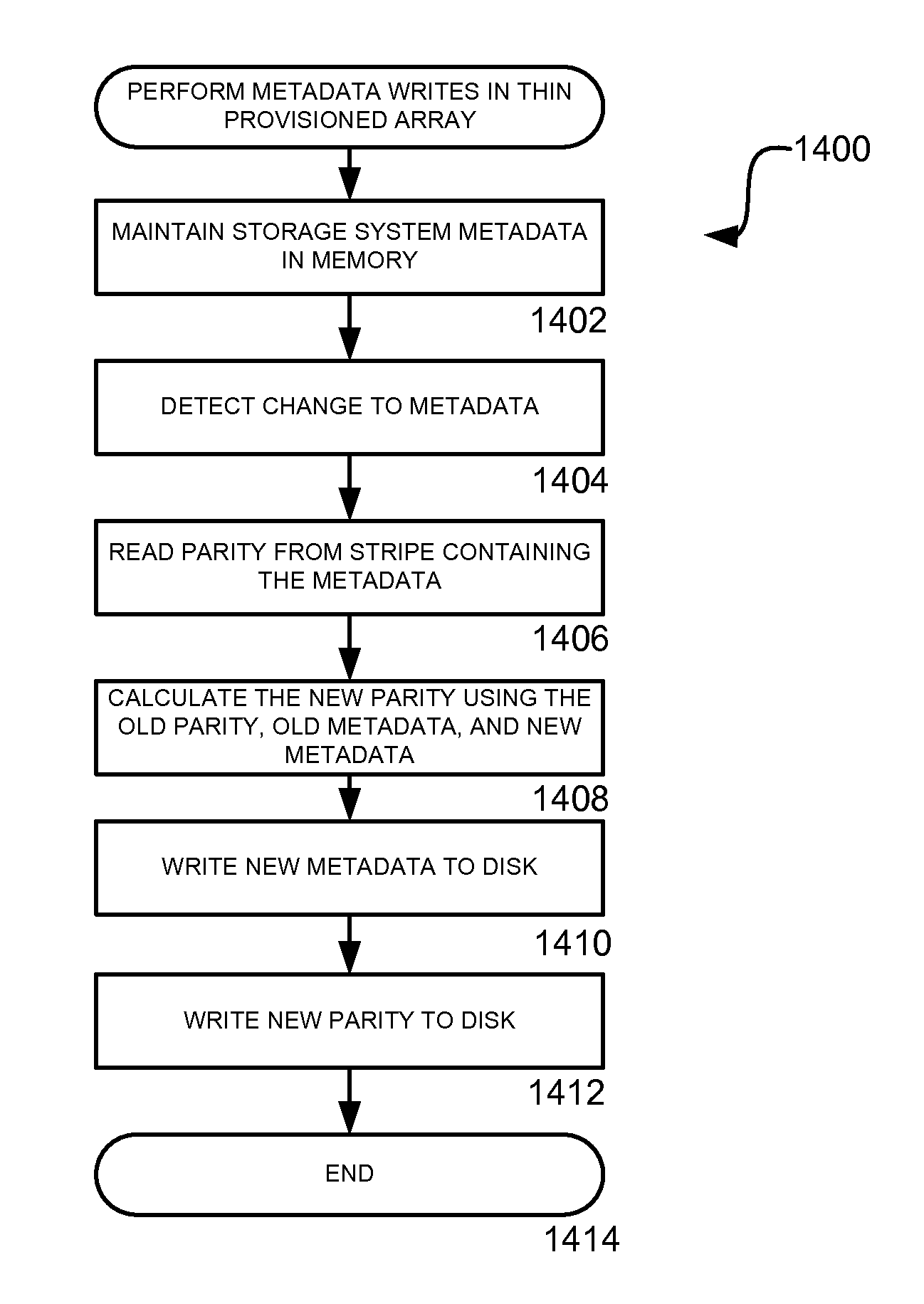
ActiveUS7711897B1Improve performanceEffective cachingMemory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionRAIDThin provisioning
A method, system, apparatus, and computer-readable medium are provided for improving storage in a disk array are provided. According to aspects of the invention, a redundant disk array is combined with a mechanism for thin provisioning of the array. Thin provisioning refers to a process of allocating physical capacity to logical volumes on an as-needed basis. Data structures containing a mapping between the logical location of stored data and its actual location on a physical device are maintained. Through the use of the thin provisioning mechanism, physical storage space can be allocated sequentially, regardless of the order of logical writes. In this manner, the data stored on the array grows in a linear manner. The data structures maintained by the thin provisioning mechanism can be used to identify the portions of a device or an array that have been previously written. This information allows redundant arrays, such as RAID arrays, to perform initialization, rebuild, and data migration operations only on portions that been written, and not on areas that have not been utilized by a higher layer.
Owner:AMZETTA TECH LLC
Cache-based storage system architecture
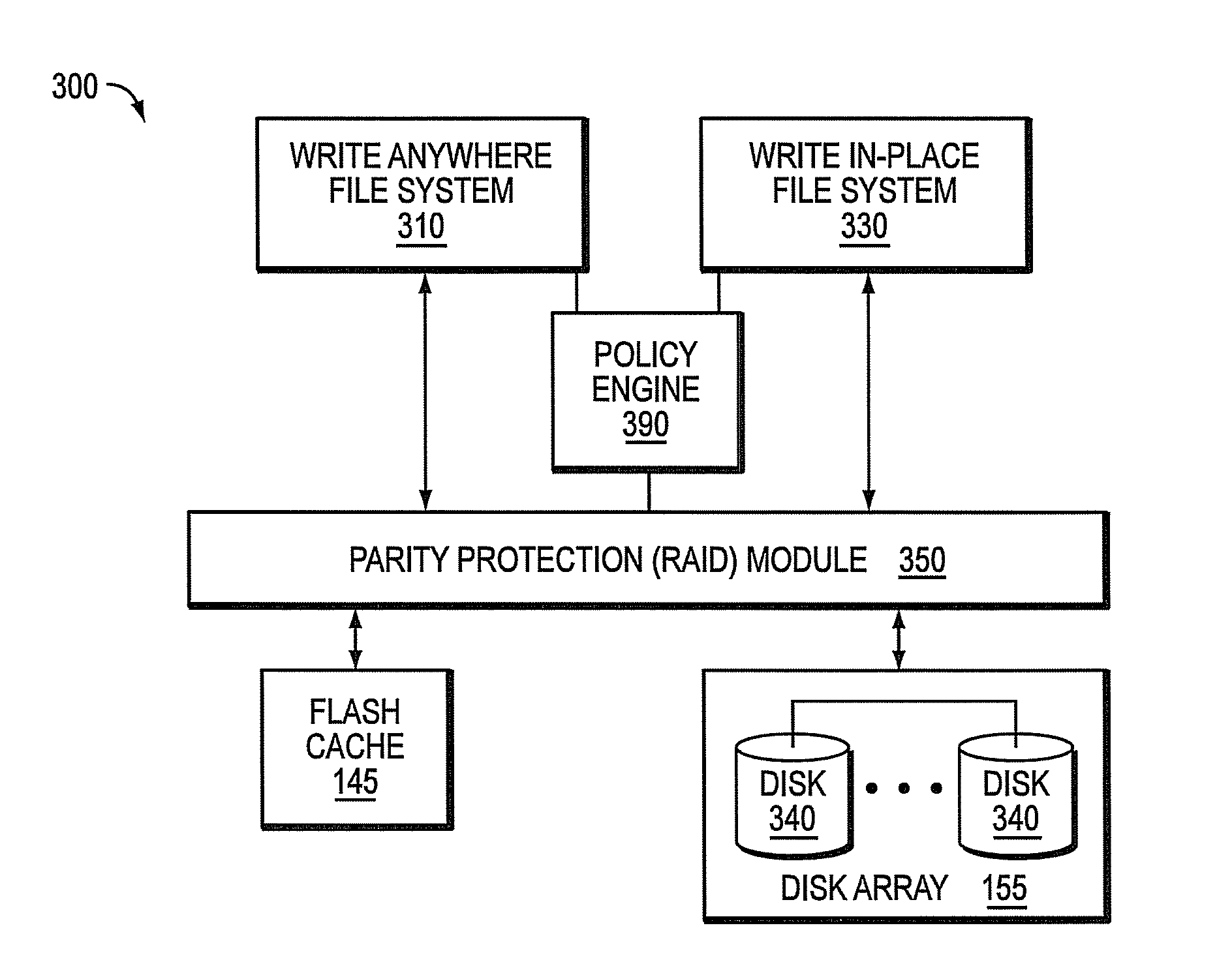
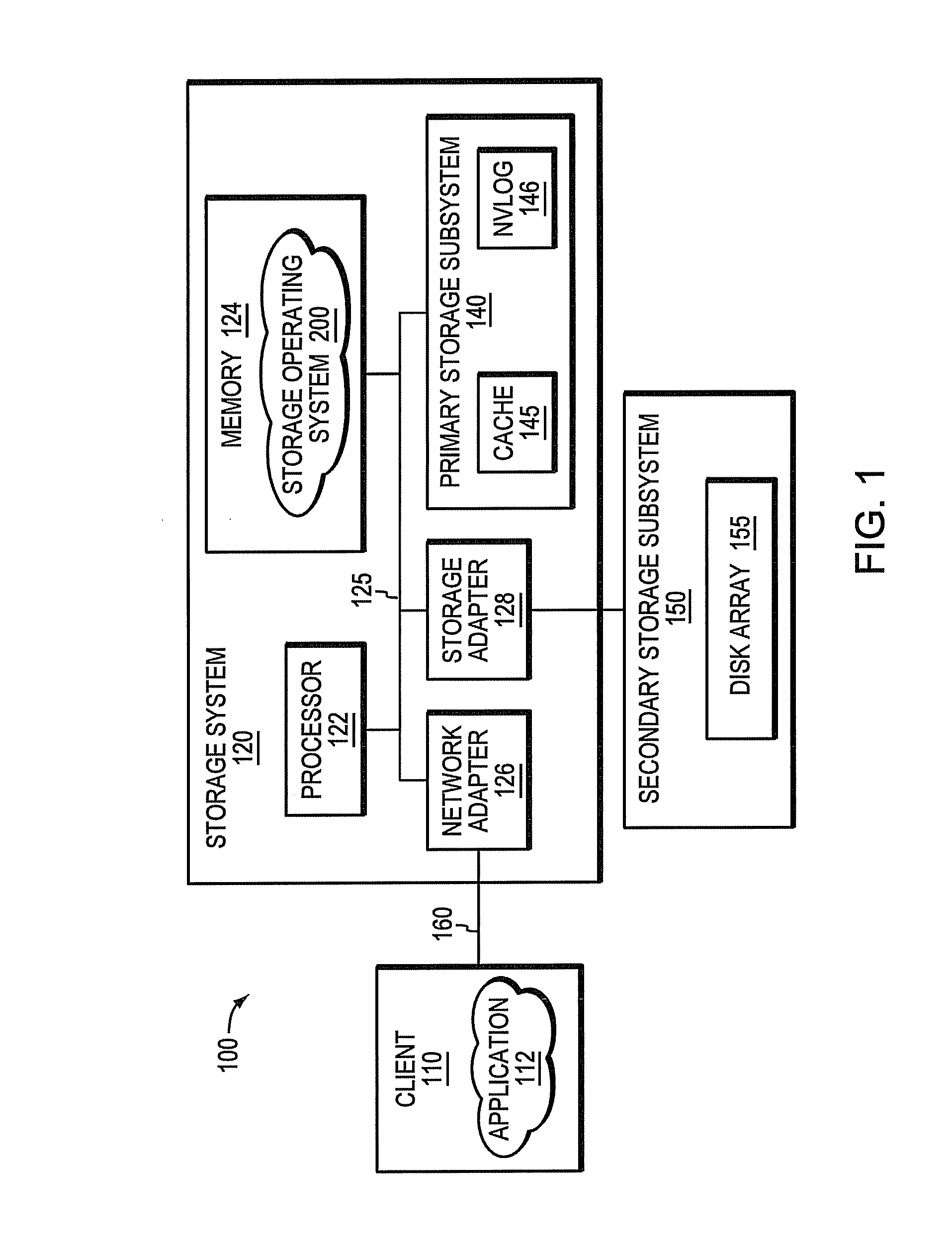
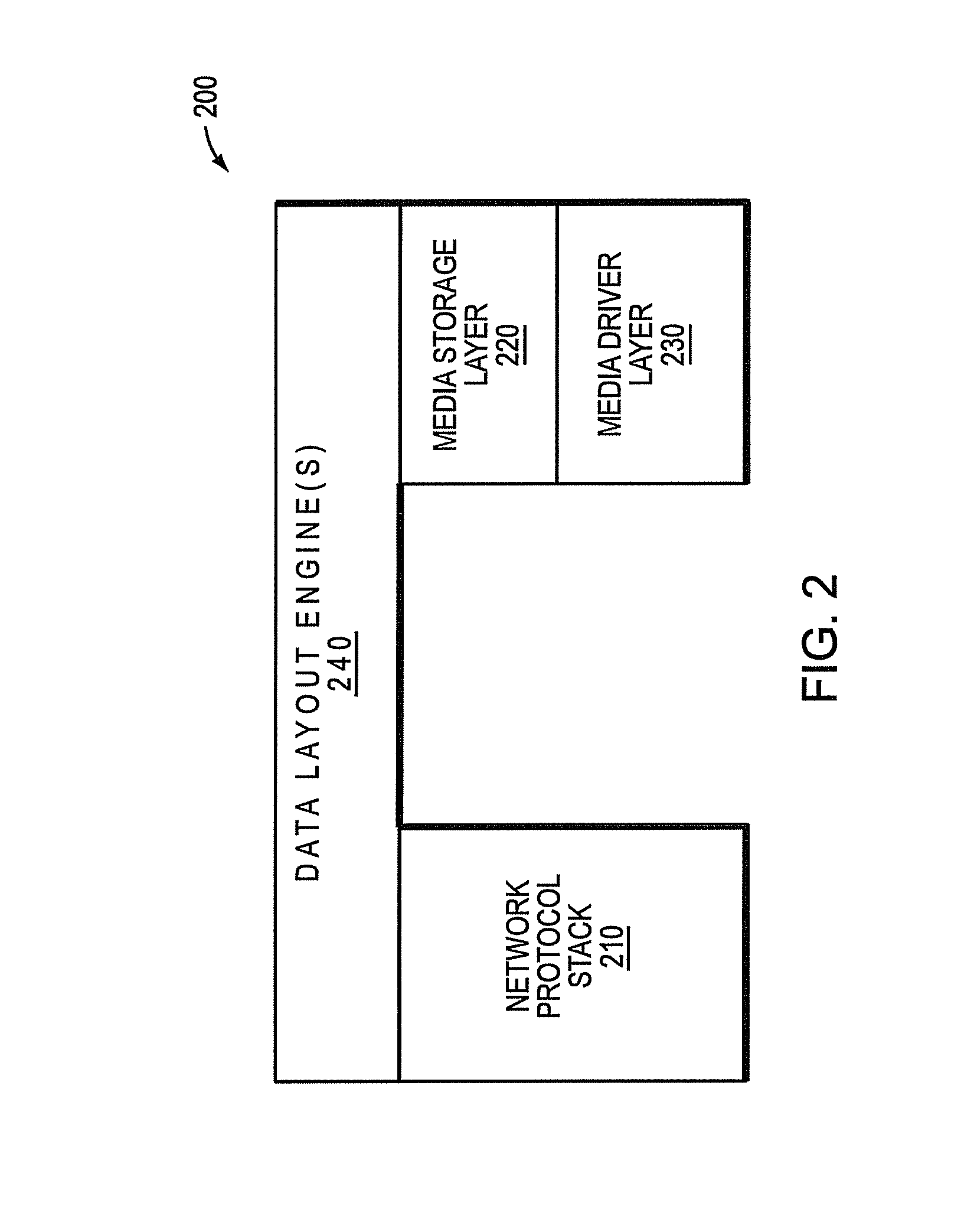
ActiveUS8549222B1Improve write performanceImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionMagnetic storageData access
A cache-based storage architecture has primary and secondary storage subsystems that are controlled by first and second data layout engines to provide a high-performance storage system. The primary storage subsystem illustratively comprises non-volatile electronic storage media configured as a cache, while the secondary storage subsystem comprises magnetic storage media configured as a disk array. The data layout engines illustratively implement data layout techniques that improve read and write performance to the primary and secondary storage subsystems. To that end, the data layout engines cooperate to optimize the use of the non-volatile cache as a primary storage stage that efficiently serves random data access operations prior to substantially transposing them into sequential data access operations for permanent (or archival) storage on the disk array.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
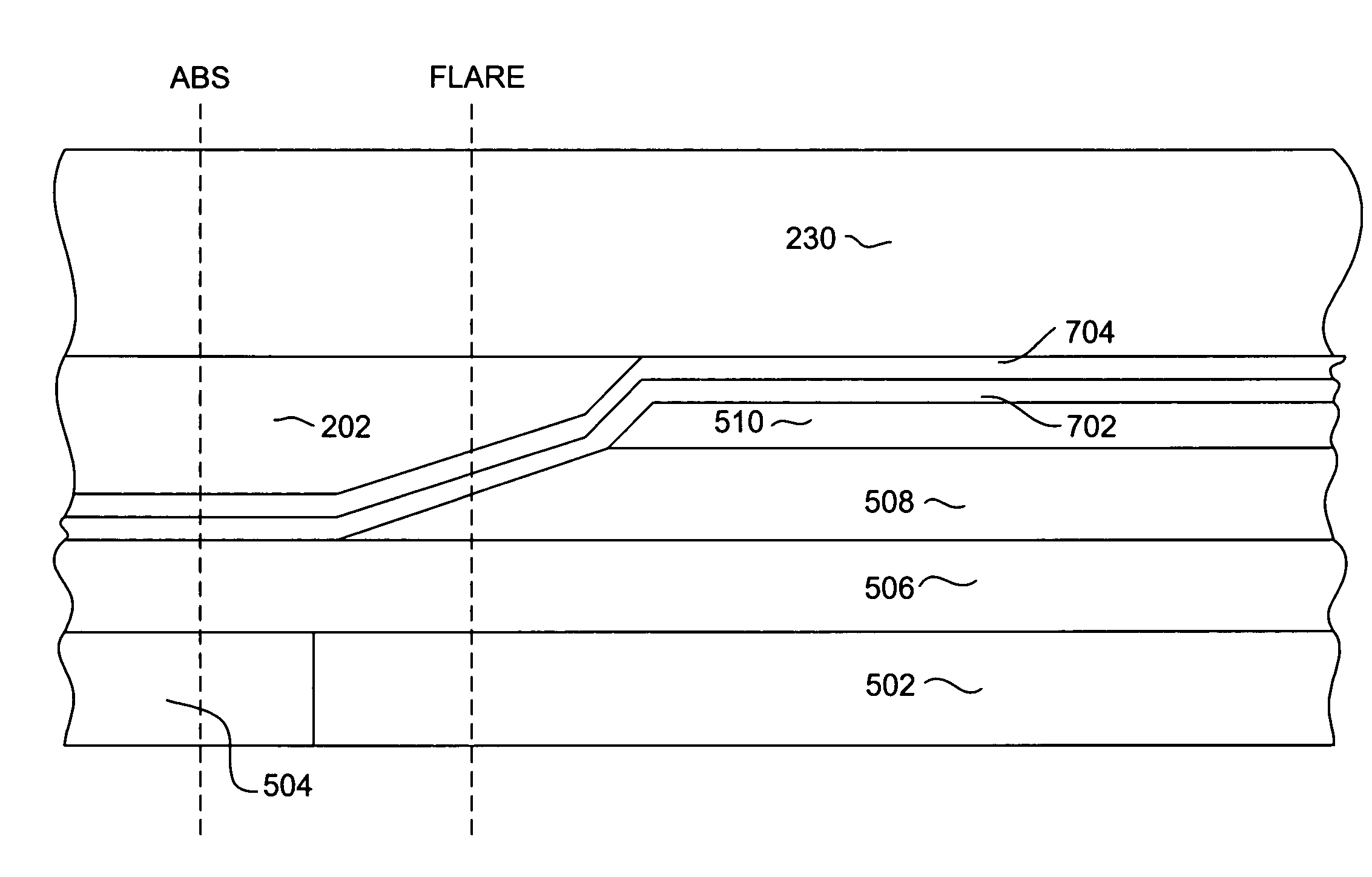
Perpendicular magnetic recording head with flare and taper configurations
ActiveUS7212379B2Improve performanceImprove write performanceManufacture head surfaceHeads using thin filmsEngineeringData recording
A magnetic write head for use in perpendicular magnetic data recording. The write head includes a write pole and a trailing shield having a tapered surface. A return pole stitched to the trailing shield is magnetically connected with the write pole at a location away from the air bearing surface (ABS).
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method of managing files for optimal performance
ActiveUS20050256838A1Desired performanceImprove write performanceInput/output to record carriersProgram control using stored programsFile systemTerm memory
A method of storing a file in a memory. An explicit command is issued to a file system to store the file in accordance with a desired performance characteristic of the file such as enhanced write performance, enhanced read performance or enhanced latency performance. The file system stores the file in the memory in accordance with the desired performance characteristic. Preferably the desired performance characteristic is achieved by storing the file in a physically contiguous portion of the memory or in a logically contiguous portion of the memory. After the explicit command has been issued for each of a plurality of files, the files may be stored concurrently.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL ISRAEL LTD
Trailing edge taper design and method for making a perpendicular write head with shielding
ActiveUS20050219747A1Improved write field writeImproved write write gradient performanceManufacture head surfaceHeads using thin filmsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
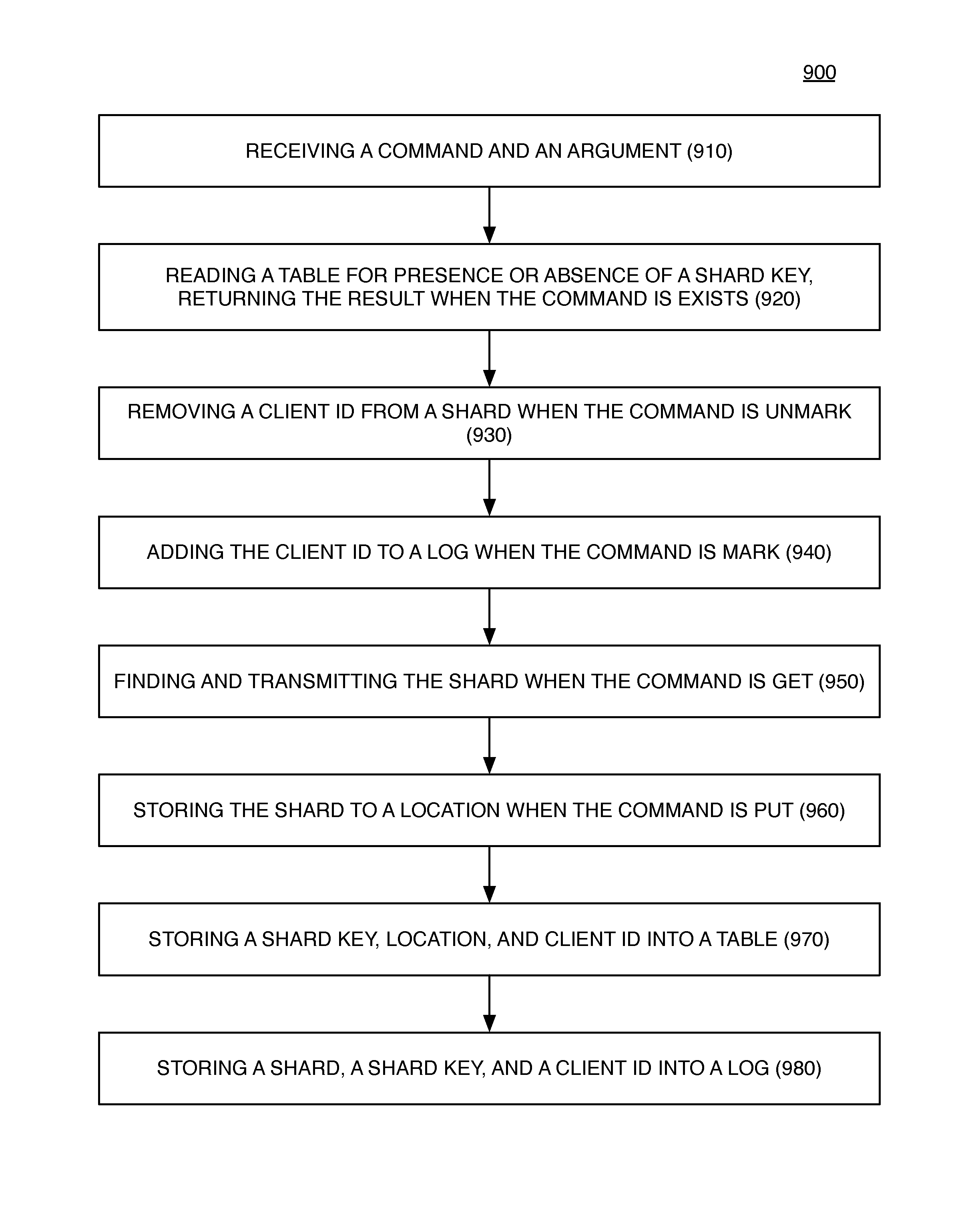
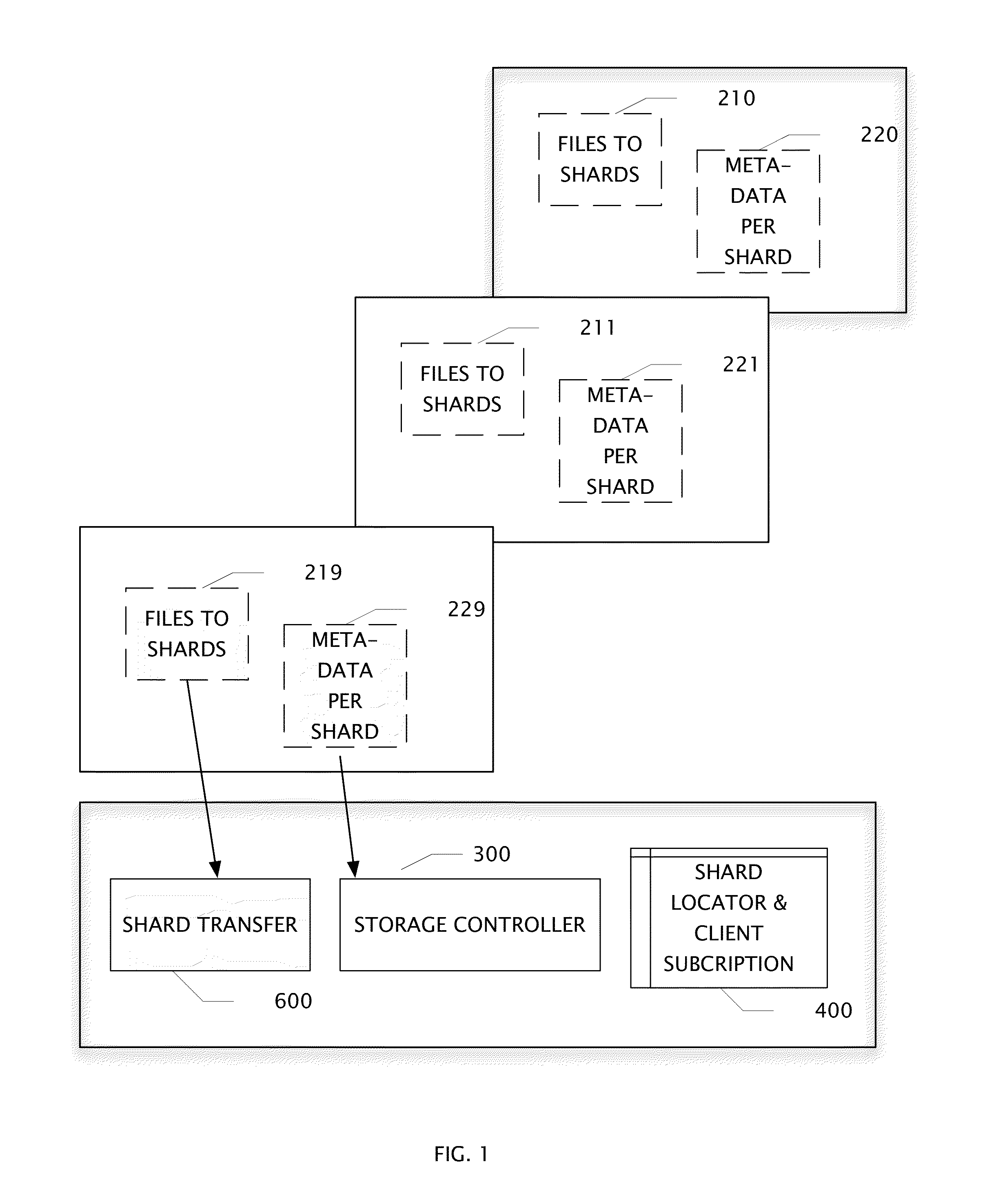
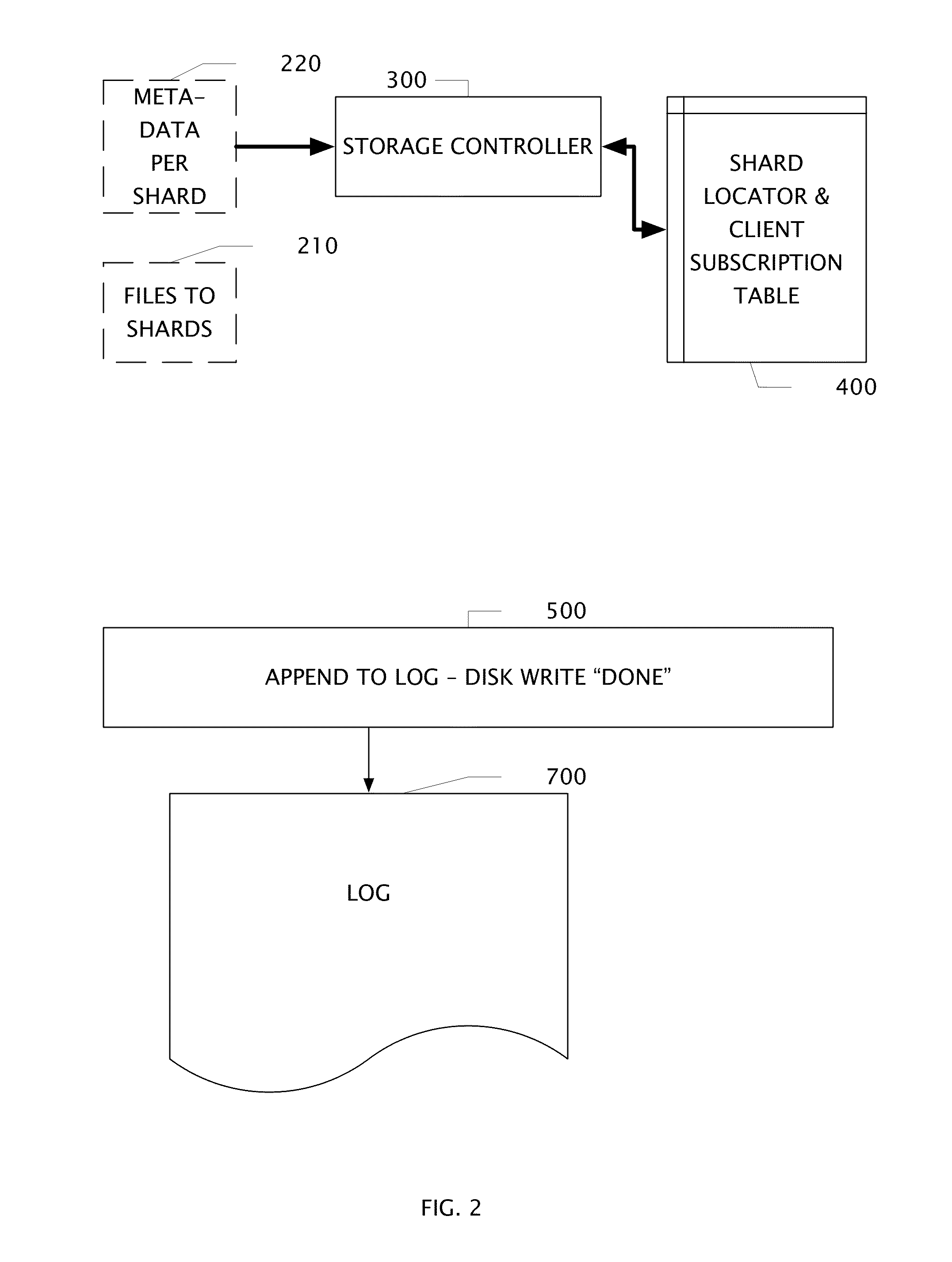
Log Access Method Storage Control Apparatus, Archive System, and Method of Operation
ActiveUS20140372383A1High performance encoding and compaction circuitAvoids duplicate storageDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsAccess methodClient-side
A file shard store includes high performance encoding and compaction circuits. An apparatus and its method of operation avoids duplicate storage of file fragments. A plurality of tables control write operations into a plurality of log segments. Shard keys are transferred to uniquely identify fragments of files which may have been previously stored and associated with one or more of client subscribers. An apparatus comprises a plurality of location / subscription tables, a shard transfer circuit, a storage control circuit, an append-to-log circuit coupled to a large storage array, and a log segment compactor circuit.
Owner:BARRACUDA NETWORKS
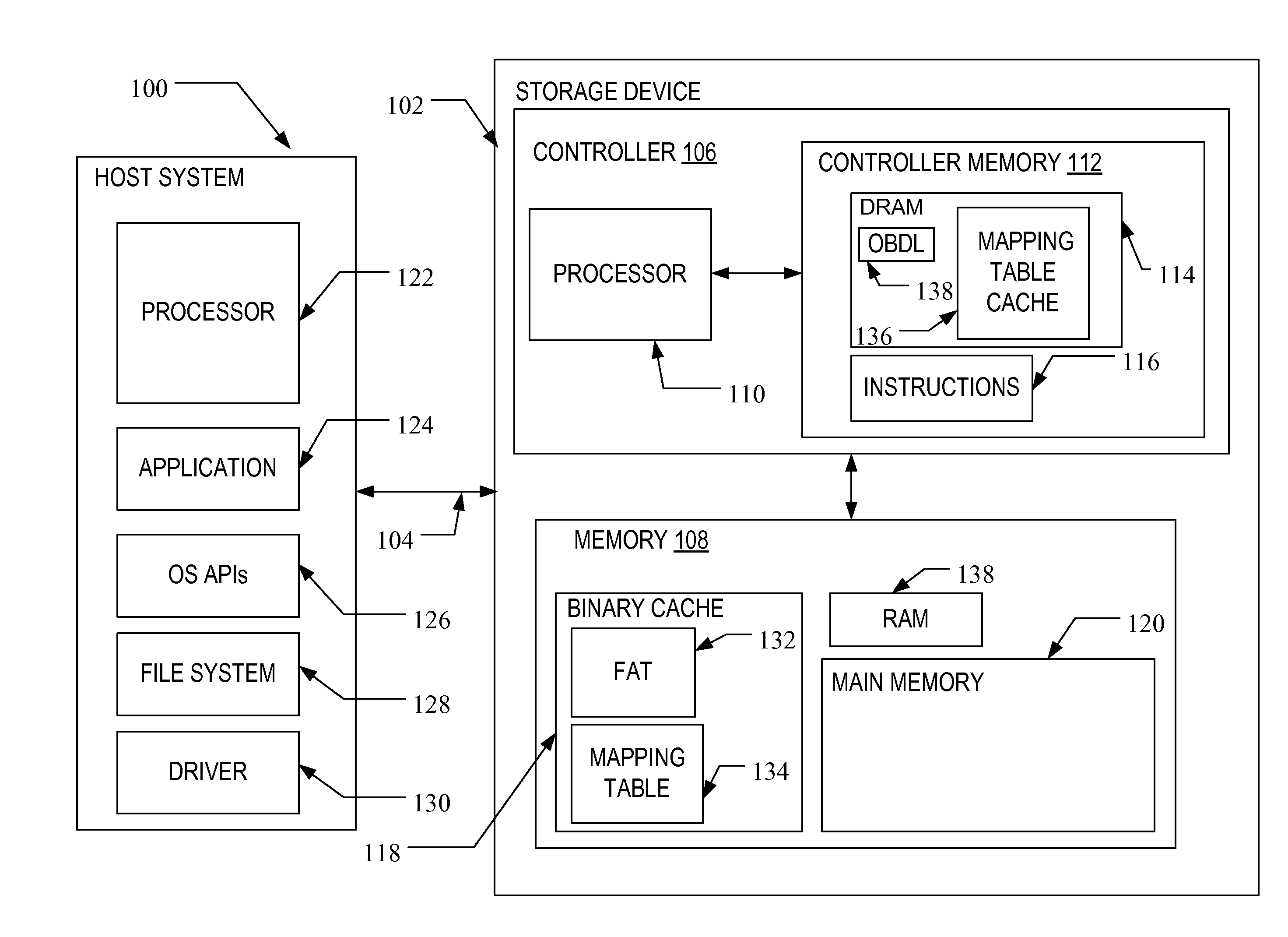
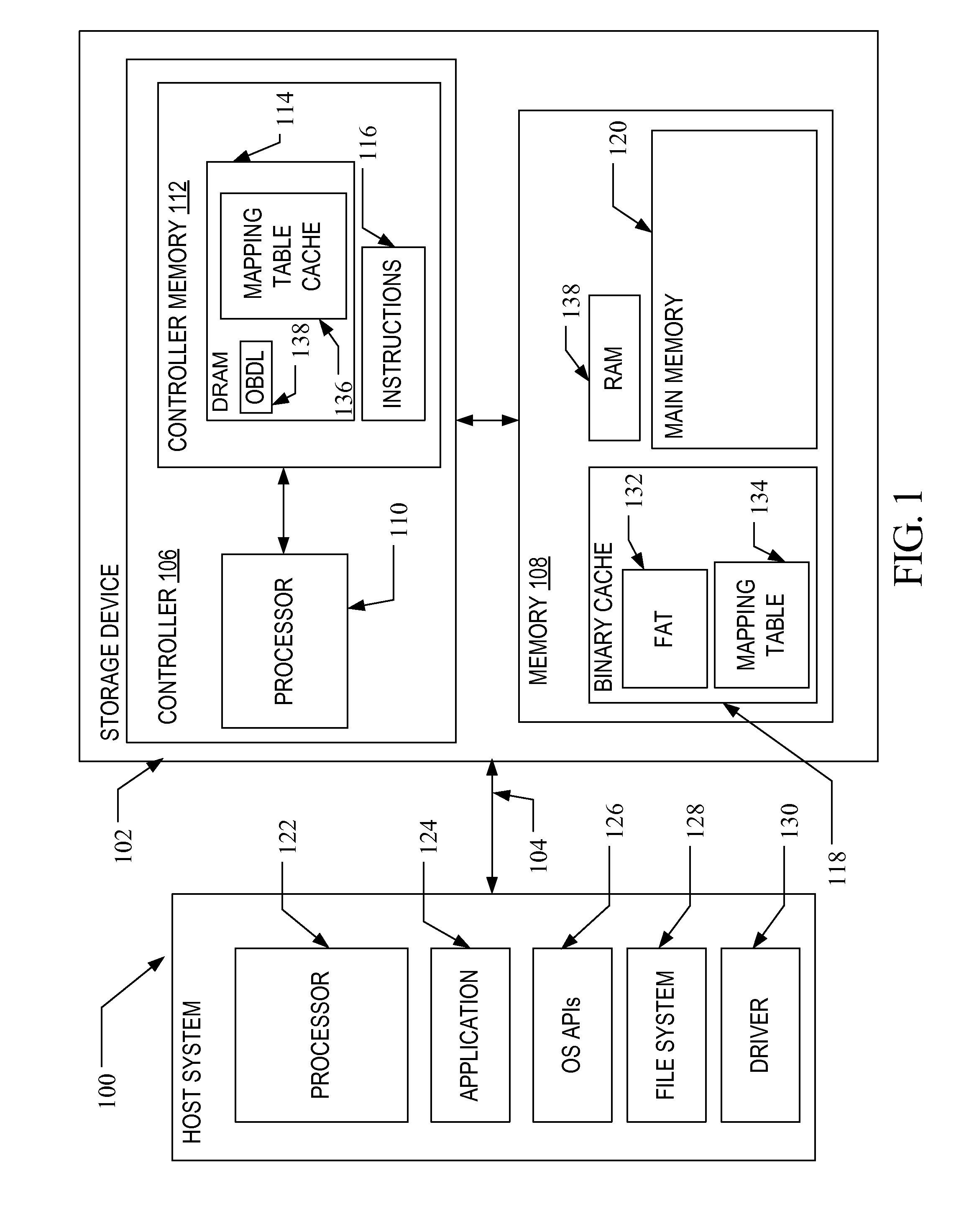
Method and system for interleaving pieces of a mapping table for a storage device
ActiveUS20150347026A1Improve efficiencyImprove read performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersContiguityVolatile memory
A method and system are disclosed for handling logical-to-physical mapping in a storage device. The method includes the storage device storing in fast access memory, such as DRAM, only a fixed-size subset of the primary mapping table in non-volatile memory, along with contiguity information of physical addresses for logical address not in the subset that are adjacent to the logical addresses in the subset. The system includes a storage device having volatile memory, non-volatile memory and a controller in communication with the volatile and non-volatile memory that is configured to carry out the method noted above.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Asymmetrical memory cells and memories using the cells
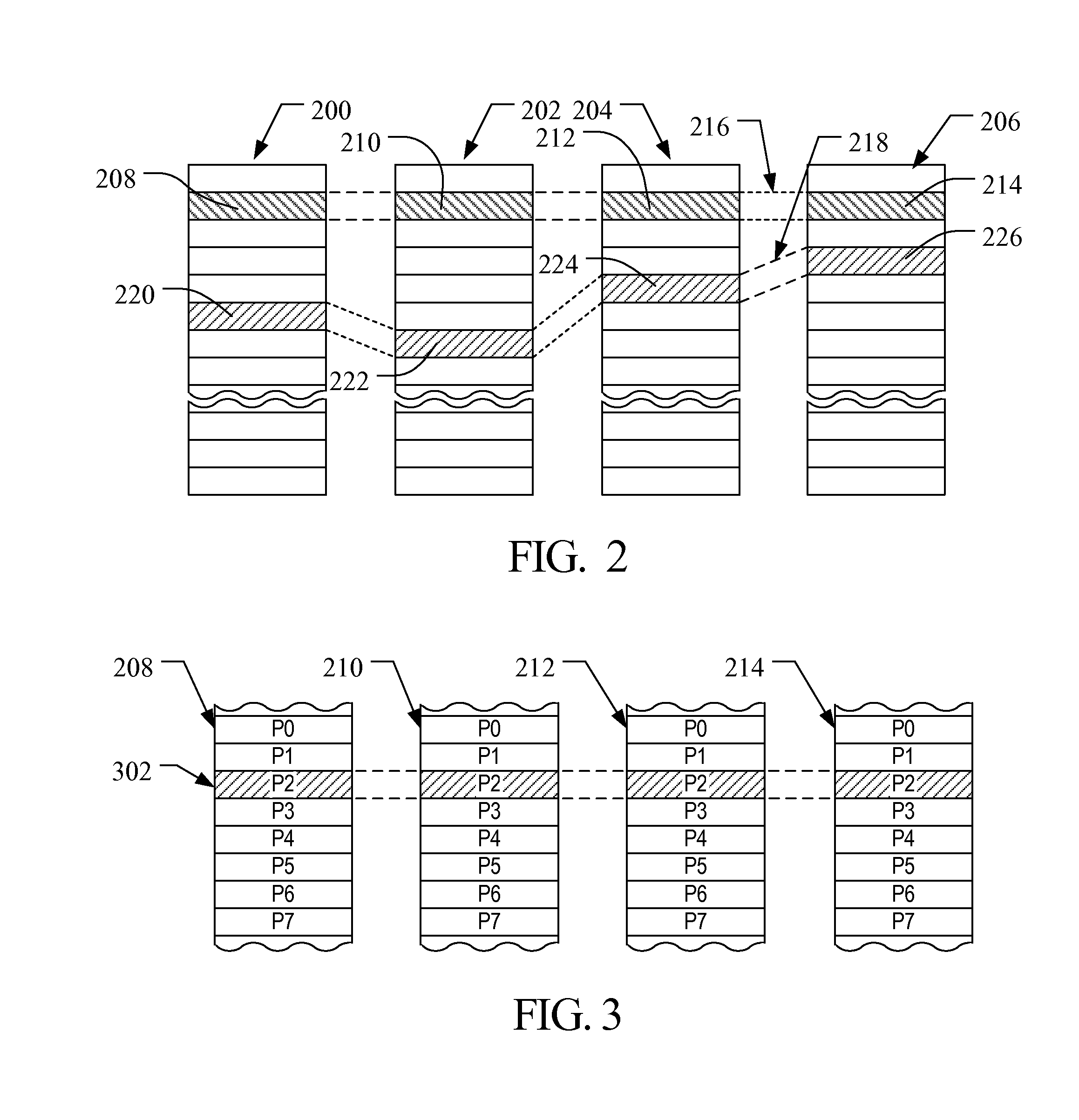
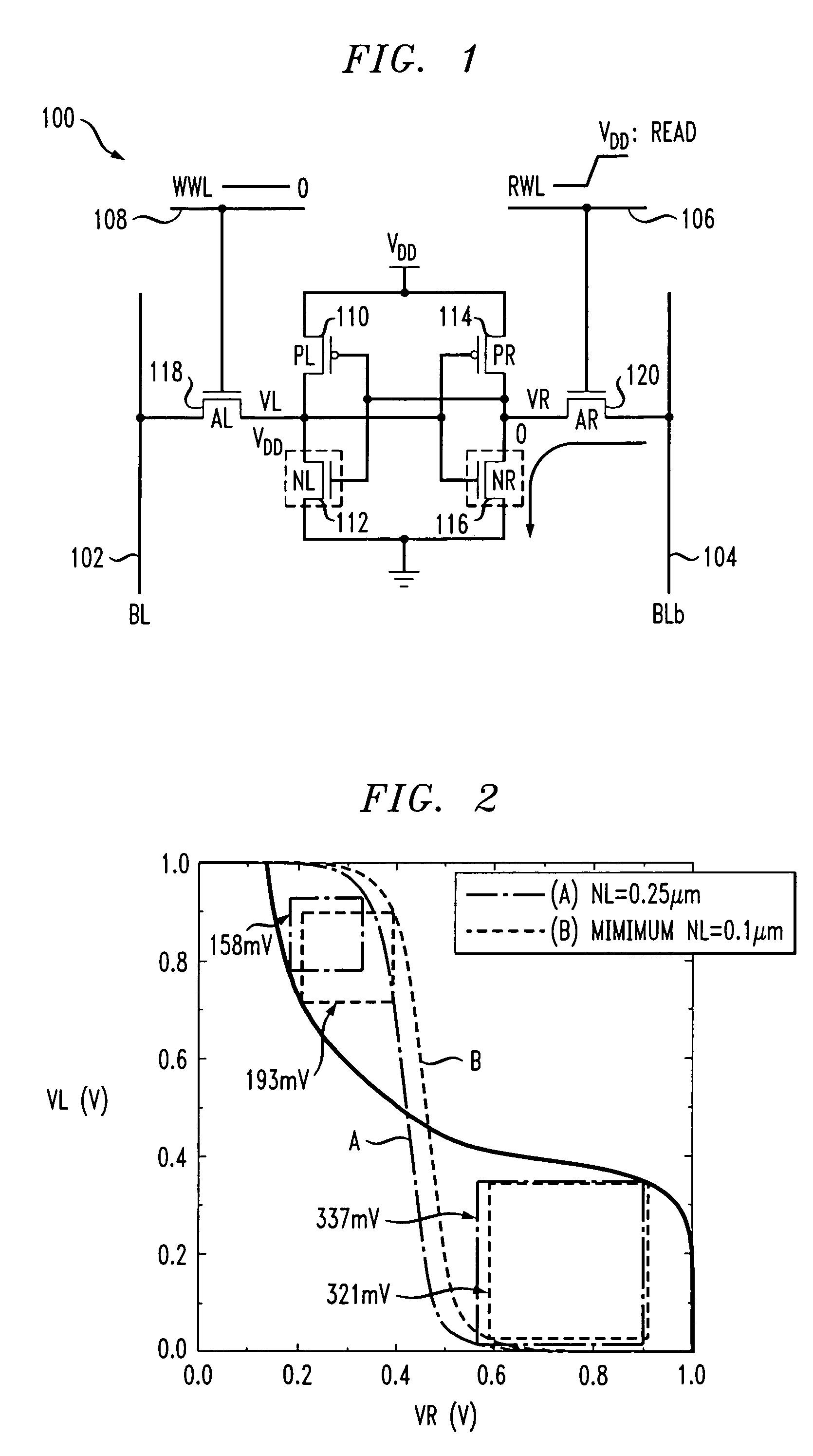
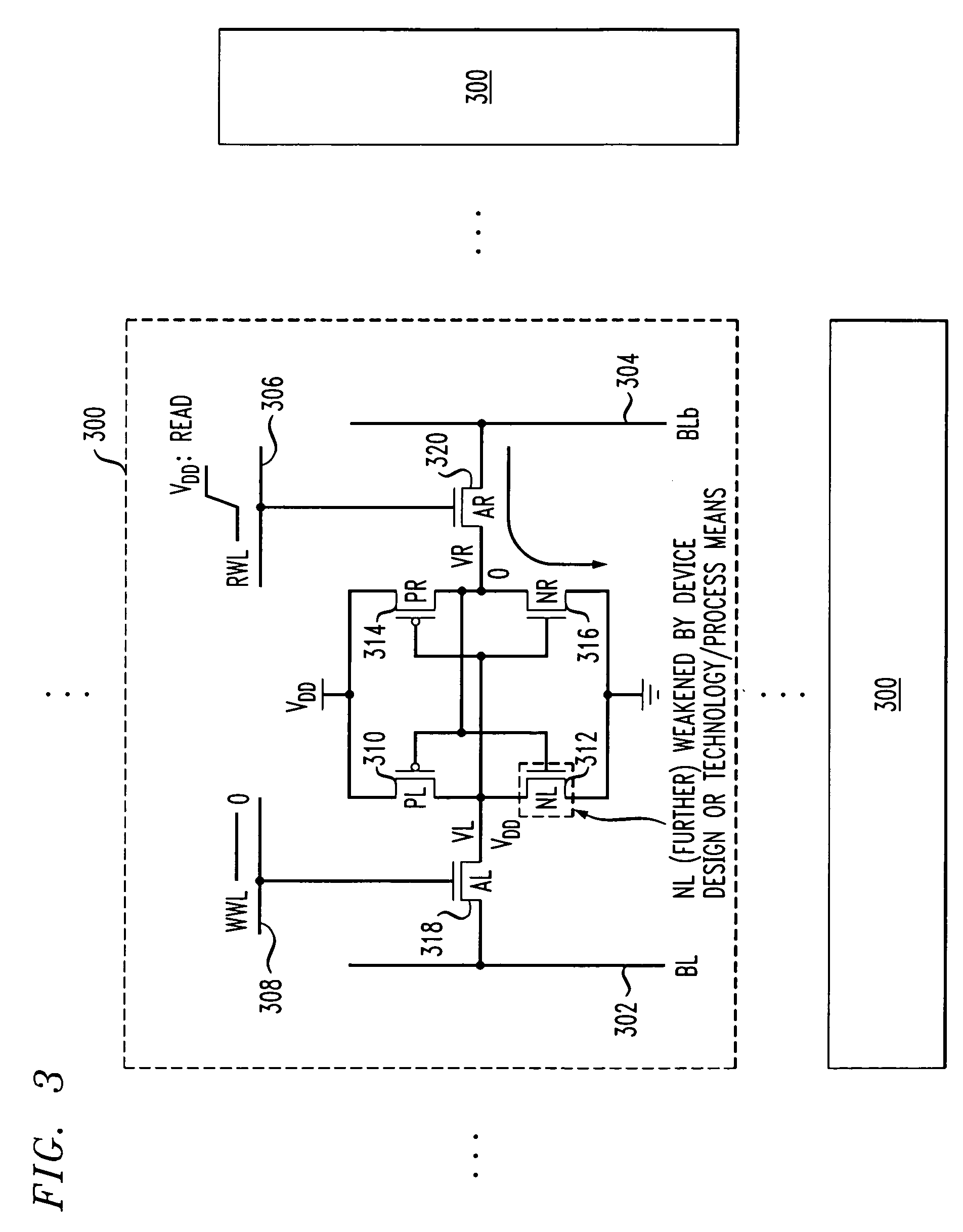
ActiveUS7362606B2Improve stabilityImprove write performanceTransistorDigital storageBit lineNon symmetric
Techniques are provided for asymmetrical SRAM cells which can be improved, for example, by providing one or more of improved read stability and improved write performance and margin. A first inverter and a second inverter are cross-coupled and configured for selective coupling to true and complementary bit lines under control of read and write word lines. The first inverter is formed by a first, n-type, FET (NFET) and a second, p-type, FET (PFET). Process and / or technology approaches can be employed to adjust the relative strength of the FETS to obtain, for example, read margin, write margin, and / or write performance improvements.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Method and system for internal cache management of solid state disk based on novel memory
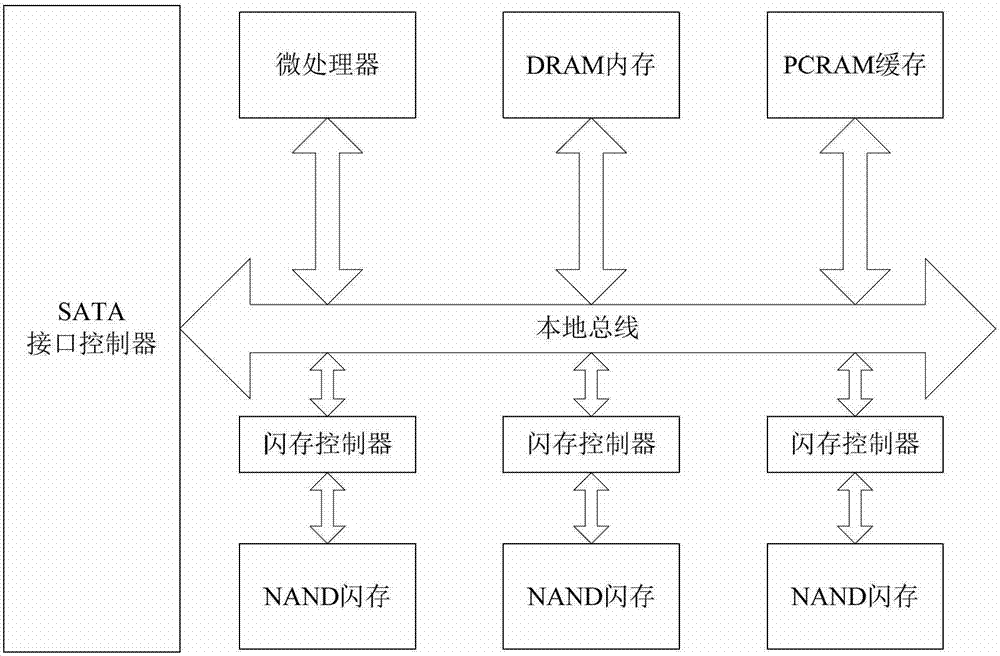
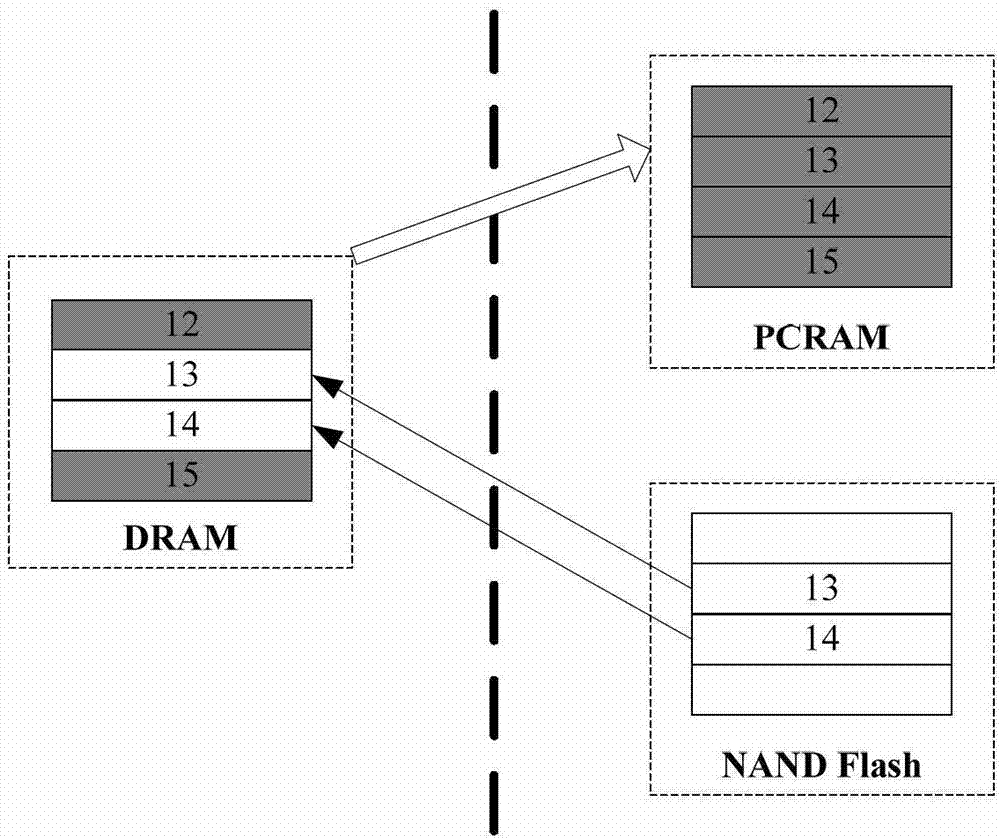
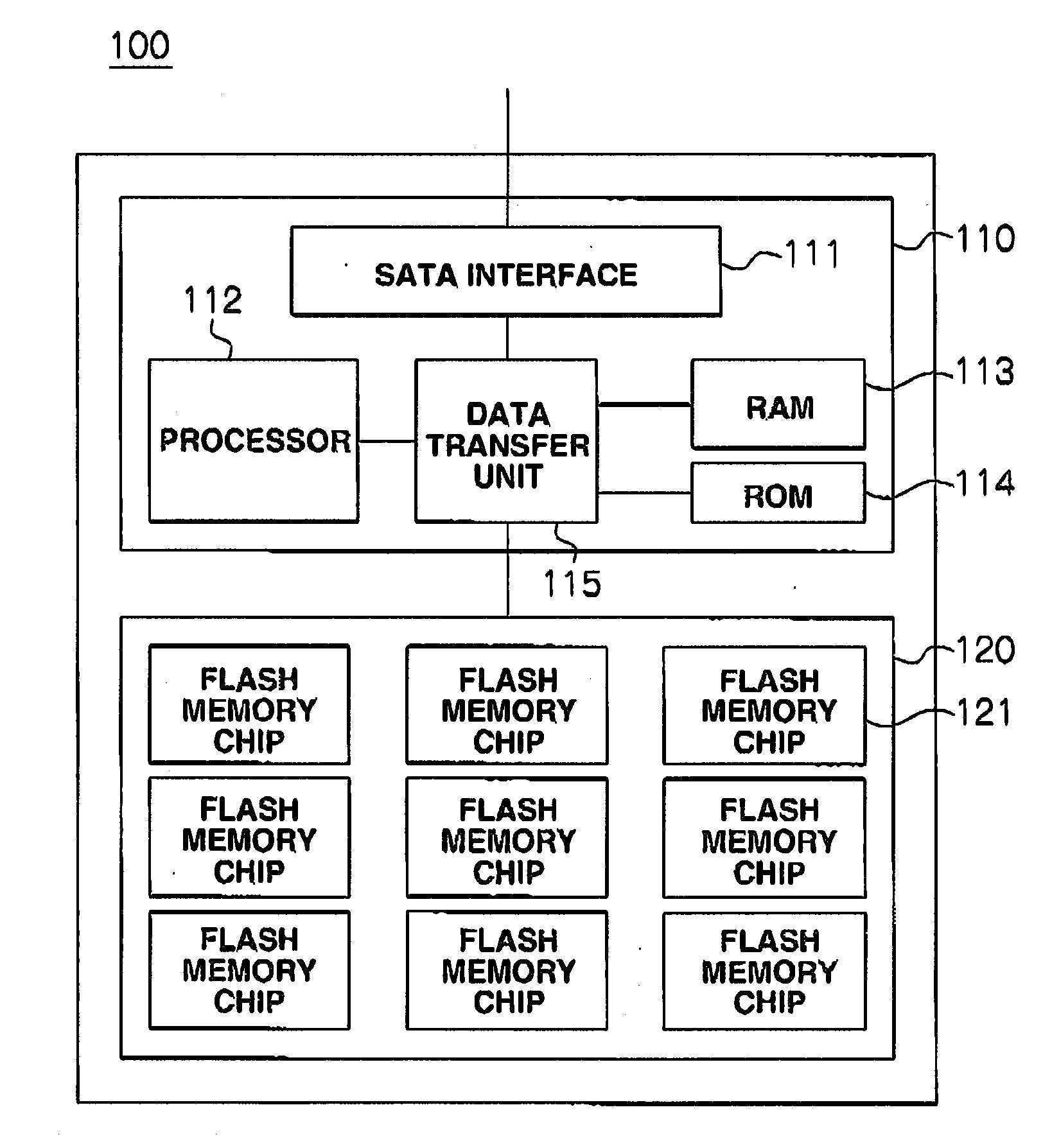
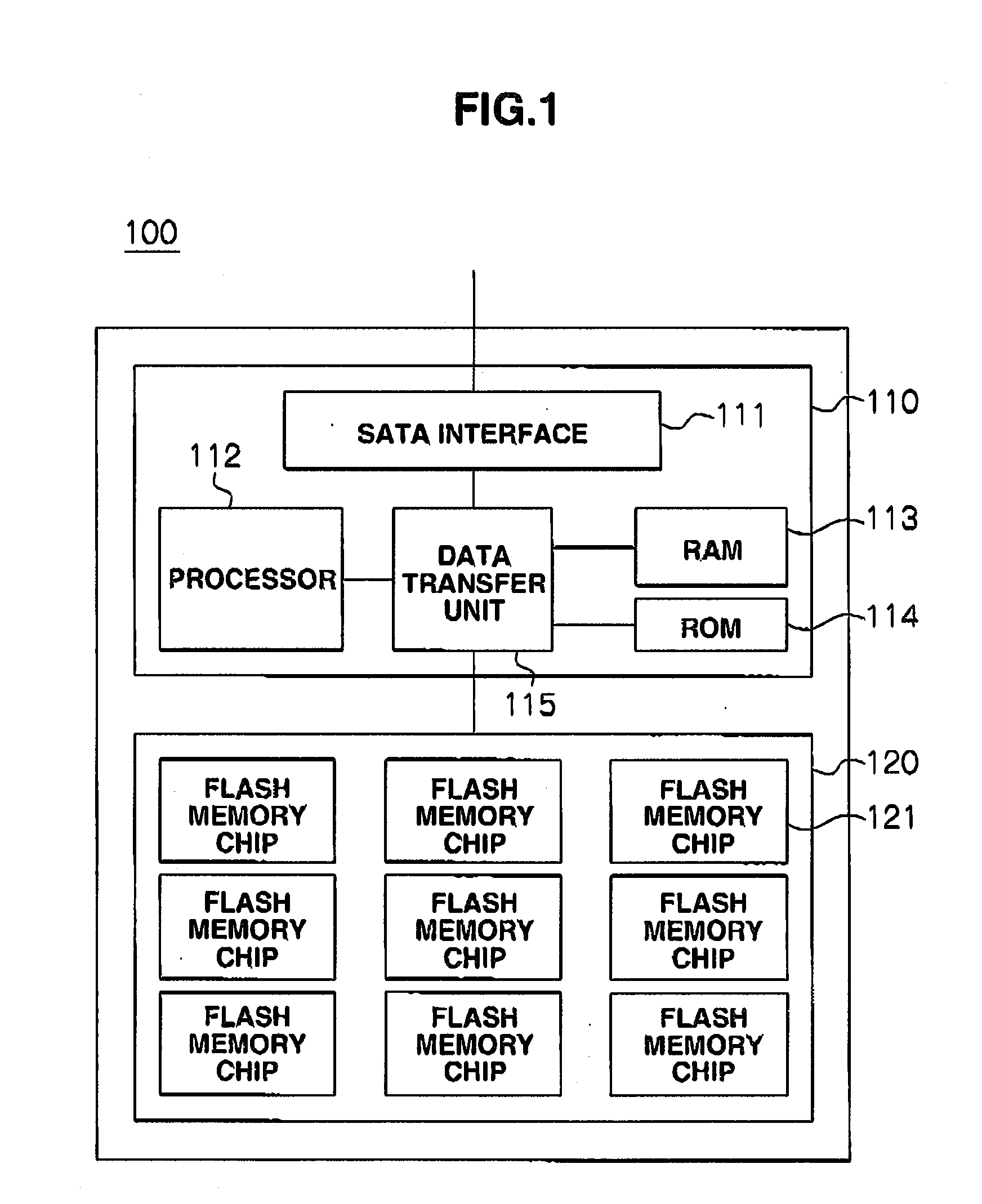
ActiveCN103049397AOvercome read and write imbalanceEasy to operateMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFlash memory controllerCache management
The invention provides a method and a system for internal cache management of a solid state disk based on a novel memory. The system for internal cache management of the solid state disk comprises an SATA (serial advanced technology attachment) interface controller, a microprocessor, a DRAM (dynamic random access memory), a local bus, a flash controller, an NAND flash and a PCRAM (phase change random access memory) cache. The PCRAM cache comprises a data block displacement area and a mapping table storage area, wherein the data block replacement area is used for storing data blocks displaced to the PCRAM cache from the DRAM, and the mapping table storage area is used for storing mapping tables among logic addresses and physical addresses of data pages. By the method for internal cache management of the SSD (solid state disk) based on the PCRAM, write cache for the solid state disk is realized to overcome read-write imbalance of the solid state disk, write performances are effectively improved, random write operation and wiping operation of the solid state disk are decreased, accordingly, the service life of the solid state disk is prolonged, and the integral I / O (input / output) performance of the solid state disk is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-performance reliable solid-state disk realizing method
ActiveCN103488583AImprove performanceImprove reliabilityInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRAIDData error
The invention provides a high-performance reliable solid-state disk realizing method. The method includes: (1), dividing all flash memory chips in a solid-state disk into groups and forming an RAID (redundant array of independent disks) 4-level flash array in each group by N successive flash chips; (2), receiving and storing data through a cache; (3), judging whether the cache is filled up or not, if yes, entering the step (4), and if not, returning to the step (2); (4), extracting N-1 data blocks from the cache and computing check values of the N-1 data blocks; making up the N-1 data blocks and the check values into filled stripe data and writing back the flash array; returning to the step (2). The flash chips in the solid-state disk are used for establishing the RAID4-level physical array to assure data reliability. Faults at different levels including page level, block level, or even chip level can be processed. Besides, writing-in performance is improved by writing of filled stripes and sequence, and spatial and performance loss resulted from data errors can be reduced to the utmost.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Magnetic disk cache system based on solid-state disk
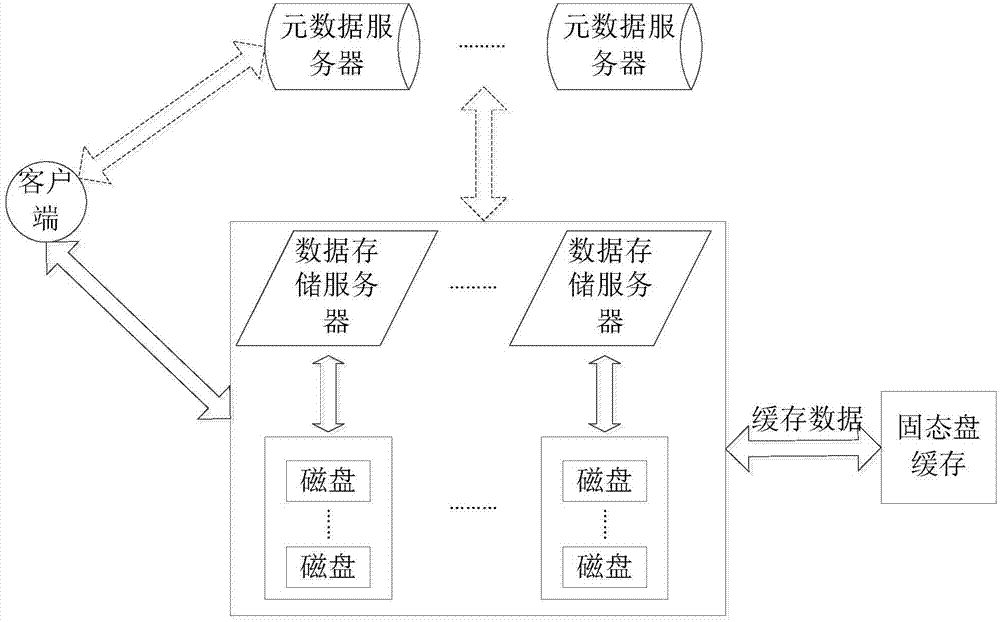
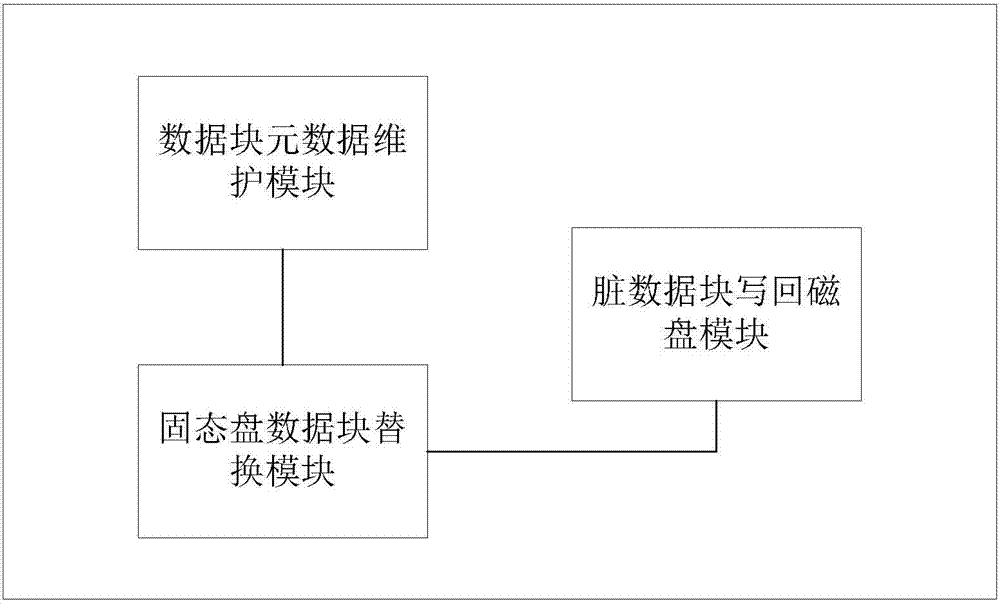
ActiveCN103885728AImprove read and write performanceLower read latencyInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMagnetic disksDirty data
The invention discloses a magnetic disk cache system based on a solid-state disk and belongs to the technical field of cache systems in computer data storage systems. The magnetic disk cache system based on the solid-state disk comprises a data block metadata maintenance module, a solid-state disk data replacement module and a dirty data block writing-back disk module. According to the magnetic disk cache system based on the solid-state disk, the reading and writing performance of disk data in a large-scale storage environment is improved through the solid-state disk, and the data block reading and writing hit rate and the cache space utilization rate are high; meanwhile, it is guaranteed that data blocks cached under the condition that a computer is restarted due to faults can not be lost easily, the cold-to-hot convergence time of solid-state disk equipment is shortened, and the problems that according to a computer data storage system in the prior art, the cache space is limited, cached data can be lost easily, and the cache space can not be fully utilized can be solved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Video data storage method and system
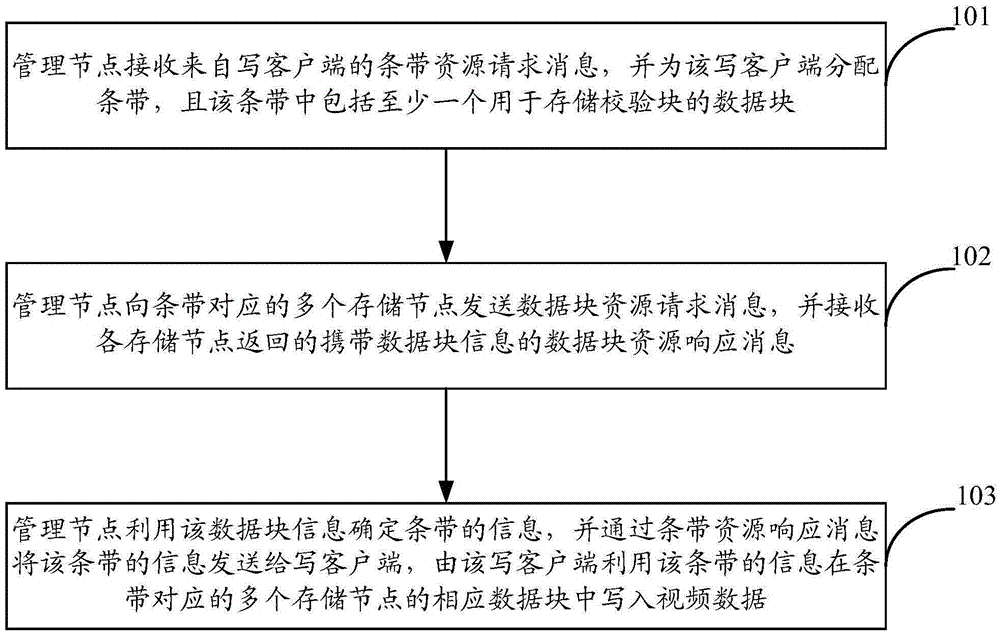
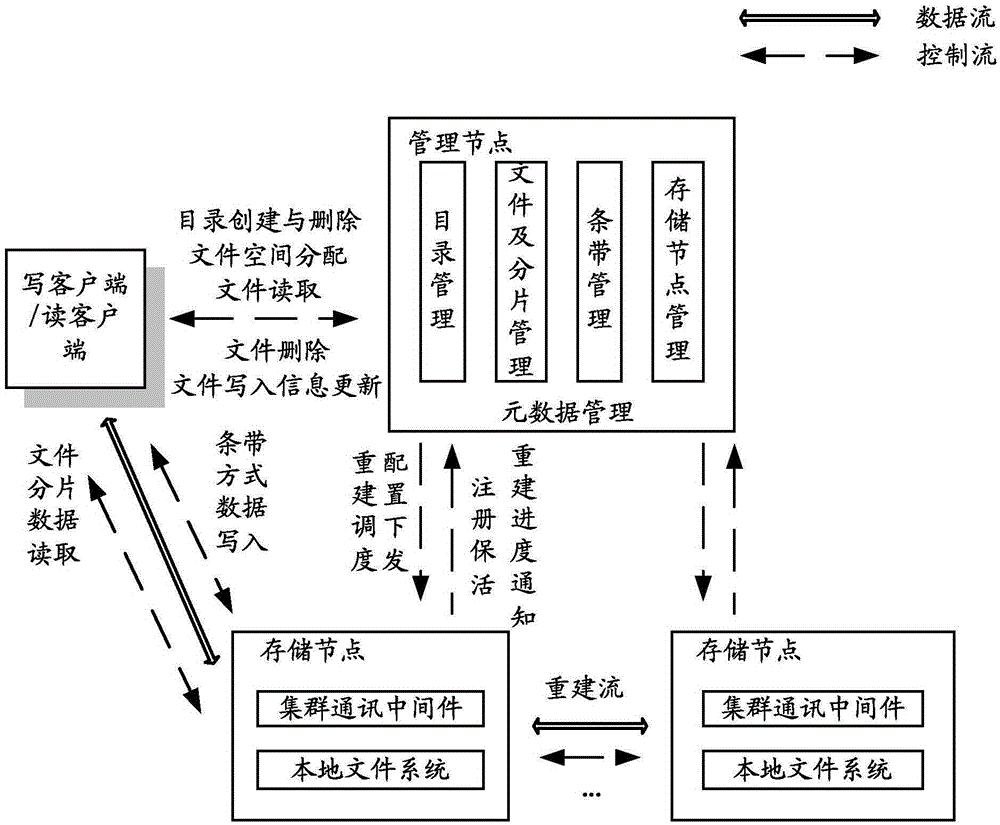
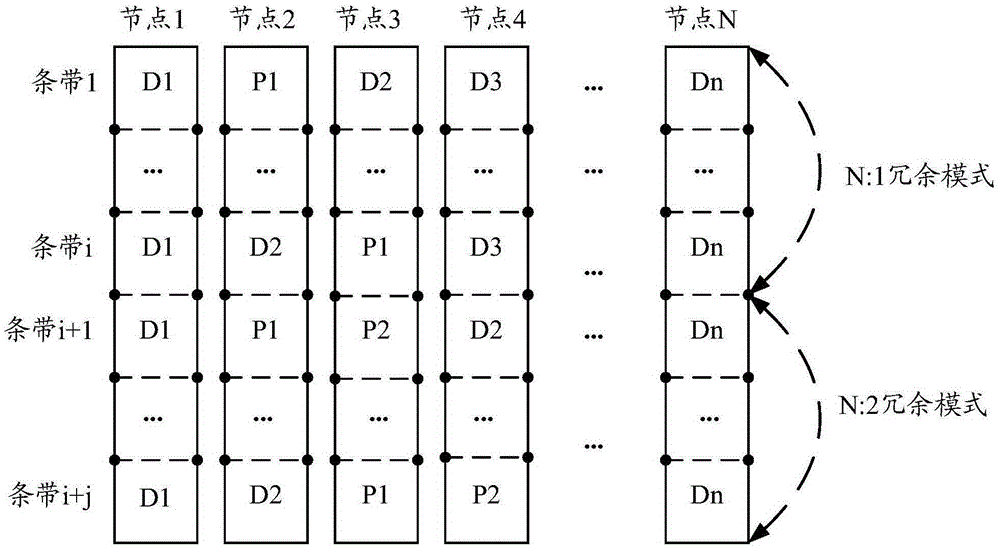
ActiveCN105404469AImprove space utilizationIncrease profitTelevision system detailsInput/output to record carriersVideo monitoringDistributed computing
The invention provides a video data storage method and system, which are applied to a distributed video monitoring system comprising a management node, storage nodes, a writing client and a reading client. The method comprises the steps that the management node receives a stripe resource request message from the writing client and allocates stripes to the writing client, wherein each stripe comprises at least one data block used for storing verifying blocks; the management node sends a data block resource request message to the storage nodes corresponding to the stripes and receives a data block resource response message carrying data block information and returned by each storage node; and the management node determines information of the stripes by utilizing the data block information and sends the information of the stripes to the writing client through a stripe resource response message, and the writing client writes video data into corresponding data blocks of the storage nodes corresponding to the stripes by utilizing the information of the stripes. Through the technical scheme provided by the invention, high writing performance, high space utilization rate and high reconstruction performance are supported.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVIEW TECH CO LTD
Programming method and device for a buffer cache in a solid-state disk system
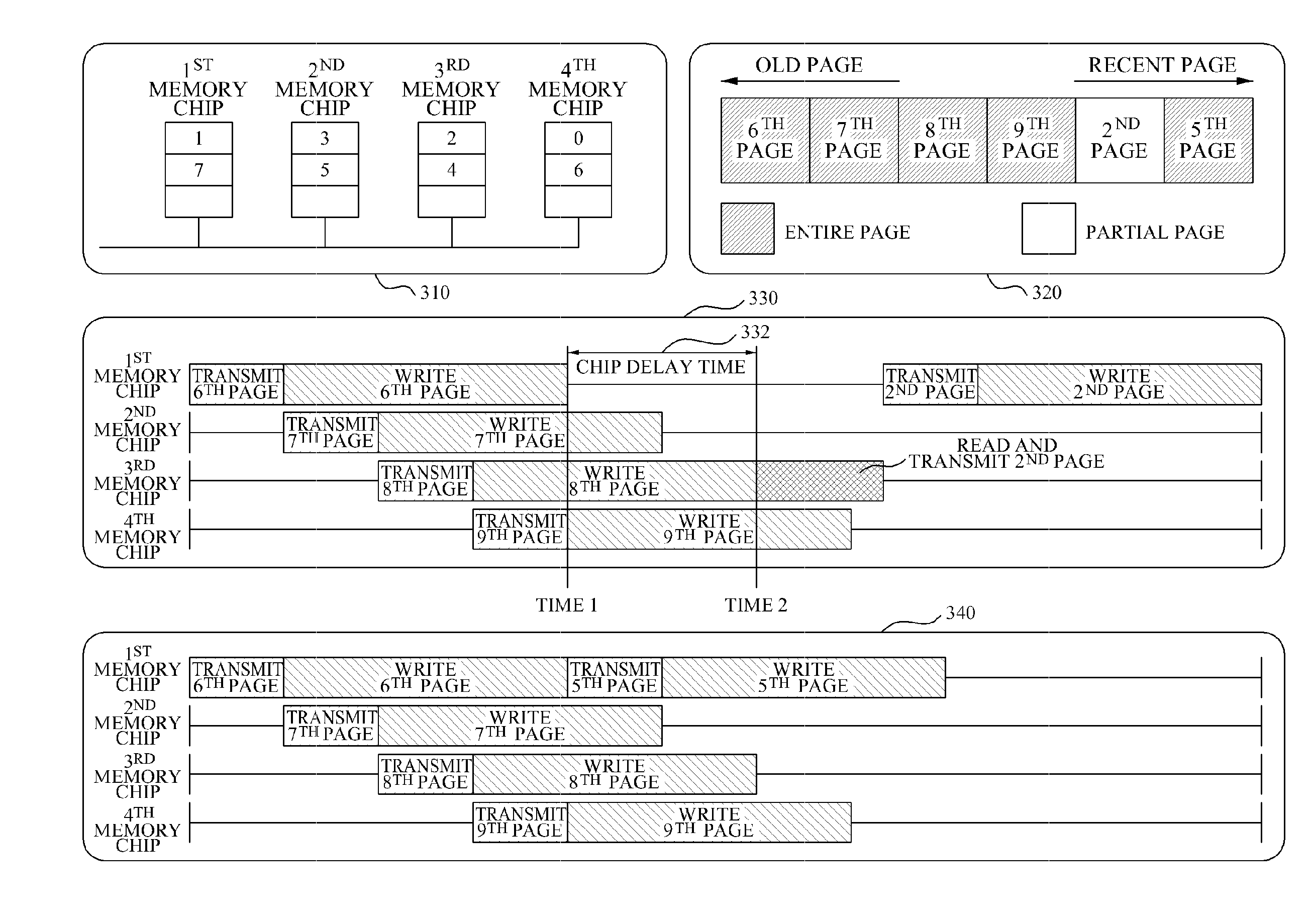
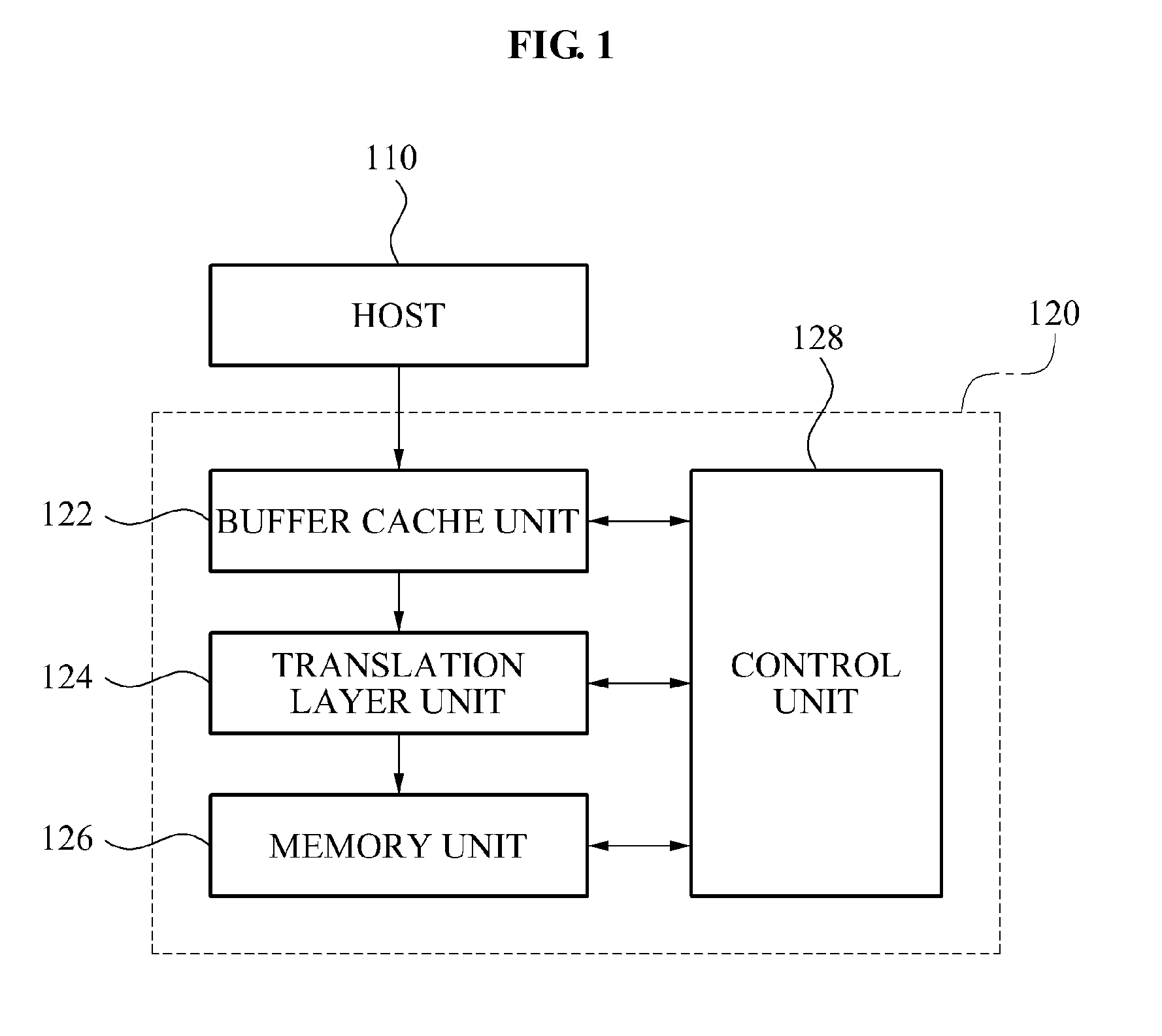
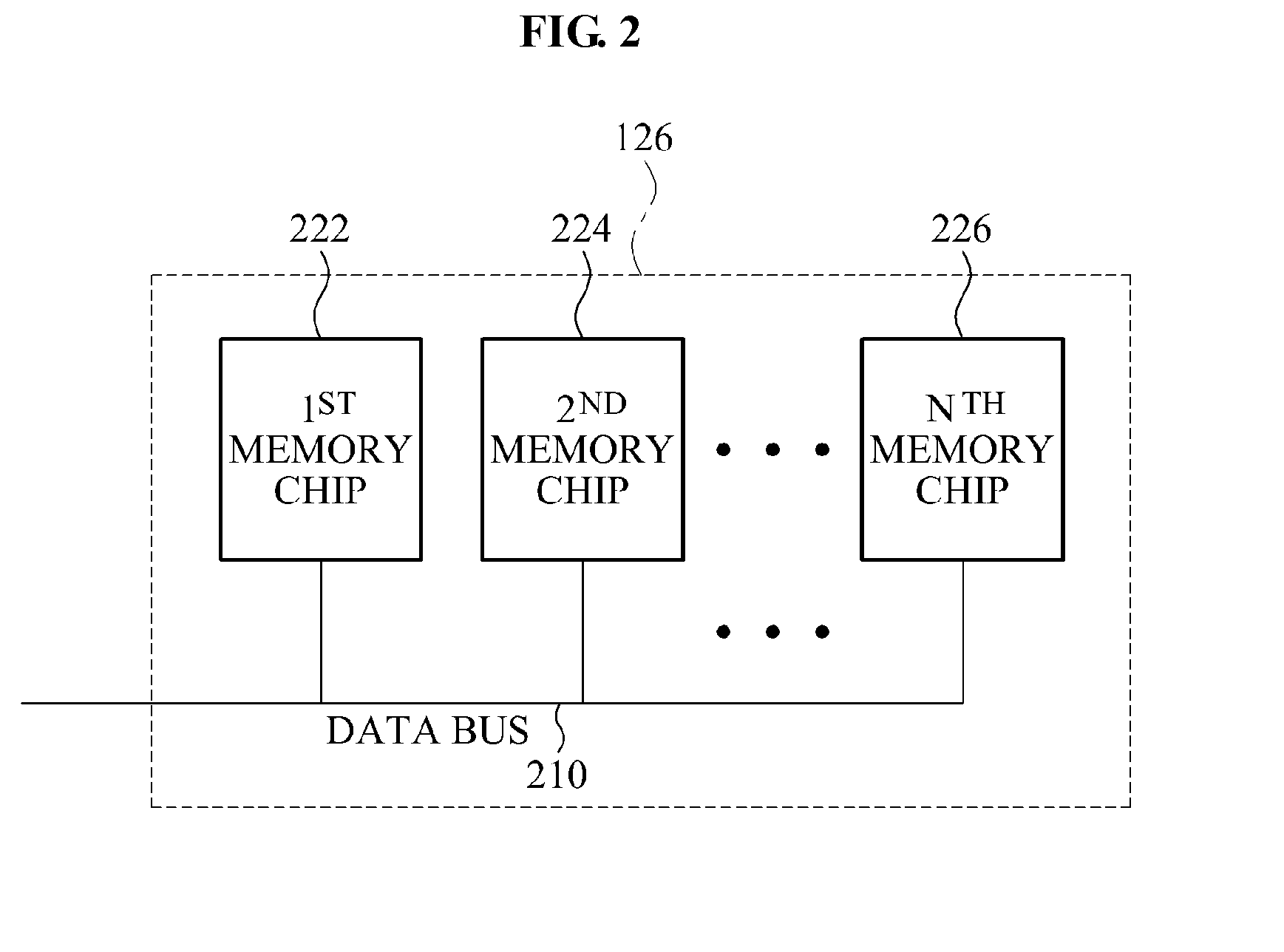
ActiveUS20110296089A1Improve write performanceReduce delaysMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersMemory chipControl unit
Provided are a method and apparatus for programming a buffer cache in a Solid State Disk (SSD) system. The buffer cache programming apparatus in the SSD system may include a buffer cache unit to store pages, a memory unit including a plurality of memory chips, and a control unit to select at least one of the page as a victim page, based on a delay occurring when a page is stored in at least one target memory chip among the plurality of memory chips.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Magnetic recording medium, magnetic storage apparatus and recording method
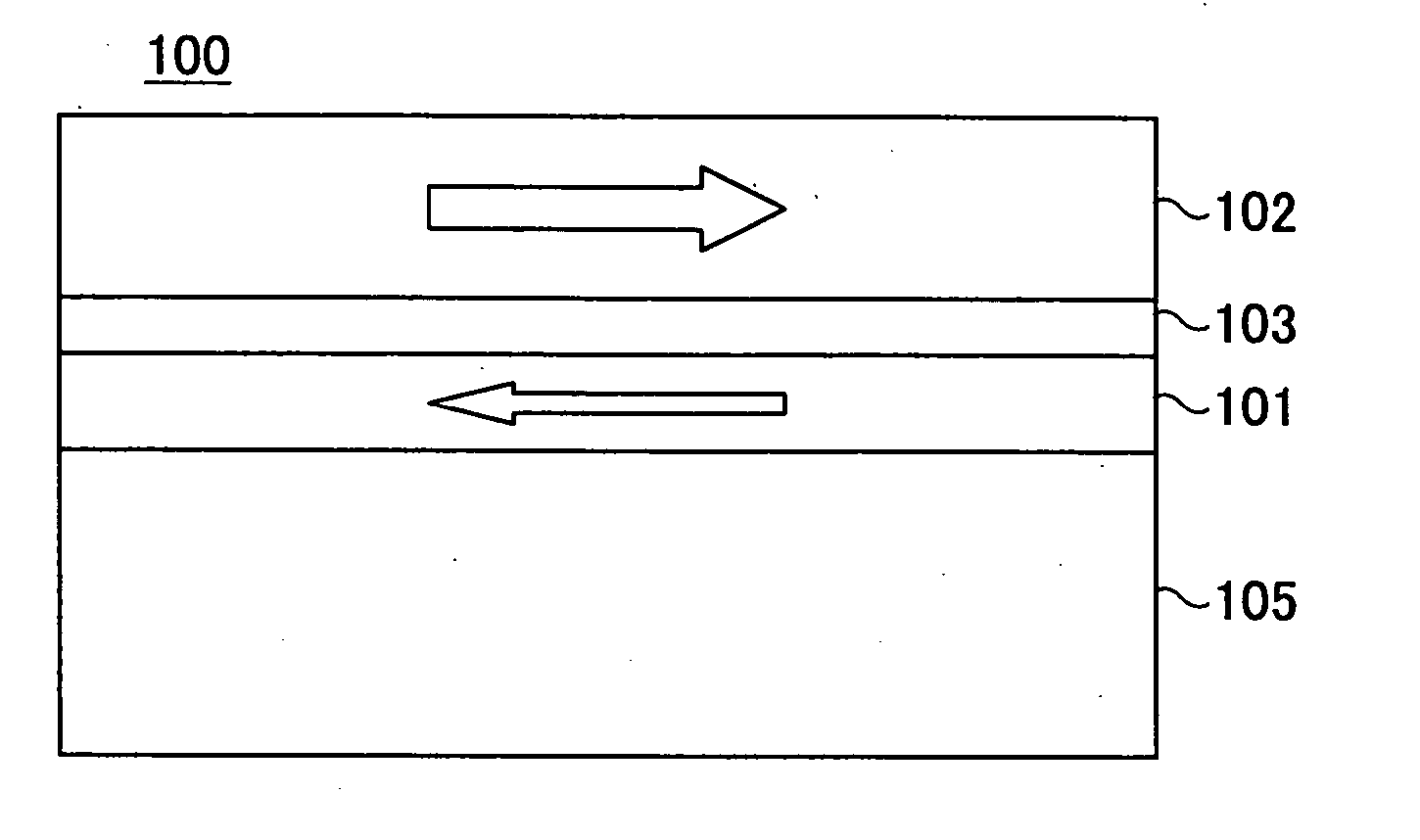
InactiveUS20050053803A1Improve write performanceHigh-density recordingDifferent record carrier formsMechanical record carriersNuclear magnetic resonanceMagnetic storage
A magnetic recording medium is provided with a first magnetic layer, a nonmagnetic coupling layer provided on the first magnetic layer, and a second magnetic layer provided on the nonmagnetic coupling layer. The first and second magnetic layers are exchange-coupled, and have magnetization directions which are mutually parallel in a state where no external magnetic field is applied thereto, and the first magnetic layer switches the magnetization direction thereof before the second magnetic layer in response to a recording magnetic field which switches the magnetization directions of the first and second magnetic layers.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Storage system and data write method
InactiveUS20090210611A1Reducing average write processing timeImprove write performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsManagement unitMemory management unit
The size of a memory management unit in a low-performance non-volatile memory device is maintained, and the size of write data is compared with the size of the memory management unit. If the size of the write data is smaller than that of the memory management unit, the write data is cached by the high-performance non-volatile memory device; or if the size of the write data is not smaller, the write data is written to the low-performance device. Subsequently, a plurality of address values for the write data cached by the high-performance device are referred to; an address segment that is equal to the size of the memory management unit and in which the cached address values are consecutive; and data contained in that address segment is copied from the high-performance device to the low-performance device.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method, device and system for data storage
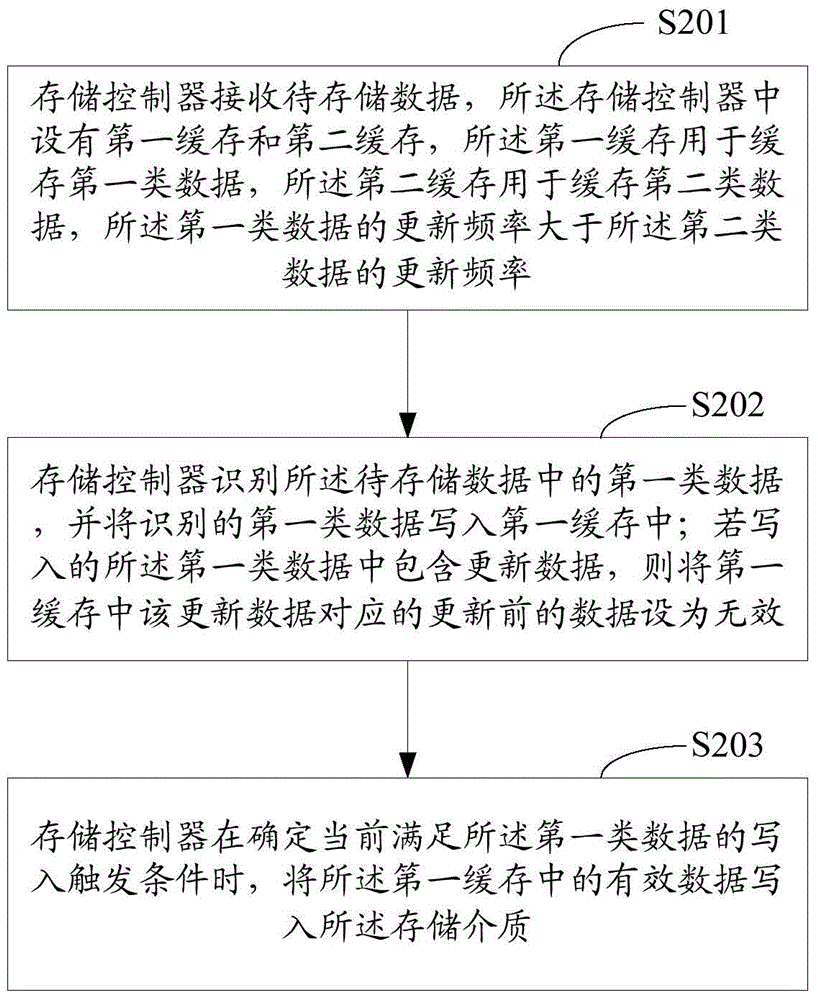
ActiveCN104461935AReduce data volumeReduce the number of writesMemory adressing/allocation/relocationControl storeData store
The invention relates to the technical field of electronics, in particular to a method, device and system for data storage. The method, device and system for data storage are used for solving the problems that a storage device is low in writing performance and short in service life. The data storage method provided by the embodiment includes the steps that a storage controller receives data to be stored and is internally provided with a first cache and a second cache, the first cache is used for caching the first type of data, the second cache is used for caching the second type of data, and the updating frequency of the first type of data is larger than that of the second type of data; the storage controller recognizes the first type of data in the data to be stored and writes the recognized first type of data into the first cache; if the first type of data written in comprise updated data, the data, which correspond to the updated data and are not updated yet, in the first cache are set to be invalid; when the storage controller determines that the writing-in triggering condition of the first type of data is met currently, the valid data in the first cache are written into a storage medium.
Owner:XFUSION DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
Perpendicular magnetic recording medium and hard disk drive using the same
ActiveUS20080180843A1Improve write performanceStable productionNanoinformaticsPatterned record carriersHard disc driveInter layer
Embodiments of the present invention provide a perpendicular magnetic recording medium having an improved writing property due to the exchange spring effect and capable of stable production. According to one embodiment, a perpendicular magnetic recording medium includes a non-magnetic substrate; an adhesion layer; a soft magnetic underlayer; a seed layer; and intermediate layer; a magnetic recording layer at least including a perpendicular recording layer, a writing assist layer, and a magnetic coupling layer disposed between the perpendicular recording layer and the writing assist layer; a protective layer, and a lubrication layer, in which the saturation magnetization of the magnetic coupling layer is lower than the saturation magnetization of the writing assist layer, the saturation magnetization of the magnetic coupling layer is 300 kA / m (300 emu / cc) or lower, and the thickness of the magnetic coupling layer is 1 nm or more and 3 nm or lower.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
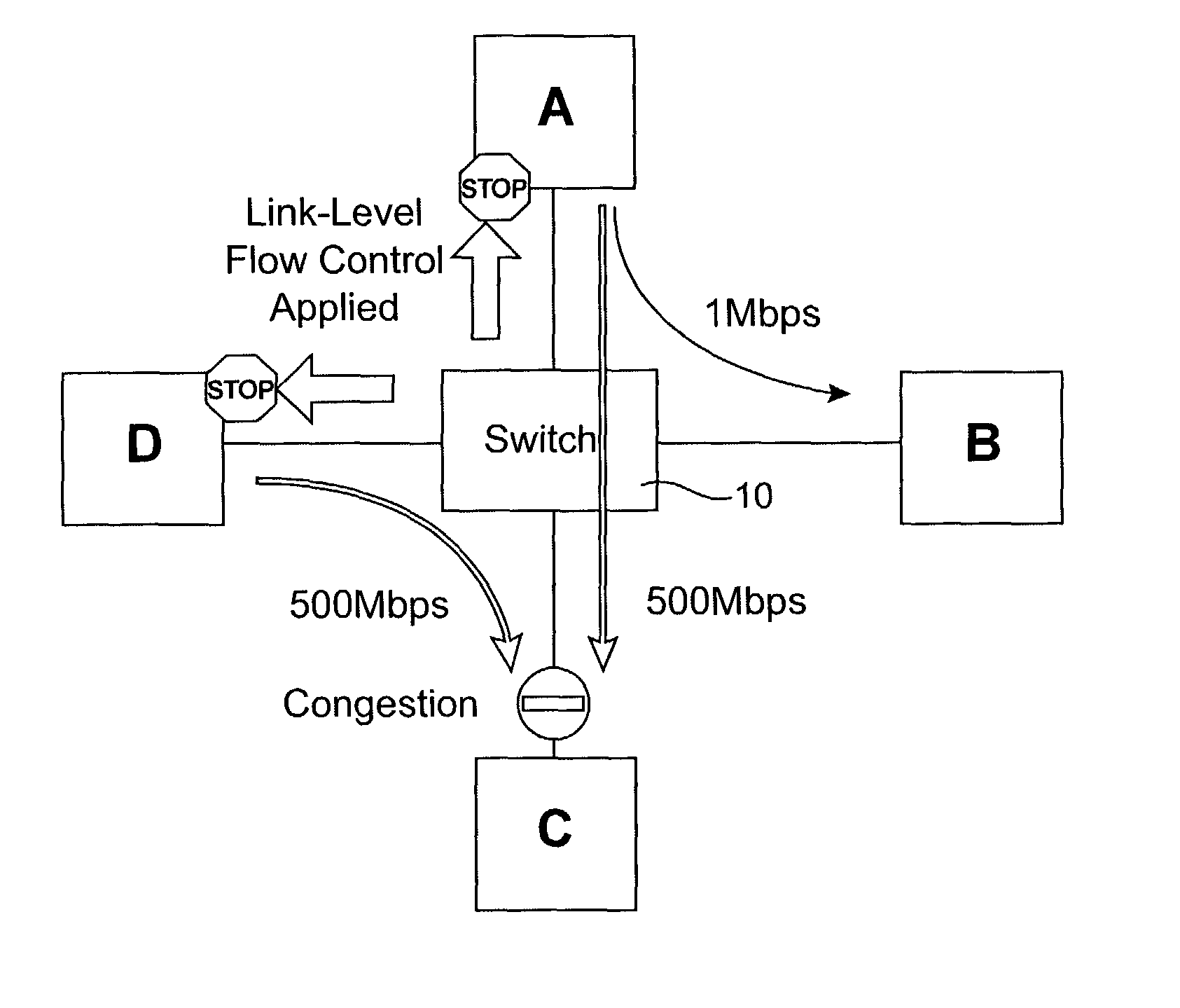
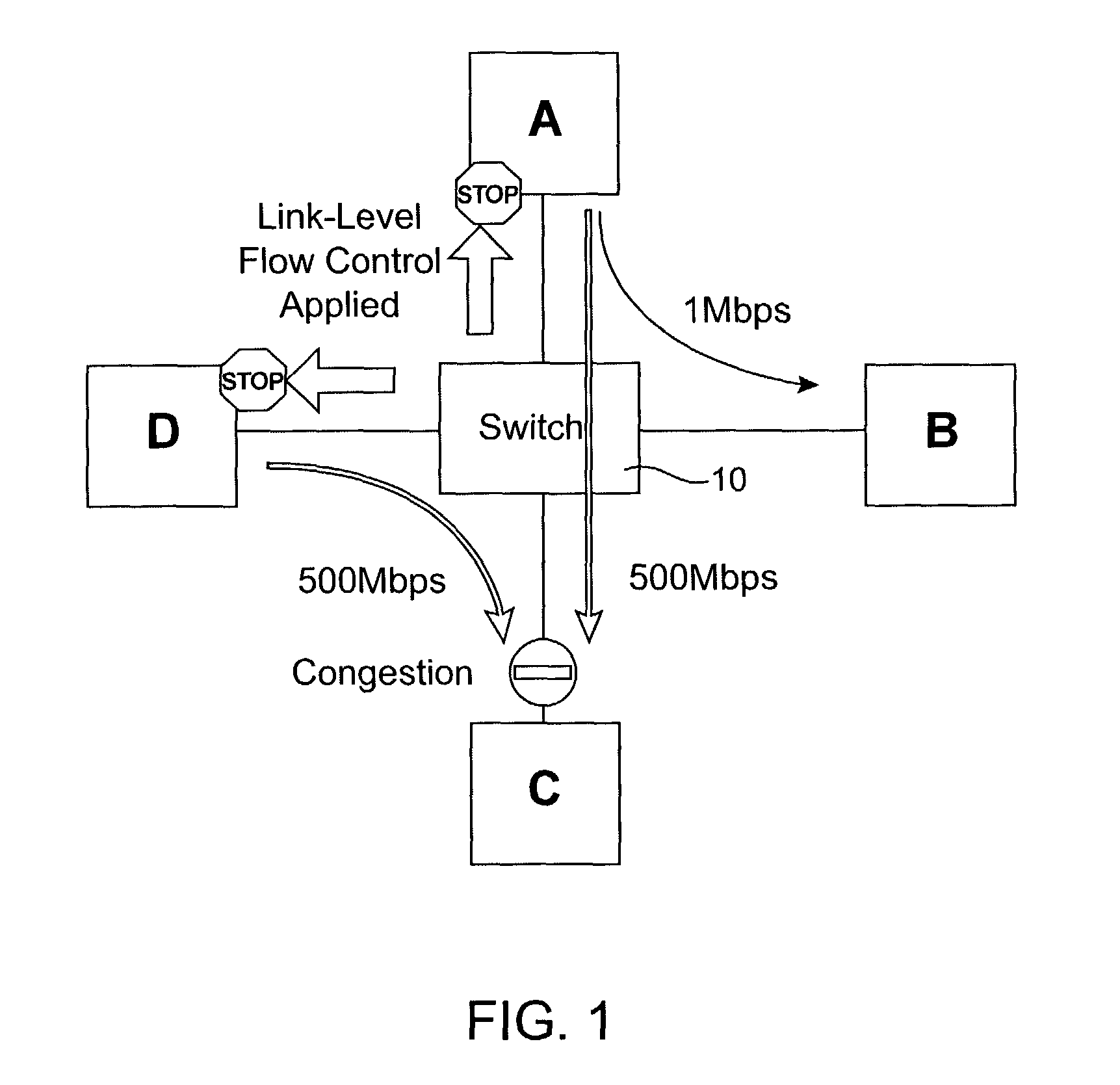
Network congestion management systems and methods
InactiveUS8051197B2Avoid cloggingImprove write performanceEnergy efficient ICTError preventionSCSIStructure of Management Information
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method of managing non-volatile memory device and memory system including the same
InactiveUS20100211820A1Improve write performanceImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesMemory systemsMemory block
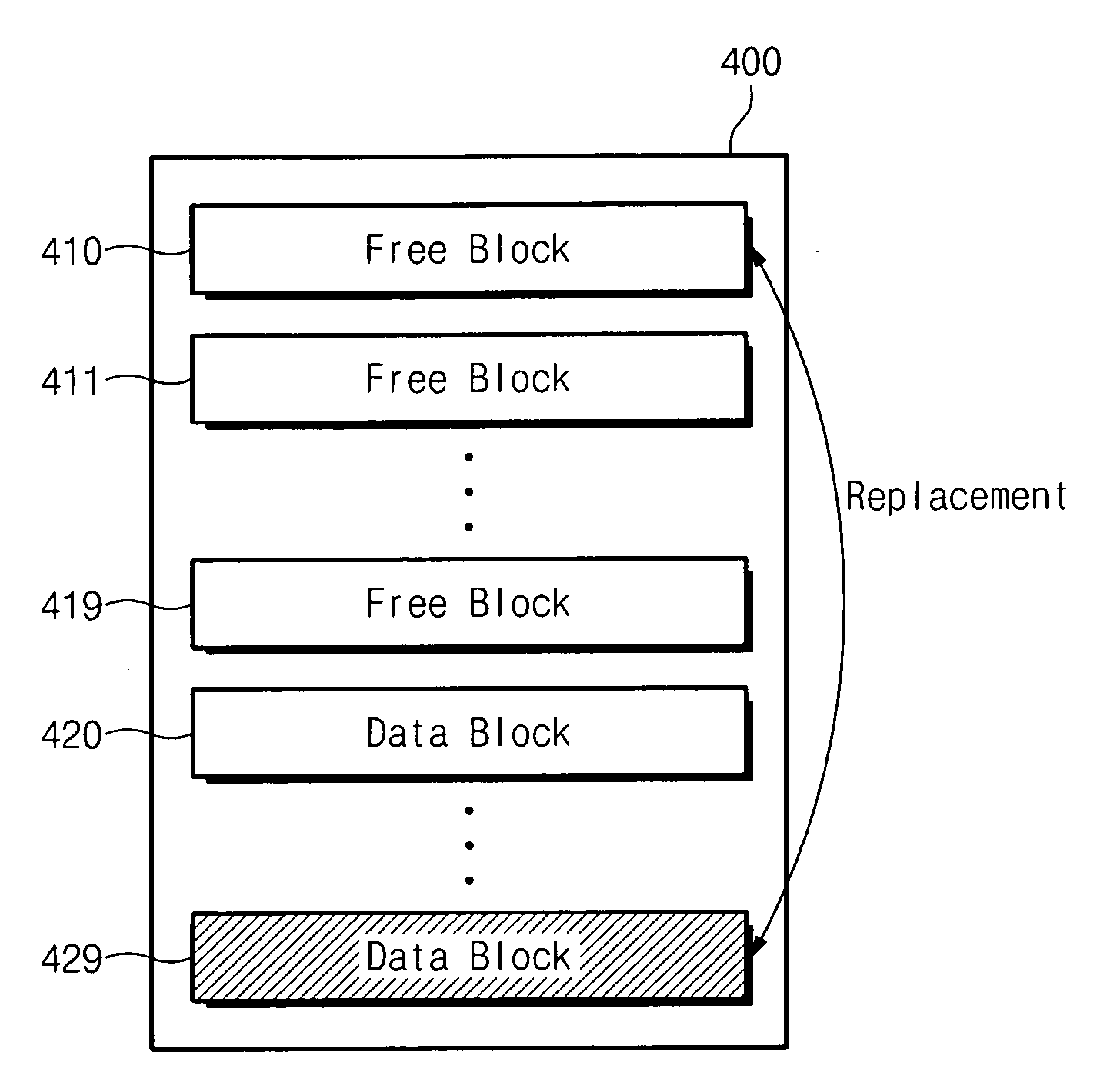
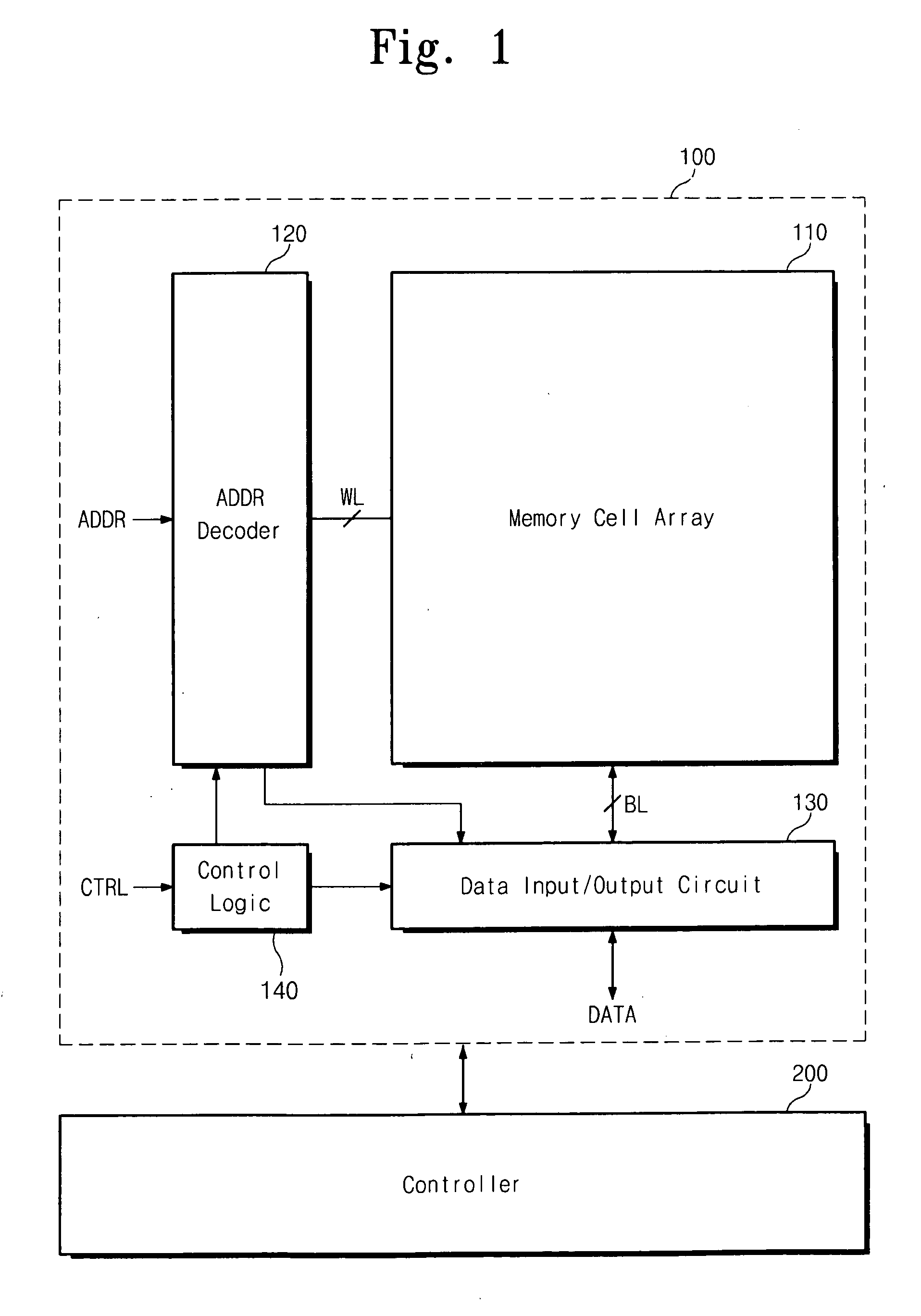
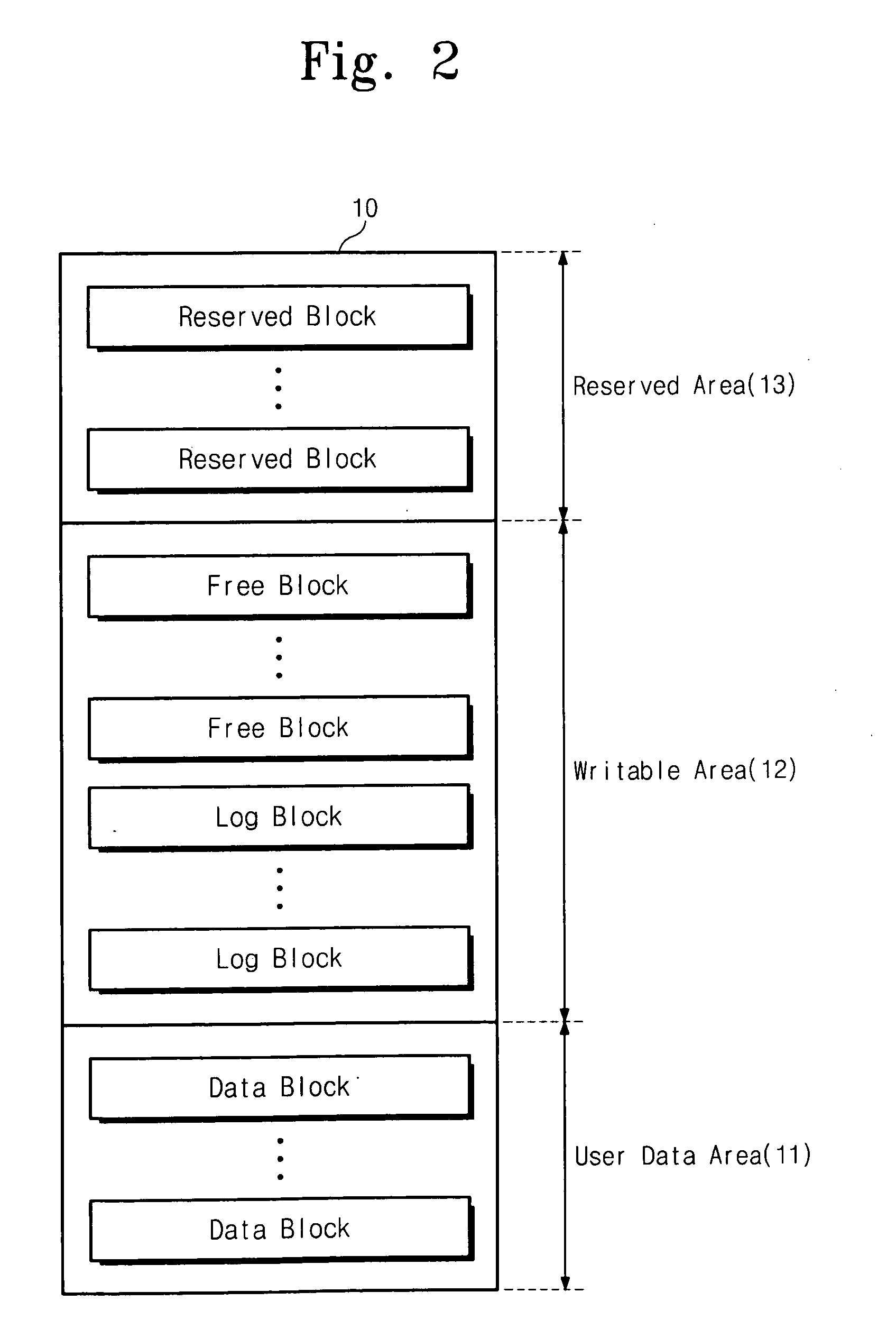
Disclosed is a method of managing a non-volatile memory device having a plurality of memory blocks which includes assigning the plurality of memory blocks of the non-volatile memory device into a user data area and a writable area; determining whether any of the plurality of memory blocks of the nonvolatile memory device are runtime bad blocks; and replacing each determined runtime bad block from among the plurality of memory blocks with a memory block of the writable area.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method, system, apparatus, and computer-readable medium for improving disk array performance
ActiveUS7802063B1Improve performanceEffective cachingMemory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data processing detailsRAIDThin provisioning
Owner:AMZETTA TECH LLC
Method and device for writing data and redundant array of inexpensive disk
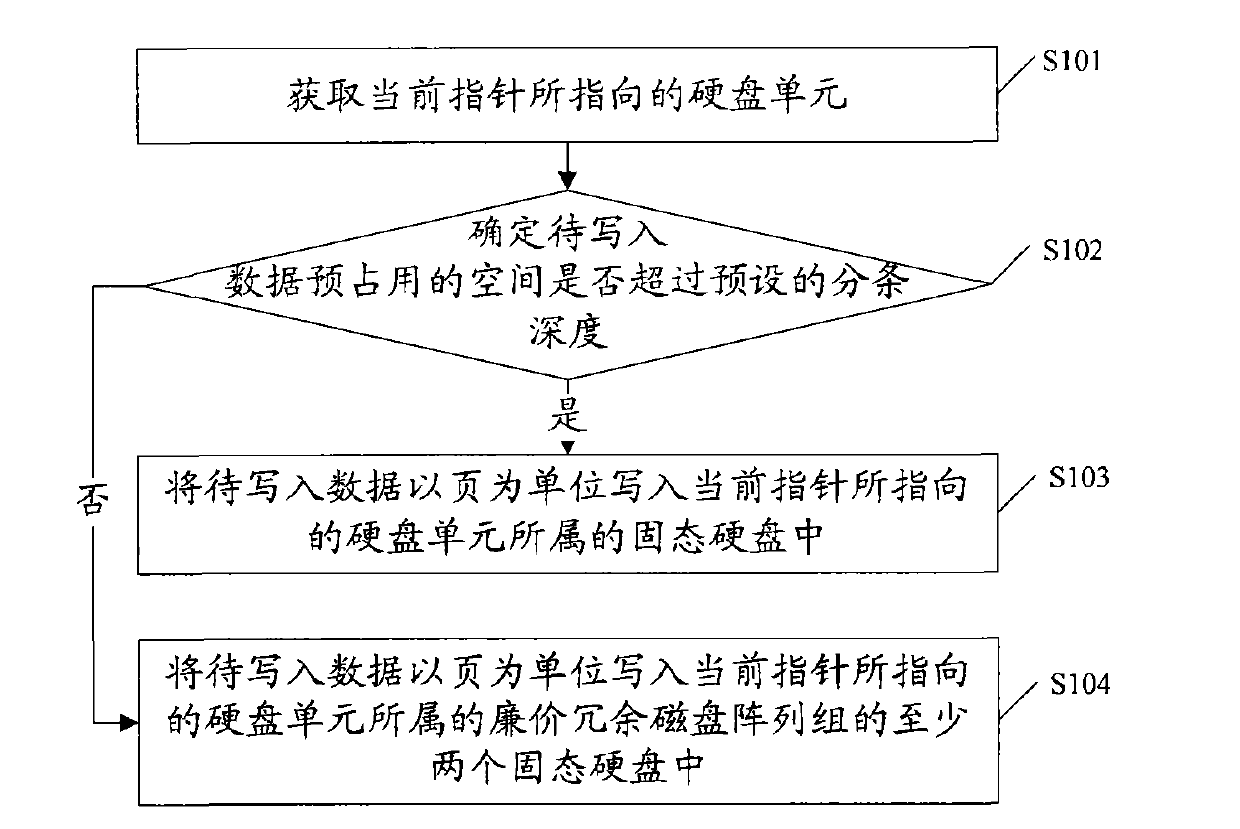
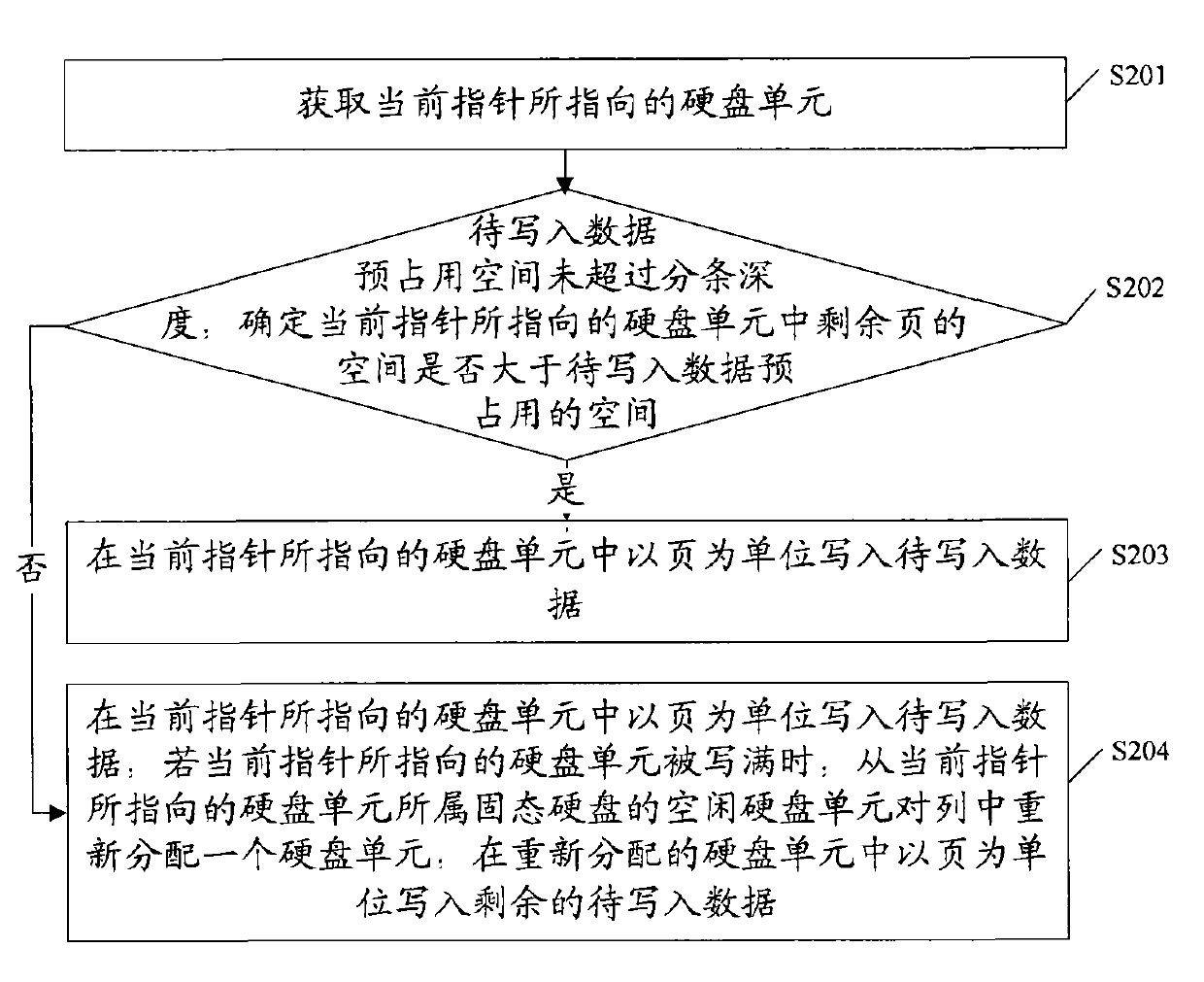
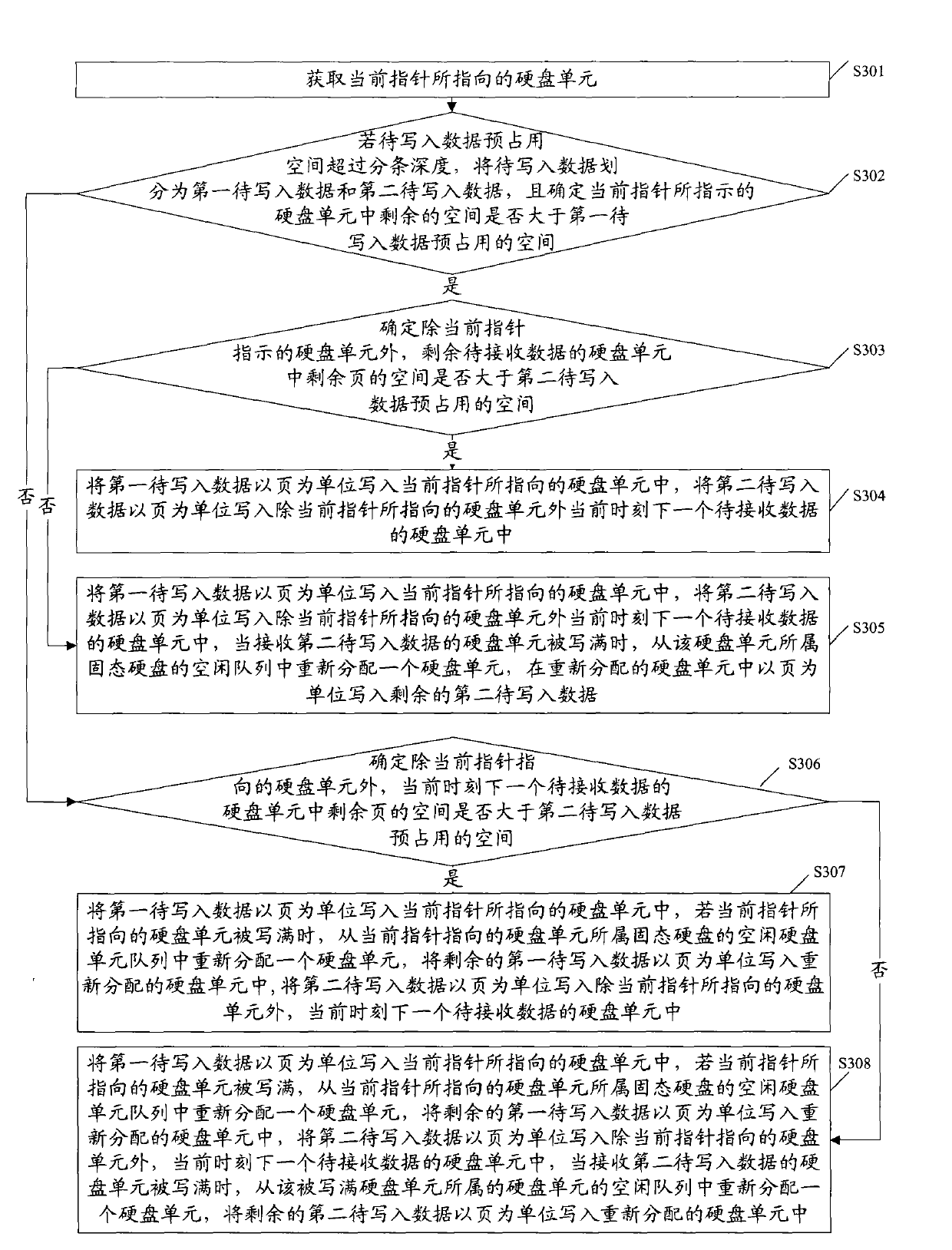
The invention relates to a method for writing data, which comprises the following steps of: acquiring a disk unit (DU) pointed by a pointer currently; when space pre-occupied by data to be written does not exceed preset striping depth, writing the data to be written into a solid state disk (SSD) the DU belongs to by page; and when the space pre-occupied by data to be written exceeds the preset striping depth, writing the data to be written into at least two SSDs that the DU belongs to in a redundant array of inexpensive disk (RAID) group by pages. The embodiment of the invention also provides a device for writing the data and the redundant array of inexpensive disk. In the technical scheme, the data are written into the SSDs sequentially, so the processing process of a controller is simplified, and the writing performance of the SSDs is improved.
Owner:CHENGDU HUAWEI TECH
File storage method and system
ActiveCN104462563AImprove write performanceAvoid it happening againClosed circuit television systemsSpecial data processing applicationsSmall filesFile storage
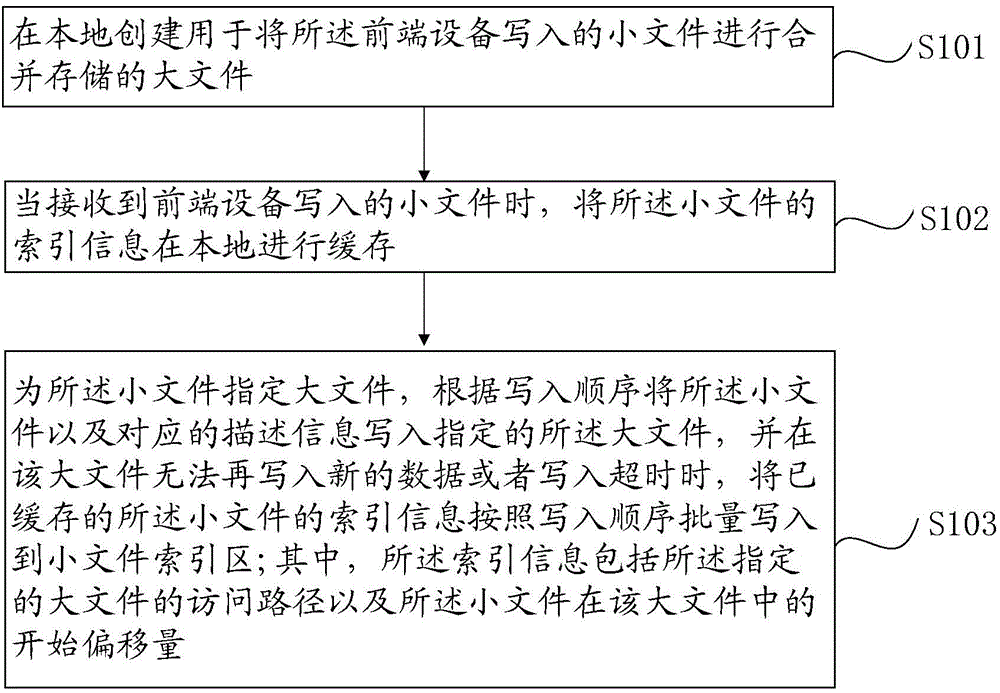
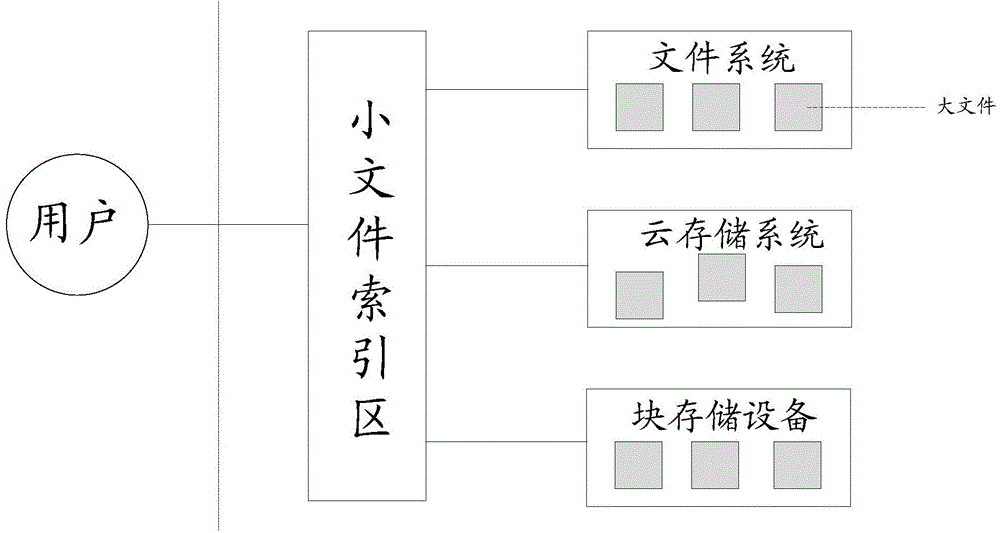
The invention provides a file storage method which is applied to a storage device. The file storage method includes the steps that large files for merging and storing small files written by a front-end device are created in local; when the small files written by the front-end device are received, index information of the small files is cached in local; the large files are appointed for the small files, the small files and corresponding description information are written into the appointed large files according to the written-in sequence, and the cached indexing information of the small files is written into small file indexing areas in batch according to the written-in sequence when new data cannot be written into the large files any more or writing is timed out, wherein the indexing information comprises access paths of the appointed large files and starting offset of the small files in the large files. By means of the file storage method, the written-in performance of the small files can be improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVIEW TECH CO LTD
Write buffer detector, addressing method of written data and parallel channel write method
InactiveCN102521160AAvoid misjudgmentPrevent missed judgmentInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPage address registerWrite buffer
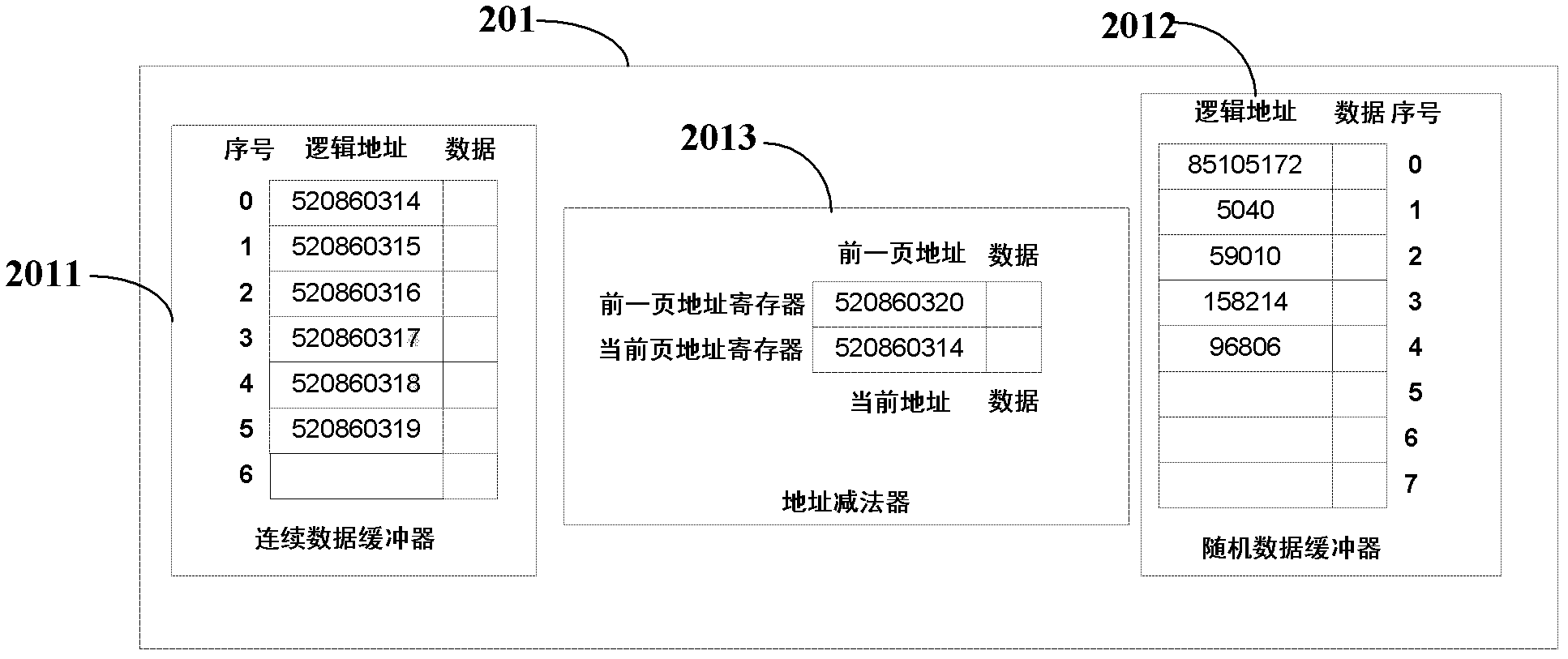
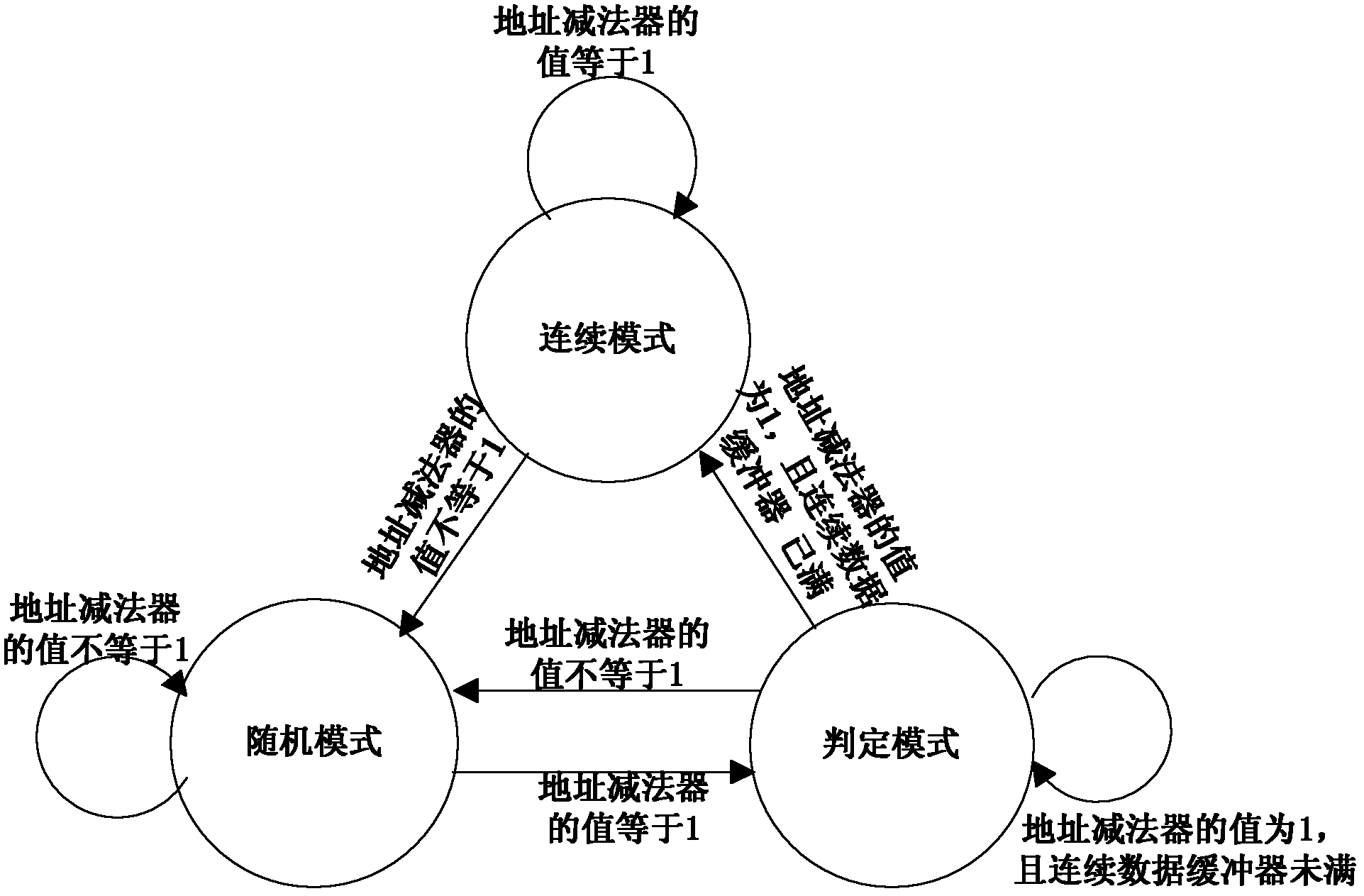
The invention provides a solid state disk (SSD) controller based on a write buffer detector, an addressing method of written data and an optional parallel channel write method, which achieve accurate judgment on address characteristics of data, respectivelycache continuous address data and random address data, write different write strategies according to different data types, and improve write speed of random data. The write buffer detector comprises an address subtractor, a continuous data buffer and a random data buffer, wherein the address subtractor is used for conducting subtraction on current page addresses and previous page addresses and comprises a previous page address register and a current page address register, the previous page address register is used for storing data and addresses at the previous page, and the current page address register is used for storing data and addresses at the current page; the size of the continuous data buffer is set to be a parameter Sequential-Buffer-Size, the continuous data buffer is used for caching data which is probably judged to be continuous access data, and data in the continuous data buffer is judged to be continuous data if the length of data in the continuous data buffer reaches the set parameter; and the random data buffer is used for caching random access data.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
LUN CACHE method for FC-SAN memory system
InactiveCN1545033AImprove write performanceMemory adressing/allocation/relocationOperational systemSCSI
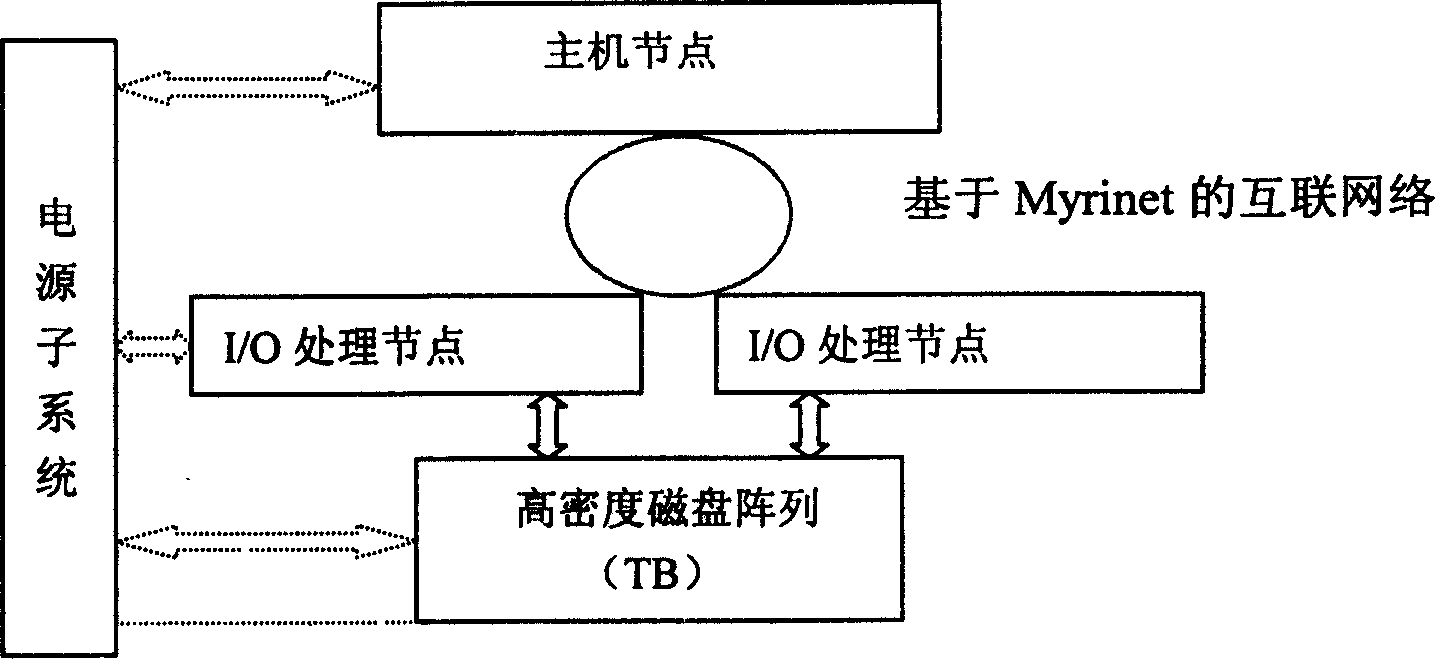
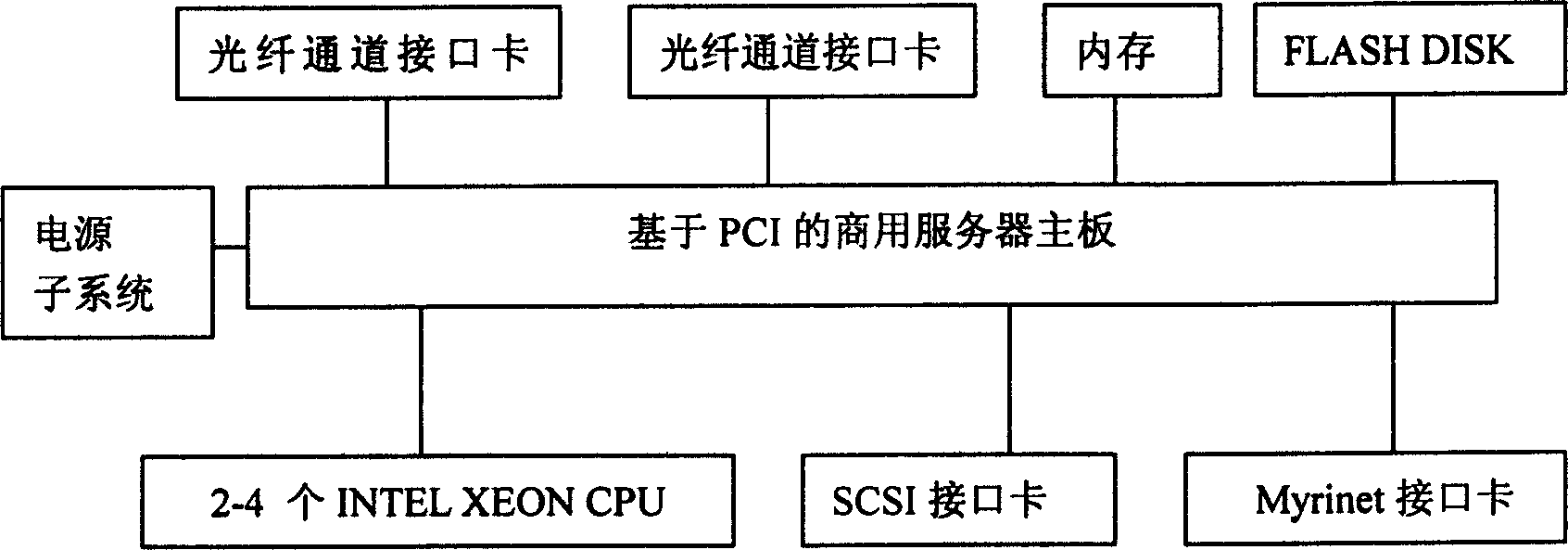
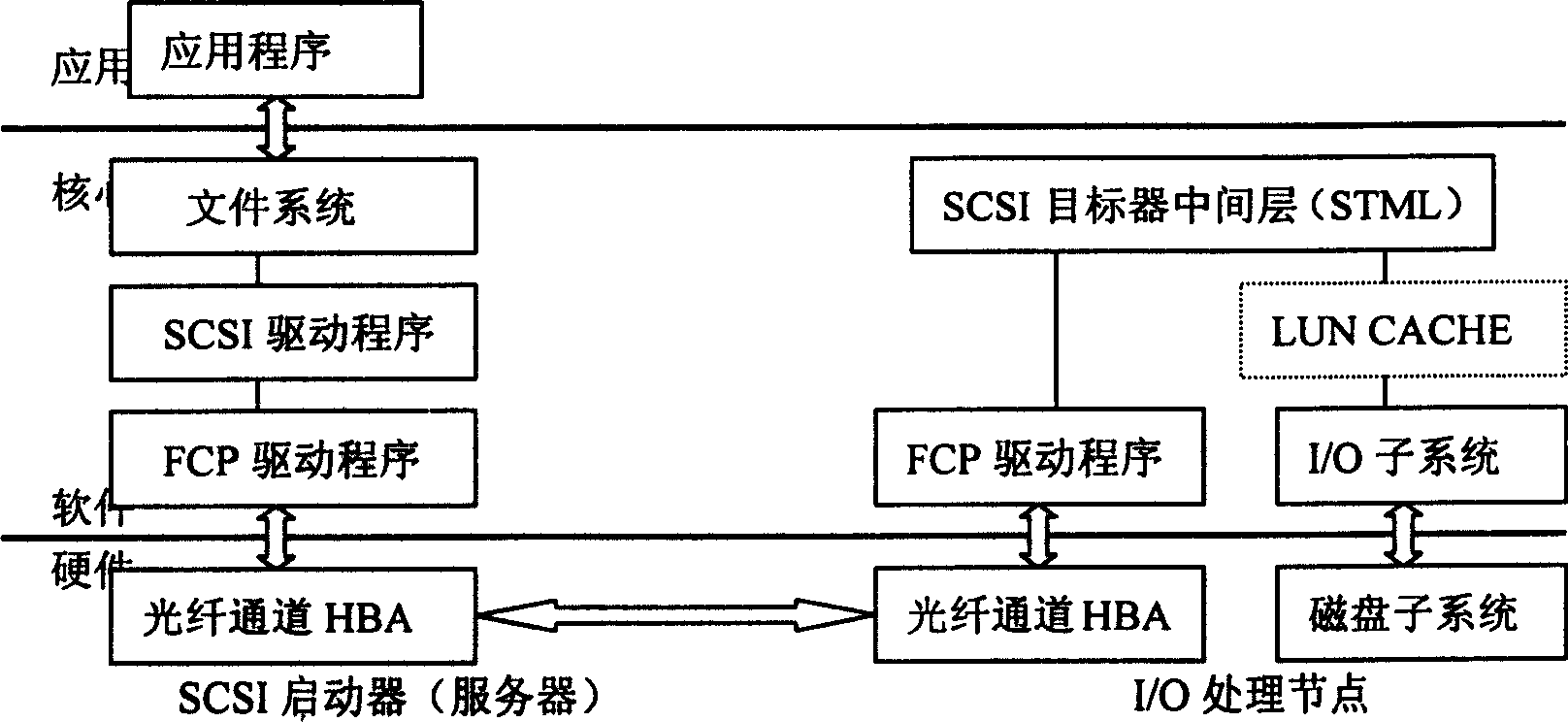
The invention is an LUN CACHE method for an FC-SAN storage subsystem, and its character: it is implemented by a logic unit number cache (LUN CACHE) module operating in an embedded system of I / O processing nodes in the FC-SAN; it uses an improved CACHE displacement arithmetic to enhance the utilization ratio of CACHE, so as to complete the read-write operation in the I / O processing nodes by caching but not sending to a concrete SCSI device; uses a delayed write technique to update the data on the background, extremely improving the repose time; uses a mechanism of read-write lock to ensure a consistency of data sharing among multiple users; makes the LUN CACHE completely transparent for a user by the good design of interface devices. It is tested that the read-write operation performance is extremely enhanced by using the LUN CACHE than before.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Flash data management method and system
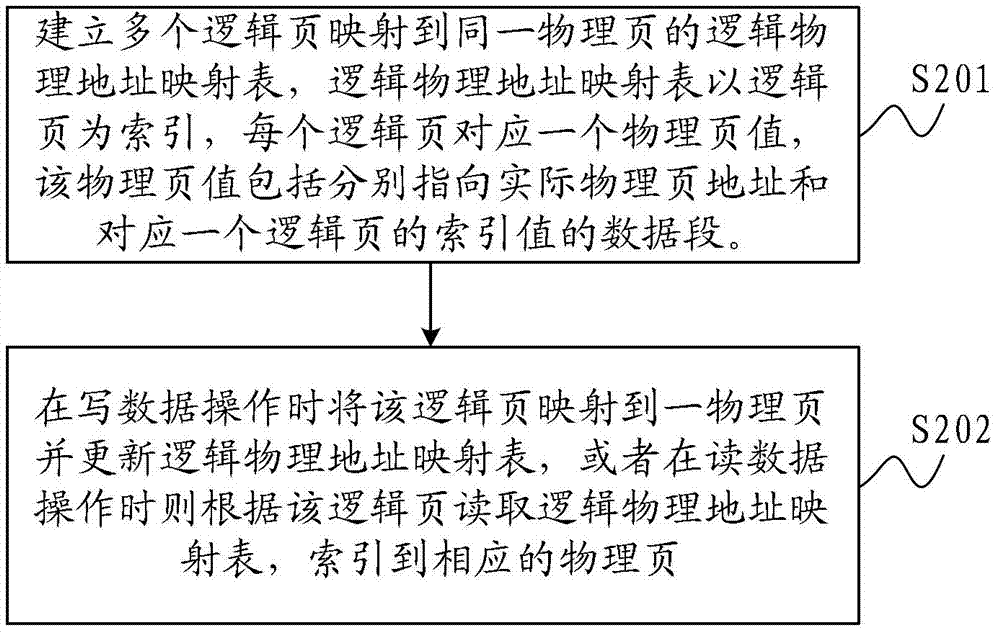
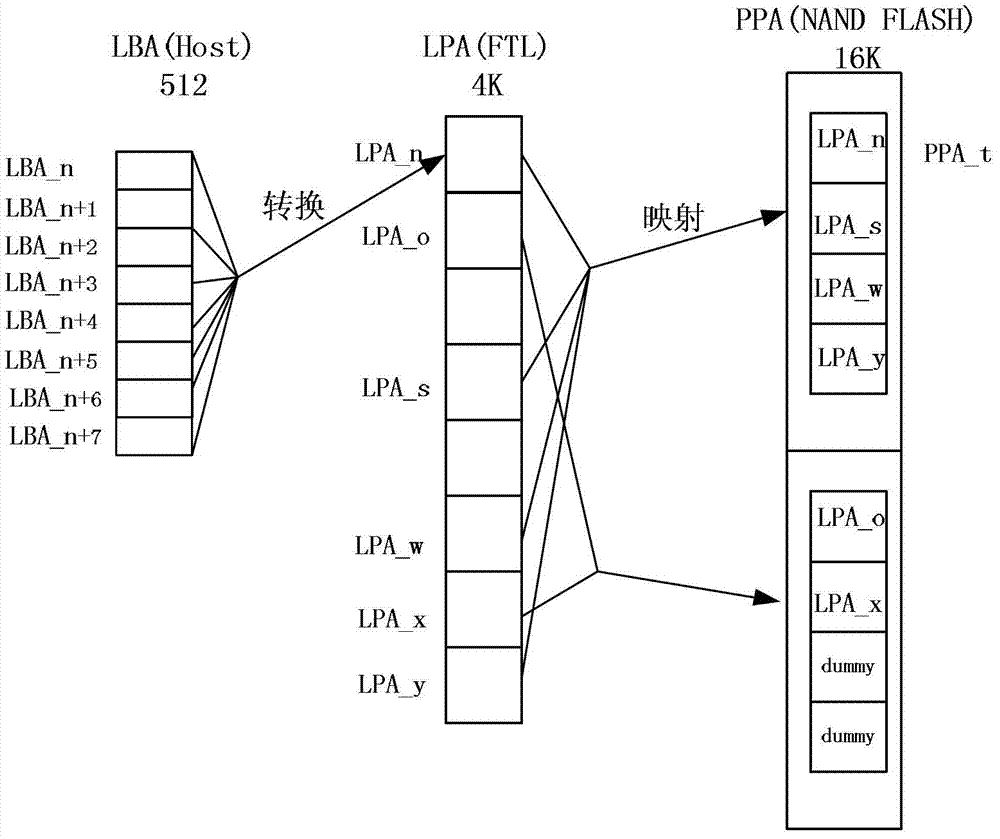
InactiveCN102866955AReduce stepsImprove write performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationAddress mappingManagement system
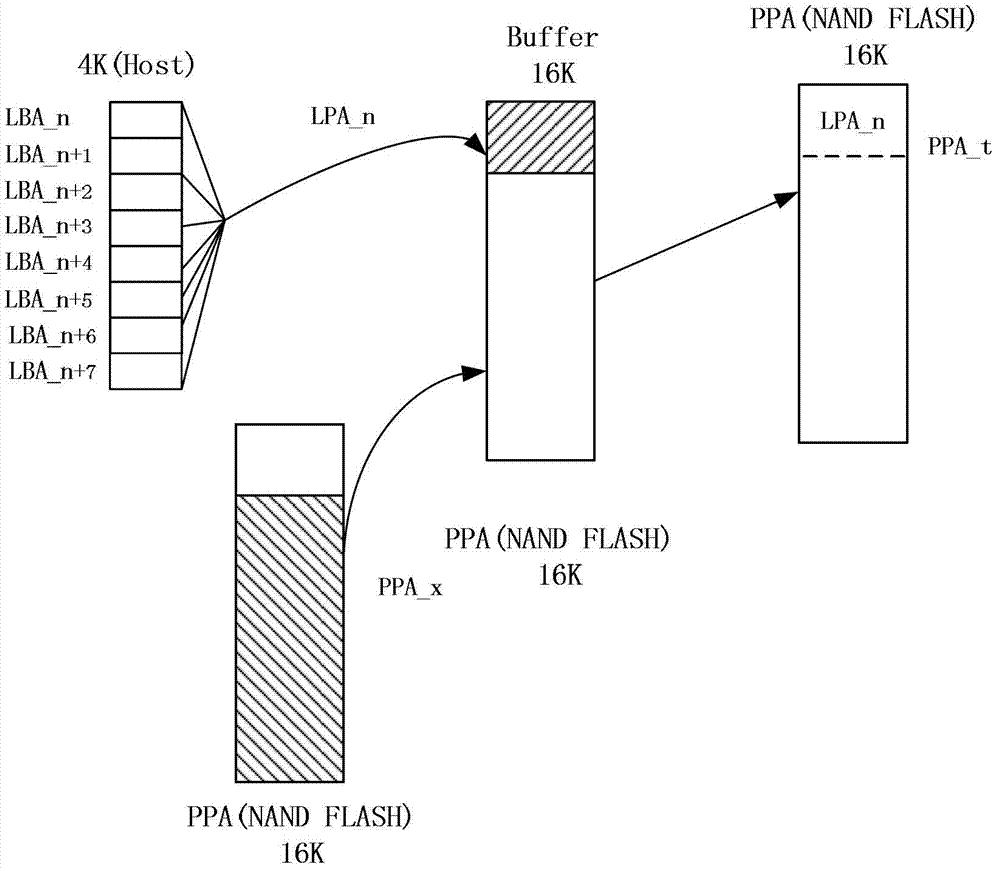
The invention is adapted to the technical field of a solid-state storage technology, in particular to a flash data management method and a flash data management system. The flash data management method comprises the following steps of: managing address mapping, building a logic physical address mapping table mapped on the same physical page by a plurality of logic pages, setting the logic pages as index of the logic physical address mapping table, wherein each logic page corresponds to a physical page value, the physical page value comprises data segments of index values which respectively point to the actual physical page address and correspond to one of the logic pages, and arbitrary logic sequences between the plurality of logic pages in the physical page are relevant; and mapping the logic page to the physical page and updating the logic physical mapping table during writing data operation, or reading the logic physical address mapping table according to the logic pages during reading data operation, and indexing to the corresponding physical page. Therefore, the plurality of logic pages can be mapped to the same physical page according to the size of the physical page and the sizes of the logic pages, reduction of ready-modify-write (RMW) operation is facilitated, and the writing performance is improved.
Owner:RAMAXEL TECH SHENZHEN
File system journal management
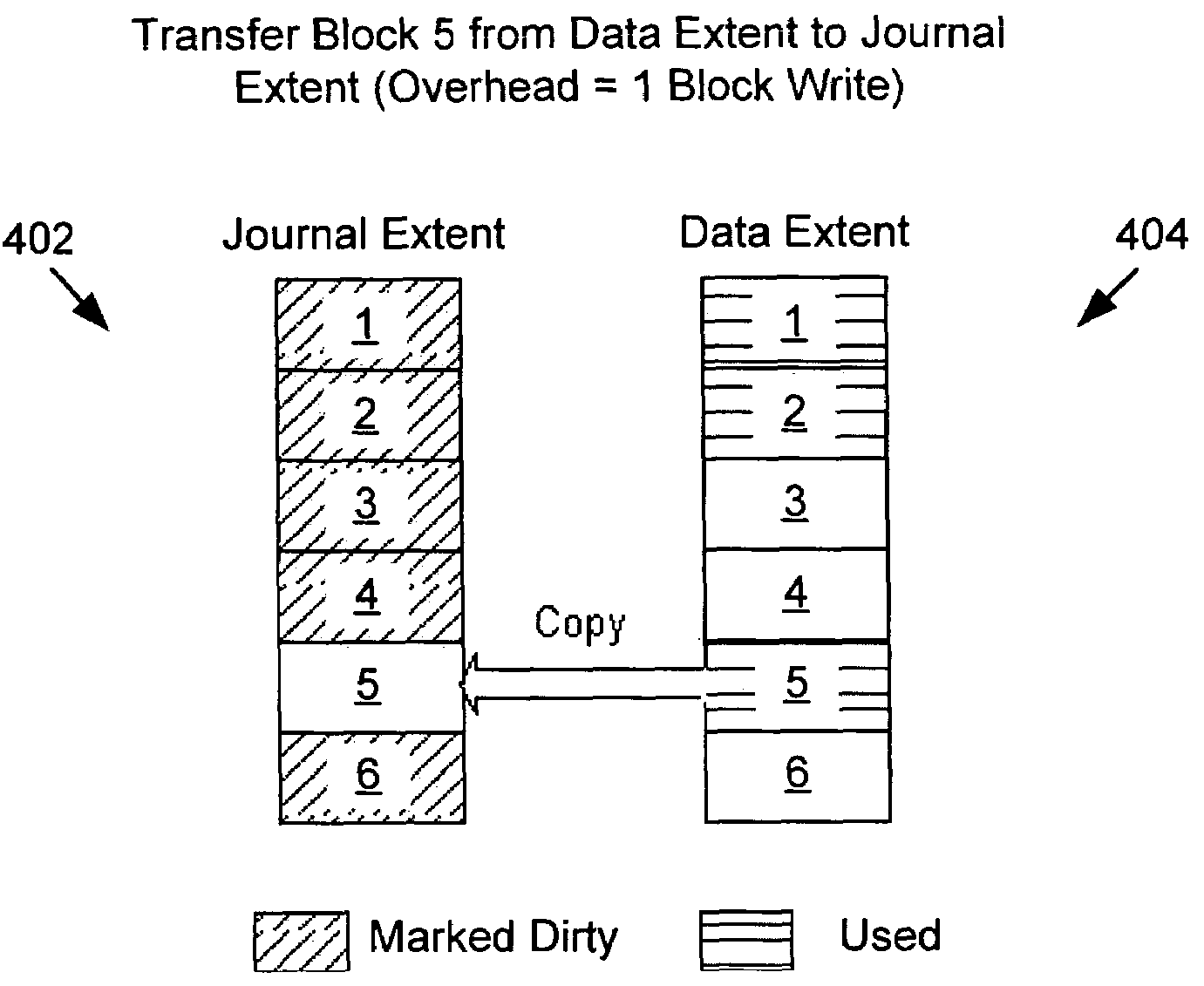
ActiveUS7010721B2Improve write performanceMemory loss protectionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFile systemData storing
A method for data journaling includes writing data into at least one block in a journal storage area, and marking each written block as dirty. If the number of blocks in the journal storage area marked as dirty is greater than the number of blocks in a corresponding data storage area that have been used and whose corresponding blocks in the journal storage area are not marked as dirty, then those used blocks are copied to the corresponding blocks in the journal storage area, and a message is transmitted instructing a meta-data server to swap the data storage area and the journal storage area. If this condition is not so, the blocks in the journal storage area marked as dirty are copied to corresponding blocks in the data storage area, and a message is transmitted instructing the meta-data server to commit the data stored in the journal storage area.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com