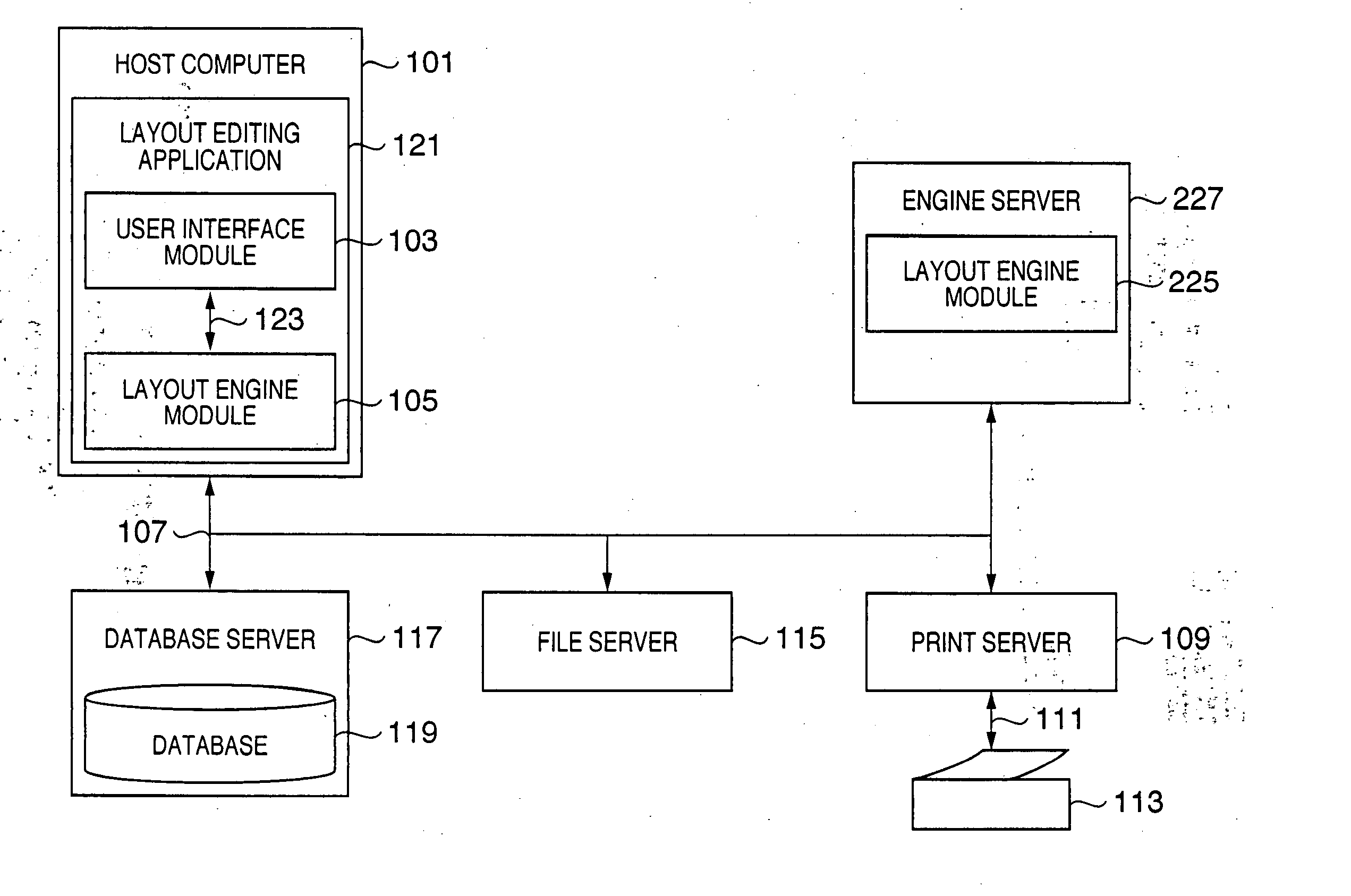
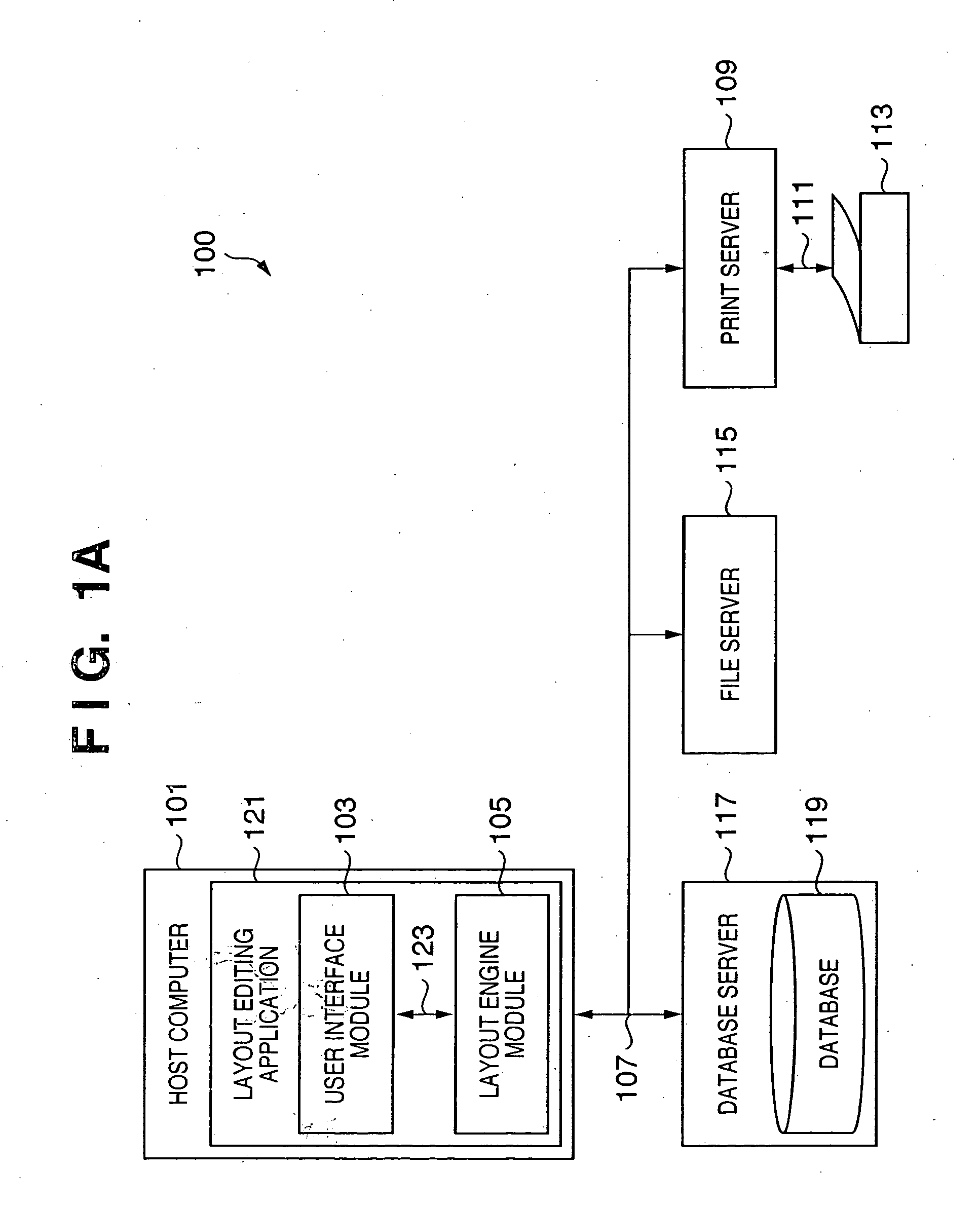
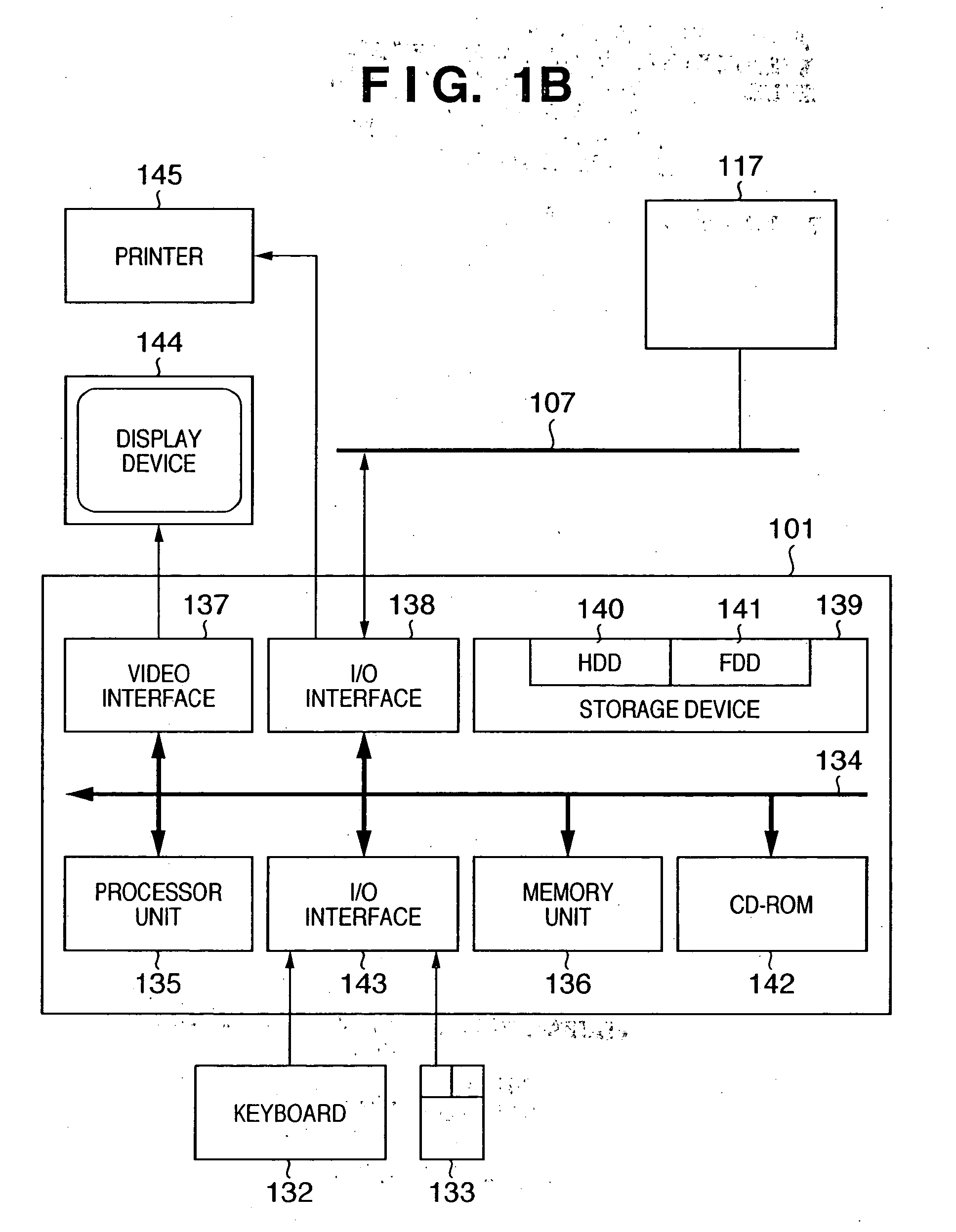
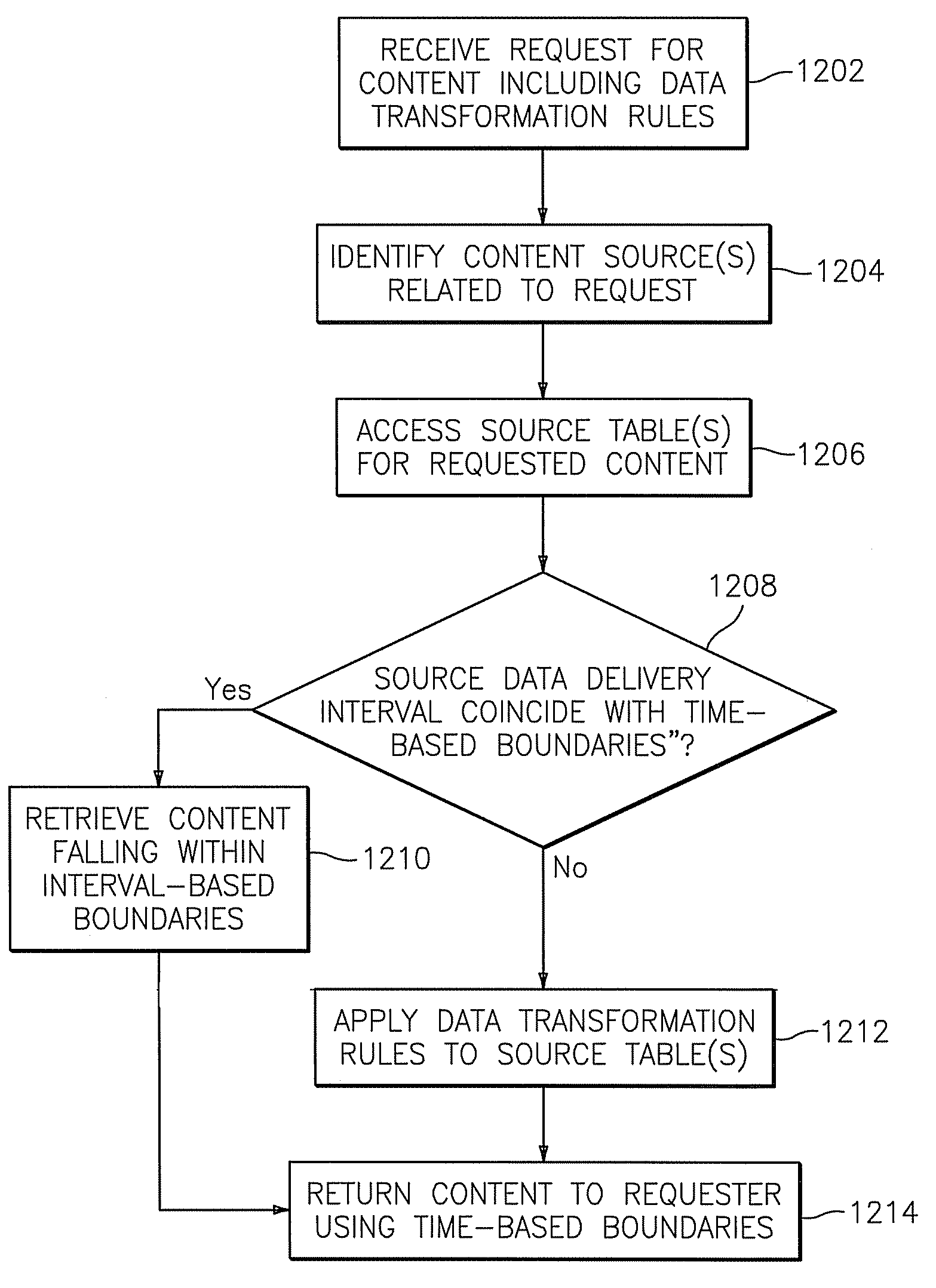
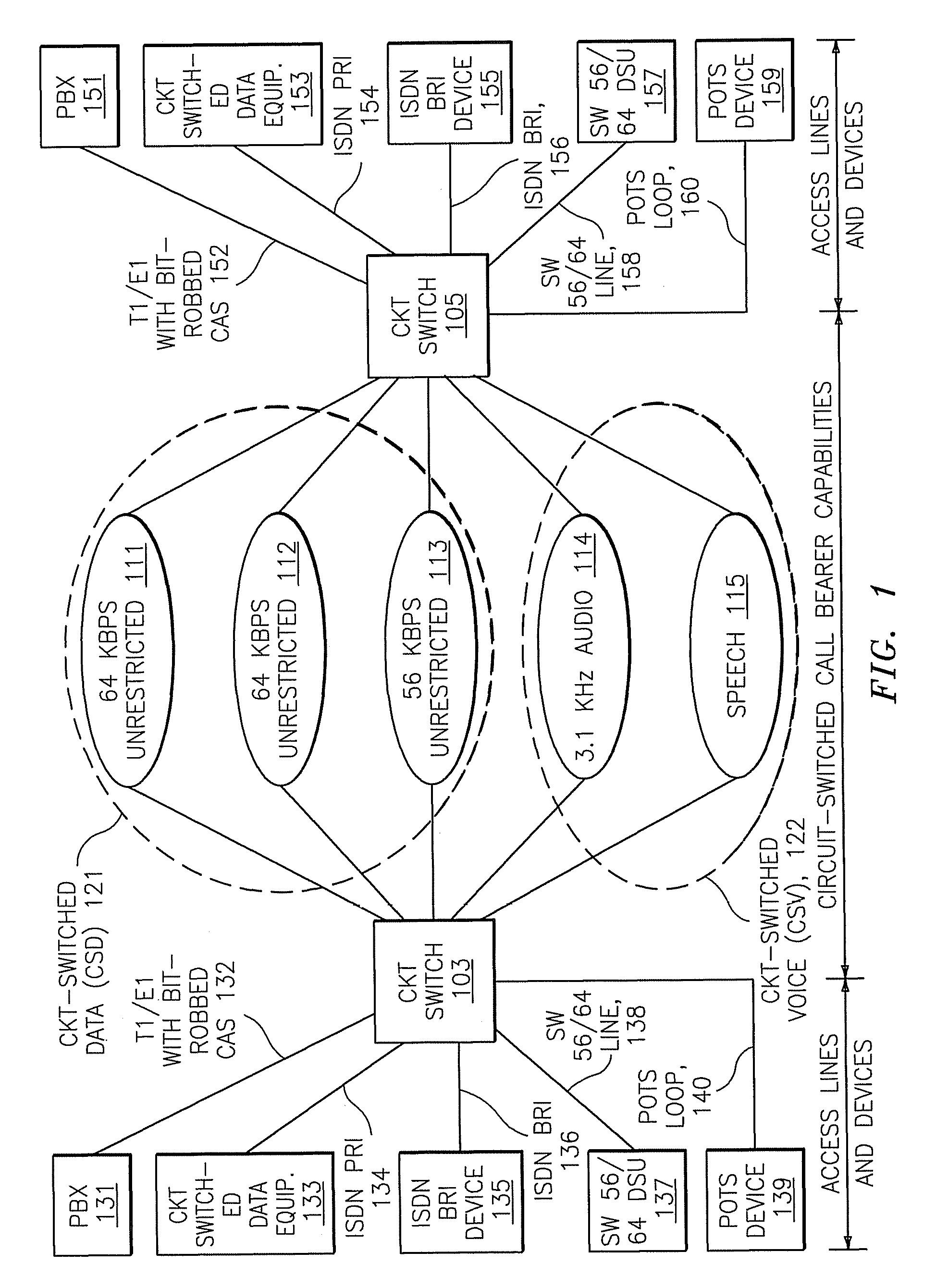
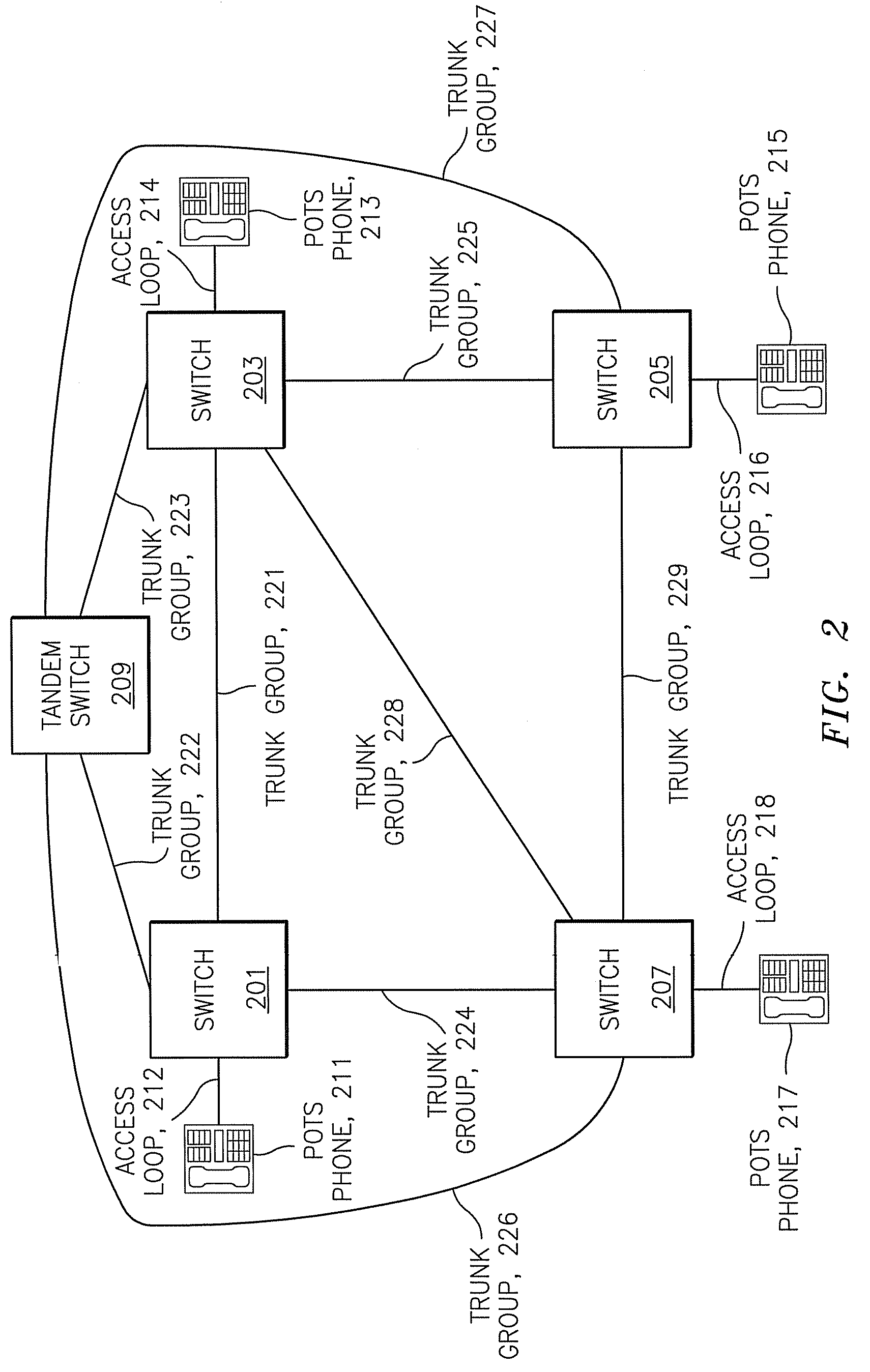
Patents
Literature
263 results about "Data layout" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A data layout is a structure applied to a system that defines how the data fields are organized. Data layouts can be different for each system. Different systems organize their data based on their core functionality. A CRM systems data layout may focus mainly on customer and account data where an eCommerce platform...
Efficient data layouts for convolutional neural networks
Systems and methods for efficient implementation of a convolutional layer of a convolutional neural network are disclosed. In one aspect, weight values of kernels in a kernel stack of a convolutional layer can be reordered into a tile layout with tiles of runnels. Pixel values of input activation maps of the convolutional layer can be reordered into an interleaved layout comprising a plurality of clusters of input activation map pixels. The output activation maps can be determined using the clusters of the input activation map pixels and kernels tile by tile.
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
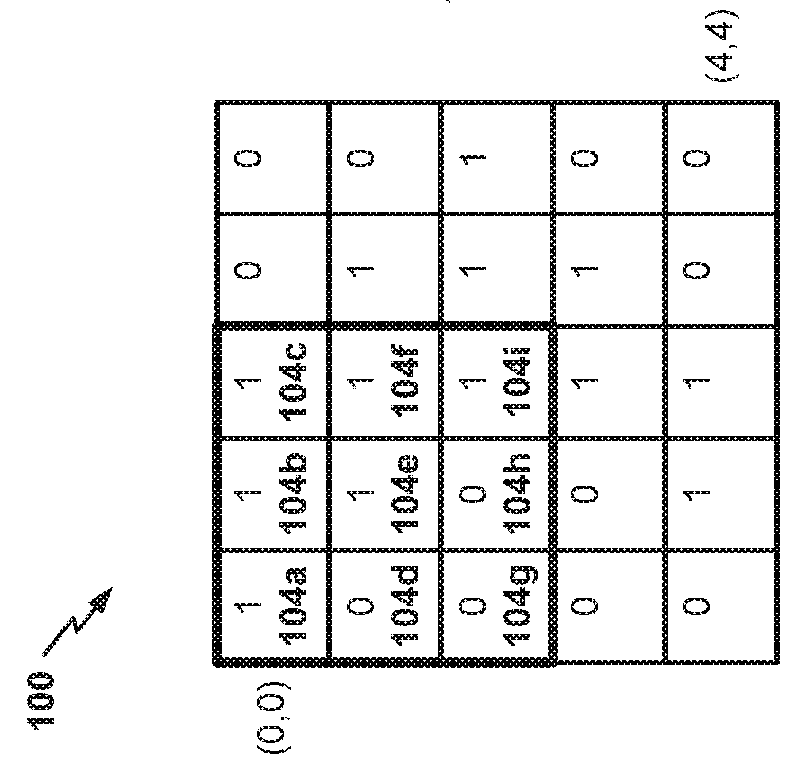
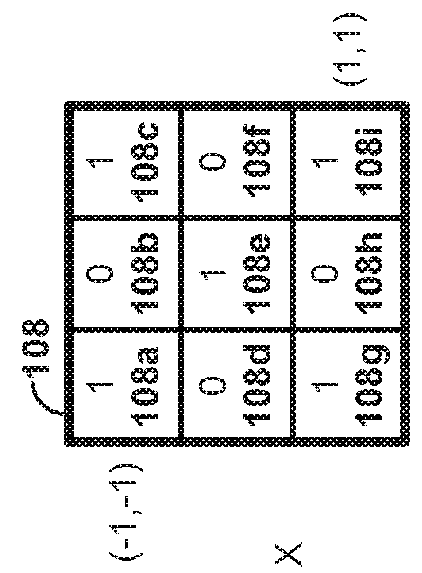
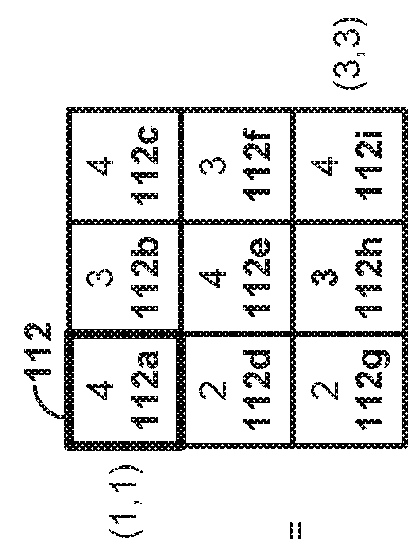
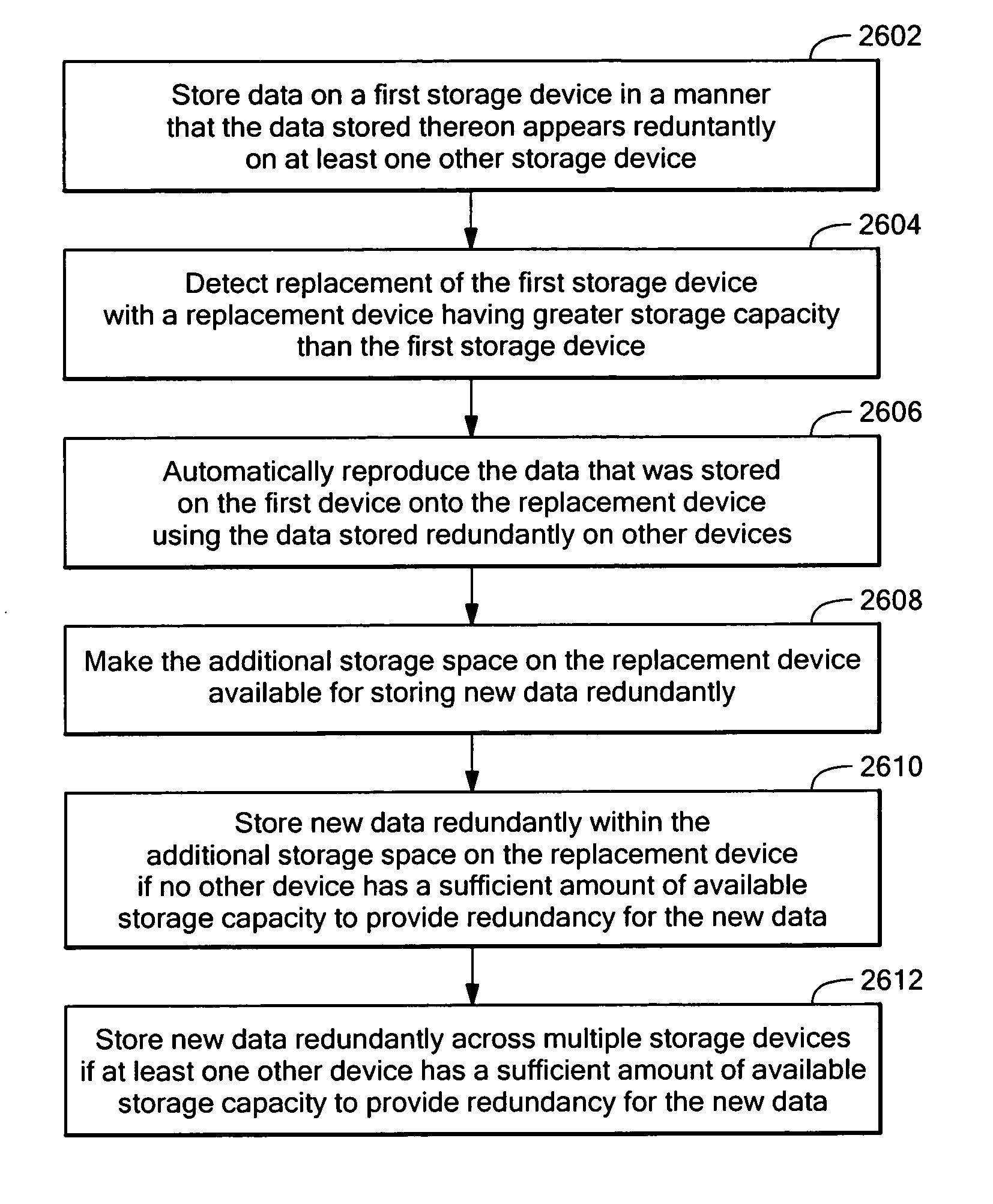
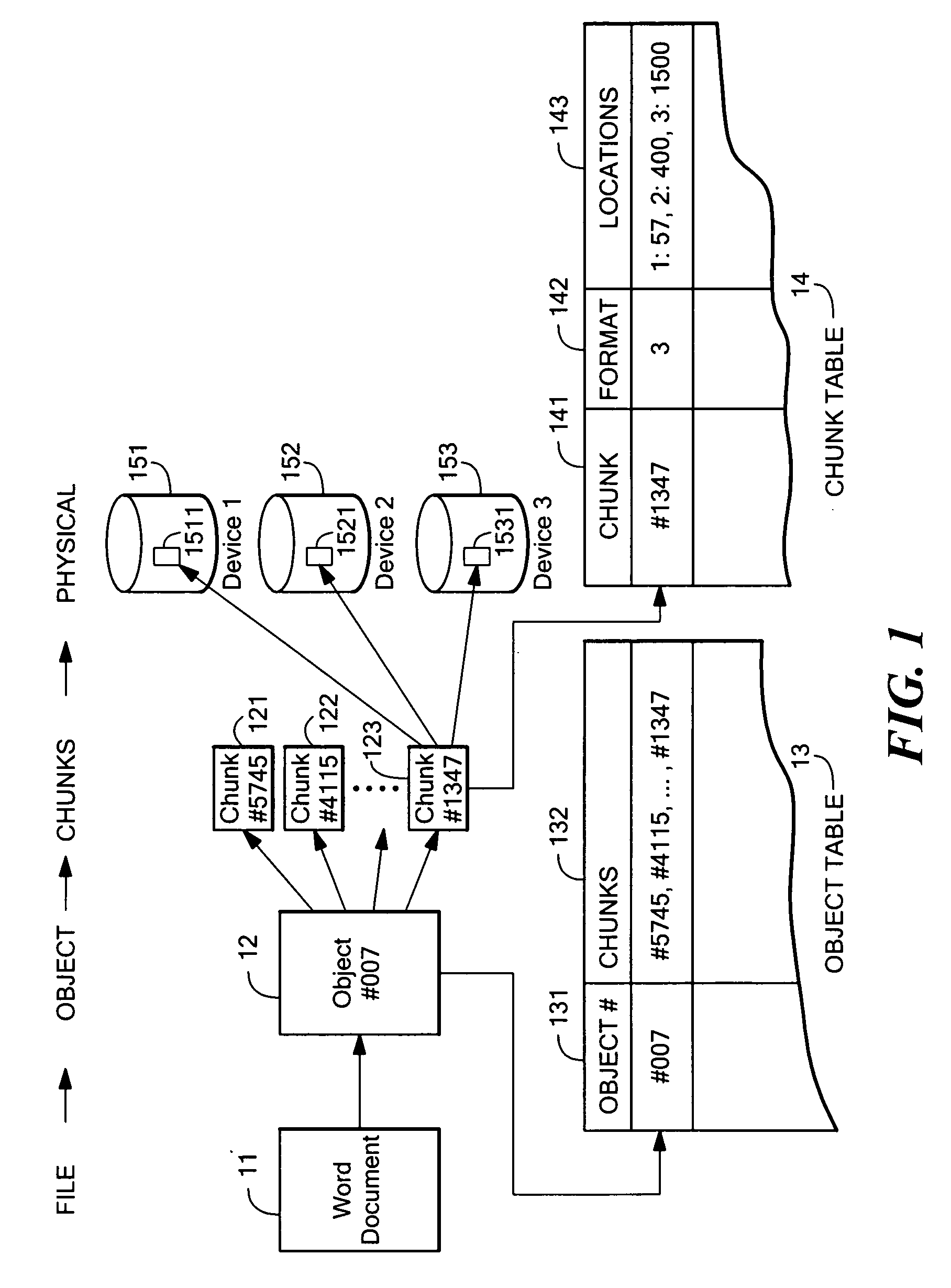
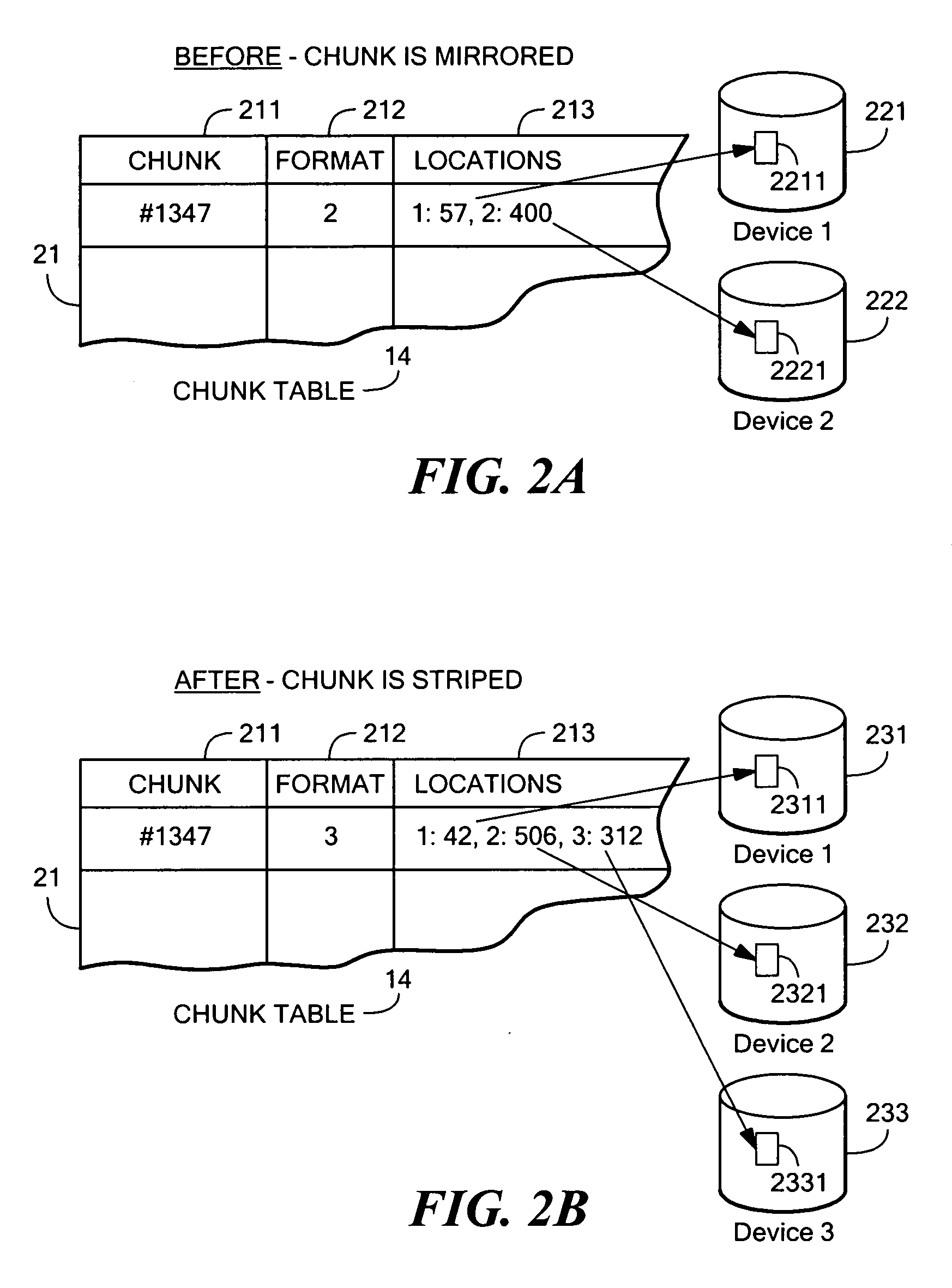
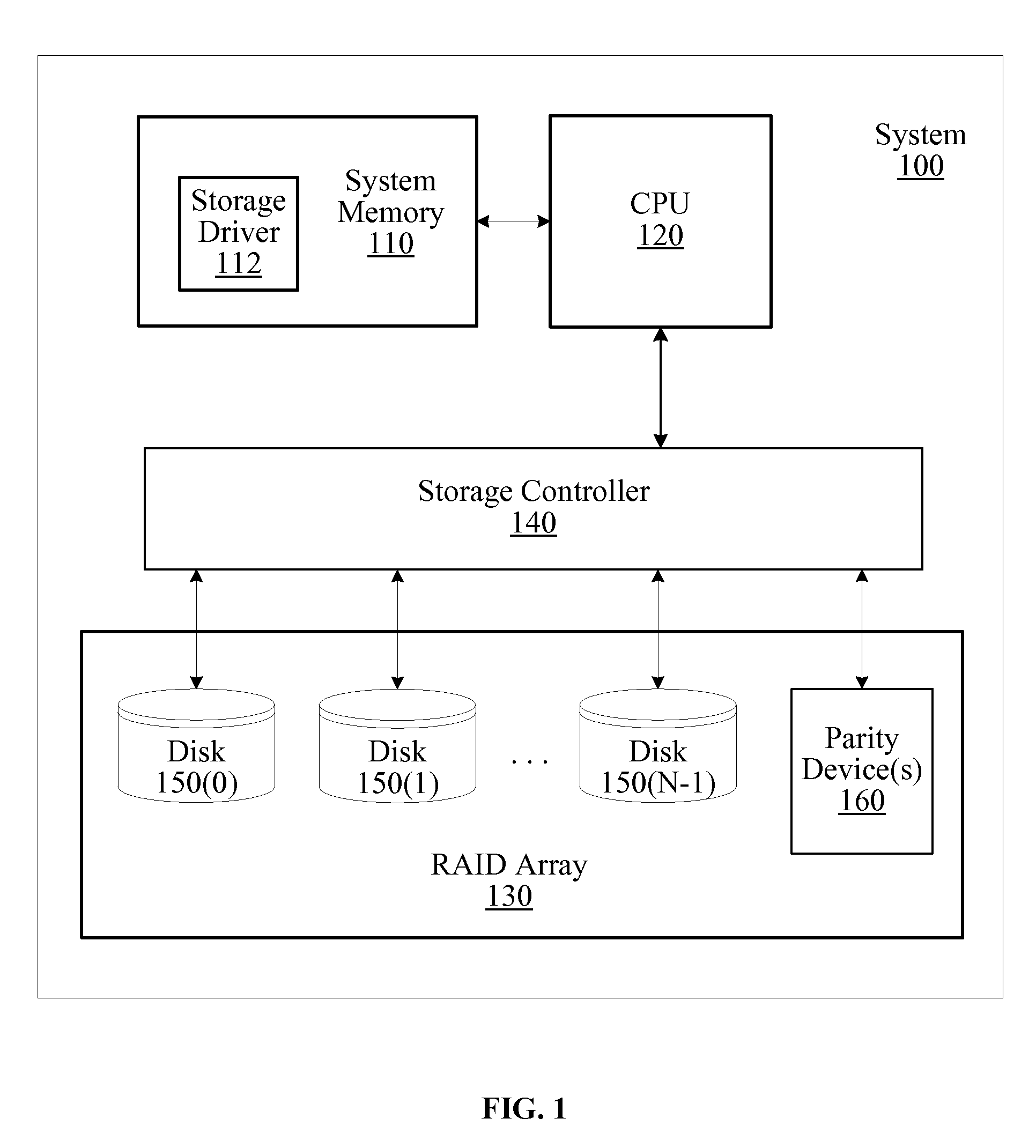
Dynamically expandable and contractible fault-tolerant storage system permitting variously sized storage devices and method
ActiveUS20060112222A1Improve storage efficiencyInput/output to record carriersMemory loss protectionData layoutOperating system
A dynamically expandable and contractible fault-tolerant storage system permits variously sized storage devices. Data is stored redundantly across one or more storage devices if possible. The layout of data across the one or more storage devices is automatically reconfigured as storage devices are added or removed in order to provide an appropriate level of redundancy for the data to the extent possible. A hash-based compression technique may be used to reduce storage consumption. Techniques for freeing unused storage blocks are also disclosed.
Owner:STORCENTRIC DIP LENDER LLC
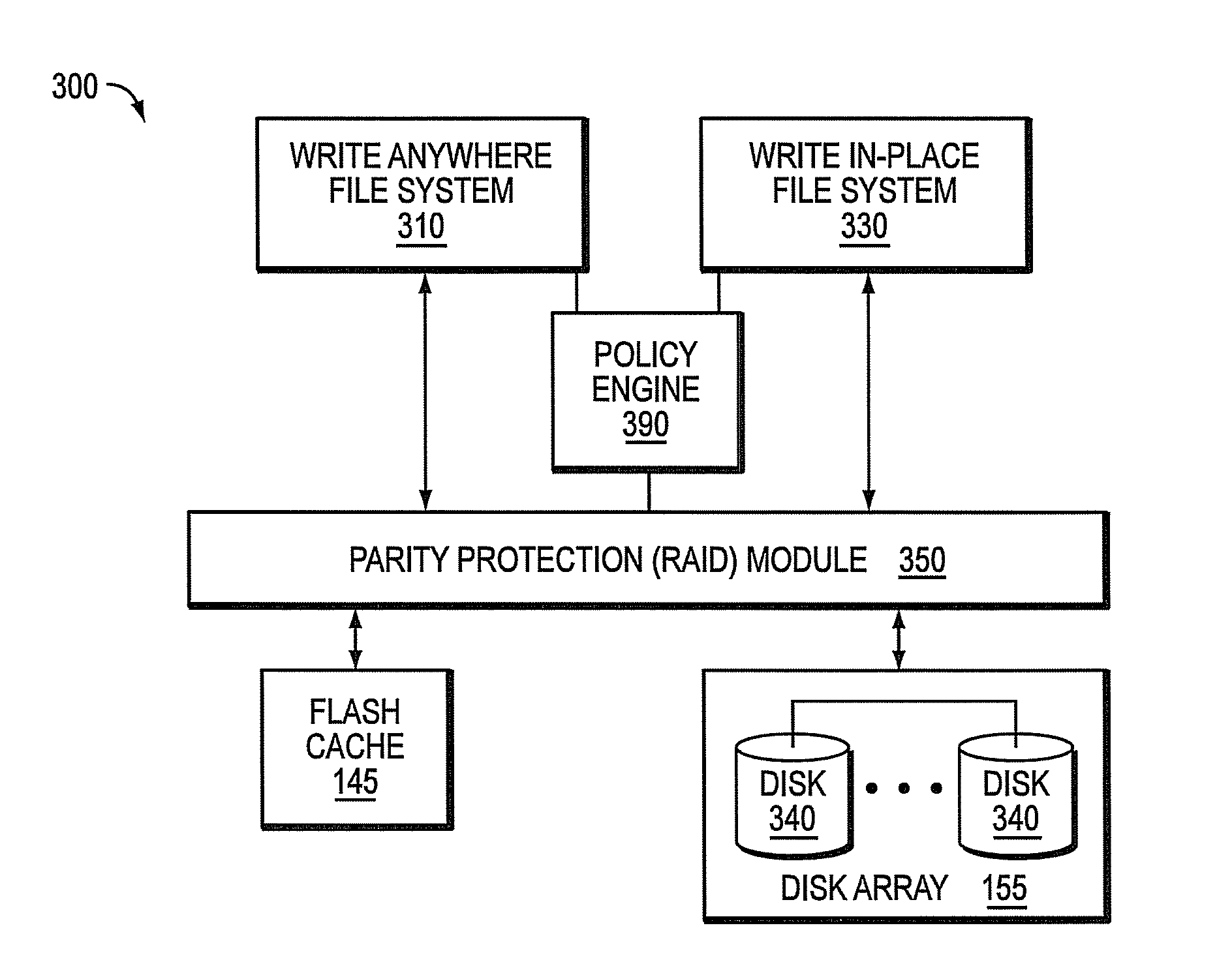
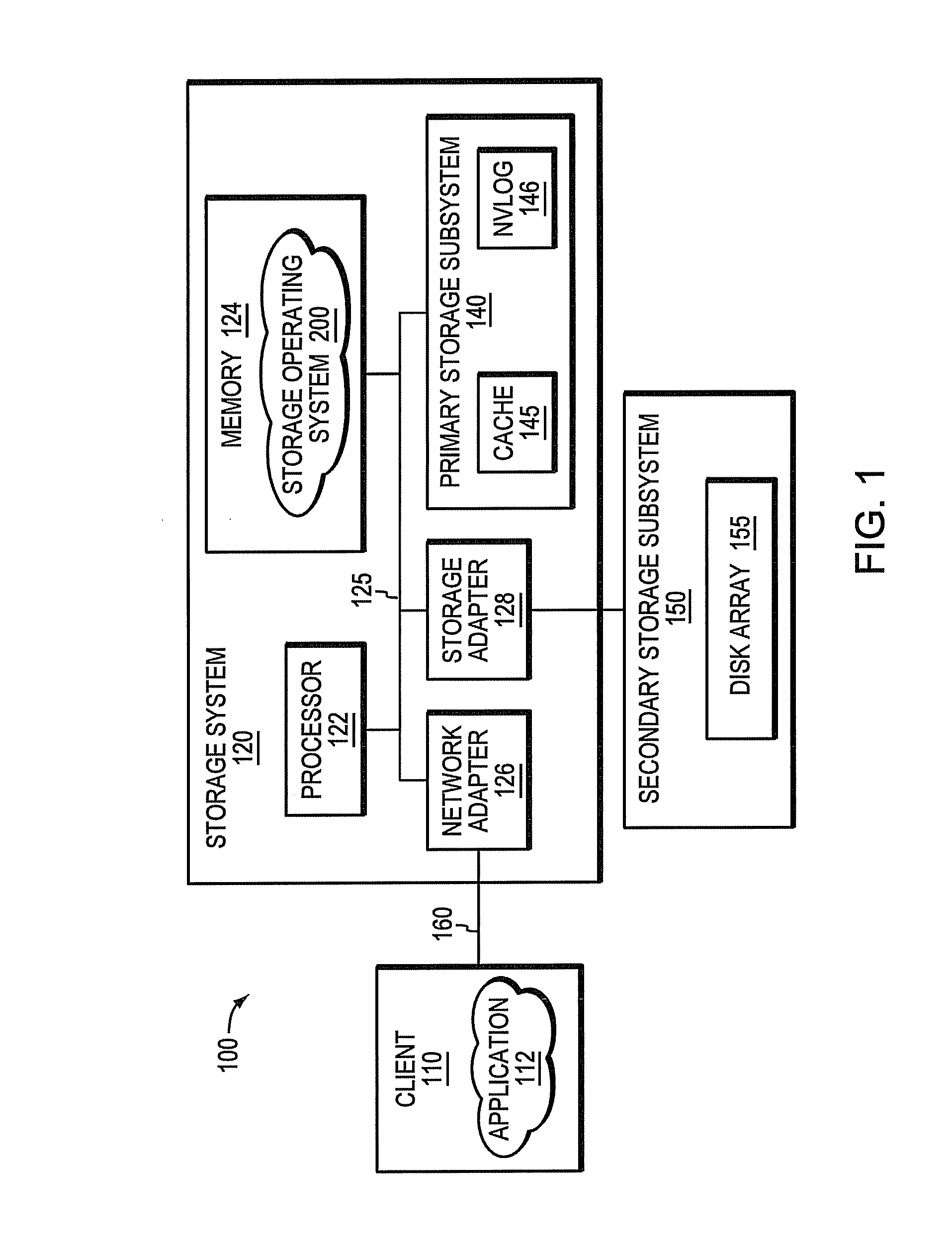
Cache-based storage system architecture
ActiveUS8549222B1Improve write performanceImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionMagnetic storageData access
A cache-based storage architecture has primary and secondary storage subsystems that are controlled by first and second data layout engines to provide a high-performance storage system. The primary storage subsystem illustratively comprises non-volatile electronic storage media configured as a cache, while the secondary storage subsystem comprises magnetic storage media configured as a disk array. The data layout engines illustratively implement data layout techniques that improve read and write performance to the primary and secondary storage subsystems. To that end, the data layout engines cooperate to optimize the use of the non-volatile cache as a primary storage stage that efficiently serves random data access operations prior to substantially transposing them into sequential data access operations for permanent (or archival) storage on the disk array.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
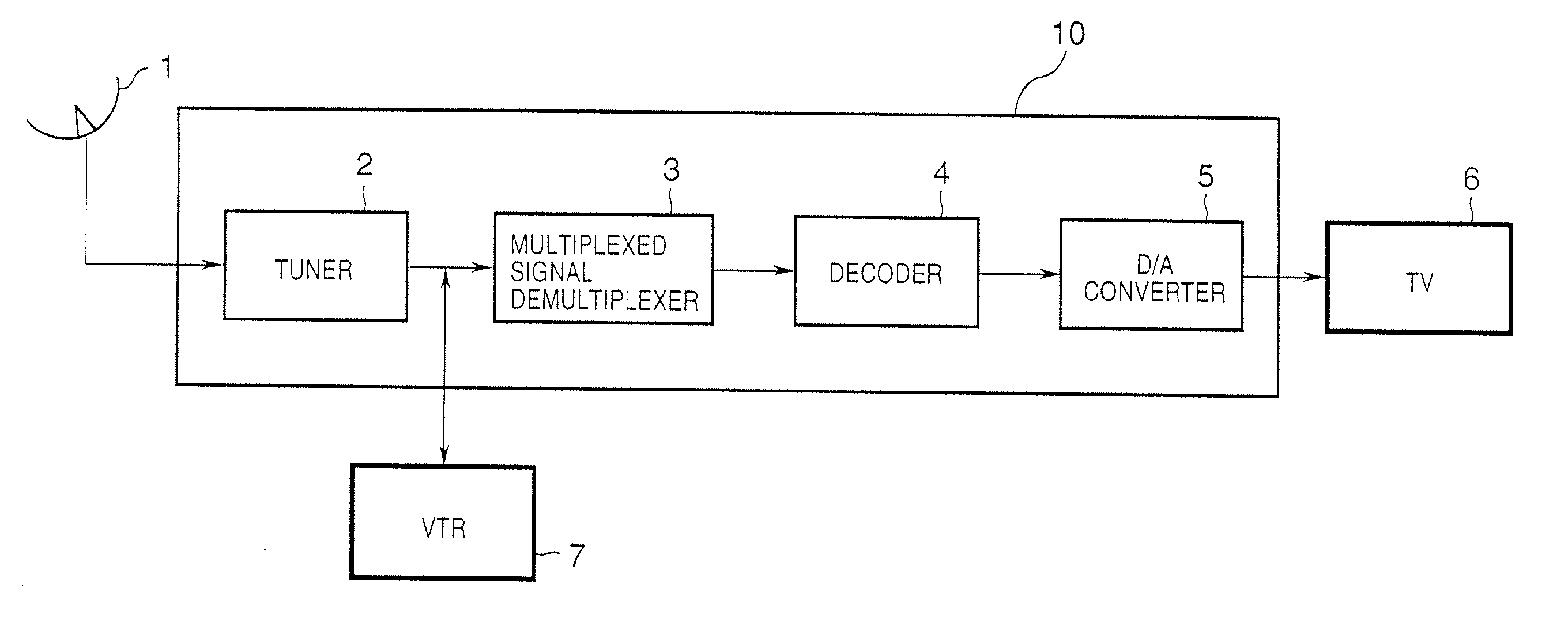
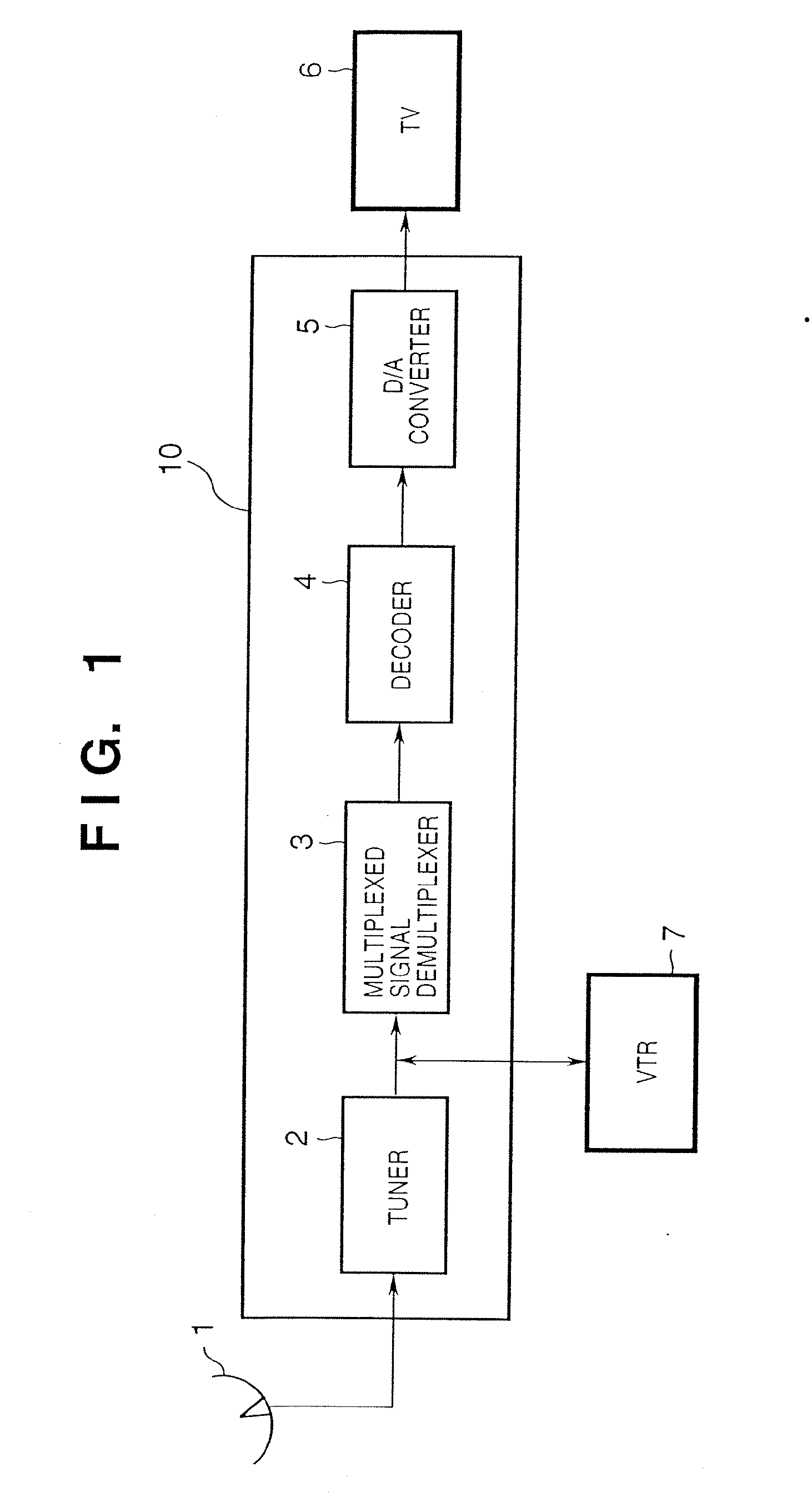
Receiving apparatus and method
InactiveUS20060282874A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer graphics (images)Data layout
Upon reproducing a TV program, it is a common practice to display video data sent from a broadcast station as it is, and the display pattern (layout) is not effectively changed (e.g., an object in video data is erased, or the object size is changed). A program ID from additional data contained in received TV information is detected, and when layout setting data corresponding to the detected program ID is stored in a memory, the corresponding layout setting data is read out from the memory to display program video data in the set layout. When a new layout is set, the user selects an object for which a layout is to be adjusted from objects that form image data in TV information, and adjusts movement, upscaling / downscaling, display ON / OFF of the selected object.
Owner:CANON KK
Layout control method, layout control apparatus, and layout control program
InactiveUS20050172226A1Easy to operateShearing machinesNatural language data processingComputer scienceData layout
To implement an efficient user operation by making it possible to set links between a plurality of containers at once by one operation, in a layout control method which sets a link between partial display regions to connect them to each other, the partial display regions receiving assigned data and laying out the data on a page, and adjusts the position of each partial display region on the basis of the data assigned to it, a plurality of links are set for a plurality of partial display regions, the plurality of partial display regions are designated, the position information of each designated partial display region is acquired, and in a case where setting of a plurality of links is instructed, a plurality of links are set for the plurality of designated partial display regions, on the basis of the acquired position information.
Owner:CANON KK
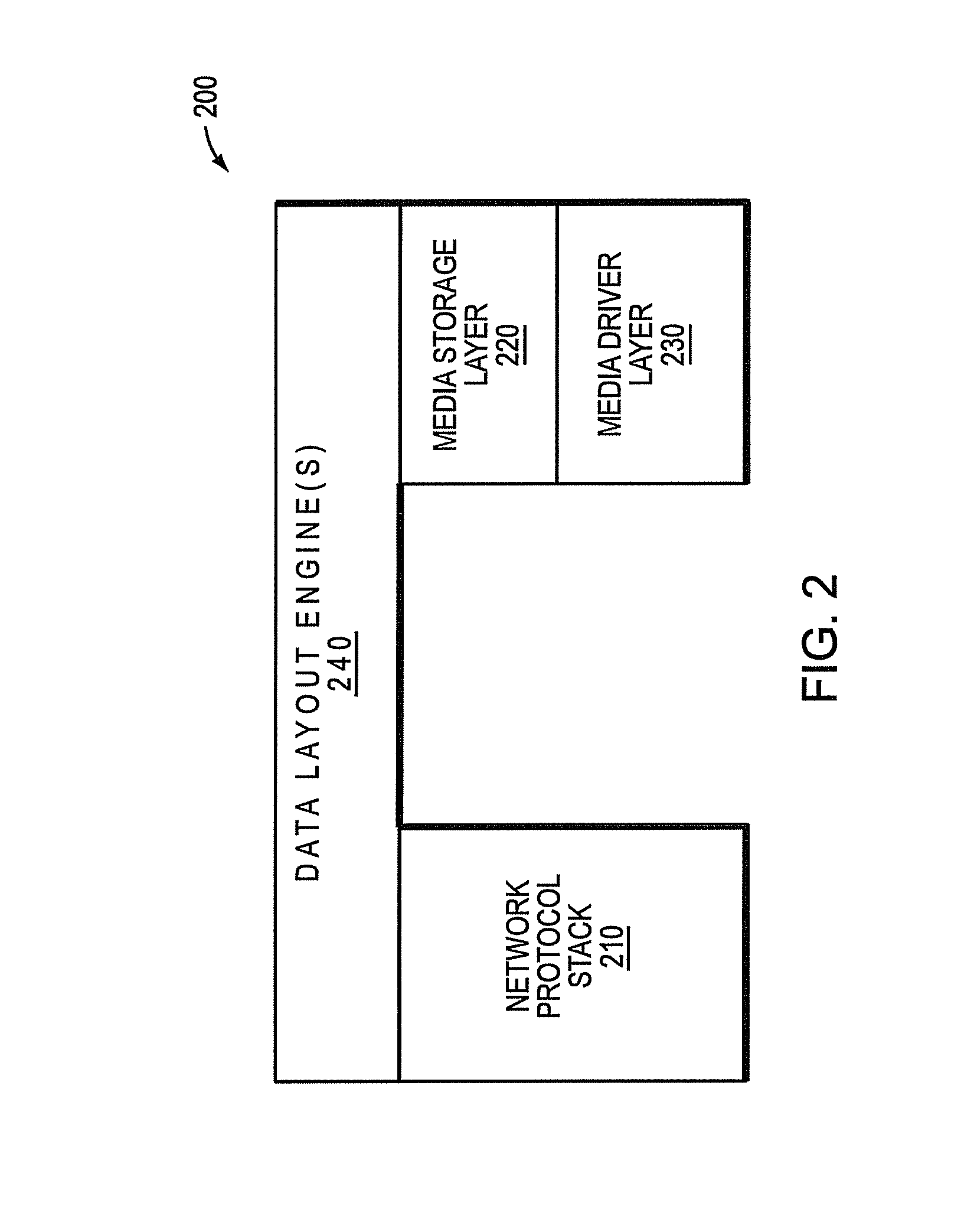
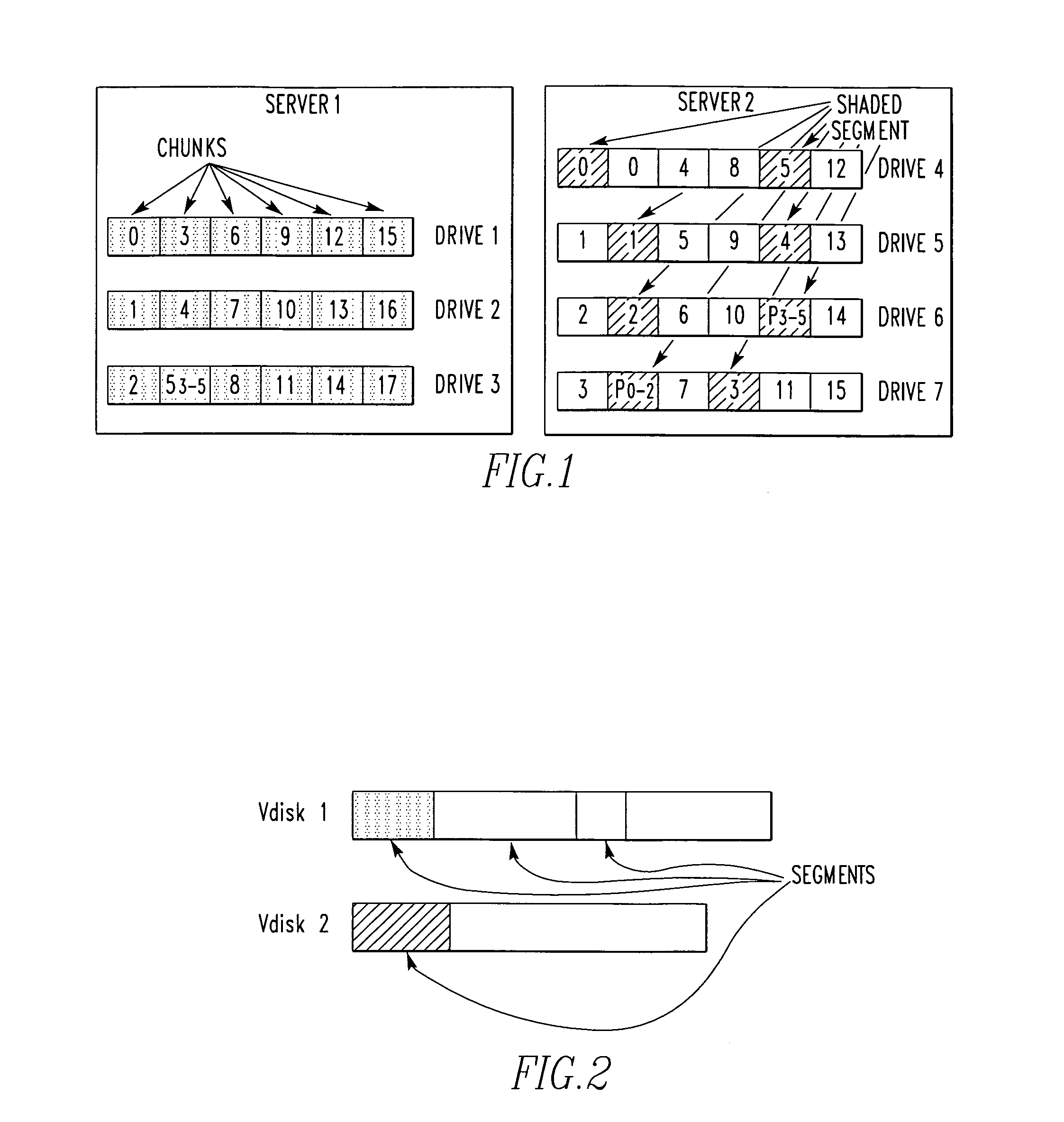
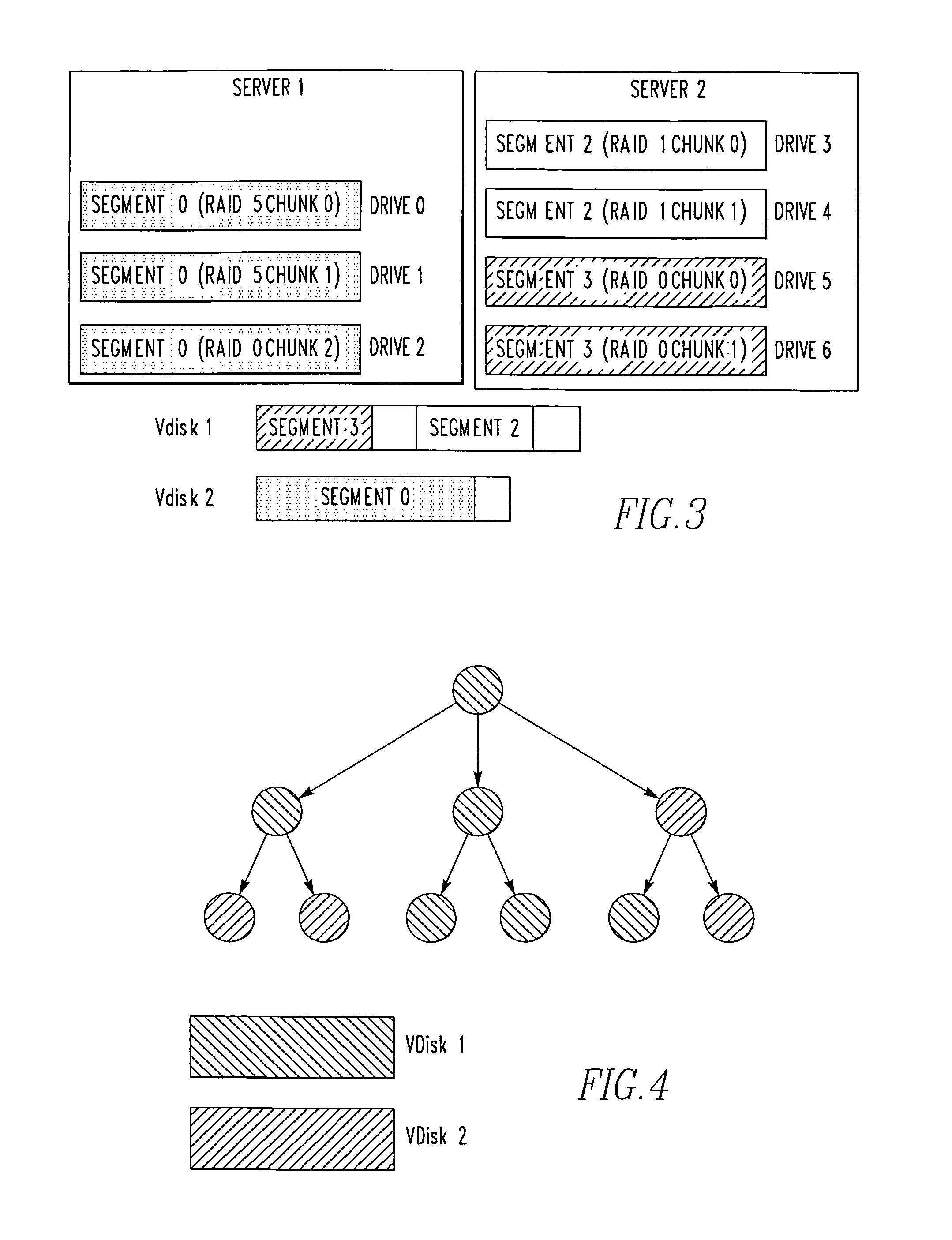
Media aware distributed data layout
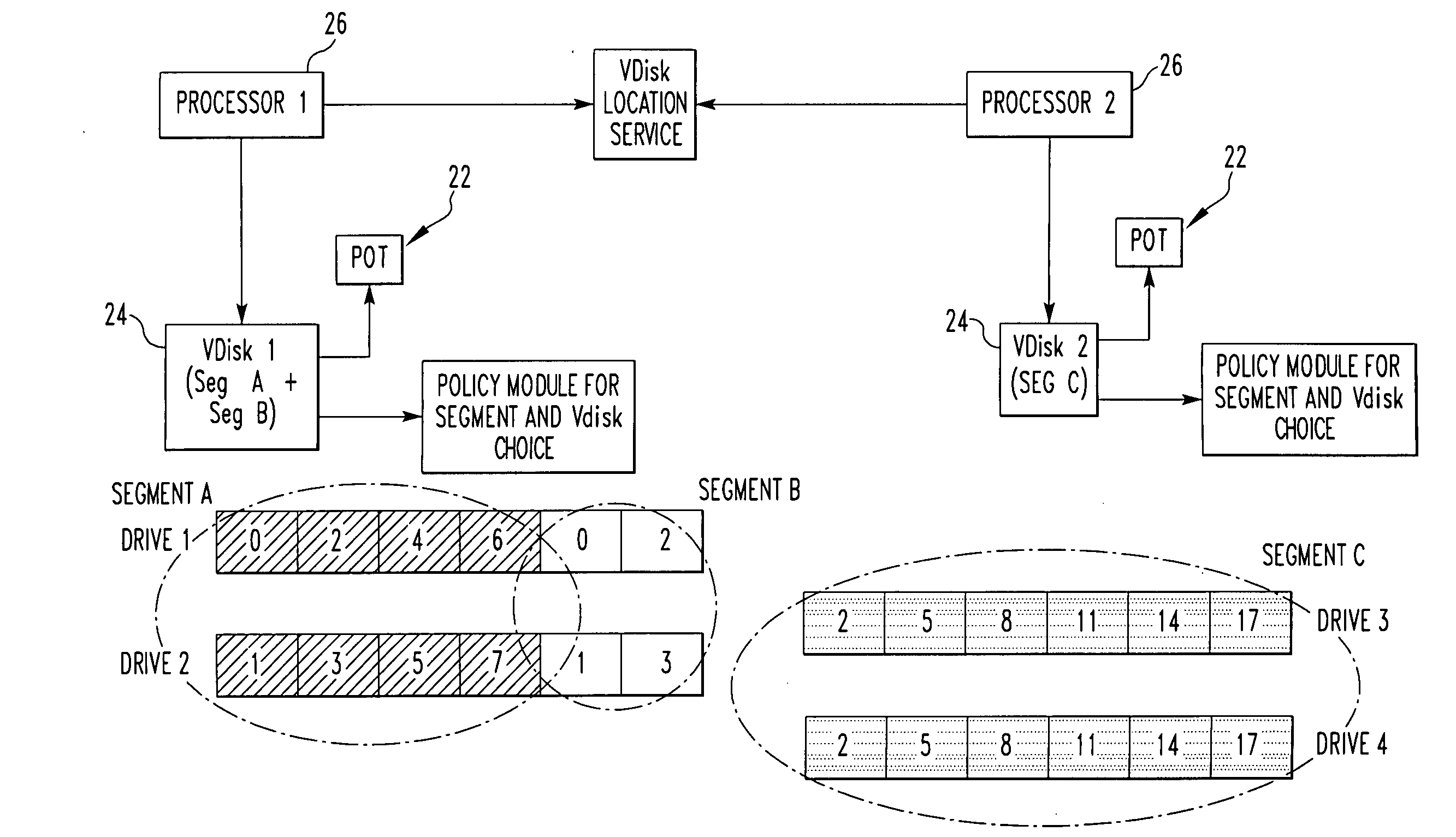
InactiveUS20100011037A1Reduce amountLimited amountData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsClass of serviceInode
A storage system comprises a plurality of vdisks, with each vdisk containing a plurality of storage segments, and each segment providing a specific class of service (CoS). Each vdisk stores files with data and meta data distributed among its storage segments. A storage system comprises a memory having multiple classes of service. The system comprises an interface for storing a file as blocks of data associated with a class of service in the memory. The interface chooses the class of service for a block on a block by block basis. A file system for storing a file comprises a plurality of vdisks, with each vdisk having a plurality of inodes. Each inode of each vdisk stores data on one or more segments, with each segment having a different class of service. The system comprises a controller which stores data of a file in an inode of a vdisk, in one or more segments of that vdisk. A file system for storing a file comprises a plurality of vdisks, and each vdisk having a plurality of inodes. The system comprises a controller including a plurality of processors, with each processor serving one or more of the vdisks. A file system for storing comprises a plurality of vdisks, with each vdisk having a plurality of inodes, a plurality of inodes of at least one vdisk storing data on a plurality of segments, each segment having a different class of service. The system comprises a controller which stores data of the file in one or more segments of one vdisk. A method for storing a file.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
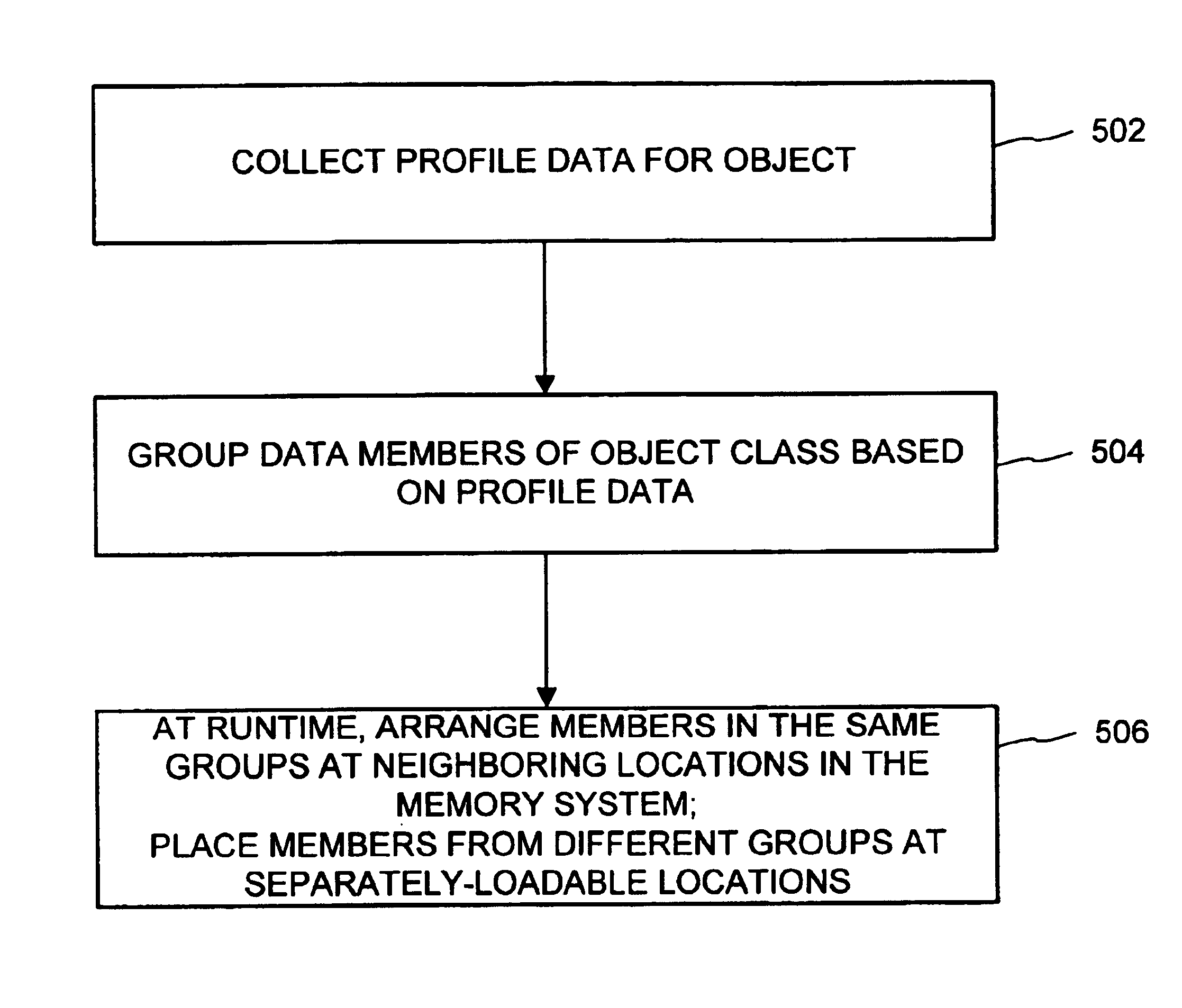
Profile-driven data layout optimization
InactiveUS6862729B1Easy to useImprove performanceProgram loading/initiatingMemory systemsObject ClassAnalysis data
Data layout optimization arranges data members within memory to enhance software performance. Profiling data is consulted to determine how to group data members for an object class into groups. One technique groups the data members based on how frequently the data members are referenced in memory. Another technique groups the data members based on their affinities for one another in time as determined by observing when references to the data members take place. A variety of options when collecting the profiling data and grouping the data members is supported. The data member grouping is recorded in metadata associated with a definition of the object class. At runtime, a class loader places the data members of an object in memory according to the metadata. Data members of different groups can be placed in separately-loadable units of memory in the memory system. Subsequently, when the data members are referenced in memory, more frequently referenced data members, including those that tend to be referenced at times close to each other, reside at neighboring locations in the memory system.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method to reduce I/O for hierarchical data partitioning methods
InactiveUS6055539AGenerate efficientlyShort training timeData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalRecordsetMulti processor
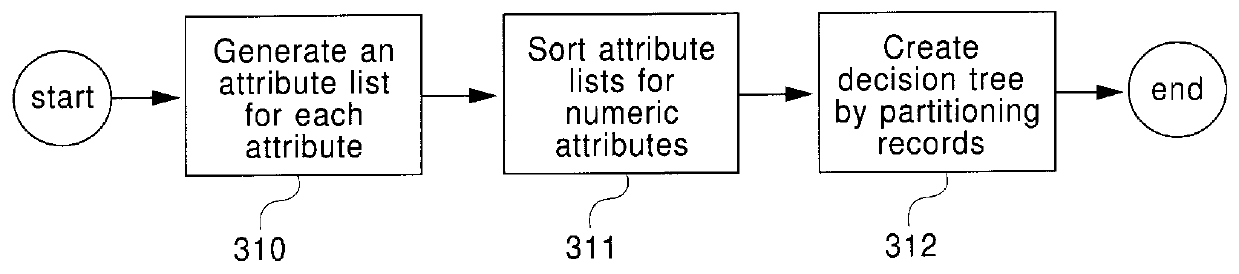
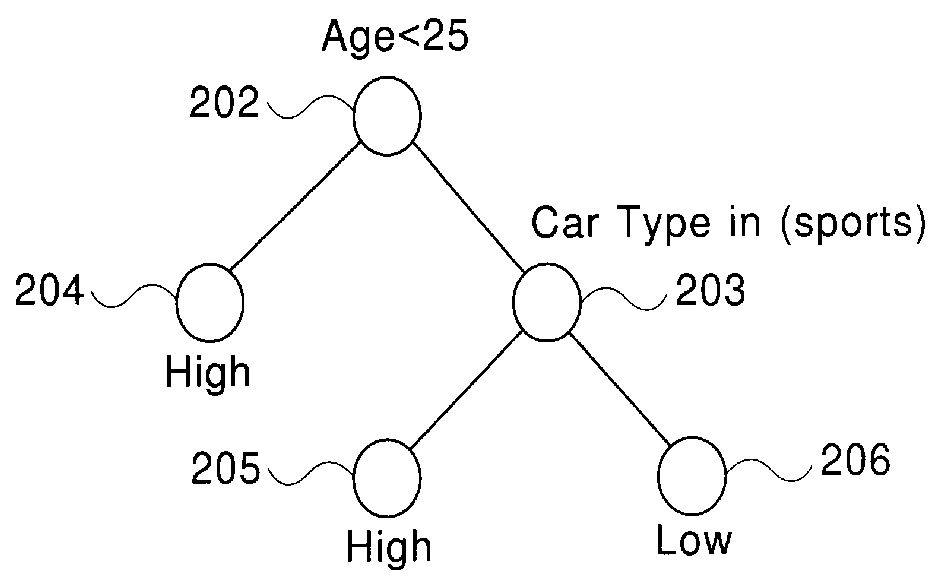
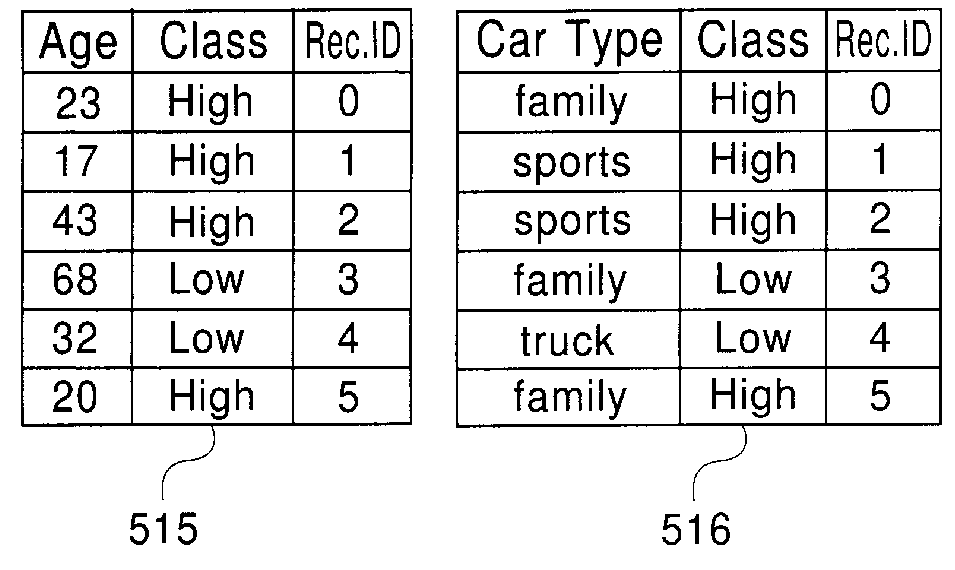
A method and system for generating a decision-tree classifier from a training set of records, independent of the system memory size. The method includes the steps of: generating an attribute list for each attribute of the records, sorting the attribute lists for numeric attributes, and generating a decision tree by repeatedly partitioning the records using the attribute lists. For each node, split points are evaluated to determine the best split test for partitioning the records at the node. Preferably, a gini index and class histograms are used in determining the best splits. The gini index indicates how well a split point separates the records while the class histograms reflect the class distribution of the records at the node. Also, a hash table is built as the attribute list of the split attribute is divided among the child nodes, which is then used for splitting the remaining attribute lists of the node. The method reduces I / O read time by combining the read for partitioning the records at a node with the read required for determining the best split test for the child nodes. Further, it requires writes of the records only at one out of n levels of the decision tree where n> / =2. Finally, a novel data layout on disk minimizes disk seek time. The I / O optimizations work in a general environment for hierarchical data partitioning. They also work in a multi-processor environment. After the generation of the decision tree, any prior art pruning methods may be used for pruning the tree.
Owner:IBM CORP
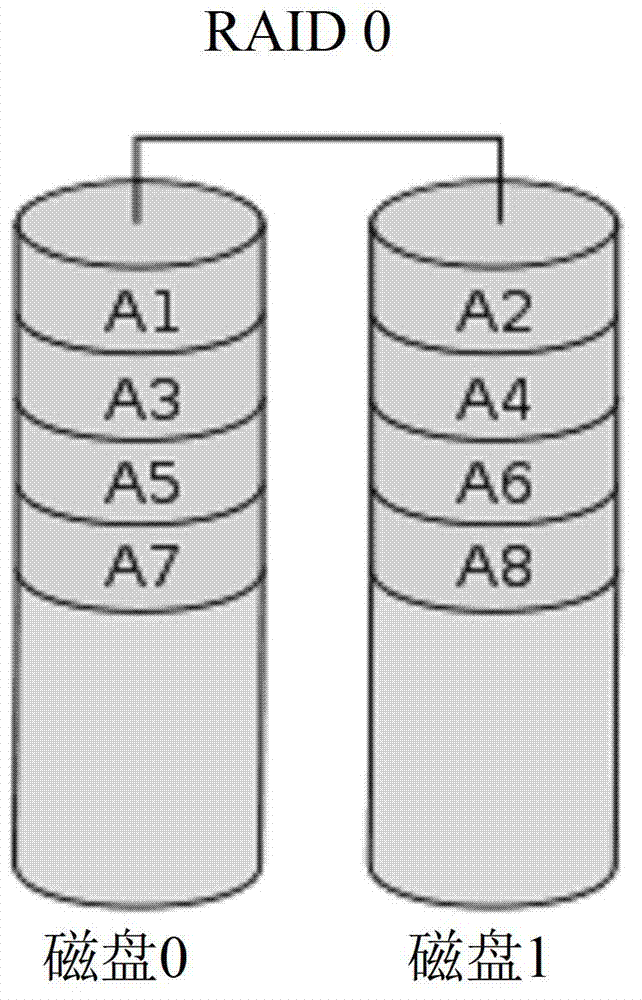
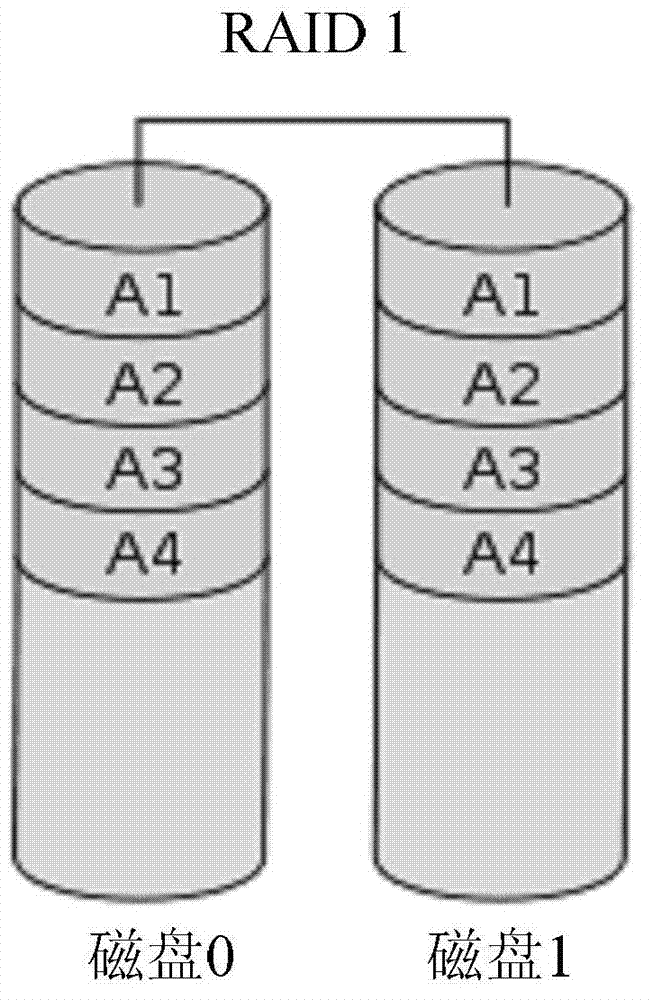
Raid with redundant parity
InactiveUS20090113235A1Shorten the timeImprove reliabilityRedundant data error correctionMemory systemsRAIDHard disc drive
Methods and apparatus of the present invention include storing redundant parity information in storage devices that are configured in a RAID array. Conventional hard disk drives are configured to store data in RAID 3 or RAID 4 data layouts. A storage controller is configured to generate the parity information for the data written to the hard disk drives. One or more of the devices storing the parity information may be a flash storage device.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
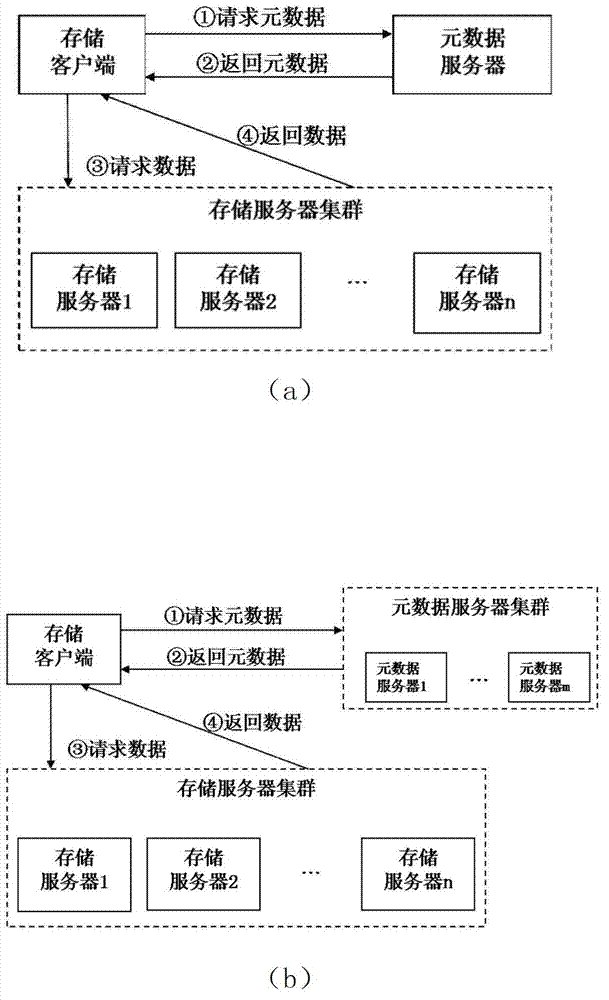
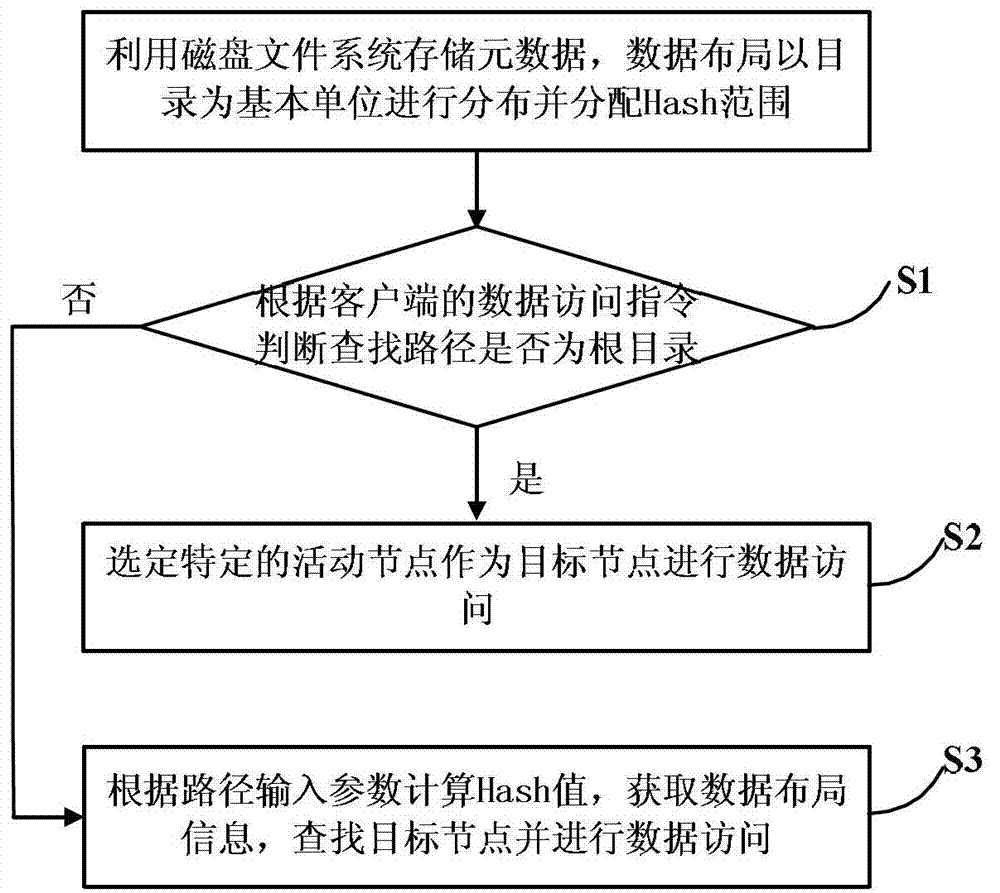
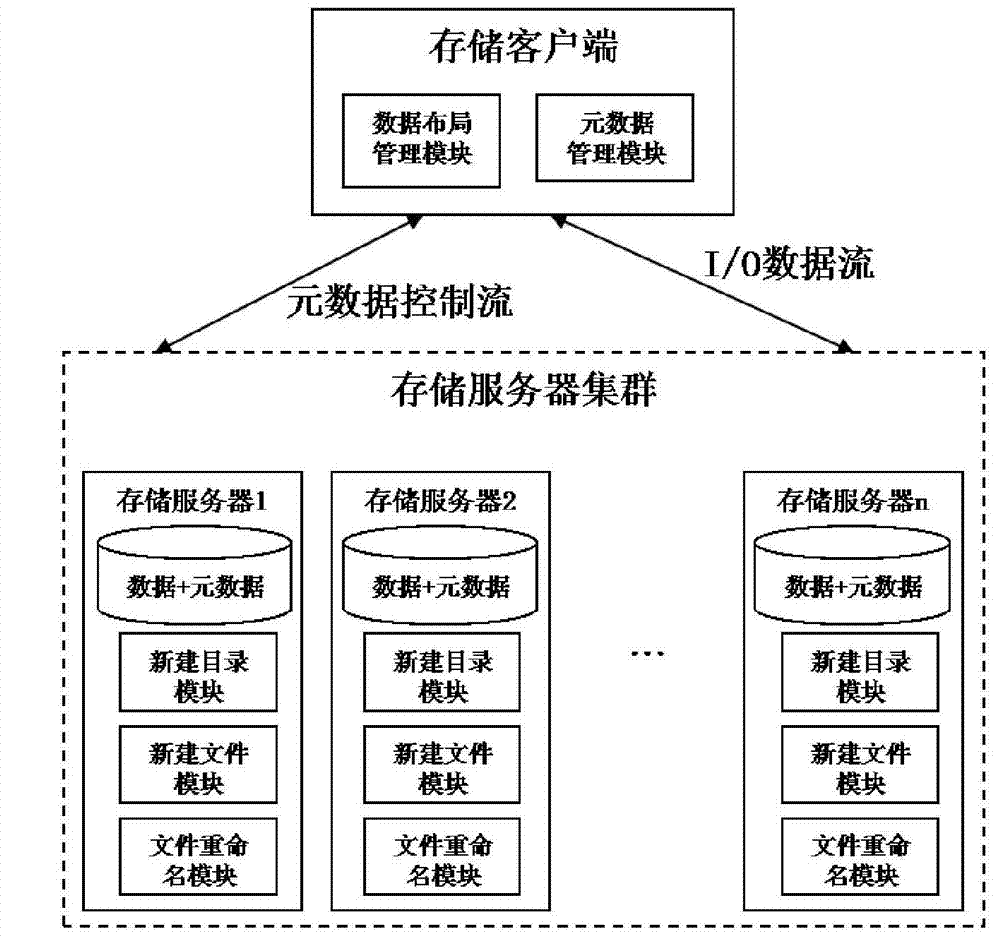
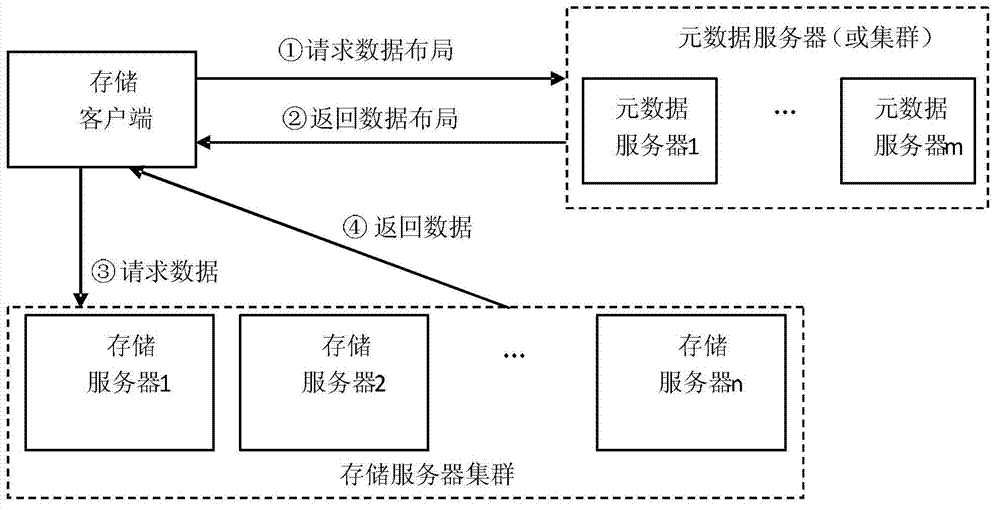
Method and system for managing data of cluster storage system
ActiveCN102855284AEliminate performance bottlenecksEliminate data consistencySpecial data processing applicationsFile systemMetadata management
The invention discloses a method and a system for managing data of a cluster storage system and belongs to the technical field of cluster storage. The method includes that a disk file system is used for storing and managing meta data, and the data are distributed by using a catalogue as a basic unit; a client senses data distribution information and sends a data access instruction, a storage server judges whether a finding path is a root catalogue according to the data access instruction of the client, a specific active node is selected to be a target node for data access if the finding path is the root catalogue, otherwise, a Hash value is calculated according to path input parameters to obtain the data distribution information, and finding the target node for data access. According to the method and the system for managing the data of the cluster storage system, a series of relevant problems of performance bottlenecks, single point faults, data inconsistency and the like of meta data management are eliminated, system expansibility is obviously improved, and linear expansion increase of system concurrency and performances is achieved.
Owner:北京联创信安科技股份有限公司
Intelligent hash data layout method, cluster storage system and cluster storage method
ActiveCN102855294AEliminate dependenciesReduce load pressureSpecial data processing applicationsThree levelExtensibility
The invention discloses an intelligent hash data layout method, a cluster storage system and a cluster storage method. The intelligent hash data layout method is used for laying out storage nodes in a data volume. Data is distributed through a hash distribution method by taking a directory as a basic unit. The parent directory of a file utilizes extended attributes to record the mapping information of the storage nodes. Sub-files are distributed in the storage nodes to which the parent directory belongs. The distribution method of the sub-files in the storage nodes to which the parent directory belongs specifically comprises one of the following situations that: the sub-files are distributed in the storage nodes to which the parent directory belongs through the hash distribution method; the sub-files are distributed in the storage nodes to which the parent directory belongs through a zonal two-level distribution method; the sub-files are distributed in the storage nodes to which the parent directory belongs through a duplicate two-level distribution method; and the sub-files are firstly distributed in the storage nodes to which the parent directory belongs through the zonal two-level distribution method and then are distributed through a duplicate three-level distribution method. The system and the methods provided by the invention have the advantages that the extensibility, the performance, the availability and the applicability of the cluster storage system can be remarkably improved, and the load pressure of a storage server can be greatly decreased.
Owner:中关村科技租赁股份有限公司
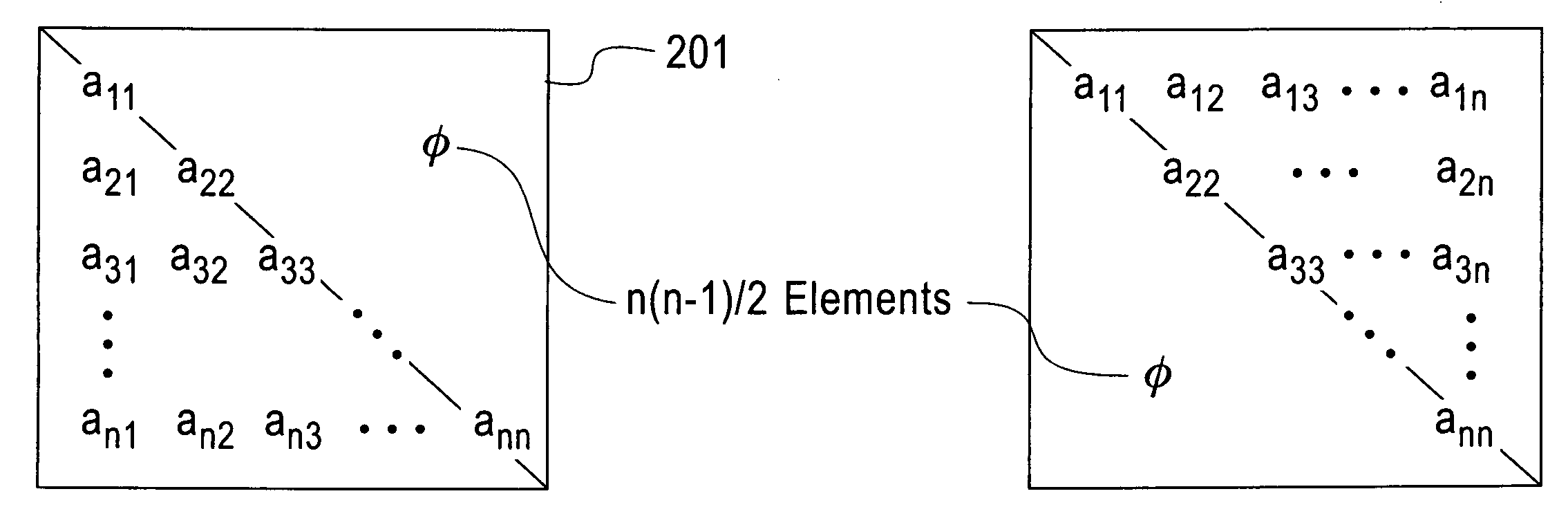
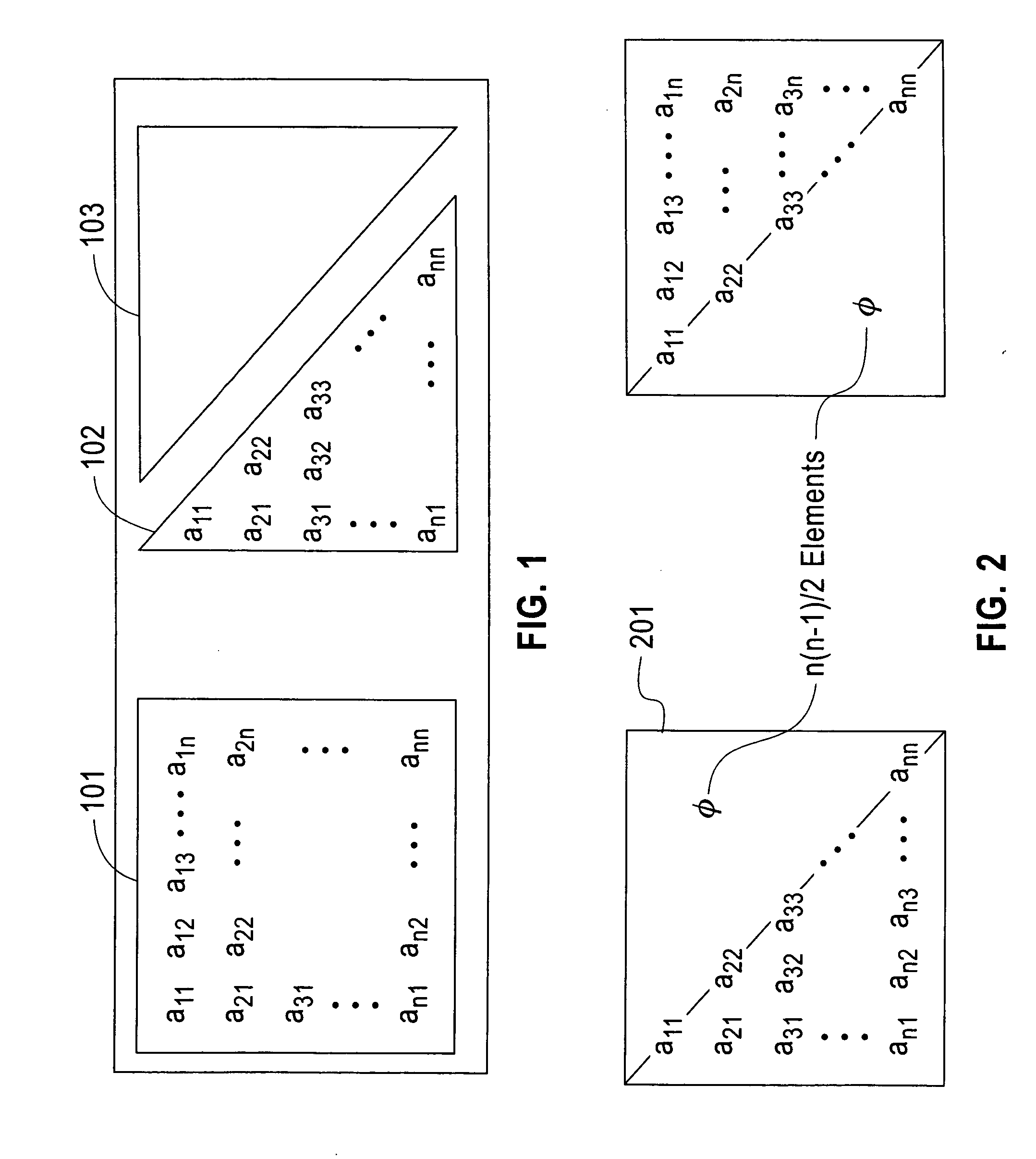
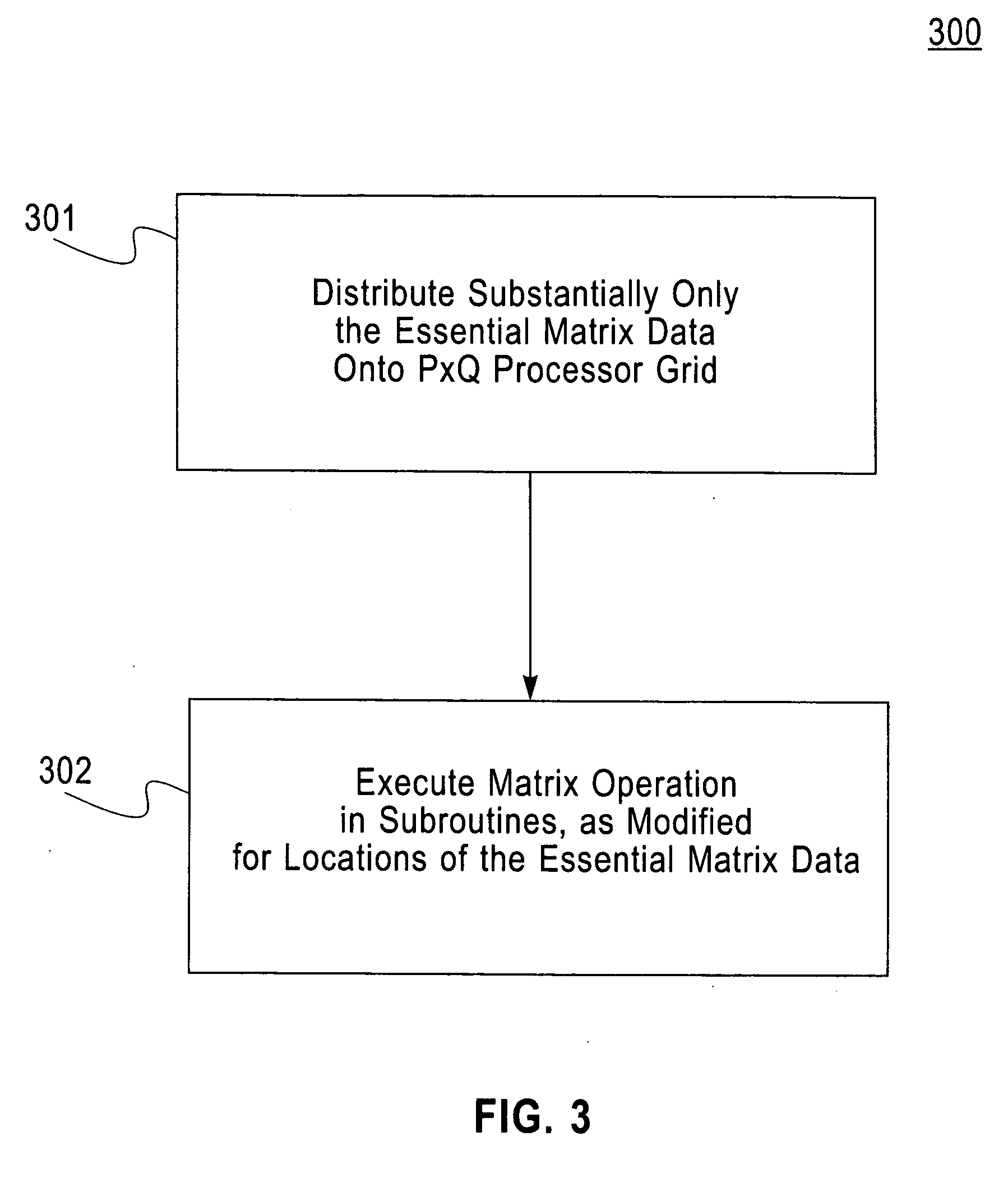
Method and structure for improving processing efficiency in parallel processing machines for rectangular and triangular matrix routines
InactiveUS20060265445A1Reduce storageImprove efficiencyData mergingComplex mathematical operationsDistributed memoryData preparation
A computerized method (and structure) of linear algebra processing on a computer having a plurality of processors for parallel processing, includes, for a matrix having elements originally stored in a memory in a rectangular matrix AR or especially of one of a triangular matrix AT format and a symmetric matrix AS format, distributing data of the rectangular AR or triangular or symmetric matrix (AT, AS) from the memory to the plurality of processors in such a manner that keeps all submatrices of AR or substantially only essential data of the triangular matrix AT or symmetric matrix AS is represented in the distributed memories of the processors as contiguous atomic units for the processing. The linear algebra processing done on the processors with distributed memories requires that submatrices be sent and received as contiguous atomic units based on the prescribed block cyclic data layouts of the linear algebra processing. This computerized method (and structure) defines all of its submatrices as these contiguous atomic units, thereby avoiding extra data preparation before each send and after each receive. The essential data or AT or AS is that data of the triangular or symmetric matrix that is minimally necessary for maintaining the full information content of the triangular AT or symmetric matrix AS.
Owner:IBM CORP
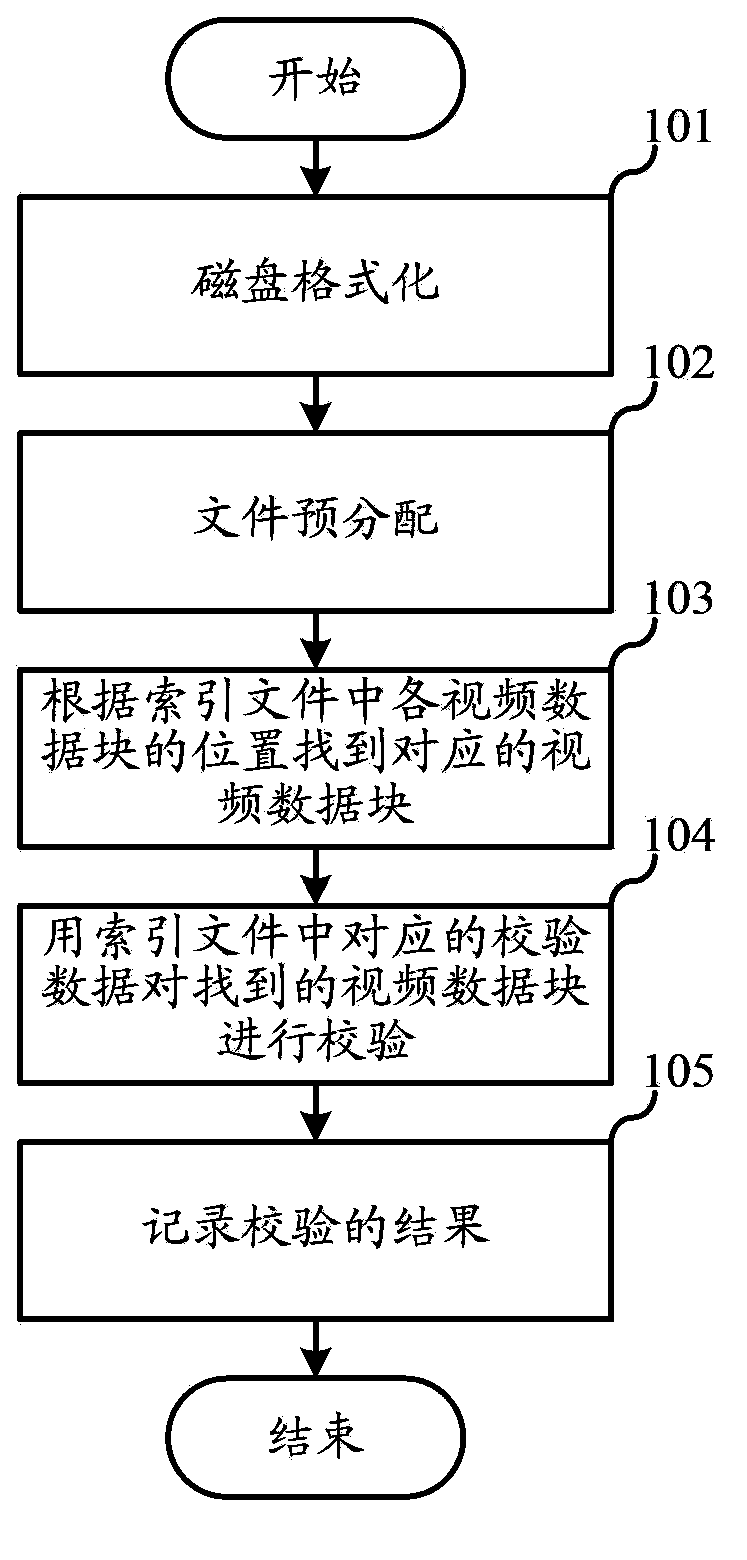
Storing and repairing method and storing and repairing device for repairable video monitoring data
ActiveCN103678026AAchieve fixJudgment integrityRedundant data error correctionSpecial data processing applicationsVideo monitoringVideo storage
The invention relates to the field of video storage, and discloses a storing and repairing method and a storing and repairing device for repairable video monitoring data. By using the storing and repairing method, positions of metadata, index files and video recording files of a file system on a magnetic disk are fixed according to characteristics of video storage; when the file system is damaged, the metadata of the file system are reestablished by a preset rule, and the original pre-distributed file is recovered; and because the positions of the file data in the magnetic disk are not changed, the data which are written in the magnetic disk cannot be lost. The storing and repairing method can support different file systems, and does not depend on the metadata of the original file system; and monitoring software is not required to be written in the magnetic disk, extra backup space is not required, and the video data can be repaired. A partition formatting mode of the magnetic disk is fixed according to specifications of different file systems; and data layouts formed by formatting at different times are the same as long as the data are in the same partition of the magnetic disk.
Owner:HANGZHOU HIKVISION SYST TECH
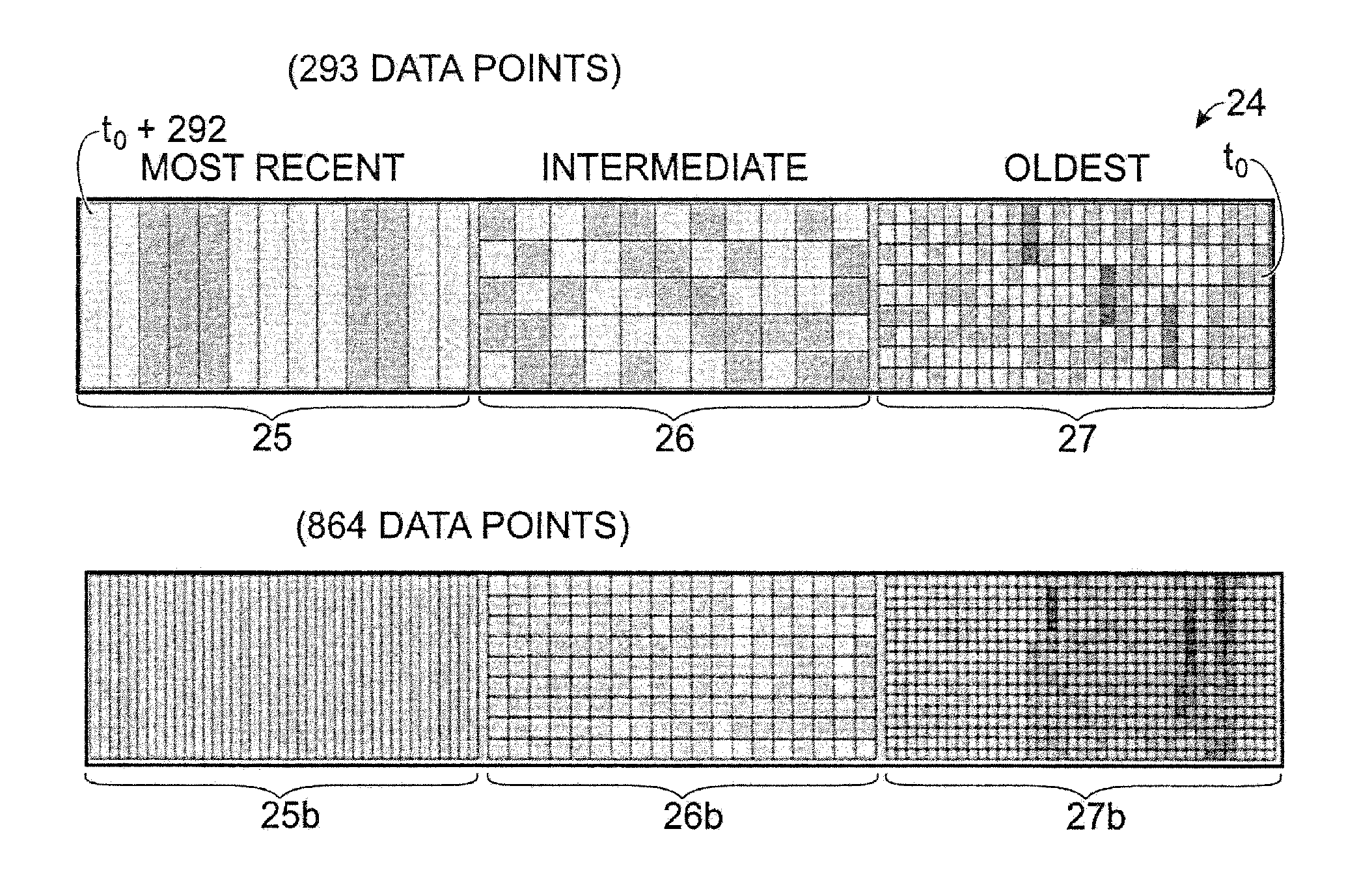
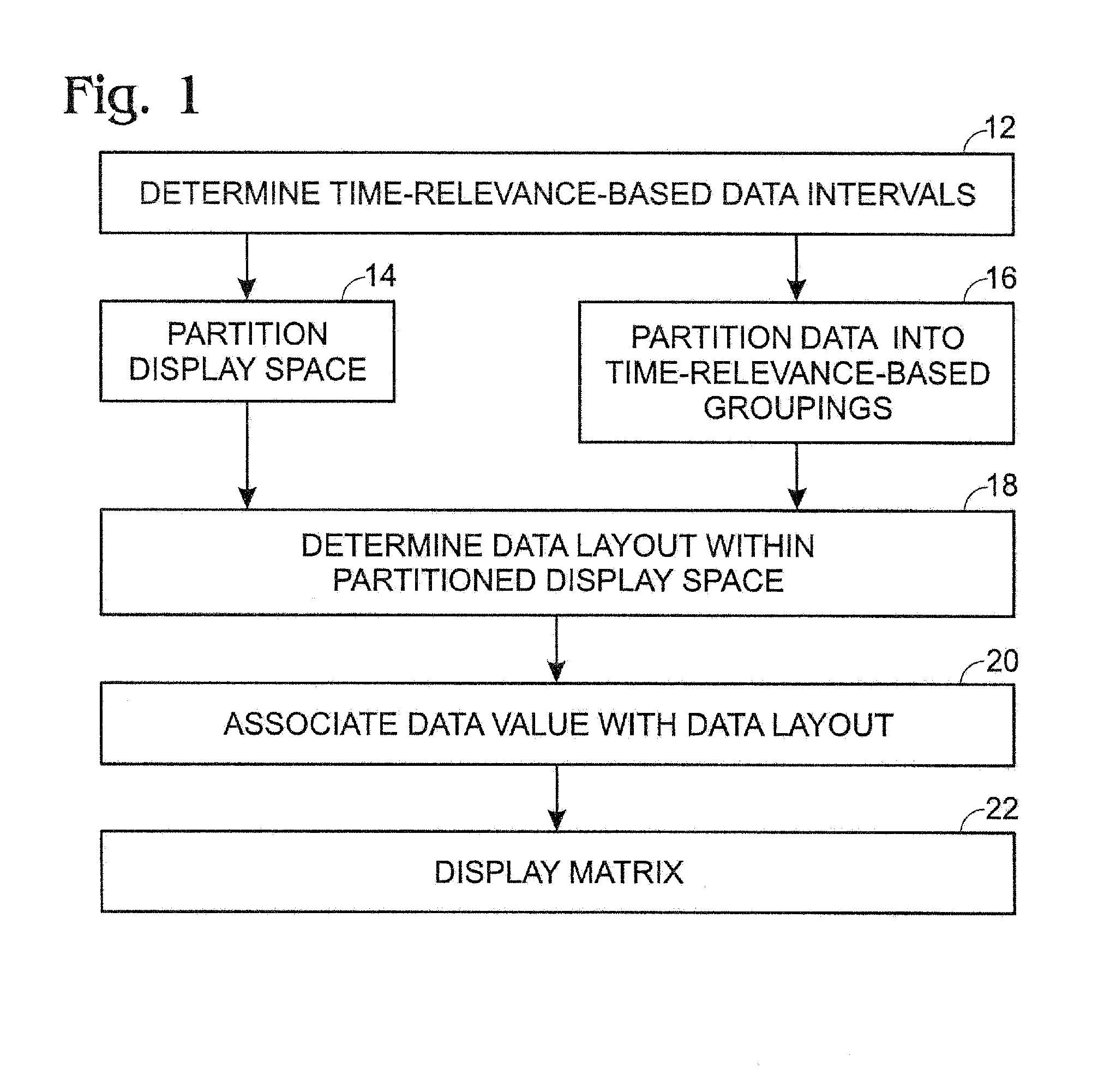
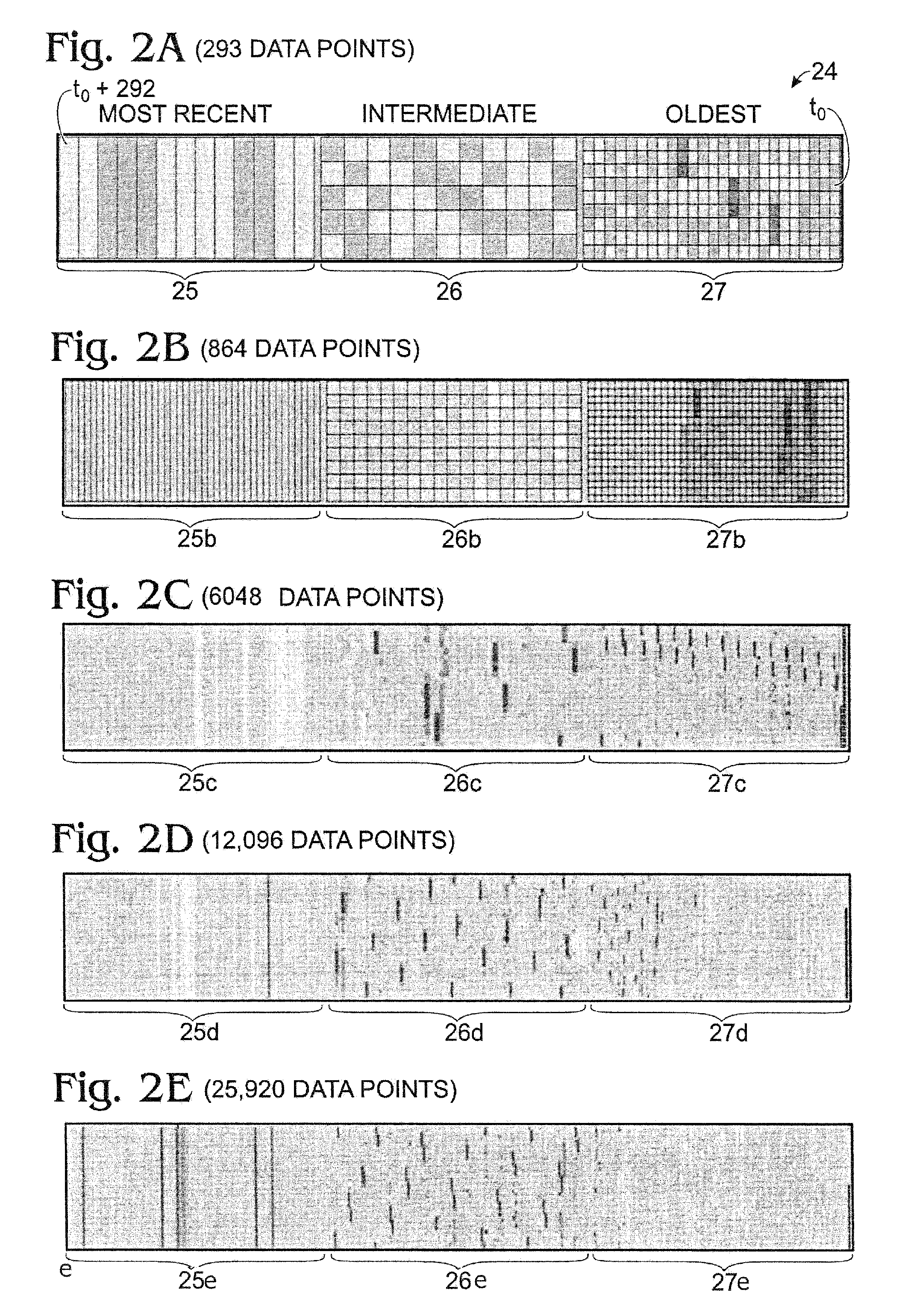
Time relevance-based visualization of data
A method for displaying a time-series data set. The method may include determining a number of data intervals for the data set, determining a data resolution for each data interval, partitioning a display space into a number of substantially equally sized partitions equal to the number of data intervals, partitioning the dataset into a number of time-relevance-based subsets equal to the number of partitions based on the currentness of the data and the desired data resolution for each partition, determining a data layout for each partition, and associating the data values for each subset with the corresponding layout. Furthermore, the first subset may consist of more current data at a first resolution and the second subset may consist of data that is less current than the first subset at a lower resolution than the first resolution.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
File system block-level tiering and co-allocation
ActiveUS20160283140A1Input/output to record carriersSpecial data processing applicationsFile systemData layout
Embodiments of the invention relate to intra-block organized storage placement. One embodiment includes obtaining a file in a file system. The file is separated into multiple blocks. The multiple blocks are separated into at least two correlated sub-blocks. Intra-file block organized storage placement on different memory devices is determined for the at least two correlated sub-blocks in a file system metadata layout.
Owner:IBM CORP
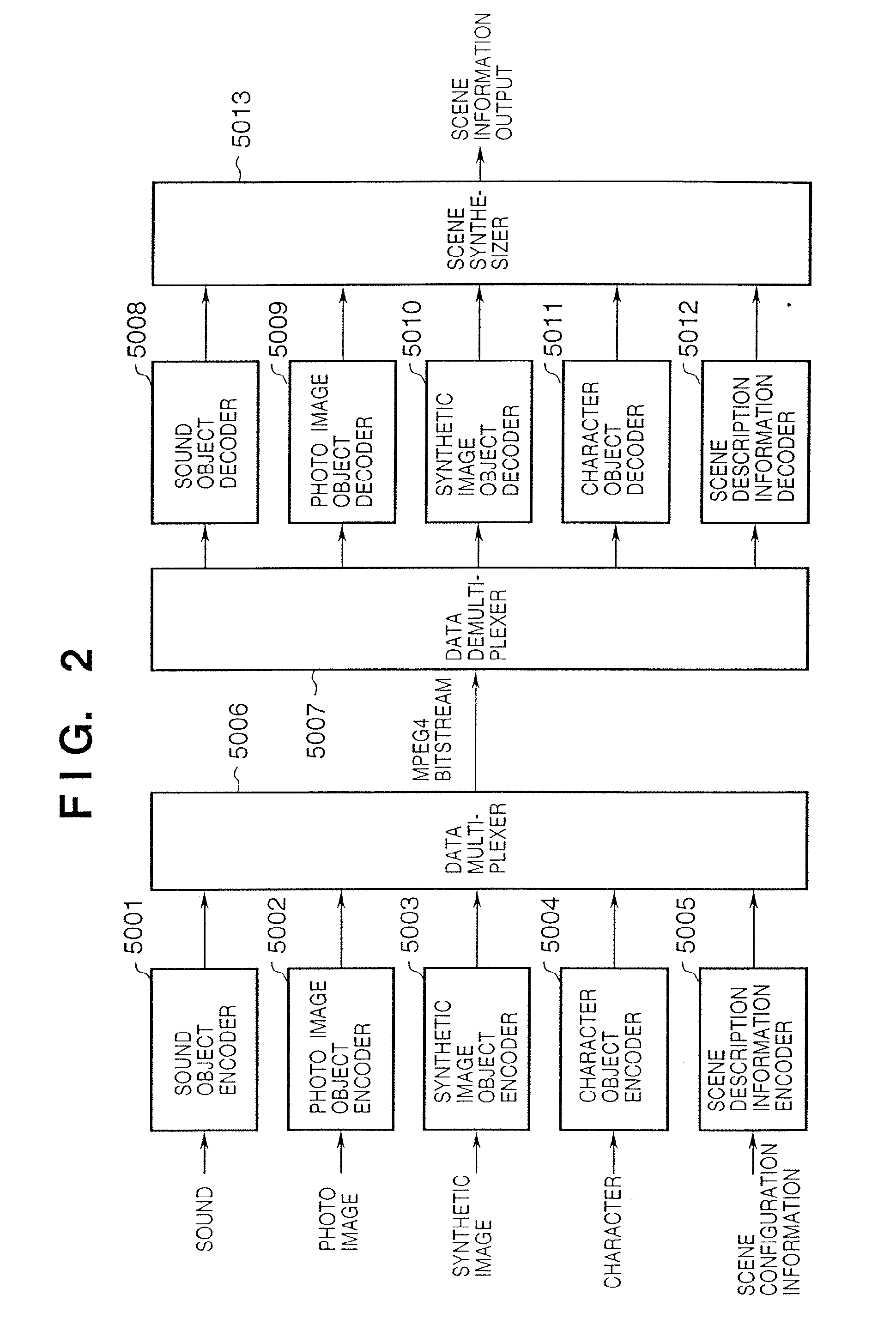
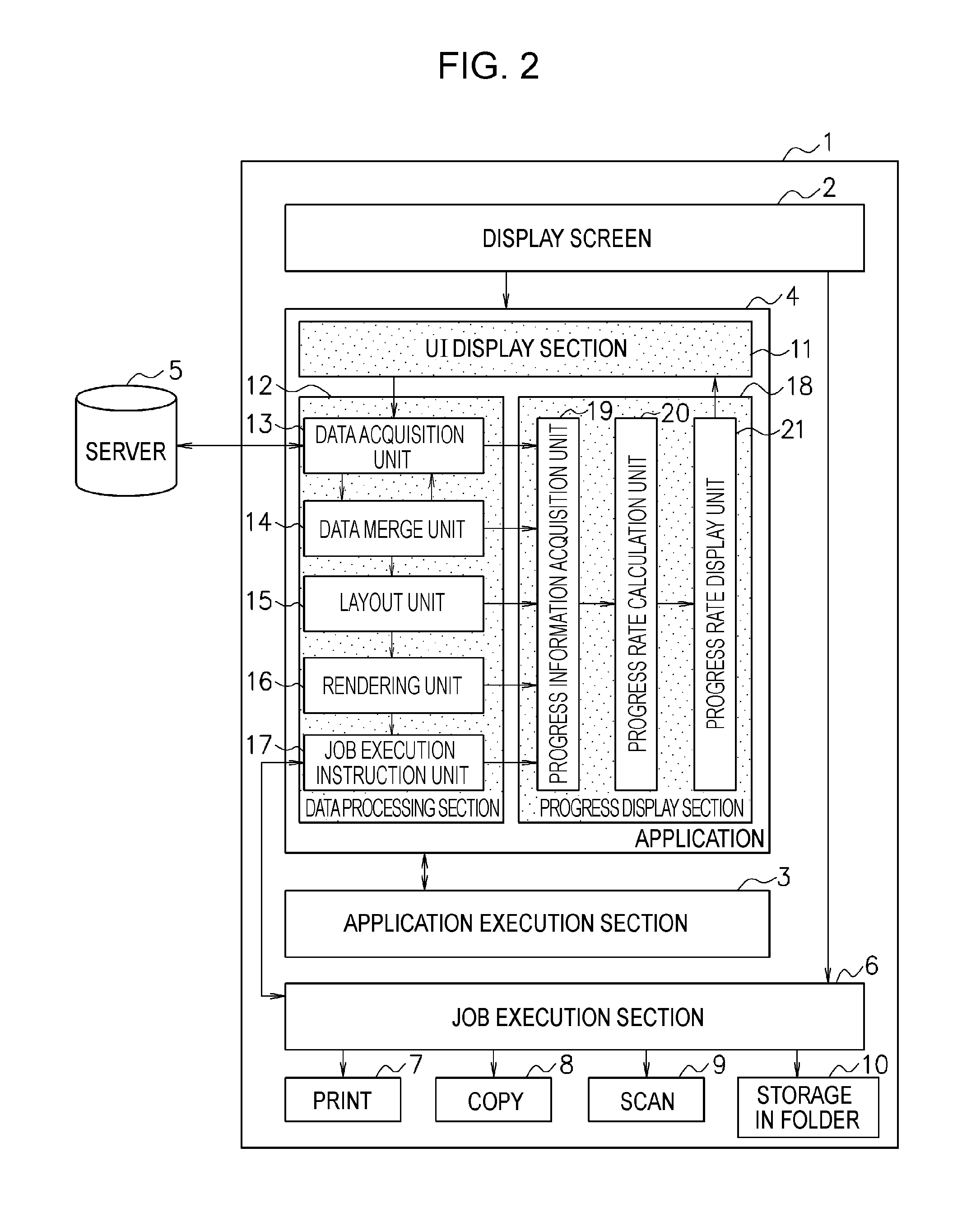
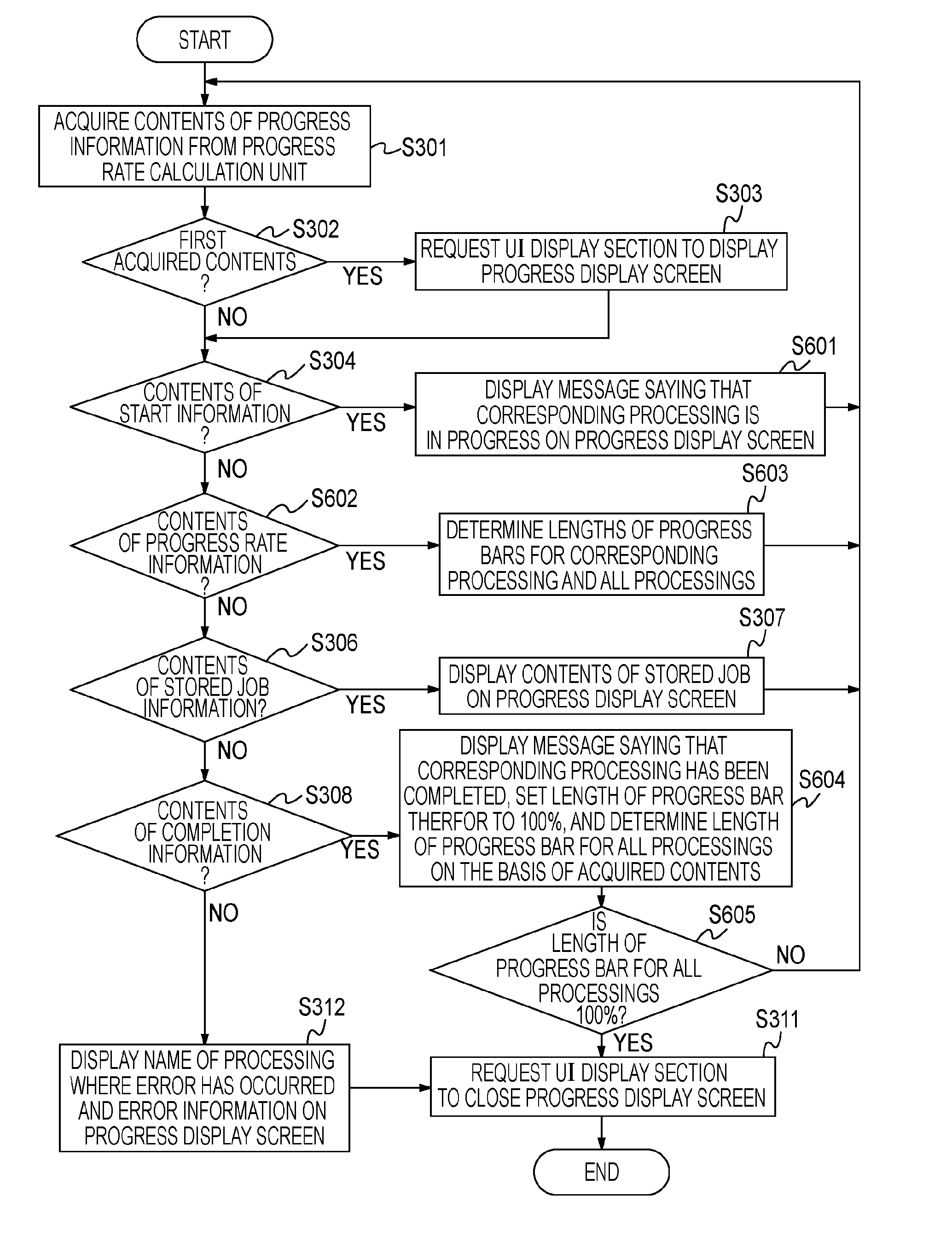
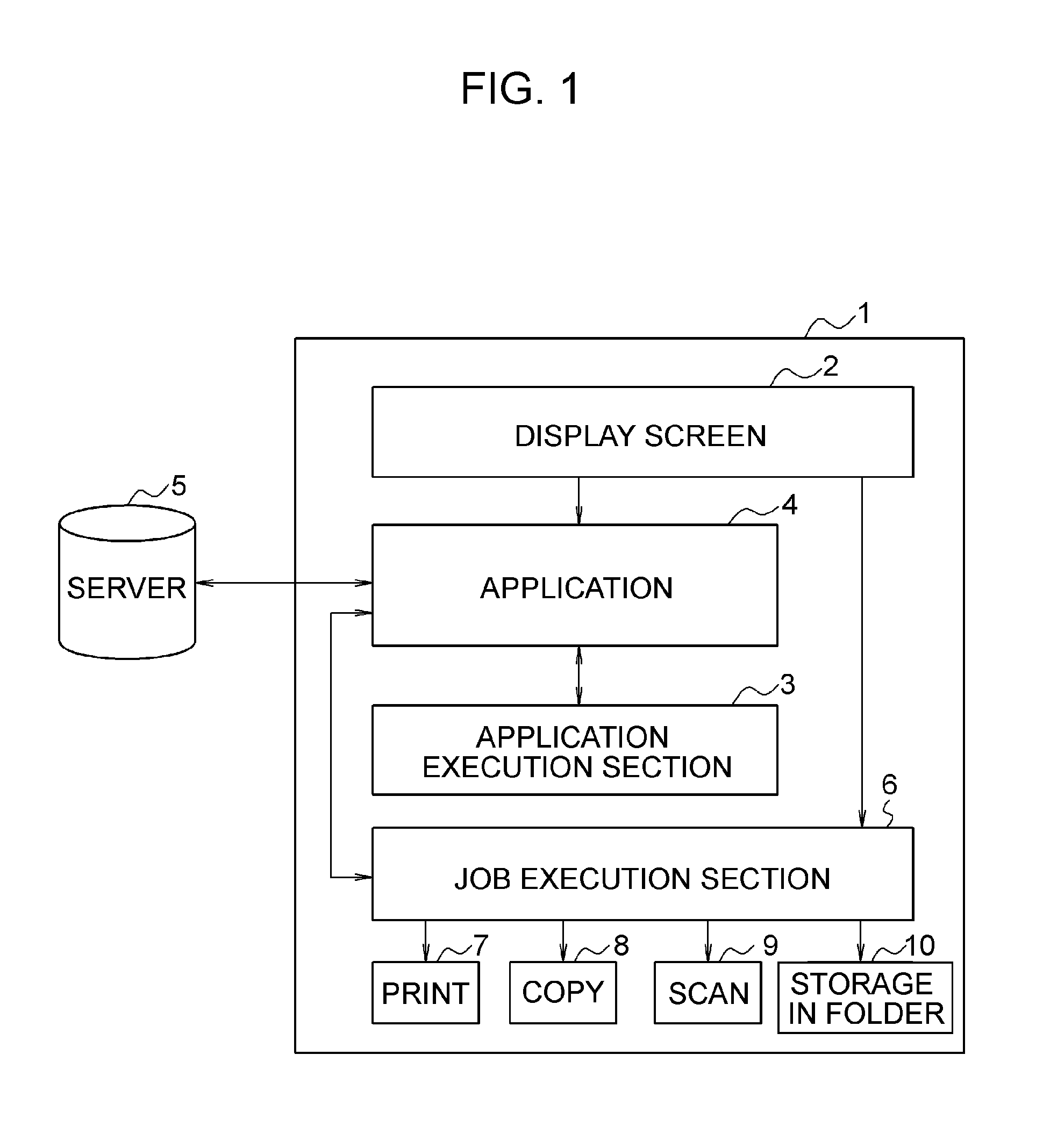
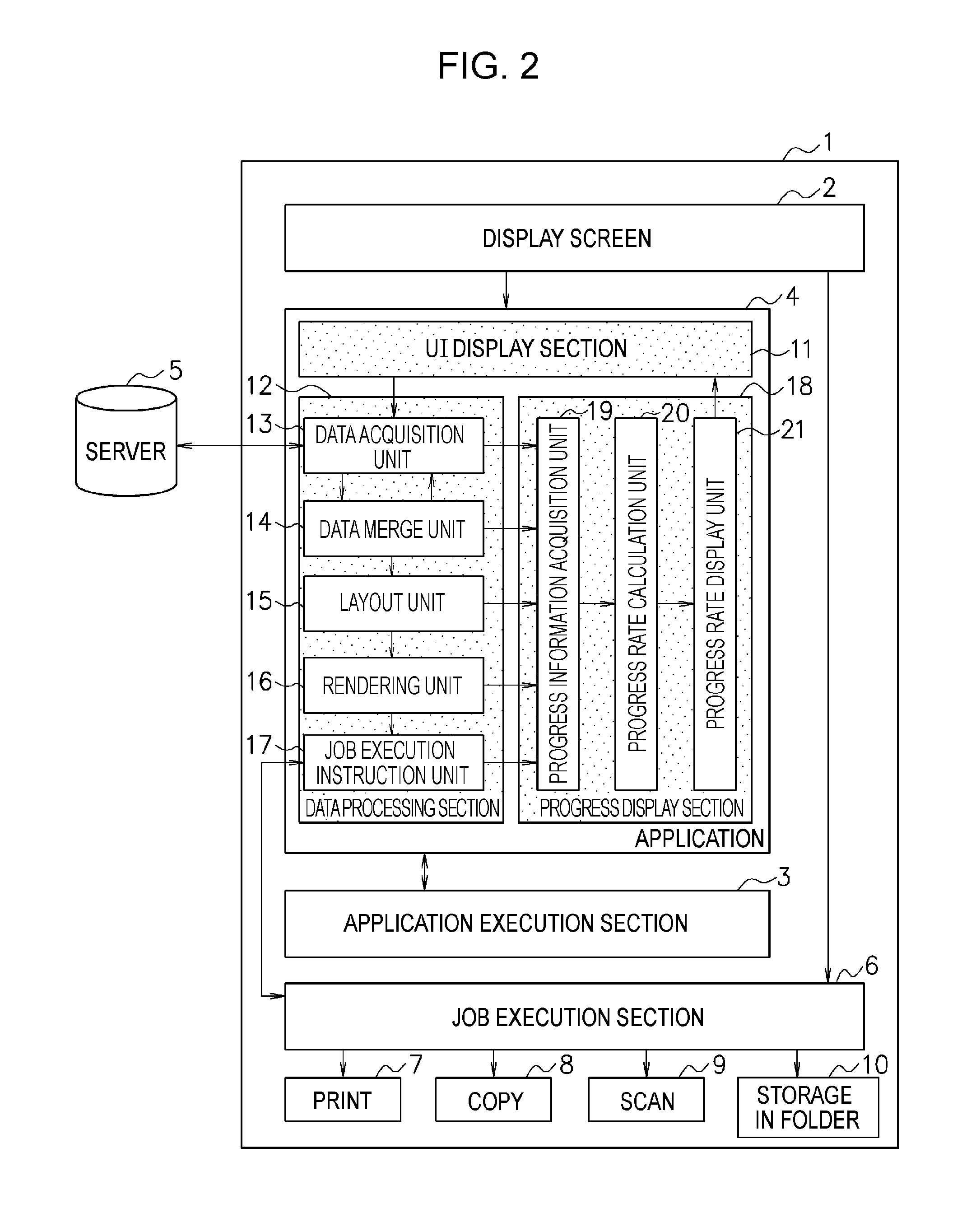
Data processing method, data processor, and program
An apparatus performs a data processing, including a data layout processing, to generate processed data. When the data processing has been completed, the apparatus performs a data output processing for outputting the processed data. The apparatus is further configured to output a current progress status of a processing that includes the data processing and the data output processing.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and system for data layout and replacement in distributed streaming caches on a network
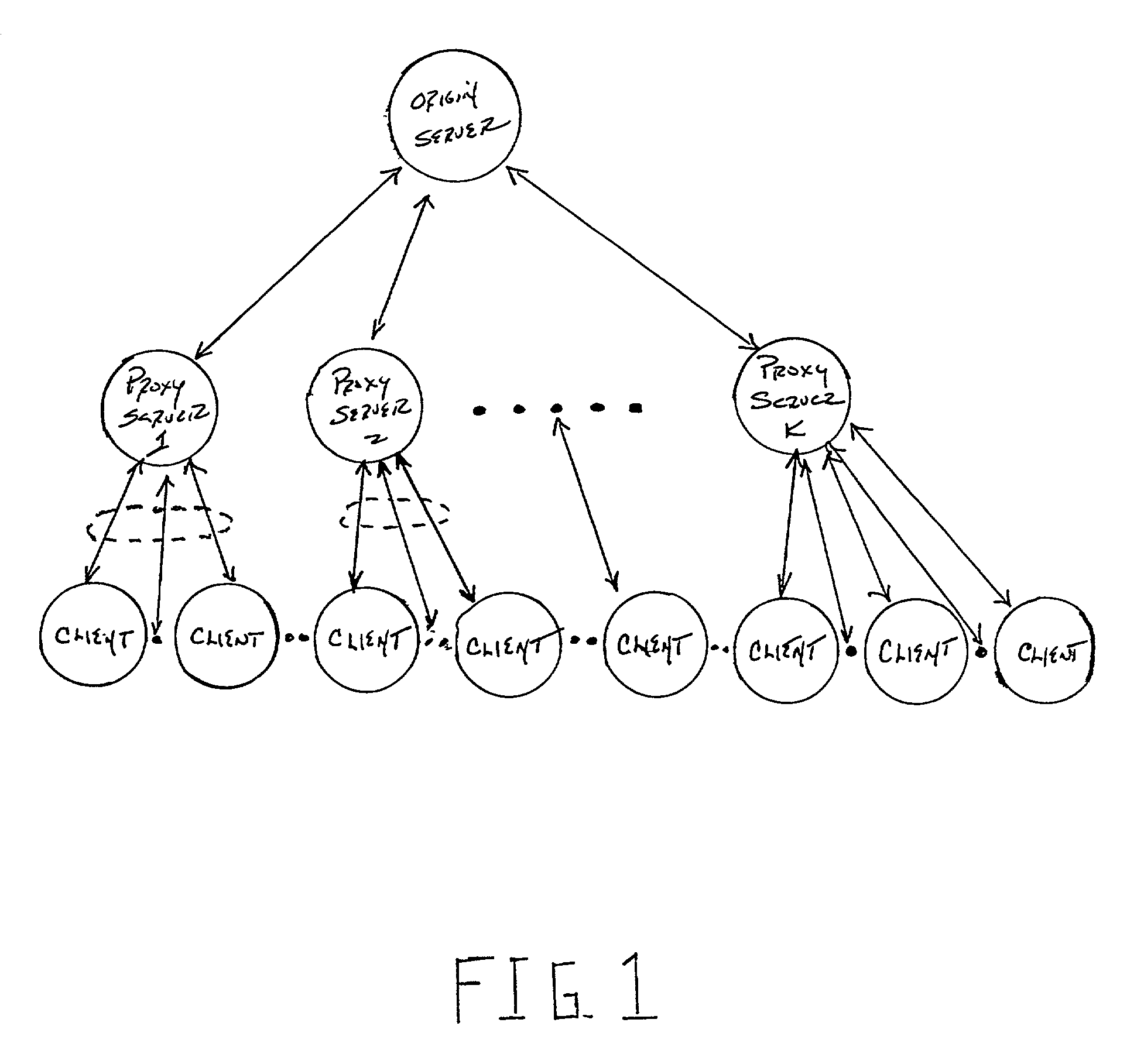
ActiveUS7085843B2Lower latencyReduce in quantityMultiple digital computer combinationsTwo-way working systemsData segmentNetwork connection
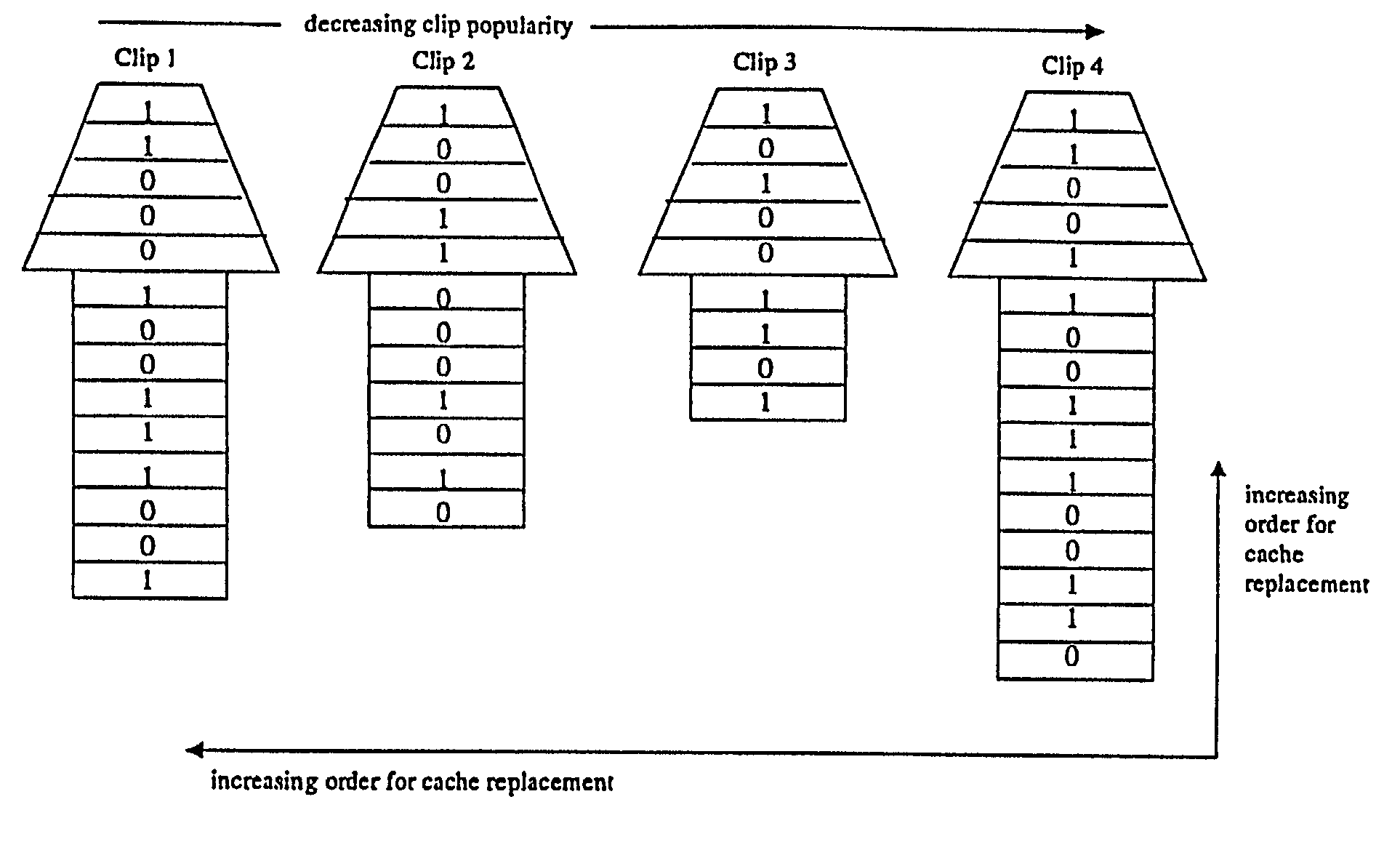
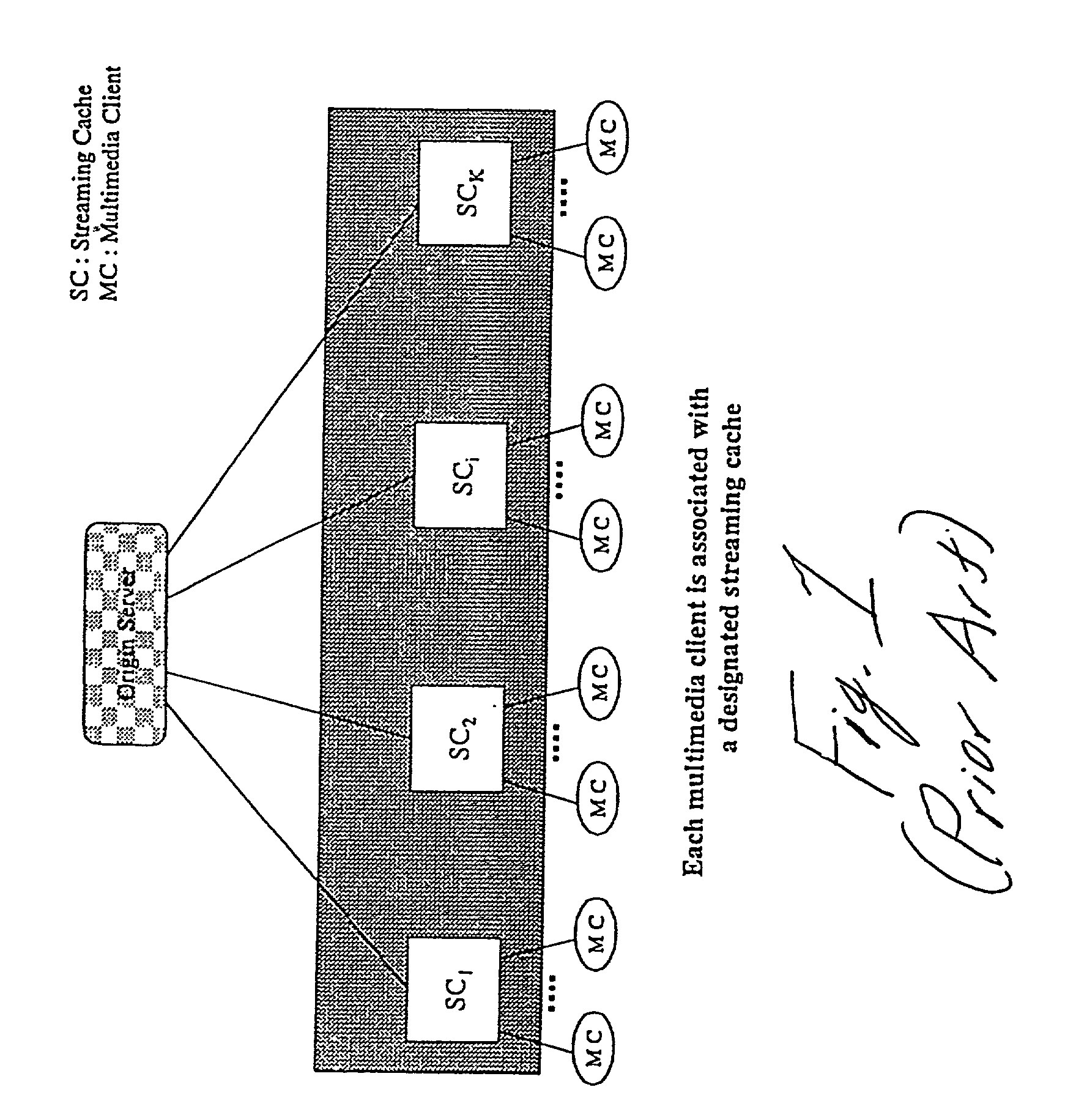
A system and method for segmenting, distributing and replacing streaming multimedia clips in a network system including at least one origin server connected to a plurality of streaming caches via an interactive distribution network, such as the Internet. The at least one origin server stores a plurality of streaming multimedia clips in an associated memory and segments the clips into a plurality of data segment of exponentially increasing size; the origin server then distributes the plurality of data segments to the plurality of streaming caches where each streaming cache decides whether to store or discard each segment in accordance with a predefined probability. Another aspect of the invention involves replacing stored data segments at each of the plurality of streaming caches as needed. In one embodiment, a hotness rating is computed for each streaming multimedia clip stored in an SC. Clips are replaced as needed based on their hotness rating relative to other clips. In a second embodiment, a potential function is computed for each segment stored in an SC. Segments are replaced as needed based on their potential function value relative to other stored segments.
Owner:SOUND VIEW INNOVATIONS
Data processing apparatus, data processing method, program for implementing the method, and storage medium storing the program
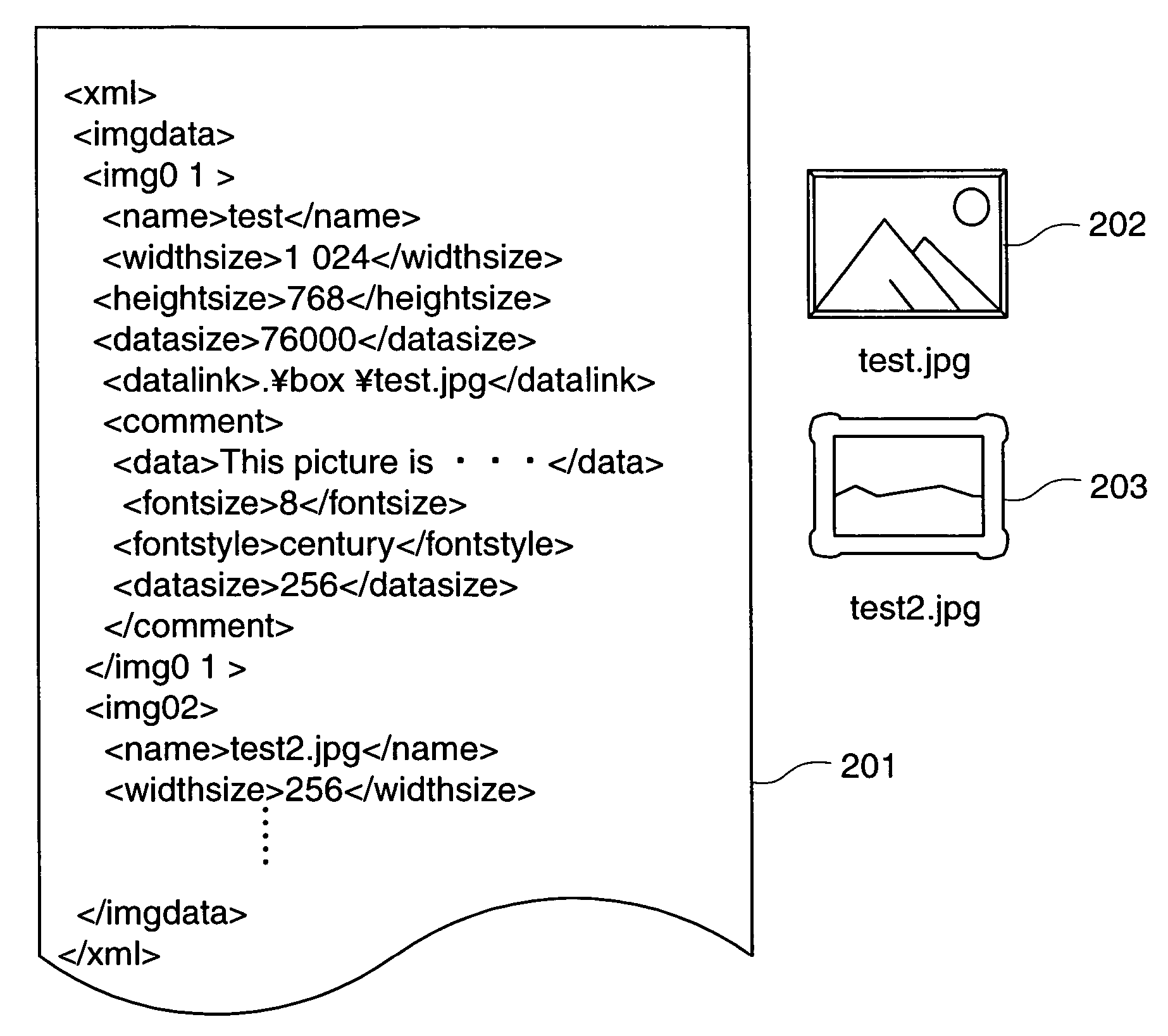
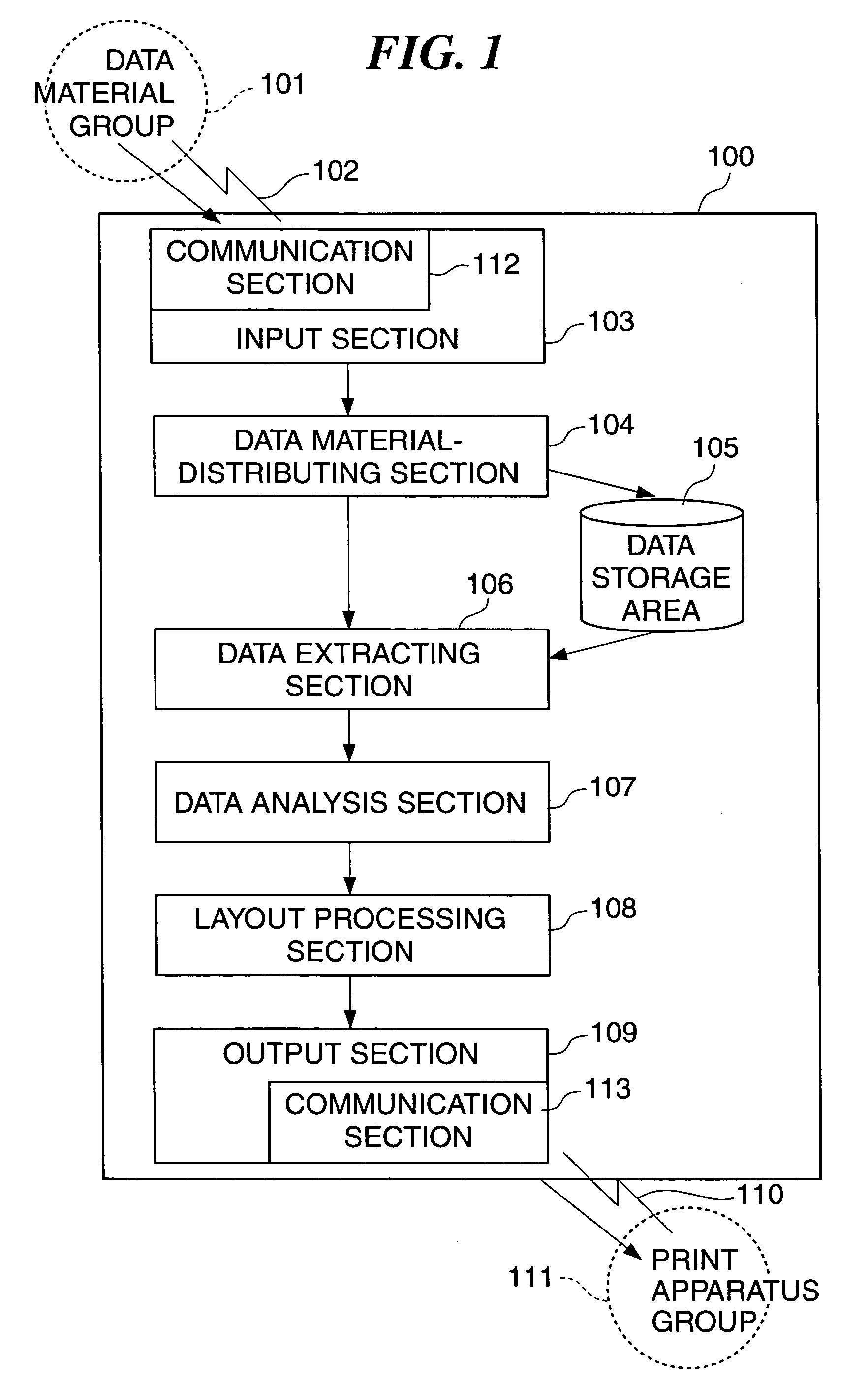
InactiveUS20050183010A1Special data processing applicationsDigital output to print unitsPaper documentDocument preparation
A data processing apparatus which is capable of automatically calculating layout information suitable for various materials and outputting a document interpretable by a driver of a printing apparatus. An input section 103 inputs data. A data analysis section 107 analyzes the input data. A layout processing section 108 generates layout information on the data based on a result of the analysis by the data analysis section. The layout processing section 108 lays out the data based on the generated layout information and converts the data laid out into a document printable by the printing apparatus.
Owner:CANON KK
Data processing method, data processor, and program
An apparatus performs a data processing, including a data layout processing, to generate processed data. When the data processing has been completed, the apparatus performs a data output processing for outputting the processed data. The apparatus is further configured to output a current progress status of a processing that includes the data processing and the data output processing.
Owner:CANON KK
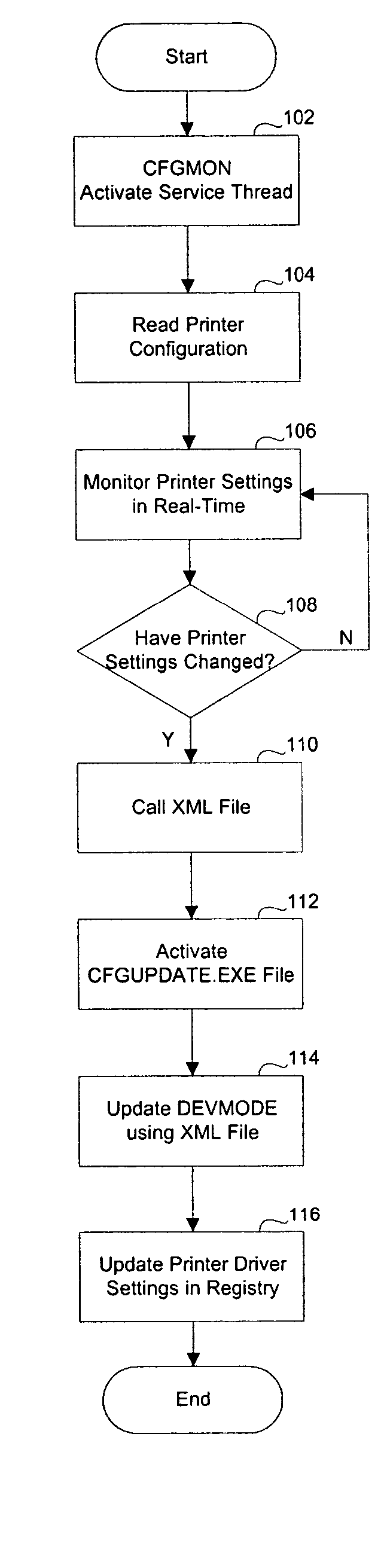
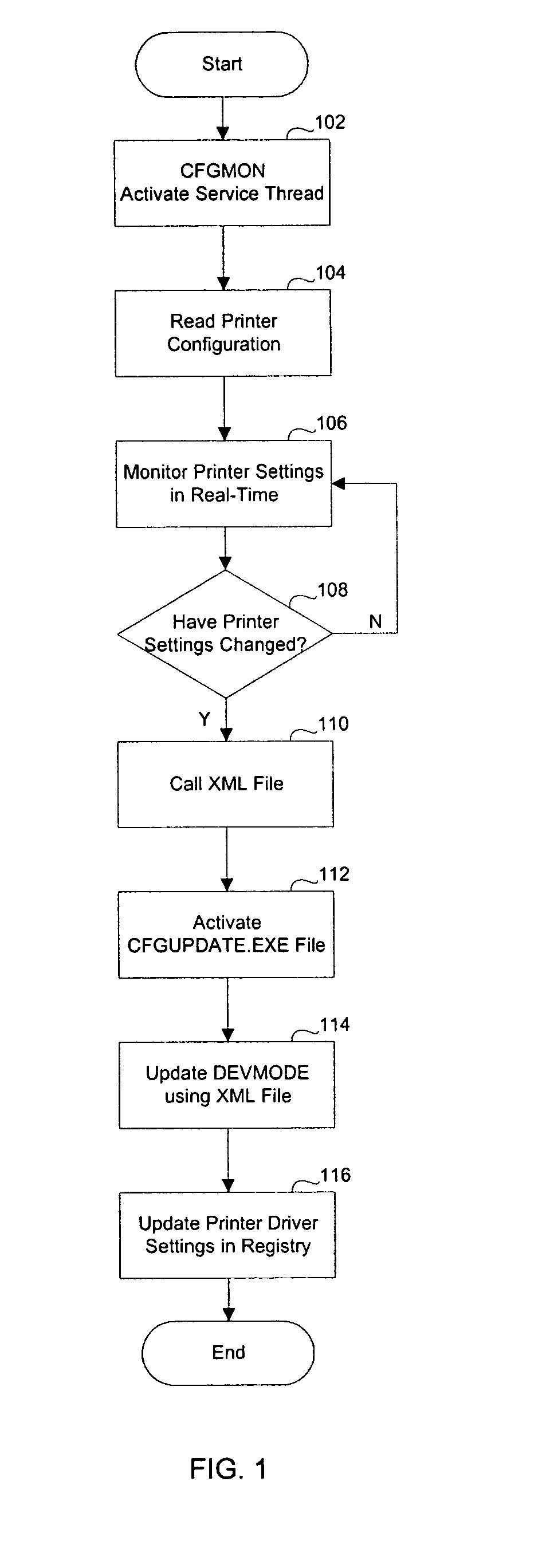
Method and system to automatically update in real-time a printer driver configuration
InactiveUS20050068558A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsCD-ROMData layout
The present invention is directed to a method and system for automatically and continuously updating a printer driver configuration. A first computer program residing on a controller, which acts to monitor the printer configuration, is activated. The printer configuration is read from the controller configuration and updates the DEVMODE data. The detection of a change in any attribute of the printer configuration causes a second program to activate. DEVMODE data is updated using a data layout described in an XML file. The data layout in the XML file will be packaged with the controller during building, as well as available on a CD-ROM, other portable device, or stored on a central location and accessed over a computer network for the updating printer drivers on the controller when new versions are released. The second program retrieves current printer configuration data using SNMP communications and writes this data to the registry. The registry is then updated by the second computer program using to account for the changes detected by the first computer program in accordance with the data layout of the XML file.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
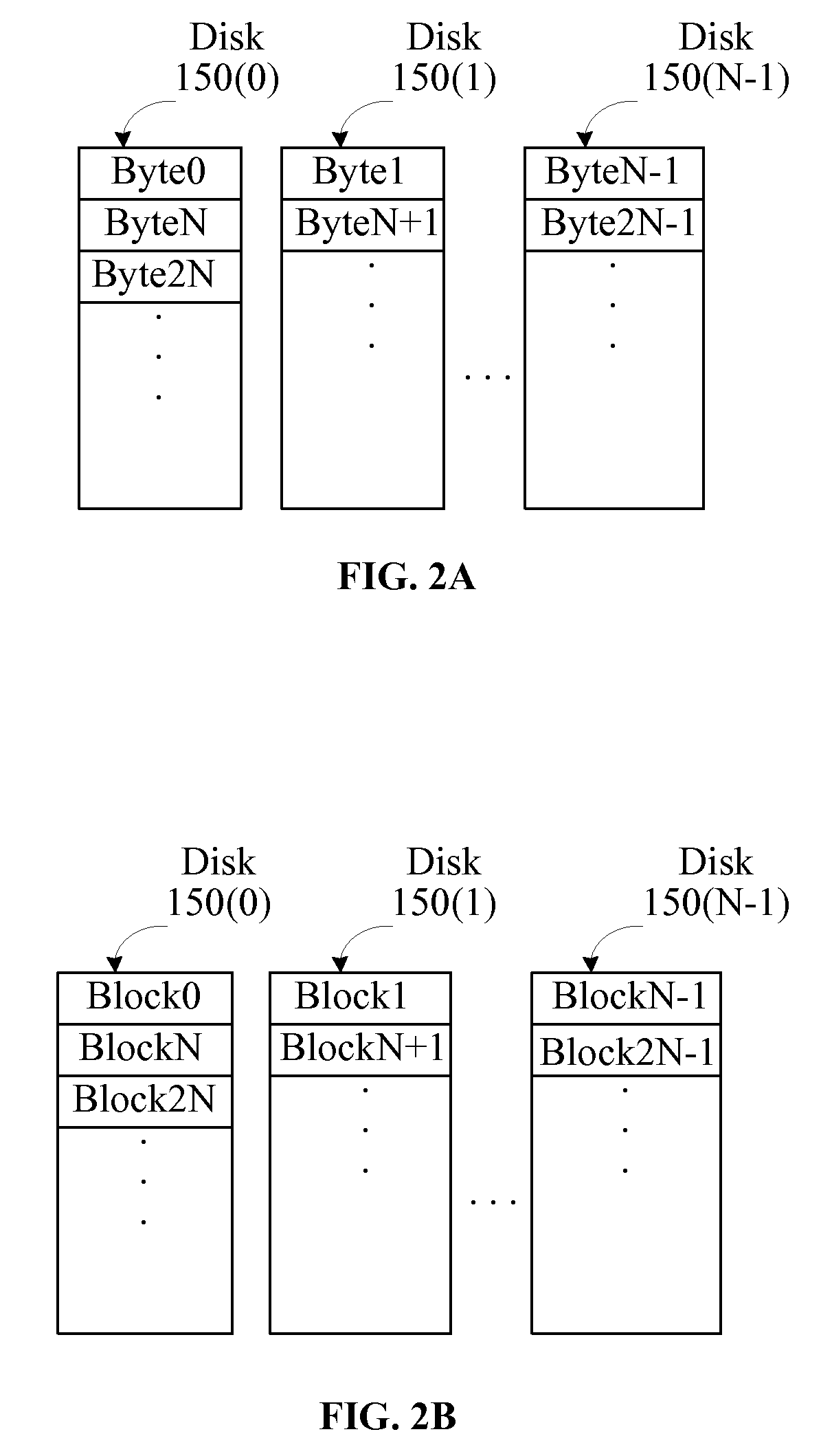
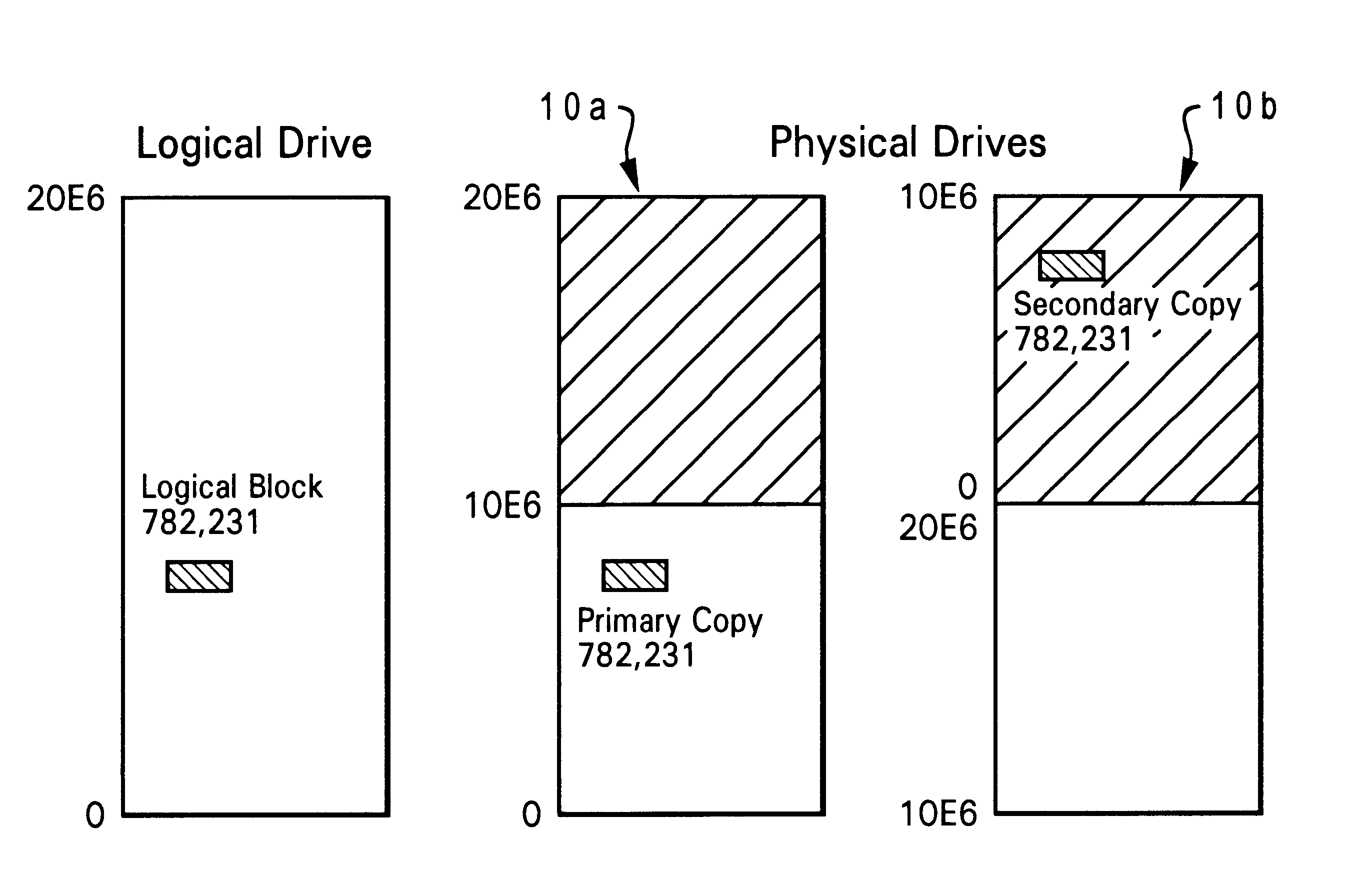
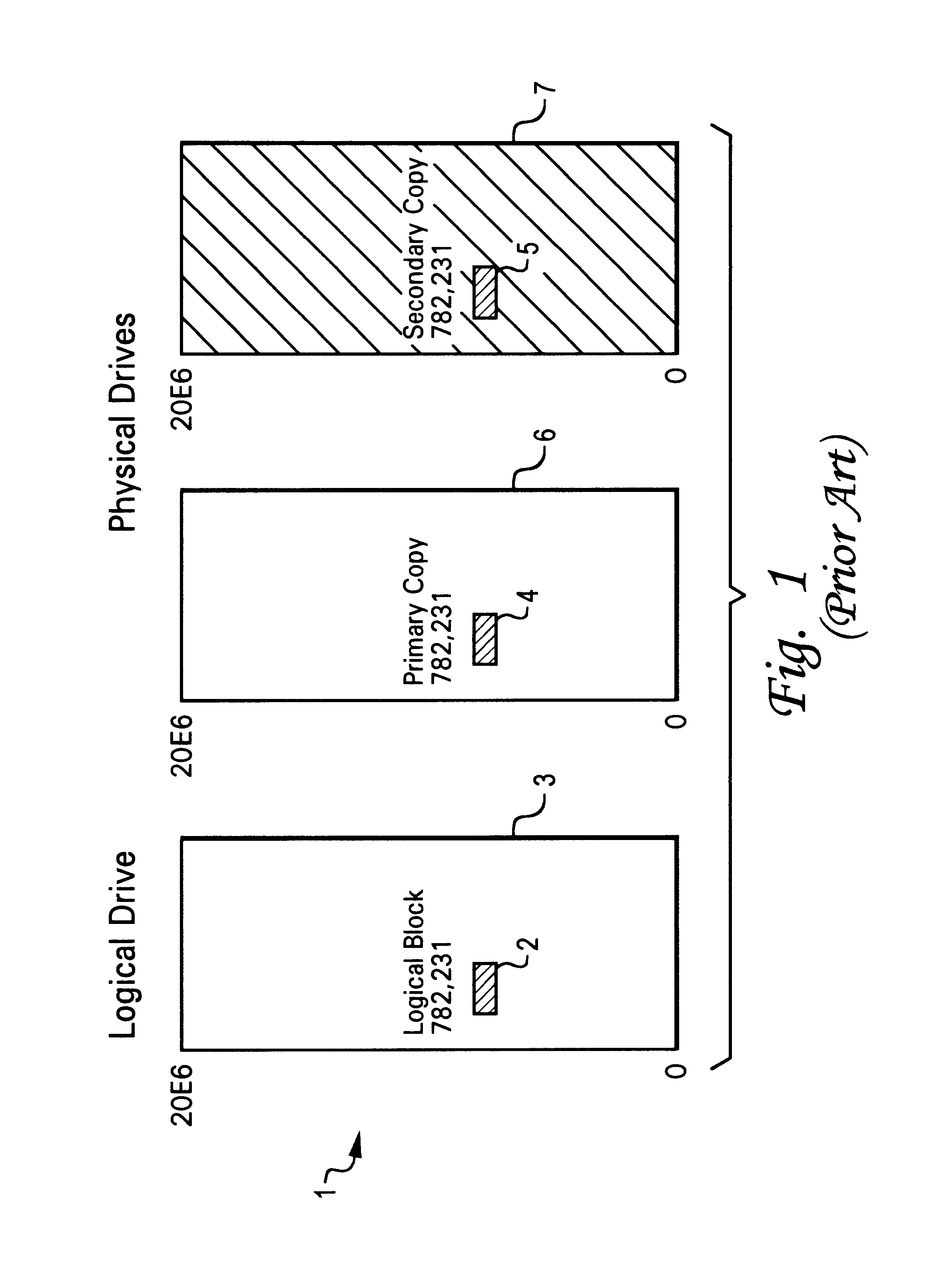
Physical data layout to reduce seeks in a raid system
A data storage subsystem which reduces seek time, by defining a logical storage space wherein part of the logical storage space is defined to correspond to a primary storage space of a first physical data storage device, and correspond to a secondary storage space of a second physical data storage device, and another part of the logical storage space is defined to correspond to a primary storage space of the second physical data storage device, and correspond to a secondary storage space of the first physical data storage device. For hard disk drives having an arm assembly with a read / write head, the average seek distance for both drives reduced, since the pivoting arm assembly need not travel as far to reach each physical storage address within a primary storage area. The invention may additionally take advantage of geometric or other aspects of the storage devices which result in some portion of the device having a faster access time that another portion. For hard disk drives which assign a larger number of logical blocks to the outer tracks of the disk than to the inner tracks, the storage controller can map the primary storage space of a given one of the drives to the outer tracks of the drive.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method and system for data layout and replacement in distributed streaming caches on the Internet
InactiveUS6999988B2Reducing ICP message exchangeInconsistency problemAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsMultiple digital computer combinationsDistributed cacheThe Internet
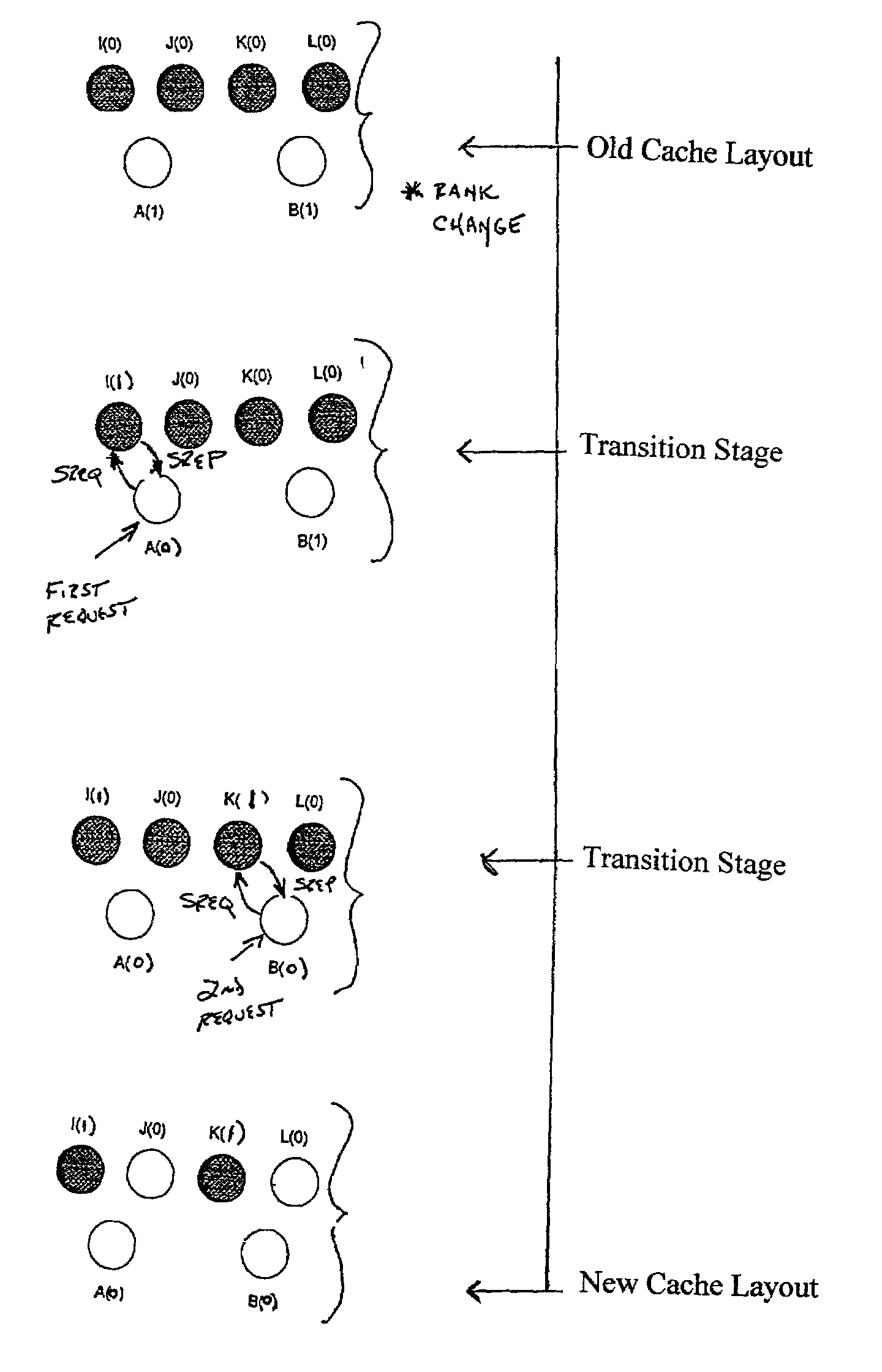
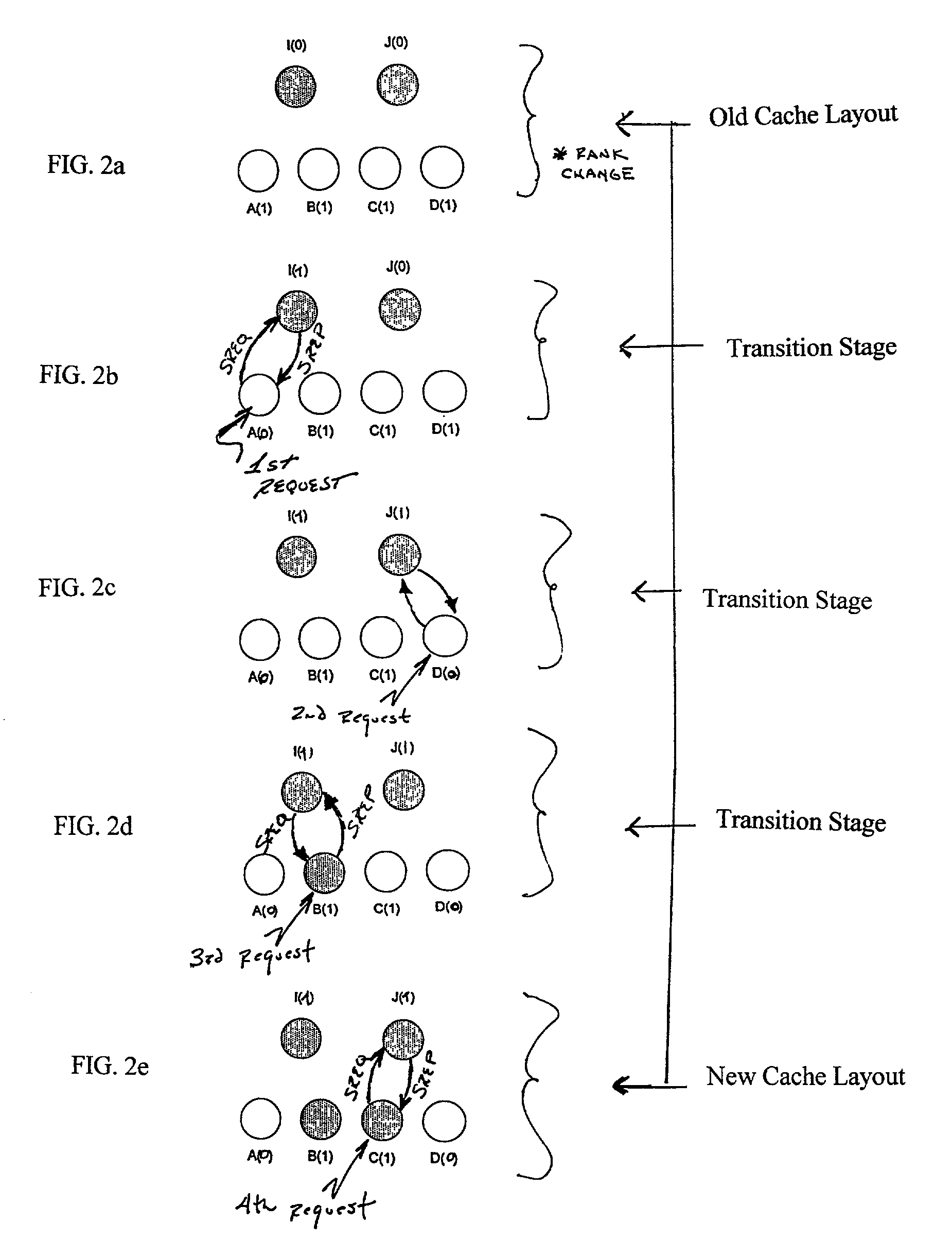
A cache replacement system and method for changing the number of cached copies of segments of a media clip in response to rank change for the media clip is disclosed. Whenever rank change for a media clip is detected at an origin server, rank change information is distributed to proxy servers organized in a loosely coupled distributed cache. Each proxy server uses this information to recompute caching probabilities for segments of the media clip in order to determine which segments of the clip to store or discard, thereby forming a new cache layout for the clip at each proxy server. Segments are neither added nor deleted to build the new cache layout until client requests for segments of the clip are received at proxy servers. Upon receiving client requests, construction of the new cache layout occurs on a segment-by-segment basis by employing techniques of lazy caching and token exchange.
Owner:SOUND VIEW INNOVATIONS
Emulated tape-based storage media
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method and system for determining optimal data layout using blind justice
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Gray-code-based distributed data layout method and query method
InactiveCN102890678AImplement aggregation queryImprove the efficiency of sequential accessSpecial data processing applicationsTheoretical computer scienceEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of a database, and discloses a gray-code-based distributed data layout method. The method comprises the steps of: dividing a range of each attribute into a plurality of equal portions; encoding according to a gray code order; marking a certain attribute value of a tuple comprising a plurality of attributes through the gray codes of the equal portions of the attribute value, namely an index code of the attribute value; forming an index key value of the tuple by mixing the index code of each attribute value in the tuple, wherein the tuple achieves the distributed data layout according to the order of the gray codes, the distributed data layout is deployed on a distributed system, the bitmap index of content perception is achieved at a host computer terminal of the system and the content perception is stored in a file name, and physical storage of data and statistical index of the data are achieved on a slave terminal of the system. The invention also discloses a query method employing the database formed by means of the method. The data layout obtained by the method can meet the requirements of data processing such as exact matching search, range search, multi-dimensional search, multi-attribute search and aggregated analysis, and the method is high in disc access efficiency.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Methods, systems, and computer program products for implementing logical and physical data models
Exemplary embodiments include a method for implementing standardized enterprise warehouse system processes, including: extracting content from one or more source systems that provide a feed for the content; loading extracted content into one or more standardized data layout tables defined by the data control structure and based upon the meta-data and rules, wherein the extracted content in condition for transformation and data warehouse loading and the standardized data layout tables comprise a logical data model; and propagating the extracted content into a physical data model.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
Storage space allocation method and device
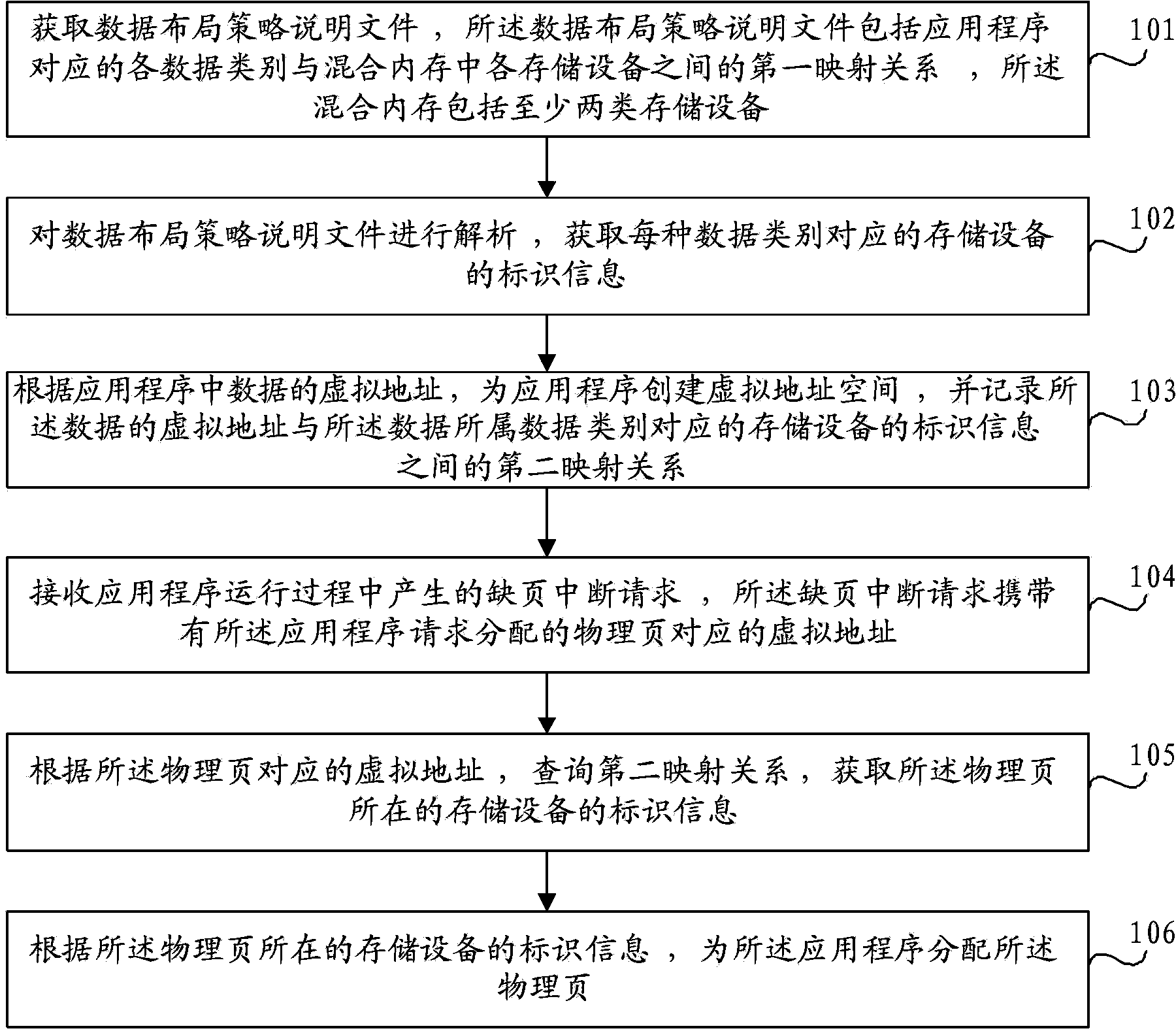
ActiveCN103853665AImprove adaptabilityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationApplication softwareData layout
Embodiments of the invention provide a storage space allocation method and device. The method includes: acquiring a data layout strategy description file; analyzing the data layout strategy description file to obtain storage device identifiers corresponding to data classes; creating a virtual address space for an application, and recording a second mapping relation between virtual addresses of data and the storage device identifiers corresponding to the data classes that the data belong to; receiving a missing page interrupt request when the application runs; querying the second mapping relation according to virtual addresses of physical pages in the missing page interrupt request to obtain the storage device identifiers of the physical pages; allocating the physical pages for the application according to the storage device identifiers of the physical pages. The storage space allocation method and device according to the technical scheme has the advantages that storage performance of a hybrid memory can be improved and implementation is simple.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
System and method for creating customizable nodes in a network diagram
InactiveUS7603632B1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsGraphical user interface
The present invention permits customization of shapes, sizes, and layout for data of nodes within a network diagram based upon node category or nodes selected by the user. The invention also permits a user to create his or her own data template for the layout of data within a certain category of nodes. The invention further provides a filter that highlights nodes in a network diagram according to parameters selected by a user. The invention can include a graphical user interface that permits rapid and easy selection of various options for nodes displayed within a network diagram. The system and method of the present invention also organizes and generates a network diagram that permits a user to display one or more nodes at one magnification level while displaying other nodes at a different magnification level.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Storage system condition indicator and method
InactiveCN101095116AInput/output to record carriersRedundant data error correctionFault toleranceHash function
Owner:德洛博公司
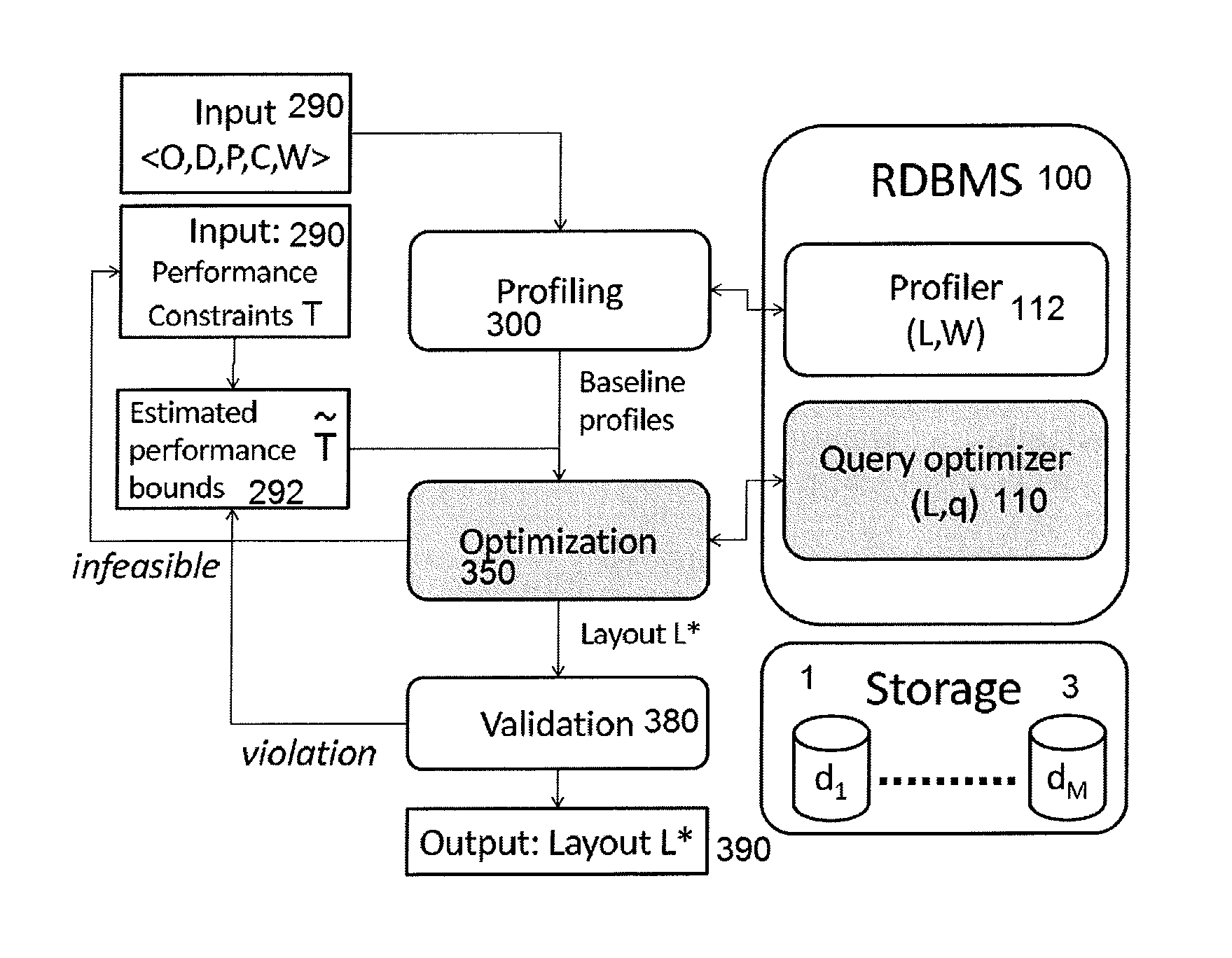
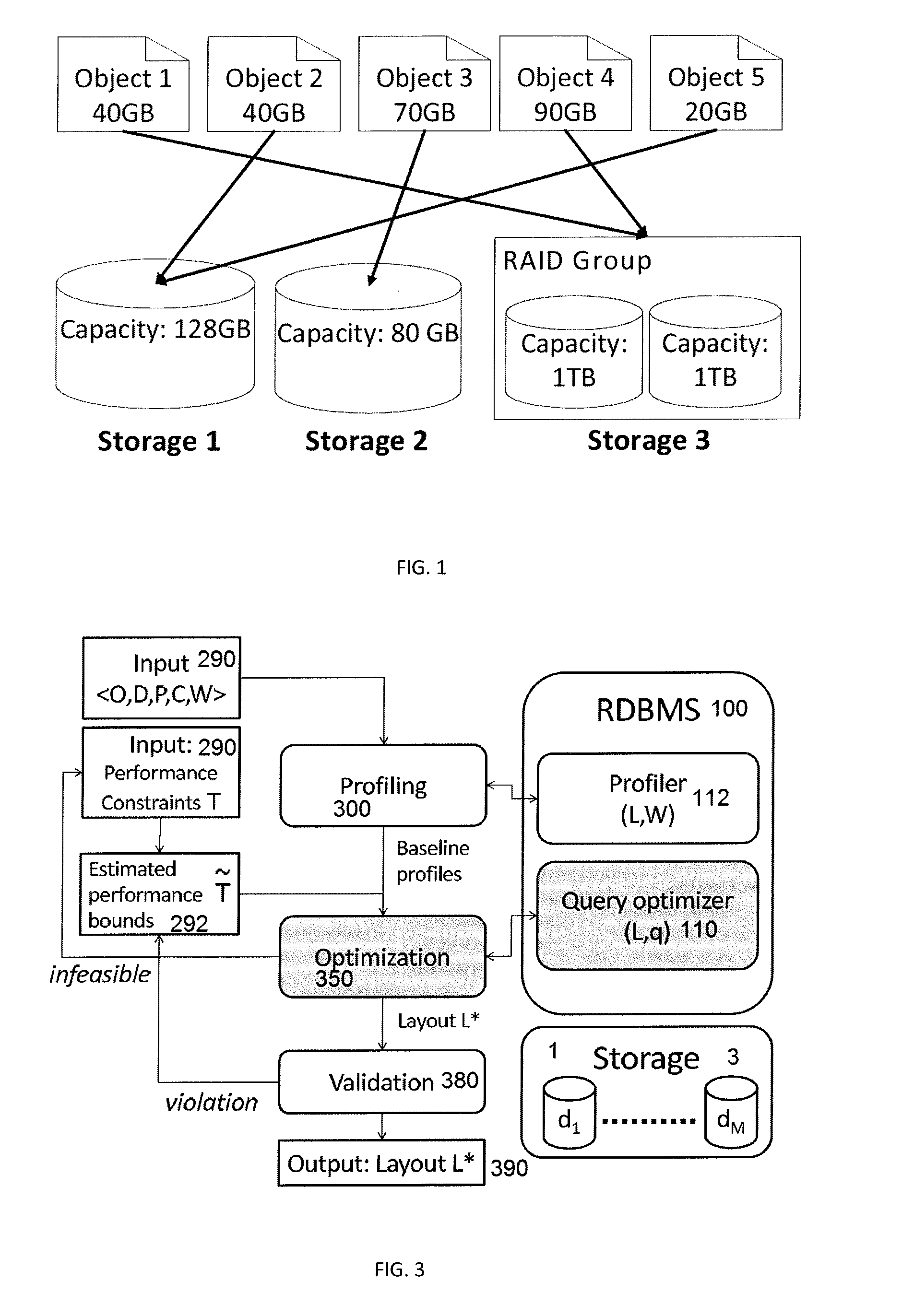
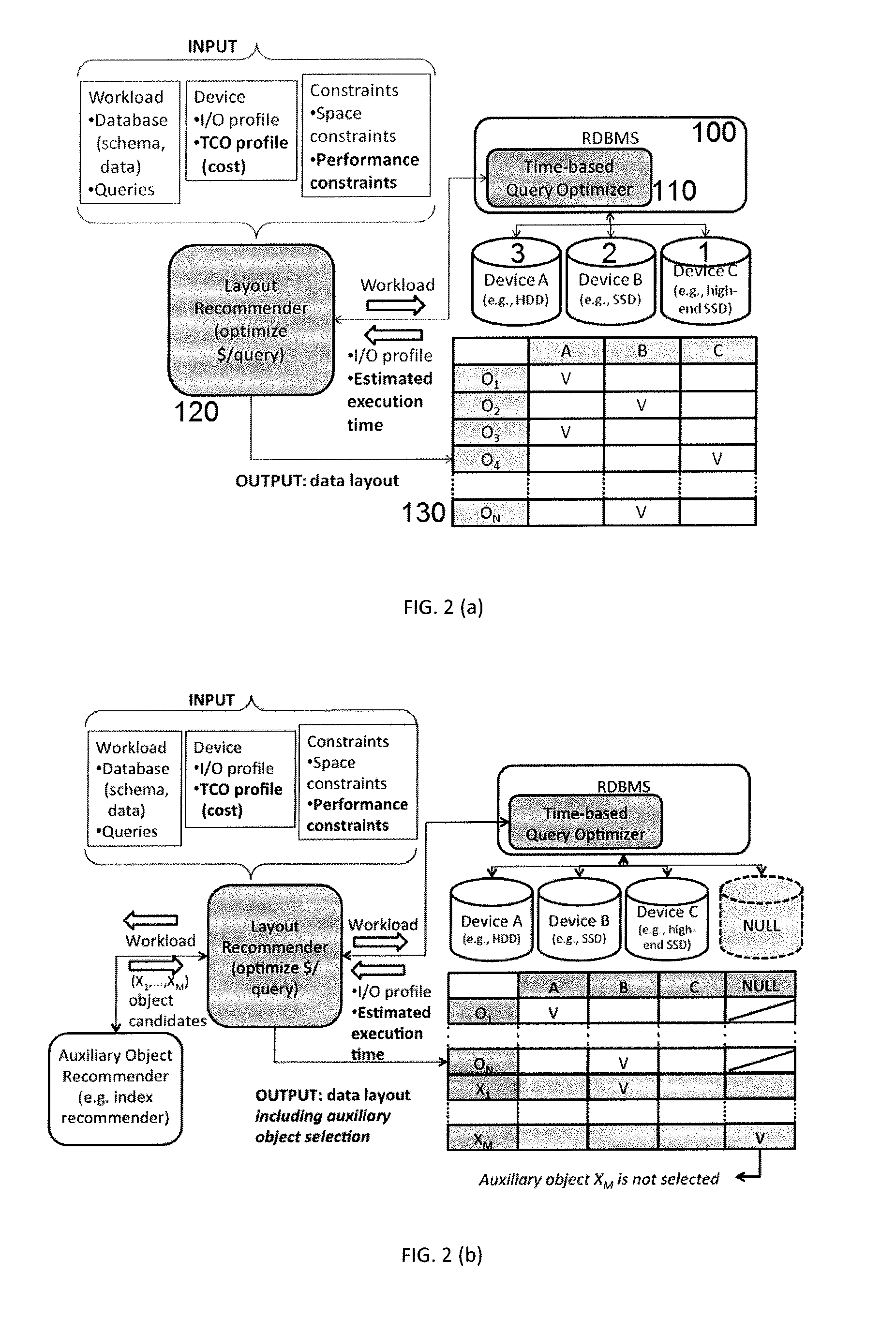
Cost-Effective Data Layout Optimization Over Heterogeneous Storage Classes
InactiveUS20140214793A1Optimize layoutDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsQuery optimizationRelational database management system
A system to optimize layout of database objects in a relational database management system stored on a plurality of storage classes each characterized by a price and a storage capacity includes a time-based query optimizer and a layout recommender coupled to the time-based query optimizer to estimate a total cost of operation (TCO) for a query workload on each data layout. The layout recommender includes an auxiliary object selection comprising database objects that include auxiliary objects that are optional to place with auxiliary object candidates being given from an auxiliary object recommender component.
Owner:NEC LAB AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com