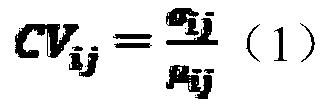Patents
Literature
172 results about "Downscaling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Downscaling is any procedure to infer high-resolution information from low-resolution variables. This technique is based on dynamical or statistical approaches commonly used in several disciplines, especially meteorology, climatology and remote sensing. The term downscaling usually refers to an increase in spatial resolution, but it is often also used for temporal resolution.
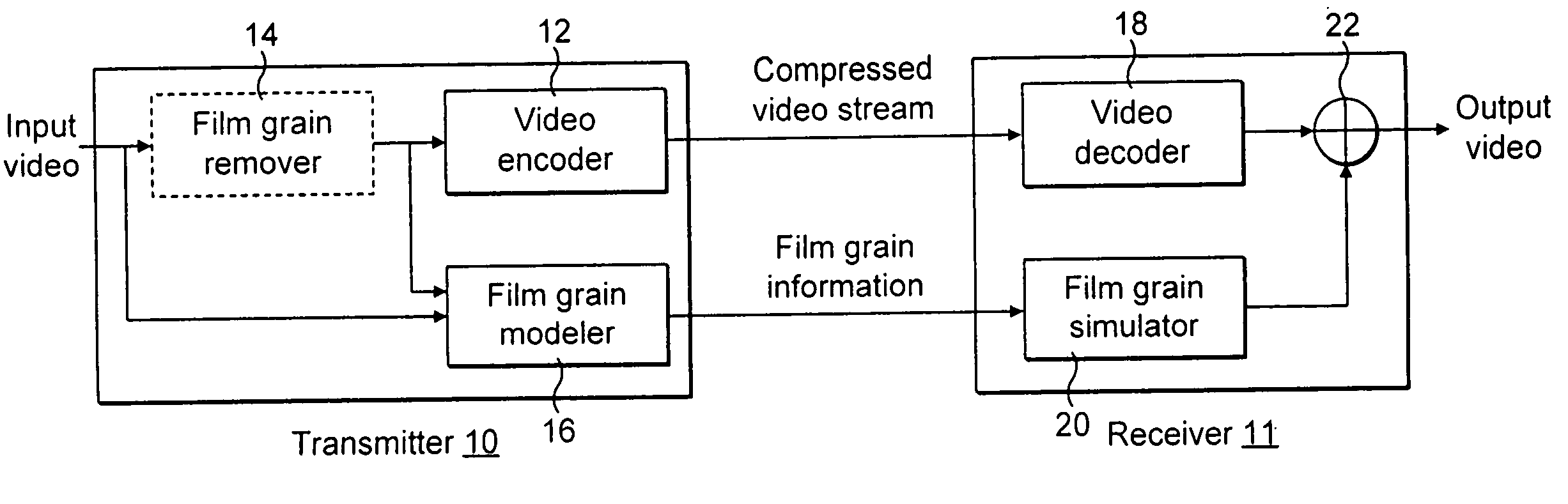
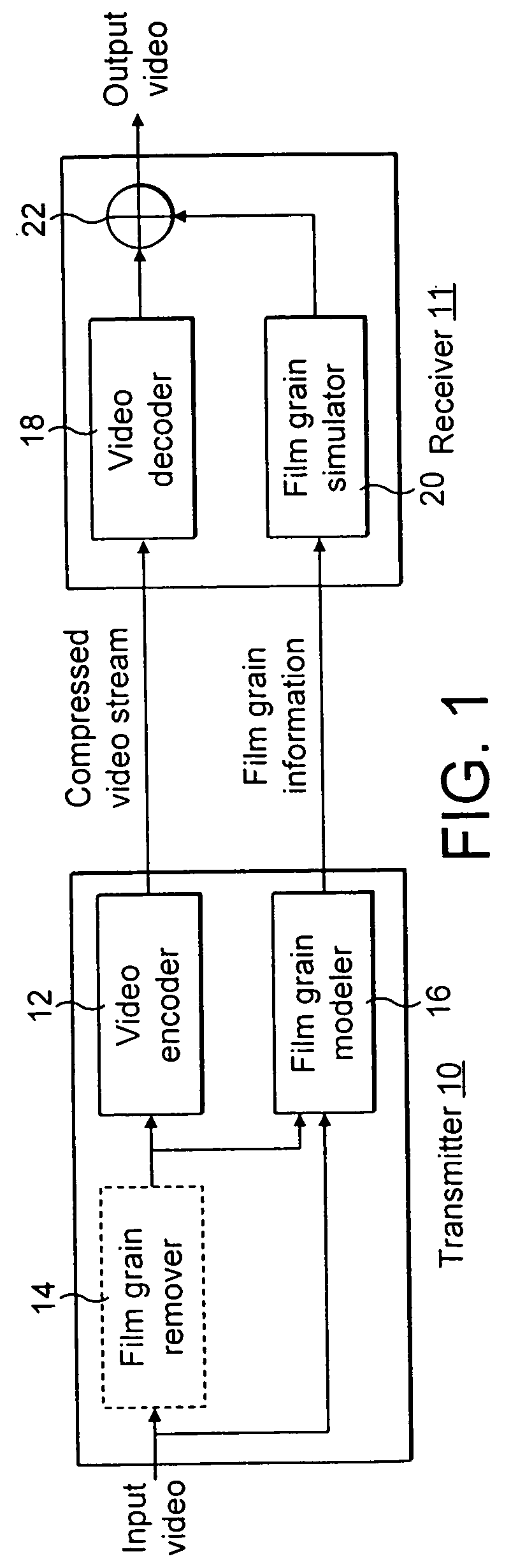
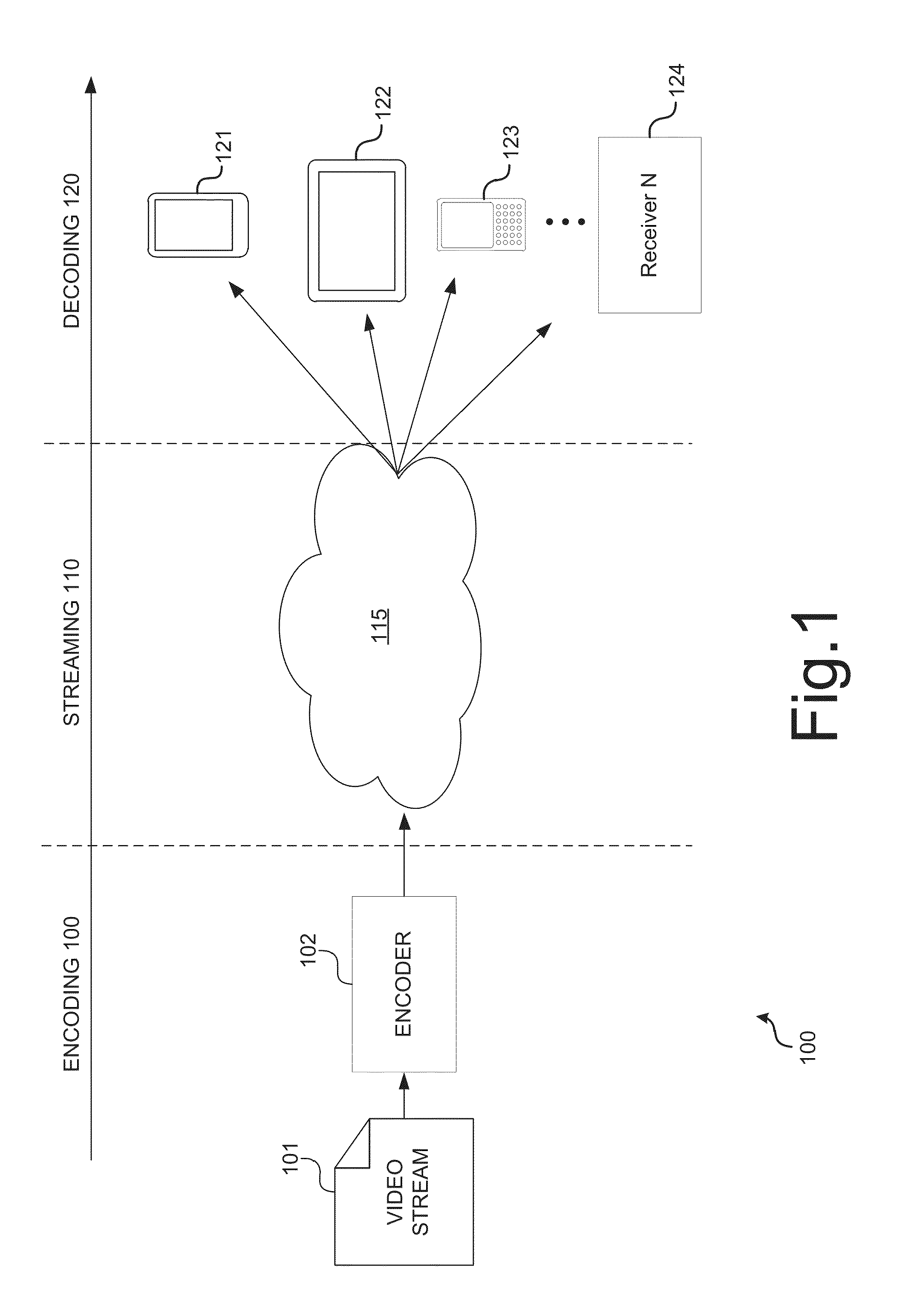
Real-time video coding/decoding
ActiveUS20050276323A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionMotion vectorDownscaling
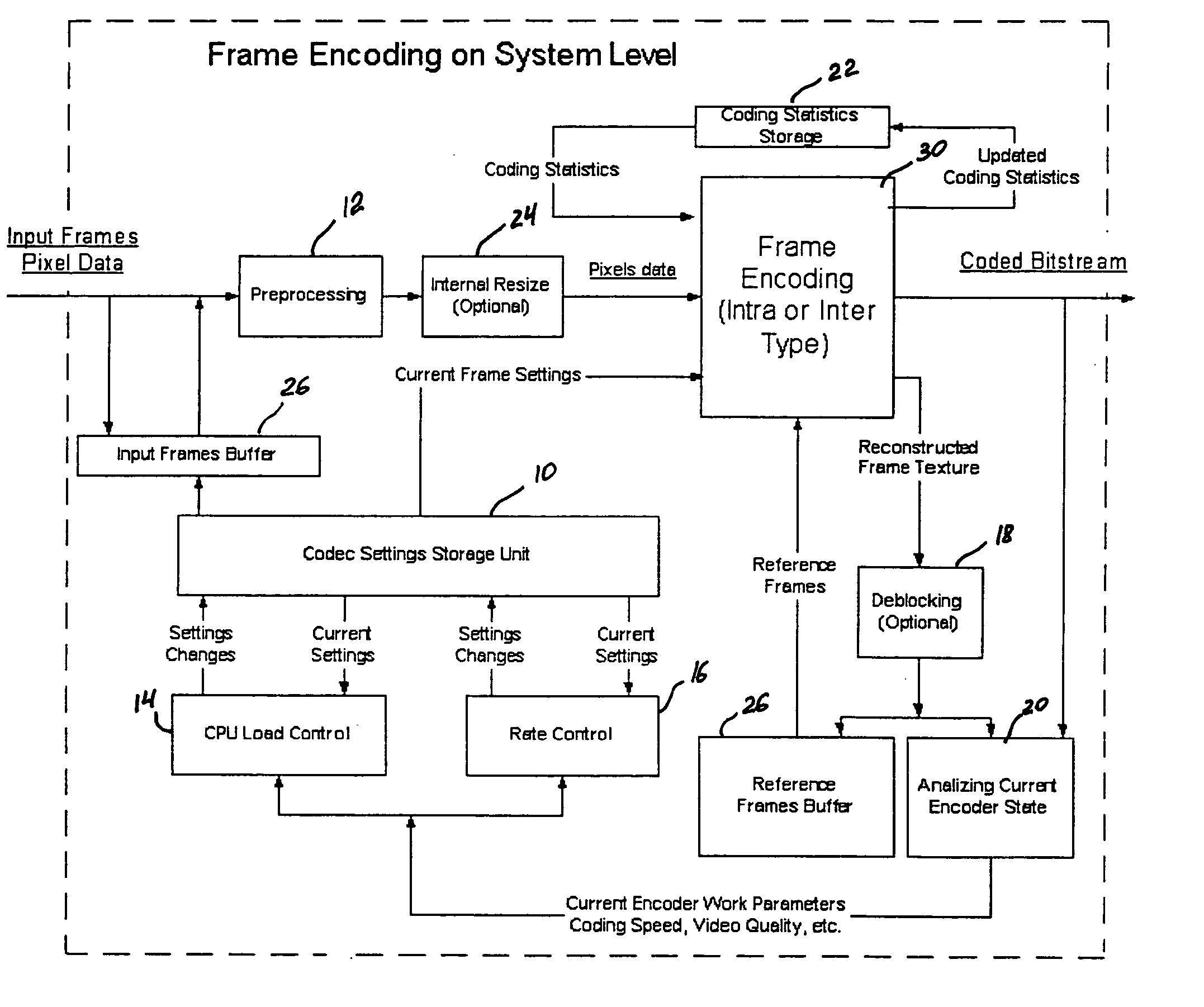
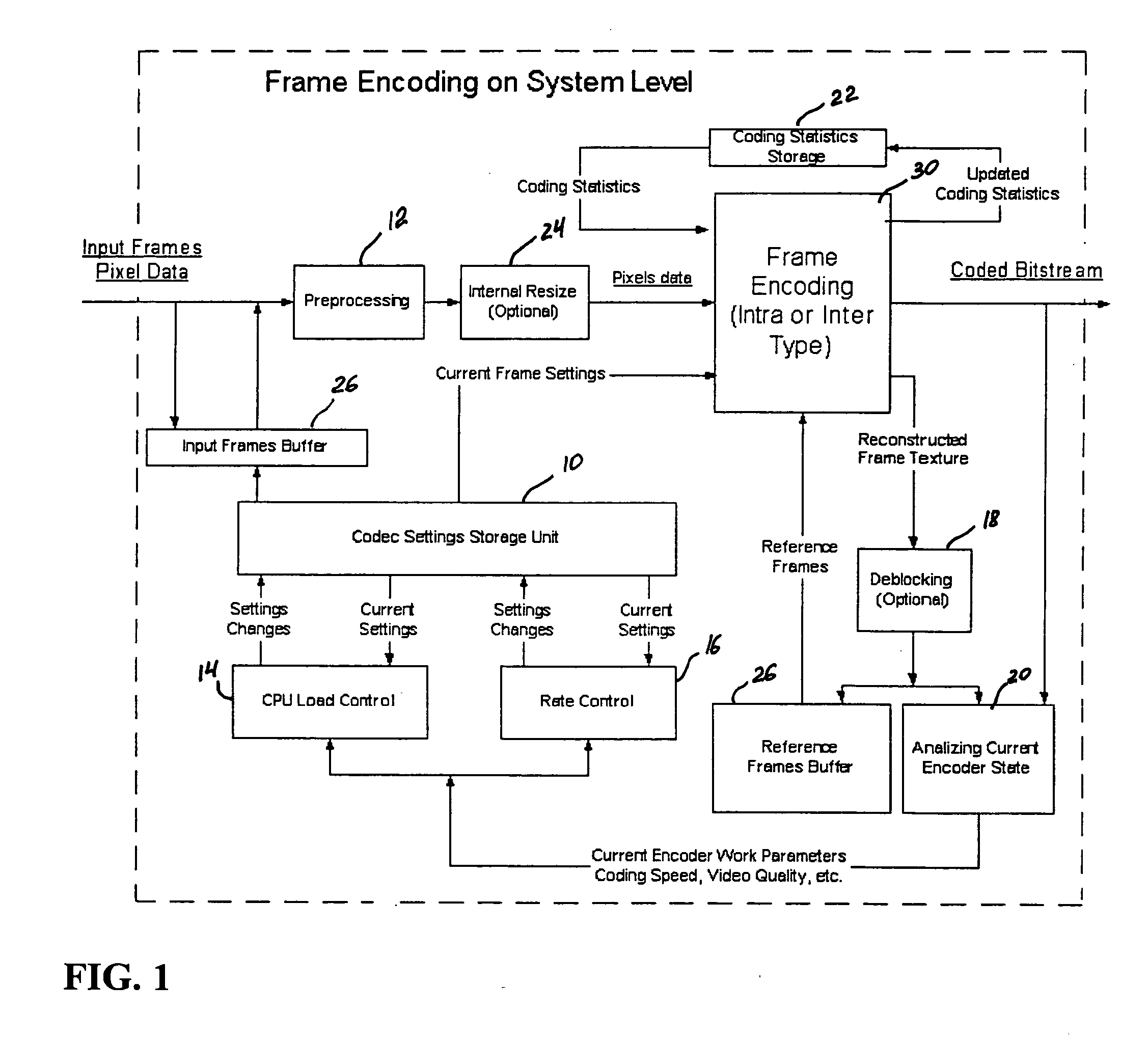
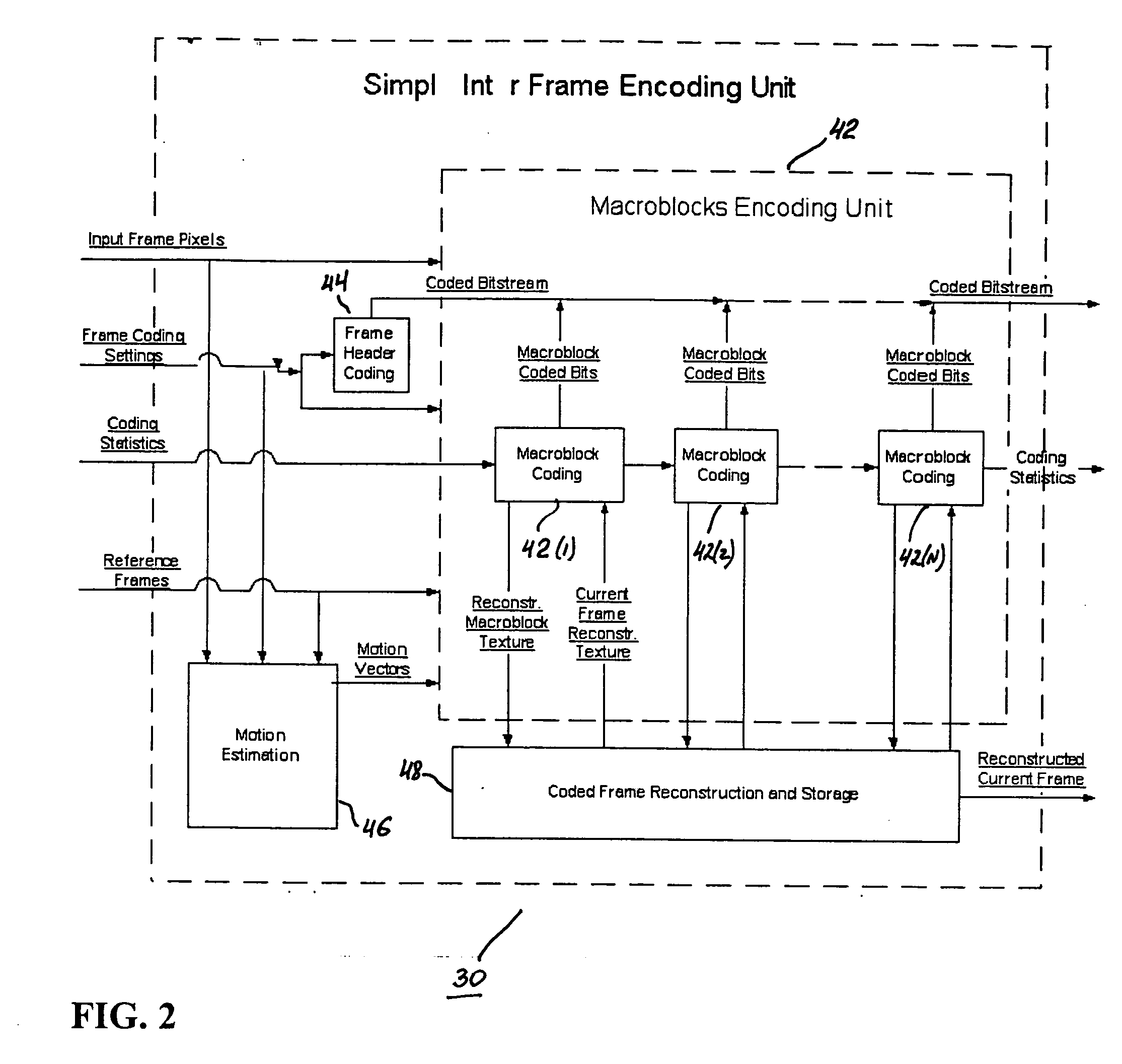
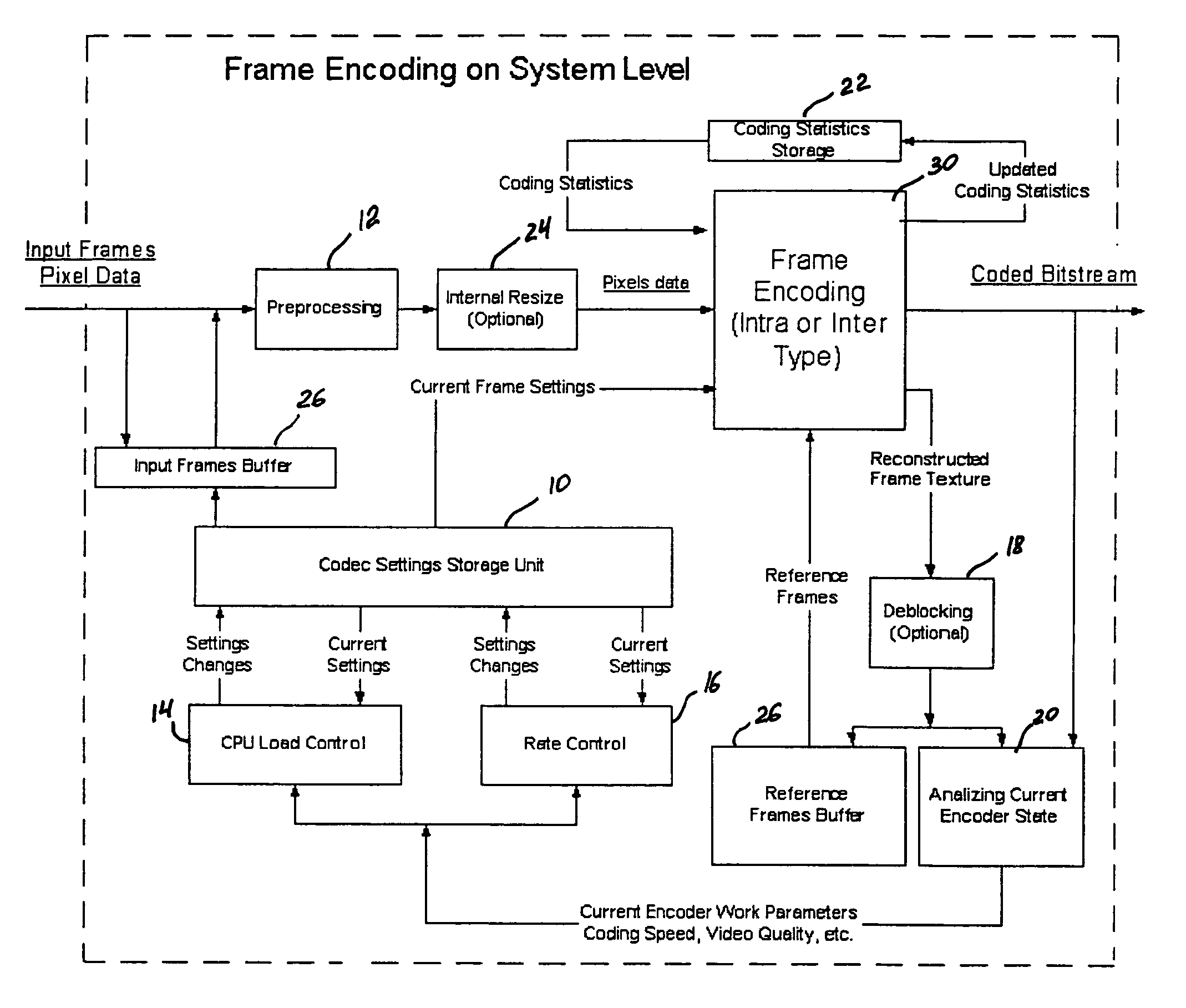
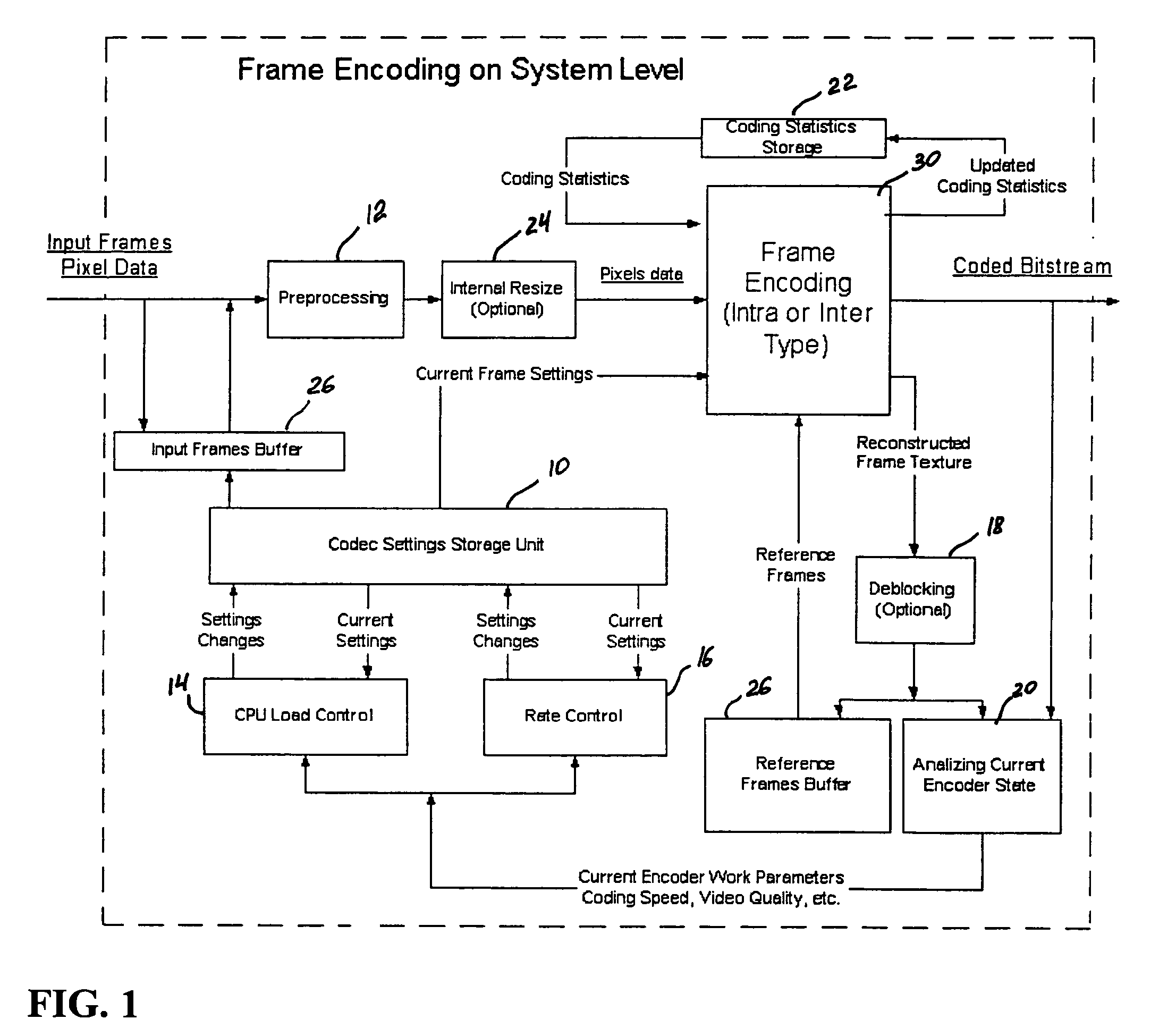
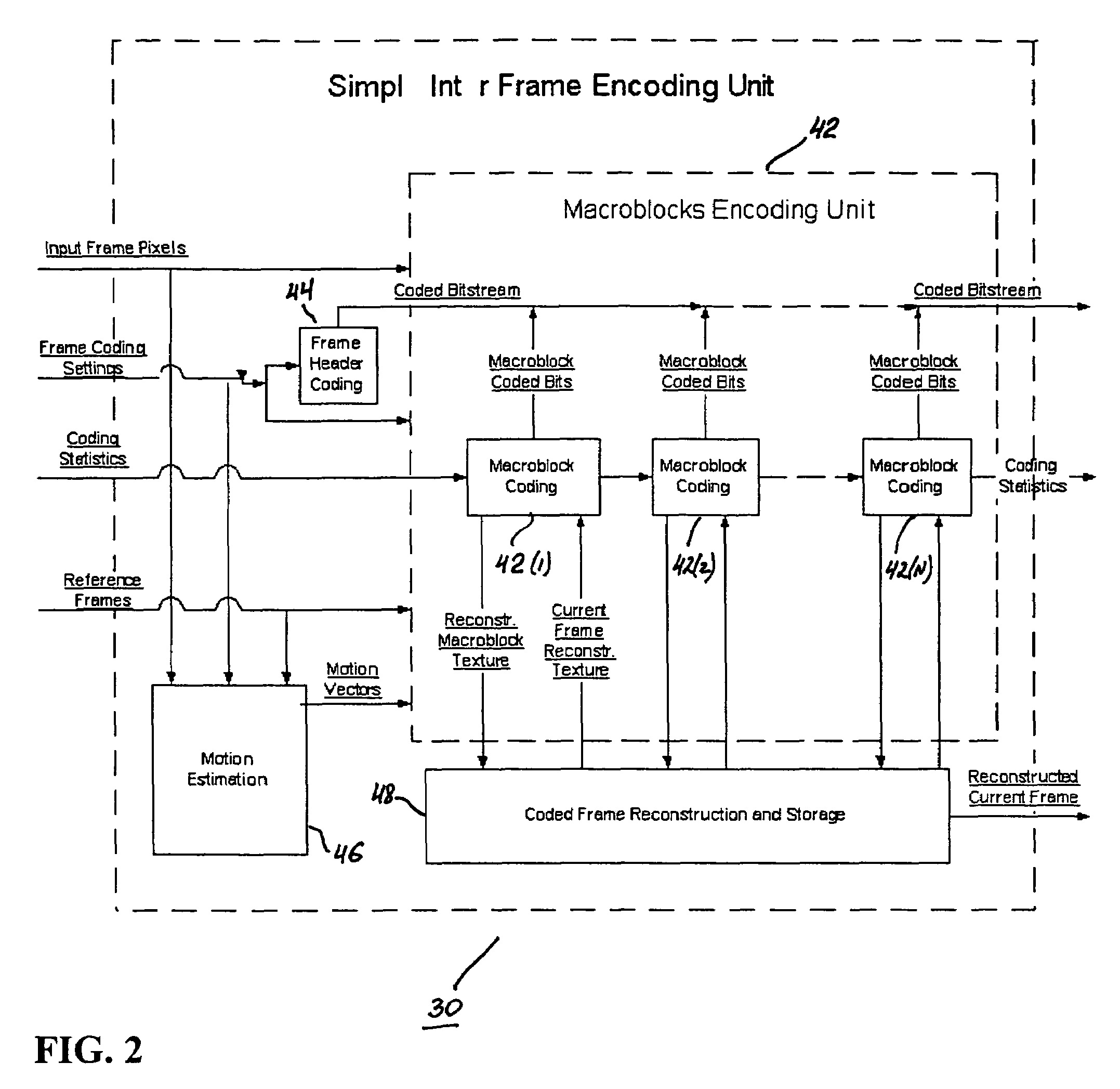
A video codec for real-time encoding / decoding of digitized video data with high compression efficiency, comprising a frame encoder receiving input frame pixels; a codec setting unit for setting and storing coding setting parameters; a CPU load controller for controlling desired frame encoding time and CPU loading; a rate controller for controlling frame size; a coding statistics memory for storing frequency tables for arithmetic coding of bitstream parameters and a reference frame buffer for storing reference frames. The frame encoder comprises a motion estimation unit, a frame head coding unit, a coded frame reconstruction and storage unit and a macroblock encoding unit. The macroblock encoding unit provides calculation of texture prediction and prediction error, transforming texture prediction error and quantization of transform coefficient, calculation of motion vector prediction and prediction error and arithmetic context modeling for motion vectors, header parameters and transform coefficients. The codec also includes a deblocking unit for processing video data to eliminate blocking effect from restored data encoded at high distortion level, which may be a part of encoder or decoder, an internal resize unit, providing matching downscaling of a frame before encoding and upscaling of decoded frame according to the coding setting parameters, and a noise suppression unit.
Owner:BEAMR IMAGING LTD
Real-time video coding/decoding
Owner:BEAMR IMAGING LTD
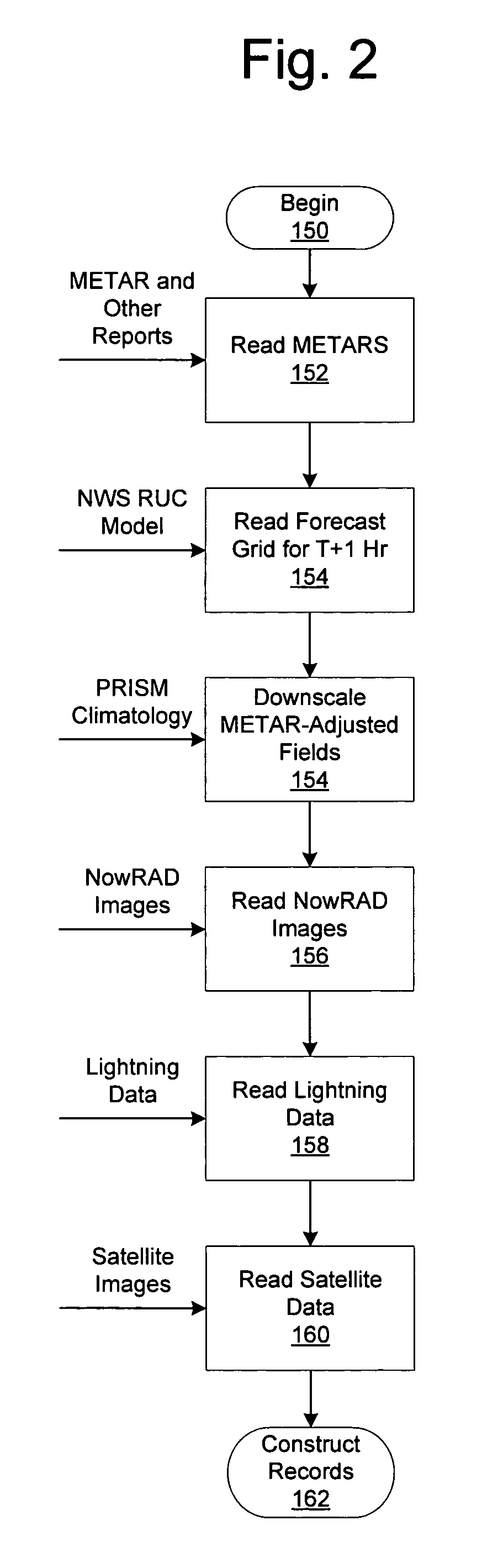
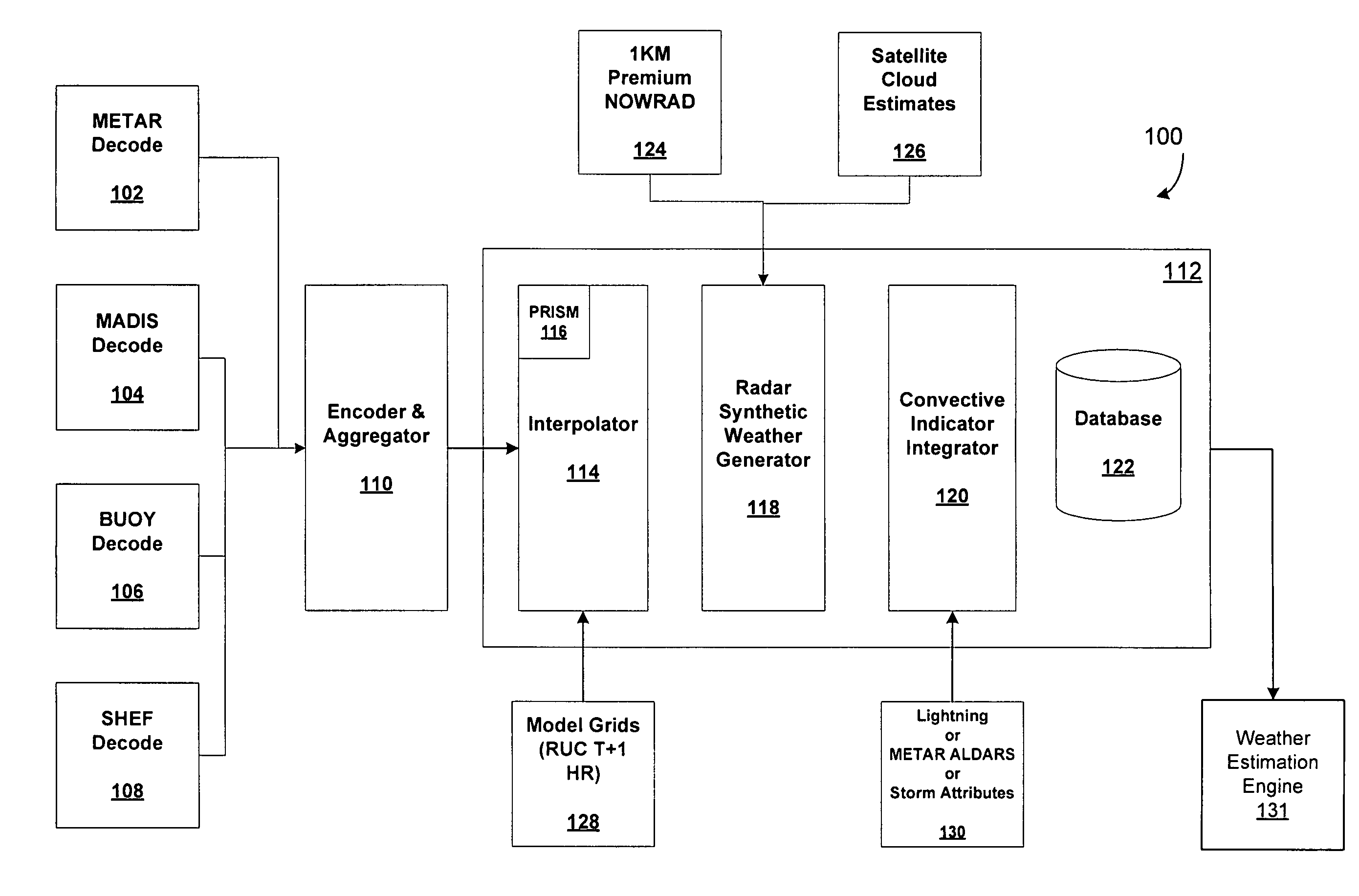
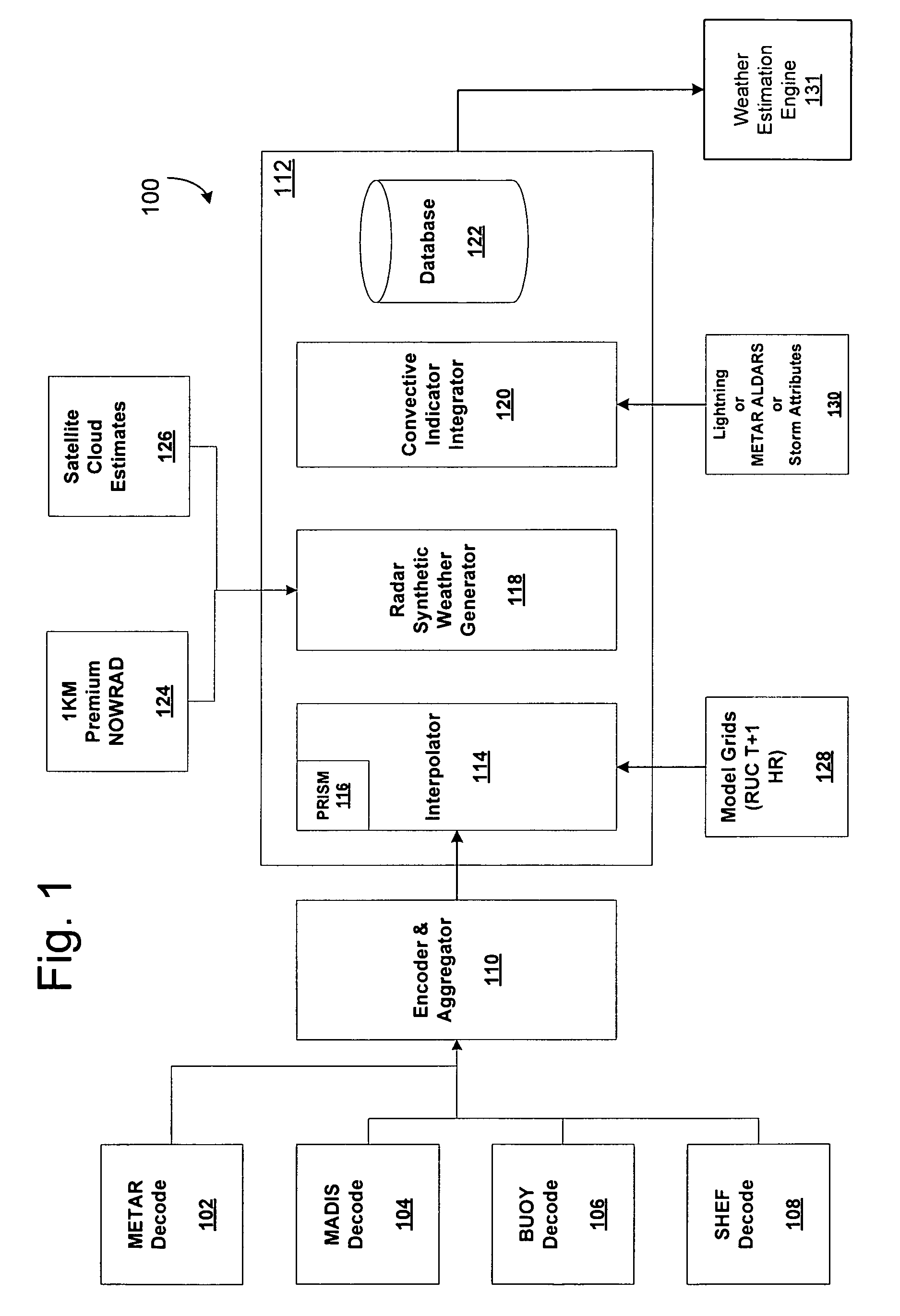
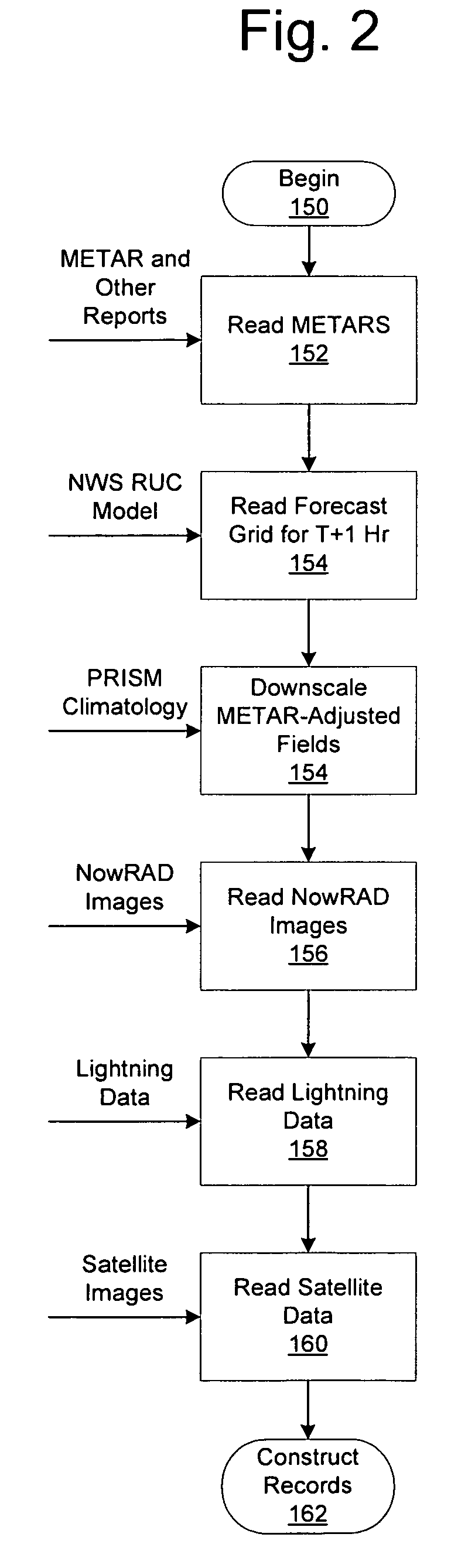
System for producing high-resolution, real-time synthetic meteorological conditions for a specified location
ActiveUS7082382B1Weather condition predictionDigital computer detailsAtmospheric sciencesSatellite imagery
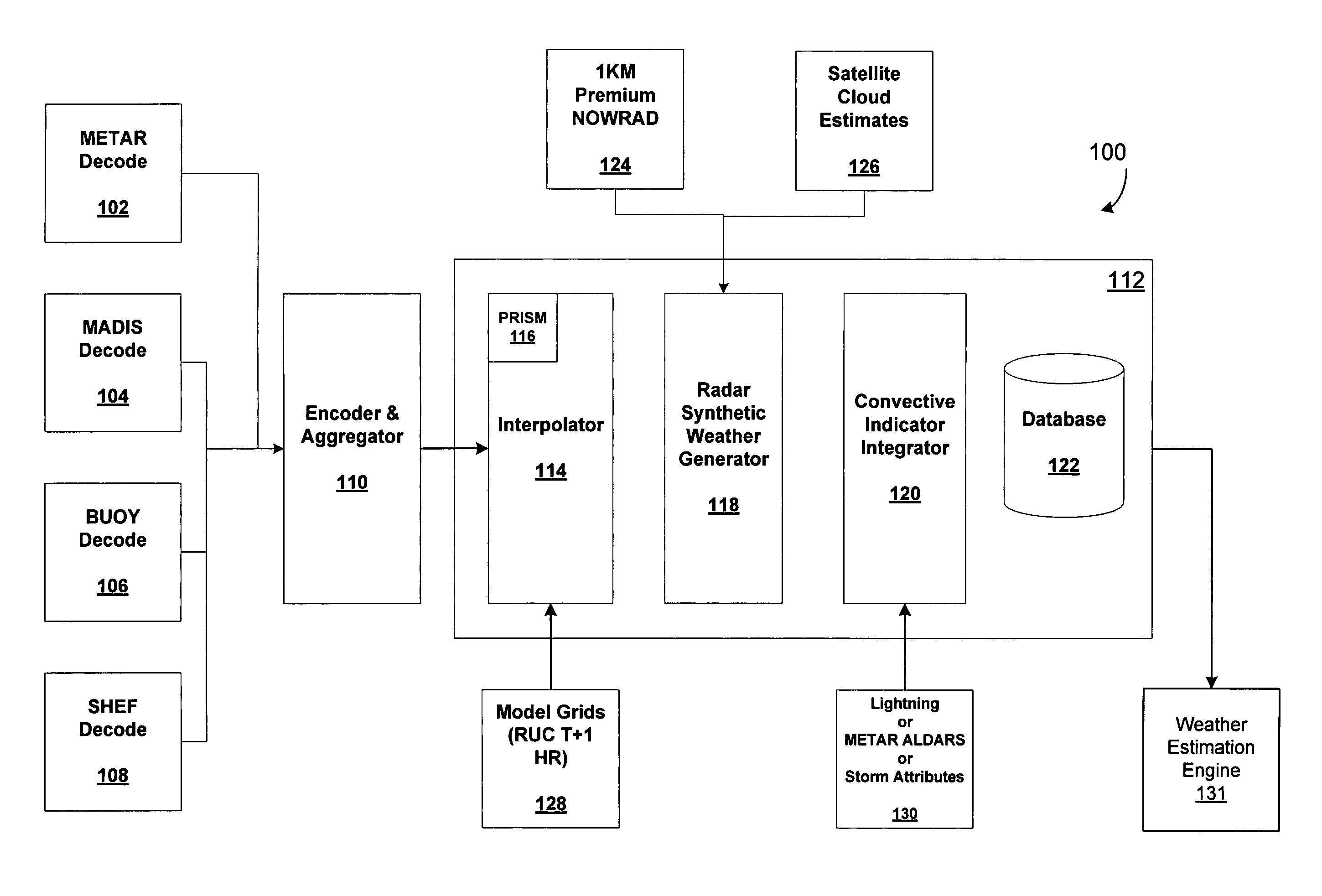
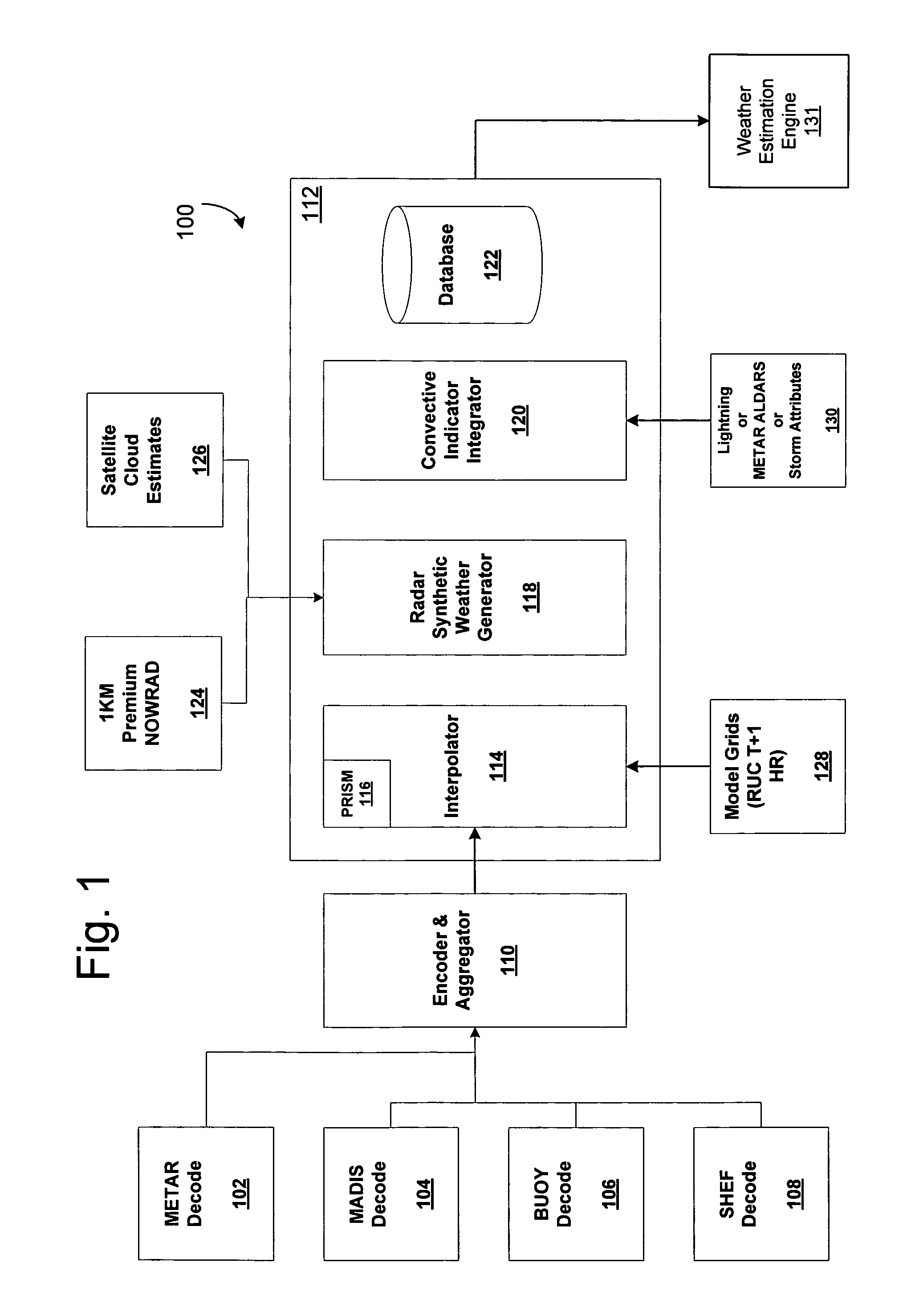
Methods and articles of manufacture for estimating or deriving weather observations / conditions for any given location using observed weather conditions from neighboring locations, radar data, lightning data, satellite imagery, etc. An initial estimate of weather conditions for a location is made based on a downscaling process using the current conditions the neighboring locations. A measure of corroboration between the radar data and surface weather conditions at official observing stations may be established. Through the results of the downscaling process, radar calibration statistics and estimates of ground-based precipitation, the corroboration can be iteratively tuned, resulting in a weather conditions vector containing associated meteorological fields for locations that lie between or near the sparse network of official observing sites from which an estimate of the weather conditions may be made.
Owner:DTN LLC
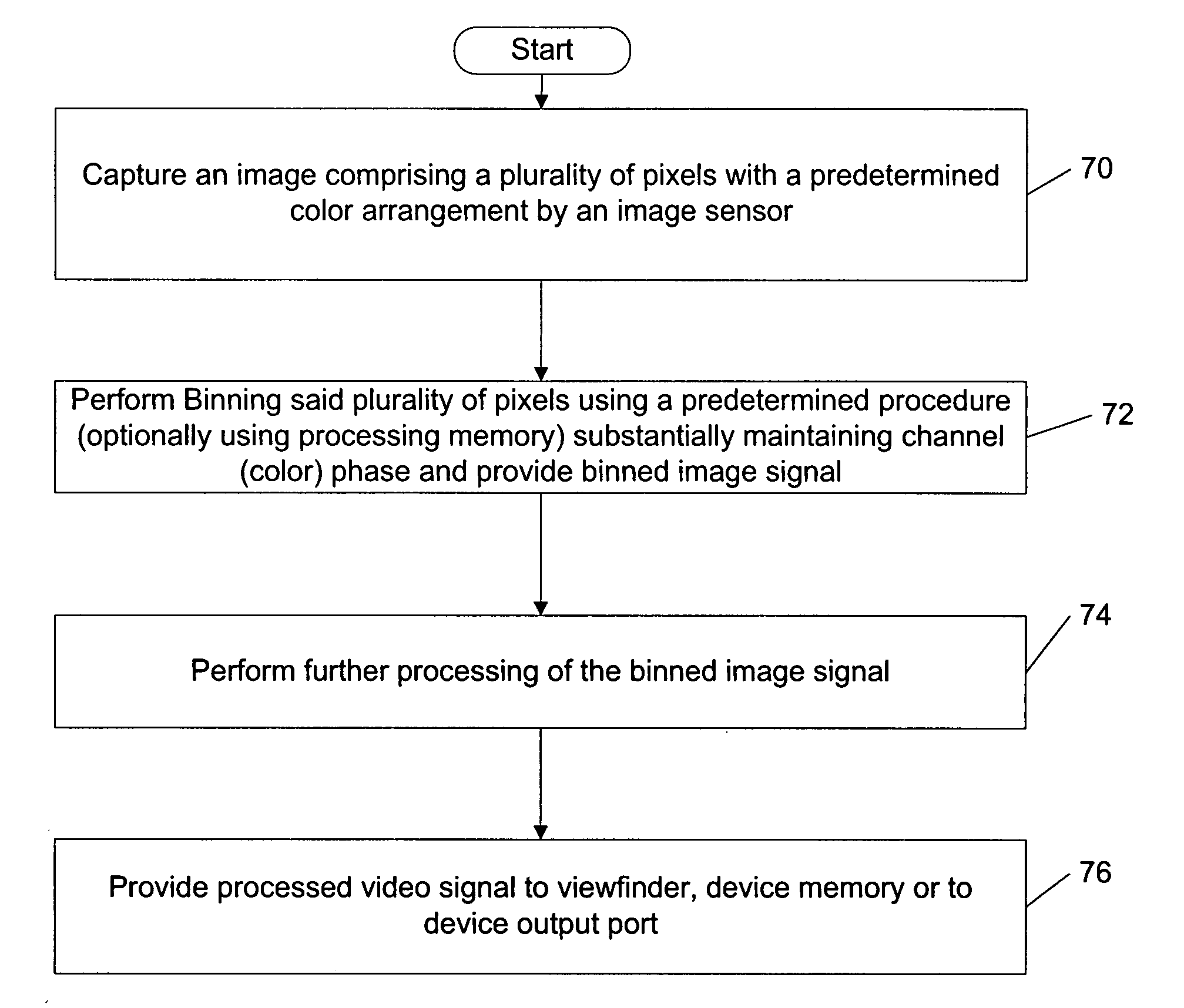
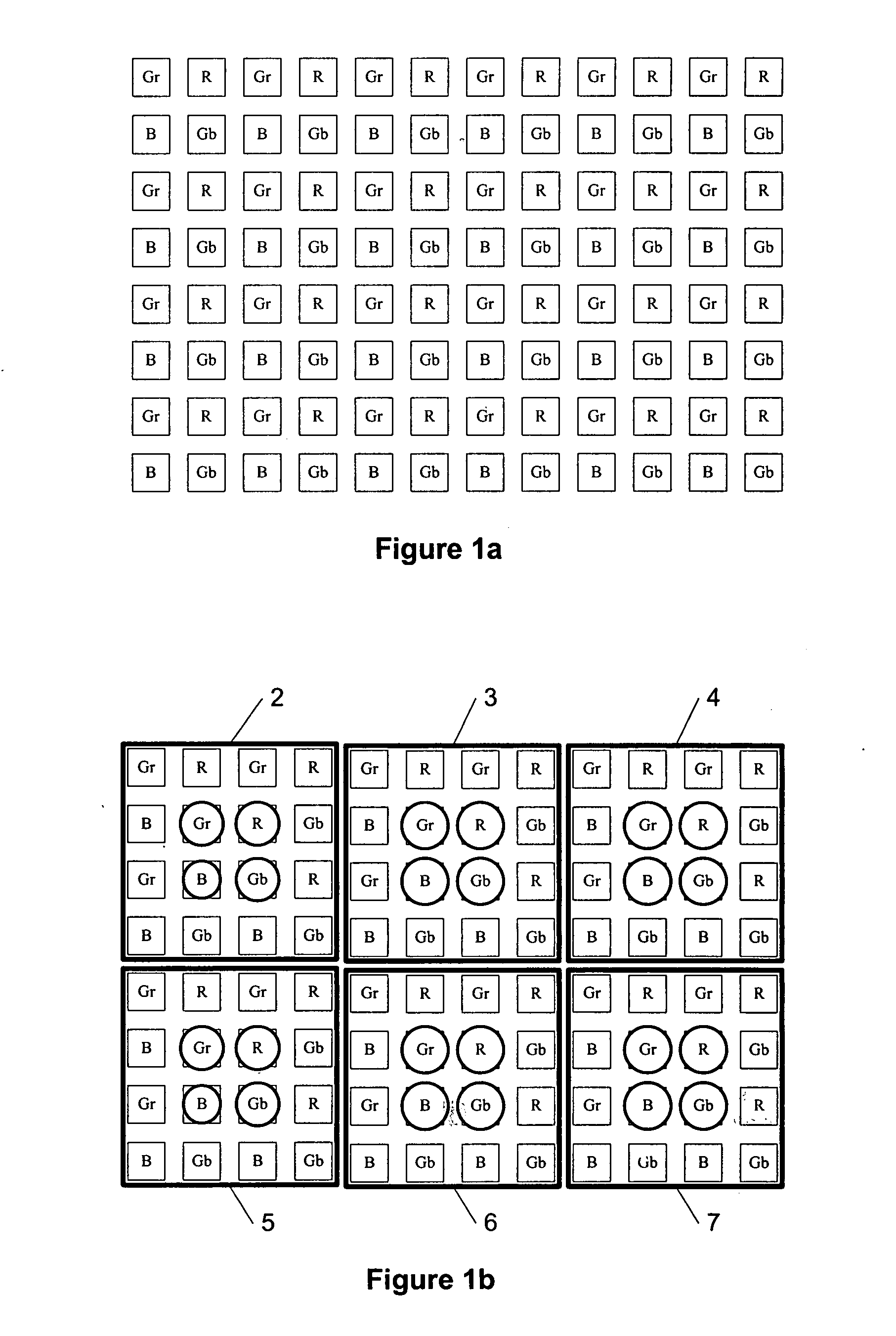
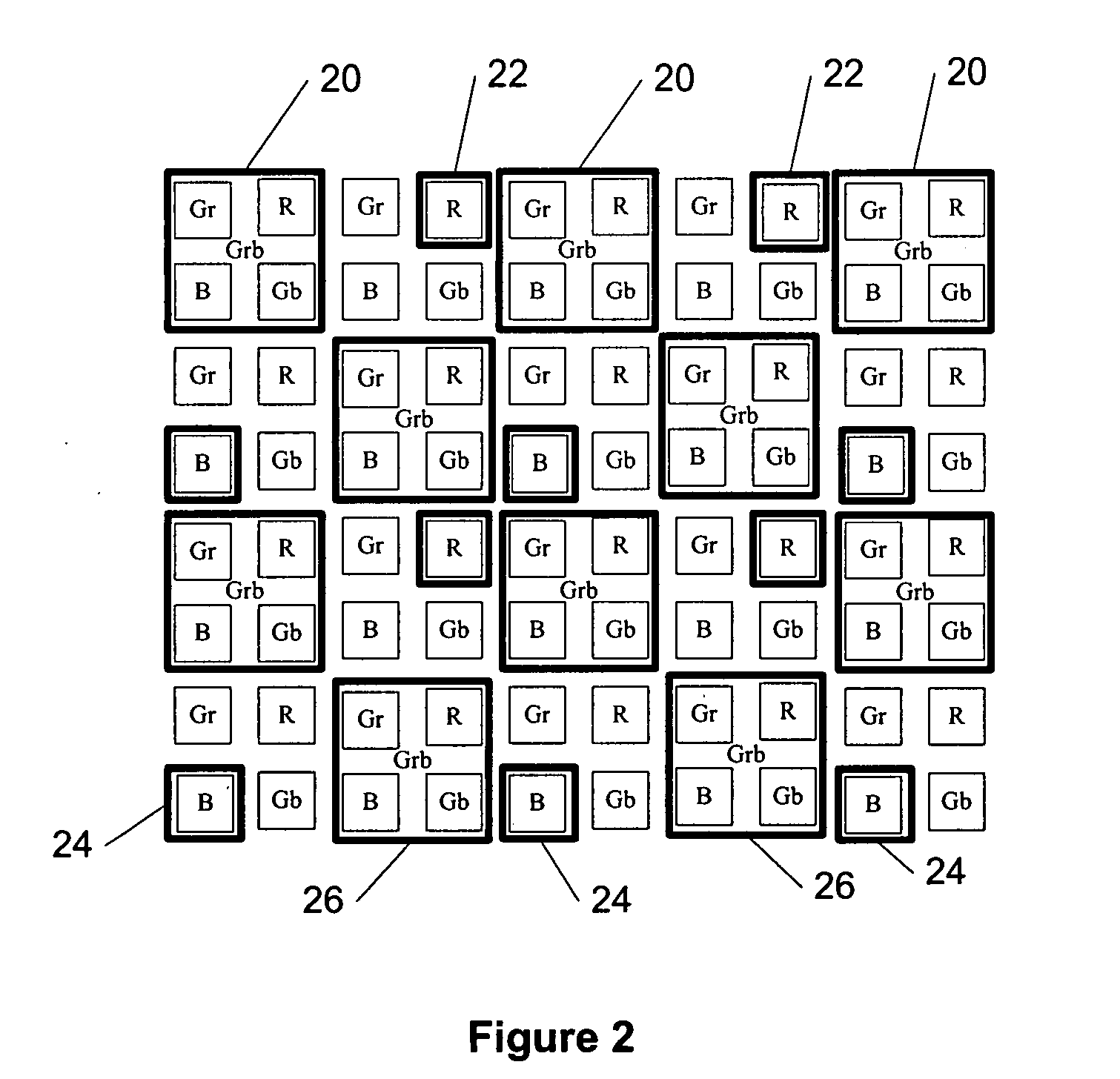
Image downscaling by binning
InactiveUS20080260291A1Geometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer visionDownscaling
The specification and drawings present a new method, apparatus and software product for image binning (downscaling) according to a predetermined procedure for a pre-selected color arrangement (e.g., a Bayer arrangement) by substantially maintaining a phase of channels (represented by selected colors) for reducing / elimination of artifacts in images taken by an electronic device. Several binning or scaling modes where the center points of each binned (e.g., averaged) pixel are arranged in the pre-selected color arrangement and maintain the phase of the channels are described.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
System for producing high-resolution, real-time synthetic meteorological conditions for a specified location
ActiveUS7200491B1Weather condition predictionIndication of weather conditions using multiple variablesSatellite imageryAtmospheric sciences
Methods and articles of manufacture for estimating or deriving weather observations / conditions for any given location using observed weather conditions from neighboring locations, radar data, lightning data, satellite imagery, etc. An initial estimate of weather conditions for a location is made based on a downscaling process using the current conditions the neighboring locations. A measure of corroboration between the radar data and surface weather conditions at official observing stations may be established. Through the results of the downscaling process, radar calibration statistics and estimates of ground-based precipitation, the corroboration can be iteratively tuned, resulting in a weather conditions vector containing associated meteorological fields for locations that lie between or near the sparse network of official observing sites from which an estimate of the weather conditions may be made.
Owner:DTN LLC
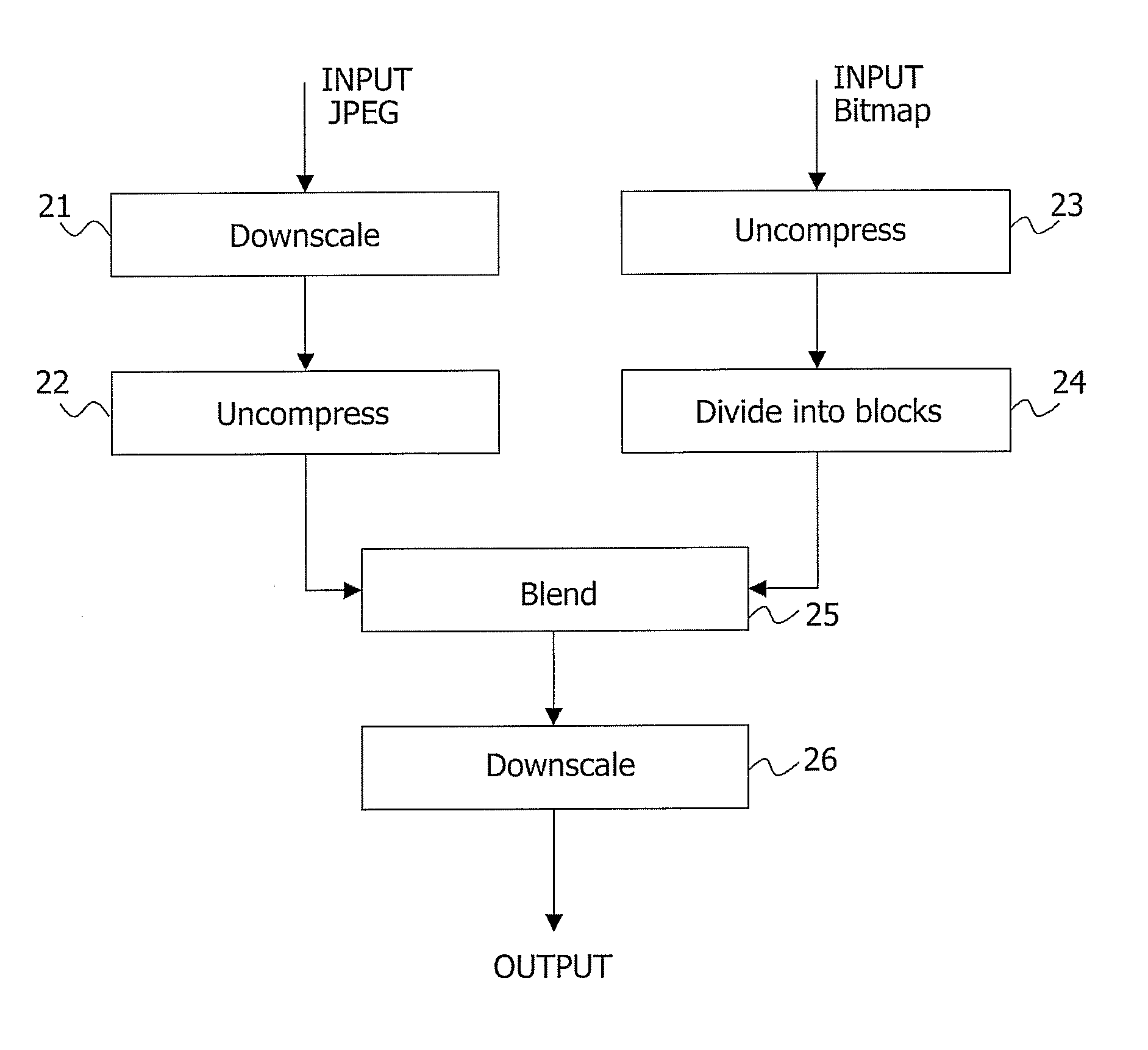
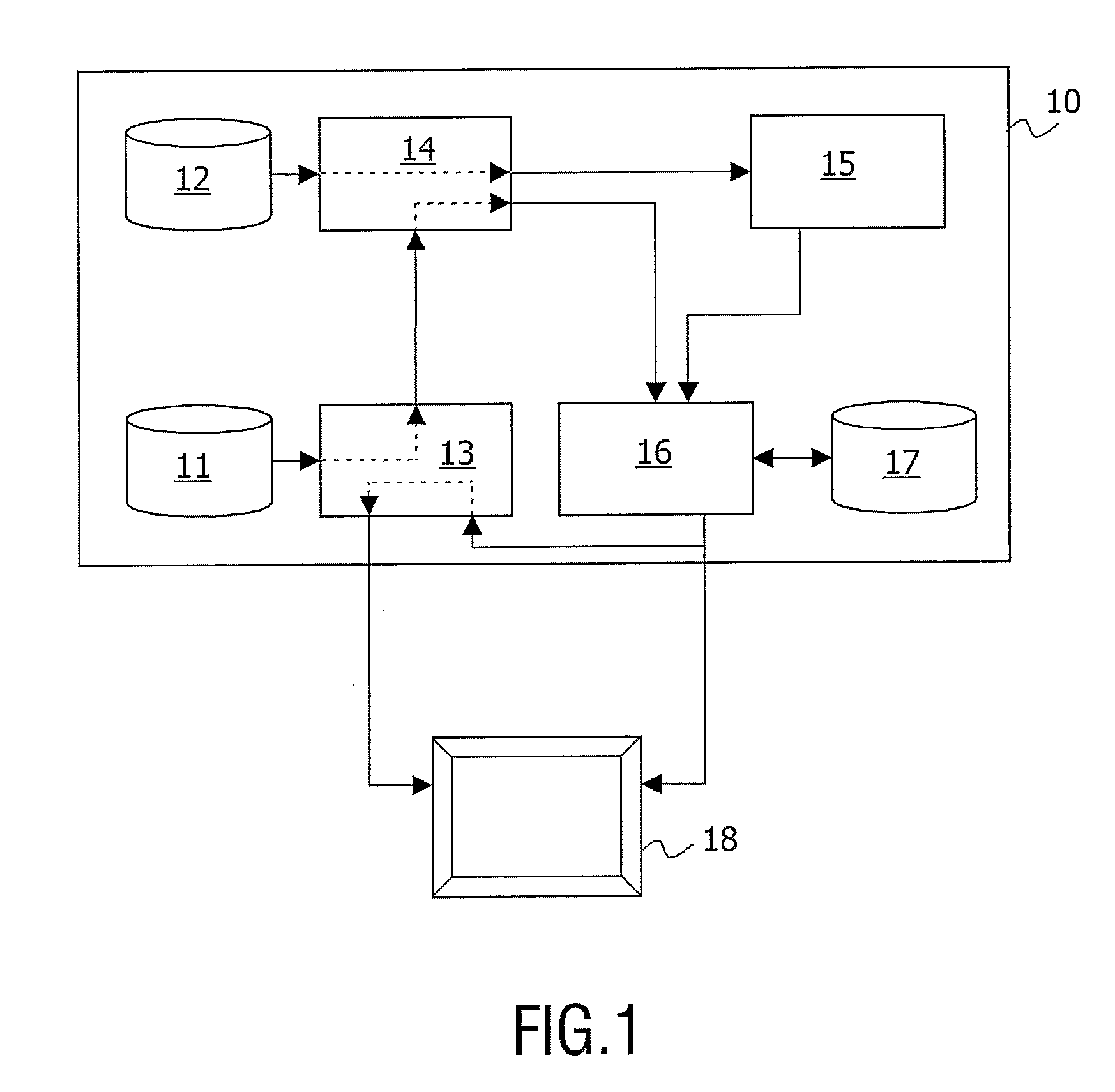
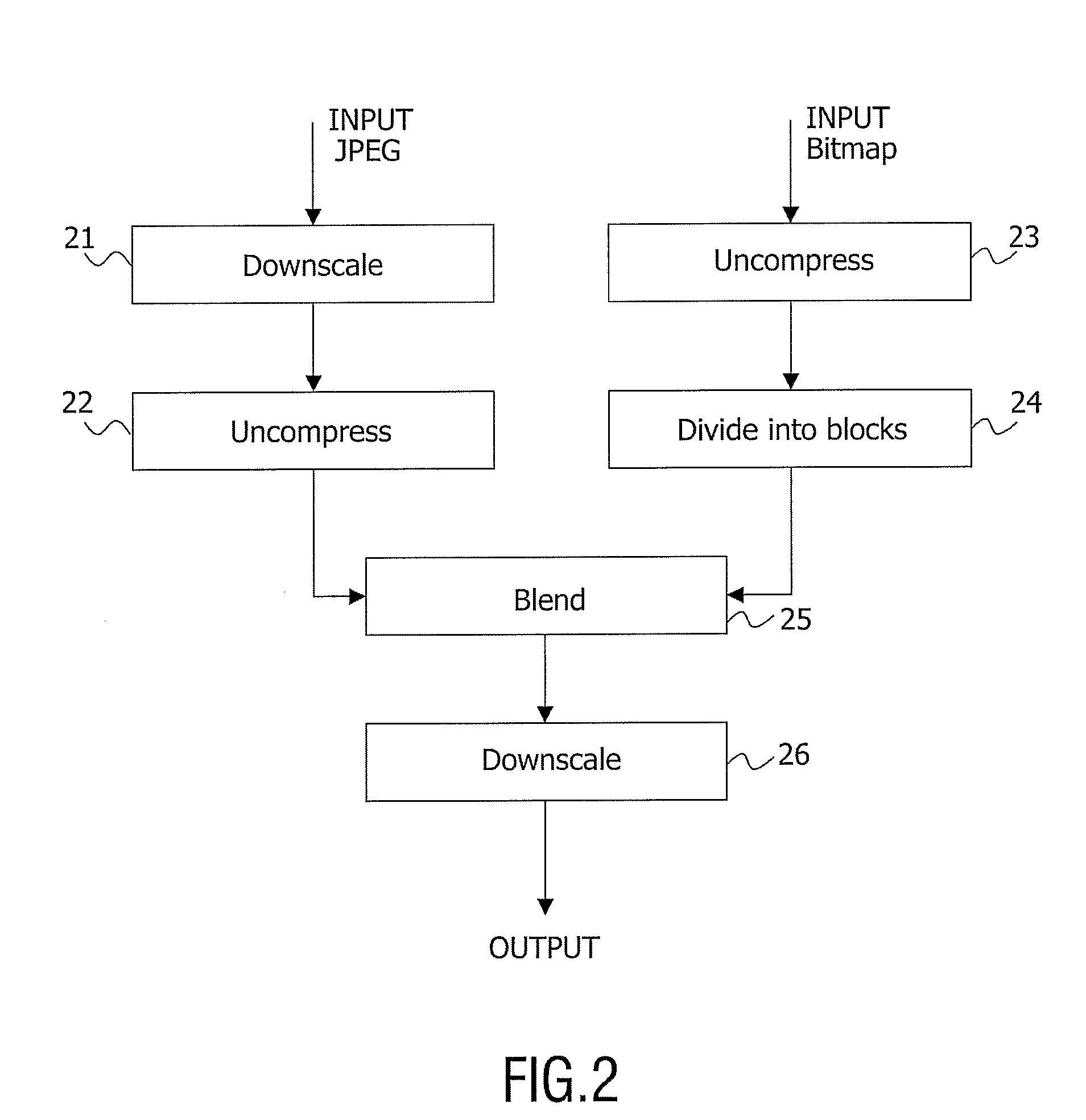
Device and Method of Downscaling and Blending Two High Resolution Images
InactiveUS20070248284A1Downscaling and blendingTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionJPEGHigh resolution image
The present invention relates to the field of downscaling and blending of two high resolution images, and particularly to a device and a method allowing for downscaling and blending of a HD JPEG background image and a HD bitmap image, which is overlaid on the JPEG background image. The device comprises means for downscaling the background image by a pre-determined factor n1, n2, . . . nN; means for uncompressing the downscaled background image and the high-resolution bitmap image; means for dividing the uncompressed high-resolution bitmap image into blocks of n1×n2× . . . ×nN pixels, whereby the size of each block correspond to the size of each pixel of the downscaled background image; and, means (16) for blending each of the blocks of the uncompressed high-resolution bitmap image with each of the pixels of the downscaled background image and thus producing a blended image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Scaled motion search section with downscaling filter and method for use therewith
InactiveUS20100316129A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImage resolutionMotion vector
A scaled motion search section can be used in a video processing device that processes a video input signal that includes a plurality of pictures. The scaled motion search section includes a downscaling module that downscales the plurality of pictures to generate a plurality of downscaled pictures, wherein the downscaling module includes a horizontal downscaling filter and a vertical downscaling filter, and wherein the vertical downscaling filter generates downscaled pixels for a macroblock pair using only pixels from the macroblock pair. A reduced-scale motion search module generates a plurality of motion vector candidates at a downscaled resolution, based on the plurality of downscaled pictures. A full-scale motion search module generates a plurality of motion search motion vectors at a full resolution, based on a plurality of reference pictures and further based on the plurality of motion vector candidates.
Owner:VIXS SYSTEMS INC
Land surface soil moisture downscaling method based on multisource remote sensing satellite merged data
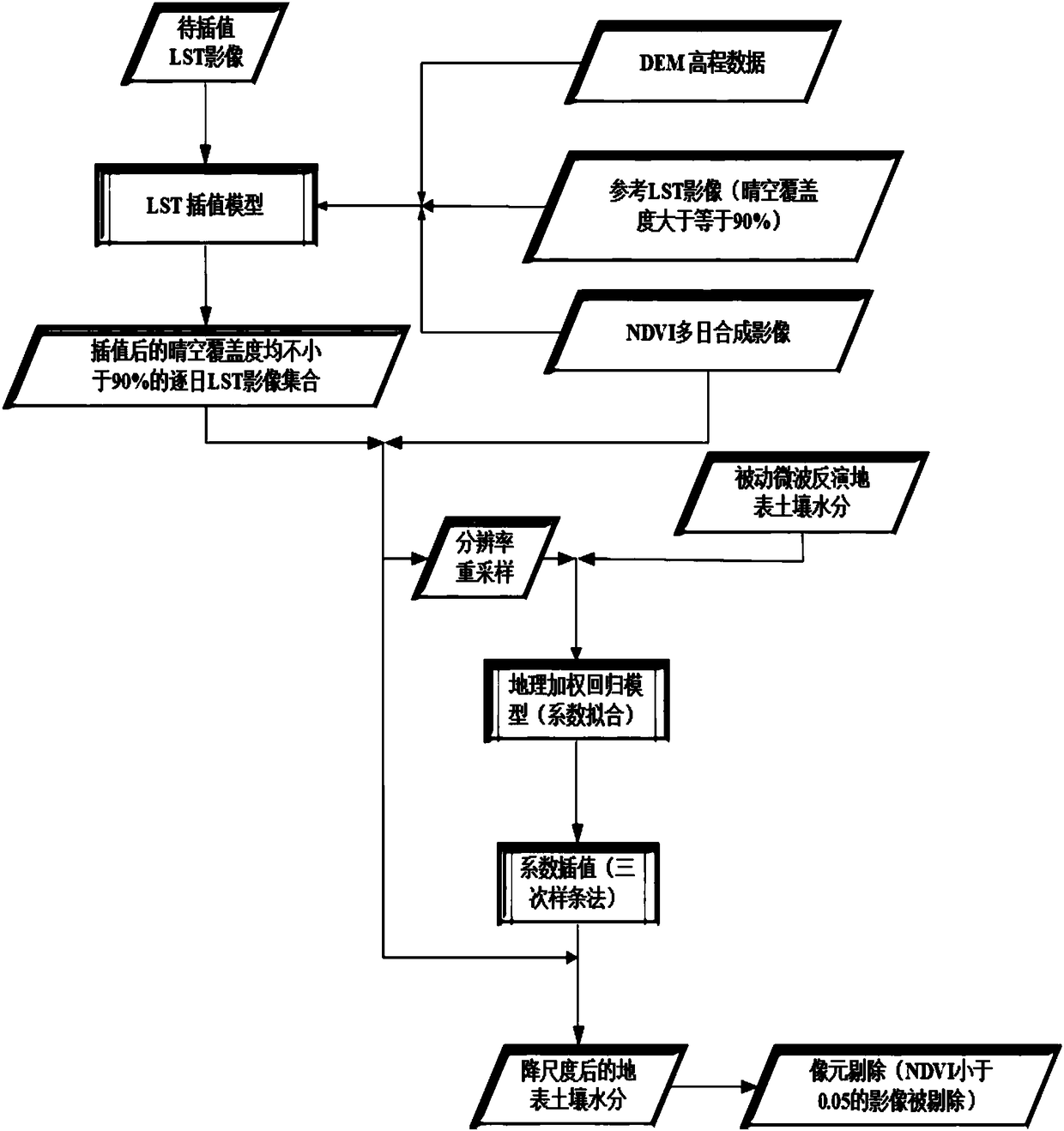
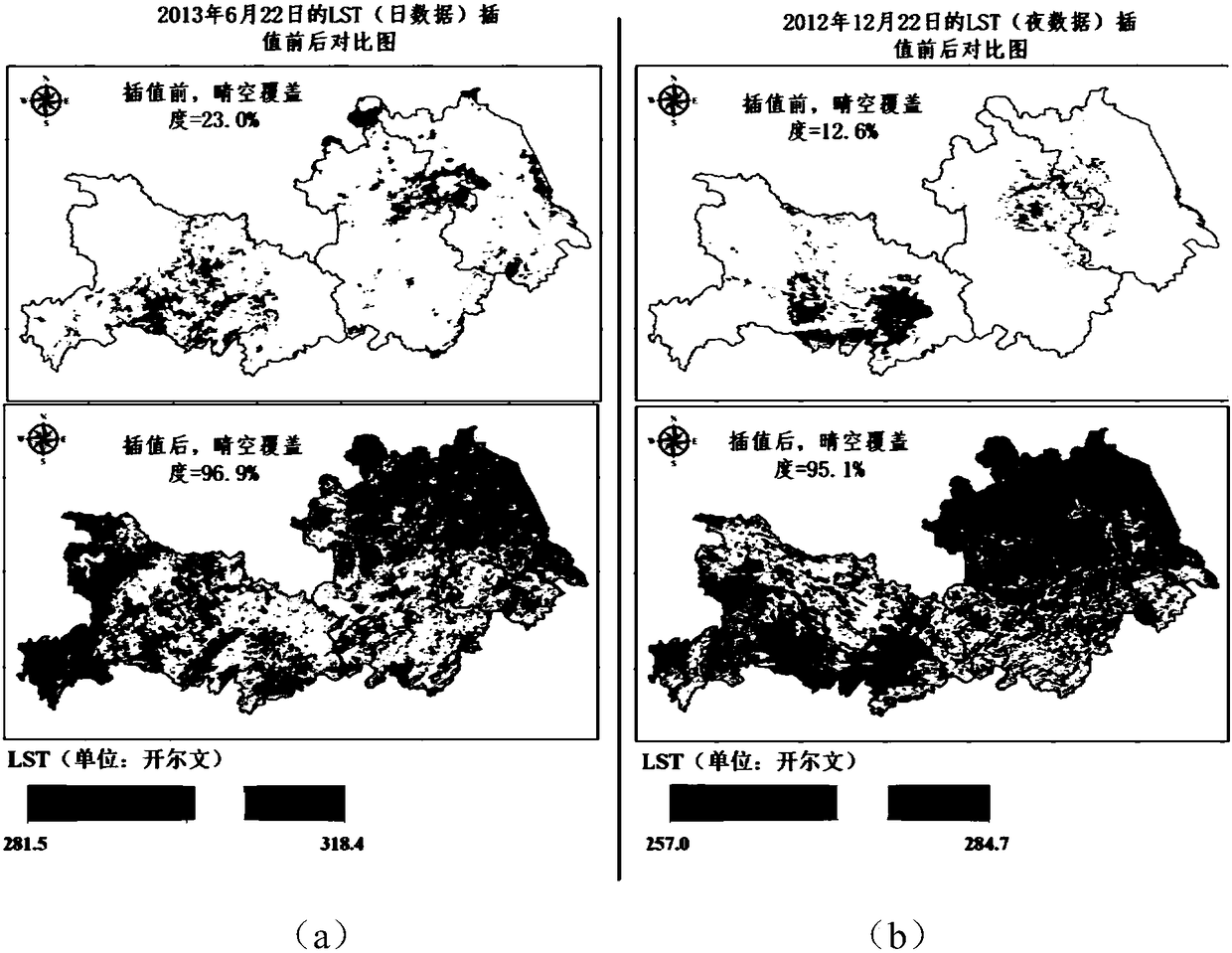
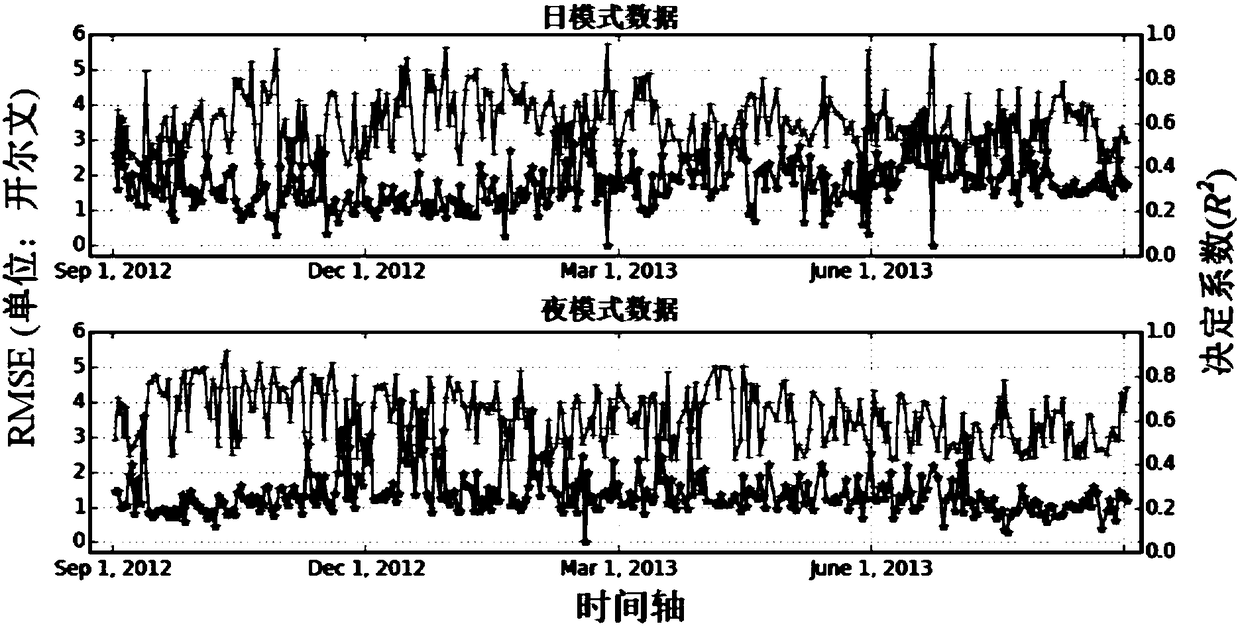
The invention discloses a land surface soil moisture downscaling method based on multisource remote sensing satellite merged data and is particularly applicable to cloudy and rainy areas. The method comprises the following steps: collecting and arranging a passive microwave soil moisture data set, an LST (land surface temperature) and NDVI (normalized difference vegetation index) data set and DEM(digital elevation model) data; performing spatial interpolation on LST images with serious pixel deletion affected by cloud and rain by adopting an NDVI and DEM data set as auxiliary data to obtain aday-by-day LST data set almost totally covering a research area; constructing a mathematic relation model for microwave soil moisture with optical remote sensing LST and NDVI by a geographical weighted regression model, and obtaining a land surface soil moisture data set with high spatial resolution with the mathematic relation model. Through the adoption of the method, reliability of a descalingresult and universality of descaling in the wide-range research area are improved effectively, and precision and efficiency of wide-range space mapping and monitoring for soil moisture content in thecloudy and rainy areas are improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
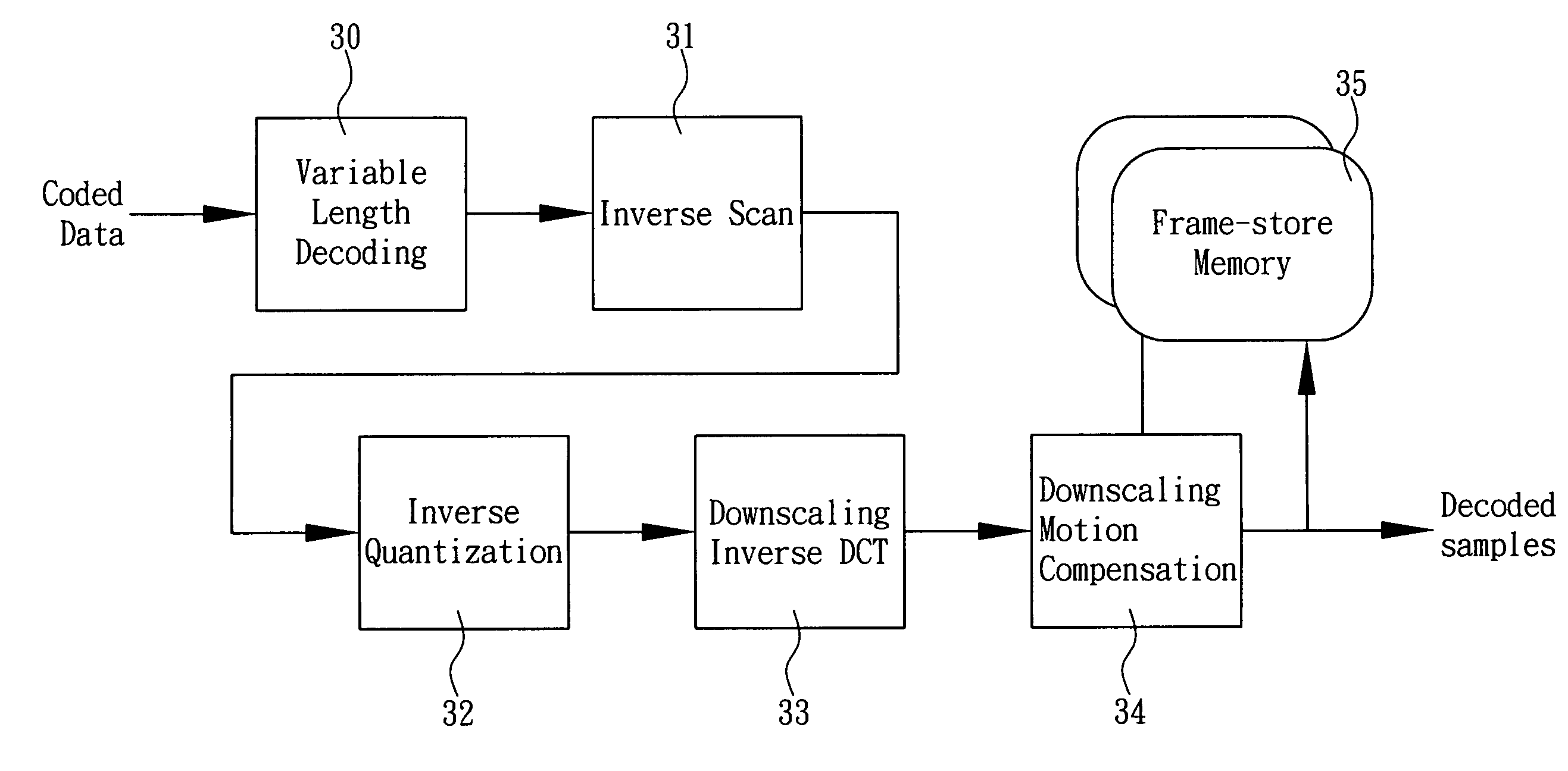
Low-complexity spatial downscaling video transcoder and method thereof
ActiveUS7180944B2Reduce calculationExtensive computationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImage resolutionMotion vector
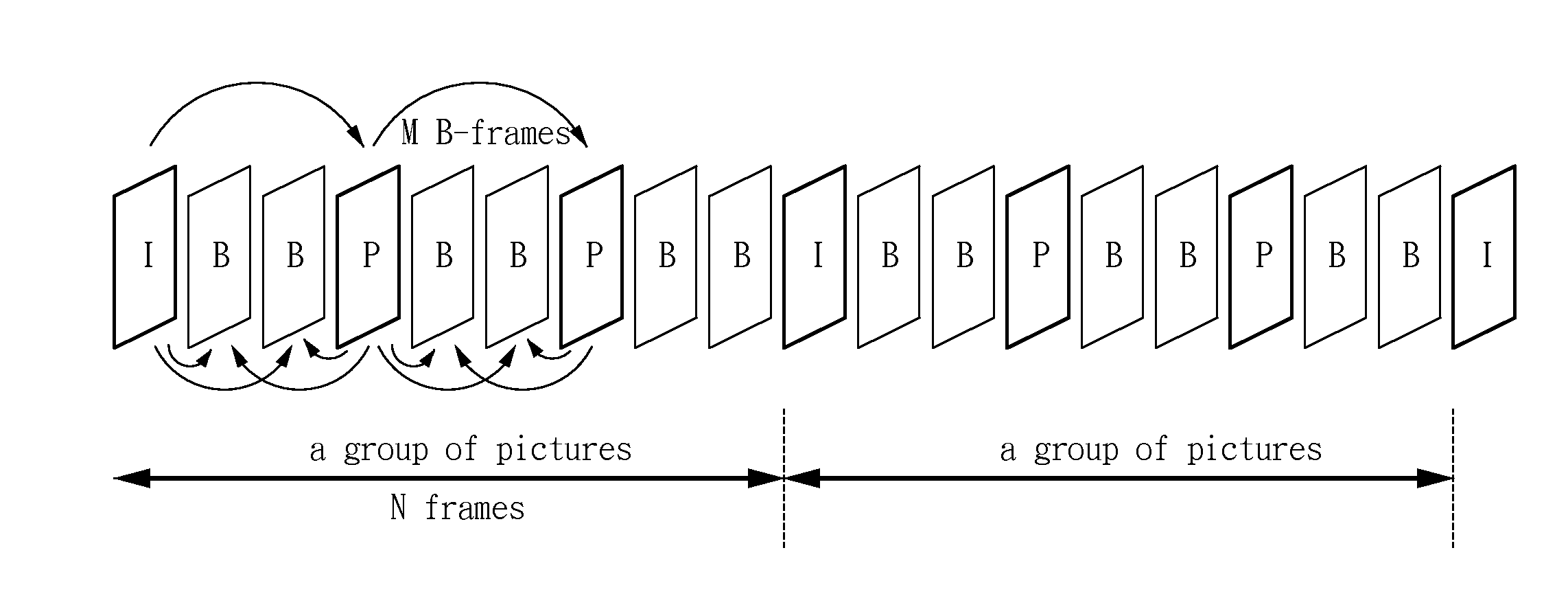
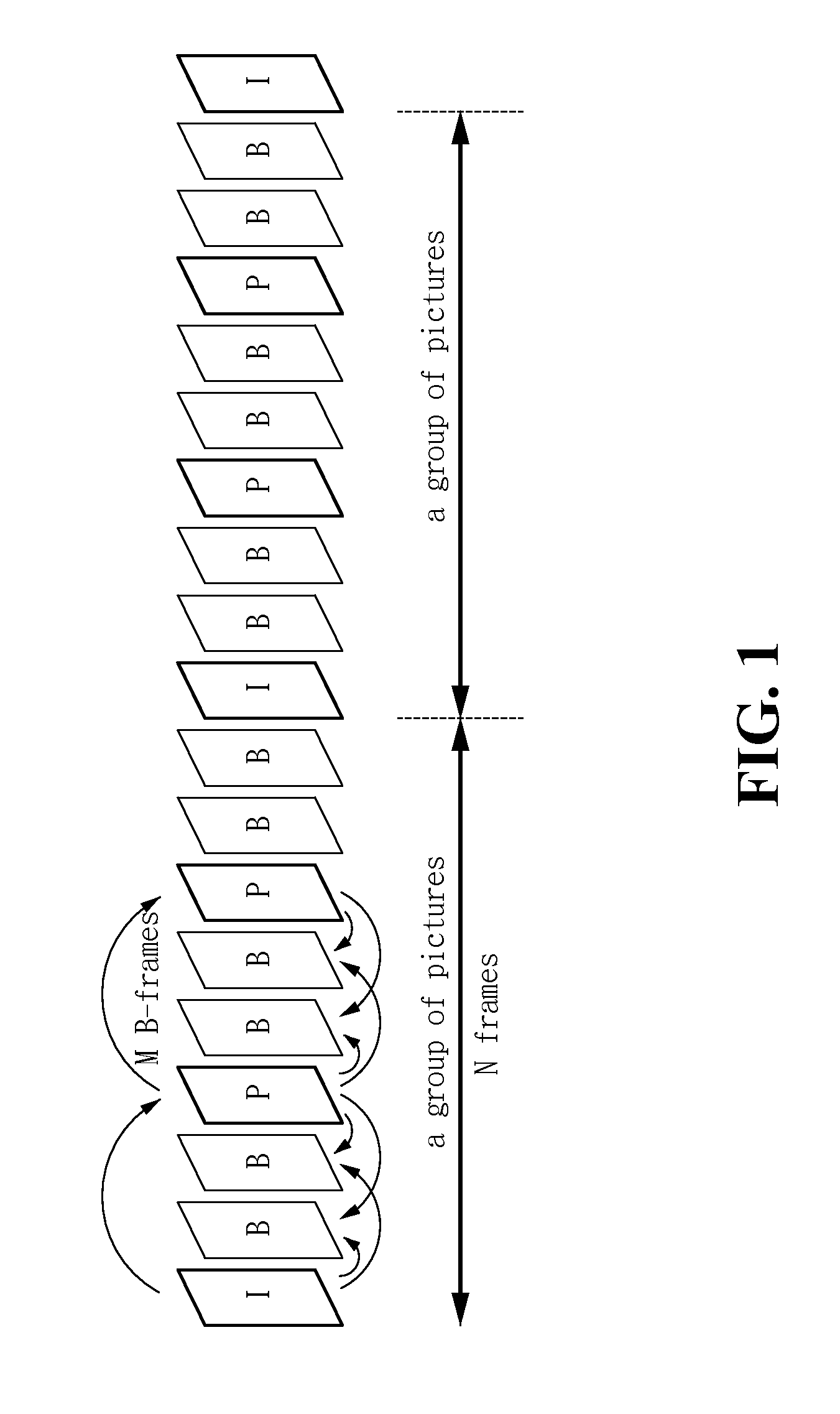
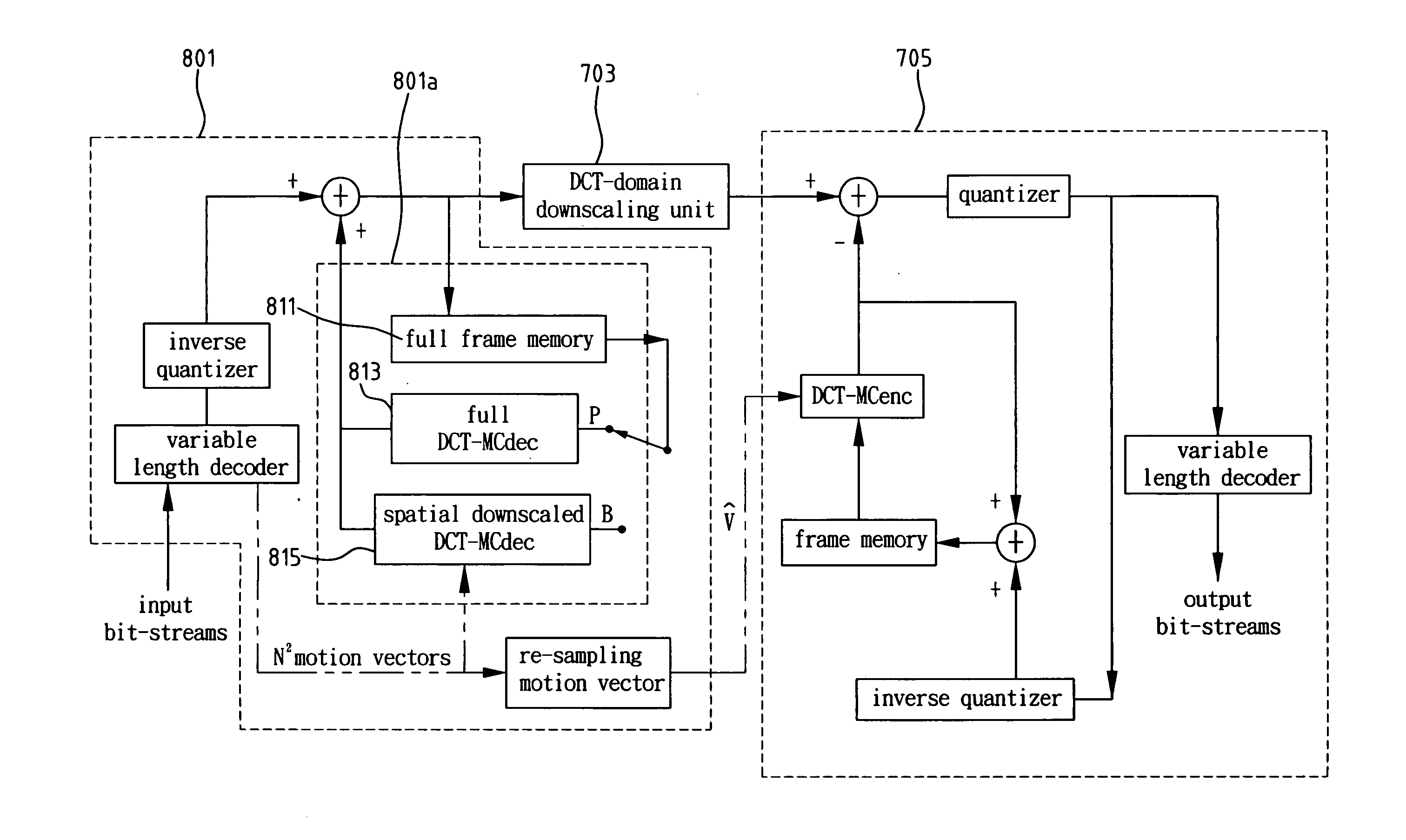
A low-complexity spatial downscaling video transcoder and method thereof are disclosed. The transcoder comprises a decoder having a reduced DCT-MC unit, a DCT-domain downscaling unit, and an encoder. The decoder performs the DCT-MC operation at a reduced-resolution for P- / B-frames in an MPEG coded bit-stream. The DCT-domain downscaling unit is used for spatial downscaling in the DCT-domain. After the downscaling and the motion vectors re-sampling, the encoder determines the encoding modes and outputs the encoded bit-stream. Compared with the original CDDT, this invention can achieve significant computation reduction and speeds up the transcoder without any quality degradation.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Wind speed forecasting method based on fine boundary layer mode for wind farm in complex terrain
ActiveCN102930177AGuaranteed impactAccurate calculationSpecial data processing applicationsICT adaptationTerrainPredictive methods
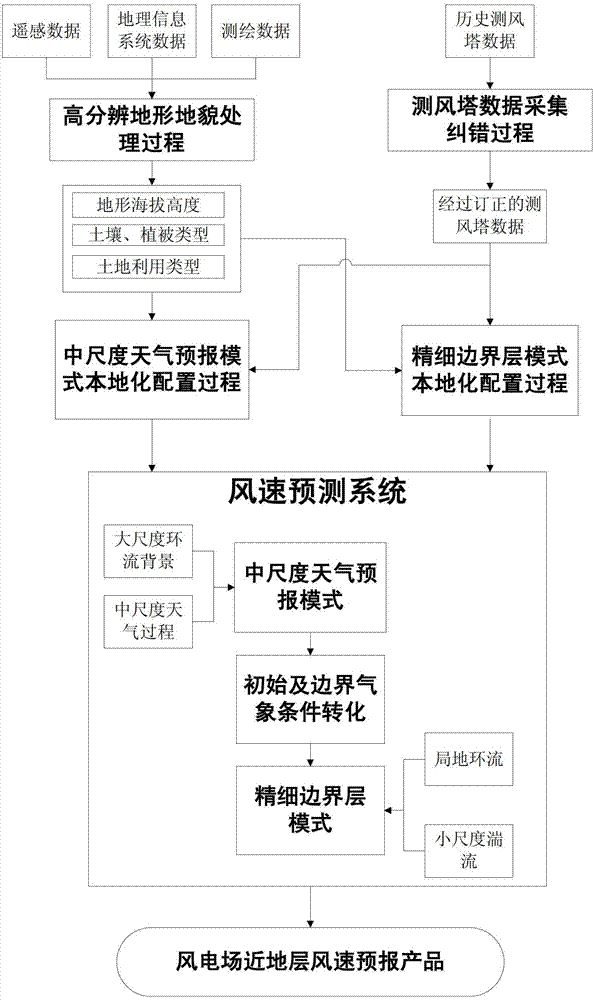
The invention discloses a wind speed forecasting method based on fine boundary layer figure mode for a wind farm in complex terrain. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring historical wind measuring tower data; converting acquired terrain data of a geological information system and the like into static data which can be directly called by a mesoscale weather forecast mode and the fine boundary layer figure mode; carrying out wind farm localization configuration for the mesoscale weather forecast mode and the fine boundary layer figure mode, so as to achieve optimal mode meteorological environment simulation; and taking the mesoscale weather forecast mode and the fine boundary layer figure mode as main body to build a wind farm wind speed forecasting system, and carrying out dynamically adjustable wind farm wind speed forecasting for areas 500 square kilometers around the wind farm for 3-7 days, wherein the horizontal grid resolution is 100m, and the time interval is 5-15 minutes. According to the invention, as the fine terrain data is introduced, and the fine boundary layer figure mode is adopted for100m-resolution dynamic downscaling forecasting. Therefore, the method is more suitable for wind farm wind speed forecasting under complex terrain conditions.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH +2
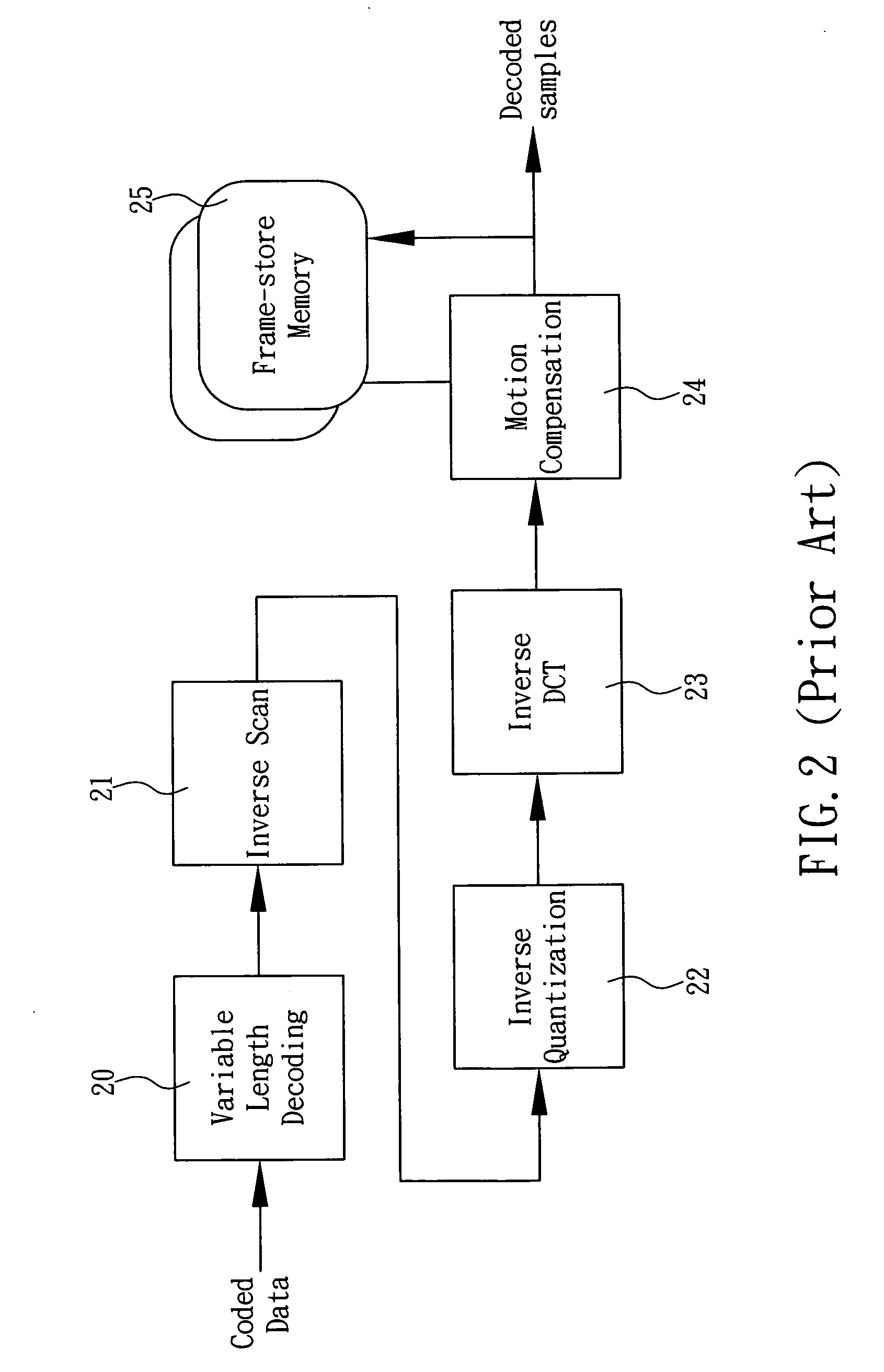
Method of downscale decoding MPEG-2 video
InactiveUS20100246676A1Reduce loadSimplify complexityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImage resolutionComputer graphics (images)
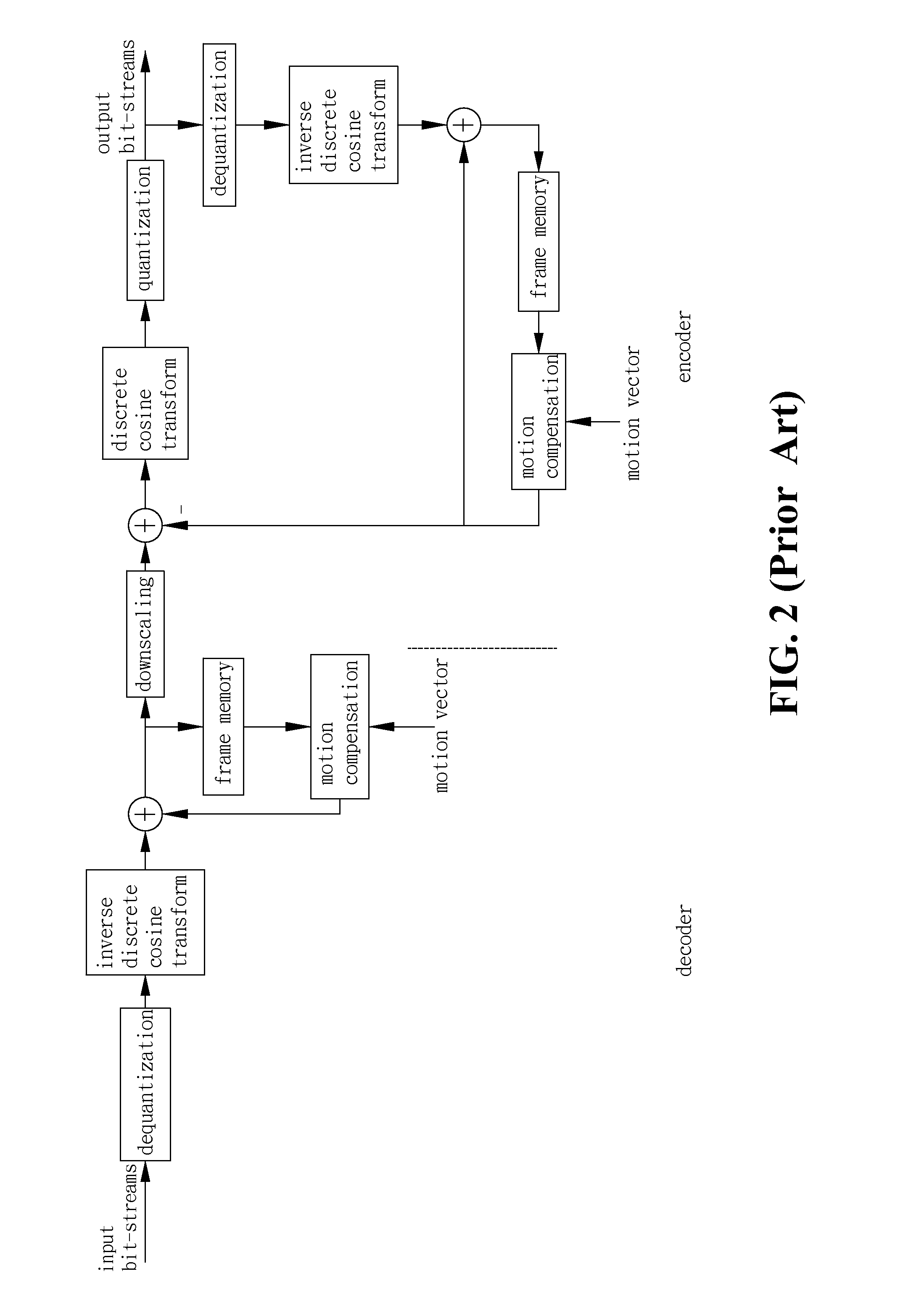
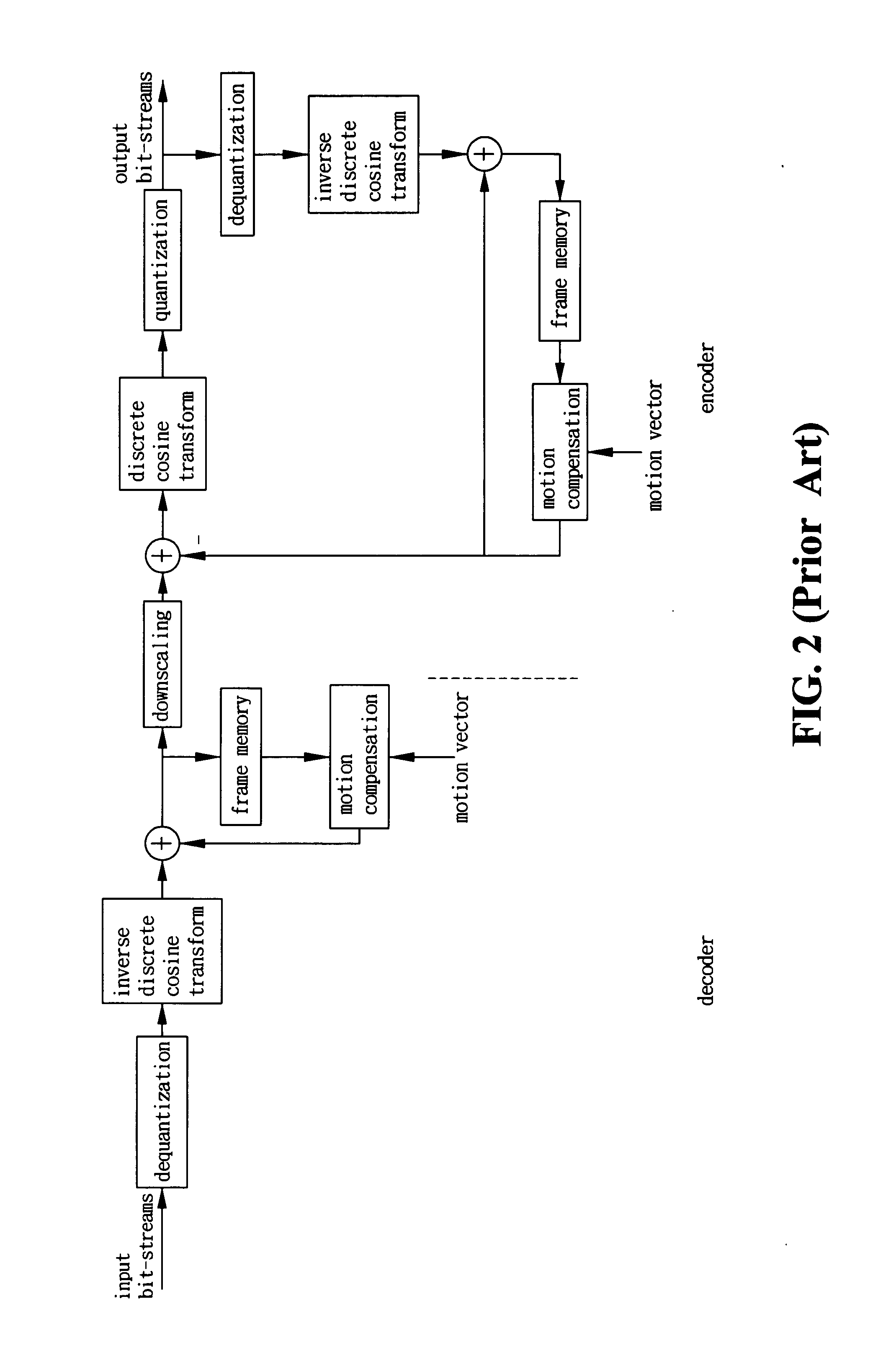
A method of downscale decoding MPEG-2 video includes an Inverse Discrete Cosine Transformation (DCT) procedure for performing a ½ horizontal downscaling to convert DCT coefficients in a 8×8 array block of the video into a 4×8 array intra-block and performing a ½ vertical downscaling to convert the intra-block into an intra-coded picture having ¼ resolution of the original; and a downscaling motion compensation procedure for performing a motion compensation to the current intra-block to obtain a predictive block having ½ horizontal size of the original, adding the predictive block with a residual block produced by the same method applied to the intra-blocks to obtain a 4×8 array inter-block, and performing a ½ vertical downscaling to the inter-block for outputting a predictive-coded picture and a bidirectional predictive-coded picture having ¼ resolution of the original, so as to simplify the complexity of the decoding computation and enhance the decoding speed.
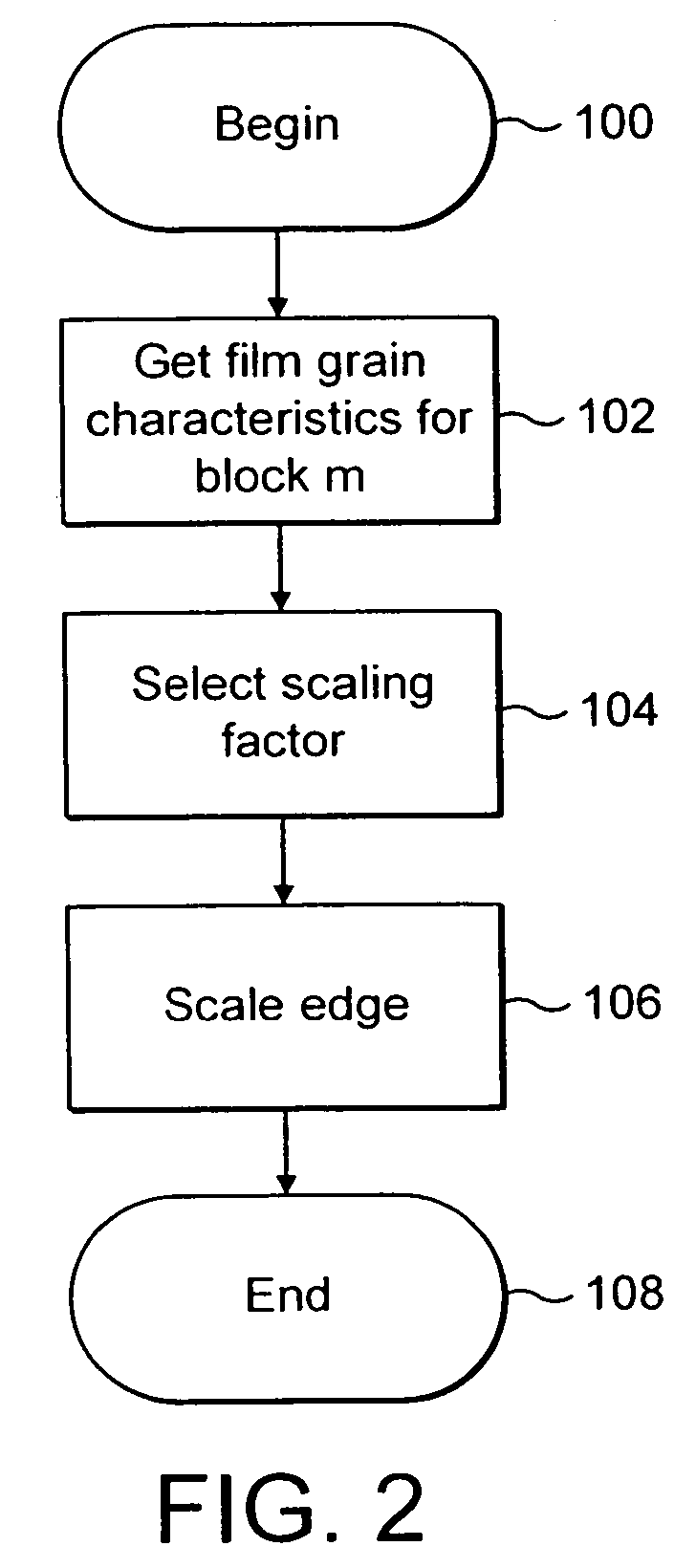
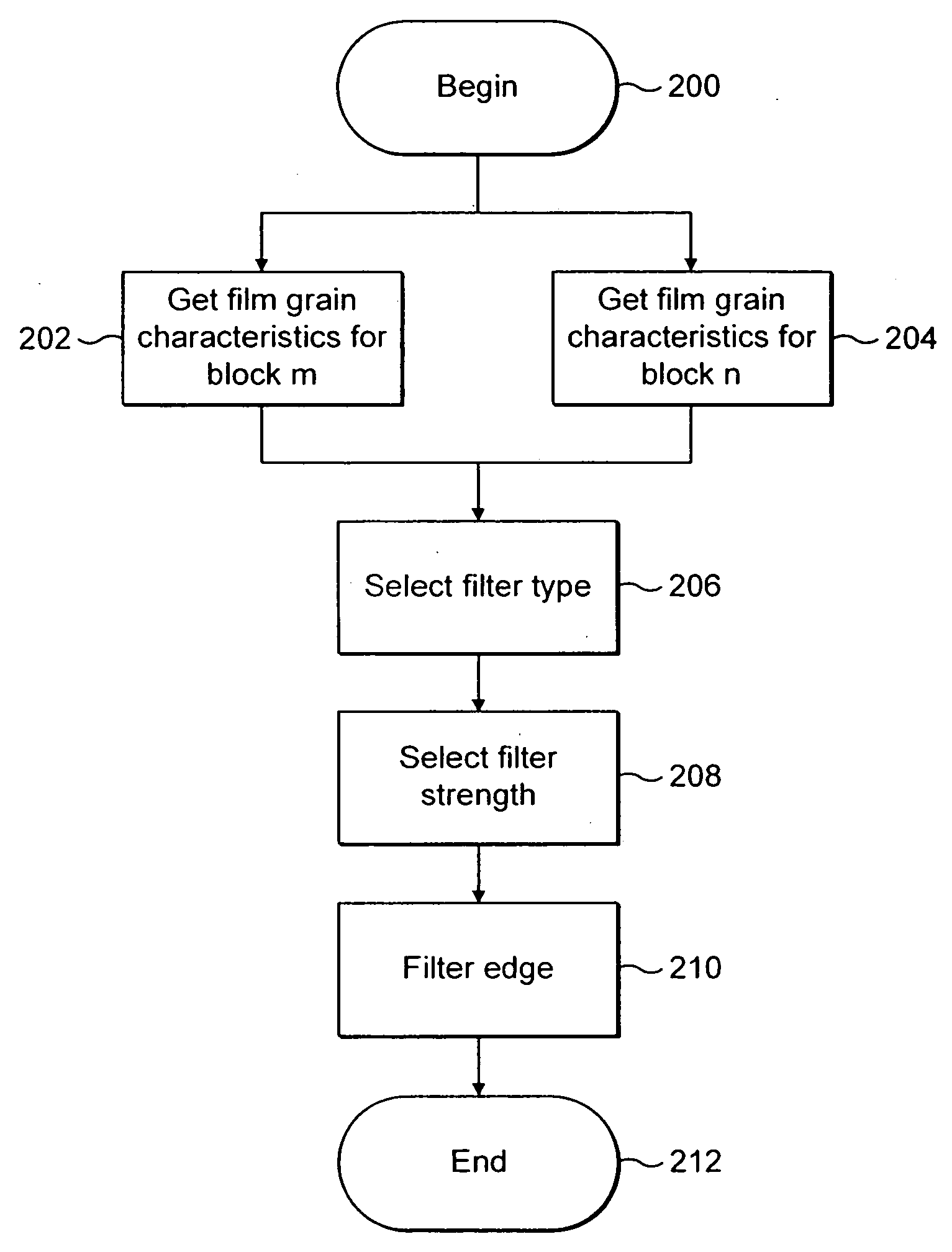
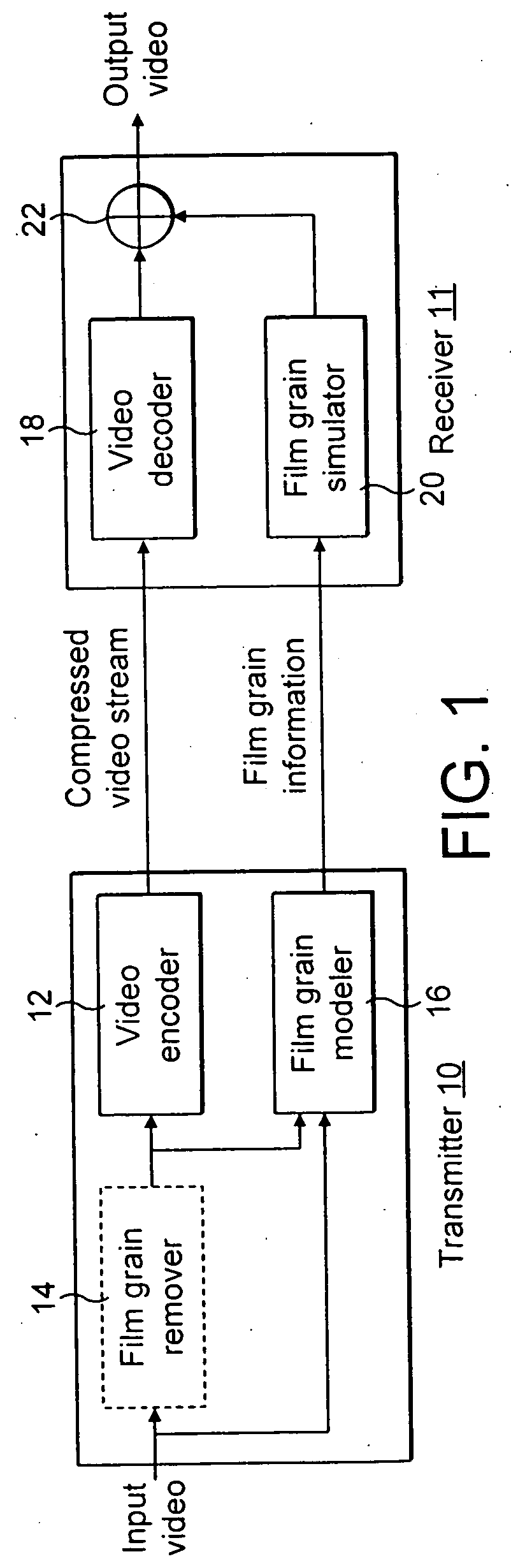
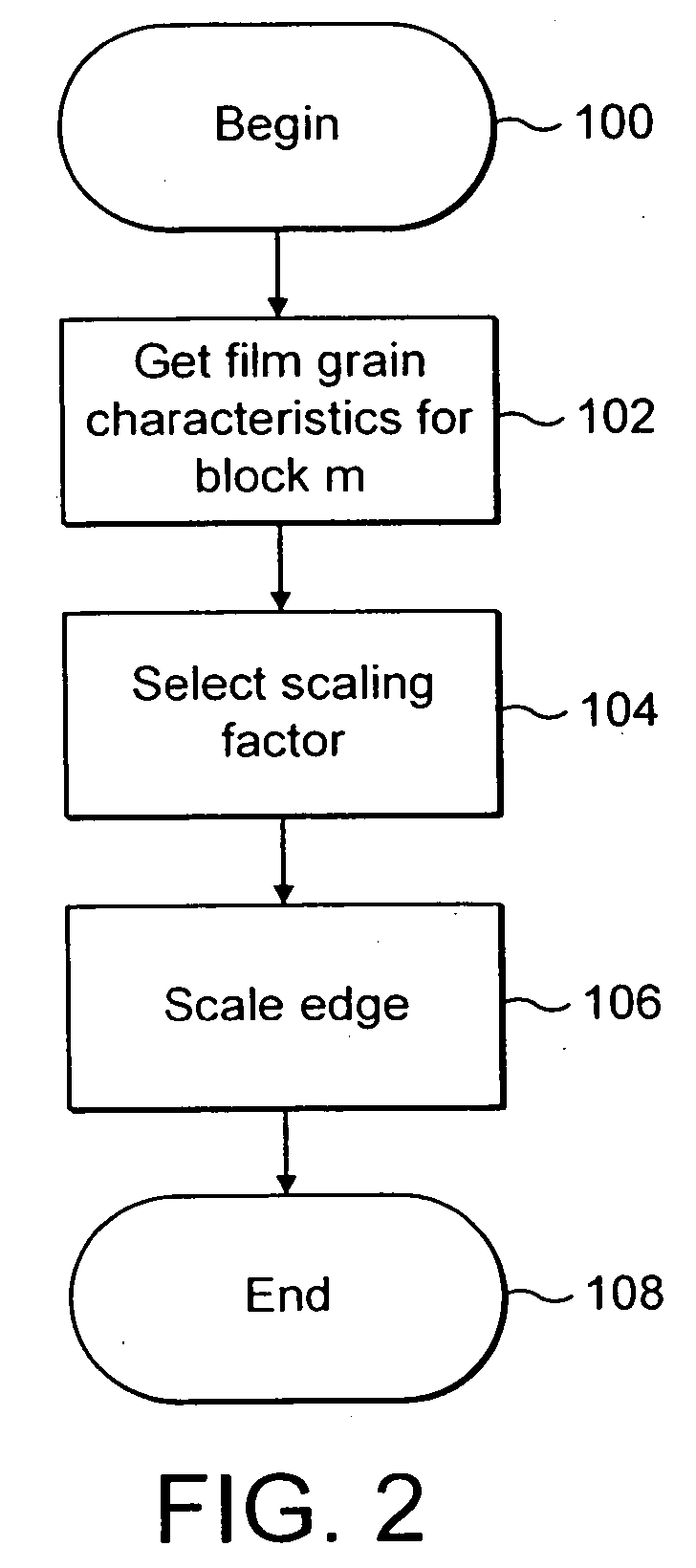
Technique for adaptive de-blocking of block-based film grain patterns
Reduction in the blockiness of a simulated film grain block can be achieved either by the use of adaptive downscaling or adaptive deblocking filtering to adjust the intensity of the pixels at the block edge in accordance with at least one film grain block parameter, such as film grain size, intensity and texture. Performing such adaptive downscaling or adaptive deblocking filtering achieves improved performance at lower computational cost by avoiding modification of film grain block pixels in lesser affected areas.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
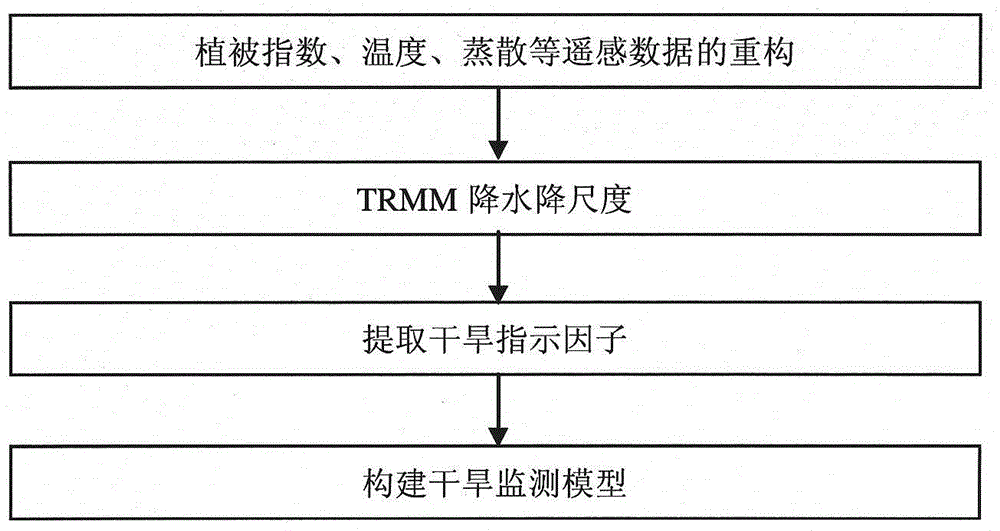
Data mining-based drought monitoring method
The invention discloses a data mining-based drought monitoring method. The method comprises the following steps: 1, data reconstruction is carried out on an MODIS vegetation index product, a land surface temperature product and an evapotranspiration product; 2, according to the vegetation index obtained in the first step and DEM data, downscaling is carried out on a TRMM rainfall product; 3, a vegetation anomaly index, a temperature anomaly index, an evapotranspiration anomaly index and a rainfall anomaly index are extracted again; and 4, a classification and regression tree model is used for building a statistical regression rule and a linear fitting model to obtain a drought monitoring model. Compared with the prior art, the method of the invention comprehensively considers multi-source remote sensing spatial information, such as the rainfall, the evapotranspiration, the vegetation growth state, the land using type, the altitude and other factors, in the case of drought monitoring, spatial data mining is adopted, the drought monitoring model is built, and the drought monitoring precision is improved.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
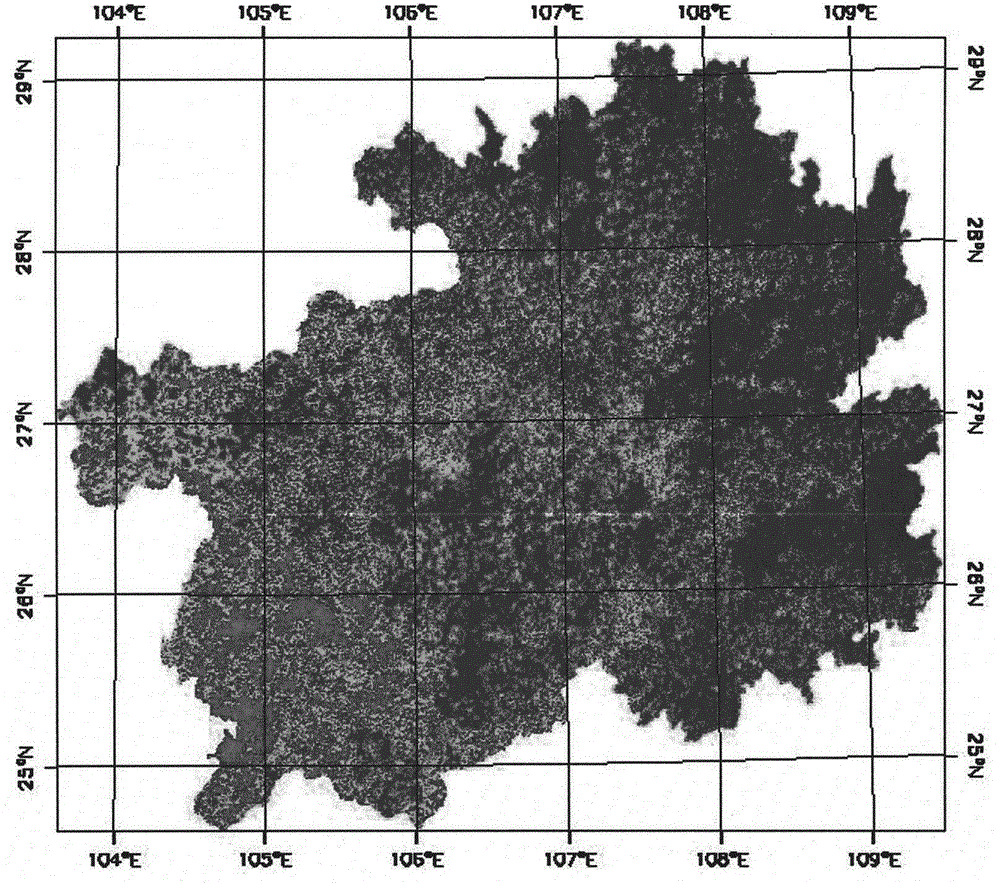
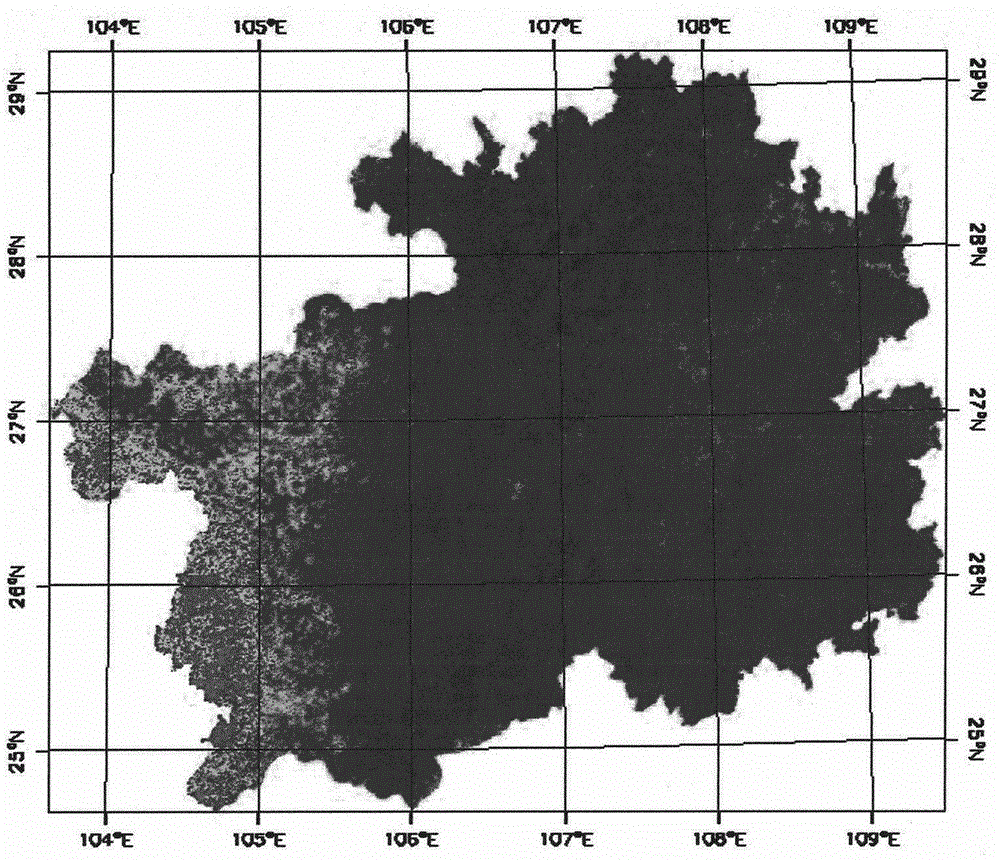
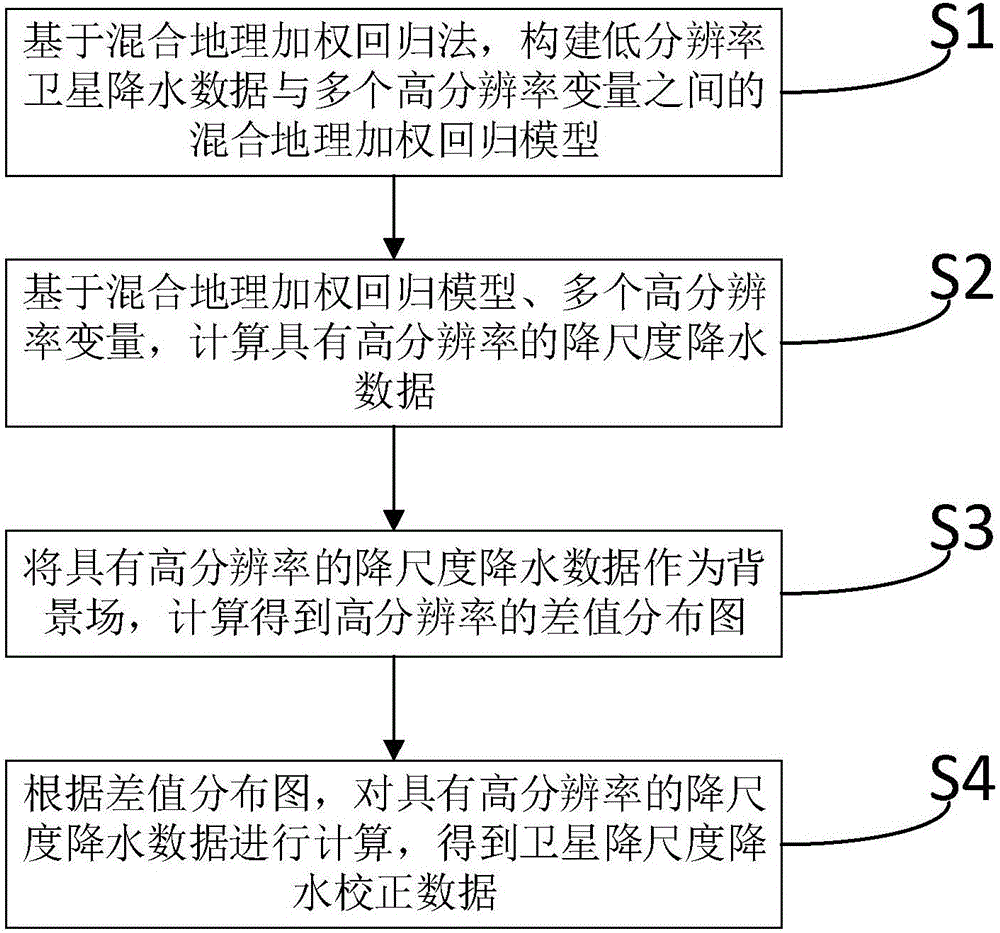
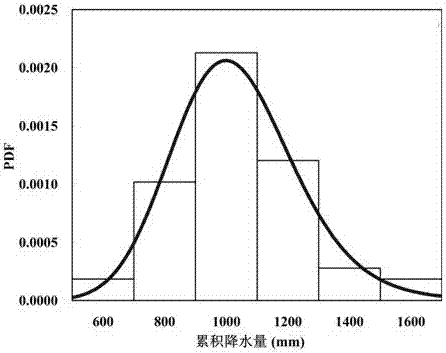
Downscaling compensation technique for satellite precipitation data
ActiveCN106776481AHigh resolutionHigh precisionComplex mathematical operationsSatellite precipitationImage resolution
The invention discloses a downscaling compensation technique for satellite precipitation data. Firstly, based on a mixed geographically weighted regression method, a mixed geographically weighted regression between low resolution satellite precipitation data and multiple high resolution variables is constructed. Secondly, based on the mixed geographically weighted regression and multiple high resolution variables, the downscaling precipitation data with high resolution is calculated. Thirdly, regarding the downscaling precipitation data with high resolution as an ambient field, a difference value distribution diagram with high resolution is acquired by calculating. Lastly, according to the difference value distribution diagram, the downscaling precipitation data with high resolution is calculated and the satellite downscaling precipitation compensation data is acquired. The downscaling compensation technique for satellite precipitation data is capable of obtaining high-precision satellite precipitation data with high resolution and being applied to the calculation of meteorological drought index and a driving hydrological model and providing high-precision input data for the hydrological model.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
TRMM (Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission) satellite rainfall data downscaling method based on M5-Local
ActiveCN105160192APrecise Rainfall ForecastImprove spatial resolutionWeather condition predictionSpecial data processing applicationsTerrainSatellite rainfall
The invention discloses a TRMM (Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission) satellite rainfall product downscaling method based on M5-Local and a multi-environmental factor variable. An M5-Local regression thought is adopted, and a plurality of environment stress factors with high spatial resolutions are fully utilized to improve the spatial resolution of the product. Firstly, 1km environmental variable factors, such as eight pieces of data including a vegetation index, a digital elevation model, a daytime surface temperature, a night surface temperature, a terrain moisture index, a gradient, a slope aspect and a slope length gradient, are subjected to aggregate calculating to obtain 25km which serves as an independent variable, corresponding 25km-resolution TRMM data is used as a dependent variable, an M5-Local method is adopted for modeling, the intercept of a regression modeling equation of 1km spatial resolution and a slope parameter corresponding to each environment factor variable are predicted, and a 1kmTRMM rainfall value is calculated. A downscaling result based on an M5-Local model is obviously superior to a downscaling result of a conventional regression model.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
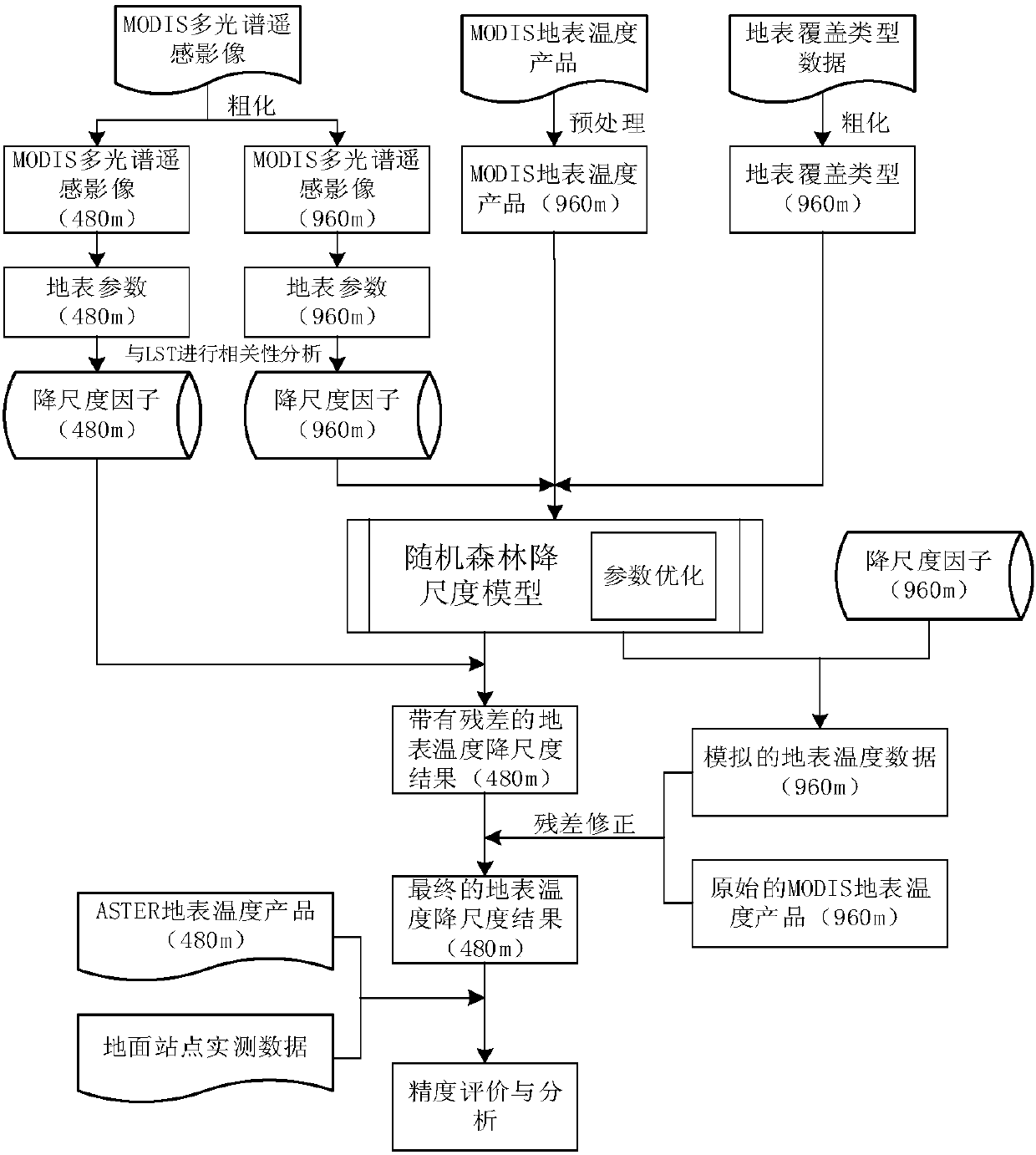
Random forest-based multifactor remote sensing surface temperature space downscaling method
ActiveCN107748736AReflect spatial changesImprove downscaling accuracyScene recognitionComplex mathematical operationsVegetationCoverage Type
The invention discloses a random forest-based multifactor remote sensing surface temperature space downscaling method. The method comprises the following steps of: inverting multiple surface parameters which can represent water body, vegetation, building and exposed soil according to surface coverage types, and selecting the surface parameters having relatively strong relevance with a surface temperature as scale factors through relevance analysis; aiming at the problem that high-temperature regions such as deserts and exposed soil are incorrect in temperature estimation, importing short infrared bands as scale factors so as to improve the downscaling precision of the high-temperature regions; and aiming at the unbalance problem of random data extraction of random forests, adopting a method of establishing different regression models under different surface coverage types to respectively carry out downscaling under the different surface coverage types, so as to obtain a high-resolutionsurface temperature image. The method has favorable applicability in a large scale or regions with complicated surface coverage, and is capable of effectively improving the downscaling precision andefficiency.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
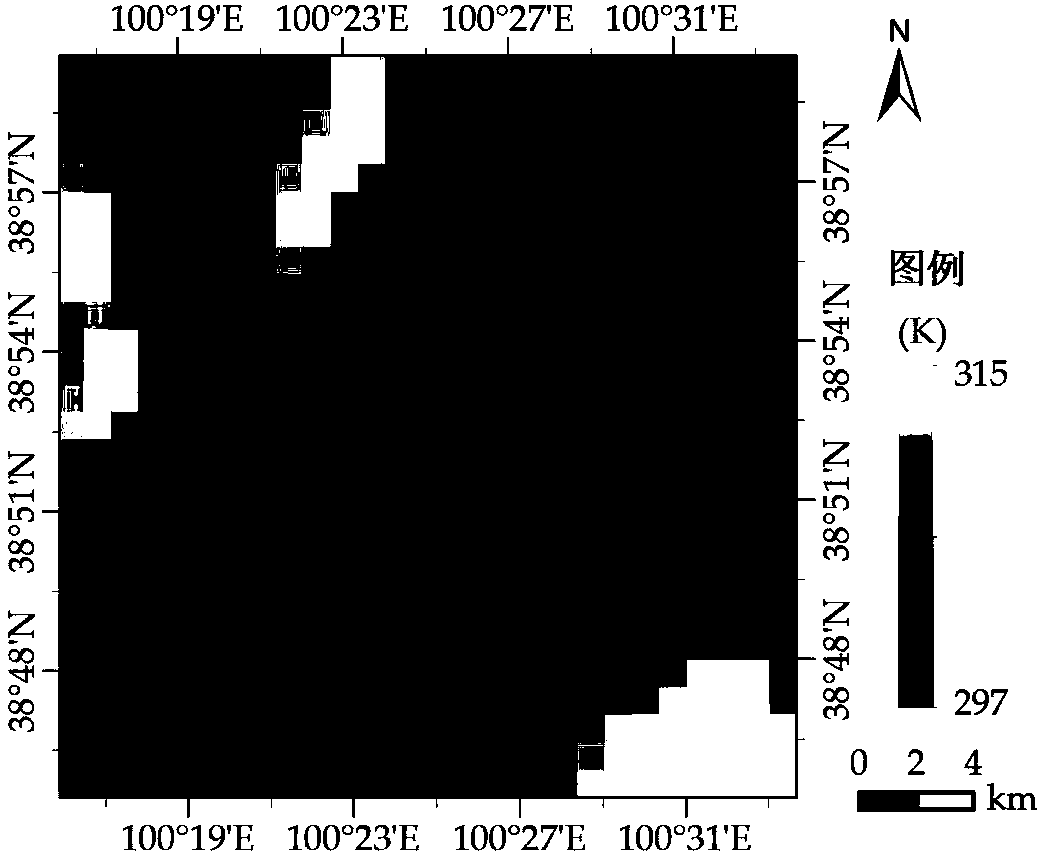
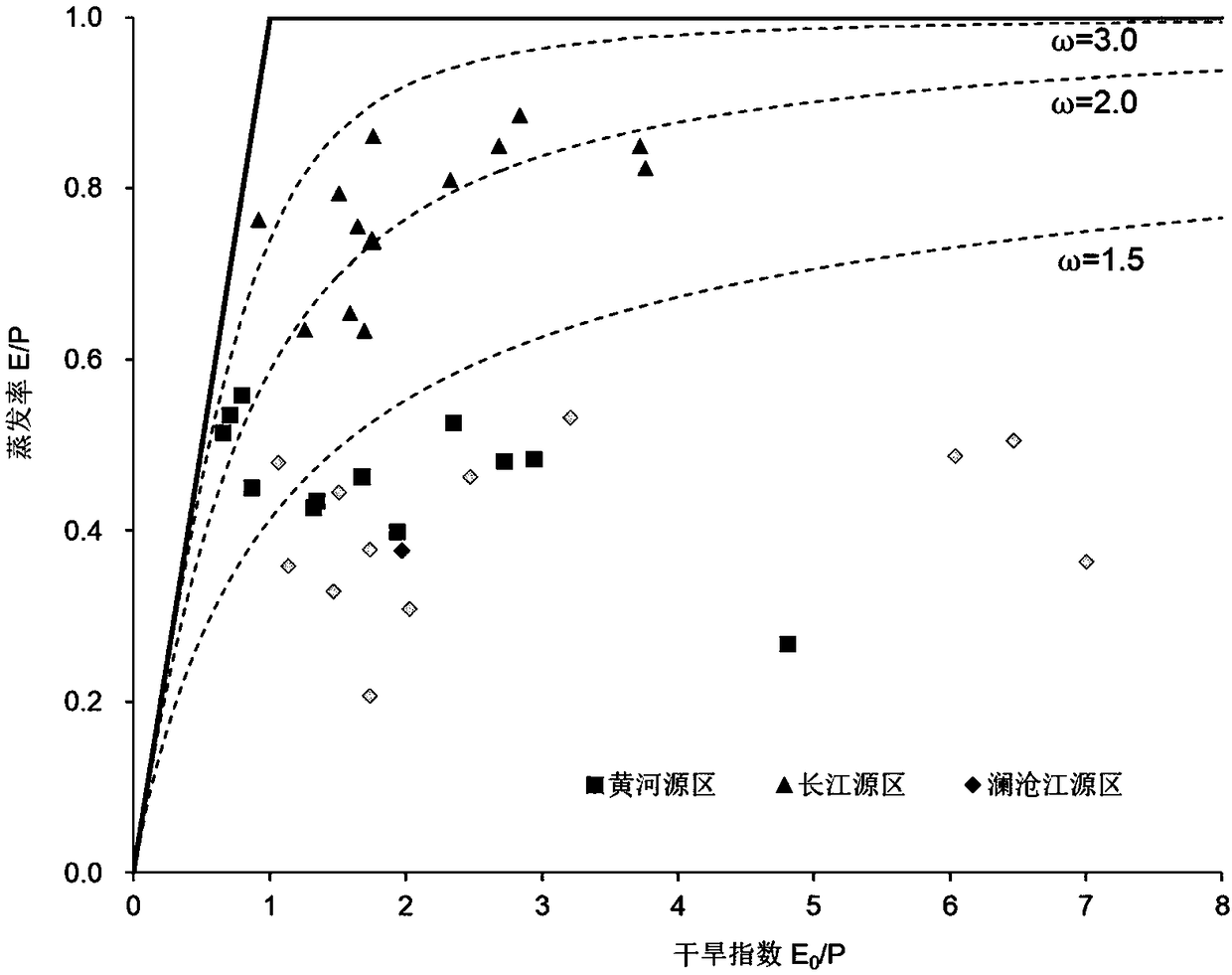
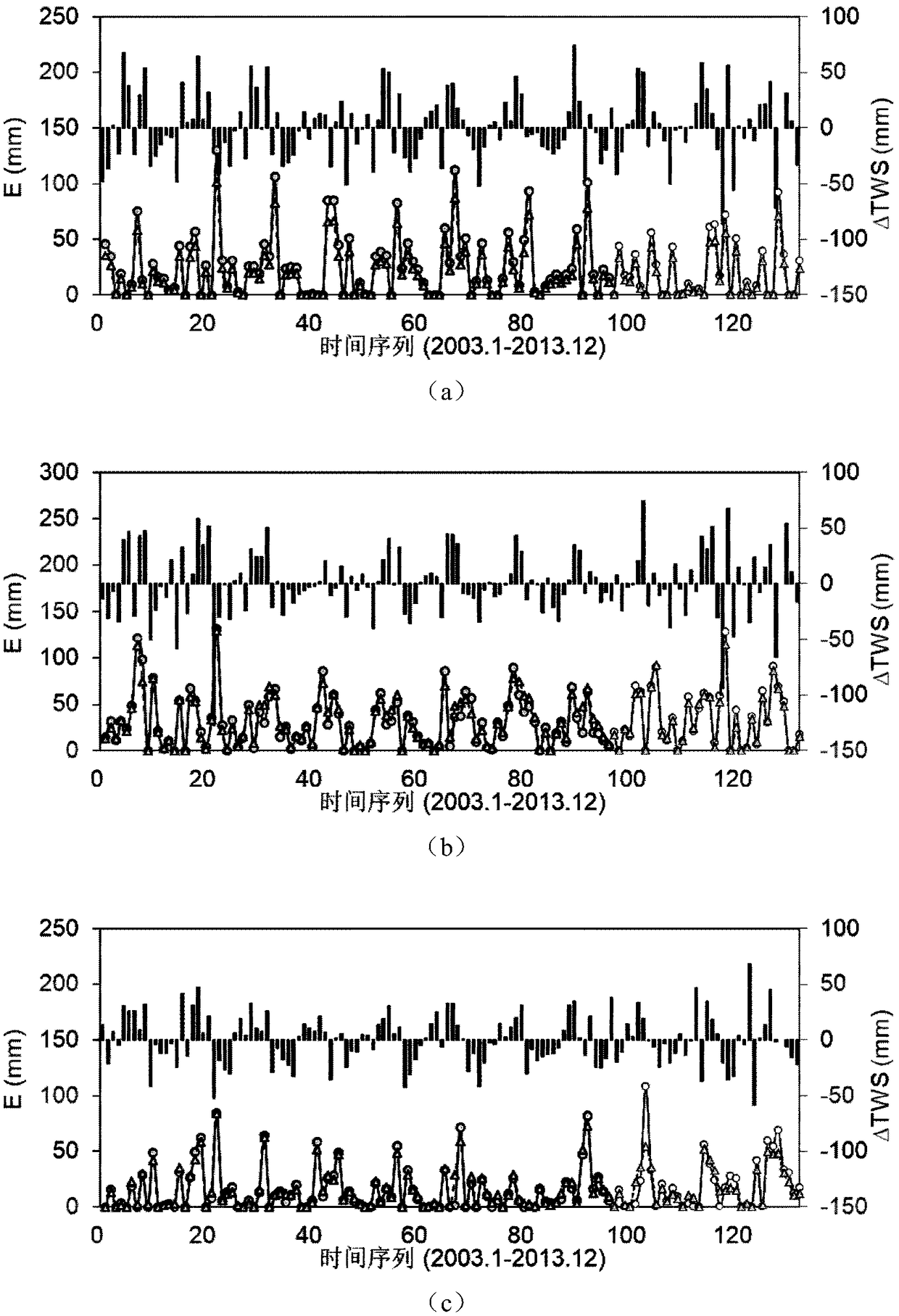
A quantitative estimation method of monthly evapotranspiration
ActiveCN109035105AImprove spatial resolutionMethod for Estimating Evapotranspiration in Enriched WatershedsData processing applicationsClimate change adaptationModel parametersDownscaling
The invention discloses a quantitative estimation method of monthly-scale evapotranspiration, which comprises the following steps: collecting hydrometeorological data in a river basin and adjusting all the data to monthly-scale; contructing the multivariate linear equation of land water storage change data, and performing spatial downscaling and filtering on the GRACE gravity satellite retrieved land water storage change data. The monthly series of actual evapotranspiration in each sub-watershed areobtained, and the trend of seasonal hydrological and climatic change and the characteristics ofspatial and temporal evolution in typical watershed are analyzed. The Budyko water-heat coupling equilibrium equation is optimized, and the quantitative estimation model of monthly actual evapotranspiration is established by using the change of land water reserves. The actual evapotranspiration parameters of monthly scale watershed are estimated quantitatively, and the monthly global evapotranspiration series are calculated according to the calibrated model parameters. The invention enriches the estimation method of river basin evapotranspiration, publishes the monthly value sequence of evapotranspiration with high spatial resolution, and provides scientific basis for scientific research and production work such as flood control and drought resistance.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Low-complexity spatial downscaling video transcoder and method thereof
ActiveUS20050169377A1Reduce calculationExtensive computationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionEncoder decoderImage resolution
A low-complexity spatial downscaling video transcoder and method thereof are disclosed. The transcoder comprises a decoder having a reduced DCT-MC unit, a DCT-domain downscaling unit, and an encoder. The decoder performs the DCT-MC operation at a reduced-resolution for P- / B-frames in an MPEG coded bit-stream. The DCT-domain downscaling unit is used for spatial downscaling in the DCT-domain. After the downscaling and the motion vectors re-sampling, the encoder determines the encoding modes and outputs the encoded bit-stream. Compared with the original CDDT, this invention can achieve significant computation reduction and speeds up the transcoder without any quality degradation.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Satellite precipitation data correction method based on multi-source information fusion and downscaling
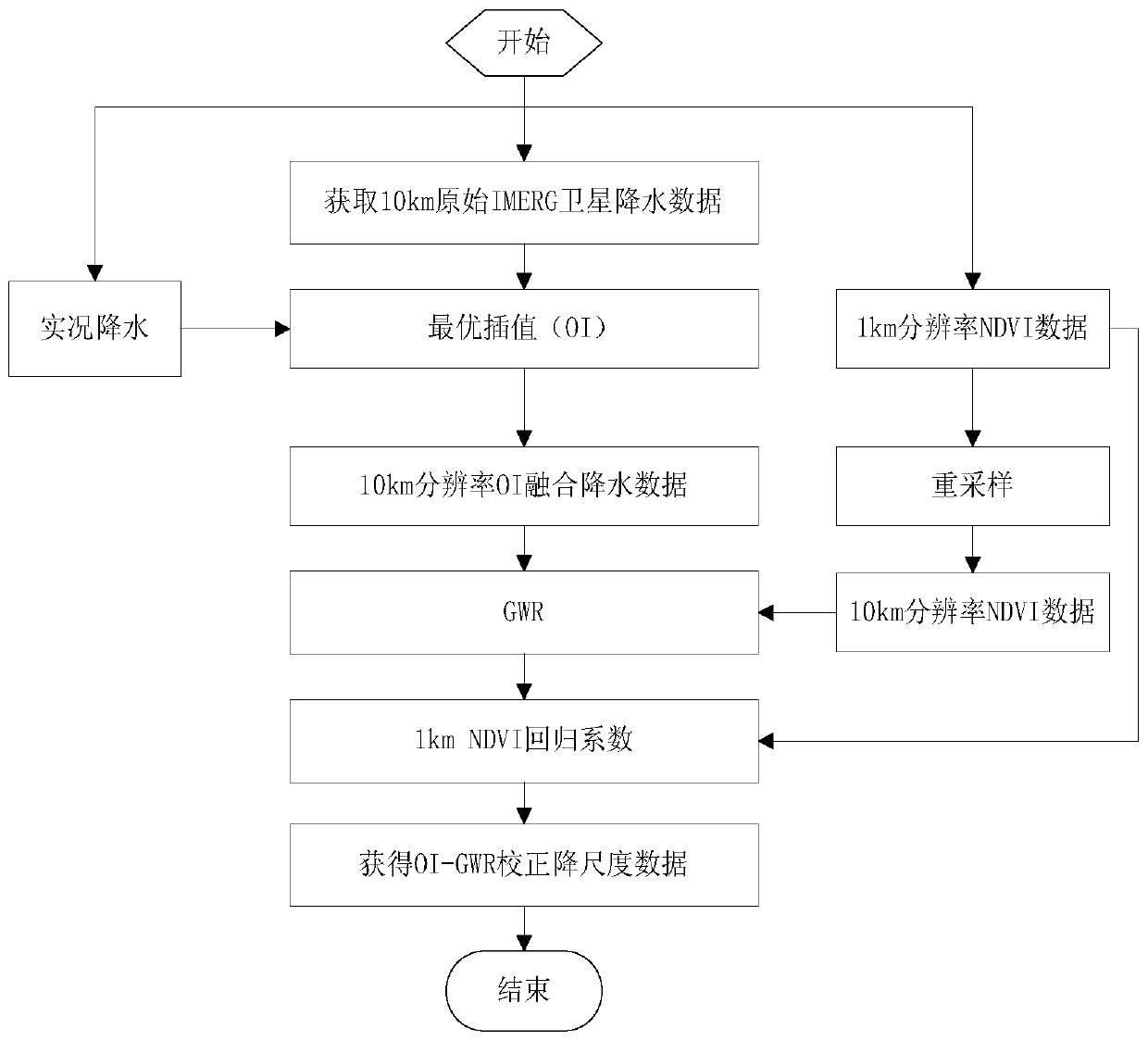
ActiveCN111078678AHigh precisionImprove spatial resolutionVisual data miningStructured data browsingSatellite precipitationAtmospheric sciences
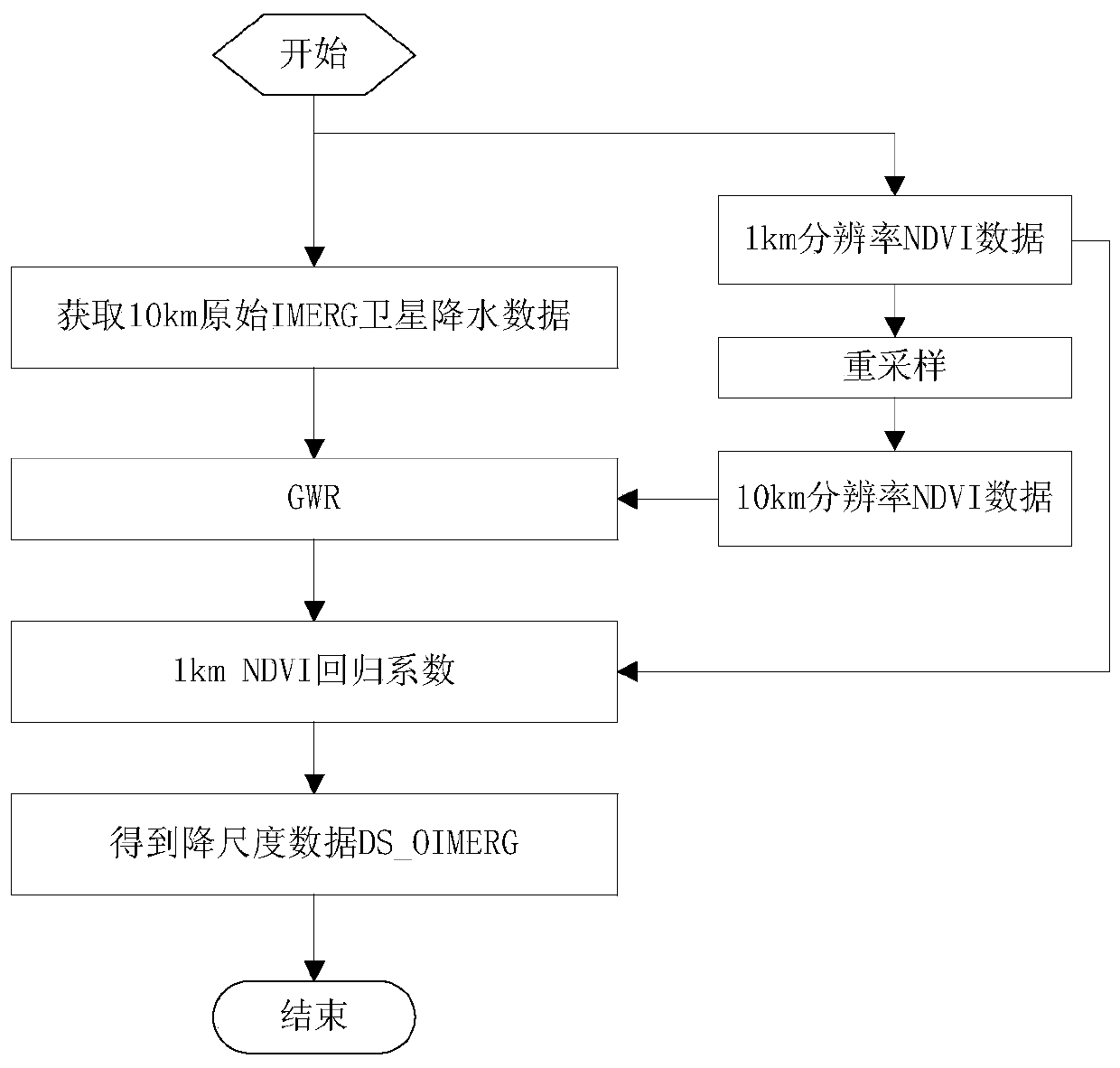
The invention discloses a satellite precipitation data correction method based on multi-source information fusion and downscaling. The method comprises the following steps: S1) acquiring live precipitation data and a satellite inversion precipitation product; S2) carrying out optimal interpolation according to the real-time rainfall data and a satellite inversion rainfall product; S3) obtaining low spatial resolution NDVI data; S4) selecting an environment variable and low spatial resolution NDVI data, and performing independent variable screening; S5) establishing a GWR downscaling model; S6)utilizing the GWR model to obtain OI-GWR corrected rainfall grid point data of the research area; and S7) checking the OI-GWR corrected precipitation grid point data of the research area by adopting10-fold cross validation. According to the method of the invention, optimal interpolation is introduced to improve the quality of original satellite precipitation data, and a better initial field is obtained; on the basis that an initial field is improved, a GWR method is used for downscaling, and the spatial resolution and precision of obtained downscaled data are improved.
Owner:INST OF DESERT METEOROLOGY CMA URUMQI
Regional meteorological drought level prediction method coupled with multi-source data
ActiveCN107316095ATo overcome the deficiency of autocorrelation propertyFitting dynamic evolution featuresClimate change adaptationForecastingDownscalingComputer science
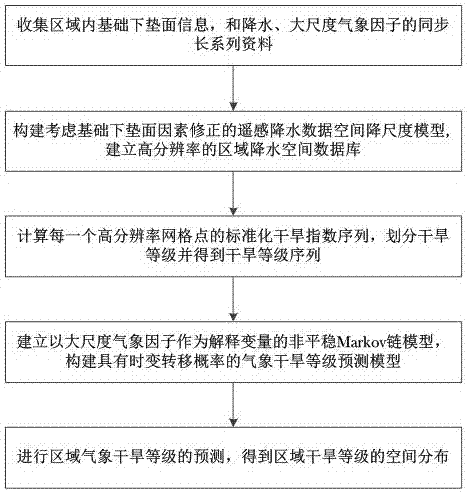
The present invention discloses a regional meteorological drought level prediction method coupled with multi-source data. The method is characterized in that: by space downscaling of the remote sensing precipitation data of the gridded satellite, a high-resolution regional precipitation space database is constructed, the drought levels are divided by using a standardized drought index, and based on the non-stationary Markov chain model, a meteorological drought level prediction model with time-varying transition probability is constructed. According to the method disclosed by the present invention, multi-source remote sensing information and basic underlying surface features are used to capture the spatial variability of regional precipitation, the lack of precipitation observed in traditional sites is made up for, the external coercion and precursor signals of the evolution of drought and flood of large-scale meteorological factors that can reflect the characteristics of atmospheric circulation are made full use of, and the mechanism of formation and development of drought and flood is taken into account to a certain extent, so that the dynamic evolution characteristics of meteorological and hydrological systems are more in line with, highly scientific and practicability are ensured, and a foundation can be laid for the establishment of a drought and flood warning system.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
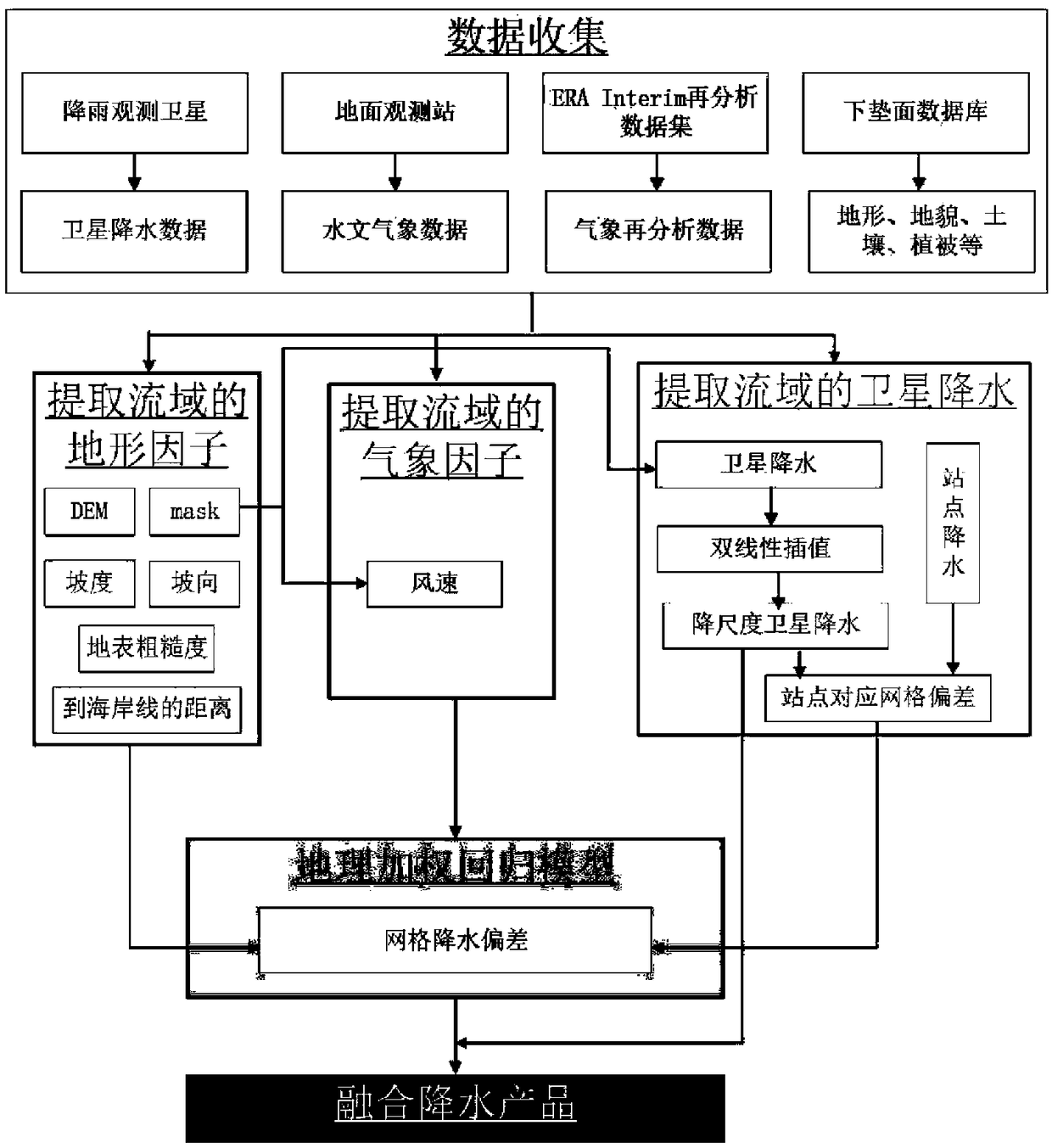
Method of using high-resolution terrain and meteorology factors for multi-source precipitation fusion
InactiveCN108647740AHigh spatio-temporal resolutionAchieve conversionCharacter and pattern recognitionTerrainSatellite precipitation
The invention discloses a method of using high-resolution terrain and meteorology factors for multi-source precipitation fusion. The method comprises the steps of: extracting DEM grid data of a targetwatershed, and obtaining a mask file of the watershed; calculating a slope, an aspect, surface roughness and a to-shoreline distance of the target watershed by the DEM grid data of the target watershed; extracting wind speed data of the watershed according to the mask file; using the mask file to extract satellite precipitation data of the watershed; carrying out downscaling on original satelliteprecipitation to obtain satellite precipitation of Rkm; calculating deviation of satellite precipitation after downscaling and actually measured site precipitation; using a geographically weighted regression model to calculate precipitation deviation of Rkm grids; and obtaining an Rkm fusion precipitation product. According to the method, site data and the satellite precipitation product are fused, downscaling is carried out on the satellite precipitation, the high-time / space-resolution precipitation product is obtained, conversion of precipitation data from points to a surface can be realized, and data support is provided for an input of a refined hydrological model.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
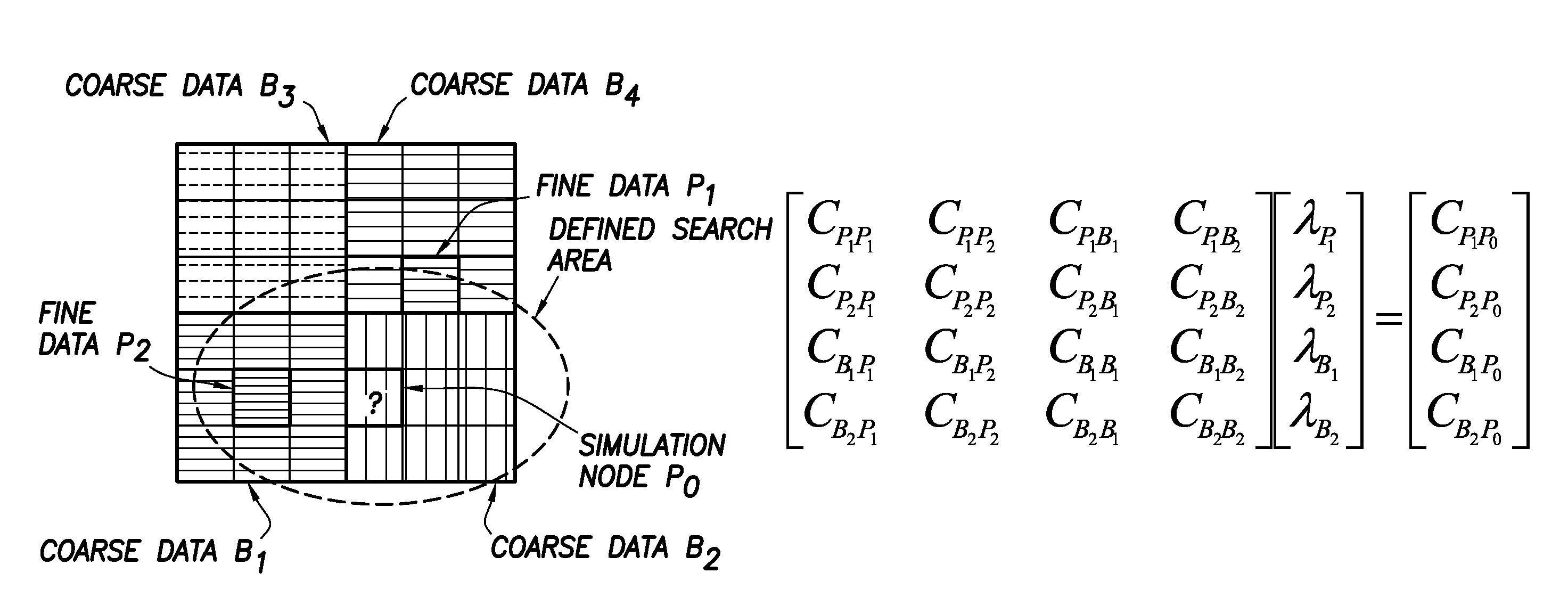
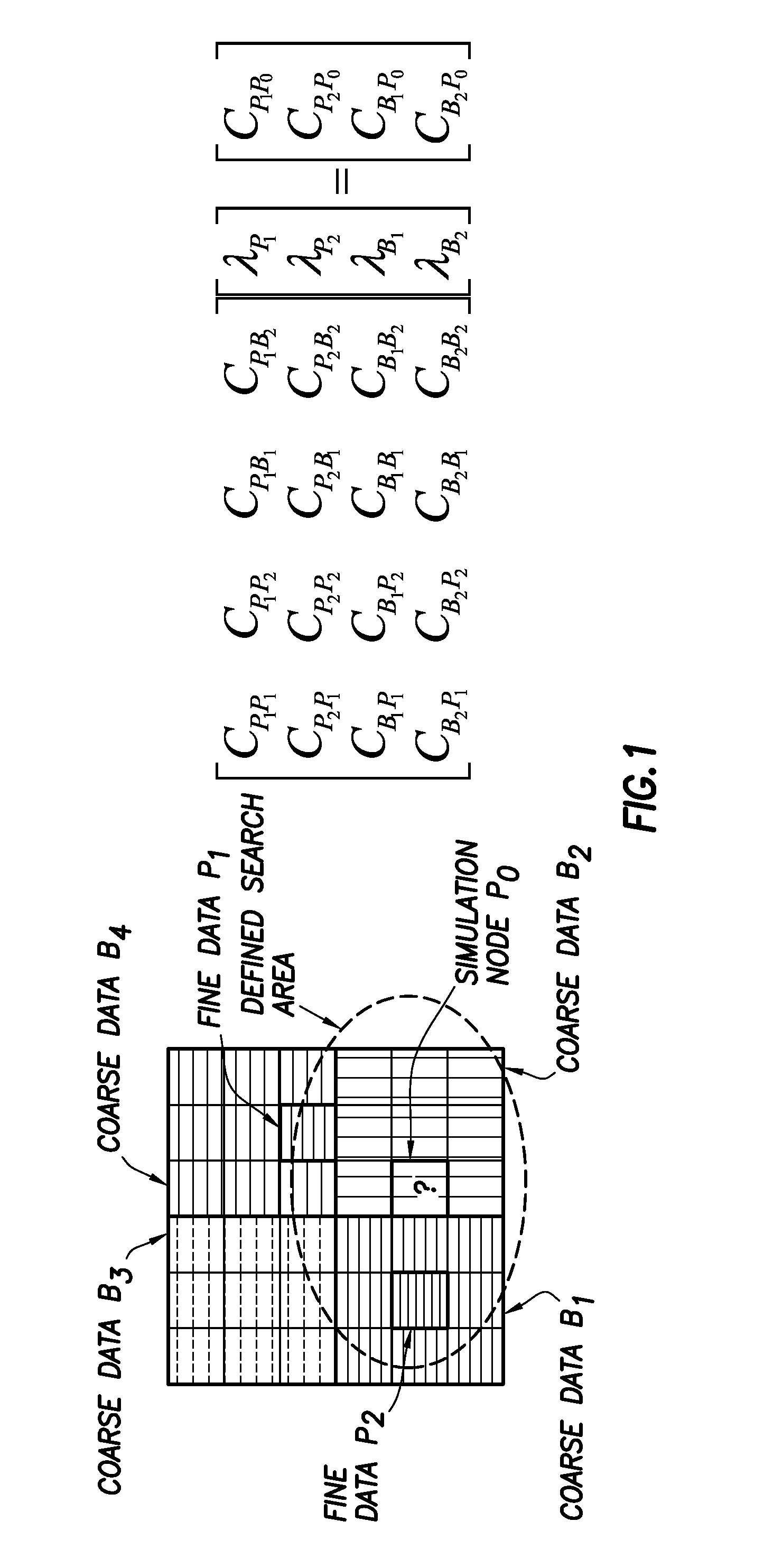
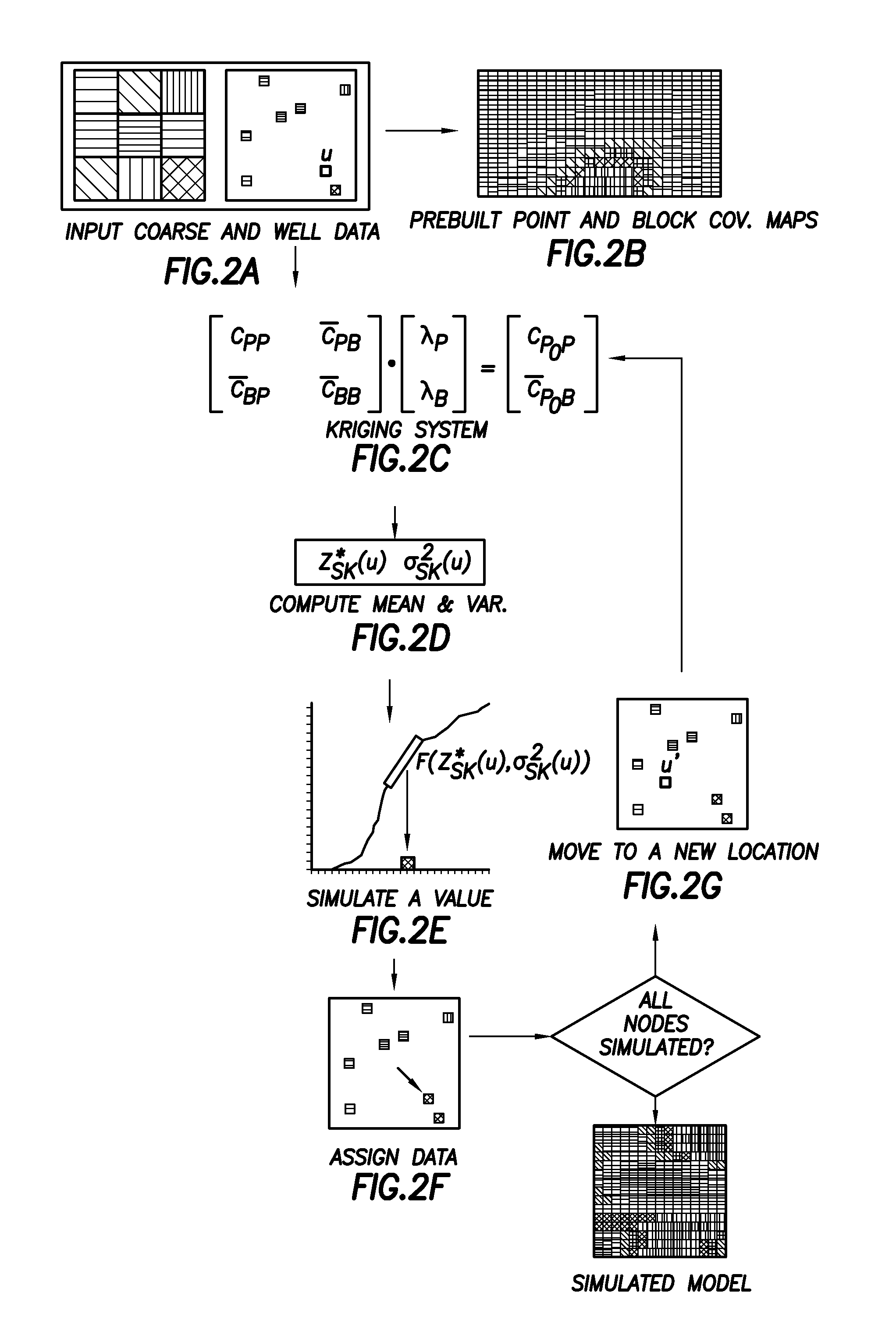
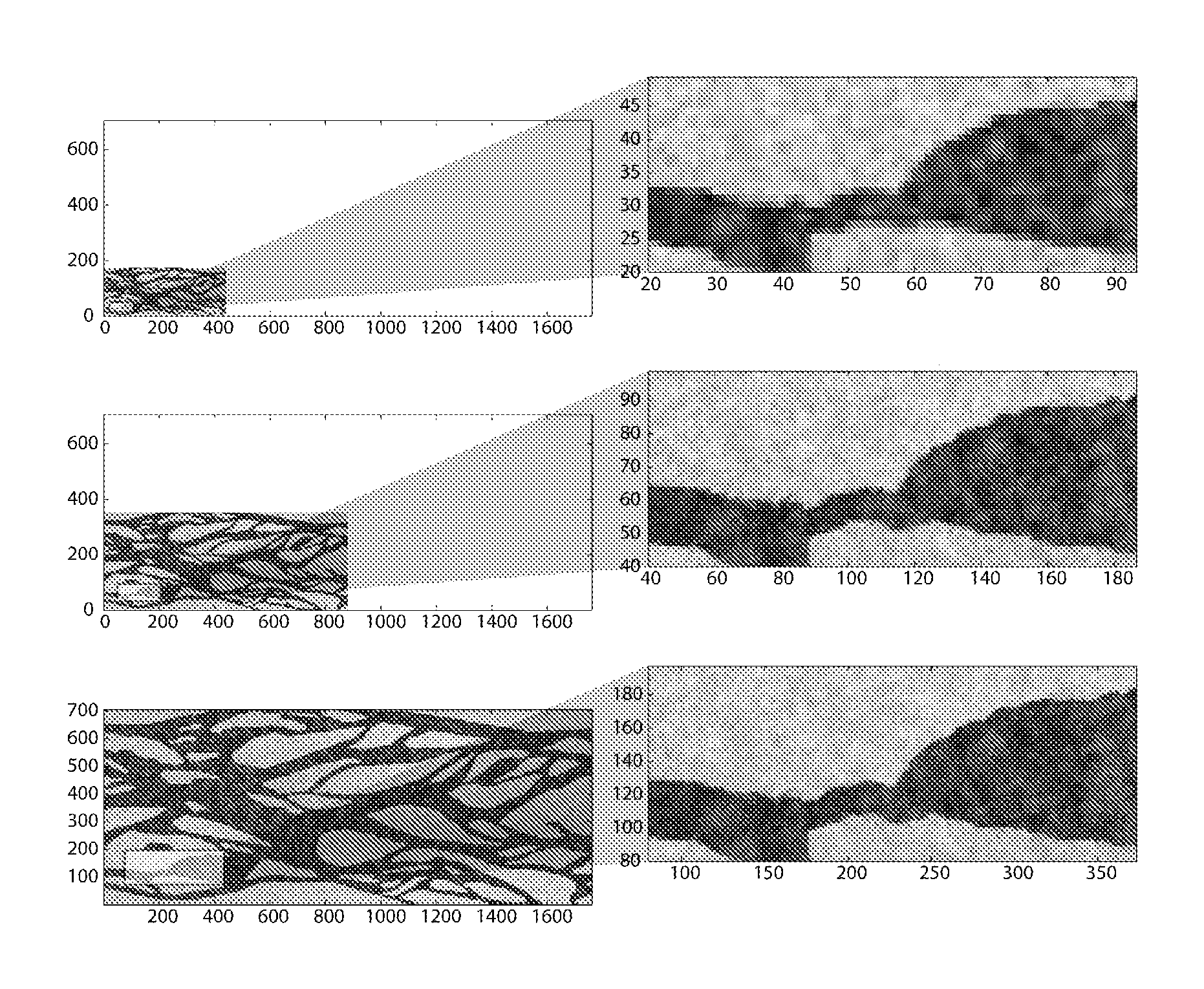
Stochastic downscaling algorithm and applications to geological model downscaling
A computer-aided method of downscaling a three-dimensional geological model by generating numerical stochastic fine-scale models conditioning to data of different scales and capturing spatial uncertainties which involves a downscaling algorithm.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Deterministic version of the multiple point geostatistics simulation/reconstruction method with the simulated/reconstructed values are directly taken from the training images without prior estimation of the conditional
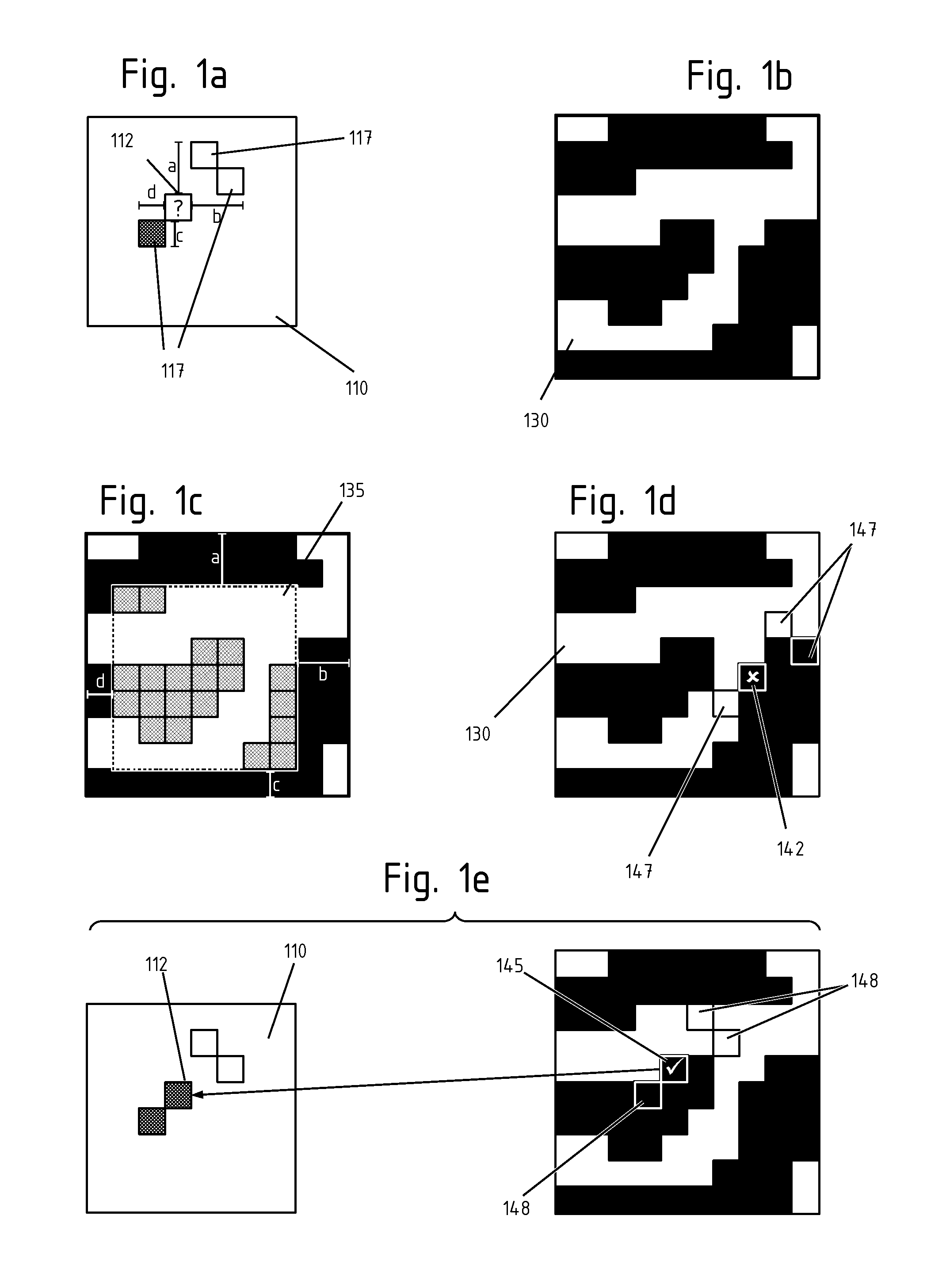
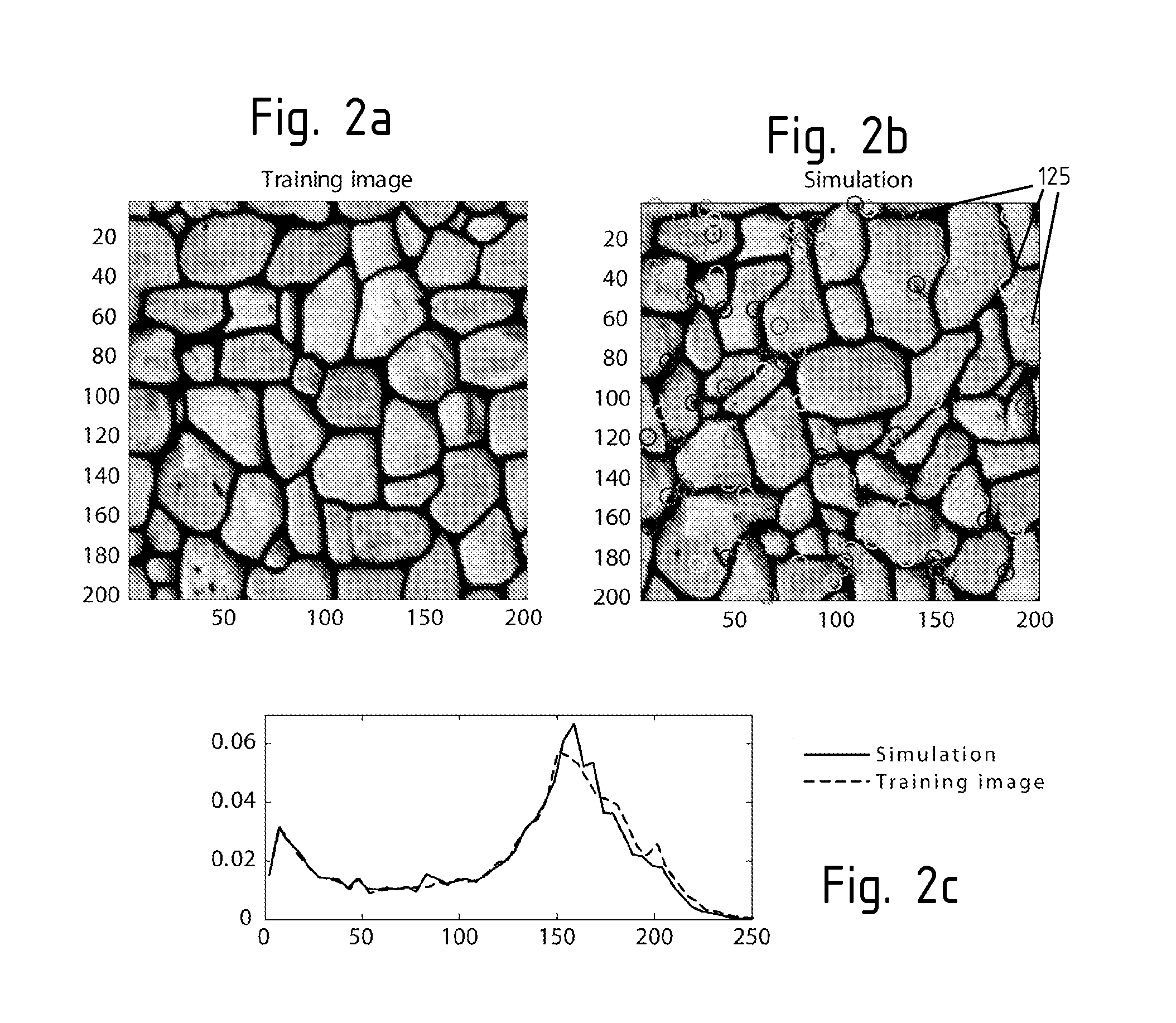
ActiveUS20110251833A1Easy to handleHigh resolutionSeismologyComputation using non-denominational number representationDigital dataPattern recognition
A method of simulating, reconstructing and scaling digital data sets, in particular images, but not exclusively. The method of the invention is based on a training image that is directly sampled each time a point in the simulation image is to be filled, and does not need the preliminary creation of a data structure storing conditional probabilities, as it is often the case in known multipoint simulation method. Accordingly, the method of the invention is less memory-demanding than conventional methods, and is better suited to simulations including continuous variables. Embodiments regarding the application to reconstruction of partial images and downscaling are also presented.
Owner:UNIV DE NEUCHATEL NEUCHATEL
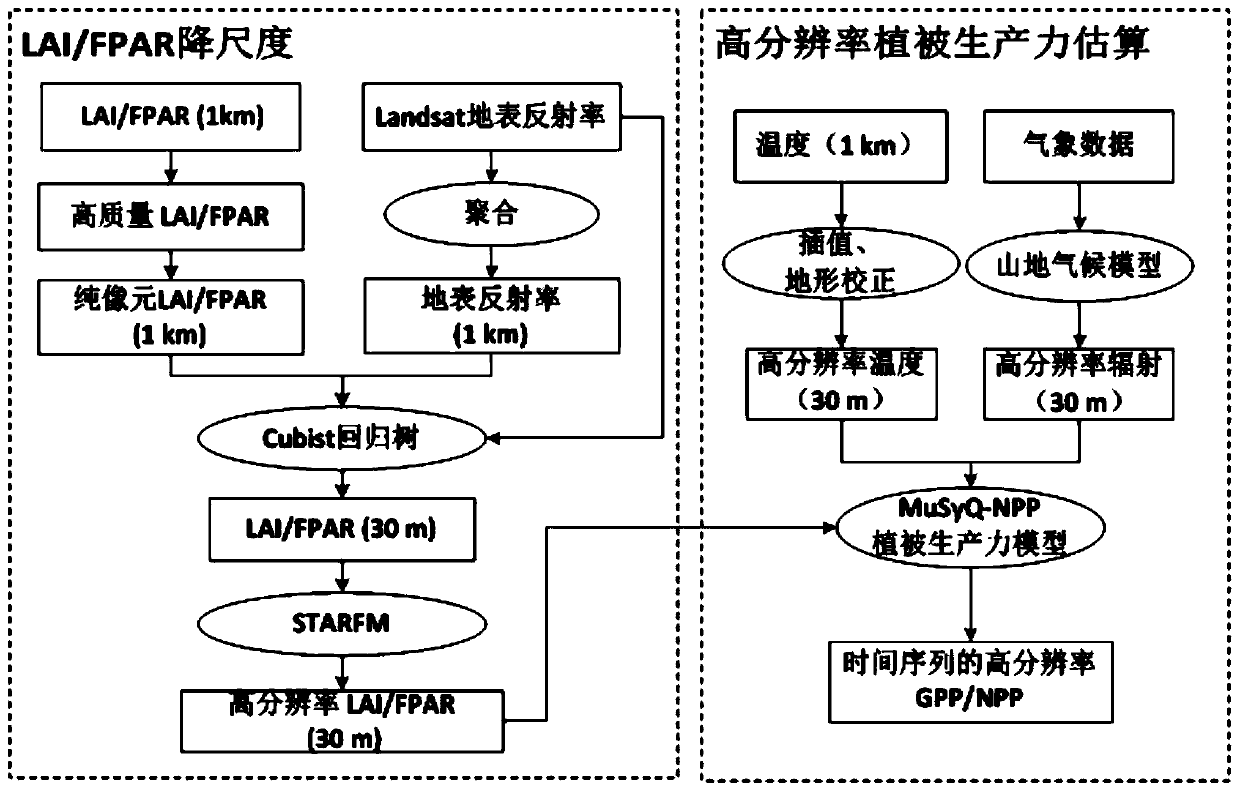
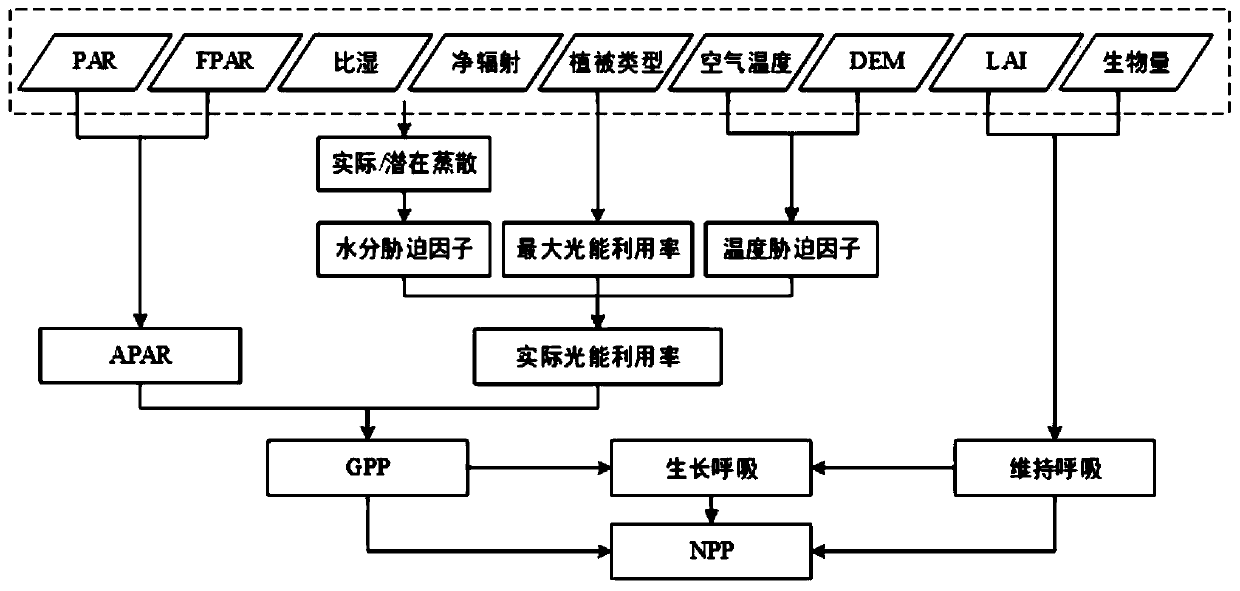
High-resolution vegetation productivity remote sensing estimation method based on downscaling
InactiveCN110276304AHigh precisionUniversalCharacter and pattern recognitionResourcesTerrainDownscaling
The invention provides a high-resolution vegetation productivity remote sensing estimation method based on downscaling. The high-resolution vegetation productivity remote sensing estimation method based on the downscaling comprises: carrying out downscaling on factors LAI / FPAR estimated by vegetation productivity, and obtaining high-resolution LAI / FPAR of a time sequence; performing spatial interpolation and terrain correction on the temperature to obtain a high-resolution temperature factor; simulating high-resolution solar short-wave radiation by using a mountainous microclimate model; inputting the downscaled high-resolution LAI / FPAR, the terrain-corrected high-resolution temperature factor and the solar short wave radiation data into a vegetation productivity model MuSyQ-NPP to obtain the high-resolution GPP / NPP of the continuous time sequence. The advantages of remote sensing data with different resolutions are fully exerted, the remote sensing data with high resolution and low resolution are fused, a technical scheme of a high-resolution vegetation productivity product with higher precision and stronger universality is constructed, and the problems that an existing vegetation productivity downscaling scheme is low in precision and insufficient in universality are solved.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
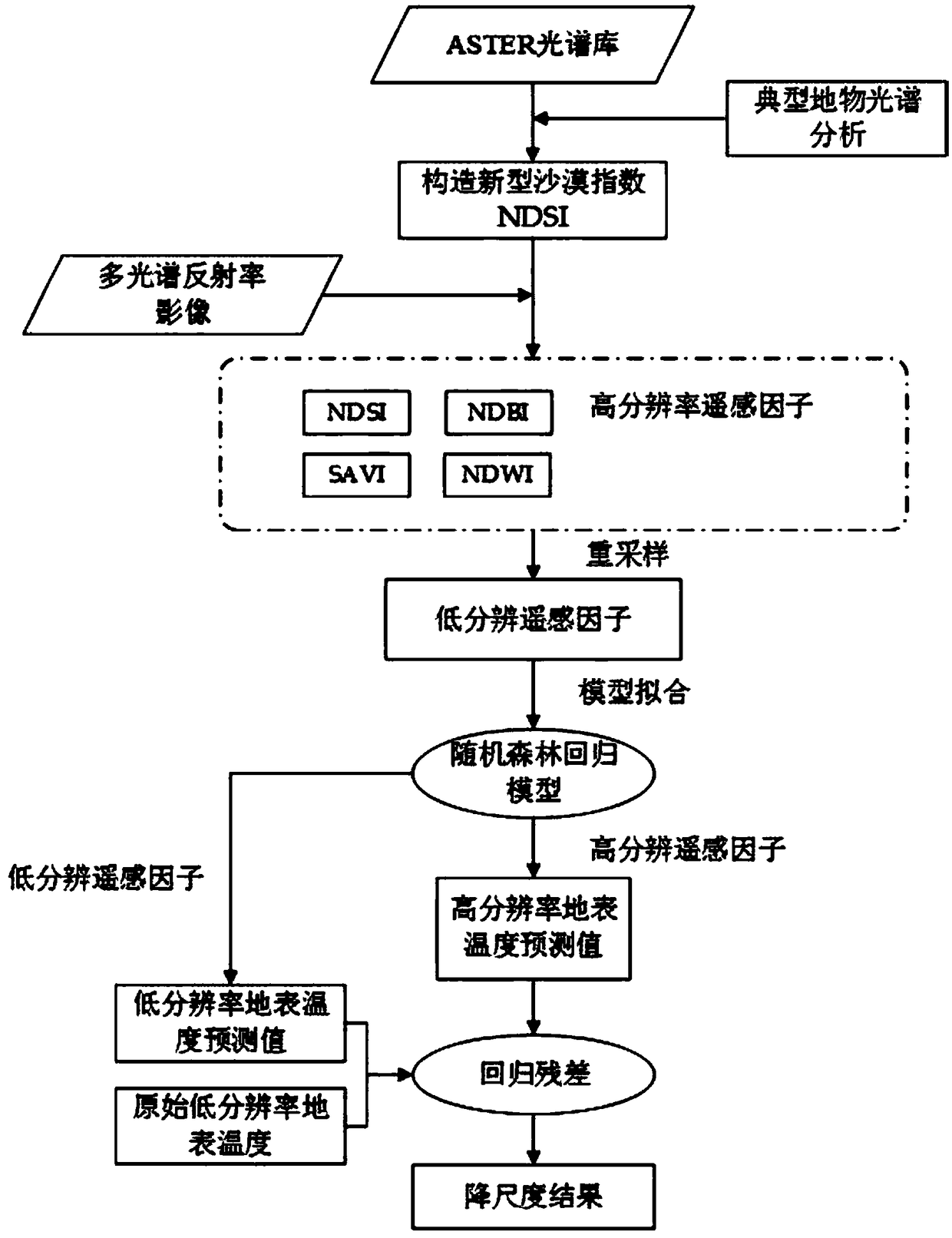
Remote sensing surface temperature spatial downscaling method based on normalized desert indexes
ActiveCN108896185AHigh resolutionImprove downscaling accuracyRadiation pyrometryInfrared remote sensingEarth surface
The invention discloses a remote sensing surface temperature spatial downscaling method based on normalized desert indexes. The method comprises the following steps: a, acquiring a multi-spectrum andthermal infrared remote sensing image which covers the range of a research area under a sunny condition, and preprocessing; b, upscaling a multi-spectral reflectivity image and a thermal infrared image to the same low resolution through a polymerization method, and constructing a new drought index according to the multi-spectral reflectivity image to represent the desert surface; c, carrying out temperature inversion on the preprocessed thermal infrared remote sensing image to obtain the surface temperature in the research area; d, taking a novel drought index, vegetation index, building indexand water body index as scale factors, establishing an earth surface temperature downscaling model with a random forest regression algorithm, and obtaining a high-resolution earth surface temperatureimage of the research area through the model; e, carrying out precision evaluation on the dimension reduction result. The method is beneficial for improving the dimension reduction precision in the desert area.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
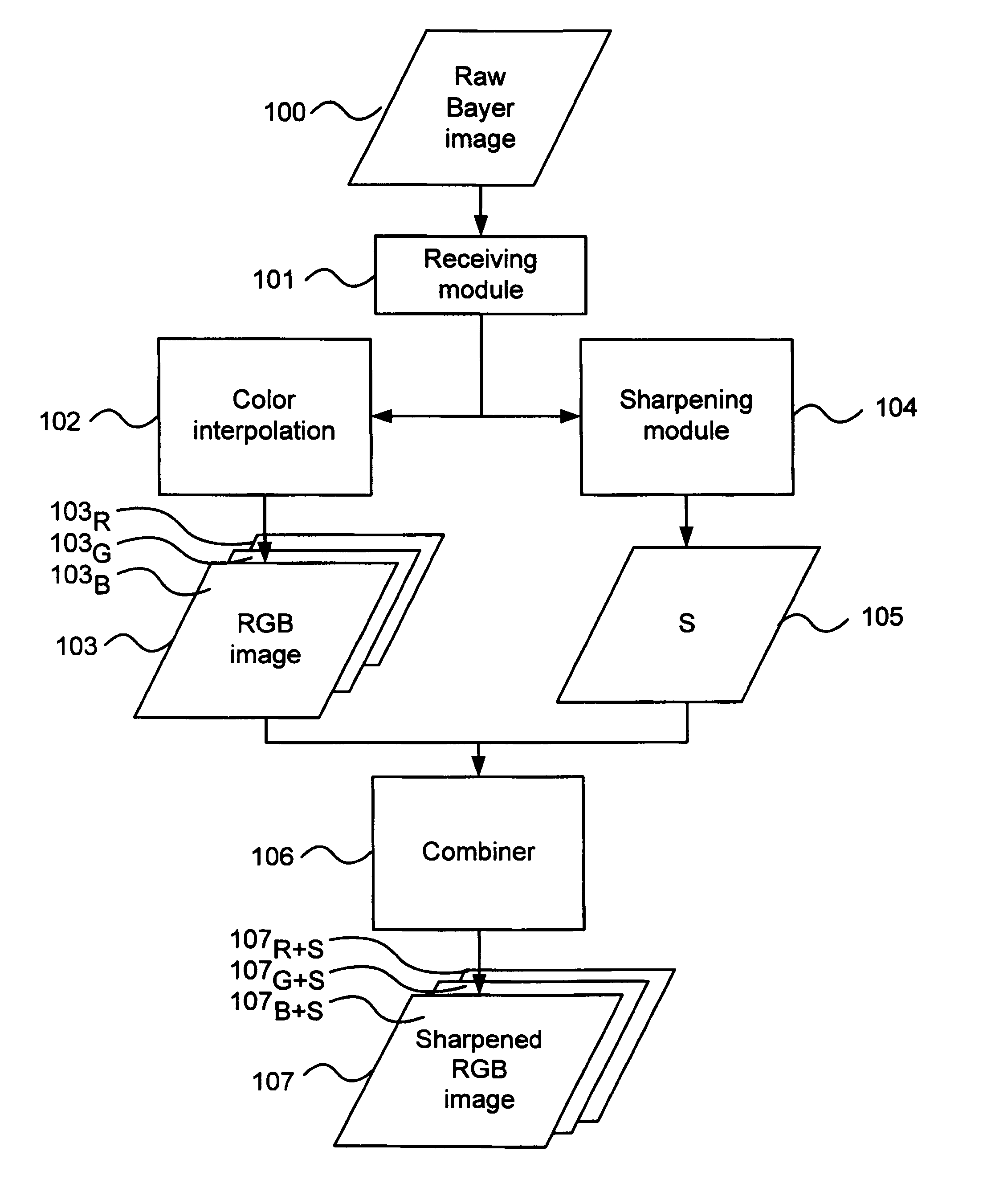
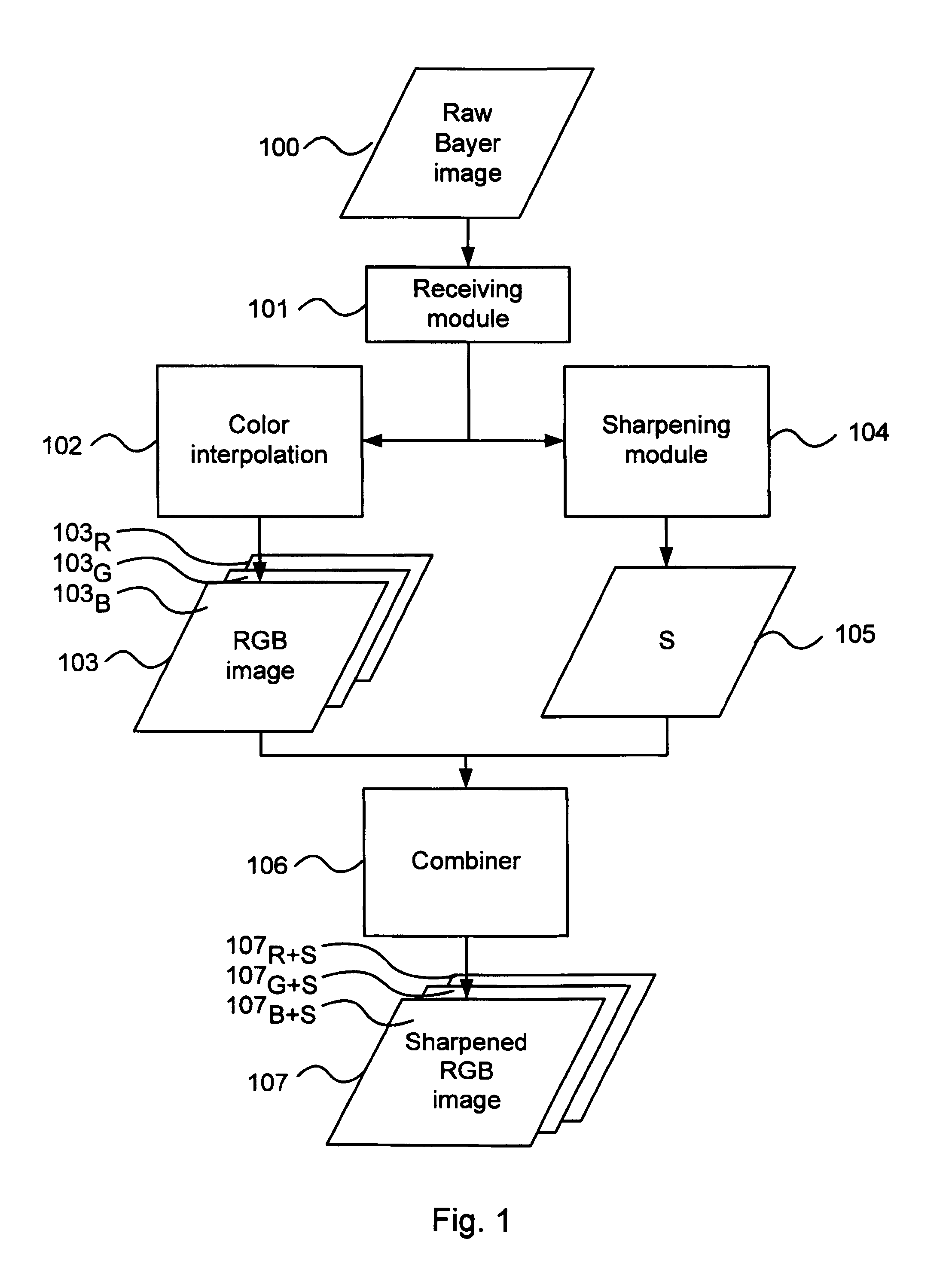
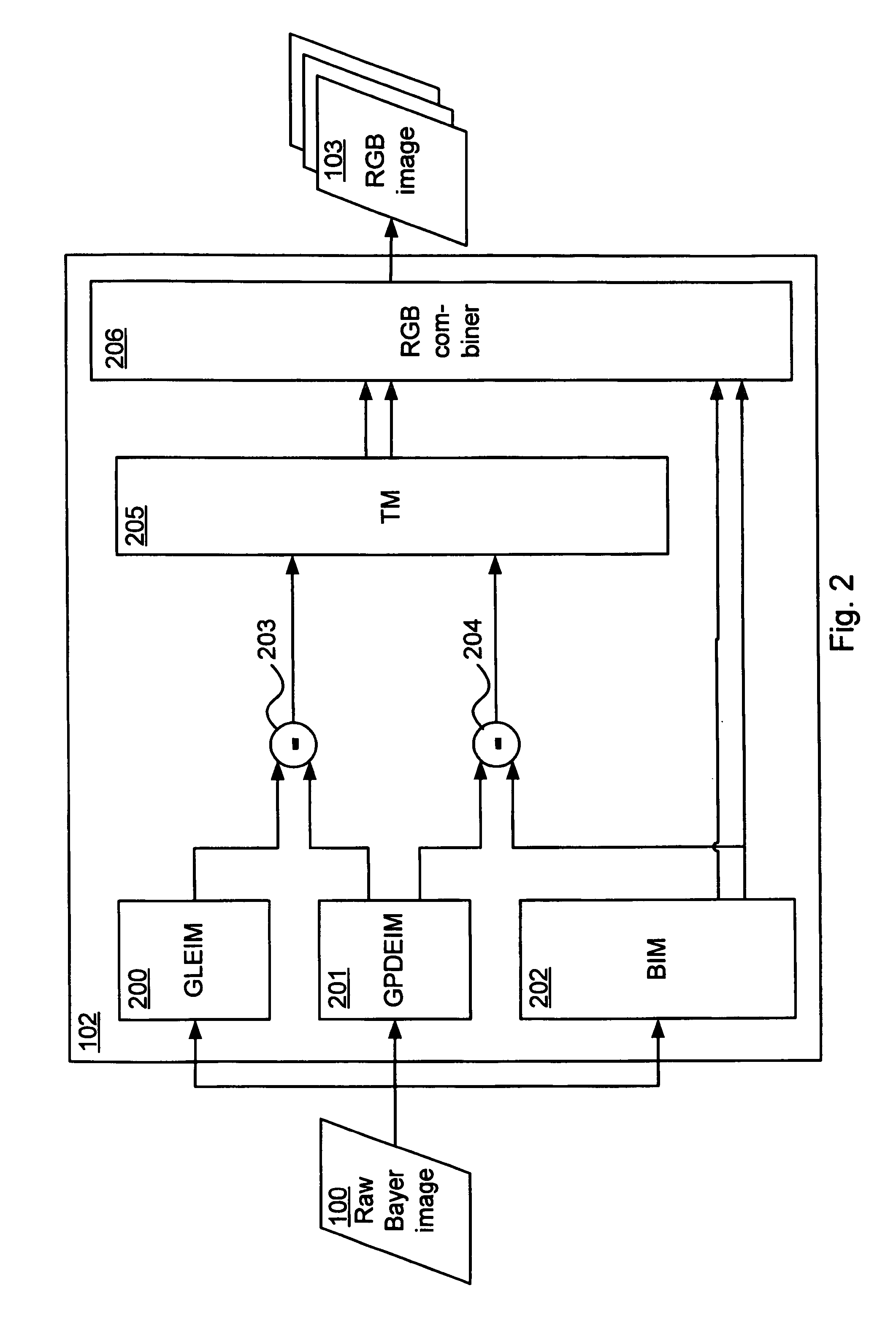
Methods and devices for image processing, image capturing and image downscaling
ActiveUS7751642B1Reducing zipperReducing maze artifactTelevision system detailsImage enhancementColor imagePower efficient
An image processing method comprises receiving a raw color image as produced by an image sensor. A color image having a plurality of pixels is generated by processing raw image data from said raw color image, wherein pixels for which color values are absent in said raw image data are assigned color values derived from present color values in said raw image data. A sharpening term is generated by processing raw image data from said raw color image. Then, an improved color image is produced by combining said color image with said sharpening term. The raw color image may be a Bayer image, and the image processing method may be implemented in a cost and power efficient integrated circuit using limited memory.
Owner:ARM LTD
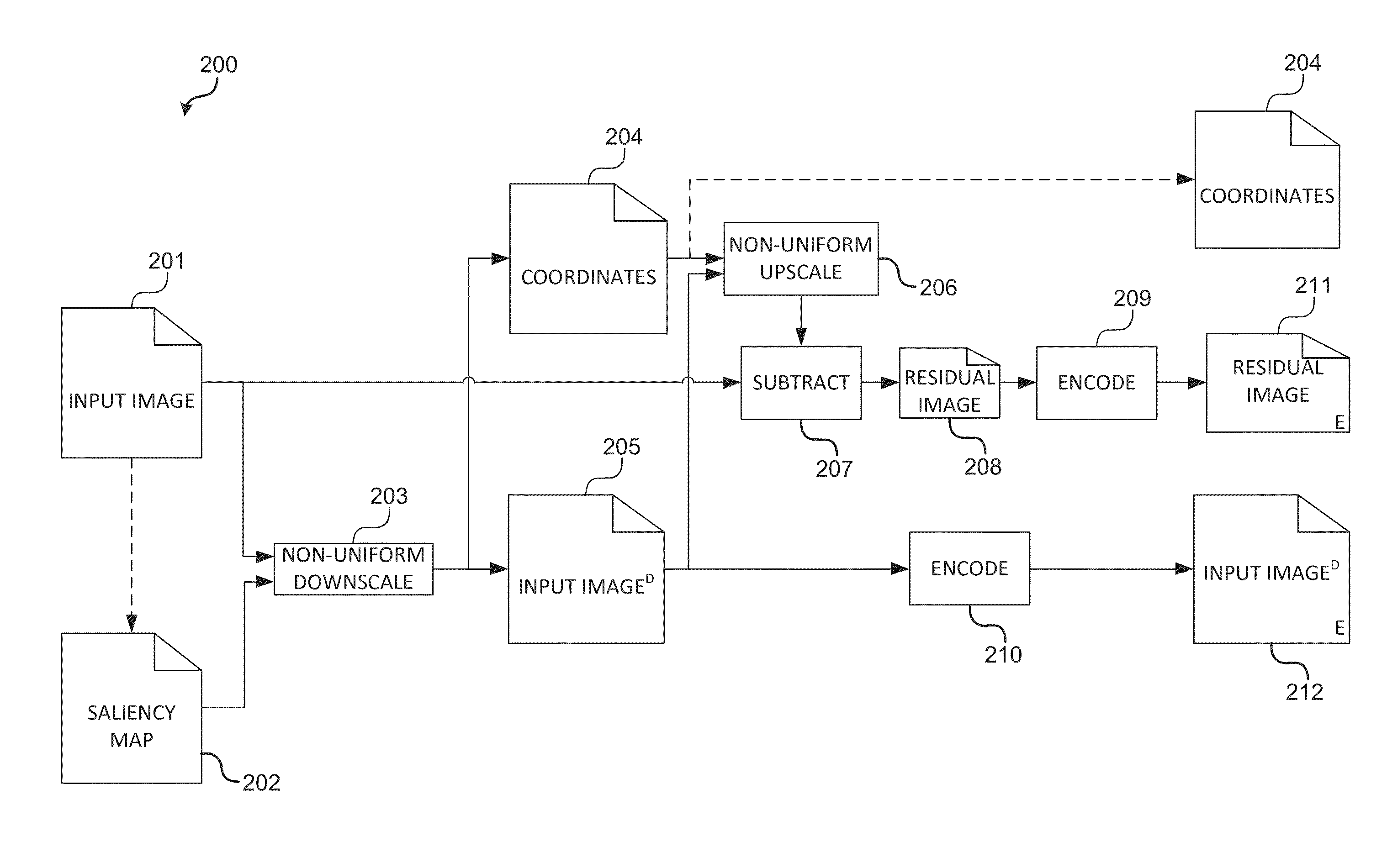
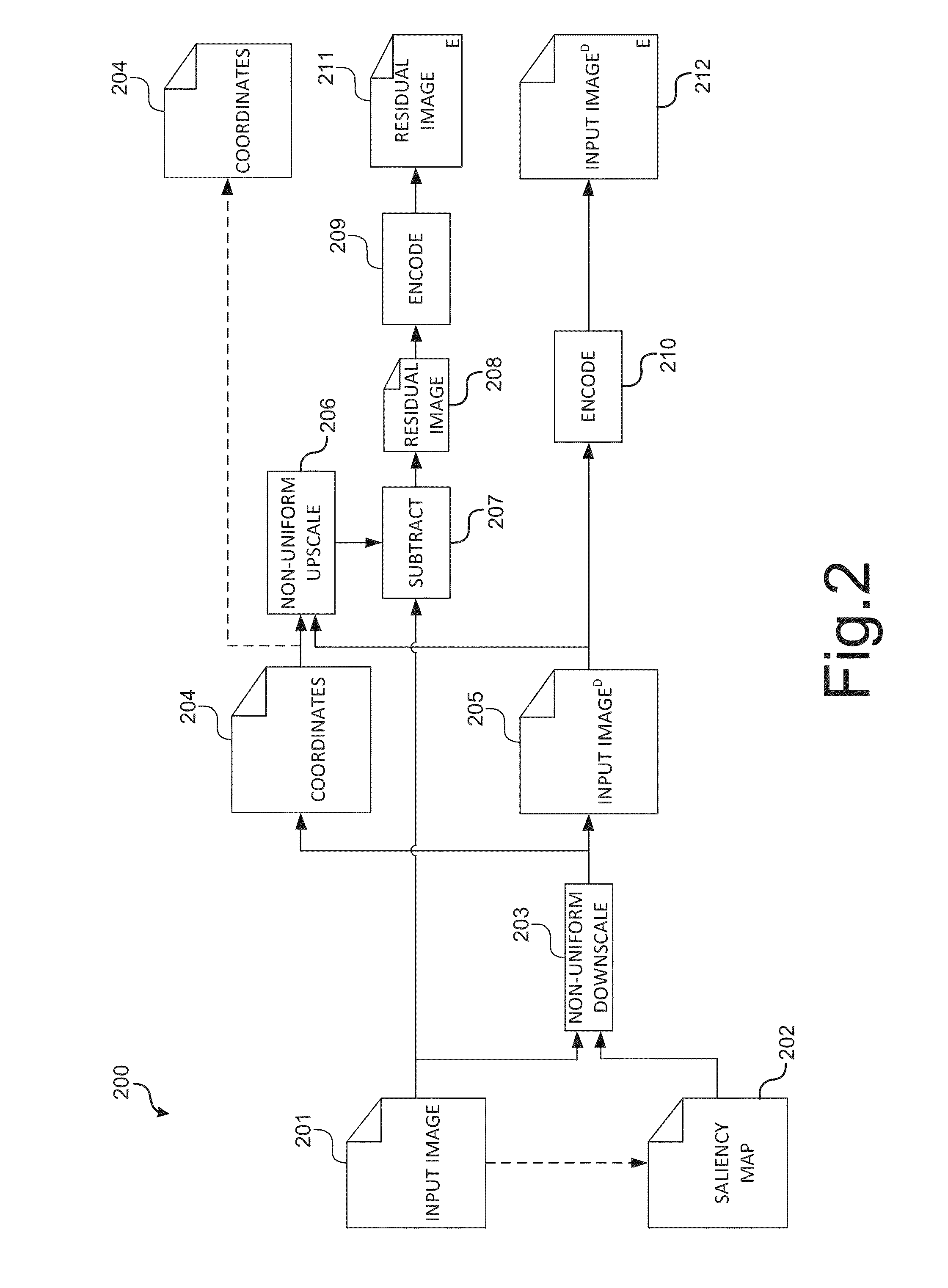
Content-aware image compression method
Methods for content-aware image compression are disclosed. One method comprises the steps of non-uniformly downscaling an original input image according to a saliency map, creating a residual image, encoding the residual image and downscaled input image, and transmitting the residual image and downscaled input image. The encoded image components are transmitted to a receiver. Downscaling may be performed using an aspect ratio that is automatically calculated from the saliency map. The saliency map may be based on an algorithm specified at an encoder or on regions of interest selected by a plurality of users of receivers that receive the transmitted encoded image components.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC +1
Technique for adaptive de-blocking of block-based film grain patterns
InactiveUS20060140278A1Quality improvementReduce computing costImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDeblocking filterDownscaling
Reduction in the blockiness of a simulated film grain block can be achieved either by the use of adaptive downscaling or adaptive deblocking filtering to adjust the intensity of the pixels at the block edge in accordance with at least one film grain block parameter, such as film grain size, intensity and texture. Performing such adaptive downscaling or adaptive deblocking filtering achieves improved performance at lower computational cost by avoiding modification of film grain block pixels in lesser affected areas.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
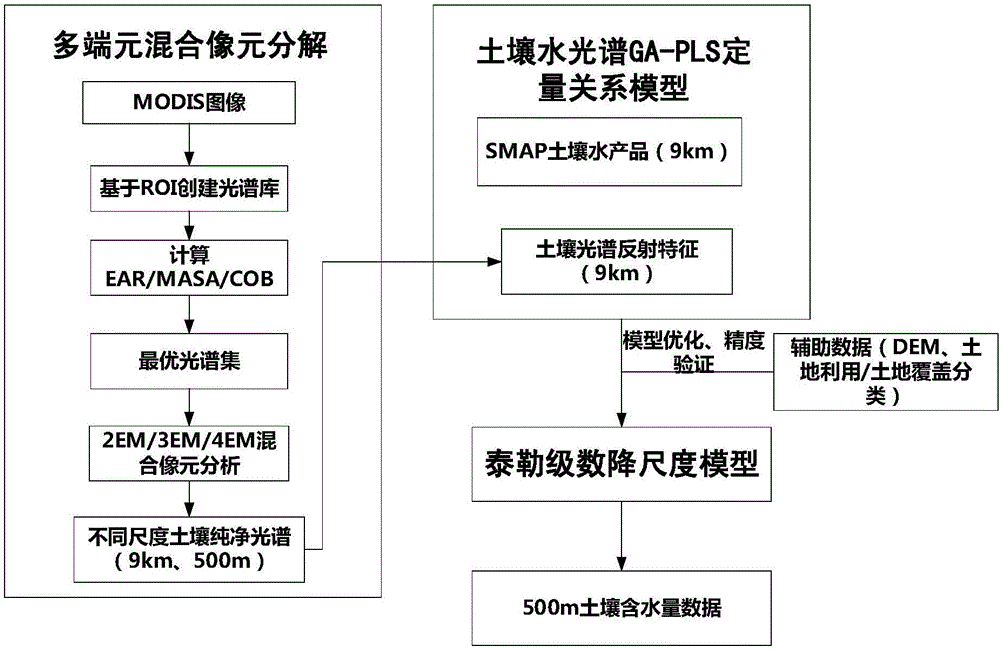
A downscaling method for a soil water content product
ActiveCN106501186AImprove accuracySatisfying large-scale watershed-scale regional researchColor/spectral properties measurementsMoisture content investigation using microwavesRelational modelDynamic monitoring
A downscaling method for a soil water content product is disclosed. The method includes A) acquiring passive microwave soil water content products of a region to be researched and optical remote sensing data at the same time, B) subjecting the optical remote sensing data to soil spectrum extraction based on a multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis process, C) building a model of a quantitative relation between soil spectrum reflection characteristics and soil water contents acquired from the passive microwave soil water content products by utilizing GA-PLS, and D) based on the model of the quantitative relation, building a soil water content downscaling model by utilizing the Taylor series expansion and acquiring soil water content data having a high spatial resolution. Advantages of passive microwave remote sensing data and optical remote sensing data on the temporal-spatial resolution are utilized in the method, and the passive microwave remote sensing data and the optical remote sensing data are effectively combined to acquire the soil water content data having the high spatial resolution, and therefore large-scale watershed scale region researching can be met, real-time or quasi real-time dynamic monitoring on watershed scale soil water contents is achieved, accuracy is high, building is easy and time and labor are saved.
Owner:中科卫星应用德清研究院 +1
Surface temperature downscaling method based on adaptive threshold value
ActiveCN107423537AHigh precisionImprove efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsUrban regionCoverage Type
The invention discloses a surface temperature downscaling method based on an adaptive threshold value. According to the method, multiple factors highly correlated with surface temperature are mainly used as downscaling factors; and a mobile window method is adopted to obtain an optimal threshold value of the downscaling factors participating in downscaling model fitting through downscaling evaluation indicators. In this way, irrelevant scale factors in a mobile window can be eliminated, scale factors highly matched with a land coverage type are selected adaptively to participate in downscaling calculation, therefore, the method has good applicability in a region with a complicated land coverage type, the precision and efficiency of surface temperature downscaling are improved, and the depth and breadth of a thermal infrared image in urban region application are expanded.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com