Patents
Literature
95 results about "Film grain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Film grain or granularity is the random optical texture of processed photographic film due to the presence of small particles of a metallic silver, or dye clouds, developed from silver halide that have received enough photons. While film grain is a function of such particles (or dye clouds) it is not the same thing as such. It is an optical effect, the magnitude of which (amount of grain) depends on both the film stock and the definition at which it is observed. It can be objectionably noticeable in an over-enlarged photographic film photograph.
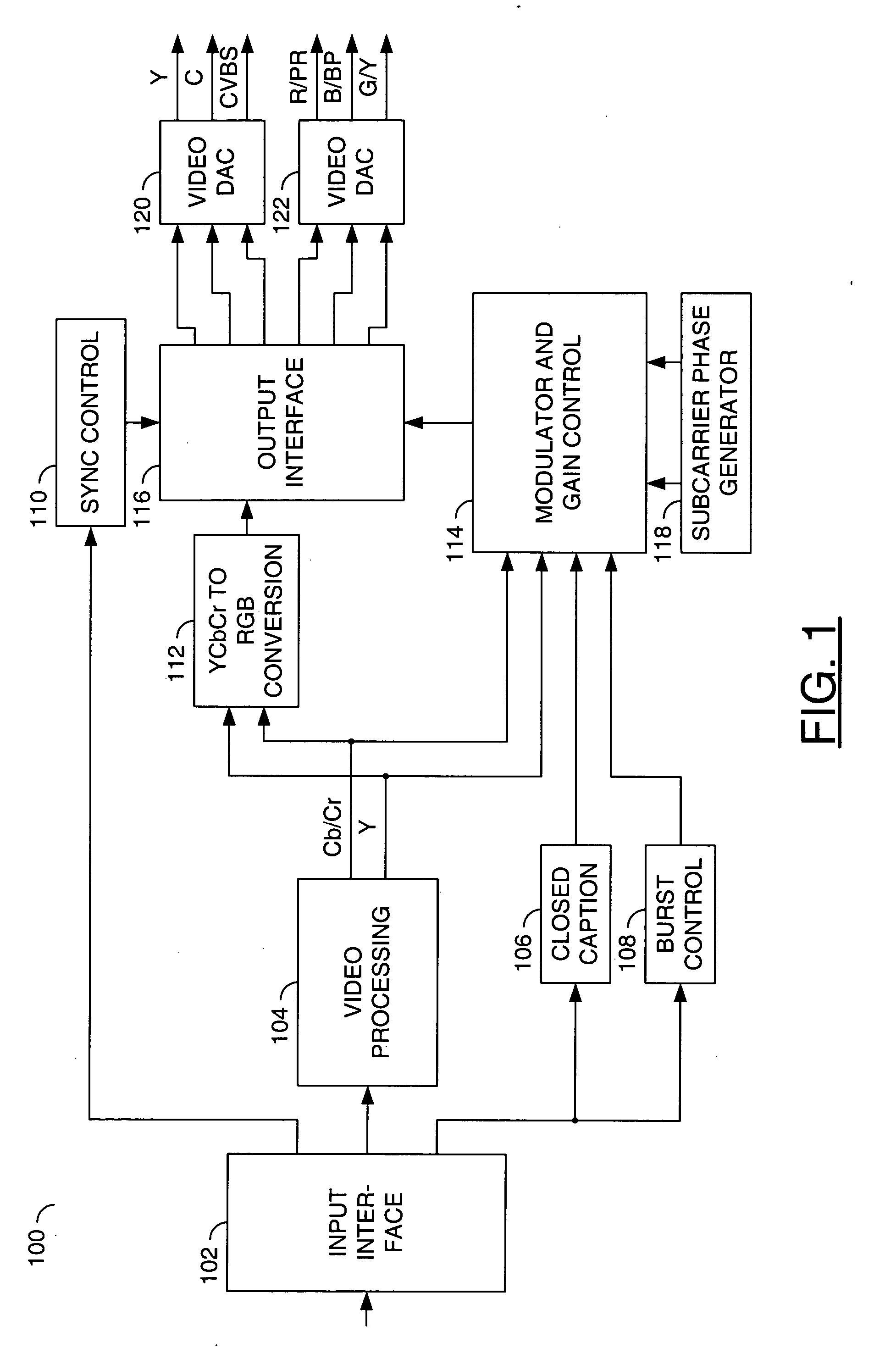
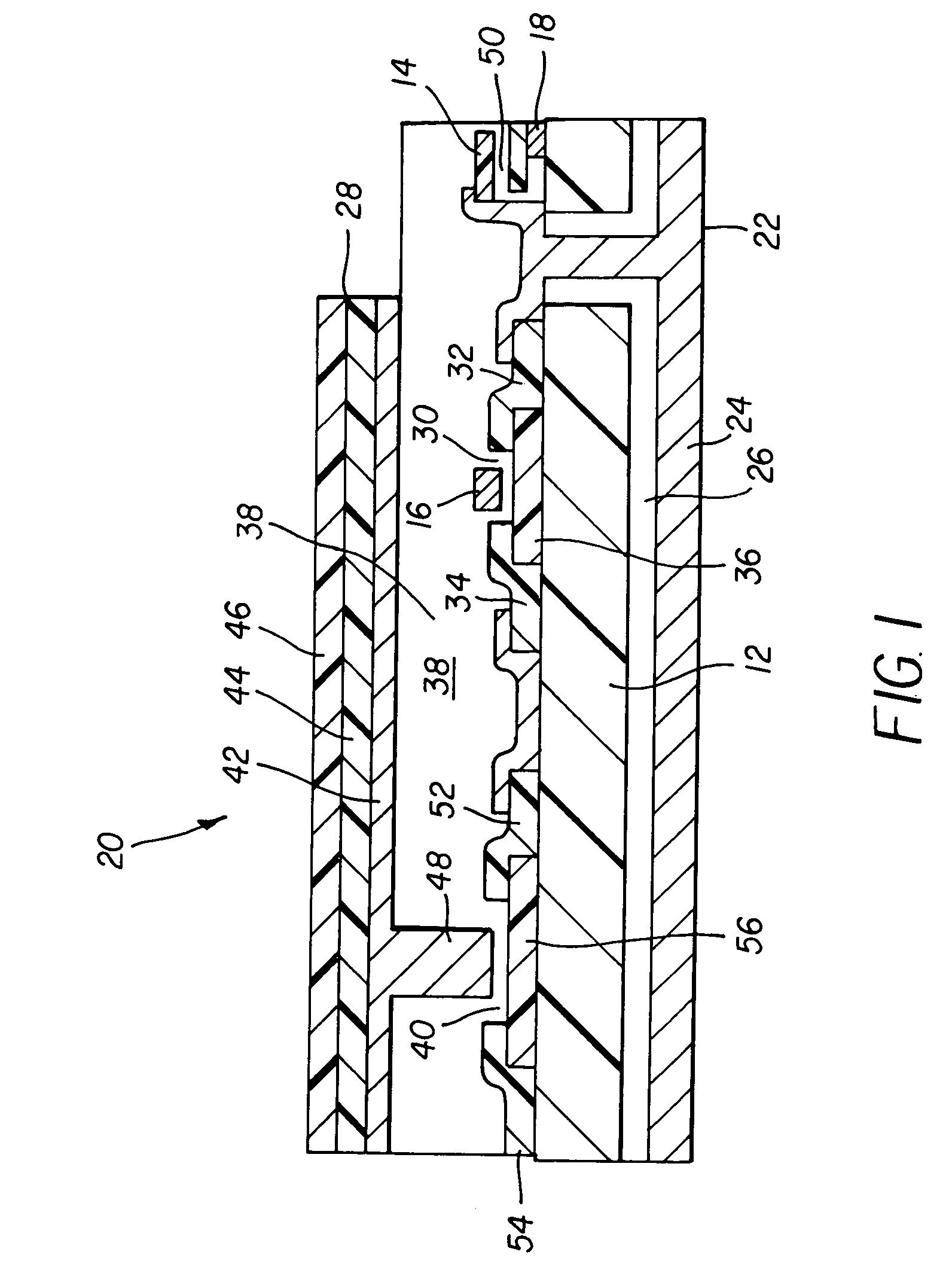
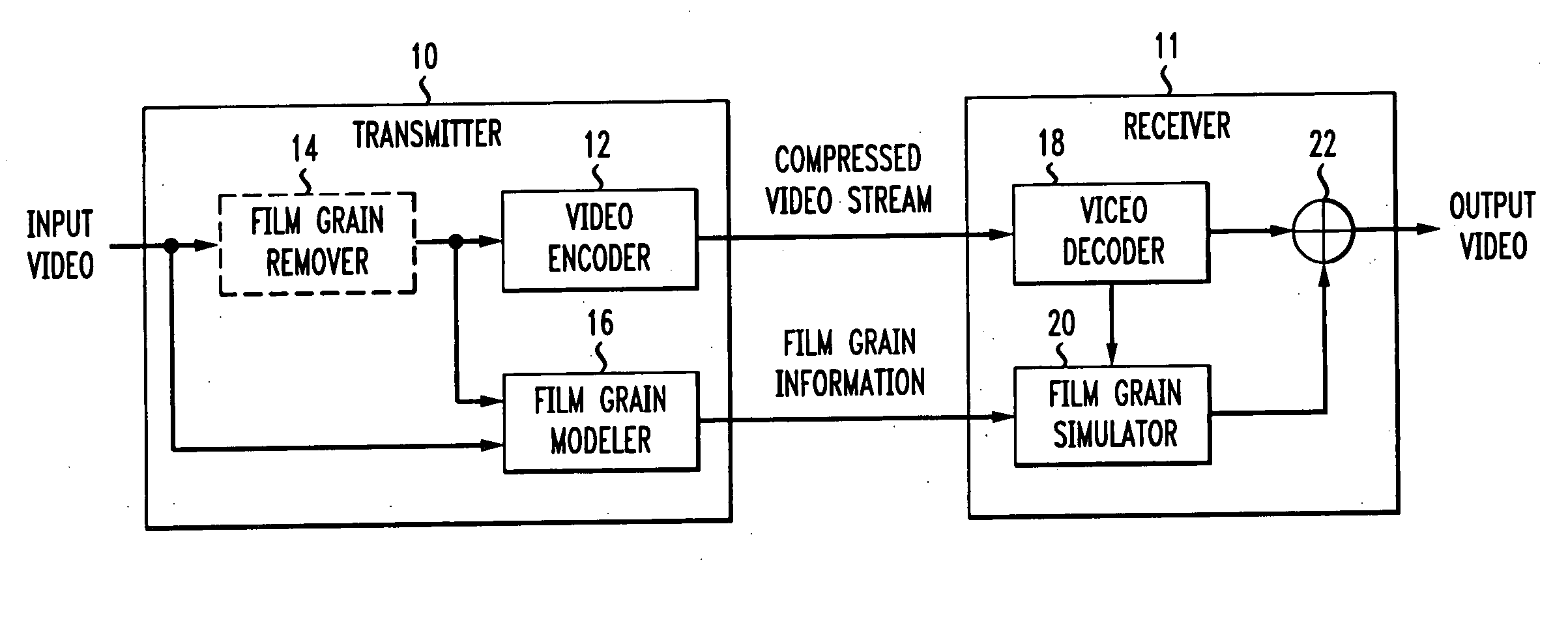
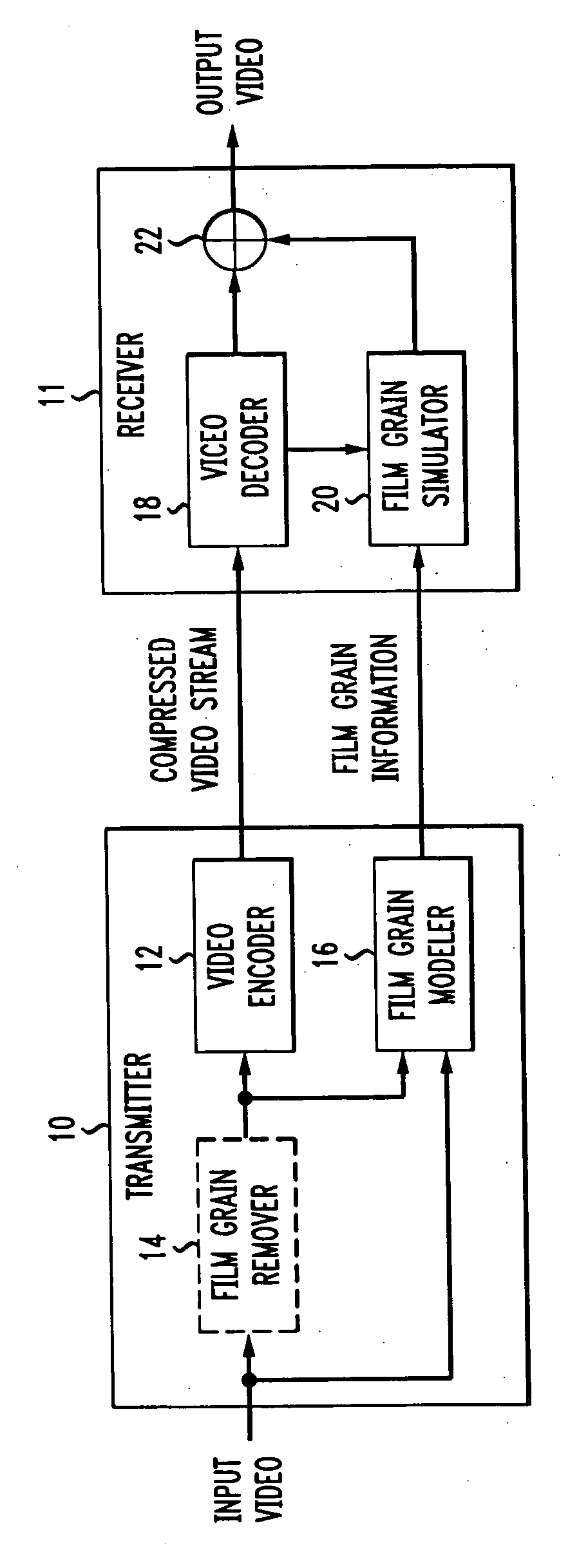
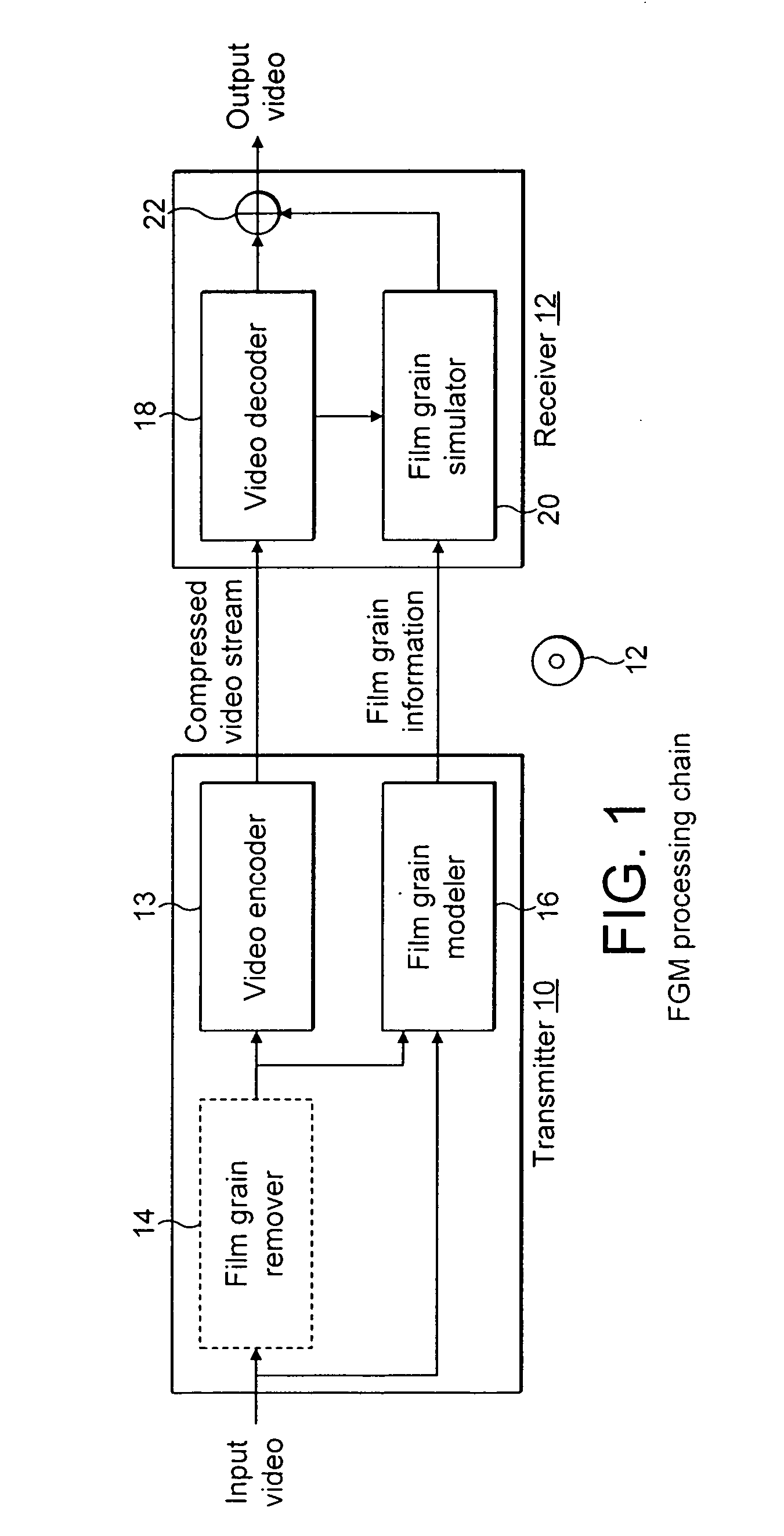
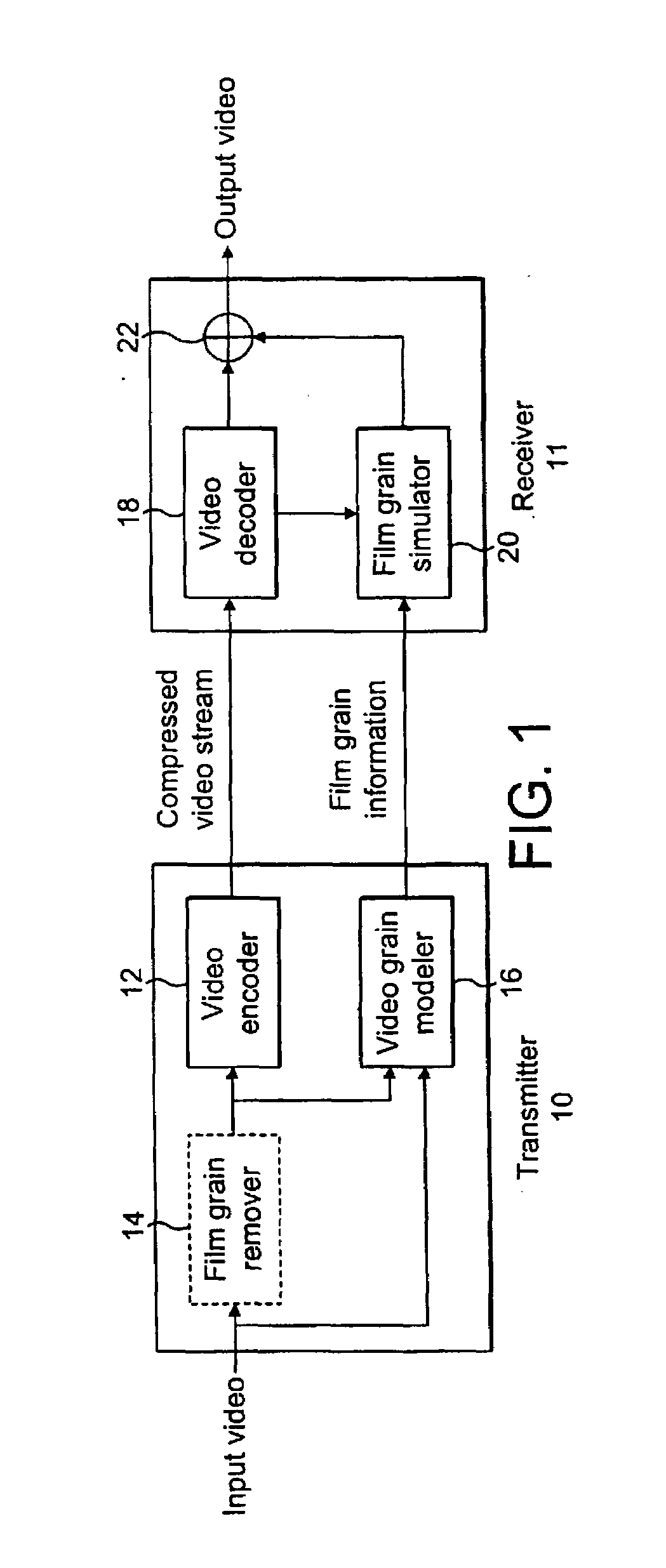
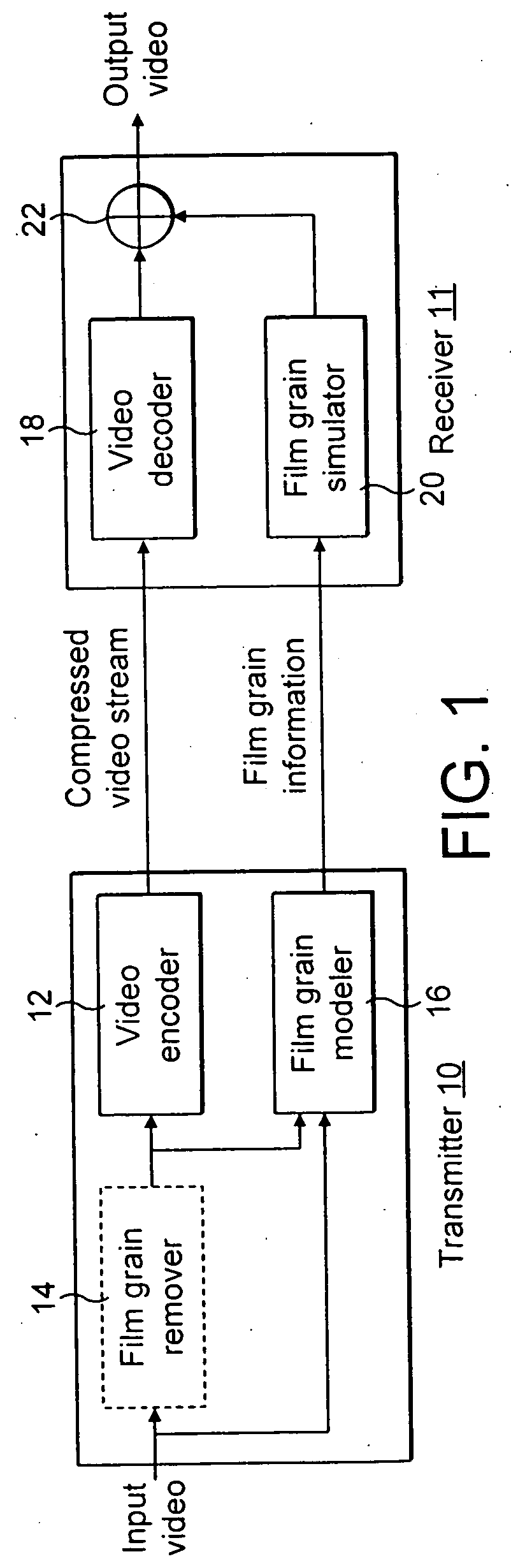
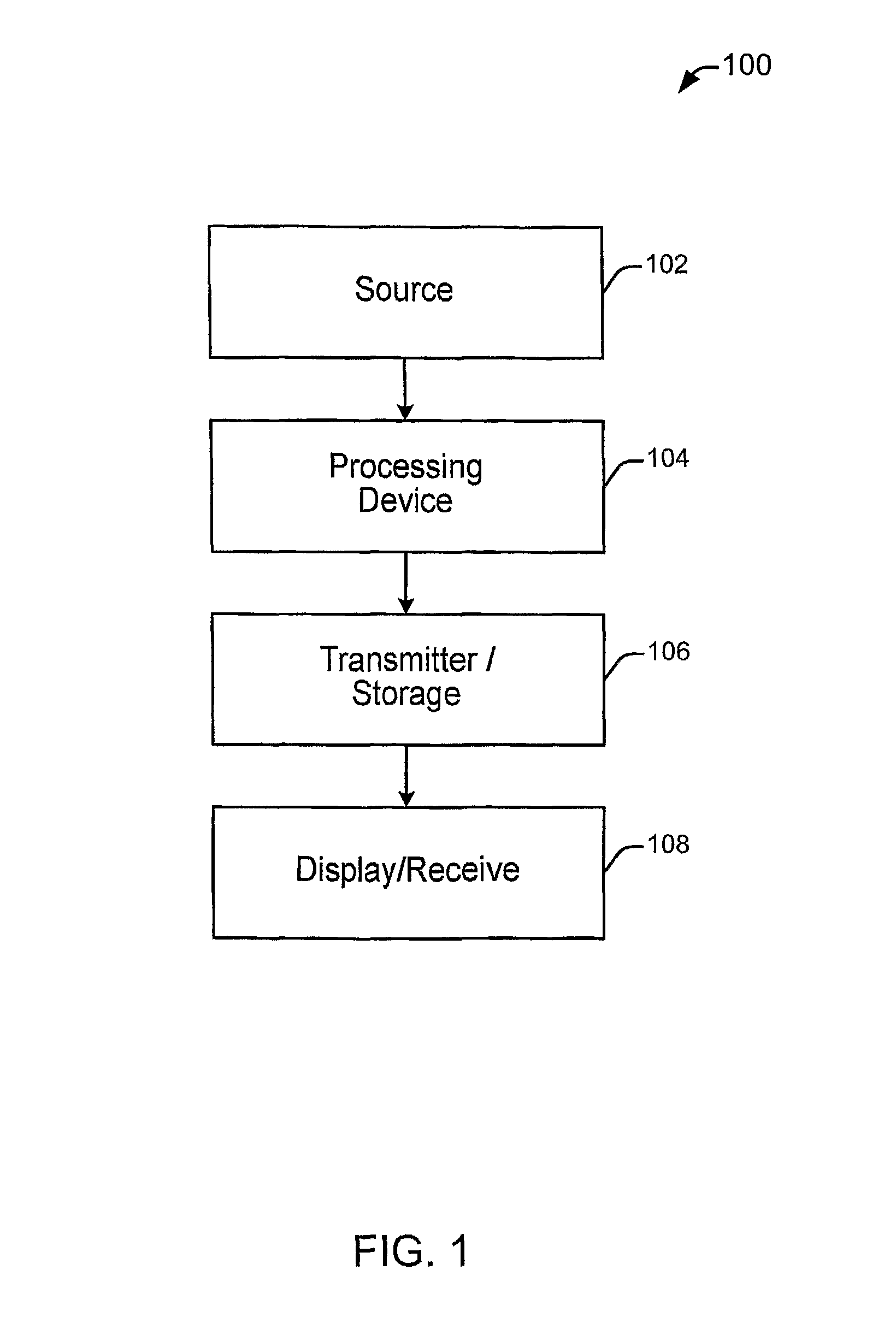
Method and apparatus for masking of video artifacts and/or insertion of film grain in a video decoder
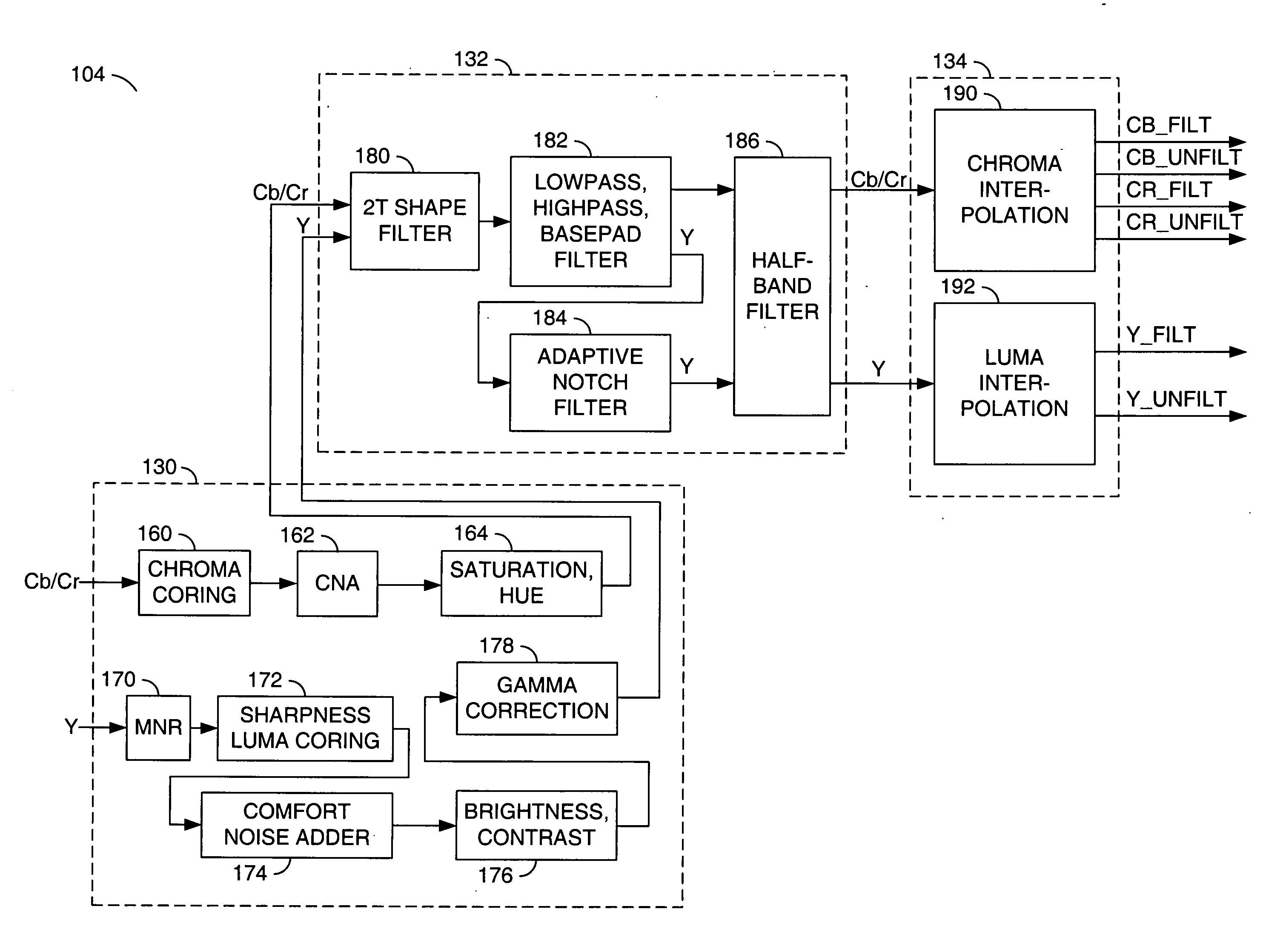
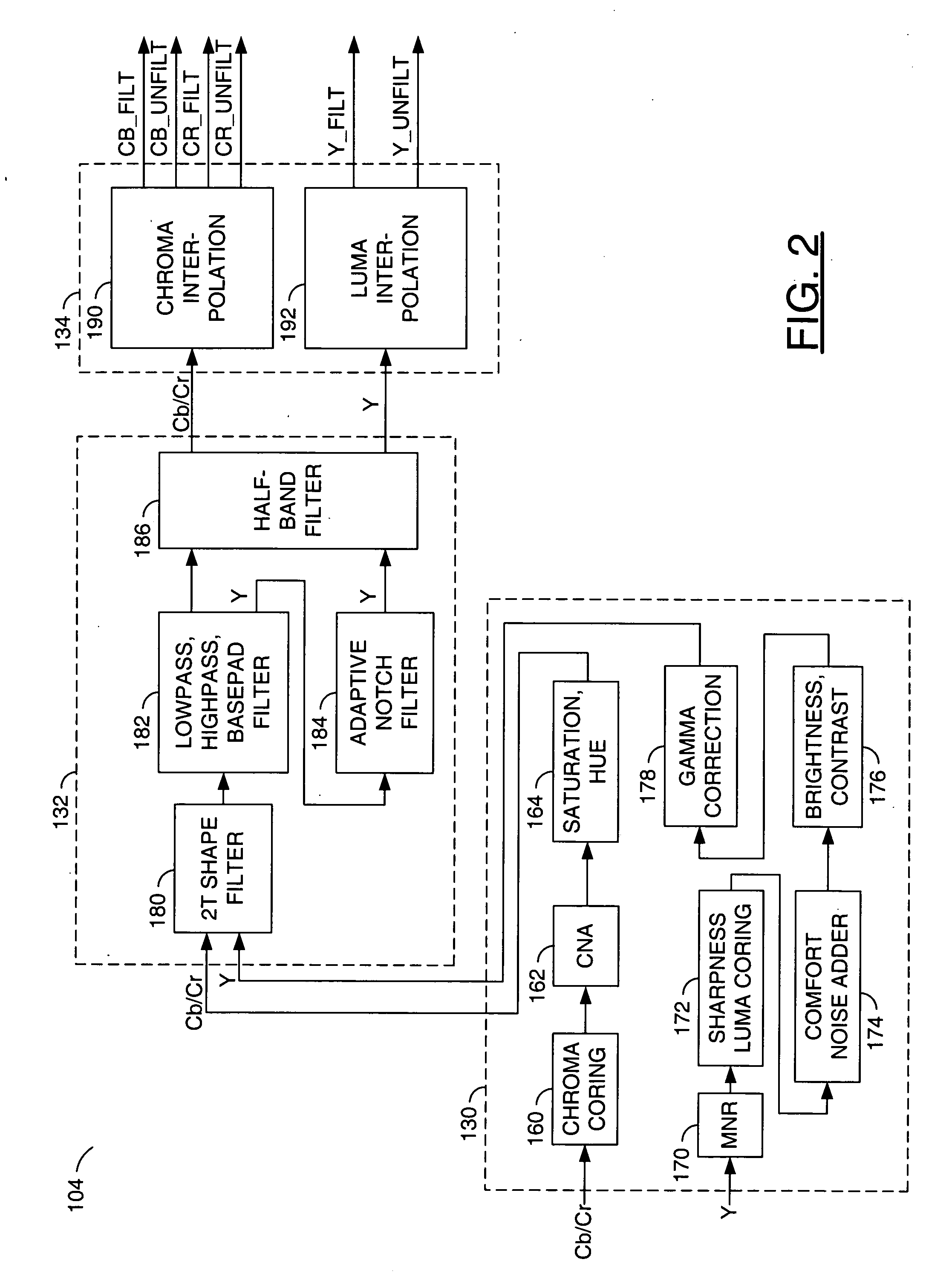
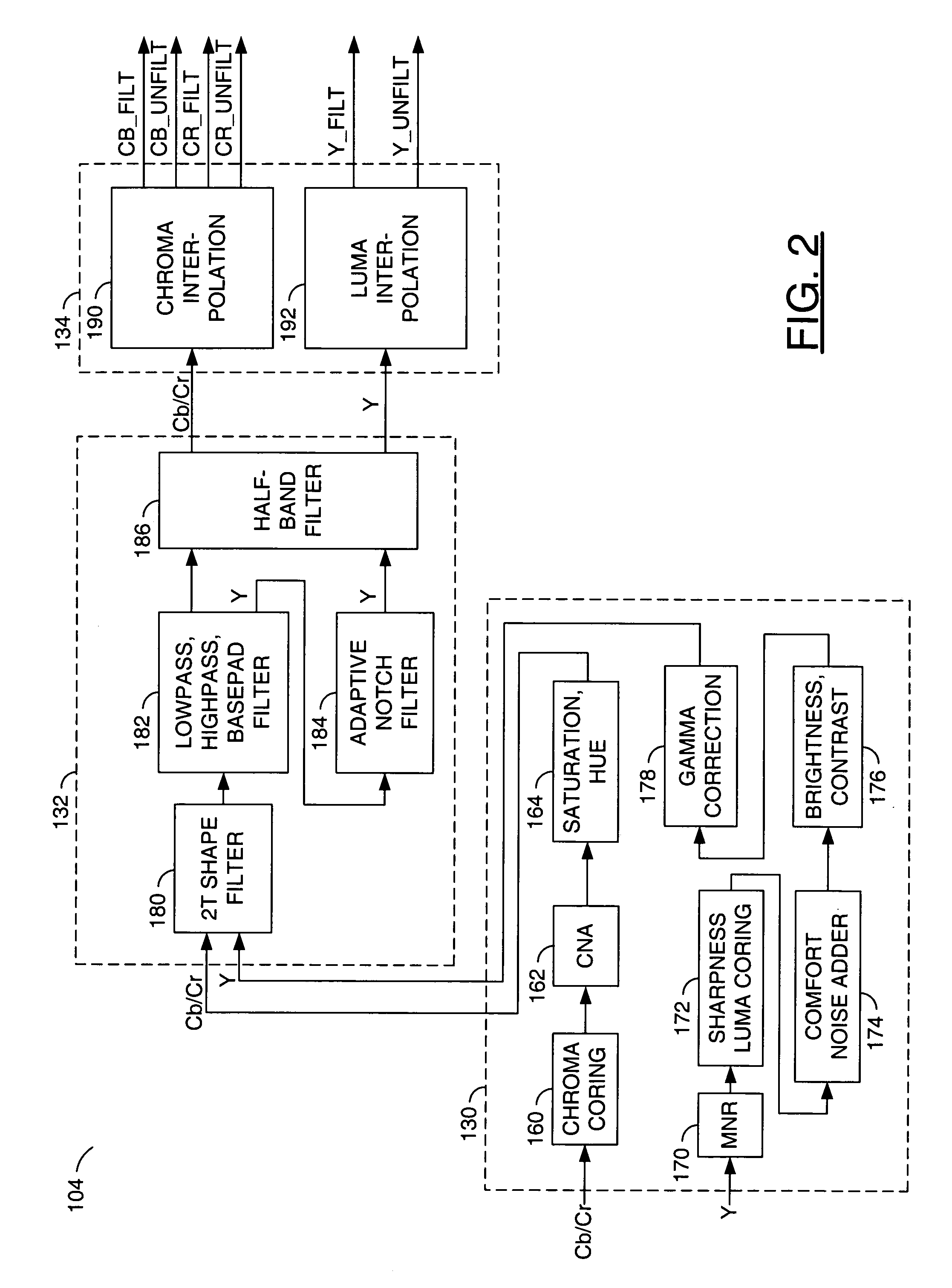
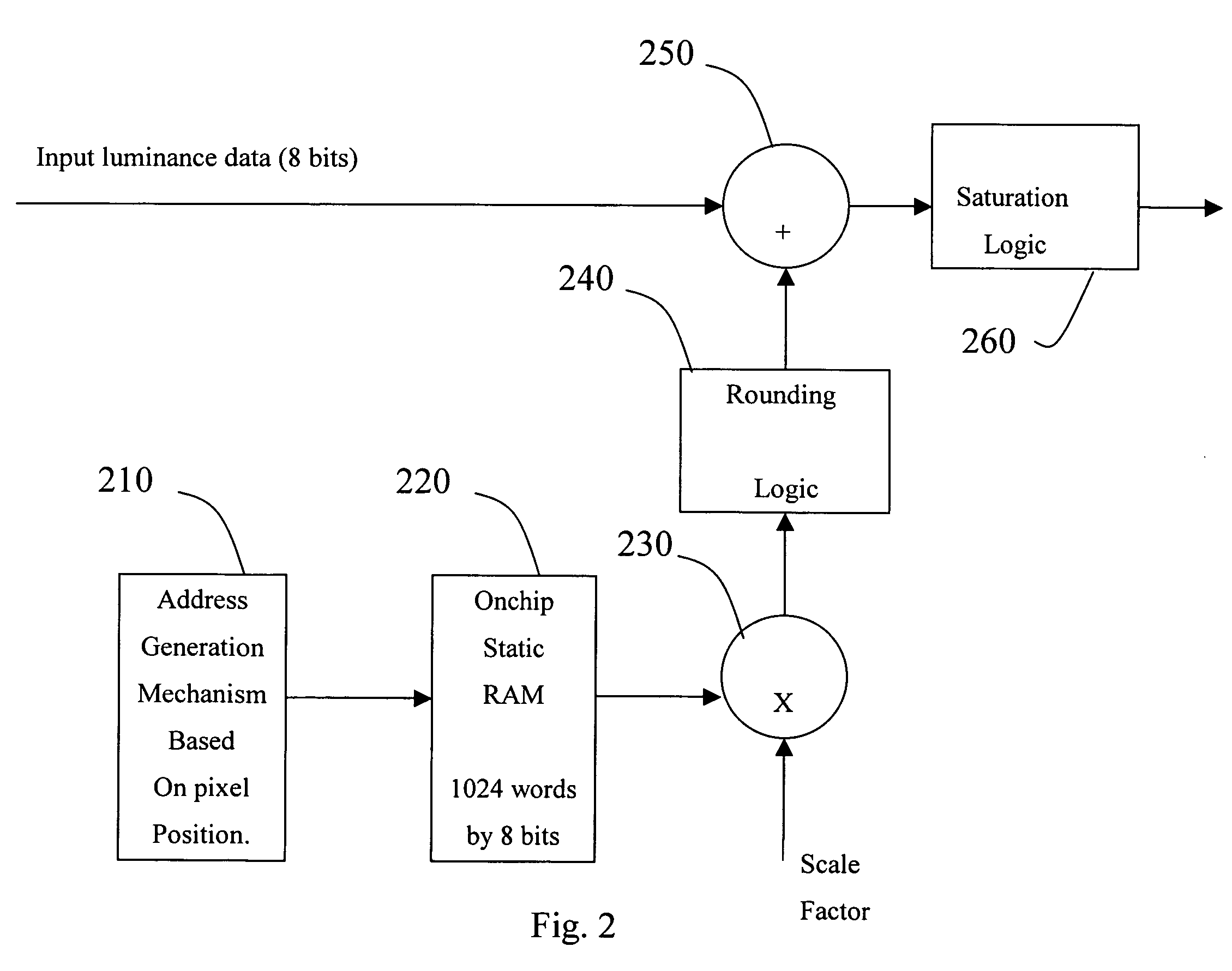
A video decoder comprising (i) a post-processing filter block, (ii) a comfort noise addition block and (iii) a video value / range adjustment block, where the comfort noise addition block is integrated into a video output path of the video decoder. The post-processing filter block may be configured to perform one or more of noise reduction, spatial filtering and temporal filtering on luminance data. The comfort noise addition block may be configured to add comfort noise to the luminance data. The video value / range adjustment block may be configured to adjust one or both of a value and a range of the luminance data.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Digital film grain
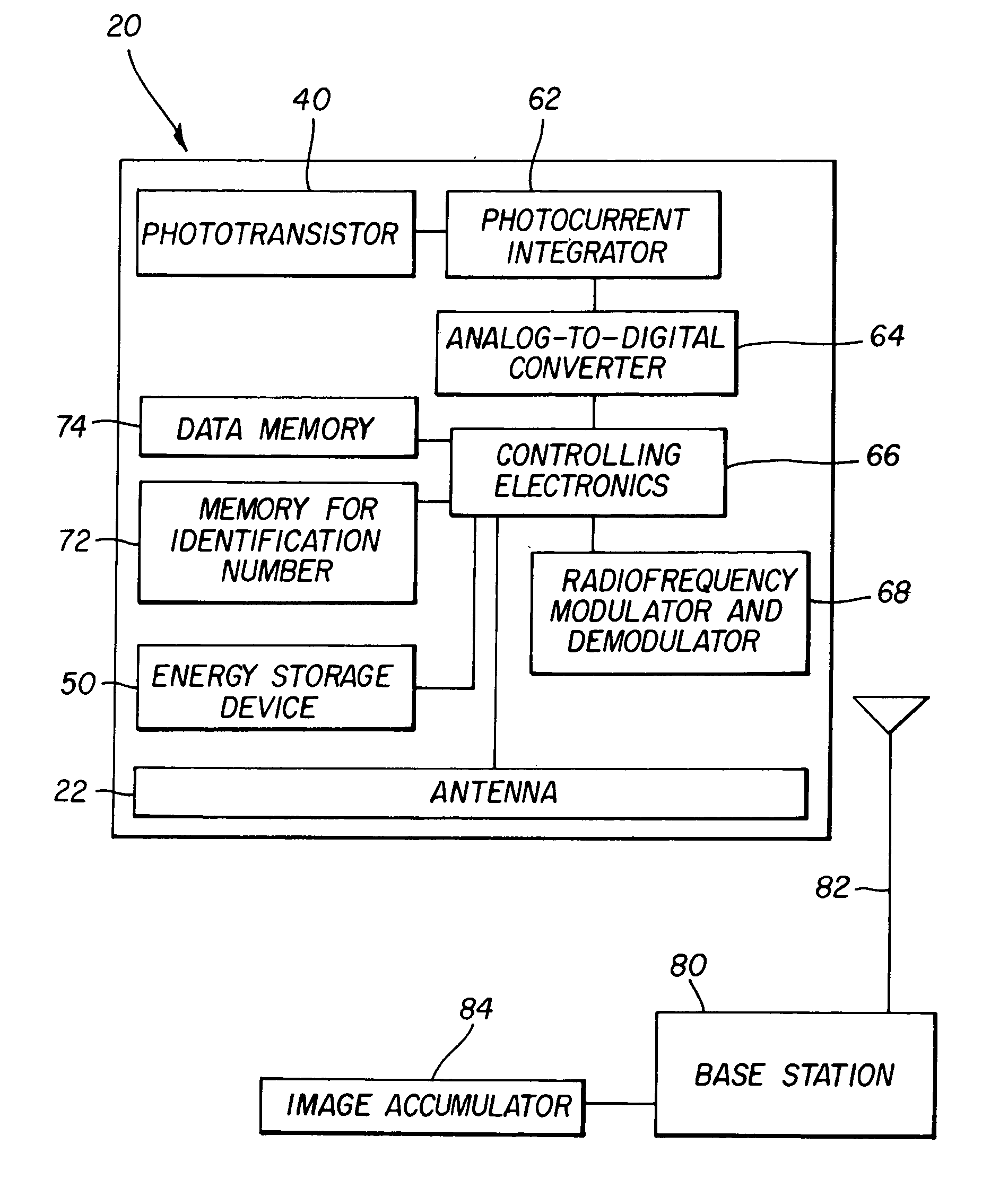
ActiveUS7015479B2Reduce lossesReduces and prevents signalTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesSheet filmRadiation flux
A digital film grain (20) comprises a phototransistor (40) which produces an electrical signal having a strength which is related to an input radiation flux. A transponder receives commands and power from a base station (80) and transmits information quantifying the radiation observed by that digital film grain. An image accumulator (84) connected to the base station (80) assembles an image from the profile of radiation reported by a distribution of digital film grains correlated to the locations of those grains.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
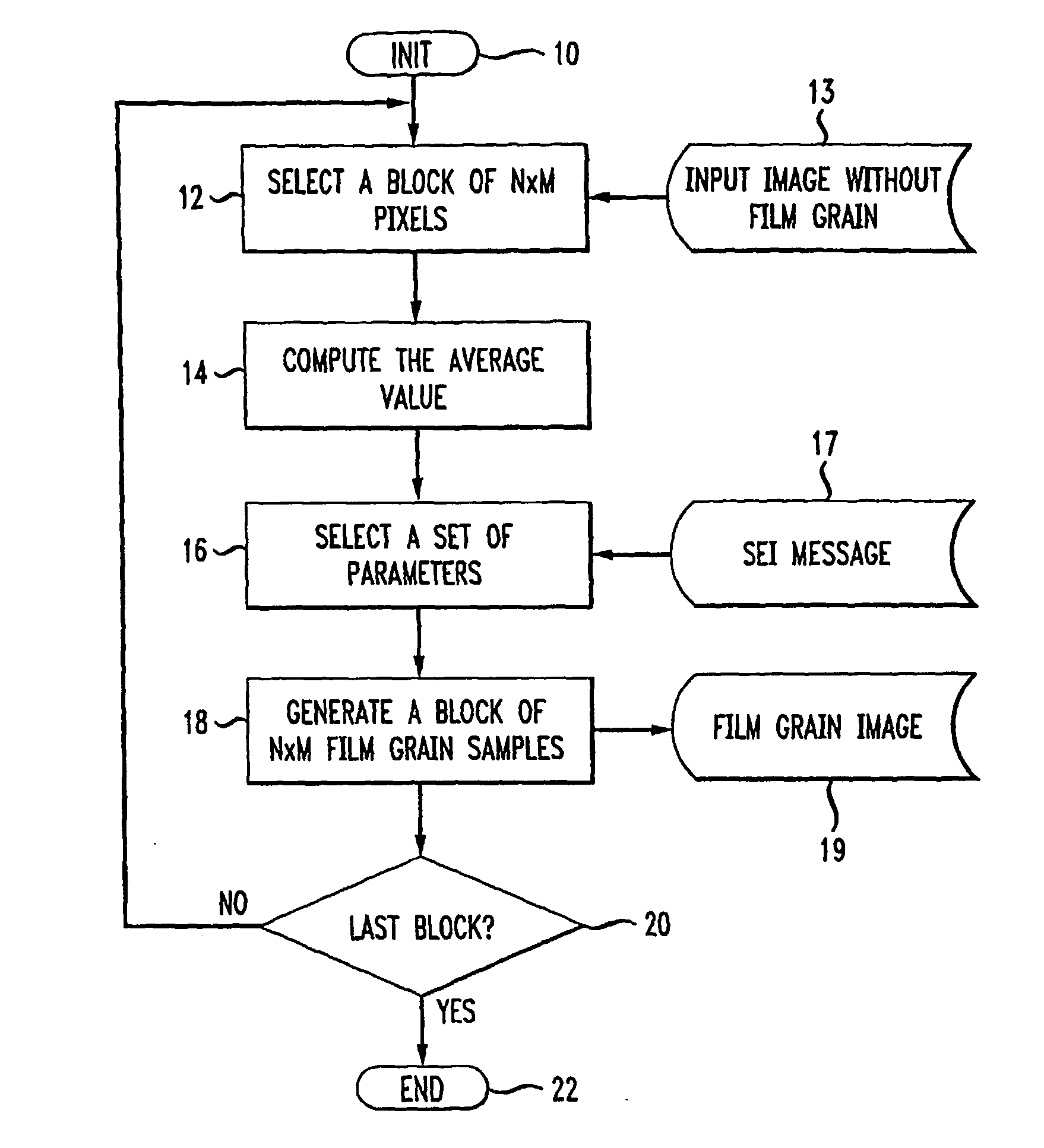
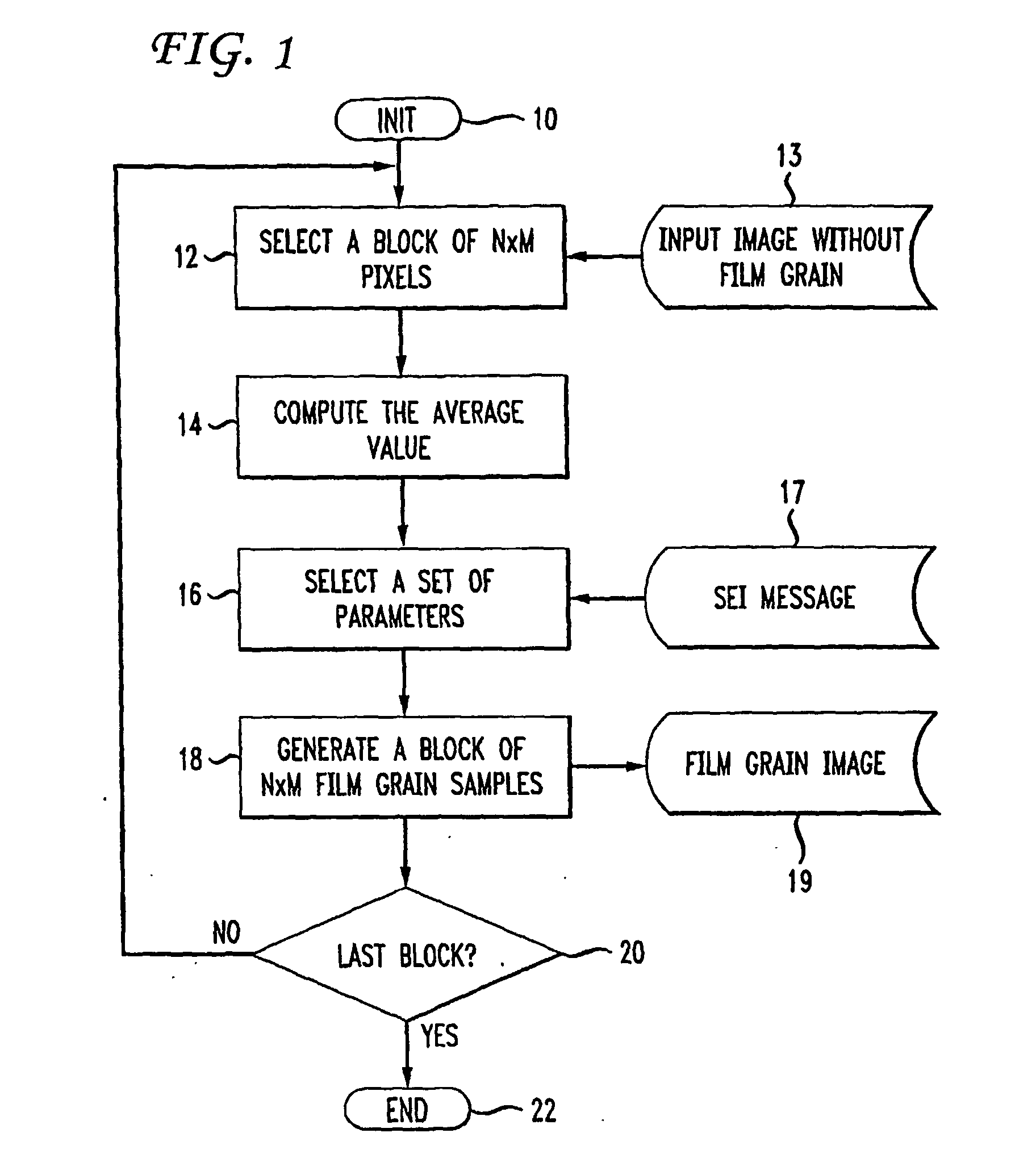
Method for simulating film grain by mosaicing pre-computer samples
InactiveUS20070058878A1Reduce complexityReduce artifactsImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImage mapComputer science
Film grain is simulated in an output image using pre-established blocks of film grain from a pool of pre-established blocks. Successive film grain blocks are selected by matching the average intensity of a block from the pool to the average intensity of a successive one of a set of M×N pixels in an incoming image. Once all of the successive pixel blocks from the image are matched to selected film grain blocks, the selected film grain blocks are “mosaiced”, that is composited into a larger image mapped to the incoming image.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
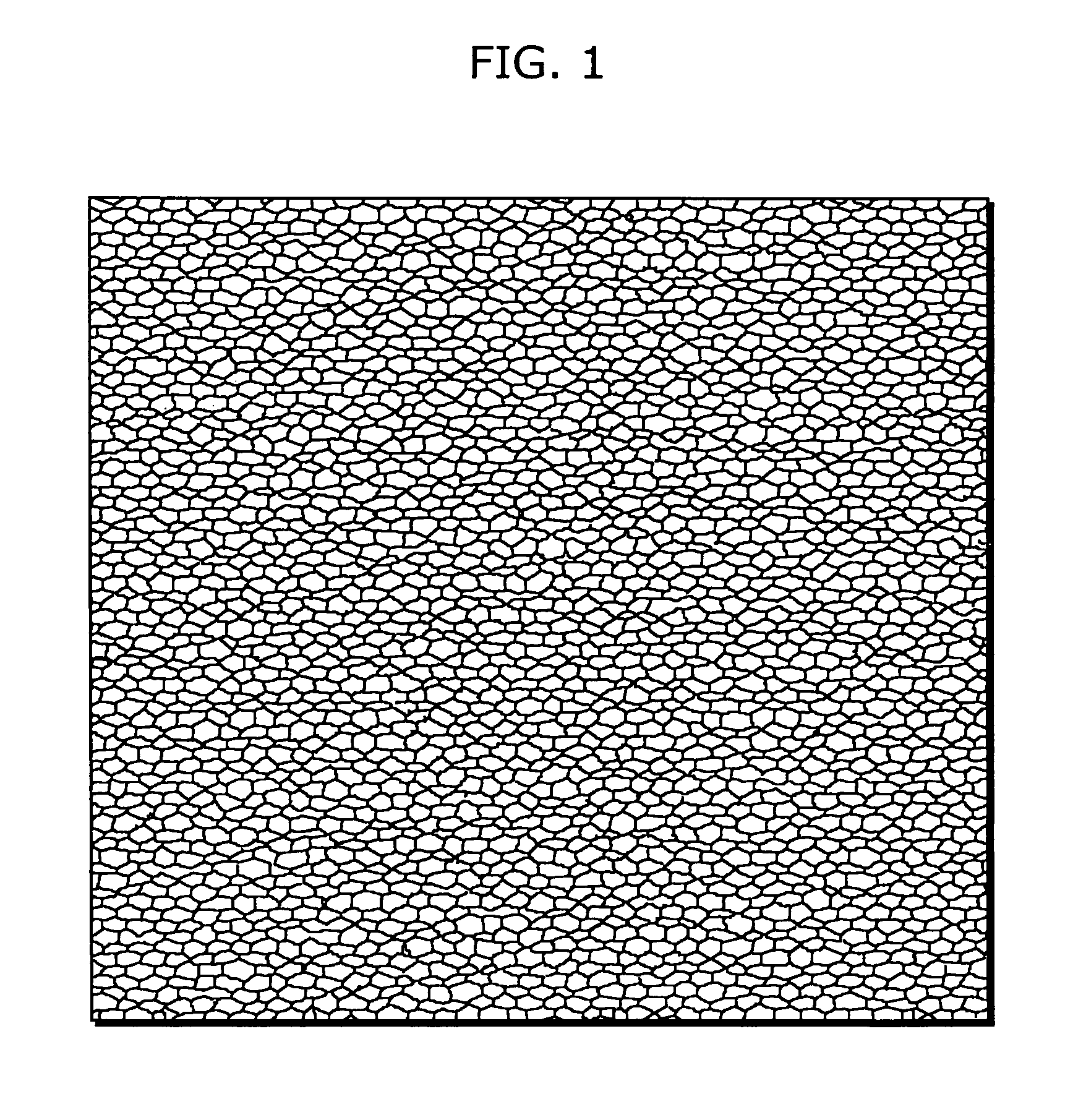
Moving picture encoding method and moving picture decoding method
InactiveUS20060256853A1Good reproducibilityImprove picture qualityImage enhancementImage analysisSuperimpositionEngineering
A moving picture coding apparatus (100) includes a coding unit (110) that generates a coded stream by coding inputted pictures and a film grain coding unit (130) that codes a representative pattern by selecting film grain components equivalent to at least one macro block and regarding the film grains as a representative pattern. On the other hand, a moving picture decoding apparatus (200) includes a decoding unit (210) that generates decoded picture data by decoding the coded stream and a film grain preparation unit (230) that prepares a superimposition pattern based on the representative pattern and additional information, and a synthesizing unit (240) that synthesizes the decoded picture data with the superimposition pattern.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
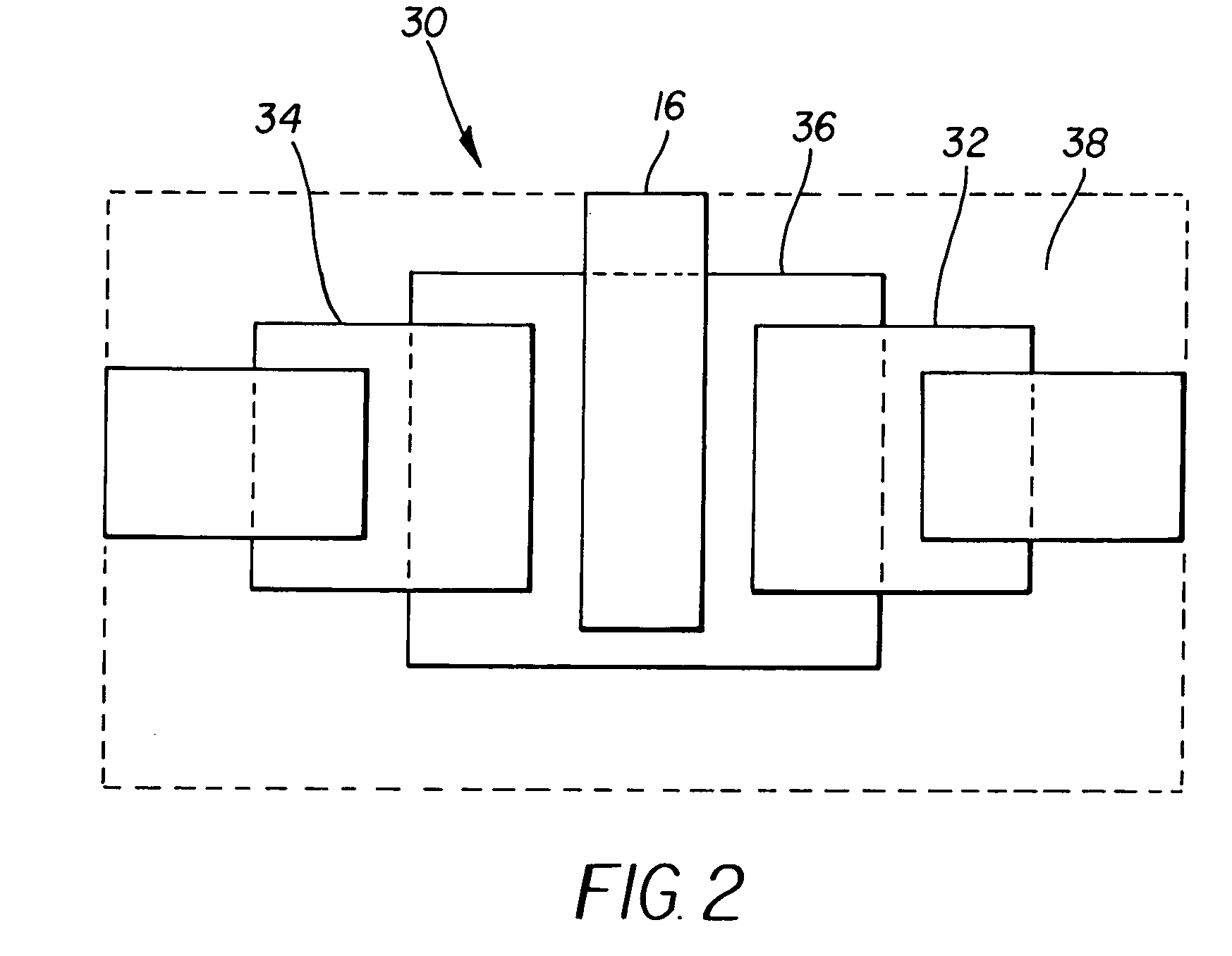
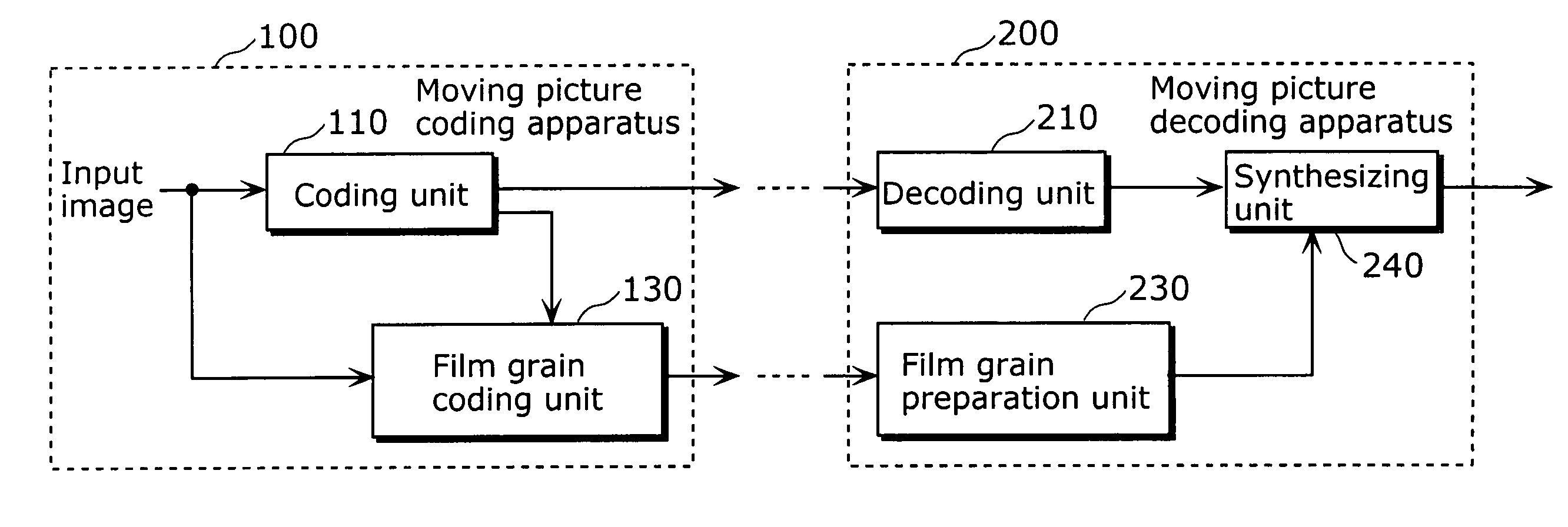
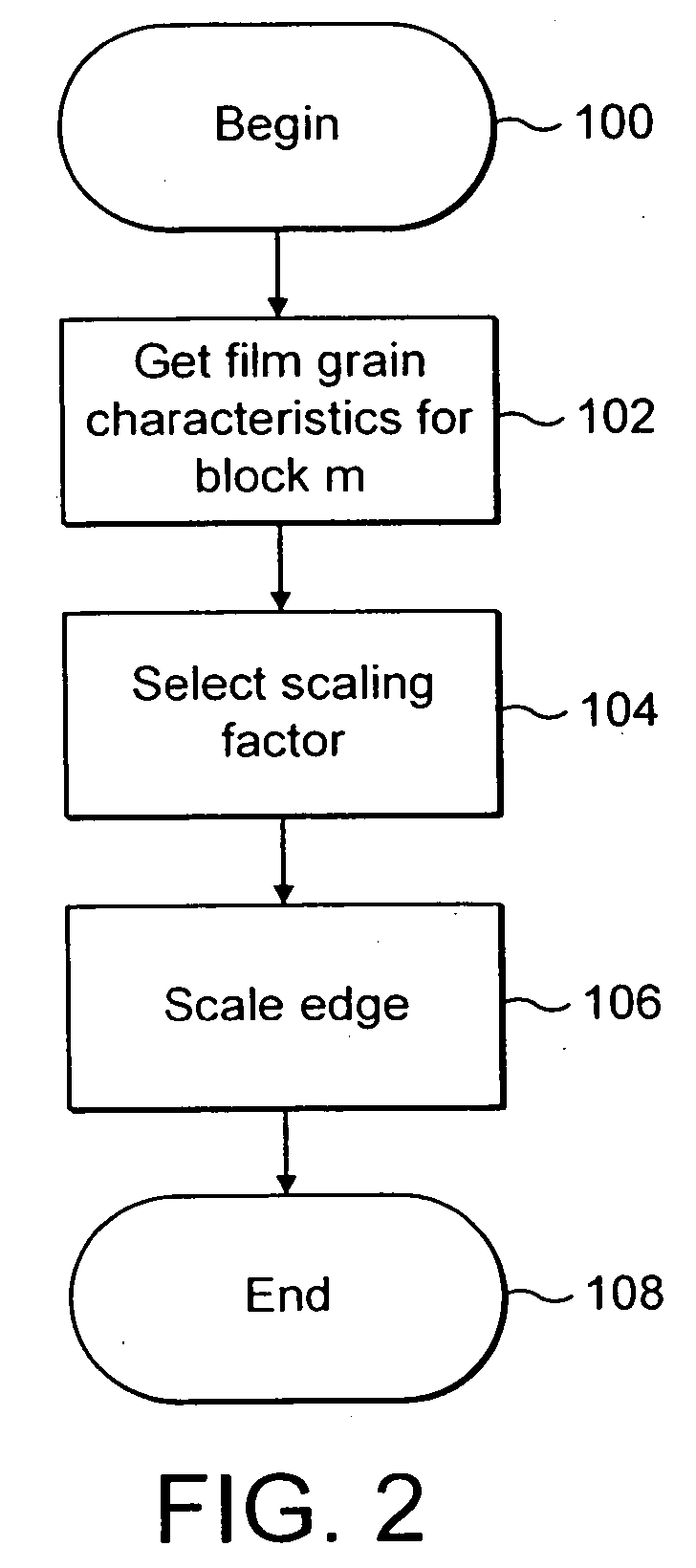
Film grain simulation method
Briefly, in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present principles, simulation of a block of film grain for addition to a block of an image occurs by first establishing at least one image parameter in accordance with at least one attribute of the block. Thereafter, a block of film grain is established in accordance with the image parameter. Deblocking filtering can be applied to the film grain block.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Film grain simulation technique for use in media playback devices
Simulation of a block of film grain for addition to a block of an image occurs by first establishing at least one parameter at least in part in accordance with an attribute of the image block At least one at least one block of film grain is simulated from at least one film grain pattern generated in accordance with the at least one parameter. In particular, the film grain pattern is generated using a bit accurate technique.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
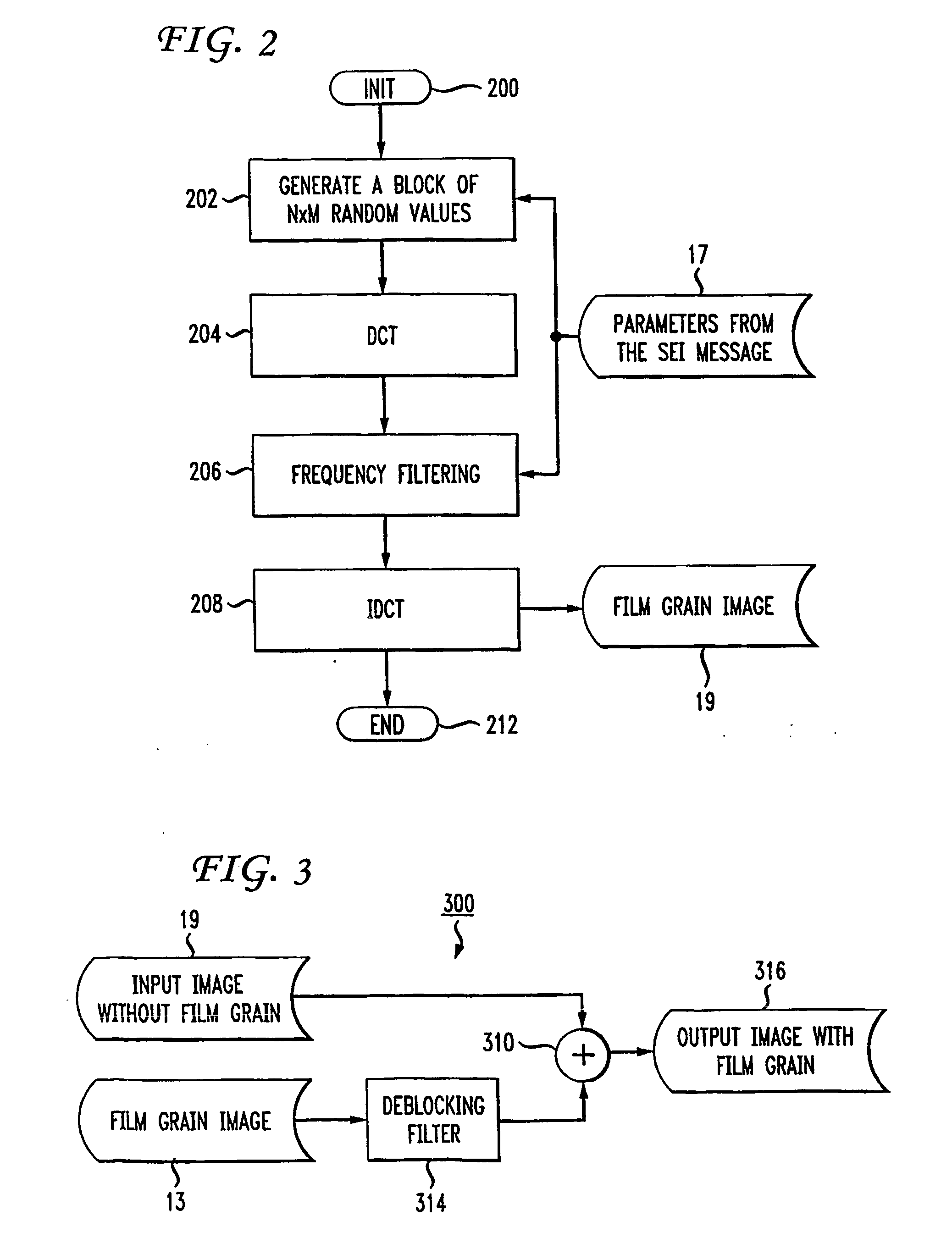
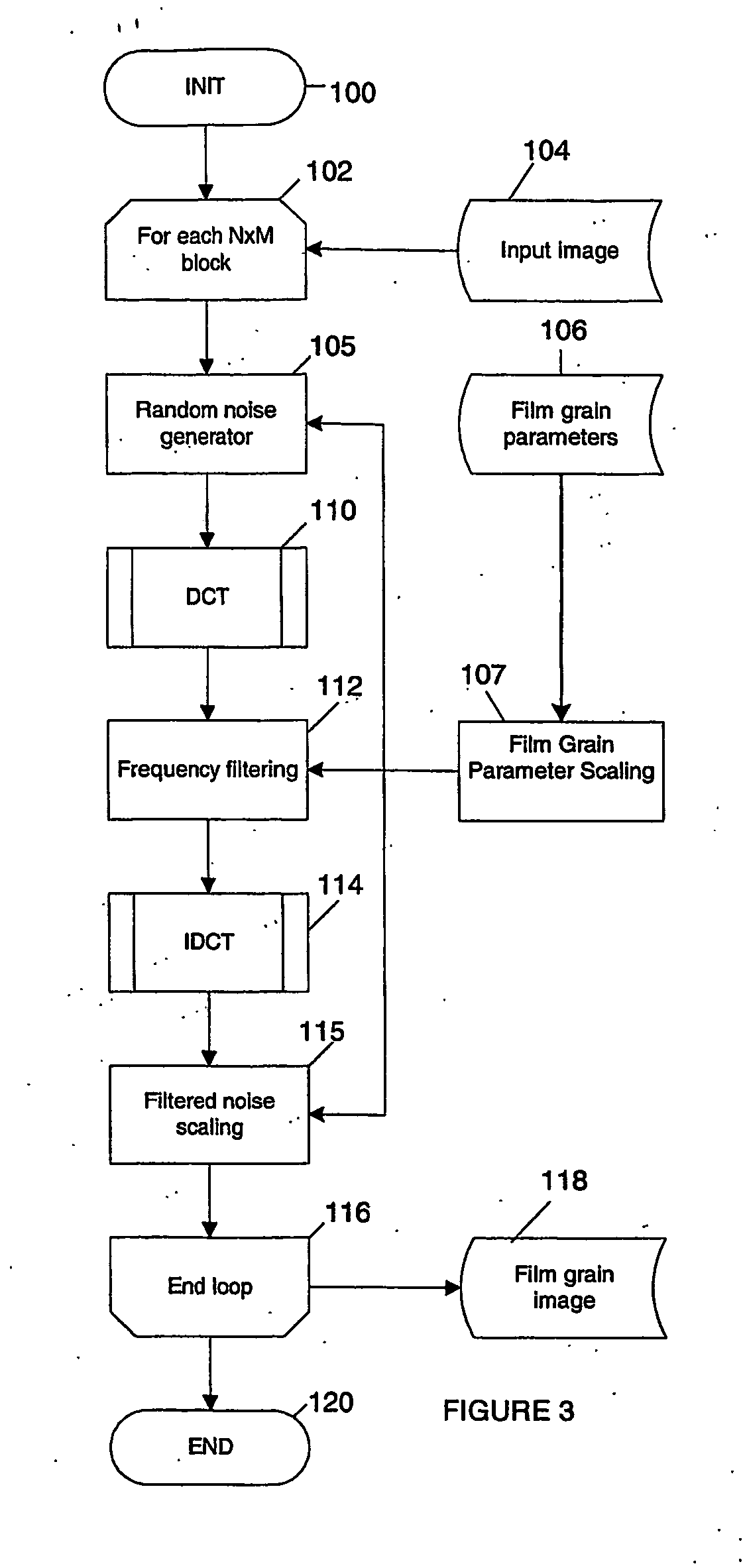
Technique for simulating film grain using frequency filtering
Simulation of film grain in an image can occur by compressing a video image, then transmitting compressed video together with a message containing at least one parameter indicative of the original film grain, to a decoder, and restoring the original grainy appearance of images by having the decoder simulating film grain based on the content of the film grain message. To improve efficiency, one or more parameters of film grain information undergo scaling in accordance with a target pixel block size for pixel blocks in the image. Such scaling allows for the use of conventional circuitry for performing block-based operations in connection with the film grain simulation.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
Technique for bit-accurate film grain simulation
The simulation of film grain in an image makes use of parameters contained in a Supplemental Enhancement Information (SEI) message that accompanies the image upon transmission. The SEI message specifies film grain simulation parameters such as the film simulation model, the blending mode, and color space.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
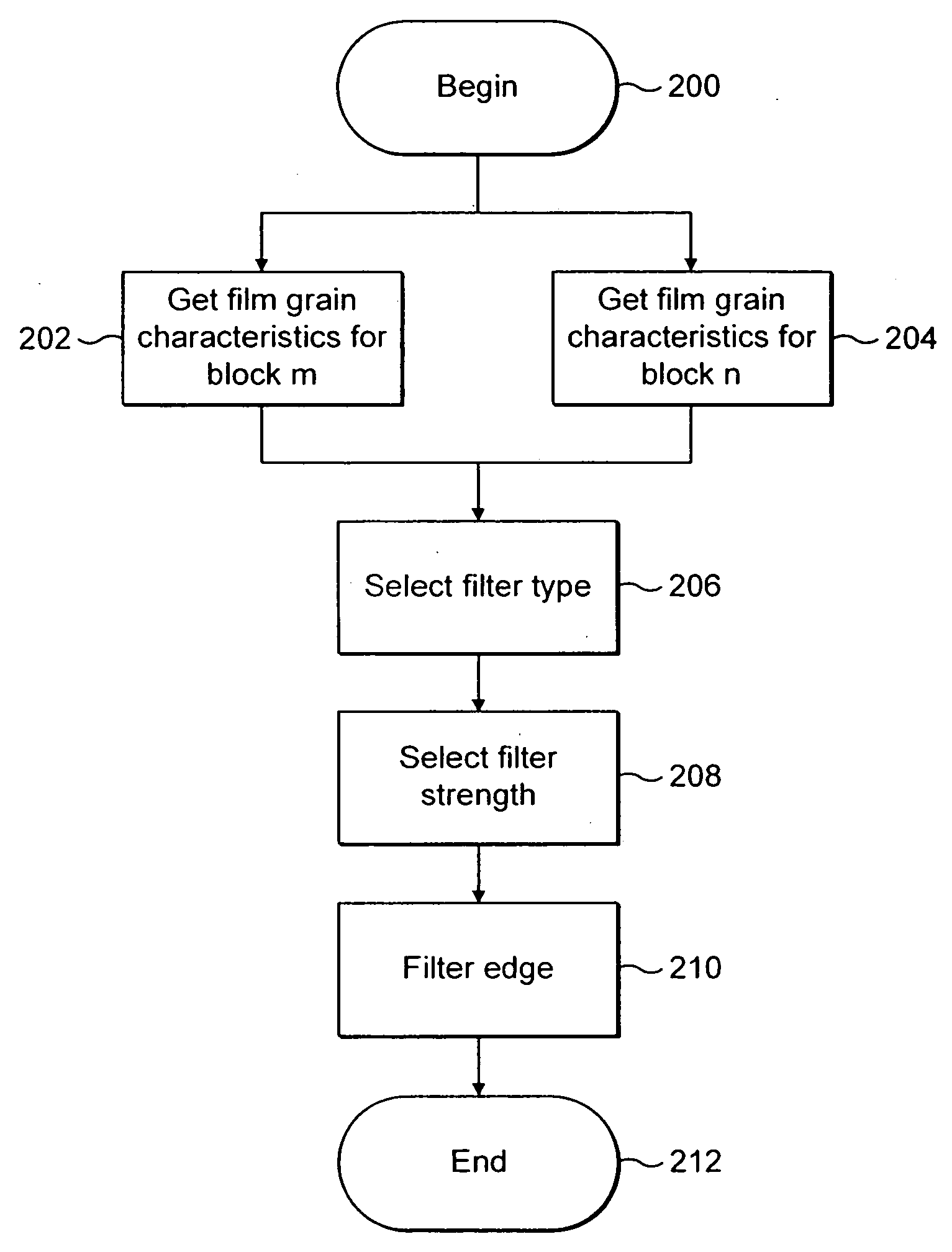
Technique for adaptive de-blocking of block-based film grain patterns
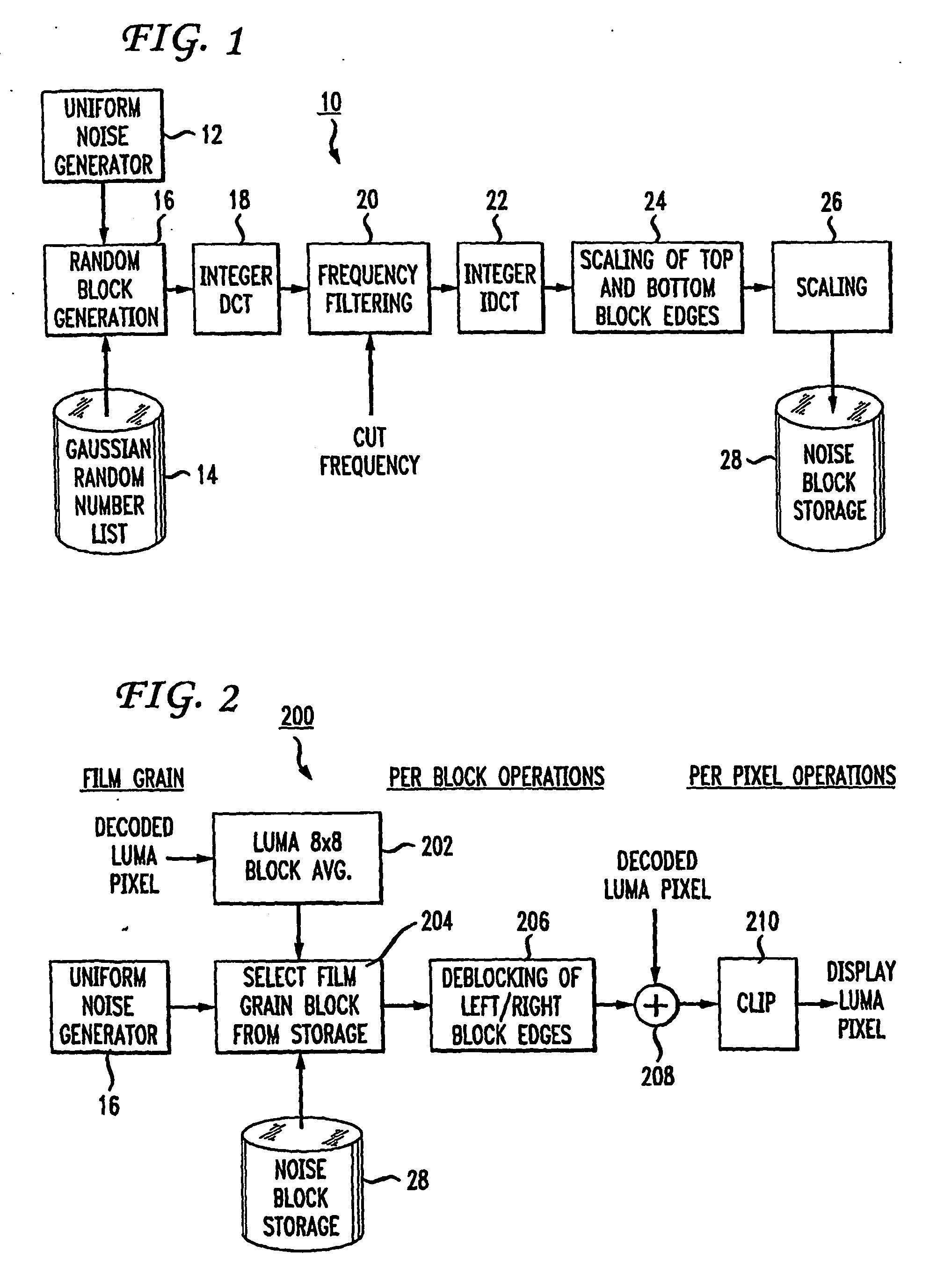
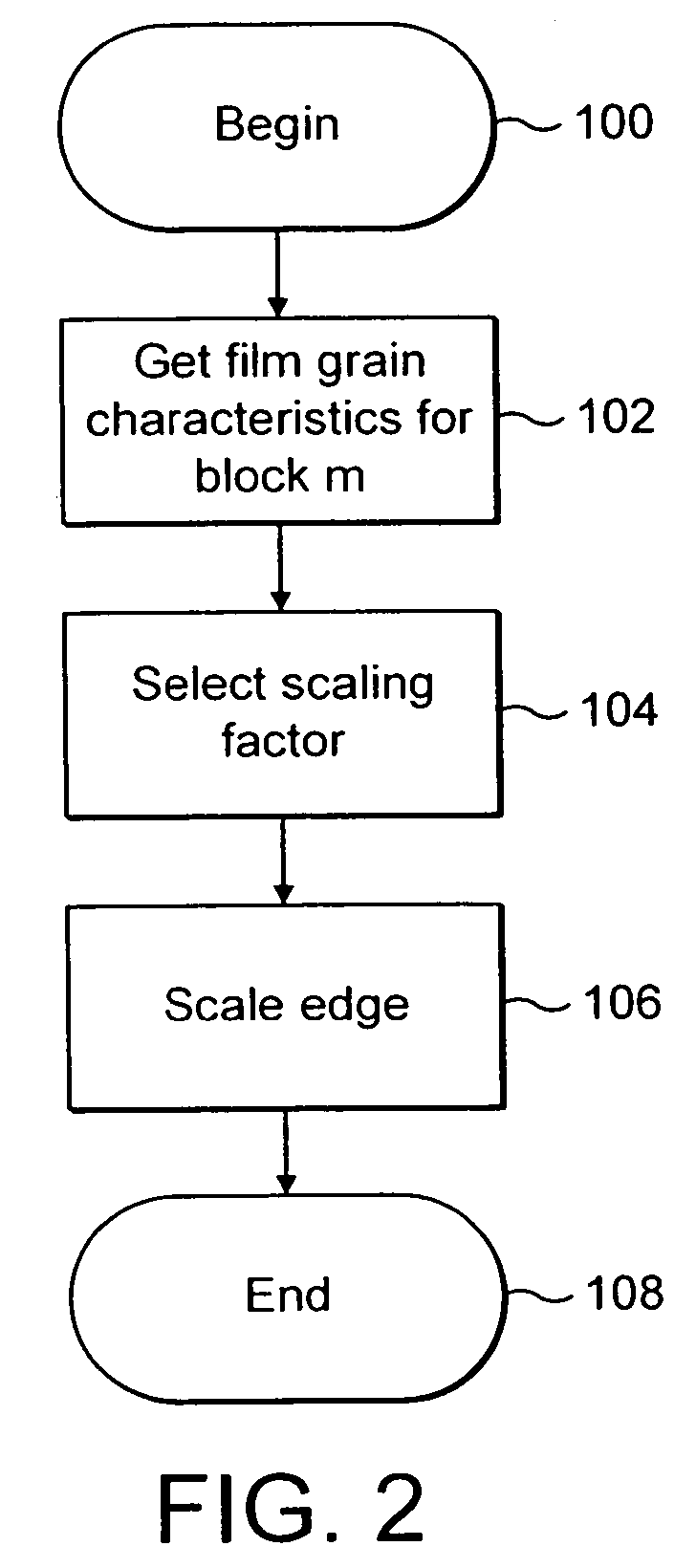
Reduction in the blockiness of a simulated film grain block can be achieved either by the use of adaptive downscaling or adaptive deblocking filtering to adjust the intensity of the pixels at the block edge in accordance with at least one film grain block parameter, such as film grain size, intensity and texture. Performing such adaptive downscaling or adaptive deblocking filtering achieves improved performance at lower computational cost by avoiding modification of film grain block pixels in lesser affected areas.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
Method and apparatus for masking of video artifacts and/or insertion of film grain in a video decoder
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for reading film grain patterns in a raster order in film grain simulation
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for reading film grain patterns in a raster order in film grain simulation including establishing a pseudo-random starting position, repeating the pseudo-random starting position for each line of a group of film grain blocks, and using a different pseudo-random starting position for each display line of a next group of film grain blocks. In various embodiments of the present invention, the different pseudo-random starting positions are triggered by resetting at least one seed value of a pseudo-random number generator implemented to determine said pseudo-random starting positions.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
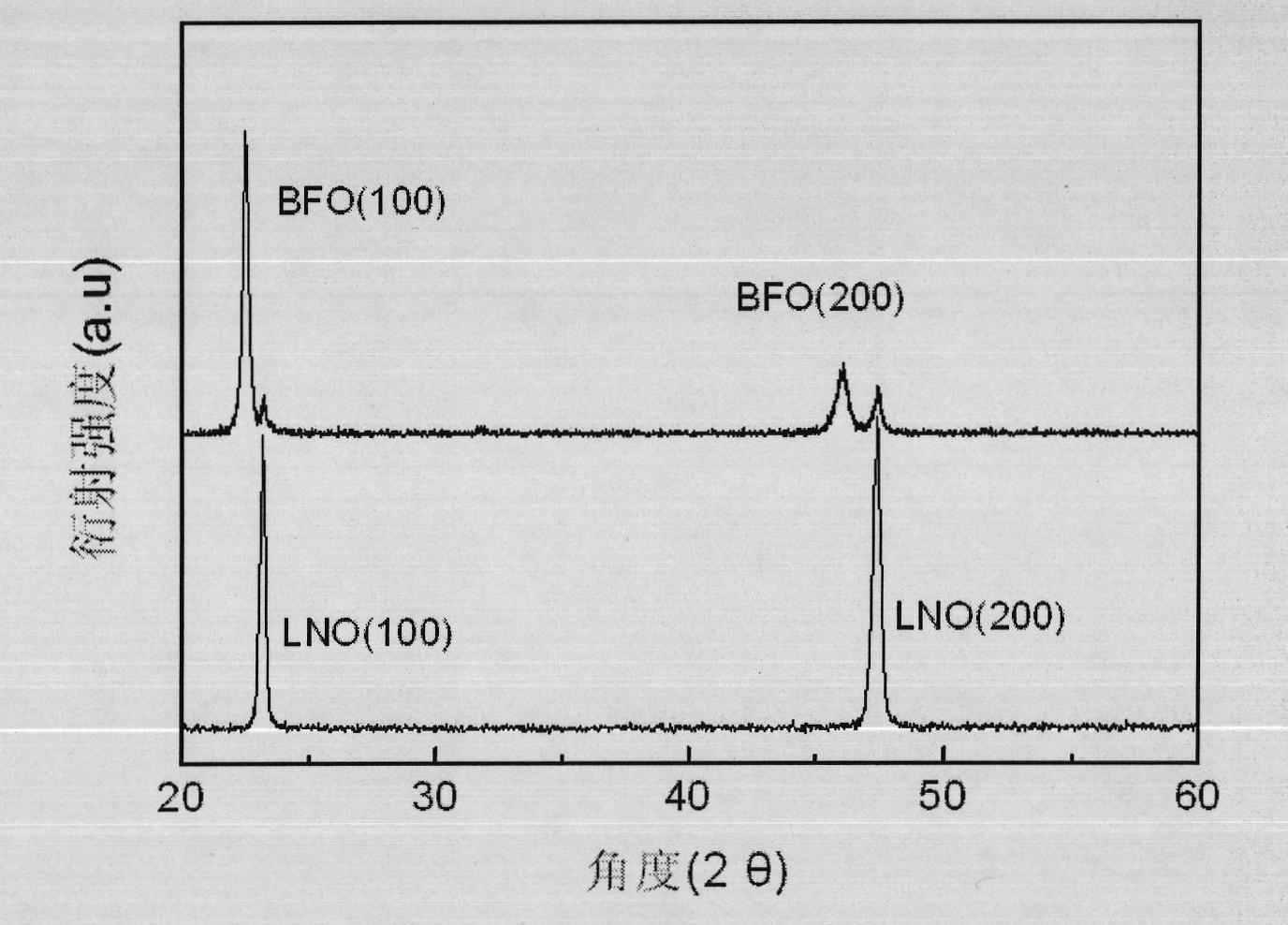
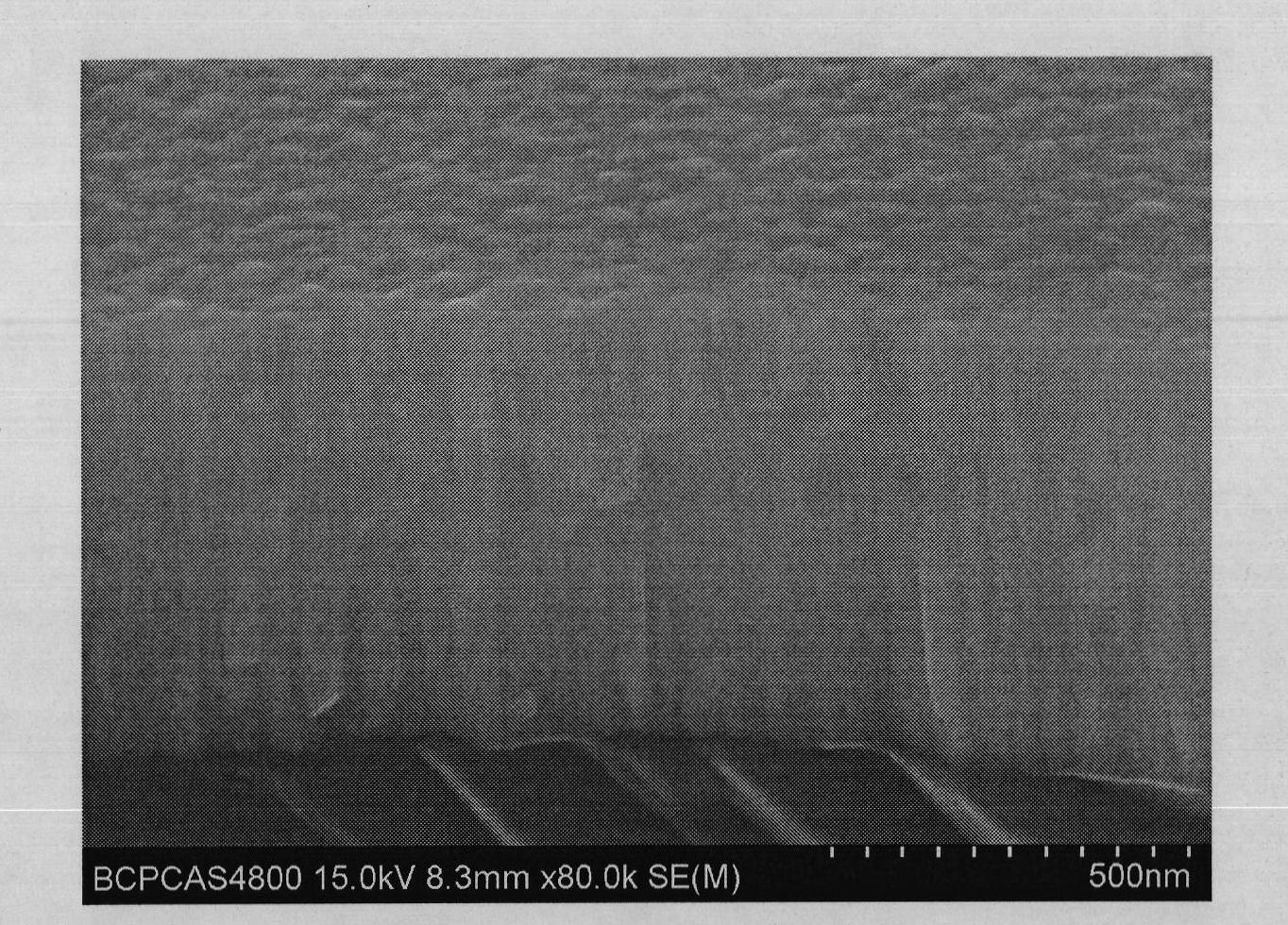
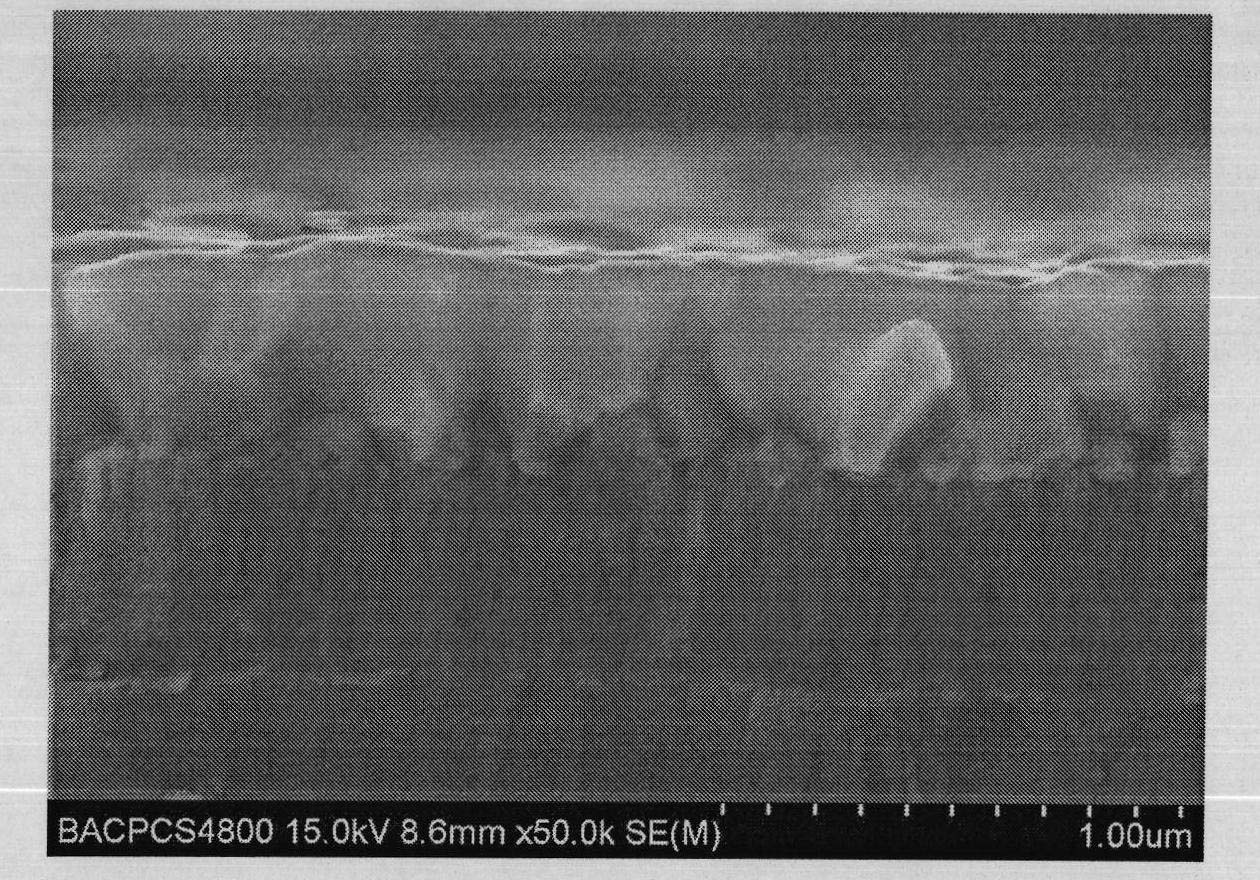
Method for preparing highly (100) oriented BiFeO3 films on Si substrate
InactiveCN102051582AHigh priceCan't solveVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCrystalliteFilm grain
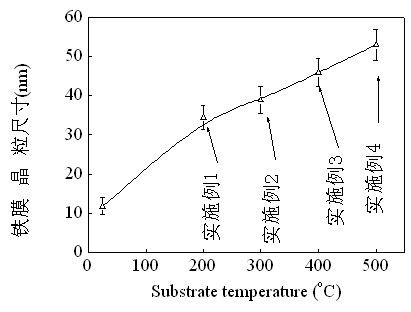
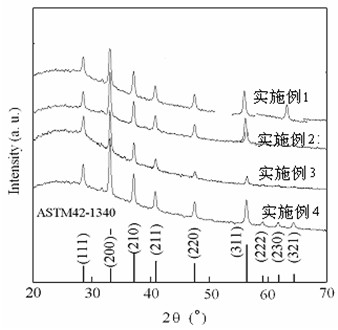
The invention discloses a method for preparing highly (100) oriented BiFeO3 films on a Si substrate, which belongs to the technical field of functional material preparation. The method comprises the following steps: the Si substrate is pre-treated; a highly oriented LaNiO3 film is prepared on the substrate by adopting the pulsed laser deposition method and a LaNiO3 target material; and a highly oriented BiFeO3 film is prepared on the LaNiO3 film by adopting the pulsed laser deposition method and a BiFeO3 target material. The product prepared by adopting the method provided by the invention has good compatibility, uniform film grain sizes, compactness in arrangement, high crystallinity and good orientation.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Process for preparing water transfer printing film
InactiveCN101695891AAvoid imprintingImprove product added valueDecorative surface effectsSputteringPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention relates to a process for preparing a water transfer printing film, which is mainly used for surface coating of workpieces. The process comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a polyvinyl alcohol film; 2) printing various patterns on the polyvinyl alcohol film, and adding a layer of bonding agent; 3) pressing logic grains on the polyvinyl alcohol film printed with the various patterns, or radiating laser film grains on the polyvinyl alcohol film in order to generate grains; 4) performing vacuum plating or sputtering on the polyvinyl alcohol film with the grains to generate metallic luster; 5) placing the polyvinyl alcohol film after the vacuum plating or sputtering on water surface, and letting a surface not printed with the pattern layer to contact the water surface; 6) spraying or coating a reducing agent on the printed surface, reducing the printed solid surface into a liquid surface, pressing a workpiece into the liquid surface from the top down, and transferring the patterns to the surface of a product through the water pressure; and 7) cleaning residues, drying, and spraying a finish paint to form a layer of transparent protective coating. The preparation process is simple and has low cost.
Owner:东莞市西迪艾史纳米科技有限公司
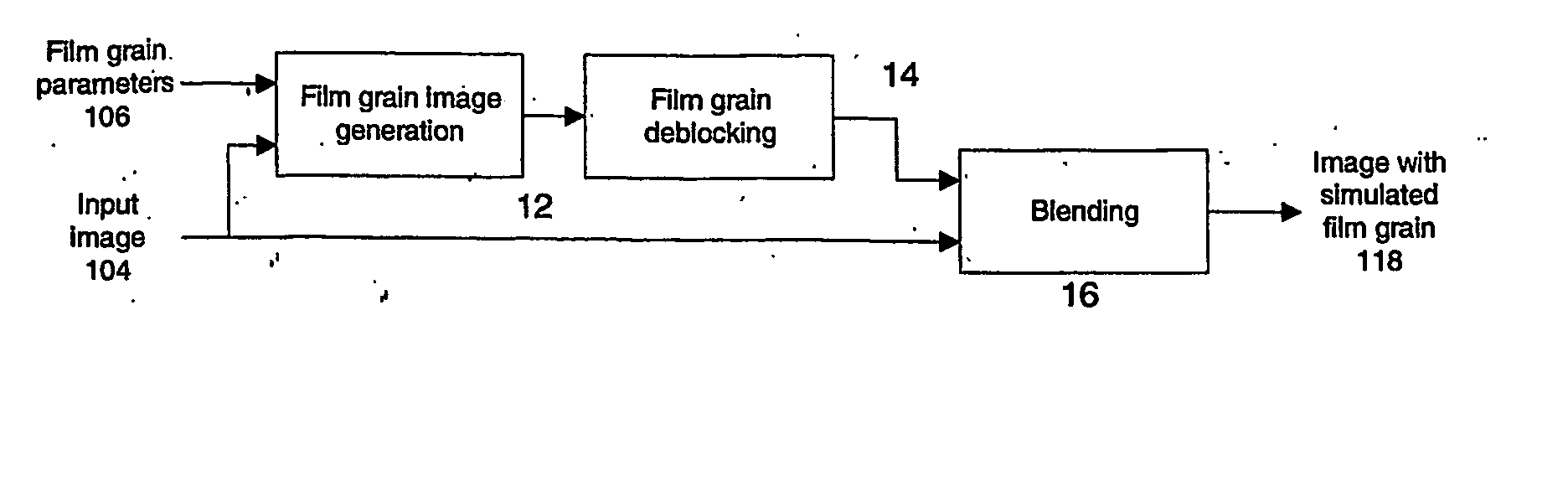
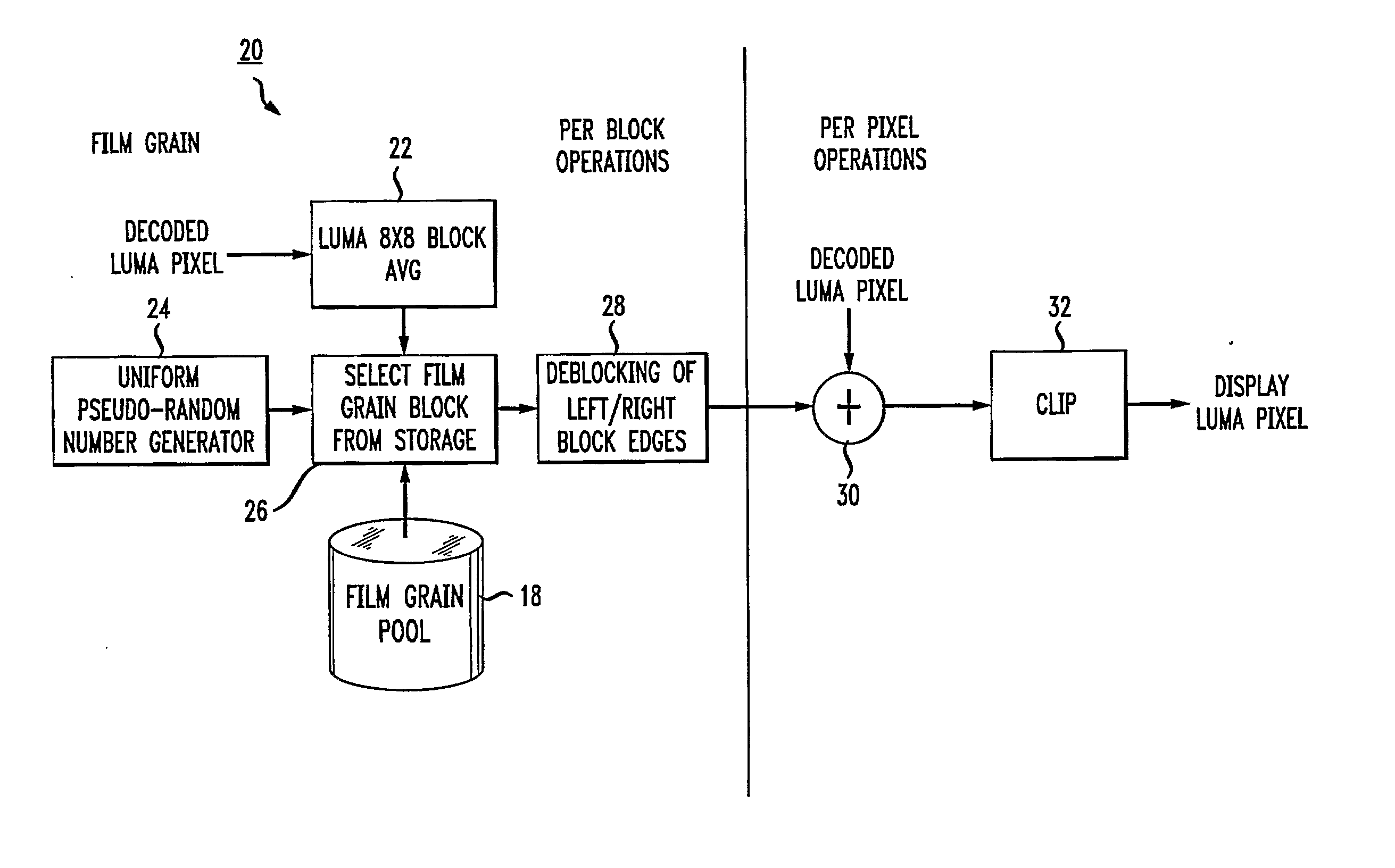
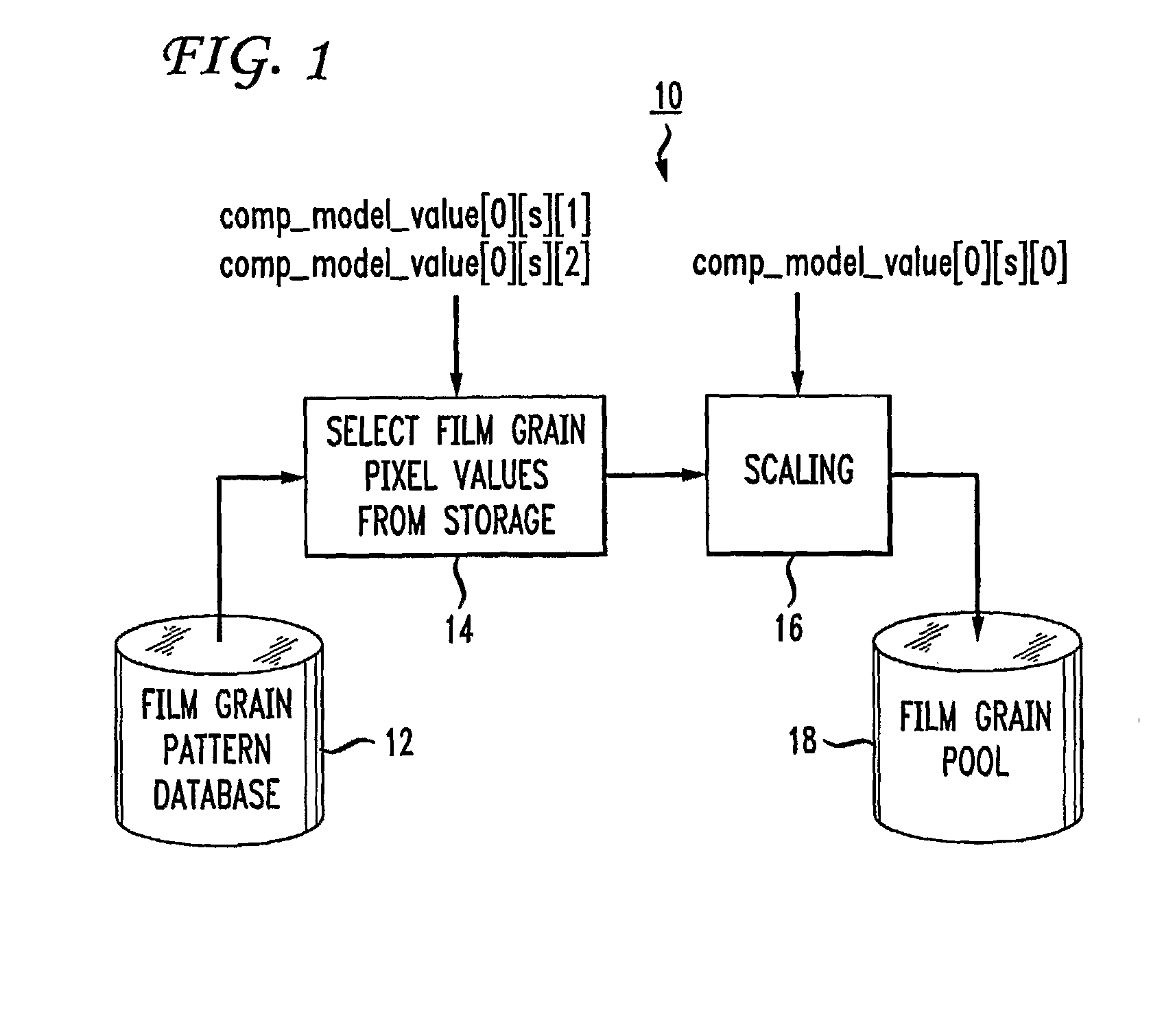
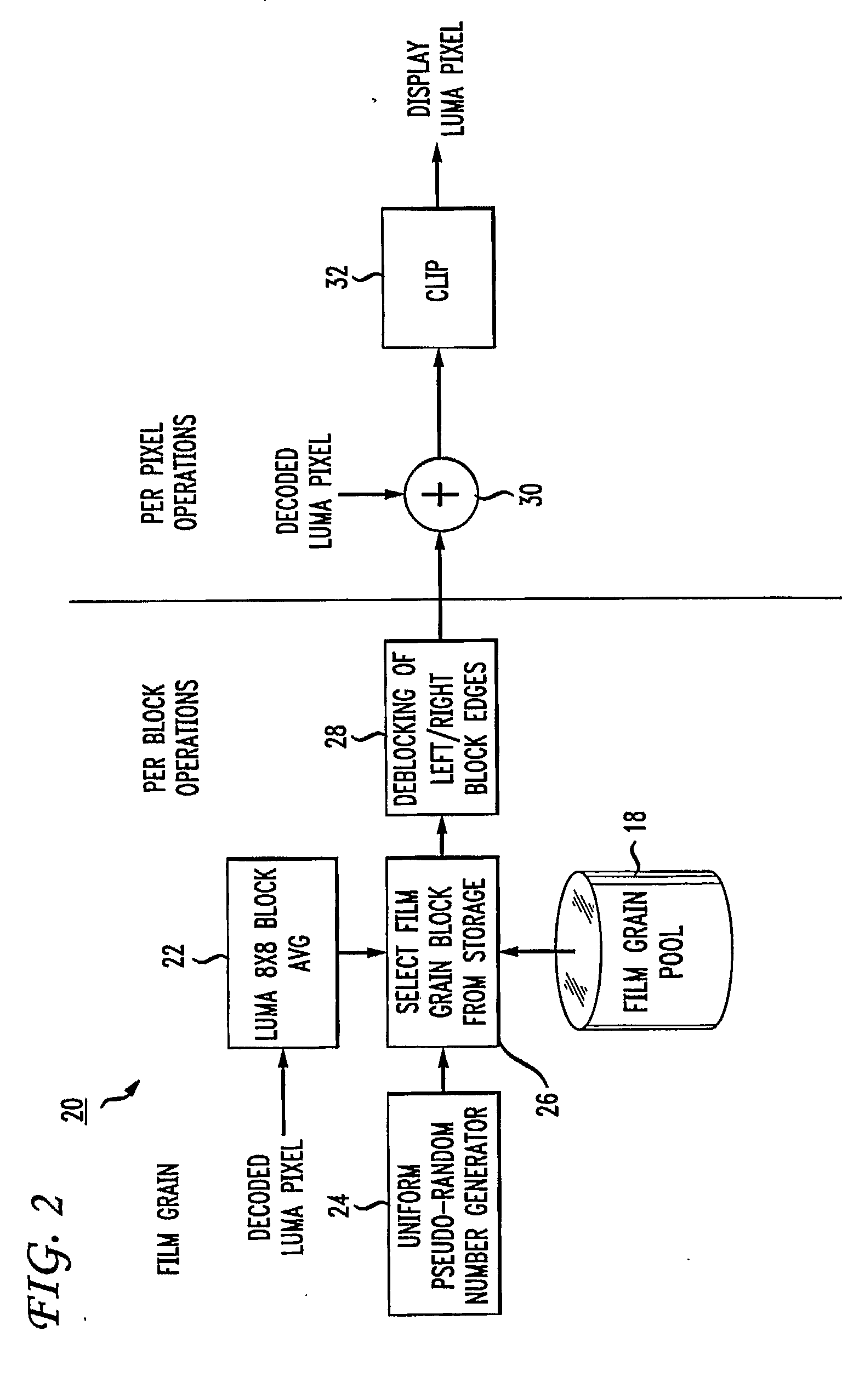
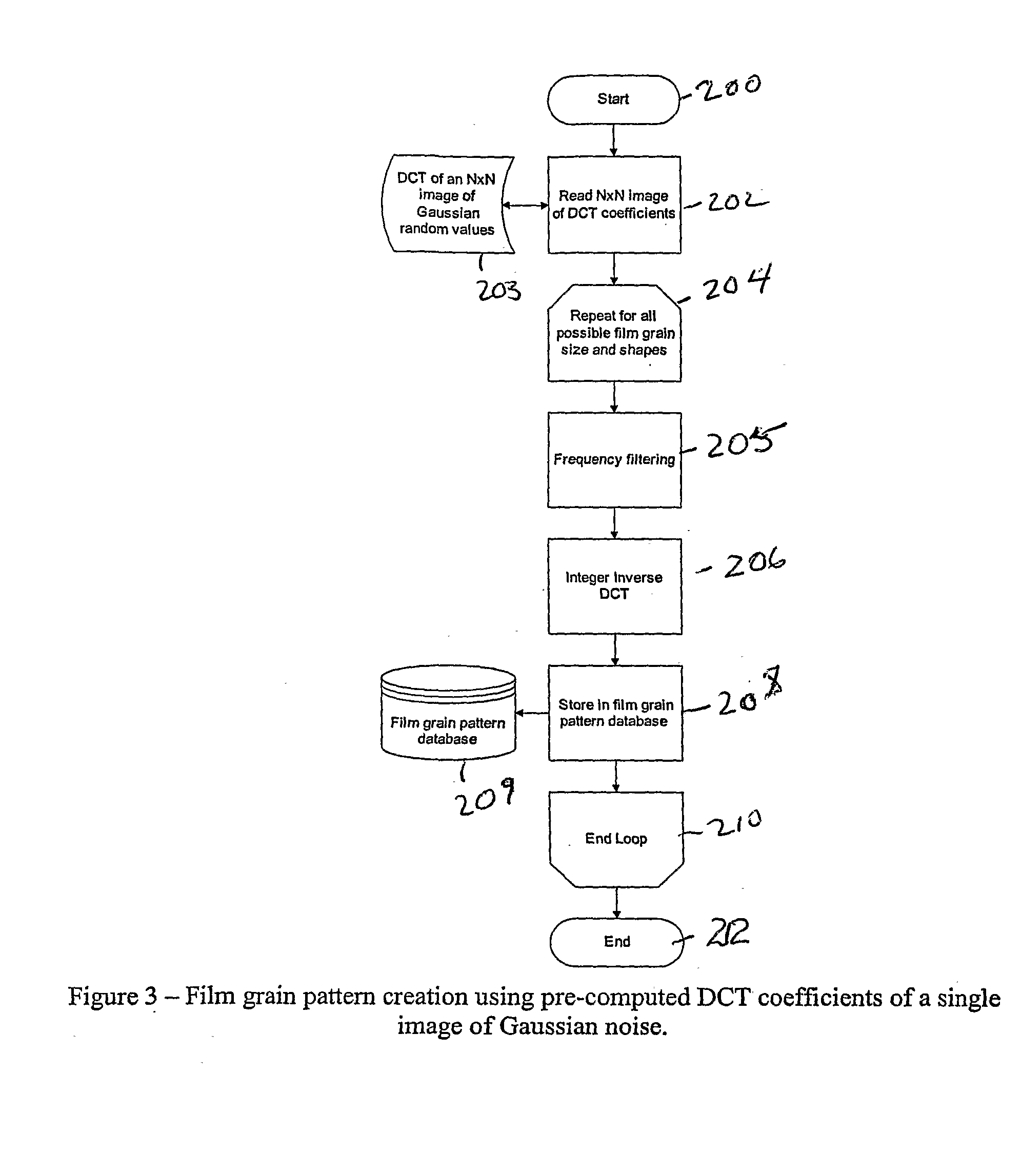
Technique for film grain simulation using a database of film grain patterns
Individual pixels in an image block undergo blending with film grain from a film grain block randomly selected from among a pool of previously established film grain blocks in accordance with a luma characteristic of the image block. Prior to blending, the selected film grain block undergoes deblocking by a deblocking filter (28). Following blending, a clipper clips the individual pixels prior to display. The pool of film grain blocks is created by scaling a set of film grain patterns in accordance with at least one parameter of a film grain information message that accompanies the image block.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
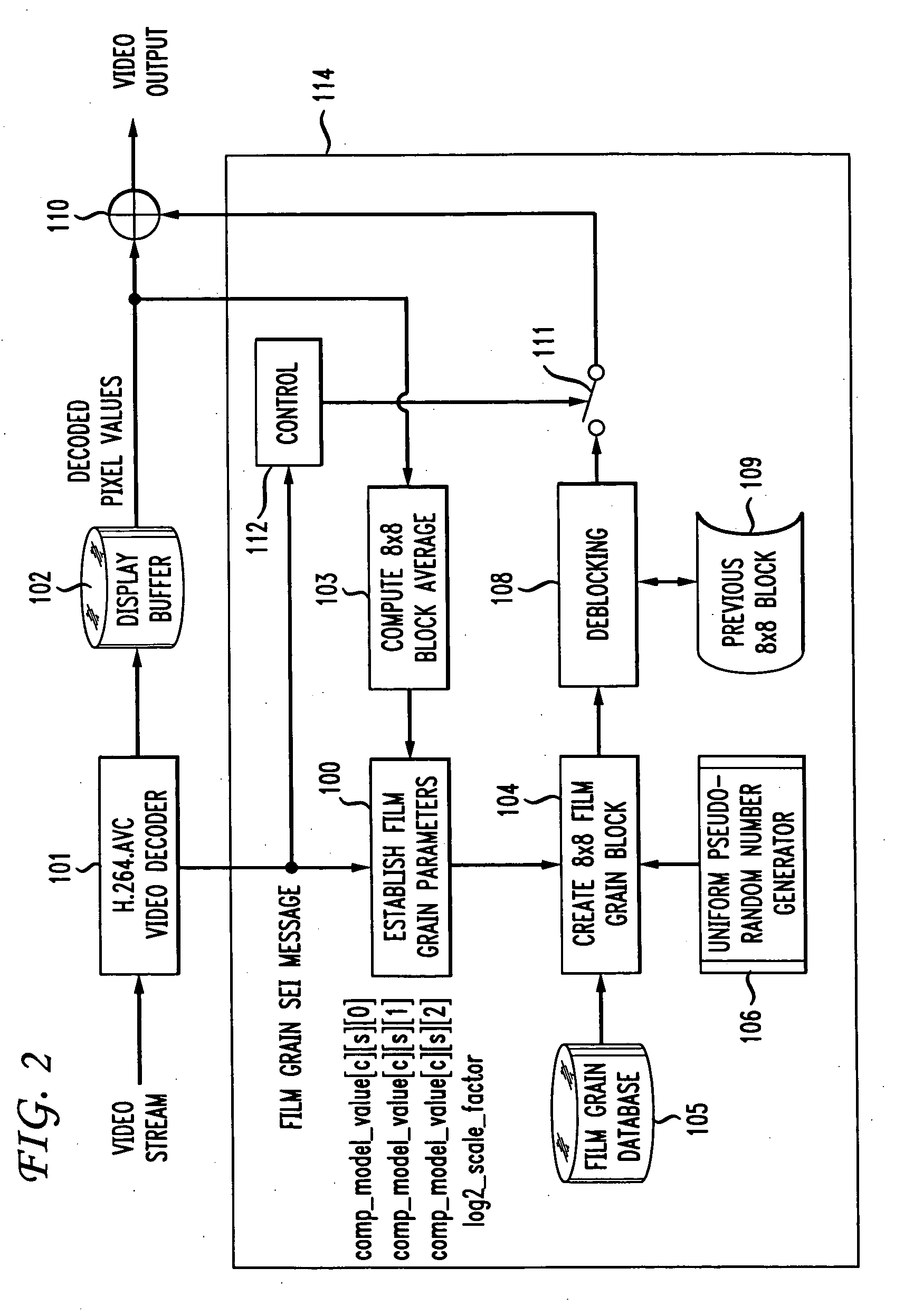
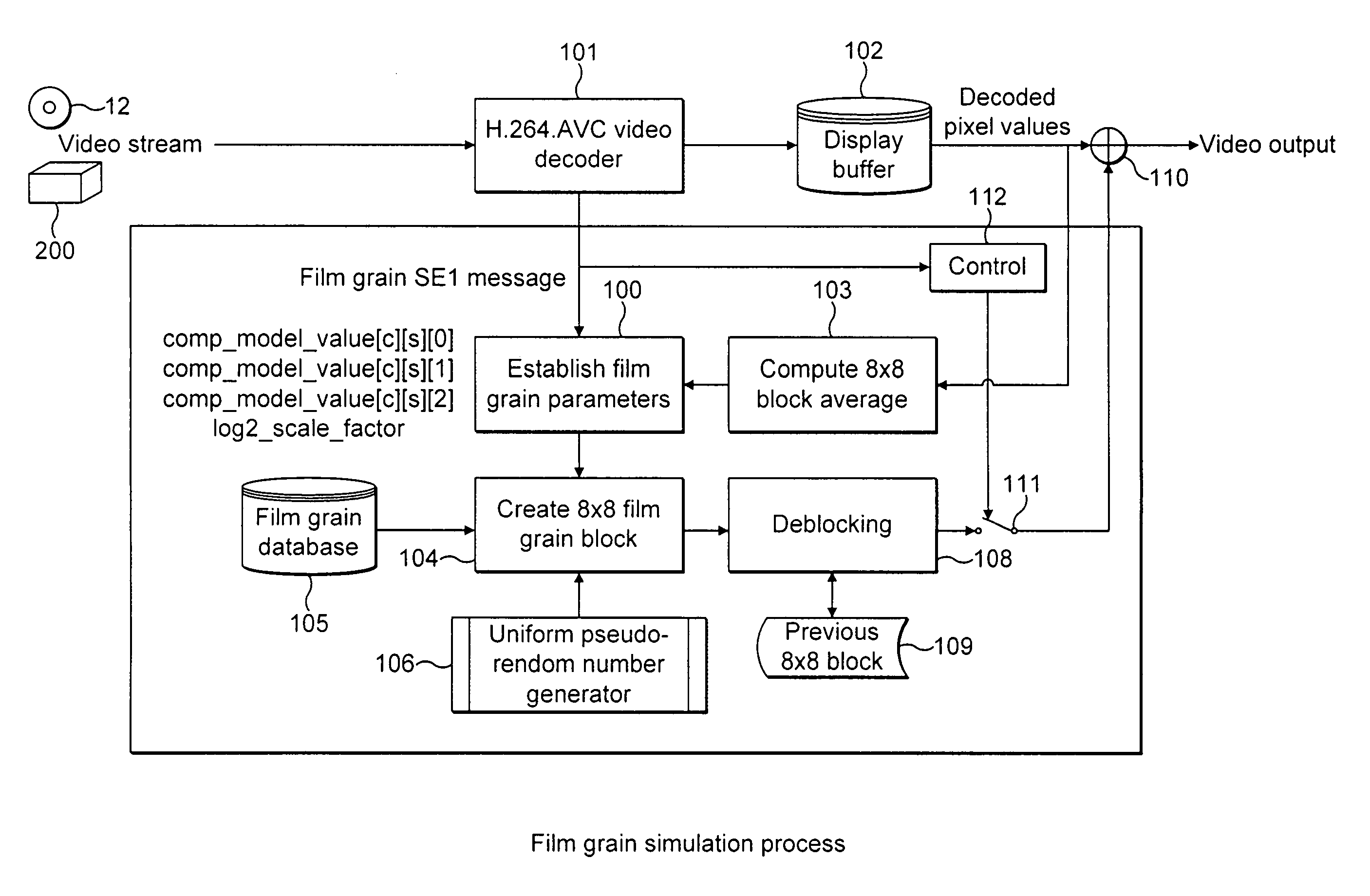
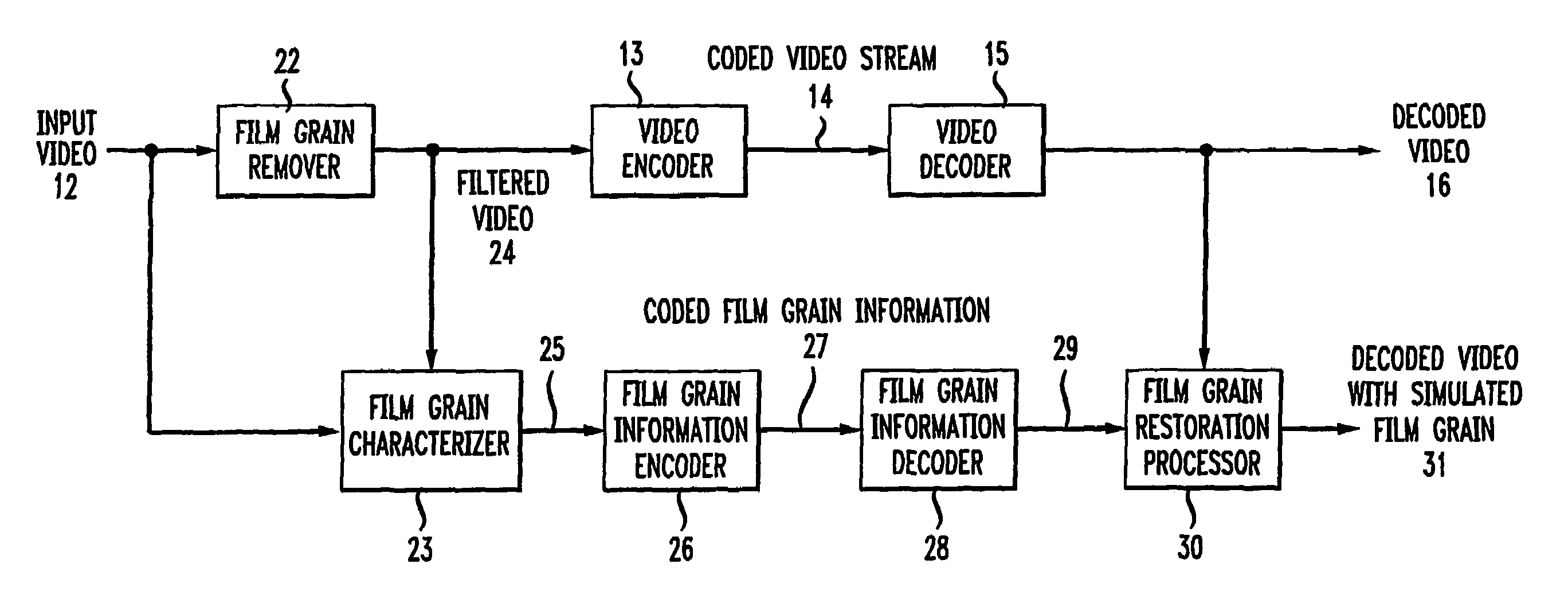
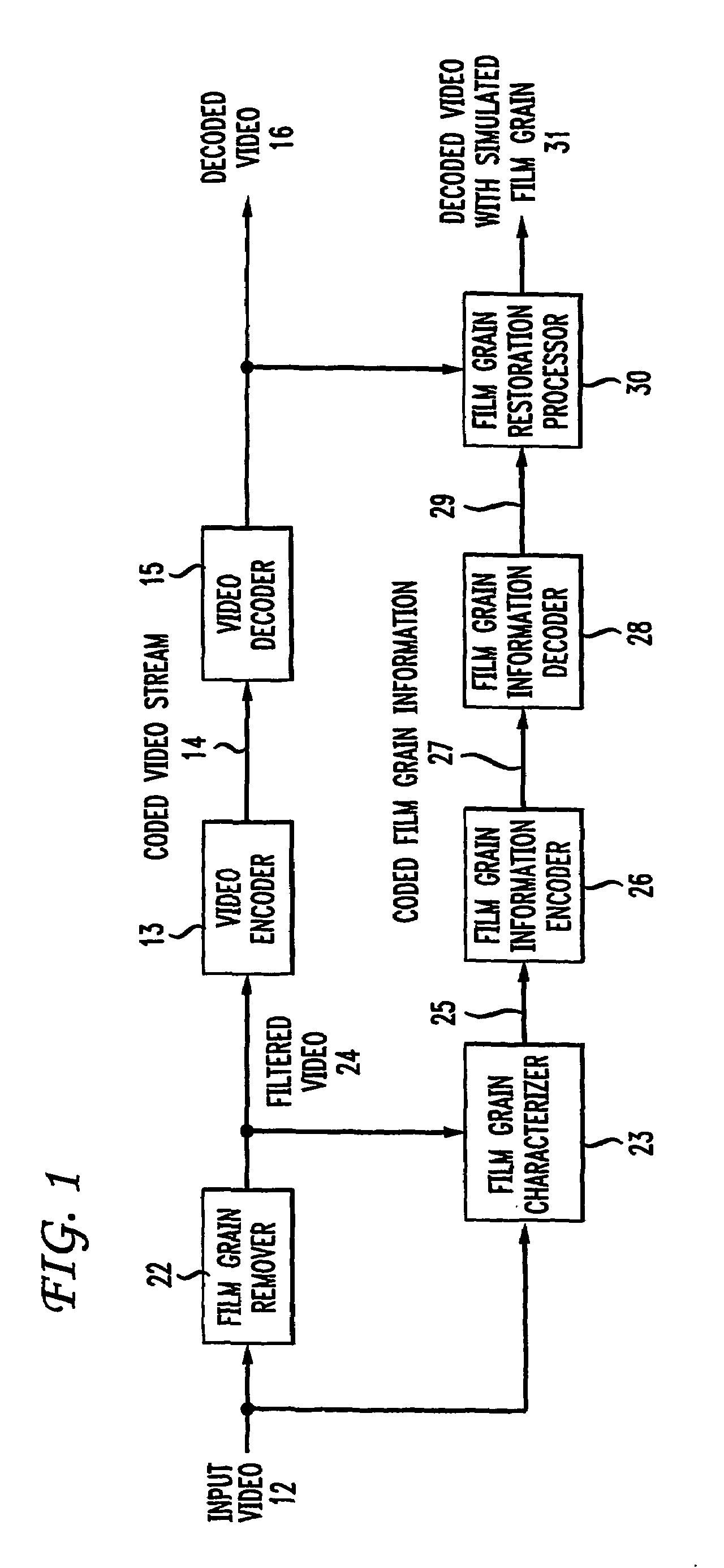
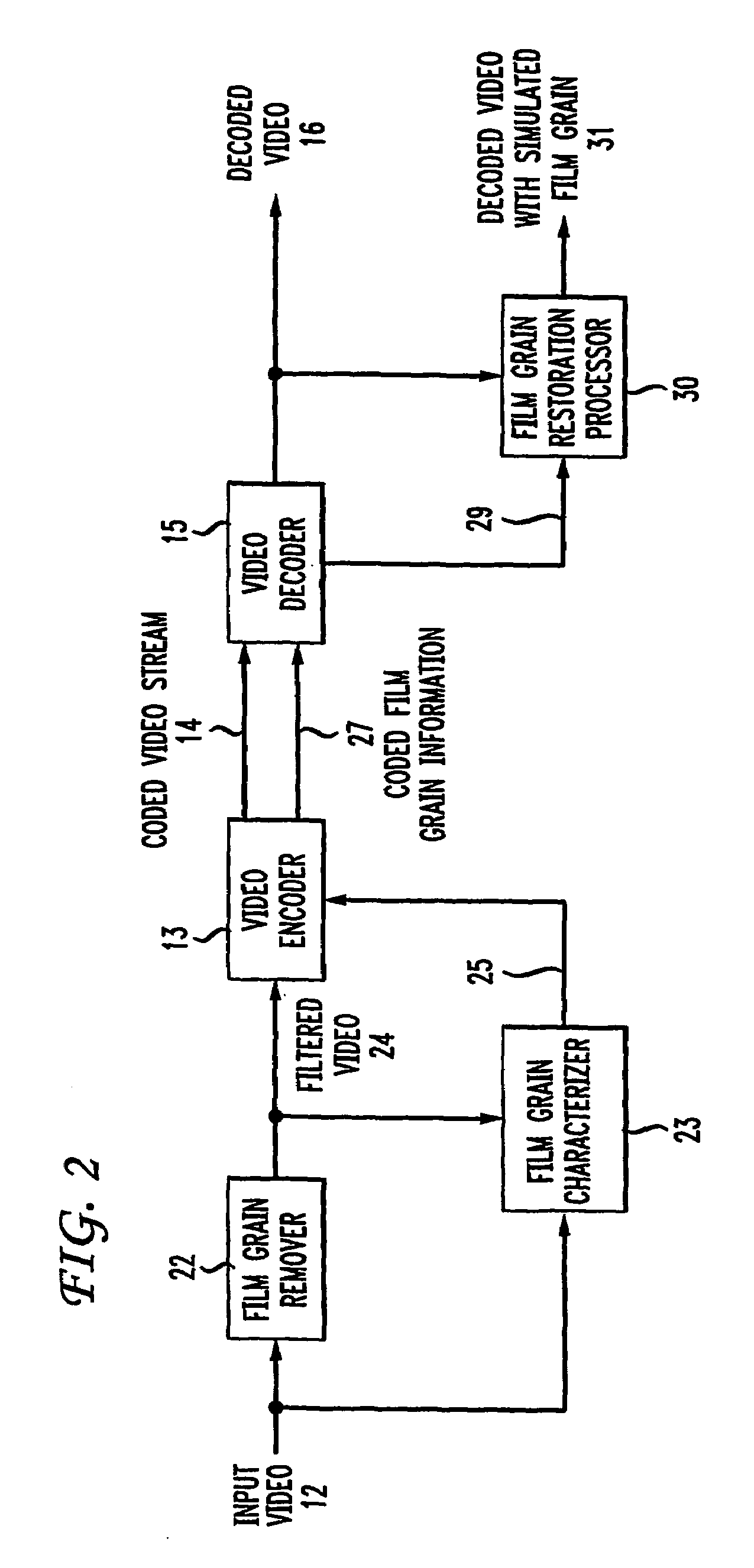
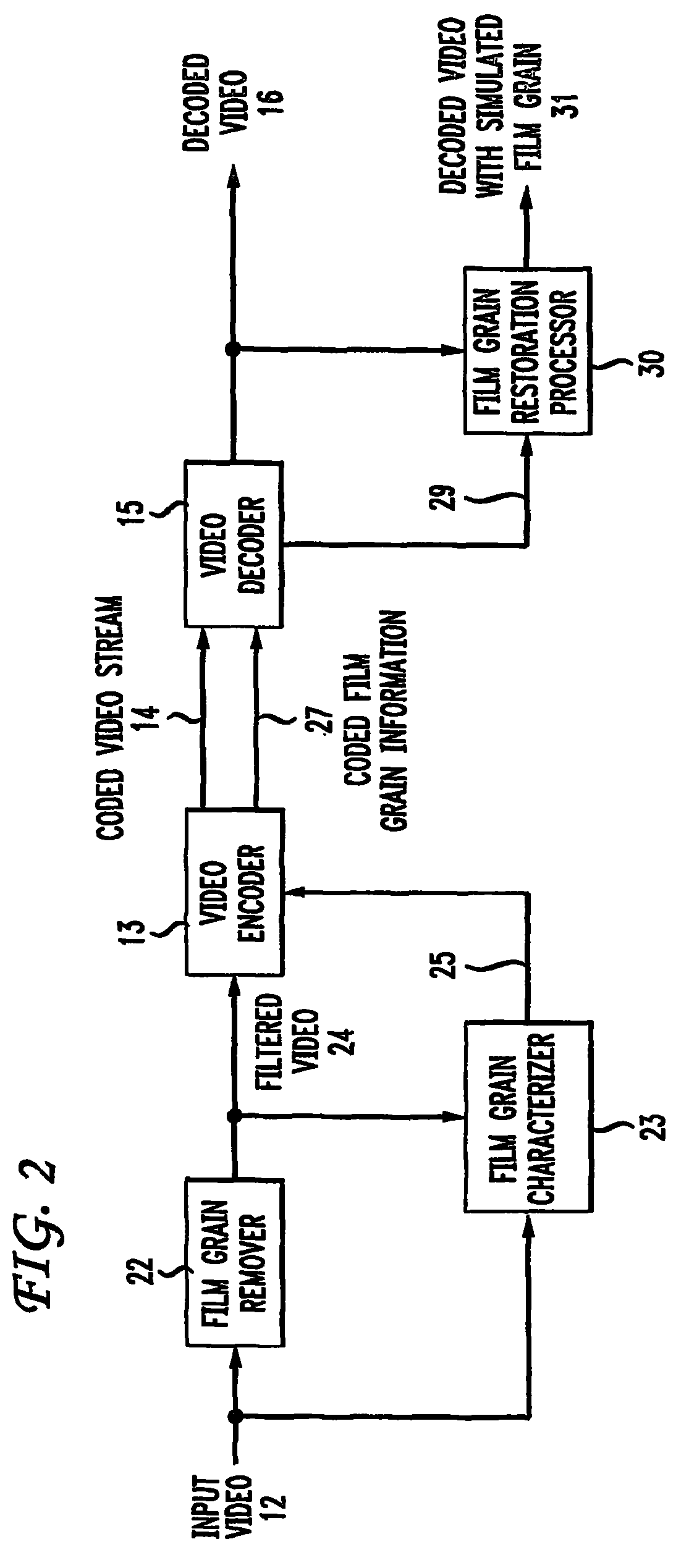
Method and apparatus for representing image granularity by one or more parameters
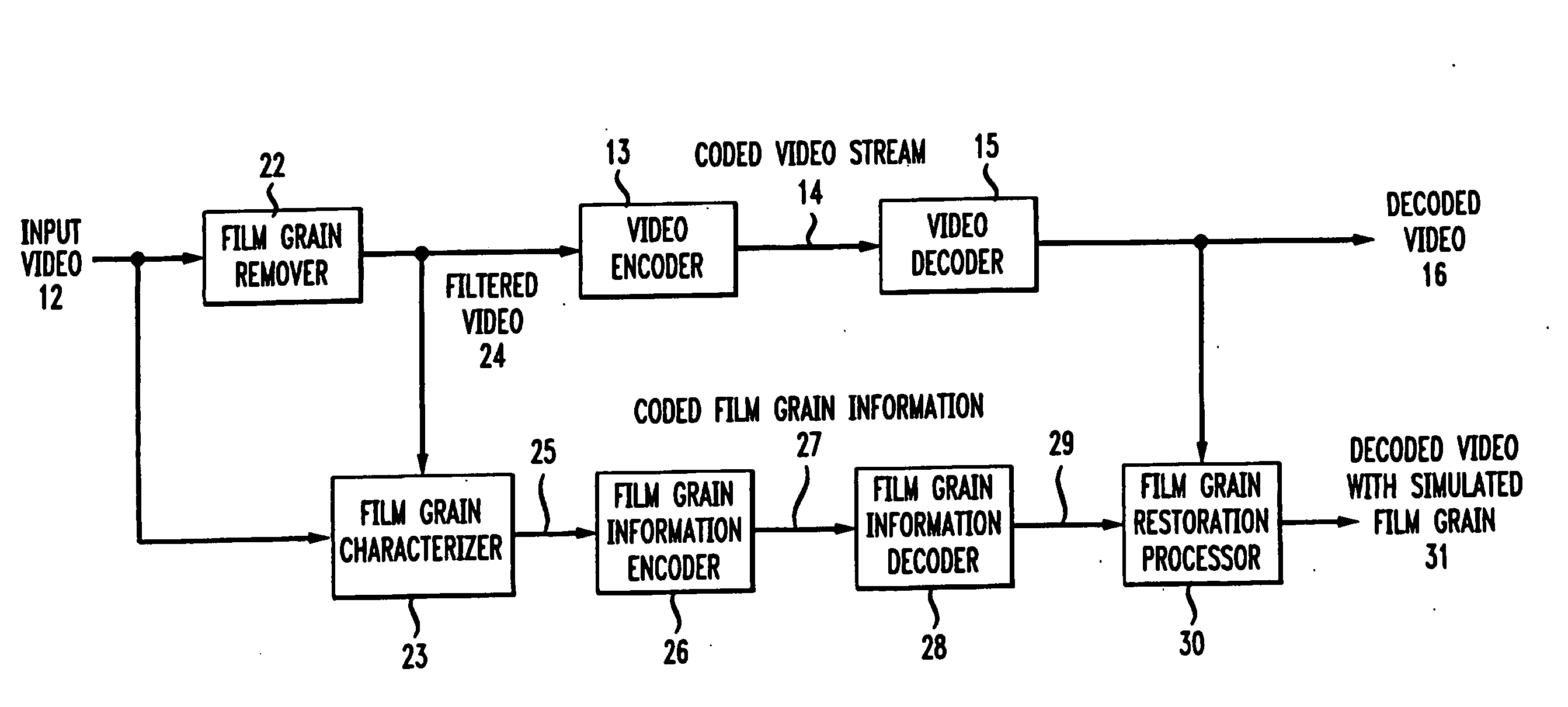
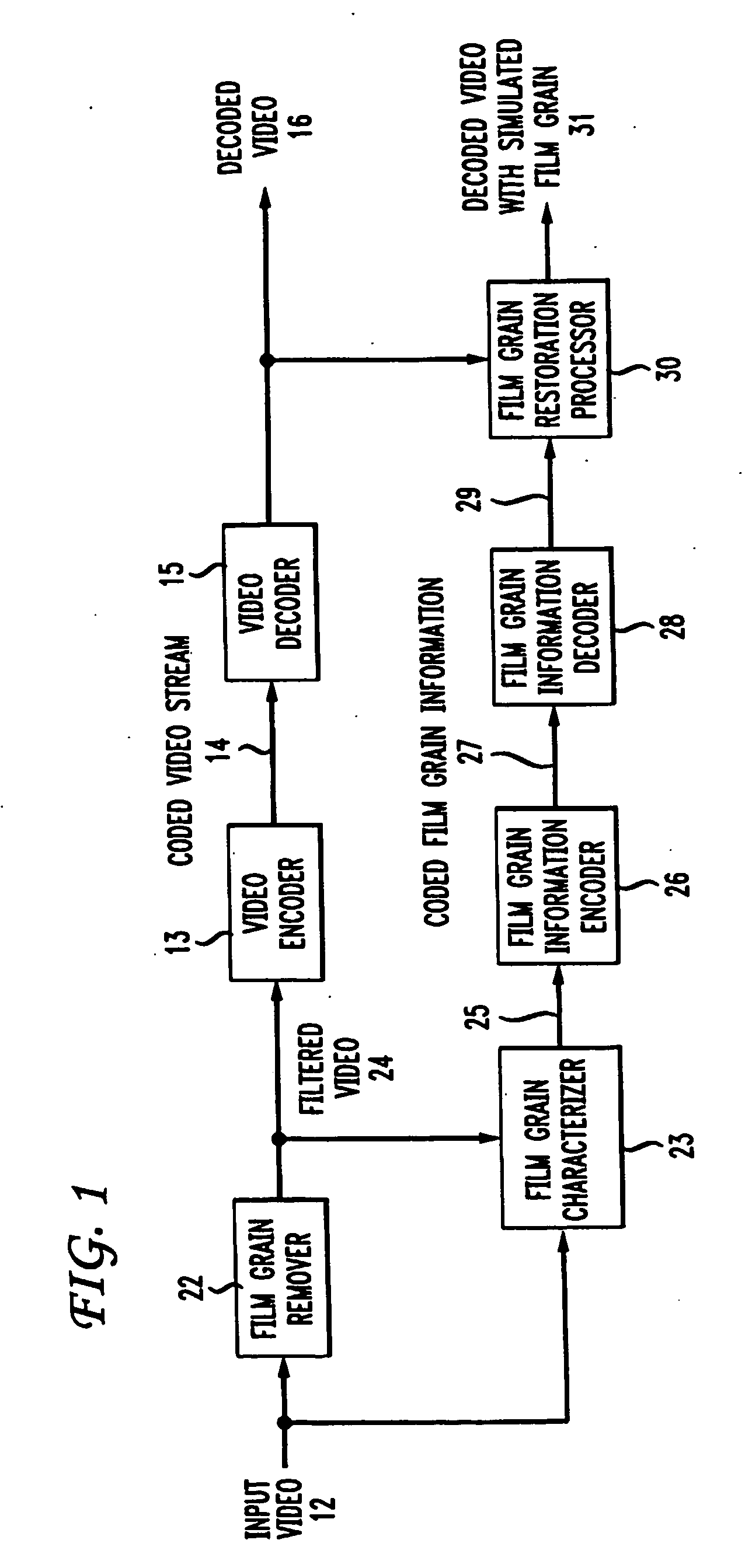
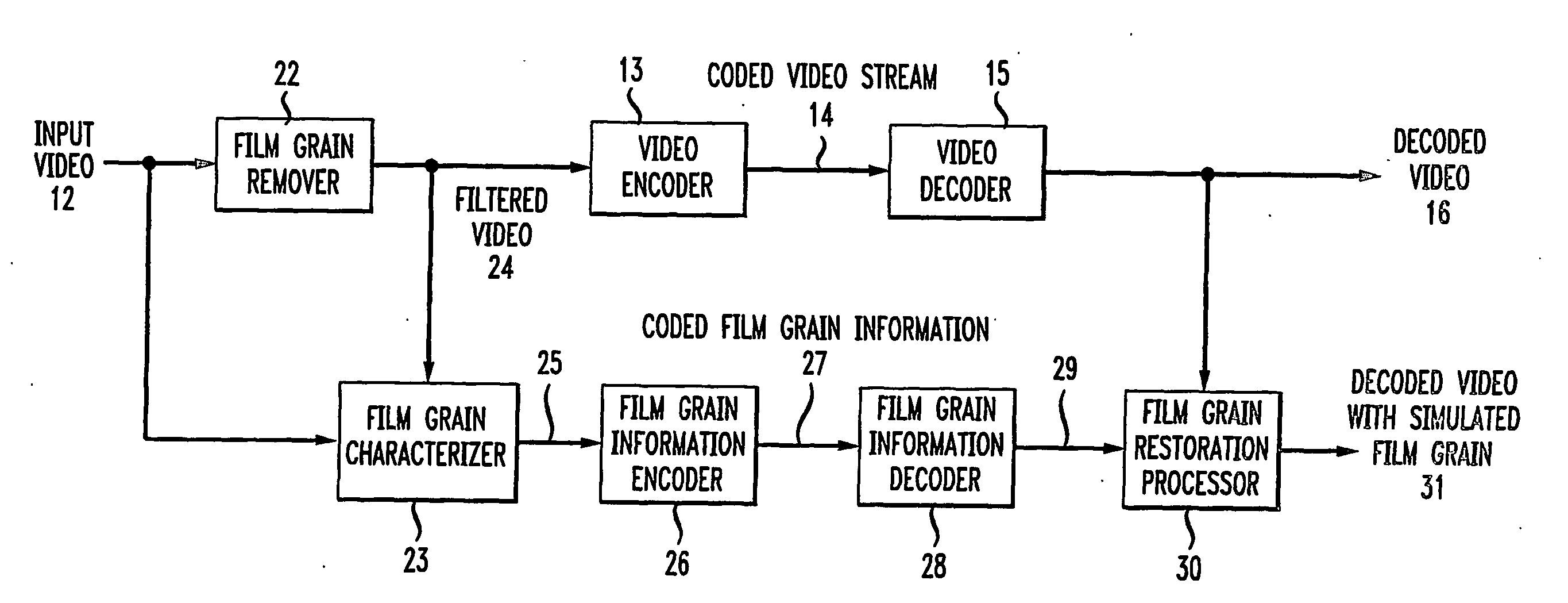
ActiveUS20070104380A1Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionGranularityIndependent parameter
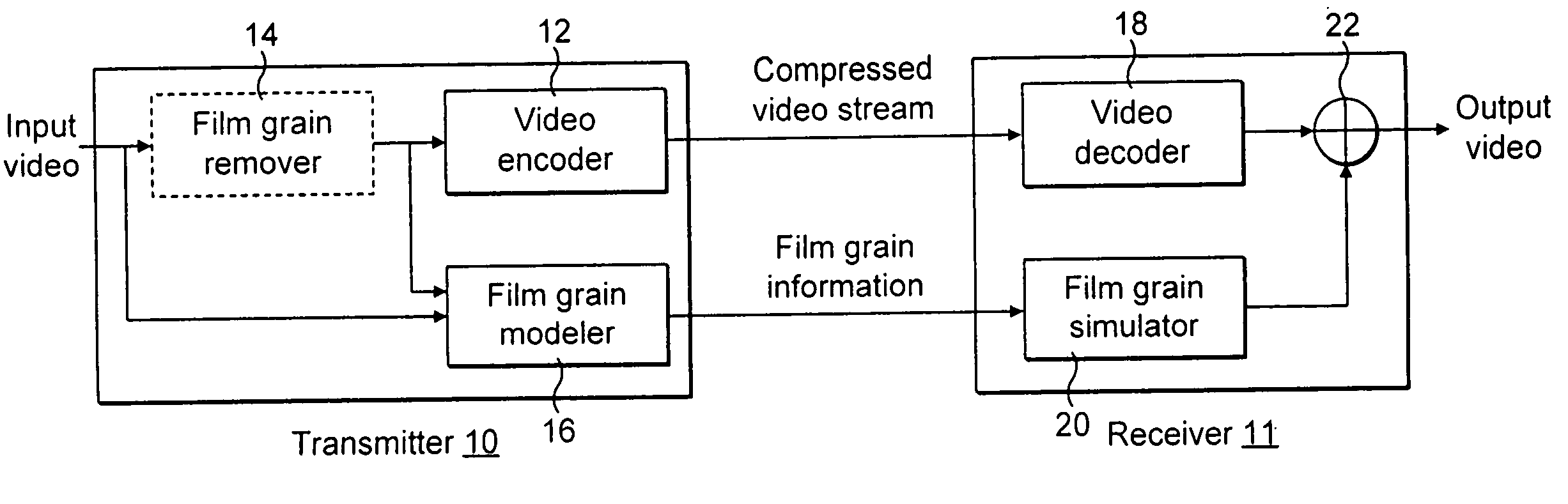
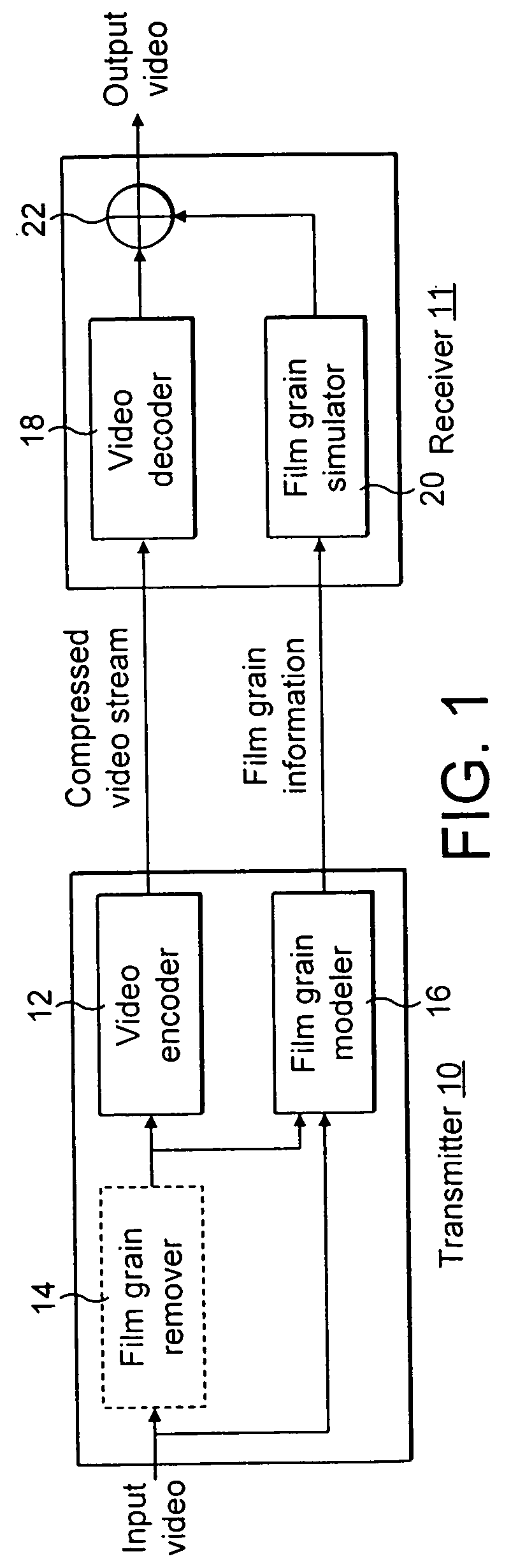
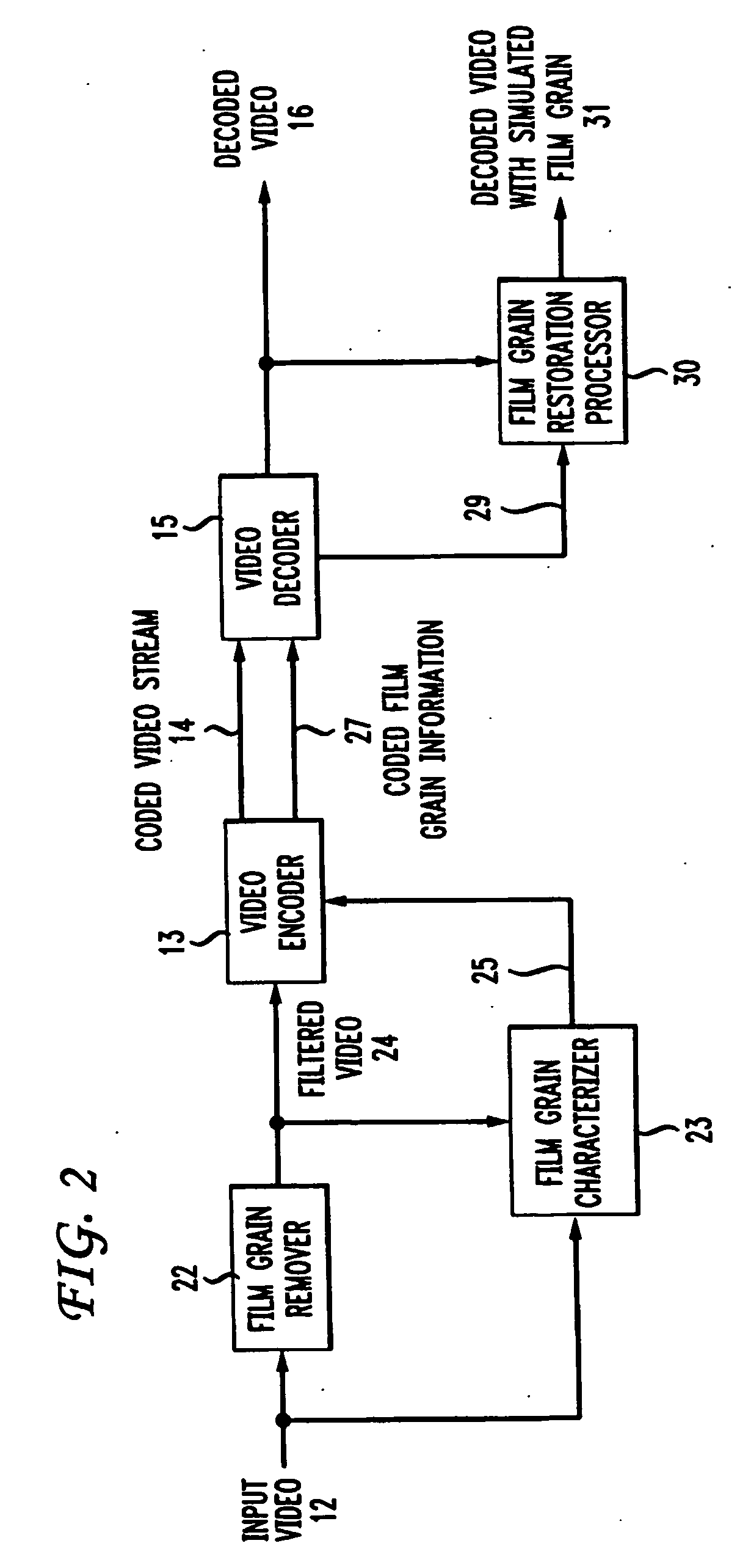
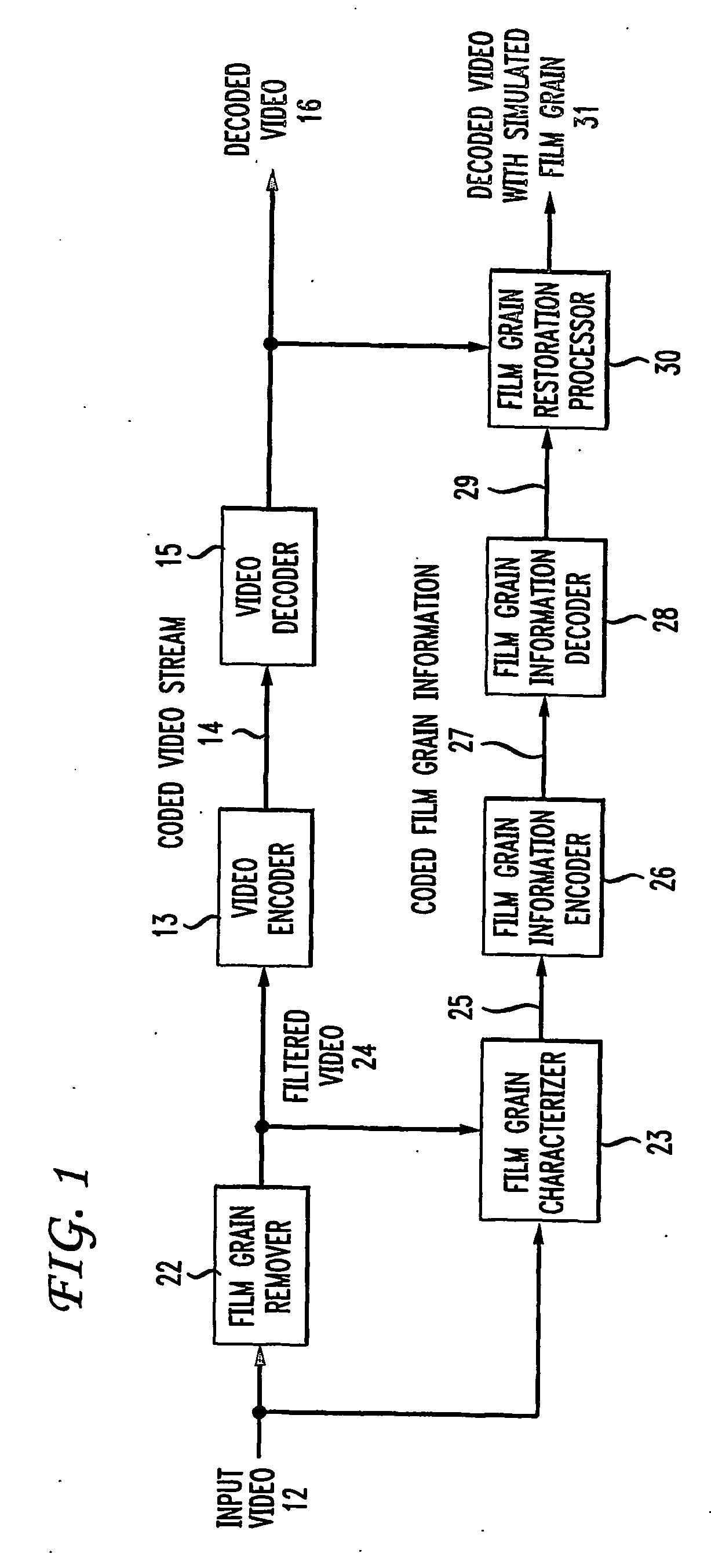
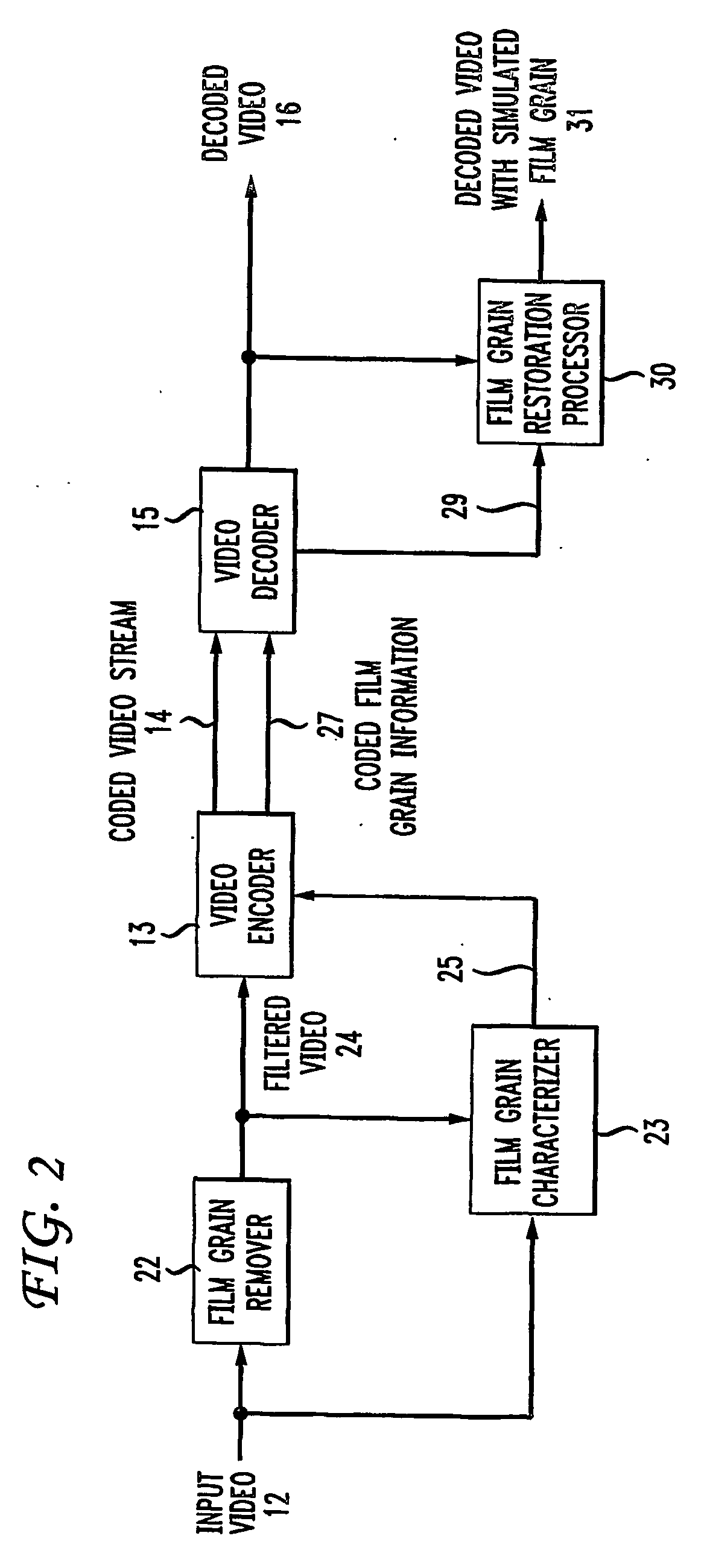
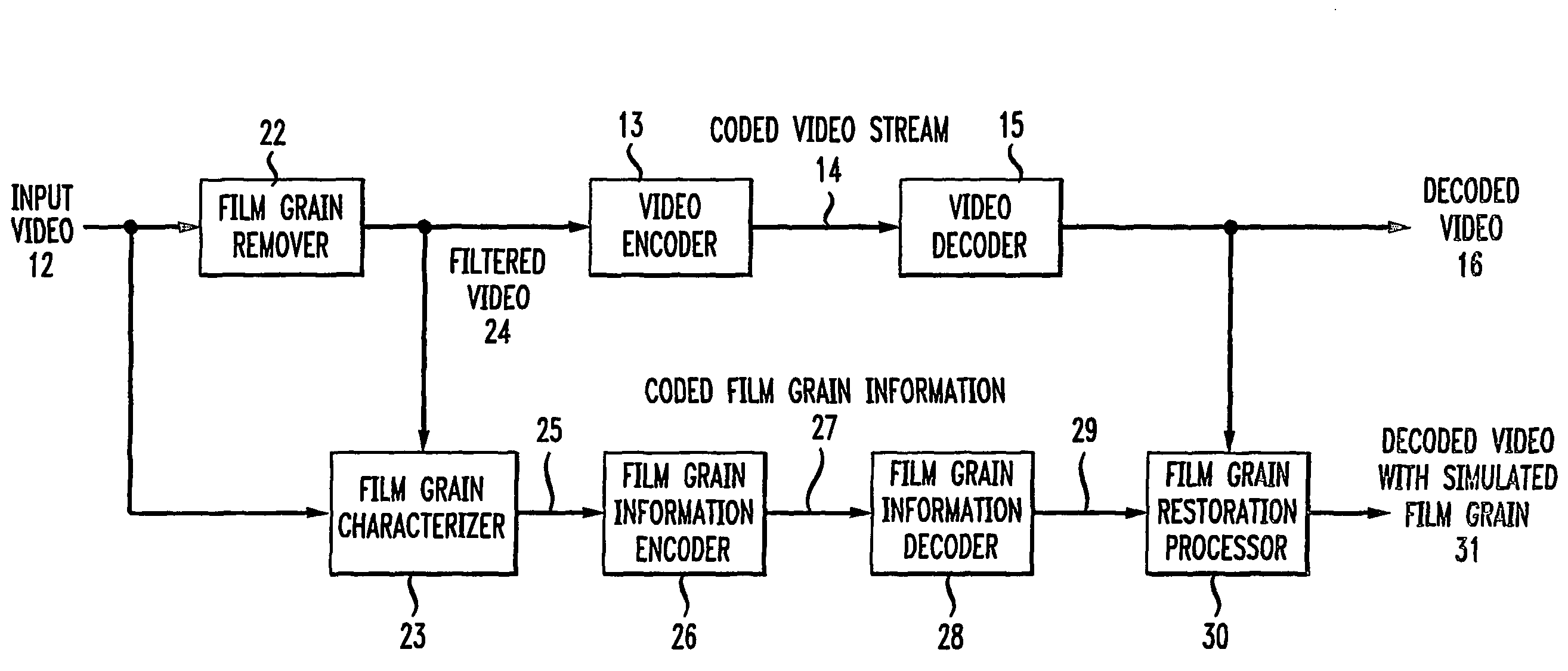
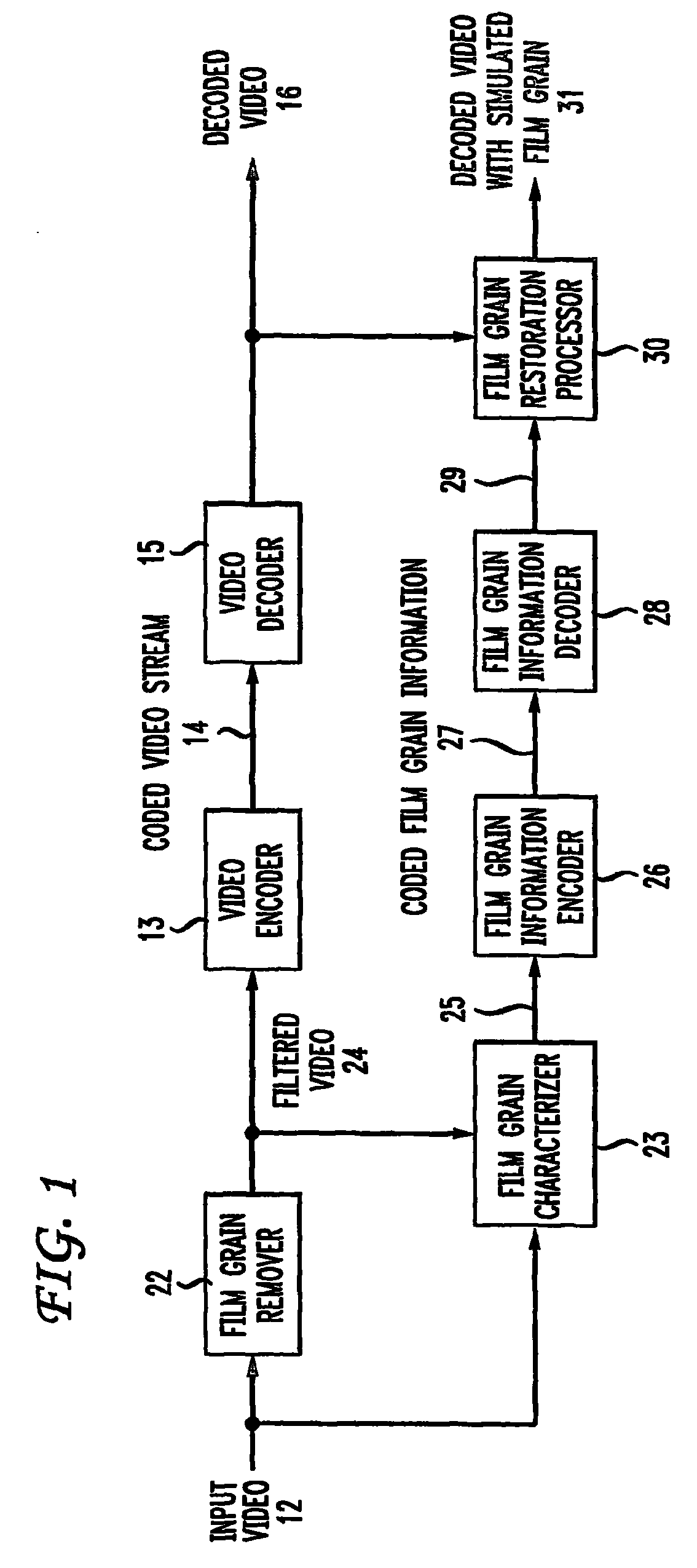
To characterize film grain, a Film Grain Characterizer (23) receives an incoming information stream (12) and a filtered information stream (24) from which the film grain has been removed. From these streams, the Film Grain Characterizer (23) outputs a message that contains an identity of a model for simulating grain, as well at least one of a set of several parameters, including correlation parameters, intensity-independent parameters and intensity-dependent parameters used by the identified model. An encoder (26, 13) encodes the film grain information for subsequent transmission.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Film grain generation and addition
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC +2
Grain-Oriented Electrical Steel Sheet Having High Tensile Strength Insulating Film and Method of Treatment of Such Insulating Film
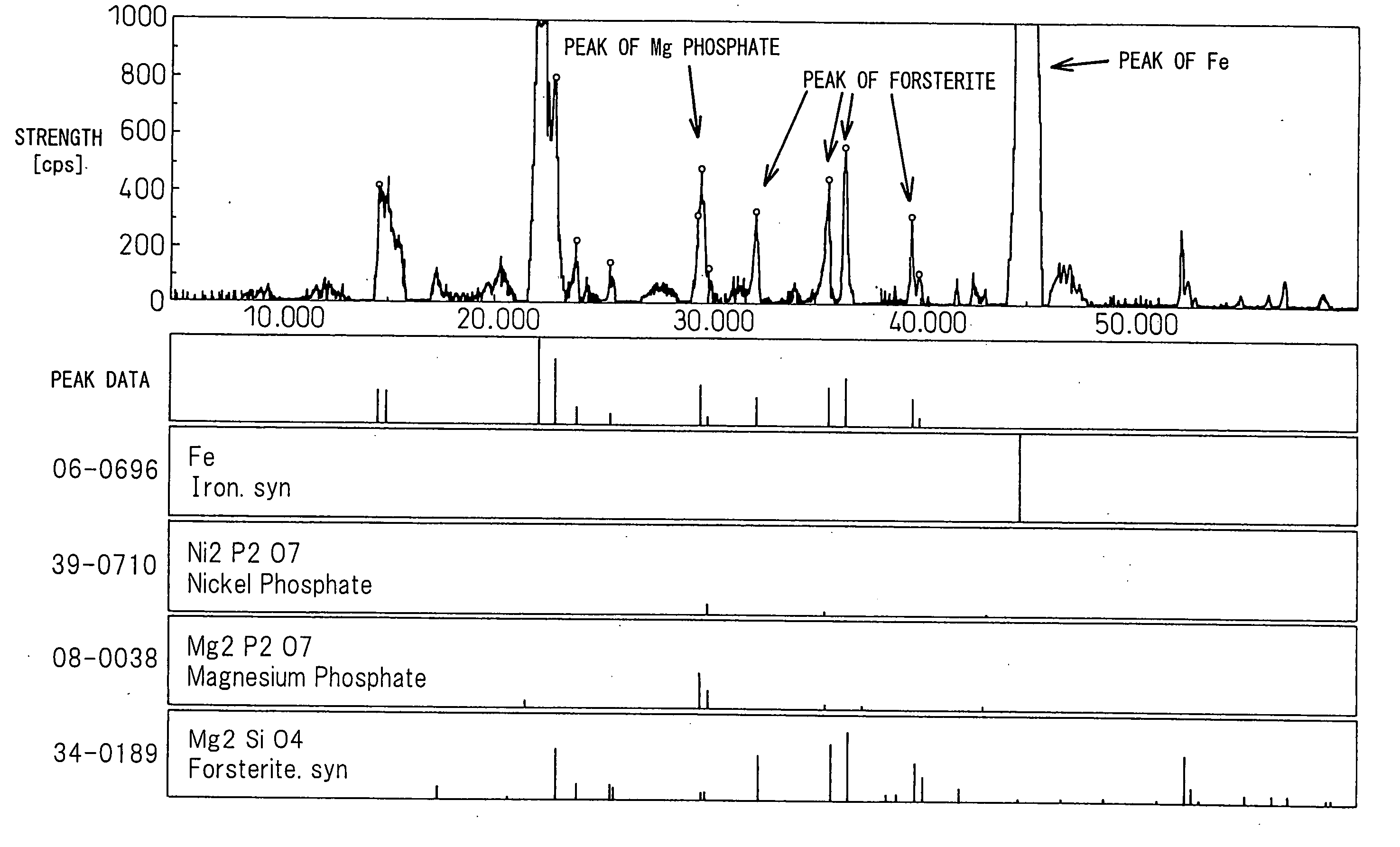
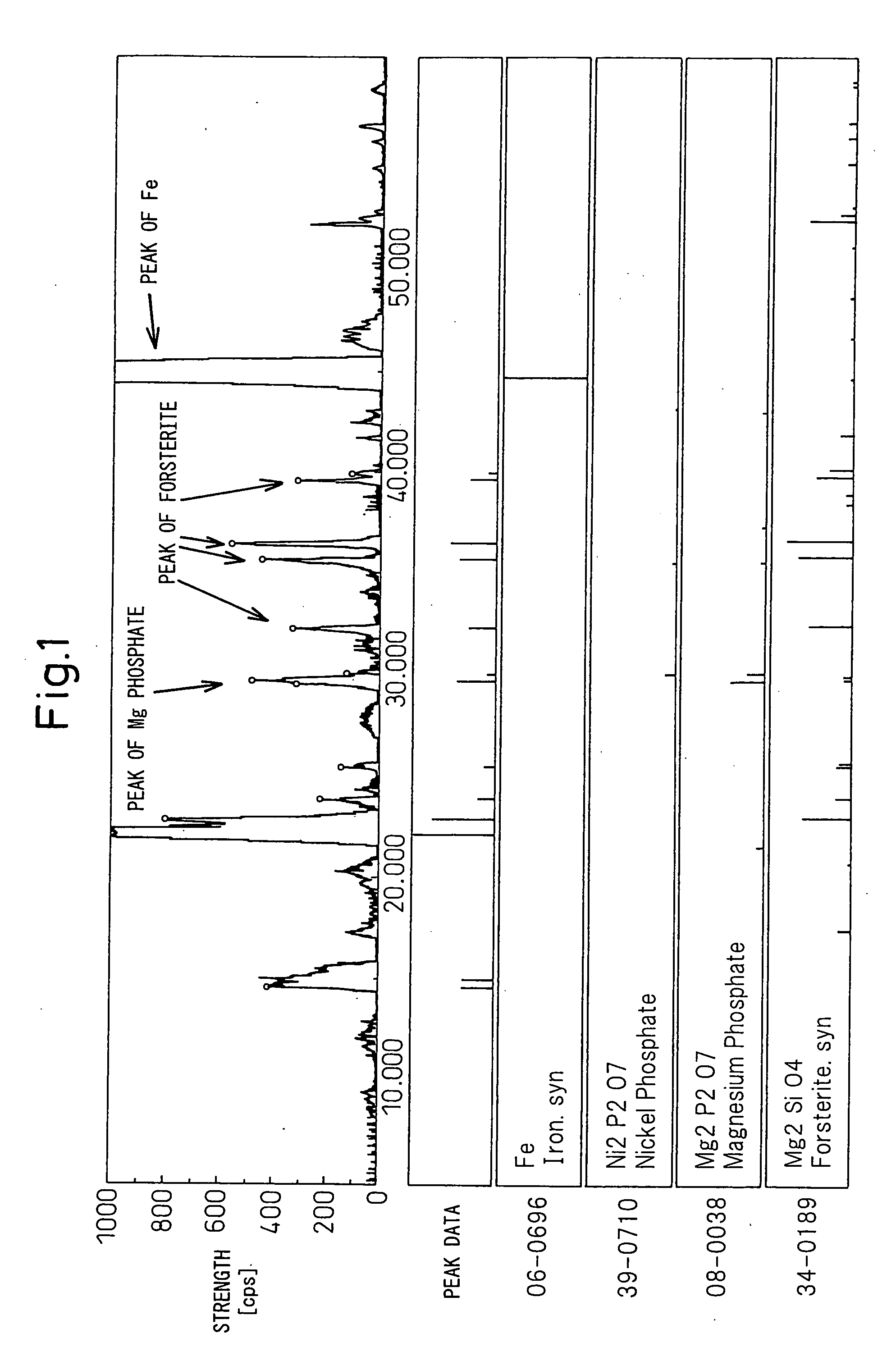
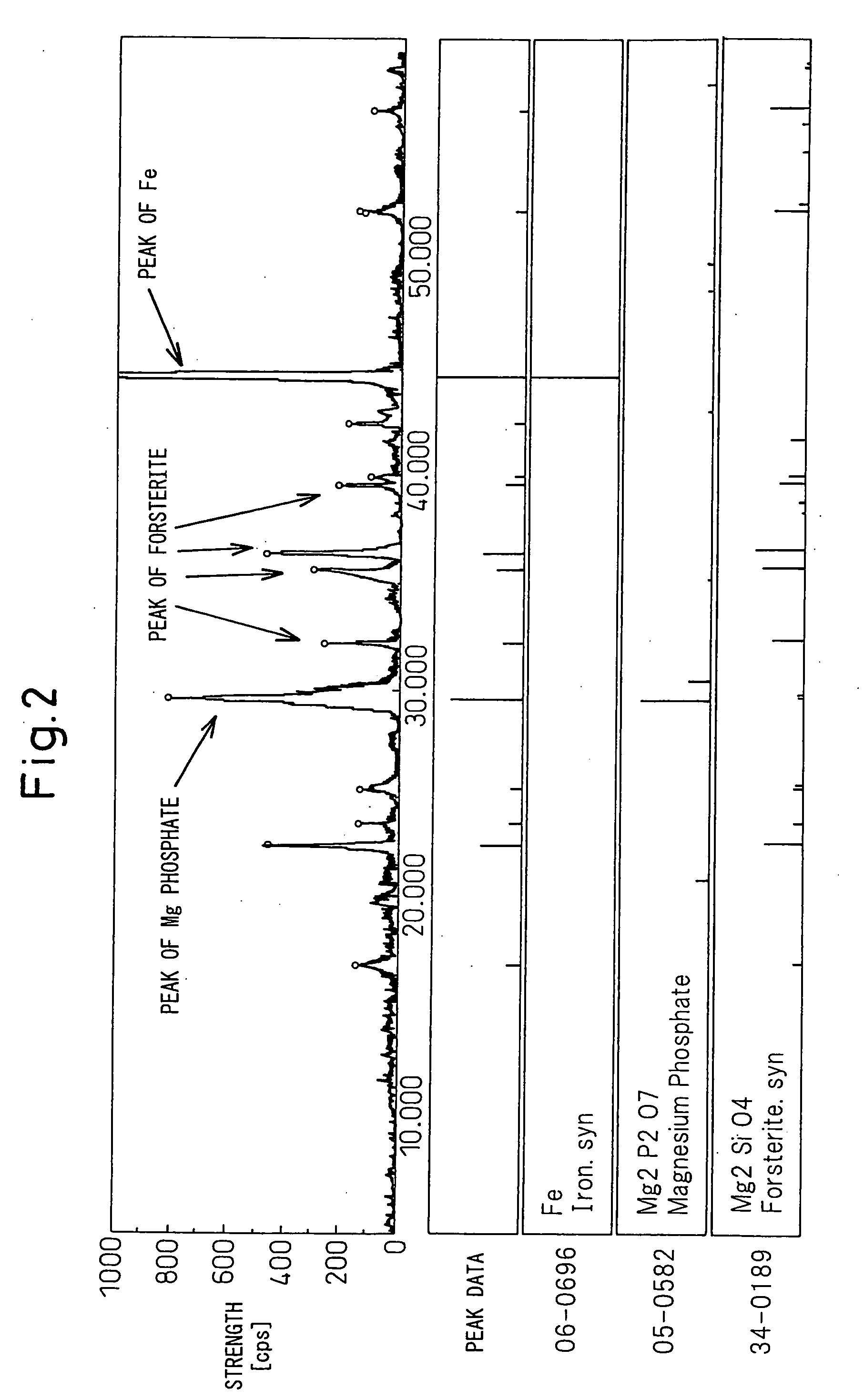
ActiveUS20090233114A1Reduced stabilityPretreated surfacesInorganic material magnetismColloidal silicaMagnesium phosphate
Grain-oriented electrical steel sheet having a chrome-free high tensile strength insulating film characterized by comprising steel sheet on the surface of which is formed an insulating film containing a phosphate and colloidal silica as main ingredients and containing crystalline magnesium phosphate uniformly dispersed over the entire surface.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
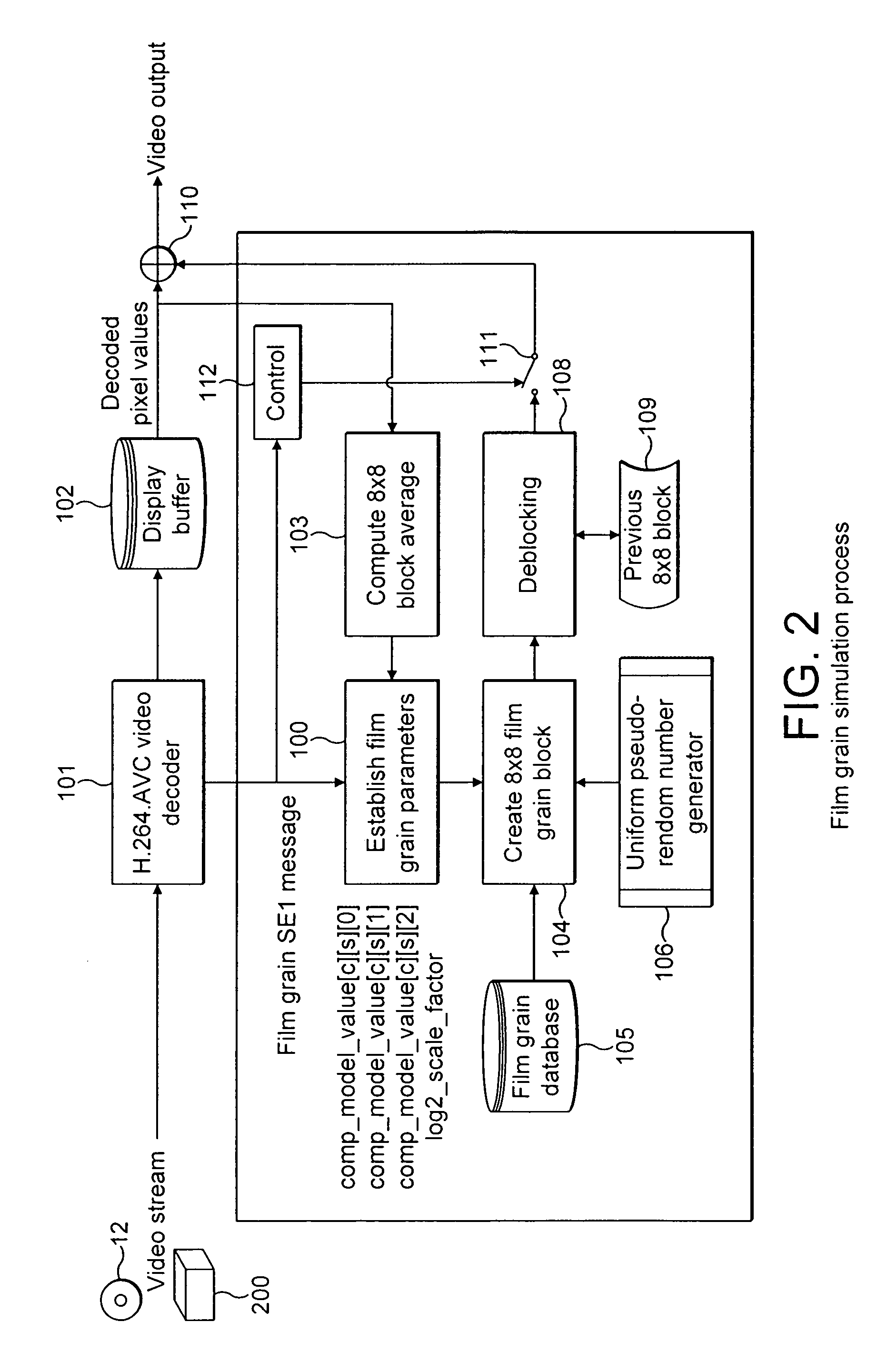
Technique for simulating film grain on encoded video
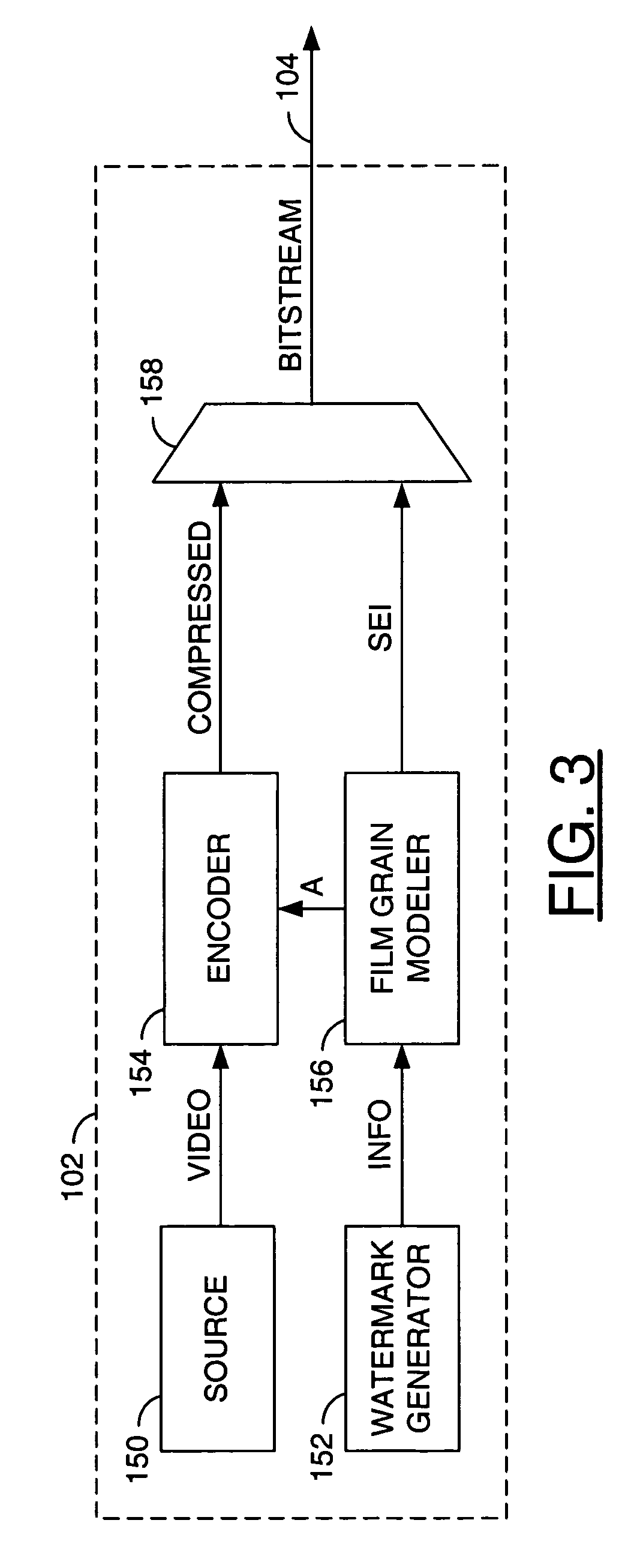
Simulating film grain in an encoded image occurs by extracting the film grain and then characterizing the film grain for encoding in a video stream to enable the film grain restoration upon decoding. Typically, the film grain is characterized based either on the type of film, or by using a particular model. In practice, the film grain particulars are transmitted as parallel information to the video coded stream, typically as a film grain Supplemental Enhancement Information (SEI) message when using the ITU T H.264 video coding standard.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Film grain generation and addition
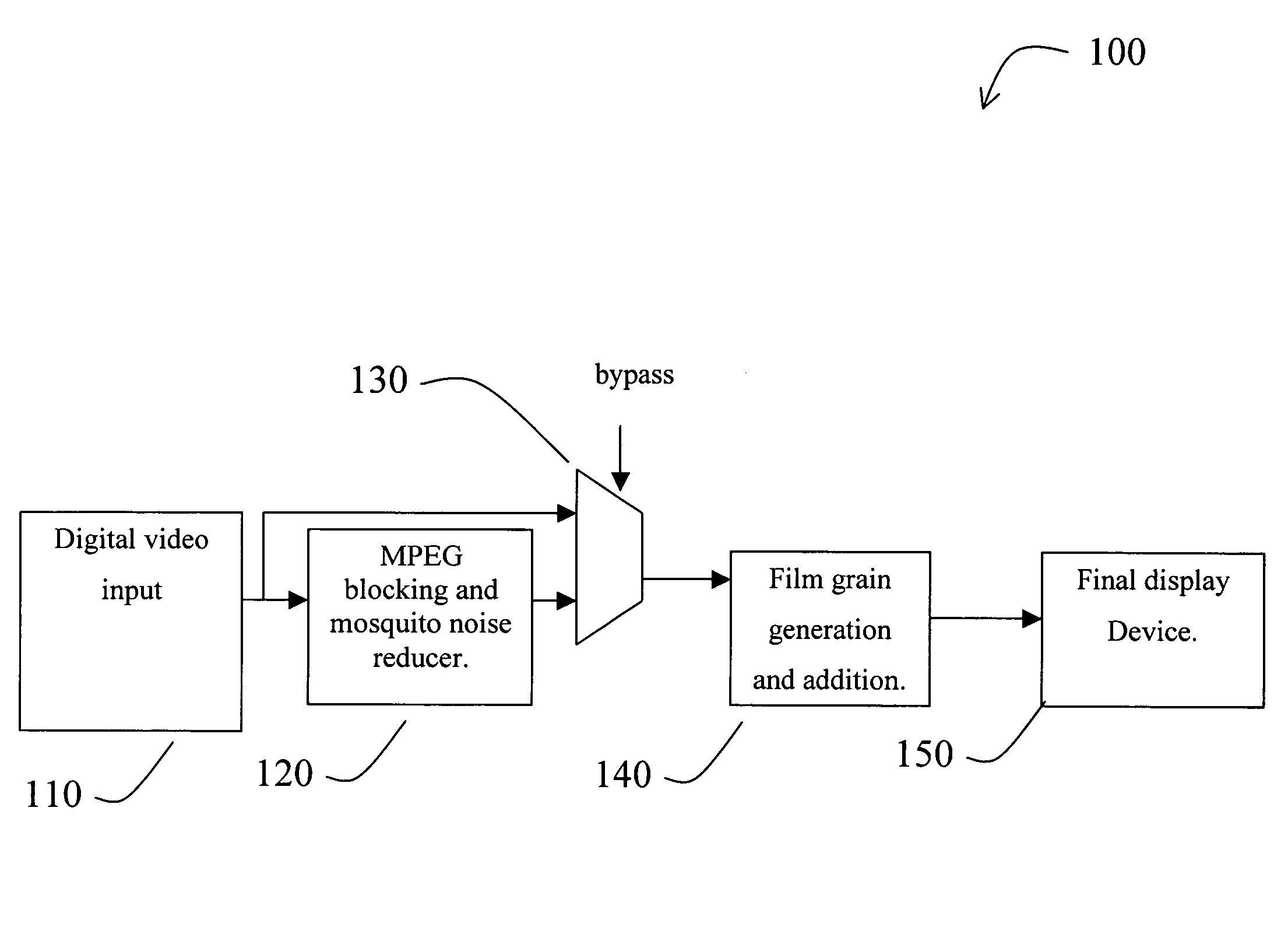
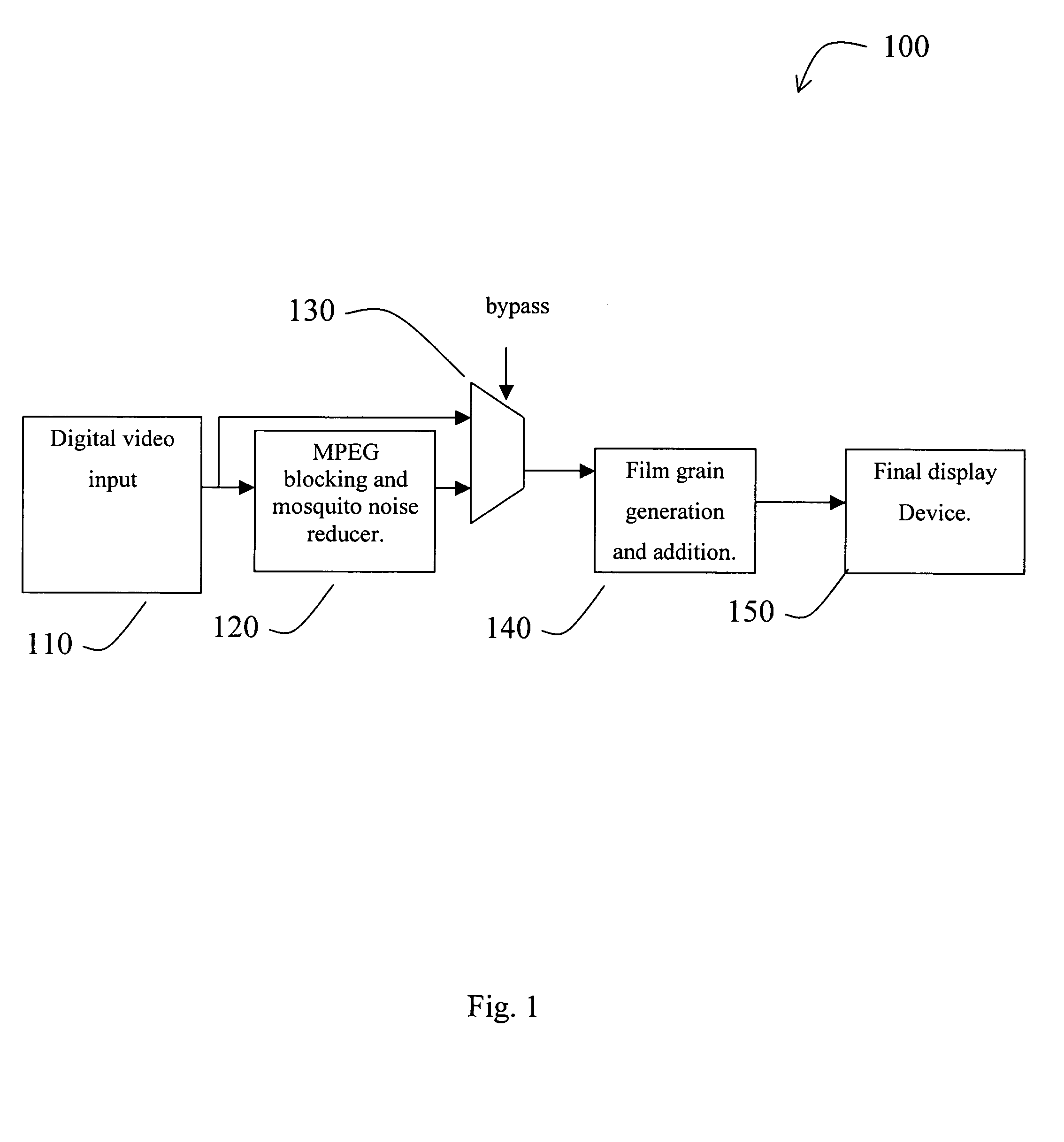
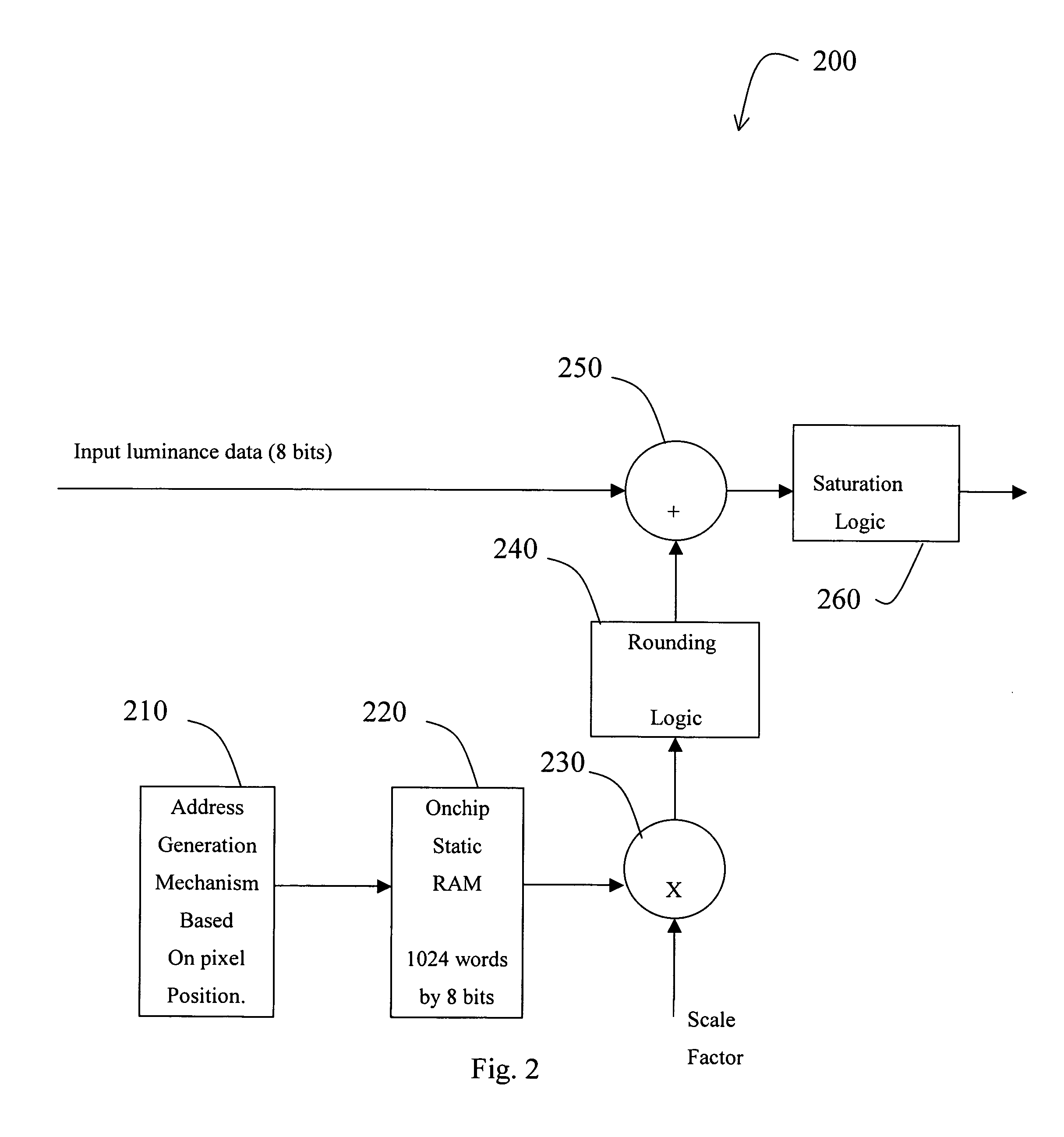
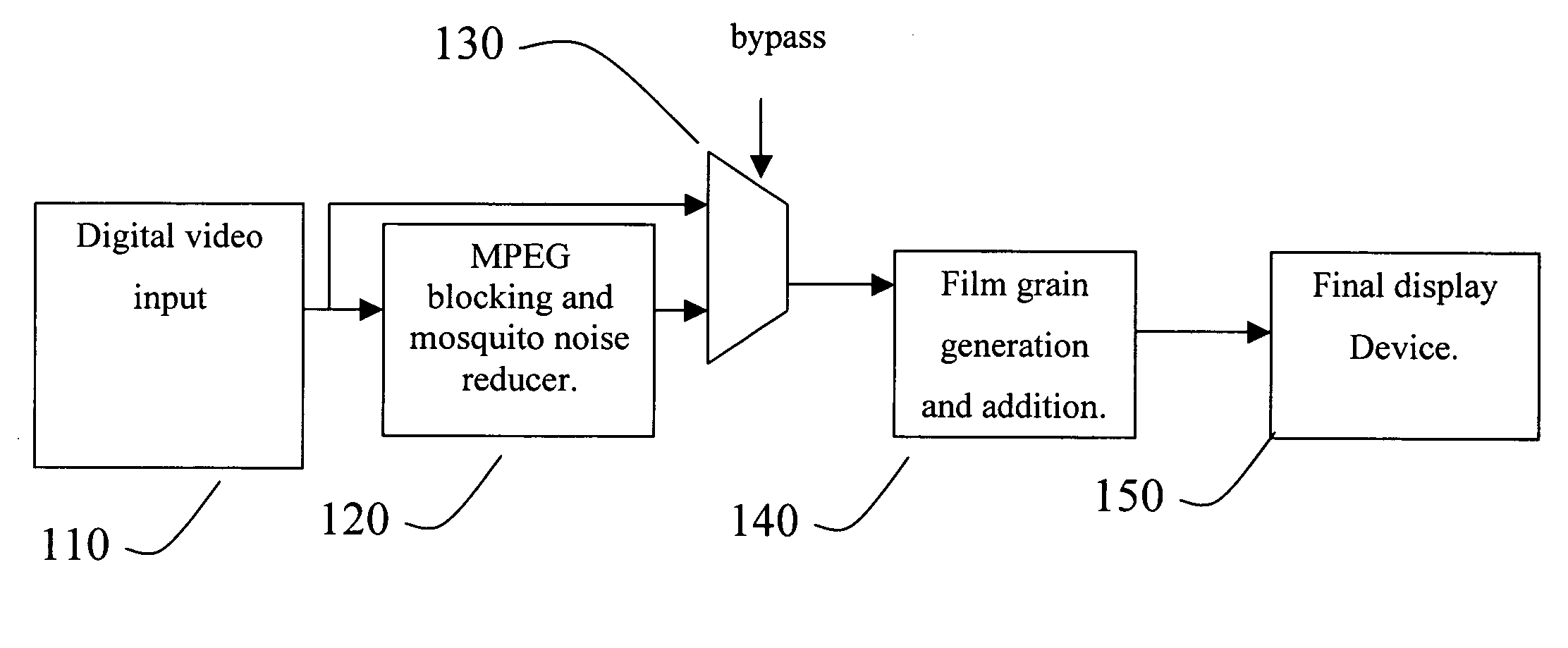
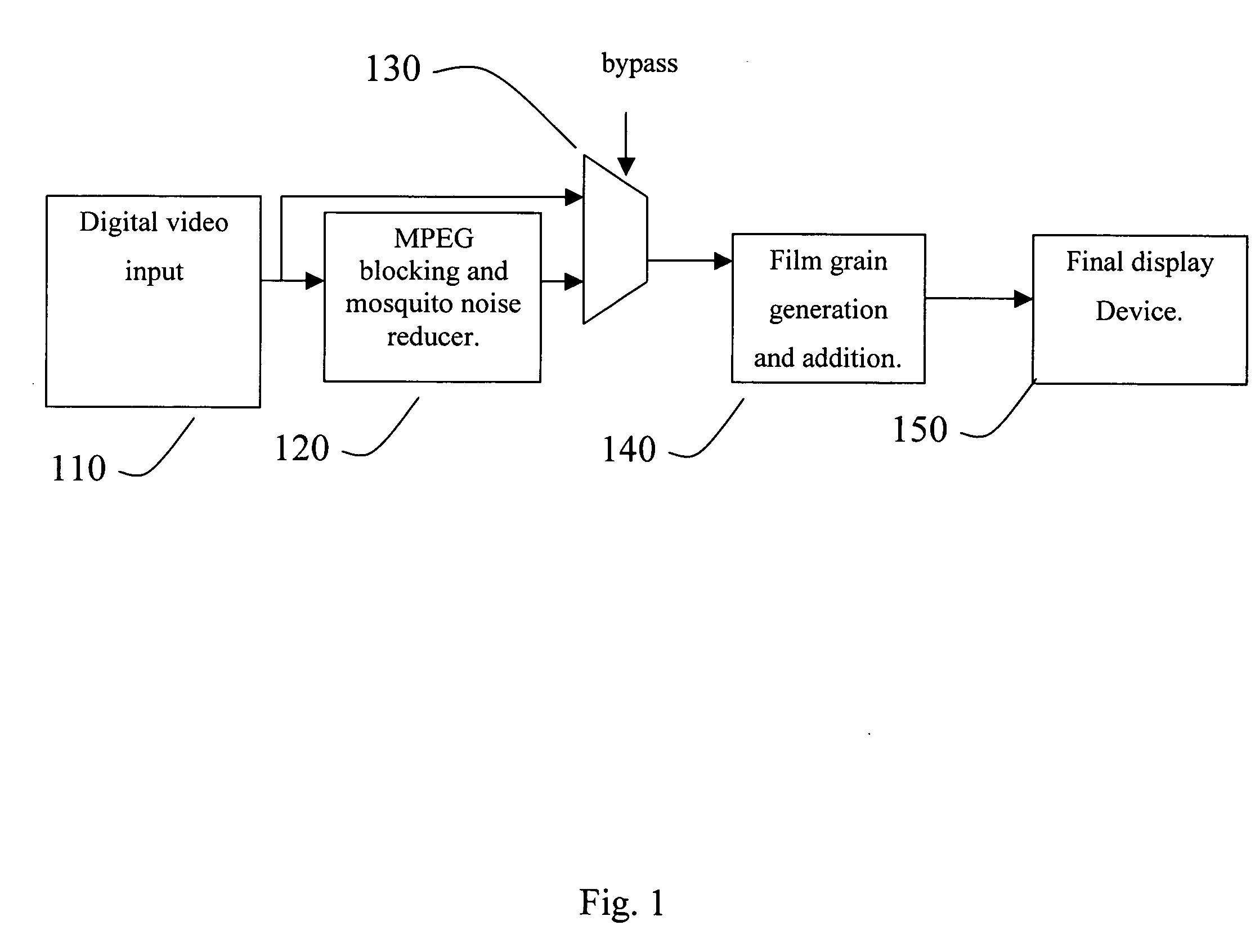
High-frequency noise is generated that approximates the appearance of traditional “film grain” for a digital video signal. By adding a relatively small amount of film grain noise, the video can be made to look more natural and more pleasing to the human viewer. The digital film grain generation can be used to mask unnatural smooth artifacts in digital video such as “blockiness” and “contouring” in the case of compressed video and / or used to provide visual enhancements or special effects to any digital video stream. The digital film grain generator can control grain size and the amount of film grain to be added.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC +2
Method and/or apparatus for video watermarking and steganography using simulated film grain
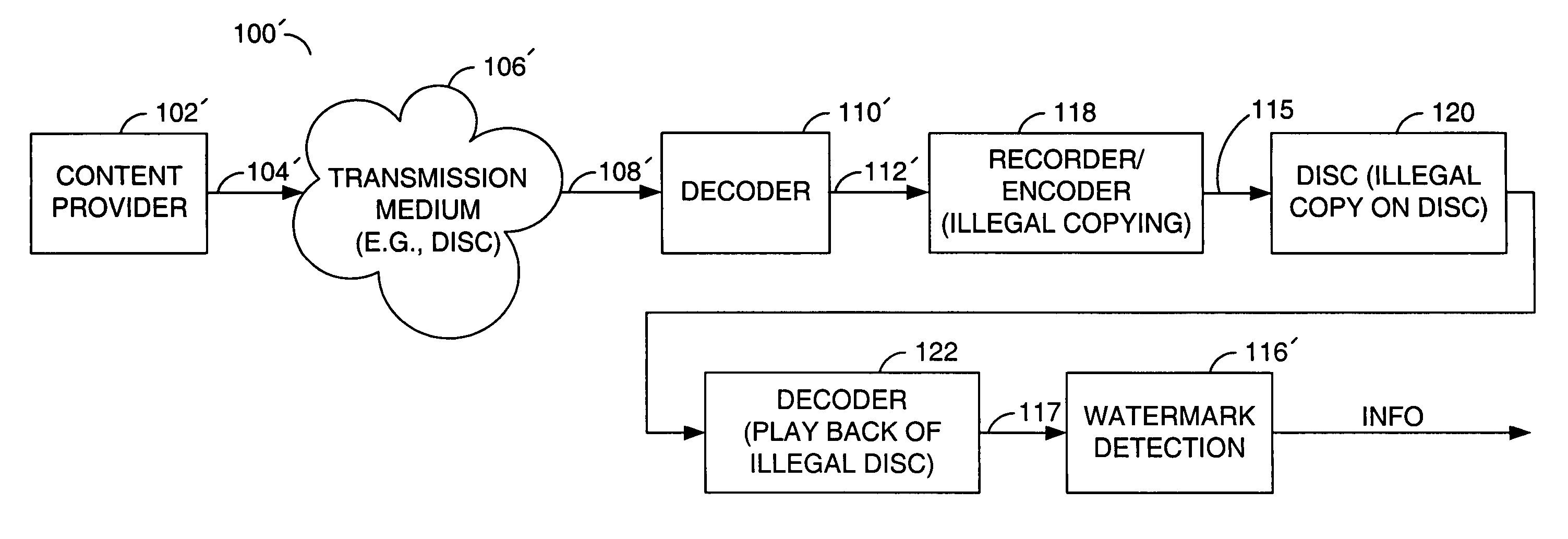
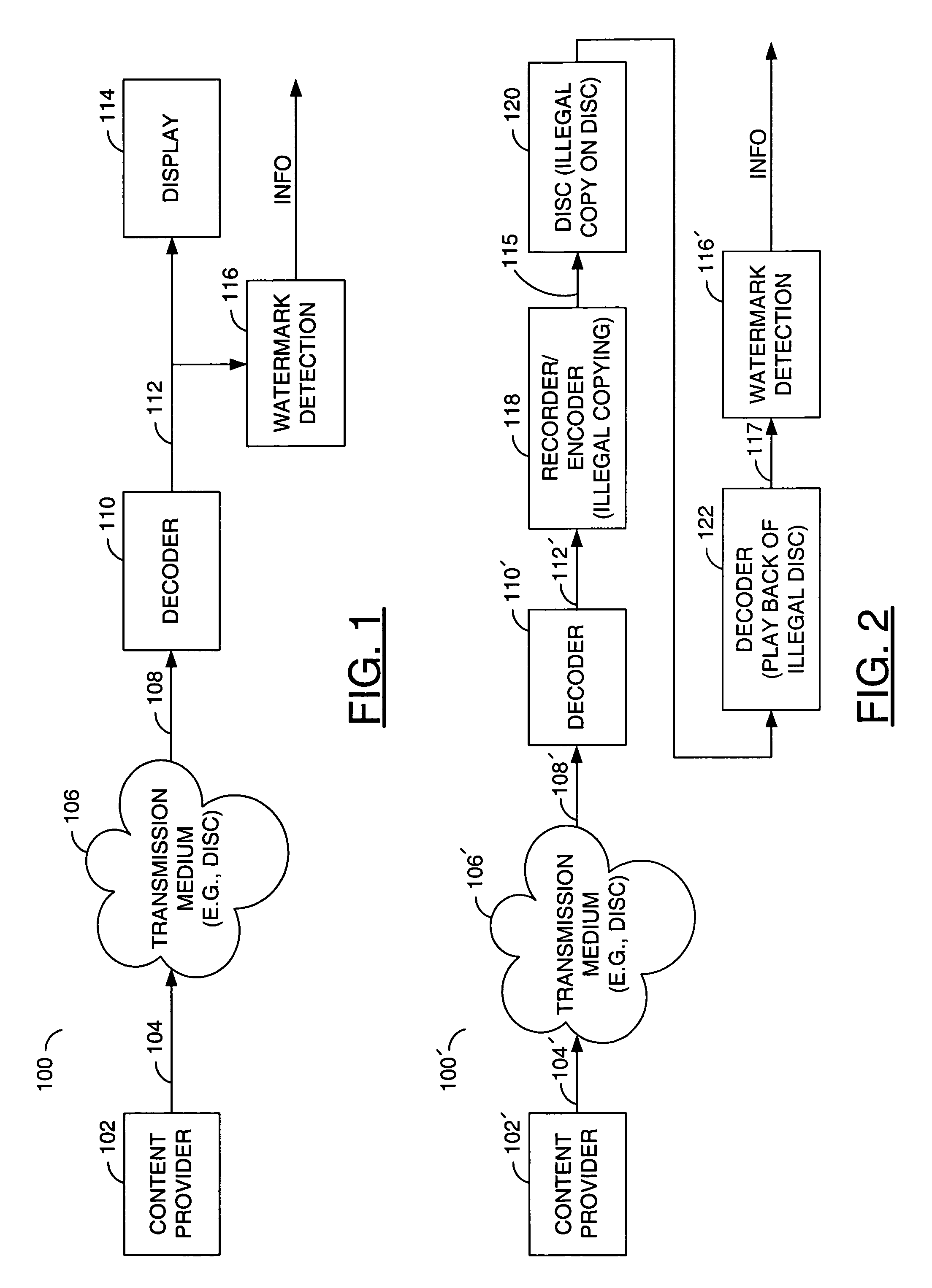
InactiveUS7596239B2Reduce complexityMinimized bitrateCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsVideo outputSteganography
An apparatus comprising a first circuit, a second circuit, and a watermark detection circuit. The first circuit may be configured to generate a bitstream, wherein the bitstream comprises a watermark message which represents hidden information. The second circuit may be configured to (i) simulate film grain in response to one or more predetermined values on the watermark message and (ii) generate a video output. The watermark detection circuit may be configured to extract hidden information from the decoded video output.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
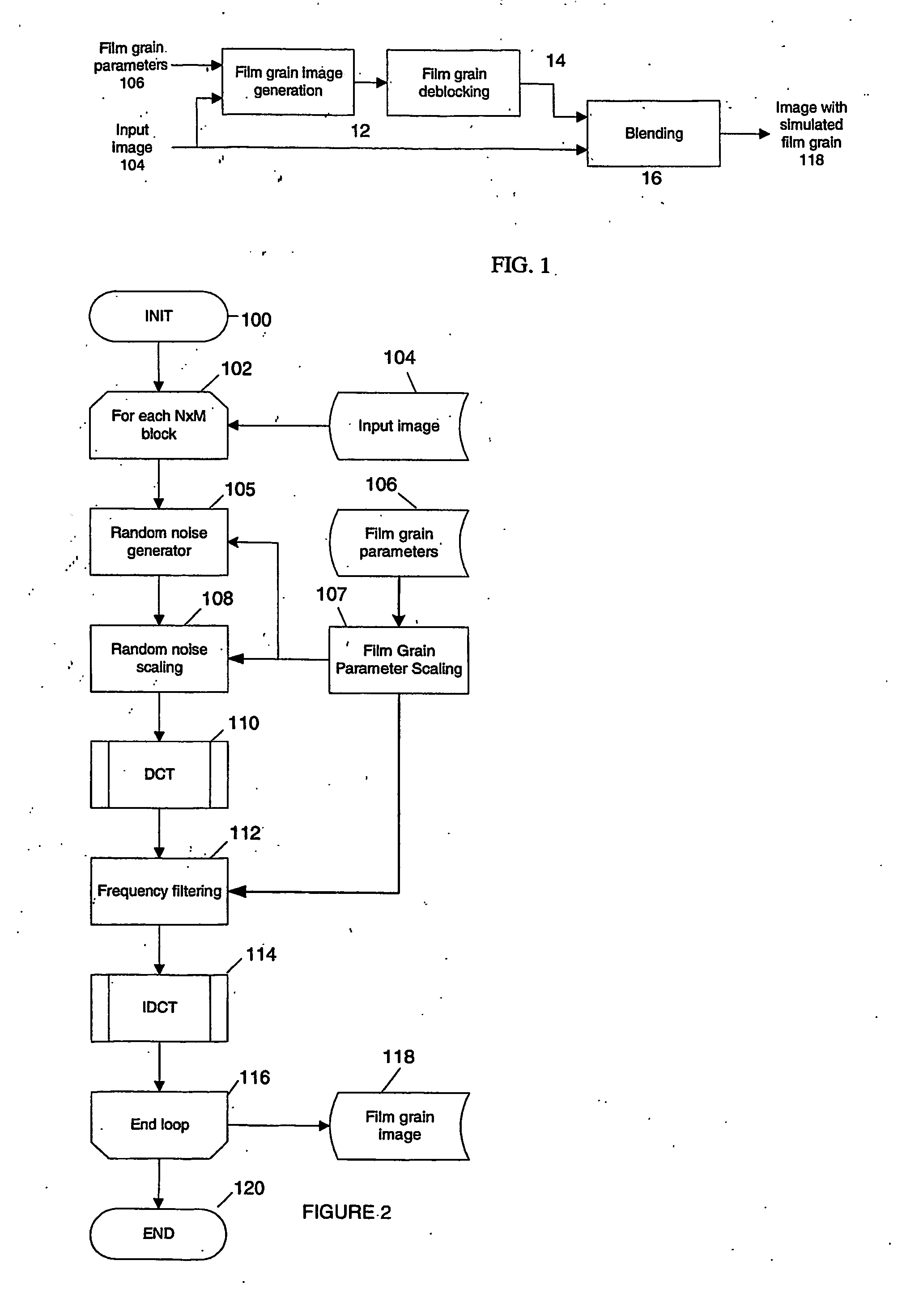
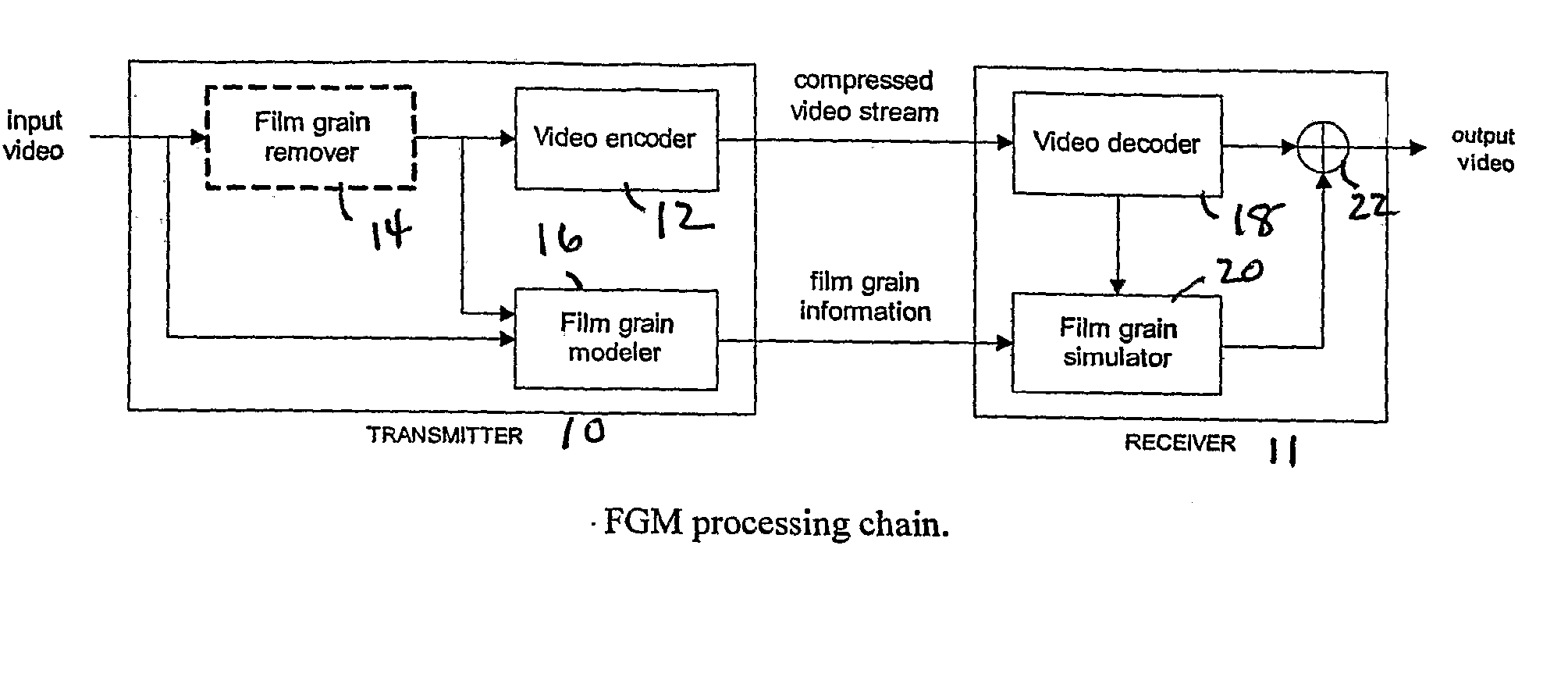
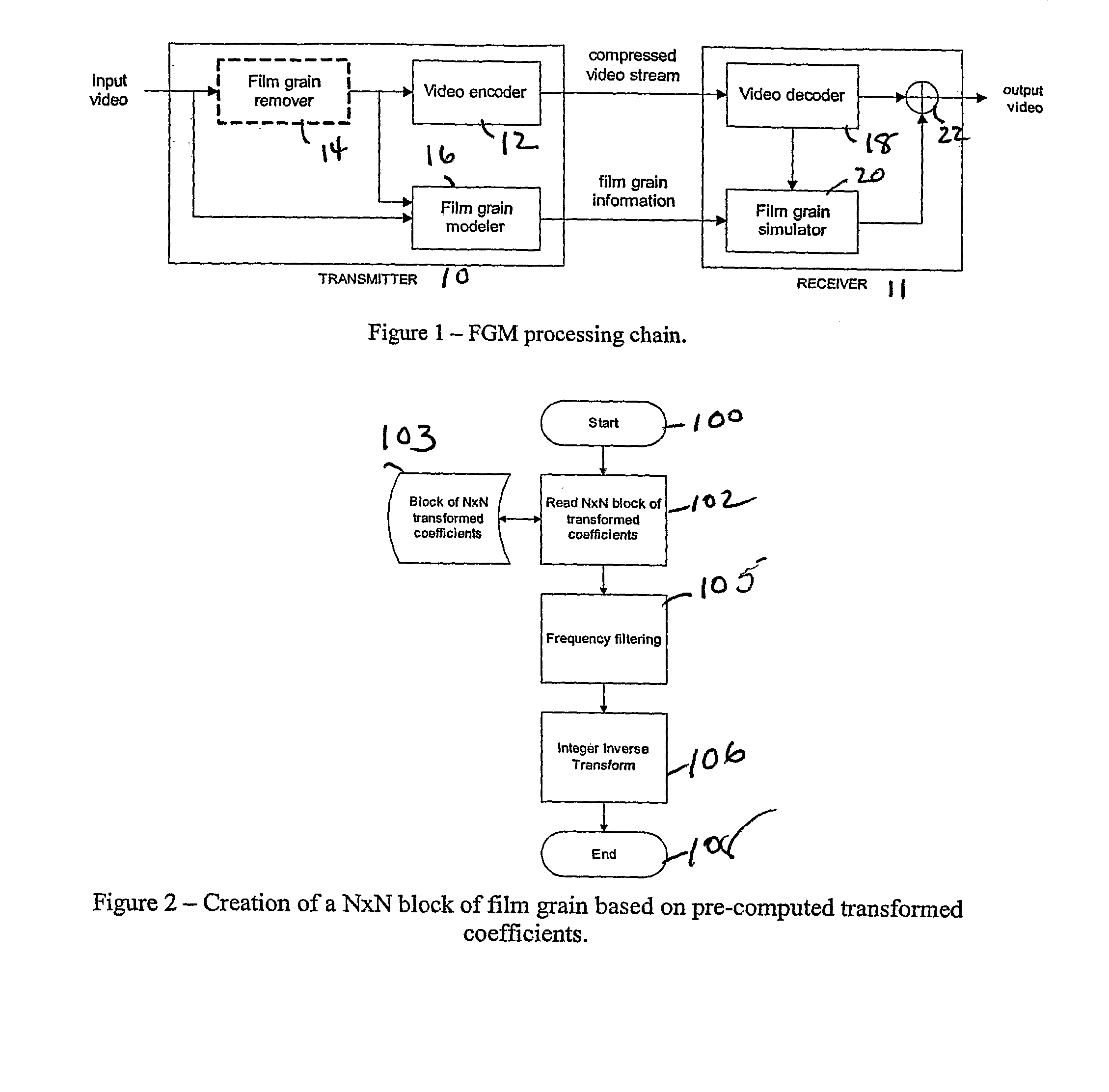
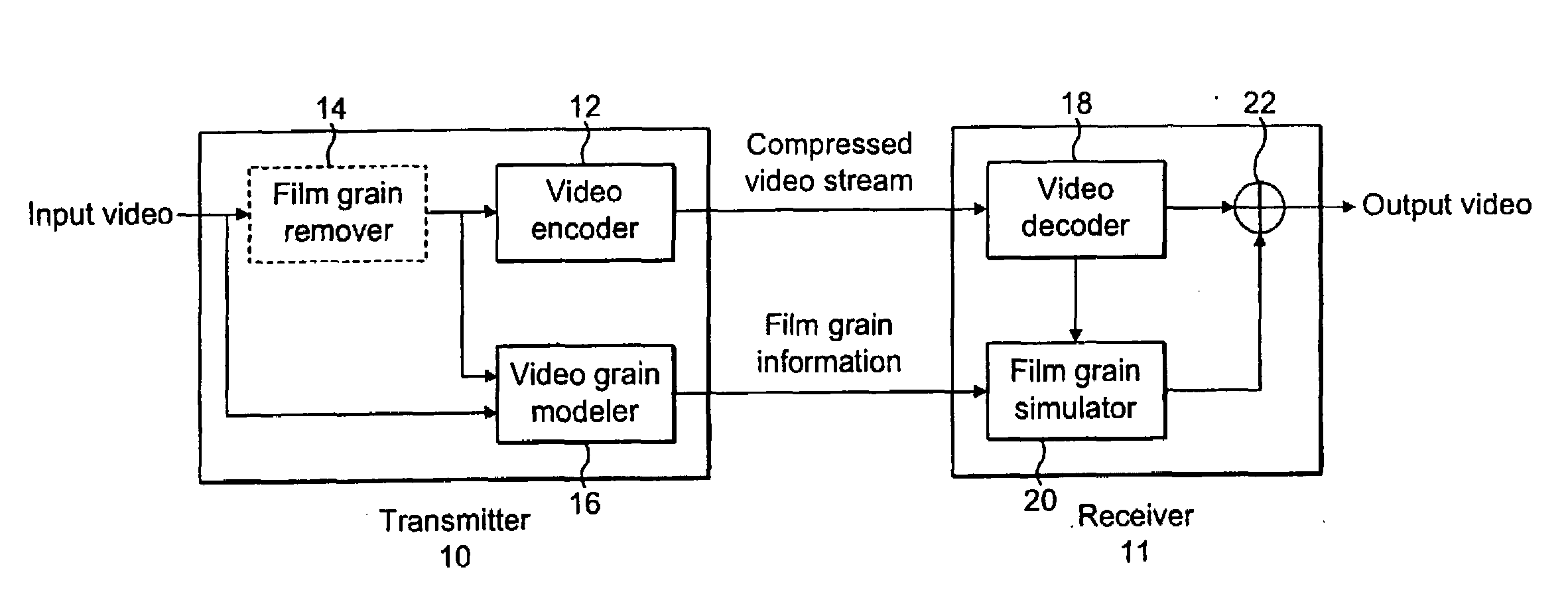
Film Grain Simulation Method Based on Pre-Computed Transform Coefficients
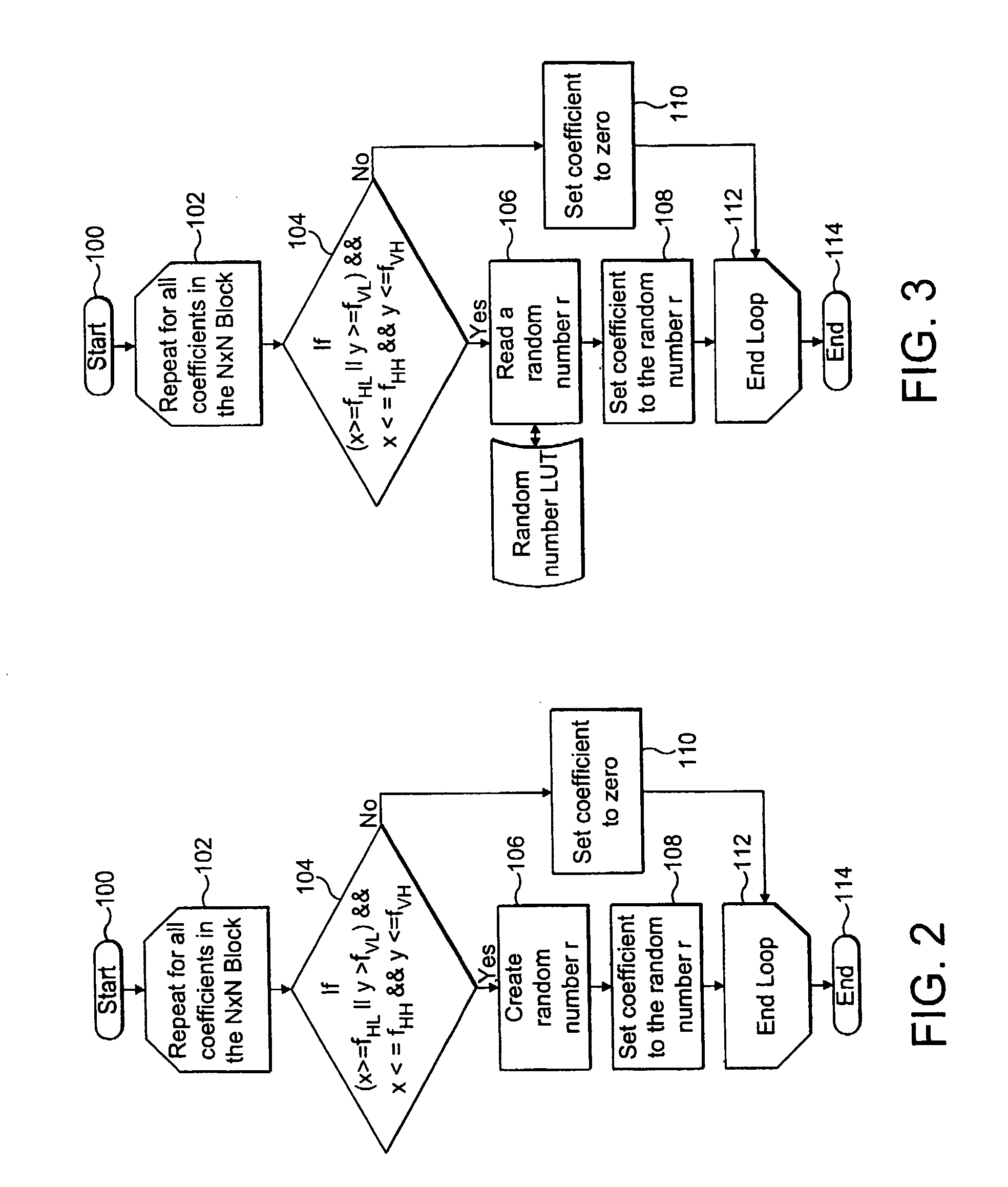
Film grain simulation within a receiver 4 occurs by first obtaining at least one block of pre-computed transformed coefficients. The block of pre-computed transformed coefficients undergoes filtering responsive to a frequency range that characterizes a desired pattern of the film grain. In practice, the frequency range lies within a set of cut frequencies fHL, fVL, fHH and fVH of a filter in two dimensions that characterizes a desired film grain pattern. Thereafter, the filtered set of coefficients undergoes an inverse transform to yield the film grain pattern.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
Low-Complexity Film Grain Simulation Technique
ActiveUS20080152250A1Reduce complexityReduce memory requirementsImage enhancementTelevision system detailsComputational physicsAnalog signal
The simulation of film grain in a video image occurs by first creating a block (i.e., a matrix array) of transformed coefficients for a set of cut frequencies fHL, fVL, fHH and fVH associated with a desired grain pattern. (The cut frequencies fHL, fVL, fHH and fVH represent cut-off frequencies, in two dimensions, of a filter that characterizes the desired film grain pattern). The block of transformed coefficients undergoes an inverse transform to yield a bit-accurate film grain sample and the bit accurate sample undergoes scaling to enable blending with a video signal to simulate film grain in the signal.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
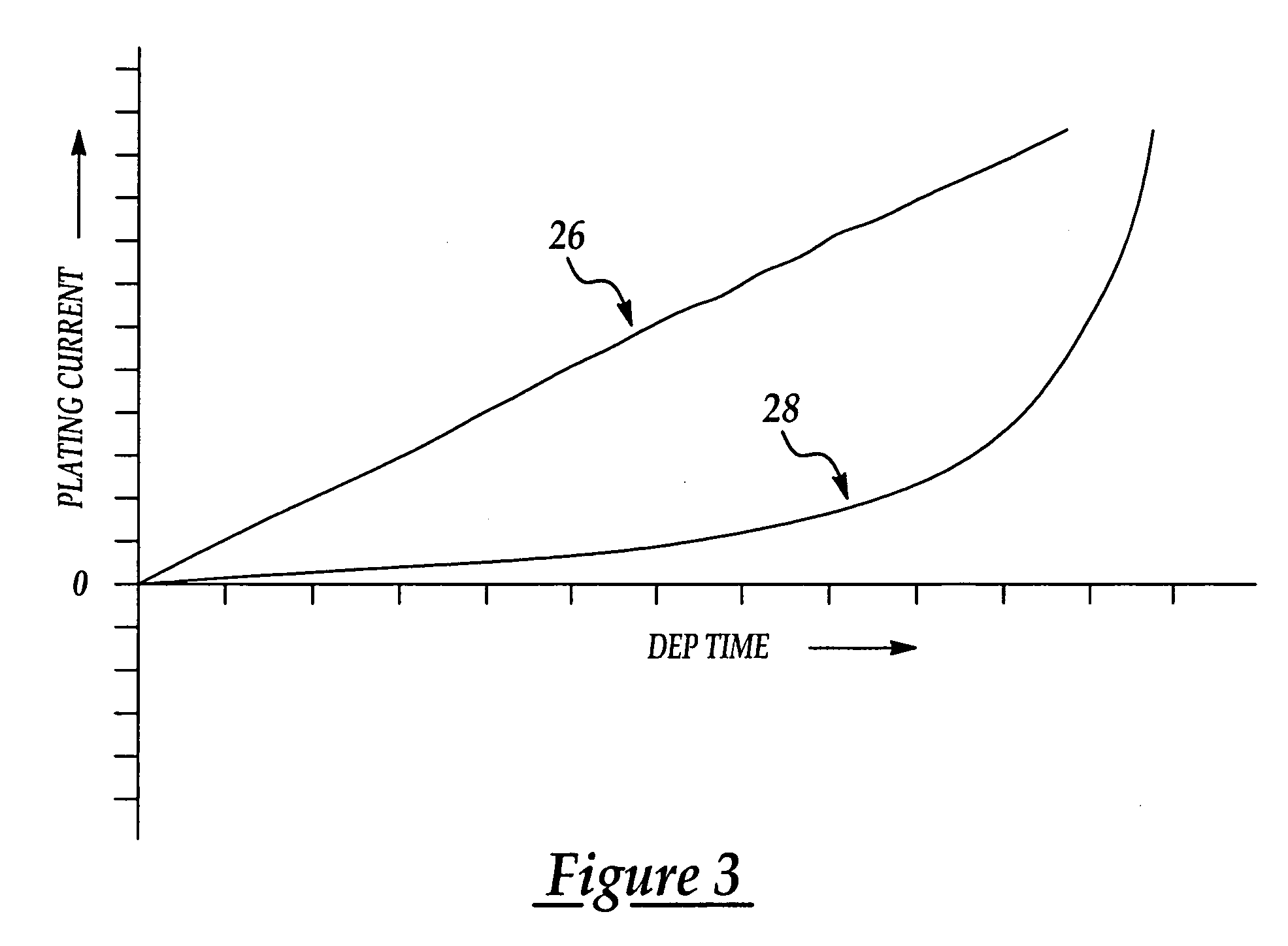
Method for electrochemical plating on semiconductor wafers
InactiveUS20060213778A1Uniform and continuous grain structureReduce thermal stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringConductive materials
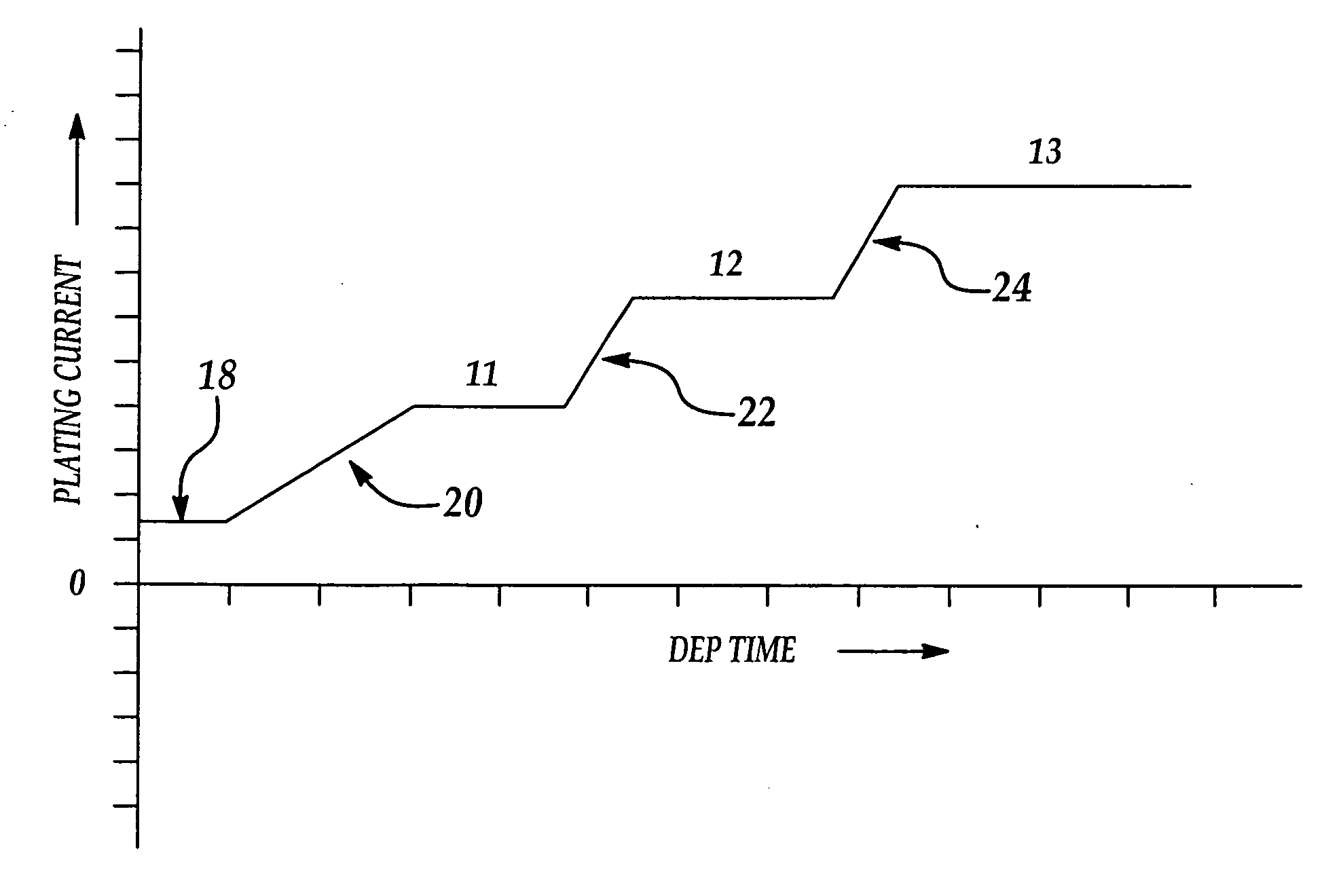
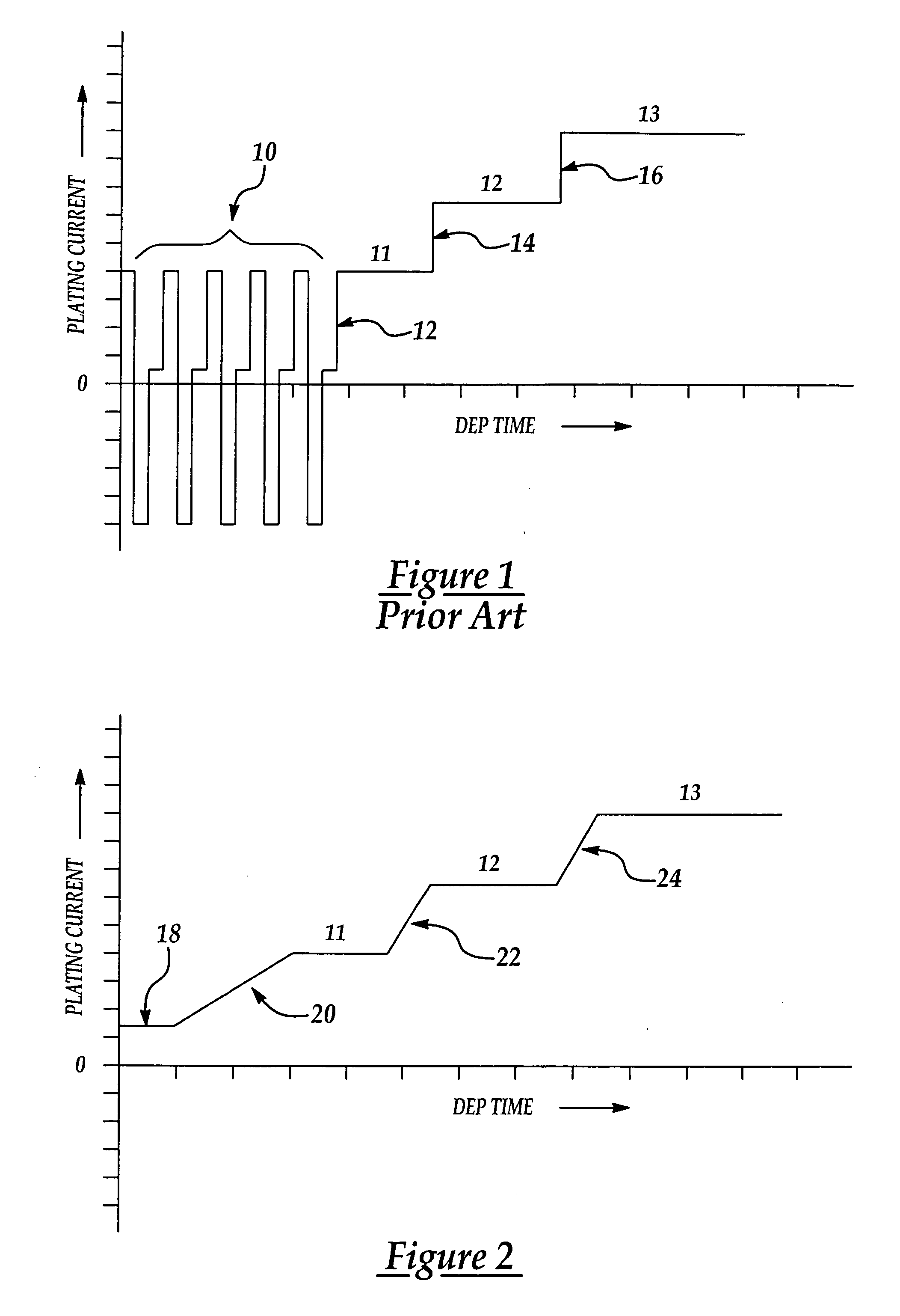
A method of electroplating conductive material on semiconductor wafers improves deposited film quality by providing greater control over the formation of the film grain structure. Better grain size control is achieved by applying a continuous DC plating current to the wafer which avoids sharp discontinuities in the current as the applied current is increased in successive stages during a plating cycle. Current discontinuities are avoided by gradually increasing the current in a ramp-like fashion between the successive plating stages.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Method and apparatus for representing image granularity by one or more parameters
ActiveUS7742655B2Image enhancementTelevision system detailsAlgorithmElectrical and Electronics engineering
To simulate film grain in a compressed video signal, a decoder (15, 28) receives a message containing information that contains a set of one or more parameters, each specifying certain attribute associated with the film grain. For example, one of the parameters will specify the model used to simulate the film grain, whereas other parameters each specify a particular factor associated with that model. Upon receipt of the message, the decoder selects the model, and simulates the film grain for addition to the video signal following decompression.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Technique for adaptive de-blocking of block-based film grain patterns
InactiveUS20060140278A1Quality improvementReduce computing costImage enhancementTelevision system detailsDeblocking filterDownscaling
Reduction in the blockiness of a simulated film grain block can be achieved either by the use of adaptive downscaling or adaptive deblocking filtering to adjust the intensity of the pixels at the block edge in accordance with at least one film grain block parameter, such as film grain size, intensity and texture. Performing such adaptive downscaling or adaptive deblocking filtering achieves improved performance at lower computational cost by avoiding modification of film grain block pixels in lesser affected areas.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL VC HLDG INC
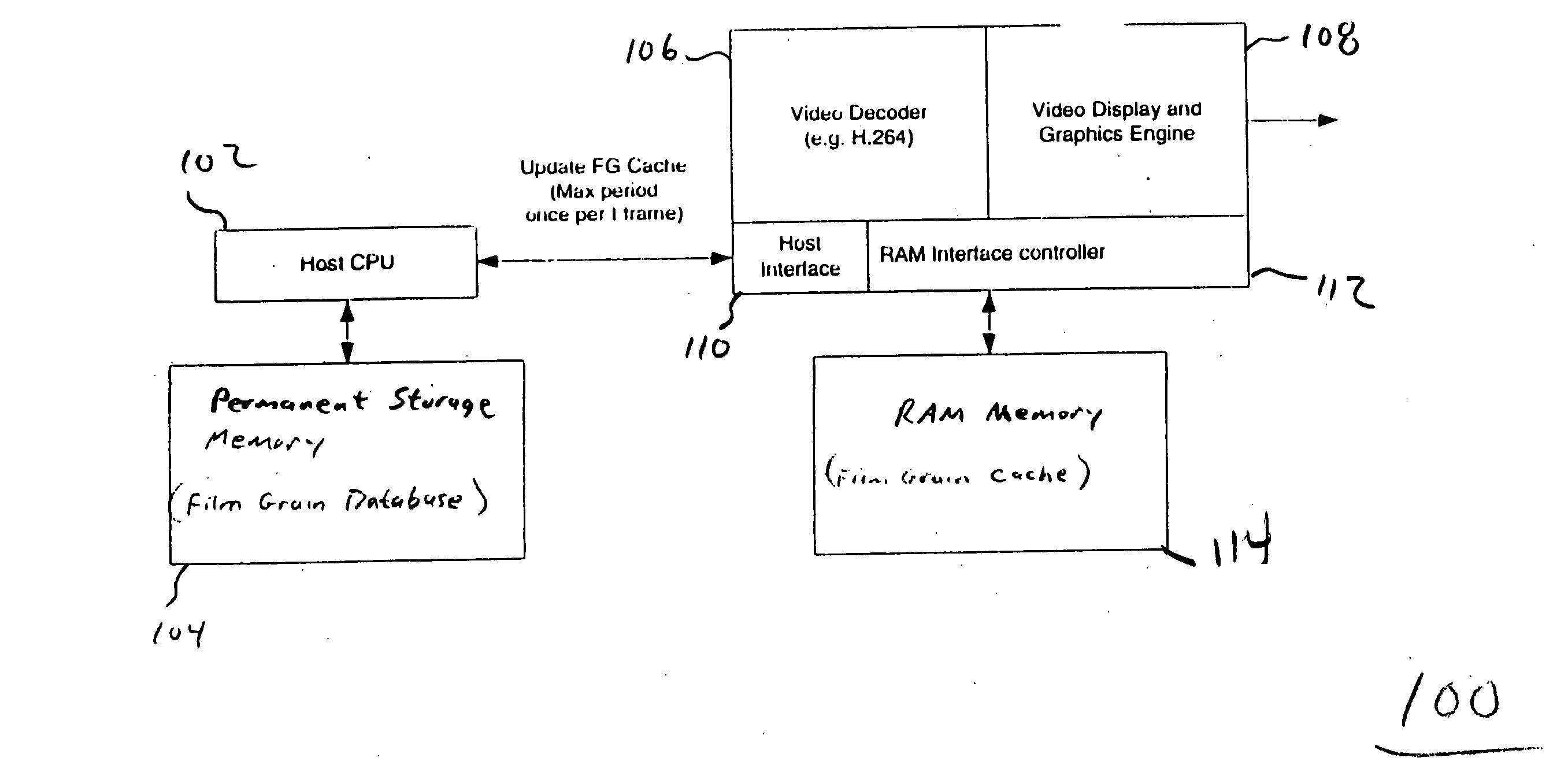
Methods, apparatus and system for film grain simulation
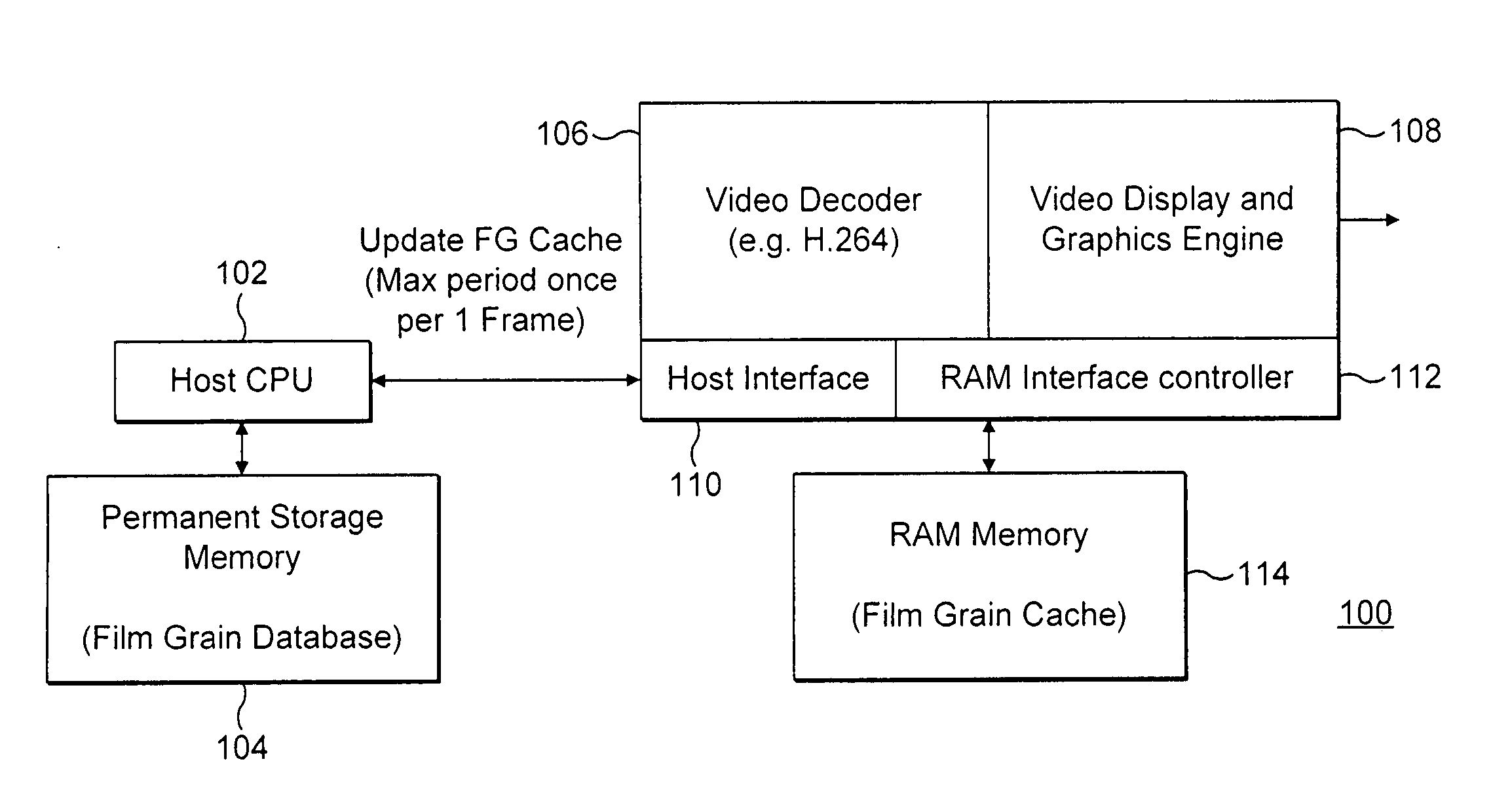
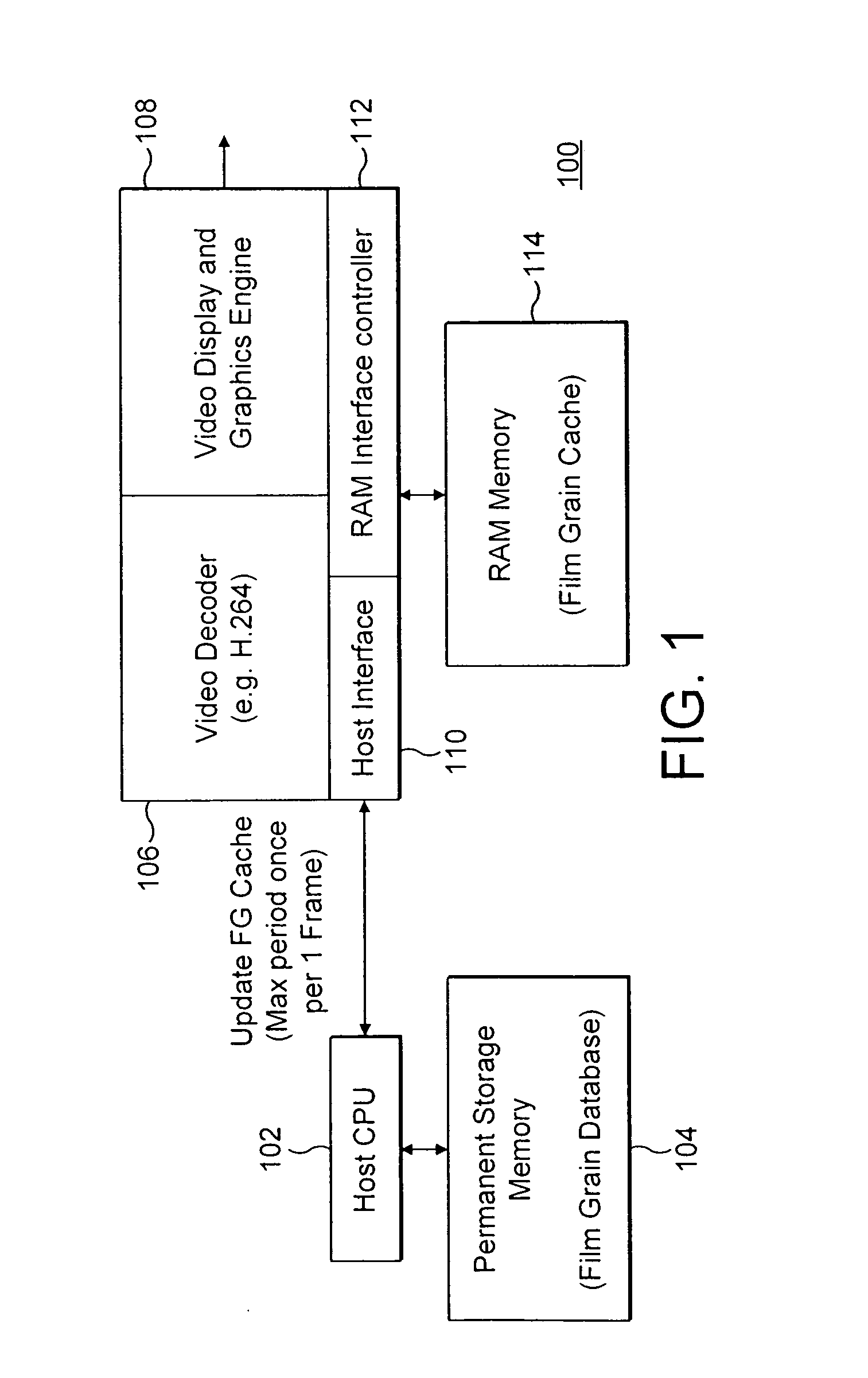
ActiveUS20060083314A1Efficient and low-cost film grain simulation implementationImage enhancementTelevision system detailsNO storageComputer science
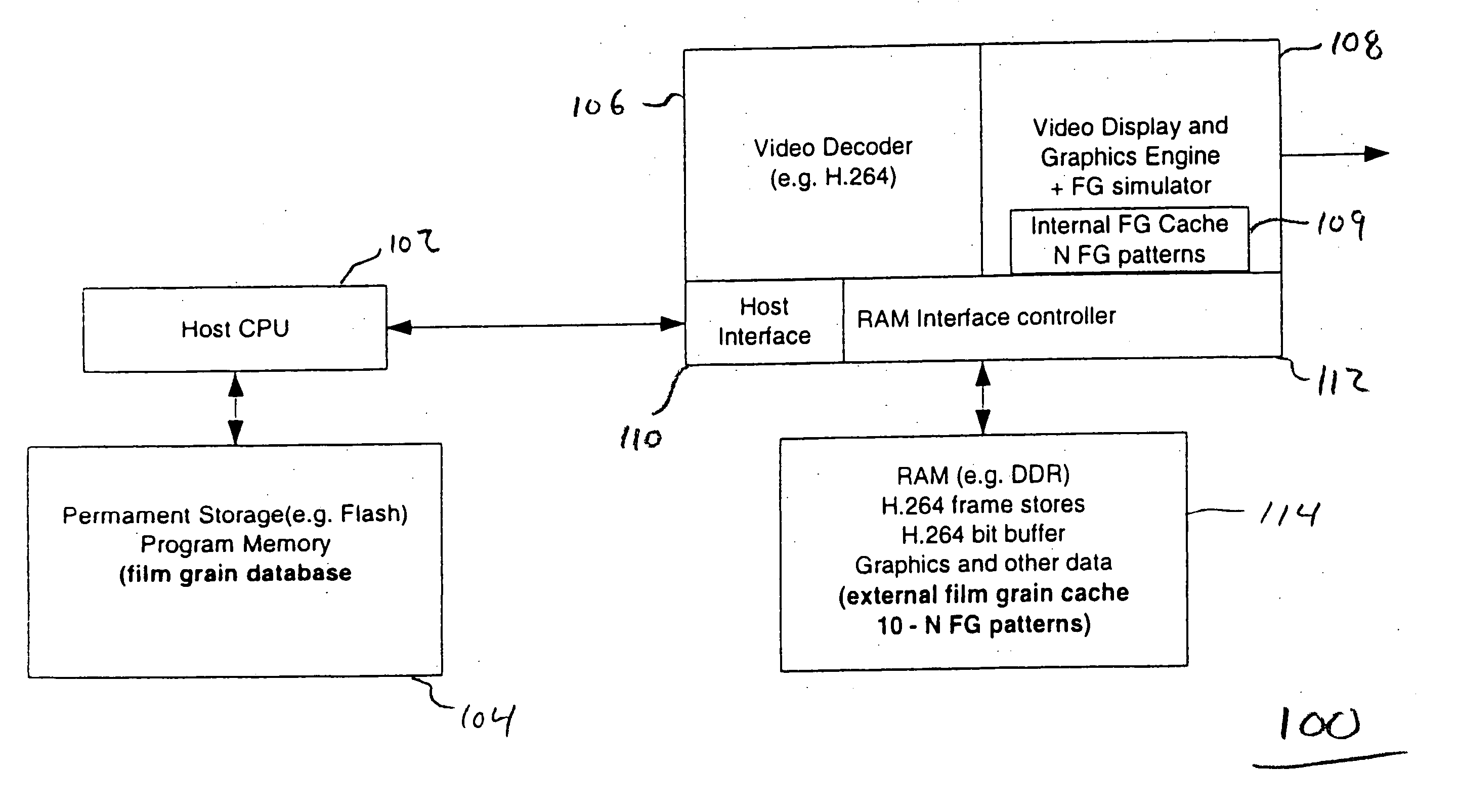
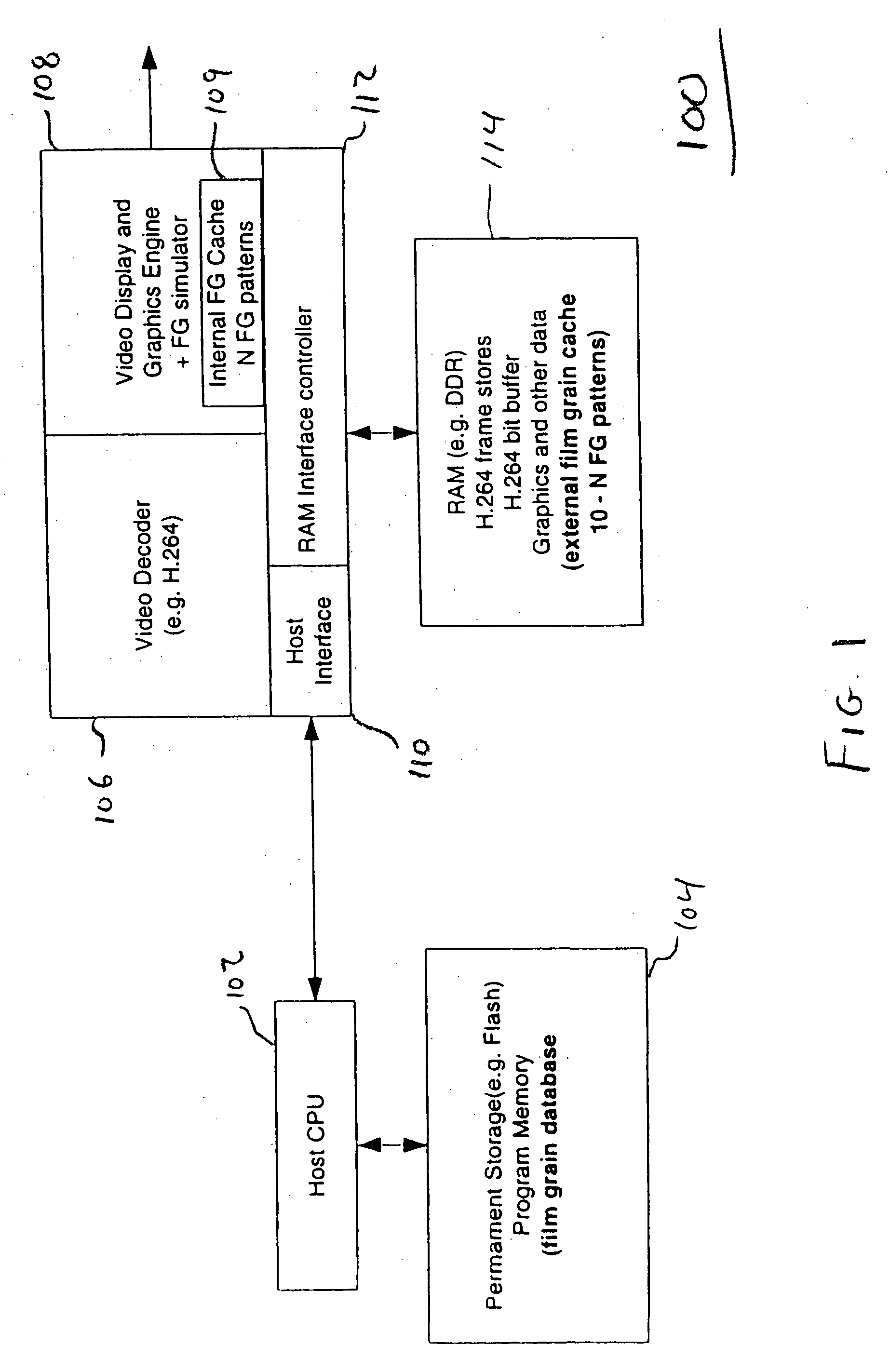
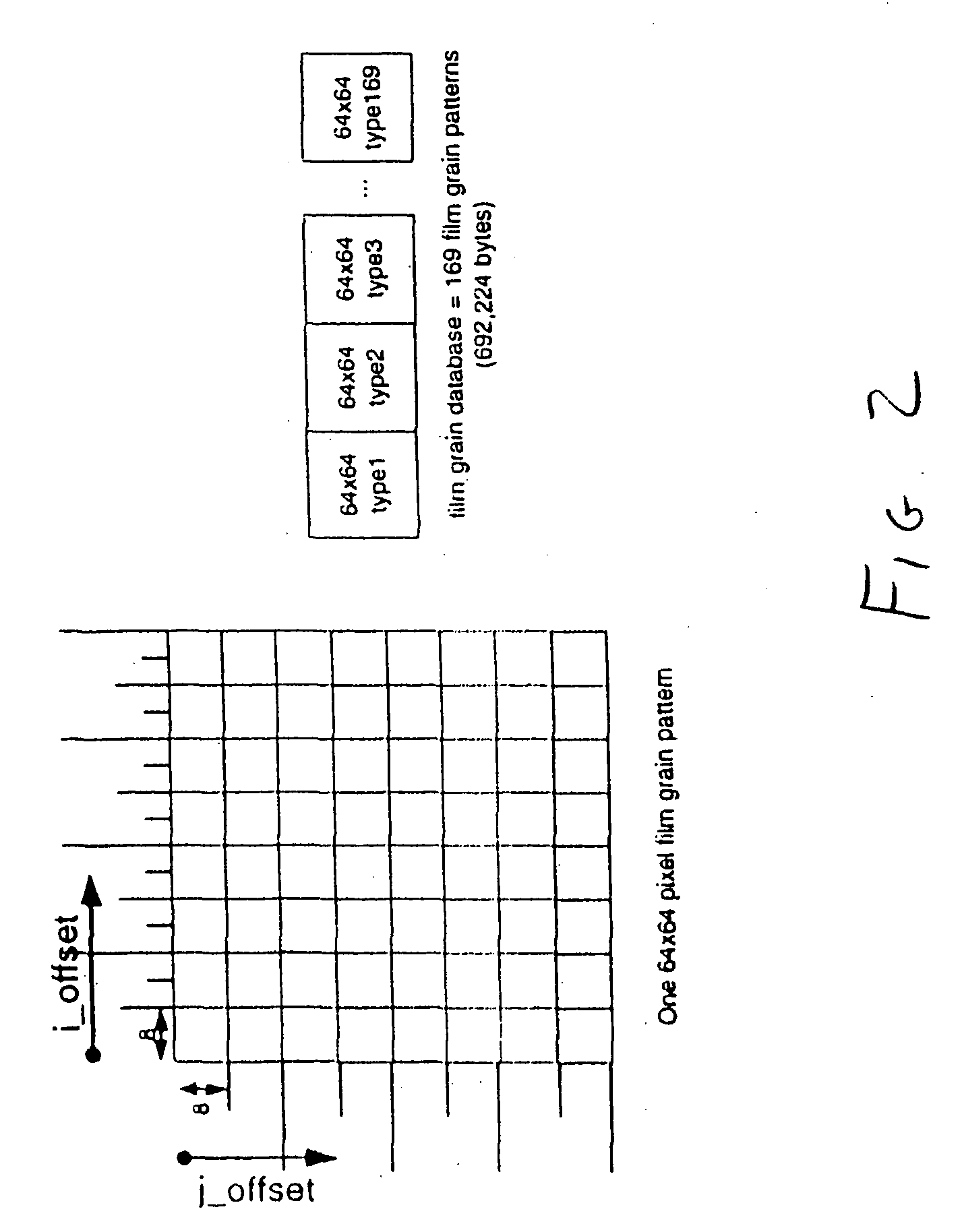
The present invention provides a method, apparatus and system for providing fast access to film grain patterns in a film grain simulation process including providing a first memory storing at least one film grain pattern and in response to a film grain pattern required by the film grain simulation process not being stored in the first memory, updating the first memory to obtain at least the required film grain pattern from at least a second memory. In one embodiment, the first memory is a local cache, the second memory is a film grain pattern database and a controller causes the examination of the local cache for a particular film grain pattern required in the film grain simulation process. In response to the required film grain pattern not being stored in the local cache, the controller causes the update of the local cache using the film grain pattern database.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Method used for preparing FeS2 film and capable of controlling precursor grain size
InactiveCN102560374ARefined grain sizeControl grain sizeFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingAlcoholControl quality
The invention discloses a method used for preparing a FeS2 film and capable of controlling precursor grain size. A coating substrate is boiled in saturation chromic acid solution, washed with deionized water, and washed and dried through ultrasonic oscillation in acetone, absolute ethyl alcohol and deionized water sequentially. A pure Fe film is sputtered, and temperature and thickness of the substrate are controlled. The pure Fe film and sulphur powder are packaged in a glass tube to be processed through sulfidizing. The method can obtain fine and even precursor ferrum film grain size, and the grain size can be controlled conveniently. The method can use optimization of different technology of optimizing precursor film sputtering and following sulfidizing and flexibly controls quality and state of the finally obtained FeS2 film. A control means and a control process are flexible, optimization of preparation technology is facilitated, and more choices for industrial production of the FeS2 film are also provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
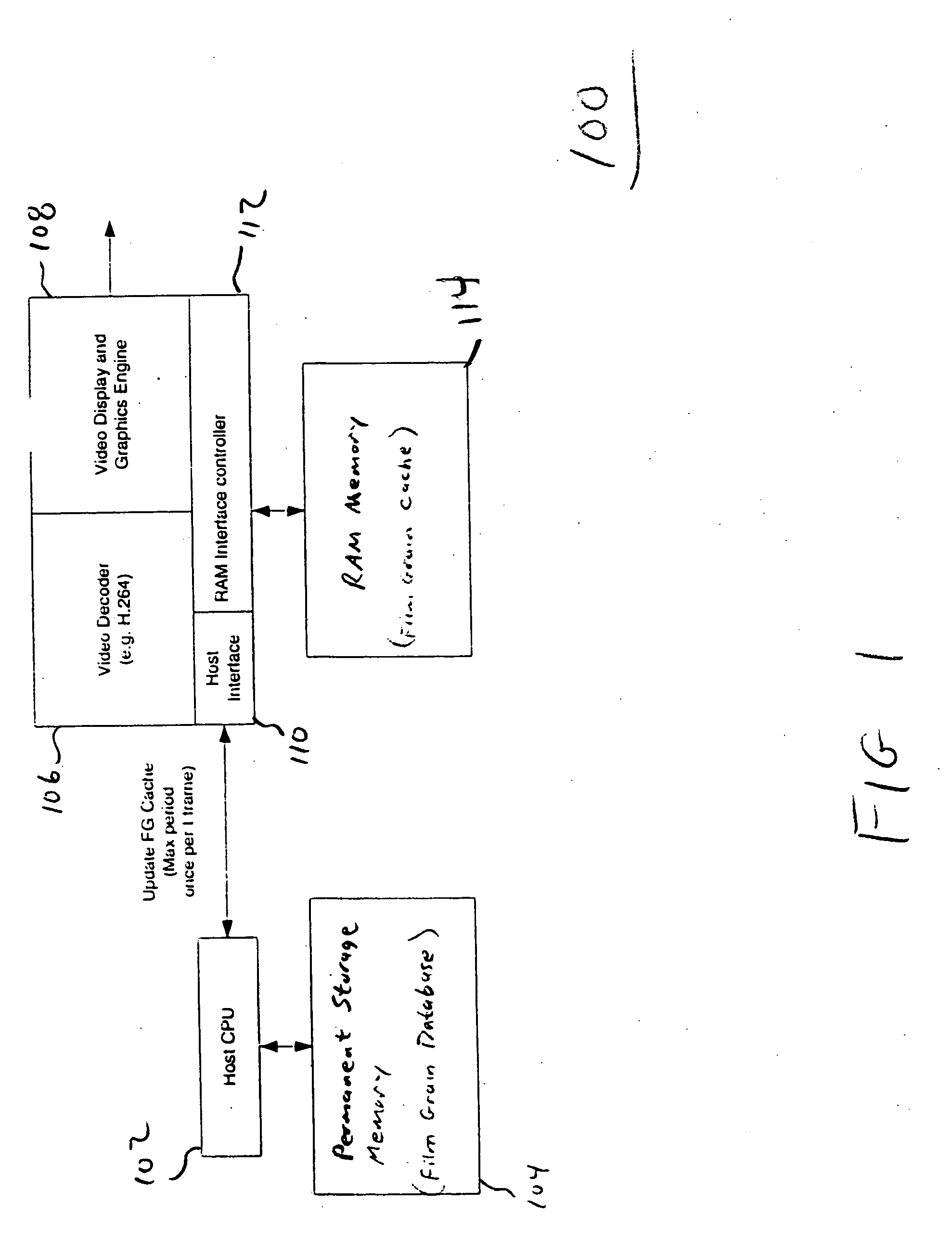
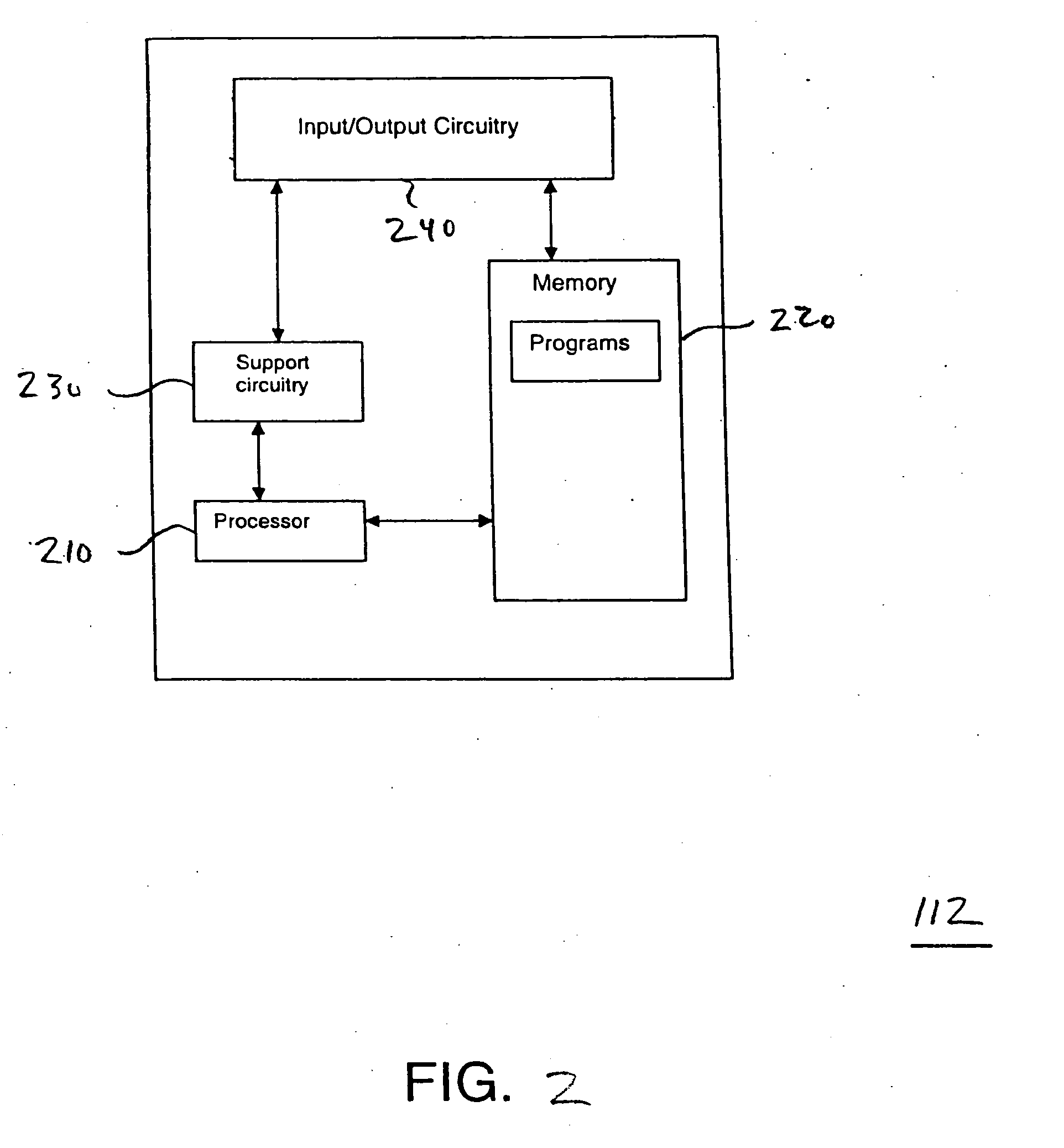
Methods, apparatus and system for film grain cache splitting for film grain simulation
The present invention provides a method, apparatus and system for film grain cache splitting for film grain simulation. In one embodiment of the present invention a method for storing film grain patterns includes storing at least a first portion of film grain patterns in an internal memory and storing at least a second portion of the film grain patterns in an external memory. That is, in the present invention a method for film grain cache splitting for film grain simulation includes splitting the storage of film grain patterns between an internal cache and an external memory. In one embodiment of the present invention, the internal cache is integrated into an integrated circuit chip of a decoder.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
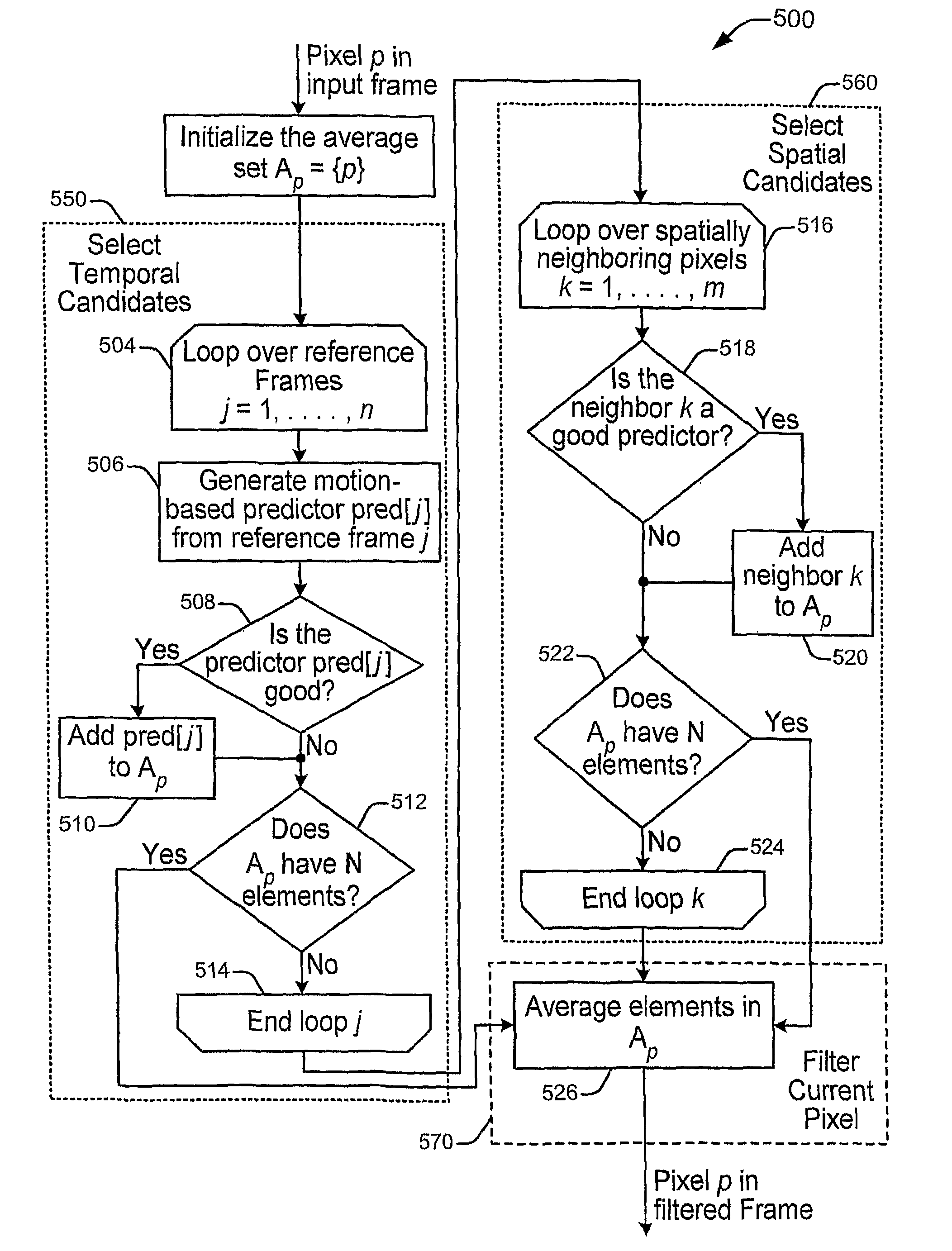
Adaptive pixel-based filtering
In an implementation, a pixel is selected from a target digital image. Multiple candidate pixels, from one or more digital images, are evaluated based on values of the multiple candidate pixels. For the selected pixel, a corresponding set of pixels is determined from the multiple candidate pixels based on the evaluations of the multiple candidate pixels and on whether a predetermined threshold number of pixels have been included in the corresponding set. Further for the selected pixel, a substitute value is determined based on the values of the pixels in the corresponding set of pixels. Various implementations described provide adaptive pixel-based spatio-temporal filtering of images or video to reduce film grain or noise. Implementations may achieve an “even” amount of noise reduction at each pixel while preserving as much picture detail as possible by, for example, averaging each pixel with a constant number, N, of temporally and / or spatially correlated pixels.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Technique for simulating film grain on encoded video
Simulating film grain in an encoded image occurs by extracting the film grain and then characterizing the film grain for encoding in a video stream to enable the film grain restoration upon decoding. Typically, the film grain is characterized based either on the type of film, or by using a particular model. In practice, the film grain particulars are transmitted as parallel information to the video coded stream, typically as a film grain Supplemental Enhancement Information (SEI) message when using the ITU T H.264 video coding standard.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com