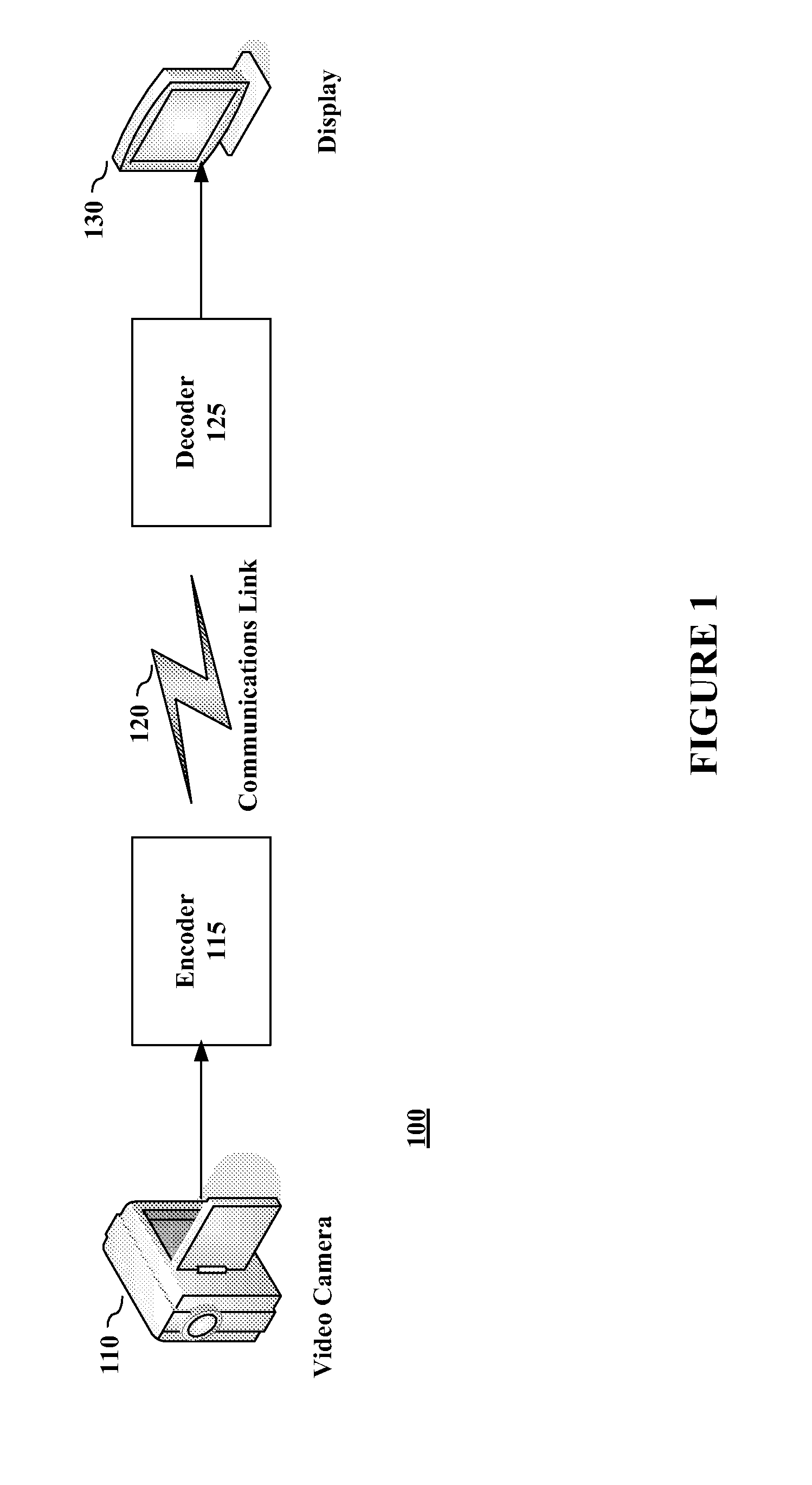
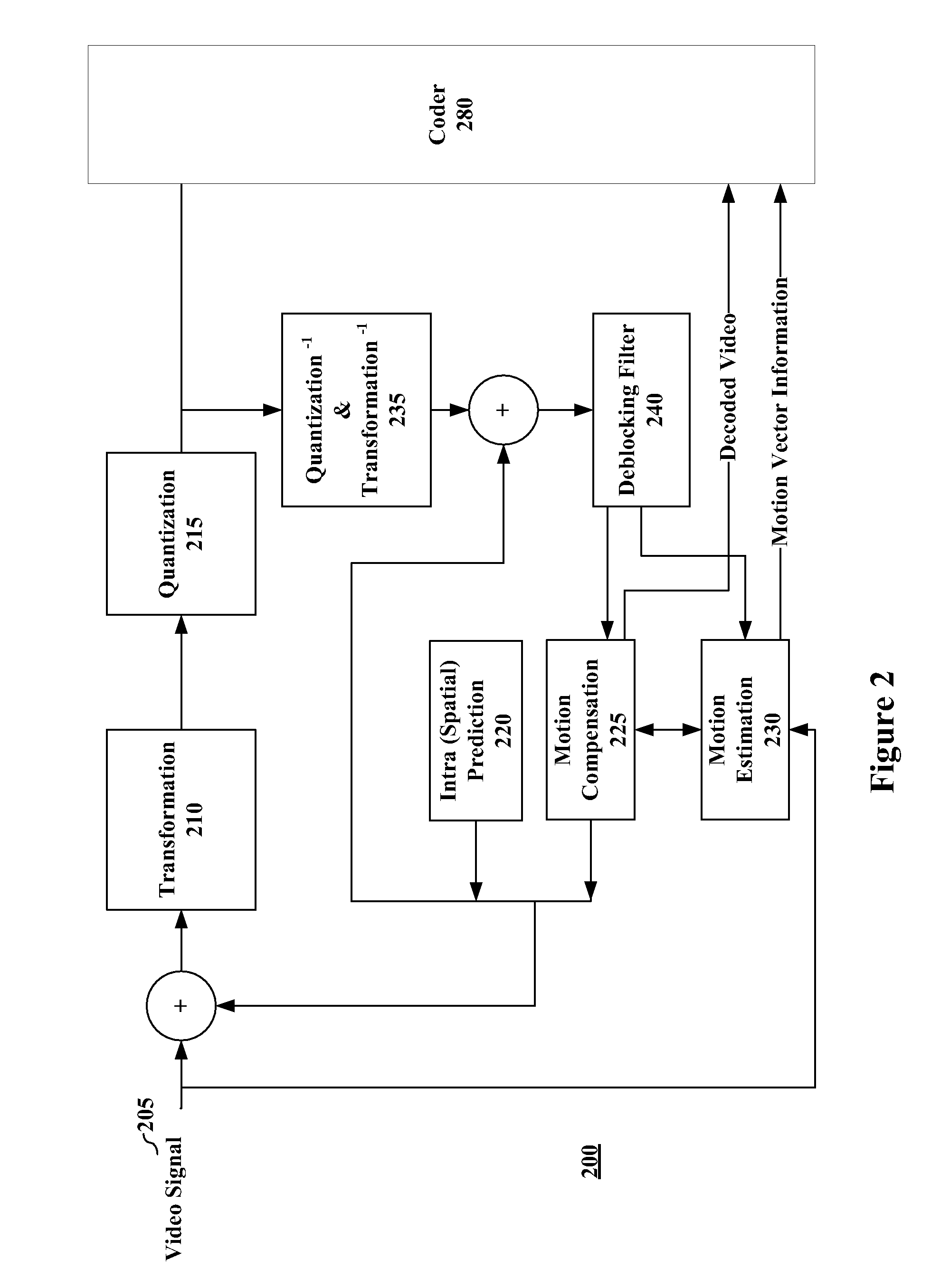
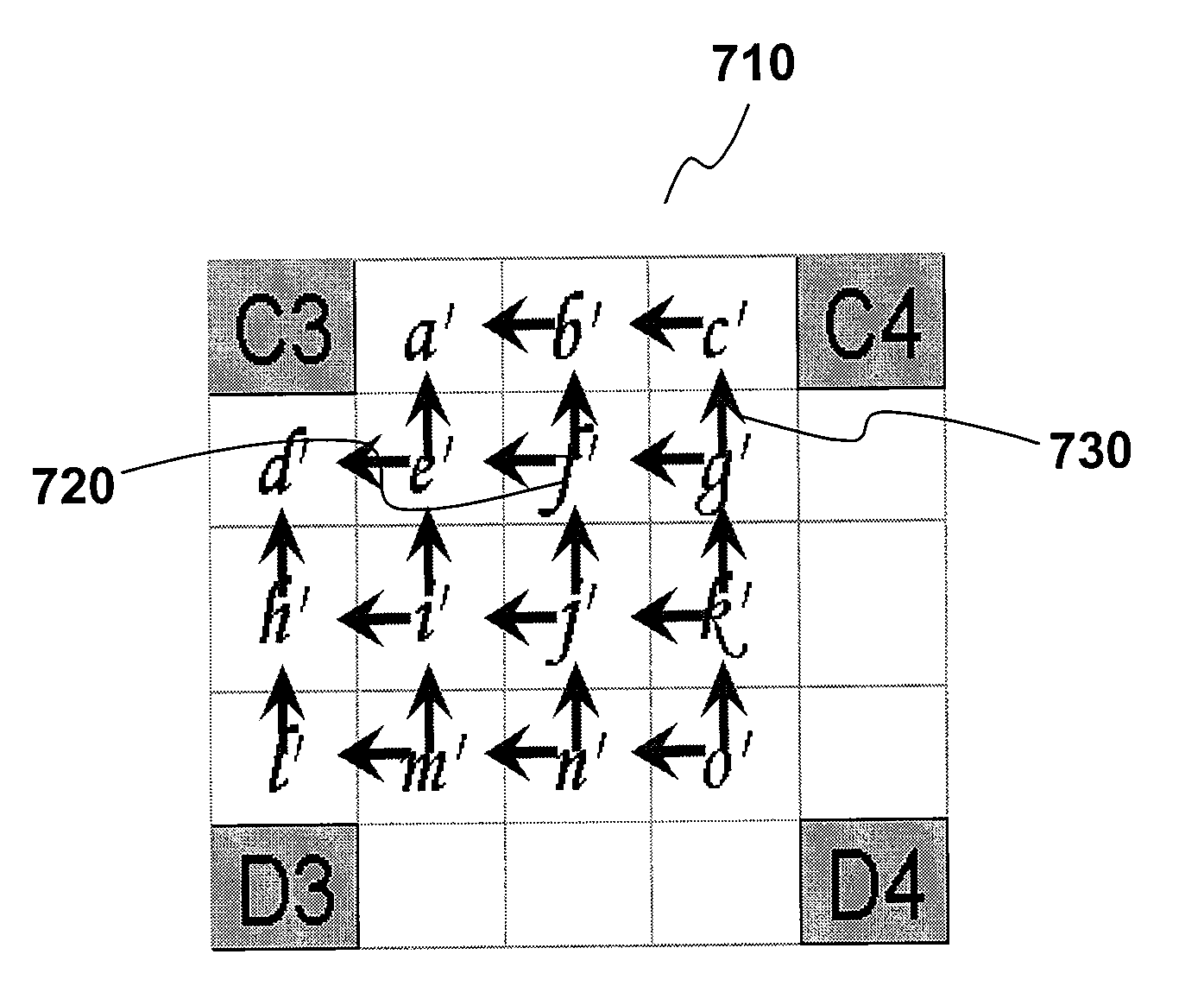
Patents
Literature
447 results about "Filter (video)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A video filter is a software component that performs some operation on a multimedia stream. Multiple filters can be used in a chain, known as a filter graph, in which each filter receives input from its upstream filter, processes the input and outputs the processed video to its downstream filter.
Screen sharing method and apparatus
ActiveUS20070263003A1Reduce distractionsColor television detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer graphics (images)Screen sharing
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Illumination flicker detection apparatus, an illumination flicker compensation apparatus, and an ac line frequency detection apparatus, methods of detecting illumination flicker, compensating illumination flicker, and measuring ac line frequency
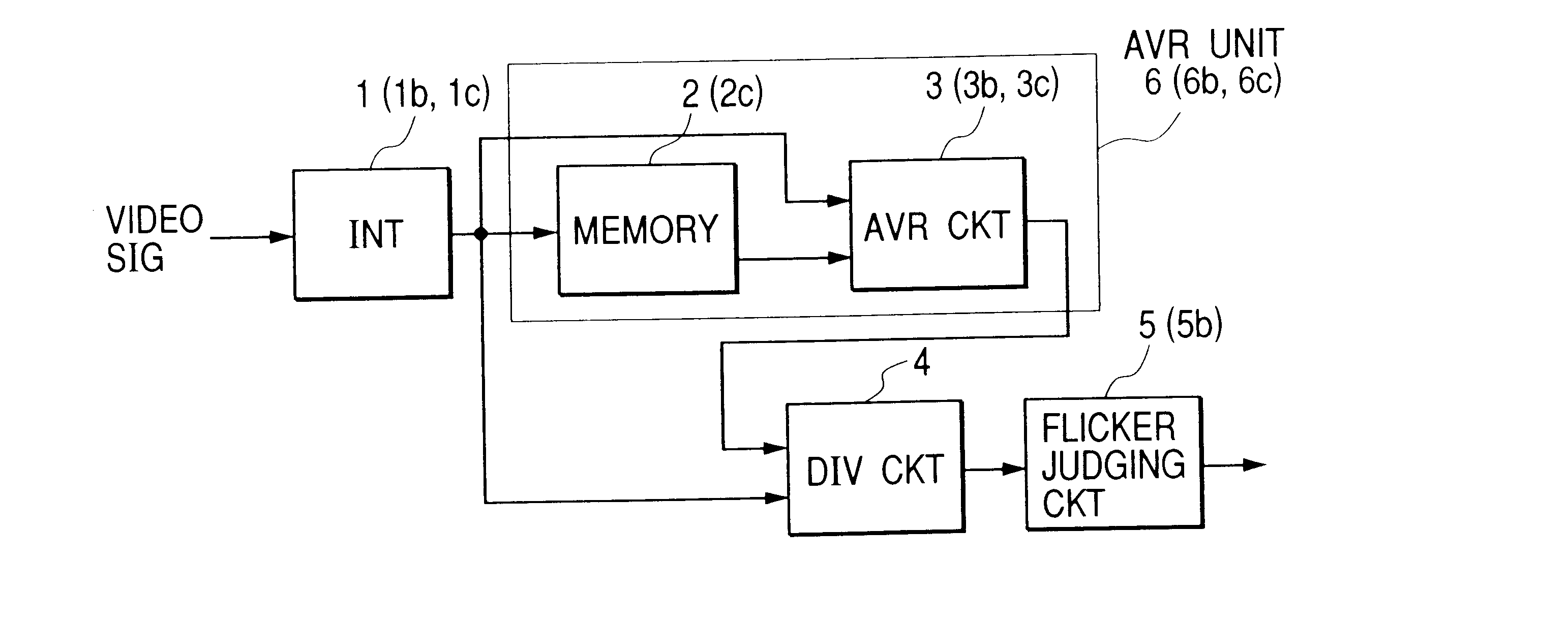
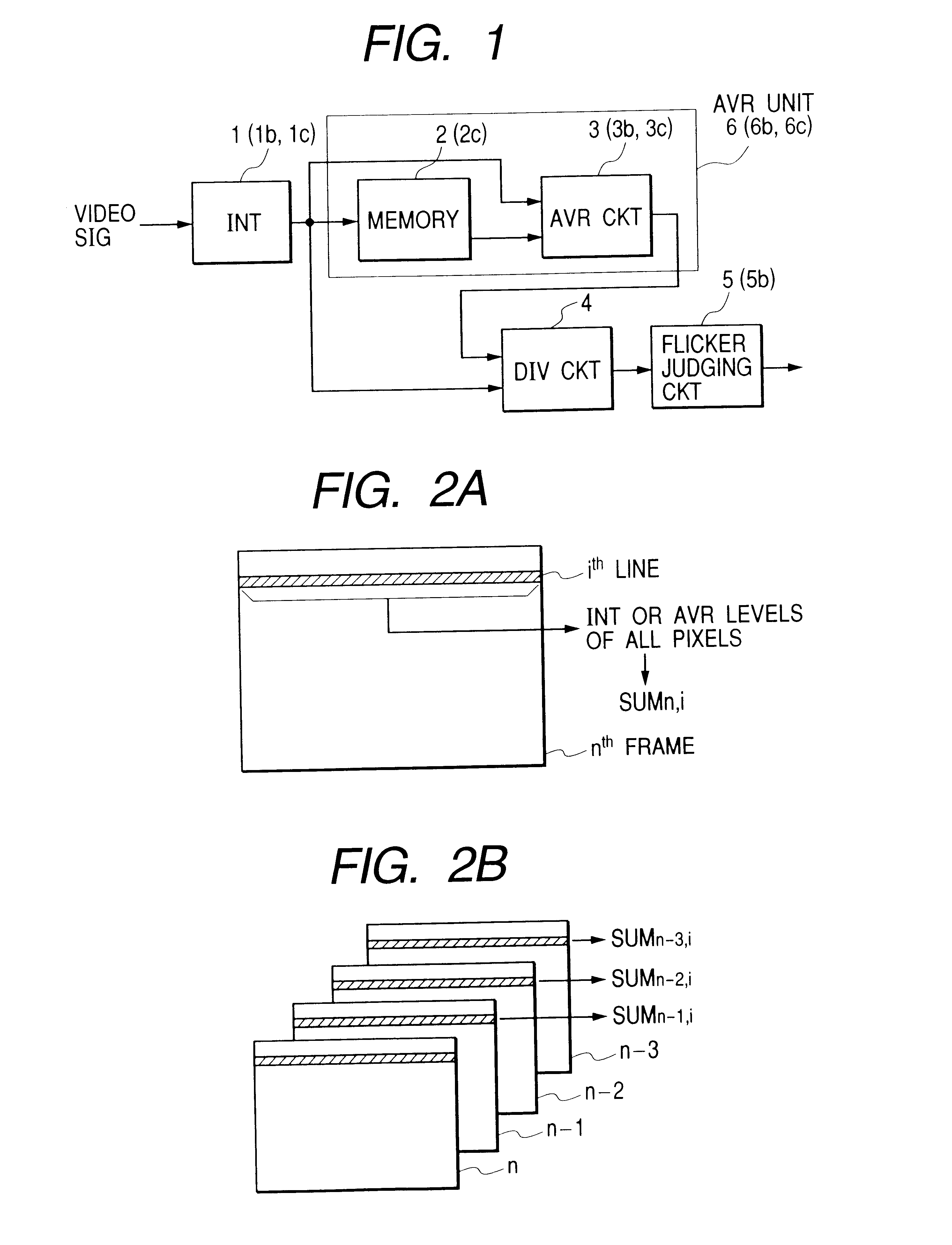
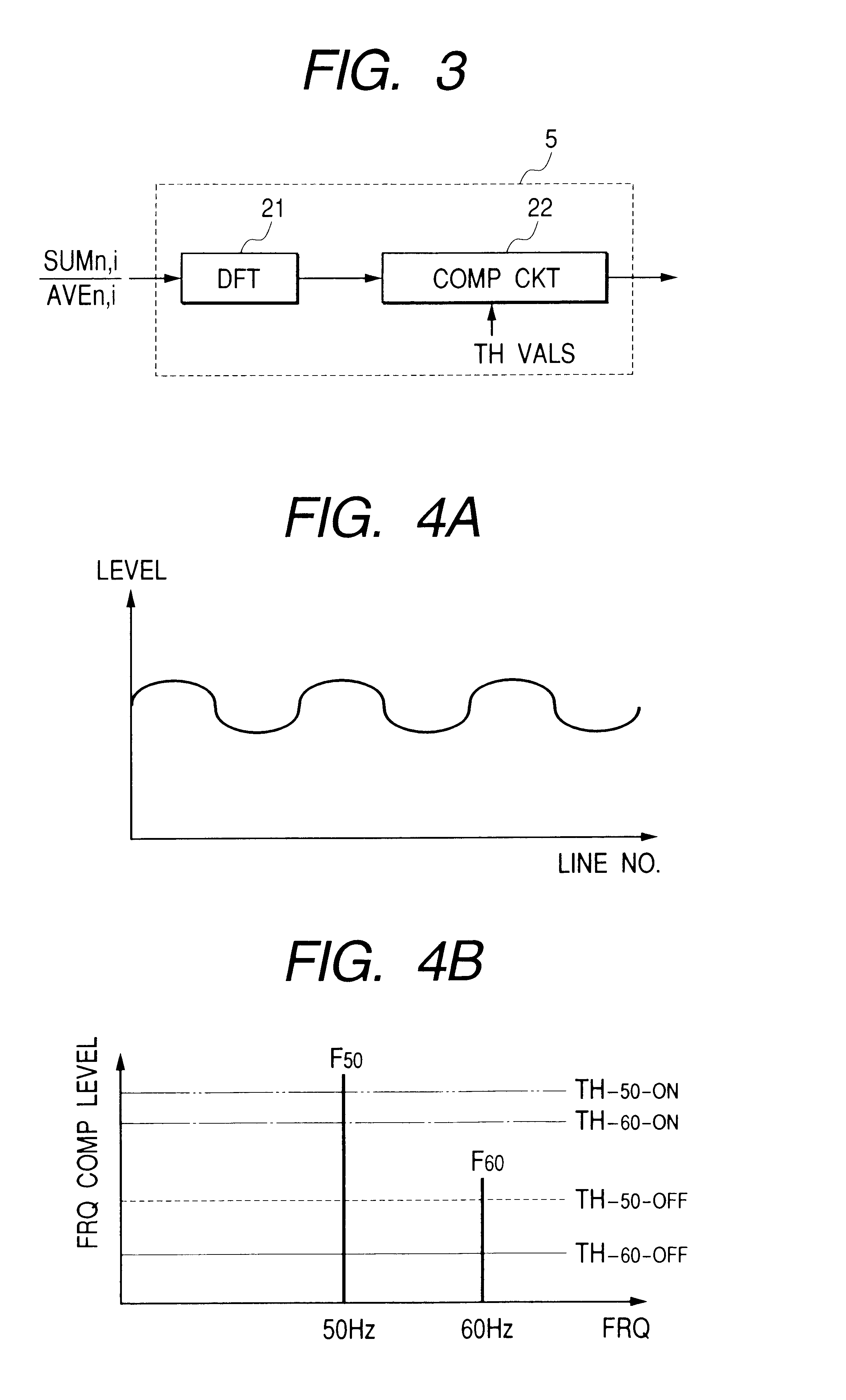
A video signal including illumination flicker component is integrated at each of unit areas (horizontal lines) in a frame (field) of the video signal. The integrated level at each of the unit areas at the frame and the integrated level at the corresponding unit area of an adjacent frame are averaged. Dividing is effected between results of the averaging and integrating every unit area. It is judged whether flicker exists in the video signal by frequency-analyzing results of the dividing result at the unit areas. The unit area may be plural adjacent lines where flickering are negligible. The averaging circuit may be circulation type of or FIR filter. Threshold level for judging the flicker is changed according to a shutter speed control signal. Flicker compensation may be executed by controlling shutter speed or the AGC according to flicker judging result. A still condition at a block in a frame may be detected from the integration result at plural frames. When the block is judged to be still, the flicker is judged. An ac line frequency detection is also disclosed to detect the frequency of the ac line from a video signal generated under illumination including flicker. An imaging circuit may be provided to generate the video signal therein.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Low noise encoding and decoding method
InactiveUS6873368B1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionLow noiseDecoding methods
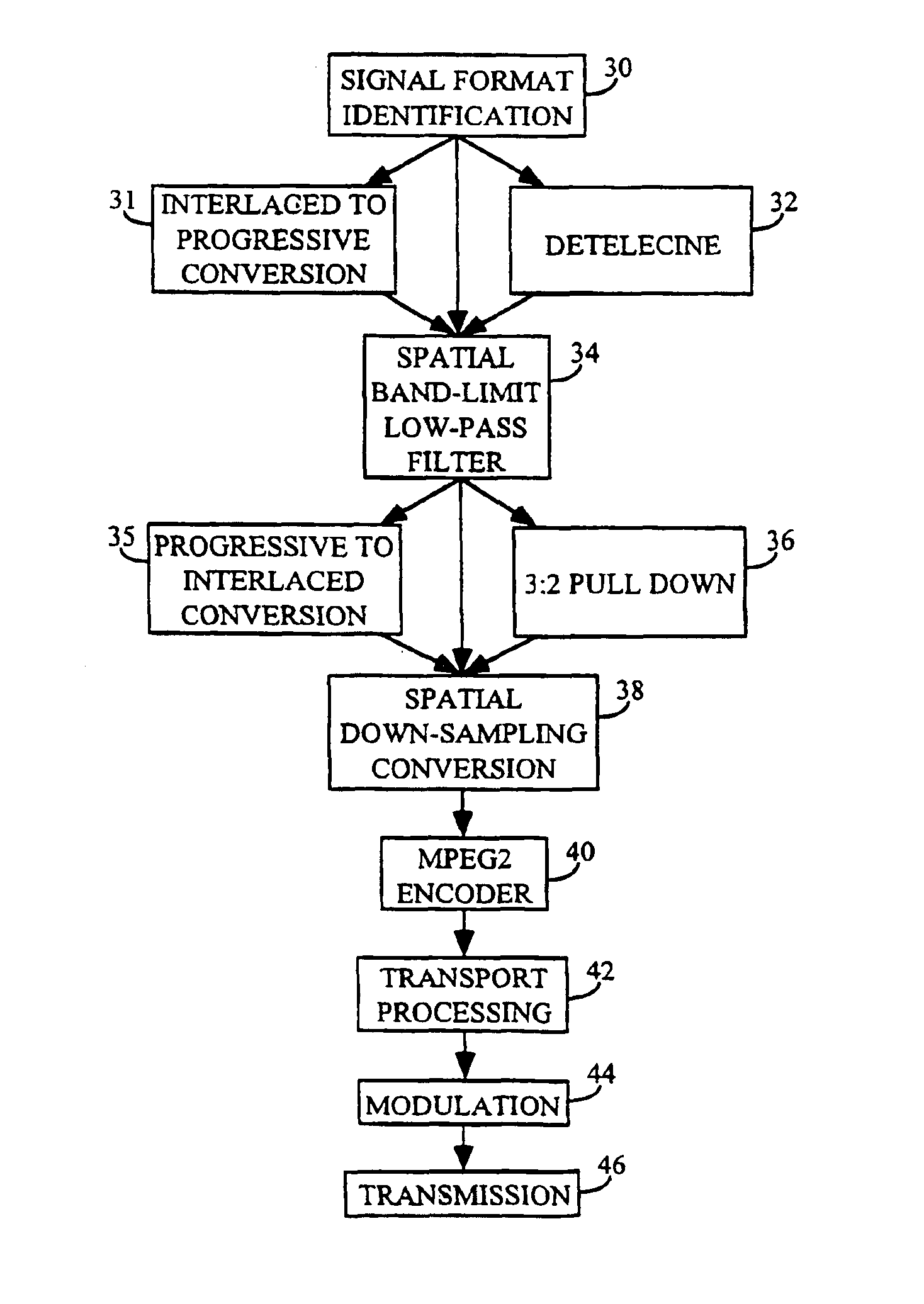
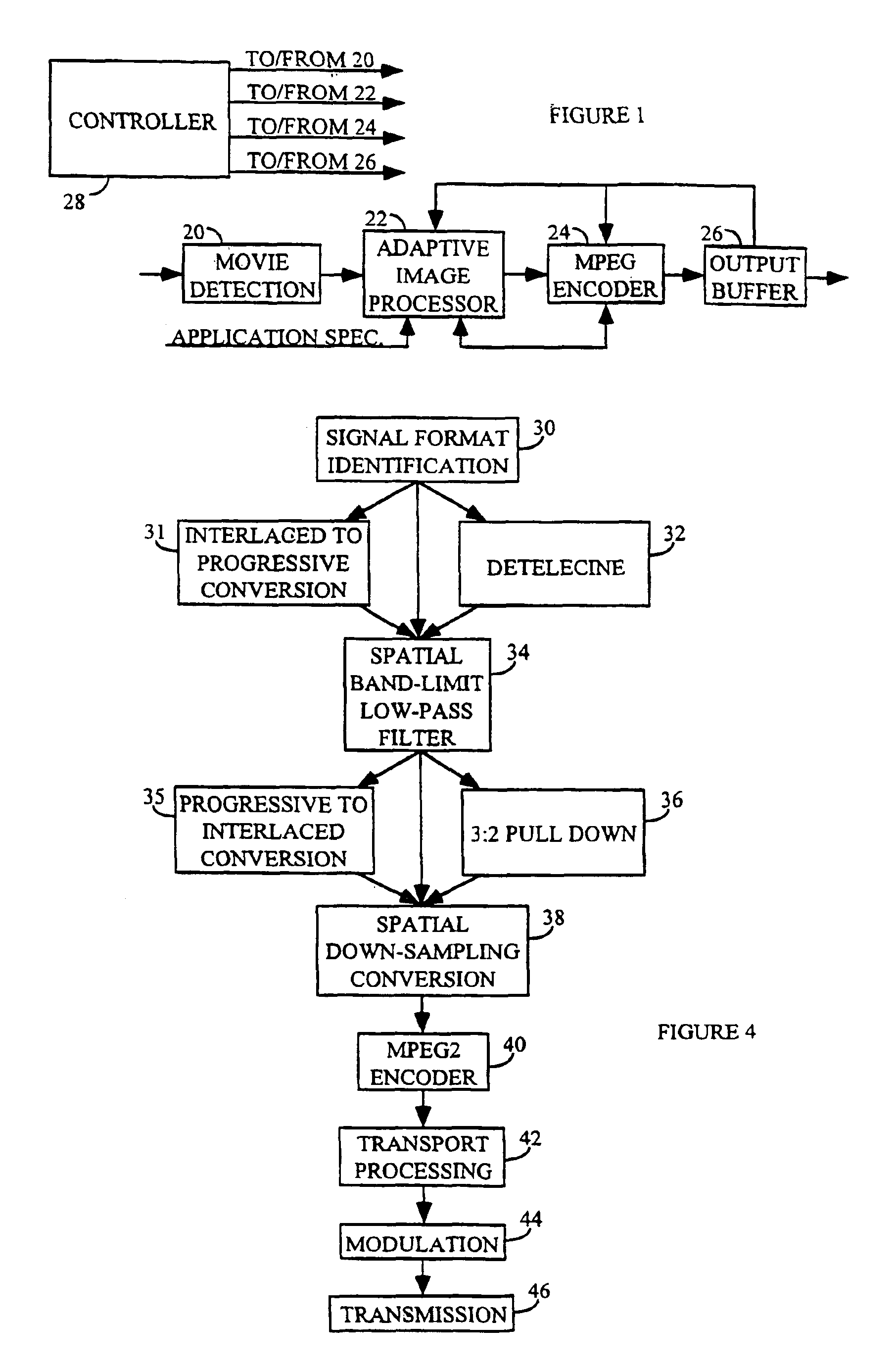
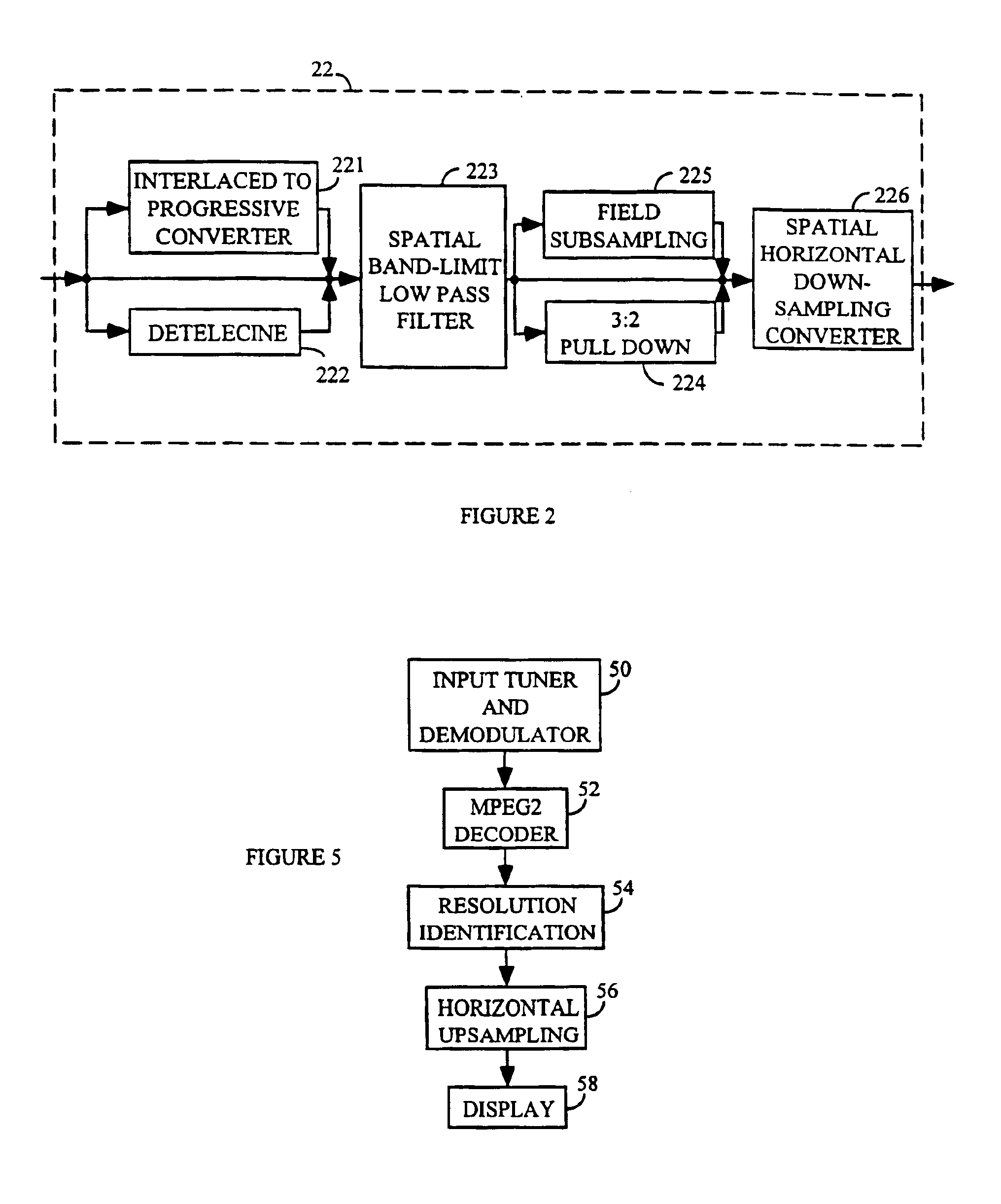
An adaptive digital image processor precedes an MPEG2 encoder. The processor receives a high definition video signal intended for broadcast or storage, and adaptively low-pass filters the signal. The signal is subjected to low-pass two-dimensional filtering to eliminate encoding artifacts and related noise. The video signal is then horizontally down-sampled to create a lower resolution hybrid signal. A receiver decodes and decompresses the hybrid signal. The hybrid signal is upsampled to its original resolution using existing hardware and software with a software modification.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Video coding method and video decoding method
InactiveUS20100220788A1Improve predictive efficiencyImprove coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSub-pixel resolutionImage resolution
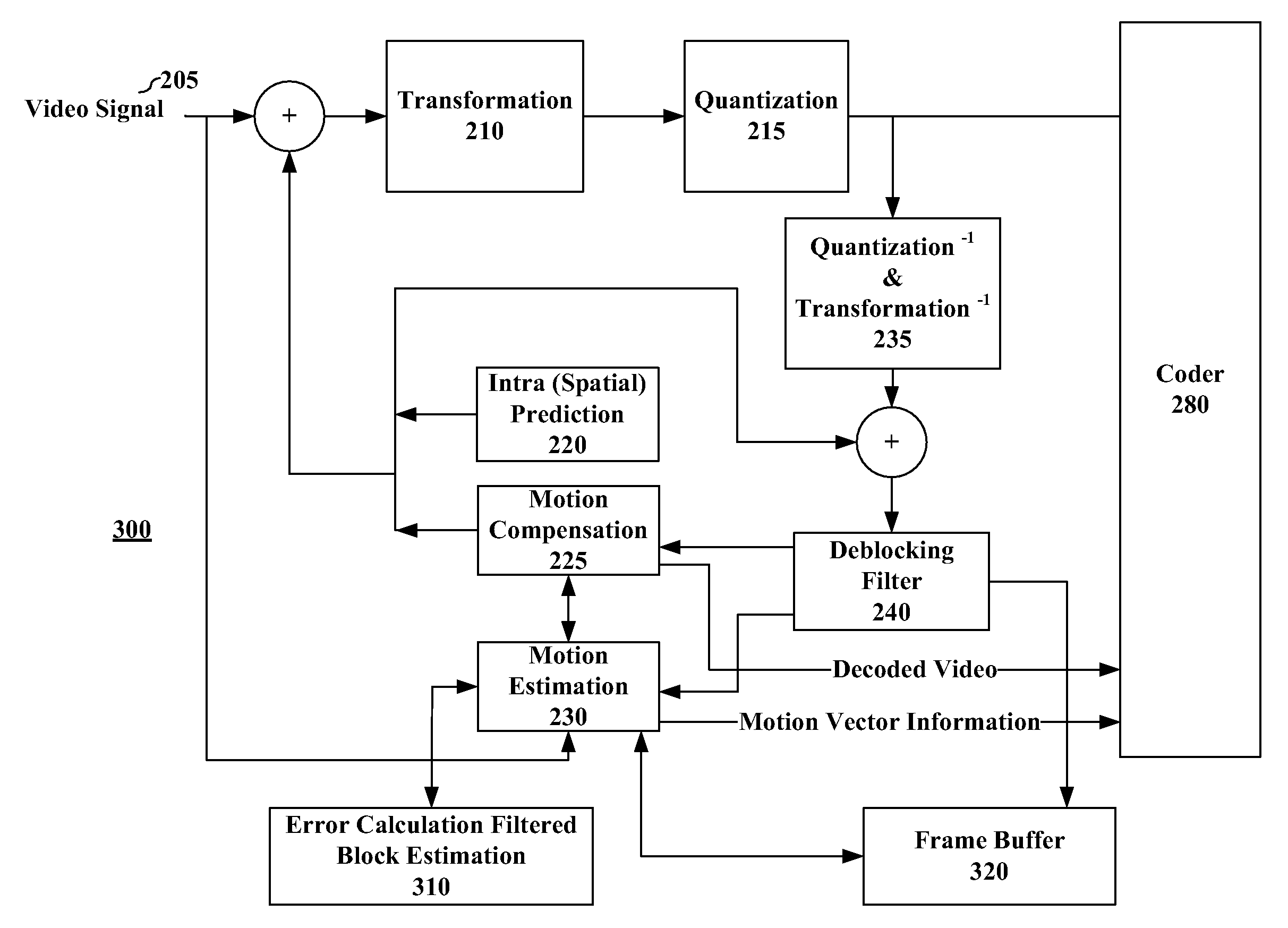
A video coding method and a video coding device can optimize prediction efficiency and coding efficiency.A video coding device (100) codes video data, by performing motion compensation with sub-pel resolution by using an adaptive interpolation filter for calculating a pixel value of a sub pixel for interpolation between full pixels configuring an input image included in the video data. The video coding device (100) includes: a motion compensation unit (160) that (i) sets a filter property for an adaptive interpolation filter on a predetermined process unit basis, and determining, for each of sub-pel positions relative to a full pixel, a plurality of filter coefficients of the adaptive interpolation filter having the set filter property, and (ii) performs the motion compensation with sub-pel resolution, by applying the adaptive interpolation filter having the determined filter coefficients to the input image; and a subtraction unit (110) that generates a prediction error, by subtracting, from the input image, a prediction image generated in the motion compensation; and a coding unit (190) that codes the prediction error.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Low-complexity deblocking filter
ActiveUS20060104349A1Minimise coding artifactMinimize artifactColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionCoding artifacts
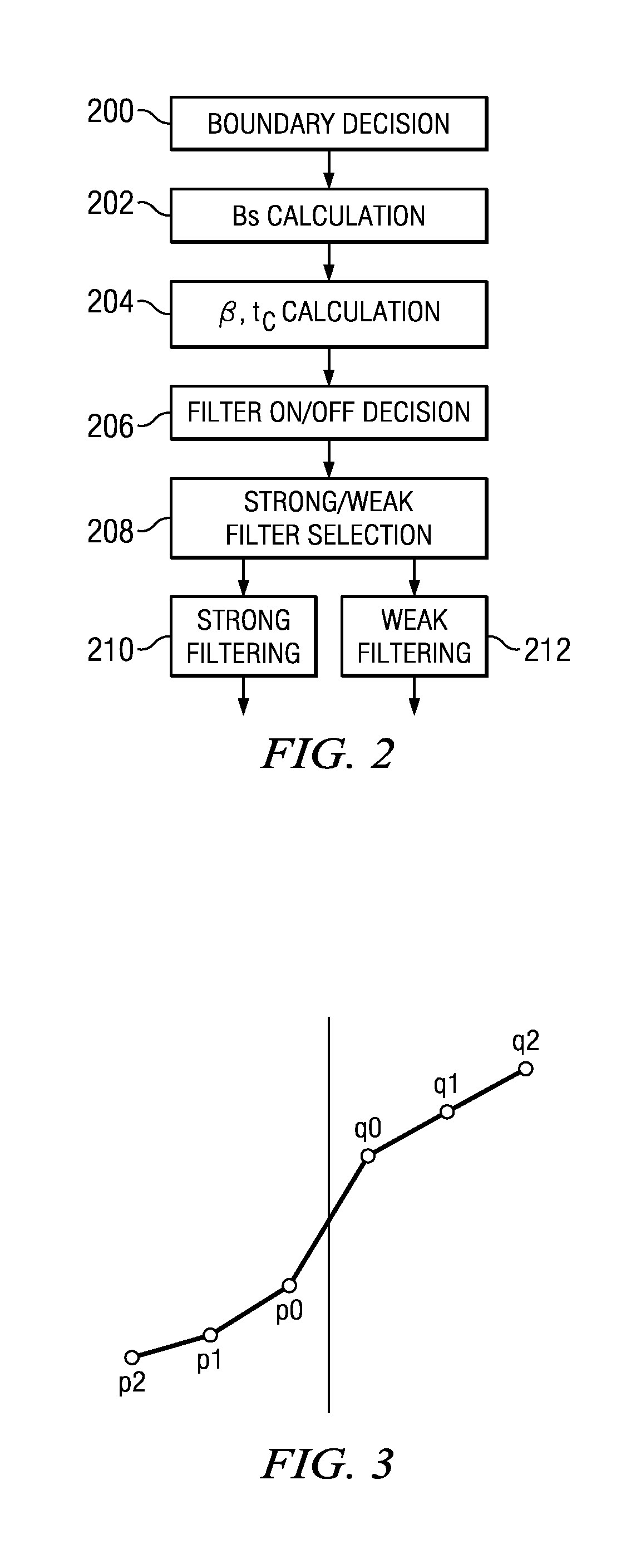
A method of filtering to remove coding artifacts introduced at block edges in a block-based video coder, the method having the steps of: checking the content activity on every line of samples belonging to a boundary to be filtered and where content activity is based on a set of adaptively selected thresholds determined using Variable-Shift Table Indexing (VSTI); determining whether the filtering process will modify the sample values on that particular line based on said content activity; and selecting a filtering mode between at least two filtering modes to apply on a block boundary basis, implying that there would be no switching between the two primary modes on a line by line basis along a given block boundary. The two filtering modes include a default mode based on a non-recursive filter, and a strong filtering mode which features two strong filtering sub-modes and a new selection criterion that is one-sided with respect to the block boundary to determine which of the two strong filtering sub-modes to use. The two strong filtering sub-modes include a new 3-tap filter sub-mode and a 5-tap filter sub-mode that permits a more efficient implementation of the filter.
Owner:CISCO SYST CANADA
Confusion of multiple filters in adaptive loop filtering in video coding
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
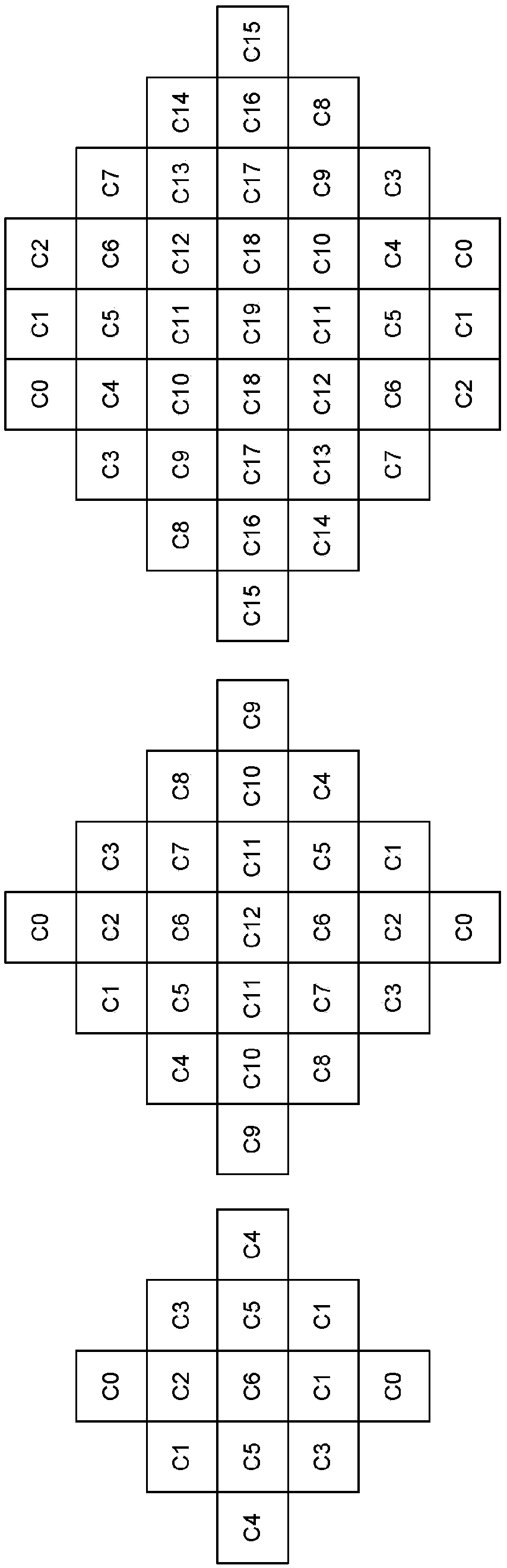
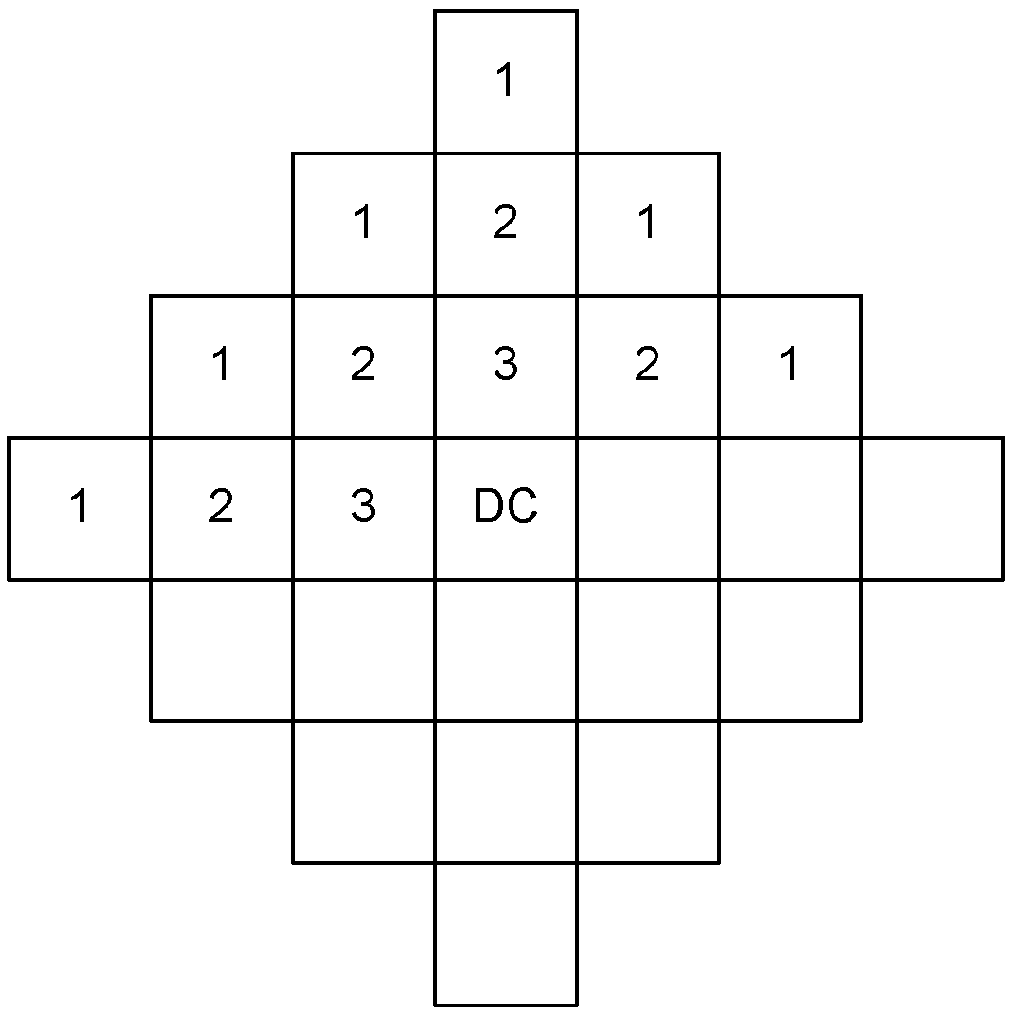
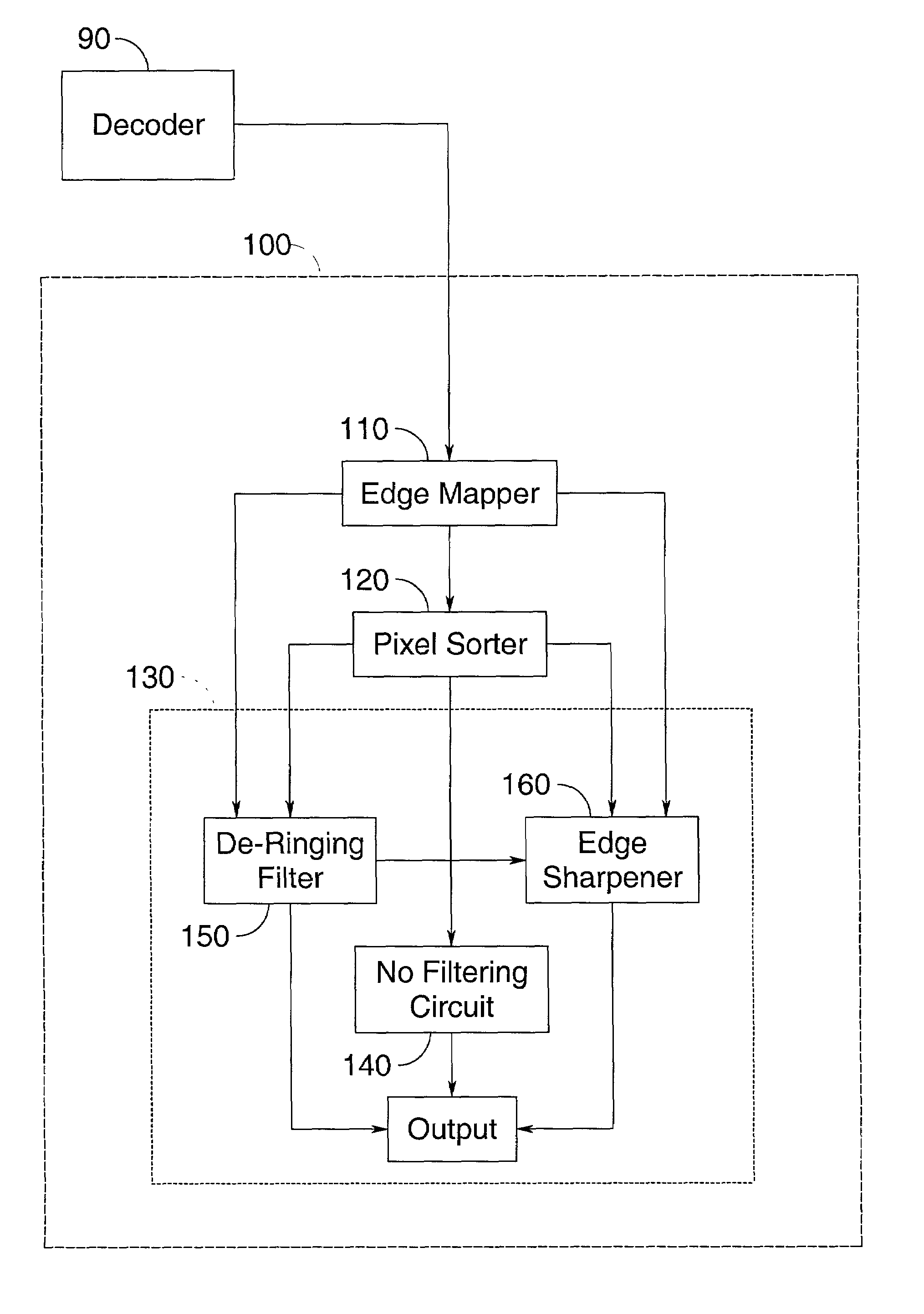
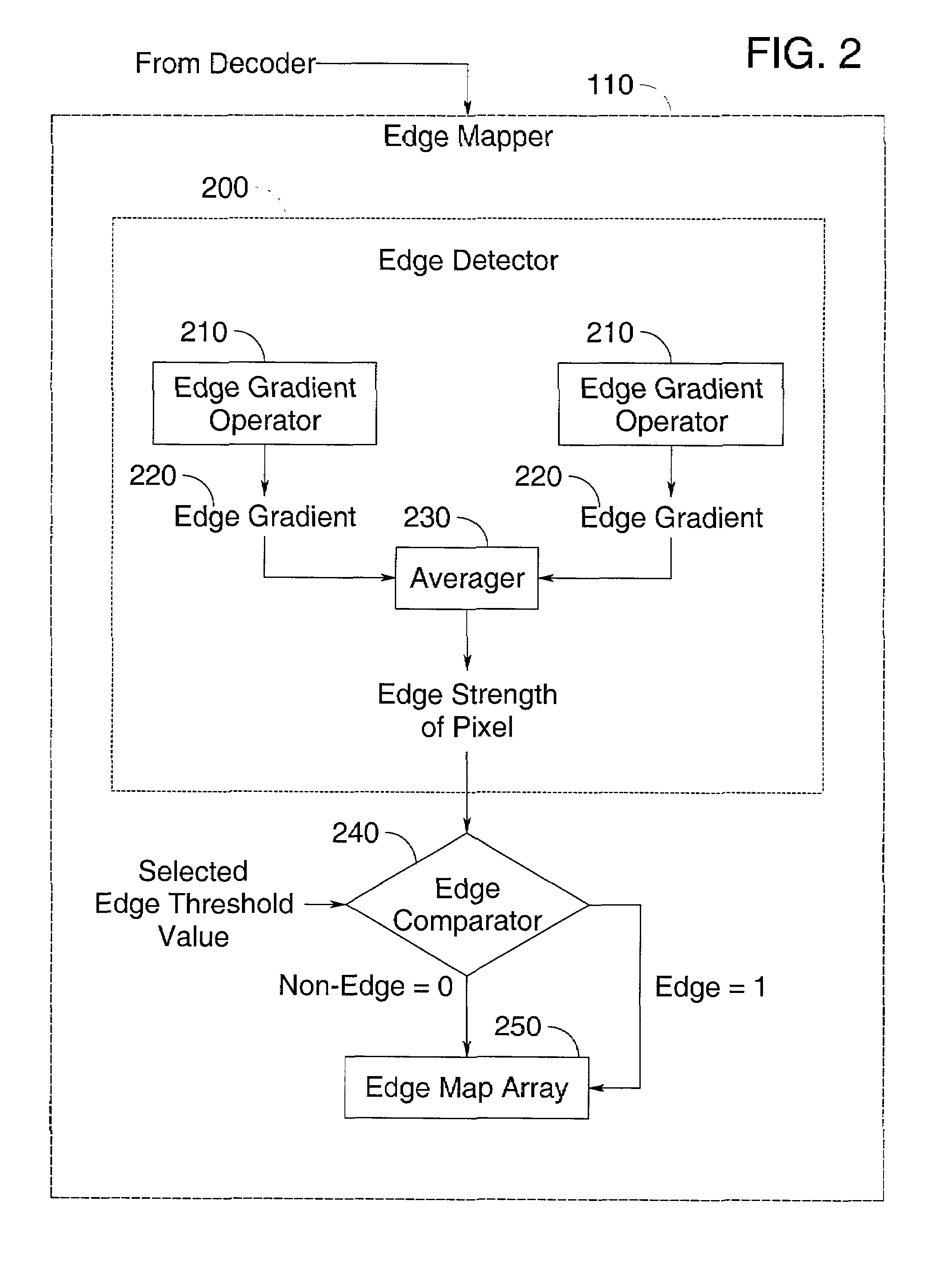
Filter for combined de-ringing and edge sharpening
InactiveUS7003173B2Reduce redundancyComputationally less-expensiveTelevision system detailsImage enhancementAdaptive filterSharpening
A filter for post-processing digital images and videos, having an edge mapper, a pixel sorter, and an adaptive filter that simultaneously performs de-ringing and edge sharpening. The combined filter is computationally simpler than known methods and can achieve removal of ringing artifacts and sharpening of true edges at the same time. The present invention also includes a preferred method of simultaneously de-ringing and edge sharpening digital images and videos.
Owner:SHARP KK
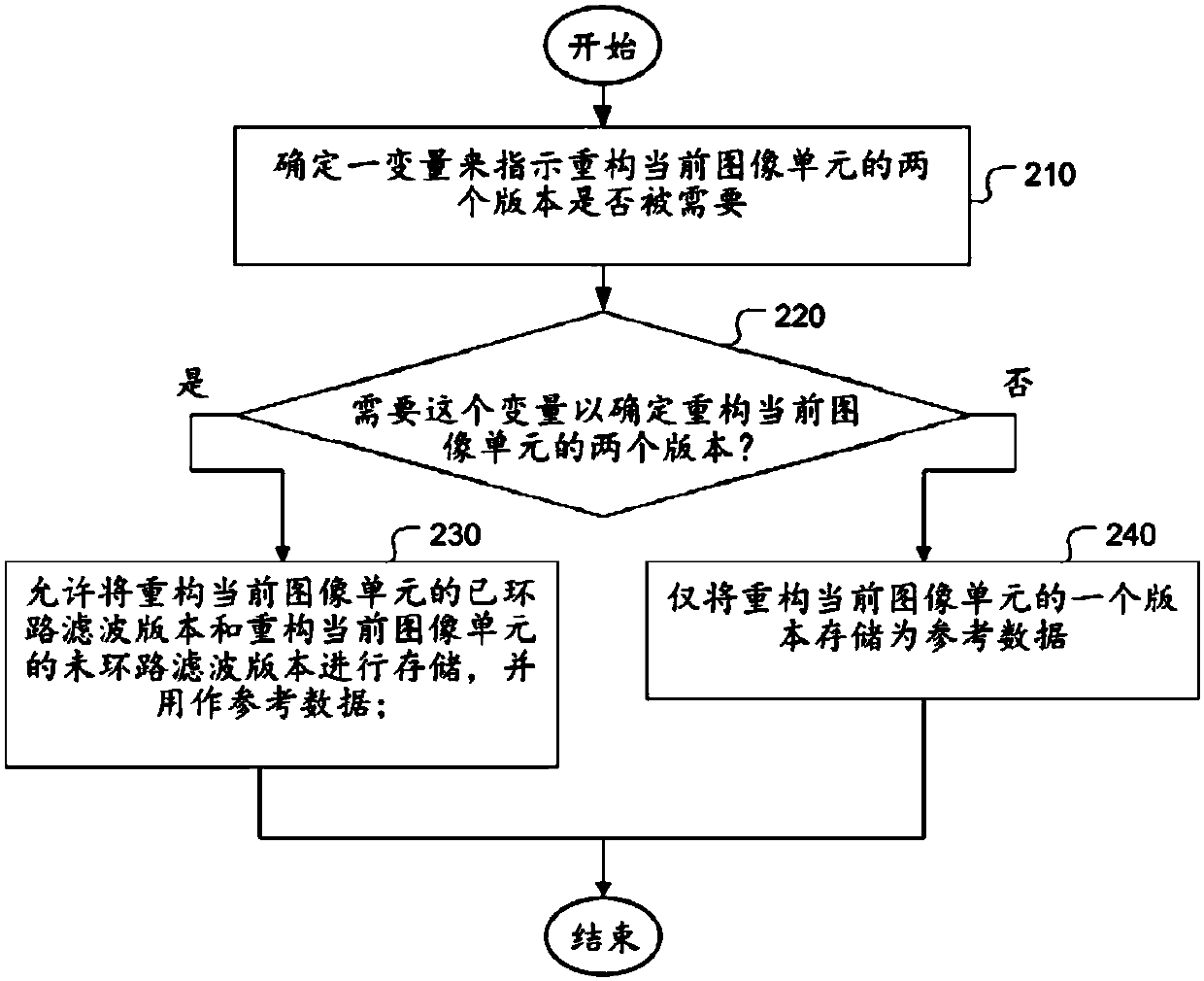
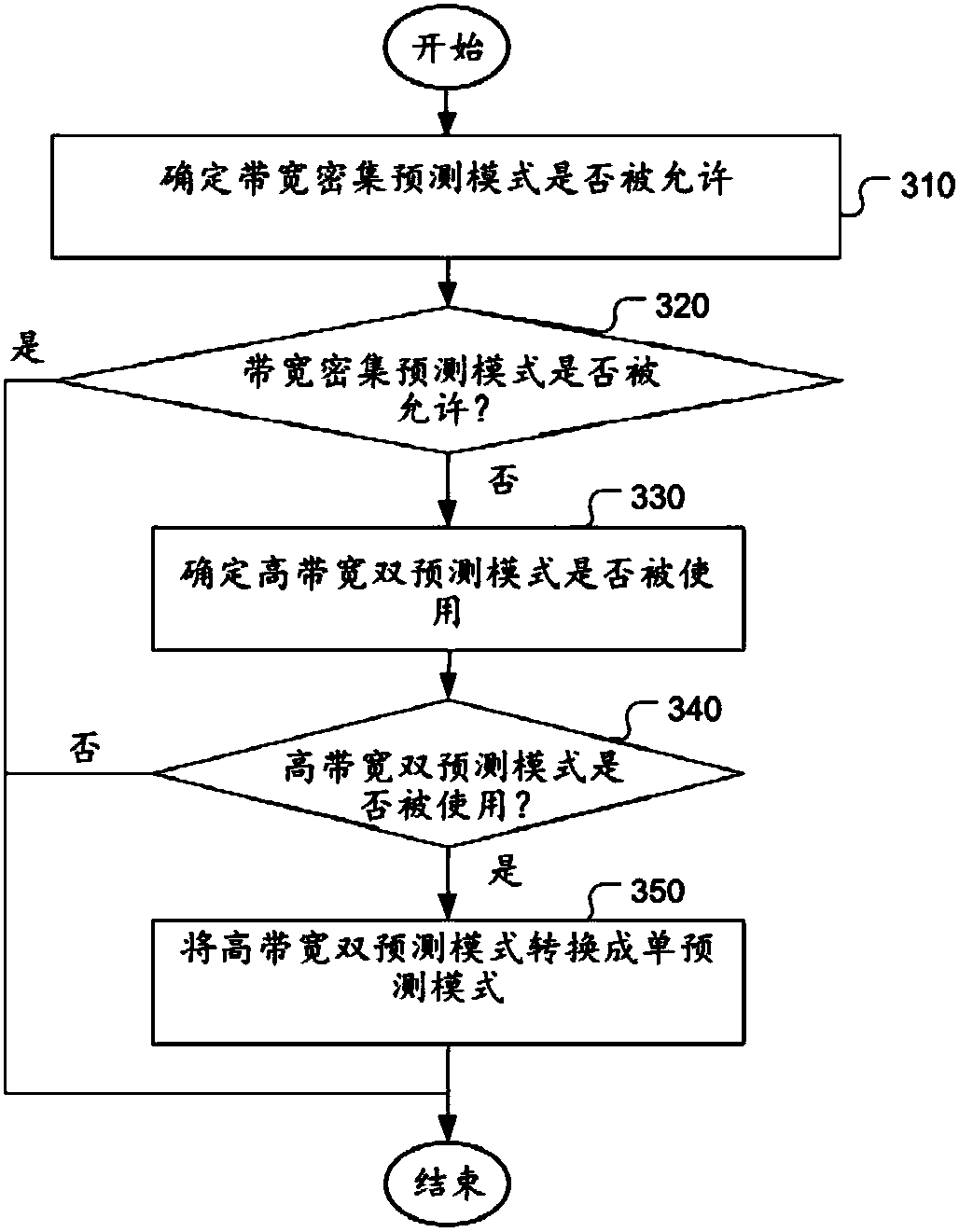
Method of system for video coding using intra block copy mode
A method and system for video system using coding modes including an Inter prediction mode and an Intra Block Copy (IntraBC) mode are disclosed. A syntax element in a bitstream is determined to indicate whether two versions of a reconstructed current image unit are needed. If two versions of the reconstructed current image unit are needed, a loop-filtered version of the reconstructed current imageunit and a non-loop-filter version of the reconstructed current image unit are allowed to be stored and used as reference data. Otherwise, only one version of the reconstructed current image unit isstored as the reference data. According to another method, bi-prediction mode is converted to uni-prediction mode for a certain prediction mode, where the bandwidth exceeds the existing worst case.
Owner:HFI INNOVATION INC
Block-Based Parallel Deblocking Filter in Video Coding
ActiveUS20130034169A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionDeblocking filter
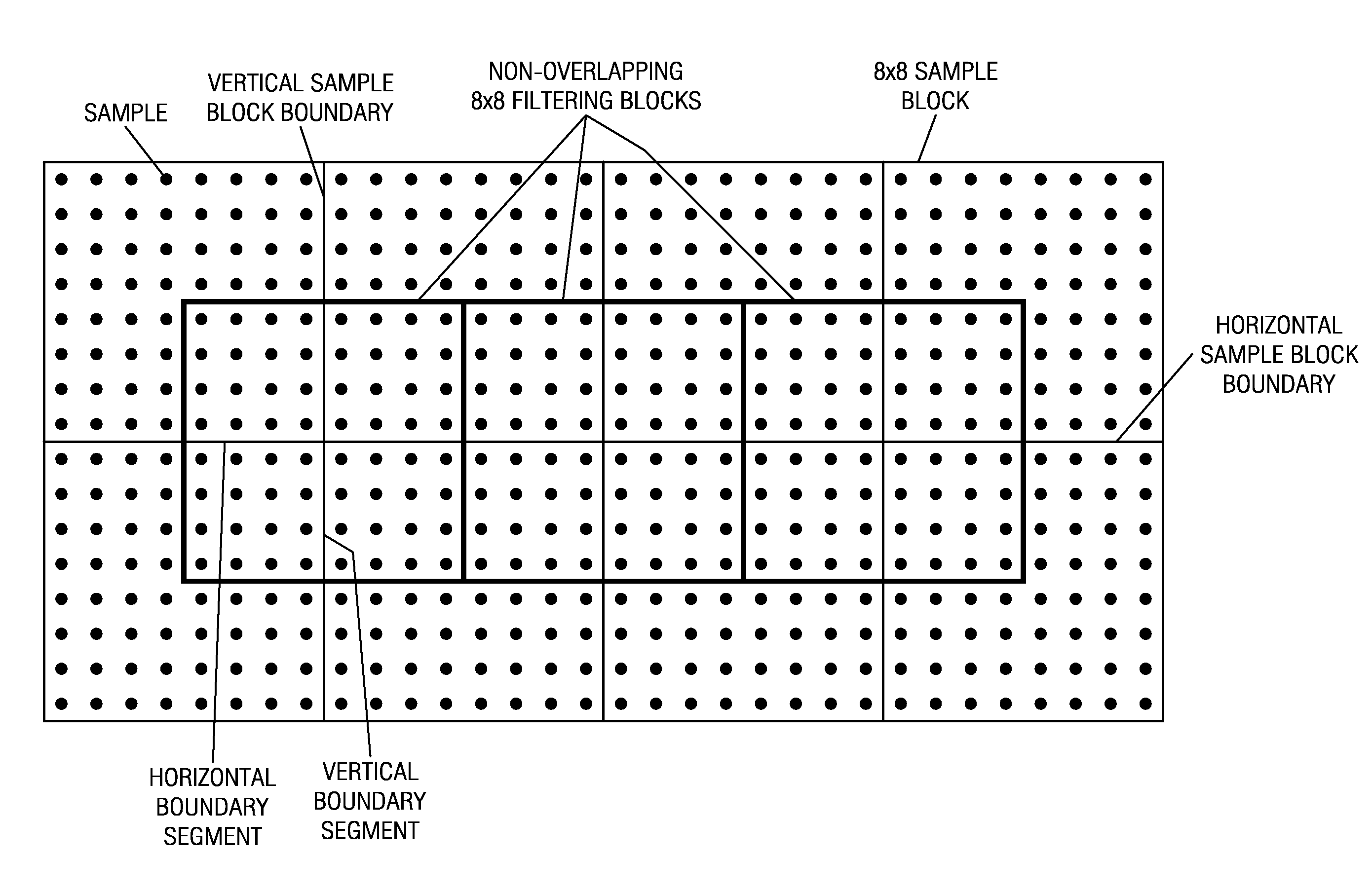
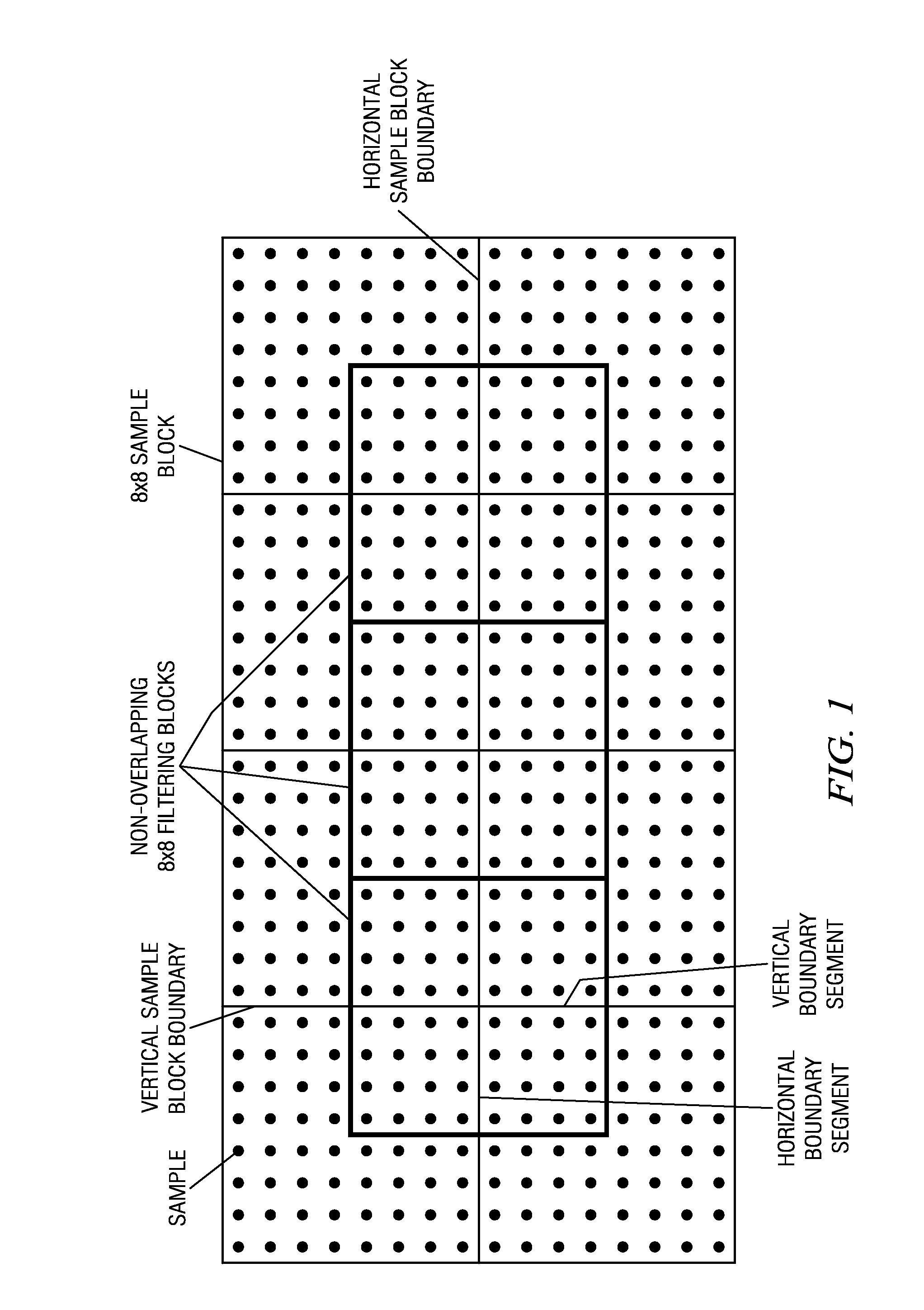
Deblocking filtering is provided in which an 8×8 filtering block covering eight sample vertical and horizontal boundary segments is divided into filtering sub-blocks that can be independently processed. To process the vertical boundary segment, the filtering block is divided into top and bottom 8×4 filtering sub-blocks, each covering a respective top and bottom half of the vertical boundary segment. To process the horizontal boundary segment, the filtering block is divided into left and right 4×8 filtering sub-blocks, each covering a respective left and right half of the horizontal boundary segment. The computation of the deviation d for a boundary segment in a filtering sub-block is performed using only samples from rows or columns in the filtering sub-block. Consequently, the filter on / off decisions and the weak / strong filtering decisions of the deblocking filtering are performed using samples contained within individual filtering blocks, thus allowing full parallel processing of the filtering blocks.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Depth image estimating method of binocular stereo video
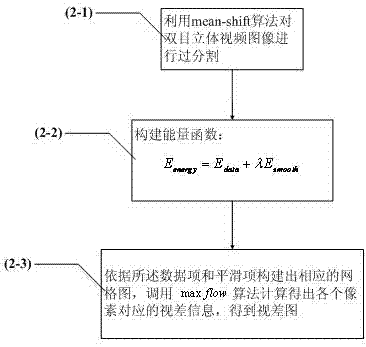
InactiveCN102523464AEliminate errorsReduce complexityImage analysisSteroscopic systemsStereoscopic videoImaging quality
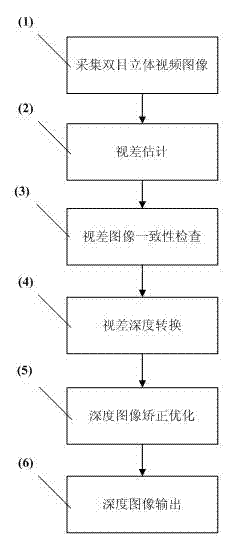
The invention discloses a depth image estimating method of a binocular stereo video, which comprises the following steps of: (1) collecting a binocular stereo video image from a binocular stereo camera; (2) performing parallax estimation based on graph cut stereo matching on the binocular stereo video image; (3) performing uniformity check on a parallax image obtained by the graph cut stereo matching, and deleting the unreliable matching by self-adapting matching to reduce the wrong matching of the depth image; (4) converting the parallax image into a depth image according to the relation of the parallax and the depth; (5) performing correction optimization on the obtained depth image by a multilateral filter; and (6) outputting the depth image to finish the depth image estimation of the binocular stereo video. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of effectively eliminating the errors in the depth image estimation, and finally obtaining an accurate and dense depth image so as to satisfy the demand of rebuilding image quality based on a real scene.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
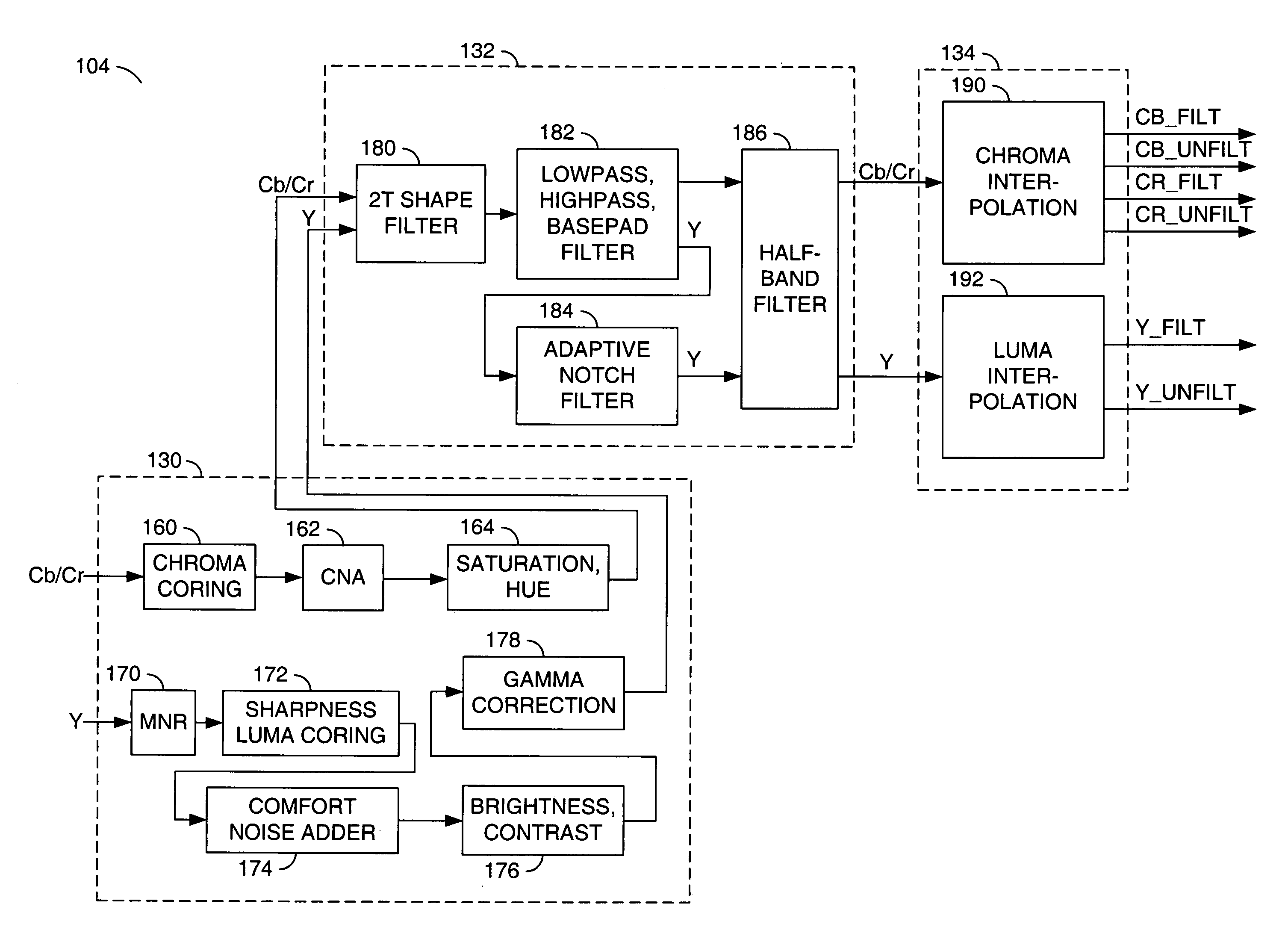
Method and apparatus for masking of video artifacts and/or insertion of film grain in a video decoder
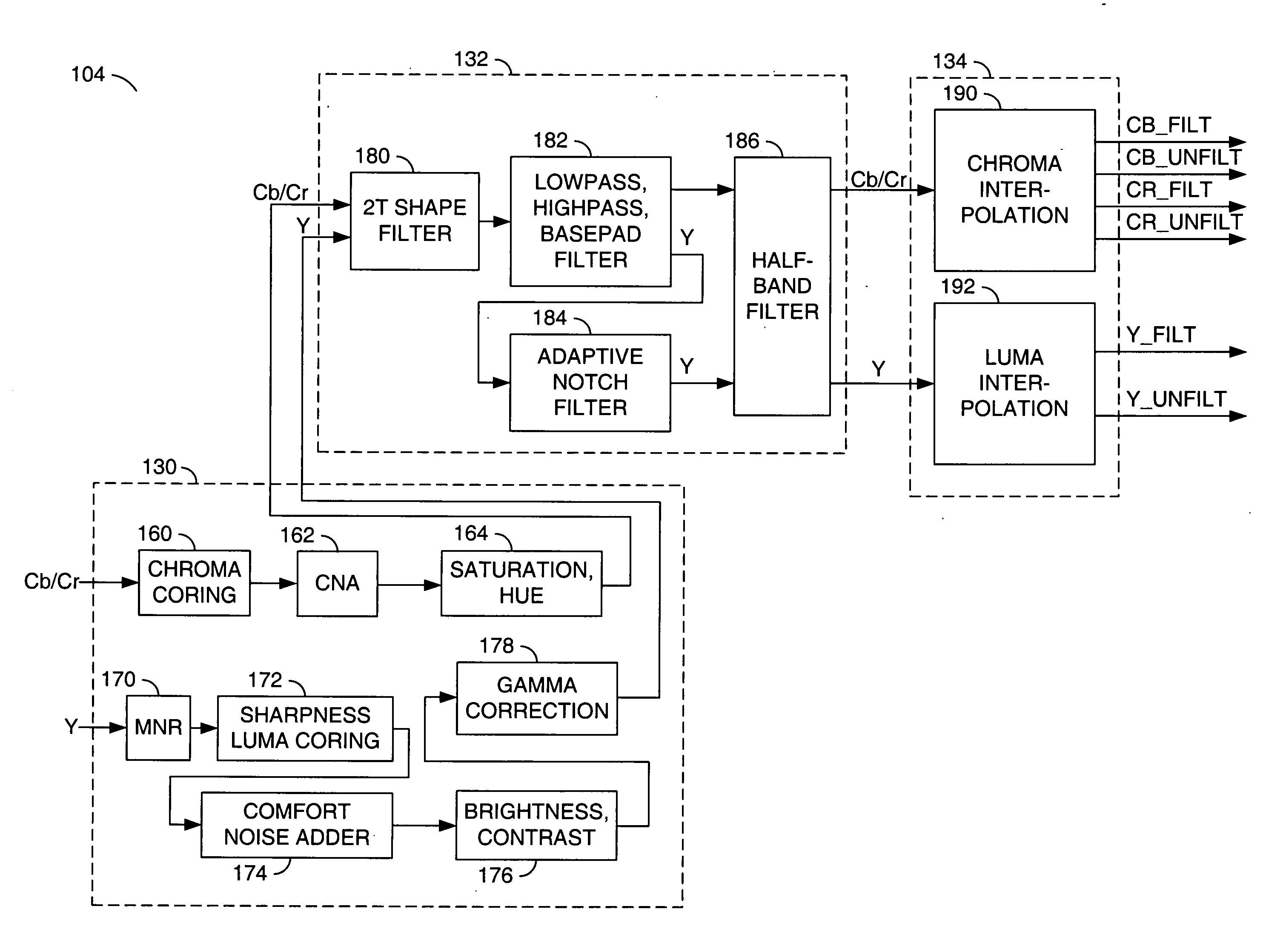
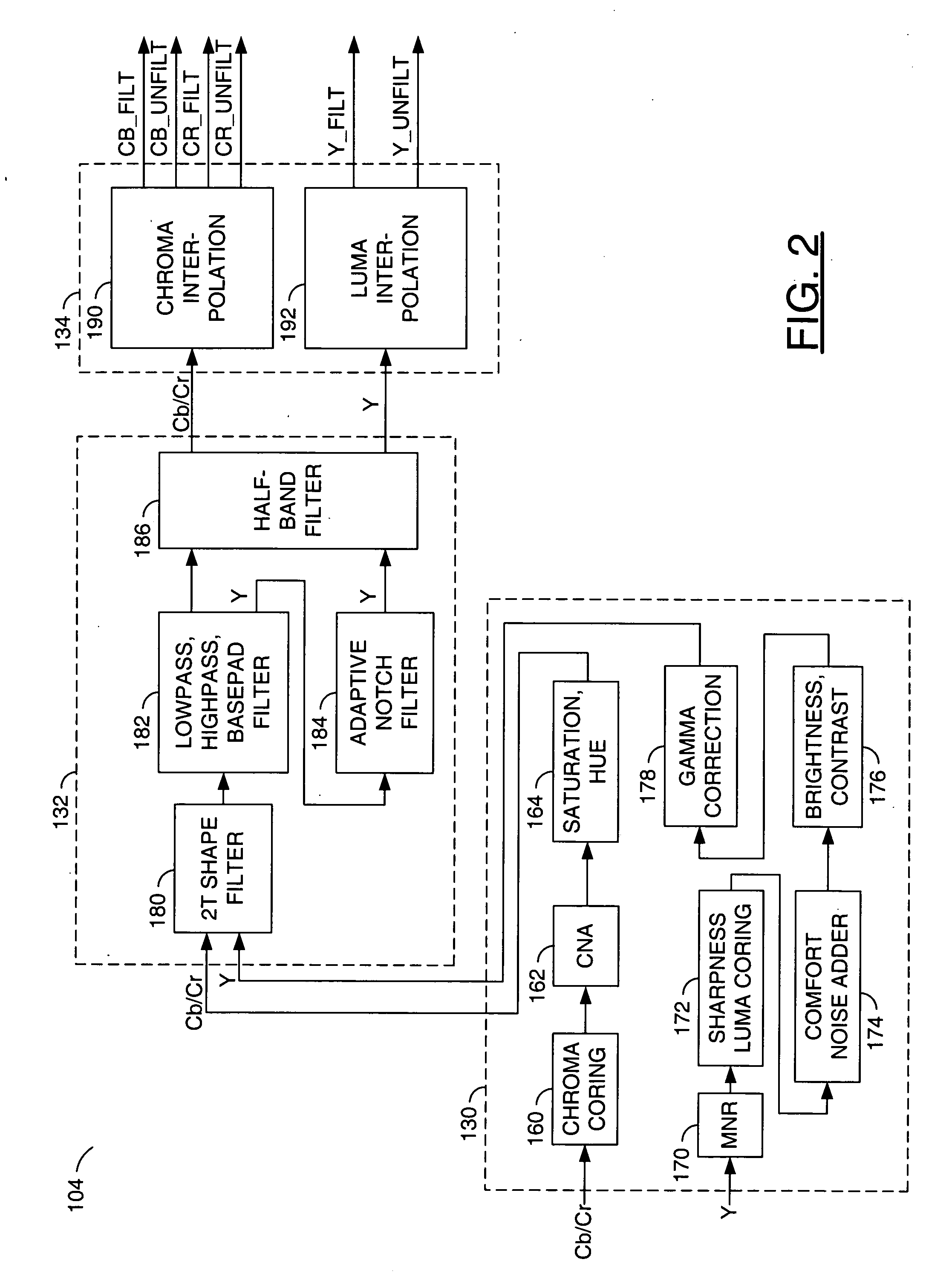
A video decoder comprising (i) a post-processing filter block, (ii) a comfort noise addition block and (iii) a video value / range adjustment block, where the comfort noise addition block is integrated into a video output path of the video decoder. The post-processing filter block may be configured to perform one or more of noise reduction, spatial filtering and temporal filtering on luminance data. The comfort noise addition block may be configured to add comfort noise to the luminance data. The video value / range adjustment block may be configured to adjust one or both of a value and a range of the luminance data.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Methods and apparatus for removing compression artifacts in video sequences
InactiveUS6993191B2Cancel noiseIncrease amplitudeTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsLow-pass filterCompression artifact
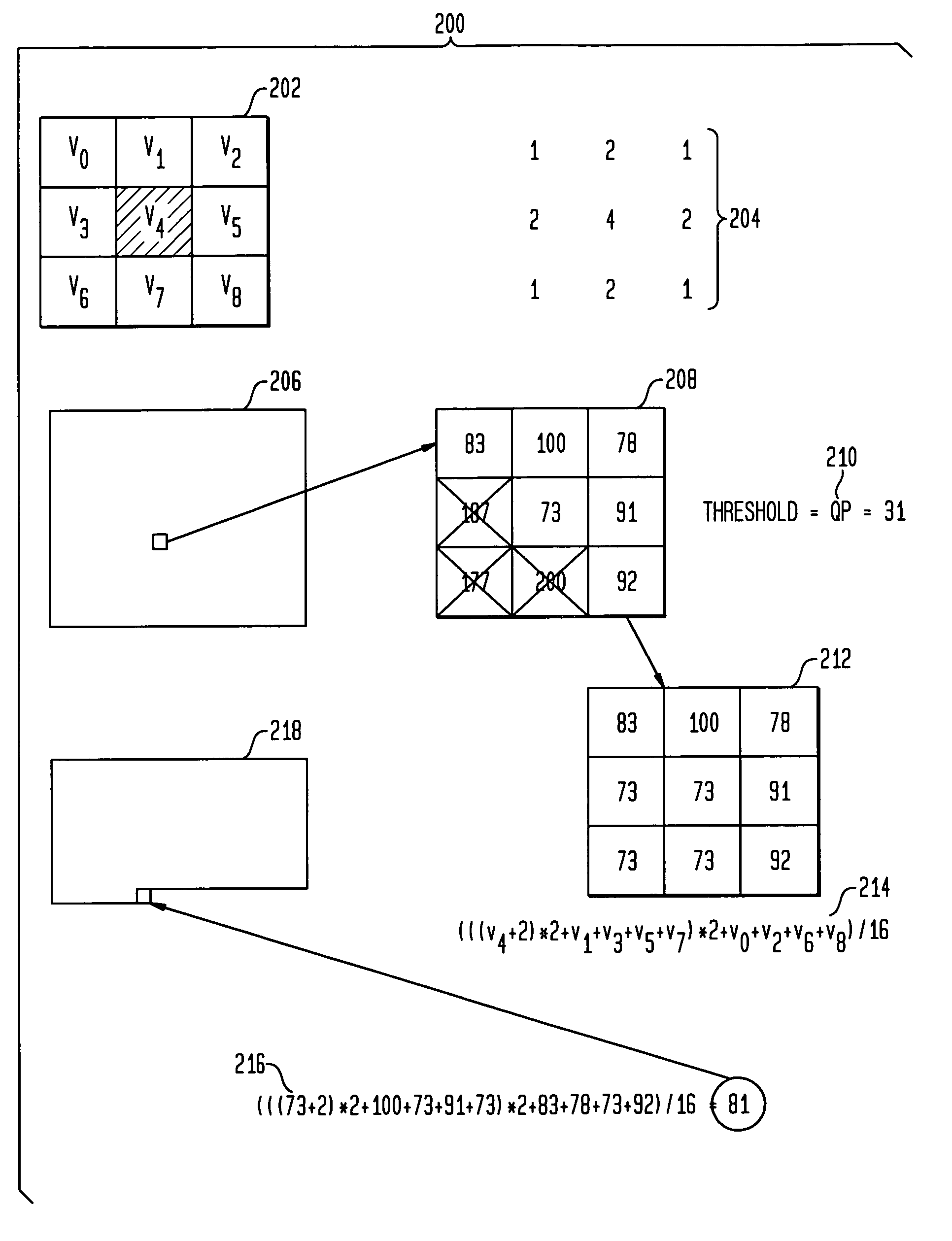
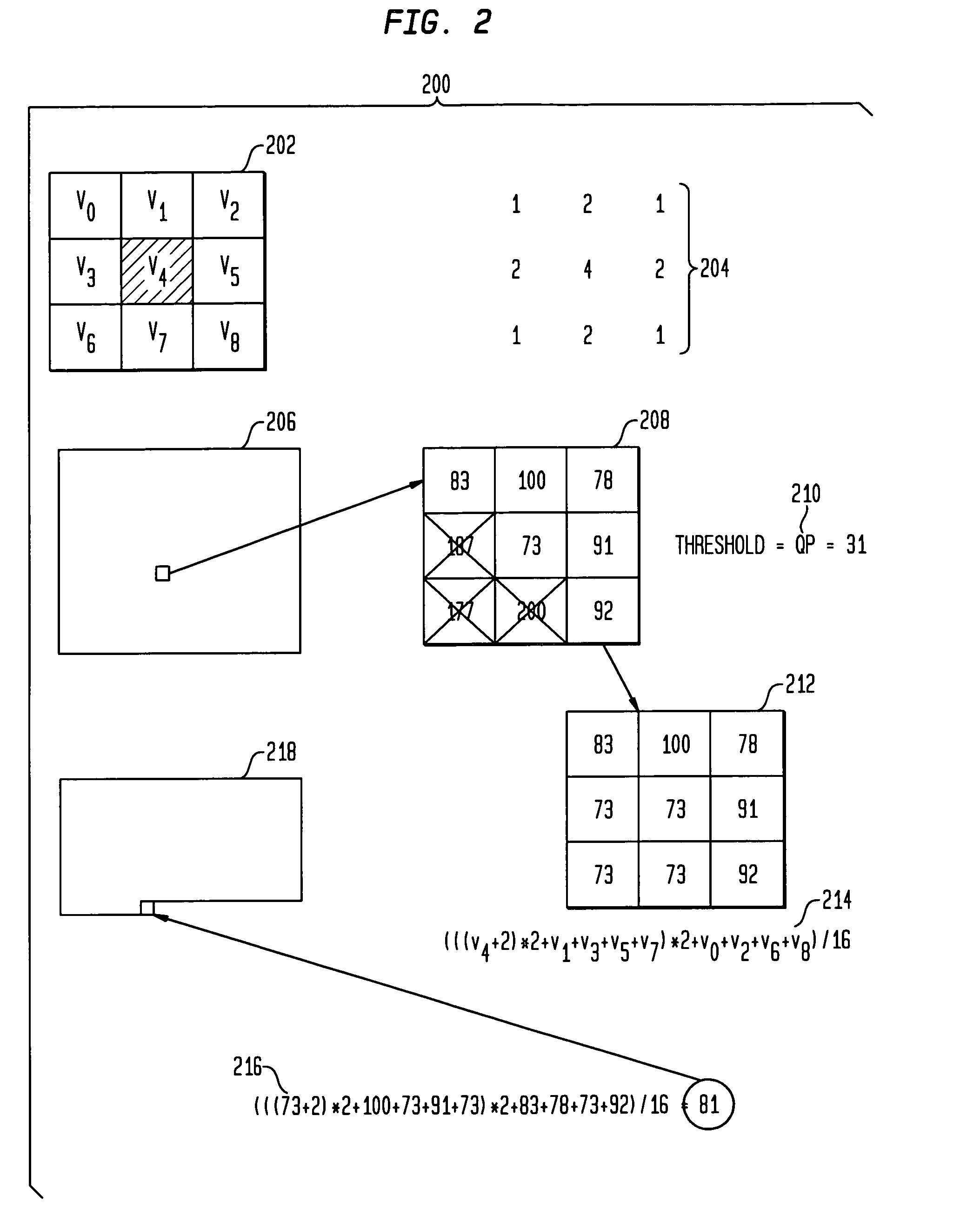
Techniques for removing ringing artifacts from video data. A deringing filter in accordance with the present invention preserves real image edges in a video frame, while smoothing out the interiors of objects. In one aspect, a 9-tap low-pass filter is applied to an adaptive processing window. The filter window is initialized with the values in a 3×3 mask centered on the position whose output is computed. Then all values that are very different from the central one are replaced with the central value. The deringing filter varies between 3×3 low-pass and identity, depending on how much the central value differs from its surrounding ones. A deblocking filter in accordance may also be suitably used in conjunction with the deringing filter.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
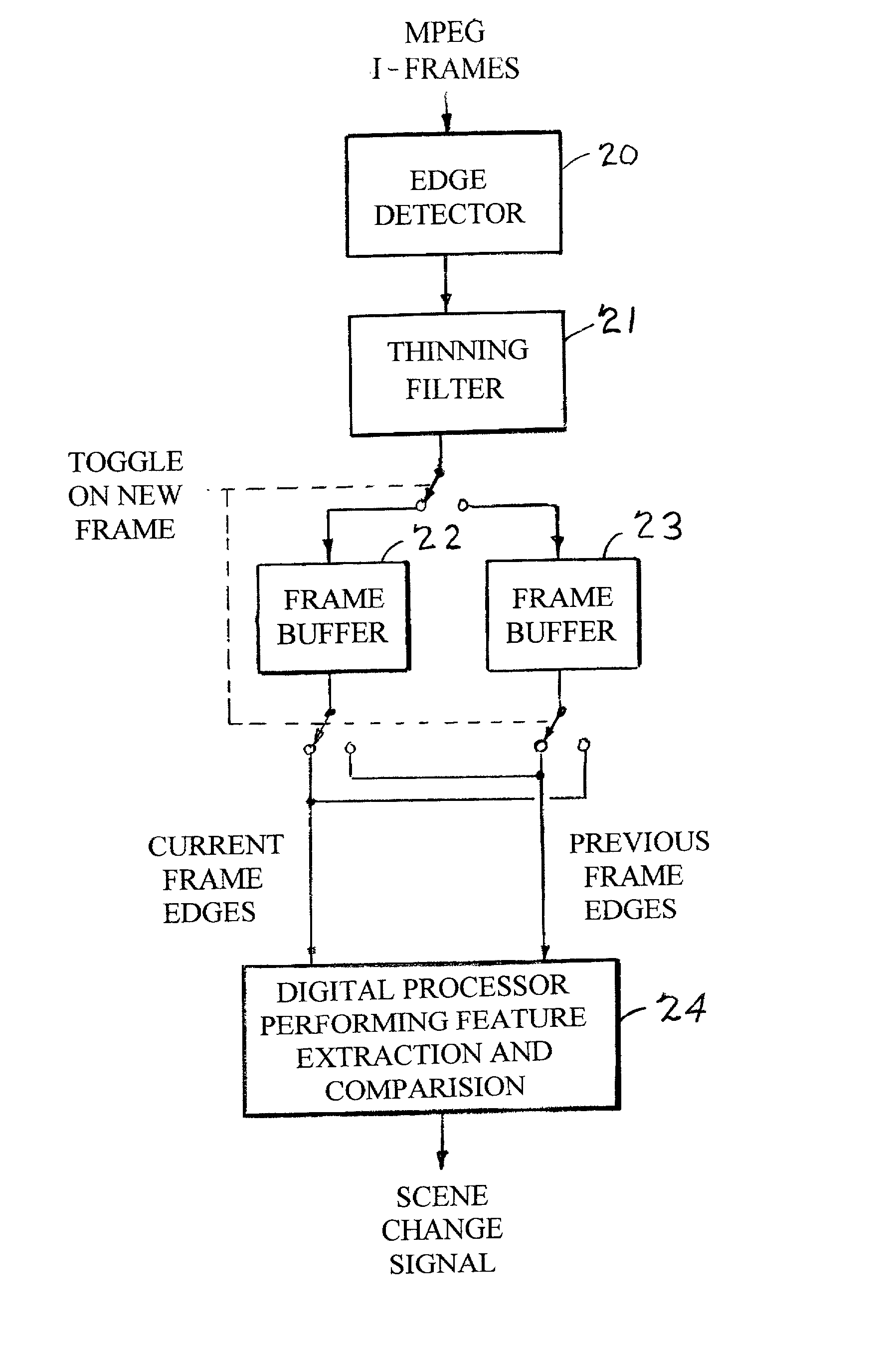
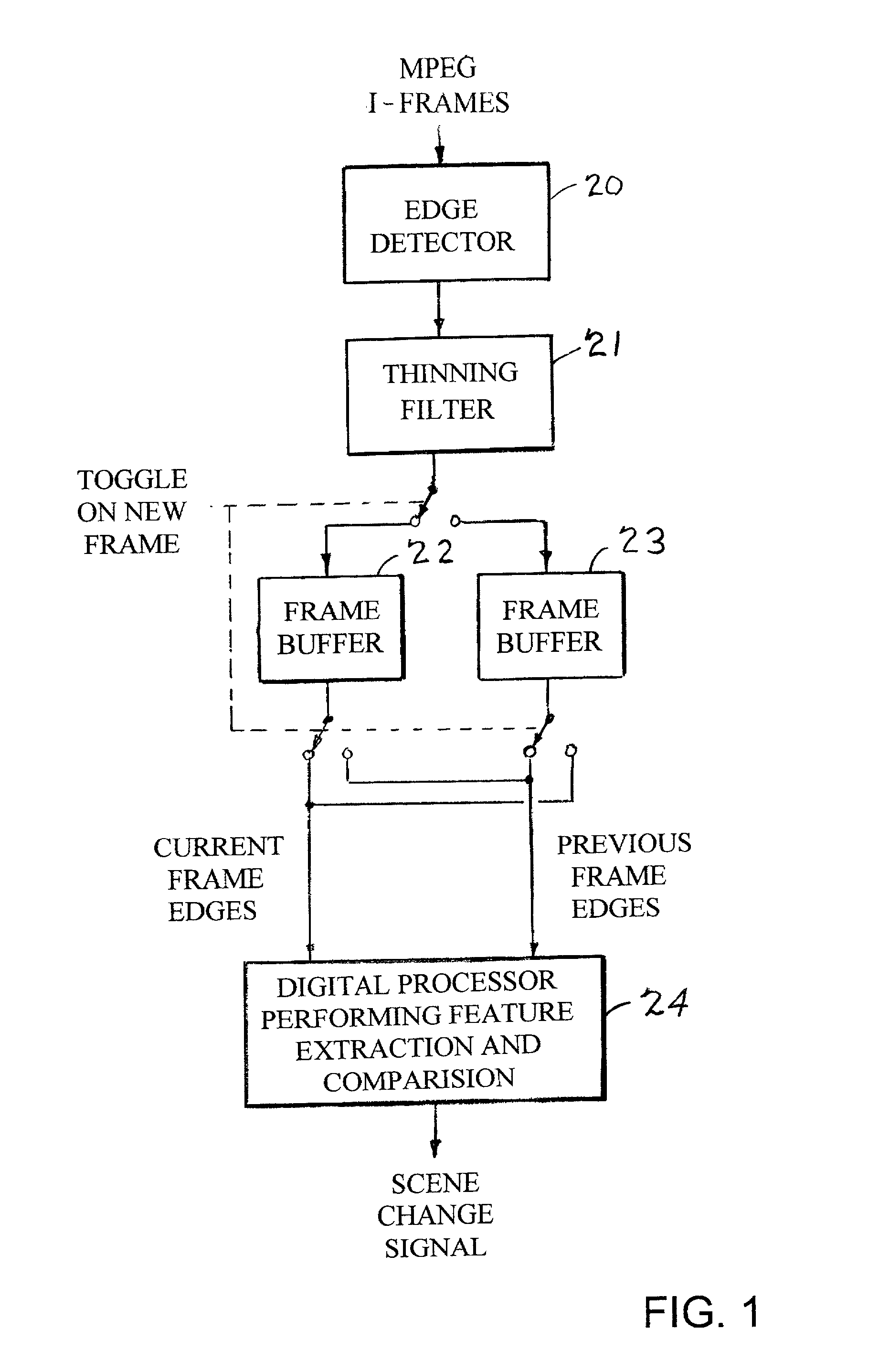
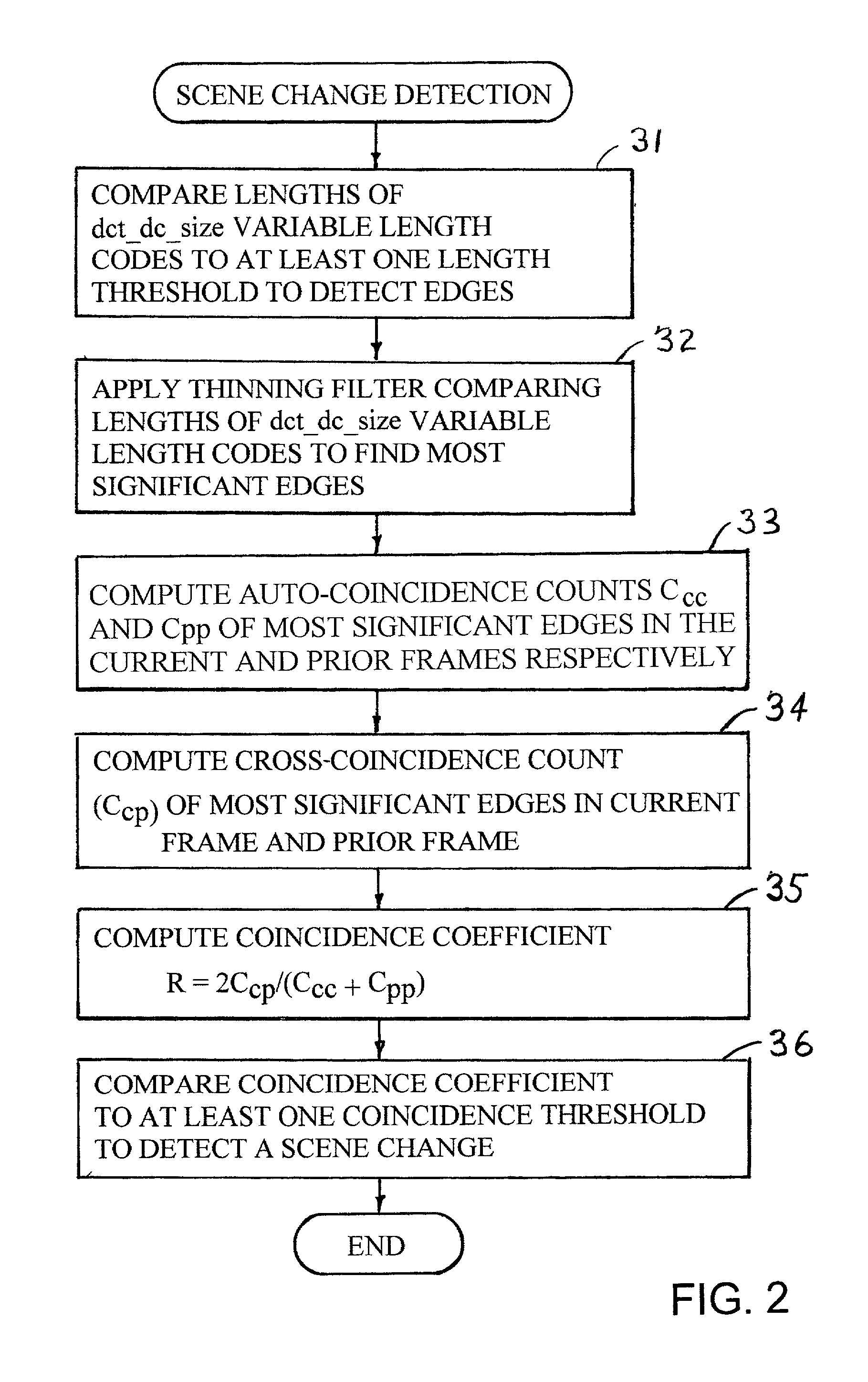
Edge detection based on variable-length codes of block coded video
ActiveUS20030142750A1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesVariable-length codePattern recognition
Edges are detected in block coded video by a threshold comparison upon the lengths of variable-length codes used for encoding the differential DC coefficients of the pixel blocks. A thinning filter compares the code lengths of the differential DC coefficients of adjacent blocks in order to retain the edge indications of more significant edges and to exclude the edge indications of less significant edges. The edge indications can be split into substantially independent channels for luminance or chrominance, for edges having positive or negative horizontal gradient components, and for edges having positive or negative vertical gradient components. The edge indications for successive frames in an MPEG sequence are compared to each other in various ways in order to detect scene changes.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Adaptive noise intensity video denoising method and system thereof
InactiveCN102368821AKeep Edges SharpImprove time and efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsPattern recognitionNoise reduction
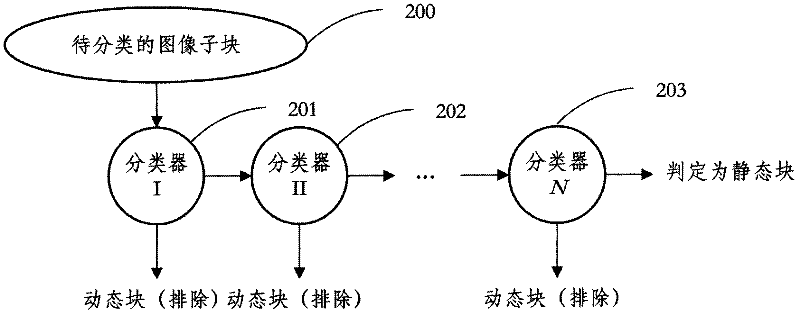
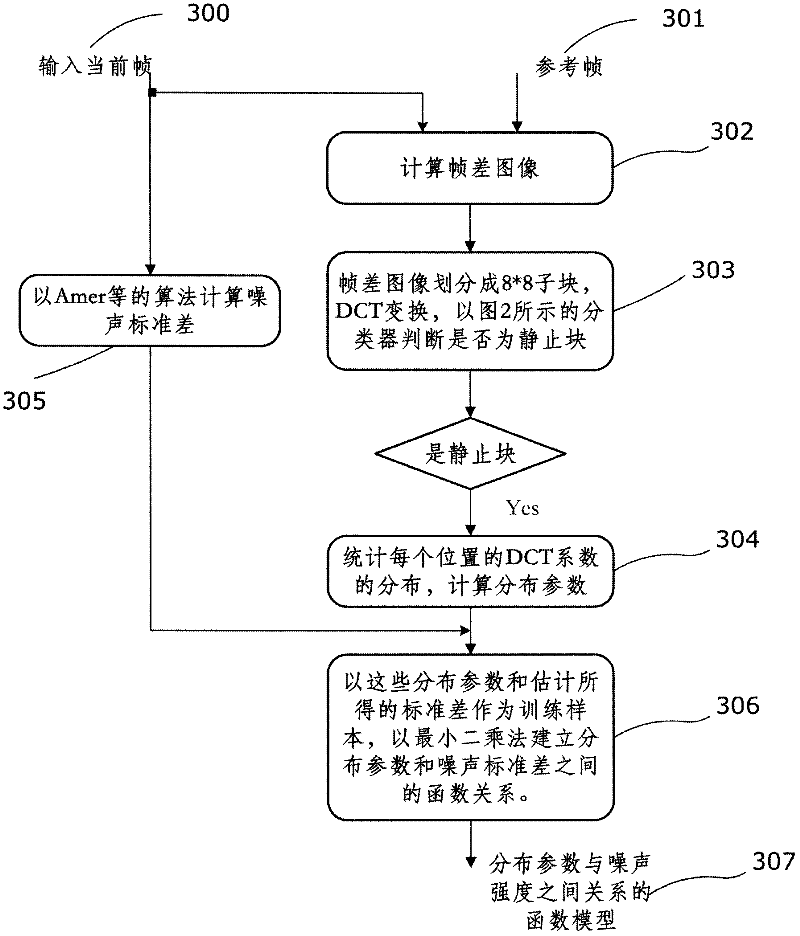
The invention discloses an adaptive noise intensity video denoising method which is based on motion detection and is embedded in an encoder. The method comprises the following steps: (1) taking a sum of regularization frame differences in a neighborhood as an observed value, dividing input pixels into a static pixel and a dynamic pixel and using filters in different supporting domains for the two kinds of the pixels, wherein a filtering coefficient is adaptively determined according to noise intensity and an image local characteristic; (2) taking a single DCT coefficient or the sum of the several DCT coefficients as the characteristic, using AdaBoost as a tool to construct a cascade-form classifier and using the classifier to select a static block; (3) establishing a function model of connection between DCT coefficient distribution parameters of the video noise intensity and the static block and using the model to estimate the noise signal standard difference. By using noise intensity estimation embedded in the video encoder and a noise reduction technology provided in the invention, few computation costs can be used to acquire the parameters and the information needed by noise filtering. A time efficiency is good. Because a reliable clue is used to determine whether the pixels accord with a static hypothesis, the filter of the invention can effectively filter the noise and simultaneously maintain marginal sharpness of the static image. And motion blur caused by filtering in a motion area can be avoided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Motion-compensated inverse filtering with band-pass filters for motion blur reduction
InactiveUS20070126928A1Reduce motion blurReduce relative motionTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesBandpass filteringMotion vector
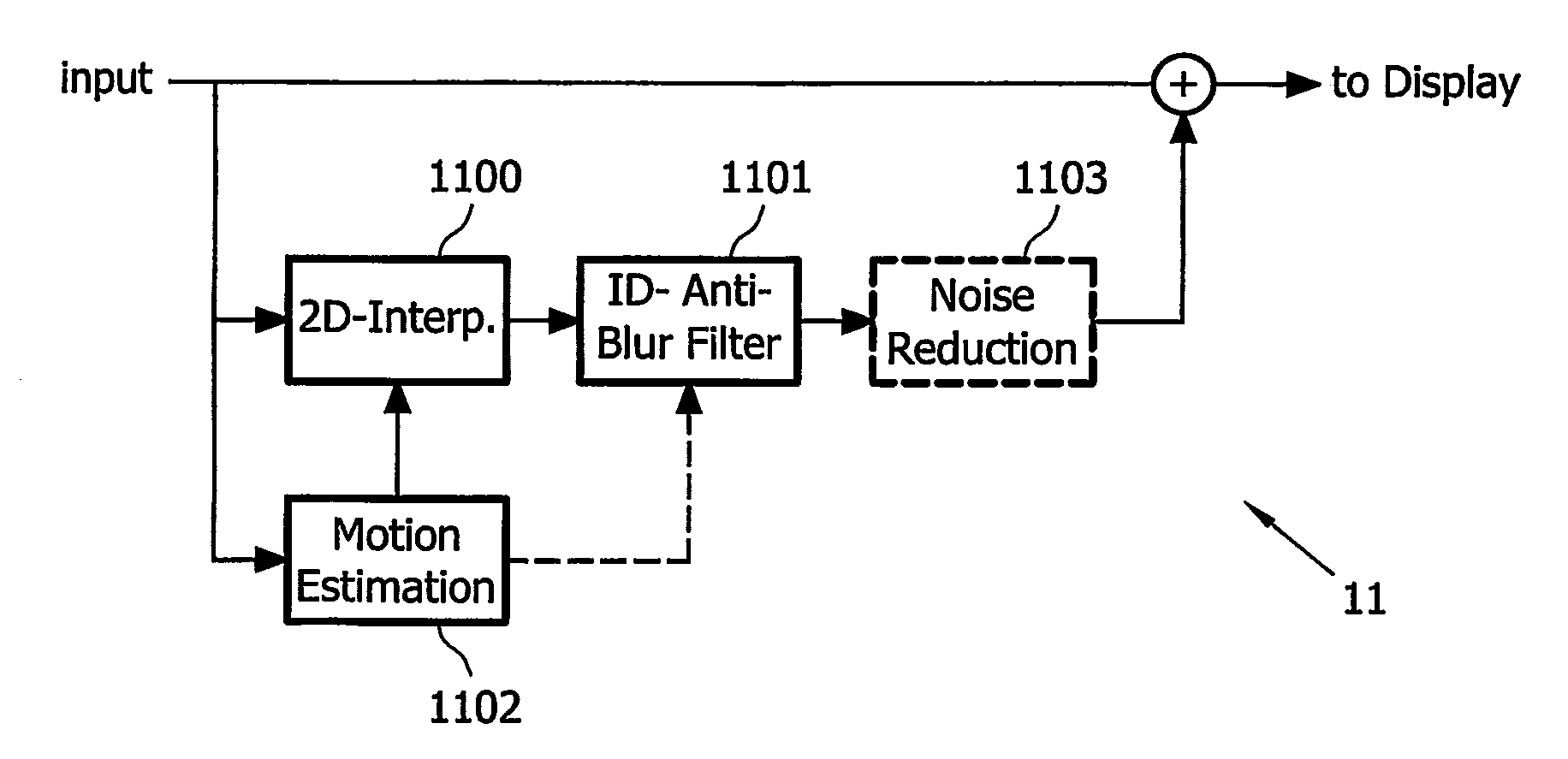
This invention relates to a method, a computer program, a computer program product, and a device for reducing motion blur of images of a video signal shown on a hold-type display (101), comprising estimating (1102) motion vectors of moving components in said images of said video signal; band-pass filtering (1100, 1101) said video signal with respect to a spatial frequency domain, wherein said band-pass filtering at least partially depends on said estimated motion vectors, and wherein with increasing length of said estimated motion vectors, the passband of said band-pass filtering adaptively shifts from high spatial frequencies to medium spatial frequencies; and combining (1104) said video signal and said band-pass filtered video signal to produce an input video signal for said hold-type display.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
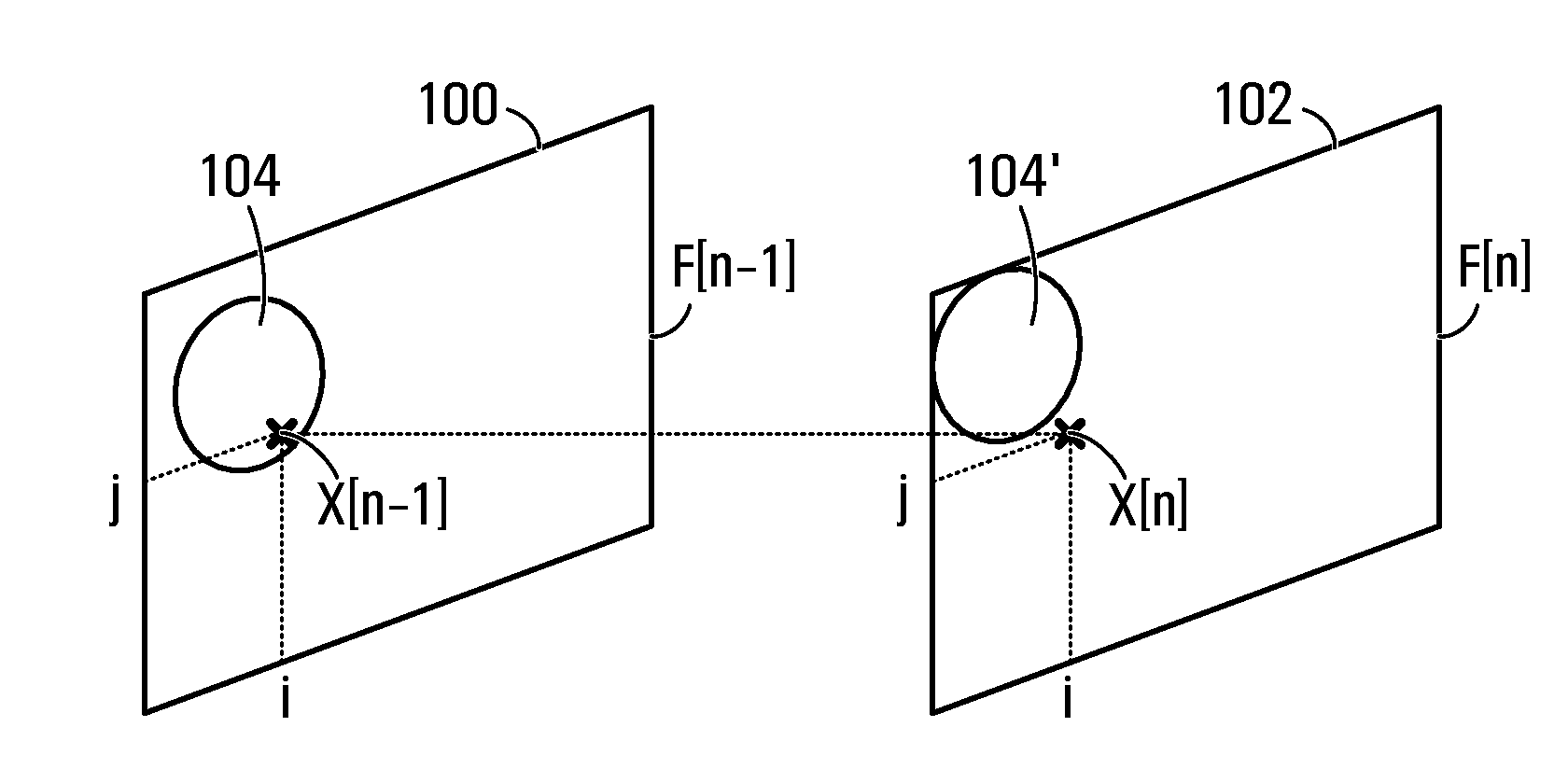
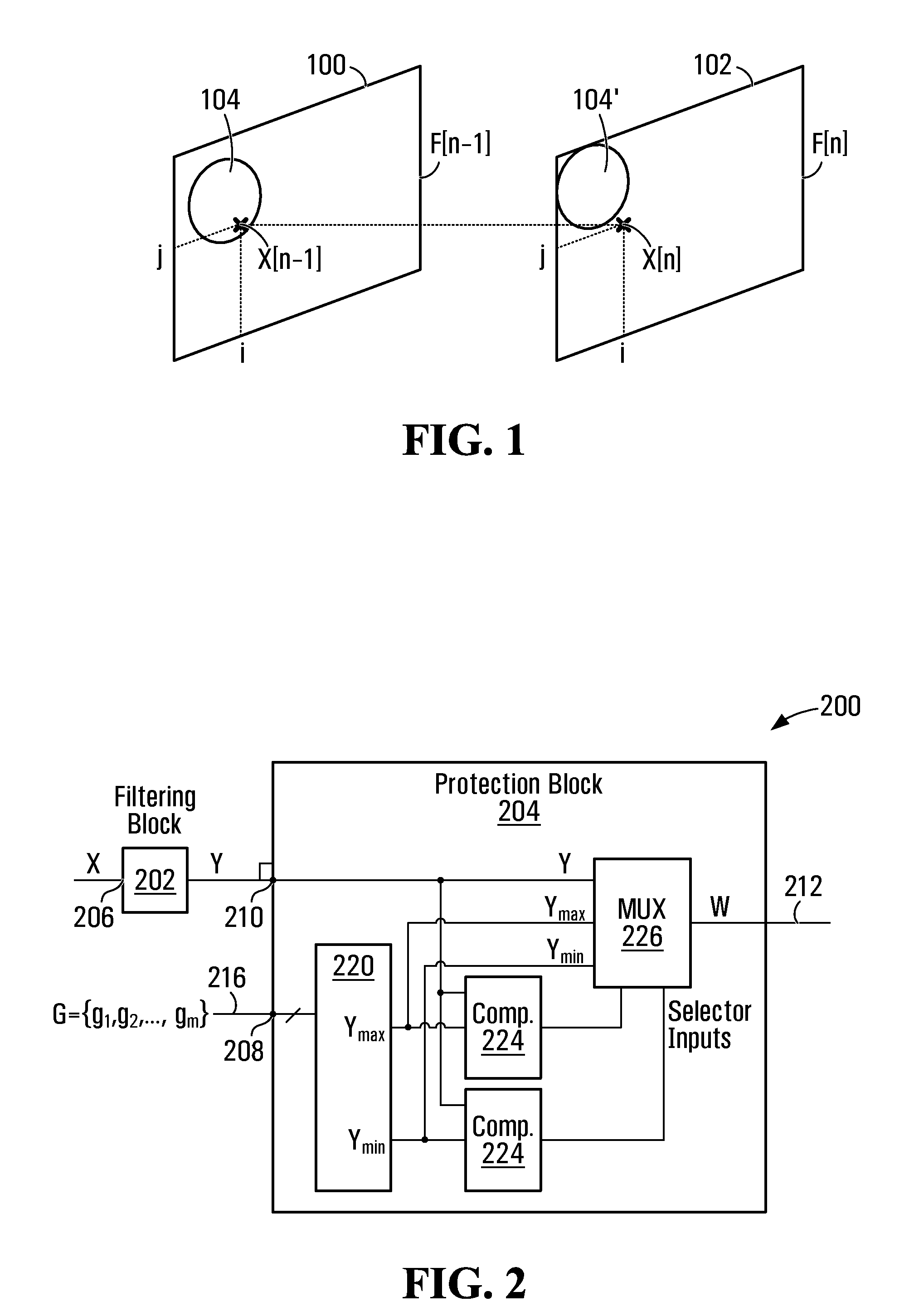
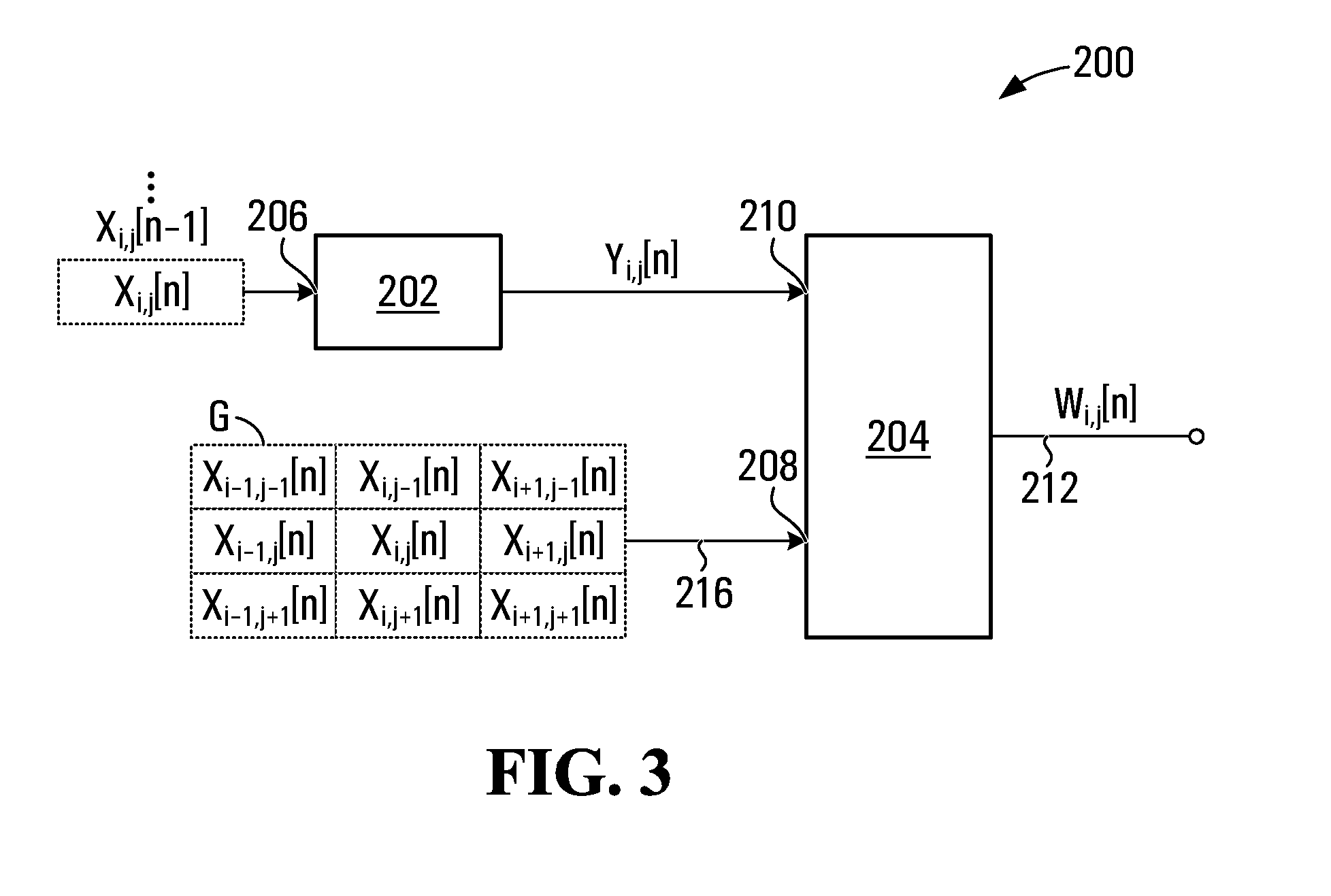
Protection filter for image and video processing
ActiveUS20100061648A1Reduce Motion ArtifactsMitigate artifact static artifactImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionVideo processing
A filter includes a conventional filtering block and a protection block. The conventional filtering block receives input values and provides filtered values. The protection block receives filtered values and a group of input values proximate the current input, to ensure that the output is lies within a range computed for the current input. The range is determined by the protection block based on the group of input values proximate the current input. Any algorithm or statistical function may be applied to the group of input values to determine the range. If a filtered value provided by the conventional filtering block is outside the range, then the protection block computes and outputs a value that is within the range. The filter may be used in temporal or spatial filtering of images and video to mitigate artifacts such as motion artifacts and static artifacts.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
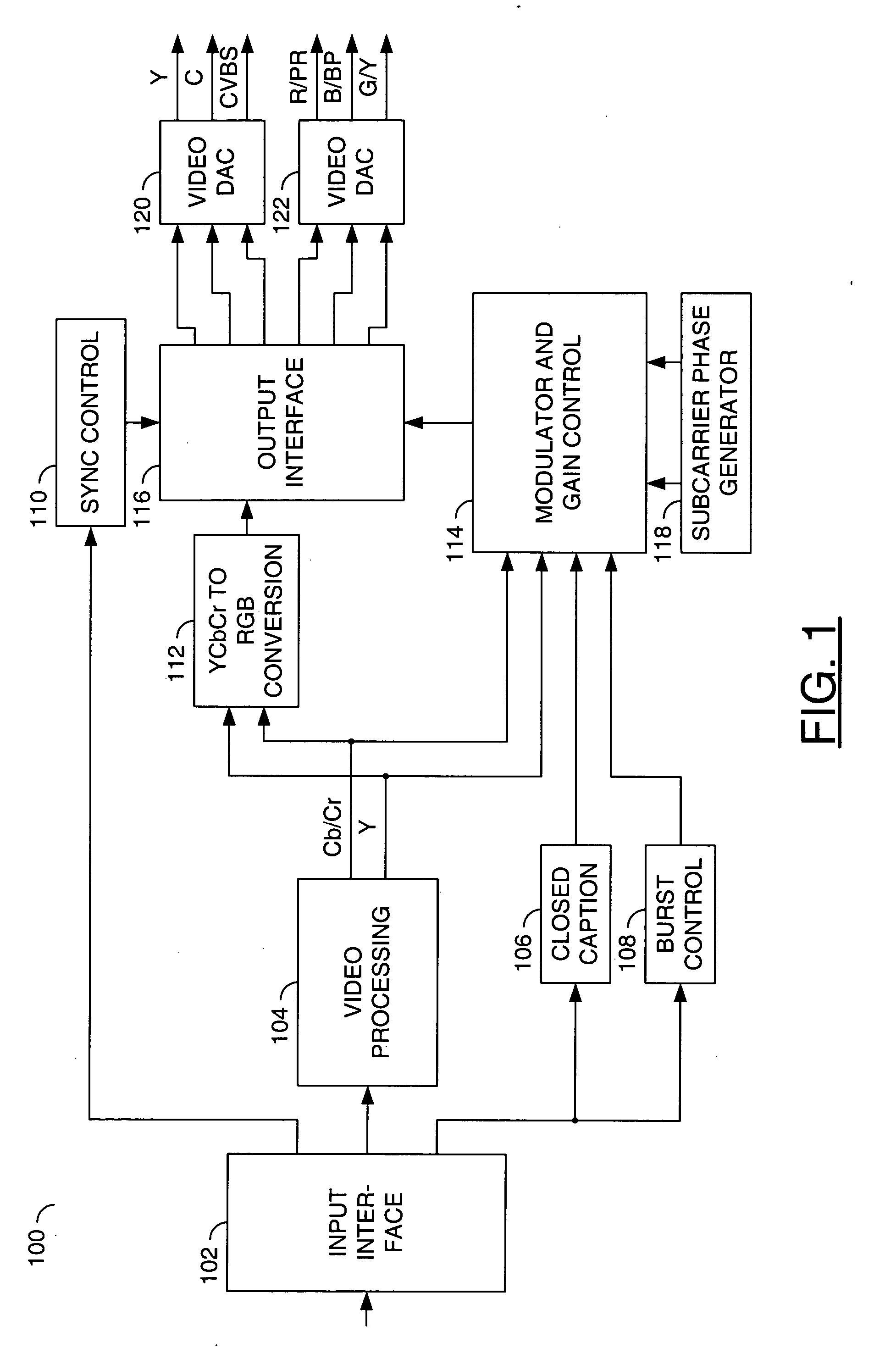
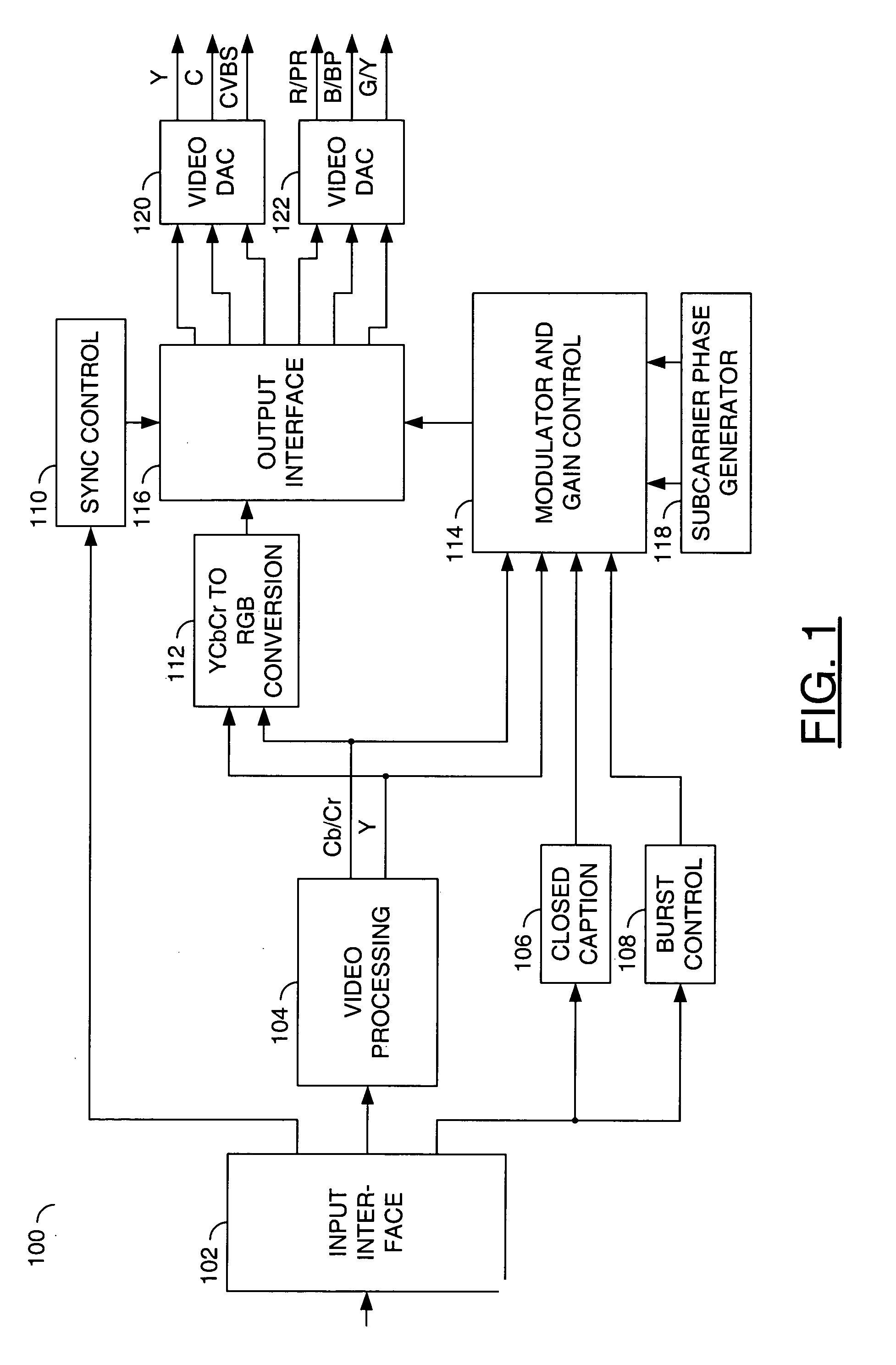
Video signal processing apparatus and method
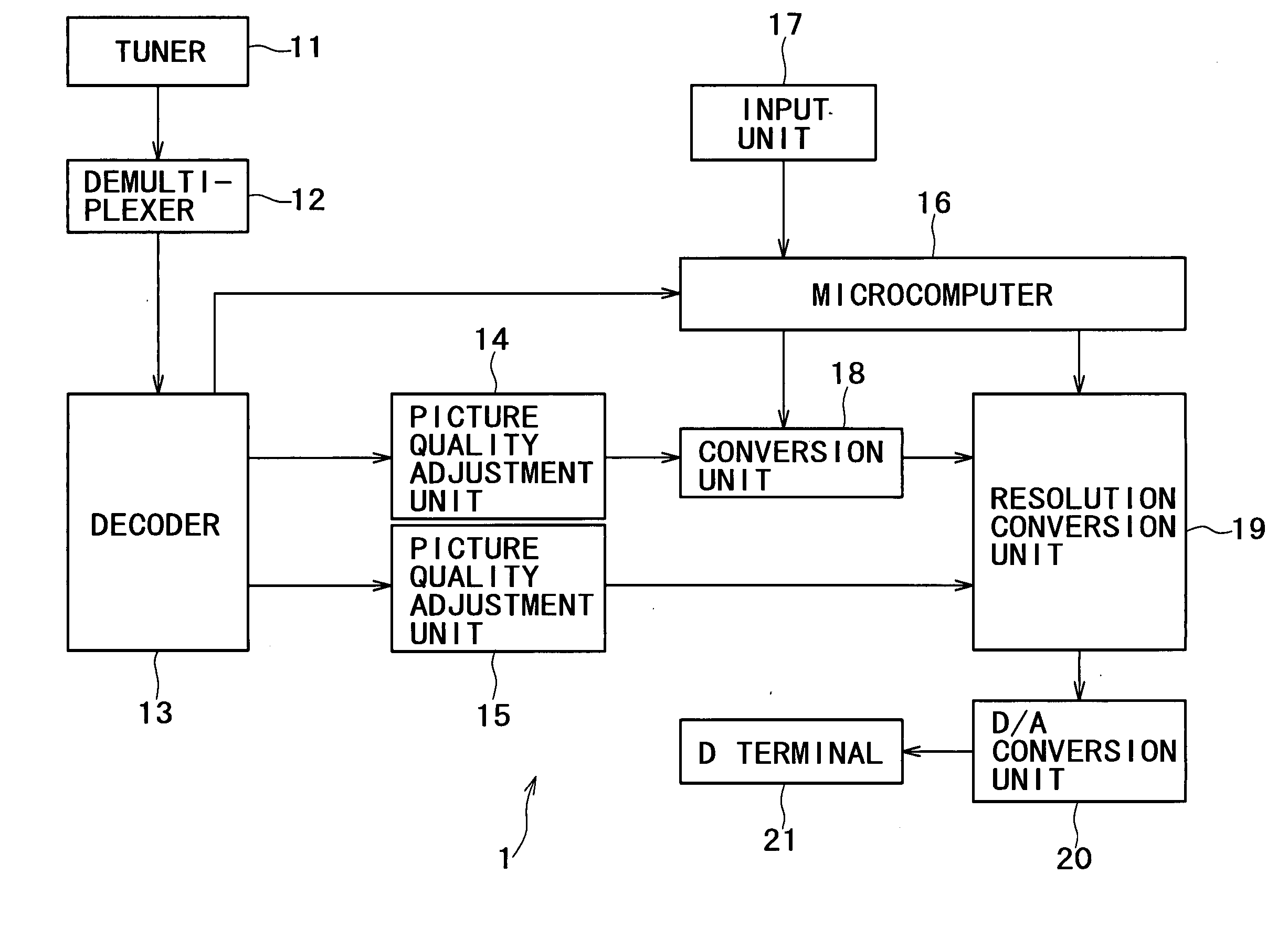
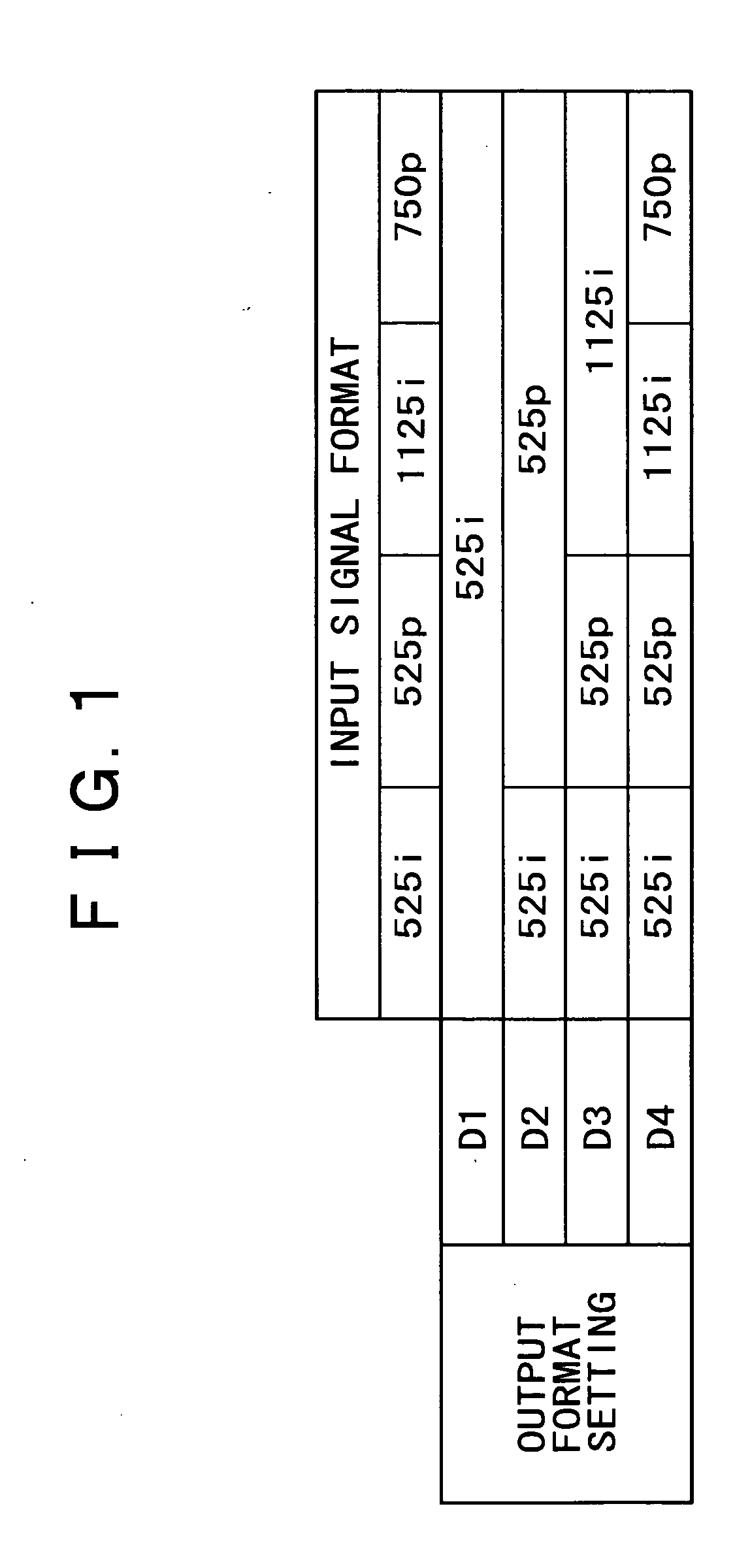
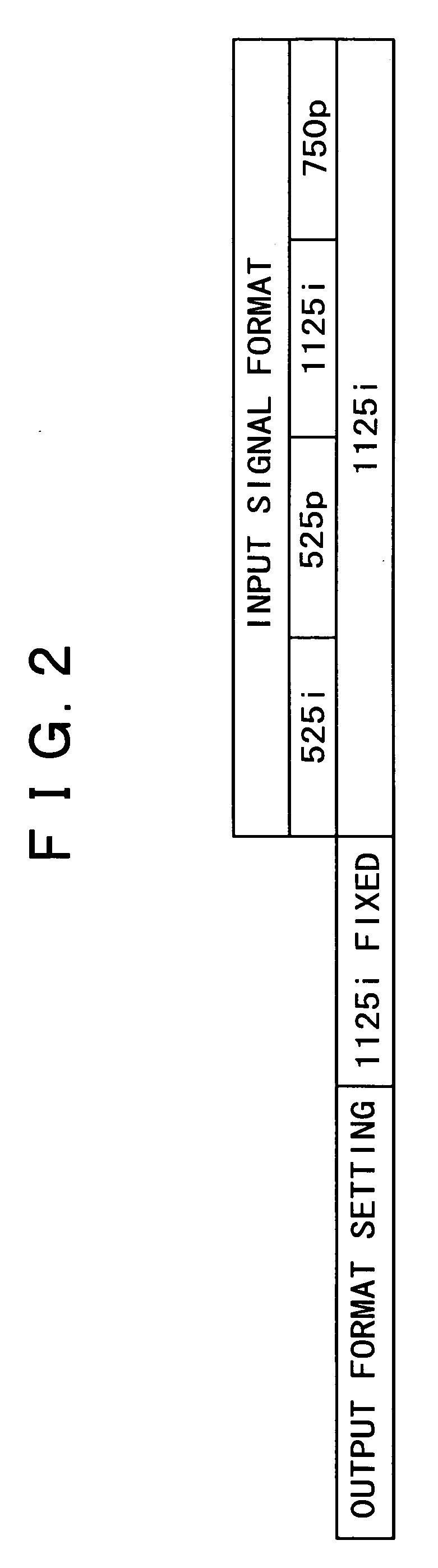
InactiveUS20050231641A1Improve picture qualityEfficient use ofTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMicrocomputerComputer graphics (images)
A video signal processing apparatus and a video signal processing method are capable of outputting a display having a high picture quality by effectively utilizing an output resolution. A microcomputer controls a shrinkage filter, a memory and an enlargement filter to carry out a resolution conversion process of converting the signal format of a video signal into a selected output signal format depending on the output format setting of a D terminal of the video processing apparatus, and outputs the video signal.
Owner:SONY CORP
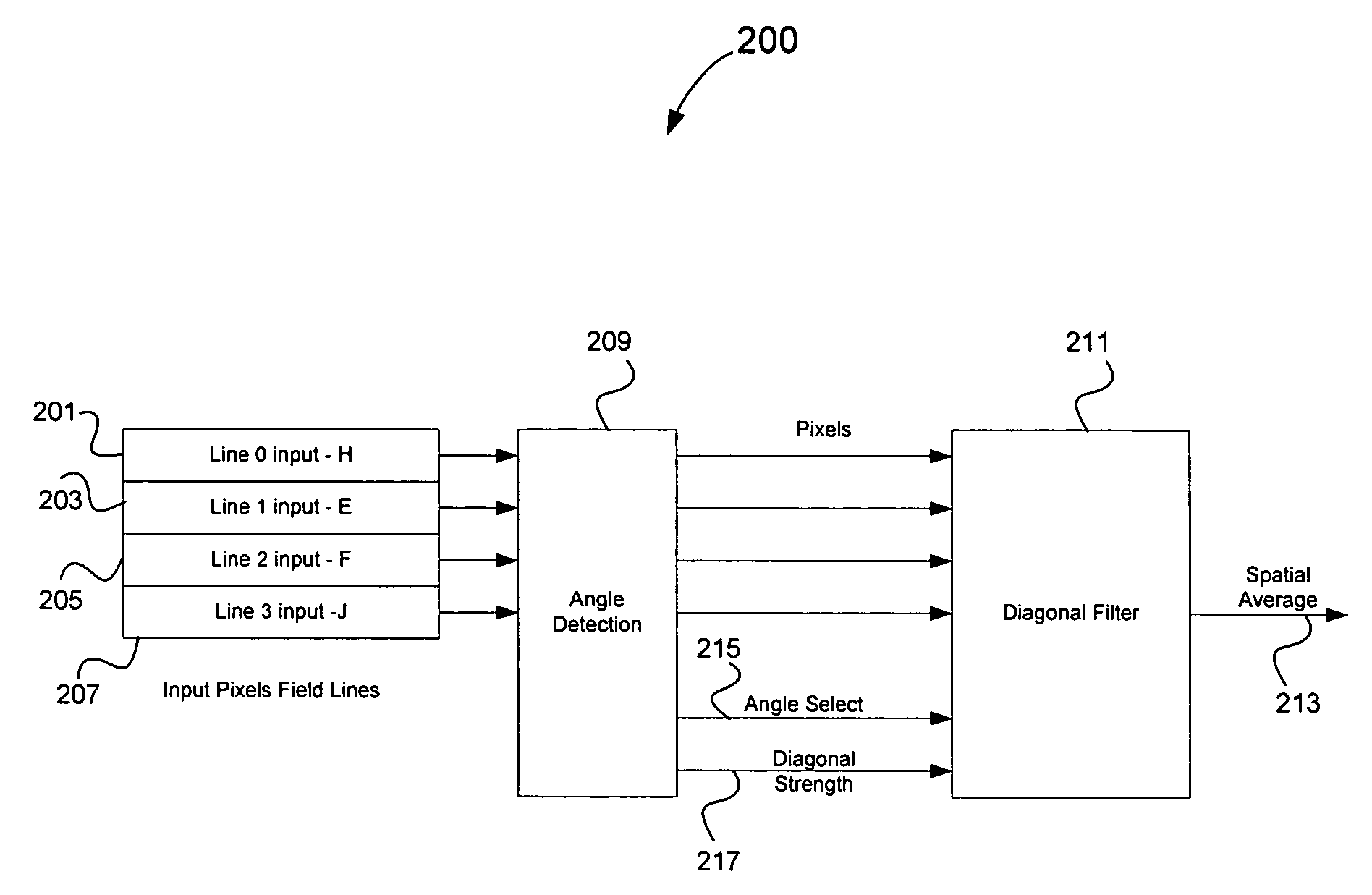
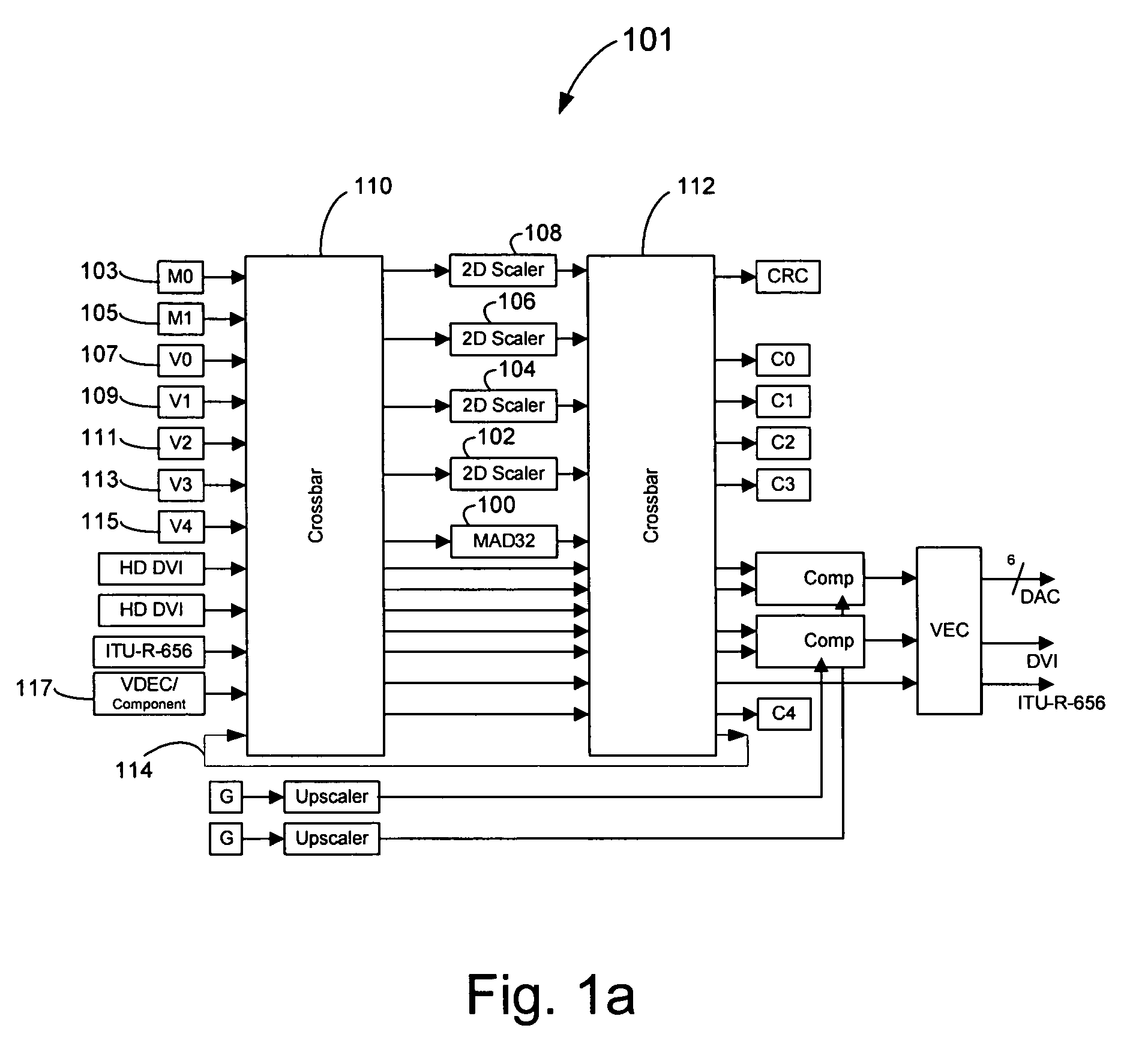
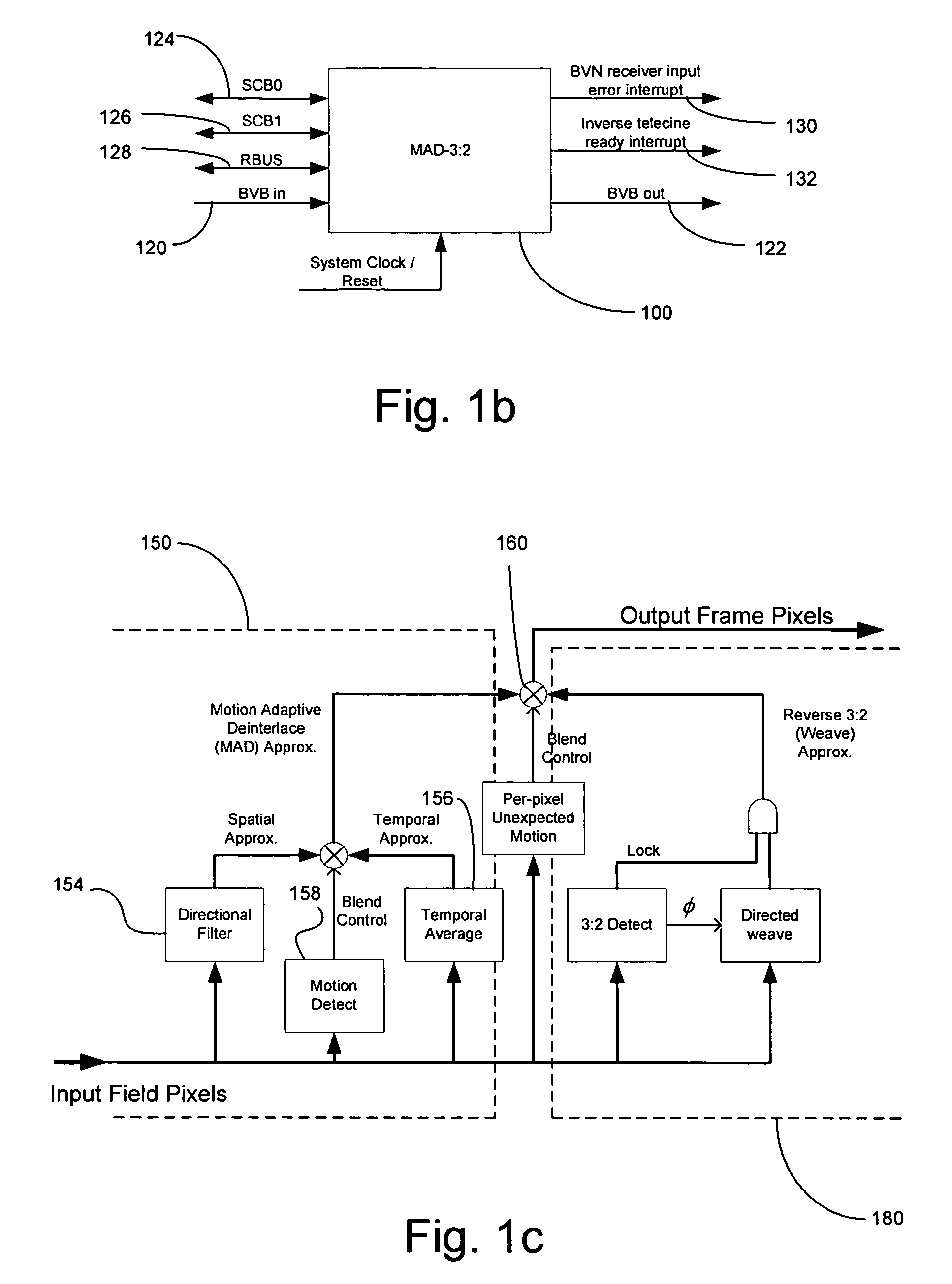
Method and system for motion adaptive deinterlacer with integrated directional filter
InactiveUS7349028B2Television system detailsBrightness and chrominance signal processing circuitsInterlaced videoComputer graphics (images)
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for masking of video artifacts and/or insertion of film grain in a video decoder
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
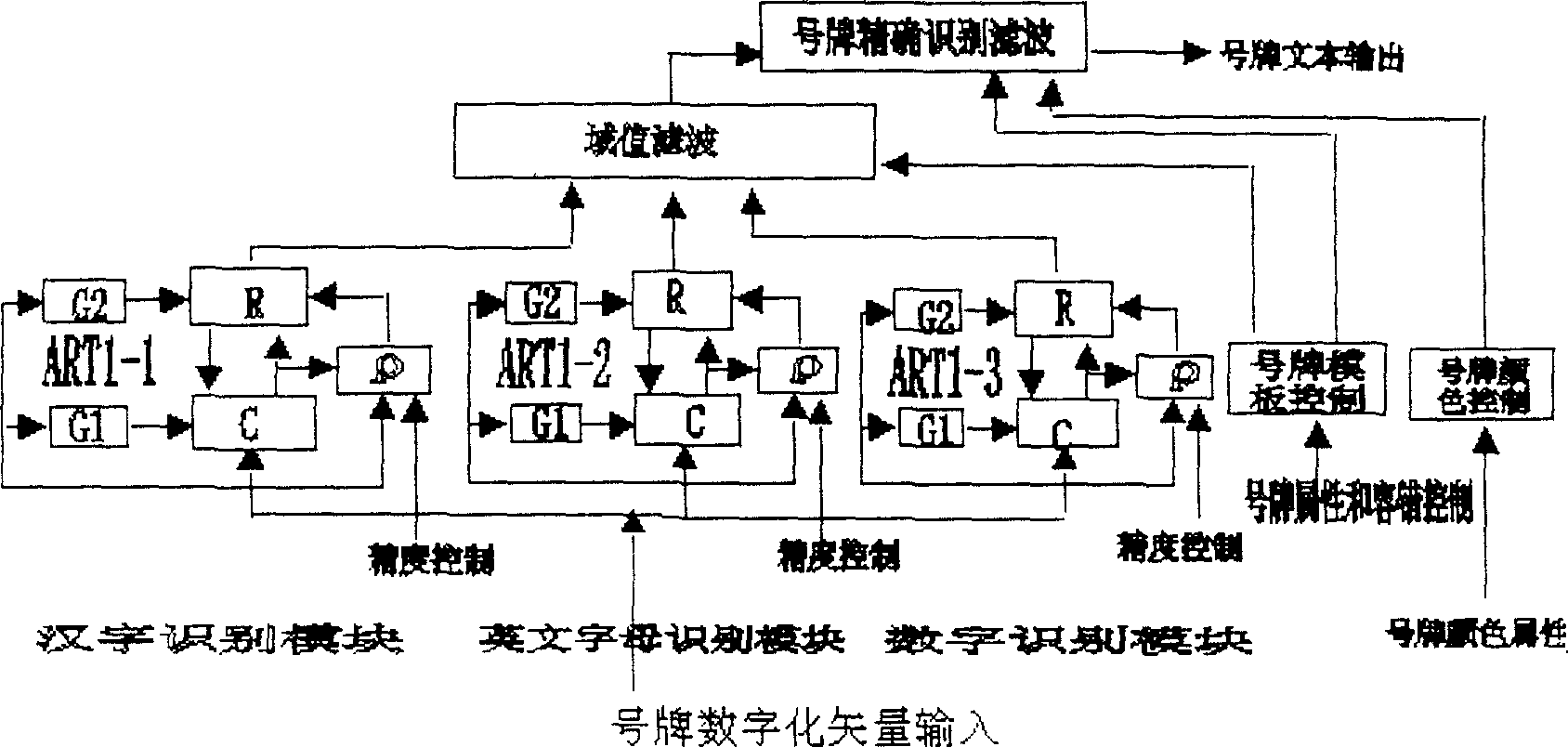
Identification method of mobile number plate based on three-channel parallel artificial nerve network
InactiveCN1694130AOvercoming the contradiction between precision and class diffusionSystem stabilityRoad vehicles traffic controlArtificial neural networkReal-time computing
The invention relates to a floating number plates discriminating method, which is based on the three-road parallel manmade nerve-net. The identify steps are that adopting the video burst mode to catch the video automatically for the collection of video pictures of the moving vehicle, character cutting the part of pictures of the number plates and then being the input signal of the nerve-net; said nerve-net adopts three standard self-adapt vibrate net each of which has its own work, the three nets are the Chinese characters identify net, the English characters identify net and the data identify net, all of which identify the inputted vector signals at one time, and outputs the most similar sort unity respectively, through controlling the property of the Territory value and the identify accurately according to the number plates and filter, at last add a color property of number plates as the output of the discriminating results. Adopting the method of the invention can identify the number plates of vehicle fast and accurately under the largest driving speed of the vehicles.
Owner:ANHUI VOCATION TECH CO LTD
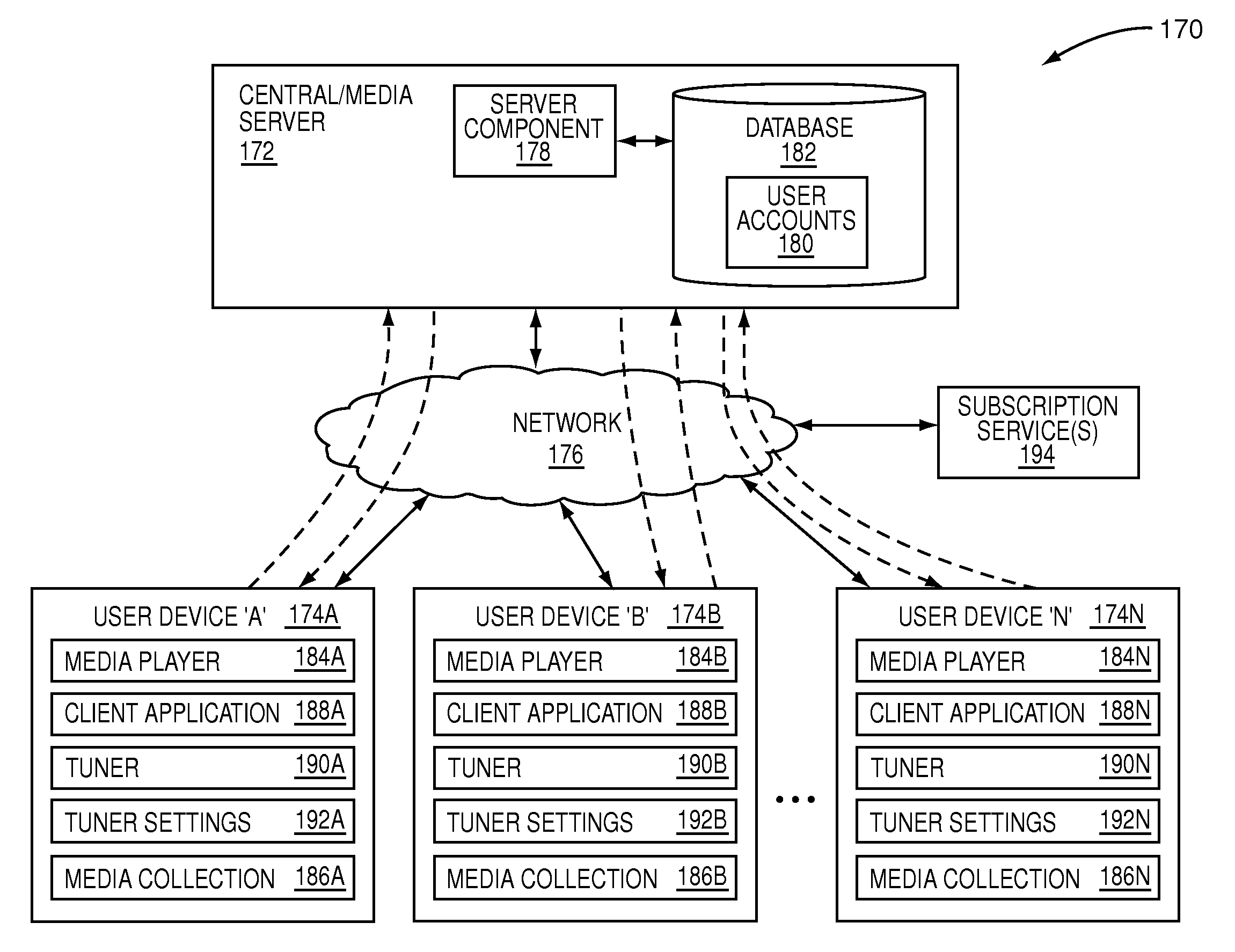
System and method for generating dynamically filtered content results, including for audio and/or video channels
InactiveUS20090164448A1Generate efficientlyHighly relevantMetadata audio data retrievalMetadata video data retrievalAudio frequencyInformation retrieval
A system and method for allowing a user to more effectively generate focused content results, including audio and / or video content. Content is dynamically filtered to generate content results in response to initial filtering settings or characteristics. The content results are provided to a user. Once the user finds and selects a content result of interest, additional filtering characteristics associated with the selected result are provided to the user as a suggestion for additional filtering. In this manner, the user is made aware of additional filtering settings or characteristics that can be used to focus the search results. Subsequent filter settings and filtering operations can be based on characteristics of previous relevant results in an iterative and dynamic manner. Focused results are more likely produced, because additional filtering settings are provided and adjusted according to characteristics of results deemed relevant by the user.
Owner:CONCERT TECH
Filtering method and system
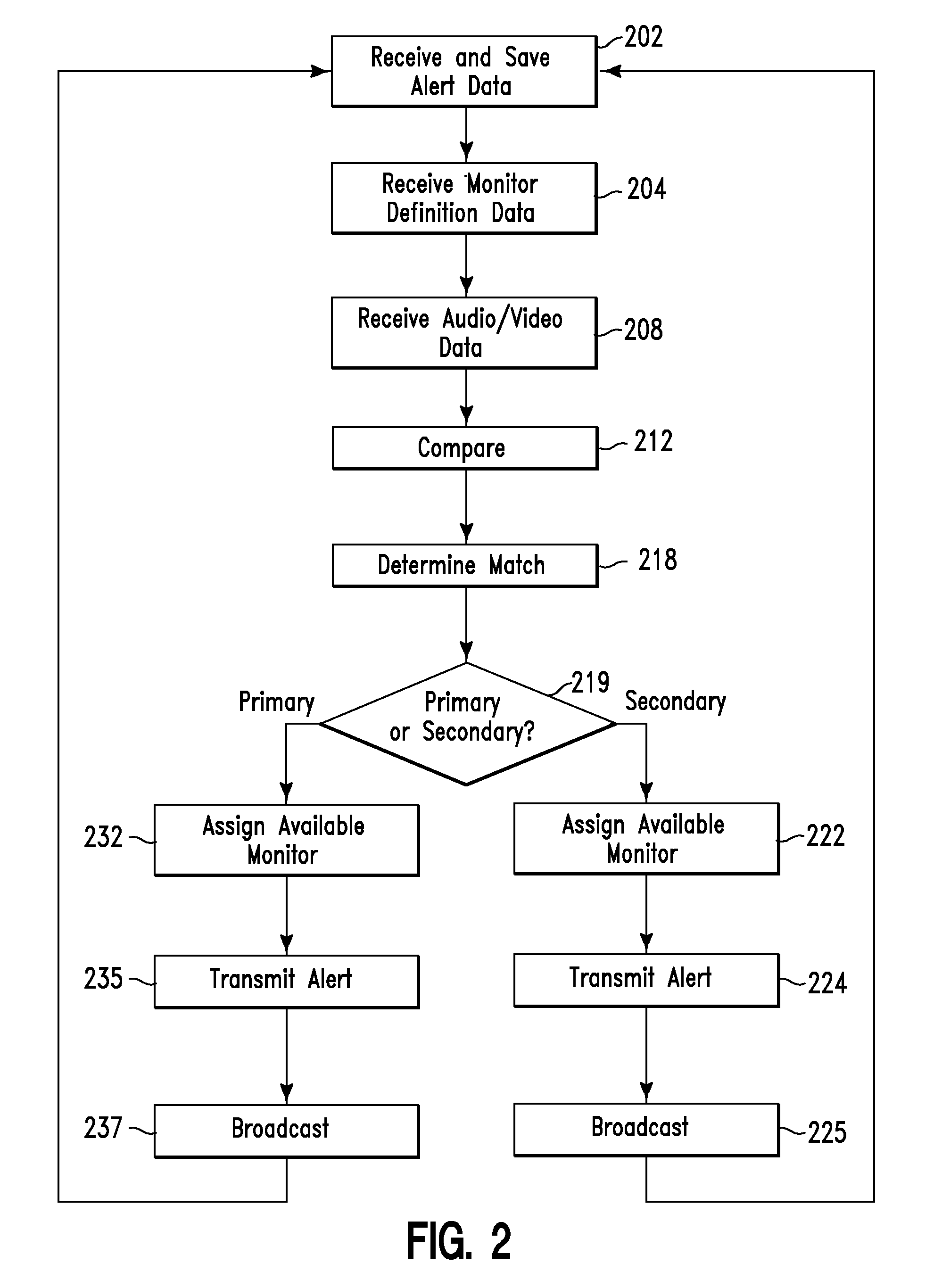
InactiveUS20110285542A1Electrical cable transmission adaptationSelective content distributionData packTelecommunications
An alert generation method and system. The method includes receiving by a computer processor, alert data indicating filters for specified alert types associated with possible future events. The computer processor receives monitor definition data and media generated audio / video data; compares the alert data to the media generated audio / video data; determines a first alert type matches first audio / video data of the media generated audio / video data; and determines that the first audio / video data comprises a primary event. The computer processor broadcasts the primary event.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
Switched filter up-sampling mechanism for scalable video coding
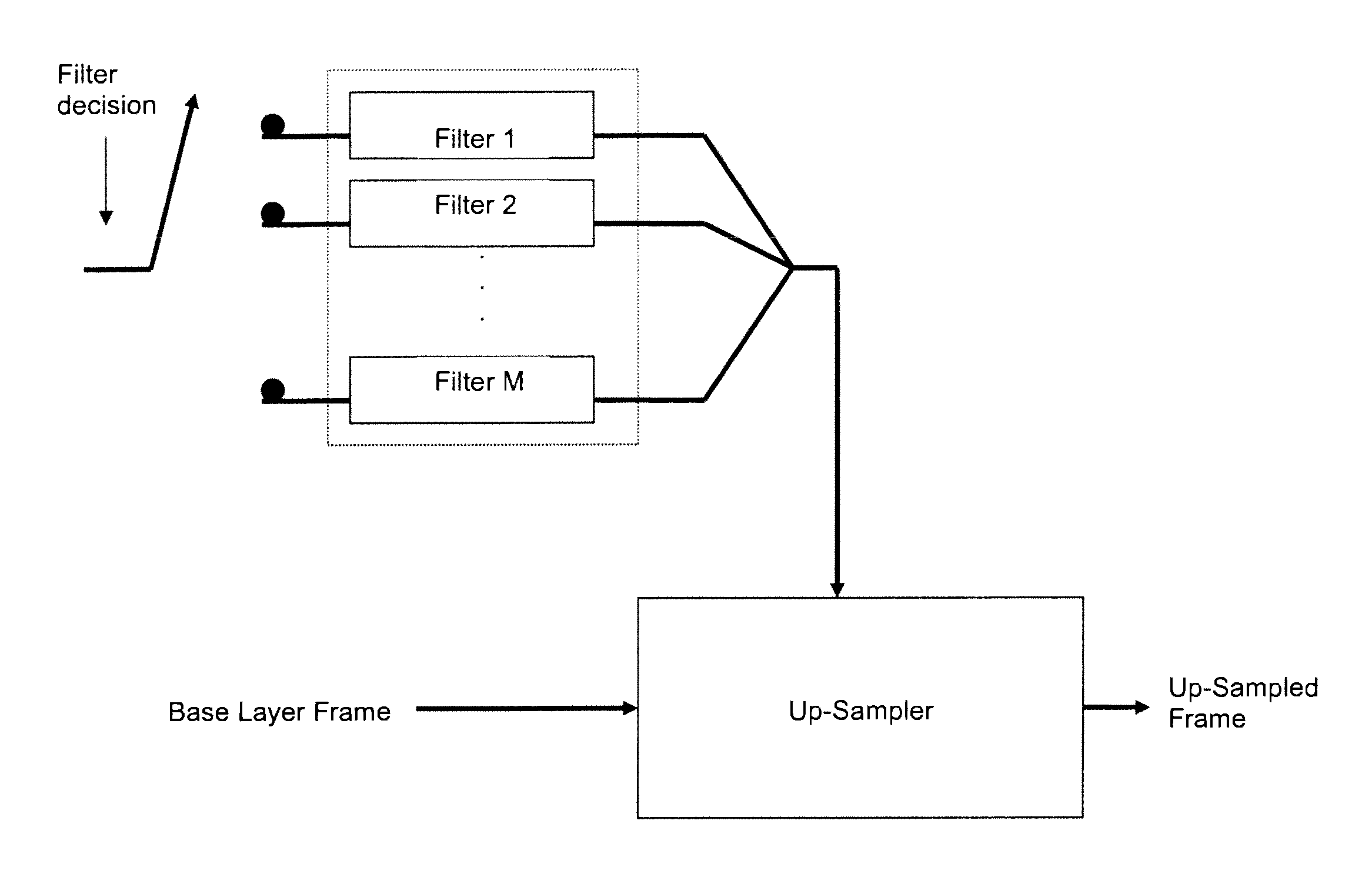
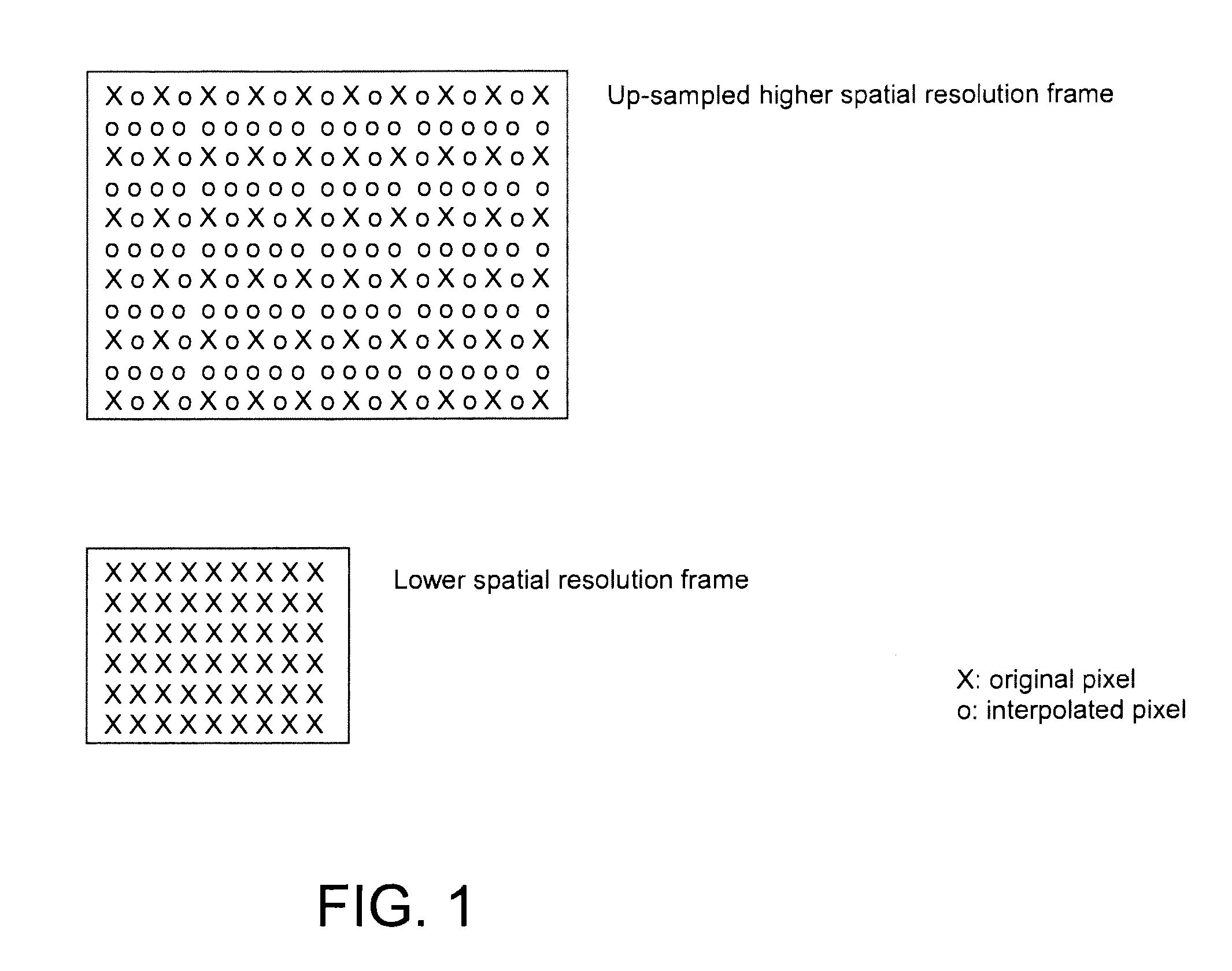
InactiveUS20070217502A1Reduce computational complexityImprove performanceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureSwitched filters
An improved switched filter up-sampling mechanism for scalable video coding. A filter switching mechanism of the present invention takes advantage of the best performance of each of the filters in a collaborative manner. The switching process of the present invention can be generalized to more filter choices and potentially relieve the computational complexity due to the added freedom and flexibility of filter choices.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Apparatus, a method and a computer program for video processing
ActiveUS20110170609A1Pleasant reproductionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo processingComputer program
There is disclosed apparatuses, methods and computer program products for coding and decoding and specifically but not only for coding and decoding of image and video signals. It is determined whether two adjacent blocks of pixels of an image have a flat nature. The result of the determining is used to select a filter among at least a first filter and a second filter for filtering a block boundary between two adjacent blocks of pixels. The second filter is selected when said determining indicates that there are two adjacent blocks of pixels having a flat nature. At least a first reference value and a second reference value are selected for the second filter and used in filtering the block boundary.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
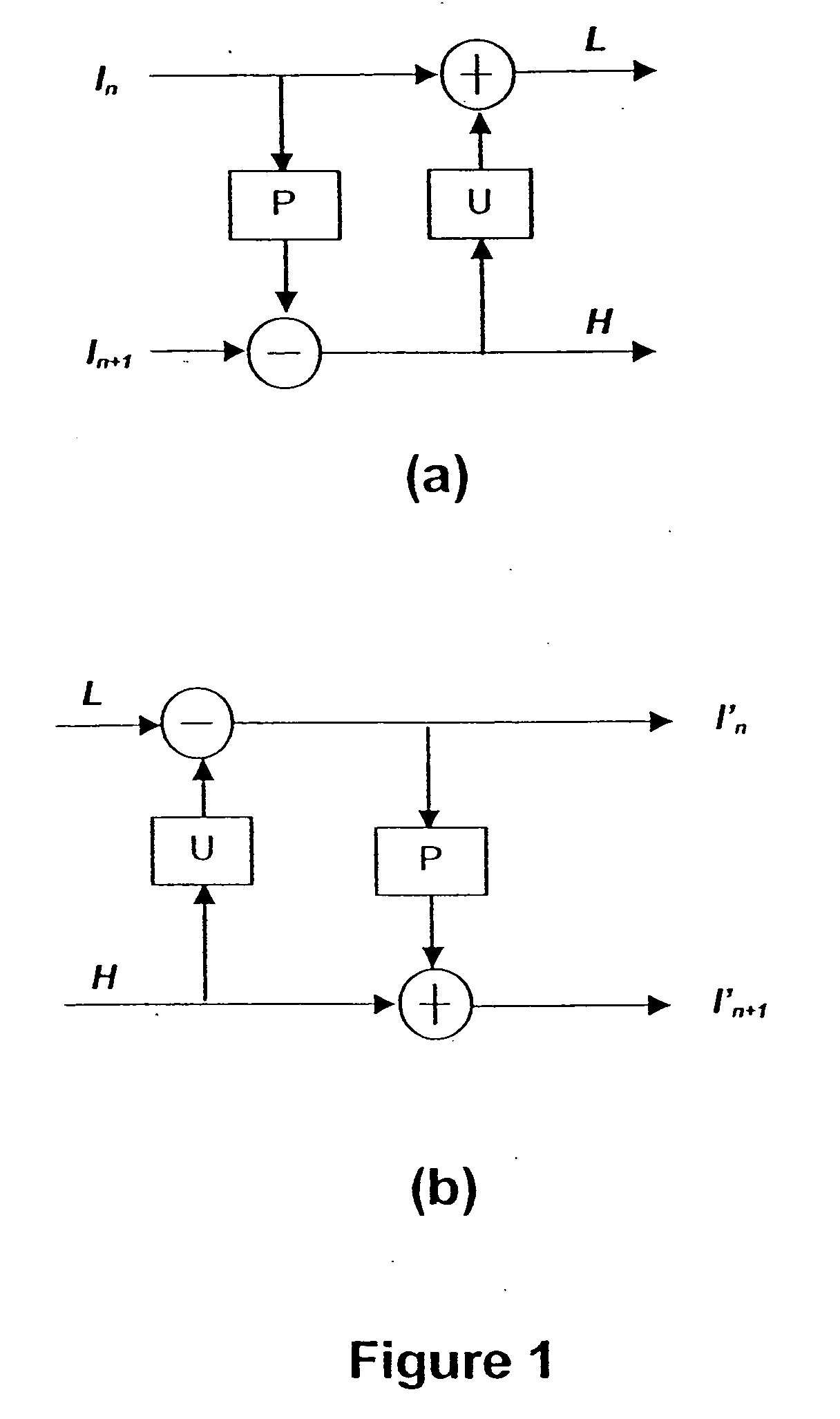
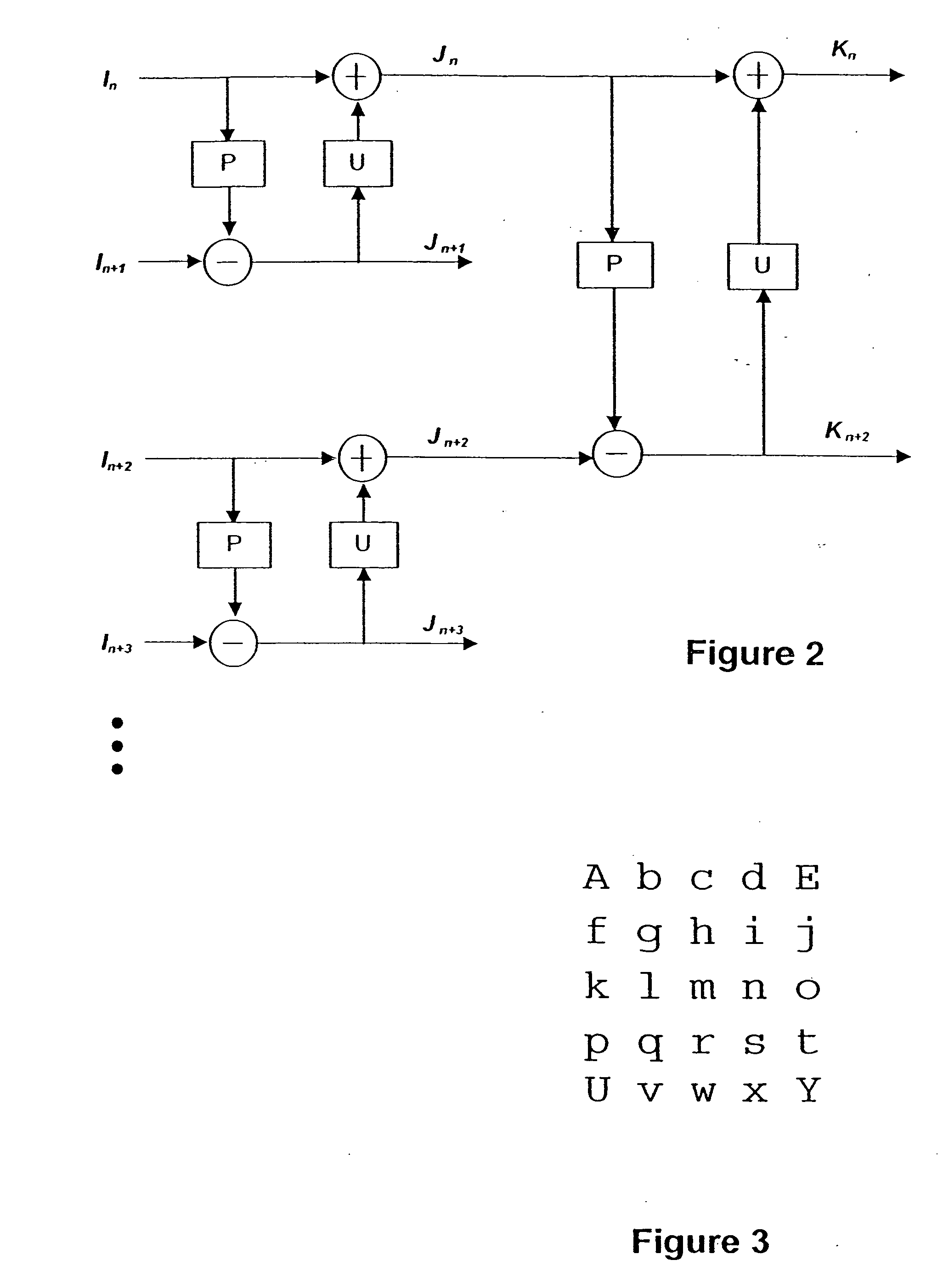
Method and apparatus for sub-pixel interpolation for updating operation in video coding
InactiveUS20070110159A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoFrame based
In the video encoding and decoding of digital video sequence having a prediction operation and an update operation, the update operation includes interpolation to generate energy distributed interpolation. Prediction is carried out on each block based on motion compensated prediction with respect to a reference frame and a motion vector in order to provide a corresponding block of prediction residues. Updating is carried out on a reference video frame based on motion compensated prediction with respect to the block of prediction residues and a reverse direction of the motion vector. The interpolation filter is determined based on the motion vector and the sample values of sub-pixel are interpolated using the block prediction residues by treating the sample values outside the block of prediction residues to be zero. Interpolation is performed along horizontal direction and vertical direction separately using one dimensional interpolation filter.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
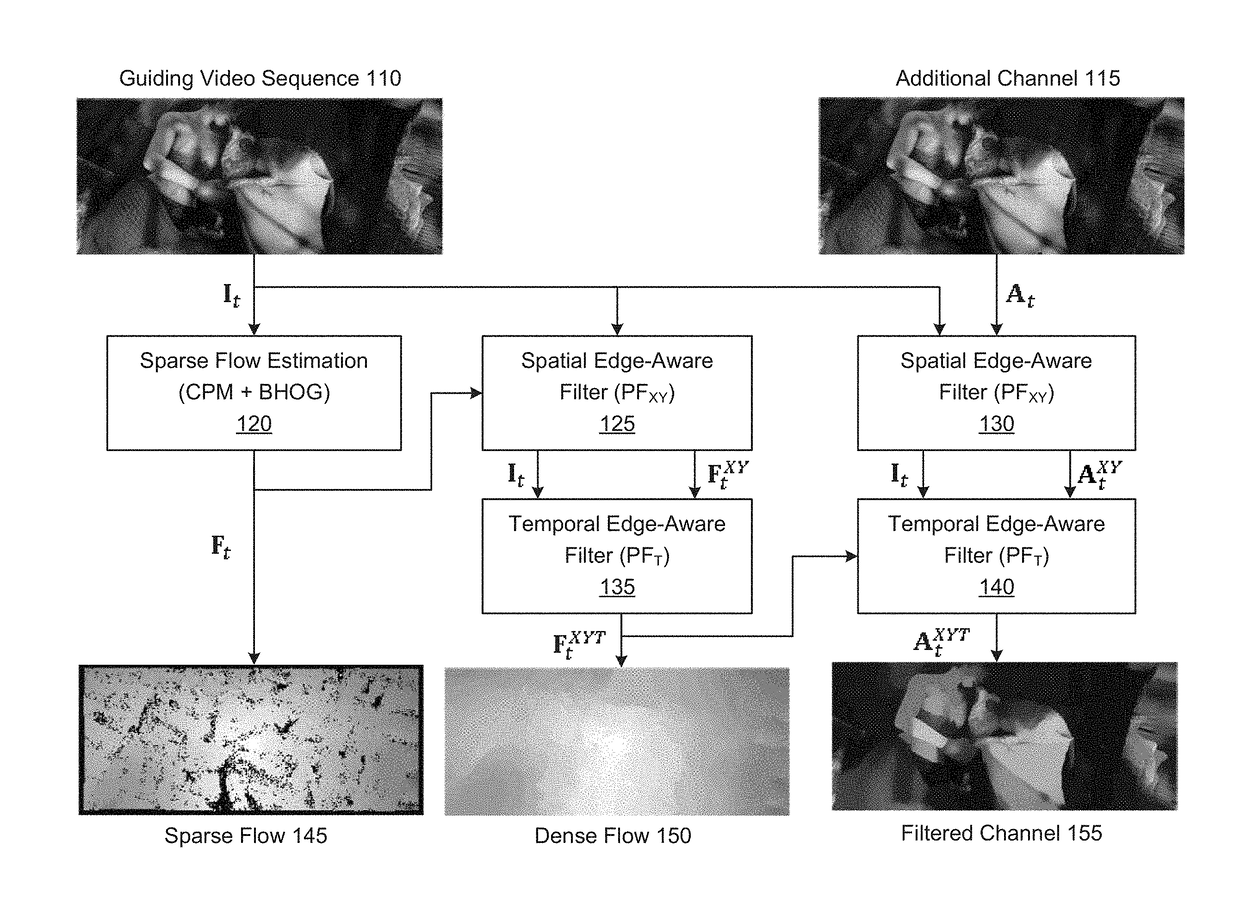
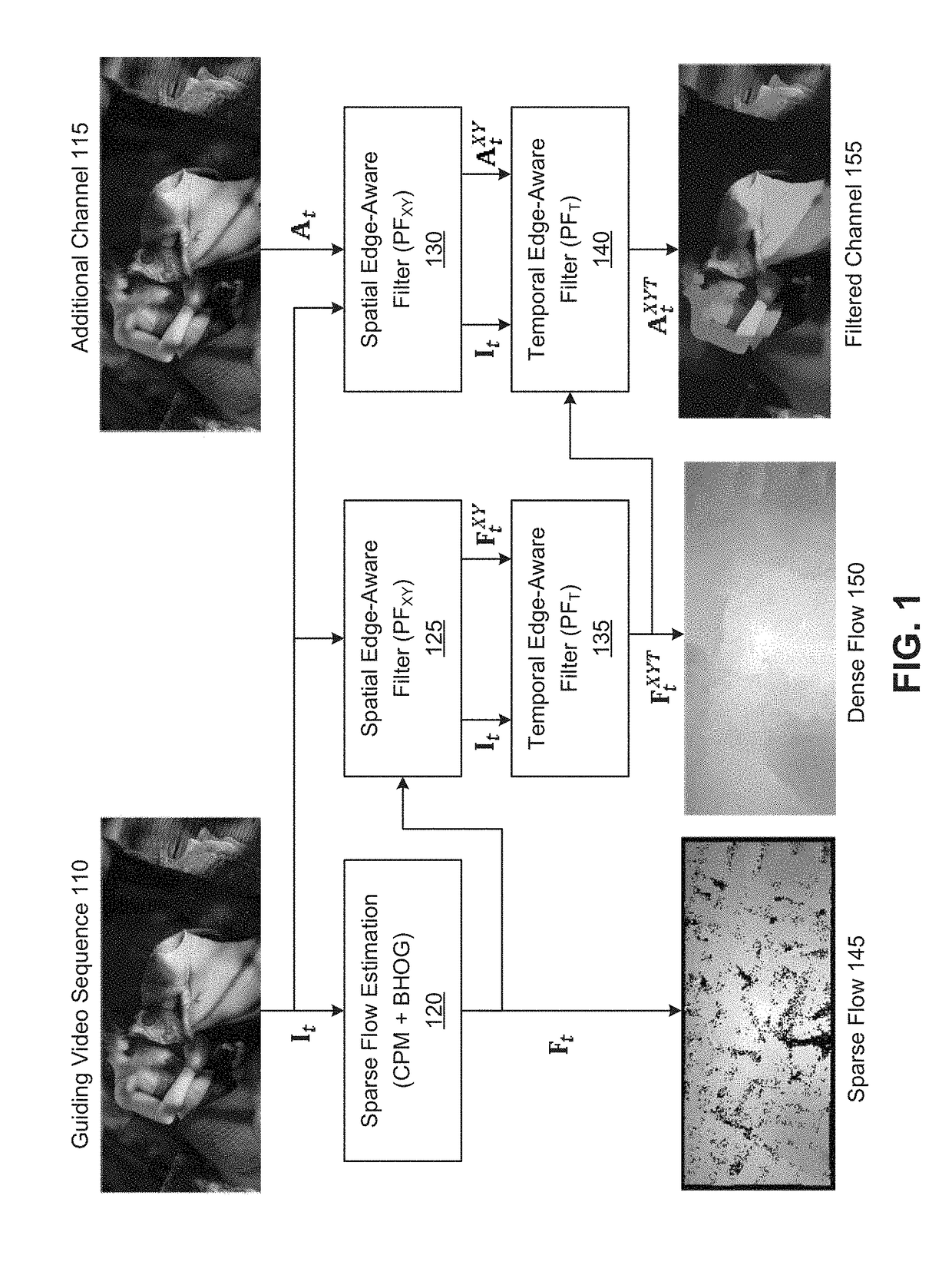
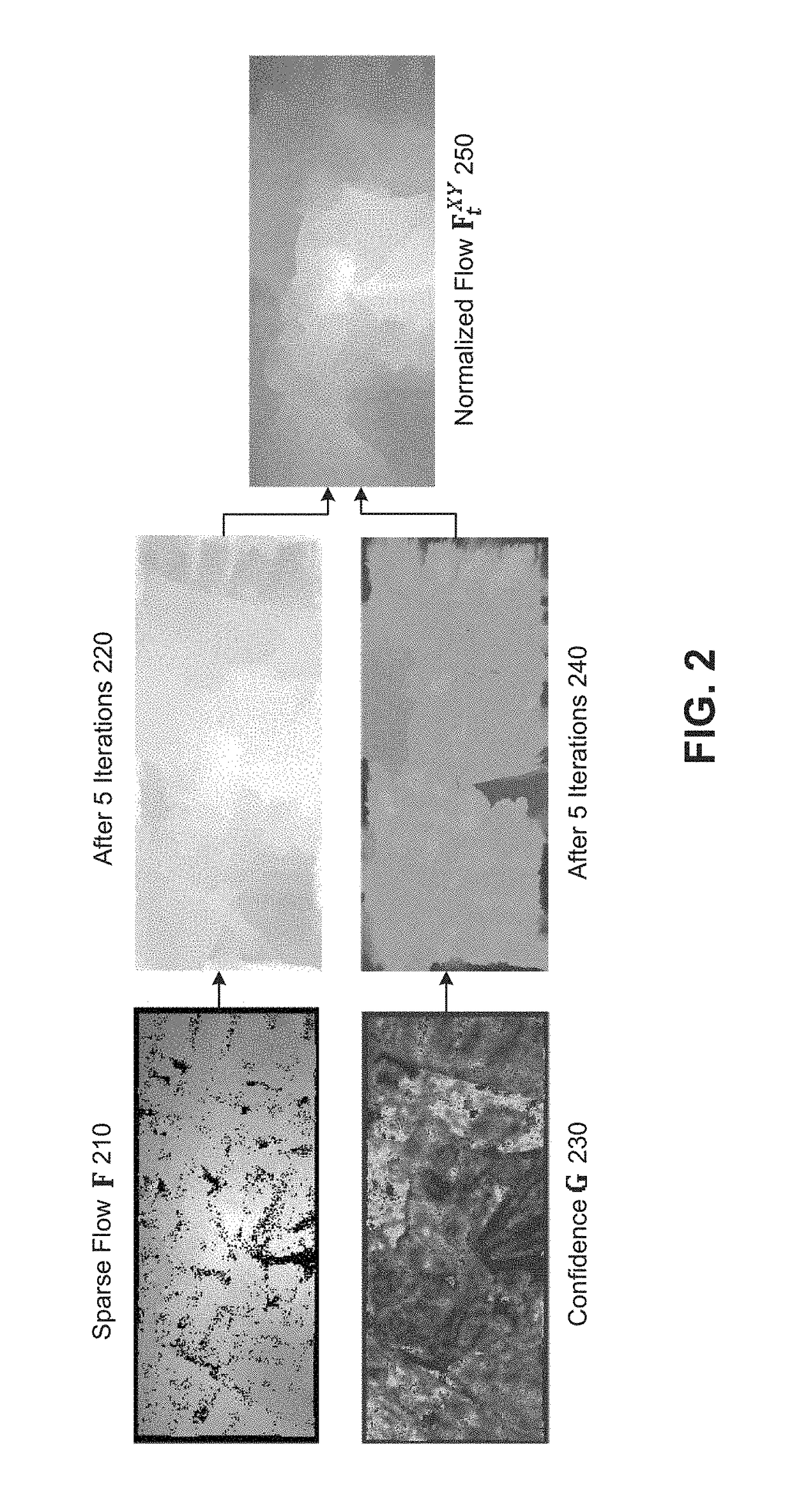
Edge-aware spatio-temporal filtering and optical flow estimation in real time
The disclosure provides an approach for edge-aware spatio-temporal filtering. In one embodiment, a filtering application receives as input a guiding video sequence and video sequence(s) from additional channel(s). The filtering application estimates a sparse optical flow from the guiding video sequence using a novel binary feature descriptor integrated into the Coarse-to-fine PatchMatch method to compute a quasi-dense nearest neighbor field. The filtering application then performs spatial edge-aware filtering of the sparse optical flow (to obtain a dense flow) and the additional channel(s), using an efficient evaluation of the permeability filter with only two scan-line passes per iteration. Further, the filtering application performs temporal filtering of the optical flow using an infinite impulse response filter that only requires one filter state updated based on new guiding video sequence video frames. The resulting optical flow may then be used in temporal edge-aware filtering of the additional channel(s) using the nonlinear infinite impulse response filter.
Owner:ETH ZURICH EIDGENOESSISCHE TECHN HOCHSCHULE ZURICH +1
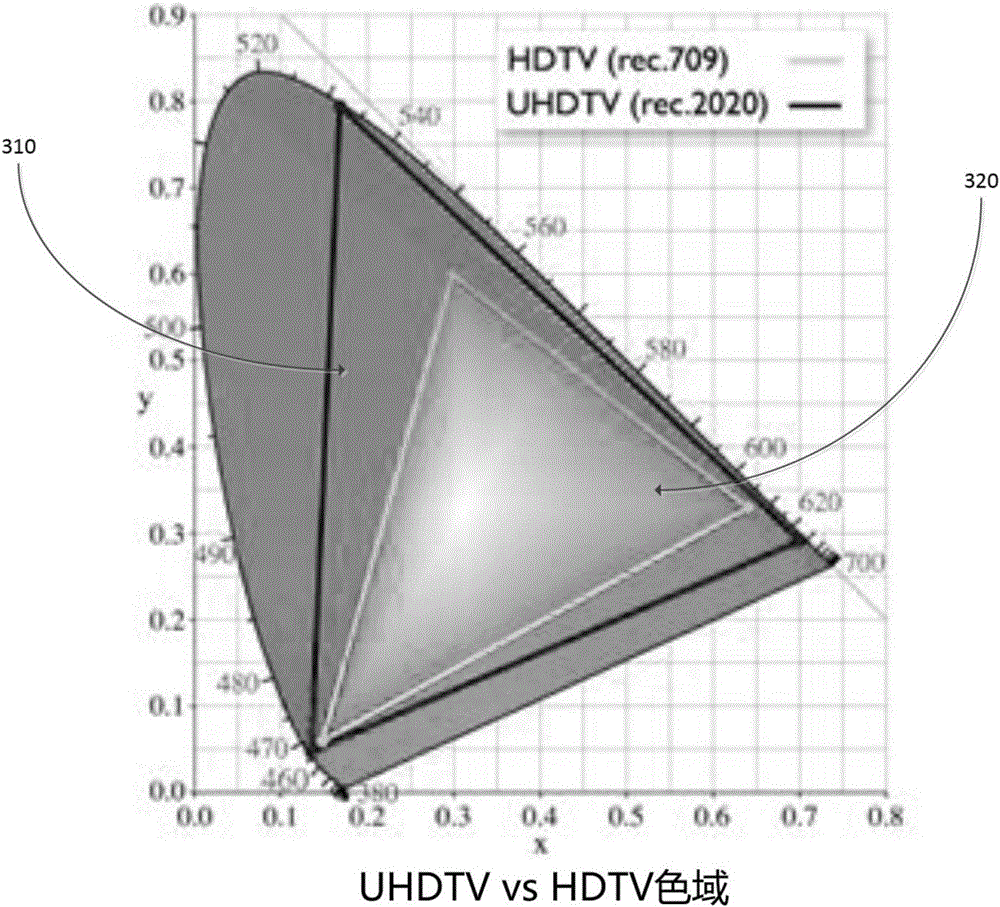
Color gamut scalable video coding device and method for the phase alignment of luma and chroma using interpolation
ActiveCN105830440AColor signal processing circuitsDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionGamut
The invention discloses a color gamut scalable video coding device and a method for the phase alignment of luma and chroma using interpolation. According to the invention, a video coding device and a method are used for receiving a picture associated with a first color space, wherein the picture comprises a first component at a first sampling location (CO), a second component at a second sampling location (LO) and the second component at a third sampling location (L4). A first interpolation filter is applied to the second component at the second sampling location (LO) and the second component at the third sampling location (L4) to determine the second component at the first sampling location (L(C0)). The second component at the first sampling location (L(C0)) may be associated with the first color space. A color conversion model is applied to the first component at the first sampling location (CO) and to the second component at the first sampling location (L(C0) ) to translate the first component at the first sampling location to a second color space.
Owner:VID SCALE INC
A method of adapting video images to small screen sizes
InactiveCN102124727ATelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesCropping systemFeature extraction
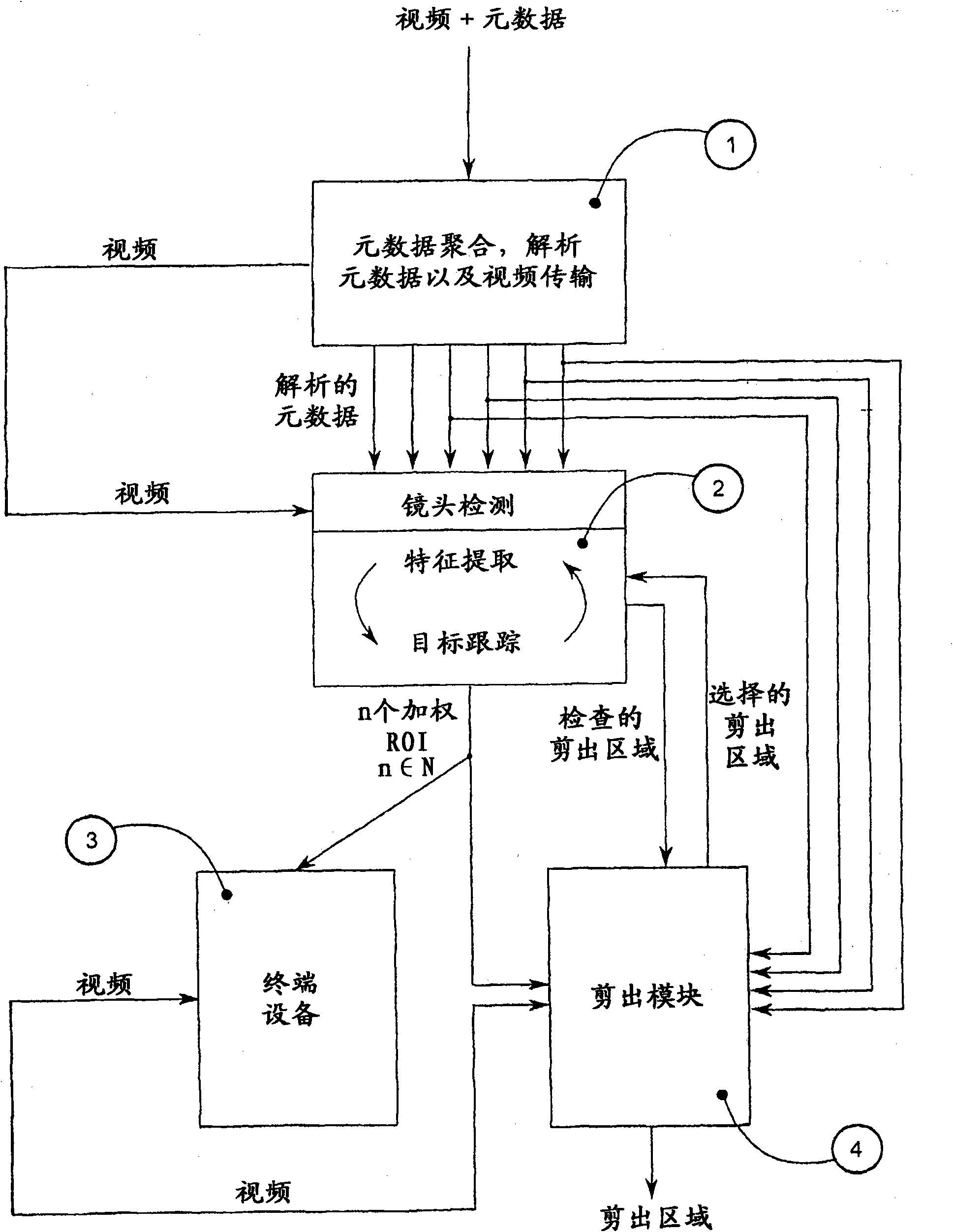
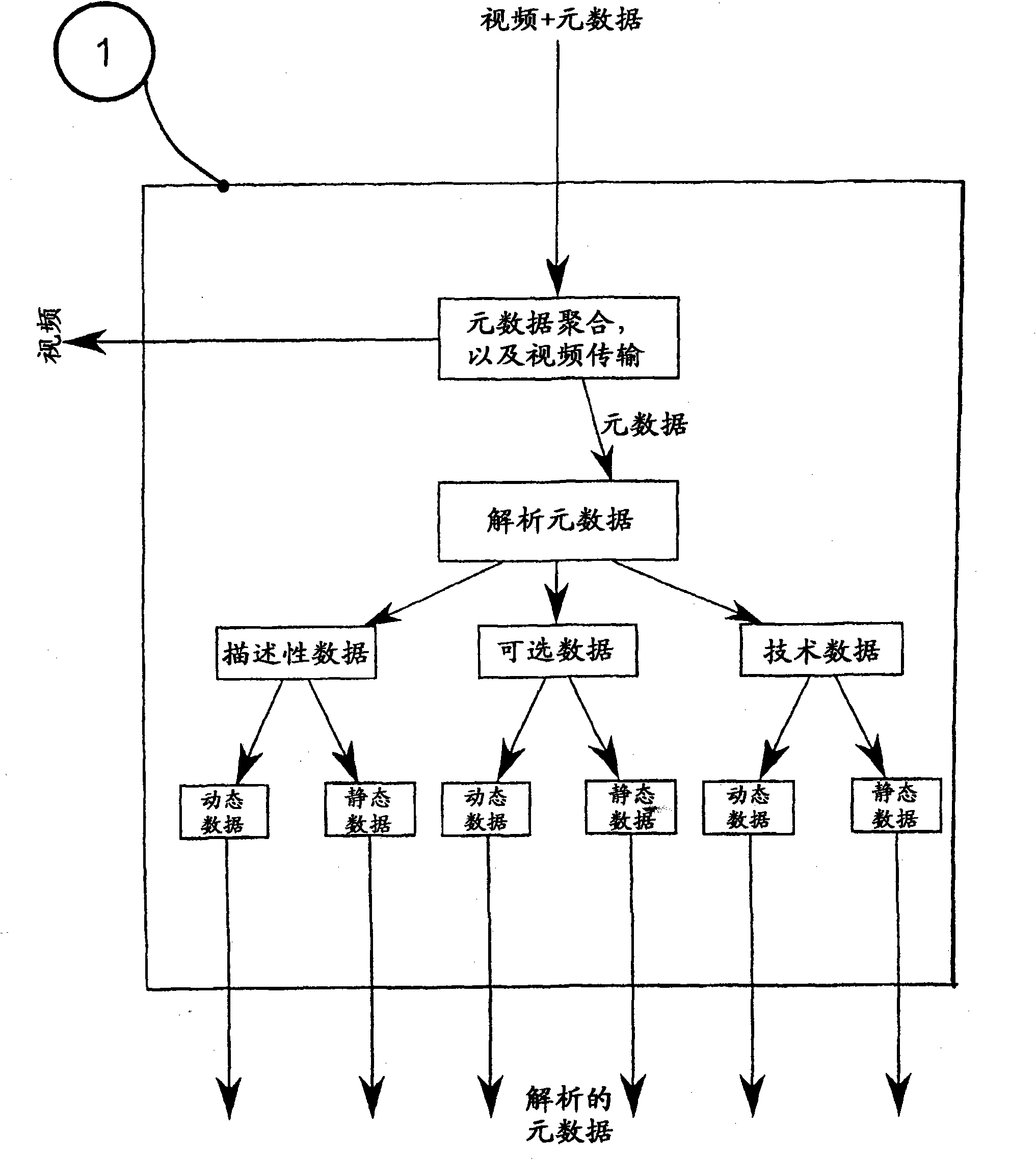
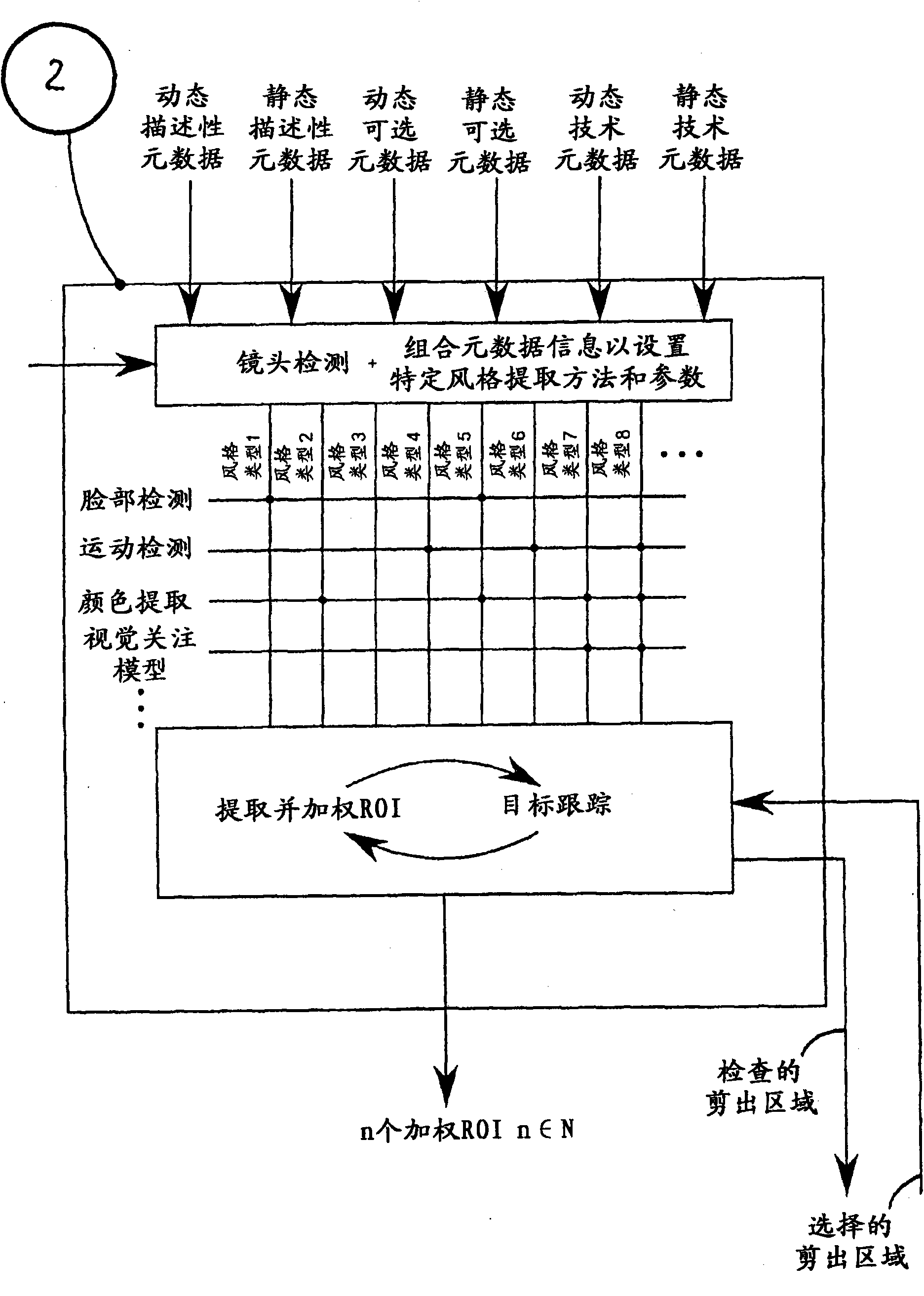
In order to improve a cropping system by obtaining the coverage of a wide range of contents for smaller sized displays of handheld devices, the invention proposes a method starting from a metadata aggregation and the corresponding video, e.g. in post-production, programme exchange and archiving, wherein (a) the video is passed through a video analysis to deliver video, e.g. by use of motion detection, morphology filters, edge detection, etc., (b) the separated video and metadata are combined to extract important features in a context wherein important information from the metadata is categorised and is used to initialise a dynamically fitted chain of feature extraction steps adapted to the delivered video content, (c) extracted important features are combined to defione regions of interest (ROI) which are searched in consecutive video frames by object tracking, said object tracking identifies the new position and deformation of each initialised ROI in consecutive video frames and returns this information to the feature extraction thereby obtaining a permanent communication between said feature extraction and said object tracking, (d) one or several ROIs are extracted and inputted video frame by video frame into a cropping step (e); based on weighting information a well composed image part is cropped by classifying said supplied ROIs by importance, and (f) said cropped image area(s) are scaled to the desired small screen size.
Owner:无线电技术研究学院有限公司 +2
In-Loop Noise Reduction Within an Encoder Framework
InactiveUS20080056366A1Reduce noiseEasy to adjustColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoPattern recognition
An apparatus and method are described for filtering noise internally within a video encoding framework. In various embodiments of the invention, an in-loop noise filter is integrated within an encoding device or framework that reduces noise along a motion trajectory within a digital video signal. This integration of in-loop noise reduction allows both noise filtering parameters and encoding parameters to be more easily related and adjusted. The in-loop noise filter leverages characteristics of digital video encoding processes to reduce noise on a video signal and improve encoding efficiencies of a codec.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
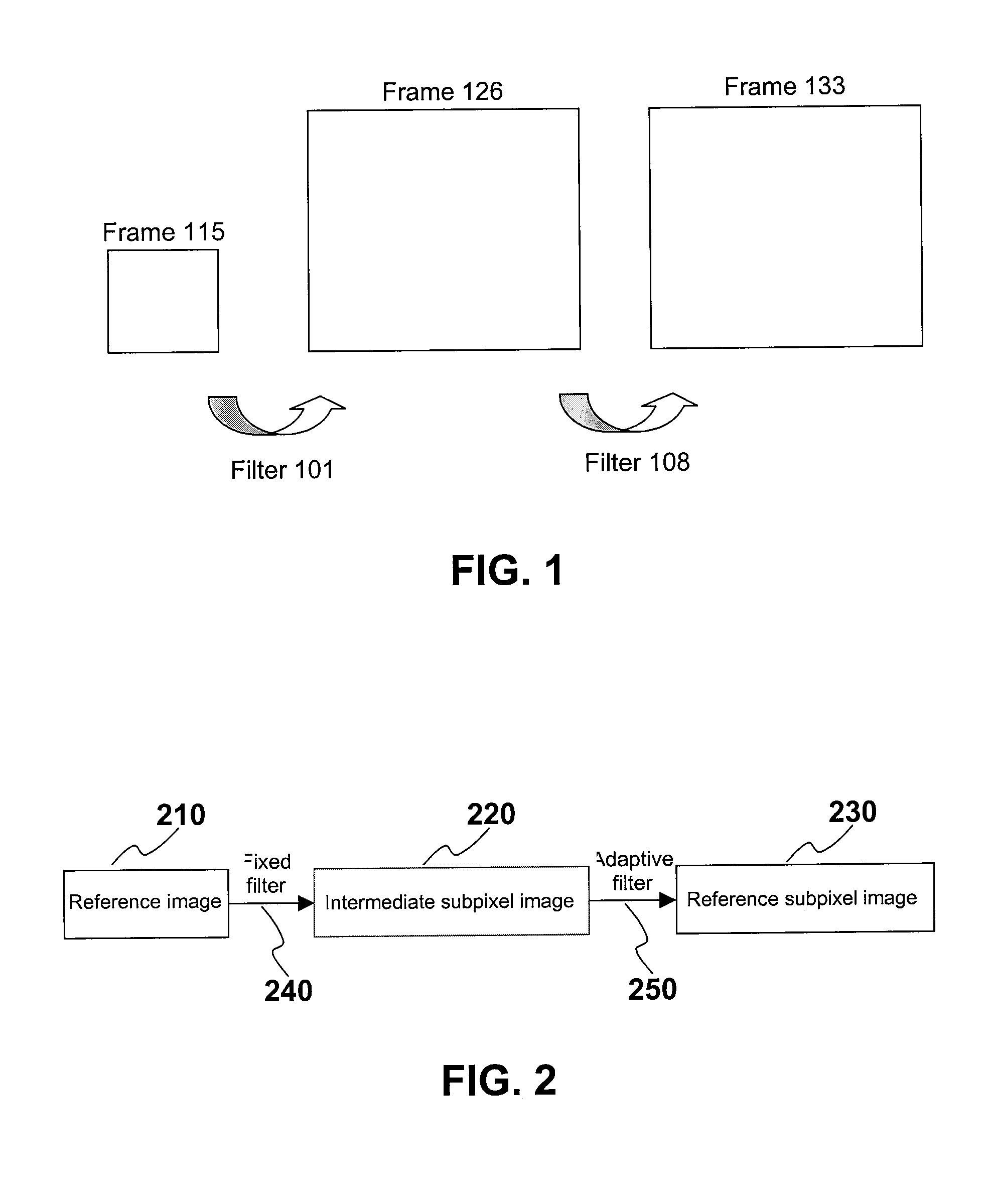
Method for motion compensation
ActiveUS20090092328A1Reduce complexityLow data requirementsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningAdaptive filterComputer graphics (images)
A method for use in video compression is disclosed. In particular, the claimed invention relates to a method of more efficient fractional-pixel interpolation in two steps by a fixed filter (240) and an adaptive filter (250) for fractional-pixel motion compensation.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com