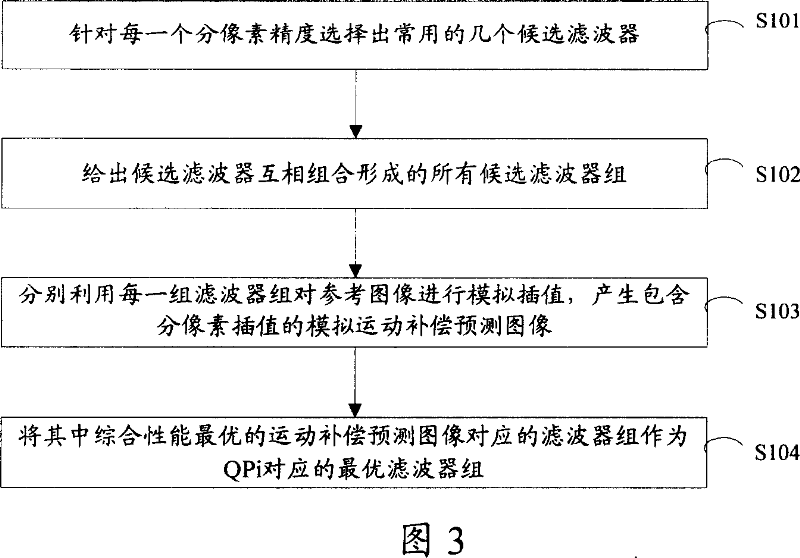
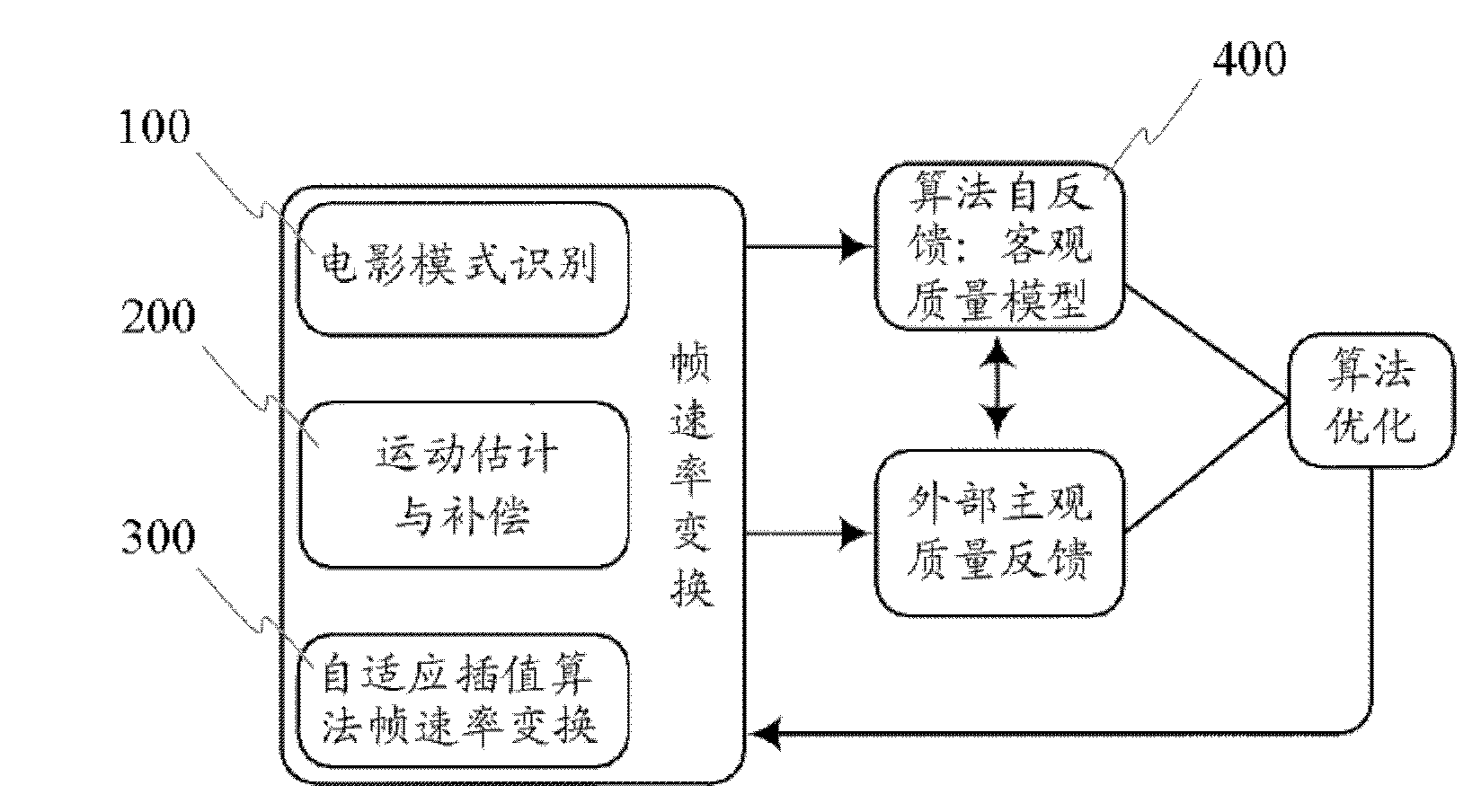
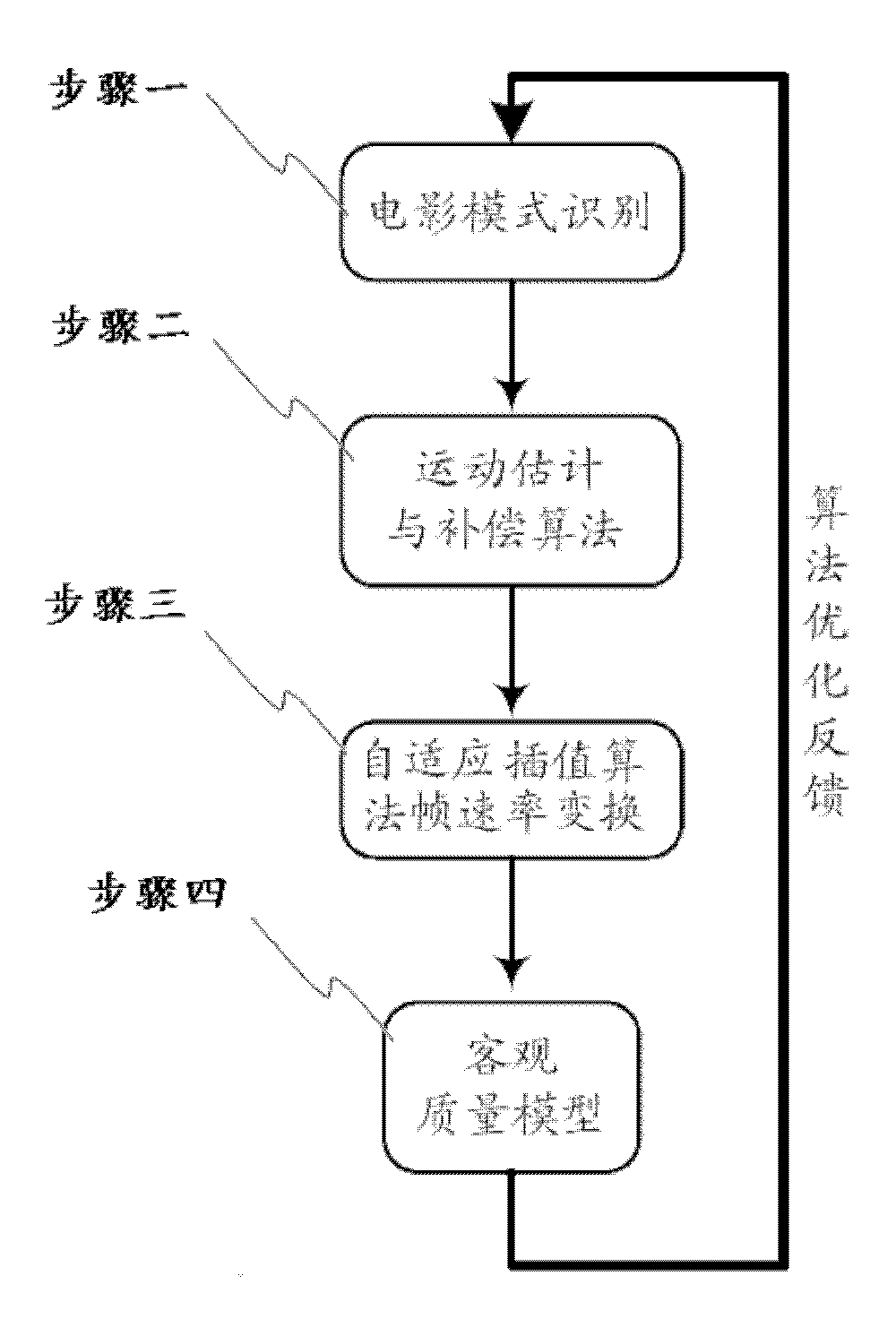
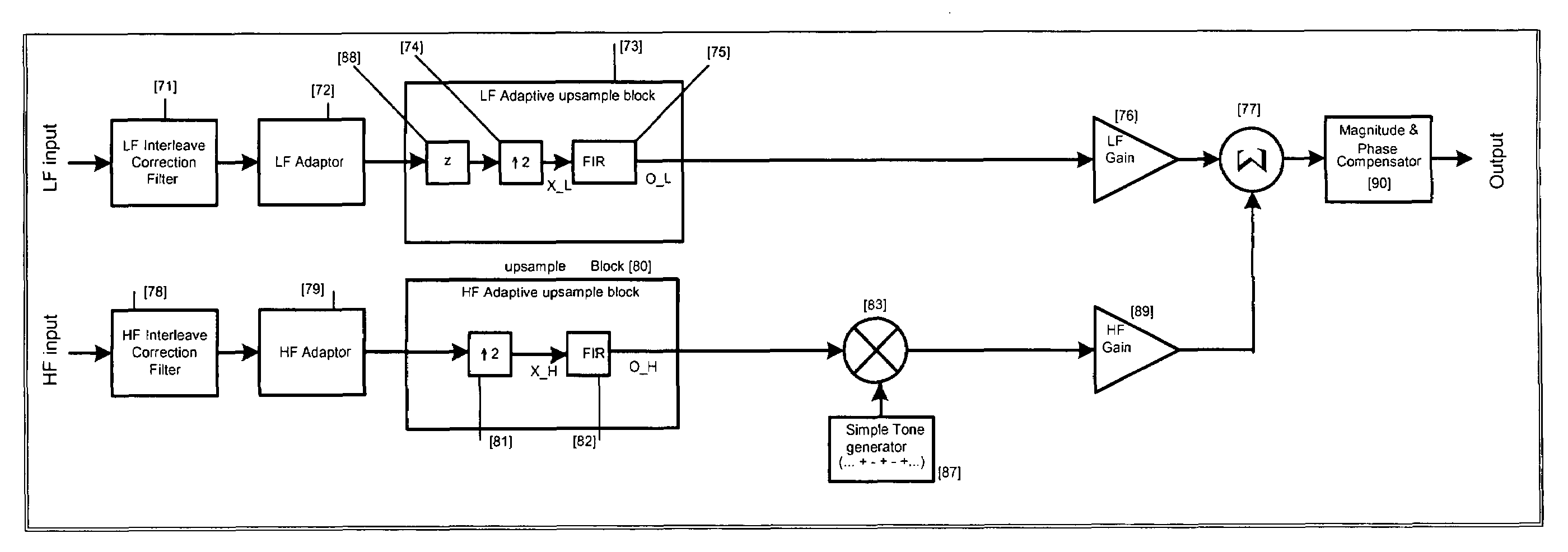
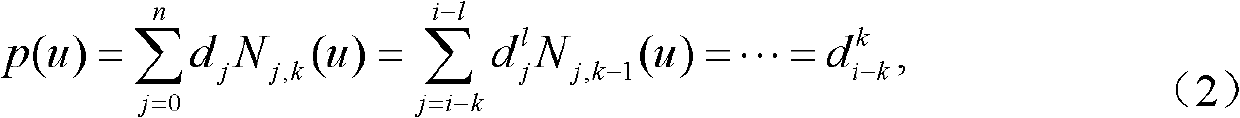Patents
Literature
158 results about "Adaptive interpolation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
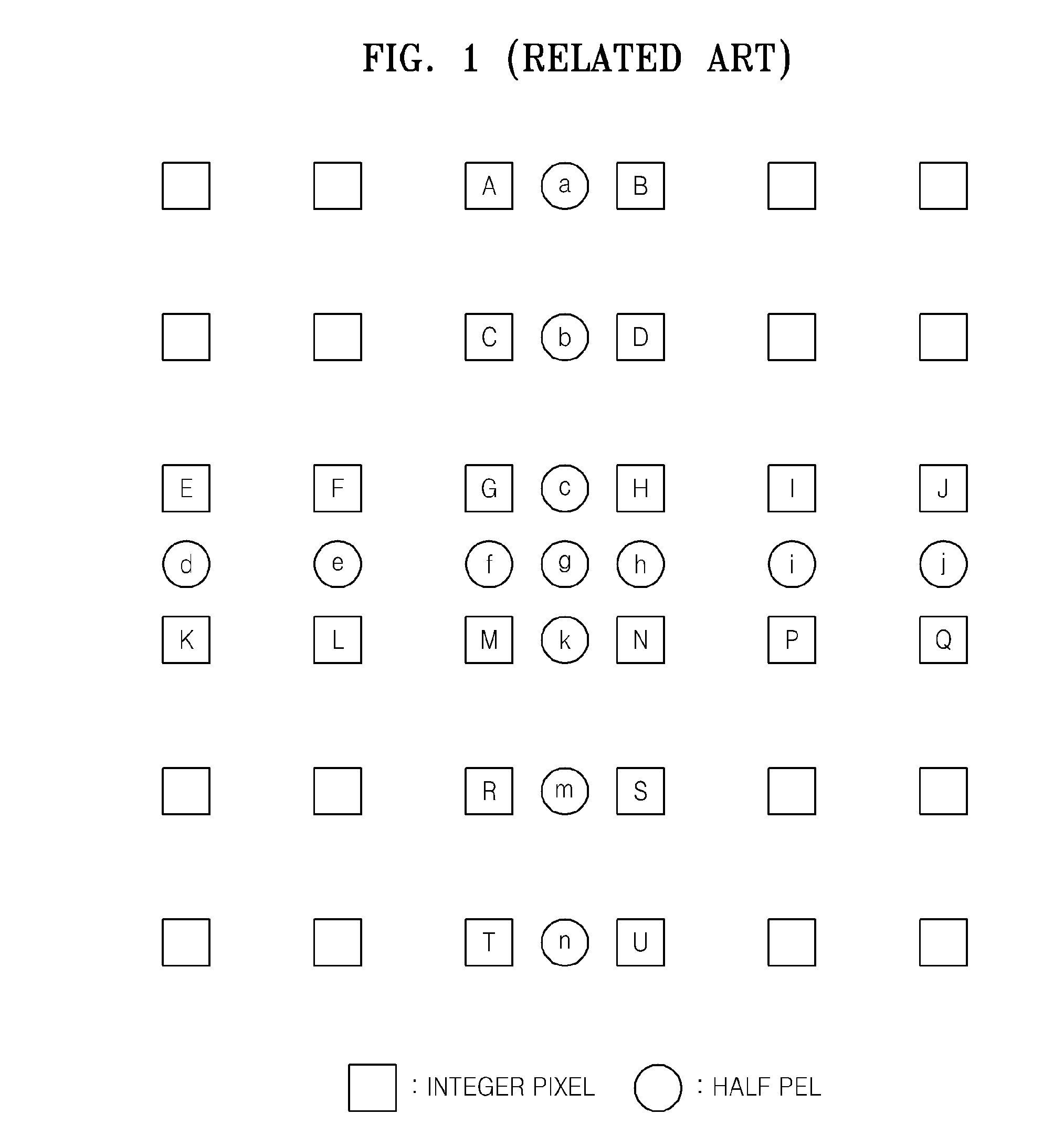
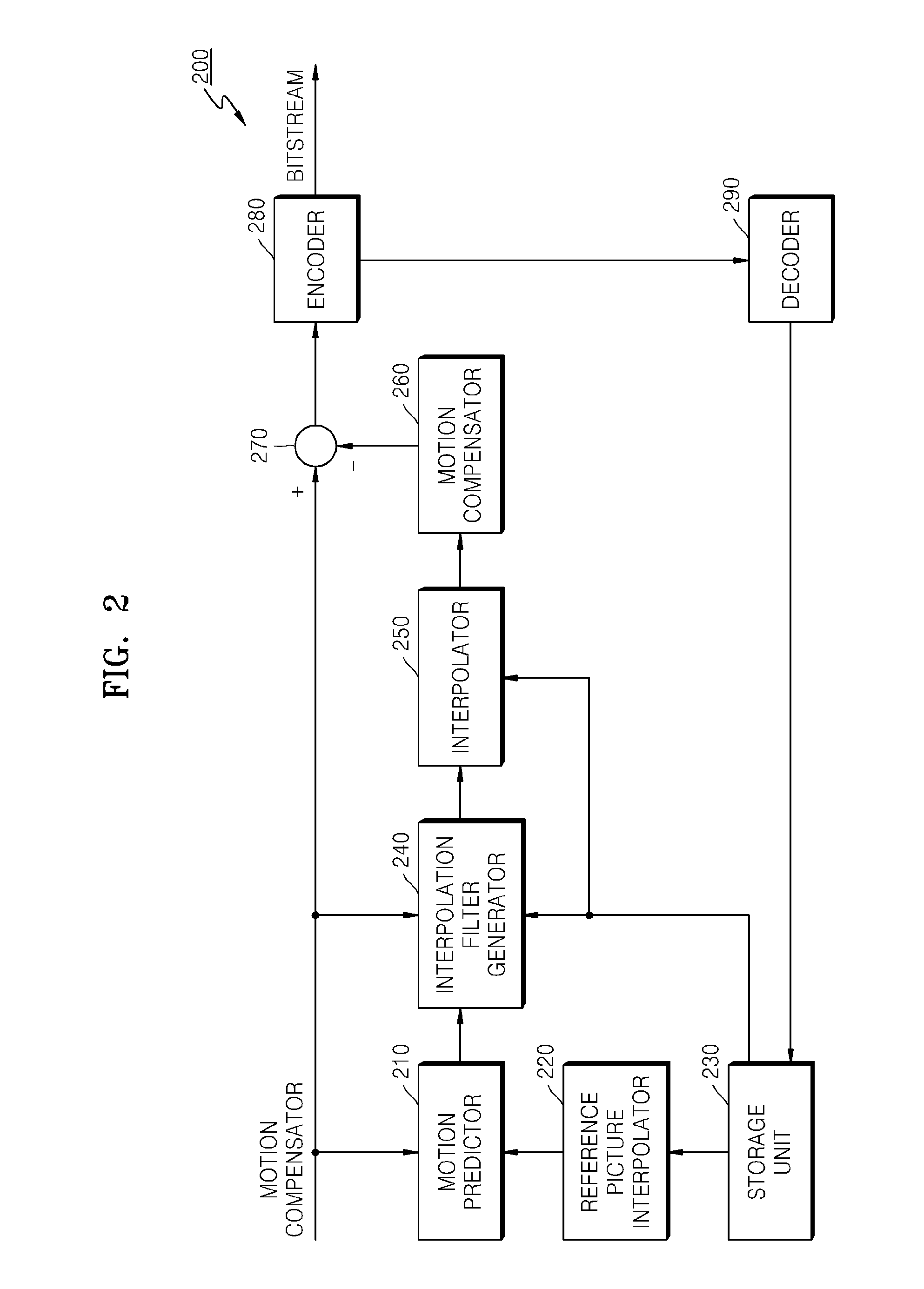
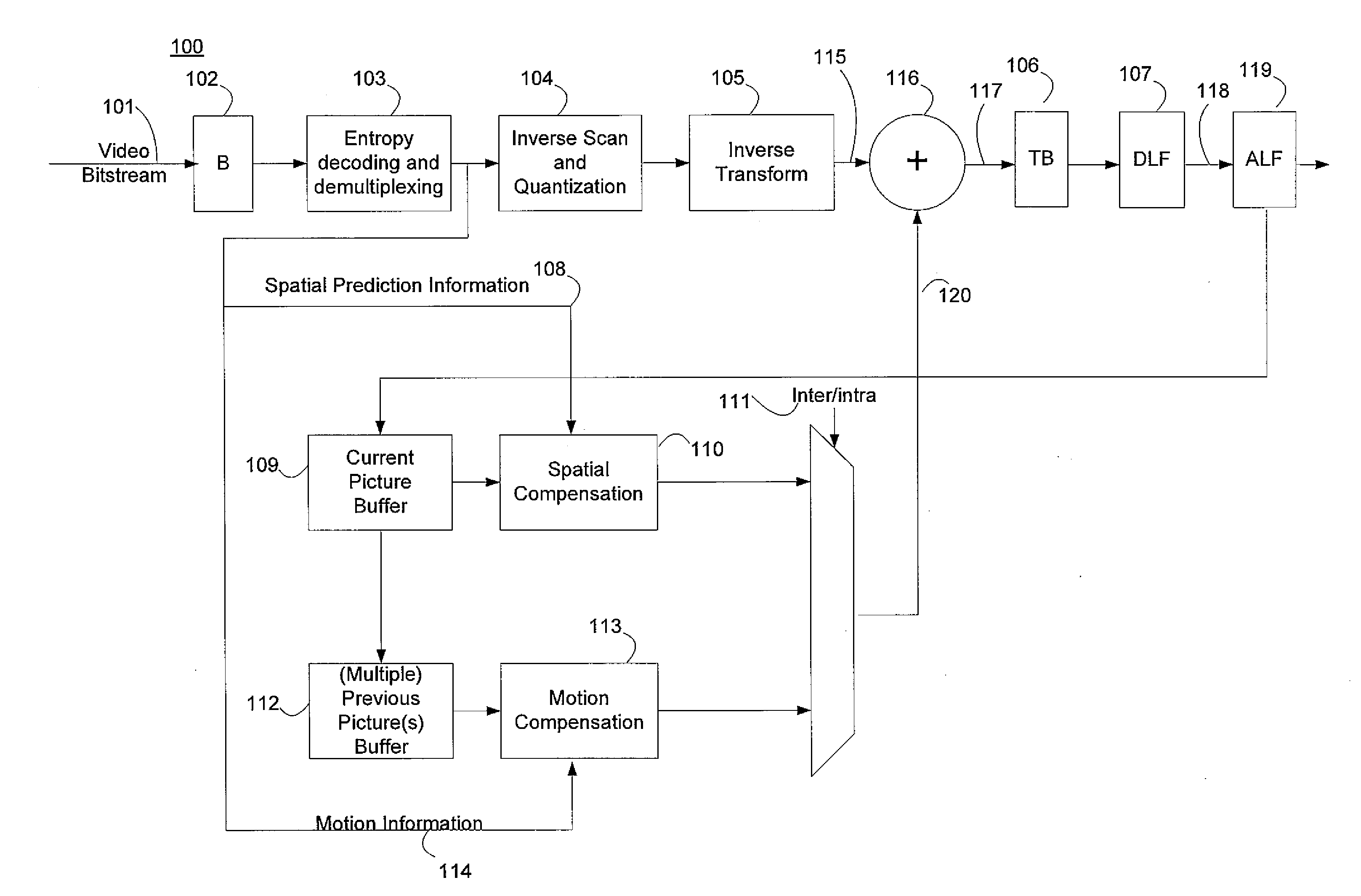
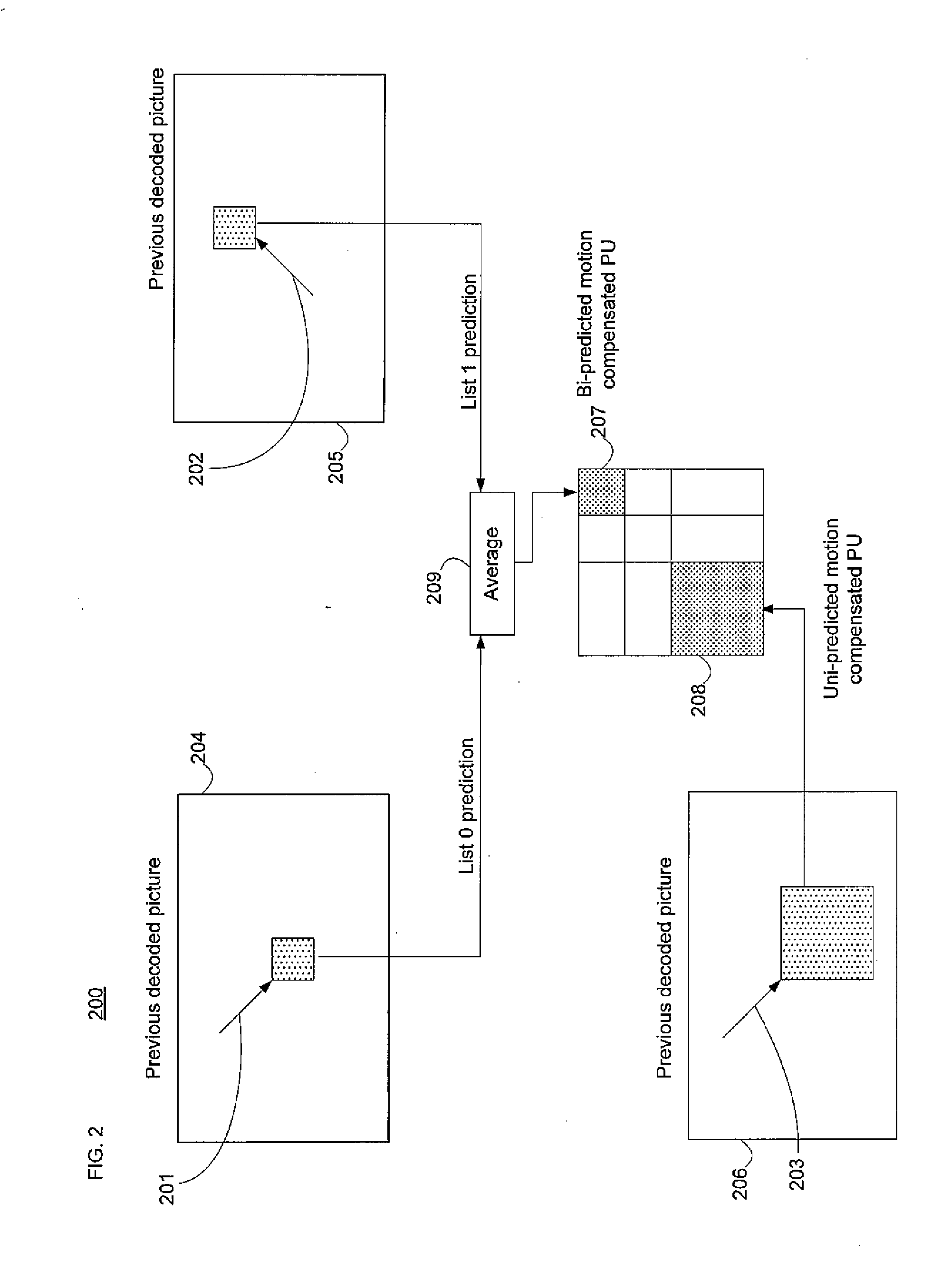
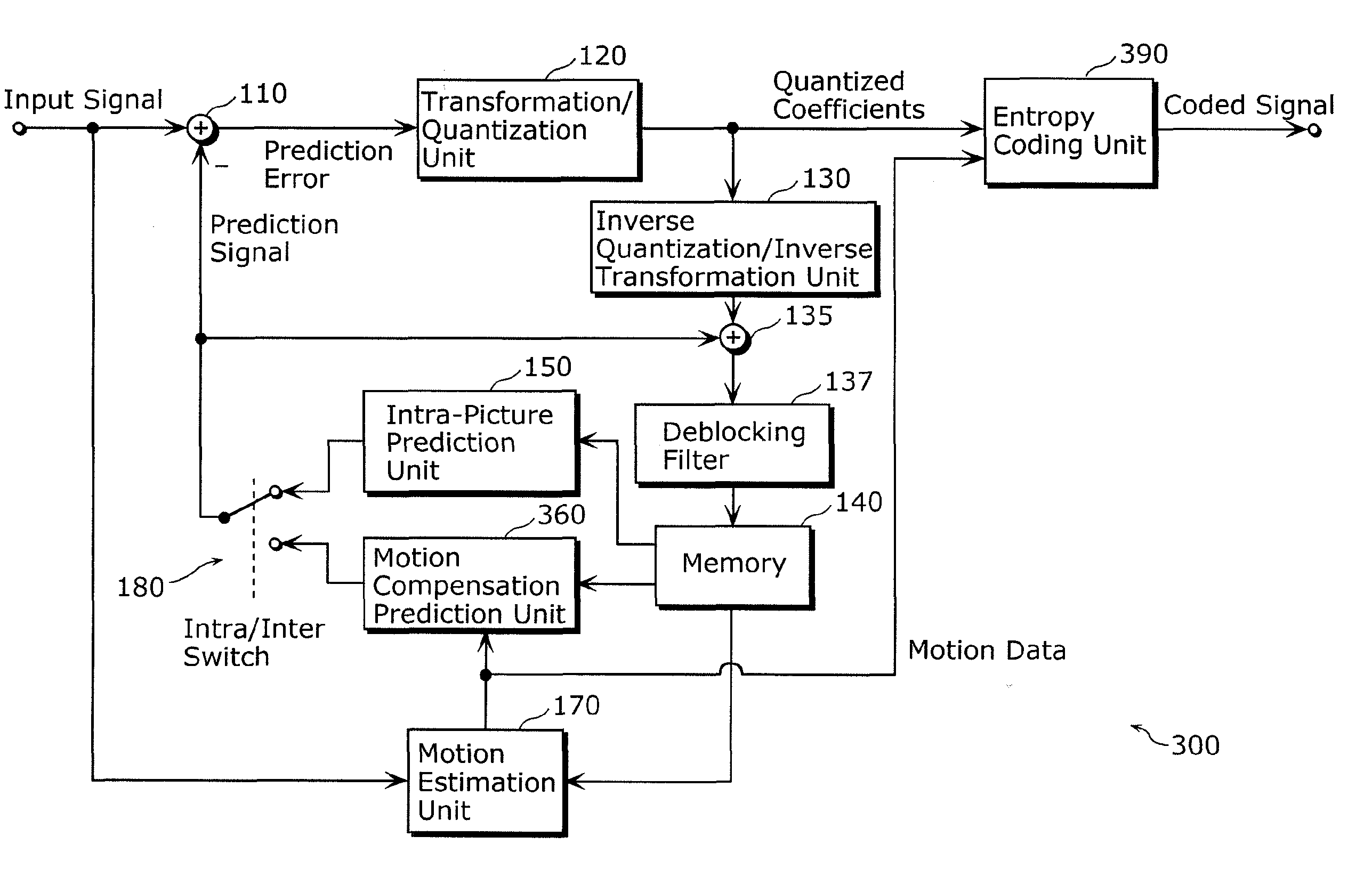
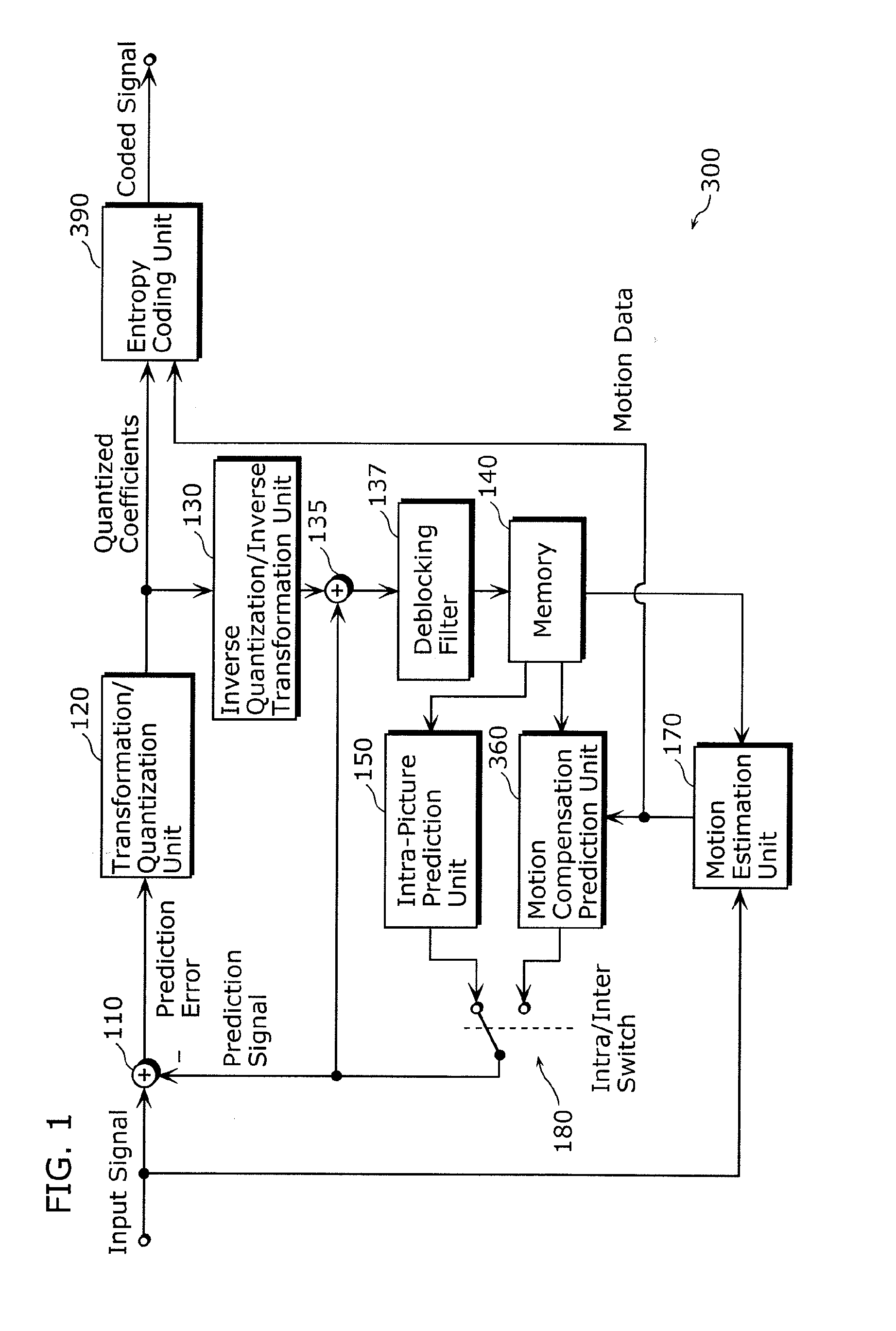
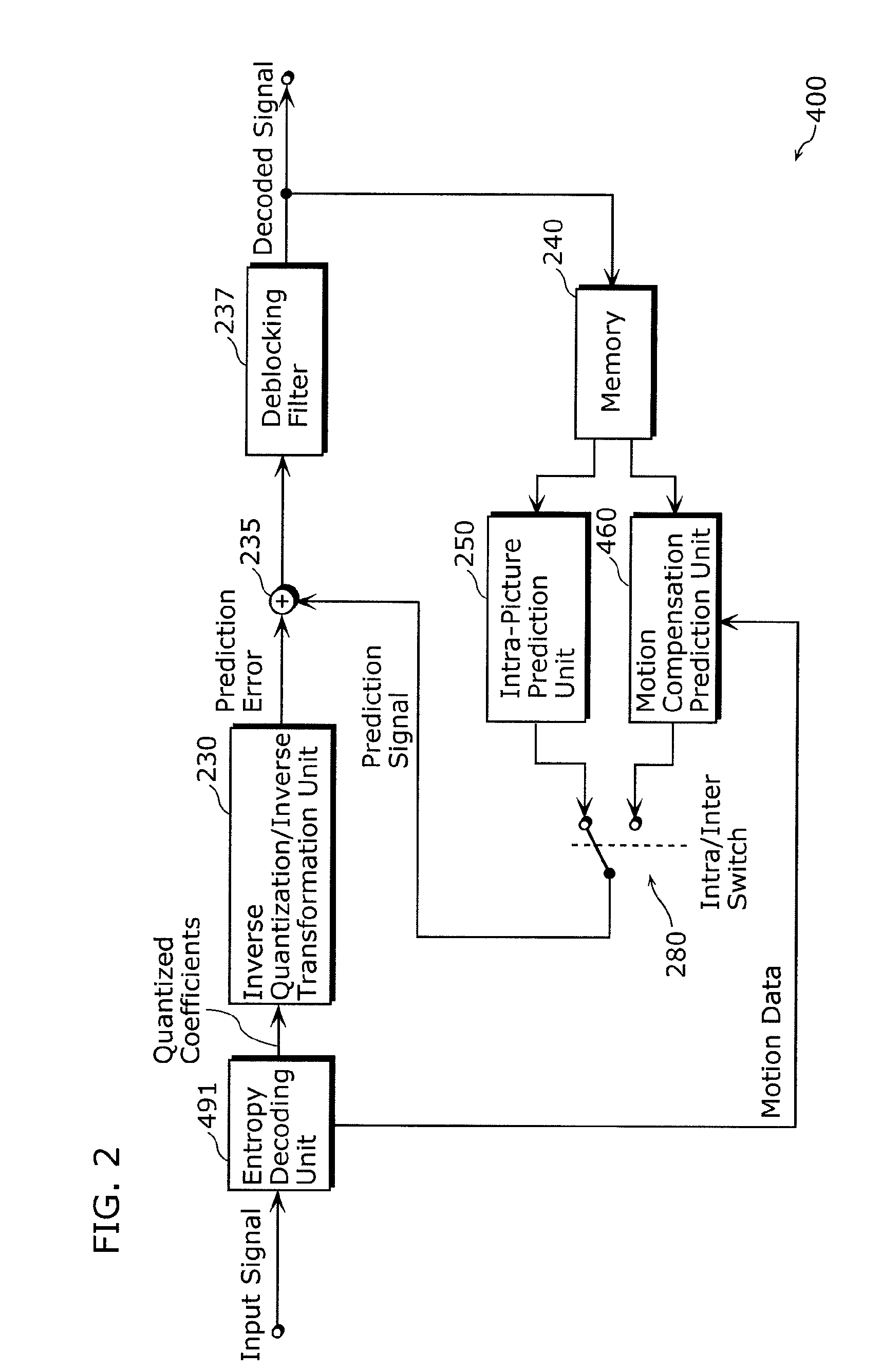
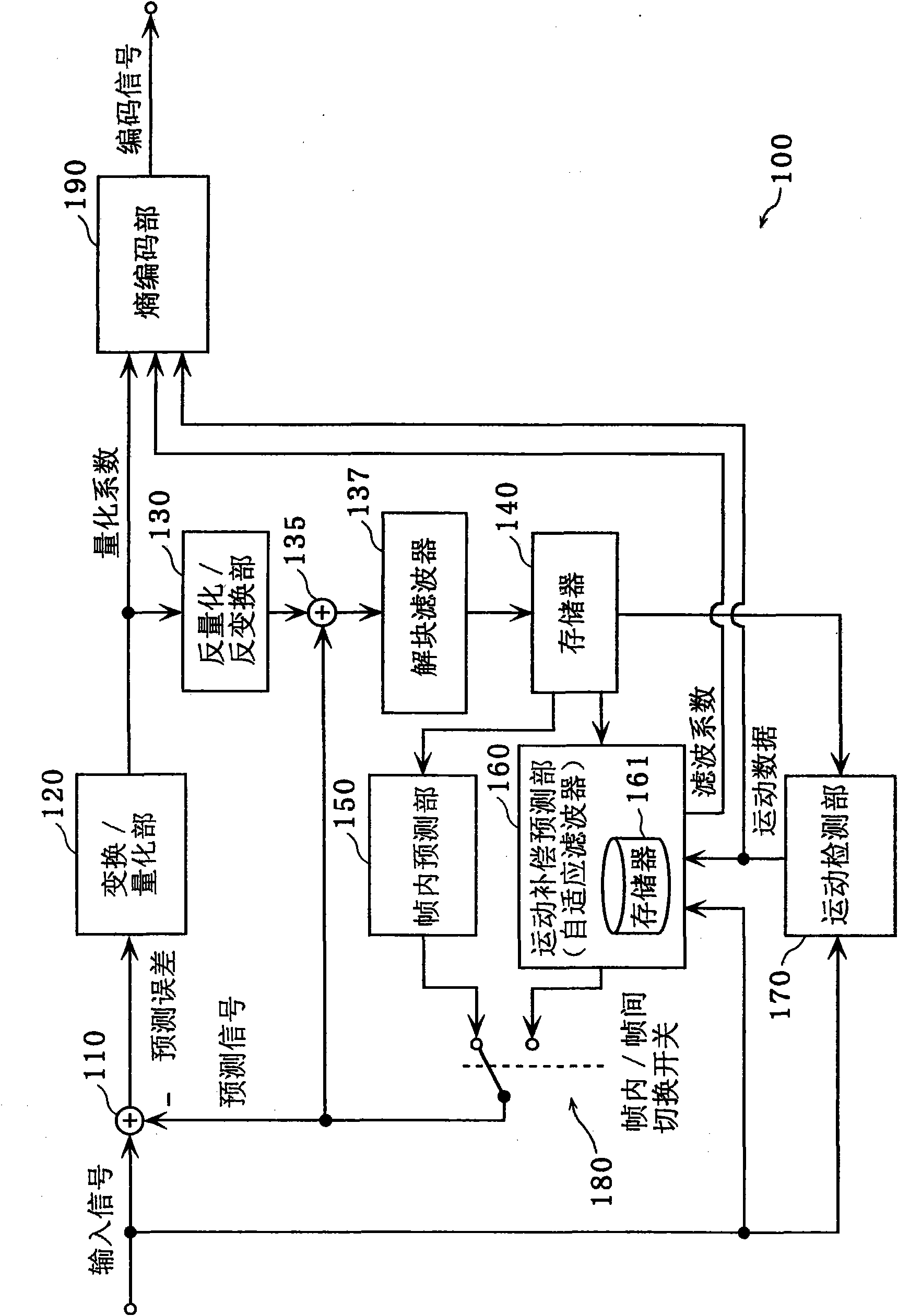
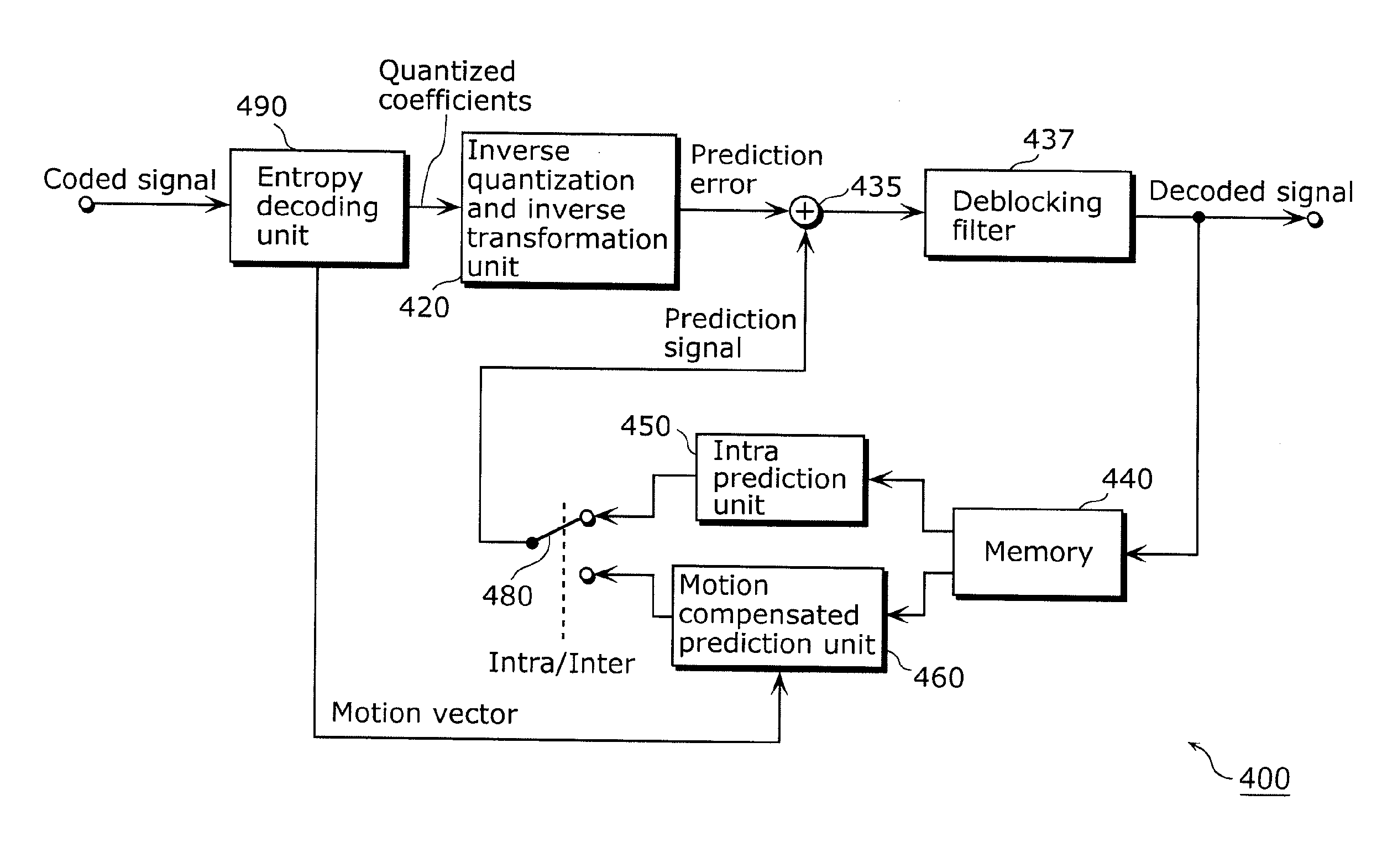
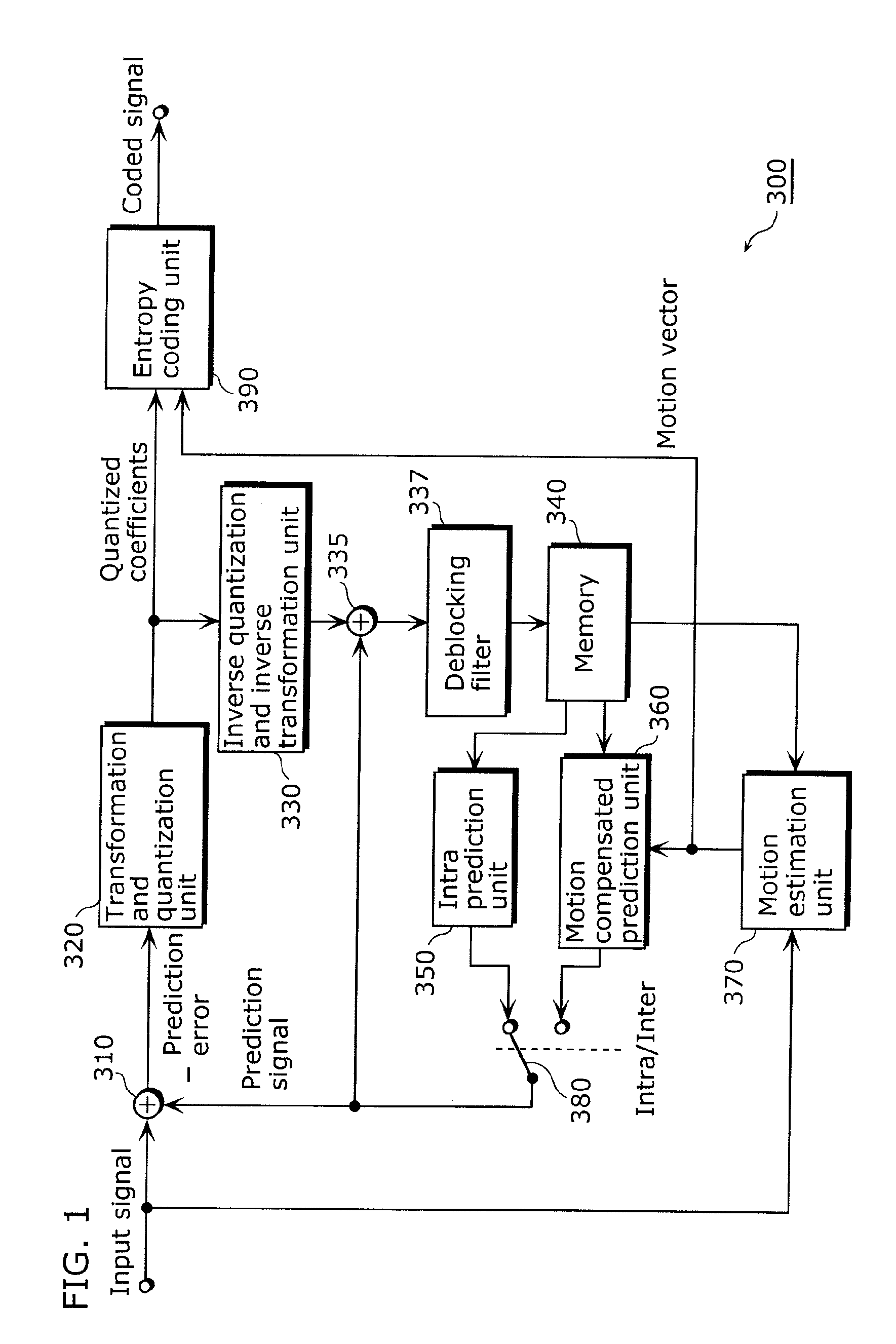
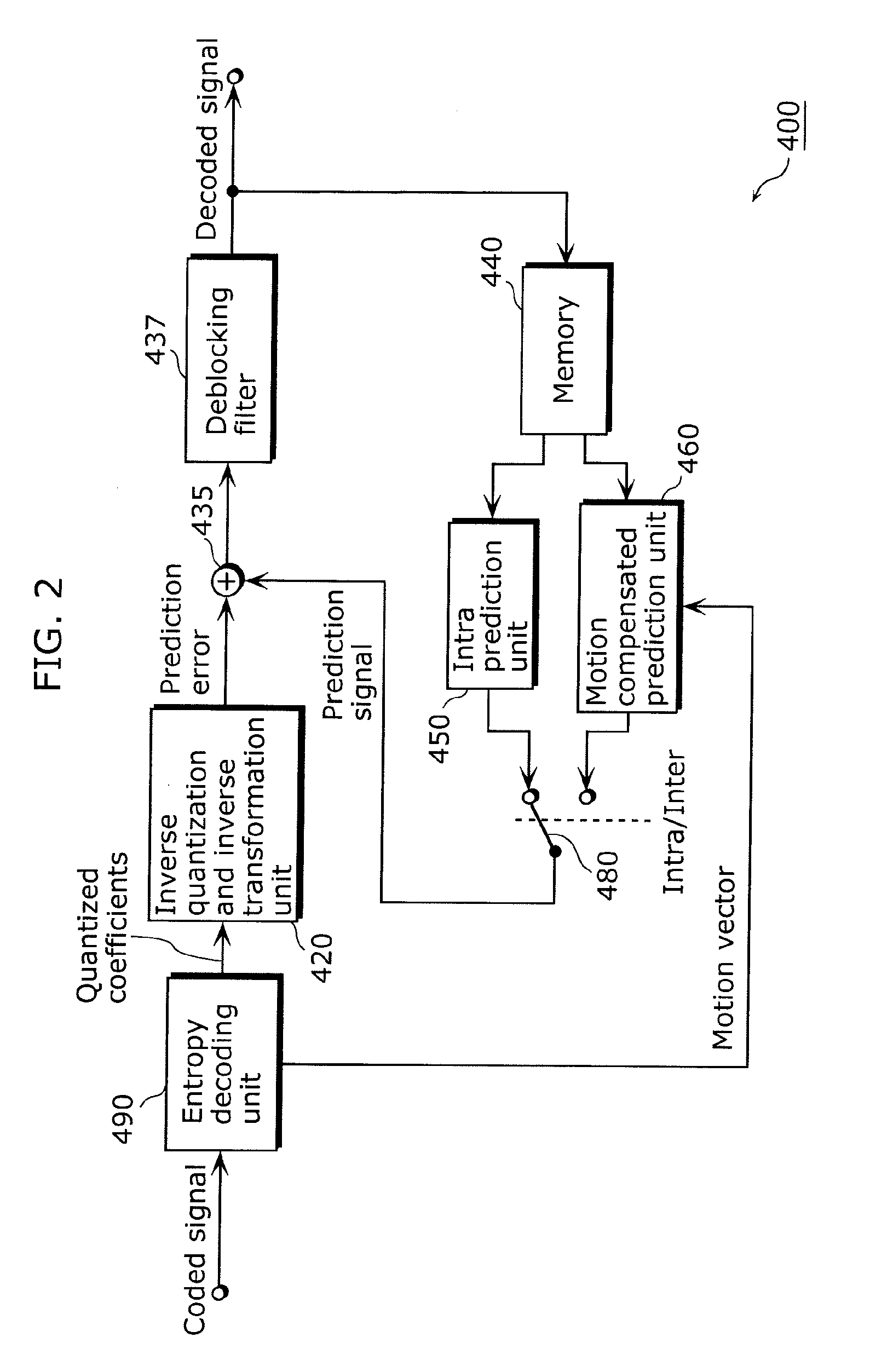
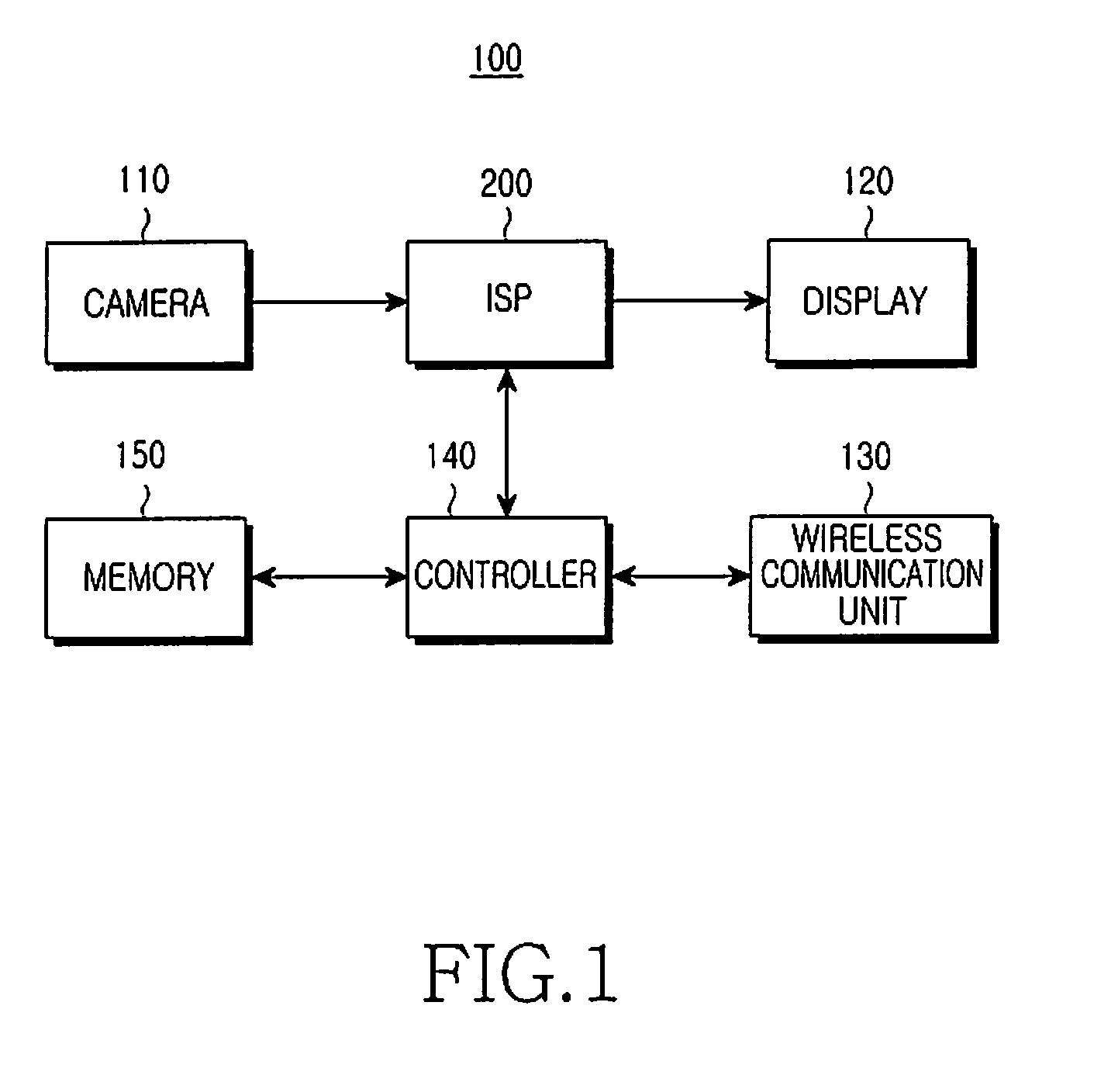
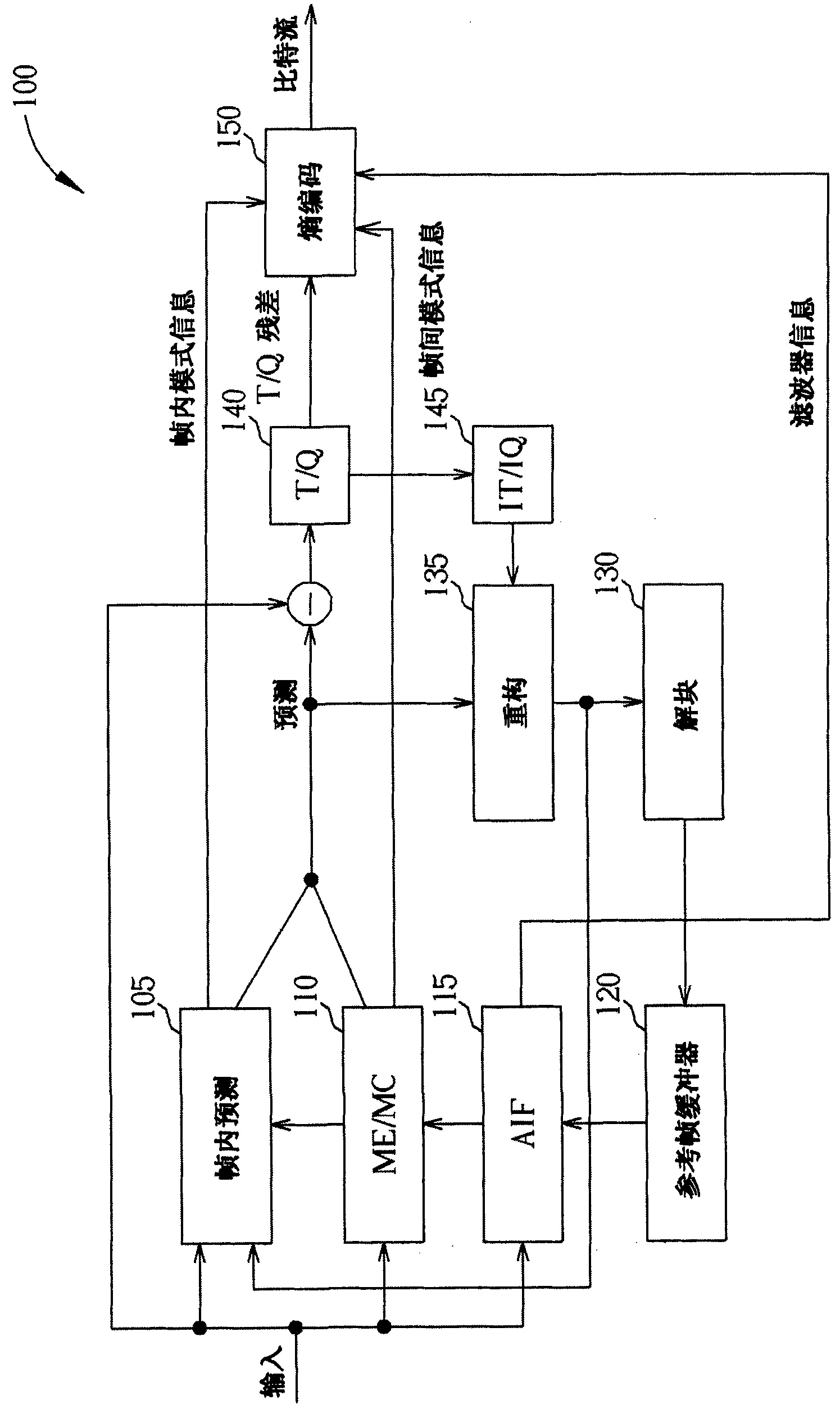
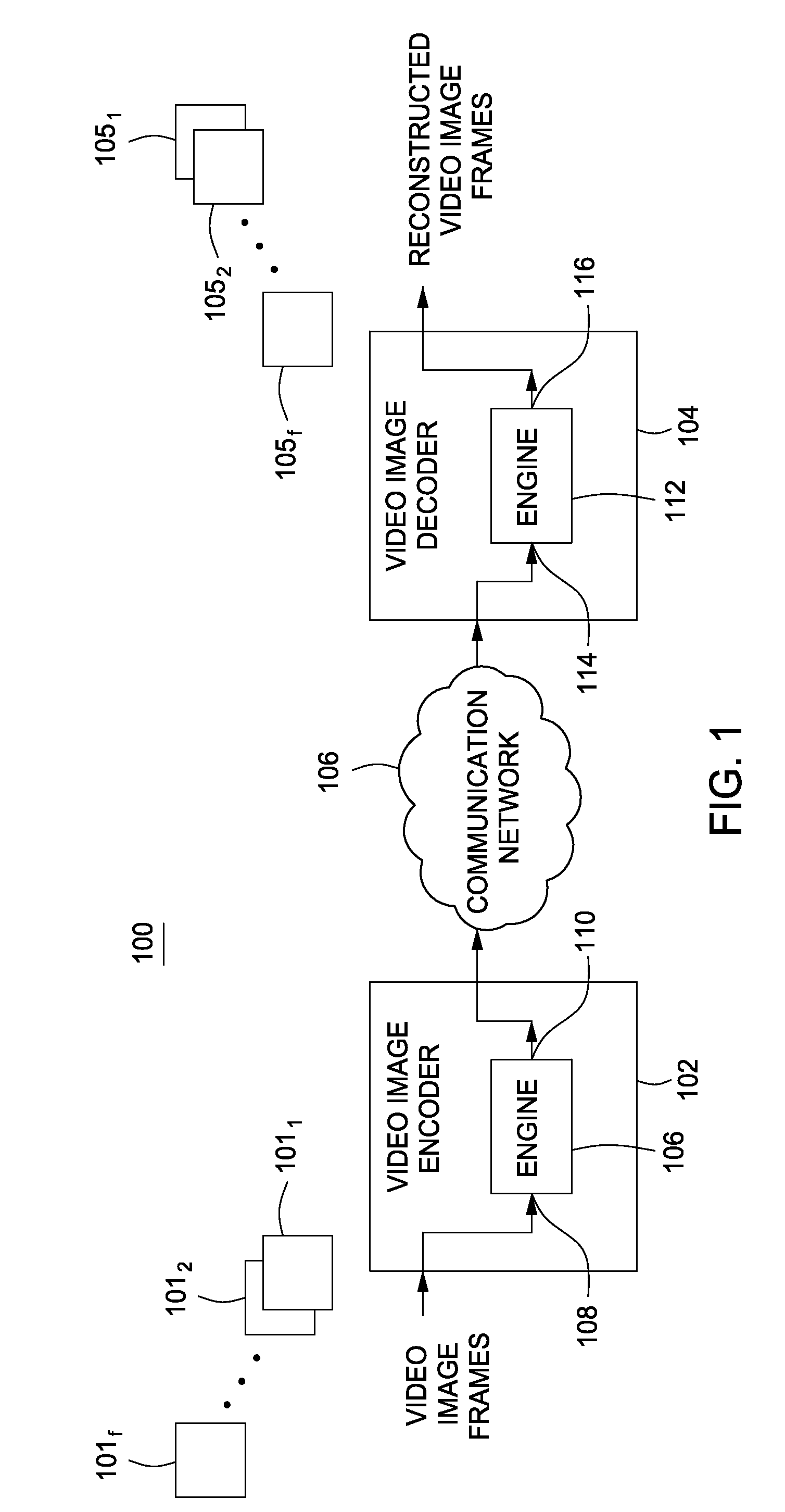
Method and apparatus for video encoding and decoding using adaptive interpolation
ActiveUS20060294171A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingMotion vector
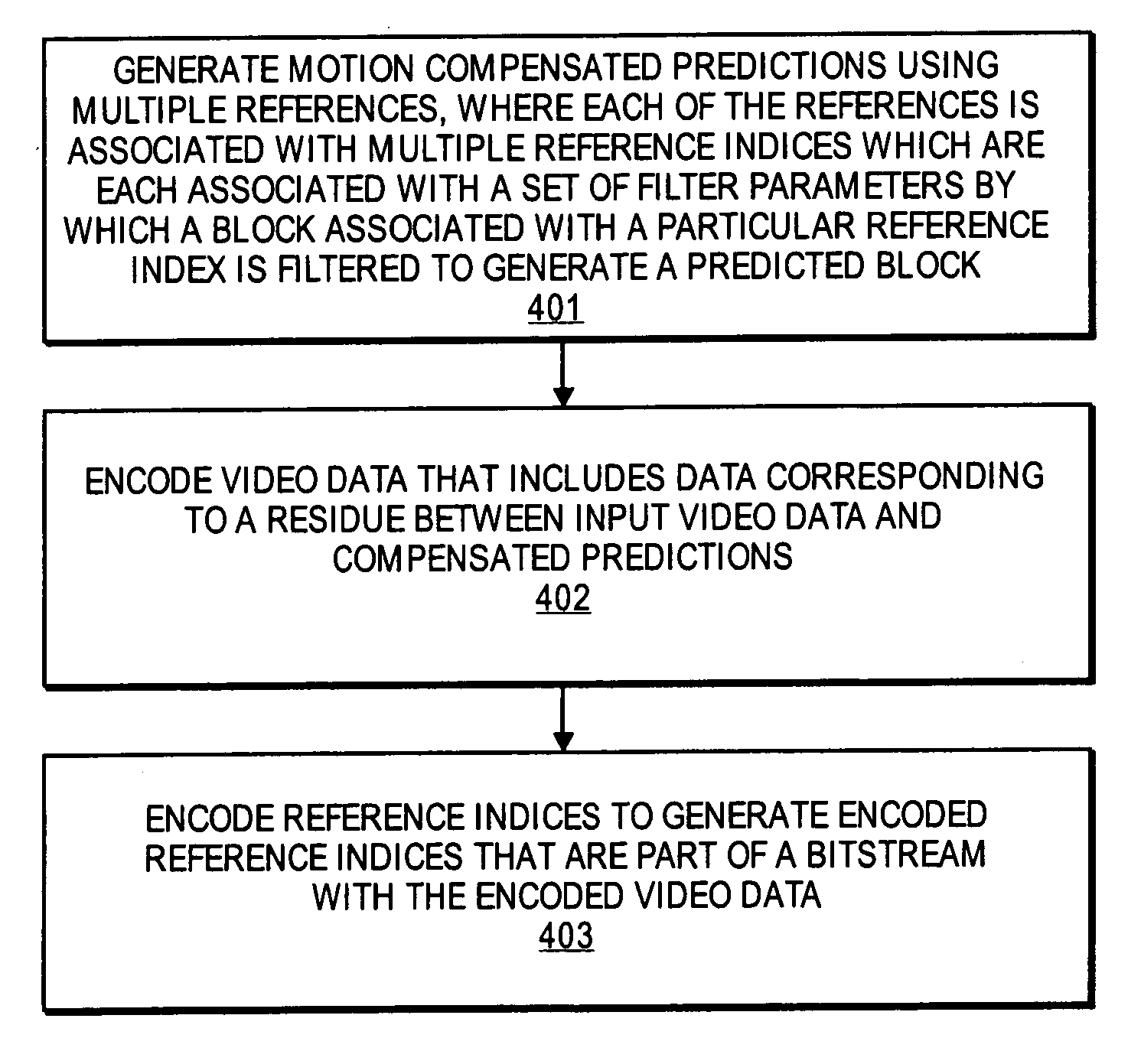
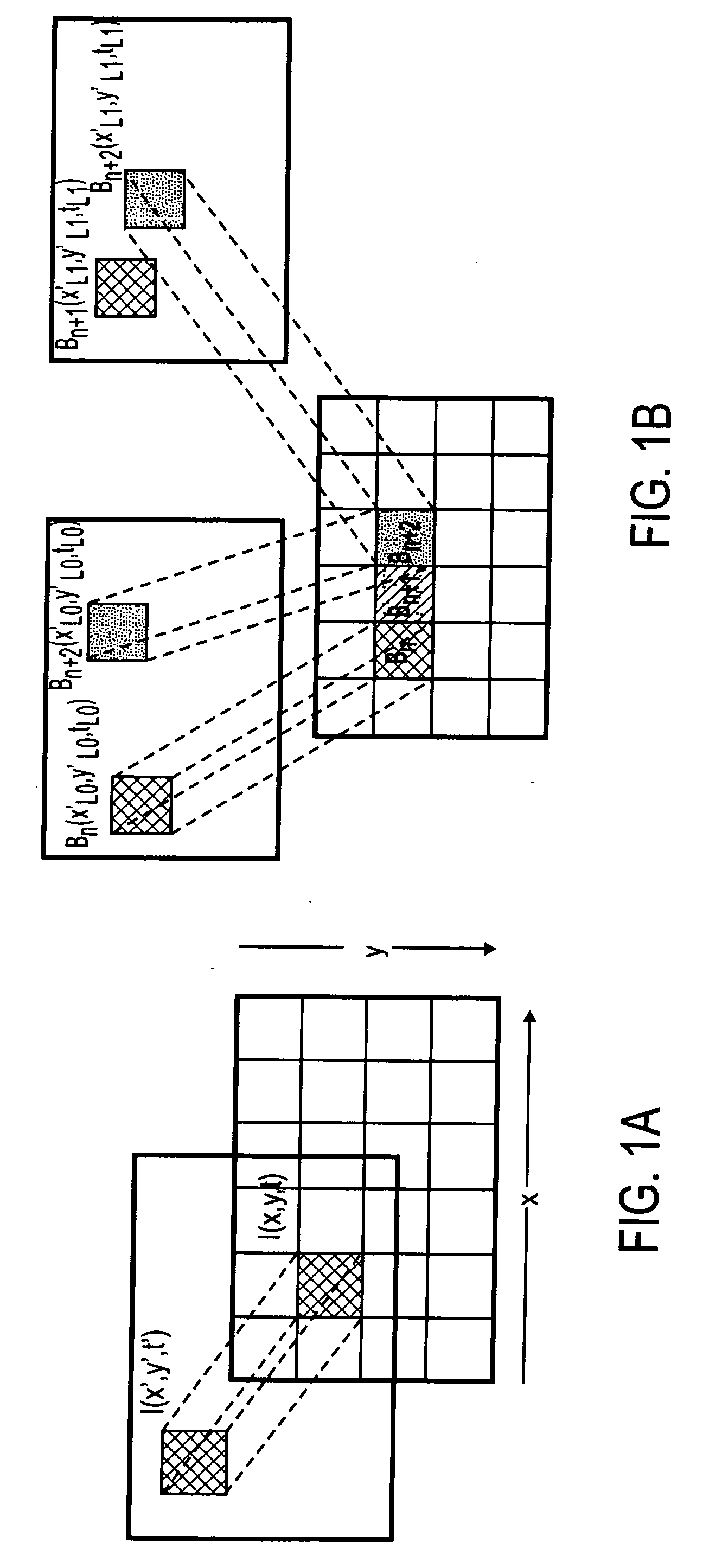
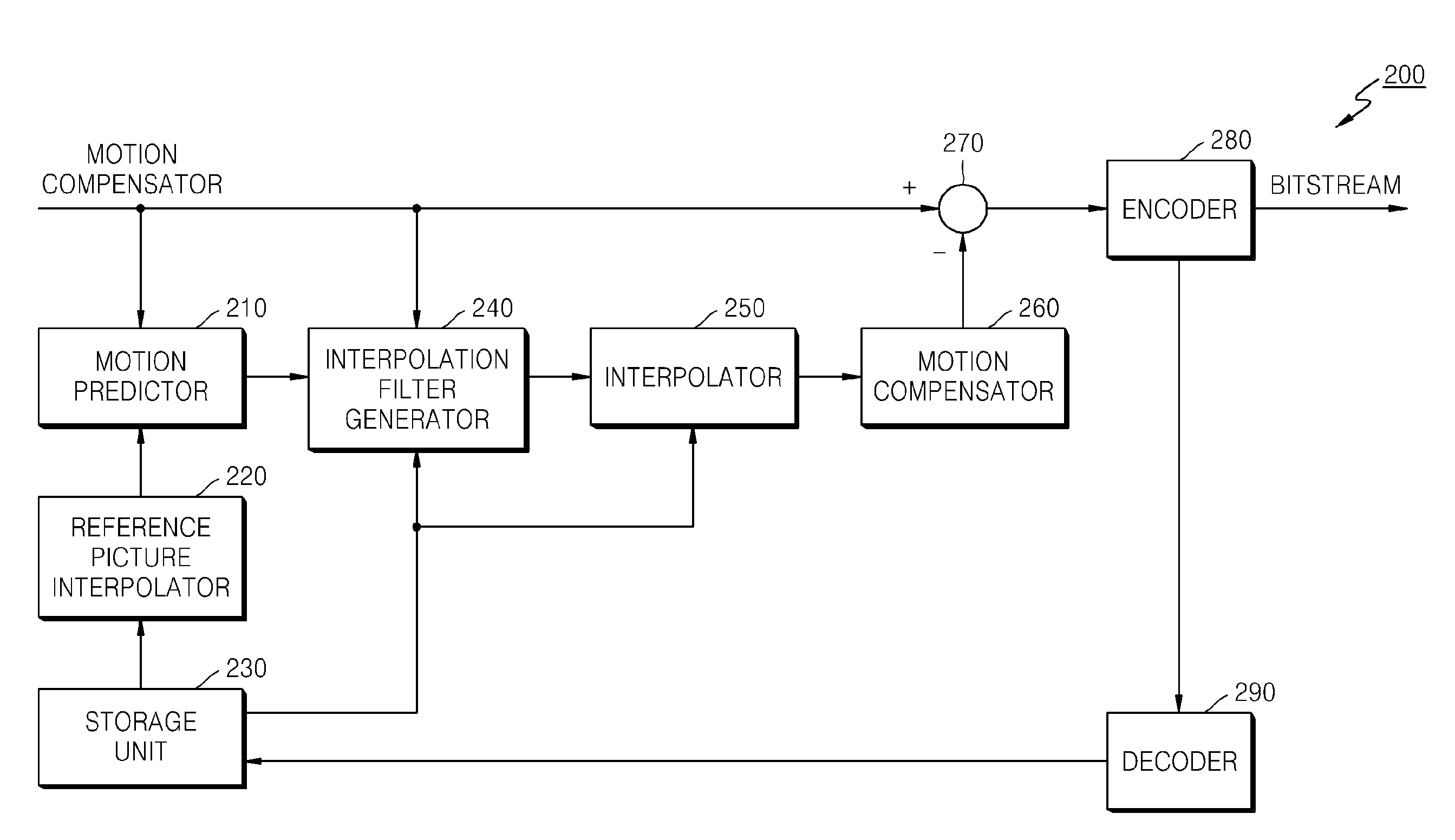
A method and apparatus is disclosed herein for video encoding and / or decoding using adaptive interpolation is described. In one embodiment, the decoding method comprises decoding a reference index; decoding a motion vector; selecting a reference frame according to the reference index; selecting a filter according to the reference index; and filtering a set of samples of the reference frame using the filter to obtain the predicted block, wherein the set of samples of the reference frame is determined by the motion vector.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
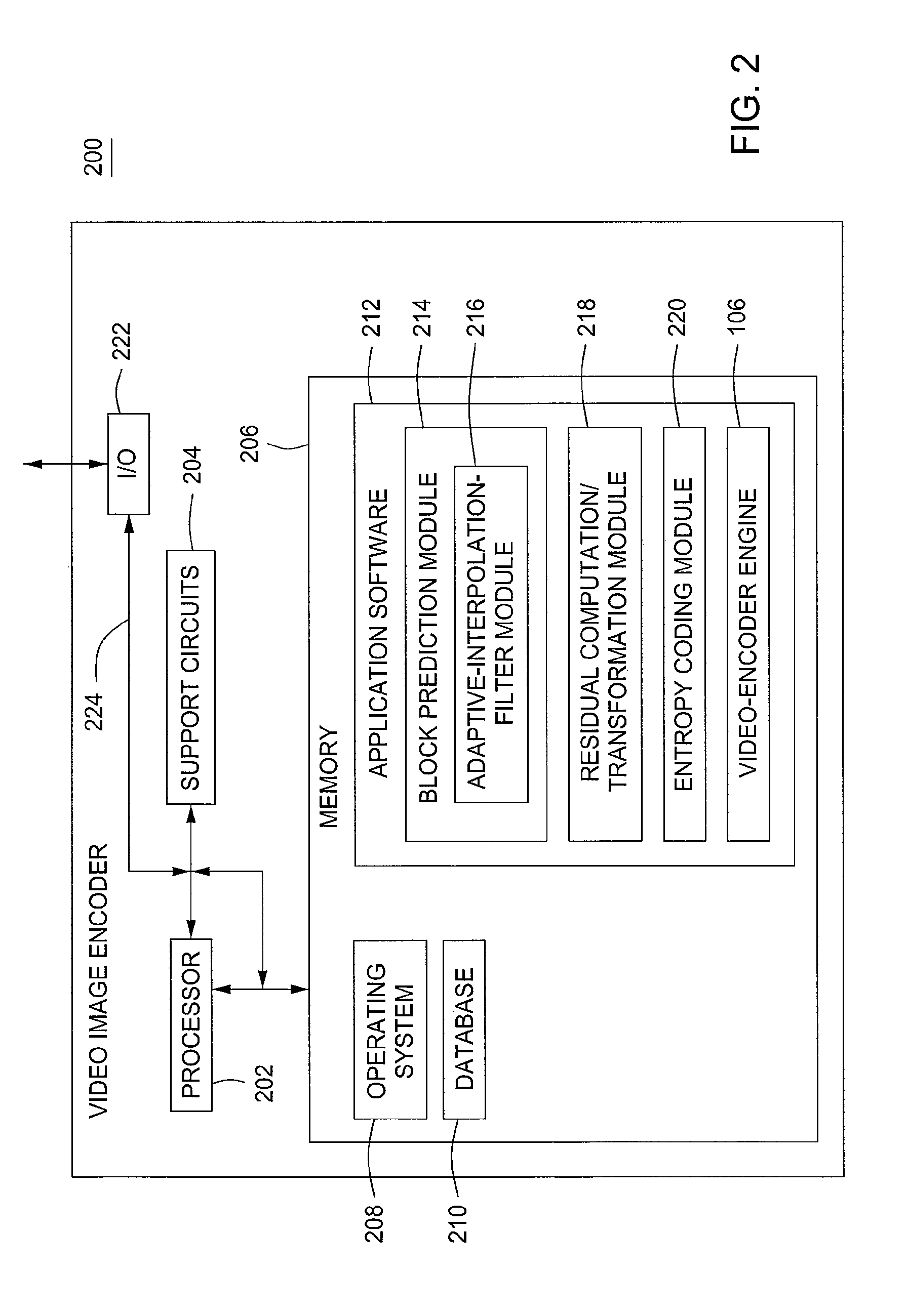
Method and apparatus for encoding and decoding image using adaptive interpolation filter
InactiveUS20080175322A1Minimize the differenceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDecoding methodsImage resolution
Provided are an image encoding method and apparatus for generating an interpolation filter using an adjacent area of a current block and a corresponding adjacent area of a reference picture and interpolating the reference picture using the generated interpolation filter, and an image decoding method and apparatus therefor. By interpolating an adjacent area of a reference picture corresponding to an adjacent area of a current block according to fractional pixel resolution of a motion vector of the current block and determining interpolation filter coefficients to minimize a difference between an interpolated adjacent area of the reference picture and the adjacent area of the current block, an interpolation filter needed for motion compensation of the current block is adaptively generated using information on the adjacent area.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
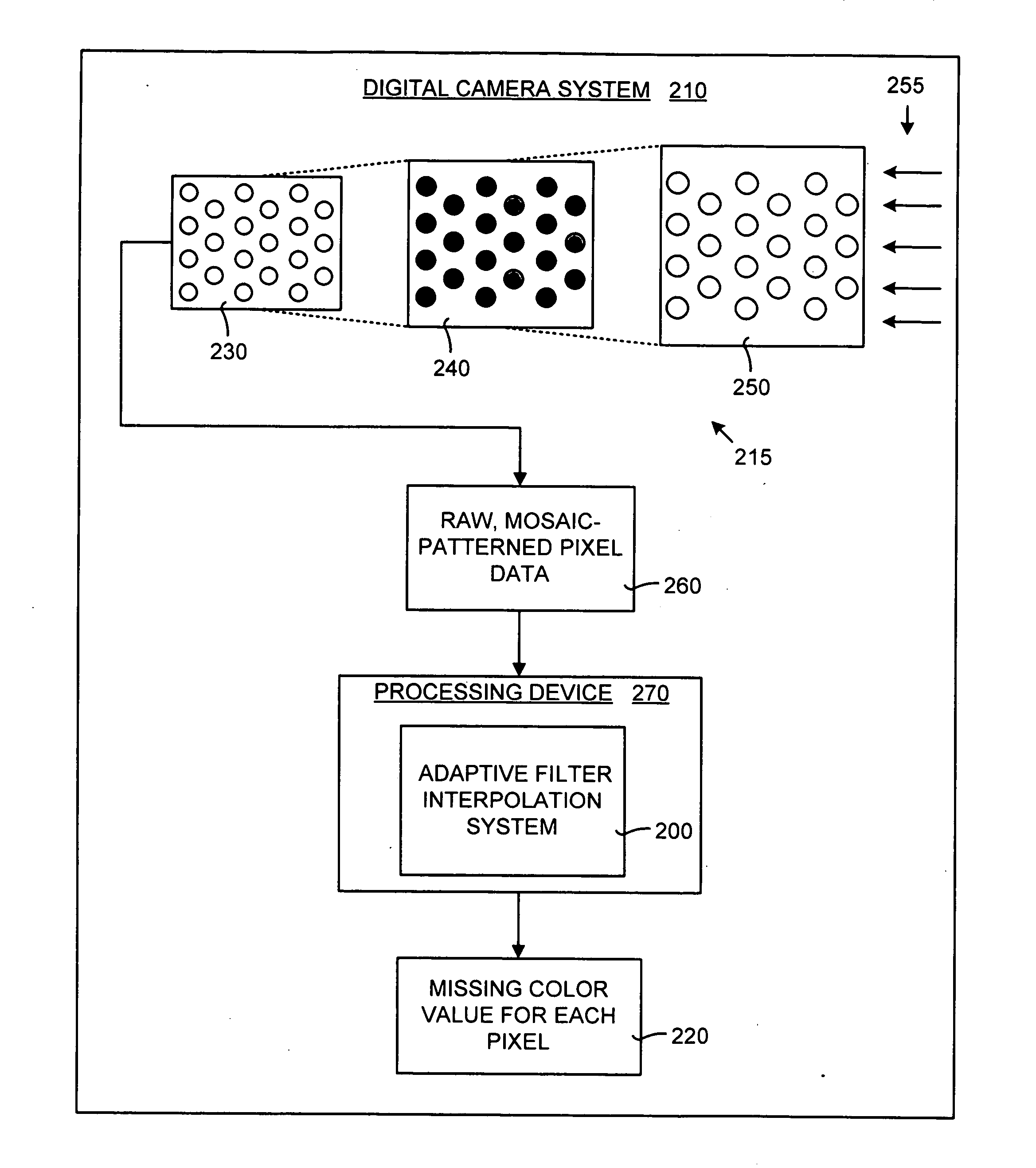
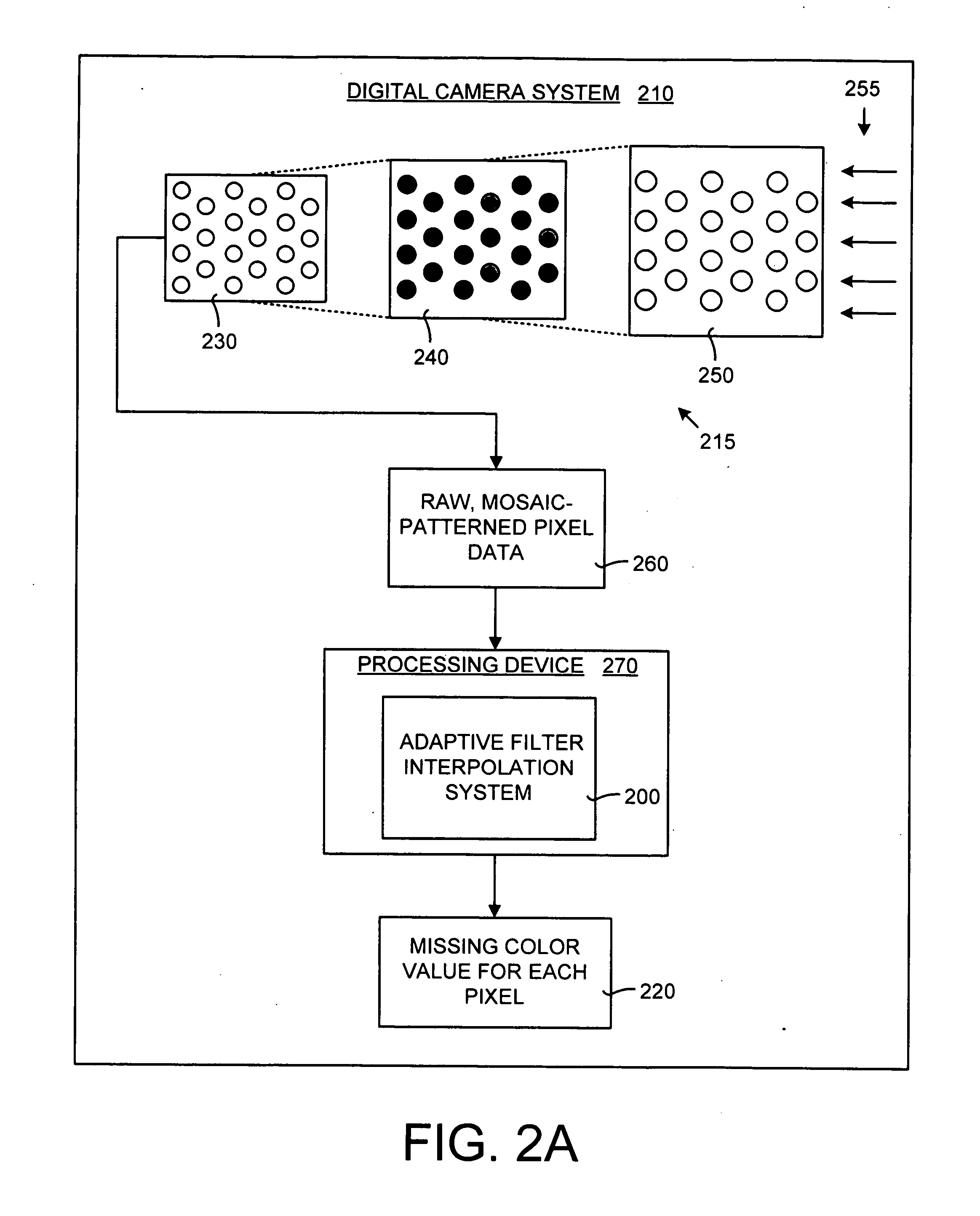
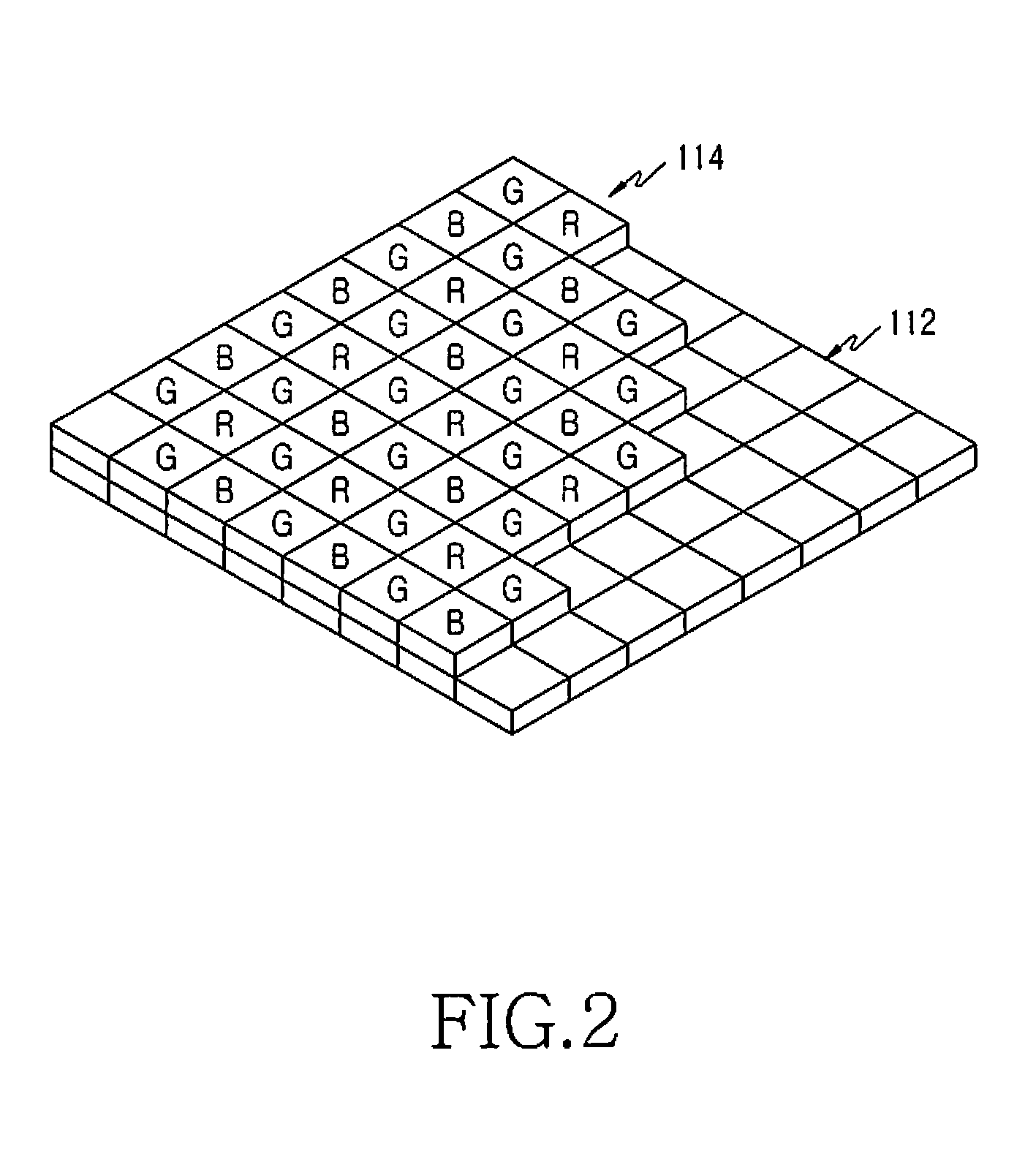
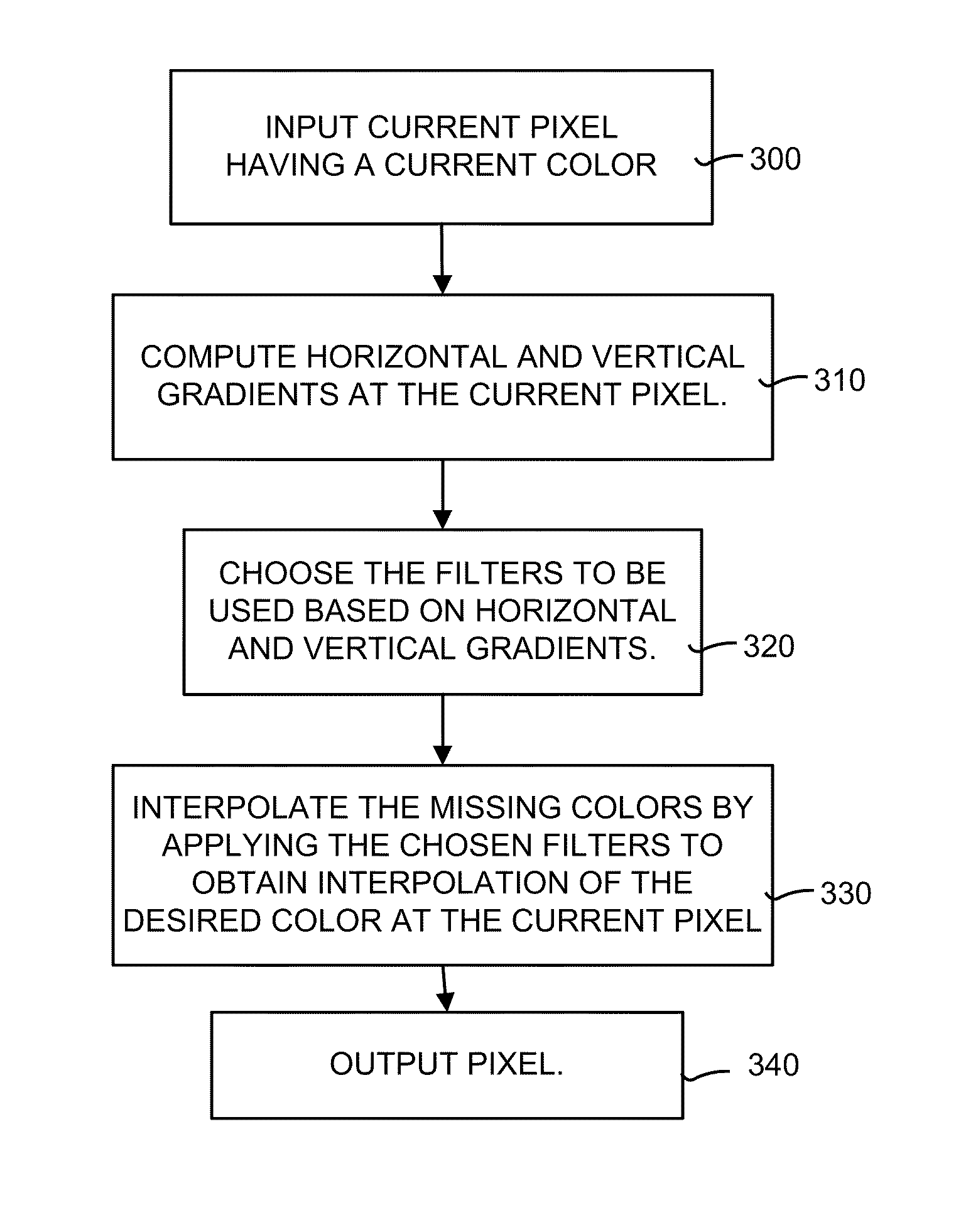
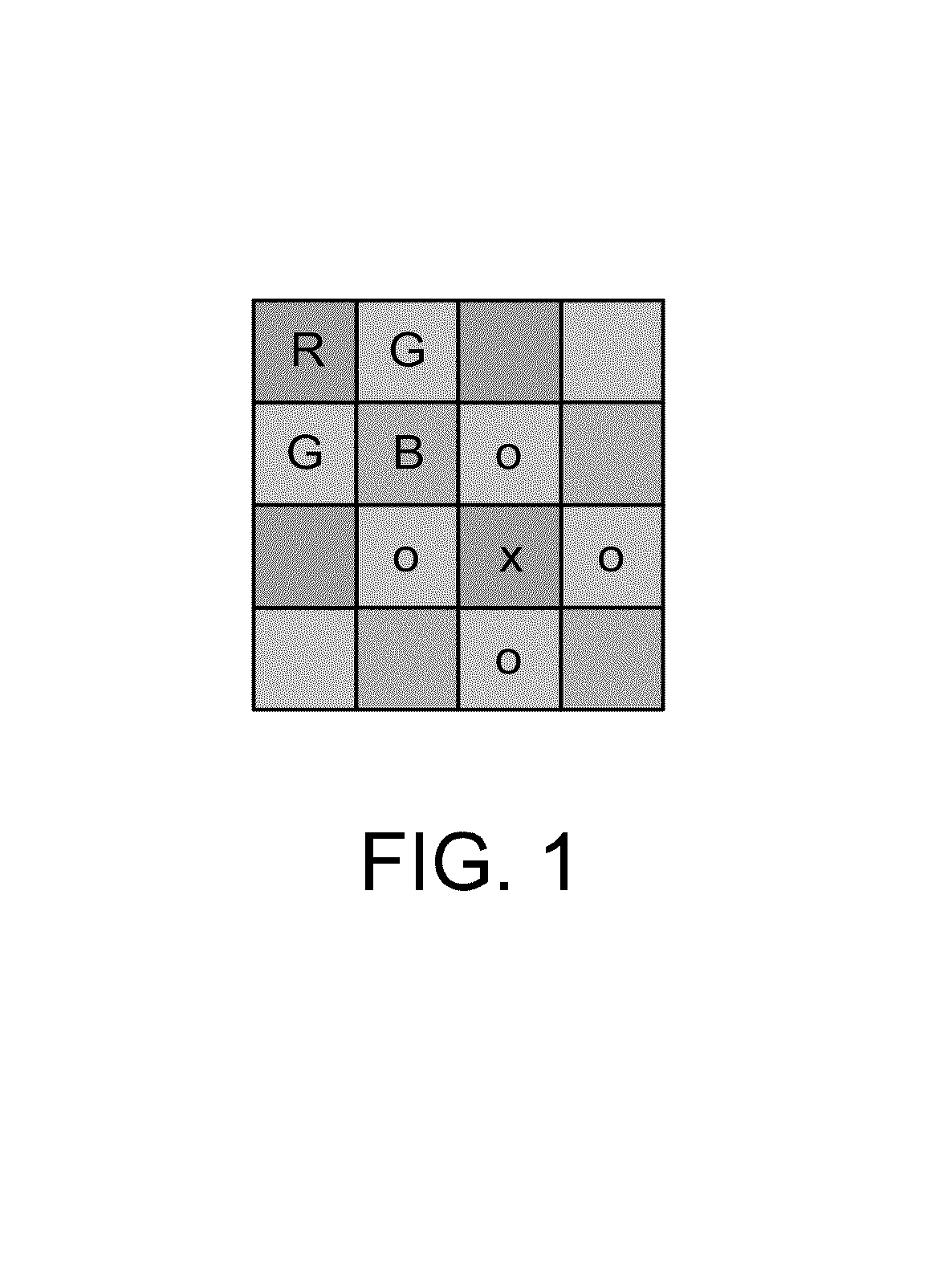
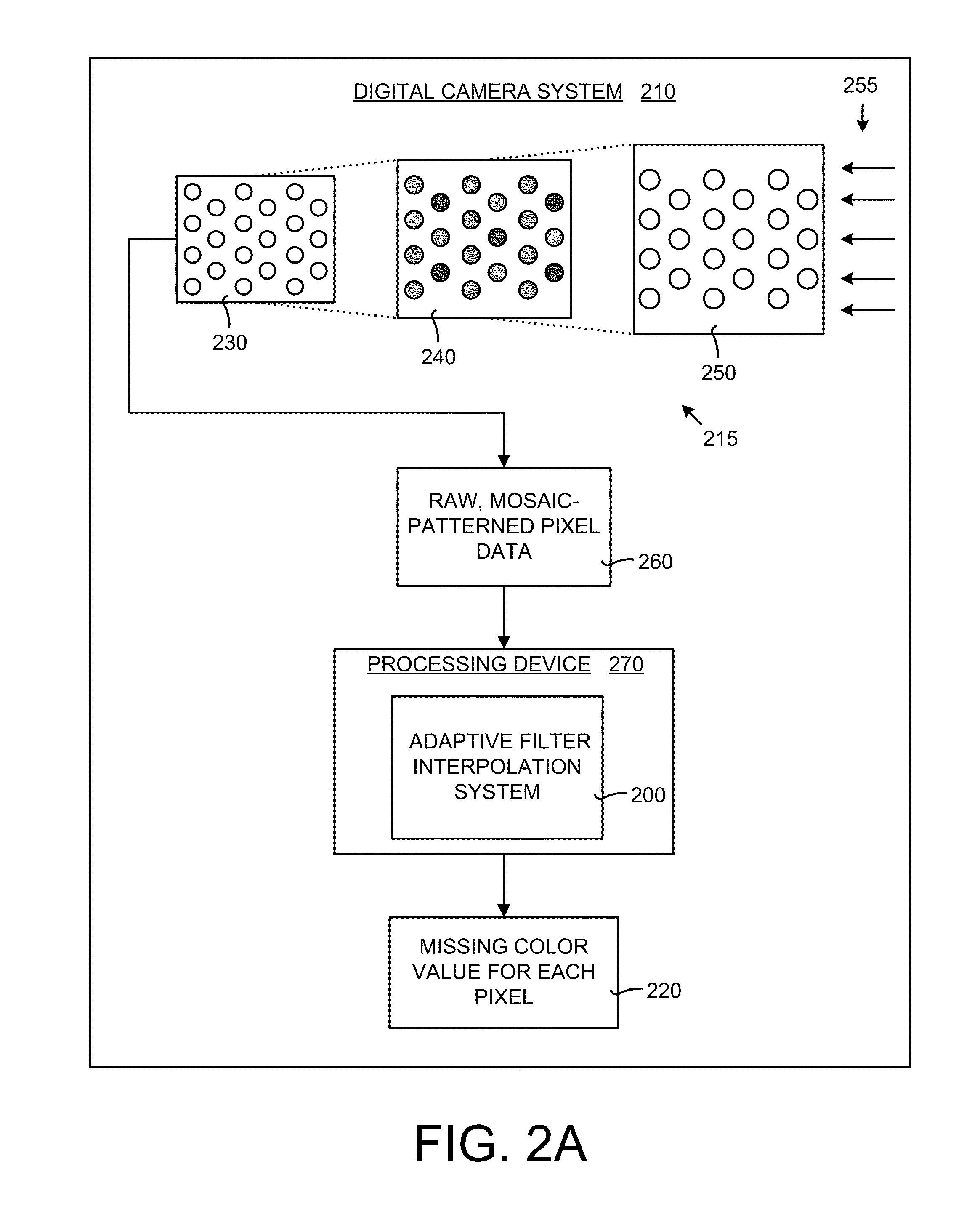
System and method for adaptive interpolation of images from patterned sensors
ActiveUS20050200733A1Computationally efficientImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageGrating
A adaptive filter interpolation method and system for the demosaicing of color images. In general, input pixels are input in a Bayer-mosaiced pattern (only one color per pixel), and output pixels are in full RGB mode (three color values per pixel). For each pixel location, in raster scan order, the processing steps can be summarized as follows. Following a regular raster scanning order (from left to right and top to bottom), for each pixel location horizontal and vertical gradients are first computed (whose computation depends on the available color for that pixel), and from those the appropriate interpolation filters are chosen from a small set of predetermined filters. Then, the chosen filters are applied to interpolate the missing data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
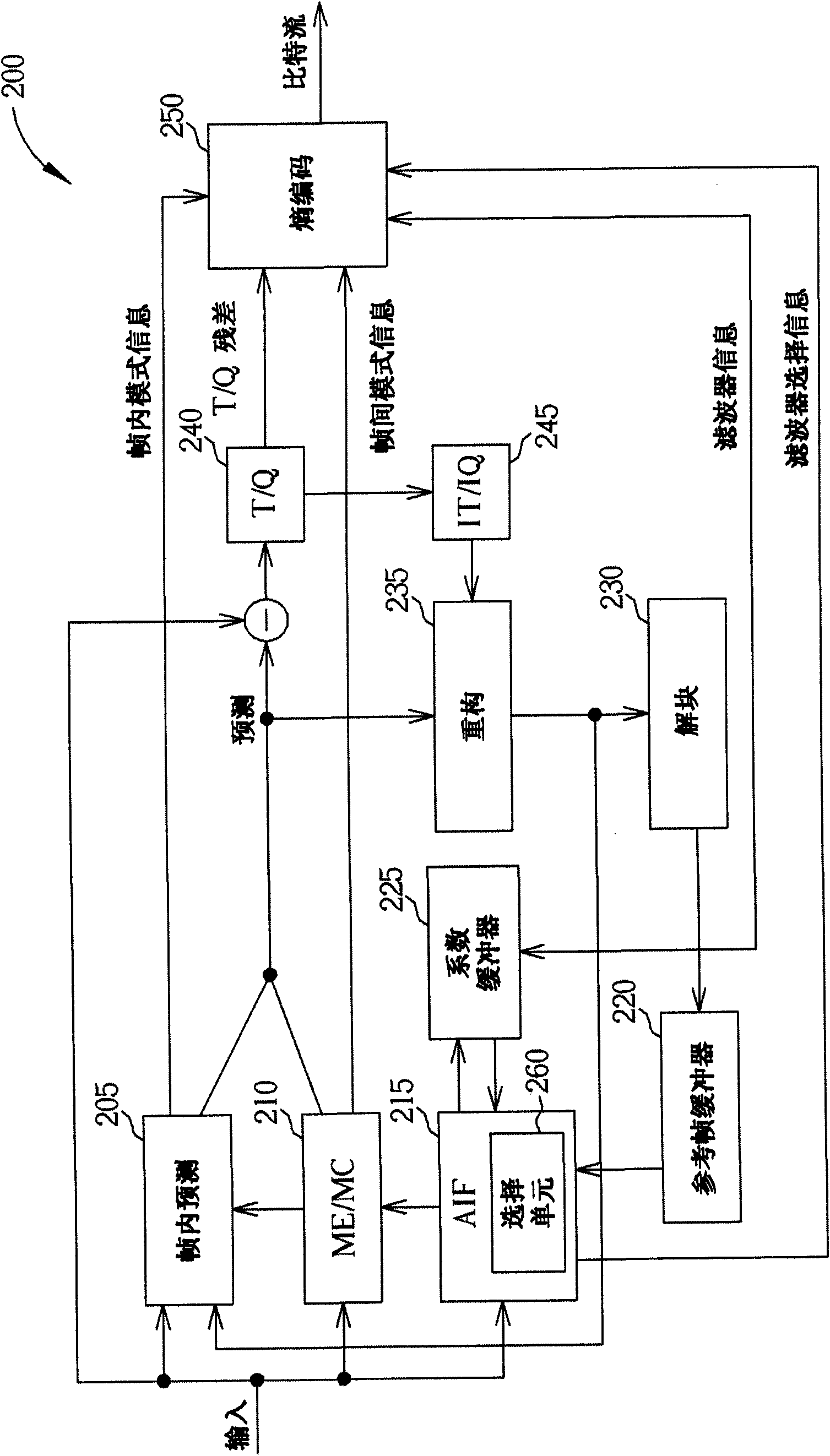
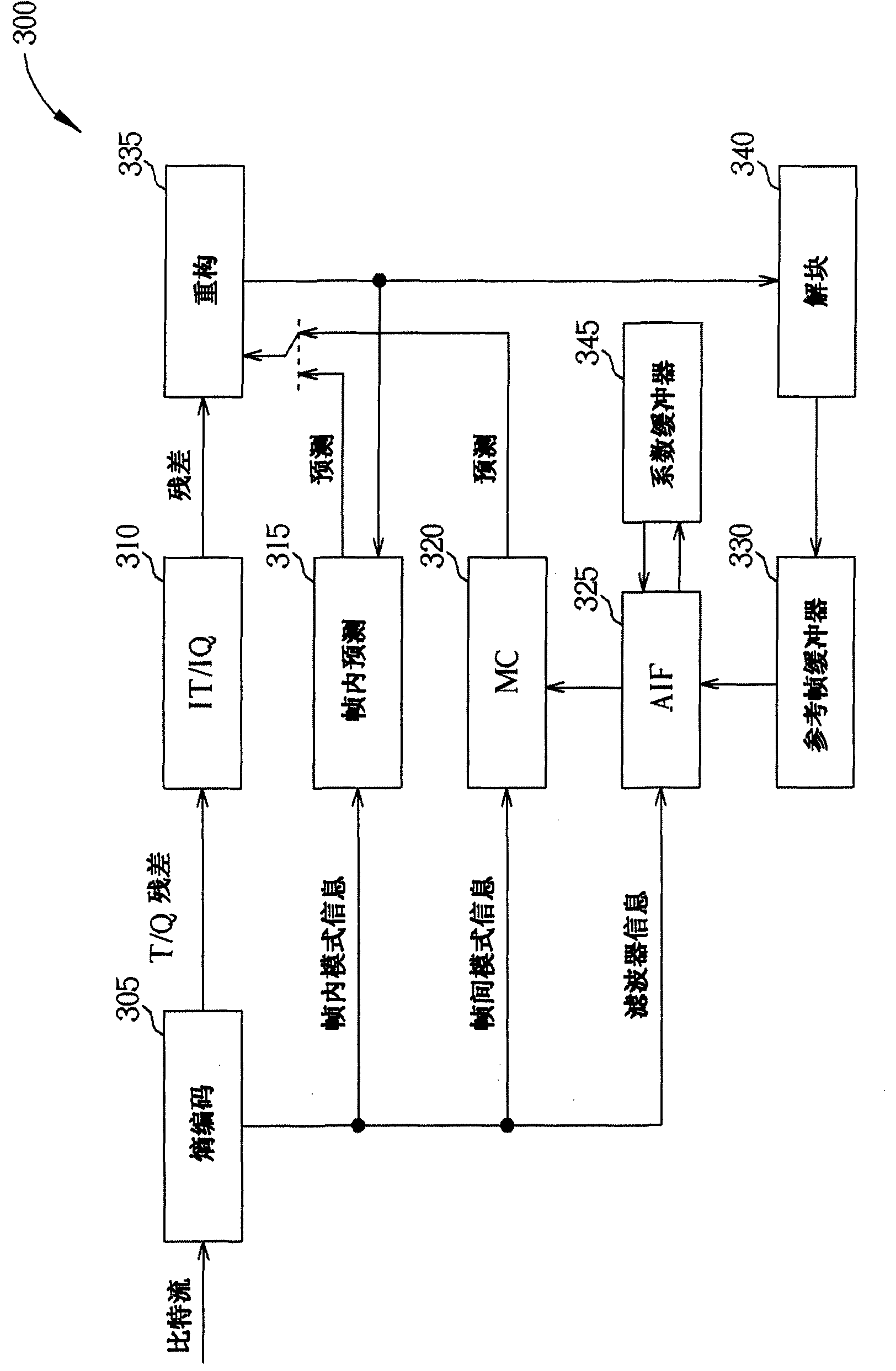
Method and System for Adaptive Interpolation in Digital Video Coding
InactiveUS20120134425A1Improve coding efficiencyReduce memory requirementsColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionDigital video
Disclosed are techniques for adaptive interpolation filtering of luminance and chrominance samples in the context of motion compensation in video encoding or decoding. A two-dimensional interpolation filter of n×m coefficients may be separable, i.e., it may be separated into two one-dimensional filters with m and n coefficients, respectively. The bitstream may include, per video unit and sub-sample position, information indicating whether to use a newly-generated, a cached, or a default filter that may be a separable two-dimensional filter. The information may be structured in a way that takes advantage of the two-dimensional filter being separable. When a newly-generated filter is signalled, the bitstream may contain information pertaining to the characteristics of the newly-generated filter, such as its coefficients. A decoder may fetch this information from the bitstream to create the filters which are applied to samples of the video unit. An encoder may create a bitstream as described.
Owner:KOSSENTINI FAOUZI +4
Video coding method and video decoding method
InactiveUS20100220788A1Improve predictive efficiencyImprove coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSub-pixel resolutionImage resolution
A video coding method and a video coding device can optimize prediction efficiency and coding efficiency.A video coding device (100) codes video data, by performing motion compensation with sub-pel resolution by using an adaptive interpolation filter for calculating a pixel value of a sub pixel for interpolation between full pixels configuring an input image included in the video data. The video coding device (100) includes: a motion compensation unit (160) that (i) sets a filter property for an adaptive interpolation filter on a predetermined process unit basis, and determining, for each of sub-pel positions relative to a full pixel, a plurality of filter coefficients of the adaptive interpolation filter having the set filter property, and (ii) performs the motion compensation with sub-pel resolution, by applying the adaptive interpolation filter having the determined filter coefficients to the input image; and a subtraction unit (110) that generates a prediction error, by subtracting, from the input image, a prediction image generated in the motion compensation; and a coding unit (190) that codes the prediction error.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
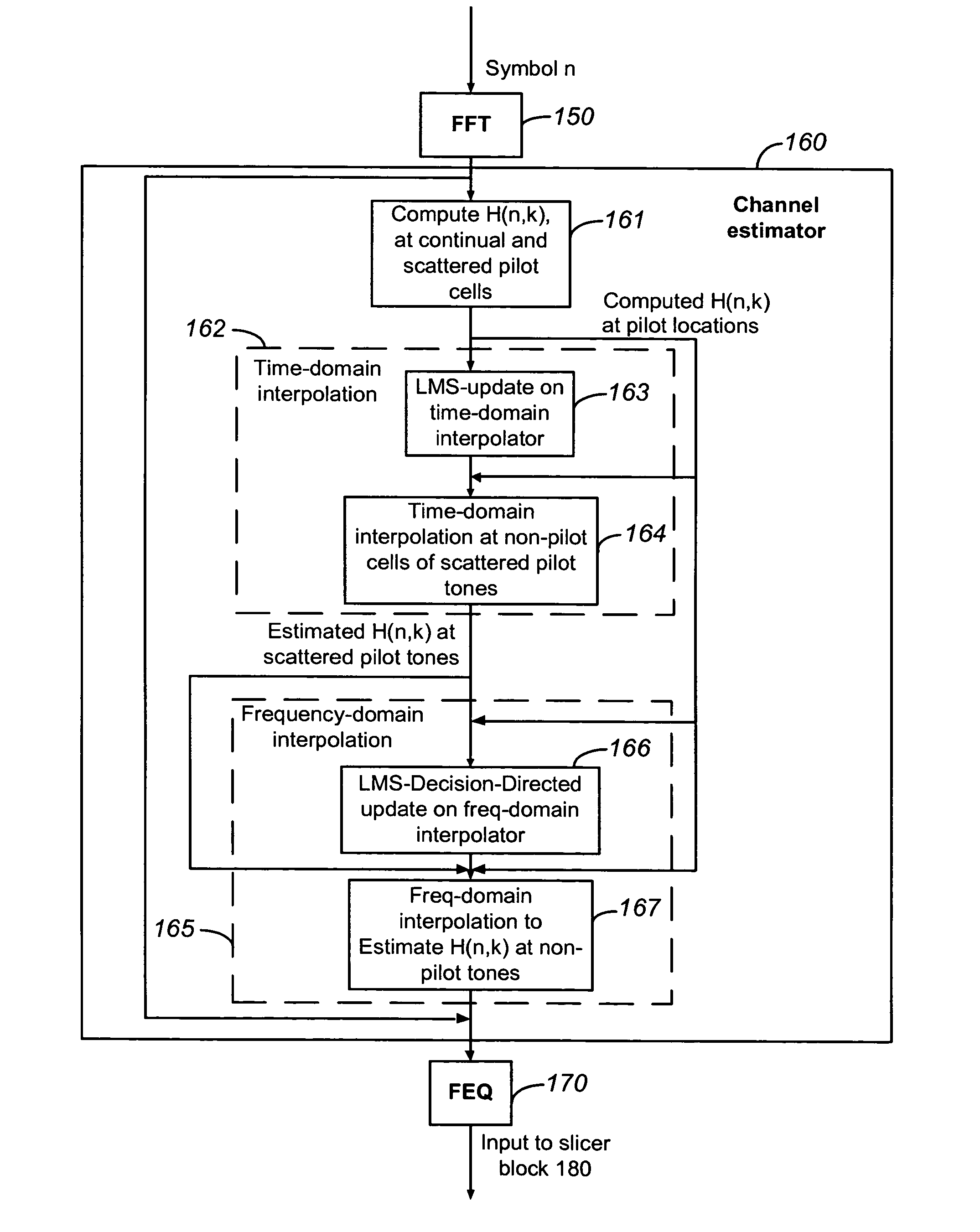
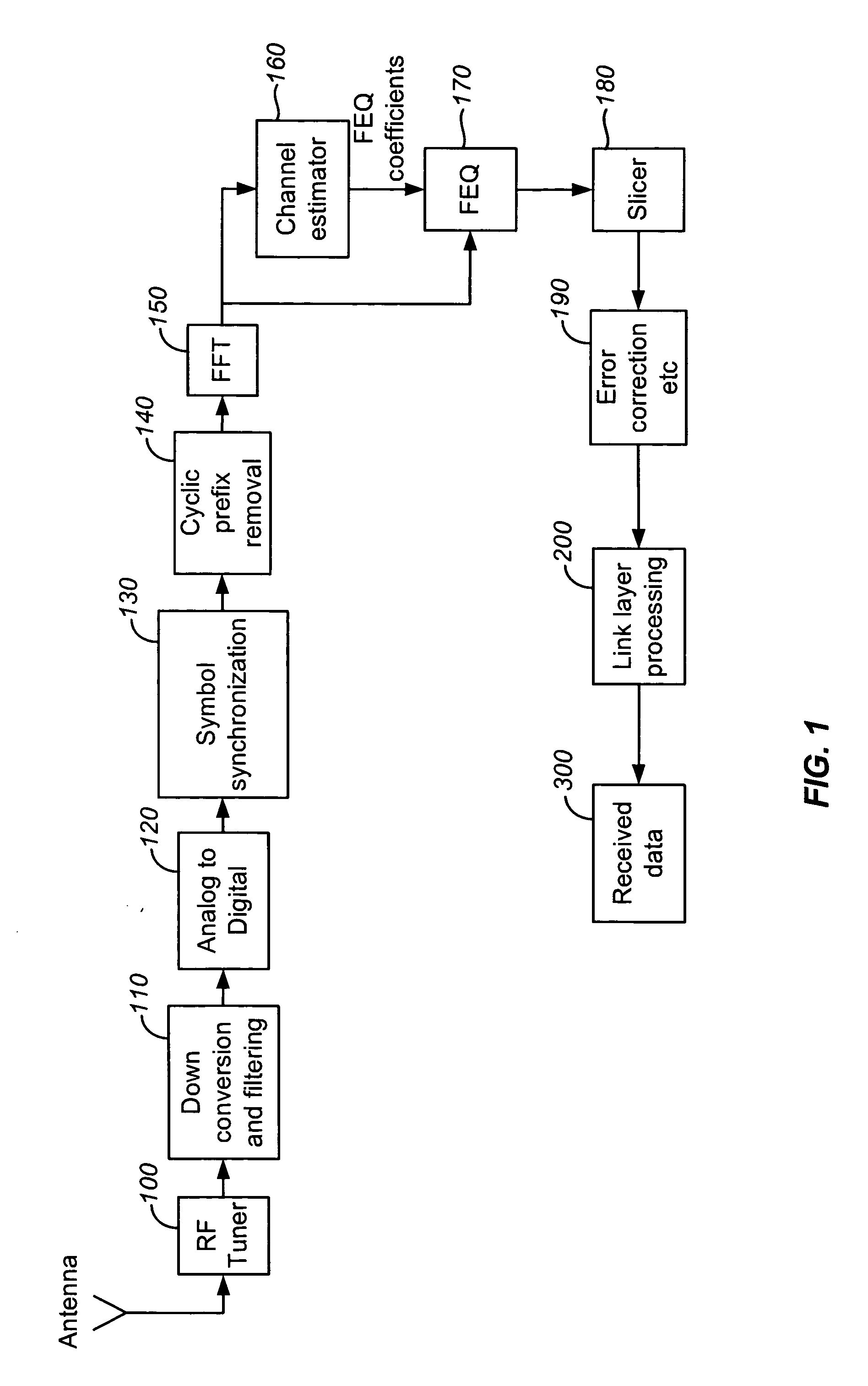
Adaptive interpolator for channel estimation
InactiveUS20060269016A1Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionTime domainCommunications system
A method for channel estimation in a wireless communication system includes the following steps. Channel transfer function is computed at continual and scattered pilot cells using transmitted and received signals at the continual and scattered pilot cells. Time-domain adaptive interpolation is performed to obtain channel transfer function at non-pilot cells of the scattered pilot tones using the channel transfer function computed at continual and scattered pilot cells. Frequency-domain adaptive interpolation is performed to obtain channel transfer function at non-pilot cells of non-pilot tones using the channel transfer function computed at continual and scattered pilot cells.
Owner:MEDIAPHY CORP
Video coding method and video decoding method
InactiveCN101822061ATelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionVideo encoding
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
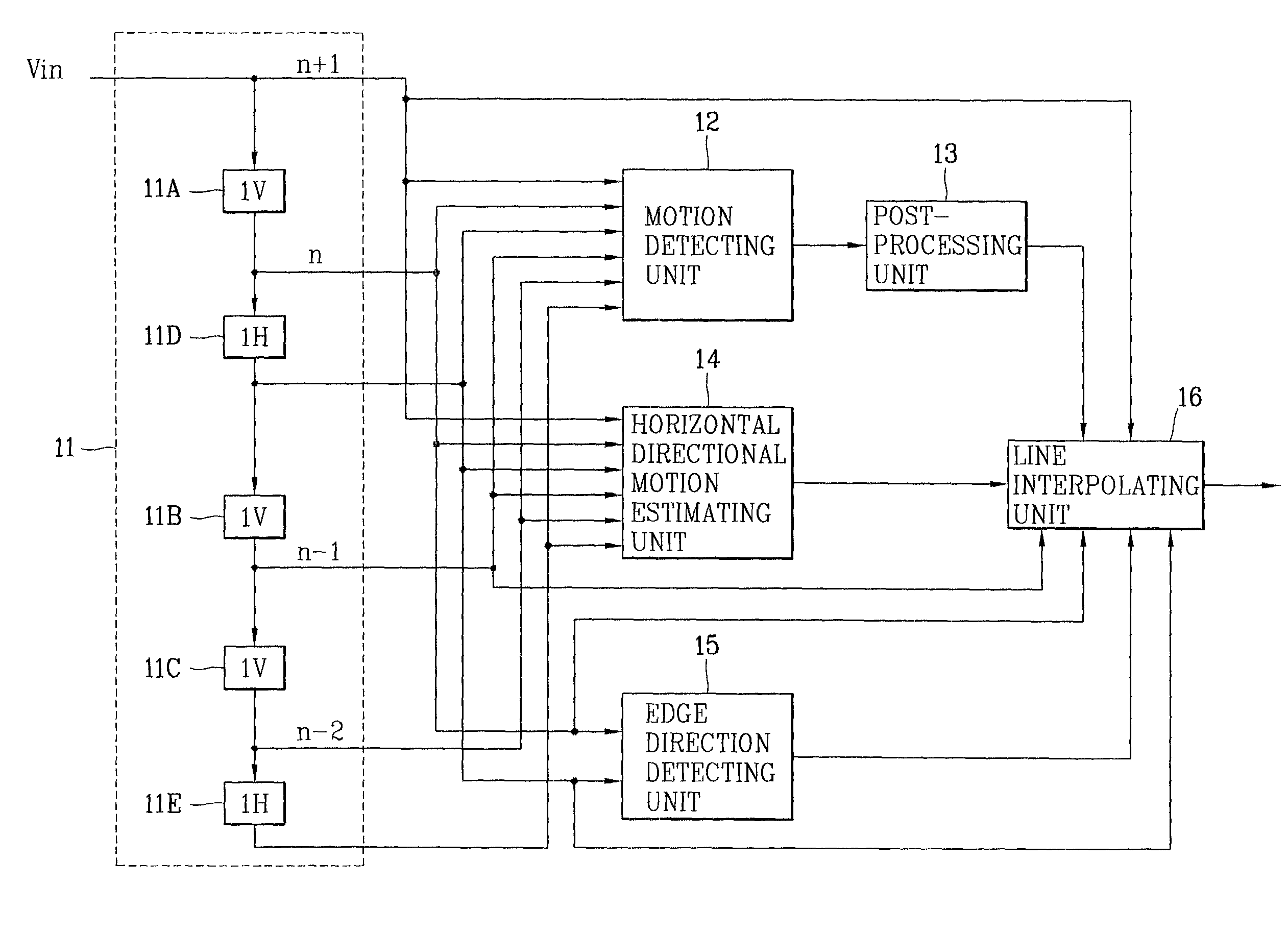
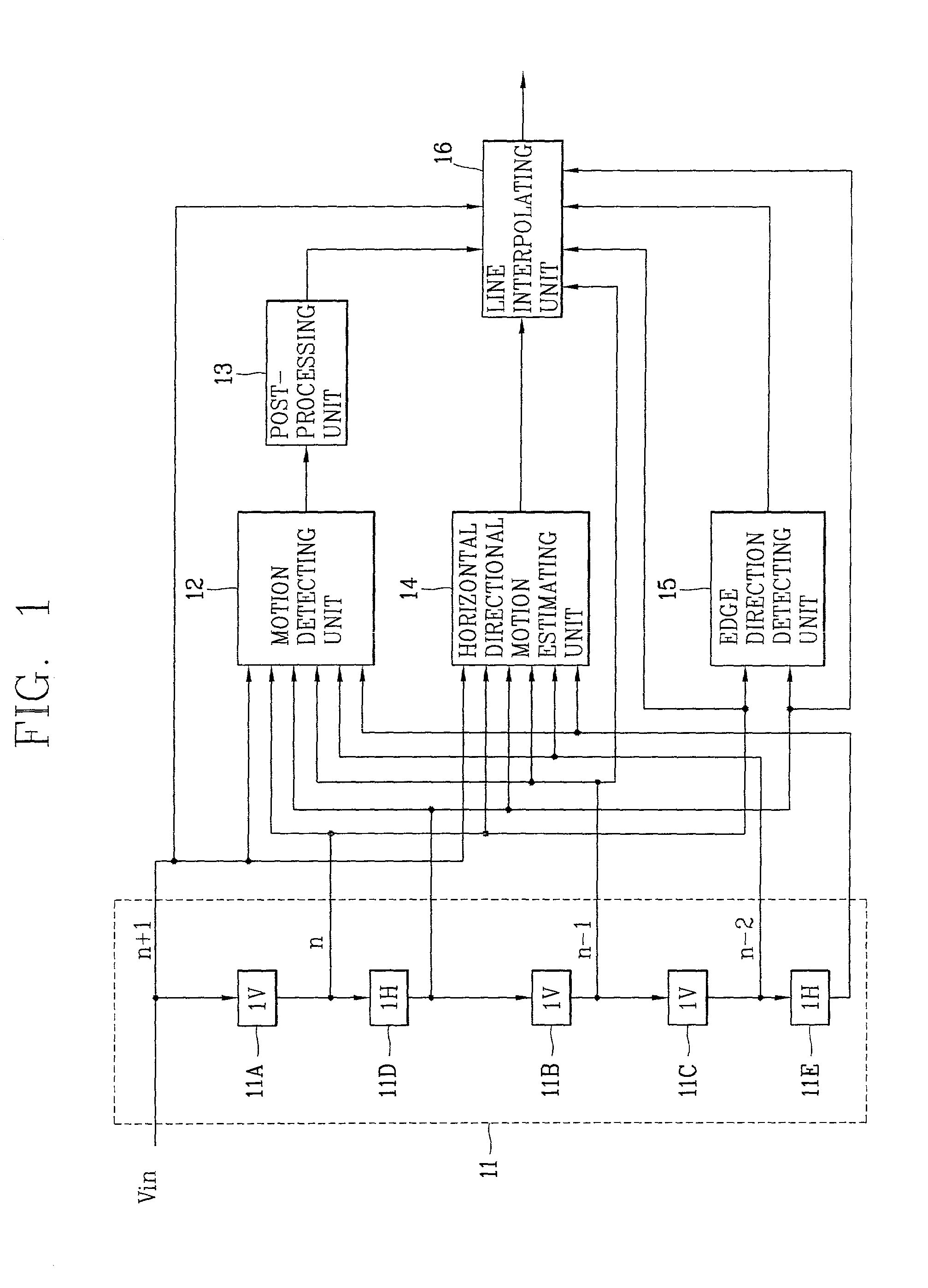
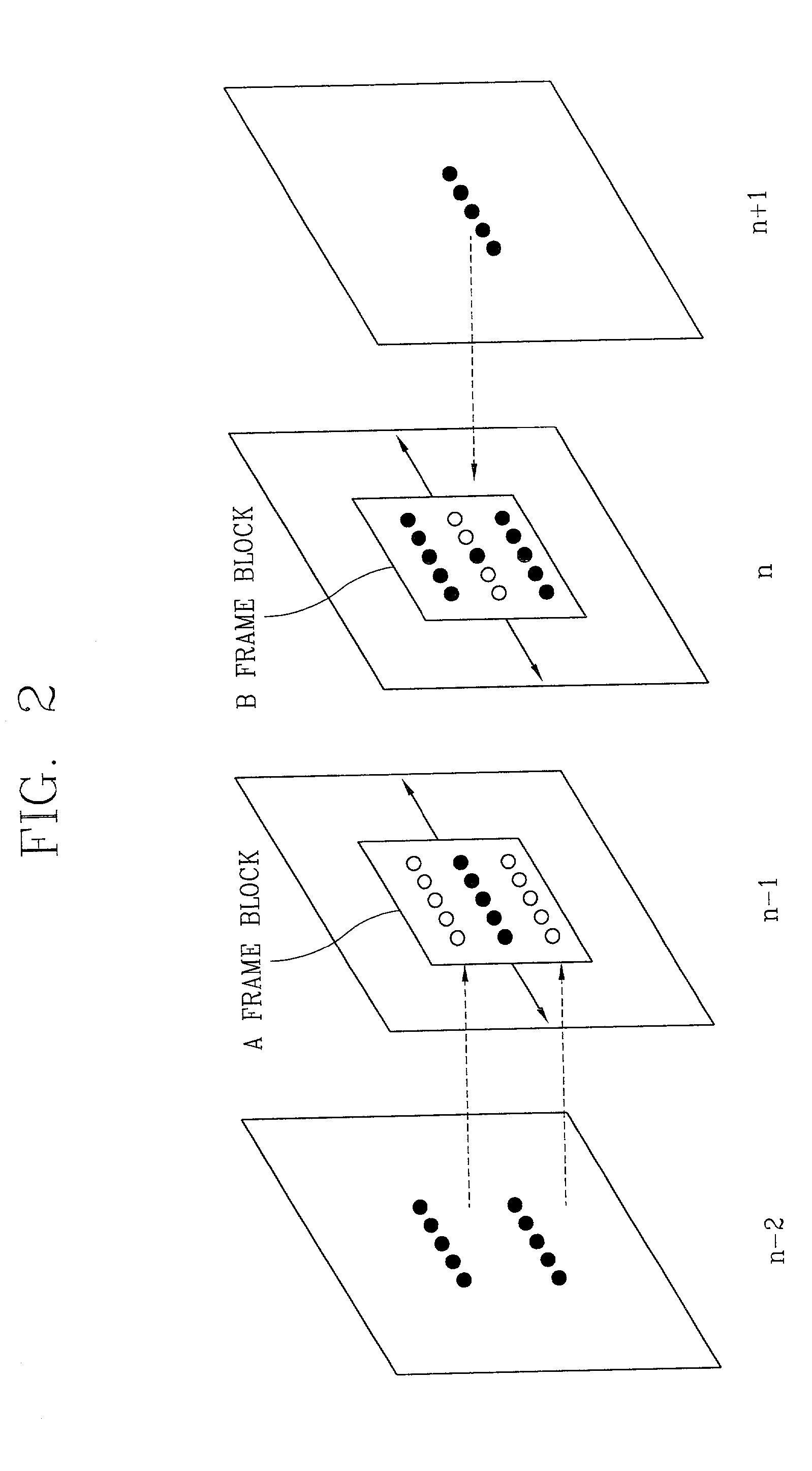
Motion-adaptive interpolation apparatus and method thereof
InactiveUS6985187B2Improve picture qualitySimple hardware structureTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesInter frameSelf adaptive
A motion-adaptive interpolation apparatus and method are disclosed. After an image signal is received and horizontal directional inter-frame motion information of a field to be currently interpolated is estimation, and interpolating is suitably performed based on the motion information. According to one aspect of the present invention, a basic unit image region is set for a pizel to be interpolated, a block matching error (BME) is obtained by moving the basic unit image region at certain intervals in a different direction, a linear interpolated pixel value is detected in consideration of the block matching error, and a final interpolation value is calculated and outputted by applying a rule and filtering based on the linear interpolated pizel value. Thus, a picture quality is improved after de-interlacing, and a circuit for implementation of the operation is simplified, so that a unit cost can be reduced.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Method for determining filter coefficient of two-dimensional adaptive interpolation filter
InactiveUS20100135398A1Efficiently determinedSolve the excessive calculationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionSub-pixel resolutionImage resolution
A method for efficiently determining an appropriate filter coefficient of a two-dimensional adaptive interpolation filter with less calculation, the method including: a motion estimating step (S100) of estimating at sub-pel resolution, for each of blocks constituting a current picture, a motion of an image of the block from a reference picture as a motion vector; an identifying step (S102) of identifying at least one block having a motion vector specifying a sub-pel position (p, q) on the reference picture from among the blocks having motion vectors estimated at sub-pel resolution; and a determining step (S104) of determining a filter coefficient of the sub-pel position (p, q) based on an image of the at least one block identified in the identifying step and an image of at least one block of the reference picture specified by the motion vector of the at least one block identified in the identifying step.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
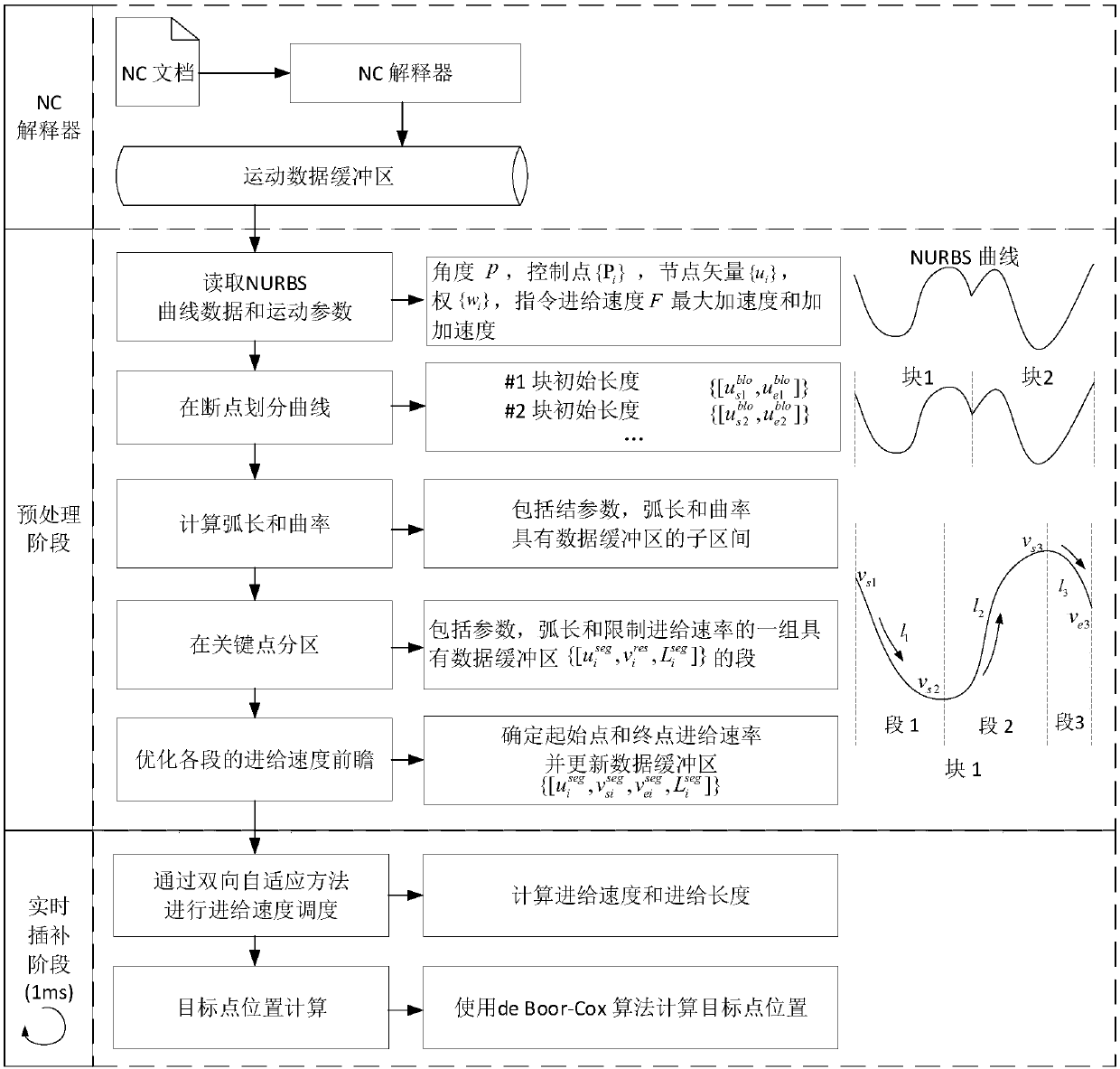
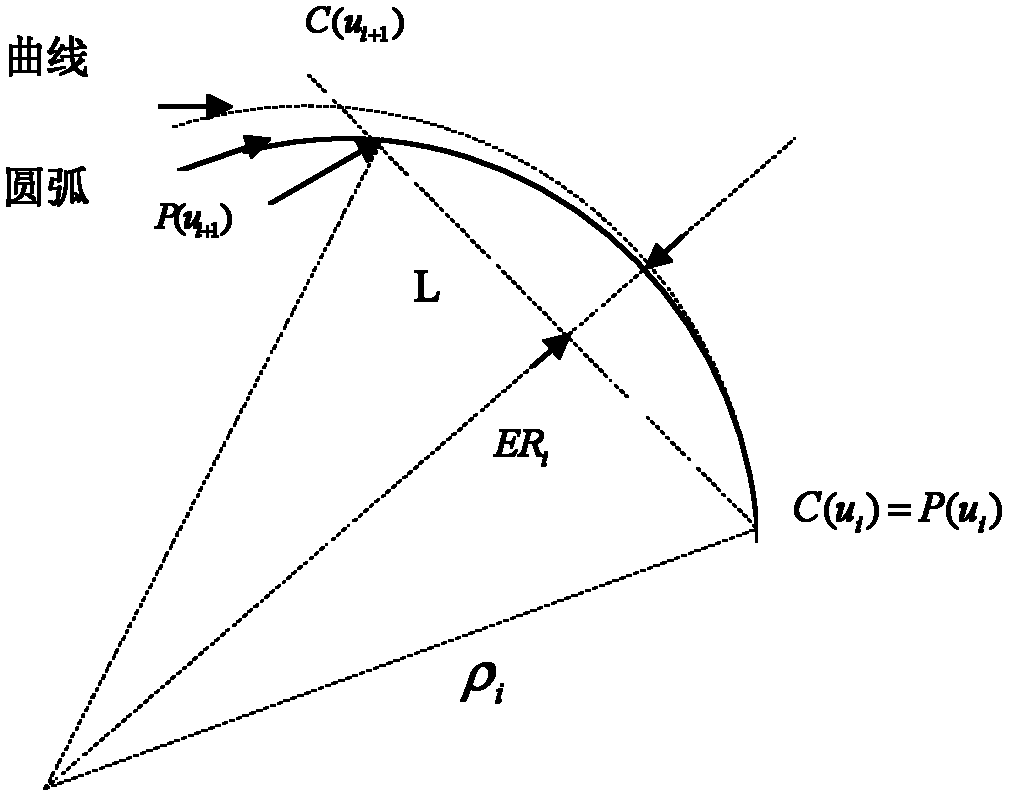
NURBS curve bi-directional adaptive interpolation algorithm based on S-curve acceleration and deceleration algorithm
ActiveCN107817764AGuaranteed speed smoothnessHigh precisionNumerical controlAlgorithmMotion parameter
The present invention relates to an NURBS curve bi-directional adaptive interpolation algorithm based on an S-curve acceleration and deceleration algorithm, belonging to the field of motion control. The method comprises the steps of: (1) employing an NC interpreter to obtain NURBS curve data and motion parameters; (2) performing scanning to obtain key characteristics of a NURBS curve, the key characteristics comprising breaking points of the NURBS curve, dividing the NURBS curve into blocks according to the breaking points, and calculating an arc length and a curvature of the NURBS curve of each block; dividing the blocks into sections according to curvature of each block; and (3) employing the curve data and motion parameters of each section obtained in the step (2) to obtain a feeding length of each period in each section, and finding new interpolating points. The NURBS curve bi-directional adaptive interpolation algorithm considers constraint of a curvature extreme point and curvatures in nearby areas thereof on the speed so as to ensure that a planning speed is in a constraint range and precision of speed planning and interpolation is improved; and moreover, interpolations in two directions can be accurately met, and speed smoothness of the whole interpolation process can be ensured.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
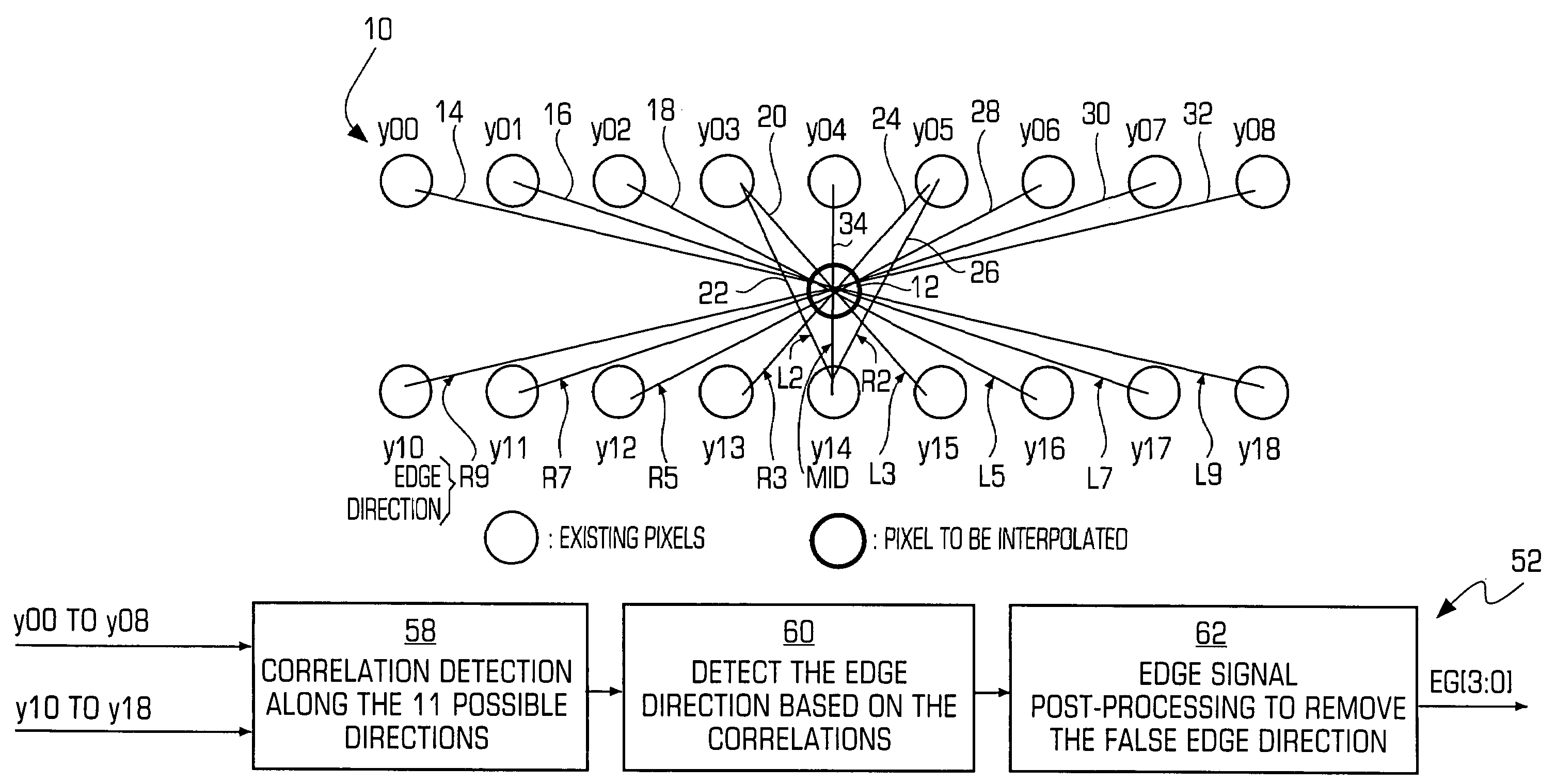
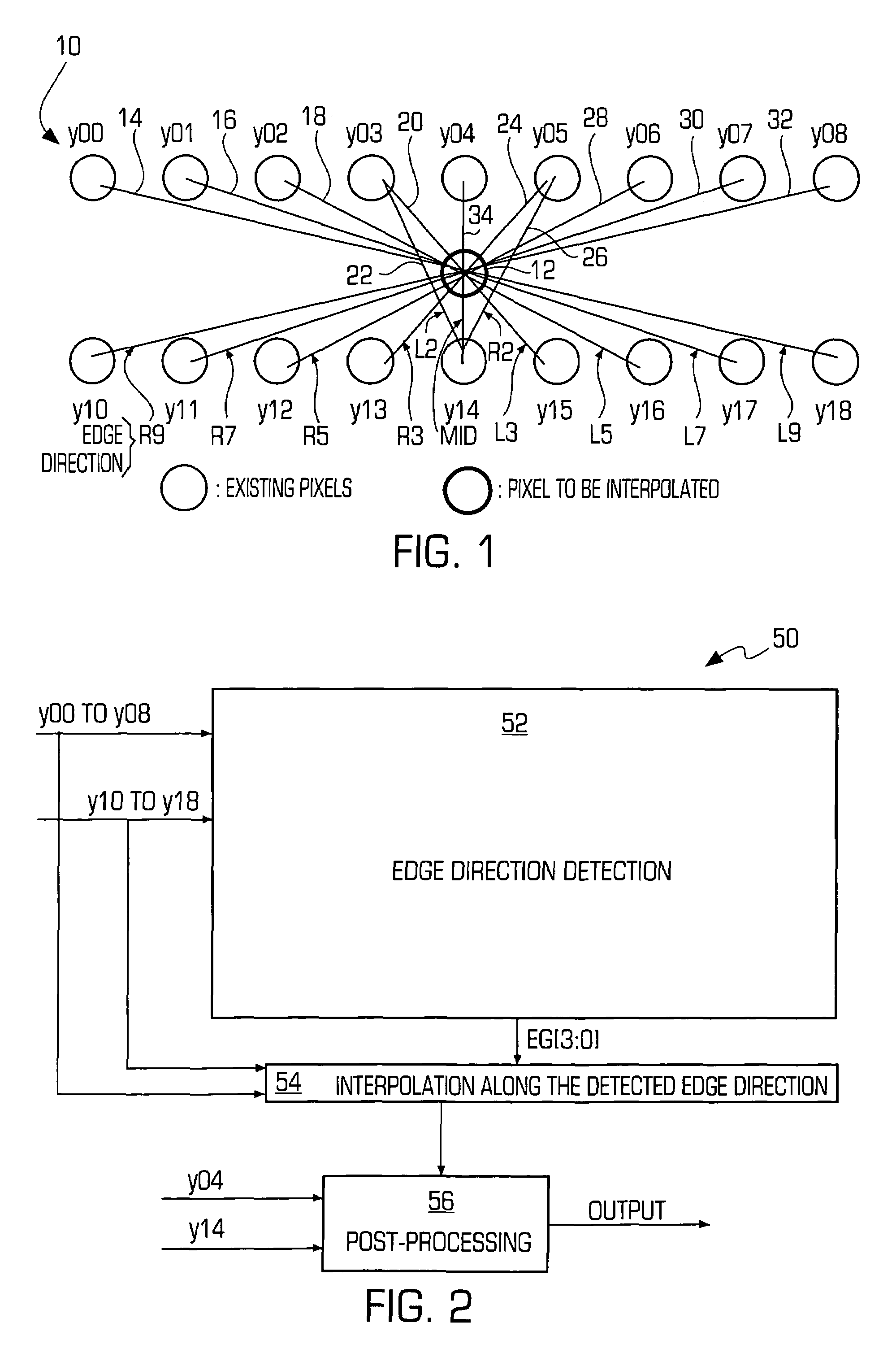
Method and system for advanced edge-adaptive interpolation for interlace-to-progressive conversion
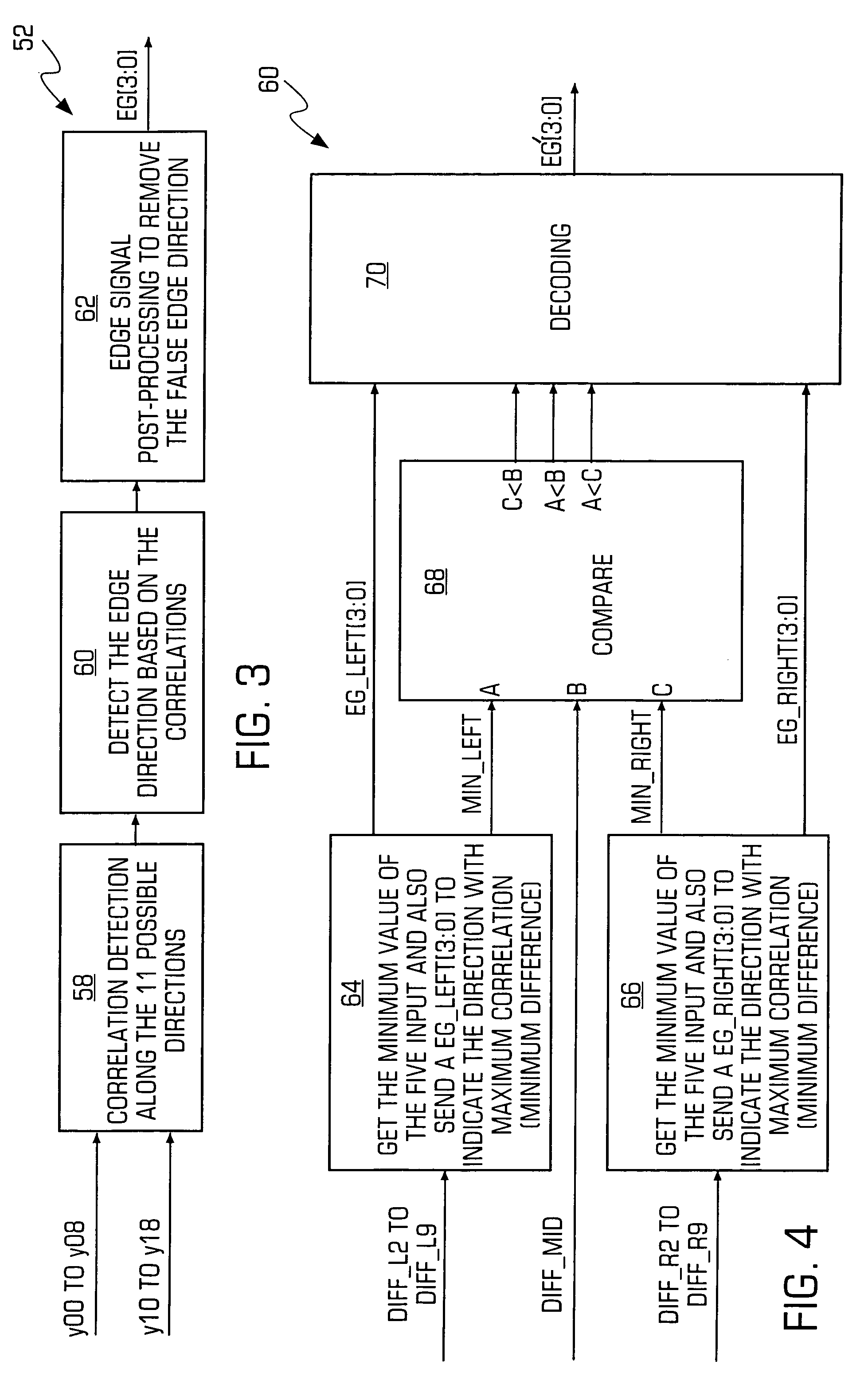
InactiveUS7242819B2Reduce calculationImproved edge detectionImage enhancementImage analysisImproved methodDirection detection
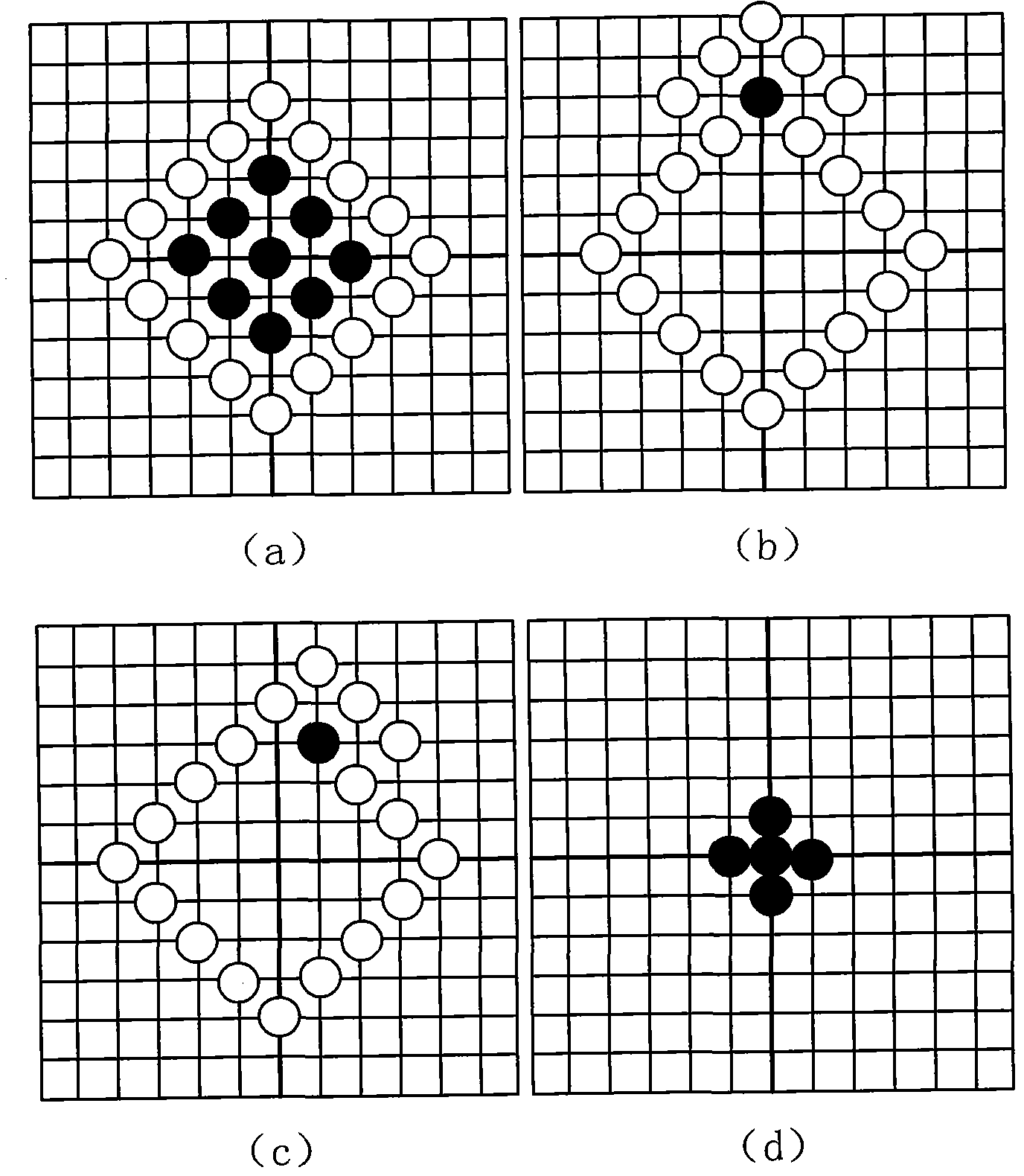
An improved method and system for edge adaptive interpolation. The method uses a “9×2” window to detect the edge direction with post-processing to remove any artifacts due to the possible false edge detection, and a hierarchical scheme is employed to reduce the computation required. The method detects if there is edge existing along the current pixel. If there is no edge, then the edge detection output will be 90 degrees (the interpolation will be performed along the vertical direction). If an edge does exist, the method determines whether the edge direction falls within a first or second direction group. Once the edge direction is assigned to a particular group (e.g., 0–90 degrees or 90–180 degrees), the edge direction will be detected among five (5) possible directions. To further improve the edge detection precision, and also to remove the possibility of false edge direction detection, a post-processing technique may be applied to the edge direction signal. After the edge signal post-processing, the edge direction information is then passed to an edge adaptive interpolation block to perform the interpolation along the edge direction detected. Still another post-processing technique may be applied to the edge adaptive interpolated signal to further remove the possible noise due to an incorrect edge direction detection.
Owner:ENTROPIC COMM INC
Margin-oriented self-adaptive image interpolation method and VLSI implementation device thereof
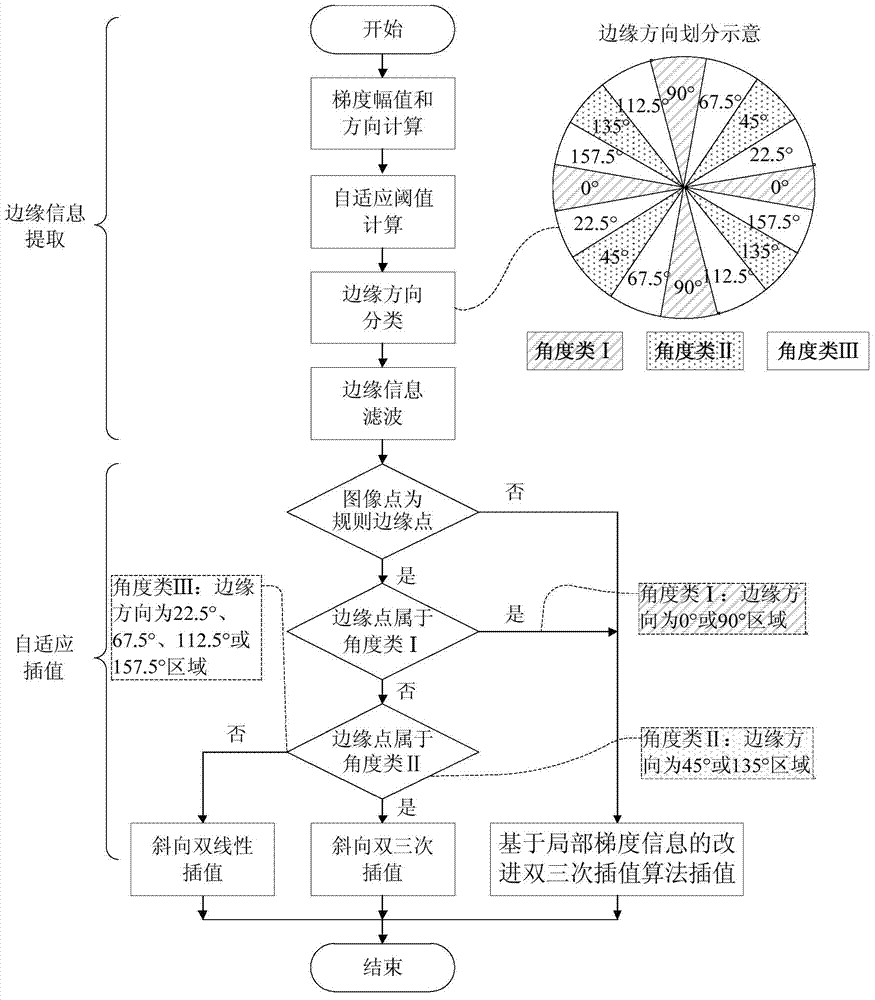
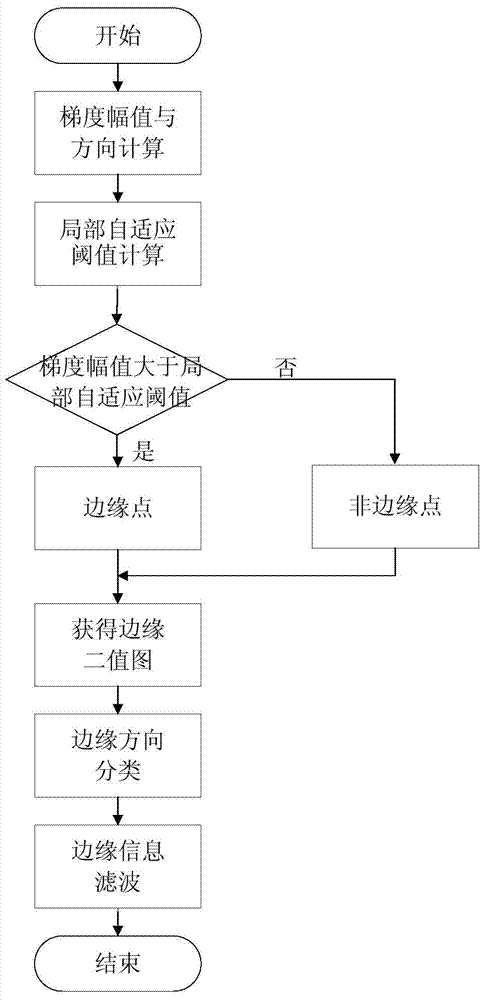
ActiveCN103500435AGuaranteed accuracyProtectImage enhancementImage analysisVlsi implementationsSynchronous control
The invention discloses a margin-oriented self-adaptive image interpolation method and a VLSI implementation device thereof. The method comprises the steps that the gradient magnitude and the gradient direction of a source image pixel are computed, and marginal information is obtained by comparing the gradient magnitude and a local self-adaptive threshold value, wherein the marginal direction is perpendicular to the gradient direction; the marginal direction is classified, filtering is conducted through the marginal information, and an image is divided into a regular marginal area and a non-marginal area; the regular marginal area interpolation is conducted in the marginal direction, and an improved bicubic interpolation method, a slant bicubic interpolation method and a slant bilinear interpolation method based on local gradient information are adopted to conduct image interpolation according to the classification of the marginal information; image interpolation is conducted on the non-marginal area through the improved bicubic interpolation method based on the local gradient information. The VLSI implementation device comprises a marginal information extraction module, a self-adaptive interpolation module, an input line field synchronous control module and an after-scaling line field synchronous control module. The margin-oriented self-adaptive image interpolation method and the VLSI implementation device of the margin-oriented self-adaptive image interpolation method can effectively improve the effect of image interpolation with high-magnification scaling, and is beneficial to integrated circuit framework achieving.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
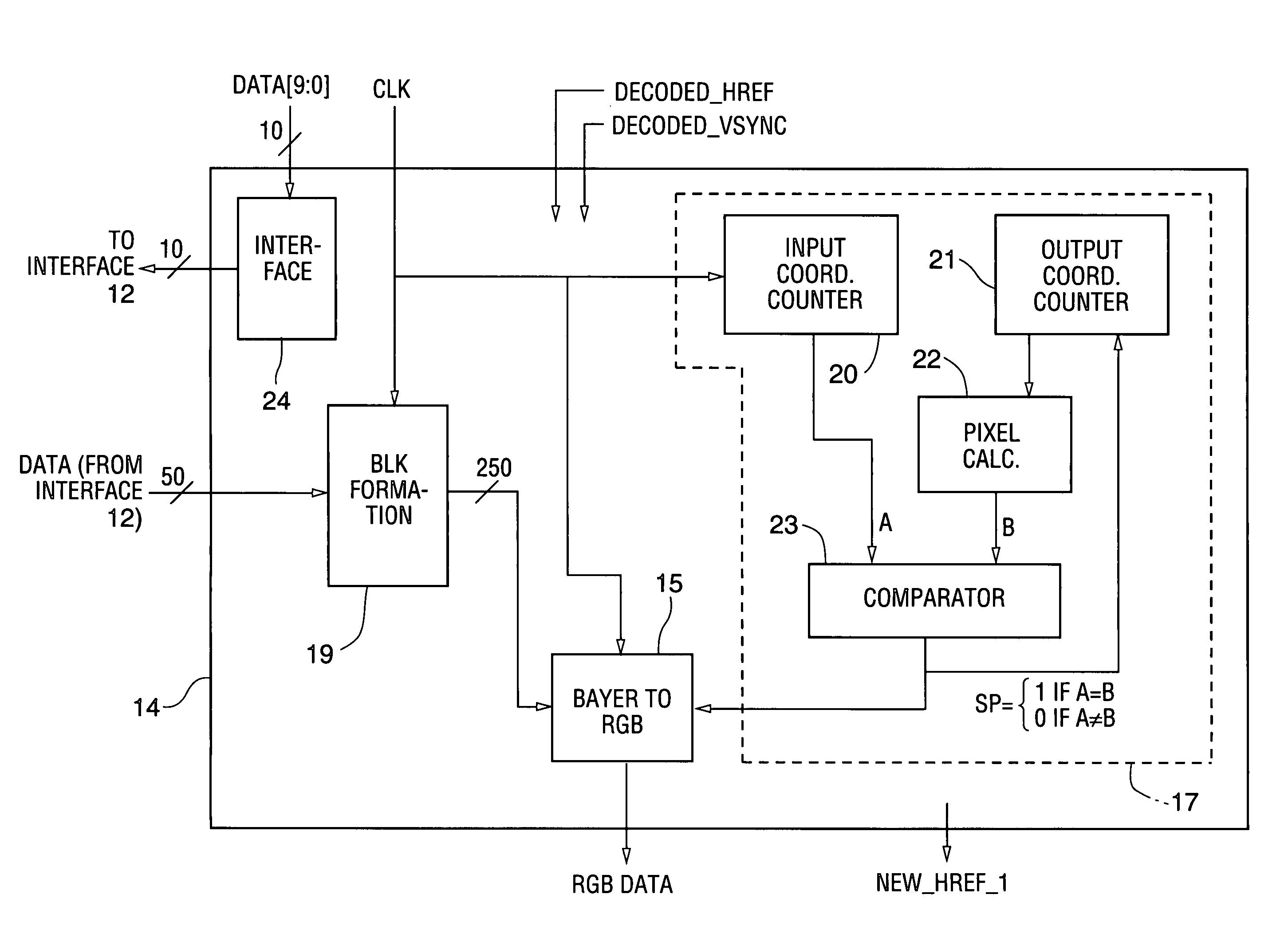
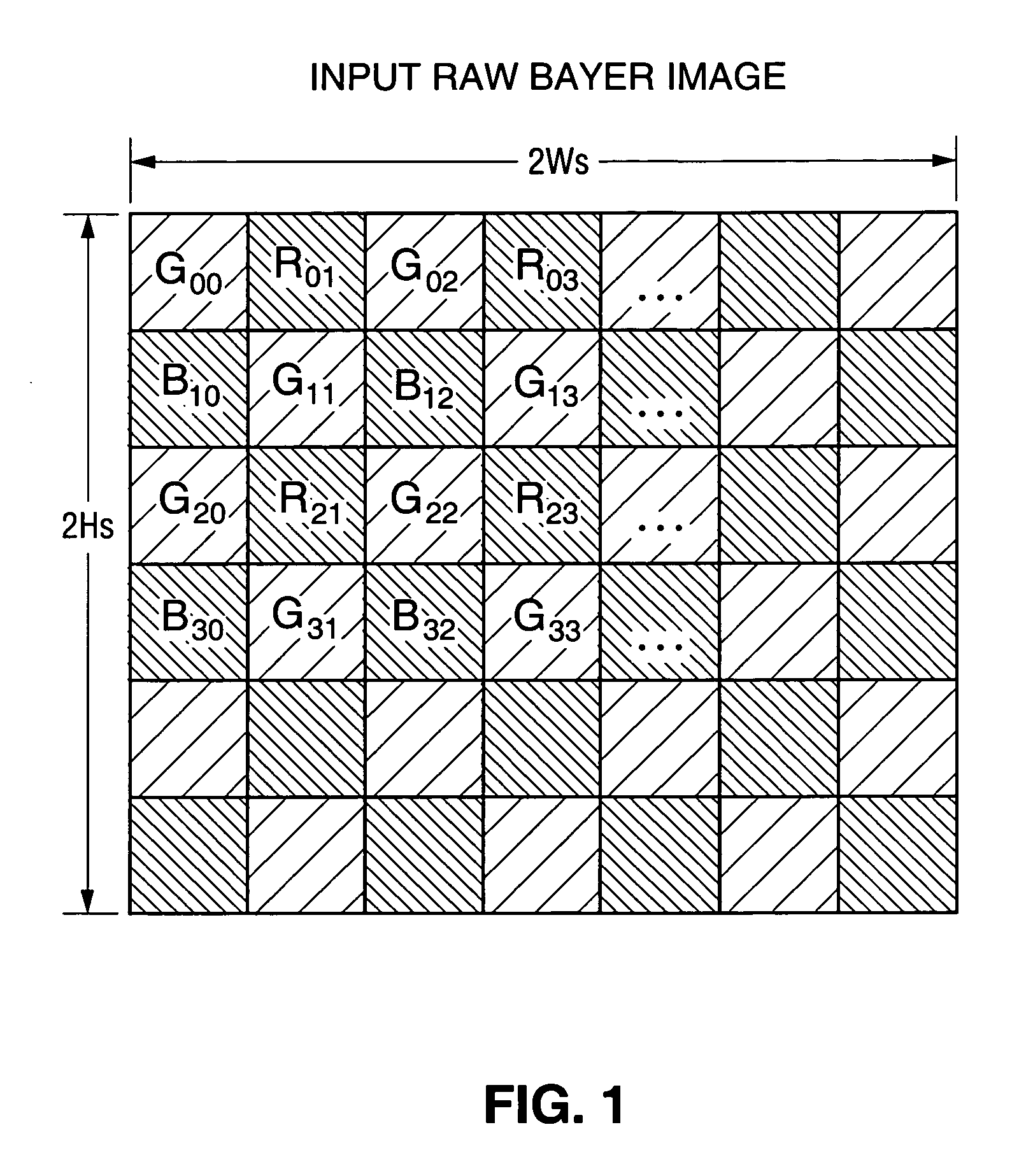
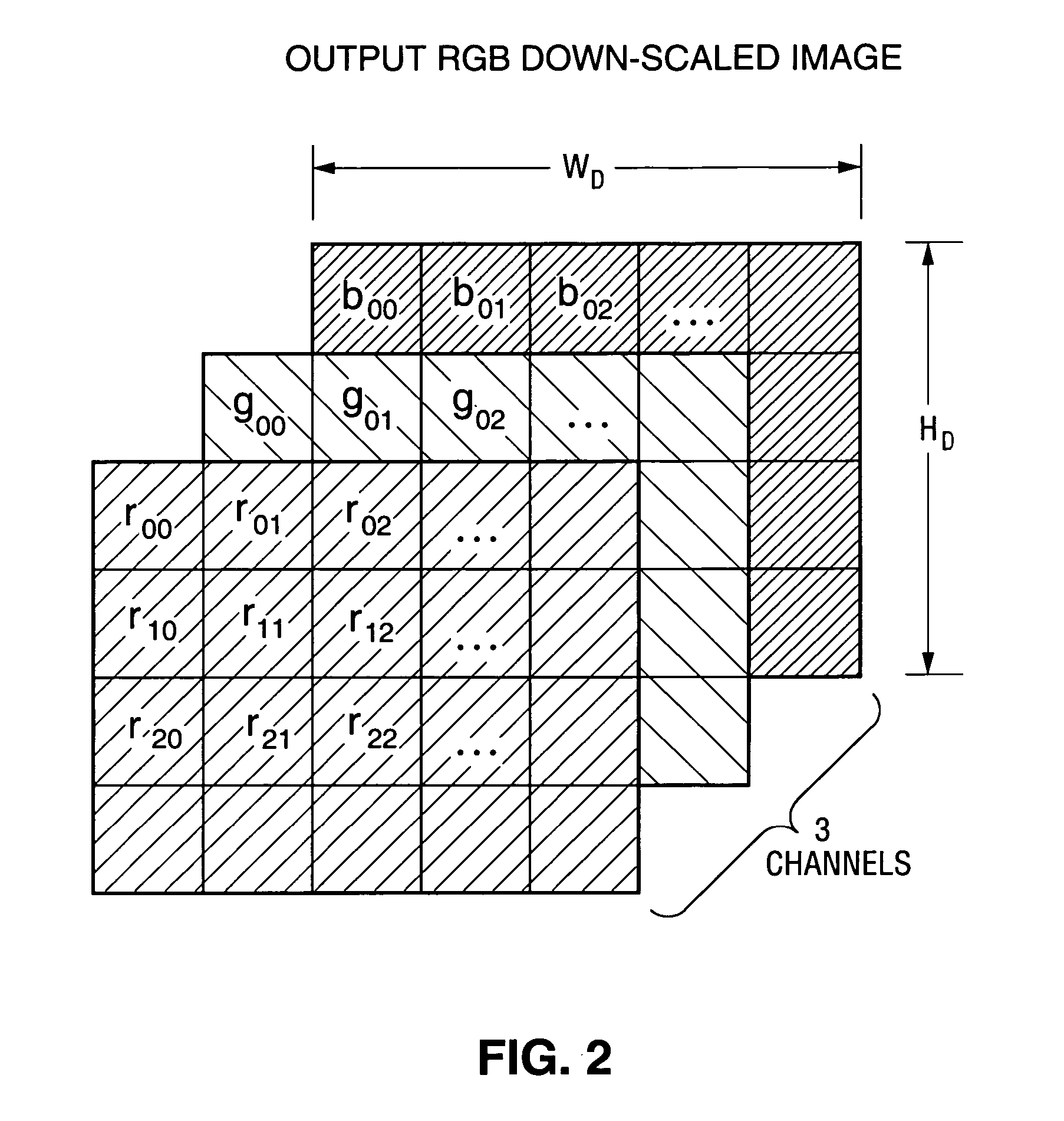
Method and circuit for integrated de-mosaicing and downscaling preferably with edge adaptive interpolation and color correlation to reduce aliasing artifacts
InactiveUS20070133902A1Reduce artifactsAvoid excessive computationGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionIntegrated operations
In a class of embodiments, a method and circuit for de-mosaicing and downscaling image data (e.g., image data in raw Bayer image format) in a single, integrated operation, rather than two separate and sequential de-mosaicing and downscaling operations. Some embodiments of the method include a step of displaying the de-mosaiced and downscaled data (e.g., on an LCD of a digital camera to perform an image preview operation). In typical embodiments, the method includes the steps of: determining sampling points (one sampling point for each output image pixel); and filtering the input image data to generate color component values of output image data (e.g., red, green, and blue color components of output image data in RGB format) at each sampling point without producing unacceptable aliasing artifacts. In typical embodiments, the filtering step implements an edge adaptive interpolation algorithm and performs color correlation between red and green channels and between blue and green channels to reduce aliasing artifacts.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Edge-adaptive interpolation and noise filtering method, computer-readable recording medium, and portable terminal
ActiveUS20110032396A1Accurate analysisCancel noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPattern recognitionSelf adaptive
An edge-adaptive interpolation and noise filtering method is provided including performing primary interpolation on a first color, based on a first preset number of directions, with respect to a first color window obtained from an input image window, estimating an edge direction within a primary interpolated first color window obtained by the primary interpolation, based on a second preset number of directions, the second preset number of directions being larger than the first preset number, with respect to the primary interpolated first color window, performing secondary interpolation on the first color, based on the estimated edge direction, with respect to the primary interpolated first color window, and performing interpolation on a second color, based on the estimated edge direction, with respect to a second color window obtained from the input image window.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Self-adaptive interpolation process method and coding/decoding module
ActiveCN101043621ASave energyReduce dataPulse modulation television signal transmissionReference imageMotion prediction
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Speed conversion processing module and method of high definition digital video frame
InactiveCN102131058AGood handling qualityEliminates grooming imperfectionsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDigital videoObjective quality
The invention provides a speed conversion processing module of a high definition digital video frame. The module provided by the invention comprises a film mode recognition pretreatment module, a movement estimation and compensation module, an adoptive interpolation algorithm frame speed conversion module and an objective quality evaluation module. The invention also provides a speed conversion method of the video frame. The method comprises the following steps: recognizing the type of a video source and determining the video format of the video source, interweaving or reversely intersecting a video stream, completing restoration from a video field to the frame and eliminating the dressing defect of an image; estimating a movement vector between the frames by using a movement estimation and compensation algorithm, recognizing whether a moving object is shielded or not and determining the position of the moving object; according to the movement estimation information, adaptively carrying out weighted average interpolation between the unshielded frames of the moving object, or adaptively carrying out protective interpolation on different areas based on the shielded image situation of the moving object; and establishing an objective evaluation model of video processing quality, and correcting adjustable parameters of frame speed conversion by using quality grade provided by the objective evaluation model, thereby optimizing the processing quality of the video.
Owner:BEIJING WISDOM ELVES TECH
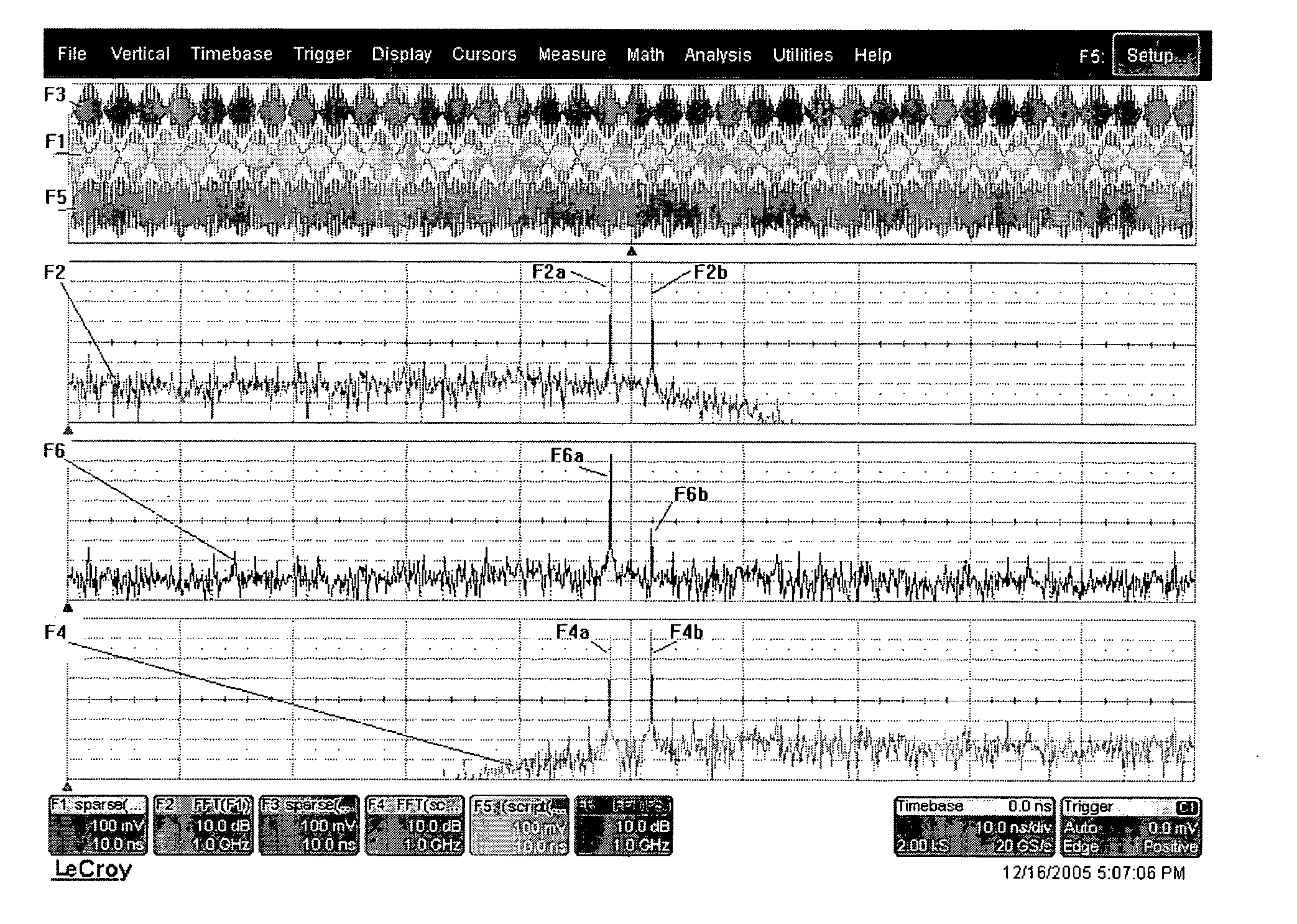
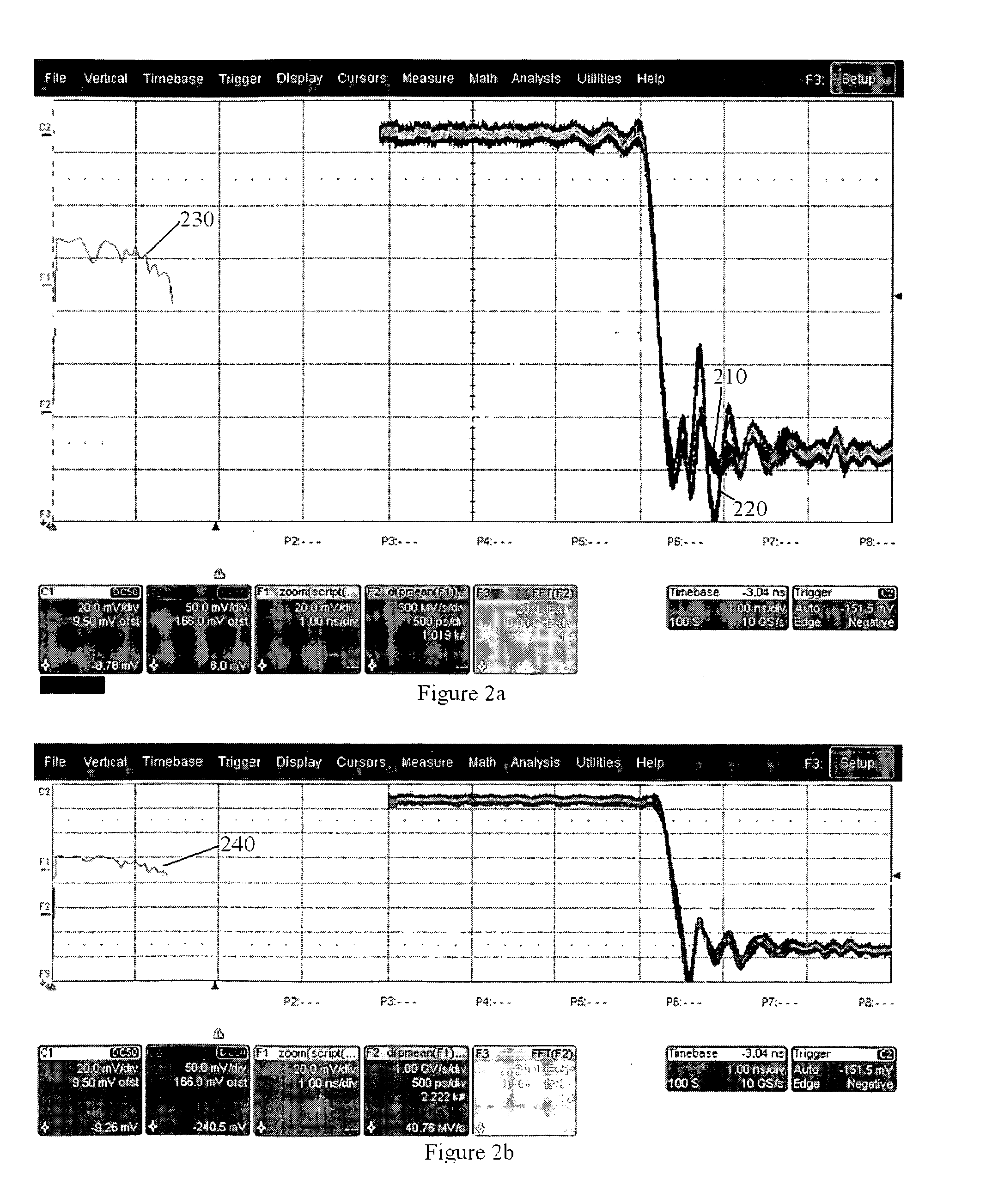
Adaptive interpolation for use in reducing signal spurs
A method and apparatus for acquiring an analog signal. The method of the invention comprising the steps of acquiring a first portion of the analog signal by a first channel, the first portion of the analog signal spanning a first bandwidth range, and acquiring a second portion of the analog signal by a second channel, the second portion of the analog signal spanning a second bandwidth range adjacent the first bandwidth range. At least one spur in the signal acquired by the first channel corresponding to a portion of the analog signal that should have properly been acquired by the second channel is offset with an opposite spur in the second channel.
Owner:TELEDYNE LECROY
NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Spline) curve adaptive interpolation control method based on de Boor algorithm
InactiveCN102608956AReduce complexityAvoid iterative solution processProgramme controlComputer controlPulse numberSelf adaptive
The invention discloses a NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Spline) curve adaptive interpolation control method based on a de Boor algorithm. An upper computer calculates an interpolation point and transfers the calculated coordinate value list to a lower computer; and the lower computer converts the coordinate value into corresponding pulse number and sends a pulse to a motor driver which controls a motor to rotate and drives a mechanical structure to act. The NURBS curve adaptive interpolation control method comprises the following steps: a parameter value in a curve definition domain is set to calculate a corresponding point p(u) on the B-spline curve; and a NURBS curve adaptive interpolation module based on the de Boor algorithm applies the de Boor algorithm to the NURBS curve interpolation by use of a recursion formula of the de Boor algorithm. The invention provides the NURBS curve adaptive interpolation control method based on the de Boor algorithm, which reduces the complexity and has good real-time performance and relatively high interpolation efficiency.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
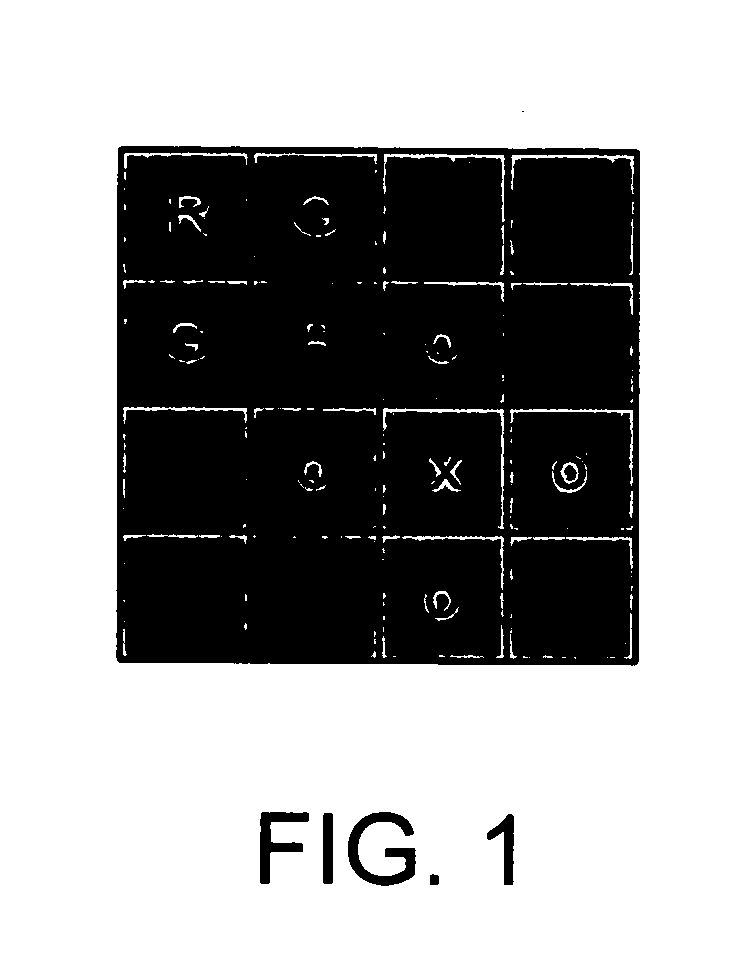
Method and apparatus for processing image
ActiveUS20140153823A1Eliminate generationRemove color distortionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsImaging processingPixel value difference
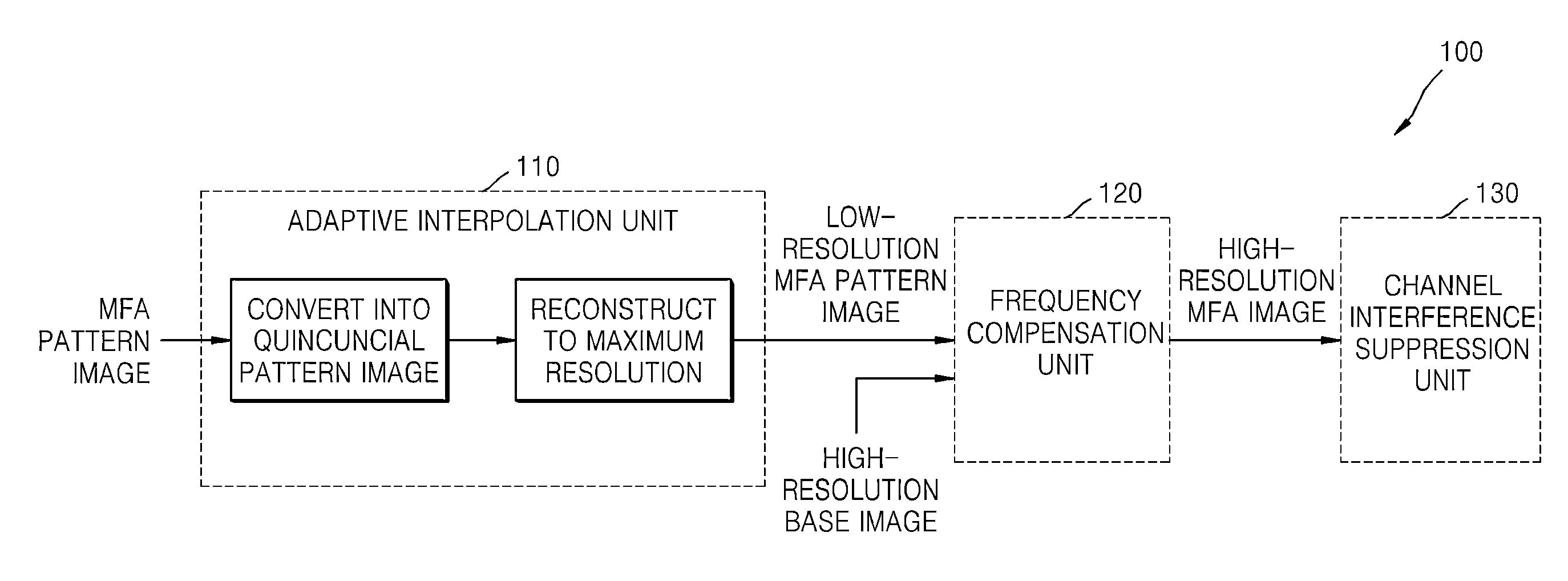
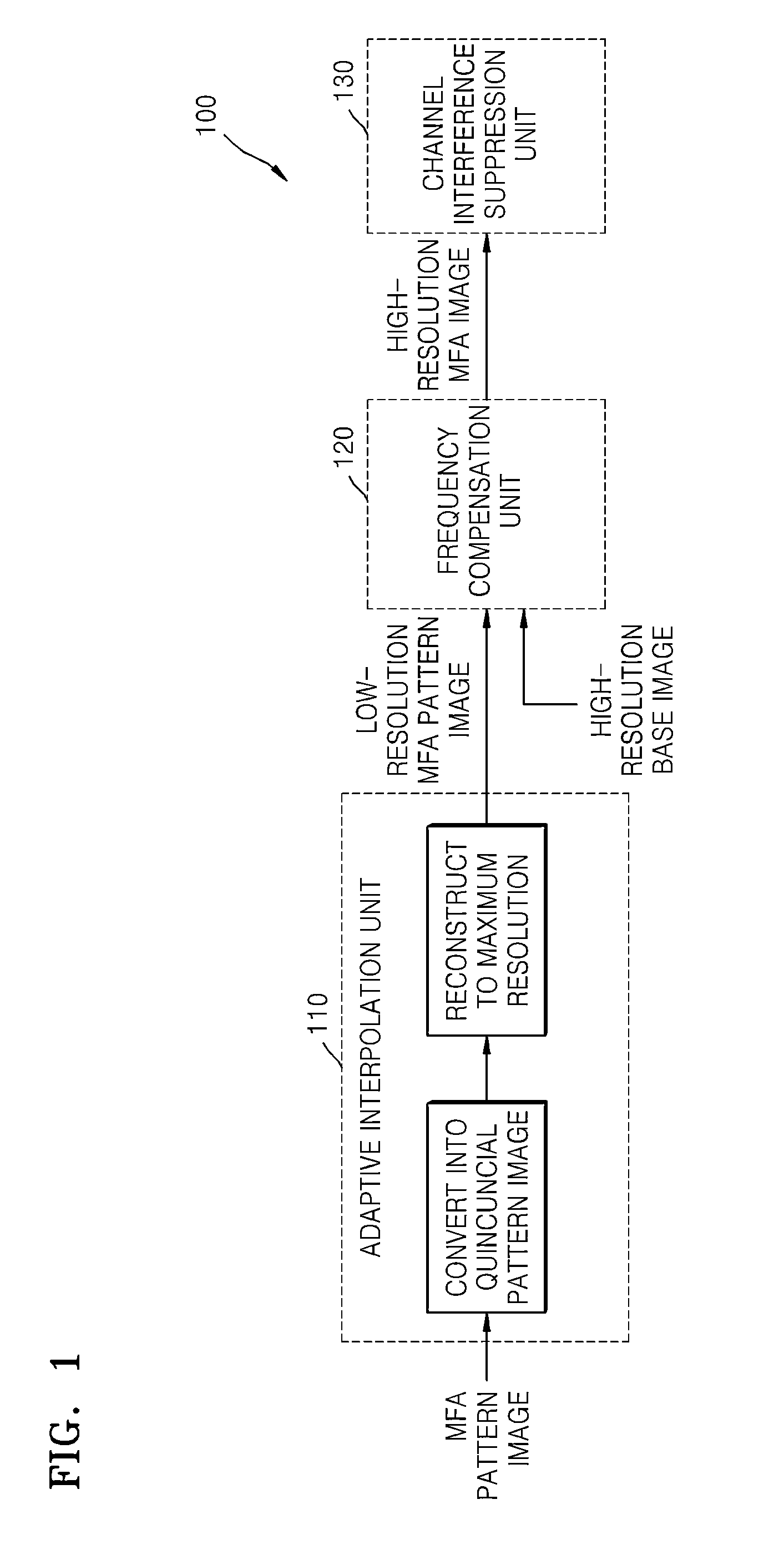
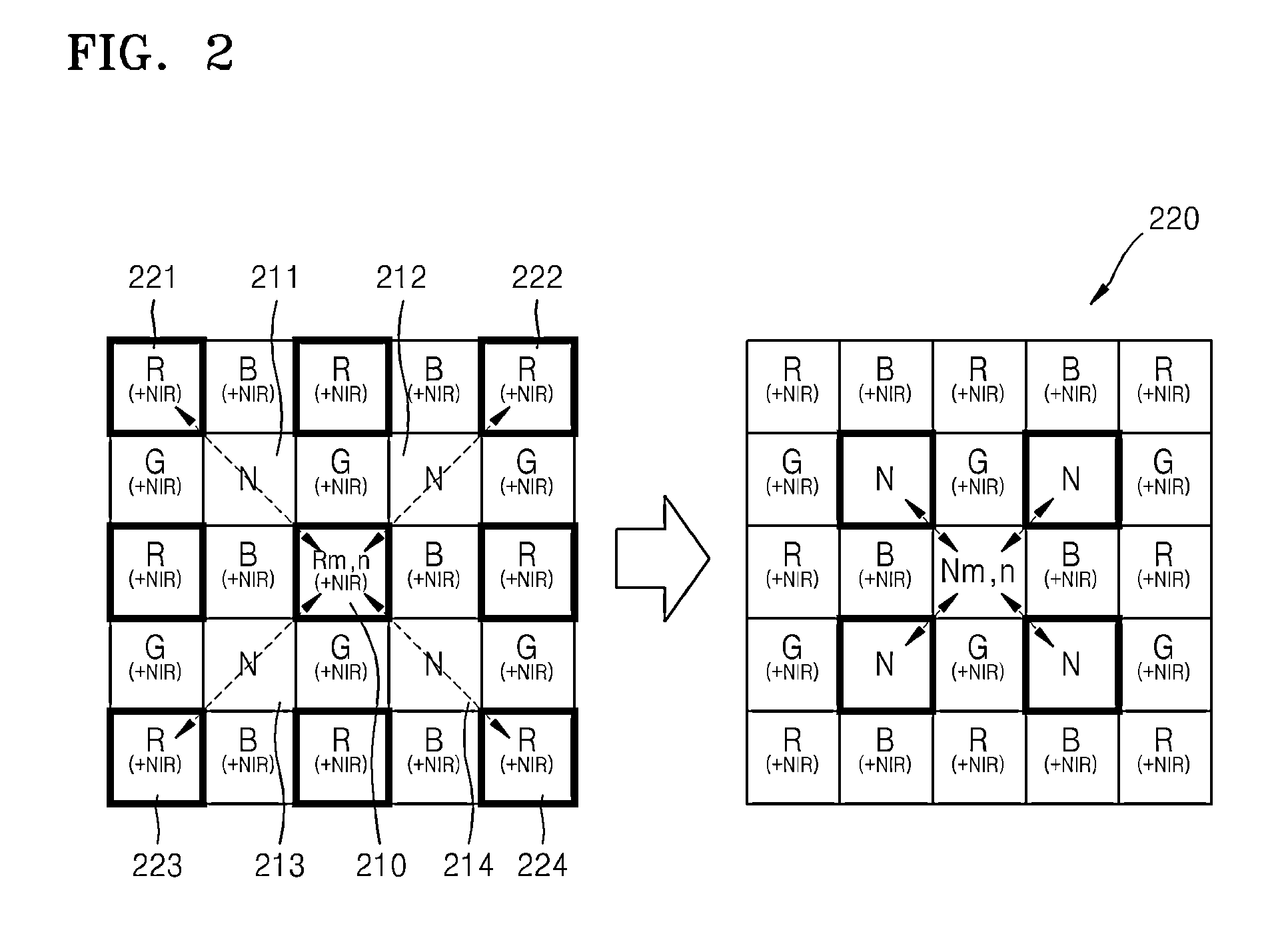
An image processing apparatus includes an adaptive interpolation device which converts a MFA pattern image into a quincuncial pattern image based on difference values, and interpolates color channels and an NIR channel, based on difference values of the converted quincuncial pattern image in vertical and horizontal pixel directions; a frequency compensation device which obtains a high-resolution MFA image using high-frequency and medium-frequency components of a high-resolution base image, based on linear regression analysis and compared energy levels of MFA channel images to an energy level of a base image; and a channel interference suppression device which removes color distortion generated between each channel of the high-resolution MFA image, and another channel of the high-resolution MFA image and a base channel using a weighted average of pixel value differences between each channel of the high-resolution MFA image, and the other channel of the high-resolution MFA image and the base channel.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV +1
Adaptive interpolation
ActiveUS20070273567A1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionAnalog signalSelf adaptive
A method and apparatus for acquiring an analog signal. The method of the invention comprising the steps of acquiring a first portion of the analog signal by a first channel, the first portion of the analog signal spanning a first bandwidth range, and acquiring a second portion of the analog signal by a second channel, the second portion of the analog signal spanning a second bandwidth range adjacent the first bandwidth range. At least one spur in the signal acquired by the first channel corresponding to a portion of the analog signal that should have properly been acquired by the second channel is offset with an opposite spur in the second channel.
Owner:TELEDYNE LECROY
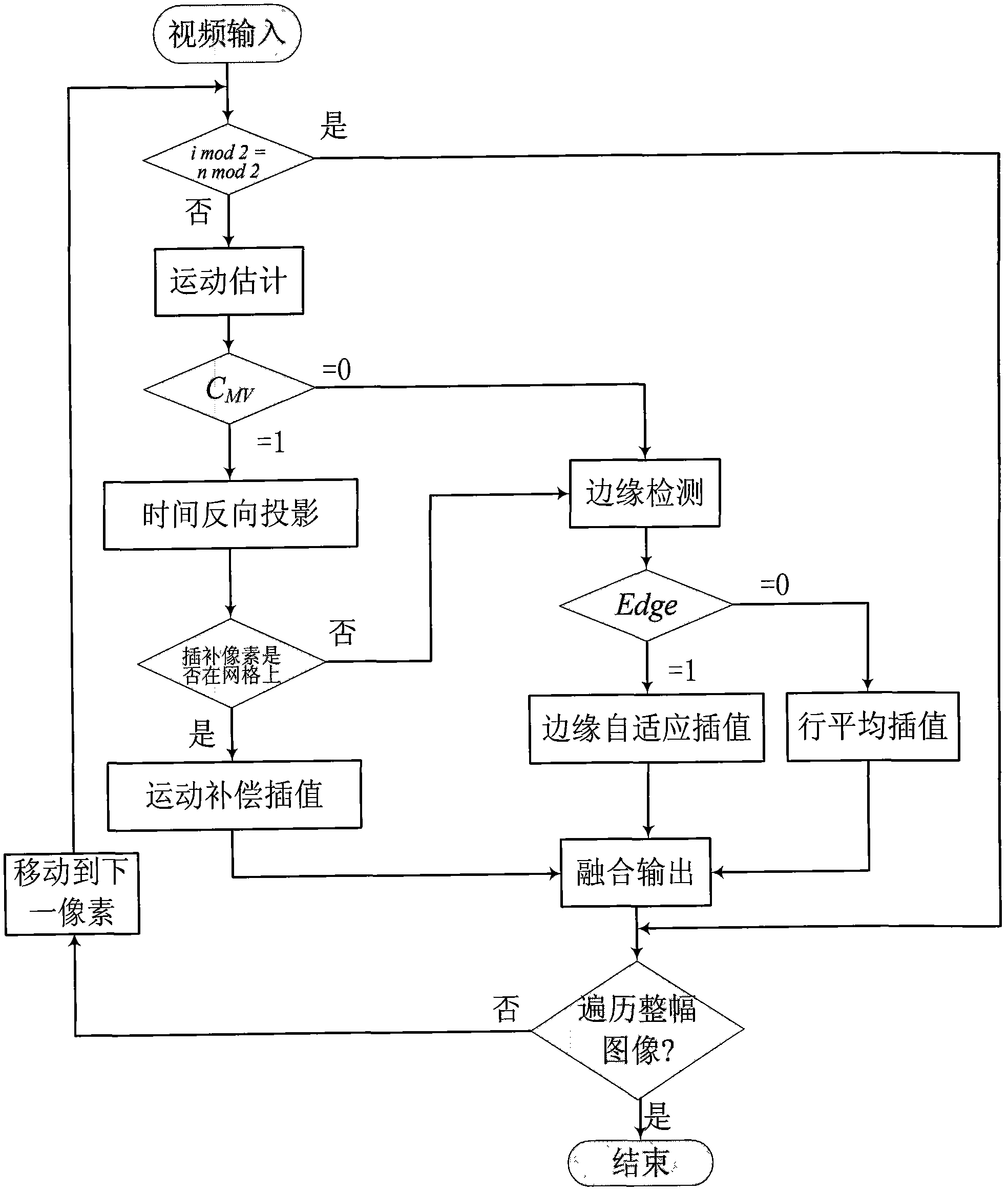
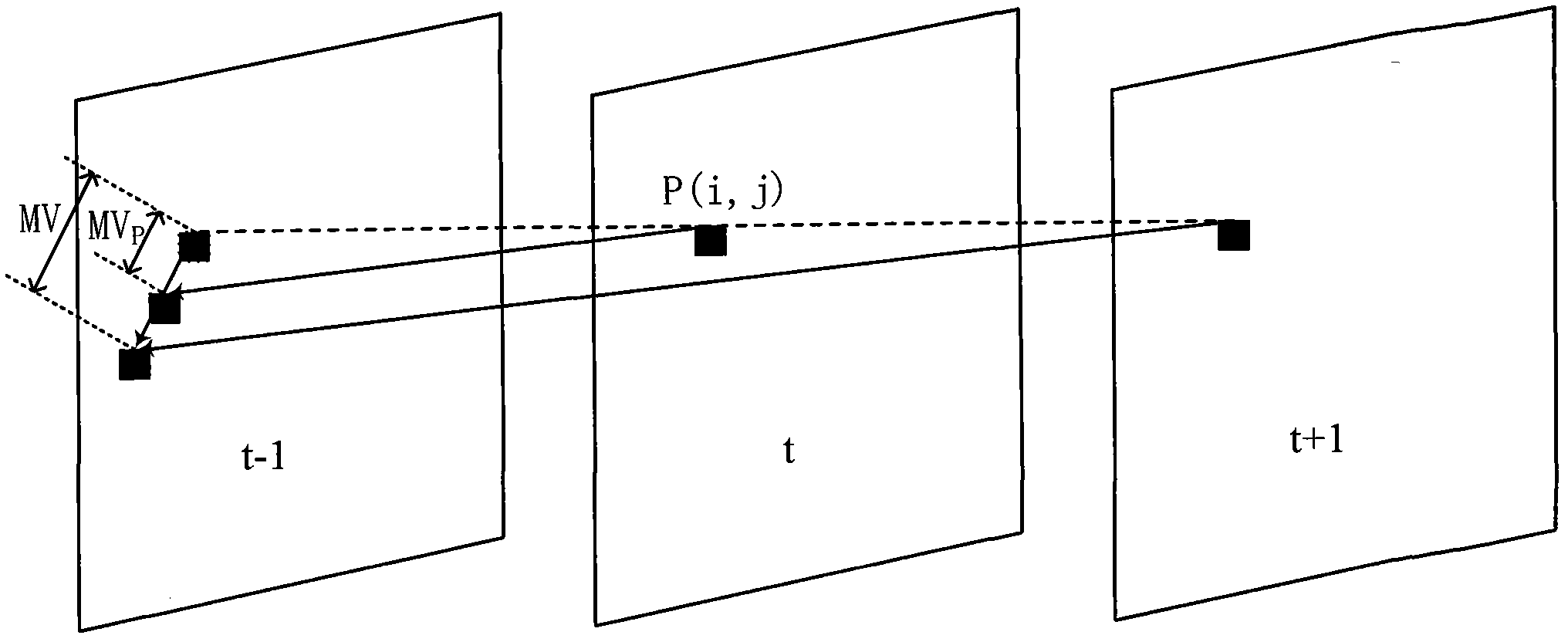
Motion compensation de-interlacing method based on adaptive interpolation
InactiveCN102025960AImprove continuityProtect sharpnessTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMotion vectorBack projection
The invention discloses a motion compensation de-interlacing method based on adaptive interpolation, which belongs to the technical field of image signal processing. The method comprises the following steps: performing motion estimation on an input video image by a centre bias diamond search algorithm to obtain a motion vector of a corresponding location; interpolating pixel points by a motion compensation method of time back projection; performing edge detection on the pixel points not meeting the motion compensation conditions; and judging whether the pixel point to be processed is on the edge. The edge direction of the pixel points on the edge is calculated and directional interpolation is performed; average interpolation is performed on the pixel points which are not on the edge; and the entire image is traversed to finish the de-interlacing processing of the entire image. Through the invention, adaptive selective interpolation is performed on the information such as motion vector and edge, the advantages of motion compensation interpolation and edge adaptive directional interpolation are automatically combined, the interpolation error caused by inaccurate motion estimation is suppressed, and the edge continuity and picture sharpness are protected.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Single pass adaptive interpolation filter
InactiveCN102037732ATelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionIndirect Expenditures
Owner:MEDIATEK SINGAPORE PTE LTD SINGAPORE
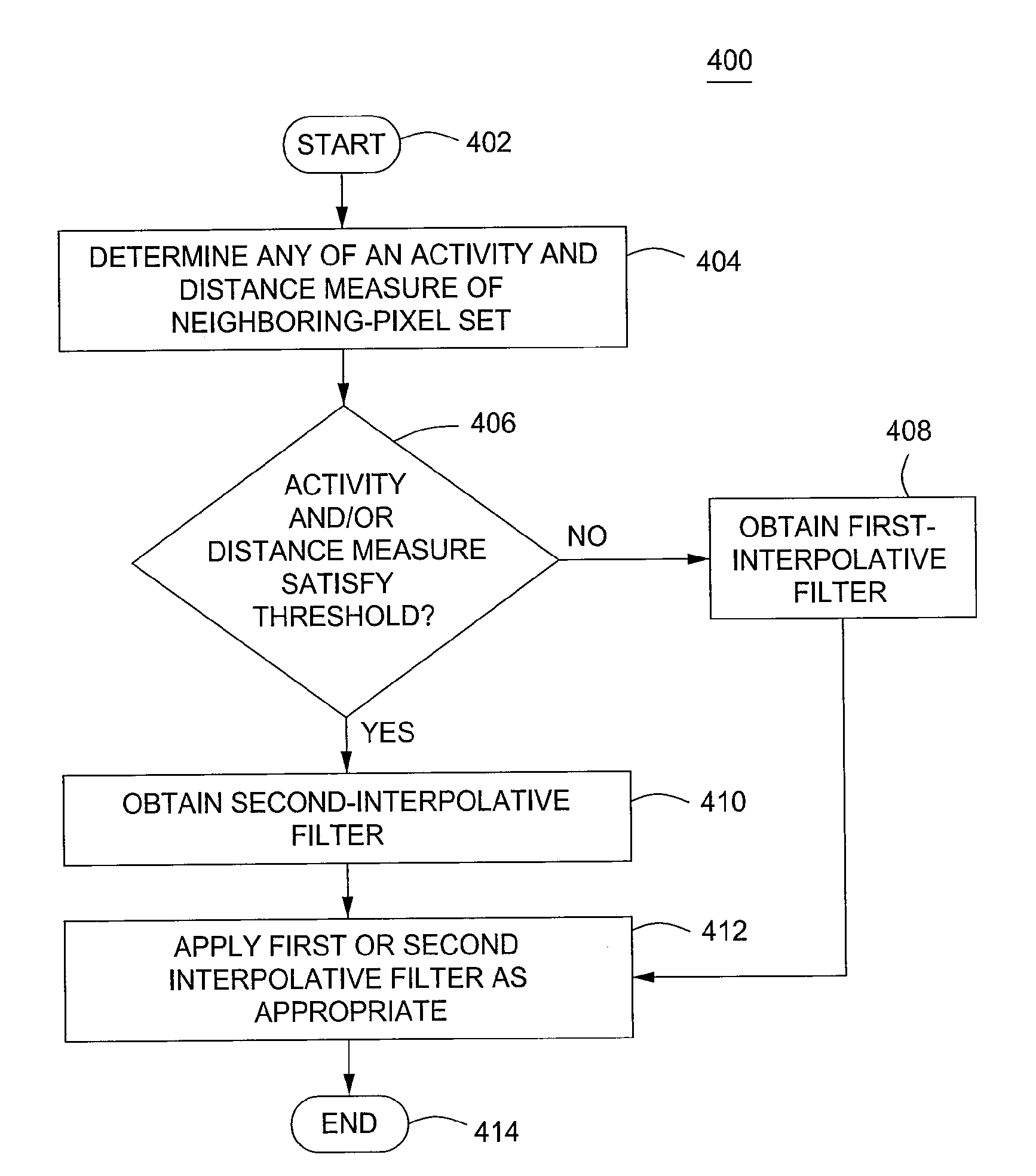
Intra prediction with adaptive interpolation filtering for image compression
ActiveUS20100111431A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionImage compression
A method and apparatus for adaptive interpolation filtering for image compression is disclosed. The method includes determining an activity measure associated with a set of pixels neighboring a pixel undergoing intraframe prediction or a distance measure between at least one pixel in the set of pixels and the pixel undergoing intraframe prediction, and selecting a filter for filtering at least a portion of the set of pixels in accordance with the at least one of the activity measure or the distance measure.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
System and method for adaptive interpolation of images from patterned sensors
ActiveUS7643676B2Computationally efficientImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPattern recognitionColor image
A adaptive filter interpolation method and system for the demosaicing of color images. In general, input pixels are input in a Bayer-mosaiced pattern (only one color per pixel), and output pixels are in full RGB mode (three color values per pixel). For each pixel location, in raster scan order, the processing steps can be summarized as follows. Following a regular raster scanning order (from left to right and top to bottom), for each pixel location horizontal and vertical gradients are first computed (whose computation depends on the available color for that pixel), and from those the appropriate interpolation filters are chosen from a small set of predetermined filters. Then, the chosen filters are applied to interpolate the missing data.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Computed tomography device and method using circular-pixel position-adaptive interpolation
ActiveUS20100119034A1Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationComputed tomographyX-ray
A method of computed-tomography and a computed-tomography apparatus where a interpolation kernel width is adaptively determined as a function of the distance from the x-ray source to the reconstruction pixel. The width of the kernel is the projection of the reconstruction pixel on the detector. The method can be implemented in the channel direction. The method can also be implemented in the segment direction, or in the channel and segment directions at the same time. Backprojection is performed using the adaptive kernel width and may by used with helical and circular scanning, and with cone-beam or fan beam x-ray CT.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Adaptive nonlinear image enlargement using wavelet transform coefficients
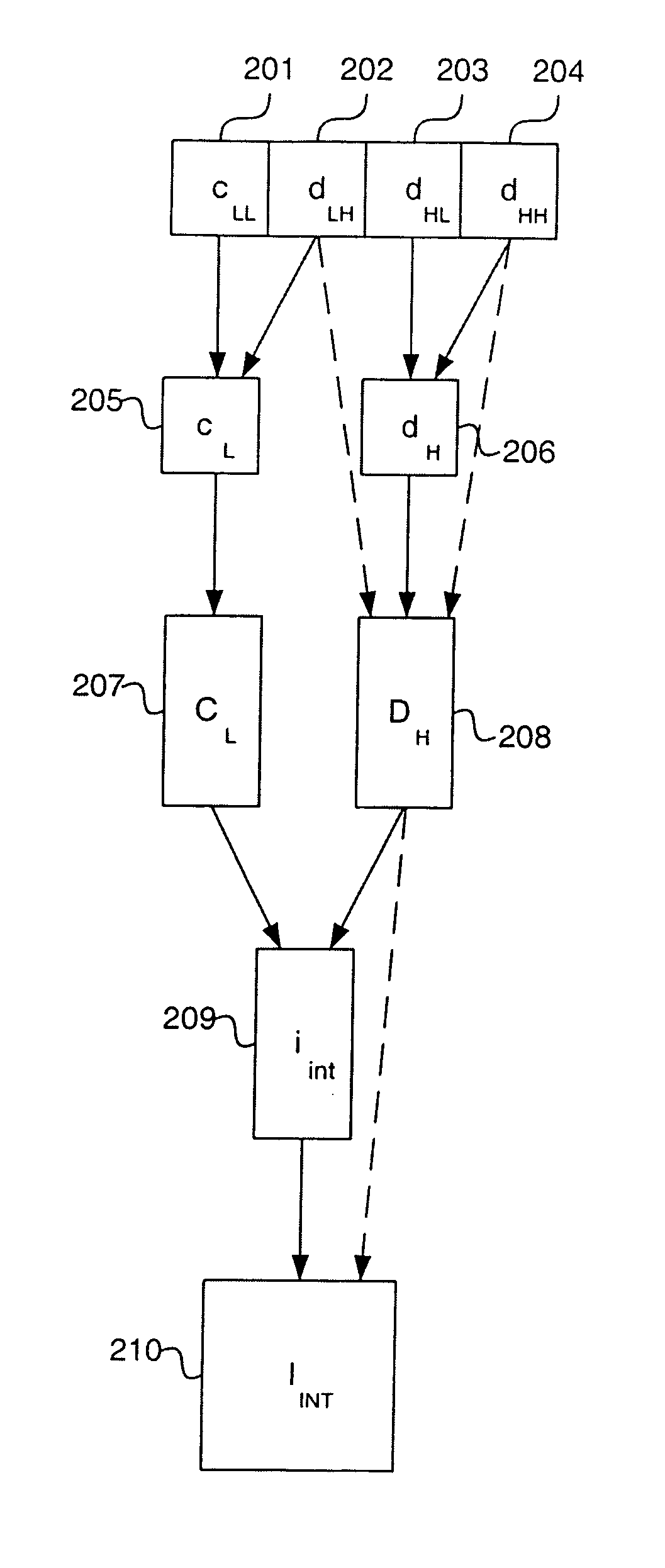
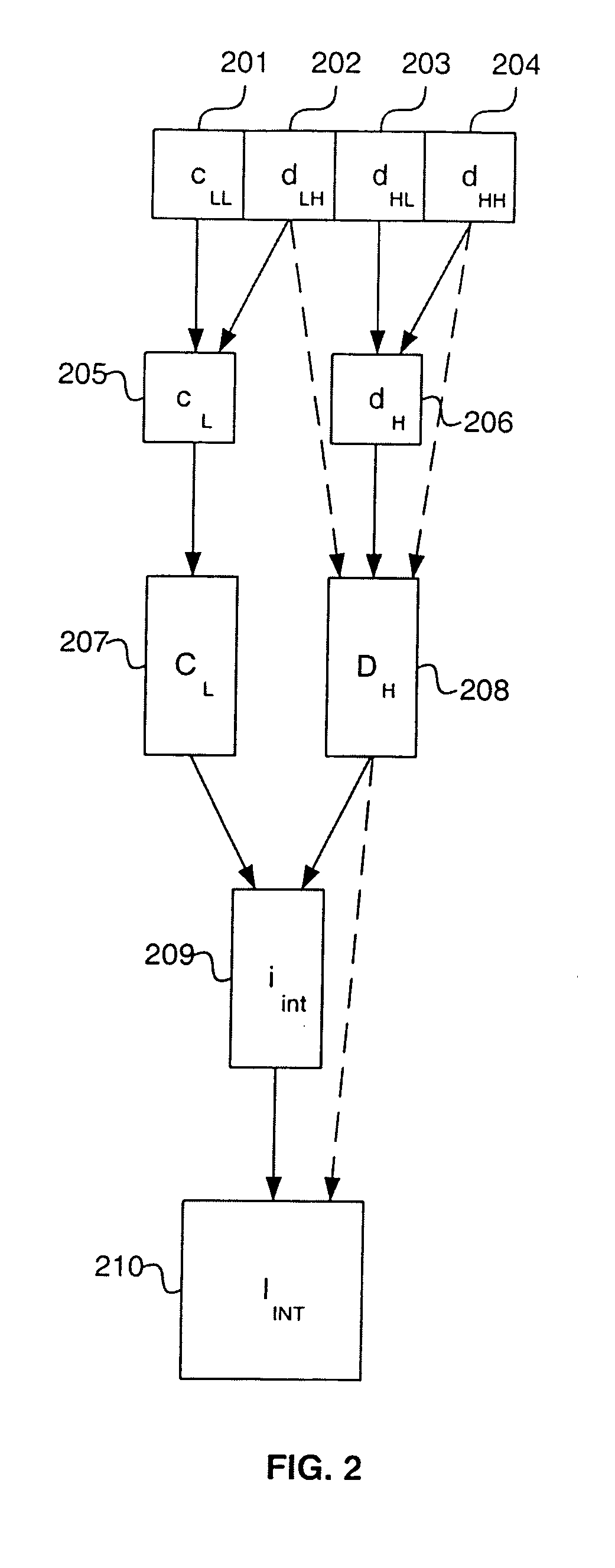
A method and apparatus for enlargement and resolution enhancement of images in the wavelet domain is described. In one embodiment, the method comprises receiving a wavelet representation of an image, where the wavelet representation comprises wavelet coefficients, and performing localized adaptive interpolation on the wavelet coefficients in the wavelet domain.
Owner:RICOH KK
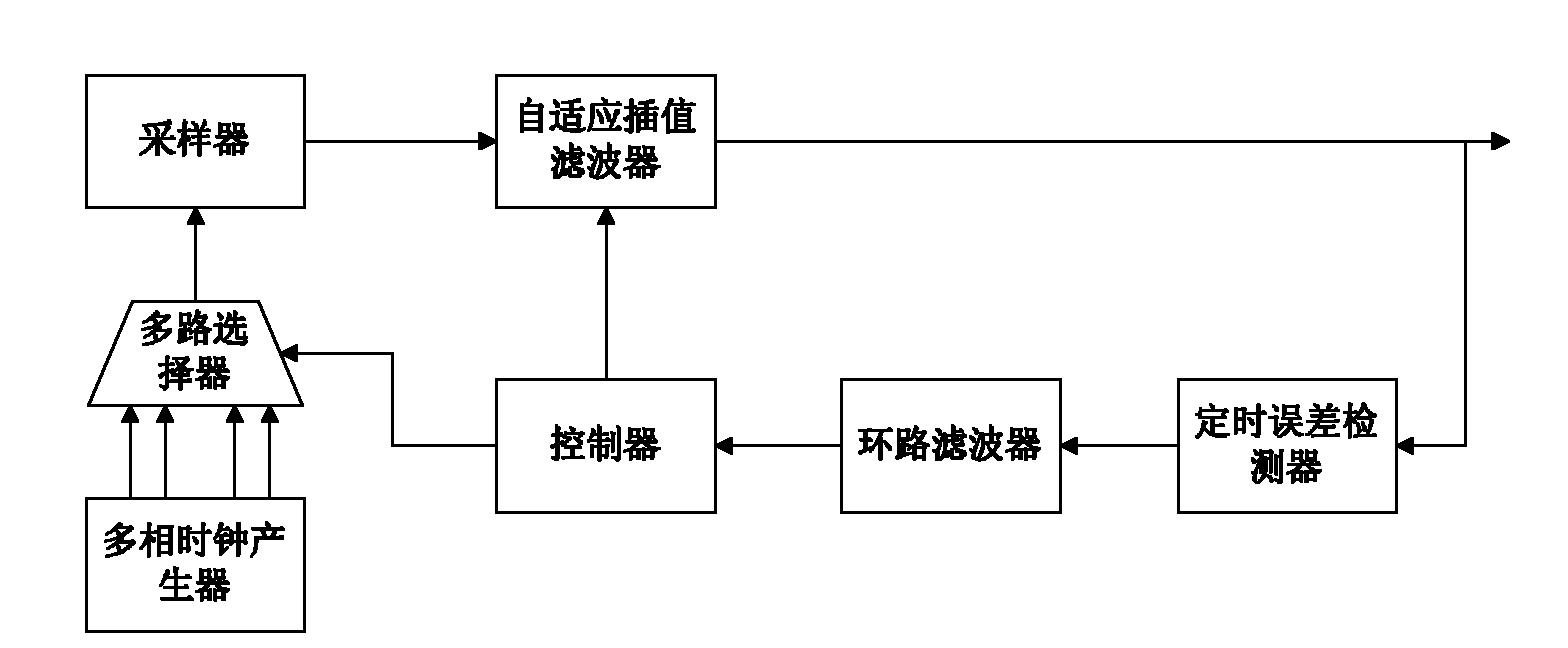
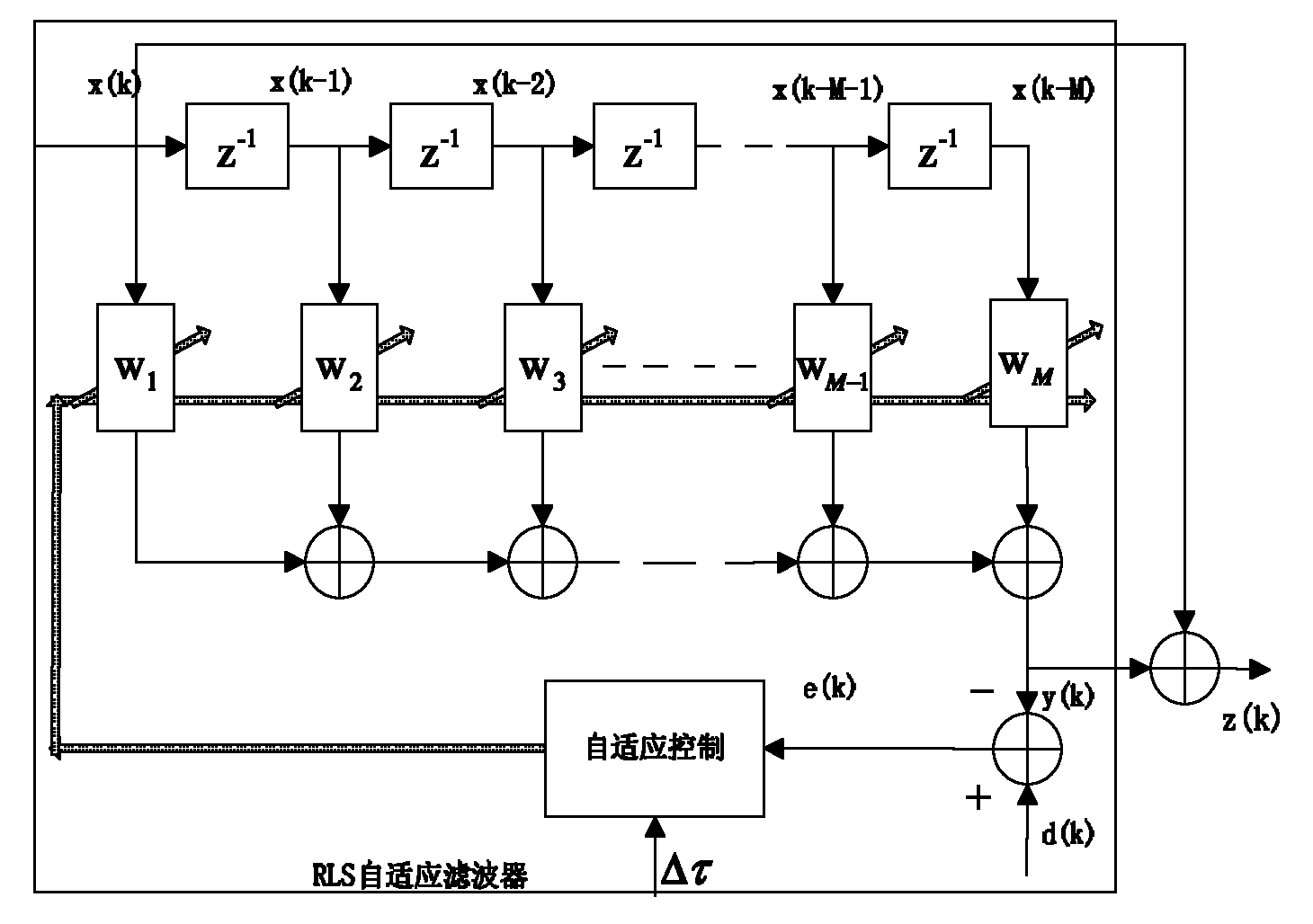
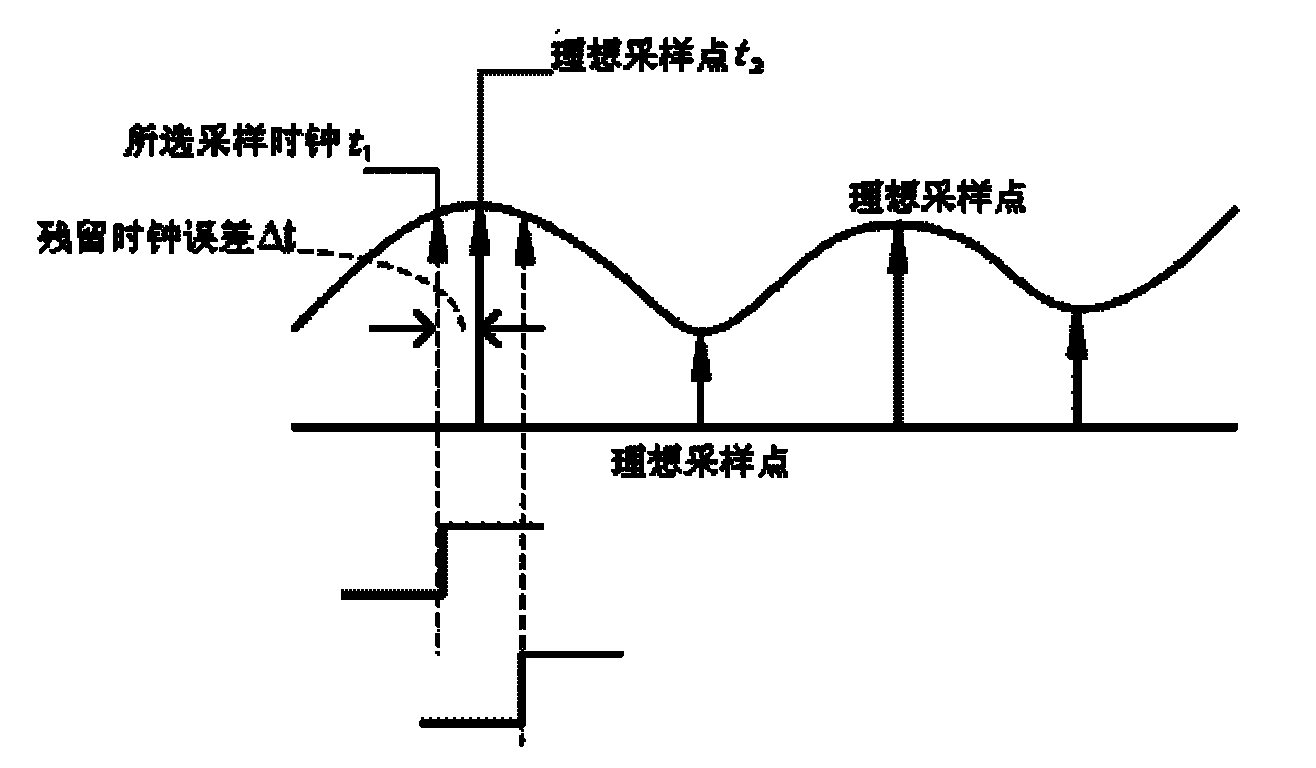
Timing synchronization device based on symbol rate adaptive-interpolation and synchronization method thereof
InactiveCN101895334AReduce the sampling frequencyReduce power consumptionRadio transmission for post communicationHigh level techniquesLoop filterMultiplexer
The invention provides a timing synchronization device based on a symbol rate adaptive-interpolation and a synchronization method thereof, belonging to the wireless communication technical field. The device comprises a sampler, an adaptive-interpolation filter, a timing error detector, a loop filter, a controller, a multi-phase clock generator and a multiplexer, wherein, the sampler is connected with the adaptive-interpolation filter; the adaptive-interpolation filter is connected with the timing error detector; the timing error detector is connected with the loop filter; the loop filter is connected with the controller; the controller is connected with the adaptive-interpolation filter and the multiplexer; the multi-phase clock generator is connected with the multiplexer; and the multiplexer is connected with the sampler. The invention greatly lowers sampling frequency so as to reduce power consumption, obtains the result close to an ideal sampling value, reduces the number of multiphase clocks and lowers complexity.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
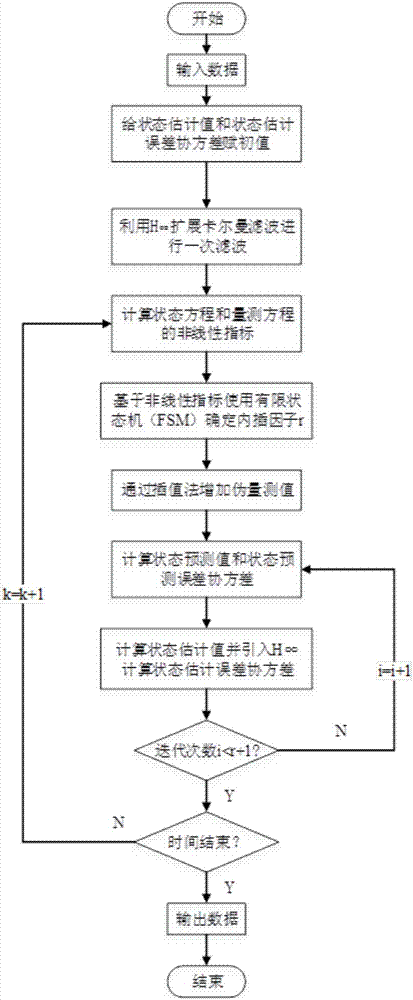
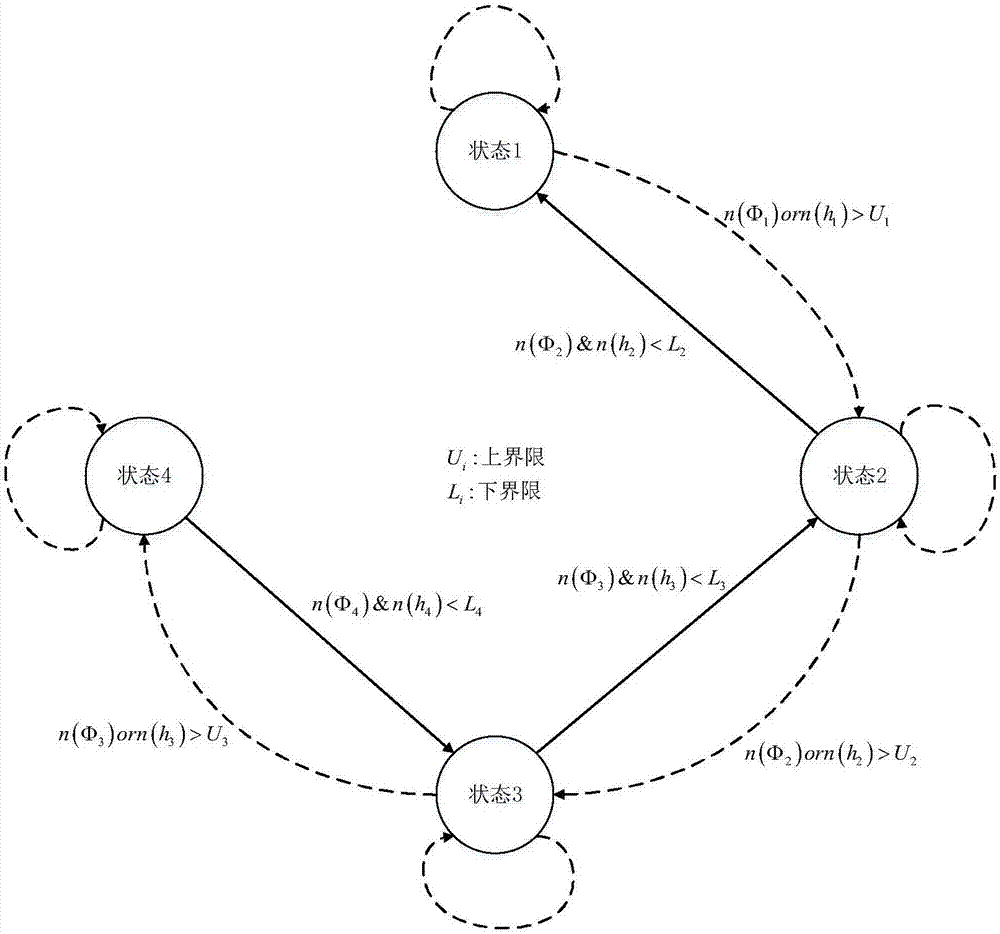
Interpolation H infinite expanded Kalman filtering generator dynamic state estimation method
ActiveCN107425548AImprove robustnessRobustSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsDynamo-electric machine testingState predictionEstimation methods
The invention discloses an interpolation H infinite expanded Kalman filtering (IHEKF) generator dynamic state estimation method comprising an adaptive interpolation part and a multi-step prediction and correction part; the method comprises the following steps: firstly, calculating state equation and measurement equation non-linear indexes before the multi-step prediction and correction part, using a limit state machine to determine an interpolation factor, and using an interpolation method to add a pseudo measurement value between two real measurement values according to the interpolation factor; carrying out multi-step prediction and correction according to the added pseudo measurement value, using an expanded Kalman filtering prediction step to obtain a state predicted value and a state prediction error covariance, further introducing H infinite into the expanded Kalman filtering correction step so as to correct the predicted value, thus obtaining a generator power angle, an electric angle speed estimation value and an estimation error covariance in a dynamo-electric transient process. According to example analysis results, the generator dynamic state estimation method can be accurately applied to the generator dynamic state estimation, and has excellent robustness.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
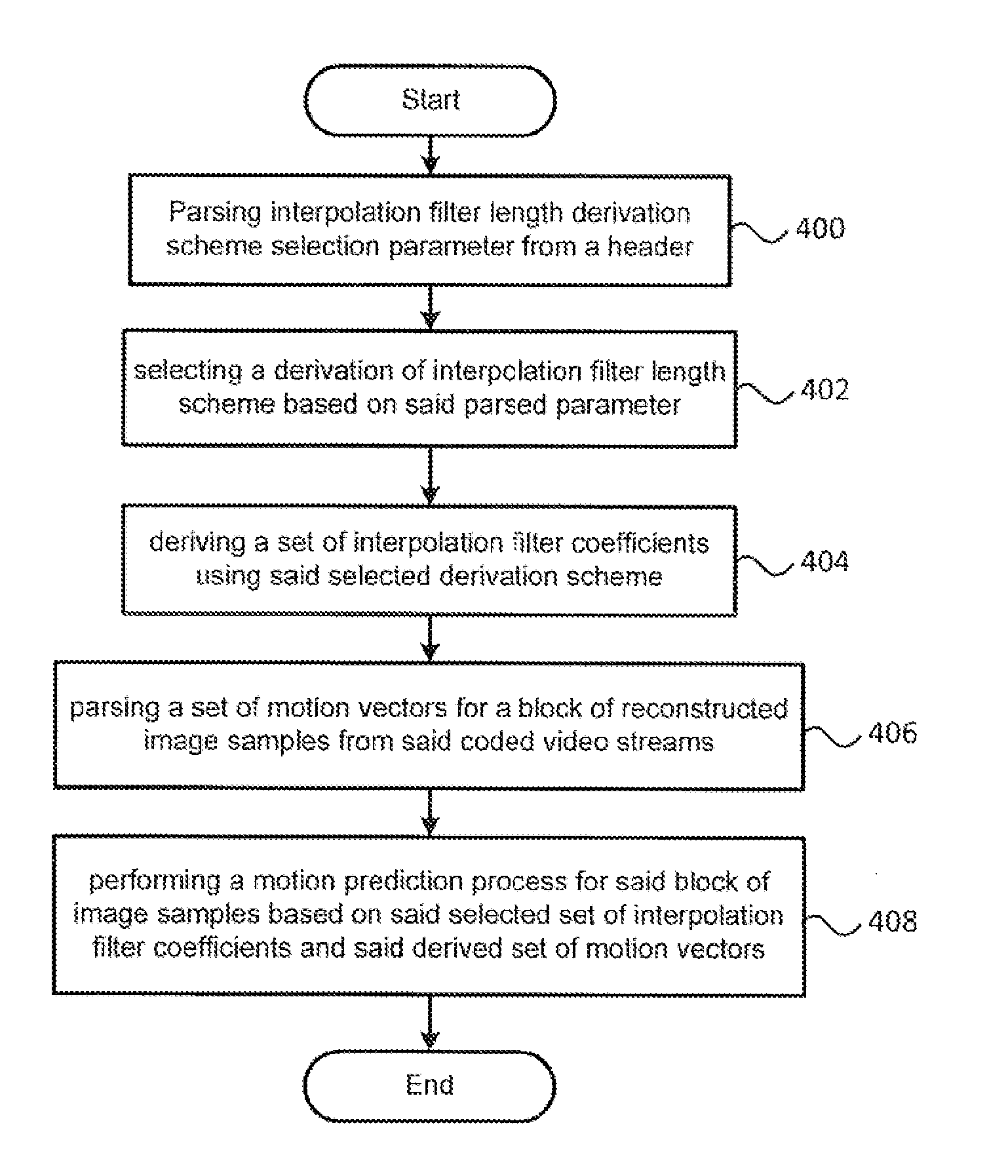
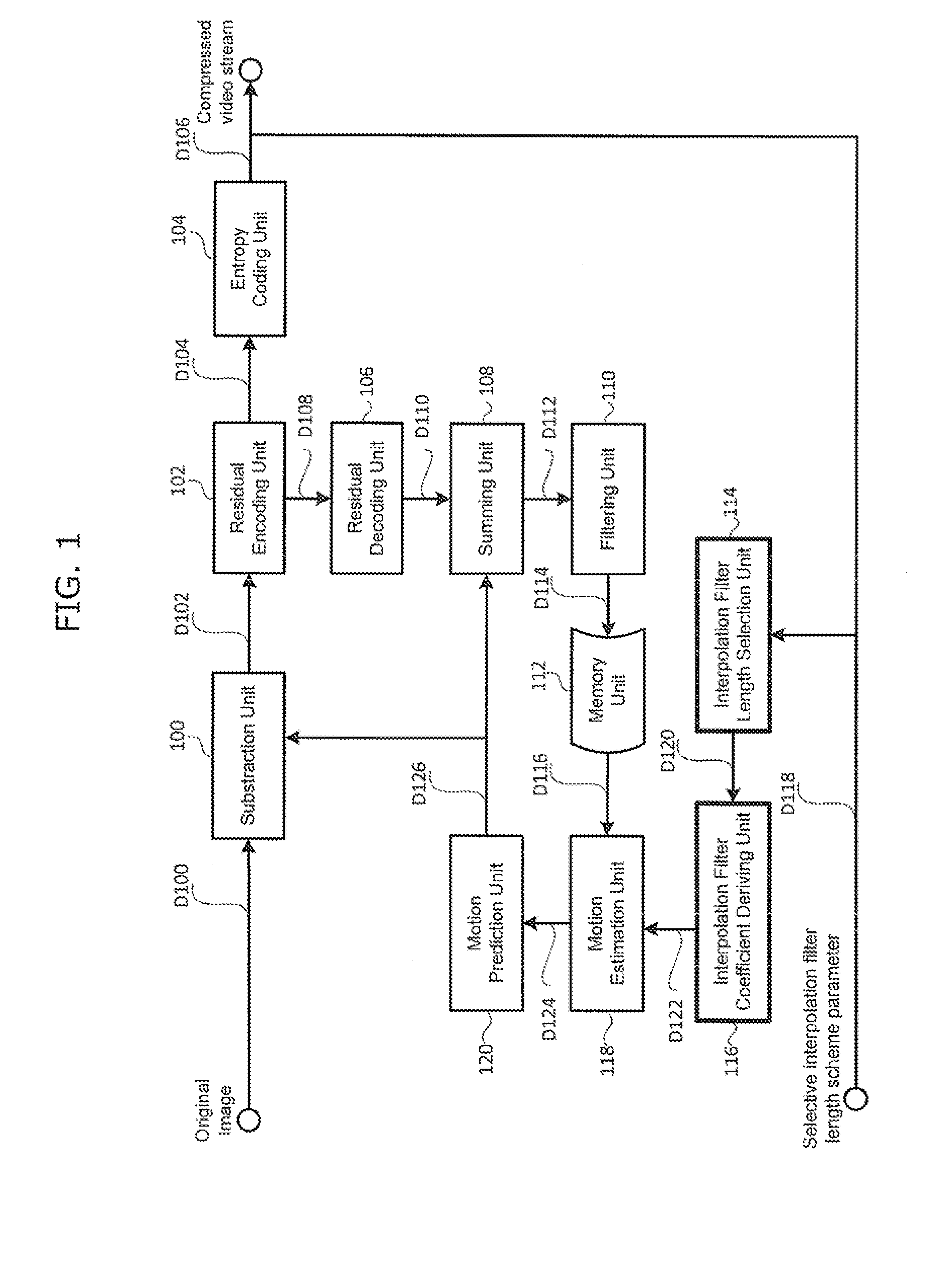
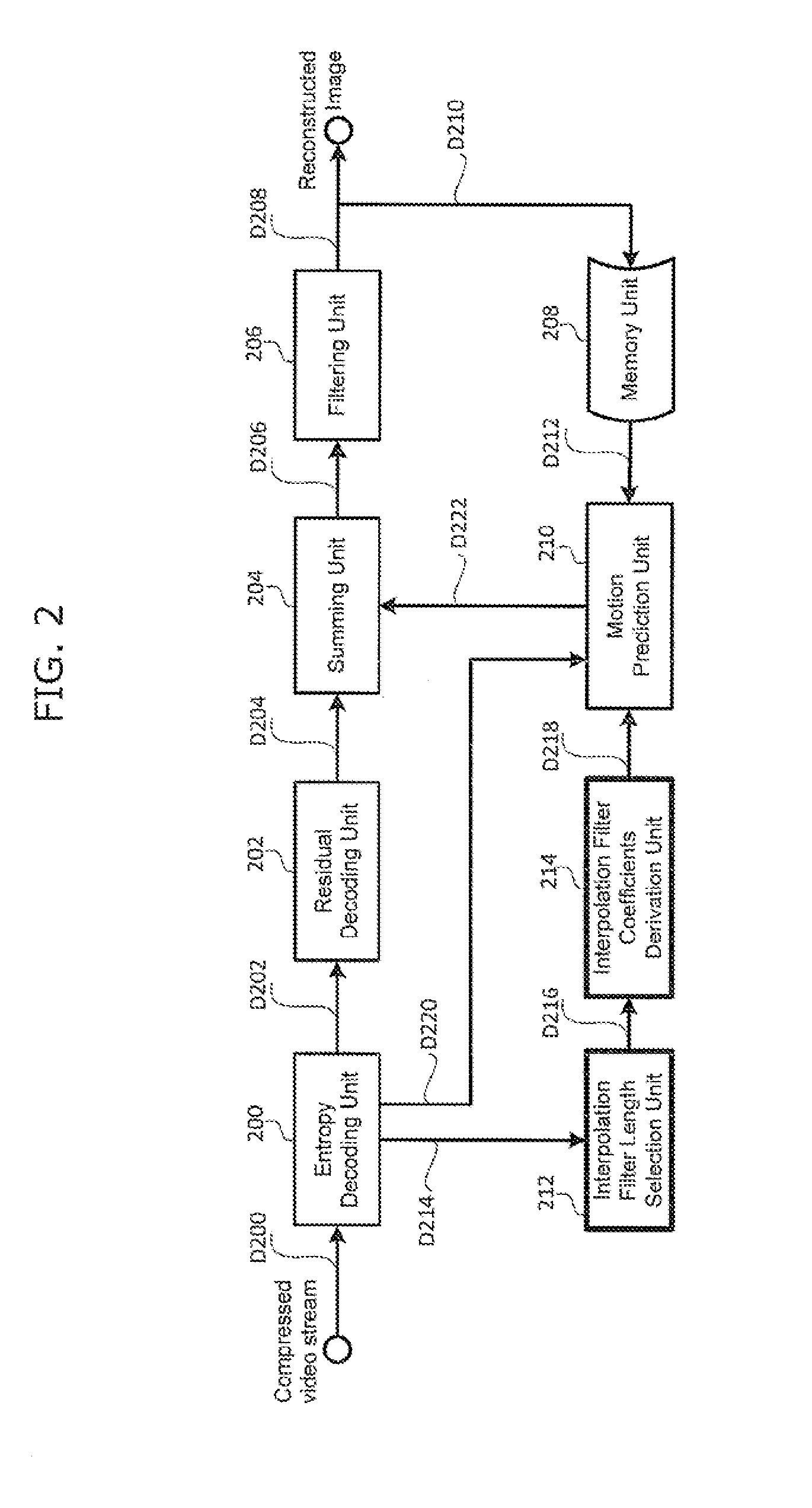
Methods and apparatuses for encoding and decoding video using adaptive interpolation filter length
InactiveUS20120230393A1Reducing memory bandwidth usageReduce memory bandwidthColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionImage resolutionVideo encoding
Recent video coding schemes support different size of interpolation filter length for interpolation process. However, the schemes are using fixed, one sized interpolation filter length for all different size of picture resolutions and all different size of inter predicted units, leading to undesired large memory bandwidth usage. Especially for large spatial resolution images or large prediction blocks, the required memory bandwidth is substantially increased by using fixed interpolation filter length. The current invention provides methods and apparatuses for selecting the different interpolation filter coefficients adaptively based on a pre-determined interpolation filter length selection scheme. The benefit of the current invention is in the form of saving memory bandwidth usage.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Layered scene decomposition CODEC system and methods
ActiveUS20190068973A1Reduced system transmission latencyHigh bandwidth rateImage analysisGeometric image transformationDecompositionComputer graphics (images)
A system and methods for a CODEC driving a real-time light field display for multi-dimensional video streaming, interactive gaming and other light field display applications is provided applying a layered scene decomposition strategy. Multi-dimensional scene data is divided into a plurality of data layers of increasing depths as the distance between a given layer and the plane of the display increases. Data layers are sampled using a plenoptic sampling scheme and rendered using hybrid rendering, such as perspective and oblique rendering, to encode light fields corresponding to each data layer. The resulting compressed, (layered) core representation of the multi-dimensional scene data is produced at predictable rates, reconstructed and merged at the light field display in real-time by applying view synthesis protocols, including edge adaptive interpolation, to reconstruct pixel arrays in stages (e.g. columns then rows) from reference elemental images.
Owner:AVALON HOLOGRAPHICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com