Adaptive interpolation
a technology of real-time oscilloscope and interpolation, applied in the field of real-time oscilloscope, can solve the problems of truncated sinc filter failing to reject an undesired frequency, affecting the use of the maximum theoretical available bandwidth,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
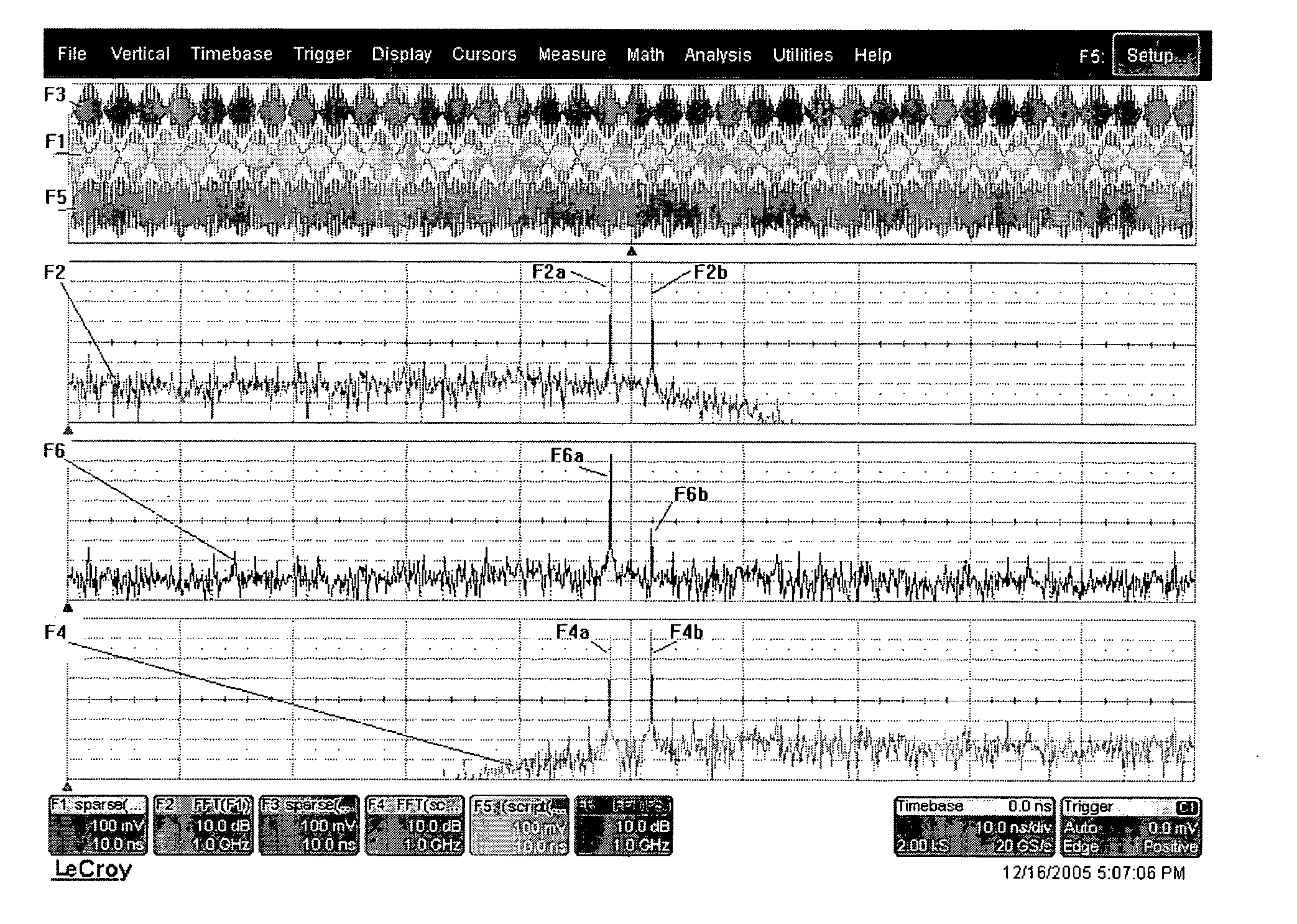
[0035]FIG. 8 is a flowchart diagram detailing the preferred functioning of a HF adaptive upsample filter (block 80 of FIG. 11);
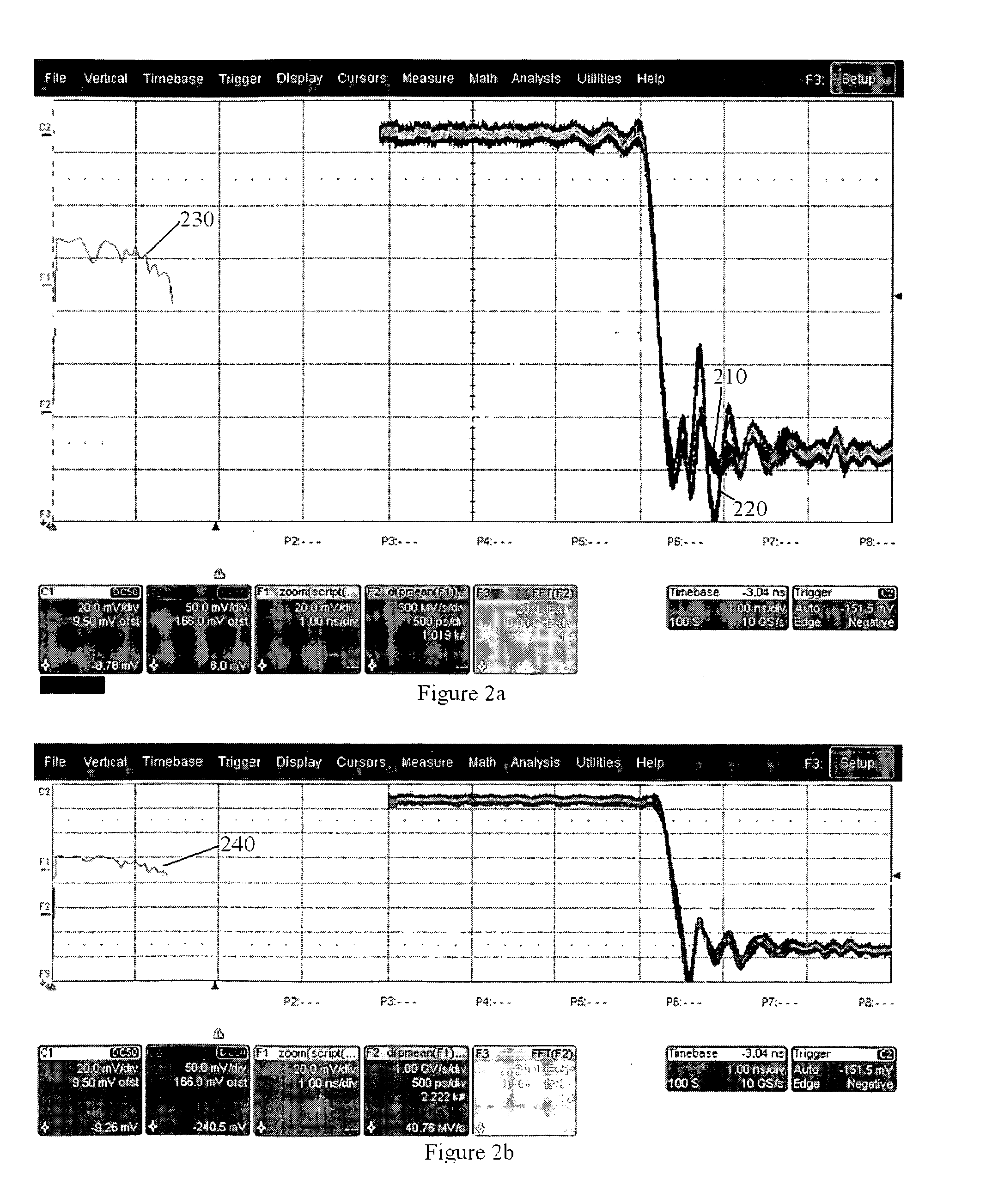
[0036]FIG. 9 is a graphical representation of an impulse response during various steps of a time-domain calibration process in the simplified case of flat group delay and the appearance of a brief impulse, such as the calibration pulse itself, on the instrument calibrated in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention;
[0037]FIG. 10 is a block diagram depicting various hardware elements of the DSO in the preferred embodiment of the present invention;
[0038]FIG. 11 is a block diagram depicting various software elements in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention;
[0039]FIG. 12 is a block diagram showing how the inputs and DBI hardware outputs are connected to the scope front-end in accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention;
[0040]FIG. 13 depicts the desired arrangement of the bands and LO and sampling c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com