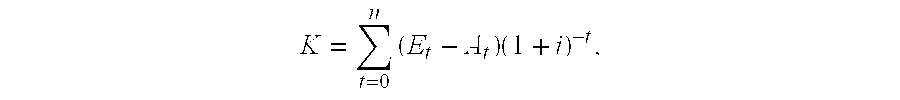Patents
Literature
87 results about "Unit cost" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The unit cost is the cost incurred by a company to produce, store and sell one unit of a particular product. Unit costs include all fixed costs and all variable costs involved in production.
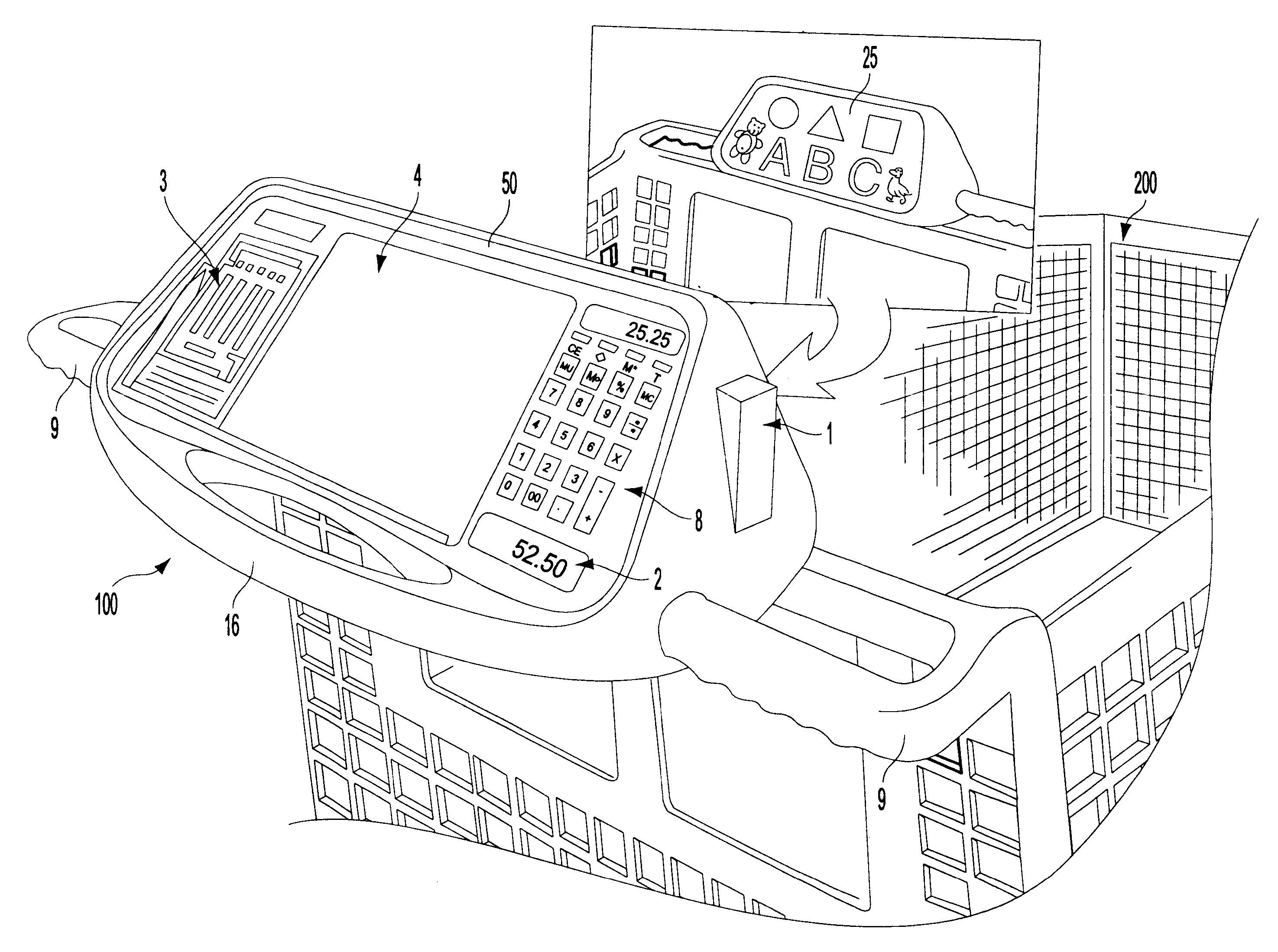
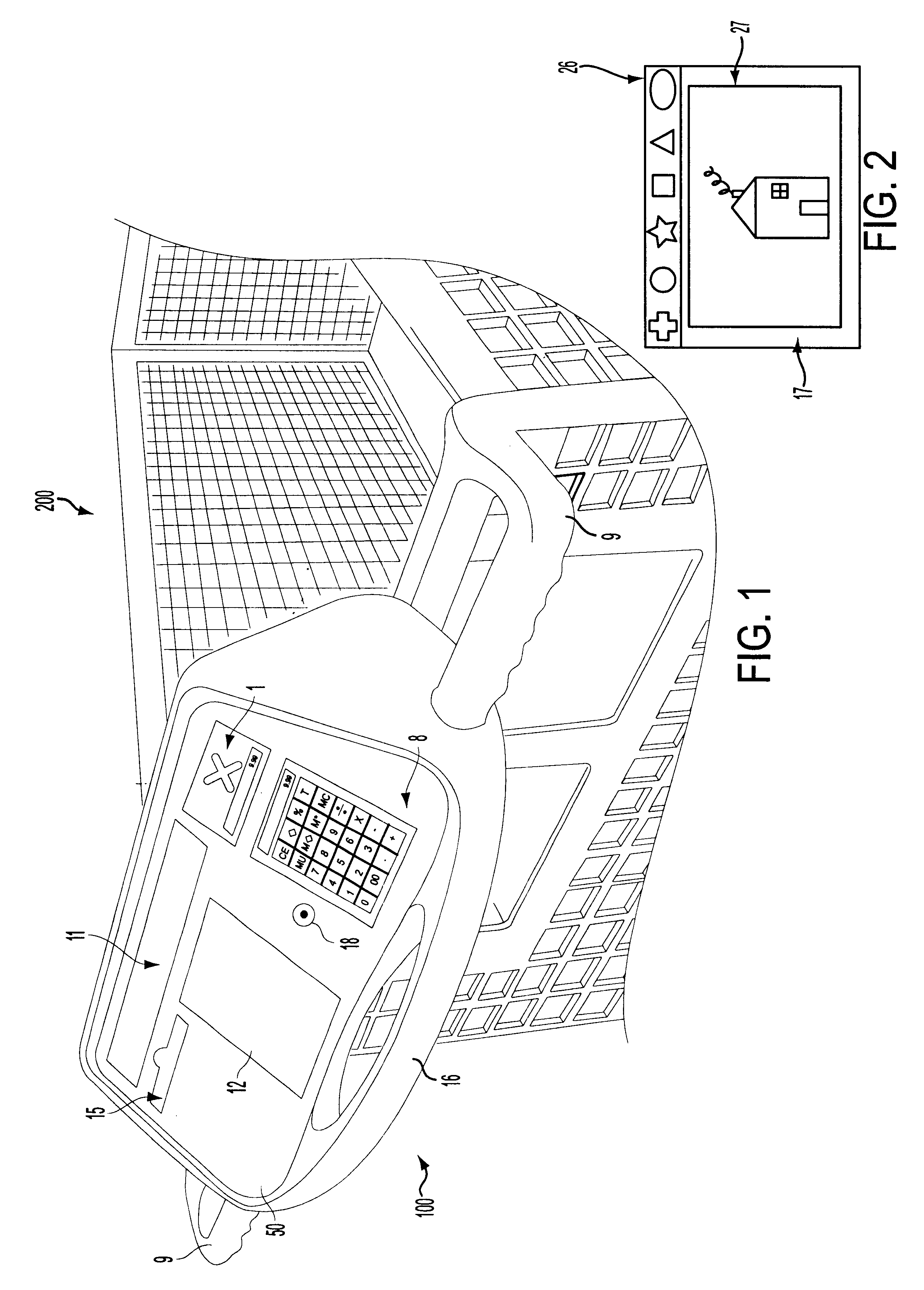
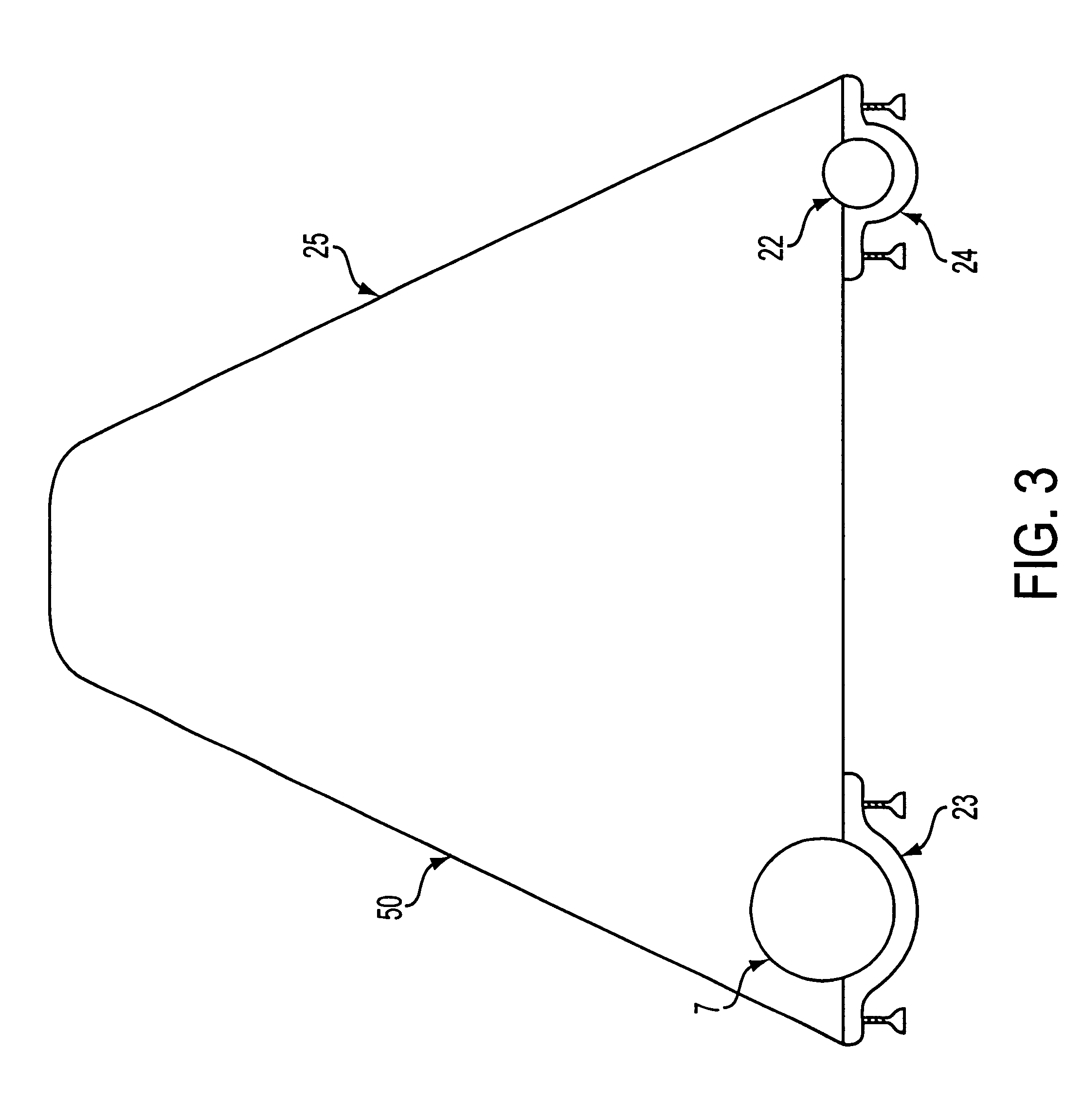
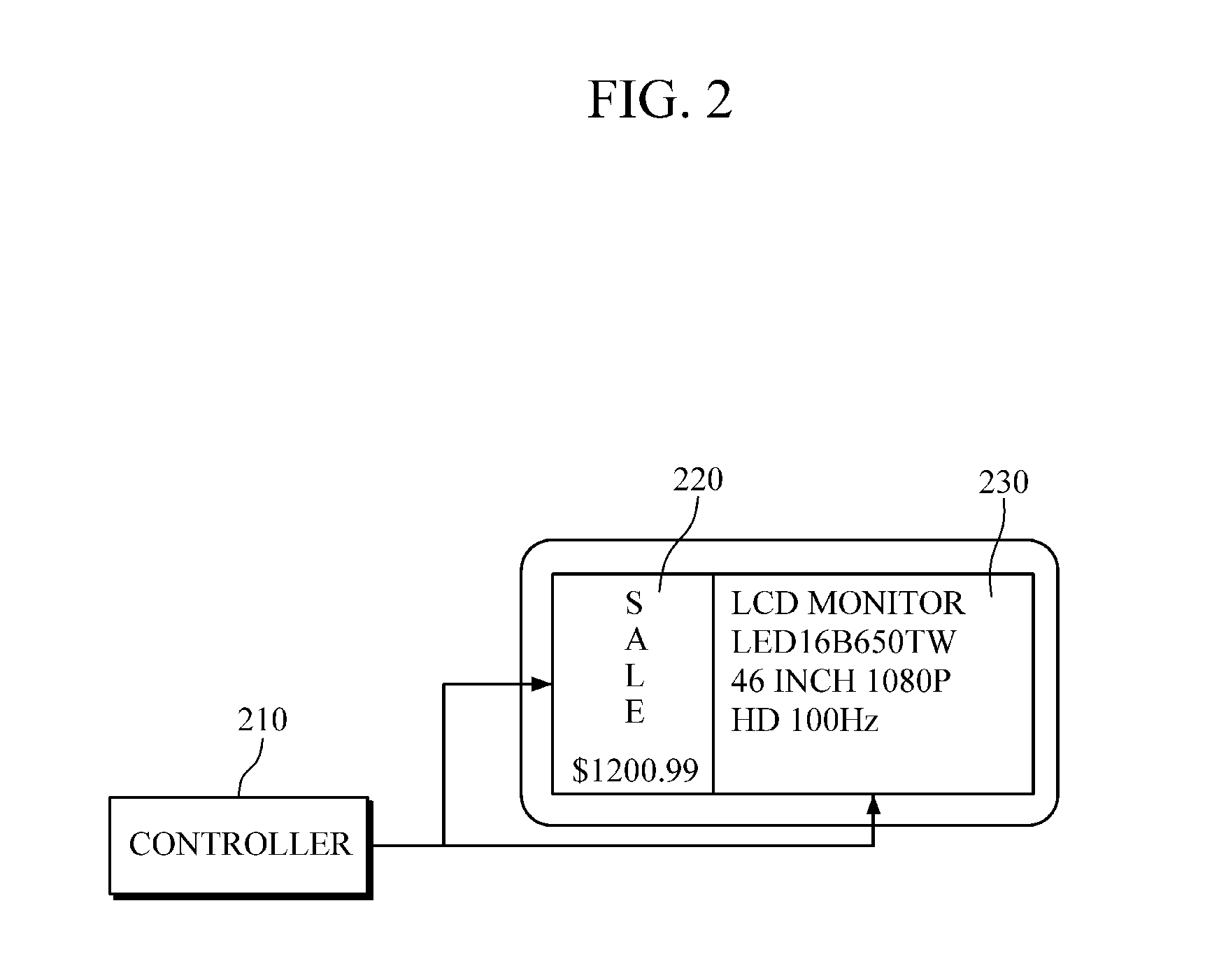
Self scanning and check out shopping cart-based electronic advertising system
InactiveUS6484939B1Credit registering devices actuationCash registersComputer graphics (images)Barcode
A console for the input and display of consumer product information such as pricing, etc. The console may be built into the handle of the shopping cart or as a retrofit application on existing handles. The console has a product information input device for numerical values such as product pricing, cost per unit, etc. The apparatus has a calculator and output display for such data. Some space on the console will likely be dedicated to a display panel for advertising. The console may be equipped with a bar code scanner as an alternate means of inputting such consumer data. The console should have an output display, such as a monitor, and / or a readout in order to display the product information such as: cost per unit. A video monitor may be used in connection with the console in order to provide advertising information related to products.
Owner:SMART MEDIA OF DELAWARE
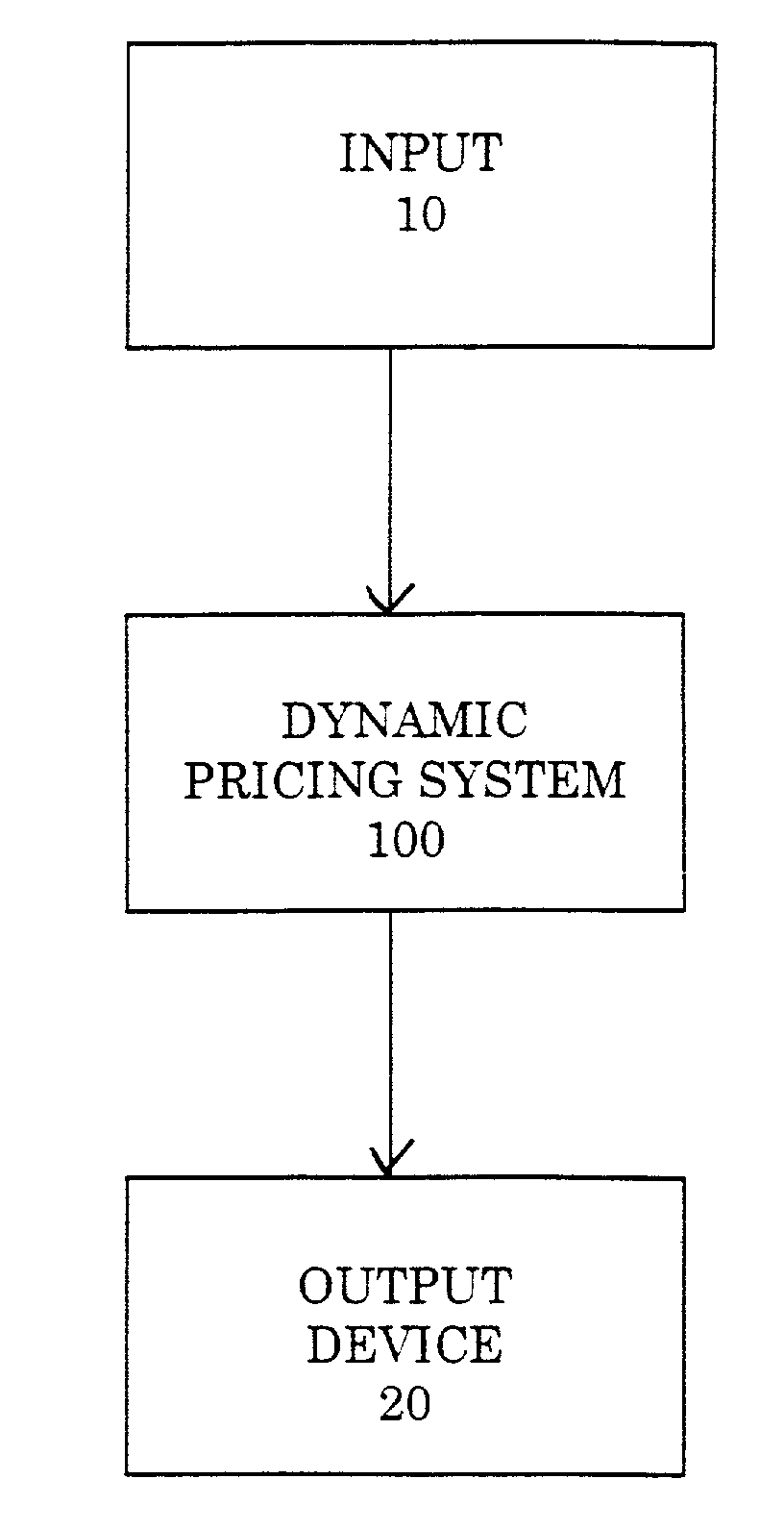
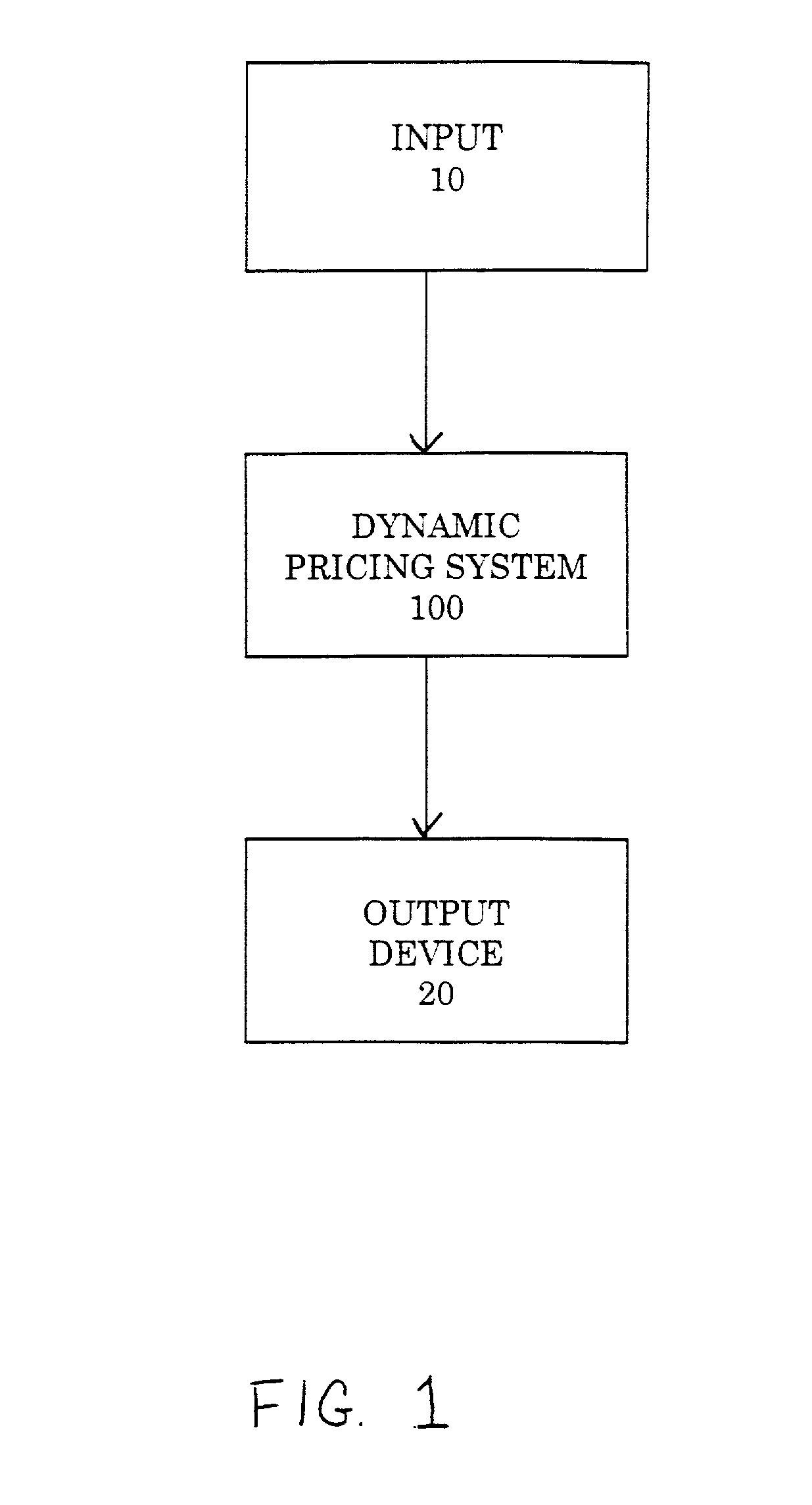
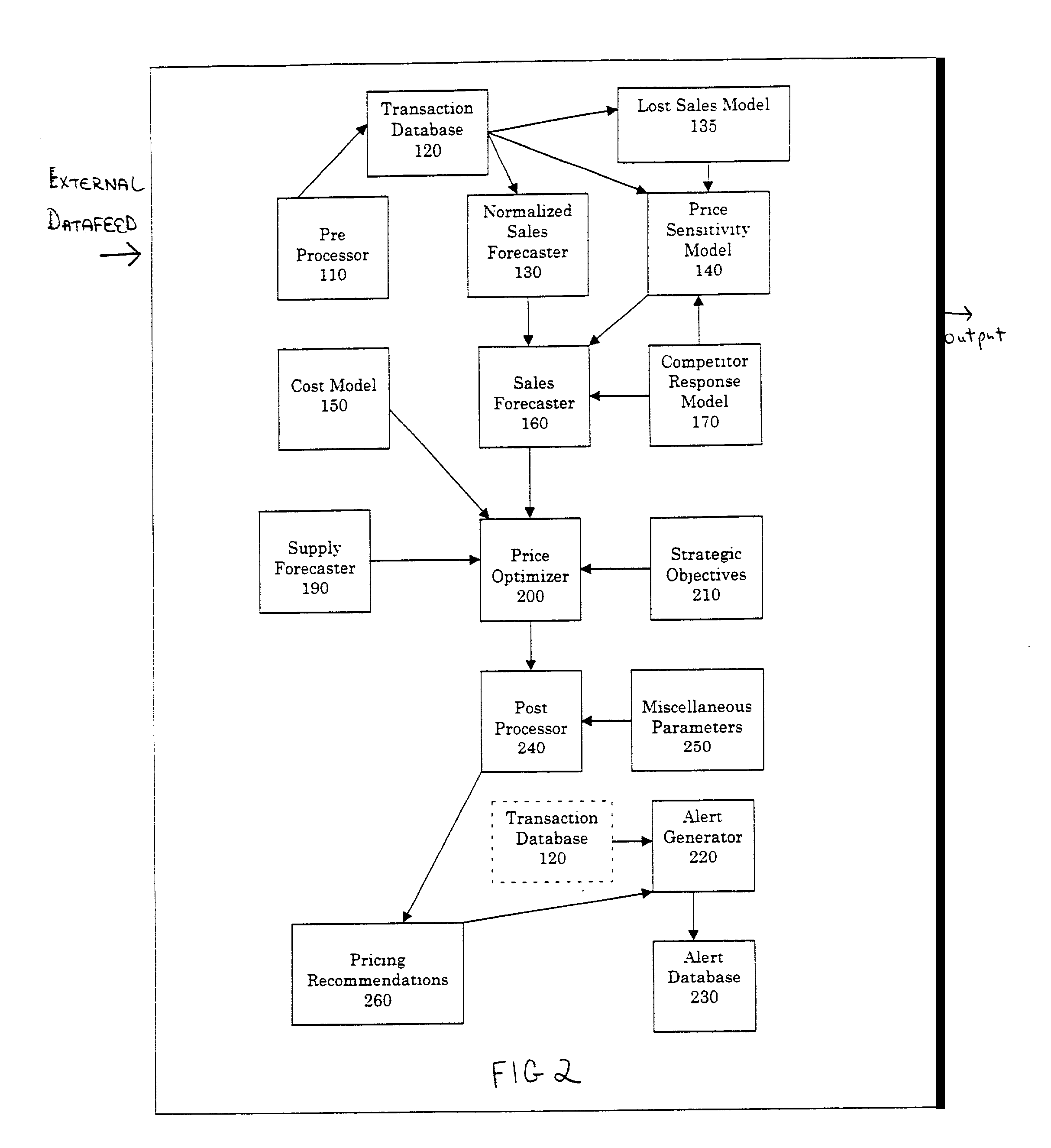
Dynamic pricing system
ActiveUS7133848B2Improve forecast accuracyBuying/selling/leasing transactionsElectric/magnetic computingProduct typeUnit cost
The present invention provides a dynamic pricing system that generates pricing recommendations for each product in each market. In particular, the system normalizes historic pricing and sales data, and then analyzes this historic data using parameters describing the user's business objectives to produce a pricing list to achieve these objectives. The system uses historical market data to forecast expected sales according to a market segment, product type, and a range of future dates and to determine the effects of price changes on the forecasted future sales. The system further calculates unit costs for the product. The system then estimates profits from sales at different prices by using the sales forecasts, adjusting these sales forecasts for changes in prices, and the costs determinations. The system optionally optimizes prices given current and projected inventory constraints and generates alerts notices according to pre-set conditions.
Owner:BLUE YONDER GRP INC
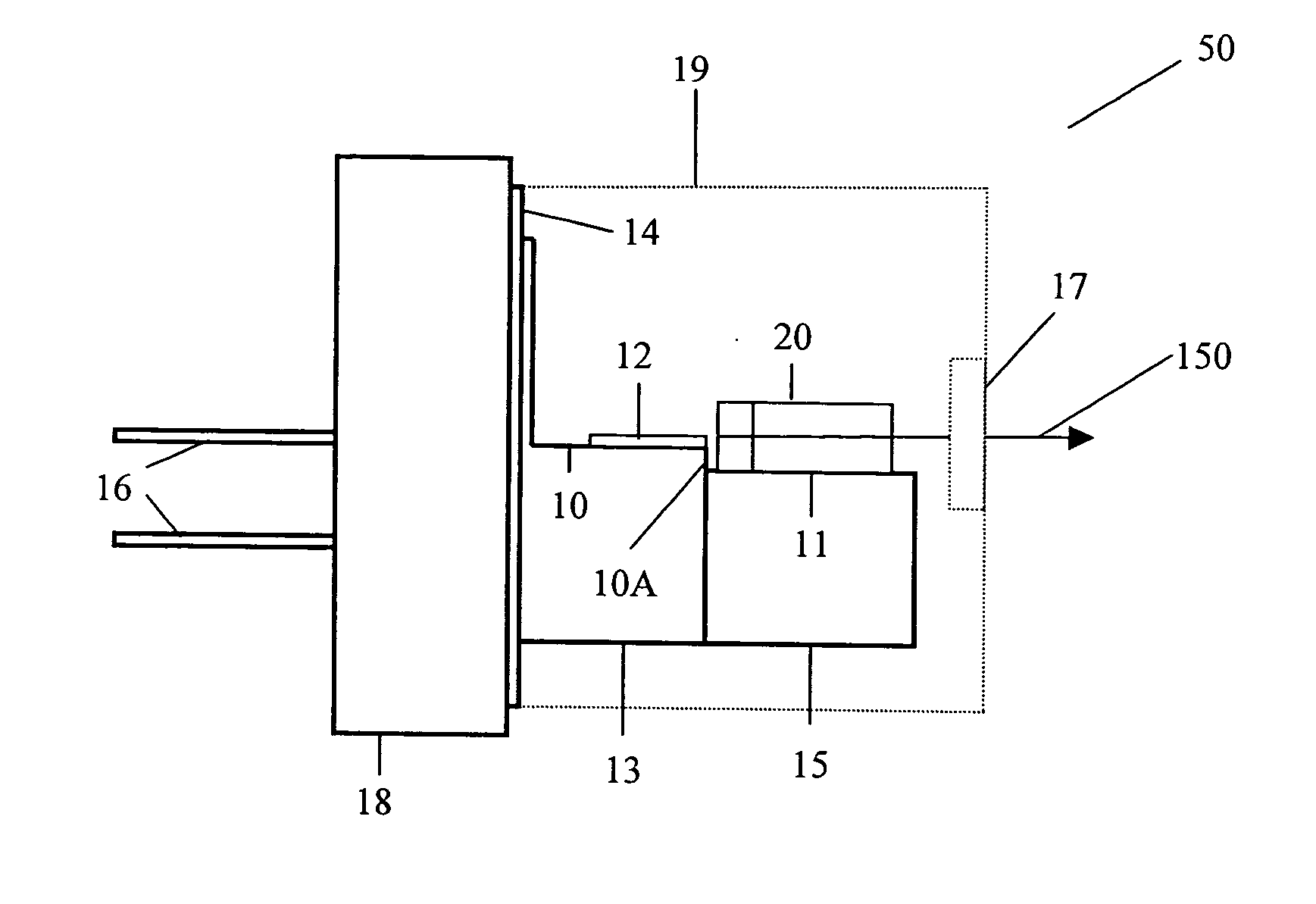
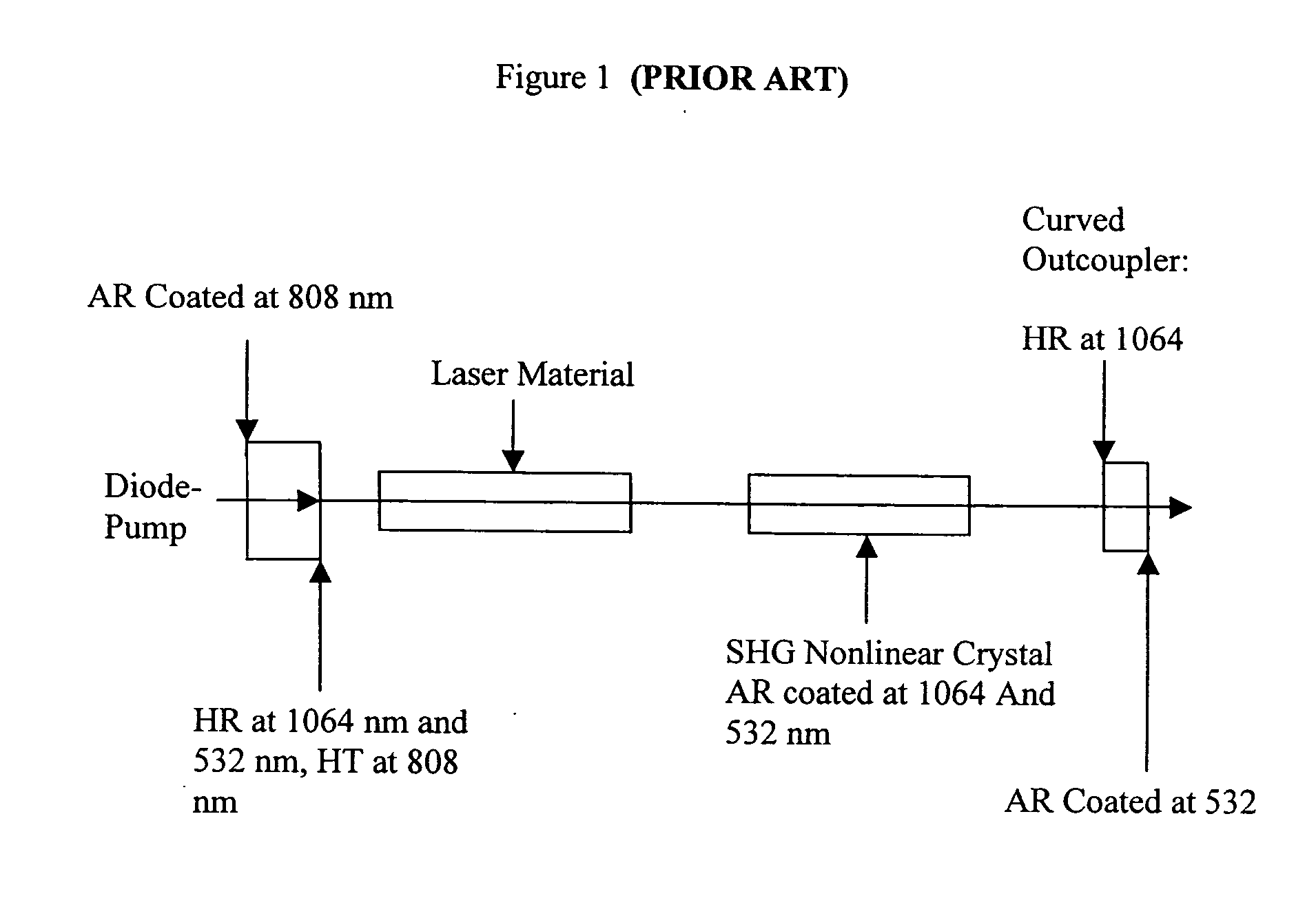
High density methods for producing diode-pumped micro lasers
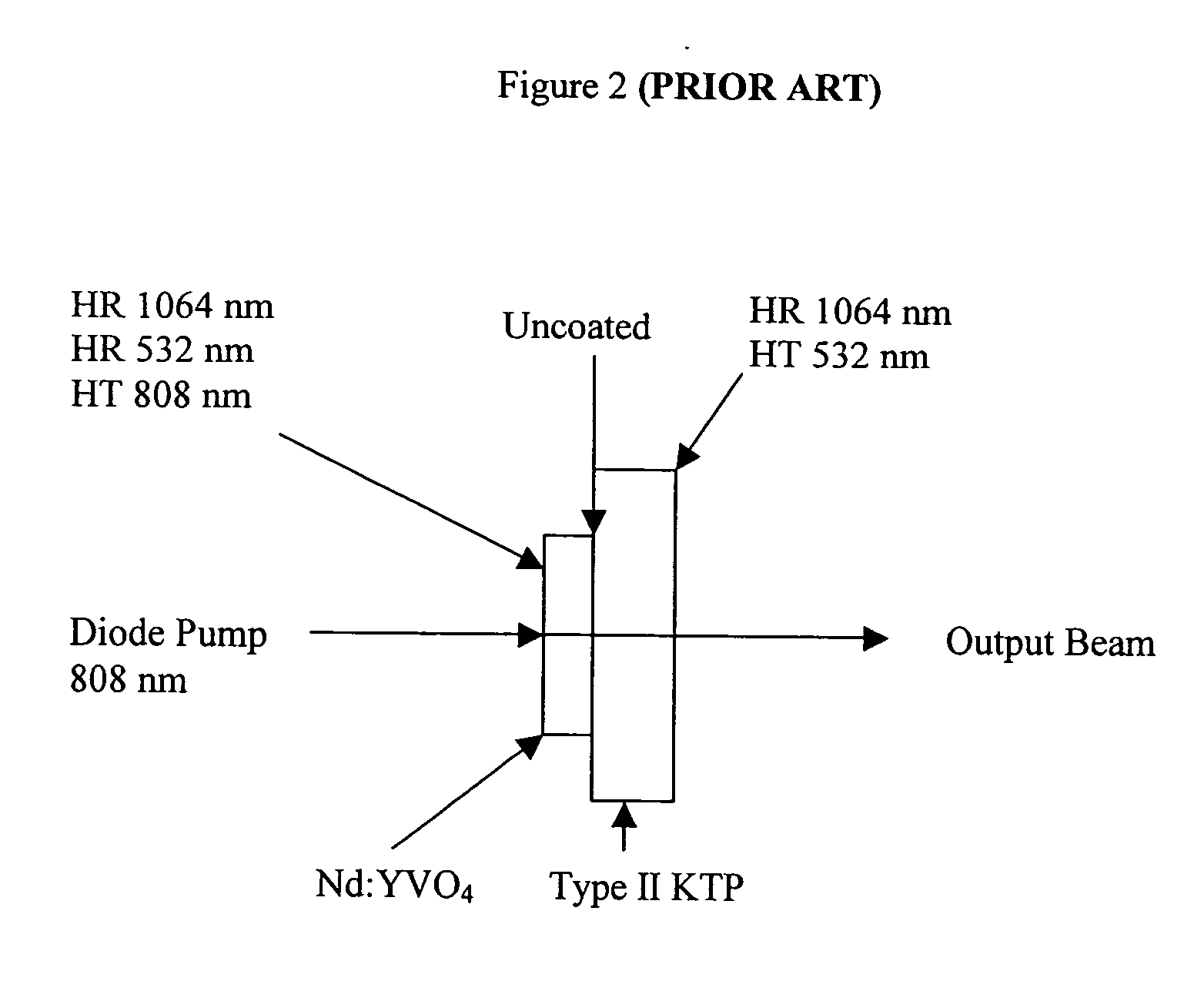
InactiveUS20050063441A1Low-cost high-densityHigh beam qualityMicrobiological testing/measurementActive medium materialLow noiseMicrochip laser
A miniaturized laser package is provided comprising a standard semiconductor laser package modified to accept a solid state microchip assembly pumped by the diode laser. Standard packages described in the invention include TO and HHL packages all of which are characterized by small dimensions, well sealed housing, robust mounting features, known characterized materials and economical production and assembly techniques characteristic of the semiconductor processing industry. In particular, the microchip lasers are produced using high density techniques that lend themselves to mass production, resulting in very low unit costs. At the same time, the compact laser devices provide a solution to the problem of providing laser radiation at high beam quality and good reliability features with a variety of wavelengths and operational characteristics and low noise features not available from diode lasers yet relying primarily on standardized designs, materials and techniques common to diode laser manufacturing. The devices constructed according to methods taught by the invention can therefore be readily integrated into numerous applications where power, reliability and performance are at a premium but low cost is essential, eventually replacing diode lasers in many existing systems but also enabling many new commercial, biomedical, scientific and military systems.
Owner:SNAKE CREEK LASERS
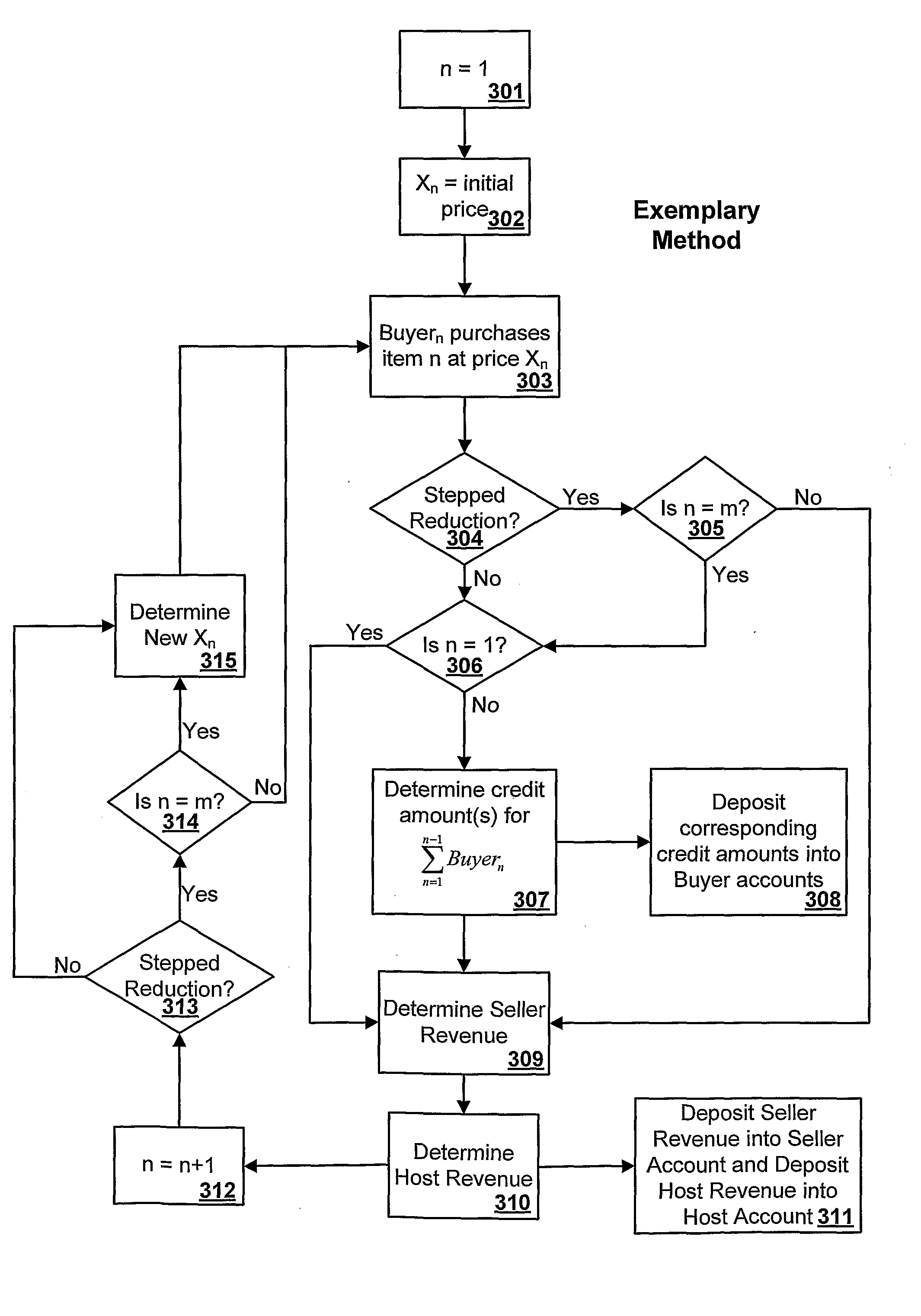
Methods and systems for optimal pricing
InactiveUS20090327062A1Low costIncrease unit outputComplete banking machinesFinanceUnit costComputer science
The systems and methods disclosed relate to the buying and selling of products. More particularly, the systems and methods relate to providing all buyers with the cost savings benefit of economies of scale. Economy of scale benefits involve unit (product) cost reductions which result from increasing total unit output, or sales. Typically, as a seller sells more of a unit, the cost per unit will eventually decline. Such a system discourages initial buyers and rewards later buyers. The present systems and methods can provide economy of scale benefits to all buyers and sellers of products.
Owner:BOTES ANDRIES STEPHANUS
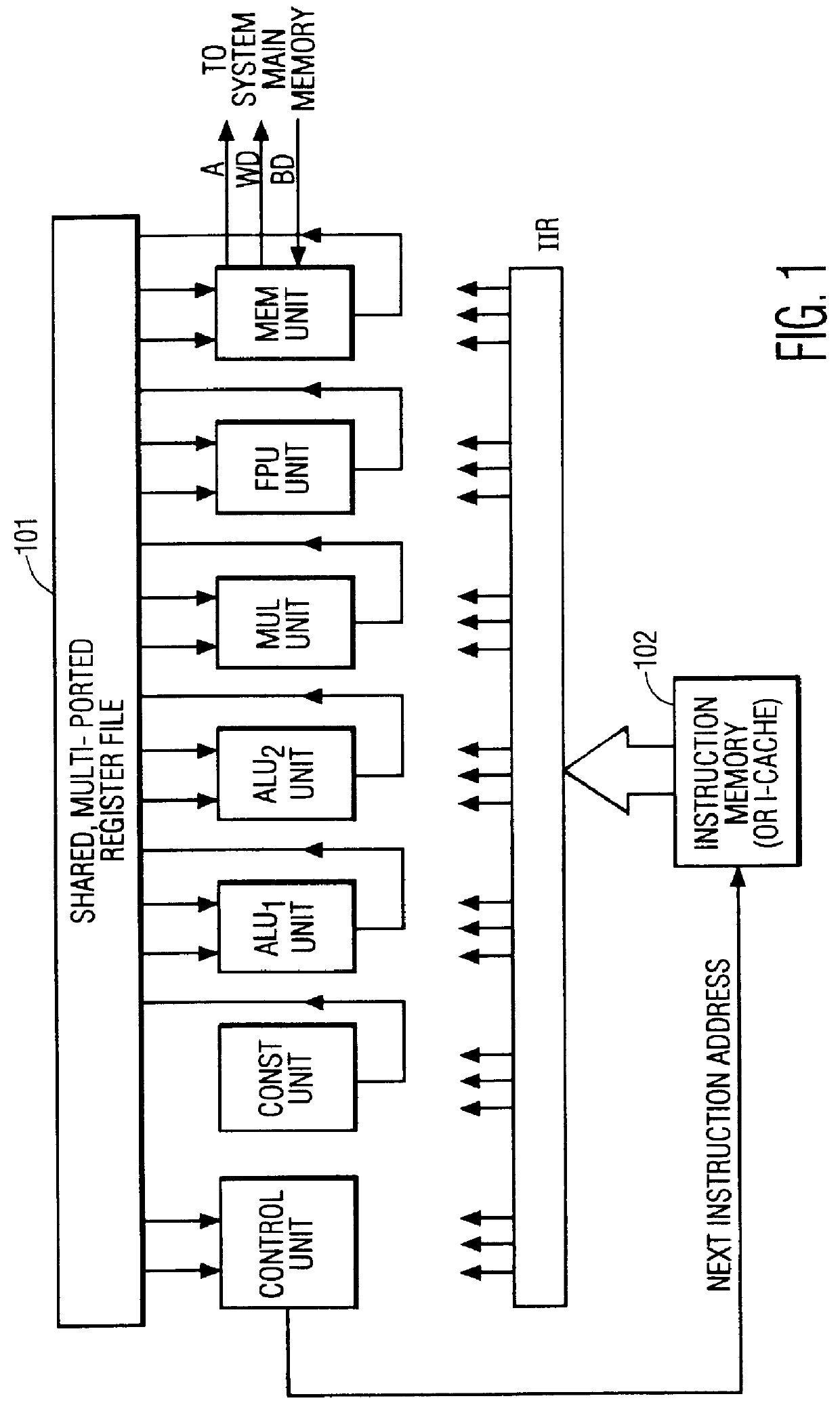
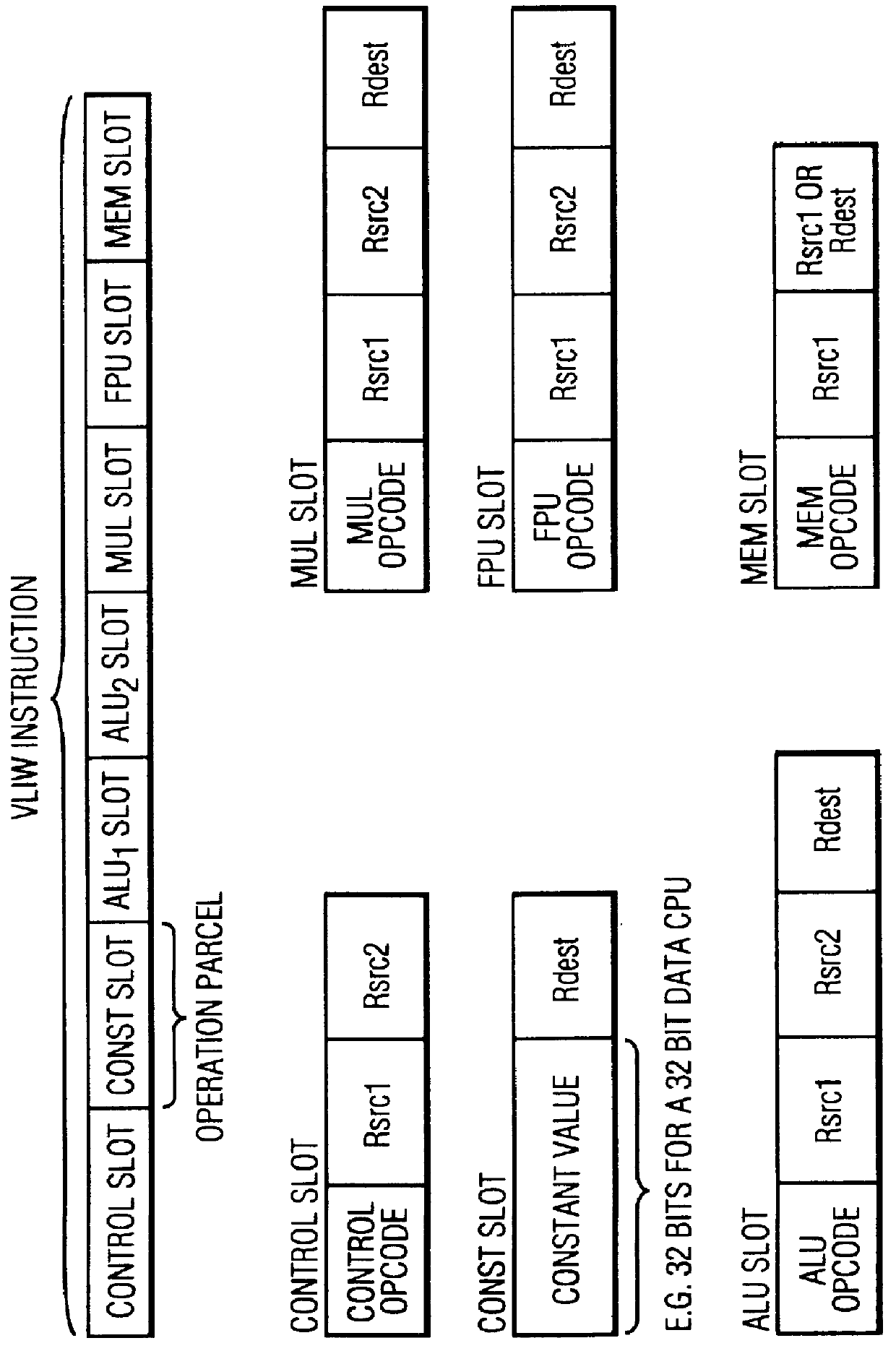
VLIW processor with less instruction issue slots than functional units
InactiveUS6122722AImproved cost-efficiencyRegister arrangementsGeneral purpose stored program computerComputer architectureProcessor register
Owner:FOOTHILLS IP LLC
Semiconductor device and its manufacturing method
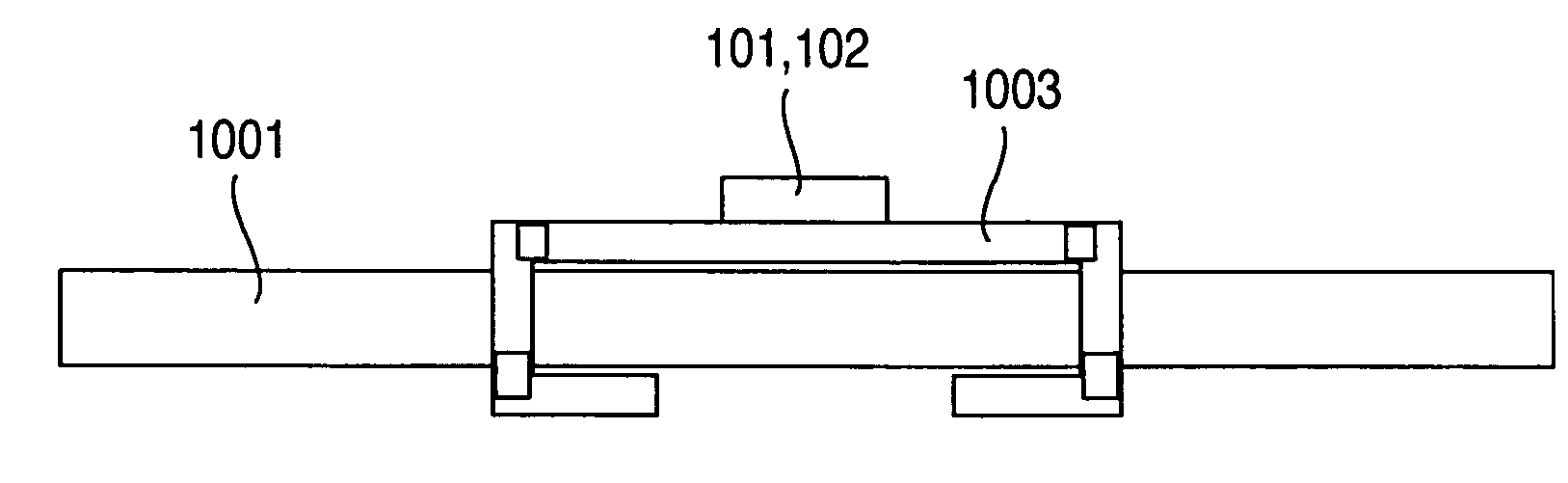
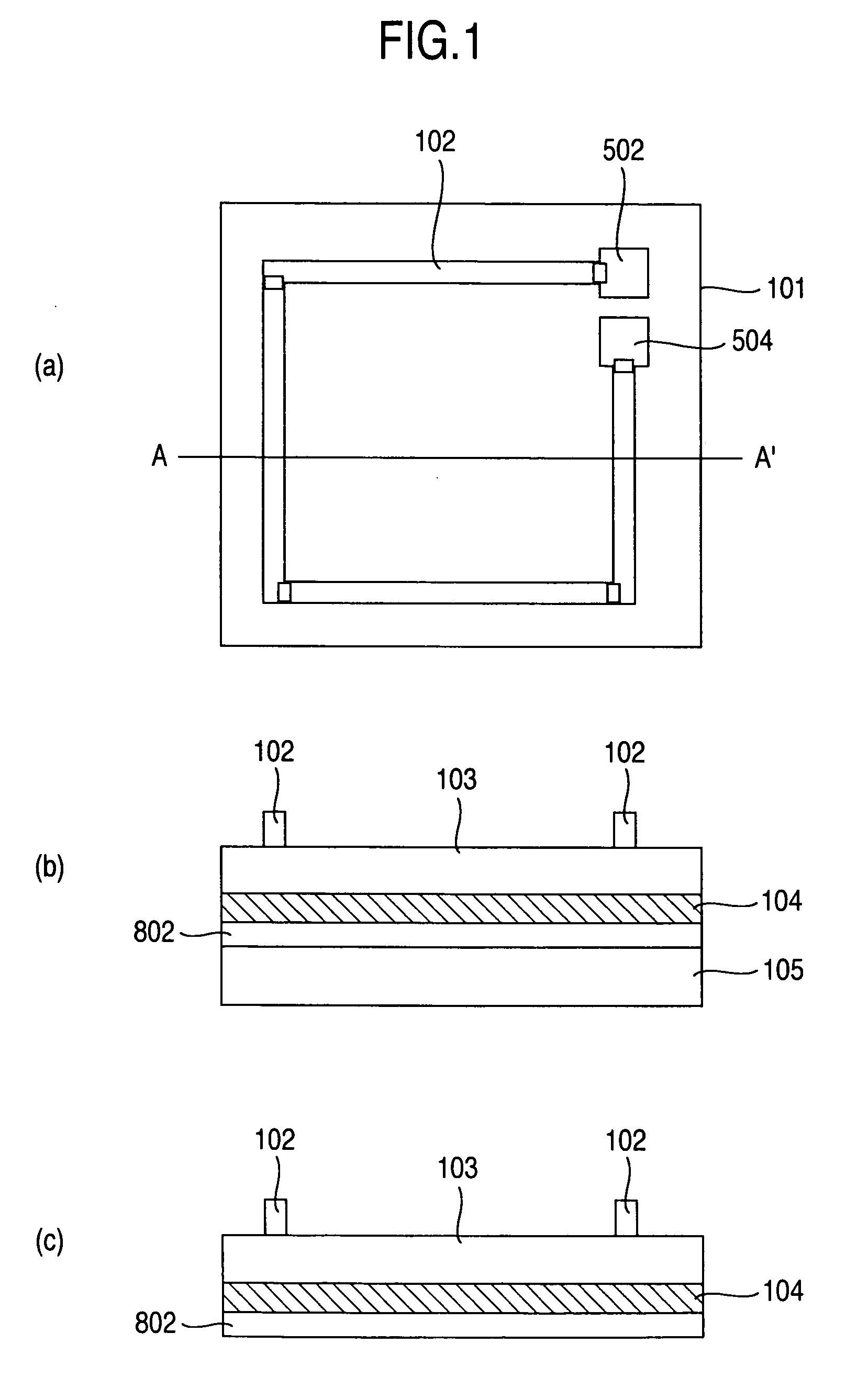
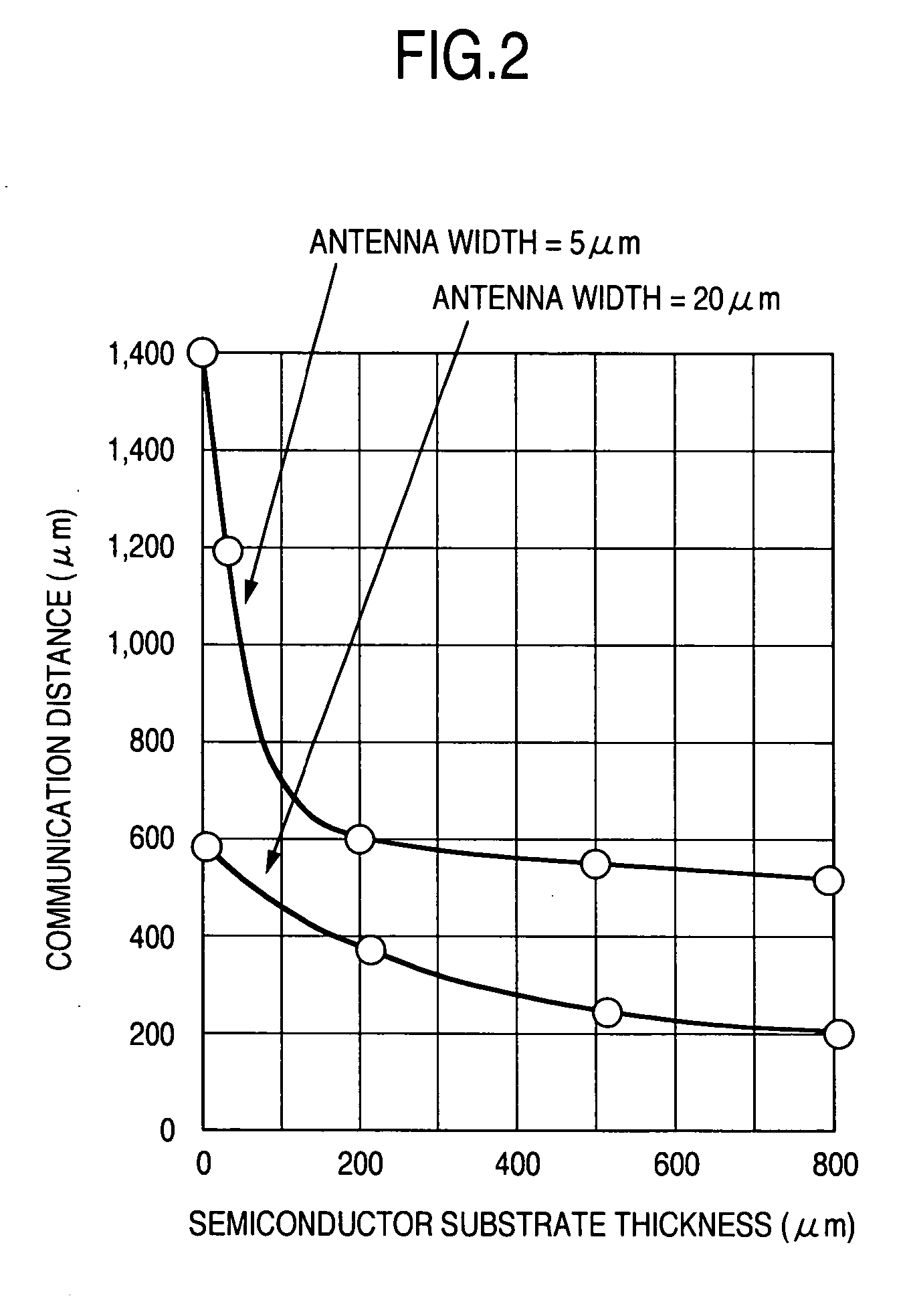
InactiveUS20060260546A1Antenna supports/mountingsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialEddy current
An issue of reducing a product manufacture unit cost exists in wireless IC chips which are required to be disposable because the wireless IC chips circulate in a massive scale and require a very high collection cost. It is possible to increase the communication distance of a wireless IC chip with an on-chip antenna simply contrived for reduction of the production unit cost by increasing the size of the antenna mounted on a wireless IC chip or by increasing the output power of a reader as in a conventional way. However, because of the circumstances of the applications used and the read accuracy of the reader, the antenna cannot be mounted on a very small chip in an in-chip antenna form. When an AC magnetic field is applied to an on-chip antenna from outside, eddy current is produced in principle because the semiconductor substrate is conductive. It has been fount that the thickness of the substrate can be used as a design parameter because of the eddy current. Based on this finding, according to the invention, the thickness of the substrate is decreased to reduce or eliminate the energy loss due to the eddy current to utilize the electromagnetic wave energy for the semiconductor circuit operation as originally designed. With the thickness reduction, it is possible to increase the communication distance by preventing ineffective absorption of energy and thereby increasing the current flowing through the on-chip antenna.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
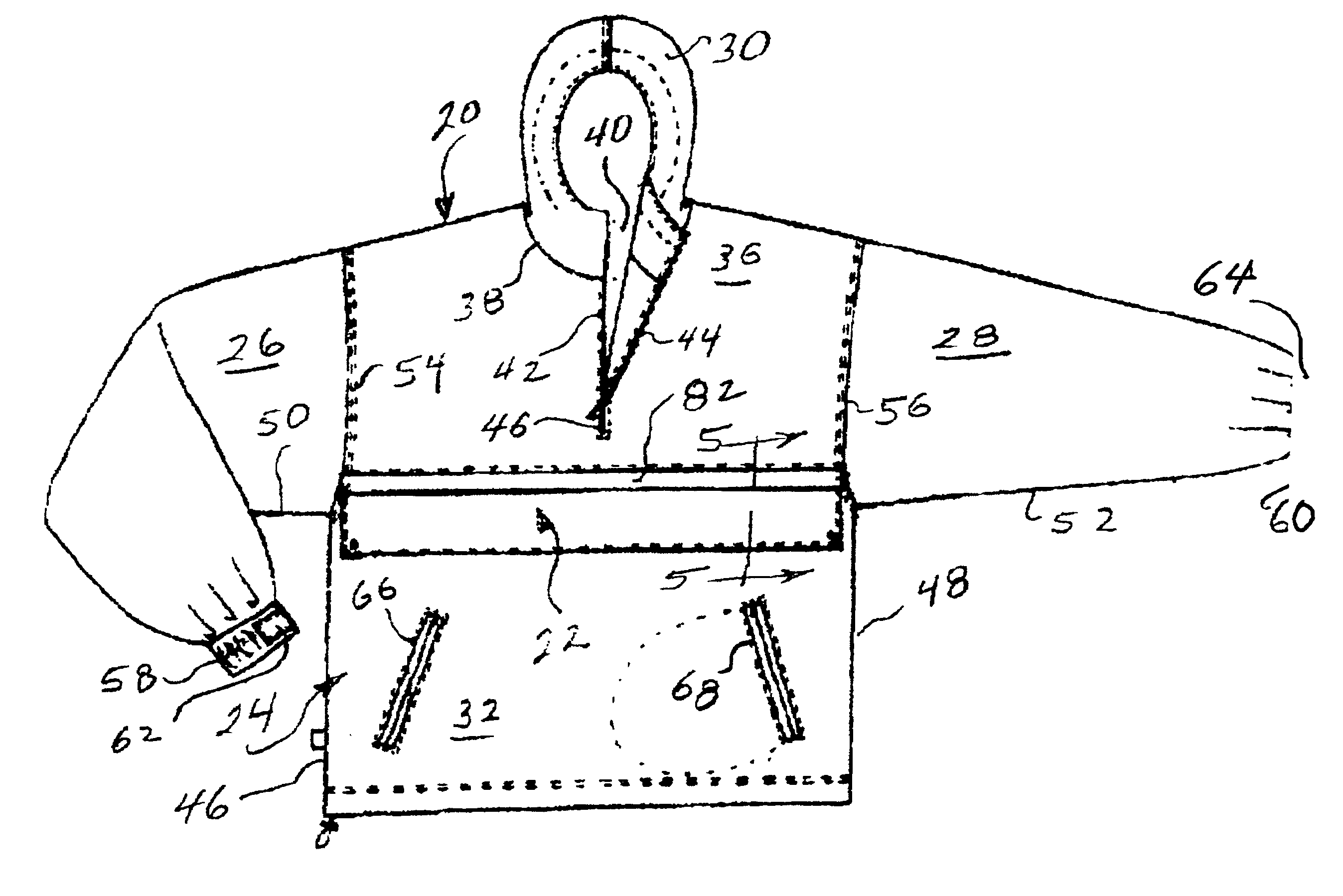
Pullover jacket with customized decorative band
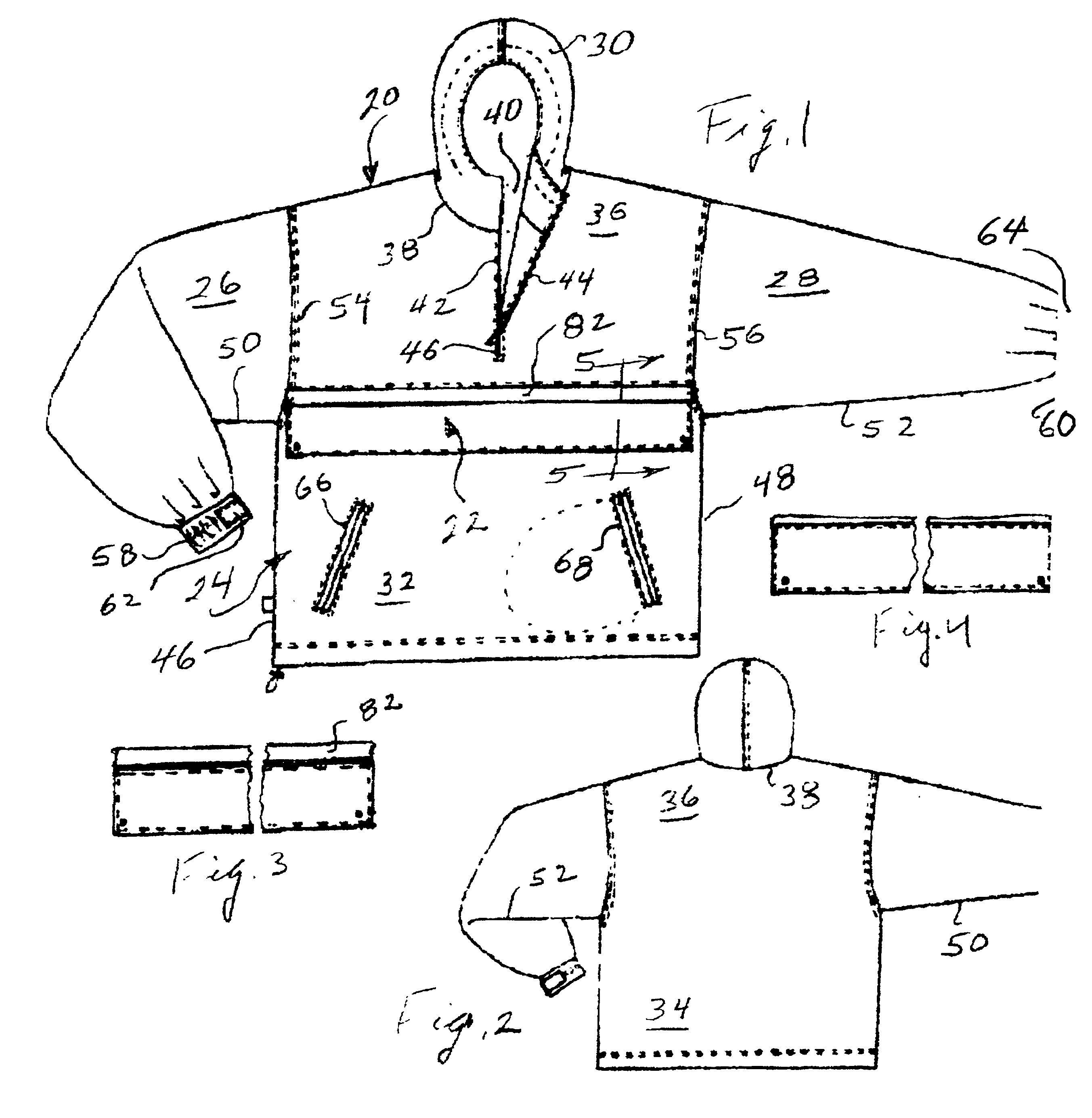
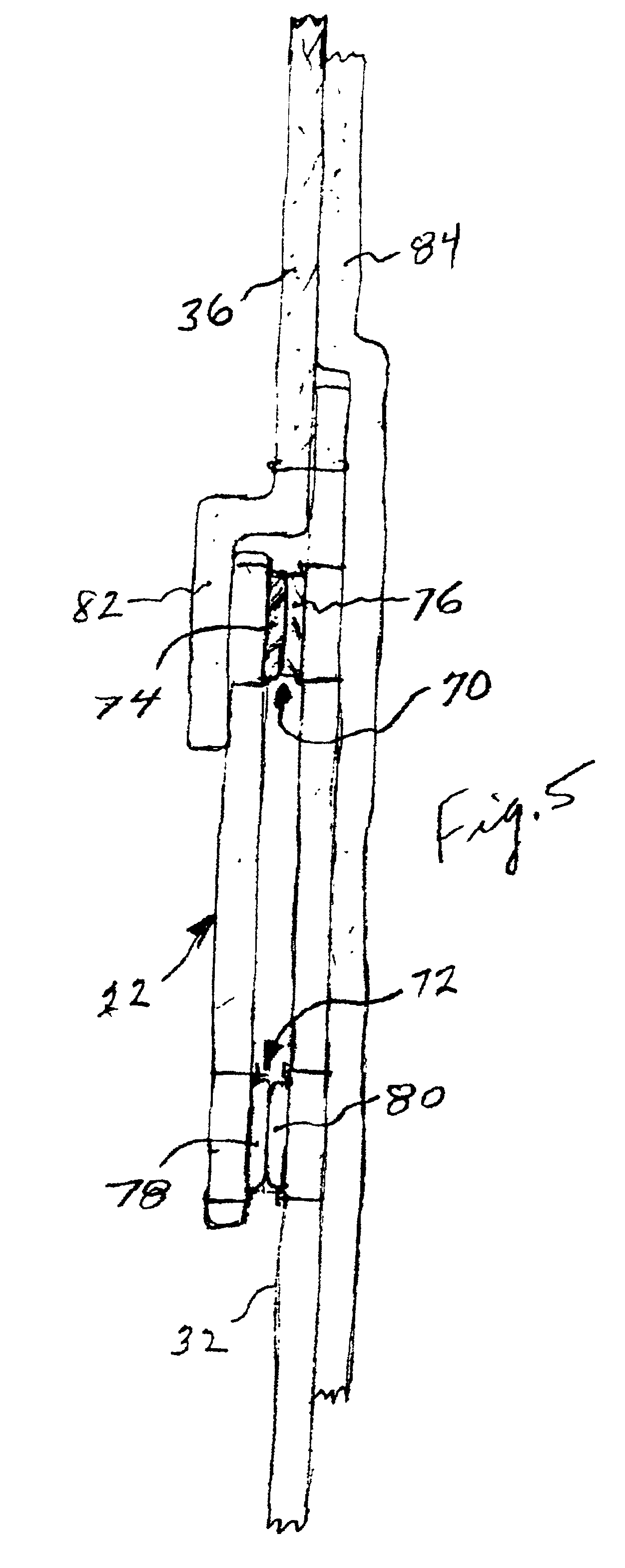
InactiveUS6848118B2Economical inventoryEasy to assembleGarment special featuresJacketsArchitectural engineeringUnit cost
A product and process involve providing customized pullover jackets, units of which are characterized by (1) pullover body construction units of a type having a fabric configuration that facilitates slipping over the head and shoulders; and (2) decorative band construction units of a type having distinguishable color and design for affixation to said pullover body construction. The process comprises acquiring a relatively small inventory of body construction units of different sizes, acquiring a relatively large inventory of band construction units of different colors or designs, and receiving and fulfilling orders for the customized pullover jackets from customers. The body construction units account for the major component of unit cost. The band construction units account for a minor component of unit cost. The customized jackets are assembled by joining mating fasteners on the upper and lower edges of selected band construction and corresponding upper and lower points on selected body constructions. Extending from each body construction is an elongated flap that overlaps the upper edge of the band construction.
Owner:CHARLES RIVER APPAREL
Control device of a storage system comprising storage devices of a plurality of types
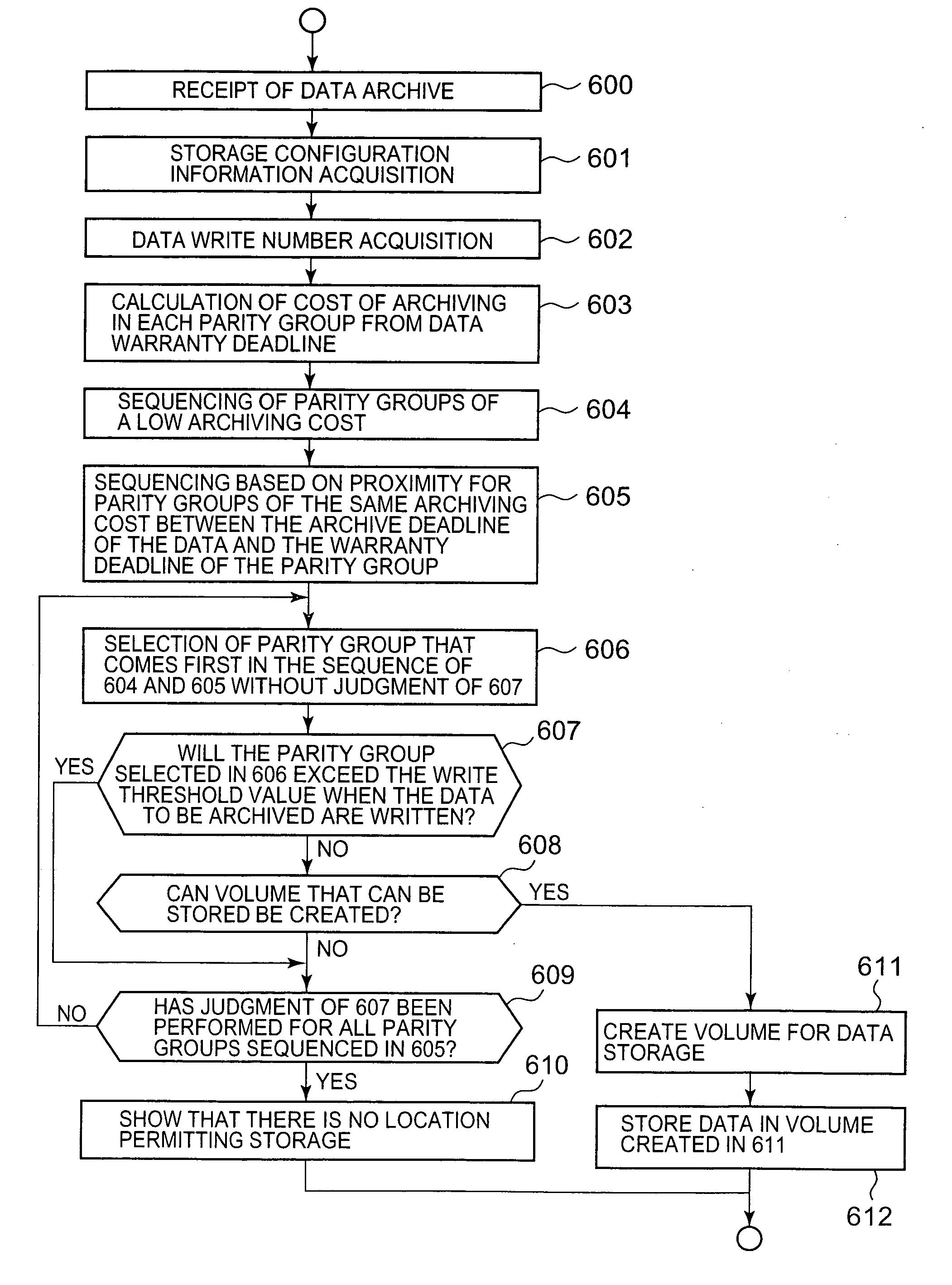
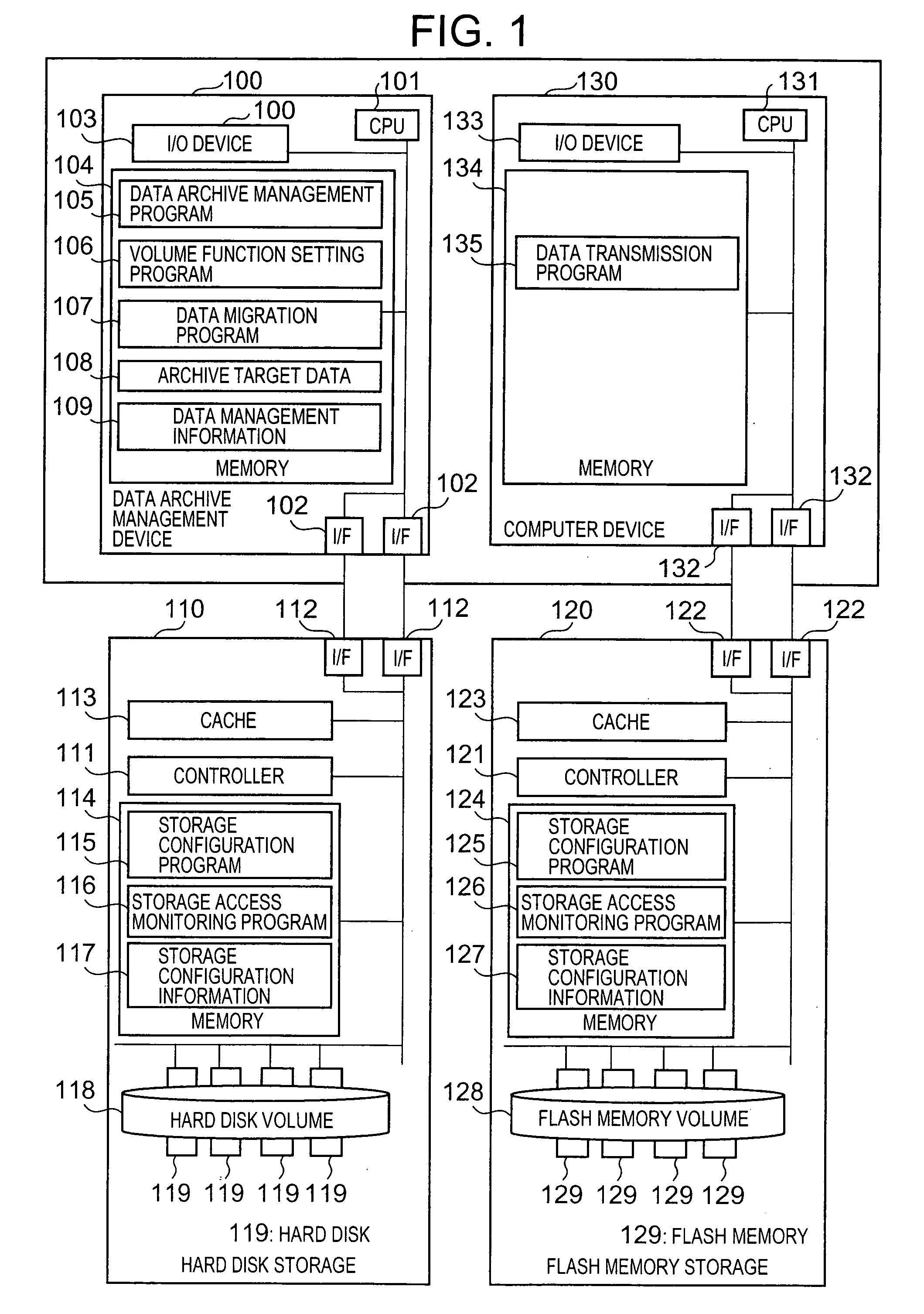
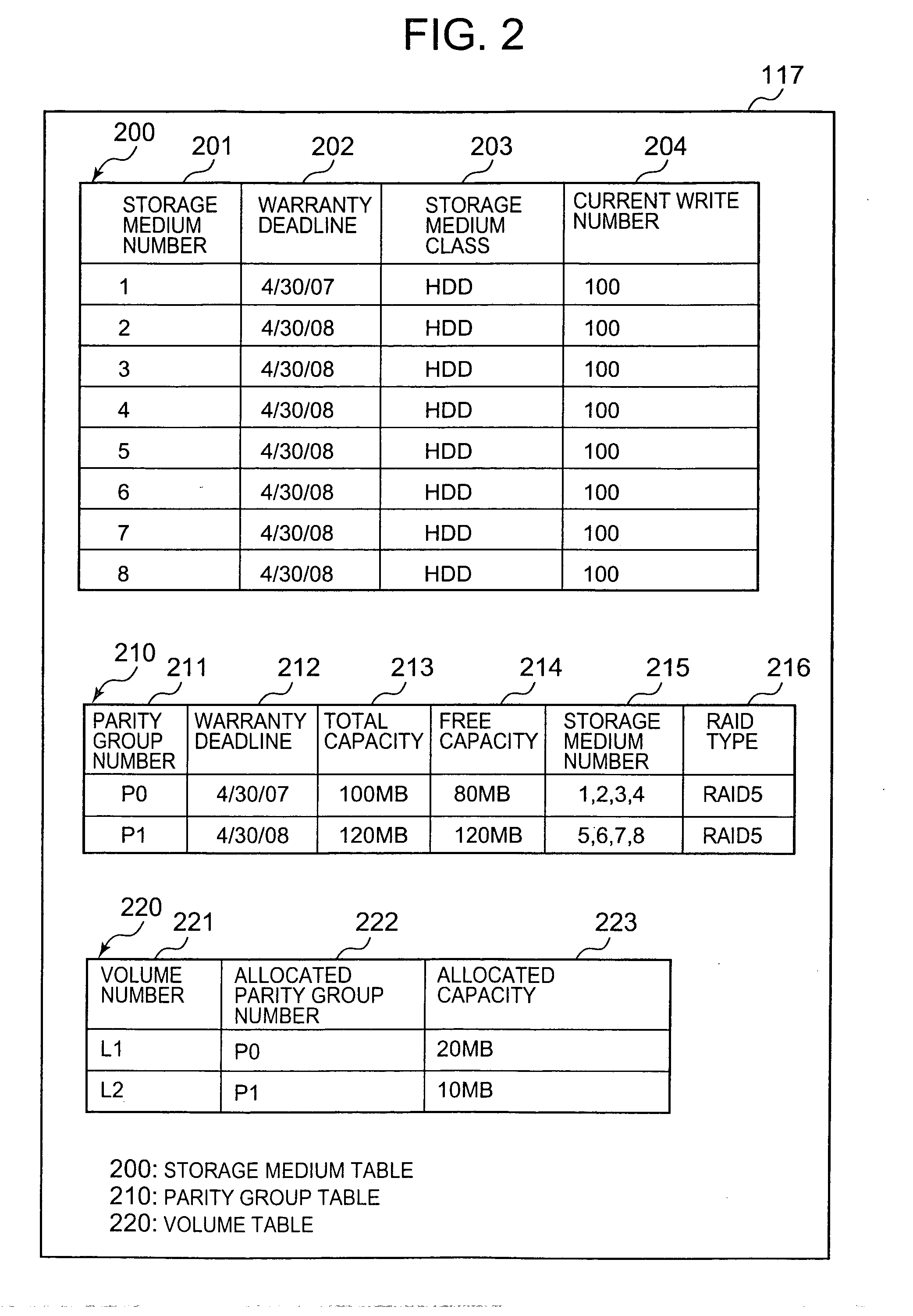
InactiveUS20080005508A1Digital data information retrievalMemory loss protectionUnit costData storing
The control device acquires the archive deadline of archive target data and acquires, for storage devices of a plurality of types, a warranty deadline for the quality of data stored by the storage device and the unit cost which is the cost for each predetermined storage size of the storage device. The storage control device is a storage device which acquires a data migration cost and which obtains a storage destination for the archive target data from storage devices of a plurality of types on the basis of the archive deadline, warranty deadline, unit cost and data migration cost thus acquired. The storage control device selects a storage device for which the total cost is minimum when the archive target data is archived until the archive deadline.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Hardware-adaptable watermark systems
ActiveUS20170004597A1Details involving processing stepsImage watermarkingGeneral purposeCost effectiveness
There are many advantages to implementing a watermark-based system using dedicated hardware, rather than using software executing on a general purpose processor. These include higher speed and lower power consumption. However, hardware implementations incur substantial design and development costs. Moreover, because each watermarking application has its own design constraints and parameters, it has not been cost-effective to develop a hardware chip design for each, since such chips would typically not be manufactured in volumes sufficient to bring per-unit costs down to an acceptable level. The present technology provides various techniques for making watermarking hardware adaptable, so that a single chip can serve multiple diverse watermark applications. By so-doing, the advantages of hardware implementation are made available where it was formerly cost-prohibitive, thereby enhancing operation of a great variety of watermark-based systems.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Apparatus and methods for streamlined term adjustment
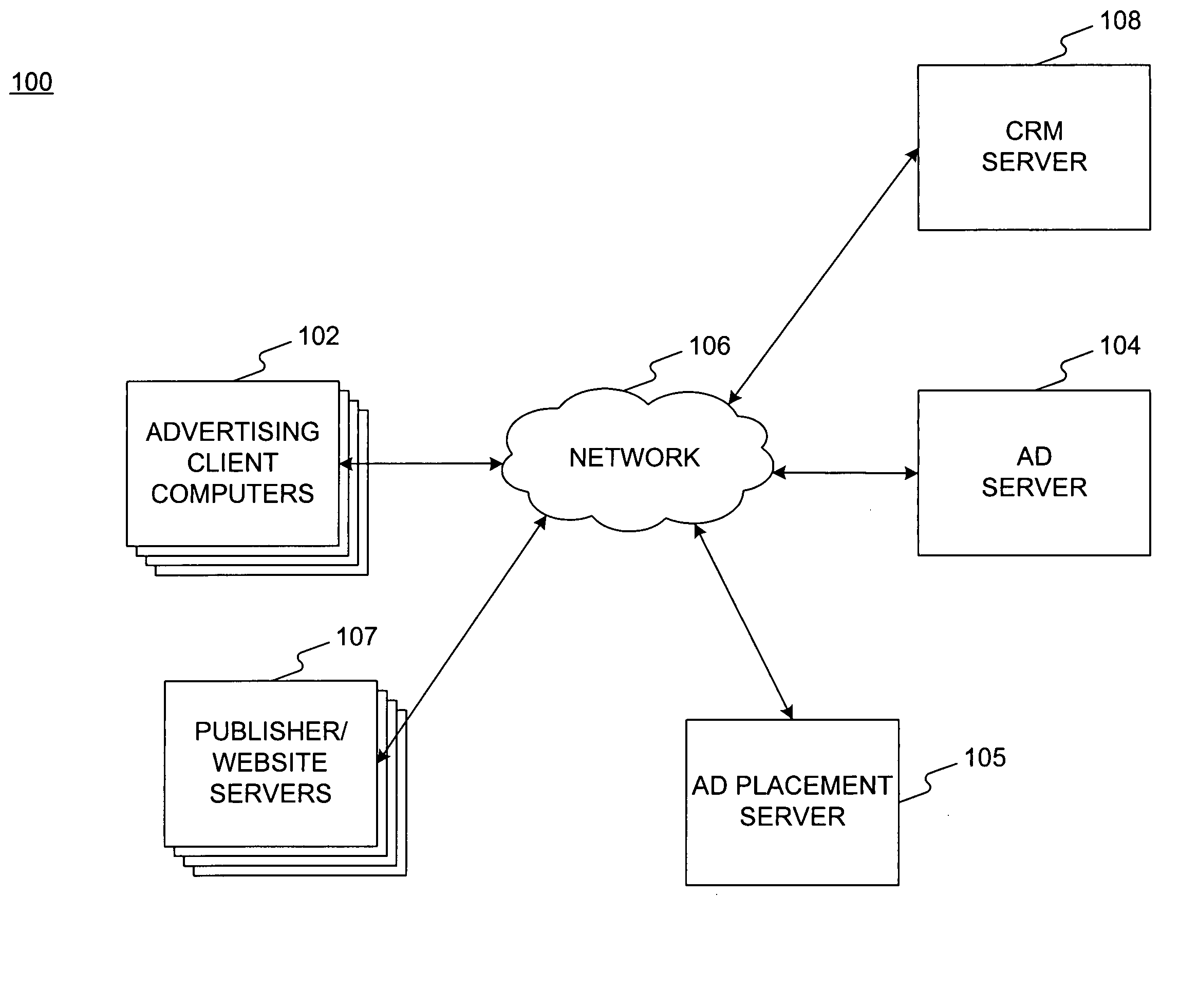
Embodiments consistent with the present invention enable an advertising client to vary terms of an advertising campaign automatically in order to react to changing business conditions. An advertising client and a publisher establish terms of an advertising campaign including a unit cost for placement of advertisements and a range of acceptable changes. The unit cost may use any pricing model, such as cost per mille, cost per click, or cost per action. During the advertising campaign, the advertising client may submit a change that is automatically implemented to alter the advertising campaign.
Owner:ADVERTISING COM
Computer-implemented method and system for designing transportation routes
InactiveUS6996507B1Facilitate comparison of different layoutsGreat cost-effectivenessGeometric CADLiquid/gas jet drillingLand coverUnit cost
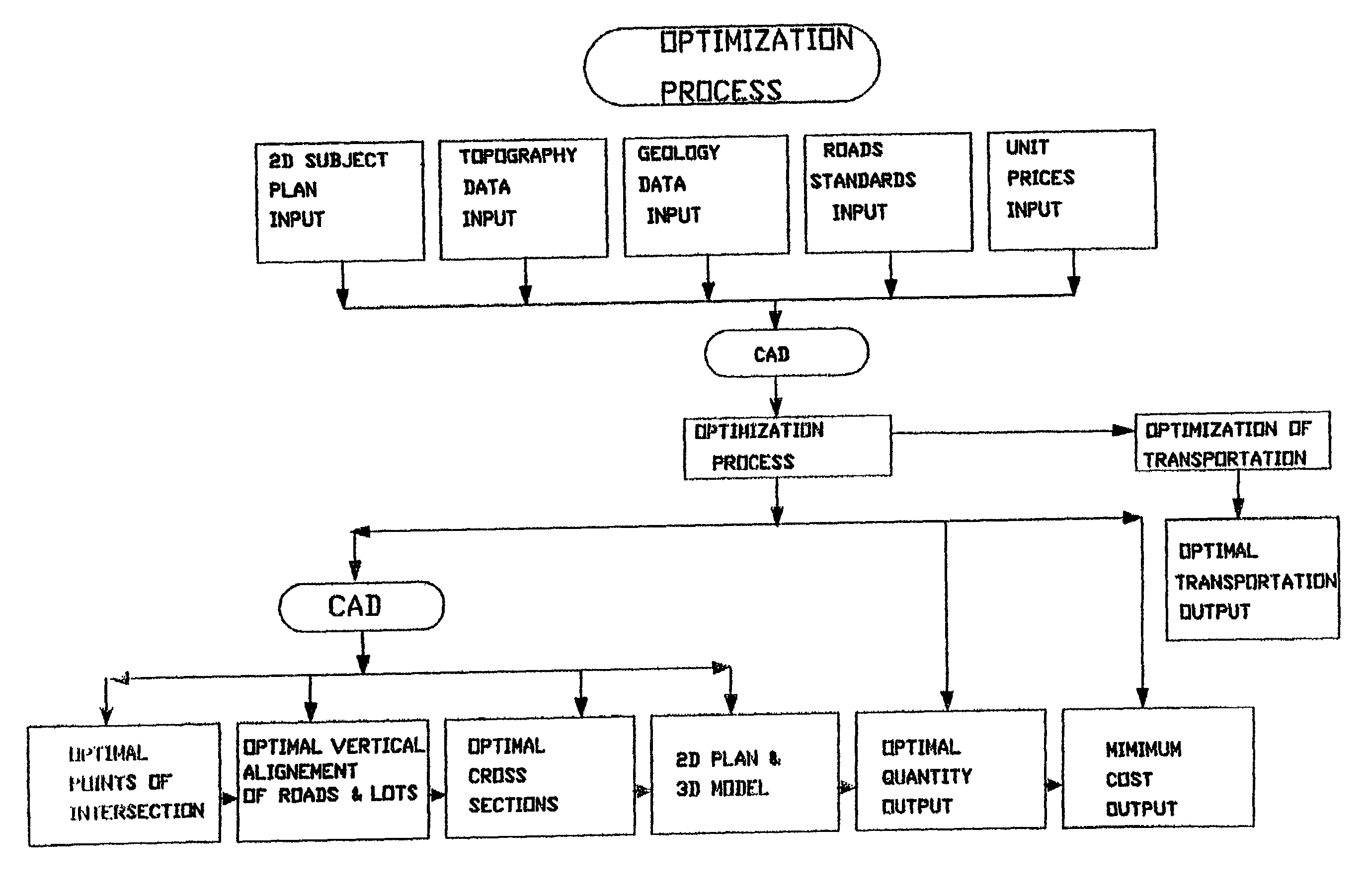
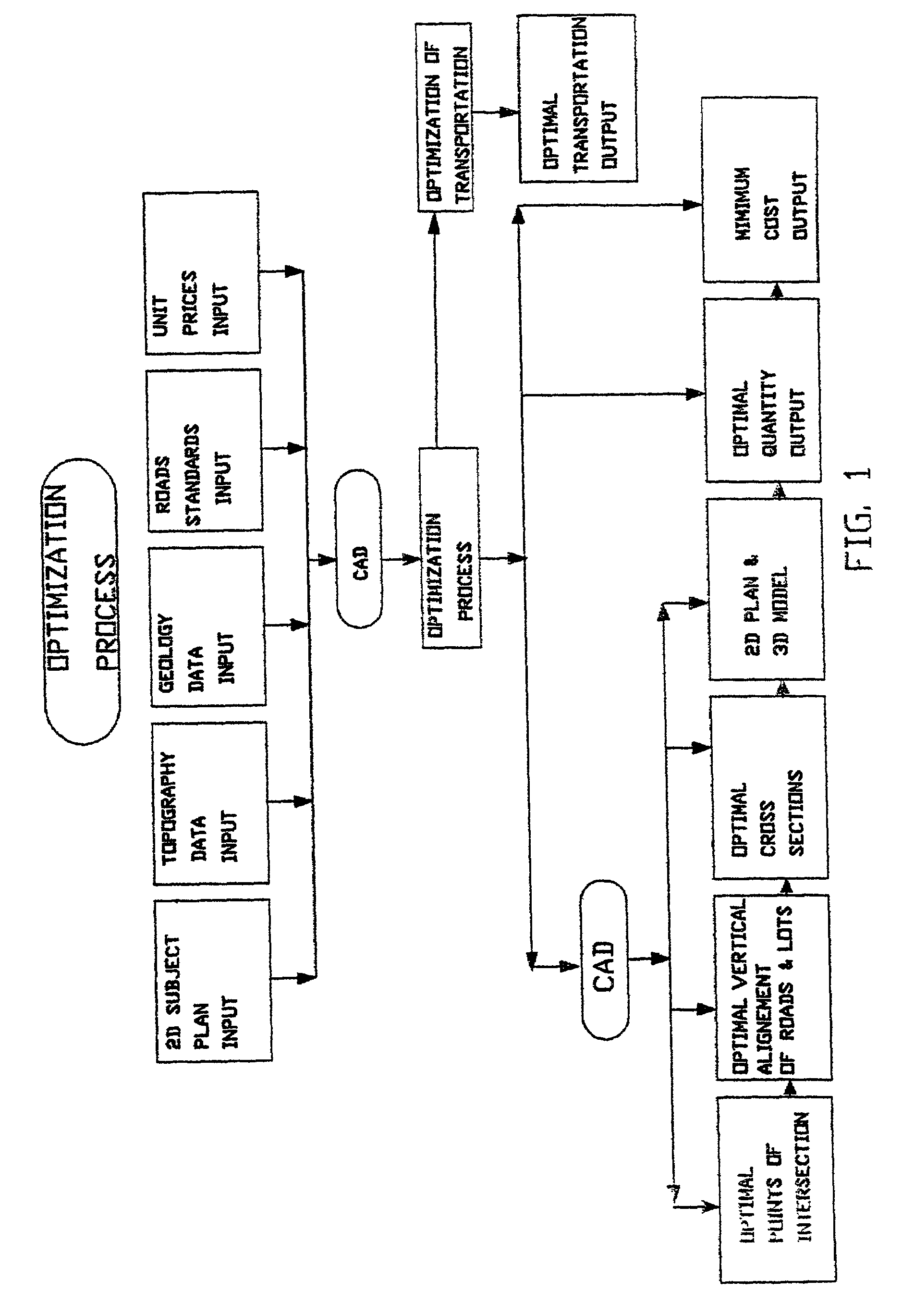
A computer-implemented method and system for designing transportation routes, wherein design criteria to be met in respect of at least one of said transportation routes are supplied and route profile data are obtained showing land heights at sampled points along each of said at least one transportation route. Per-unit cost estimates in respect of land-cut and land-fill operations are supplied, and a height profile is computed of the at least one transportation route which meets the design criteria and for which the land-cut and land-fill operations are adjusted to give a minimum cost.
Owner:MAKOR ISSUES & RIGHTS
System and method for providing cost transparency to units of an organization
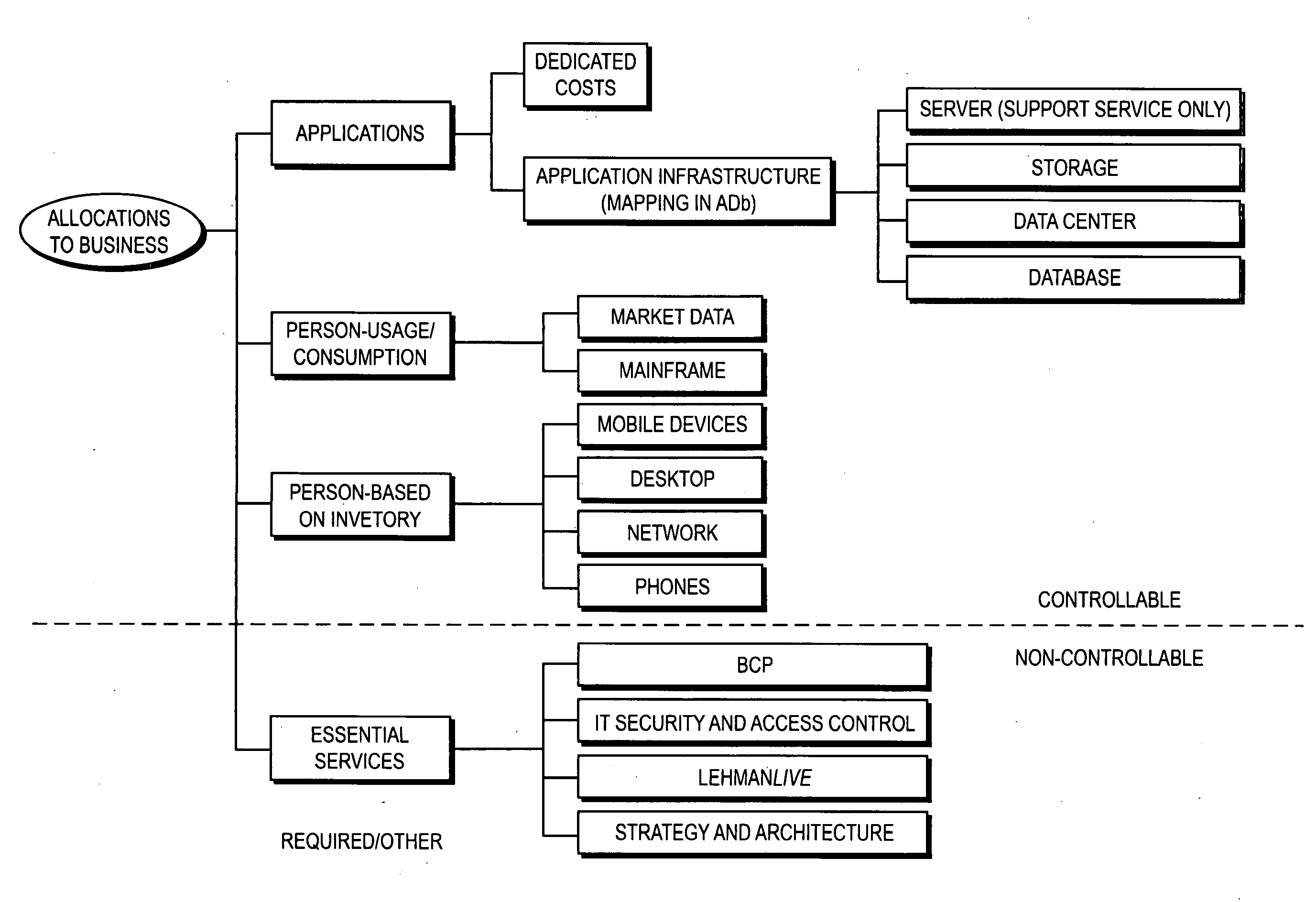
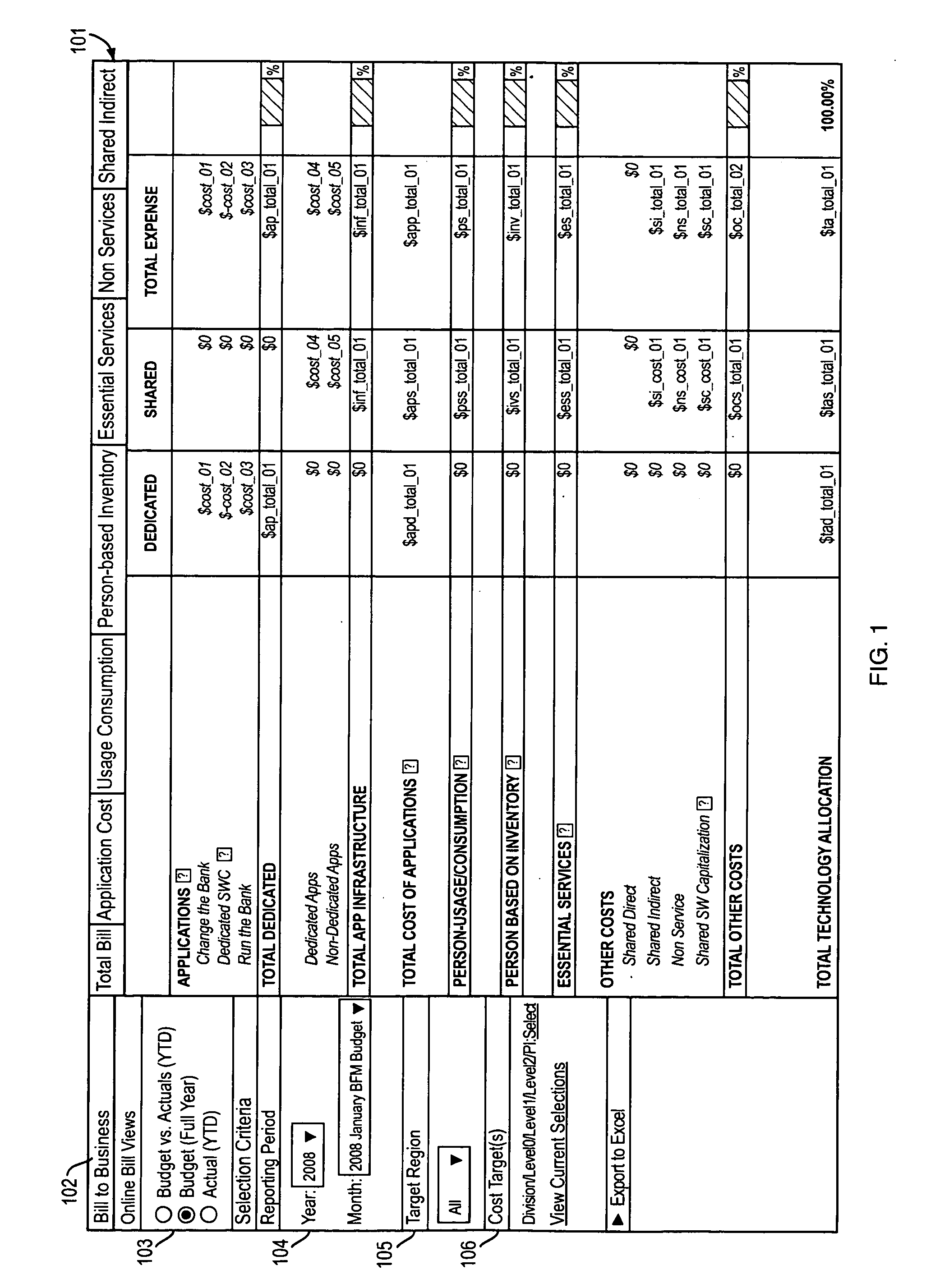
InactiveUS20100005014A1Eliminate the problemComplete banking machinesFinanceApplication softwareUnit cost
A system and method provide transparency of costs allocated to a unit of an organization. The method includes steps to receive asset information for an application at a cost transparency engine and identify a direct dependency of the application and an indirect dependency of the application using the asset information for the application. An infrastructure cost for the application is determined based on the direct dependency, the indirect dependency, component consumption by the application, and a unit cost of a service supporting the component. A report is generated, via a reporting tool, presenting the infrastructure cost for the application.
Owner:BARCLAYS CAPITAL INC
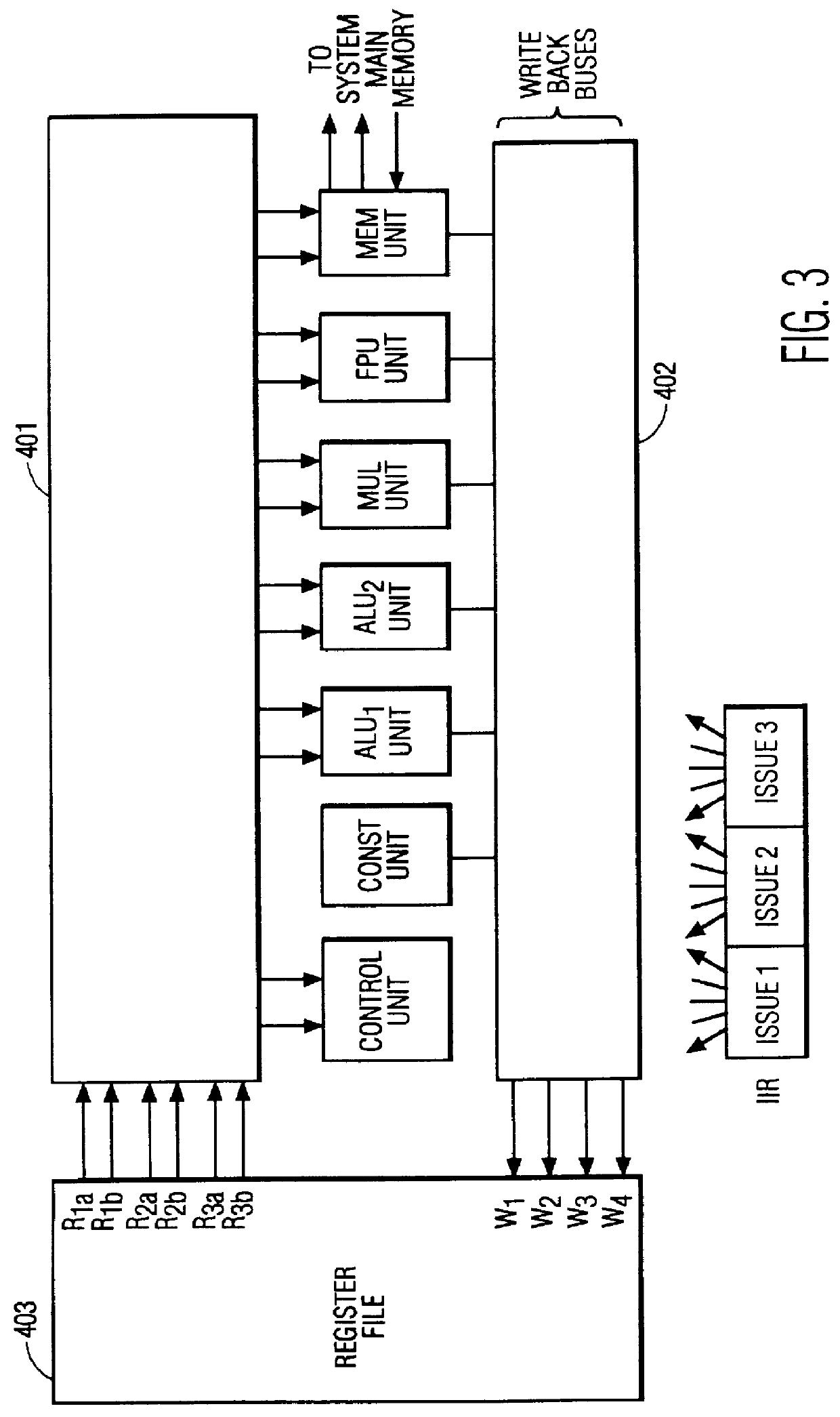
VLIW processor with write control unit for allowing less write buses than functional units
InactiveUS6044451AImproved cost-efficiencyRegister arrangementsGeneral purpose stored program computerProcessor registerUnit cost
Owner:FOOTHILLS IP LLC
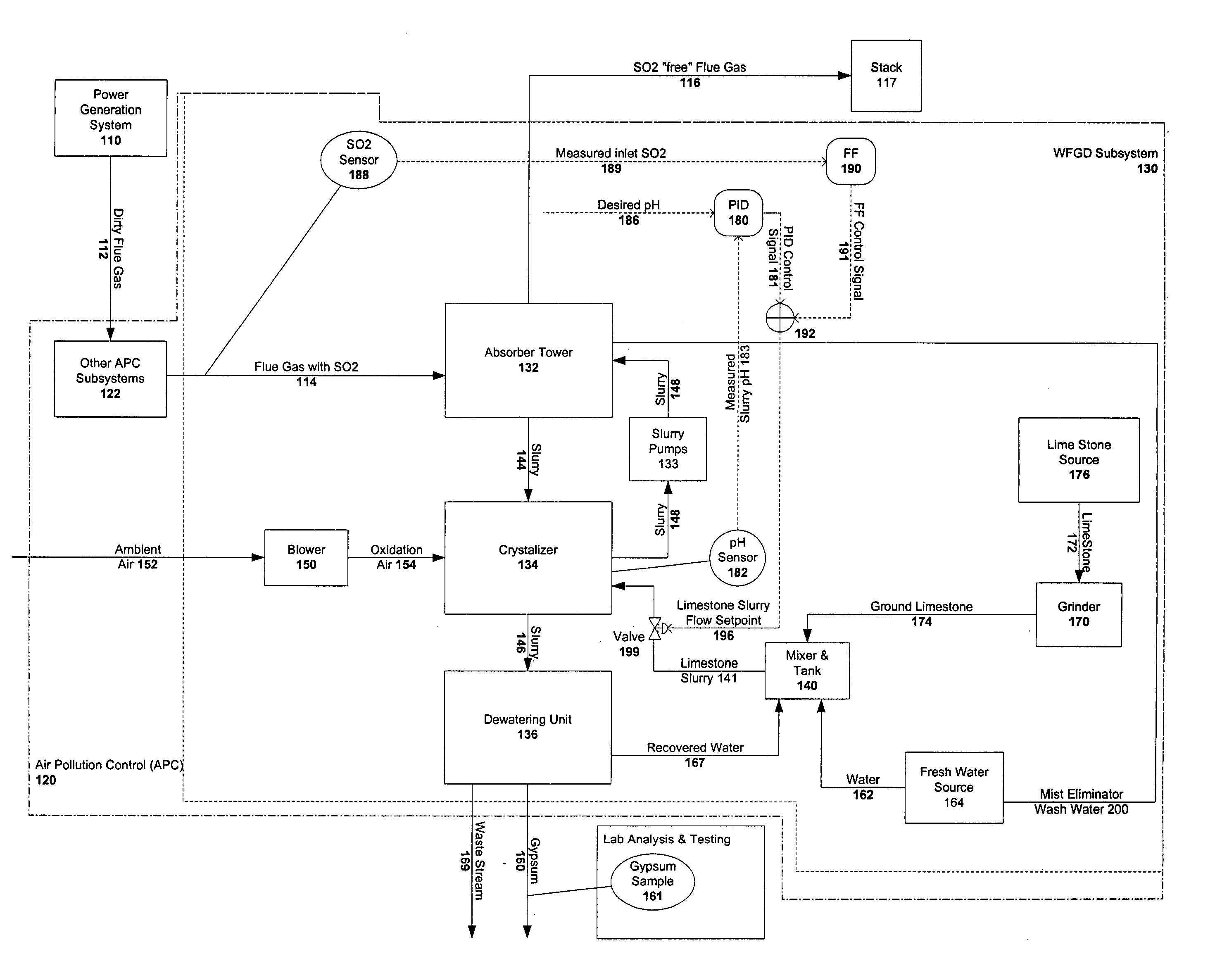
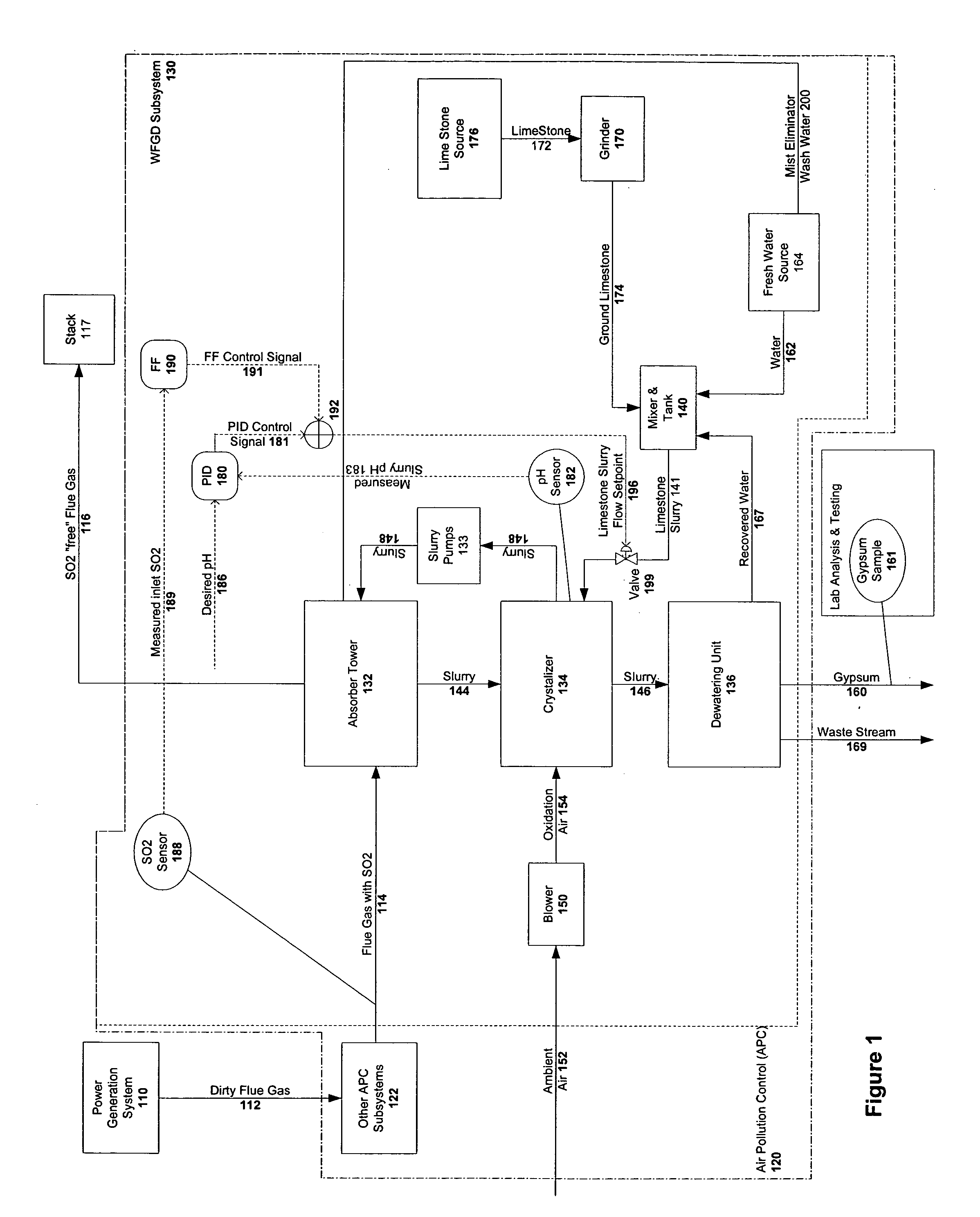
Cost based control of air pollution control
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Hardware-adaptable watermark systems
ActiveUS9819950B2Details involving processing stepsCharacter and pattern recognitionGeneral purposeCost effectiveness
There are many advantages to implementing a watermark-based system using dedicated hardware, rather than using software executing on a general purpose processor. These include higher speed and lower power consumption. However, hardware implementations incur substantial design and development costs. Moreover, because each watermarking application has its own design constraints and parameters, it has not been cost-effective to develop a hardware chip design for each, since such chips would typically not be manufactured in volumes sufficient to bring per-unit costs down to an acceptable level. The present technology provides various techniques for making watermarking hardware adaptable, so that a single chip can serve multiple diverse watermark applications. By so-doing, the advantages of hardware implementation are made available where it was formerly cost-prohibitive, thereby enhancing operation of a great variety of watermark-based systems.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
Cost based control of air pollution control
ActiveUS20060047526A1Reduce oxidationReduce removalCombination devicesFinanceOperational systemControl system
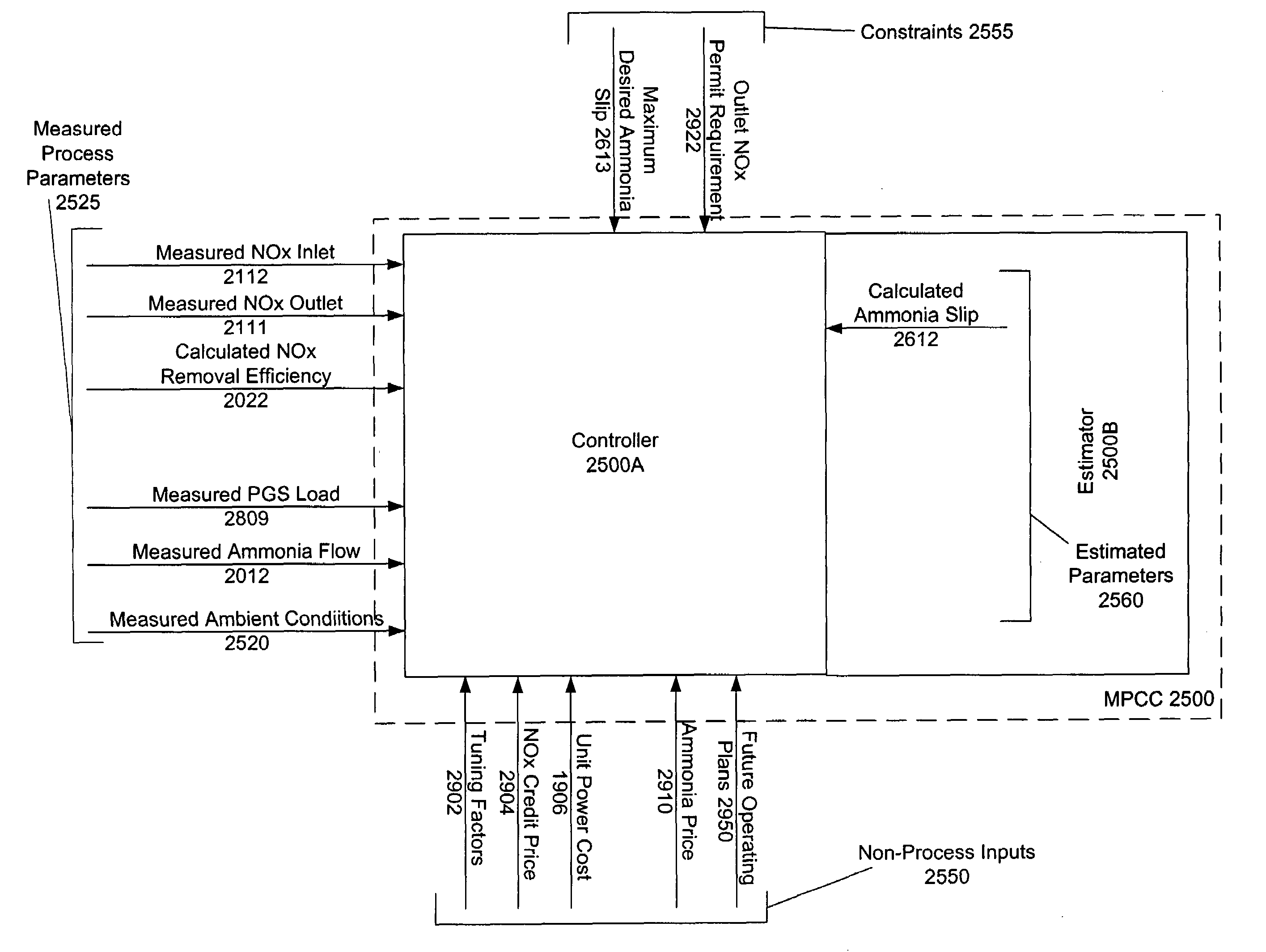
A controller for directing operation of an air pollution control (APC) system, requires a consumable to perform a process to control emissions of a pollutant. The process has multiple process parameters (MPPs). One or more of the MPPs is a controllable process parameters (CTPPs) and one of the MPPs is an amount of the pollutant (AOP) emitted by the system. A defined AOP value (AOPV) represents a limit on an actual value (AV) of the emitted AOP. An interface receives a value corresponding to a unit cost of the consumable. A control processor determines the cost of operating the system based on the received value corresponding to the unit cost of the consumable, and directs control of at least one of CTPPs based on the current value of that CTPP and the determined operating cost.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
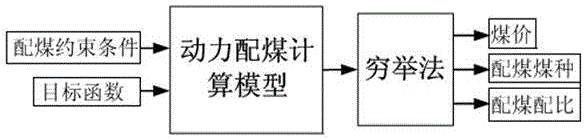
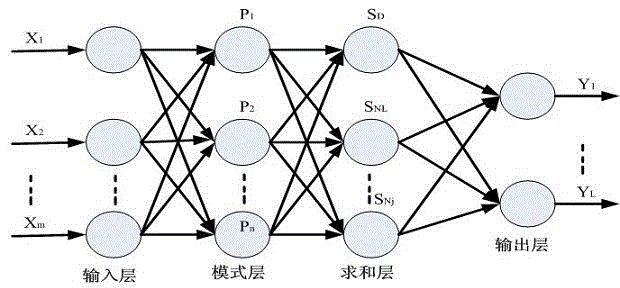
Method for acquiring coal parameter of thermal power generating unit boiler cost minimum mixed coal
InactiveCN104156781AGuaranteed reasonablenessGuaranteed economyForecastingMathematical modelProcess engineering
The invention discloses a method for acquiring a coal parameter of thermal power generating unit boiler cost minimum mixed coal. The method adopts the objective functions that high-grade coal composition is minimum, poor coal composition is maximum and raw coal unit cost is minimum to establish a dynamic coal composition mathematical model, and predicts the model according to a general regression neural network, so that the acquired coal quality parameter value of the mixed coal is more reasonable, and rationality and economy of boiler operation are ensured. The method comprises the following steps: adopting the objective functions that high-grade coal composition is minimum, poor coal composition is maximum and raw coal unit cost is minimum, adopting the constraint conditions of single coal database, boiler design coal quality and historical coal data, establishing the dynamic coal composition mathematical model, and adopting the general regression neural network technology to establish coal quality characteristic prediction model for the mixed coal. The method is suitable for acquiring the coal parameter of thermal power generating unit boiler cost minimum mixed coal.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Method for optimizing arrangement and distribution of multi-target emergency rescue resources
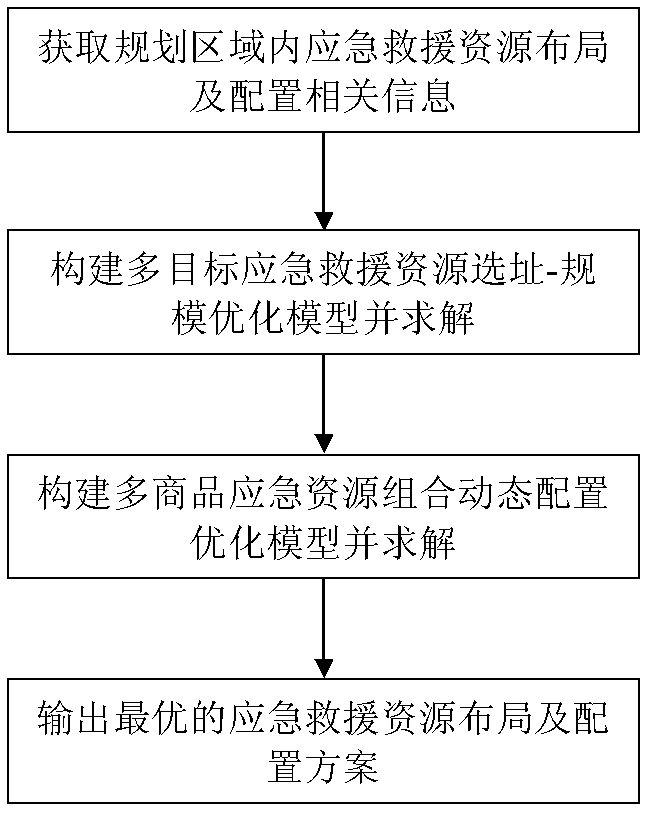
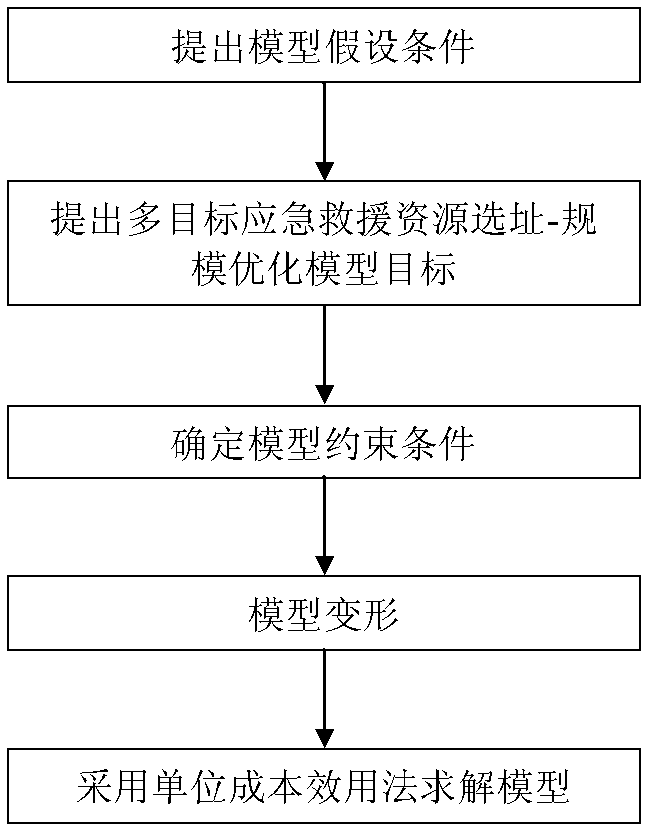
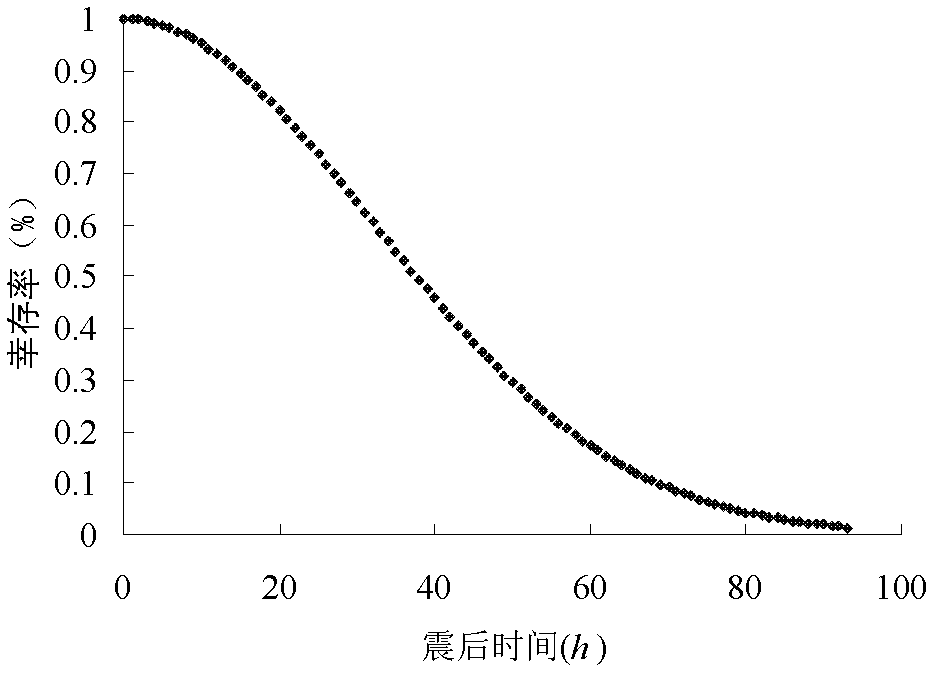
InactiveCN102542359AOptimize resource locationResource optimizationForecastingRelevant informationConfiguration optimization
The invention provides a method for optimizing arrangement and distribution of multi-target emergency rescue resources and relates to the field of emergency rescue resource distribution decision. The method comprises the following steps that: obtaining related information, such as emergency rescue resource requiring places within a planned area, required resource variety, required scale, estimated survival rate of affected people in the requiring places under various disaster conditions, disaster probability, spare resource place positions, and the like; establishing a multi-target emergency rescue resource address-scale optimizing model according to the obtained related information, and solving the model by adopting a unit cost utility method; establishing a multi-goods emergency rescue resource combined dynamic distribution optimizing model according to the obtained related information, and solving the model by adopting an algorithm combined with an ideal point method and a unit cost method; and outputting an optimal scheme for the arrangement and distribution of the emergency rescue resources. According to the method, a practical reference scheme for the arrangement and distribution of the emergency rescue resources can be supplied to an emergency decider.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Microfabricated fuel heating value monitoring device
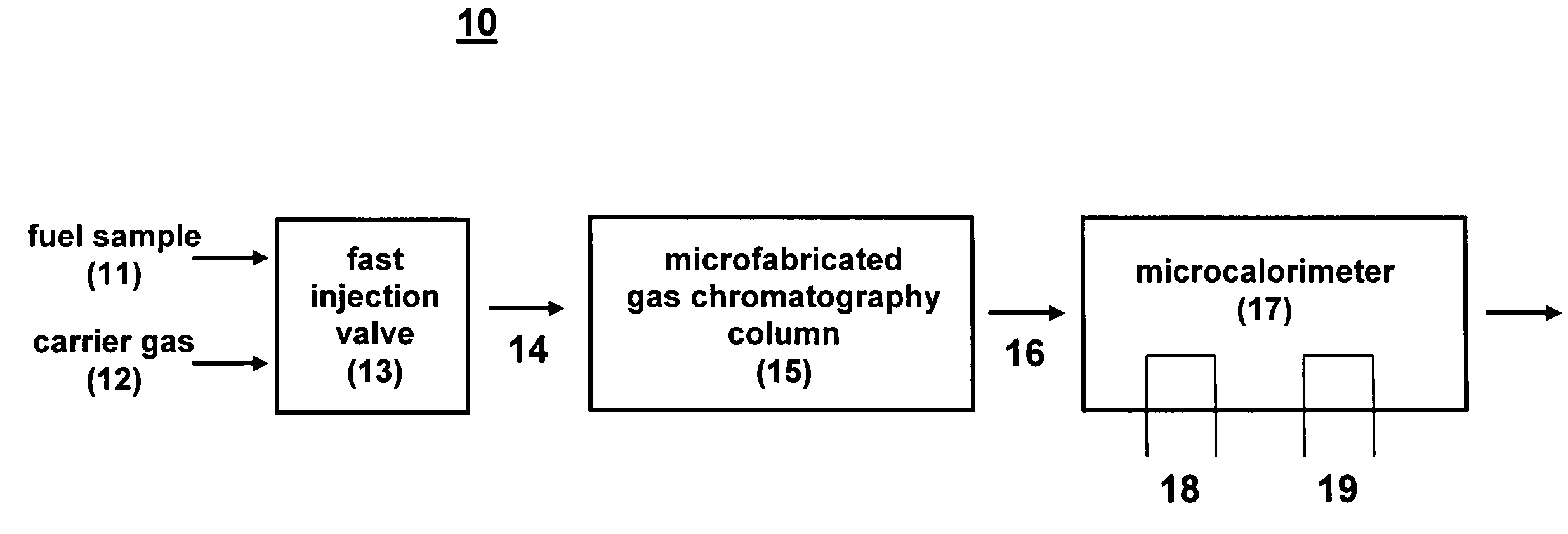
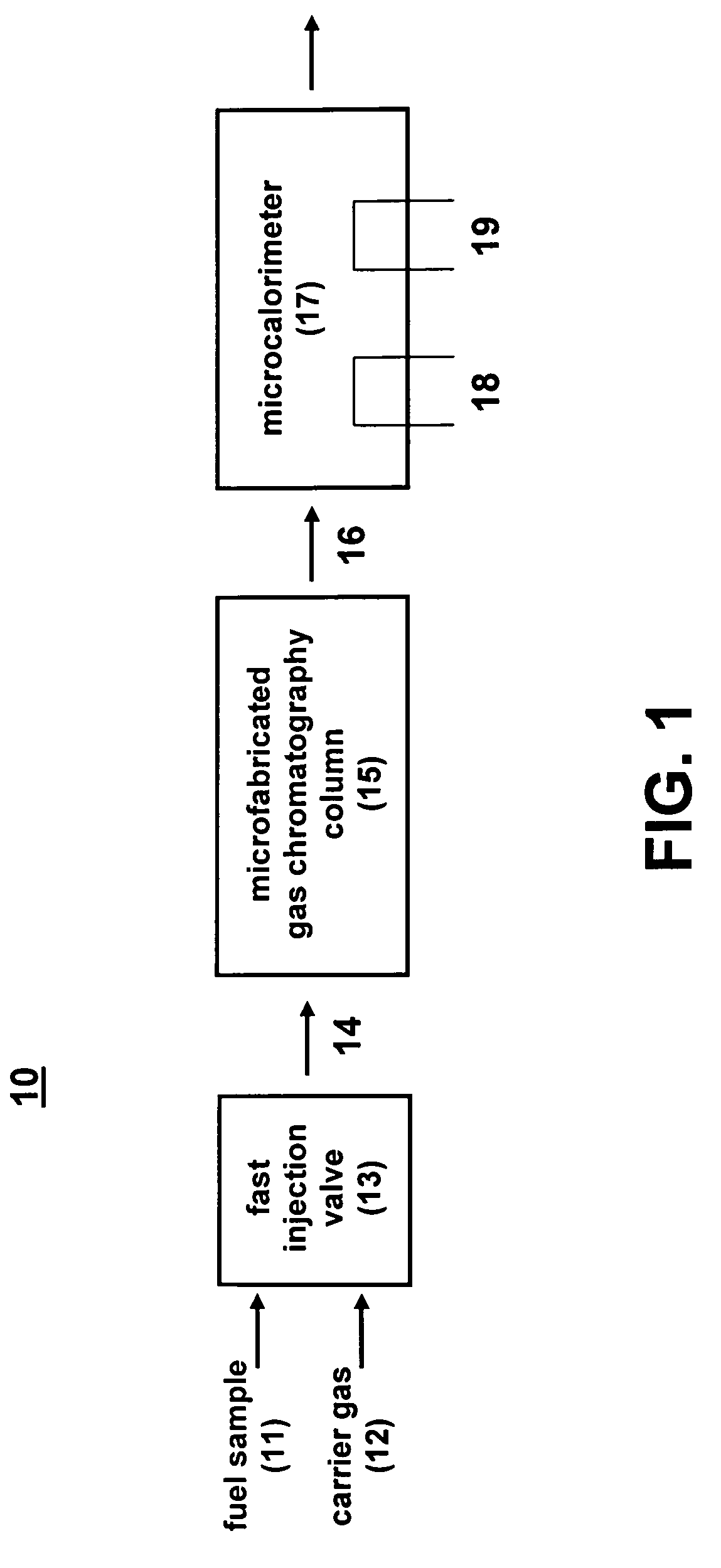
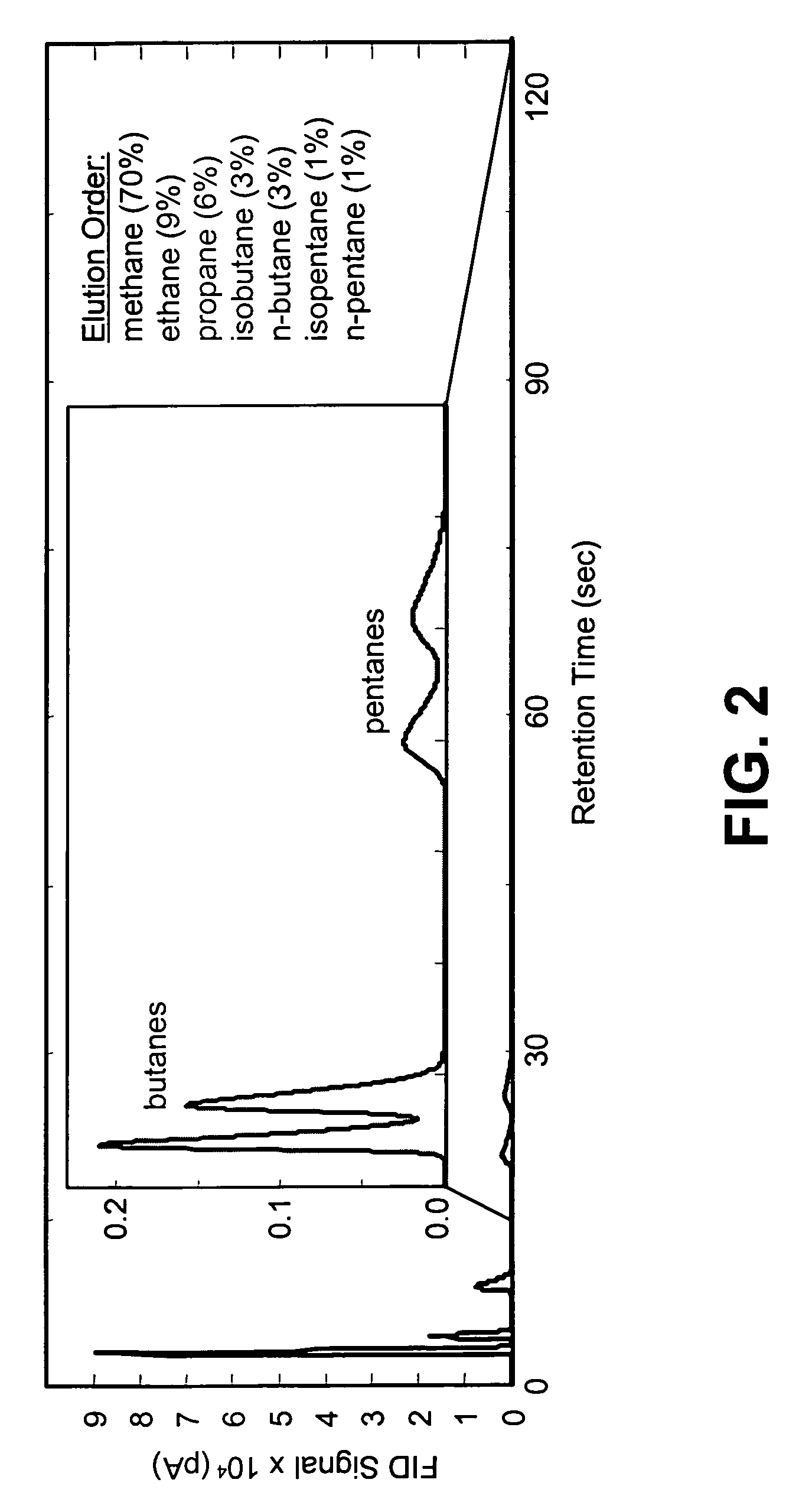
ActiveUS7708943B1Low costChemical analysis using combustionComponent separationContinuous feedbackUnit cost
A microfabricated fuel heating value monitoring device comprises a microfabricated gas chromatography column in combination with a catalytic microcalorimeter. The microcalorimeter can comprise a reference thermal conductivity sensor to provide diagnostics and surety. Using microfabrication techniques, the device can be manufactured in production quantities at a low per-unit cost. The microfabricated fuel heating value monitoring device enables continuous calorimetric determination of the heating value of natural gas with a 1 minute analysis time and 1.5 minute cycle time using air as a carrier gas. This device has applications in remote natural gas mining stations, pipeline switching and metering stations, turbine generators, and other industrial user sites. For gas pipelines, the device can improve gas quality during transfer and blending, and provide accurate financial accounting. For industrial end users, the device can provide continuous feedback of physical gas properties to improve combustion efficiency during use.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
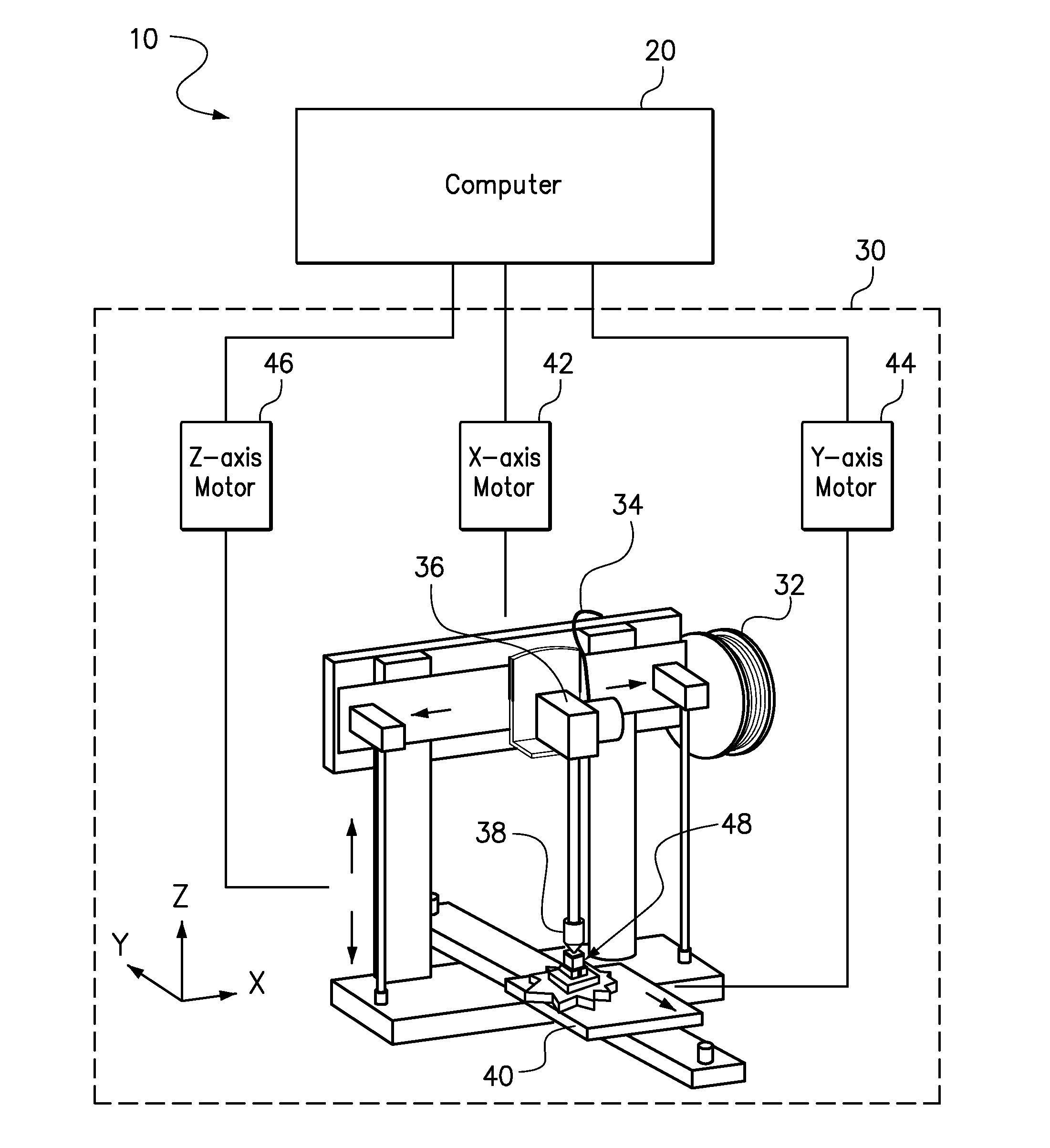
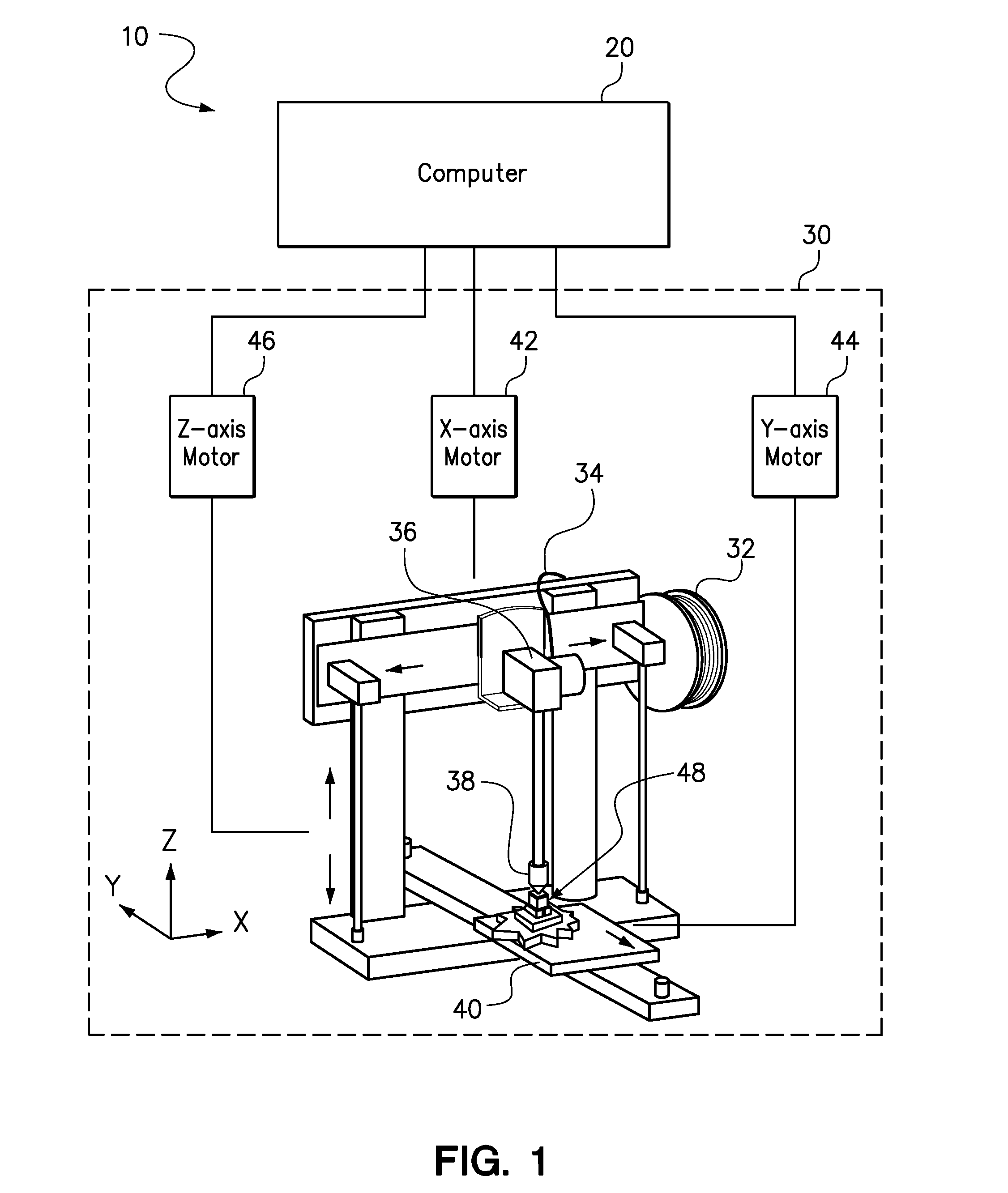
Modifying a three-dimensional object to be printed without exceeding a time or cost threshold
A method and a computer program product for performing the method are provided. The method includes identifying a data file including parameters for causing a three-dimensional printer to print a three-dimensional model of an object, identifying a total time or total cost threshold for printing the three-dimensional model of the object on the three-dimensional printer, obtaining a unit time or unit cost for one or more resources required for printing, modifying one or more of the parameters of the data file so that the three-dimensional model of the object can be printed without exceeding the time or cost threshold, and causing the three-dimensional printer to print the three-dimensional model of the object using the modified parameters.
Owner:LENOVO ENTERPRISE SOLUTIONS SINGAPORE
Electrophoresis display and driving method thereof
ActiveCN101751867AReduce the driving voltageSmall sizeStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsData controlElectrophoresis
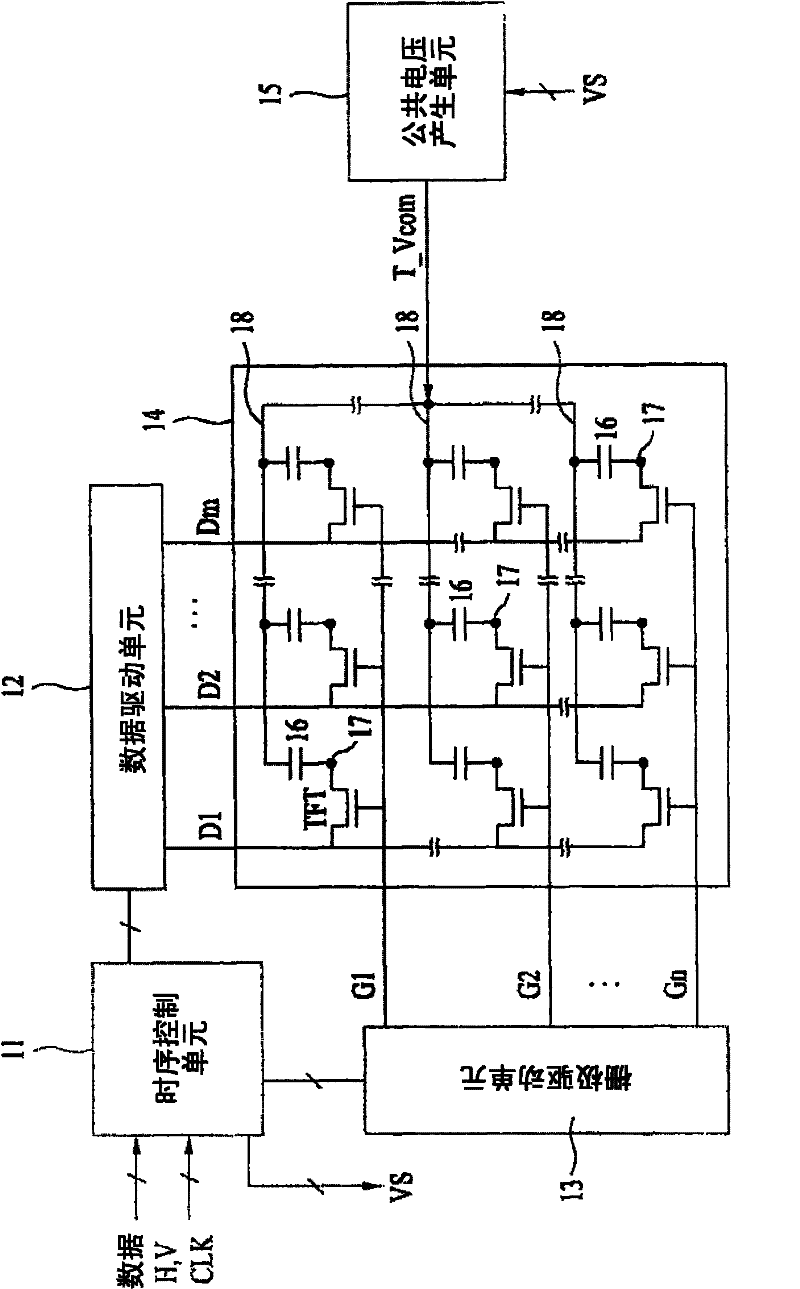
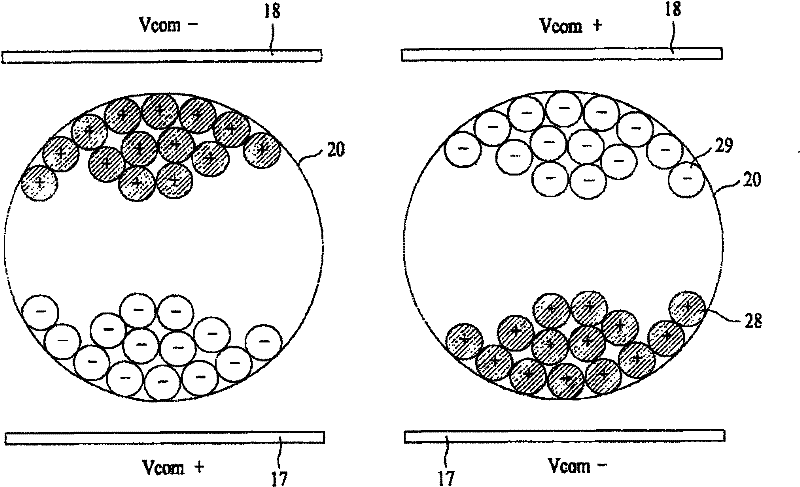
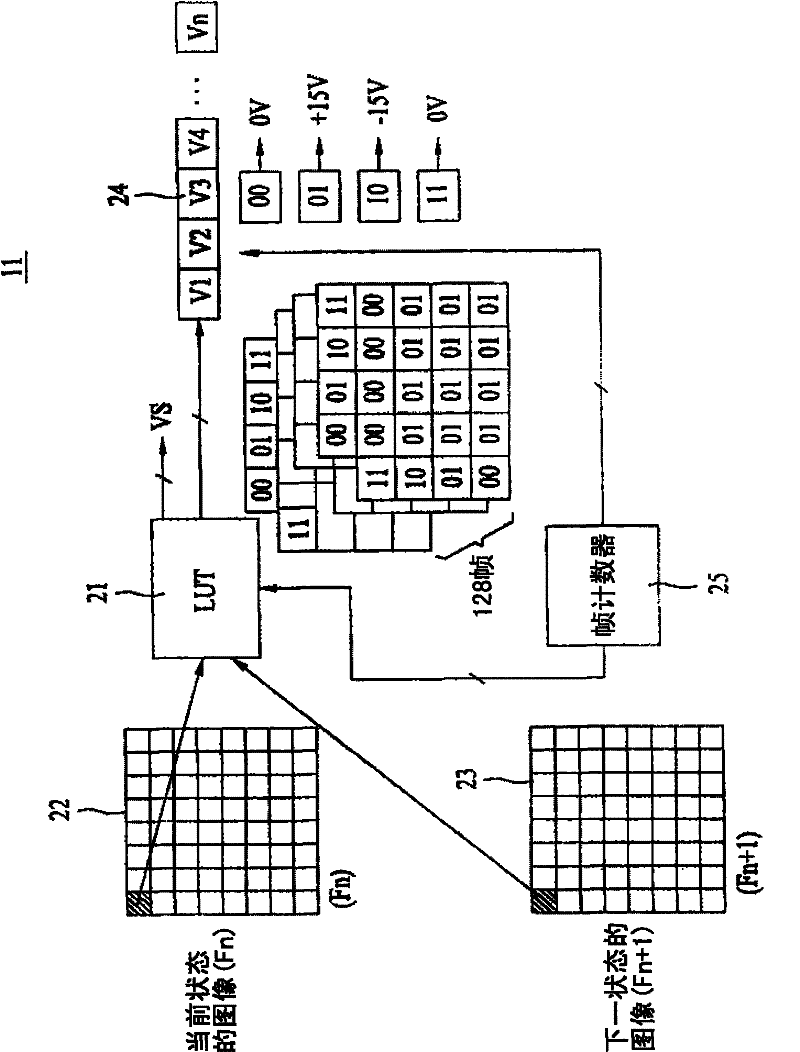
An electrophoresis display and a driving method thereof are disclosed. The present invention relates to an electrophoresis display electrophoresis display that is able to reduce the size of circuits for driving a display panel by decreasing driving voltages required to display images and the unit cost of the product. An electrophoresis display includes a display panel comprising a plurality of pixel cells to display an image, a data driving unit supplying a pixel voltage to a plurality of data lines provided in the display panel, a common voltage generating unit generating a common voltage swinging to reverse electric potential and supplying the common voltage to a common electrode of the display panel, and a timing control unit generating a data control signal and a common voltage control signal and controlling a driving timing of the data driving unit and the common voltage generating unit.
Owner:E INK CORP
Method for generating process chains
A method for generating process chains for product manufacturing is provided. In accordance with the method, all available data pertaining to the component to be manufactured is collected and the component to be manufactured is subdivided into component elements which can be manufactured independently of one another. On the basis of this subdivision, process blocks for manufacturing the component elements are defined. The method further includes collecting all possible core technologies for the individual process blocks, where the core technologies are those manufacturing processes and machining processes through which alternative manufacturing processes and machining processes differ from one another. The method includes generating all possible manufacturing process chains by combining all core technologies of one process block with the core technologies of the other process blocks, and reducing all possible manufacturing process chains to a subset of possible manufacturing process chains. This reduction is based upon geometric and / or technological boundary conditions. Particularized manufacturing process chains for this subset of manufacturing process chains are generated, with identical input states and output states being applied or being defined for all manufacturing process chains. The method ascertains data pertaining to per-unit costs for the component to be manufactured, resulting from the use of the particularized manufacturing process chains; ascertains data pertaining to the technological risk and / or to the reliability of the ascertained per-unit costs for the particularized manufacturing process chains; and performs capital value calculations for the particularized manufacturing process chains on the basis of the particular per-unit costs. The method then selects the optimum manufacturing process chain for the component, at least on the basis of the capital value calculations and the data pertaining to risk and / or reliability.
Owner:MTU AERO ENGINES GMBH
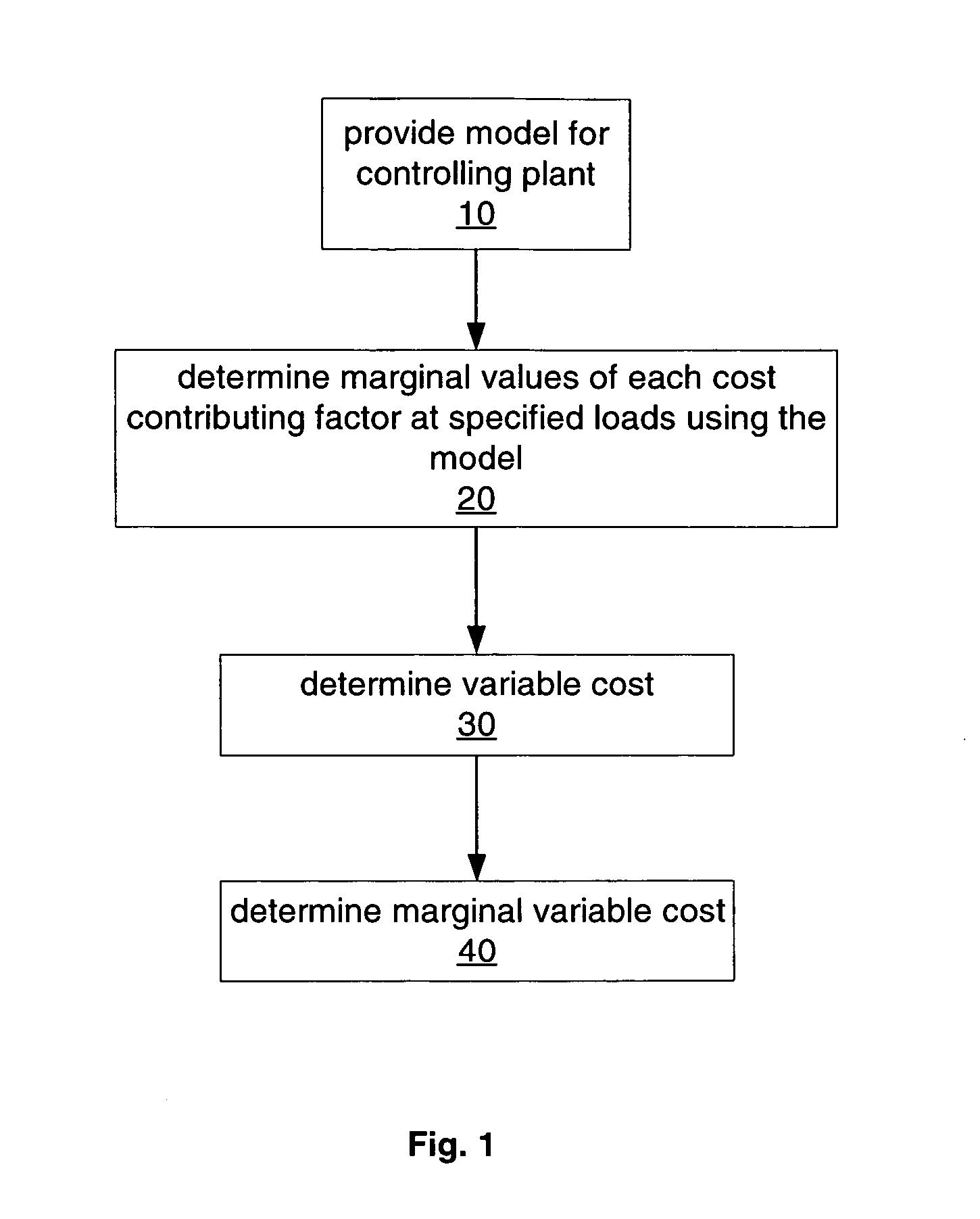
Method and system for calculating marginal cost curves using plant control models
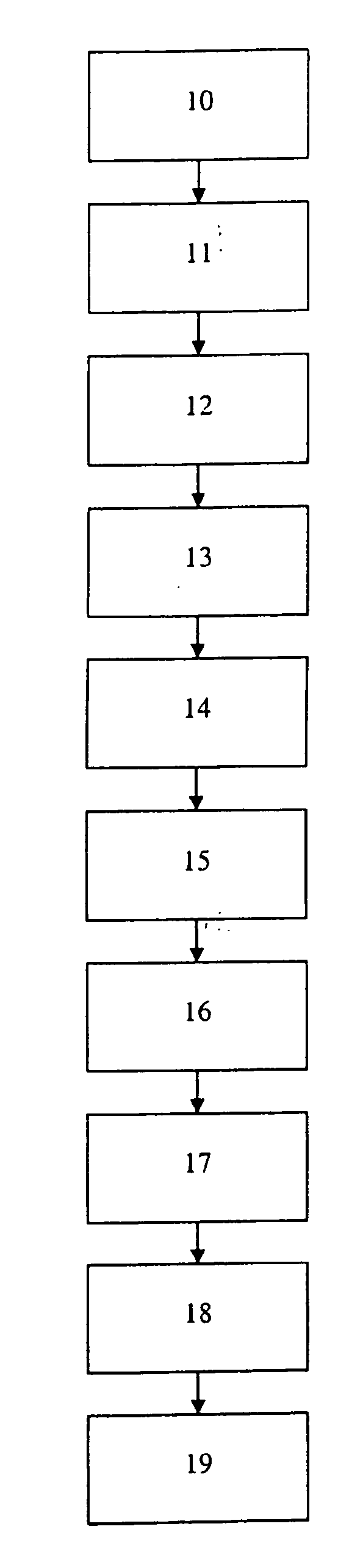
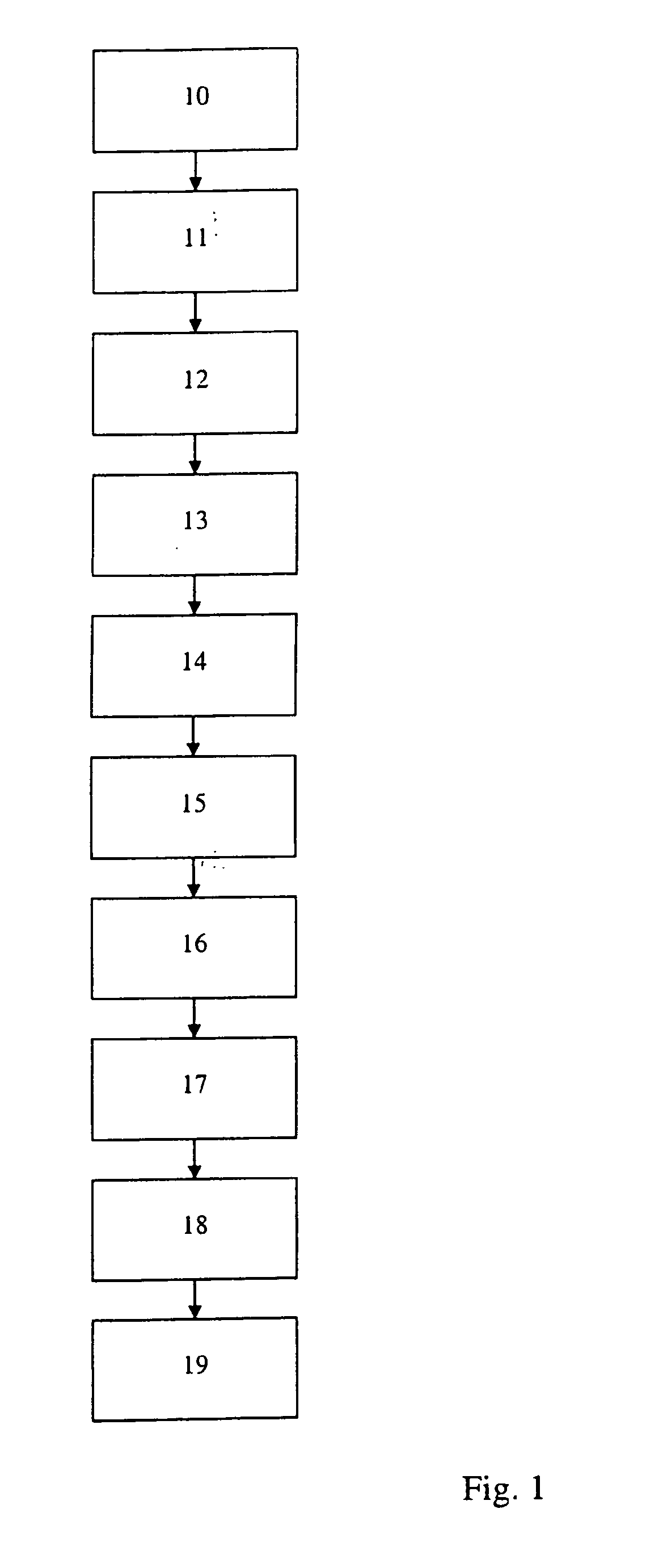
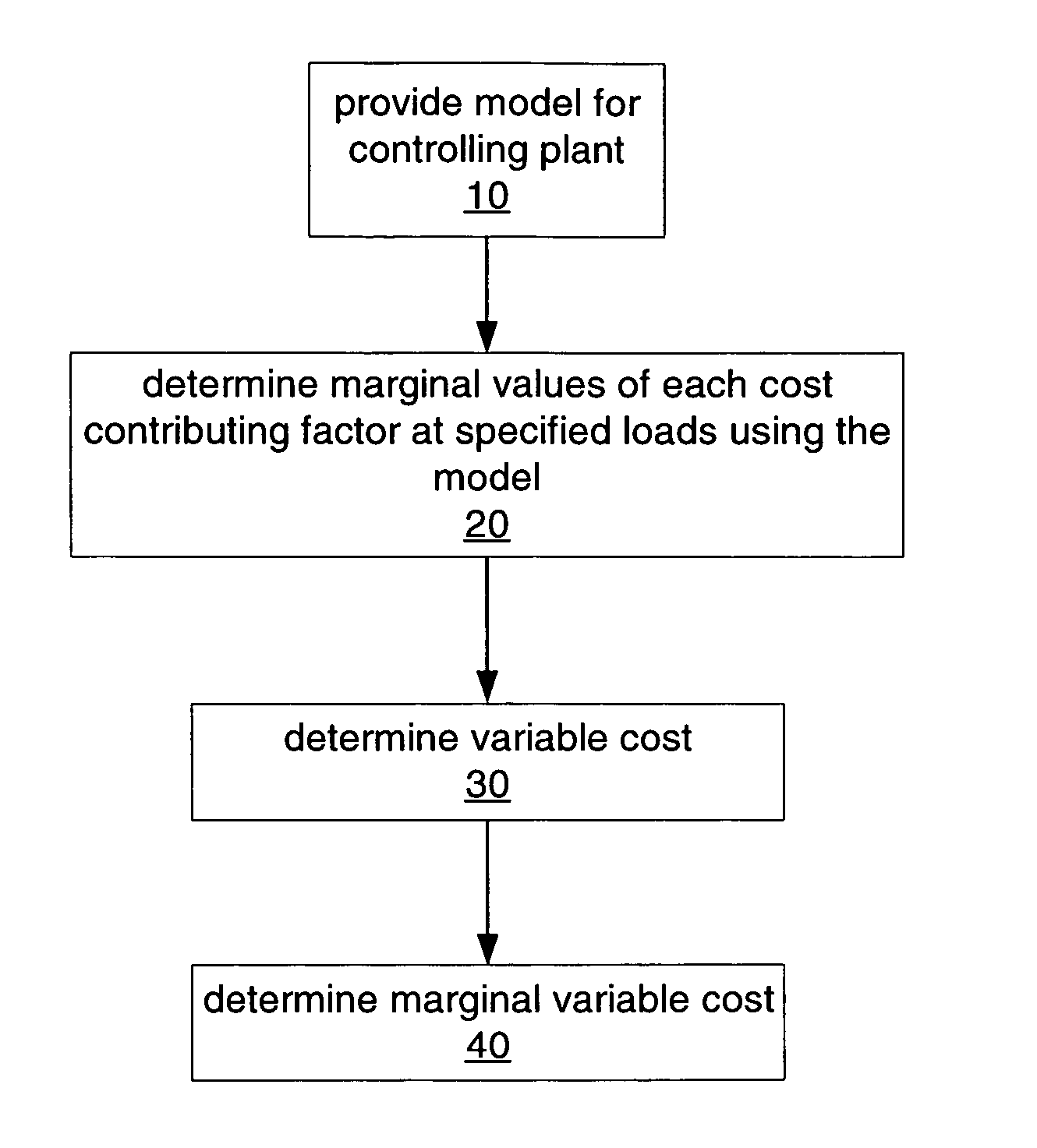
ActiveUS20060089730A1Mechanical power/torque controlData processing applicationsUnit costLoad following power plant
A method and system are provided for calculating a marginal cost curve for a plant at a plant load range comprising a plurality of specified plant loads. The method includes providing a model used for controlling the plant. The model relates plant load and one or more given cost contributing factors. The marginal value for each of the one or more given cost contributing factors at each of the plurality of specified plant loads is determined using the model. A variable cost at each of the plurality of specified plant loads is determined by: (i) multiplying the marginal value of each of the one or more given cost contributing factors at each of the plurality of specified plant loads by a respective unit cost of each of the one or more given cost contributing factors, and (ii) if there are a plurality of given cost contributing factors, summing the results of (i) at each of the plurality of specified plant loads. A marginal variable cost is determined at each of the plurality of specified plant loads by computing a derivative of the variable cost at each of the plurality of specified plant loads. A collection of marginal variable costs at the plurality of specified plant loads defines the marginal cost curve for the plant at the plant load range.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
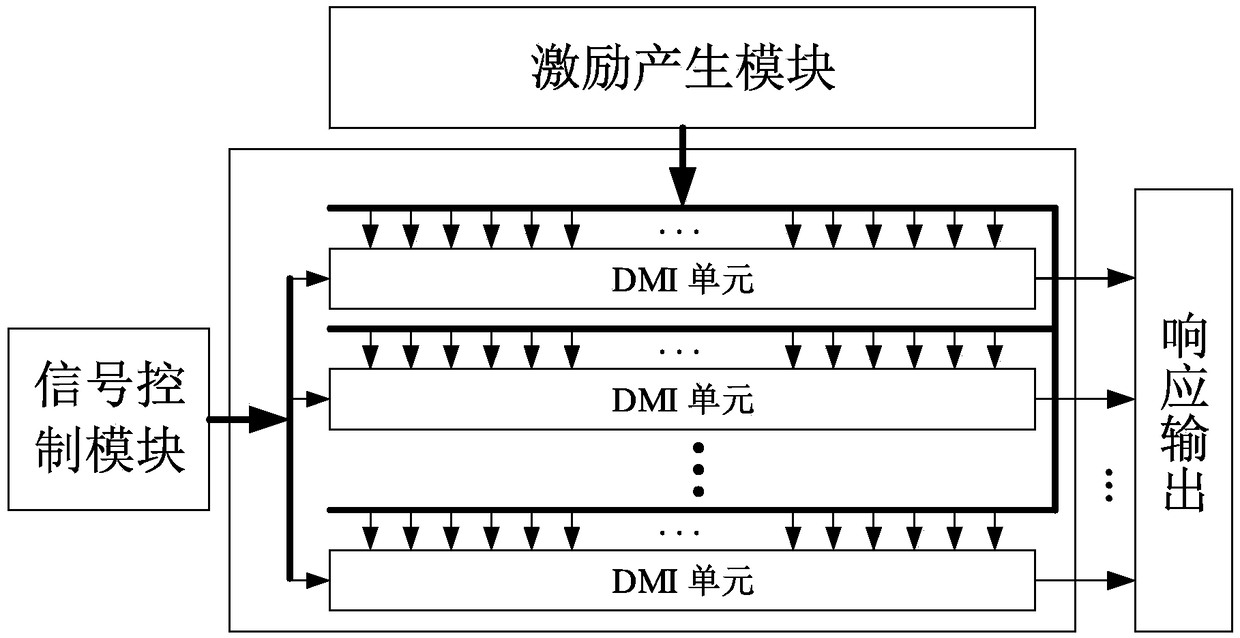
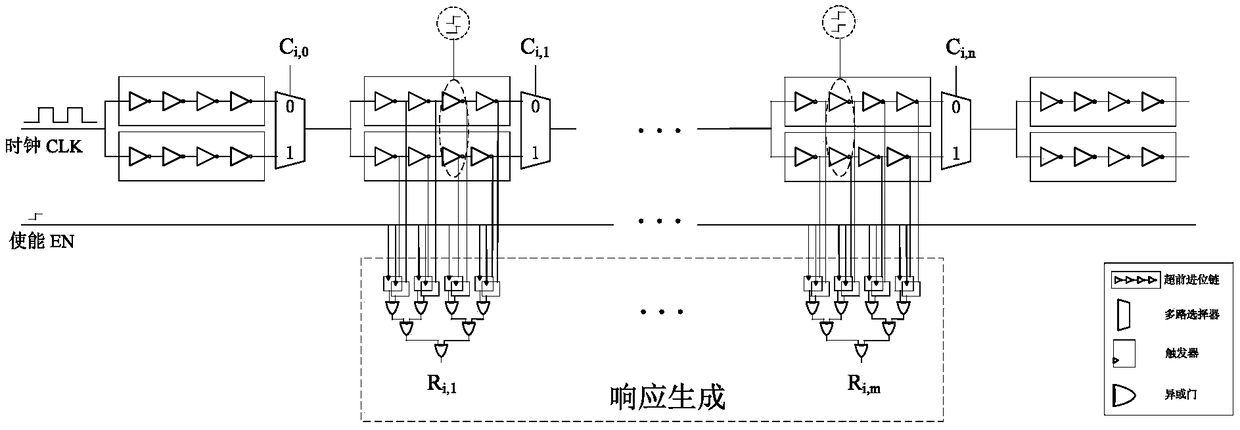
A configurable physically non-clonable function circuit based on delay chain
ActiveCN109460681ASave resourcesLower unit costInternal/peripheral component protectionOn boardFpga chip
The invention provides a configurable physical non-clone function circuit based on delay chain, which comprises a signal control module, an excitation generation module and at least one delay multi-excitation unit. The delay multi-excitation unit comprises a delay chain; The clock source in the circuit is generated by multiplying the clock of FPGA chip on board and controlled by signal control module. The delay chain is composed of inverting blocks which are configured by the carry-forward chain in series. The random difference of the response of different inverting blocks to the signal is extracted to generate the excitation response pair. The circuit uses fewer resources than other delay-type physical non-clonable function circuits under the condition of generating the same bit sequenceby adjusting the configuration signal of the excitation generation module, thus greatly reducing the unit cost.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method and device for designing a data network
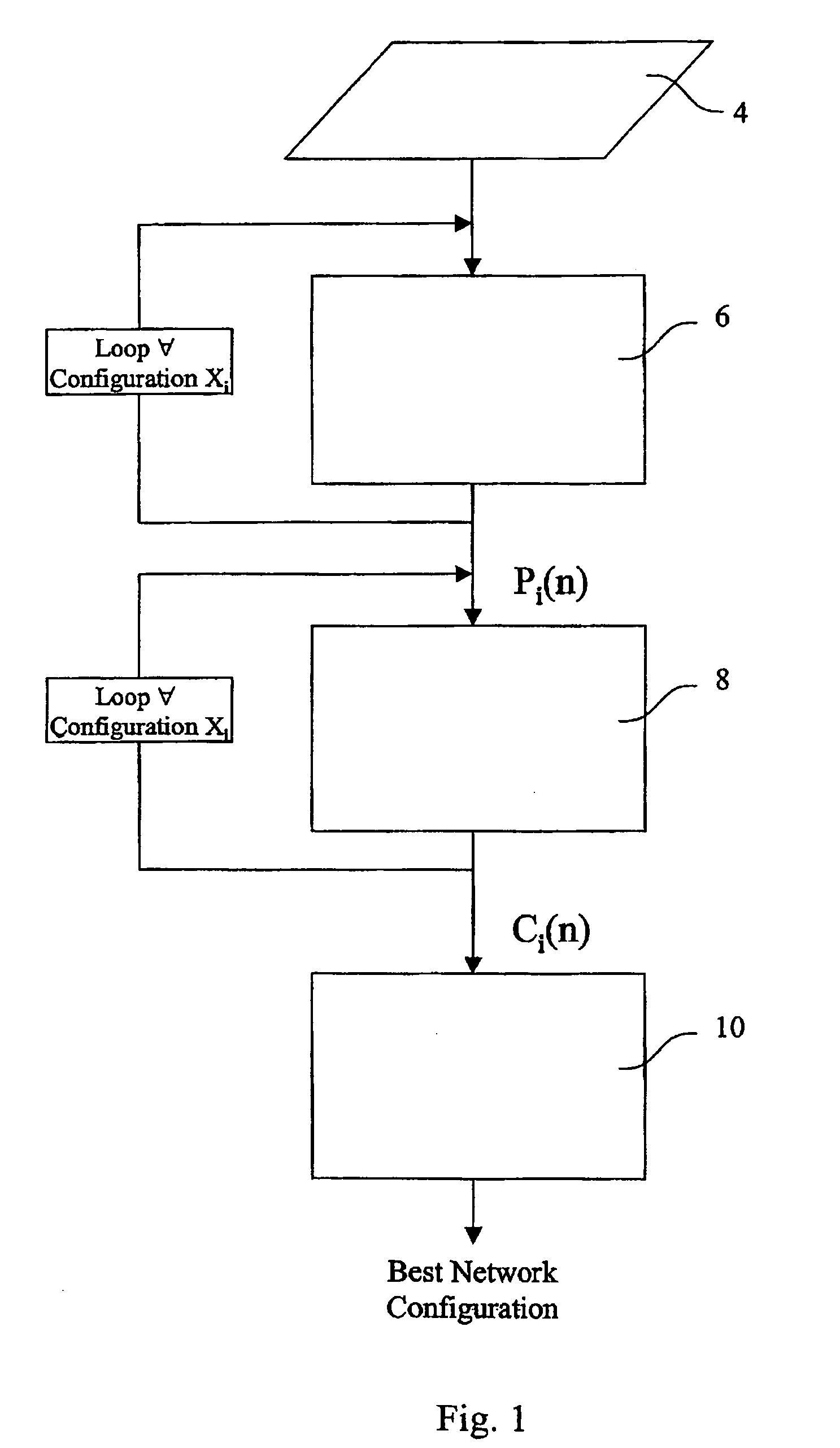
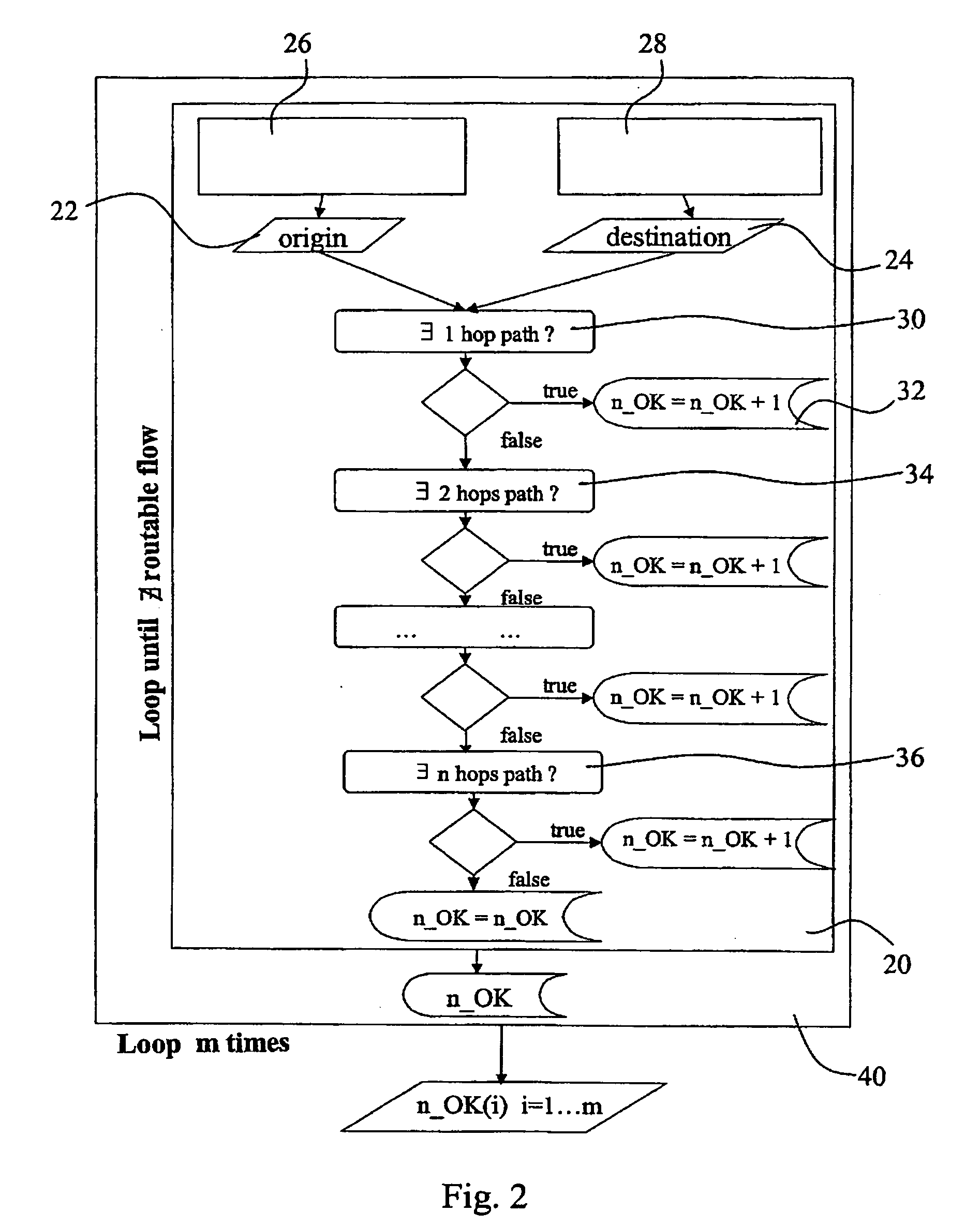
InactiveUS20060067234A1Error preventionTransmission systemsComputational probabilityTraffic capacity
A method of designing a transport network having a plurality of network elements and a plurality of connections between the network elements by (a) defining a first network configuration and at least one alternative network configuration for the same transport network; (b) calculating for each network configuration, a probability function representing, for each maximum number of routable flows, the probability of routing such a number of flows in the network configuration currently considered; (c) calculating for each network configuration, a unit-cost-per-flow function calculated as the ratio between a sum of the costs relative to the network elements of the network configuration currently considered and the probability function; and (d) comparing the unit-cost-per-flow functions of the network configurations considered, for choosing a network configuration having a lowest unit-cost-per-flow value.
Owner:TELECOM ITALIA SPA
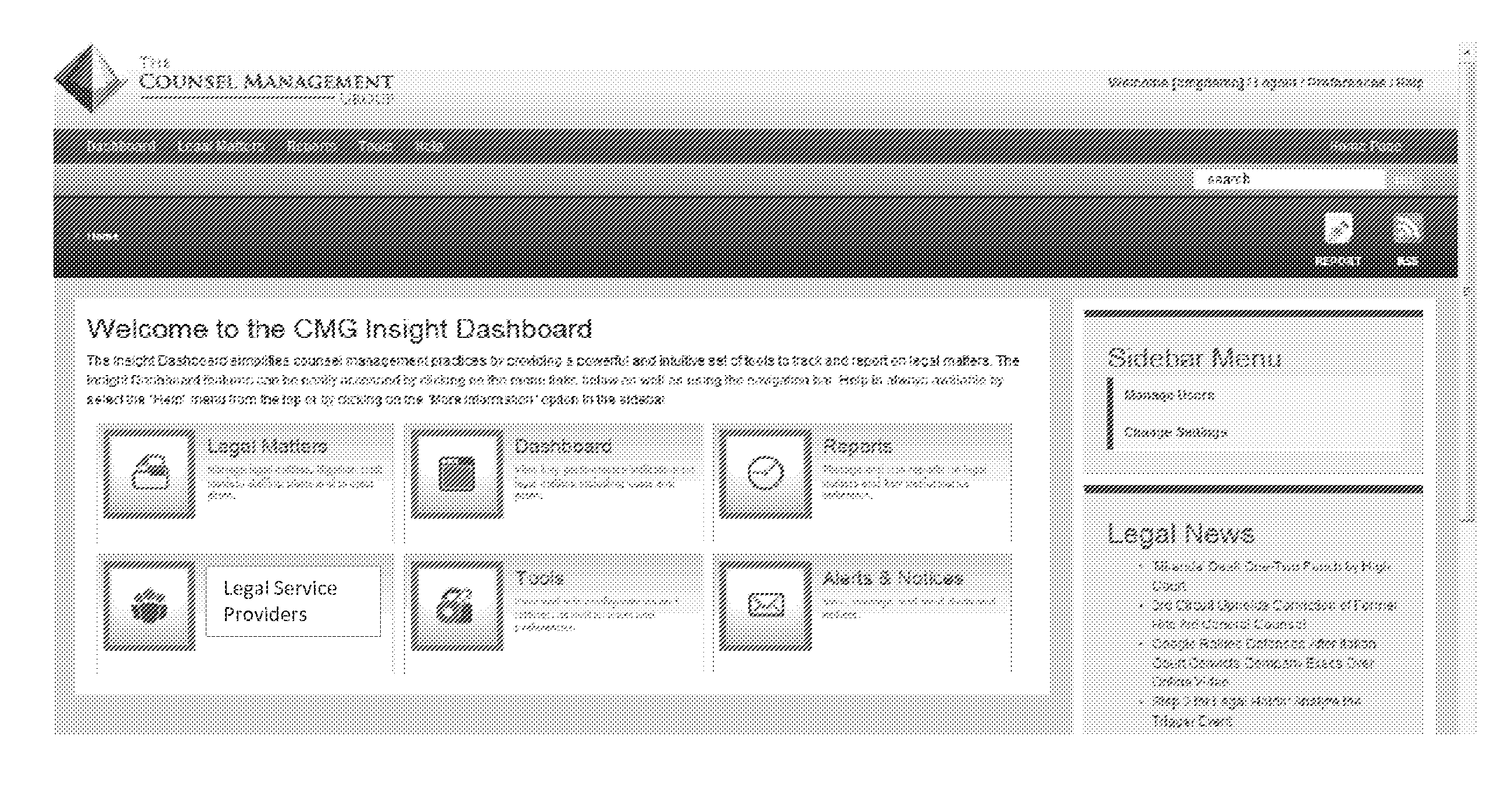
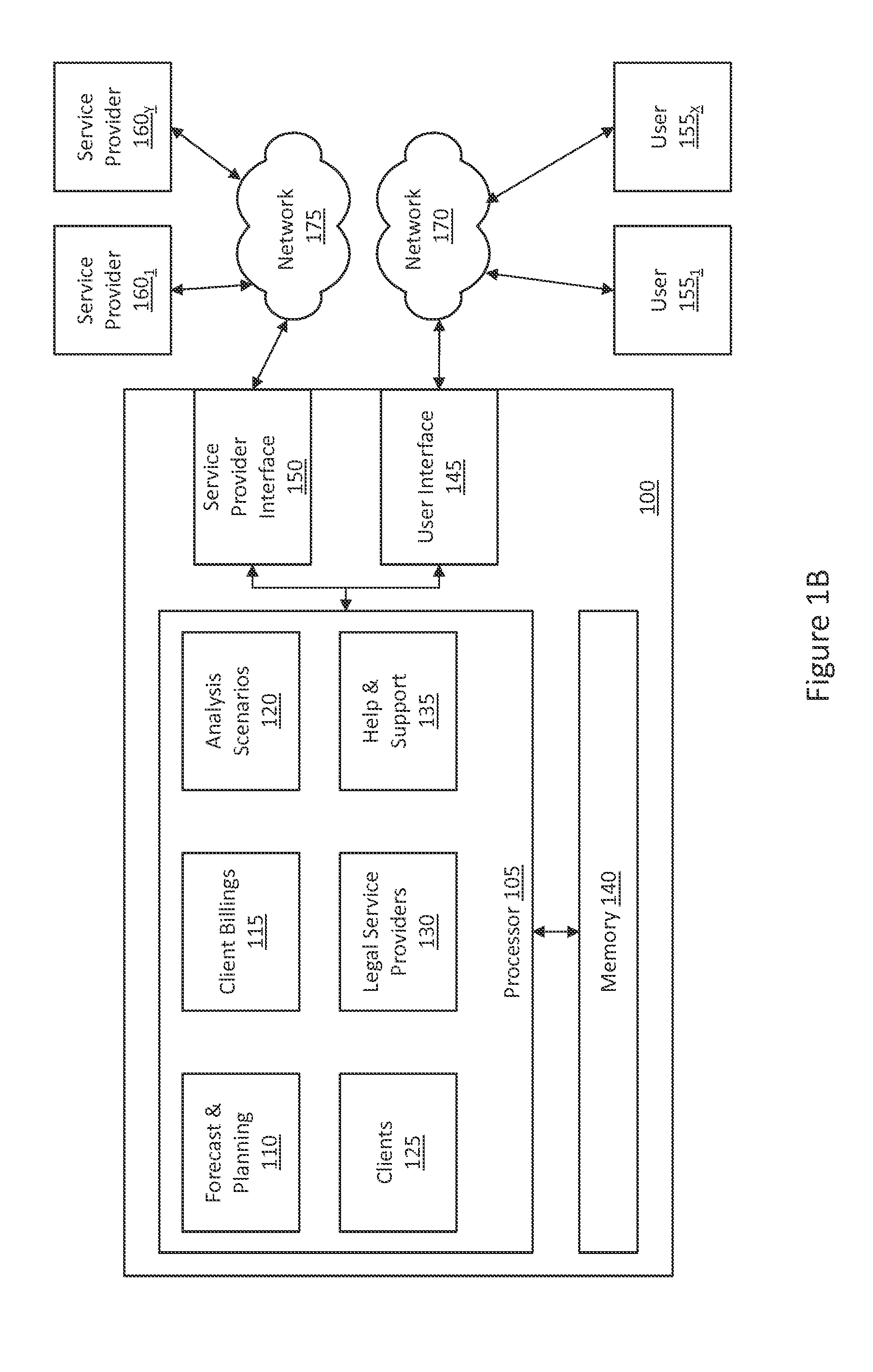
Systems and Methods for Analysis of Legal Service Providers and Comparative Unit Costs or Ratio Costs
ActiveUS20140012623A1Reliable trackingAssess the financial performance of legal service providersMarket predictionsMarket data gatheringGraphicsService provision
Systems and methods for analyzing legal service providers and unit or ratio costs are provided. Billing data from legal services providers is analyzed to identify common tasks based on task codes. The common tasks are then analyzed to determine a unit cost or ratio cost for the tasks or a ratio cost for the tasks compared to the total costs for a matter. Analysis constraints are applied to the billing data to generate a cost model, which can be output in a variety of different graphical formats. This output, which identifying at least some of the total matter costs on a unit cost or ratio cost basis, allows for comparison of legal services provided by a number of different legal services providers. It also allows for comparing price quotes from a number of legal services providers against each other and against historical cost information.
Owner:THE COUNSEL MANAGEMENT GRP
Electronic information label and displaying method thereof
InactiveUS20160071476A1Easy to useMinimizeAdvertisementsCo-operative working arrangementsDisplay deviceElectronic information
A technology regarding electronic labels that electronically show information regarding products displayed in a store.The proposed invention independently displays product information of different types through two displays and thus reduces power consumption by using LCD panels. In addition, other aspects of the proposed invention make better use of space by mounting a display panel on a bezel area, and also lower a product's unit cost of production as products, more specifically the two displays therein, may be controlled using only one controller. Furthermore, the proposed invention may allow for the displayed product information to be changed even when the electronic label is in sleep mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Device for adjusting length of string
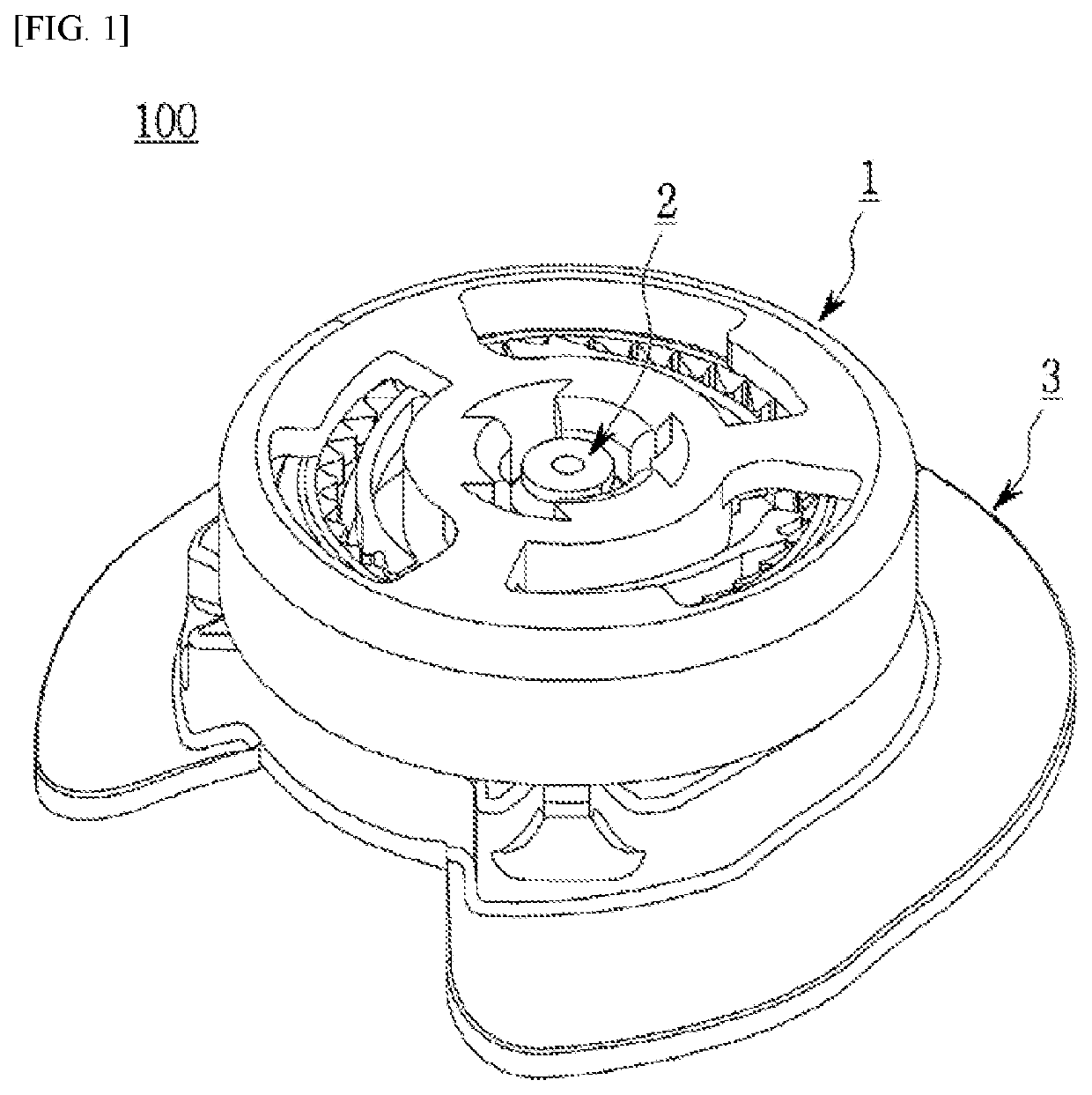
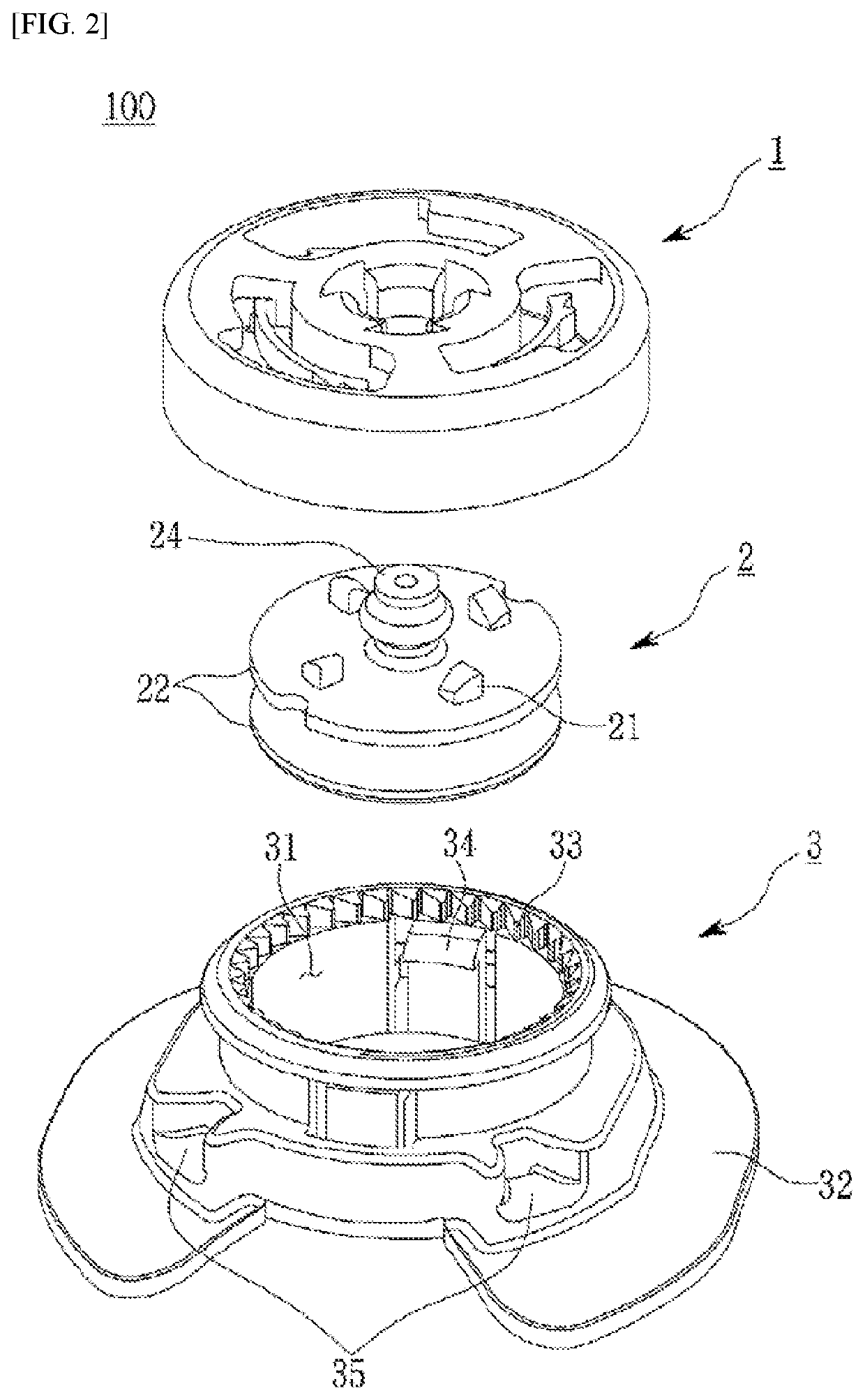
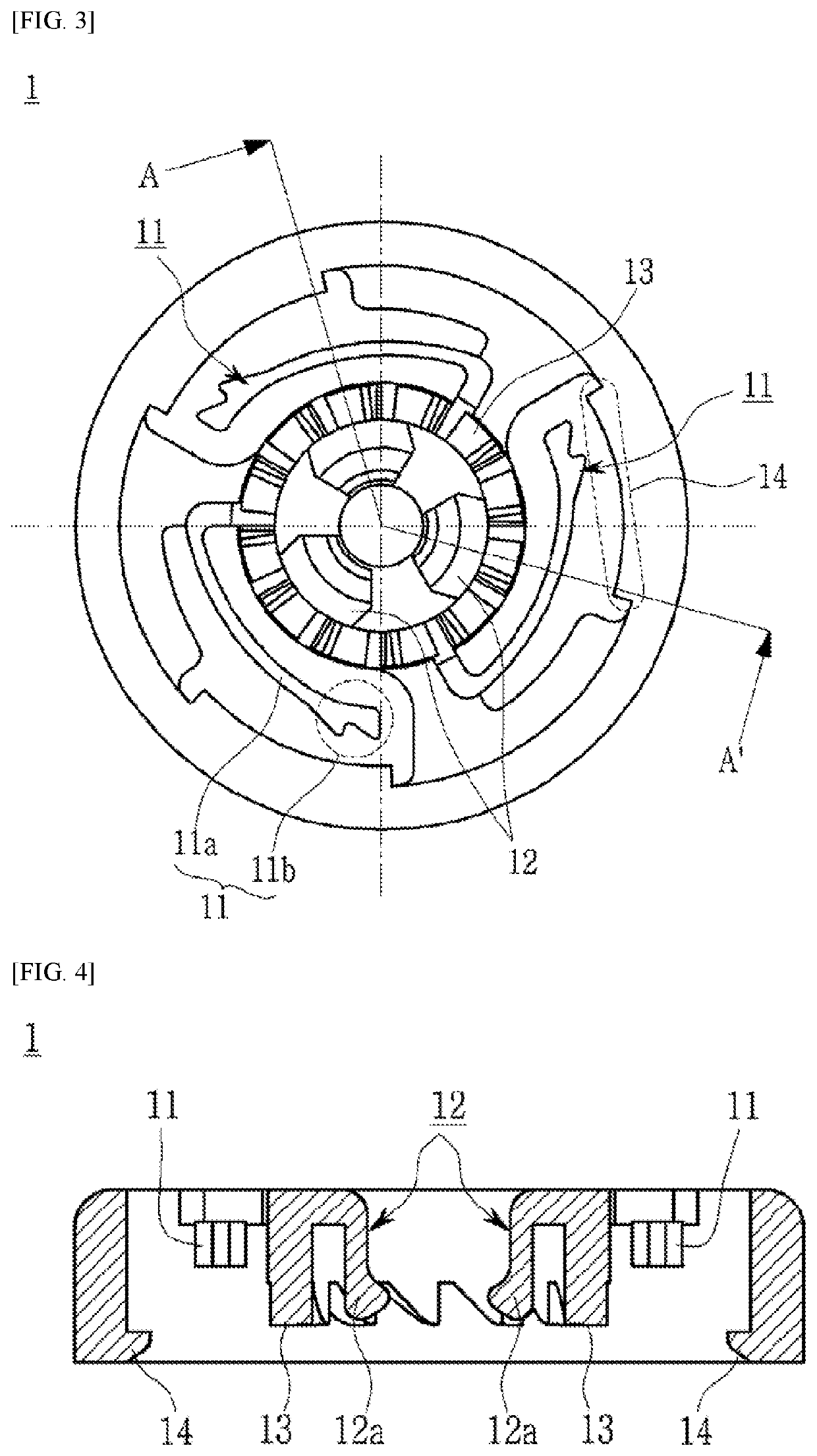
Provided is a device having an improved structure that lowers the unit cost and failure rate of a product by reducing the number of components and improves the assemblability, consistency in quality, operational stability, and convenience of future servicing of the product. In the device, a shaft and a shaft coupling part of a winding drum are simply coupled without a separate coupling member as a protruding portion formed on the shaft becomes caught in a catching portion formed on the shaft coupling part.
Owner:SO YOUN SEO
Liquid crystal display device
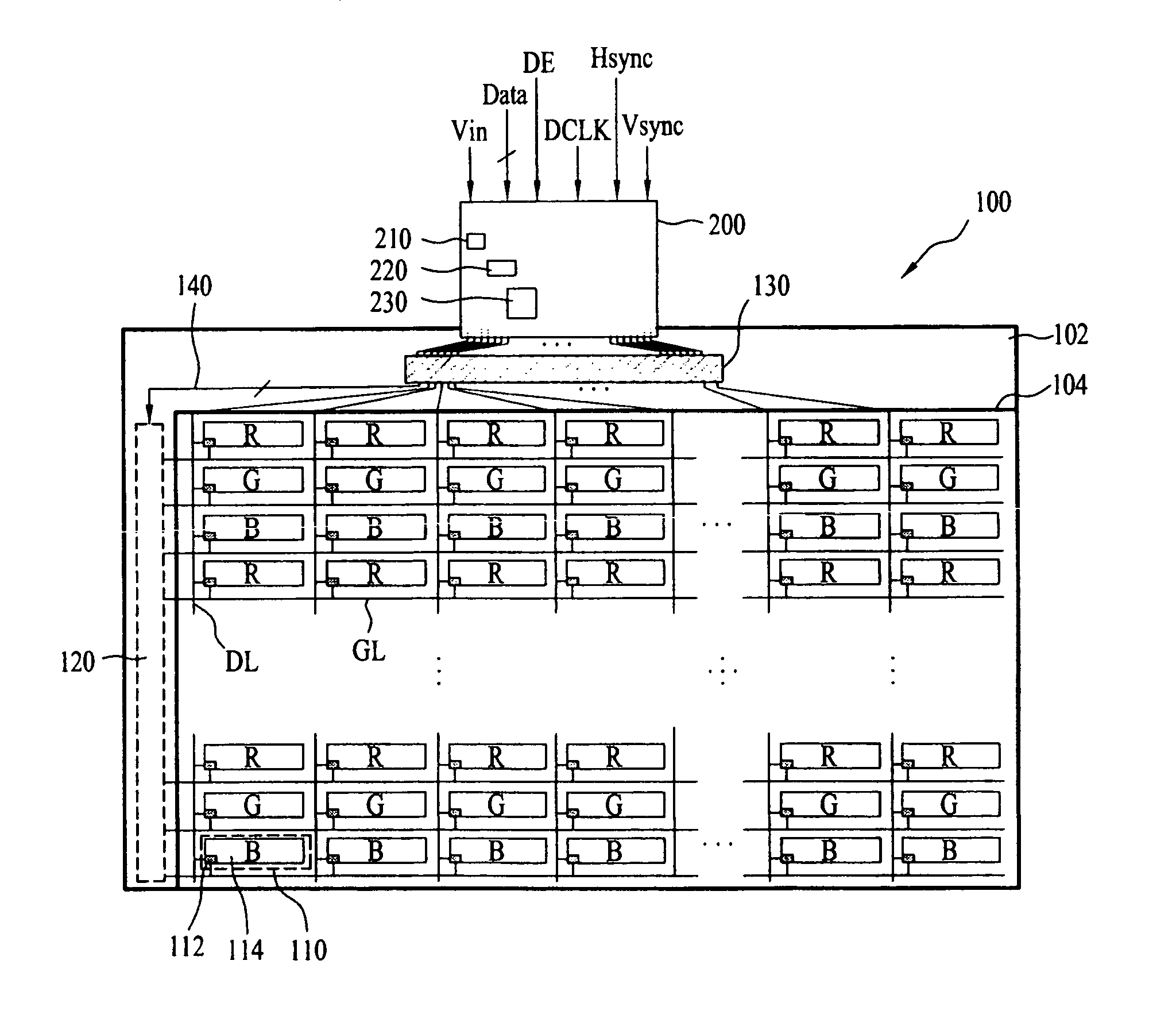
ActiveUS20080186421A1Lower unit costInhibit deteriorationStatic indicating devicesKitchen equipmentLiquid-crystal displayElectrical polarity
A liquid crystal display device is disclosed, which can reduce a unit cost and prevent deterioration of picture quality caused by unfilled pixel cells, the liquid crystal display device comprising a liquid crystal panel including a plurality of pixel cells formed at every regions defined by ‘n’ gate lines and ‘m’ data lines, three colors alternatively arranged along the data line direction, and the same colors arranged along the gate line direction; a gate built-in circuit, built-in the liquid crystal panel, for supplying gate-on voltages to the gate lines; and a driving integrated circuit, formed in the liquid crystal panel, for driving the gate built-in circuit, inverting a polarity of video signal in the unit of each data line and at least three gate lines, and supplying the video signal having the inverted polarity to the data lines.
Owner:LG PHILIPS LCD CO LTD
Method for determining inlet-outlet line investment contour line for site selection of proposed substation and application manner
ActiveCN103207953AEasy to fixEasy to analyzeSpecial data processing applicationsTotal investmentSimulation
The invention relates to a method for determining an inlet-outlet line investment contour line for site selection of a proposed substation and an application manner. The method comprises the following steps of: inputting the final positions, line attributes, buckling factors, unit costs and other parameters of inlet-outlet lines of all voltage grades as well as the geographical range for site selection of the substation in a human-machine interaction manner; calculating the total investment of all the inlet-outlet lines at all points of the substation in the range by a computer; connecting points with the same investment on a plane by a curve to form a closed or non-closed line; drawing one line every one investment difference according to a set difference value; and marking the line like marking the contour line of a topographic map.
Owner:YUNNAN HENGAN ELECTRIC POWER ENG CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com