Patents
Literature
2395results about "Details involving processing steps" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
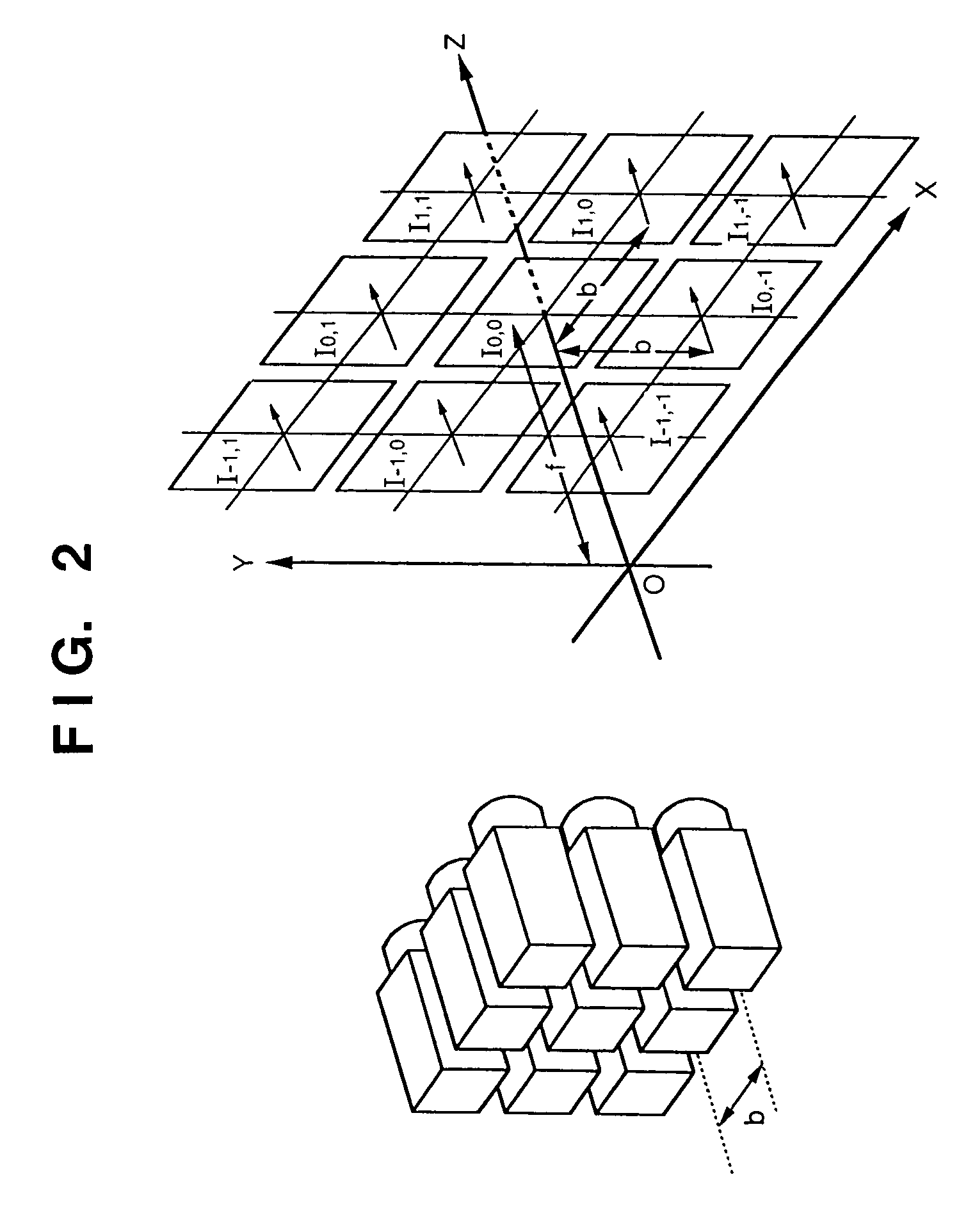
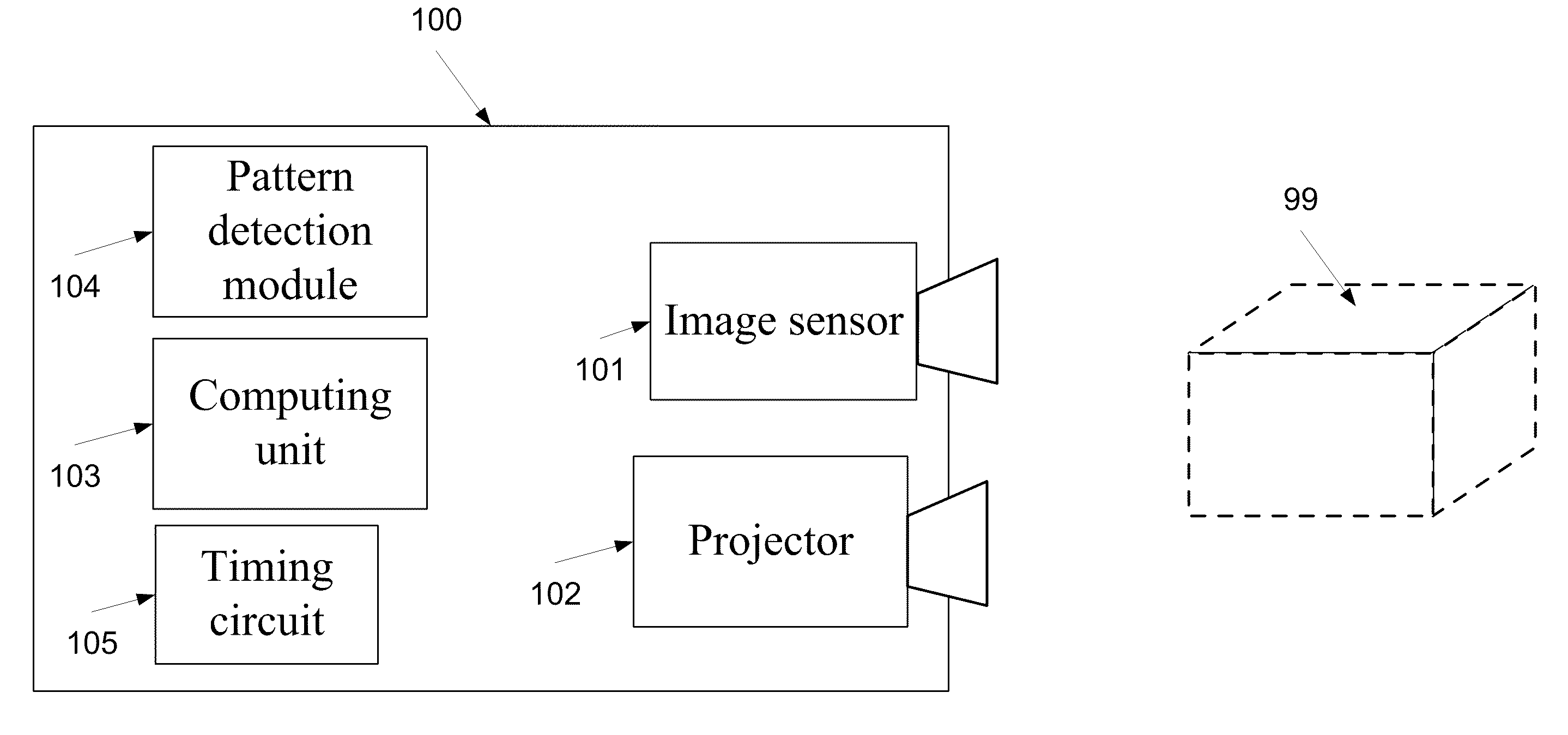
3D imaging system
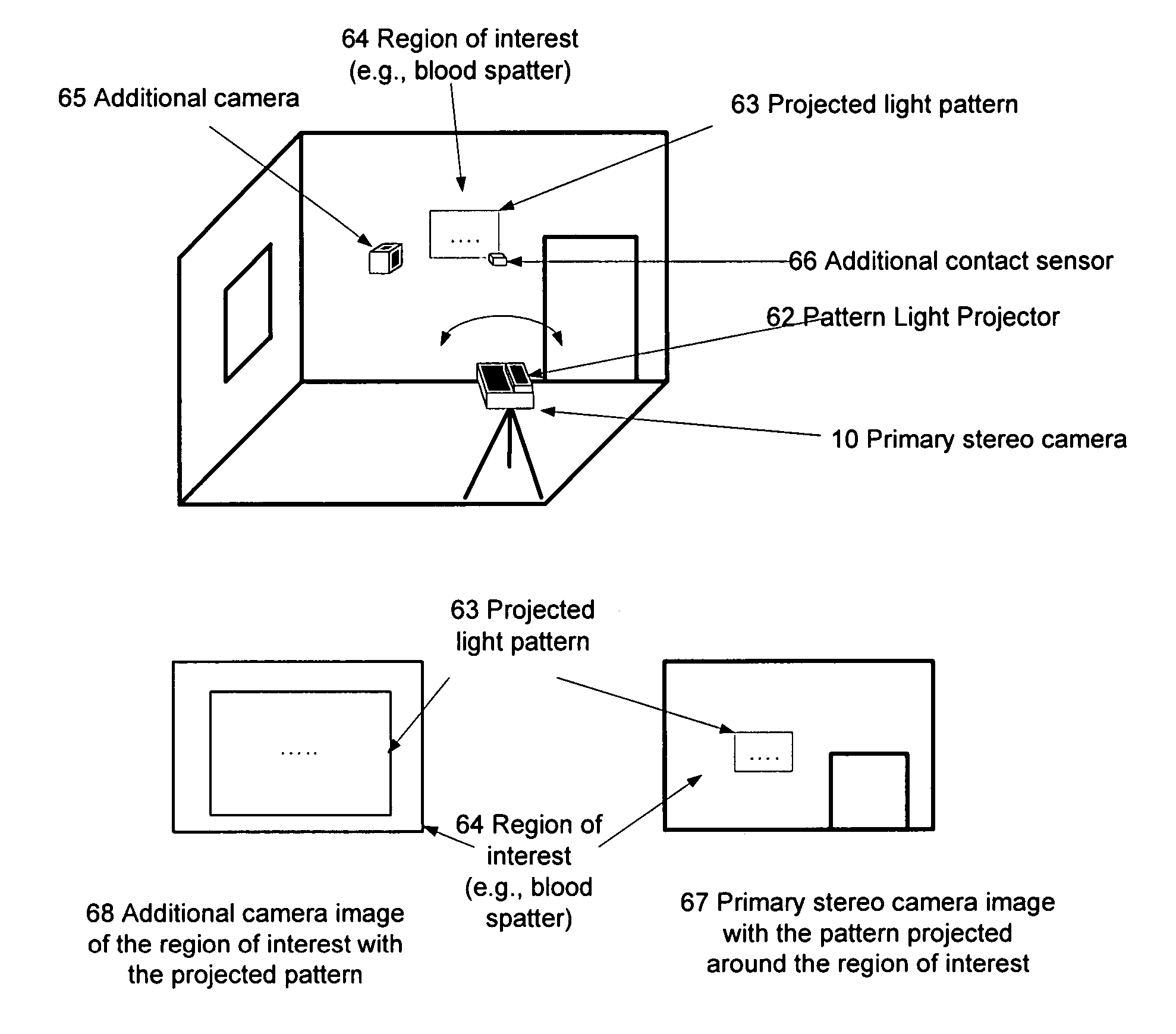
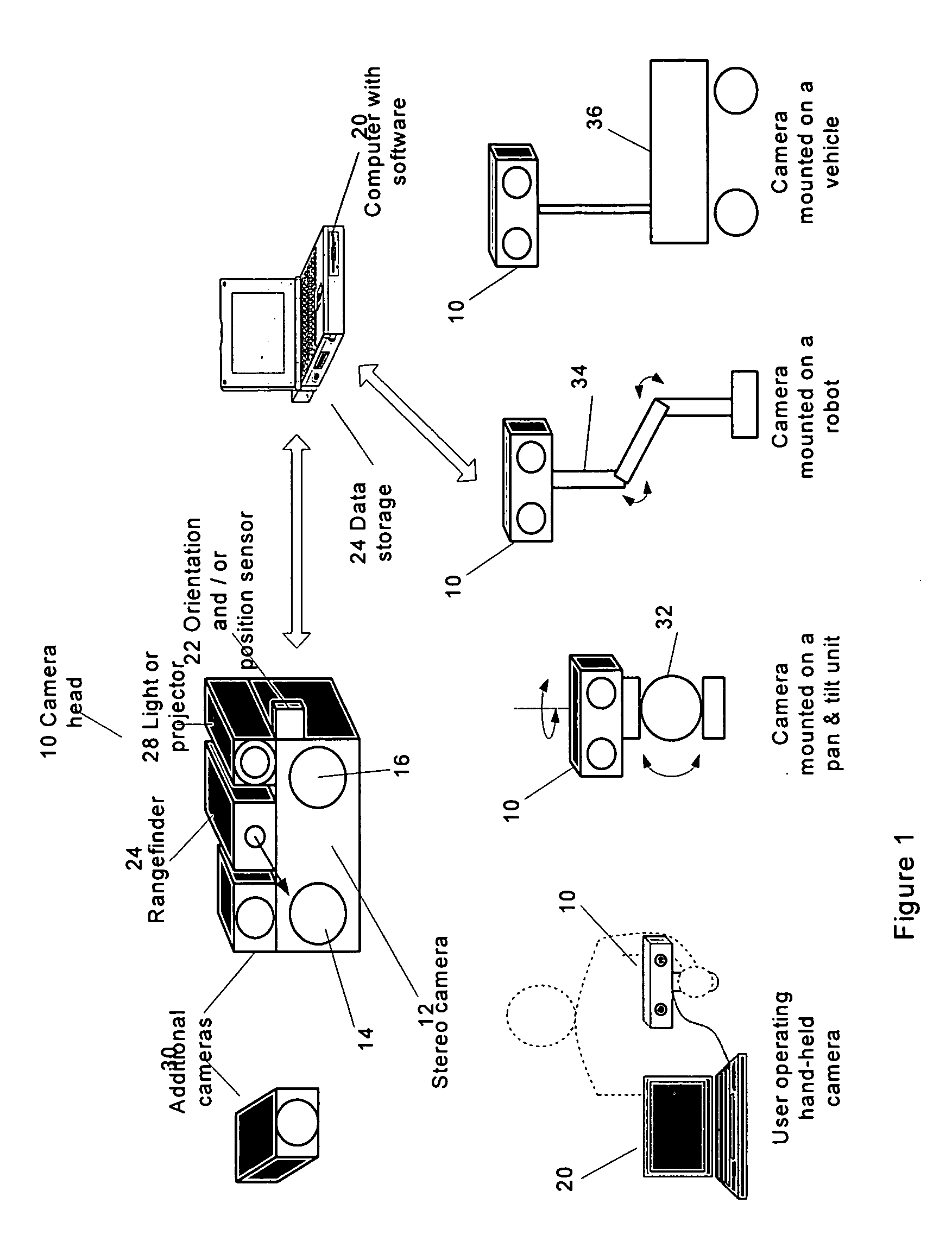
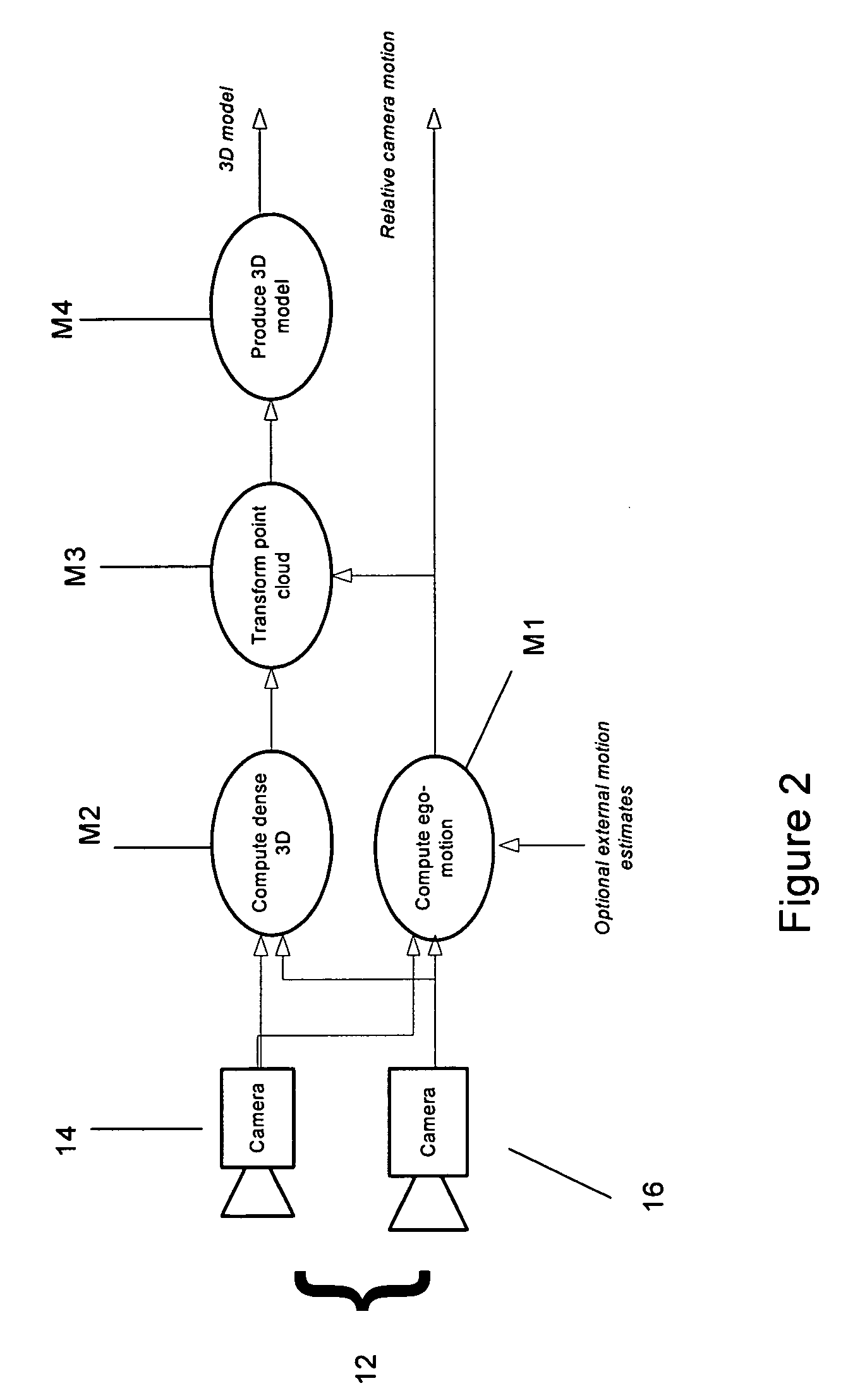
The present invention provides a system (method and apparatus) for creating photorealistic 3D models of environments and / or objects from a plurality of stereo images obtained from a mobile stereo camera and optional monocular cameras. The cameras may be handheld, mounted on a mobile platform, manipulator or a positioning device. The system automatically detects and tracks features in image sequences and self-references the stereo camera in 6 degrees of freedom by matching the features to a database to track the camera motion, while building the database simultaneously. A motion estimate may be also provided from external sensors and fused with the motion computed from the images. Individual stereo pairs are processed to compute dense 3D data representing the scene and are transformed, using the estimated camera motion, into a common reference and fused together. The resulting 3D data is represented as point clouds, surfaces, or volumes. The present invention also provides a system (method and apparatus) for enhancing 3D models of environments or objects by registering information from additional sensors to improve model fidelity or to augment it with supplementary information by using a light pattern projector. The present invention also provides a system (method and apparatus) for generating photo-realistic 3D models of underground environments such as tunnels, mines, voids and caves, including automatic registration of the 3D models with pre-existing underground maps.
Owner:MACDONALD DETTWILER & ASSOC INC
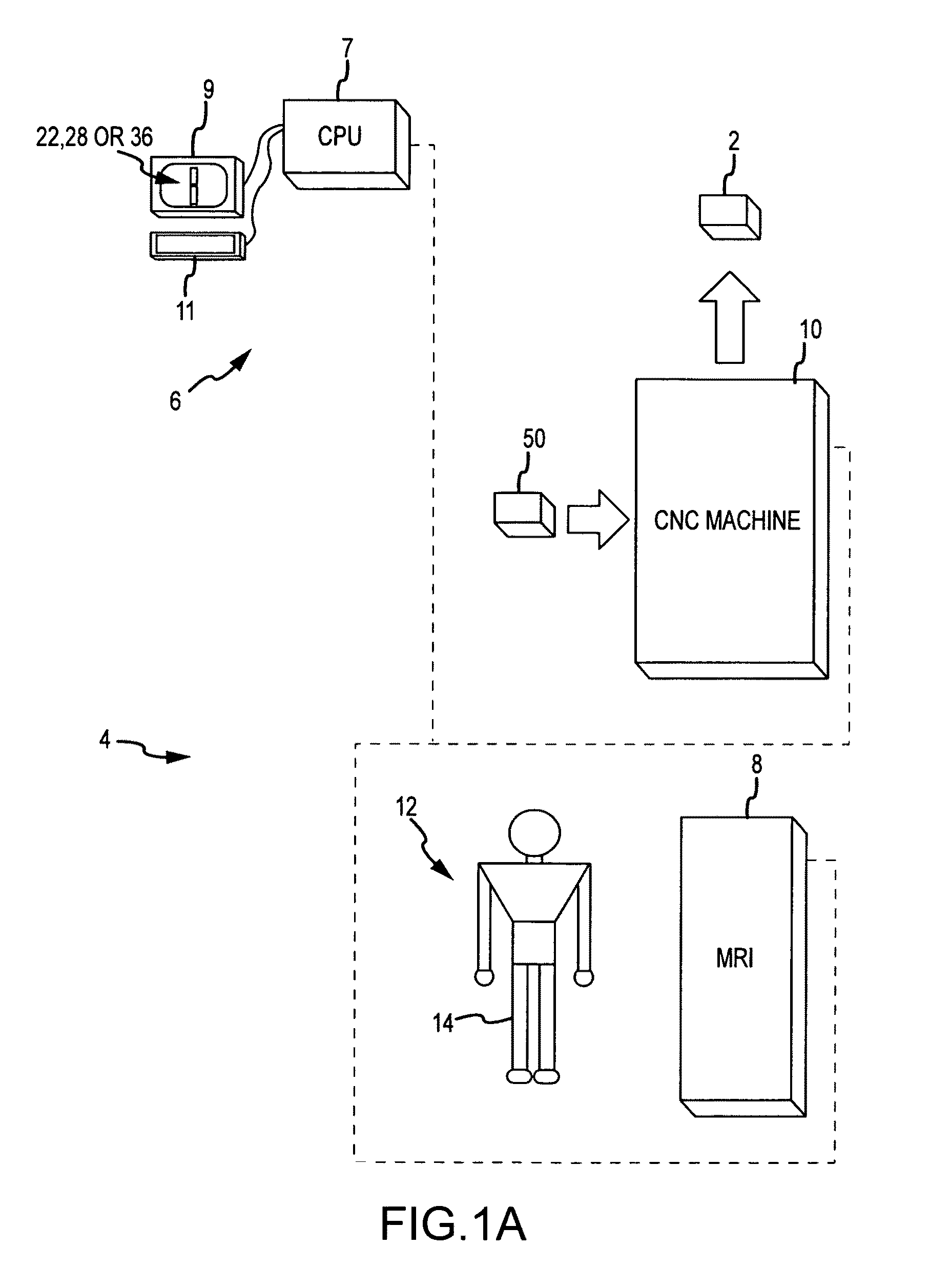
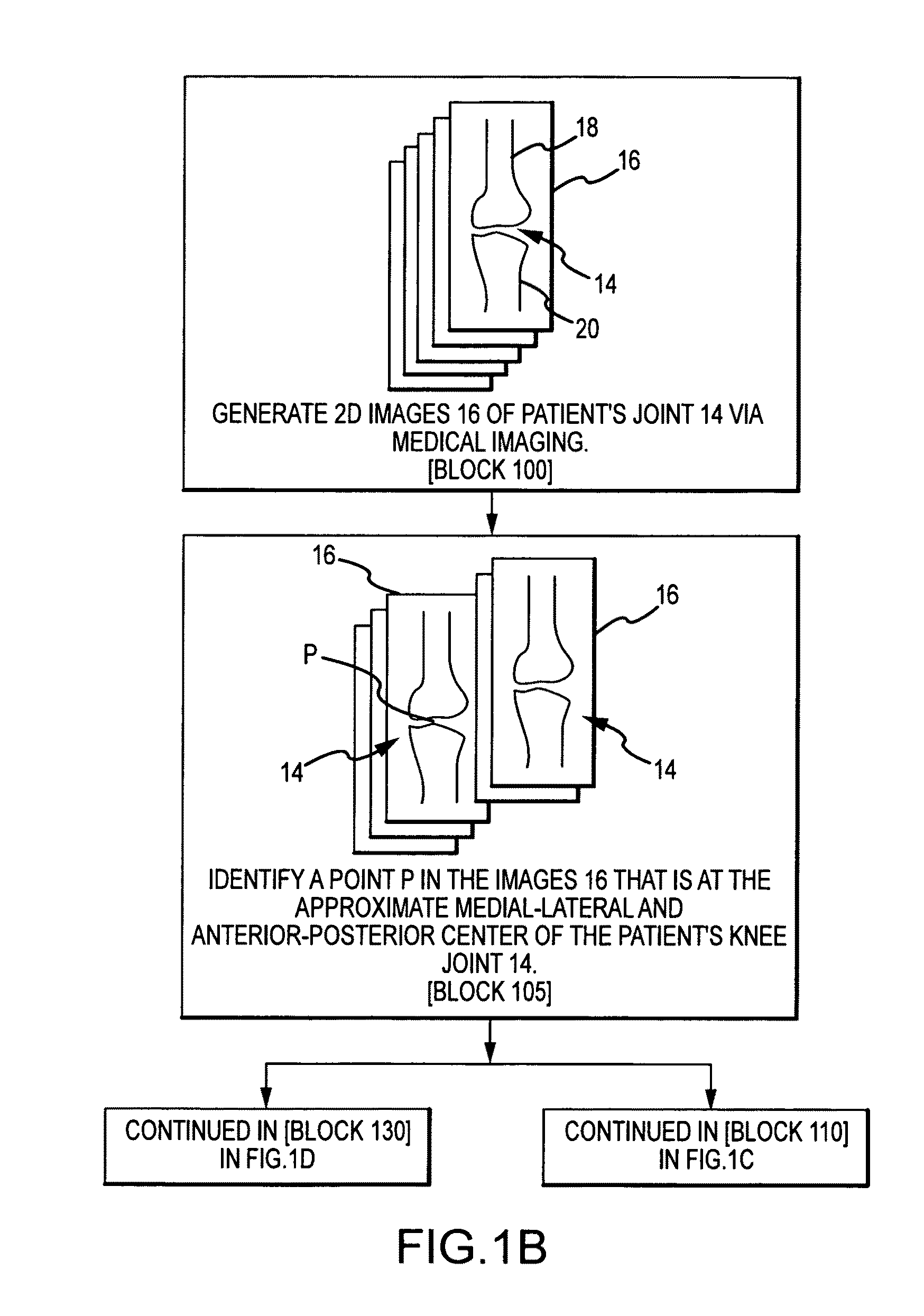
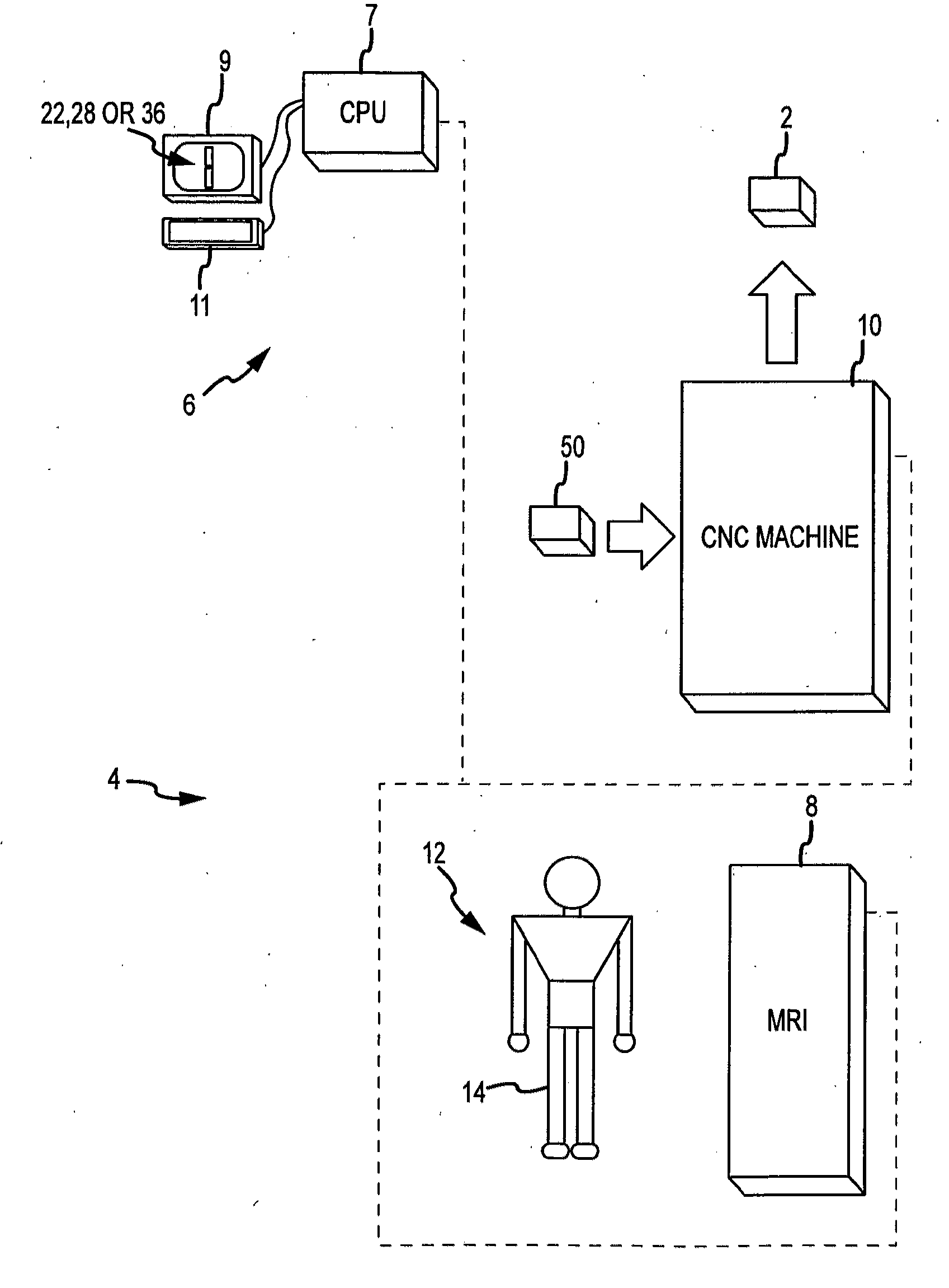
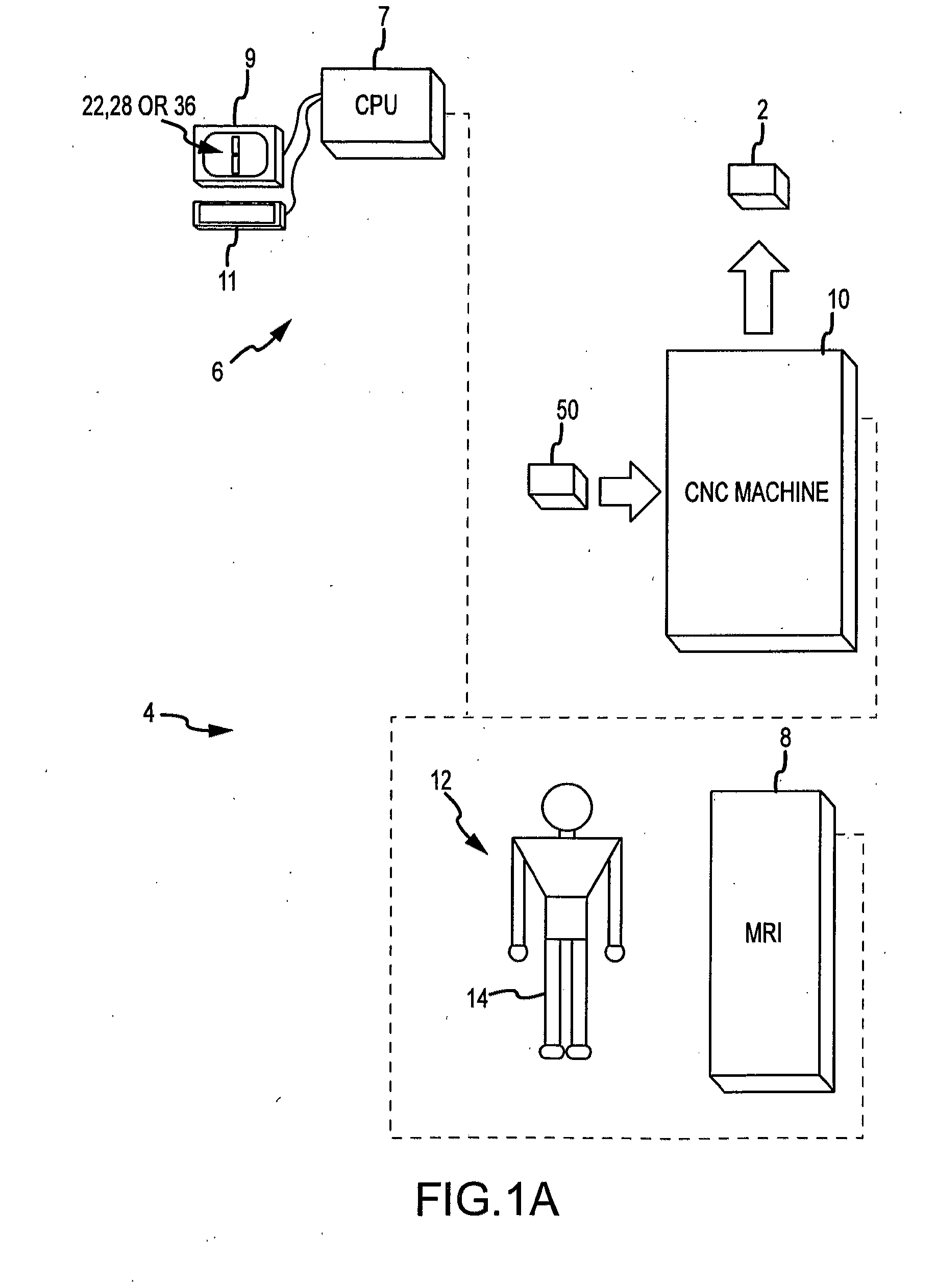
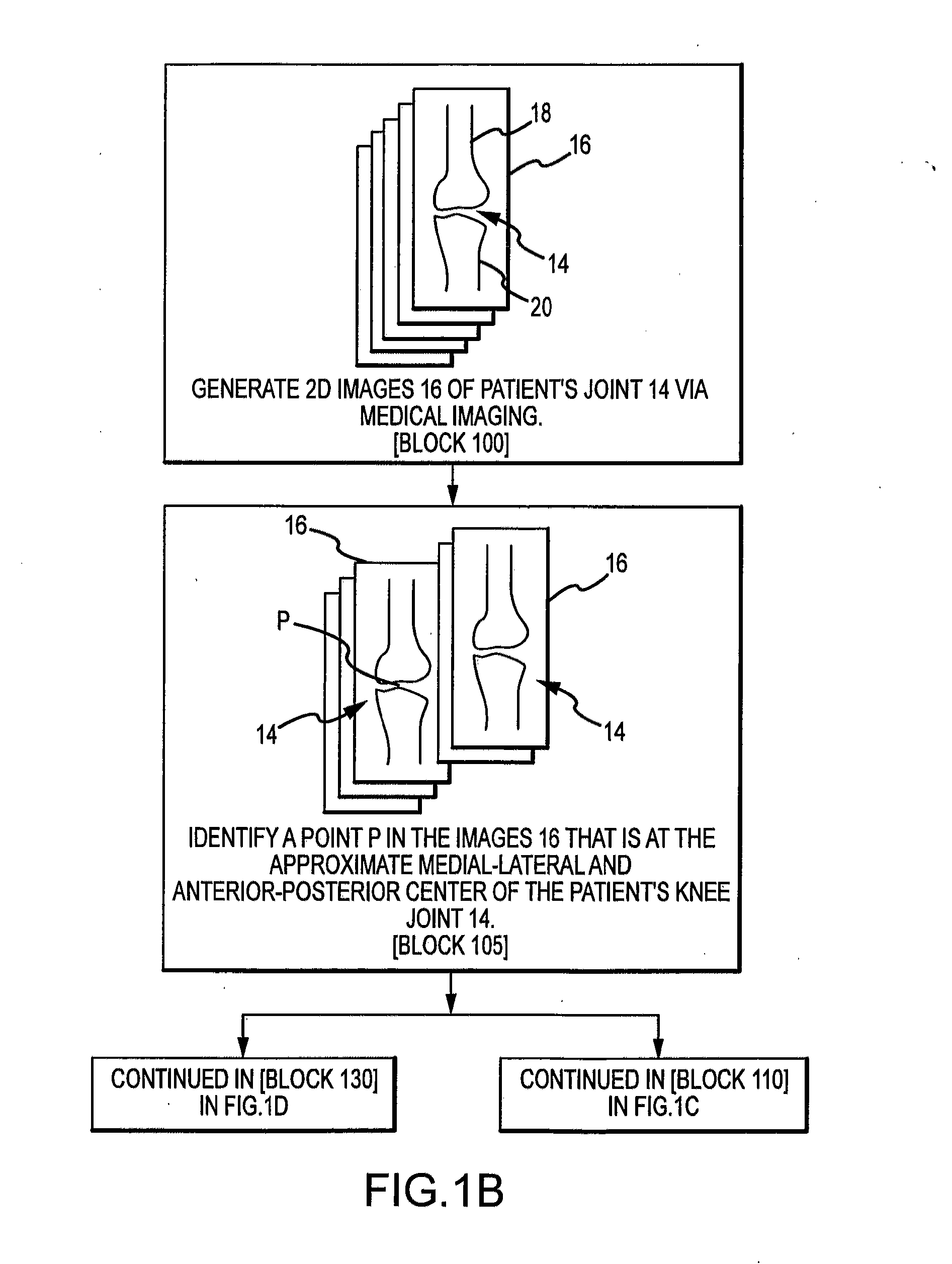
System and method for image segmentation in generating computer models of a joint to undergo arthroplasty
ActiveUS8160345B2Details involving processing stepsImage enhancementMedical imagingImage segmentation
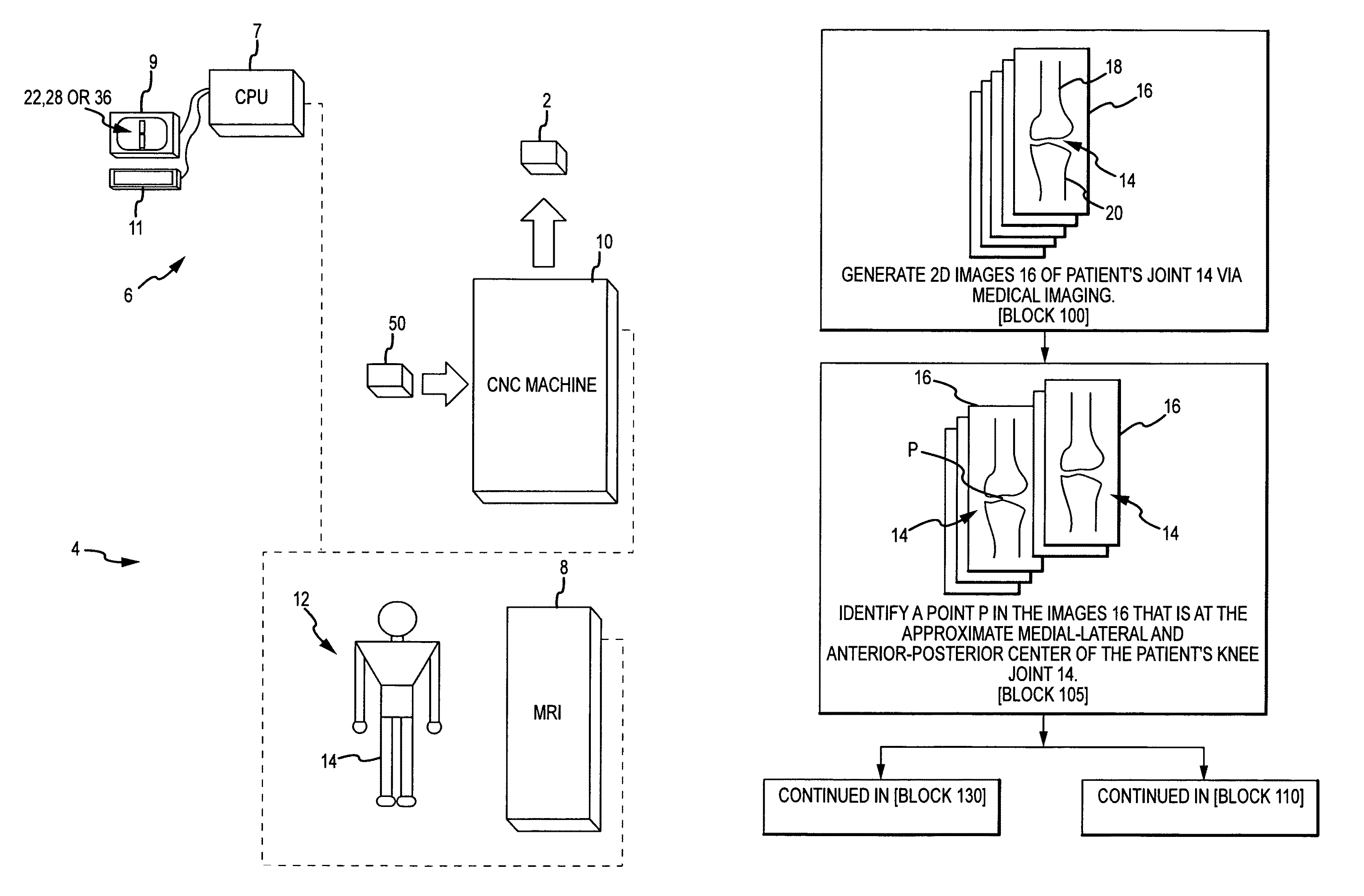
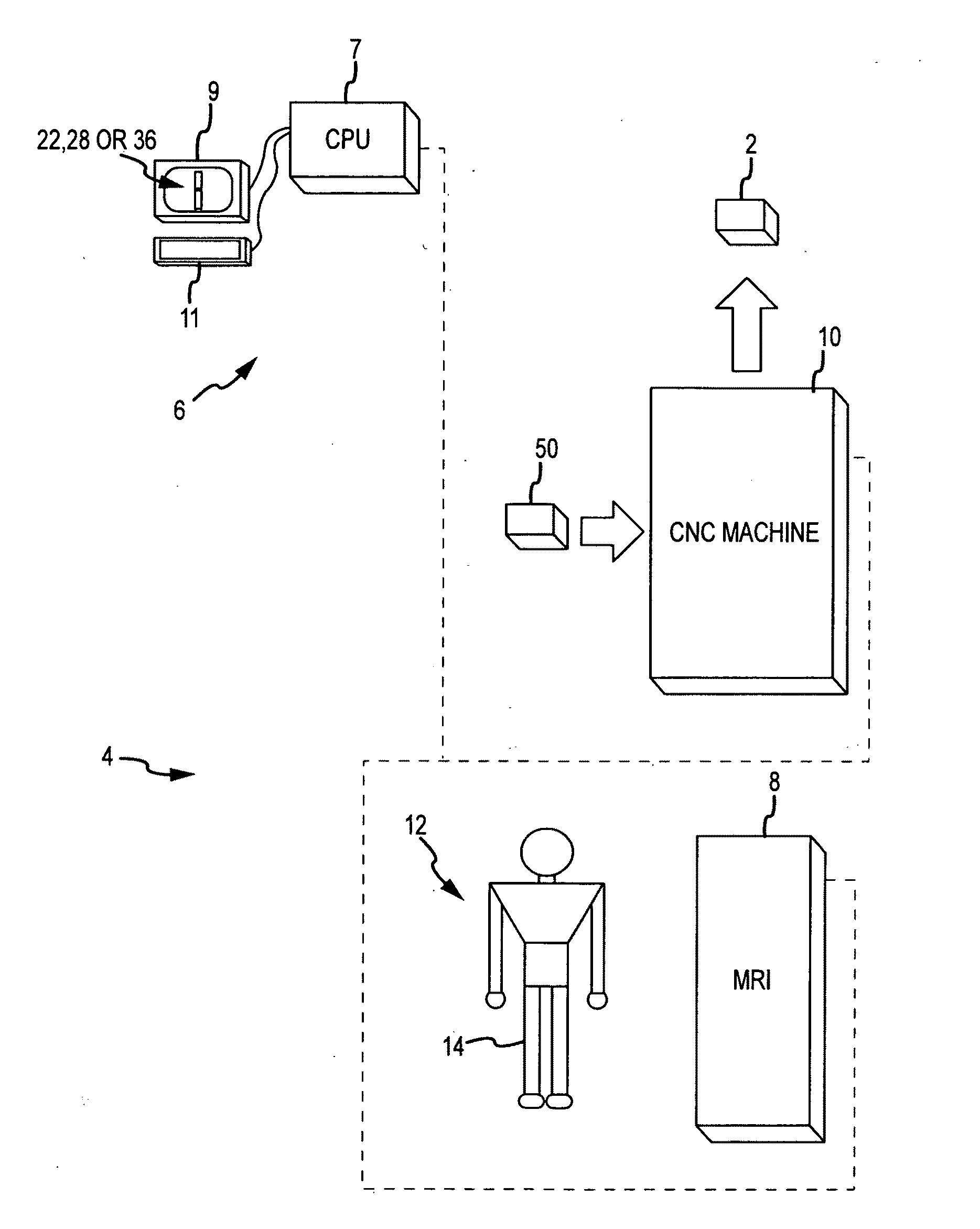
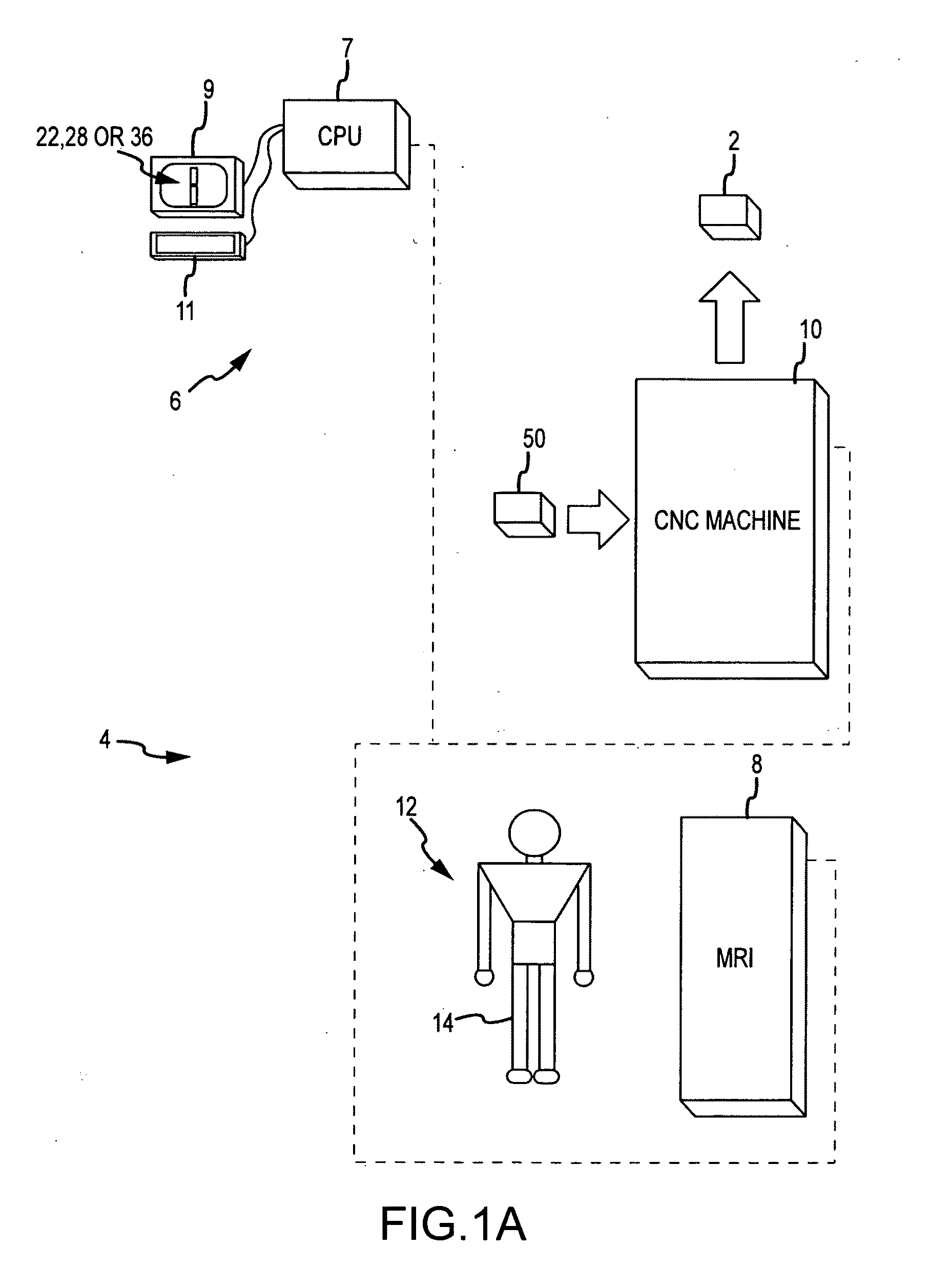
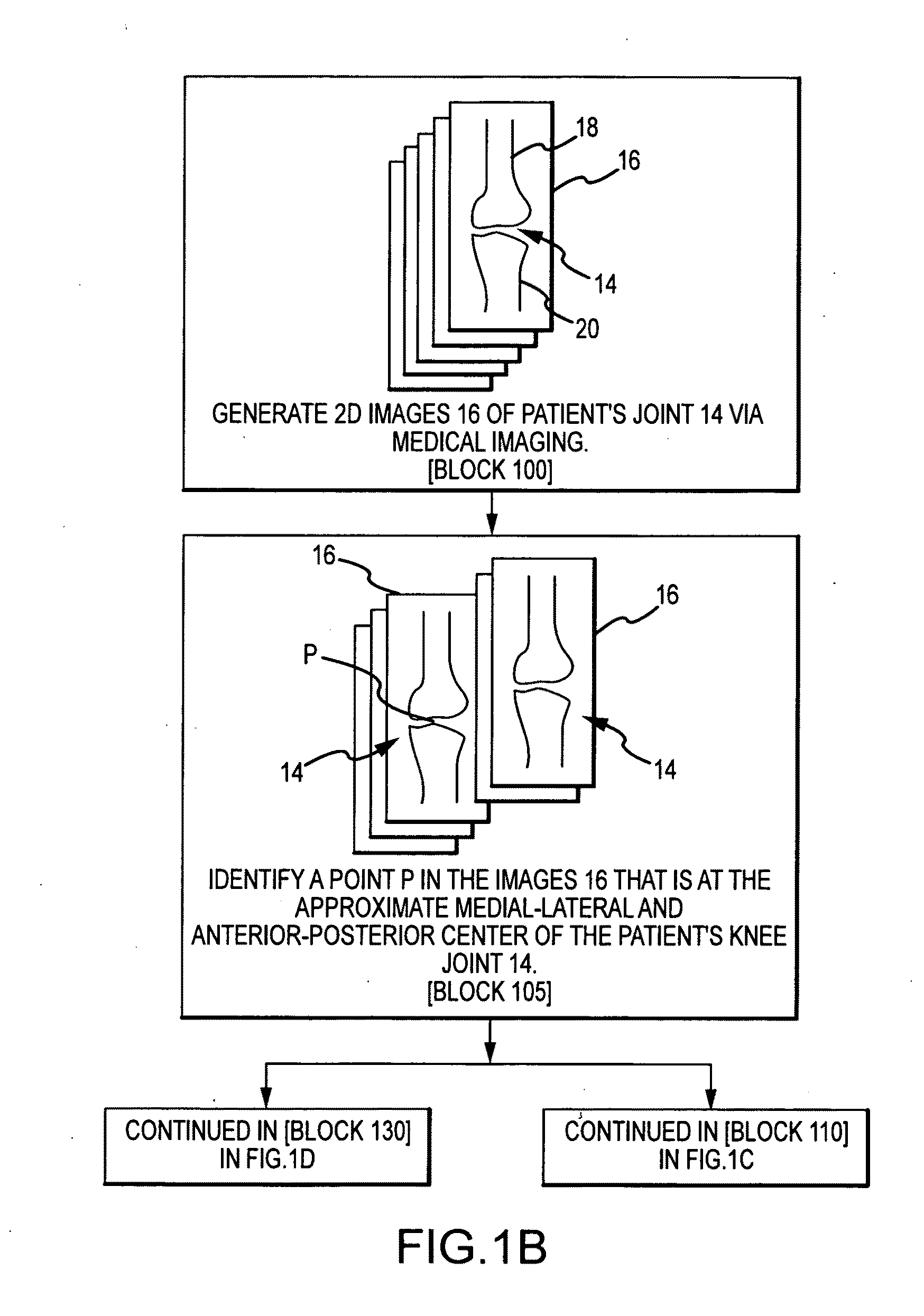
A custom arthroplasty guide and a method of manufacturing such a guide are disclosed herein. The guide manufactured includes a mating region configured to matingly receive a portion of a patient bone associated with an arthroplasty procedure for which the custom arthroplasty guide is to be employed. The mating region includes a surface contour that is generally a negative of a surface contour of the portion of the patient bone. The surface contour of the mating region is configured to mate with the surface contour of the portion of the patient bone in a generally matching or interdigitating manner when the portion of the patient bone is matingly received by the mating region. The method of manufacturing the custom arthroplasty guide includes: a) generating medical imaging slices of the portion of the patient bone; b) identifying landmarks on bone boundaries in the medical imaging slices; c) providing model data including image data associated with a bone other than the patient bone; d) adjusting the model data to match the landmarks; e) using the adjusted model data to generate a three dimensional computer model of the portion of the patient bone; f) using the three dimensional computer model to generate design data associated with the custom arthroplasty guide; and g) using the design data in manufacturing the custom arthroplasty guide.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
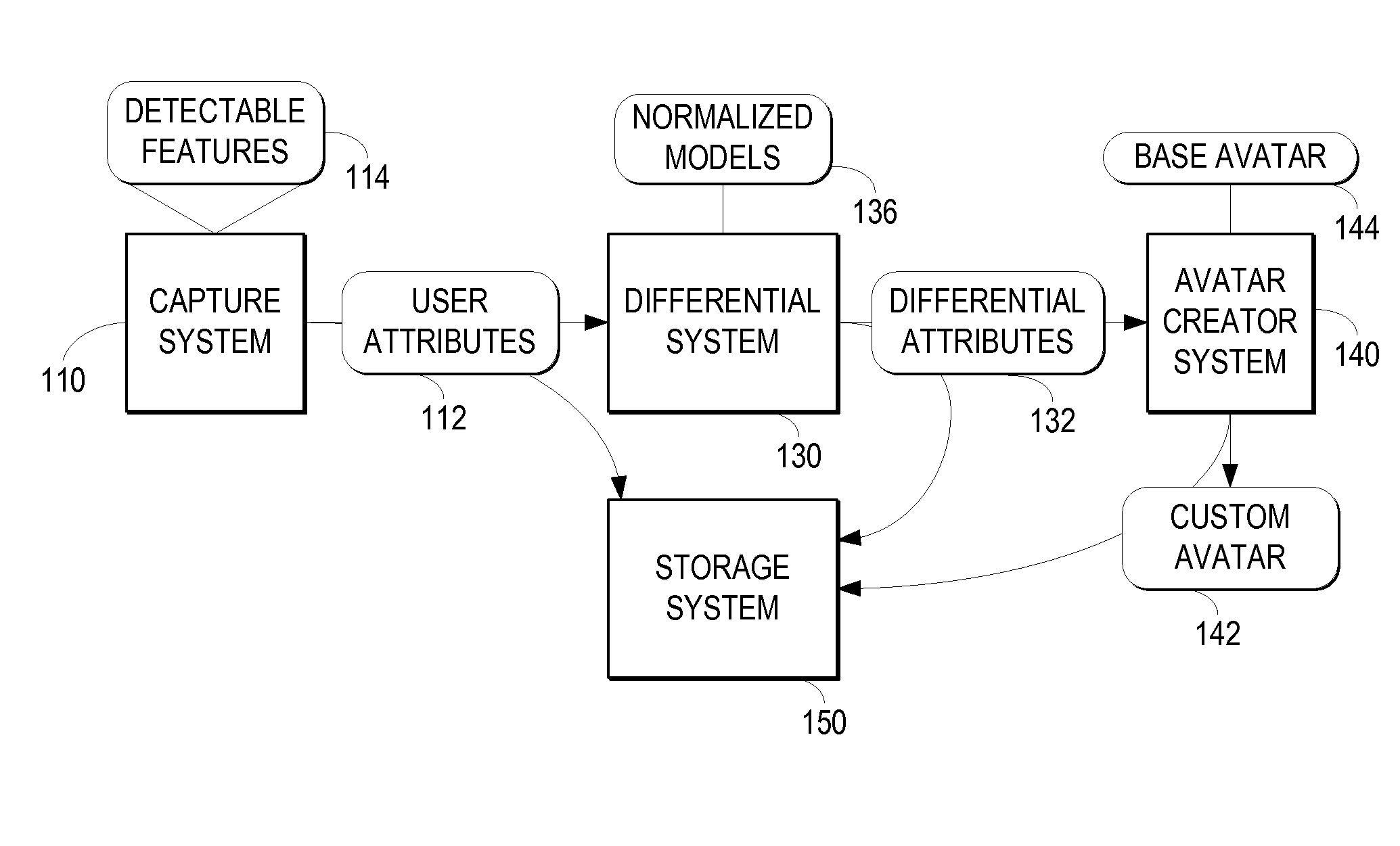
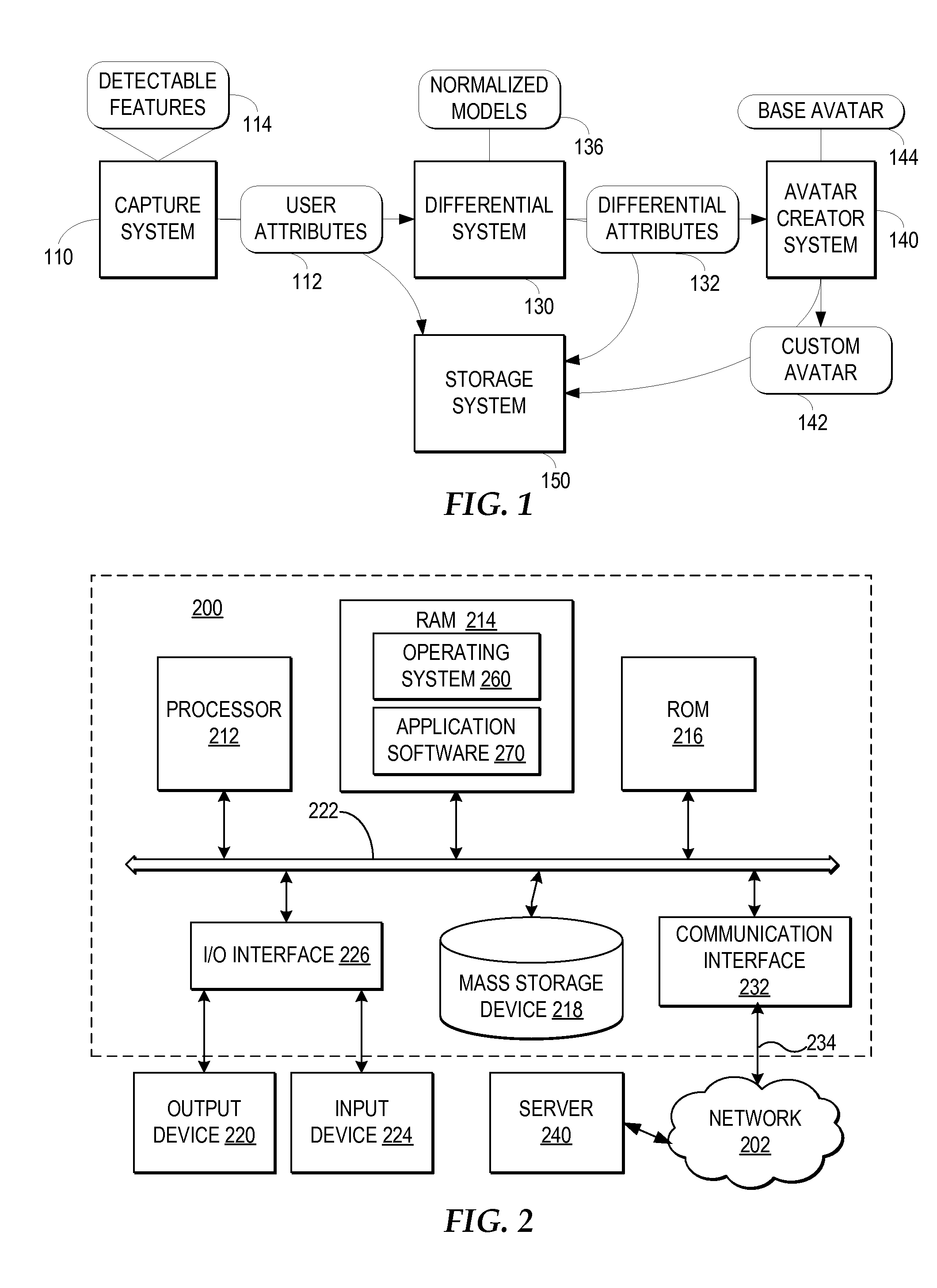
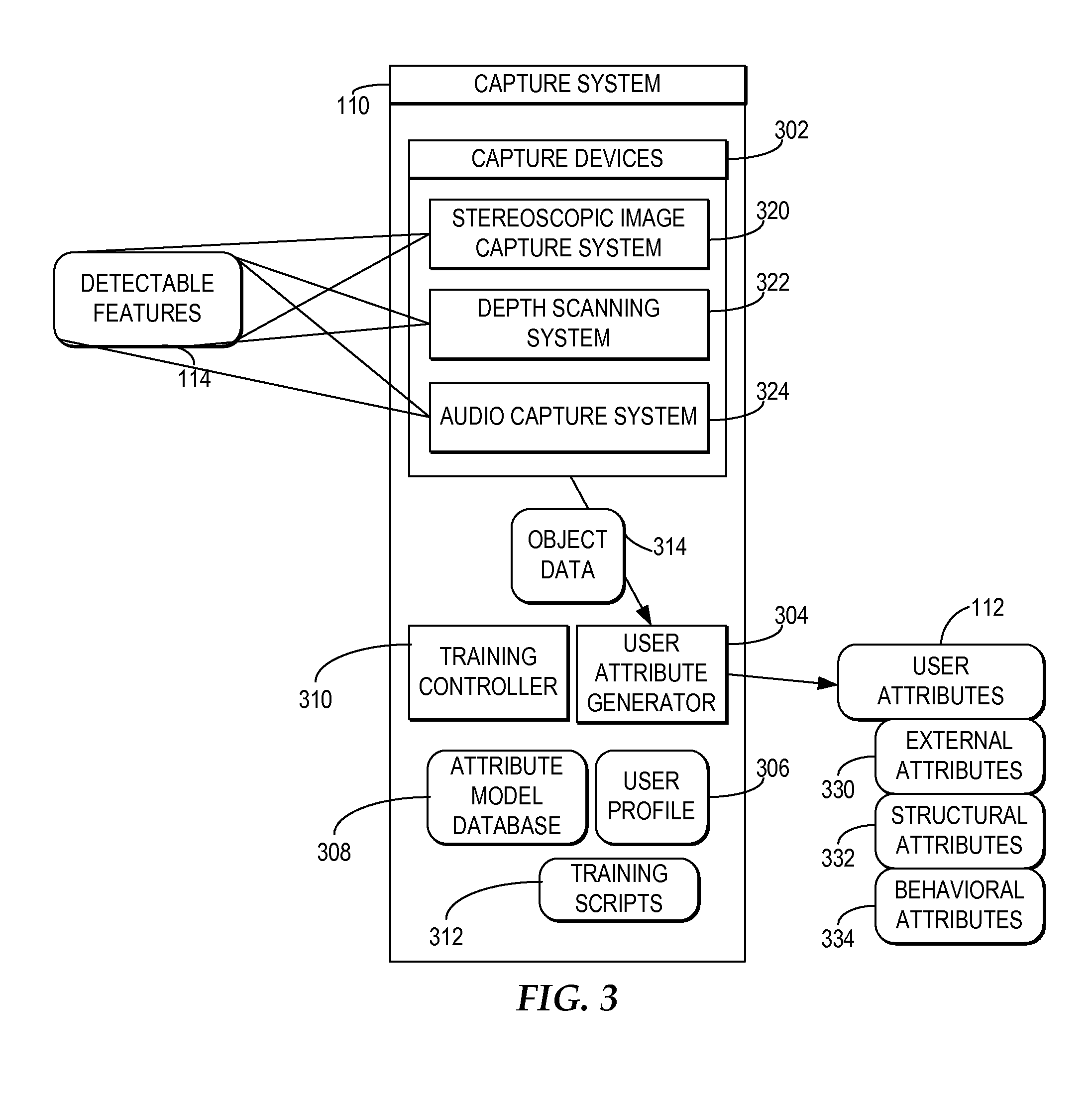
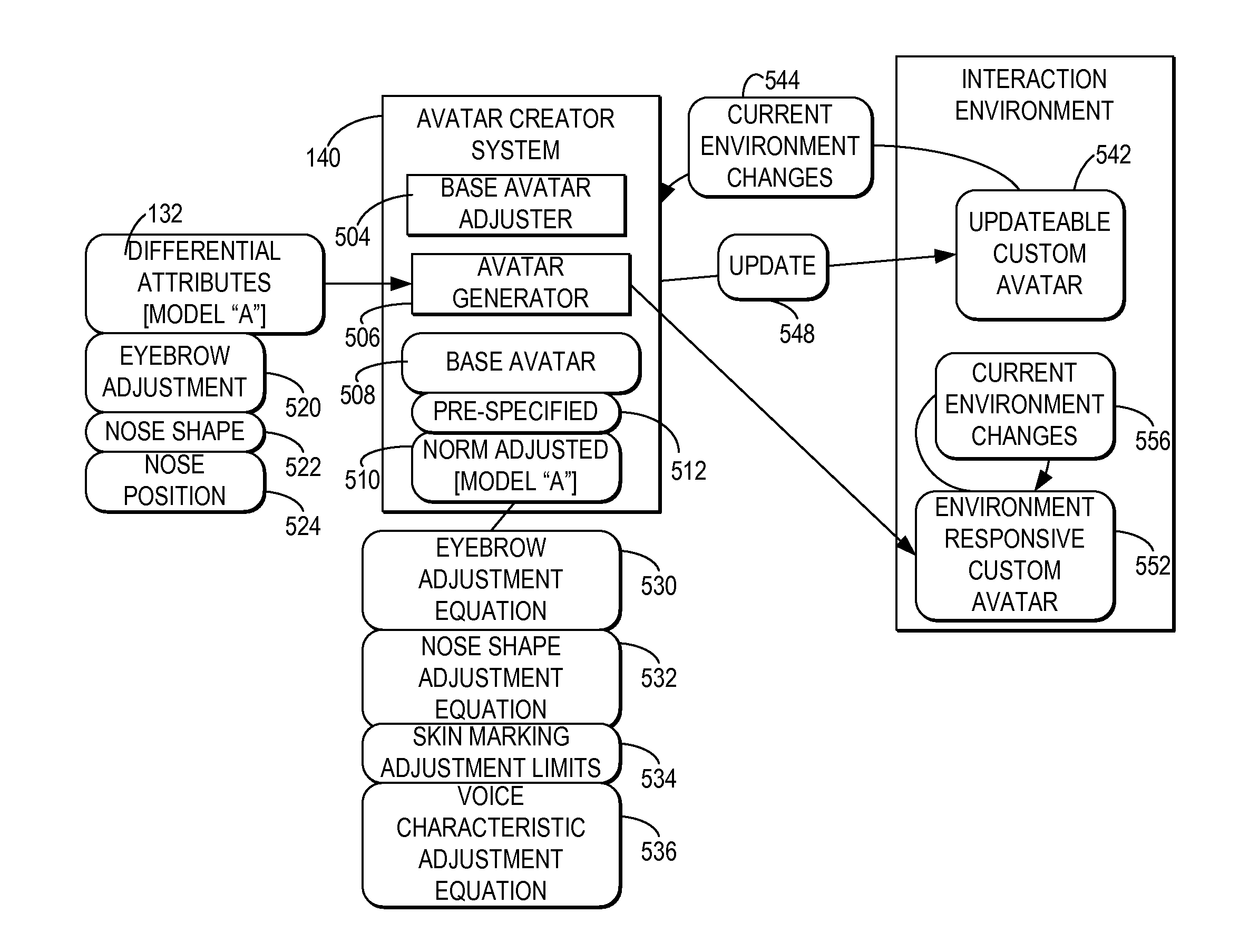
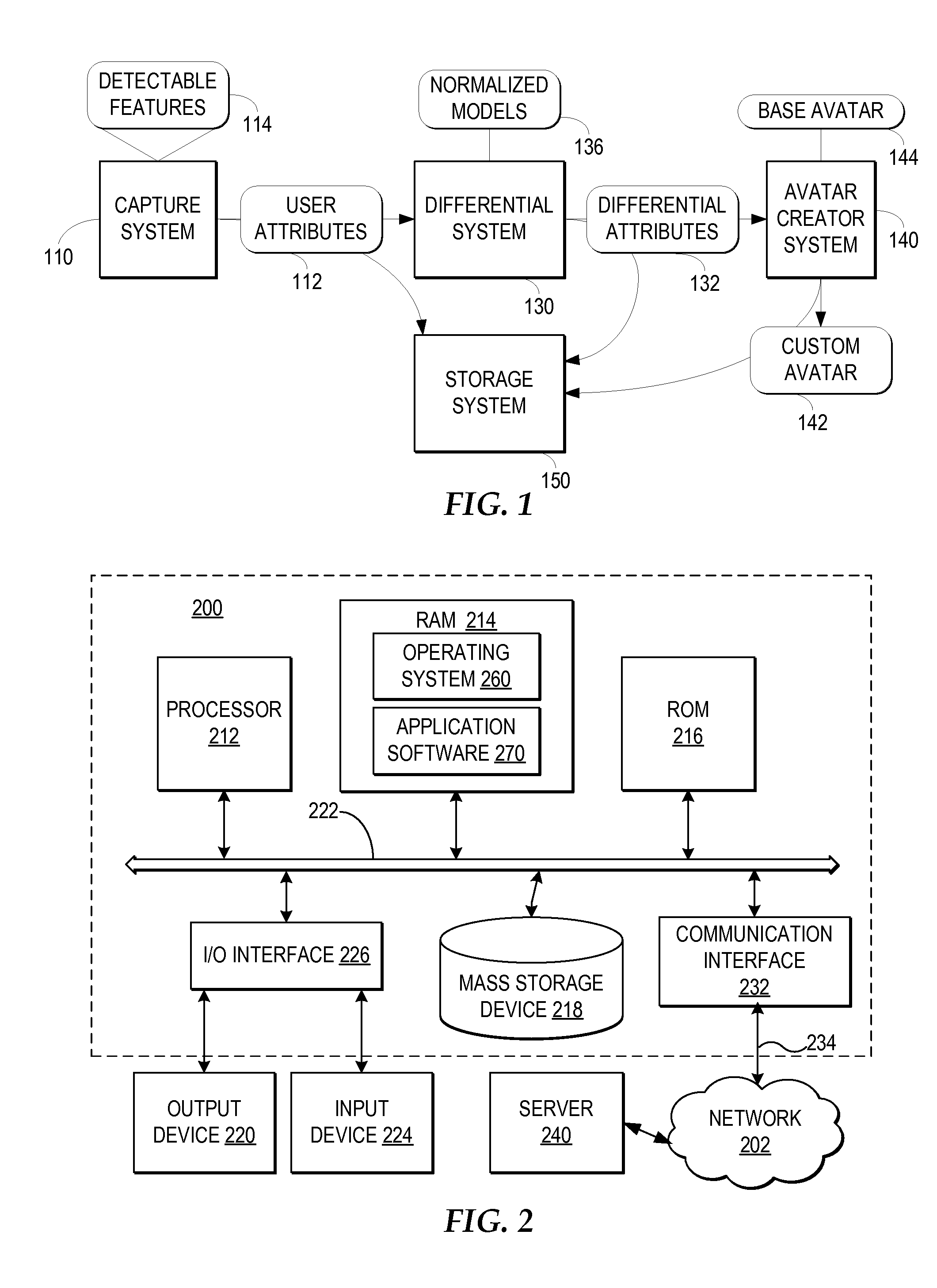
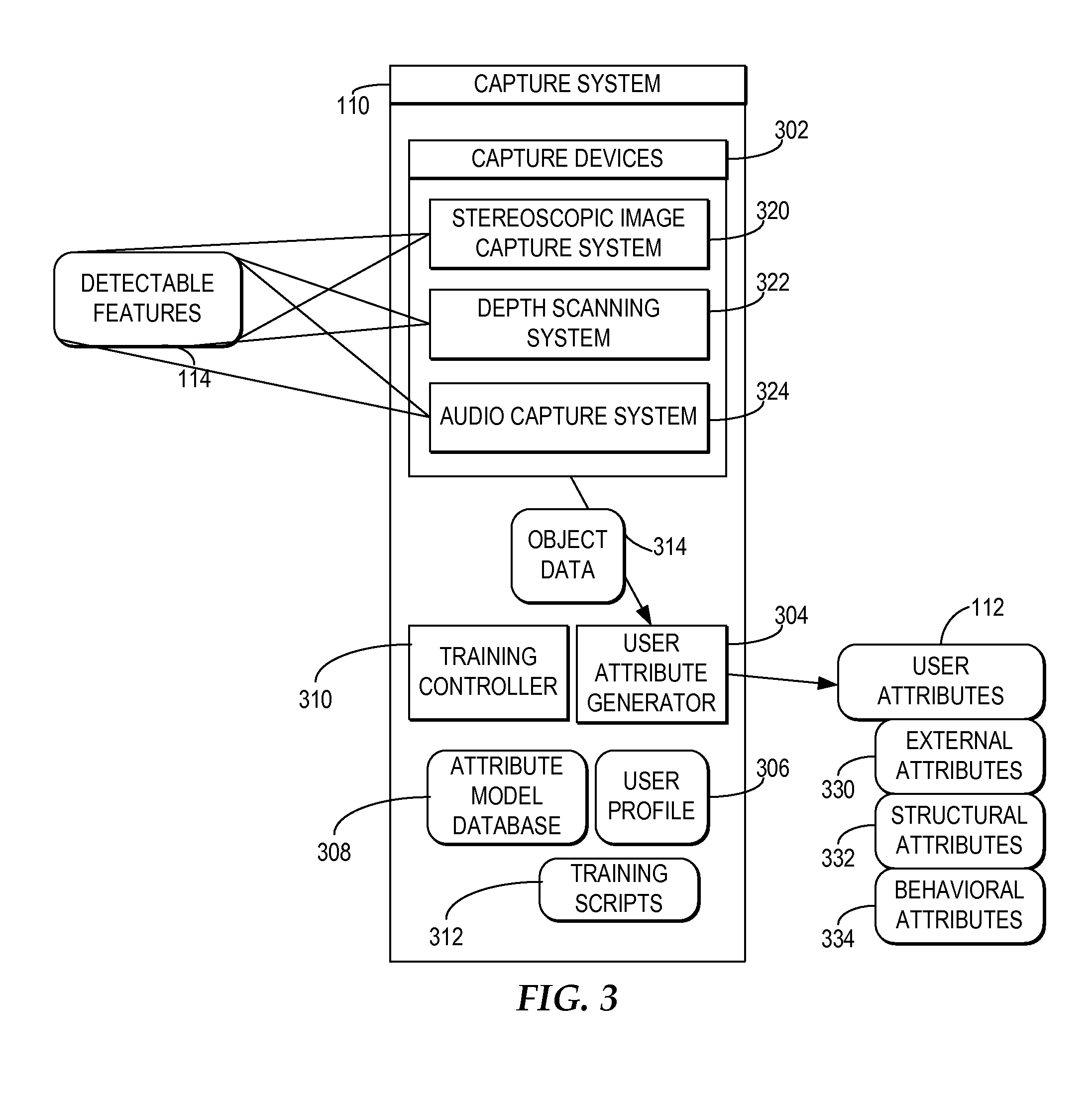
Creating a Customized Avatar that Reflects a User's Distinguishable Attributes
A capture system captures detectable attributes of a user. A differential system compares the detectable attributes with a normalized model of attributes, wherein the normalized model of attributes characterize normal representative attribute values across a sample of a plurality of users and generates differential attributes representing the differences between the detectable attributes and the normalized model of attributes. Multiple separate avatar creator systems receive the differential attributes and each apply the differential attributes to different base avatars to create custom avatars which reflect a selection of the detectable attributes of the user which are distinguishable from the normalized model of attributes.
Owner:KING COM
Creating a customized avatar that reflects a user's distinguishable attributes
A capture system captures detectable attributes of a user. A differential system compares the detectable attributes with a normalized model of attributes, wherein the normalized model of attributes characterize normal representative attribute values across a sample of a plurality of users and generates differential attributes representing the differences between the detectable attributes and the normalized model of attributes. Multiple separate avatar creator systems receive the differential attributes and each apply the differential attributes to different base avatars to create custom avatars which reflect a selection of the detectable attributes of the user which are distinguishable from the normalized model of attributes.
Owner:KING COM
System and method for image segmentation in generating computer models of a joint to undergo arthroplasty
ActiveUS20110282473A1Image enhancementDetails involving processing stepsImage segmentationMedical imaging
A custom arthroplasty guide and a method of manufacturing such a guide are disclosed herein. The guide manufactured includes a mating region configured to matingly receive a portion of a patient bone associated with an arthroplasty procedure for which the custom arthroplasty guide is to be employed. The mating region includes a surface contour that is generally a negative of a surface contour of the portion of the patient bone. The surface contour of the mating region is configured to mate with the surface contour of the portion of the patient bone in a generally matching or interdigitating manner when the portion of the patient bone is matingly received by the mating region. The method of manufacturing the custom arthroplasty guide includes: a) generating medical imaging slices of the portion of the patient bone; b) identifying landmarks on bone boundaries in the medical imaging slices; c) providing model data including image data associated with a bone other than the patient bone; d) adjusting the model data to match the landmarks; e) using the adjusted model data to generate a three dimensional computer model of the portion of the patient bone; f) using the three dimensional computer model to generate design data associated with the custom arthroplasty guide; and g) using the design data in manufacturing the custom arthroplasty guide.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
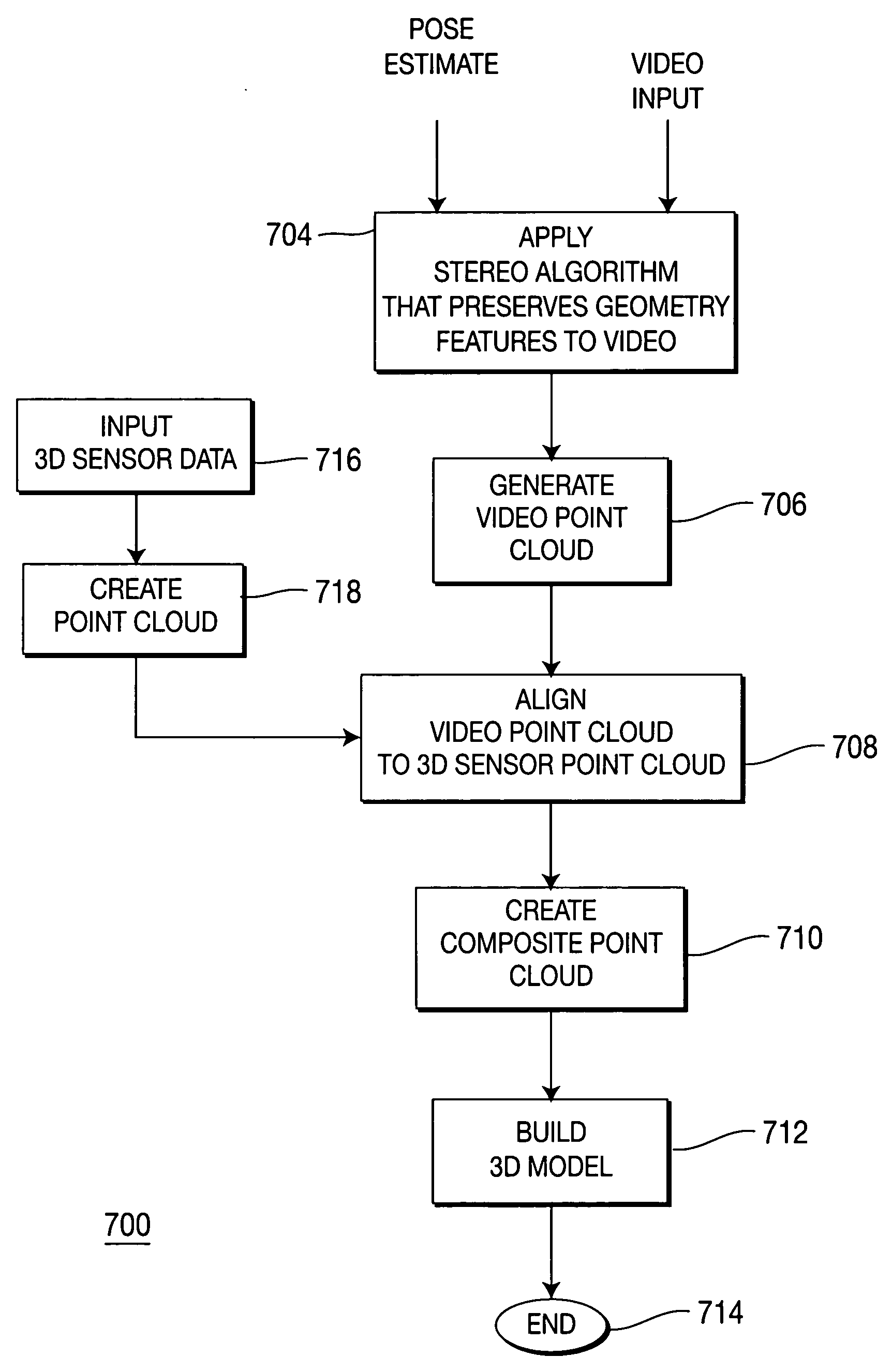
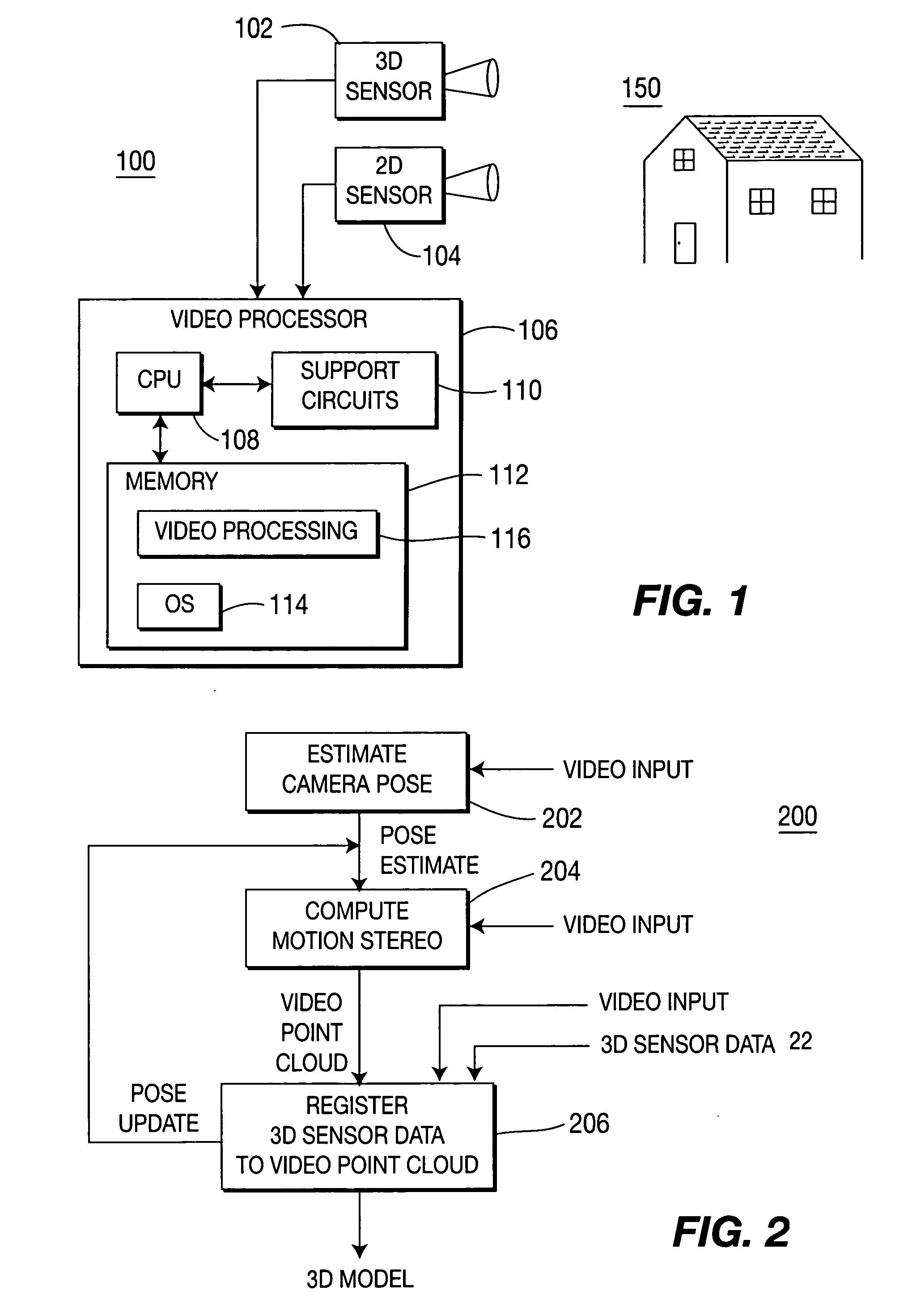
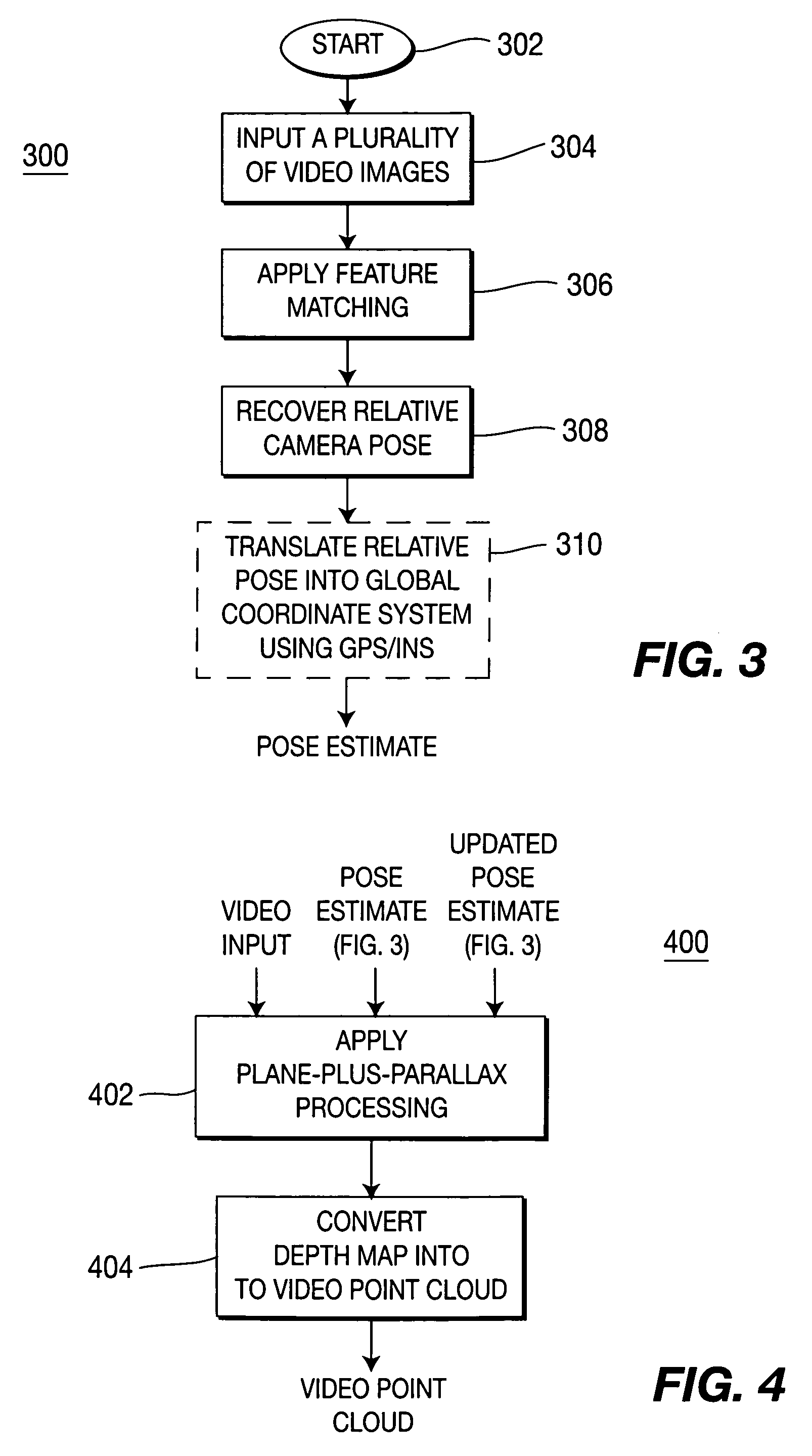
Method and apparatus for aligning video to three-dimensional point clouds
A method and apparatus for performing two-dimensional video alignment onto three-dimensional point clouds. The system recovers camera pose from camera video, determines a depth map, converts the depth map to a Euclidean video point cloud, and registers two-dimensional video to the three-dimensional point clouds.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
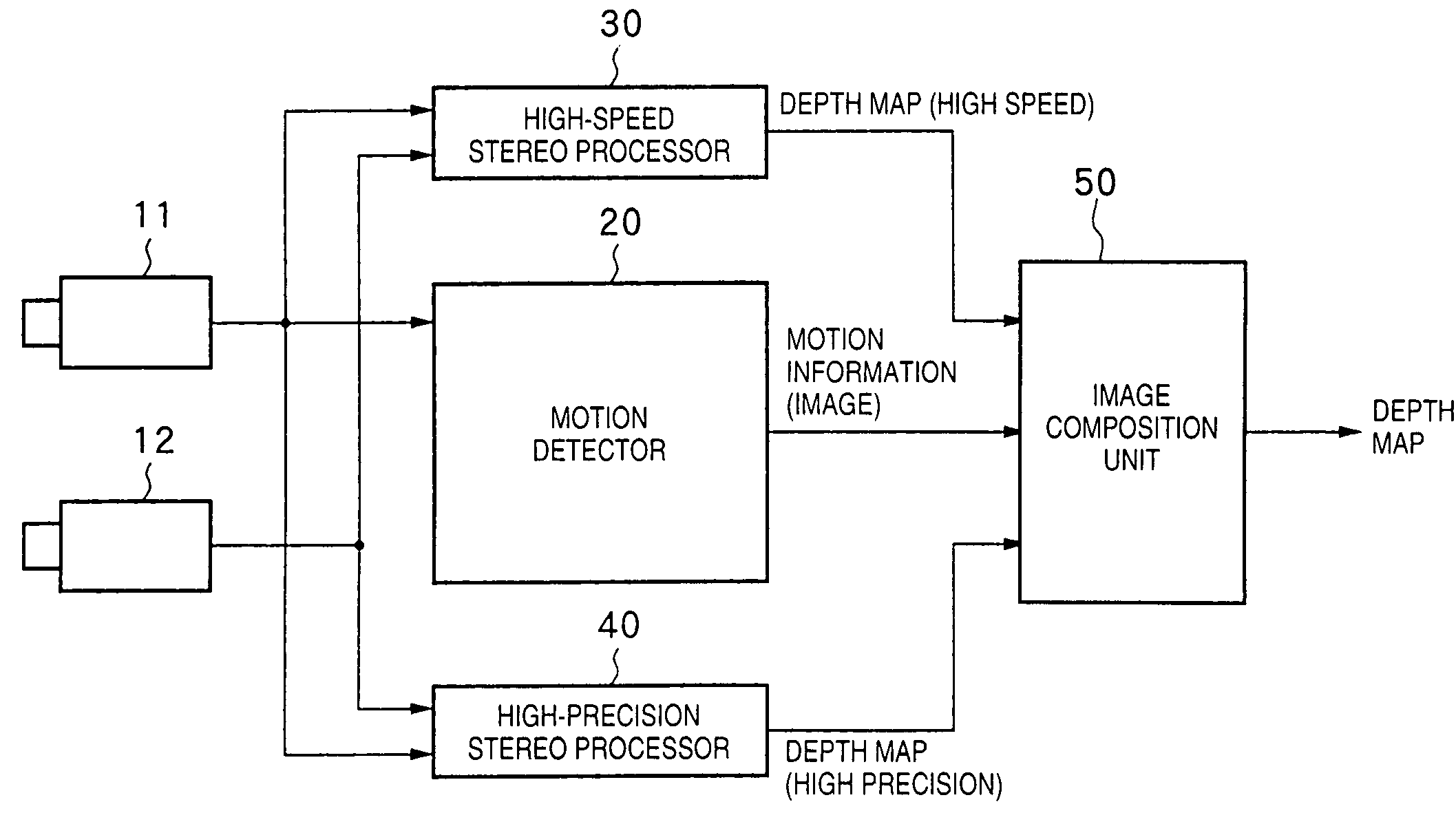
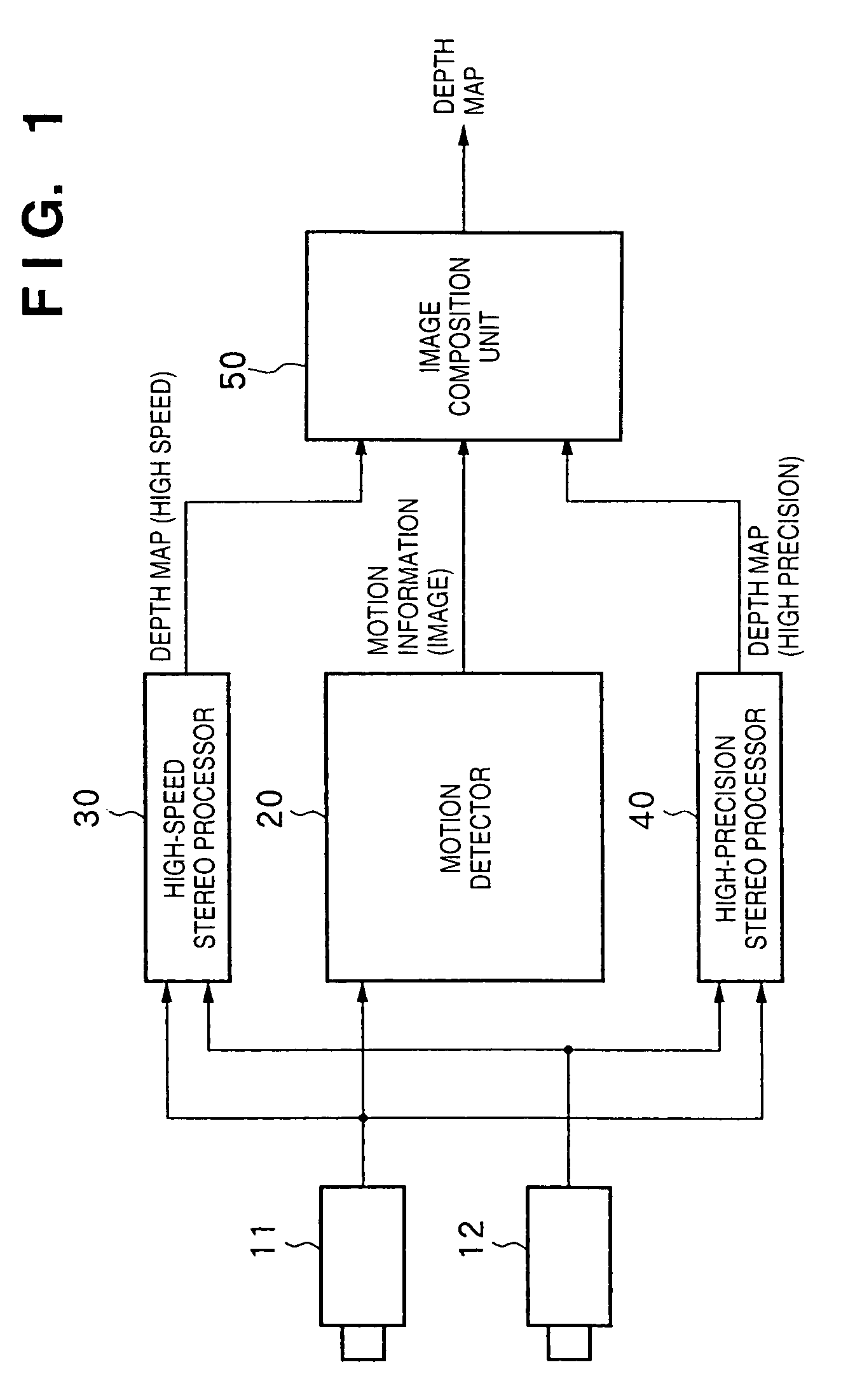
Depth information measurement apparatus and mixed reality presentation system
InactiveUS7295697B1Improve accuracyImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsStereophonic soundStereo image
There is disclosed a depth information generation apparatus capable of acquiring high-precision depth information within a short computation time. A depth information generation apparatus of this invention generates depth information at the capture position of a reference image from the reference image, and at least one peripheral image that forms a stereo image pair with the reference image, and has a high-speed stereo processor (30) for generating depth information at high speed from the reference image and peripheral image, and a high-precision stereo processor (40) for generating high-precision depth information. A motion detector (20) detects a motion in an image, and instructs an image composition unit (50) to select the output from the high-speed stereo processor (30) for a portion with a large motion, and the output from the high-precision stereo processor (40) for other portions. The image composition unit (50) composites the outputs from the high-speed stereo processor (30) and high-precision stereo processor (40) in accordance with an instruction from the motion detector (20), and outputs a depth map as final depth information.
Owner:CANON KK
System and method for image segmentation in generating computer models of a joint to undergo arthroplasty
ActiveUS20120192401A1Image enhancementDetails involving processing stepsImage segmentationMedical imaging
A custom arthroplasty guide and a method of manufacturing such a guide are disclosed herein. The method of manufacturing the custom arthroplasty guide includes: a) generating medical imaging slices of the portion of the patient bone; b) identifying landmarks on bone boundaries in the medical imaging slices; c) providing model data including image data associated with a bone other than the patient bone; d) adjusting the model data to match the landmarks; e) using the adjusted model data to generate a three dimensional computer model of the portion of the patient bone; f) using the three dimensional computer model to generate design data associated with the custom arthroplasty guide; and g) using the design data in manufacturing the custom arthroplasty guide.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Three-dimensional digital magnifier operation supporting system
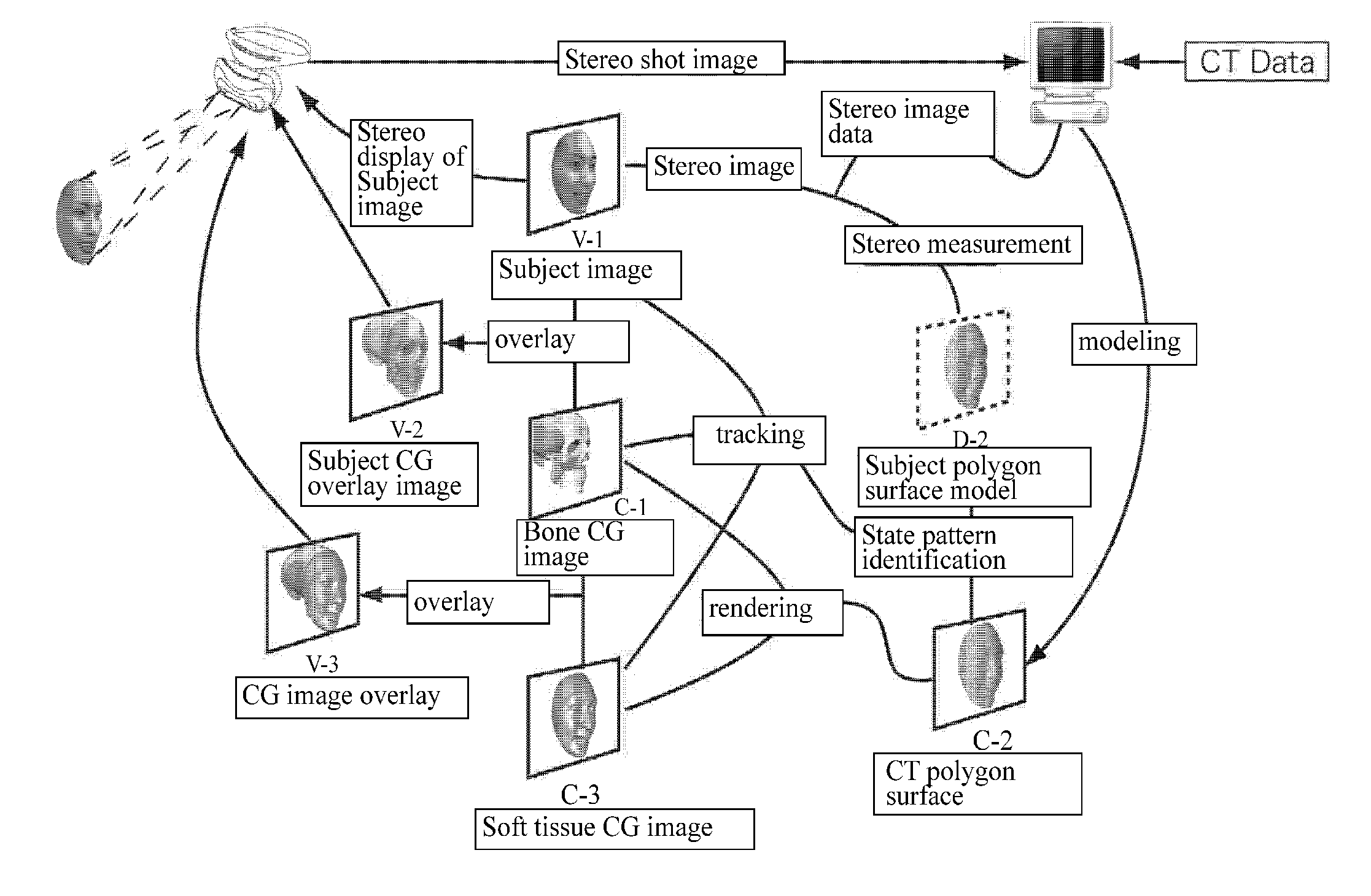
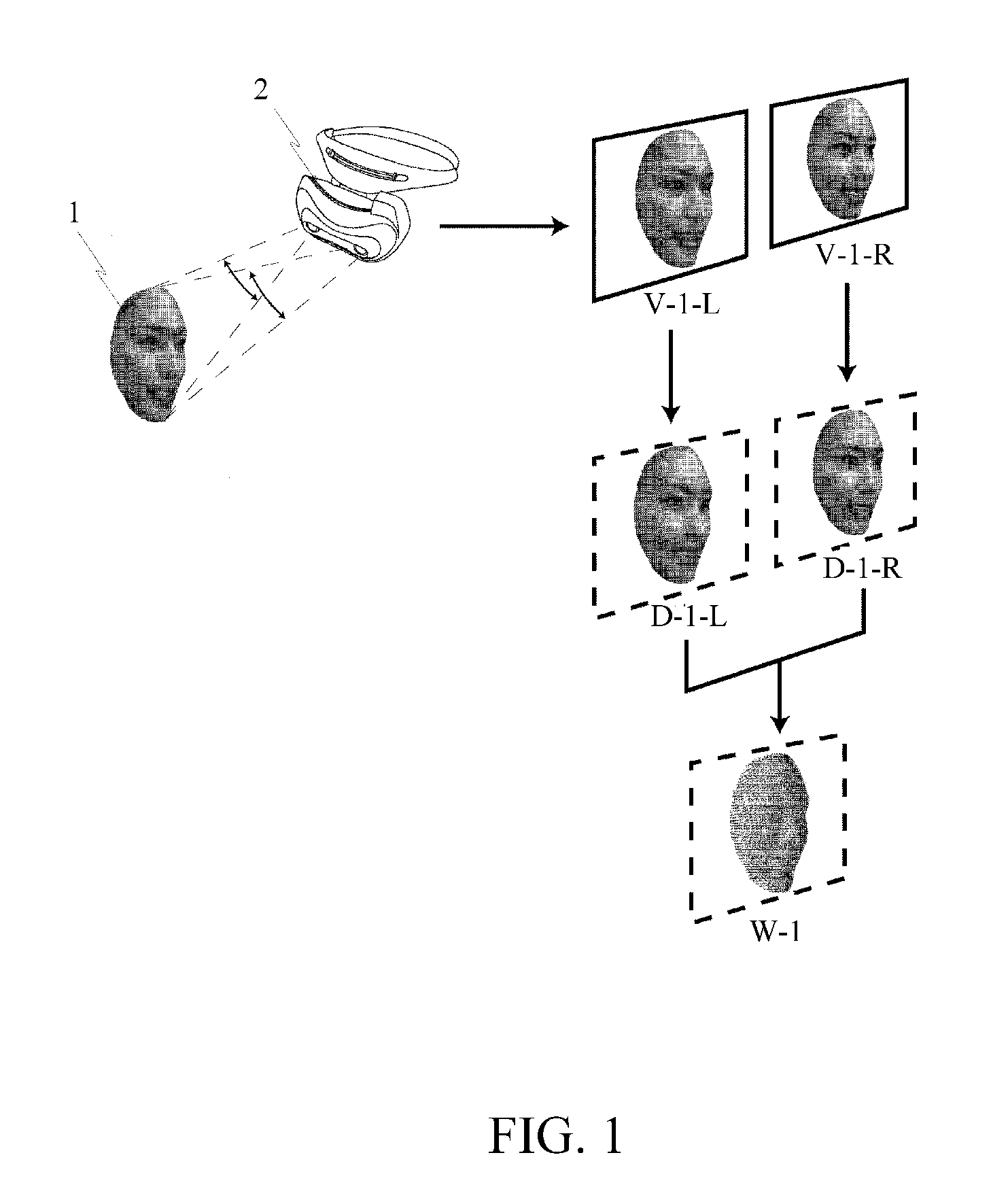
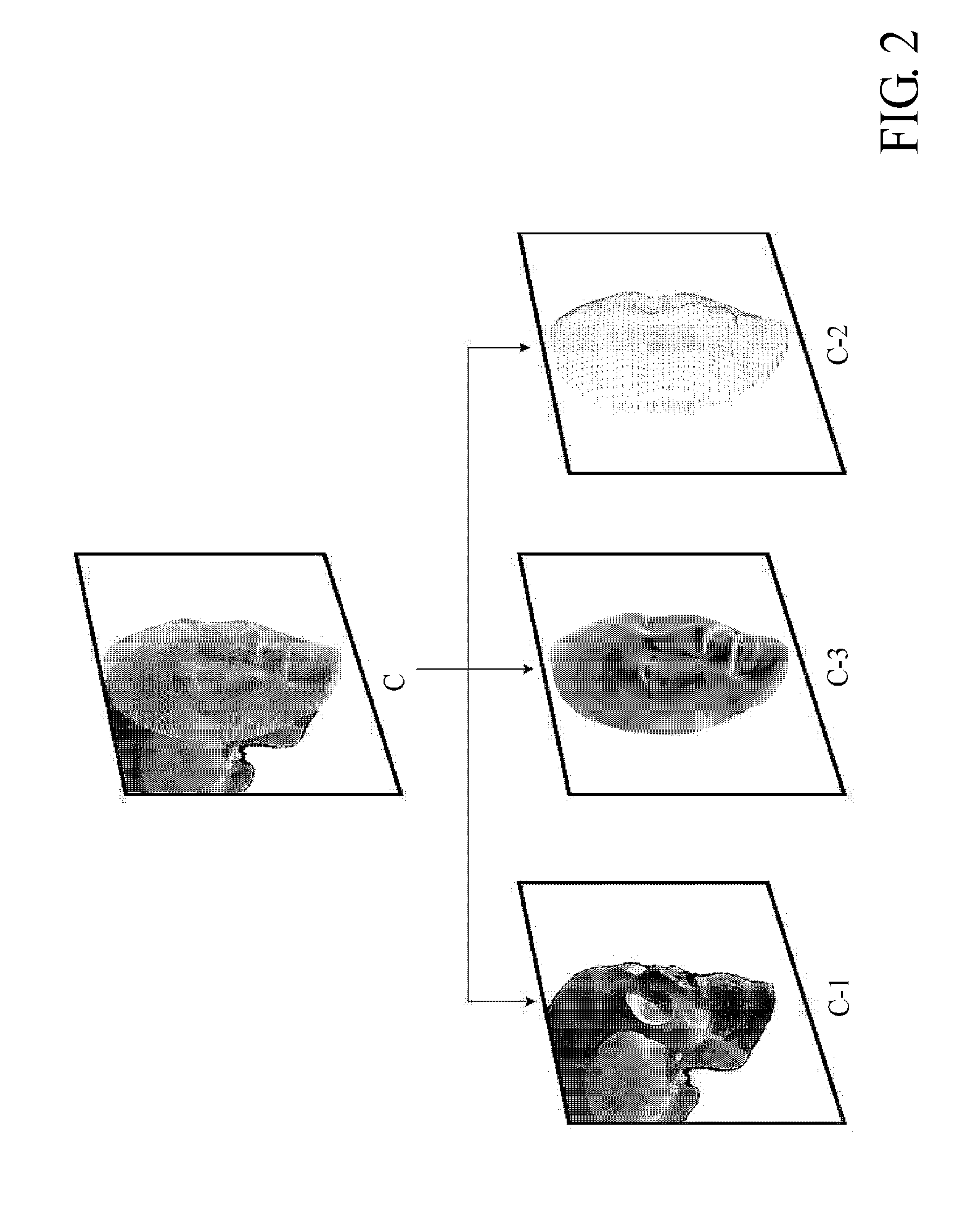
The simulation regarding the state change of the subject in a real space provides a system which represents impacts to three-dimensional computer graphics caused by changes of state of three-dimensional computer graphics composed and fixed to subject, and state of image taking space by simulation, surface polygon model and similar surface polygon model 1 is selected, according to shape pattern, from surface polygon model 2 measures, in a three-dimensional way, subject image existing in the same space, a tracking process is performed on the computer graphics, following to the relative position change of the position changes of the subject and the camera caused in real three-dimensional space, subjects in the visual field of the camera and virtual three-dimensional computer graphics image is unified and displayed by displaying computer graphics image having the same relative position change on the image.
Owner:ATSUSHI TAKAHASHI
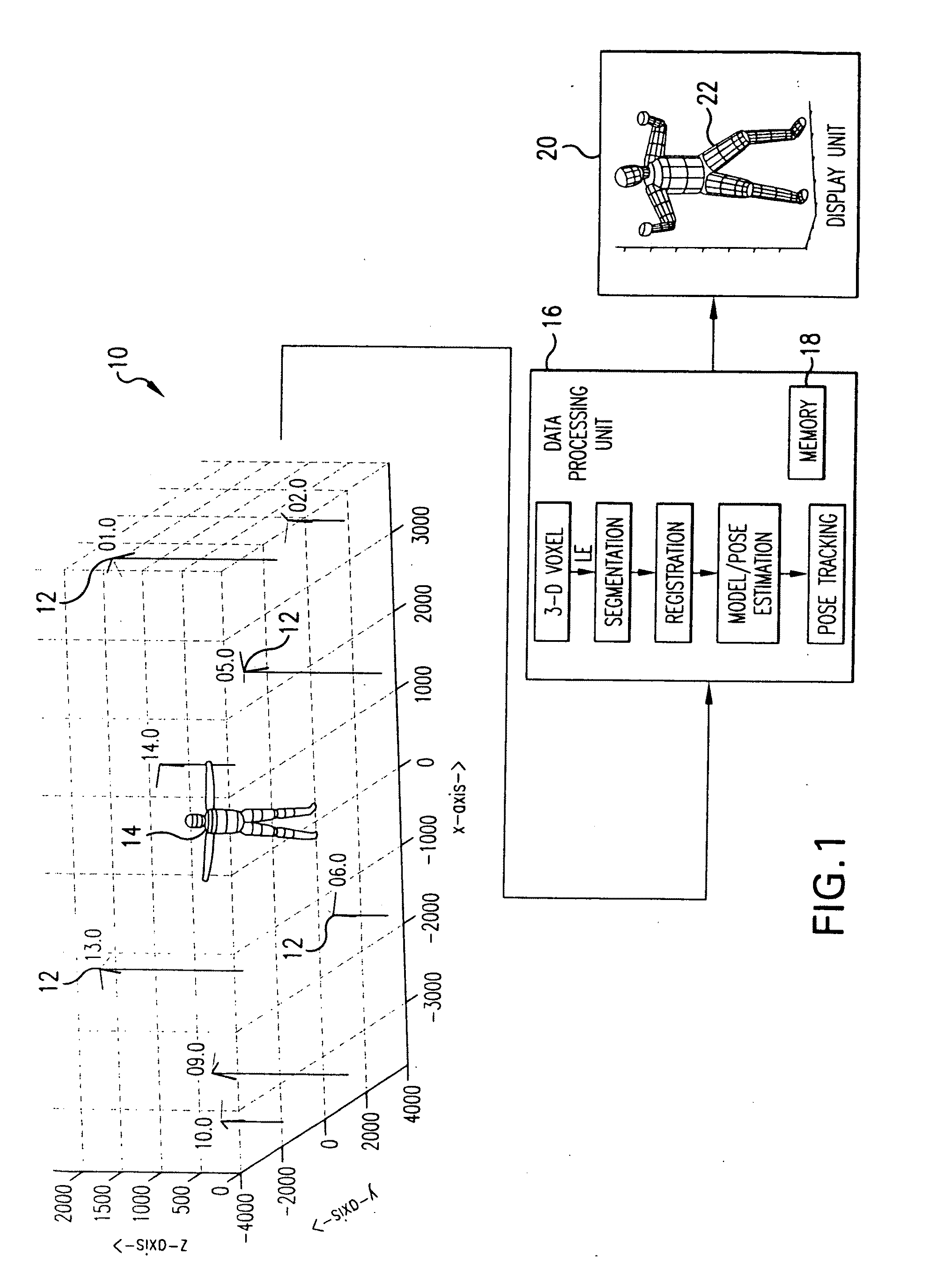
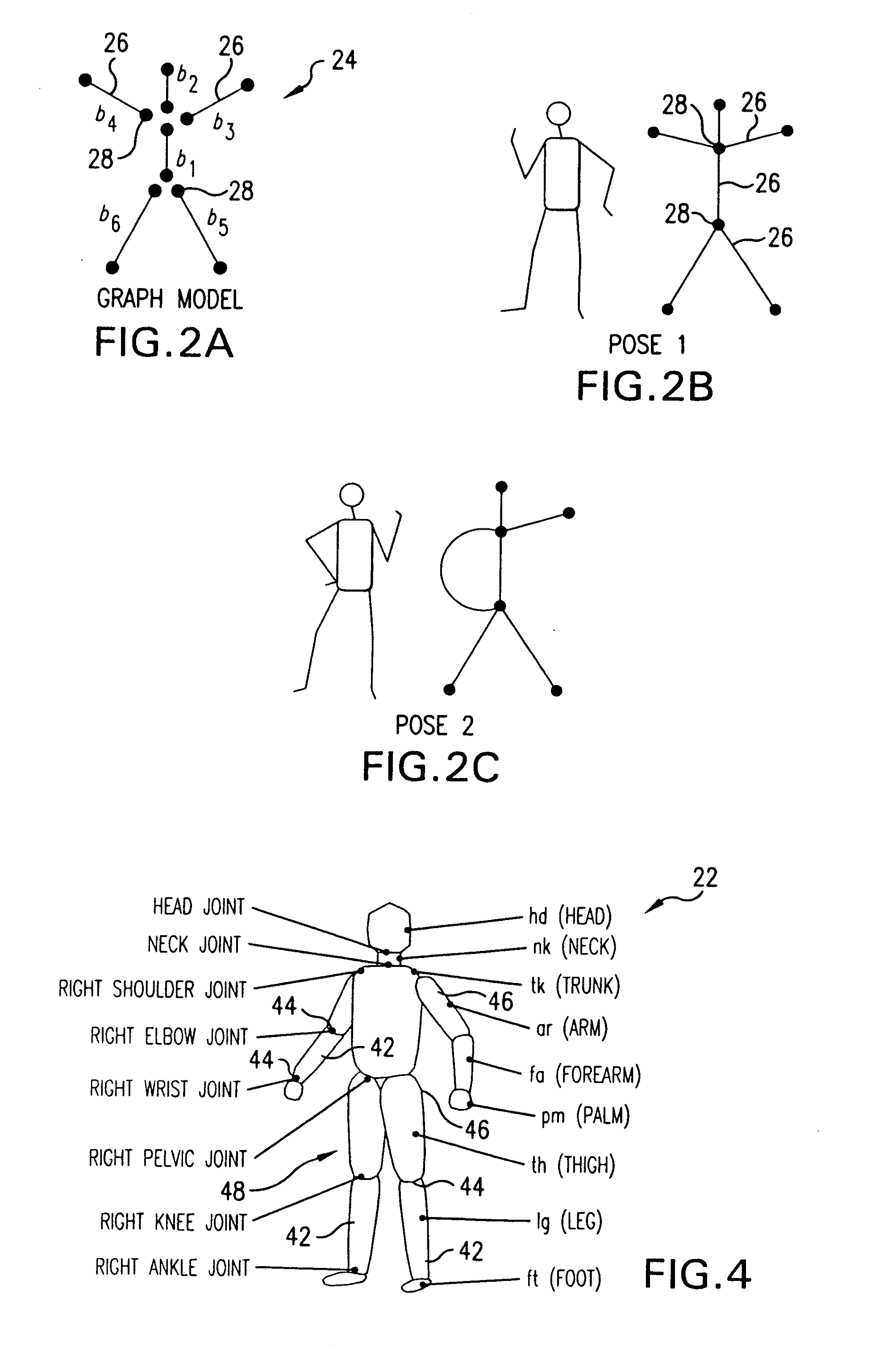
Method and system for markerless motion capture using multiple cameras
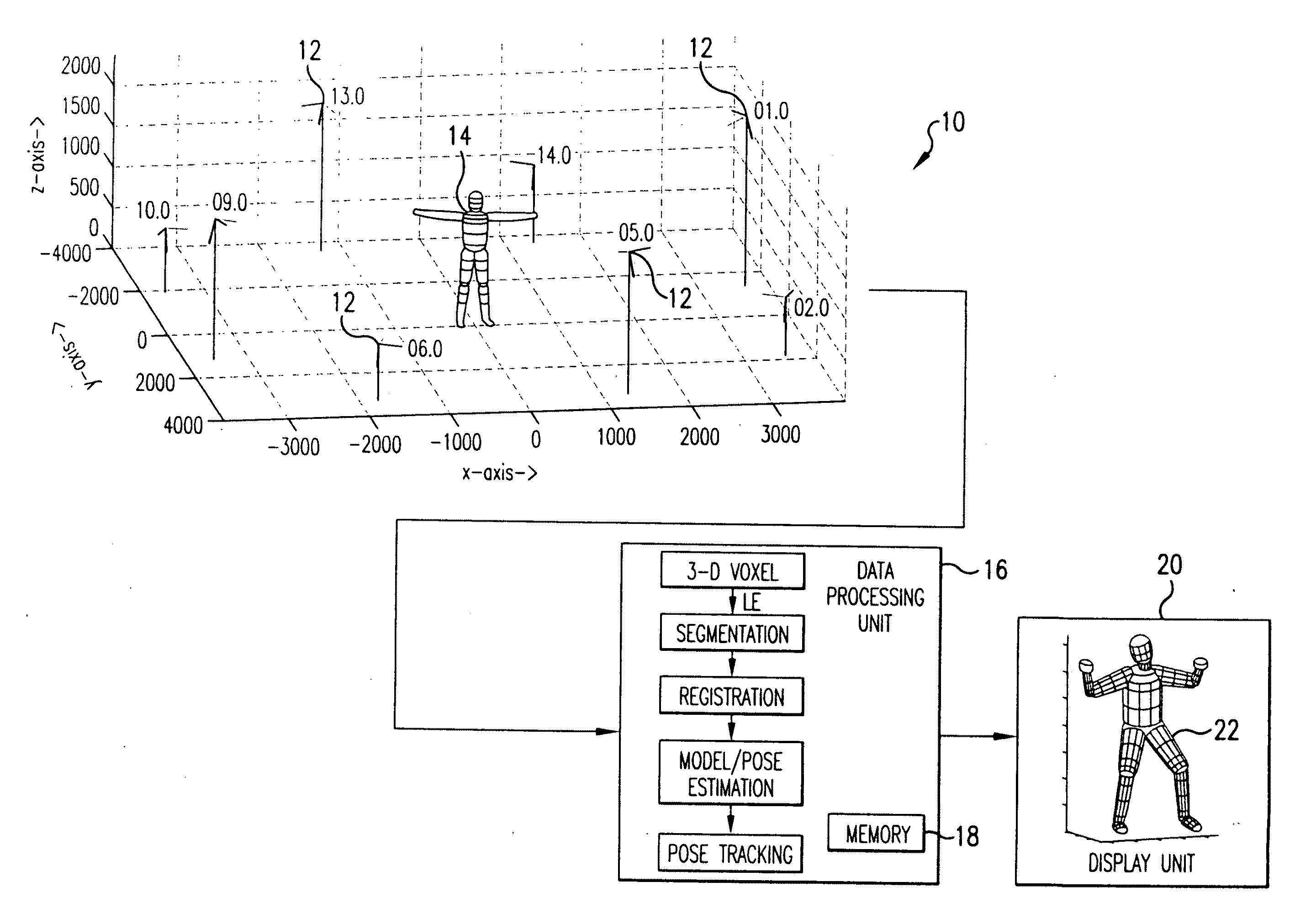
InactiveUS20090232353A1Accurate estimateAccurate presentationImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsProbabilistic methodVoxel
Completely automated end-to-end method and system for markerless motion capture performs segmentation of articulating objects in Laplacian Eigenspace and is applicable to handling of the poses of some complexity. 3D voxel representation of acquired images are mapped to a higher dimensional space (k), where k depends on the number of articulated chains of the subject body, so as to extract the 1-D representations of the articulating chains. A bottom-up approach is suggested in order to build a parametric (spline-based) representation of a general articulated body in the high dimensional space followed by a top-down probabilistic approach that registers the segments to an average human body model. The parameters of the model are further optimized using the segmented and registered voxels.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
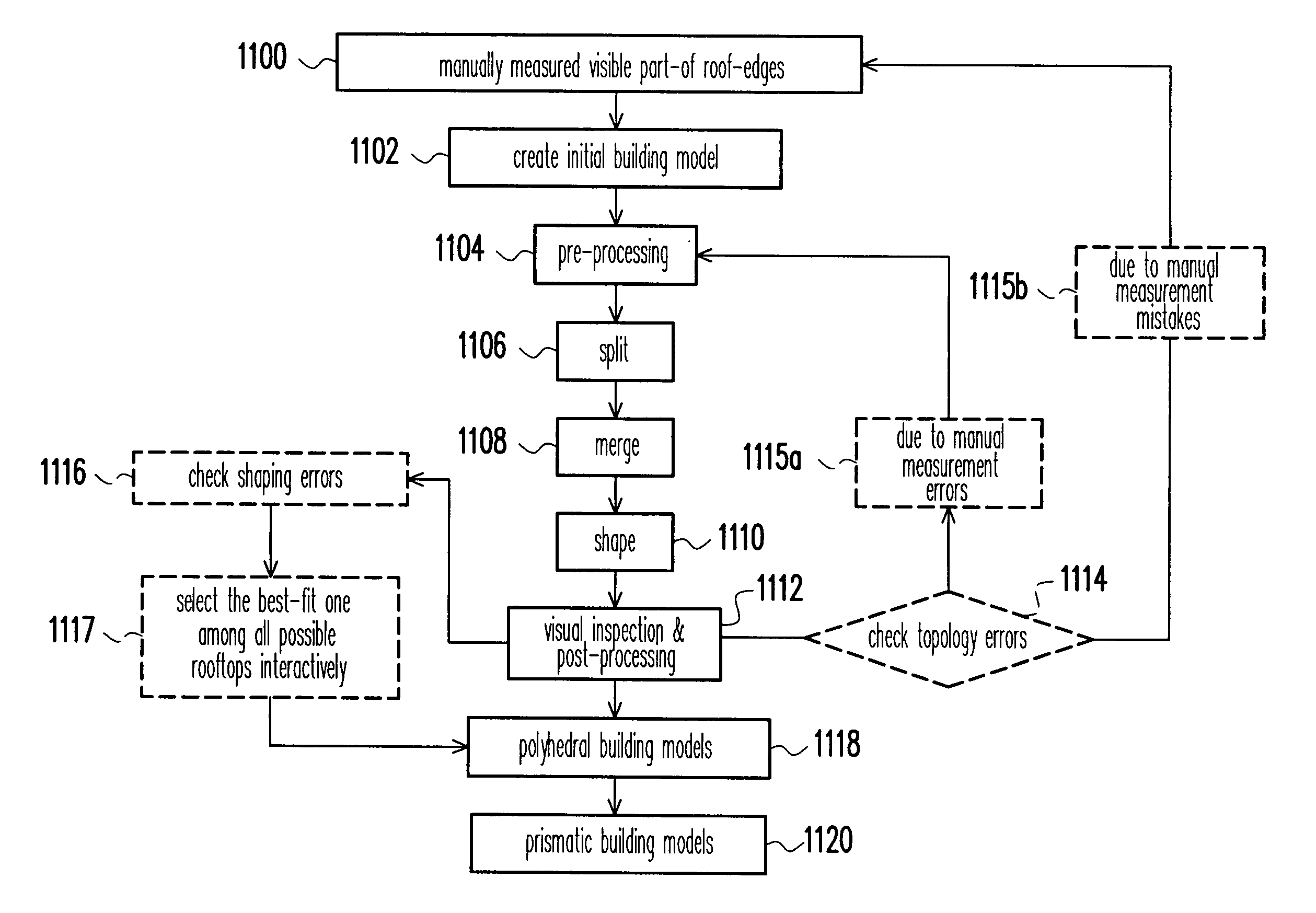
Semi-automatic reconstruction method of 3-D building models using building outline segments
InactiveUS7133551B2Operator's job is thus simplifiedOperator's workload is thus dramatically reducedGeometric CADDetails involving processing stepsArchitectural engineeringReconstruction method
A semi-automatic reconstruction method of 3-D building models using building outline segments is introduced. The core technology of the present invention is called the “Split-Merge-Shape” algorithm. The Split and Merge processes sequentially reconstruct the topology between any roof-edges of the buildings and then reform them as enclosed regions. The Shape process uses height information and consecutive-coplanar analysis to determine the shapes and heights of the roofs. After generating polyhedral building models, prismatic building models can also be generated by using a semi-automatic procedure. An existing digital topographic map of buildings can be directly used to reconstruct their 3-D models without any excess stereo-measurements. In addition to cost reduction, high efficiency, high quality, and minimization of manual operations, the integration of photogrammetric mapping with 3-D building modeling in one procedure is possible, which is the most cost-effective approach for 3-D mapping.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
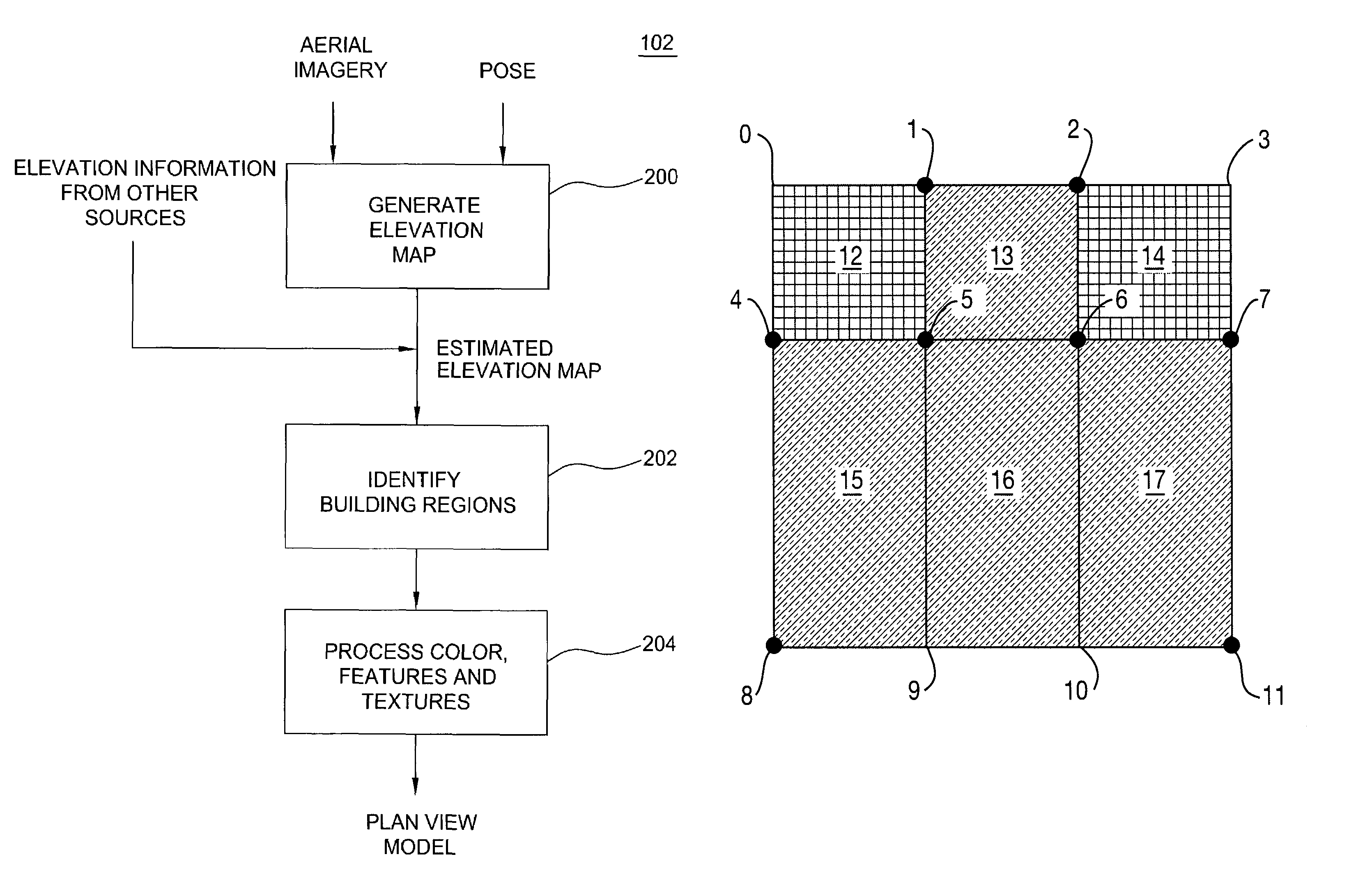
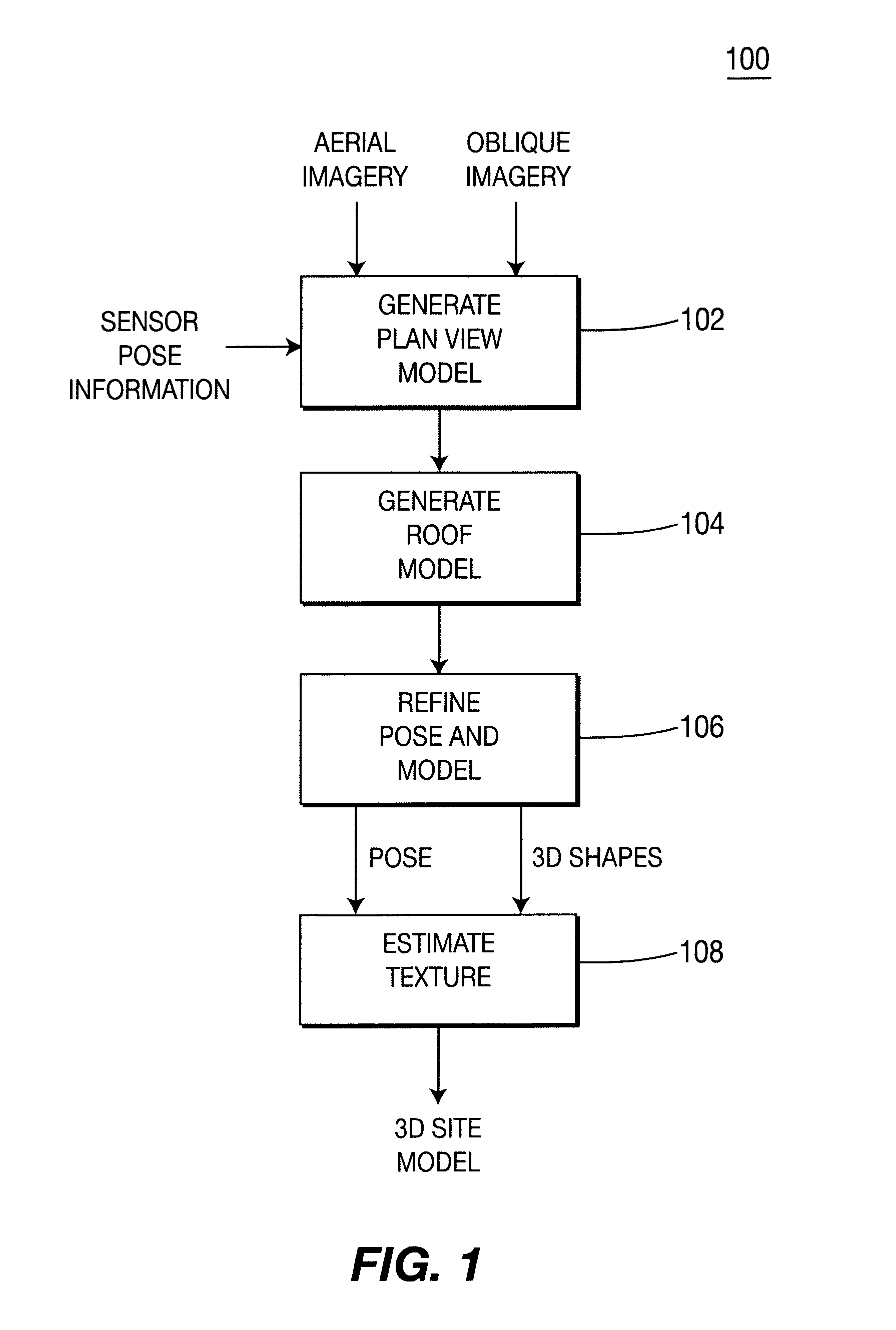
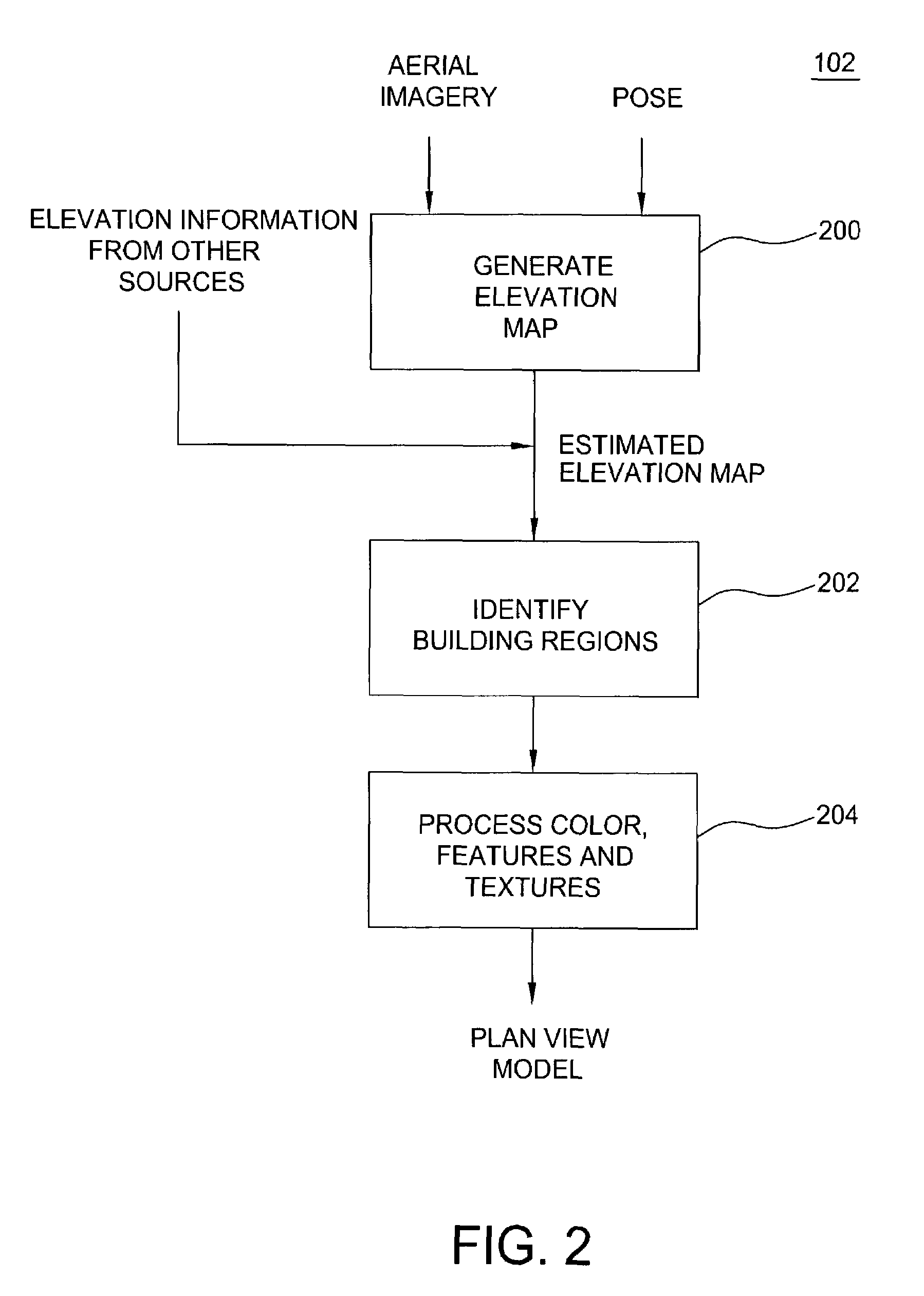
Method and apparatus for automatically generating a site model
ActiveUS7509241B2Overcome disadvantagesPrecise definitionGeometric CADDetails involving processing stepsSite modelView model
A method and apparatus for automatically combining aerial images and oblique images to form a three-dimensional (3D) site model. The apparatus or method is supplied with aerial and oblique imagery. The imagery is processed to identify building boundaries and outlines as well as to produce a depth map. The building boundaries and the depth map may be combined to form a 3D plan view model or used separately as a 2D plan view model. The imagery and plan view model is further processed to determine roof models for the buildings in the scene. The result is a 3D site model having buildings represented rectangular boxes with accurately defined roof shapes.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Aerial roof estimation systems and methods
Methods and systems for roof estimation are described. Example embodiments include a roof estimation system, which generates and provides roof estimate reports annotated with indications of the size, geometry, pitch and / or orientation of the roof sections of a building. Generating a roof estimate report may be based on one or more aerial images of a building. In some embodiments, generating a roof estimate report of a specified building roof may include generating a three-dimensional model of the roof, and generating a report that includes one or more views of the three-dimensional model, the views annotated with indications of the dimensions, area, and / or slope of sections of the roof. This abstract is provided to comply with rules requiring an abstract, and it is submitted with the intention that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:EAGLEVIEW TECH
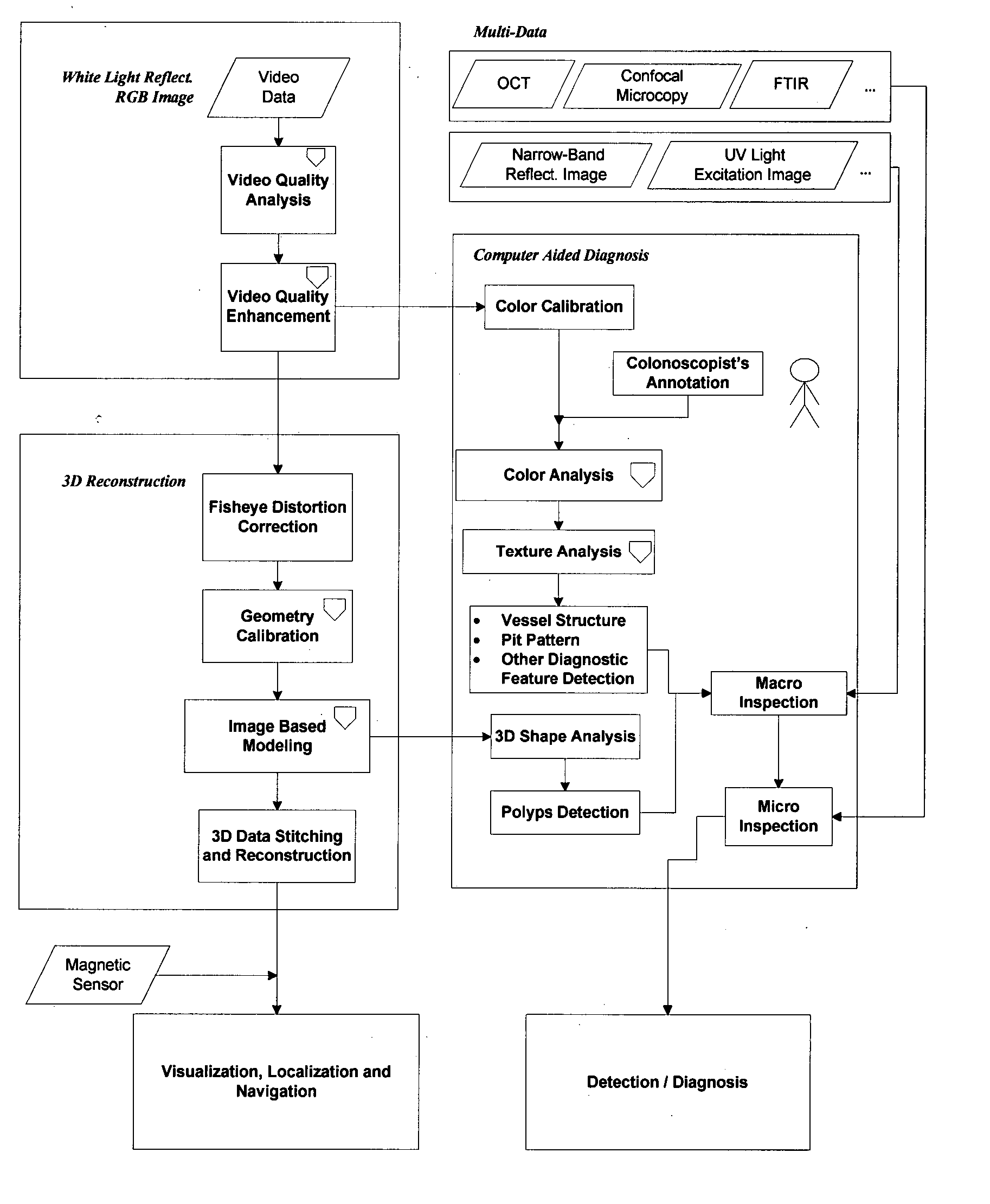
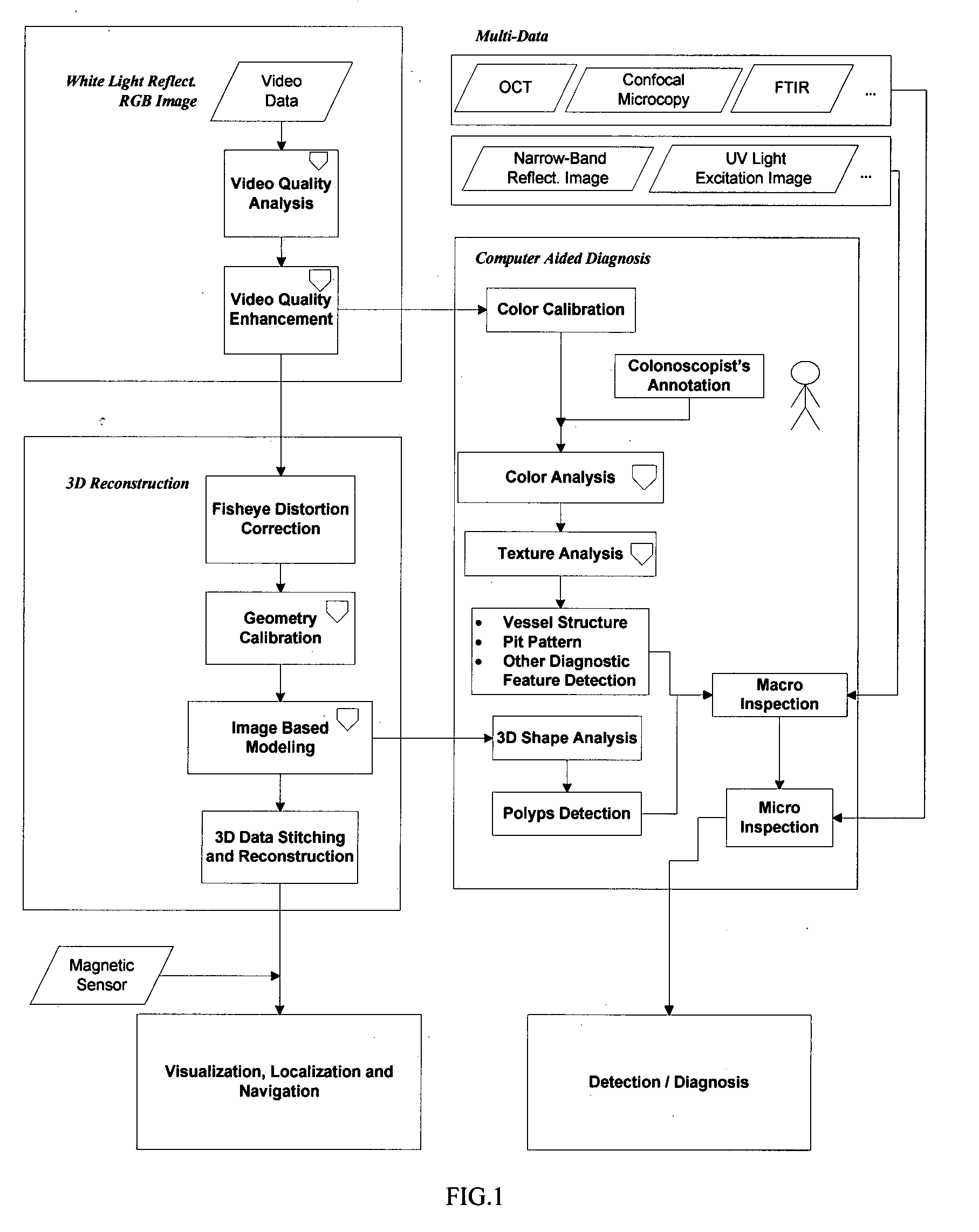
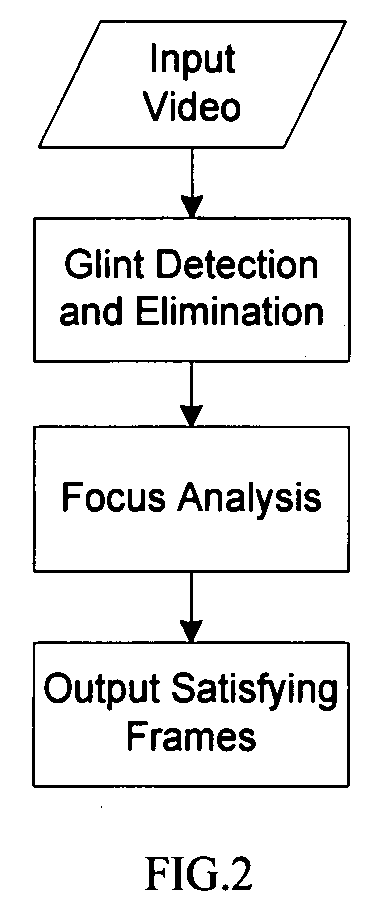
Computer aided diagnosis using video from endoscopes
A process for providing computer aided diagnosis from video data of an organ during an examination with an endoscope, comprising analyzing and enhancing image frames from the video and detecting and diagnosing any lesions in the image frames in real time during the examination. Optionally, the image data can be used to create a 3 dimensional reconstruction of the organ.
Owner:CADES SCHUTTE A LIMITED LIABILITY LAW PARTNERSHIP
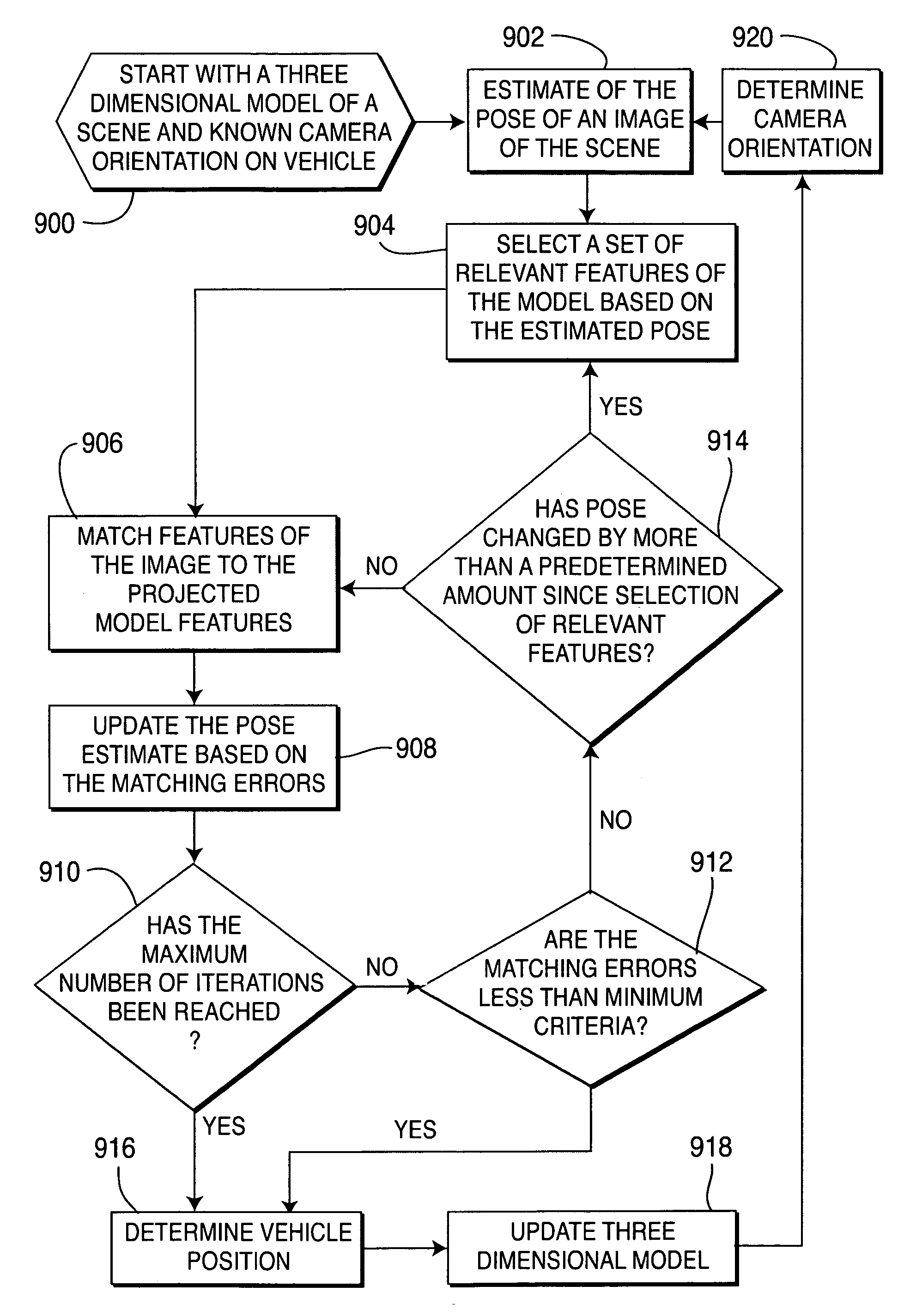
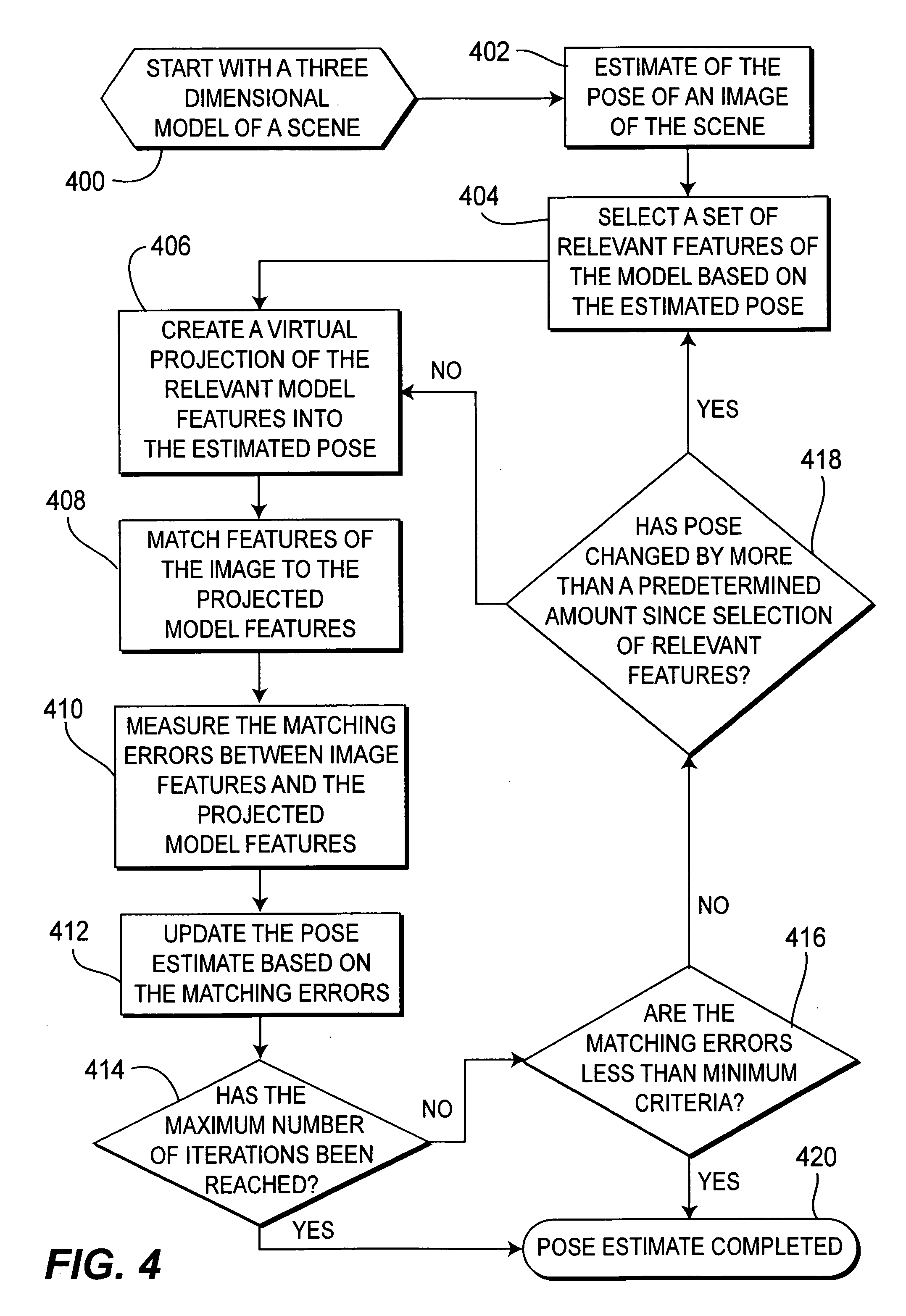
Method of pose estimation and model refinement for video representation of a three dimensional scene
InactiveUS6985620B2Accurate estimatePrecise positioningImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsViewpointsModel refinement
The present invention is embodied in a video flashlight method. This method creates virtual images of a scene using a dynamically updated three-dimensional model of the scene and at least one video sequence of images. An estimate of the camera pose is generated by comparing a present image to the three-dimensional model. Next, relevant features of the model are selected based on the estimated pose. The relevant features are then virtually projected onto the estimated pose and matched to features of the image. Matching errors are measured between the relevant features of the virtual projection and the features of the image. The estimated pose is then updated to reduce these matching errors. The model is also refined with updated information from the image. Meanwhile, a viewpoint for a virtual image is selected. The virtual image is then created by projecting the dynamically updated three-dimensional model onto the selected virtual viewpoint.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Generating simulated images from design information
ActiveUS20170148226A1Image enhancementDetails involving processing stepsSimulationDesign information
Methods and systems for generating simulated images from design information are provided. One system includes one or more computer subsystems and one or more components executed by the computer subsystem(s), which include a generative model. The generative model includes two or more encoder layers configured for determining features of design information for a specimen. The generative model also includes two or more decoder layers configured for generating one or more simulated images from the determined features. The simulated image(s) illustrate how the design information formed on the specimen appears in one or more actual images of the specimen generated by an imaging system.
Owner:KLA CORP
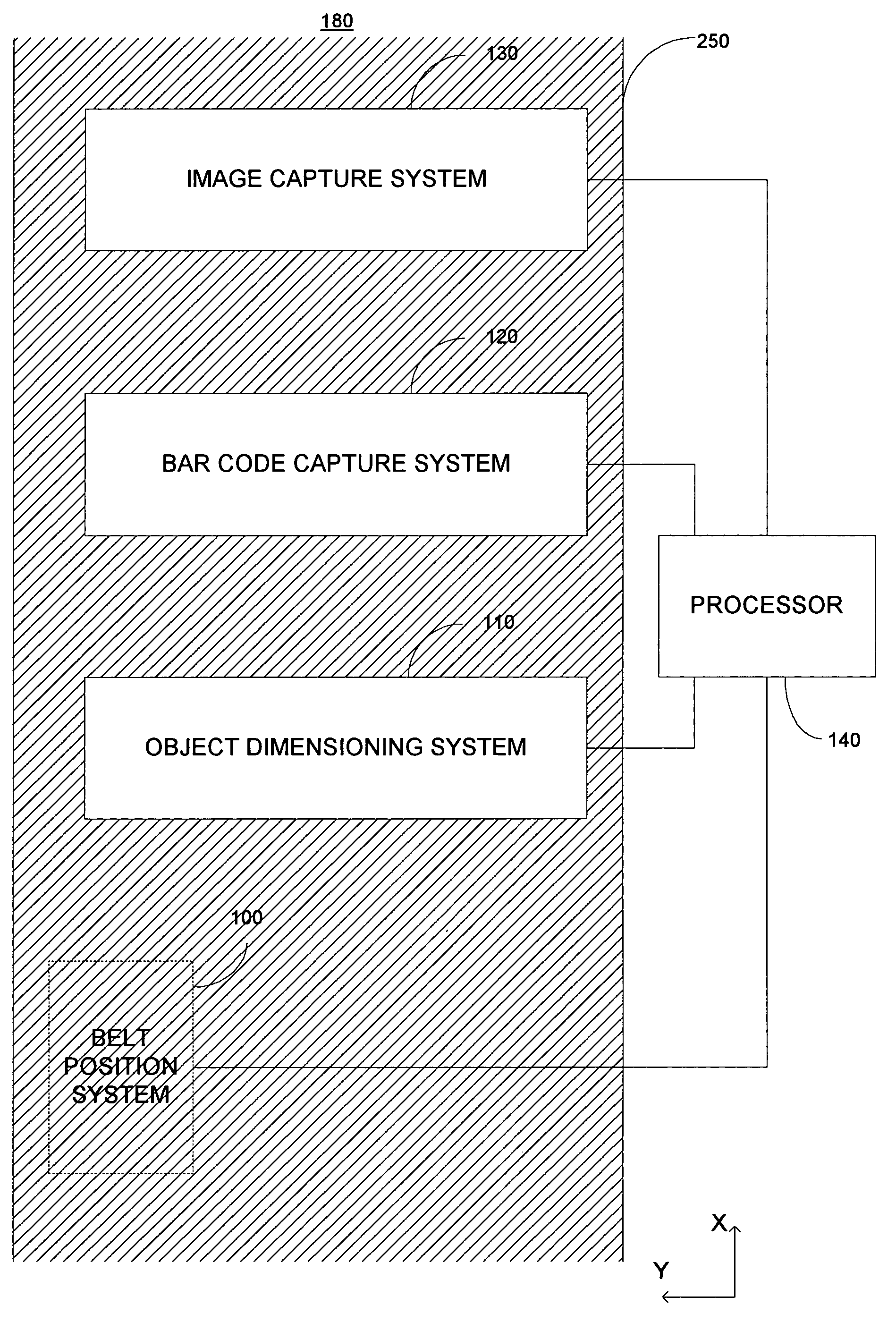
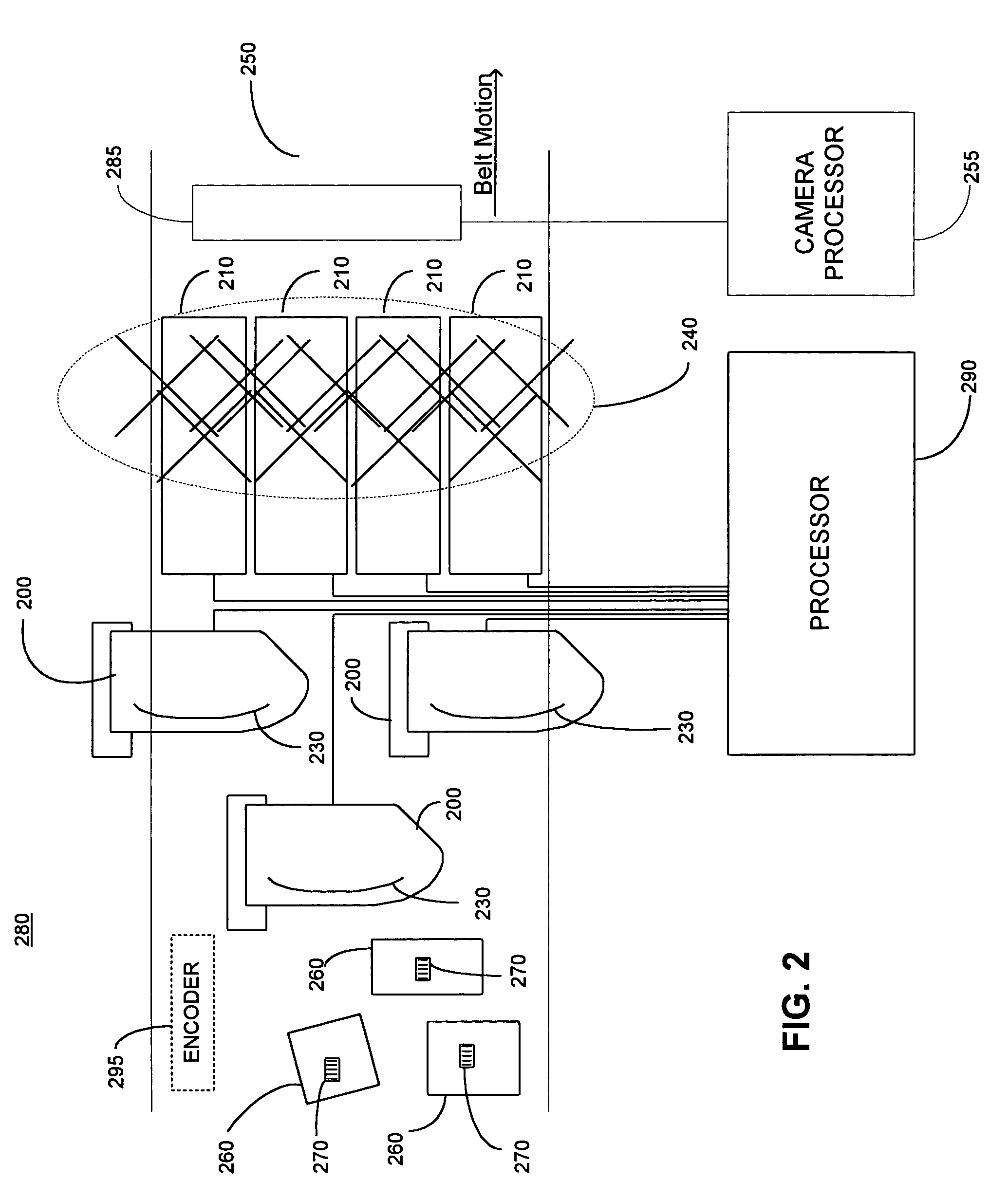
System and method for dimensioning objects
InactiveUS7137556B1Efficient accessImprove reliabilityImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsTemporal informationChemical signature
An information system for storing, retrieving, processing and displaying information captured about objects passing an information capture system. The captured and processed object information may include, for example, a visual representation of the object, a height representation of the object, an identification code from the object, dimensional information about the object, chemical signature information from the object, temperature information, date and time information, and a three dimensional model of the object. The various types of information can be accessed by users via a software interface.
Owner:BONNER BRETT BRACEWELL +2
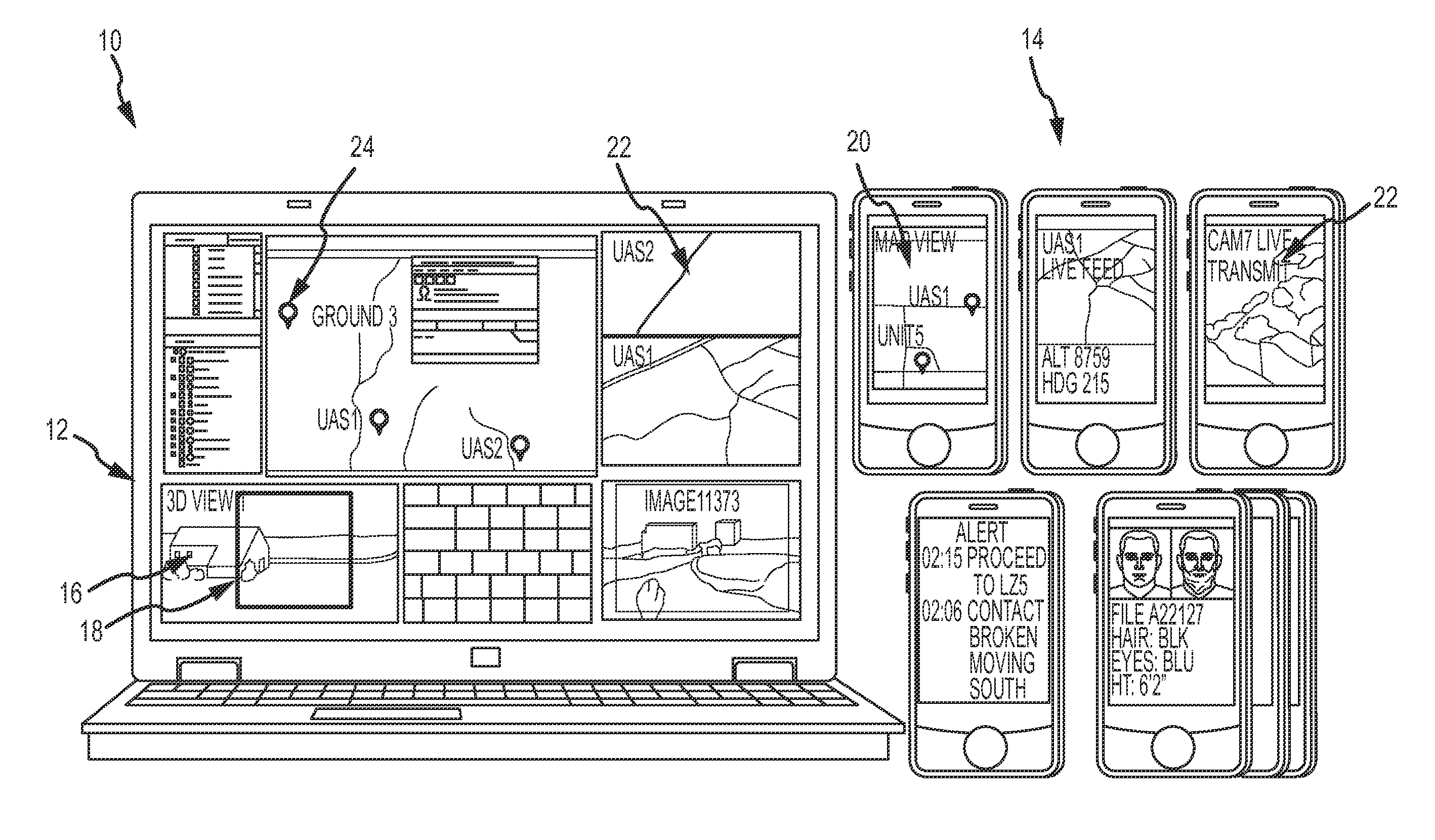
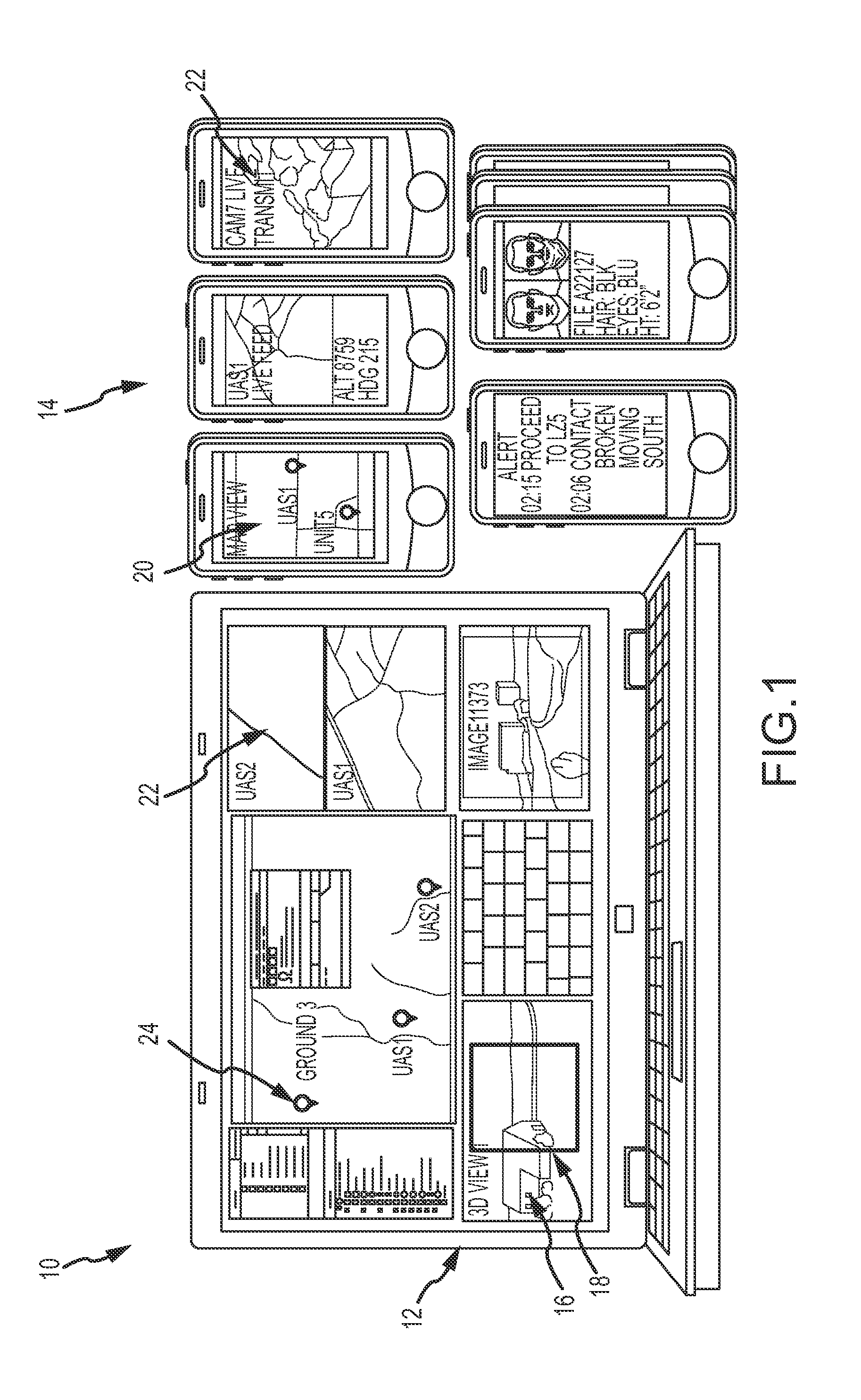
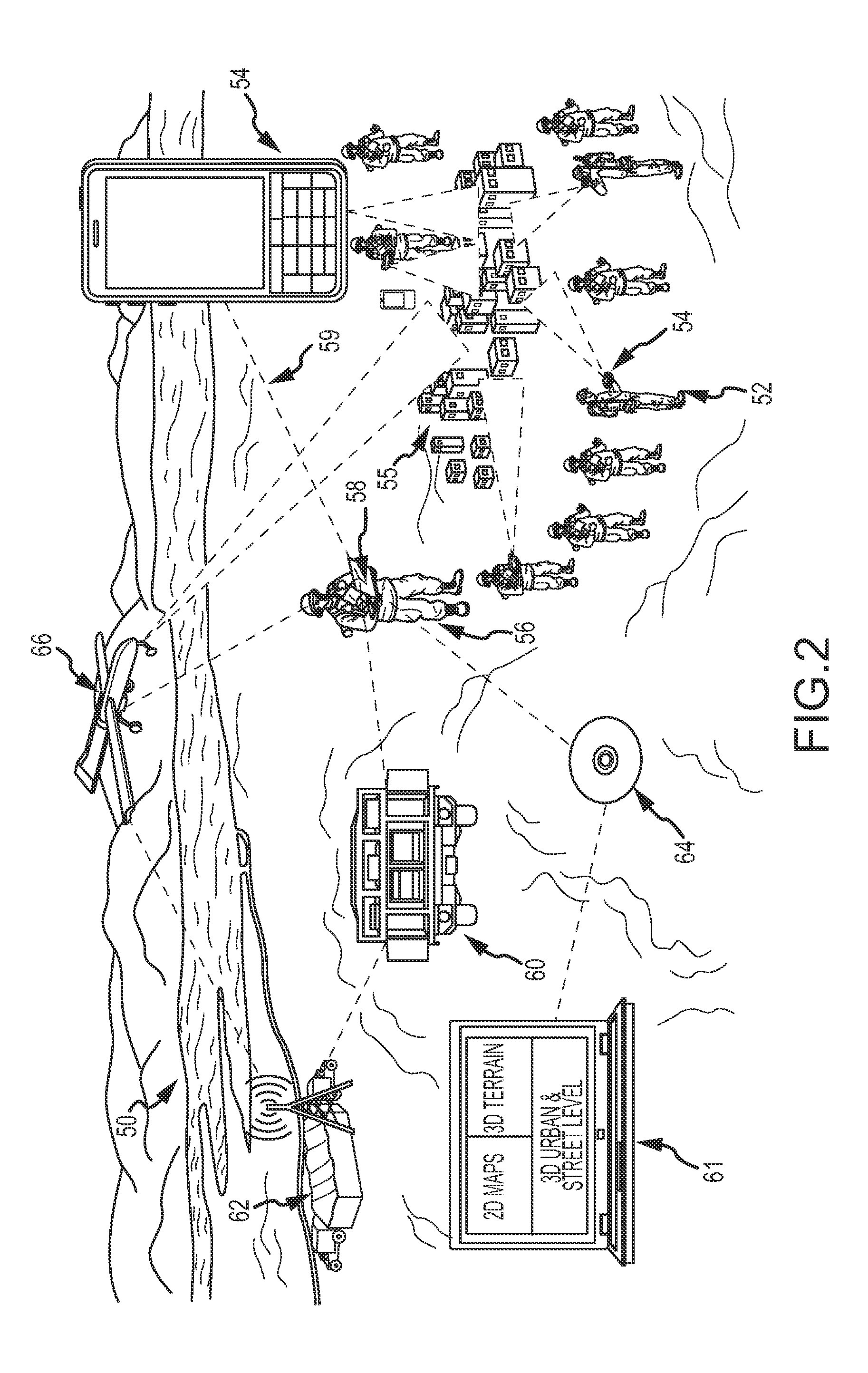
ENHANCED SITUATIONAL AWARENESS AND TARGETING (eSAT) SYSTEM
InactiveUS20120019522A1Enhanced situational awareness and targetingDetails involving processing stepsAiming meansComputer graphics (images)Display device
eSAT pushes 3D scene awareness and targeting to forward positioned mobile operators and their handheld devices in environments such as found in military theaters of operation, border control and enforcement, police operations, search & rescue and large commercial industrial operations. A host computer hosts a 3D model of a scene and dynamically captures and transmits a windowed portion of the visual representation of that 3D model over a wireless network to the mobile operators' handheld devices. The windowed portion of the visual representation is streamed directly to the operators' handheld device displays. The mobile operators may interact with and control the 3D model via the wireless network. The host computer may synthesize the visual representation of the 3D model with live feeds from one or more of the handheld devices or other assets to improve situational awareness. Either the mobile operators or host operator can make point selections on the visual representation to extract geo-coordinates from the 3D model as a set of target coordinates.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
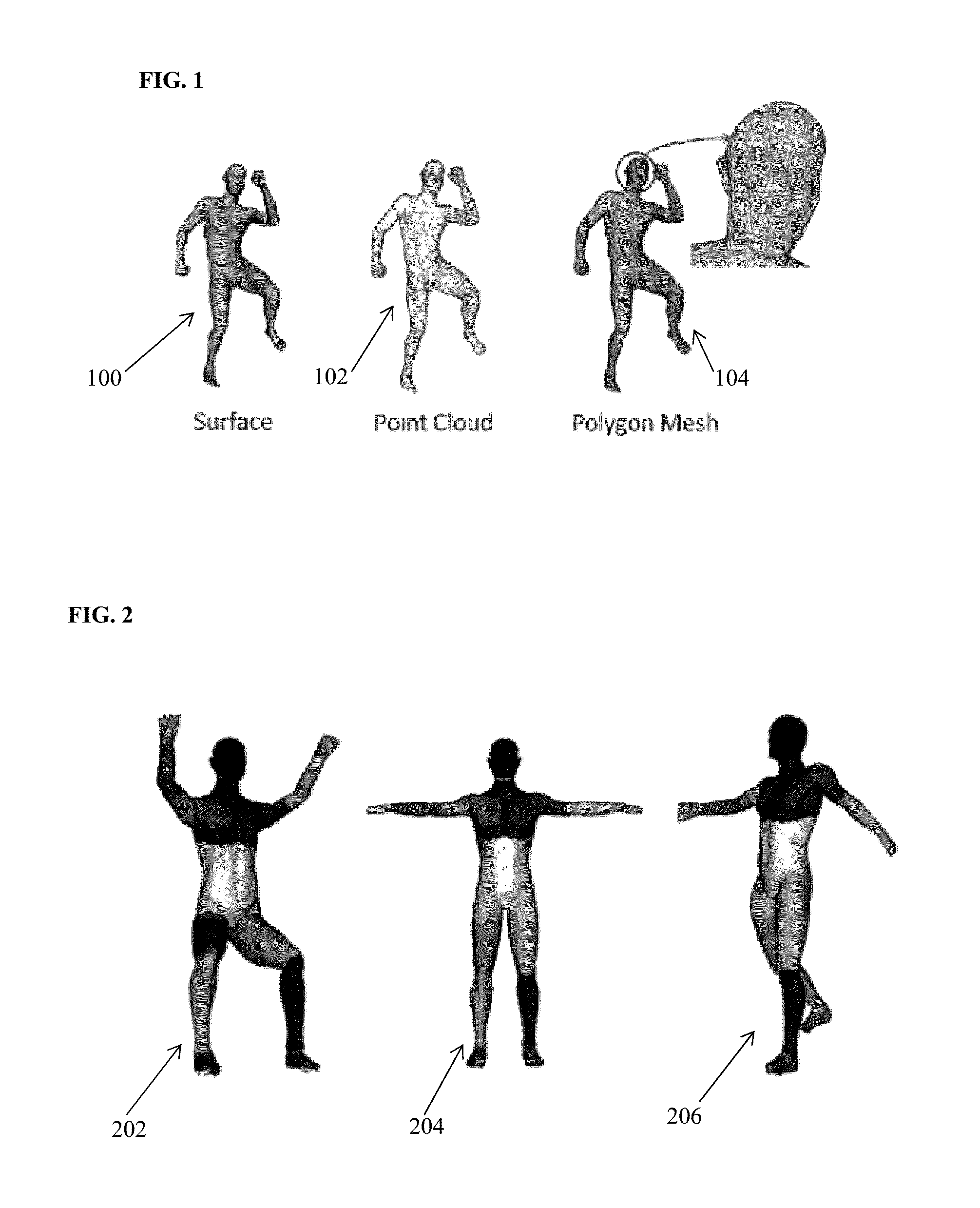
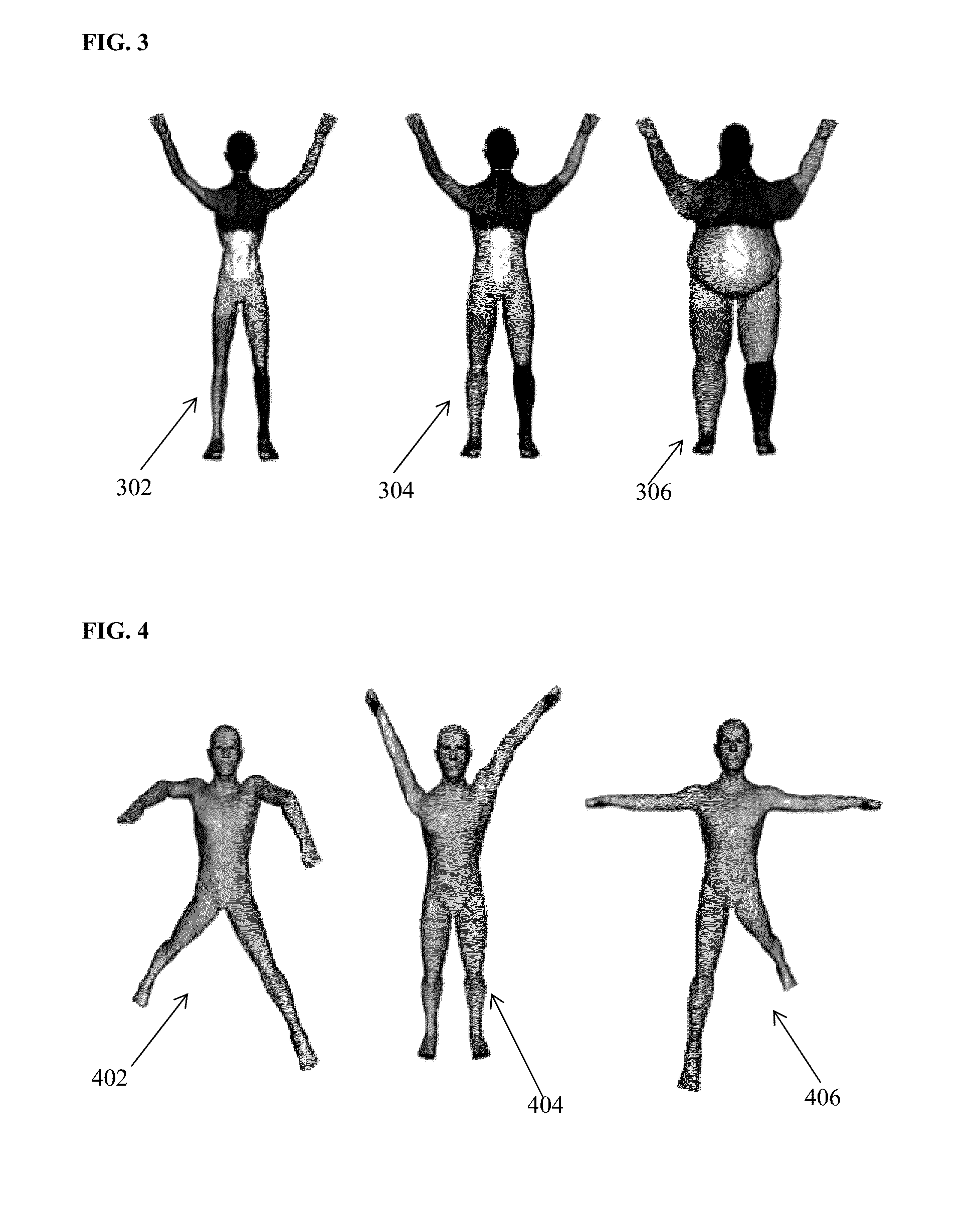
Method and System for Constructing Personalized Avatars Using a Parameterized Deformable Mesh
A method and apparatus for generating a 3D personalized mesh of a person from a depth camera image for medical imaging scan planning is disclosed. A depth camera image of a subject is converted to a 3D point cloud. A plurality of anatomical landmarks are detected in the 3D point cloud. A 3D avatar mesh is initialized by aligning a template mesh to the 3D point cloud based on the detected anatomical landmarks. A personalized 3D avatar mesh of the subject is generated by optimizing the 3D avatar mesh using a trained parametric deformable model (PDM). The optimization is subject to constraints that take into account clothing worn by the subject and the presence of a table on which the subject in lying.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Adaptive 3D image modelling system and apparatus and method therefor
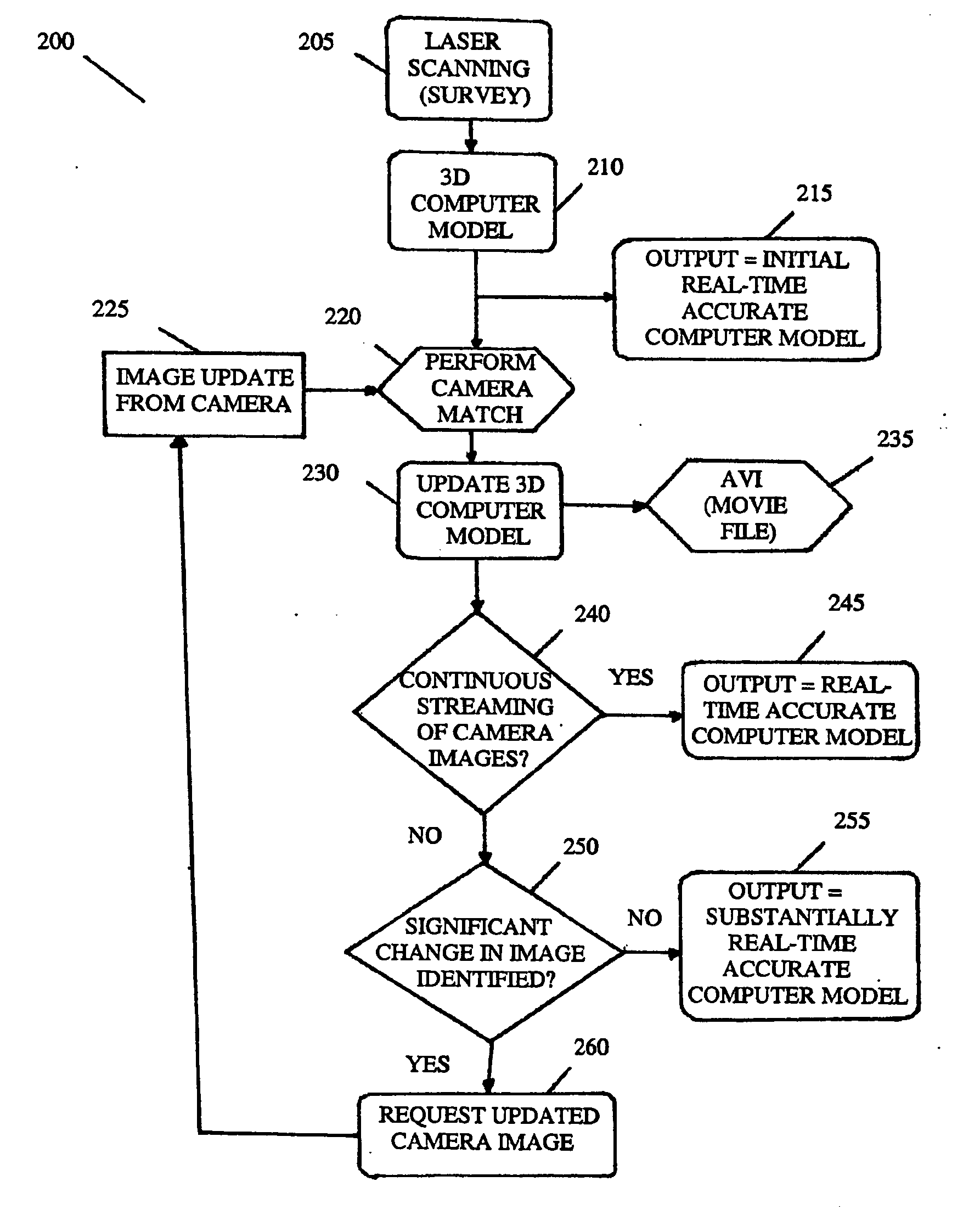
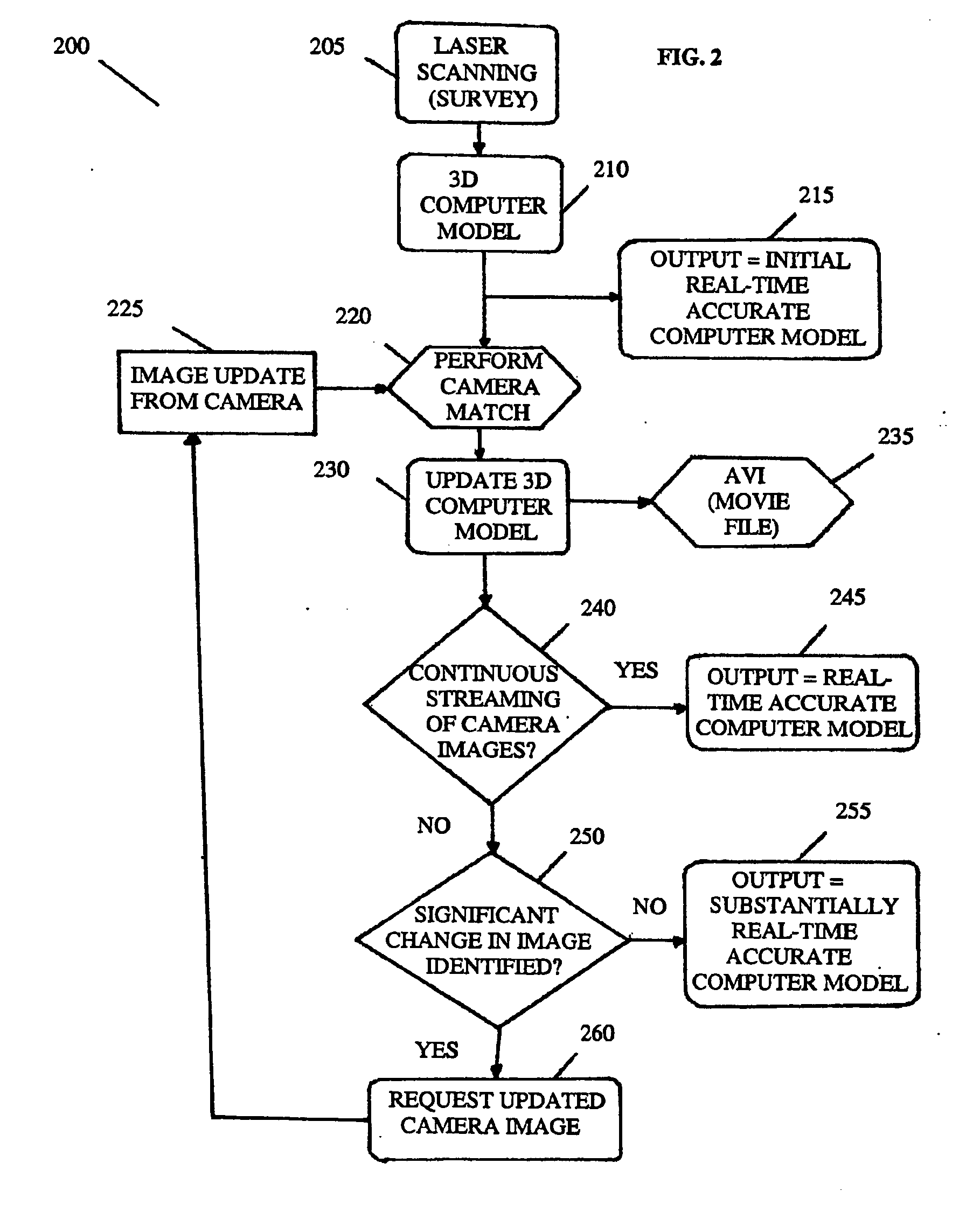
A system which resolves accuracy problems with 3D modeling techniques by using a 3D computer model that is updated using views provided by, say, a camera unit or camera system. The 2D images provided by matching the perspective view of an image within the model to that of an image of the environment. The 3D computer model can therefore be updated remotely, using 2D data.
Owner:MARZELL LAURENCE
Aerial roof estimation systems and methods
Methods and systems for roof estimation are described. Example embodiments include a roof estimation system, which generates and provides roof estimate reports annotated with indications of the size, geometry, pitch and / or orientation of the roof sections of a building. Generating a roof estimate report may be based on one or more aerial images of a building. In some embodiments, generating a roof estimate report of a specified building roof may include generating a three-dimensional model of the roof, and generating a report that includes one or more views of the three-dimensional model, the views annotated with indications of the dimensions, area, and / or slope of sections of the roof. This abstract is provided to comply with rules requiring an abstract, and it is submitted with the intention that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:EAGLEVIEW TECH
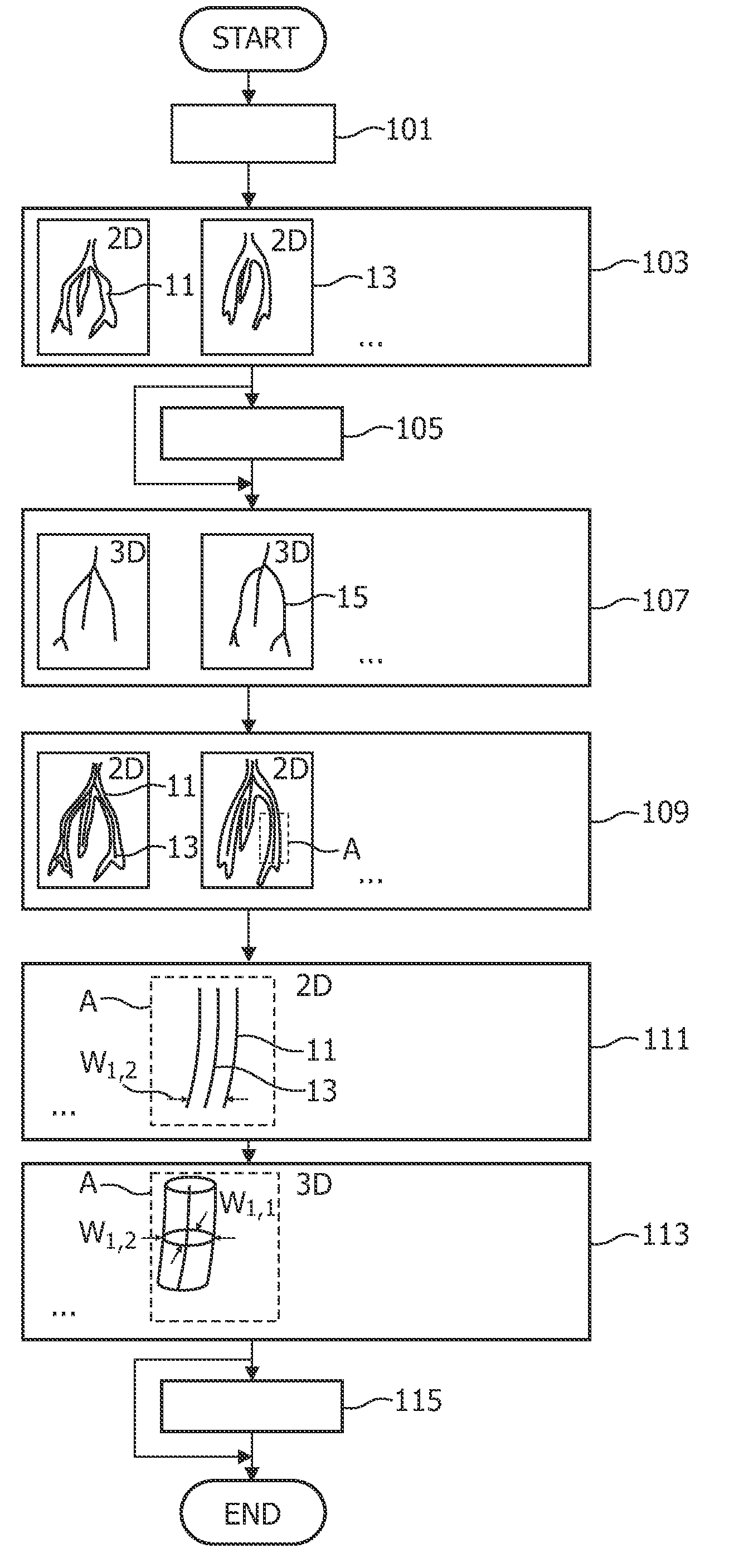
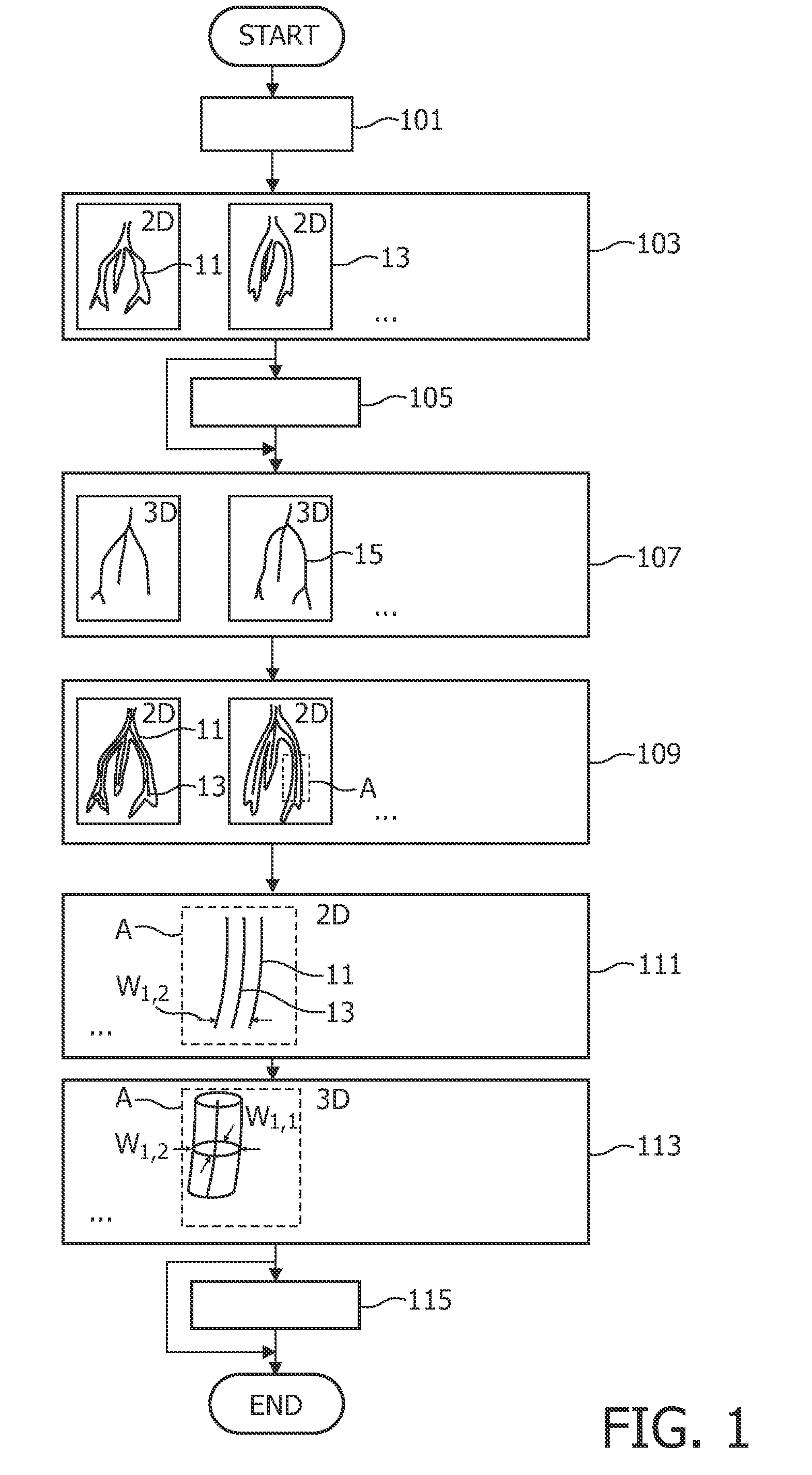
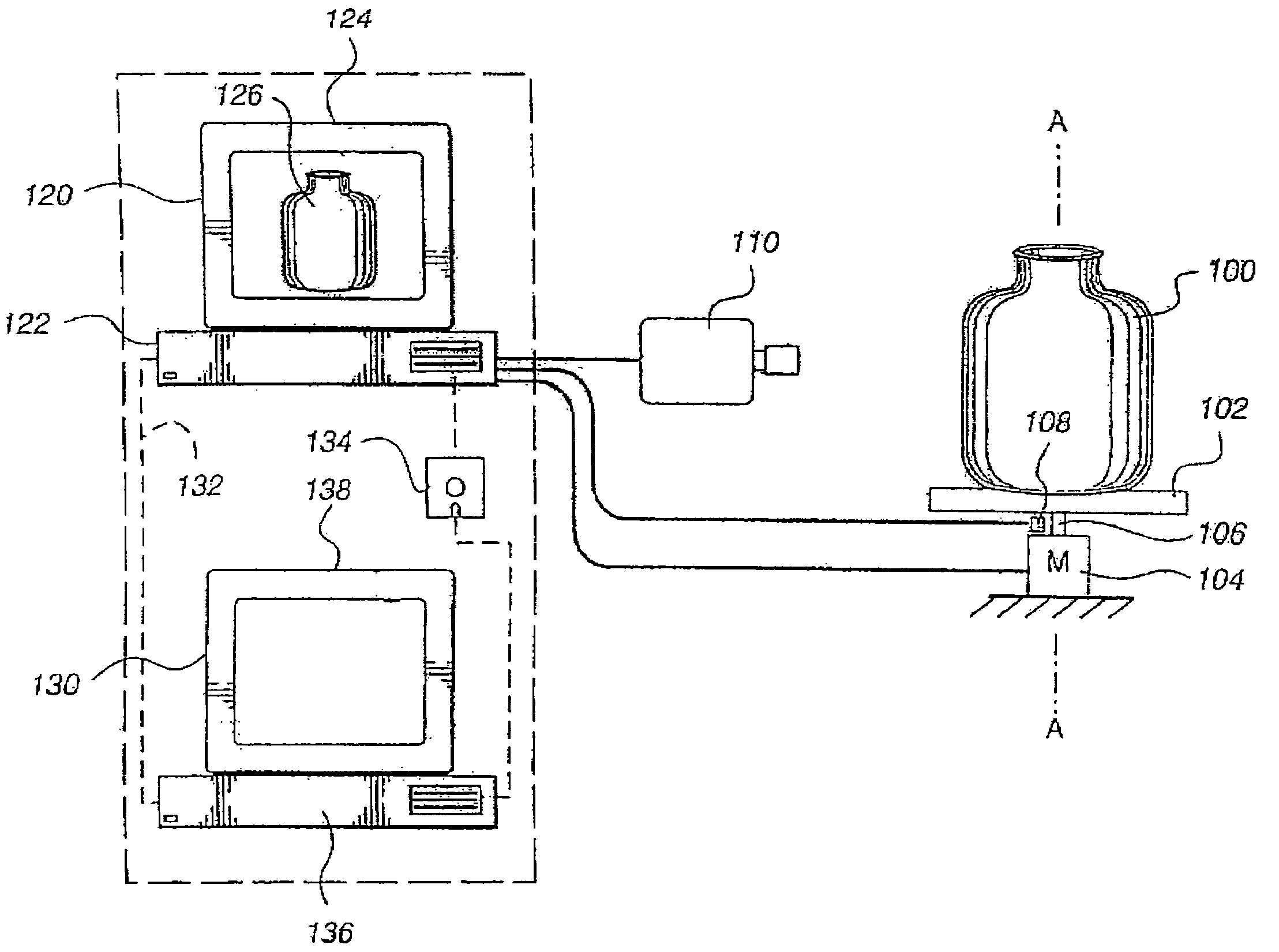
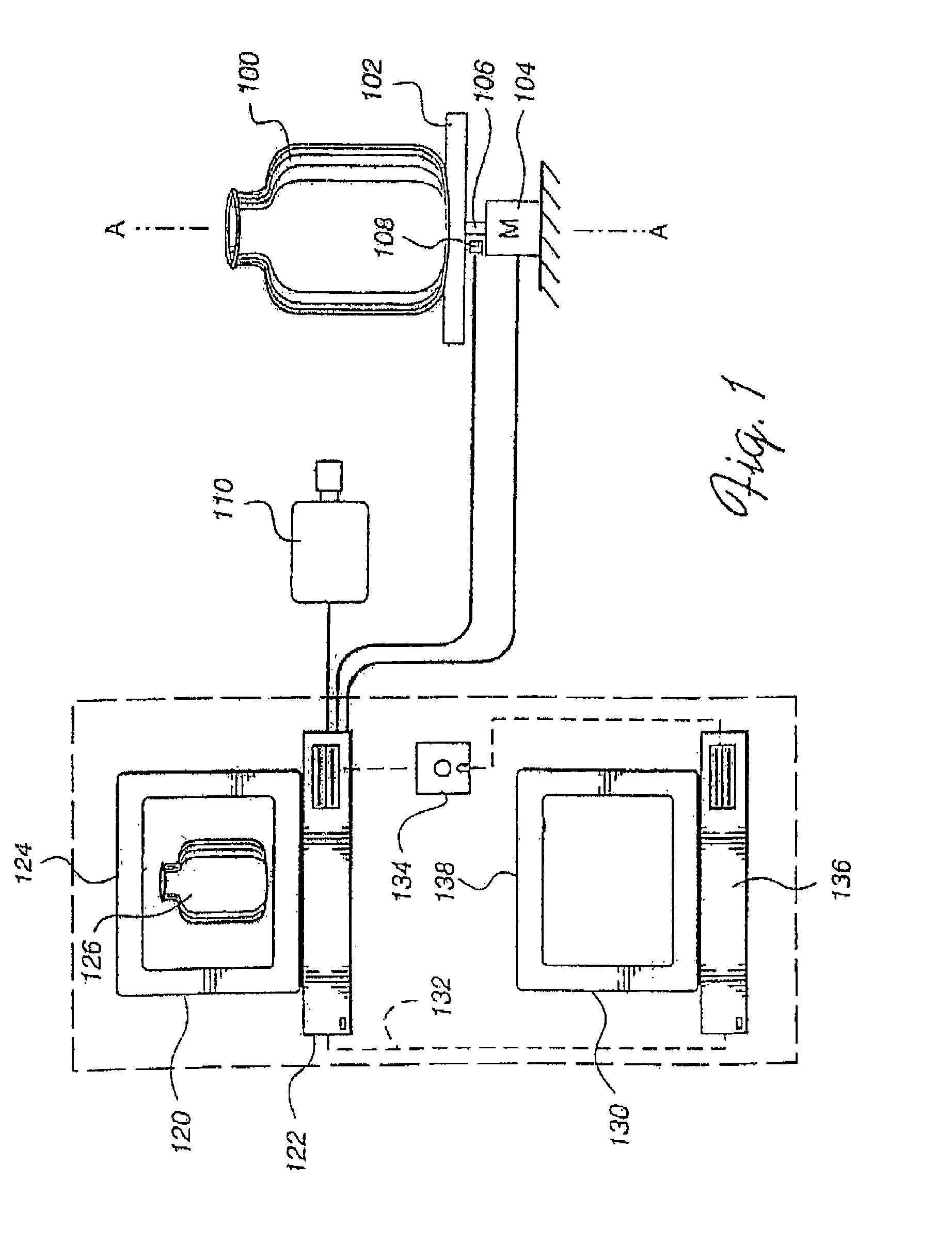
Method for acquiring 3-dimensional images of coronary vessels, particularly of coronary veins
InactiveUS20100189337A1Quality improvementImprove representationImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsVeinX-ray
A method and an apparatus for acquiring 3-dimensional images of coronary vessels (11), particularly of coronary veins, is proposed. 2-dimensional X-ray images (13) are acquired within a same phase of a cardiac motion. Then, a 3-dimensional centerline model (15) is generated based on these 2-dimensional images. From 2-dimensional projections of the centerline model into respective projection planes, the local diameters (w) of the vessels in the projection plane can be derived. Having the diameters, a 3-dimensional hull model of the vessel system can be generated and, optionally, 4-dimensional information about the vessel movement can be derived.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
CAD modeling system and method
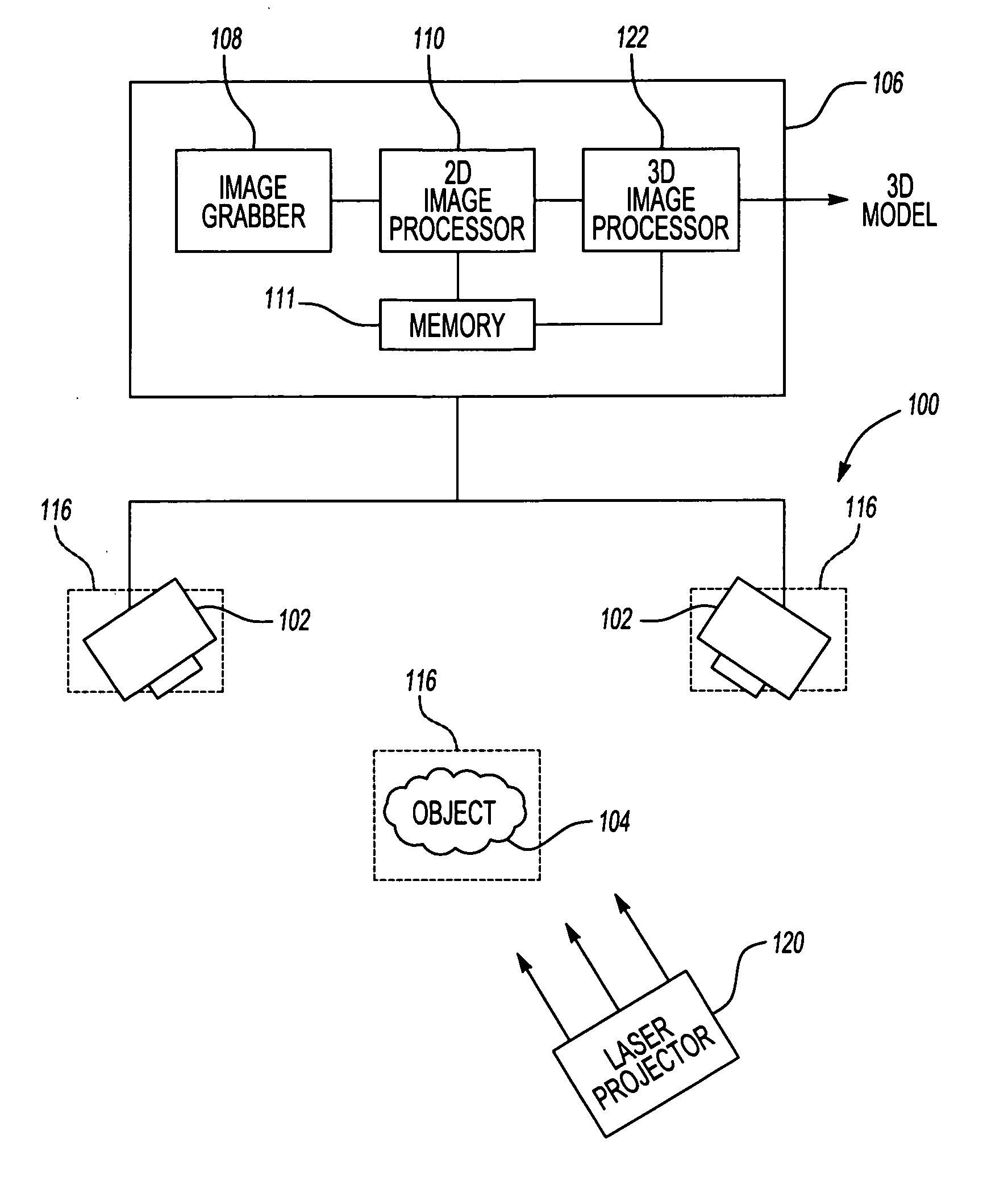
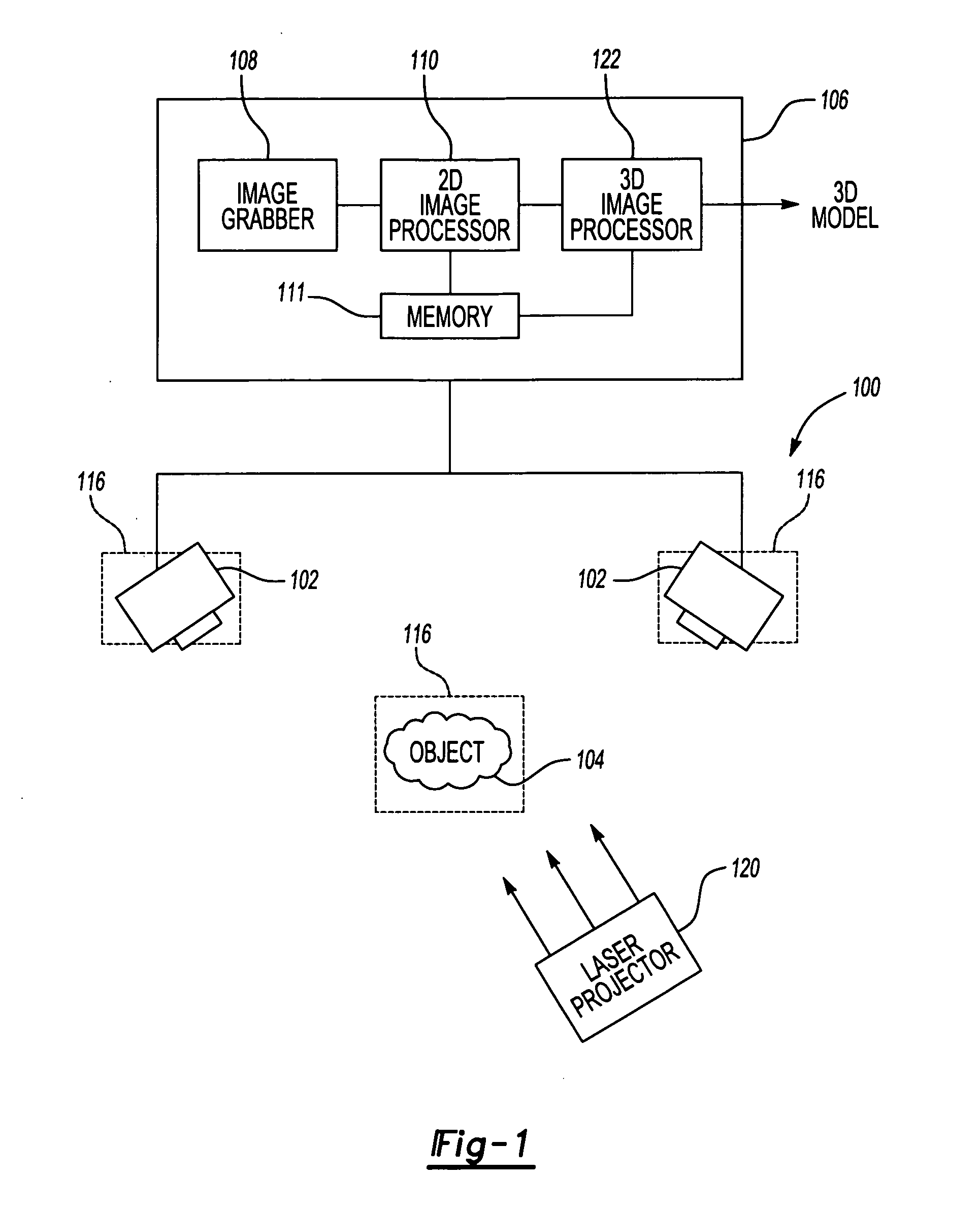
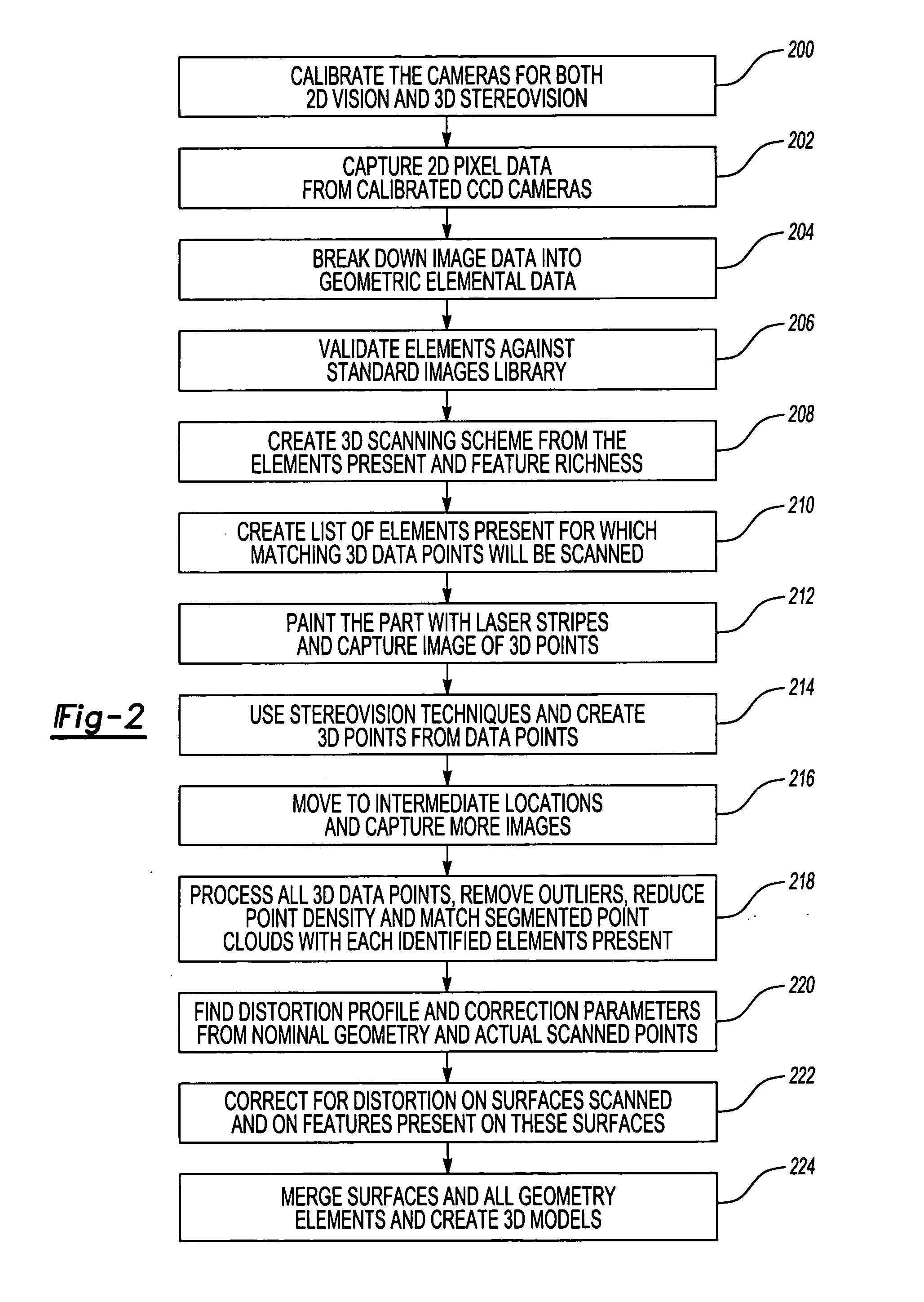
ActiveUS20050135670A1Scanning speed can not be increasedSolve the slow scanning speedDetails involving processing stepsImage analysisGeometric elementDistortion
A 3D object modeling system and method system and method captures a 2D representation of the object to be modeled and breaks the 2D image into its geometric elements. The 3D stereoscopic image is then fitted to the geometric elements generated from the 2D image to generate the final model. The 3D stereoscopic image may be compared with the geometric elements to detect distortions in the object, allowing the distortions to be corrected in the final model to ensure that the model accurately depicts the original object.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
Devices and methods of generating three dimensional (3D) colored models
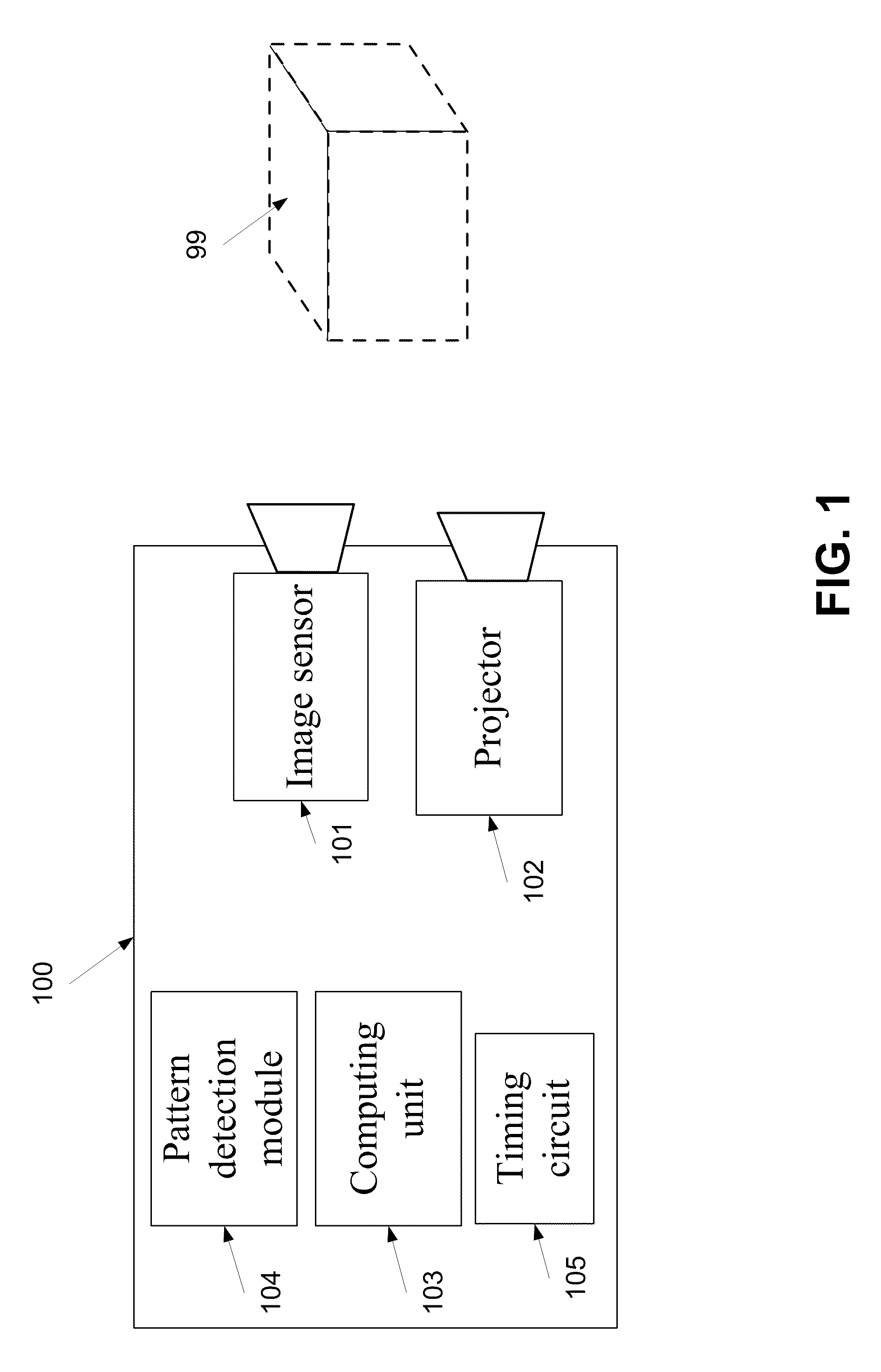
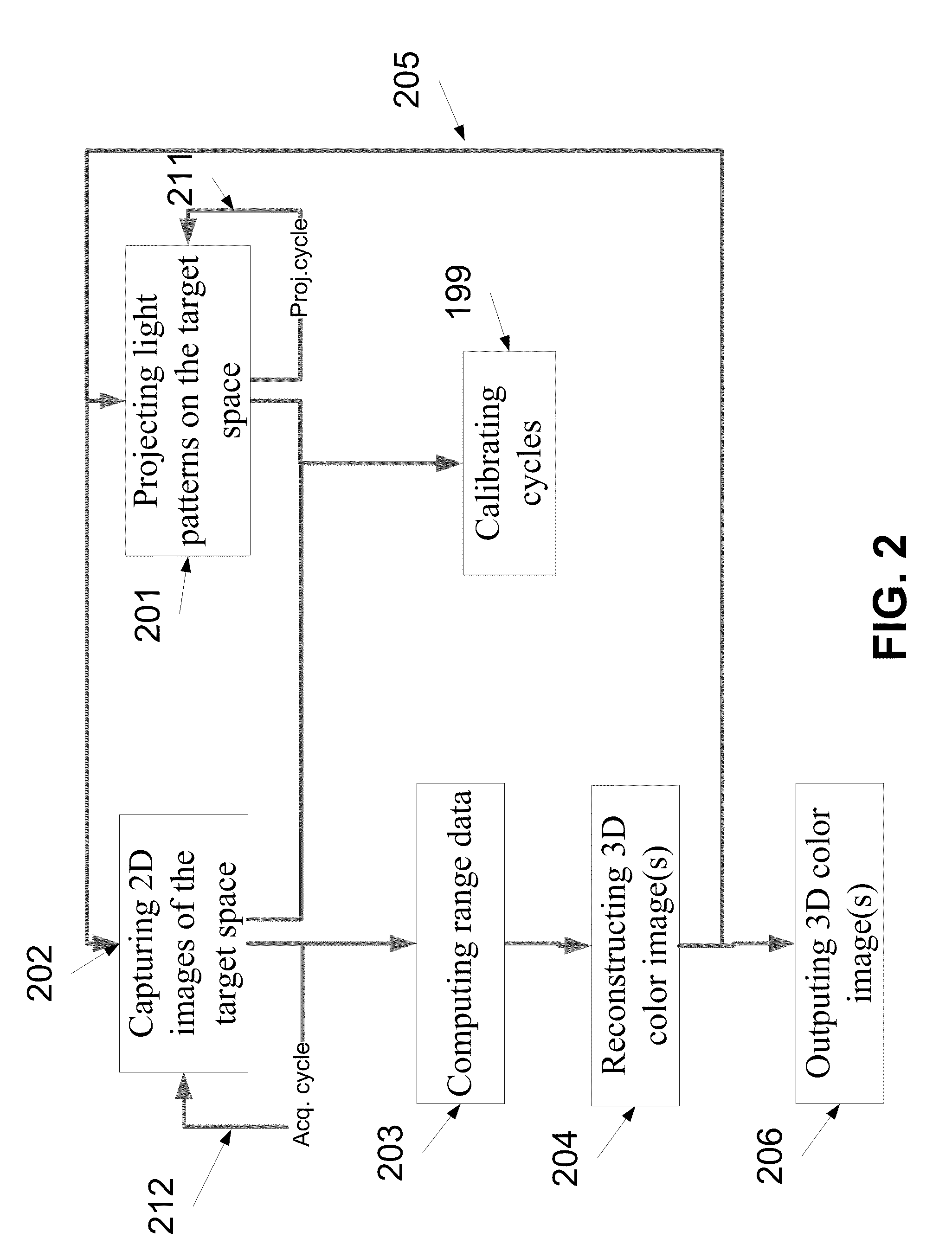
A method of forming at least one three dimensional (3D) color image of at least one object in a target space. The method comprises projecting, each of a plurality of projection cycles, a sequence comprising a plurality of gray coded light patterns, each colored in one of red green or blue, on a target space, capturing a plurality of two dimensional (2D) images of the target space during a plurality of acquisition cycles, each the acquisition cycle being timed to correspond with the projection of at least a sub sequence of the sequence, the sub sequence comprising red, green, and blue gray coded light patterns of the plurality of gray coded light patterns, extracting range data and color texture information of at least one object in the target space from the plurality of 2D images, and forming a 3D color image of the range data and color texture information.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD +1
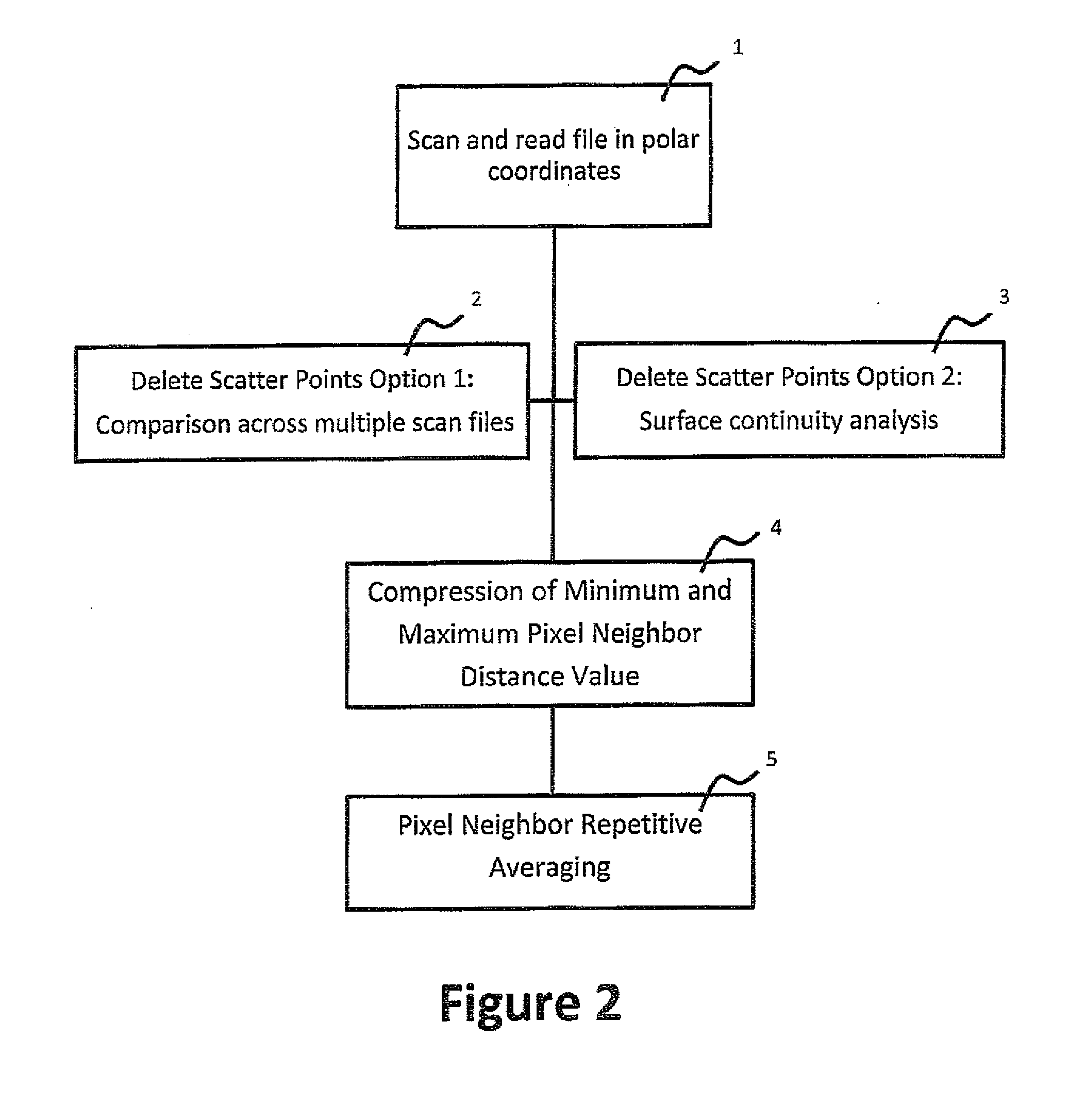
Method of generating a smooth image from point cloud data
A method for processing an array of pixels in a point cloud, comprises calculating local error limits for each distance value for each pixel in the processed point cloud data set. One may then determine the error bar. One begins a distance value adjusting loop by for each pixel in the processed point cloud data set by calculating the difference between the distance value in the pixel of the point cloud data set being processed and each of the neighboring pixels or the most suitable neighboring pixel distance value is determined whether the difference is within the range defined by the error bar. It the difference is not within the error bar, the distance value is changed for the pixel being processed by a small fraction while keeping the new distance value within the range defined by the original distance value for the pixel being processed plus or minus the error bar. If the difference is within the error bar the distance value in the pixel being processed is replaced by a weighted average value. The number of neighboring pixels with their distance values within the error bar for the pixel being processed is counted and if the count is greater than a predetermined threshold, average the counted distance values and substitute the average for the pixel distance value, but if the count is below the threshold leave the pixel distance value unchanged. It is determined whether loop exit criteria have been met and if loop exit criteria have not been met beginning the loop again, and if loop exit criteria have been met, terminating the loop.
Owner:ASKAN YOLDAS
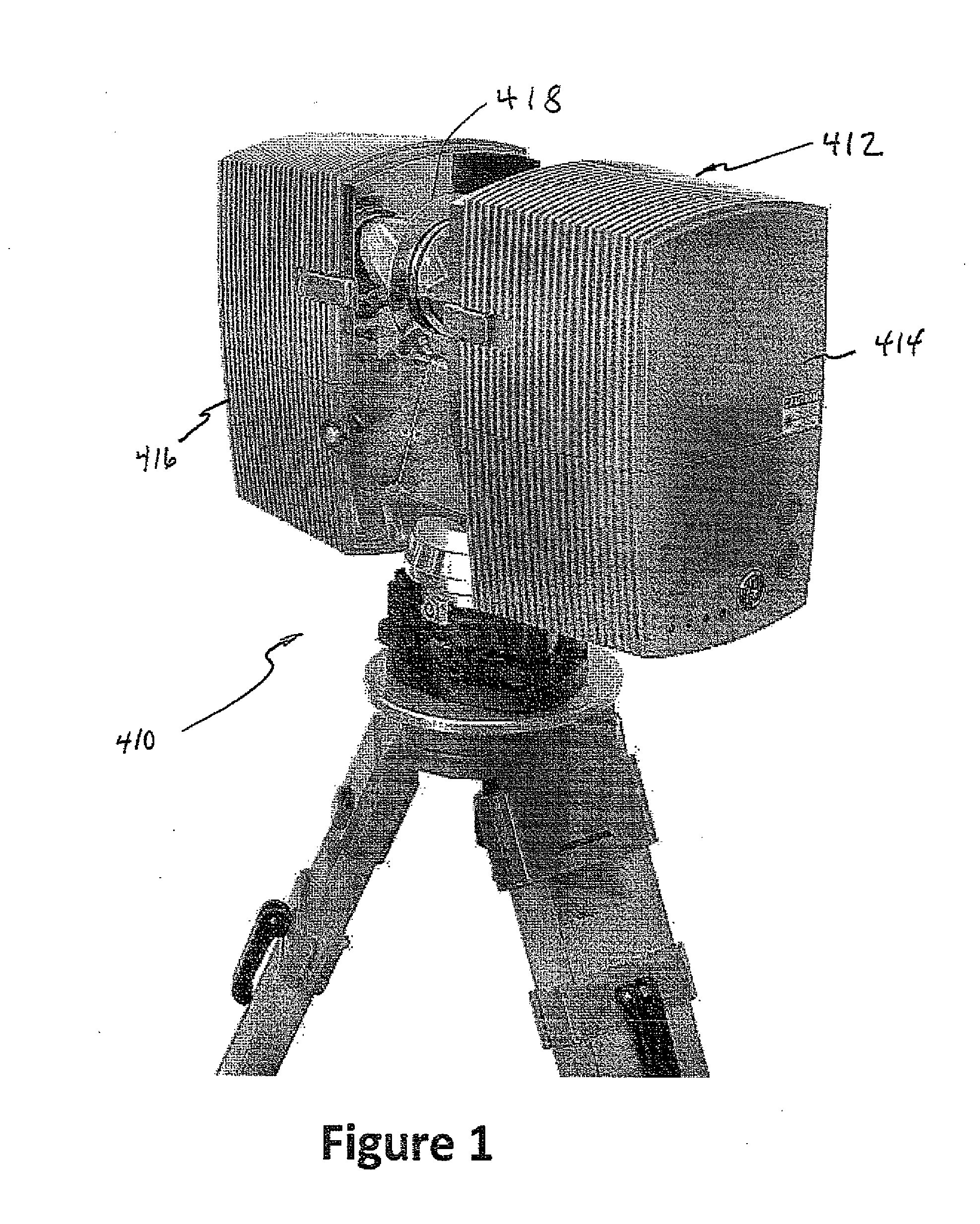
Method and apparatus for scanning three-dimensional objects
InactiveUS7098435B2Improve system accuracyReduce system costImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsVisibilityComputer vision
Apparatus and method for creating 3D imagery of an object using calibration means to transfer data to a reference frame and visibility analysis to determine and resolve occlusion.
Owner:WAVEWORX
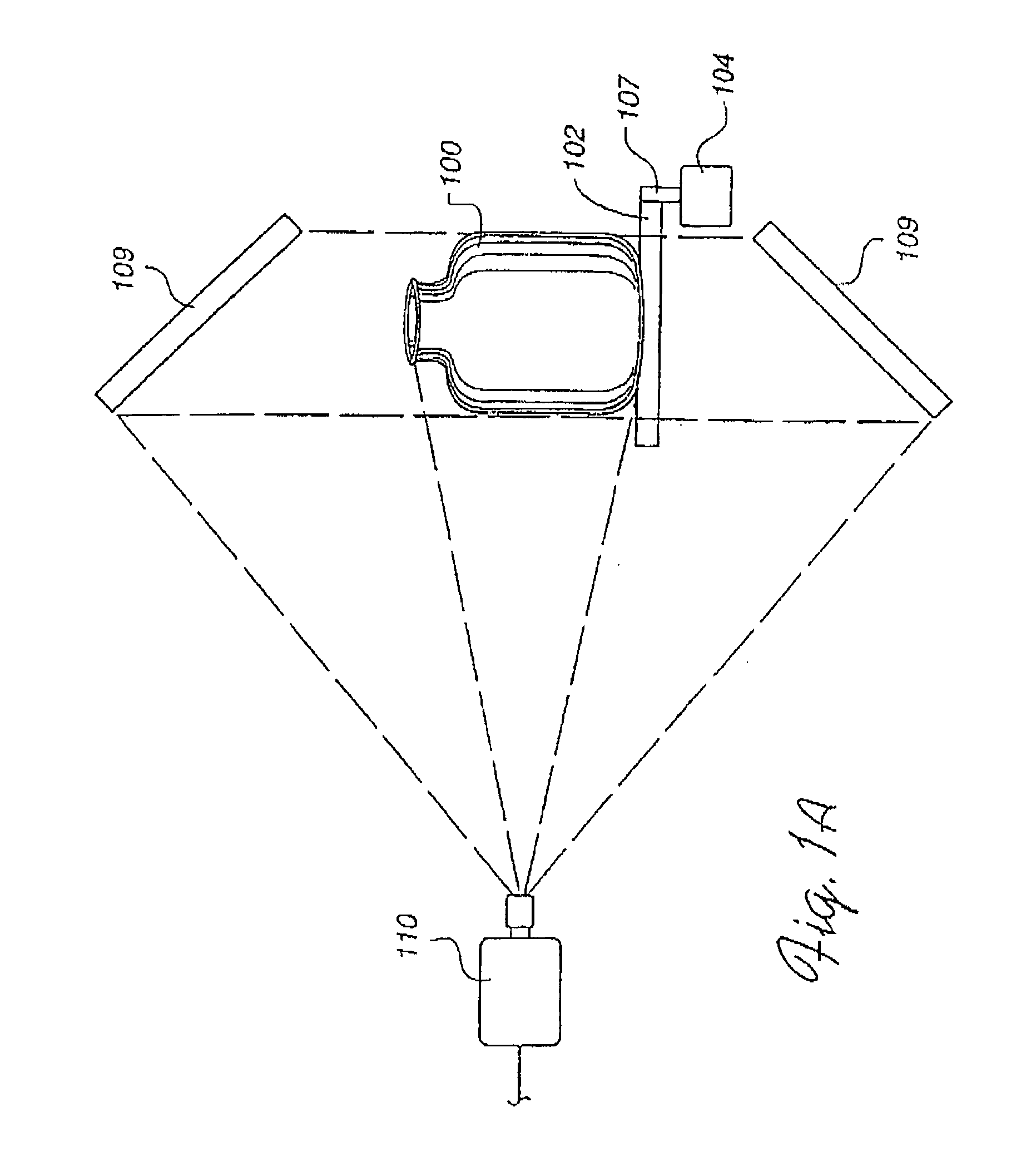
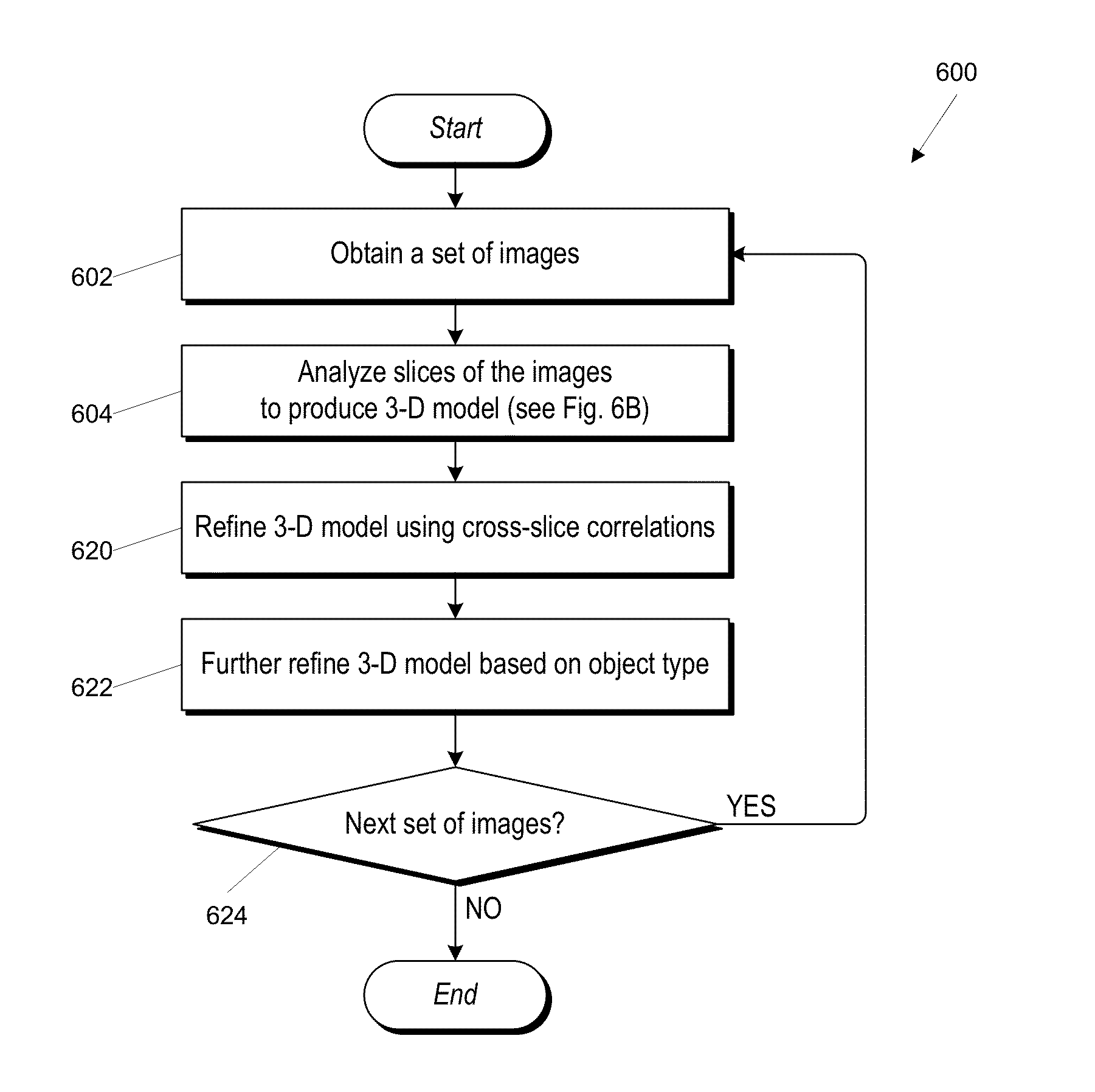
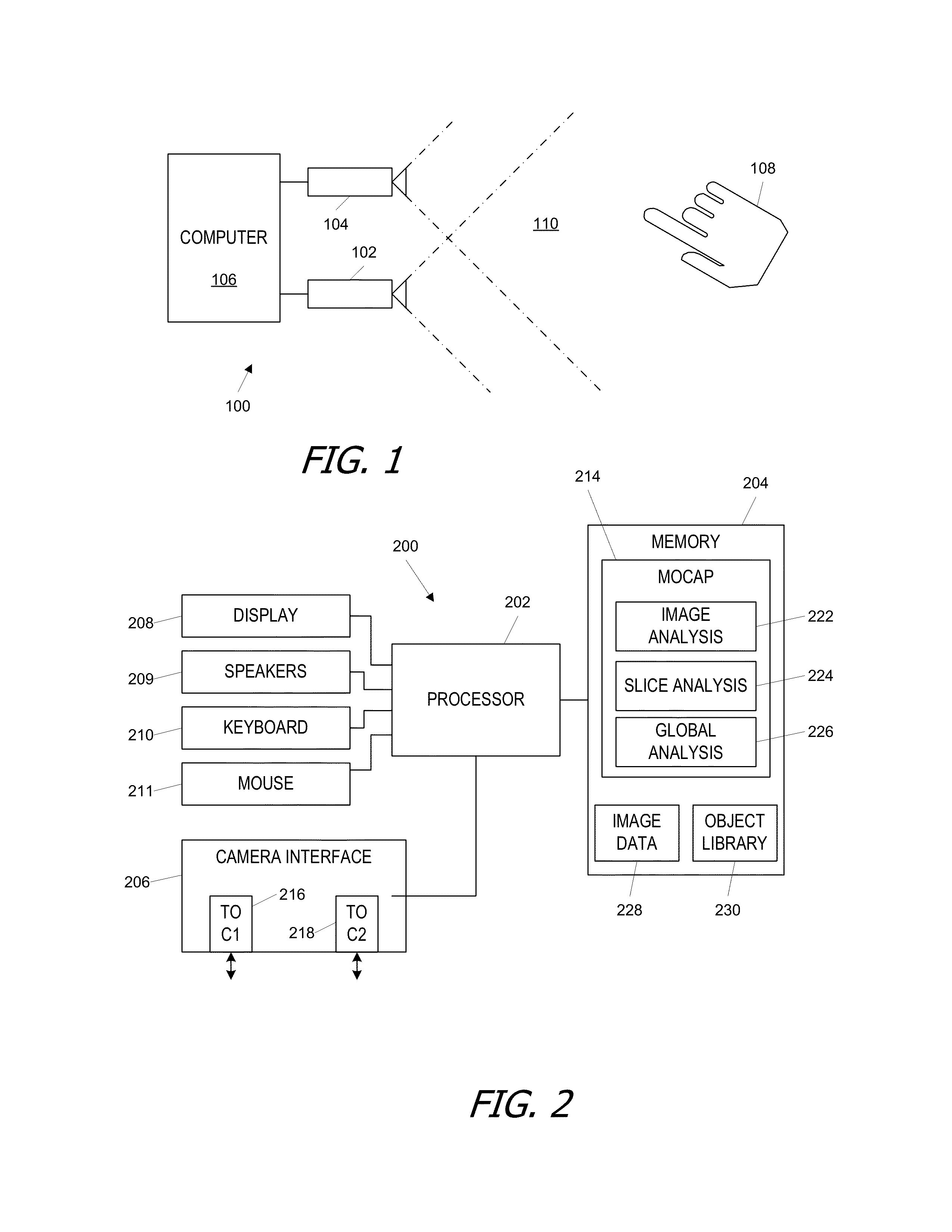
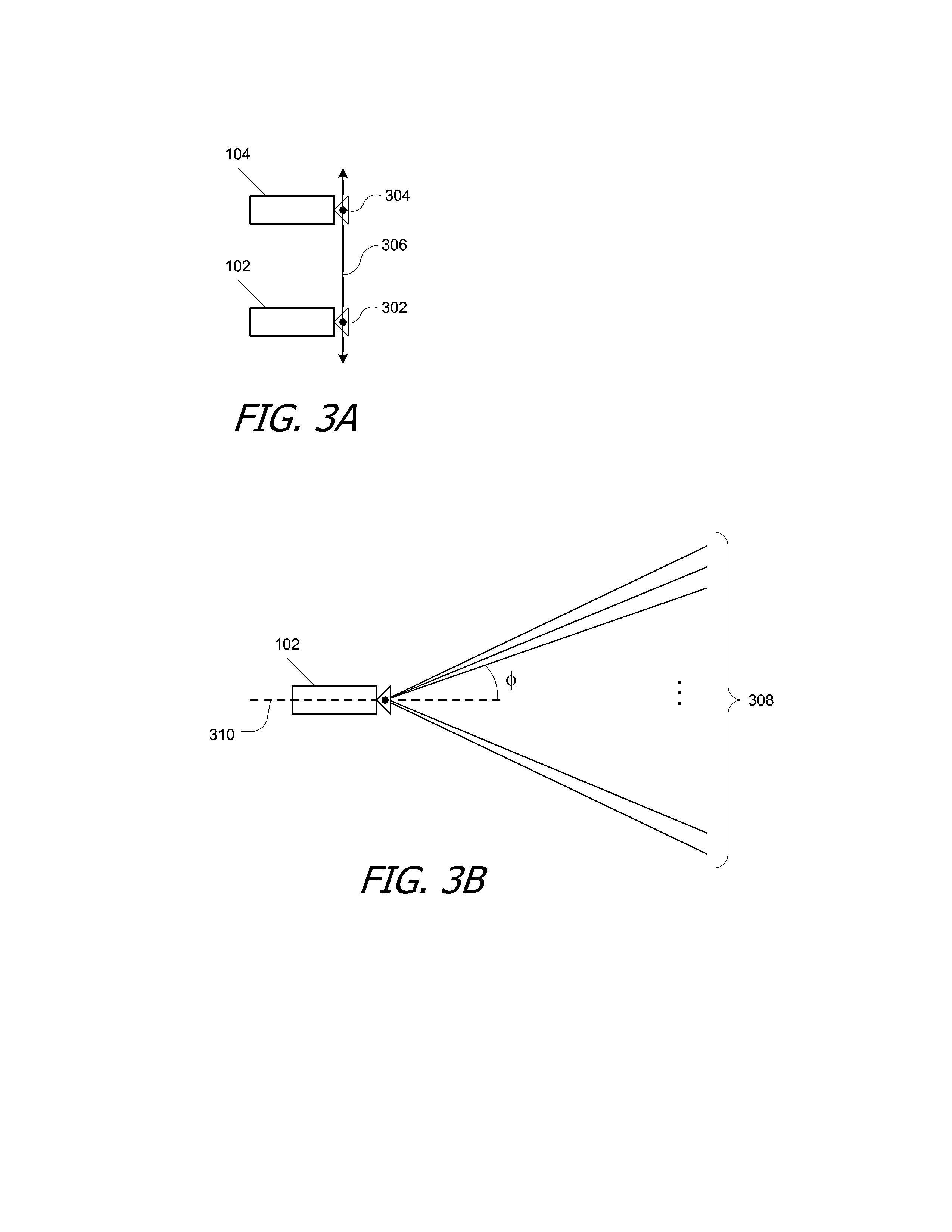
Motion capture using cross-sections of an object
InactiveUS20130182079A1Image enhancementDetails involving processing stepsEllipseThree-dimensional space
An object's position and / or motion in three-dimensional space can be captured. For example, a silhouette of an object as seen from a vantage point can be used to define tangent lines to the object in various planes (“slices”). From the tangent lines, the cross section of the object is approximated using a simple closed curve (e.g., an ellipse). Alternatively, locations of points on an object's surface in a particular slice can also be determined directly, and the object's cross-section in the slice can be approximated by fitting a simple closed curve to the points. Positions and cross sections determined for different slices can be correlated to construct a 3D model of the object, including its position and shape. A succession of images can be analyzed to capture motion of the object.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP TWO LTD
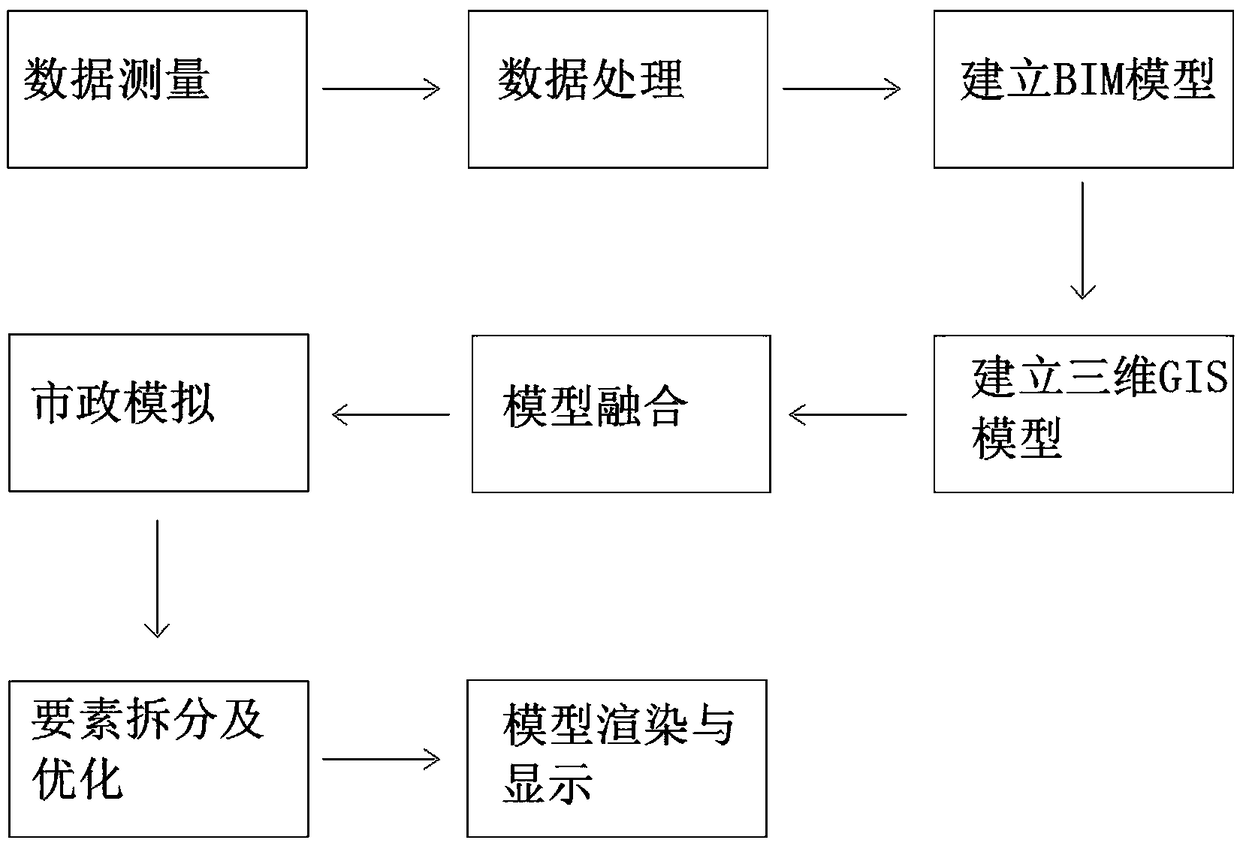
A 3D city modeling method based on BIM and GIS
ActiveCN109410327AImprove elevation accuracyLow costDetails involving processing stepsGeographical information databasesInterior spacePoint cloud
The invention discloses a three-dimensional city modeling method based on BIM and GIS, comprising the following steps: data measurement, data processing, establishing BIM model, establishing three-dimensional GIS model, model fusion, municipal simulation, element separation and optimization, model rendering and display; through BIM, the precise height of the building can be easily obtained, appearance size and interior space information, thus through combining BIM and GIS, buildings are modeled first, and then the architectural spatial information is shared with the surrounding geographic environment, and applied to urban 3D GIS analysis, so that the cost of building spatial information can be reduced. At that same time, after the data is collected, point cloud and aerial photograph data are calculated and simulated by data classification comparison, so that the elevation information of the ground object is perfect, the elevation precision of the building model is high, and the roof ismore fine. The invention does not need a large amount of manual interaction modeling, and the data are collected by the unmanned aerial vehicle and the unmanned vehicle, and the efficiency is high, the production period is short, and the timeliness is strong.
Owner:GUANGDONG BOZHILIN ROBOT CO LTD
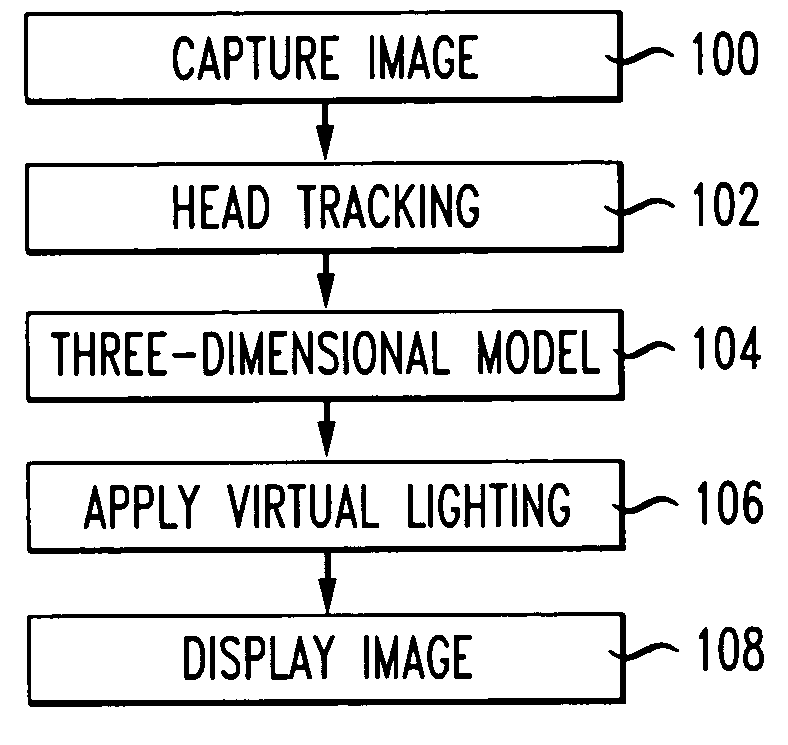
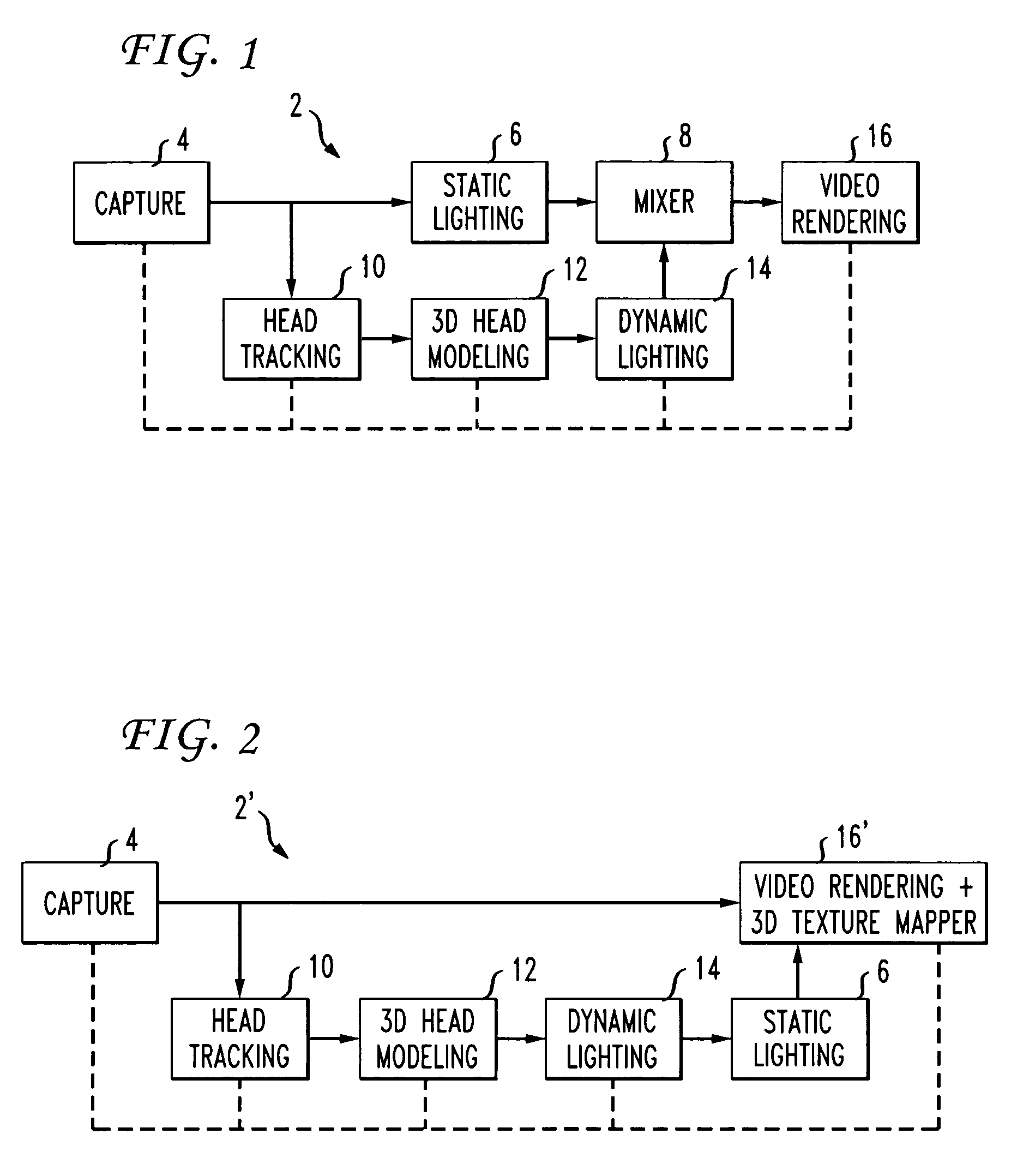
Digitally-generated lighting for video conferencing applications
ActiveUS6980697B1Improve the environmentAverage office or home environment) are poor can be greatly improvedImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsTelecommunications networkComputer graphics (images)
A method of improving the lighting conditions of a real scene or video sequence. Digitally generated light is added to a scene for video conferencing over telecommunication networks. A virtual illumination equation takes into account light attenuation, lambertian and specular reflection. An image of an object is captured, a virtual light source illuminates the object within the image. In addition, the object can be the head of the user. The position of the head of the user is dynamically tracked so that an three-dimensional model is generated which is representative of the head of the user. Synthetic light is applied to a position on the model to form an illuminated model.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
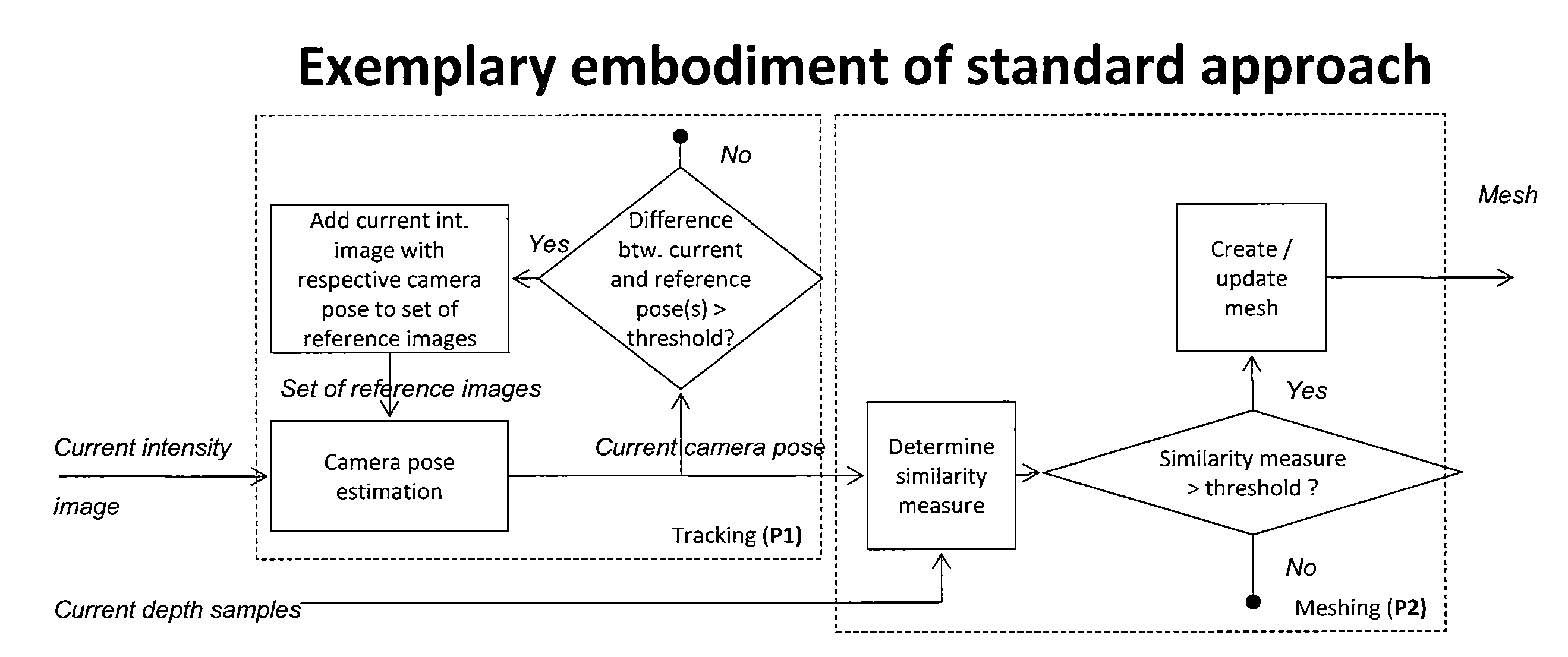
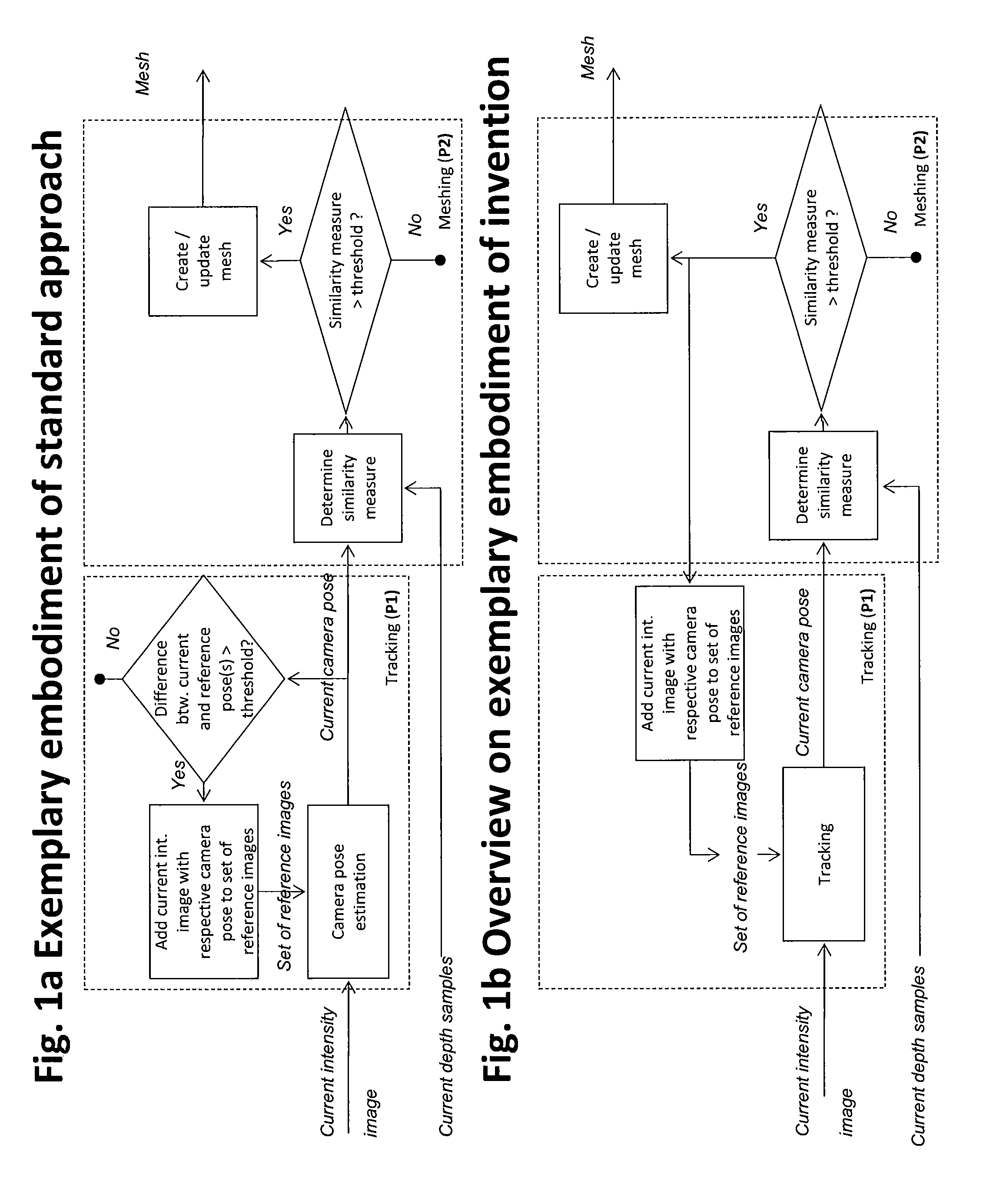
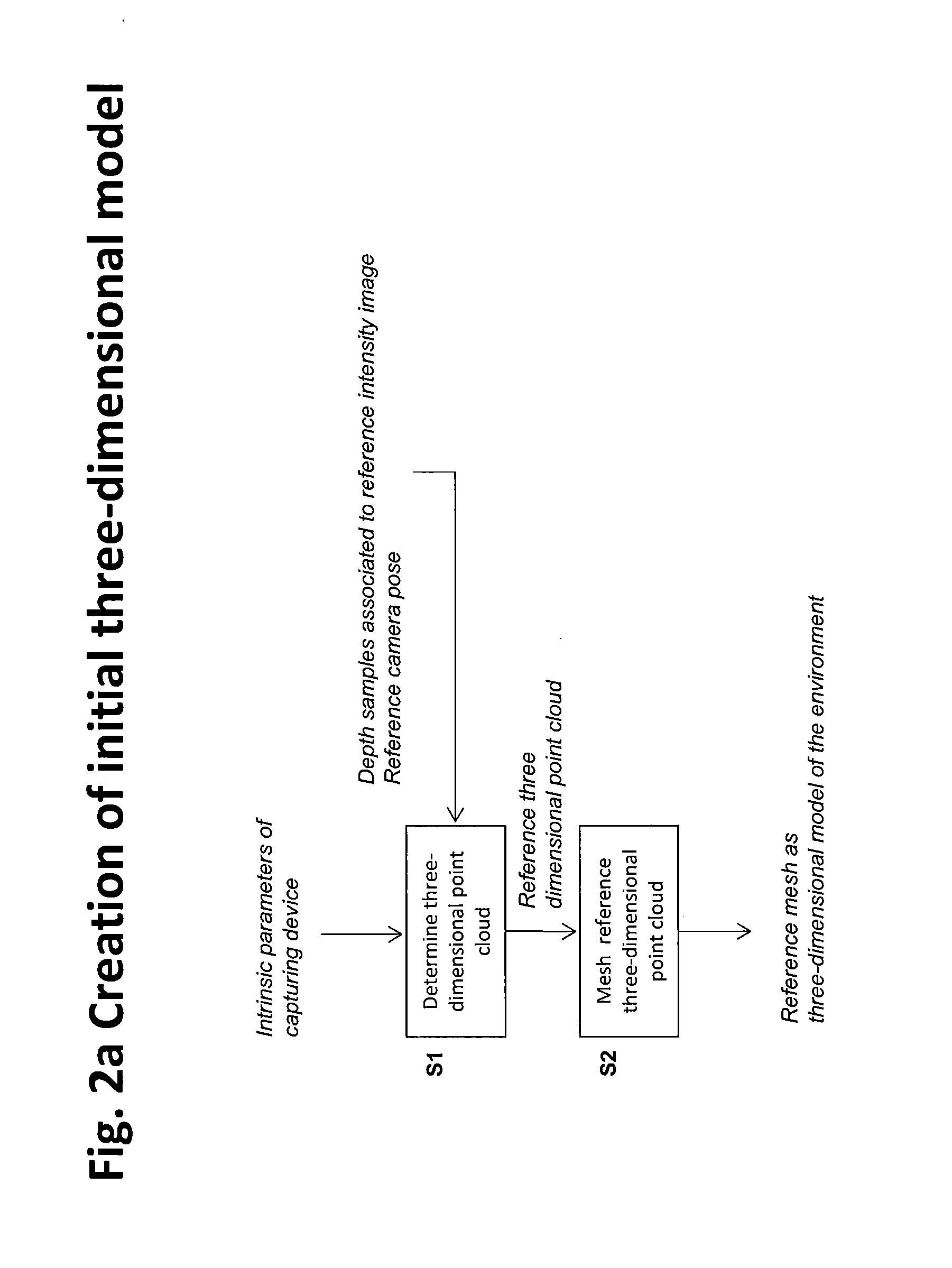
Method for estimating a camera motion and for determining a three-dimensional model of a real environment
ActiveUS20140293016A1Closed loopDetails involving processing stepsImage enhancementPostural orientationComputer science
A method for estimating a camera motion and for determining a three-dimensional model of an environment is provided that includes the steps of: providing intrinsic parameters of a camera; providing a set of reference two-dimensional imaged points captured by the camera at a first camera pose and reference depth samples; determining a three-dimensional model of the environment; providing a set of current two-dimensional imaged points captured by the camera at a second camera pose and current depth samples associated to the set of current two-dimensional imaged points and determining a current three-dimensional model; estimating a camera motion between the first camera pose and the second camera pose; determining a similarity measure between the three-dimensional model and the current three-dimensional model, and if it is determined that the similarity measure meets a first condition, updating the three-dimensional model of the environment and adding the set of current two-dimensional imaged points to the set of reference two-dimensional imaged points.
Owner:APPLE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com