Patents
Literature
110results about How to "Improve system accuracy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Speech recognition semantic classification training
ActiveUS20100023331A1Improve system accuracyDigital computer detailsDigital dataNatural language processingSpeech identification
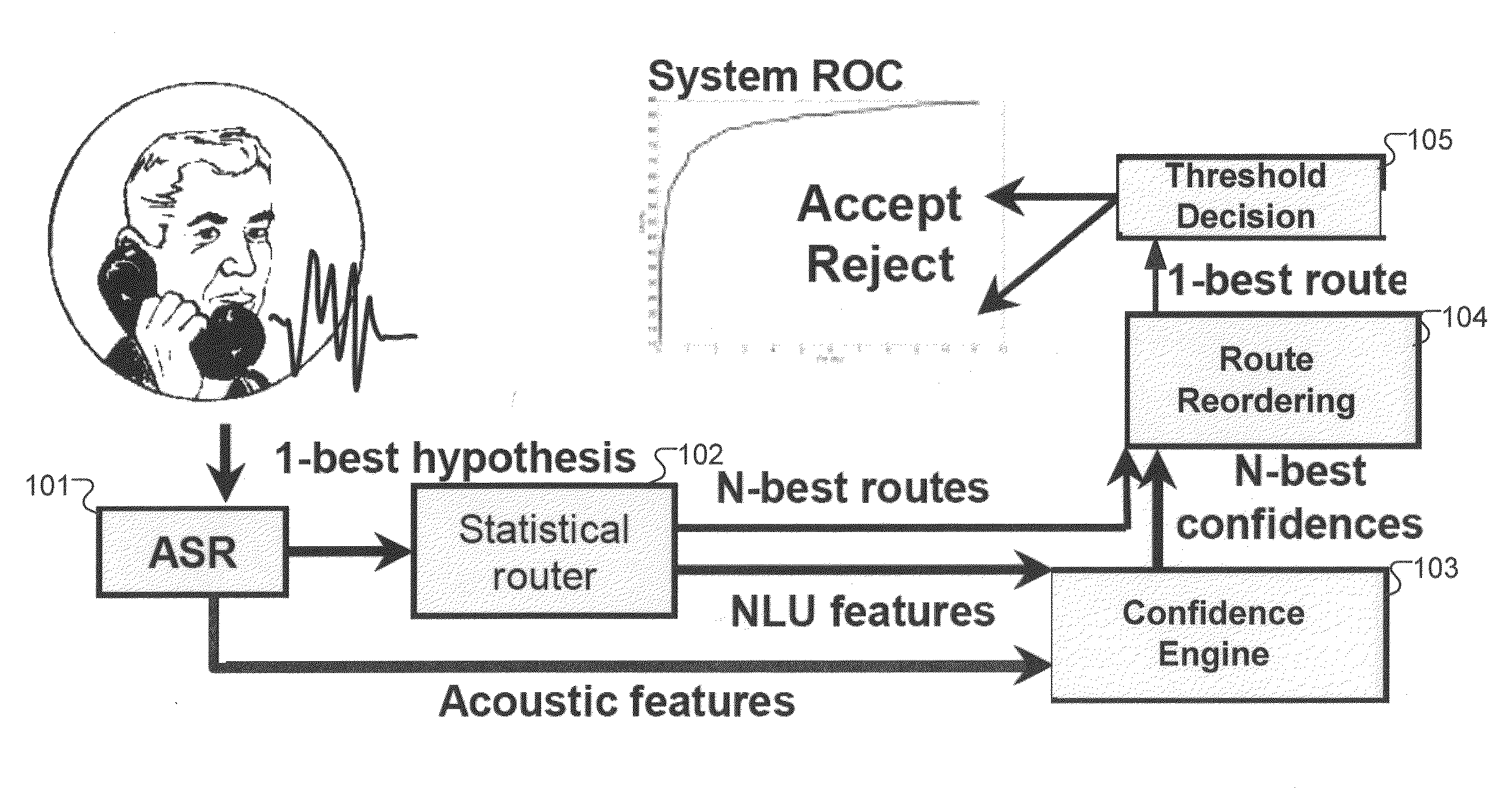
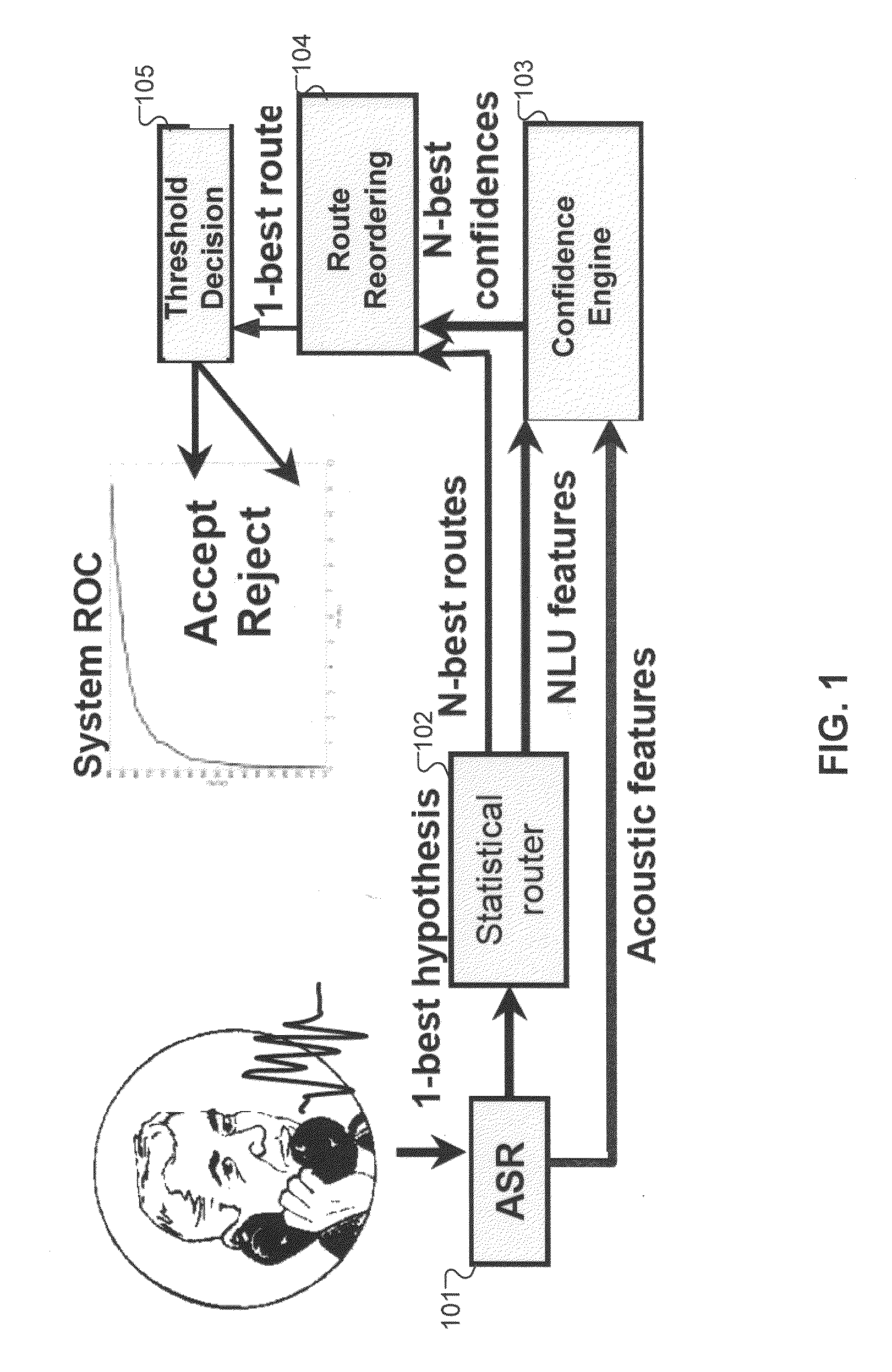
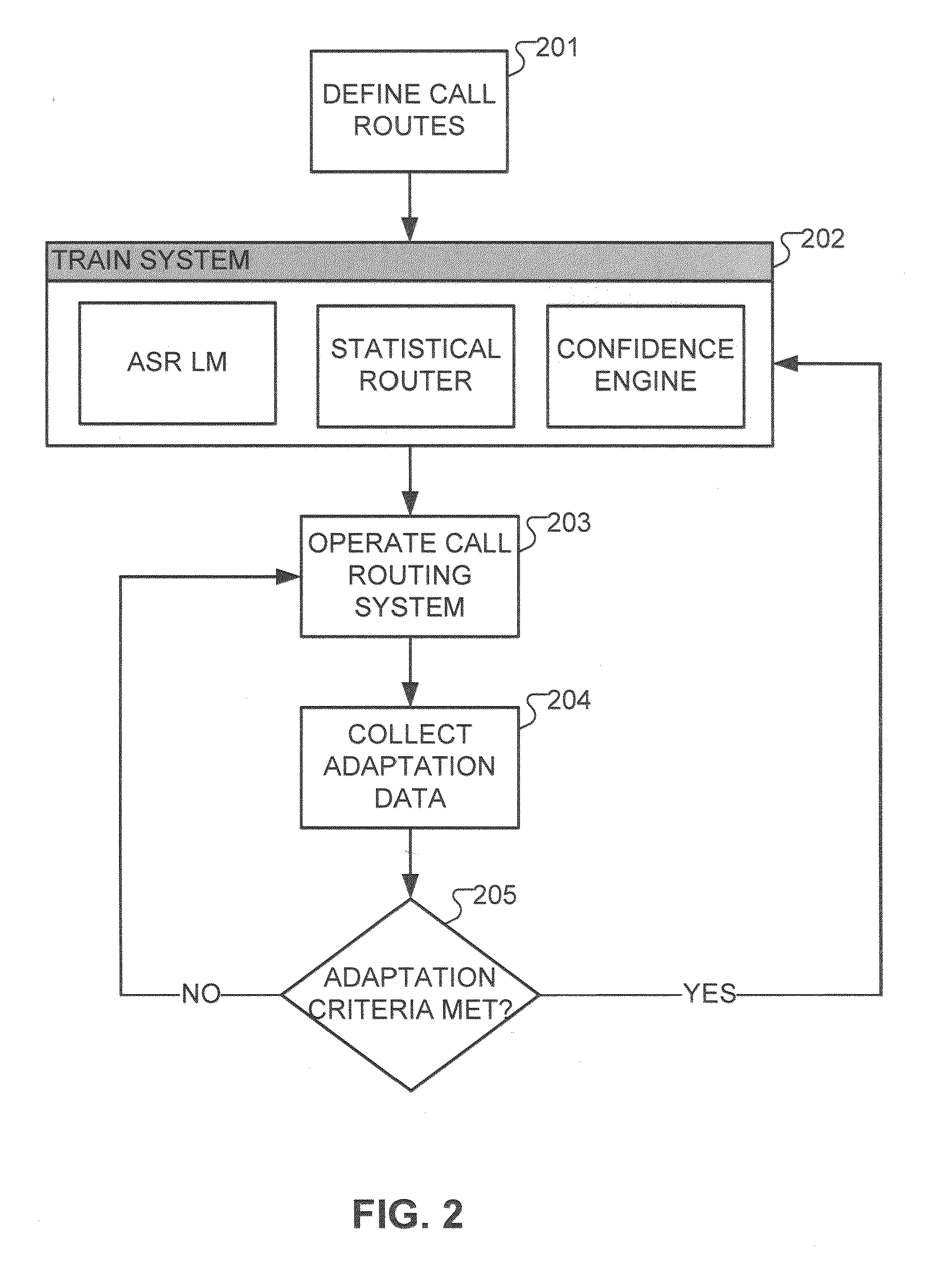
An automated method is described for developing an automated speech input semantic classification system such as a call routing system. A set of semantic classifications is defined for classification of input speech utterances, where each semantic classification represents a specific semantic classification of the speech input. The semantic classification system is trained from training data having little or no in-domain manually transcribed training data, and then operated to assign input speech utterances to the defined semantic classifications. Adaptation training data based on input speech utterances is collected with manually assigned semantic labels. When the adaptation training data satisfies a pre-determined adaptation criteria, the semantic classification system is automatically retrained based on the adaptation training data.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
System for determining the position of an object
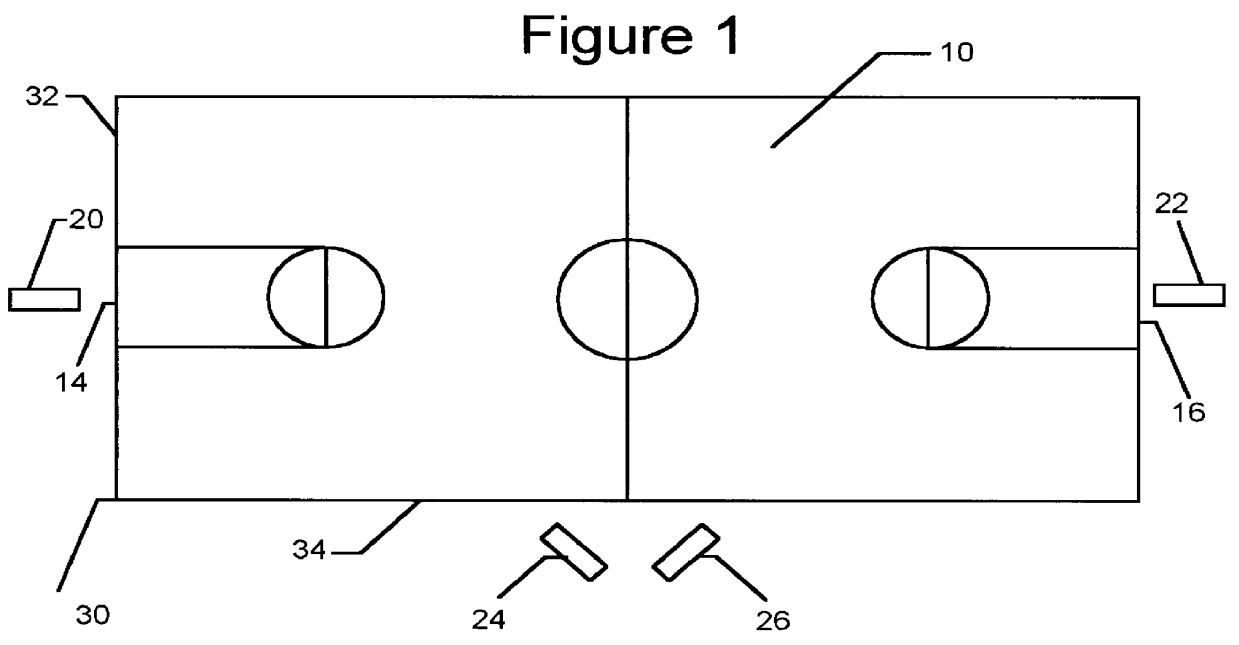
InactiveUS6133946AError minimizationImprove accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisGraphicsThe Internet
A system determines the vertical position of an object and report that vertical position in a format suitable for use on a television broadcast, a radio broadcast, the Internet or another medium. One example of a suitable use for the system includes determining the height that a basketball player jumped and adding a graphic to a television broadcast that displays the determined height. The system includes two or more cameras that capture a video image of the object being measured. The object's position in the video images is determined and is used to find the three dimensional location of the object. The three dimensional location includes a height coordinate. In some cases, the height coordinate is the desired vertical position. In other cases, the height or size of the object may be subtracted from the height coordinate to determined the vertical position.
Owner:SPORTSMEDIA TECH CORP
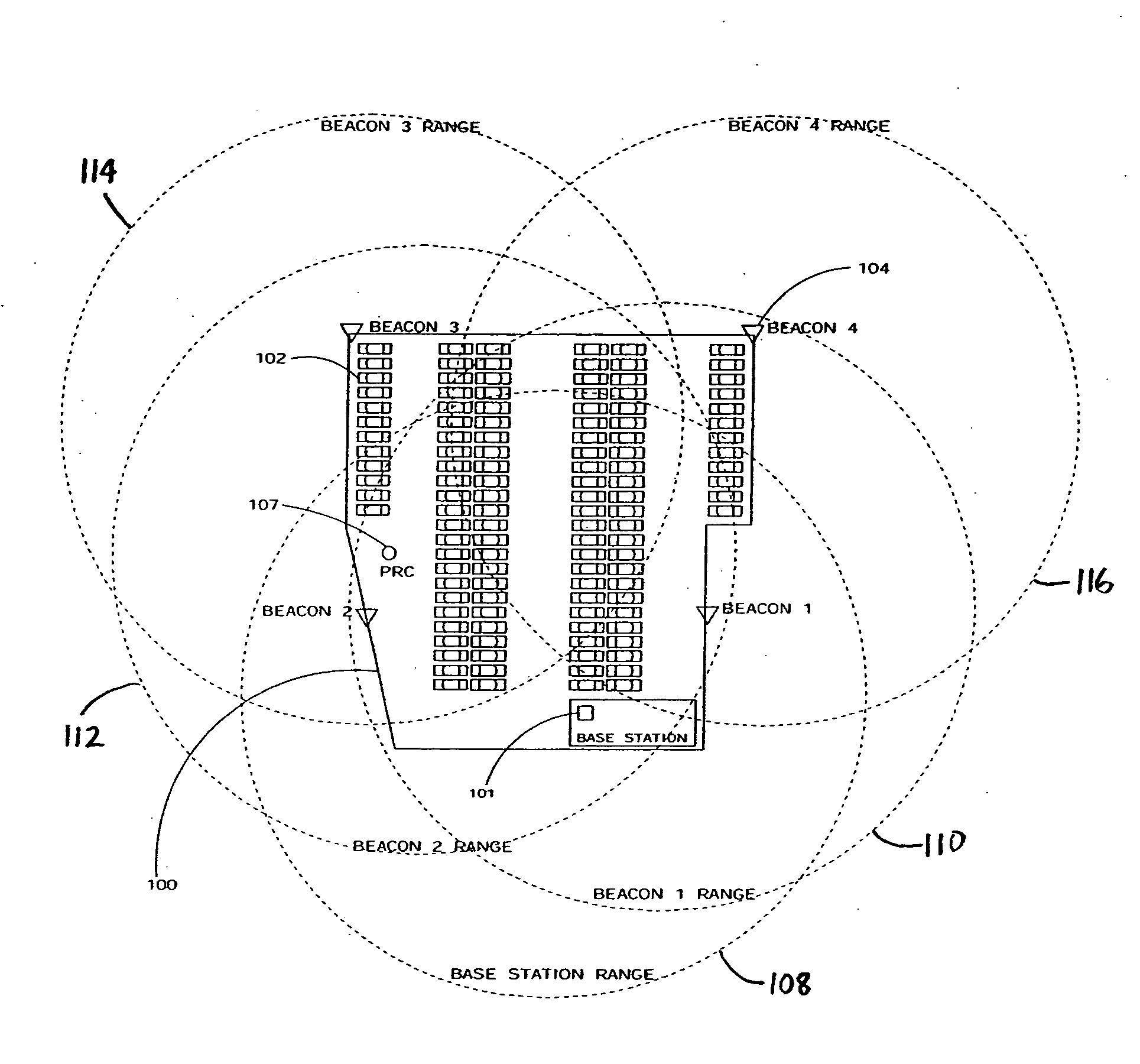
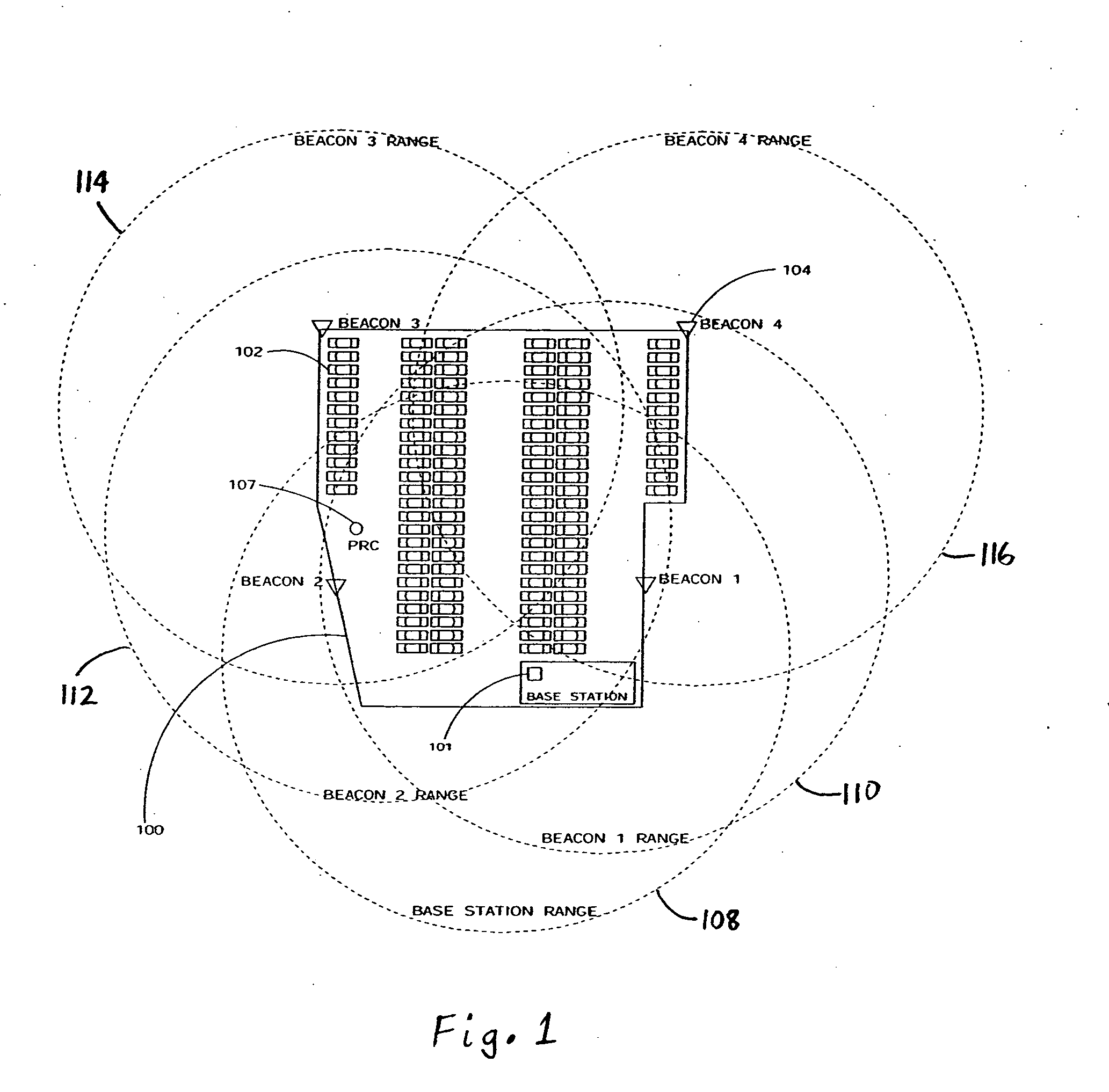
Method and system for location of objects within a specified geographic area
InactiveUS20070184852A1Reduce the impactEnhance location calculation accuracyRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationTransceiverDevices fixation
A method and system for determining the location of objects within a geographic area is disclosed. In one embodiment, the system includes a plurality of portable transceiver devices each coupled to a respective object located within the geographic area; a plurality of stationary transceiver devices fixed at predetermined locations within the geographic area, wherein the plurality of stationary transceiver devices are each configured to determine received signal strength (RSSI) values of signals transmitted by the plurality of portable transceiver devices; and a base station, comprising a base station transceiver device and a computer coupled to the base station transceiver device, wherein the base station is configured to receive RSSI values from at least one of the plurality of stationary transceiver devices and calculate a location of at least one portable transceiver device based on the received RSSI values.
Owner:LOTTRAK
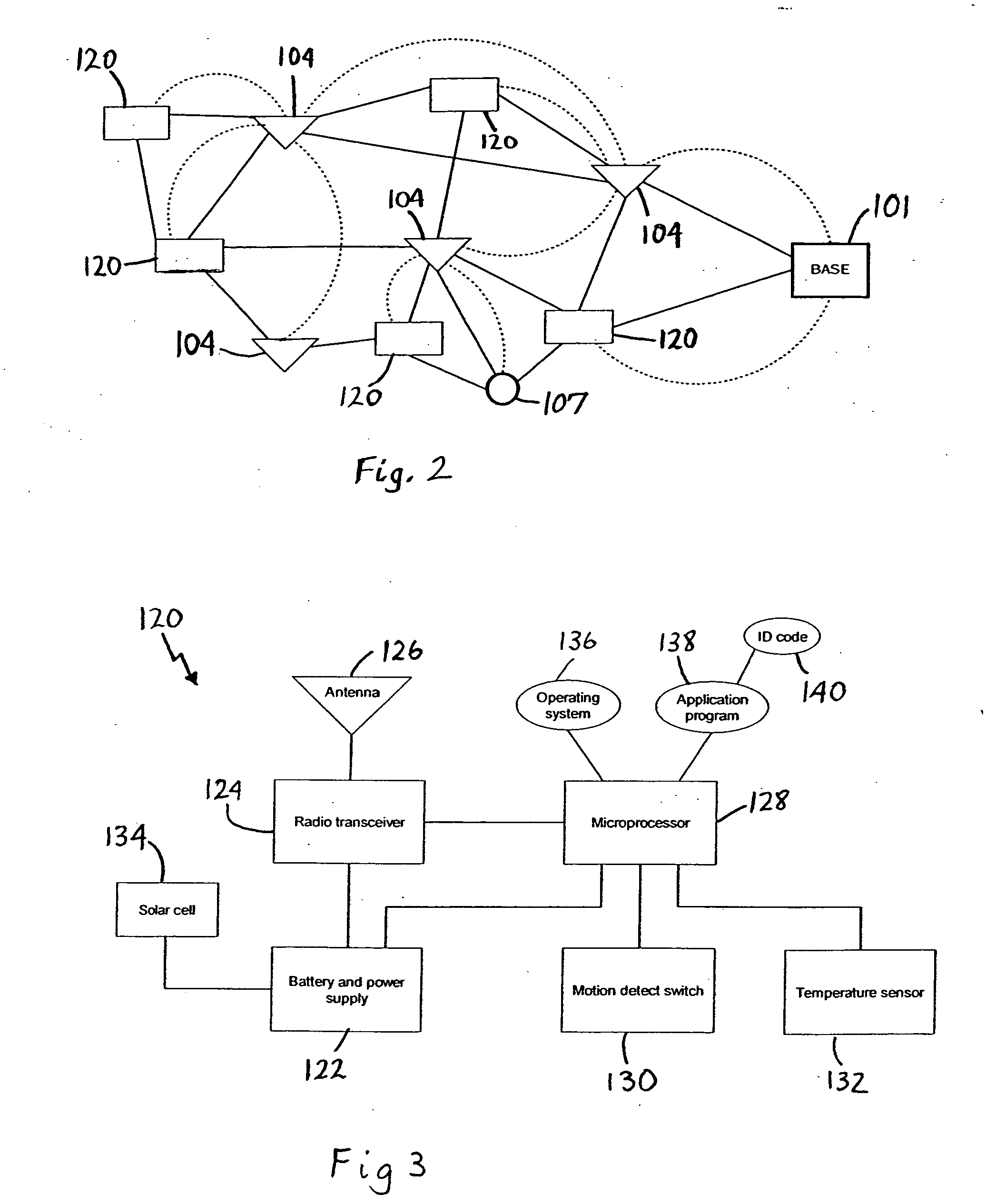
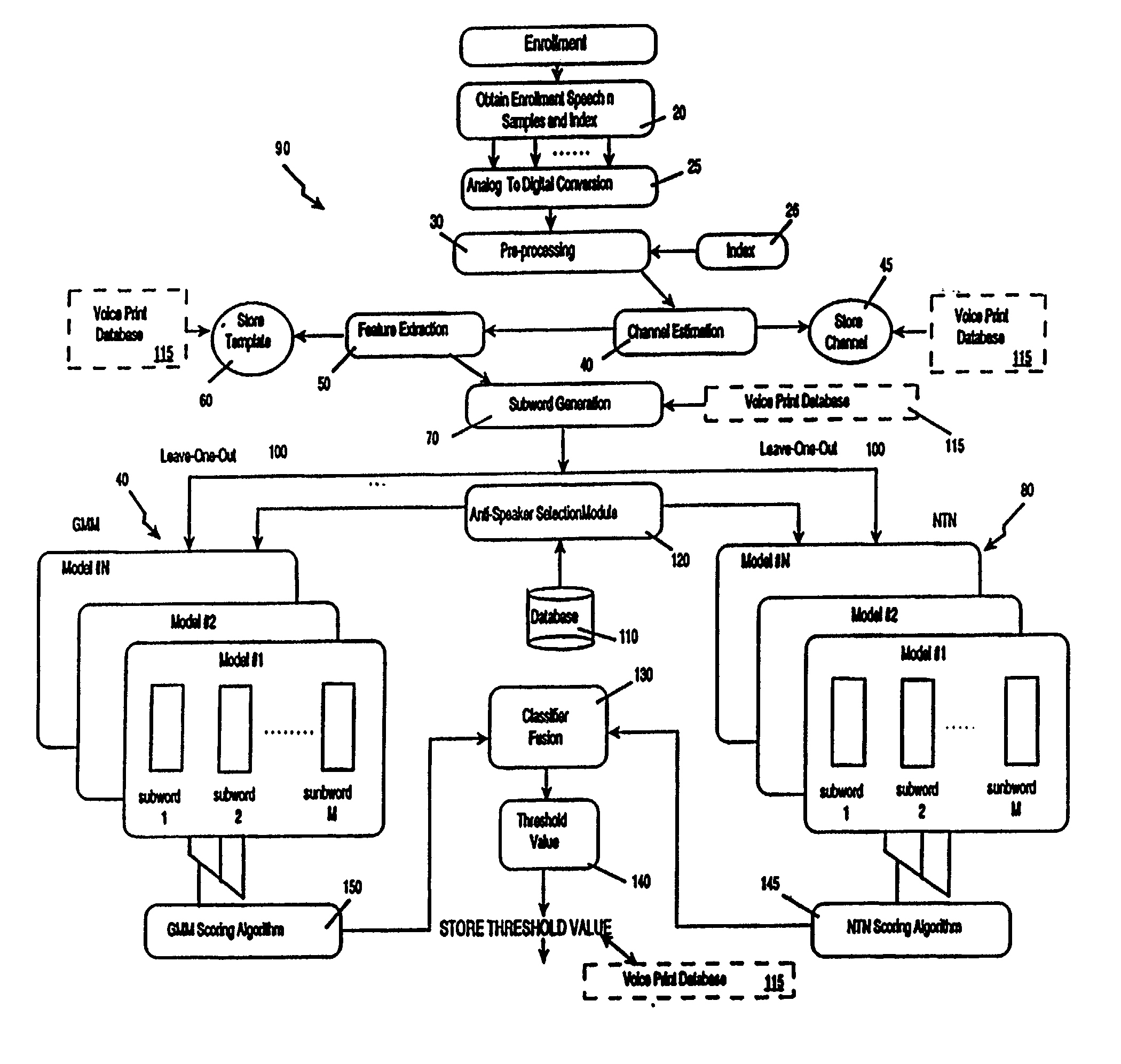
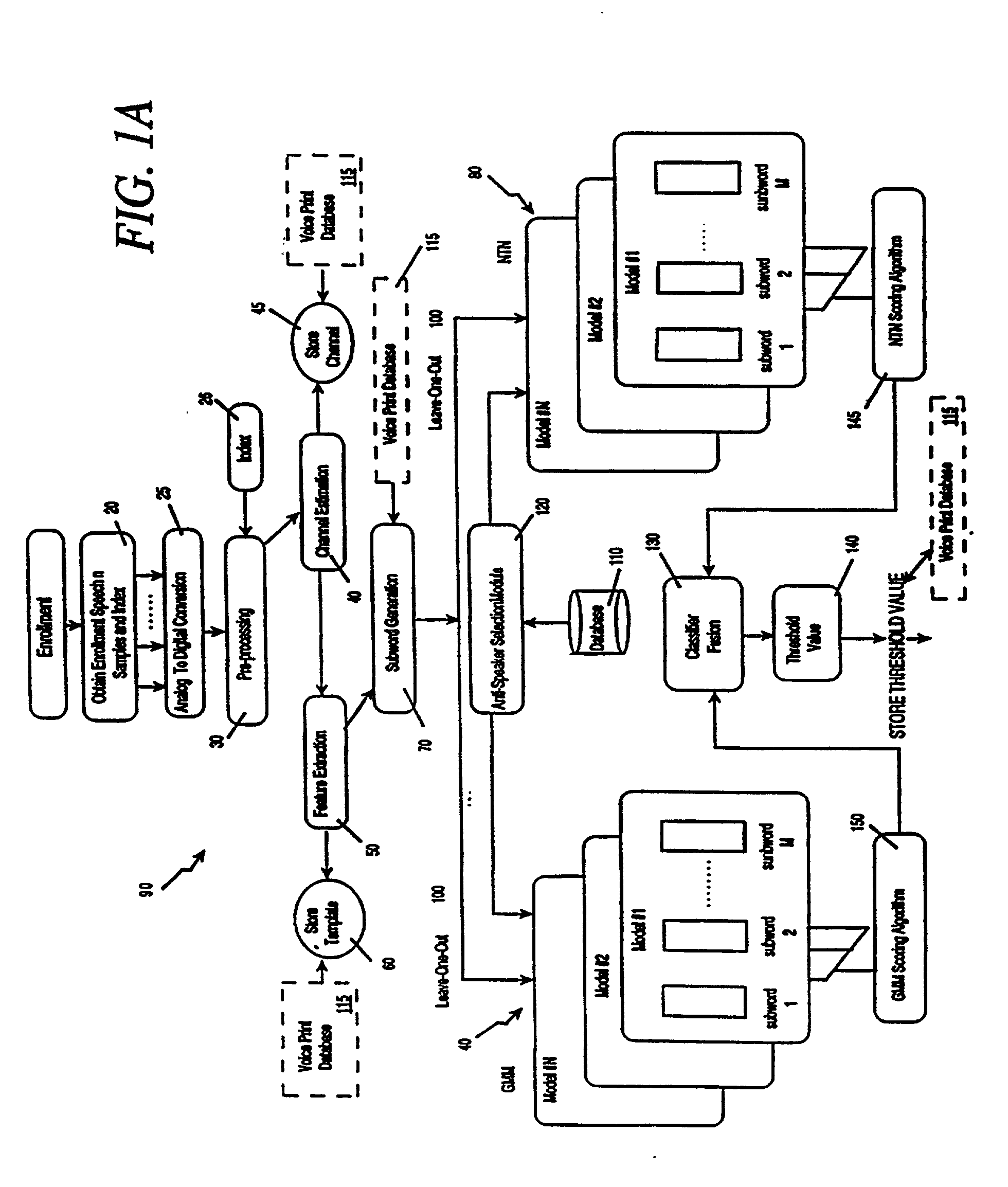
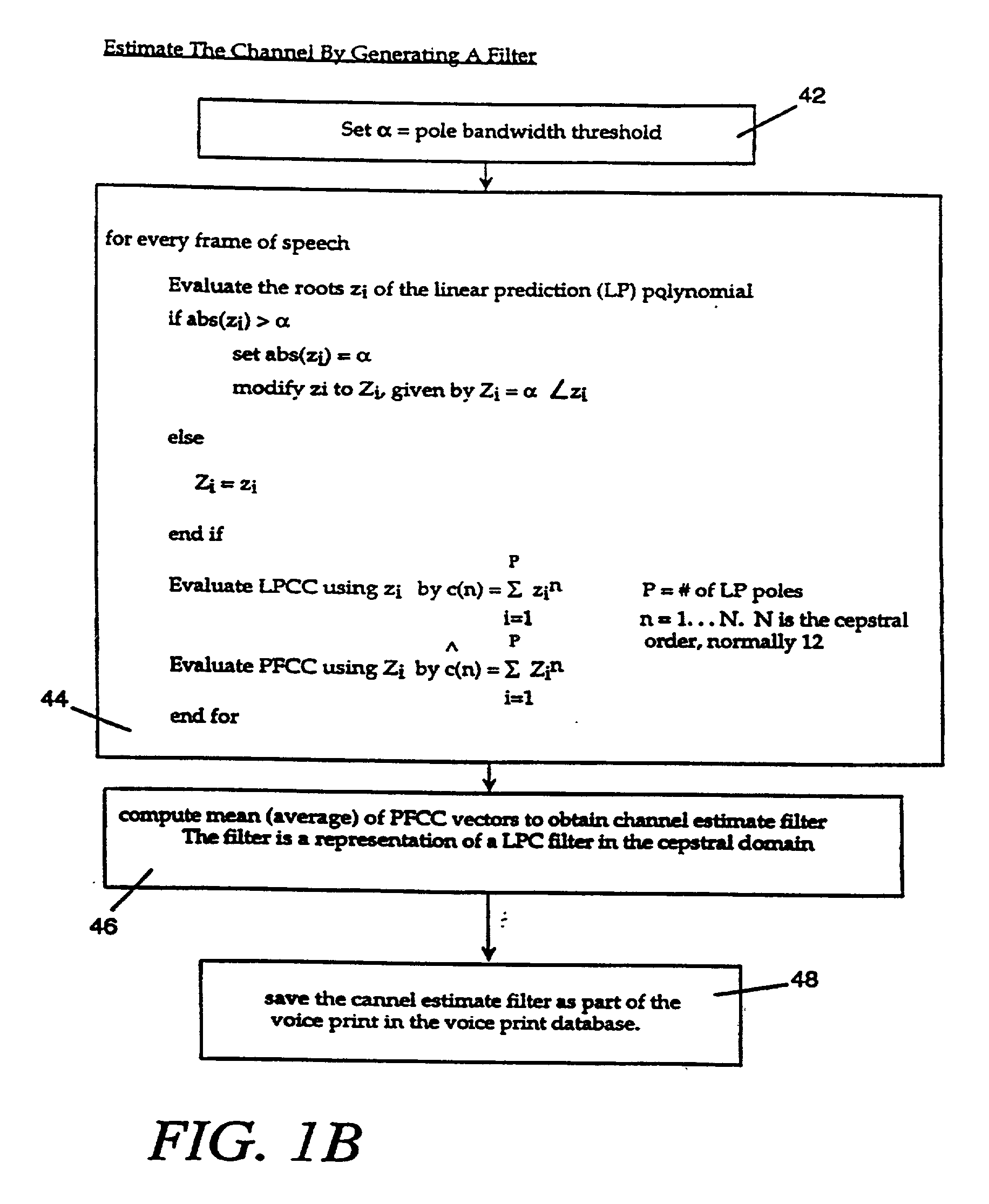
Voice print system and method
InactiveUS20030009333A1Increase in sizeImprove generalization abilitySpeech recognitionSpeech segmentationSpeaker verification
The voice print system of the present invention is a subword-based, text-dependent automatic speaker verification system that embodies the capability of user-selectable passwords with no constraints on the choice of vocabulary words or the language. Automatic blind speech segmentation allows speech to be segmented into subword units without any linguistic knowledge of the password. Subword modeling is performed using a multiple classifiers. The system also takes advantage of such concepts as multiple classifier fusion and data resampling to successfully boost the performance. Key word / key phrase spotting is used to optimally locate the password phrase. Numerous adaptation techniques increase the flexibility of the base system, and include: channel adaptation, fusion adaptation, model adaptation and threshold adaptation.
Owner:SPEECHWORKS INT
System and method for mining surprising temporal patterns
InactiveUS6189005B1Improve system accuracyAccurate representationData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalMinimum description lengthMachine learning
A system and method for data mining is provided in which temporal patterns of itemsets in transactions having unexpected support values are identified. A surprising temporal pattern is an itemset whose support changes over time. The method may use a minimum description length formulation to discover these surprising temporal patterns.
Owner:IBM CORP
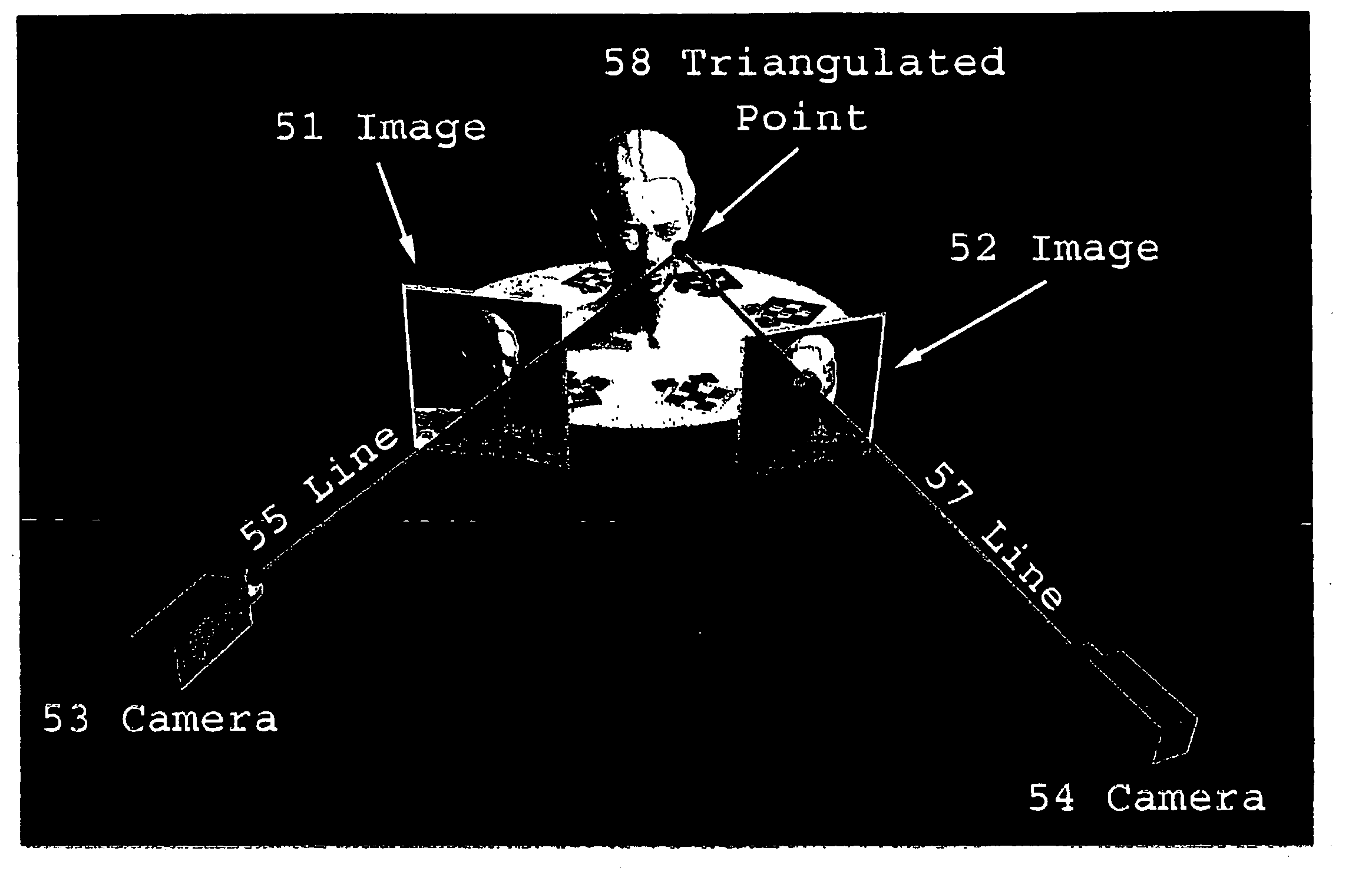
Method and apparatus for scanning three-dimensional objects
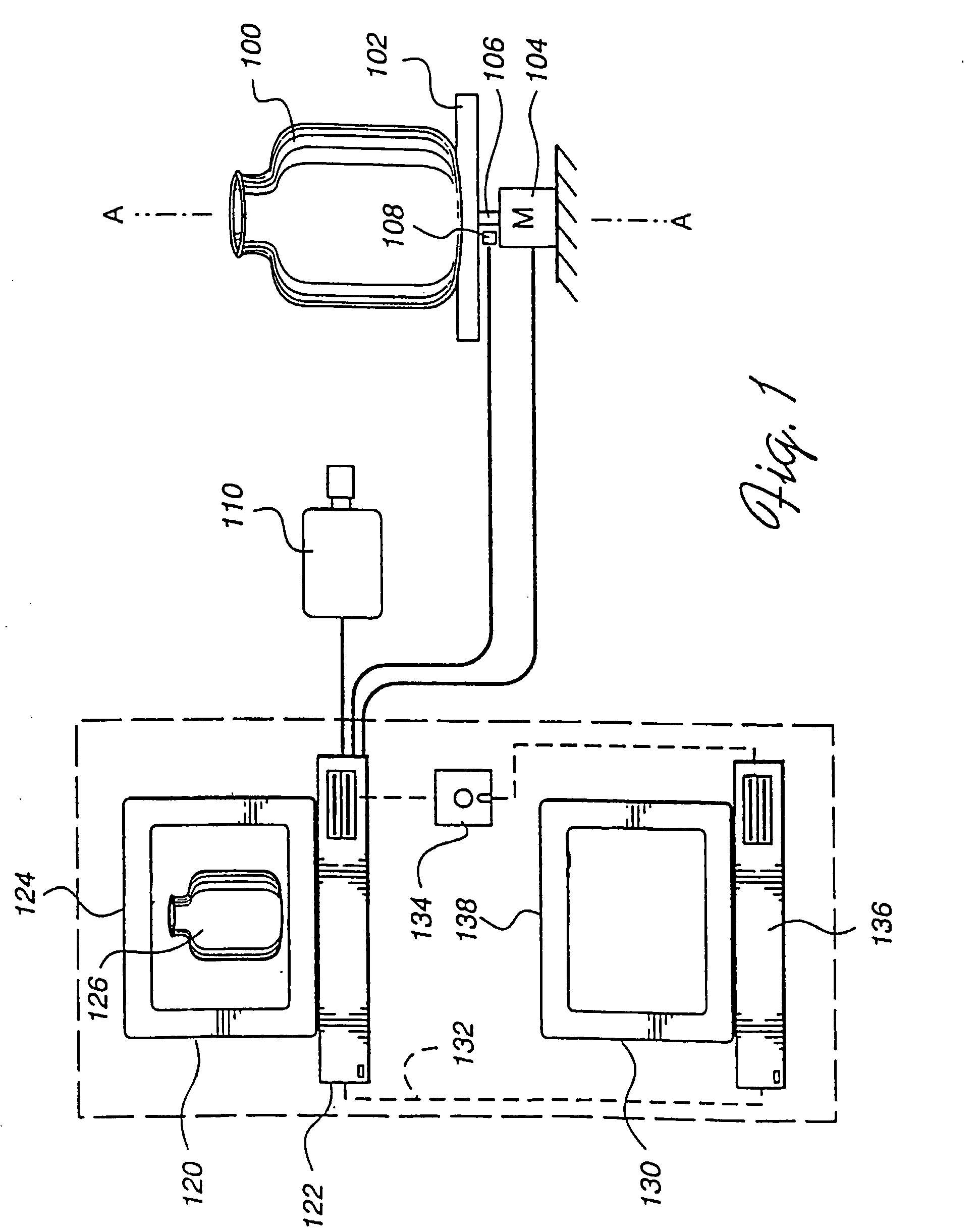
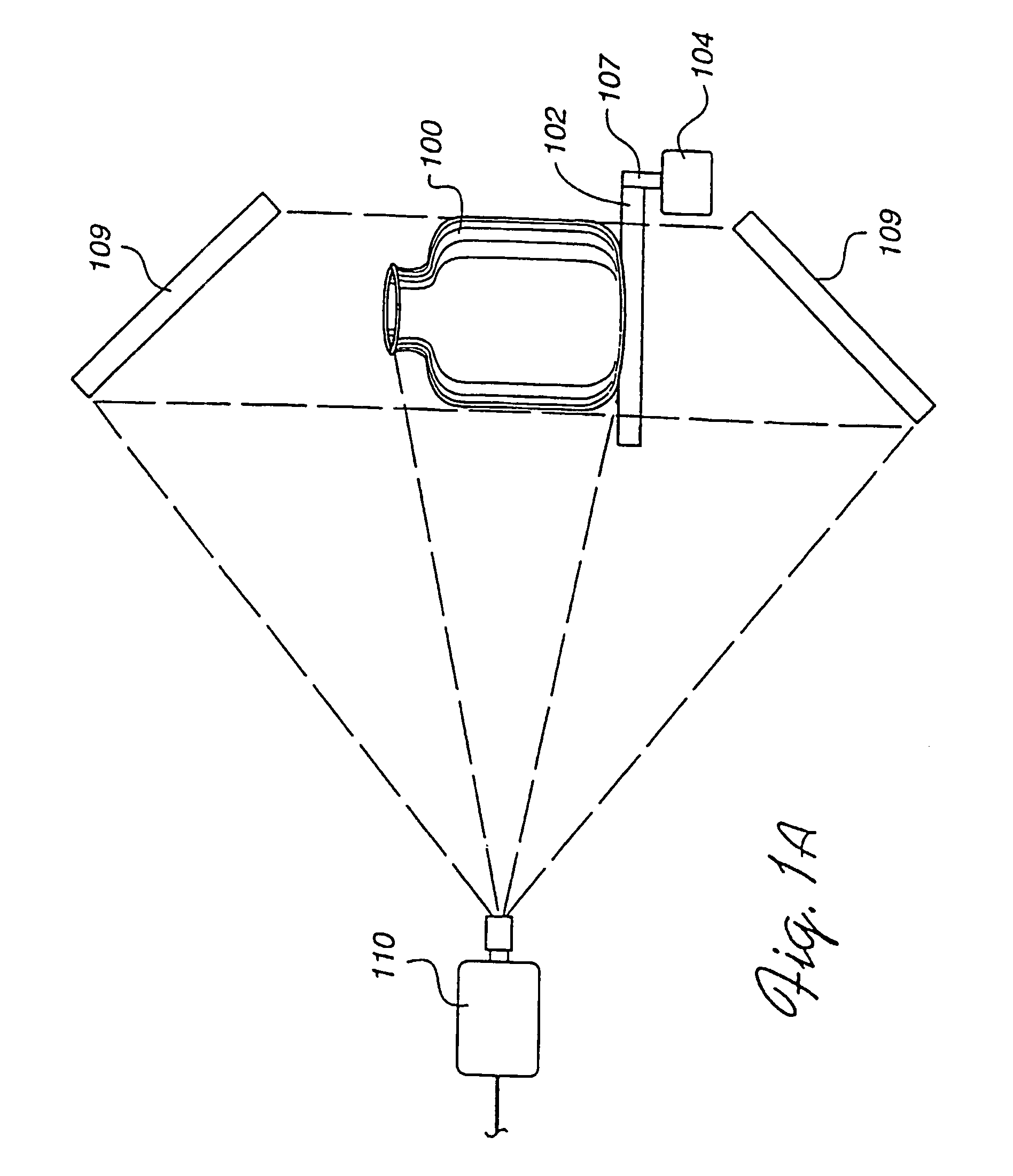
InactiveUS6858826B2Improve system accuracyReduce system costImage enhancementImage analysisVisibilityComputer vision
Apparatus and method for creating 3D imagery of an object using calibration means to transfer data to a reference frame and visibility analysis to determine and resolve occlusion.
Owner:WAVEWORX
Method and apparatus for determining a measure of similarity between natural language sentences
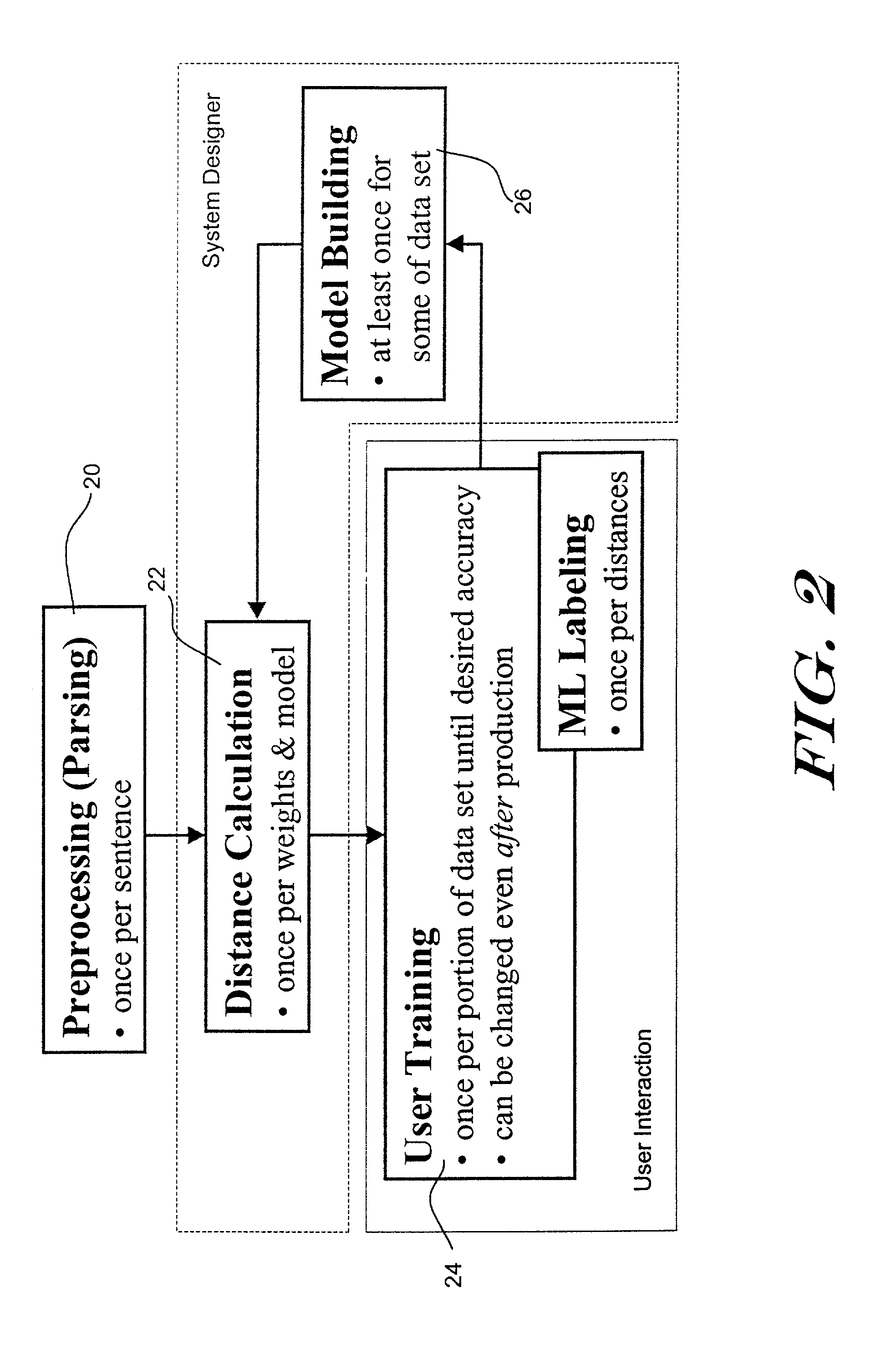
ActiveUS7295965B2Easy to customizeImprove system accuracyData processing applicationsSpeech recognitionSimilarity measureHuman language
Systems and methods for classifying natural language (NL) sentences using a combination of NL algorithms or techniques is disclosed. Each NL algorithm or technique may identify a different similarity trait between two or more sentences, and each may help compare the meaning of the sentences. By combining the various similarity factors, preferably by various weighting factors, a distance metric can be computed. The distance metric provides a measure of the overall similarity between sentences, and can be used to assign a sentences to an appropriate sentence category.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
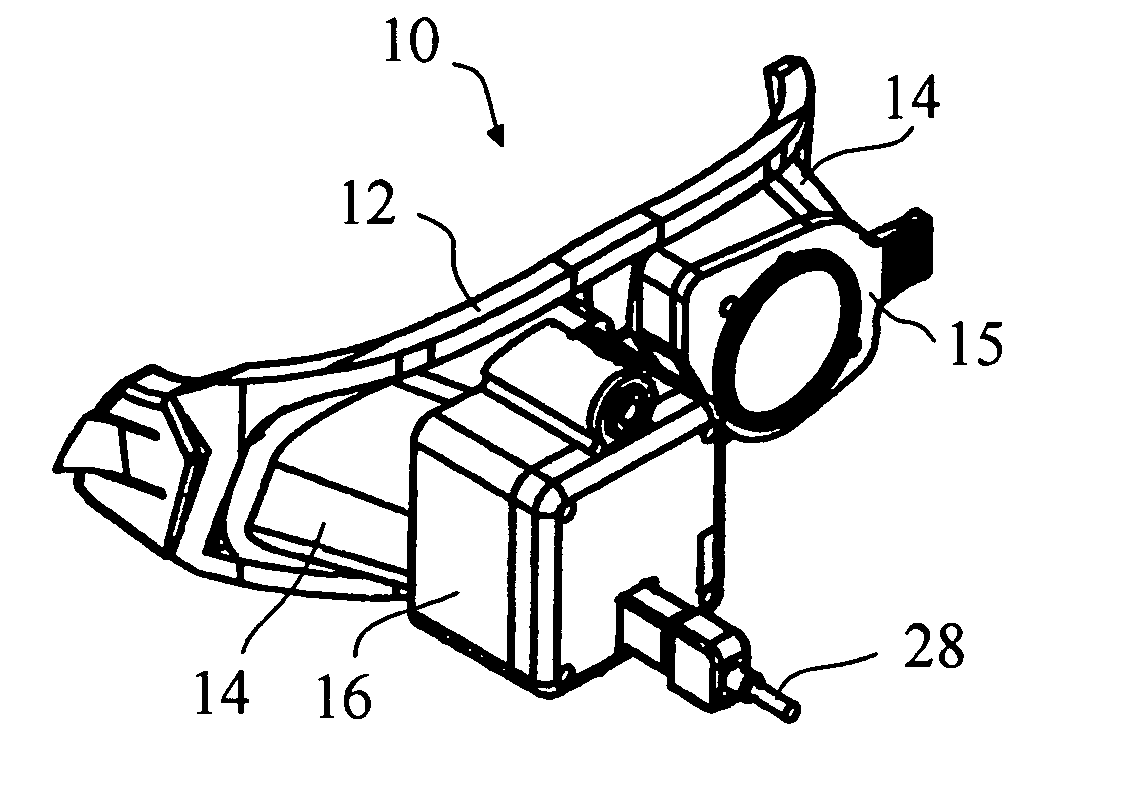
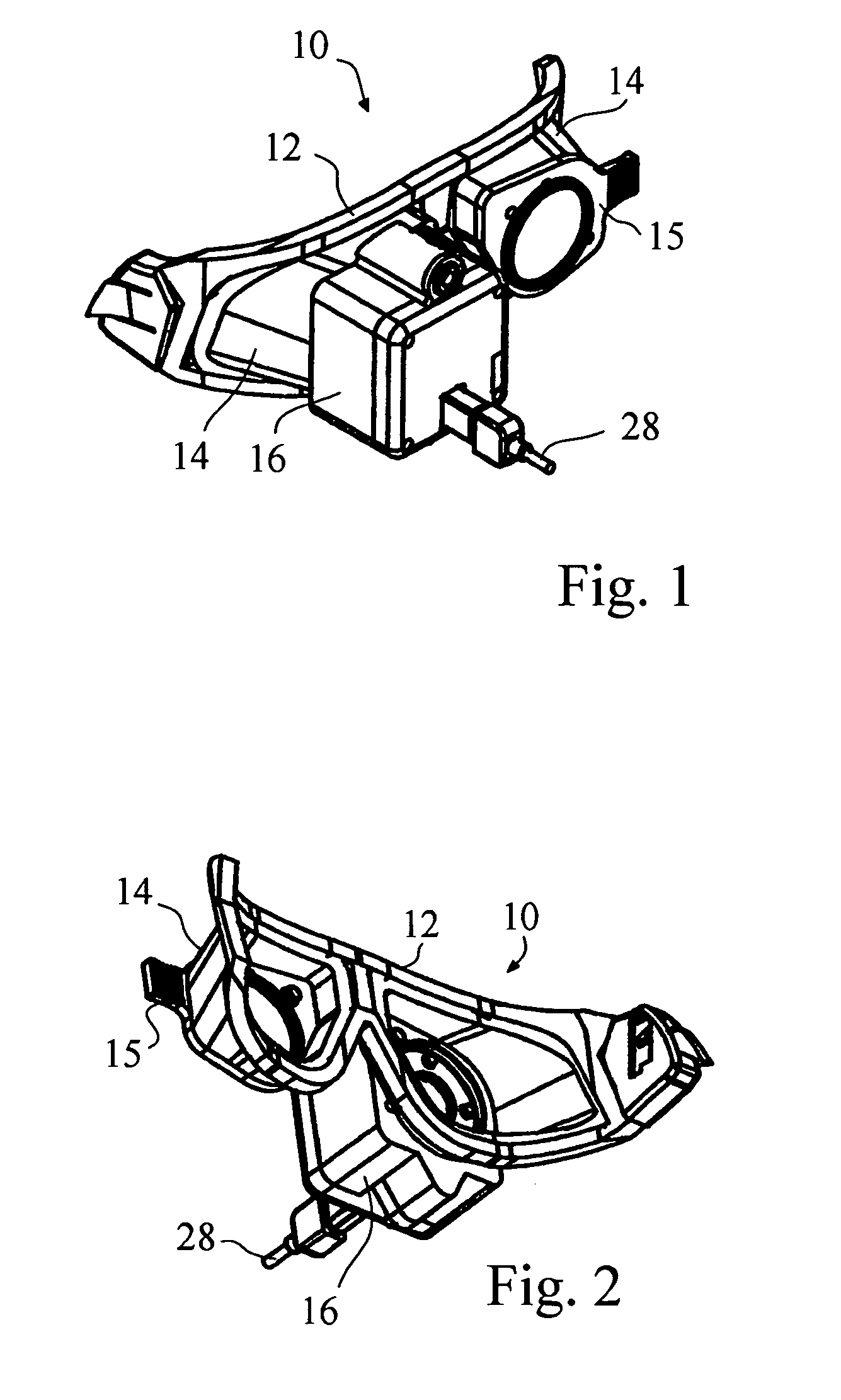
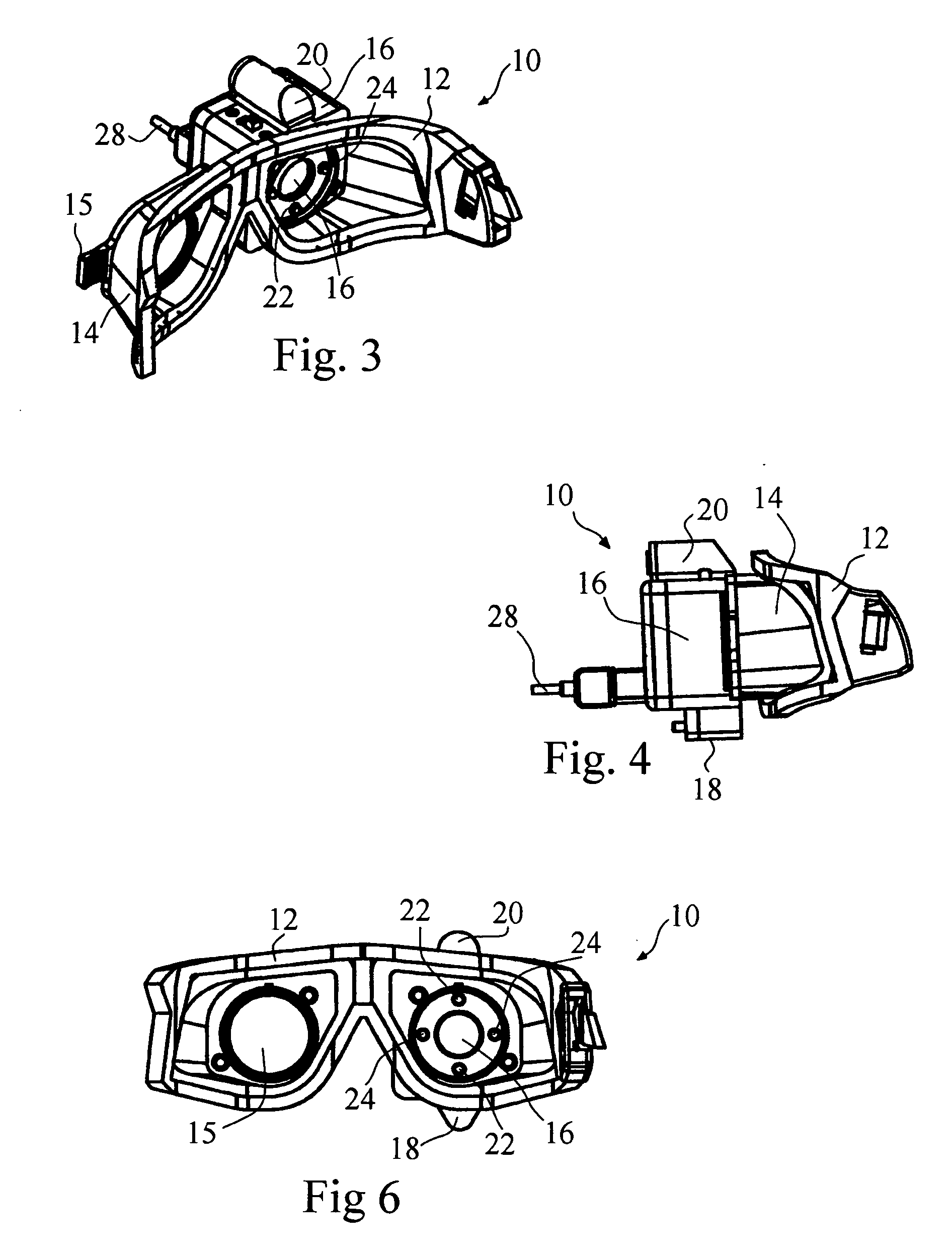
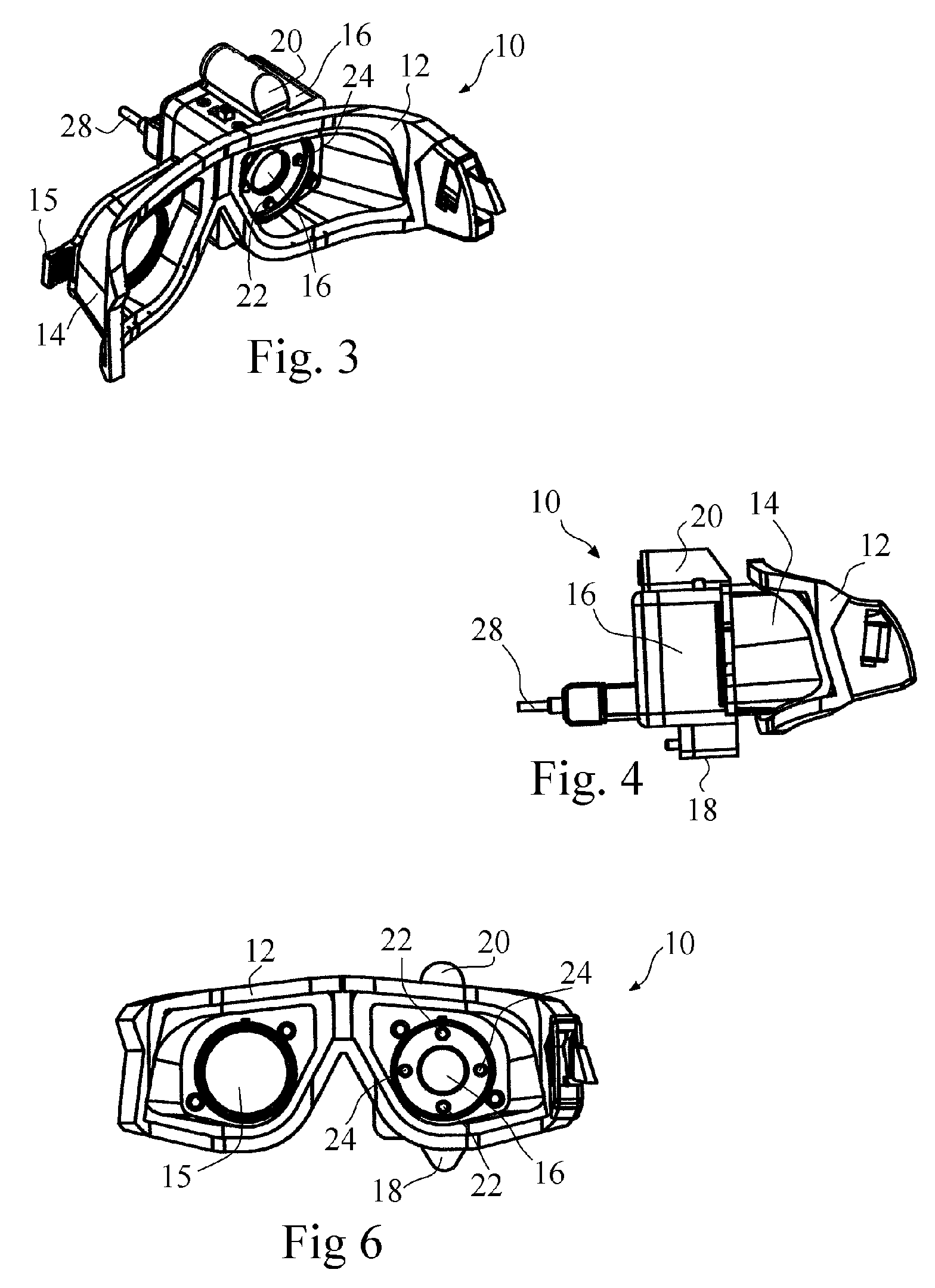
Portable video oculography system
A goggle based light-weight VOG system includes at least one digital camera connected to and powered by a laptop computer through a firewire connection. The digital camera may digitally center the pupil in both the X and Y directions. A calibration mechanism may be incorporated onto the goggle base. An EOG system may also be incorporated directly into the goggle. The VOG system may track and record 3-D movement of the eye, track pupil dilation, head position and goggle slippage. An animated eye display provides data in a more meaningful fashion. The VOG system is a modular design whereby the same goggle frame or base is used to build a variety of digital camera VOG systems.
Owner:128 GAMMA LIQUIDATING TRUST +1
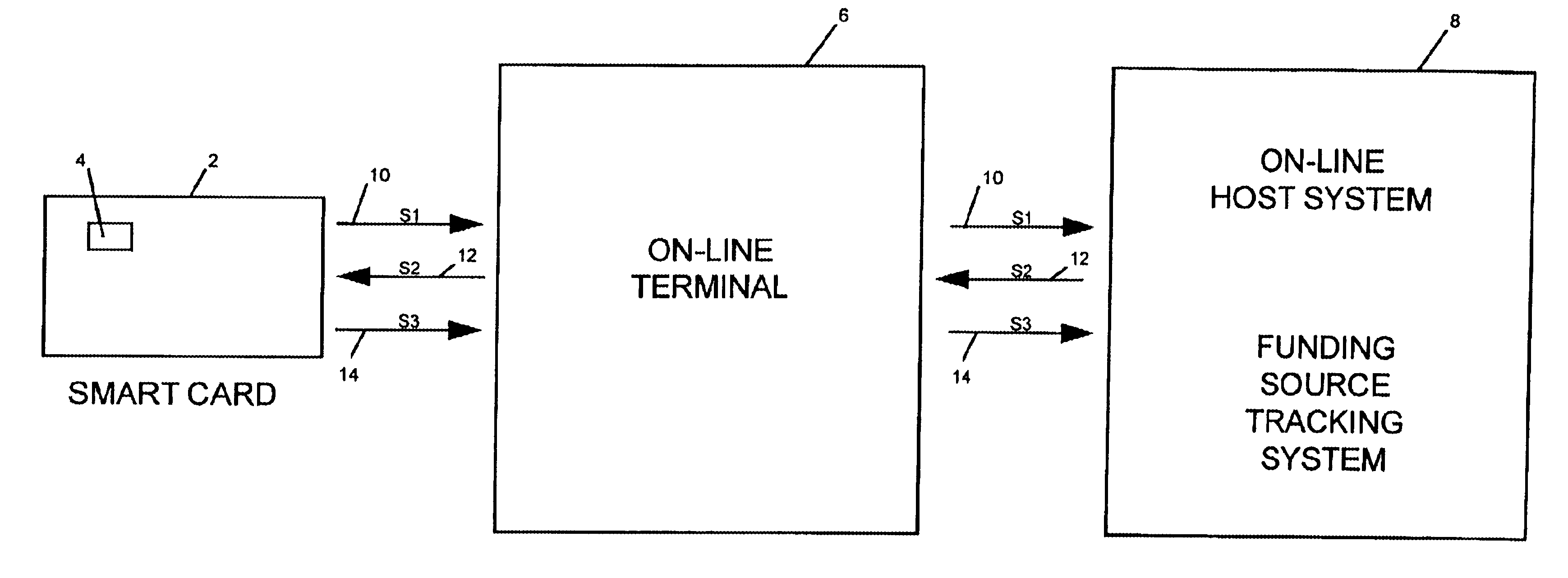
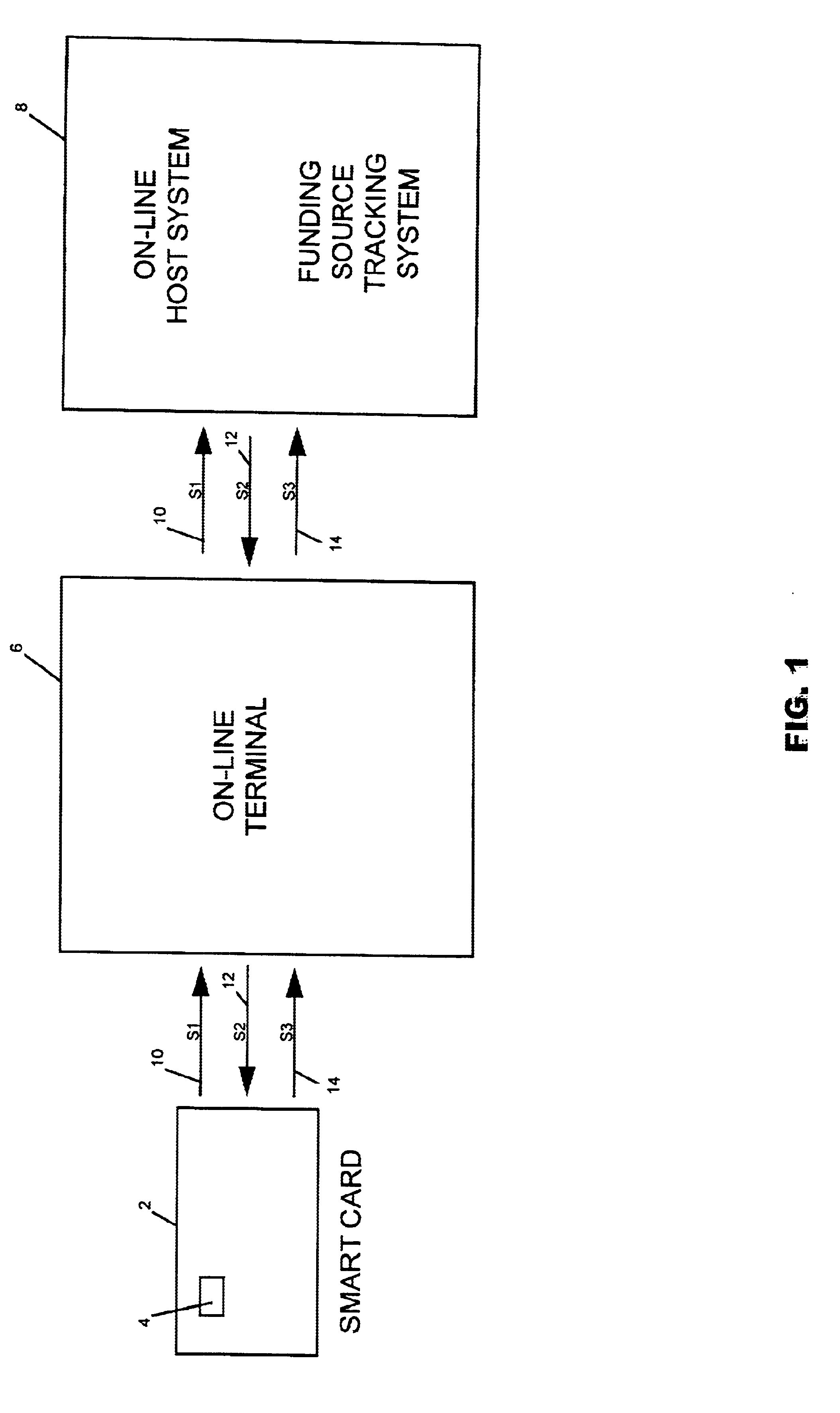
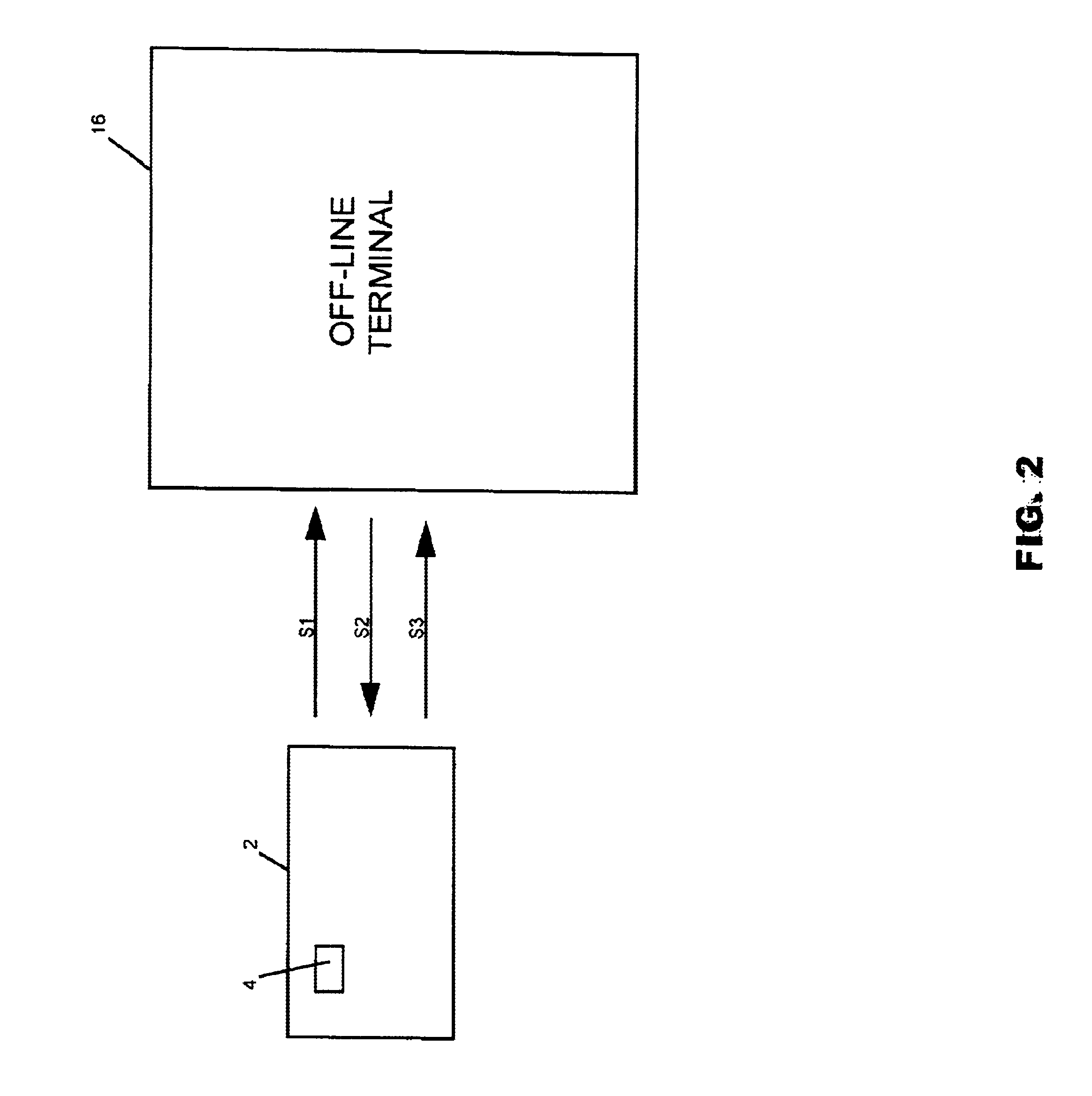
Method and system of tracking and providing an audit trail of smart card transactions
InactiveUS6913193B1Accelerated programPrevent fraudPayment architectureSpecial data processing applicationsSmart cardComputer terminal
A method and system for tracking and providing an audit trail for off-line smart card transactions includes storing information representing a monetary transaction in a permanent memo on an smart card microprocessor and holding the transaction amount in escrow until the stored information is transmitted from the smart card, for example, at an on-line terminal, to a host on-line system for logging to a tracking system. The monetary transaction includes a transaction with an off-line device, such as another smart card. The escrowed transaction amount represents, for example, a load transaction to one of the smart cards and an unload transaction to other smart card. Once the memo is deleted from the respective smart cards, the load values of the respective smart cards are incremented or decremented by the transaction amount. Alternatively, the smart cards may be provided with a card-to-card key, in which case, a permanent memo is stored only on the receiving smart card.
Owner:CITICORP CREDIT SERVICES INC (USA)
Method and apparatus for scanning three-dimensional objects
InactiveUS20050180623A1Improve accuracyImprove system accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisVisibilityComputer vision
Apparatus and method for creating 3D imagery of an object using calibration means to transfer data to a reference frame and visibility analysis to determine and resolve occlusion.
Owner:MUELLER FREDERICK E
Monolithic Geared Optical Reflector
InactiveUS20120140219A1Improve system accuracyShorten assembly timeRadiation pyrometryAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyOptical instrumentEngineering
A novel monolithic geared optical reflector apparatus which is configured from a gear blank machined to have an integral shaft and integral reflective surface with desired optical properties is introduced herein. Such a rotating mirror device is beneficially capable of being configured into any optical instrument, such as, but not limited to a spectrophotometer, wherein the reflector is adapted to accurately point to a plurality of locations within or out of the system via gear to gear rotation.
Owner:THERMO ELECTRON SCI INSTR
Control of respiratory oxygen delivery
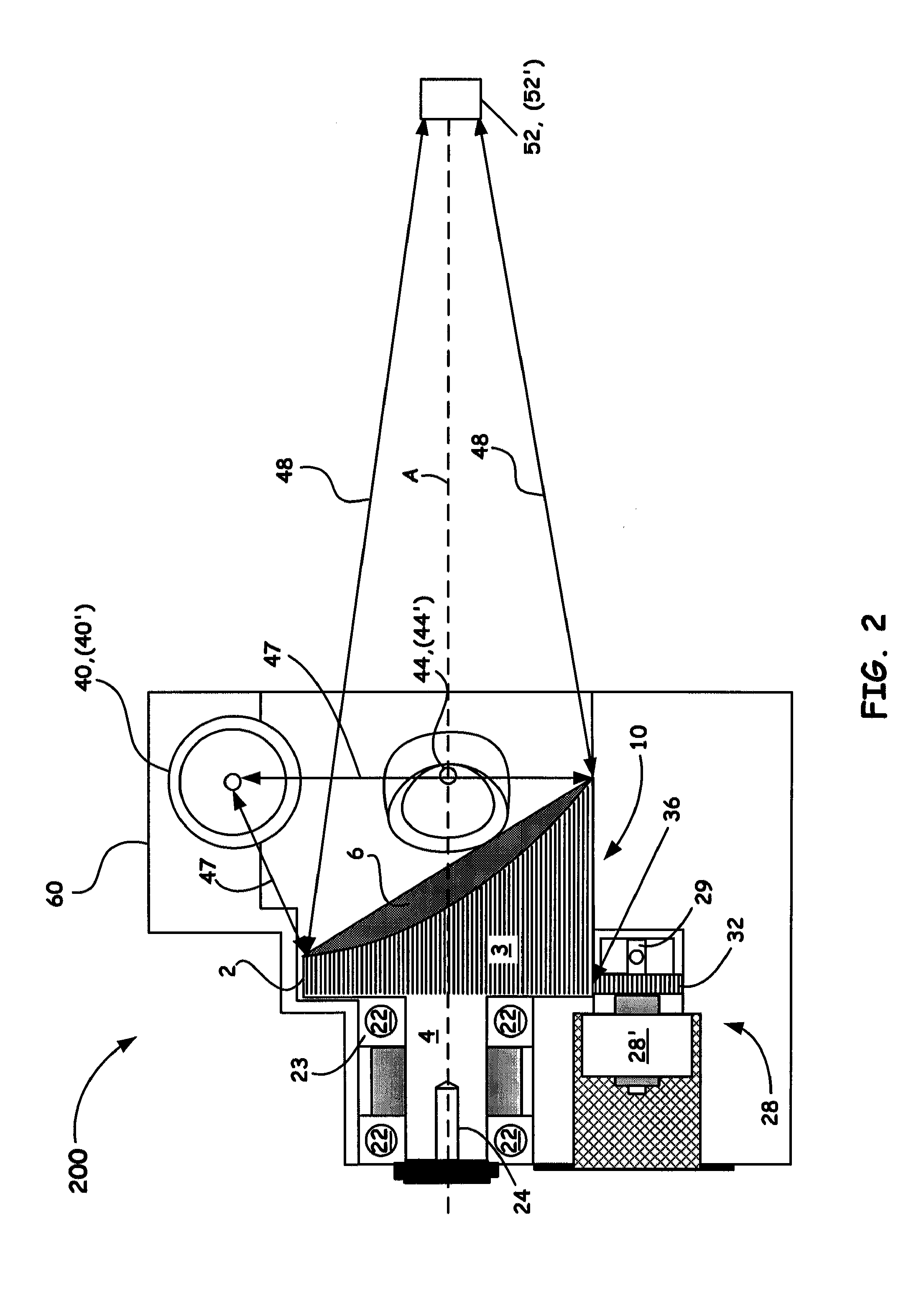
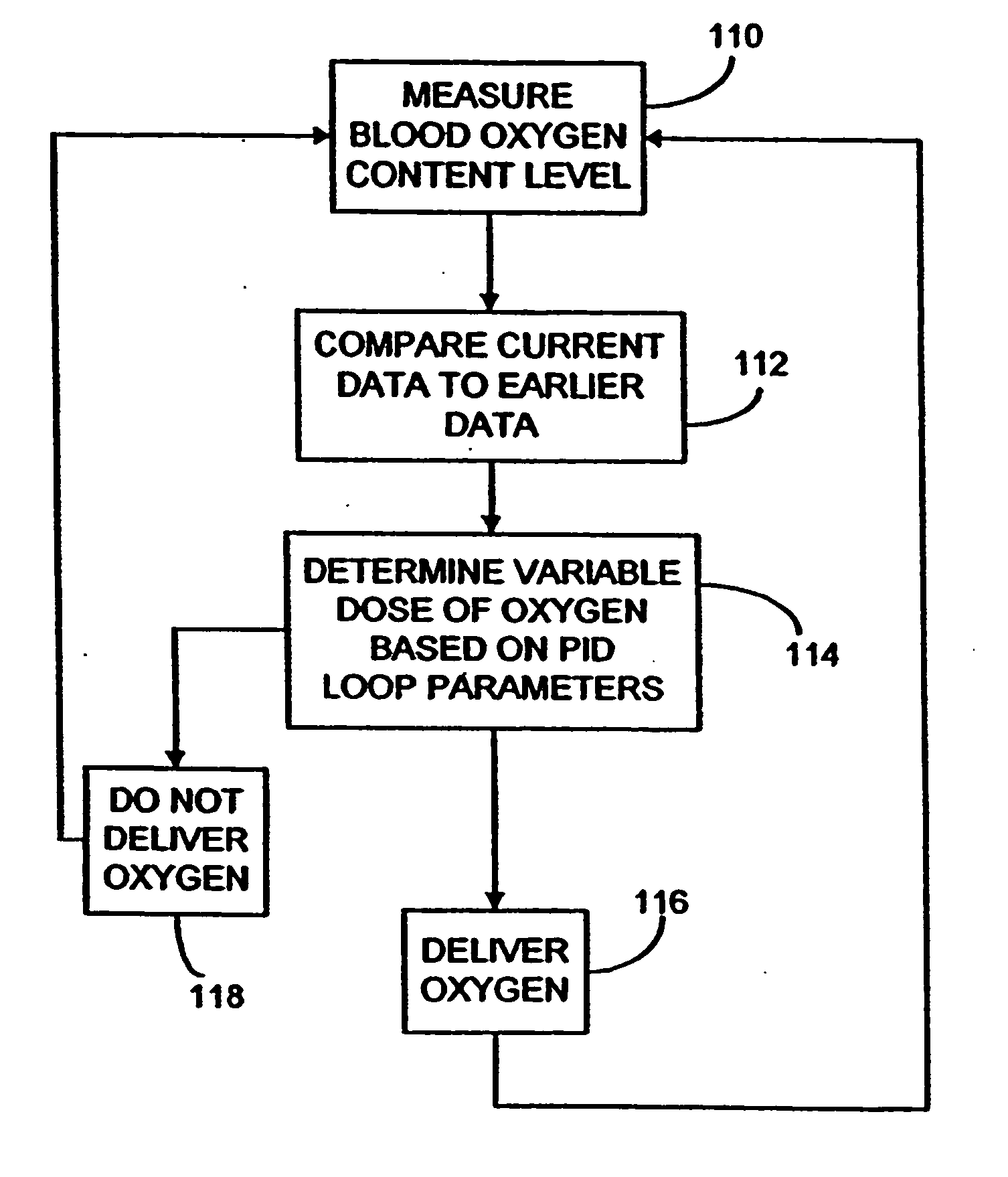
InactiveUS20060213519A1Improve accuracyImprove system accuracyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksDuring expirationExhalation
Methods and systems for supplying respiratory oxygen to users when the users are inhaling are disclosed. The methods and systems may rely on delivery devices that are selectively placed in fluid communication with either a respiration sensor or a source of oxygen. The methods and systems may actively monitor for exhalations, as well as monitor for oxygen in the oxygen source. The respiration sensor may preferably be a flow sensor.
Owner:MINNESOTA INNOVATIVE TECH & INSTR MITI
Inertial measurement system and method with bias cancellation
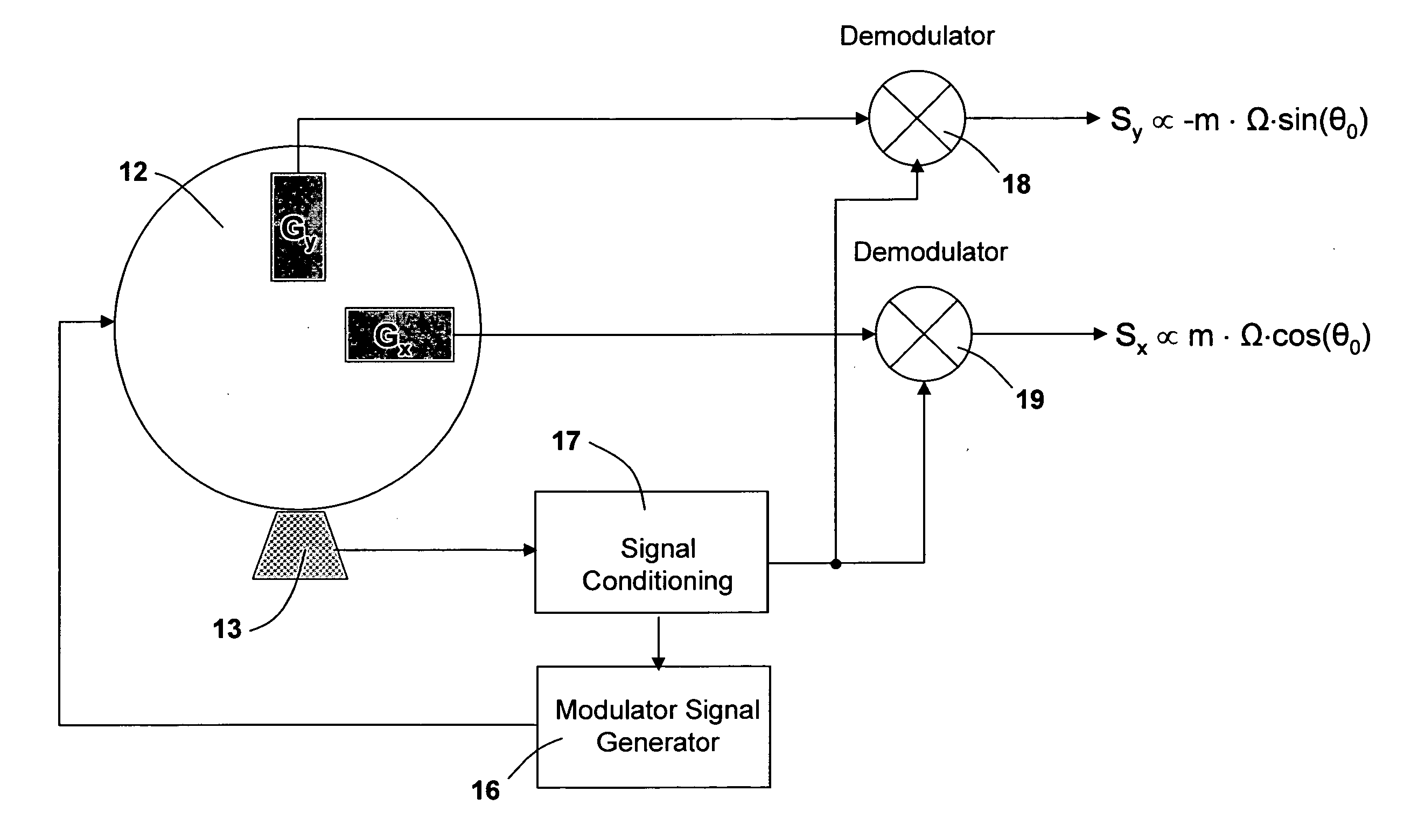
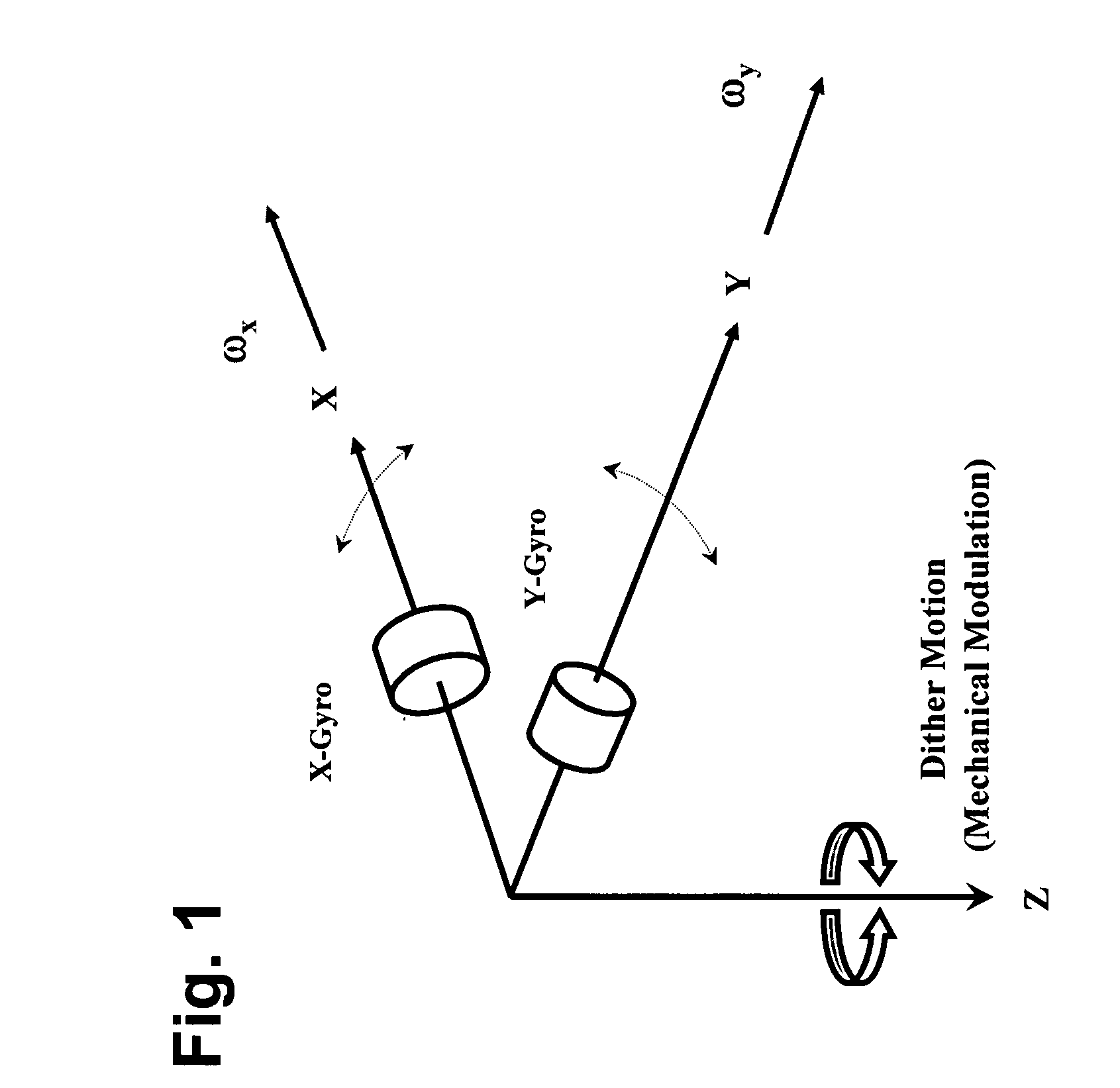
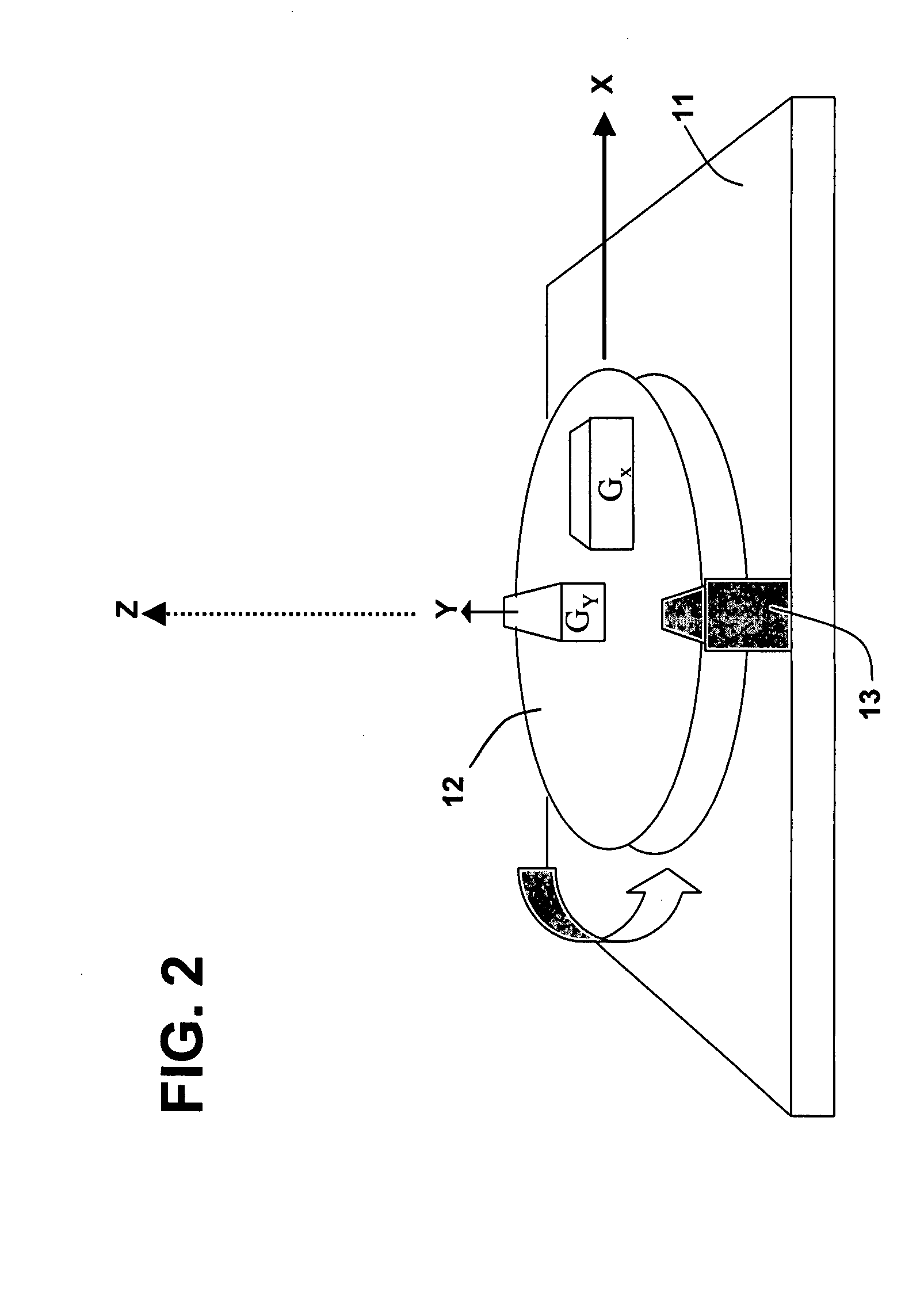
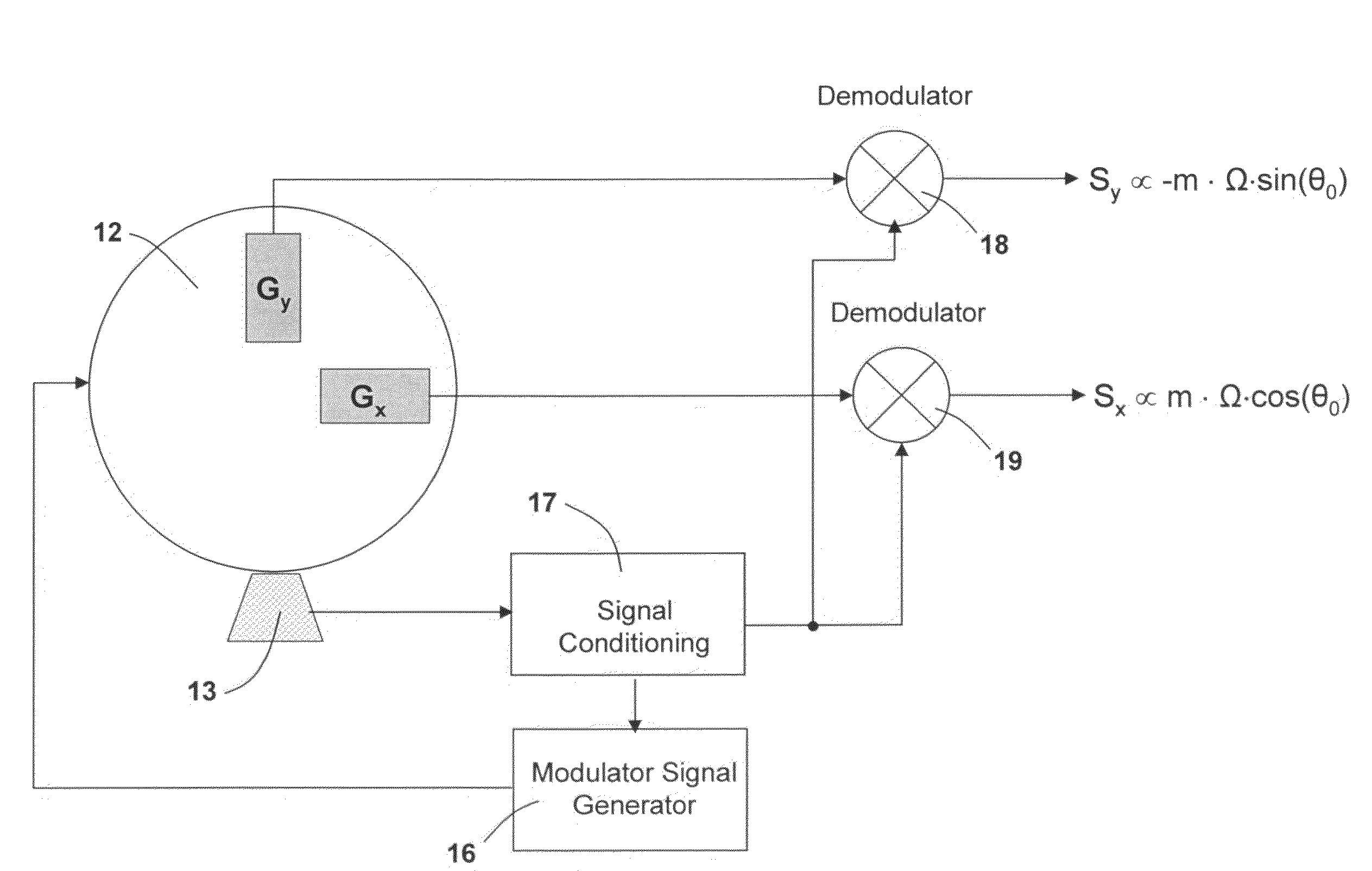
ActiveUS20070240486A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioReduce sensitivityAcceleration measurement using interia forcesNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsEngineeringSignal-to-noise ratio
System having one or more inertial sensors in which one or more of the sensor input axes are modulated in orientation about an axis substantially perpendicular to the input, or sensitive, axis of the sensor and, in some embodiments, by also enhancing the accuracy of such a system to provide improved signal to noise ratio and reduced sensitivity to errors in alignment of the sensor axes to the dither axes.
Owner:EMCORE INC
Sensor assembly
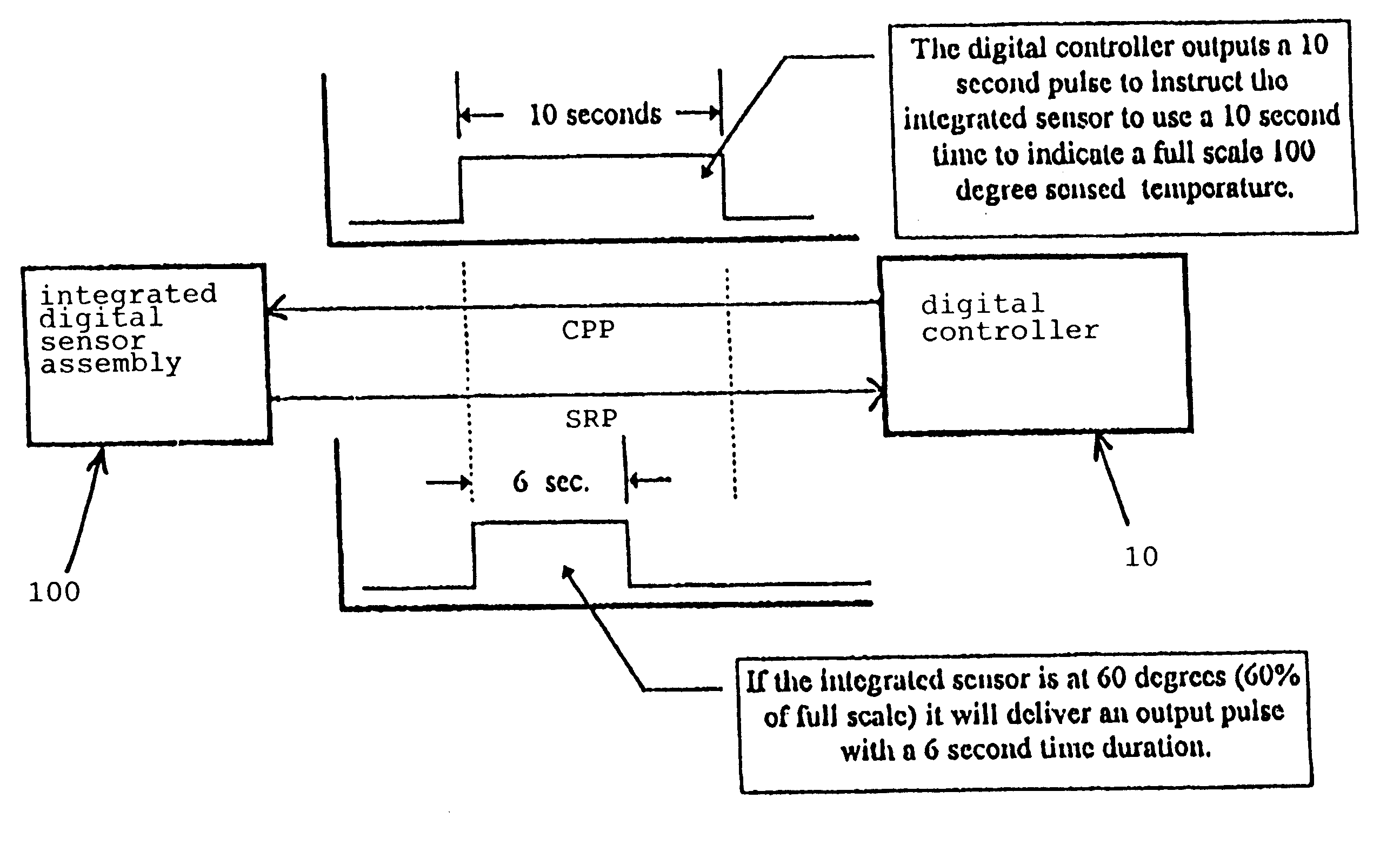
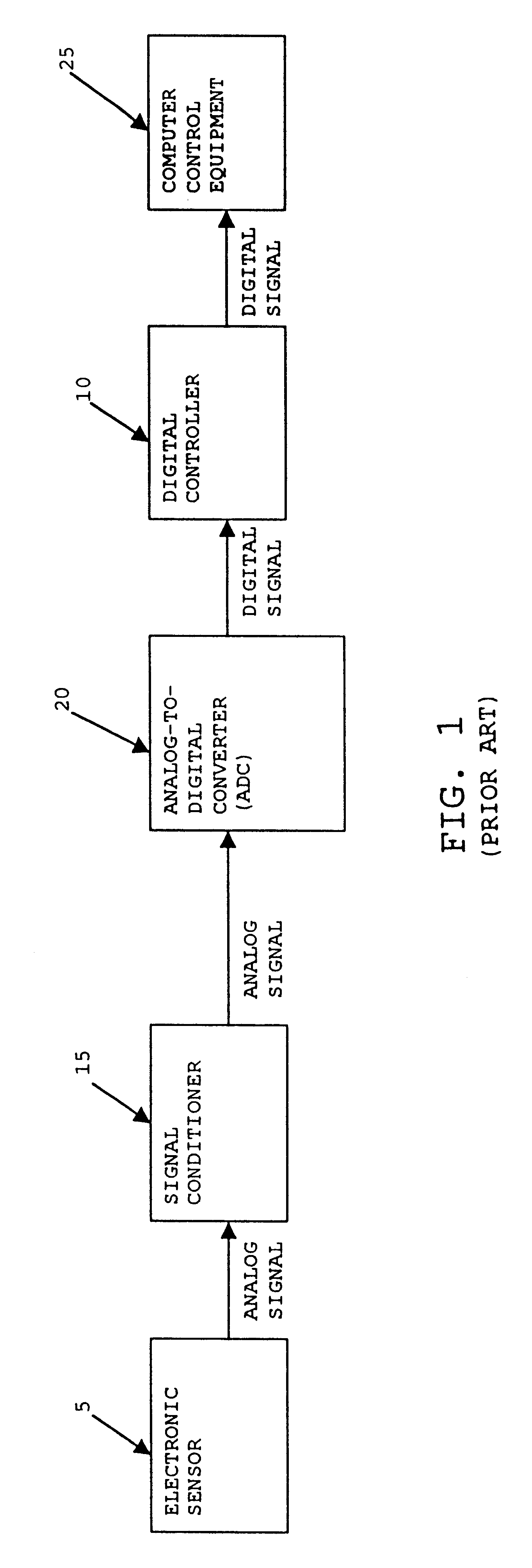
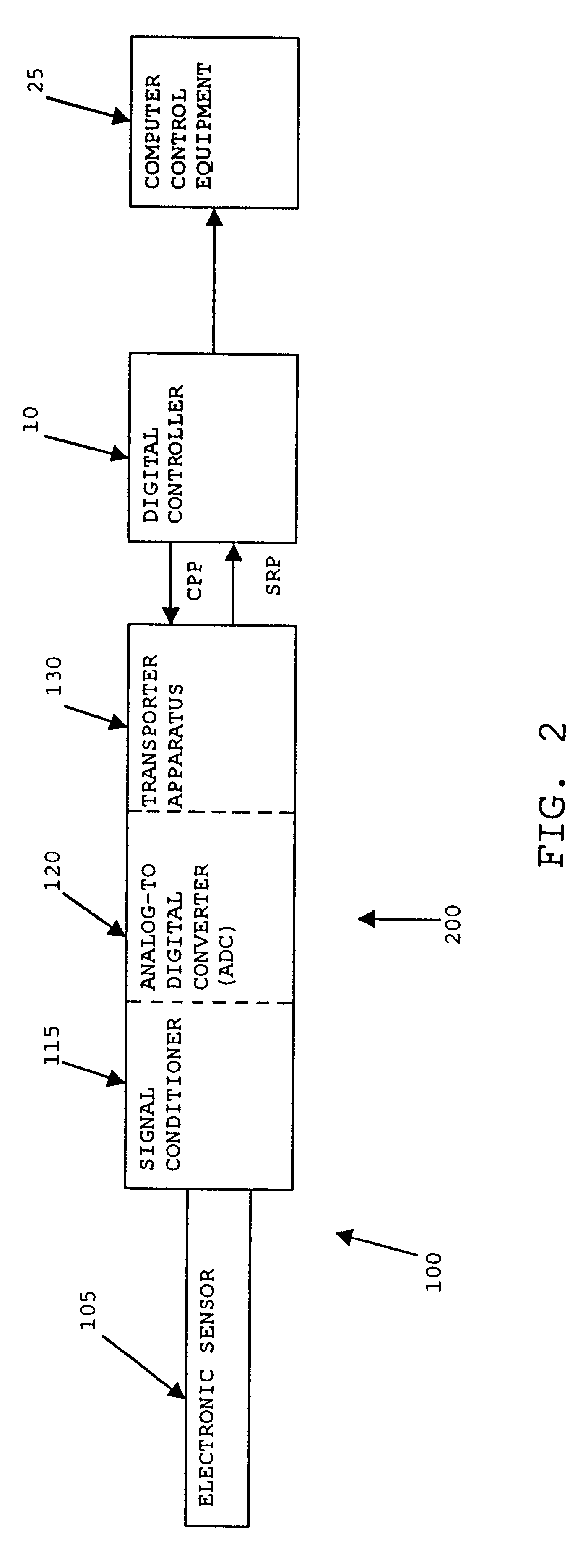
InactiveUS6233532B1Quickly and conveniently replacedLow costElectric signal transmission systemsComputer controlComputer hardwareData reporting
A sensor assembly and a method for sensing physical conditions and reporting on the same are disclosed. The sensor assembly comprises an electronic sensor, a dedicated signal conditioner and a dedicated ADC, all integrated directly with the electronic sensor into a single pre-assembled and pre-calibrated package. The sensor assembly also comprises transponder apparatus for enabling the sensor assembly to adapt its output signal so as to properly match the specific input requirements of a particular digital controller. More particularly, the sensor assembly's transponder apparatus is constructed so as to measure the time duration of a programming pulse sent to the sensor assembly (the "Controller Programming Pulse", or "CPP"), and then to use the time duration of the CPP to generate a time-proportioned reporting pulse ("the Sensor Reporting Pulse", or "SRP") so as to report sensor data to the digital controller.
Owner:DOVER ASSOCS
Integrated navigation system for autonomous underwater robot and method
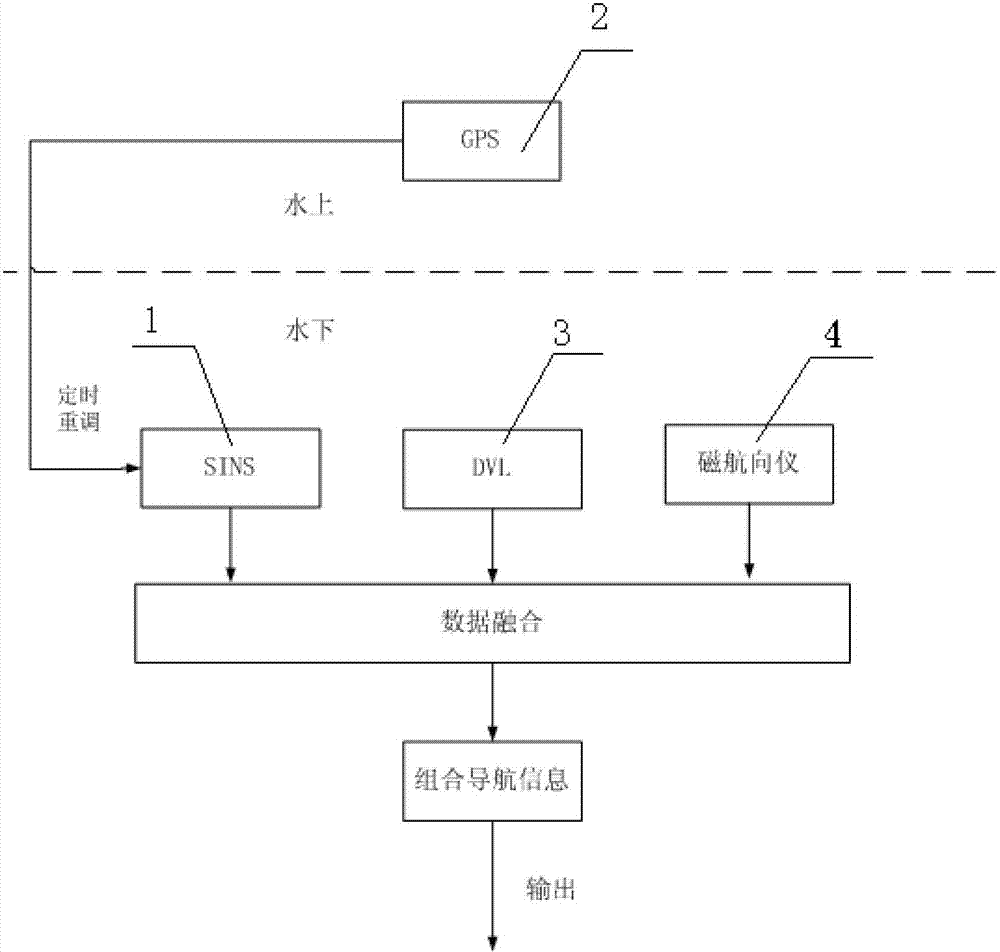
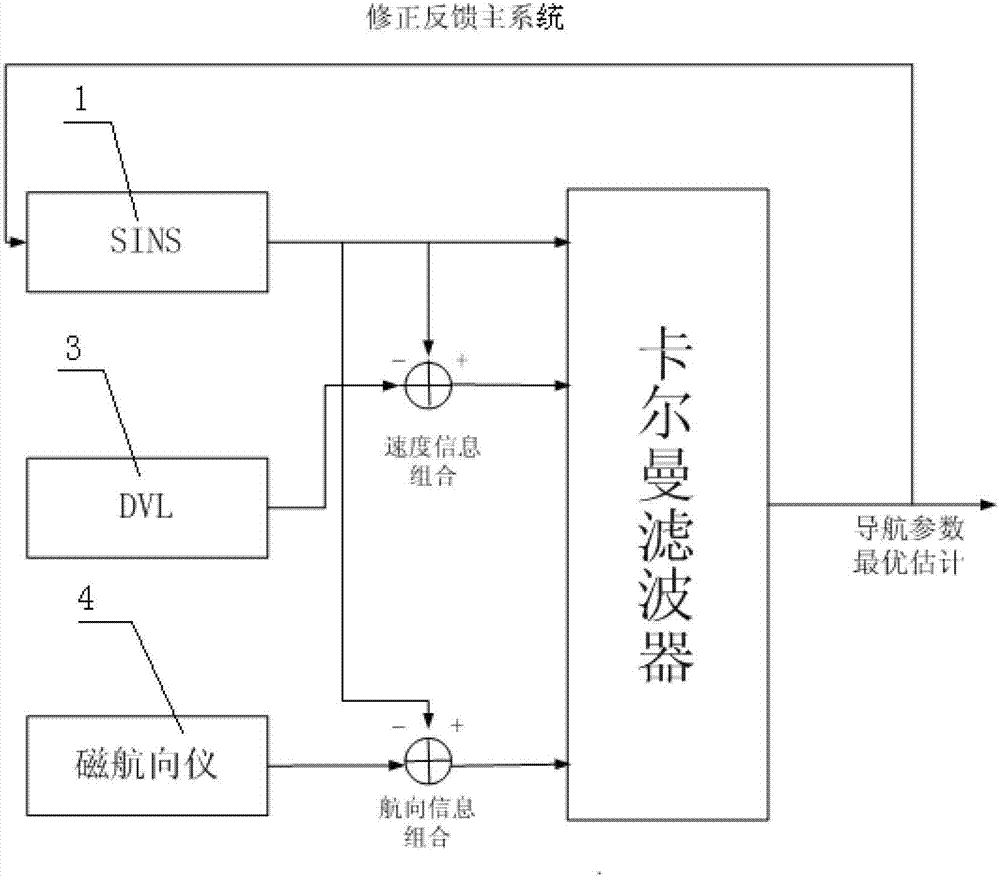
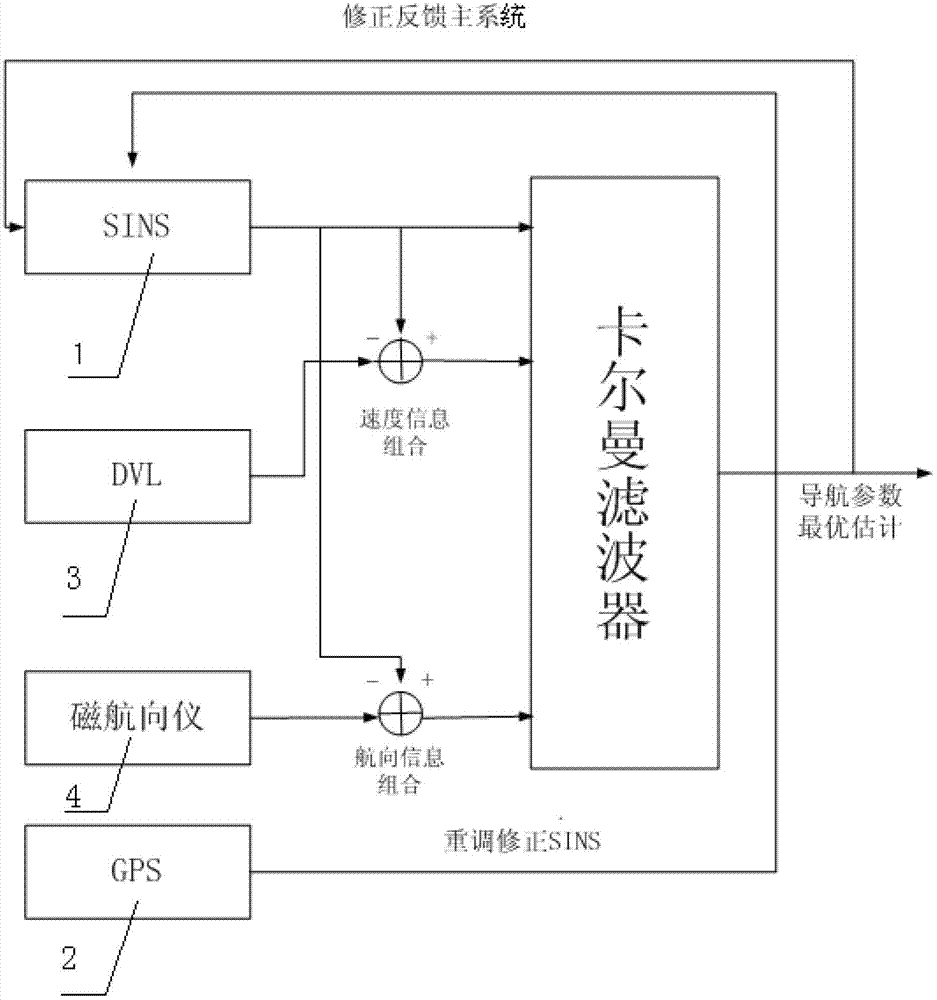
InactiveCN102829777AImprove system accuracyHigh precisionNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSelf adaptiveGeographic coordinate system
The invention discloses an integrated navigation system for an autonomous underwater robot. The integrated navigation system is composed of a strapdown inertial navigation system, a global positioning navigation system, a Doppler speed meter and a magnetic heading device, wherein the speed information, the position information and the gesture information relative to the earth along a geographic coordinate system are calculated by the strapdown inertial navigation system; initial absolute position information and speed information of the autonomous underwater robot are obtained by the global positioning navigation system; the speed information is calculated by the Doppler speed meter; the heading information is calculated by the magnetic heading device; the timing for the strapdown inertial navigation system is readjusted by the global positioning navigation system; and the system is used for performing data fusion on the speed information, the position information and the gesture information outputted by the strapdown inertial navigation system, the speed information calculated by the Doppler speed meter and the heading information calculated by the magnetic heading device through self-adaption fuzzy Kalman filtering, so that accurate integrated navigation information is obtained.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and system for generating a medical report and computer program product therefor
ActiveUS20140324477A1Improve generationEasy to operateMedical report generationOffice automationComputerized systemComputer science
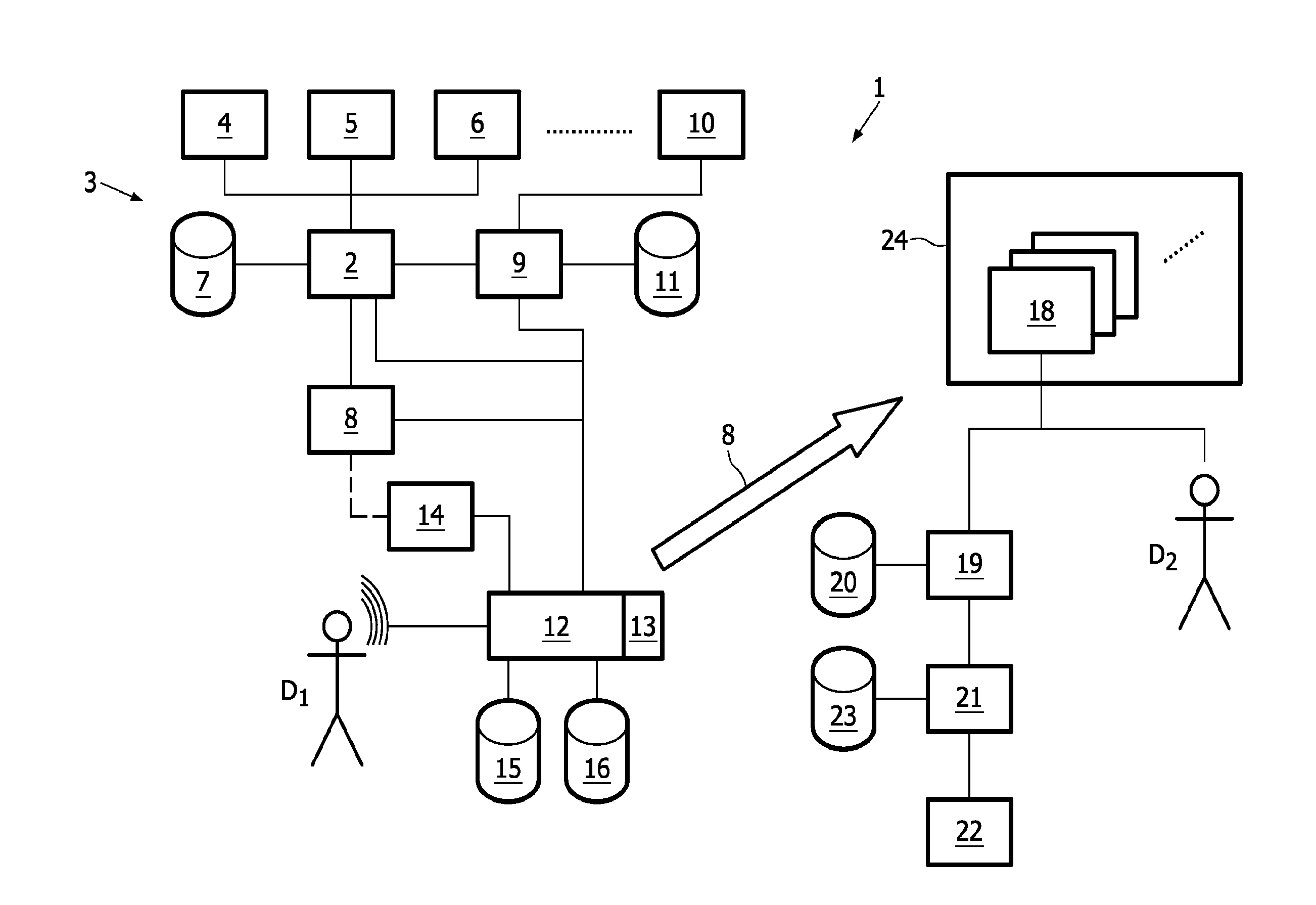
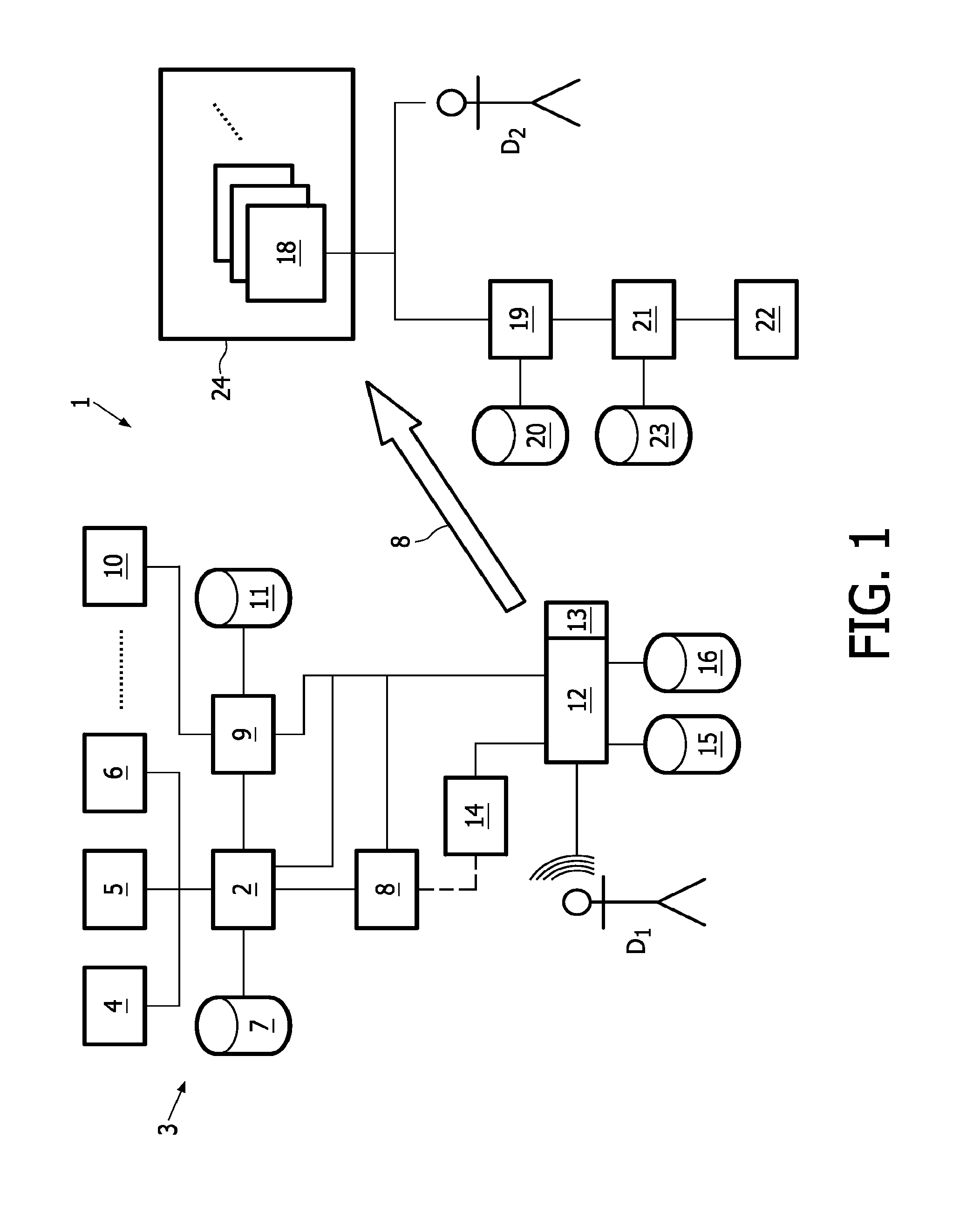
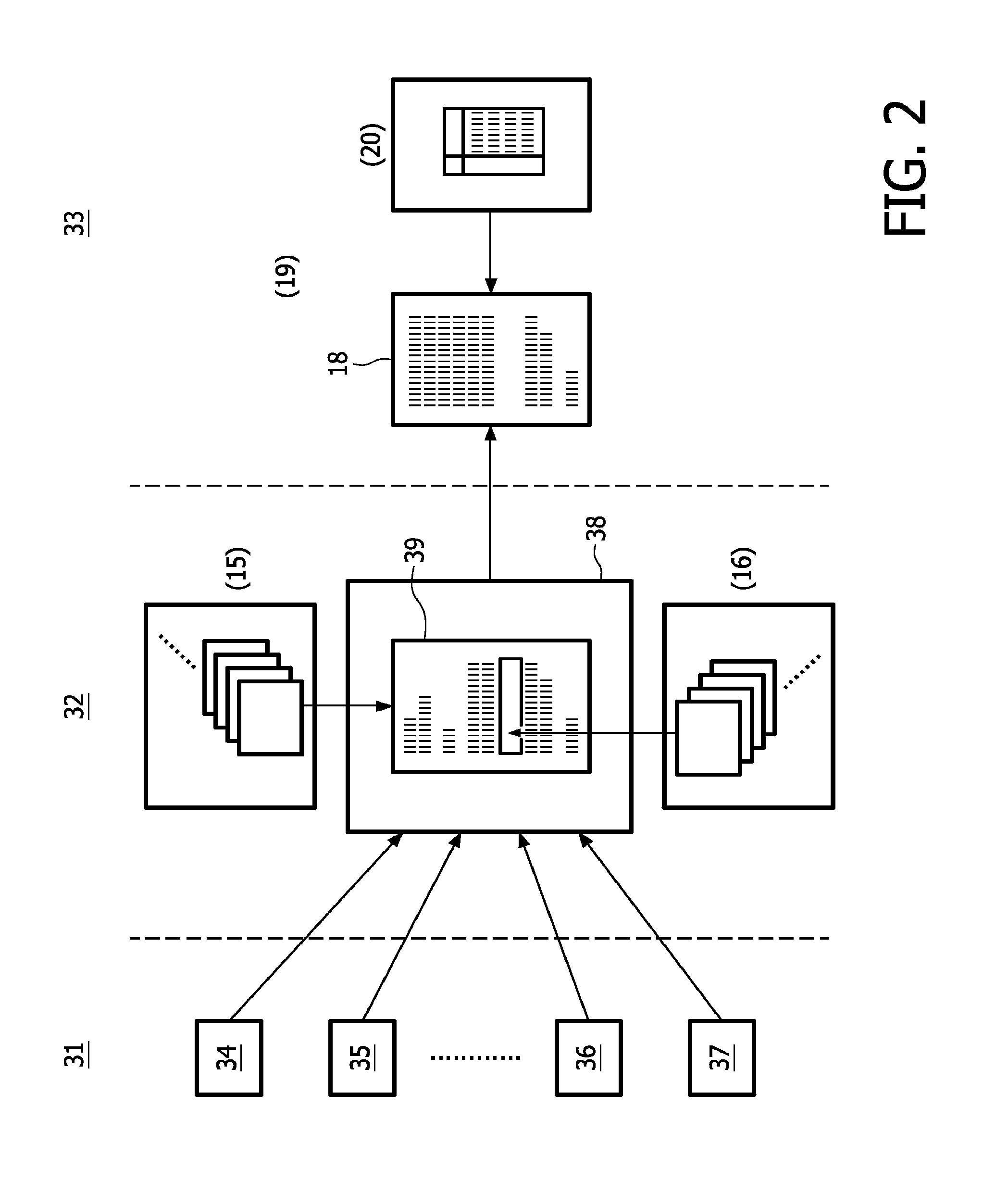
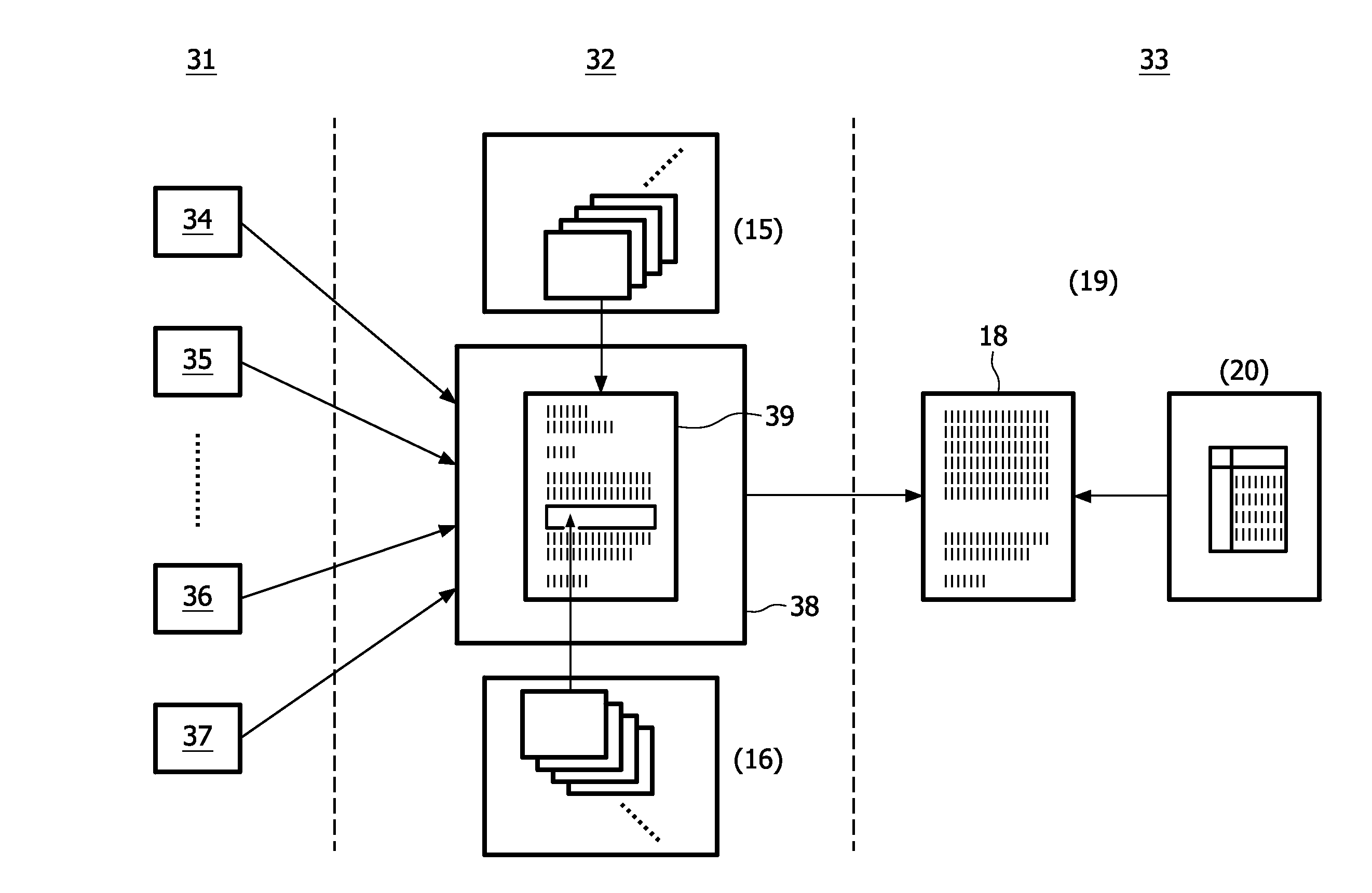
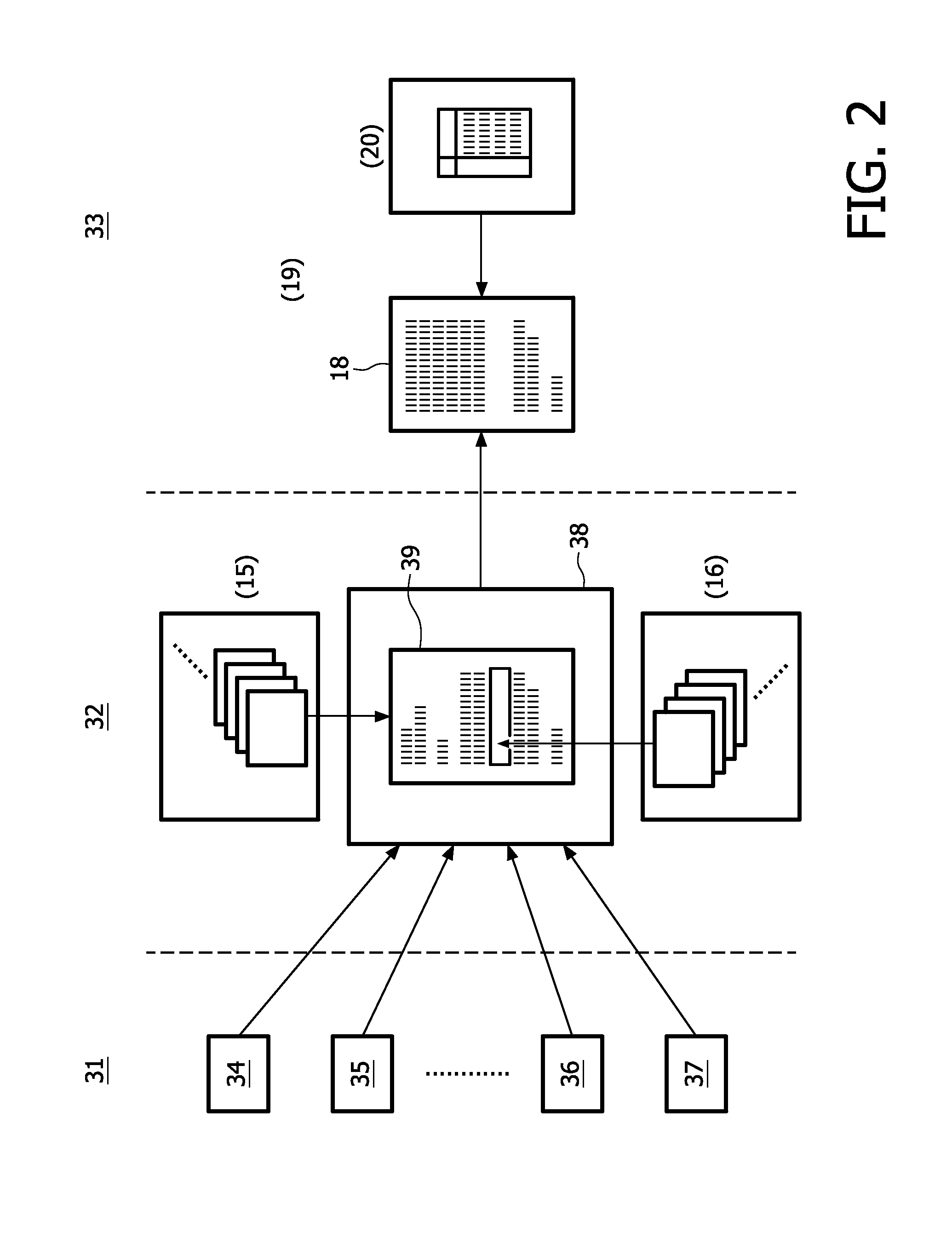
A method and a system for generating, with the assistance of a computer system (12), a medical report (18) suitable for automatic billing, where an electronic template (39) suited for a specific patient's condition is selected out of a plurality of given electronic templates stored in storage means (15); personal data of the specific patient's and previously stored in storage means (11) are automatically entered into the selected electronic template; and medical report text passages and instructions are entered into the selected template by dictating and using a speech recognition system (13); additionally, condition data are automatically entered on the basis of condition information as far as stored in storage means (7) into the selected template, and code data associated with these condition information are automatically embedded in the selected template; and when entering medical report text passages, at least one predetermined voice macro stored in the storage means (16) together with code data embedded therein is called in; the code data thus embedded in the medical report (18) being applicable when coding the medical report for automatic billing.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method to estimate location and orientation of an object
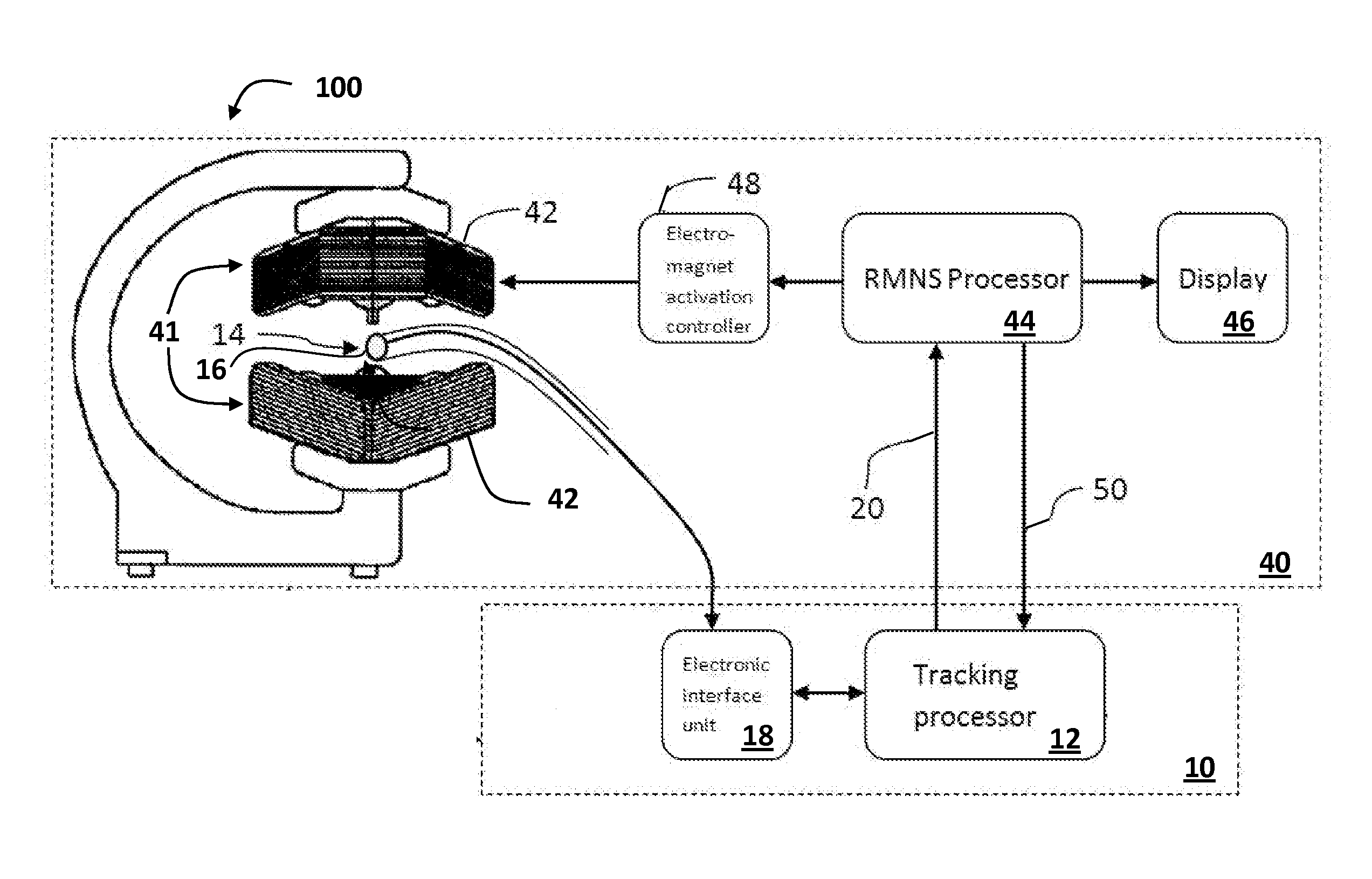
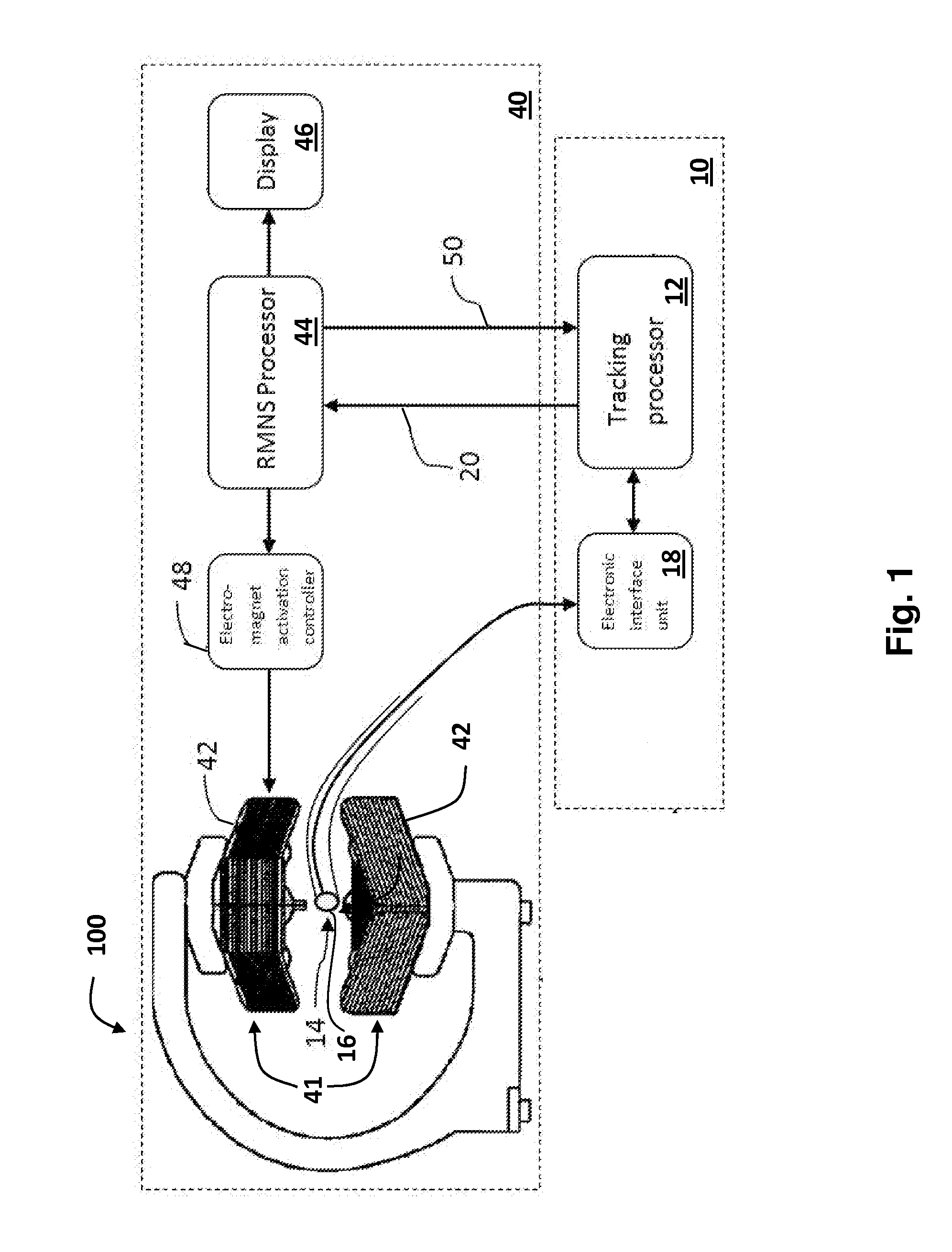
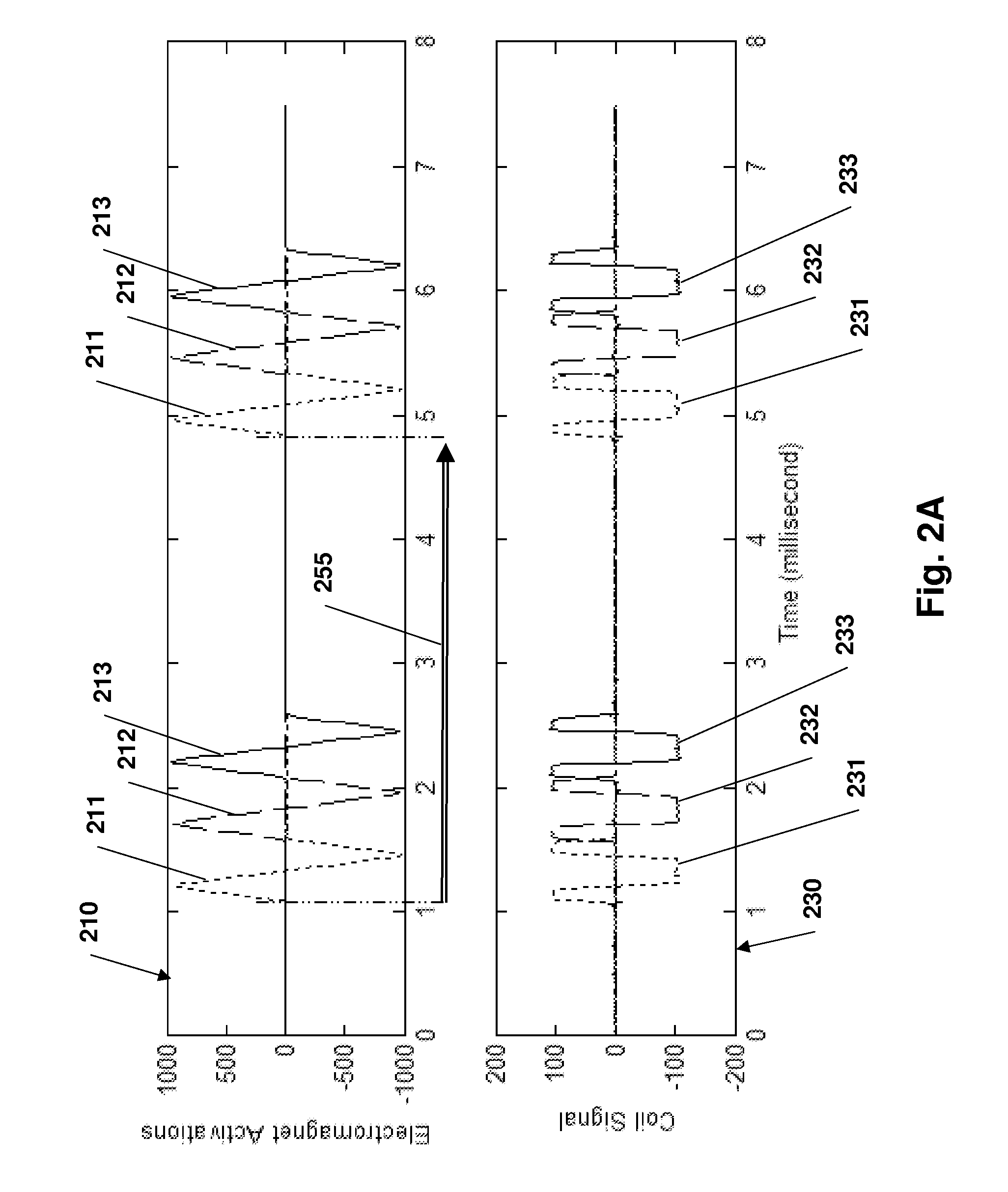
InactiveUS20130303878A1Improve system accuracyEliminate needSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringLocation trackingNavigation system
A tracking system for estimating the position and orientation of an object inside a patient comprising electromagnets that generate magnetic fields used to navigate an object, including rotating and translating the object, are used to track the position of the object. Position tracking of the object is concurrent with navigating the object; or interleaved with navigating the object. Using the same electromagnets for navigation and tracking ensure coordinate system registration between the navigation system and the position tracking system. A tracking sensor attached to the object comprises at least a single coil generating signals in response to time varying tracking magnetic field generated by the electromagnets. Iterative algorithm is used to estimate position and orientation from sensor's signal. Linearly time varying current in the tracking electromagnets is produced by applying calculated voltage waveform to the electromagnet coils.
Owner:ENAV MEDICAL
Calibration ring for developing and aligning view dependent image maps with 3-D surface data
InactiveUS7271377B2Improve accuracyImprove system accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisVisibilityData transmission
Apparatus and method for creating 3D imagery of an object using calibration means to transfer data to a reference frame and visibility analysis to determine and resolve occlusion.
Owner:MUELLER FREDERICK E
Foundation-based atmosphere profile microwave detector
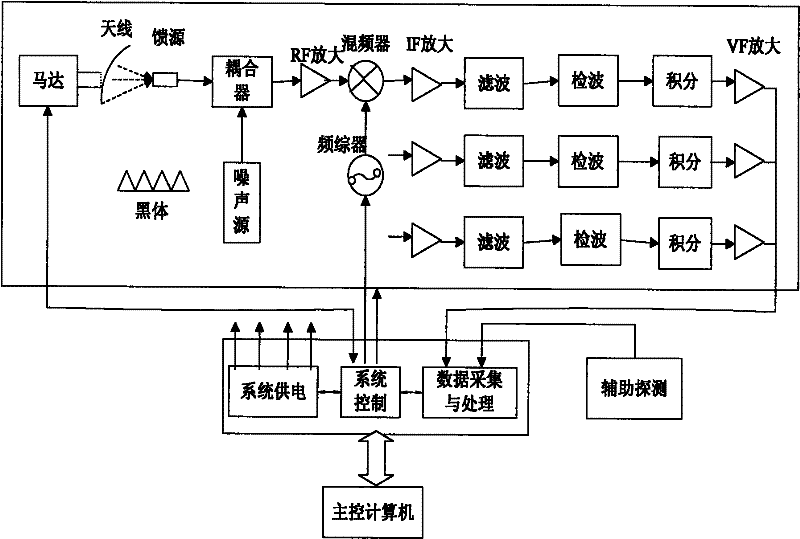
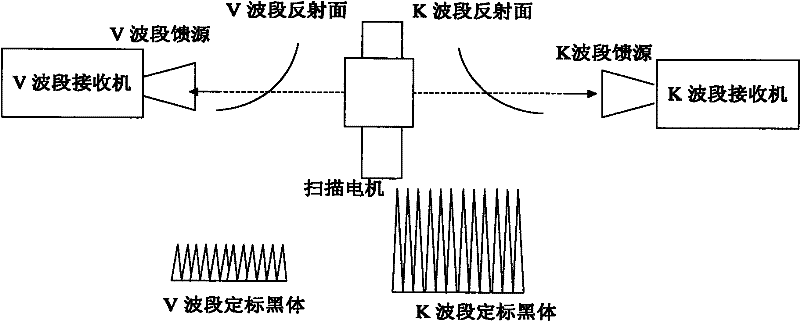
InactiveCN102243304AReduce axial (transverse) dimensionsIncrease in sizeICT adaptationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionIntegratorIntermediate frequency
The invention provides a foundation-based atmosphere profile microwave detector. The detector is characterized by comprising an antenna feeder unit, a radiometer receiving unit and a scanning mechanism unit, wherein the antenna feeder unit comprises two independent antenna feeder sub-units for two wavebands and is provided with two-frequency independent reflective surfaces; the two independent antenna reflective surfaces are arranged at two ends of the output shaft of a scanning motor respectively, can realize beam scanning through motor rotation, and are used for receiving microwave radiation of atmosphere and an internal calibration reference source; the radiometer receiving unit comprises a directional coupler, a radio amplifier, a power divider, a band pass filter, a square law detector, an integrator and a video amplifier, and is used for realizing intermediate frequency detection of a received signal; the scanning mechanism unit comprises a scanning shaft, a scanning step motor, two front ends and a sub-miniature type A (SMA) connector; and driven by the scanning motor, the scanning shaft drives the two reflective surfaces to circumferentially scan so as to realize observation on sky in different incident angles and measurement on an internal calibration blackbody and acquire data which is acquired in a measurement and periodic internal calibration unit.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
Three Axis Aerodynamic Control of Guided Munitions
InactiveUS20080029641A1Improve system accuracyImprove performanceSelf-propelled projectilesEngineeringBevel gear
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Method and system for generating a medical report and computer program product therefor
ActiveUS20100114598A1Improve report generationImprove generationOffice automationSpeech recognitionComputerized systemComputer science
A method and a system for generating, with the assistance of a computer system(12), a medical report (18) suitable for automatic billing, wherein an electronic template (39) suited for a specific patient's condition is selected out of a plurality of given electronic templates stored in storage means (15); personal data of the specific patient's and previously stored in storage means (11) are automatically entered into the selected electronic template; and medical report text passages and instructions are entered into the selected template by dictating and using a speech recognition system (13); additionally, condition data are automatically entered on the basis of condition information as far as stored in storage means (7 ) into the selected template, and code data associated with these condition information are automatically embedded in the selected template; and when entering medical report text passages, at least one predetermined voice macro stored in storage means (16) together with code data embedded therein is called in; the code data thus embedded in the medical report (18) being applicable when coding the medical report for automatic billing.
Owner:NUANCE COMM INC
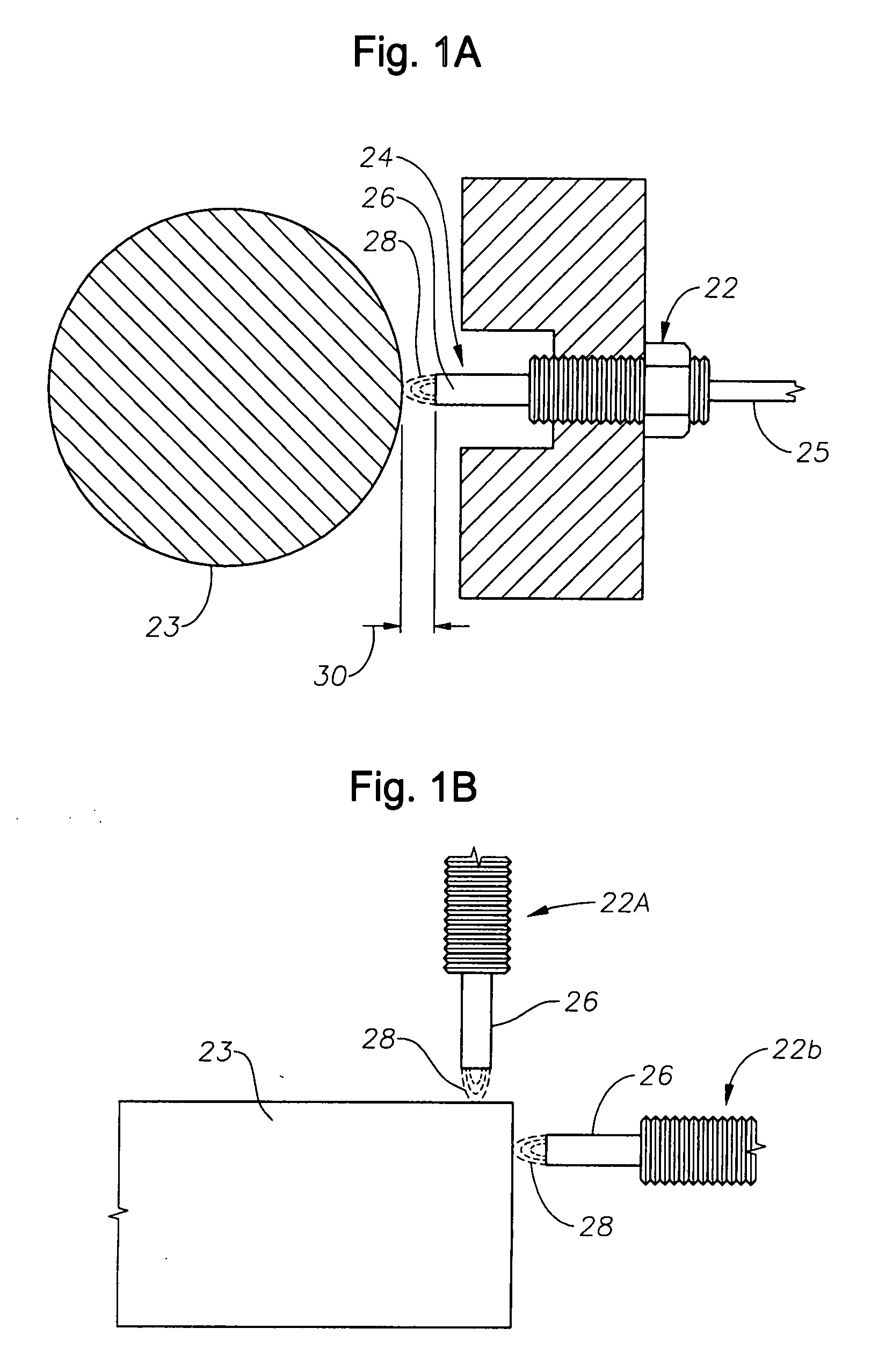
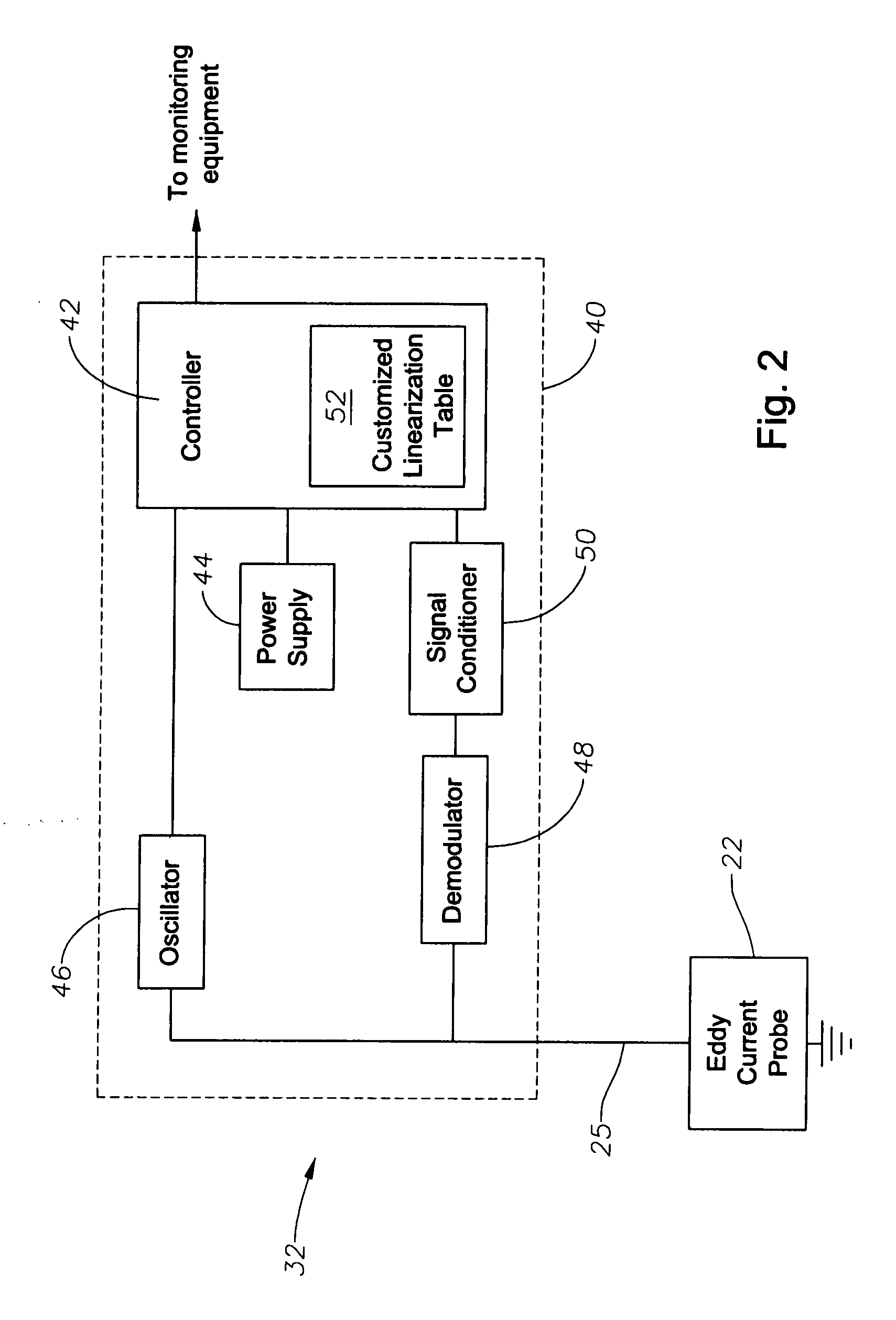
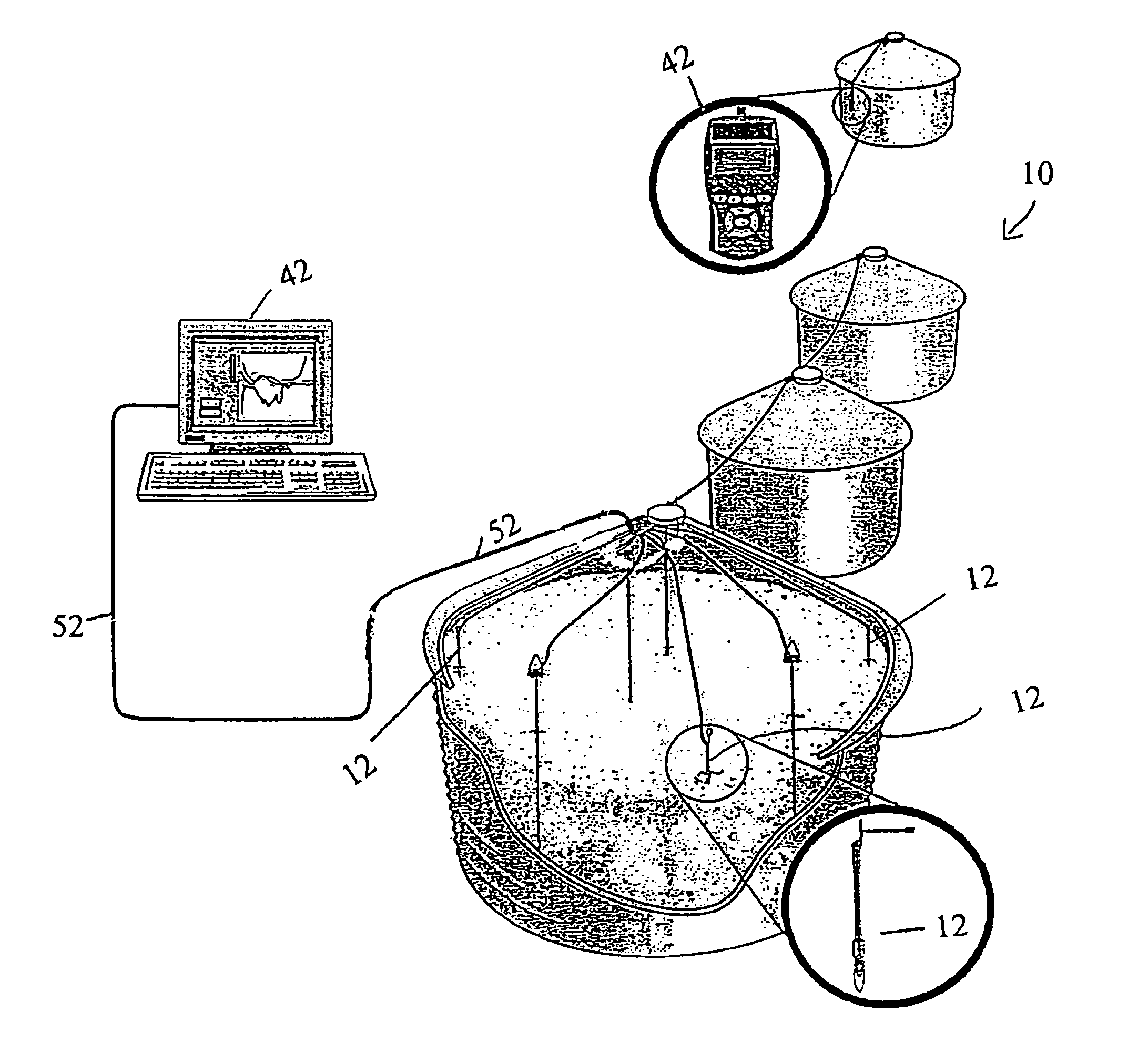
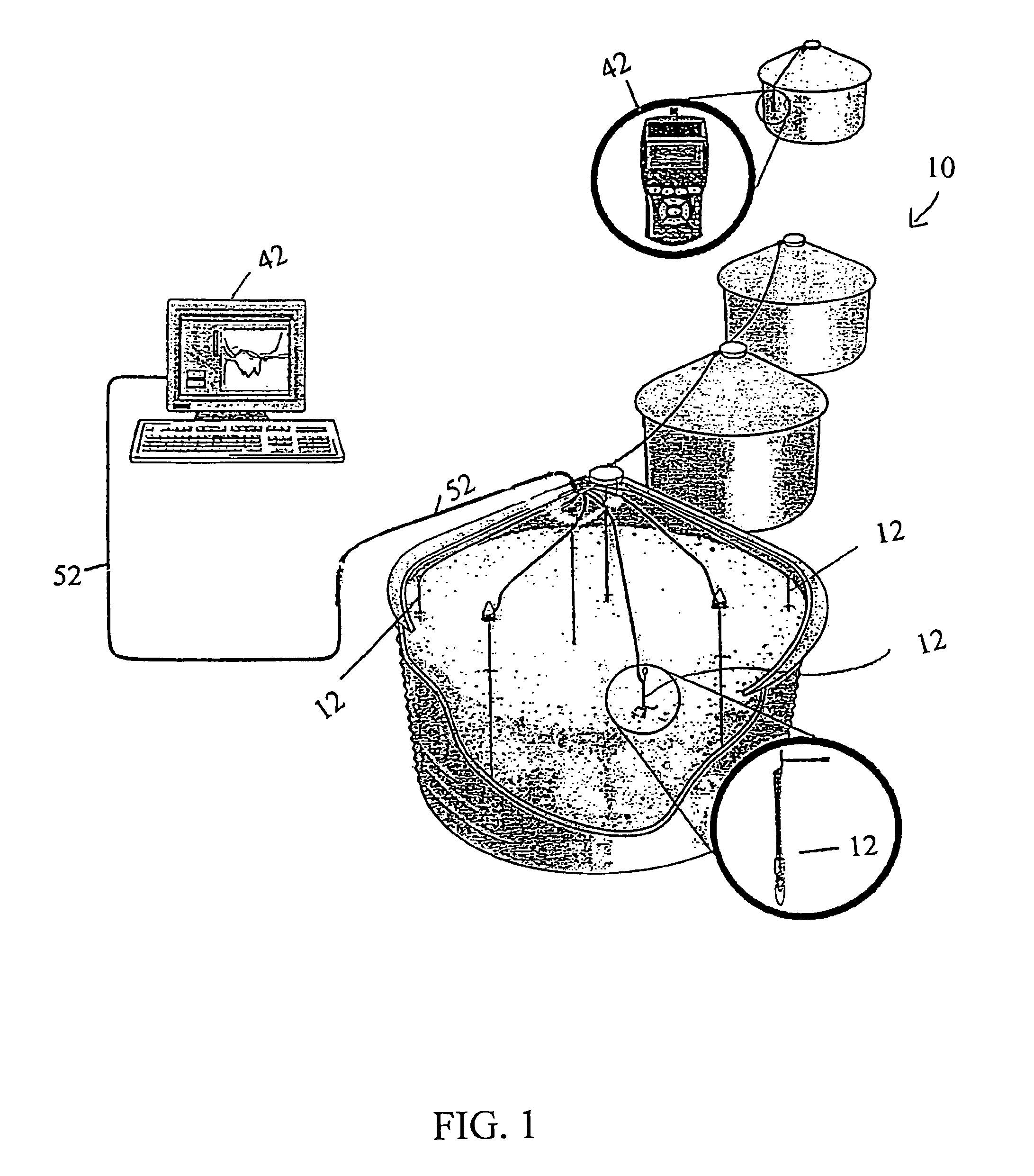
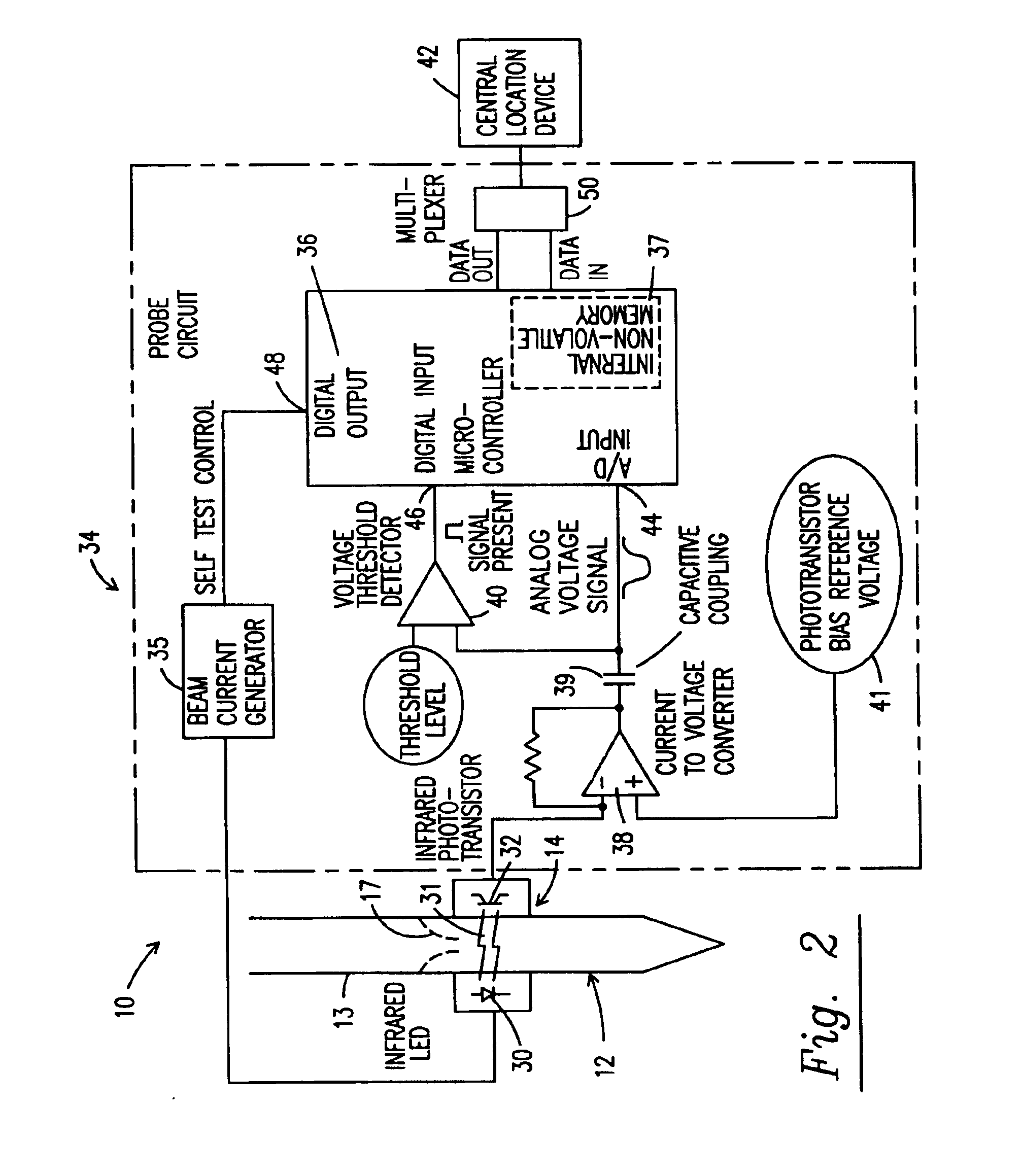
Proximity probe transmitter
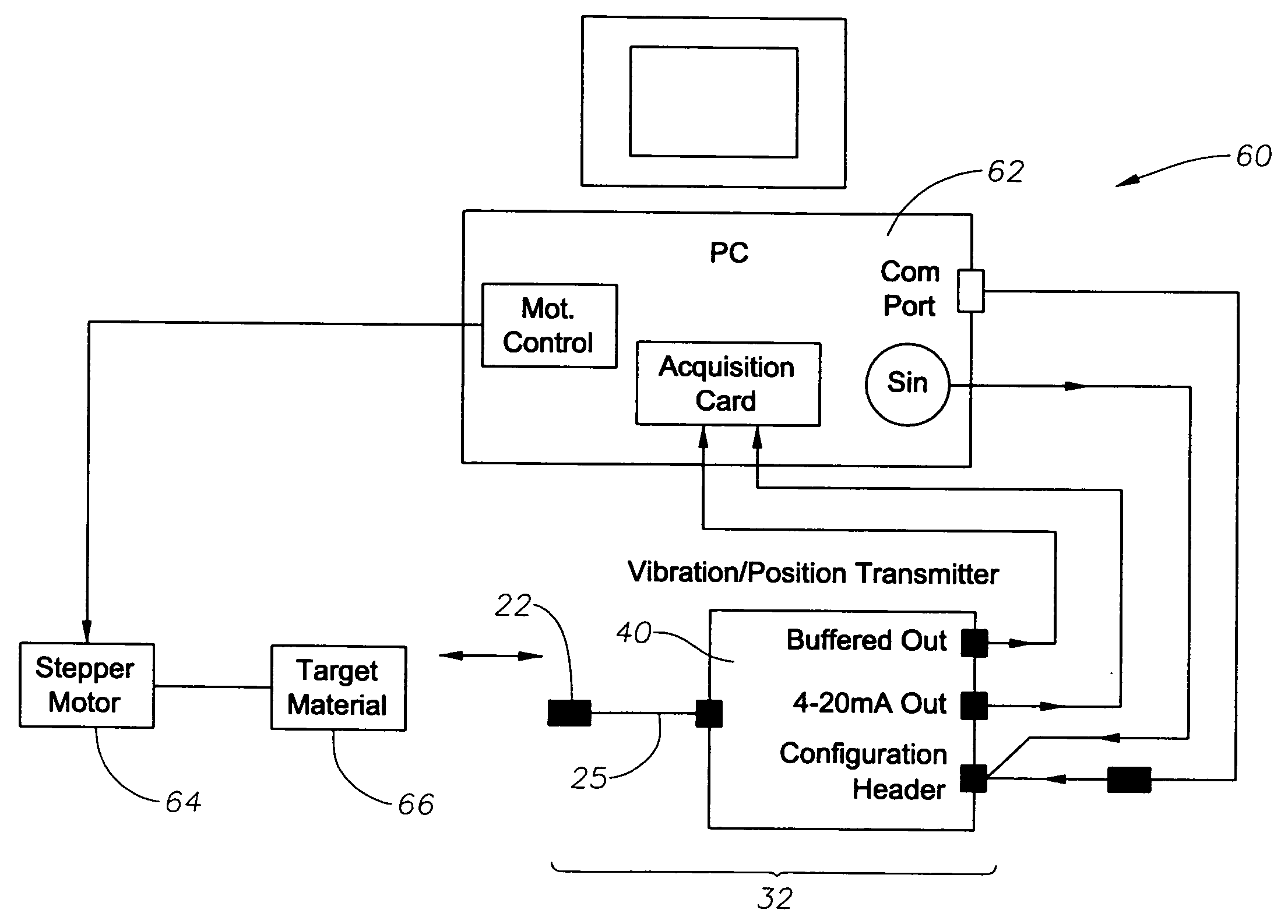
ActiveUS20080054891A1Eliminate power consumptionEliminate needVibration measurement in solidsUsing electrical meansCoaxial cableImpedance properties
A digital based two wire proximity transmitter system and a method for calibrating the system, wherein the transmitter includes a customized linearization table uniquely generated during calibration to take into account the unique impedance properties of a particular probe / coaxial cable configuration. During calibration, the probe is positioned adjacent a calibration target. The calibration target is selected to have the same material characteristics as the target to be monitored during actual operation of the transmitter in the field. At a fixed distance between the probe and calibration target, the resonant frequency of the probe / cable system is determined. Thereafter, utilizing this resonant frequency to excite the probe, the voltage response of the probe / cable system is determined as the distance between the probe and the target material is incrementally changed. The voltage output is used to build a table for incremental distances, wherein each distance is characterized by a non-linear output that has been equated to a linear output. This uniquely generated table is subsequently downloaded into the transmitter for reference during monitoring.
Owner:METRIX INSTR
Portable video oculography system with integral light stimulus system
A goggle based light-weight VOG system includes at least one digital camera connected to and powered by a laptop computer through a firewire connection together with an integral visual light stimulus source. The digital camera may digitally center the pupil in both the X and Y directions. A calibration mechanism may be incorporated onto the goggle base. An EOG system may also be incorporated directly into the goggle. The VOG system may track and record 3-D movement of the eye, track pupil dilation, head position and goggle slippage. An animated eye display provides data in a more meaningful fashion. The VOG system is a modular design whereby the same goggle frame or base is used to build a variety of digital camera VOG systems.
Owner:NEUROLIGN USA LLC +1
Laser diode based multiple-beam laser spot imaging system for characterization of vehicle dynamics
ActiveUS20120044477A1Improve system accuracyImprove accuracyTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesDevices using optical meansVehicle dynamicsLaser imaging
The invention is related to a laser diode based multiple beam laser spot imaging system for characterization of vehicle dynamics. A laser diode based, preferably VCSEL based laser imaging system is utilized to characterize the vehicle dynamics. One or more laser beams are directed to the road surface. A compact imaging system including an imaging matrix sensor such as a CCD or CMOS camera measures locations or separations of individual laser spots. Loading status of vehicles and vehicles' pitch and roll angle can be characterized by analyzing the change of laser spot locations or separations.
Owner:TRUMPF PHOTONIC COMPONENTS GMBH
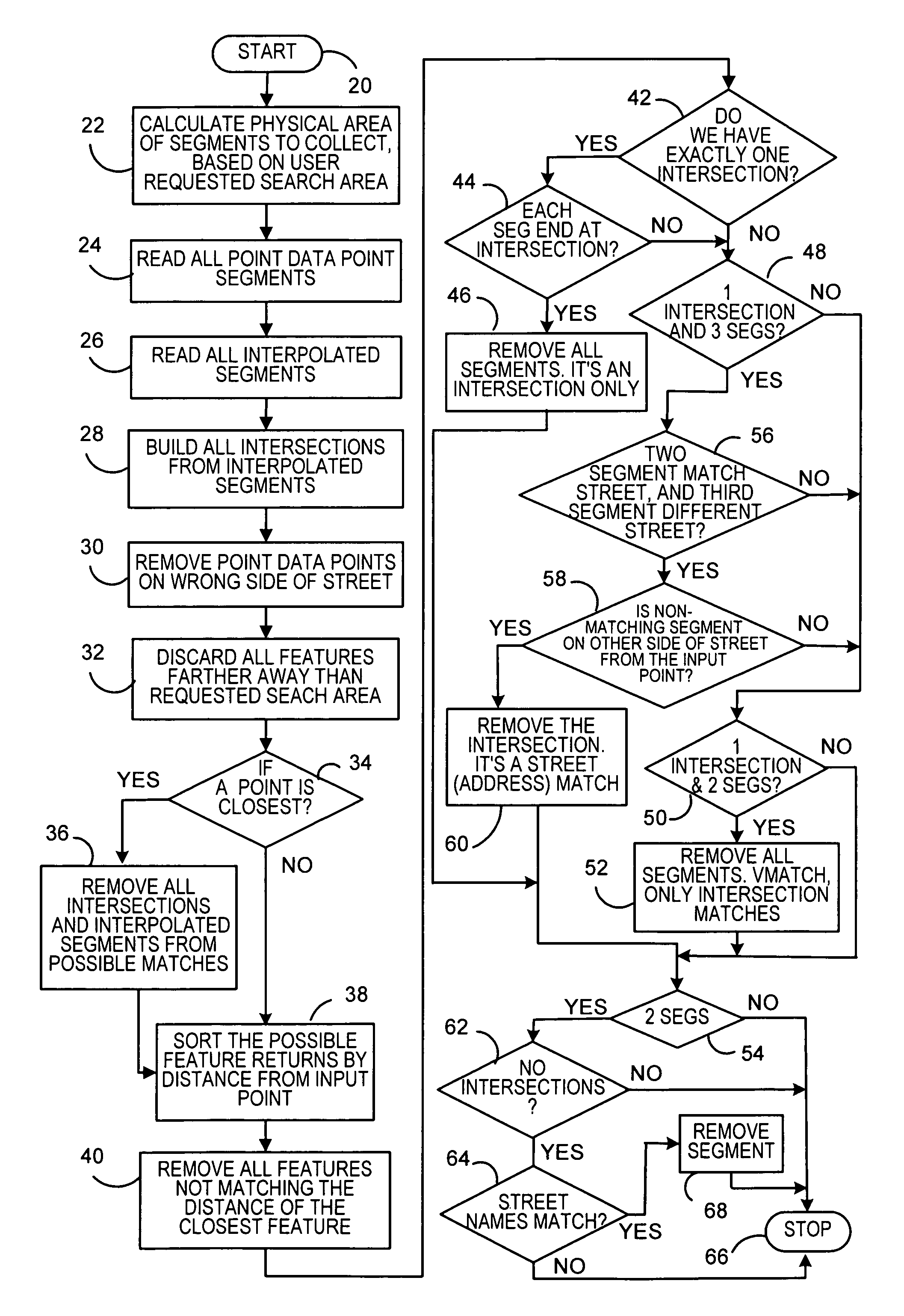
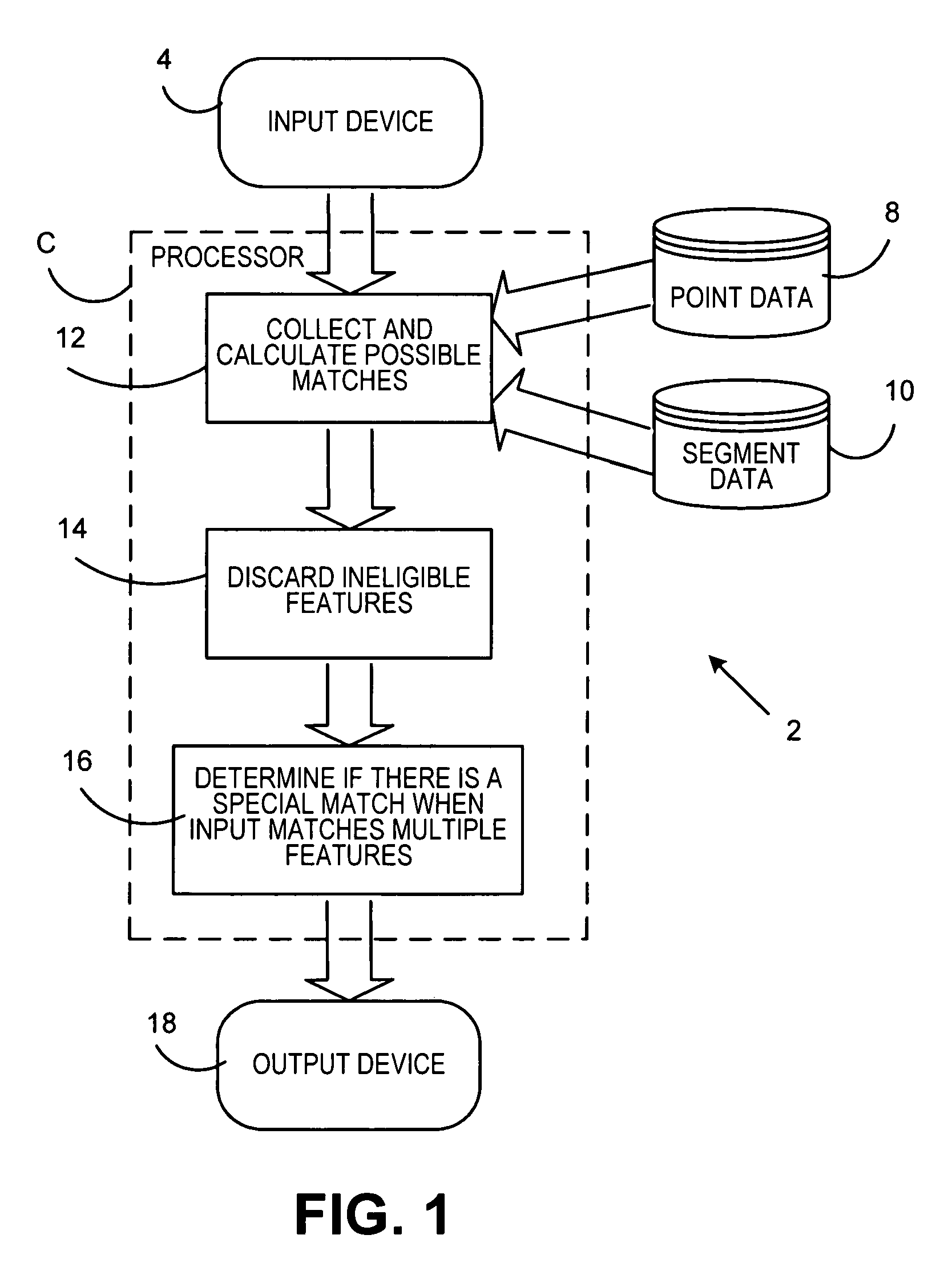
Reverse geocoding system using combined street segment and point datasets
ActiveUS7668651B2Improve system accuracyInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlData setLongitude
A reverse geocoding system and method processes a point level dataset and a street segment dataset to determine an address for a particular latitude and longitude of an input point entered into the system. A determination is made if the point level dataset contains a point level data address match to the entered latitude and longitude data within the closest street segment and without crossing the street segment. Any such point level data address match is output. When no such point level data address match is made, the system computes an interpolated address from a range of addresses of the closest street segment in the street segment dataset based on the entered latitude and longitude of the input point in relation to said range of addresses for the closest street segment. The interpolated address from the closest street segment in the street segment dataset is output. The street segment dataset may also contain unranged street segments without ranges of addresses.
Owner:PRECISELY SOFTWARE INC
Implantable enzyme-based monitoring system having improved longevity due to improved exterior surfaces
InactiveUS6934572B2Improve biocompatibilityImprove accuracy and responsivenessCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringIonBiomedical engineering
An implantable enzyme-based monitoring system suitable for long term in vivo use to measure the concentration of prescribed substances such as glucose is provided. In one embodiment, the implantable enzyme-based monitoring system includes at least one sensor assembly, an outer membrane surrounding the sensor assembly and having a window therein, and a polymeric window cover affixed to the outer membrane and covering the window. Preferably, the outer membrane of the monitoring system is silicone and the window cover is a polymer of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA), N,N,-dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate (DMAEMA) and methacrylic acid (MA). Also provided herein is an implantable enzyme-based monitoring system having at least one sensor assembly, an outer membrane surrounding the sensor assembly and a coating affixed to the exterior surface of the outer membrane, wherein the coating resists blood coagulation and protein binding to the exterior surface of the outer membrane. Preferably, the coating is polyethylene glycol (PEG) and heparin in an 80:20 molar ratio. Finally, provided herein is a method of coating the exterior surface of the outer membrane of an implantable enzyme-based monitoring system comprising the steps of forming hydroxyl groups on the silicone surface by plasma etching; reacting the silicone surface with amino functionalized silane, thereby forming amino groups on the silicone surface; simultaneously, covalently binding polyethylene glycol (PEG) and heparin to the amino groups; and ionically binding heparin to the monitoring system surface.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN FOUND FOR SCI RES
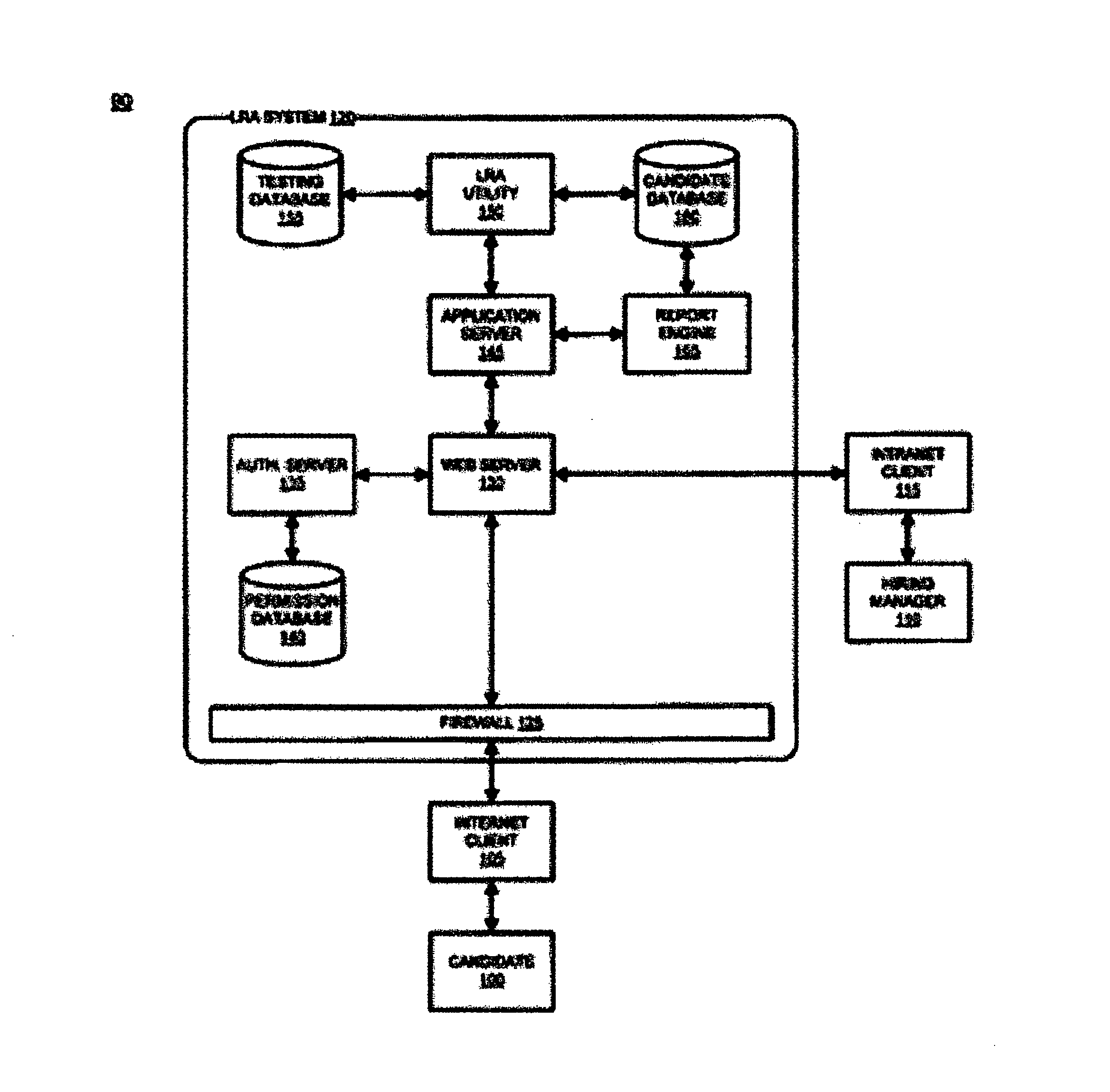
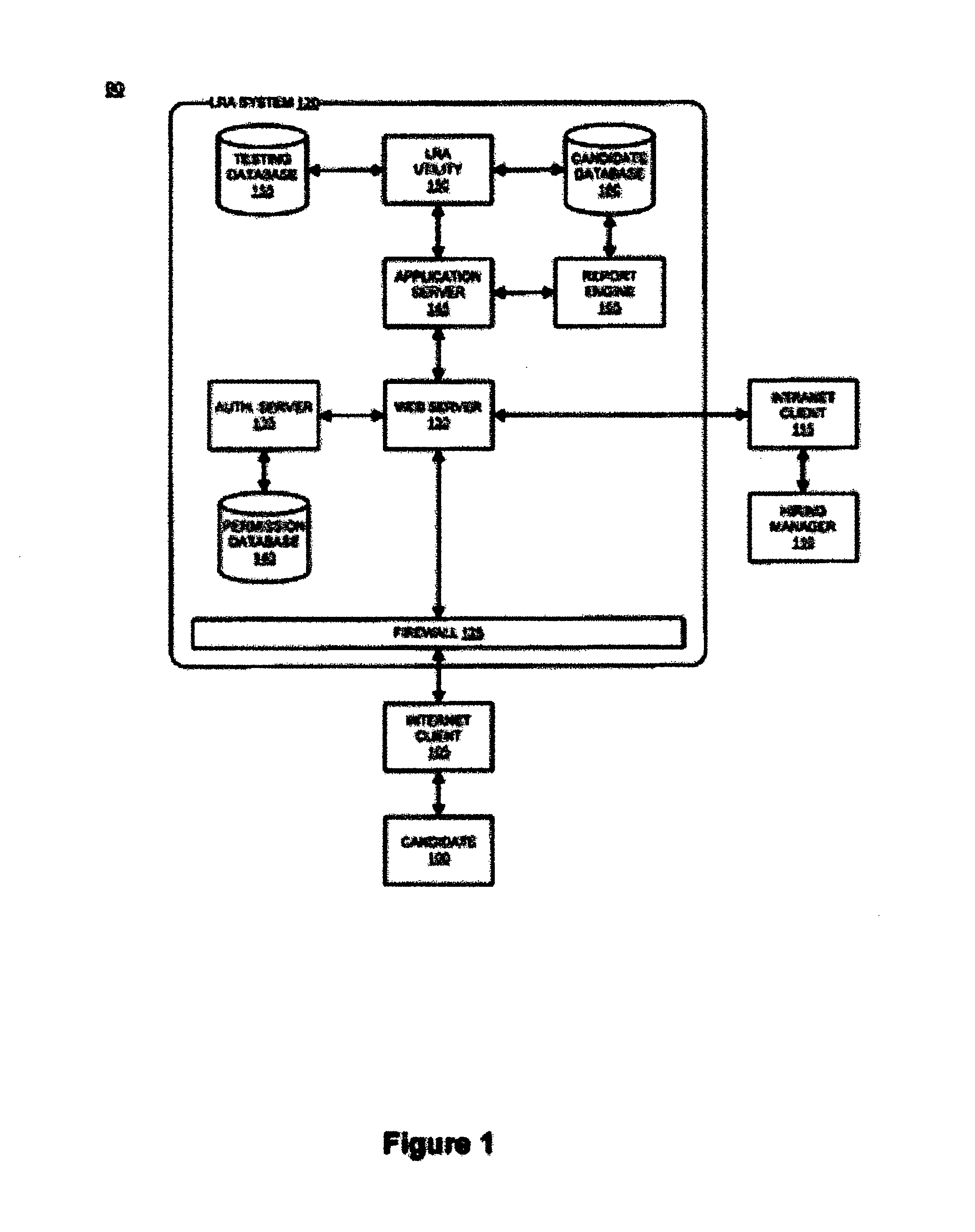
Labor resource testing system and method
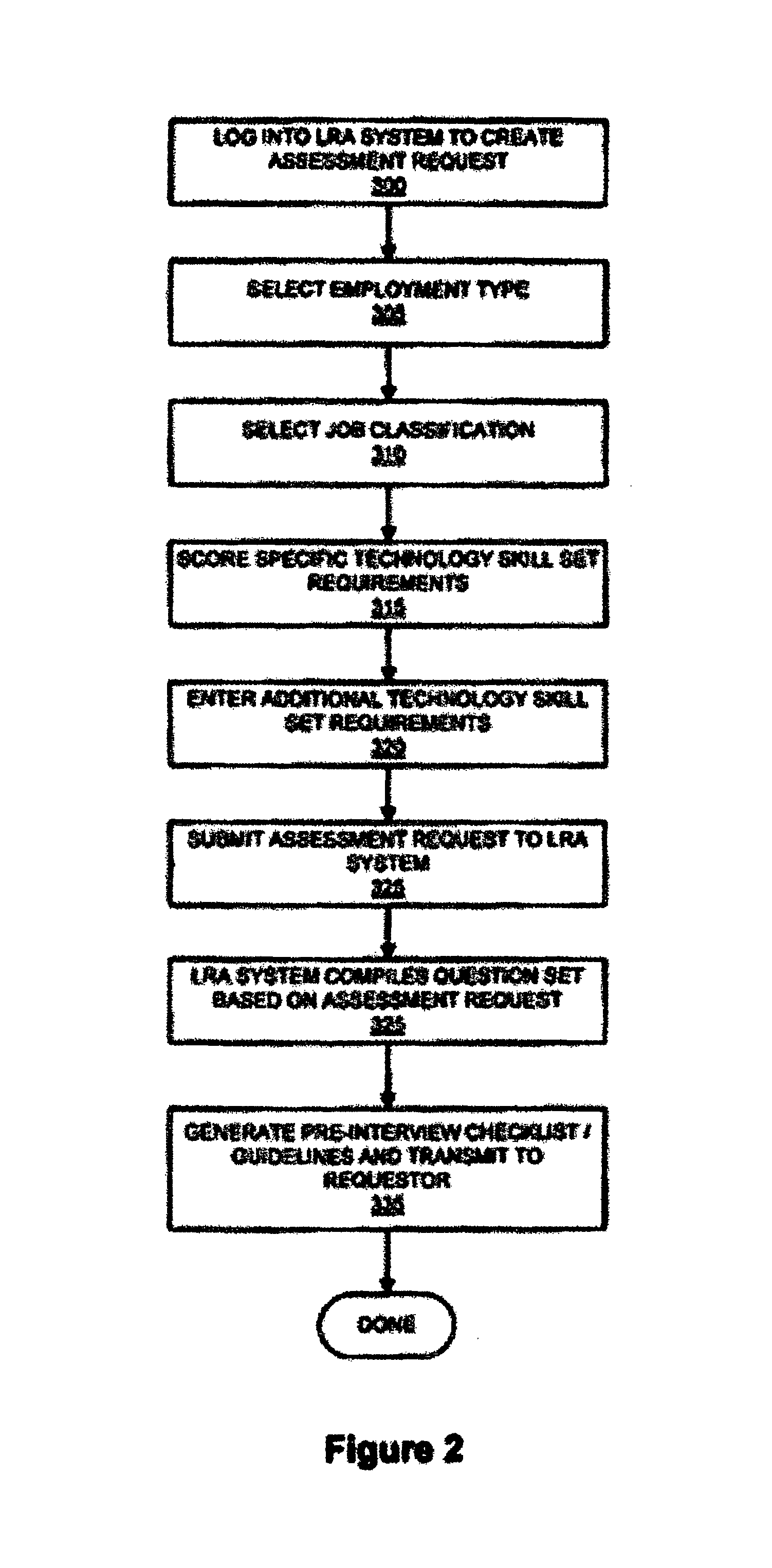
ActiveUS8517742B1Effectively scoreImprove system accuracyResourcesElectrical appliancesProgramming languageSkill sets
A system and method for testing labor resources is disclosed. The method includes defining core skill set requirements for a project and / or job and defining each according to expertise and experience requirements is disclosed. The defined skill set requirements and their corresponding expertise levels are provided into a tool via a web interface where they are used to compile an examination from questions selected from a database. The invention further administers the compiled examination to one or more candidates, scores the examination, transmits results and analysis to a hiring manager and accepts subjective input from the hiring manger following a personal interview. Subjective input is used to adjust future weighting values of the examination questions.
Owner:AMERICAN EXPRESS TRAVEL RELATED SERVICES CO INC
Sensor output analog processing-A microcontroller-based insect monitoring system
InactiveUS6882279B2Accurate countLarge electronicRadiation pyrometryPhotometryBiotechnologyMicrocontroller
A system for automated monitoring of pest insects in stored products to help identify insect species and improve reliability across adverse external conditions, including environmental, biological and aging. The system includes sensor units having a microcontroller which collects, analyzes, and stores data from at least one signal pulse created by an insect falling through the sensor unit.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Inertial measurement system and method with bias cancellation
ActiveUS7481109B2Improve system accuracyEnhanced signalWave based measurement systemsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
System having one or more inertial sensors in which one or more of the sensor input axes are modulated in orientation about an axis substantially perpendicular to the input, or sensitive, axis of the sensor and, in some embodiments, by also enhancing the accuracy of such a system to provide improved signal to noise ratio and reduced sensitivity to errors in alignment of the sensor axes to the dither axes.
Owner:EMCORE INC
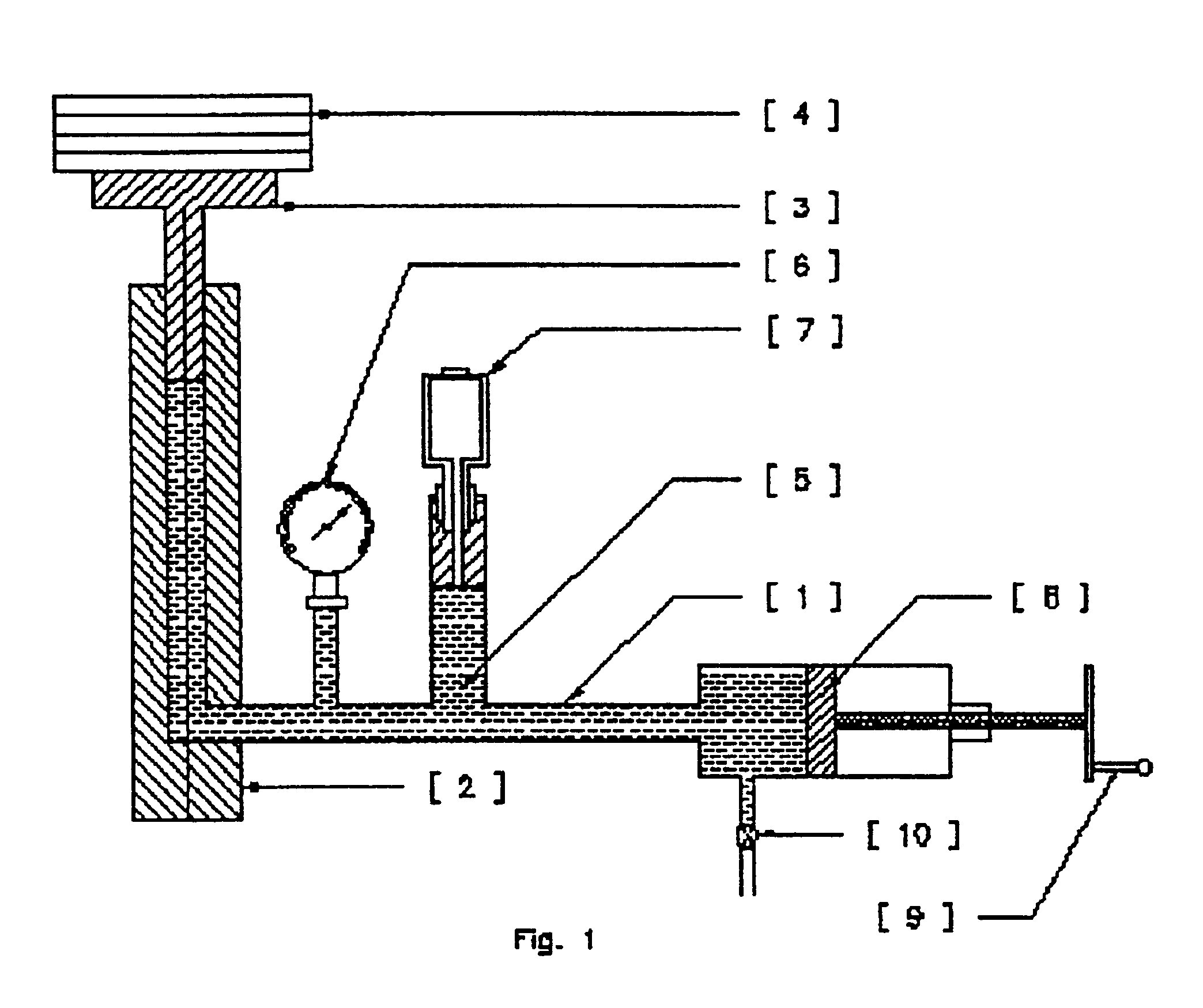
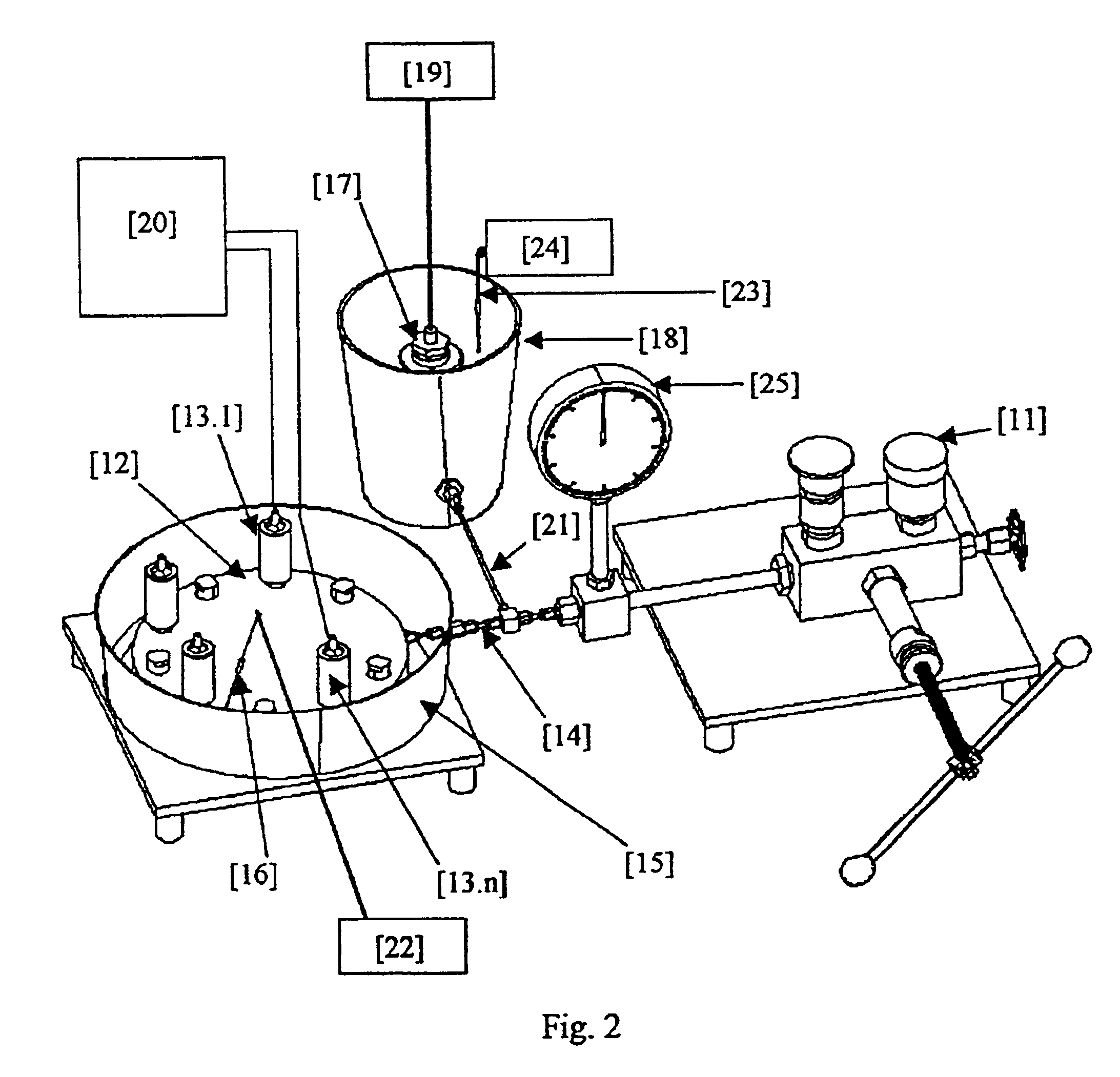
System for calibration of pressure transducers
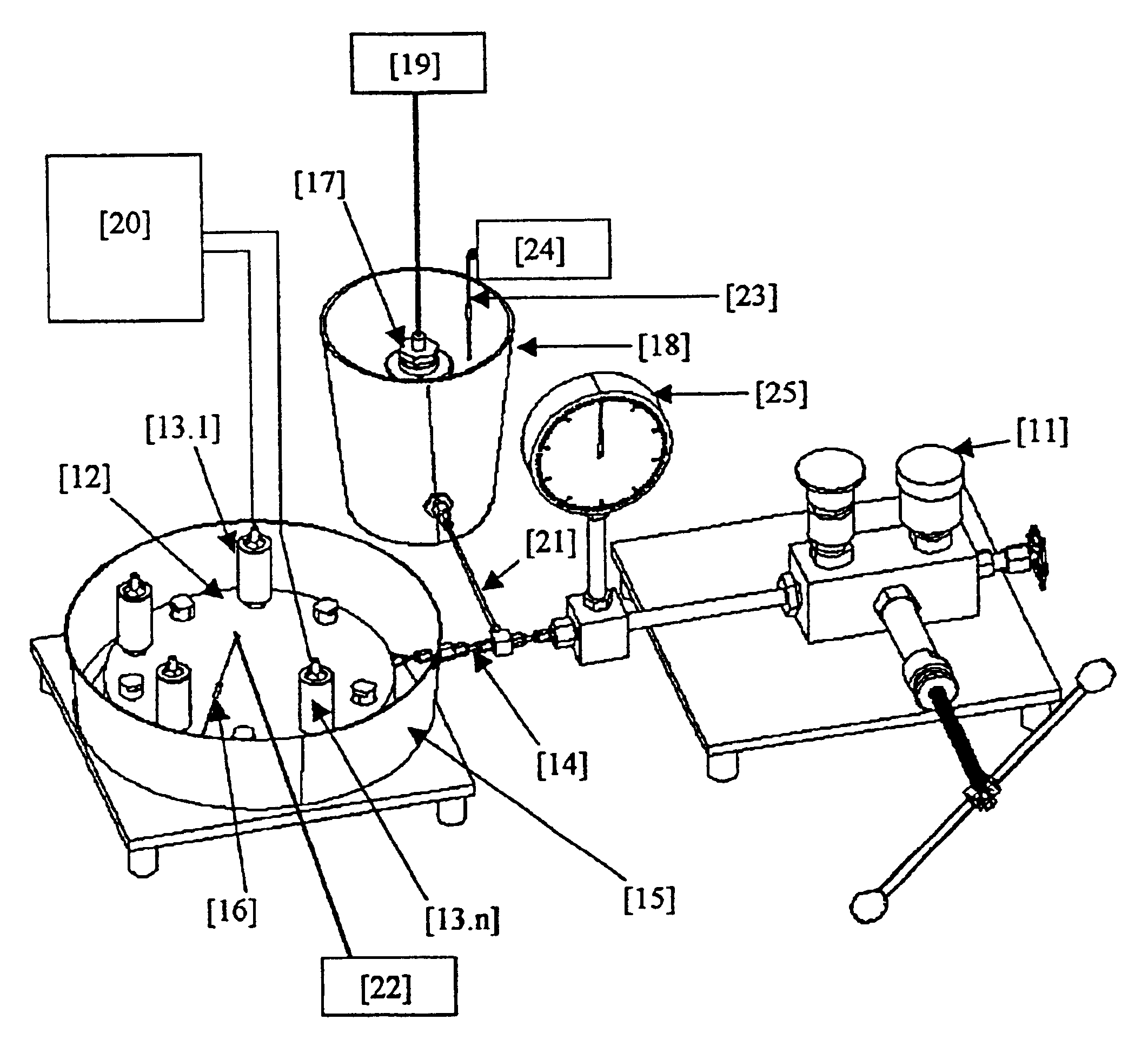
InactiveUS6848292B2Facilitates study of temperature-dependence sensitivityIncrease pressureFluid pressure measurementChemical methods analysisTransducerEngineering
The present invention relates to system for calibrating plurality of pressure transducers, said system comprising plurality of pressure transducers (13.1 to 13.n) mounted on a mounting means (12) which receives pressure input from a pressure source (11) via a hollow pipe (14) and distributes the pressure evenly to all the pressure transducers, said plurality of pressure transducers are mounted on the mounting means and placed inside a vessel (15) as to vary the temperature of the pressure transducers, said pressure source is also connected to a standard pressure transducer (17) whose temperature is maintained at the same level as that of pressure transducers (13.1 to 13.n).
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com