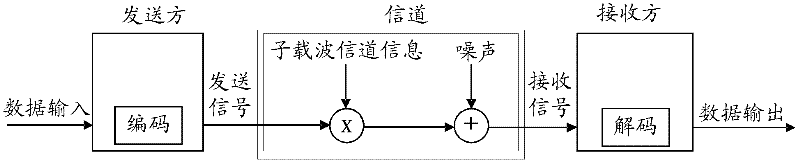
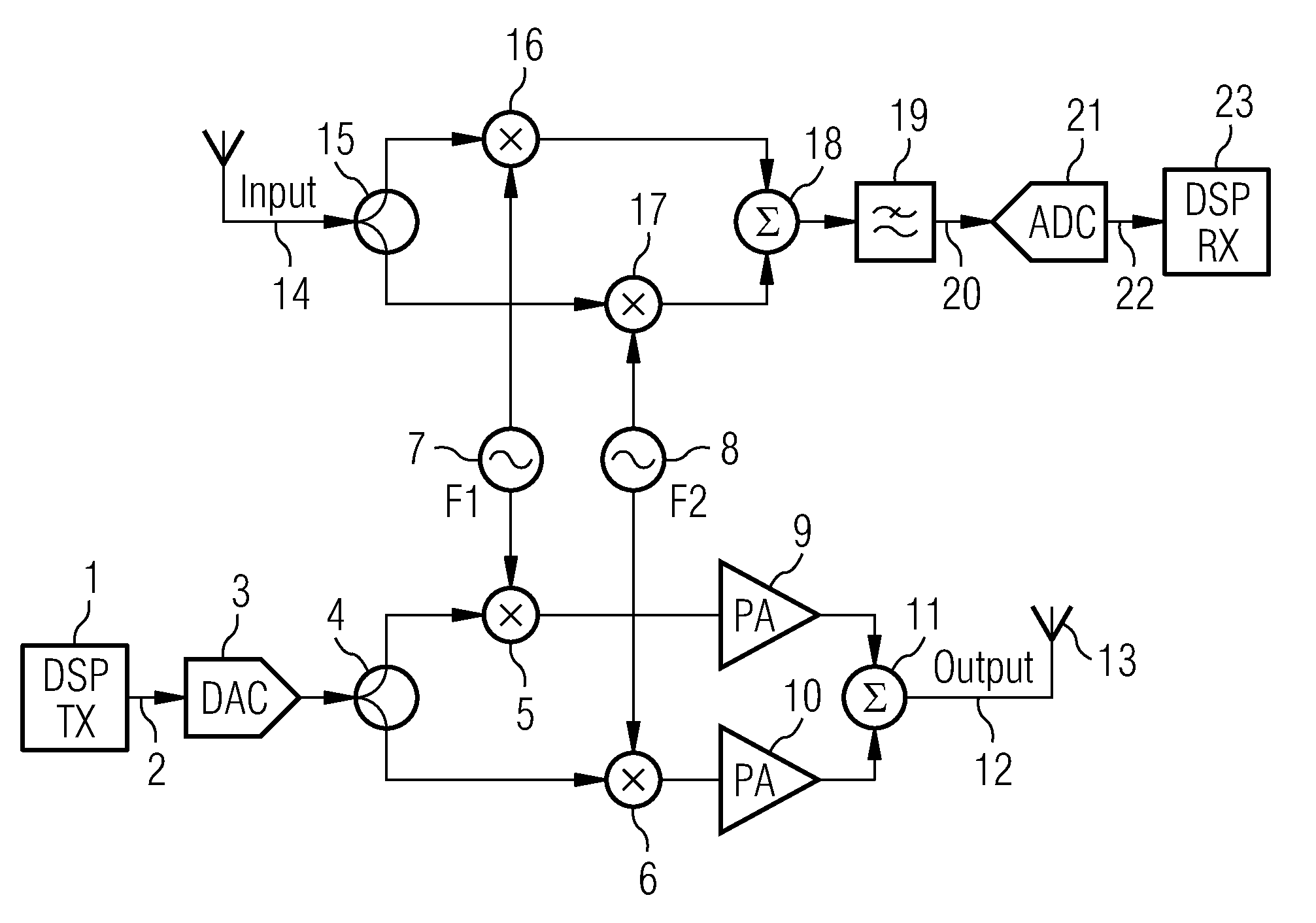
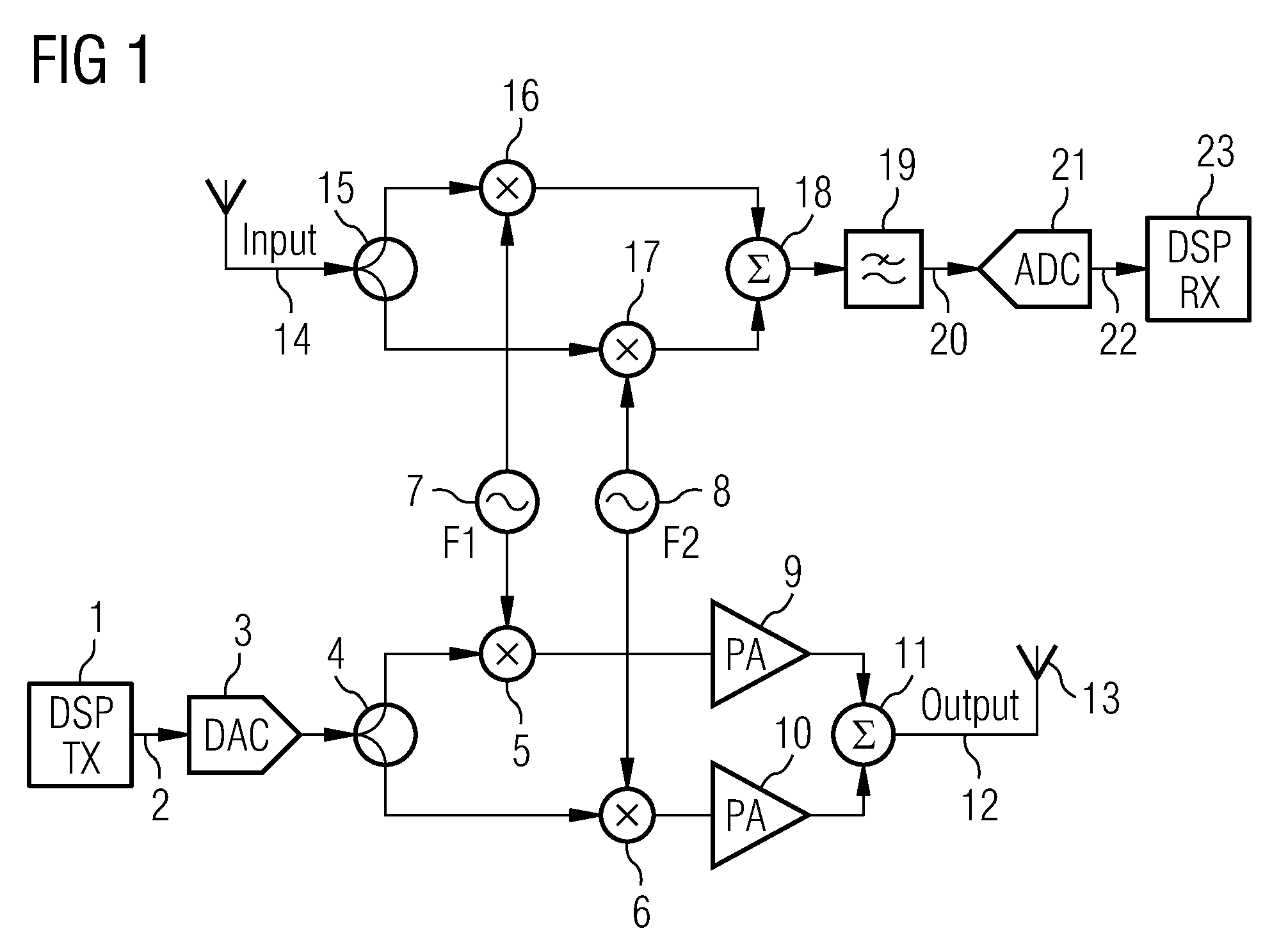
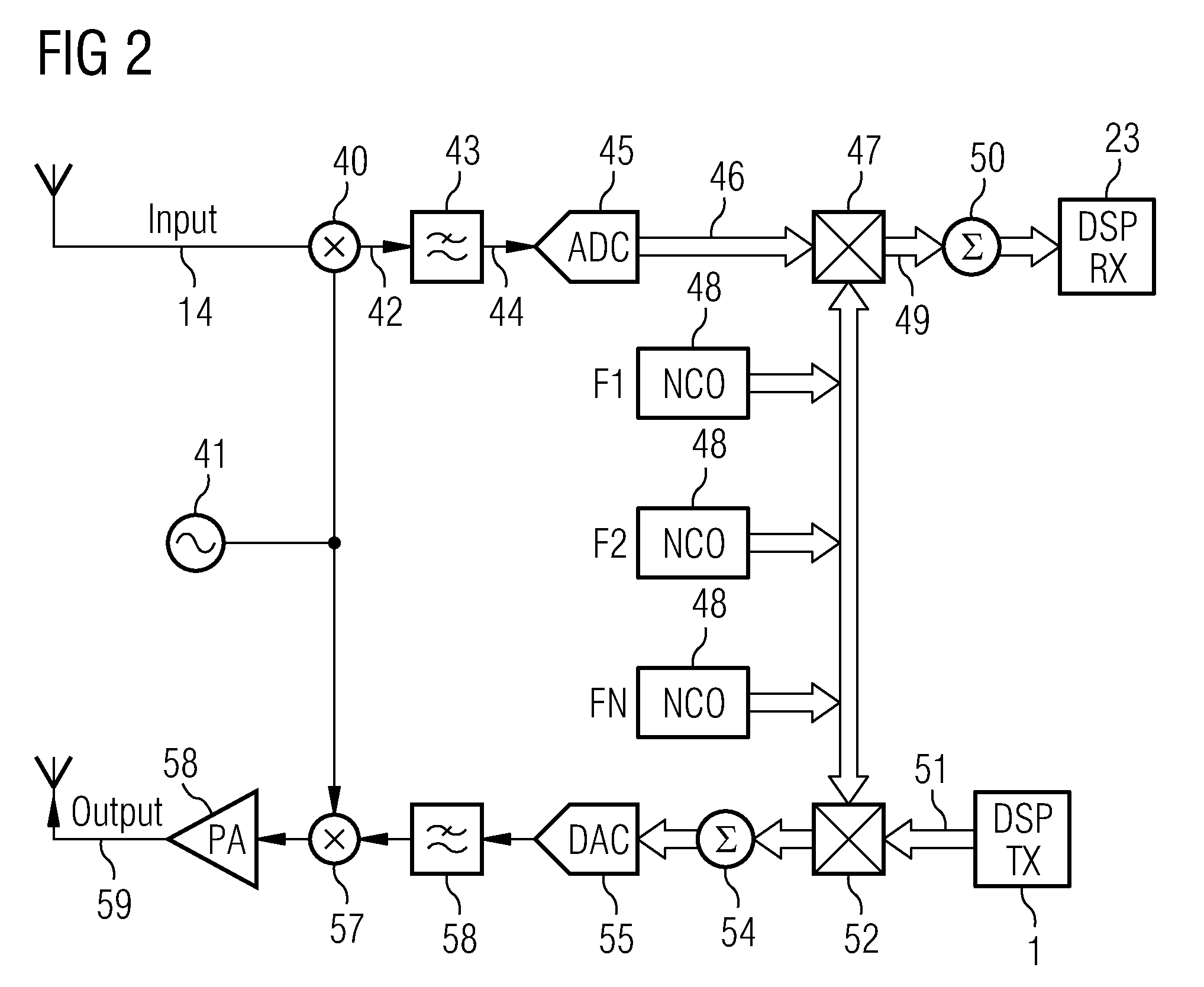
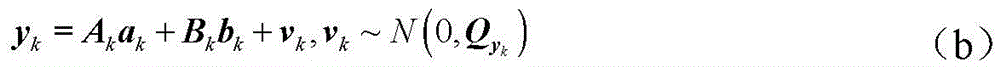Patents
Literature
86results about How to "Reduce multipath effects" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
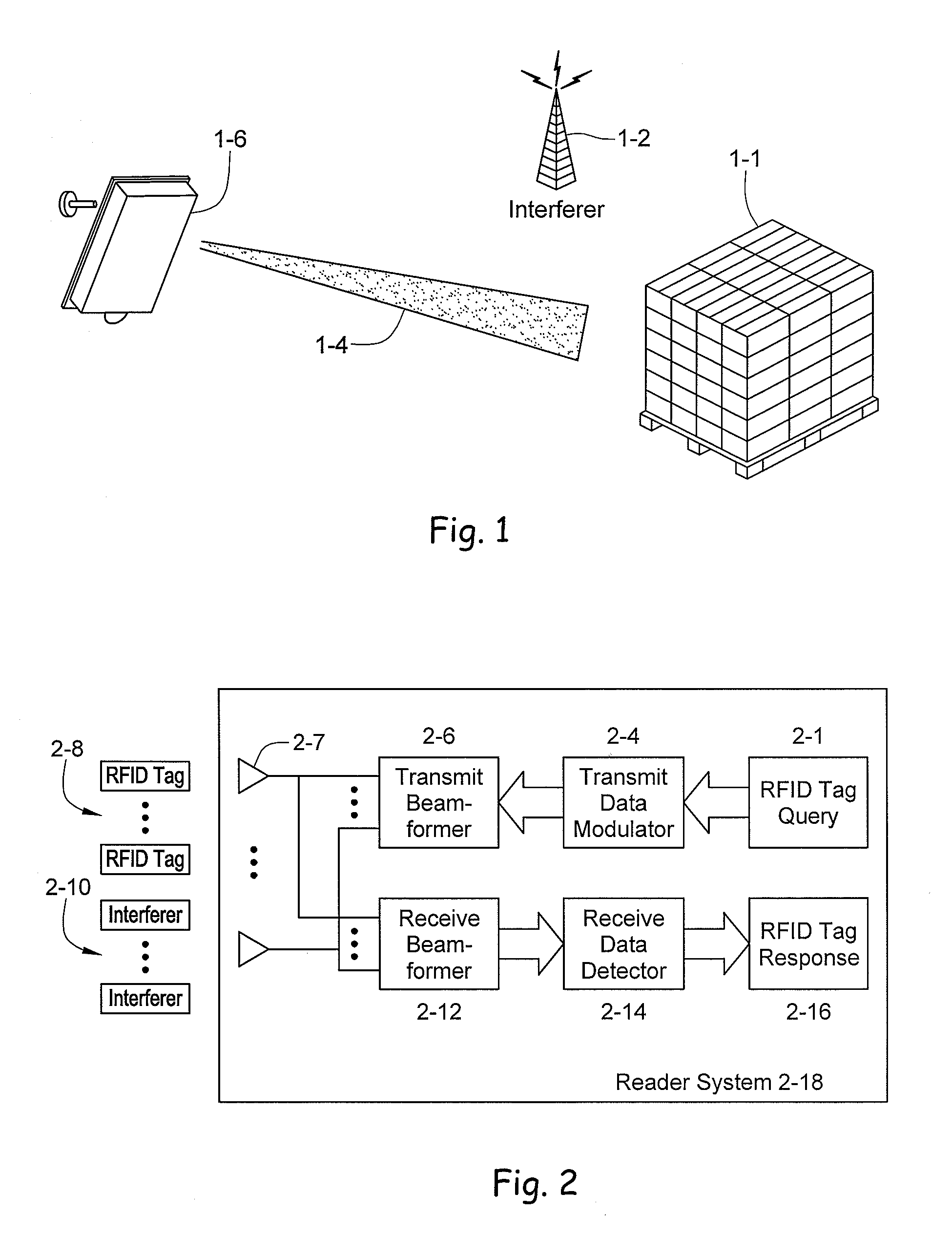
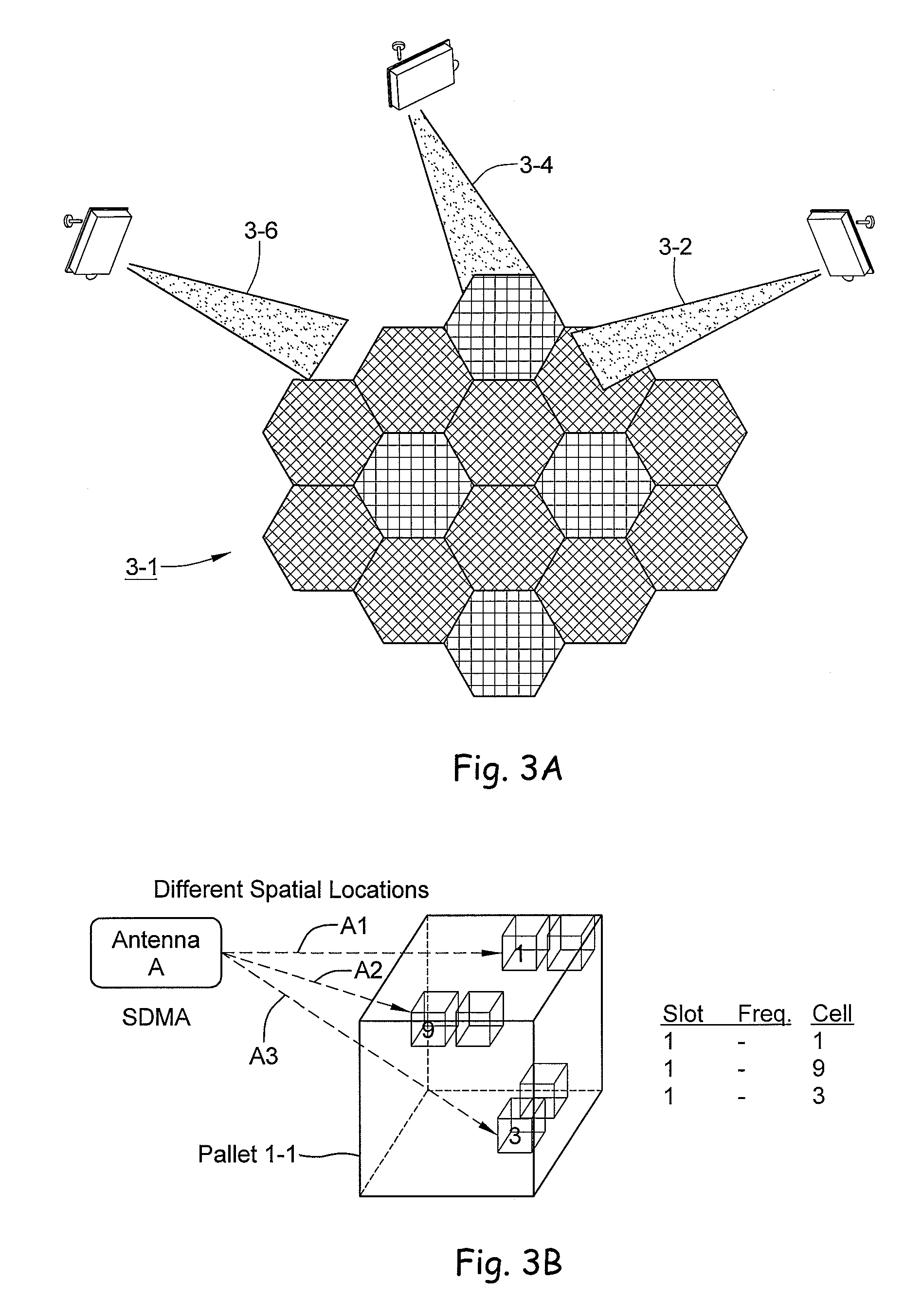
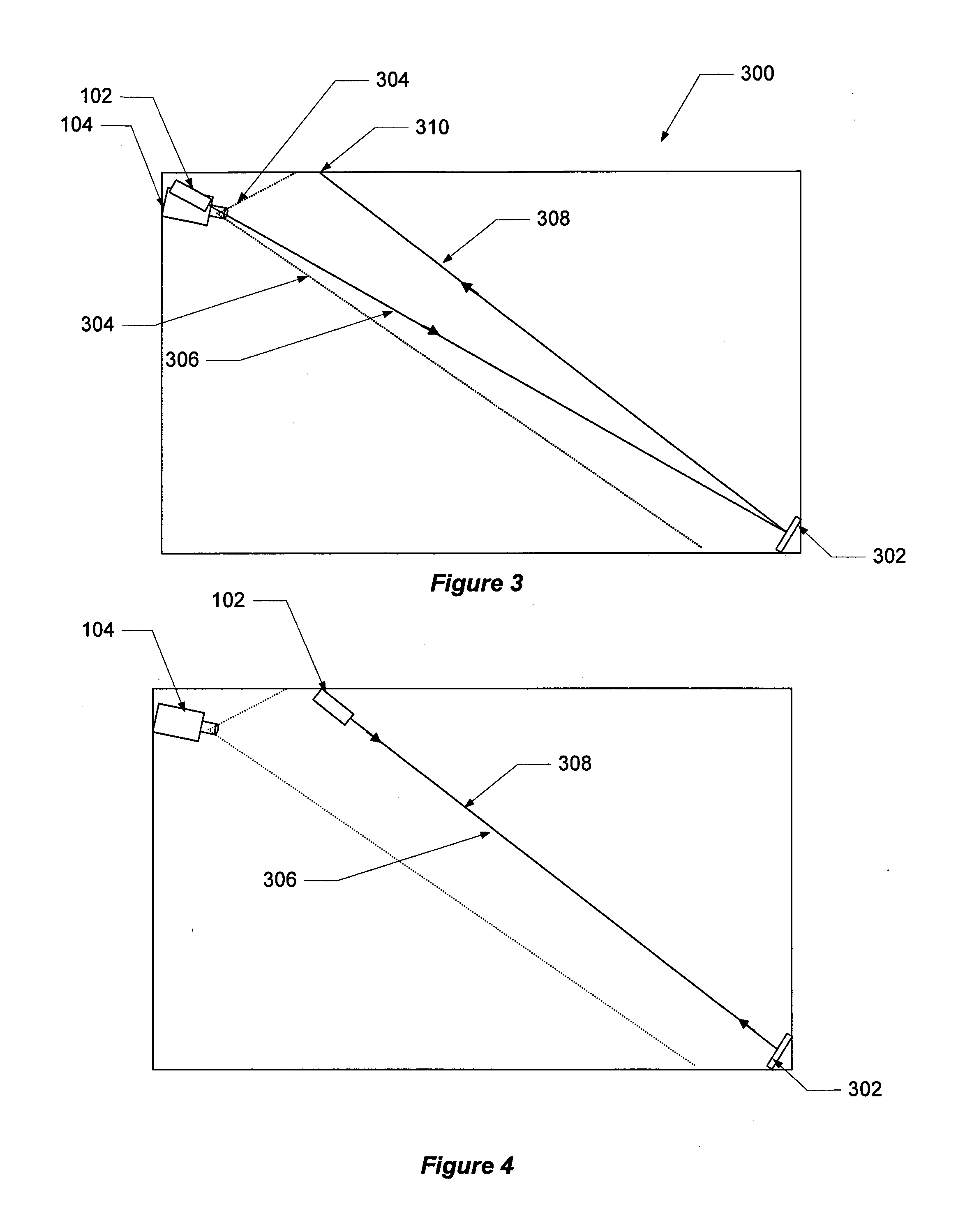
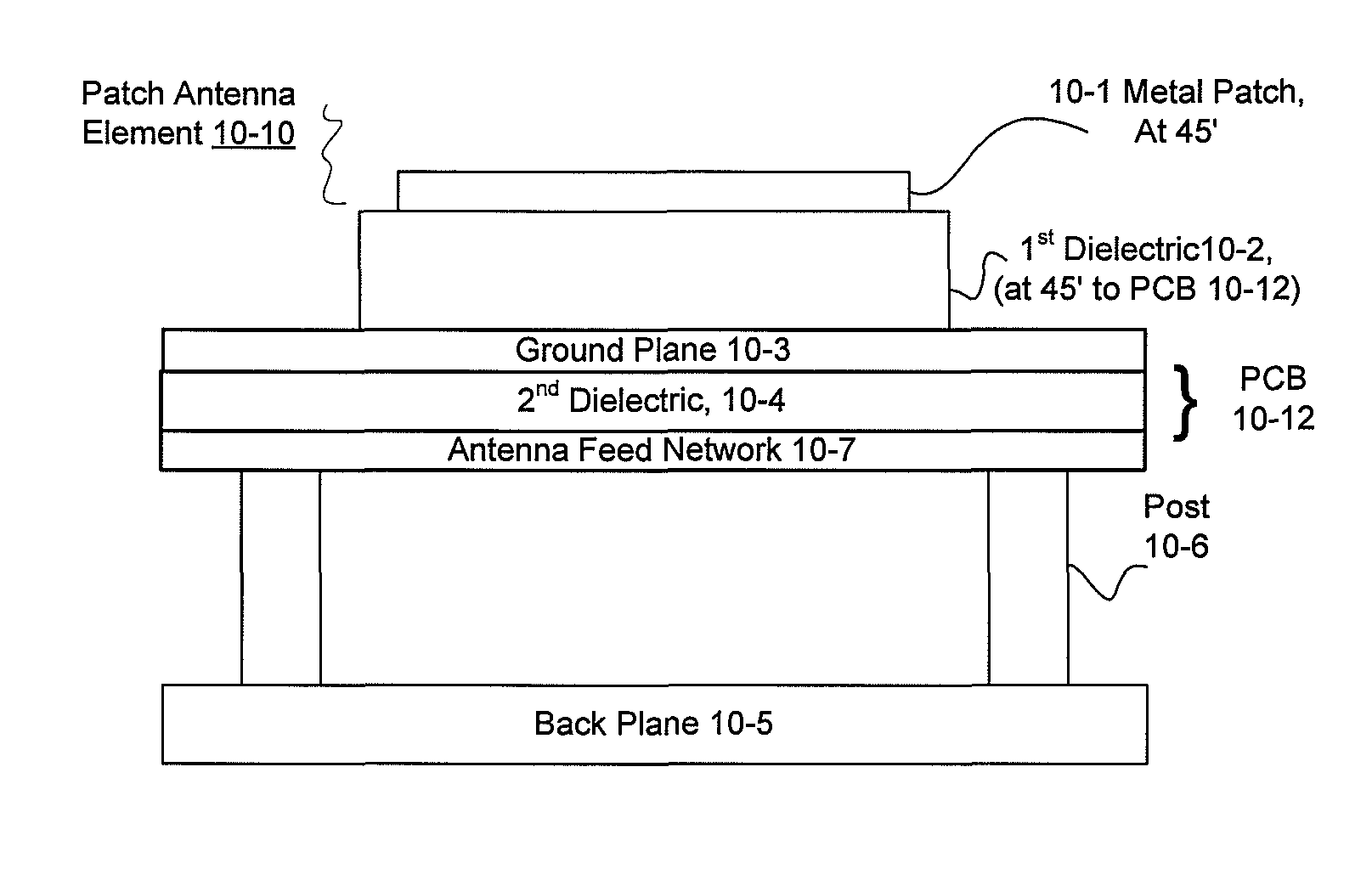
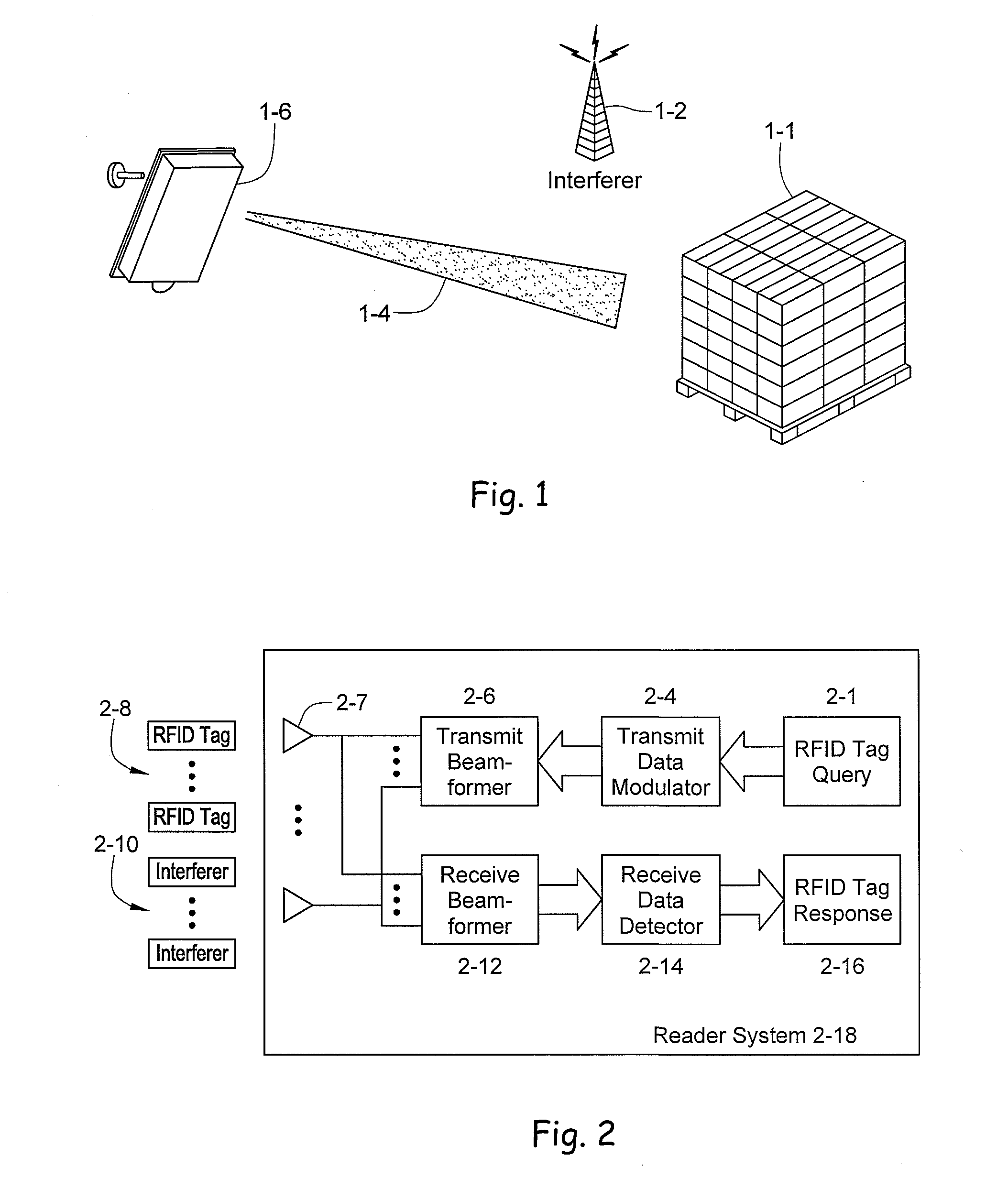
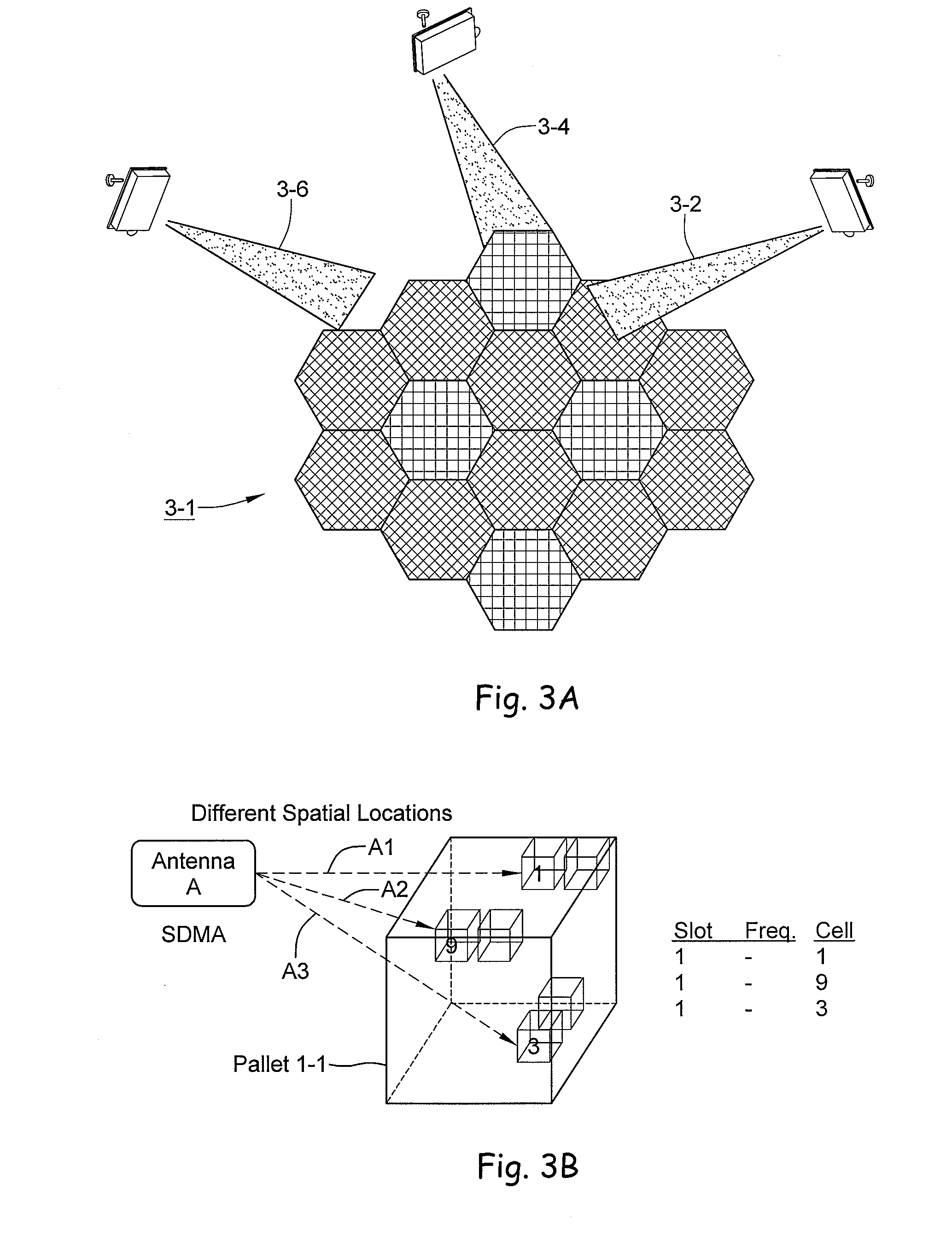
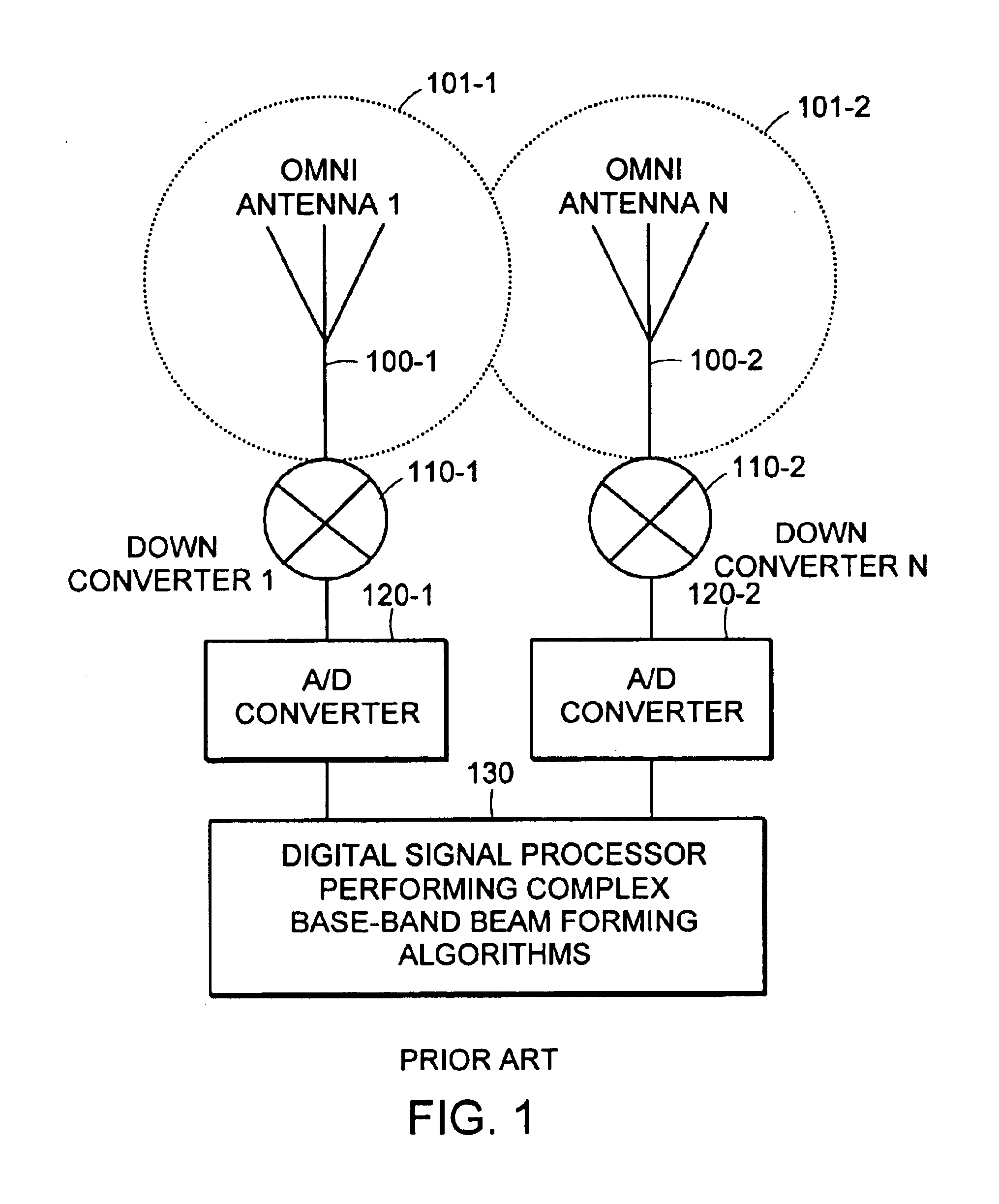
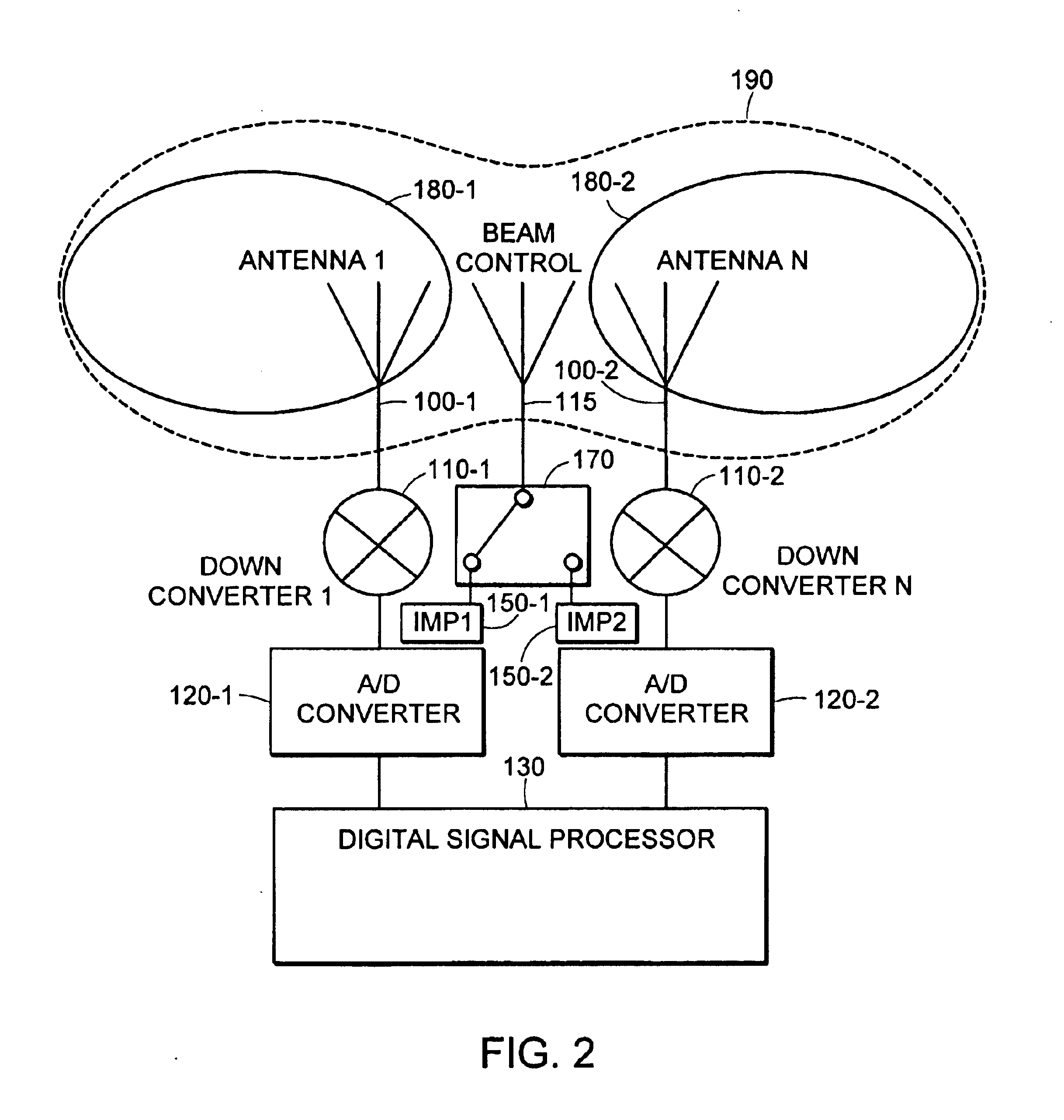
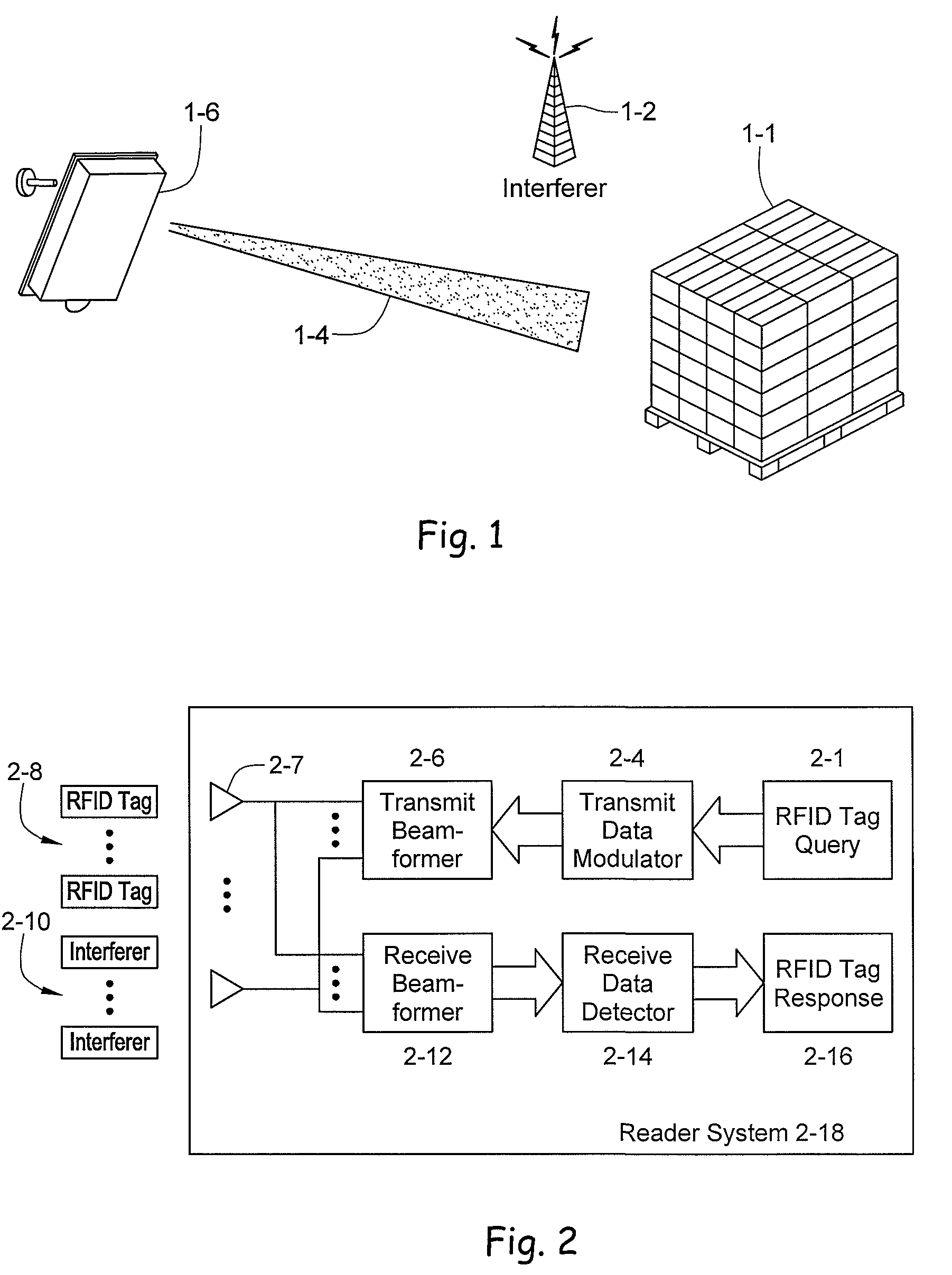
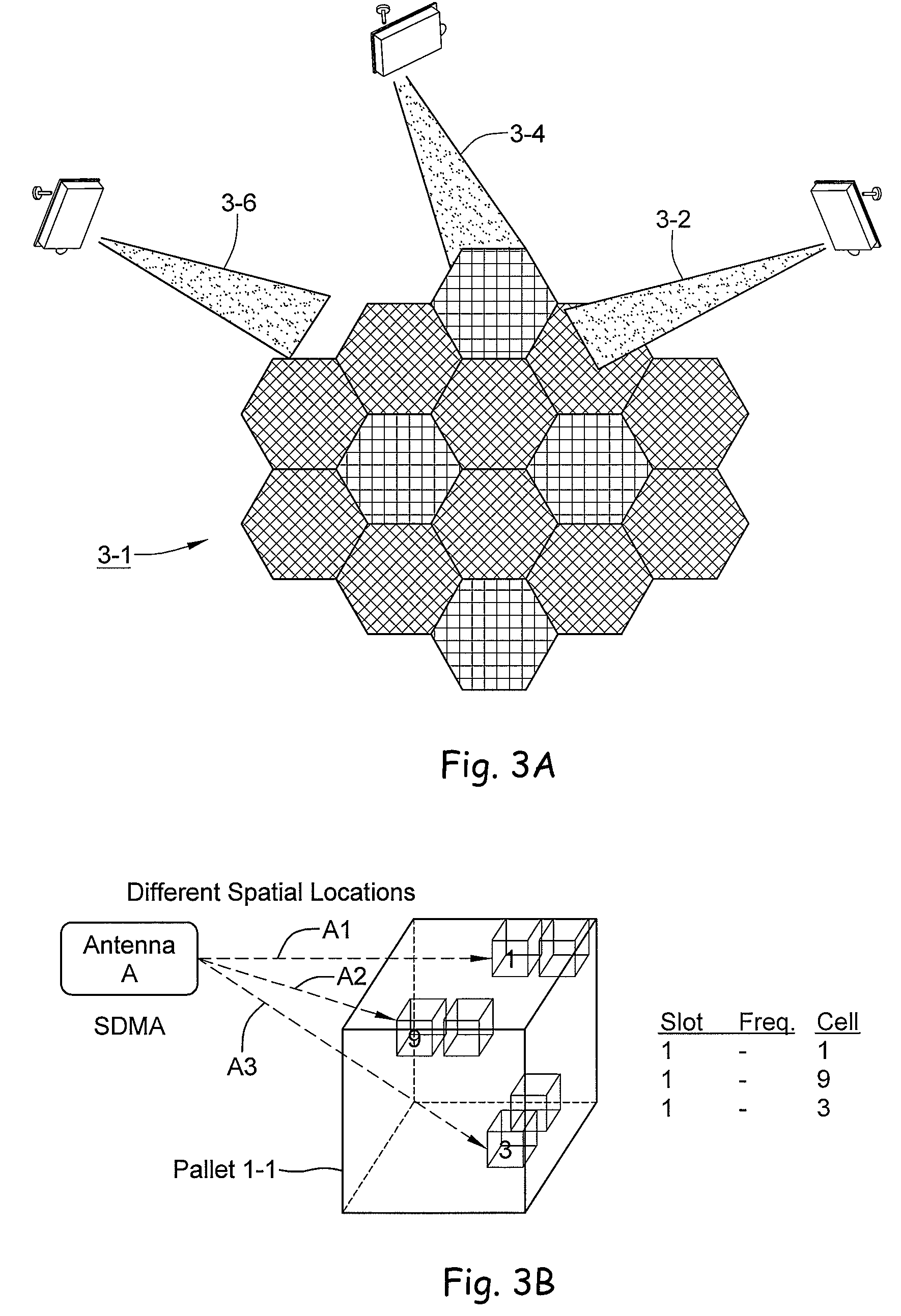
RFID beam forming system
ActiveUS20080012710A1Improve accuracyReduce multipath effectsMemory record carrier reading problemsBroadcast transmission systemsMulti bandLight beam
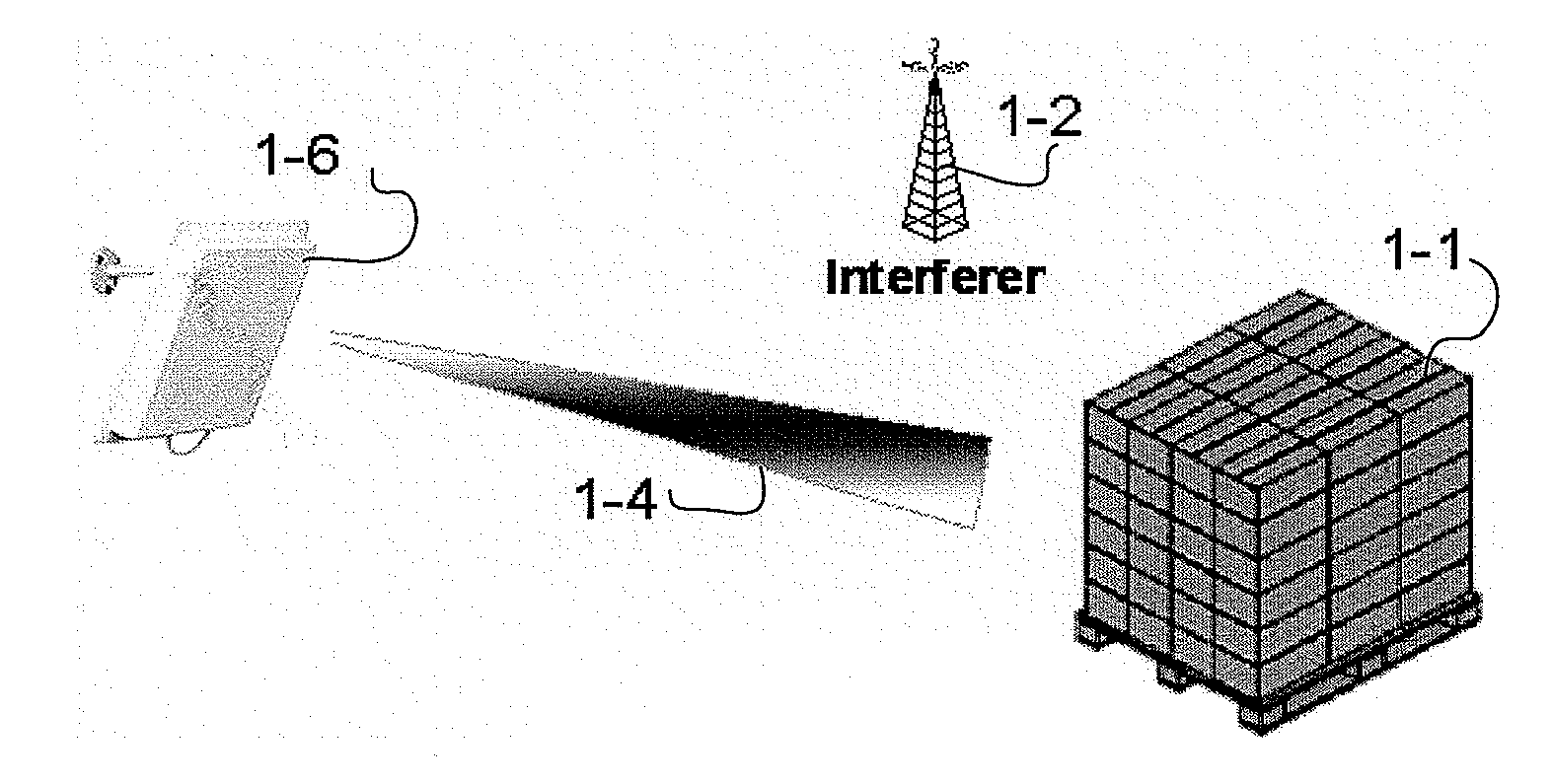
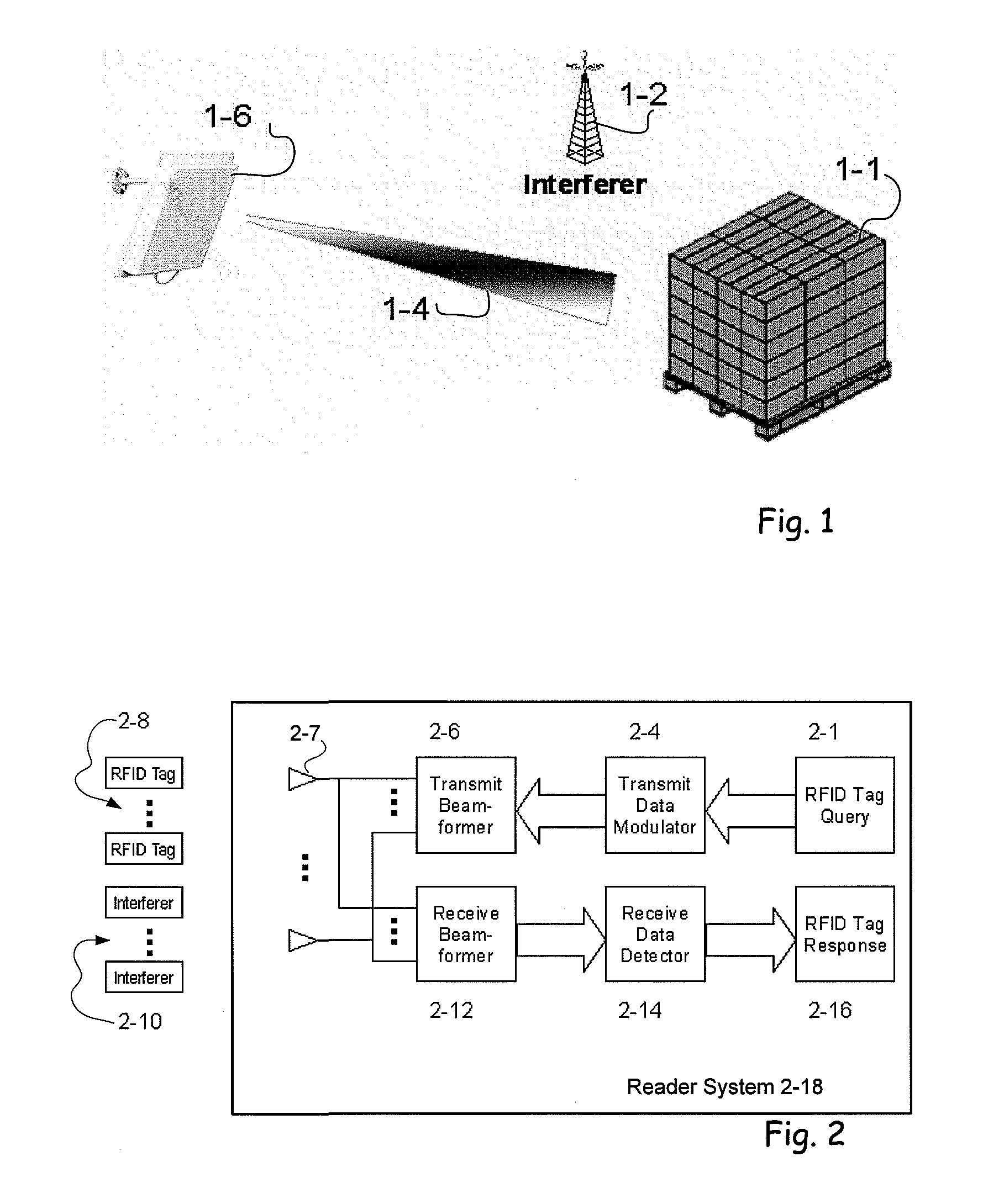
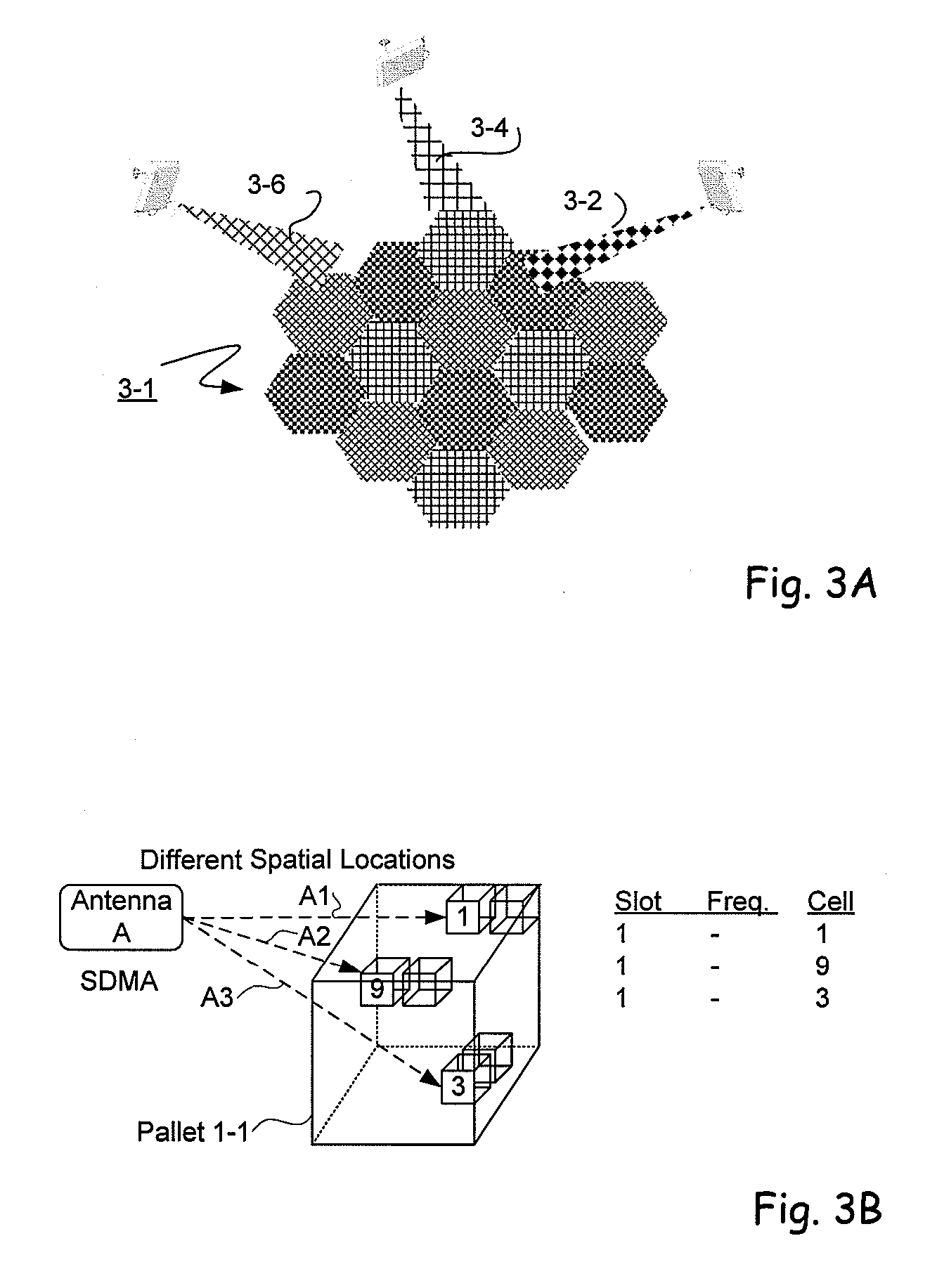
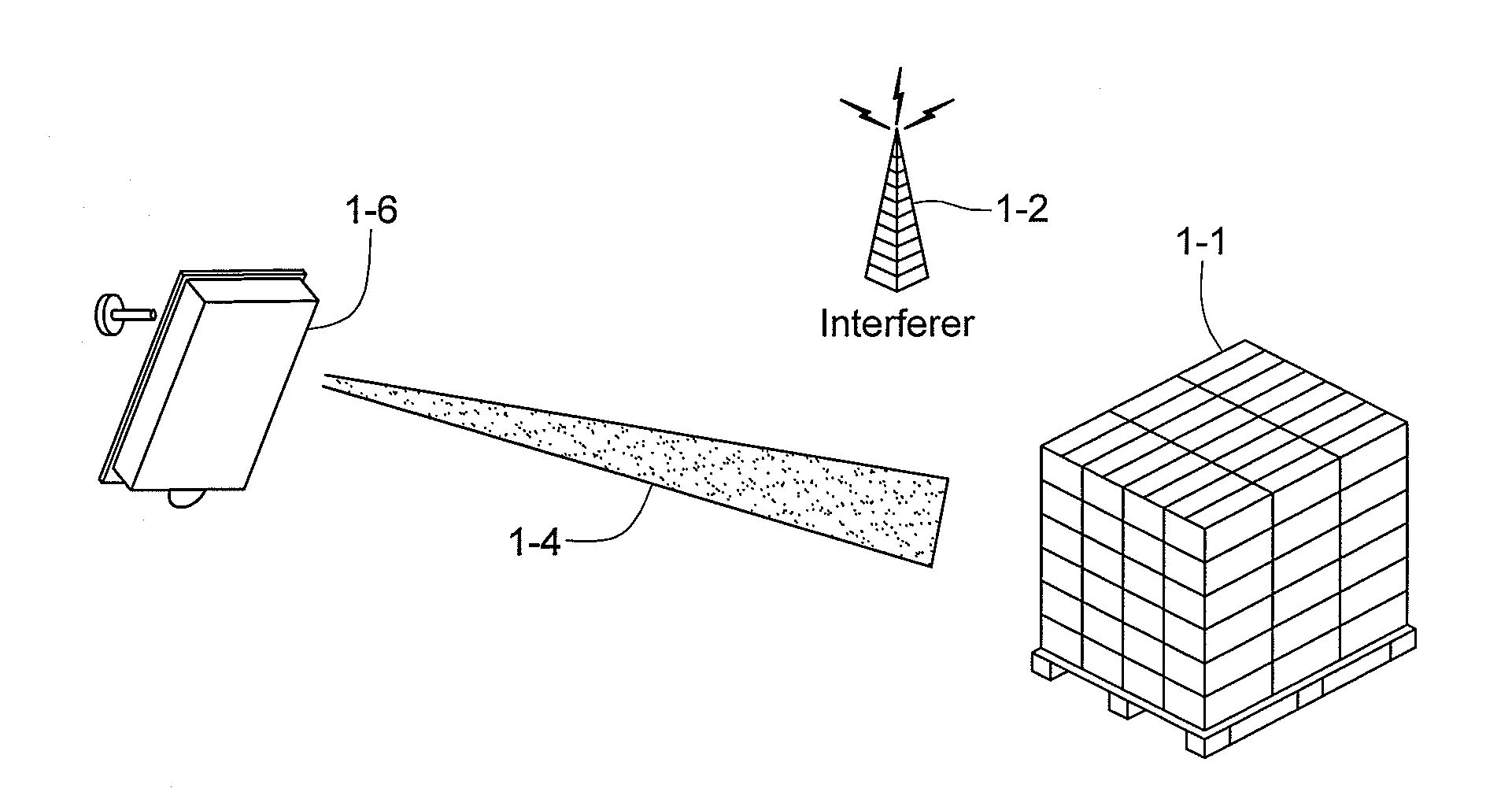
A multi-protocol, multi-band array antenna system may be used in Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) system reader and sensory networks. The antenna array may include array elements with an integrated low noise amplifier. The system may employ digital beam forming techniques for transmission and steering of a beam to a specific sensor tag or group of tags in an cell. The receive beam forming network is optimized for detecting signals from each sensor tag. Narrow and wideband interferences may be excised by an interference nulling algorithm. Space division multiplexing may be used by the antenna system to enhance system processing capacity.
Owner:MOJIX
RFID beam forming system
ActiveUS7873326B2Improve accuracyReduce multipath effectsSimultaneous aerial operationsMemory record carrier reading problemsMulti bandMulti protocol
Owner:MOJIX
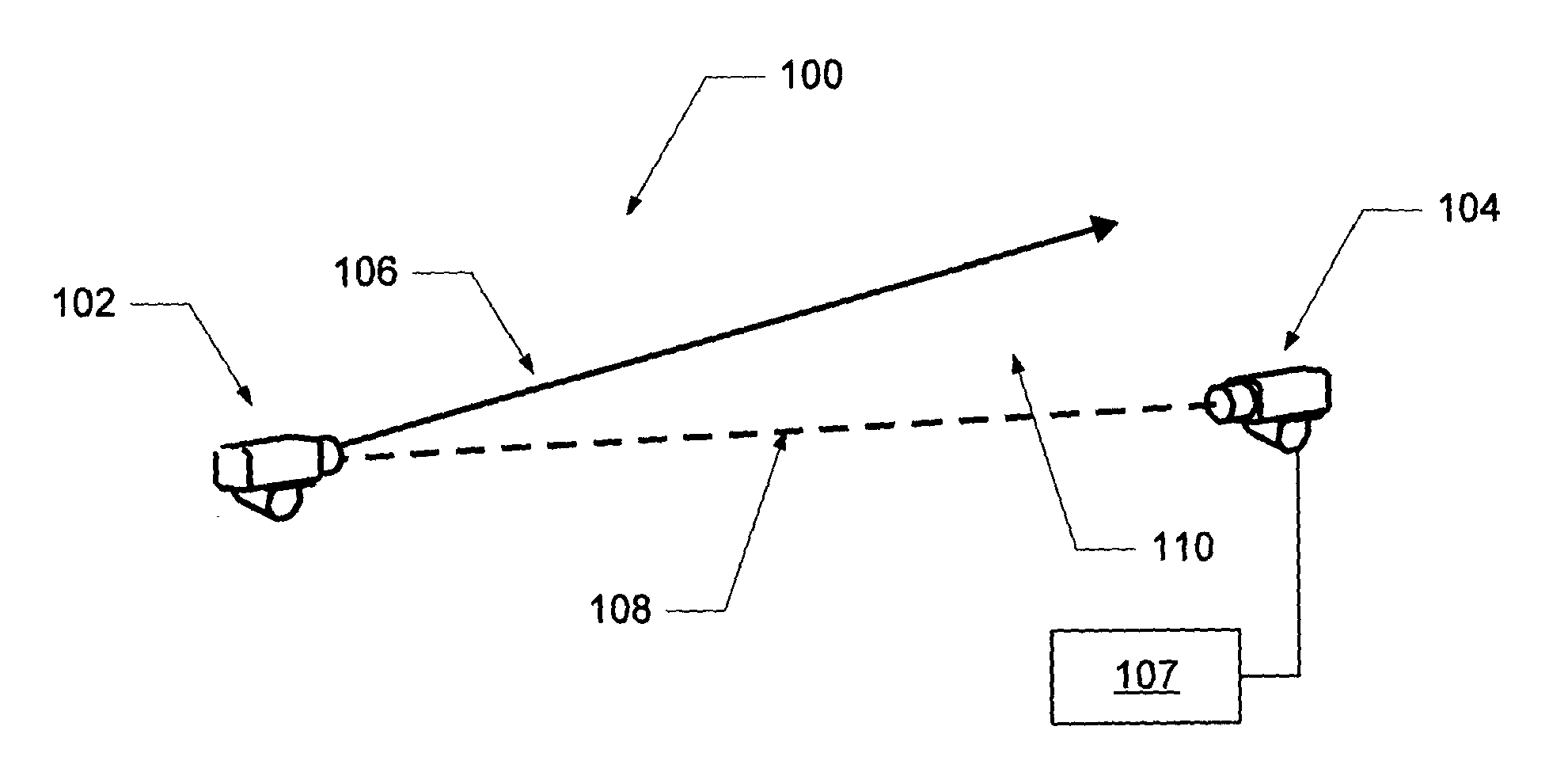
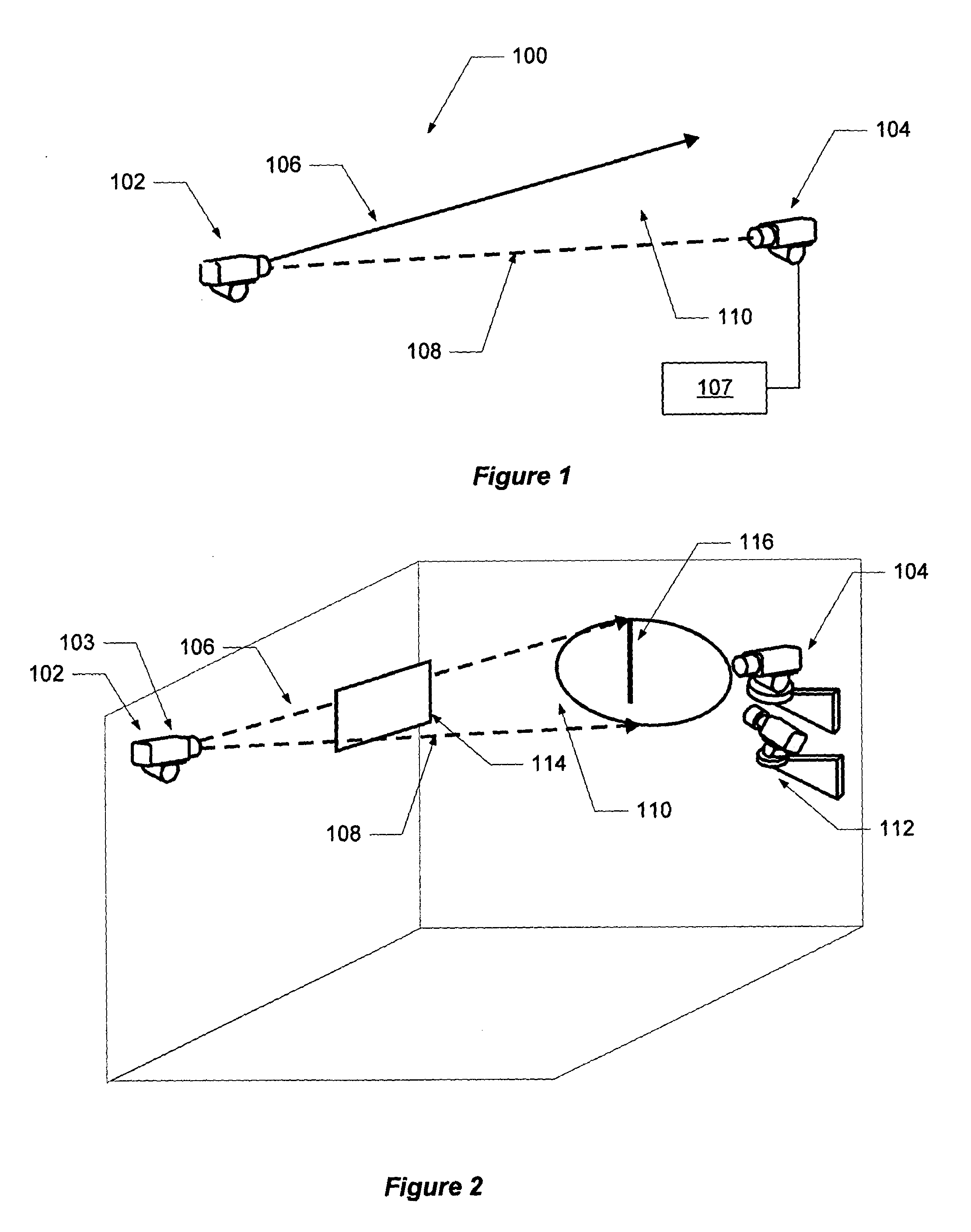
Particle detection
ActiveUS20110058167A1Reduce multipath effectsReduce sensitivityTelevision system detailsScattering properties measurementsAir volumeUsability
A particle detection system (100), such as an active video smoke detection system, includes at least one illumination means (102) for directing a beam (106) of radiation through at least part of the air volume being monitored (110), an image sensor (104) is positioned to capture images of at least part of a beam (106) from illumination means (102); and means to analyse (107) the captured images to detect the presence of particles within the volume. At least 29 different aspects are described for improving the sensitivity, usability, and robustness of particle detection. These include, for example, configuring illumination means (102) to create a curtain of light or a rapidly-scanned beam across the air volume (110), and configuring a reflector to steer or change direction of a beam reflected from illumination means (102).
Owner:GARRETT THERMAL SYST LTD
RFID antenna system
InactiveUS20080030422A1Improve accuracyReduce multipath effectsSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMulti bandEngineering
A multi-protocol, multi-band array antenna system may be used in Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) system reader and sensory networks. The antenna array may include array elements with an integrated low noise amplifier. The system may employ digital beam forming techniques for transmission and steering of a beam to a specific sensor tag or group of tags in an cell. The receive beam forming network is optimized for detecting signals from each sensor tag. Narrow and wideband interferences may be excised by an interference nulling algorithm. Space division multiplexing may be used by the antenna system to enhance system processing capacity.
Owner:MOJIX
Low cost multiple pattern antenna for use with multiple receiver systems
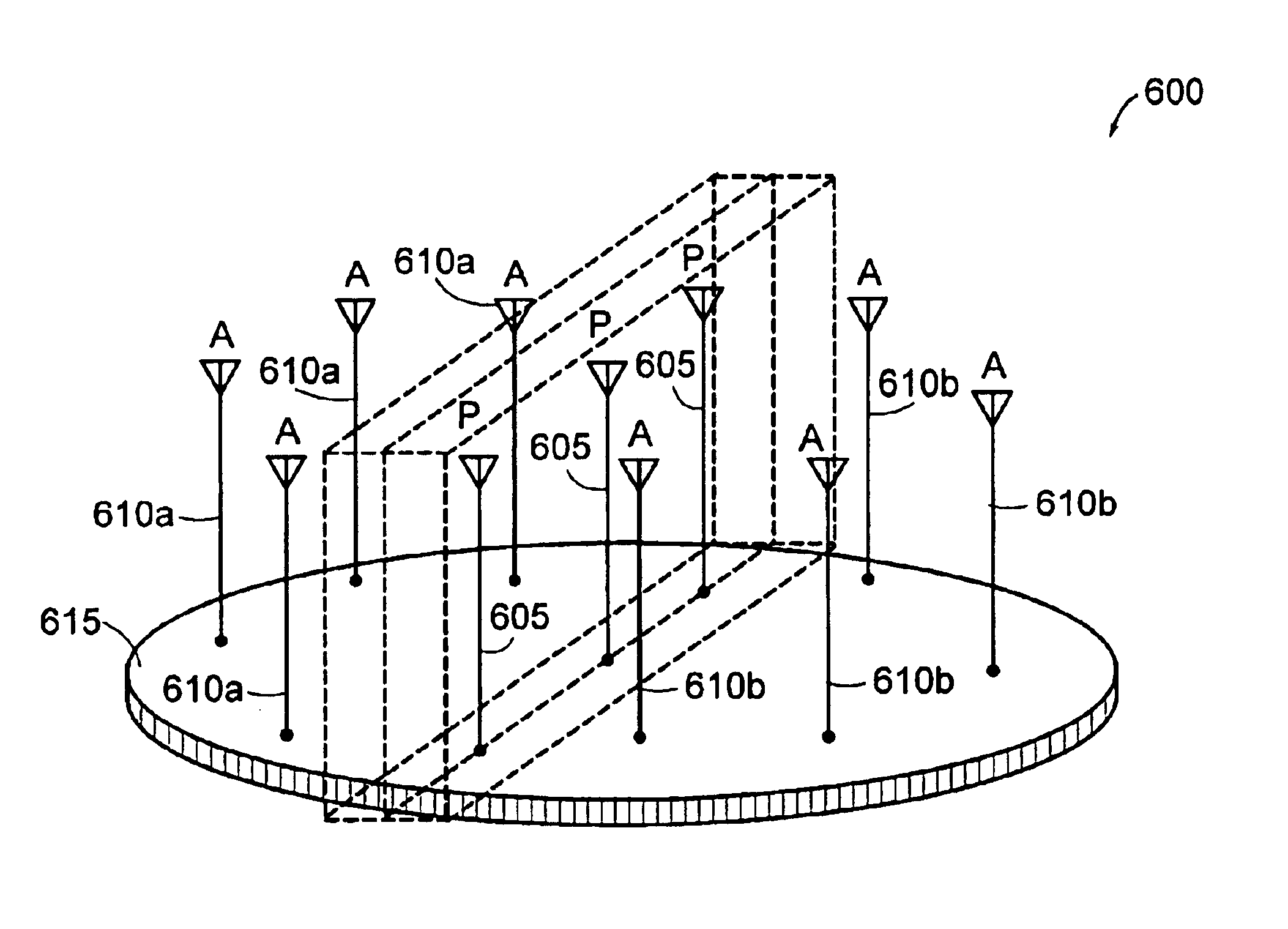
InactiveUS6894653B2Low costImprove performanceAntenna supports/mountingsIndividually energised antenna arraysIntermediate frequencyOmni directional
An antenna assembly includes at least two active or main radiating omni-directional antenna elements arranged with at least one beam control or passive antenna element used as a reflector. The beam control antenna element(s) may have multiple reactance elements that can electrically terminate it to adjust the input or output beam pattern(s) produced by the combination of the active antenna elements and the beam control antenna element(s). More specifically, the beam control antenna element(s) may be coupled to different terminating reactances to change beam characteristics, such as the directivity and angular beamwidth. Processing may be employed to select which terminating reactance to use. Consequently, the radiator pattern of the antenna can be more easily directed towards a specific target receiver / transmitter, reduce signal-to-noise interference levels, and / or increase gain by using Radio Frequency (RF), Intermediate Frequency (IF), or baseband processing. A Multiple-Input, Multiple-Output (MIMO) processing technique may be employed to operate the antenna assembly with simultaneous beam patterns.
Owner:IPR LICENSING INC
RFID antenna system
InactiveUS7667652B2Improve accuracyReduce multipath effectsSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMulti bandEngineering
A multi-protocol, multi-band array antenna system may be used in Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) system reader and sensory networks. The antenna array may include array elements with an integrated low noise amplifier. The system may employ digital beam forming techniques for transmission and steering of a beam to a specific sensor tag or group of tags in an cell. The receive beam forming network is optimized for detecting signals from each sensor tag. Narrow and wideband interferences may be excised by an interference nulling algorithm. Space division multiplexing may be used by the antenna system to enhance system processing capacity.
Owner:MOJIX
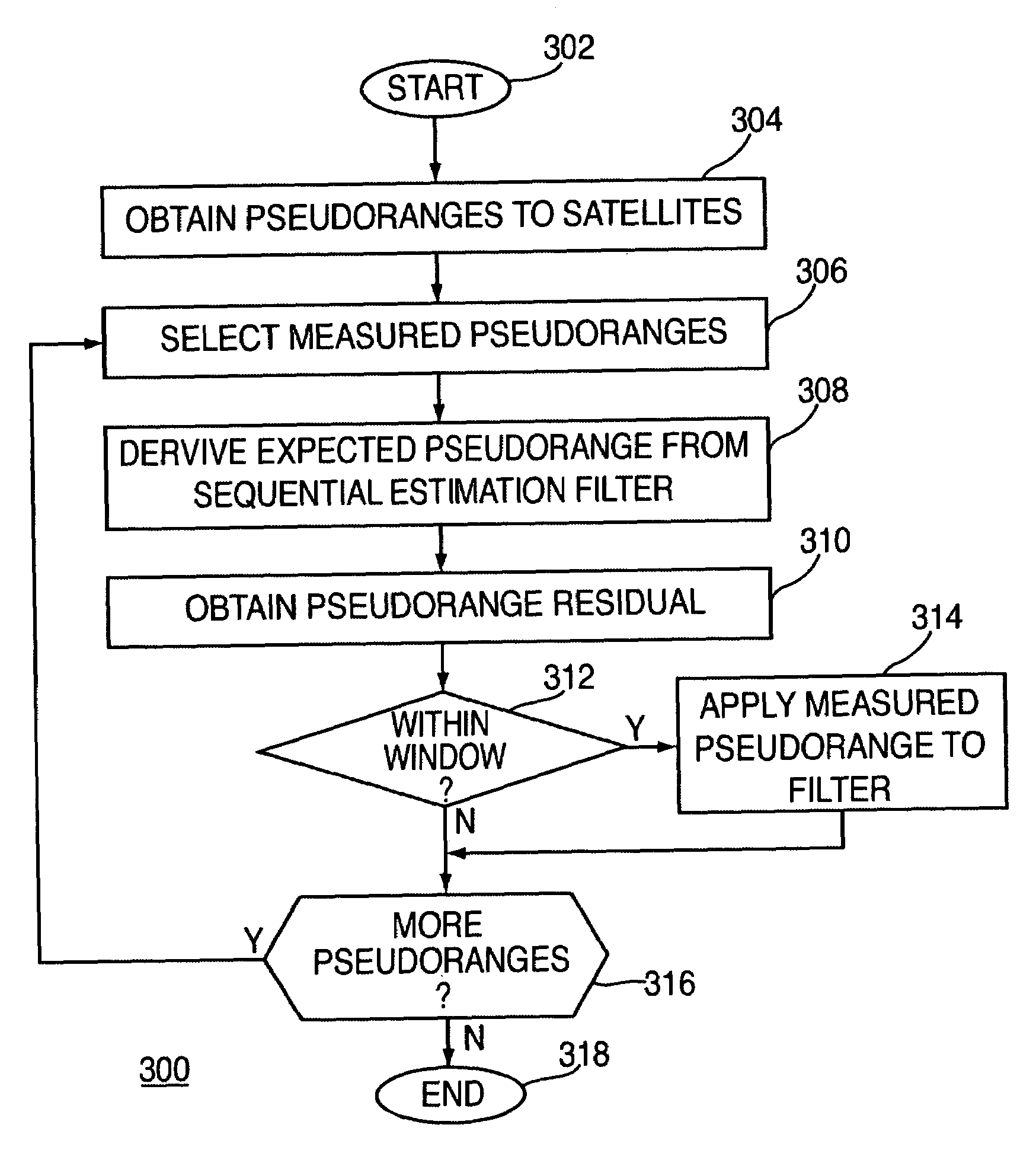
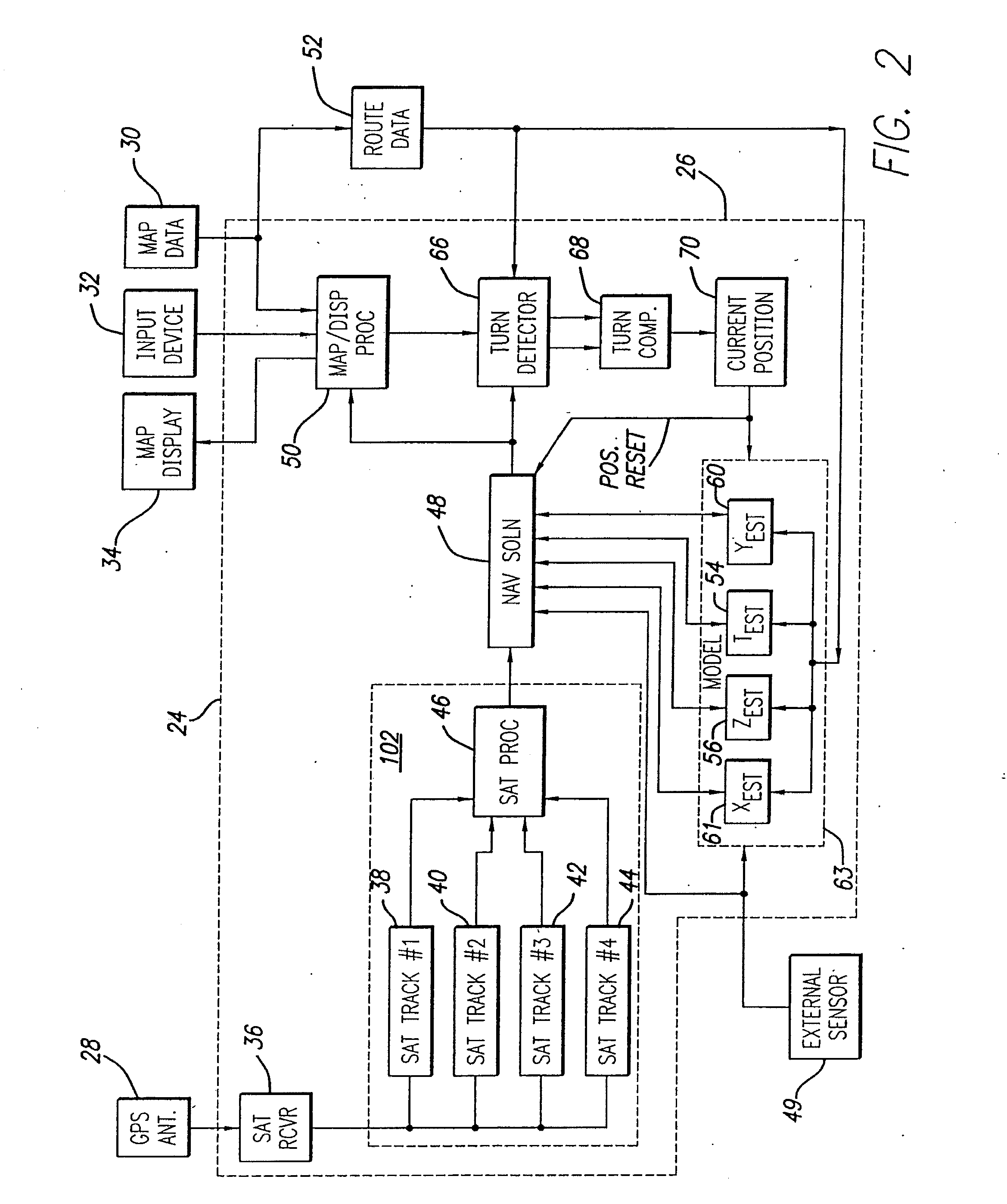
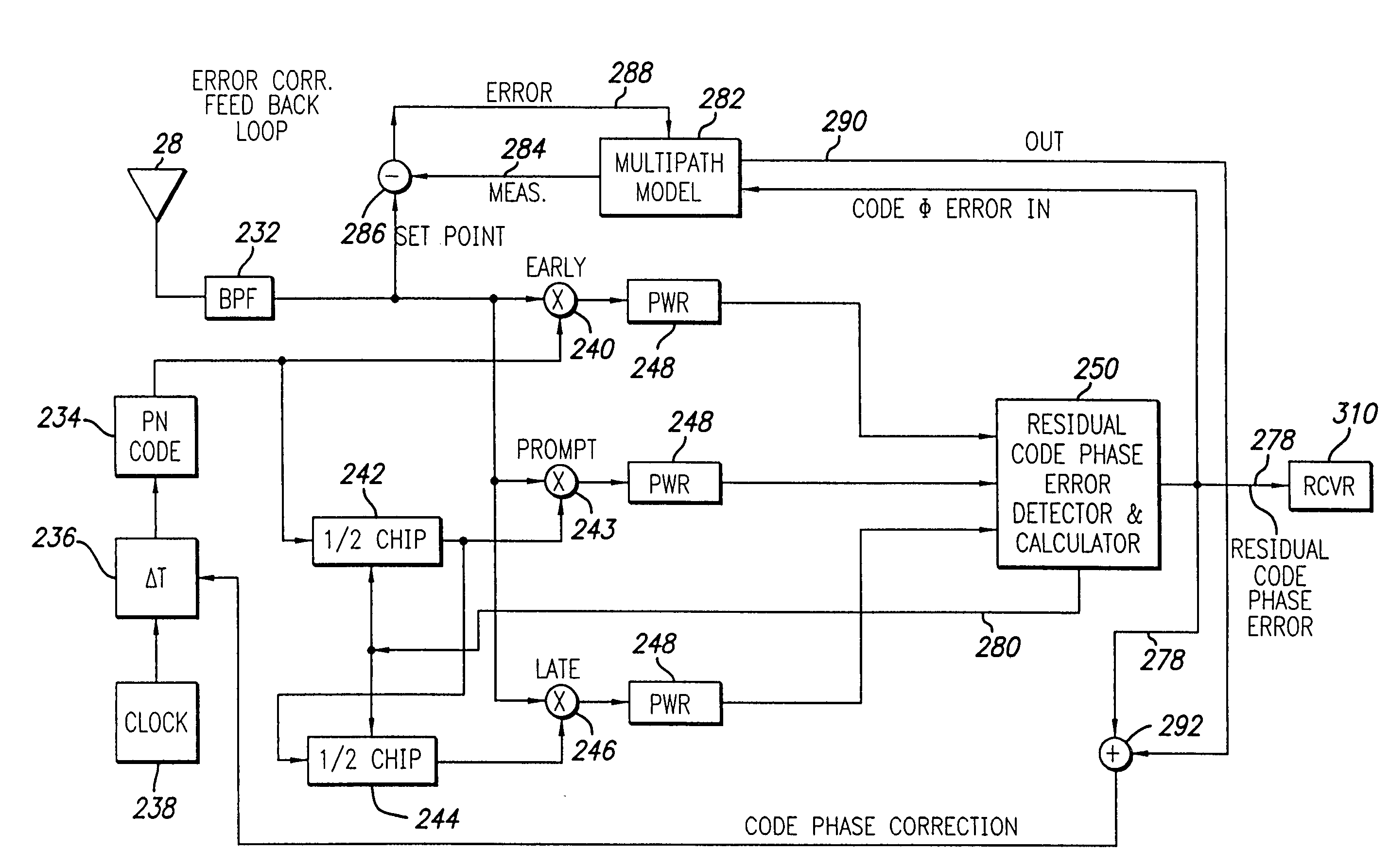
Method and apparatus for mitigating multipath effects at a satellite signal receiver using a sequential estimation filter
ActiveUS7095370B1Reduce multipath effectsPosition fixationBeacon systemsSatelliteSequential estimation
A method and apparatus for mitigating multipath effects in a satellite signal receiver is described. In one example, measured pseudoranges are obtained from the satellite signal receiver to a plurality of satellites. For each measured pseudorange: an expected pseudorange is derived from a sequential estimation filter in the satellite signal receiver. The measured pseudorange and the expected pseudorange are differenced to compute a pseudorange residual. The measured pseudorange is applied to the sequential estimation filter only if the pseudorange residual is within a window.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and method to estimate the location of a receiver in a multi-path environment
InactiveUS7030814B2Reduce multipath effectsOvercome limitationsDirection finders using radio wavesPosition fixationTimestampConvolution
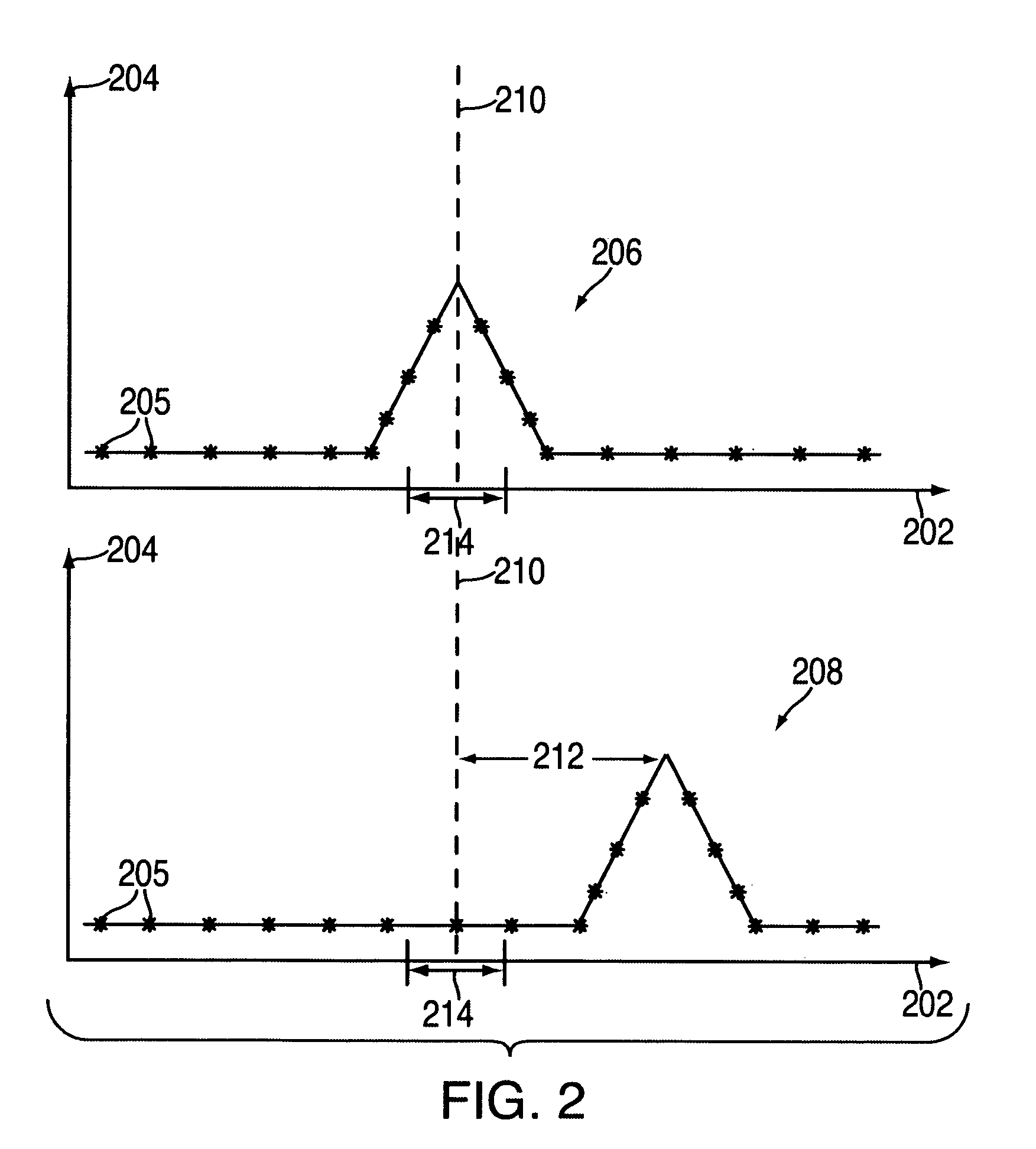
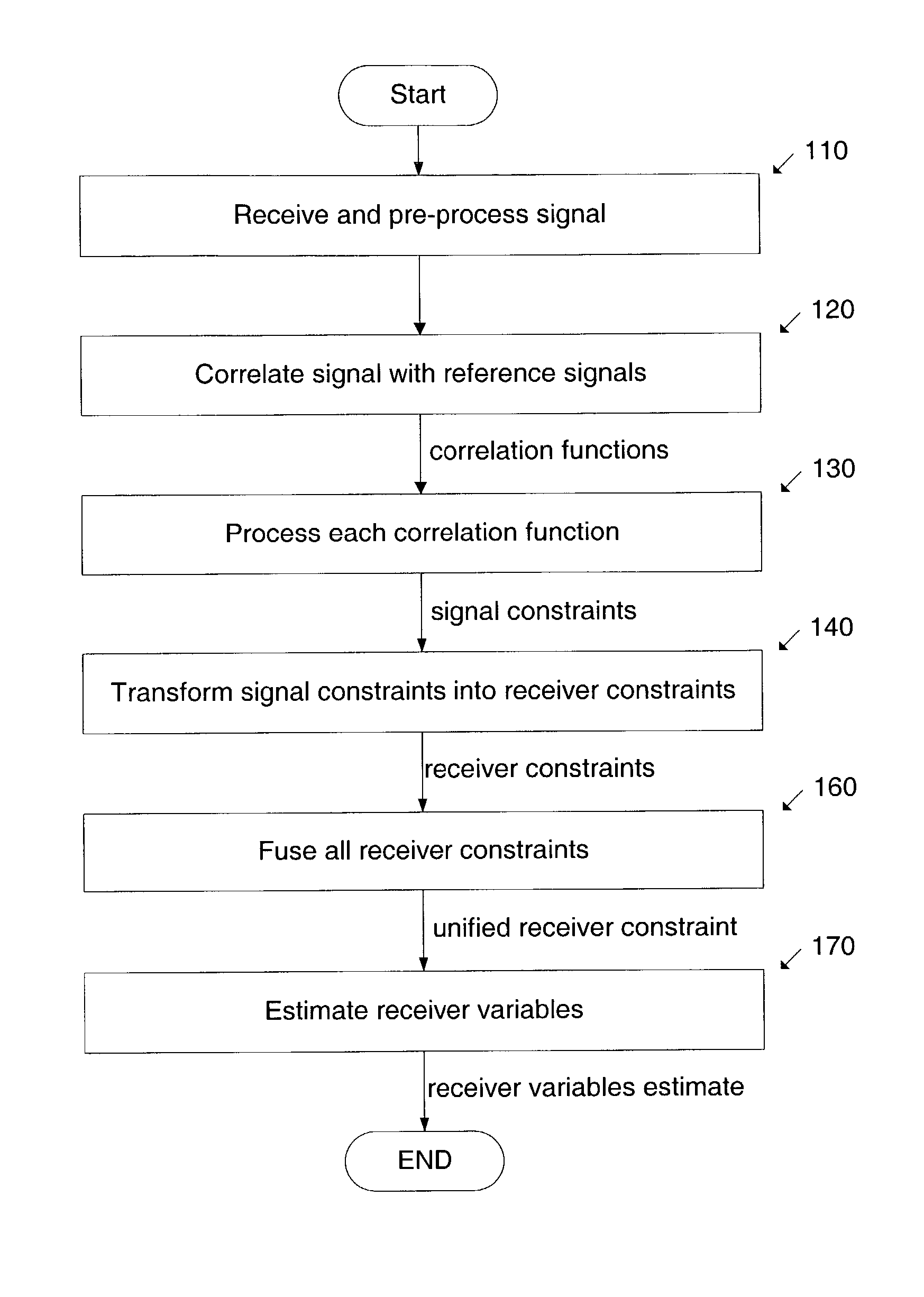
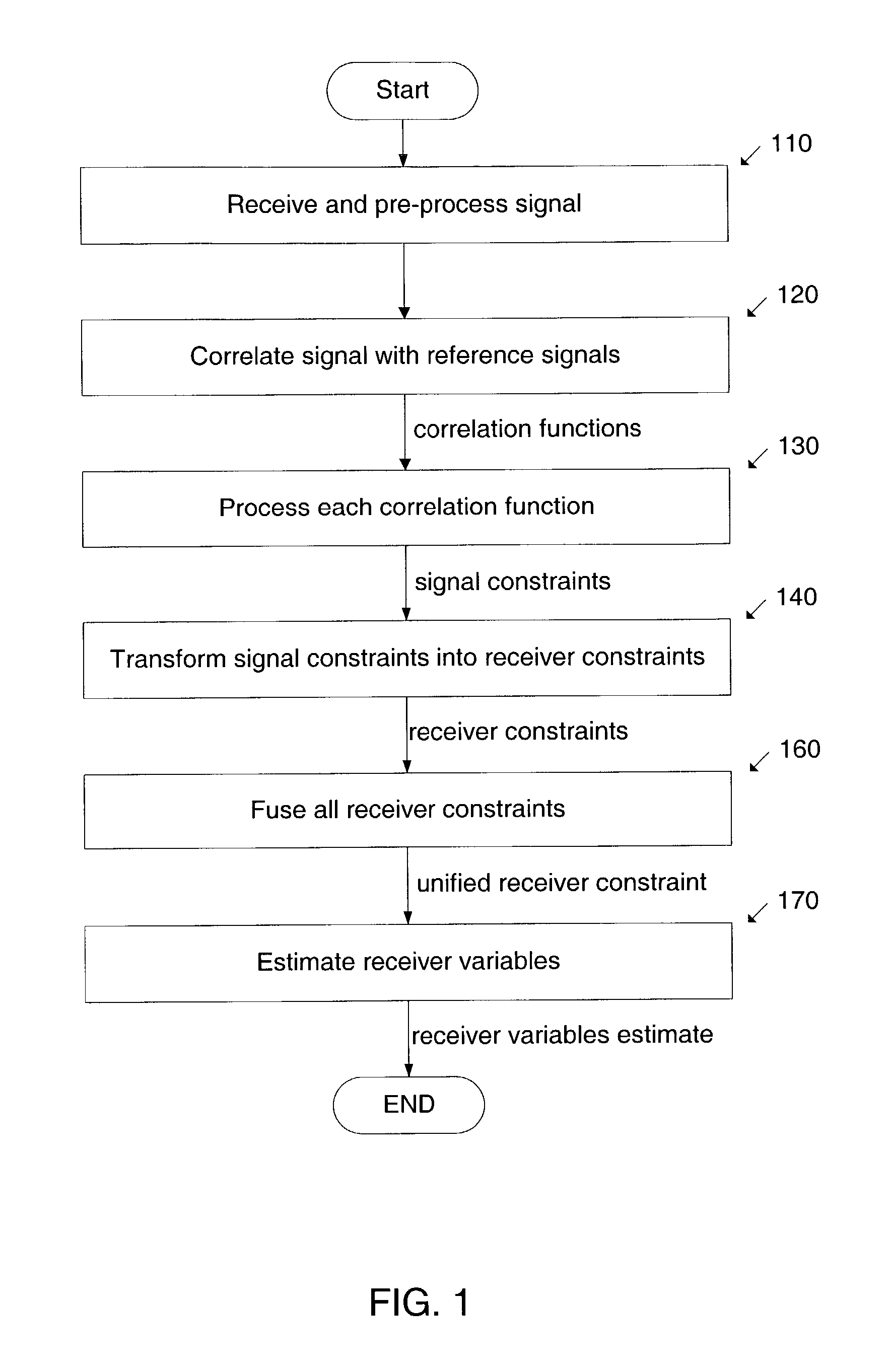
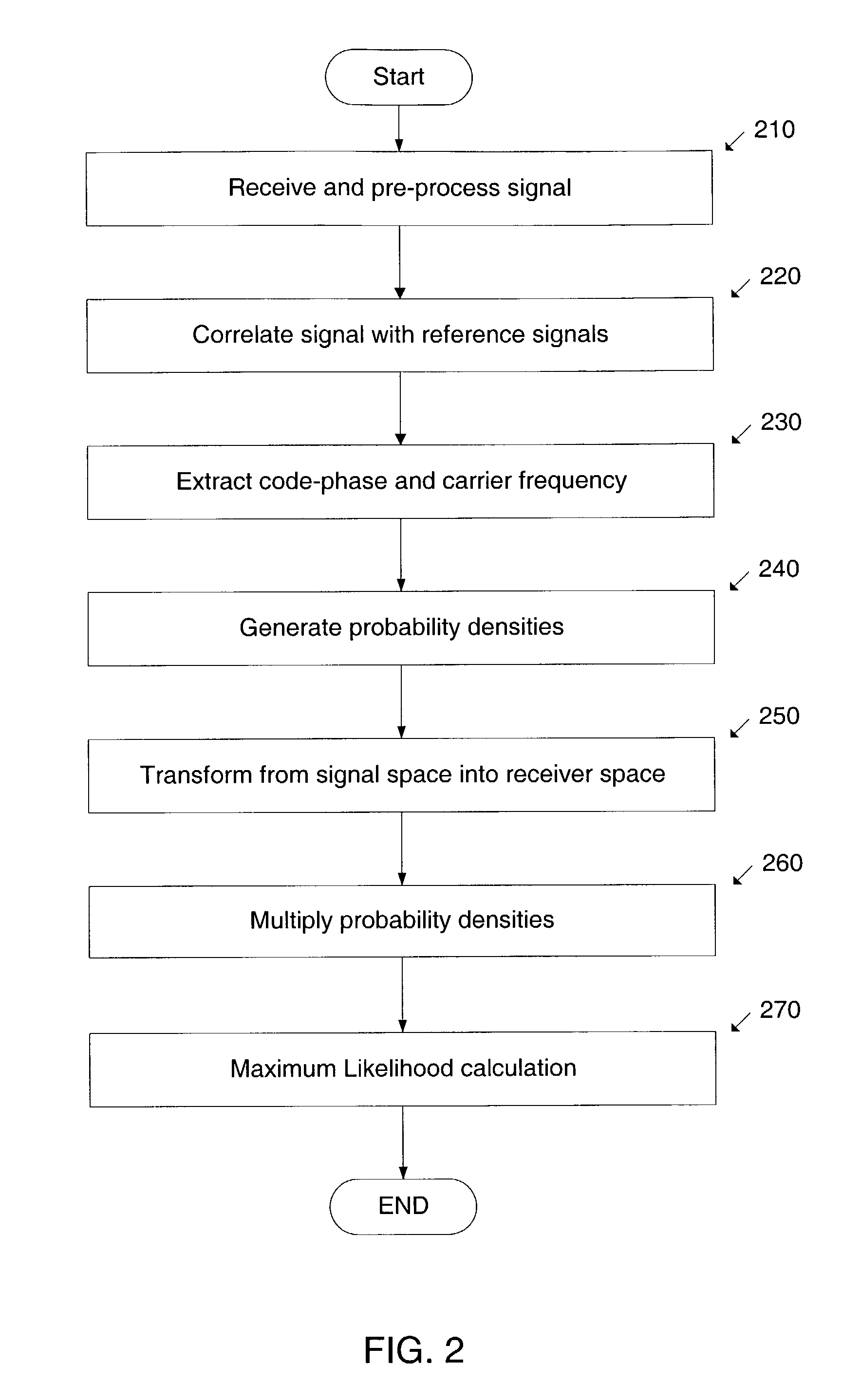
System and method to determine the location of a receiver in a multipath environment are provided. The received signal is correlated with the reference signals associated with the transmitting sources. Each correlation function is processed to derive various types of signal constraints, such as probability densities and uncertainty regions or intervals. In some embodiments, these constraints are for the code-phases and the Doppler frequencies. These signal constraints are transformed into constraints on the receiver variables and then fused together into a unified receiver constraint. A-priori constraints, such as constraints on the location of the receiver or the timestamp, may be incorporated into the unified receiver constraint. Some embodiments estimate a location based also on the estimated Doppler frequency. The constraints used by the invention are based on models of multipath effects and are geared towards mitigating these effects. In one of these models, a probability density for code-phase is obtained by convolving a gaussian distribution with an exponential distribution that describes the extra delay introduced by multipath. Another approach is based on identifying outliers in the set of code-phases. In other approaches, uncertainty region constraints and probability densities are combined. The present invention achieves faster and more sensitive signal acquisition and higher location accuracy in multipath environment, without compromising performance in other environments.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
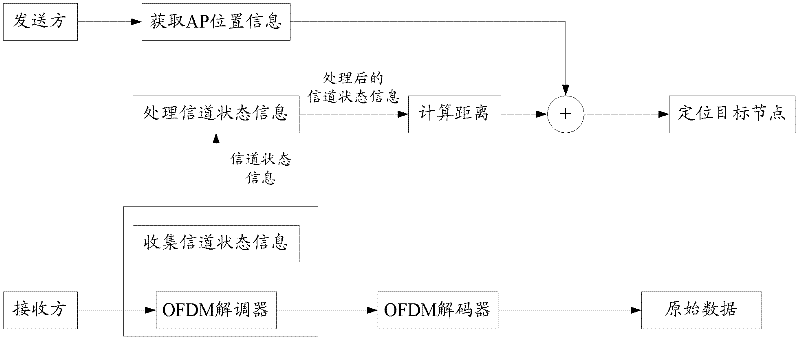
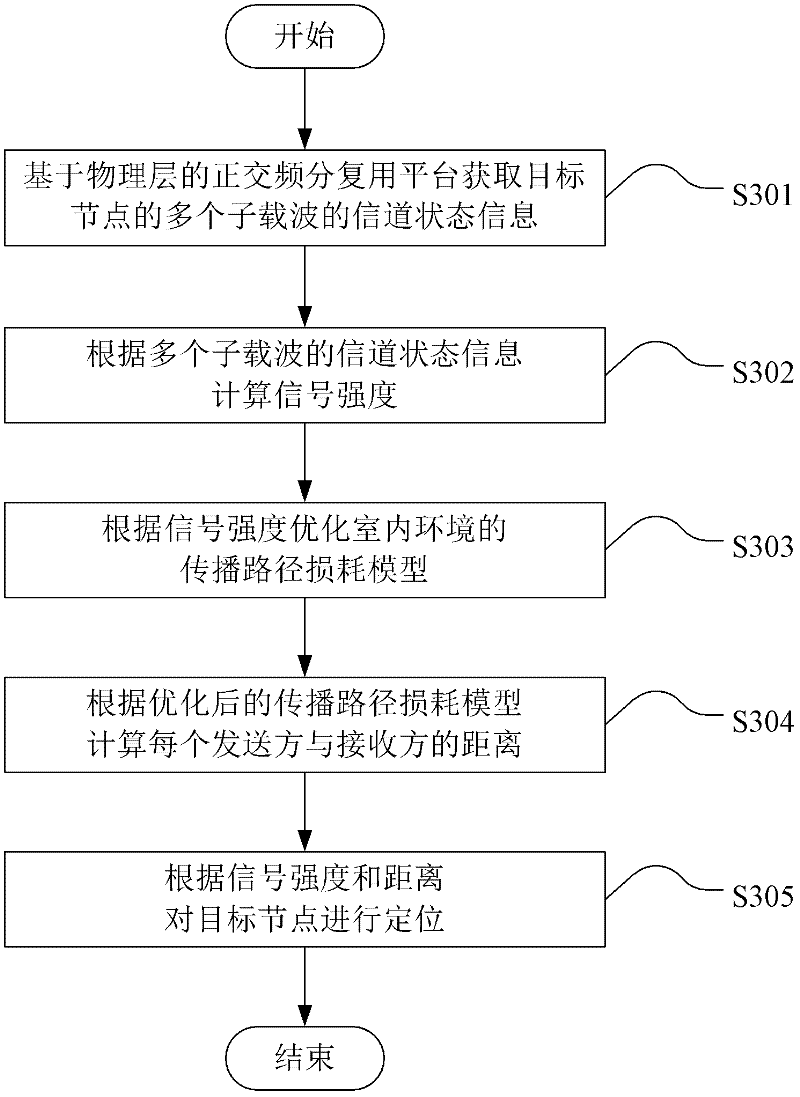
Physical-layer-based method and device for realizing indoor positioning of wireless network
ActiveCN102421189AReduce multipath fadingAccurate calculationWireless communicationTelecommunicationsSubcarrier
The embodiment of the invention discloses a physical-layer-based method and device for realizing indoor positioning of a wireless network. The method comprises the steps of: acquiring the channel state information of a plurality of subcarriers of a target node based on an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) platform of a physical layer; calculating signal intensity according to the channel state information of the plurality of subcarriers; optimizing a propagation path loss model of an indoor environment according to the signal intensity; calculating the distance between each sending party and each receiving party according to the optimized propagation path loss model; and positioning the target node according to the signal intensity and the distances. In the embodiment of the invention, under the condition that an indoor environment multipath effect is ubiquitous, the precise channel state information is utilized to calculate the signal intensity in the wireless local area network so as to further realize the indoor positioning, the frequency diversity of the channel state information is utilized to reduce multipath attenuation and reduce the influences of the indoor environment multipath effect and frequency selective attenuation, and thus, the position information of the target node can be calculated more precisely and the positioning precision is increased.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
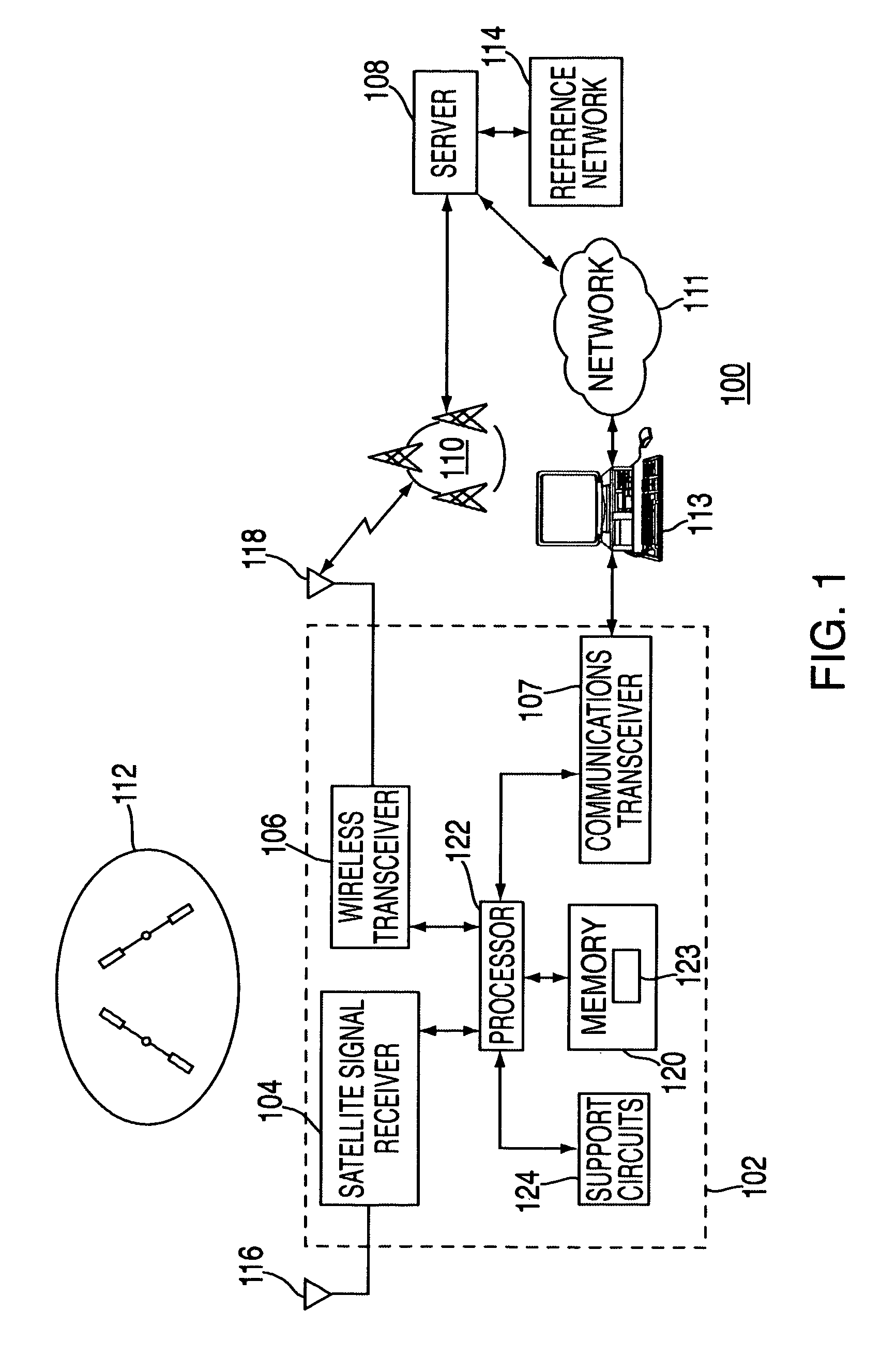
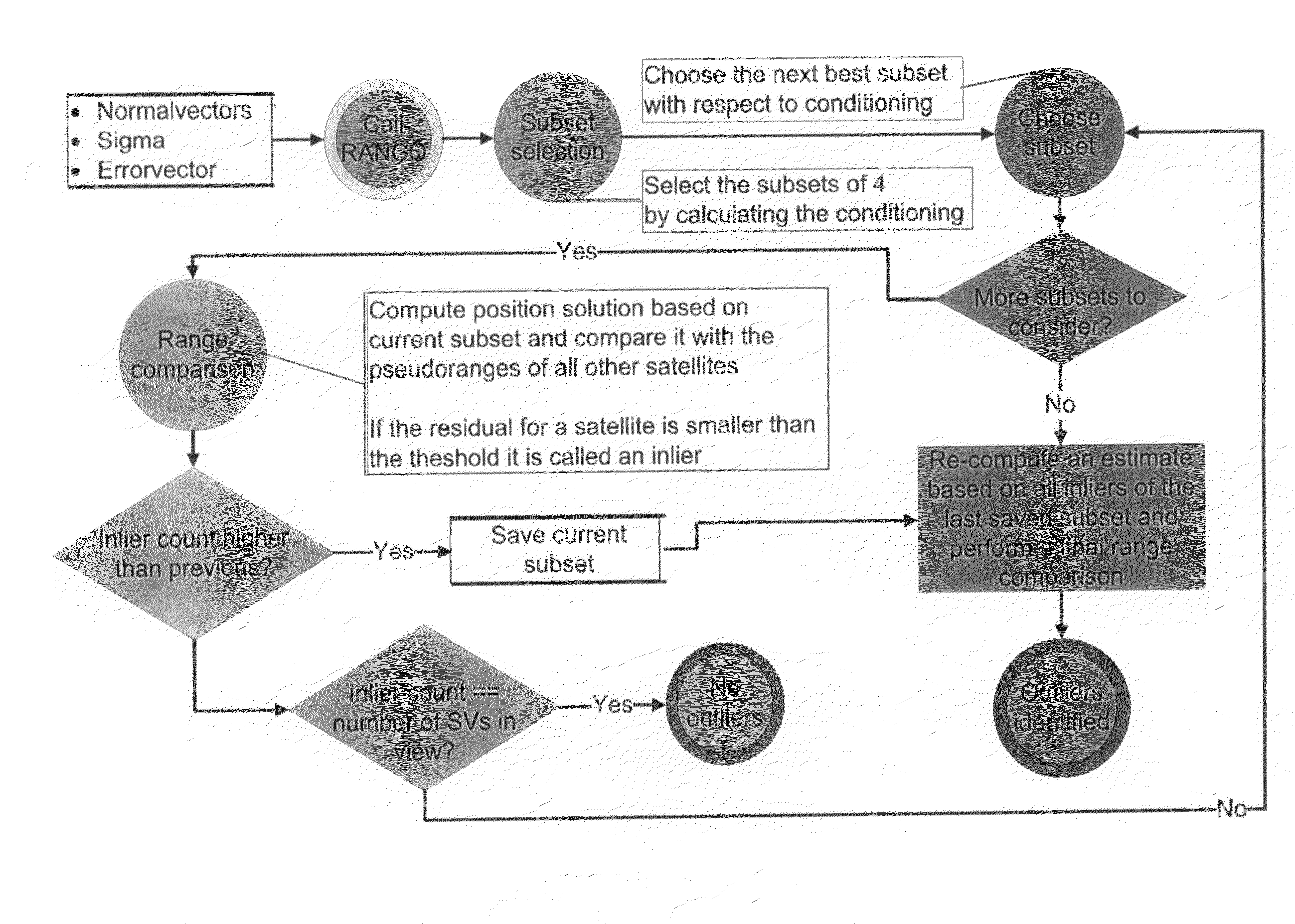
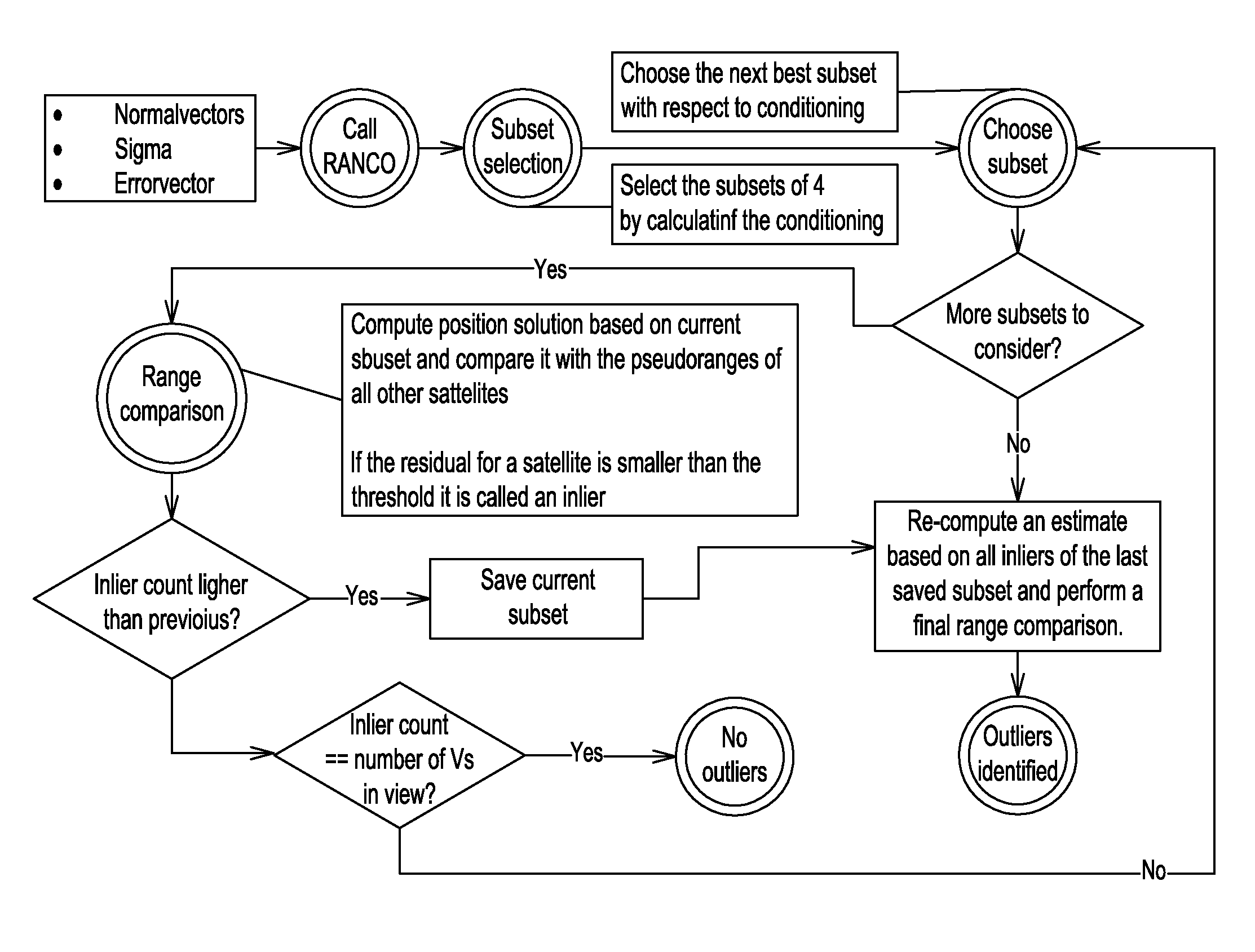
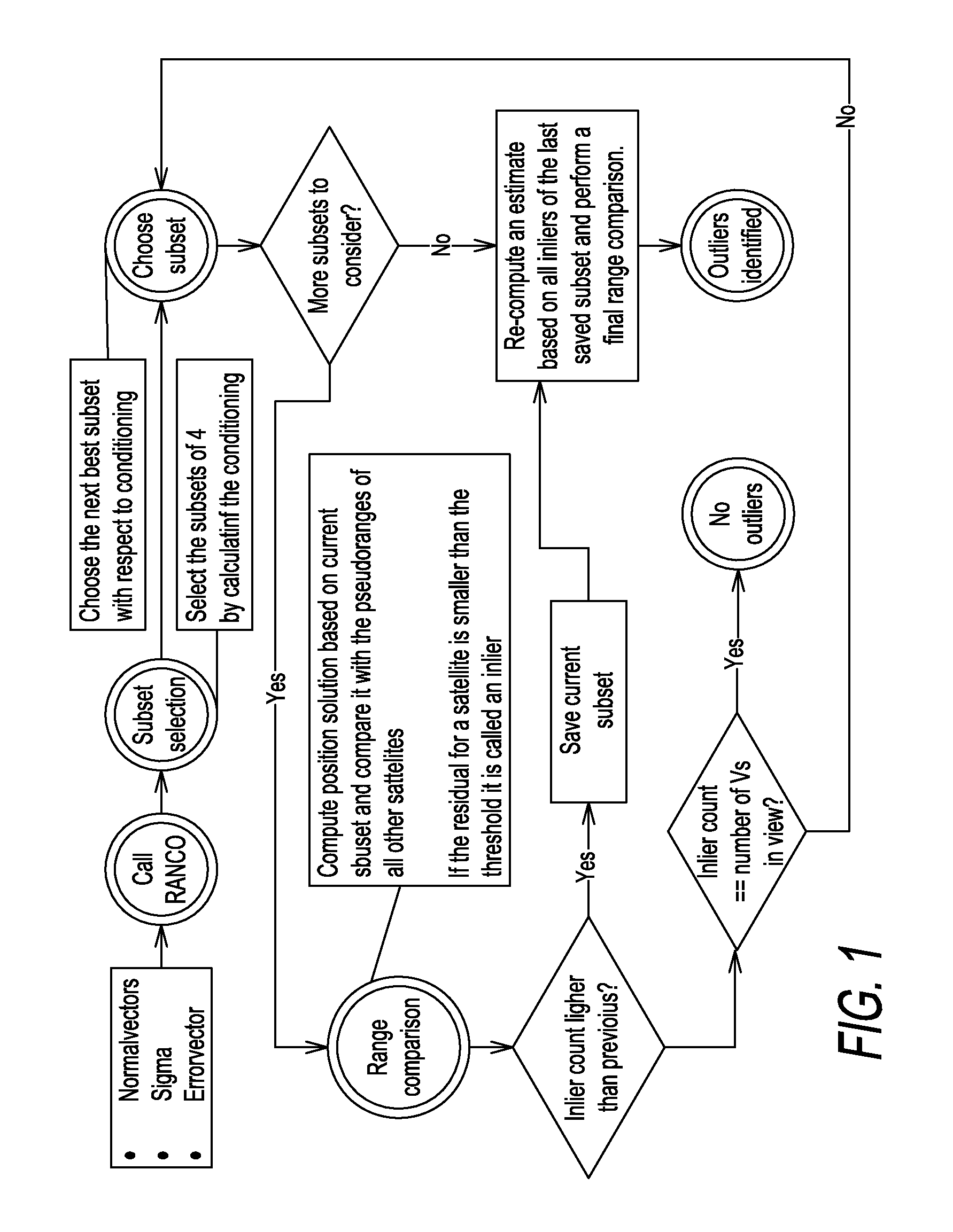
Method of operating a satellite navigation receiver
InactiveUS20090273511A1Improve performanceSensitive to errorBeacon systemsSatellite radio beaconingSatellite navigationEnvironmental geology
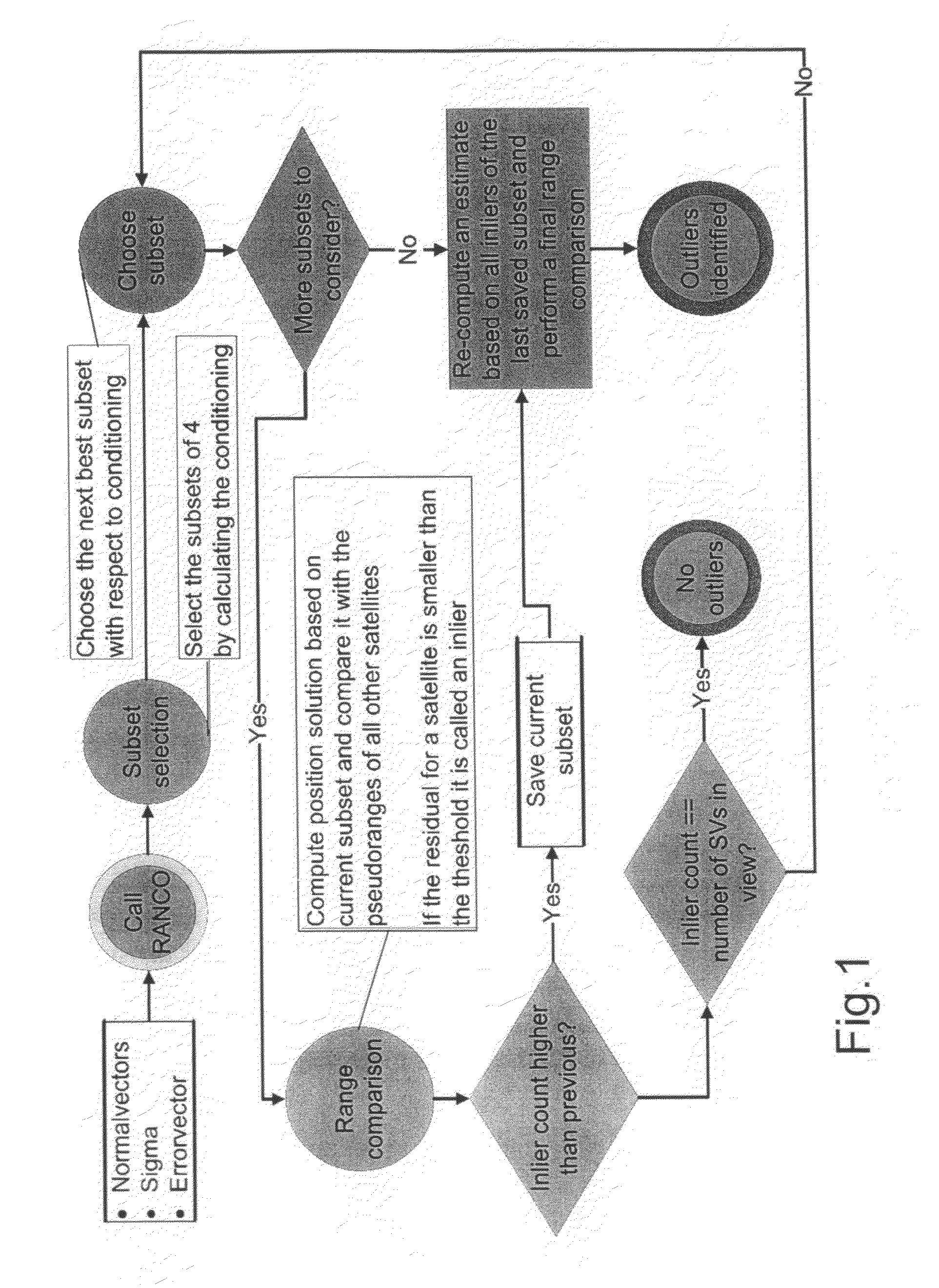
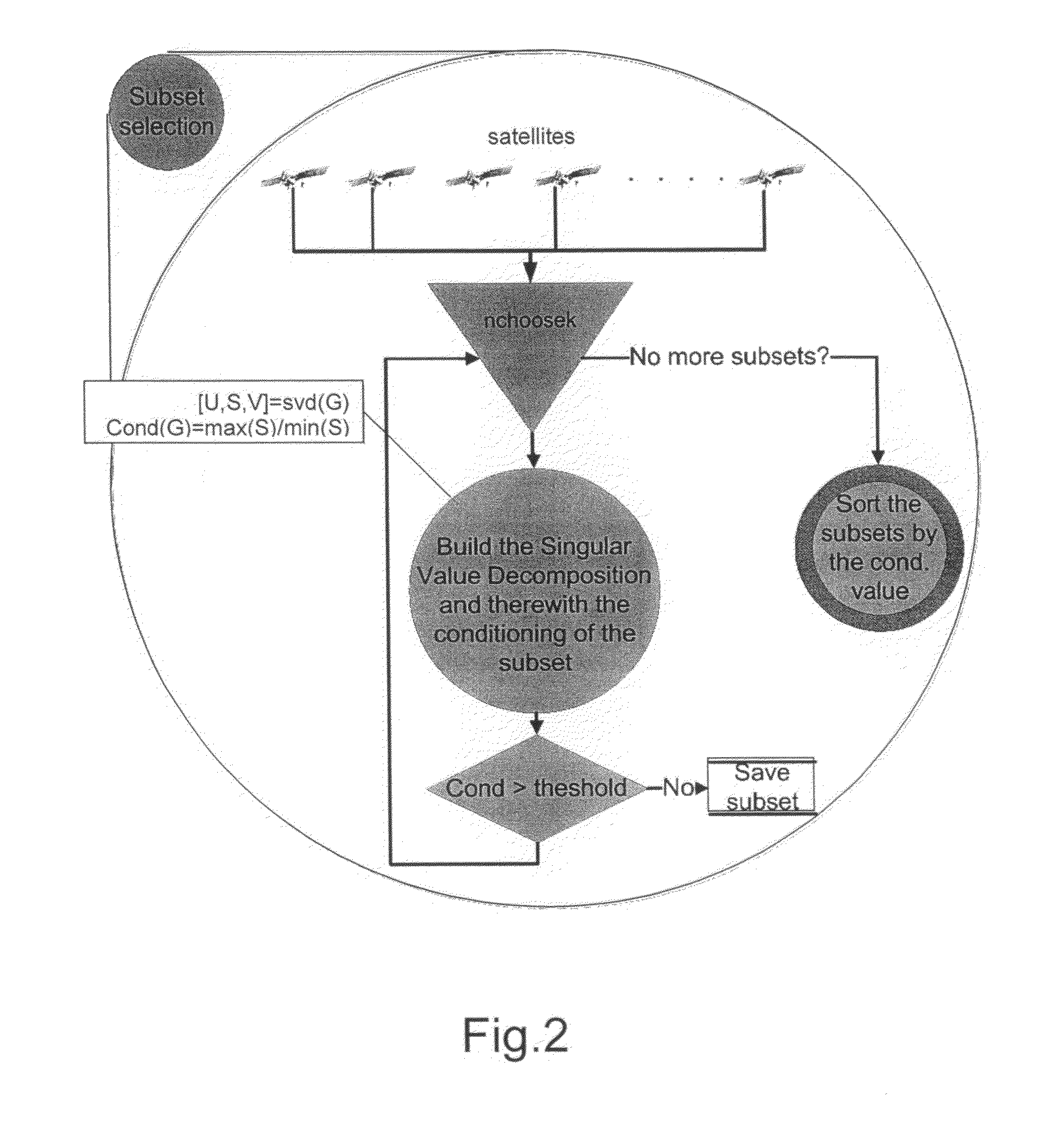
A receiver operating with satellite navigation signals estimates its position by means of a multiplicity of signals each transmitted by another satellite. A subset of satellites is used to calculate the position estimation and checking the pseudoranges of all received satellite signals that did not contribute to this particular estimate with respect to their consensus with this estimate. The subset with the best consensus is determined by combining the subsets with respect to the consensus with all ranging sources in view. Consensus in this context refers to pseudoranges that coincide in a position solution in a consistent way. The satellites with a bias in pseudorange higher than a threshold are identified as faulty satellites, after knowing all consistent satellites. This identifying information is then used to exclude the faulty satellites for the determination of position, velocity, and time in the receiver.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
Multipath Processing for GPS Receivers
InactiveUS20080205493A1Reduce multipath effectsSimple technologyInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationGps receiverEngineering
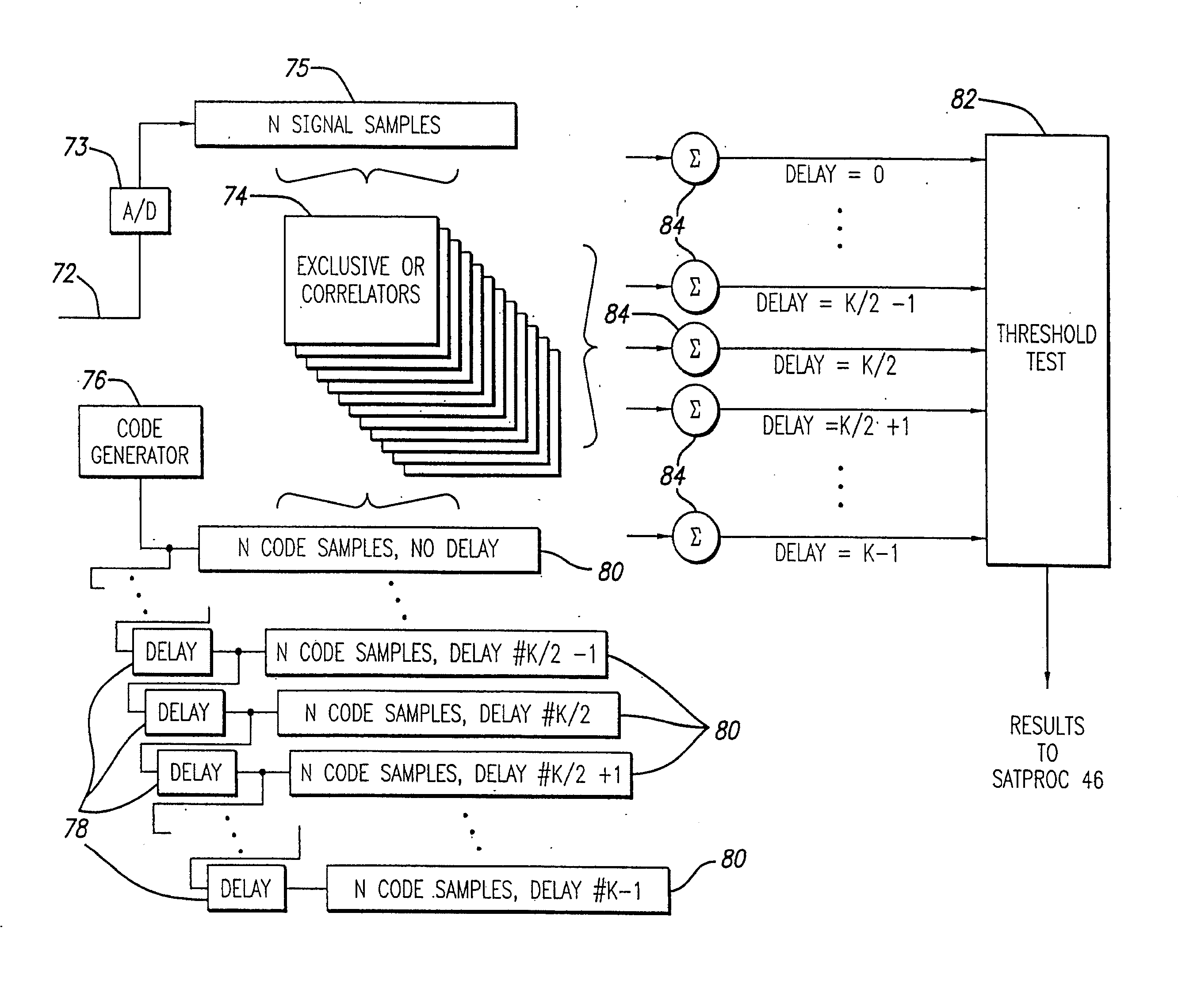
A GPS receiver system determines the presence of trackable signals at code delays less than the prompt delay being tracked for a particular signal and changes the prompt delay to correspond to the smallest code delay having a trackable signal. Trackable signals at large code delays are multipath signals and may be separately tracked to aid in dead reckoning. The trackable signals at code delays not adjacent to the current tracked prompt delay may be tracked in the same channel as the prompt delay so that all satellite channels are continuously evaluated for multipath signals being tracked or a non-satellite specific channel may be used to sequentially step through the satellite signals to evaluate multipath on a satellite by satellite basis.
Owner:KOHLI SANJAI +1
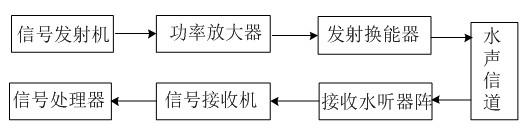
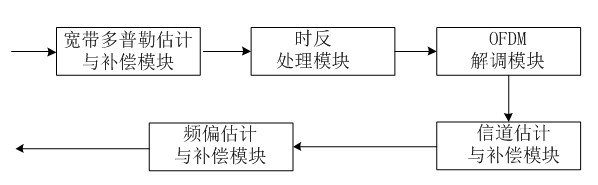
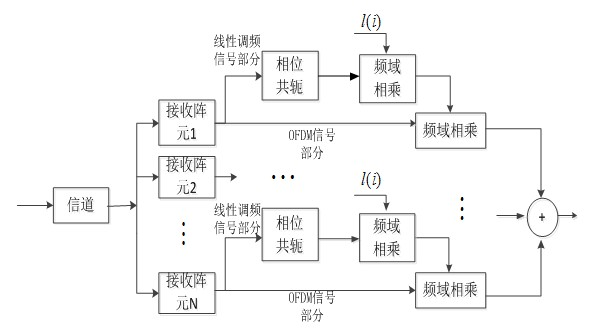
Underwater sound communication device and method based on time reversal and orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) combined treatment
InactiveCN102546511AReduce multipath effectsEliminate delayMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksEngineeringCombined treatment
The invention discloses an underwater sound communication device and a method based on time reversal and orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) combined treatment. The underwater sound communication device comprises a signal transmitter, a power amplifier, a transmitting transducer, a receiving hydrophone array, a signal receiver and a signal processor, wherein the signal processor comprises a broadband Doppler estimation and compensation module, a time reversal processing module, an OFDM demodulation module, a channel estimation and compensation module and a frequency deviation estimation and compensation module. In the underwater sound communication device, the space time focusing characteristics of the time reversal are utilized to eliminate the multipath influence of the channel; a pulse channel response length can be shortened by the time reversal so as to reduce the length of an OFDM symbol guard interval and improve the communication efficiency; and because the guard interval is reduced, the length of the OFDM symbol can be shortened so as to enlarge a subcarrier frequency interval. With the method disclosed by the invention, interference among subcarriers can be reduced, and the available rate of the OFDM underwater sound communication is further improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
RFID reader
InactiveUS9141836B2Maximize probabilityReduce multipath effectsSpatial transmit diversityMemory record carrier reading problemsEngineeringTransmitter
An RFID reader is provided. The RFID reader includes a transmitter section and a receiver section. The transmitter section is configured to transmit a first RF signal which includes several carrier frequencies that are effective to simultaneously illuminate a tag at the plurality of carrier frequencies. The receiver section is configured to receive a second RF signal which includes several frequencies which each have the same information.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
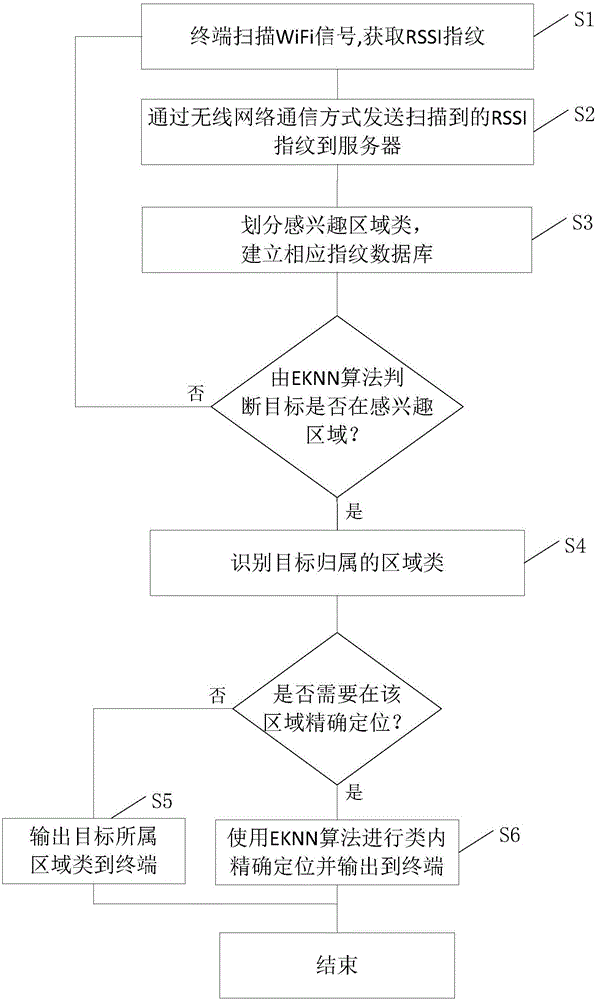
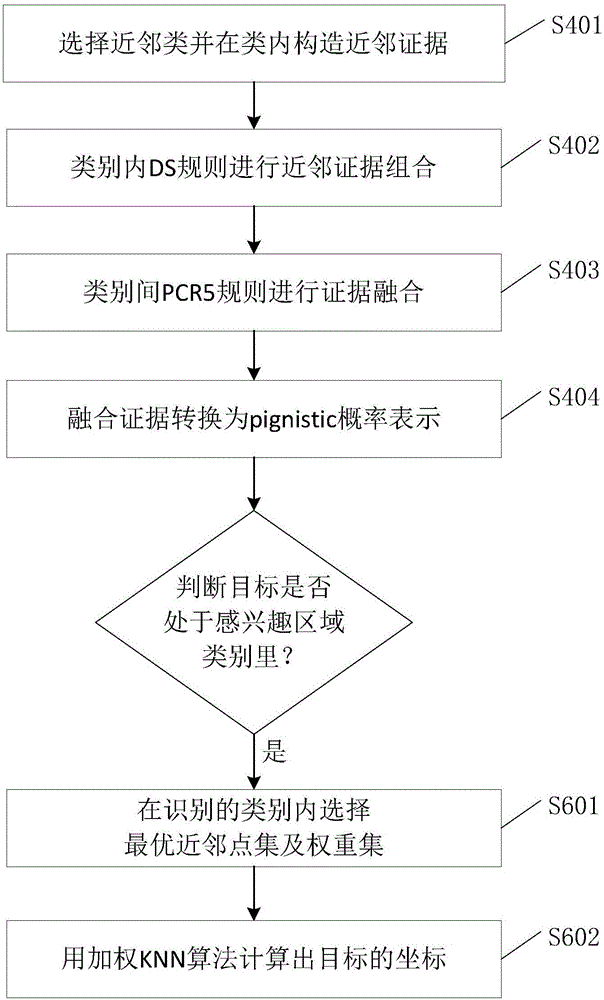
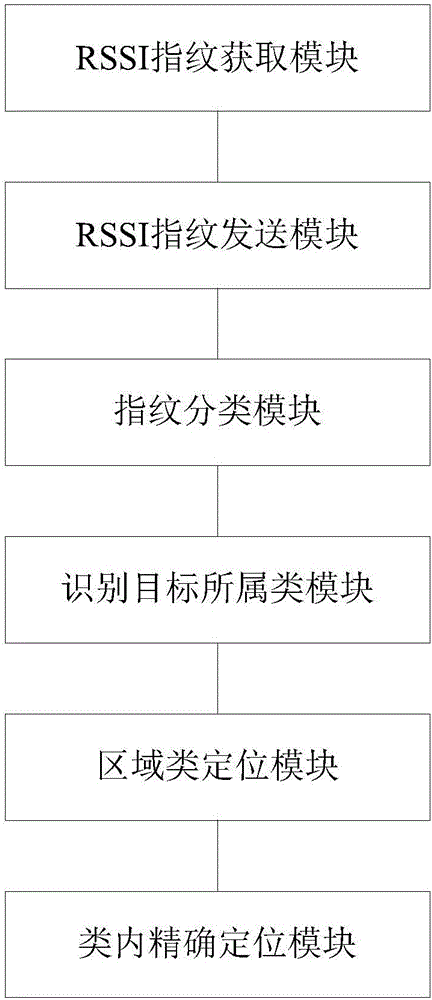
Indoor area WiFi positioning method and system based on EKNN (Evidence K Nearest Neighbor)
ActiveCN106507475AReduce multipath effectsReduce distractionsWireless communicationAlgorithmNear neighbor
The invention discloses an indoor area WiFi positioning method and a system based on EKNN (Evidence K Nearest Neighbor). The positioning method comprises the following steps: a terminal scans WiFi signals, and a received signal strength indicator (RSSI) fingerprint is acquired; the scanned RSSI fingerprint is sent to a server in a wireless network communication mode; a region of interest class is divided, and a corresponding fingerprint database is built at the server side; a target attribution region class is recognized, and at the server side, through the integrated EKNN positioning algorithm, the target attribution region class is recognized; the target attribution region class is outputted to the terminal, and if no precise positioning is needed, the region class of the target is outputted; and finally, the EKNN algorithm is used for intra-class precise positioning. According to the WiFi positioning method based on the EKNN algorithm, requirements of indoor region of interest recognition and precise positioning are met, and the region recognition precision, the positioning precision and the positioning efficiency are enhanced to a certain degree.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method of operating a satellite navigation receiver
InactiveUS8106823B2Reduce multipath effectsImprove performanceSatellite radio beaconingSatellite navigationPseudorange
A receiver operating with satellite navigation signals estimates its position by means of a multiplicity of signals each transmitted by another satellite. A subset of satellites is used to calculate the position estimation and checking the pseudoranges of all received satellite signals that did not contribute to this particular estimate with respect to their consensus with this estimate. The subset with the best consensus is determined by combining the subsets with respect to the consensus with all ranging sources in view. Consensus in this context refers to pseudoranges that coincide in a position solution in a consistent way. The satellites with a bias in pseudorange higher than a threshold are identified as faulty satellites, after knowing all consistent satellites. This identifying information is then used to exclude the faulty satellites for the determination of position, velocity, and time in the receiver.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
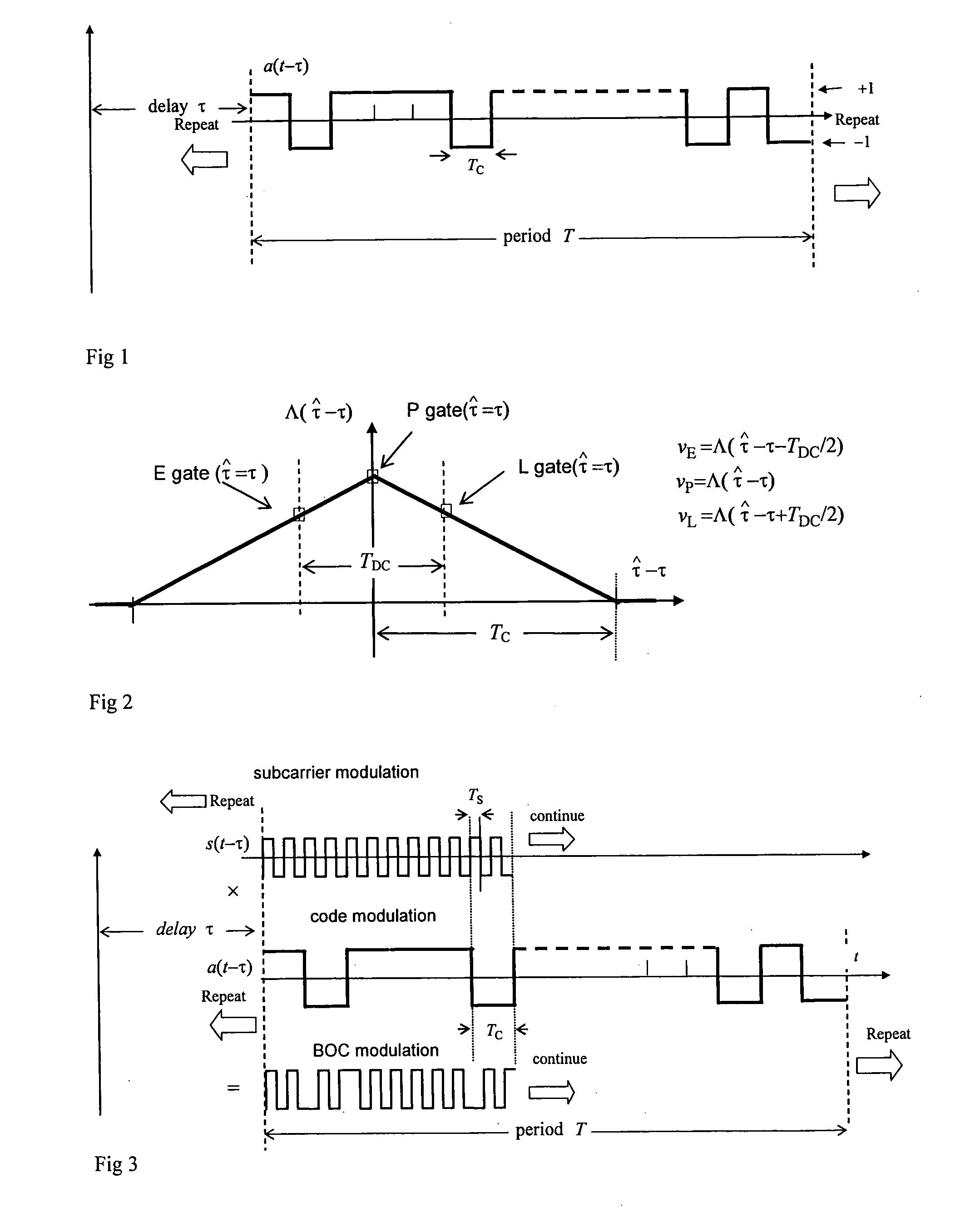
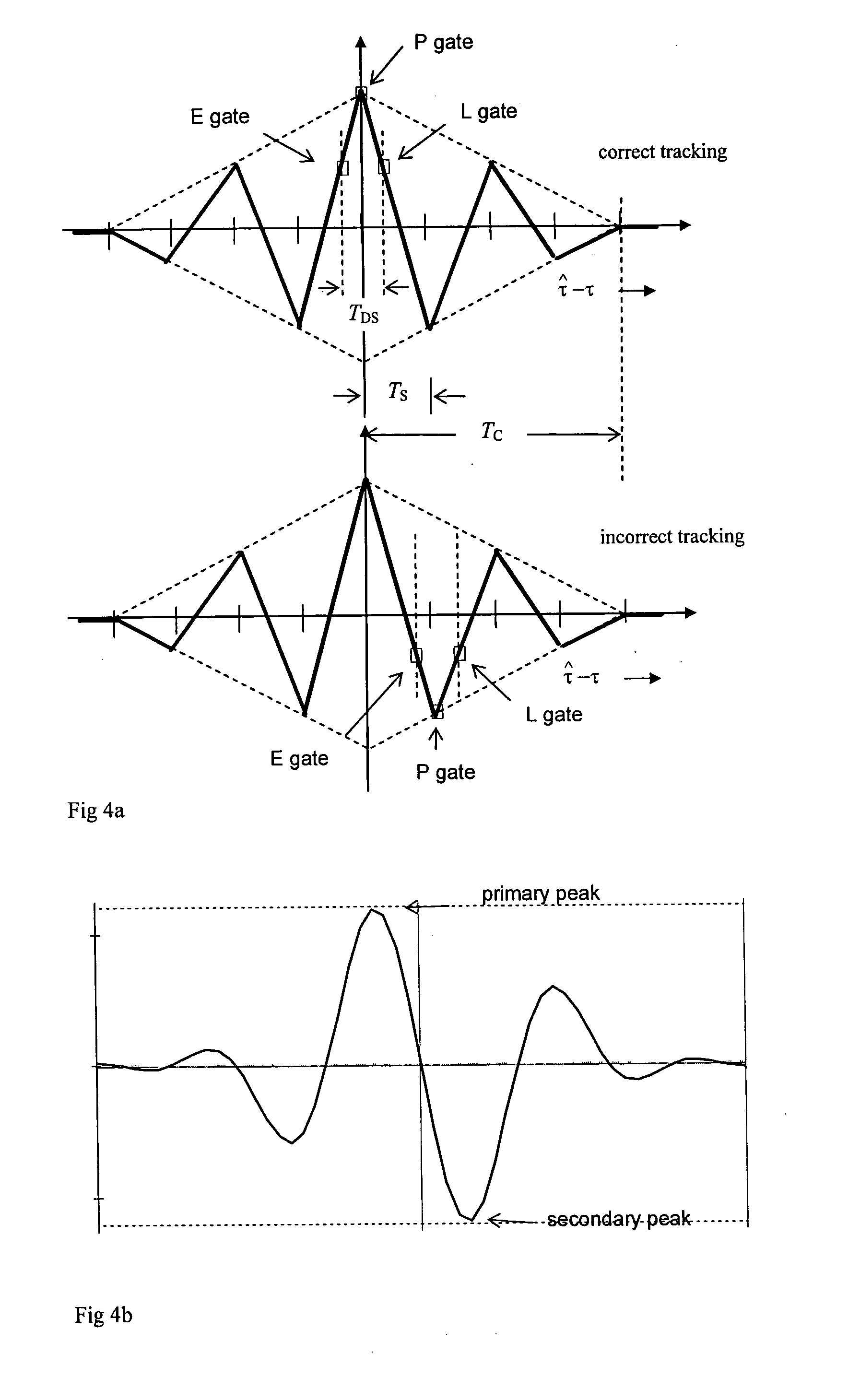
Receiver of multiplexed binary offset carrier (MBOC) modulated signals
InactiveUS20100135364A1Reduce multipath effectsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSatellite radio beaconingMultiplexingModulation function
A receiver for receiving a navigation signal comprising a carrier modulated by a code modulation function of a given code rate and further modulated by a composite sub-carrier modulation function having first and second components with two different rates both of which arc different to the code rate, the receiver comprising processing means arranged to: generate a first estimate of delay based on the code modulation only; generate a second estimate of delay based on the first component of the sub-carrier modulation only; and generate a third estimate of delay based on the second component of the sub-carrier modulation only; and determine a further delay estimate from the first second and third delay estimates.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SURREY
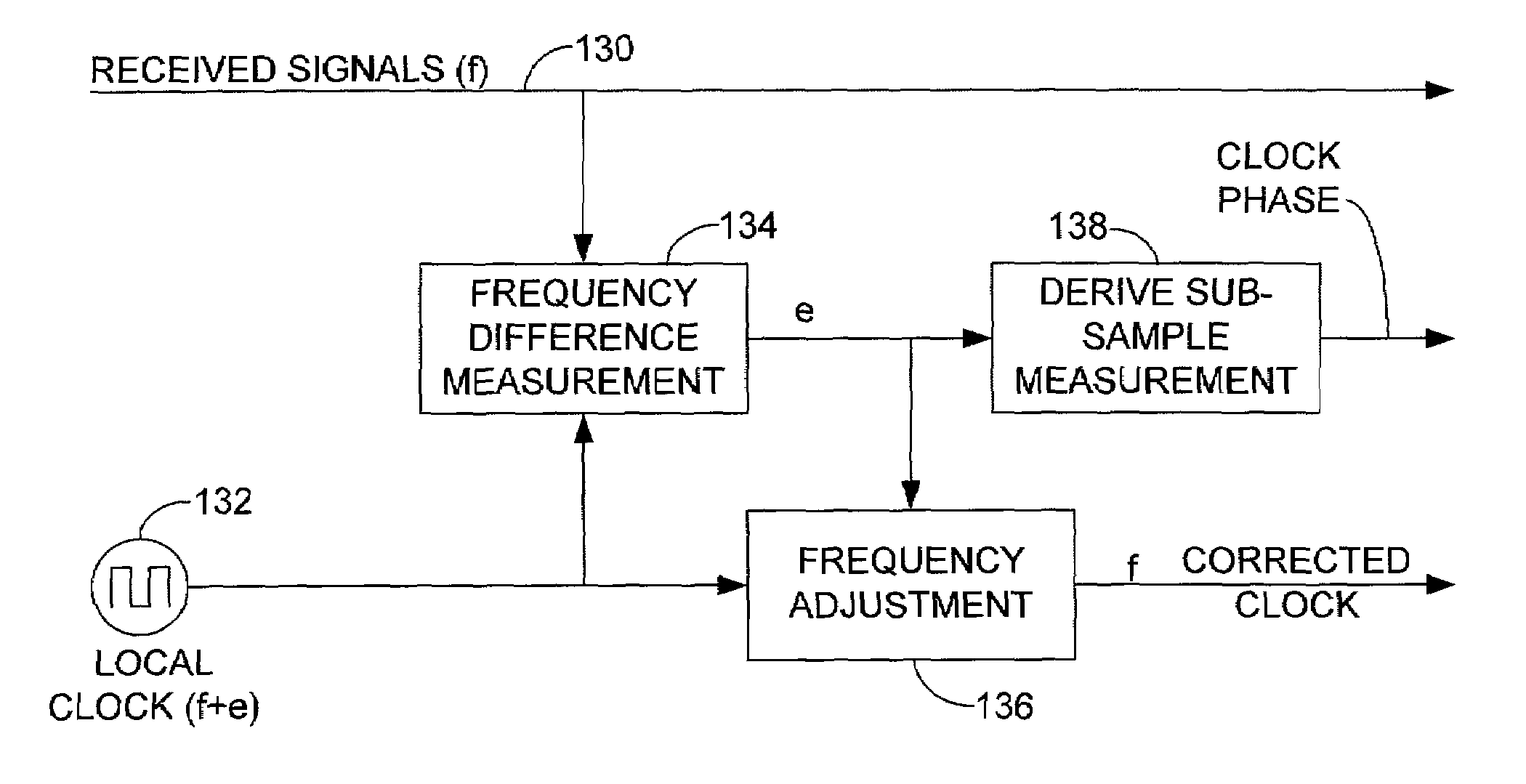
Method and apparatus for processing digitally sampled signals at a resolution finer than that of a sampling clock
InactiveUS7133480B2High level of temporal accuracyReduce multipath effectsModulated-carrier systemsPosition fixationImage resolutionFrequency shift
A method and related apparatus for reproducing a periodic signal received over a communication channel, or signal window of a desired profile, wherein the resolution of the reproduced signal or window is not limited by a digital sampling interval. The profile can be selected to match and compensate for known or estimated characteristics of a communication channel. A frequency difference, due to a Doppler frequency shift or other errors between received signals and locally generated signals, is determined in a receiver and utilized to derive a fine code phase measurement that is then usable to generate a succession of magnitudes that reproduce the desired signal or window profile.
Owner:LEICA GEOSYSTEMS INC
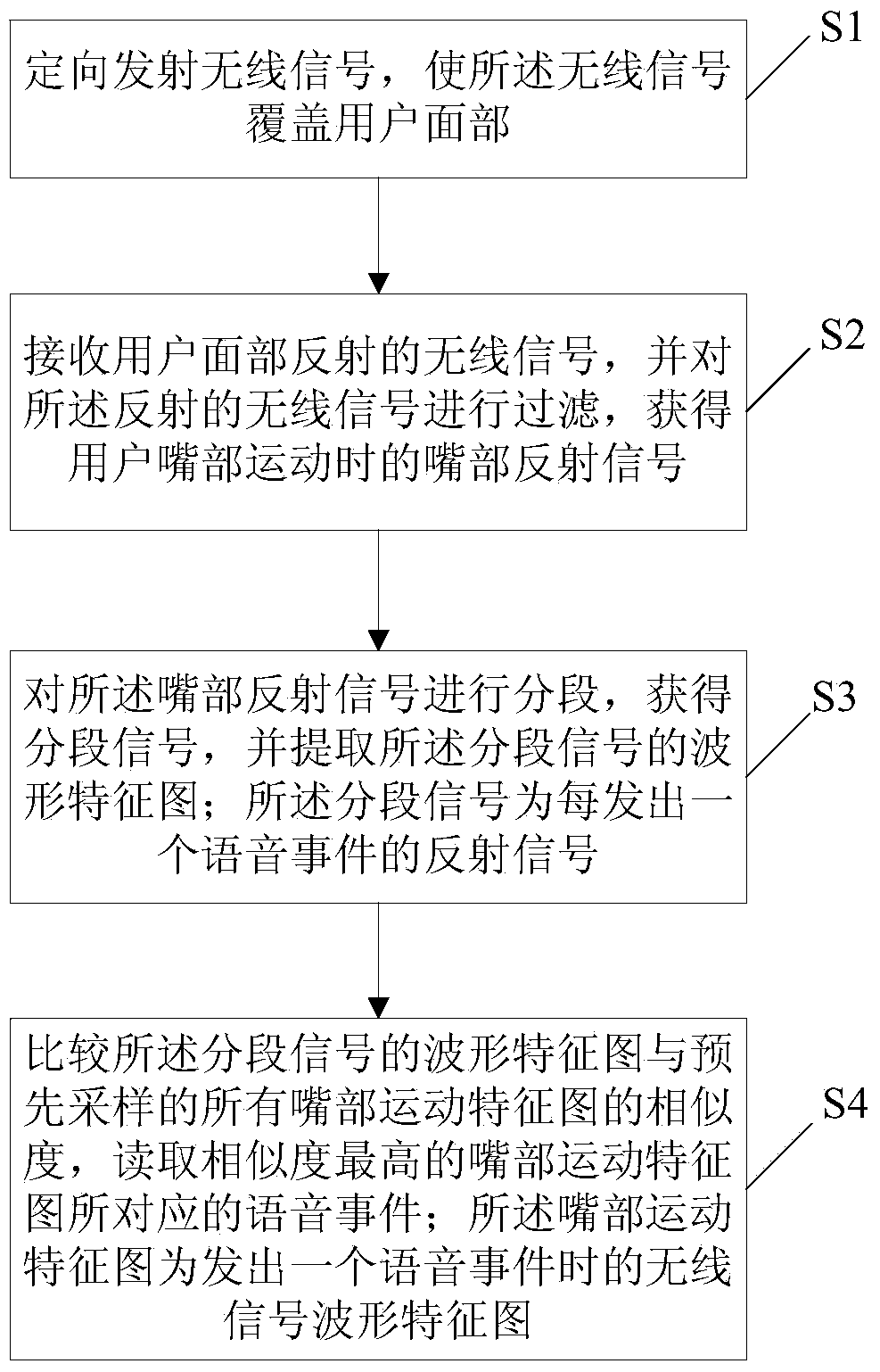
Lip language recognition method and system
ActiveCN104217218AImprove accuracyHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionSpeech soundLanguage recognition
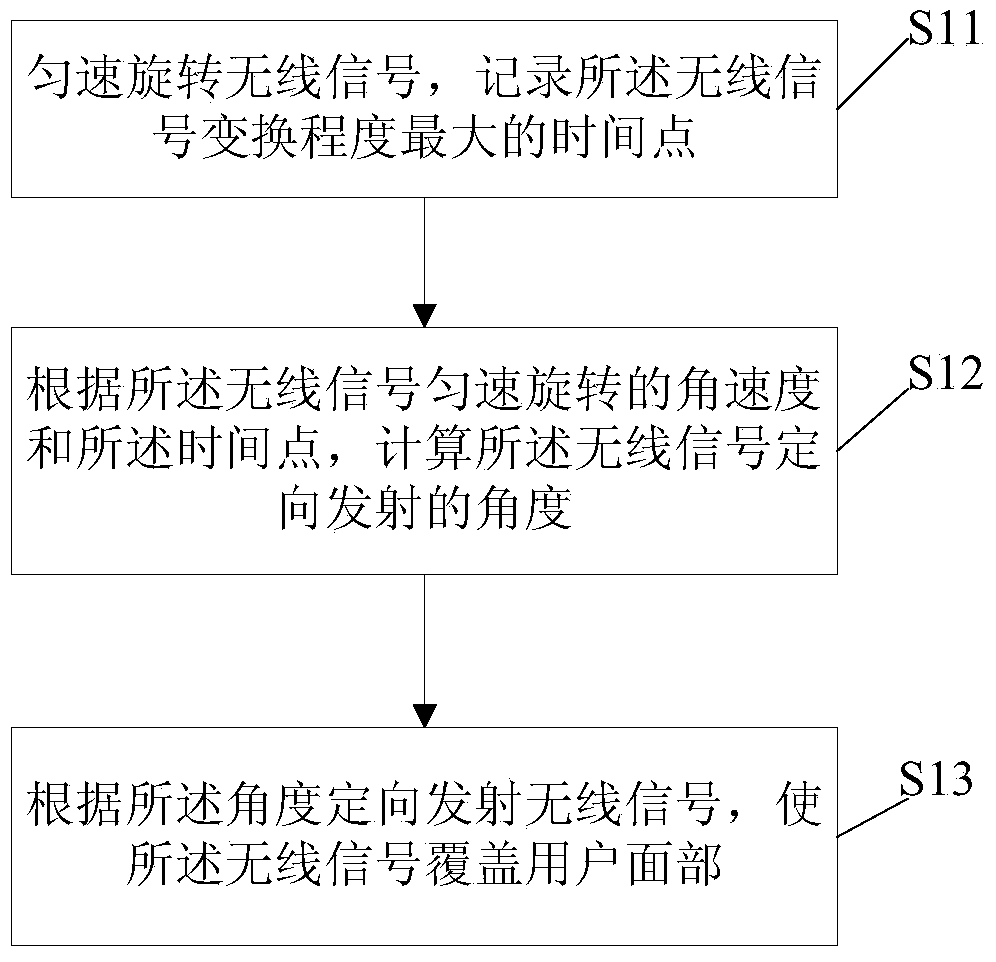
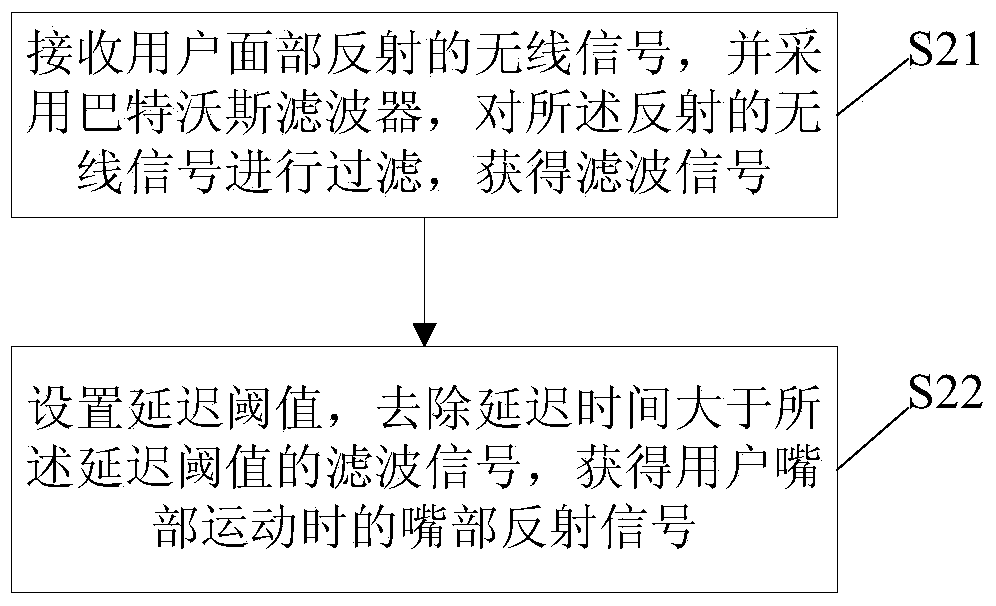
The invention discloses a lip language recognition method. The lip language recognition method comprises the steps of transmitting wireless signals directionally so that the wireless signals cover the face of a user; receiving wireless signals reflected by the face of the user, filtering the reflected wireless signals, and obtaining reflected signals of the mouth during the user's mouth motion; segmenting the reflected signals of the mouth, obtaining segmented signals, and obtaining waveform characteristic patterns of the segmented signals; enabling the segmented signals to be reflected signals each time a voice event is sent; comparing the similarity of the waveform characteristic patterns of the segmented signals with all mouth motion characteristic patterns sampled in advance, and reading the voice event corresponding to the mouth motion characteristic pattern highest in similarity. Correspondingly, an embodiment of the invention further provides a lip language recognition system. By the adoption of the lip language recognition method and system, the user's mouth motion can be detected through the wireless signals to achieve lip language recognition, and recognition efficiency and the accurate rate are improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HKUST FOK YING TUNG RES INST
Miniature unmanned plane RTK relative positioning method based on difference air pressure height constraints
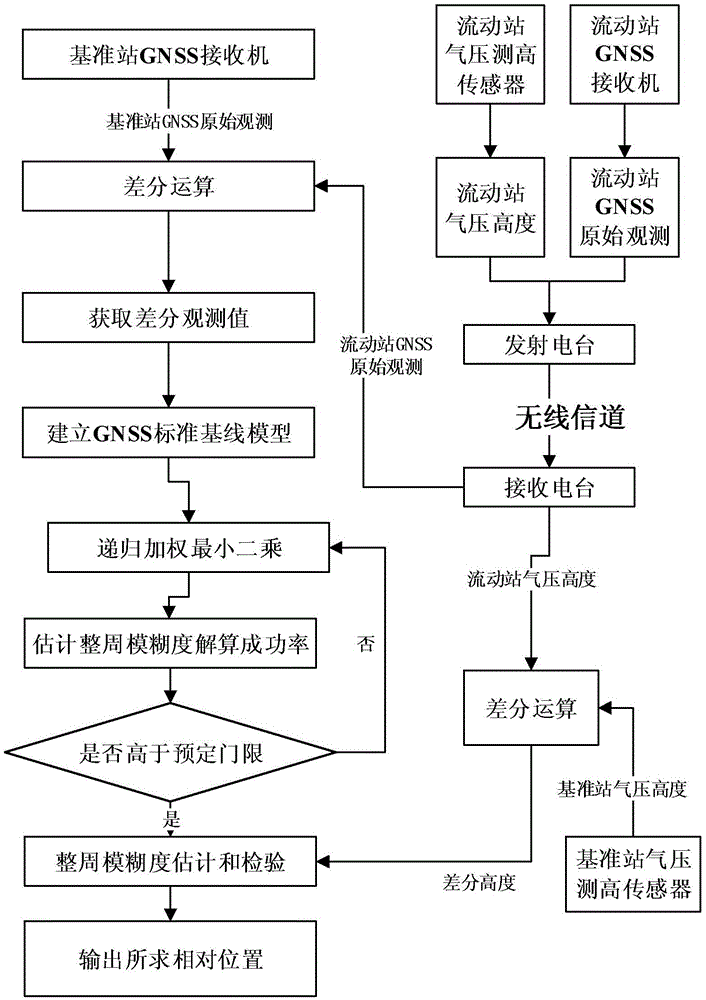
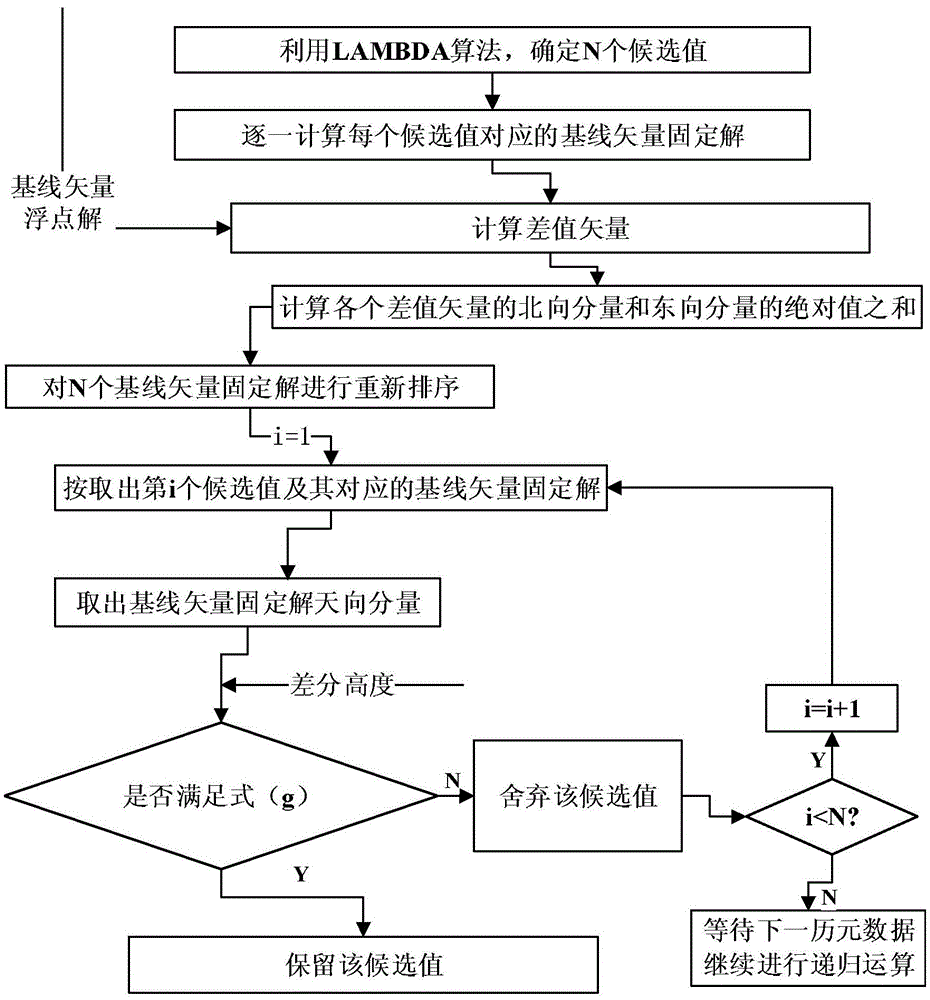
InactiveCN105467415AReduce mistakesReduce multipath effectsHeight/levelling measurementSatellite radio beaconingEngineeringFloating point
Provided is a miniature unmanned plane RTK relative positioning method based on difference air pressure height constraints, comprising: installing GNSS receivers of a same model, antennas, barometric leveling sensors and radio stations both on a reference station and a mobile station; transmitting the GNSS original observed value of the mobile station to the reference station, and performing difference recursion treatment on the original observed value of the reference station; employing an LAMBDA algorithm to determine N baseline vector residence values, respectively calculating the difference vector with a baseline vector floating point solution, and performing ordering again according to the absolute value sum of north and east components; transmitting the barometric height of the mobile station to the reference station through the radio stations, and performing difference with the barometric height of the reference station to obtain a difference height; and successively examining the sky direction component of a baseline vector fixed solution, and determining a relative position if meeting difference height constrains. The miniature unmanned plane RTK relative positioning method can utilize the difference height information of the reference station and the mobile station to discriminate a correct baseline vector fixed solution, does not need to use a measurement type receiver with a multi-path inhibition function, and can be used for low cost RTK application.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Household electrical appliance control method and control system based on indoor positioning
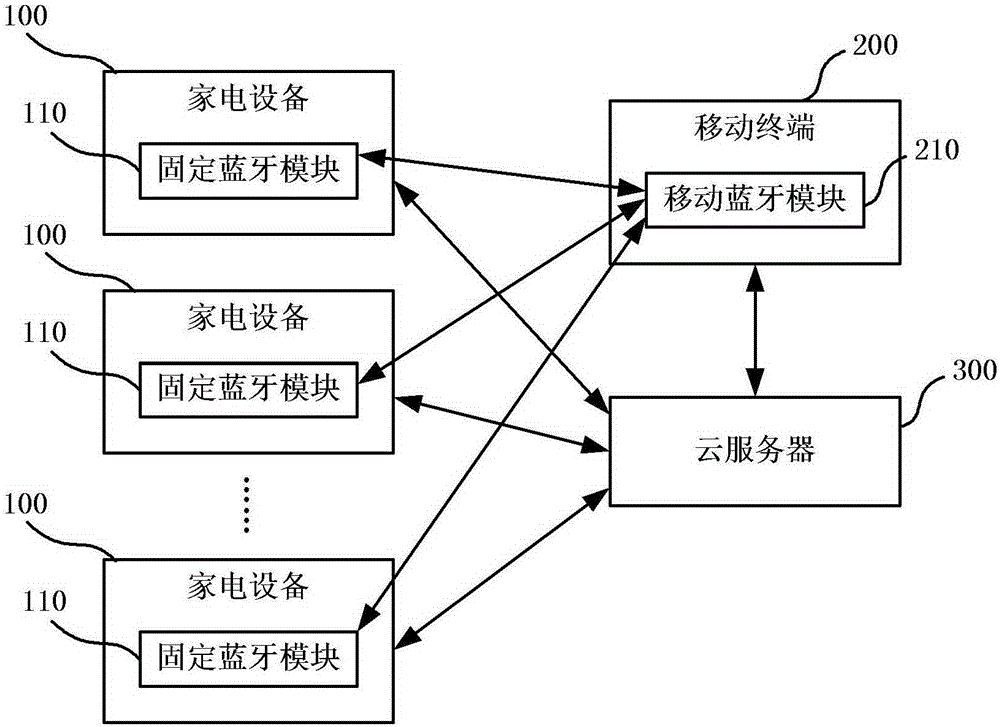
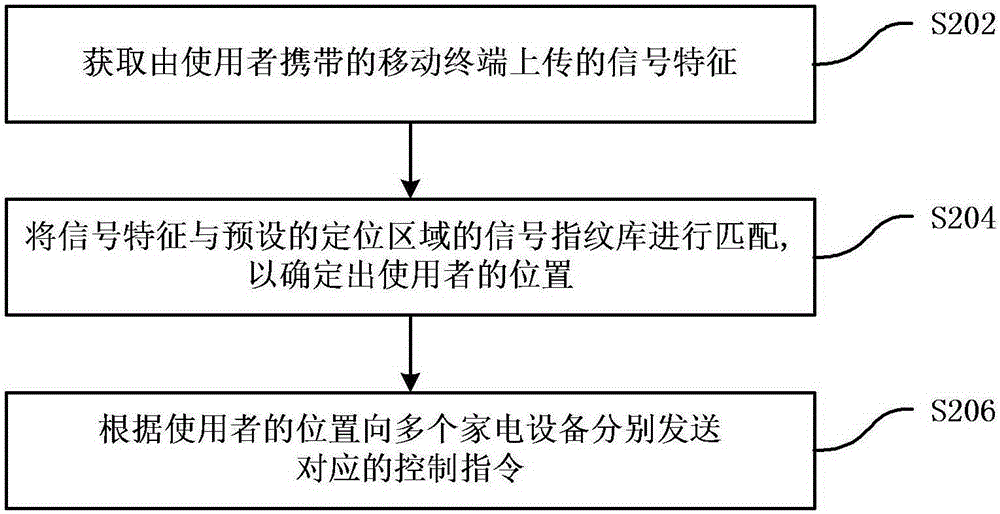
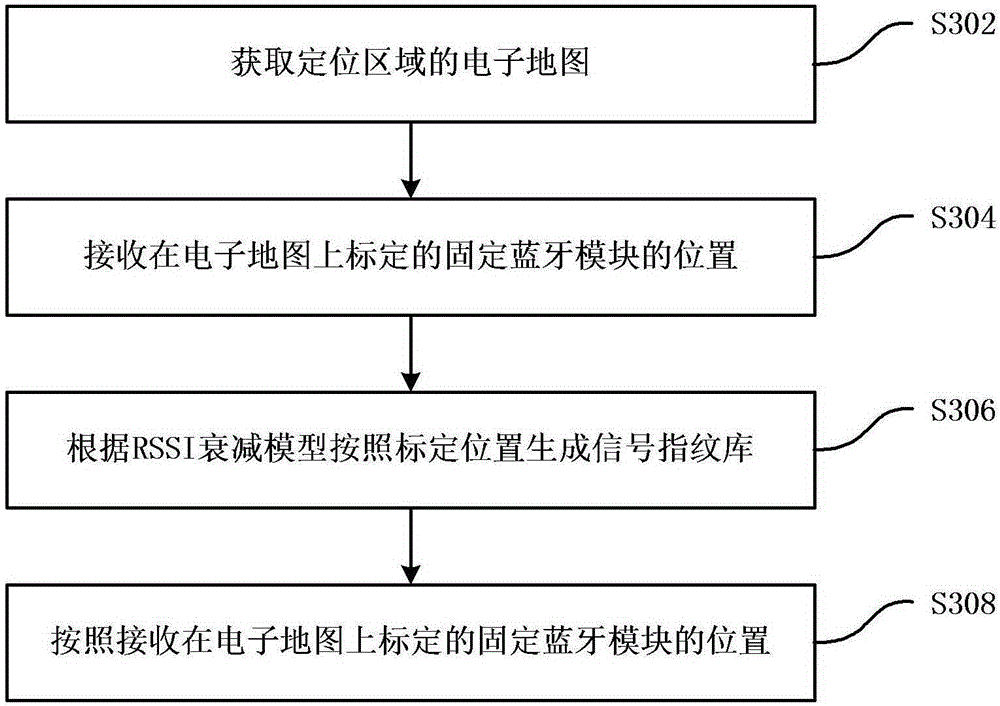
ActiveCN106406106AMeet the use requirementsImprove completenessComputer controlLocation information based serviceControl systemComputer module
The invention provides a household electrical appliance control method and control system based on indoor positioning. The household electrical appliance control method based on indoor positioning includes: obtaining signal features uploaded by a mobile terminal carried by a user, wherein the signal features are obtained by extraction according to broadcasting signals of a plurality of fixed bluetooth modules in a positioning area received by a mobile bluetooth module of the mobile terminal, and the plurality of fixed bluetooth modules are arranged in a plurality of household electrical appliance devices in the positioning area; matching the signal features with a preset signal fingerprint database of the positioning area in order to determine the position of the user, wherein the signal fingerprint database stores the signal features corresponding to different positions in the positioning area; and sending corresponding control instructions to the plurality of household electrical appliance devices according to the position of the user in order to adjust the work states of the plurality of household electrical appliance devices. By employing the scheme, accurate indoor positioning can be realized by employing the low-power-consumption bluetooth technology, and remote intelligent control of the household electrical appliances is realized.
Owner:QINGDAO HAIER AIR CONDITIONER GENERAL CORP LTD
Multipath processing for GPS receivers
InactiveUS7301992B2Reduce multipath effectsSimple technologyInstruments for road network navigationPosition fixationSatelliteDead reckoning
A GPS receiver system determines the presence of trackable signals at code delays less than the prompt delay being tracked for a particular, signal and changes the prompt delay to correspond to the smallest code delay having a trackable signal. Trackable signals at large code delays are multipath signals and may be separately tracked to aid in dead reckoning. The trackable signals at code delays not adjacent to the current tracked prompt delay may be tracked in the same channel as the prompt delay so that all satellite channels are continuously evaluated for multipath signals being tracked or a non-satellite specific channel may be used to sequentially step through the satellite signals to evaluate multipath on a satellite by satellite basis.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
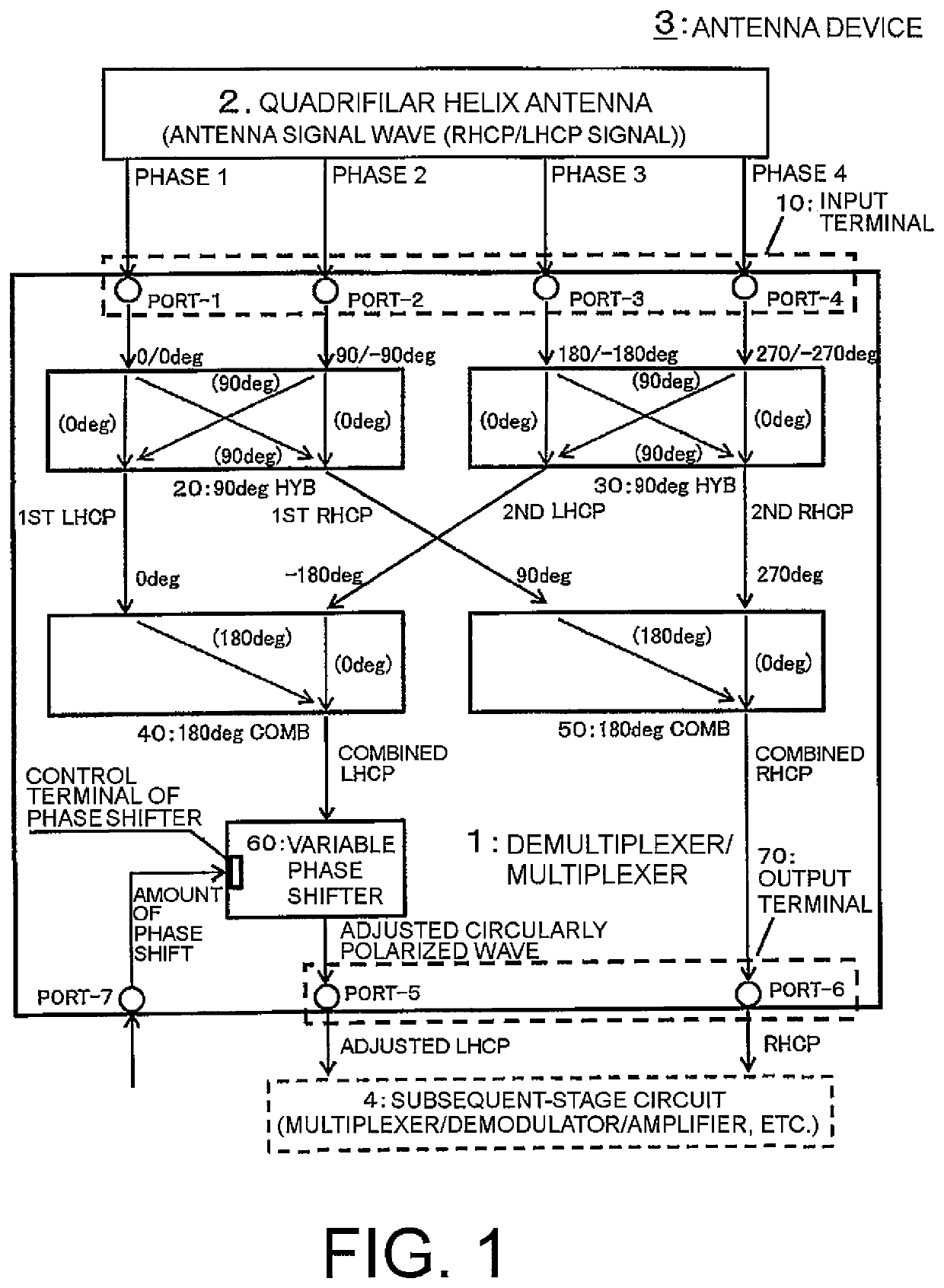
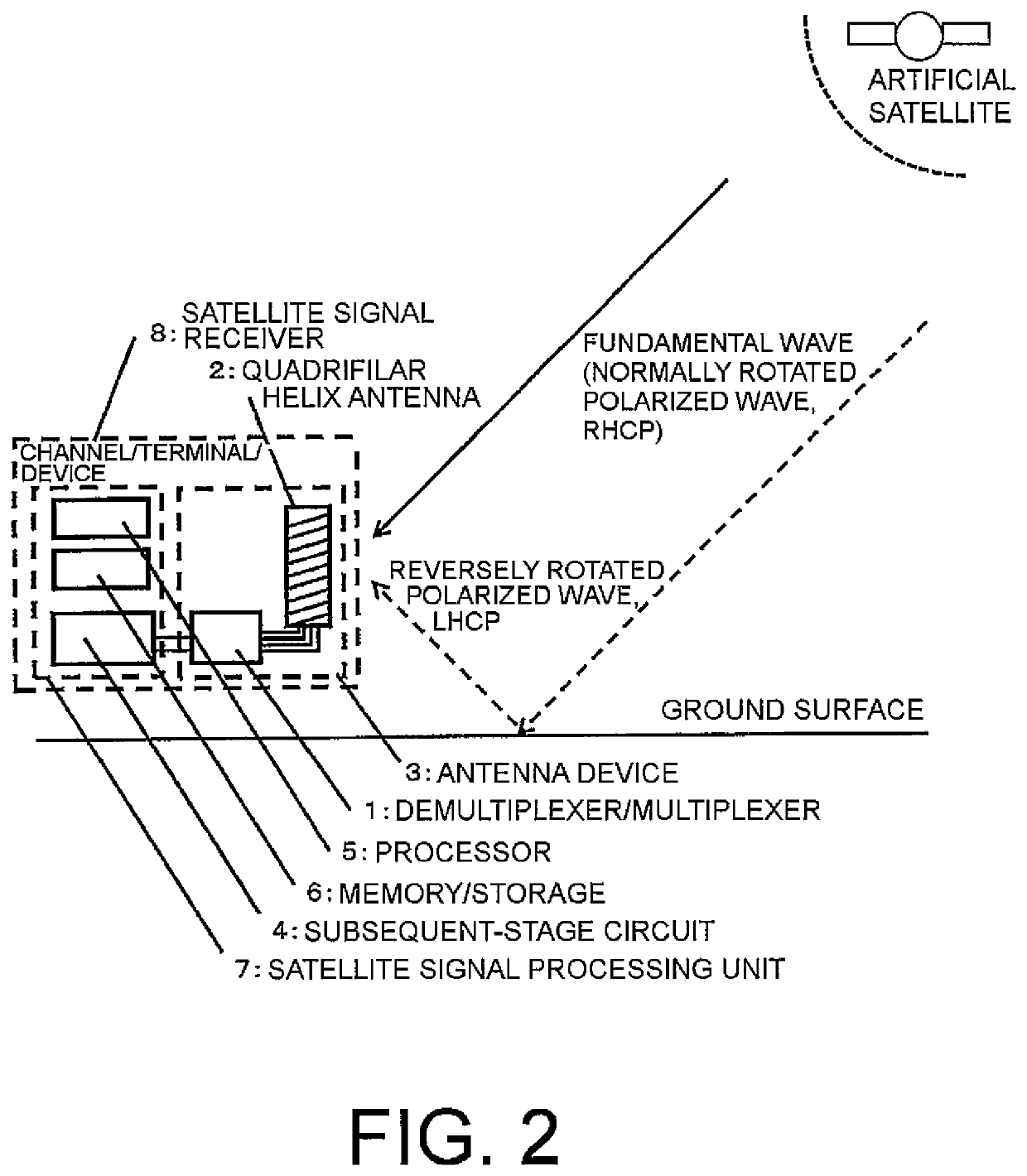
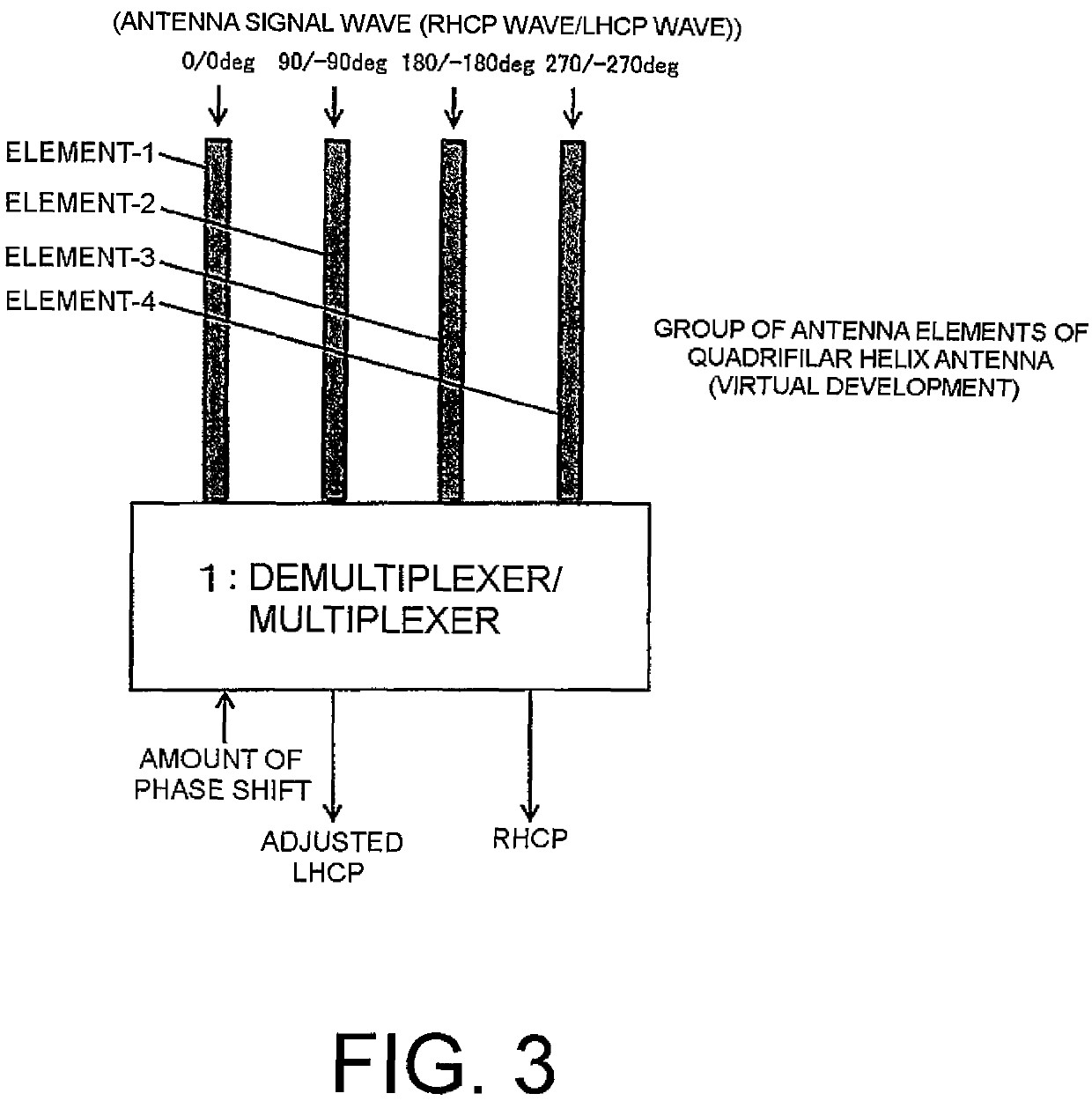
Demultiplexer/multiplexer, antenna device, and fading elimination method
ActiveUS10530033B2Reduce multipath effectsParticular array feeding systemsLogperiodic antennasFrequency mixerSoftware engineering
Owner:NEC CORP
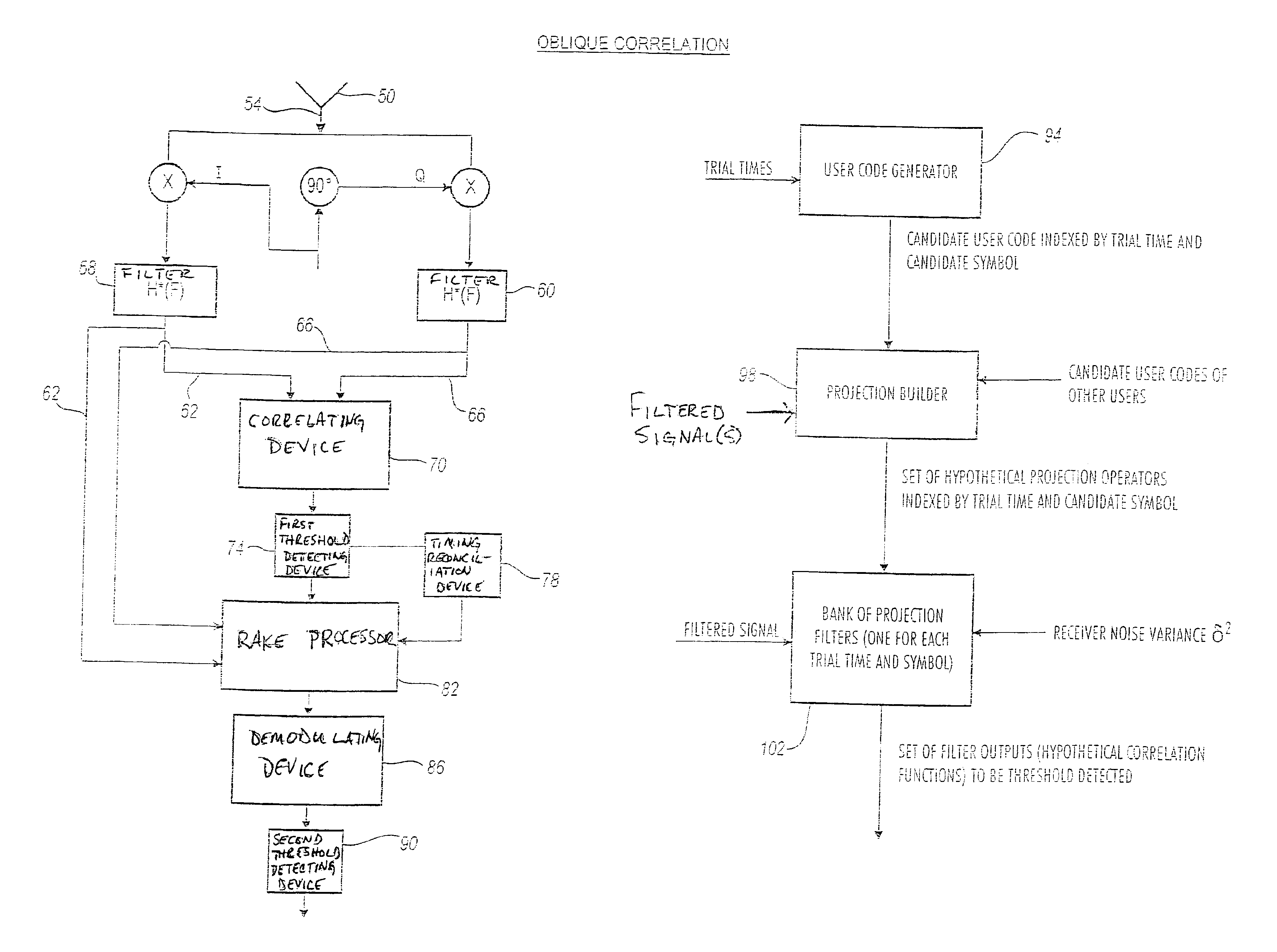
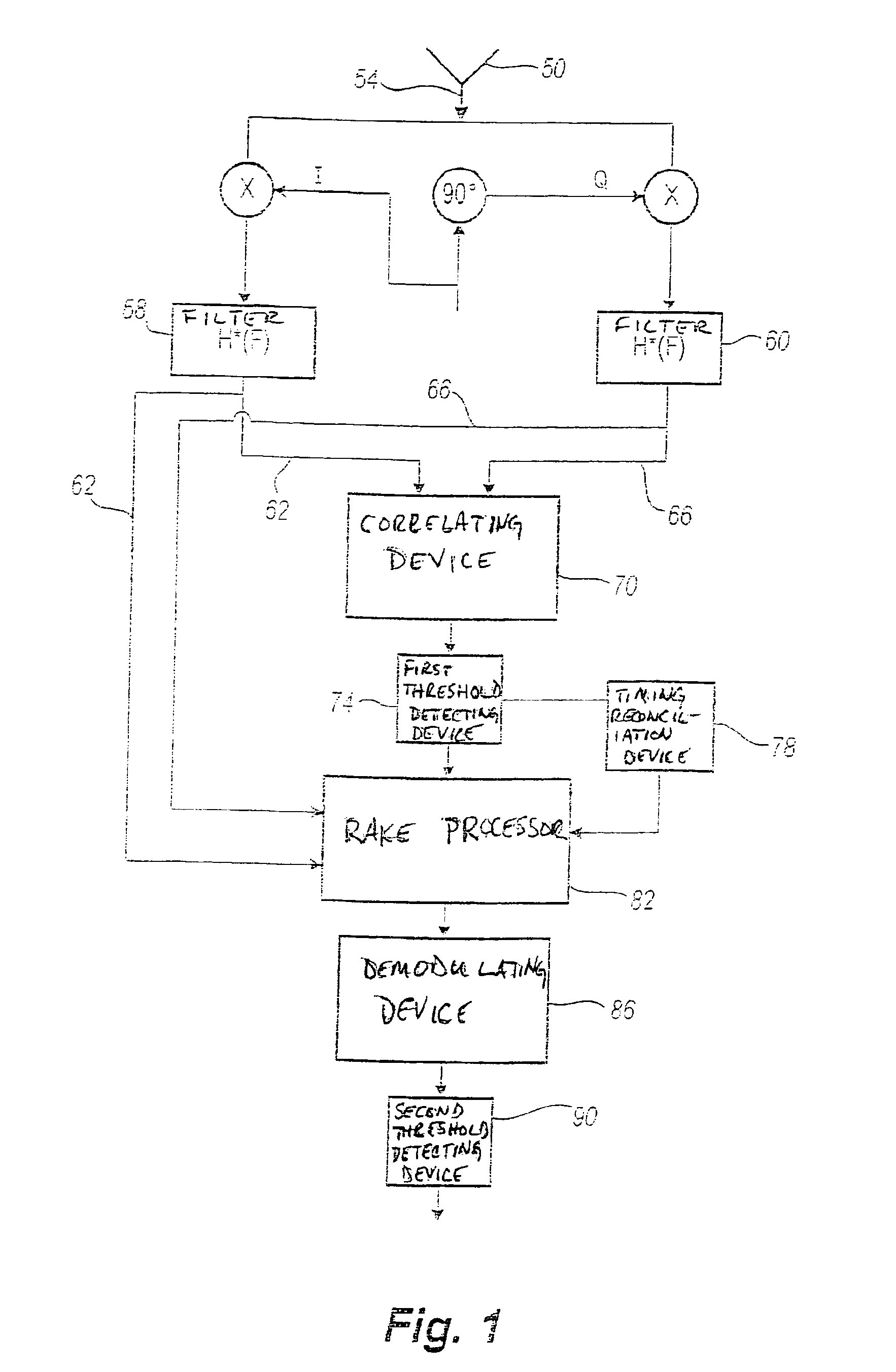
Rake receiver for spread spectrum signal demodulation
InactiveUS6947474B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioEliminate distractionsSpatial transmit diversityBeacon systems using radio wavesRake receiverEngineering
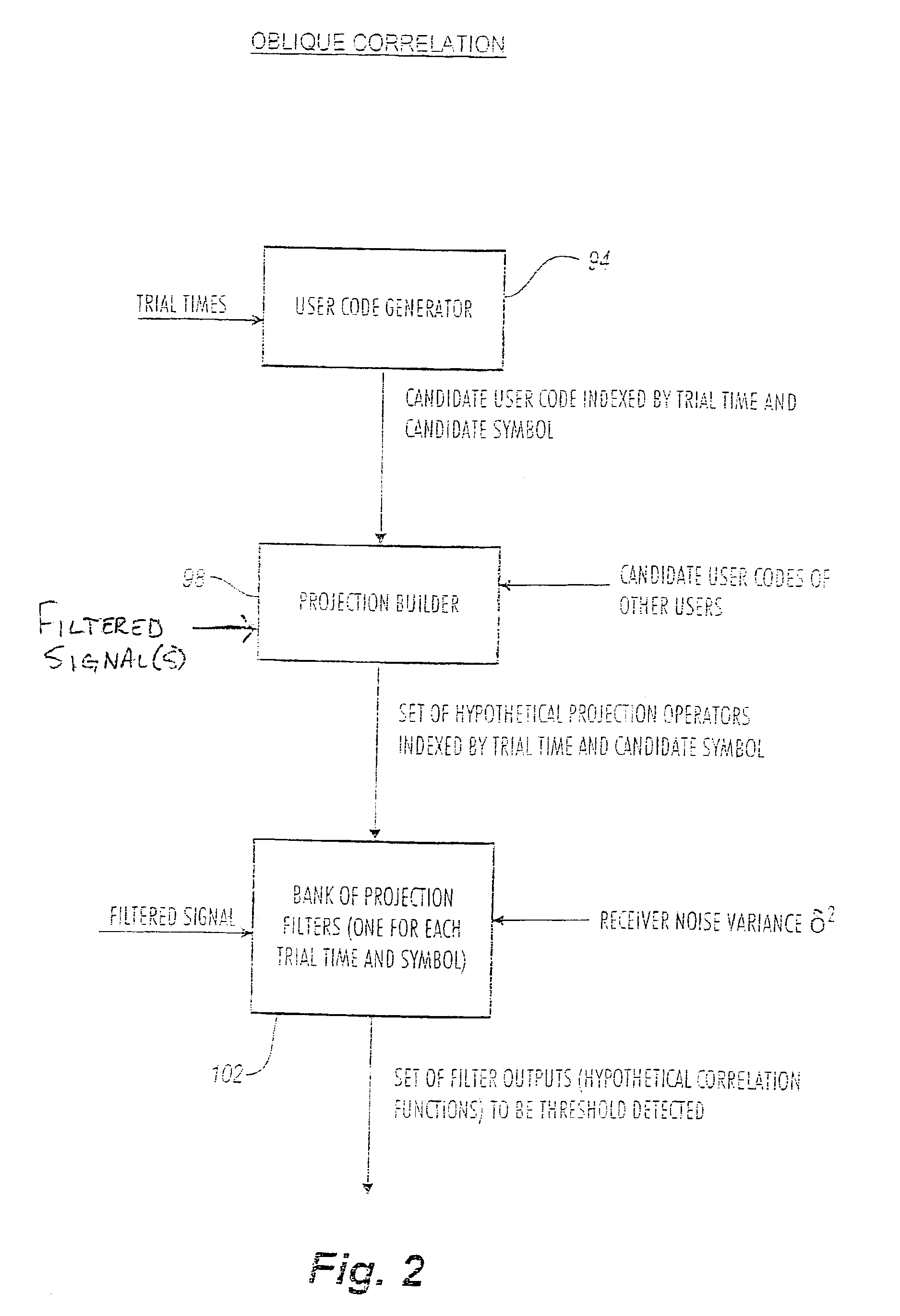
The architecture of the present invention is premised upon an algorithm involving integration of oblique correlators and RAKE filtering to null interference from other spread spectrum signals. The oblique correlator is based on the non-orthogonal projections that are optimum for nulling structured signals such as spread spectrum signals. In one configuration, space spanned by a first signal associated with a first emitter is orthogonal to an interference space associated with one or more signals of one or more other emitters. RAKE filtering is used to rapidly steer the beam of the multi-antenna system and to mitigate the effects of multipath.
Owner:III HLDG 1
RFID reader
InactiveUS20080315996A1Maximising read probabilityMaximize probabilitySpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsTransmitter
An RFID reader comprises a receiver section for receiving an RF signal and a transmitter section for transmitting an RF signal. The reader is a multicarrier RFID reader and both the transmitted RF signal and the received RF signal comprise at least two frequencies.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
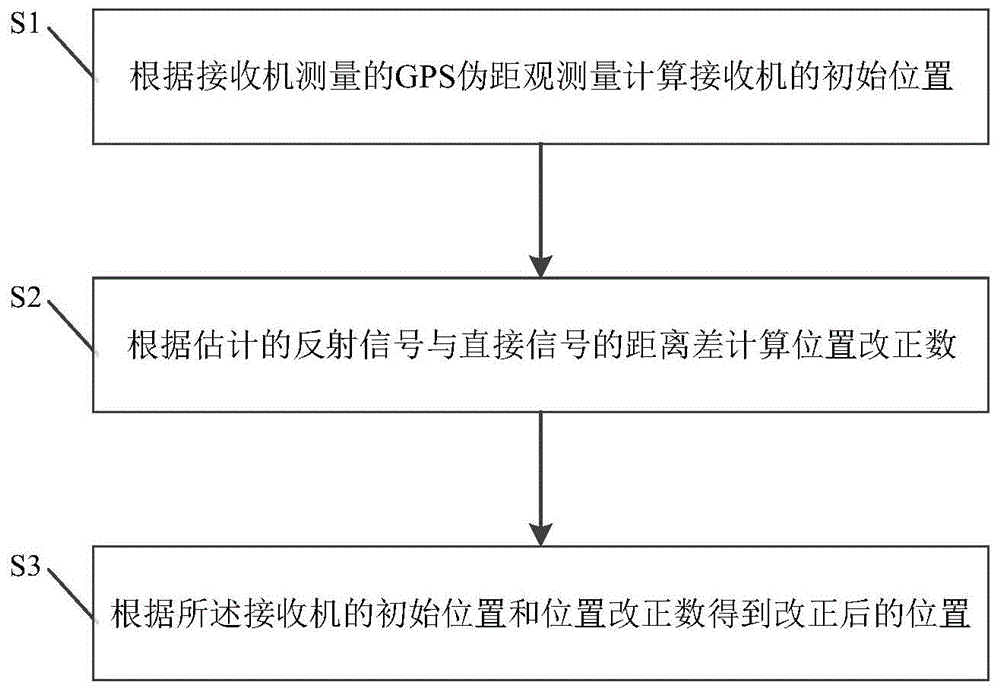
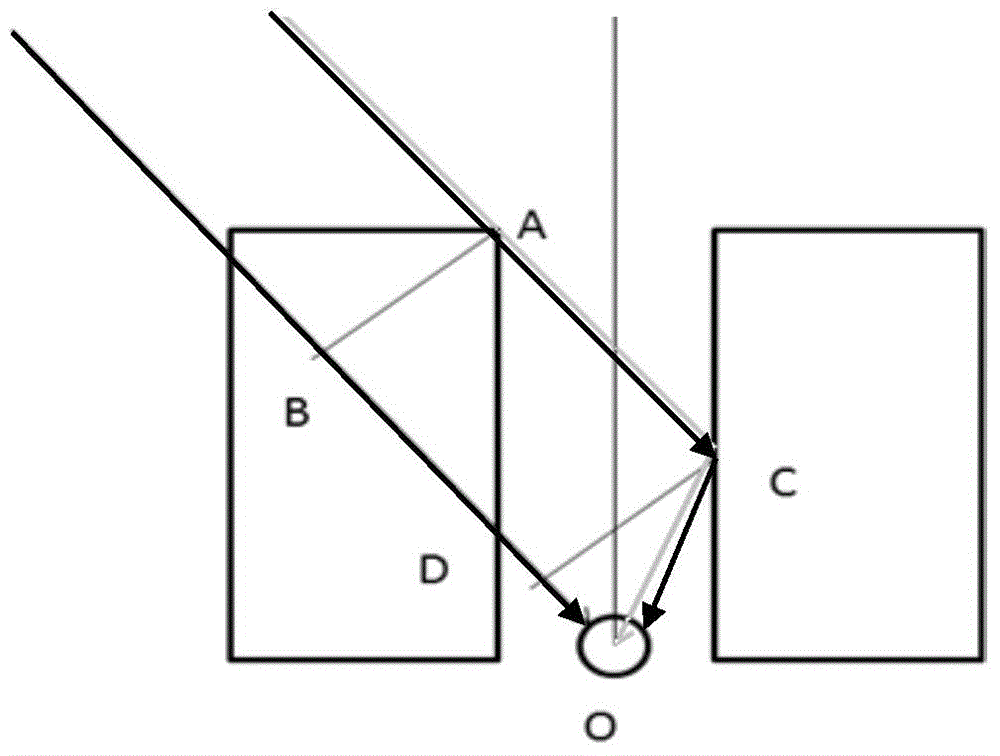
GPS multi-path effect correction and positioning method and system
ActiveCN105652292AHigh positioning accuracyReduce multipath effectsSatellite radio beaconingMulti pathUrban building
The invention relates to a PS multi-path effect correction and positioning method and system. The method comprises: S1, an initial position of a receiver is calculated according to a GPS pseudo-range observation value measured by the receiver; S2, a position correction value is calculated based on an estimated distance difference between a reflection signal and a direct signal; and S3, according to the initial position of the receiver and the position correction value, a corrected position is obtained. According to the invention, the position correction value is calculated based on the estimated distance difference between the reflection signal and the direct signal and thus the position of the receiver can be corrected, so that the multi-path effect is reduced and the positioning precision of the GPS in an urban building compact district can be substantially improved. Moreover, the method is simple; the cost is low; and the method and system can be directly applied to a positioning mode of a GPS phone.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Dynamic positioning method and device
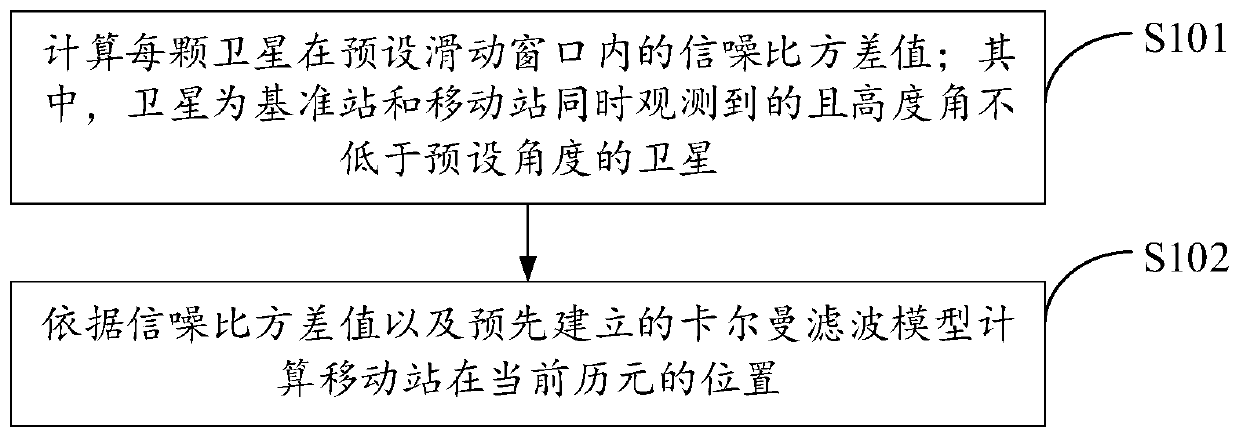
ActiveCN110058281AEasy to filterEasy to eliminateSatellite radio beaconingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Slide window
The embodiments of the invention provide a dynamic positioning method and a device, and relate to the technical field of positioning. The dynamic positioning method includes the steps that the variance value of signal-to-noise ratio of each satellite in a preset sliding window is calculated, wherein the satellite is a satellite observed simultaneously by a base station and a mobile station, and analtitude angle is not lower than a preset angle; and the position of the mobile station at the current epoch is calculated based on the variance value of the signal-to-noise ratio and a pre-established kalman filter model. Because low-elevation satellites are more prone to being affected by multi-path, the satellites whose altitude angles are lower than the preset angles are eliminated first before the variance value of the signal-to-noise ratio is calculated, so that the impact of the multi-path effects is reduced effectively; and the variance value of the signal-to-noise ratio is involved in the calculation process of the kalman filter, so that multi-path errors can be better filtered and eliminated, and therefore, the accuracy of RTK positioning results is improved.
Owner:HUNAN GOKE MICROELECTRONICS
Method for pretreating bridge monitoring signals
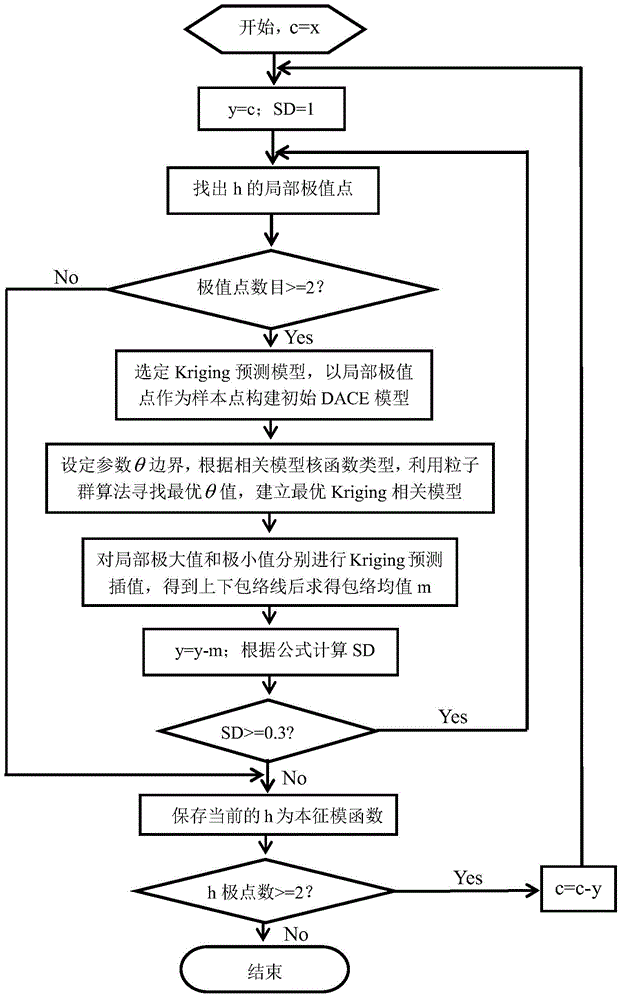
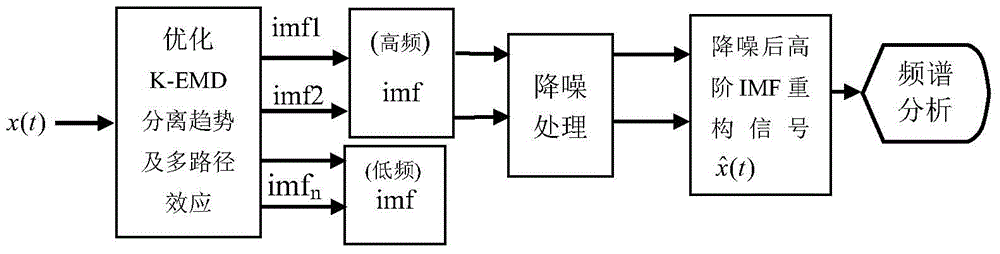
ActiveCN104897180AAvoid falling intoCapable of global optimizationSpecial purpose recording/indication apparatusLocal optimumPretreatment method
The invention relates to the bridge field, especially to a method for pretreating bridge monitoring signals. The method includes pretreating bridge monitoring signals with an EMD decomposition method with added Kriging interpolation, wherein particle swarm optimization (PSO) is employed to optimize related model parameter theta involved in a K-EMD process. PSO has overall optimization capability, prevents signal processing from being optimized partially, and ensures the value is overall optimal.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
Signal separation estimation theory-based satellite navigation signal multipath interference suppression method
InactiveCN102508265AEliminate multipath effectsReduce mistakesSatellite radio beaconingPrior informationIntermediate frequency
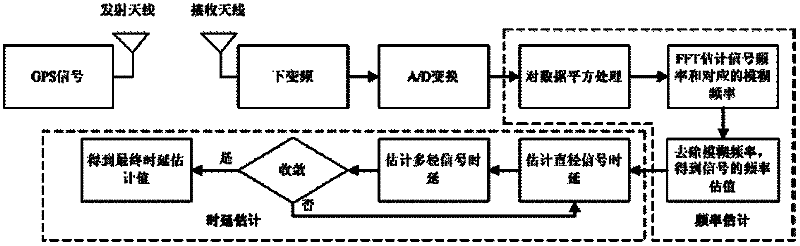
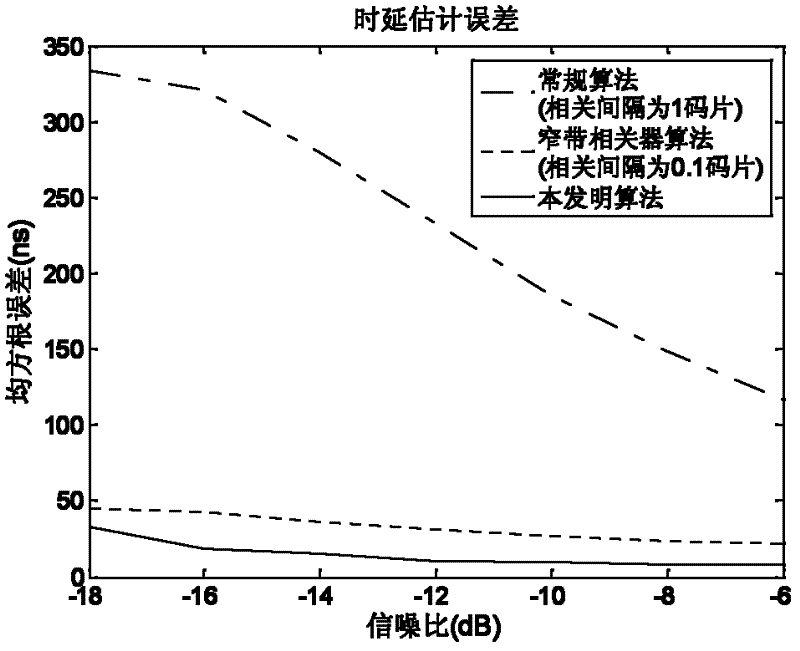
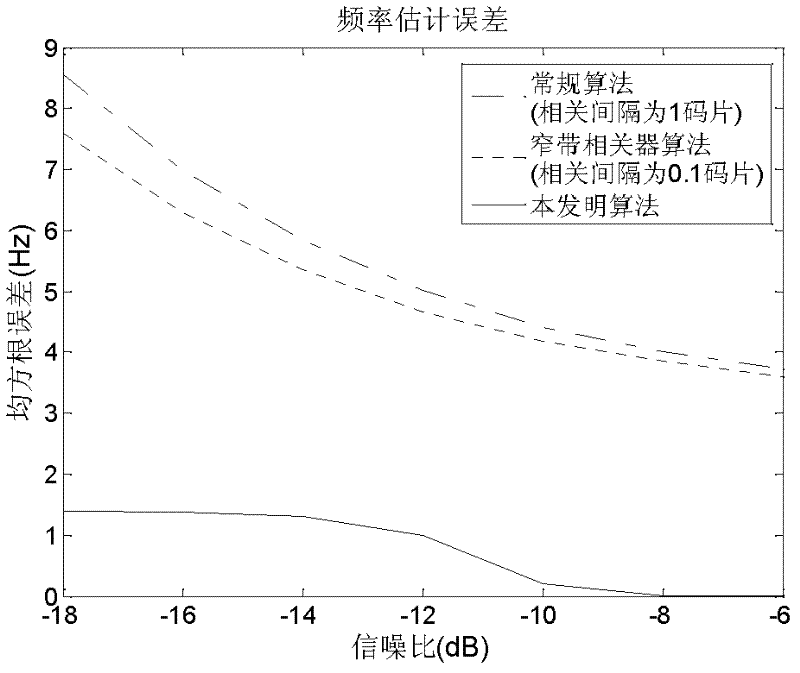
The invention discloses a signal separation estimation theory-based satellite navigation signal multipath interference suppression method, which mainly relates to a time delay estimation algorithm and a frequency estimation algorithm of a diameter signal and a multipath signal of a satellite navigation system. The method comprises the following steps of: estimating a satellite signal frequency which includes Doppler under the condition that a time delay is unknown, eliminating a fuzzy frequency according to the intermediate frequency value of the satellite signal and prior information in which a Doppler frequency shift range is known, and estimating the time delays of the diameter signal and the multipath signal respectively by using the signal separation estimation theory. By the signal separation estimation theory-based satellite navigation signal multipath interference suppression method, the time delay information and the frequency information of the diameter signal can be directly estimated and the aim of eliminating multipath signal influence can be fulfilled in a multipath environment.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Apparatus and method for mitigating multipath effects and improving absorption of an automotive radar module
ActiveUS10074907B2Reduce multipath effectsReduce radiationAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadiating element housingsRadar systemsRadar radiation
Owner:VEONEER US LLC
High-frequency epoch-by-epoch phase difference method for single-frequency GNSS phase stability monitoring
ActiveCN105425248AReduce multipath effectsSatellite radio beaconingPhase differenceStatistical analysis
The invention discloses a high-frequency epoch-by-epoch phase difference method for single-frequency GNSS phase stability monitoring, comprising the following steps: using a single-frequency GNSS receiver to perform high-frequency observation on a station point, and calculating the phase difference between adjacent epochs; using the least squares method to detect a station 3D (NEU) coordinate correction number time series within the interval of adjacent epochs under continuous epochs; getting the mean and standard deviation of the NEU coordinate through statistical analysis of the time series; and calculating the anomaly ratio. The phase observation stability of the single-frequency GNSS receiver is evaluated by calculating the continuous observation anomaly ratio using the method. Single-point real-time high-frequency GNSS phase data quality monitoring is carried out based on single-frequency GNSS data. The GNSS phase stability can be evaluated without the need for high-precision clock difference or model correction.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com