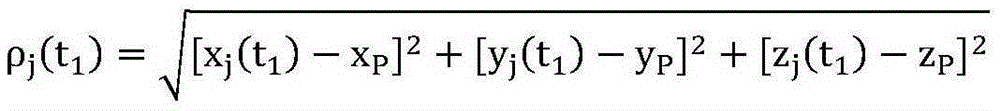High-frequency epoch-by-epoch phase difference method for single-frequency GNSS phase stability monitoring
A phase difference and epoch-by-epoch technology, which is applied in the field of high-frequency phase difference by epoch, can solve the problems of inability to provide precise positioning and station management
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
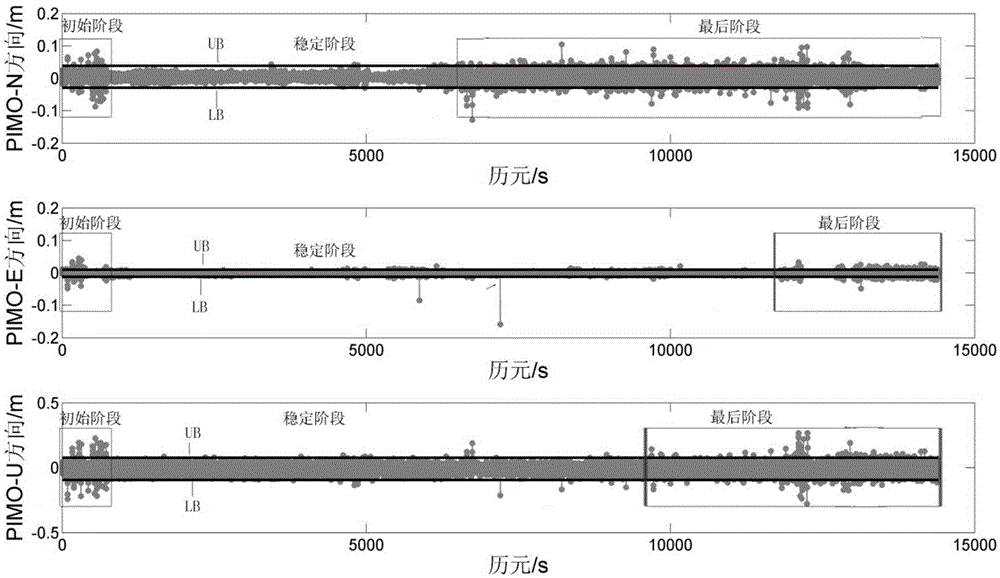
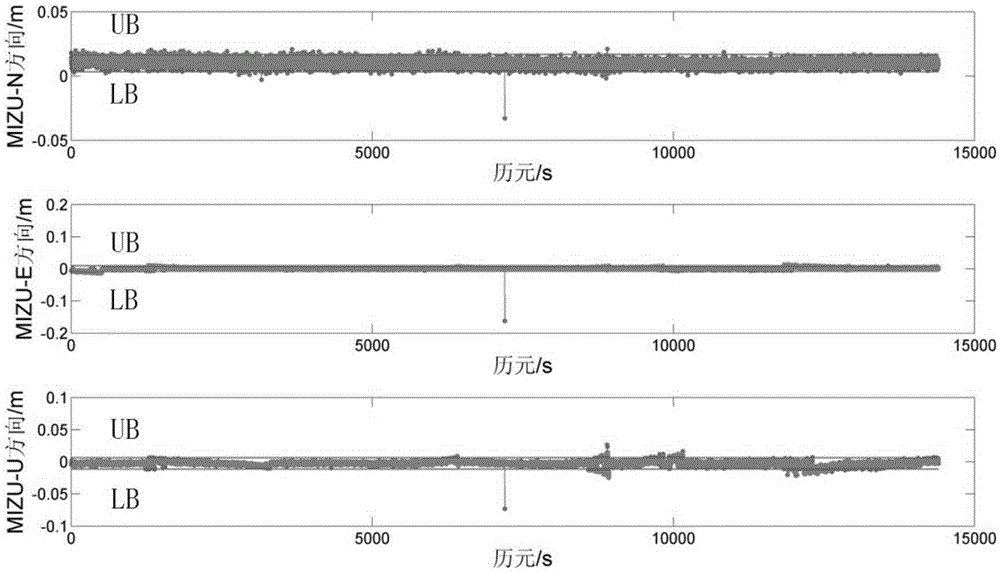
[0053] The present invention is a high-frequency epoch-by-epoch phase difference method for single-frequency GNSS phase stability monitoring, which has universal characteristics and can replace data post-processing analysis with single-point real-time monitoring; the evaluation method can eliminate tides, multipath effects, and ionization layer and troposphere, ambiguity, clock bias, hardware delay, etc. without the need for high-precision clock bias, various model corrections, etc.
[0054] The method for monitoring the stability of the phase by using the single-frequency GNSS receiver through the high-frequency epoch-by-epoch phase difference includes the following steps:
[0055] (1) Calculate the phase difference by epoch
[0056] Use a single-frequency GNSS receiver to perform high-frequency (eg 1 Hz) observations on a station P. Under the condition that the number of observation satellites is more than 3, the phase data of two adjacent epochs are collected at high frequ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com