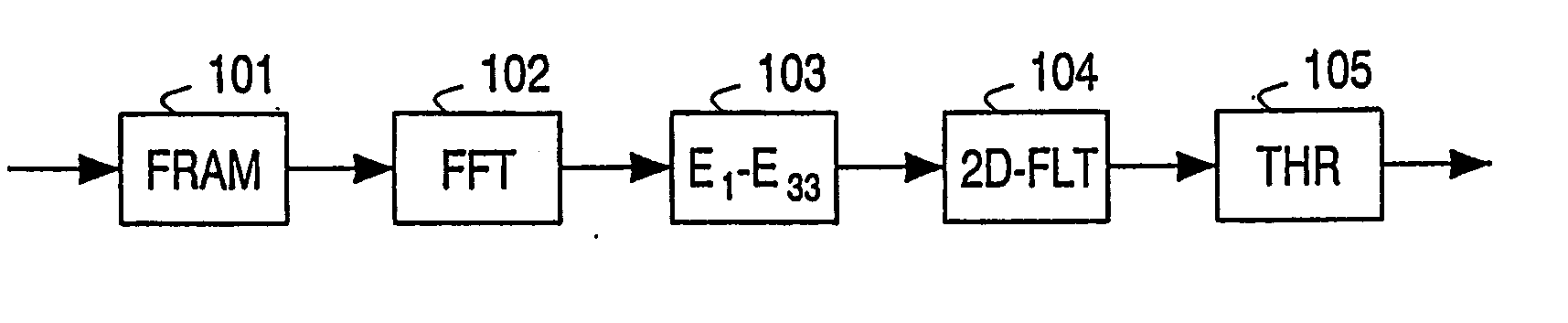
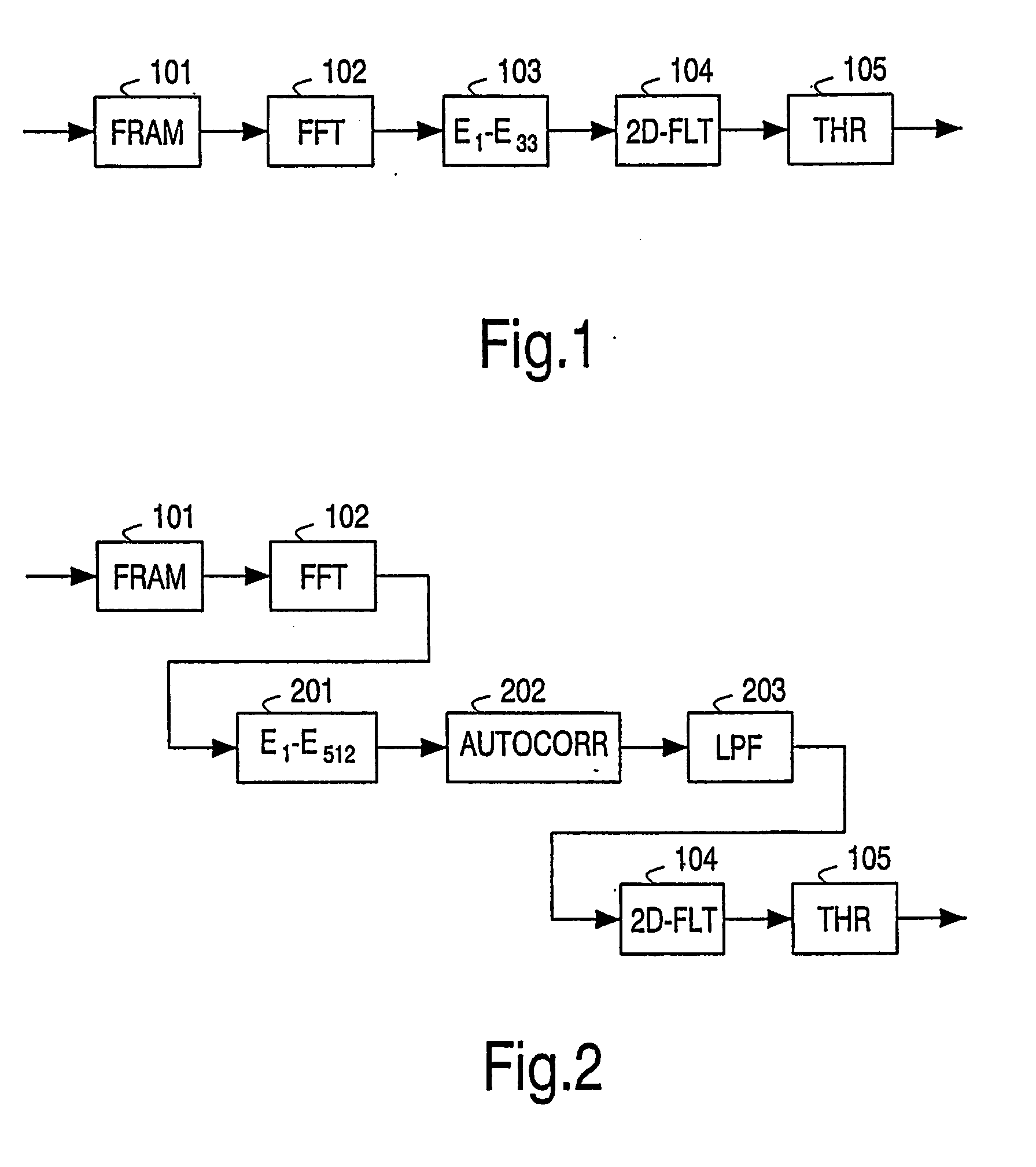
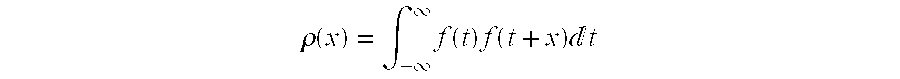Patents
Literature
1820 results about "Correlation function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A correlation function is a function that gives the statistical correlation between random variables, contingent on the spatial or temporal distance between those variables. If one considers the correlation function between random variables representing the same quantity measured at two different points then this is often referred to as an autocorrelation function, which is made up of autocorrelations. Correlation functions of different random variables are sometimes called cross-correlation functions to emphasize that different variables are being considered and because they are made up of cross-correlations.
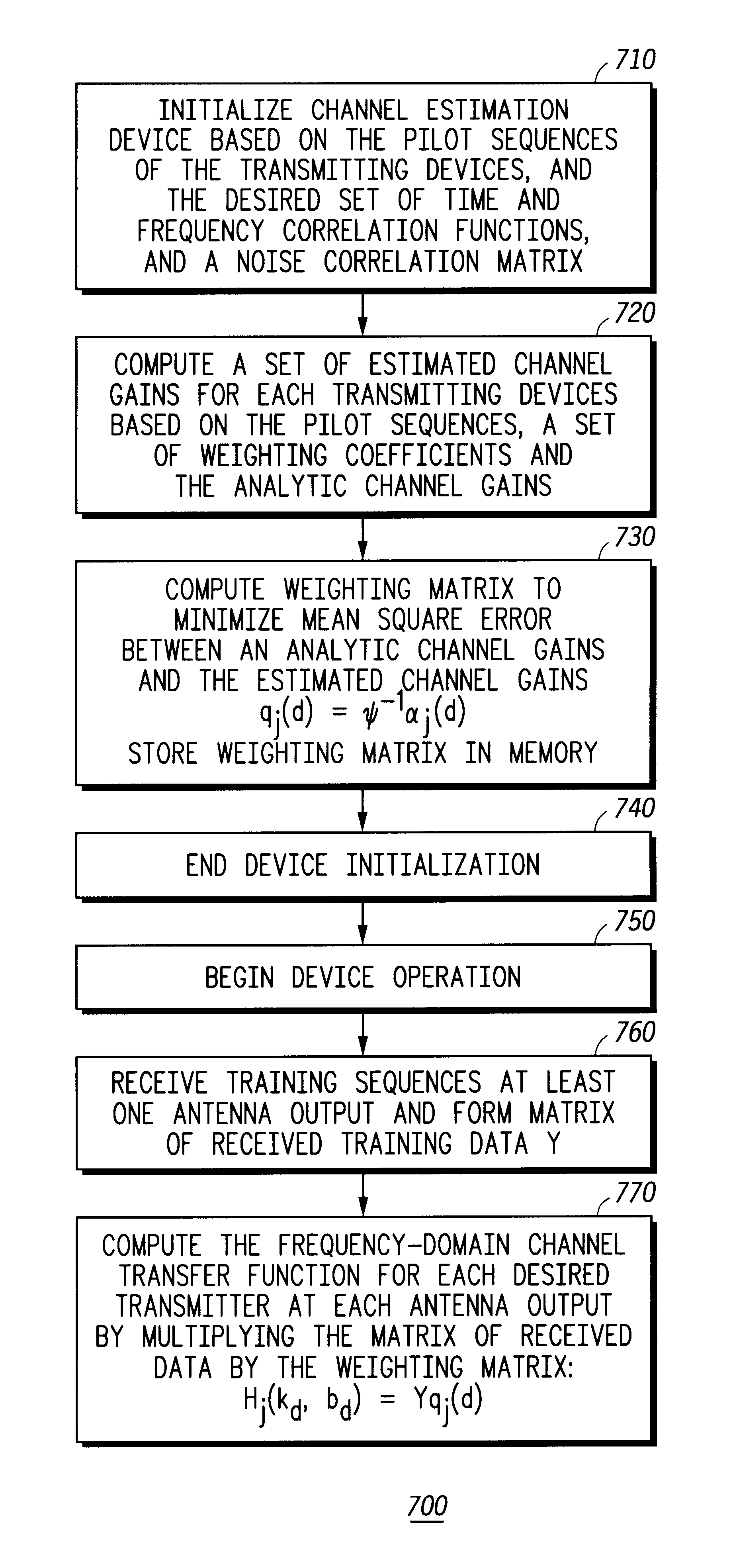
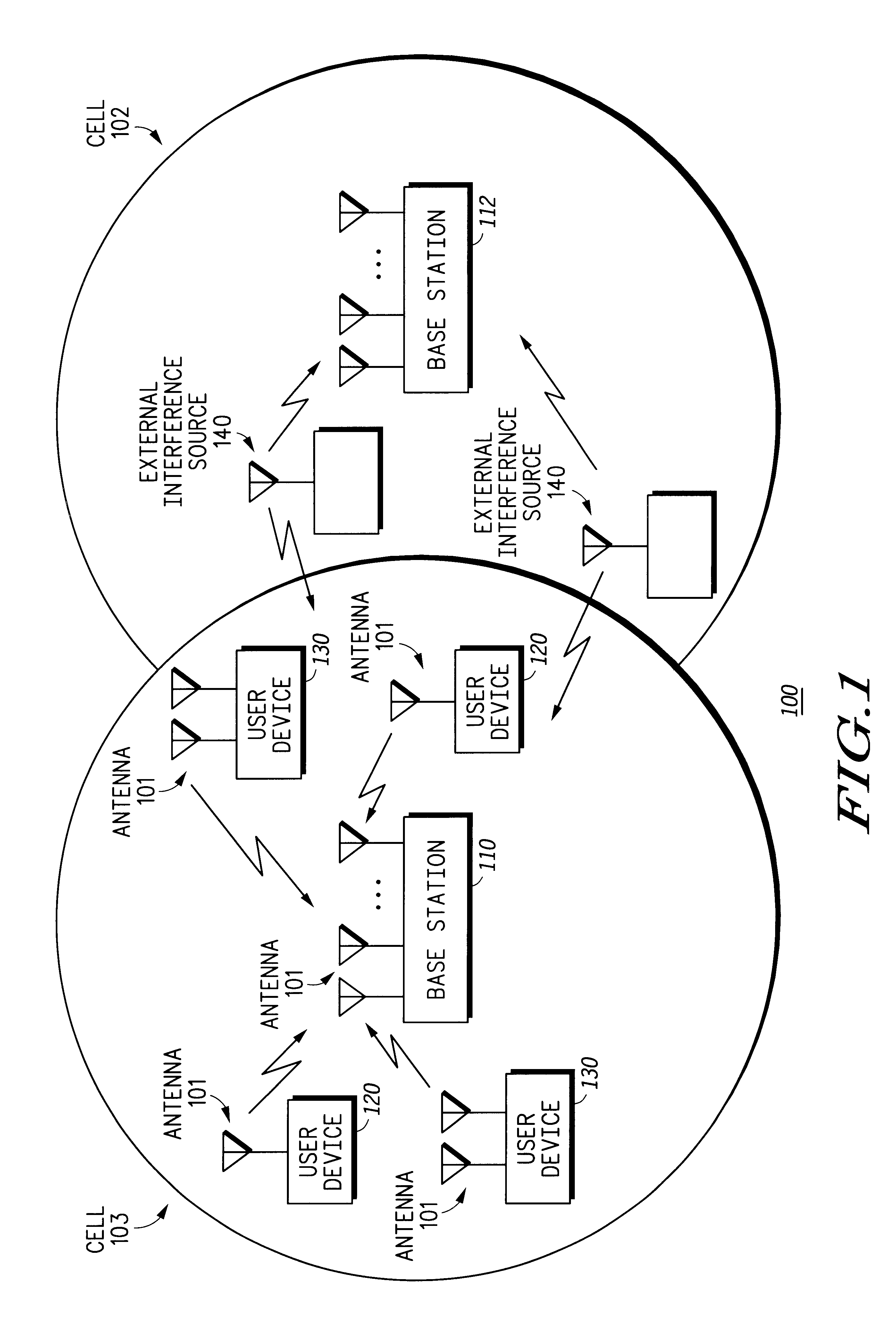
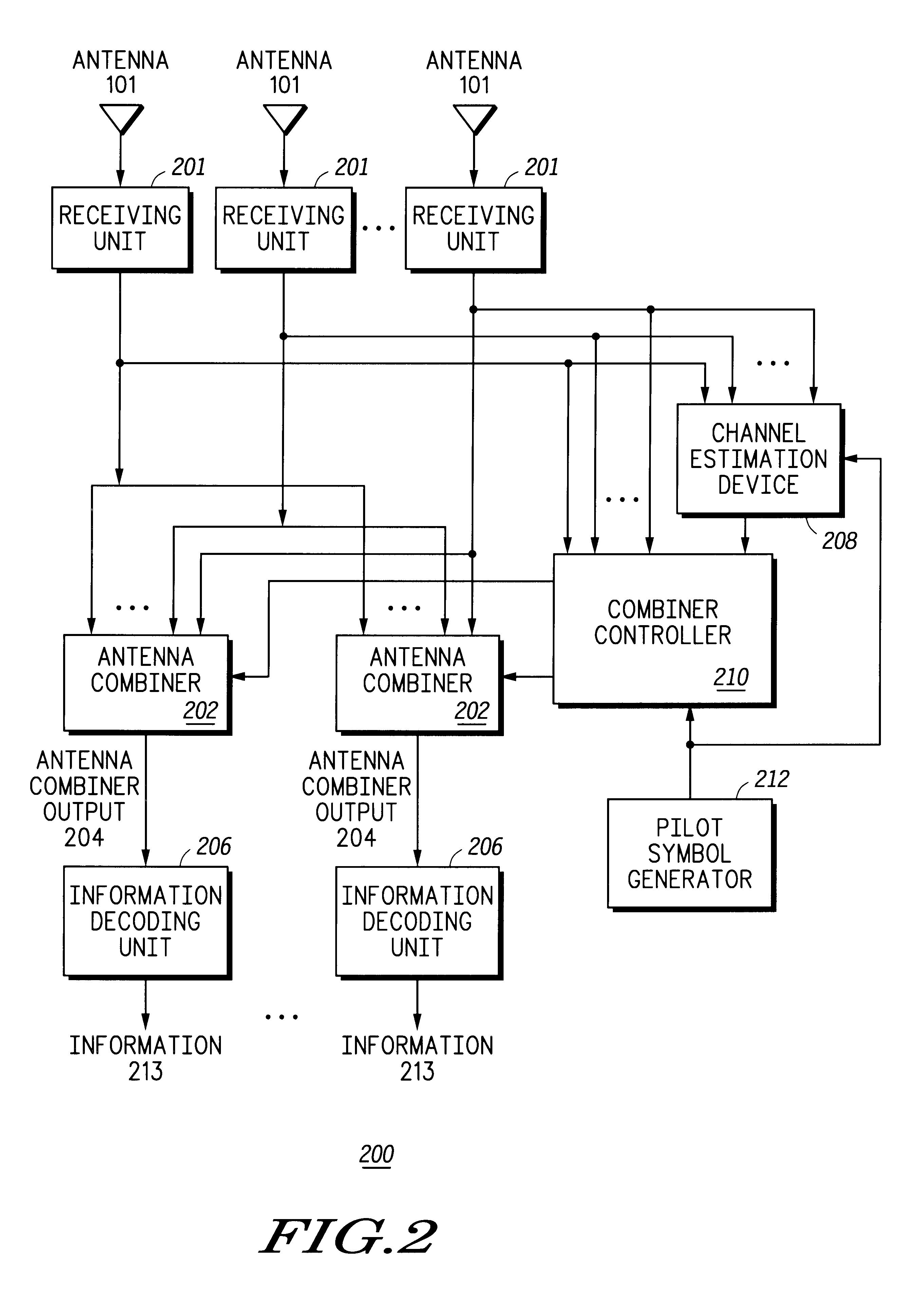
Method and device for multi-user channel estimation
InactiveUS6765969B1Modulated-carrier systemsChannel estimationComputation complexityWeight coefficient
The invention computes frequency-domain channel gains by compiling a set of estimated channel gains as a function of pilot sequences, a set of analytical channel gains variables, and a set of weighting coefficients variables. A plurality of weighting coefficients are computed as a function of time and frequency correlation functions, a noise correlation matrix, and pilot sequences. A weighting matrix is computed from the weighting coefficients. After receiving a training sequence from at least one transmitter, a received data matrix is computed from the training sequence. The weighting matrix and the received data matrix are used to compute the frequency-domain channel gains. The invention also provides a method for reducing the computational complexity of estimating the time and frequency response of at least one desired signal received by at least one antenna. Also, the time and frequency response of at least one desired signal received by at least one antenna can be both interpolated and predicted with the present invention.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
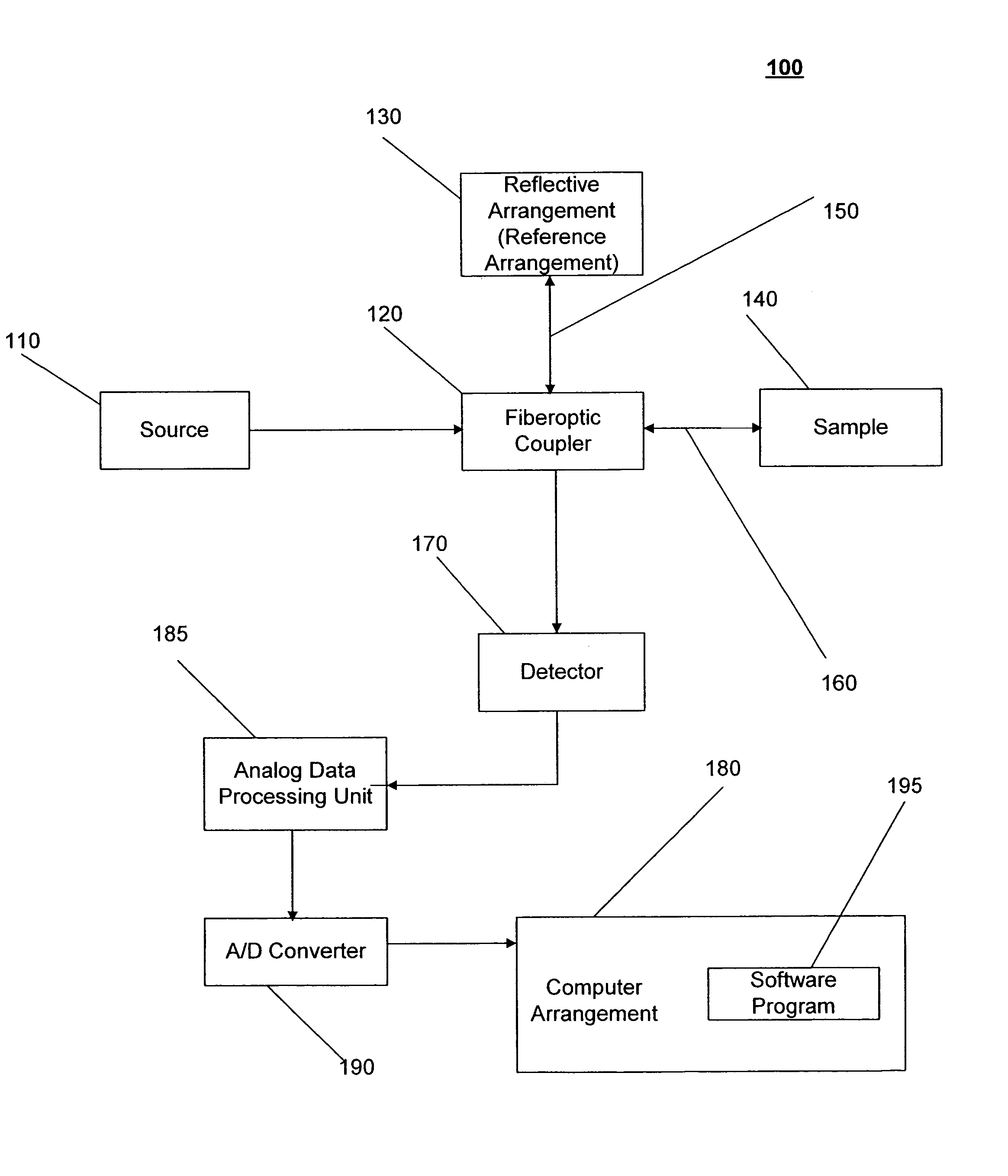
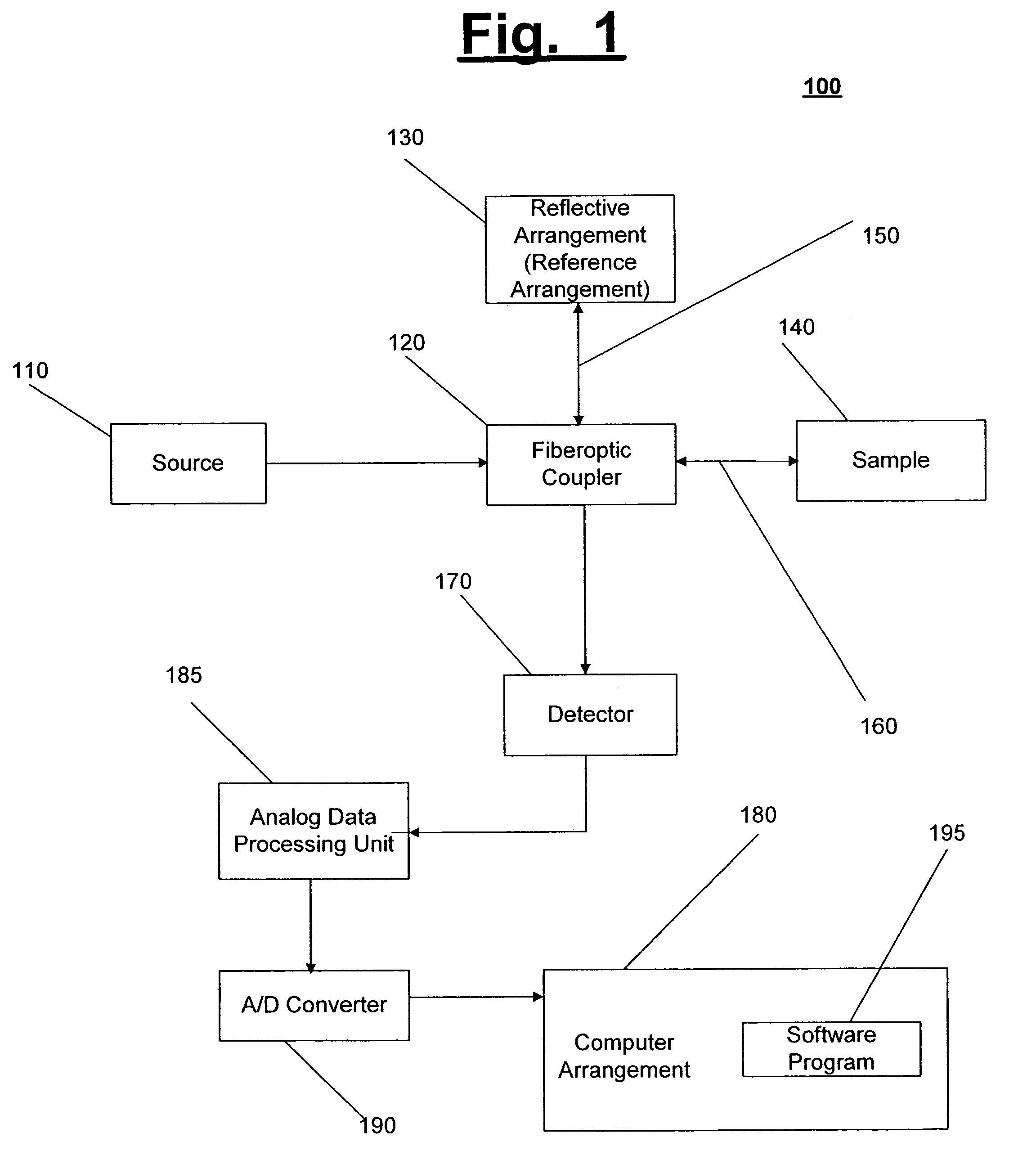
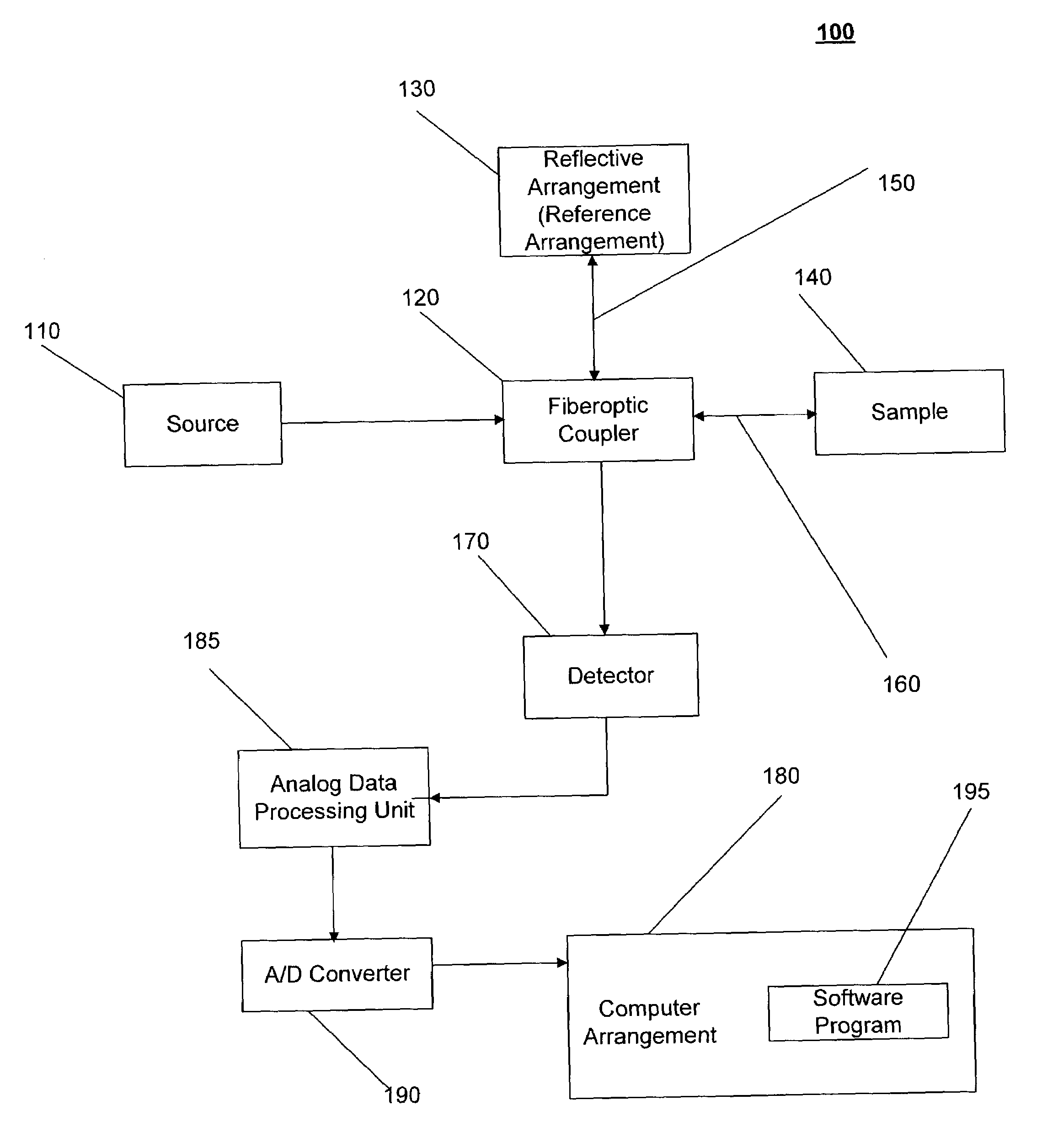
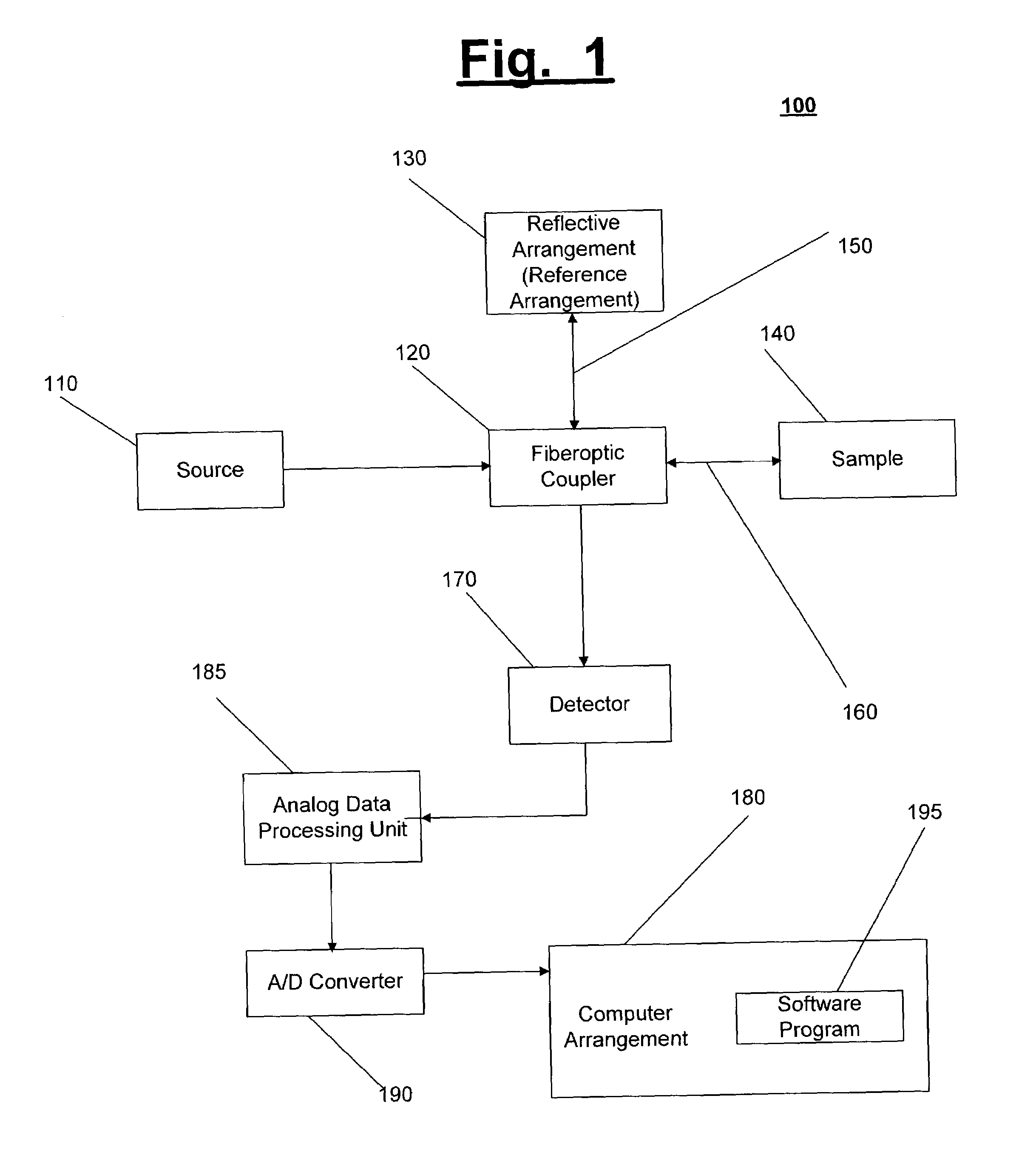
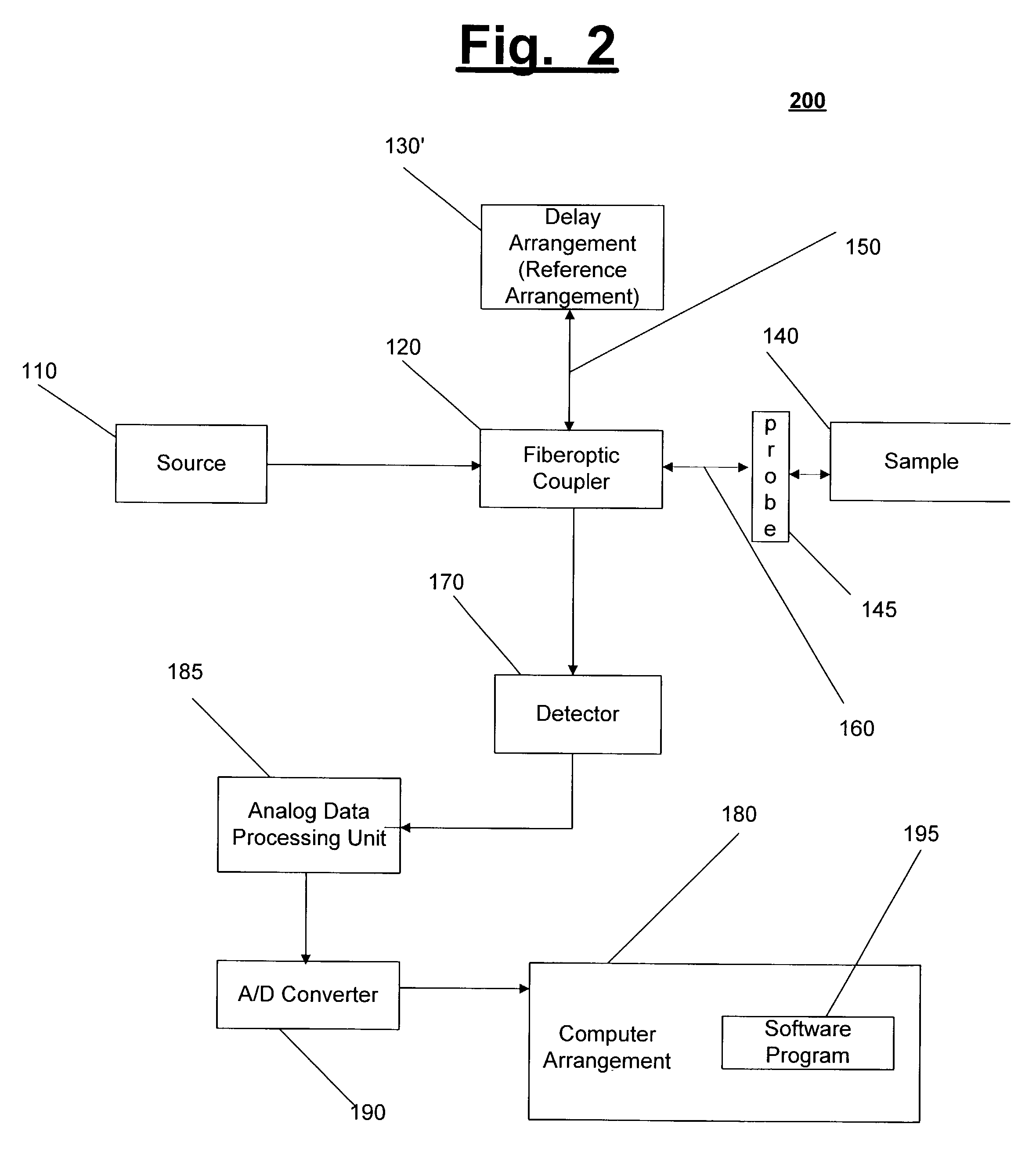
Systems and methods for imaging a sample
InactiveUS7148970B2Side lobes in the coherence envelope are reduced or eliminatedCompensation for dispersionUsing optical meansCorrelation functionComputational physics
A system and method for imaging a sample are provided. In particular, a first combination of light and a second combination of light are received, in which a first cross correlation function is associated with the first combination and a second cross correlation function is associated with the second combination. Each of the first and the second combinations includes a first portion of light which is received from a reference arrangement and a second portion of light which is received from the sample, and a first relative position of the sample associated with the first combination is different than a second relative position of the sample associated with the second combination. In an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the first cross correlation function is transformed into a first complex cross spectral density and the second cross correlation function is transformed into a second complex cross spectral density. Moreover, a third complex cross spectral density can be determined which is approximately an average of the first complex cross spectral density and the second complex cross spectral density.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
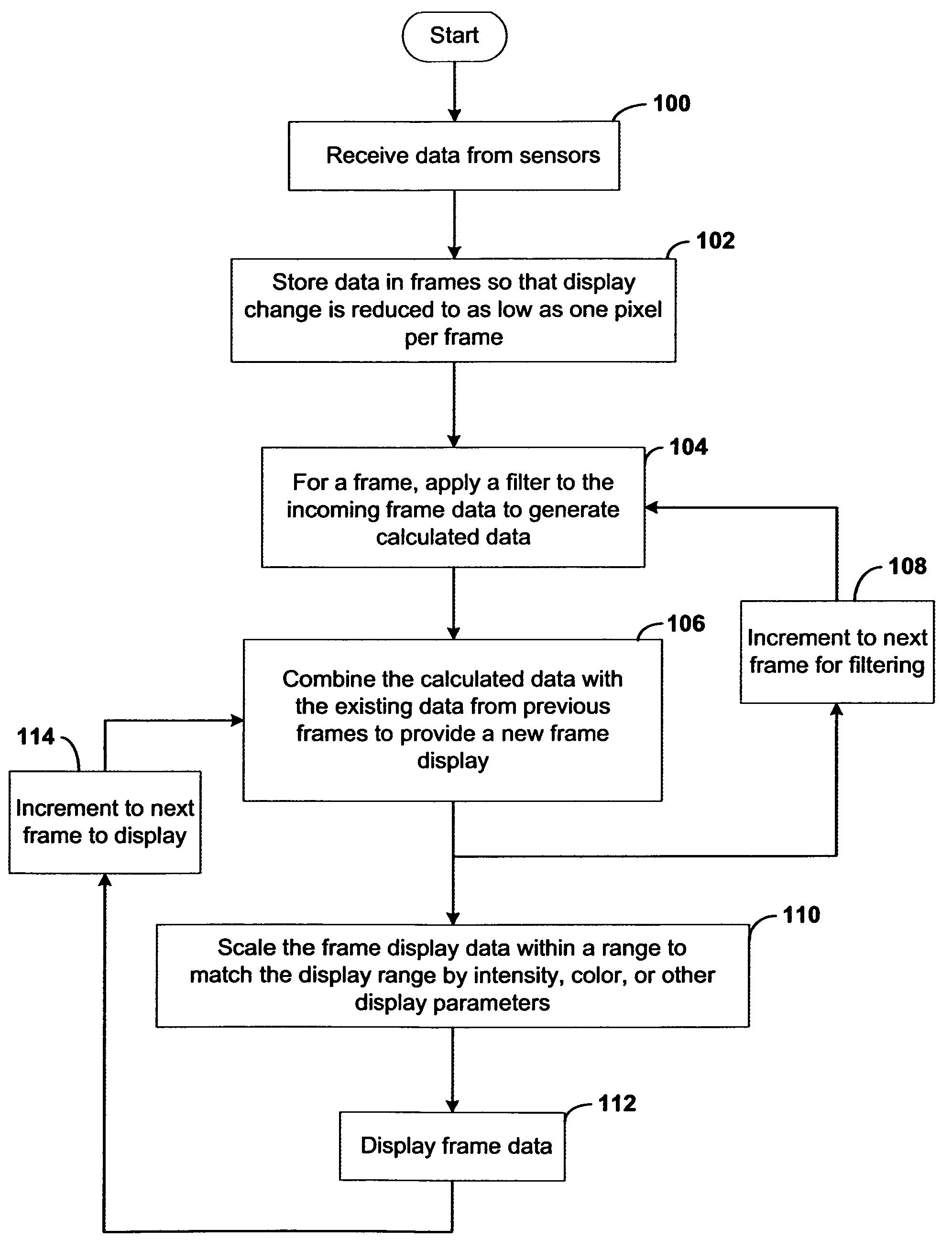
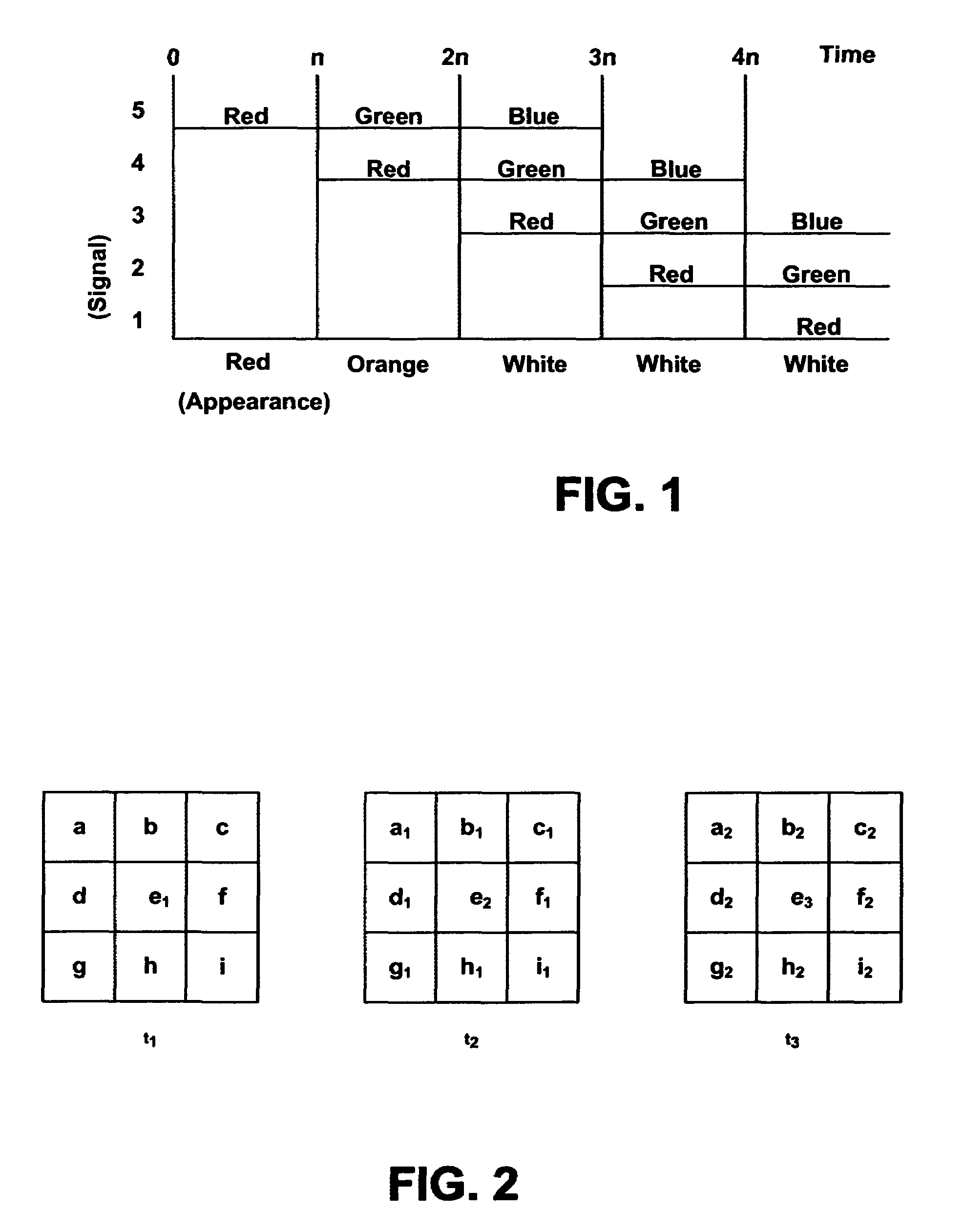
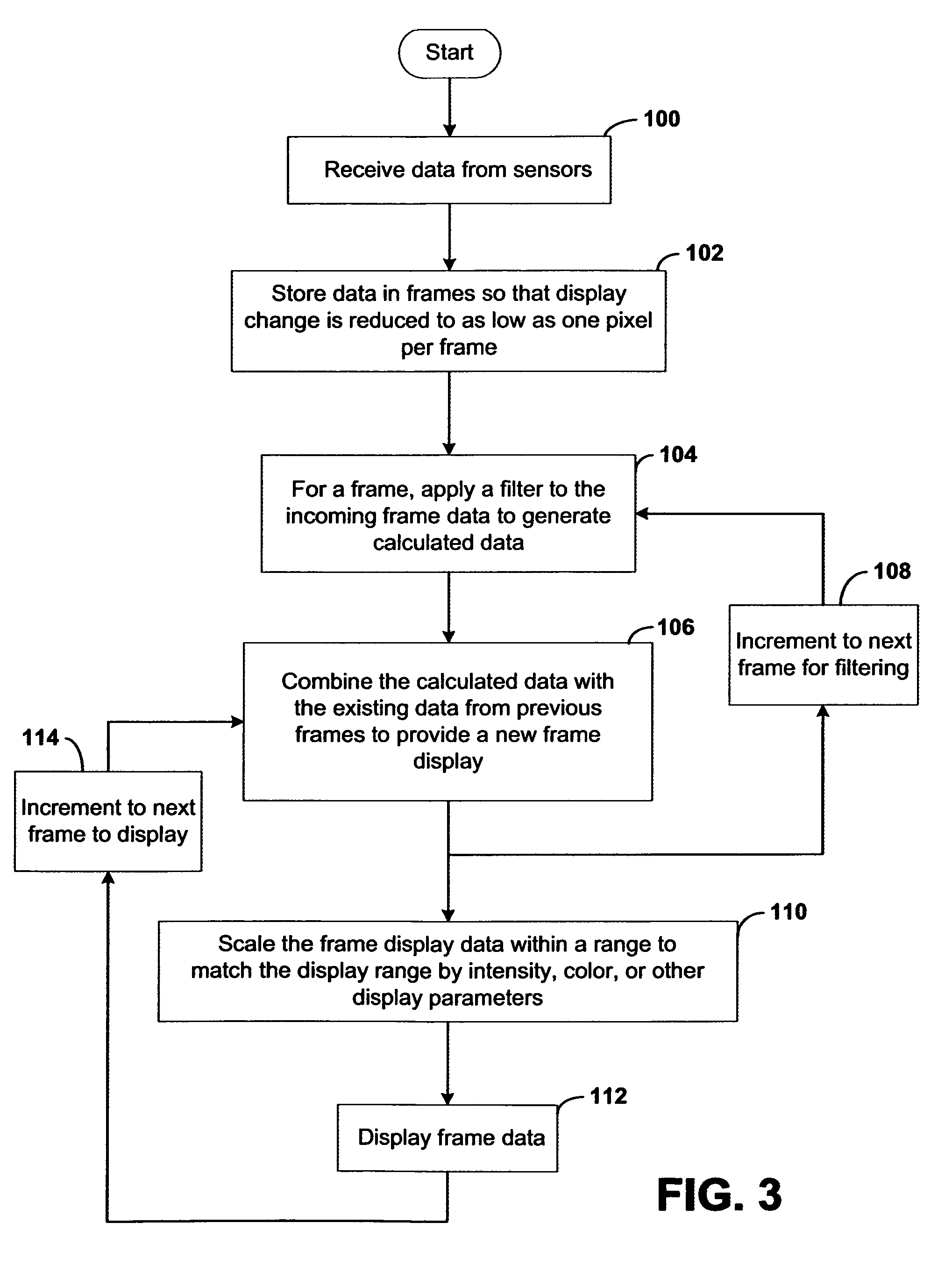
Systems and methods for displaying changes in biological responses to therapy
InactiveUS7720306B2Better convey information to the viewerImprove visibilityDrawing from basic elementsPerson identificationCorrelation functionDisplay device
Systems and methods of this invention display data using pixels with information indicated by color and intensity changes, particularly used for monitoring of physiological variables in real time. For certain methods, physiological data can be acquired by sensors, acquired data can be stored in data frames, data frames can be processed using computer-implemented methods, and processed data frames can be scaled to a display frame for display on a display device. Using such methods, a spot made up of a group of pixels can be updated during a time frame, or cycle using a computer-implemented method, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division or a time dependent function. Newly received data can be combined with prior received data to indicate time-dependent changes. In this way, each spot contains a cumulative history of data starting at some initial time. In other embodiments, visual contrast can be enhanced between desired data and other data. In further embodiments, two or more different types of data can be plotted together to indicate relationships between variables. Real time monitoring of signals during therapeutic treatment using light, electricity or other nerve or muscle stimuli can allow a user to monitor physiological responses during stimulation and to make rapid decisions about medical treatment.
Owner:PHOTOMED TECH
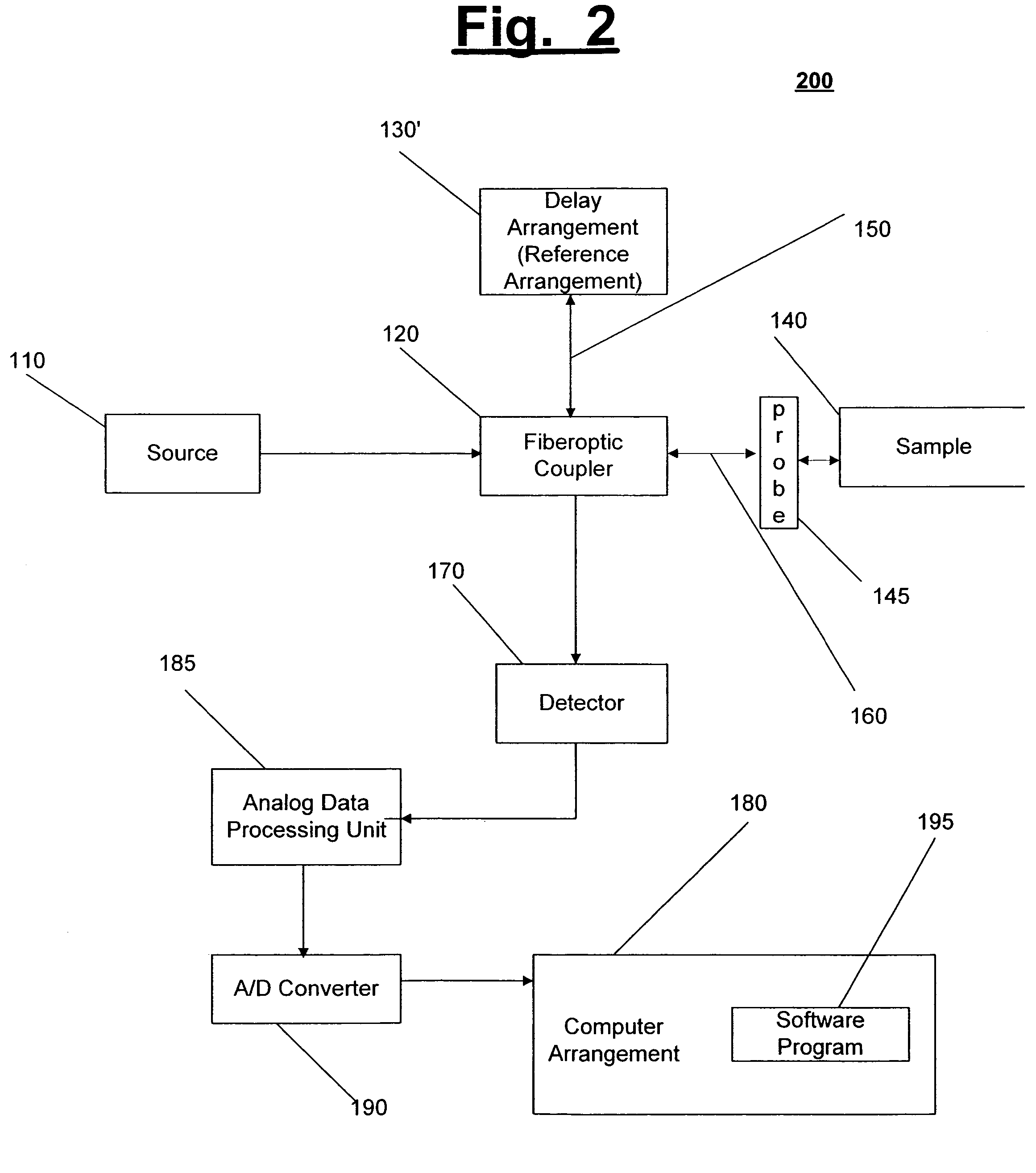
Systems and methods for imaging a sample
InactiveUS6980299B1Side lobes in the coherence envelope are reduced or eliminatedCompensation for dispersionUsing optical meansCorrelation functionComputational physics
A system and method for imaging a sample are provided. In particular, a first combination of light and a second combination of light are received, in which a first cross correlation function is associated with the first combination and a second cross correlation function is associated with the second combination. Each of the first and the second combinations includes a first portion of light which is received from a reference arrangement and a second portion of light which is received from the sample, and a first relative position of the sample associated with the first combination is different than a second relative position of the sample associated with the second combination. In an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the first cross correlation function is transformed into a first complex cross spectral density and the second cross correlation function is transformed into a second complex cross spectral density. Moreover, a third complex cross spectral density can be determined which is approximately an average of the first complex cross spectral density and the second complex cross spectral density.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
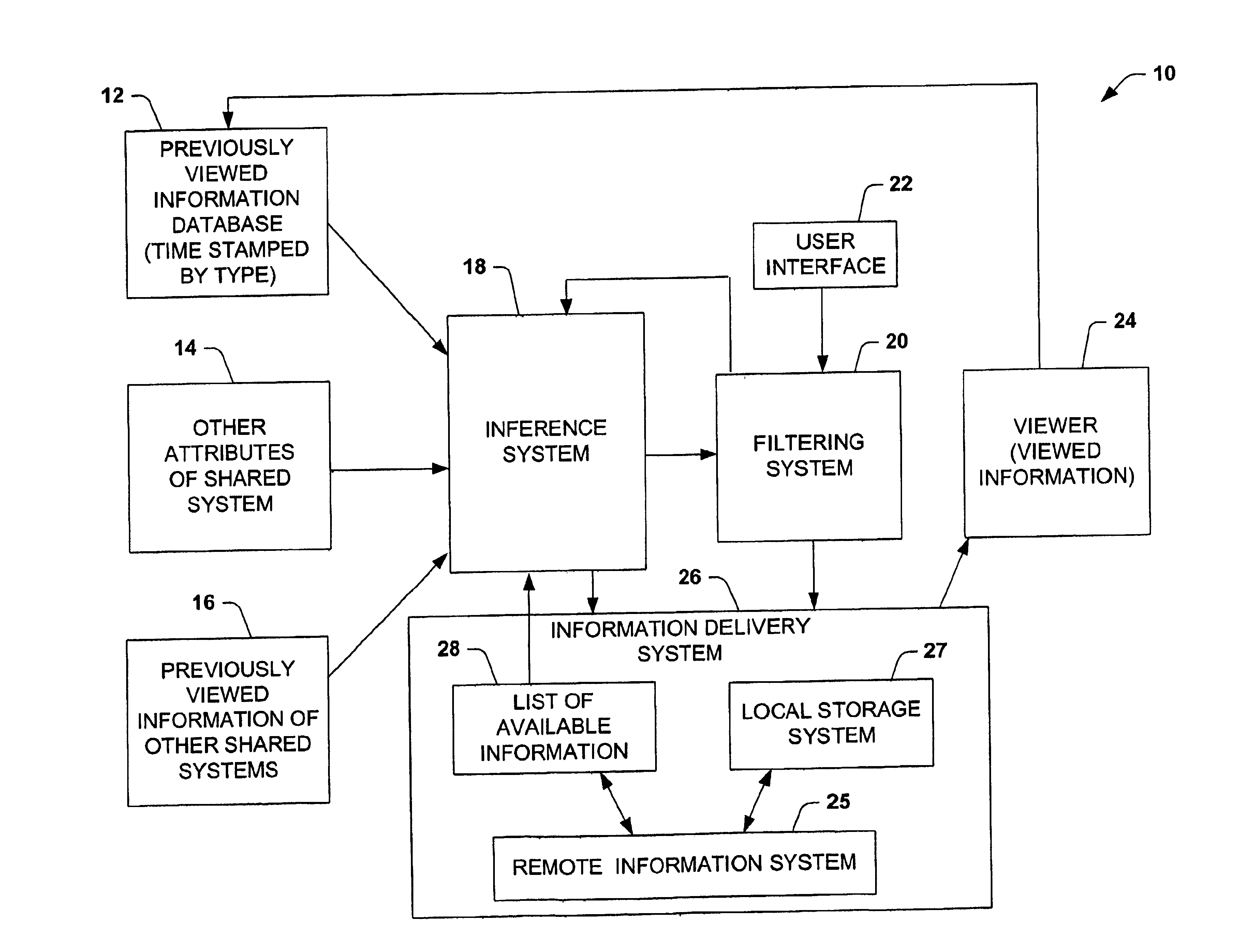
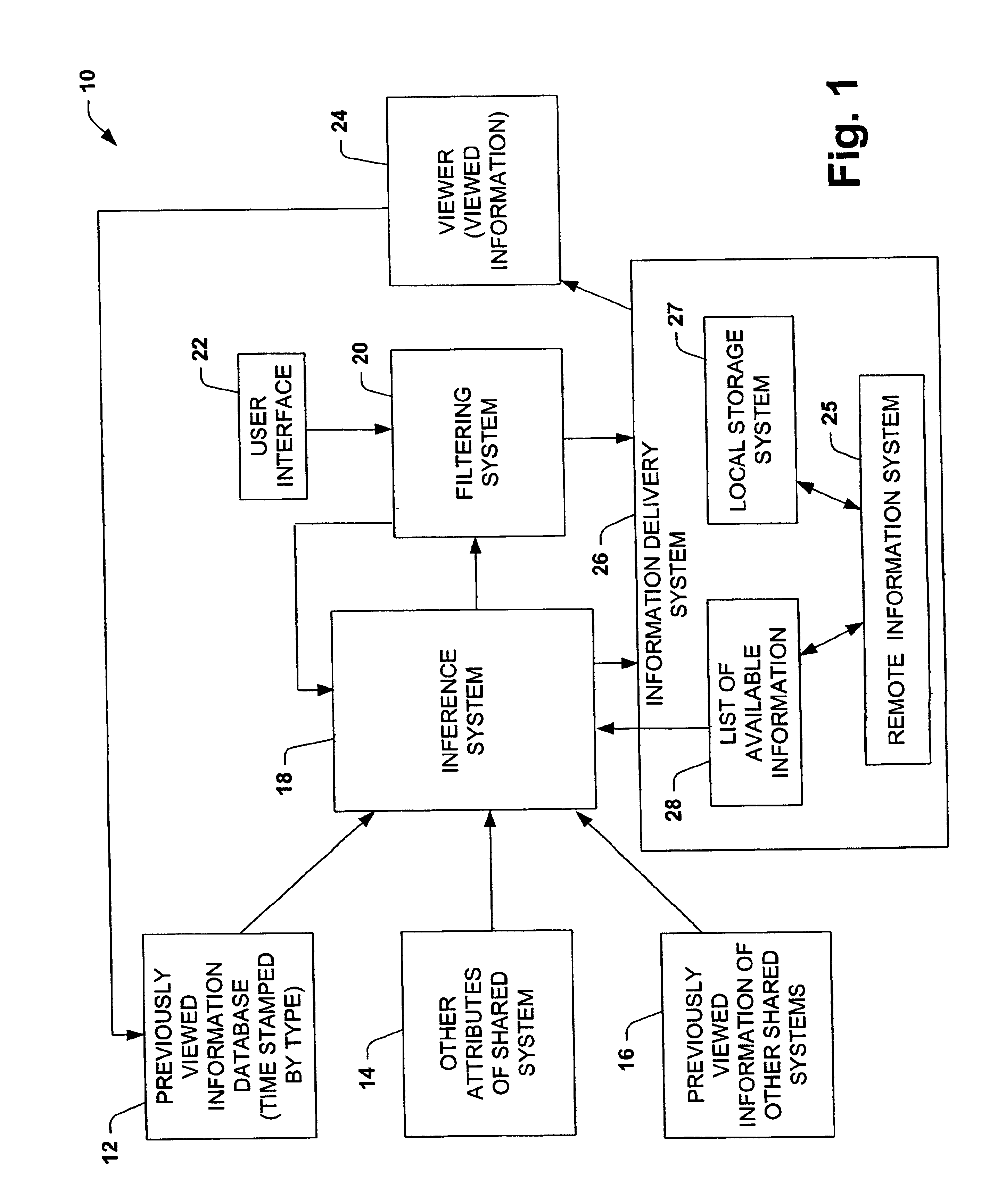
Training, inference and user interface for guiding the caching of media content on local stores
InactiveUS6947935B1Low costIncrease value densityTelevision system detailsData processing applicationsTime segmentCorrelation function
The present invention is related to a system and method of caching data employing probabilistic predictive techniques. The system and method has particular application to multimedia systems for providing local storage of a subset of available viewing selections by assigning a value to a selection and retaining selections in the cache depending on the value and size of the selection. The value assigned to an item can represent the time-independent likelihood that a user will review an item at some time in the future. An initial value of an item can be based on the user's viewing habits, the user's viewing habit over particular time segment (e.g., early morning, late morning, early afternoon, late afternoon, primetime, late night) and / or viewing habits of a group of user's during a particular time segment. A value assigned to a selection dynamically changes according to a set of cache retention policies, where the value can be time-dependent functions that decay based on the class of the item, as determined by inference about the class or via a label associated with the item. A selections value may be reduced as the selection ages because a user is less likely to view the selection over time. Additionally, a value of a selection may change based on changes on a user's viewing habits, changes in time segments or a user's modification of the cache retention policies.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
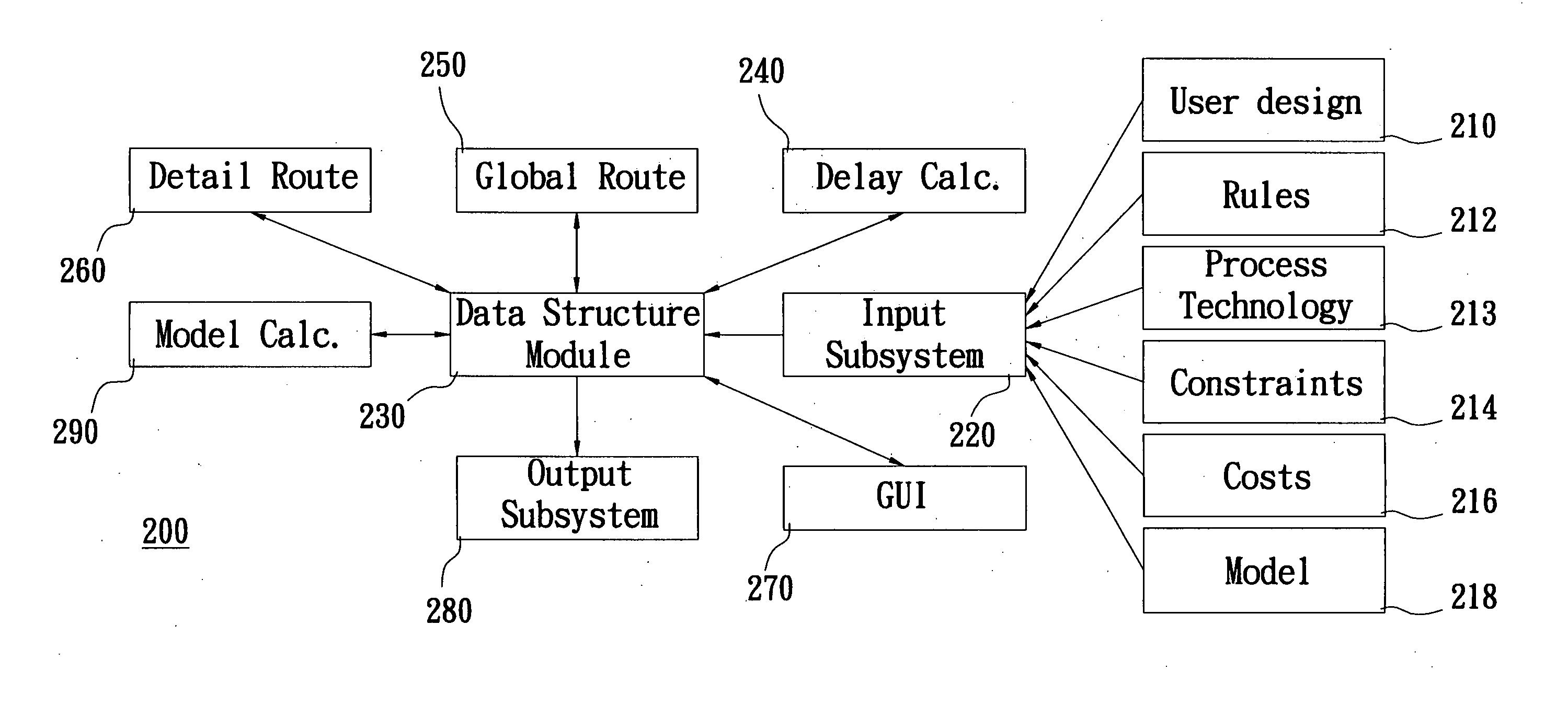
Apparatus for a routing system
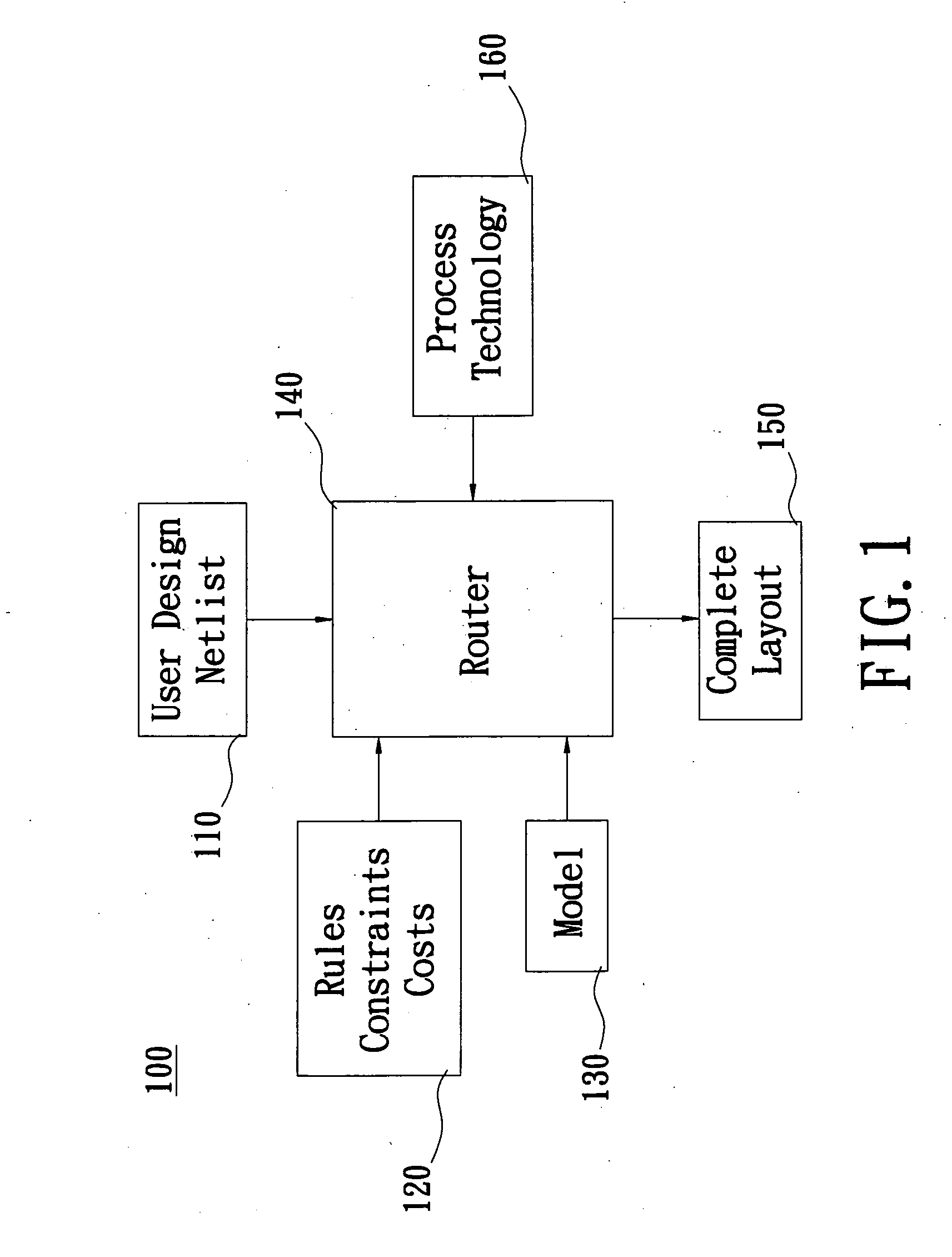
InactiveUS20070106971A1Reduce violationsReduce processComputer programmed simultaneously with data introductionComputer aided designAlgorithmGrid based
The invention details methods and apparatus for a routing system or router that includes a model. The model can be in many different forms including but not limited to: resolution enhancement technologies such as OPC; lithography model including but not limited to aerial image; pattern-dependent functions; functions for timing / signal integrity / power; manufacturing process variations; and measured silicon data. In one embodiment, the model can be described as input to the system and the model calculator can interact either with the data structure or the query engine of the detail router or both. The model calculator can accept input as a set of geometry description and produce output to guide the query functions. An example technique called set intersection is disclosed herein to combine multiple models in the system. A preferred embodiment of this invention includes a full chip grid-based router being aware of manufacturability.
Owner:LIZOTECH
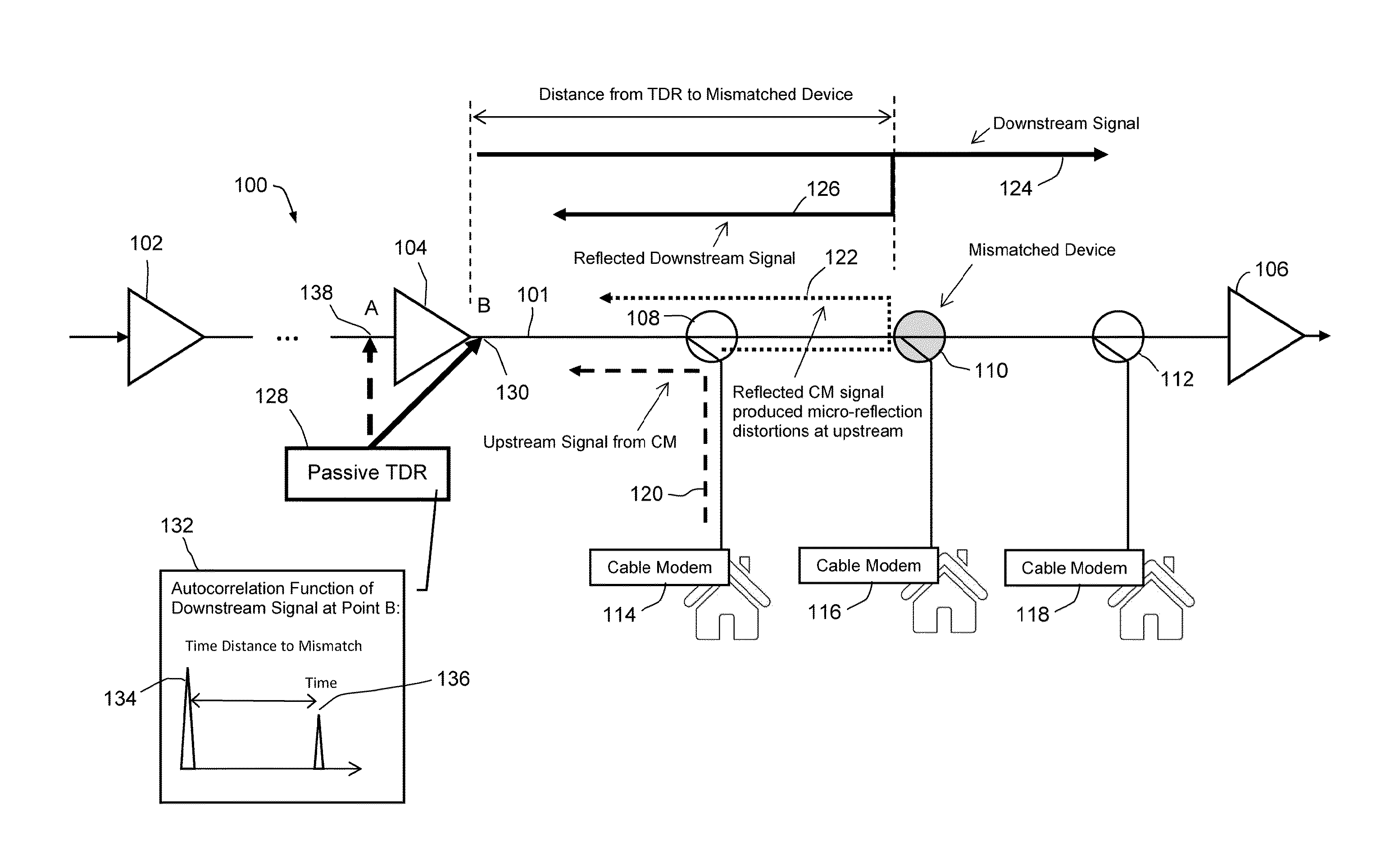
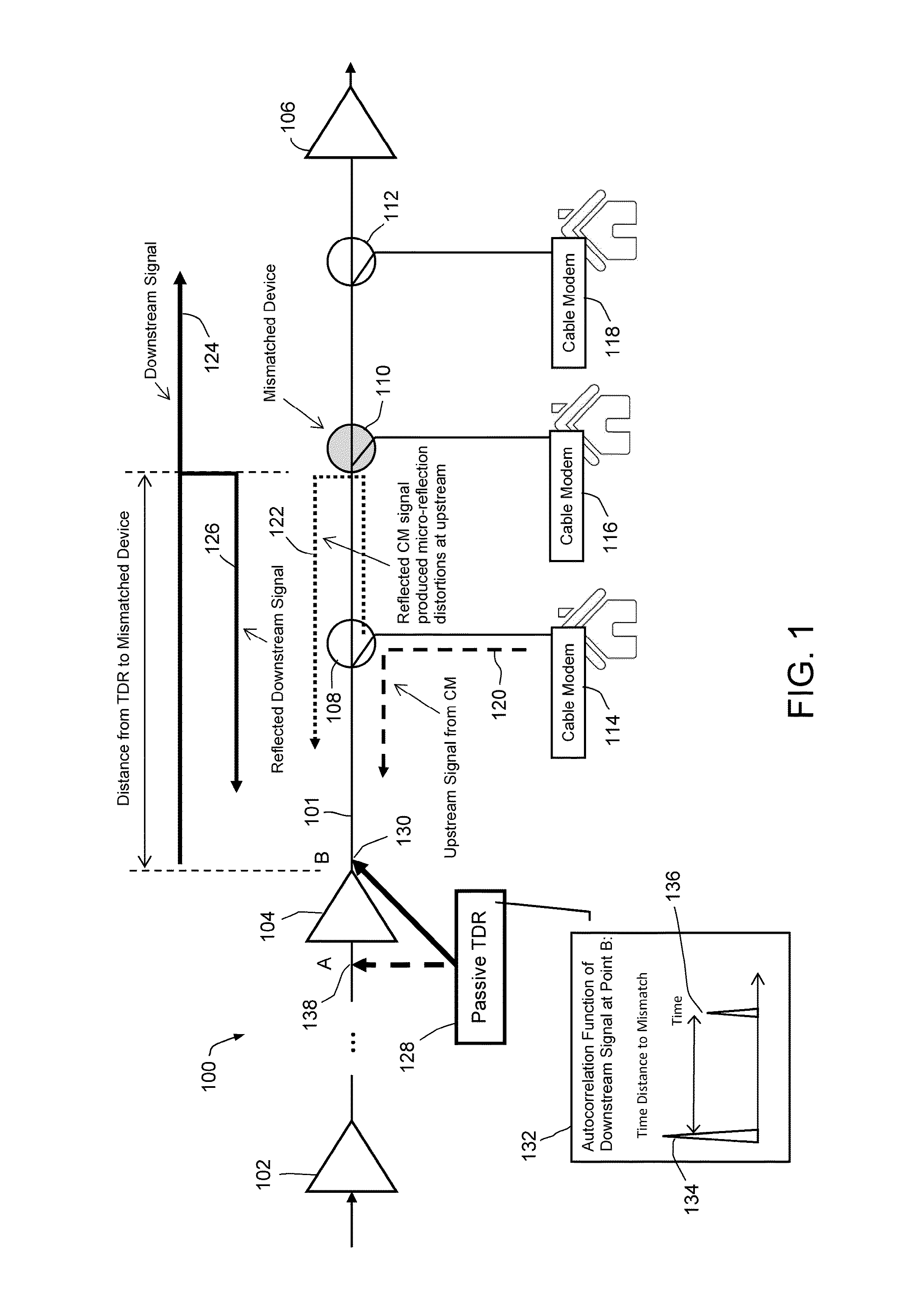
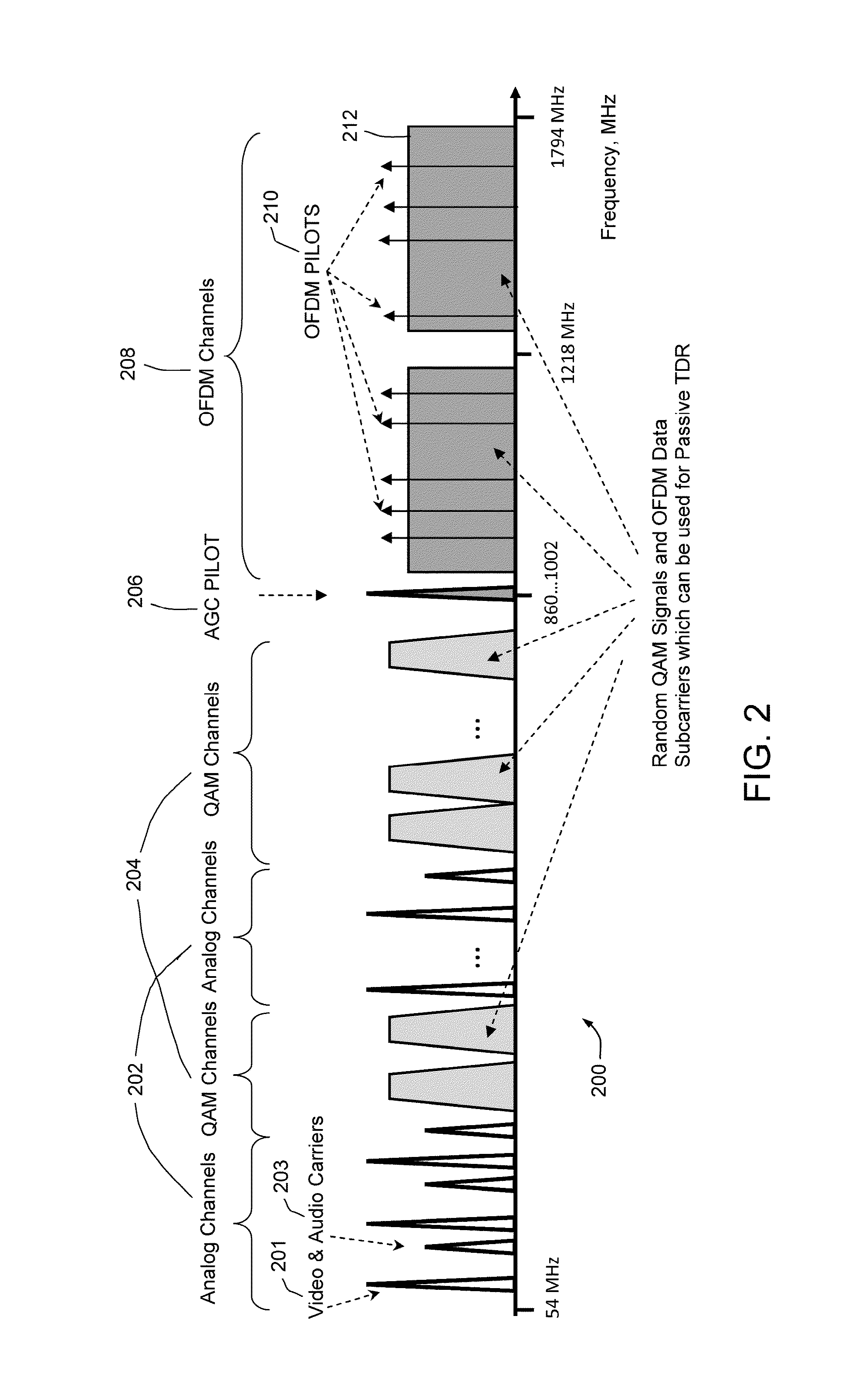
Passive time domain reflectometer for HFC network
ActiveUS9414126B1High detection sensitivityHigh sensitivityTelevision systemsLine-transmission monitoring/testingTime-domain reflectometerCable transmission
Detecting a linear impairment in a cable under test by using a random signal transmitted down the cable. The impairment causes a reflected signal to be combined with the random signal. The combined signal extends over a plurality of sub-bands. A method and apparatus perform the steps of: (a) receiving the combined signal from a test point upstream from the impairment; (b) tuning to each sub-band and receiving a part of the combined signal within each sub-band; (c) determining an autocorrelation function of each part of the combined signal of each sub-band, to produce a plurality of autocorrelation functions; (d) combining the autocorrelation functions to form a combined function; (e) detecting the reflected signal from the combined function; and (f) determining, from the combined function, a time delay associated with the reflected signal and the distance from the test point to the impairment.
Owner:ARCOM DIGITAL
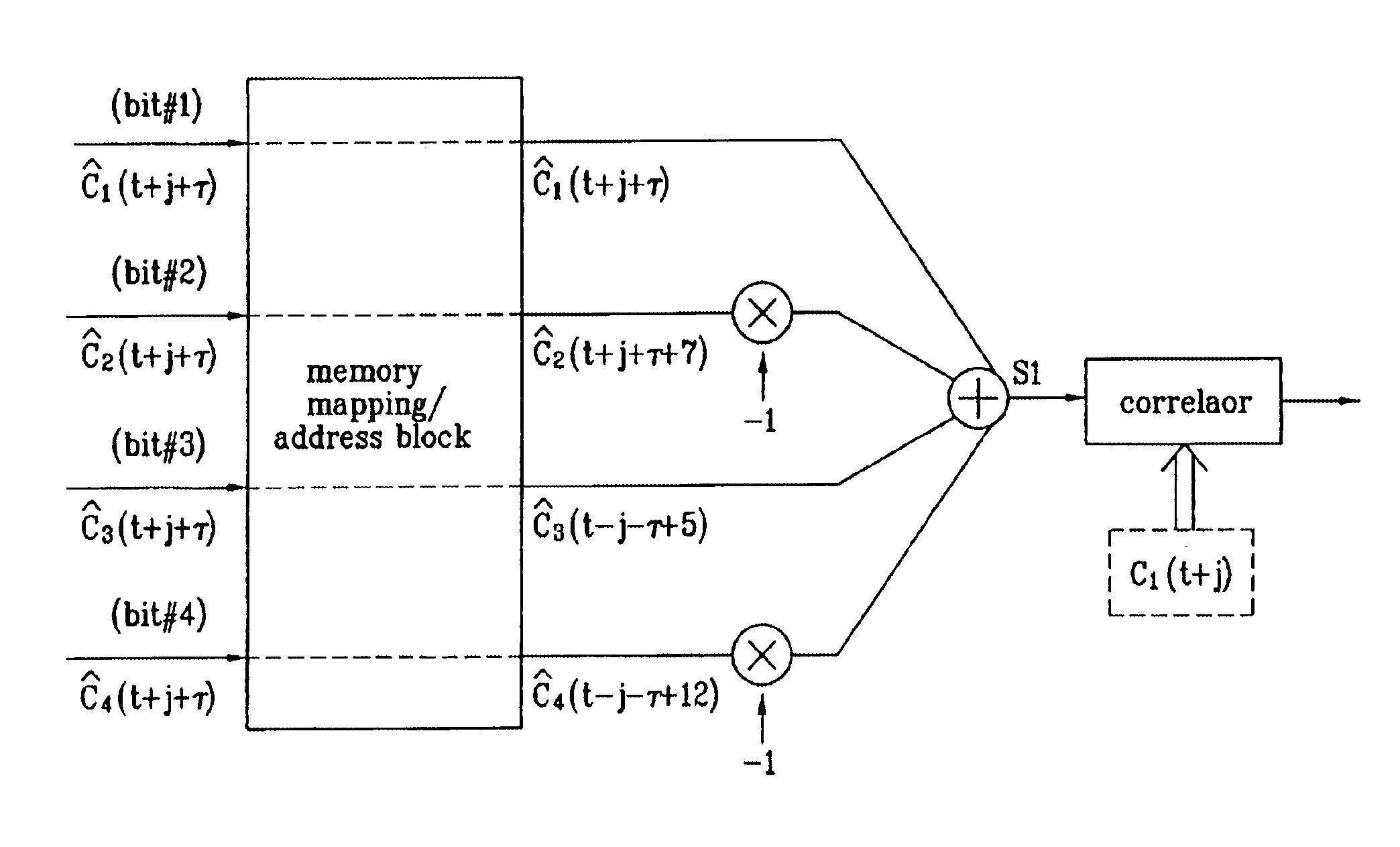
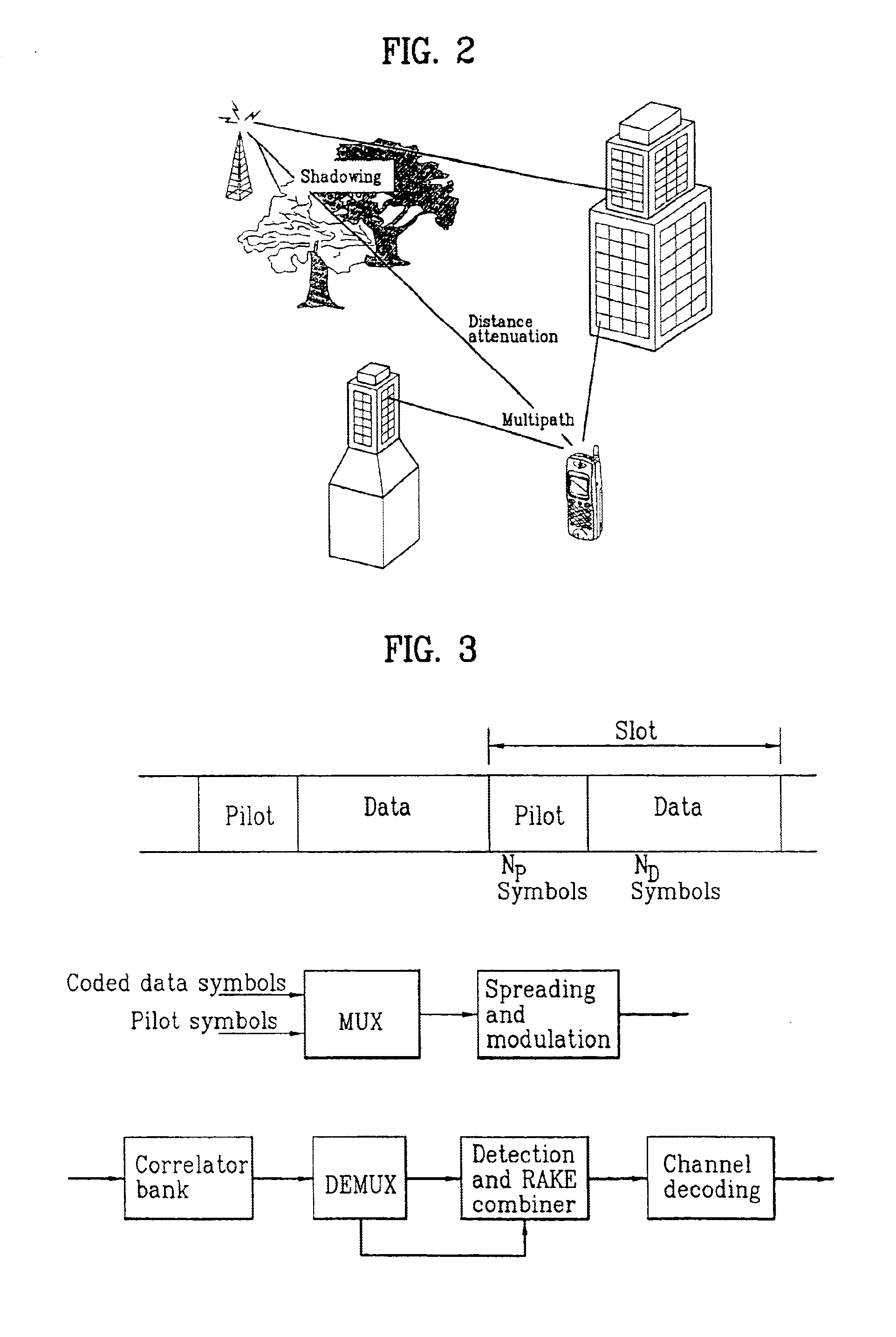
Pilot signals for synchronization and/or channel estimation
InactiveUS6987746B1Optimal autocorrelation resultEliminate and prevent sidelobesSynchronisation arrangementTime-division multiplexCode division multiple accessCorrelation function
The frame words of the preferred embodiment are especially suitable for frame synchronization and / or channel estimation. By adding the autocorrelation and cross-correlation functions of frame words, double maximum values equal in magnitude and opposite polarity at zero and middle shifts are obtained. This property can be used to slot-by-slot, double-check frame synchronization timing, single frame synchronization and / or channel estimation and allows reduction of the synchronization search time. Further, the present invention allows a simpler construction of a correlator circuit for a receiver. A frame synchronization apparatus and method using an optimal pilot pattern is used in a wide band code division multiple Access (W-CDMA) next generation mobile communication system. This method includes the steps of storing column sequences demodulated and inputted by slots, in a frame unit, in detecting frame synchronization for upward and downward link channels; converting the stored column sequences according to a pattern characteristic related to each sequence by using the pattern characteristic obtained from the relation between the column sequences; adding the converted column sequences by slots; and performing a correlation process of the added result to a previously designated code column.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Fingerprint extraction
InactiveUS20060041753A1Electrophonic musical instrumentsUser identity/authority verificationFrequency spectrumCorrelation function
Fingerprints are bit strings extracted from a media signal (e.g. an audio or video clip) to identify said media signal. Typically, they are derived from a perceptual property of the signal, for example, the spectral energy distribution of an audio fragment or the luminance distribution of a video image. A method and arrangement for extracting a fingerprint is here disclosed which is robust with respect to shifts of the perceptual property. Such shifts occur, inter alia, when the fingerprint is derived from a logarithmically mapped spectral energy distribution of an audio signal and said audio signal is subjected to speed changes. According to the invention, the fingerprint is not derived from the perceptual property as such, but from its auto-correlation function.
Owner:GRACENOTE
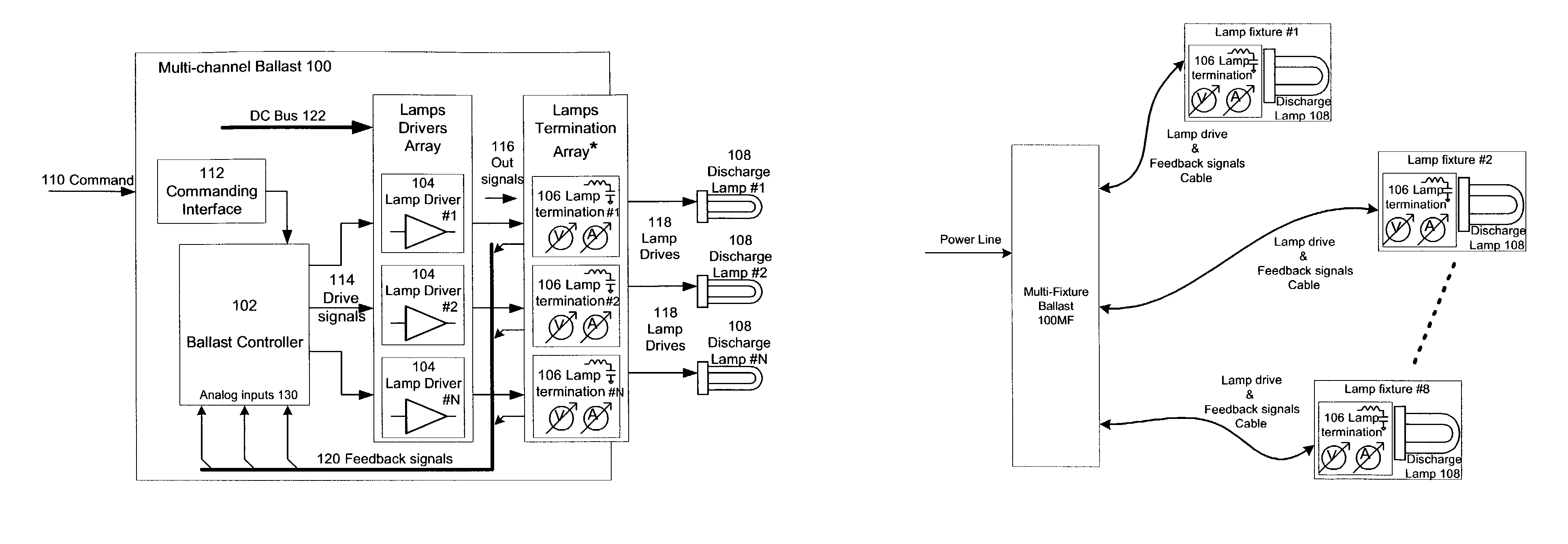
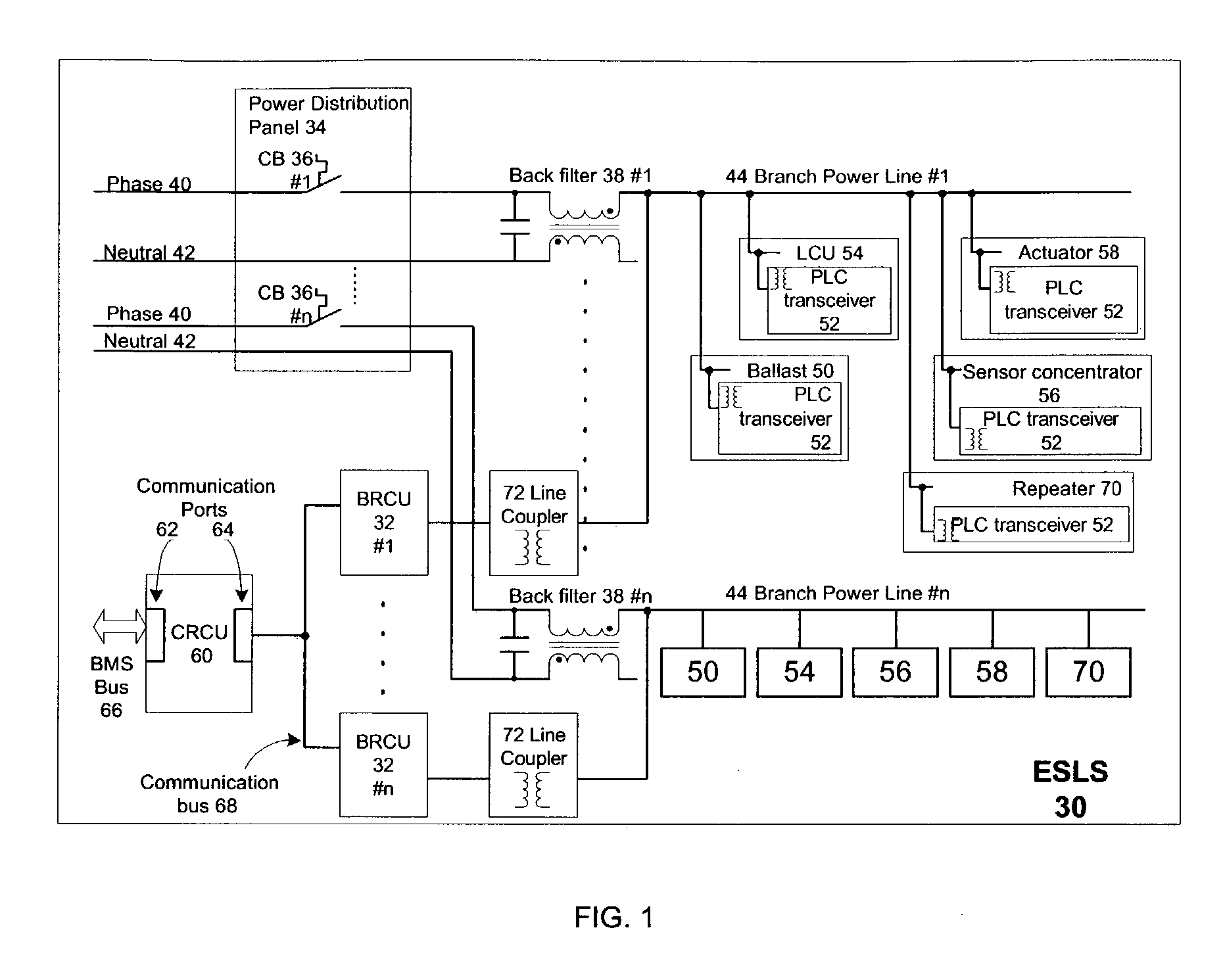
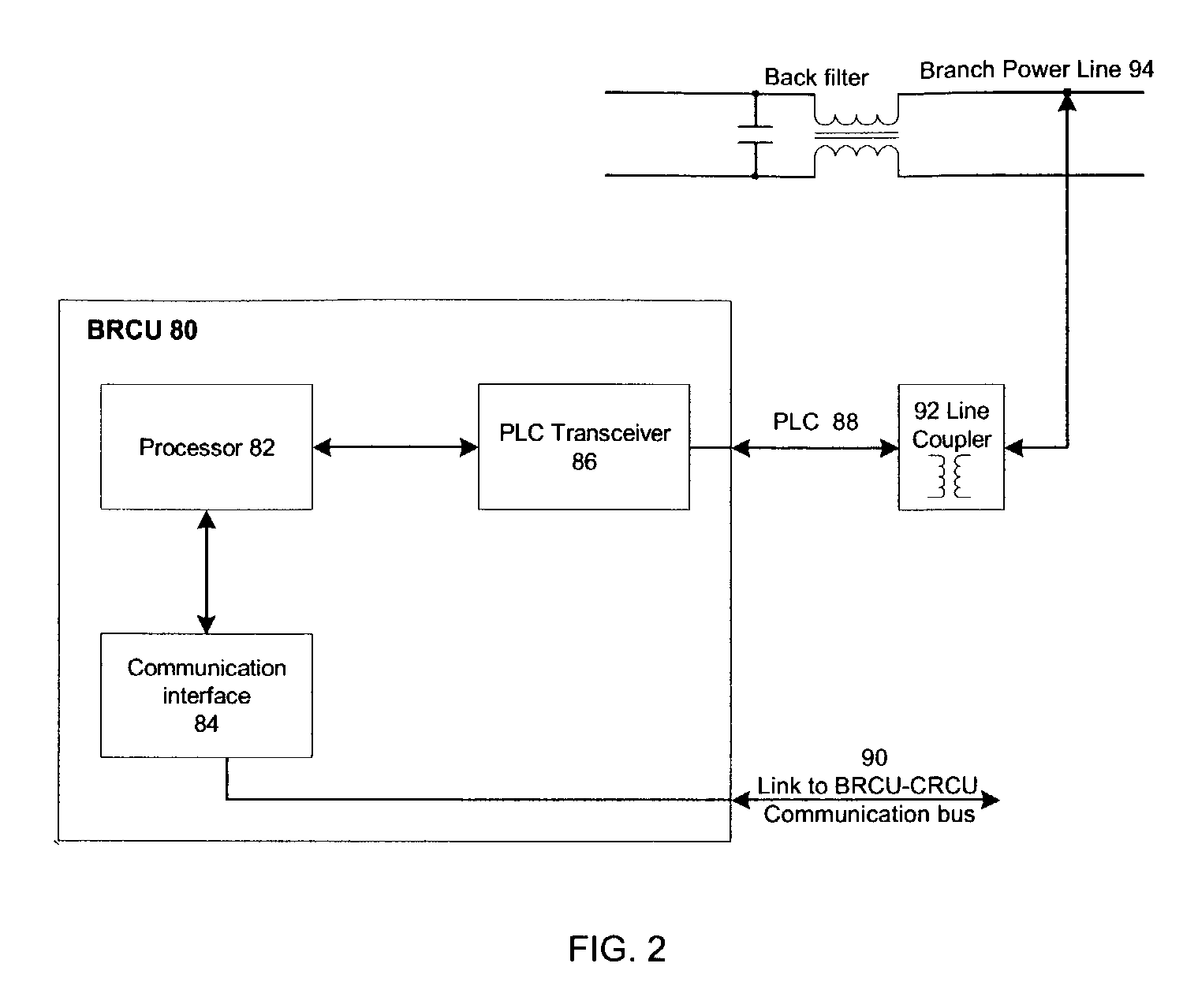
Multiple channel ballast and networkable topology and system including power line carrier applications
InactiveUS7009348B2Efficient qualityExtend lamp lifeAnalogue/digital conversionElectric light circuit arrangementLoop controlElectric power system
Control systems and methods for independent control of power systems, particularly lighting network branches, and separate control of individual branch components. Multi-branch systems comprise independently controllable branches that inter-communicate via PLC communications. In each branch, components such as ballasts, local control units, sensors, actuators, and repeaters, may exchange commands and queries independently of a branch remote control unit (BRCU). Alternatively, a BRCU may manage or arbitrate communications, or interact with other BRCUs, other control units and external management systems. Ballasts include a multi-channel ballast that enables close-loop control of individual fixtures, or of individual dimmable or non-dimmable lamps within a fixture. The close-loop control is facilitated by sampling circuits / sensors co-located with each controlled fixture or lamp. All controllers are preferably implemented using an integrated digital controller. The PLC communication is preferably carried out by a direct spread spectrum method that eliminates side lobes from a cross-correlation function, using an anti-collision protocol.
Owner:S T L ENERGY SOLUTIONS & TECH
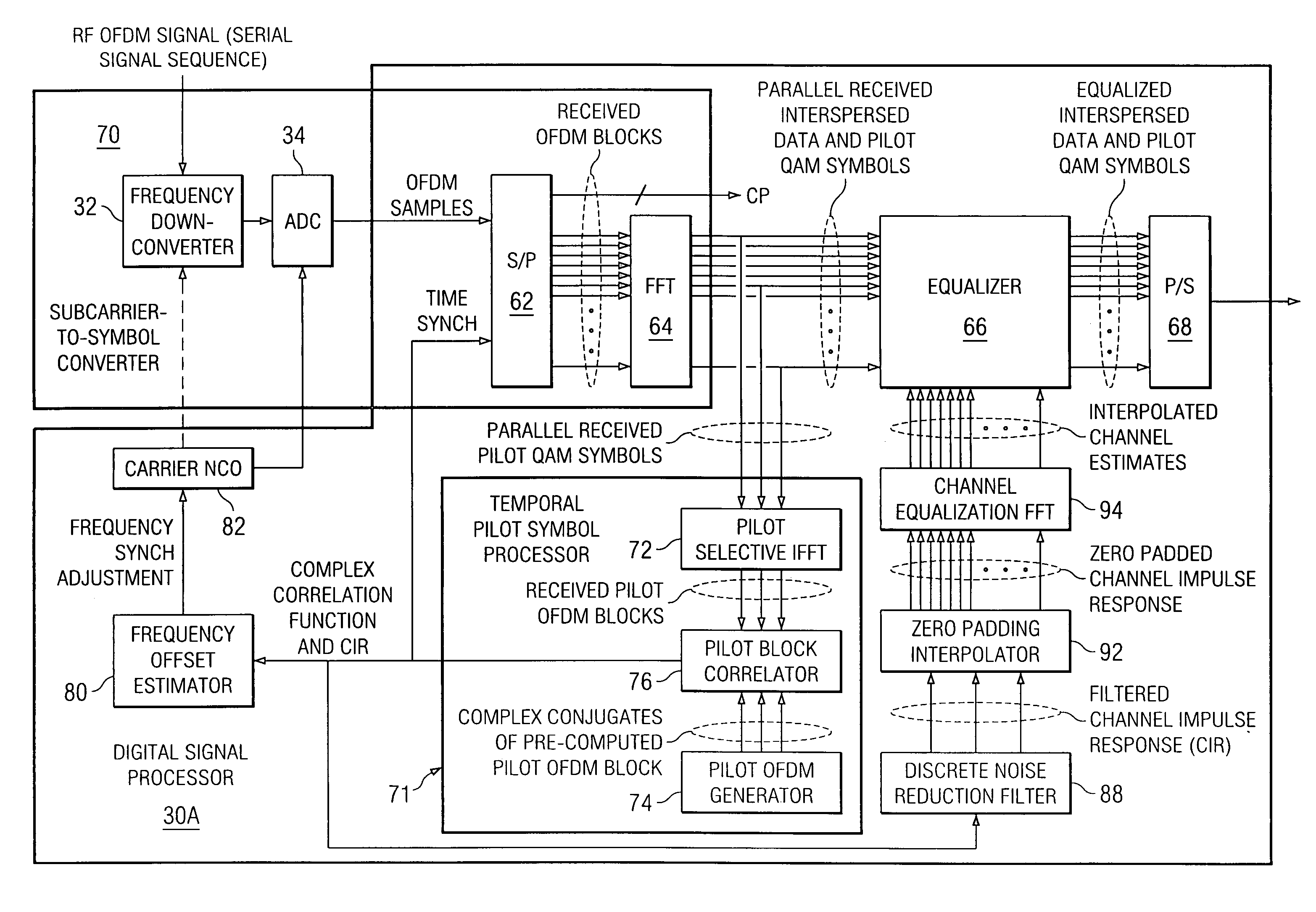
Method and apparatus for multicarrier channel estimation and synchronization using pilot sequences
ActiveUS7139320B1Extension of timeTransmission path divisionSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlPilot systemChannel impulse response
Method and apparatus for OFDM synchronization and channel estimation. In a temporal embodiment, received embedded system pilot symbols are inverse Fourier transformed at expected index locations and correlated with computed complex conjugates of inverse Fourier transforms of pilot symbols for providing a correlation function for the channel impulse response. In a frequency domain embodiment, embedded system pilot symbols are augmented with pilot-spaced inferred guard band symbols, multiplied by scaled complex conjugates of computed pilot systems, and inverse Fourier transformed into the channel impulse response. Time and frequency are synchronized in feedback loops from information in the channel impulse response. The channel impulse response is filtered, interpolated, and then Fourier transformed for determining channel estimates for equalization.
Owner:RADIA COMM
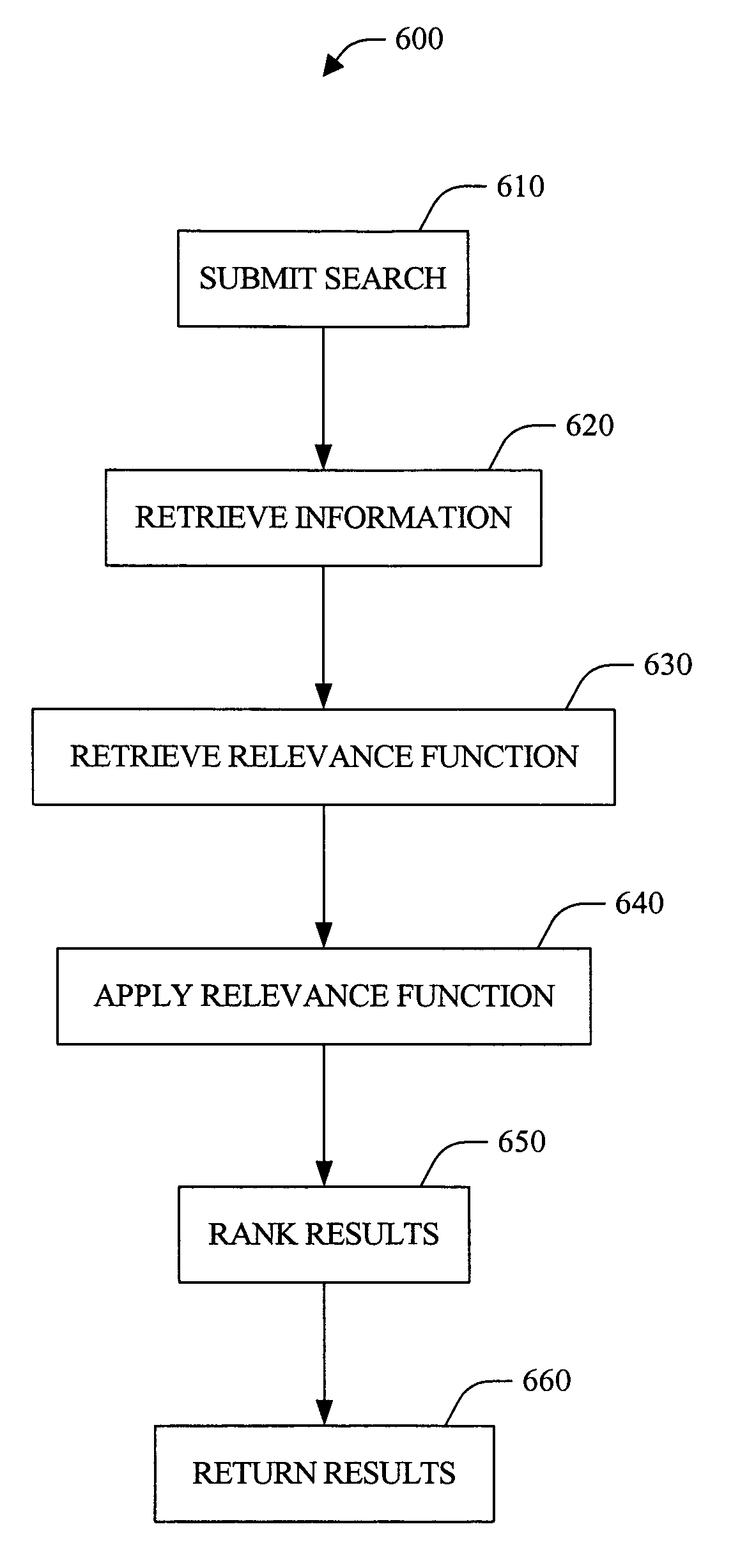
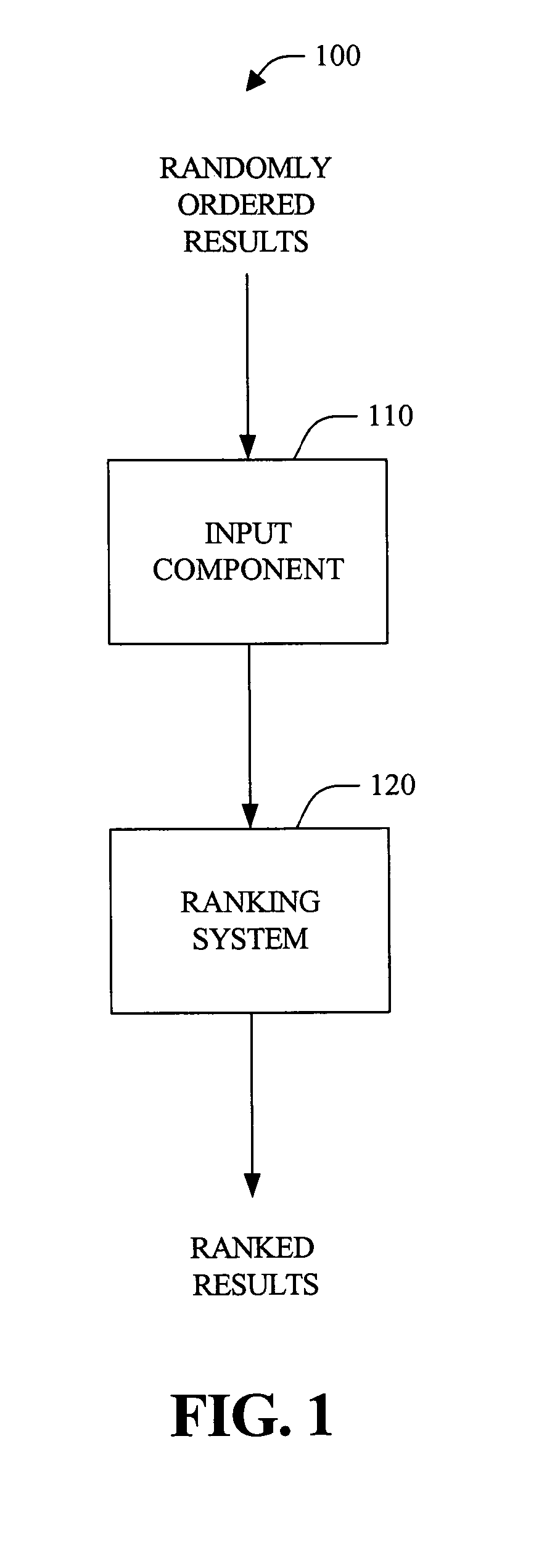
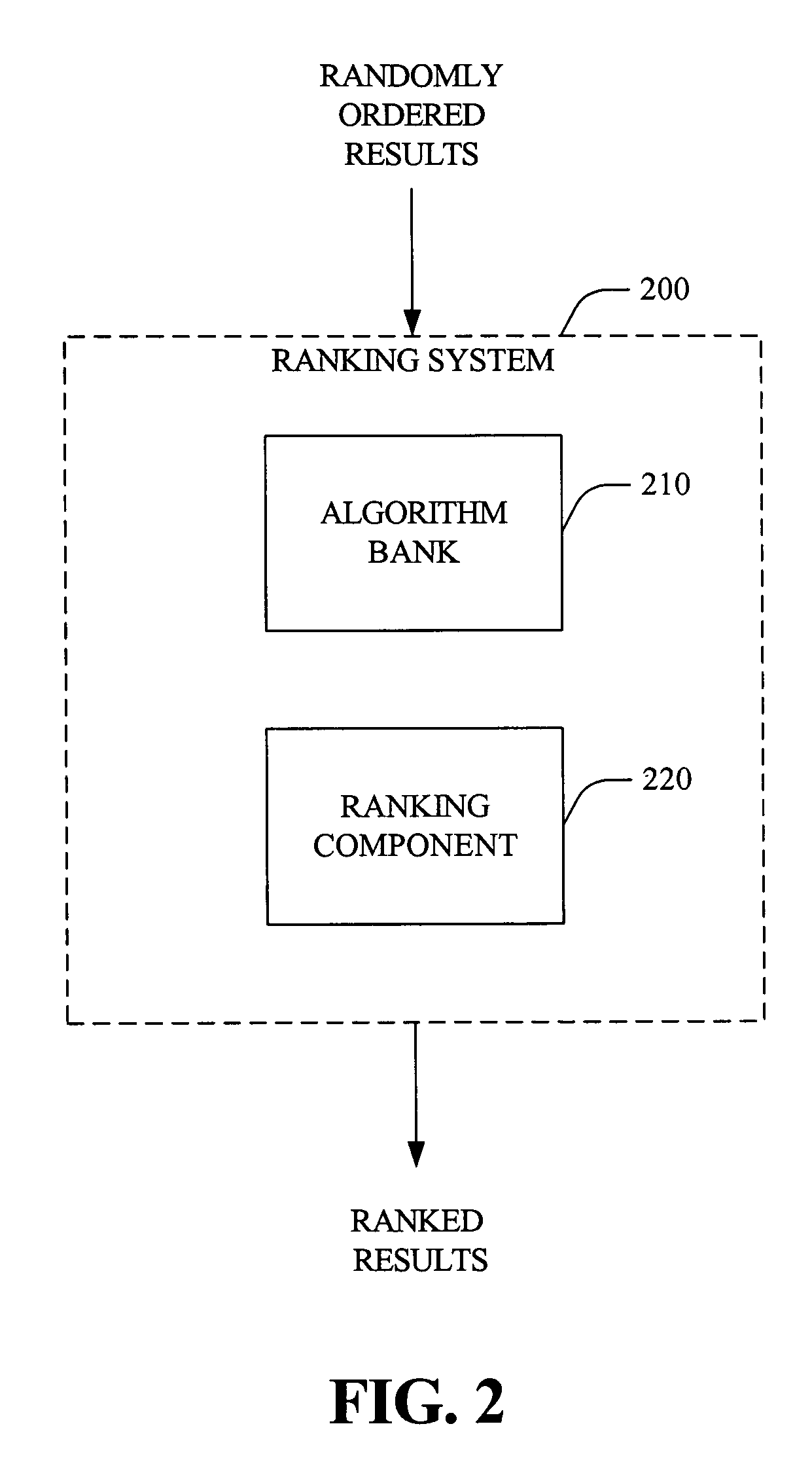
Systems and methods that rank search results
ActiveUS20050234904A1Facilitate ranking search resultEasy to operateDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsRankingCorrelation function
The present invention provides systems and methods that rank search results. Such ranking typically includes determining a relevance of individual search results via one or more feature-based relevance functions. These functions can be tailored to users and / or applications, and typically are based on scoped information (e.g., lexical), digital artifact author related attributes, digital artifact source repository attributes, and / or relationships between features, for example. In addition, relevance functions can be generated via training sets (e.g., machine learning) or initial guesses that are iteratively refined over time. Upon determining relevance, search results can be ordered with respect to one another, based on respective relevances. Additionally, thresholding can be utilized to mitigate returning results likely to be non-relevant to the query, user and / or application.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
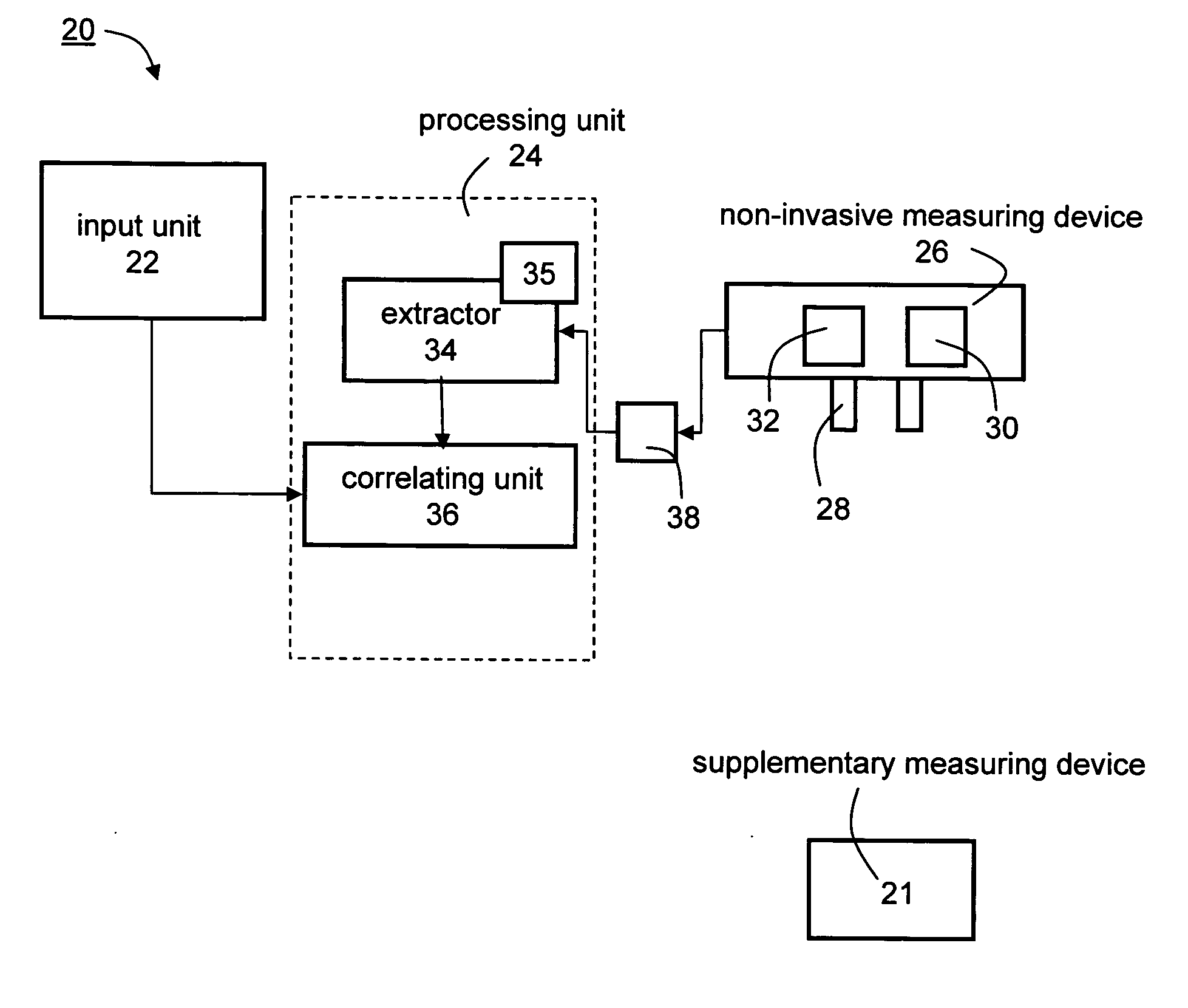
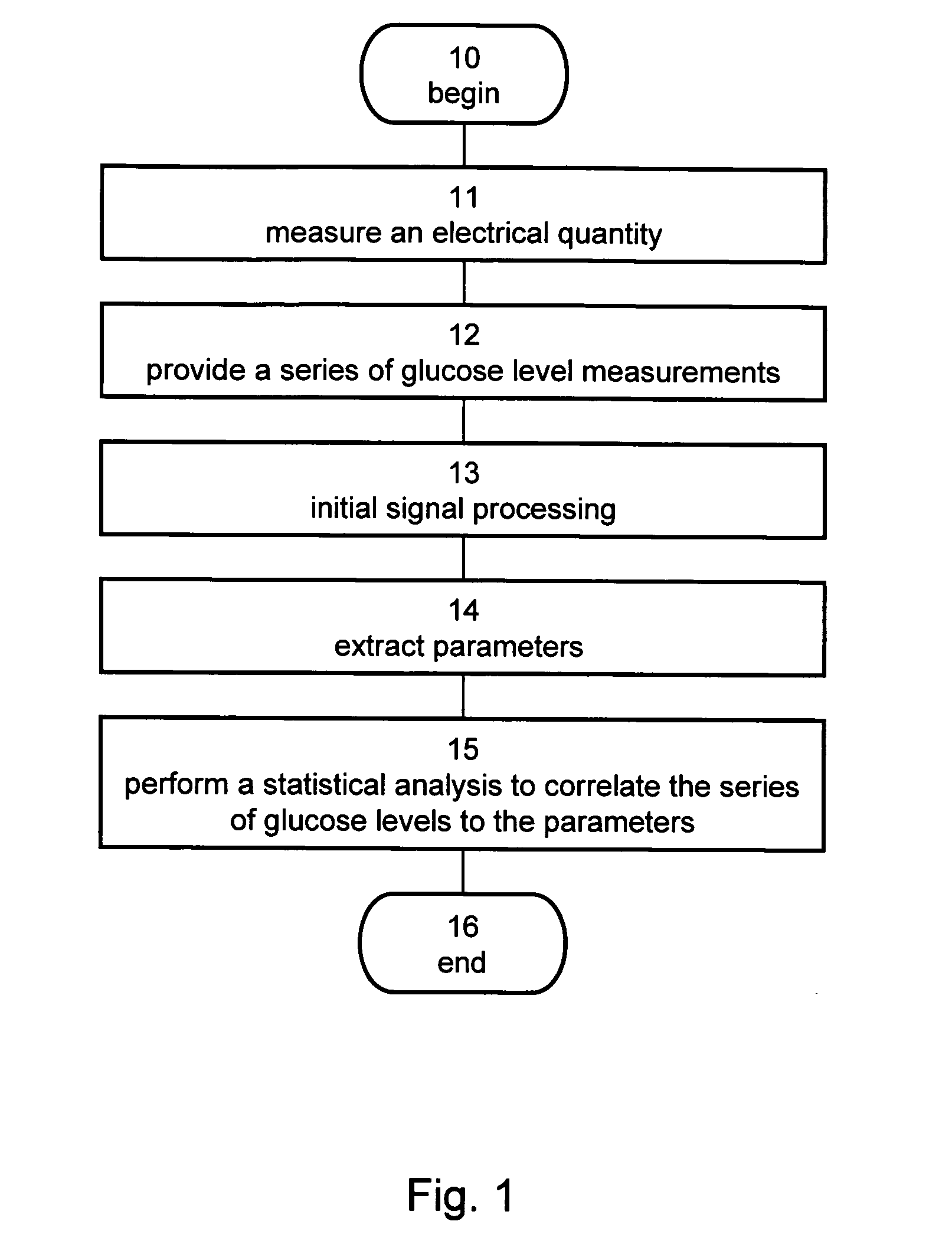
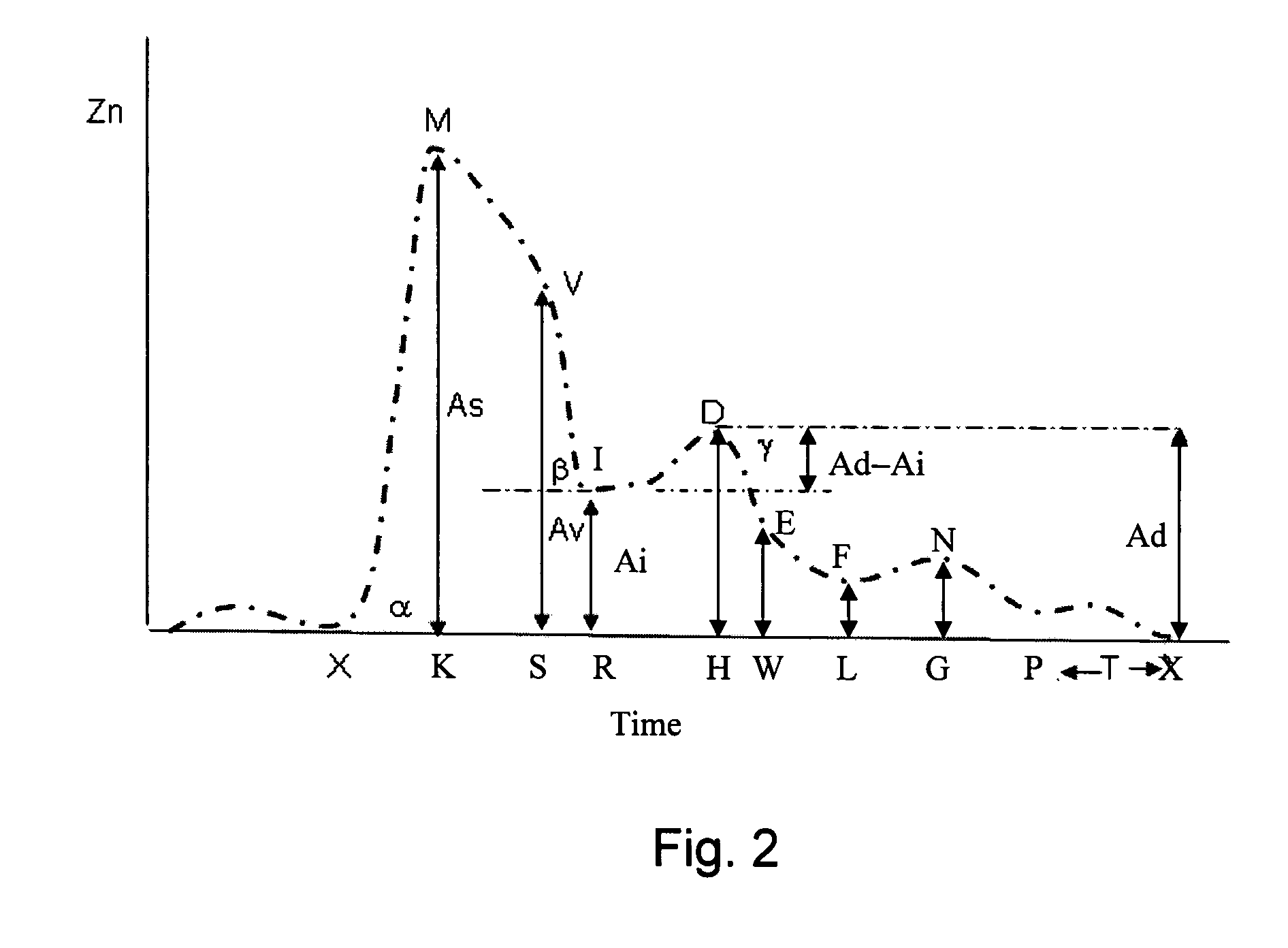
Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring
InactiveUS20090240440A1Accurate and reliable non-invasive glucose level monitoringDigital computer detailsDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurement deviceMedicine
A monitoring system for monitoring the glucose level of a subject having a glucose level history is disclosed. The system comprises (a) a non-invasive measuring device, operable to measure and record an electrical quantity from a section of the subject body, so as to provide a time-dependence of the electrical quantity over a predetermined time-period. The system further comprises (b) a processing unit, communicating with the non-invasive measuring device. The processing unit comprises: an extractor, for extracting a plurality of parameters characterizing the time-dependence, a correlation function calculator for calculate a subject-specific correlation function, and an output unit, communicating with the correlation function calculator and configured to output the glucose level of the subject. The subject-specific correlation function describes the glucose level history and is defined over a plurality of variables, each corresponding to a different parameter.
Owner:BIG GLUCOSE
Systems and methods that rank search results
ActiveUS7761447B2Efficiently and effectively rank search resultNonobviousDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsRankingCorrelation function
The present invention provides systems and methods that rank search results. Such ranking typically includes determining a relevance of individual search results via one or more feature-based relevance functions. These functions can be tailored to users and / or applications, and typically are based on scoped information (e.g., lexical), digital artifact author related attributes, digital artifact source repository attributes, and / or relationships between features, for example. In addition, relevance functions can be generated via training sets (e.g., machine learning) or initial guesses that are iteratively refined over time. Upon determining relevance, search results can be ordered with respect to one another, based on respective relevances. Additionally, thresholding can be utilized to mitigate returning results likely to be non-relevant to the query, user and / or application.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
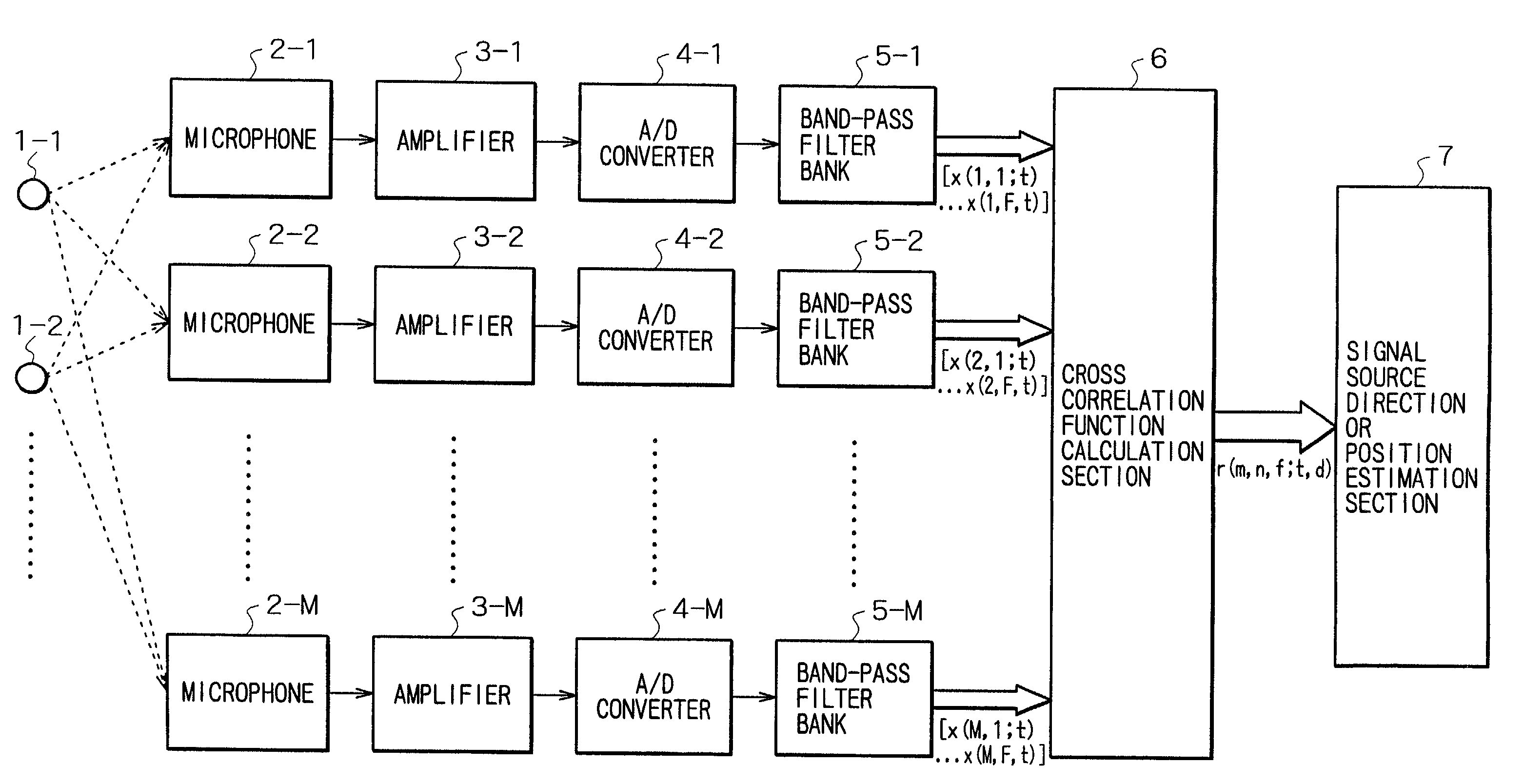
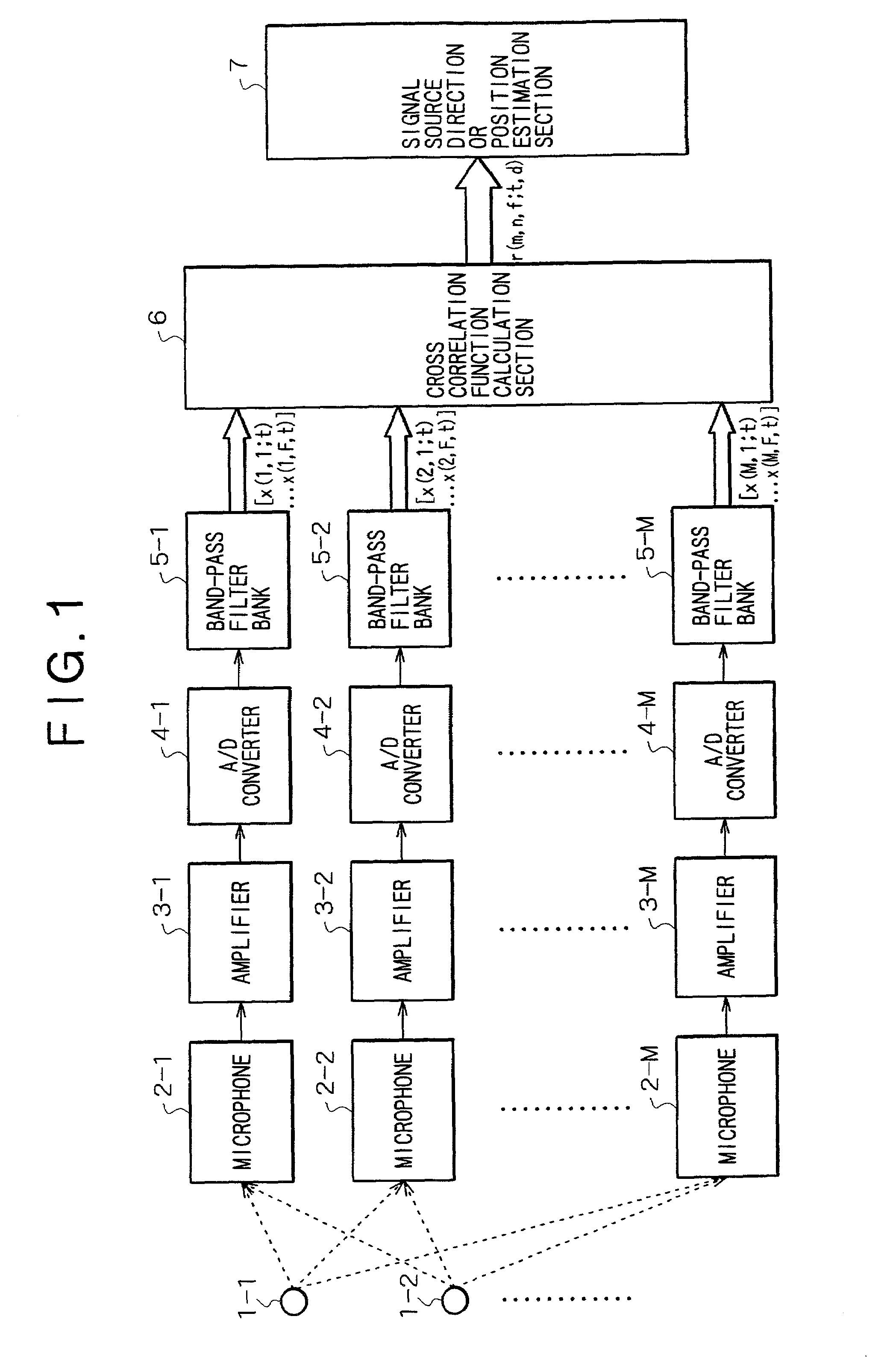
Signal processing apparatus and signal processing method
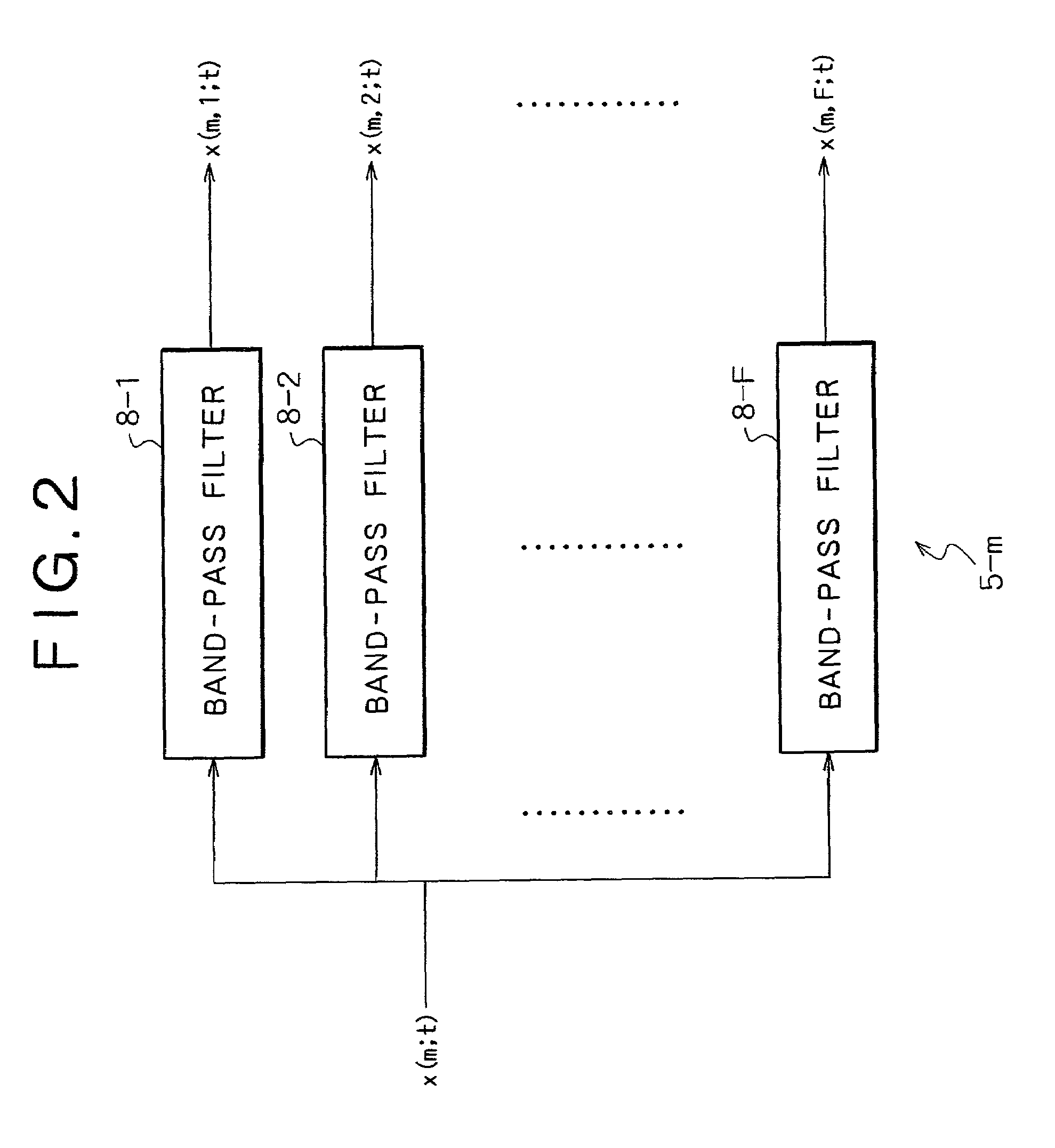
InactiveUS7054452B2Influence of noise can be suppressedTelevision conference systemsPosition fixationSound sourcesBand-pass filter
The invention provides a method and apparatus by which the direction in or the position at which a signal source such as a sound source is present is estimated. A signal or signals from a signal source or a plurality of signal sources are received by a plurality of reception apparatus, and the received signals are decomposed into signals of different frequency bands by a plurality of band-pass filters. Then, cross correlation functions between the different frequency band signals are calculated for individual combinations of the reception apparatus for the individual corresponding frequency bands. If the power of noise having no directivity is high in some of the frequency bands, then the cross correlation functions of the frequency band do not exhibit a maximum value. Therefore, an influence of the noise can be suppressed effectively when delay times of the individual reception apparatus which depend upon the direction or directions or the position or positions of the signal source or sources are estimated.
Owner:SONY CORP
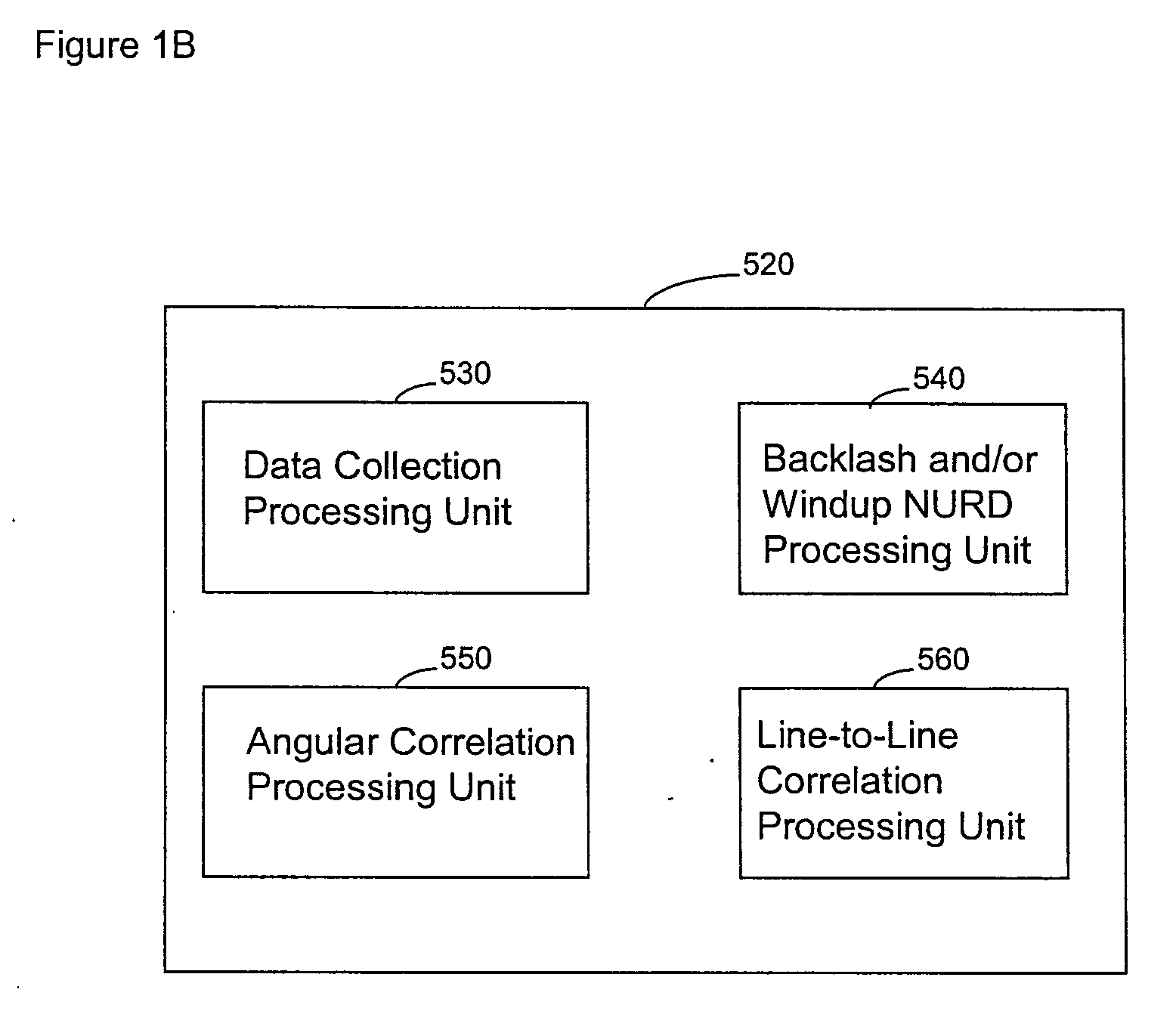
System and method for reducing angular geometric distortion in an imaging device
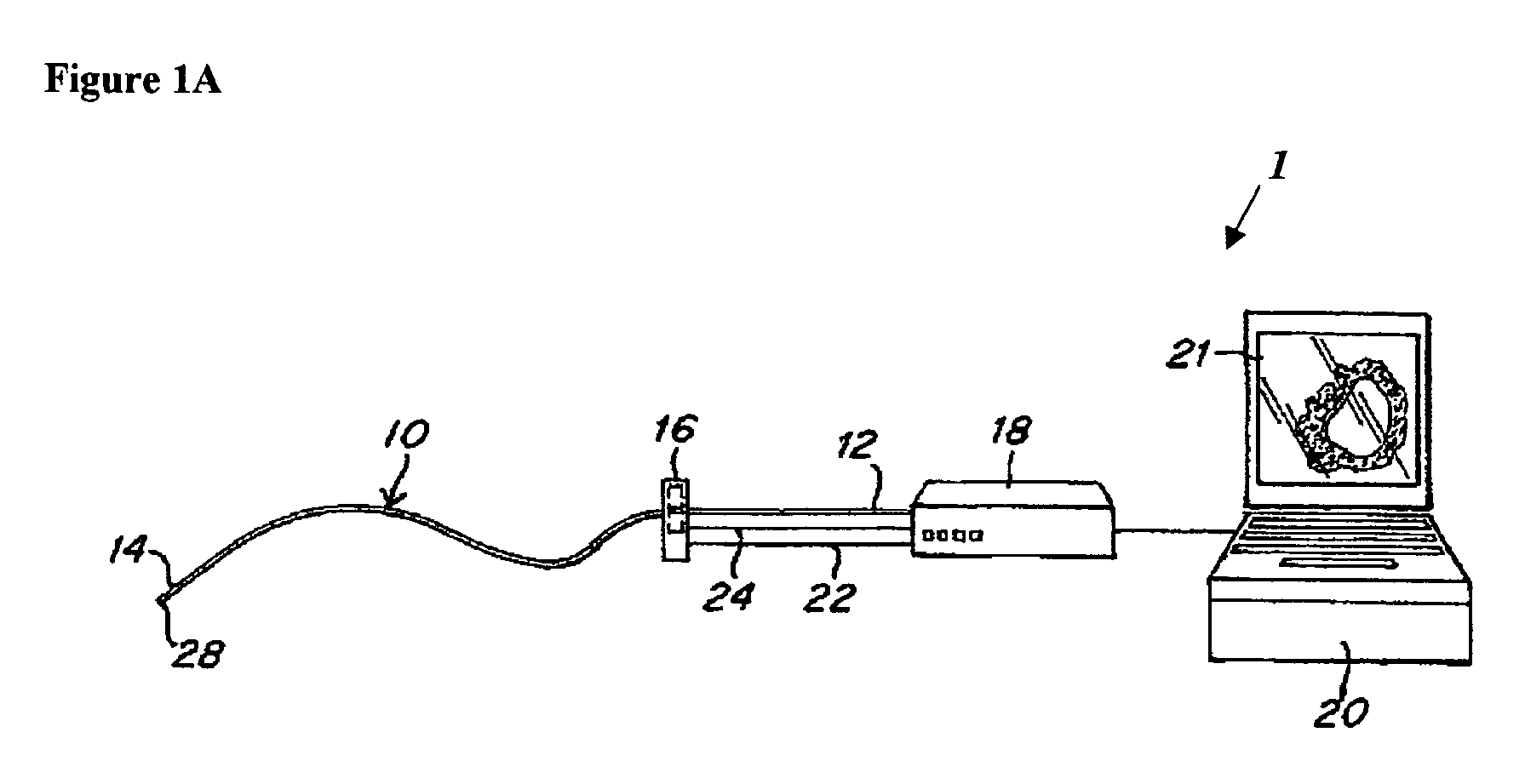
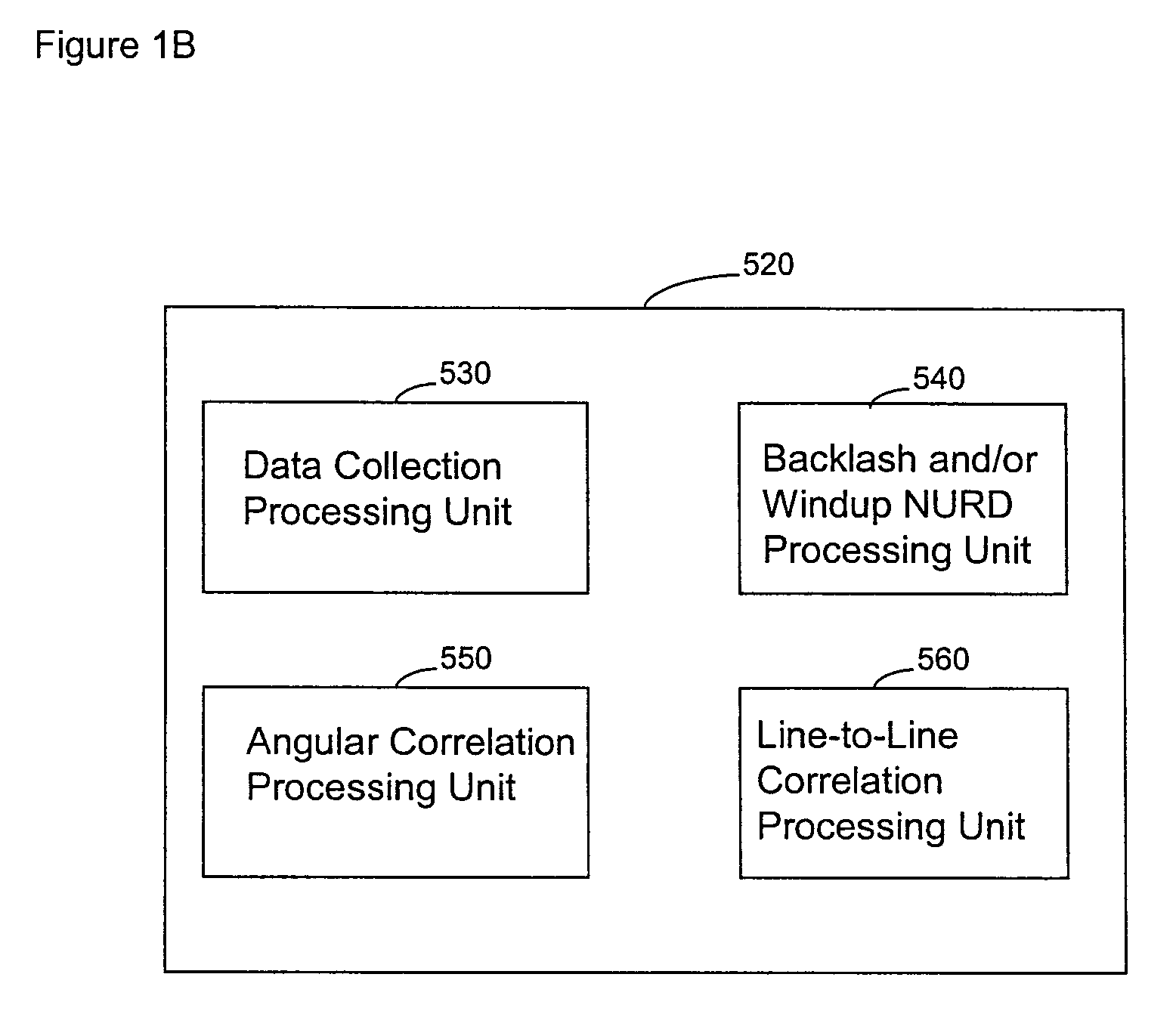
ActiveUS20070106155A1Reduce geometric distortionReduce and substantially eliminate angular geometric distortionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterTreatment choicesTreatment options
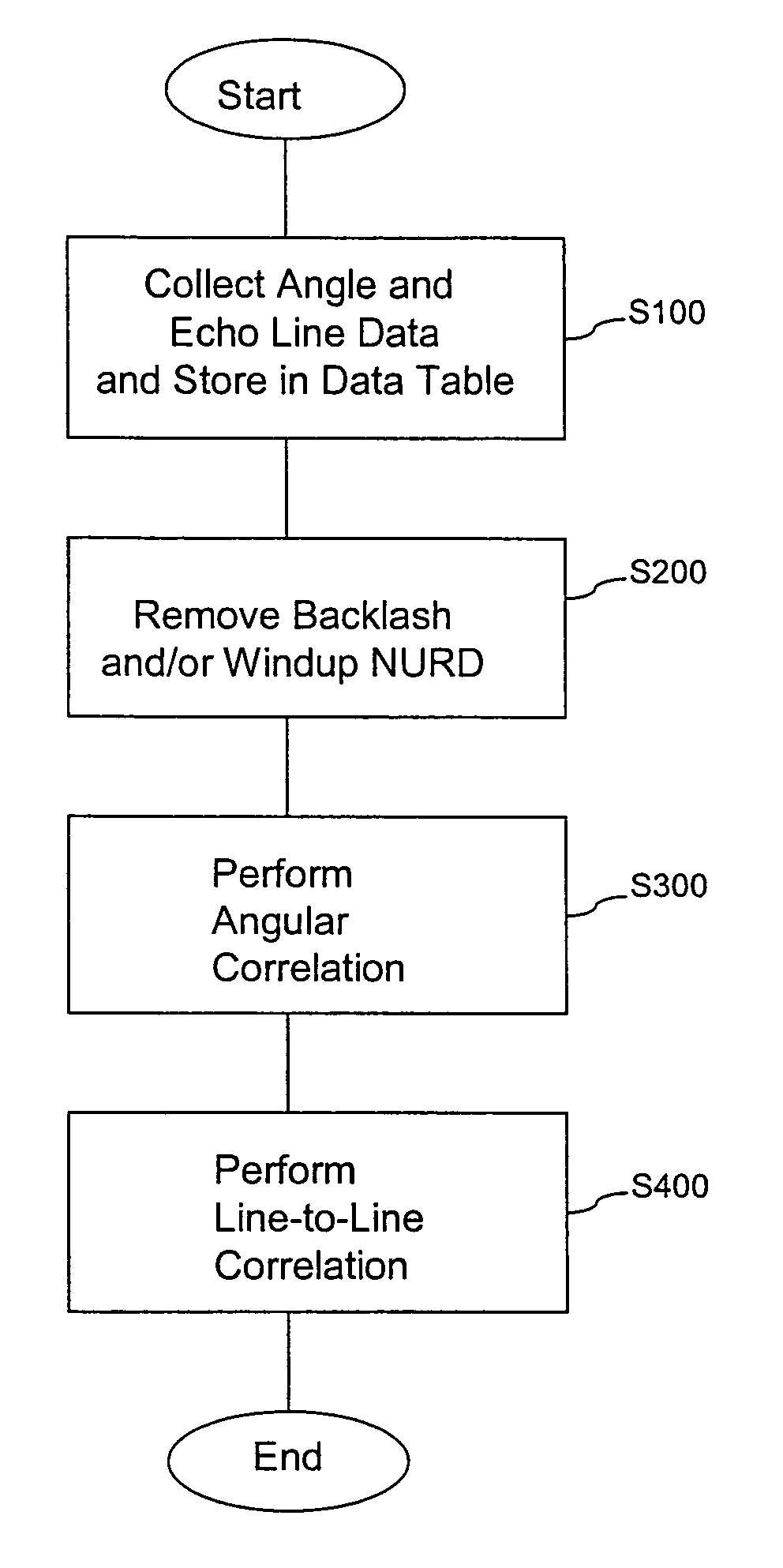
A system and method are provided for significantly reducing or substantially eliminating angular geometric distortions in devices designed for imaging and / or inspection of an interior portion or surface of a cavity. A series of processing steps or methods may be employed to eliminate Non-Uniform Rotational Distortion (NURD) in such devices, for example, unidirectional and bi-directional intravascular ultrasonic (IVUS) imaging systems. The system may include a processor and an electronic module which control operation of a transducer assembly provided at a distal end of a catheter assembly. The system invokes a first processing step or method to collect and store raw angle and line data, as well as one or more of second and third processing steps or methods which adjust for NURD experienced during backlash of a bi-directional imaging system and a fourth processing step or method which performs a line-to-line correlation function. The system and method provide more accurate and reliable angular orientations of anomalies identified during imaging and / or inspection of the interior portion or surface of the cavity, thus facilitating diagnosis and treatment options.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
Systems and methods for correlating images in an image correlation system with reduced computational loads
InactiveUS20030026457A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionCorrelation functionPeak value
After one or both of a pair of images are obtained, an auto-correlation function for one of those images is generated to determine a smear amount and possibly a smear direction. The smear amount and direction are used to identify potential locations of a peak portion of the correlation function between the pair of images. The pair of images is then correlated only at offset positions corresponding to the one or more of the potential peak locations. In some embodiments, the pair of images is correlated according to a sparse set of image correlation function value points around the potential peak locations. In other embodiments, the pair of images is correlated at a dense set of correlation function value points around the potential peak locations. The correlation function values of these correlation function value points are then analyzed to determine the offset position of the true correlation function peak.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
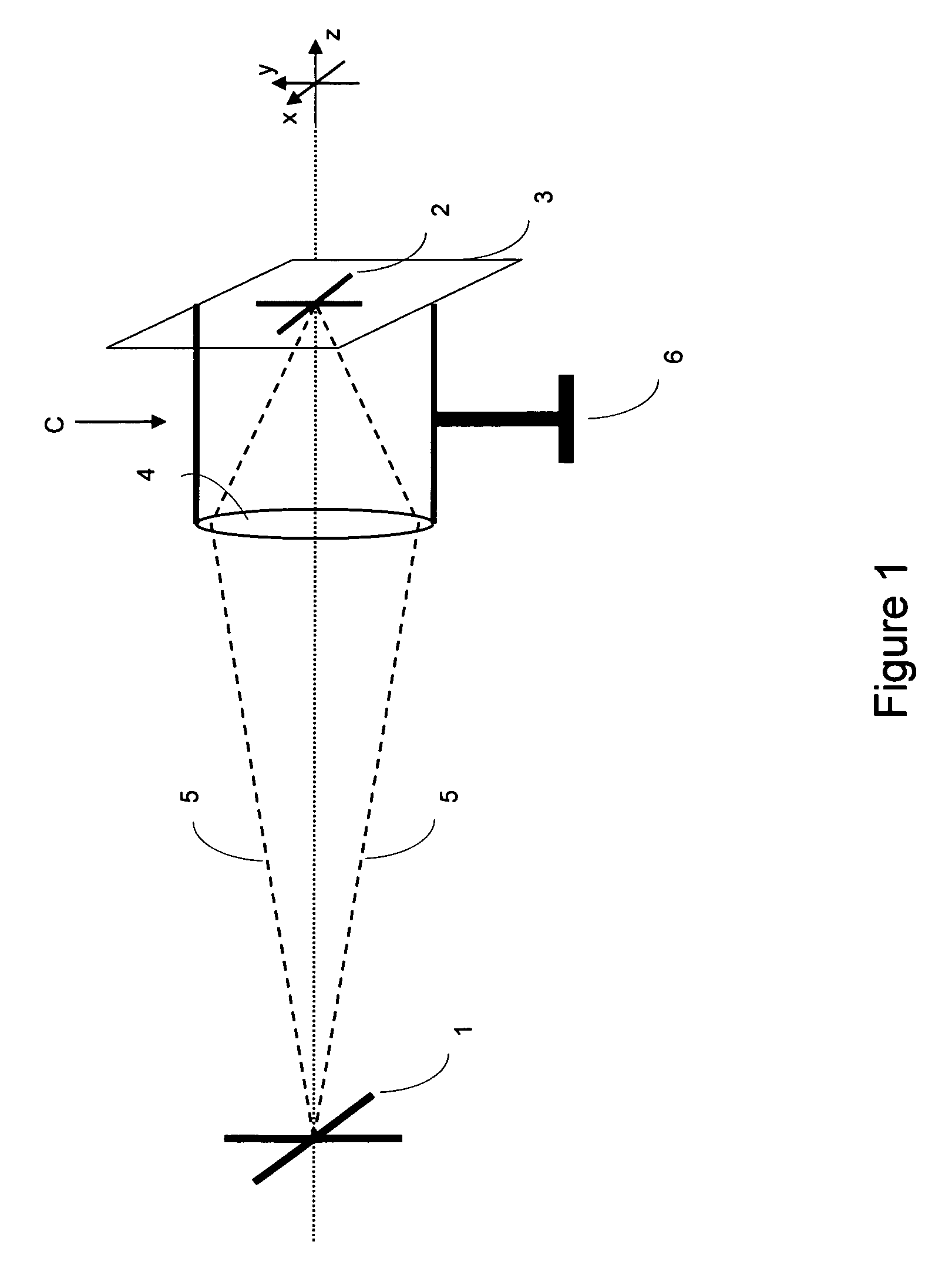
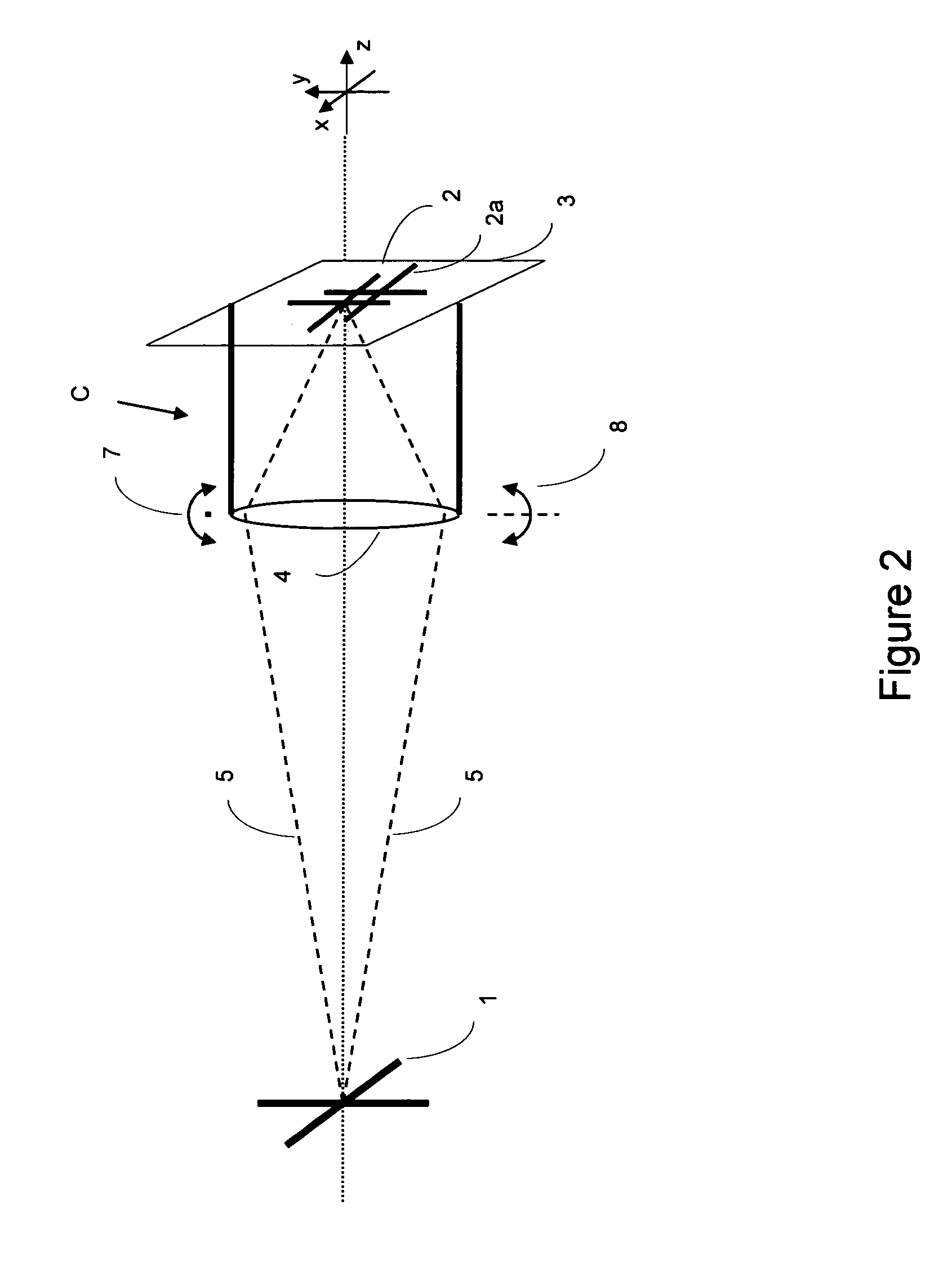
BOC signal acquisition and tracking method and apparatus
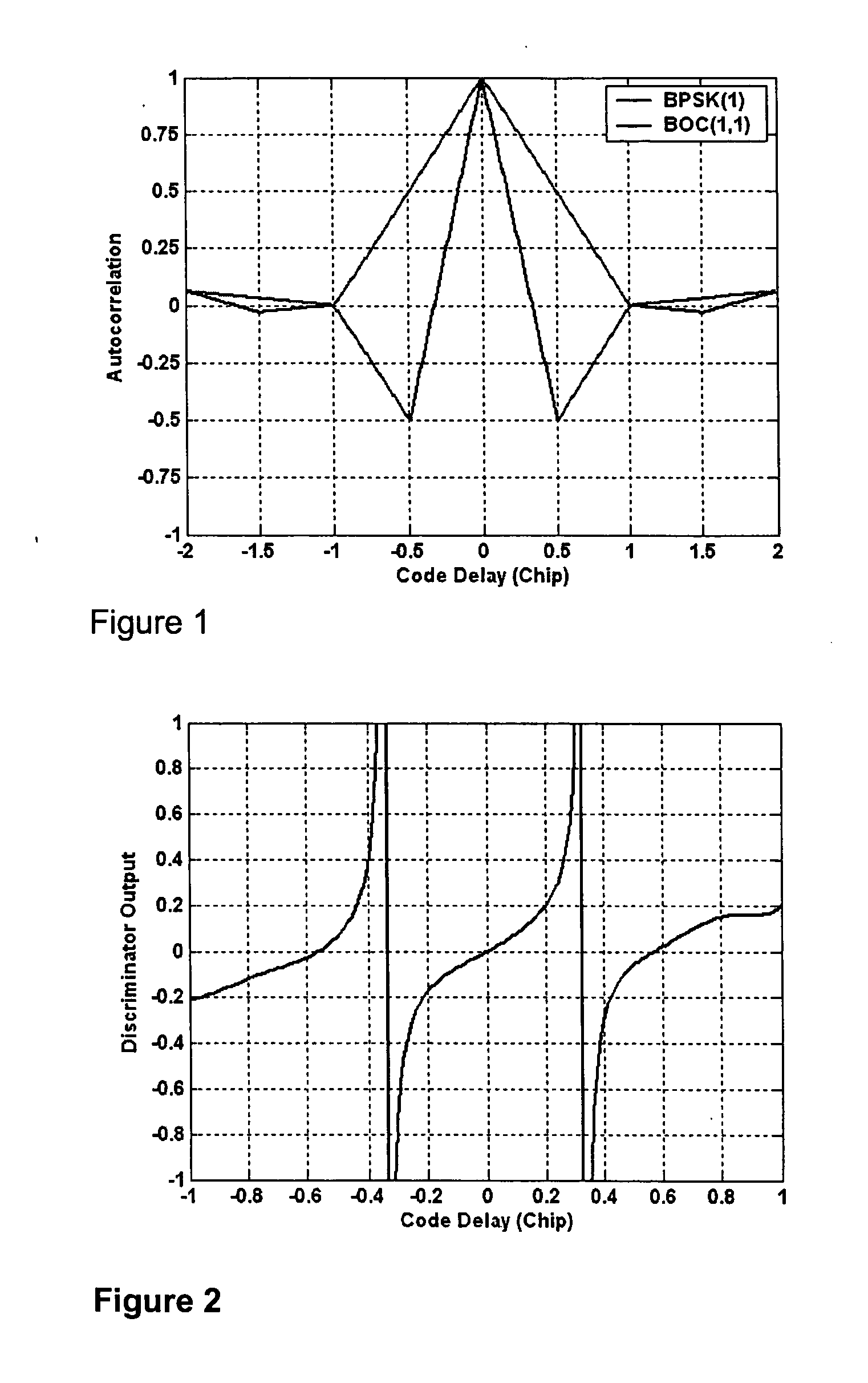
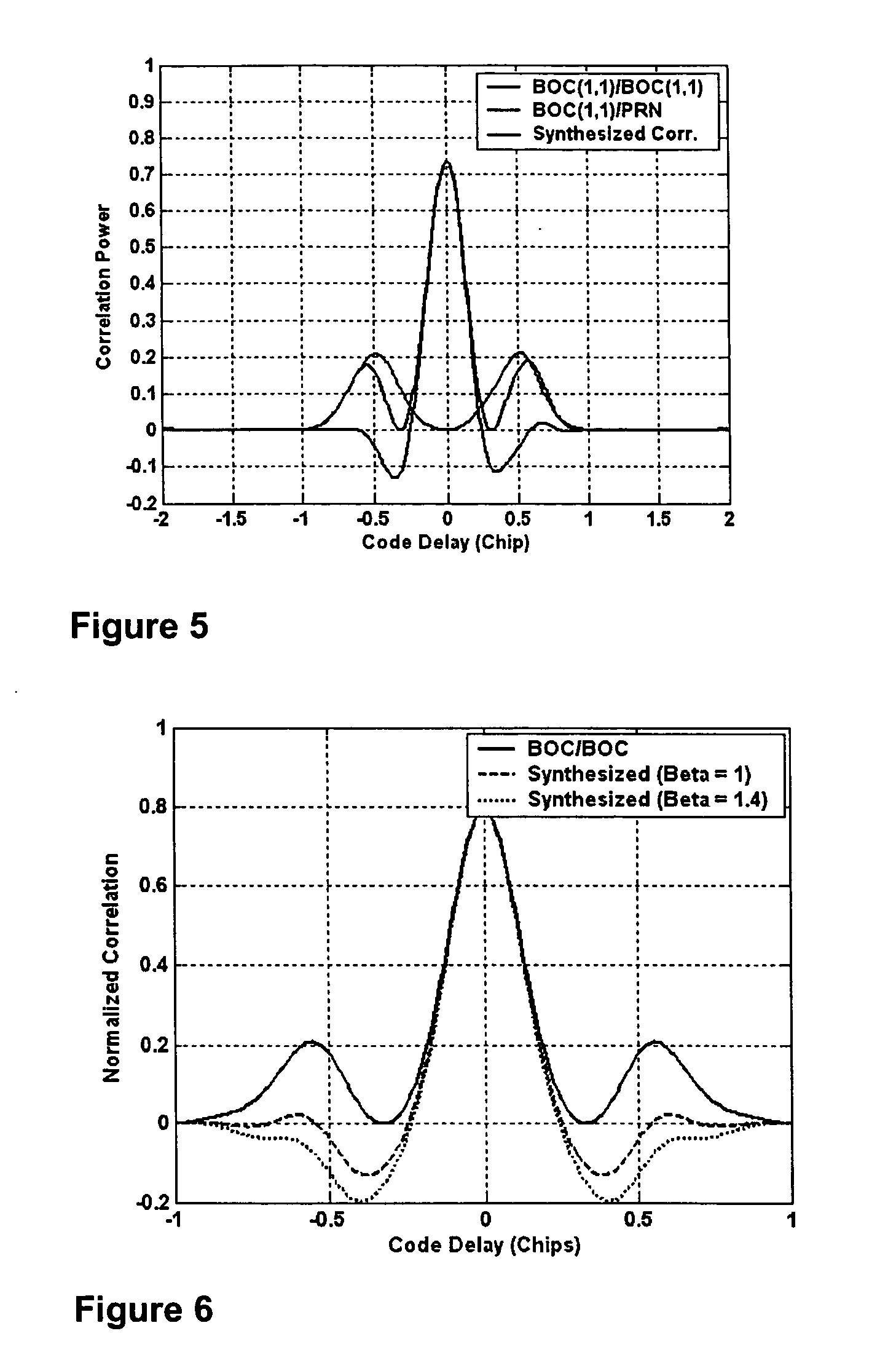
InactiveUS20050270997A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDiscriminatorCorrelation function
A method and apparatus for acquiring and tracking a BOC signal in a satellite navigation receiver includes a synthesized acquisition test function or a discriminator for code delay provided by combining a BOC autocorrelation function and a BOC / PRN cross-correlation function.
Owner:FRENCH CIVIL AVIATION UNIVERSITY +1
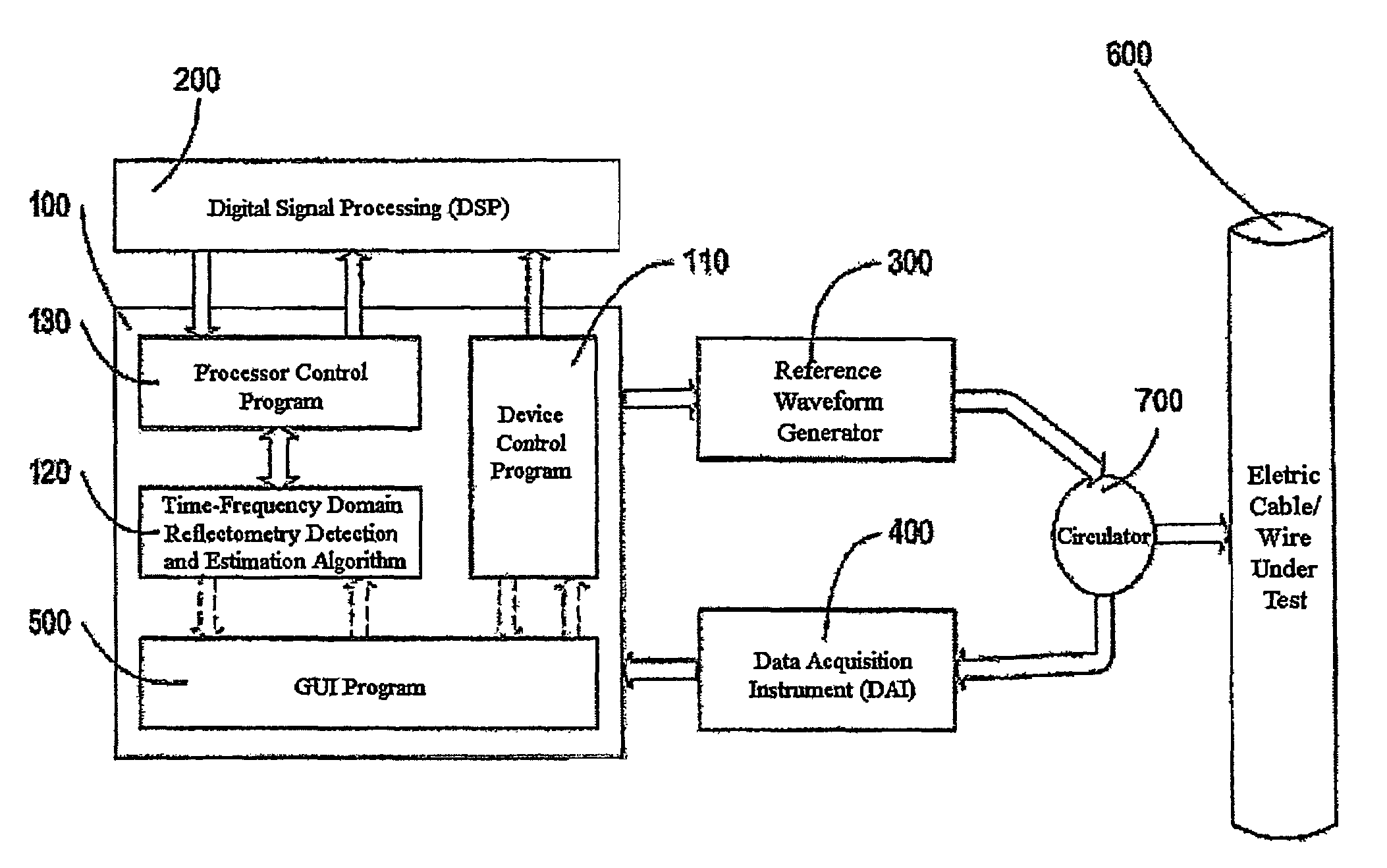
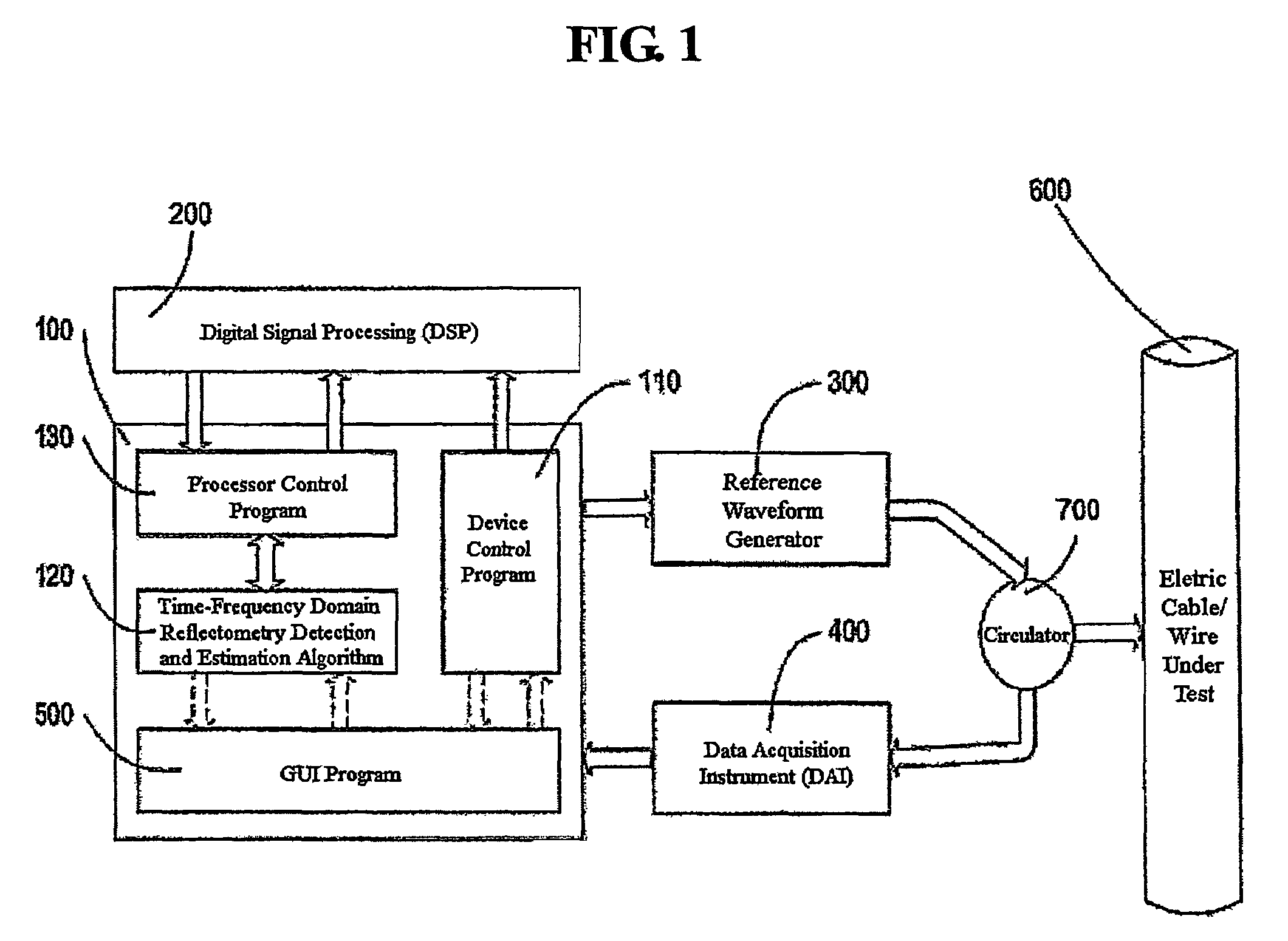
Time-frequency domain reflectometry apparatus and method
InactiveUS7337079B2Resistance/reactance/impedenceFault location by pulse reflection methodsMeasurement deviceTime delays
An apparatus and method for high-resolution reflectometry that operates simultaneously in both the time and frequency domains, utilizing time-frequency signal analysis and a chirp signal multiplied by a Gaussian time envelope. The Gaussian envelope provides time localization, while the chirp allows one to excite the system under test with a swept sinewave covering a frequency band of interest. High resolution in detection of the reflected signal is provided by a time-frequency cross correlation function. The high-accuracy localization of faults in a wire / cable can be achieved by measurement of time delay offset obtained from the frequency offset of the reflected signal. The apparatus enables one to execute an automated diagnostic procedure of a wire / cable under test by control of peripheral devices.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC CORP FOUND YONSEI UNIV
Apparatus and methods for performing acoustical measurements
InactiveUS6279379B1Good repeatabilityAbsenceVibration measurement in solidsSpectral/fourier analysisFast Fourier transformCorrelation function
Apparatus (15, 30) and methods for performing acoustical measurements are provided having some and preferably all of the following features: (A) the system (15, 30) is operated under near-field conditions; (B) the piezoelement (40) or piezoelements (40, 48) used in the system are (i) mechanically (41, 49) and electrically (13, 16) damped and (ii) efficiently electrically coupled to the signal processing components of the system; (C) each piezoelement (40, 48) used in the system includes an acoustical transformer (42, 50) for coupling the element to a gaseous test medium (9); (D) speed of sound is determined from the time difference between two detections of an acoustical pulse (81, 82) at a receiver (40, FIG. 3; 48, FIG. 7); (E) cross-correlation techniques are employed to detect the acoustical pulse at the receiver; (F) forward and inverse Fourier transforms employing fast Fourier transform techniques are used to implement the cross-correlation techniques; in such a mathematical manner that the peak of the cross-correlation function corresponds to the detection of a pulse at the receiver and (G) stray path signals through the body (31) of the acoustic sensor (15, 30) are removed from detected signals prior to signal analysis. Techniques are also provided for performing acoustical measurements on gases whose thermodynamic properties have not been measured and on mixtures of compressible gases. Methods and apparatus (29) for performing feedback control of a gas of interest in a mixture of that gas and a carrier gas are provided in which the controlled variable is the flow of the carrier gas.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
Method and apparatus for locating the source of an unknown signal
InactiveUS6618009B2Direction finders using radio wavesBeacon systems using radio wavesPhase correctionUnknown Source
A method of determining the location of an unknown source 10 transmitting a signal to satellite relays 14 and 16 comprises receiving replicas of the signal from the relays at receivers 18. The receivers 18 also transmit and receive reference signals via respective relays 14 and 16. All signals are downconverted, digitized and correlated with one another in pairs using a correlation function including a term which compensates for time varying differential frequency offset (DFO). Compensation for time varying differential time offset or time dilation is achieved by replicating or adding to signal samples and applying phase corrections. This procedure enables a correlation maximum and associated measurement results to be obtained despite the effects of relay satellite motion which mitigate against this. Results are used in a prior art geometrical technique to locate the unknown transmitter.
Owner:KRATOS INTEGRAL HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for electronically stabilizing digital images
ActiveUS7557832B2Fast readoutEffective timeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCorrelation functionConsecutive frame
An electronic image stabilizer in a digital camera compensates for camera motion-induced blurriness by segmenting exposure times into multiple shorter exposure times and summing the individual pixels from successive frames after applying an appropriate motion correction. Motion is detected by computing the correlation function between successive images, and compensation is applied by maximizing the correlation function. This avoids the need for mechanical stabilization devices in order to detect or correct the motion as is done in prior art. This method further enables the detection of moving objects in a still background, and correction of blurriness images due to such motion.
Owner:LINDENSTRUTH VOLKER +2
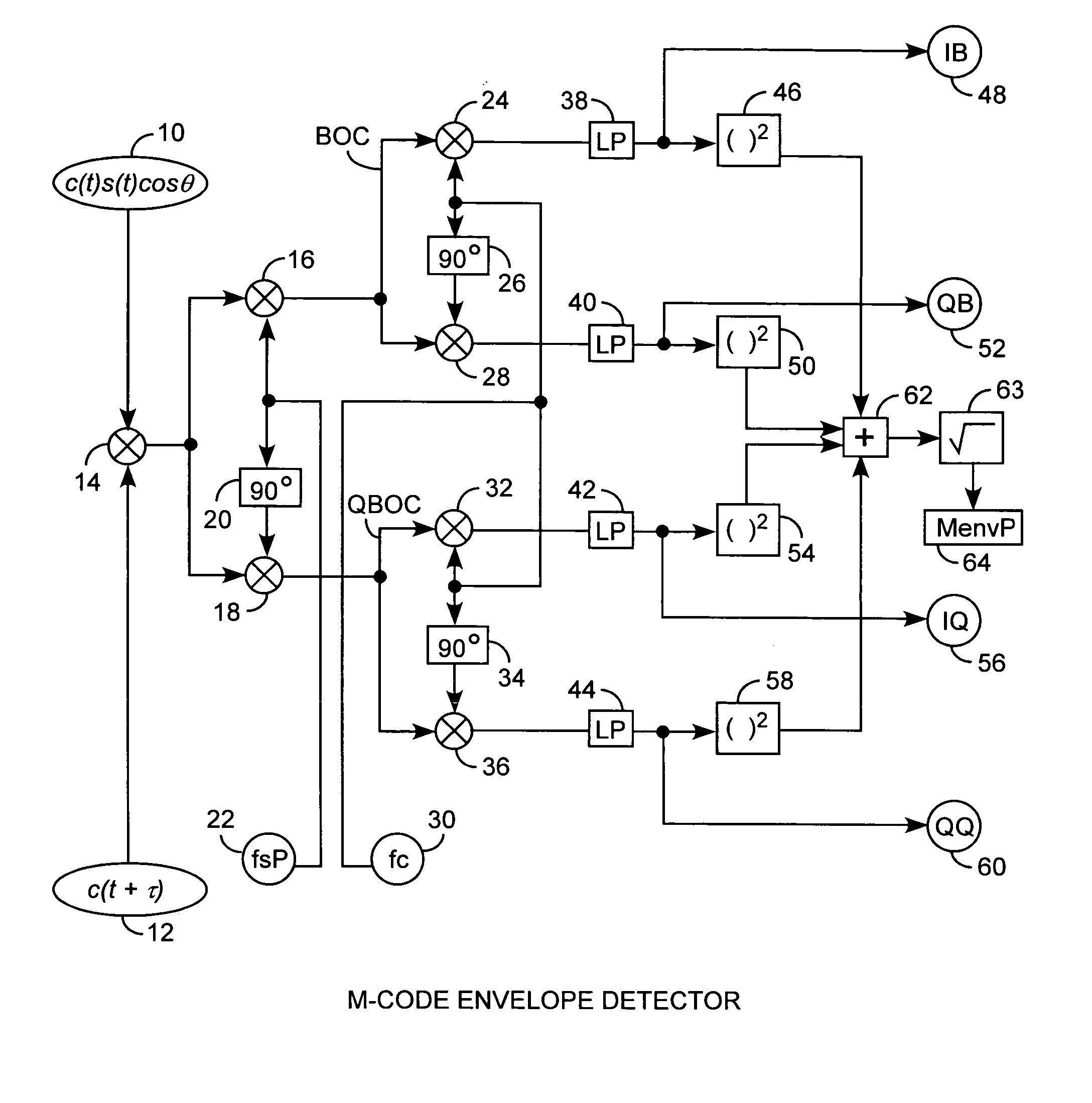
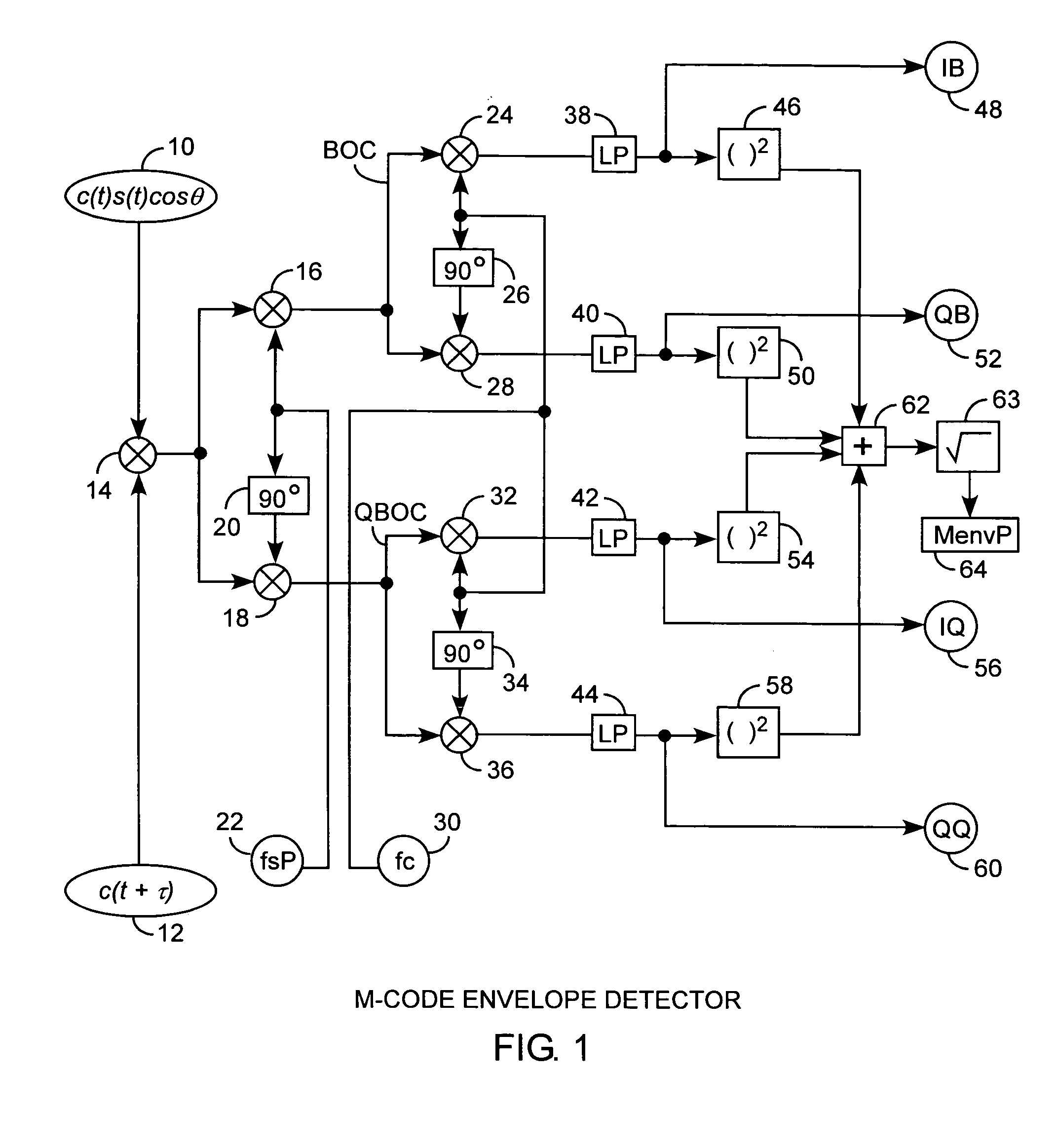
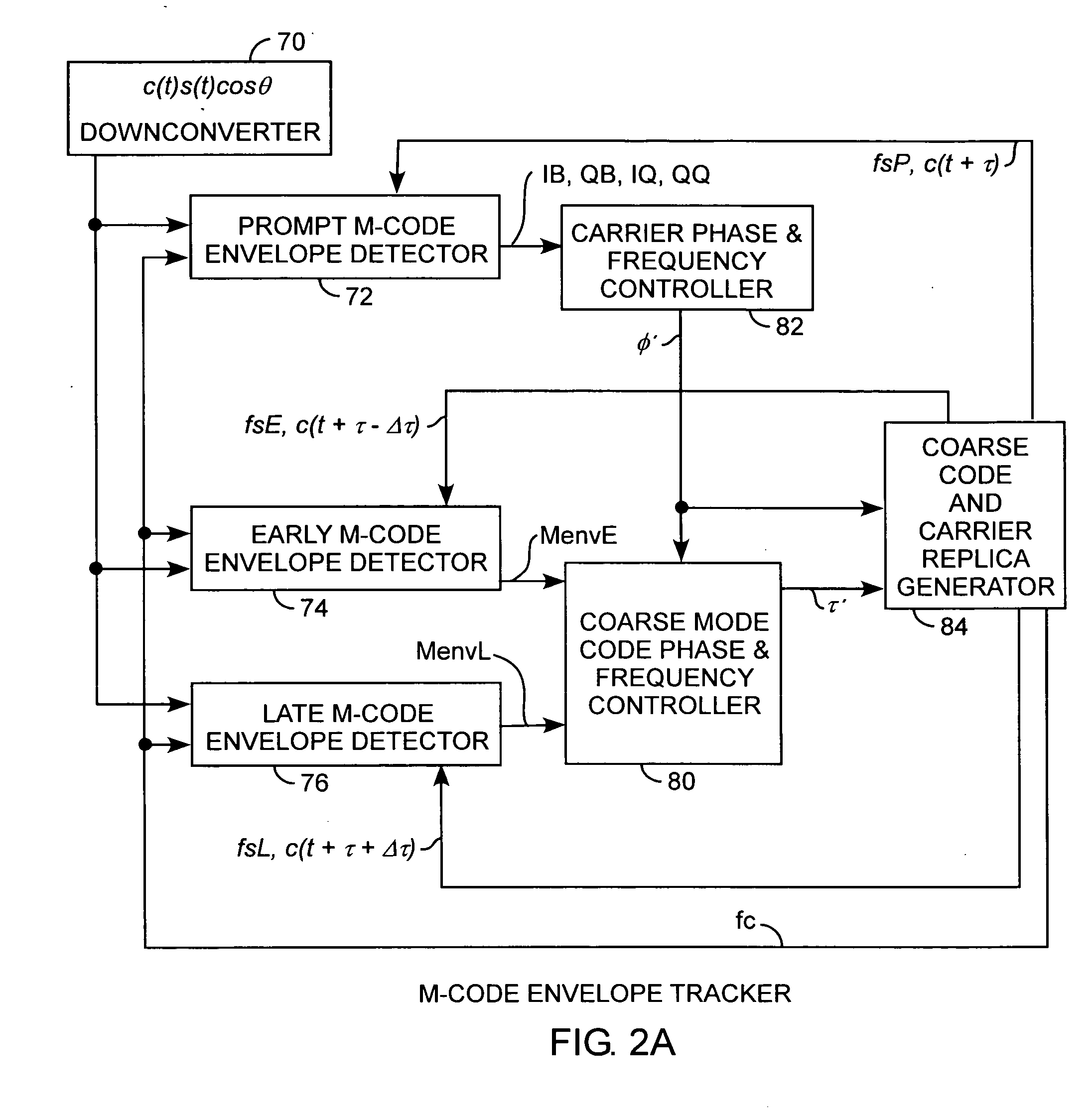
Binary offset carrier M-code envelope detector
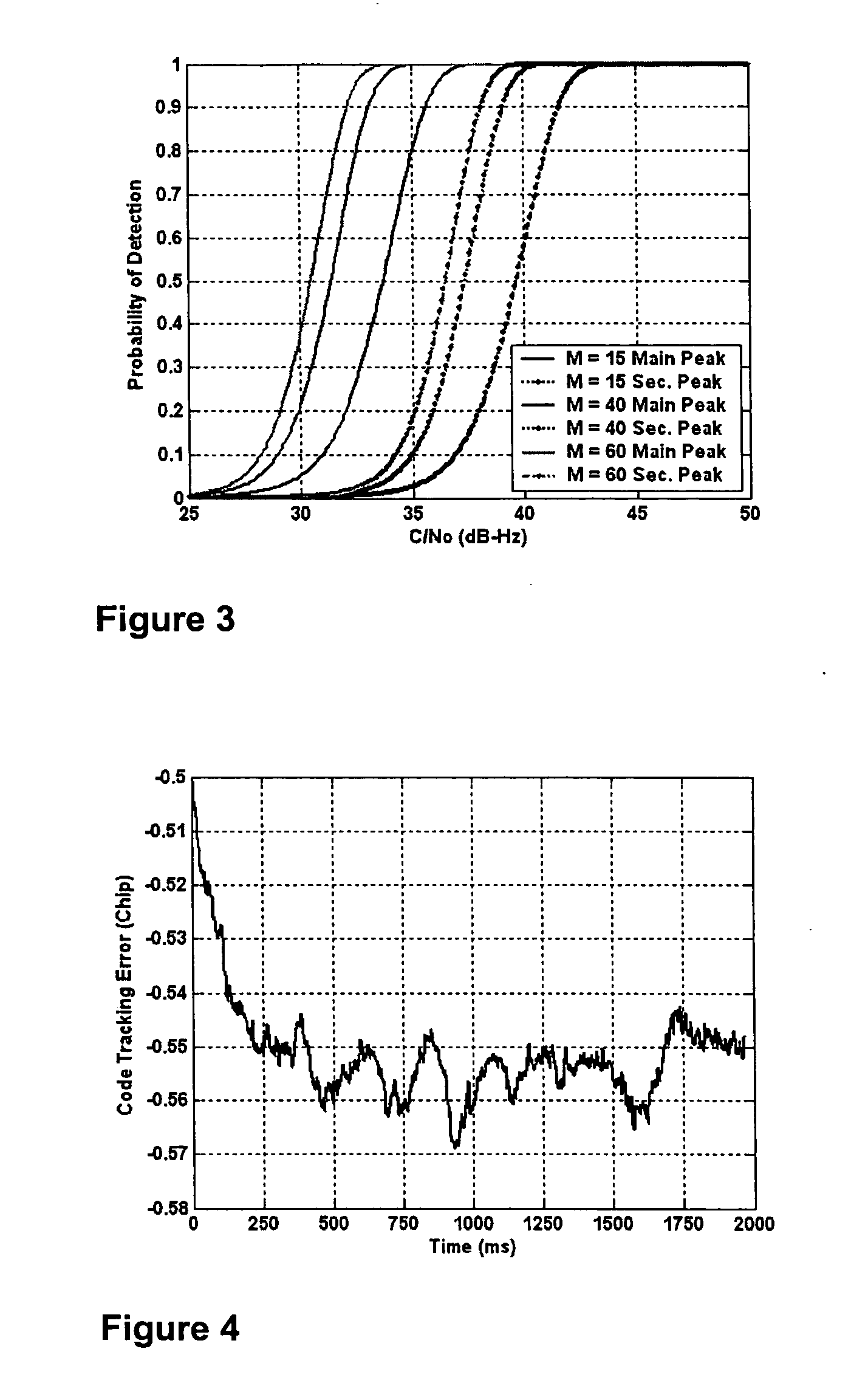
ActiveUS20050281325A1Improve acquisitionModulated-carrier systemsBeacon systemsCorrelation functionCode tracking
An M code envelope detector receives an incoming binary offset carrier (BOC) signal, such as the M code signal, and generates inphase BOC and quadraphase BOC signals, separated by an offset, that have respective ambiguous correlation envelopes, that when combined, provide a near unimodal correlation function with respect to code phase error of the BOC signal having an inherent multimodal autocorrelation function, with the near unimodal correlation envelope being tracked by early and late code replicas at broad one chip phases for providing unambiguous but nonlinear code phase error tracking, which detector is then further improved with the use of code replicas having narrow partial chip phases, such as ⅛ chip phases, for providing near linear code phase error tracking for unambiguous and accurate code tracking of the BOC signal.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
Time-of-flight measurement using pulse sequences
InactiveUS20060227315A1Accurate identificationEasy to processOptical rangefindersHeight/levelling measurementCorrelation functionPulse sequence
A method for determining the time-of-flight of a device under test, wherein a return signal returning from the device under test in response to the probing signal comprising a sequence of pulses according to a first code sequence is detected and a second code sequence from the detected return signal is derived, and a correlation function is determined by correlating the first code sequence and the second code sequence, a main peak is identified, a time position of the main peak is determined and the time-of-flight is derived from the time position.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
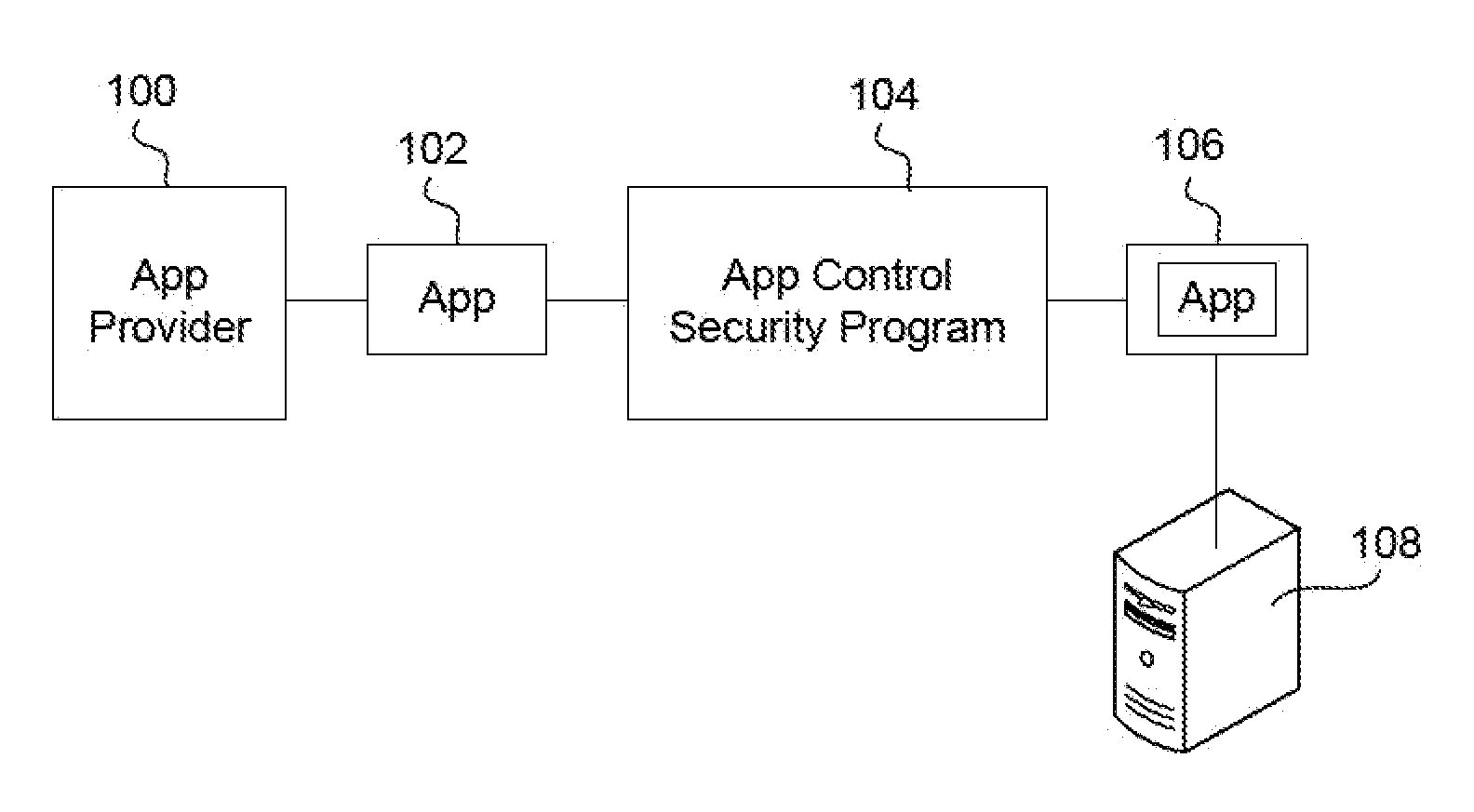
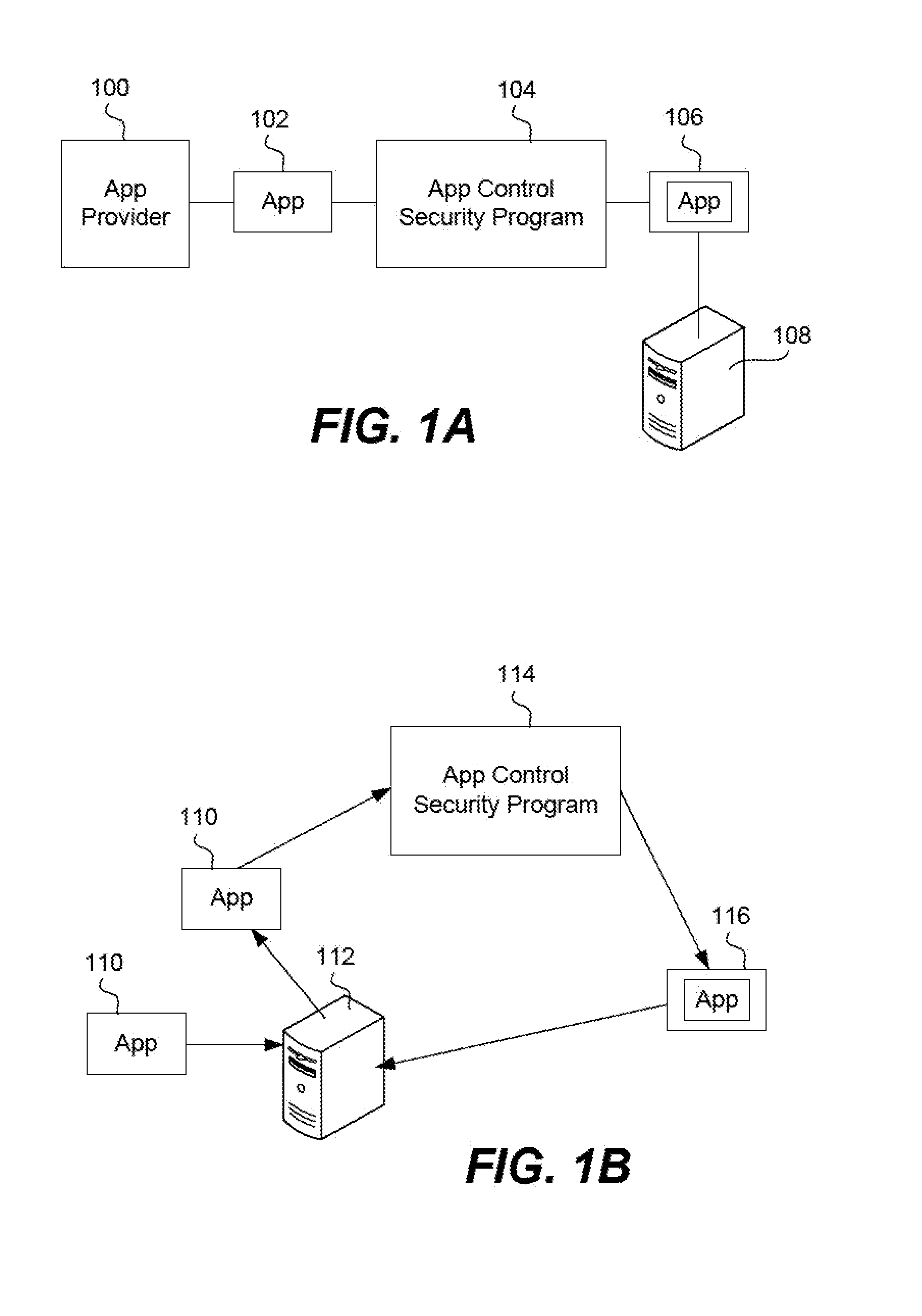
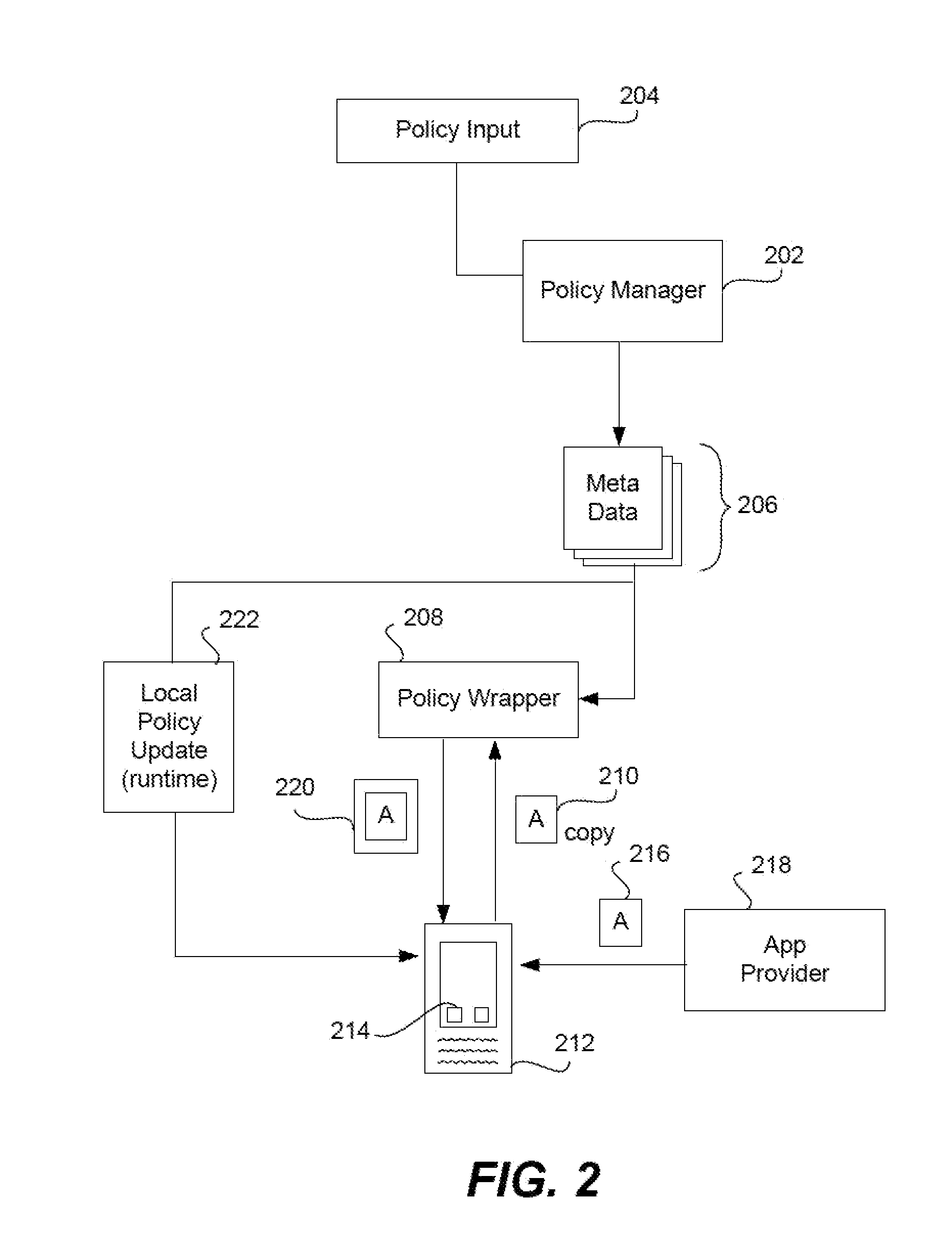
Ensuring network connection security between a wrapped app and a remote server
InactiveUS20130291086A1Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsOperational systemData stream
A network connection between an app on a mobile device and a remote server is either enabled or denied based on whether a security wrapped app can verify that the connection is with a known and trusted server. The wrapped app uses a socket interception layer injected into the app code along with a trust store, also part of the wrapped app to determine whether a network connection attempted by the app should be allowed. The layer buffers relevant function calls from the app by intercepting them before they reach the device operating system. If the layer determines that a network connection is attempted, then it snoops the negotiation phase data stream to discern when the server sends a certificate to the app. It obtains this certificate and compares it to data in the trust store and makes a determination of whether the server is known and trusted.
Owner:BLUE CEDAR NETWORKS INC
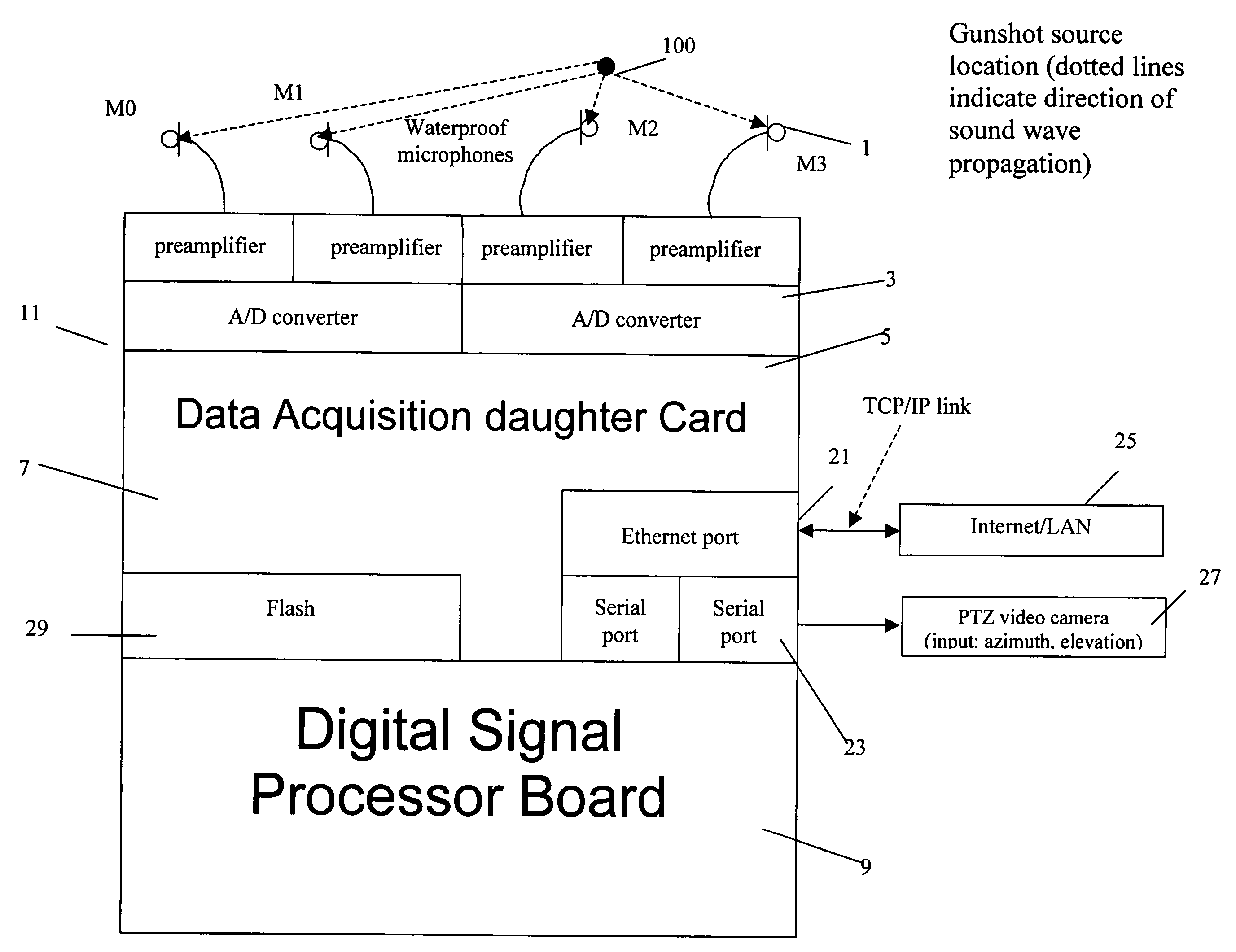
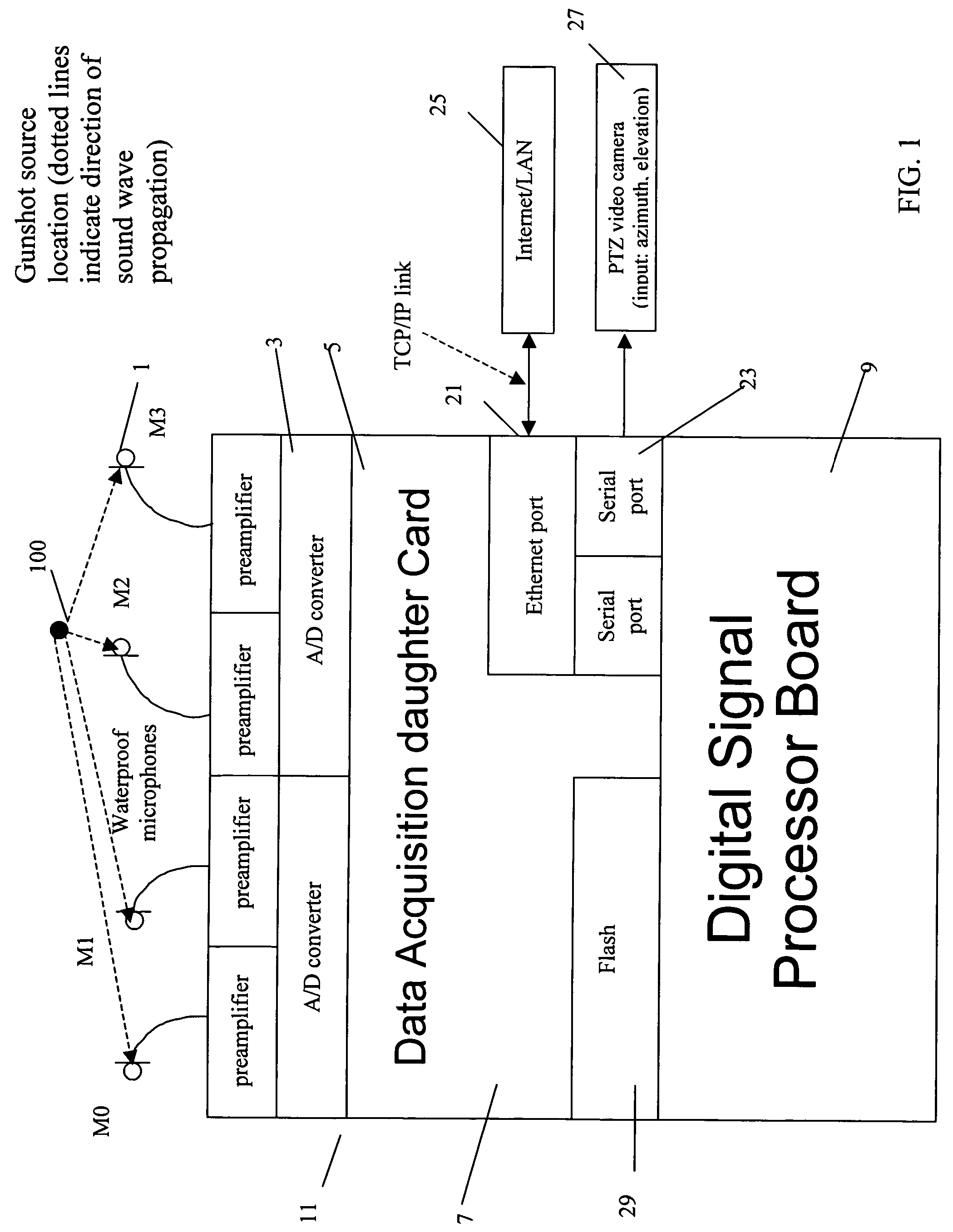
Real time acoustic event location and classification system with camera display
ActiveUS7203132B2Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesSpeech analysisThird partyEvent type
An acoustic event location and classification system comprising an array of at least two acoustic transducers arranged spaced from one another; a central data processing unit for receiving signals from the acoustic transducers and processing the signals to determine a event type and location; and an internet or LAN connection for transmitting event type and location data to a third party, wherein the central data processing unit uses a DSNN to determine the event type and generalized cross correlation functions between microphone pairs to determine the event location.
Owner:SAFETY DYNAMICS
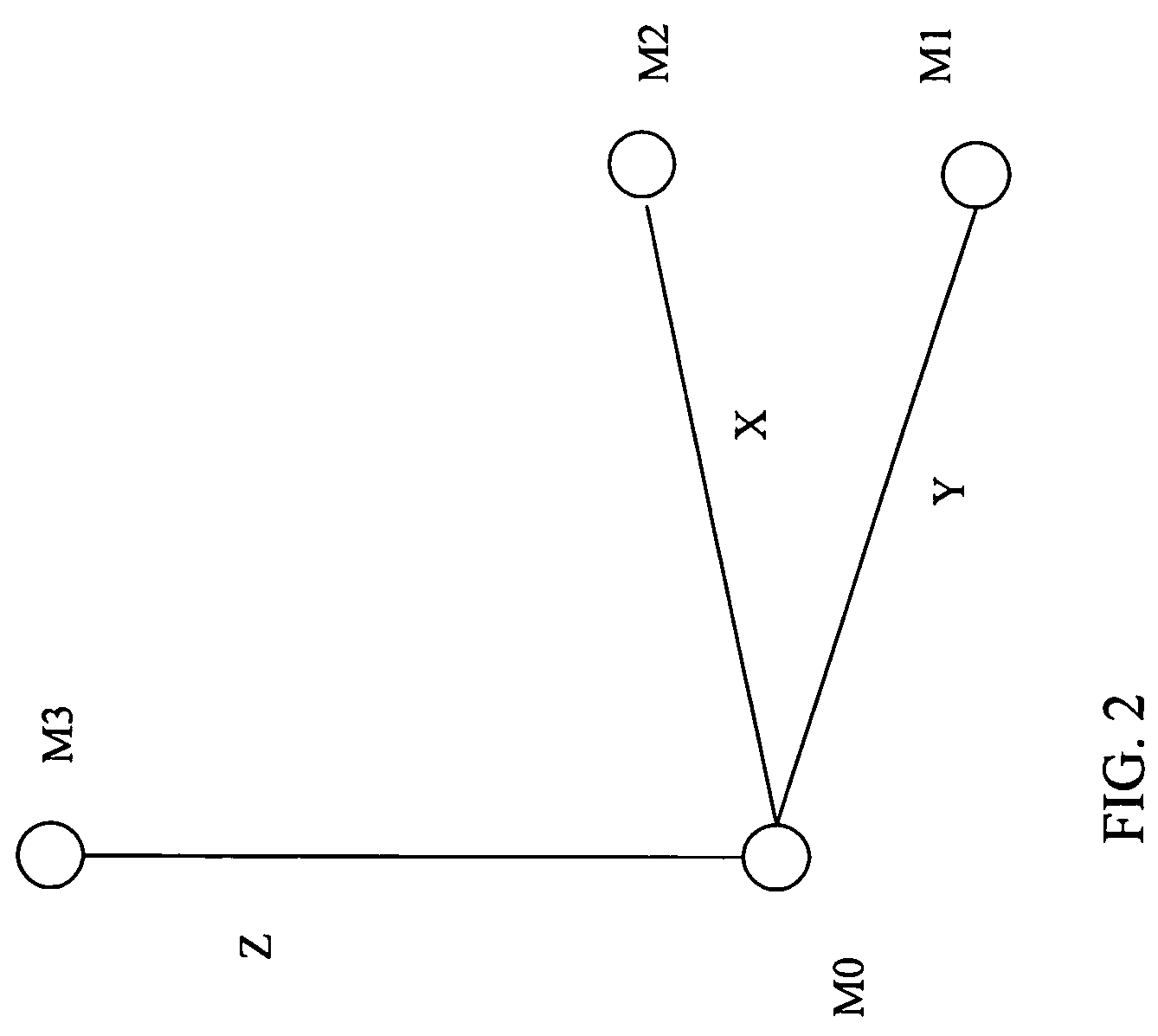
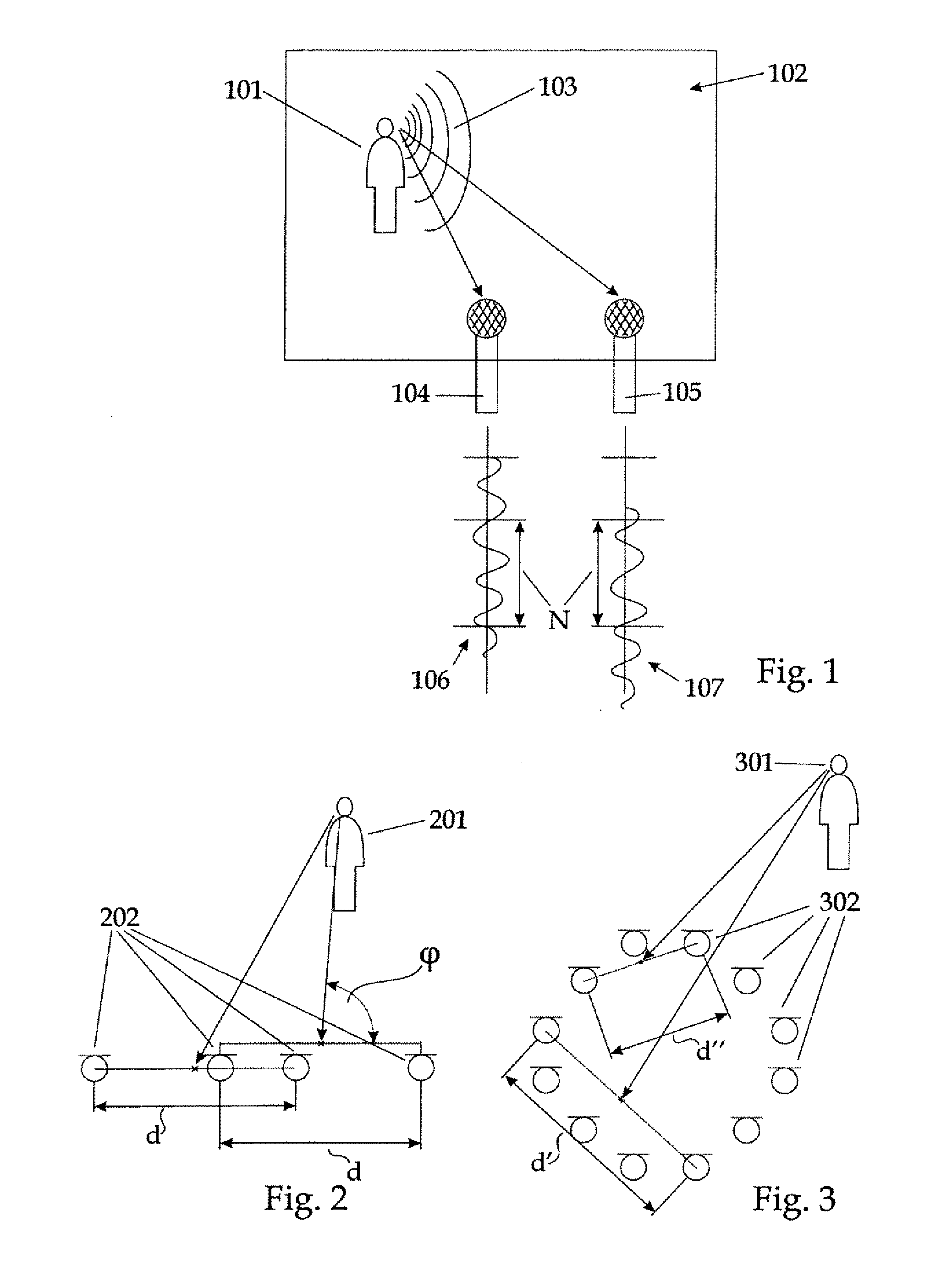
Joint position-pitch estimation of acoustic sources for their tracking and separation
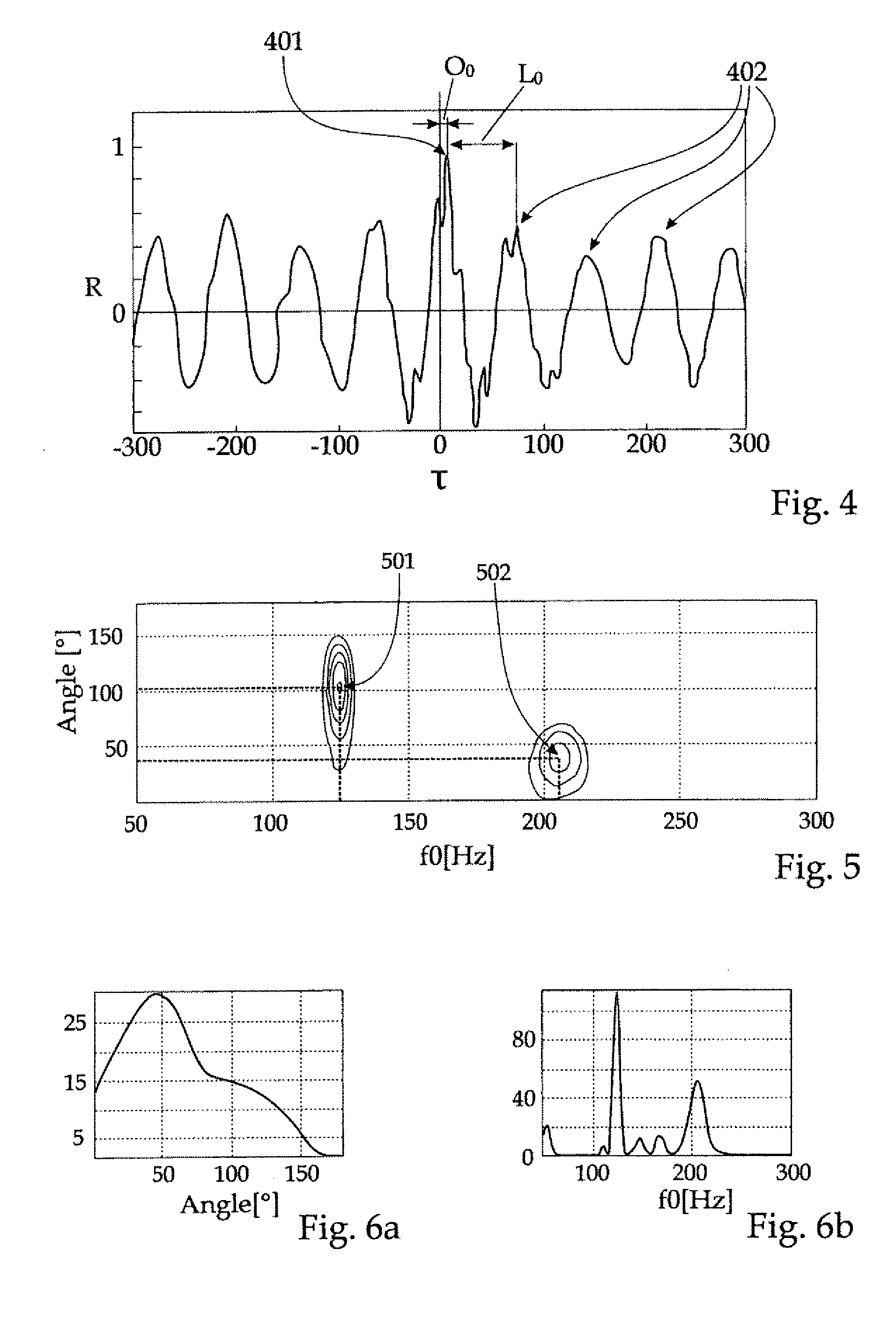
ActiveUS20100142327A1Simple methodDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesSpeech analysisSound sourcesCorrelation function
The invention relates to a method for localizing and tracking acoustic sources (101) in a multi-source environment, comprising the steps of recording audio-signals (103) of at least one acoustic source (101) with at least two recording means (104, 105), creating a two- or multi-channel recording signal, partitioning said recording signal into frames of predefined length (N), calculating for each frame a cross-correlation function as a function of discrete time-lag values (τ) for channel pairs (106, 107) of the recording signal, evaluating the cross-correlation function by calculating a sampling function depending on a pitch parameter (f0) and at least one spatial parameter (φ0), the sampling function assigning a value to every point of a multidimensional space being spanned by the pitch-parameter and the spatial parameters, and identifying peaks in said multidimensional space with respective acoustic sources in the multi-source environment.
Owner:TECHN UNIV GRAZ
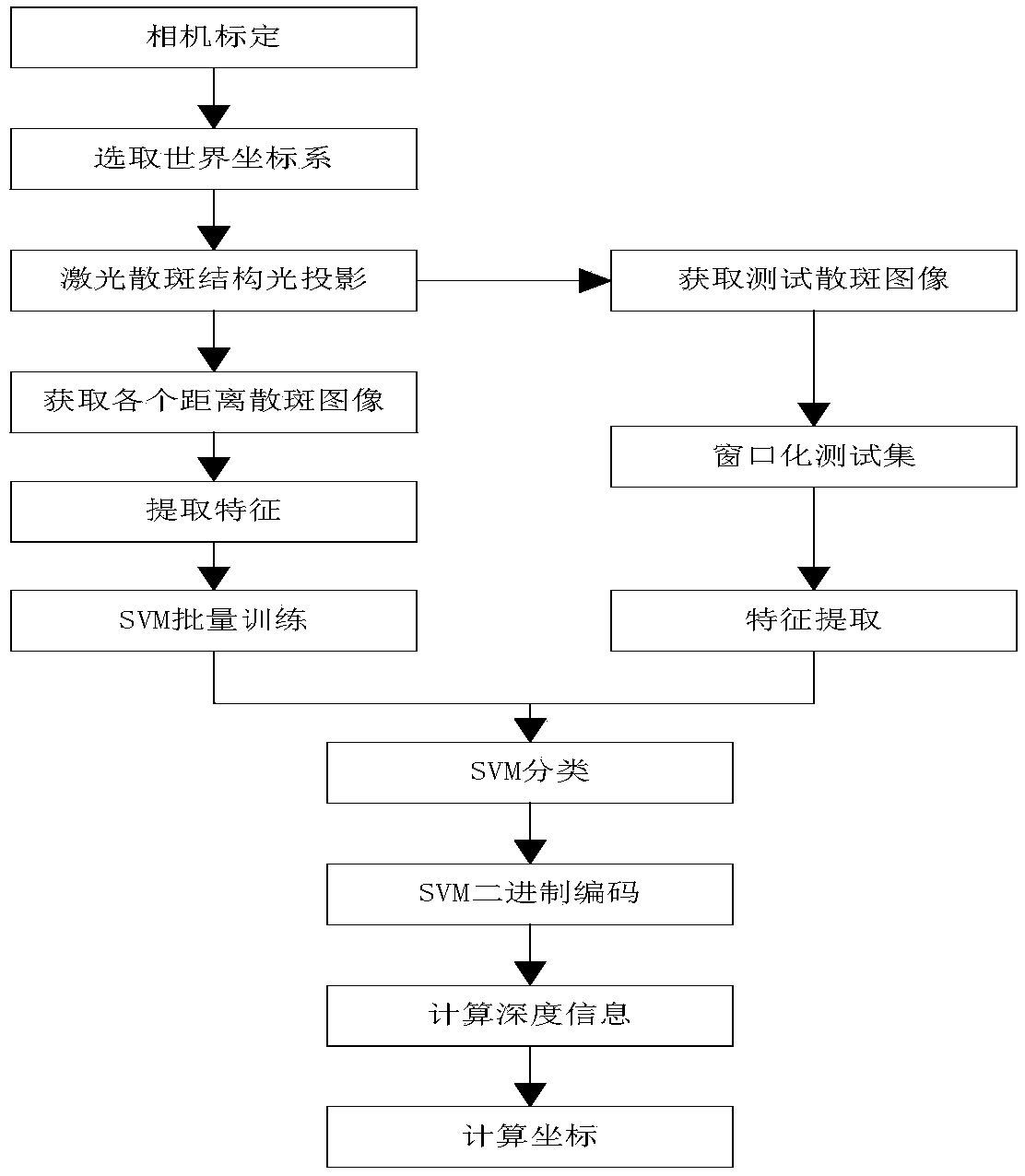
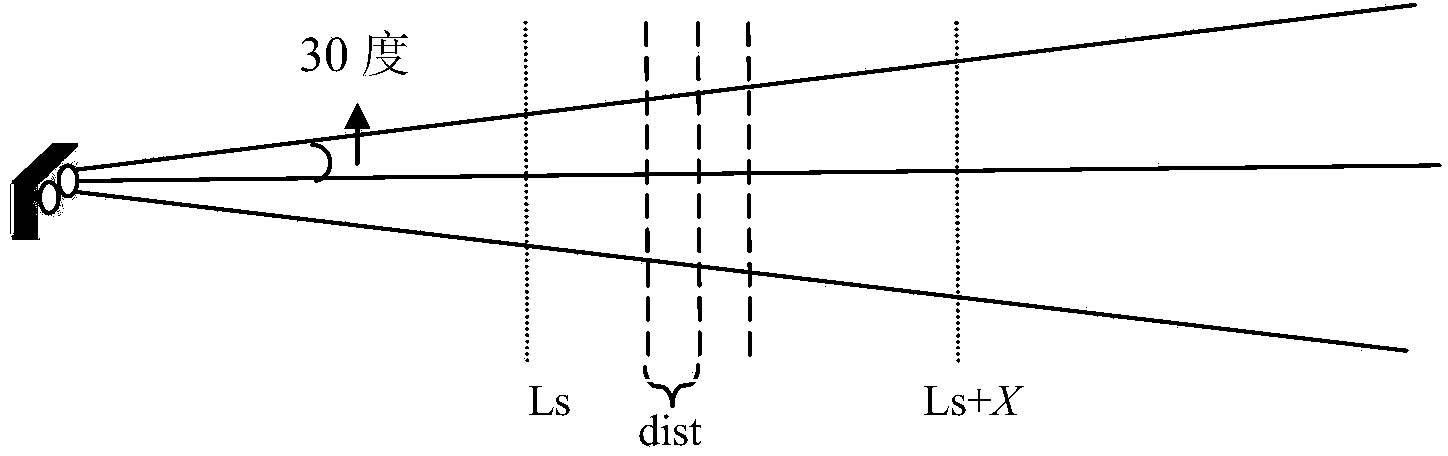
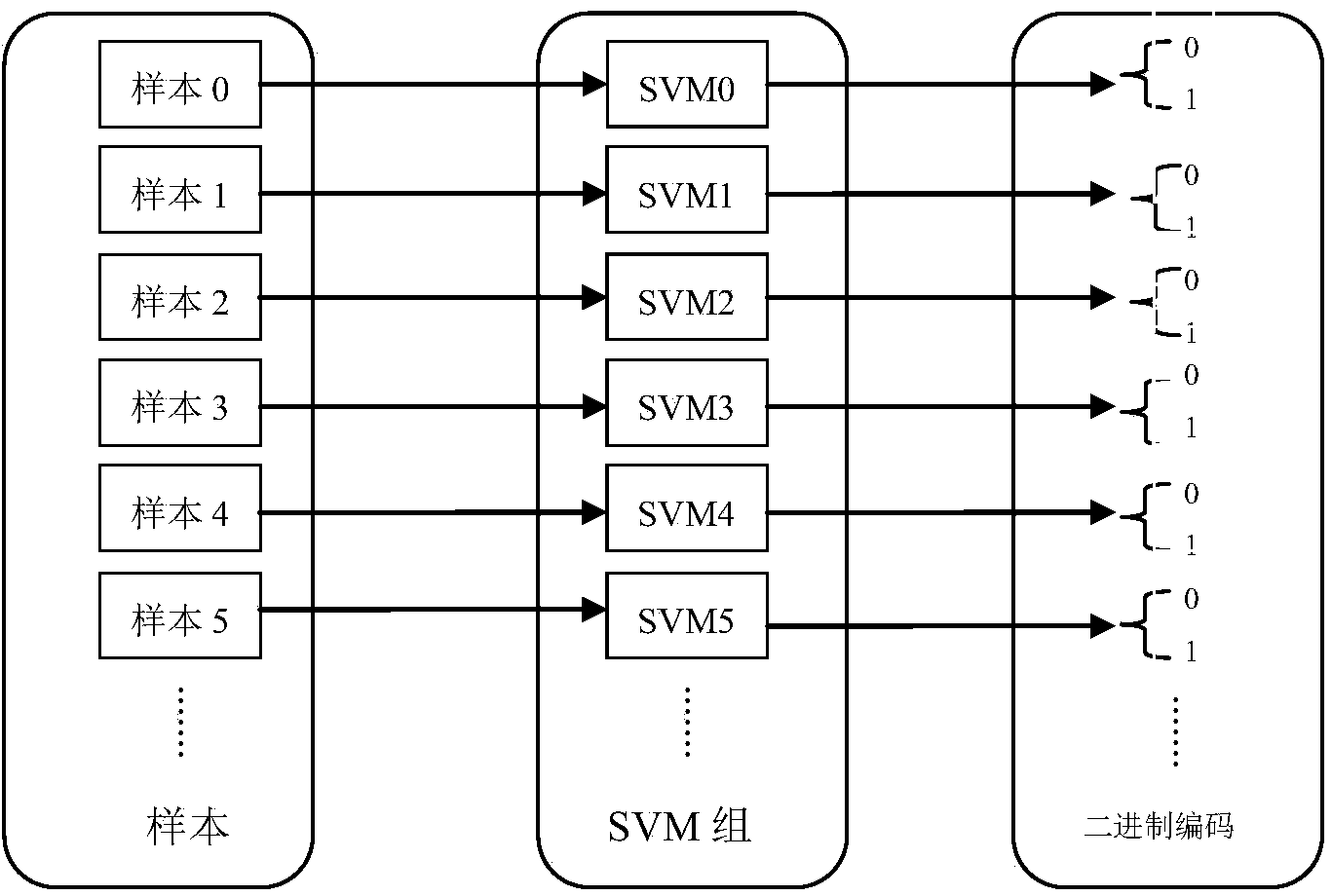
Method for three-dimensional reconstruction of laser speckle structured light and depth information
The invention provides a method for three-dimensional reconstruction of laser speckle structured light and depth information. The three-dimensional reconstruction technology is an important subject for machine vision research and refers to the content that a three-dimensional space geometrical shape of a three-dimensional body is restored through images of the three-dimensional body. Generally, three-dimensional reconstruction is conducted through the binocular parallax principle of a binocular camera or through a triangulation method or space codes are obtained through the structured light and the depth information is obtained through the triangulation method. The method aims at obtaining the depth information through the laser speckle structured light, a similar invention such as the kinect of the Microsoft Corporation also obtains the depth information (namely different depths are matched through a cross-correlation function of laser speckles) of an object through the method, and the difference is an algorithm for obtaining the depth information through the speckles. According to the method, parallel code number sorting is conducted on each pixel block one by one by a thinning window through multiple support vector machines, so that the depth of each pixel window is obtained, coordinates under a world coordinate system of the object are obtained by inversely solving a camera model through the depth information, and therefore the depth information with the higher accuracy can be obtained.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
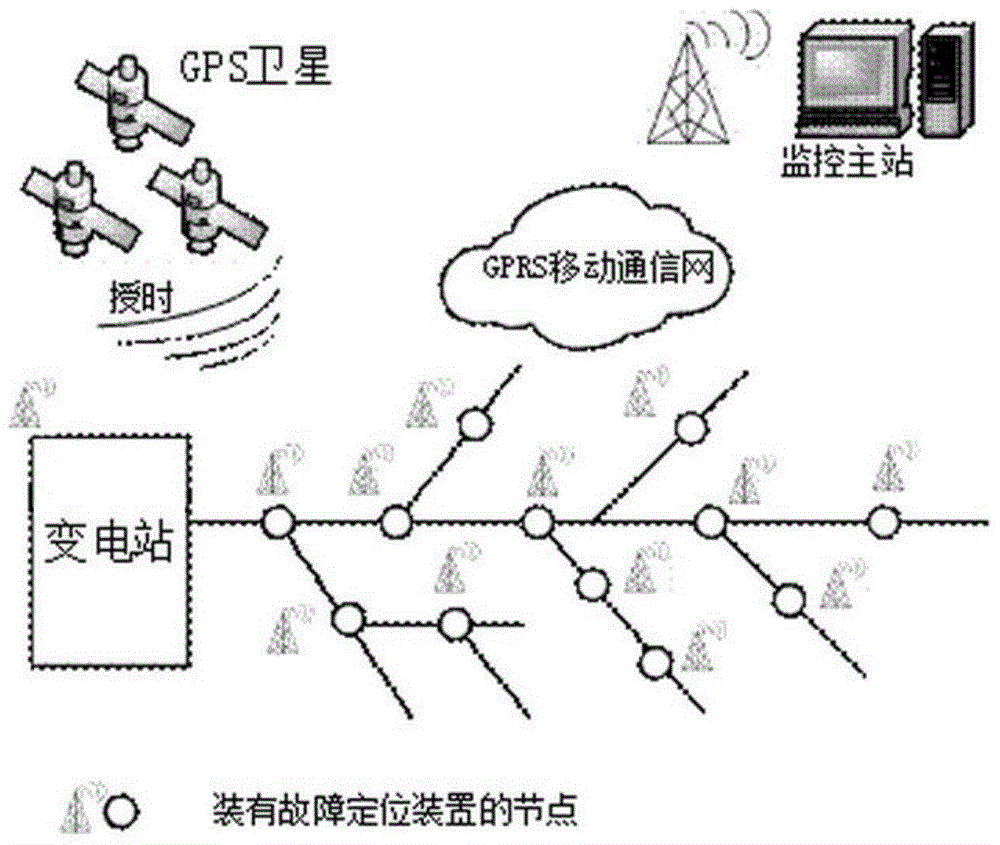
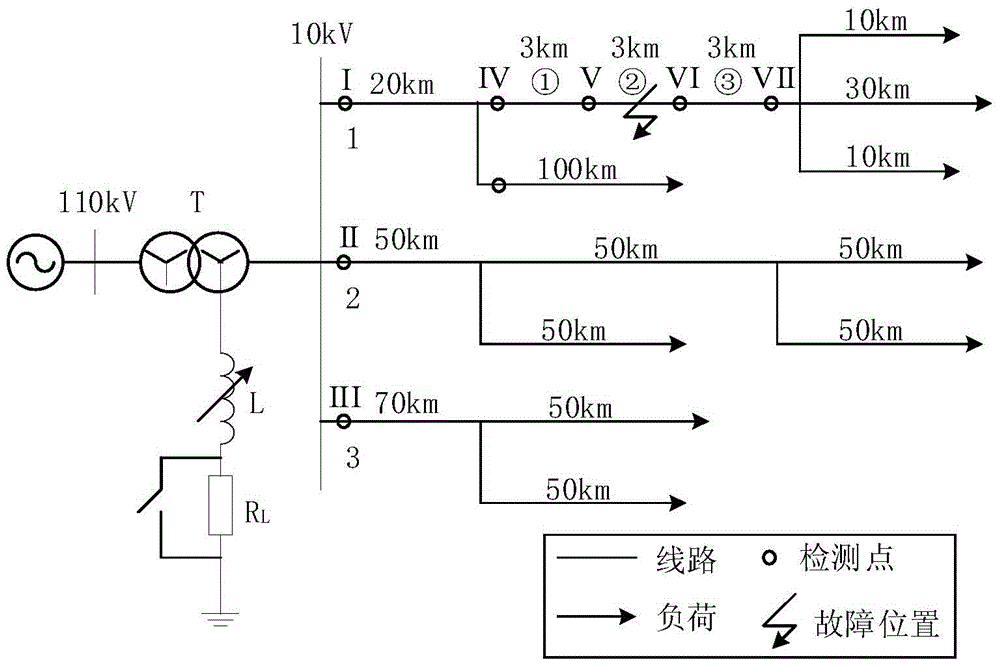
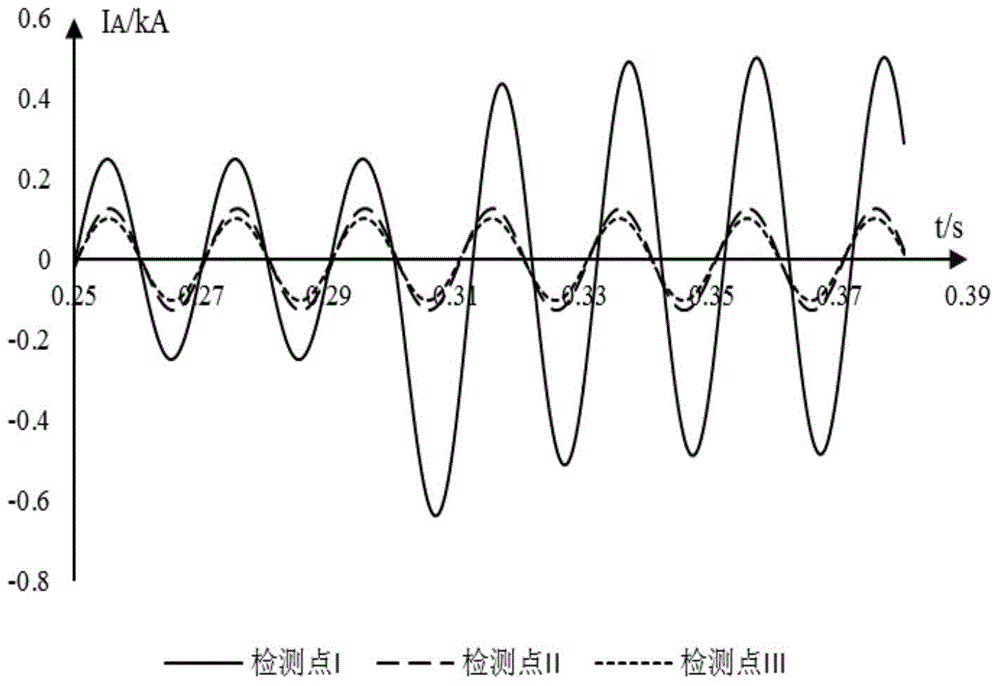
Distribution network line fault section positioning method based on full-waveform information
ActiveCN104155582AHigh sensitivityImprove reliabilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault location by conductor typesPhase currentsCorrelation function
The invention discloses a distribution network line fault section positioning method based on full-waveform information. For the grounding fault, line selection is carried out through extreme value points of a cross-correlation function of the bus zero-sequence voltage and all outgoing line zero-sequence currents, and positioning is carried out according to the adjacent detection point zero-sequence current waveform standard drift rate of the whole action process of a fault occurrence and compensation device; for the interphase fault, line selection is carried out according to the overcurrent information obtained before action of a relay protection device, and positioning is carried out according to the adjacent detection point fault phase current waveform standard drift rate. The waveform data of the whole action process of a fault and arc extinction device are utilized, the current ubiquitous problems that when a small current grounding system encounters the single-phase grounding phase, the fault current is weak, the reliability is poor, and the sensitivity is low can be well solved, and meanwhile the system cannot get interference.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAINE ENERGY TECH CO LTD
System and method for reducing angular geometric distortion in an imaging device
ActiveUS8047996B2Reducing angular geometric distortionRemove geometric distortionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterComputer moduleCorrelation function
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com