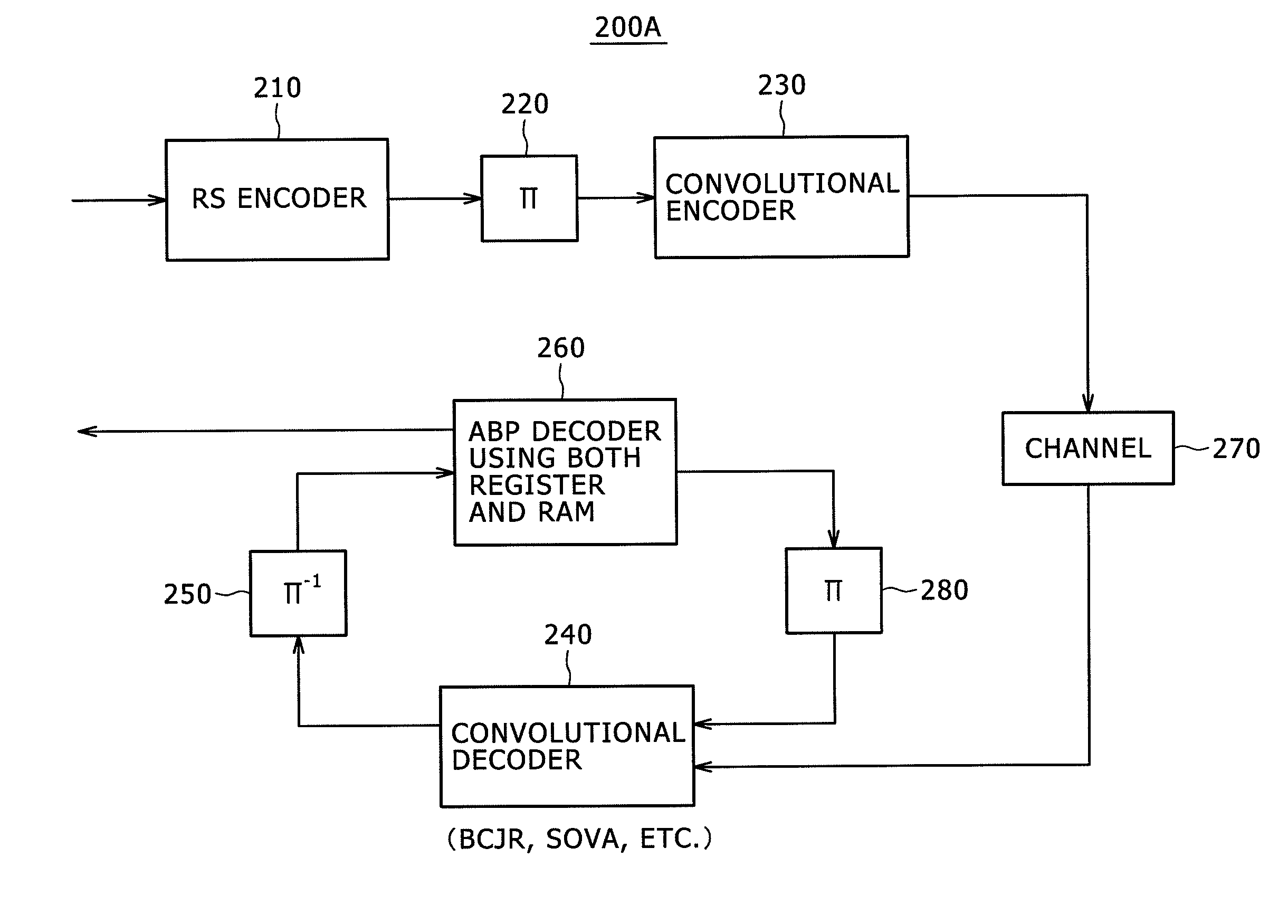
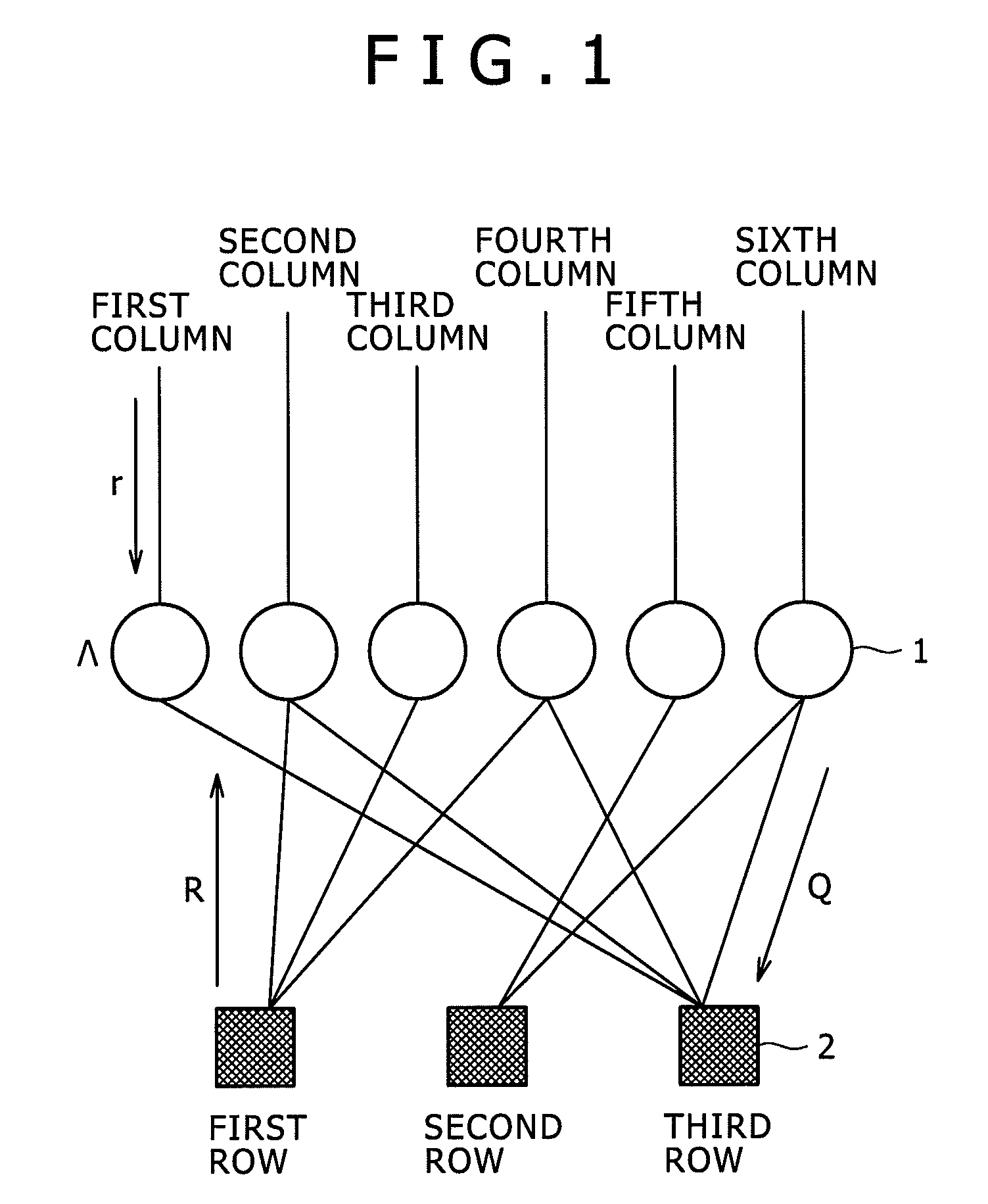
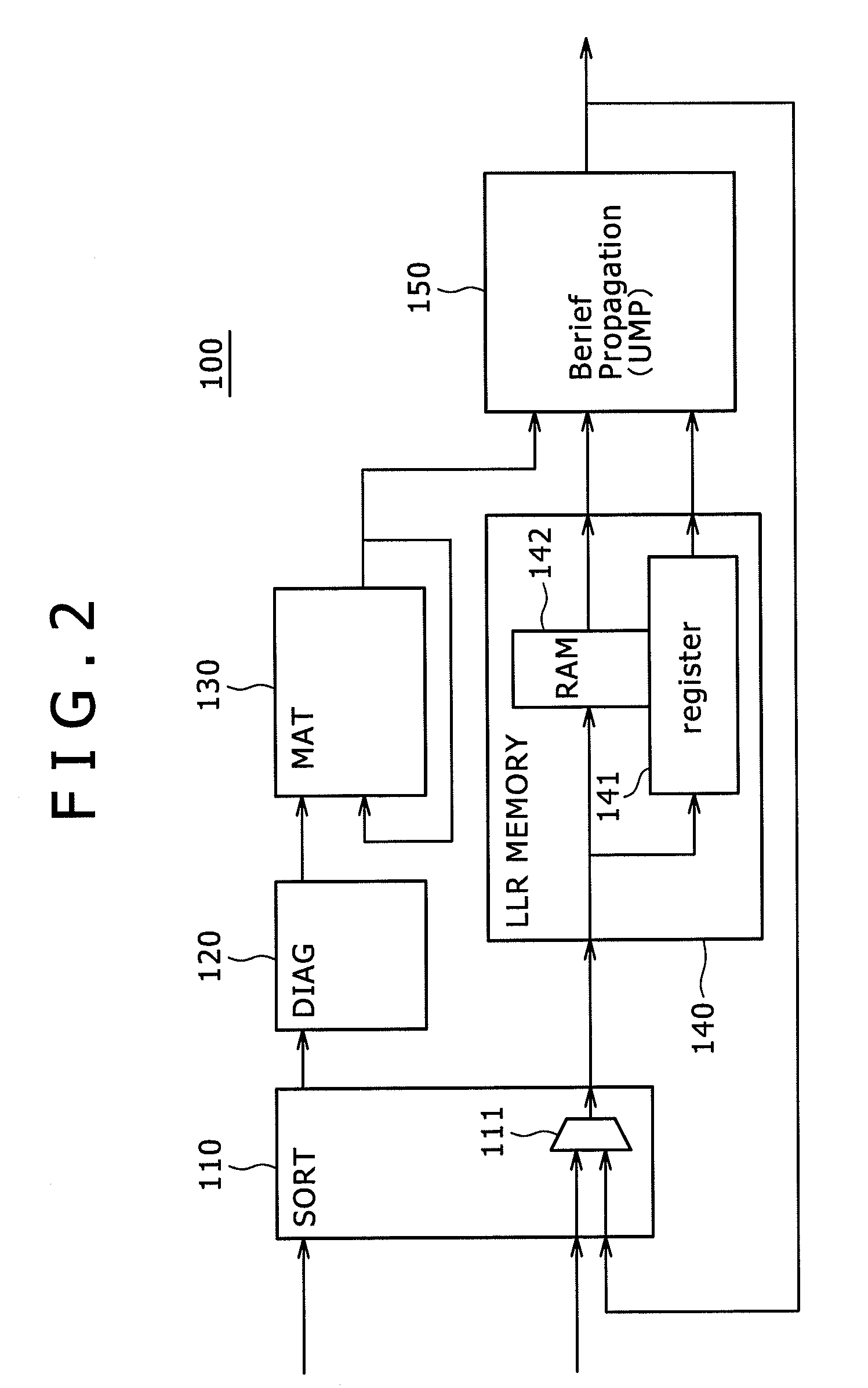
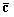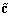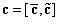Patents
Literature
126 results about "Linear code" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
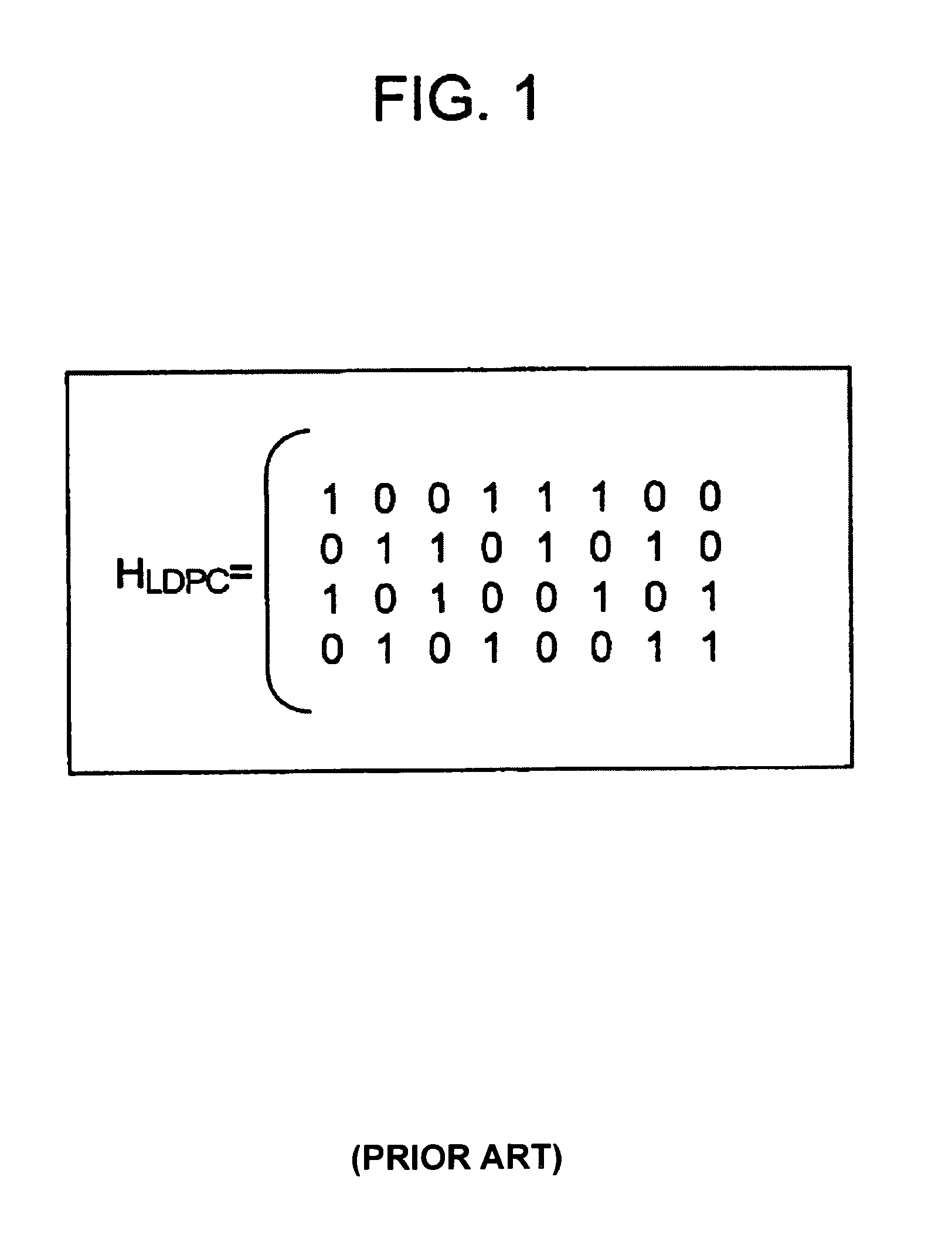
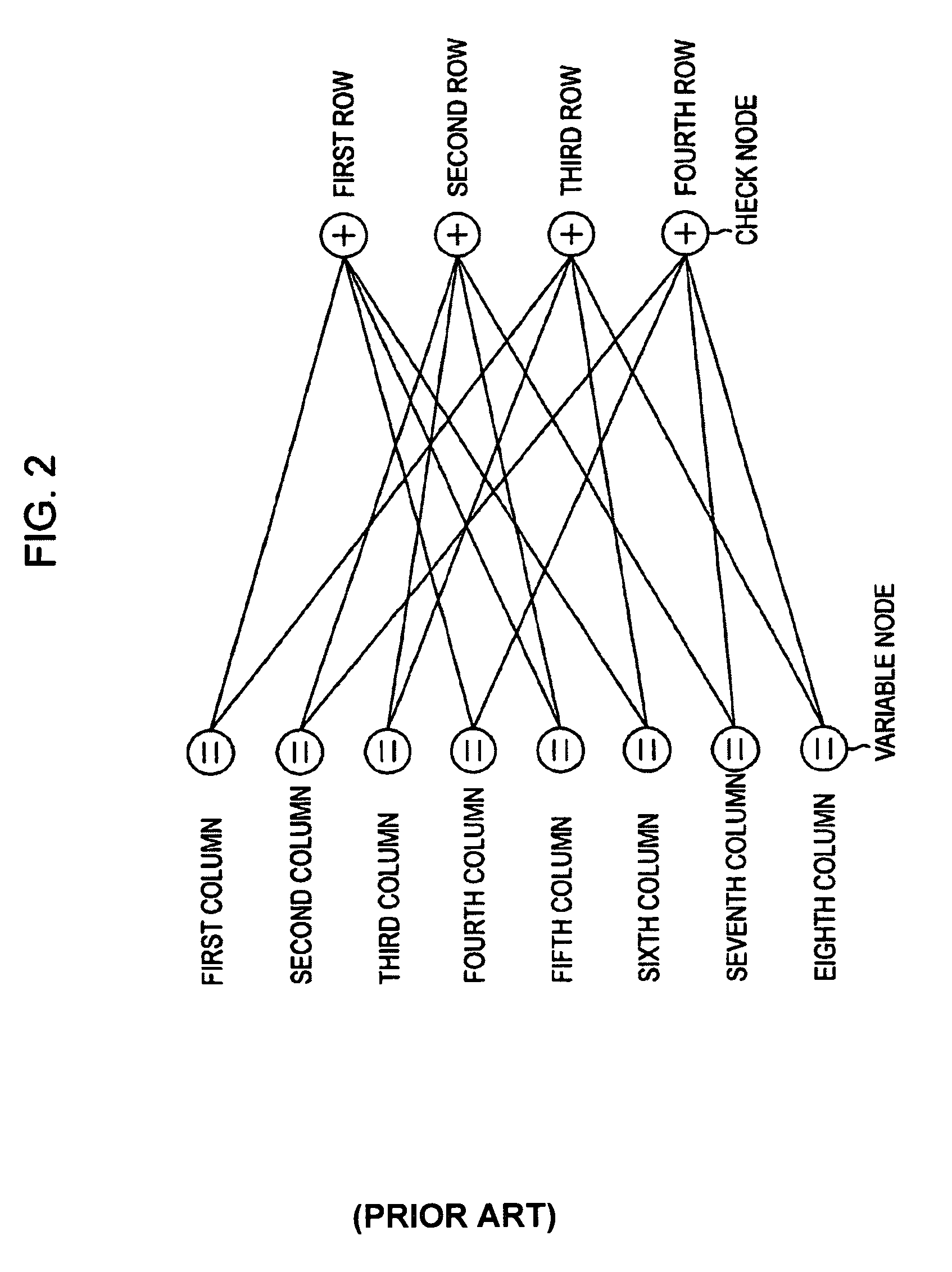
In coding theory, a linear code is an error-correcting code for which any linear combination of codewords is also a codeword. Linear codes are traditionally partitioned into block codes and convolutional codes, although turbo codes can be seen as a hybrid of these two types. Linear codes allow for more efficient encoding and decoding algorithms than other codes (cf. syndrome decoding).
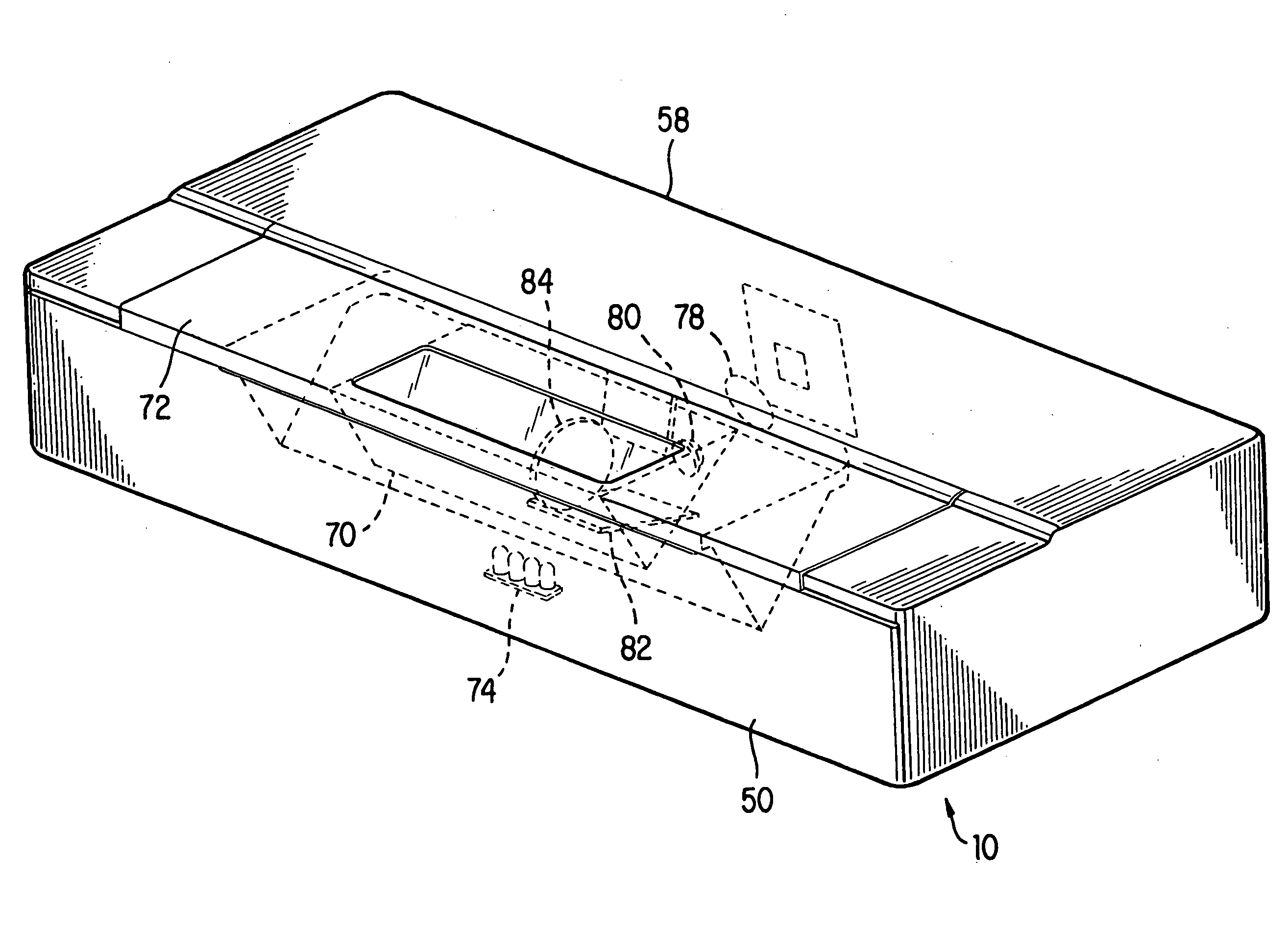
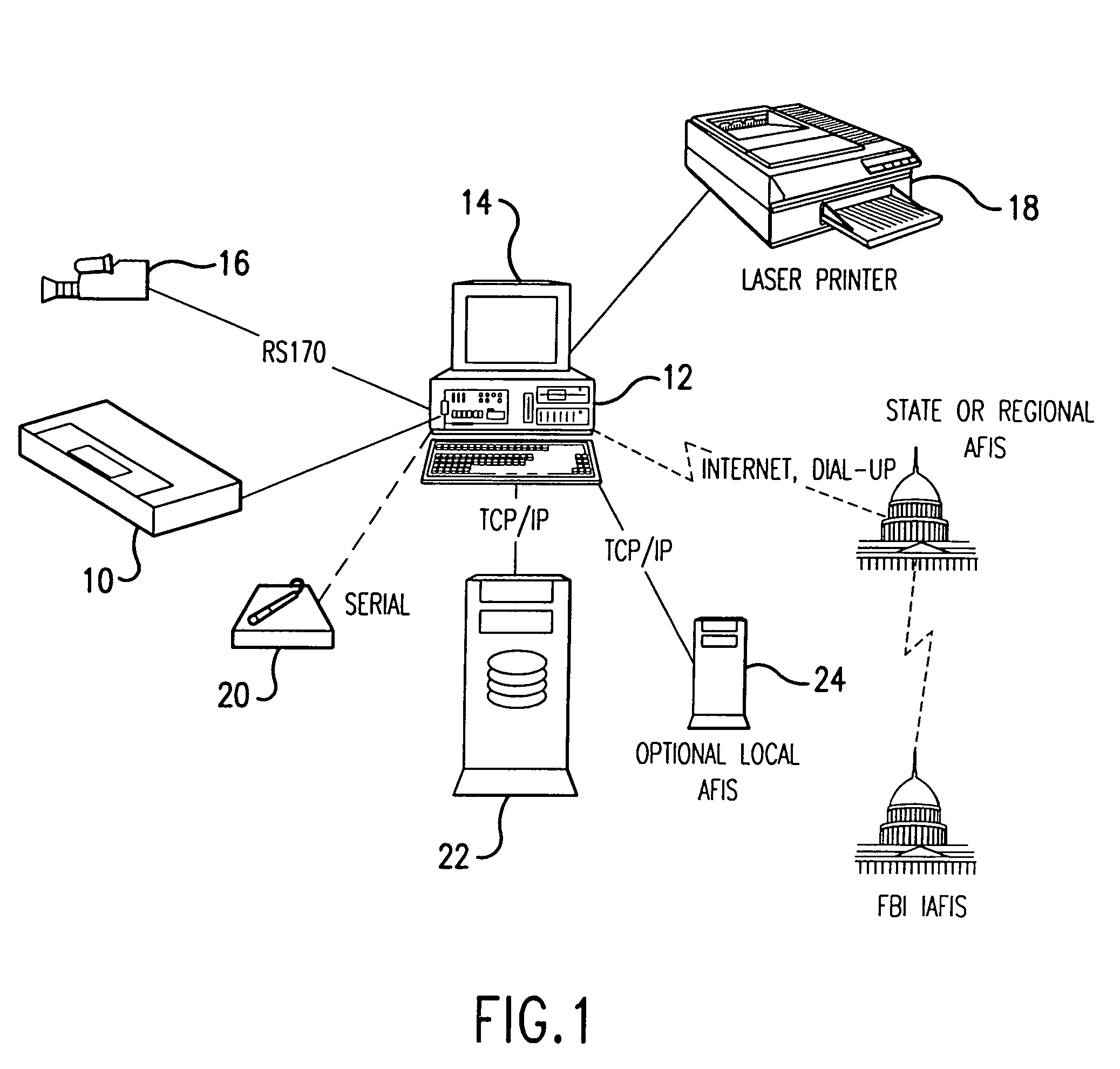
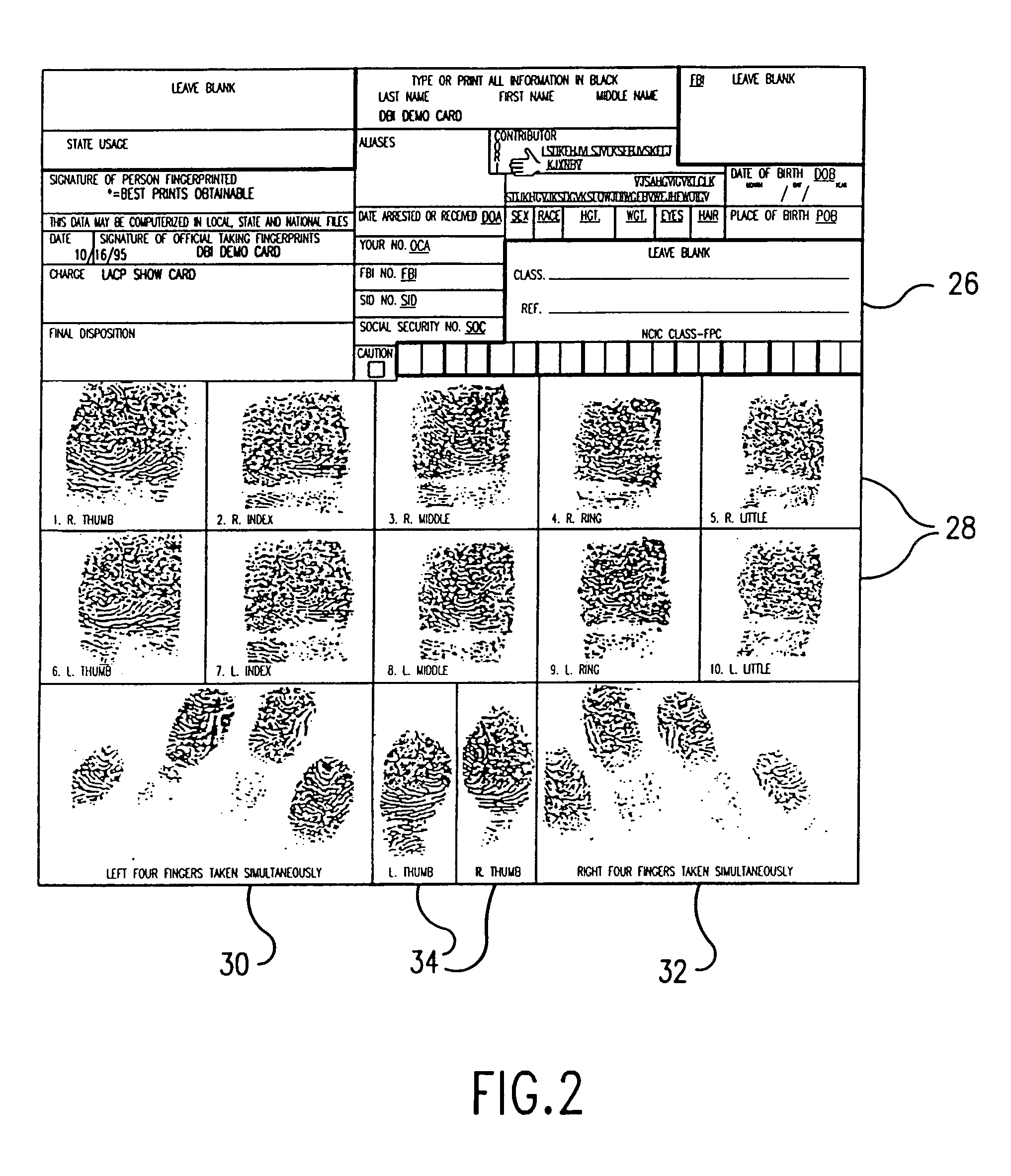
Methods for capturing fingerprint images using a moving platen
InactiveUS20050100196A1Reduce motor costAccurately and repeatable recordCharacter and pattern recognitionPrismFingerprint image
A method and apparatus whereby a fingerprint verifier has a mechanism to slide a prism over an imaged area of a camera. The position of the prism being determined by a binary absolute linear code on a sliding mechanism imaged by the same camera at the side of the fingerprint wherein the images are knitted together to simulate a large CCD.
Owner:CROSS MATCH TECH
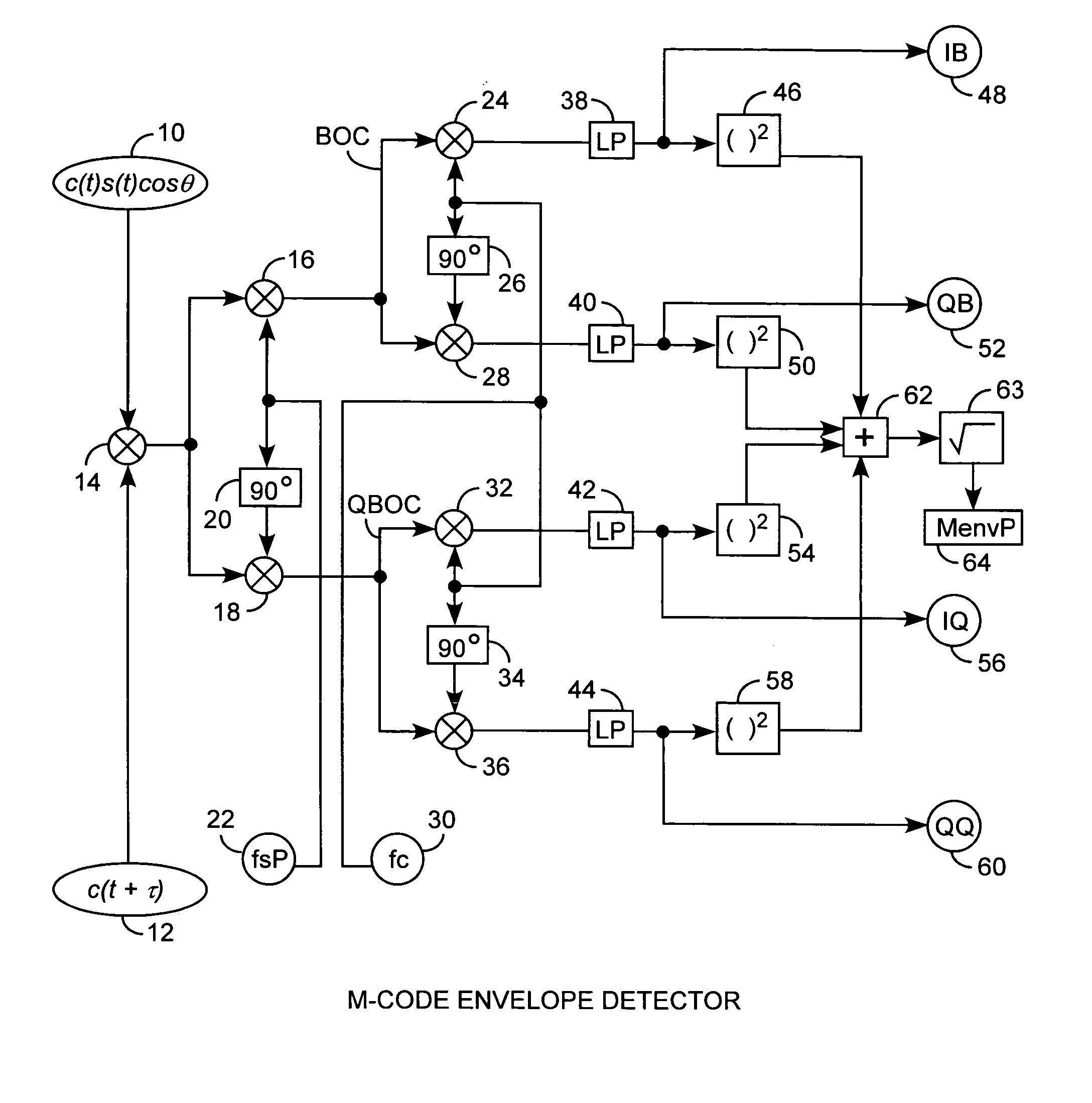
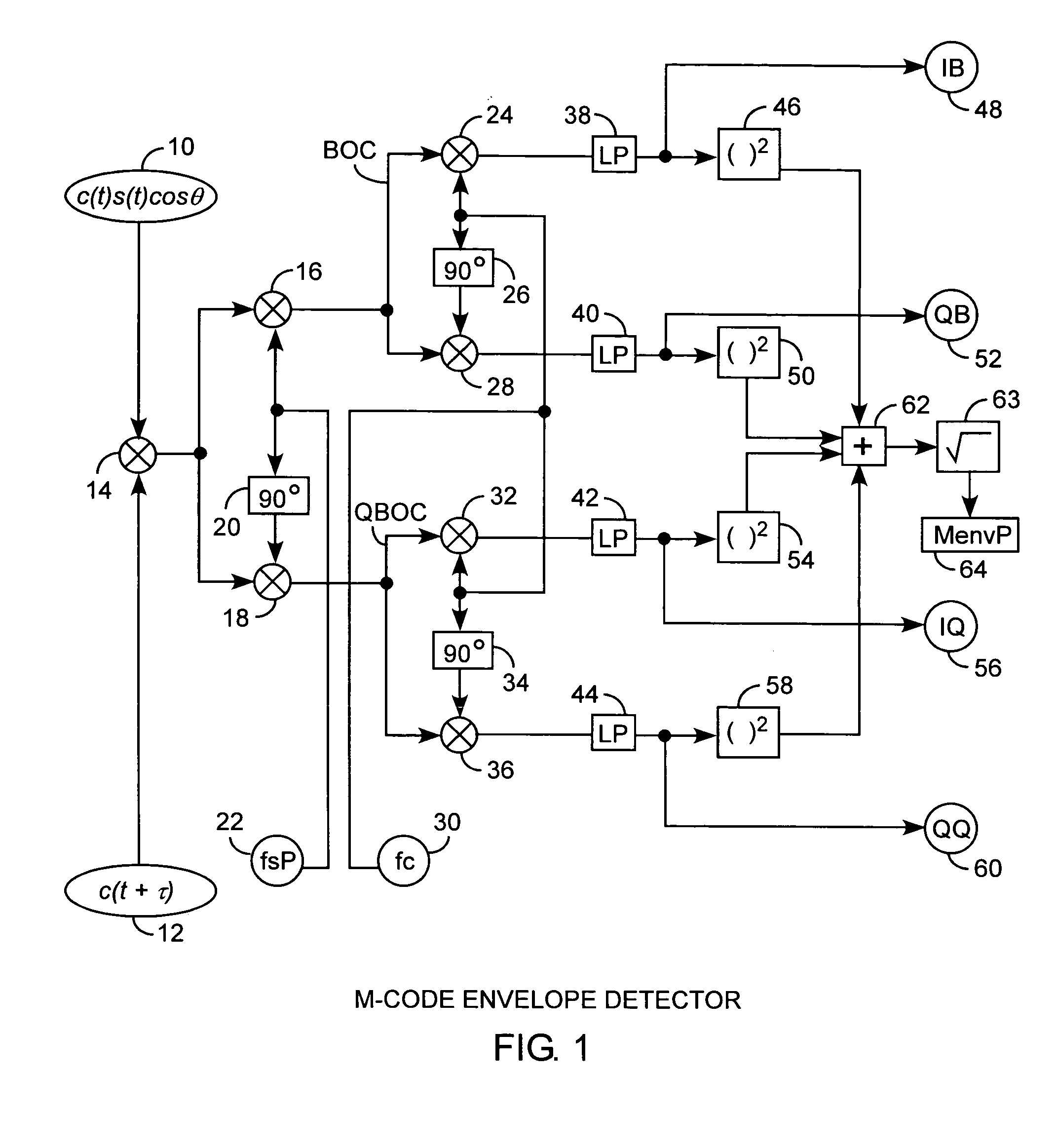
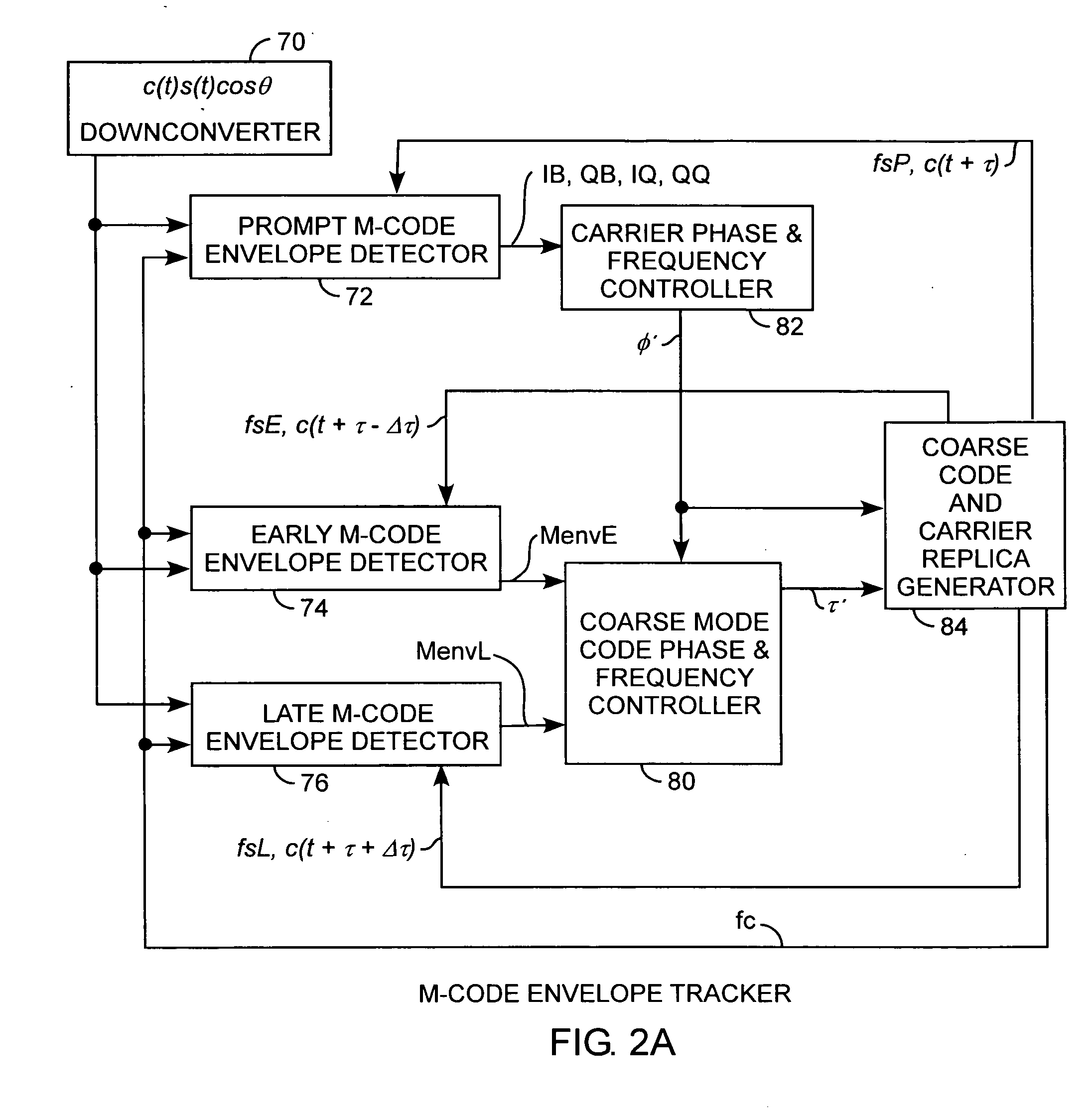
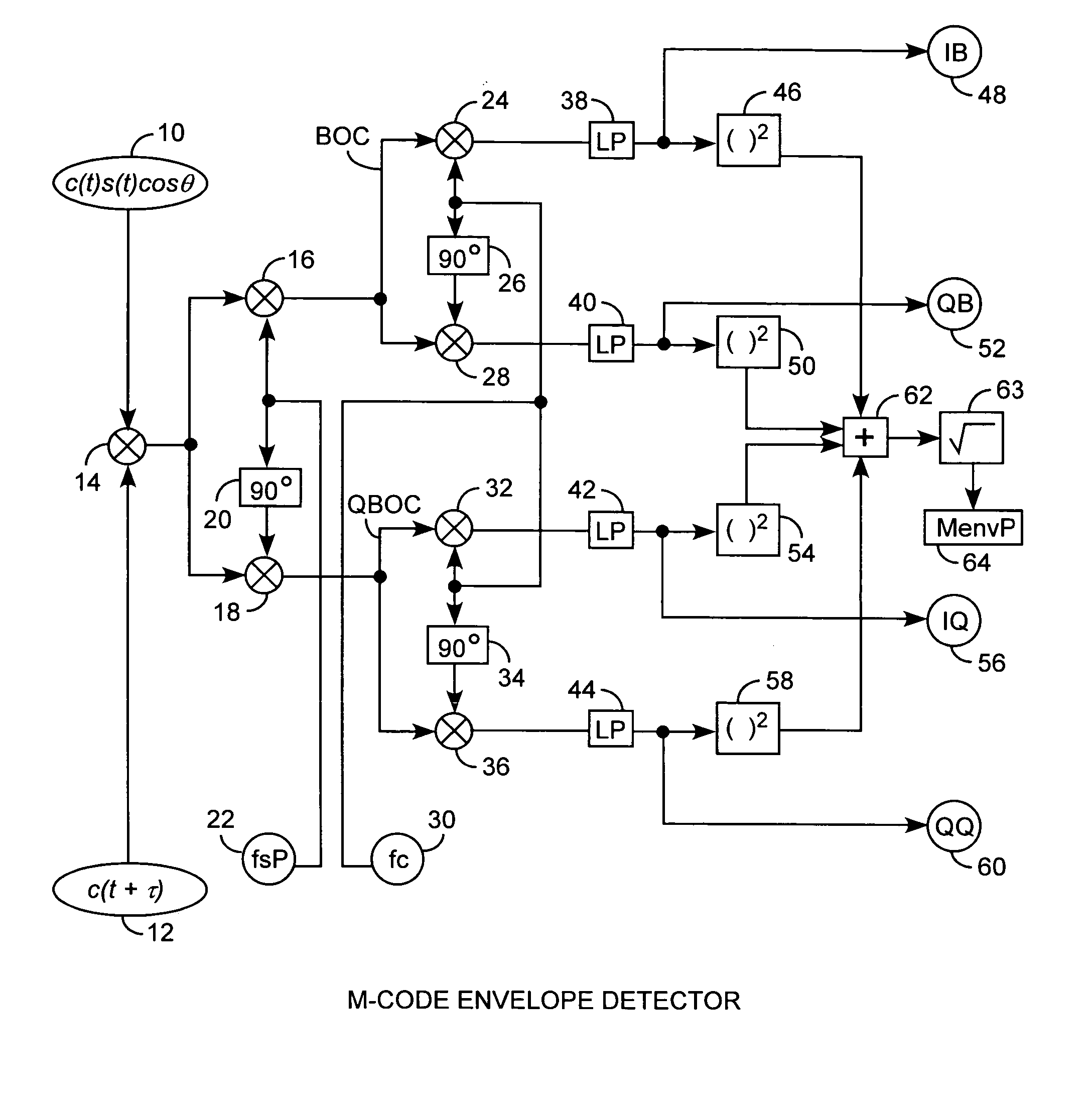
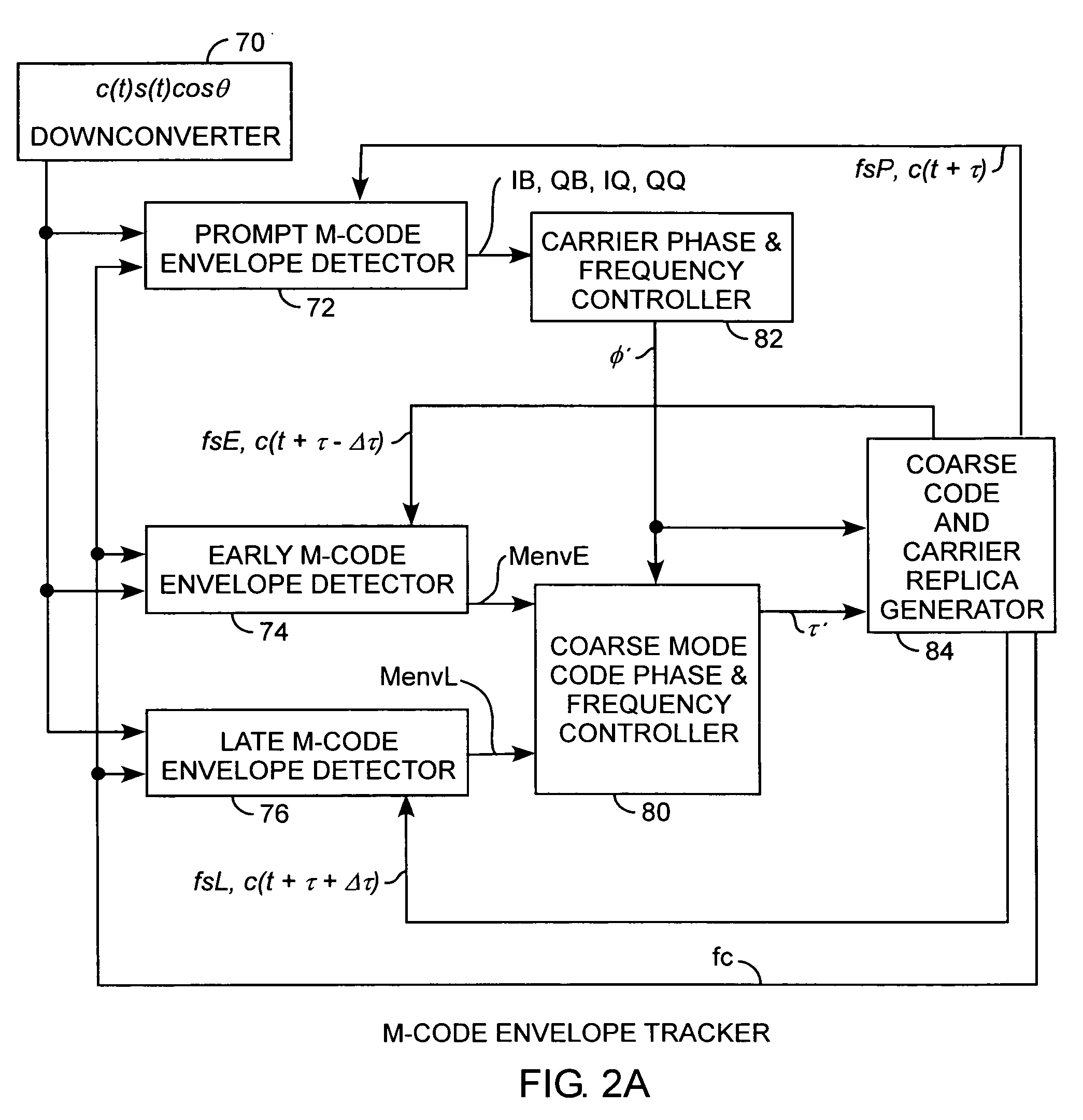
Binary offset carrier M-code envelope detector
ActiveUS20050281325A1Improve acquisitionModulated-carrier systemsBeacon systemsCorrelation functionCode tracking
An M code envelope detector receives an incoming binary offset carrier (BOC) signal, such as the M code signal, and generates inphase BOC and quadraphase BOC signals, separated by an offset, that have respective ambiguous correlation envelopes, that when combined, provide a near unimodal correlation function with respect to code phase error of the BOC signal having an inherent multimodal autocorrelation function, with the near unimodal correlation envelope being tracked by early and late code replicas at broad one chip phases for providing unambiguous but nonlinear code phase error tracking, which detector is then further improved with the use of code replicas having narrow partial chip phases, such as ⅛ chip phases, for providing near linear code phase error tracking for unambiguous and accurate code tracking of the BOC signal.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
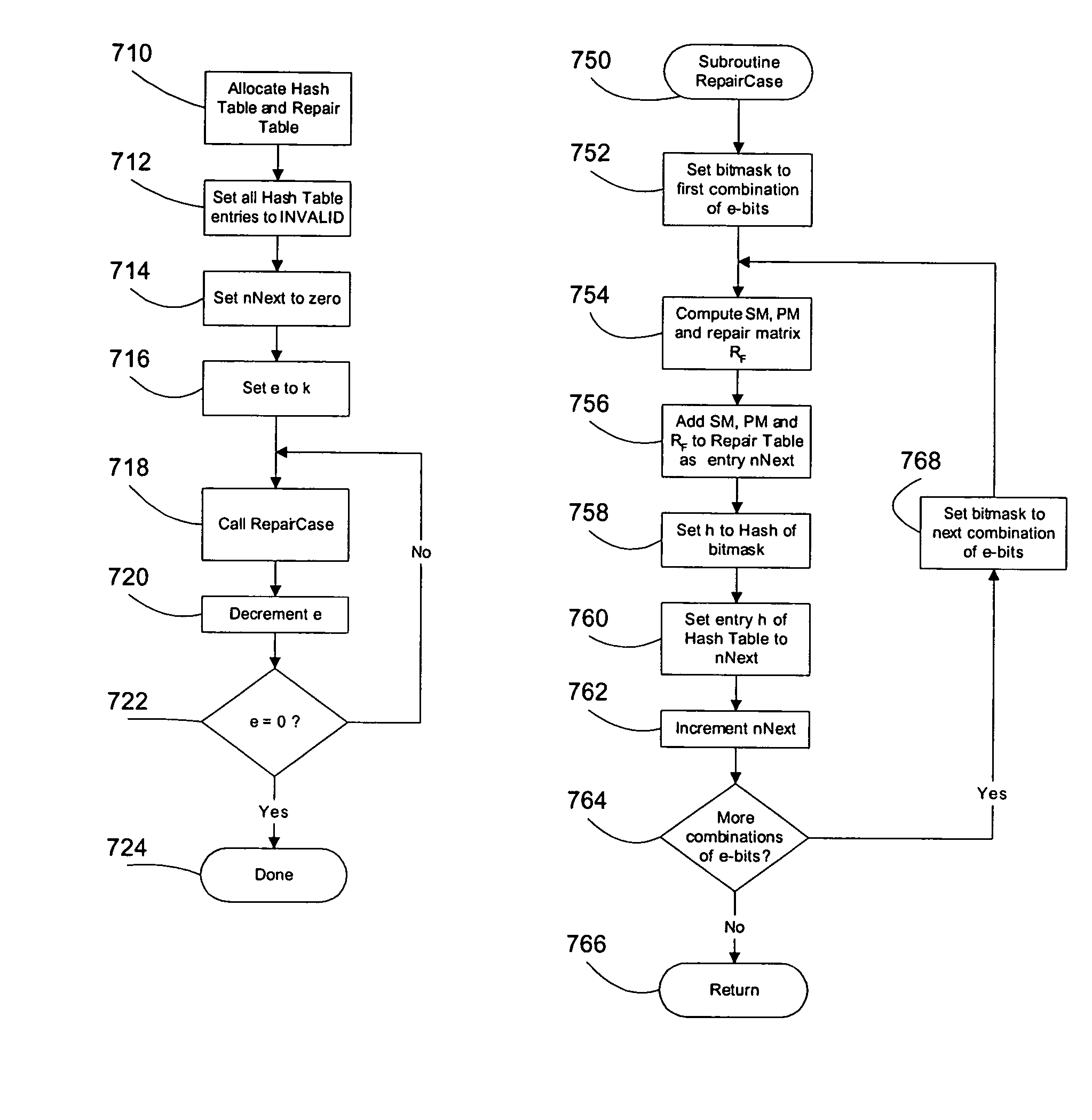
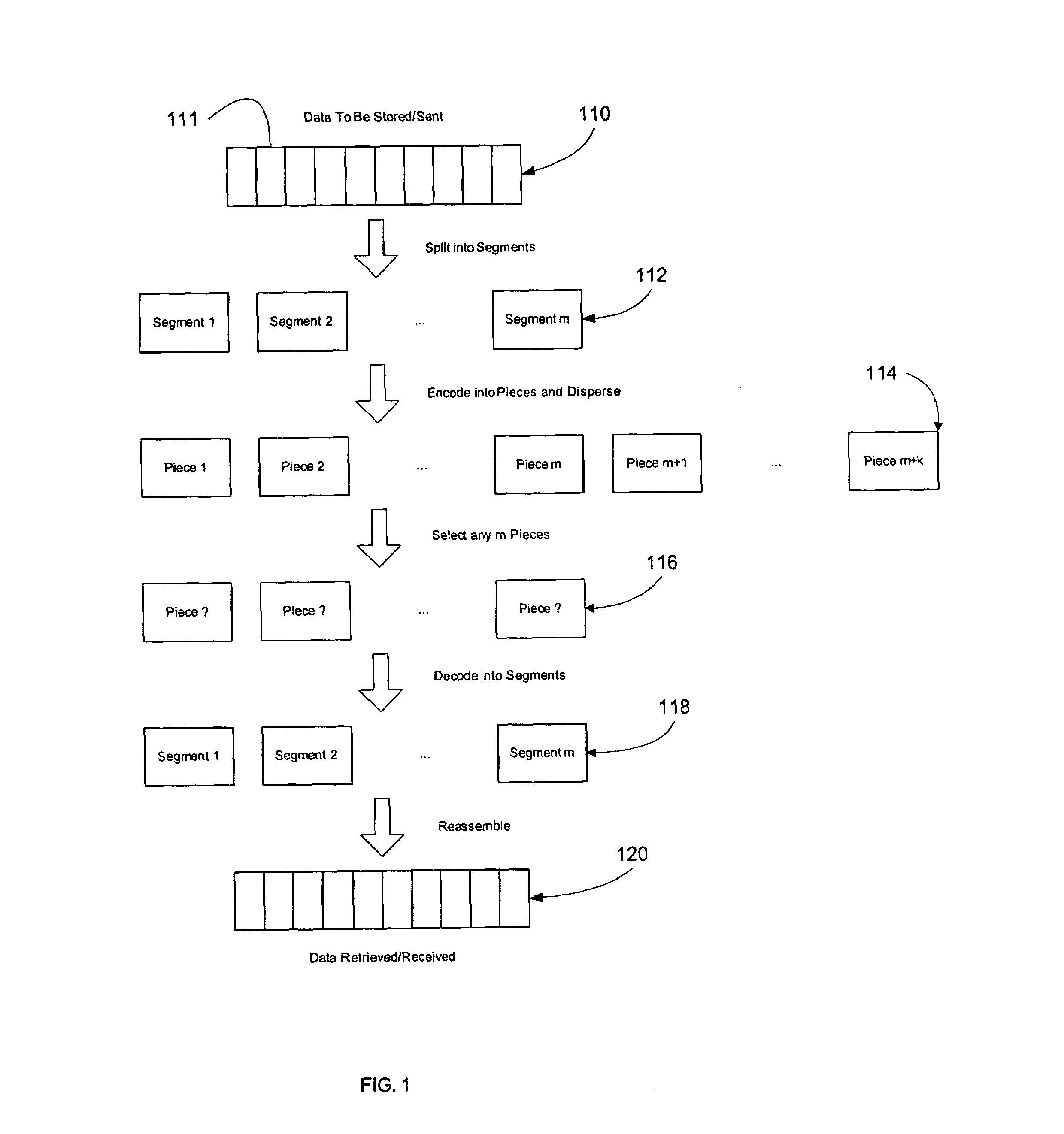
Efficient method for the reconstruction of digital information
InactiveUS7472334B1Improve decoding performanceImprove encoding performanceCode conversionCoding detailsLinear codingTheoretical computer science
Improved method of encoding and repairing data for reliable storage and transmission using erasure codes, which is efficient enough for implementation in software as well as hardware. A systematic linear coding matrix over GF(2q) is used which combines parity for fast correction of single erasures with the capability of correcting k erasures. Finite field operations involving the coding and repair matrices are redefined to consist of bitwise XOR operations on words of arbitrary length. The elements of the matrix are selected to reduce the number of XOR operations needed and buffers are aligned for optimal processor cache efficiency. Decode latency is reduced by pre-calculating repair matrices, storing them in a hashed table and looking them up using a bit mask identifying the erasures to be repaired.
Owner:SCOTT THOMAS P +1
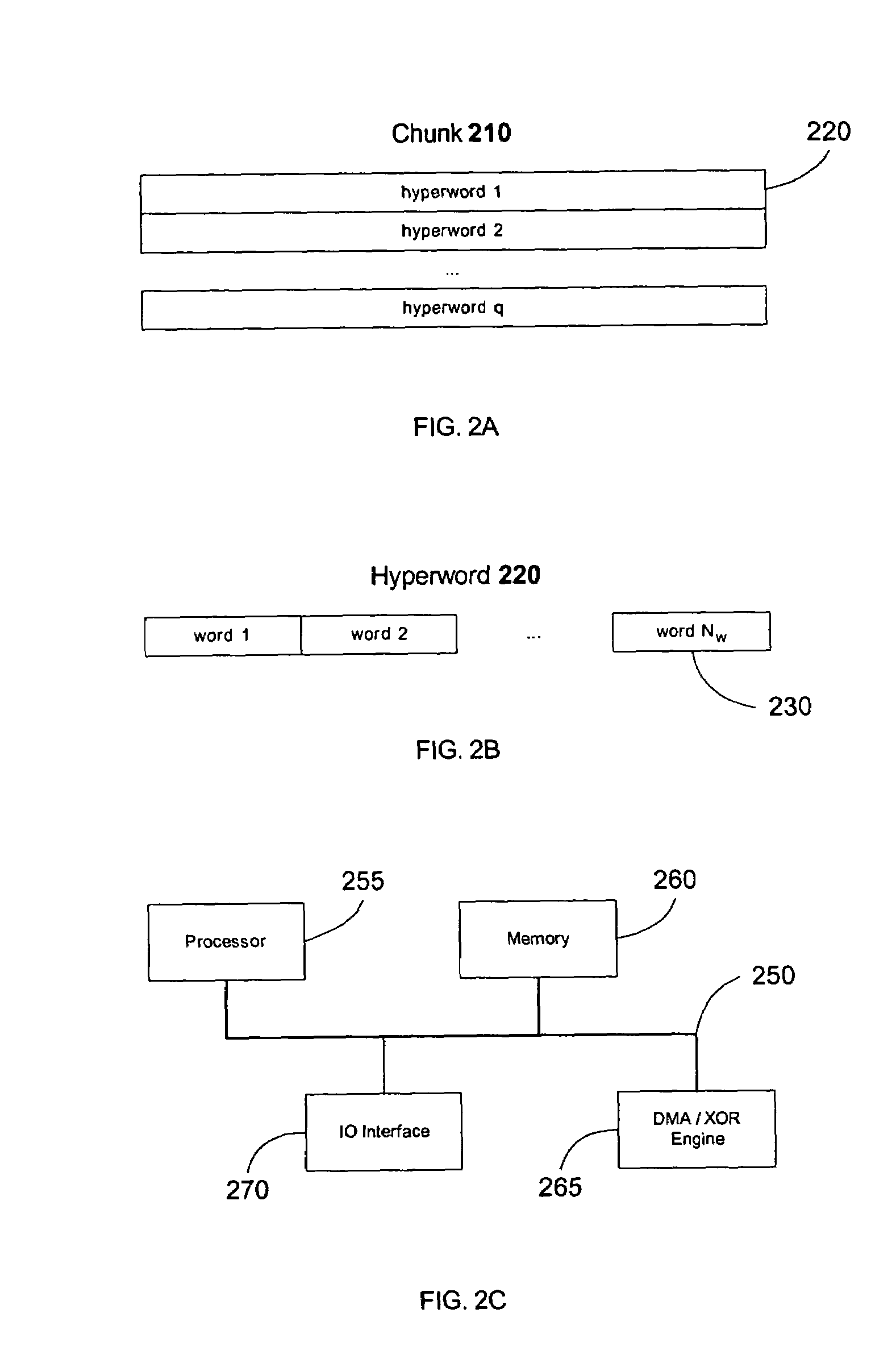
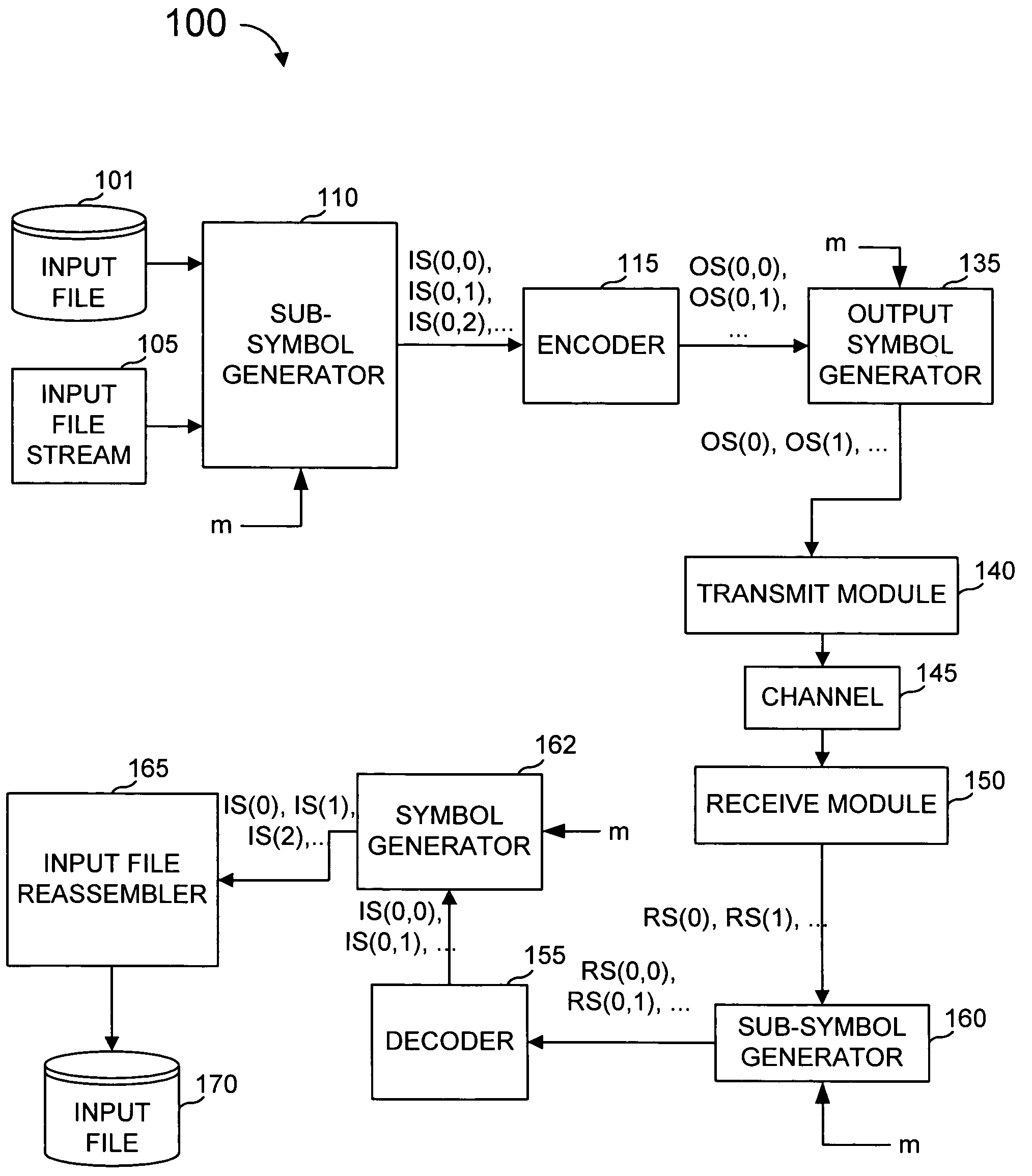
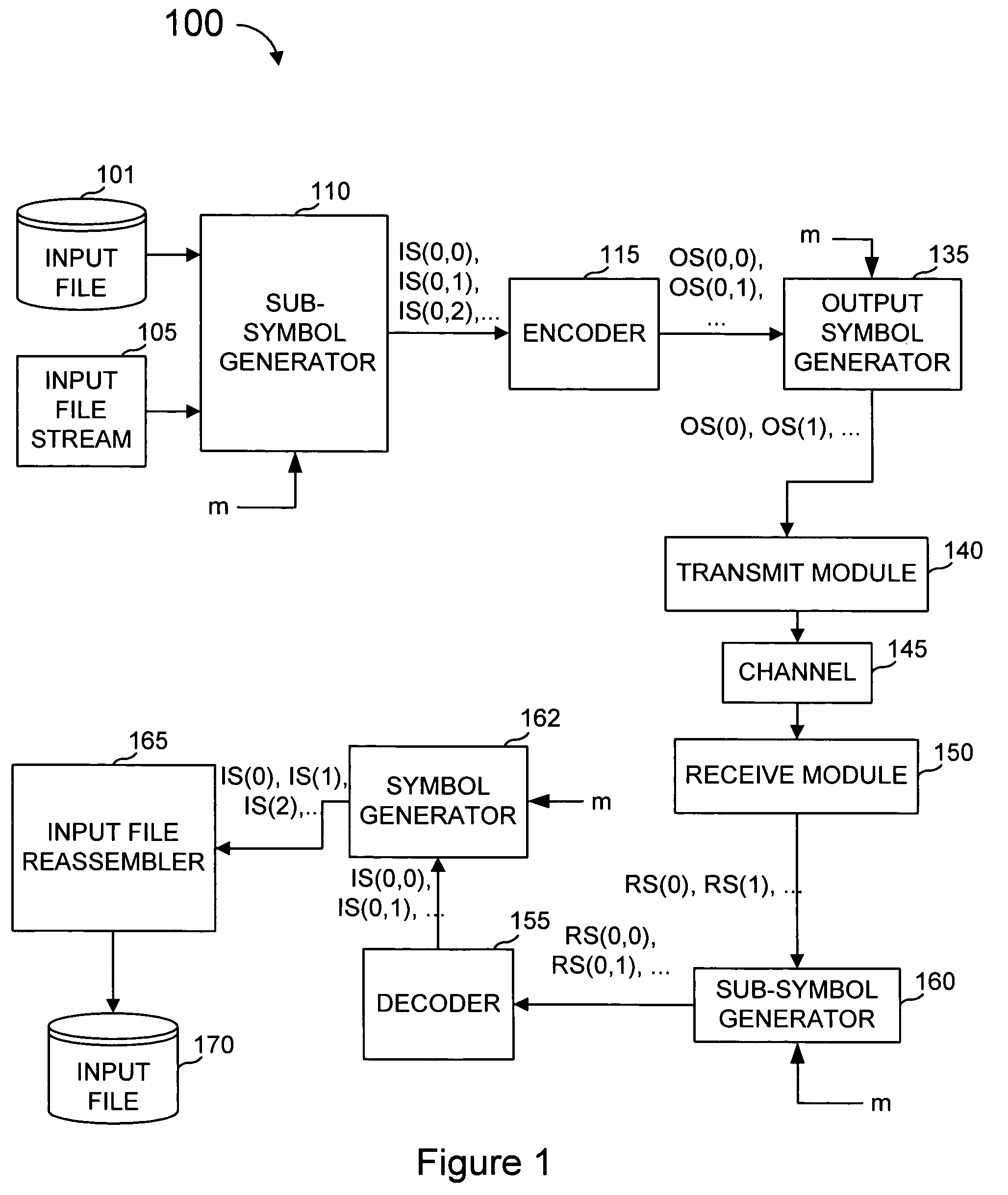
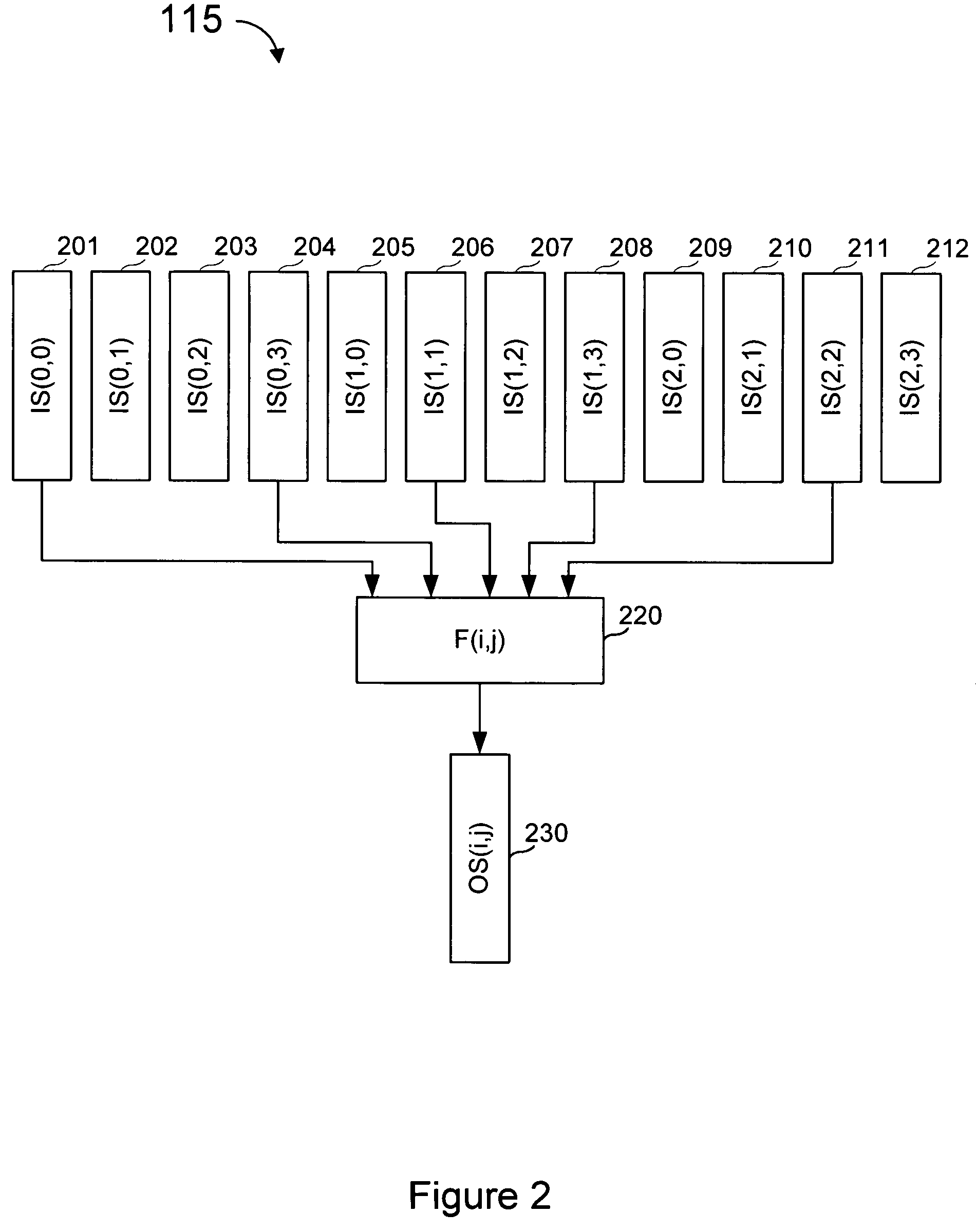
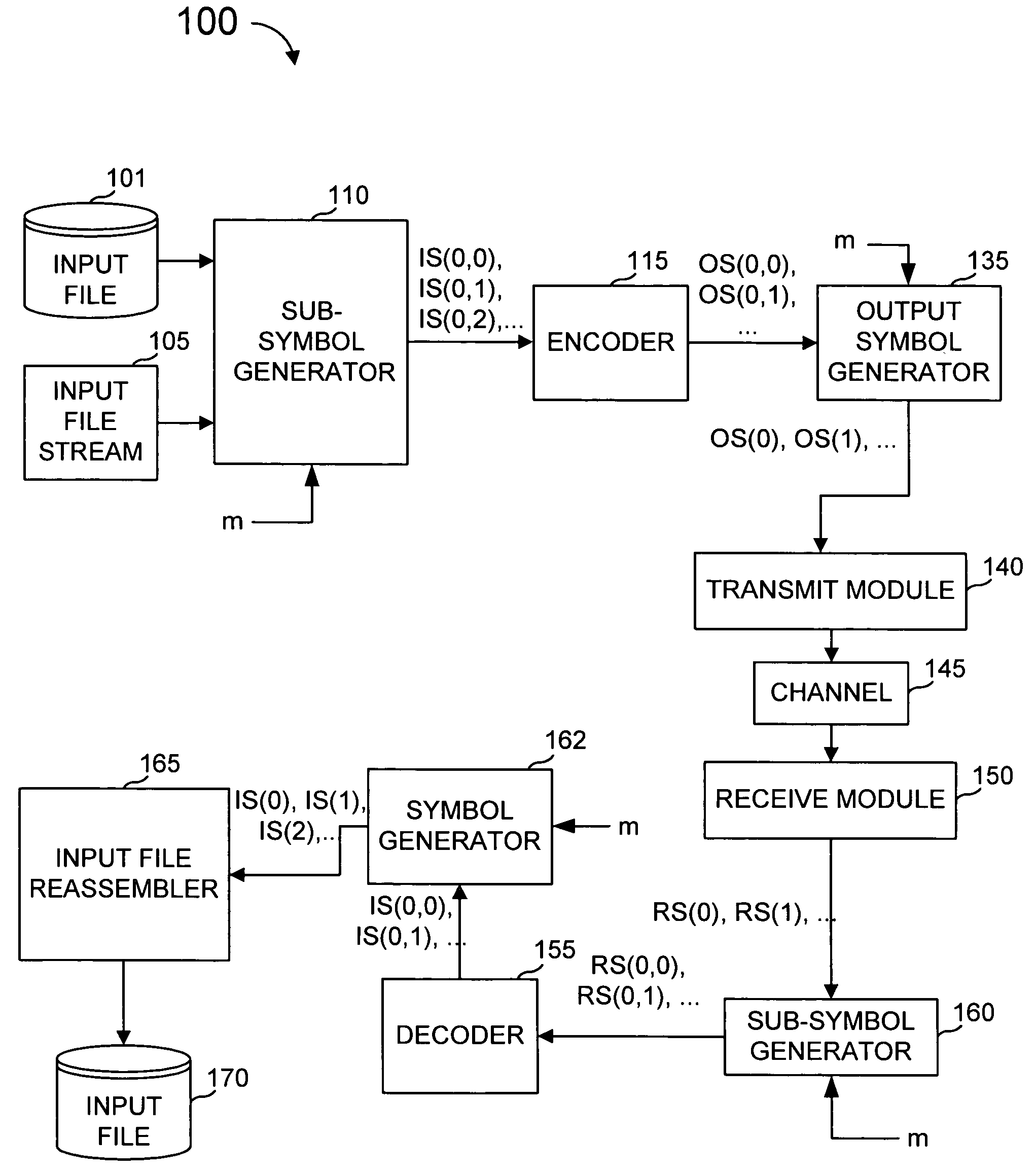
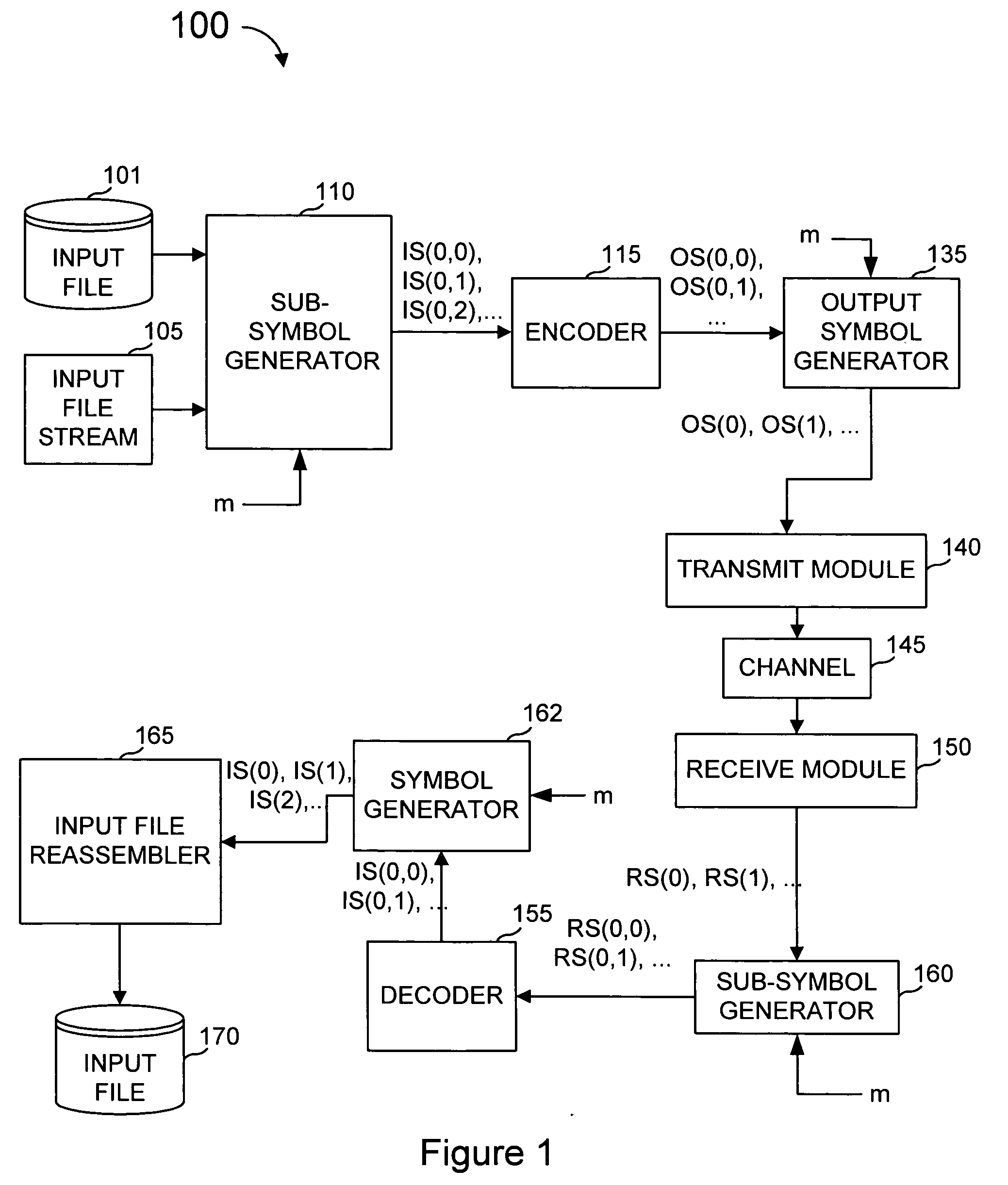
Protection of data from erasures using subsymbol based codes
ActiveUS7412641B2Reduce effortOverhead costDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionBase codeAlgorithm
An encoder uses output symbol subsymbols to effect or control a tradeoff of computational effort and overhead efficiency to, for example, greatly reduce computational effort for the cost of a small amount of overhead efficiency. An encoder reads an ordered plurality of input symbols, comprising an input file or input stream, and produces output subsymbol. The ordered plurality of input symbols are each selected from an input alphabet, and the generated output subsymbols comprise selections among an output subsymbol alphabet. An output subsymbol is generated using a function evaluator applied to subsymbols of the input symbols. The encoder may be called one or more times, each time producing an output subsymbol. Output subsymbols can then be assembled into output symbols and transmitted to their destination. The functions used to generate the output subsymbols from the input subsymbols can be XOR's of some of the input subsymbols and these functions are obtained from a linear code defined over an extension field of GF(2) by transforming each entry in a generator or parity-check matrix of this code into an appropriate binary matrix using a regular representation of the extension field over GF(2). In a decoder, output subsymbols received by the recipient are obtained from output symbols transmitted from one sender that generated those output symbols based on an encoding of an input sequence (file, stream, etc.).
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
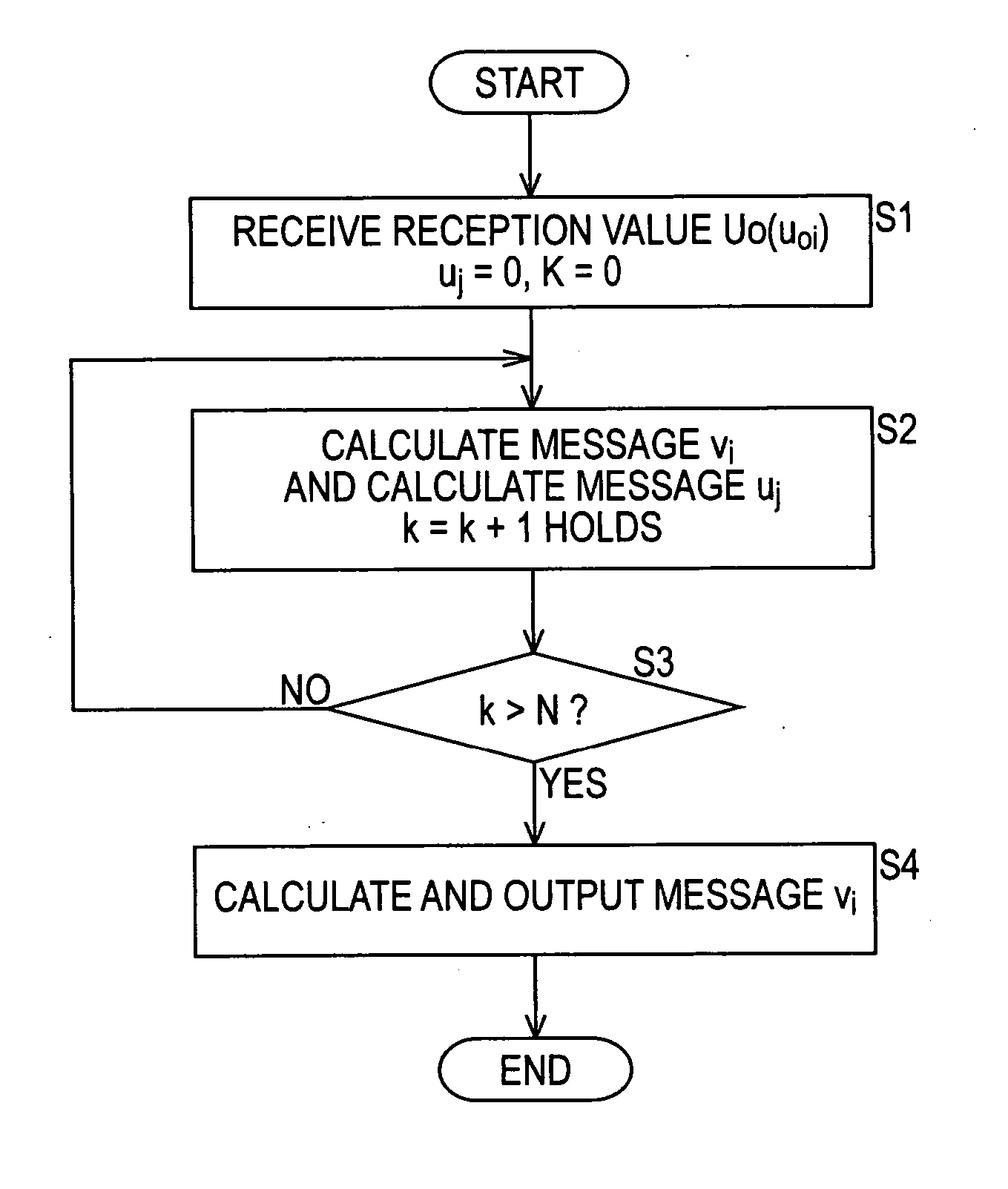
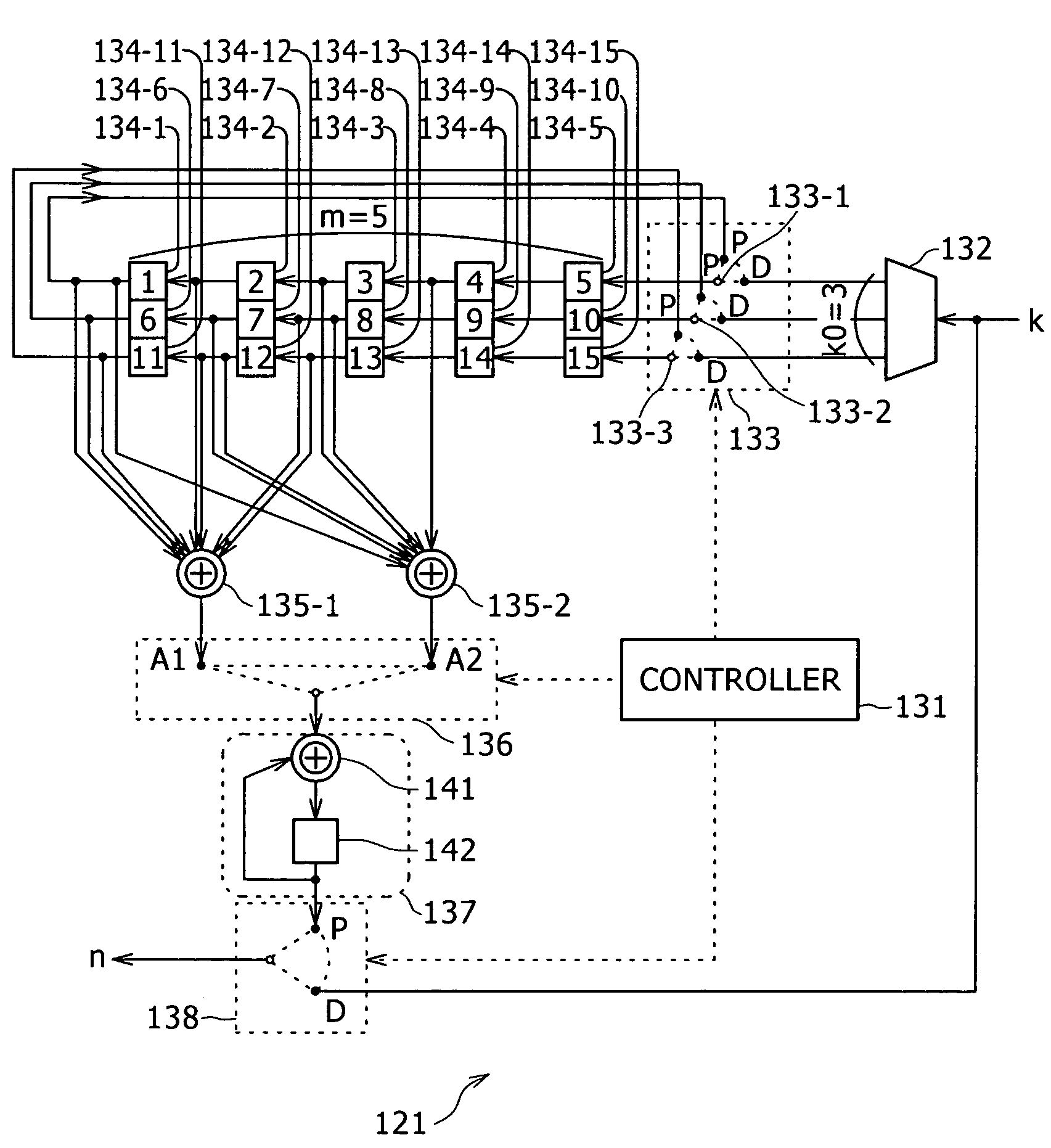
Decoding method, decoding device, program, recording/reproduction device and method, and reproduction device and method
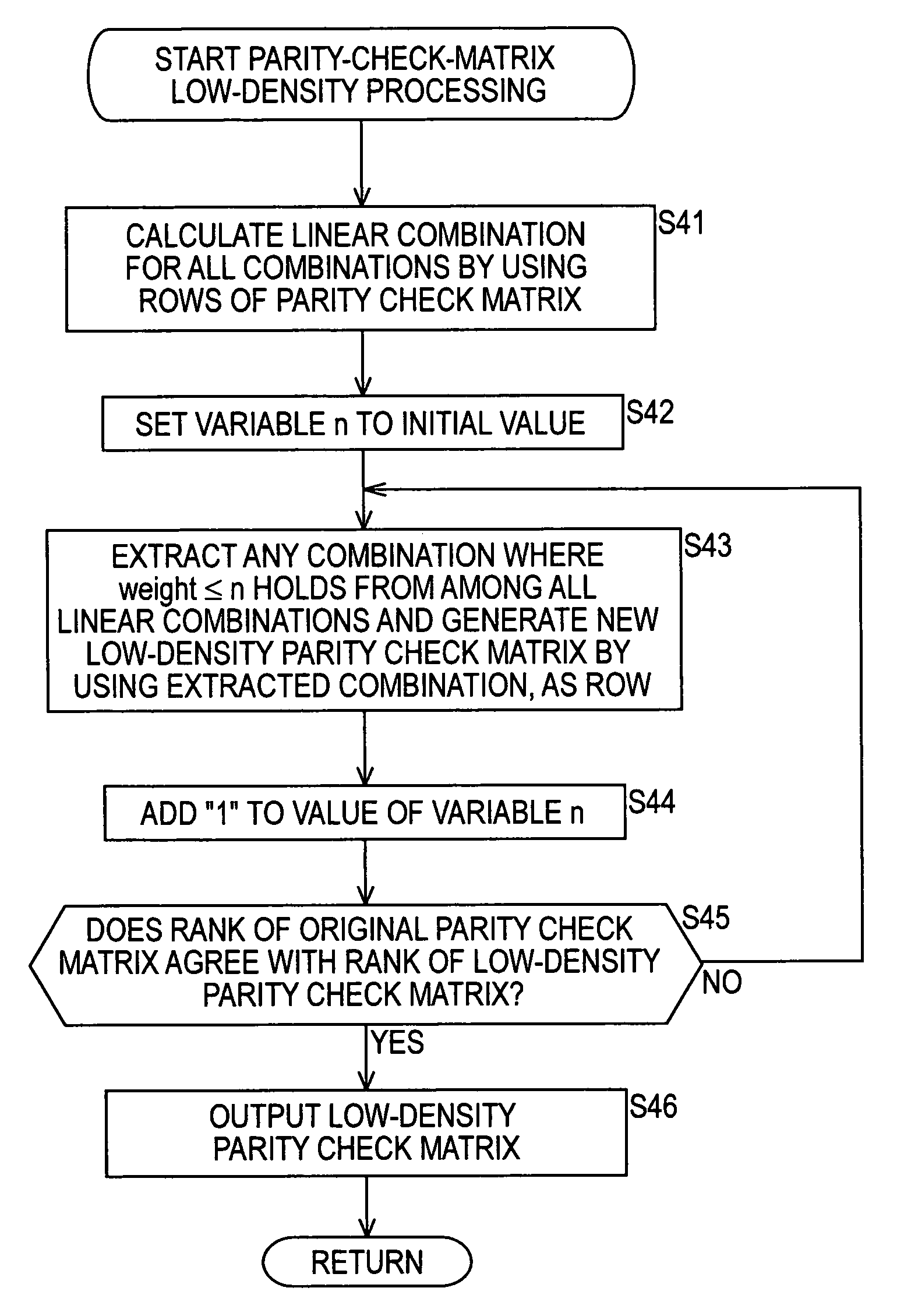
InactiveUS20060015791A1Easily performing high-performance decodingEasy to implementError detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsDecoding methodsParity-check matrix
The present invention relates to a decoding method and a decoder, a program, a recording-and-reproducing apparatus and a method, and a reproducing apparatus and a method that are suitable for decoding encoded data encoded by using a linear code on ring R. A low-density processing unit performs parity-check-matrix low-density processing, performs linear combination for rows of a parity check matrix included in an obtained reception word, and generates a parity check matrix according to the linear-combination result, thereby reducing the density of the parity check matrix used for decoding, at step S21. Then, at step S22, an LDPC decoding unit performs decoding by using a sum product algorithm (SPA) by using the parity check matrix whose density is reduced through the processing performed at step S21. Where the processing at step S22 is finished, the LDPC decoding unit finishes decoding for the reception word. The present invention can be used for an error-correction system.
Owner:SONY CORP
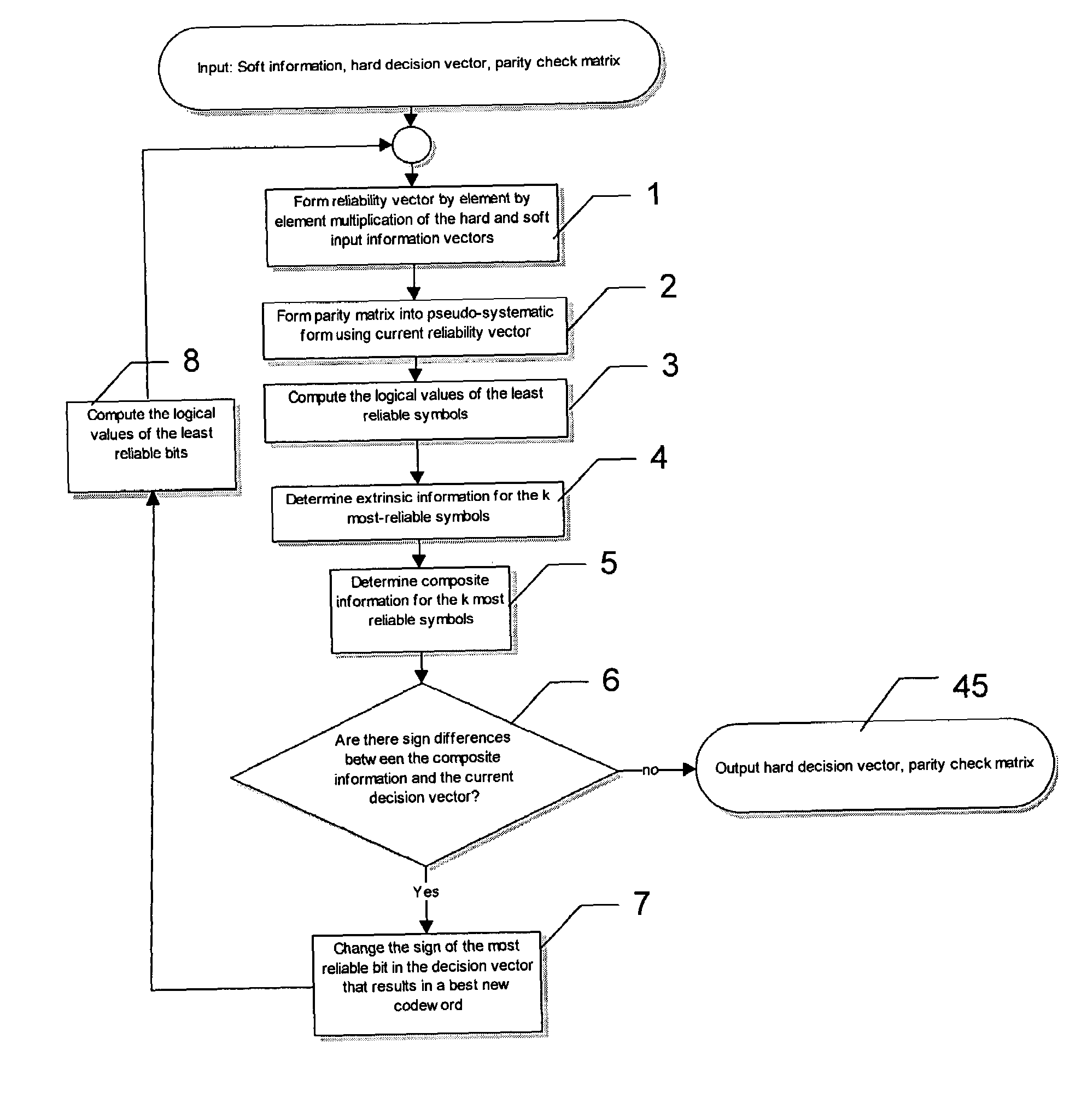
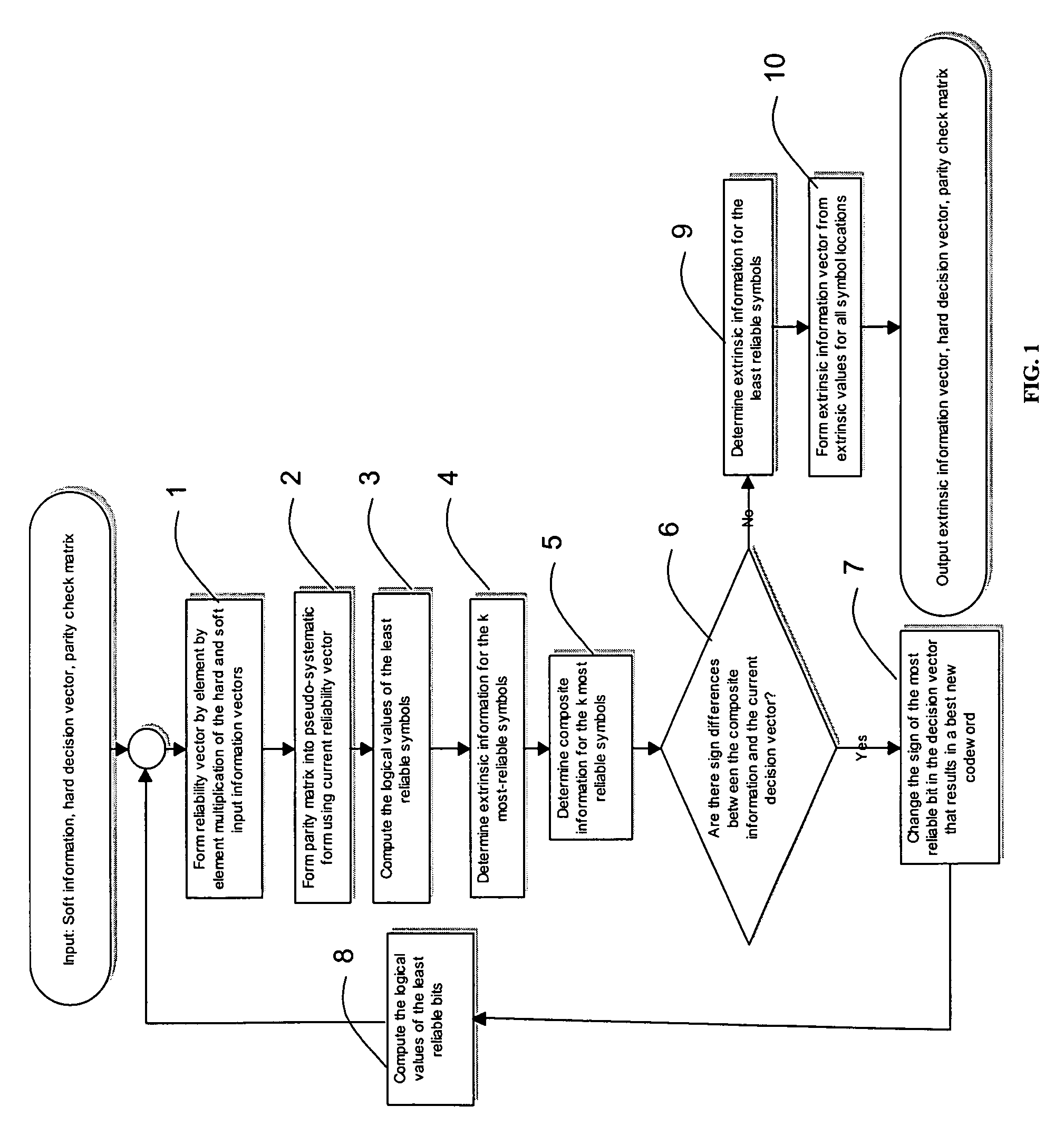
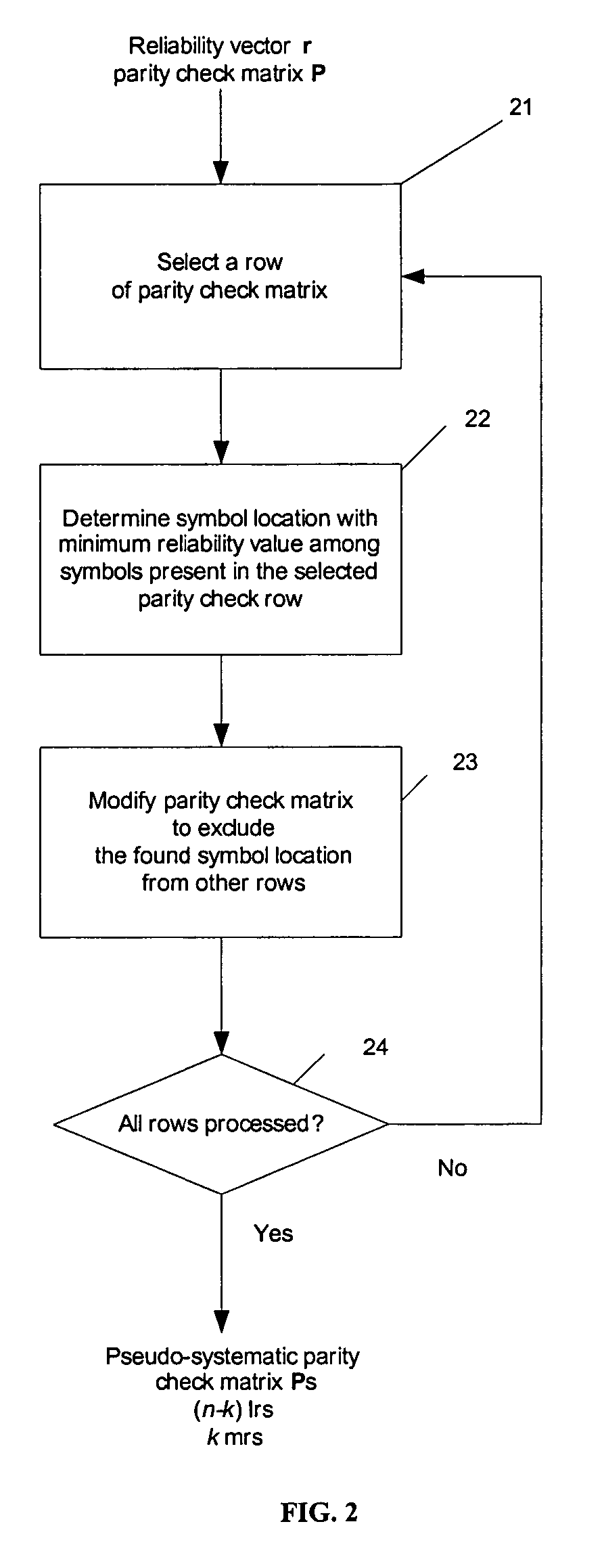
Soft input decoding for linear codes
ActiveUS7203893B2Non-binary linear block codesOther decoding techniquesParity-check matrixTheoretical computer science
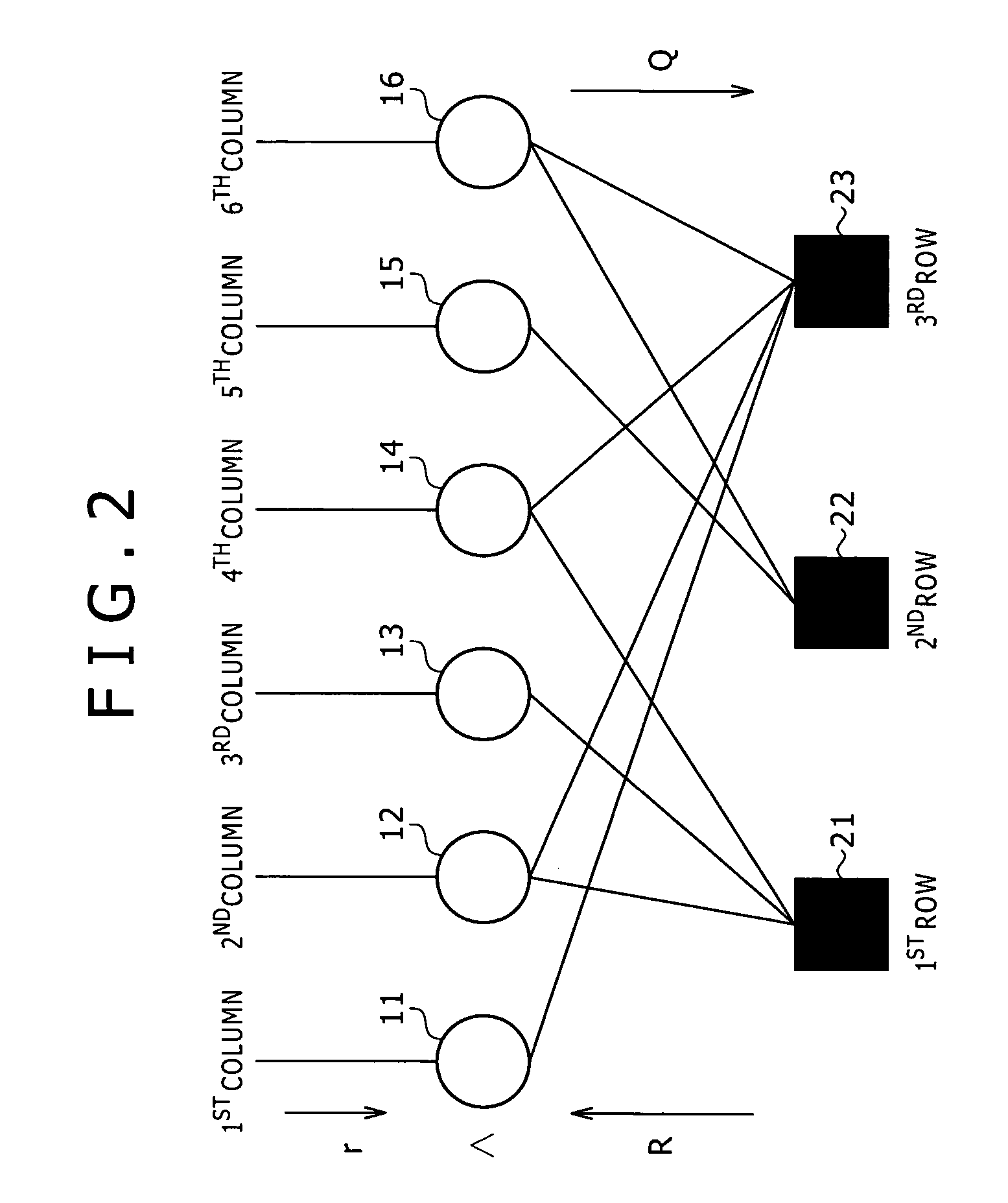
A method of decoding soft input information related to a transmitted word of a linear block code (n, k) and providing hard or soft output information is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of forming a reliability vector from the input information, identifying (n−k) linearly independent least reliable symbols and k most reliable symbols, converting a parity check matrix of the linear block code to a pseudo-systematic form with respect to the least reliable symbols, calculating extrinsic information and composite information for the most reliable symbols using the soft input information and the pseudo-systematic parity check matrix, and calculating extrinsic information for the least reliable systems using composite information for the most reliable symbols.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
Protection of data from erasures using subsymbol based codes
ActiveUS20050219070A1Reduce the amount of calculationOverhead costDigital data processing detailsError detection/correctionBase codeAlgorithm
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Electroluminescent display initial-nonuniformity-compensated drive signal
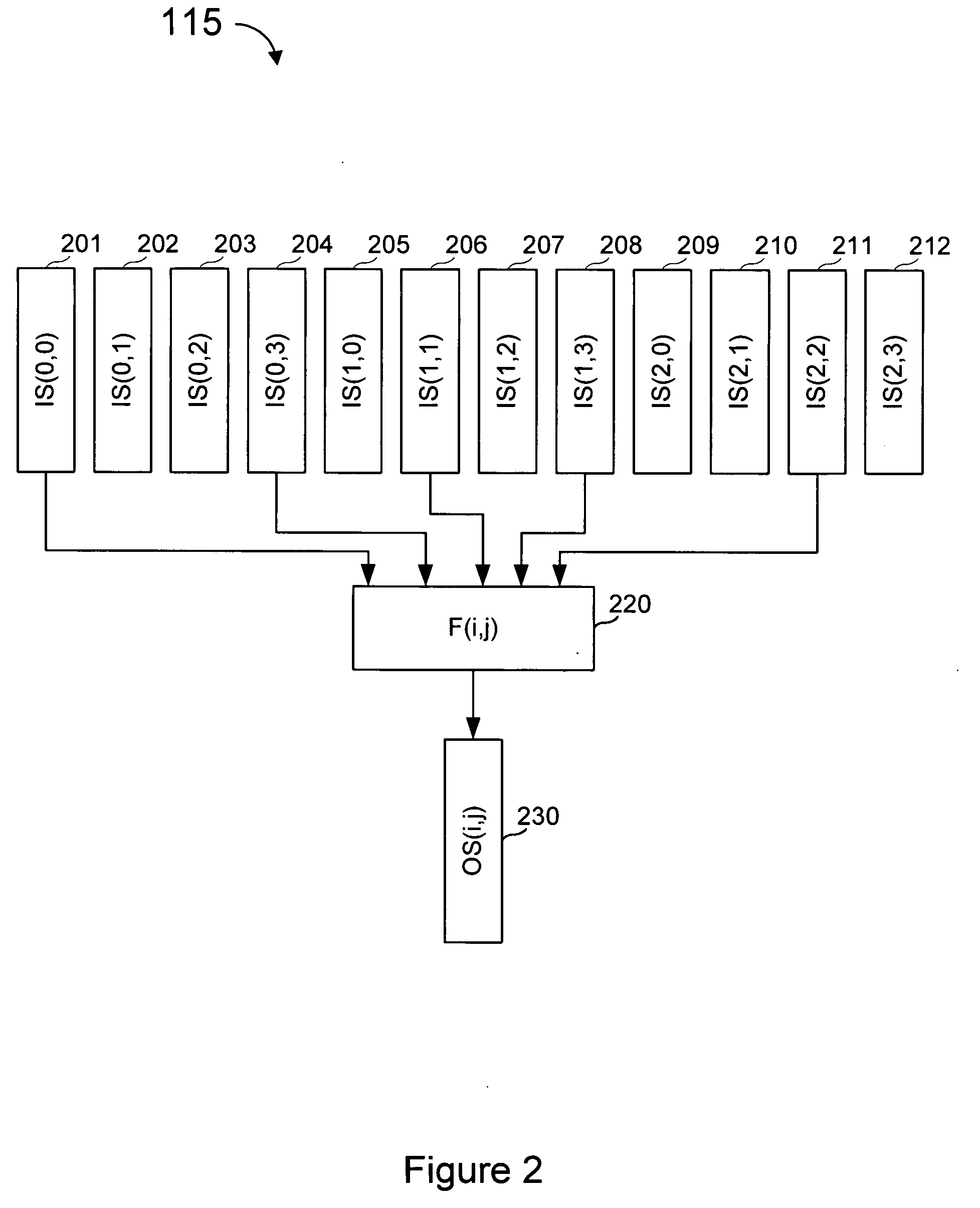
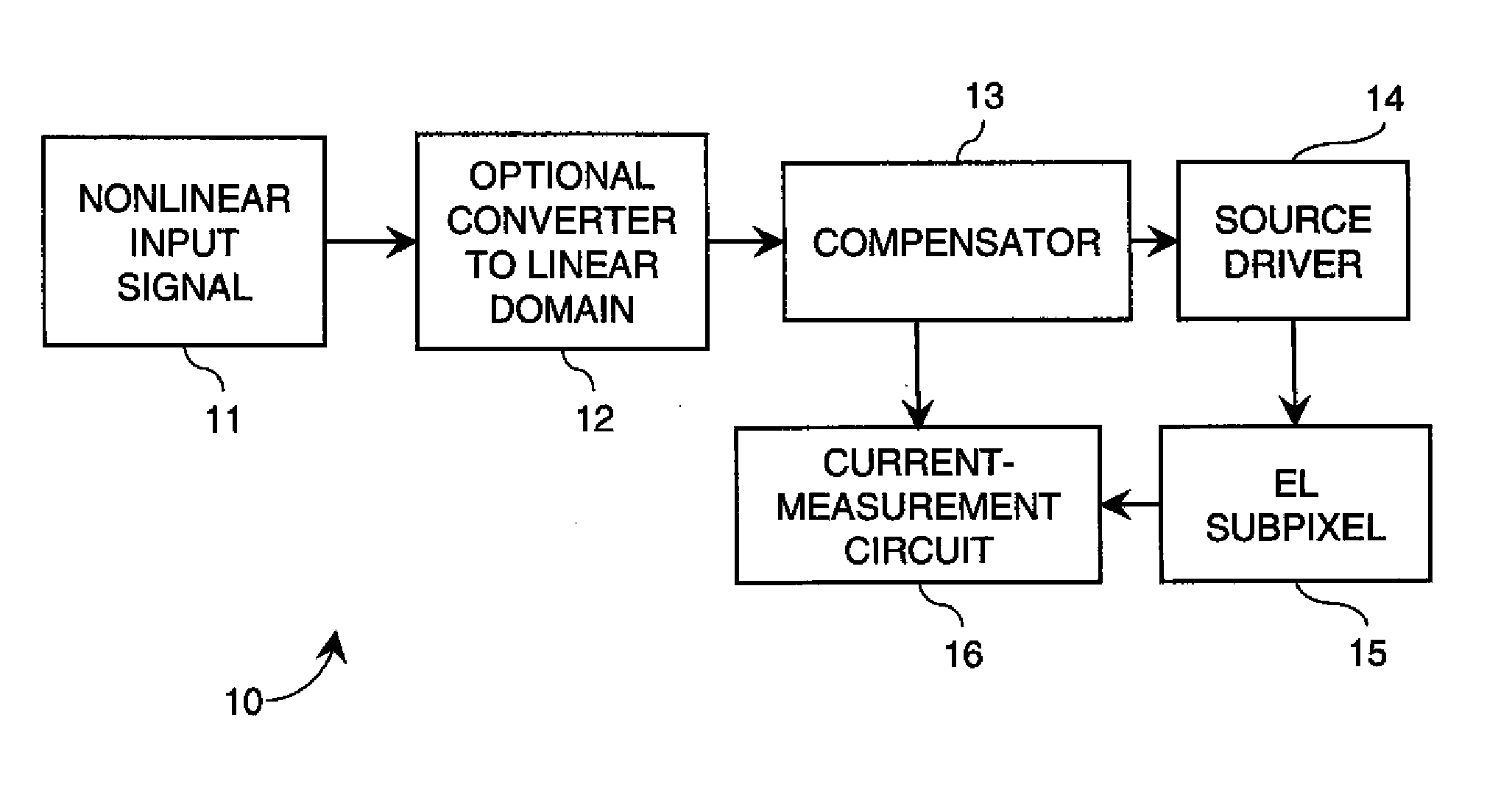
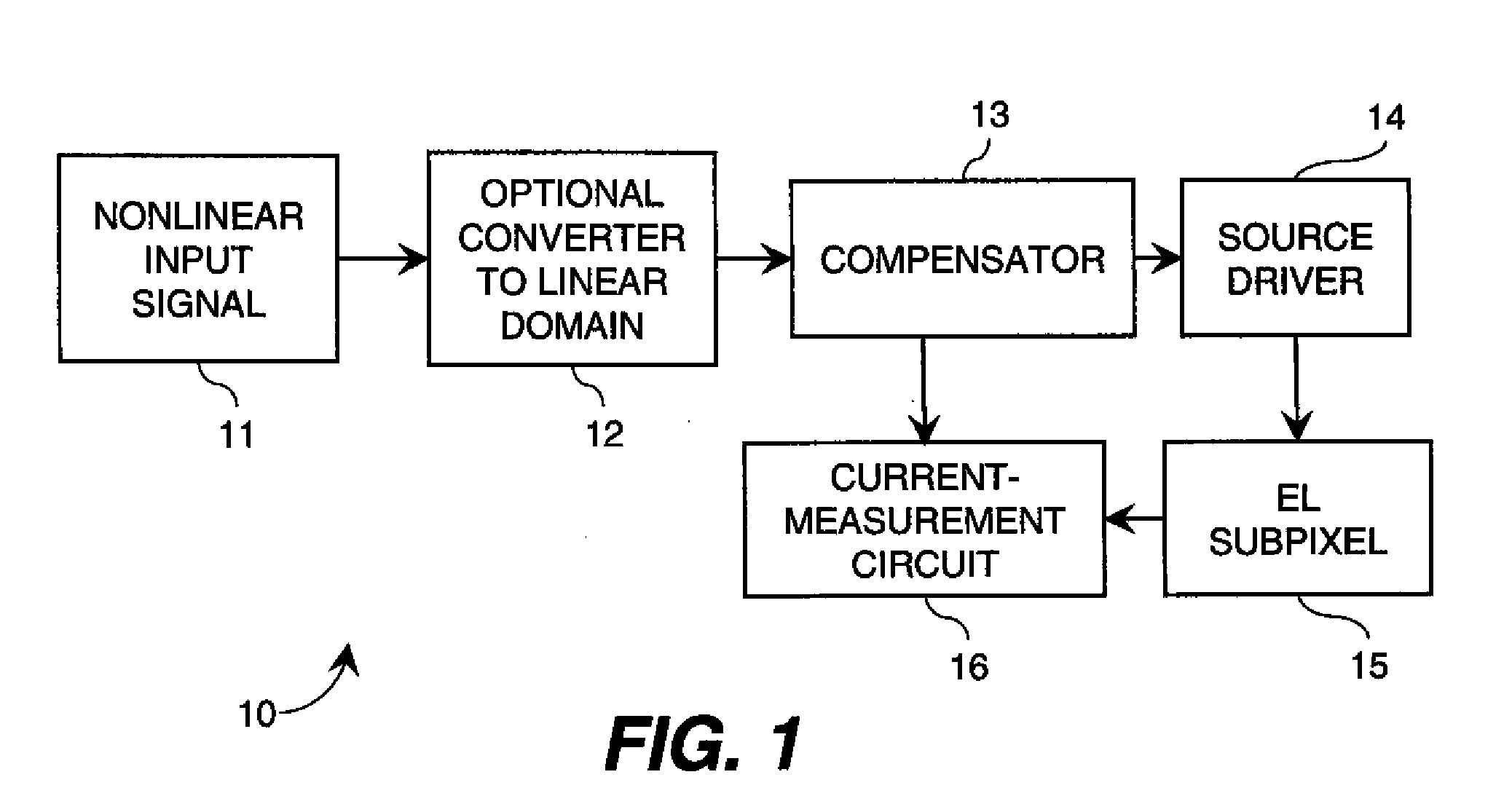
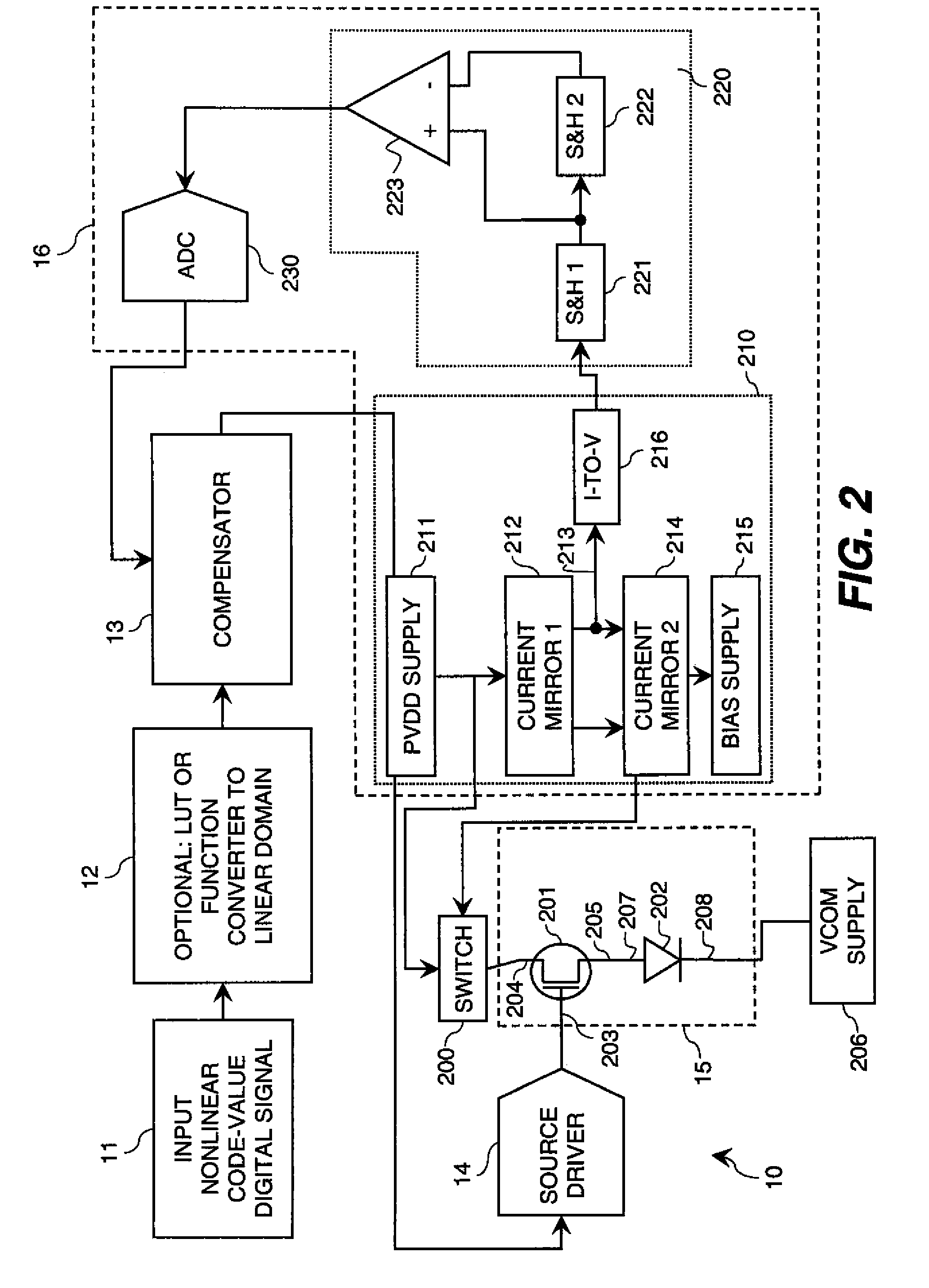
ActiveUS20100123699A1Increase the aperture ratioIncrease productionCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingEngineeringLinear code
An electroluminescent (EL) panel with 2T1C subpixels is compensated for initial nonuniformity (“mura”). The current of each subpixel is measured at a selected time to provide a status signal representing the characteristics of the subpixel. A compensator receives a linear code value and changes it according to the status signals. A linear source driver drives the panel with the changed code values.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
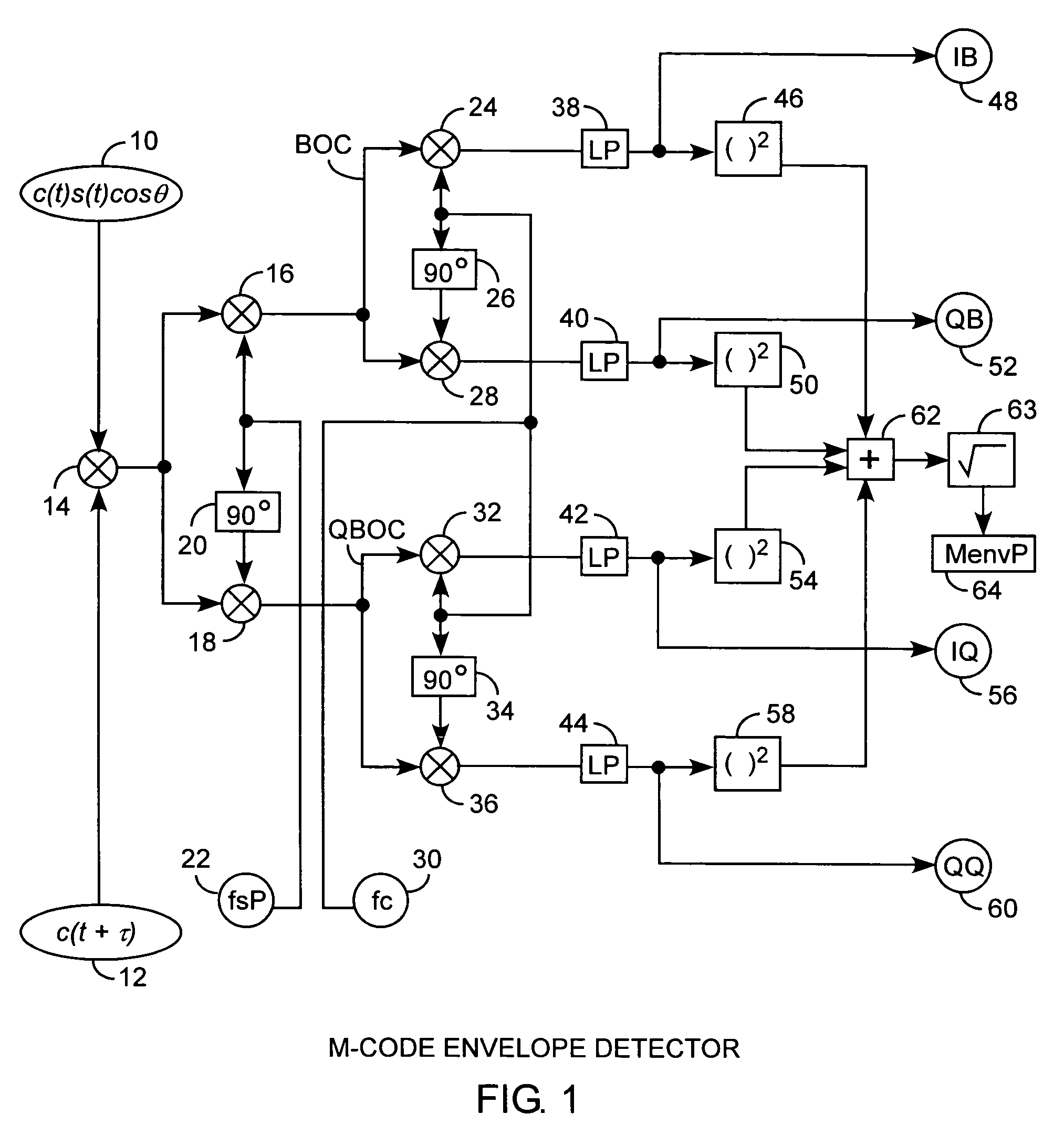
Binary offset carrier M-code envelope detector
ActiveUS7555033B2Improve acquisitionModulated-carrier systemsBeacon systemsCorrelation functionCode tracking
An M code envelope detector receives an incoming binary offset carrier (BOC) signal, such as the M code signal, and generates inphase BOC and quadraphase BOC signals, separated by an offset, that have respective ambiguous correlation envelopes, that when combined, provide a near unimodal correlation function with respect to code phase error of the BOC signal having an inherent multimodal autocorrelation function, with the near unimodal correlation envelope being tracked by early and late code replicas at broad one chip phases for providing unambiguous but nonlinear code phase error tracking, which detector is then further improved with the use of code replicas having narrow partial chip phases, such as ⅛ chip phases, for providing near linear code phase error tracking for unambiguous and accurate code tracking of the BOC signal.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
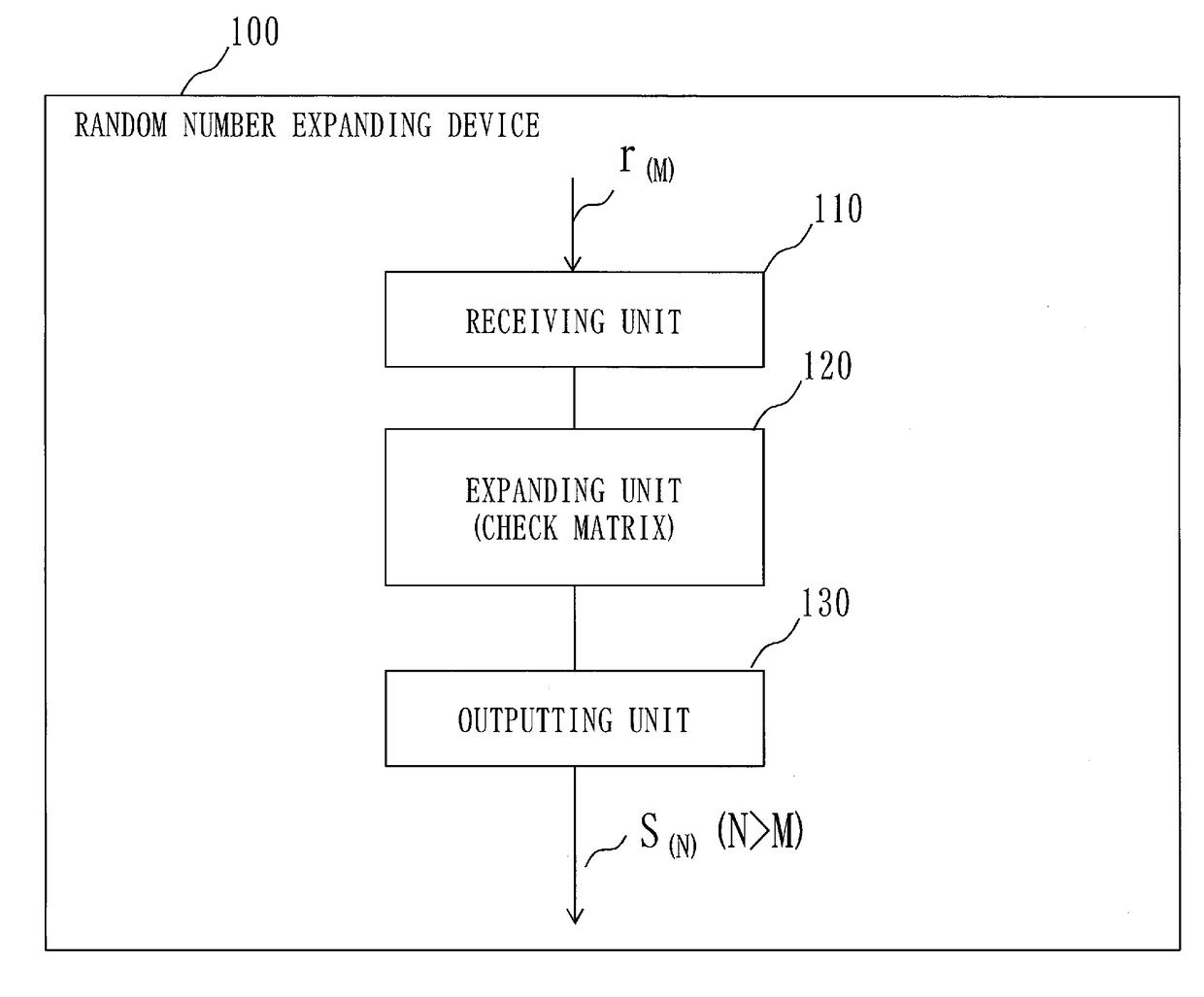
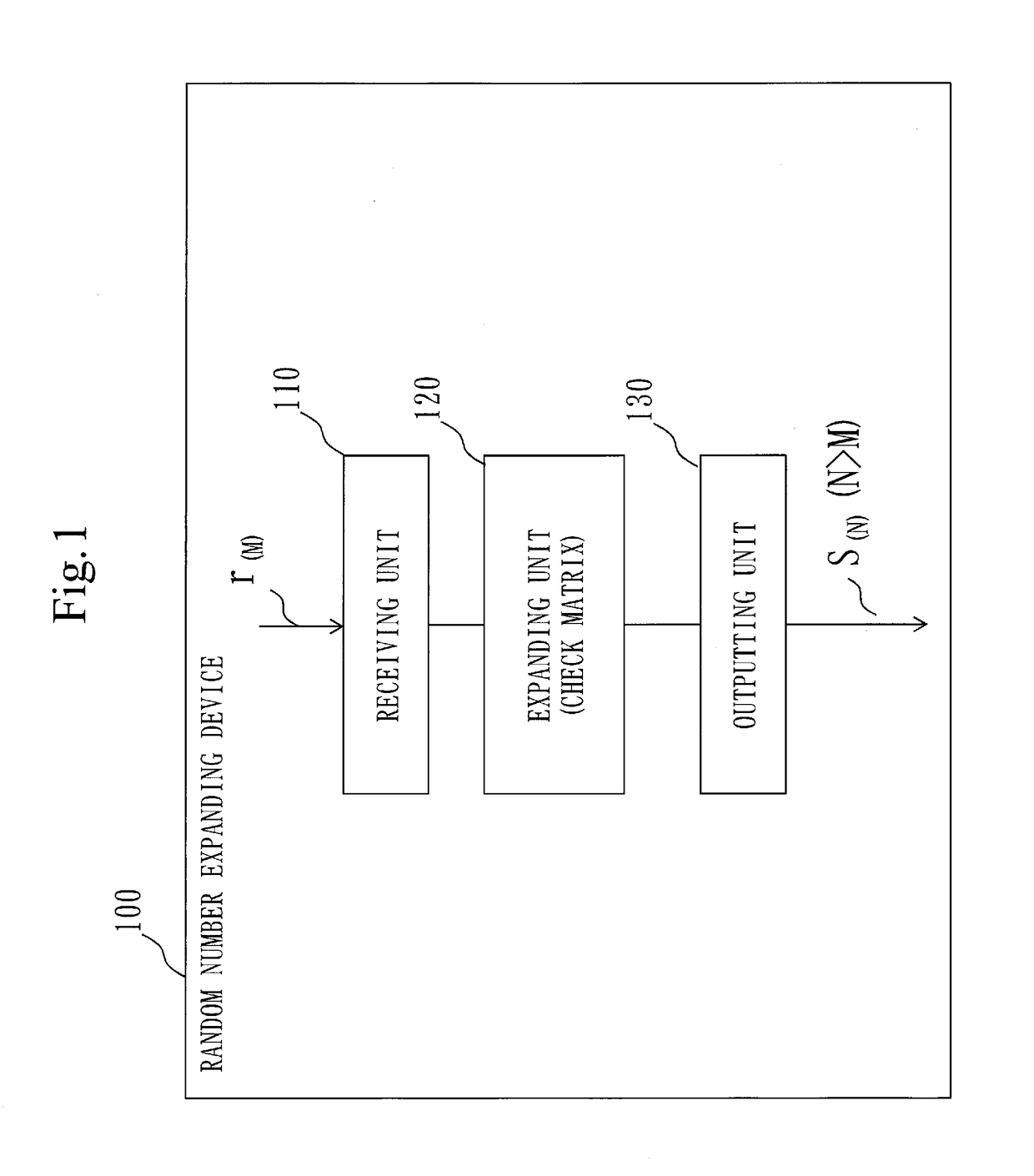
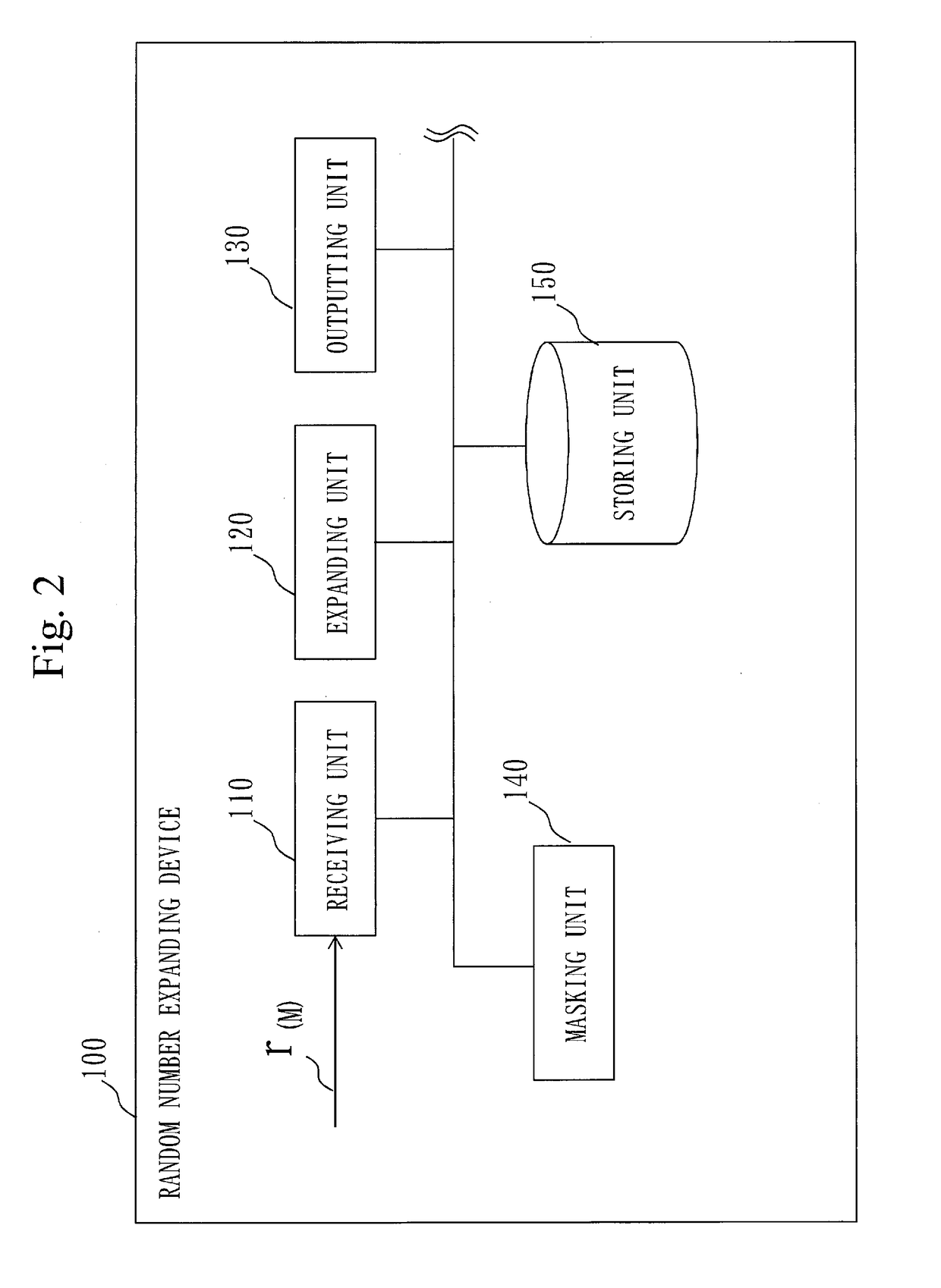
Random number expanding device, random number expanding method, and non-transitory computer readable recording medium storing random number expanding program
InactiveUS20180018147A1Reduce digitsKey distribution for secure communicationRandom number generatorsExclusive orLogical operations
A random number expanding device (100) includes an expanding unit (120) that expands a random number r(M) to an N bits random number s(N) using a logical operation that is obtained by multiplication of one matrix of a check matrix with a size of M×N and a generator matrix with a size of M×N which are determined from an (N, N−M, D) linear code for error correction by a vector in a case in which the random number r(M) is the vector with M components, the multiplication being performed through addition based on an exclusive OR. Since the random number expanding device (100) includes the expanding unit (120), it is possible to reduce the bit numbers of random numbers to be used, and counter an irradiation attack with multiple laser beams.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
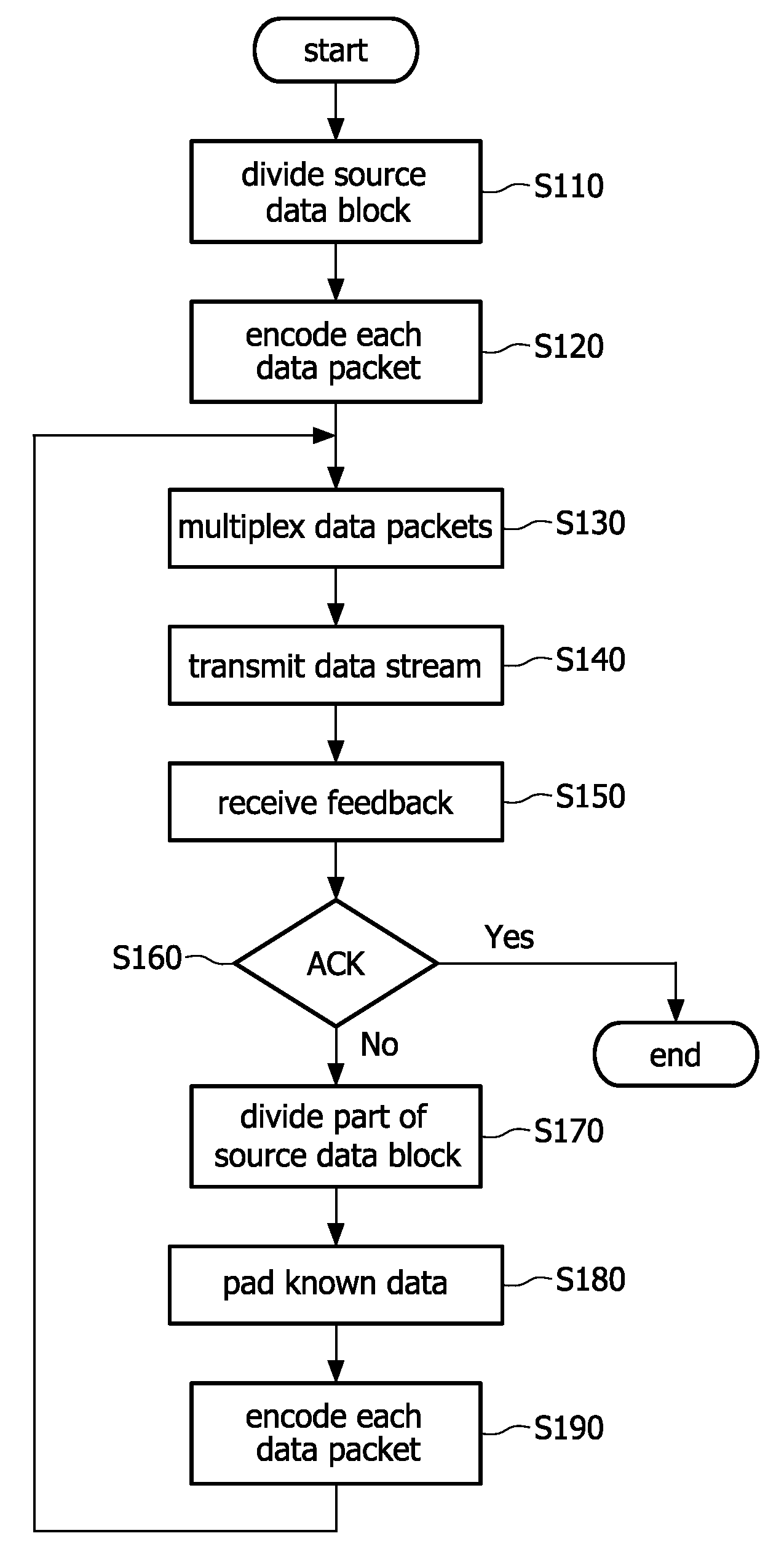
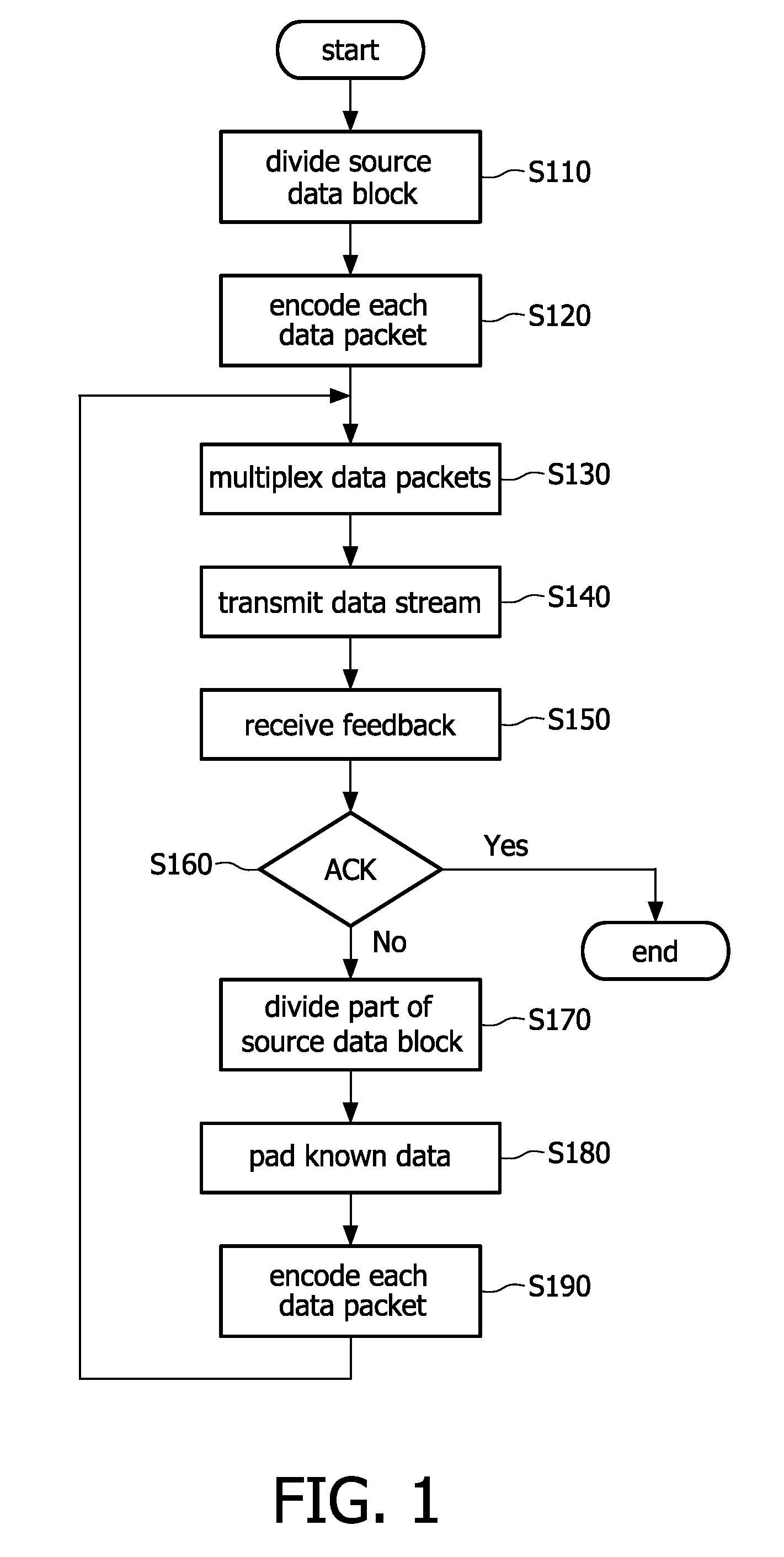
Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving a data block in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20090067424A1Easy to implementIncrease probabilityError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementData segmentCommunications system
The invention provides methods and apparatus for transmitting and receiving a source data block in a wireless communication system using hybrid automatic retransmission request protocol. According to the scheme provided by the invention, at transmitting side, the source data block or part of source data block that is not decoded correctly at receiving side is divided into a plurality of data segments, each the plurality of data segments may be paded with known data to expand the data segments to be a predetermined lengthen, the data segment is encoded with linear code to be a data packet including the data segment and a redundancy information segment or including only redundancy information, and after that the encoded data packets are transmitted. At the receiving side, when each of the received data packets includes a data segment and a redundancy information segment, decoding is performed directly based on the received data packet, decoding is performed based on the received redundancy information segment and an data segment and redundancy information segment extracted from buffered data packets with a first and second chance to restore the data segment that is not decoded correctly in previous decoding processing. With the additional decoding chance, the scheme provided by the invention can improve decoding probability and thus the transmission efficiency of the system.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Decoding apparatus, decoding method and program
InactiveUS20060192691A1Improve decoding performanceReduce probabilityAlgebraic geometric codesCode conversionLinear codeBelief propagation
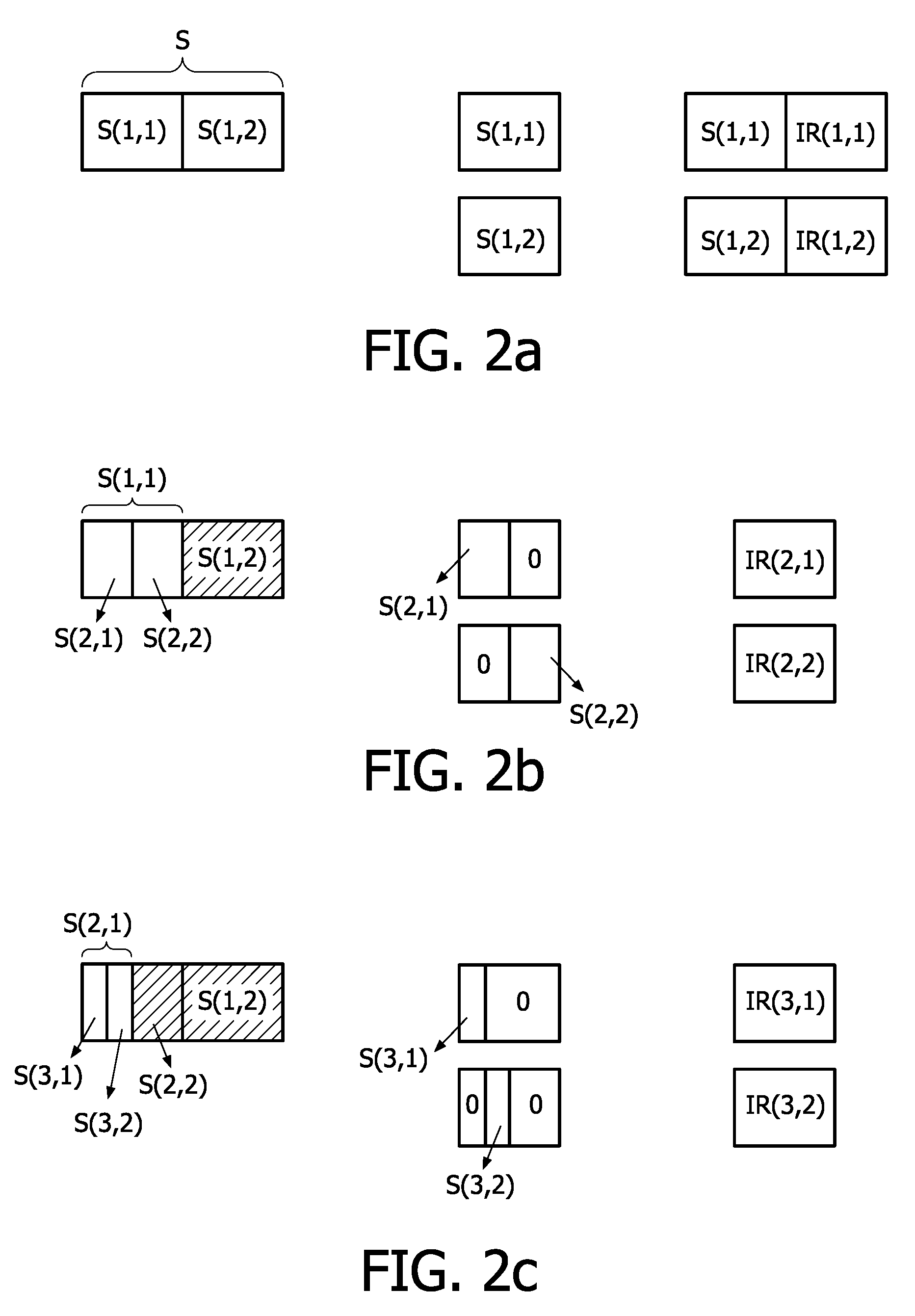
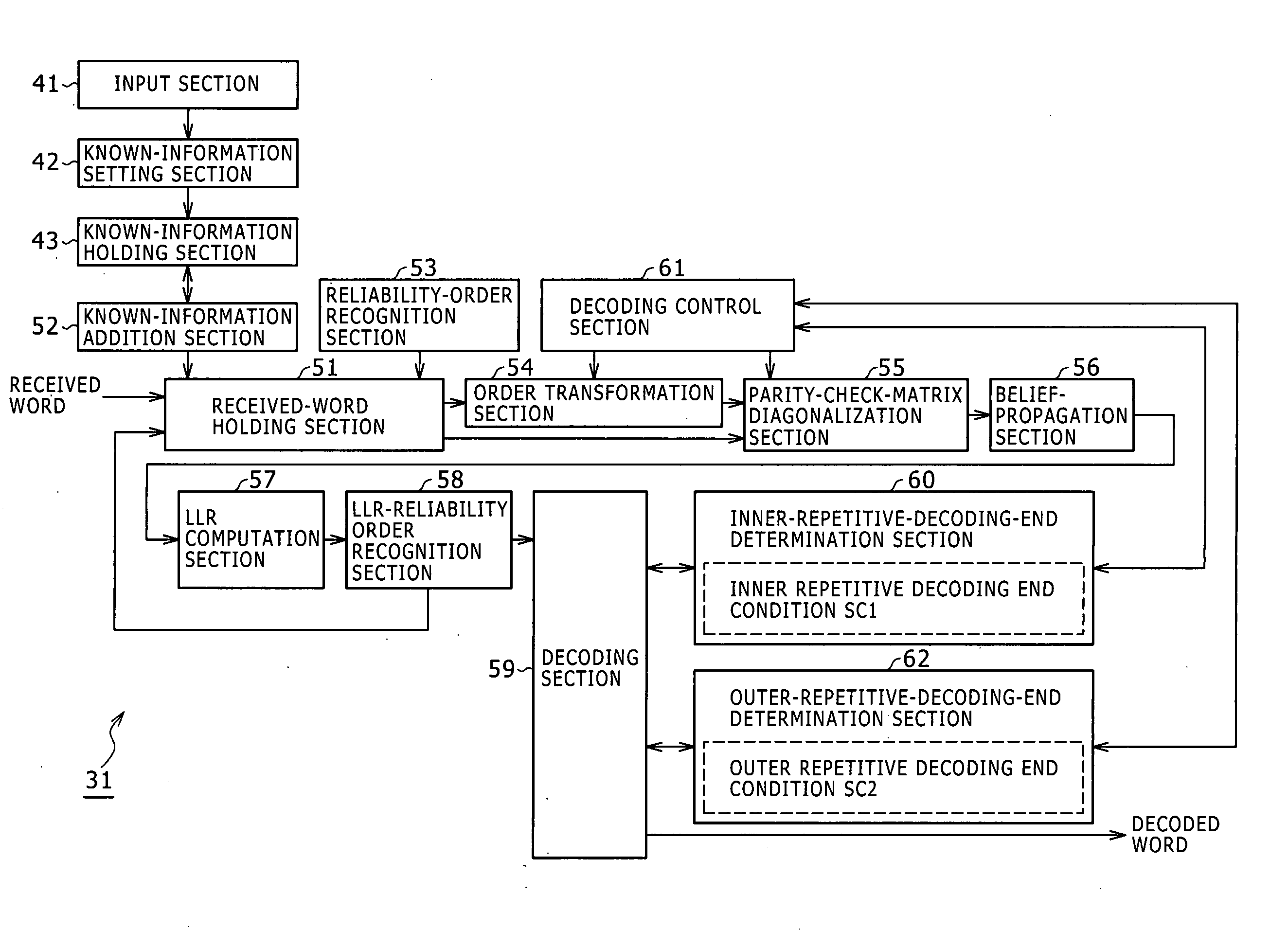
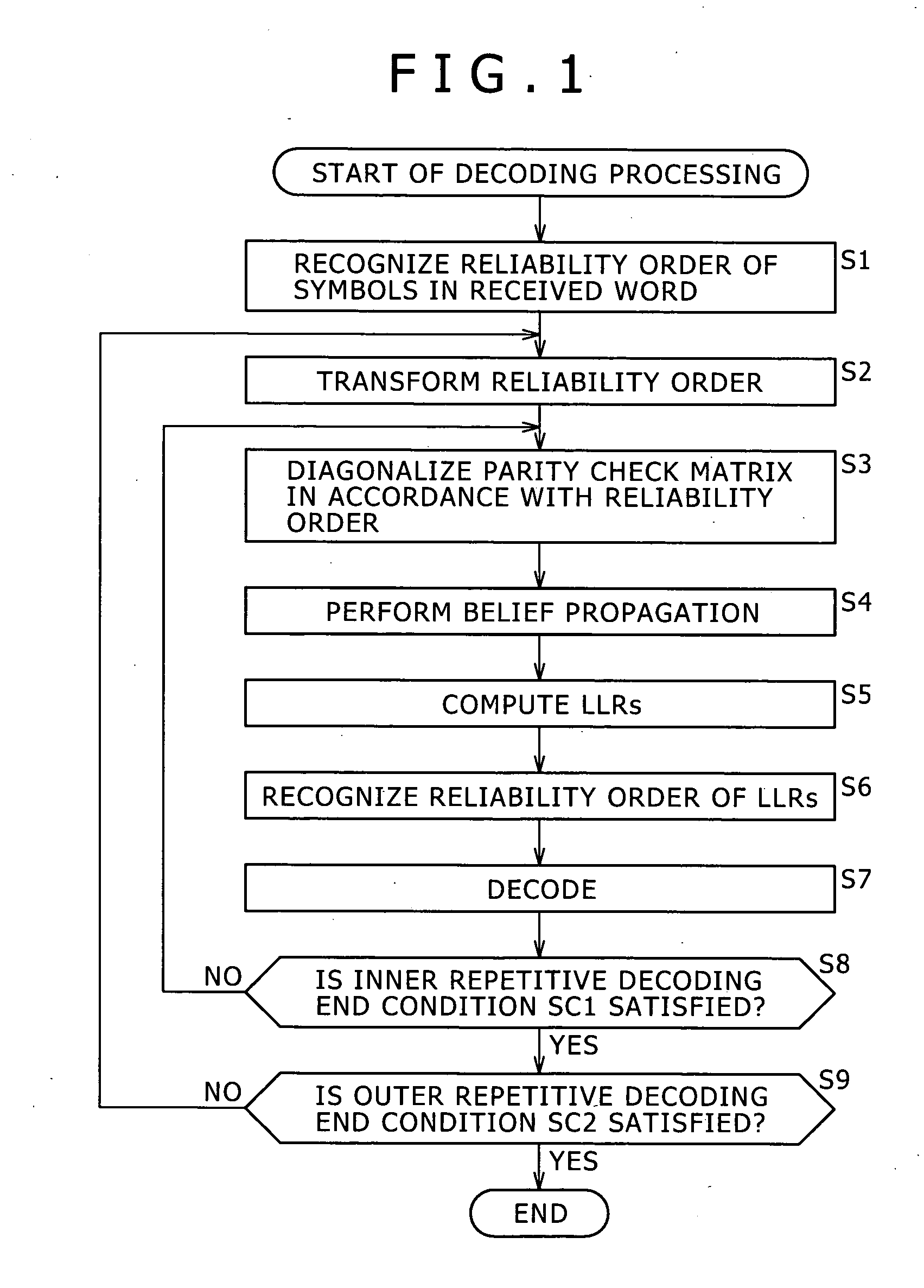
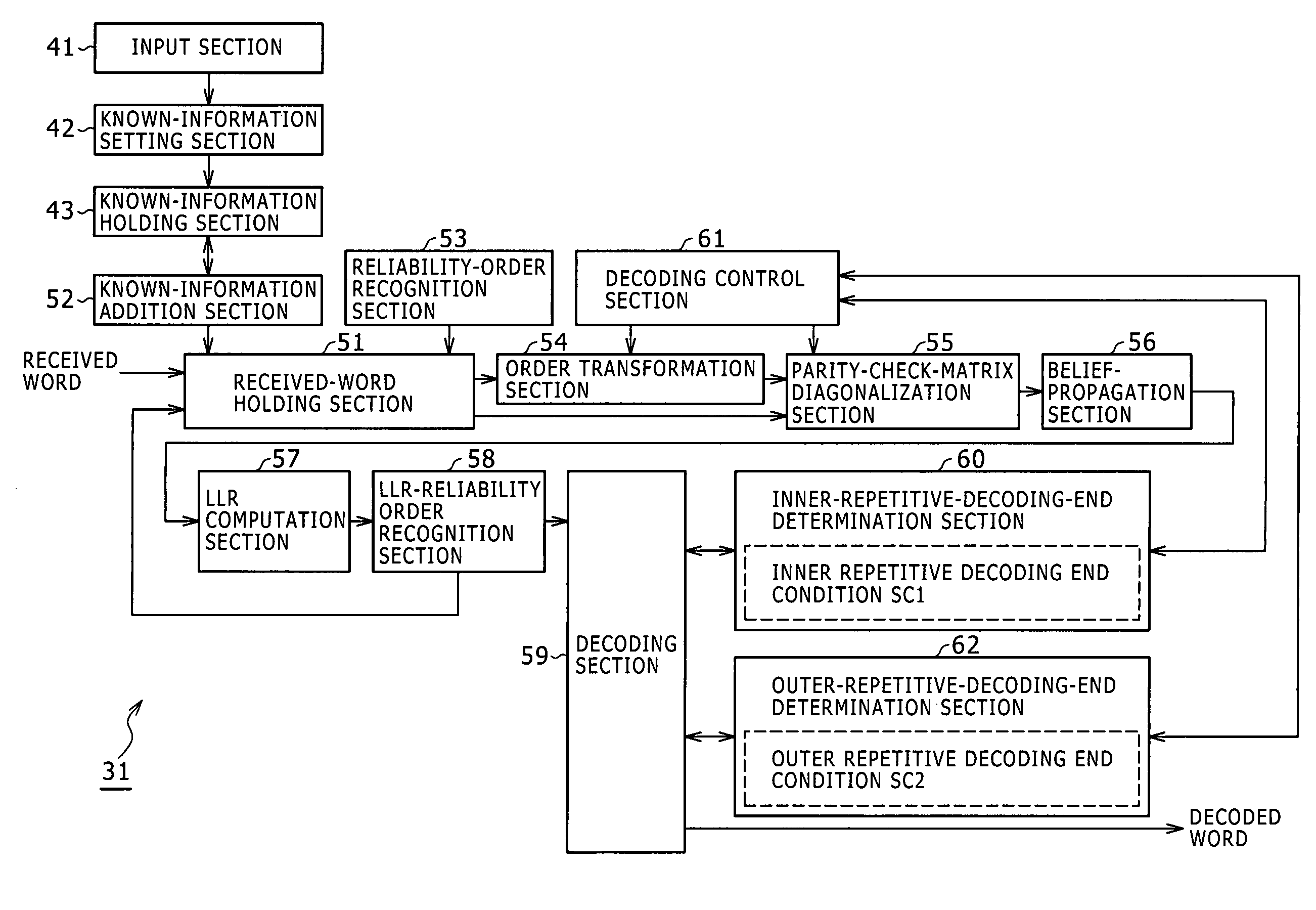
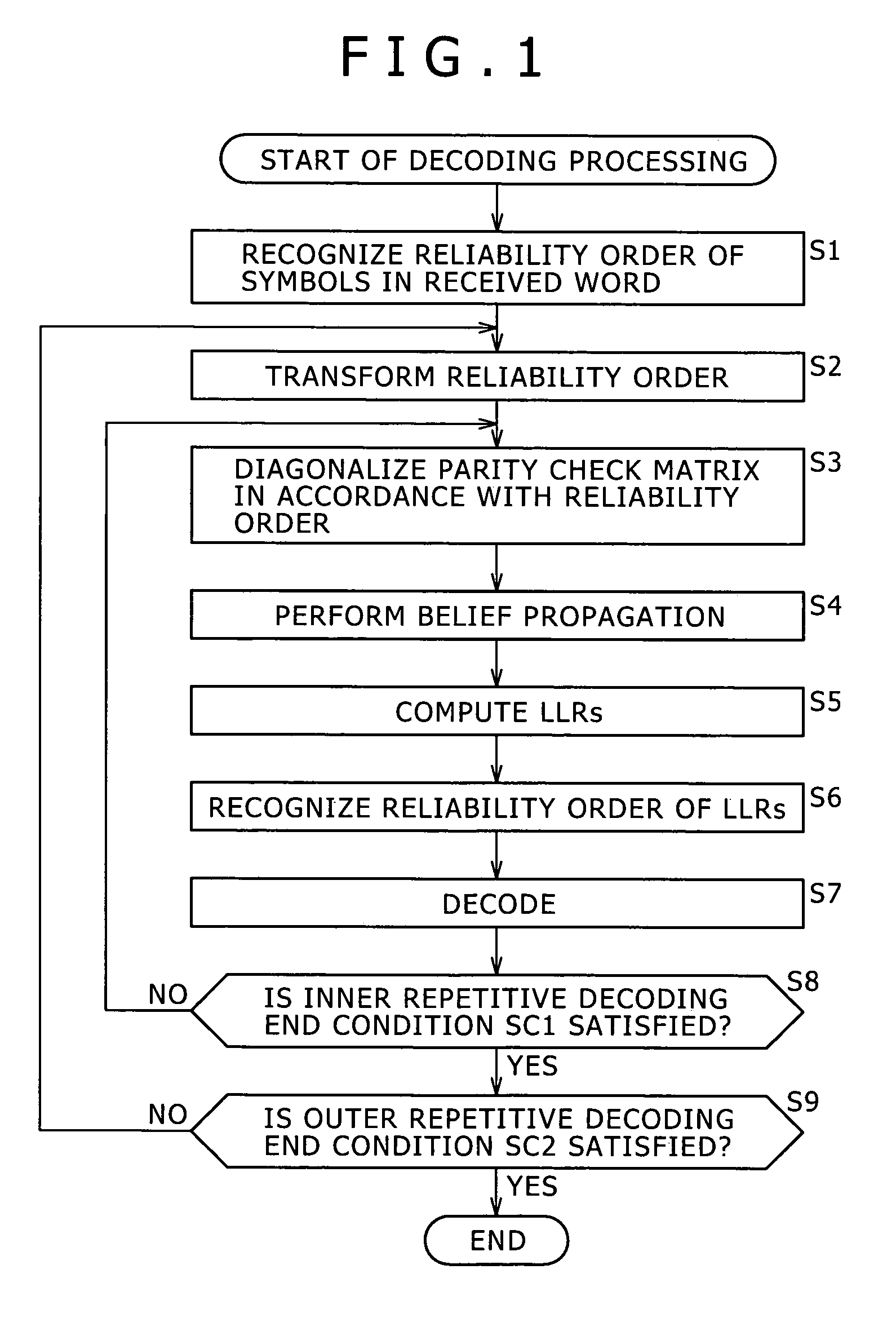
The present invention provides a decoding apparatus for carrying out a decoding process on a ring-R linear code. The decoding apparatus includes coded-word holding means for acquiring a coded word with a code length reduced by omission of some symbols from the coded word and for holding the coded word; known-information addition means for attaching a reliability level of each of the symbols omitted from the coded word to reduce its code length as known symbols each having a known value to the coded word held by the coded-word holding means as known information; and repetitive decoding means for repeatedly carrying out a decoding process using belief propagation on the coded word including the known information attached to the coded word by the known-information addition means.
Owner:SONY CORP
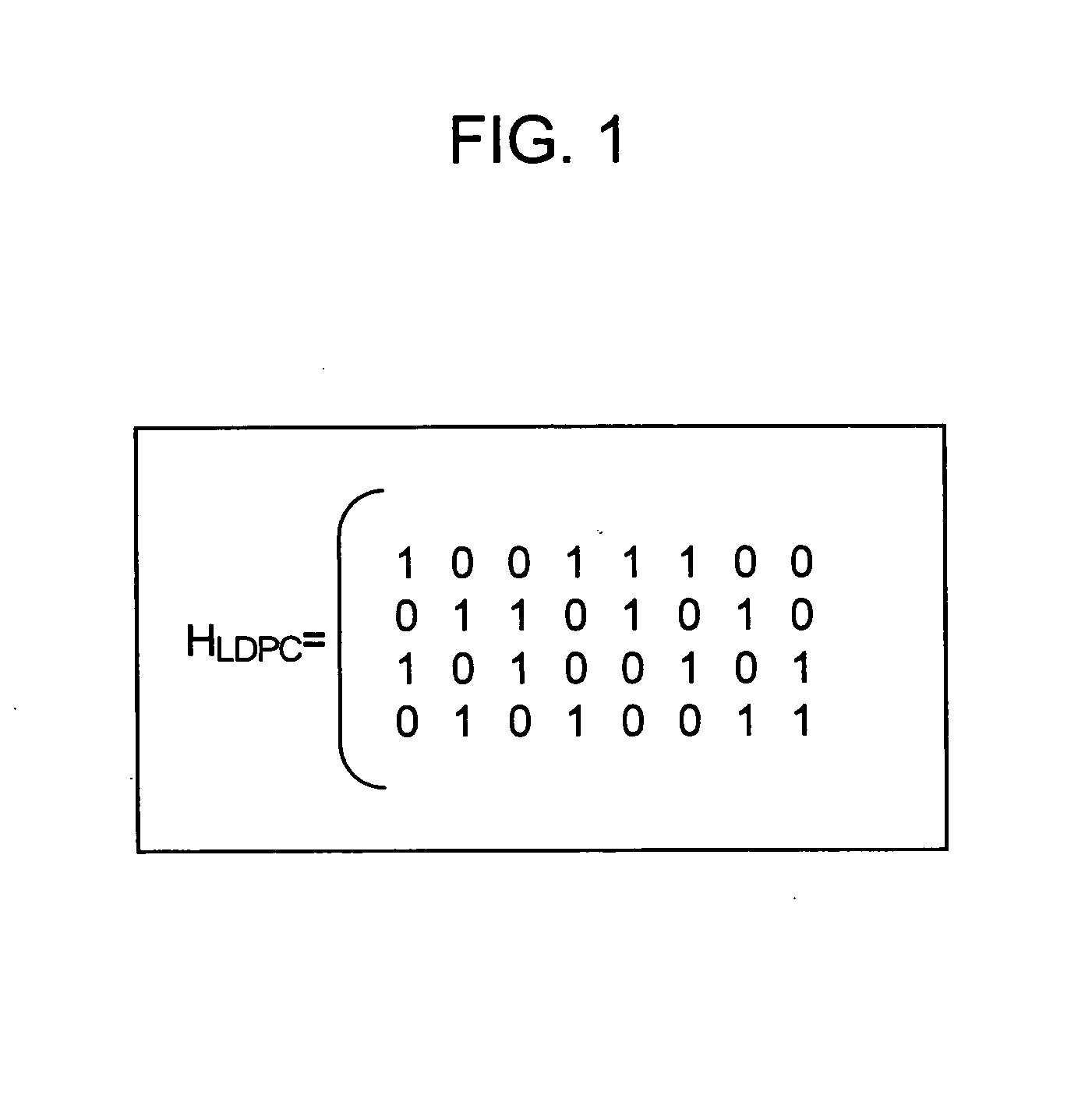
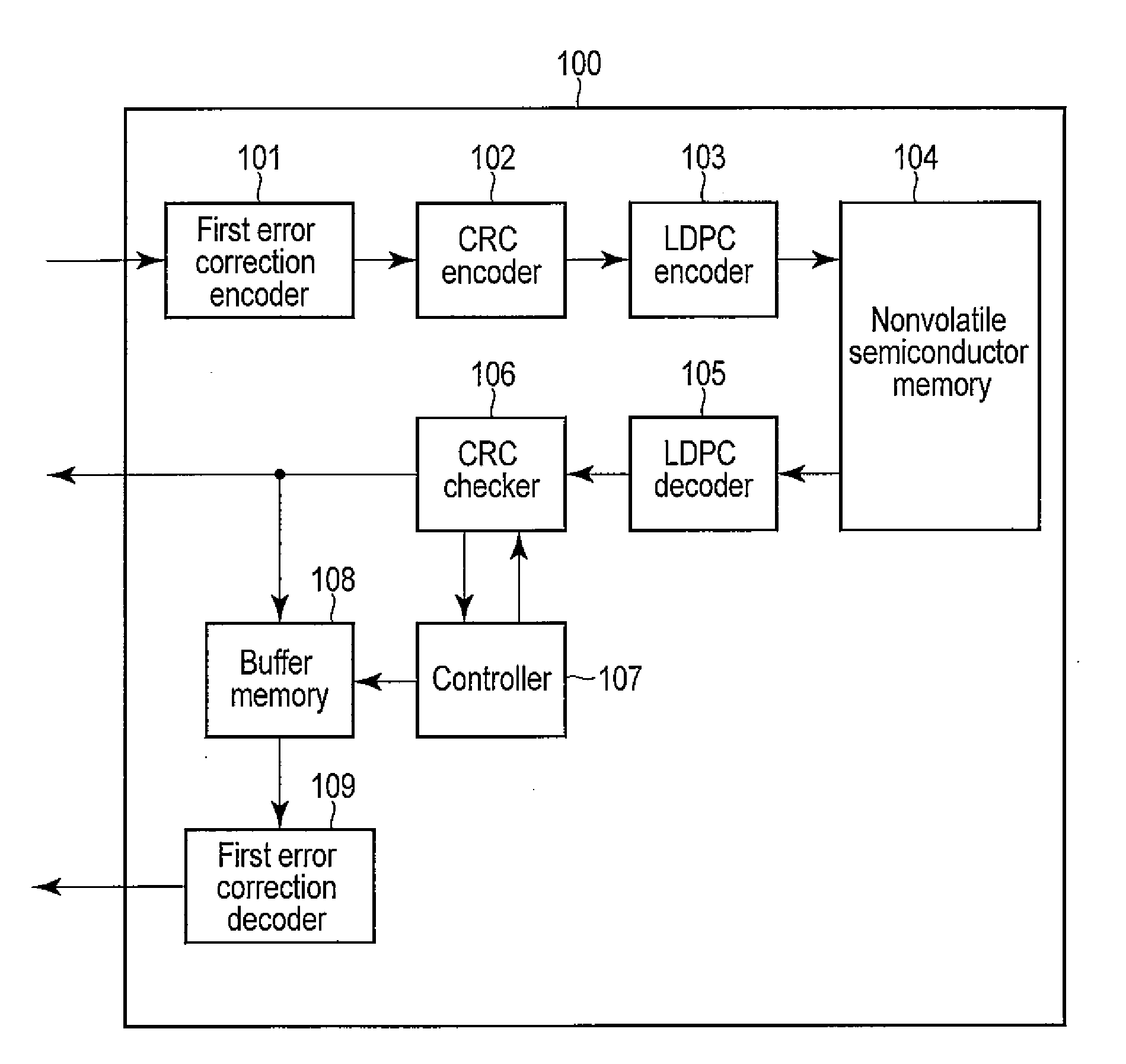
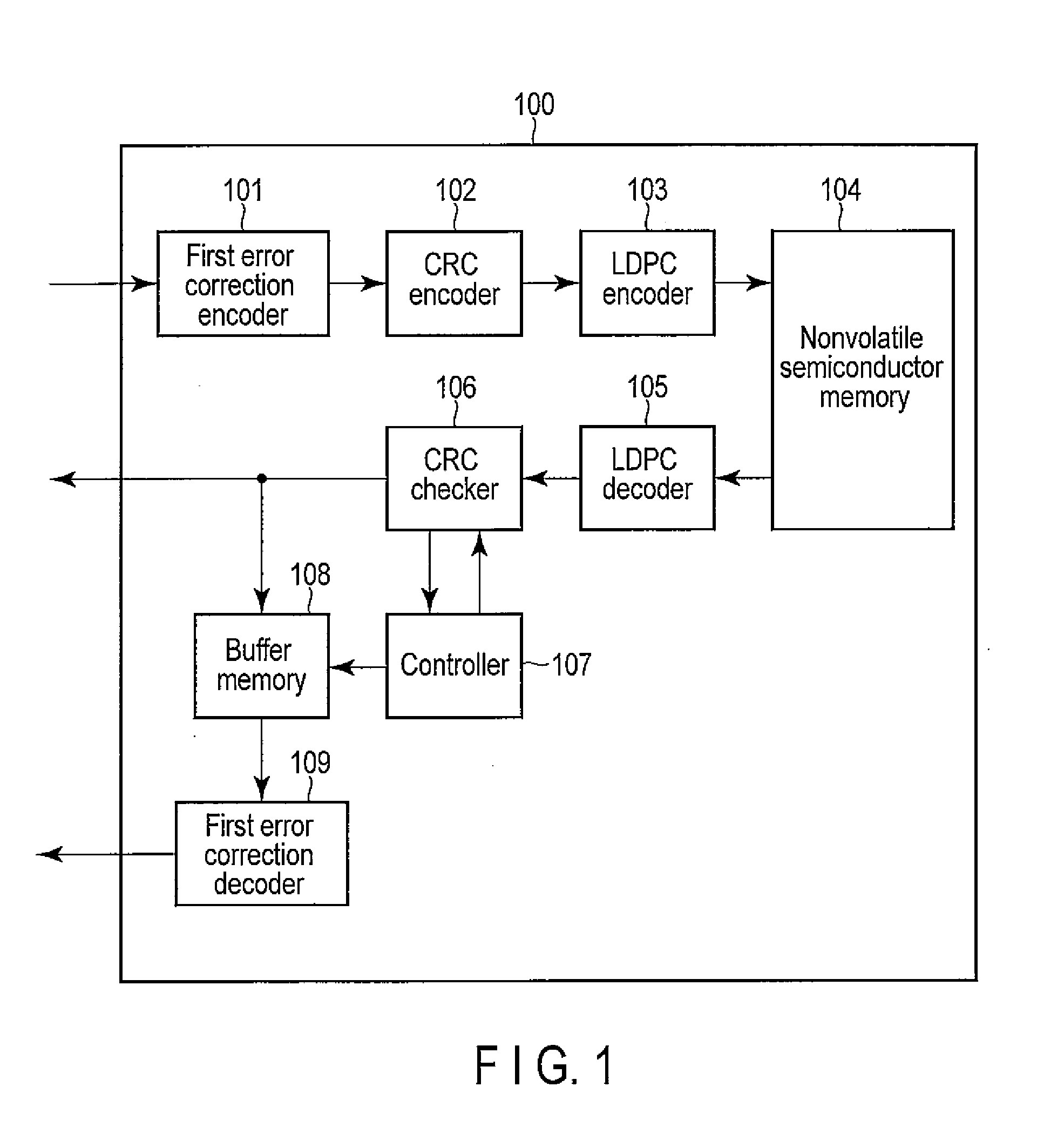
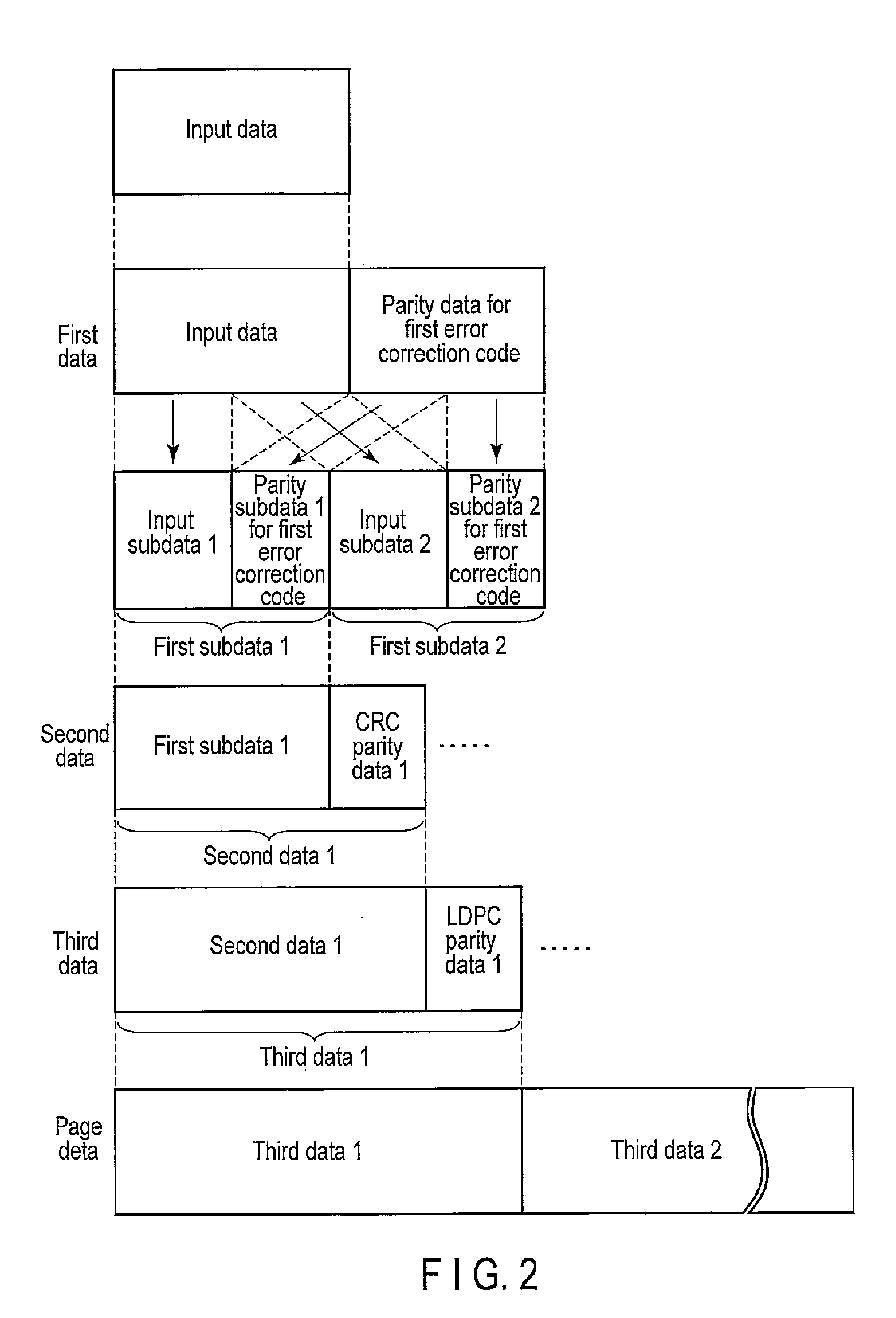
Error correction encoding apparatus, error correction decoding apparatus, nonvolatile semiconductor memory system, and parity check matrix generation method
ActiveUS20130055050A1Code conversionChecking code calculationsLinear codingTheoretical computer science
According to one embodiment, an error correction encoding apparatus includes a linear encoder and a low-density parity check (LDPC) encoder. The linear encoder supports a linear coding scheme enabling a parity check to be carried out by a division using a generating polynomial and applies the generating polynomial to input data to obtain linear coded data. The LDPC encoder applies a generator matrix corresponding to a parity check matrix for an LDPC code to the linear coded data to obtain output data. The parity check matrix satisfies Expression (1) shown in the specification.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Methods for capturing fingerprint images using a moving platen
InactiveUS7103201B2No apparent loss of accuracyMinimal lossCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
Owner:CROSS MATCH TECH
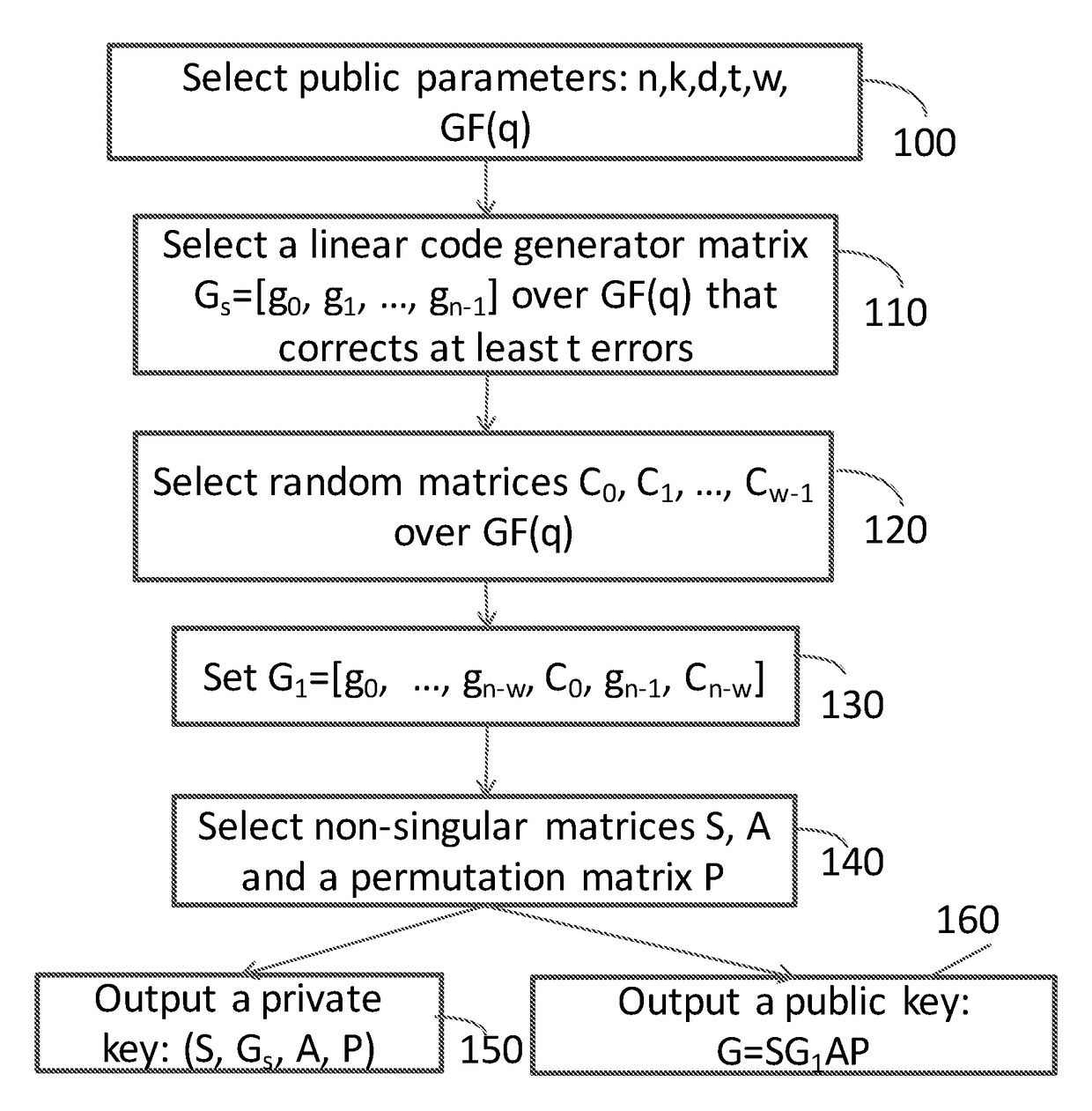
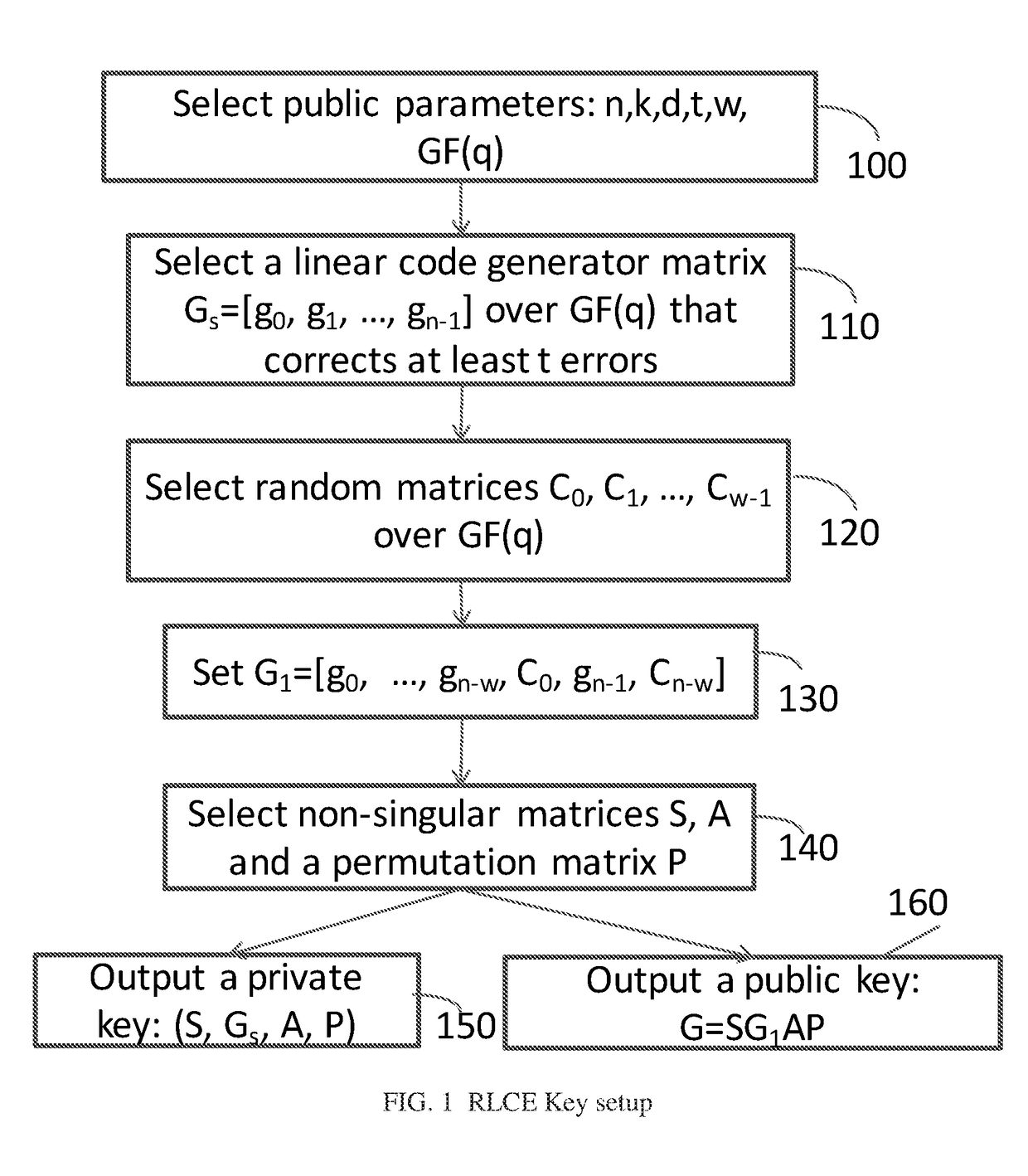
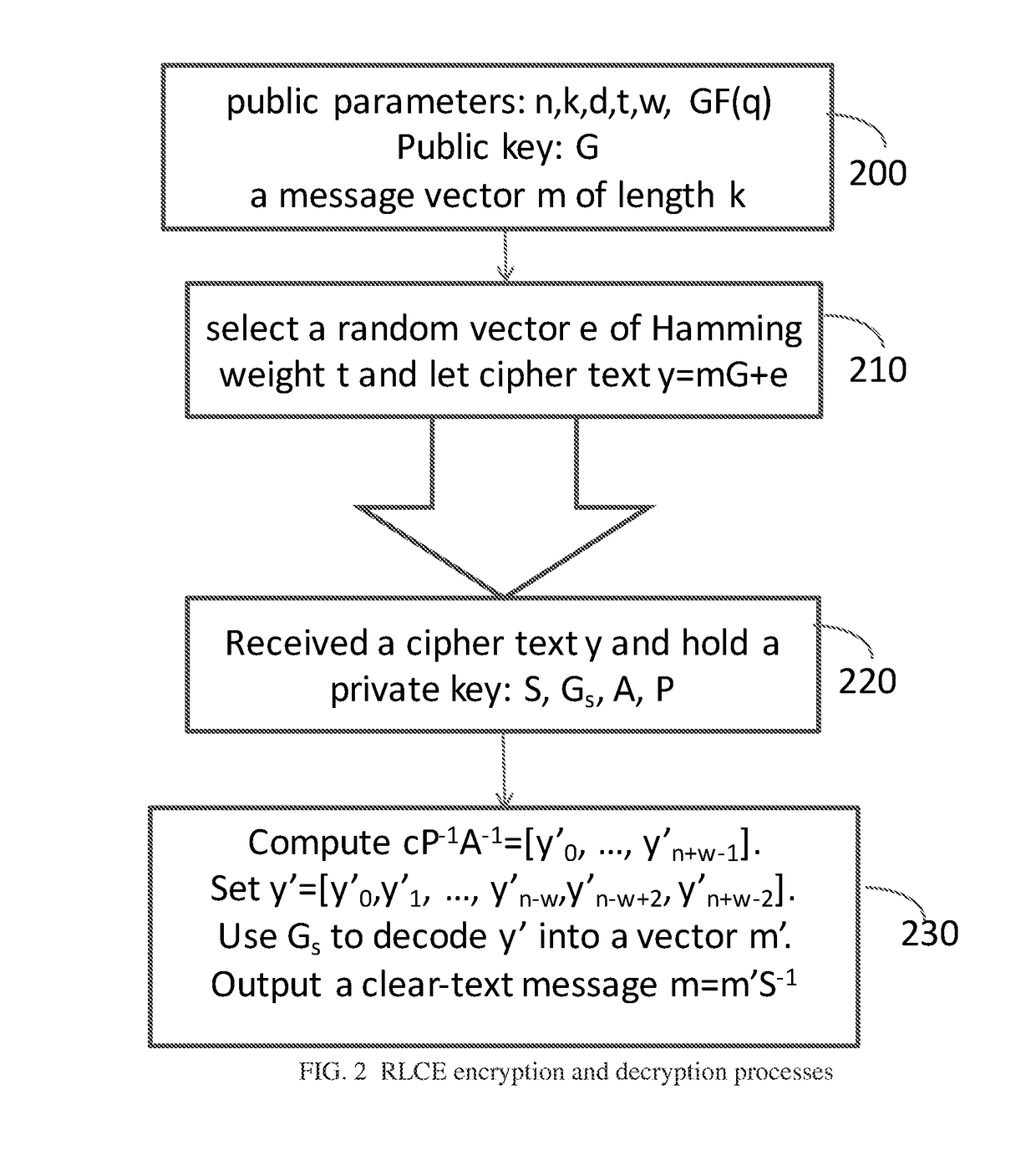
Method and Apparatus for Public Key Encryption Scheme RLCE and IND-CCA2 Security
InactiveUS20180176015A1Improve security levelKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationPlaintextMcEliece cryptosystem
Owner:WANG YONGGE
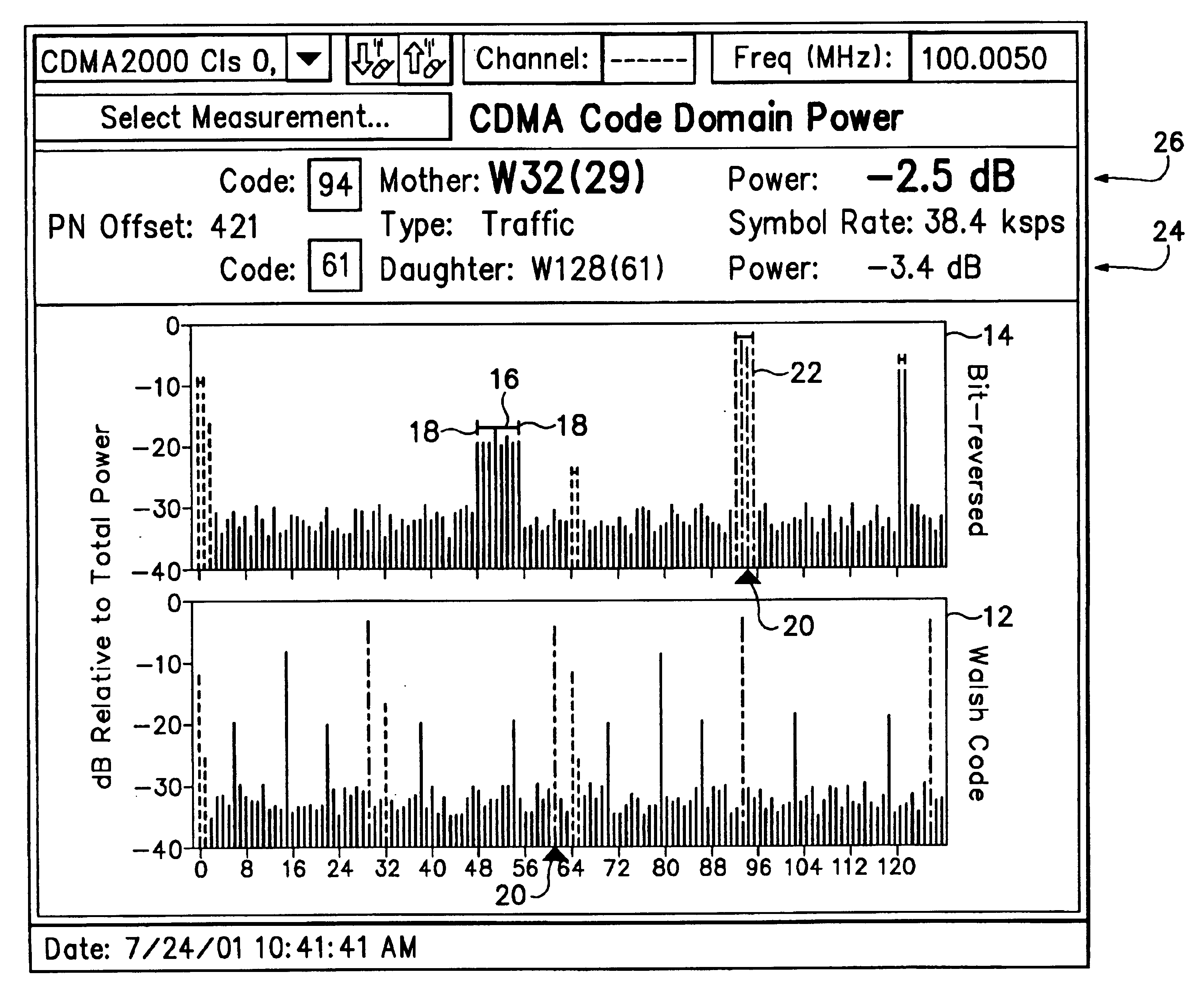
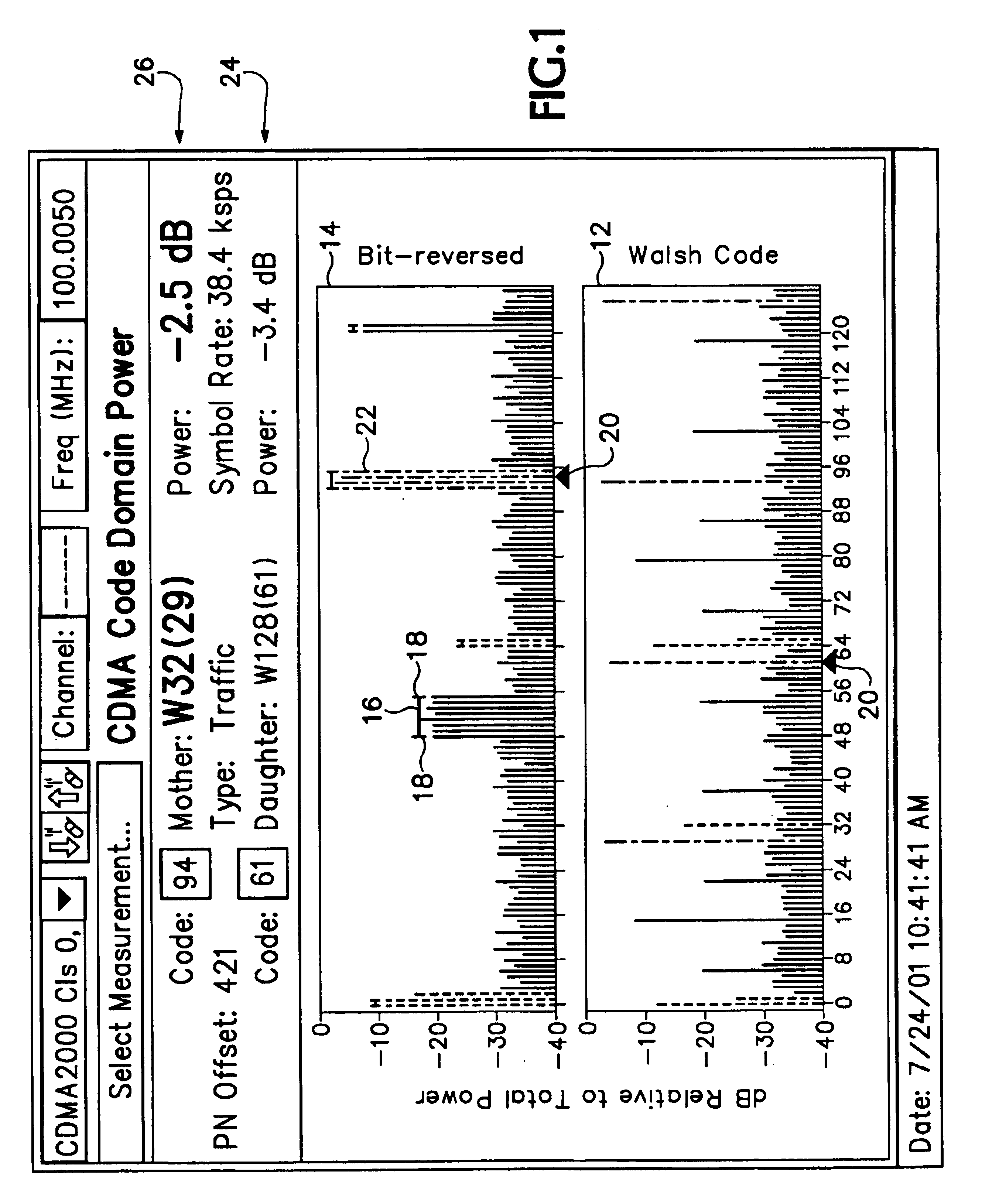
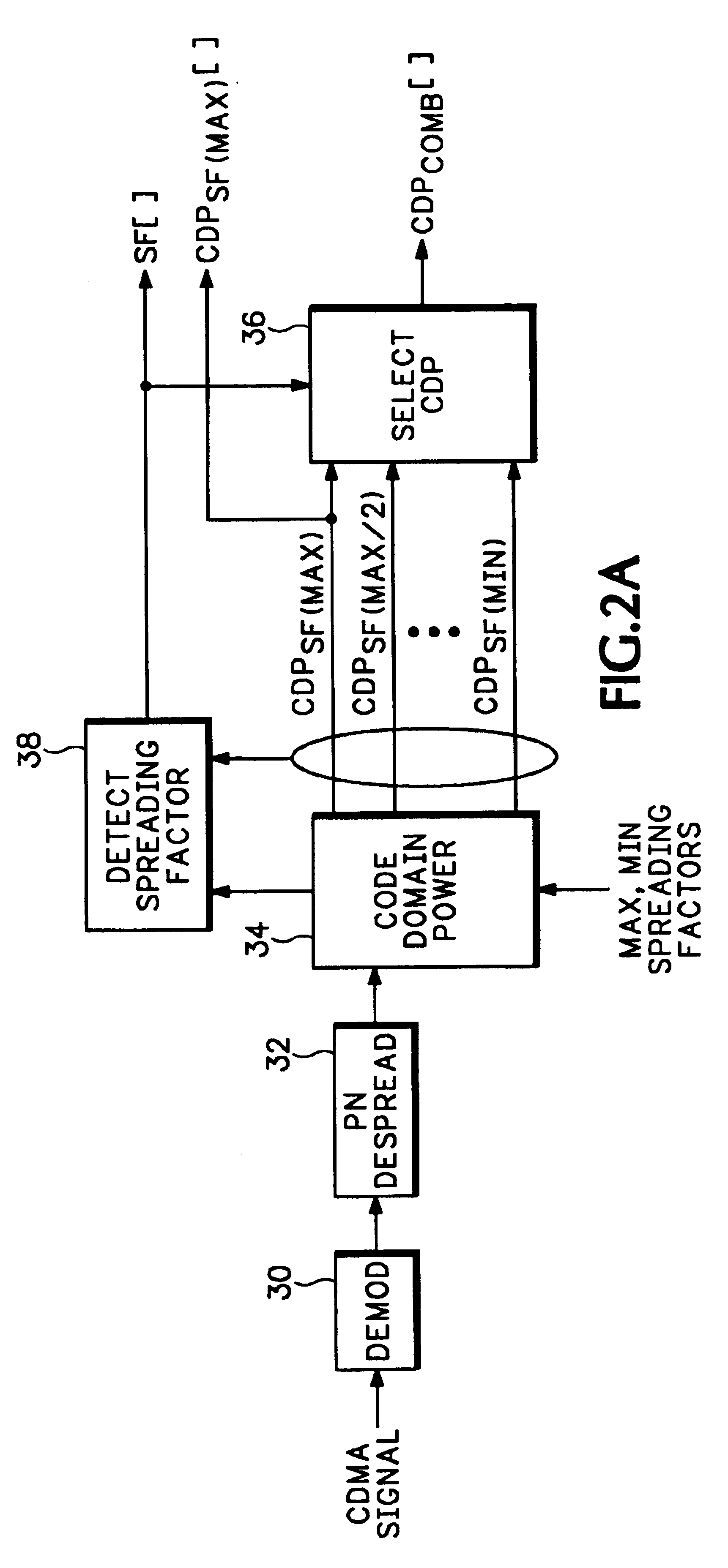
Display of code power levels and relationships of multiple spreading factor orthogonal codes in a CDMA signal
A display of code power levels and relationships of multiple spreading factor orthogonal codes in a code division multiple access (CDMA) signal has a first code graph of code domain power (CDP) for all the codes at the largest code spreading factor that includes all codes at all spreading factors plotted in a linear code indexing order and a second graph of CDP where the codes are plotted in bit-reversed order to group together the sub-codes of each code of lower spreading factor. Markers on each graph are tied together such that movement of one marker on one graph to a particular code value causes the other marker on the other graph to move to the corresponding code value. The sub-codes related to a particular code bar in the graphs indicated by the markers may be differentiated by using grey scale or color variations. A base code power level indicator, which may be in the form of a horizontal bar on the bit-reversed order graph spanning the group of sub-codes corresponding to a particular spreading factor, provides a power indication for the base code.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
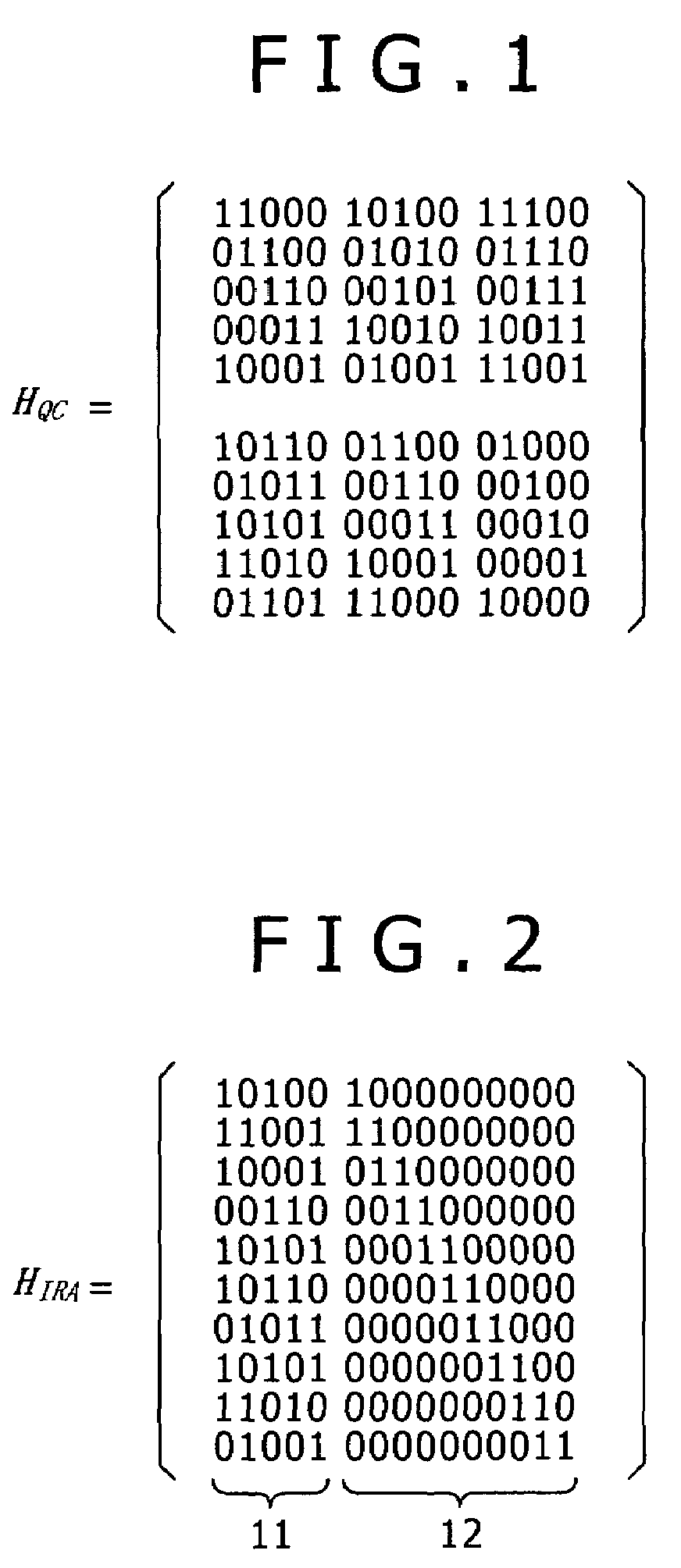
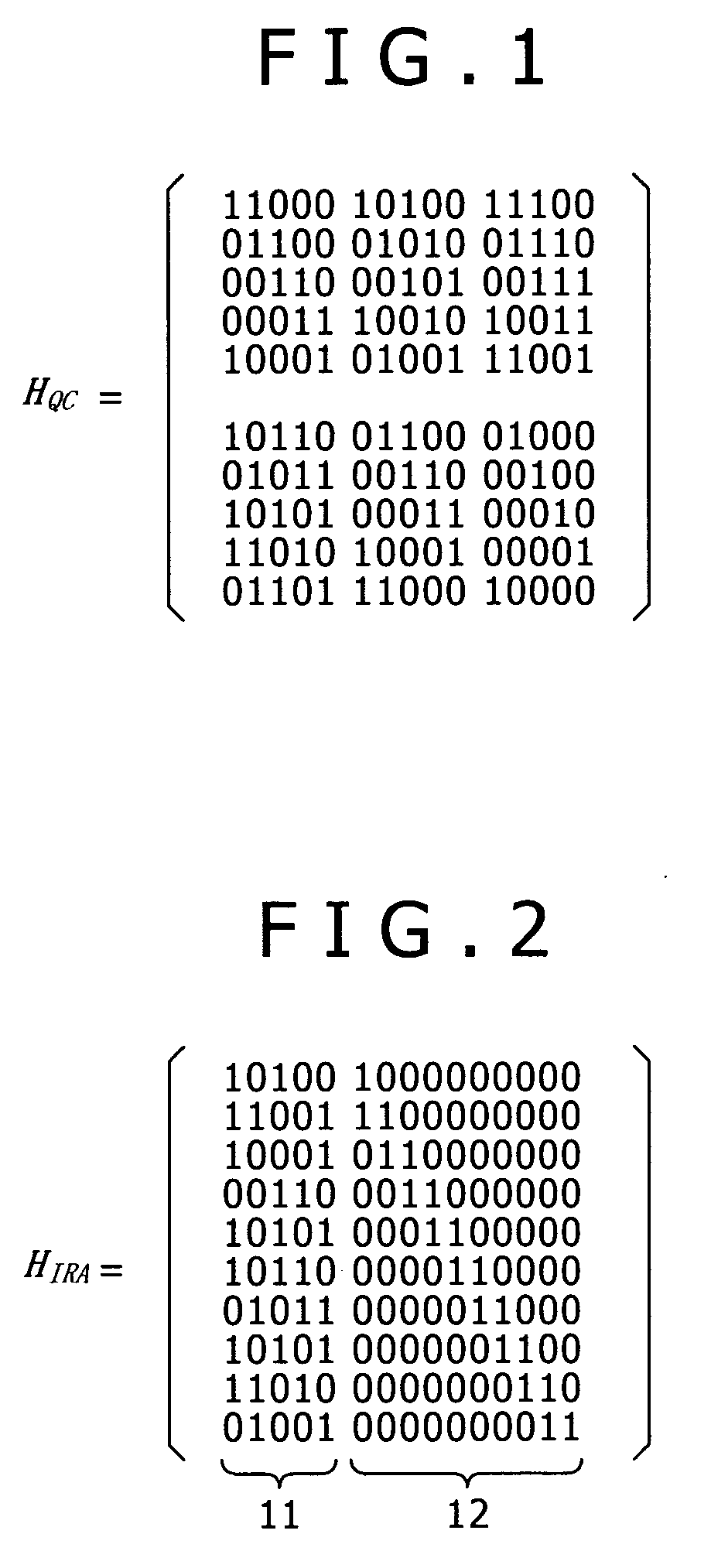
Quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check (QC-LDPC) code and correcting and linear coding method thereof
InactiveCN102055485AMinor changesNo change in performanceError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsError correction/detection using linear codesAlgorithmLinear coding
The invention relates to a quasi-cyclic low-density parity-check (QC-LDPC) code and a correcting and linear coding method thereof. The variable nodes of the LDPC code, the dimensionality of which is greater than 2, are informational nodes; and the variable nodes the dimensionality of which is 2 form a big end-to-end ring on a bipartite graph. The correcting method comprises the following implementation steps: randomly selecting one edge on the big ring the dimensionality of which is 2, cutting off the edge, and filling 0 in the corresponding position of a low-density check matrix, thereby acquiring a corrected structure of the code. The linear coding method of the corrected code comprises the following implementation steps: firstly, multiplying an input information vector s and a part of the check matrix the load of which is greater than 2 as a vector by a matrix to acquire an intermediate vector u; directly intercepting the corresponding position of the intermediate vector u to acquire a coding vector the variable node dimensionality of which is 1; computing bit by bit from a start bit according to the characteristics of the big ring on the bipartite graph to acquire a coding vector the variable node dimensionality of which is 2; and combining the two coding vectors to finally form a coding vector.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus of communication using random linear coding
InactiveUS20110044180A1Improve throughputTransmission systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer hardwareCoding block
A communication method using random linear coding is disclosed. The communication method using a random linear code comprises receiving first code blocks randomly linear-coded from a transmitter; demodulating the first code blocks using a decision distance determined in accordance with a channel status; determining whether an error has occurred in the first code blocks, using the decision distance, and transmitting a NACK signal to the transmitter, the NACK signal including information of the number of the code blocks where an error has occurred. Since a block error rate can be controlled in accordance with channel status, throughput can be improved.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
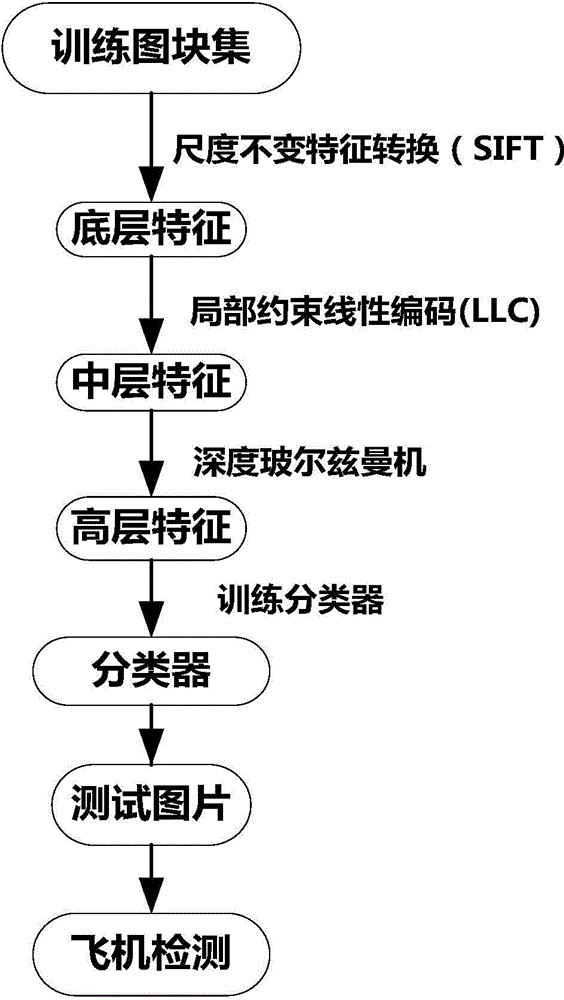
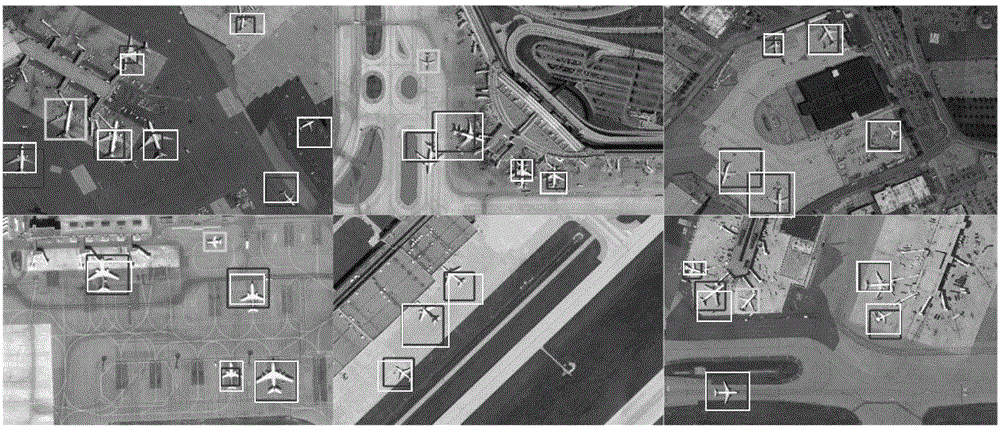
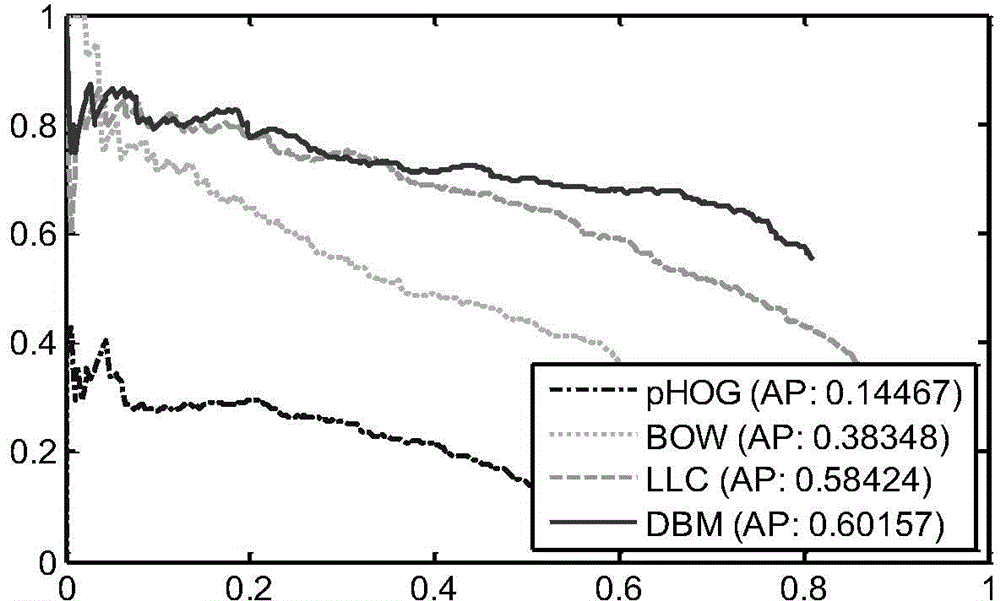
High-resolution remote sensing image airplane detecting method based on high-level feature extraction of depth boltzmann machine
InactiveCN104463248AEnhance expressive abilityExpressiveImage analysisKernel methodsJet aeroplaneScale-invariant feature transform
The invention relates to a high-resolution remote sensing image airplane detecting method based on high-level feature extraction of a depth boltzmann machine. The method comprises the steps that at first, a picture is divided into a plurality of segments, then scale-invariant feature transformation (SIFT) is utilized for extracting key points in the segments, the key points serve as low-level features of the segments, then a local restriction linear coding algorithm is utilized for coding the low-level features to obtain medium-level features, then the three-layer depth boltzmann machine is utilized for obtaining high-level features of the segments from the medium-level features, then the high-level features are utilized for training a support vector machine classifier, finally the classifier is used for detecting an airplane of the detected picture, and the airplane detection result high in accuracy and robustness can be obtained.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Encoding method and encoding apparatus
InactiveUS7484159B2Convenient ArrangementError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionShift registerParallel computing
Owner:SONY CORP
Decoding device, decoding method, receiving device, and storage medium reproducing device
InactiveUS20090158128A1Reduce circuit sizeImprove reliabilityError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesLinear codeDependability
A decoding device for a linear code on a ring R, the decoding device including: a plurality of storage media; and a processing section; wherein the processing section uses a part of reliability of all symbols at a previous time to update reliability of each symbol in a process of iterative decoding for increasing the reliability of each symbol, and further retains a part used to update retained reliability information and a part unused to update the retained reliability information on two separate storage media.
Owner:SONY SEMICON SOLUTIONS CORP
Method and apparatus for non-linear code-division multiple access technology
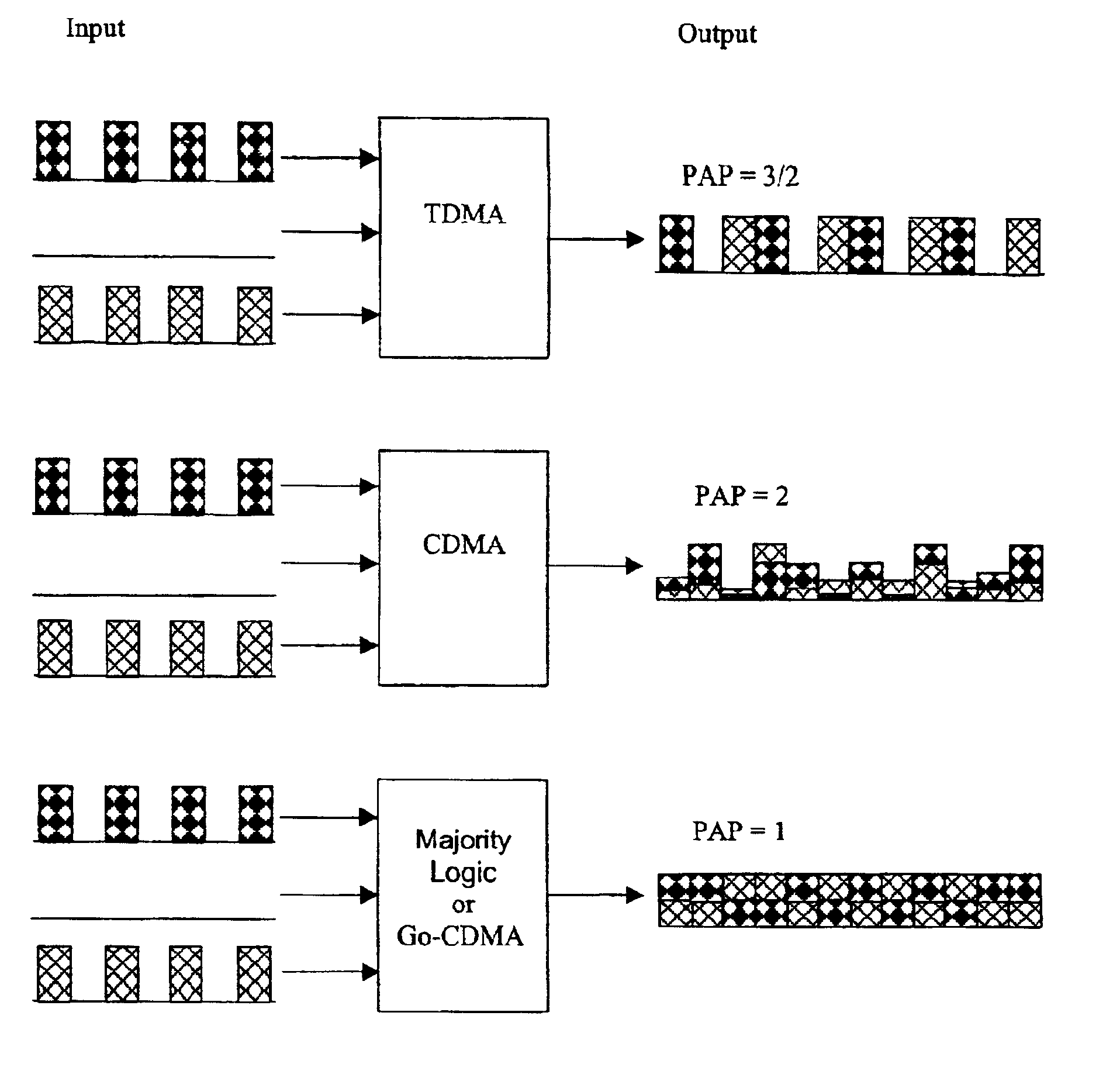
InactiveUS6956891B2High composite signalMore tolerantMultiplex code generationOrthogonal multiplexLinear codeAccess technology
A class of n×l nonlinear block codes, termed Go-CDMA codes are constructed using column-reduced and row-reduced Hadamard orthogonal matrices, termed Go-CDMA matrices. Here n,l are positive integers: n chips of user data are transmitted in frames of size l≦αn, where α is the frame expansion factor. The codes map n-vectors containing binary message data to binary or multi-level l-vectors for transmission, where l≧n. The codes are invertible maps for the binary message data, and when there is no message data in some input vector elements, and noise added between the coding and decoding, there is some error correction. The coding uses integer arithmetic and integer quantization operations, preferably certain sign operations. Go-CDMA codes may be implemented in CDMA communication systems to improve performance on many measures over conventional CDMA and TDMA systems. The coding and decoding may include scrambling and descrambling the Go-CDMA coded signal based on random codes.
Owner:GO CDMA
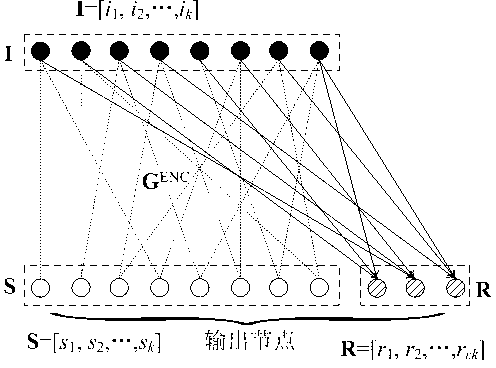
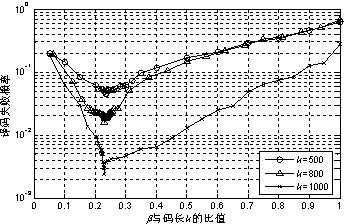
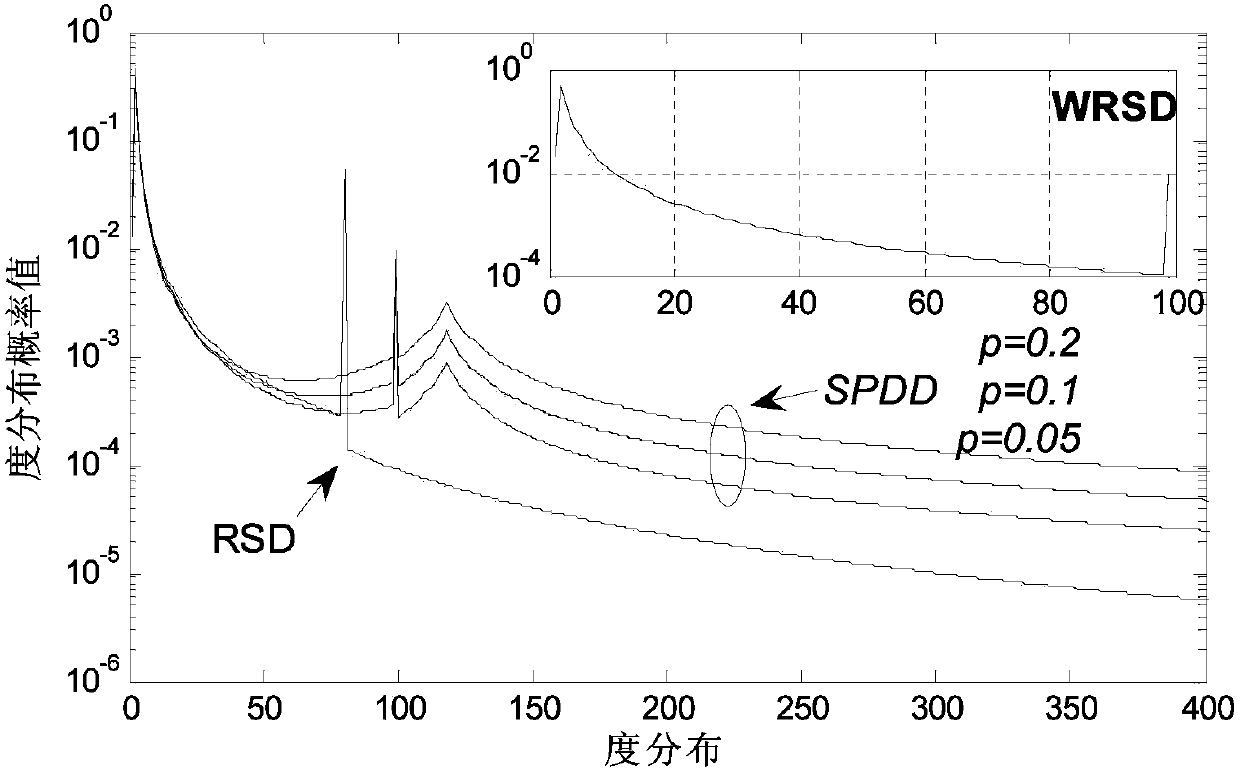
System LT code compiling method based on superposition degree
ActiveCN103346858AGuaranteed Partial Restoration PropertiesLow probability of decoding failureError preventionAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The invention provides a system LT code compiling method based on the superposition degree. The method comprises the following compiling steps: conducting initialization, defining input nodes S, middle nodes I and redundancy check nodes R, constructing a BP translatability matrix in advance, and utilizing S=I G<ENC> to generate the I; generating the R by the I in a distribution mode through the superposition degree; using the S and the R as output nodes to be sequentially sent out. SPDD degree distribution is designed and optimized for the middle nodes of system coding, a DD doping level component is arranged in a superposition mode on the basis of WRSD degree distribution, the full coverage probability on information nodes is effectively ensured, and meanwhile the method has the advantages of ensuring linear code compiling complexity and partial recovery of the middle nodes and theoretically proving the asymptotic performance of the SPDD.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Decoding method and device for decoding linear code
InactiveUS7607063B2Easy to implementLow densityError detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsDecoding methodsParity-check matrix
The present invention relates to a decoding method and a decoder, a program, a recording-and-reproducing apparatus and a method, and a reproducing apparatus and a method that are suitable for decoding encoded data encoded by using a linear code on ring R. A low-density processing unit performs parity-check-matrix low-density processing, performs linear combination for rows of a parity check matrix included in an obtained reception word, and generates a parity check matrix according to the linear-combination result, thereby reducing the density of the parity check matrix used for decoding, at step S21. Then, at step S22, an LDPC decoding unit performs decoding by using a sum product algorithm (SPA) by using the parity check matrix whose density is reduced through the processing performed at step S21. Where the processing at step S22 is finished, the LDPC decoding unit finishes decoding for the reception word. The present invention can be used for an error-correction system.
Owner:SONY CORP
Decoding apparatus, decoding method and program
InactiveUS7536628B2Improve decoding performanceReduce probabilityOther decoding techniquesAlgebraic geometric codesBelief propagationComputer science
The present invention provides a decoding apparatus for carrying out a decoding process on a ring-R linear code. The decoding apparatus includes coded-word holding means for acquiring a coded word with a code length reduced by omission of some symbols from the coded word and for holding the coded word; known-information addition means for attaching a reliability level of each of the symbols omitted from the coded word to reduce its code length as known symbols each having a known value to the coded word held by the coded-word holding means as known information; and repetitive decoding means for repeatedly carrying out a decoding process using belief propagation on the coded word including the known information attached to the coded word by the known-information addition means.
Owner:SONY CORP
Control method for code rate of three-dimensional video based on SAQD domain
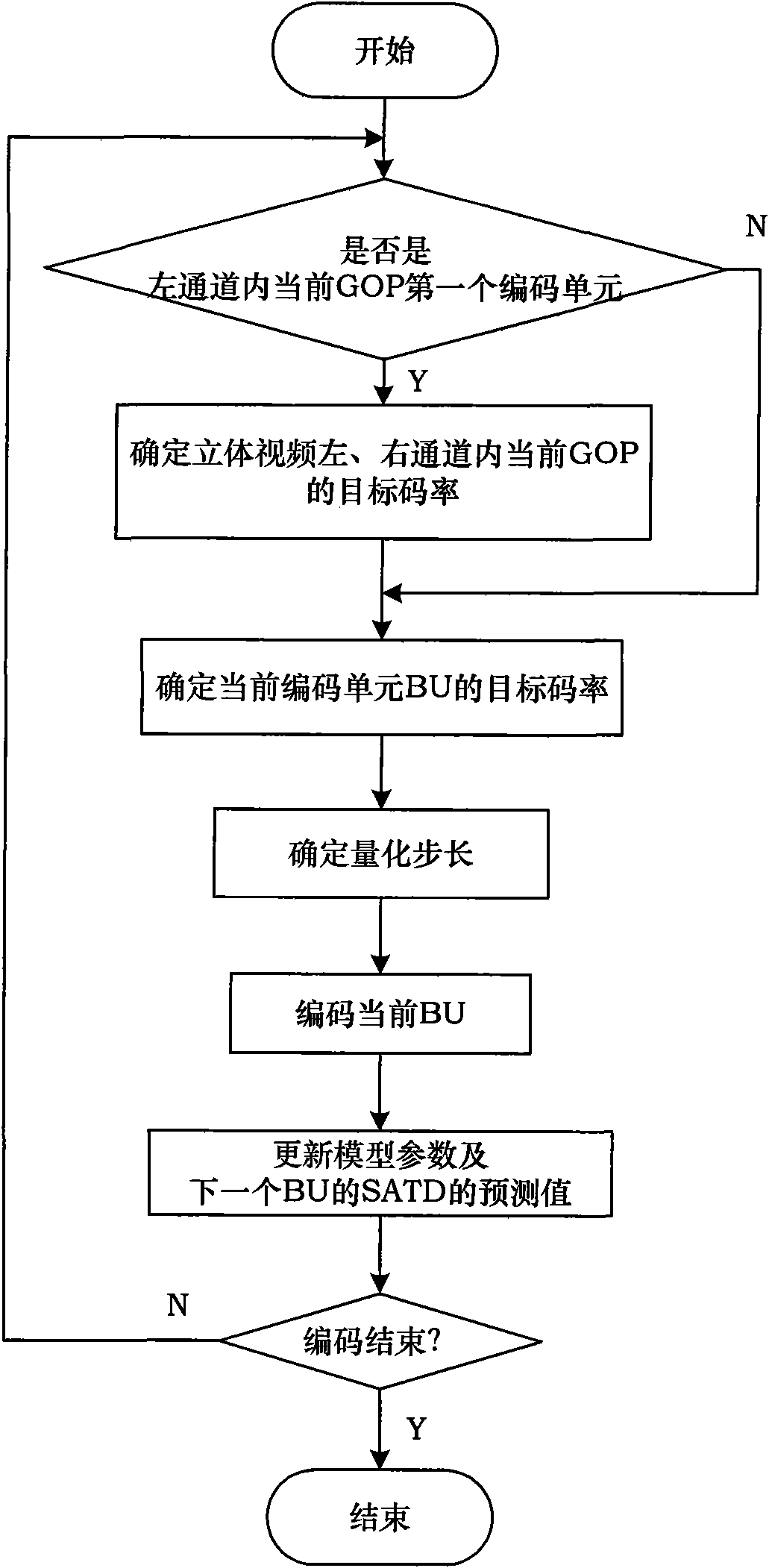
InactiveCN101883283AAccurate descriptionSolve the optimal code rate allocation problemTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationSimulationPeak value
The invention provides a control method for the code rate of a three-dimensional video based on an absolutely quantified residual error and an SAQD domain. In the method, a coding frame of a three-dimensional video with a gradable space coding structure based on an SVC solves the problem of optimal code rate distribution between the channels of the three-dimensional video by introducing the SAQD domain. The invention provides a rate model and a distortion model based on the SAQD domain and obtains the optimal code rates of a left channel and a right channel of the three-dimensional video by the resolution of an Lagrange's equation; and then, the quantified step length of each coding unit is obtained according to the calculated optimal code rate of each coding unit by the calculation of a linear code rate control model, thereby further coding each coding unit. Compared with the modes that the two channels of the three-dimensional video adopt fixed code rate distribution and a code rate control algorithm in an H.264 / SVC standard is adopted in each channel, the peak signal-to-noise ratio of a decoding image obtained by carrying out code rate control by adopting the method is higher, the bias of the output code rate of a coding end and a target code rate is smaller, and the method can adapt to the change of the bandwidth of a network fully.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Encoding method and encoding apparatus
InactiveUS20050204261A1Convenient ArrangementError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionShift registerParallel computing
Owner:SONY CORP
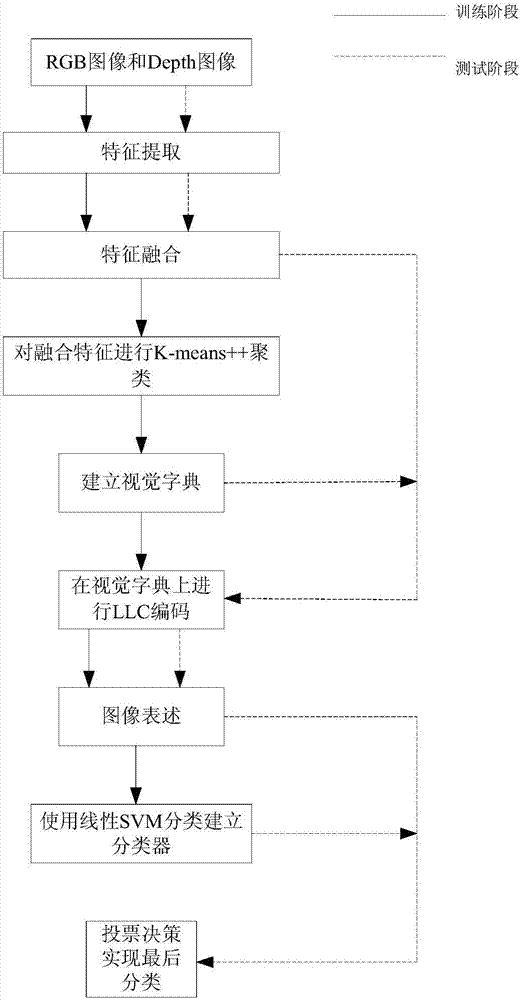
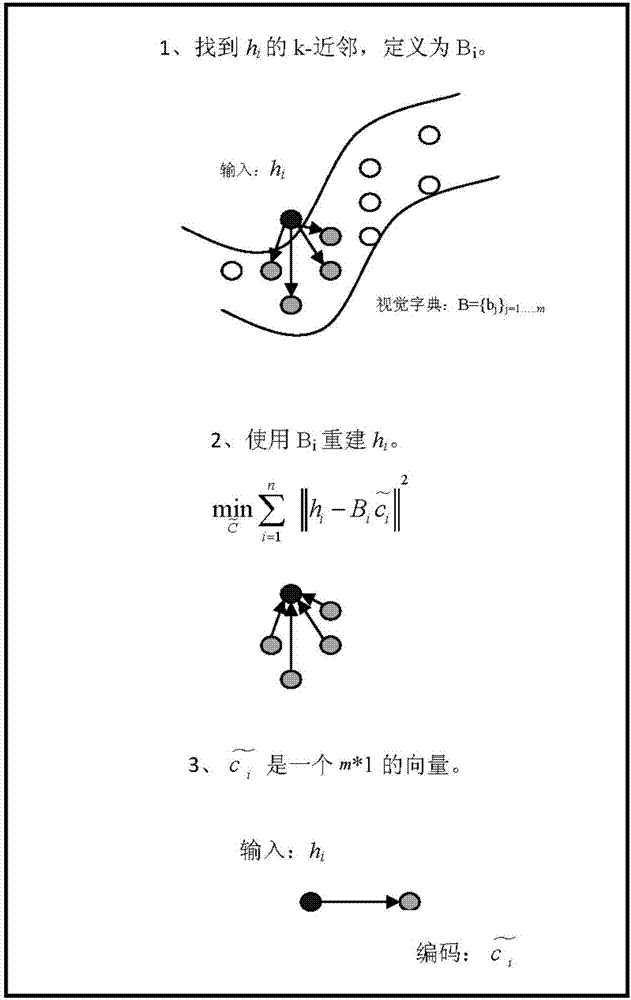
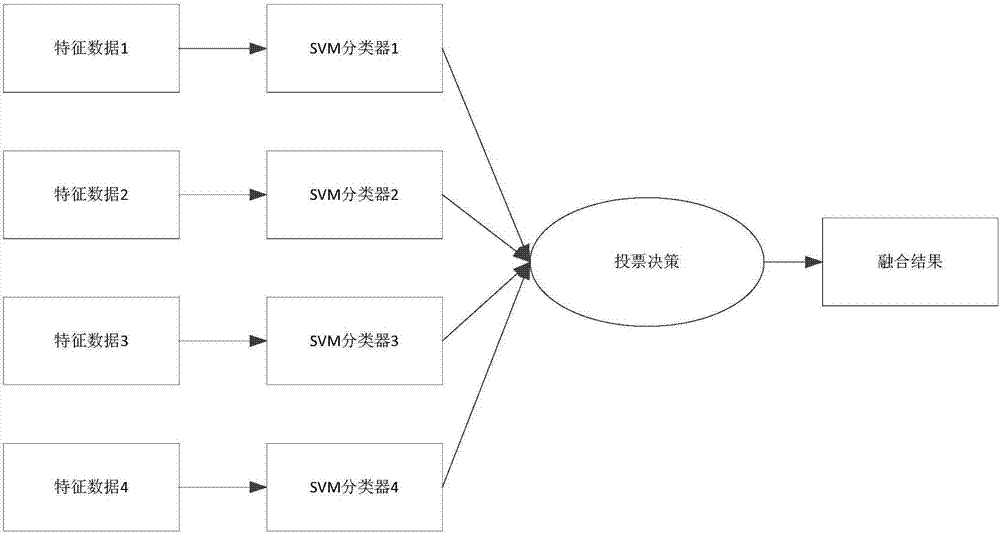
Image classification method based on RGB-D fusion feature and sparse coding
ActiveCN107085731AImprove accuracyAvoid getting stuck in a local optimumCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageImage extraction
The invention discloses an image classification method based on an RGB-D fusion feature and sparse coding. The method comprises following steps of (1) extracting dense SIFT features and PHOG features of a color image and a depth image; (2) carrying out feature fusion on the extracted features of the images by use of a linear serial connection form so as to obtain four kinds of different fusion features finally; (3) using the K-means++ clustering method to carry out clustering processing on the different fusion features so as to obtain four kinds of different vision dictionaries; (4) carrying out local restriction linear coding on each vision dictionary to obtain different image expressing sets; and (5) using the linear SVM to classify the different image expressing sets and using a vote decision method to decide final classification conditions of the obtained classification results. According to the invention, the method is high in classification precision.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Encoder home position sensing method and system
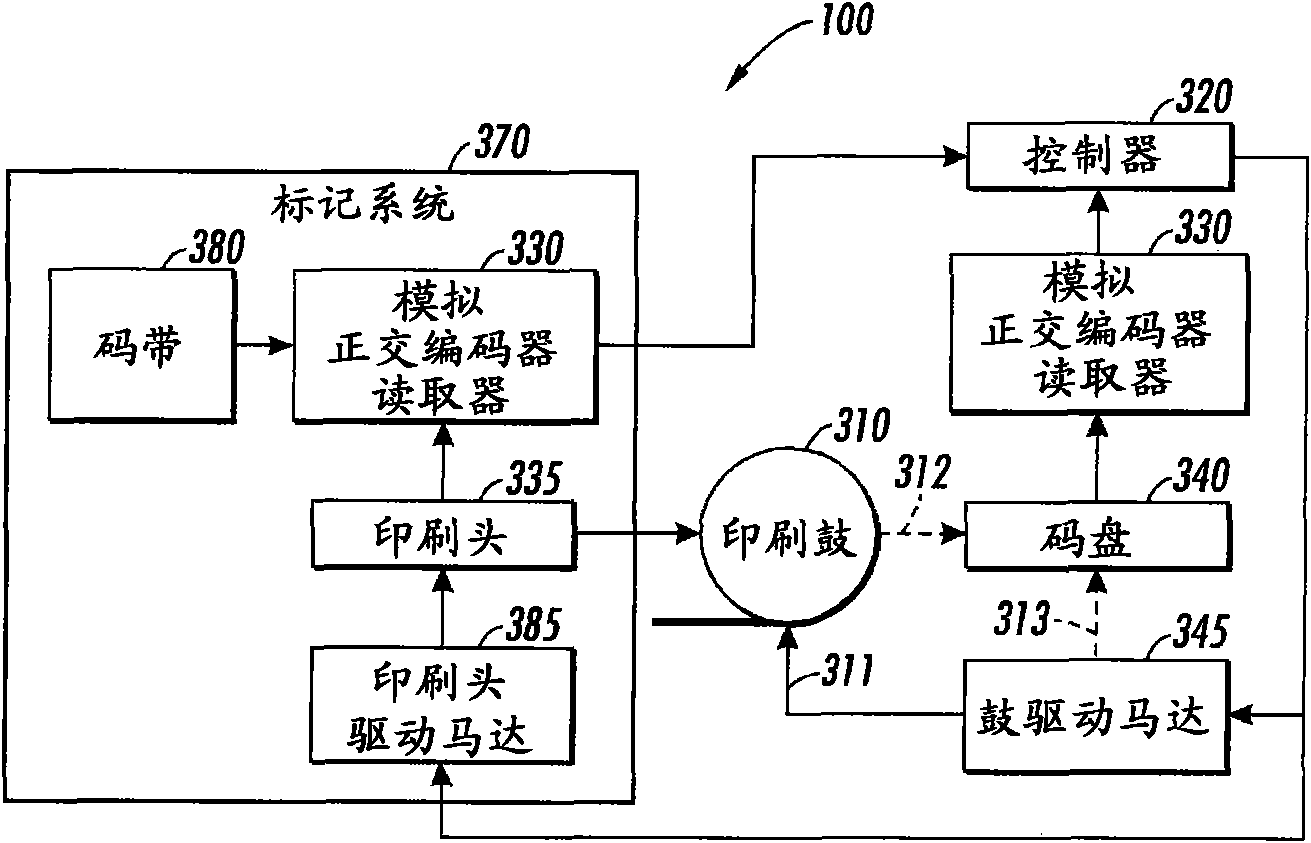
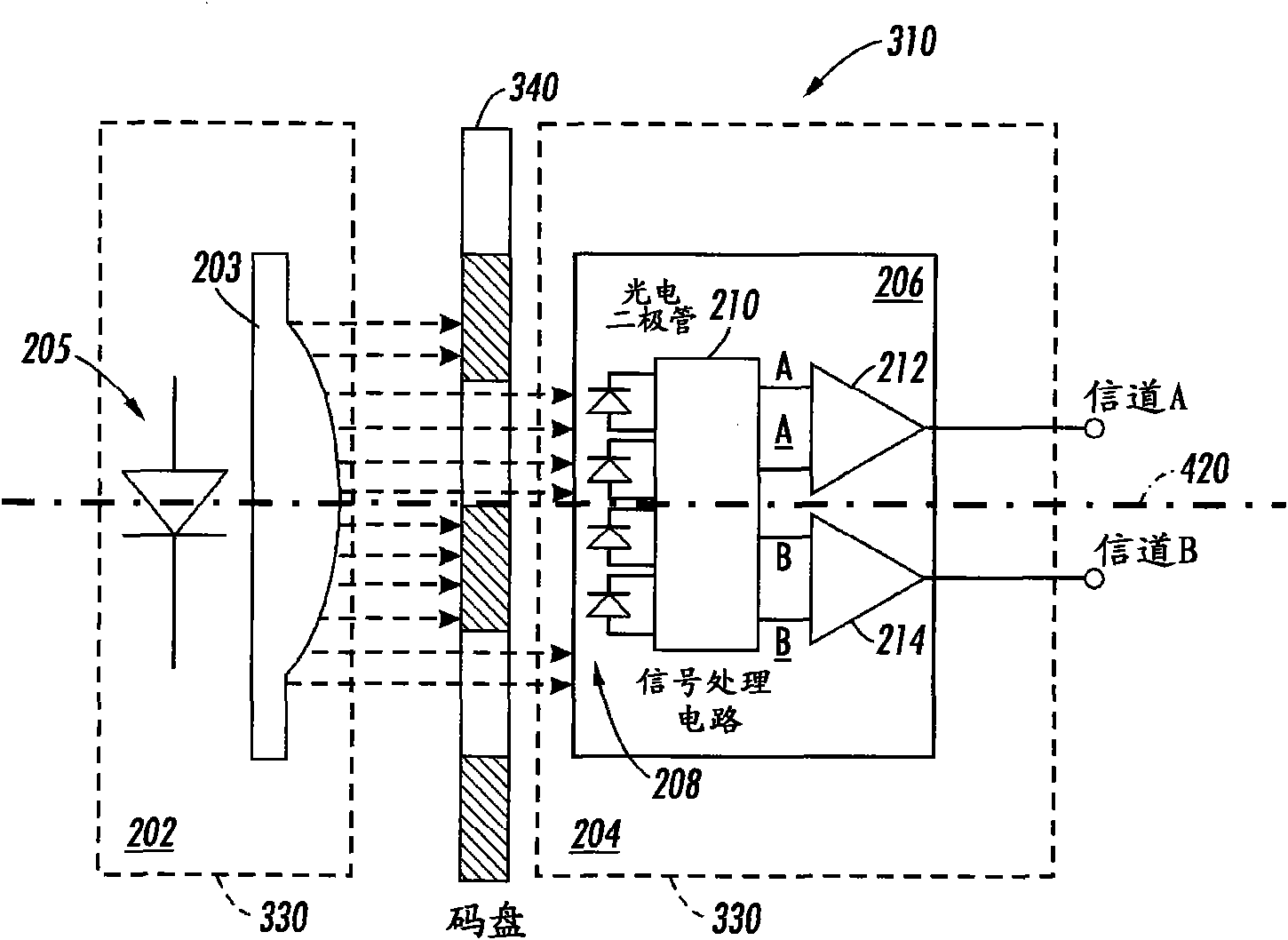
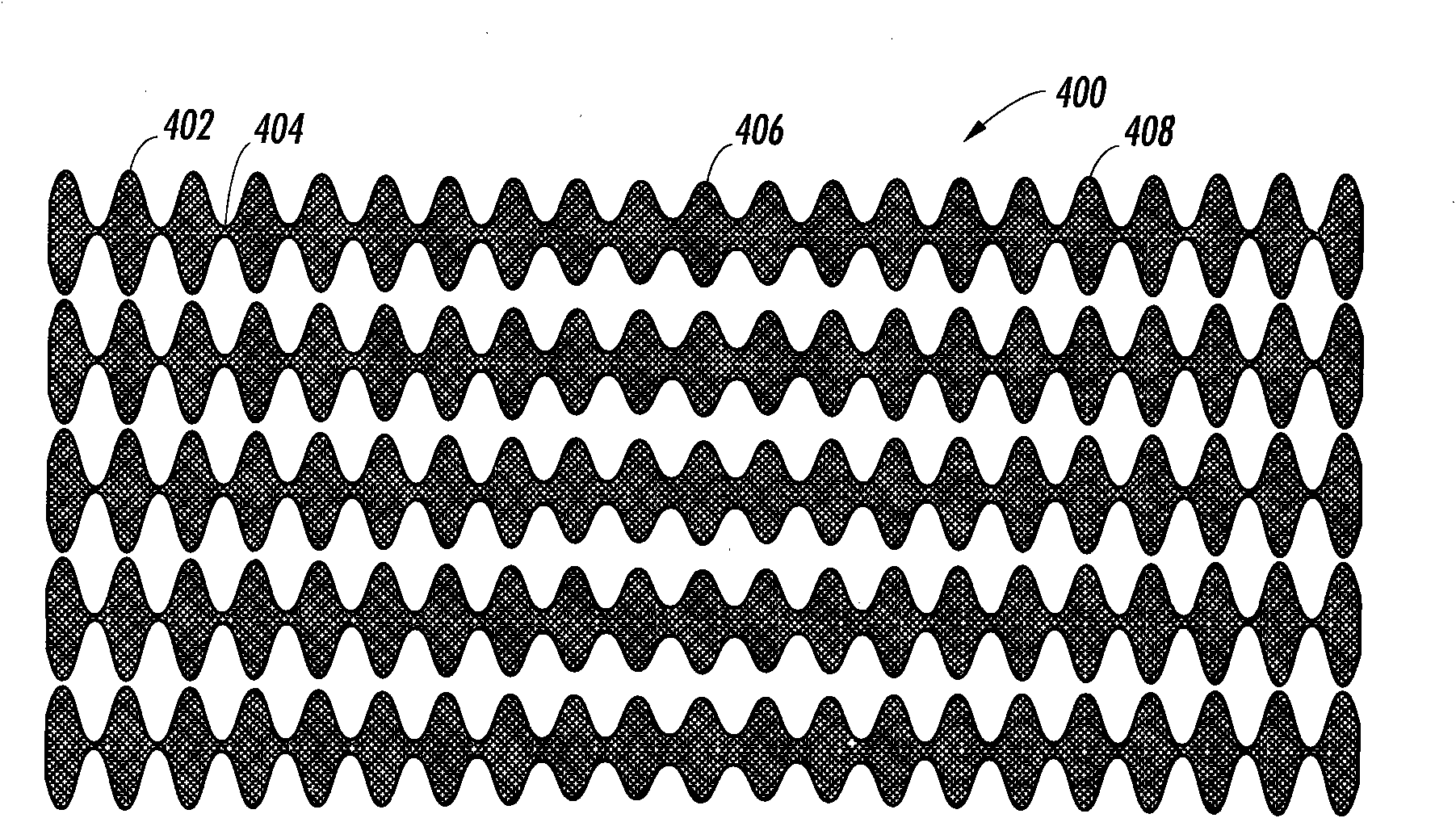
InactiveCN101614559AAccurate locationElectrographic process apparatusOther printing apparatusRing patternLinear code
The invention discloses an encoder home position sensing system and a method, comprising an analog quadrature encoder reader and either a code wheel or a code strip. The code wheel is provided with an optical track composed of annular ring patterns, the thickness of which can be modulated by a sinusoidal function about the code wheel circumference, wherein one cycle of a sine wave is corresponding to one encoder cycle. In one region of the optical track the amplitude of the sine function is changed to imbed an absolute reference home position. The region of the optical track can be sensed and used to determine an absolute system position. The linear code strip is similarly constructed with lines along the direction of motion, the thickness of which is modulated with a sine function, wherein one cycle of the sine wave is corresponding to one encoder cycle and the amplitude of the sine wave function is changed to imbed an absolute reference home position in the optical track.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Code rate controlling method for video coding based on Rho domain
ActiveCN101287123AImprove performanceGeneral formTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationMotion vectorGroup of pictures
The invention relates to a video coding code rate control method based on a Rho domain, which pertains to the technical field of multimedia communication; the invention comprises the steps as follows: the bit rate of a group of pictures (GOP) is confirmed according to a given target code rate, and the bit rate distribution of frame-level is further respectively confirmed according to three frames which are an I-frame (Intra-frame frame), a P-frame (unidirectional predictive frame) and a B-frame (bidirectional predictive frame); the characteristic parameters of the previous frames of the same type are checked to predict the slope parameter Theta of a linear code rate model, model interception difference Delta c, the ratio s of motion vector code rate and entropy coding code rate that is quantified by residual coefficient, and zero coefficient proportion Rho that meets the code rate limit is calculated; a Rho-QP mapping table is referred to obtain a quantization parameter (QP) which is used for coding the current video frame. The code rate control method of the invention is simple and practical, and has excellent performance and the original video coding standards.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com