Patents
Literature
653 results about "Erasure code" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
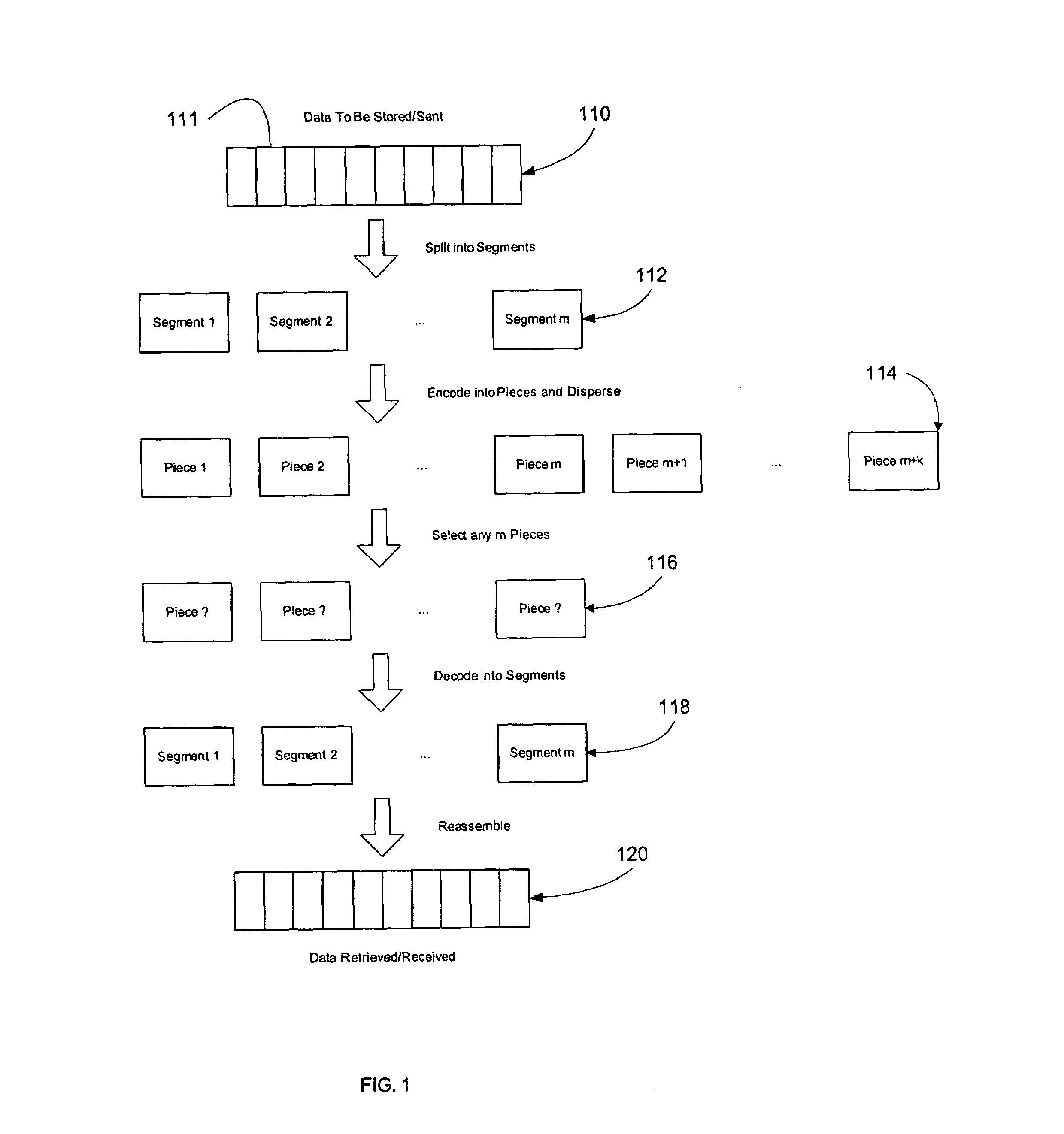
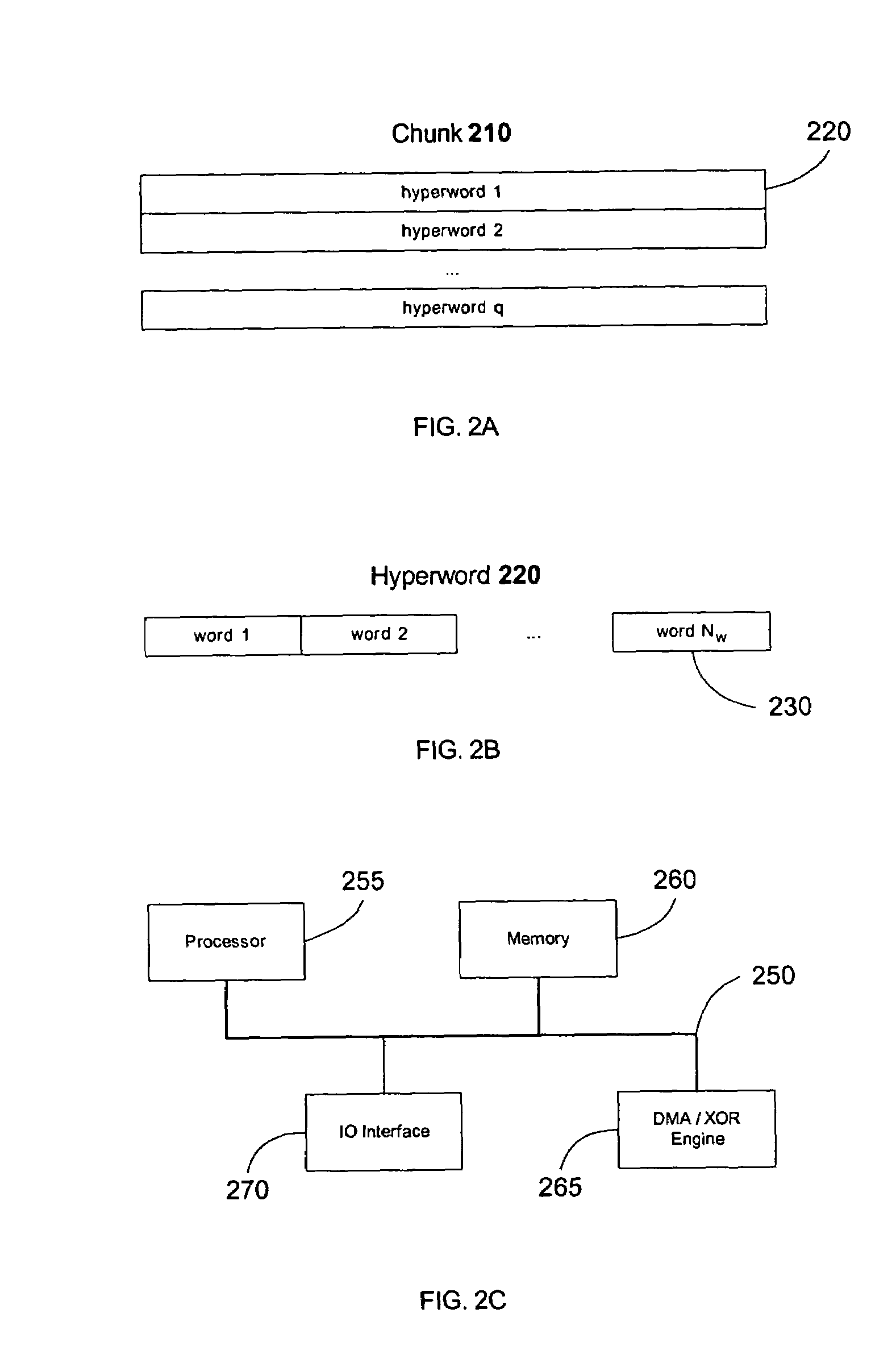
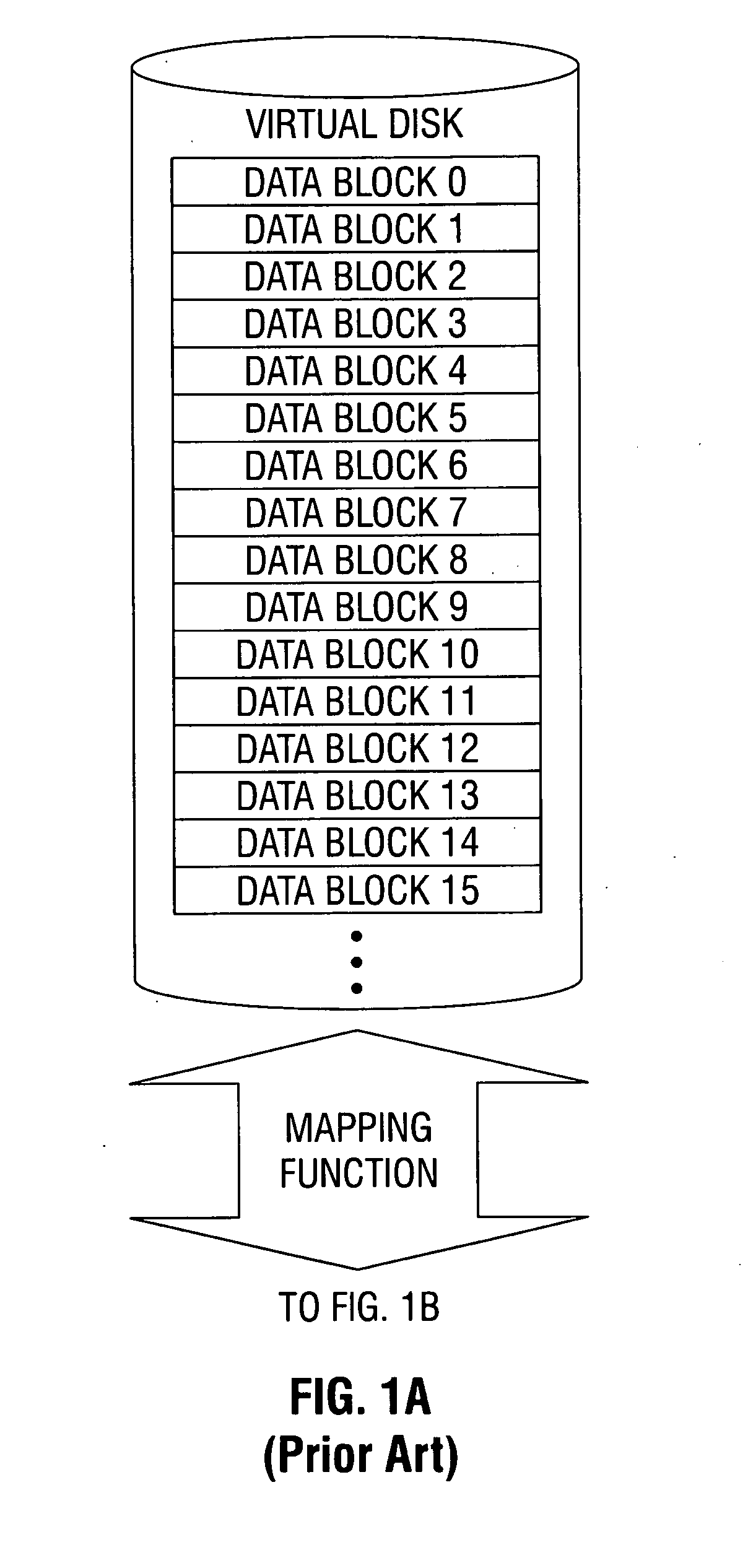
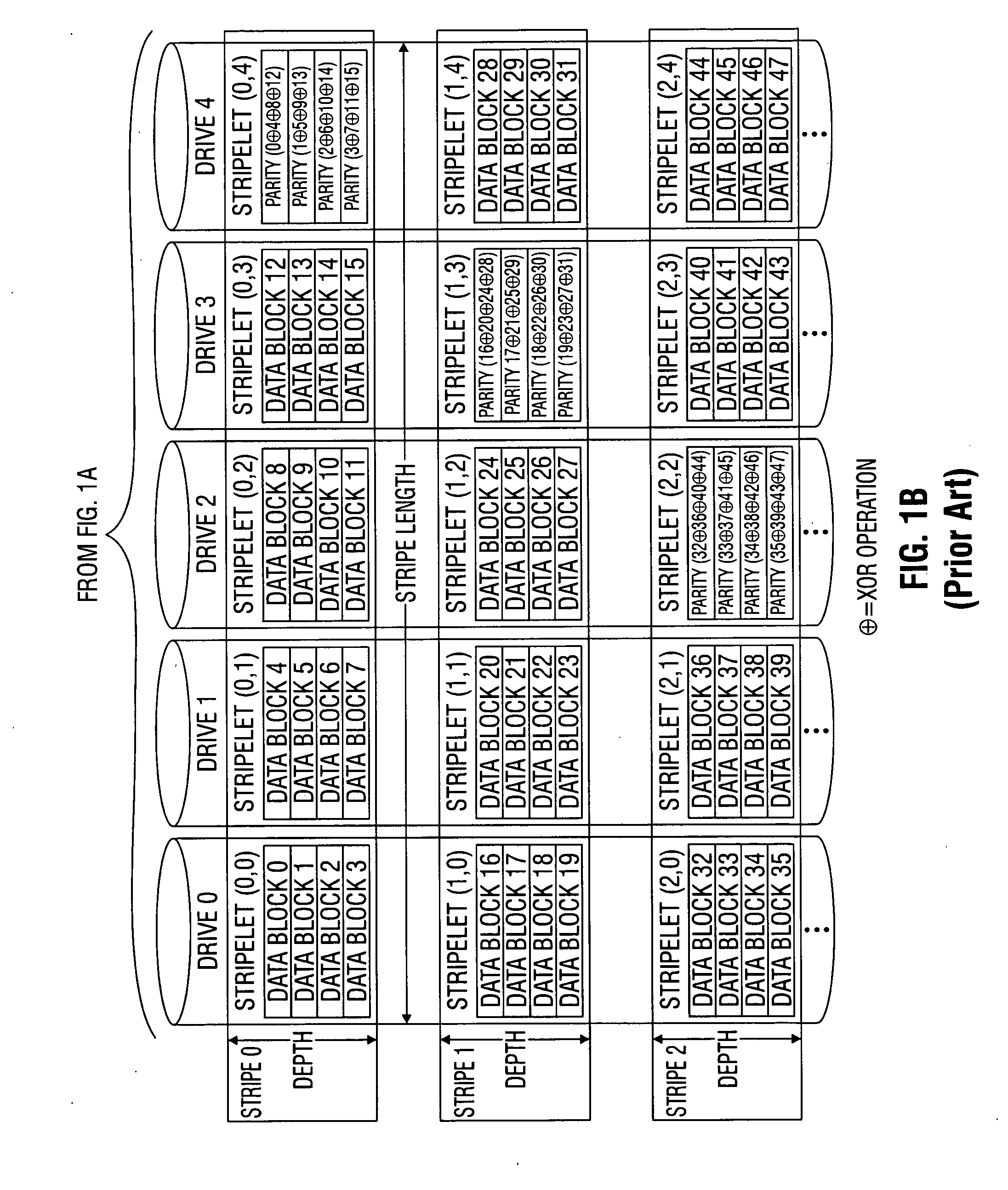
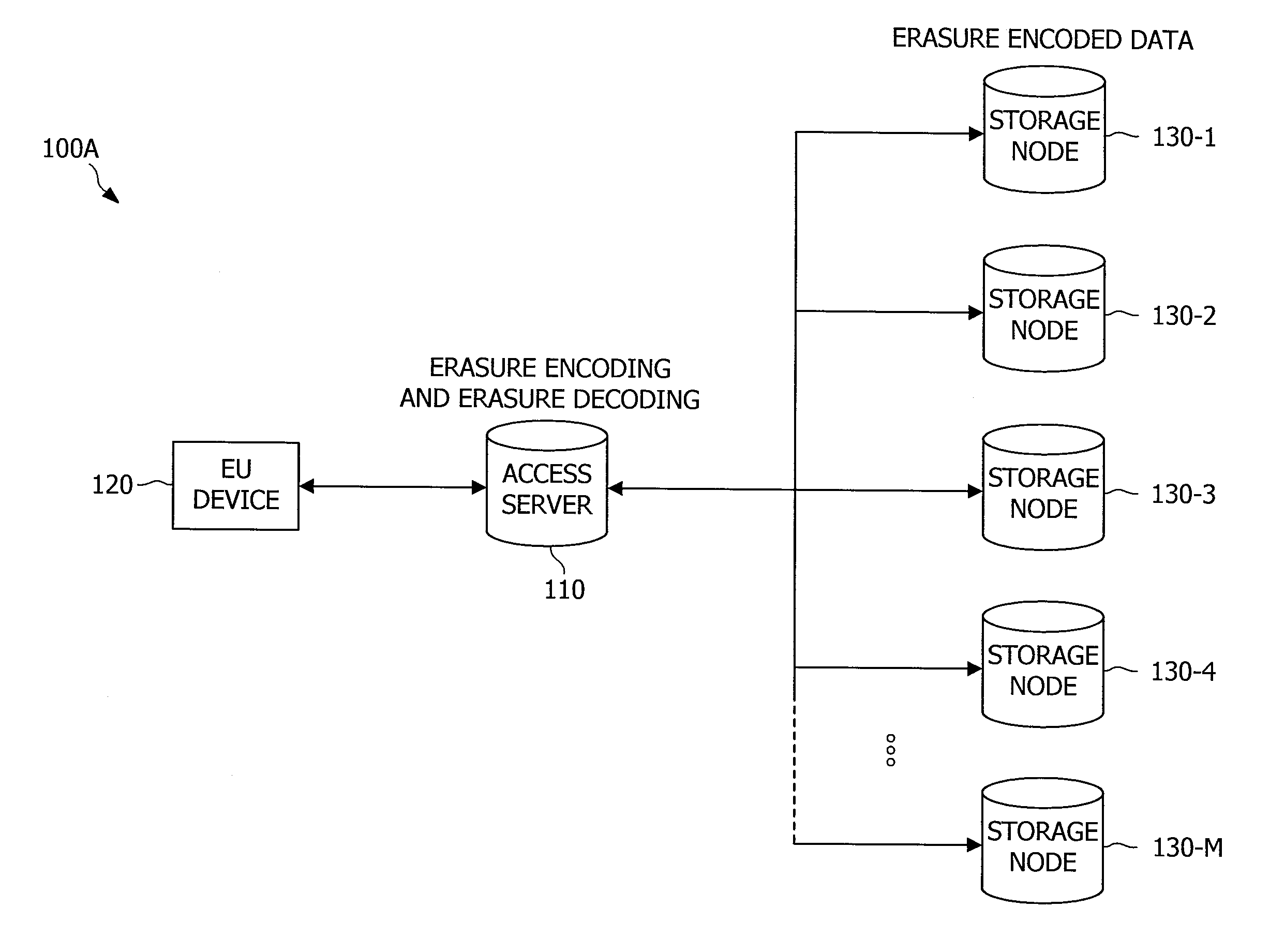
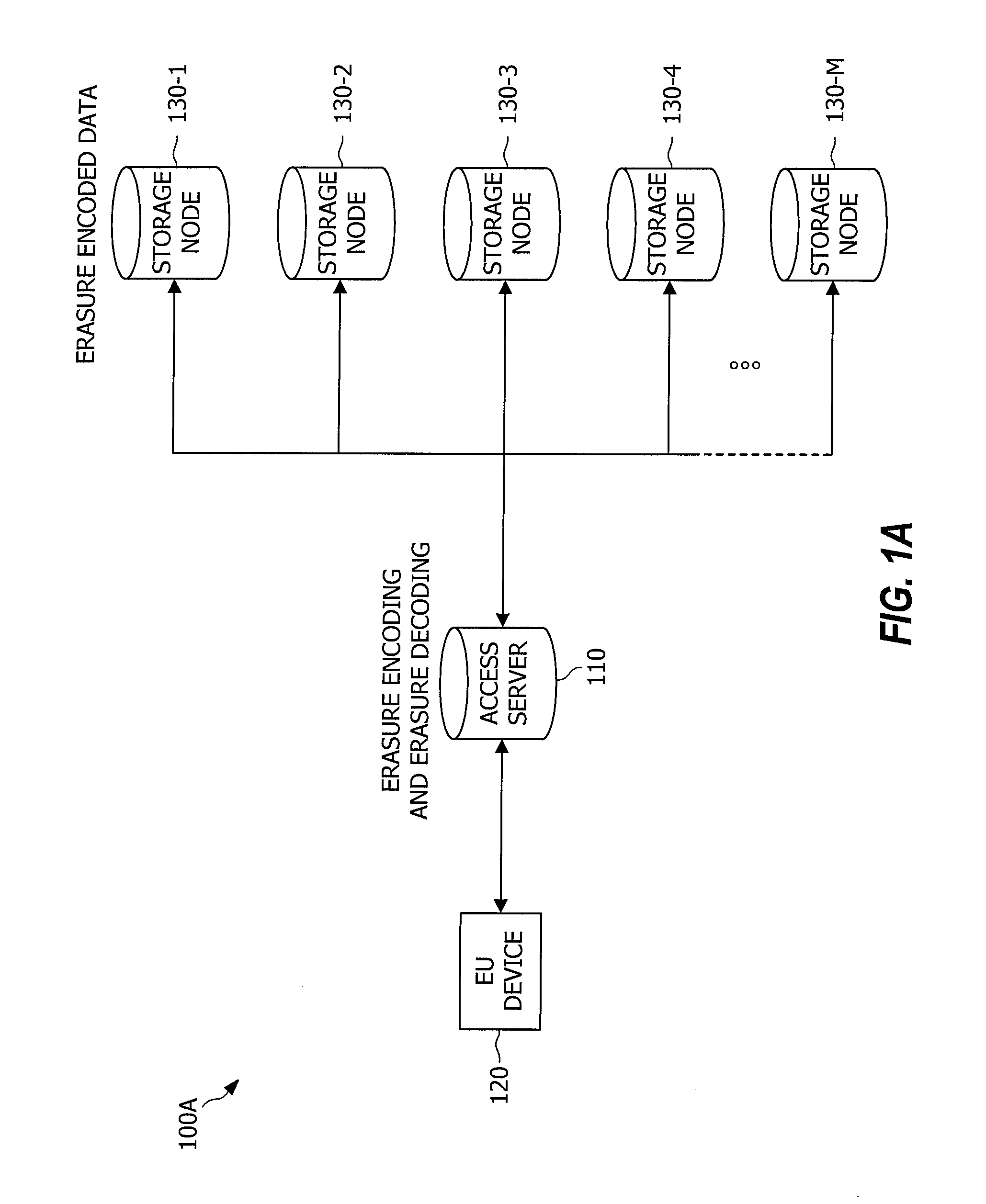
In coding theory, an erasure code is a forward error correction (FEC) code under the assumption of bit erasures (rather than bit errors), which transforms a message of k symbols into a longer message (code word) with n symbols such that the original message can be recovered from a subset of the n symbols. The fraction r = k/n is called the code rate. The fraction k’/k, where k’ denotes the number of symbols required for recovery, is called reception efficiency.
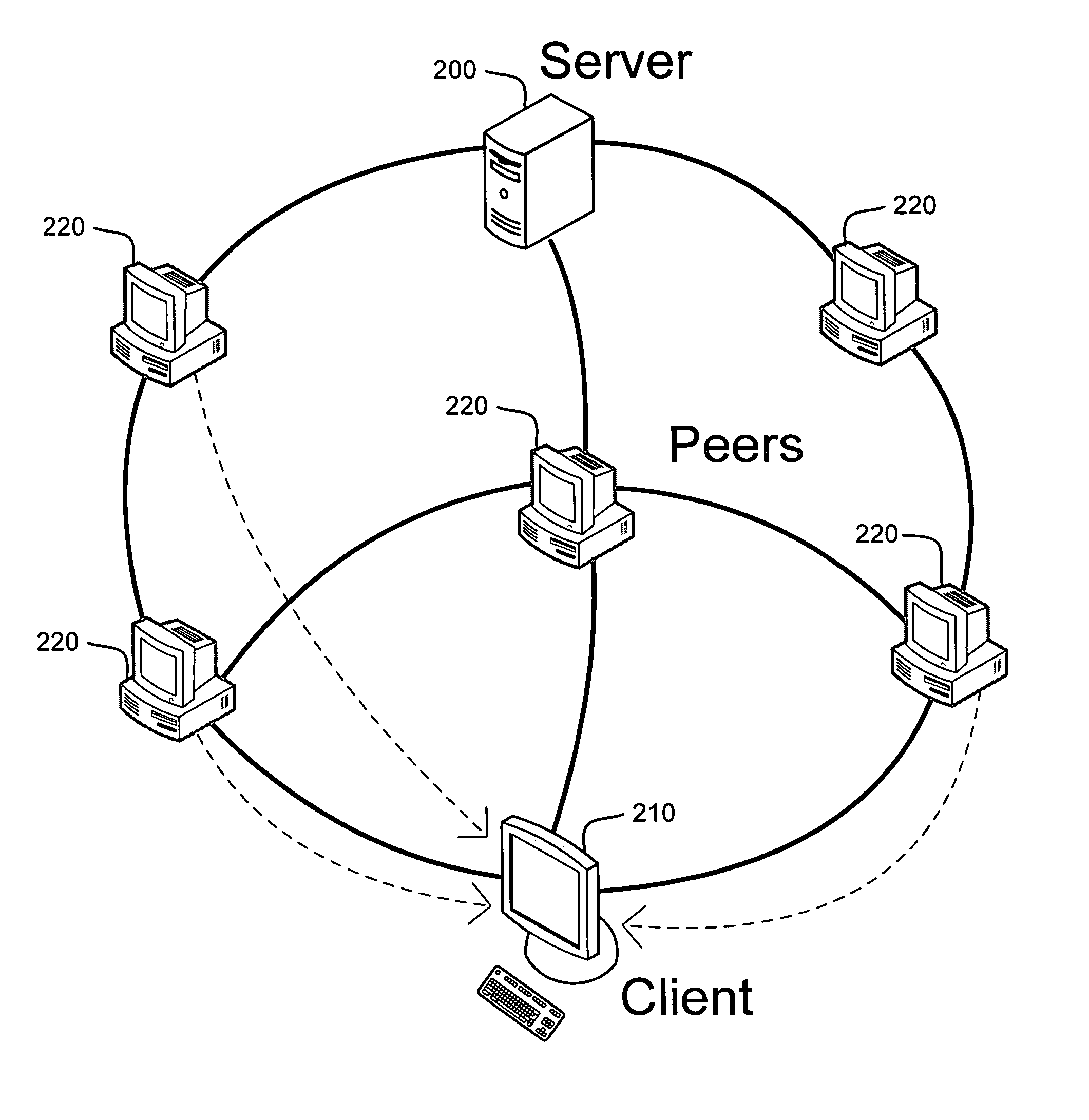
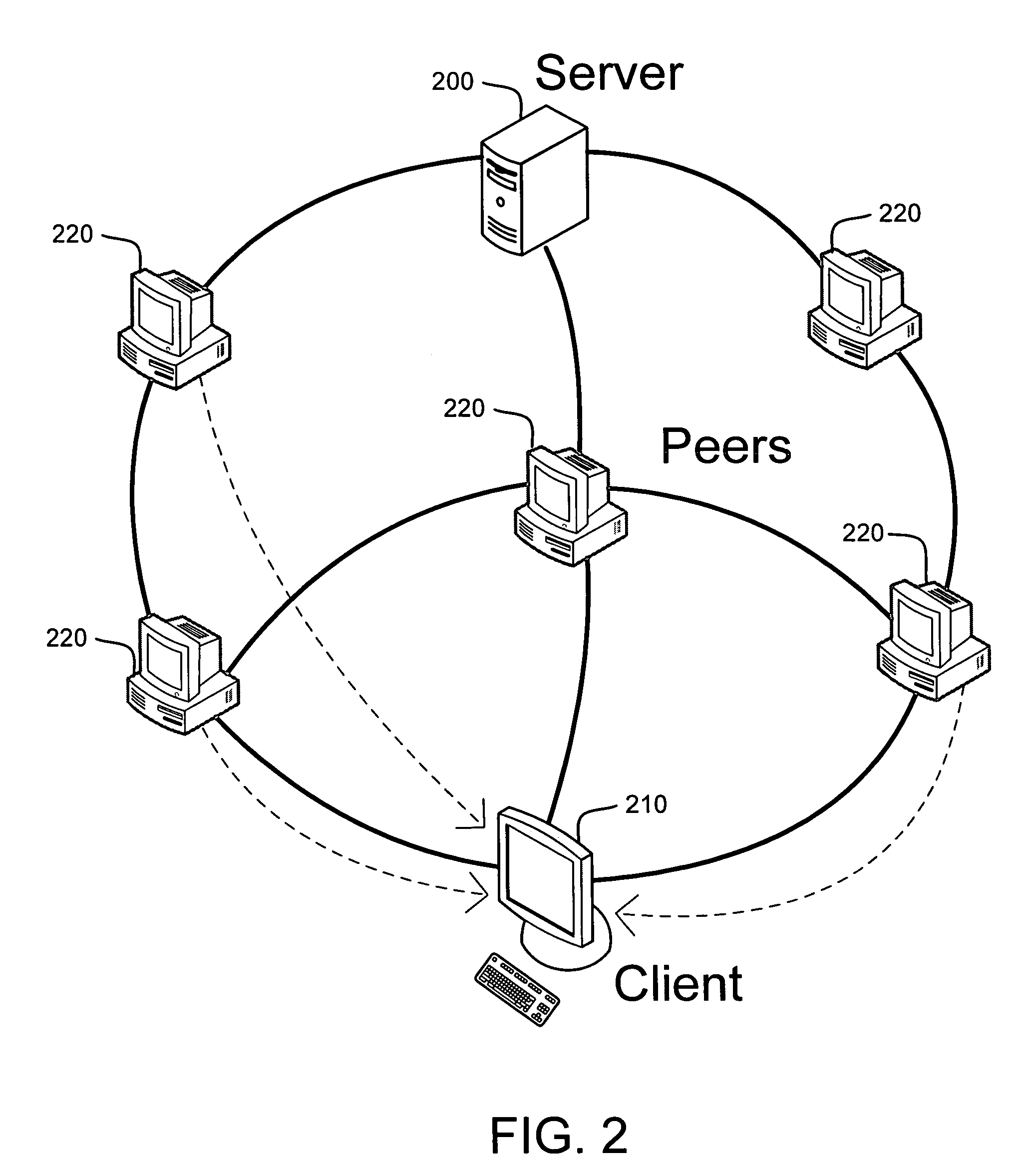
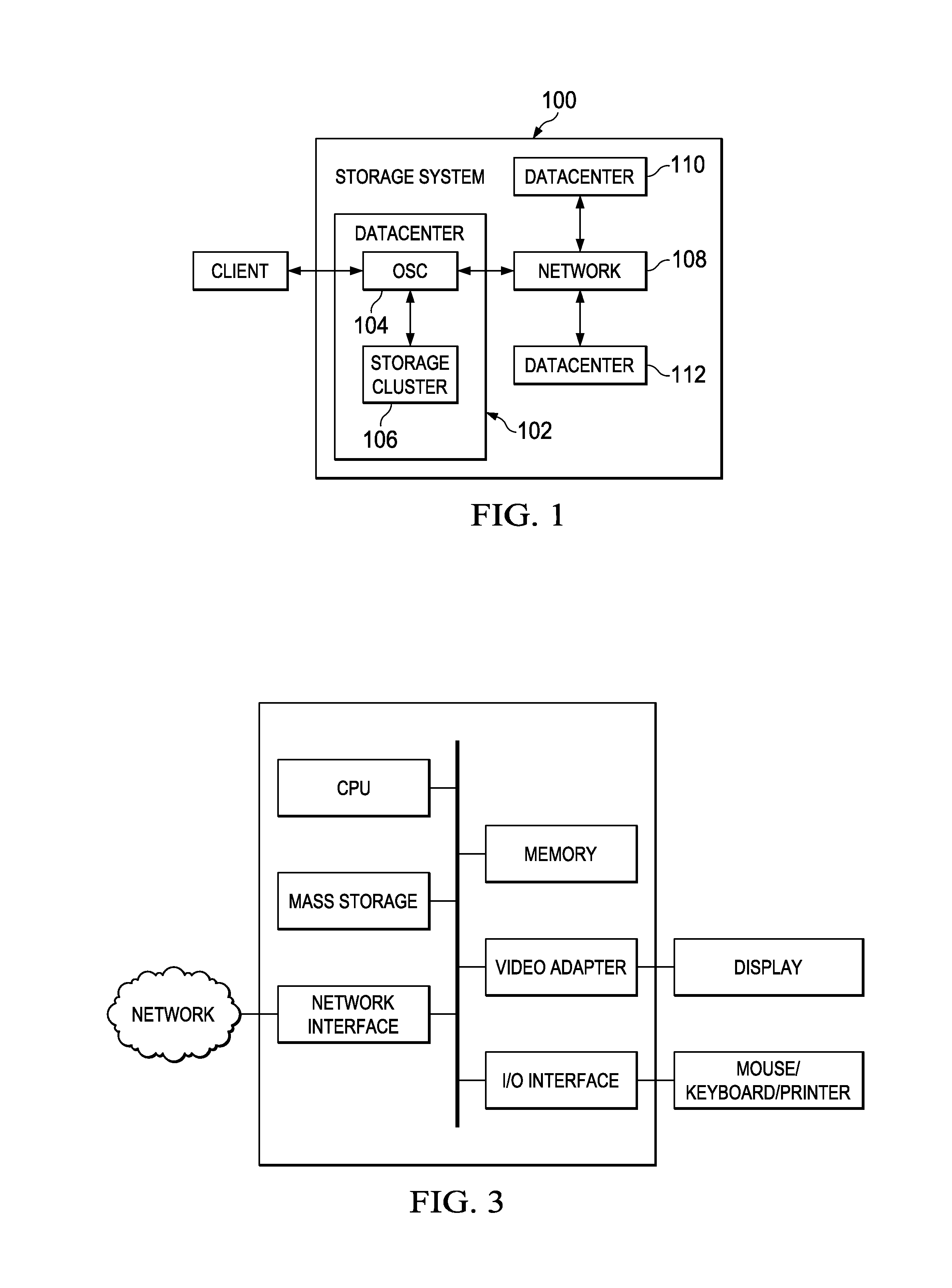
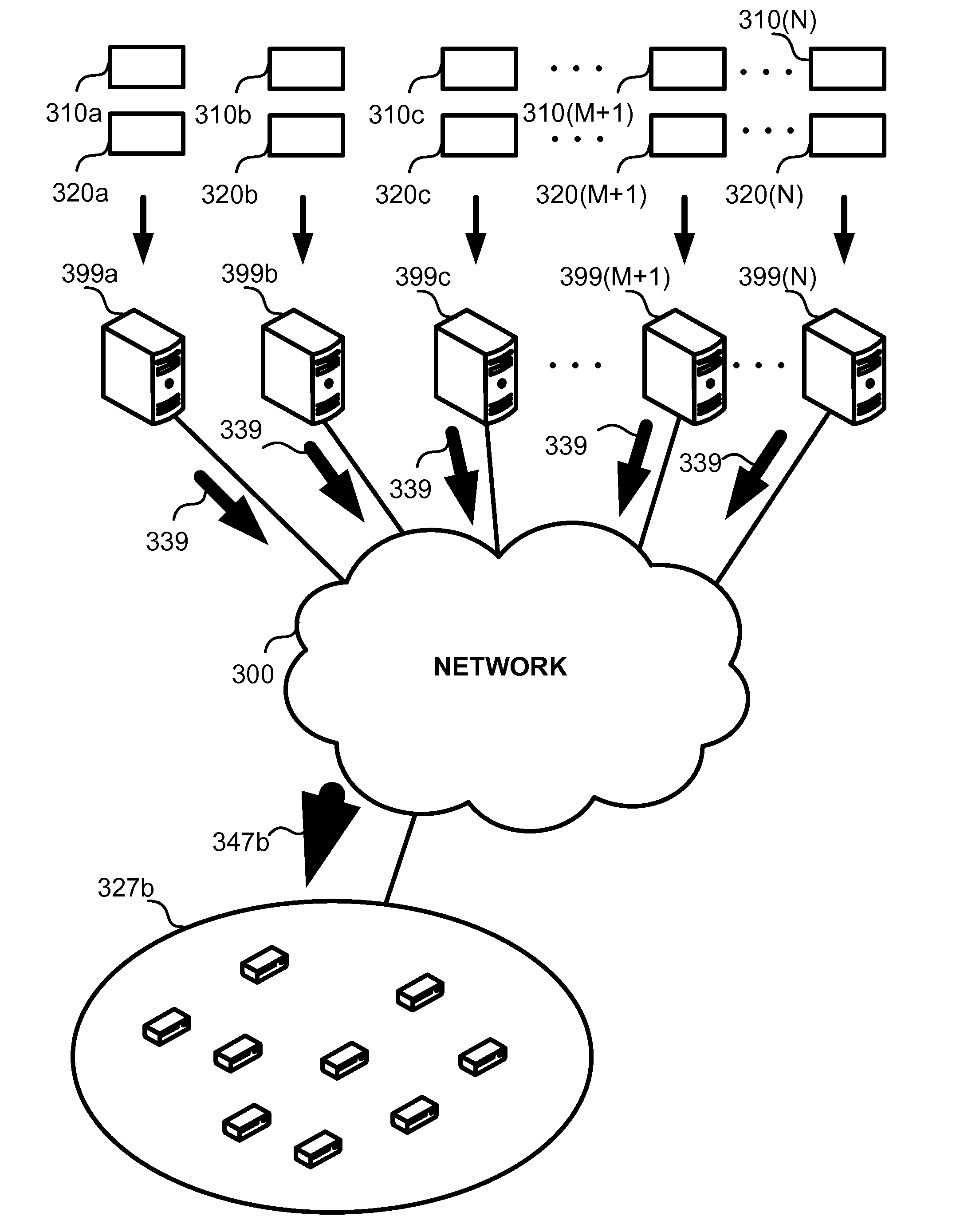
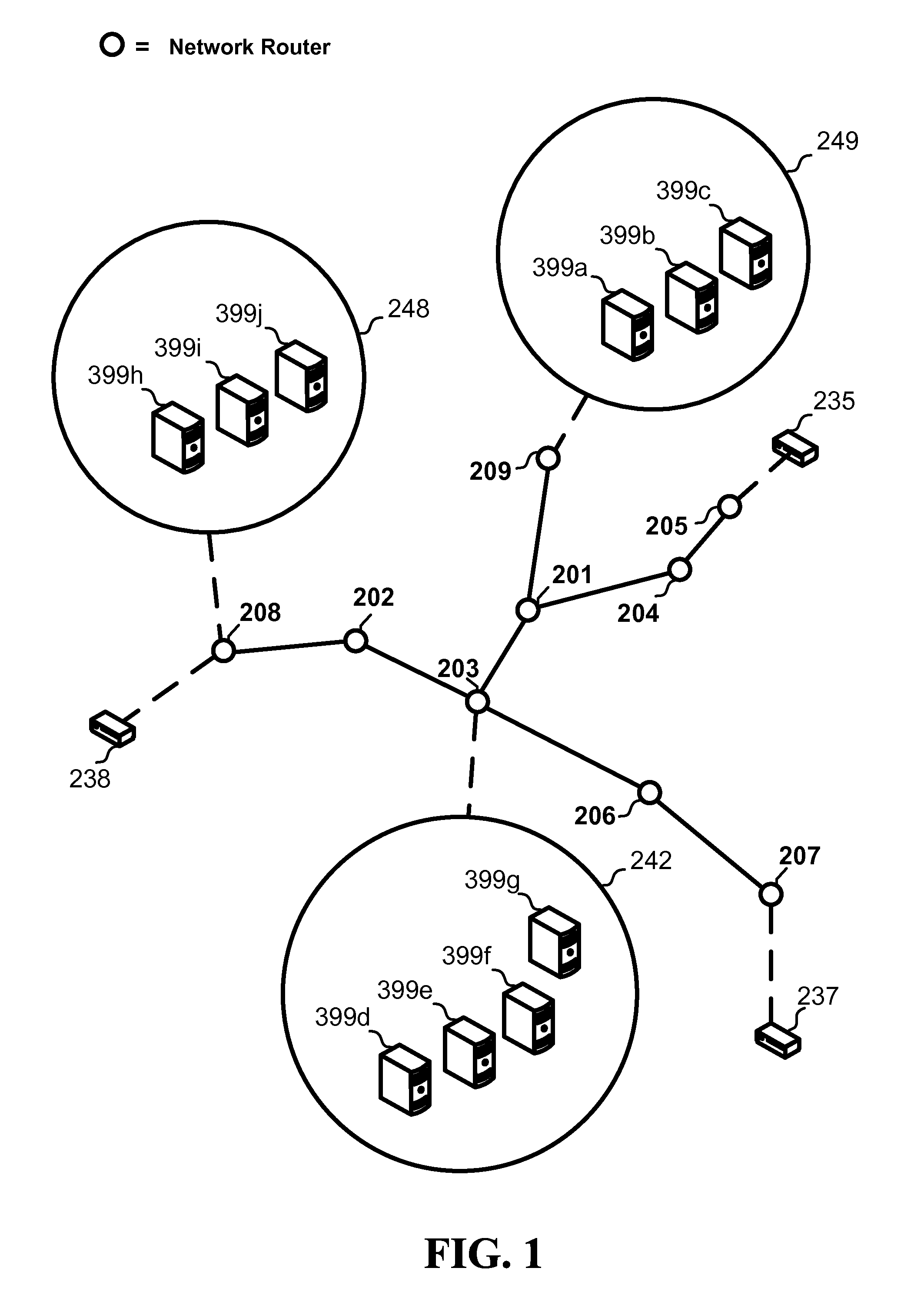
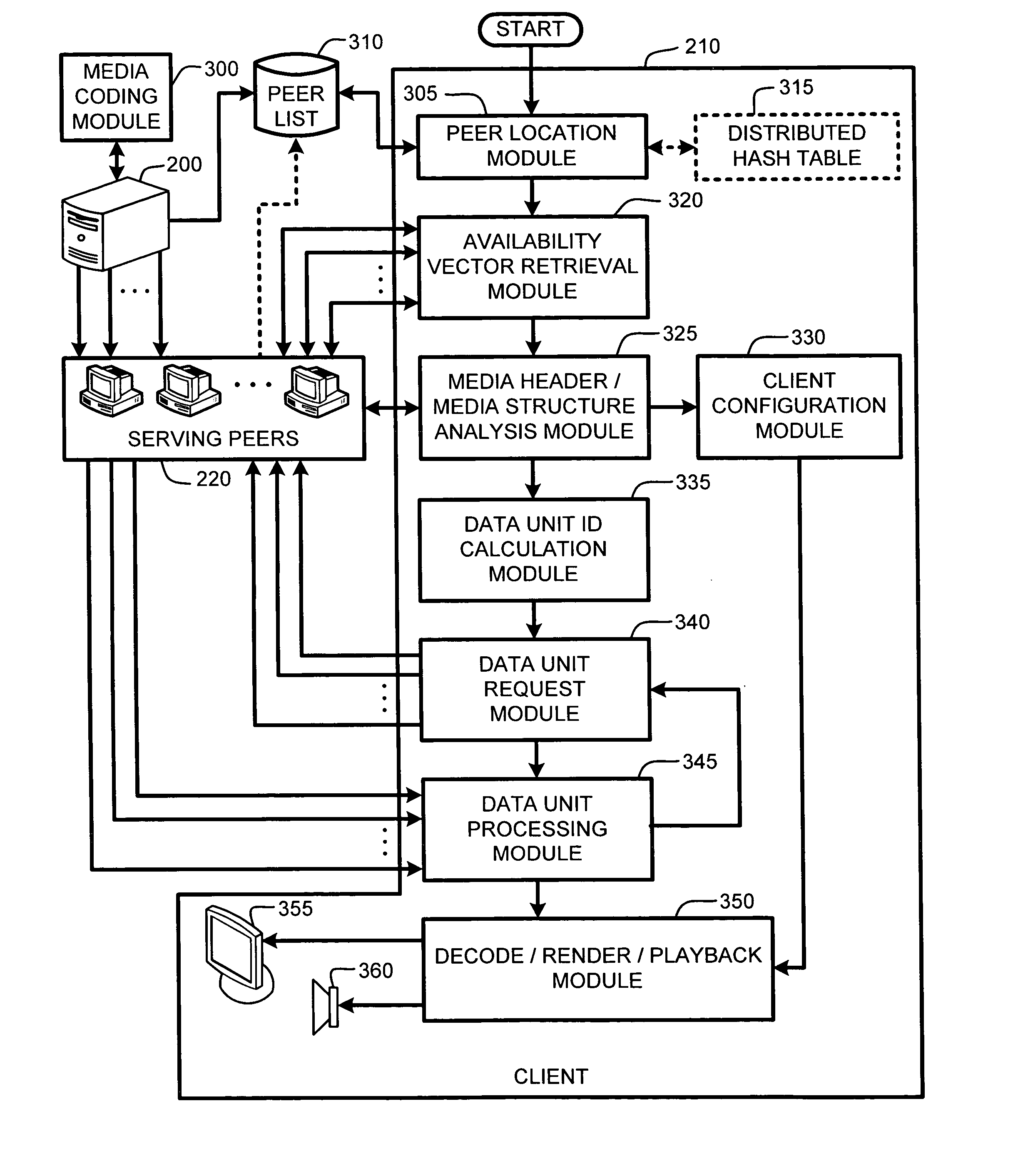
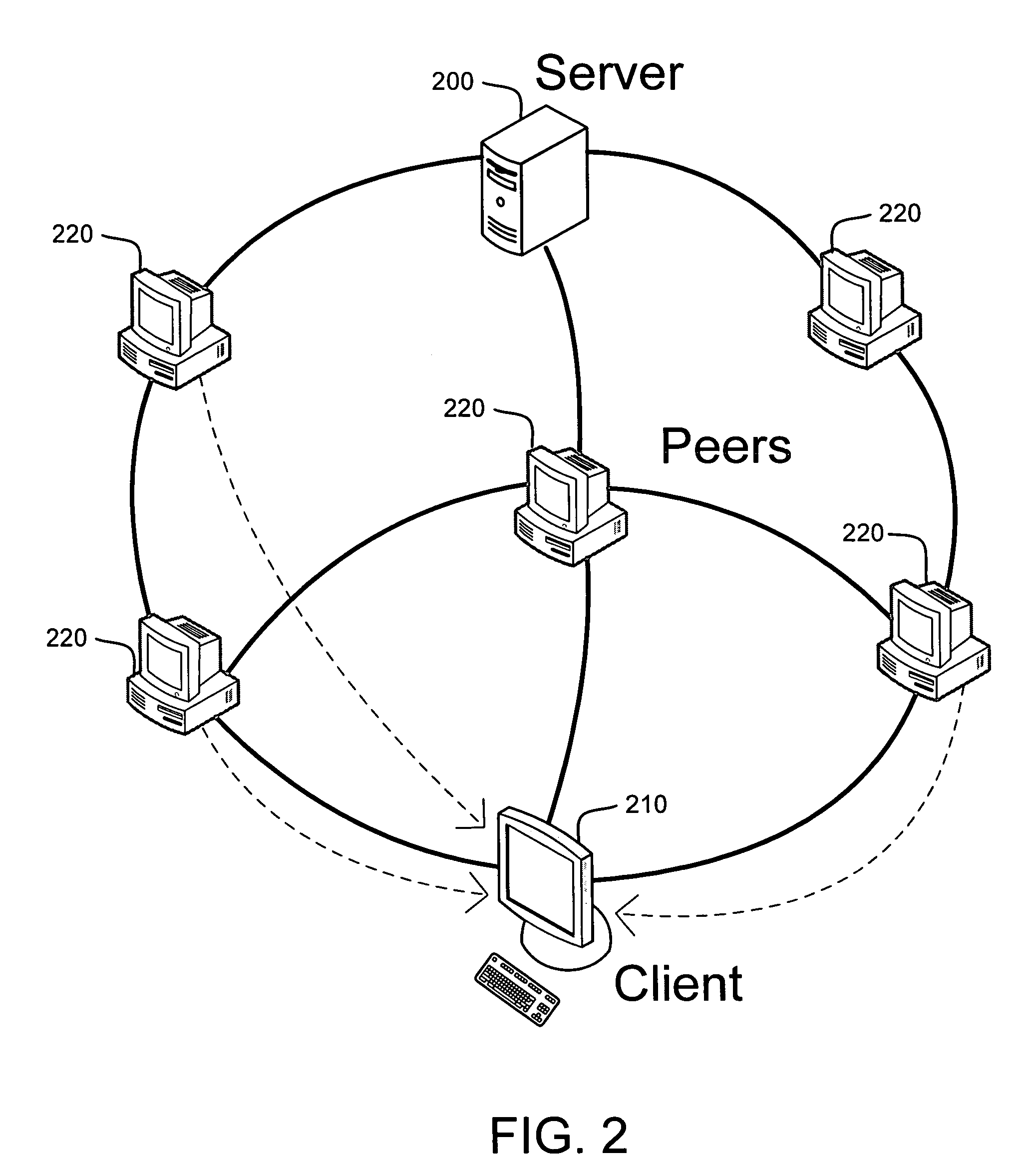
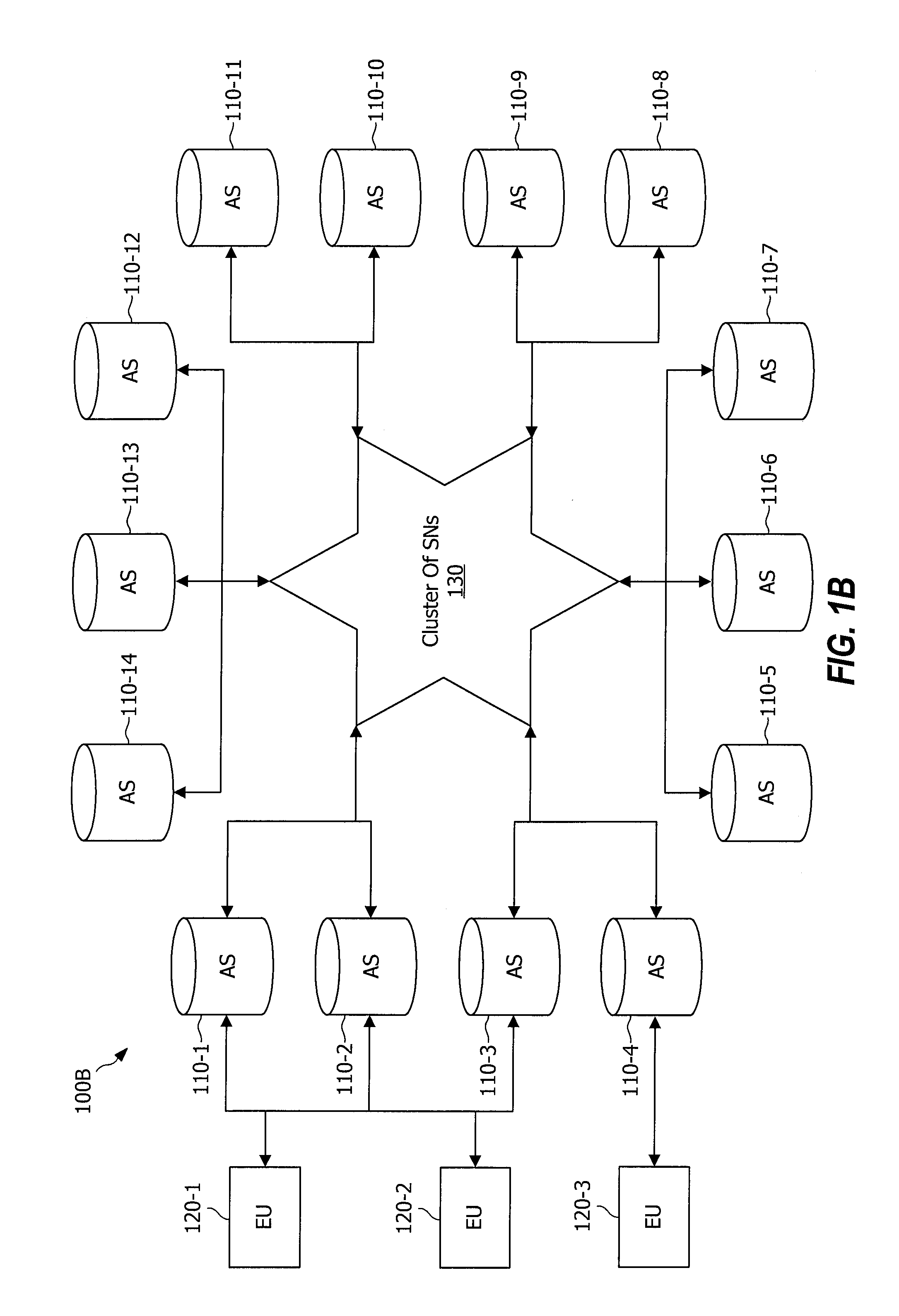
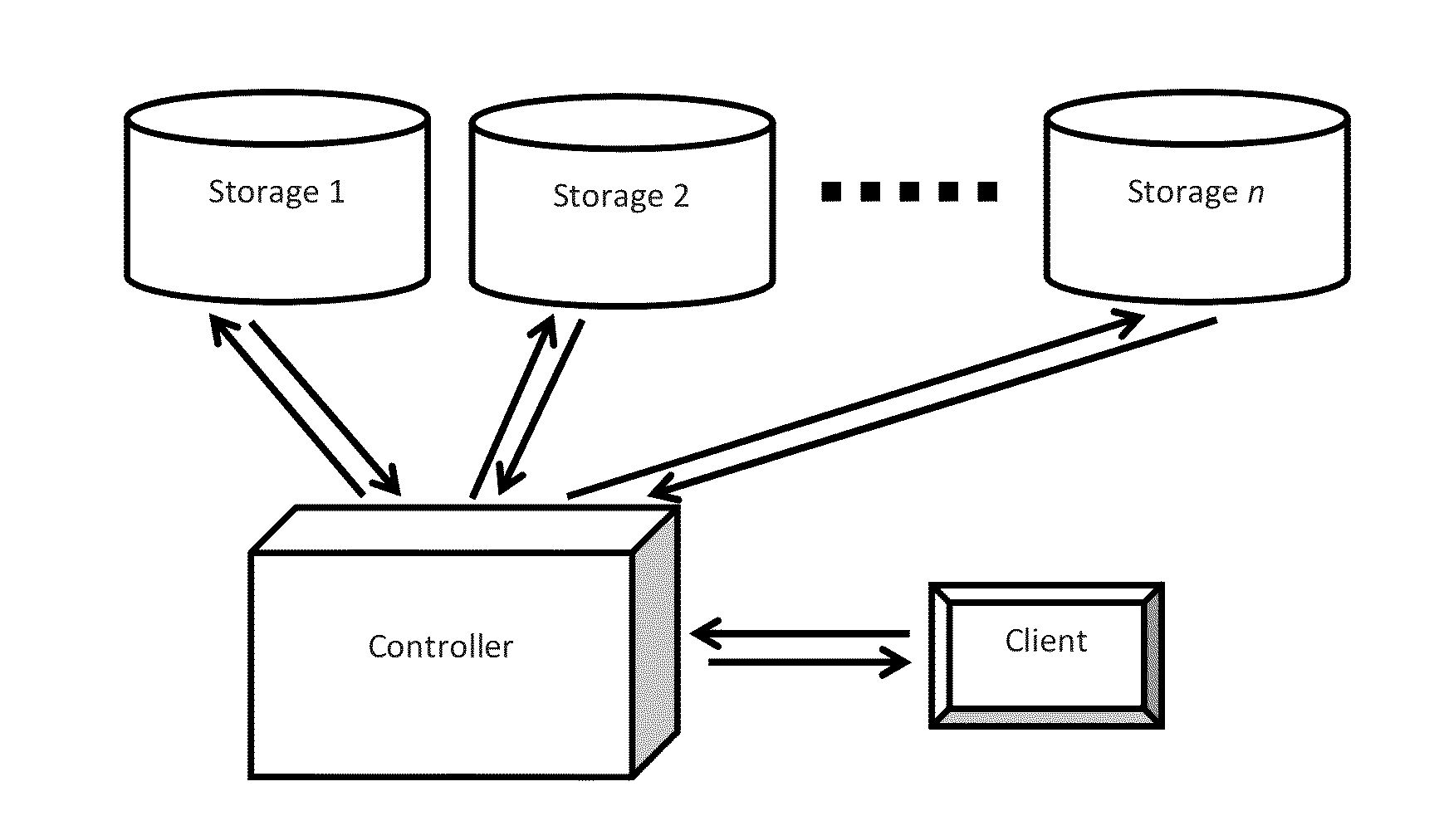
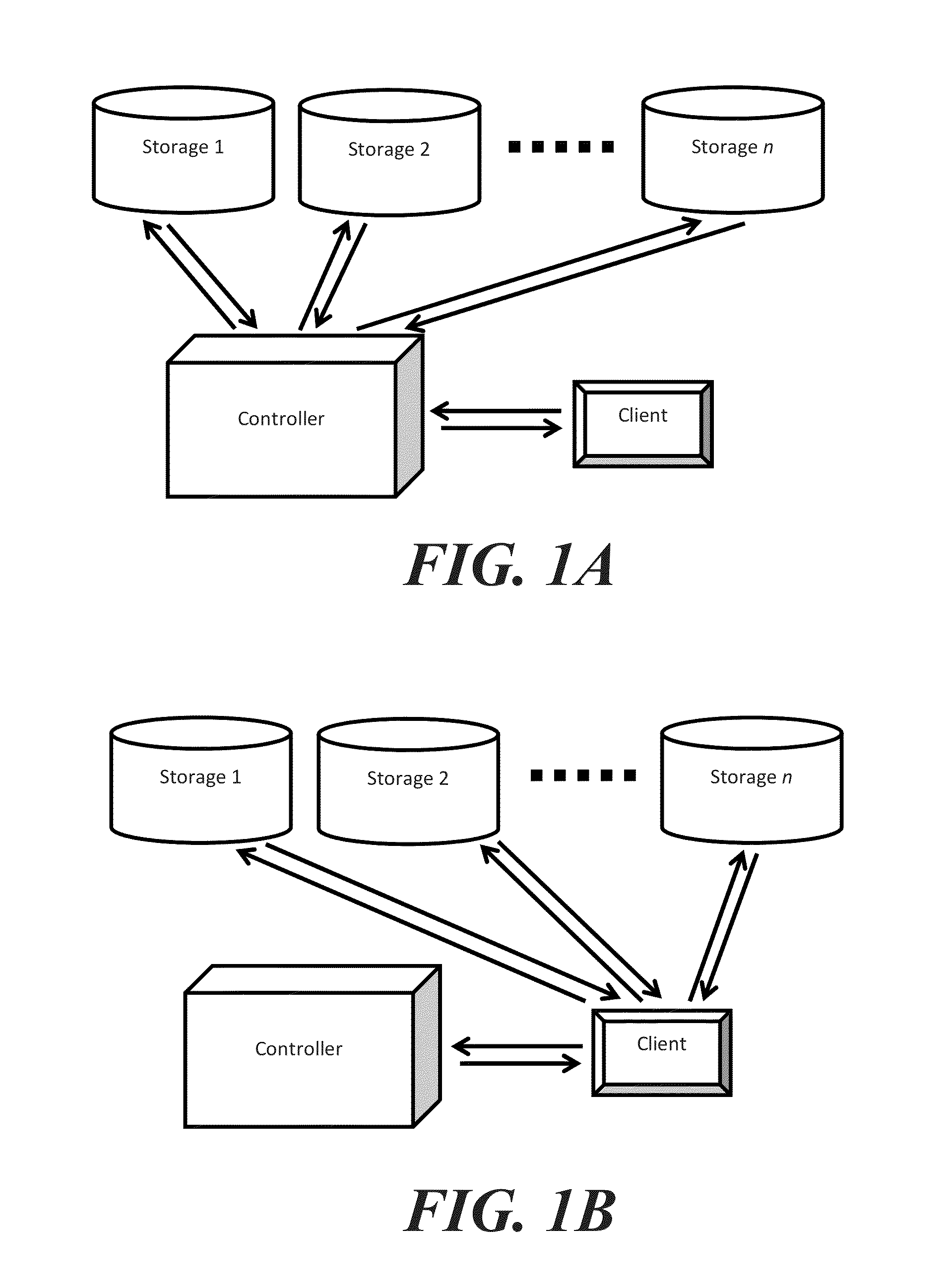
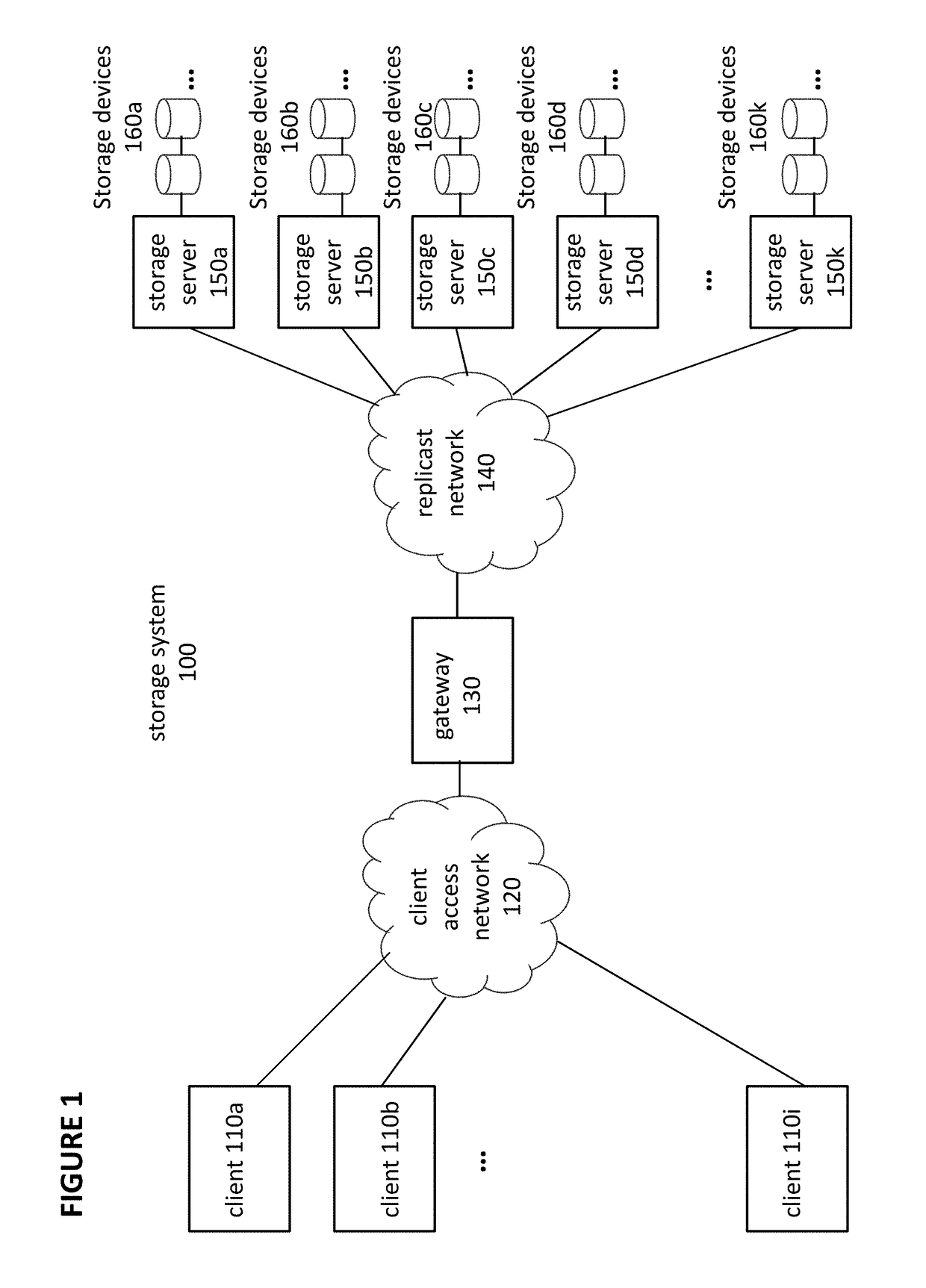
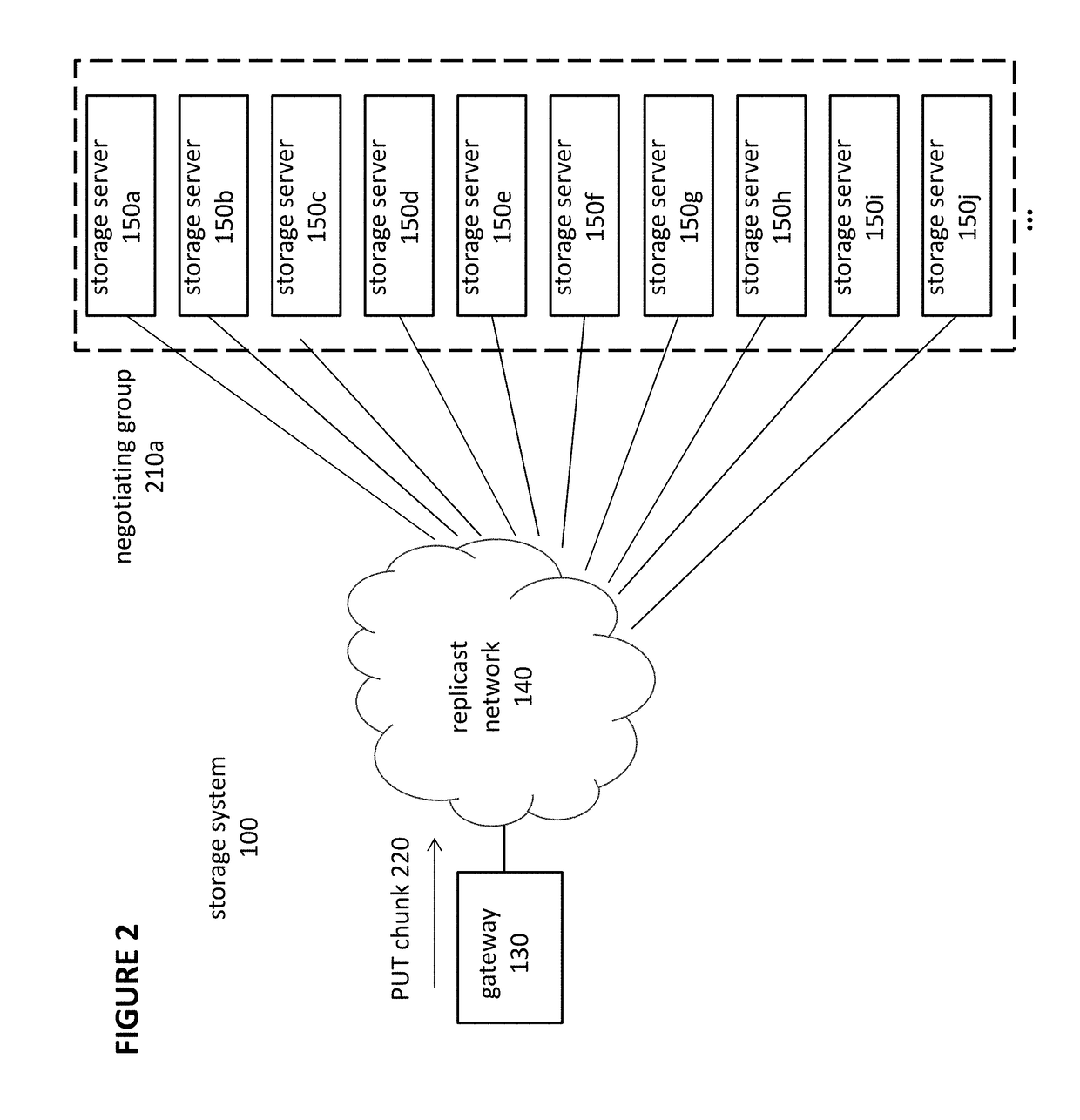
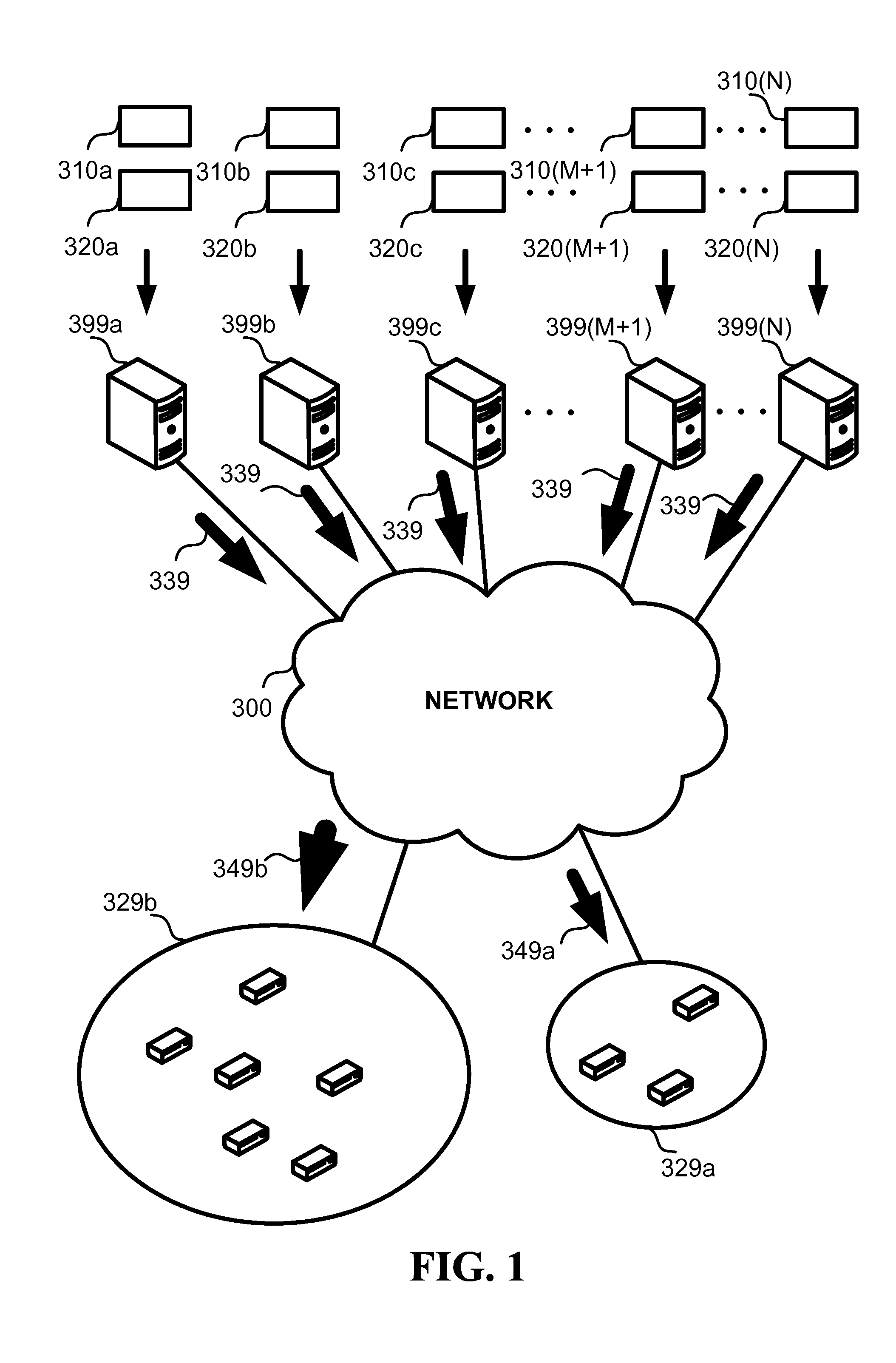
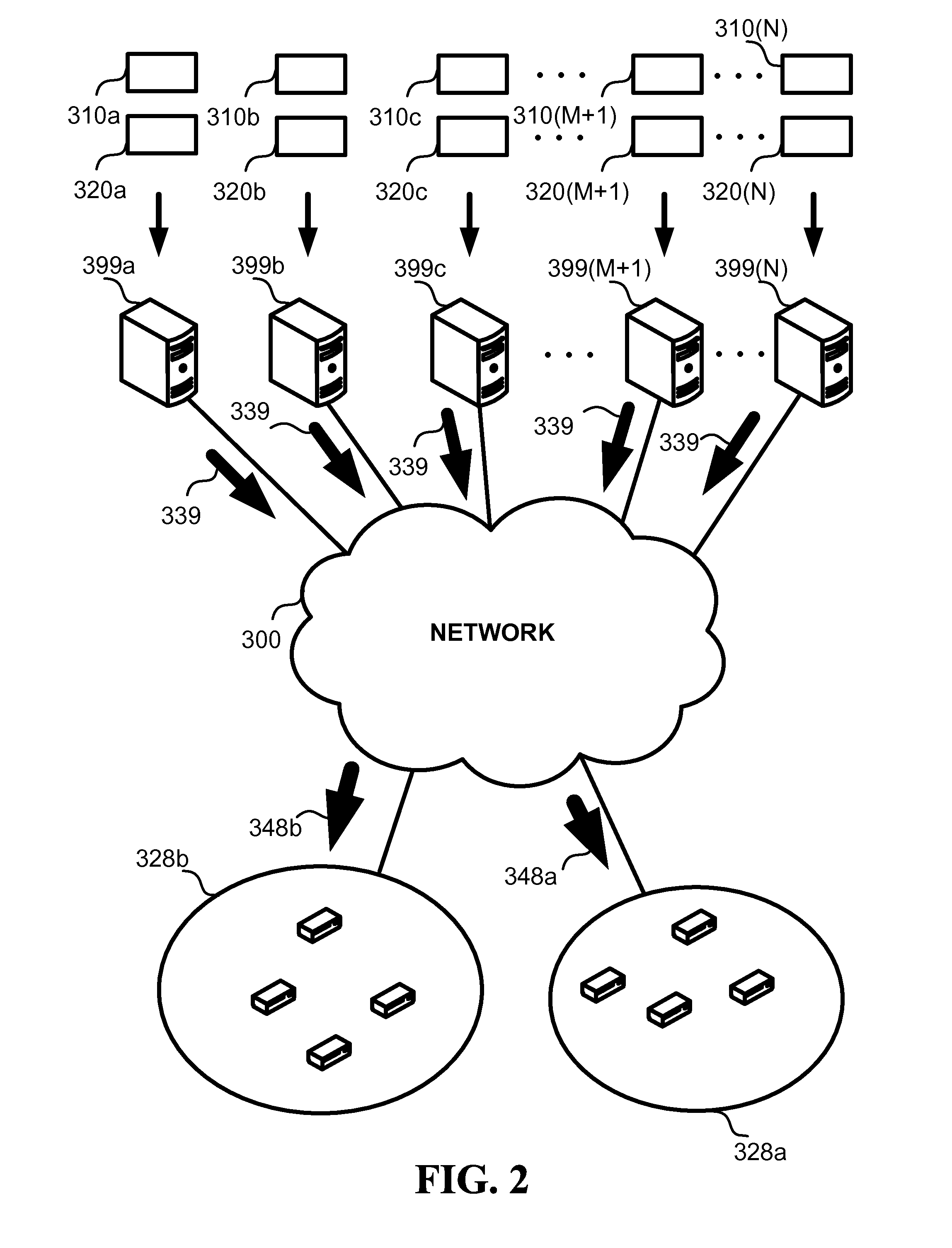
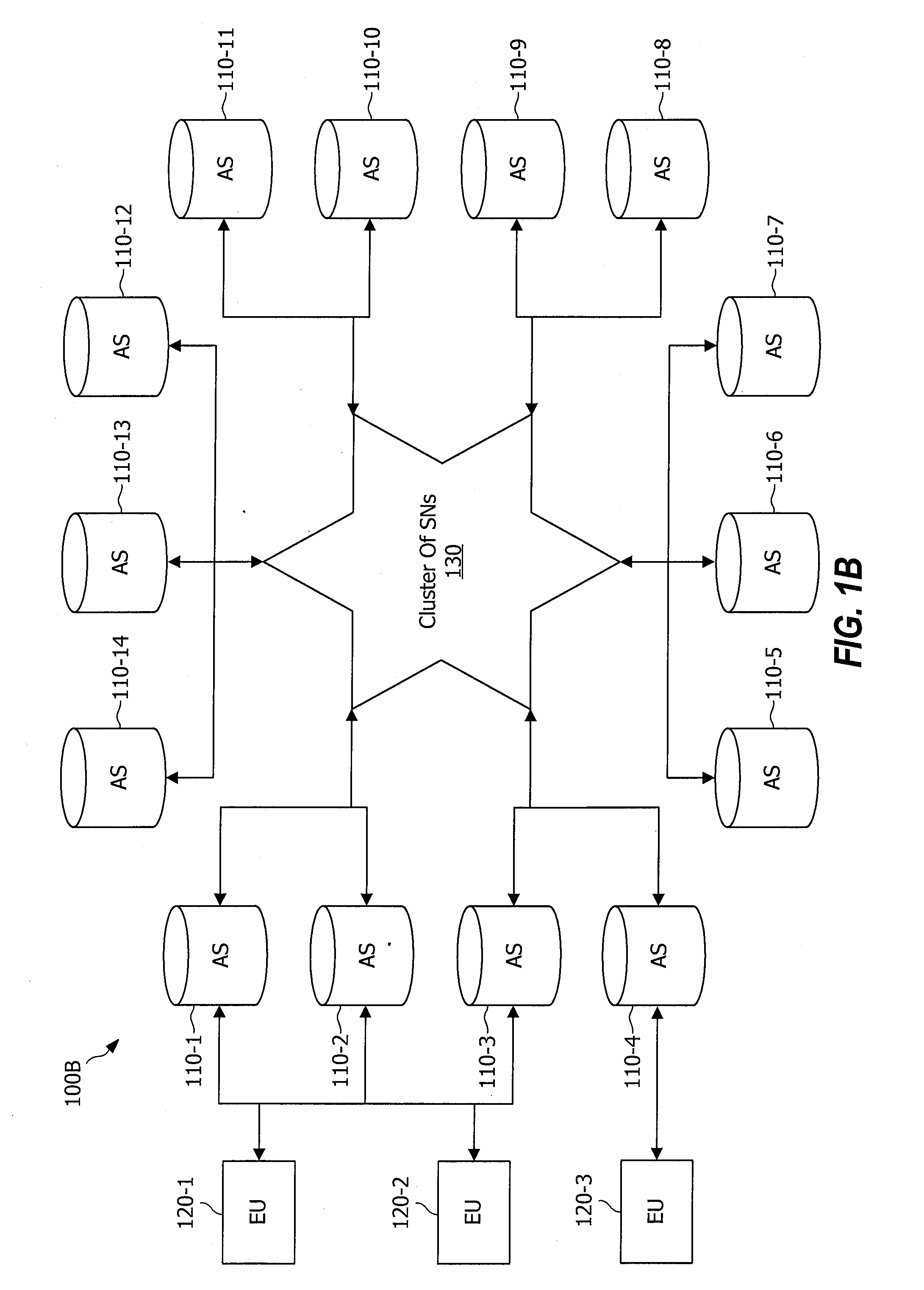
System and method for receiver-driven streaming in a peer-to-peer network
ActiveUS7174385B2Combat network packet loss and jitterMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionHigh rateClient-side
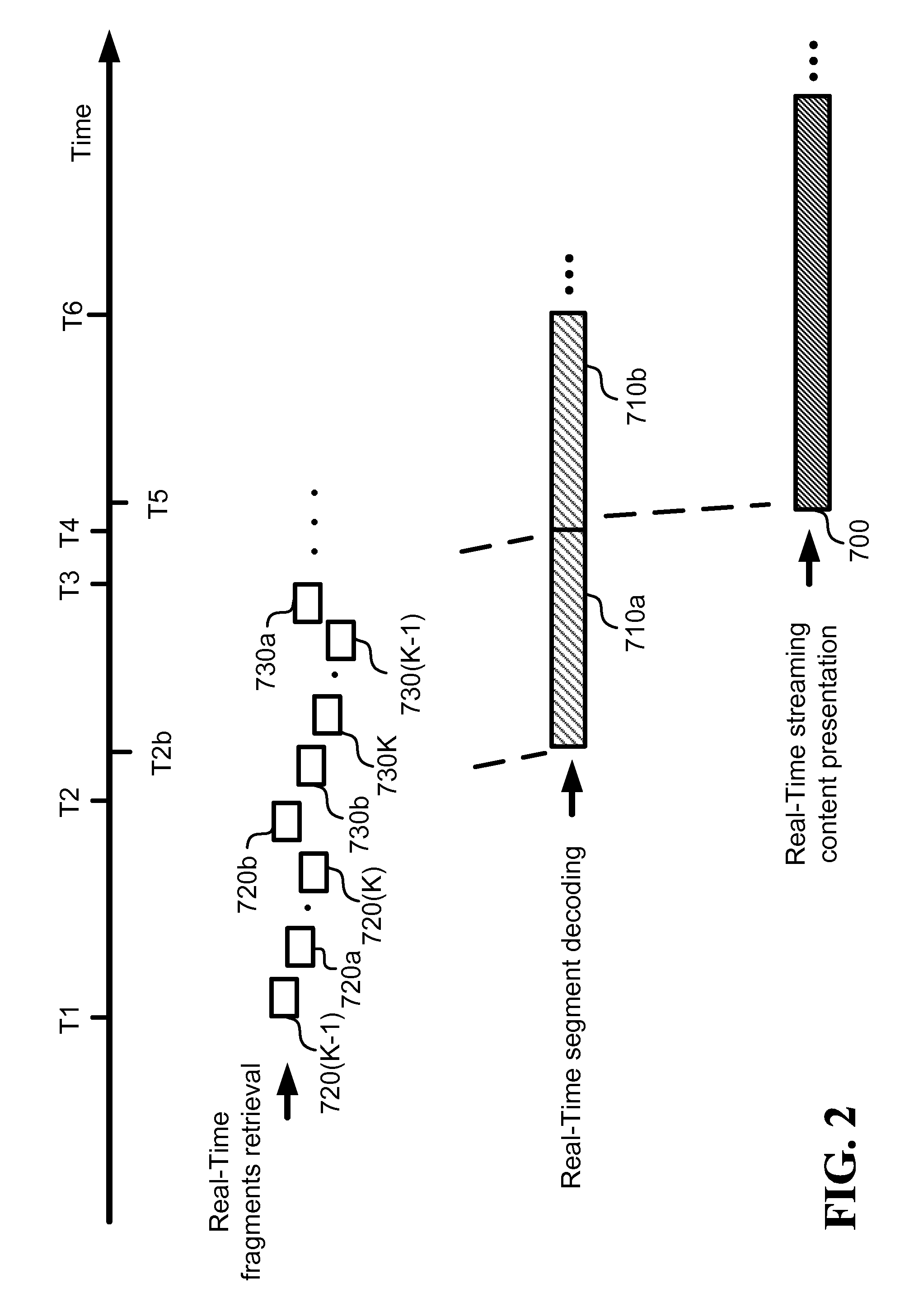
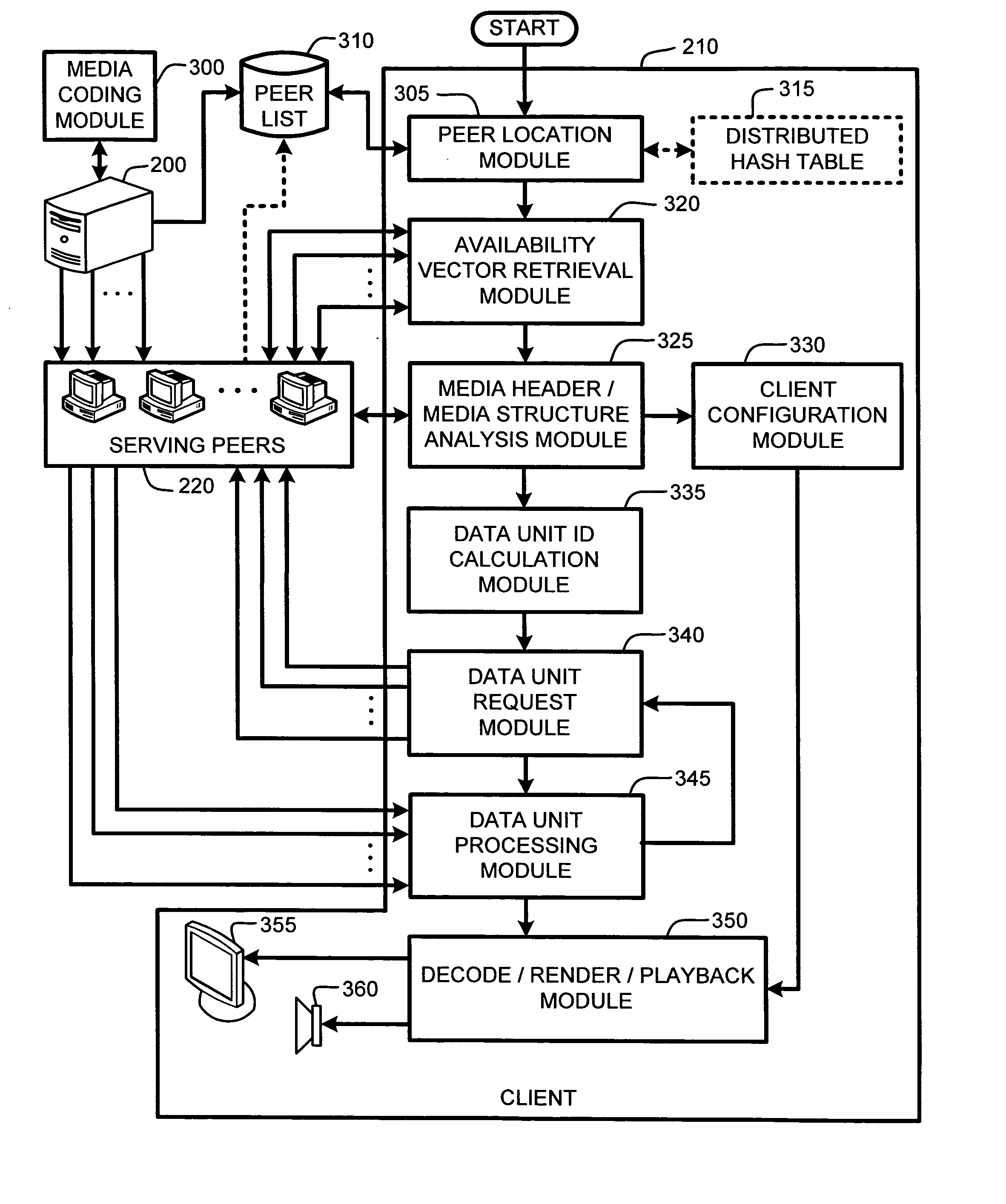
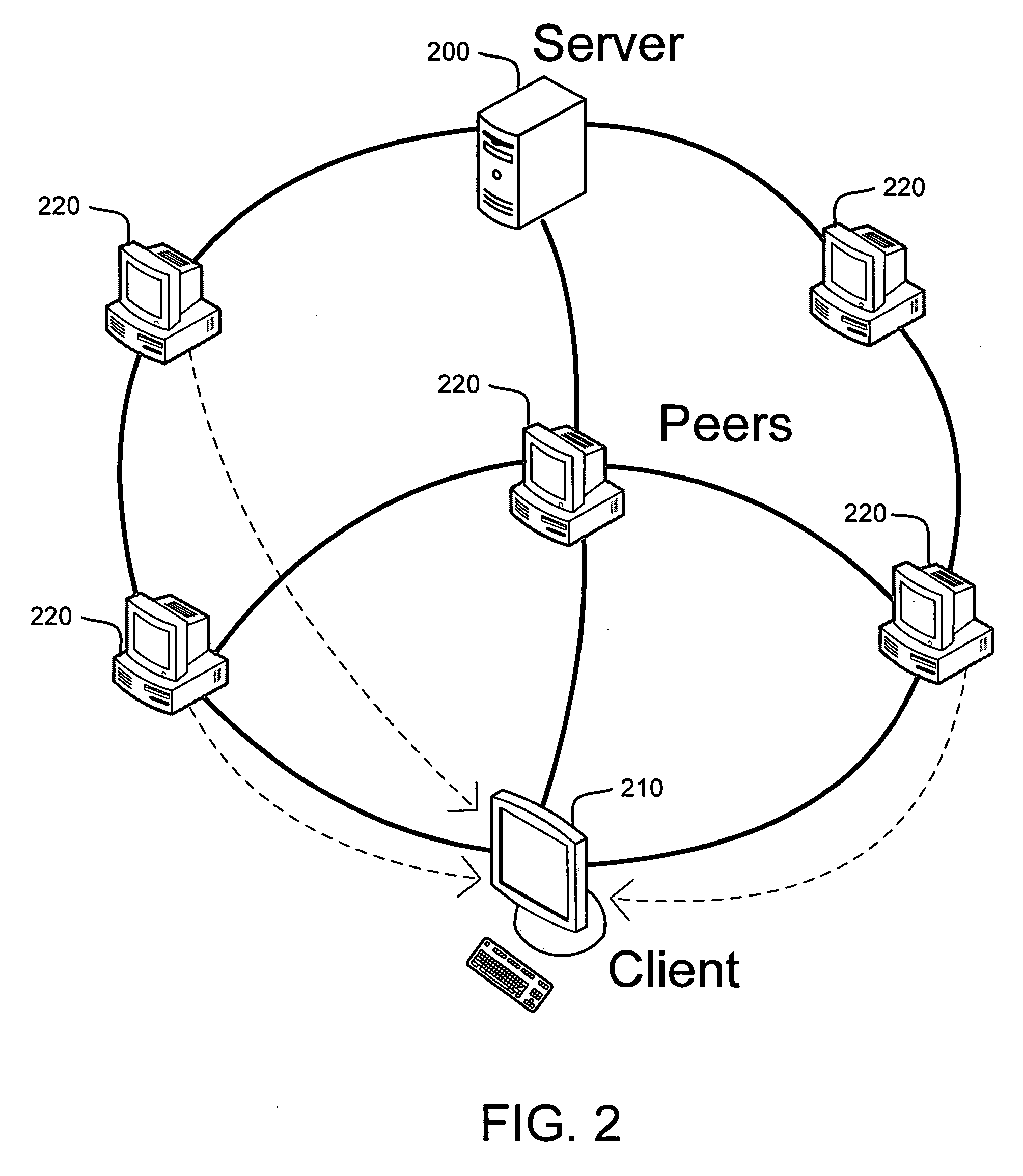
A “PeerStreamer” provides receiver-driven peer-to-peer (P2P) media streaming for loosely coupled P2P networks. Peers in the network perform only simple operations, may cache all or part of the streaming media, do not collaborate with other peers, may be unreliable, and may drop offline or come online during any given streaming session. Clients in the network operate in real-time to coordinate peers, stream media from multiple peers, perform load balancing, handle online / offline states of peers, and perform decoding and rendering the streaming media. In one embodiment, the PeerStreamer uses high rate erasure resilient coding to allow multiple serving peers to hold partial media without conflict, such that clients simply retrieve fixed numbers of erasure coded blocks regardless of where and what specific blocks are retrieved. In another embodiment, the PeerStreamer uses embedded coded media to vary streaming bitrates according to available serving bandwidths and client queue status.
Owner:ROVI TECH CORP
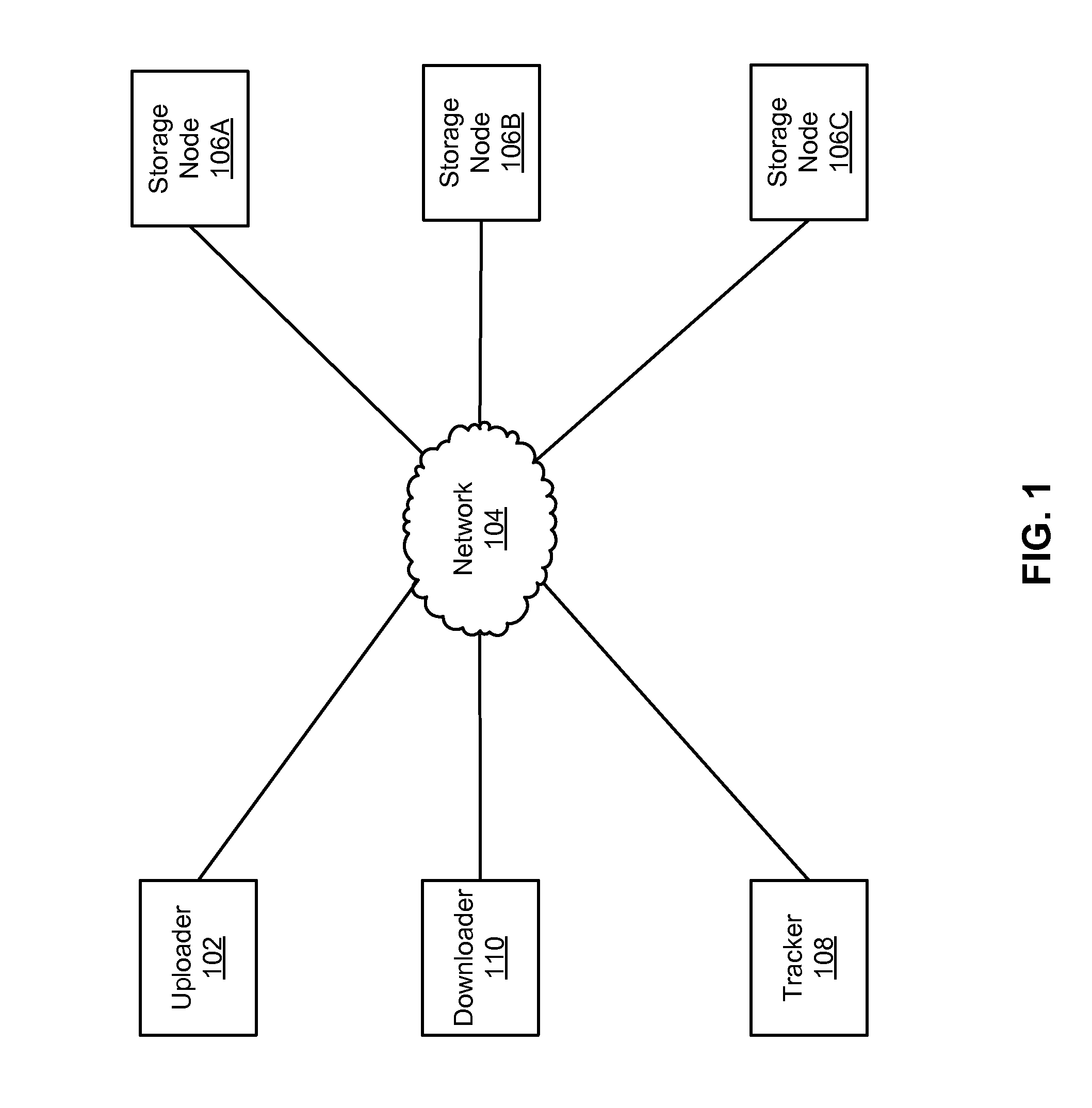
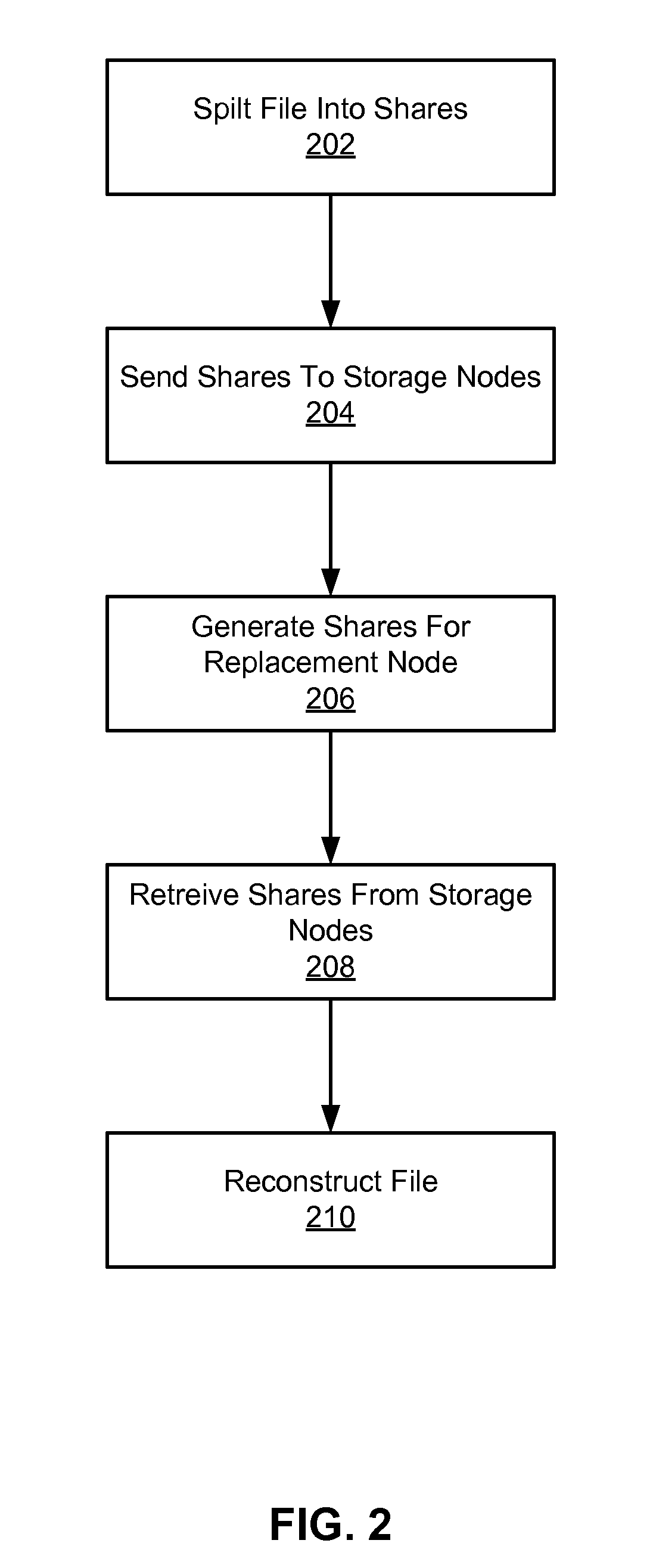
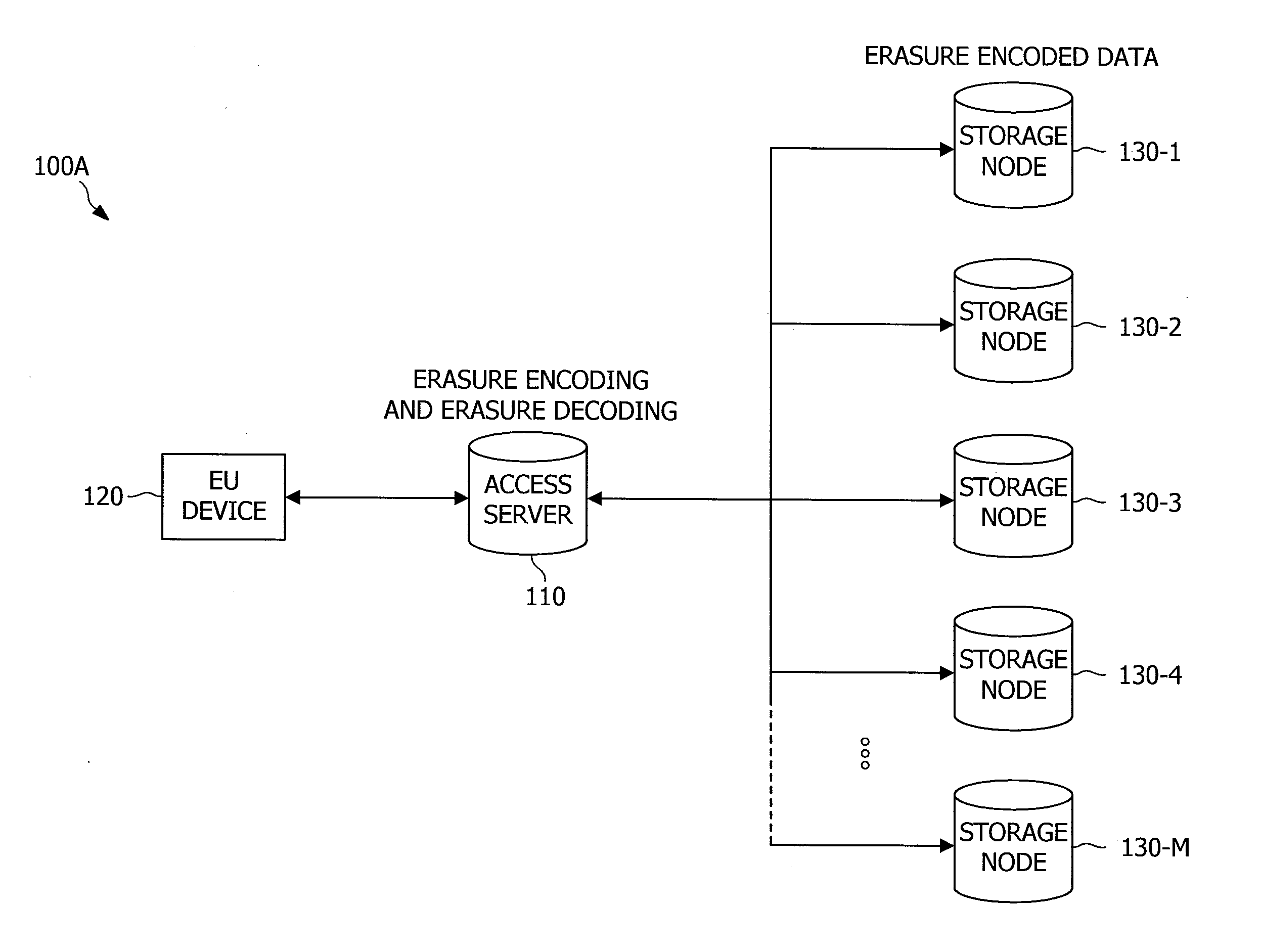
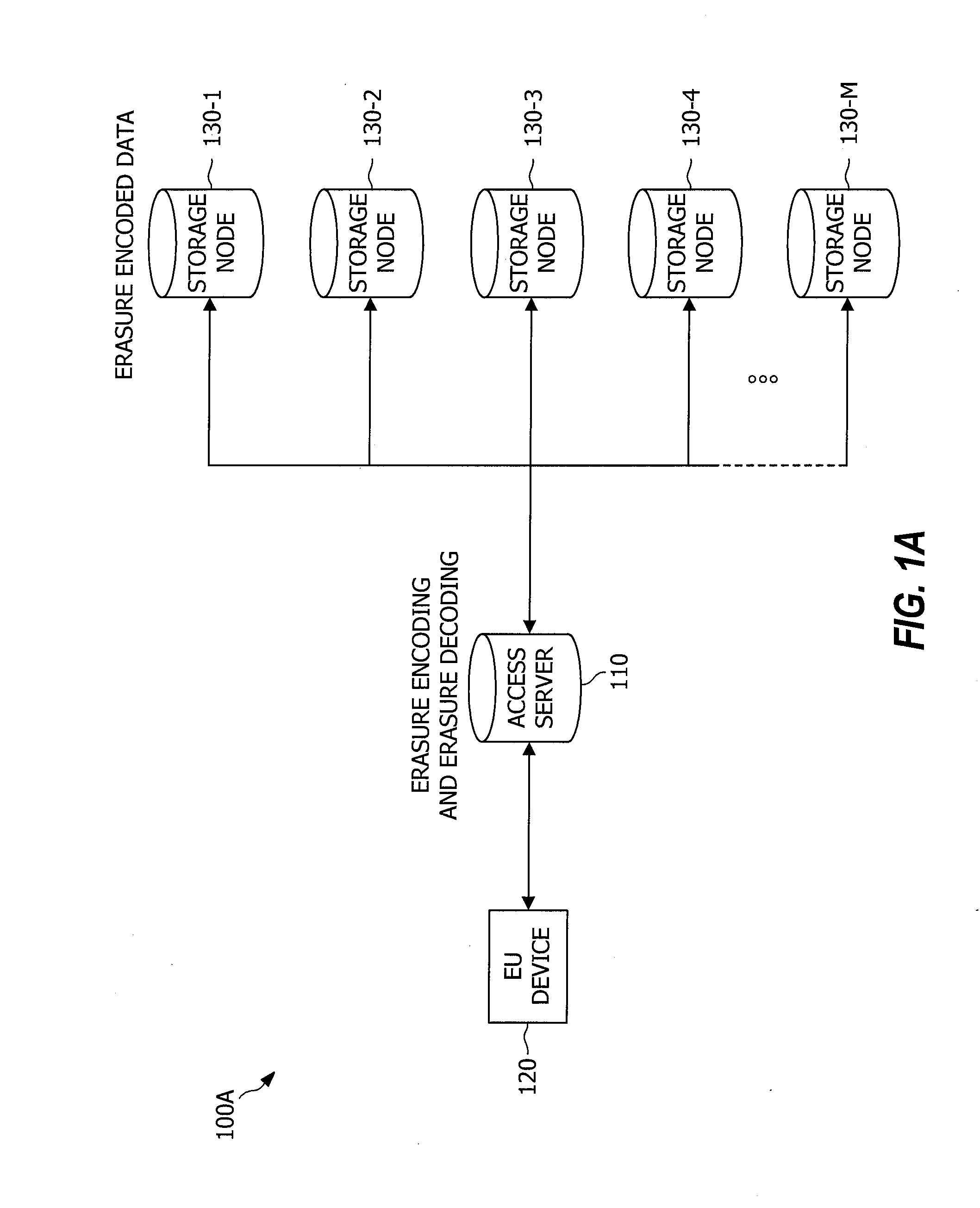
Distributed storage of recoverable data
InactiveUS8522073B2Redundant hardware error correctionInput/output processes for data processingData fileErasure code
A system, method, and computer program product replace a failed node storing data relating to a portion of a data file. An indication of a new storage node to replace the failed node is received at each of a plurality of available storage nodes. The available storage nodes each contain a plurality of shares generated from a data file. These shares may have been generated based on pieces of the data file using erasure coding techniques. A replacement share is generated at each of the plurality of available storage nodes. The replacement shares are generated by creating a linear combination of the shares at each node using random coefficients. The generated replacement shares are then sent from the plurality of storage nodes to the indicated new storage node. These replacement shares may later be used to reconstruct the data file.
Owner:BITTORRENT
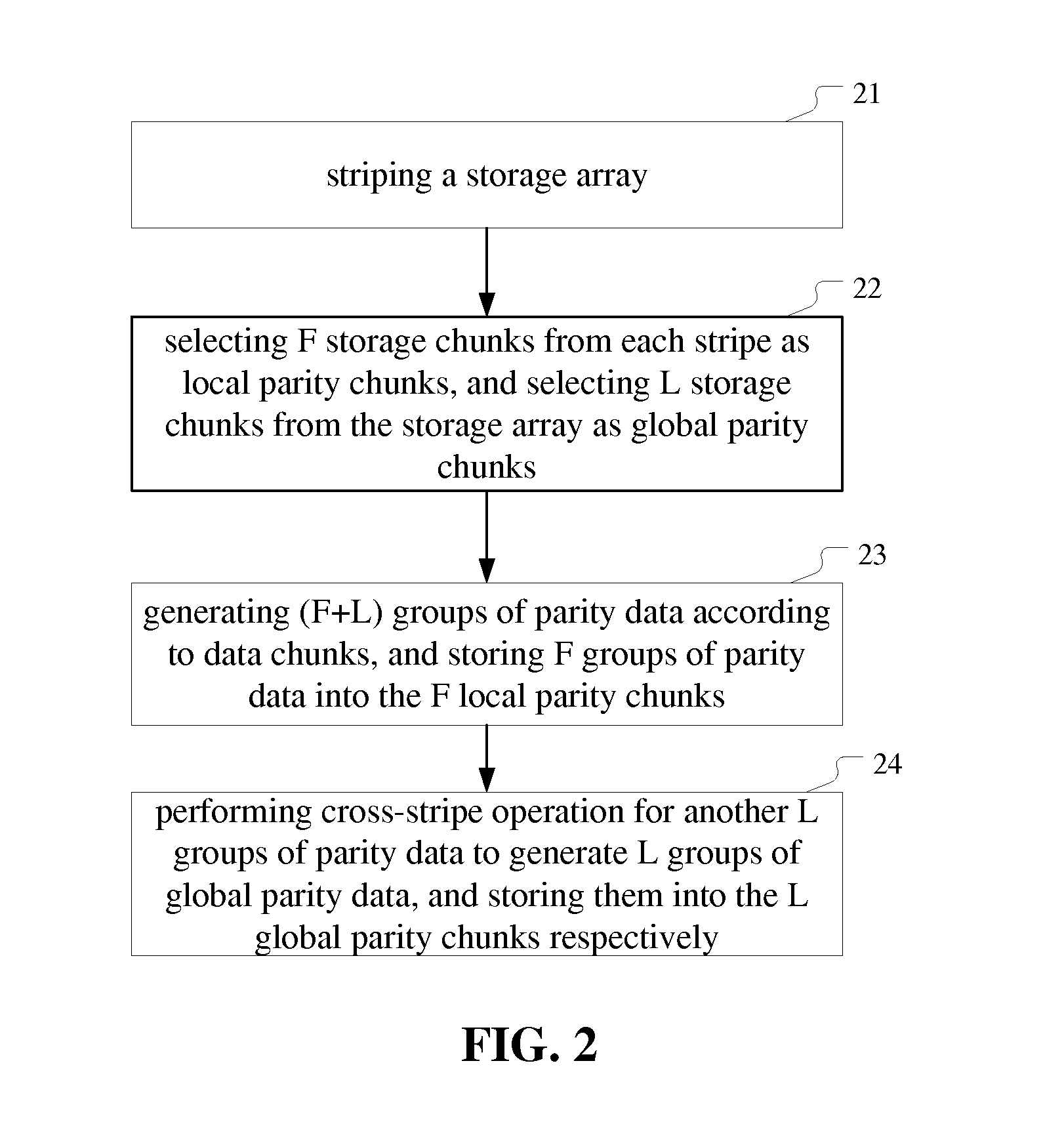
Managing a storage array
ActiveUS20140040702A1Easy to manageError capabilityCode conversionError correction/detection using interleaving techniquesFault toleranceErasure code
The present invention provides a method and apparatus of managing a storage array. The method comprises: striping the storage array to form a plurality of stripes; selecting F storage chunks from each stripe as local parity chunks, and selecting another L storage chunks from the storage array as global parity chunks; performing (F+L) fault tolerant erasure coding on all data chunks in a stripe to generate (F+L) groups of parity data, and storing F groups of parity data therein into the F local parity chunks; performing cross-stripe operation on another L groups of parity data to generate L groups of global parity data, and storing them into the L global parity chunks, respectively. The apparatus corresponds to the method. With the invention, a plurality of errors in the storage array can be detected and / or recovered to improve fault tolerance and space utilization of the storage array.
Owner:IBM CORP
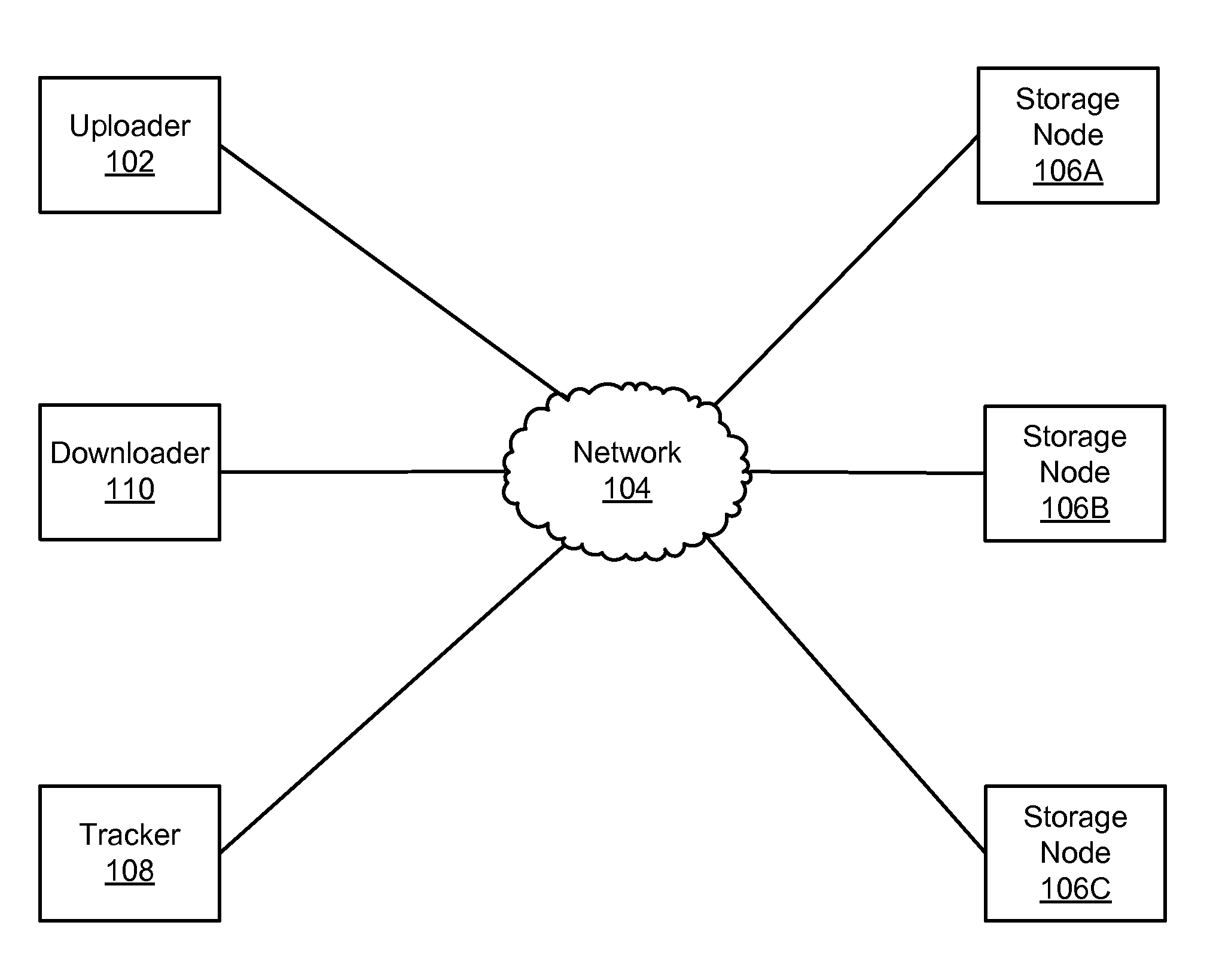
Method for erasure coding data across a plurality of data stores in a network
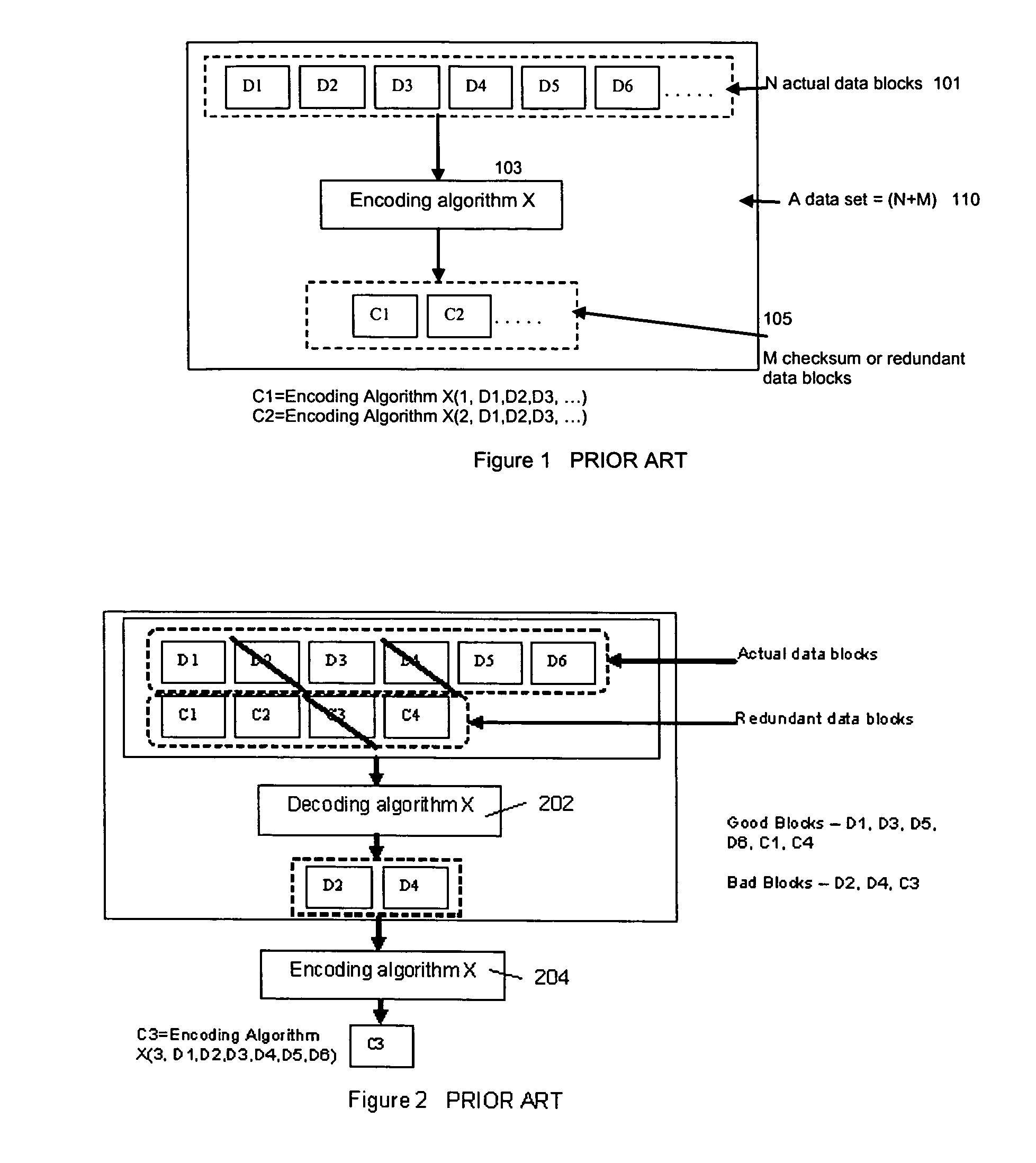
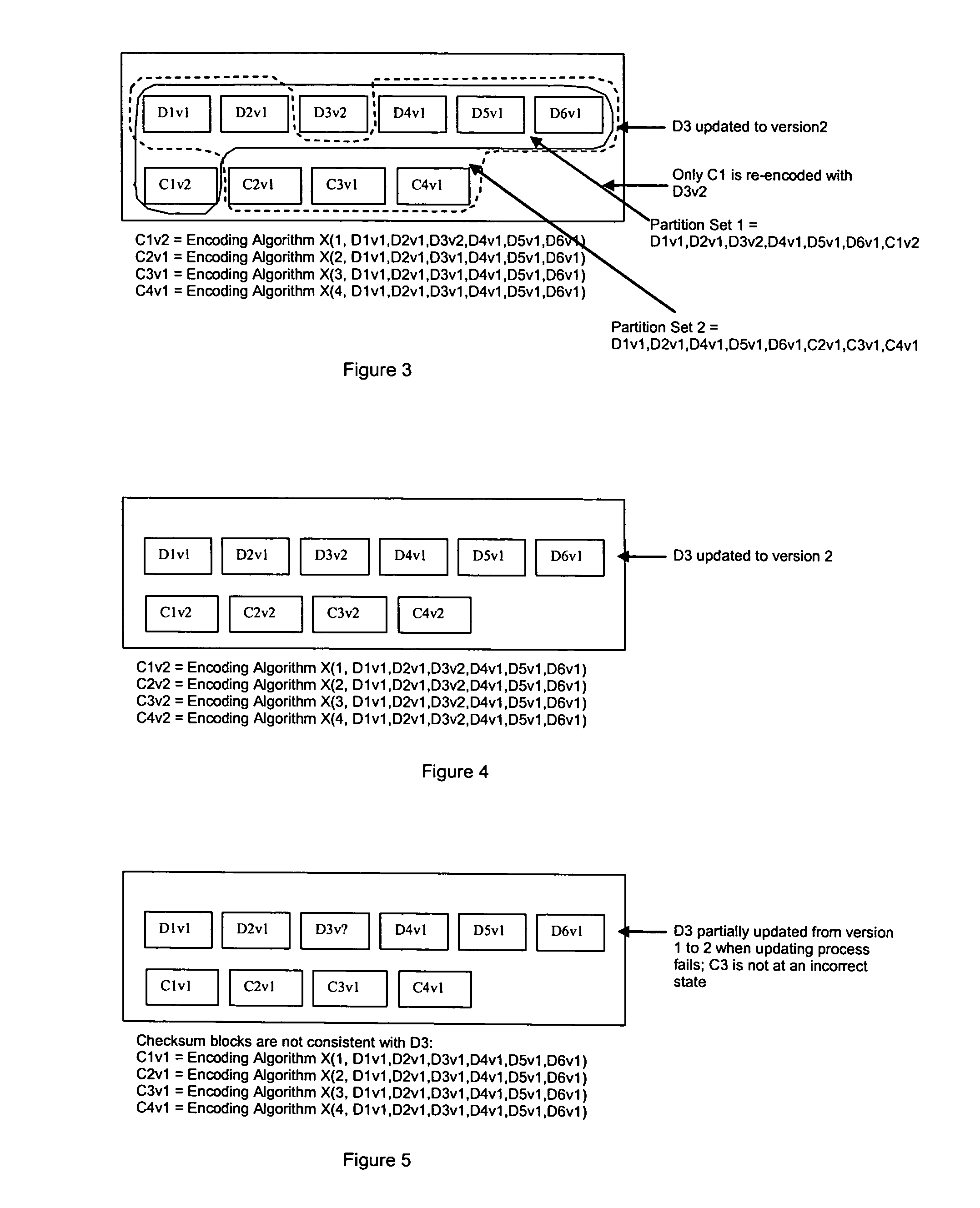
ActiveUS7681104B1Maintain data consistencyEffective applicationError preventionCode conversionData setTheoretical computer science
An efficient method to apply an erasure encoding and decoding scheme across dispersed data stores that receive constant updates. A data store is a persistent memory for storing a data block. Such data stores include, without limitation, a group of disks, a group of disk arrays, or the like. An encoding process applies a sequencing method to assign a sequence number to each data and checksum block as they are modified and updated onto their data stores. The method preferably uses the sequence number to identify data set consistency. The sequencing method allows for self-healing of each individual data store, and it maintains data consistency and correctness within a data block and among a group of data blocks. The inventive technique can be applied on many forms of distributed persistent data stores to provide failure resiliency and to maintain data consistency and correctness.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
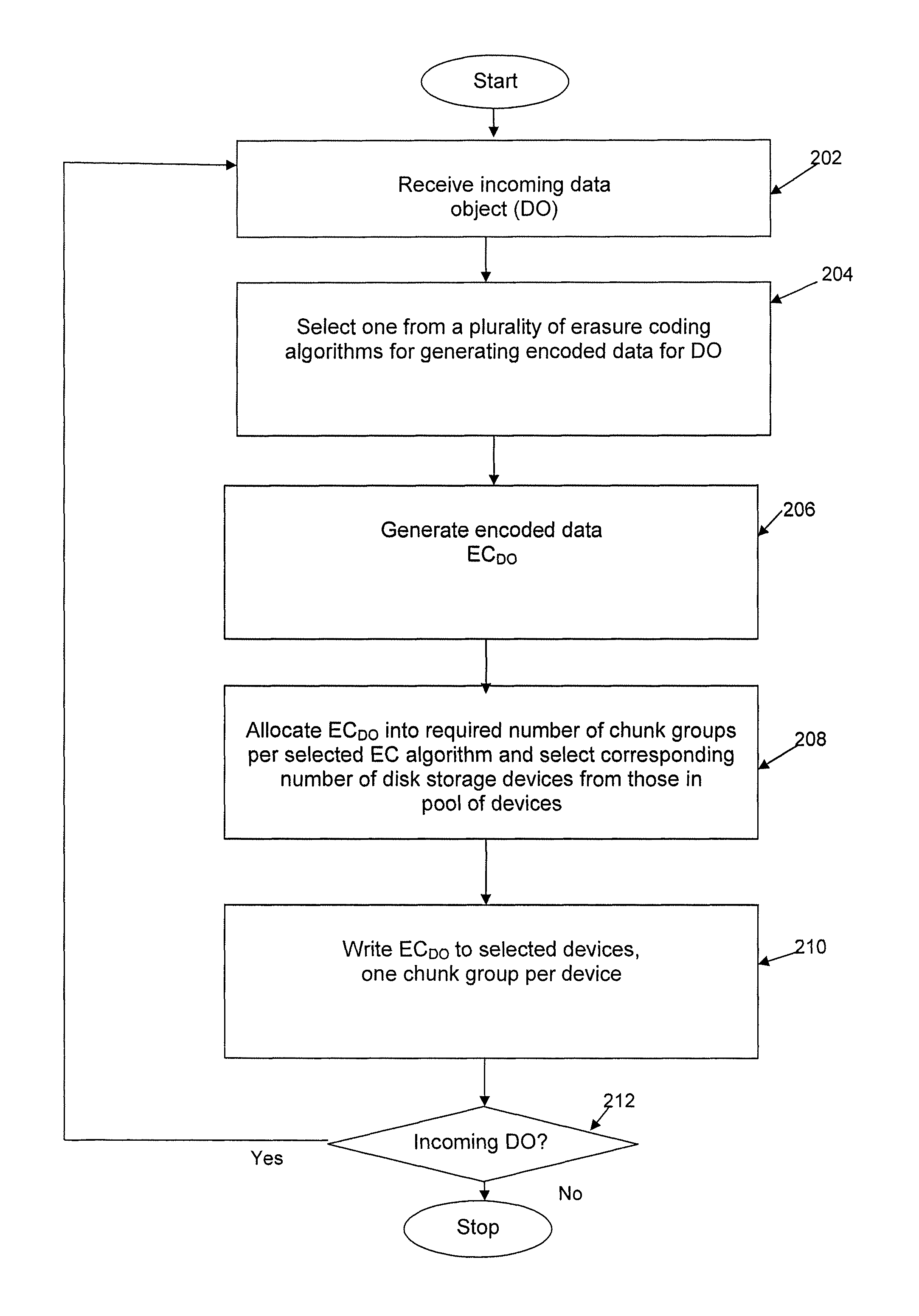
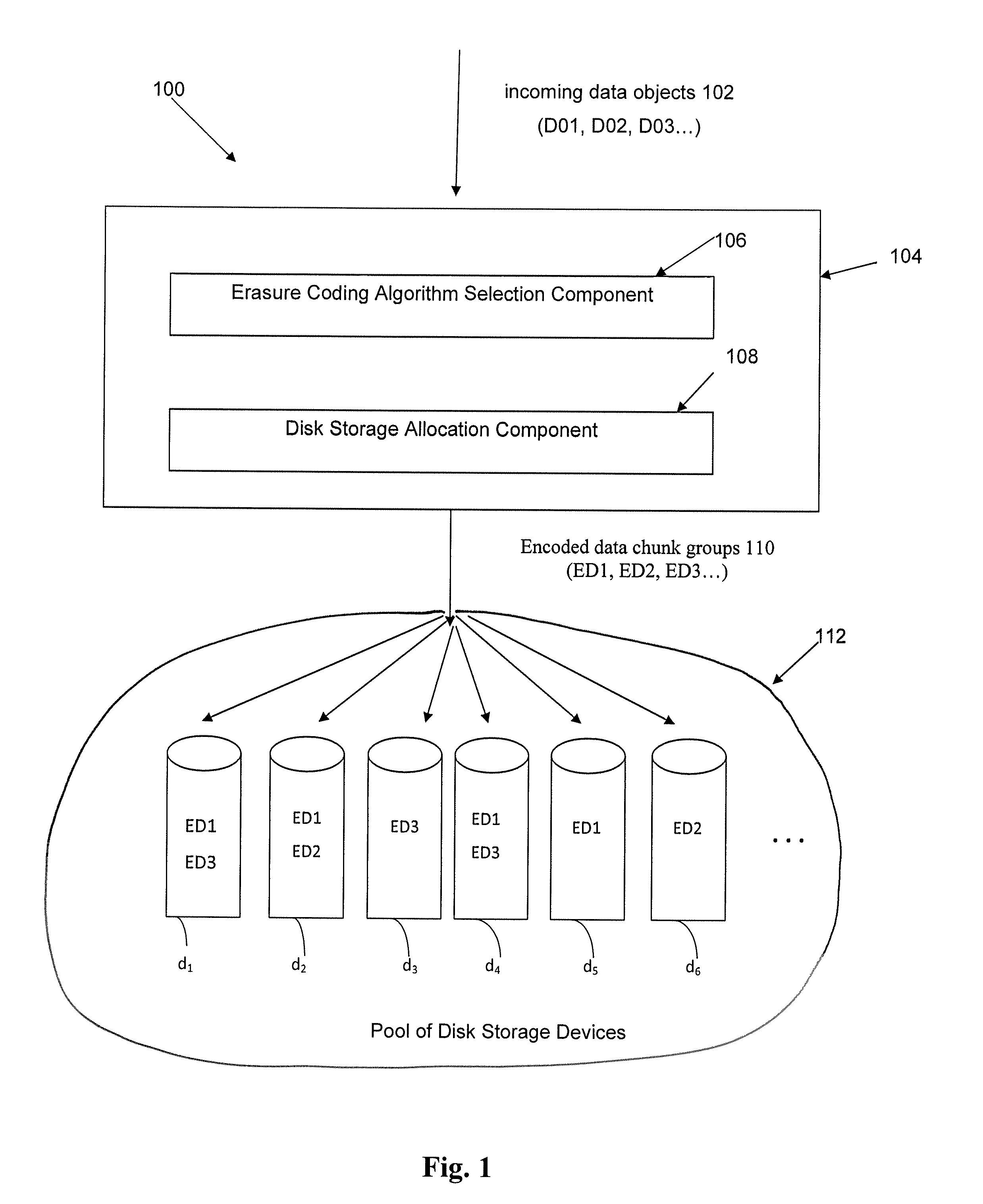
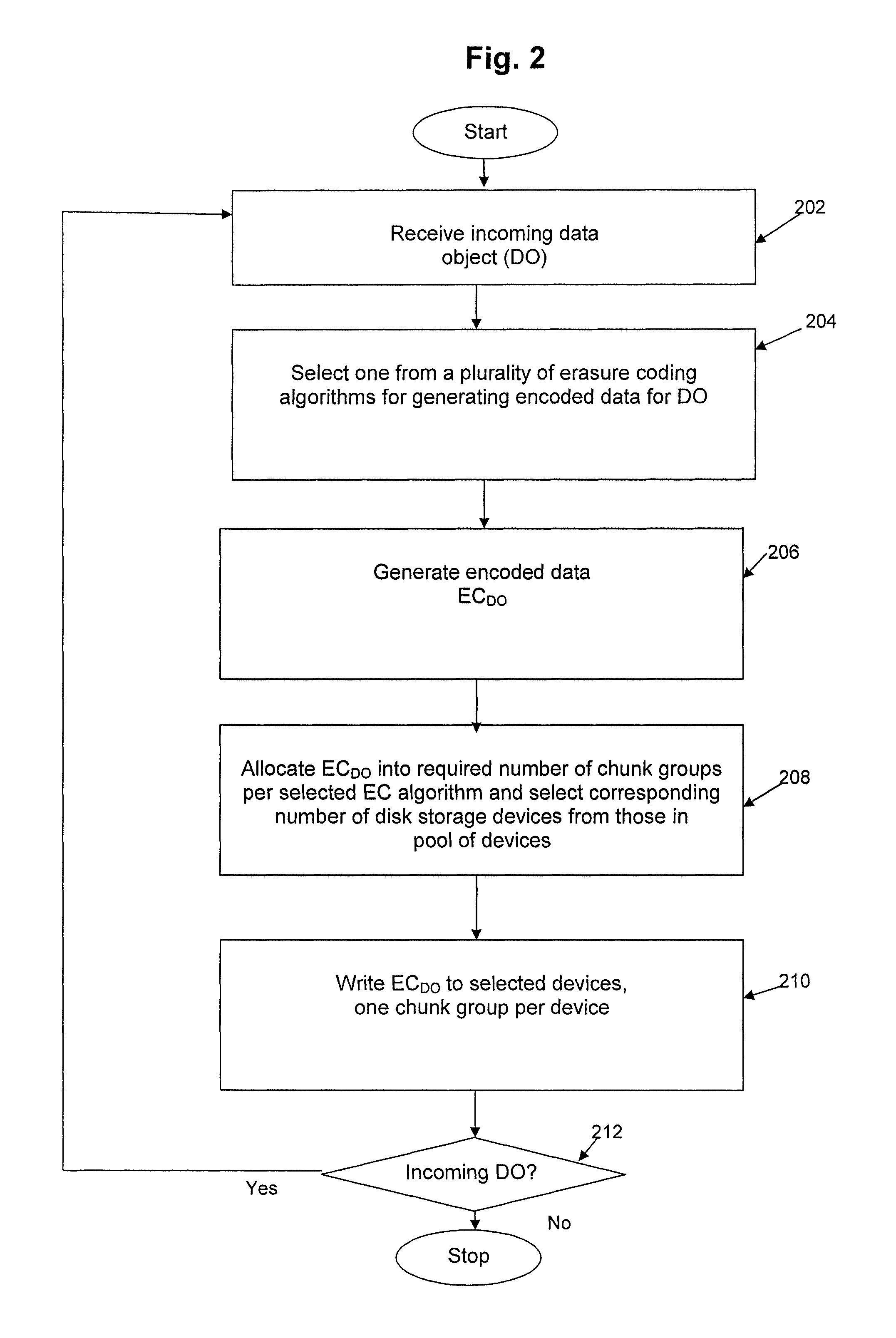
Method and apparatus for allocating erasure coded data to disk storage
Allocation process that allows erasure coded data to be stored on any of a plurality of disk drives, in a pool of drives, so that the allocation is not tied to a fixed group of drives. Still further, the encoded data can be generated by any of multiple different erasure coding algorithms, where again storage of the encoded data is not restricted to a single group of drives based on the erasure algorithm being utilized to encode the data. In another embodiment, the encoded data can be “stacked” (aligned) on select drives to reduce the number of head seeks required to access the data. As a result of these improvements, the system can dynamically determine which one of multiple erasure coding algorithms to utilize for a given incoming data block, without being tied to one particular algorithm and one particular group of storage devices as in the prior art.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
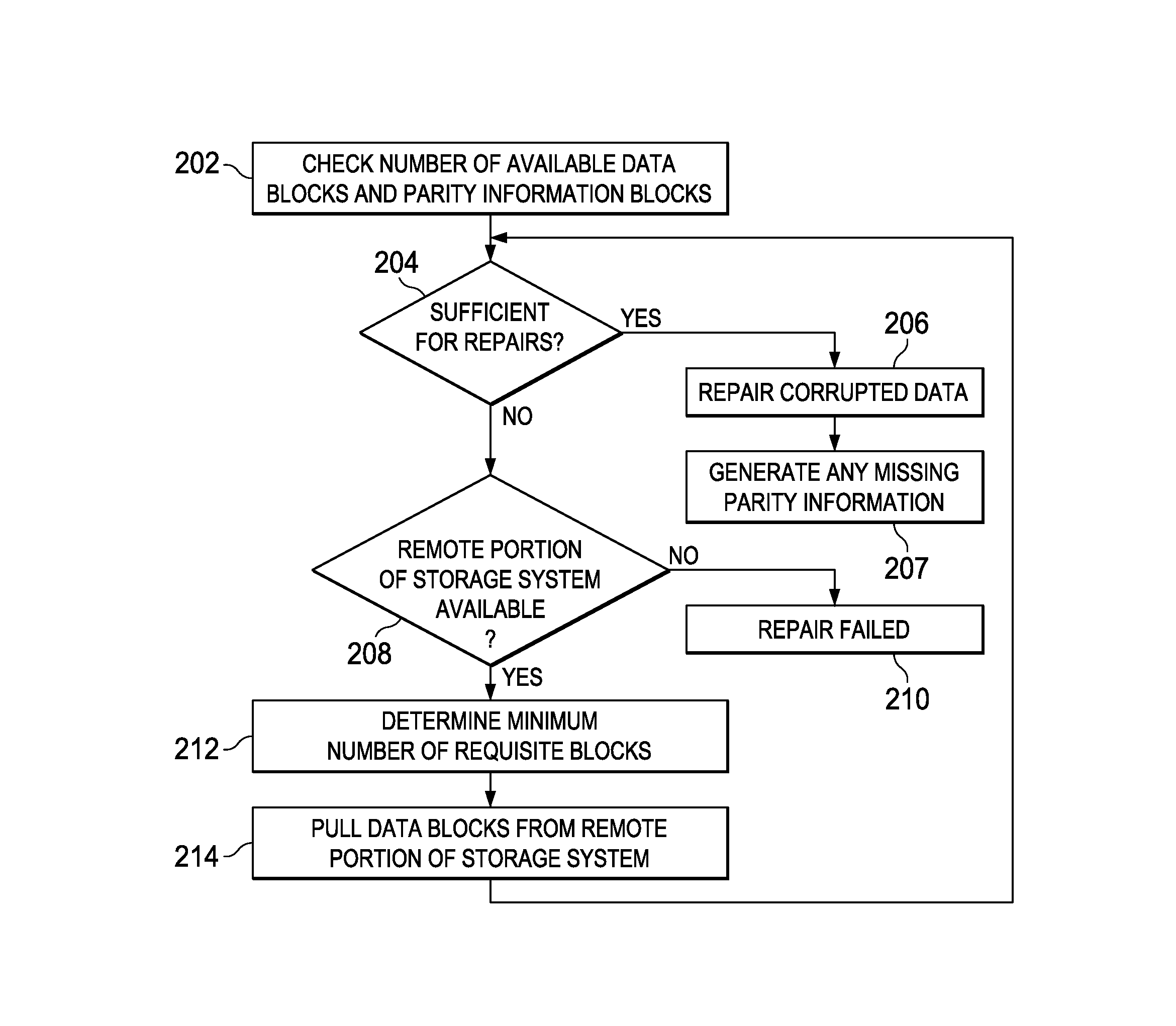
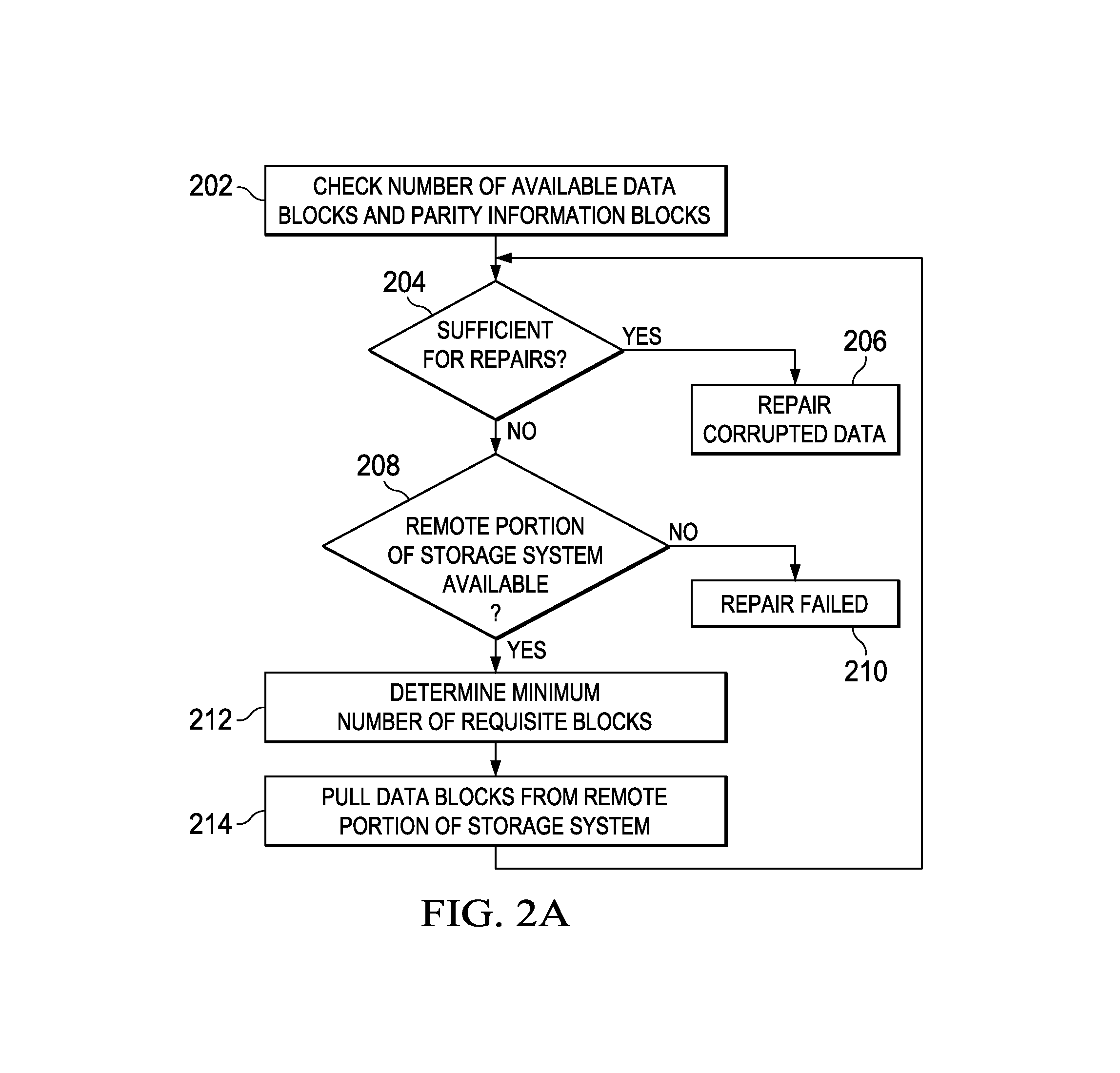
Systems and methods for data repair
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
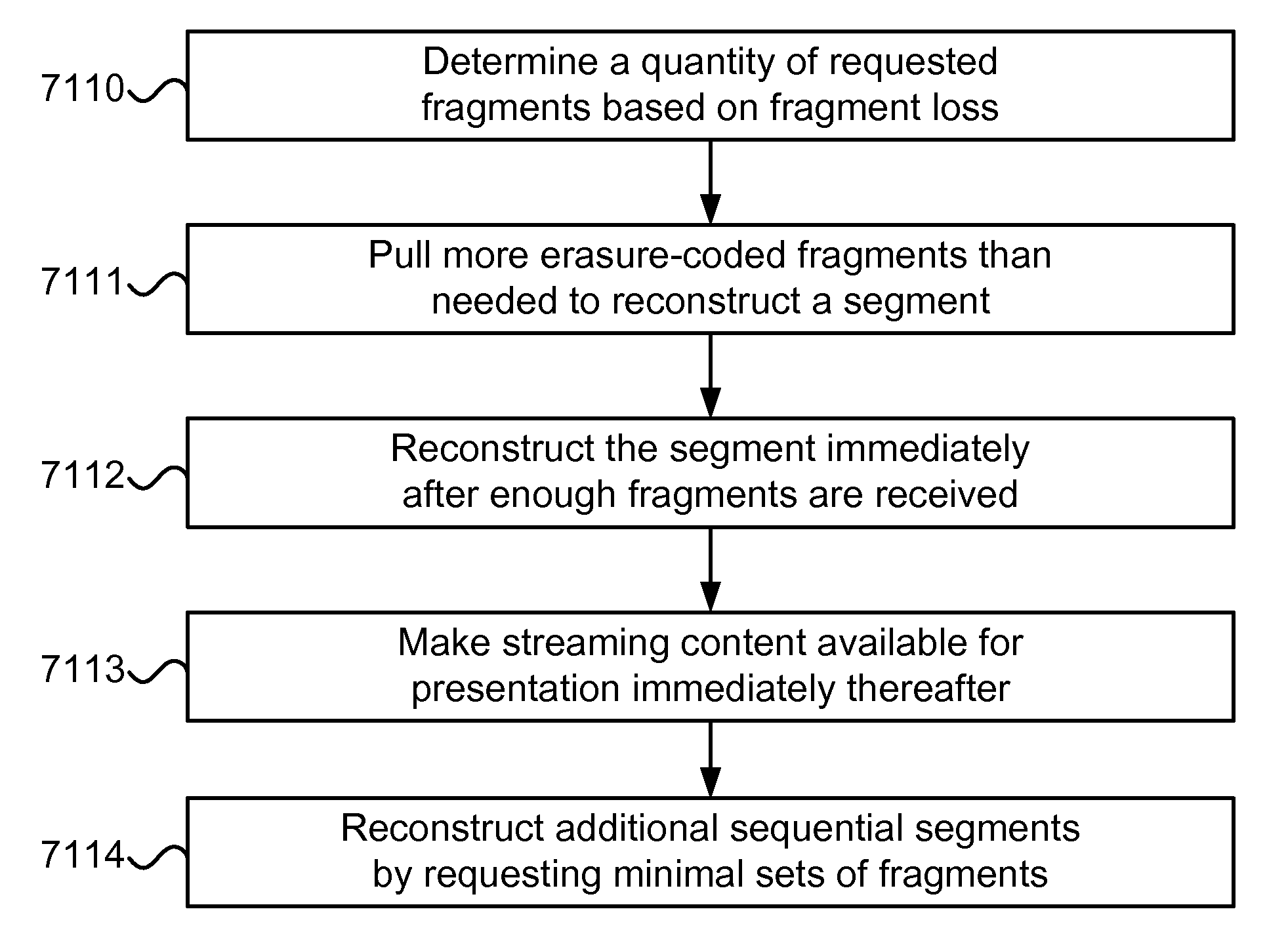
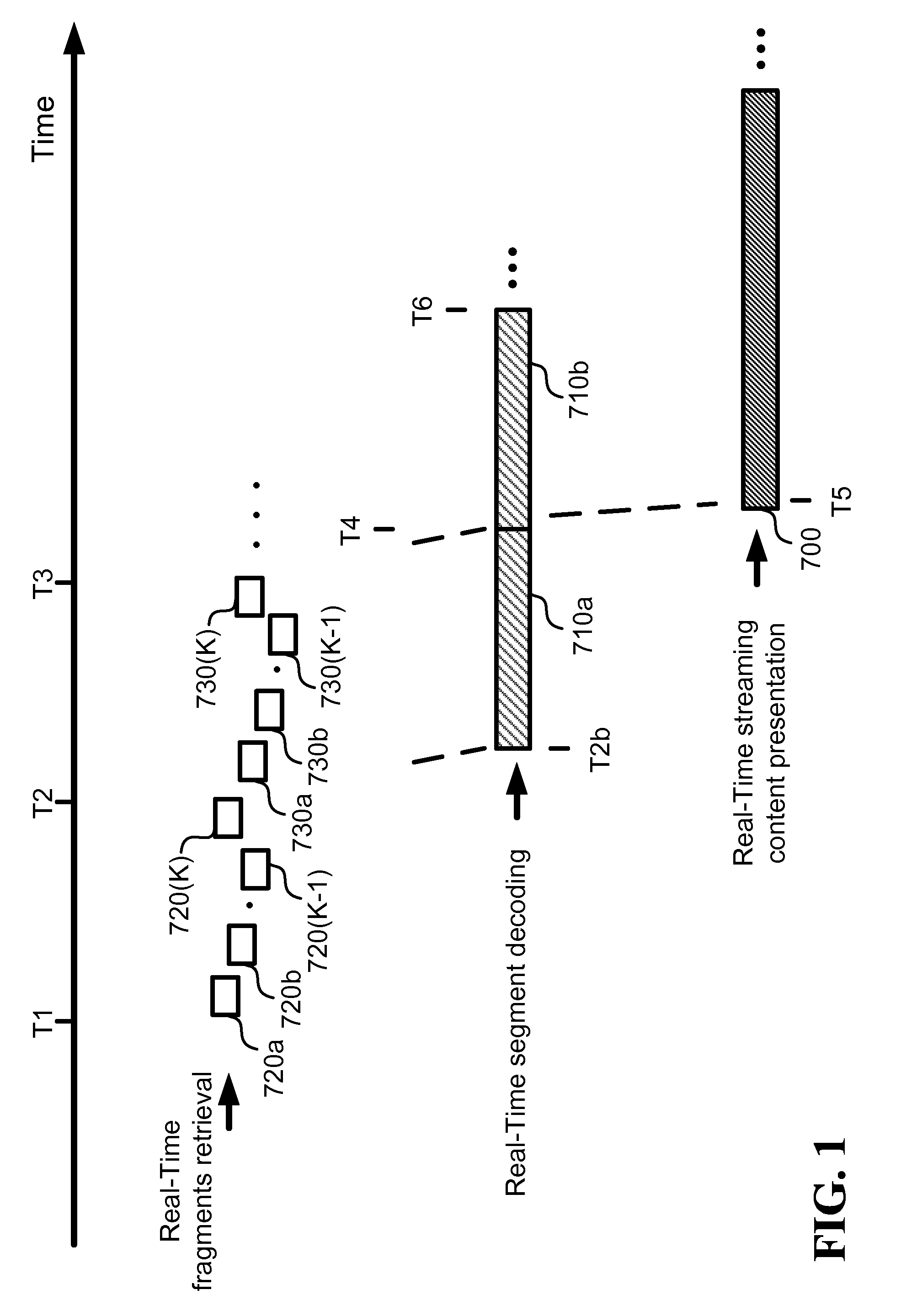
Methods and systems for fast segment reconstruction
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
System and method for distributed streaming of scalable media
ActiveUS20060053209A1Combat network packet loss and jitterMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionHigh rateClient-side
A “PeerStreamer” provides receiver-driven peer-to-peer (P2P) media streaming for loosely coupled P2P networks. Peers in the network perform only simple operations, may cache all or part of the streaming media, do not collaborate with other peers, may be unreliable, and may drop offline or come online during any given streaming session. Clients in the network operate in real-time to coordinate peers, stream media from multiple peers, perform load balancing, handle online / offline states of peers, and perform decoding and rendering the streaming media. In one embodiment, the PeerStreamer uses high rate erasure resilient coding to allow multiple serving peers to hold partial media without conflict, such that clients simply retrieve fixed numbers of erasure coded blocks regardless of where and what specific blocks are retrieved. In another embodiment, the PeerStreamer uses embedded coded media to vary streaming bitrates according to available serving bandwidths and client queue status.
Owner:ROVI TECH CORP
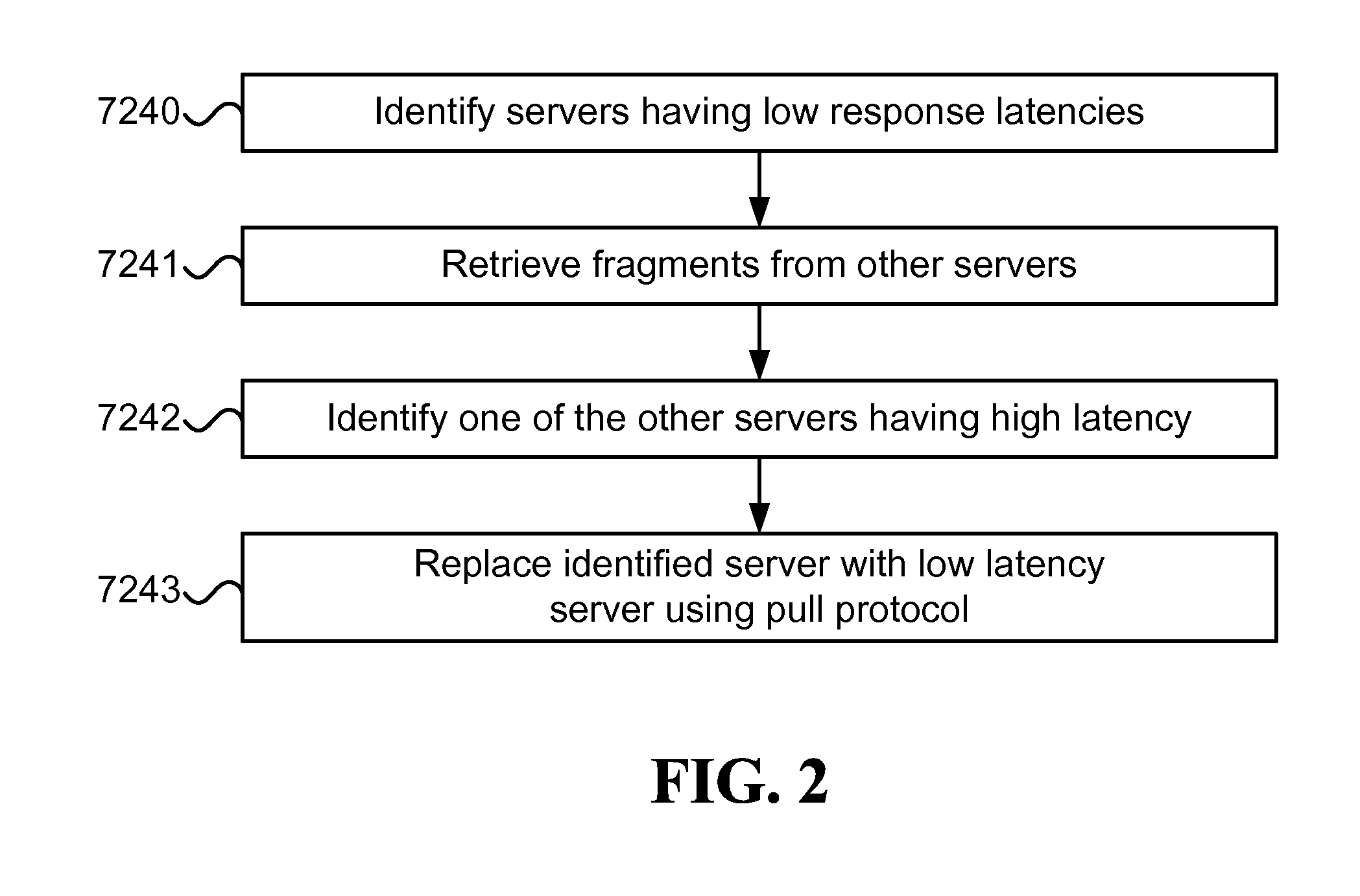
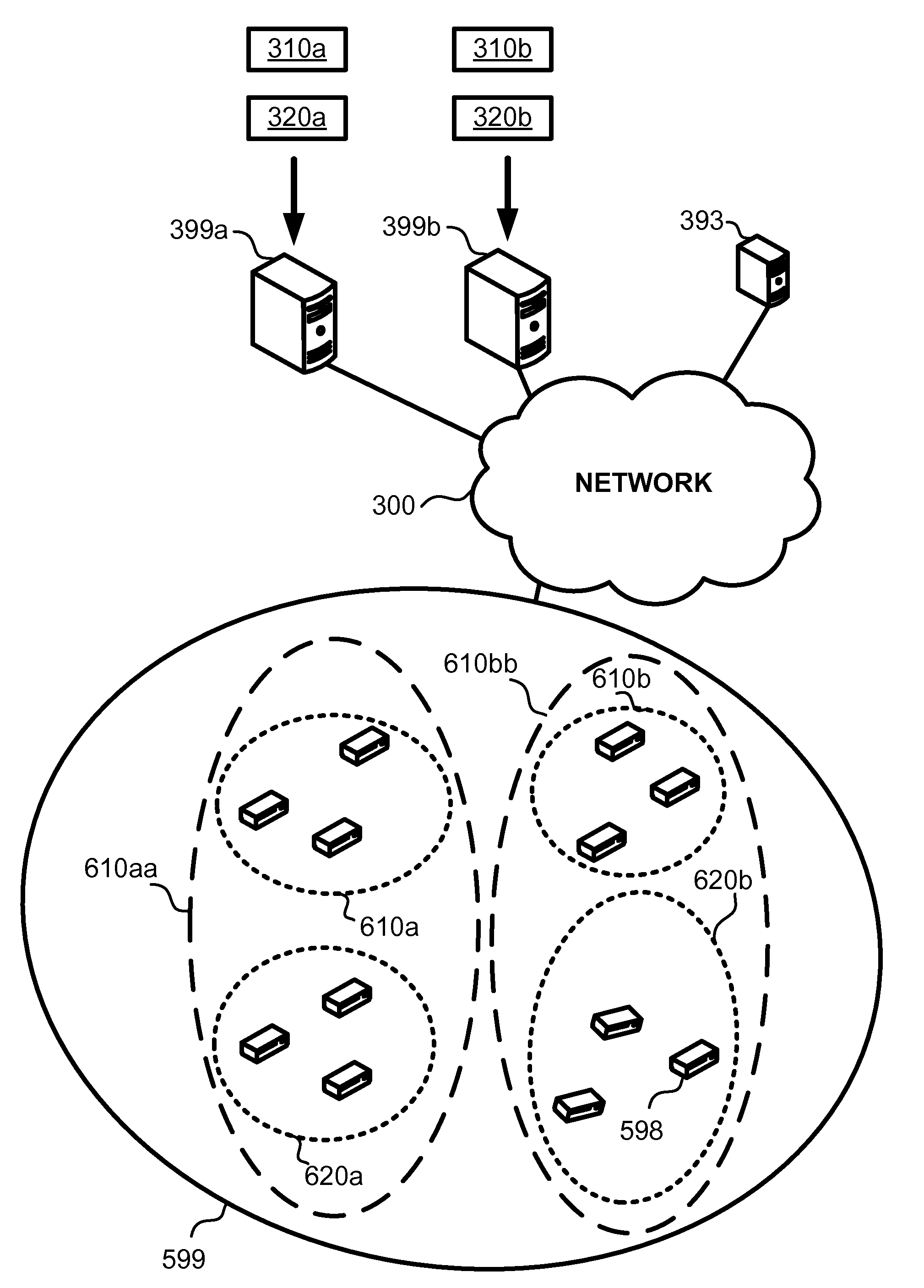
Latency based selection of fractional-storage servers
InactiveUS20100094970A1Reduce response delayOther decoding techniquesCode conversionResponse delayErasure code
Latency based selection of fractional-storage servers, including the steps of identifying a first group of fractional-storage servers estimated to have low response latencies in relation to an assembling device. Retrieving, by the assembling device from a second group of fractional-storage servers, enough erasure-coded fragments for reconstructing approximately sequential segments of streaming content. While retrieving the fragments, identifying at least one server from the second group having latency higher than a certain threshold in response to a fragment pull protocol request. And using the fragment pull protocol to replace the identified server with at least one server selected from the first group.
Owner:PATENTVC
System and method for receiver-driven streaming in a peer-to-peer network
ActiveUS20060080454A1Combat network packet lossCombat jitterMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionLoad SheddingHigh rate
A “PeerStreamer” provides receiver-driven peer-to-peer (P2P) media streaming for loosely coupled P2P networks. Peers in the network perform only simple operations, may cache all or part of the streaming media, do not collaborate with other peers, may be unreliable, and may drop offline or come online during any given streaming session. Clients in the network operate in real-time to coordinate peers, stream media from multiple peers, perform load balancing, handle online / offline states of peers, and perform decoding and rendering the streaming media. In one embodiment, the PeerStreamer uses high rate erasure resilient coding to allow multiple serving peers to hold partial media without conflict, such that clients simply retrieve fixed numbers of erasure coded blocks regardless of where and what specific blocks are retrieved. In another embodiment, the PeerStreamer uses embedded coded media to vary streaming bitrates according to available serving bandwidths and client queue status.
Owner:ROVI TECH CORP
Systems and methods for reliably storing data using liquid distributed storage
InactiveUS20160011936A1Input/output to record carriersRedundant data error correctionStreaming dataData stream
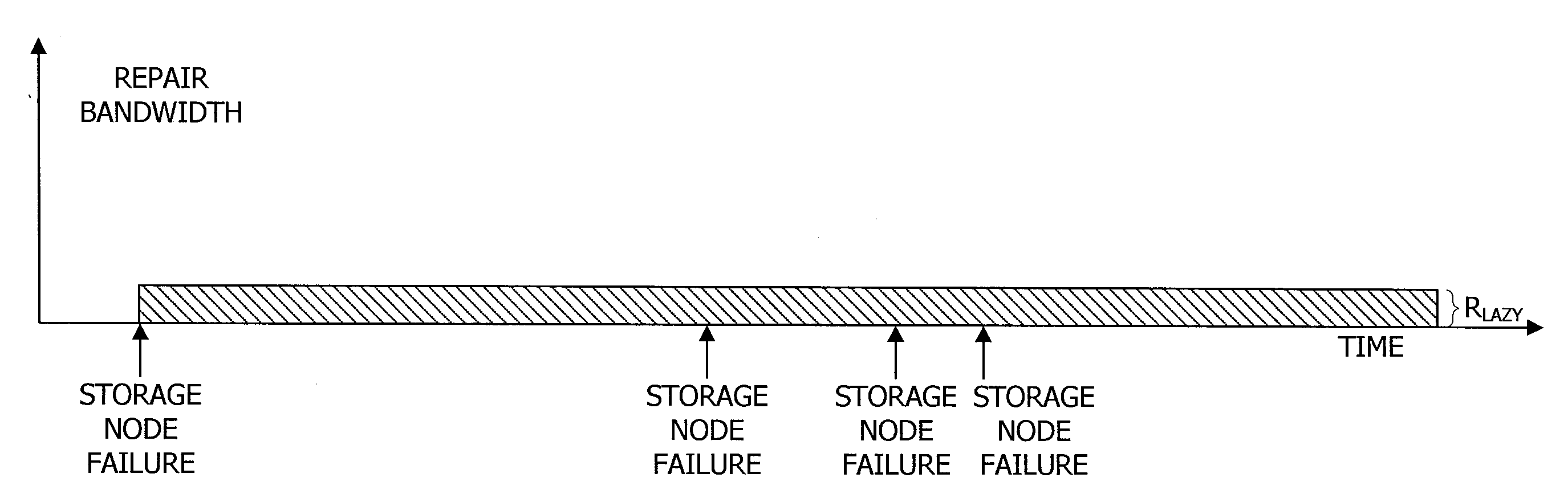
Embodiments provide methodologies for reliably storing data within a storage system using liquid distributed storage control. Such liquid distributed storage control operates to compress repair bandwidth utilized within a storage system for data repair processing to the point of operating in a liquid regime. Liquid distributed storage control logic of embodiments may employ a lazy repair policy, repair bandwidth control, a large erasure code, and / or a repair queue. Embodiments of liquid distributed storage control logic may additionally or alternatively implement a data organization adapted to allow the repair policy to avoid handling large objects, instead streaming data into the storage nodes at a very fine granularity.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
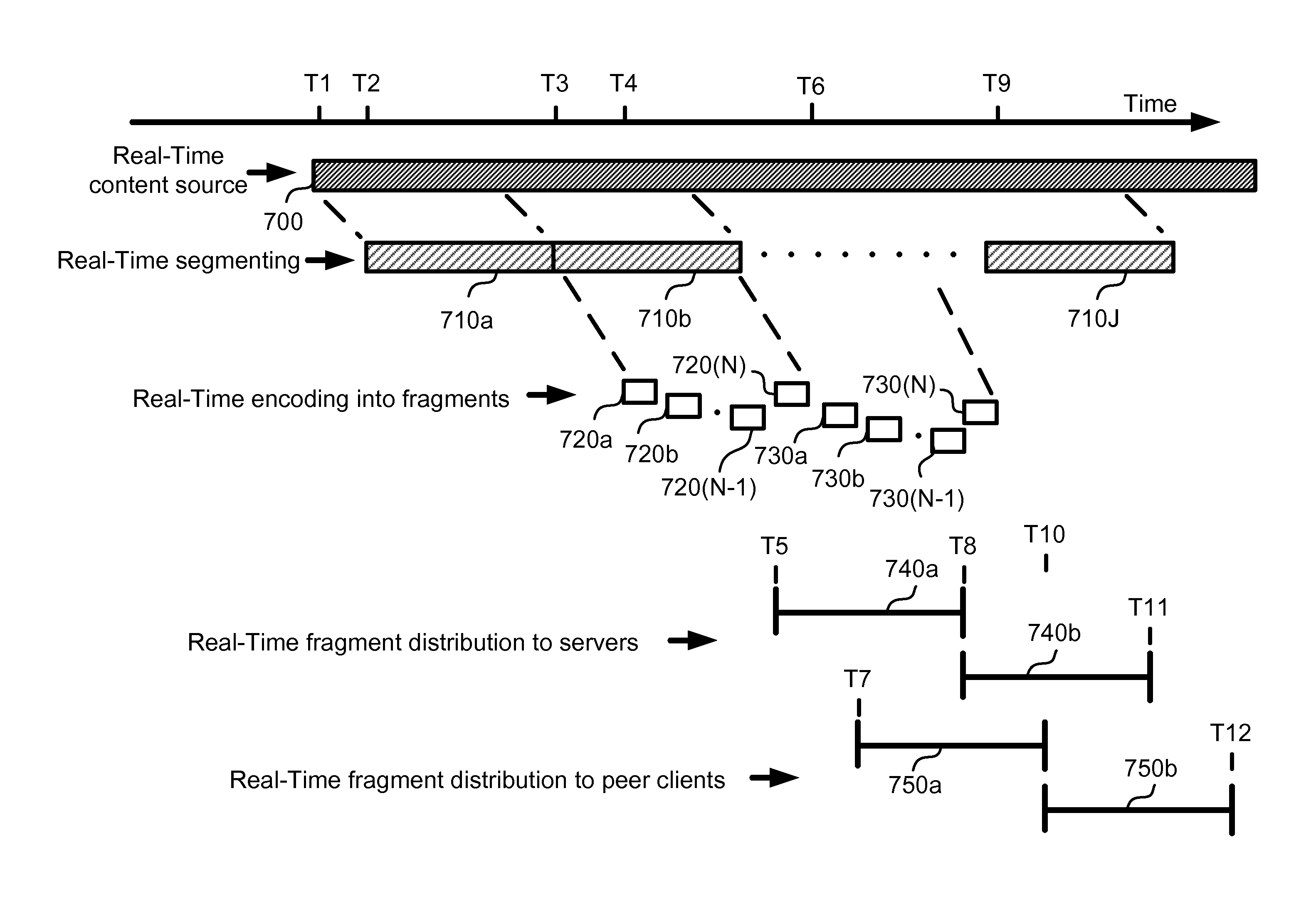
Reduction of Peak-to-Average Traffic Ratio in Distributed Streaming Systems
Reduction of peak-to-average traffic ratio in distributed streaming systems, including a large number of fractional-storage CDN servers accessed via the Internet, and storing erasure-coded fragments encoded with a redundancy factor greater than one from streaming contents, and a very large number of assembling devices obtaining the fragments from the servers in order to reconstruct the streaming contents. The assembling devices are spread over different time zones spanning at least three hours and balance the bandwidth load between the servers.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
Data storage method of cloud storage system
InactiveCN102546755ADoes not affect recoveryImprove data availabilityTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsComputer hardwareData integrity
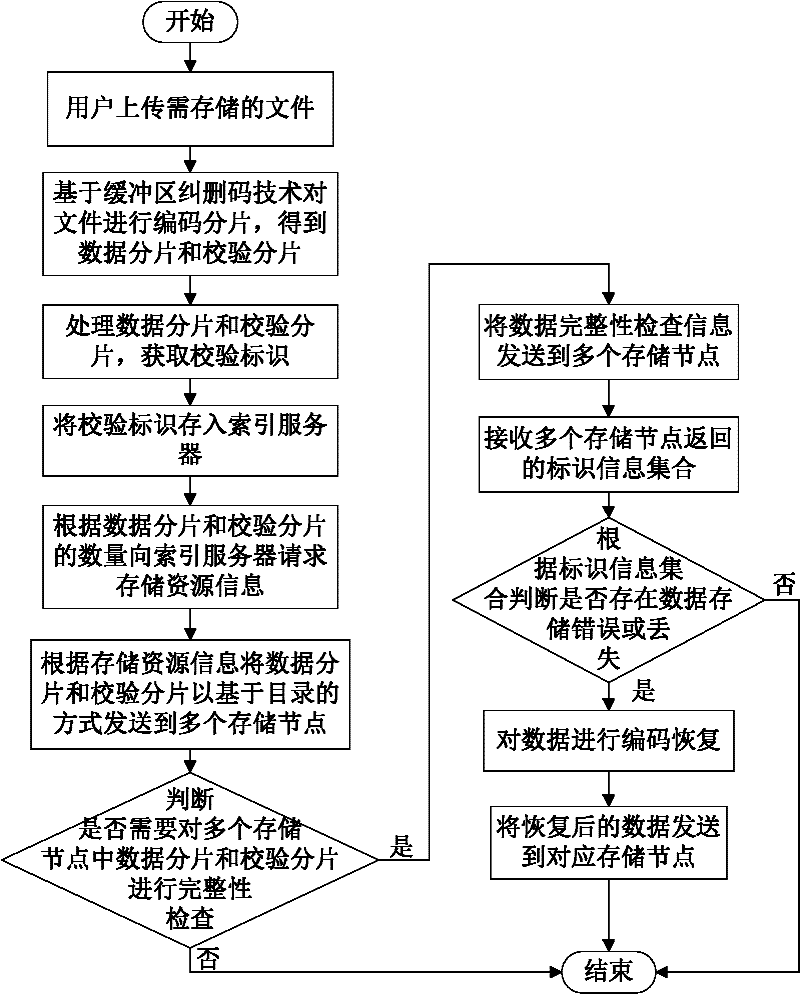
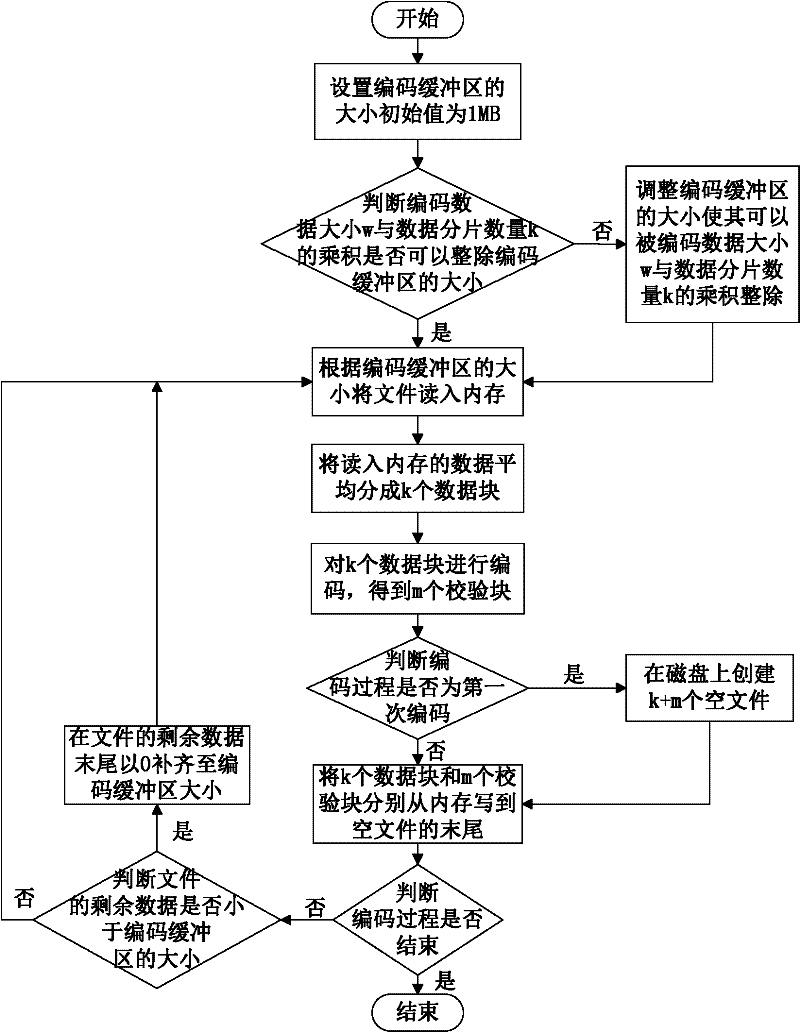
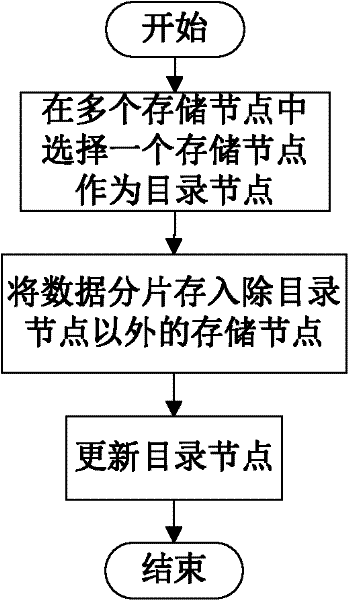
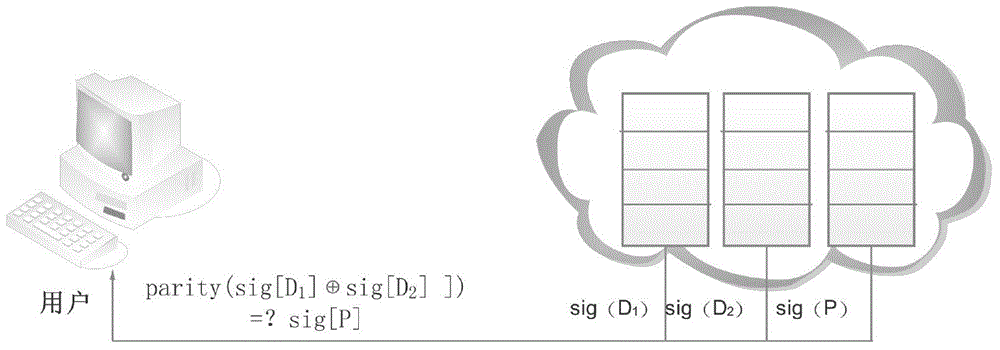
The invention discloses a data storage method of a cloud storage system, which comprises the steps of: carrying out coding fragmentation on a file on the basis of a buffer zone erasure code technology to obtain data fragments and check fragments; processing the data fragments and the check fragments to obtain a check identification; storing the check identification in an index server; requesting storage resource information to the index server according to the quantity of the data fragments and the check fragments; sending the data fragments and the check fragments to a plurality of storage nodes according to the storage resource information; judging whether needing to carry out integrity check on the data fragments and the check fragments in the storage nodes; if needing to carry out integrity check on the data fragments and the check fragments in the storage nodes, sending the data integrity check information to the storage nodes, receiving an identification information set returned by the storage nodes, and judging whether data storage errors or data losses exist according to the identification information set, if yes, coding for recovering the data, and sending the recovered data to the corresponding storage nodes.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Node consensus verification method under league chain network through asynchronous mode
InactiveCN106529951AImprove throughputImprove network throughputFinanceElectronic credentialsValidation methodsChain network
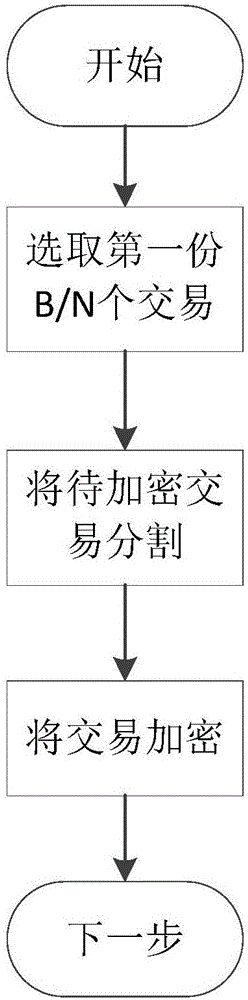
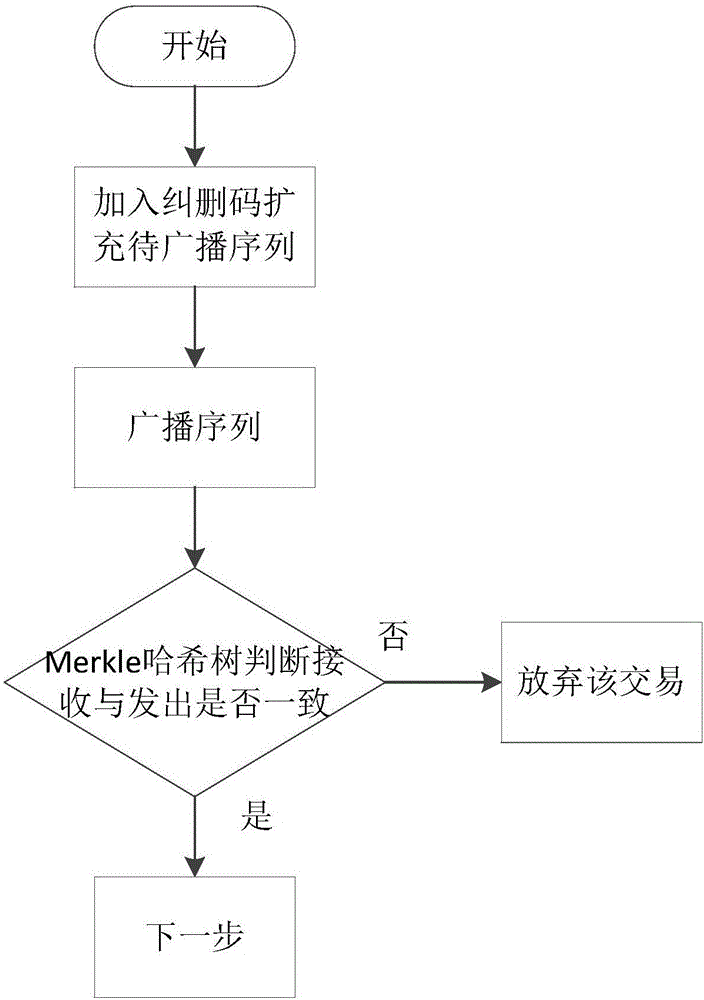
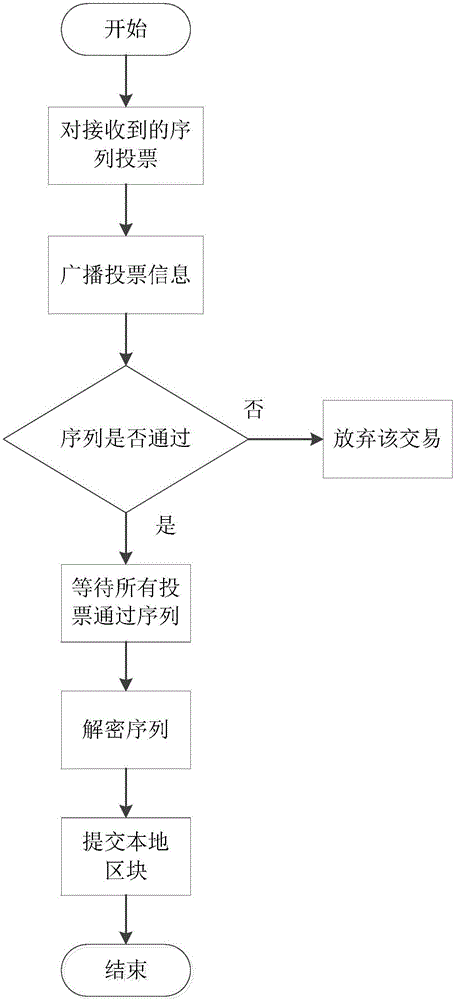
The invention discloses a node consensus verification method under a league chain network through an asynchronous mode. Each node takes a transaction request from the head of a buffer queue to act as a transaction sequence to be submitted and then encrypts the sequence by using threshold encryption; each node broadcasts the encrypted transaction sequence, ensures the integrity of the transmitted message by using an erasure code and ensures message consistency of different nodes by using a Merkle tree; and all the nodes vote the transaction sequences by using the binary Byzantine consensus agreement to reach a consensus, each node waits for local receiving all the voted transaction sequences and then decrypts the transaction sequences by using threshold decryption so as to finally obtain the decrypted transaction information to act as the transaction request written in blocks within the period. The method is completely decentralized, the system has no timeout mechanism and the broadcast message completely depends on the network bandwidth so that the method has higher network throughput when a large number of nodes exist in the network in comparison with the conventional synchronization Byzantine fault tolerance consensus method.
Owner:HANGZHOU YUNXIANG NETWORK TECH
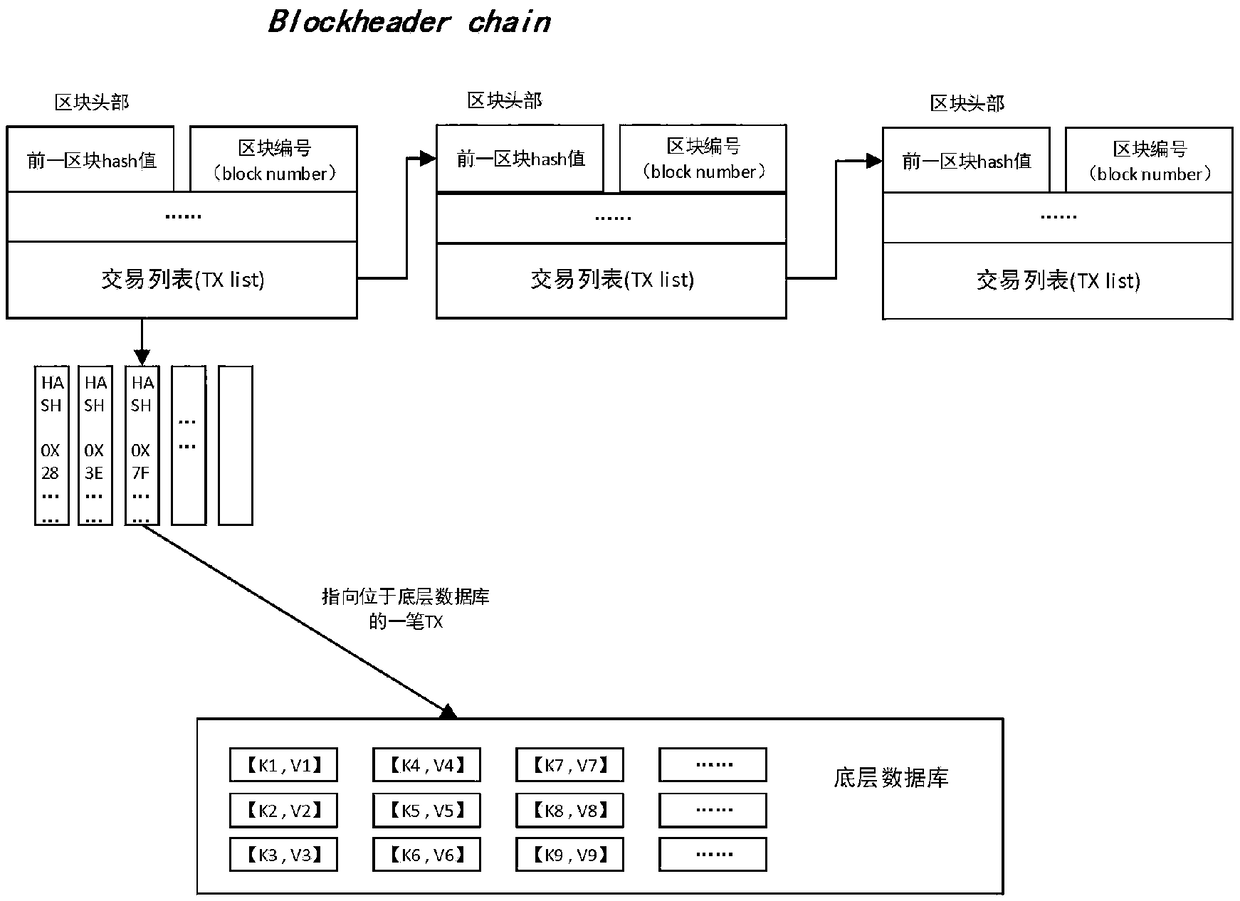
Block chain account book distributed storage technology based on erasure code
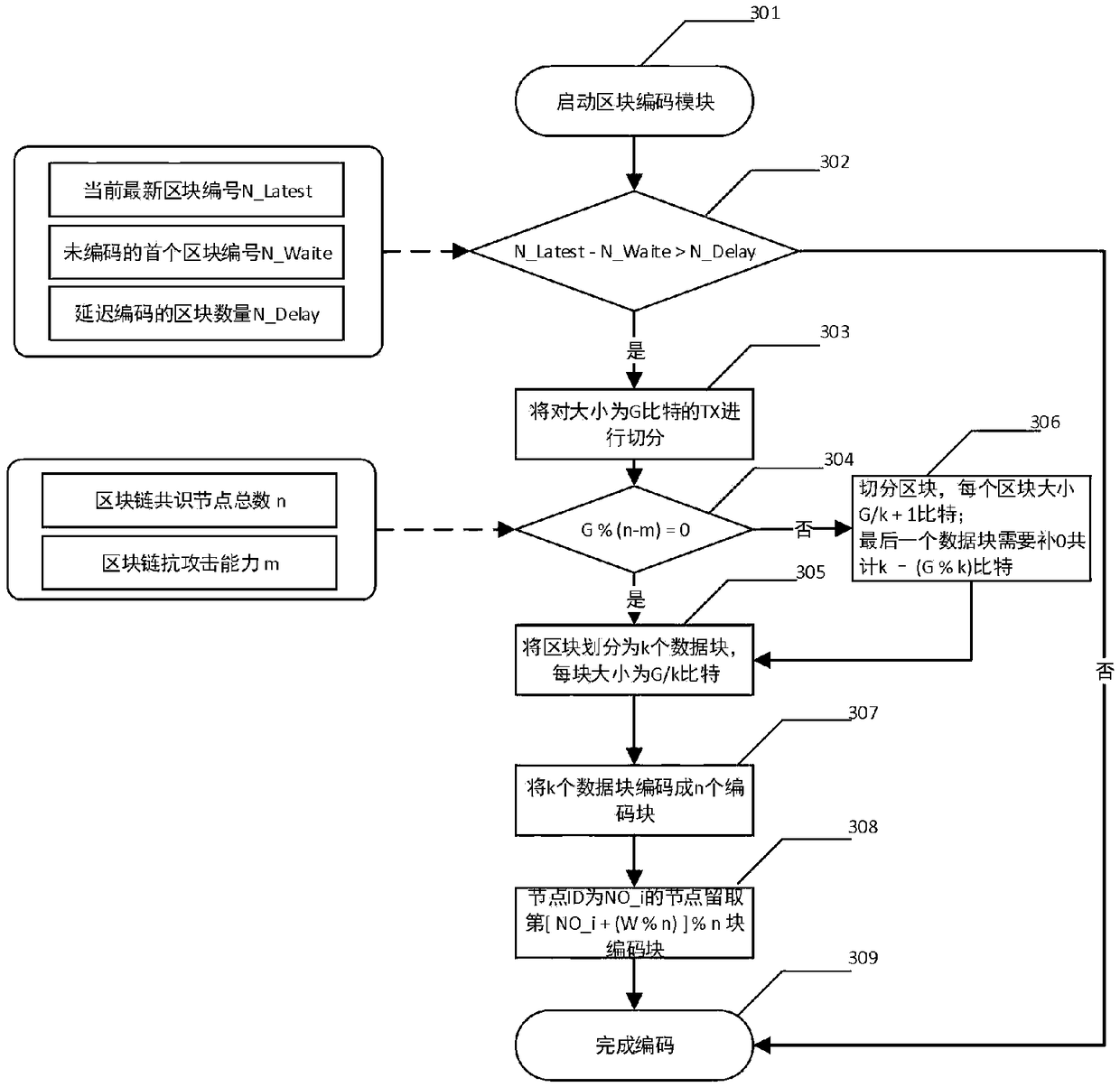
InactiveCN109359223AReduce redundancyReduce demandOther databases indexingTransmissionCoding blockComputer architecture
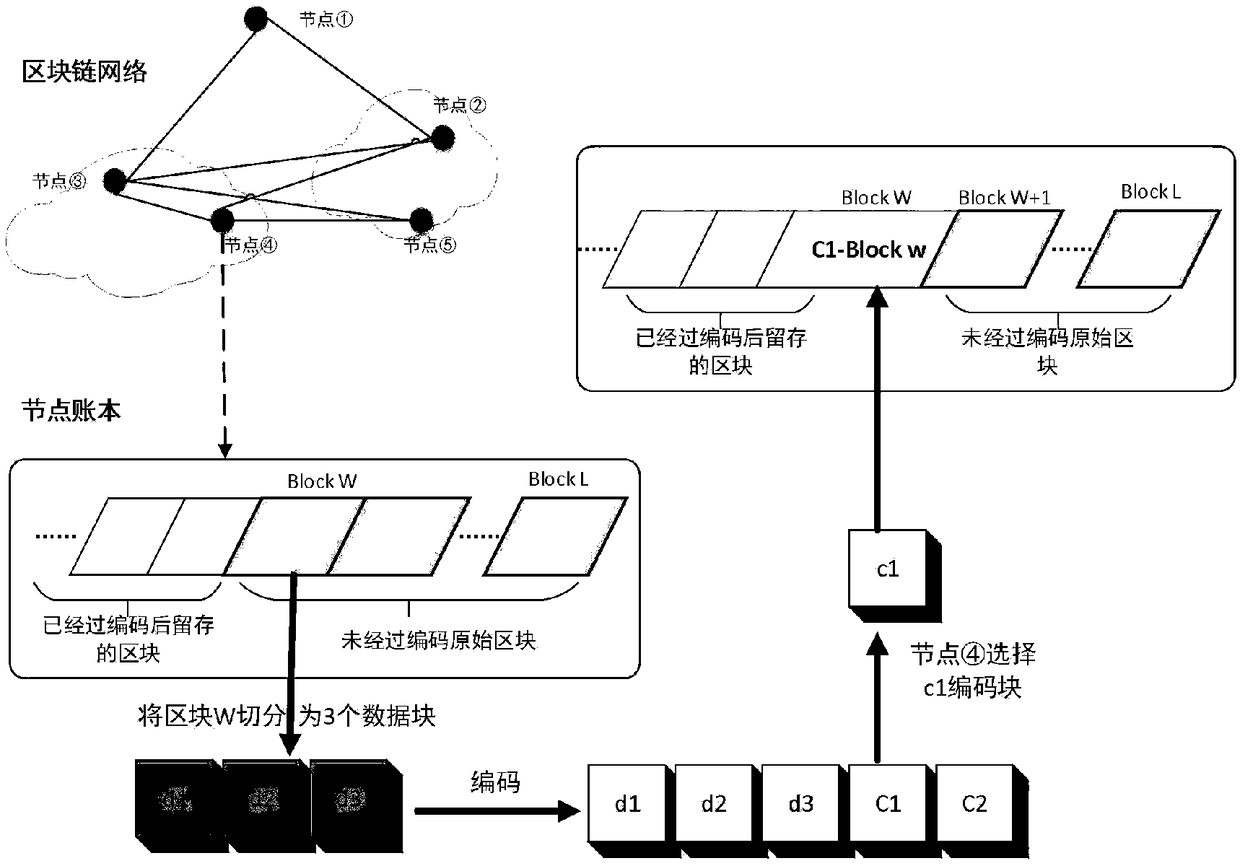
The invention relates to a block chain account book distributed storage technology based on erasure code, and belongs to the block chain technology field. The technology comprises the following steps:a) the block delay coding strategy allows to delay the coding of a certain number of new blocks to meet the synchronization requirements of other block chain consensus nodes for blocks; B) accordingto the set block coding algorithm, the blocks satisfying the coding condition are cut into k data blocks, each data block having a size of about 1 / k of the original block, and further the cut k datablocks are encoded into n (n) k encoded blocks by the erasure coding technology; (c) each block chain node reserves a part of that coding block, and finally the whole block chain network store the coding blocks decentrally; D) when the original block needs to be recovered from the encoded block, the current node collects the remaining encoded block corresponding to the block from the remaining nodes, and then recovers the original block according to the corresponding decoding algorithm. The method reduces the requirement of the block chain for storage resources and improves the utilization rate of storage space.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Systems and mehtods for reliably storing data using liquid distributed storage
Embodiments provide methodologies for reliably storing data within a storage system using liquid distributed storage control. Such liquid distributed storage control operates to compress repair bandwidth utilized within a storage system for data repair processing to the point of operating in a liquid regime. Liquid distributed storage control logic of embodiments may employ a lazy repair policy, repair bandwidth control, a large erasure code, and / or a repair queue. Embodiments of liquid distributed storage control logic may additionally or alternatively implement a data organization adapted to allow the repair policy to avoid handling large objects, instead streaming data into the storage nodes at a very fine granularity.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
System and methods for distributed data storage
InactiveUS20150142863A1Digital data information retrievalError detection/correctionCoding blockParallel computing
A systematic distributed storage system (DSS) comprising: a plurality of storage nodes, wherein each storage node configures to store a plurality of sub blocks of a data file and a plurality of coded blocks, a set of repair pairs for each of the storage nodes, wherein the system is configured to use the respective repair pair of storage nodes to repair a lost or damaged sub block or coded block on a given storage node. Also a distributed storage system DSS comprising h non-empty nodes, and data stored non homogenously across the non-empty nodes according to the storing codes (n,k). Further a method for determining linear erasure codes with local repairability comprising: selecting two or more coding parameters including r and δ; determining if an optimal [n, k, d] code having all-symbol (r, δ)-locality (“(r, δ)a”) exists for the selected r, δ; and if the optimal (r, δ)a code exists performing a local repairable code using the optimal (r, δ)a code.
Owner:SINGAPORE UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY AND DESIGN
Parity protection for data chunks in an object storage system
The present invention relates to a method and system for providing parity protection in an object storage system. The present invention allows for tracking the storage requirements for chunks in a distributed storage cluster when transitioning from replica-based protection to parity or erasure coding-based protection and when transitioning from parity or erasure coding-based protection to replica-based protection.
Owner:NEXENTA BY DDN INC
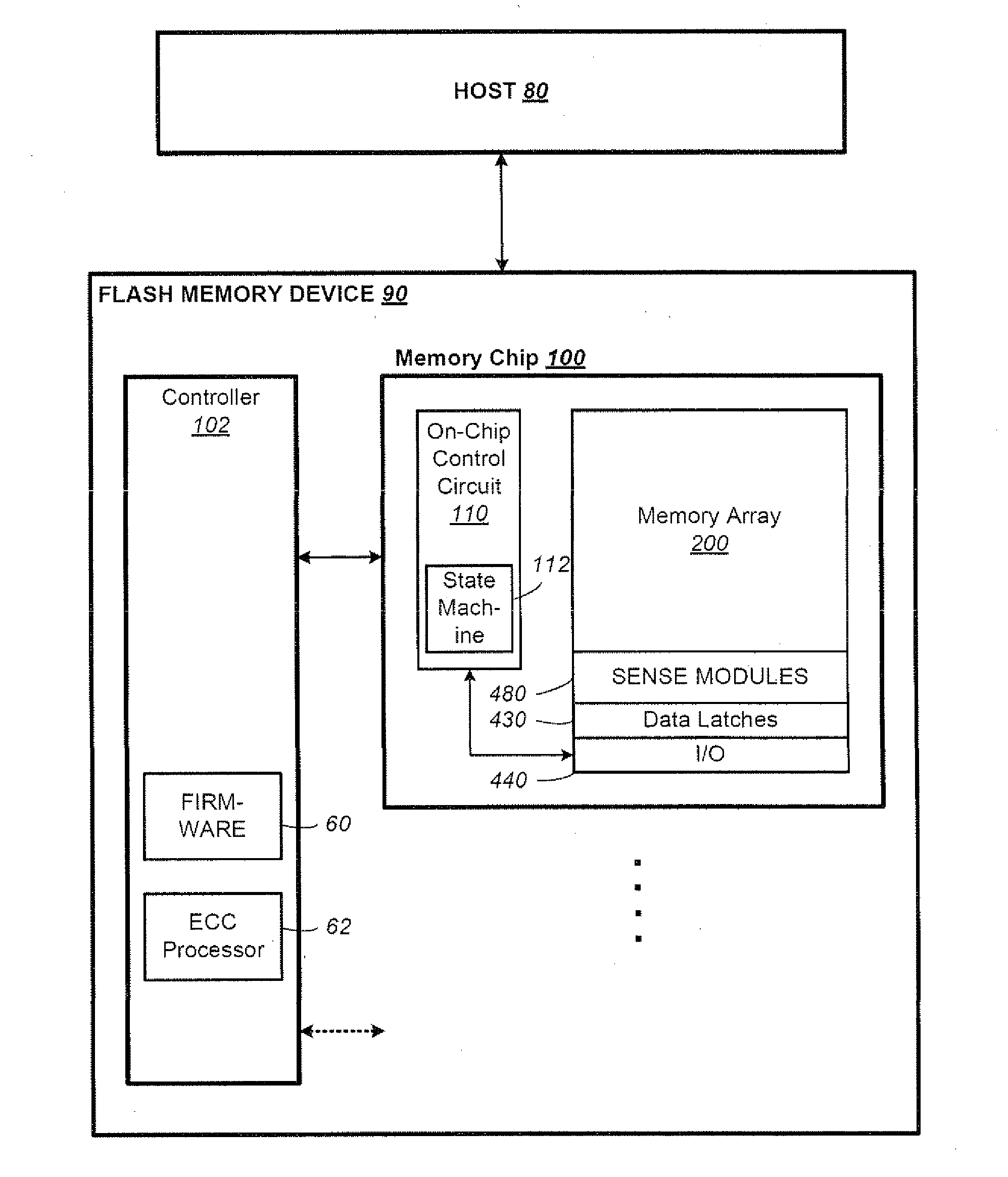
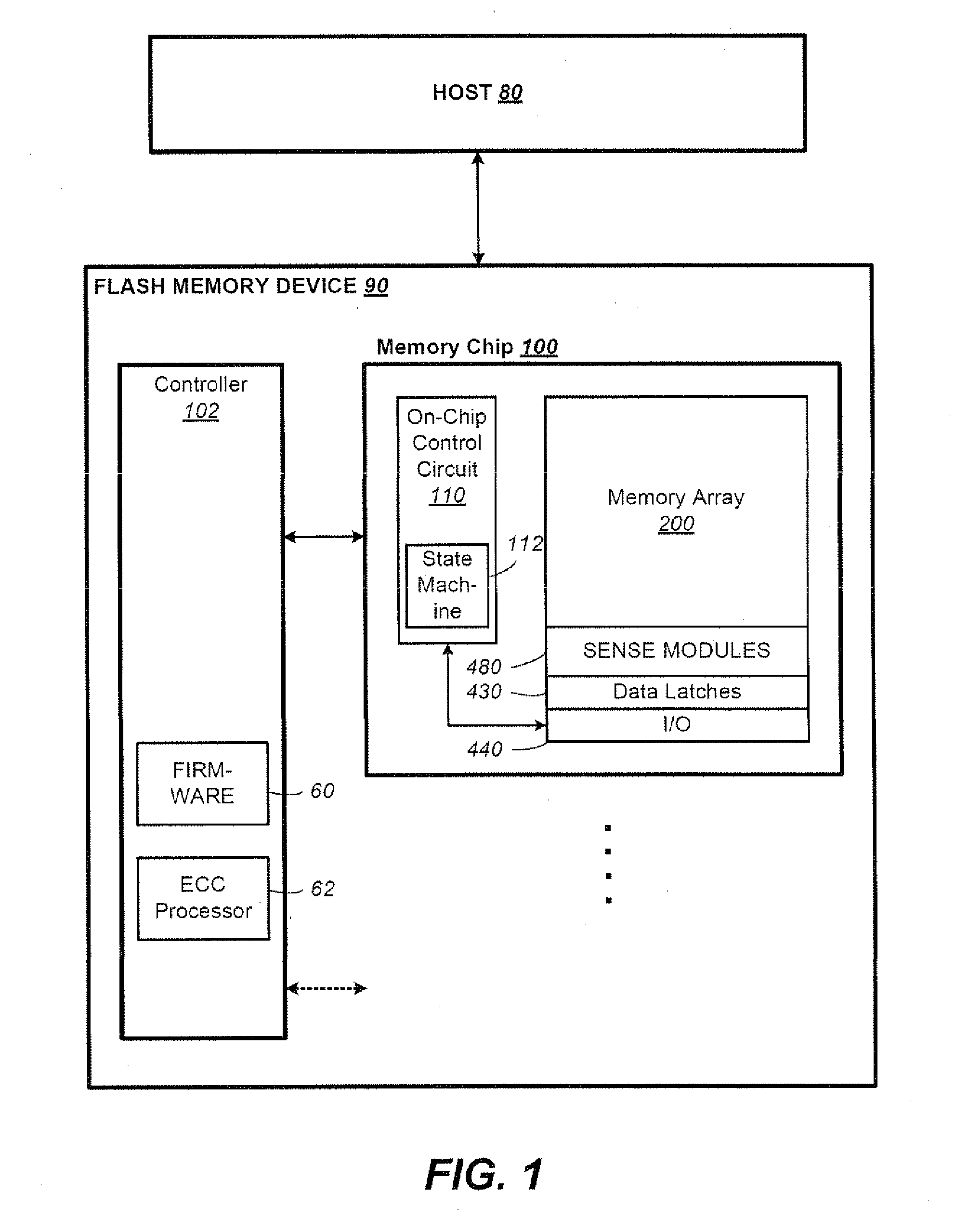
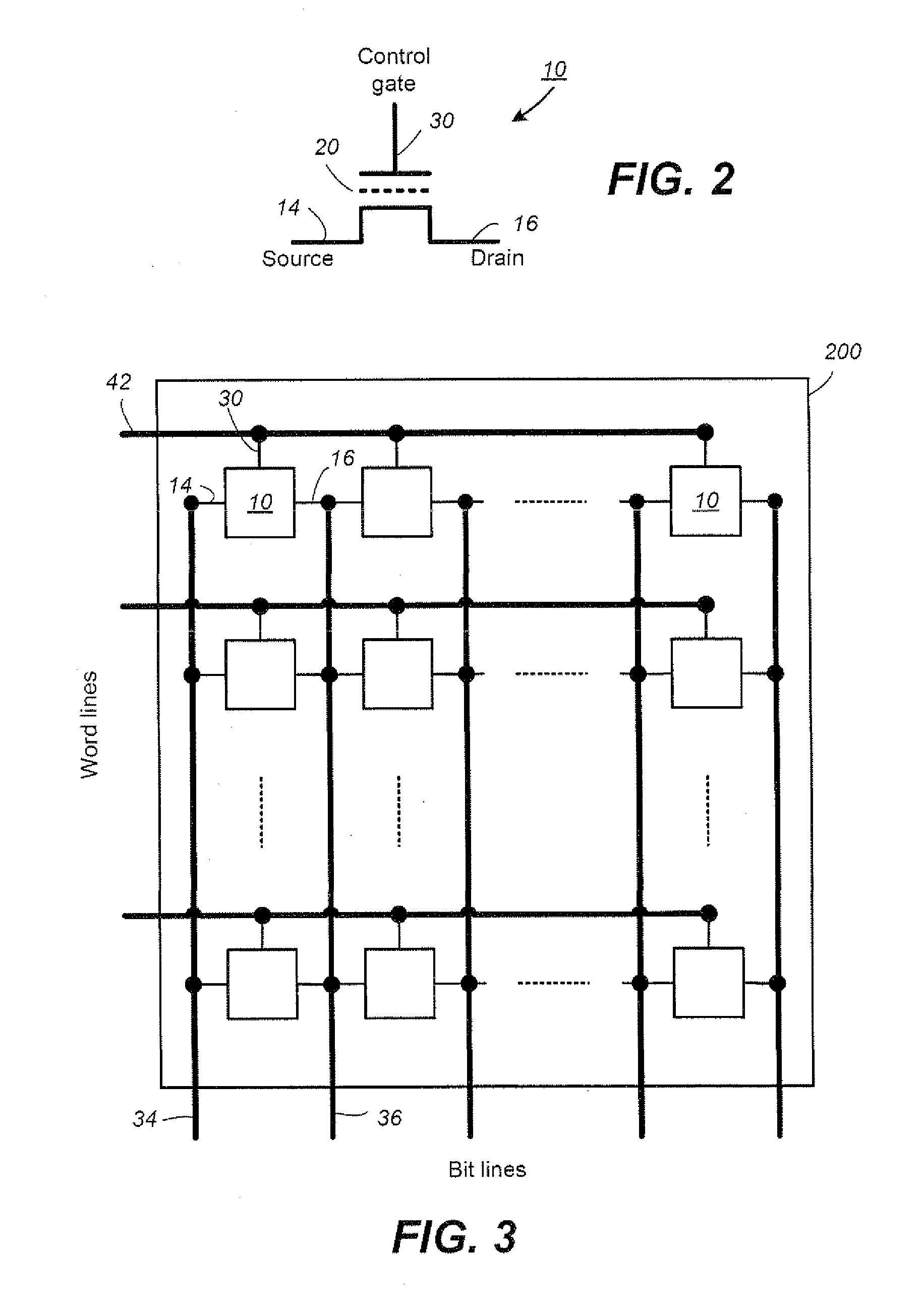
Data Recovery for Defective Word Lines During Programming of Non-Volatile Memory Arrays
The recovery of data during programming, such as in the case of a broken word-line, is considered. The arrangement described assumes that k pages may be corrupted when the system finishes programming a block. Then these corrupted pages can be recovered using an erasure code. In order to recover any k pages, the system will compute and temporarily store k parity pages in the controller. These k parity pages may be computed on-the-fly as the data pages are received from the host. Once programming of the block is finished, a post-write read may be done in order to validate that the data is stored reliably. If no problem is detected during EPWR, then the parity pages in the controller may be discarded. In case a problem is detected, and data in up to k pages is corrupt on some bad word-lines, then the missing data is recovered using the k parity pages that are stored in the controller and using the other non-corrupted pages that are read from the block of the memory array and decoded. Once the recovery is complete the block can be reprogrammed and the temporary parity pages in the controller may be discarded upon successfully reprogramming.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
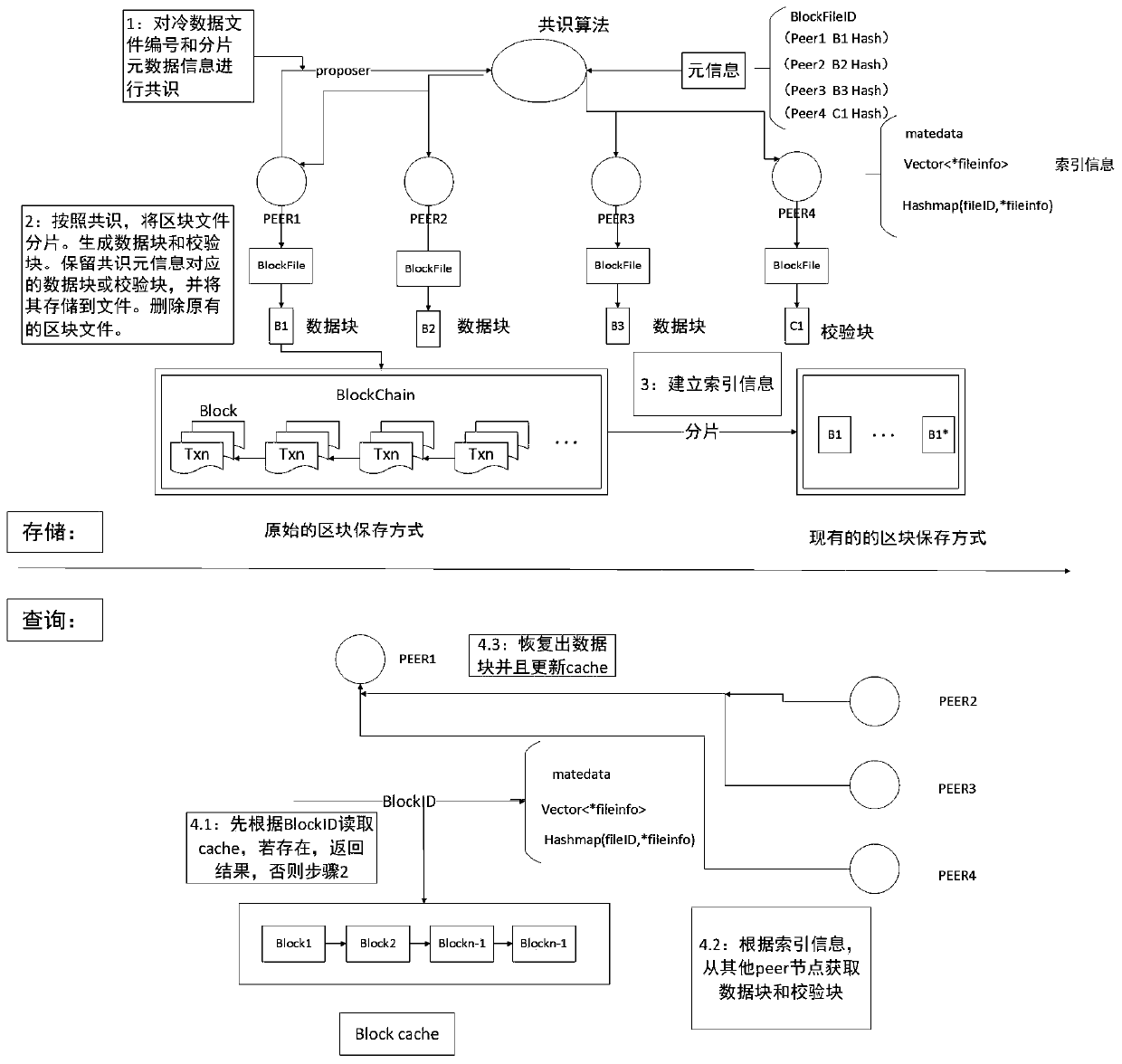
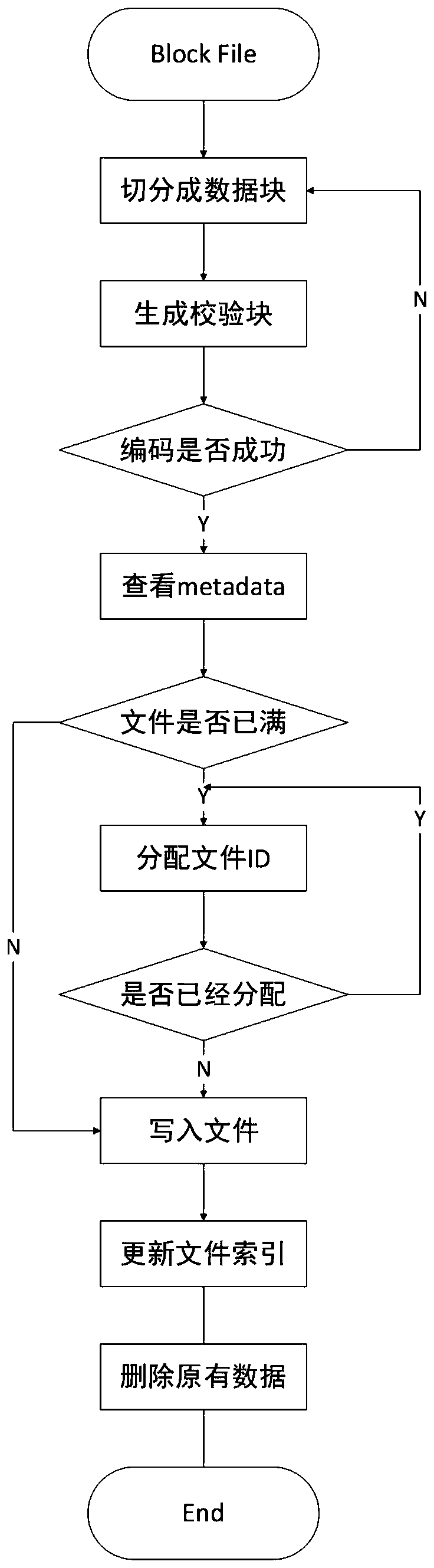
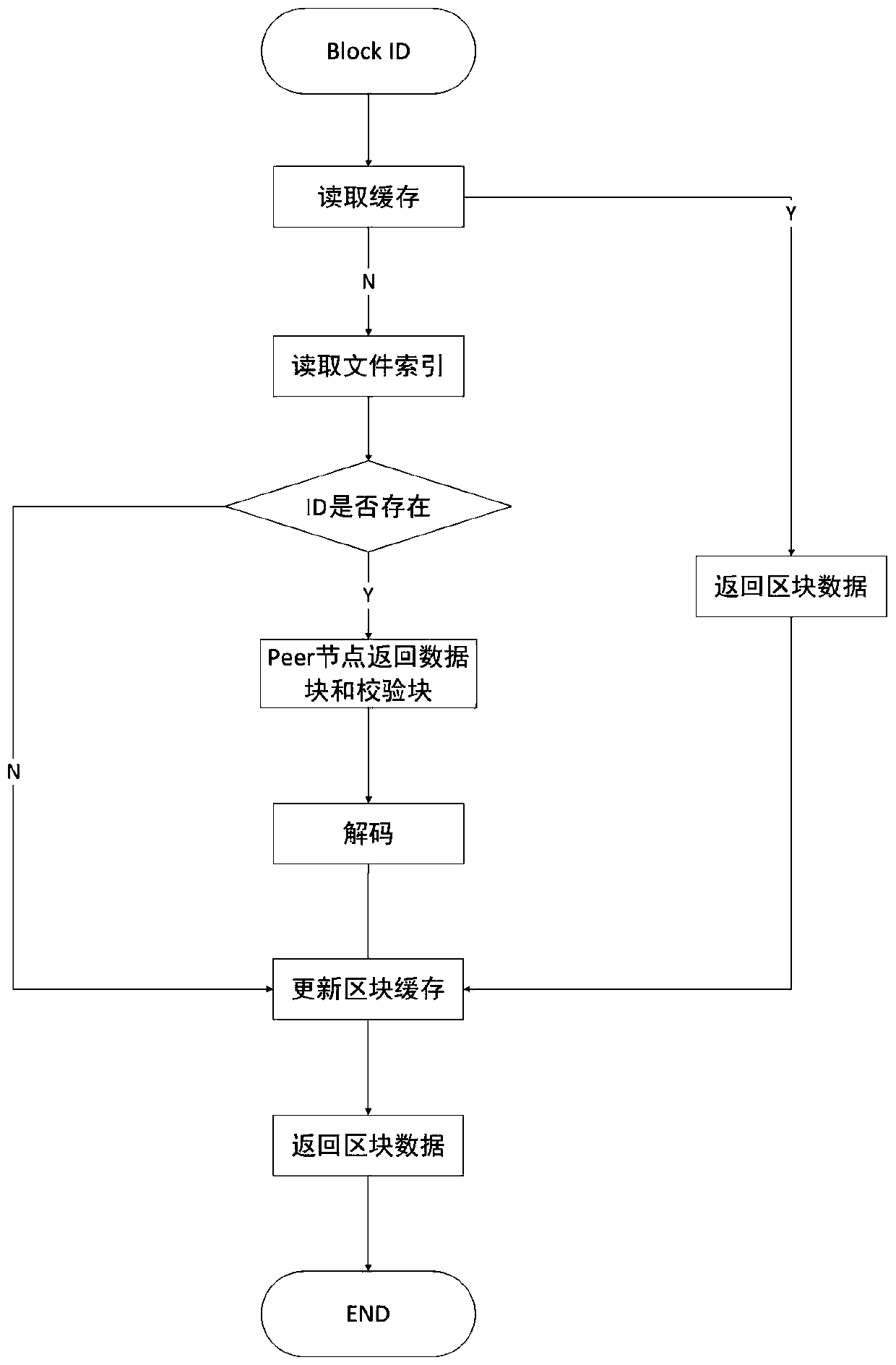
Block chain fragment storage and query method based on erasure codes
ActiveCN109871366AQuick searchEfficient queryFile access structuresSpecial data processing applicationsByzantine fault toleranceErasure code
The invention discloses a block chain fragment storage and query method based on erasure codes. When the block storage reaches a certain threshold, a block is sliced and stored. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, the meta-information of the block file fragments is consented, after the consensus is achieved, the erasure codes are utilized to fragment the block files within thethreshold value into the data blocks and the check blocks, and each node stores one part of the data blocks and the check blocks, so that the storage cost is reduced, and meanwhile, the data fault tolerance under the Bayer fault tolerance is also realized. Besides, when the block files are fragmented, the corresponding index is established, and the corresponding data block or check block can be queried from each node by utilizing the index, so that the block data can be queried efficiently under the condition that the storage space is saved.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
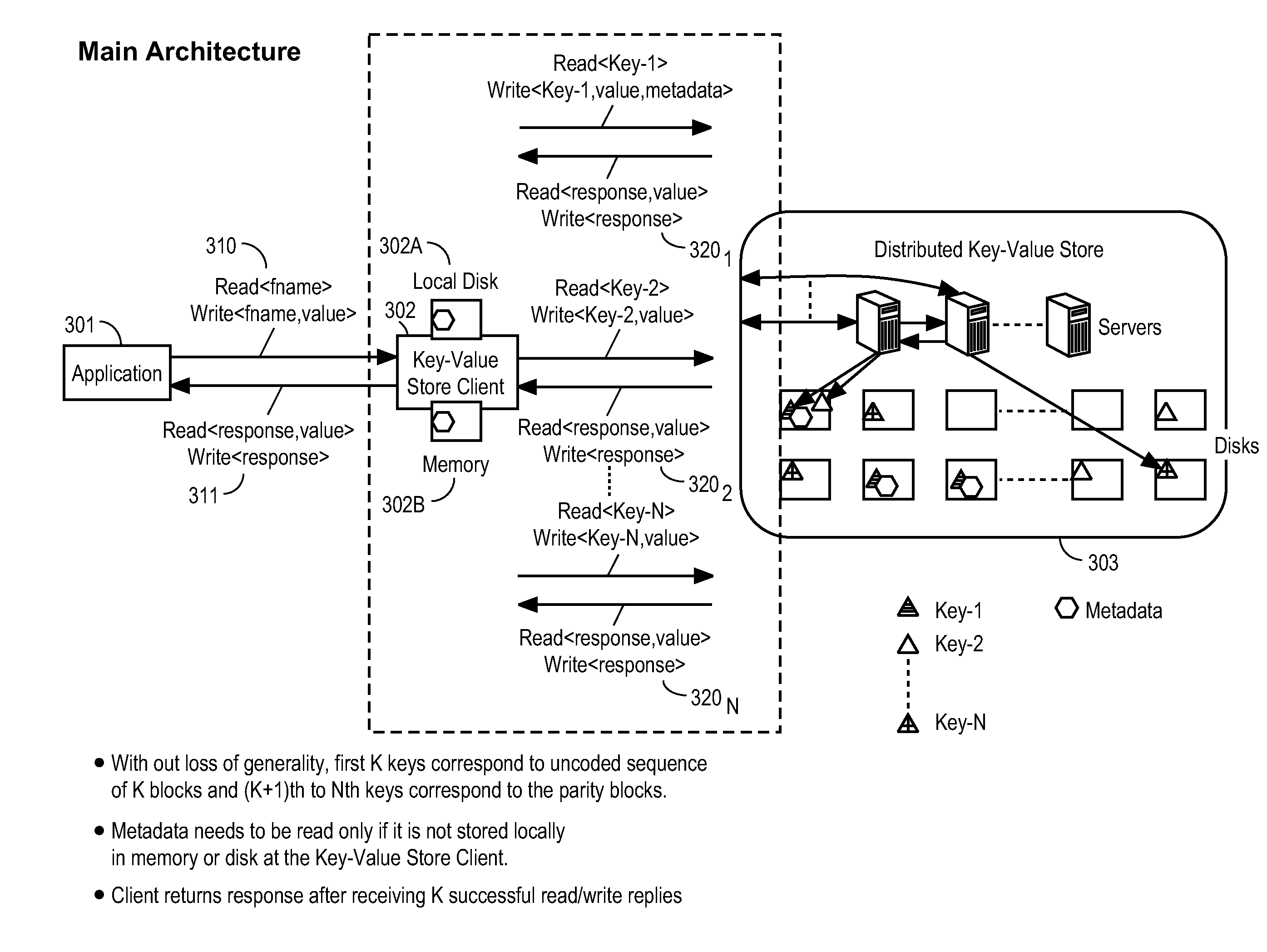
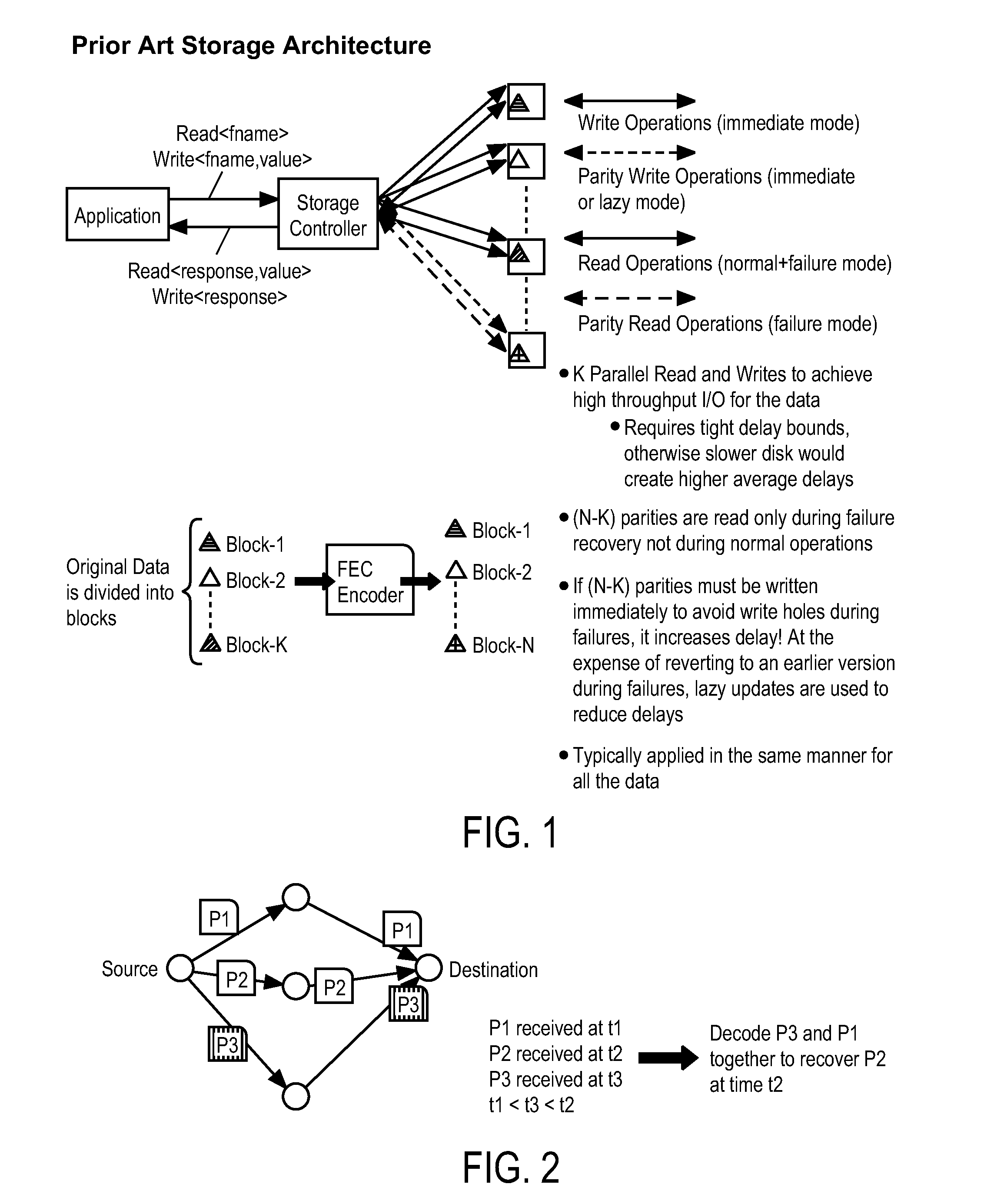
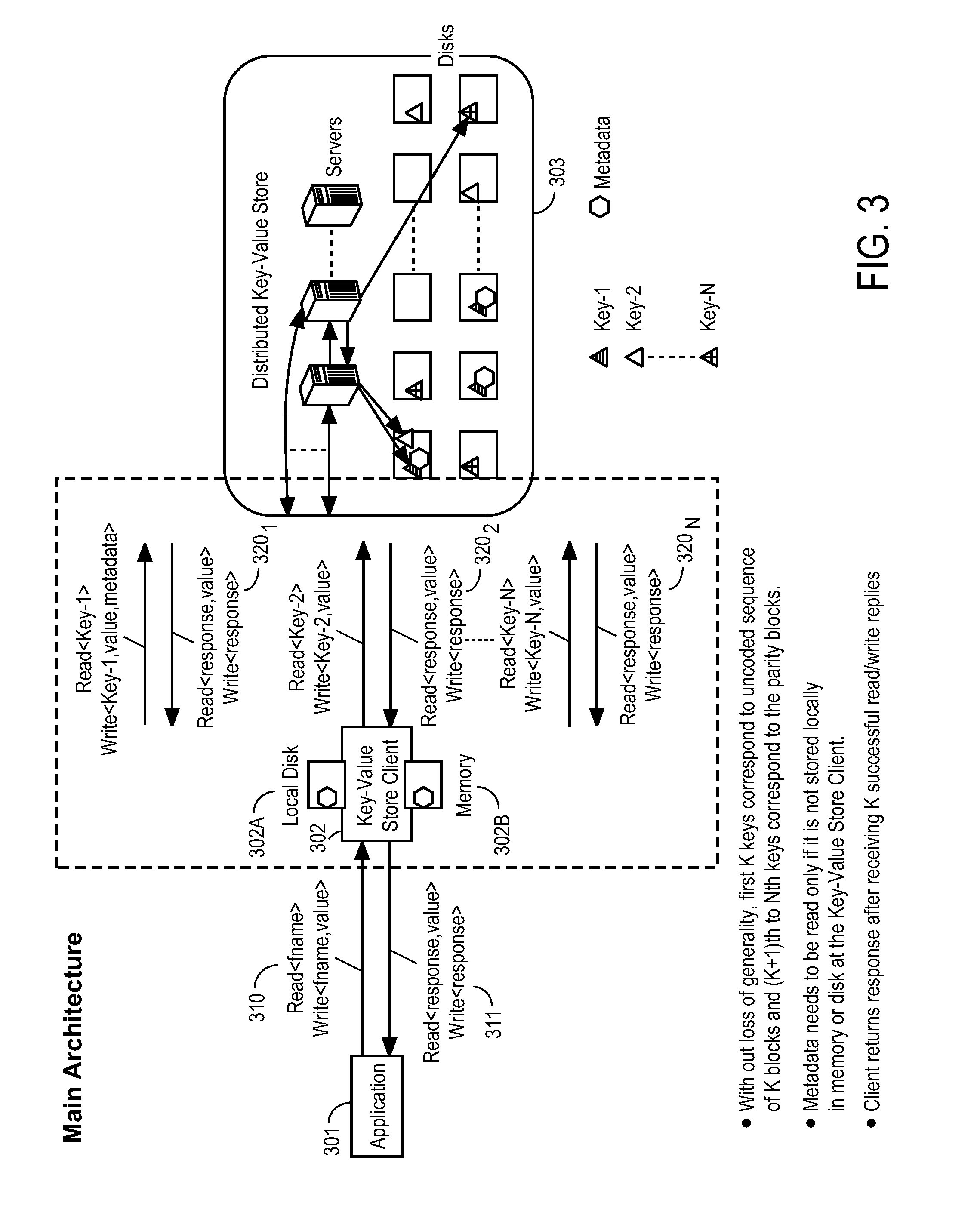
Method and apparatus for low delay access to key-value based storage systems using fec techniques
ActiveUS20150149870A1Lower latencyStatic storageForward error control useComputer architectureHybrid storage system
A method and apparatus is disclosed herein for low delay access to key-value based storage systems. In one embodiment, the method for putting data into a key-value store comprising dividing the data into K portions, where K is an integer; selecting an erasure coding to apply to the K portions as a function of delay performance of the key-value based storage system including determining a number of parity blocks to generate to satisfy one or both of a delay target of putting the object into the key-value store and a delay target of subsequent read requests based on an offline performance simulation of delay performance when different numbers of parity blocks are used given the delay distributions obtained through measurements for different request types and object sizes; applying the erasure coding to the K portions to create N blocks of data; sending the N write requests to write blocks of data to the storage system, where each block is assigned a unique key in the key-value store.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
User-oriented cloud storage data integrity protection method
InactiveCN105320899ASave storage spaceAvoid Lost Security RisksDigital data protectionData integrityOriginal data
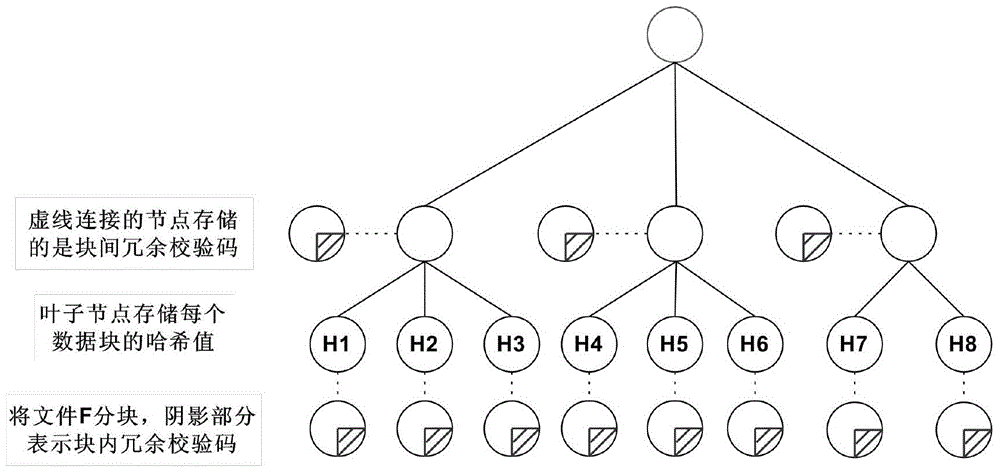
The invention discloses a user-oriented cloud storage data integrity protection method. The method includes the steps of 1, uploading, wherein a user side segments and numbers a file to generate intra-block redundancy check codes, the hash value of each file block is calculated and saved as a range-based 2-3 tree, the hash values are linked into one value and signed with private keys, and inter-block redundancy check codes are generated and encrypted with stream substitution secret keys; 2, verification, wherein a cloud management node sends a verification request to a corresponding cloud storage server, corresponding original data and algebraic signatures of the inter-block redundancy check codes corresponding to the original data are calculated and returned to the user side for data integrity verification, and the step 3 is executed if data destruction is found; 3, recovery, wherein the user side acquires all the file blocks on corresponding branch trees from a cloud side according to tree information and performs error recovery on the file blocks through erasure codes of the file blocks. According to the method, integrity verification and recovery are performed on the dynamic data stored in the cloud side from the user perspective.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
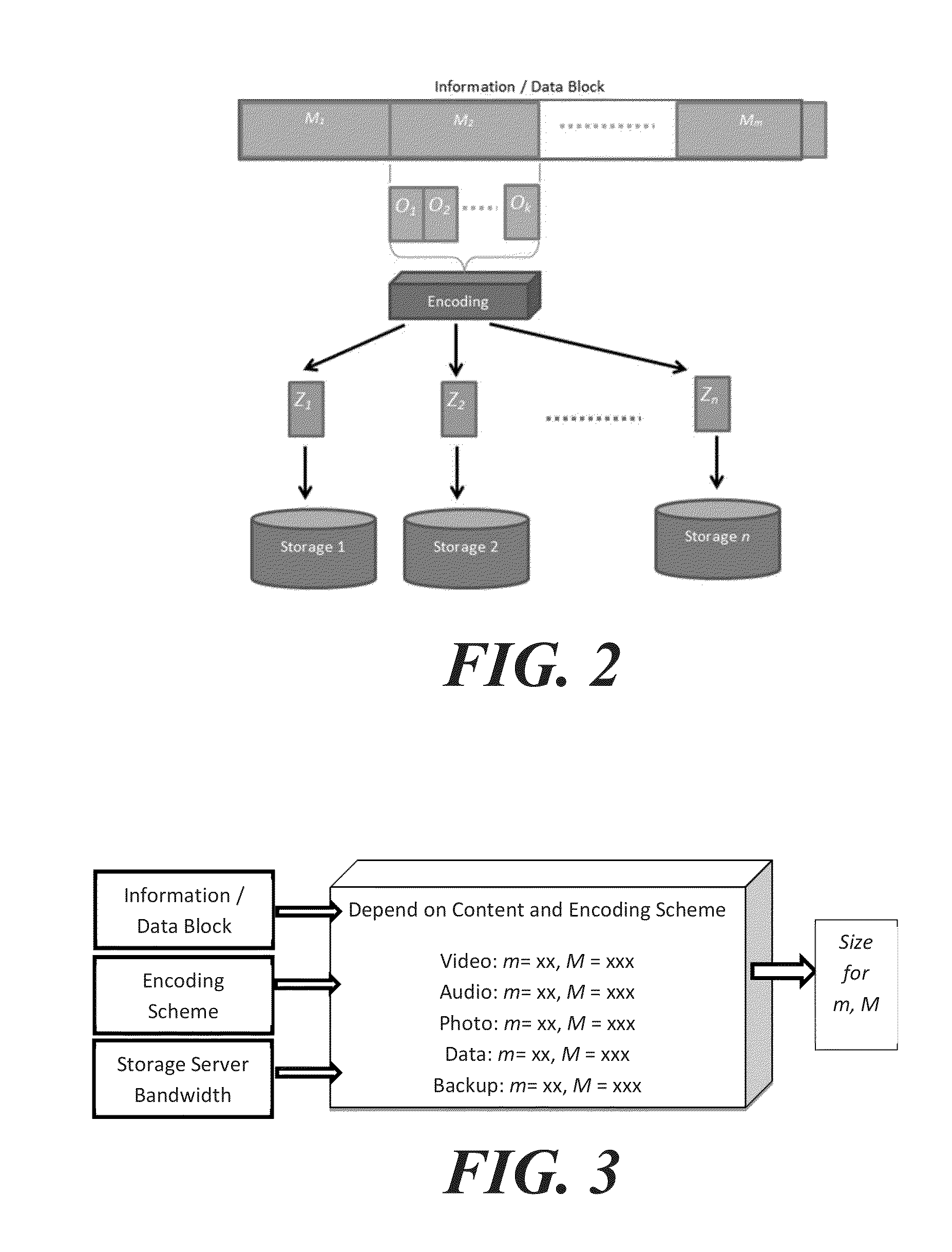
Accelerated erasure coding system and method
ActiveUS8683296B2Raise countImprove reliabilityNon-binary linear block codesError preventionProcessing coreOriginal data
An accelerated erasure coding system includes a processing core for executing computer instructions and accessing data from a main memory, and a non-volatile storage medium for storing the computer instructions. The processing core, storage medium, and computer instructions are configured to implement an erasure coding system, which includes: a data matrix for holding original data in the main memory; a check matrix for holding check data in the main memory; an encoding matrix for holding first factors in the main memory, the first factors being for encoding the original data into the check data; and a thread for executing on the processing core. The thread includes: a parallel multiplier for concurrently multiplying multiple entries of the data matrix by a single entry of the encoding matrix; and a first sequencer for ordering operations through the data matrix and the encoding matrix using the parallel multiplier to generate the check data.
Owner:STREAMSCALE
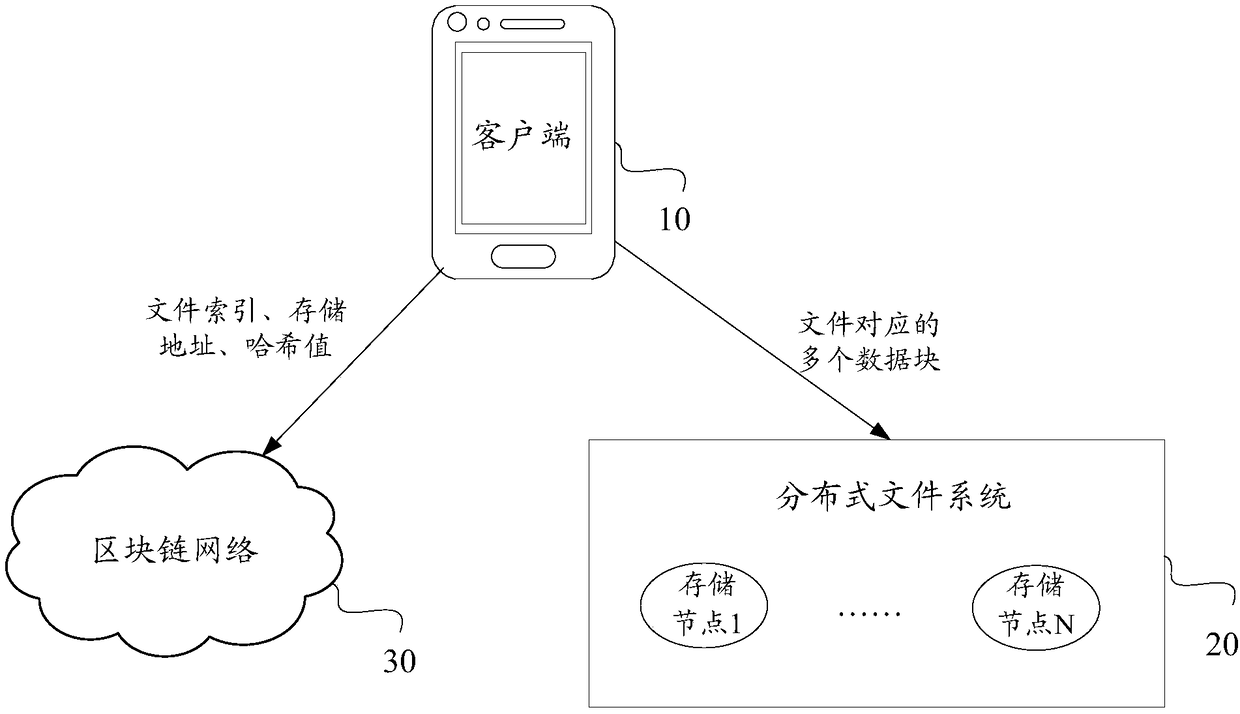
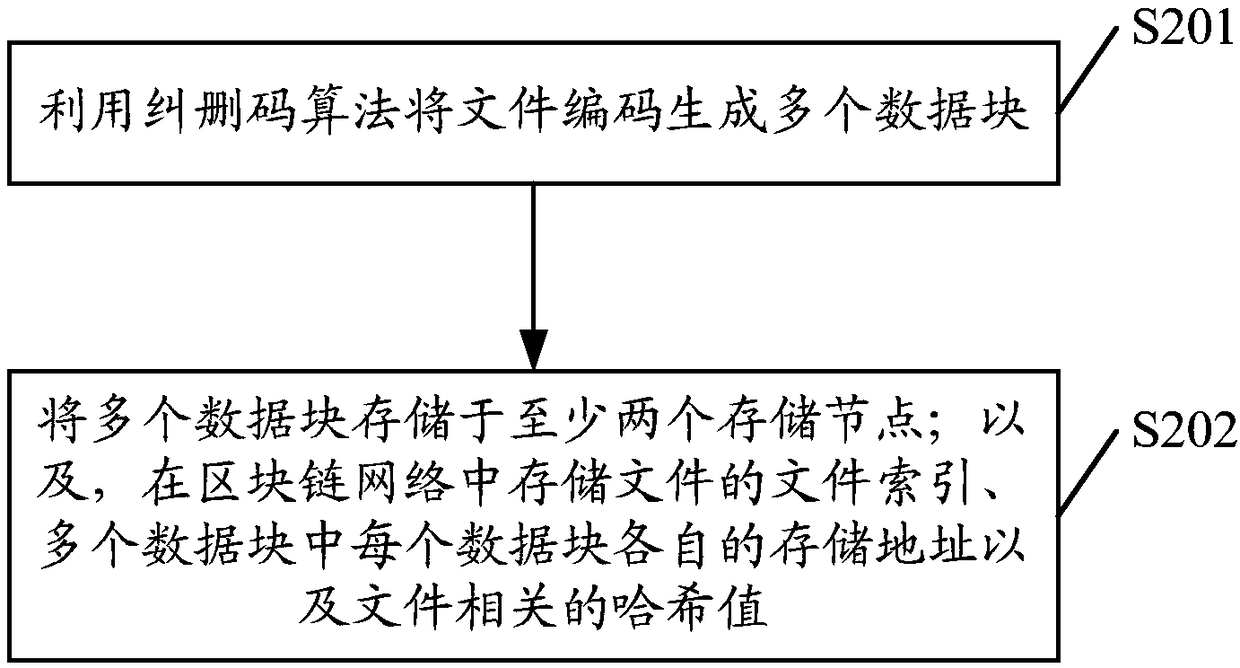
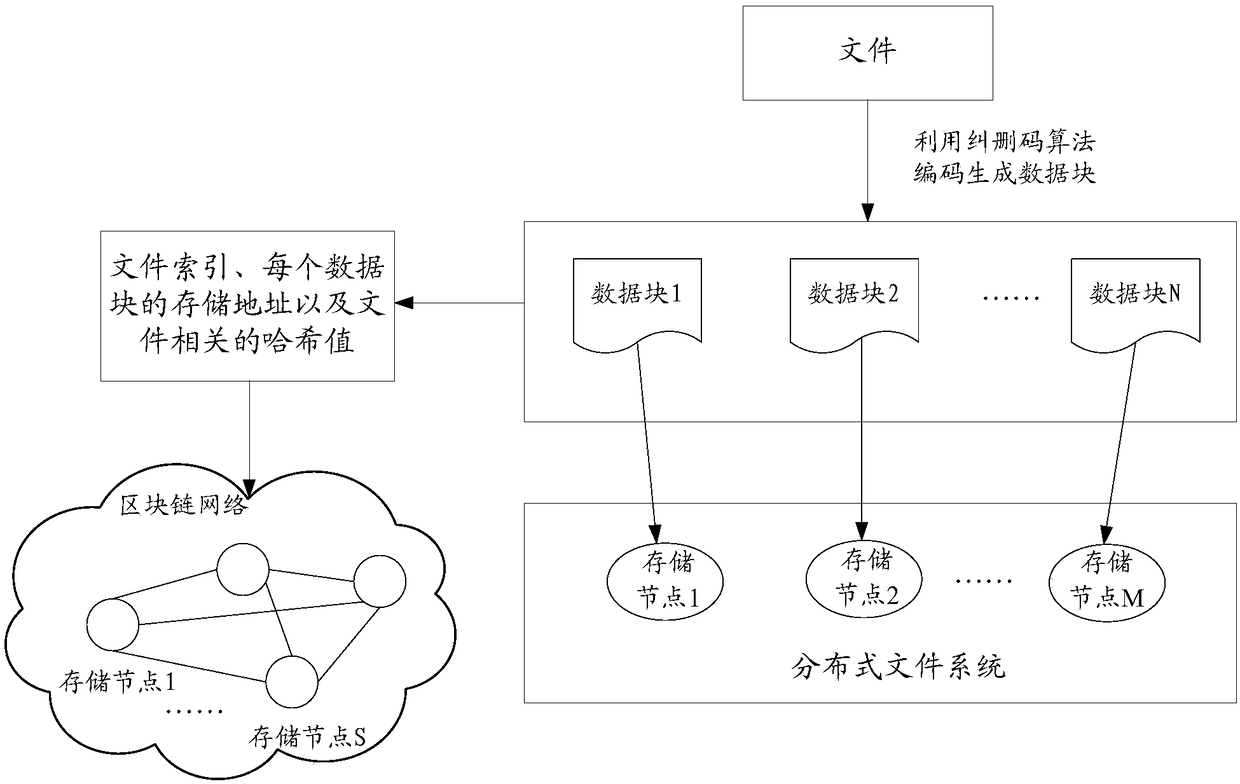
File processing method, device and equipment and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN109491968AReduce storage pressureReduce data redundancyFile access structuresRedundant data error correctionDistributed File SystemChain network
The invention discloses a file processing method, which comprises the following steps of: encoding a file into a plurality of data blocks by utilizing an erasure code algorithm, and storing the plurality of data blocks in at least two storage nodes which at least comprise storage nodes in a distributed file system; wherein one data block is only stored once; and storing the file index of the file,the respective storage address of each data block in the plurality of data blocks and the hash value related to the file in a block chain network. Therefore, the data redundancy is greatly reduced, higher data reliability is obtained with lower data redundancy, and the utilization rate of the storage space is improved. Moreover, the method adopts a mode of combined storage of the block chain network and the out-of-chain distributed storage system, so that the storage pressure of the block chain network is reduced, and the storage capacity is expanded by introducing the distributed file system. The invention further discloses a file processing device, equipment, a medium and a computer program product.
Owner:HUNDSUN TECH
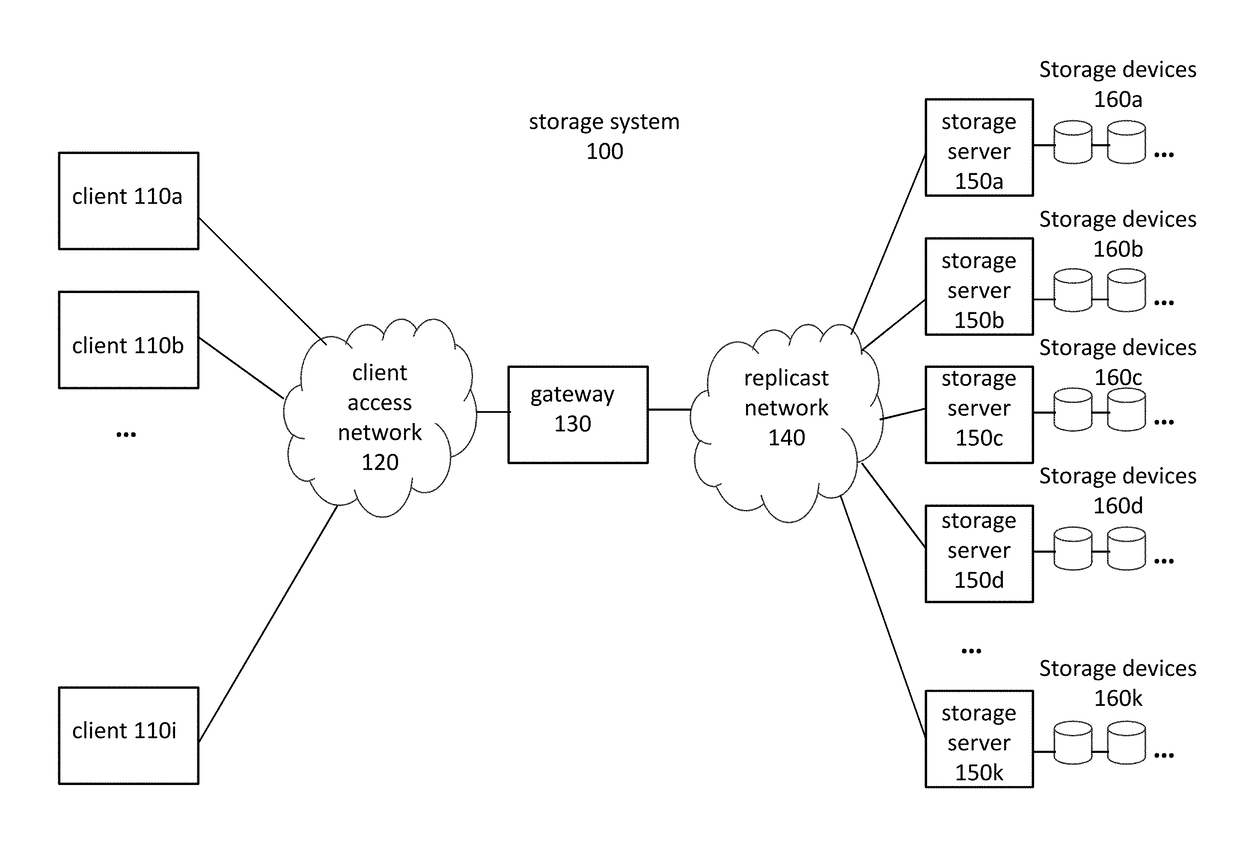
Methods and systems for using a distributed storage to its maximum bandwidth
ActiveUS20100094955A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionErasure codeDistributed computing
Using a distributed storage to its maximum bandwidth including the following steps: for each group of at least one assembling device, selecting a subgroup of fractional-storage CDN servers according to at least one criterion, whereby a plurality of server subgroups are selected for a plurality of assembling device groups. And retrieving, using a pull protocol, by the assembling devices from the subgroups of servers, erasure-coded fragments associated with multiple segments of contents, until the aggregated bandwidth used for retrieving the fragments approaches the aggregated bandwidth of the servers included in the subgroups, and as long as the aggregated bandwidth used for delivering each segment does not exceed the aggregated bandwidth of the servers storing the fragments generated from the segment.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
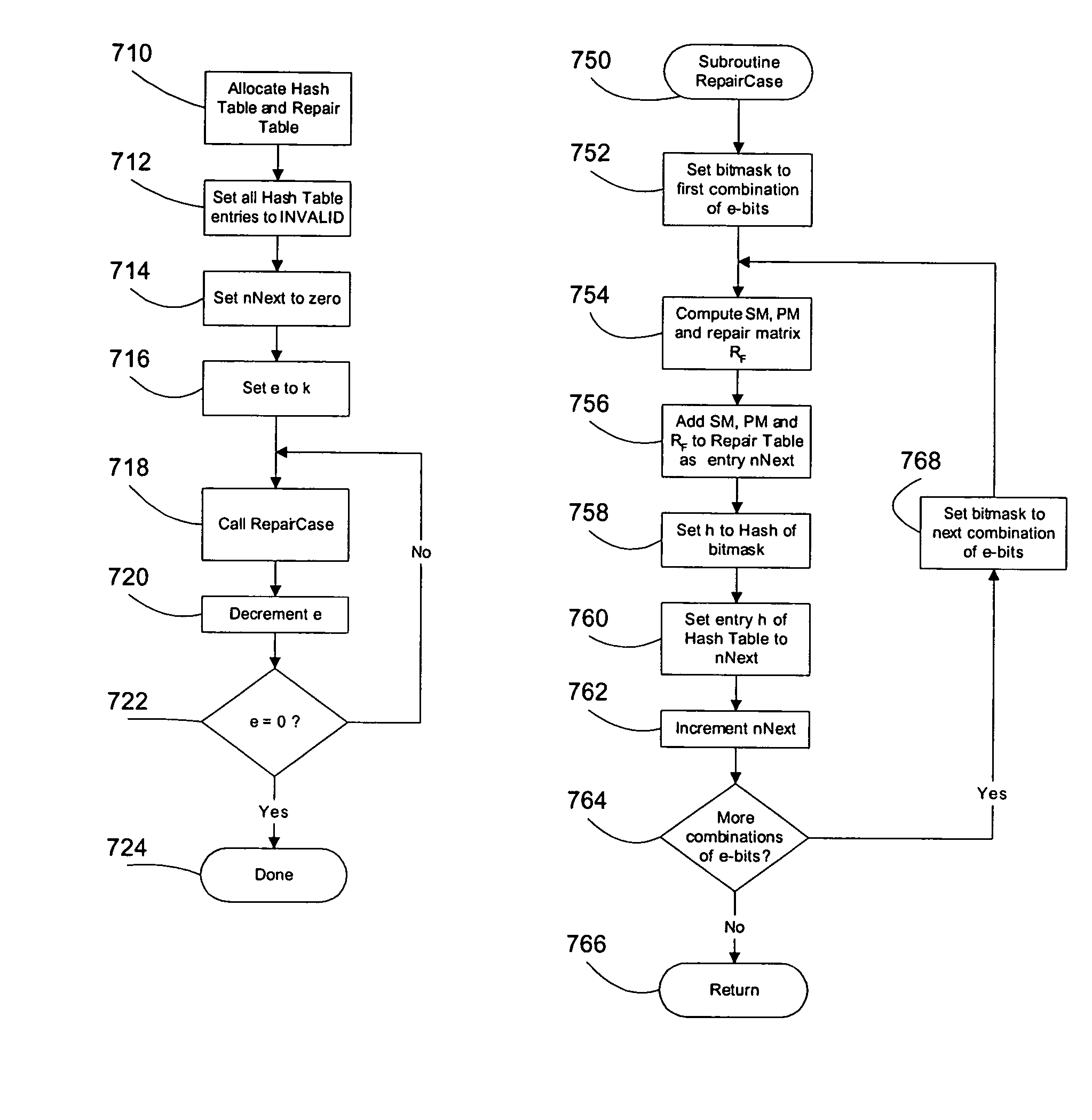
Efficient method for the reconstruction of digital information
InactiveUS7472334B1Improve decoding performanceImprove encoding performanceCode conversionCoding detailsLinear codingTheoretical computer science
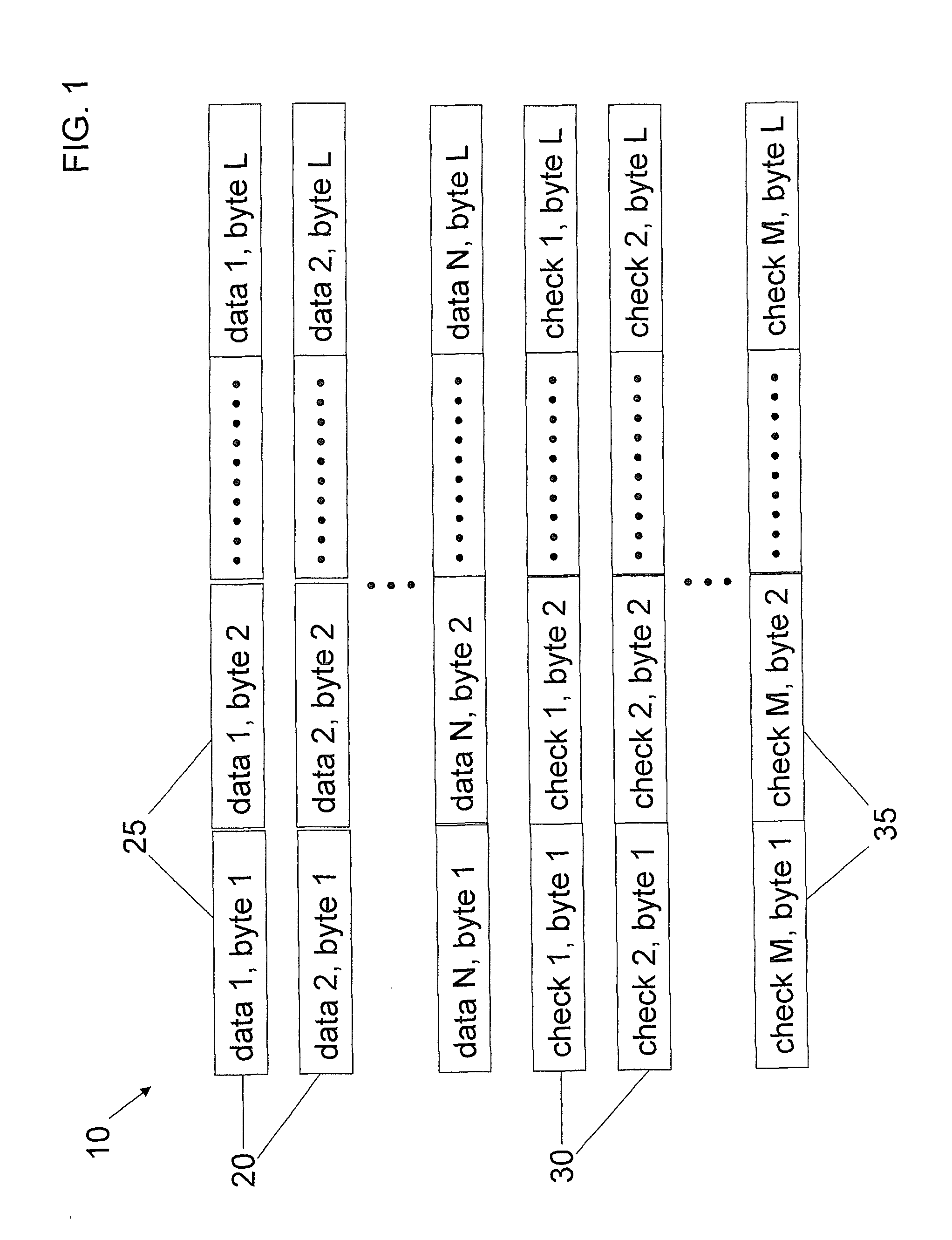
Improved method of encoding and repairing data for reliable storage and transmission using erasure codes, which is efficient enough for implementation in software as well as hardware. A systematic linear coding matrix over GF(2q) is used which combines parity for fast correction of single erasures with the capability of correcting k erasures. Finite field operations involving the coding and repair matrices are redefined to consist of bitwise XOR operations on words of arbitrary length. The elements of the matrix are selected to reduce the number of XOR operations needed and buffers are aligned for optimal processor cache efficiency. Decode latency is reduced by pre-calculating repair matrices, storing them in a hashed table and looking them up using a bit mask identifying the erasures to be repaired.
Owner:SCOTT THOMAS P +1
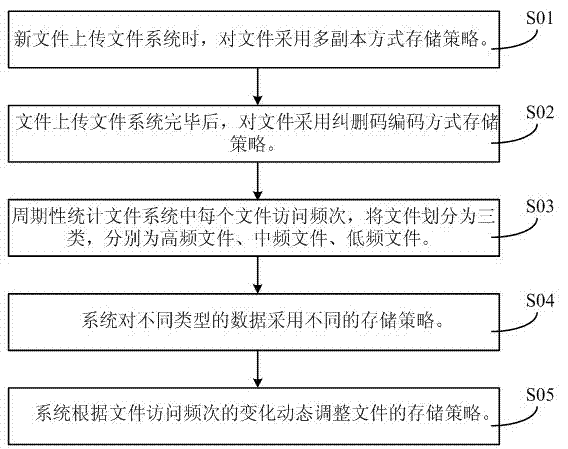
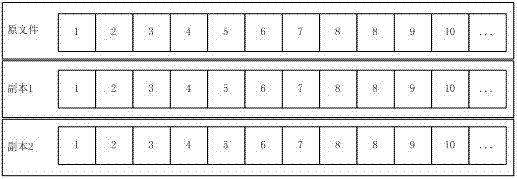
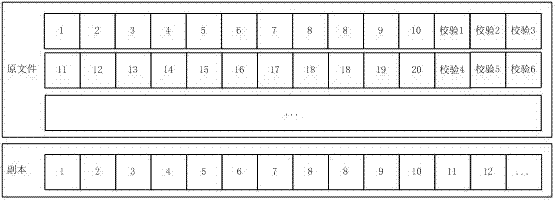
Mixed cloud storage method based on file access frequency
ActiveCN103118133AGuaranteed speedEnsure data reliabilityTransmissionFile systemResource utilization
The invention discloses a mixed cloud storage method based on file access frequency. The mixed cloud storage method based on the file access frequency includes the following steps: adopting a multi-copy mode storage strategy for a new file when the new file is uploaded to a file system; adopting an erasure code coding mode storage strategy for the file after the file is completely uploaded to the file system; periodically counting access frequency of each file in the file system, and dividing files into three categories which are respectively high frequency files, medium frequency files and low frequency files; adopting different storage strategies for different types of data and different types of files in the system; and dynamically adjusting the storage strategies of the files according to changes of the access frequency of the files in the system. The mixed cloud storage method based on the file access frequency classifies the files by periodically counting the access frequency of each file in the file system, adopts different storage strategies for different types of files, and adjusts the storage strategies of the files according to the changes of the access frequency of the files, and therefore the whole file system wholly improves system storage resource utilization rate on the premises of guaranteeing data reliability and access speed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
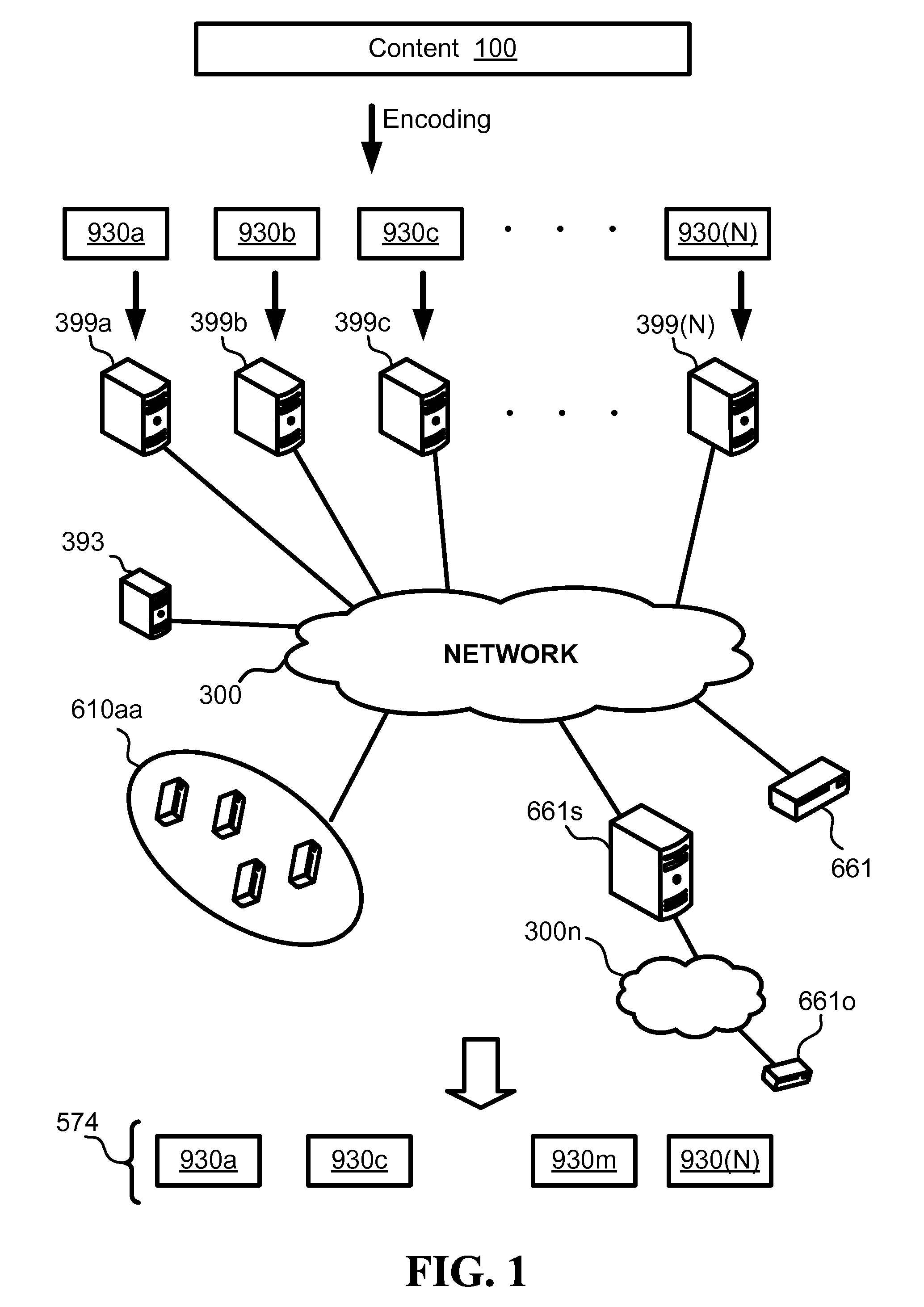
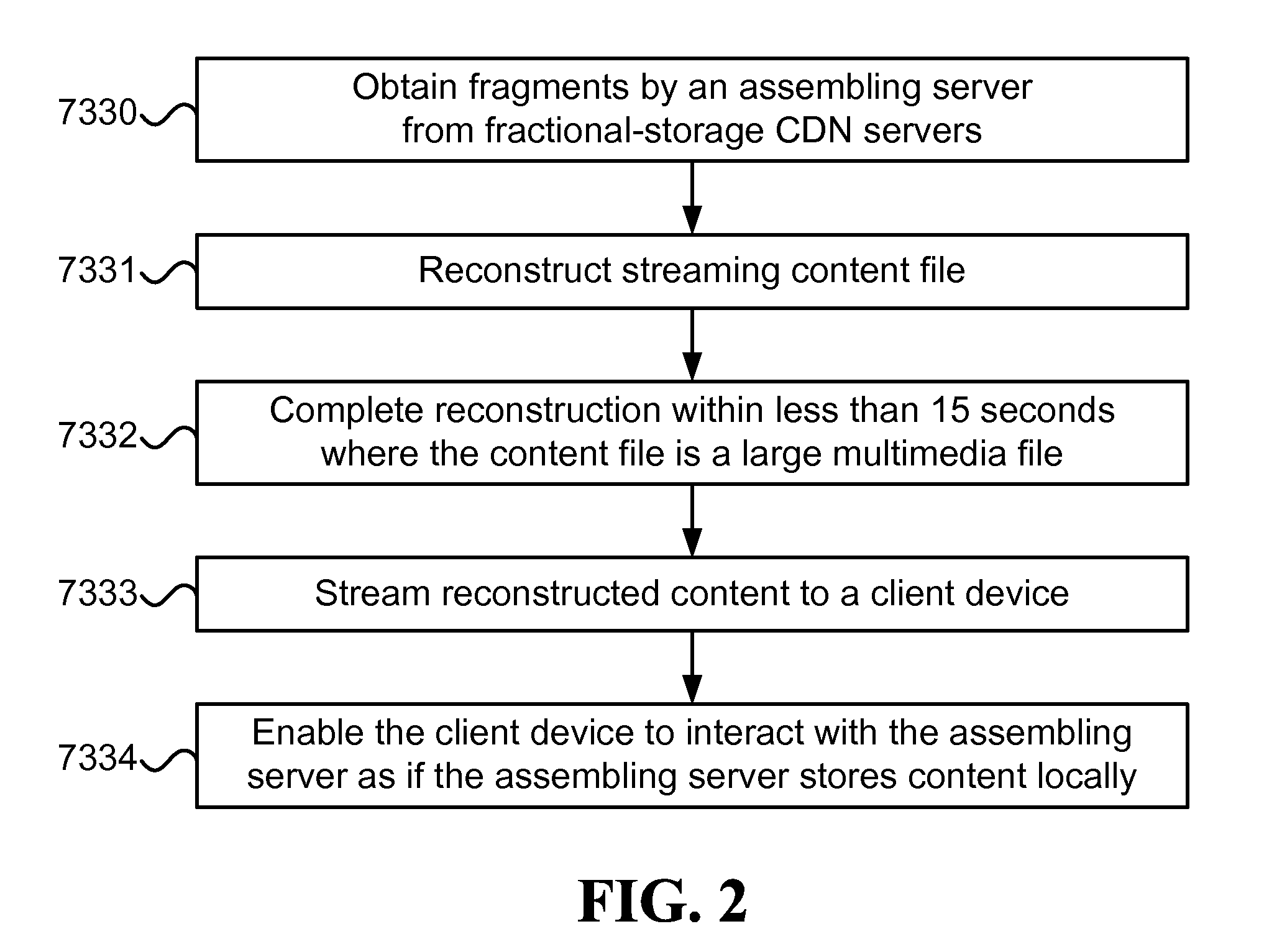
Fast retrieval and progressive retransmission of content
InactiveUS20100095012A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionThe InternetPhase retrieval
Fast retrieval and progressive retransmission of content, including the steps of obtaining erasure-coded fragments by an assembling server from fractional-storage CDN servers; reconstructing a streaming content file from the obtained fragments; and streaming the reconstructed content or a transcoded version of the content by the assembling server to a client device. Wherein most of the fractional-storage CDN servers are located close to or on the Internet backbone, and streaming the reconstructed content takes at least an order of magnitude longer than obtaining the fragments and reconstructing the content.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
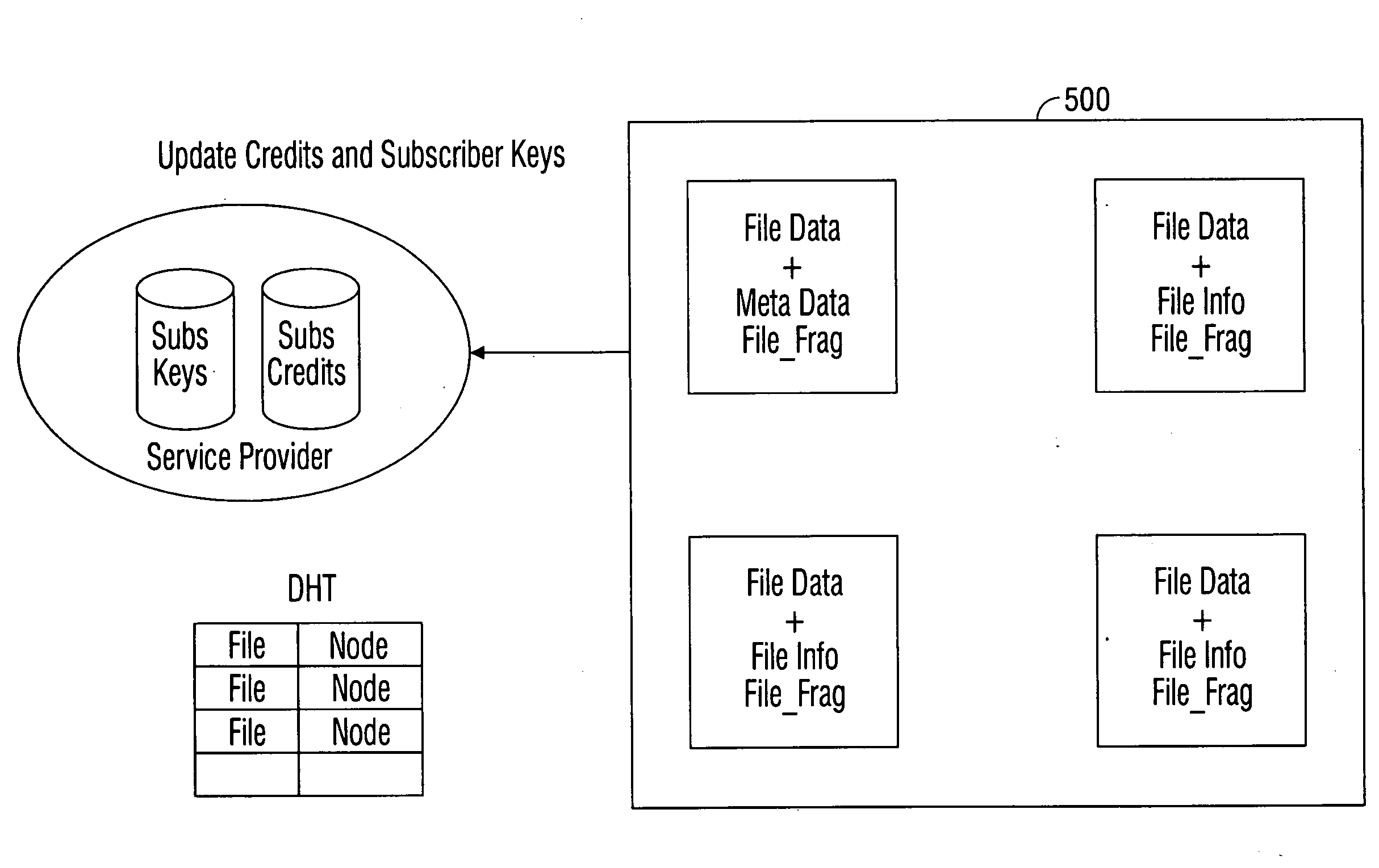
Peer-To-Peer Distributed Storage
InactiveUS20100094921A1Eliminate needMultiple digital computer combinationsSpecial data processing applicationsProgram planningData file
A system and method are provided for peer-to-peer distributed file storage in a network of connected clients. The method transmits data file peer-storage information from a first peer node to a network-connected backup manager. The backup manager creates a mapping plan, for mapping data file segments to a peer group, which typically includes a plurality of network-connected peer nodes. The backup manager transmits the mapping plan to the first peer node. The first peer node distributes the data file segments to the peer group in accordance with the mapping plan, for storage in tangible memory media. Typically, the first peer node accepts a data file and encrypts the data file. In one aspect, the backup manager creates a mapping plan for distributing (n+x) erasure-coded segments. After receipt of the mapping plan, the first peer node creates the (n+x) erasure coded file segments in preparation for distribution.
Owner:MACOM CONNECTIVITY SOLUTIONS LLC
Systems and methods for reliably storing data using liquid distributed storage
Embodiments provide methodologies for reliably storing data within a storage system using liquid distributed storage control. Such liquid distributed storage control operates to compress repair bandwidth utilized within a storage system for data repair processing to the point of operating in a liquid regime. Liquid distributed storage control logic of embodiments may employ a lazy repair policy, repair bandwidth control, a large erasure code, and / or a repair queue. Embodiments of liquid distributed storage control logic may additionally or alternatively implement a data organization adapted to allow the repair policy to avoid handling large objects, instead streaming data into the storage nodes at a very fine granularity.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com