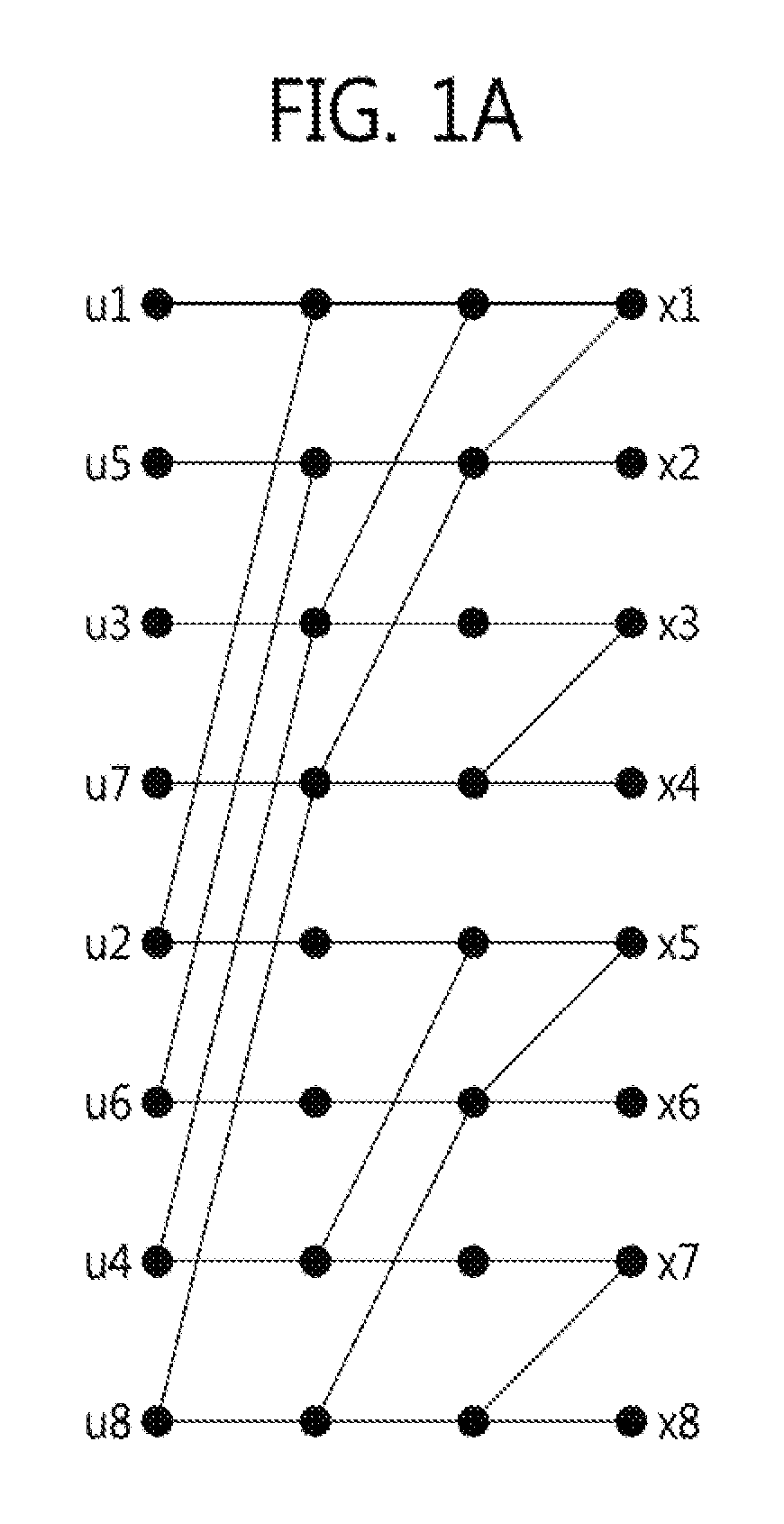
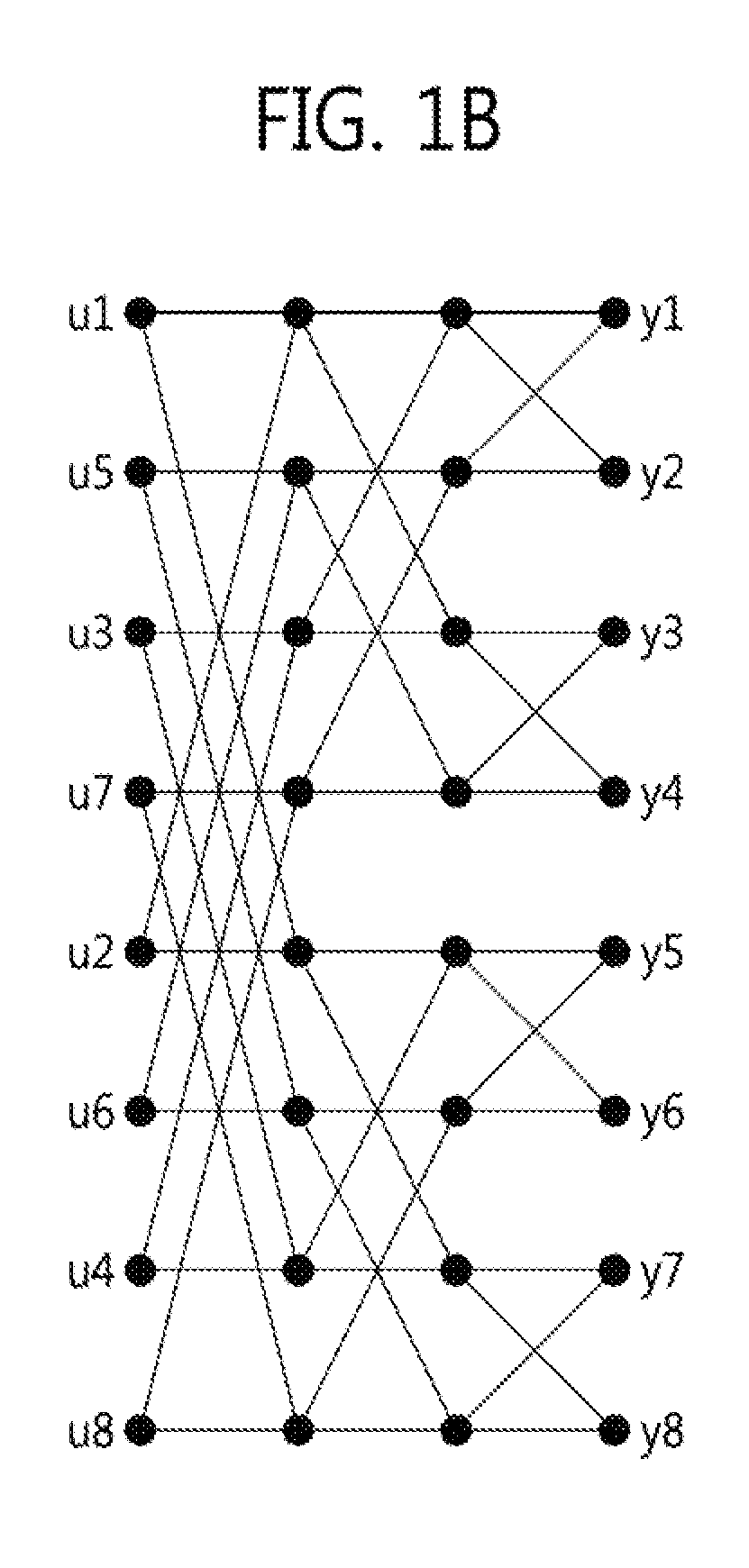
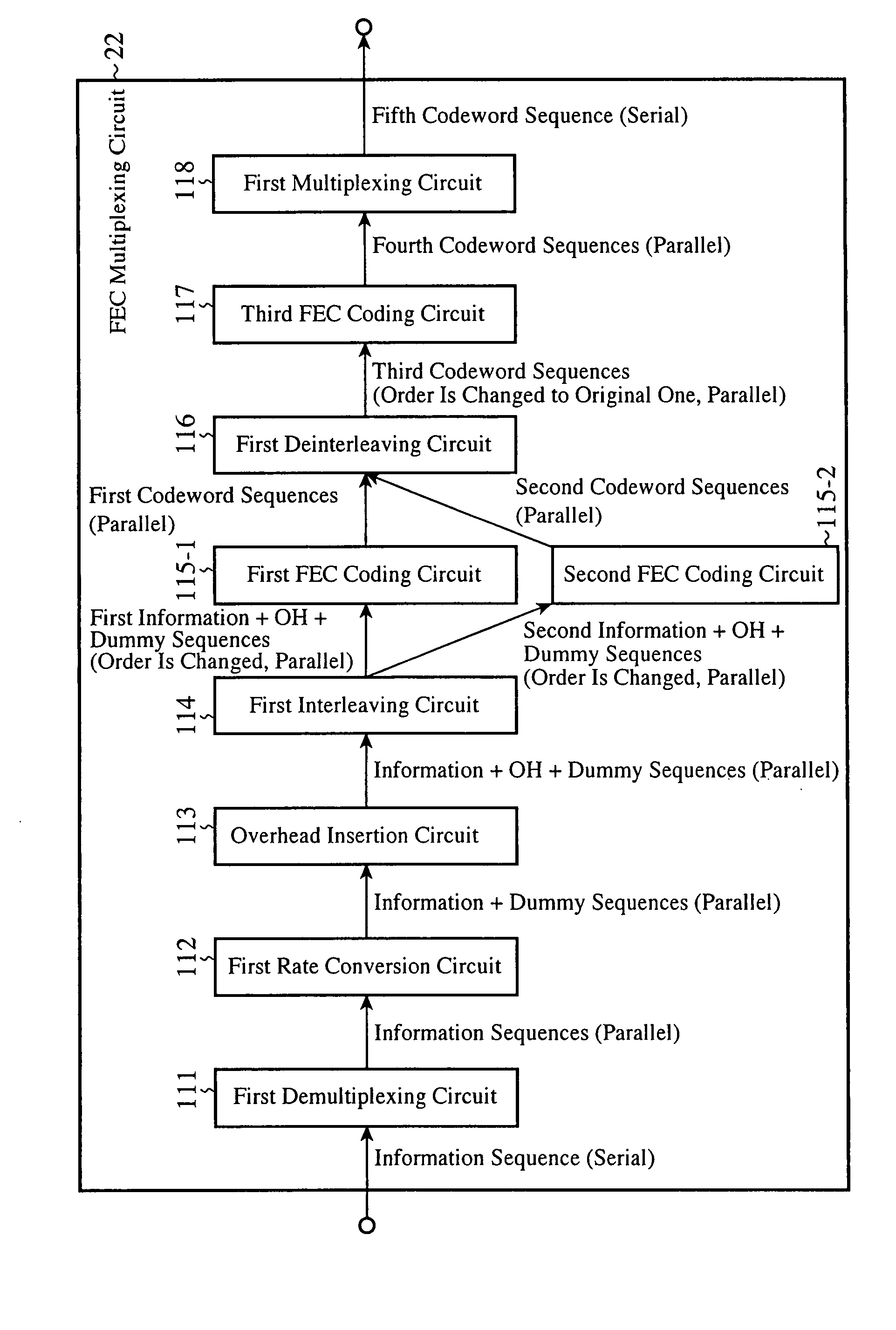
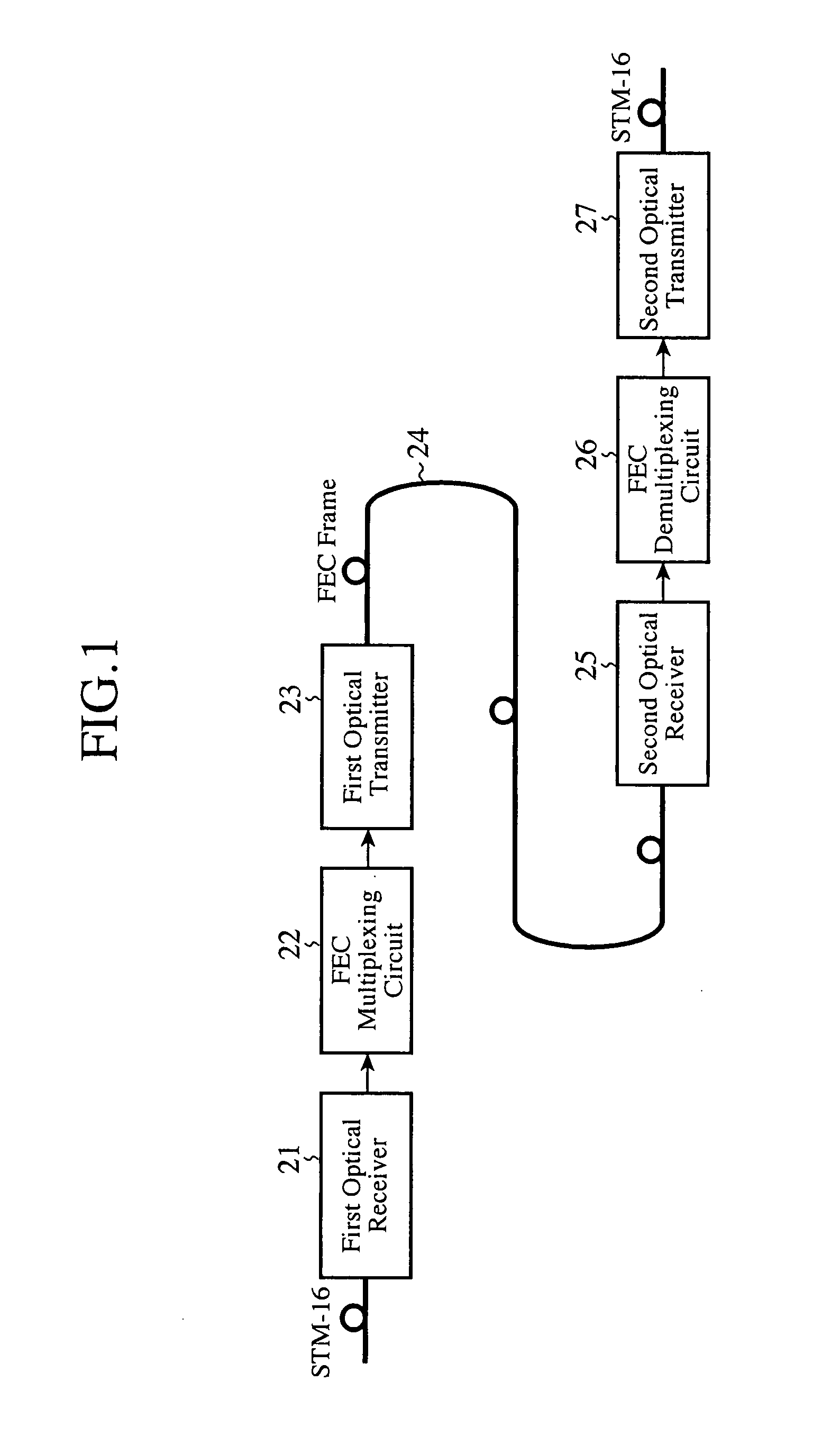
Patents
Literature
58results about "Non-binary linear block codes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polar code decoding method and decoding device
ActiveCN103368583AReduce complexityNon-binary linear block codesError preventionDecoding methodsComputer science
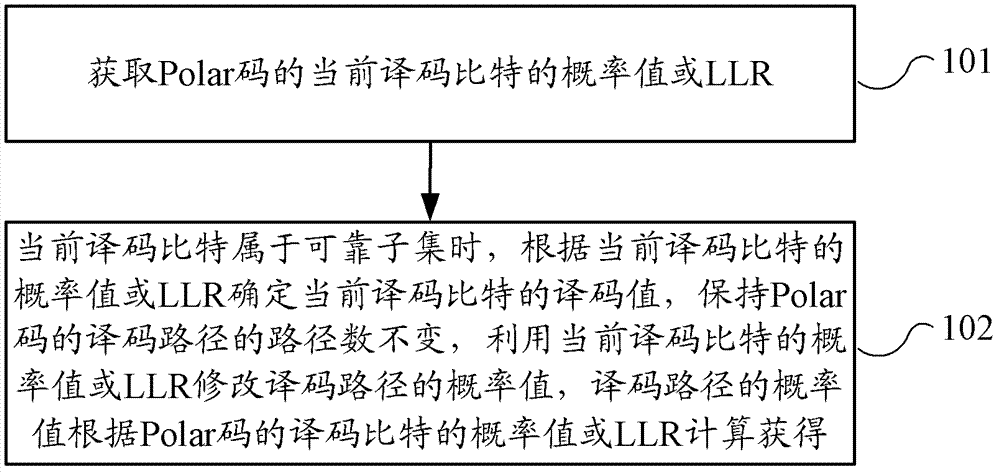
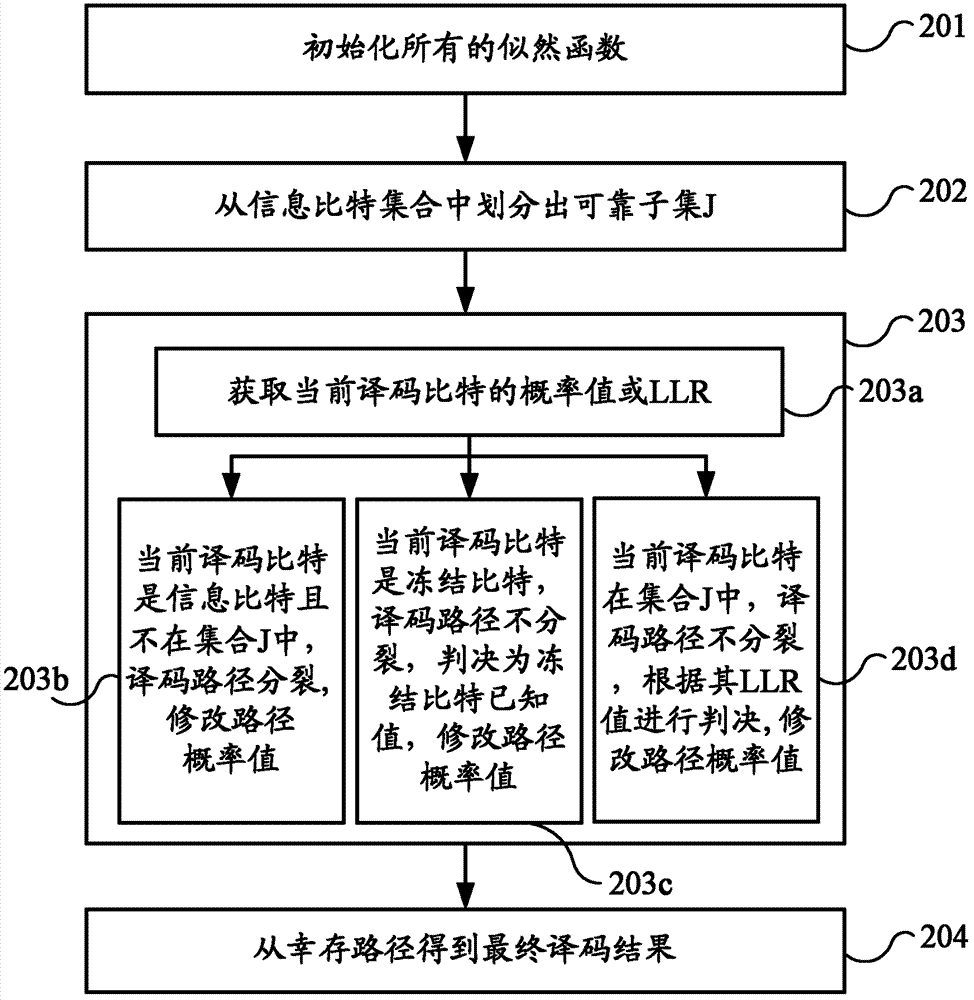
Provided are a Polar code decoding method and decoding device. A reliable subset is marked off from an information bit set of a Polar code, and the reliability of the information bits of the reliable subset is higher than that of other information bits. The method comprises: obtaining a probability value or LLR of a current decoding bit of the Polar code; when the current decoding bit belongs to the reliable subset, judging according to the probability value or LLR of the current decoding bit to determine the decoding value of the current decoding bit, keeping the number of the decoding paths of the Polar code unchanged, and modifying the probability values of all the decoding paths using the probability value or LLR of the current decoding bit; and obtaining the probability values of the decoding paths through calculation according to the probability value or LLR of the decoding bit of the Polar code. The embodiments of the present invention judge the information bits of a reliable subset without splitting decoding paths, thereby reducing the overall decoding complexity.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Accelerated erasure coding system and method
ActiveUS8683296B2Raise countImprove reliabilityNon-binary linear block codesError preventionProcessing coreOriginal data
An accelerated erasure coding system includes a processing core for executing computer instructions and accessing data from a main memory, and a non-volatile storage medium for storing the computer instructions. The processing core, storage medium, and computer instructions are configured to implement an erasure coding system, which includes: a data matrix for holding original data in the main memory; a check matrix for holding check data in the main memory; an encoding matrix for holding first factors in the main memory, the first factors being for encoding the original data into the check data; and a thread for executing on the processing core. The thread includes: a parallel multiplier for concurrently multiplying multiple entries of the data matrix by a single entry of the encoding matrix; and a first sequencer for ordering operations through the data matrix and the encoding matrix using the parallel multiplier to generate the check data.
Owner:STREAMSCALE
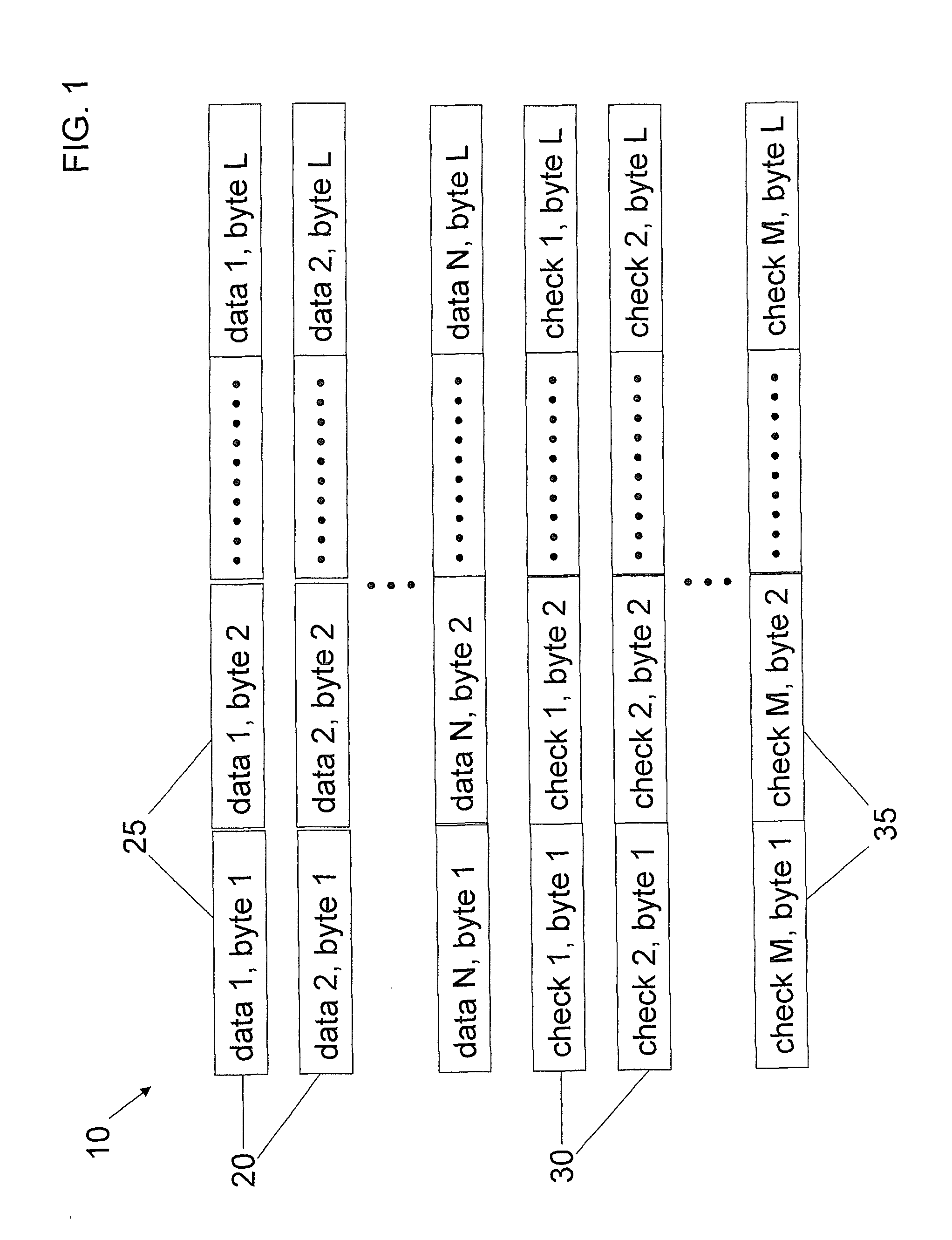
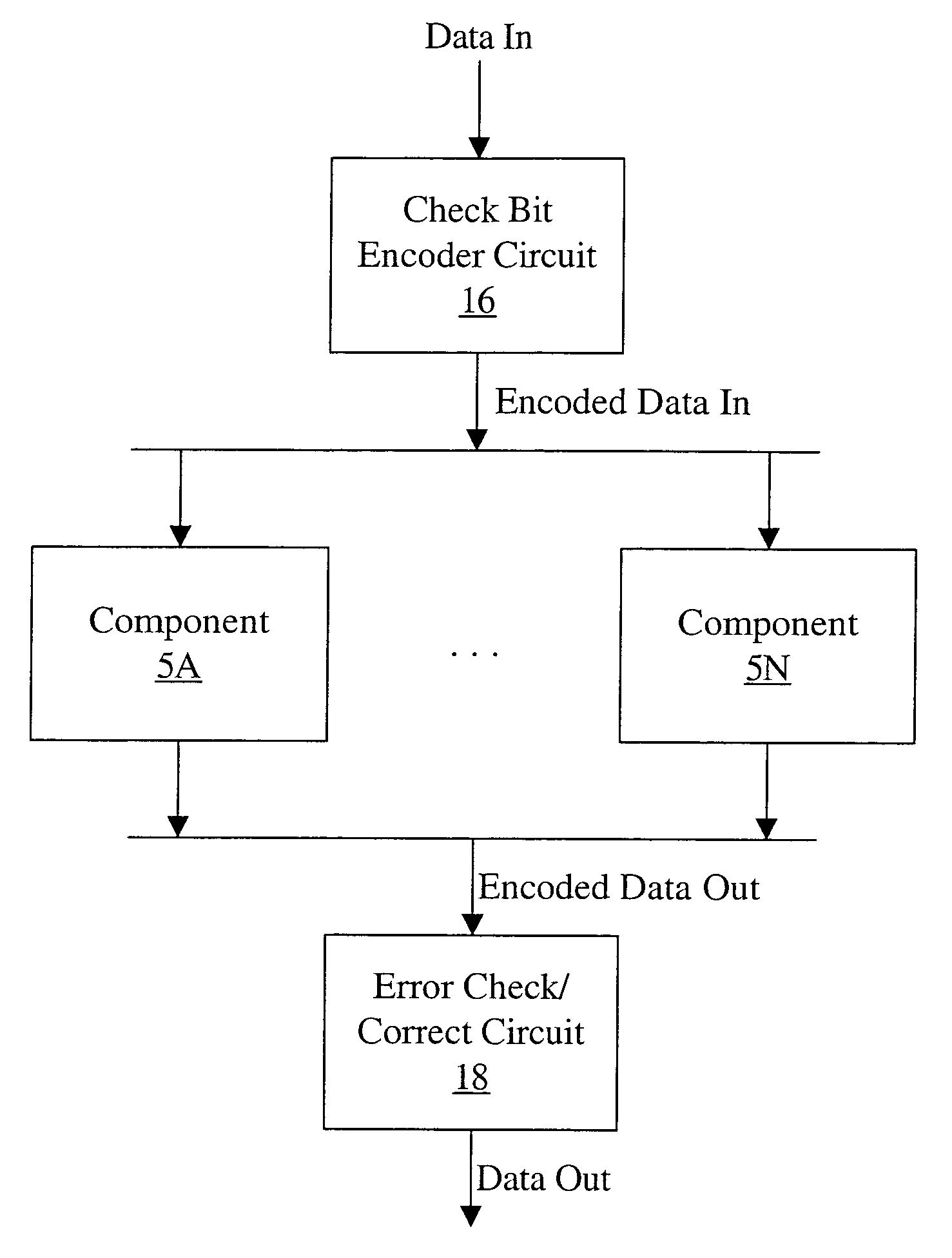
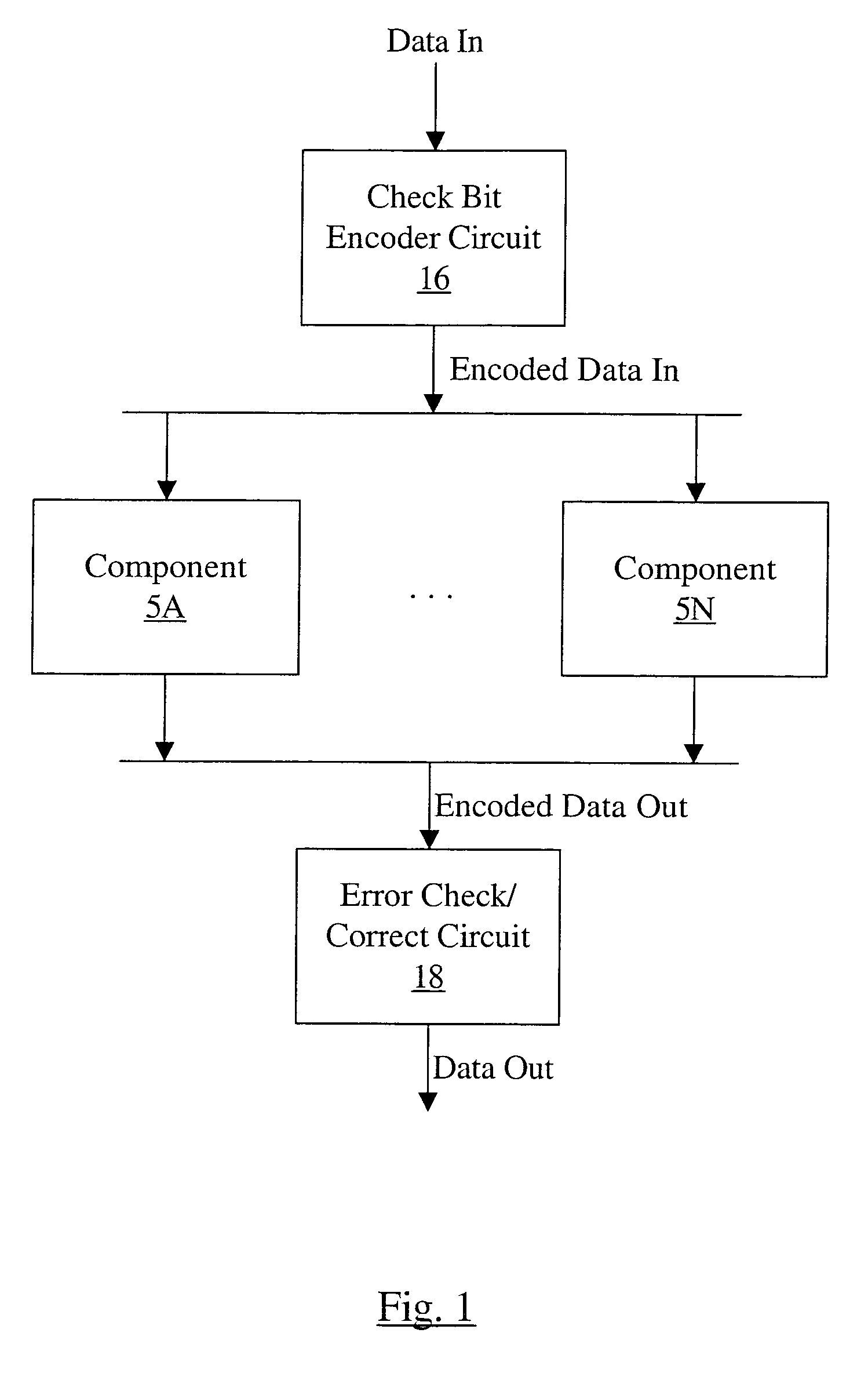
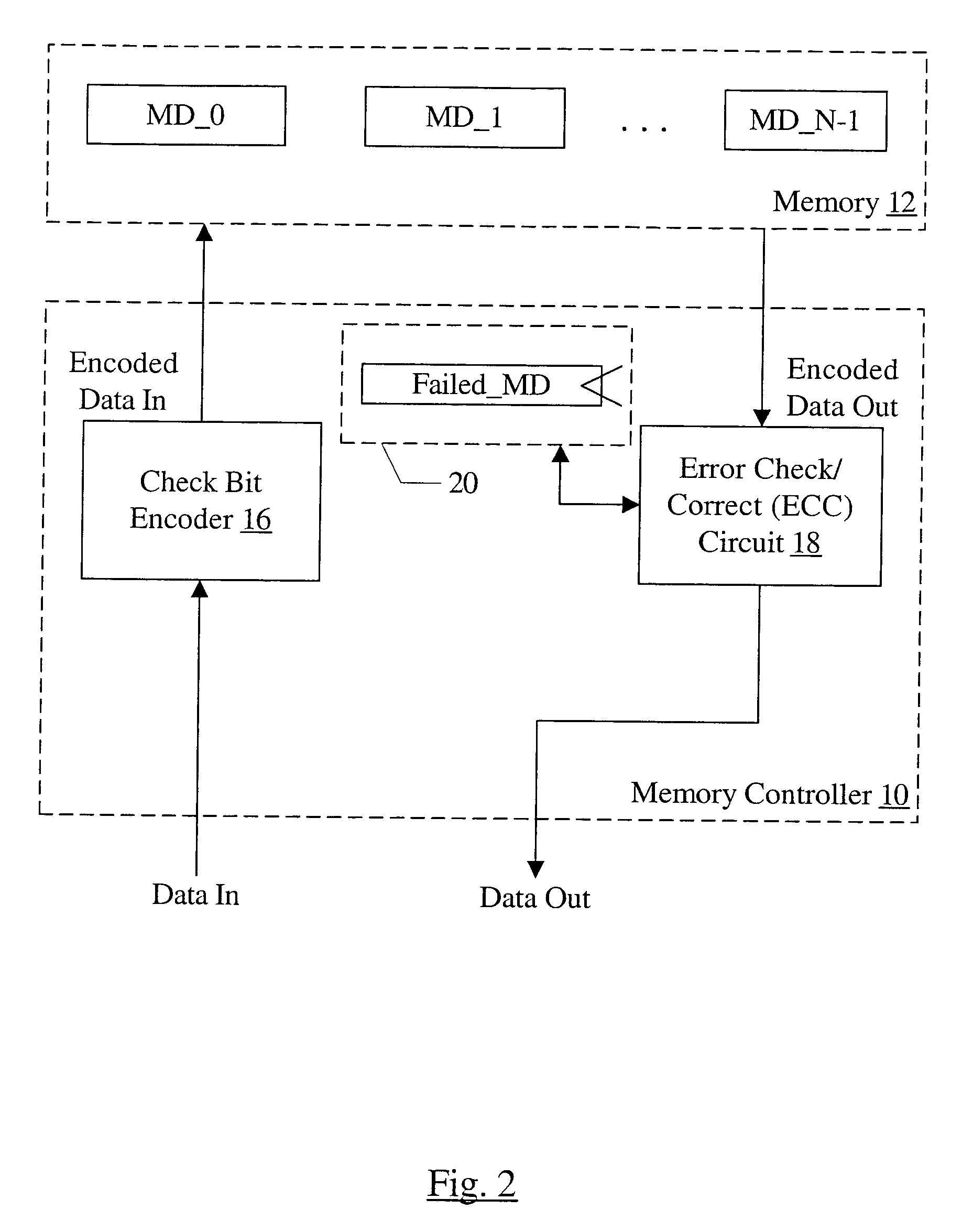
ECC for component failures using Galois fields
An apparatus comprises a check bit encoder circuit and a check / correct circuit. The apparatus operates on encoded data blocks, wherein each encoded data block includes a data block, a first plurality of check bits, and a second plurality of check bits. The encoded data block is logically arranged as an array of R rows and N columns, and each of the N columns comprises data bits from a respective one of the plurality of components. The first check bits form a first column of the array, and each of the first check bits covers a row of the array. The second check bits form a second column of the array and are defined to cover bits in the array according to a plurality of check vectors. Each check vector corresponds to a different bit in the array and is an element of a Galois Field (GF(2R)). The check vectors are derived from a plurality of unique elements of GF(2R), each of which corresponds to a different column of the array. The check vector in row X of the column is the product, in GF(2R), of the unique element for that column and alphaX, wherein alpha is a primitive element of GF(2R).
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
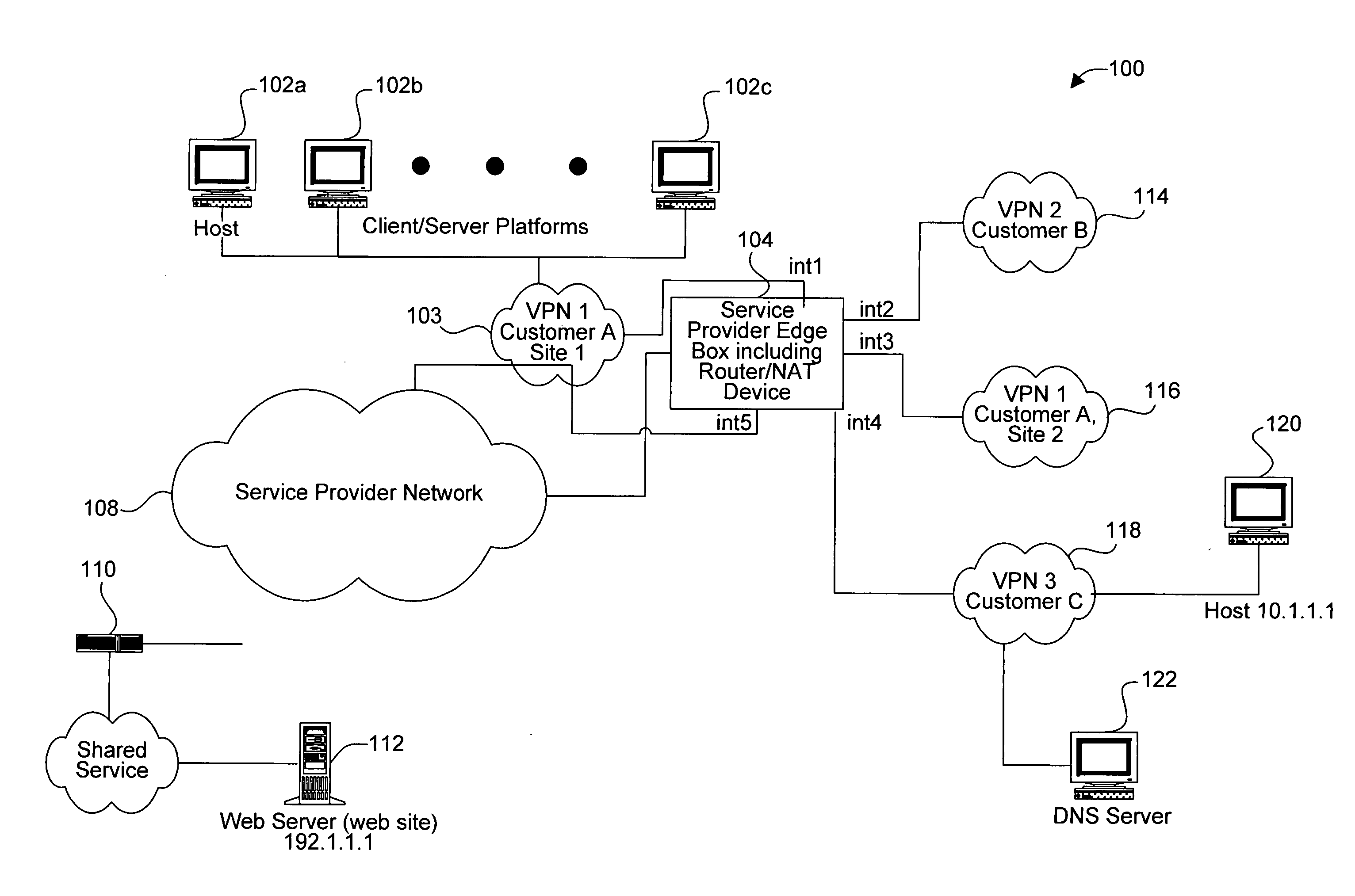
Generalized parity stripe data storage array
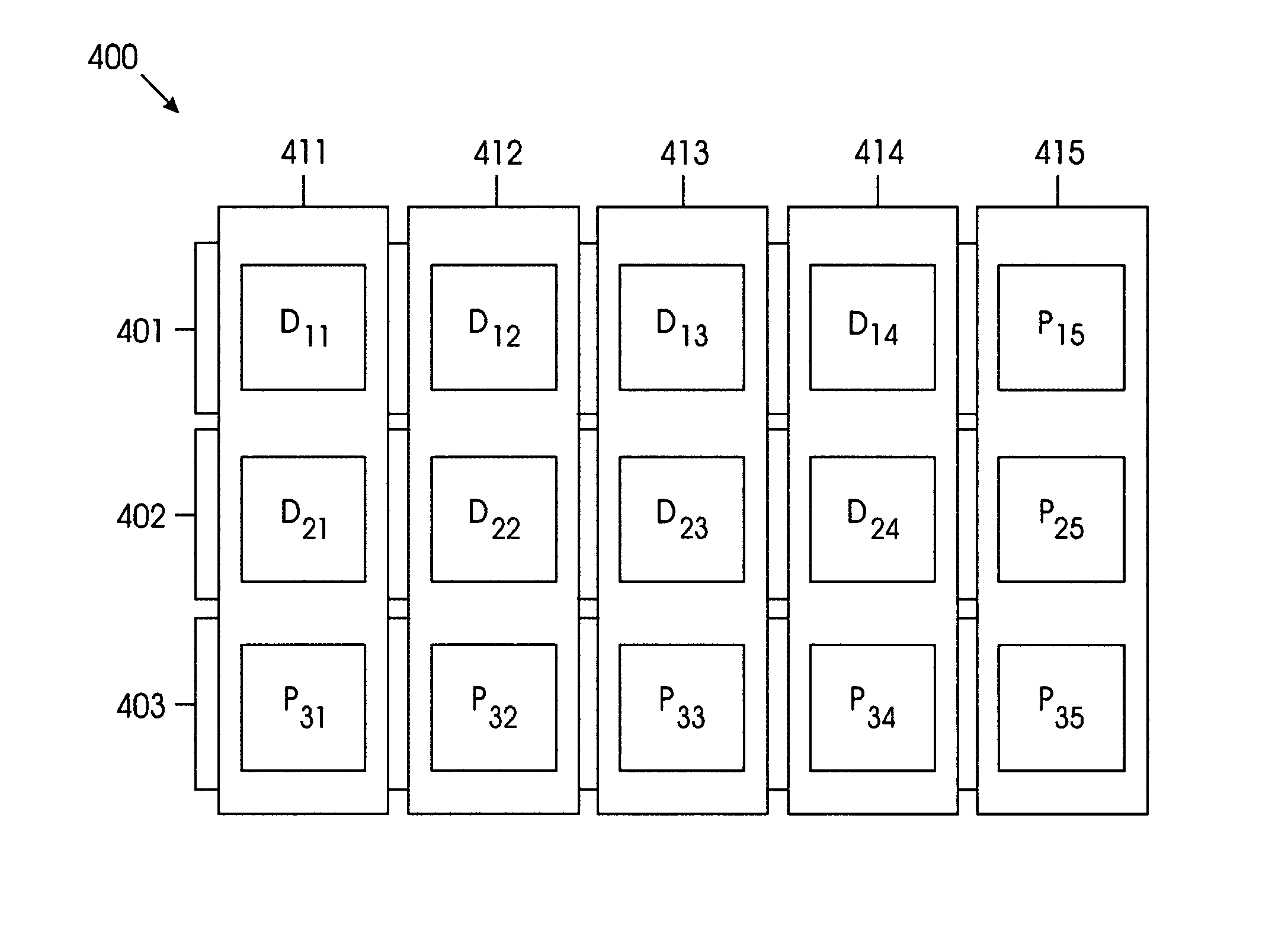
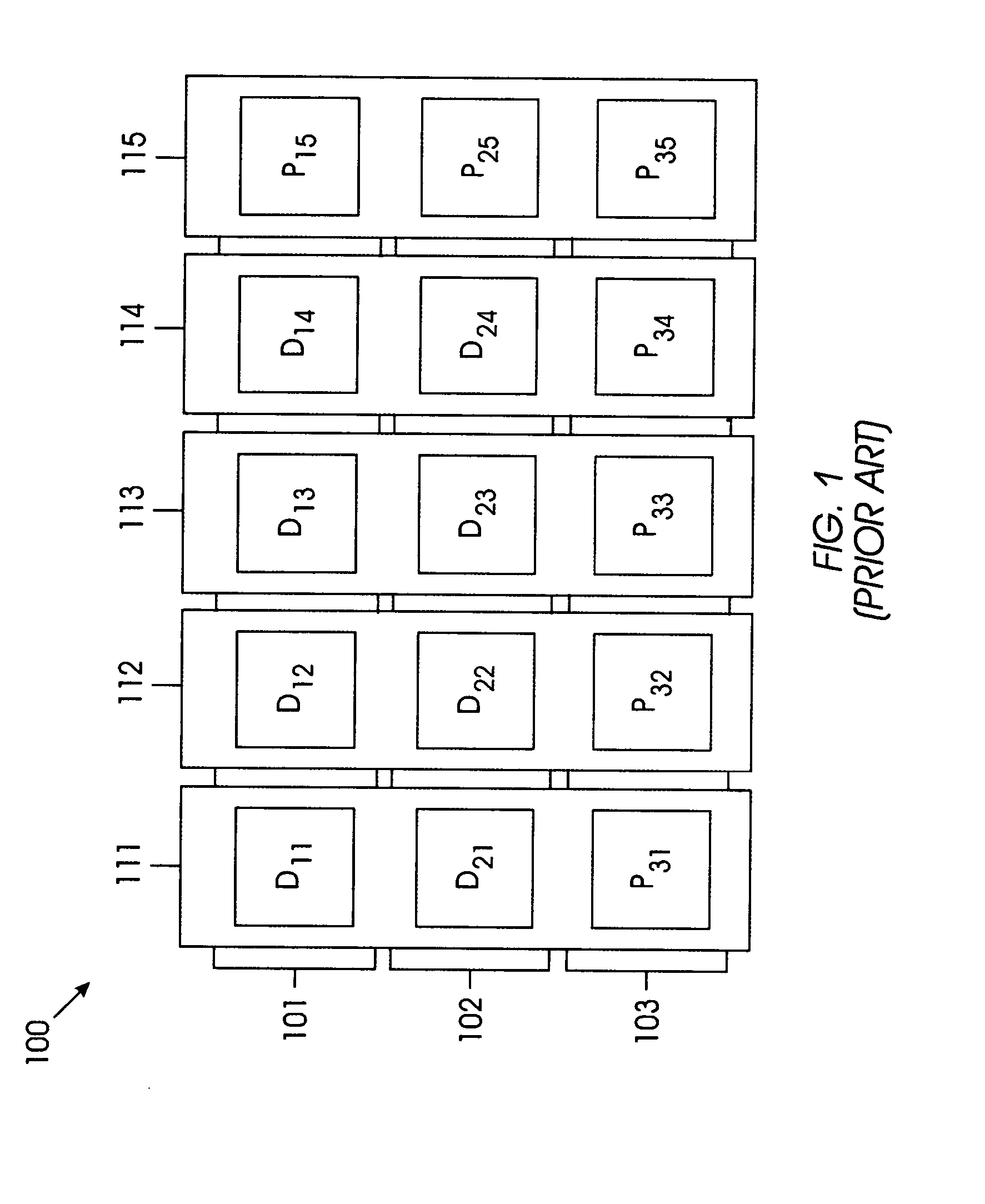
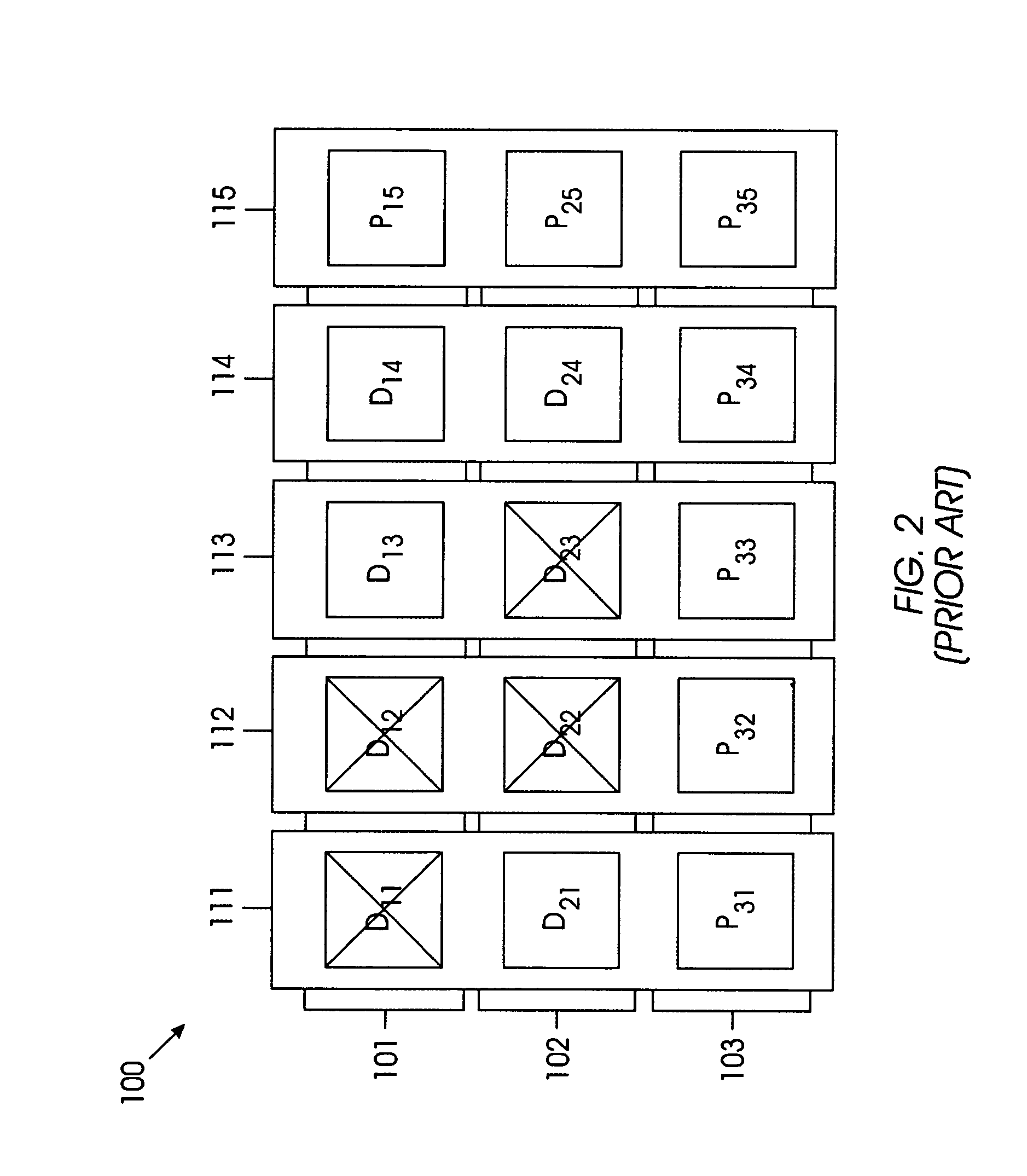
InactiveUS20050086575A1Increased Hamming distanceIncrease distanceNon-binary linear block codesError detection/correctionOn columnTheoretical computer science
The Hamming distance of an array of storage devices is increased by generating a parity check matrix based on column equations that are formed using an orthogonal parity code and includes a higher-order multiplier that changes each column. The higher order multiplier is selected to generate a finite basic field of a predetermined number of elements. The array has M rows and N columns, such that M is greater than or equal to three and N is greater than or equal to three. Row 1 through row M-2 of the array each have n-p data storage devices and p parity storage devices. Row M-1 of the array has n-(p+1) data storage devices and (p+1) parity storage devices. Lastly, row M of the array has N parity storage devices.
Owner:IBM CORP
Accelerated erasure coding system and method
ActiveUS20130173996A1Raise countImprove reliabilityNon-binary linear block codesError preventionProcessing coreOriginal data
An accelerated erasure coding system includes a processing core for executing computer instructions and accessing data from a main memory, and a non-volatile storage medium for storing the computer instructions. The processing core, storage medium, and computer instructions are configured to implement an erasure coding system, which includes: a data matrix for holding original data in the main memory; a check matrix for holding check data in the main memory; an encoding matrix for holding first factors in the main memory, the first factors being for encoding the original data into the check data; and a thread for executing on the processing core. The thread includes: a parallel multiplier for concurrently multiplying multiple entries of the data matrix by a single entry of the encoding matrix; and a first sequencer for ordering operations through the data matrix and the encoding matrix using the parallel multiplier to generate the check data.
Owner:STREAMSCALE
Method for constructing erasure correcting codes whose implementation requires only exclusive ORs
InactiveUS7350126B2Efficient implementationNon-binary linear block codesCode conversionExclusive orError correcting
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
LDPC code inspection matrix generation method and inspection matrix generation device
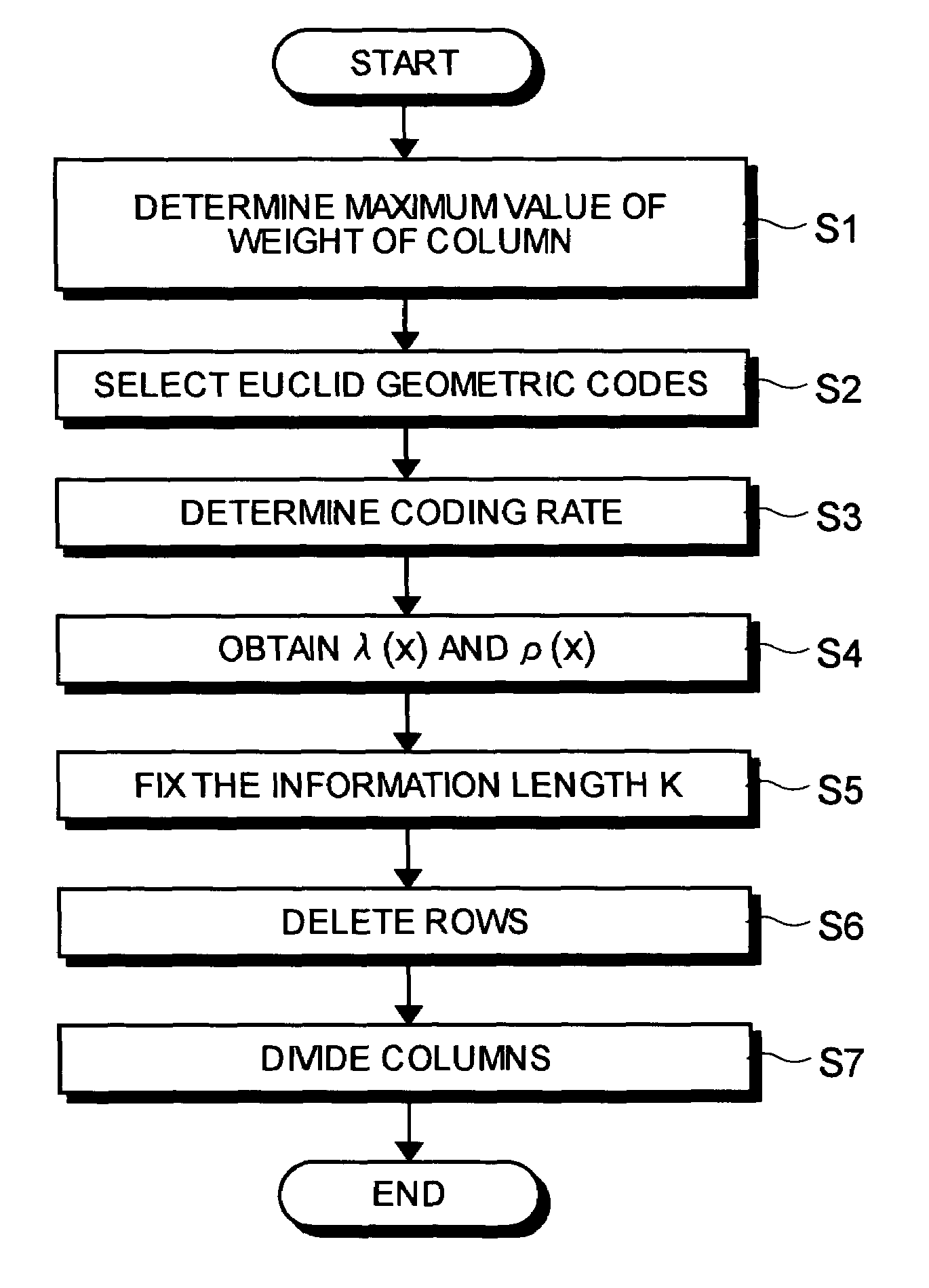
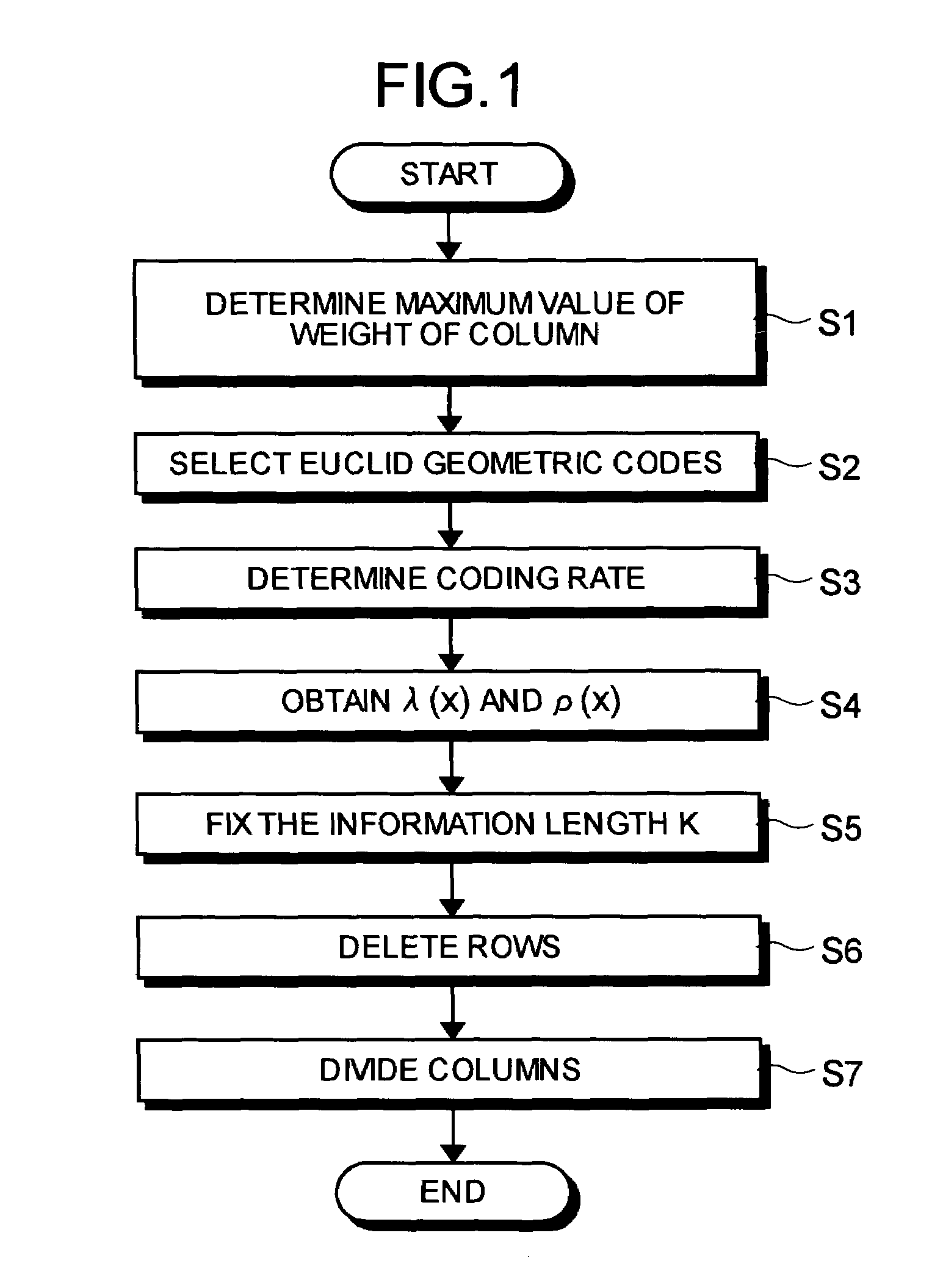
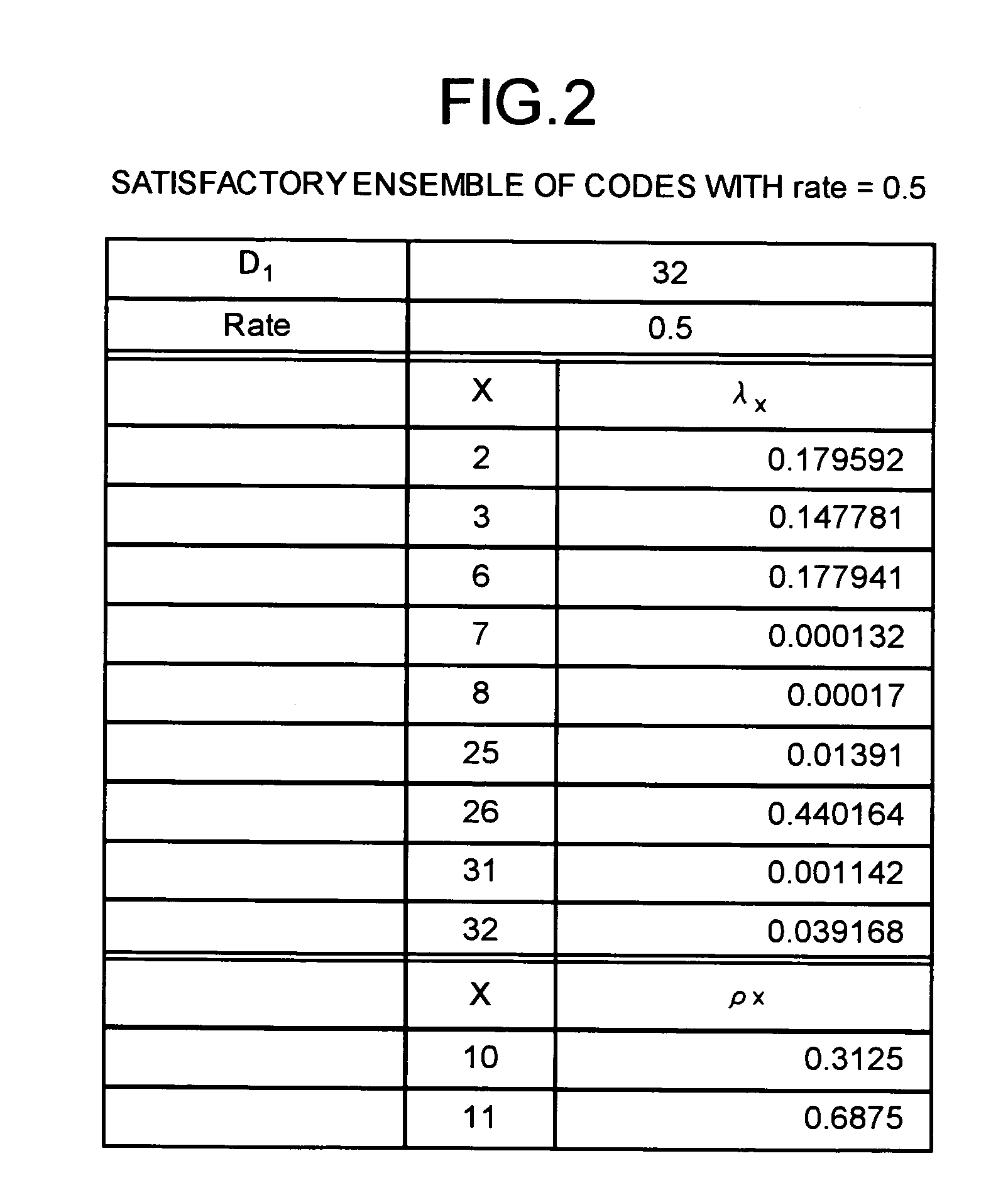
InactiveUS7089479B2Maximize noiseNon-binary linear block codesError detection/correctionLow-density parity-check codeLow density
A method of generating check matrixes for Low-Density Parity-Check codes includes determination steps of determining a maximum value of a column weight, basic Euclid geometric codes, and a coding rate respectively; a weight searching step of searching an optimum ensemble of a row weight and a column weight at one time according to a linear programming method in a state of a fixed coding rate, and so as to maximize a Gaussian noise; an information calculation step of calculating an information length based on a predetermined block length and the coding rate; a row deletion step of deleting a predetermined row based on the information length using the Euclid geometric codes; and a division step of dividing at random a row or a column of the matrixes after the row deletion in a predetermined order.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Soft input decoding for linear codes
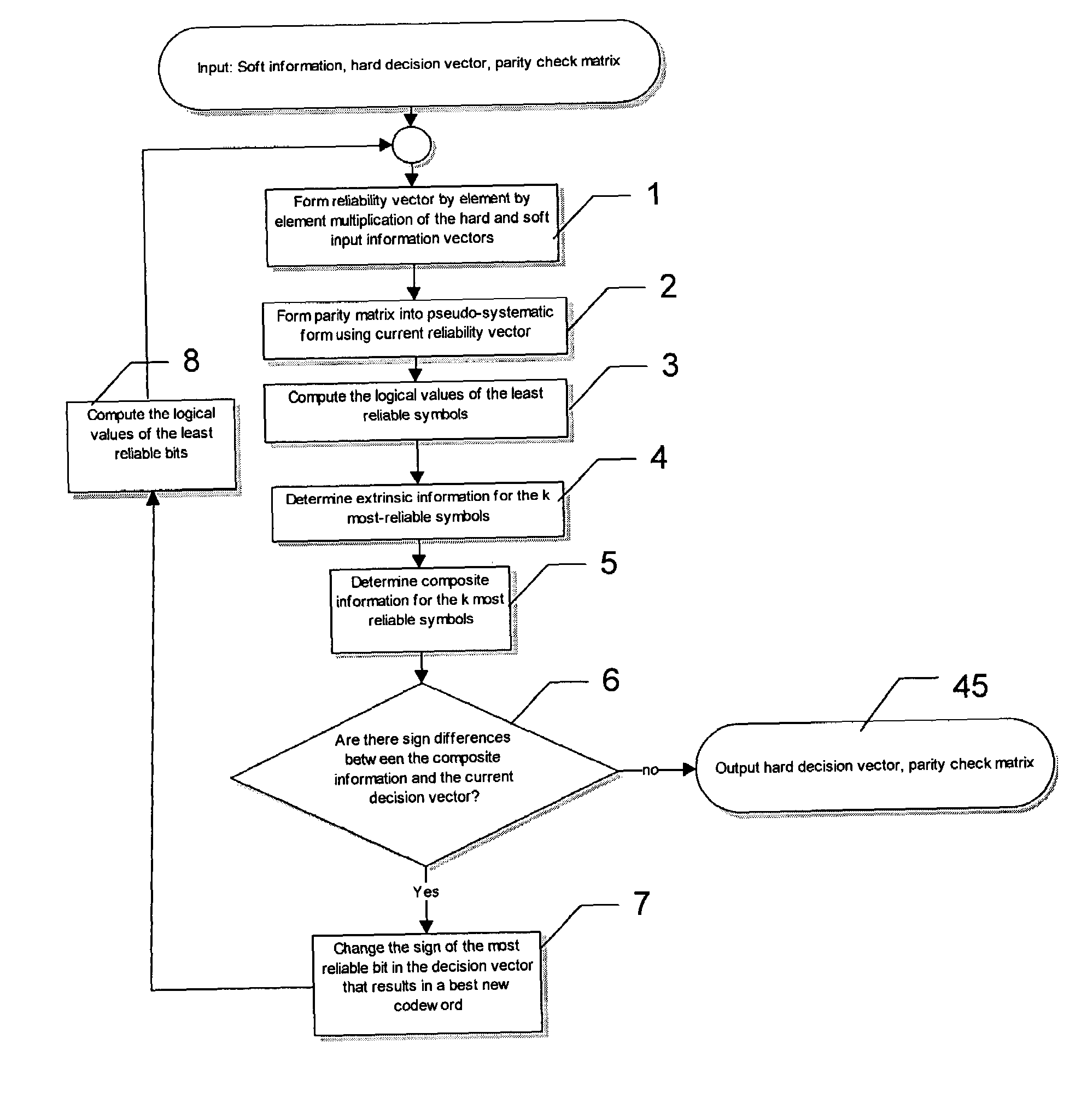
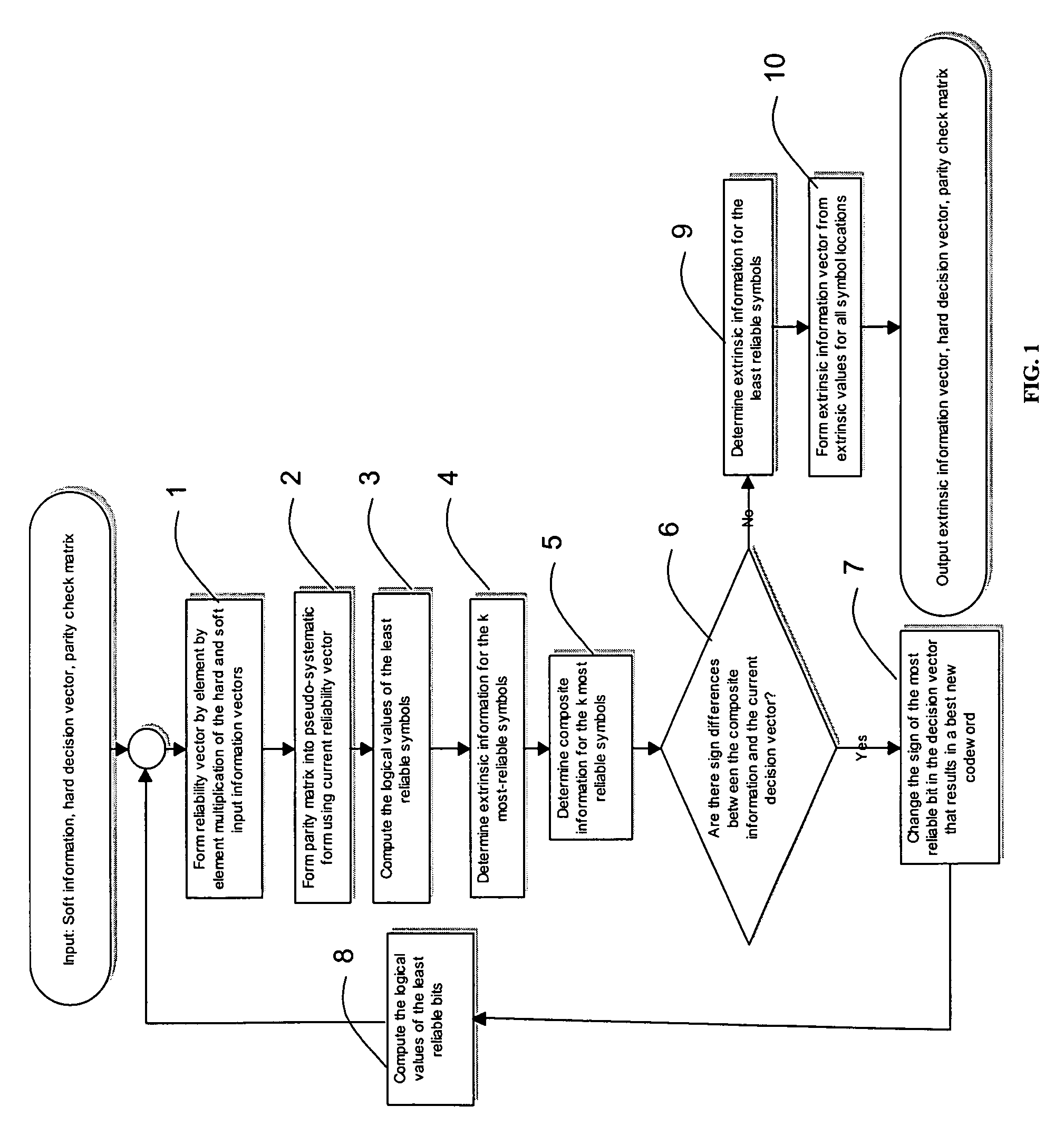
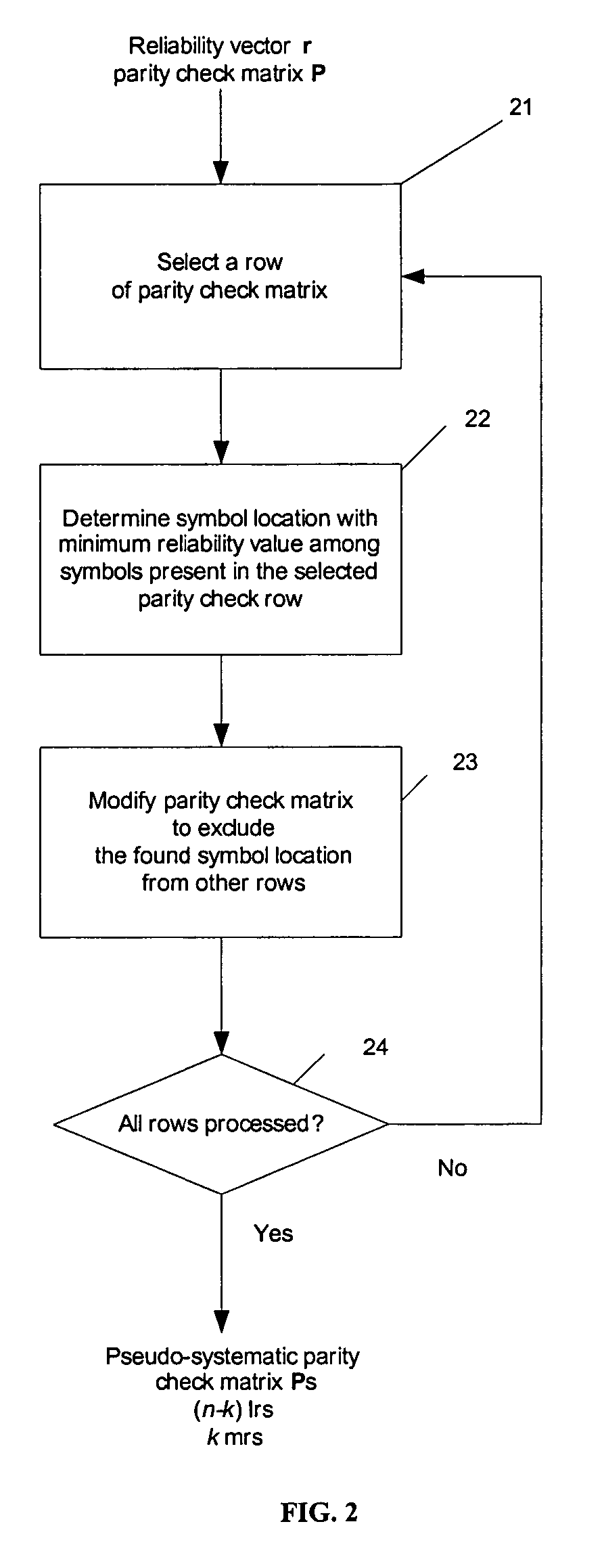
ActiveUS7203893B2Non-binary linear block codesOther decoding techniquesParity-check matrixTheoretical computer science
A method of decoding soft input information related to a transmitted word of a linear block code (n, k) and providing hard or soft output information is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of forming a reliability vector from the input information, identifying (n−k) linearly independent least reliable symbols and k most reliable symbols, converting a parity check matrix of the linear block code to a pseudo-systematic form with respect to the least reliable symbols, calculating extrinsic information and composite information for the most reliable symbols using the soft input information and the pseudo-systematic parity check matrix, and calculating extrinsic information for the least reliable systems using composite information for the most reliable symbols.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
Generalized parity stripe data storage array
InactiveUS7134066B2Increase distanceNon-binary linear block codesError detection/correctionComputer hardwareOn column
The Hamming distance of an array of storage devices is increased by generating a parity check matrix based on column equations that are formed using an orthogonal parity code and includes a higher-order multiplier that changes each column. The higher order multiplier is selected to generate a finite basic field of a predetermined number of elements. The array has M rows and N columns, such that M is greater than or equal to three and N is greater than or equal to three. Row 1 through row M−2 of the array each have n–p data storage devices and p parity storage devices. Row M−1 of the array has n−(p+1) data storage devices and (p+1) parity storage devices. Lastly, row M of the array has N parity storage devices.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
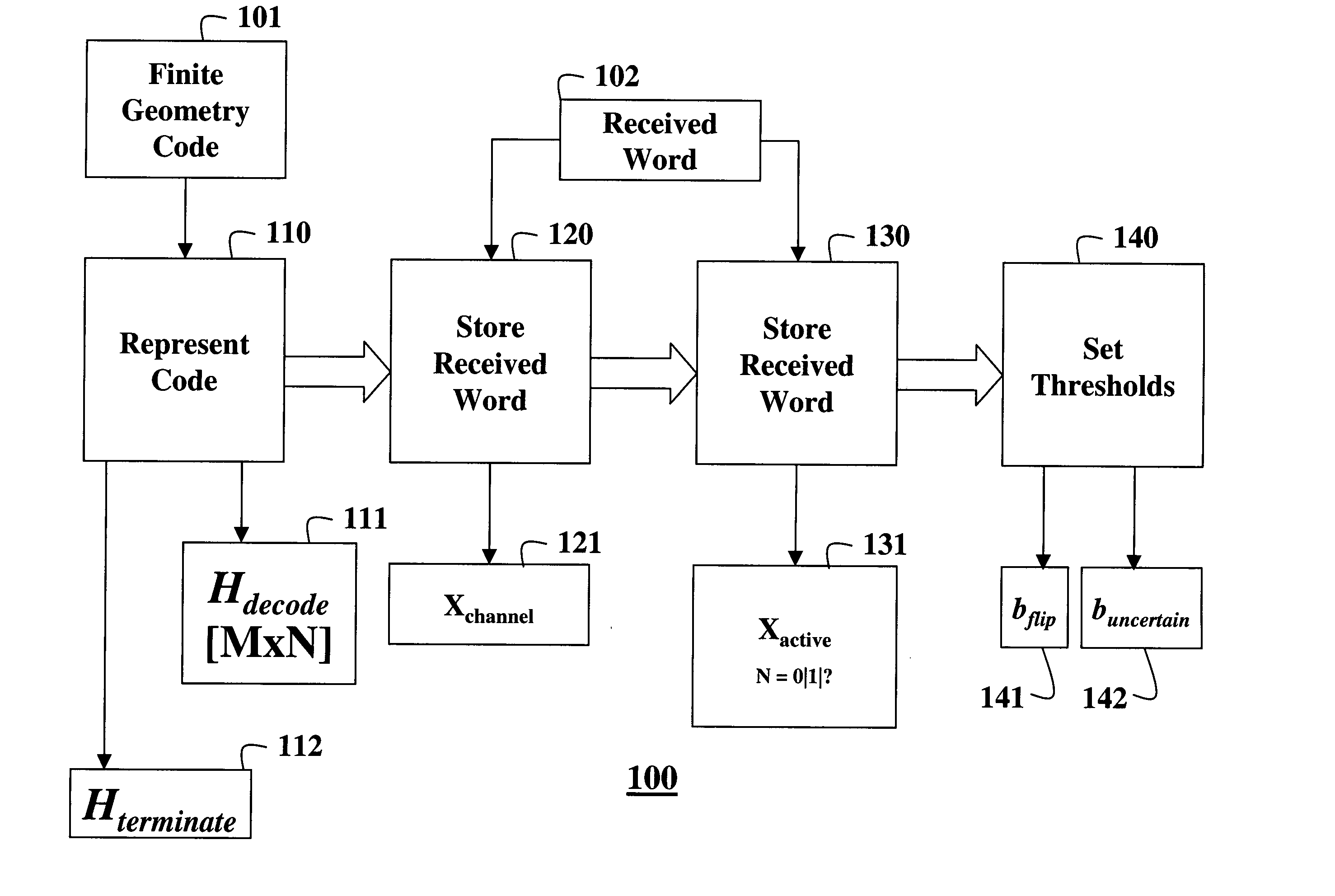
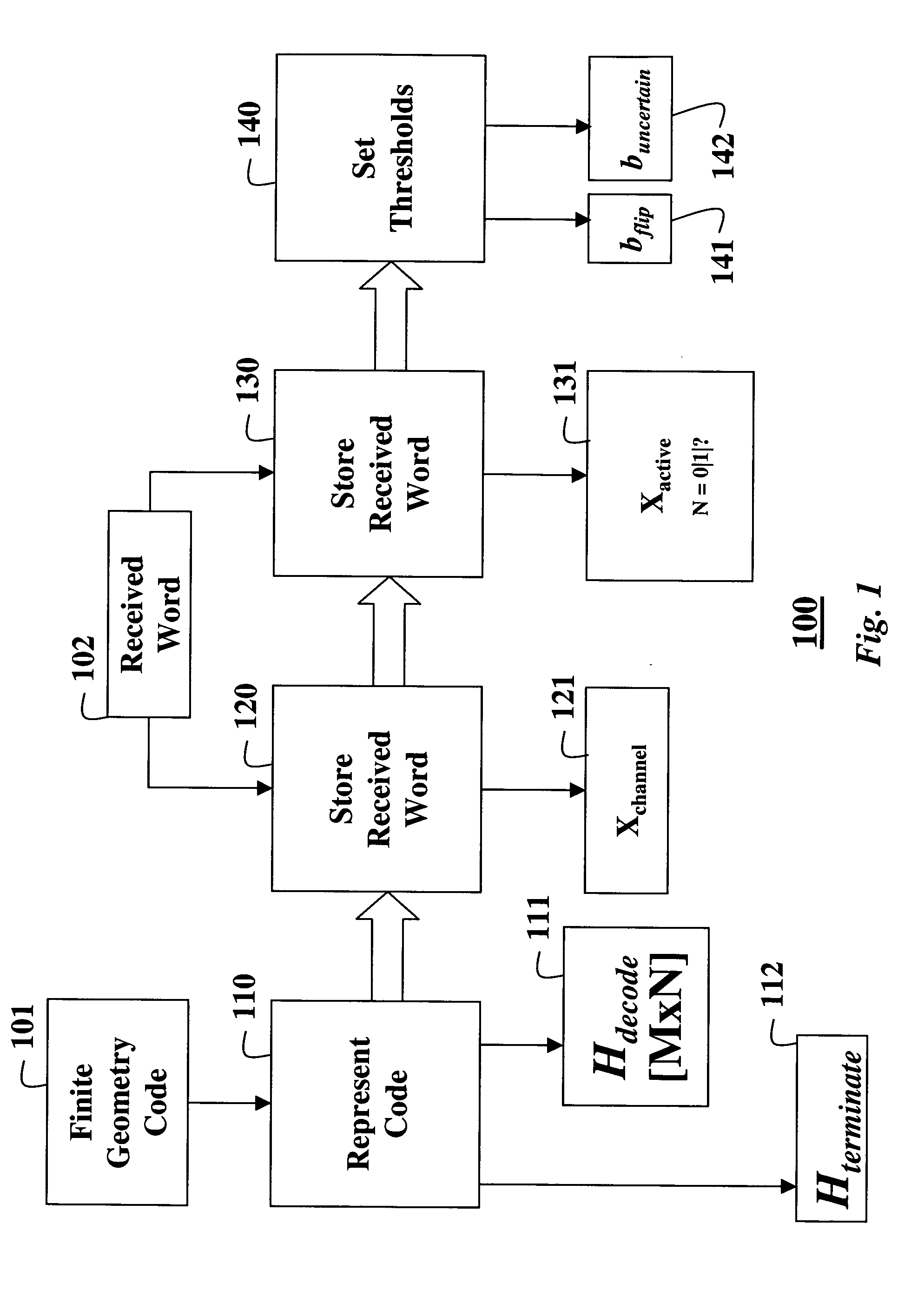
Decoding error-correcting codes based on finite geometries
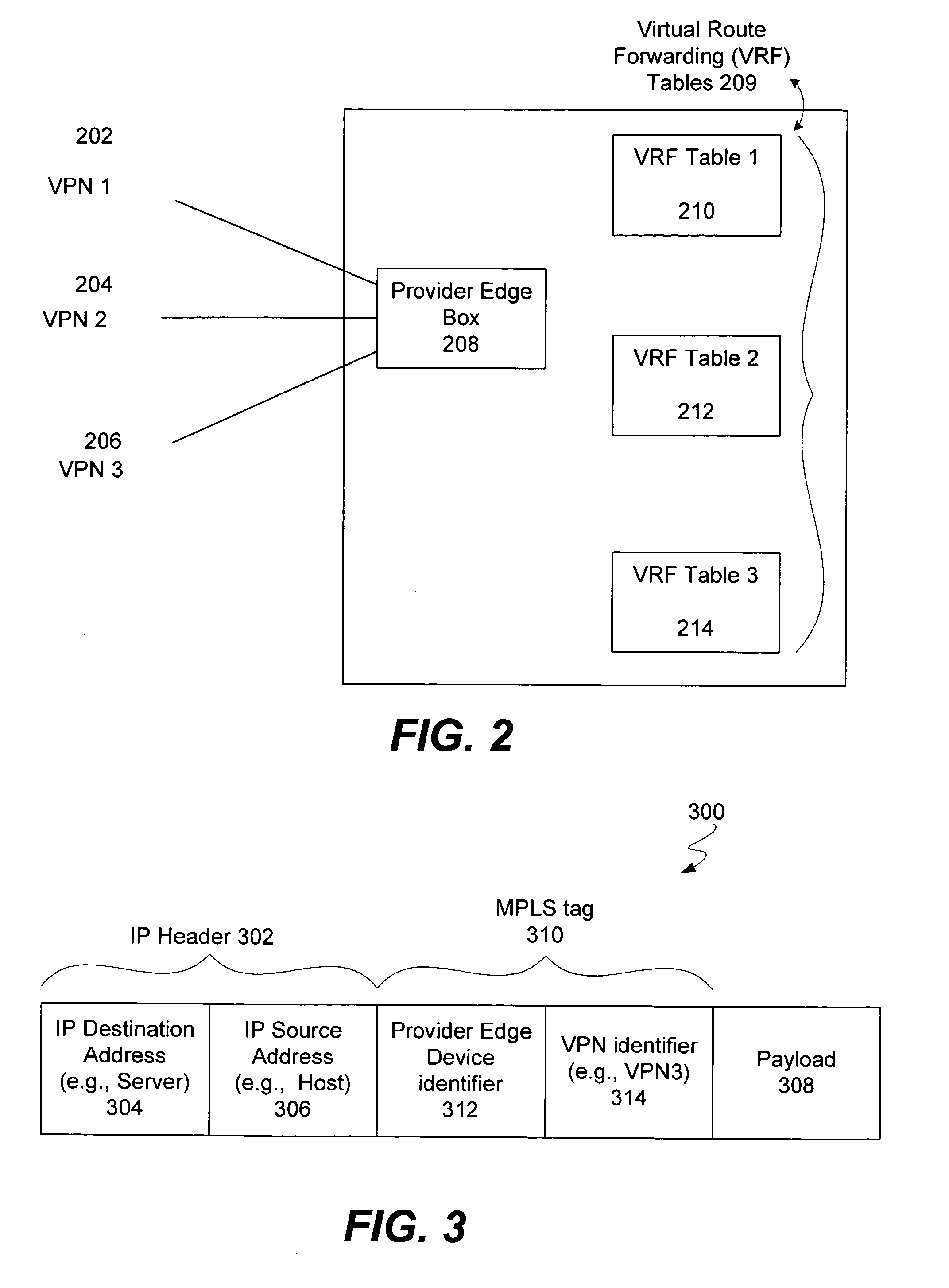
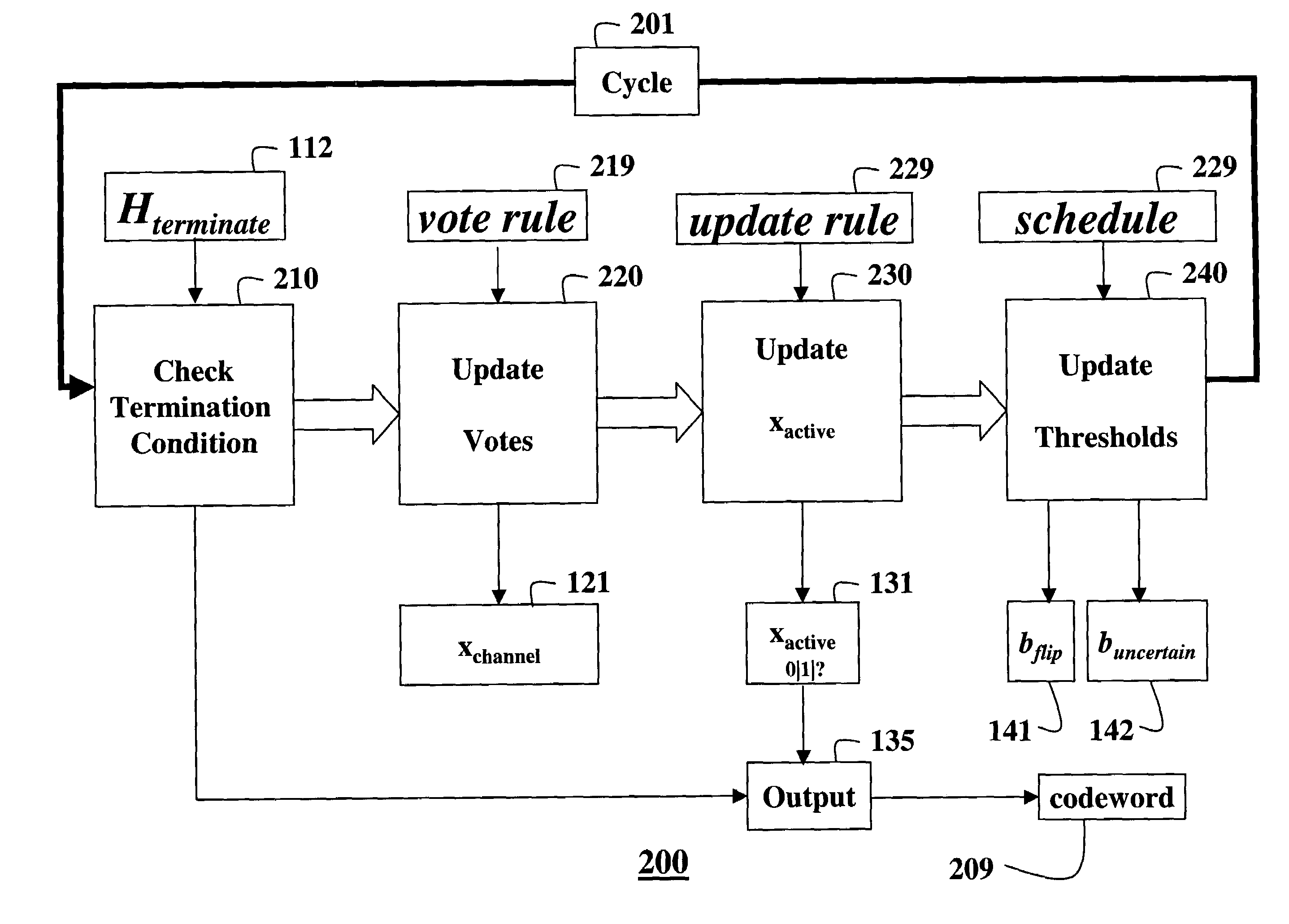
InactiveUS20050044475A1Non-binary linear block codesReed-muller codesBinary linear block codesTheoretical computer science
A method decodes a received word for a binary linear block code based on a finite geometry. First, a parity check matrix representation of the code is defined. The received word is stored in a channel register. An active register represents a current state of the decoder. Each element in the active register can take three states, representing the two possible states of the corresponding bit in the word, and a third state representing uncertainty. Votes from parity checks to elements of the active register are determined from parity checks in the matrix, and the current state of the active register. A recommendation and strength of recommendation for each element in the active register is determined from the votes. The elements in the active register are then updated by comparing the recommendation and strength of recommendation with two thresholds, and the state of the corresponding bit in the received word. When termination conditions are satisfied, the decoder outputs the state of the active register. If the decoder outputs a state of the active register that does not correspond to a codeword, a new representation for the code using a parity check matrix with substantially more rows is chosen, and the decoding cycle is restarted.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC INFORMATION TECH CENT AMERICA ITA
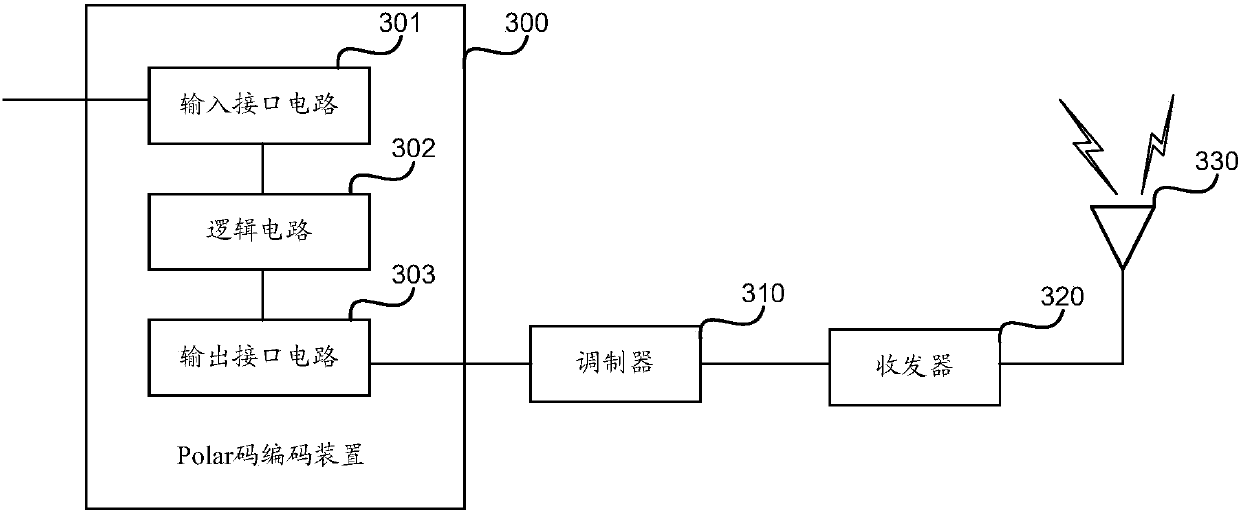
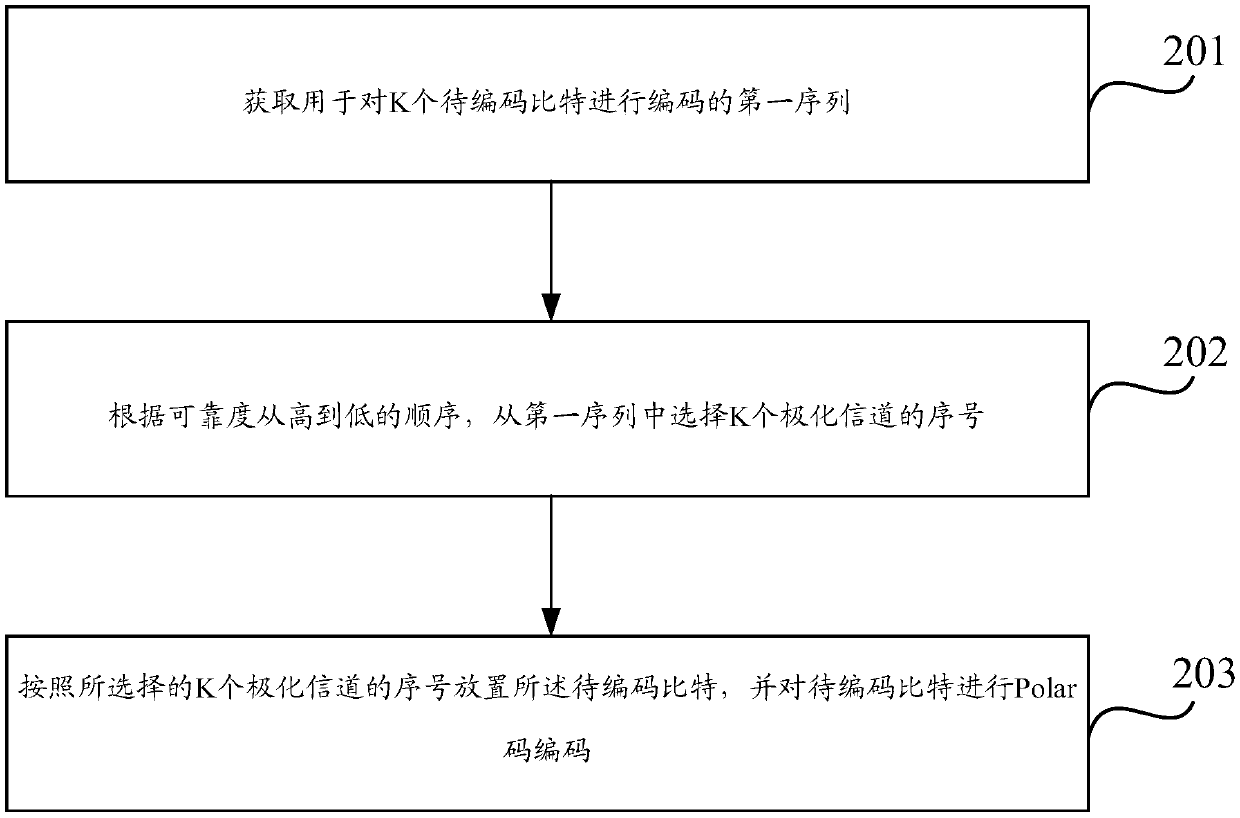
Polar code encoding method and device
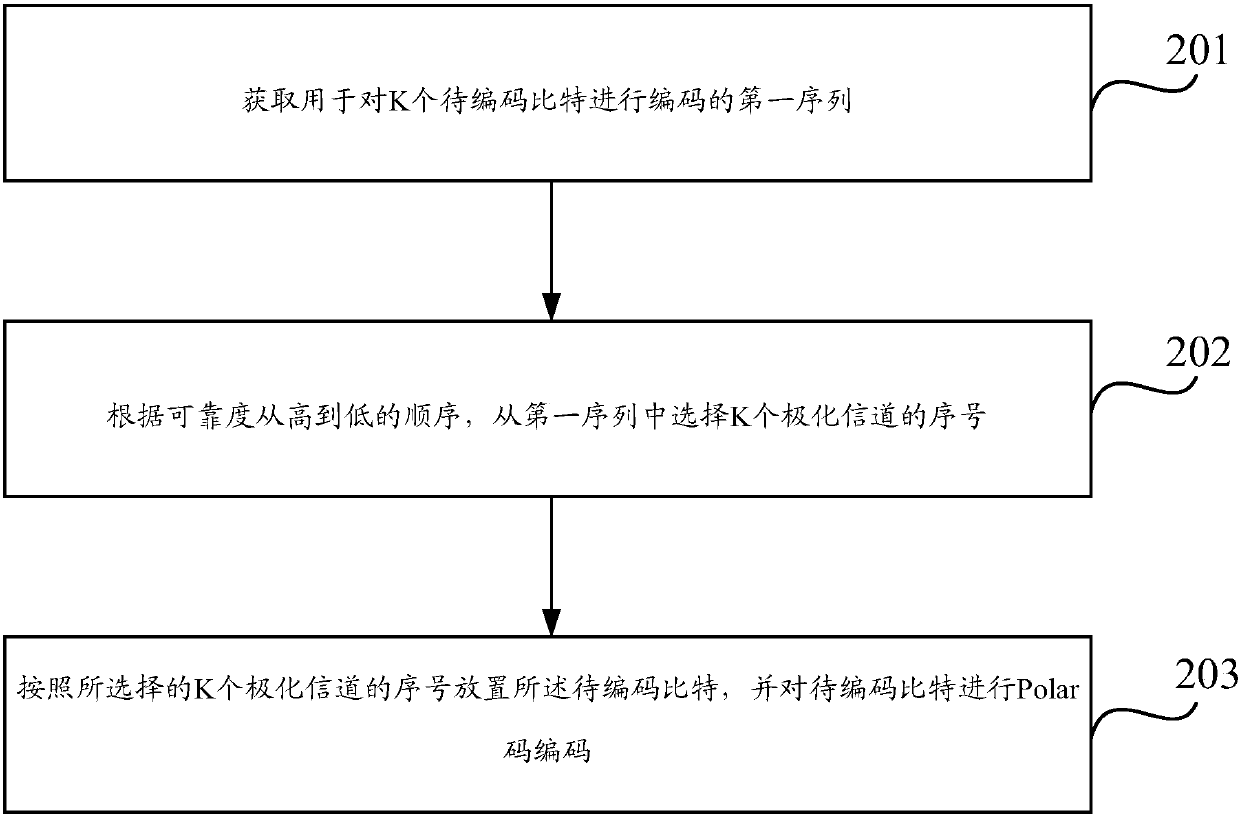
The application relates to the technical field of communication, and discloses a Polar code encoding method and device in order to improve the calculating and sorting accuracy of the reliability of polarization channels. The method includes the following steps: acquiring a first sequence used to encode K to-be-encoded bits, wherein the first sequence contains the serial numbers of N polarization channels, the serial numbers of the N polarization channels are arranged in the first sequence according to the reliability of the N polarization channels, K is a positive integer, N is the length of the mother code of a Polar code, N is a positive integer power of 2, and K<=N; selecting the serial numbers of K polarization channels from the first sequence according to the reliability from high tolow; and placing the to-be-encoded bits according to the serial numbers of the K polarization channels selected, and carrying out Polar code encoding on the to-be-encoded bits.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method for constructing erasure correcting codes whose implementation requires only exclusive ORs
InactiveUS20040260994A1Efficient implementationNon-binary linear block codesCode conversionCorrection algorithmExclusive or
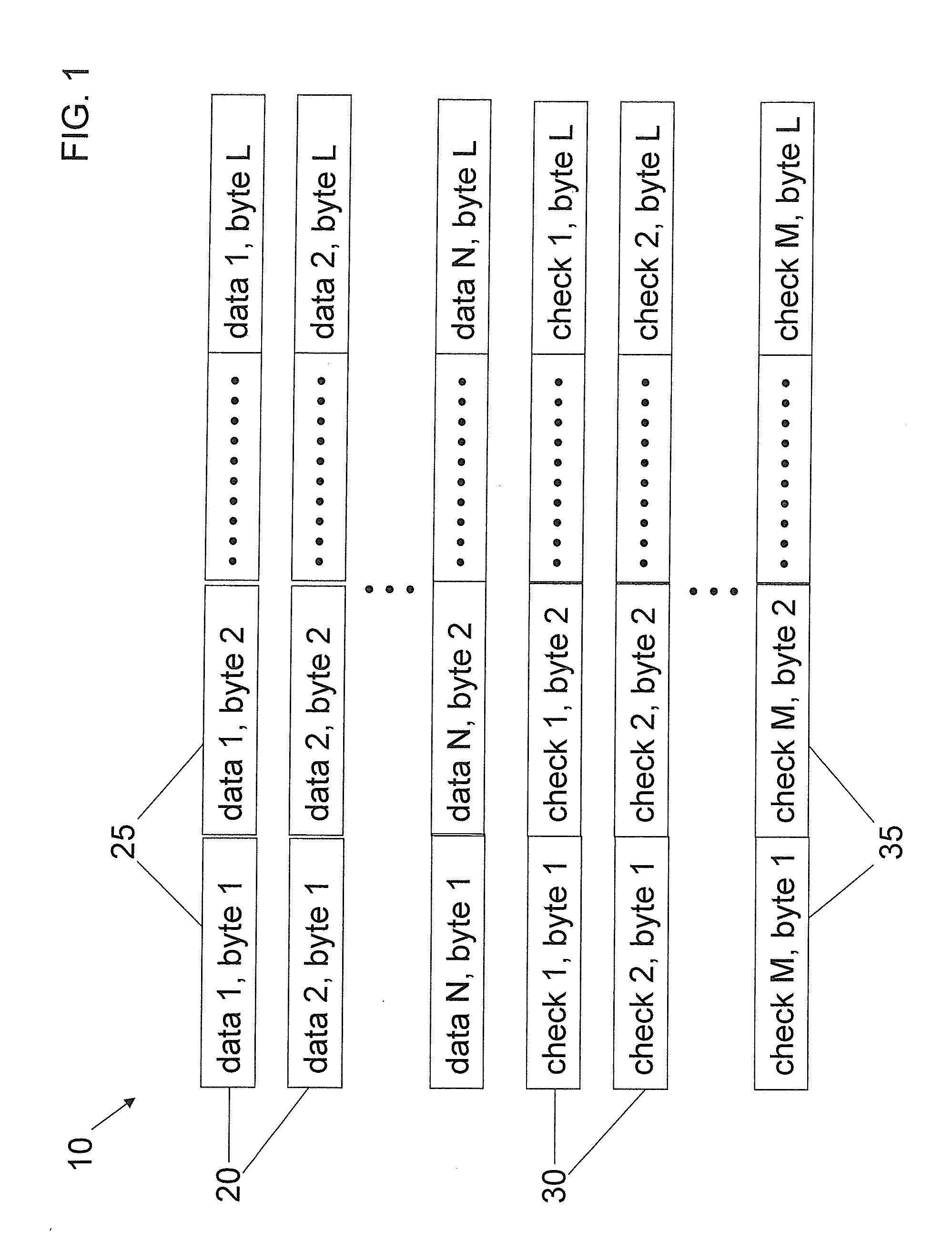
Error correcting codes of any distance (including codes of distance greater than four) use only exclusive OR (XOR) operations. Any code over a finite field of characteristic two are converted into a code whose encoding and correcting algorithms involve only XORs of words (and loading and storing of the data). Thus, the implementation of the encoding and correcting algorithms is more efficient, since it uses only XORs of words-an operation which is available on almost all microprocessors. An important code, the (3, 3) code of distance four, is also described.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
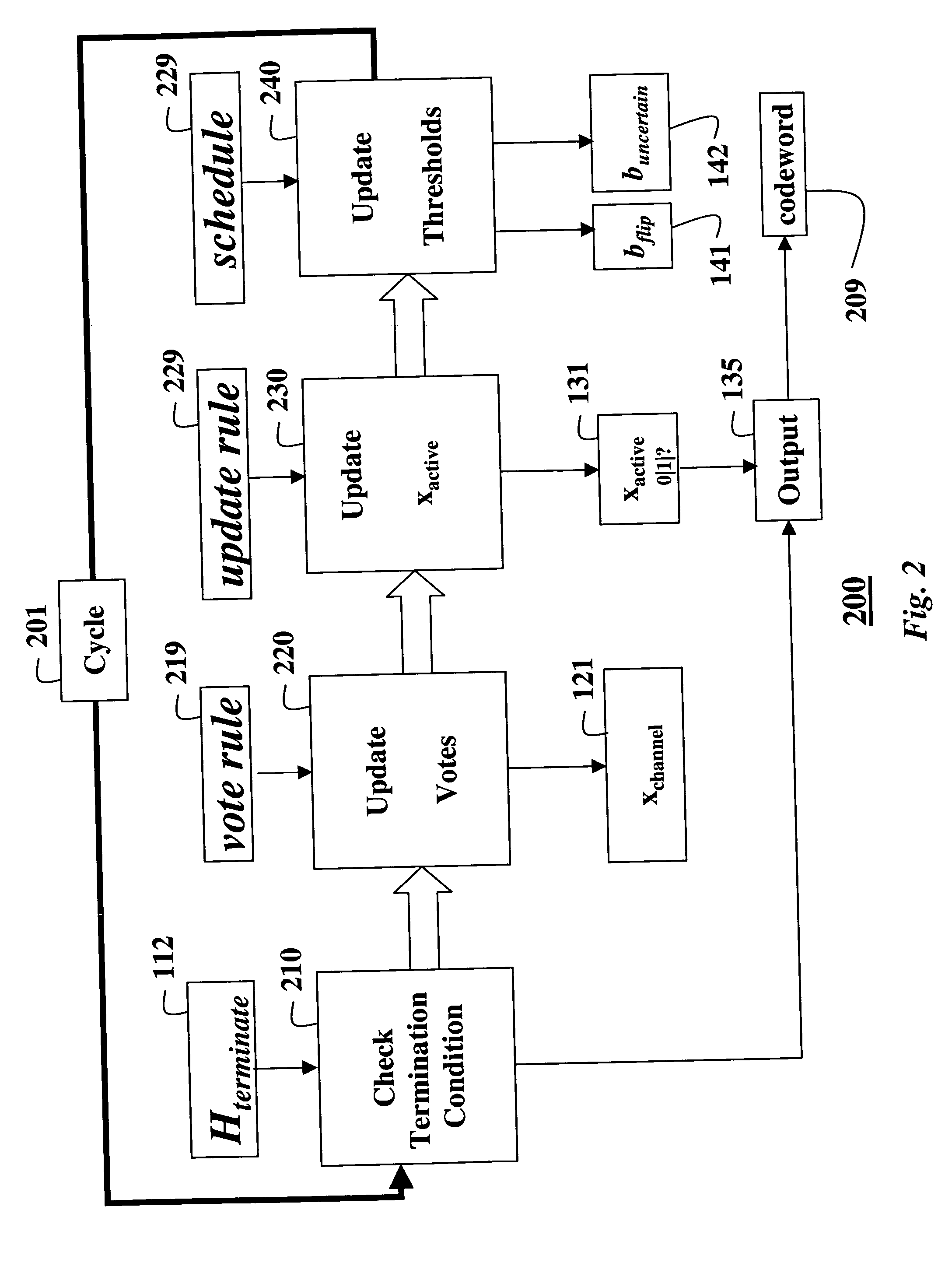
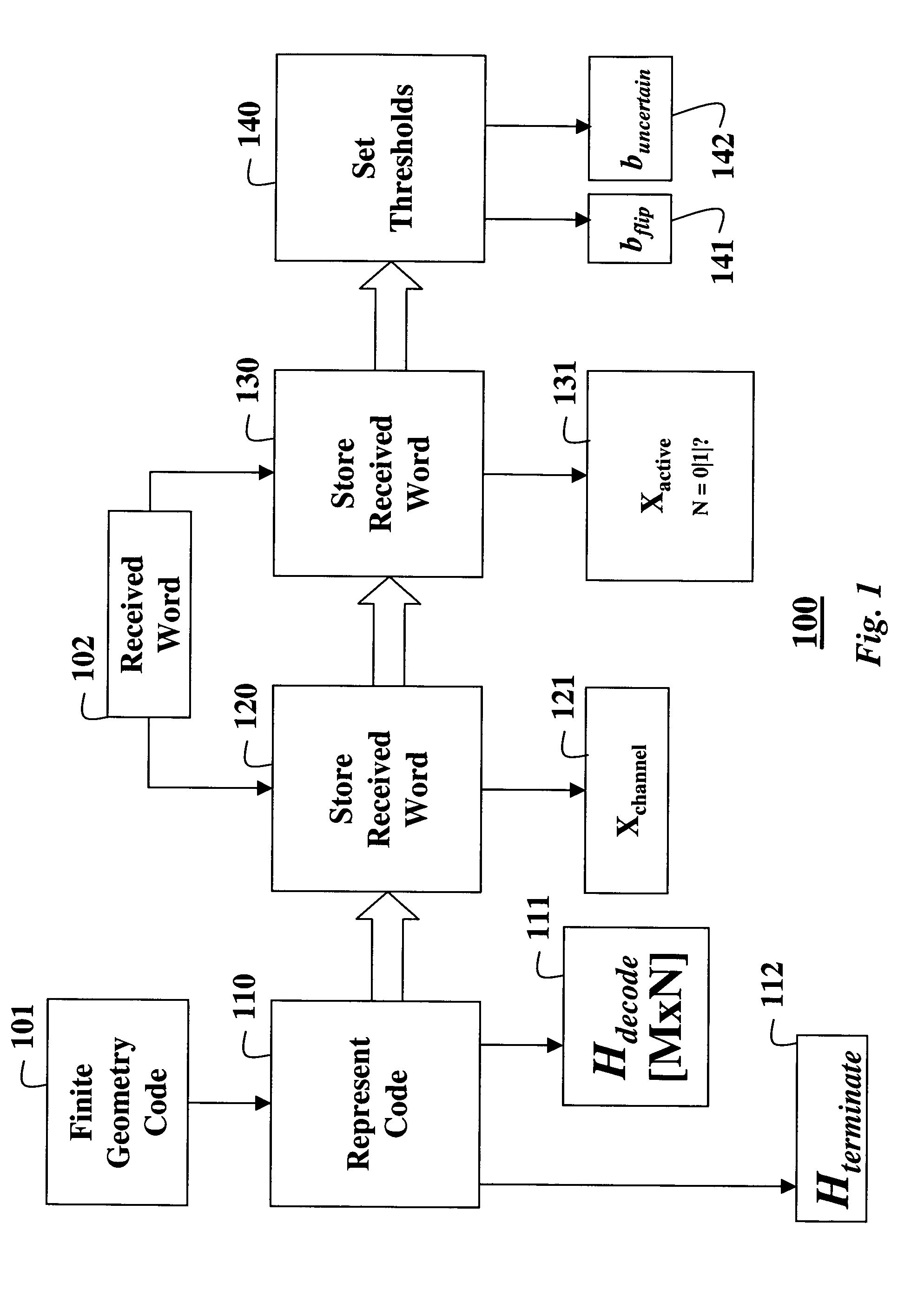
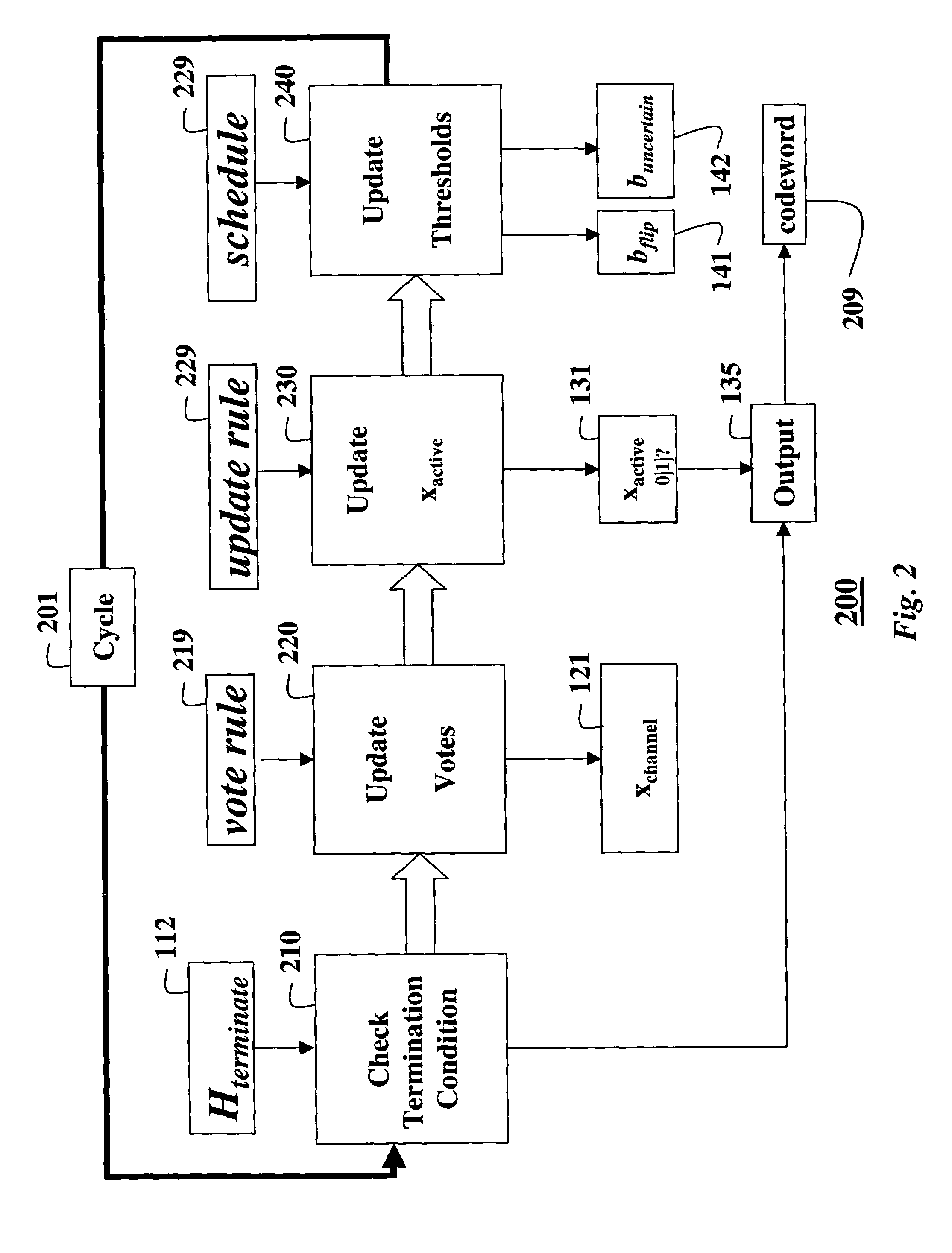
Decoding error-correcting codes based on finite geometries
InactiveUS7103825B2Non-binary linear block codesReed-muller codesProcessor registerBinary linear block codes
A method decodes a received word for a binary linear block code based on a finite geometry. First, a parity check matrix representation of the code is defined. The received word is stored in a channel register. An active register represents a current state of the decoder. Each element in the active register can take three states, representing the two possible states of the corresponding bit in the word, and a third state representing uncertainty. Votes from parity checks to elements of the active register are determined from parity checks in the matrix, and the current state of the active register. A recommendation and strength of recommendation for each element in the active register is determined from the votes. The elements in the active register are then updated by comparing the recommendation and strength of recommendation with two thresholds, and the state of the corresponding bit in the received word. When termination conditions are satisfied, the decoder outputs the state of the active register. If the decoder outputs a state of the active register that does not correspond to a codeword, a new representation for the code using a parity check matrix with substantially more rows is chosen, and the decoding cycle is restarted.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC INFORMATION TECH CENT AMERICA ITA
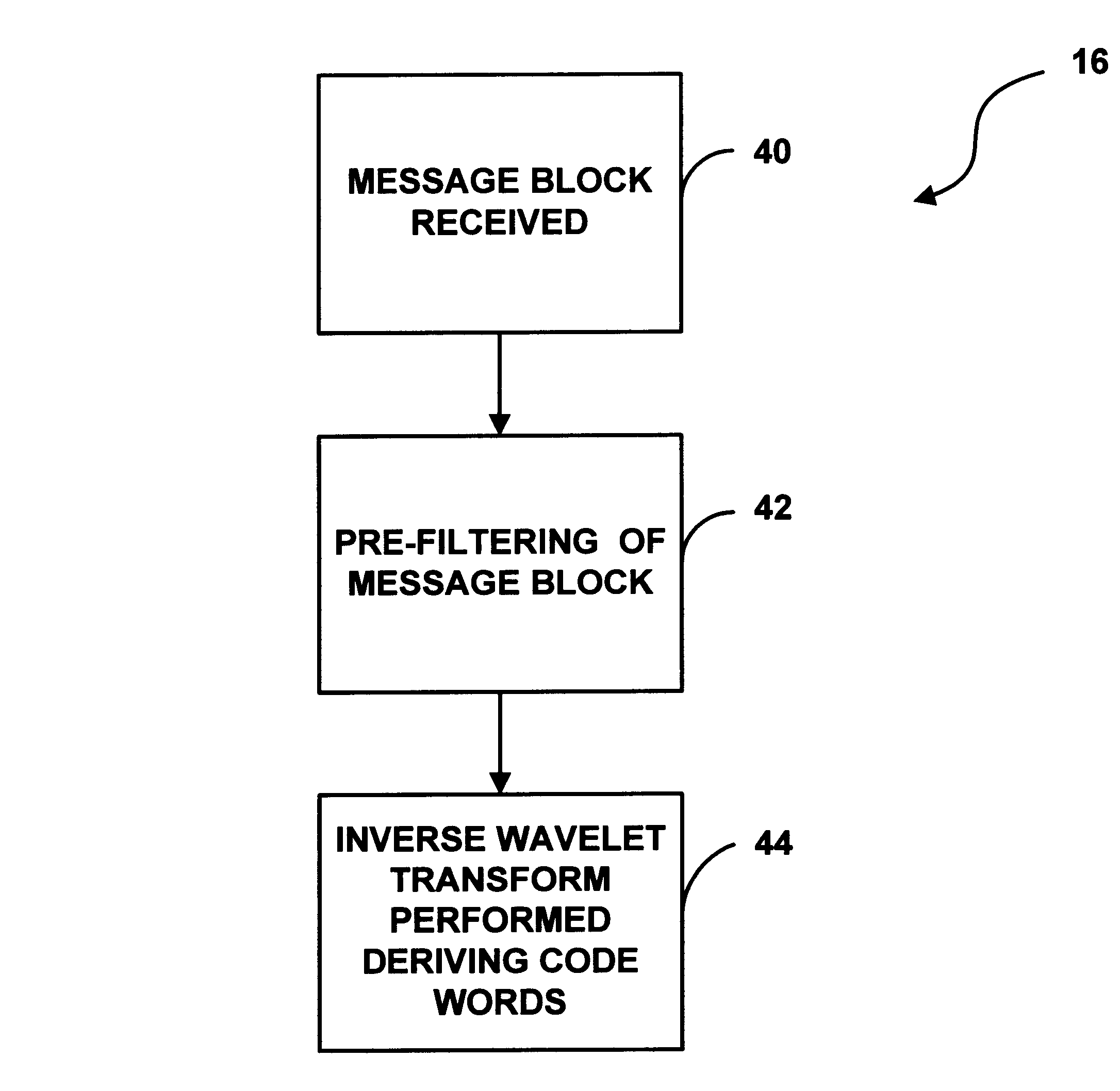
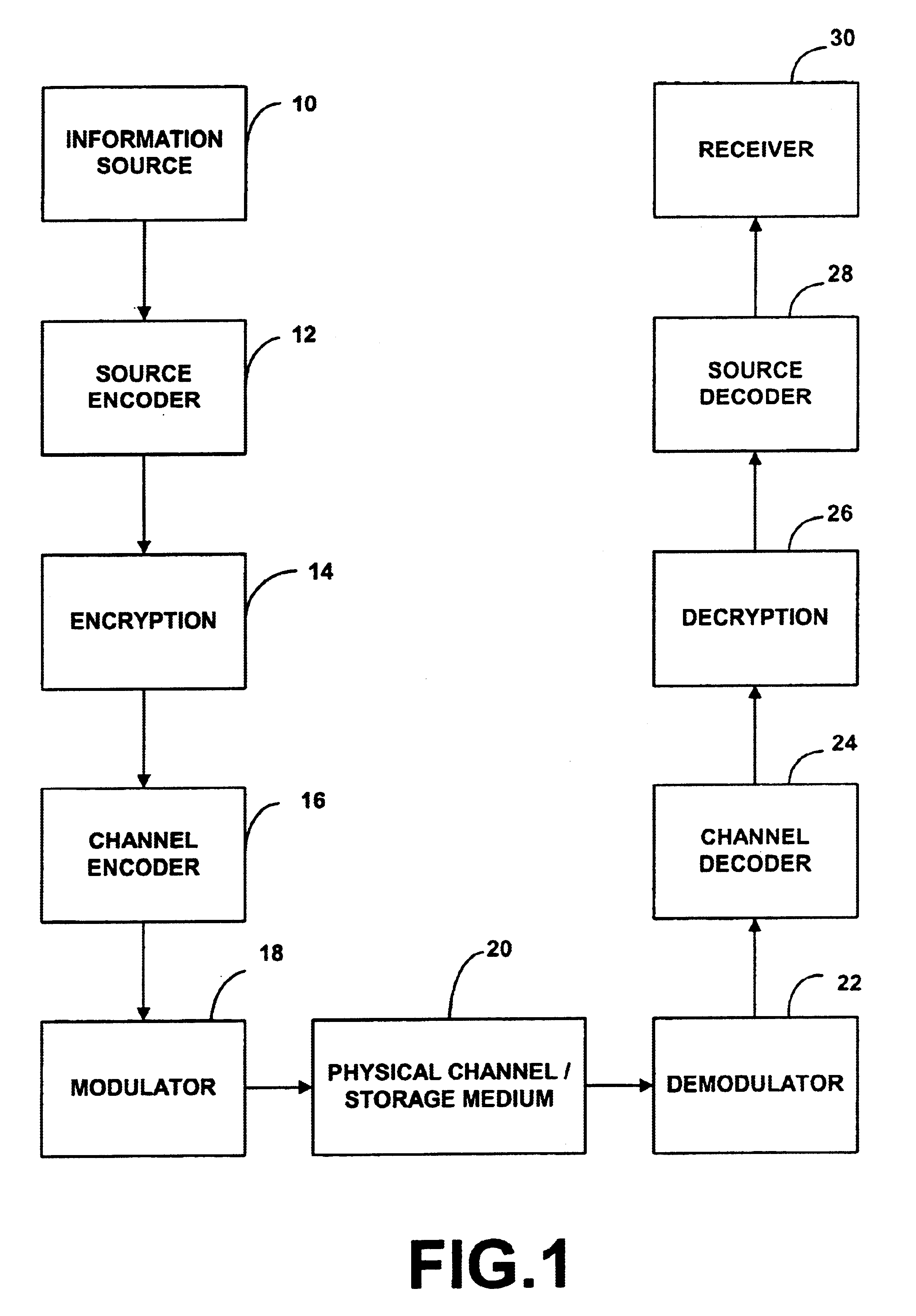
System and method for enabling efficient error correction and encryption using wavelet transforms over finite fields
InactiveUS6898756B1Quick and efficientEffective wayNon-binary linear block codesError preventionAlgorithmChannel decoder
A system and method for enabling efficient error correction and encryption using wavelet transforms over finite fields. The system and method utilizes the combination of a channel encoder and channel decoder to correct errors to source data after transmission over a physical channel or storage in a storage medium. The channel encoder mathematically generates a set of wavelet coefficients by performing a combination of filtering and / or processing of a received message vector. The wavelet coefficients are then utilized by the channel encoder to cause its filters to transform message data into transmission data. The channel decoder receives the transmitted source data in the form of a code word / channel error combination and performs filtering to render a syndrome, representative of the channel error. Analysis of the syndrome is performed to determine the actual error, which is utilized to derive the actual source data.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Sliced polar codes
ActiveUS20170244429A1Non-binary linear block codesError correction/detection using trellis codingComputer sciencePermutation matrix
An apparatus for polar coding includes an encoder circuit that implements a transformation C=u1N-sBN-s{tilde over (M)}n, wherein u1N-s, BN-s, {tilde over (M)}n, and C are defined over a Galois field GF(2k), k>1, wherein N=2n, s<N, u1N-s=(u1, . . . , uN-s) is an input vector of N−s symbols over GF(2k), BN-s is a permutation matrix, {tilde over (M)}n=((N−s) rows of Mn=), the matrix M1 is a pre-defined matrix of size q×q, 2<q and N=qn, and C is a codeword vector of N−s symbols, and wherein a decoding complexity of C is proportional to a number of symbols in C; and a transmitter circuit that transmits codeword C over a transmission channel.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Error Correction Coding Apparatus and Error Correction Decoding Apparatus
ActiveUS20080148127A1Correction capabilityPreventing circuit scaleNon-binary linear block codesError preventionComputer hardwareConcatenated error correction code
An error correction coding apparatus divides transmission information sequences in n subframes (n is an arbitrary natural number) into n1 subframes (n1 is a natural number<n) and n2 subframes (n2 is a natural number which satisfies n1+n2=n), block-codes the n1 subframes for every m1 subframes (m1 is a factor of n1) so as to generate a first error correction code, and block-codes the n2 subframes for every m2 subframes (m2 is a factor of n2) so as to generate a second error correction code.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Multi-element error correcting code transmitting and receiving apparatus, data communication system and related method
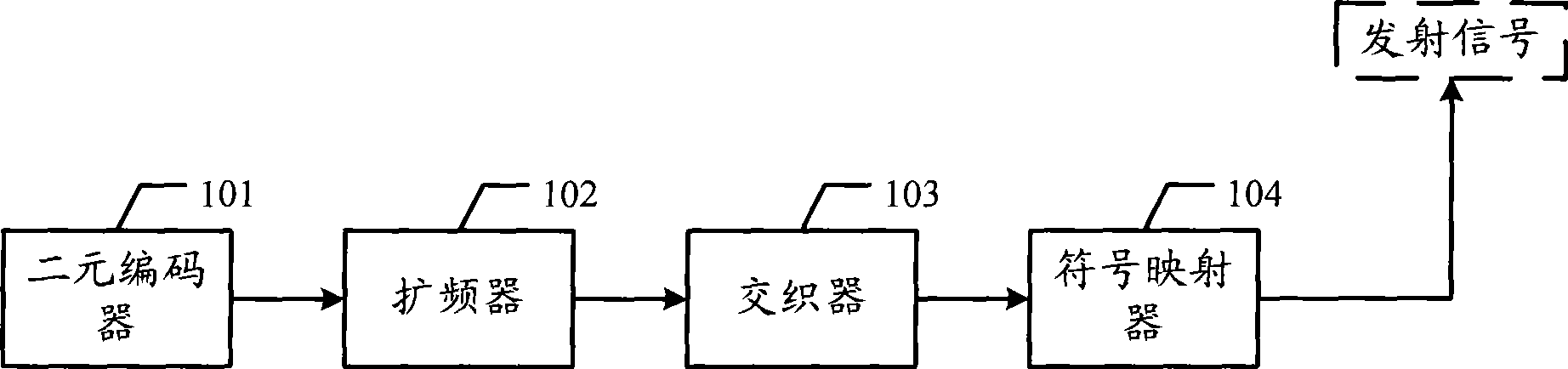
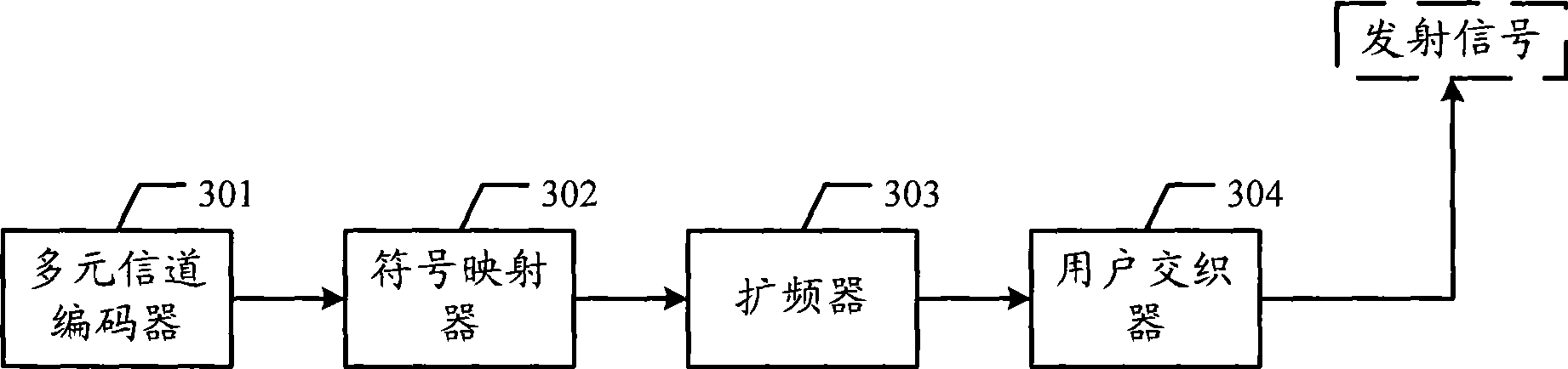
InactiveCN101425871AImprove error correction performanceImprove the ability to resist sudden errorsNon-binary linear block codesCode conversionError correctingSource data
The invention discloses a multiple-unit error correcting code transmitting and receiving device and a data transferring system as well as related methods, which can be used for reducing the complexity of operation. The multiple-unit error correcting code transmitting device comprises a multichannel decoder, a symbol mapper, a user interleaver and a frequency amplifier, wherein the multichannel decoder is used for carrying out the multiple-unit coding on the source data frames of users to obtain a coding sequence; the symbol mapper is used for carrying out the symbol mapping on the coding sequence to obtain a symbol sequence; the user interleaver is used for interleaving the symbol sequence to obtain an interleaved sequence; and the frequency amplifier is used for carrying out the frequency amplifying on the interleaving sequence to obtain a frequency amplifying sequence. The invention also provides a multiple-unit error correcting code receiving device, a data transferring system and the related methods, and can effectively reduce the complexity of operation.
Owner:GLOBAL INNOVATION AGGREGATORS LLC
Method and system for detection and correction of phased-burst errors, erasures, symbol errors, and bit errors in a received symbol string
InactiveUS20100299575A1Increase the number ofNon-binary linear block codesBurst error correctionComputer hardwareBurst error
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Raid system and data recovery apparatus using galois field
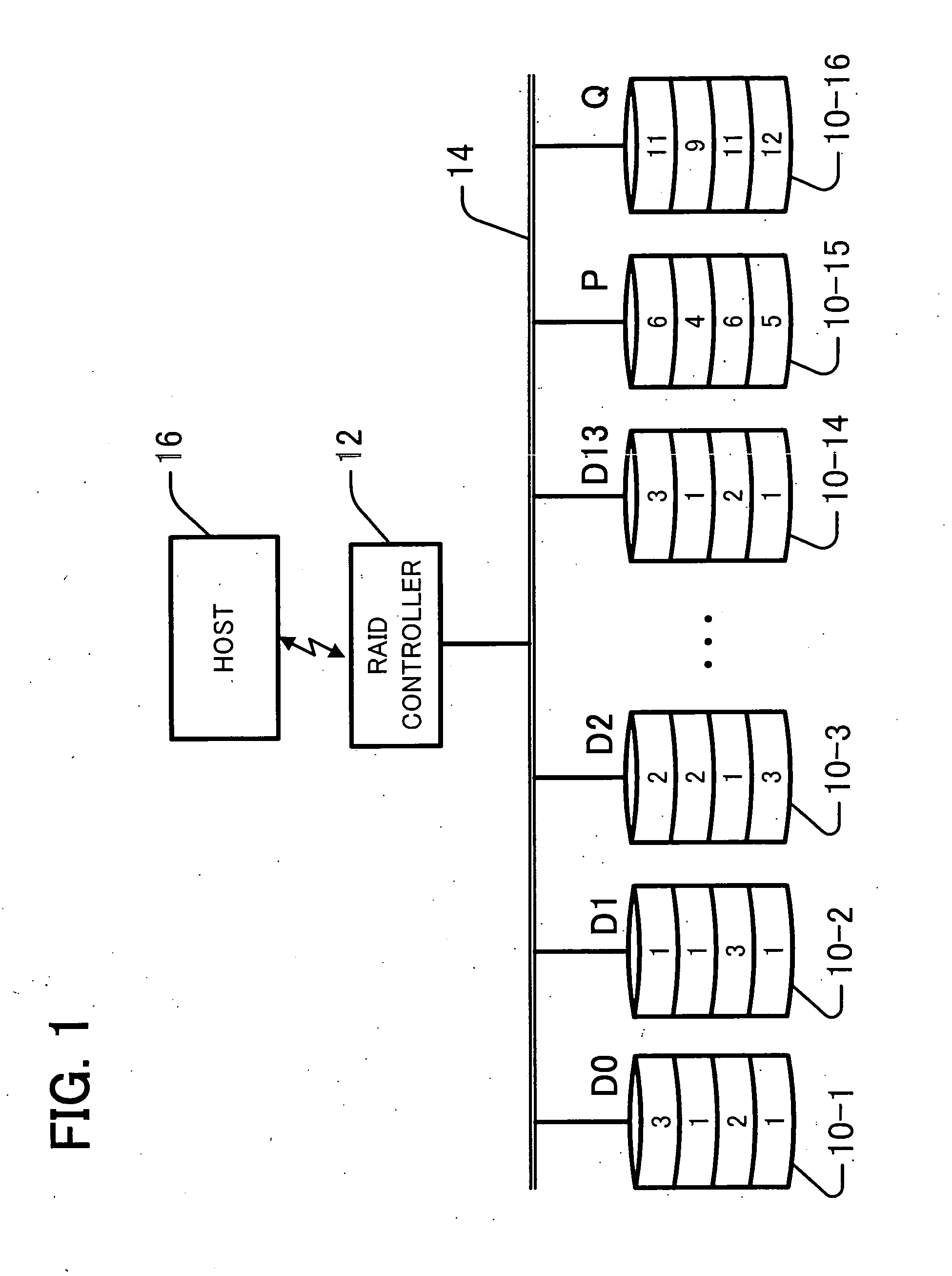
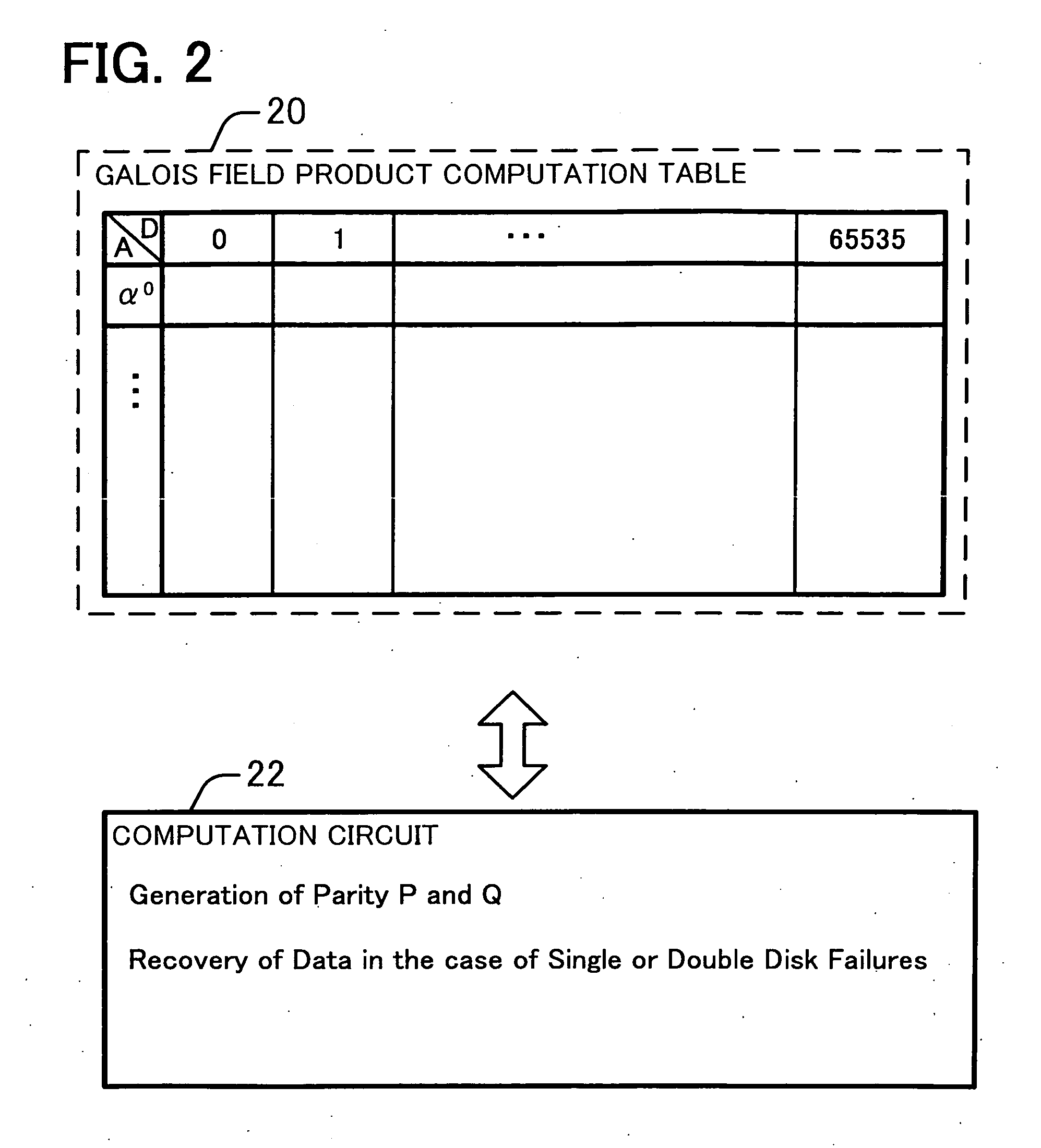
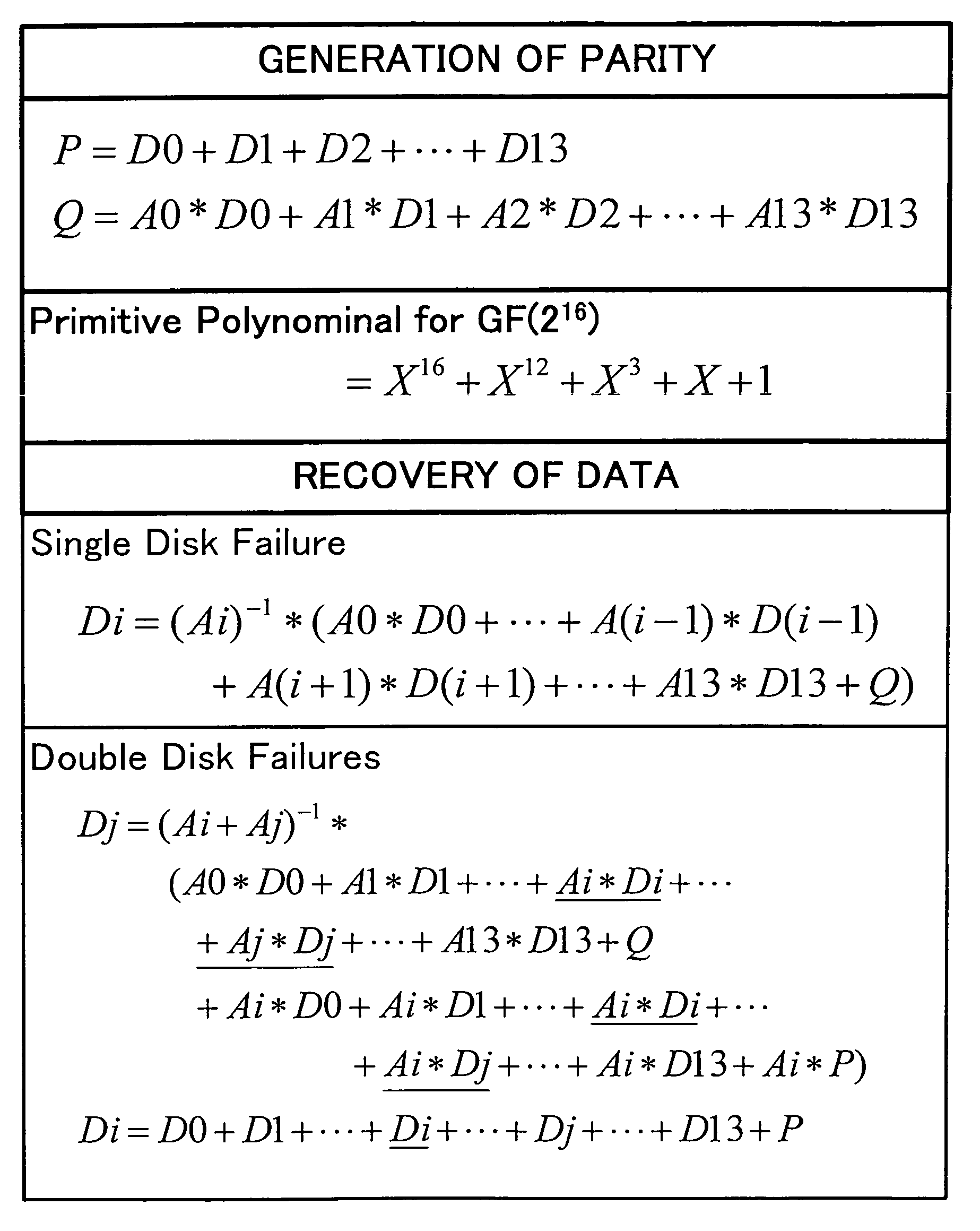
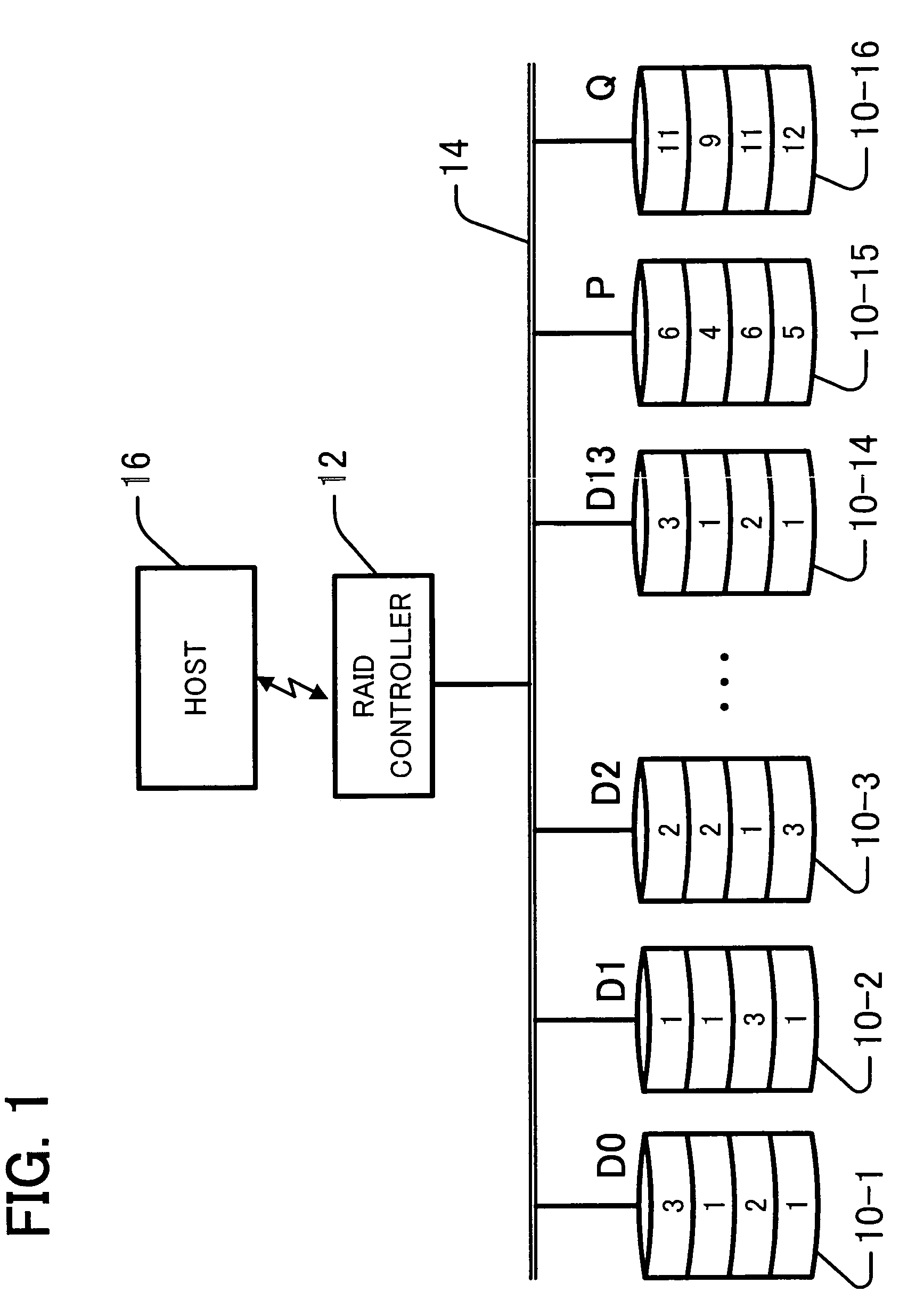
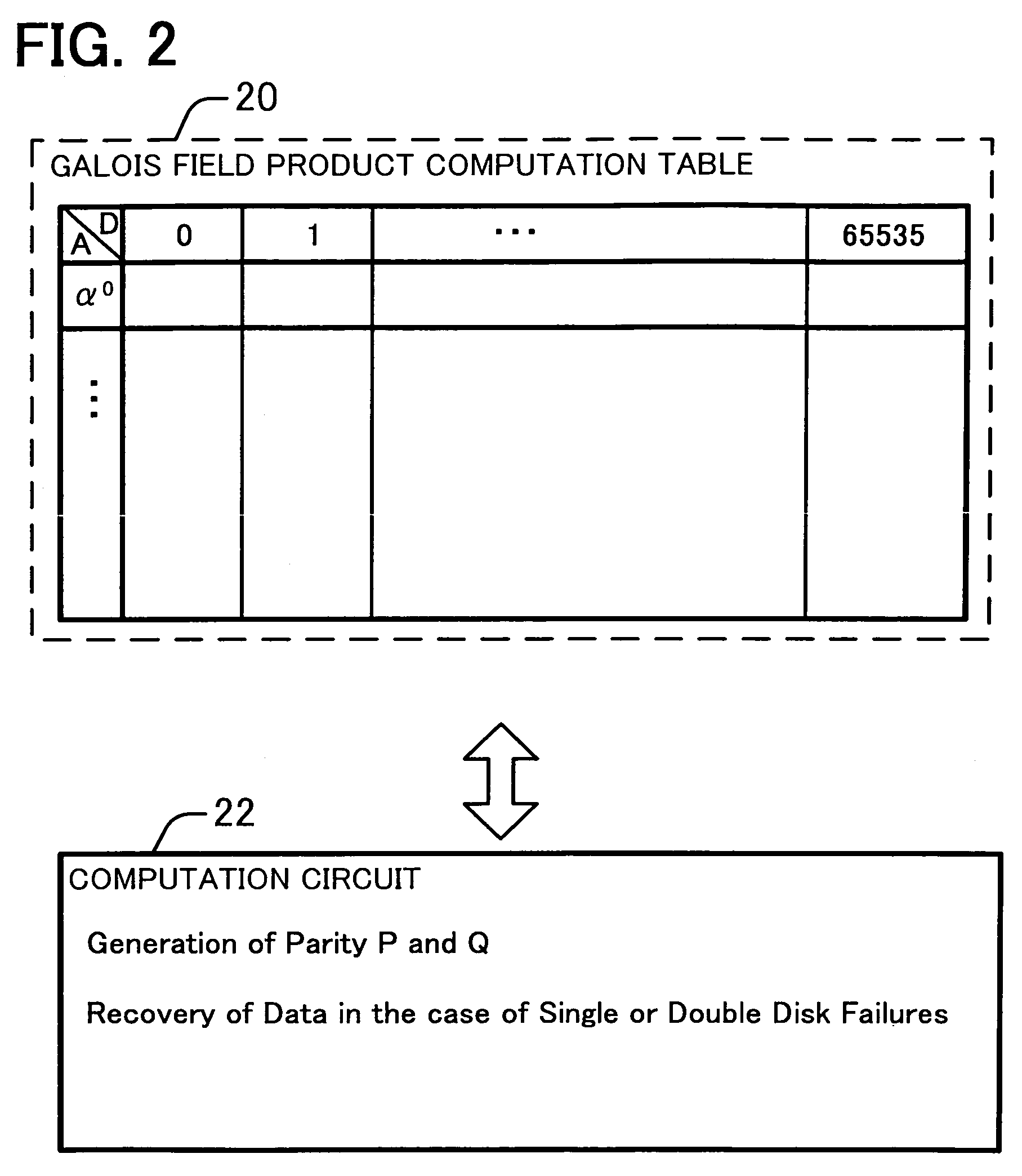
InactiveUS20080184067A1Reduce data volumeLow costNon-binary linear block codesInput/output to record carriersRAIDValue set
Disclosed is an apparatus for recovering data in the case of single or double failures of N partial data blocks generated by dividing the data where N is a natural number greater than 1. The apparatus recovers the data on the basis of a Galois field product computation table including first and second search key data, and products of the first and second search key data. The first search key data includes possible symbol values. The second search key data includes a weighting value set and an inversed weighting value set. The weighting value set includes weighting values each assigned to one of the N partial data blocks and different from each other, and is closed under addition in the Galois field. The inversed weighting value set includes multiplicative inverses of the weighting values included in the weighting value set.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Apparatus and method for encoding and decoding signals
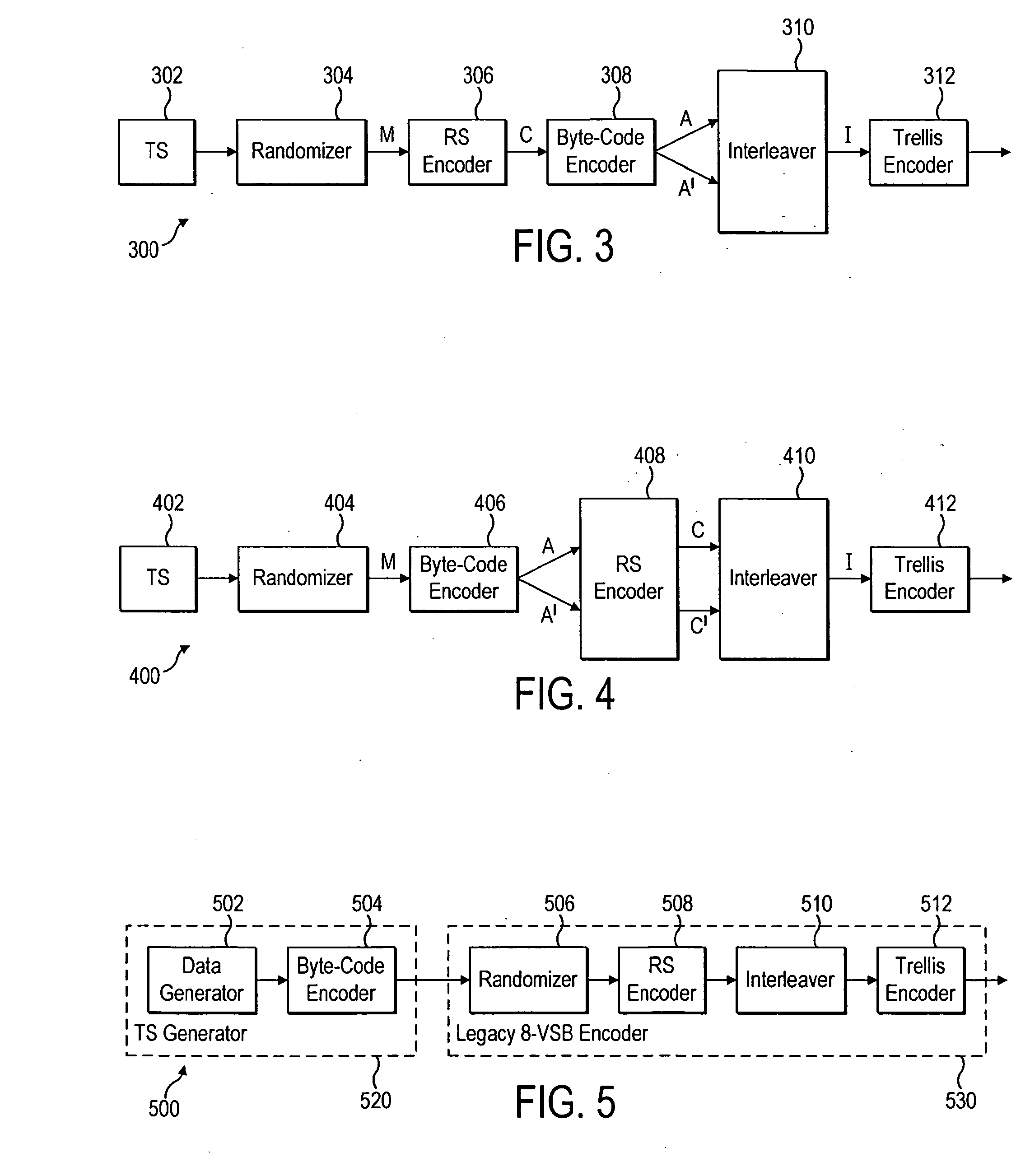
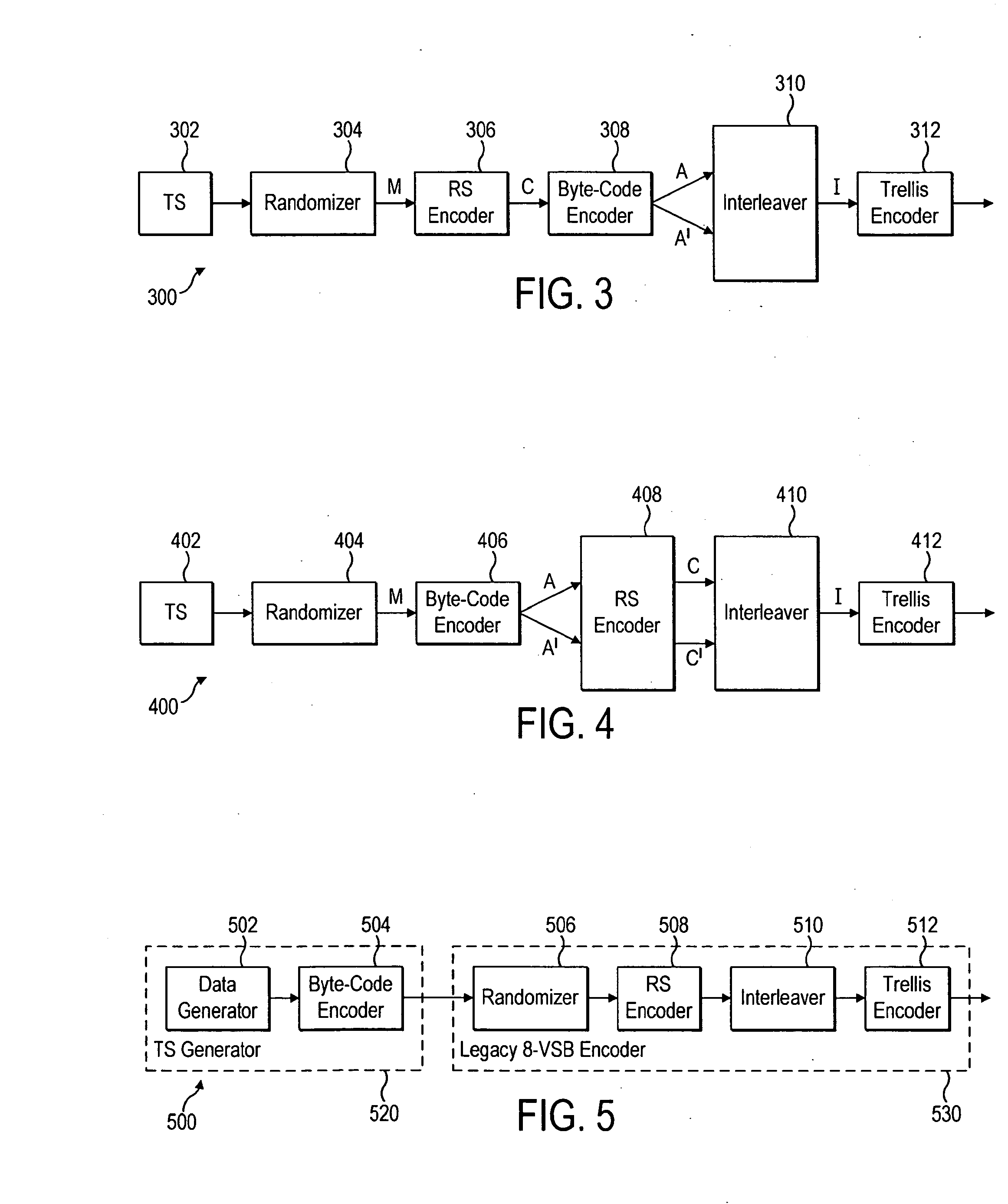
InactiveUS20100232495A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionOther decoding techniquesData setTheoretical computer science
New capabilities will allow conventional broadcast transmission to be available to mobile devices. A method is described including receiving a data set, extracting a subset, encoding the subset using a first encoding process, combining the encoded subset with the remaining portion, and encoding the combined data set including the appended subset using a second encoding process. an apparatus is described including means for extracting a subset, means for first encoding, means for combining, and means for second encoding. An apparatus for decoding includes a data identifier receiving a data set and identifying a subset of data, a first decoder decoding the subset using a first decoding process, and a second decoder combining the subset of data with a remaining portion of the data set and decoding the combined data using a second decoding process. A method for decoding is also described.
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
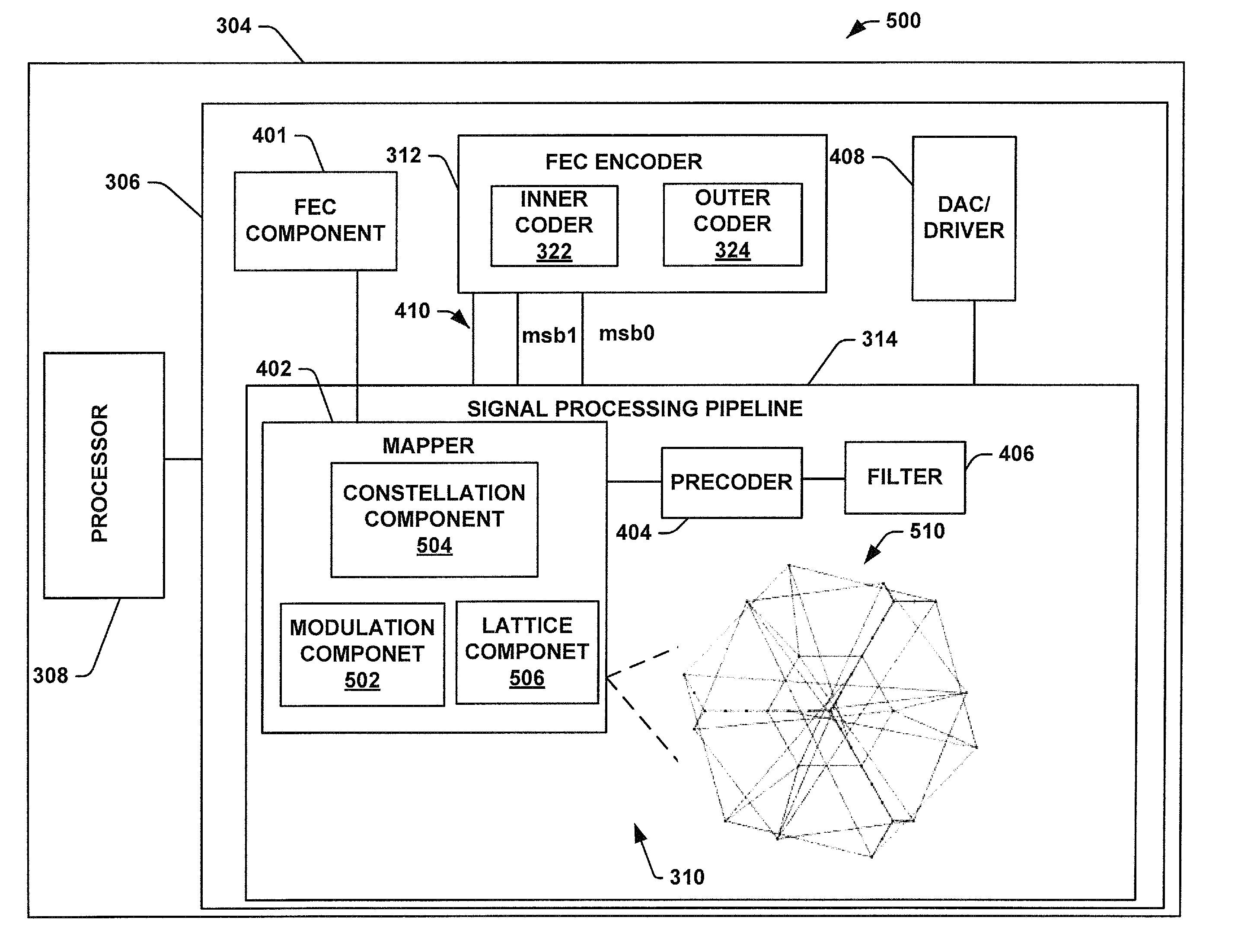
High speed transceiver based on concatenates of a leech lattice with binary and nonbinary codes
ActiveUS8989283B1Easy to implementError prevention/detection by using return channelJoint error correctionFrequency spectrumConcatenation
A transceiver architecture can contain an encoder and a decoder for communicating high speed transmissions. The encoder can modulate signal data for being mapped in a constellation that is generated based on concatenations of a leech lattice having binary and non-binary codes. The data can be transmitted at a high speed according to the constellation with an embedded leech lattice configuration in order to generate a coding gain. A decoder operates to decode the received input signal data with a decreased latency or a minimal latency with a high spectral efficiency.
Owner:MACOM CONNECTIVITY SOLUTIONS LLC
Raid system and data recovery apparatus using galois field
InactiveUS7984361B2Reduce data volumeLow costNon-binary linear block codesInput/output to record carriersRAIDValue set
Disclosed is an apparatus for recovering data in the case of single or double failures of N partial data blocks generated by dividing the data where N is a natural number greater than 1. The apparatus recovers the data on the basis of a Galois field product computation table including first and second search key data, and products of the first and second search key data. The first search key data includes possible symbol values. The second search key data includes a weighting value set and an inversed weighting value set. The weighting value set includes weighting values each assigned to one of the N partial data blocks and different from each other, and is closed under addition in the Galois field. The inversed weighting value set includes multiplicative inverses of the weighting values included in the weighting value set.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
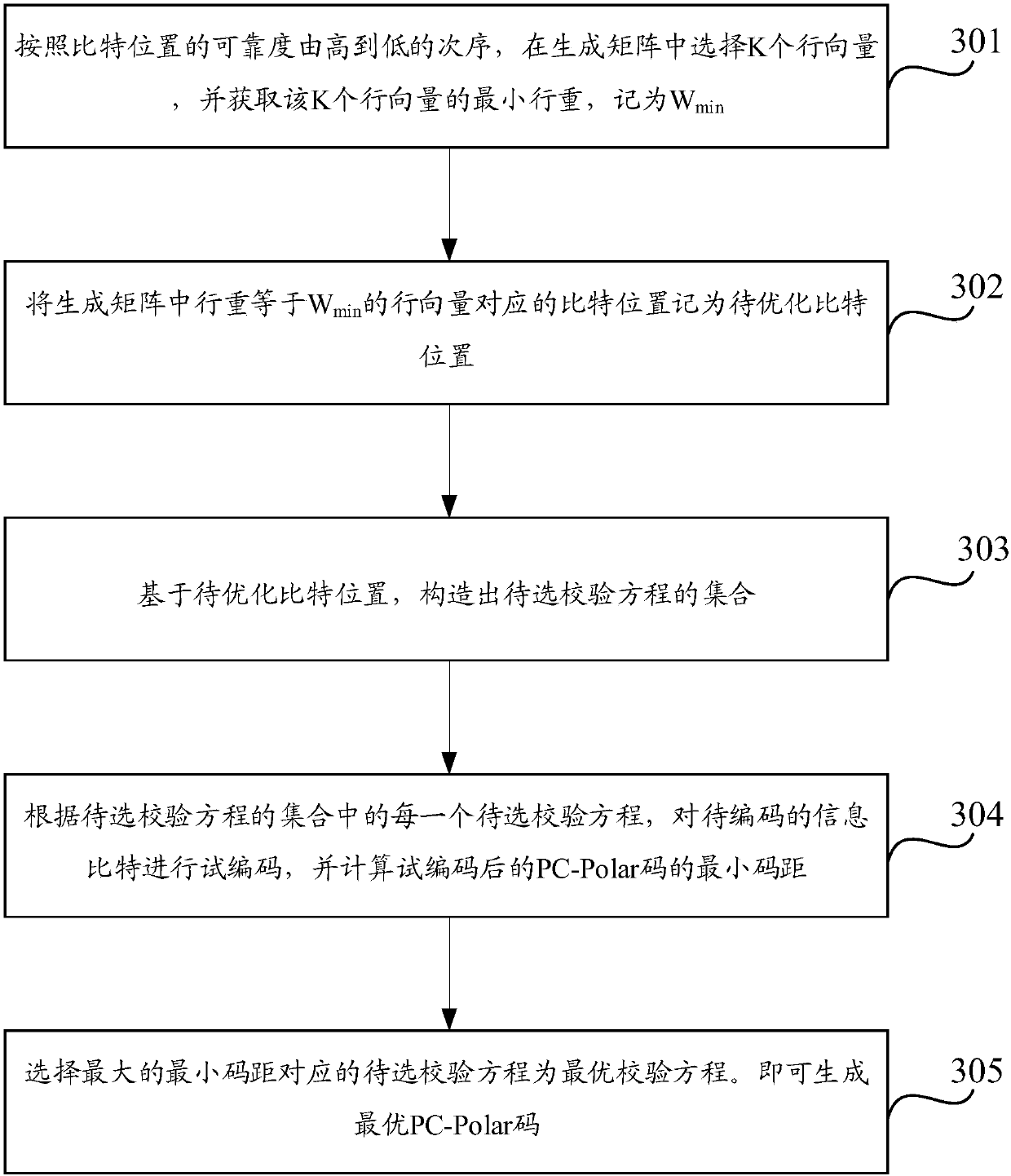
Coding method and device
The invention discloses a coding method and device, and aims to unifying coding methods of ultrashort codes. The method comprises the following steps that: a transmitting end acquires an information bit to be coded; and the transmitting end performs PC-Polar code coding on the information bit to be coded according to a first construction parameter to obtain and transmit a coded bit sequence, wherein a check equation in the first construction parameter include a first element representing the bit location of the check information and a second element representing a check bit location; the firstelement corresponds to a first vector in a generation matrix of a PC-Polar code; the second element corresponds to a second vector in the generation matrix; if the first Hamming weight of the first vector is the same as the second Hamming weight of the second vector, the third Hamming weight of a modular two vector is greater than the first Hamming weight and greater than the second Hamming weight; and if the first Hamming weight is different from the second Hamming weight, the third Hamming weight is greater than a smaller value in the first Hamming weight and the second Hamming weight.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Sliced polar codes
ActiveUS9941906B2Non-binary linear block codesError correction/detection using trellis codingComputer sciencePermutation matrix
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Encoding method and device for Polar code
The application relates to the technical field of communications, and discloses an encoding method and an encoding device for a Polar code for improving reliability calculating and ranking accuracy ofa polarization channel. The method comprises the steps of: acquiring a first sequence for encoding K bits to be coded, wherein the first sequence contains sequence numbers of N polarization channels,the sequence numbers of the N polarization channels are arranged based on the reliability of the N polarization channels in the first sequence, K is a positive integer, N is the mother code length ofthe Polar code and is a positive integer power of 2, and K is not greater than N; selecting sequence numbers of K polarization channels from the first sequence according to the order of reliability from high to low; placing the bits to be coded according to the selected K polarization channel numbers, and performing Polar code encoding on the bits to be coded.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Error correction coding apparatus and error correction decoding apparatus
ActiveUS7992069B2Correction capabilityPrevent scalingNon-binary linear block codesError preventionComputer hardwareConcatenated error correction code
An error correction coding apparatus divides transmission information sequences in n subframes (n is an arbitrary natural number) into n1 subframes (n1 is a natural number<n) and n2 subframes (n2 is a natural number which satisfies n1+n2=n), block-codes the n1 subframes for every m1 subframes (m1 is a factor of n1) so as to generate a first error correction code, and block-codes the n2 subframes for every m2 subframes (m2 is a factor of n2) so as to generate a second error correction code.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Apparatus and method for encoding and decoding signals
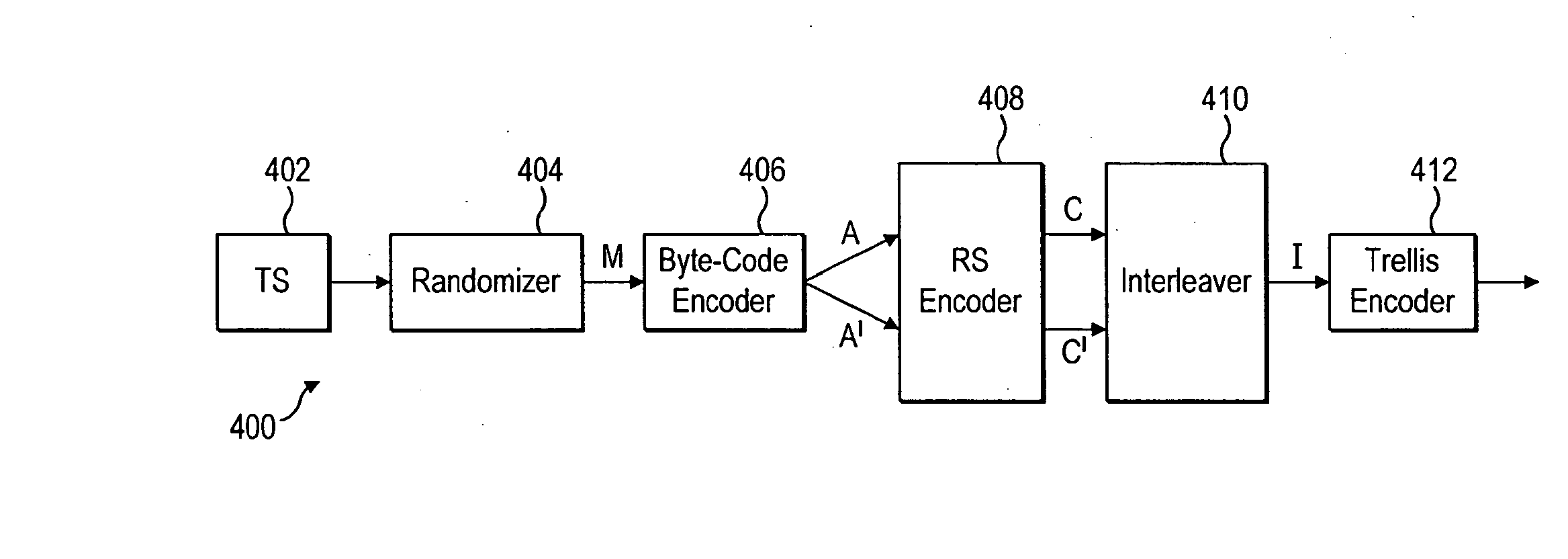
InactiveUS20100238995A1Pulse modulation television signal transmissionOther decoding techniquesNetwork packetBroadcast transmission
New capabilities will allow conventional broadcast transmission to be available to mobile devices. A method is described including the steps of receiving a packet of data having a data payload and a header, byte code encoding the data in the packet, and altering information in the header in response to the byte code encoding. An apparatus is described including an encoder receiving a packet of data and encoding the data using a byte code encoding process and a header modifier altering information in the header in response to the byte code encoding. A decoding apparatus is described including a packet identifier receiving a plurality of data packets, and identifying a data packet based on information in the header, a byte code decoder decoding the identified data packet using a byte code decoding process, and a Reed-Solomon decoder decoding at least the decoded identified data packet using a Reed-Solomon decoding process.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING INC
Error Correction Coding Using Large Fields
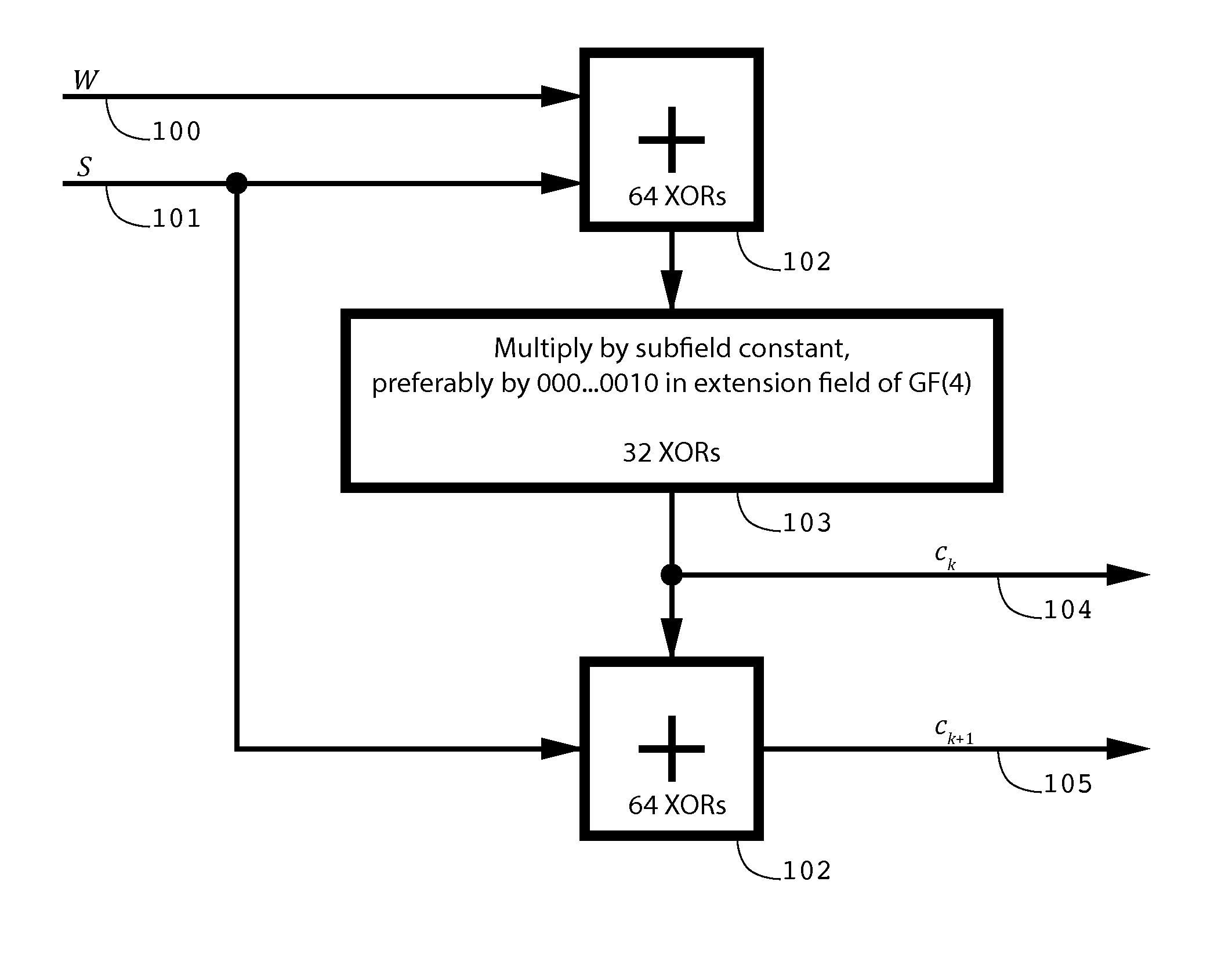
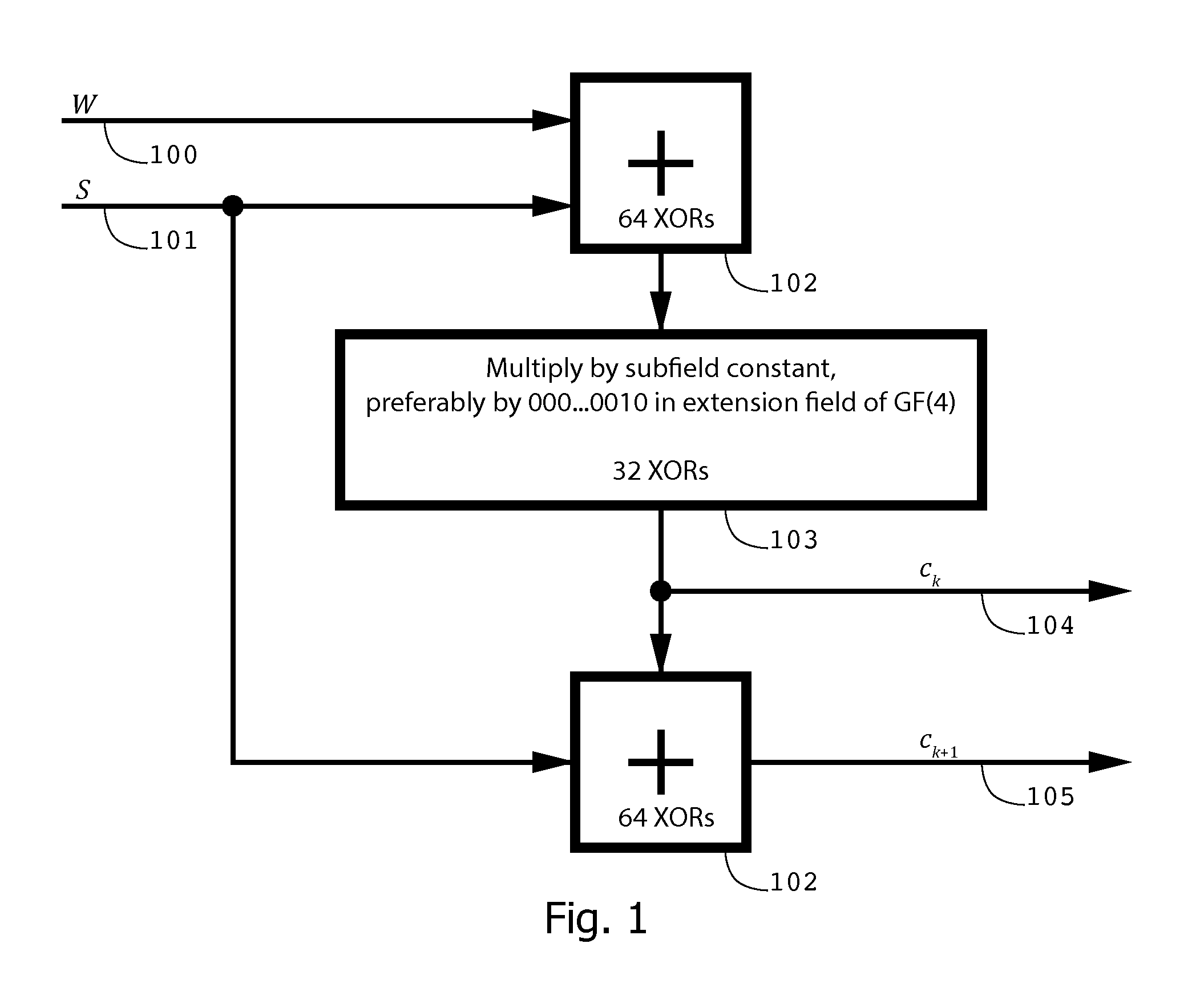
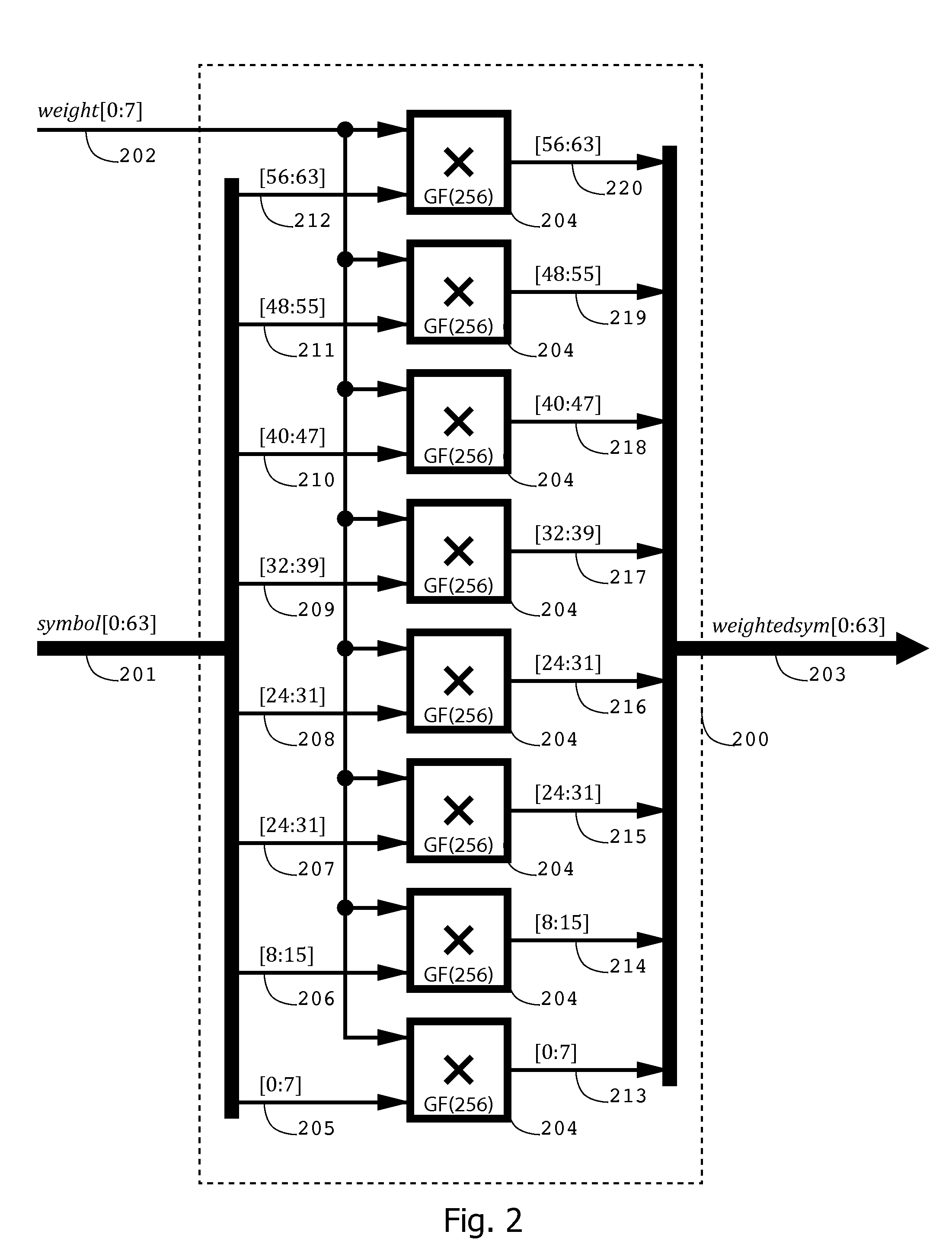
InactiveUS20140013181A1Probability of decoding failure is smallCorrection errorNon-binary linear block codesCode conversionSystems designForward error correction
An improved error correction system, method, and apparatus provides encoded sequences of finite field symbols, each with a plurality of associated weighted sums equal to zero, and decodes encoded sequences with a limited number of corruptions. Each of the multiplicative weights used in the weighted sums is preselected from a smaller subfield of a large finite field. Decoding proceeds by determining multiplicative weights using various operations over the smaller subfield. When a limited number of corruptions occur, improved system design ensures that the probability of decoding failure is small. The method and apparatus extend to determine one or more decoding solutions of an underdetermined set of equations, including detection of ambiguous solutions.
Owner:FREDRICKSON LISA
Method and system for detection and correction of phased-burst errors, erasures, symbol errors, and bit errors in a received symbol string
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
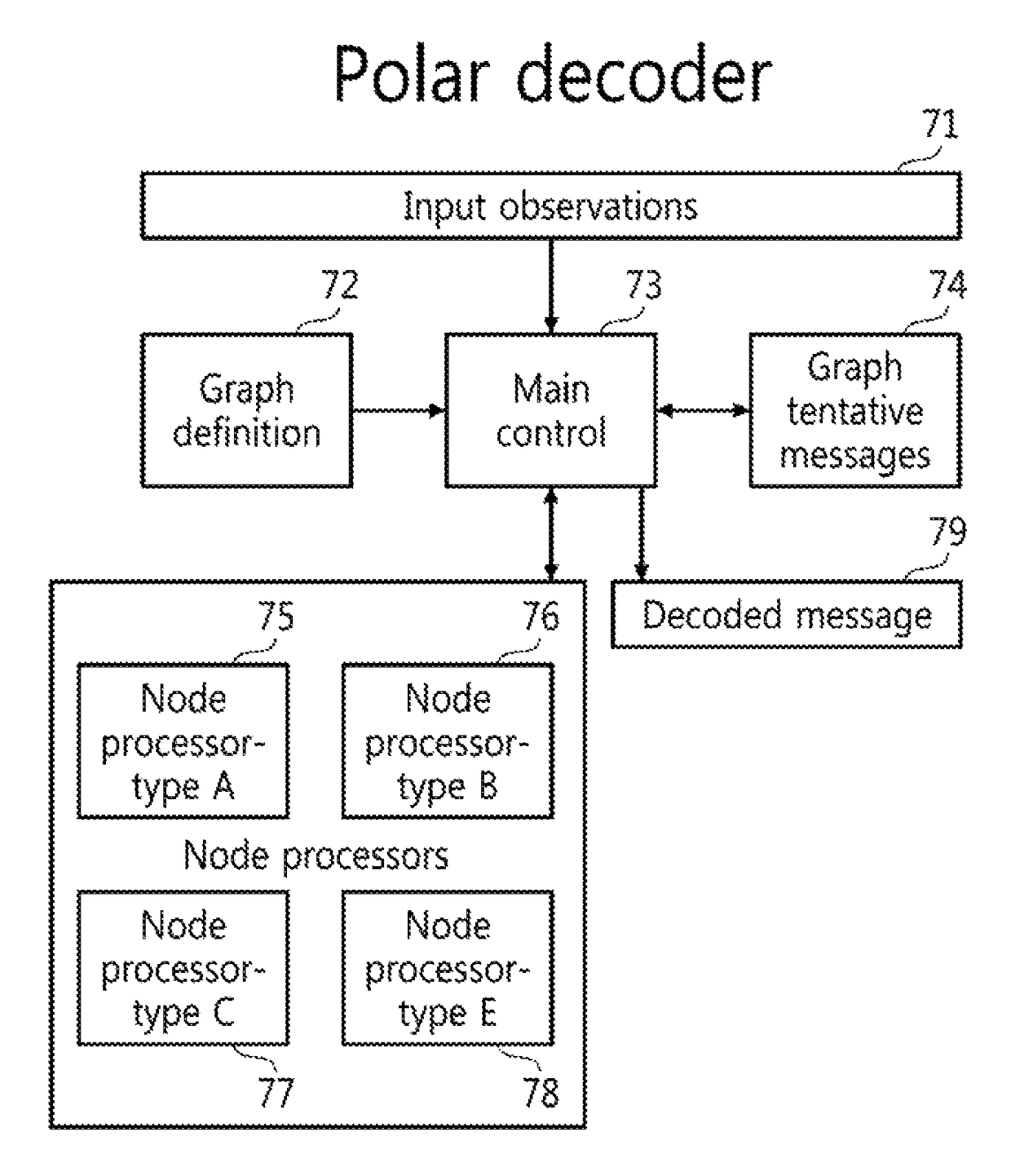
Multi-mode unrolled polar decoders
There is described a multi-mode unrolled decoder. The decoder comprises a master code input configured to receive a polar encoded master code of length N carrying k information bits and N−k frozen bits, decoding resources comprising processing elements and memory elements connected in an unrolled architecture and defining an operation path between the master code input and an output, for decoding a polar encoded code word, at least one constituent code input configured to receive a polar encoded constituent code of length N / p carrying j information bits and N / p−j frozen bits, where p is a power of 2, and at least one input multiplexer provided in the operation path to selectively transmit N / p bits of one of the master code and the constituent code to a subset of the decoding resources.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Popular searches
Securing communication Memory adressing/allocation/relocation Static storage Redundant data error correction Error correction/detection by combining multiple code structures Cyclic codes Error correction/detection using multiple parity bits Single error correction Forward error control use Error detection only
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com