Patents
Literature
695results about "Single error correction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
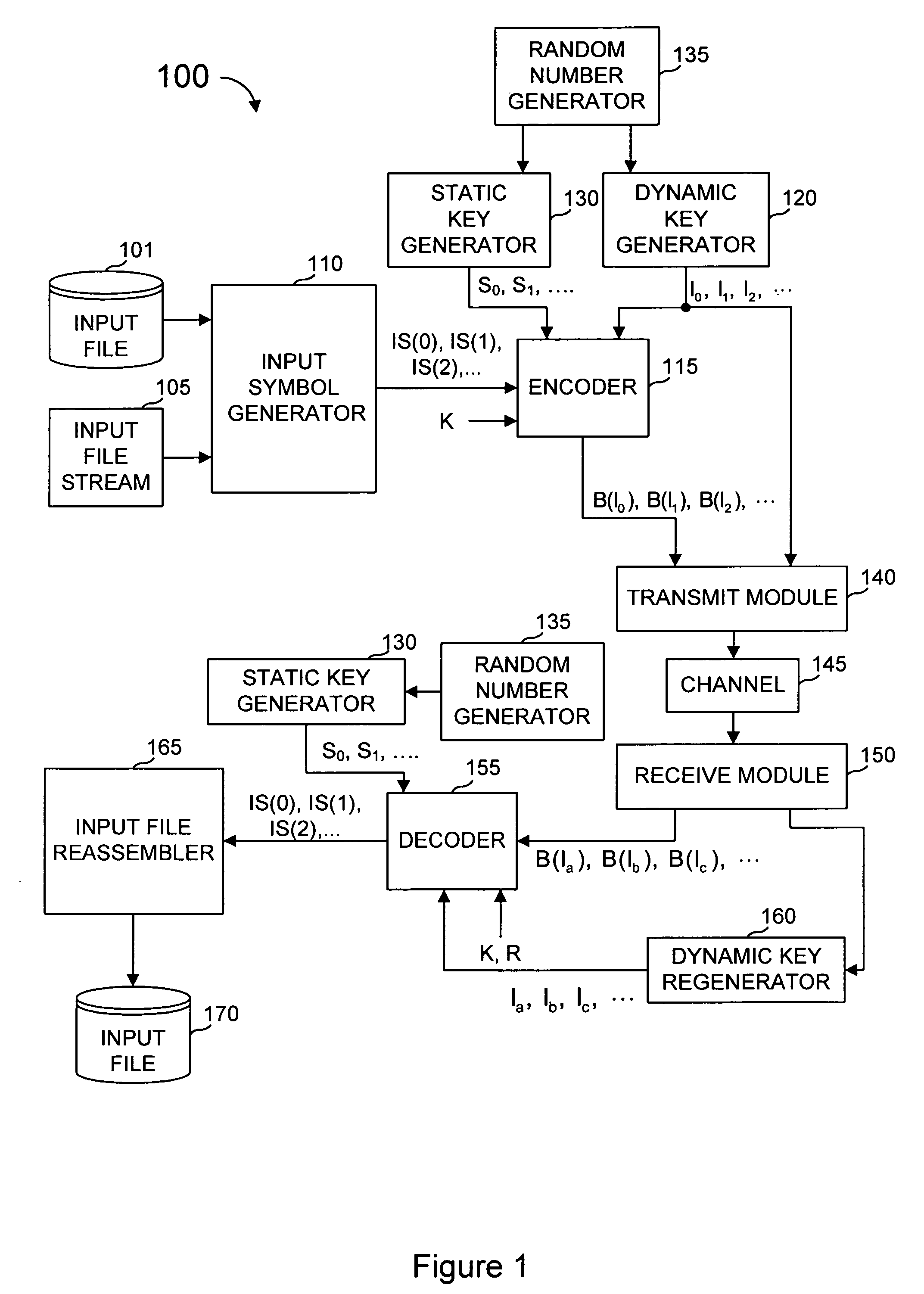
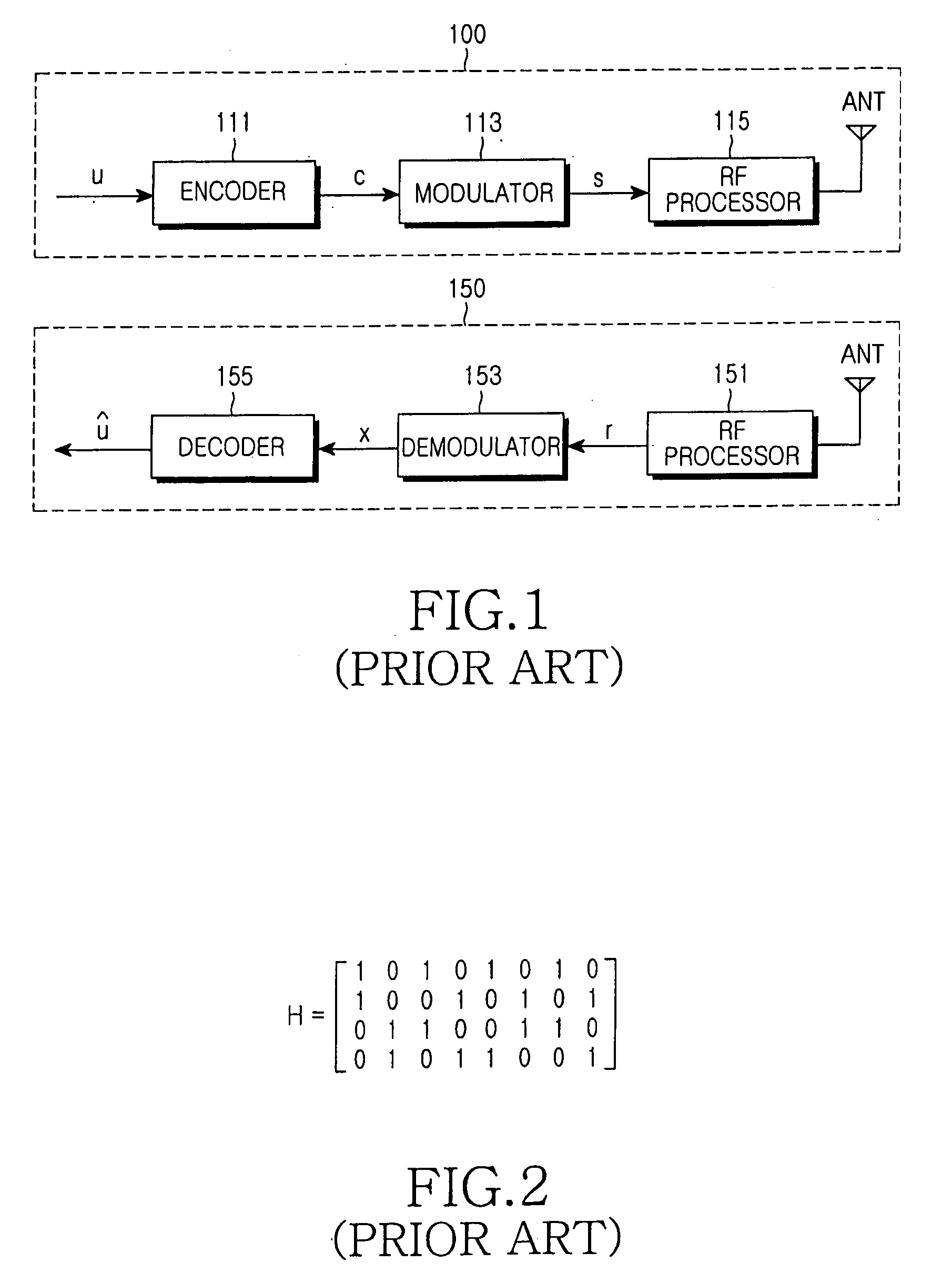
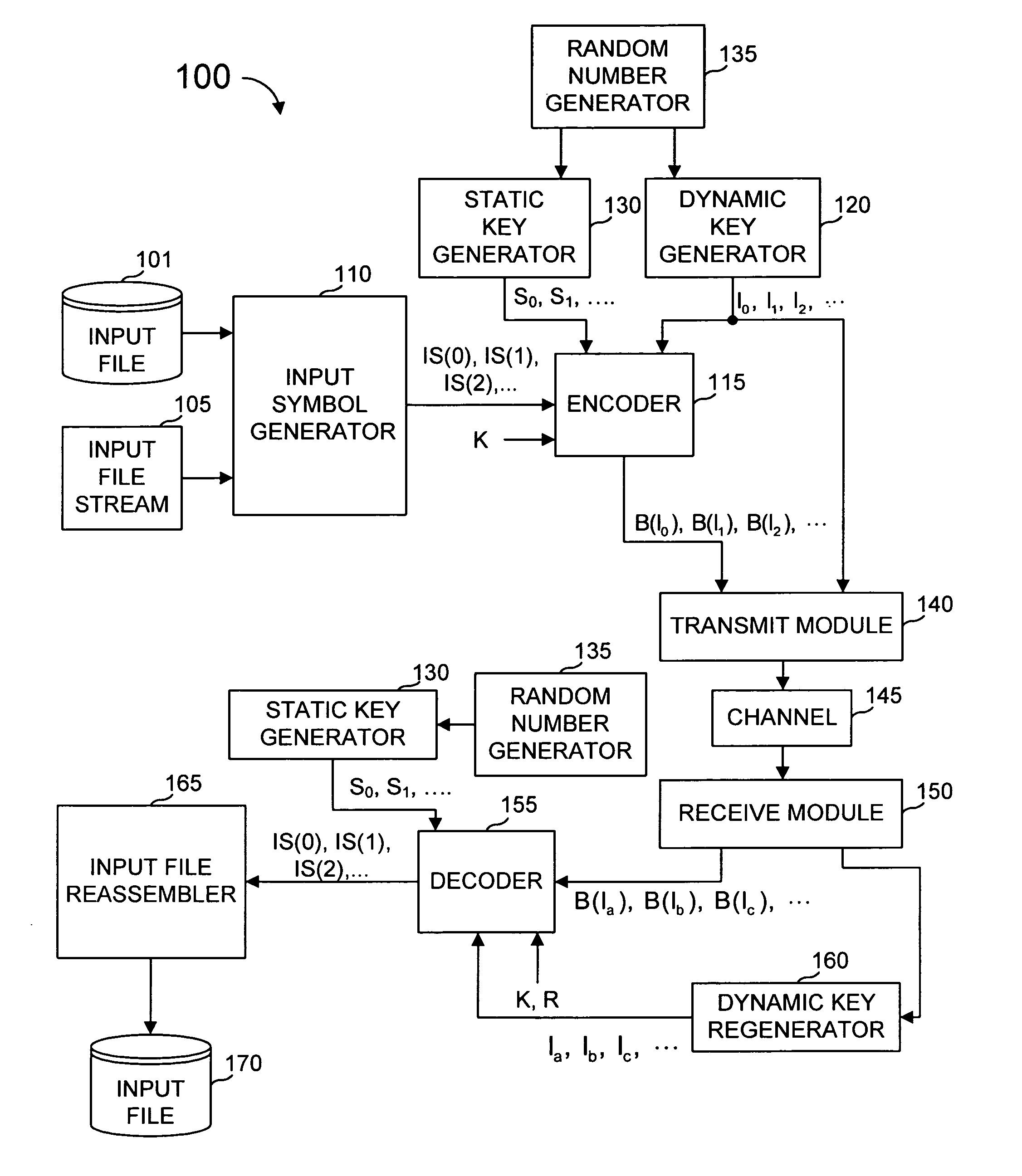
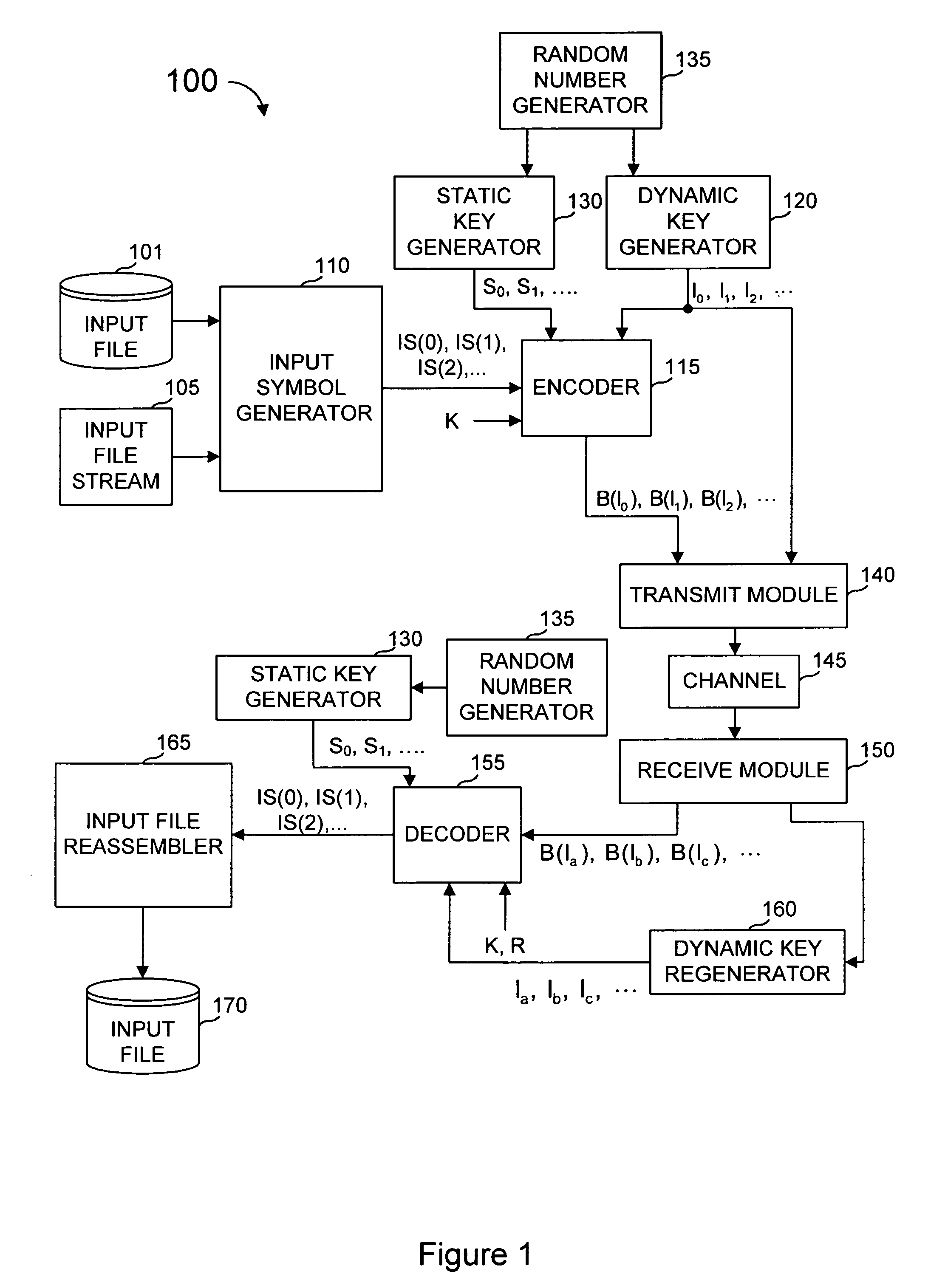
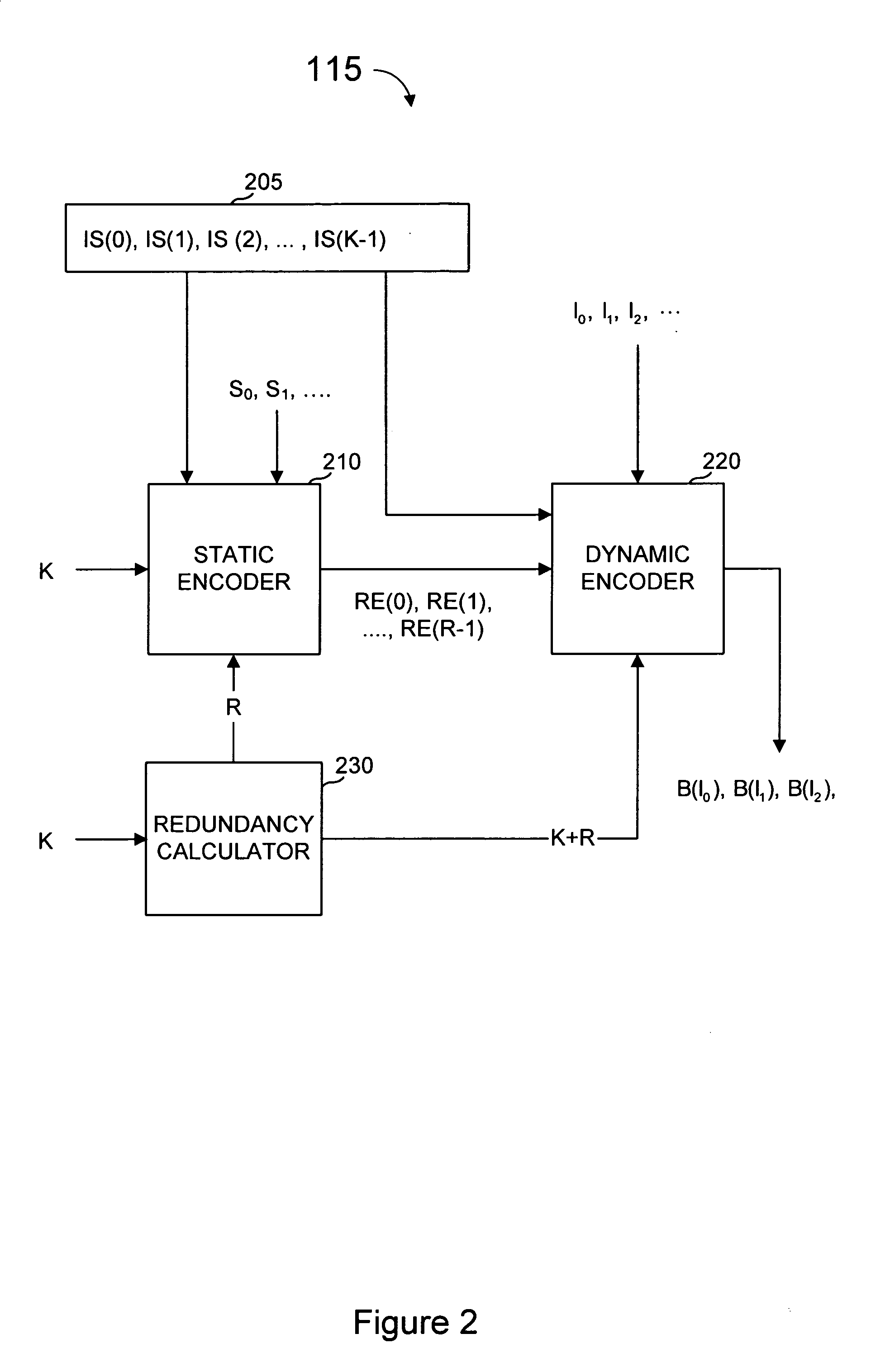
System and method for error correcting a received data stream in a concatenated system
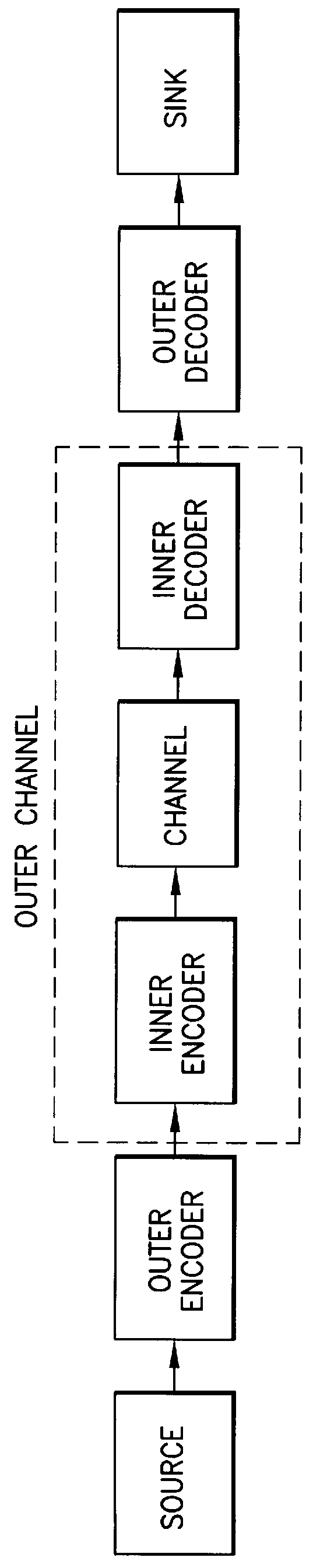
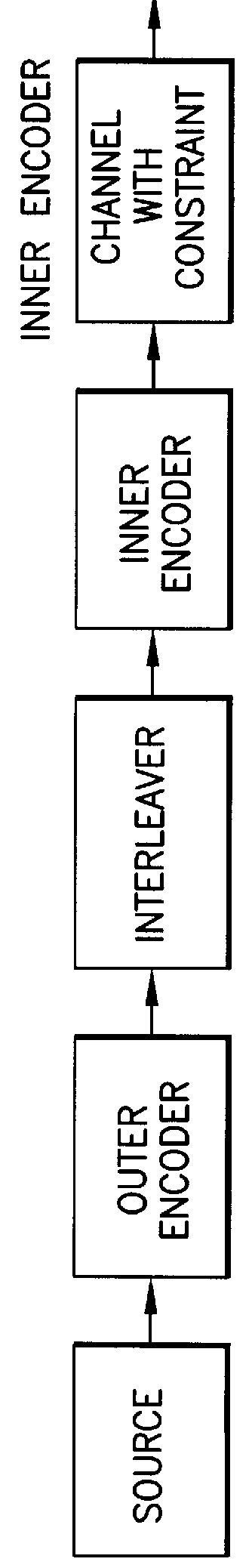
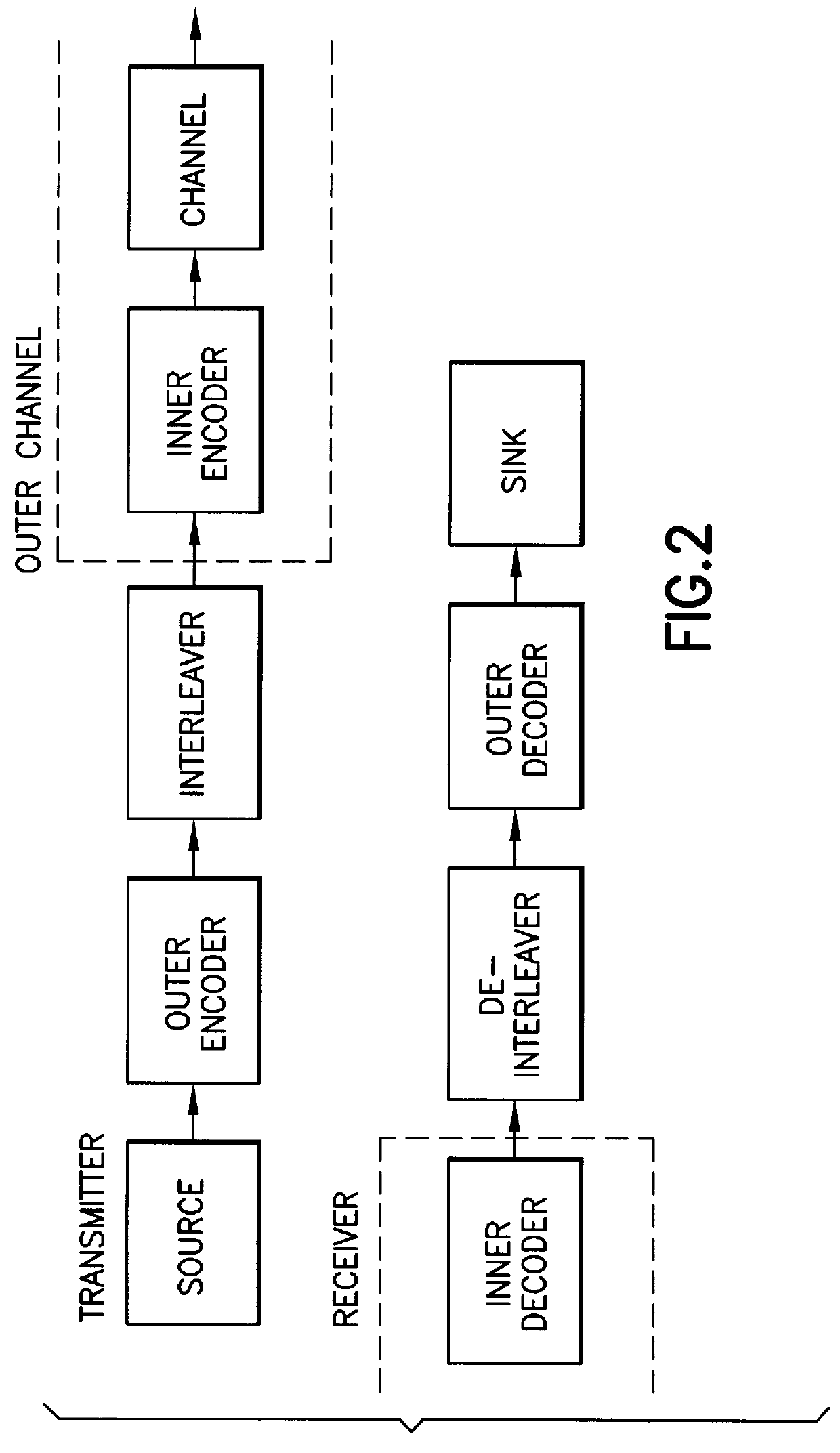
A received signal is first converted into a digital sequence that may contain "erasures" (or ambiguity symbols) as well as errors. Then iterative decoding is applied in order to eliminate or reduce the erasures. This decoding procedure works effectively with the associated transmitter that adopts a concatenation of an outer coder, a permutation and an inner coder. The principal of the invention is also applicable to a system in which the inner coder is replaced by a "digital modulator" that introduces some constraint, or a channel that introduces some memory such as partial response signaling, intersymbol interference or multipath propagation. The invention can be applied to many existing systems while maintaining "backward compatibility" in the sense that the transmitter side need not be modified.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Technique for memory imprint reliability improvement
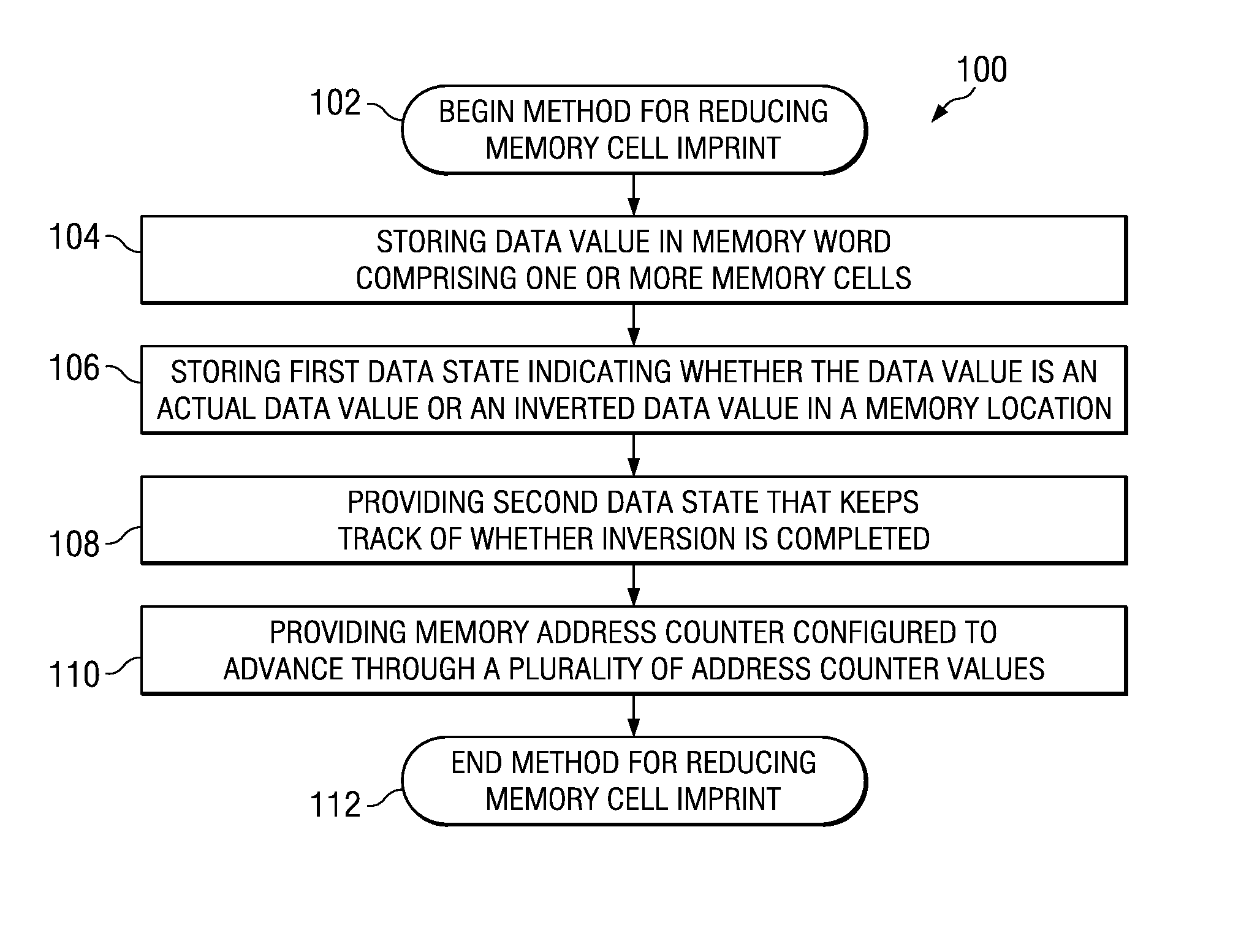
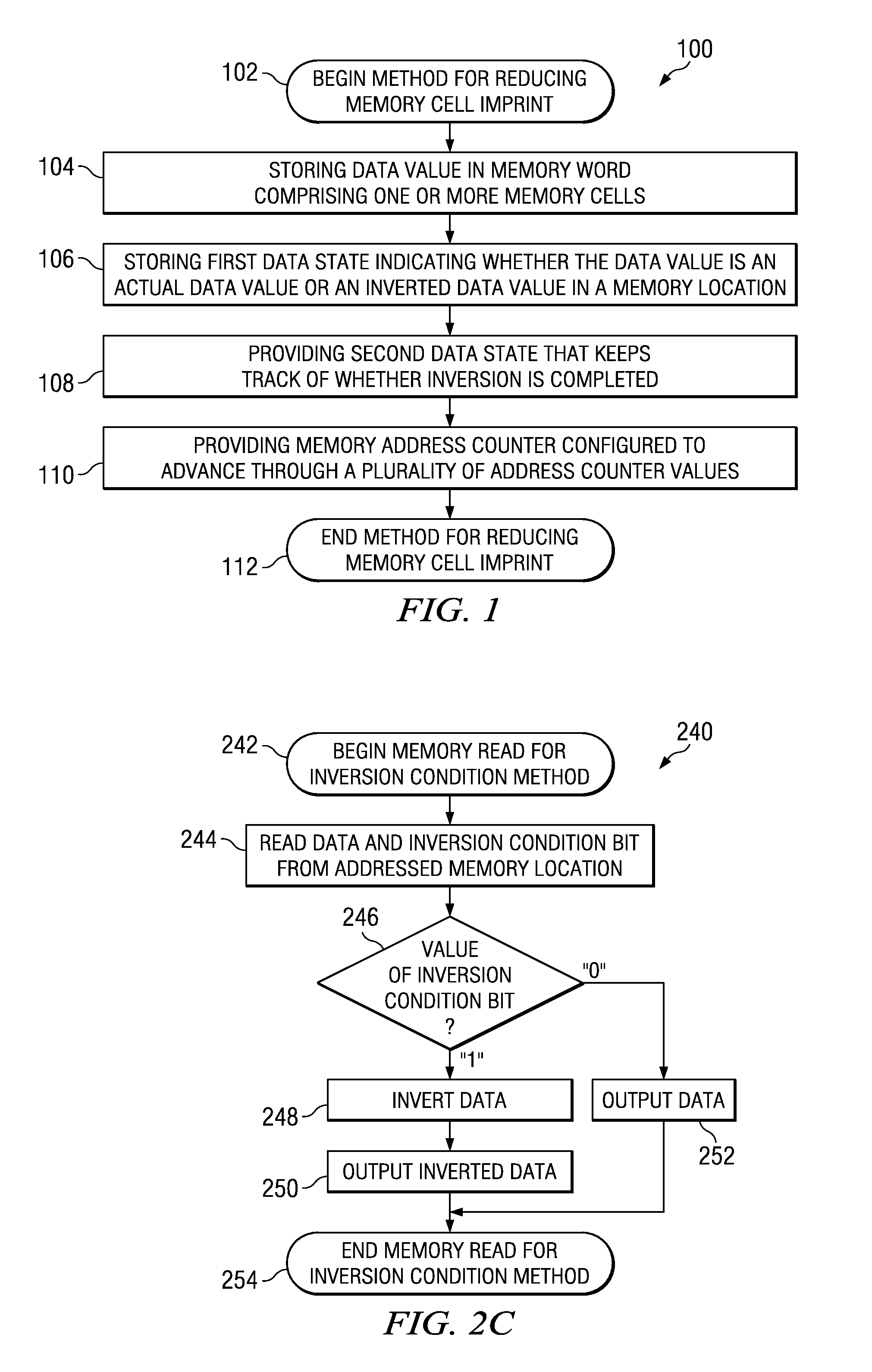
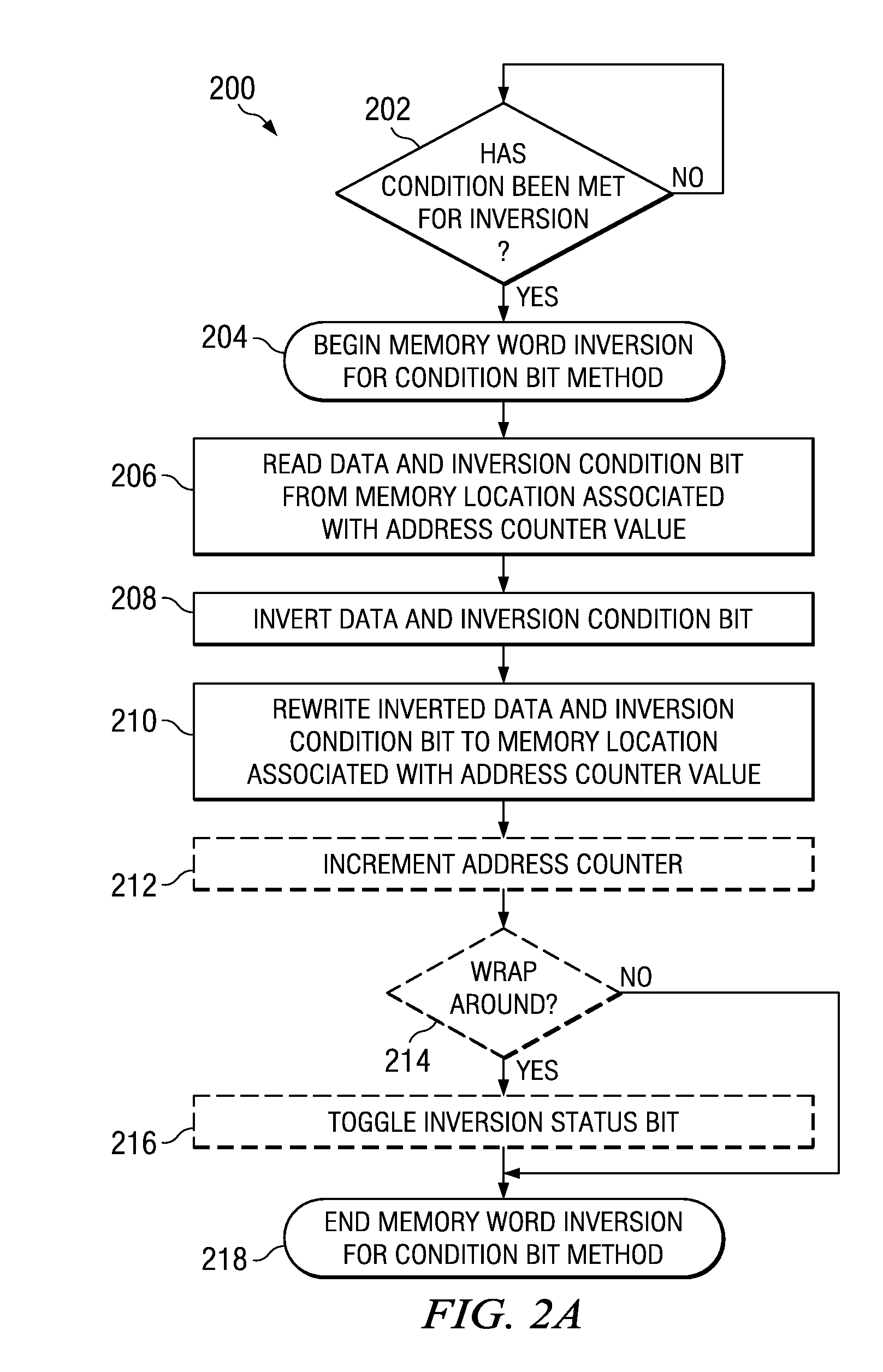
One embodiment of the present invention relates to a method of reducing imprint of a memory cell. The method comprises adding an inversion condition bit operably associated with one or more memory cells storing a memory word. The inversion condition bit indicates whether the memory word represents an actual payload or an inversion of the actual payload. The inversion condition bit and memory word are selectively toggled by a control circuitry. Inversion is performed by reading the inversion condition bit and memory word and rewriting the memory word back to the one or more memory cells in an inverted or non-inverted state, depending on an inversion condition bit. The inversion condition bit is then written to the inversion status bit value. The memory address is incremented, and the inversion status data state is toggled once the address counter addresses the entire memory array. Other methods and circuits are also disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
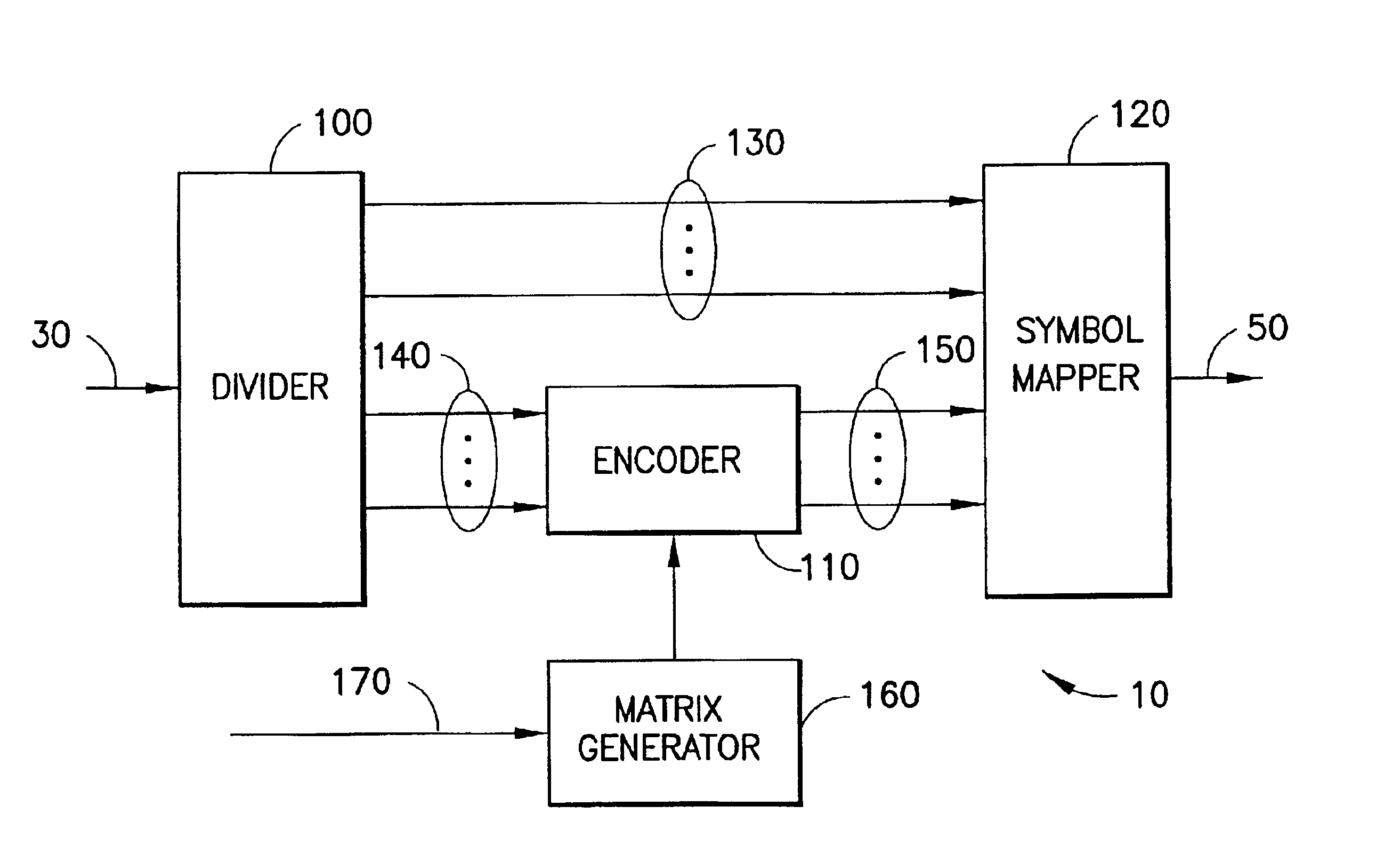
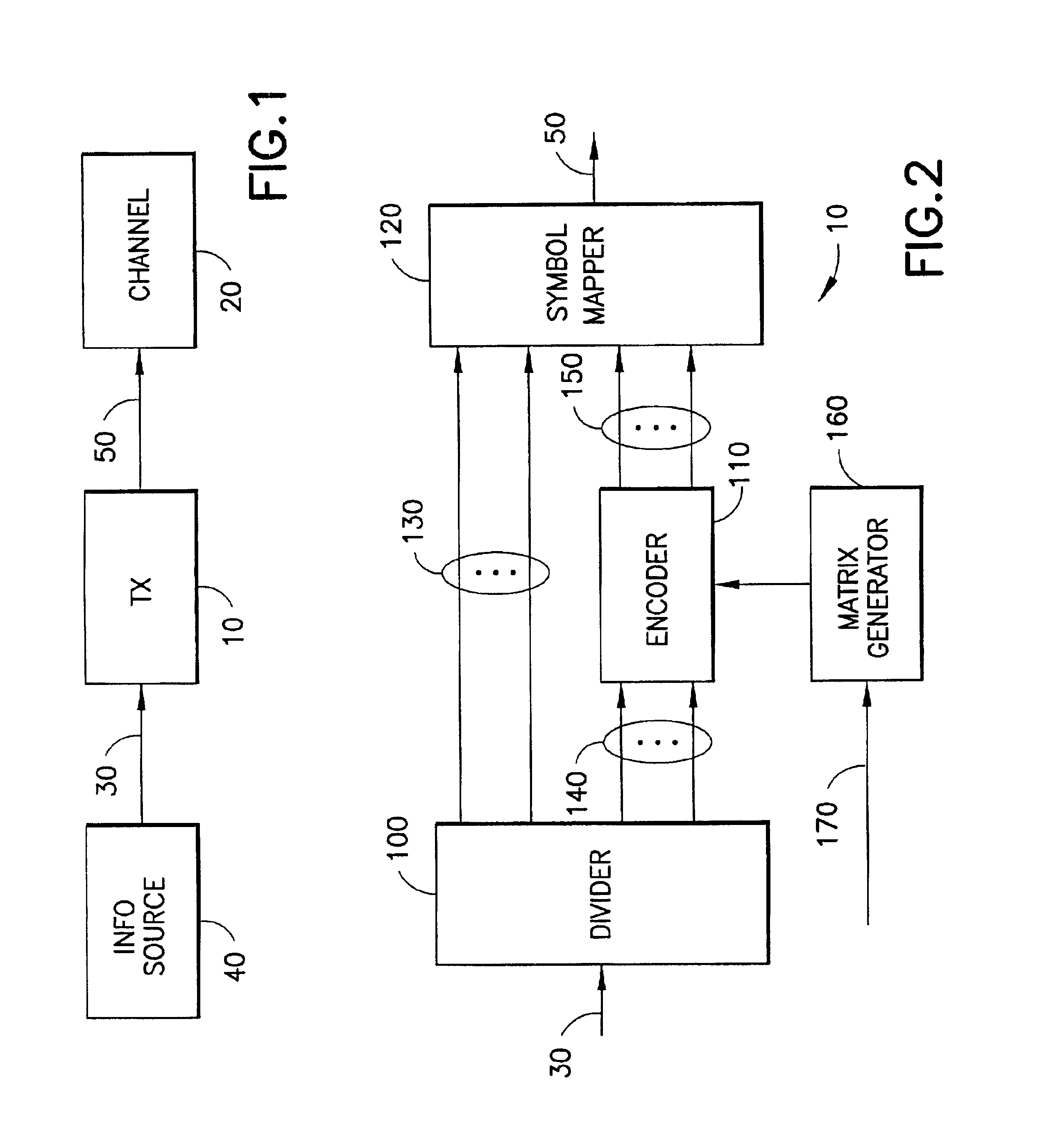
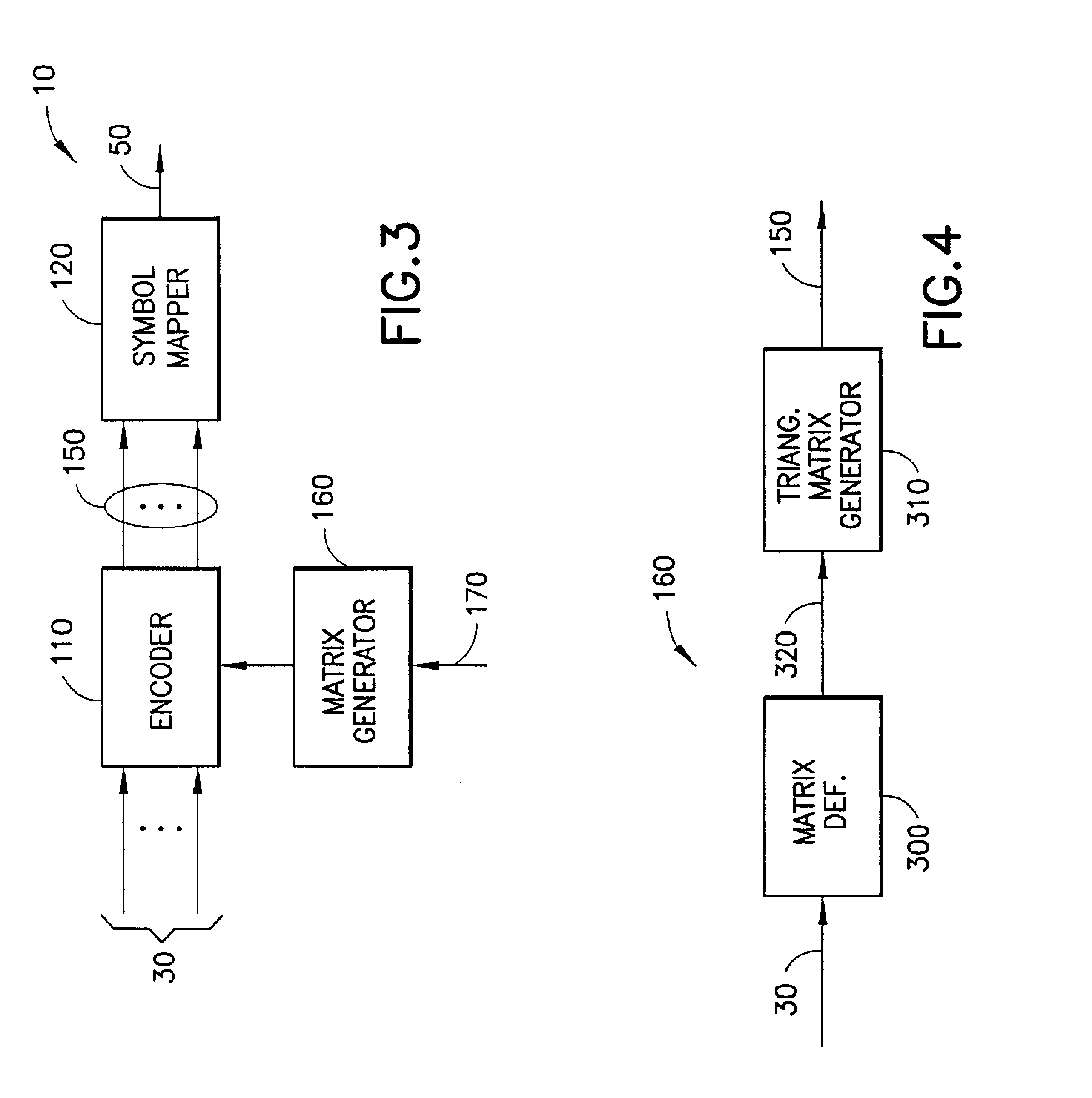
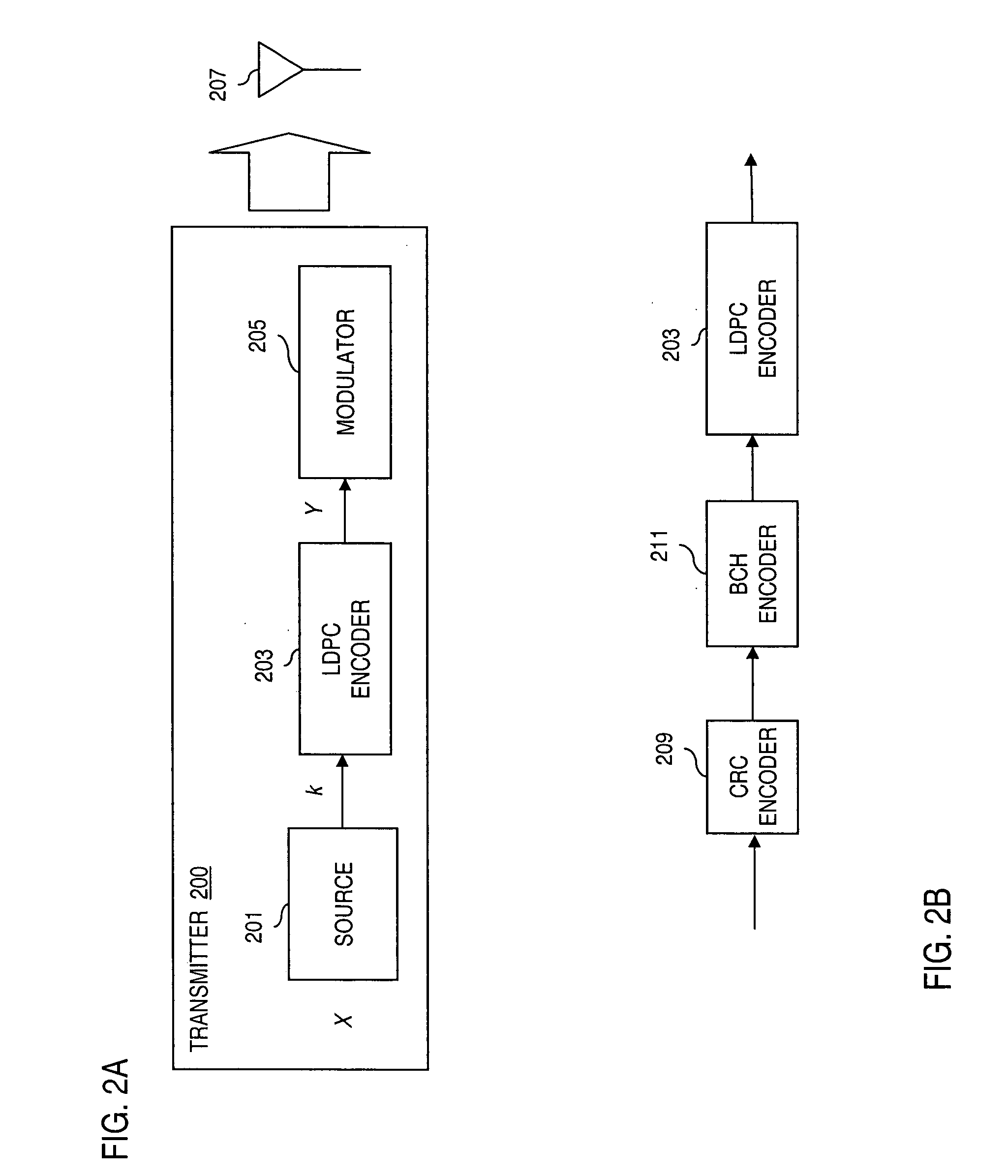
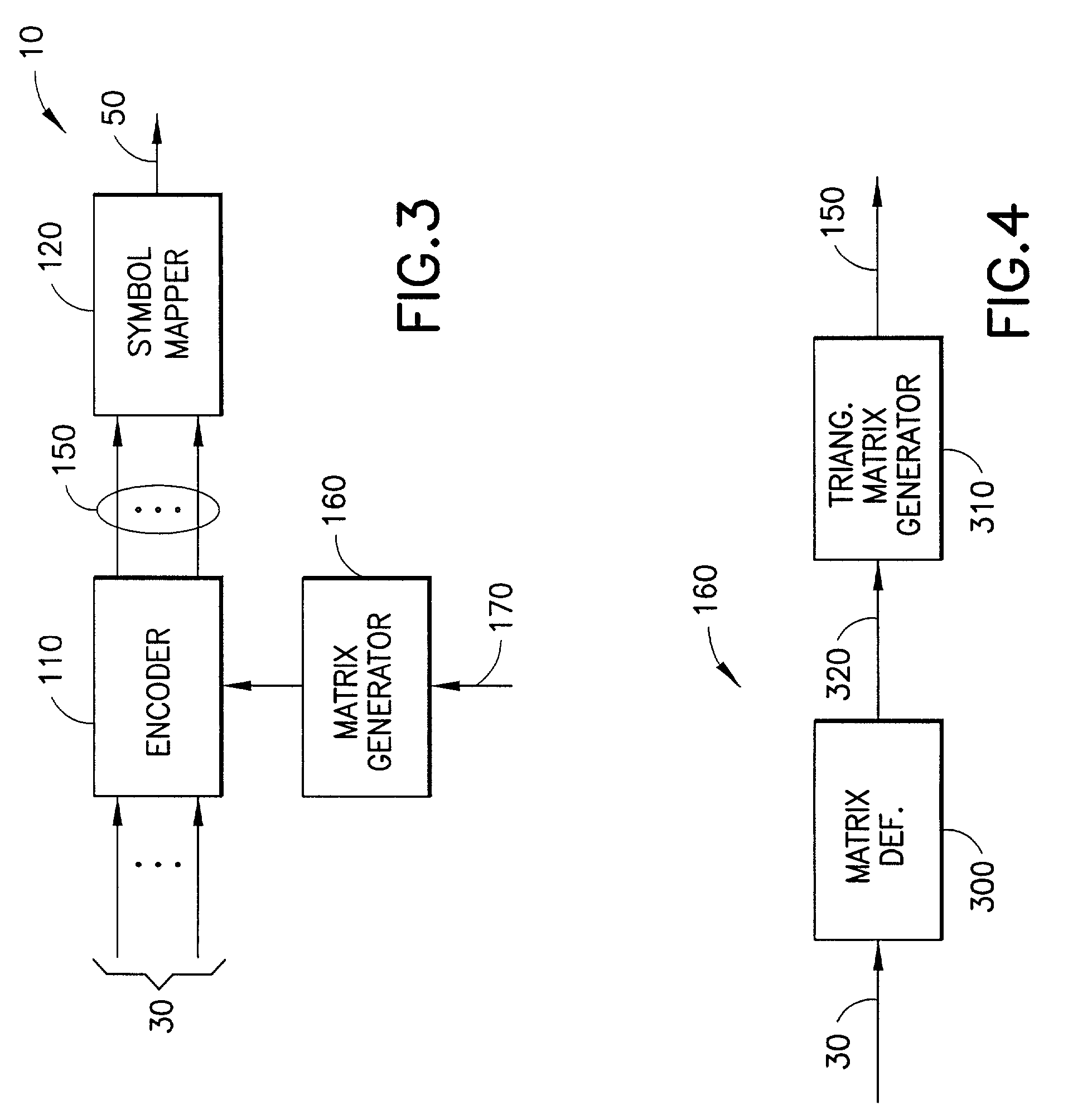
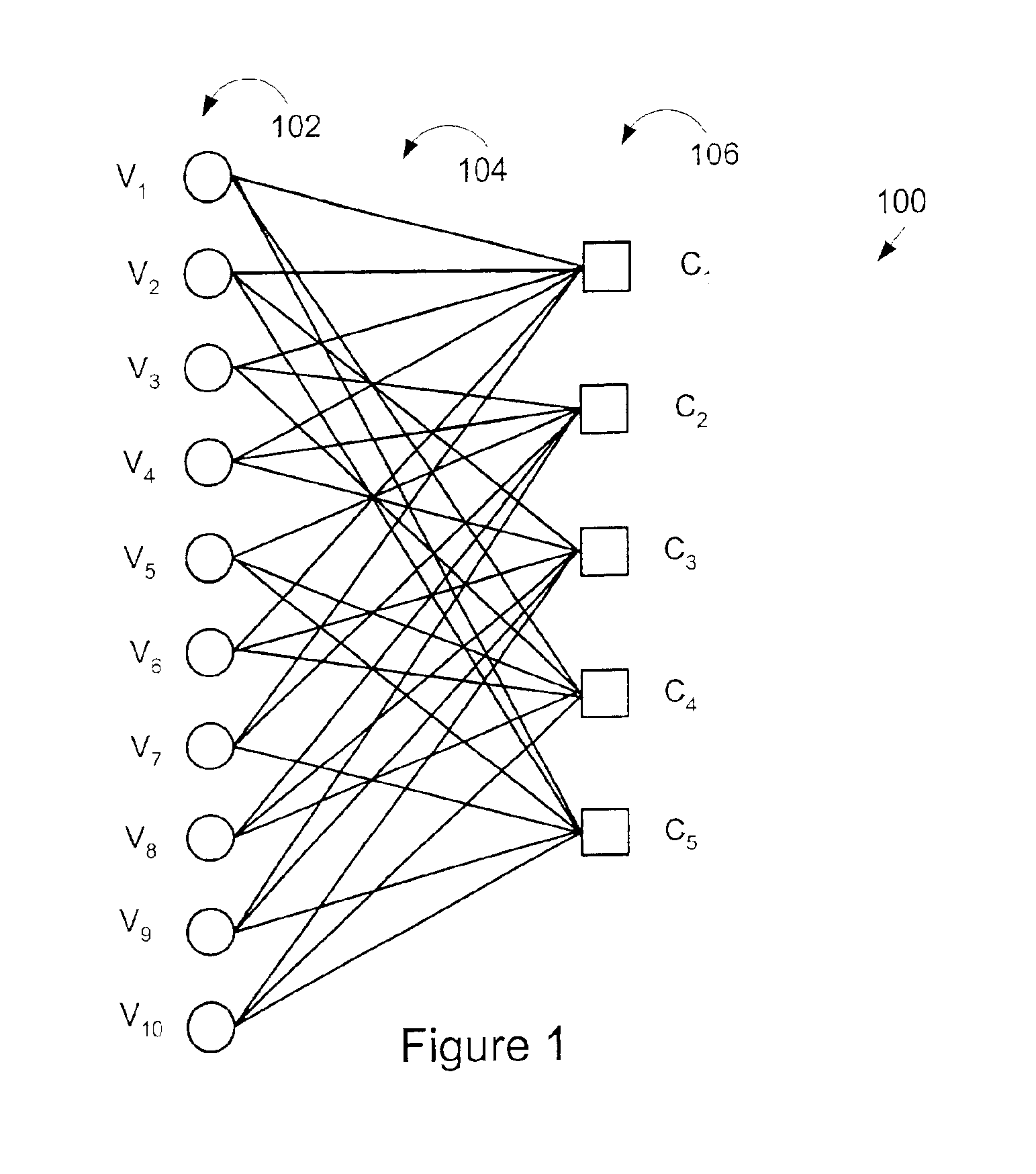
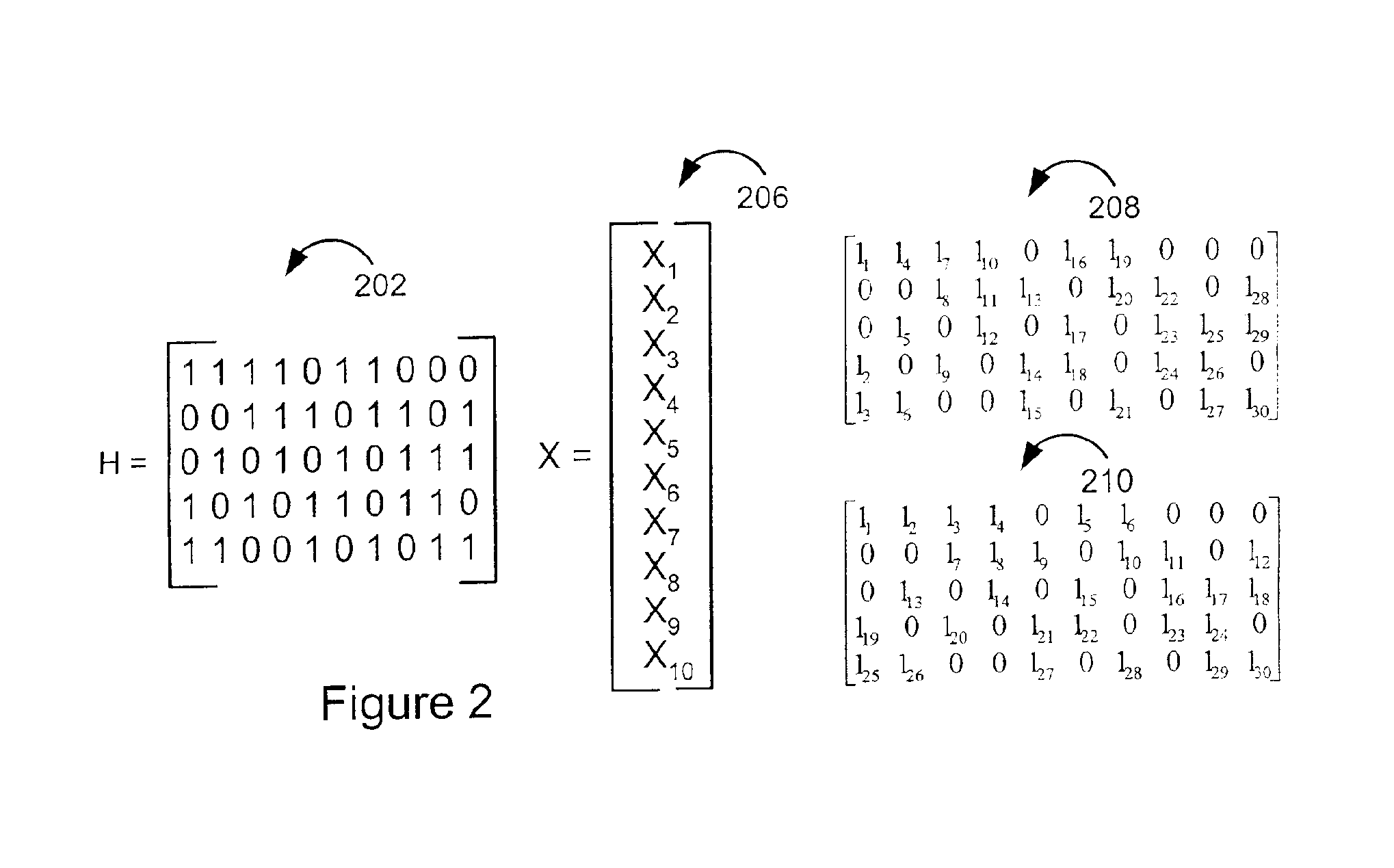
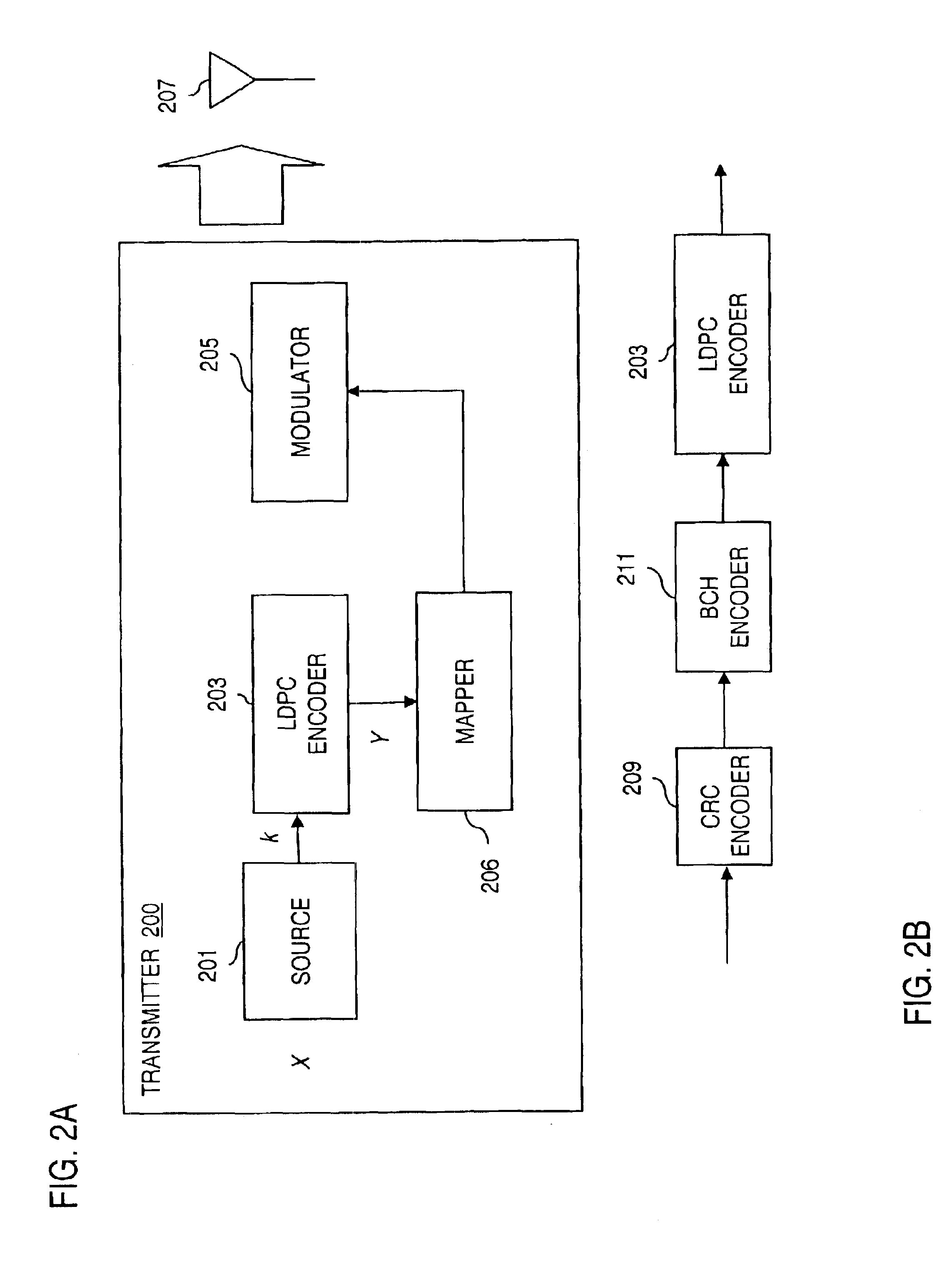
Method and apparatus for low density parity check encoding of data
InactiveUS6895547B2Improve performanceError preventionError detection/correctionTheoretical computer scienceParity-check matrix
A method for low-density parity-check (LDPC) encoding of data comprises defining a first M×N parity check matrix; generating, based on the first parity check matrix, a second parity check matrix having an M×M triangular sub-matrix; and, mapping the data into an LDPC code word based on the second parity check matrix. The method is particularly useful for data communications applications, but may also be employed in other applications such as, for example, data storage.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method and system for providing low density parity check (LDPC) encoding
ActiveUS7191378B2Readily apparentInterconnection arrangementsError correction/detection using LDPC codesAlgorithmParity-check matrix
An approach is provided for a method of encoding structure Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codes. Memory storing information representing a structured parity check matrix of Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) codes is accessed during the encoding process. The information is organized in tabular form, wherein each row represents occurrences of one values within a first column of a group of columns of the parity check matrix. The rows correspond to groups of columns of the parity check matrix, wherein subsequent columns within each of the groups are derived according to a predetermined operation. An LDPC coded signal is output based on the stored information representing the parity check matrix.
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
Multi-stage code generator and decoder for communication systems
InactiveUS7068729B2Reduce expensesOther decoding techniquesOther error detection/correction/protectionCommunications systemOrder set
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
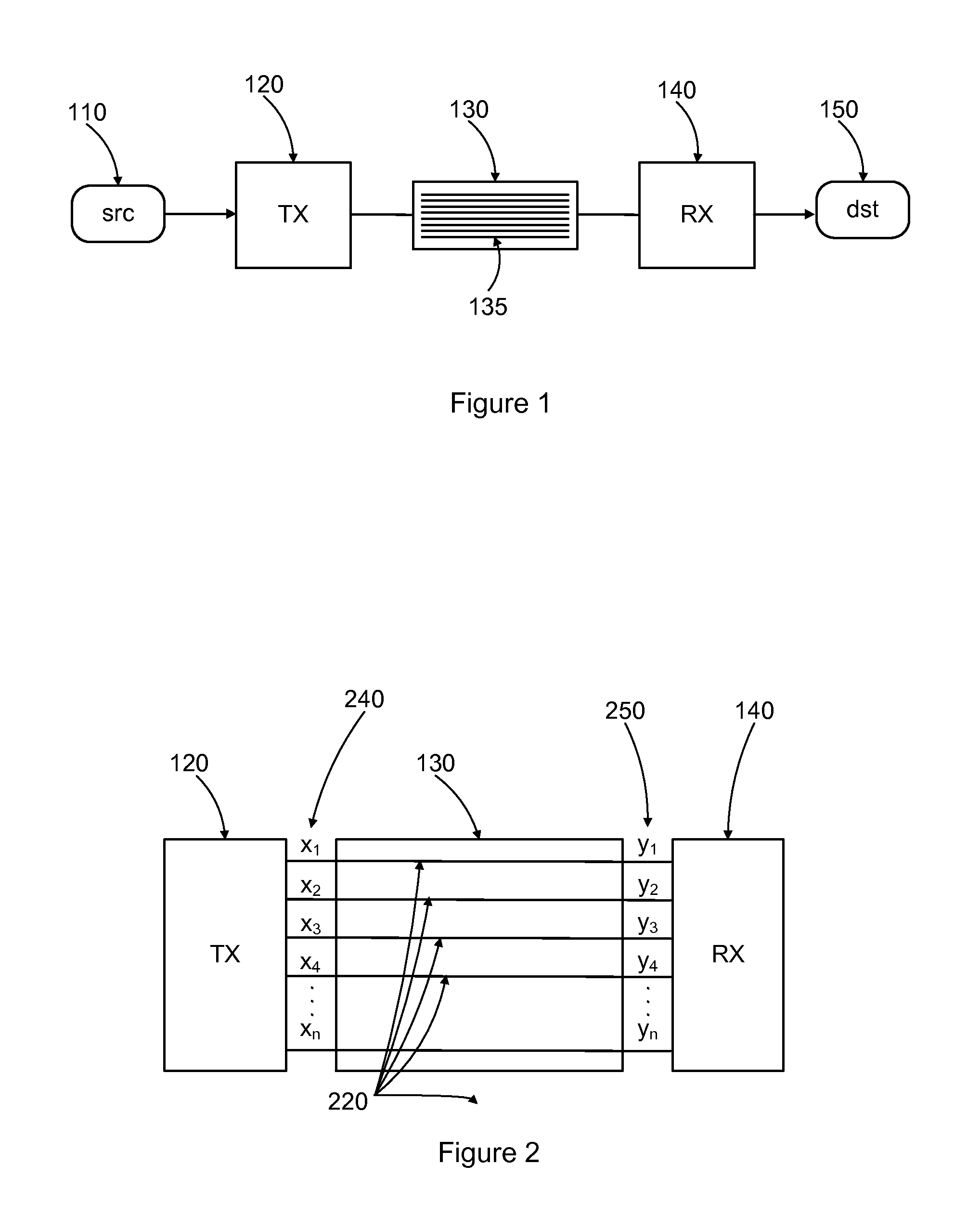
Power and pin efficient chip-to-chip communications with common-mode rejection and sso resilience
In bus communications methods and apparatus, a first set of physical signals representing the information to be conveyed over the bus is provided, and mapped to a codeword of a spherical code, wherein a codeword is representable as a vector of a plurality of components and the bus uses at least as many signal lines as components of the vector that are used, mapping the codeword to a second set of physical signals, wherein components of the second set of physical signals can have values from a set of component values having at least three distinct values for at least one component, and providing the second set of physical signals for transmission over the data bus in a physical form.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Method and apparatus for low density parity check encoding of data
InactiveUS20030037298A1Improve performanceError preventionError detection/correctionParity-check matrixTheoretical computer science
A method for low-density parity-check (LDPC) encoding of data comprises defining a first MxN parity check matrix; generating, based on the first parity check matrix, a second parity check matrix having an MxM triangular sub-matrix; and, mapping the data into an LDPC code word based on the second parity check matrix. The method is particularly useful for data communications applications, but may also be employed in other applications such as, for example, data storage.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
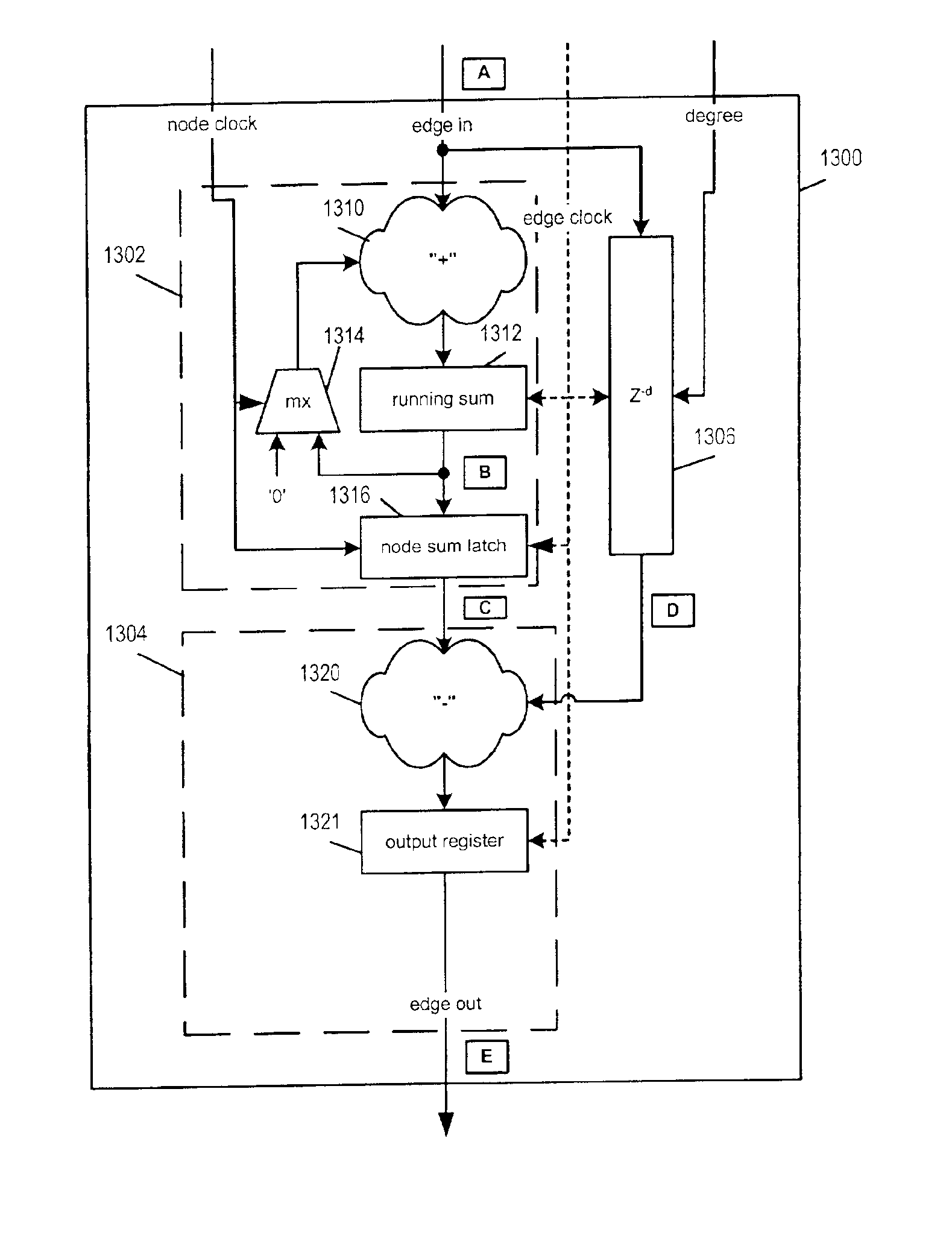
Node processors for use in parity check decoders
InactiveUS6938196B2Big errorCompensating for such errorError prevention/detection by using return channelOther decoding techniquesComputer moduleMessage processing
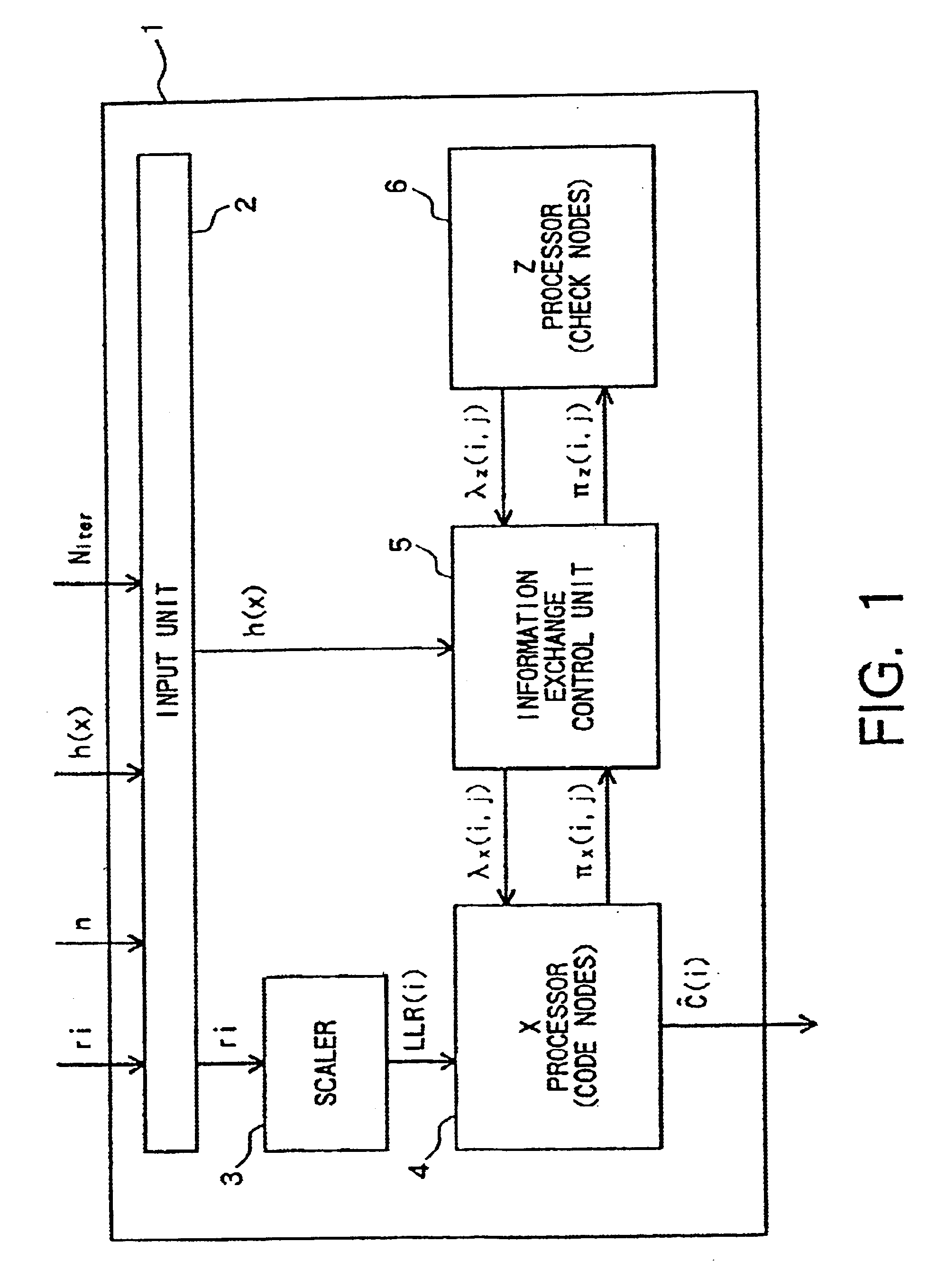
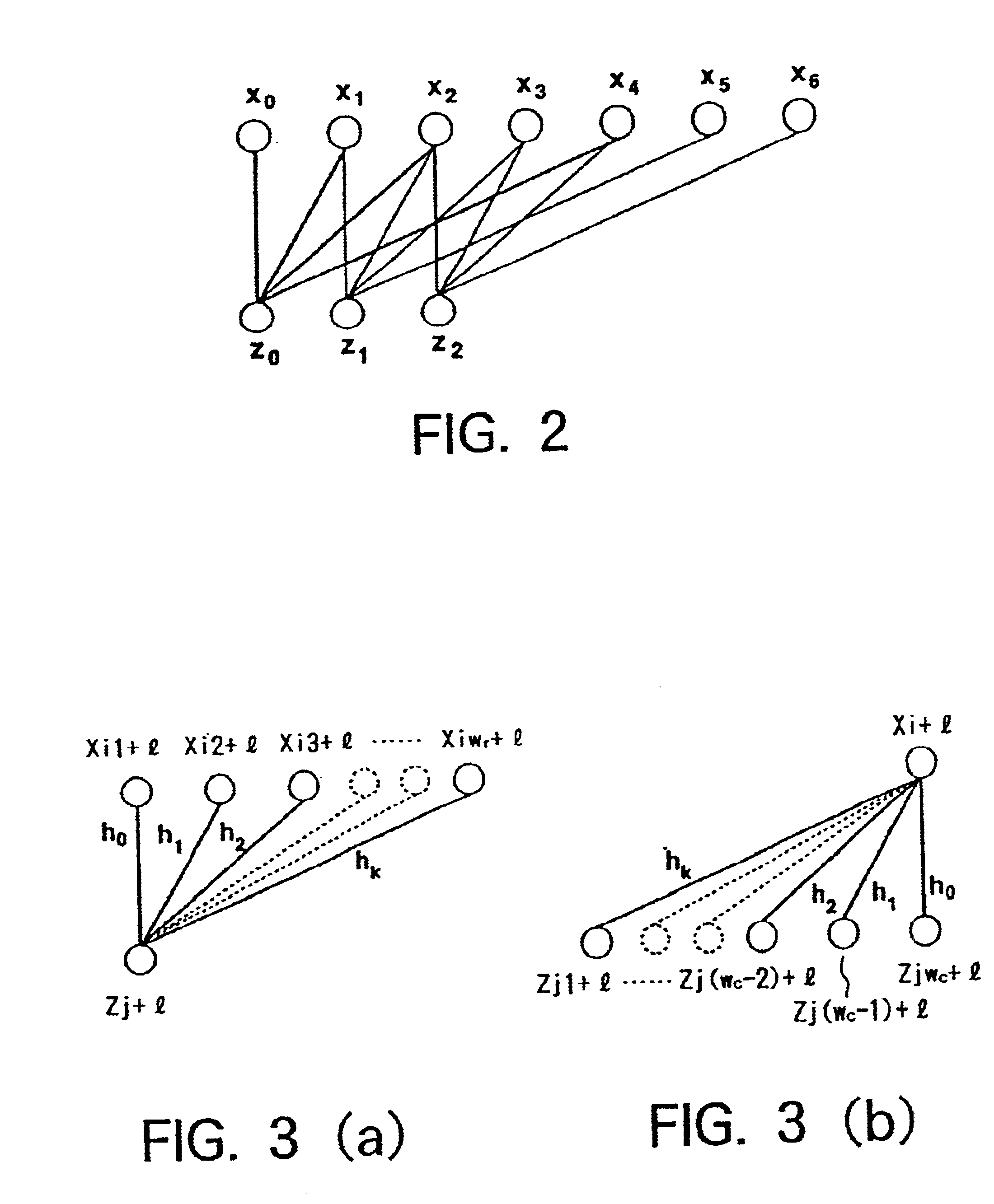
Techniques for implementing message passing decoders, e.g., LDPC decoders, are described. To facilitate hardware implementation messages are quantized to integer multiples of ½ ln2. Messages are transformed between more compact variable and less compact constraint node message representation formats. The variable node message format allows variable node message operations to be performed through simple additions and subtractions while the constraint node representation allows constraint node message processing to be performed through simple additions and subtractions. Variable and constraint nodes are implemented using an accumulator module, subtractor module and delay pipeline. The accumulator module generates an accumulated message sum. The accumulated message sum for a node is stored and then delayed input messages from the delay pipeline are subtracted there from to generate output messages. The delay pipeline includes a variable delay element making it possible to sequentially perform processing operations corresponding to nodes of different degrees.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
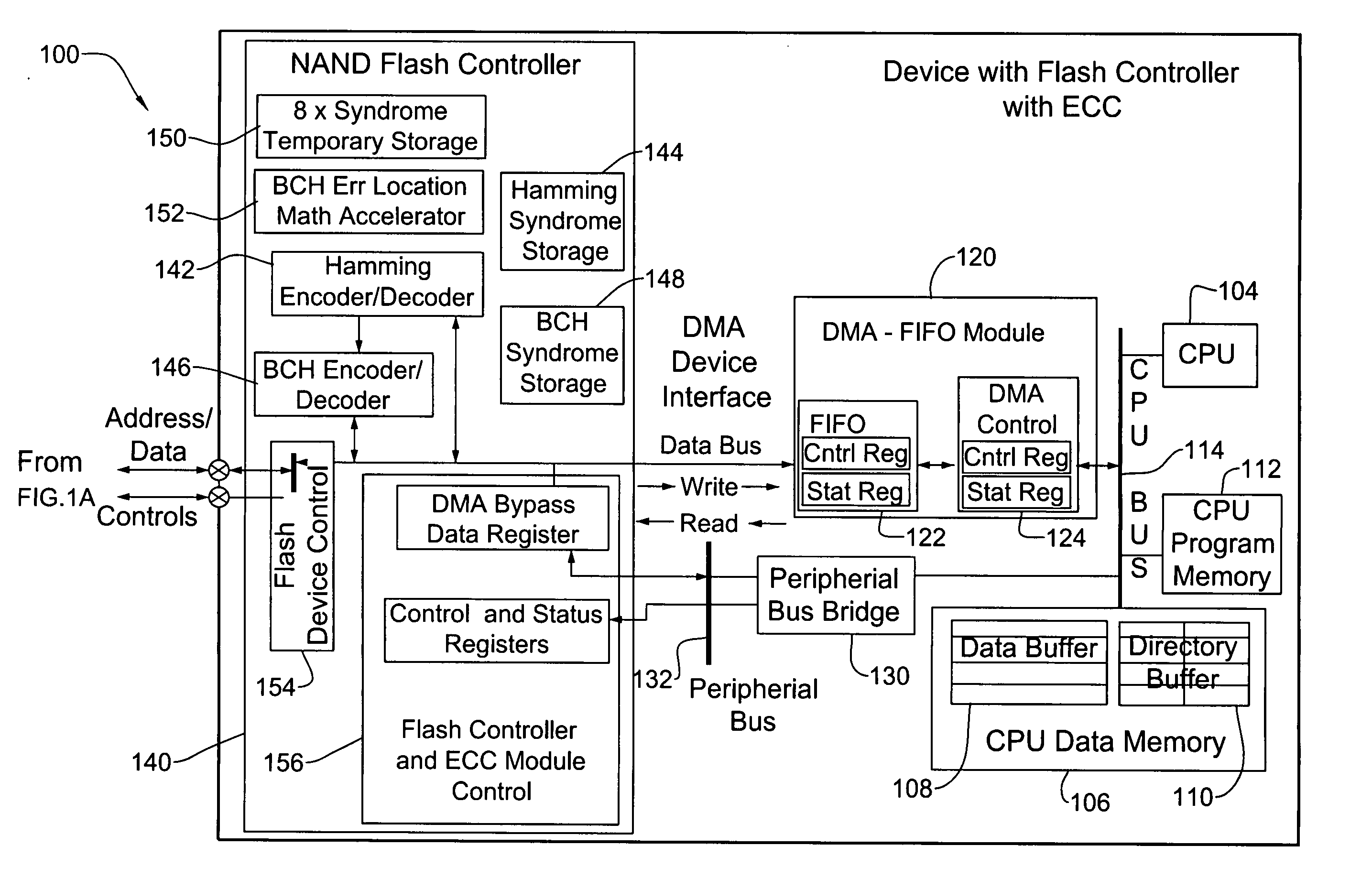
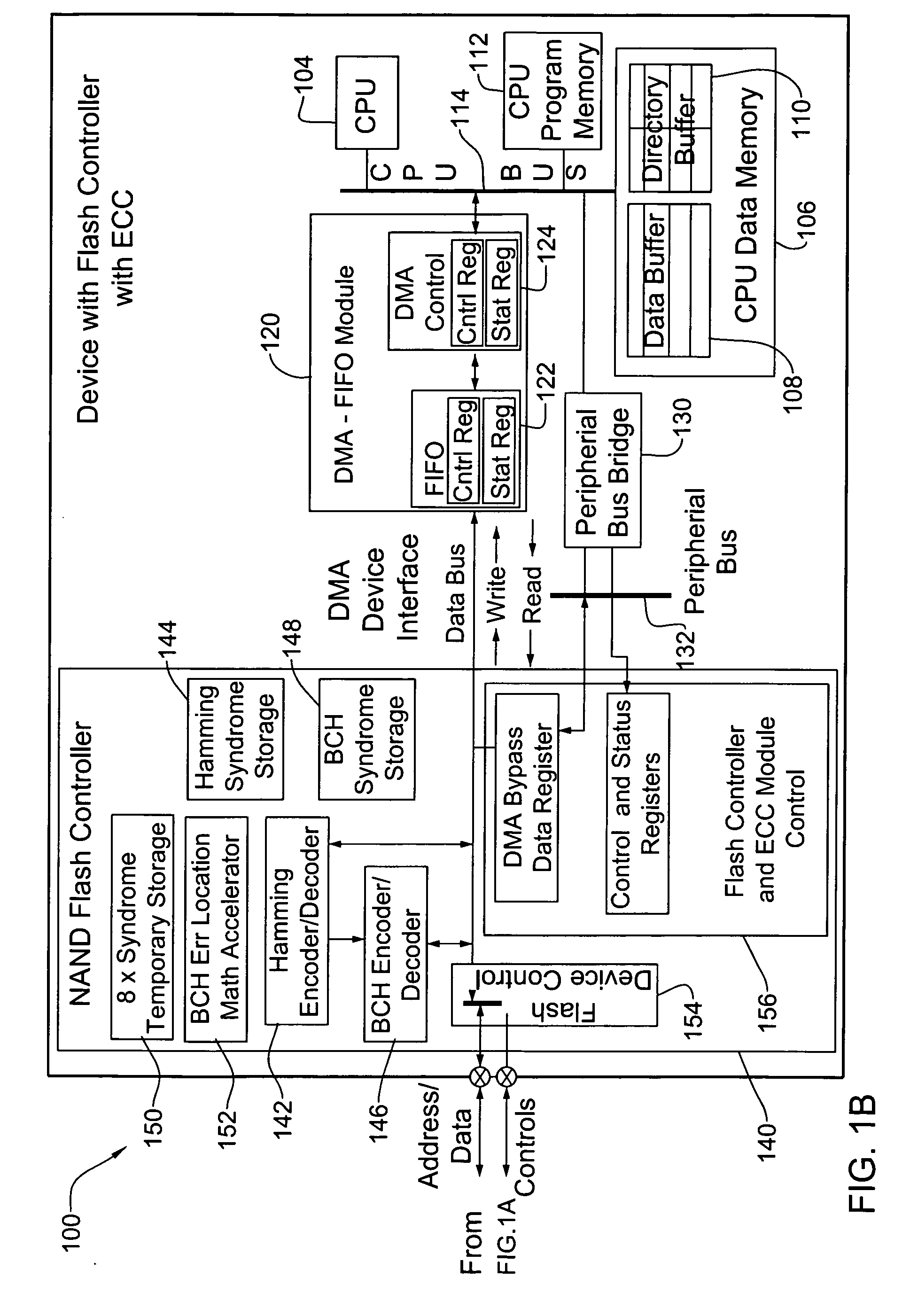
Systems and methods for error corrections
Systems and methods for error correction of data. In one embodiment of the invention, a plurality of error correction schemes are applied when encoding data and depending on the circumstances, one or more of those schemes is selected to decode the data. In one of these embodiments, the applied error correction schemes include the BCH algorithm and the Hamming algorithm.
Owner:DSP GROUP
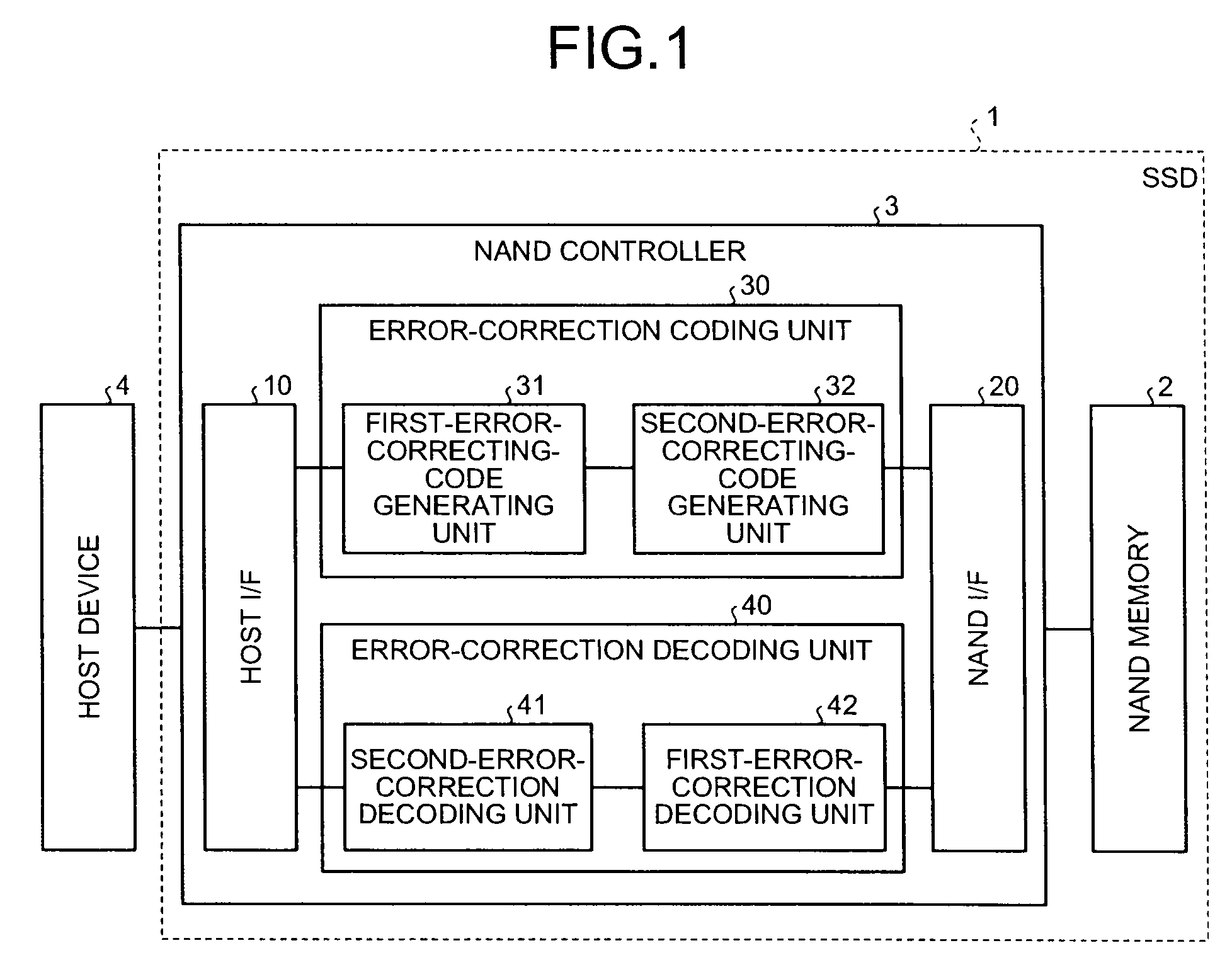
Error correcting device and error correcting method
An error correcting device for correcting erroneous data included in data read out from a nonvolatile memory includes a determining unit that determines whether the data read out from the nonvolatile memory include an error beyond an error correcting capability of the error correcting device. When the determining unit has determined that an error beyond the error correcting capability exists, the error correcting device does not perform the correction of the error.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
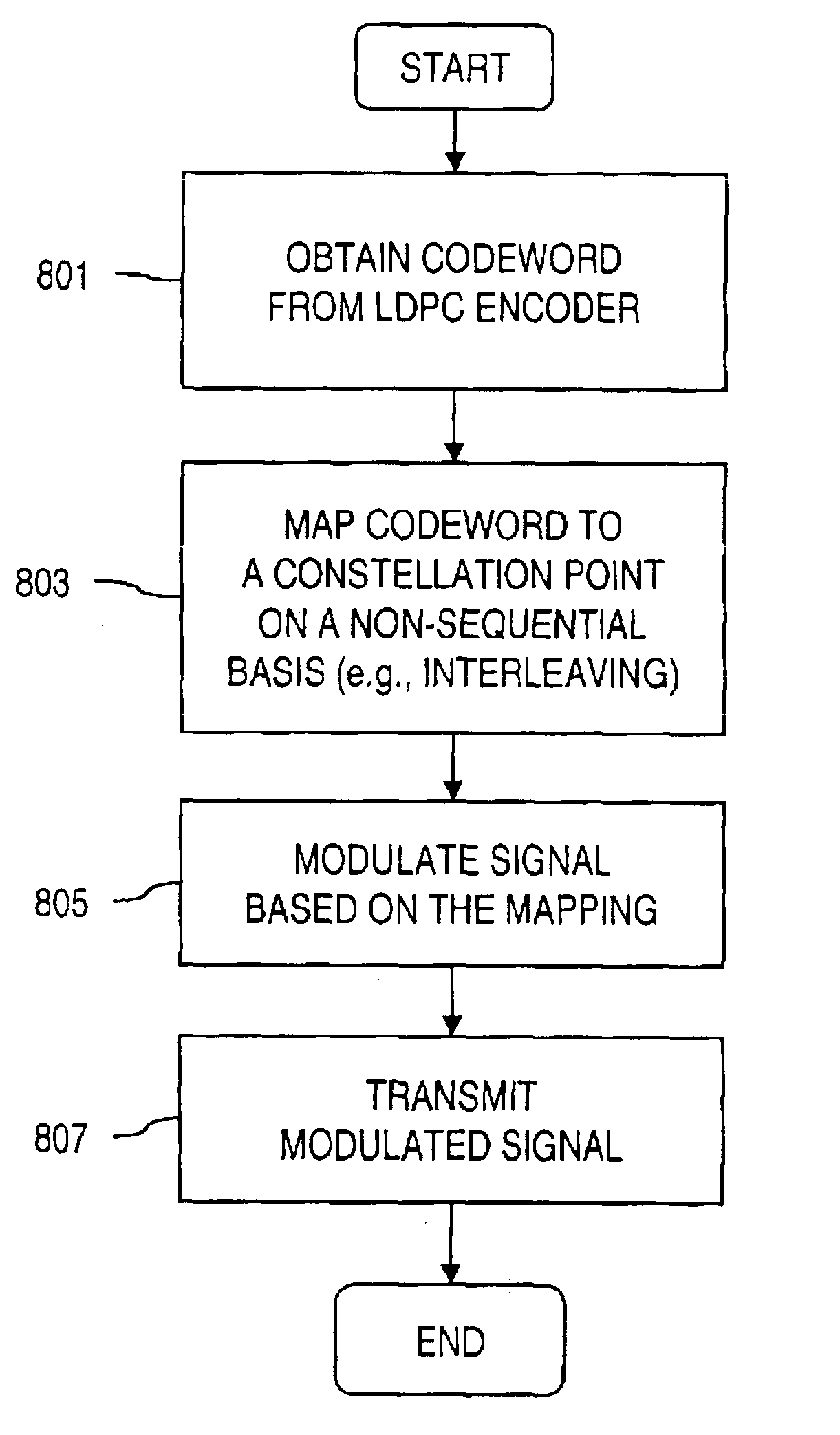
Bit labeling for amplitude phase shift constellation used with low density parity check (LDPC) codes
InactiveUS6963622B2Improve performanceError correction/detection using LDPC codesCode conversionParity-check matrixEngineering
An approach is provided for bit labeling of a signal constellation. A transmitter generates encoded signals using, according to one embodiment, a structured parity check matrix of a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) code. The transmitter includes an encoder for transforming an input message into a codeword represented by a plurality of set of bits. The transmitter includes logic for mapping non-sequentially (e.g., interleaving) one set of bits into a higher order constellation (Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK), 8-PSK, 16-APSK (Amplitude Phase Shift Keying), 32-APSK, etc.), wherein a symbol of the higher order constellation corresponding to the one set of bits is output based on the mapping.
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
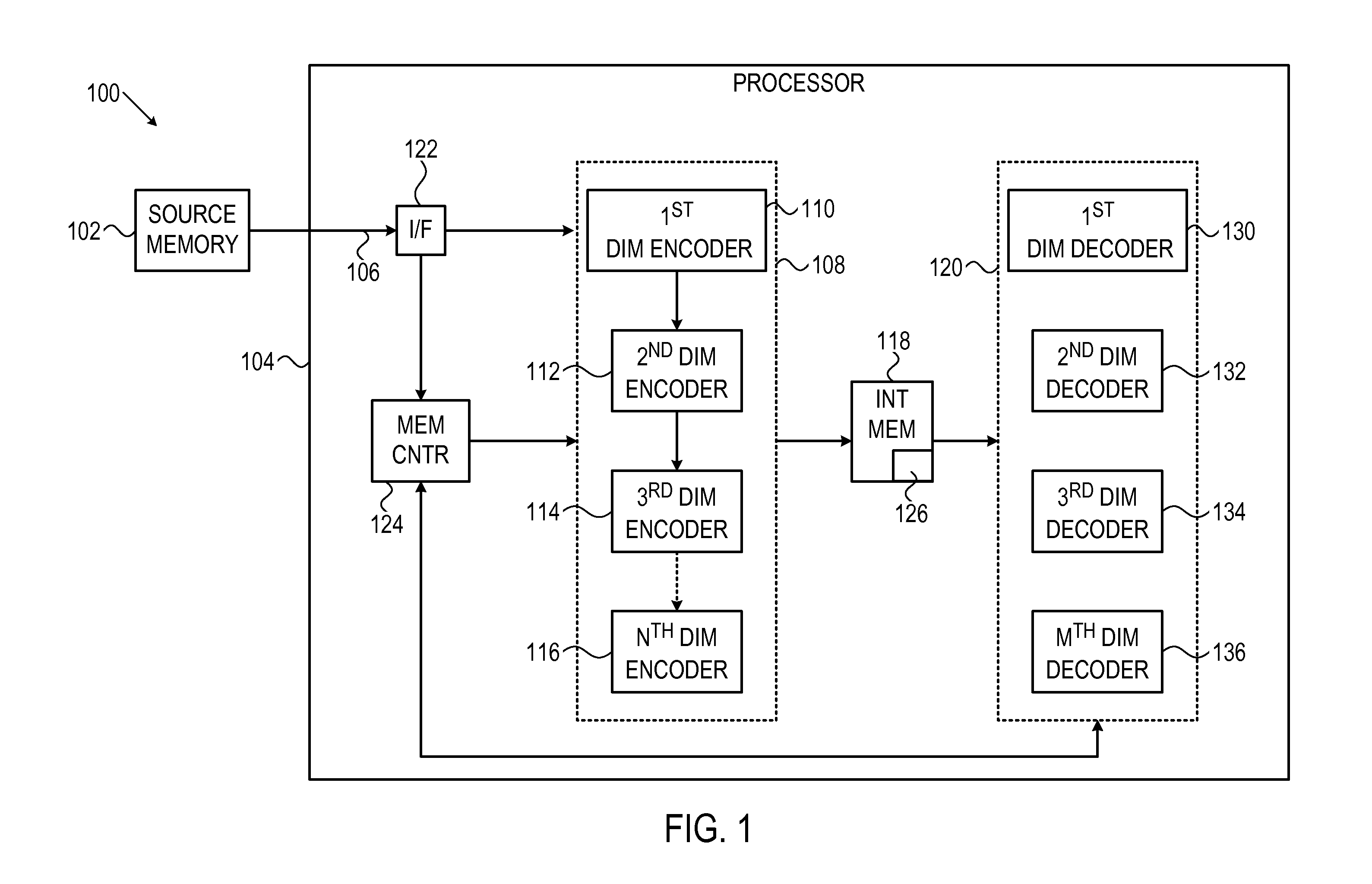
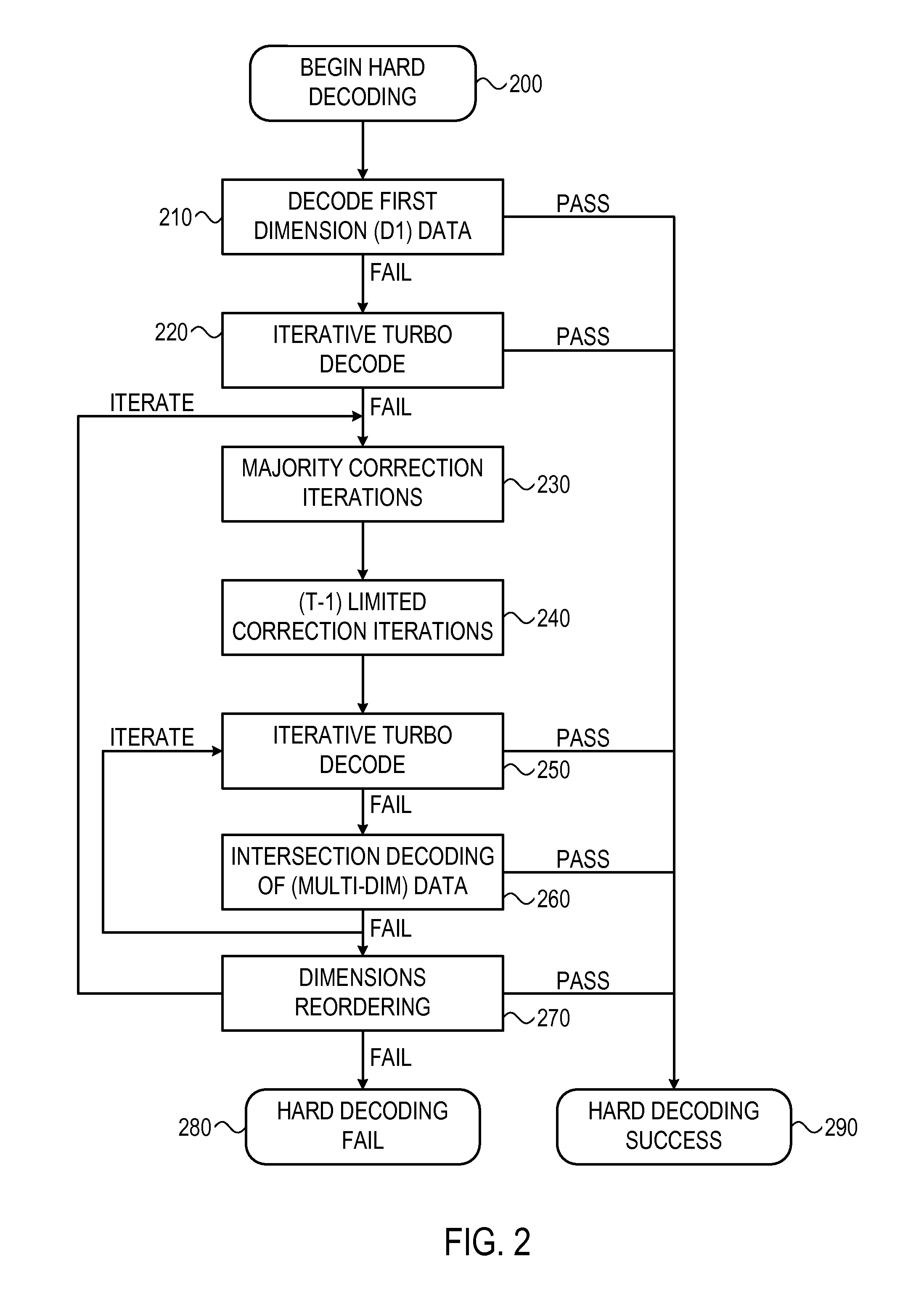
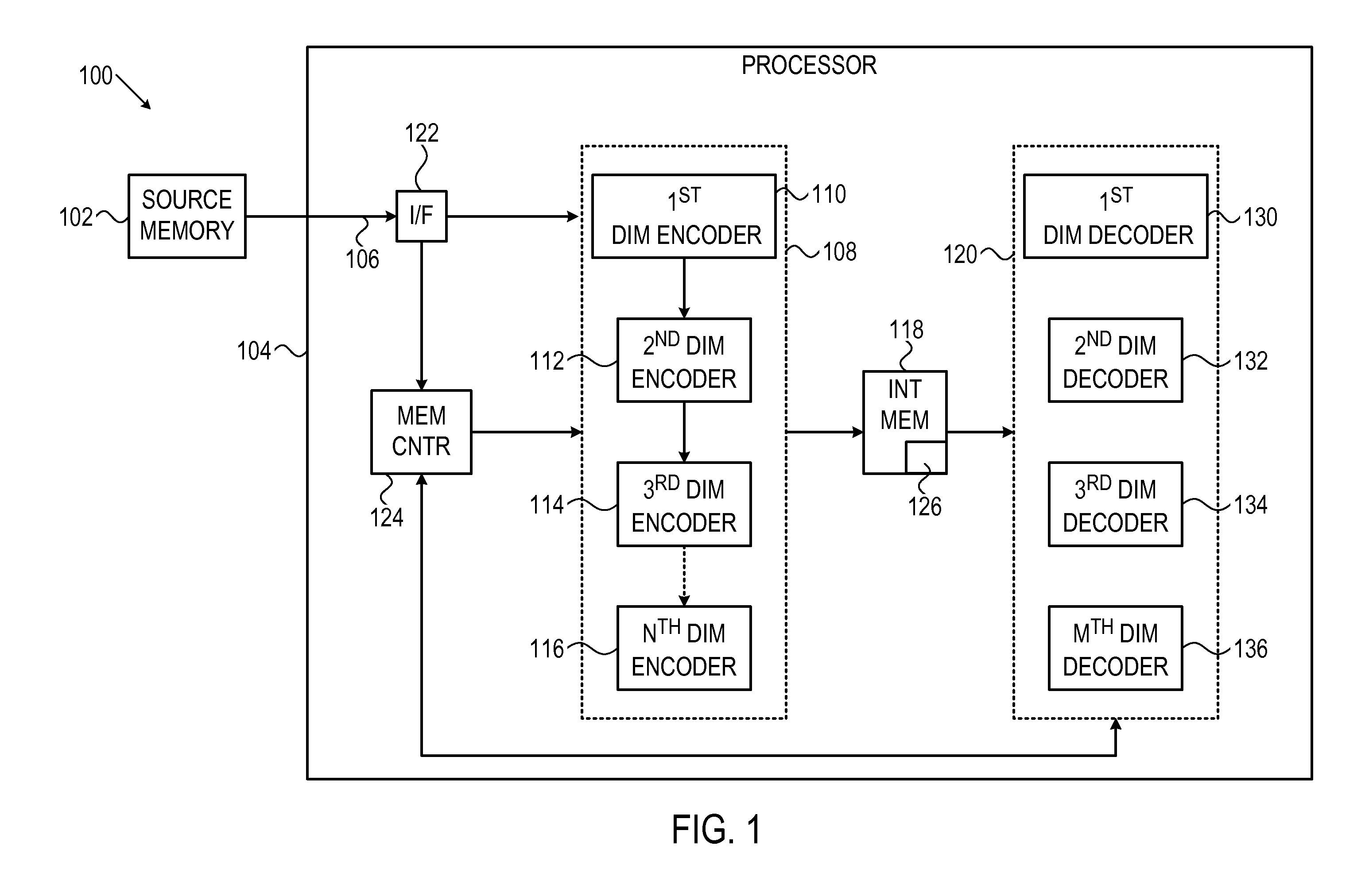
System and method for multi-dimensional encoding and decoding
ActiveUS20120005560A1Error correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesHypothesisDependability
A system and method is provided for decoding a set of bits using a plurality of hypotheses, for example, each independently tested on-the-fly. Initial bit states and associated reliability metrics may be received for the set of bits. A current hypothesis may be decoded for correcting the set of bits, wherein the current hypothesis defines different bit states and associated reliability metrics for the set of bits. If decoding the current hypothesis is not successful, a subsequently ordered hypothesis may be decoded, wherein the hypotheses are ordered such that their associated reliability metric is a monotonically non-decreasing sequence. Decoding may proceed iteratively until the current hypothesis is successful.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
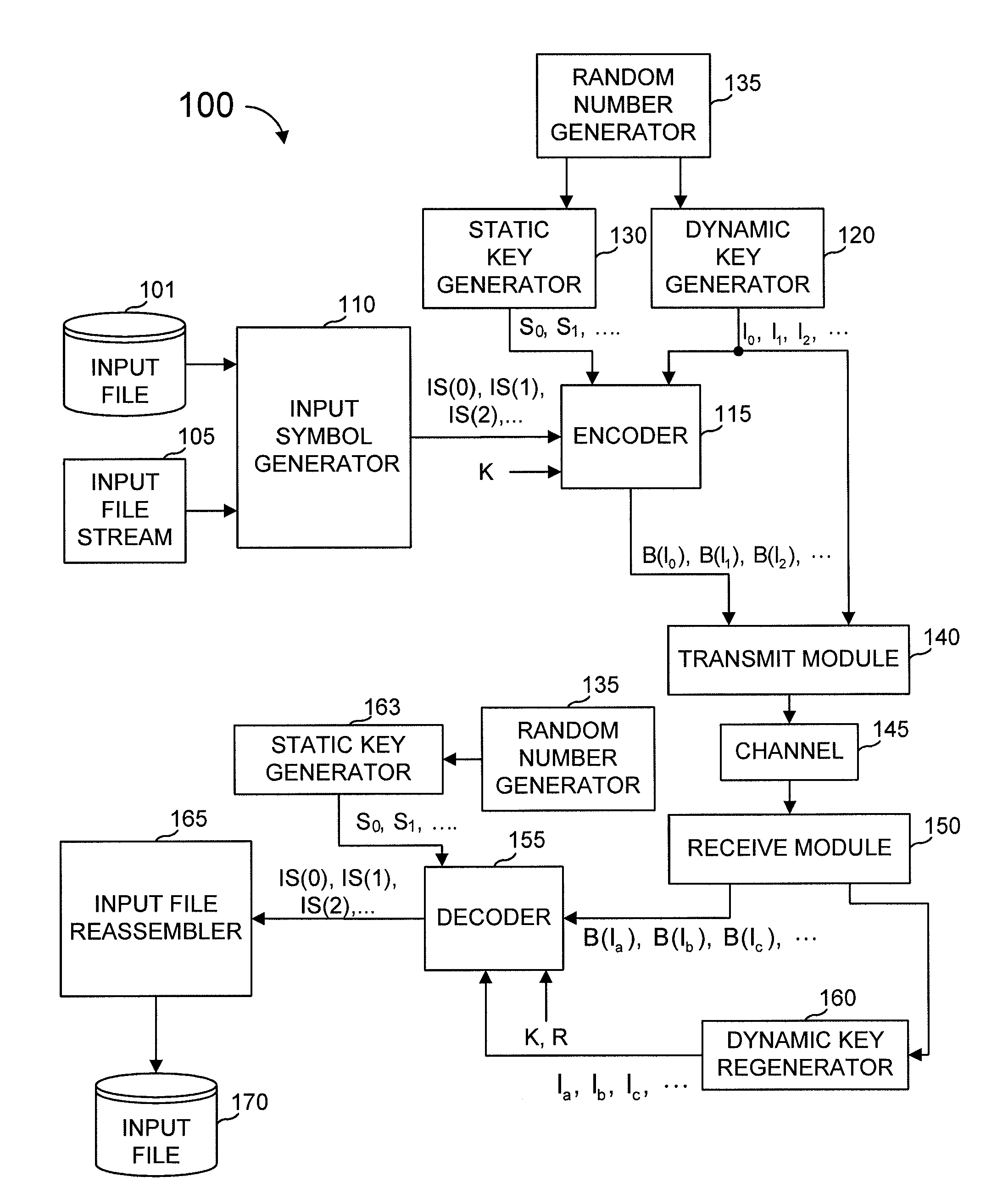
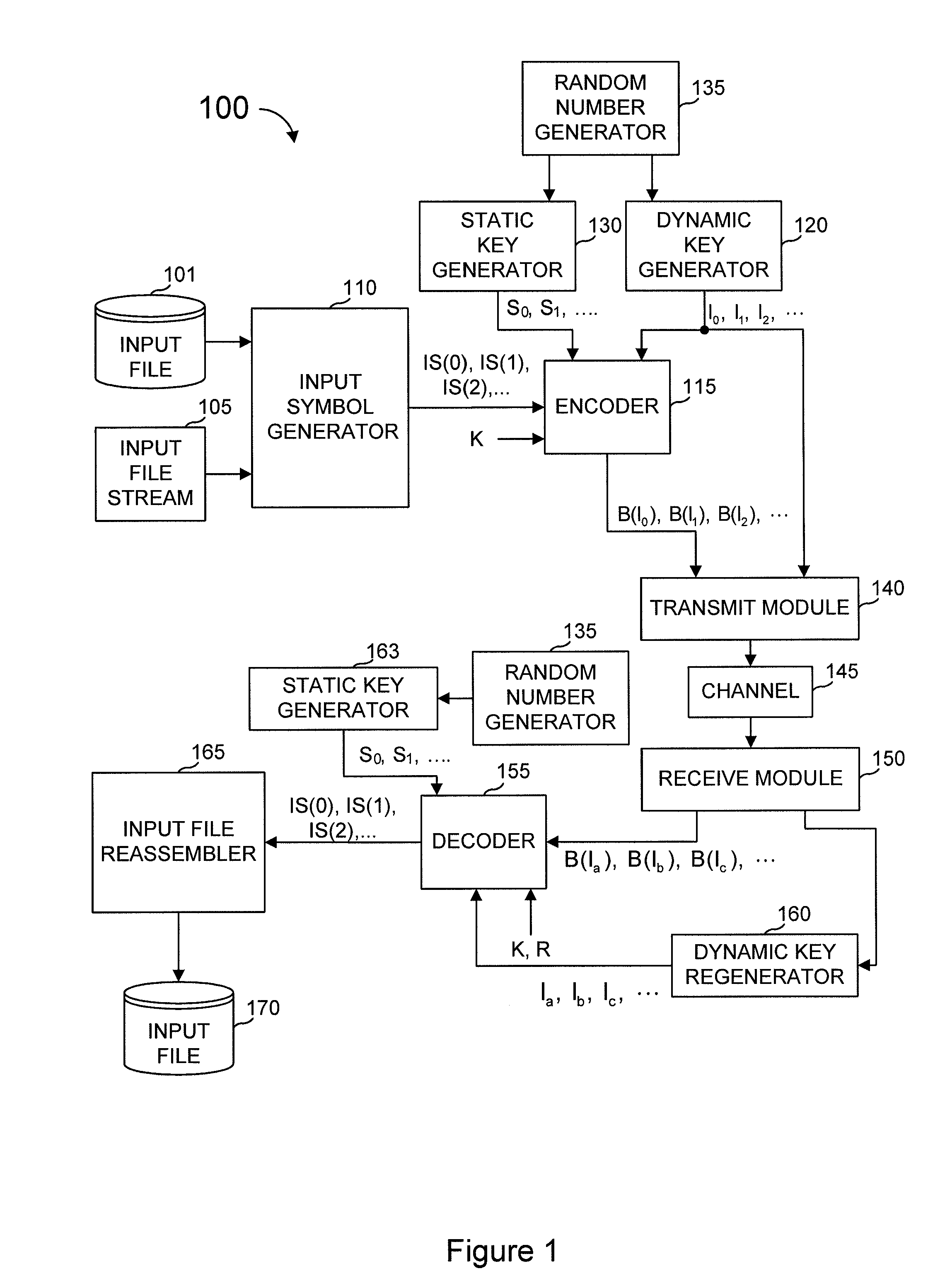
Systems and processes for decoding chain reaction codes through inactivation
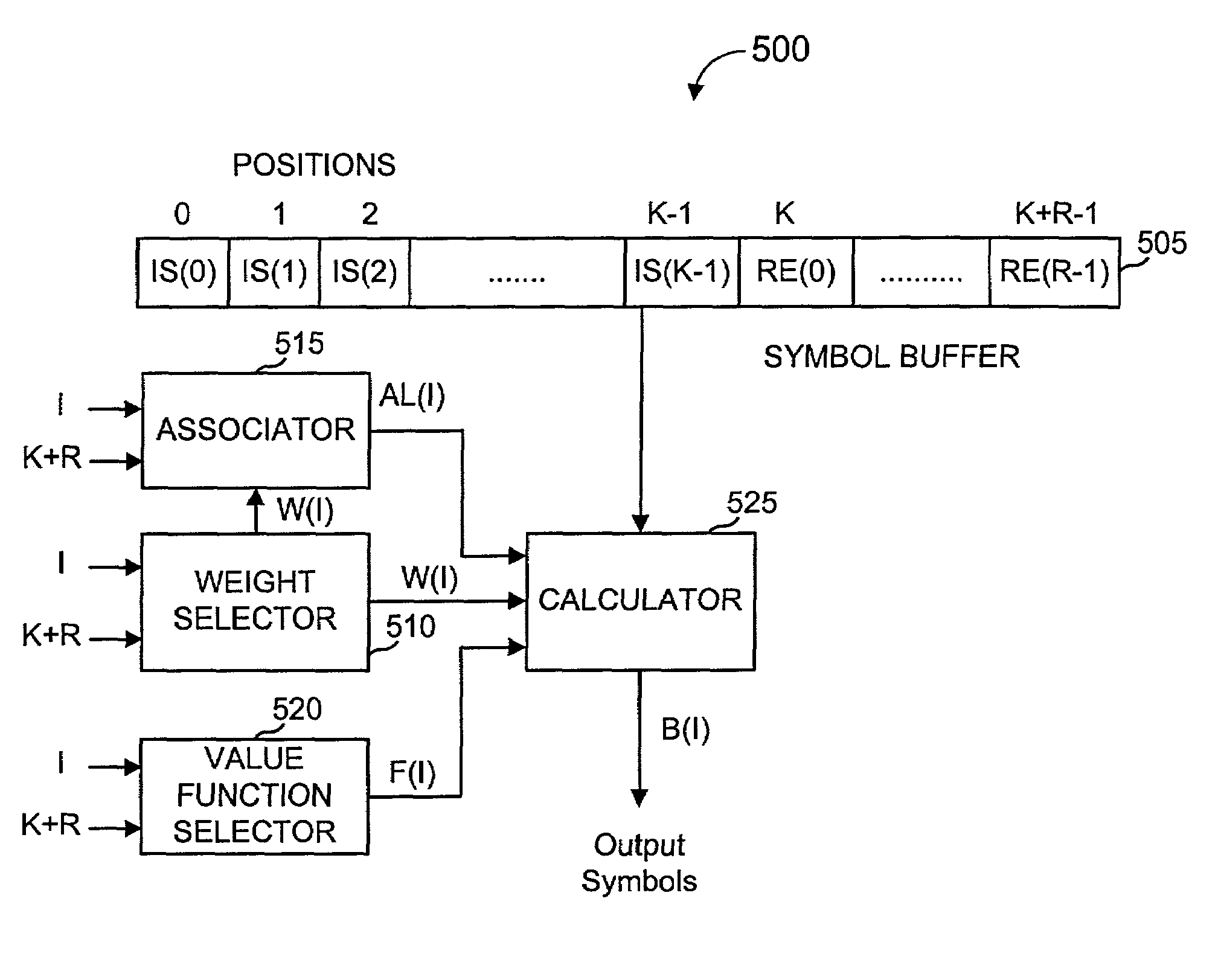
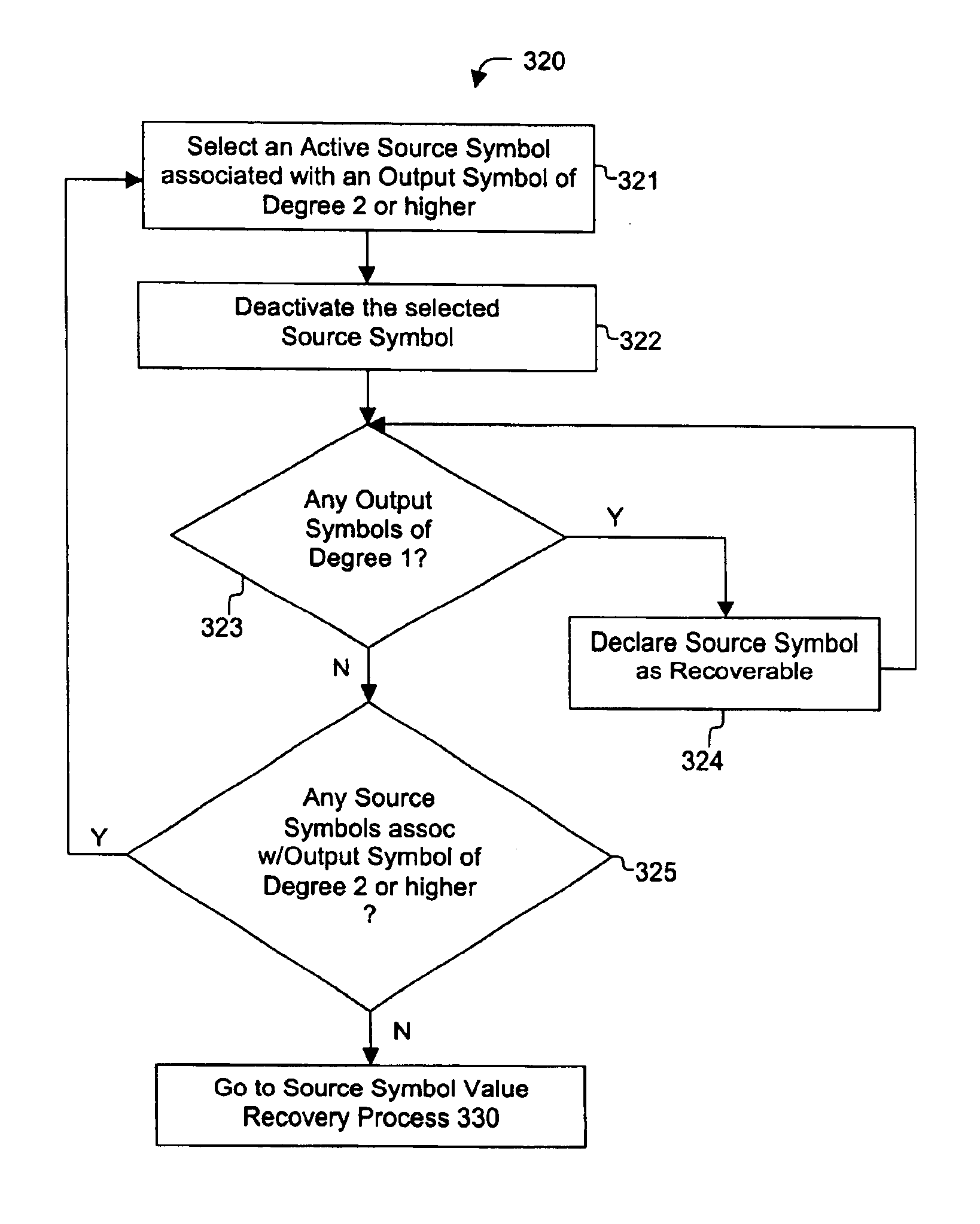
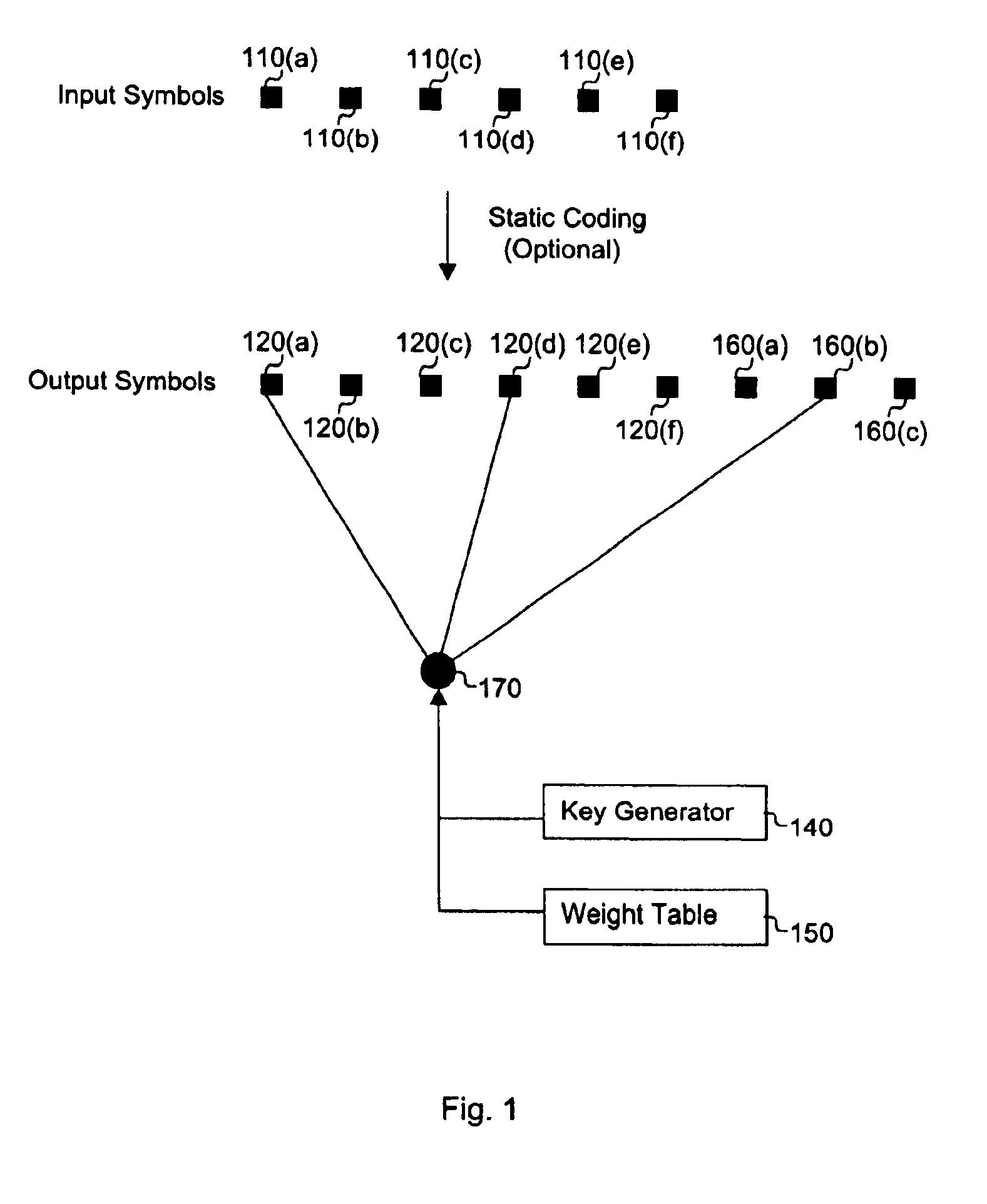
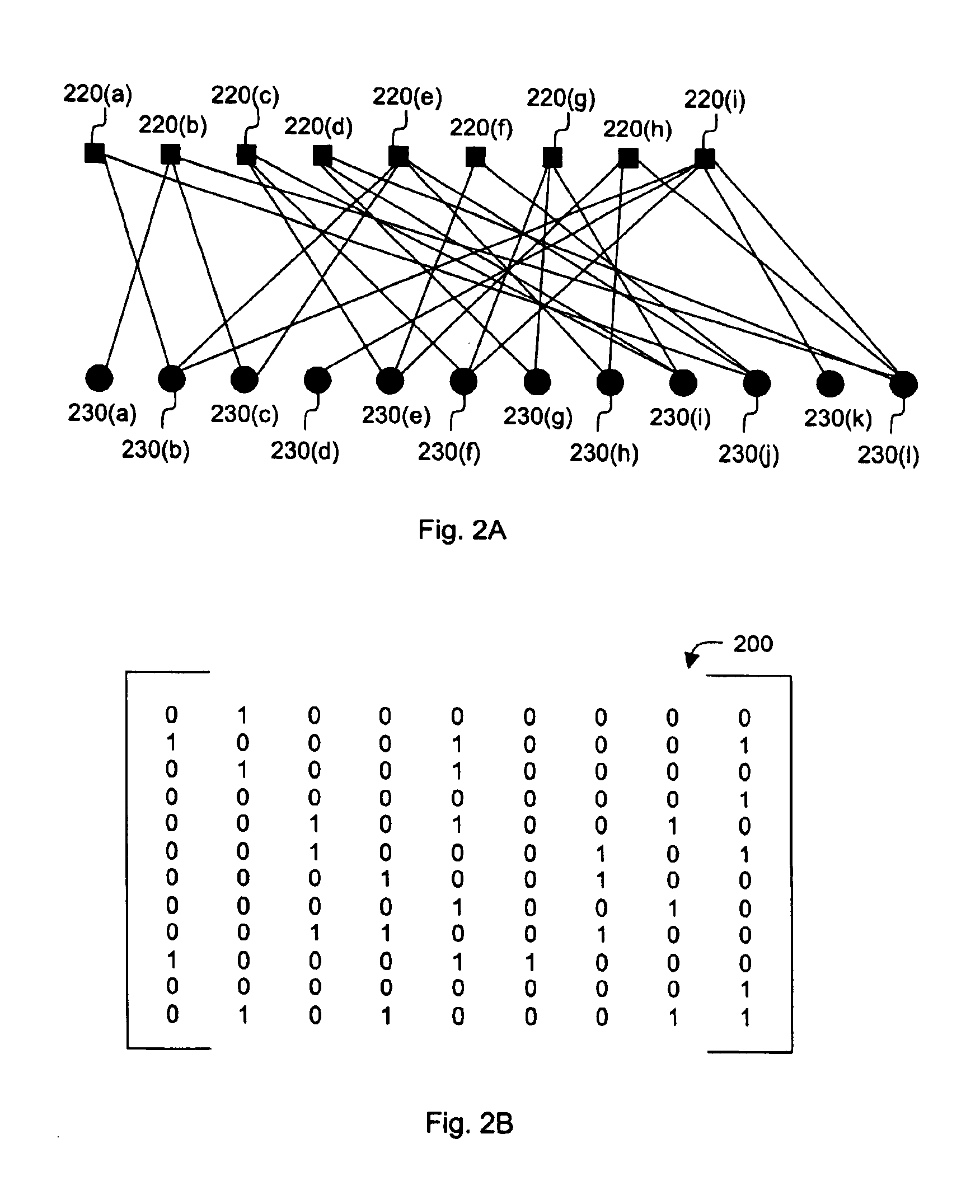
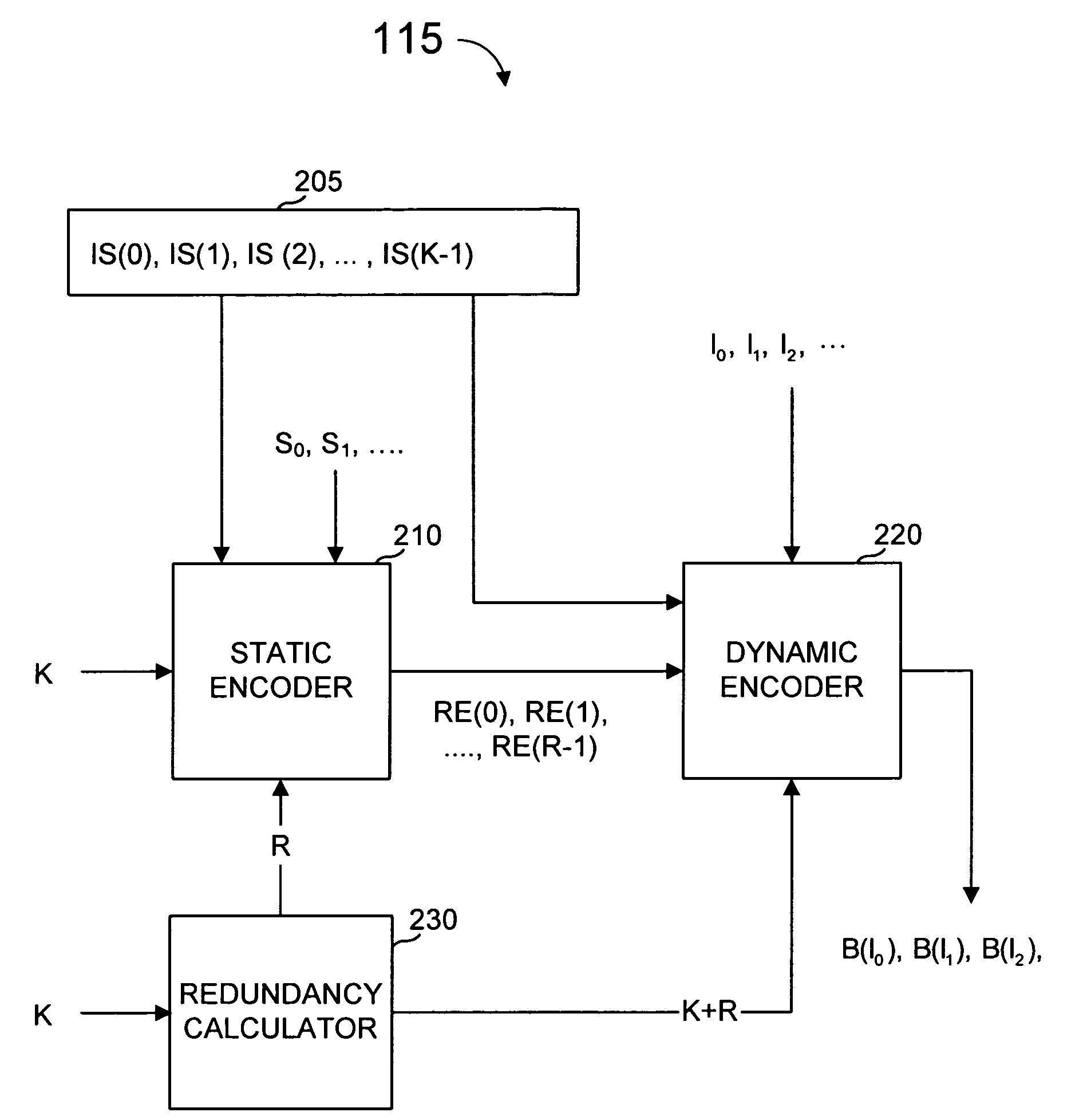
InactiveUS6856263B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelOther decoding techniquesAlgorithmChain reaction
A method for processing a chain reaction codes includes first selecting a source symbol which is associated an output symbol of degree two or higher (i.e., an output symbol which is itself associated with two or more input symbols), and subsequently deactivating the selected source symbol in an attempt to produce an output symbol of degree one. The inactivation process can be repeated either successively until an output symbol of degree one is identified, and / or whenever the decoding process is unable to locate an output symbol of degree one.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
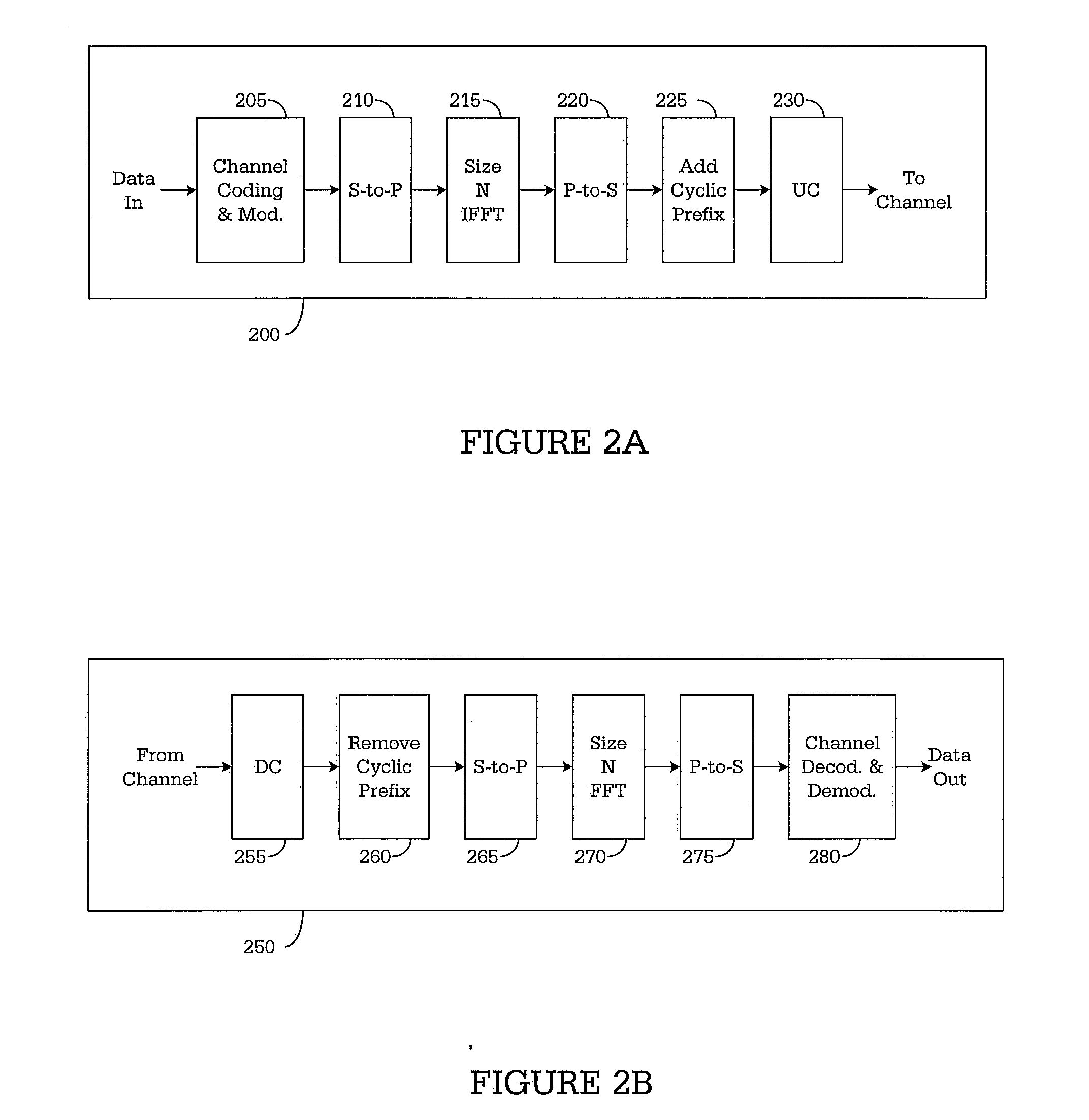
File download and streaming system
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
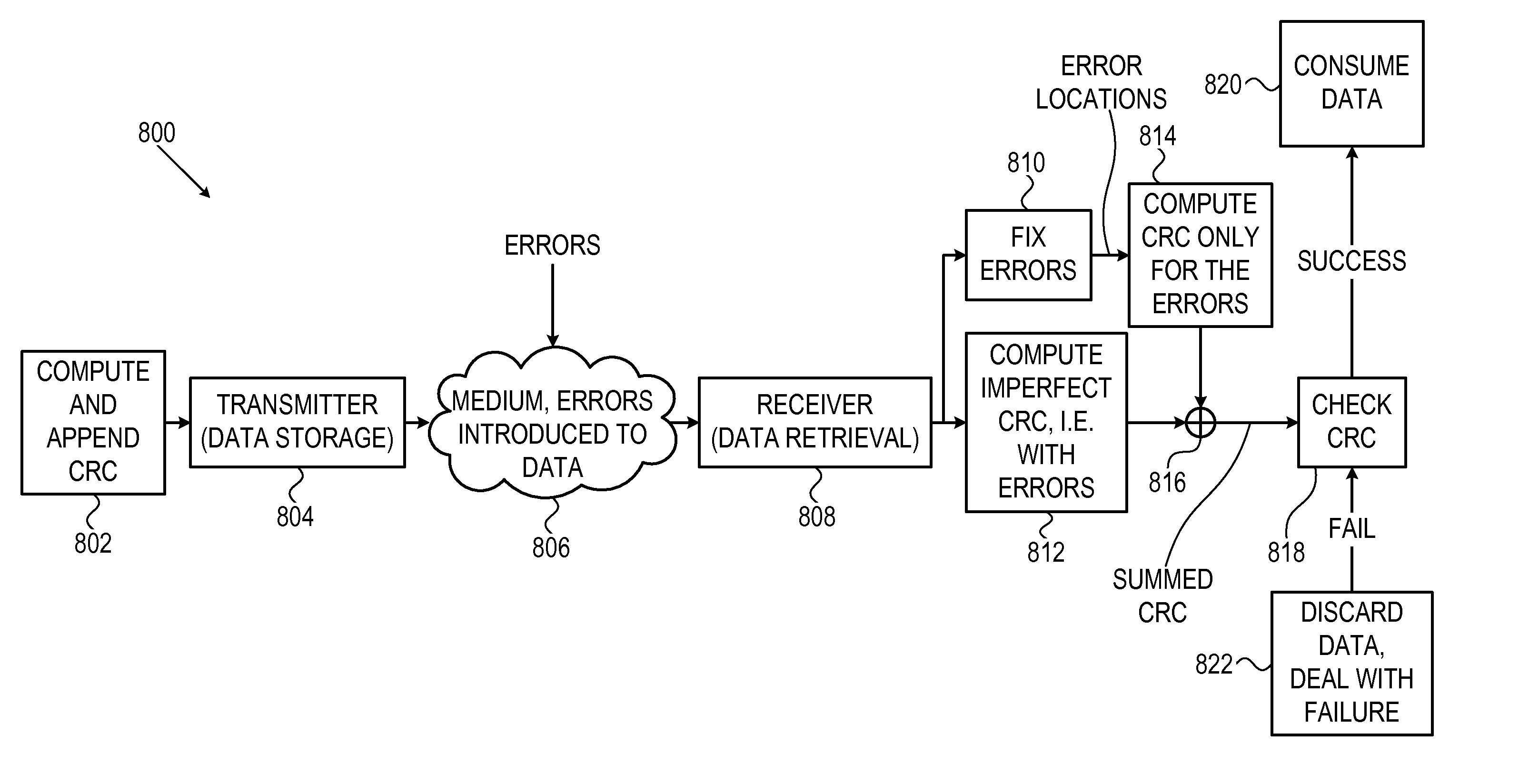
System and method for multi-dimensional encoding and decoding
ActiveUS20120005554A1Correction errorError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesData setMulti dimensional
A system and method for using a cyclic redundancy check (CRC) to evaluate error corrections. A set of data and initial CRC values associated therewith may be received. The set of data by changing a sub-set of the data may be corrected. Intermediate CRC values may be computed for the entire uncorrected set of data in parallel with said correcting. Supplemental CRC values may be computed for only the sub-set of changed data after said correcting. The intermediate and supplemental CRC values may be combined to generate CRC values for the entire corrected set of data. The validity of the corrected set of data may be evaluated by comparing the combined CRC values with the initial CRC values.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
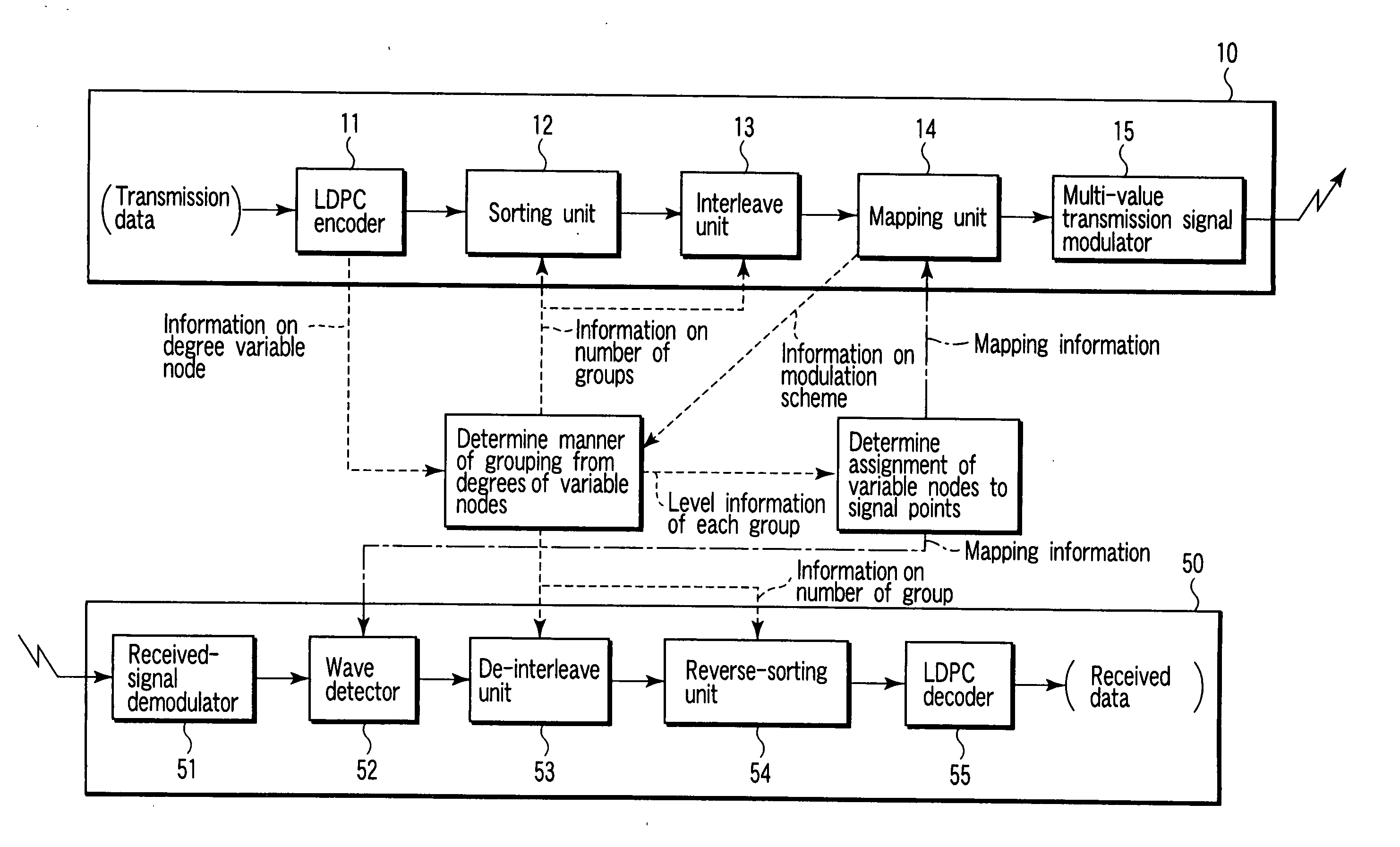
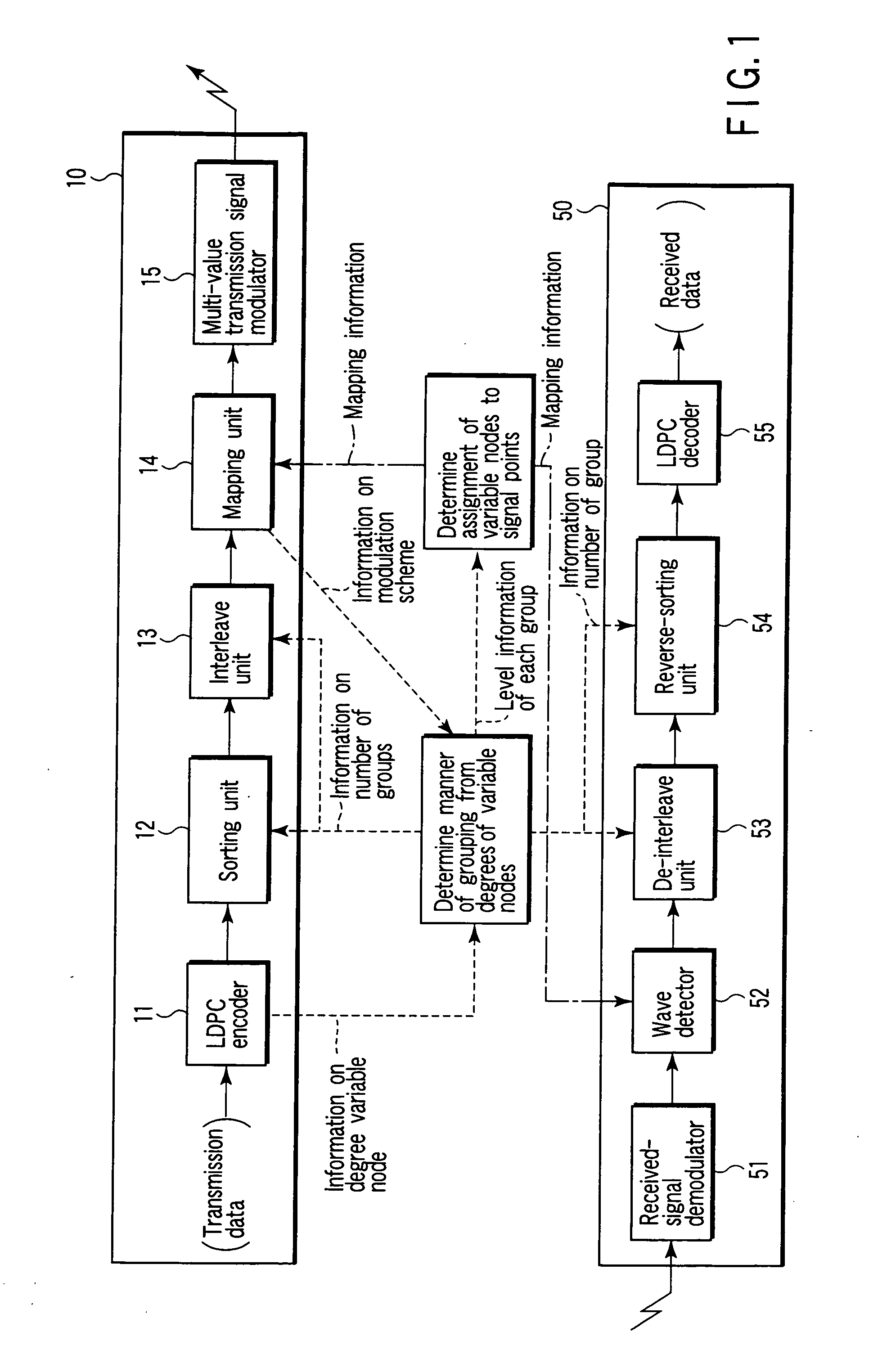
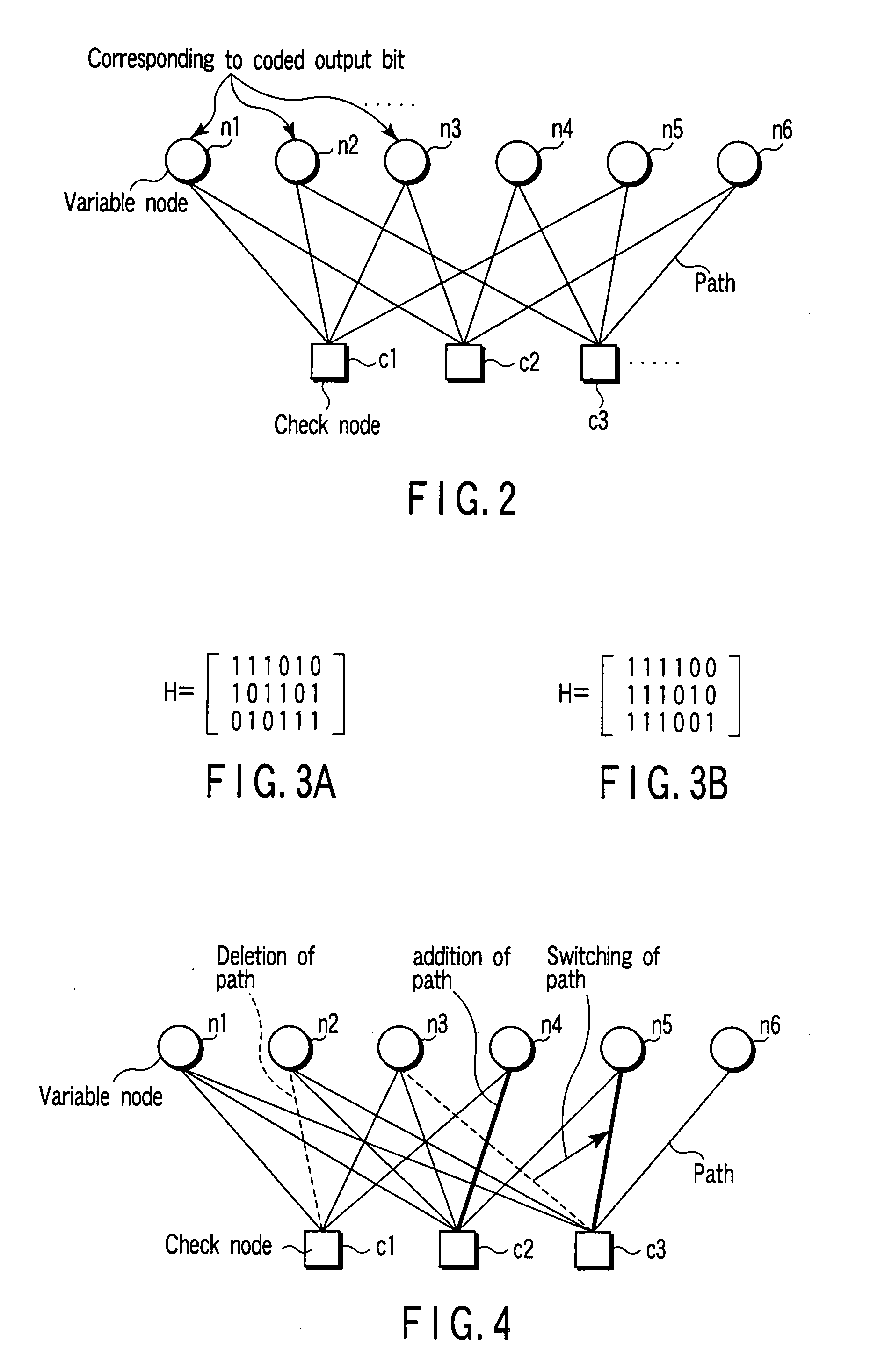
Mapping method for encoded bits using LDPC code, transmitting and receiving apparatuses employing this method, and program for executing this method
InactiveUS20050216821A1Transmission path divisionError correction/detection using LDPC codesTheoretical computer scienceParity-check matrix
A method for mapping of coded bits using a low density parity check (LDPC) code, comprises encoding information bits by using the LDPC code to generate coded bits, sorting the coded bits in accordance with degrees of variable nodes represented by a parity check matrix of the LDPC code, dividing the sorted coded bits into a plurality of groups in accordance with a using modulation scheme, and mapping the coded bits to respective modulation signal points by considering an error resistance of each of the groups and an error resistance of a corresponding one of the modulation signal points.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
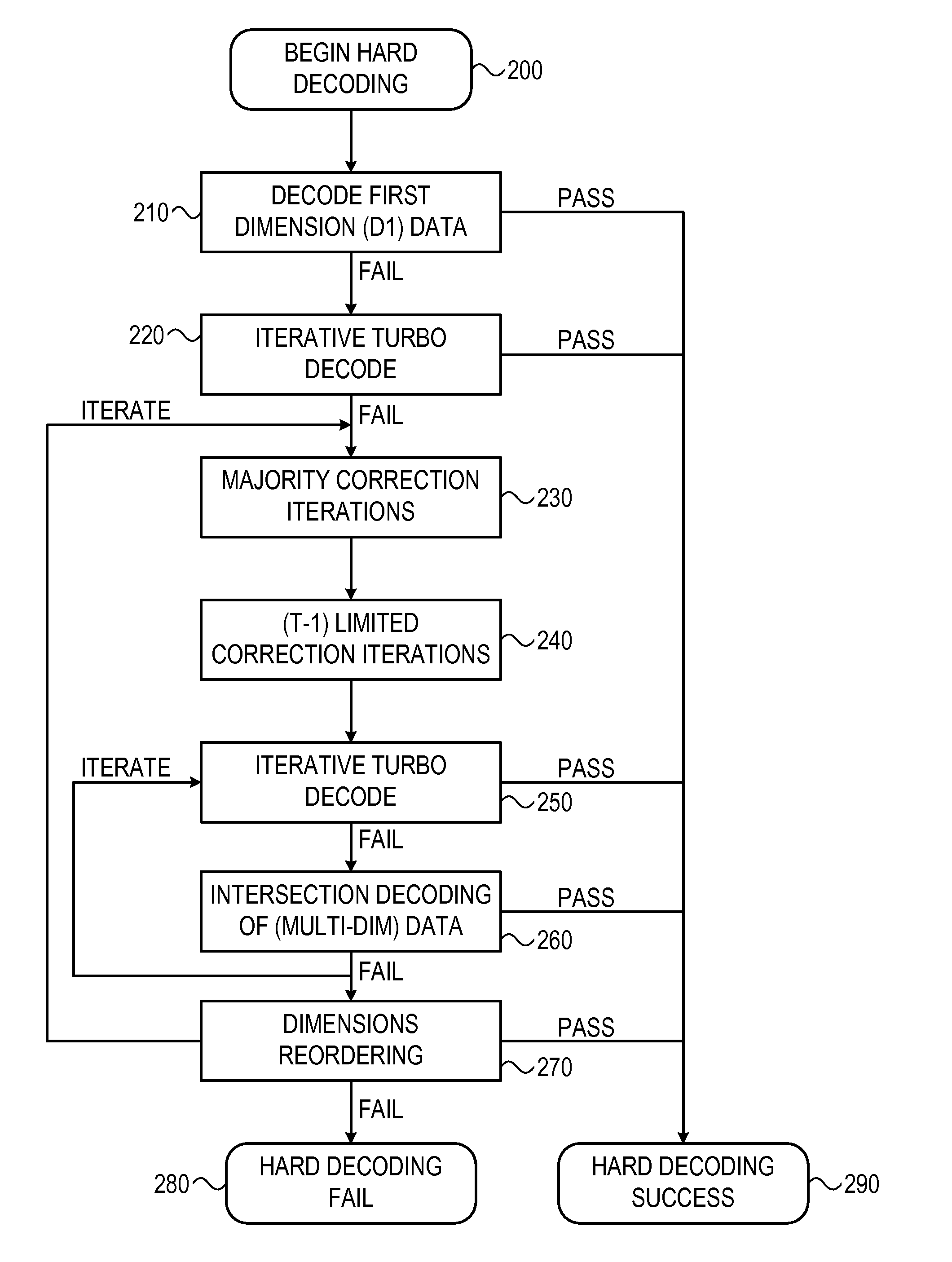
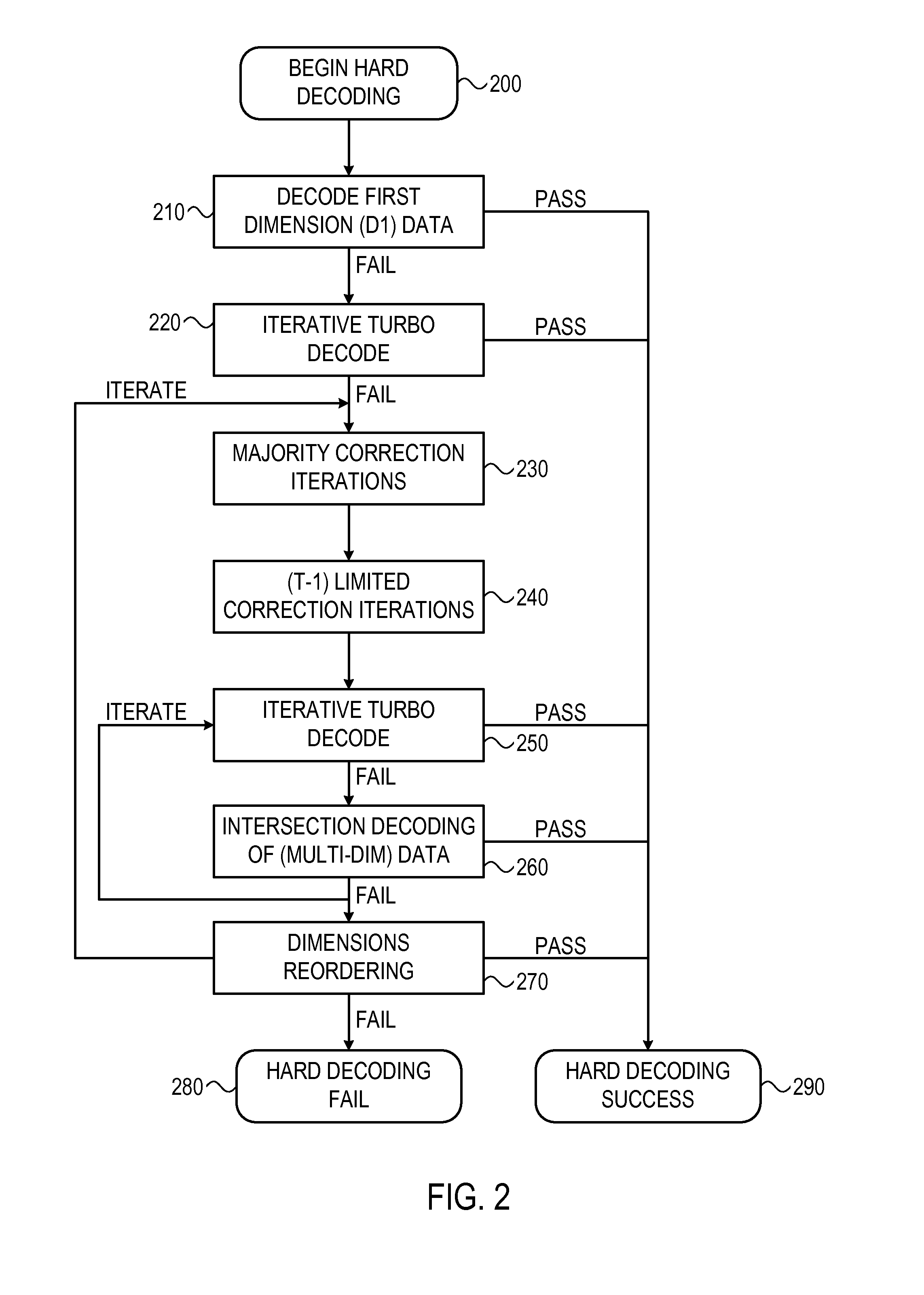
Enhanced turbo product code decoder system utilizing a codeword organization method
InactiveUS7039846B2Error preventionOther decoding techniquesMemory addressTheoretical computer science
A method and apparatus for decoding a linear block encoded string of information bits comprising: converting the string into a plurality of codewords. Performing hard and soft decisions on each codeword to generate a hard and soft decision vector. Computing the syndrome and finding the location of the two minimum values by Galois Field Arithmetic. Designating these values LOW1 and LOW2 and xoring with a Nc1, thus generating Nc2. Swapping Nc1 with Nc2 and determining the lowest soft decision value, Min1 and a next lowest value, Min2. The two bit locations creating Min1 are designated as MinA and MinB. MinA being replaced with Min2 minus the value MinA. MinB being replaced with Min2 minus the value at MinB. Generating an output codeword by subtracting Min1 from all other bit locations values and 2's complementing all soft values with 0 in their location. Creating the new soft value vector. Some embodiments include a system and method that organizes an encoded codeword. The encoded codeword has several codeword bits. The method receives the encoded codeword, assigns multiple codeword bits to at least one memory address in a plurality of memory addresses, and iteratively decodes the received codeword by utilizing the plurality of memory addresses in a predetermined order. The predetermined order is based on a dimension of the received codeword.
Owner:COMTECH TELECOMM CORP
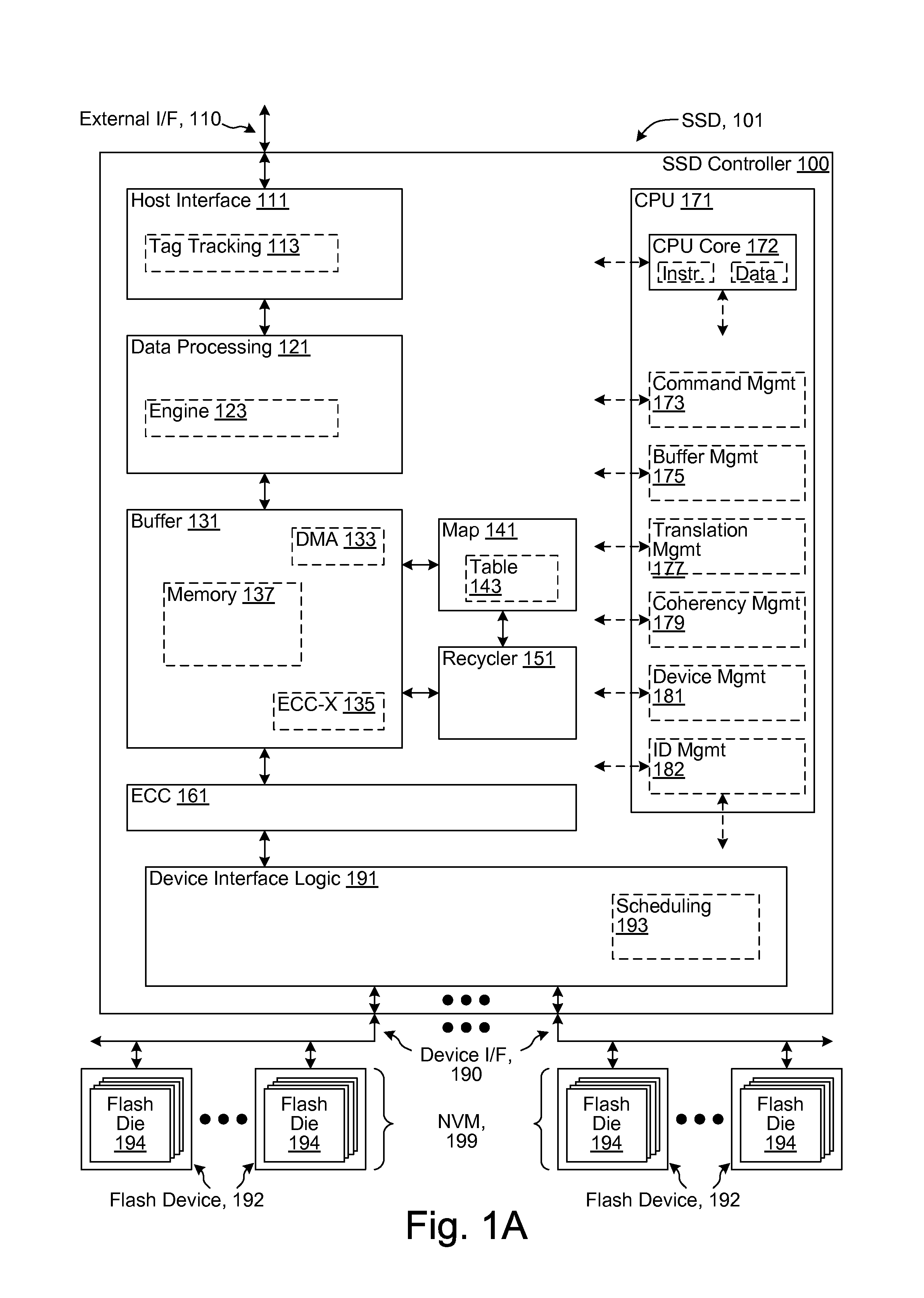
Zero-one balance management in a solid-state disk controller
An SSD controller maintains a zero count and a one count, and / or in some embodiments a zero / one disparity count, for each read unit read from an SLC NVM (or the lower pages of an MLC). In an event that the read unit is uncorrectable in part due to a shift in the threshold voltage distributions away from their nominal distributions, the maintained counts enable a determination of a direction and / or a magnitude to adjust a read threshold to track the threshold voltage shift and restore the read data zero / one balance. In various embodiments, the adjusted read threshold is determined in a variety of described ways (counts, percentages) that are based on a number of described factors (determined threshold voltage distributions, known stored values, past NVM operating events). Extensions of the forgoing techniques are described for MLC memories.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for fast encoding of data symbols according to half-weight codes
ActiveUS7721184B2Reduce expensesOther error detection/correction/protectionCode conversionHigh densityAlgorithm
Efficient methods for encoding and decoding Half-Weight codes are disclosed and similar high density codes are disclosed. The efficient methods require at most 3·(k−1)+h / 2+1 XORs of symbols to calculate h Half-Weight symbols from k source symbols, where h is of the order of log(k).
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
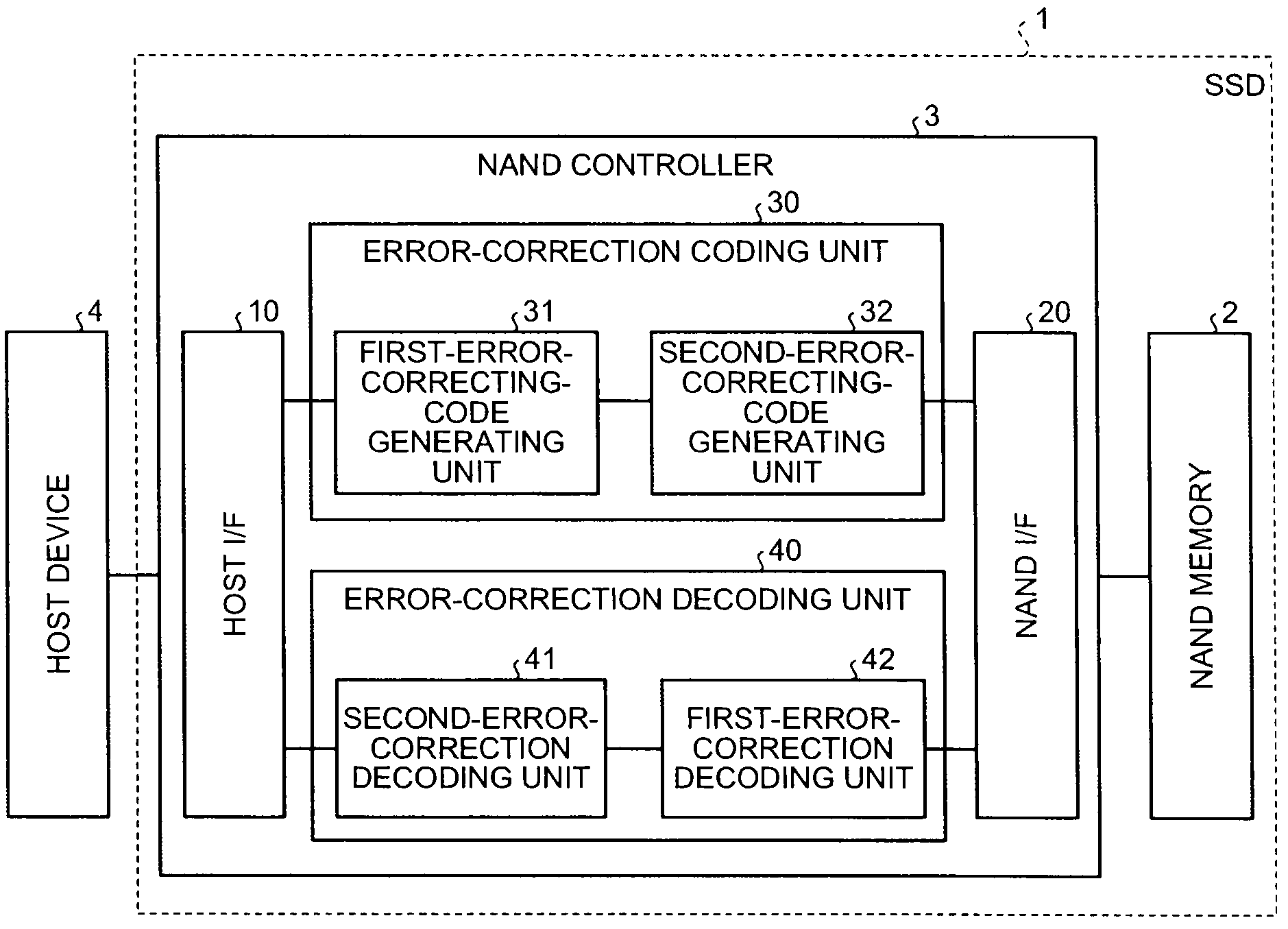
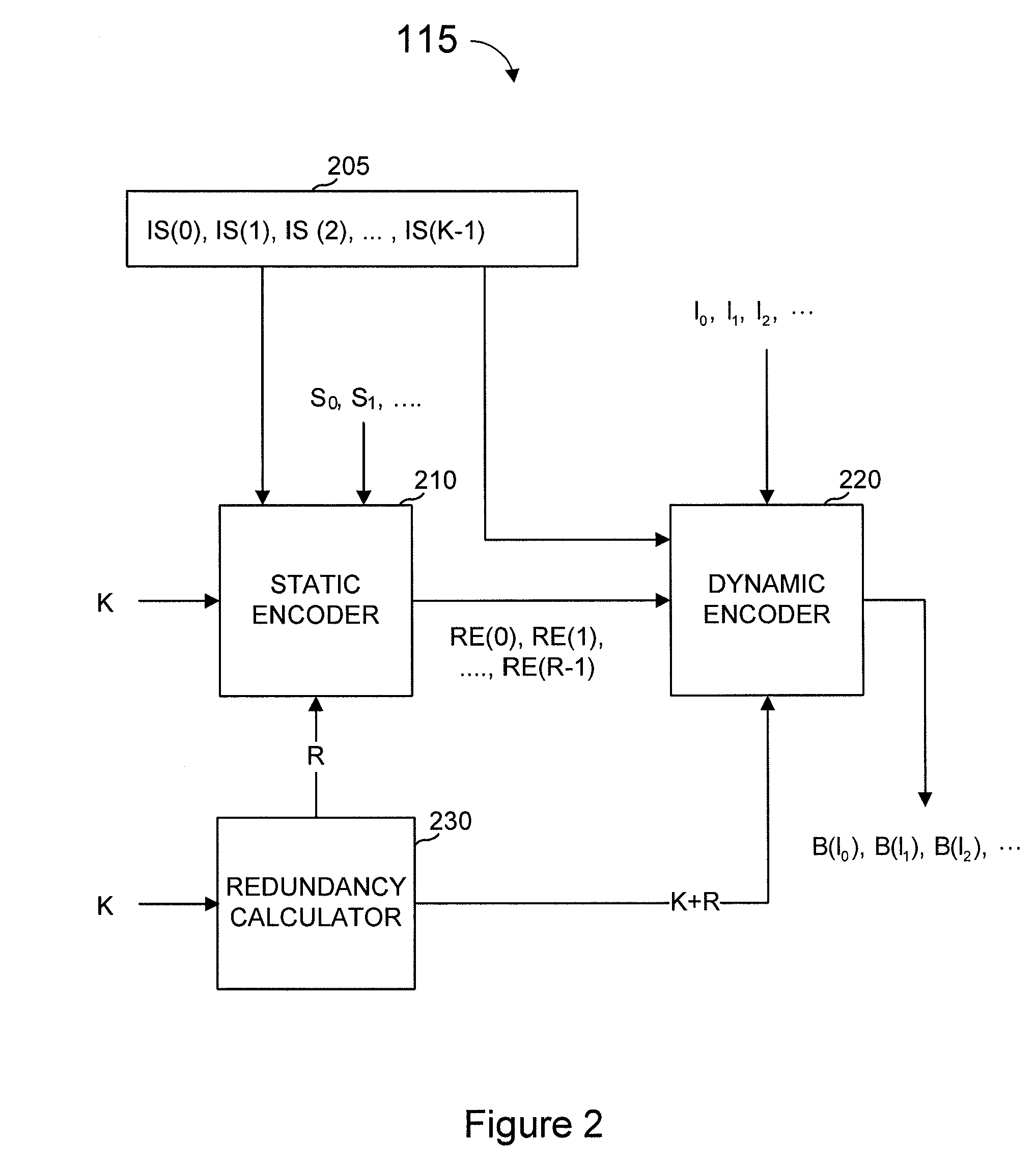
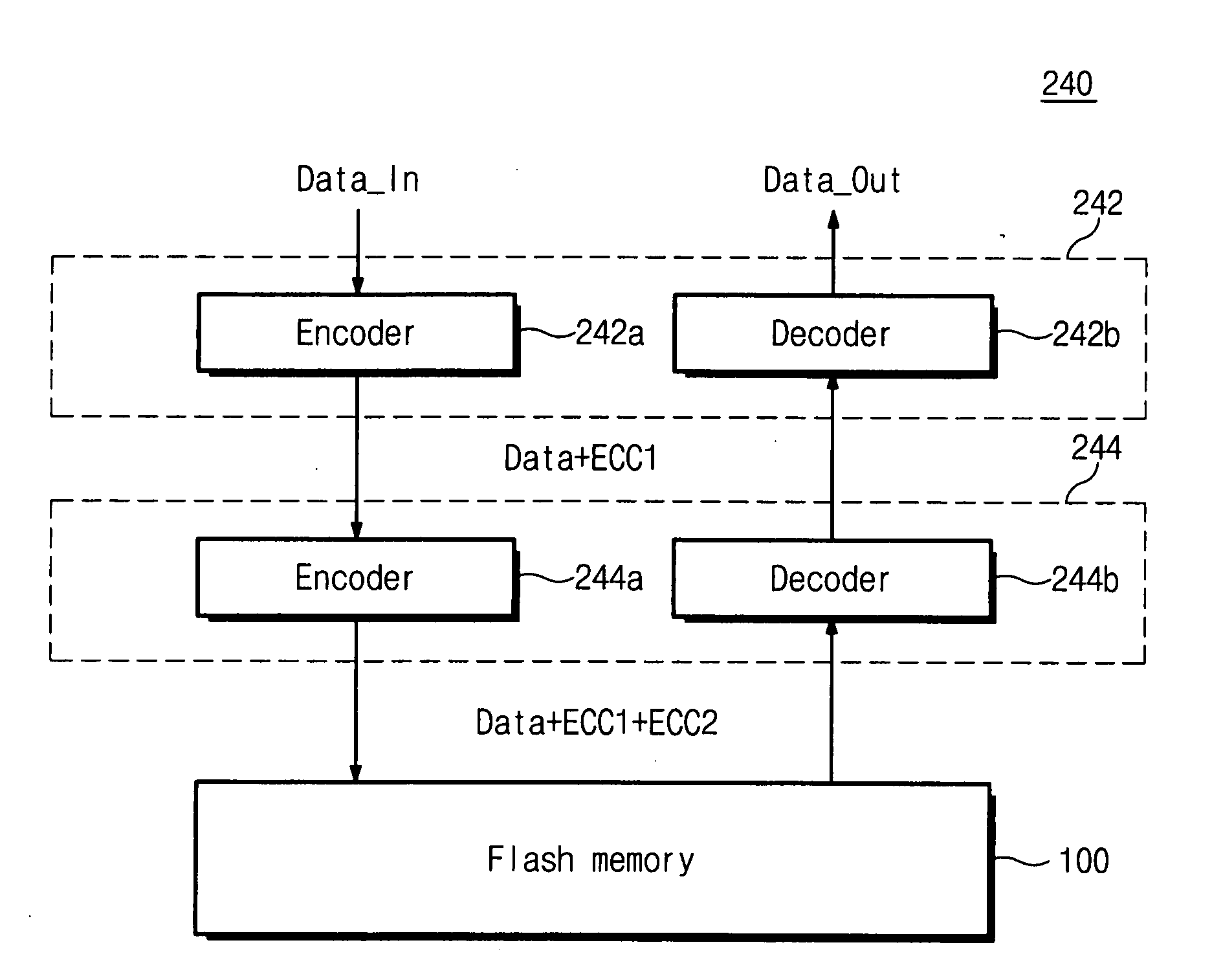
ECC controller for use in flash memory device and memory system including the same
An ECC (error correction code) controller of a flash memory device which stores an M-bit data (M being a positive integer equal to or greater than 2) comprises a first ECC block which generates a first ECC data from a program data to be stored in the flash memory device according to a first error correcting method and a second ECC block which generates a second ECC data from the first ECC data and the program data output from the first ECC block according to a second error correcting method, the program data, the first ECC data, and the second ECC data being stored in the flash memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Forward error correction for burst and random packet loss for real-time multi-media communication
ActiveUS20090193314A1Less powerFlexibility of deploymentError correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionMissing dataPacket loss
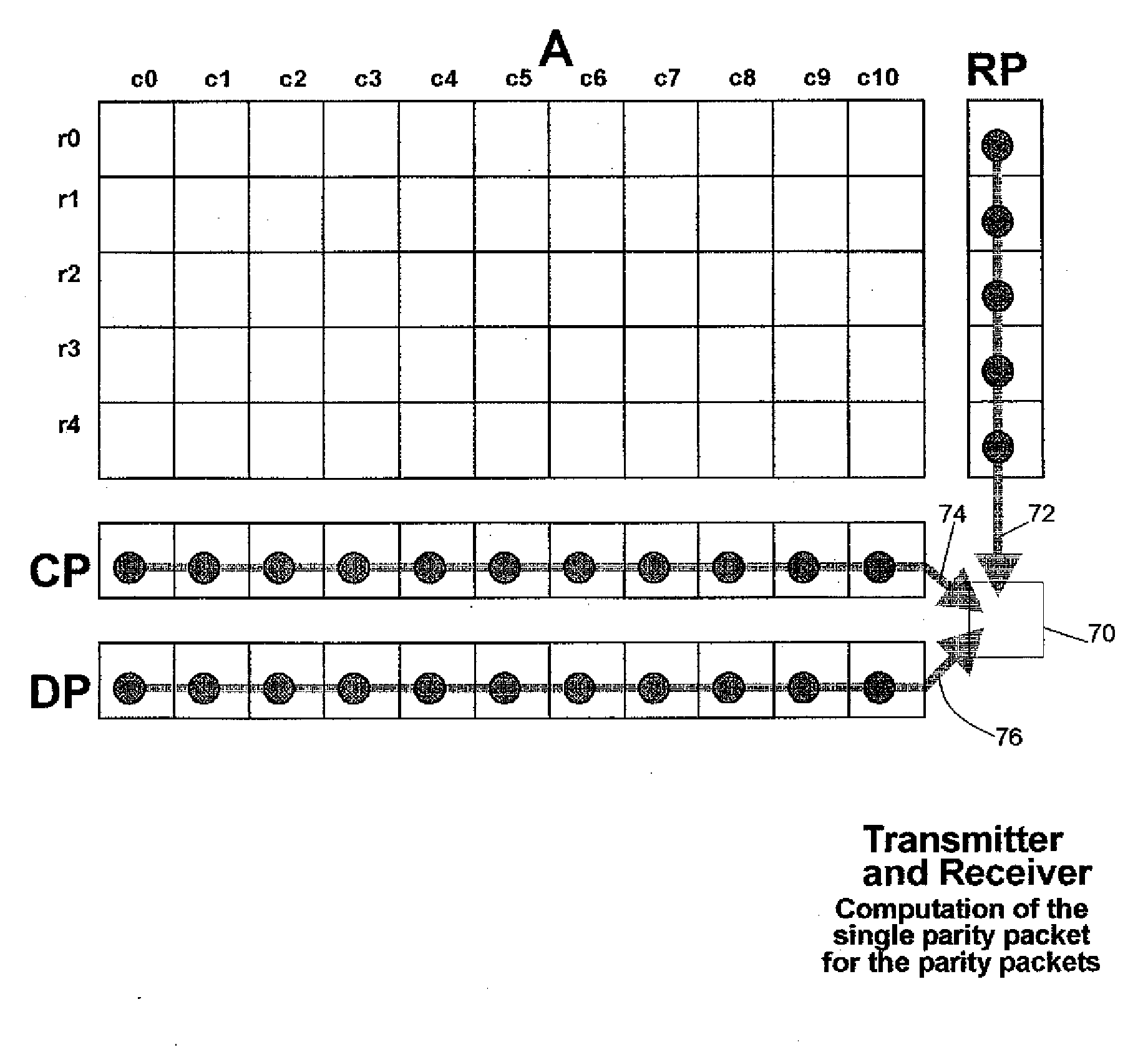
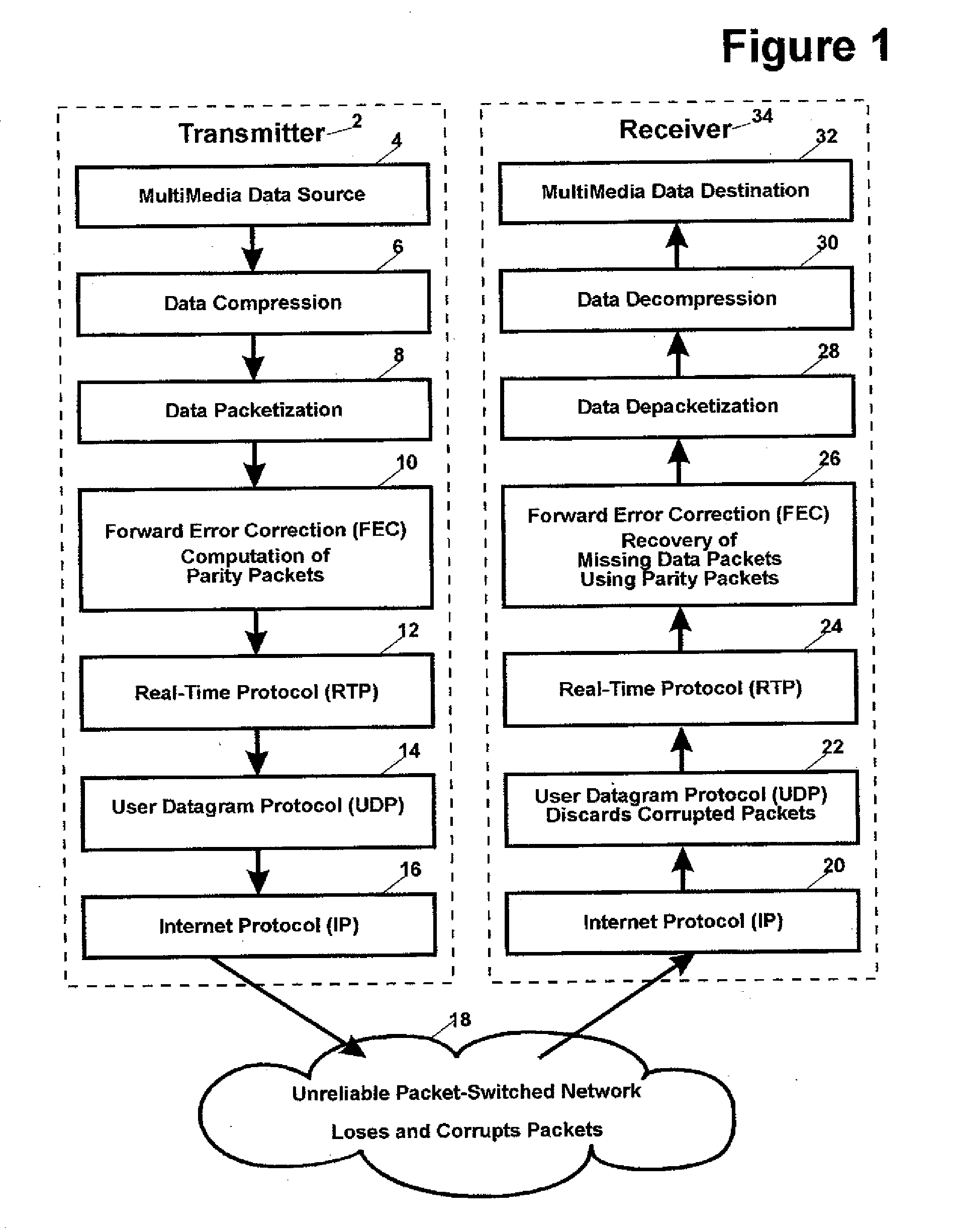
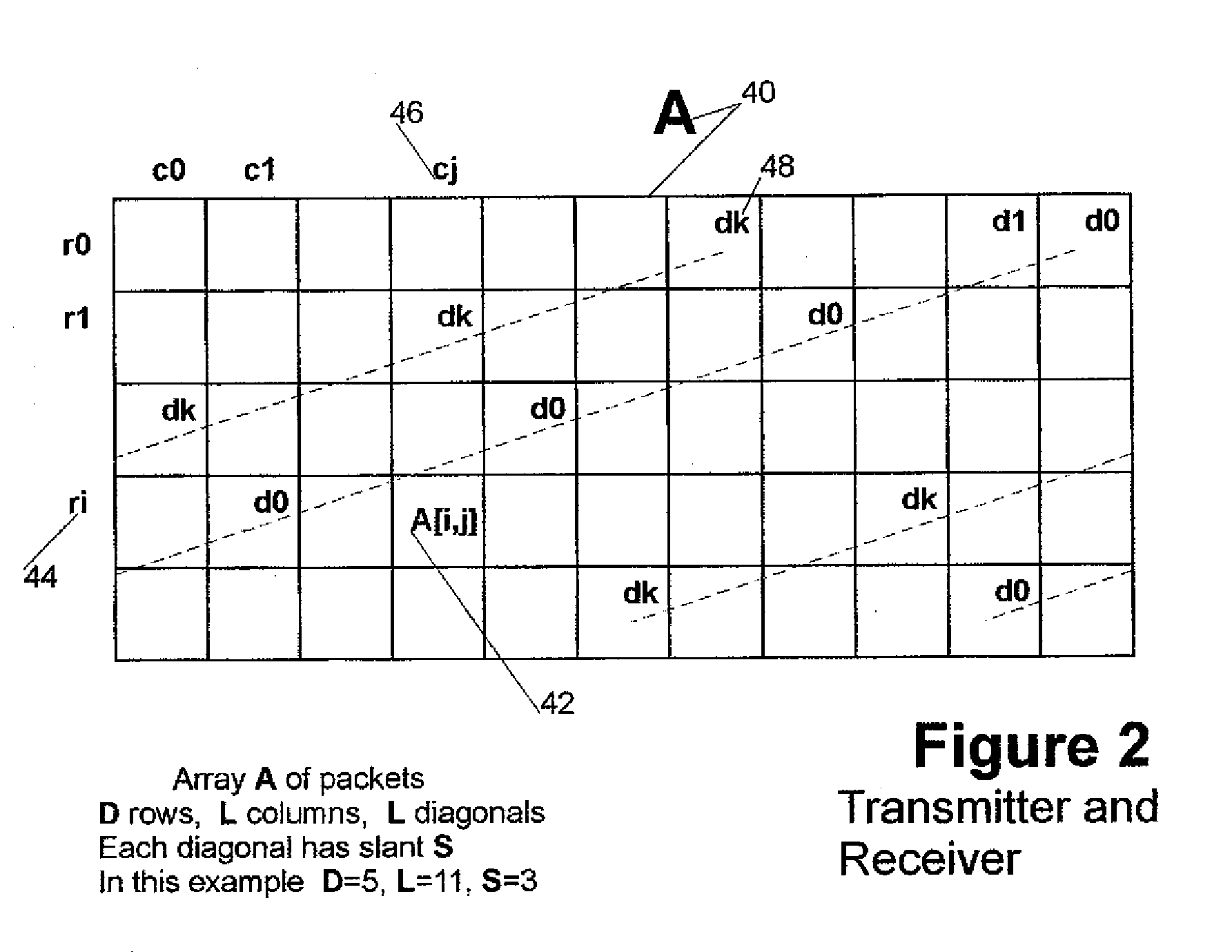
This invention relates generally to a packet recovery algorithm for real-time (live) multi-media communication over packet-switched networks, such as the Internet. Such multi-media communication includes video, audio, data or any combination thereof. More specifically, the invention comprises a forward error correction (FEC) algorithm that addresses both random and burst packet loss and errors, and that can be adjusted to tradeoff the recoverability of missing packets and the latency incurred. The transmitter calculates parity packets for the rows, columns and diagonals of a block of multi-media data packets using the exclusive or (XOR) operation and communicates the parity packets along with the multi-media data packets to the receiver. The receiver uses the parity packets to recover missing multi-media data packets in the block. The FEC algorithm is designed to be able to recover long bursts of consecutive missing data packets. If some parity packets are missing, they too can be recovered using an extra single parity packet, so that they can be used to recover other missing data packets. The invention applies to both one-way real-time streaming applications and two-way real-time interactive applications, and to both wired and wireless networks. The invention retains backwards compatibility with existing standards governing FEC for professional video over IP networks.
Owner:NEVION EURO
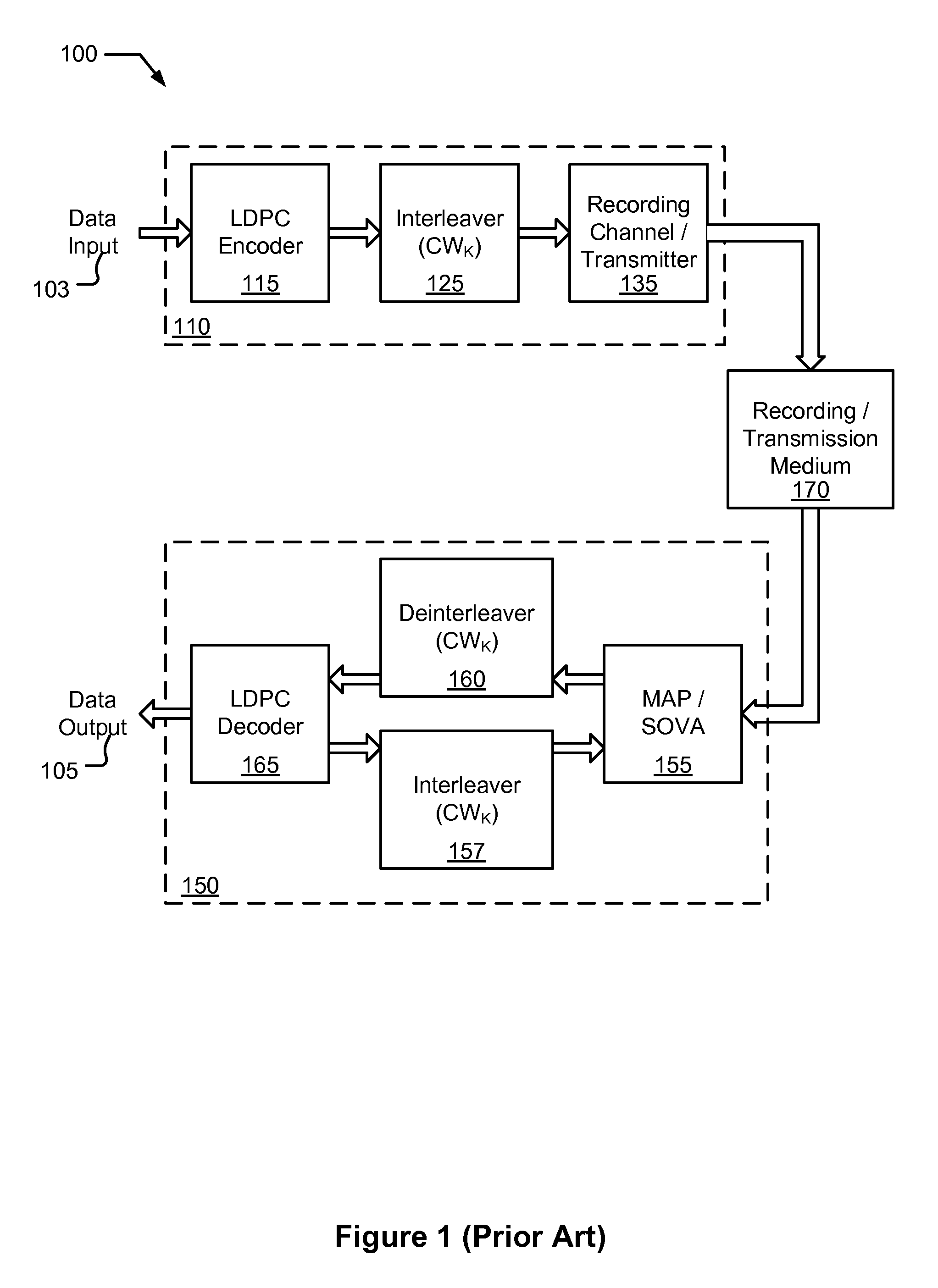
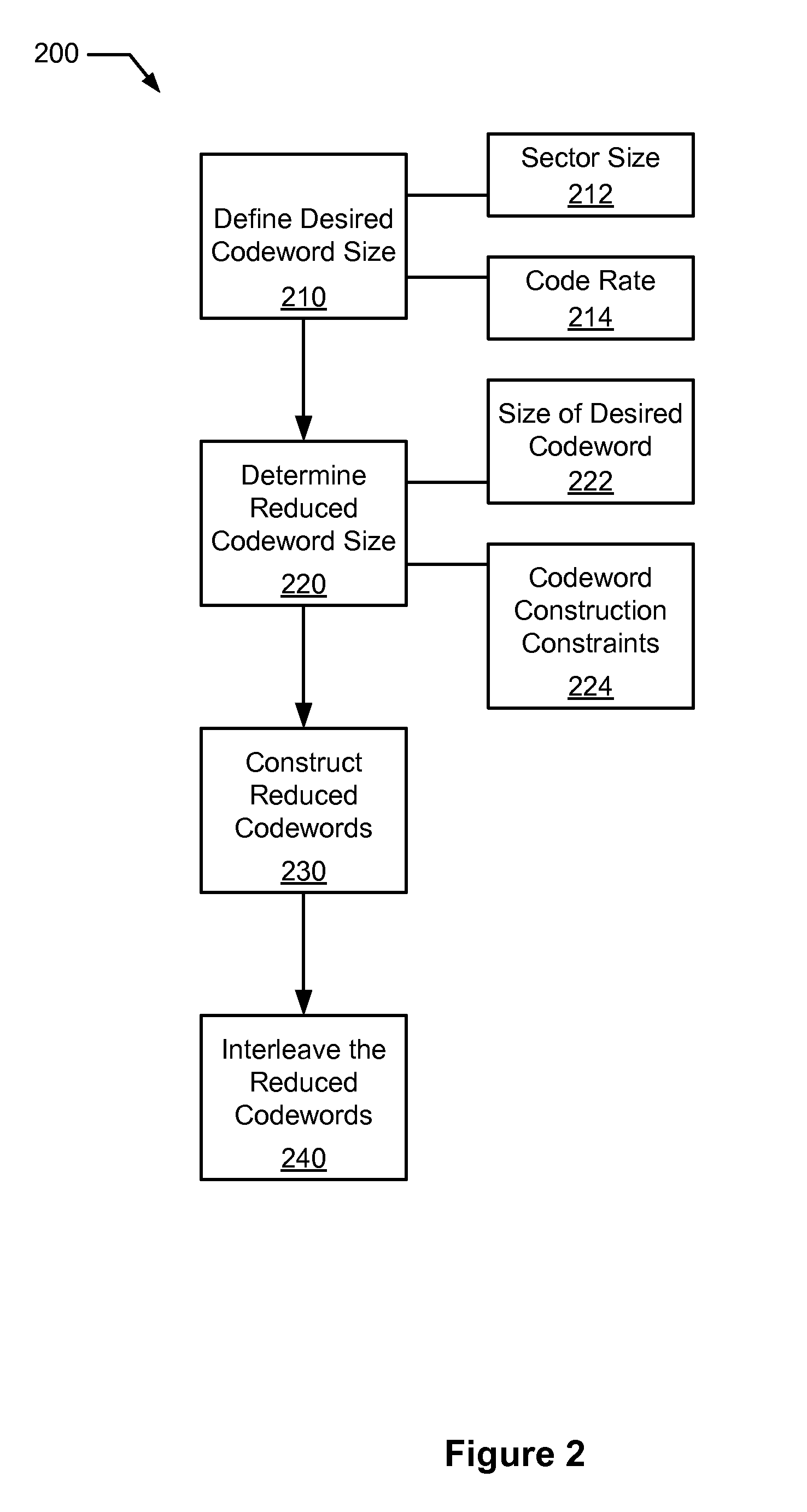
Systems and Methods for Reduced Complexity Data Processing
InactiveUS20100185914A1Reduce processing complexityReduce processCode conversionSingle error correctionProcess informationLdpc decoding
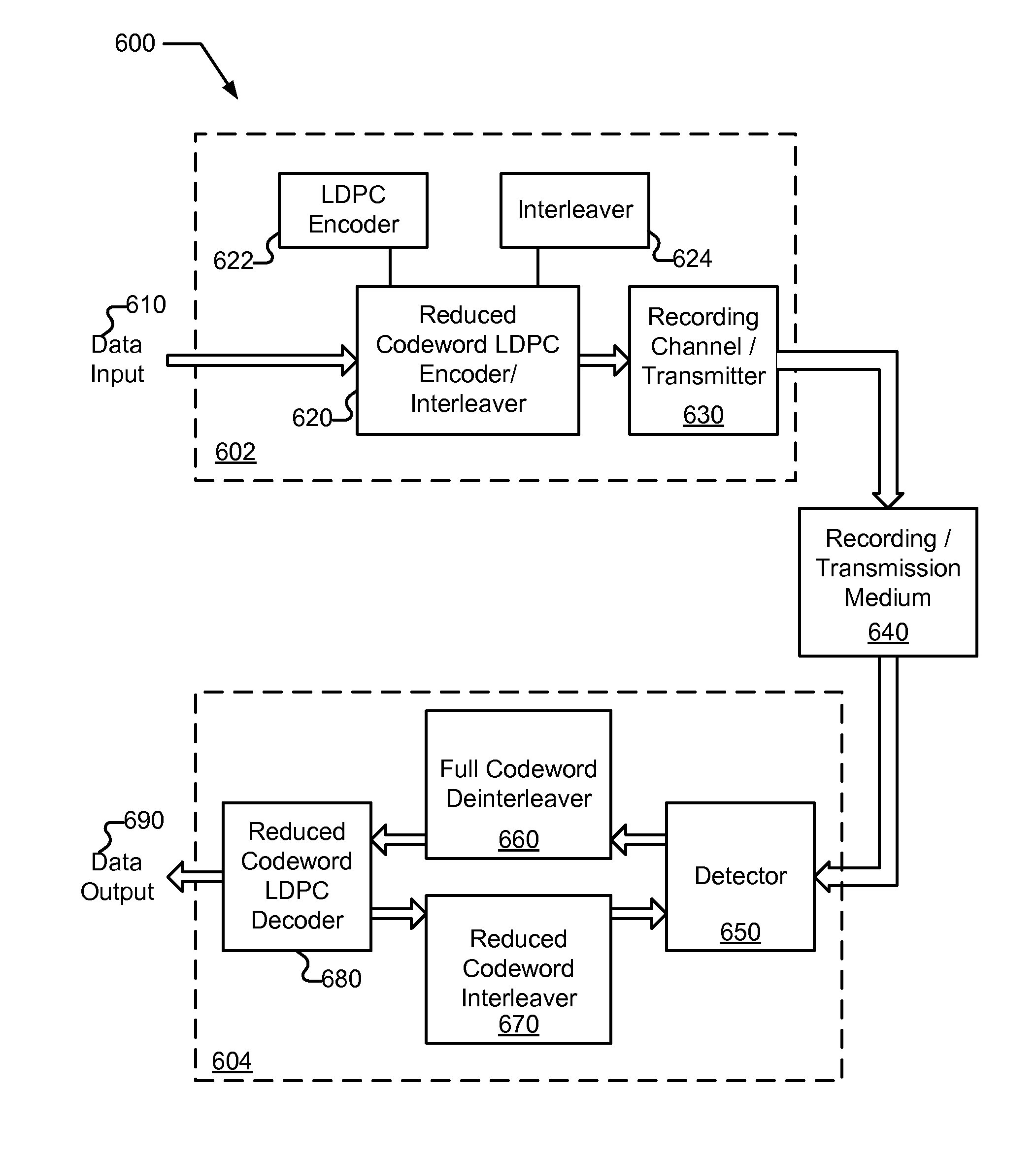
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for processing information. For example, a decoding system is disclosed that includes a de-interleaver. The de-interleaver is operable to receive an interleaved codeword that includes two or more reduced codewords interleaved together. Further, the de-interleaver is operable to provide a representation of the two or more reduced codewords. The systems also include a decoder that is operable to decode the two or more reduced codewords. In some instances of the aforementioned embodiments, the decoder is an LDPC decoder that is tailored to the size of one or both of the two or more reduced codewords.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
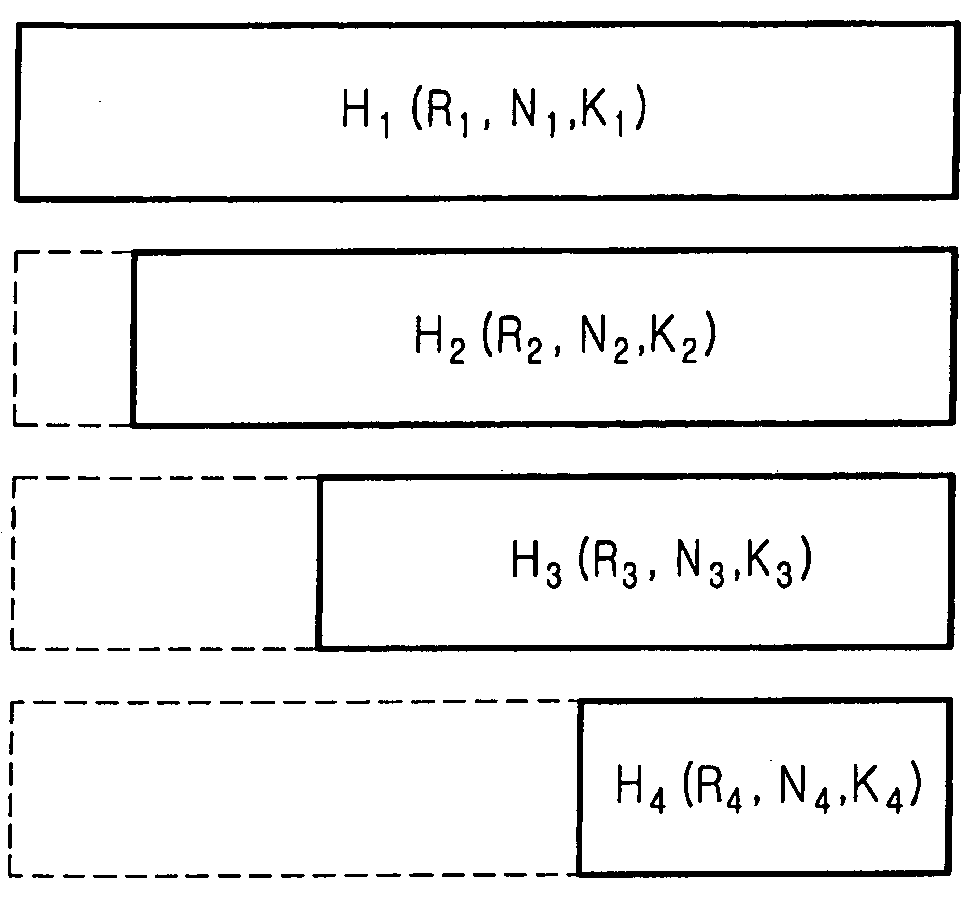
Apparatus and method for encoding and decoding block low density parity check codes with a variable coding rate
ActiveUS20050283708A1Coding complexityImprove resource efficiencyError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionTheoretical computer scienceParity-check matrix
An apparatus and method for coding a block Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) code having a variable coding rate. The apparatus receives an information word and encodes the information word into a block LDPC code based on one of a first parity check matrix and a second parity check matrix, depending on a coding rate to be applied when generating the information word into the block LDPC code.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
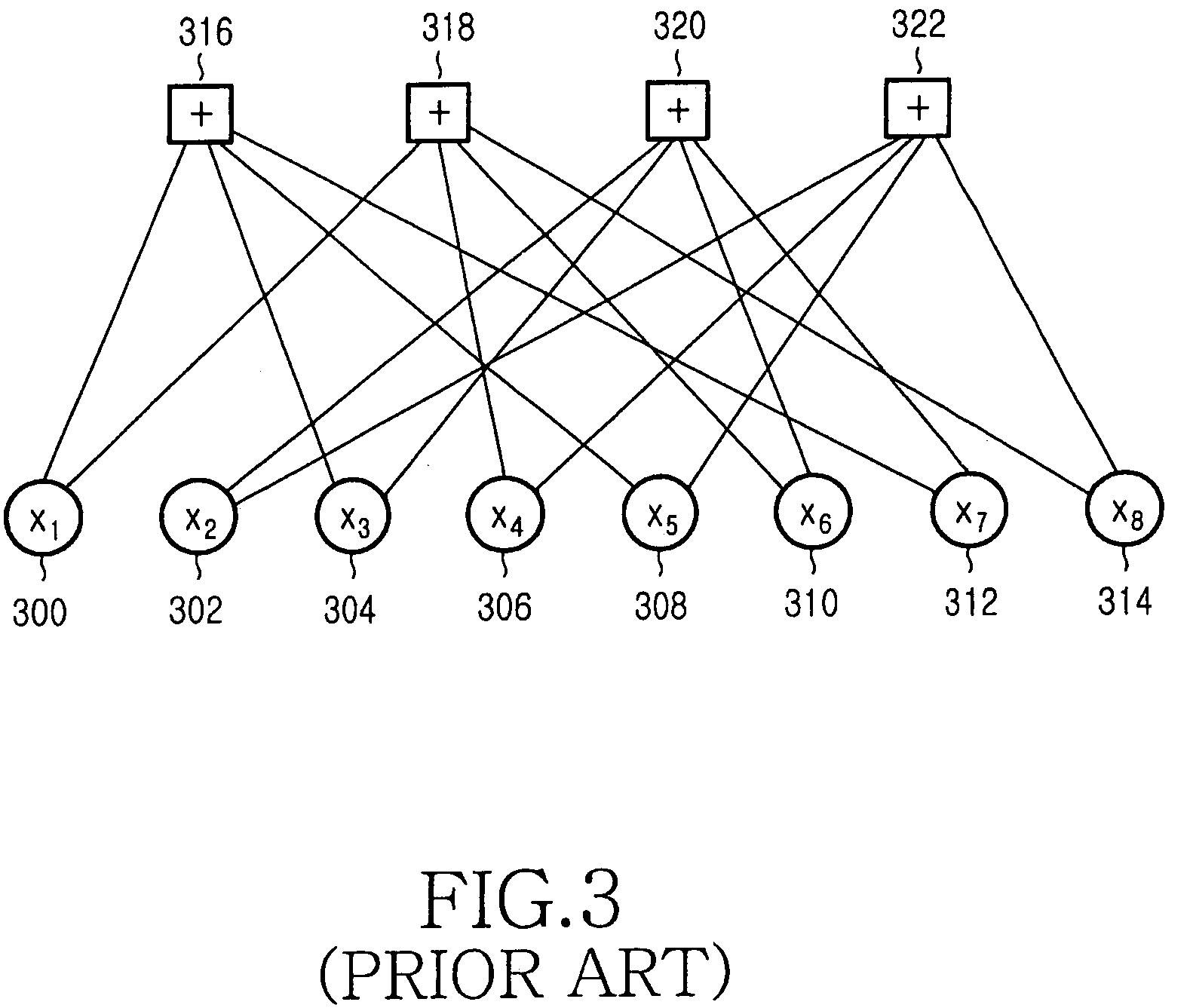
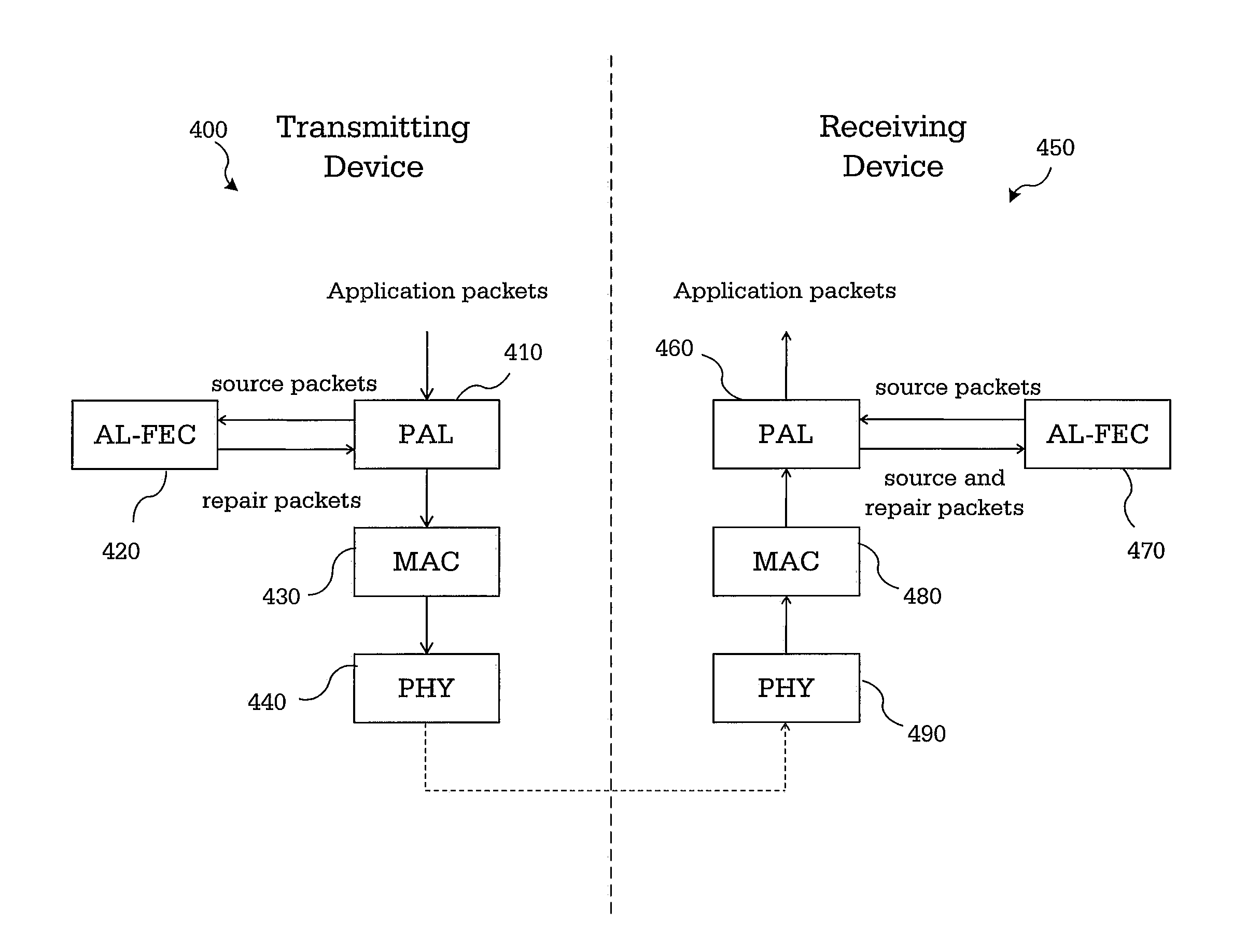
APPLICATION LAYER FEC FRAMEWORK FOR WiGig
InactiveUS20110219279A1Error correction/detection using convolutional codesError preventionComputer hardwareSingle parity check
A method and apparatus perform forward error correction in a wireless communication device in a wireless communication network. Application layer forward error correction (AL-FEC) capability information is transmitted during a capabilities exchange. A set of source packets are reshaped to k equal-sized source symbols. Systematic packets for the source symbols and at least one parity packet is encoded using a single parity check (SPC) AL-FEC code on the k source symbols. A header of each encoded packet includes a parity packet indicator. The encoded packets are processed in a media access control (MAC) layer and a physical (PHY) layer for transmission.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
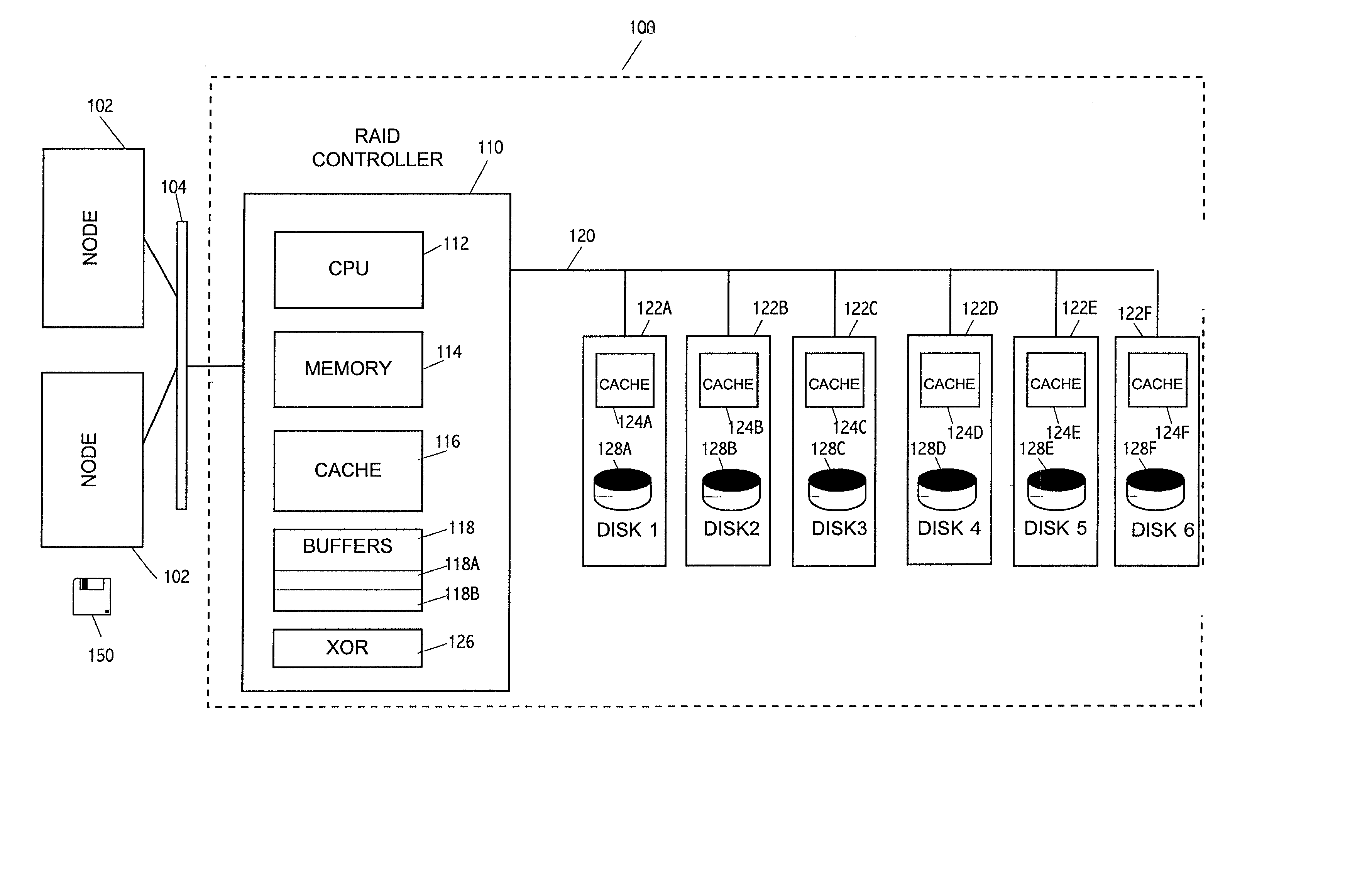
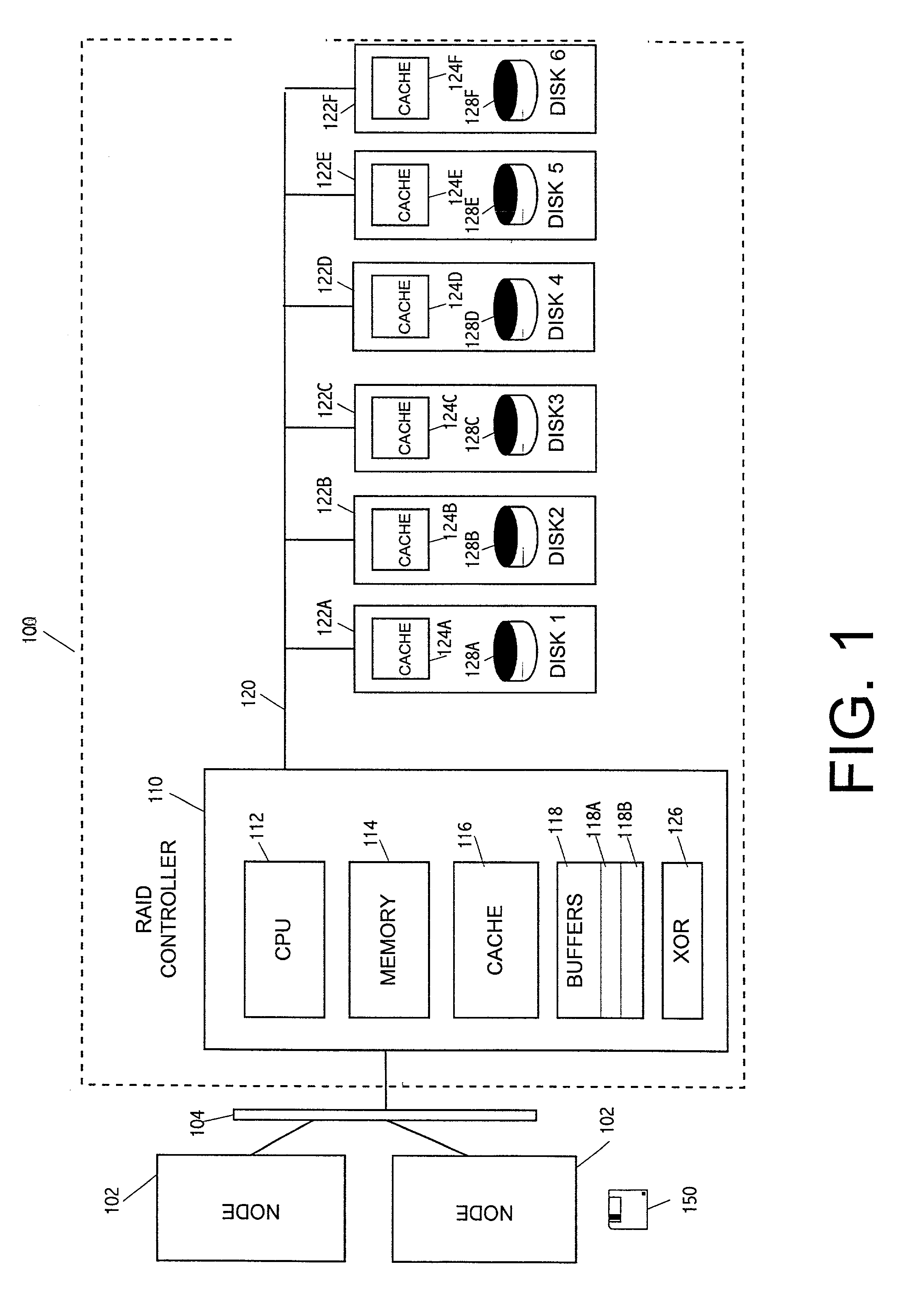
Method and apparatus for supporting parity protected raid in a clustered environment
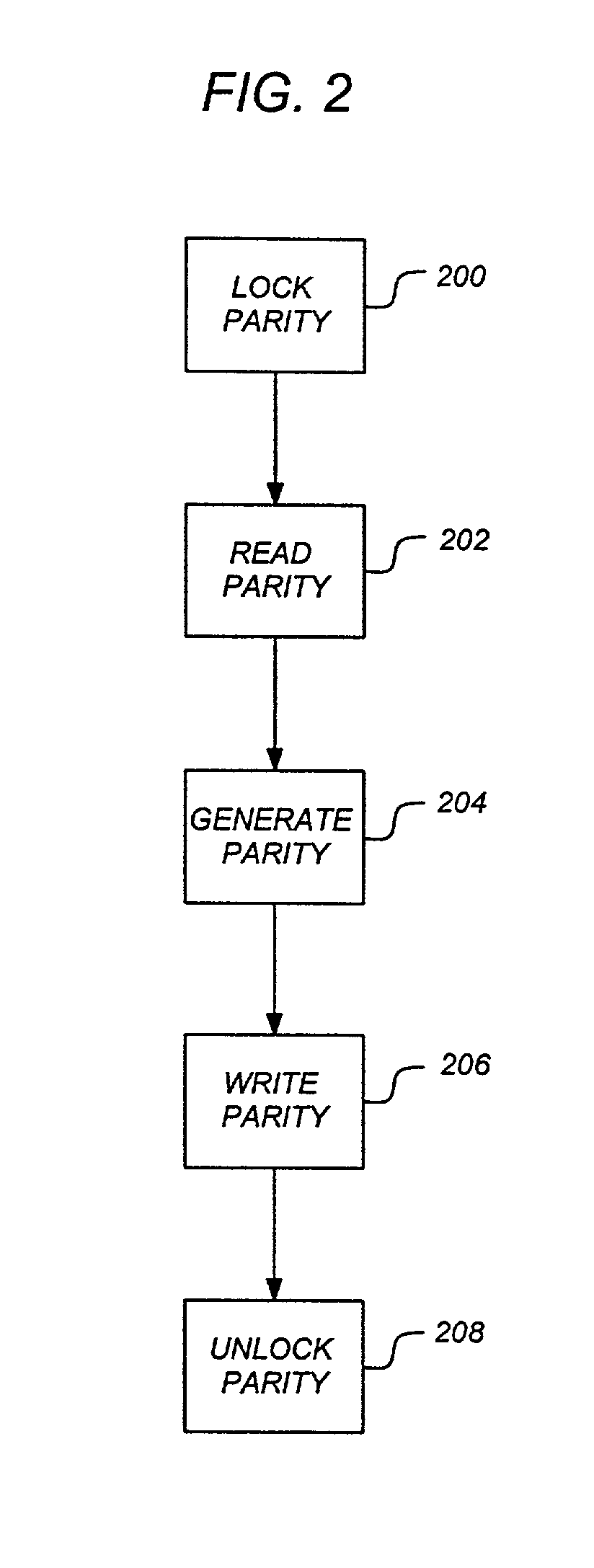
To address the requirements described above, the present invention discloses a method, apparatus, article of manufacture, and a locking structure for supporting parity protected RAID in a clustered environment. When updating parity, the parity is locked so that other nodes cannot access or modify the parity. Accordingly, the parity is locked, read, generated, written, and unlocked by a node. An enhanced protocol may combine the lock and read functions and the write and unlock functions. Further, the SCSI RESERVE and RELEASE commands may be utilized to lock / unlock the parity data. By locking the parity in this manner, overhead is minimized and does not increase as the number of nodes increases.
Owner:IBM CORP
Decoder for iterative decoding of binary cyclic codes
InactiveUS6751770B2Promote resultsEasy to implementOther decoding techniquesCode conversionTanner graphReverse order
Owner:SONY CORP
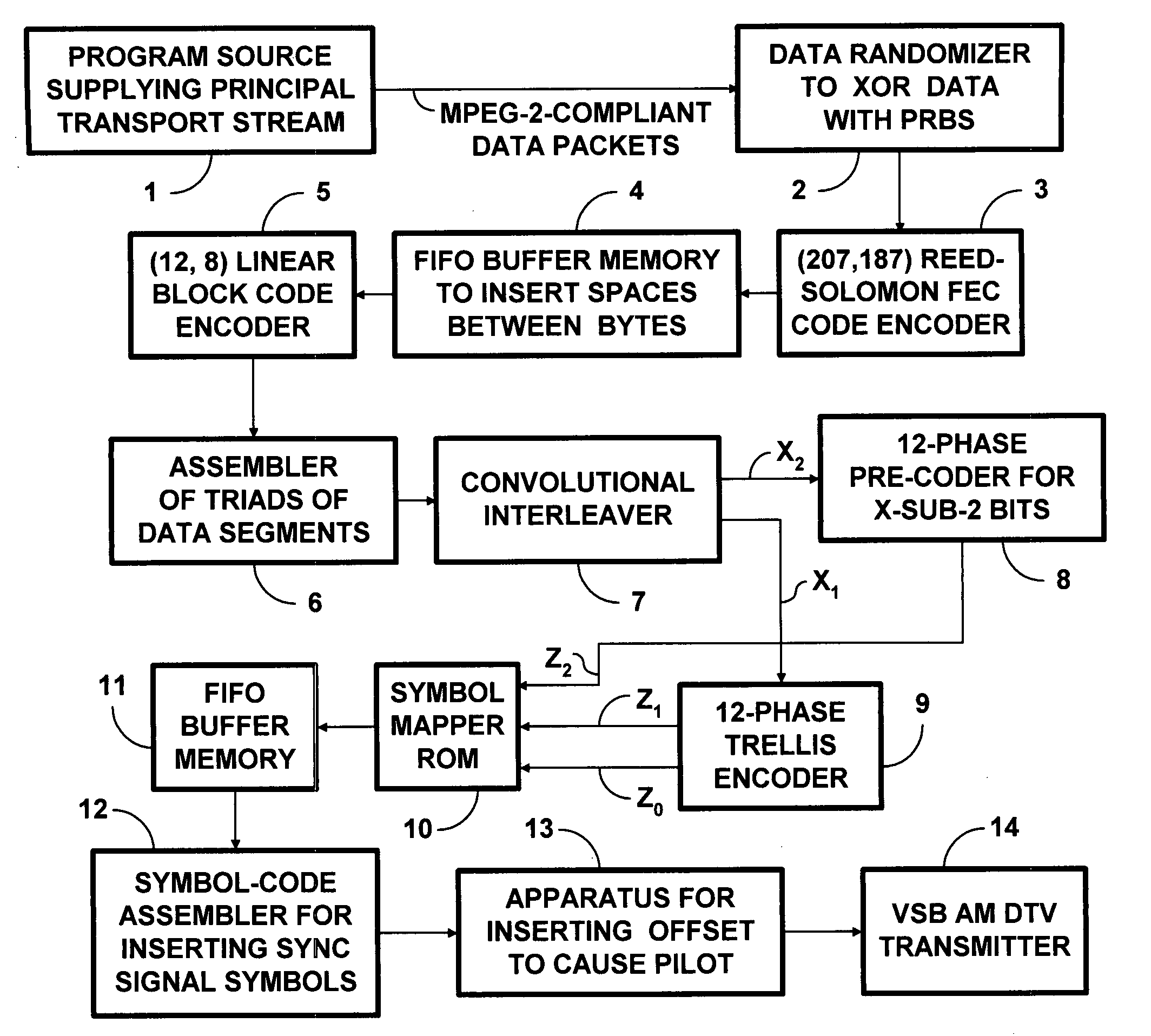
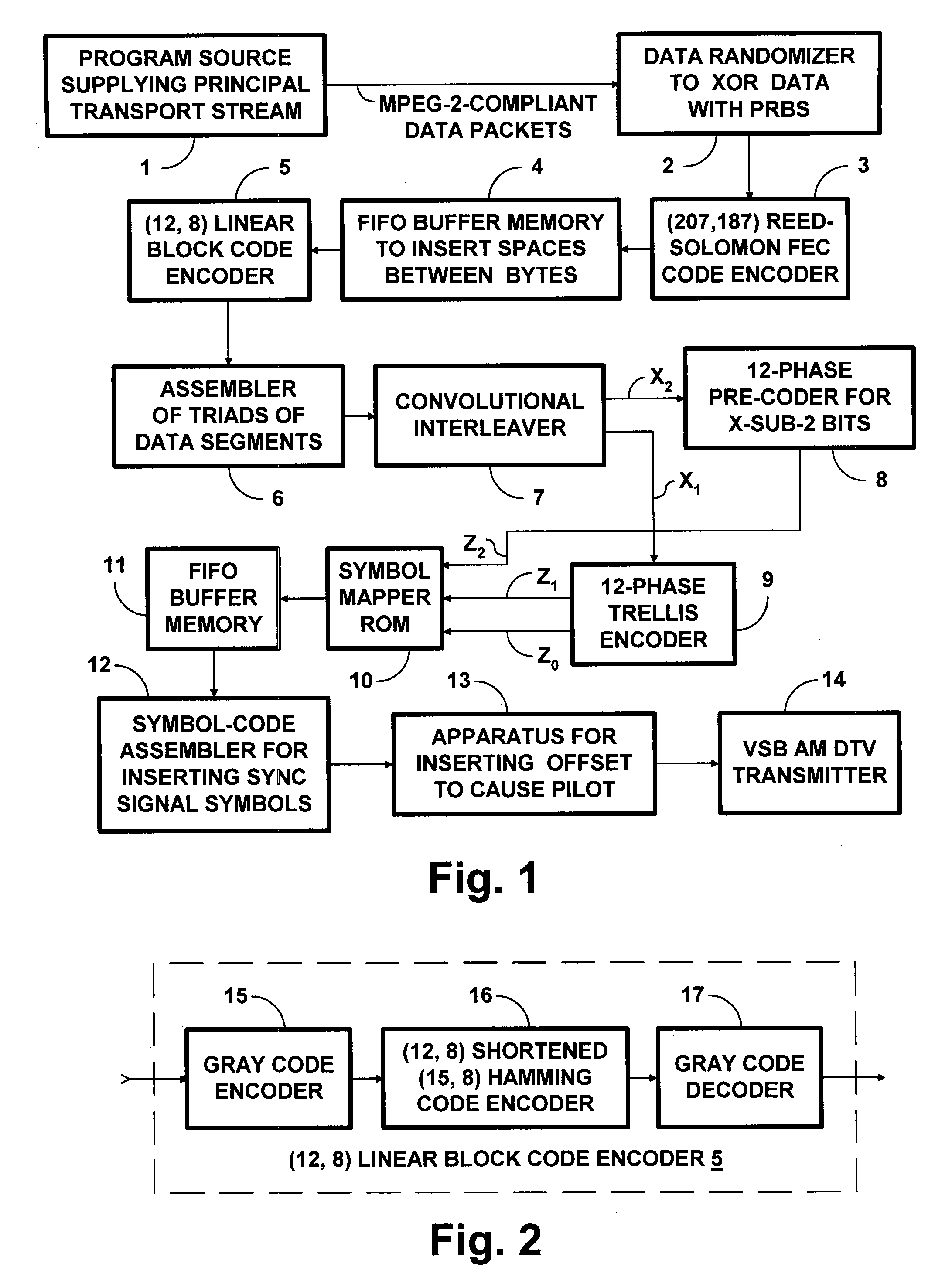
Robust DTV signals transmitted at two thirds the code rate of ordinary 8VSB DTV signals
Owner:LIMBERG ALLEN LEROY
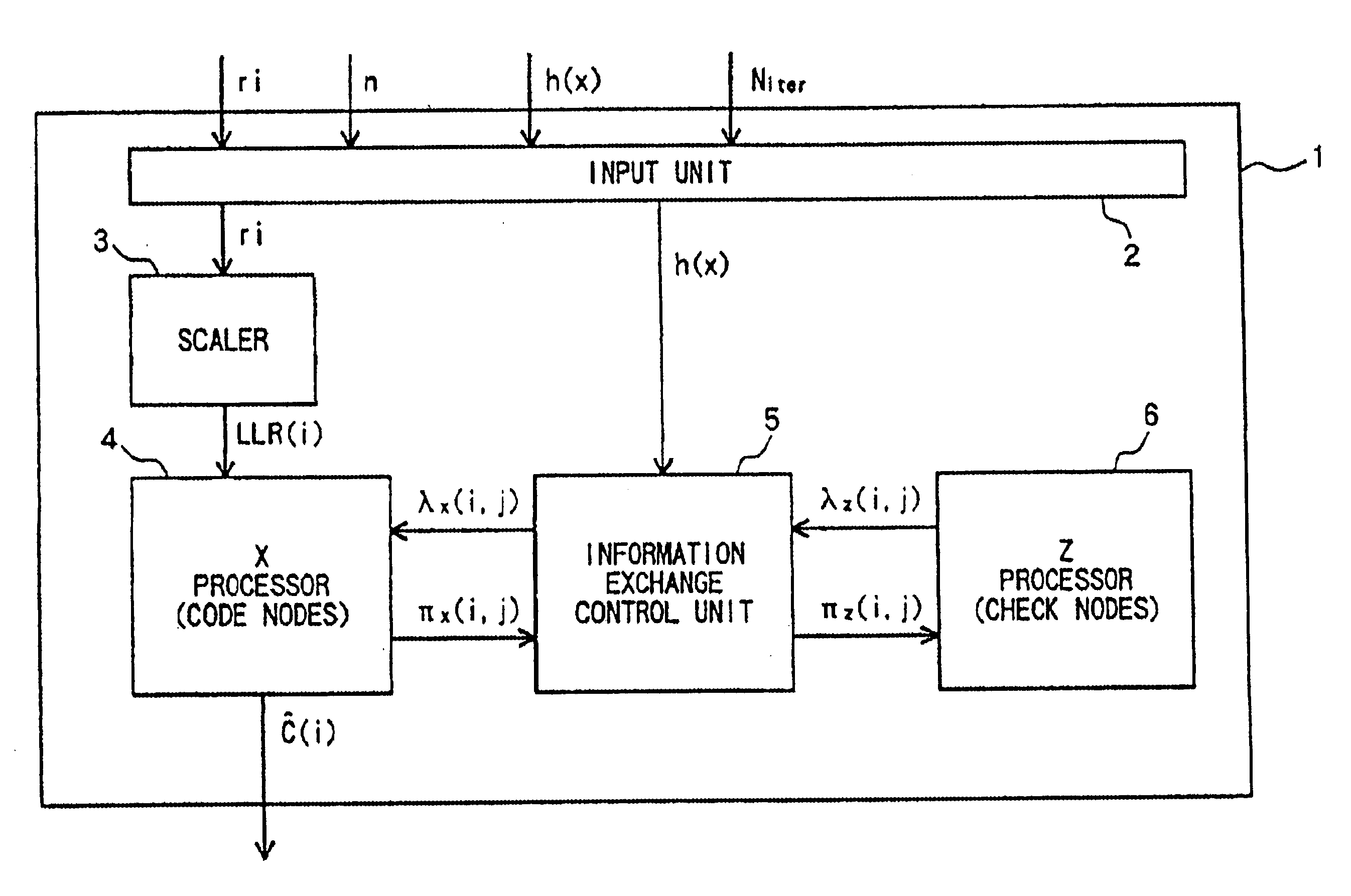
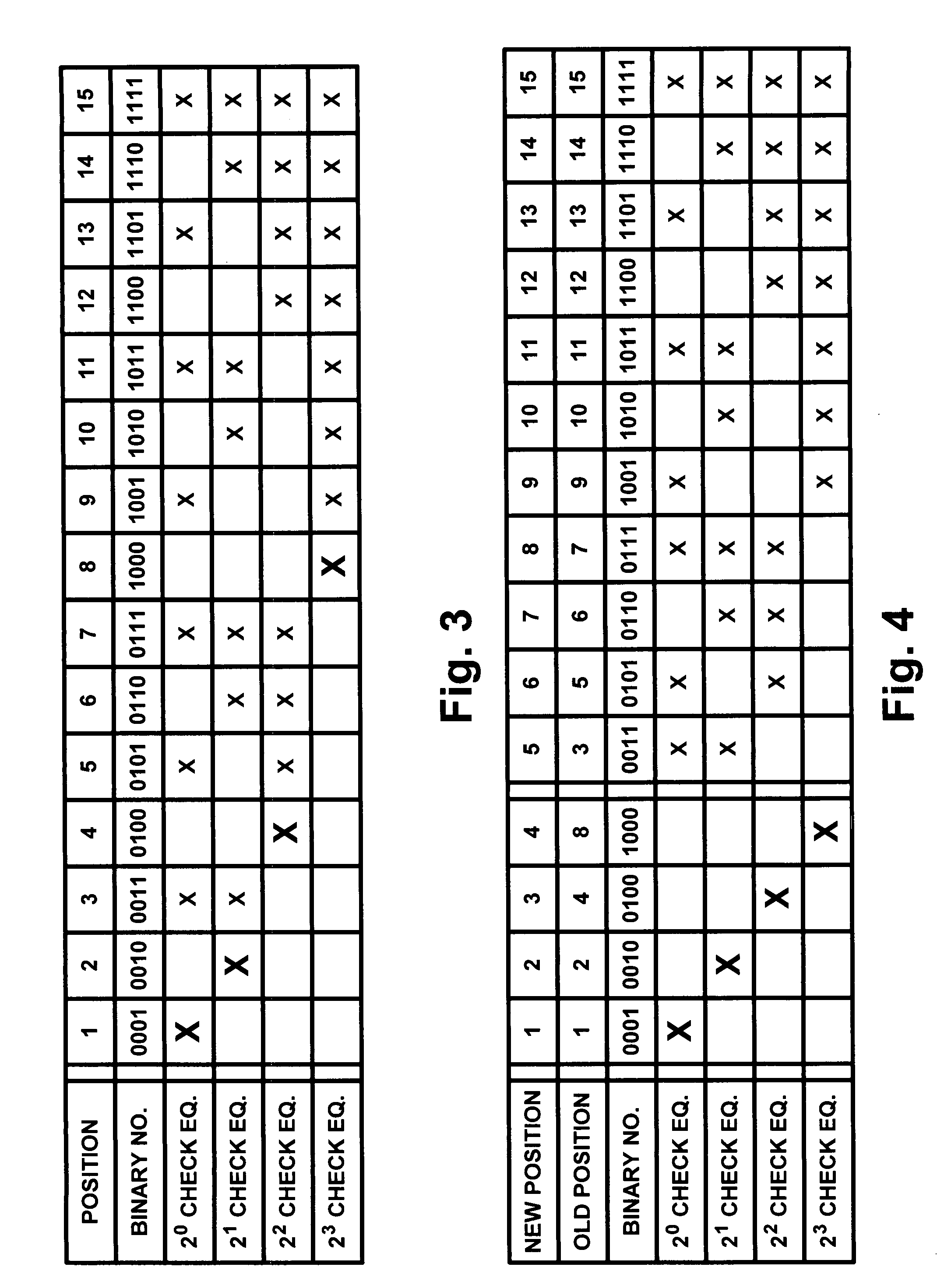
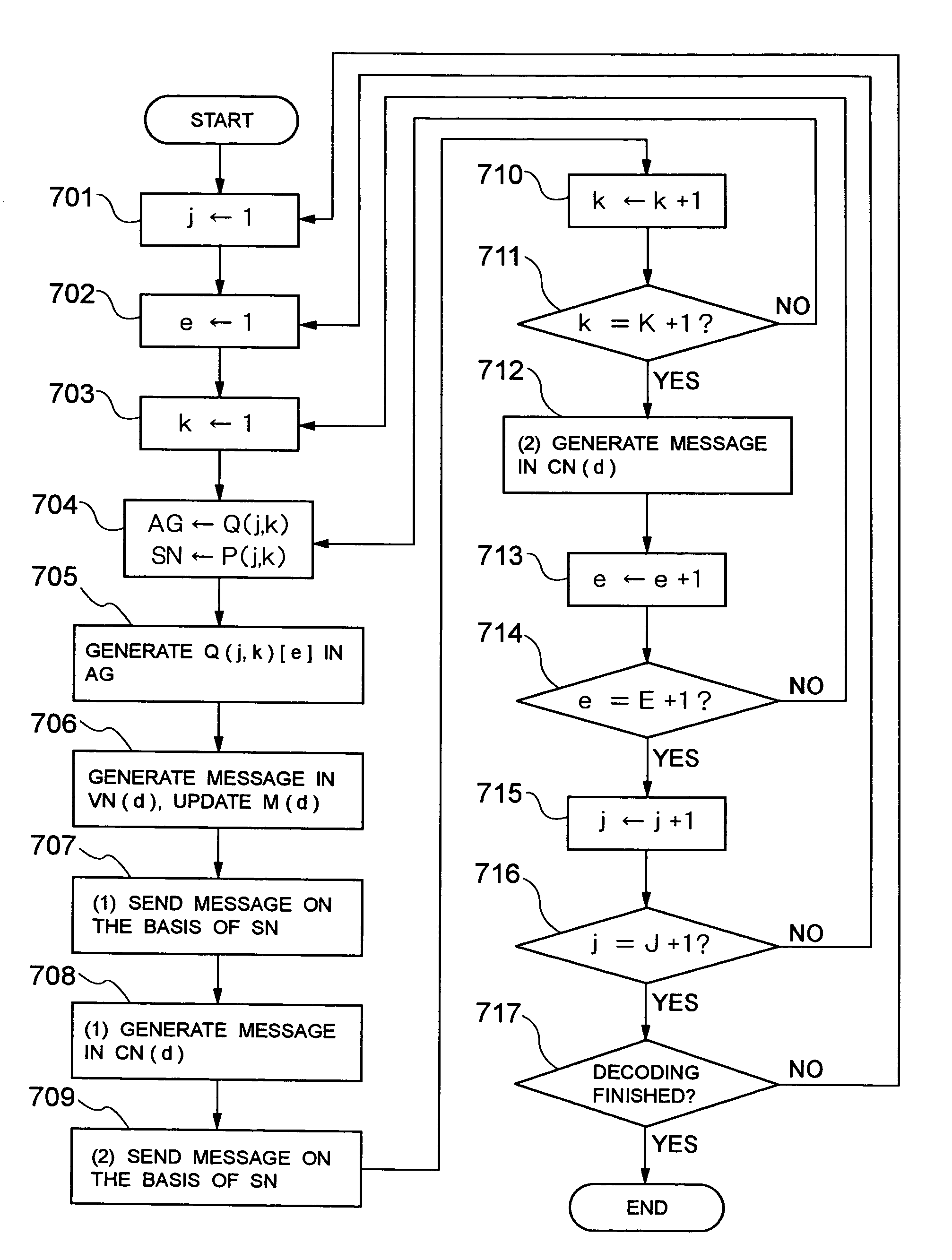
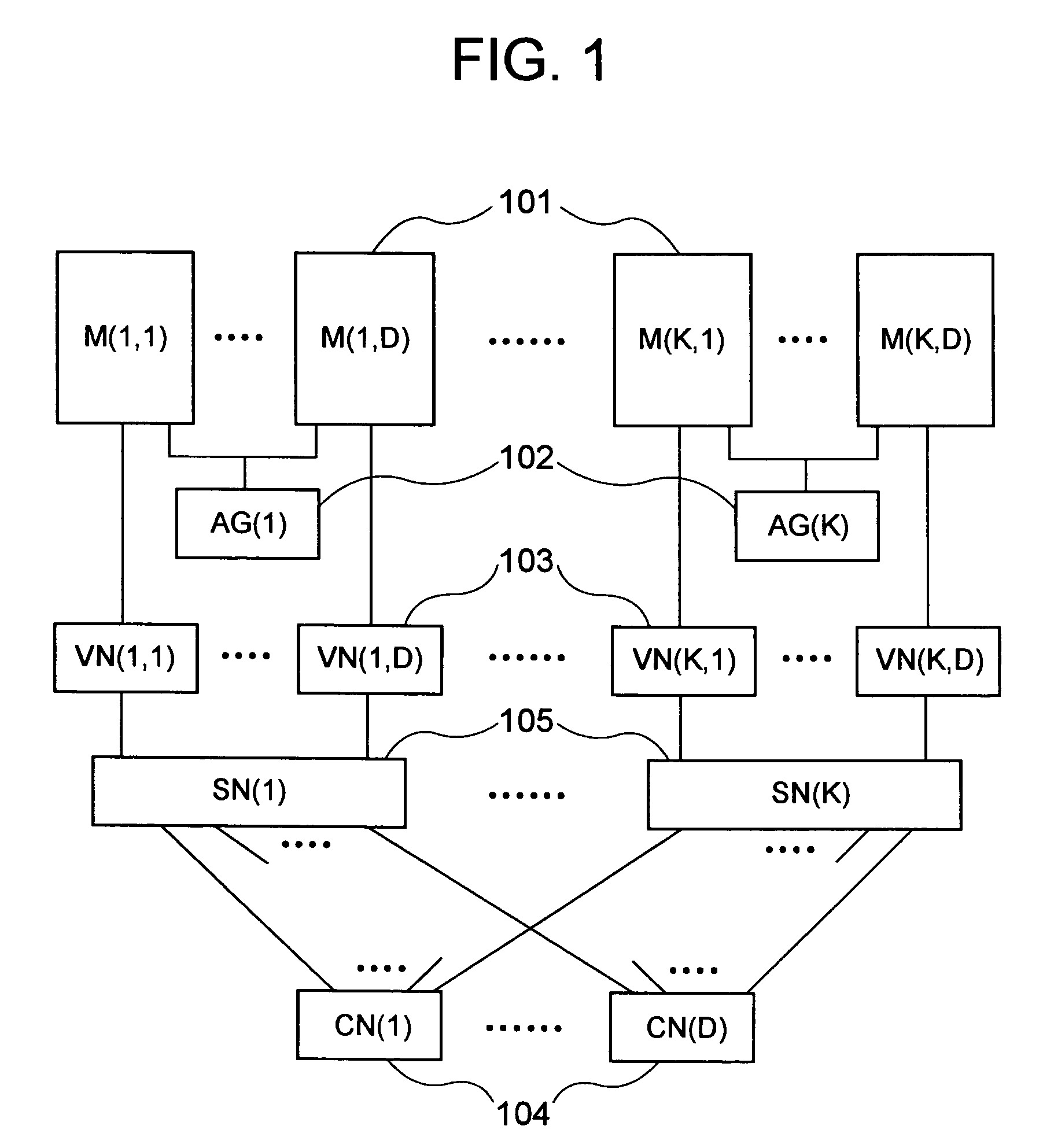
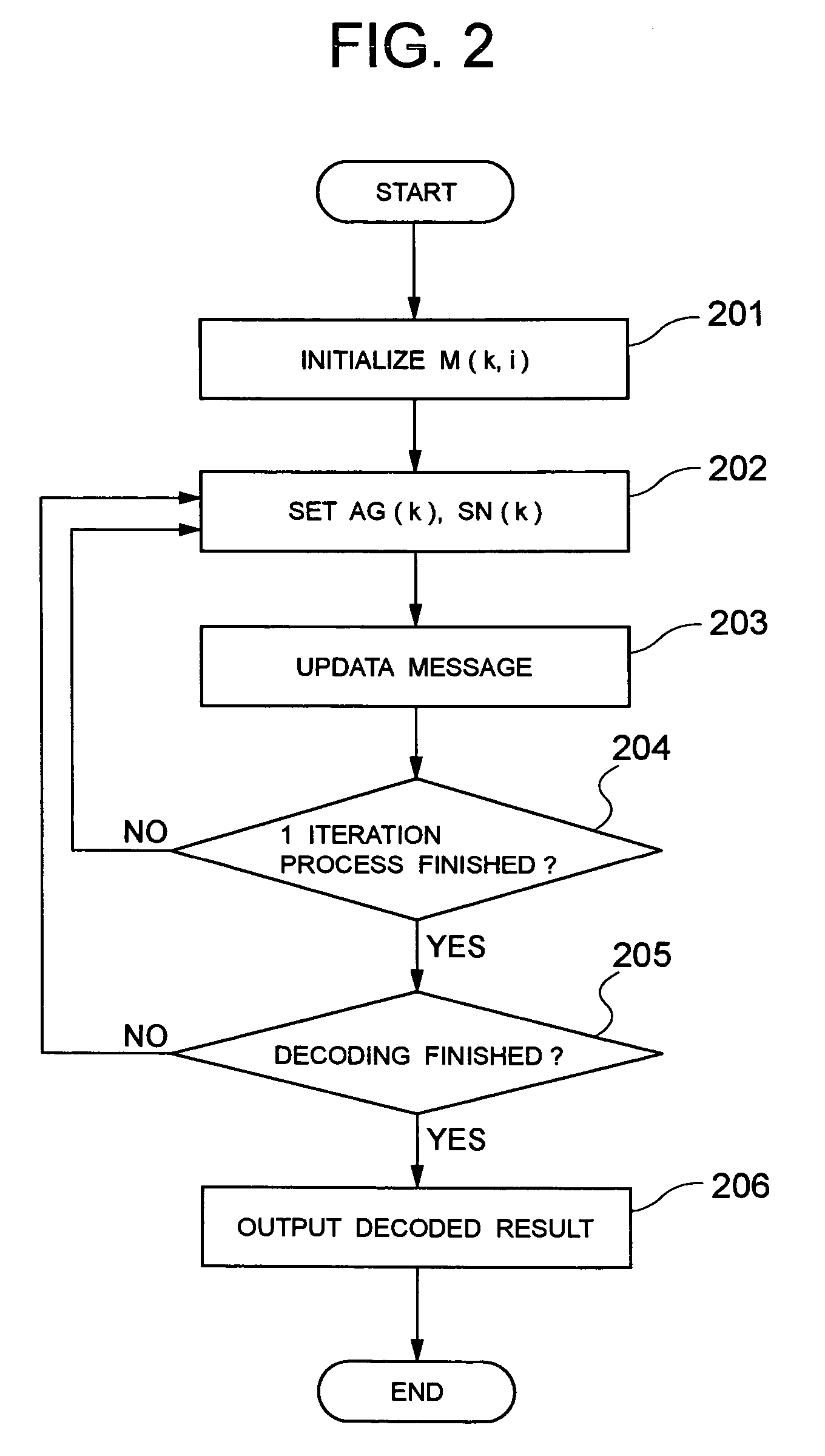
Device, program, and method for decoding LDPC codes
ActiveUS7373581B2Simpler and flexibleError preventionTransmission systemsAddress generation unitMessage passing decoding
A parallel decoder, which is simpler and more flexible than conventional devices, is provided in decoding device for a LDPC code. The present invention includes a plurality of memory units for storing a received value and a message generated during a Message-Passing decoding, a plurality of variable node function units, a plurality of check node function units, a plurality of address generation units for generating an address of each of memory units, and a plurality of shuffle network units for determining a connection between variable node function units and check node function units. An address generation unit generates an address on the basis of a plurality of permutations. Each shuffle network unit is connected to some of the variable node function units. This connection is determined on the basis of a plurality of permutations. A change of the permutations in the address generation units and a change of the permutations in the shuffle network units are performed in the same cycle in a decoding process.
Owner:NEC CORP
File download and streaming system
ActiveUS20050257106A1Reduce expensesError preventionOther decoding techniquesOrder setComputer science
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
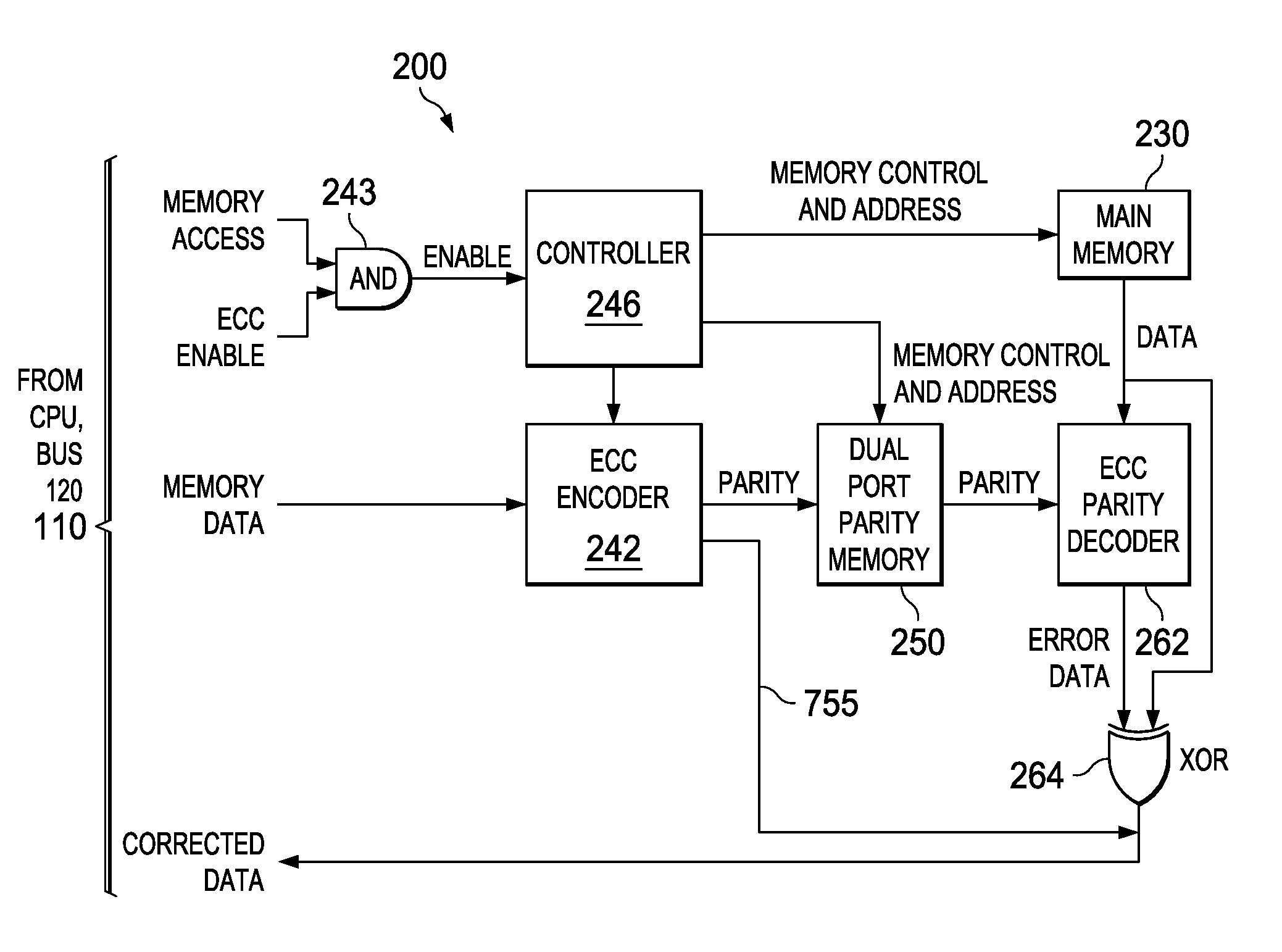
Low overhead and timing improved architecture for performing error checking and correction for memories and buses in system-on-chips, and other circuits, systems and processes
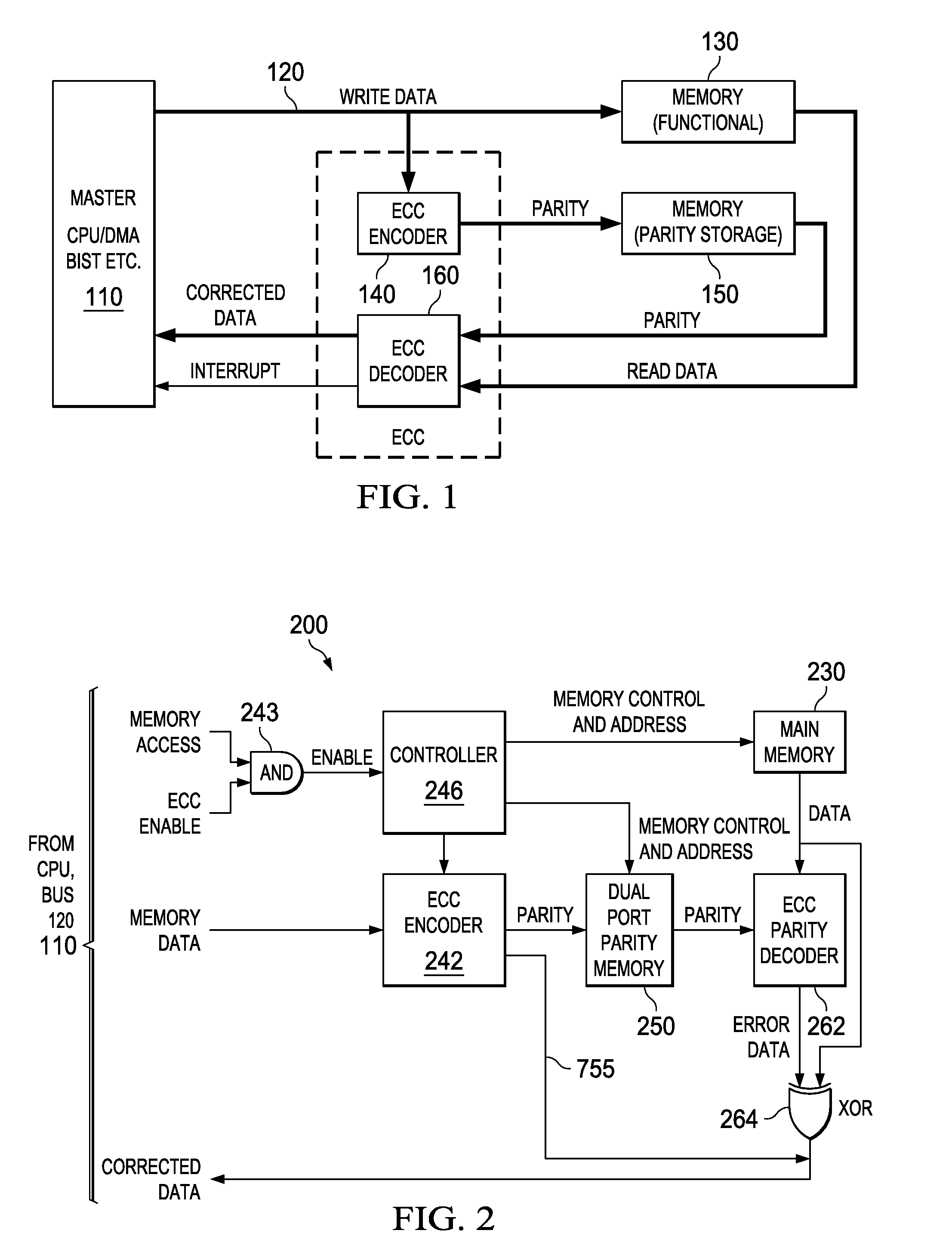
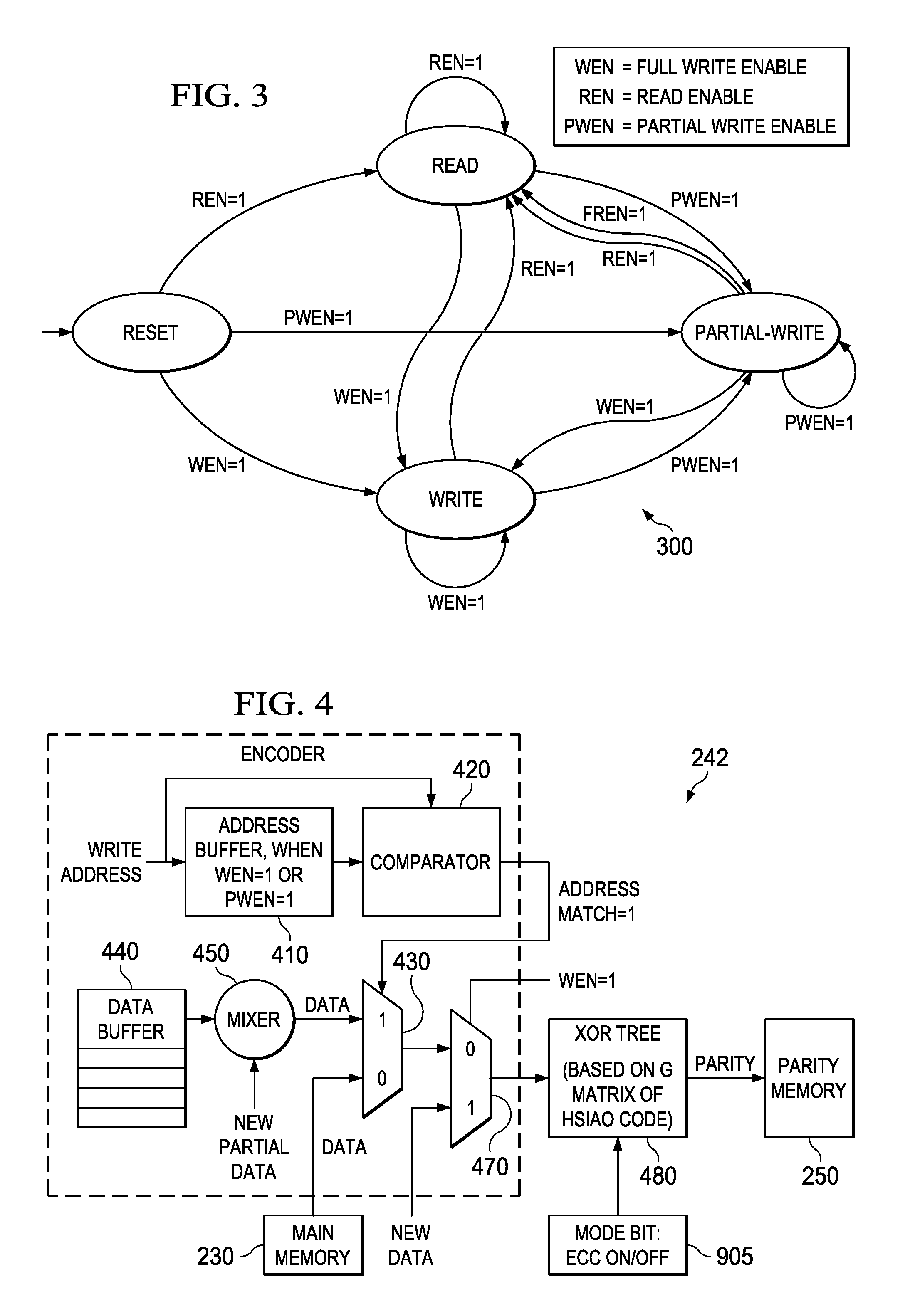
An electronic circuit (200) for use with an accessing circuit (110) that supplies a given address and a partial write data portion and also has dummy cycles. The electronic circuit (200) includes a memory circuit (230) accessible at addresses, an address buffer (410), a data buffer (440) coupled to the memory circuit (230), and a control circuit (246) operable in the dummy cycles to read data from the memory circuit (230) to the data buffer (440) from a next address location in the memory circuit (230) and to store that next address in the address buffer (410). The electronic circuit further includes a multiplexer (430), a comparing circuit (420) responsive to the given address and a stored address in the address buffer (410), to operate the multiplexer (430) to pass data from the data buffer (440) or to pass data from the memory circuit (230) instead; and a mixer circuit (450) operable to put the partial write data portion into the data taken from the selected one of the data buffer (440) or memory circuit (230). Other circuits, devices, systems, processes of operation and processes of manufacture are also disclosed.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Popular searches
Error correction/detection by combining multiple code structures Digital storage Memory systems Record information storage Error detection only Digital signal error detection/correction Substation equipment Error correction/detection using interleaving techniques Redundant data error correction Baseband systems
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com