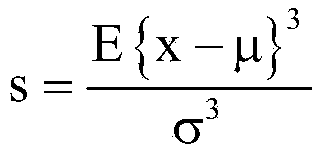Patents
Literature
149 results about "Multipath propagation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
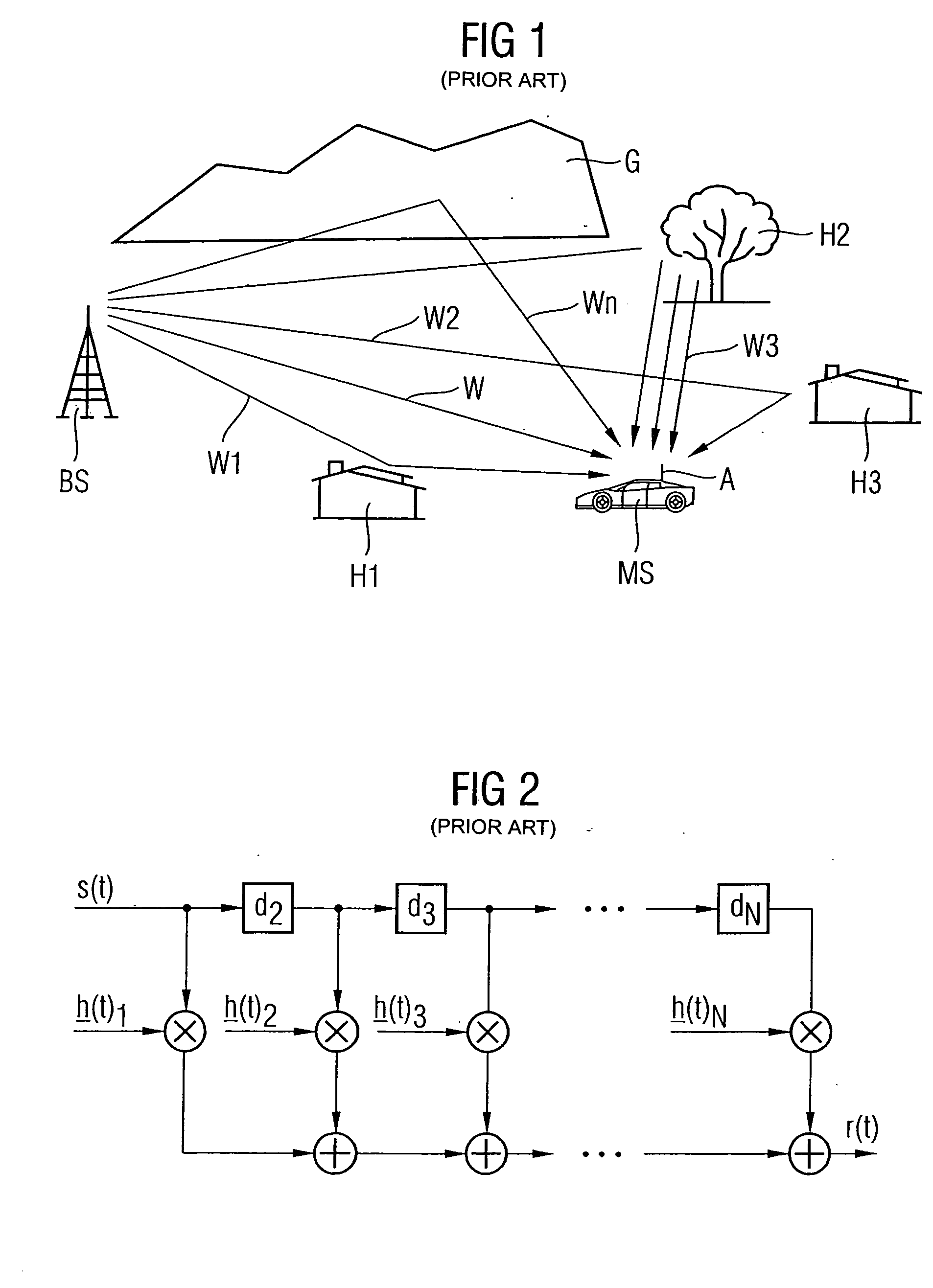
In wireless telecommunications, multipath is the propagation phenomenon that results in radio signals reaching the receiving antenna by two or more paths. Causes of multipath include atmospheric ducting, ionospheric reflection and refraction, and reflection from water bodies and terrestrial objects such as mountains and buildings.
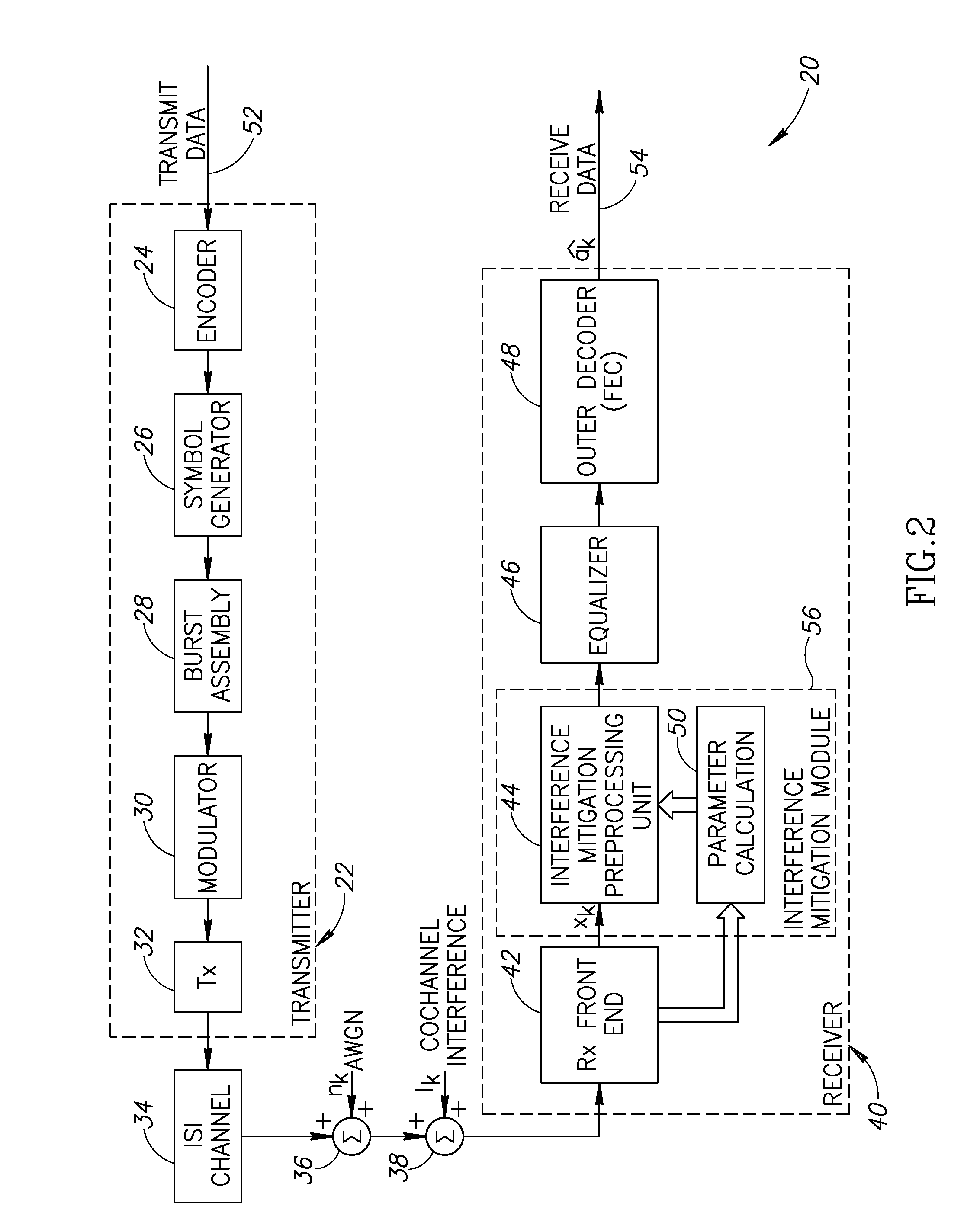
System and method for error correcting a received data stream in a concatenated system
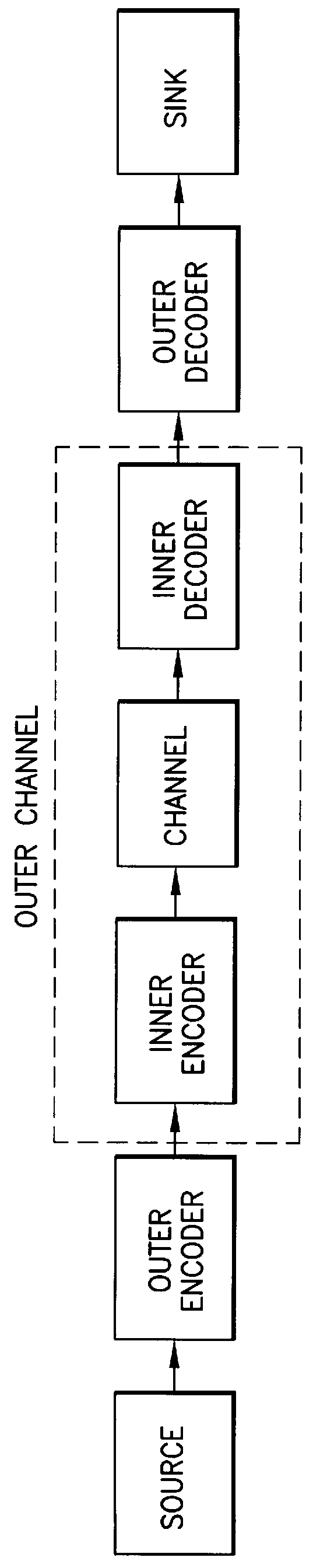
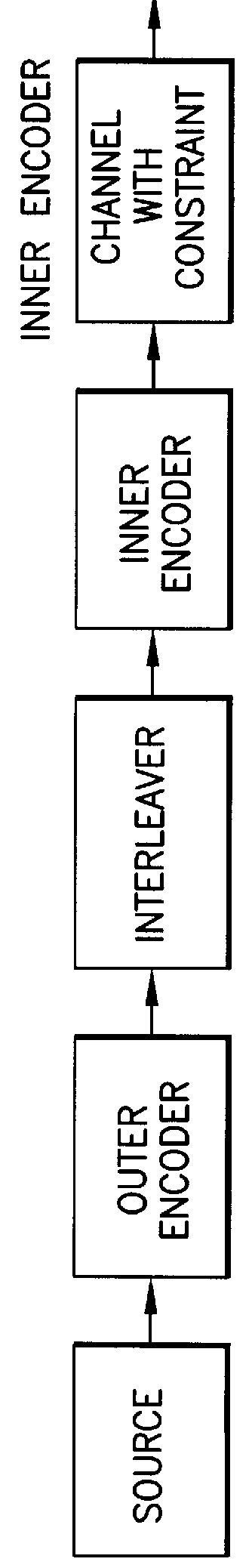
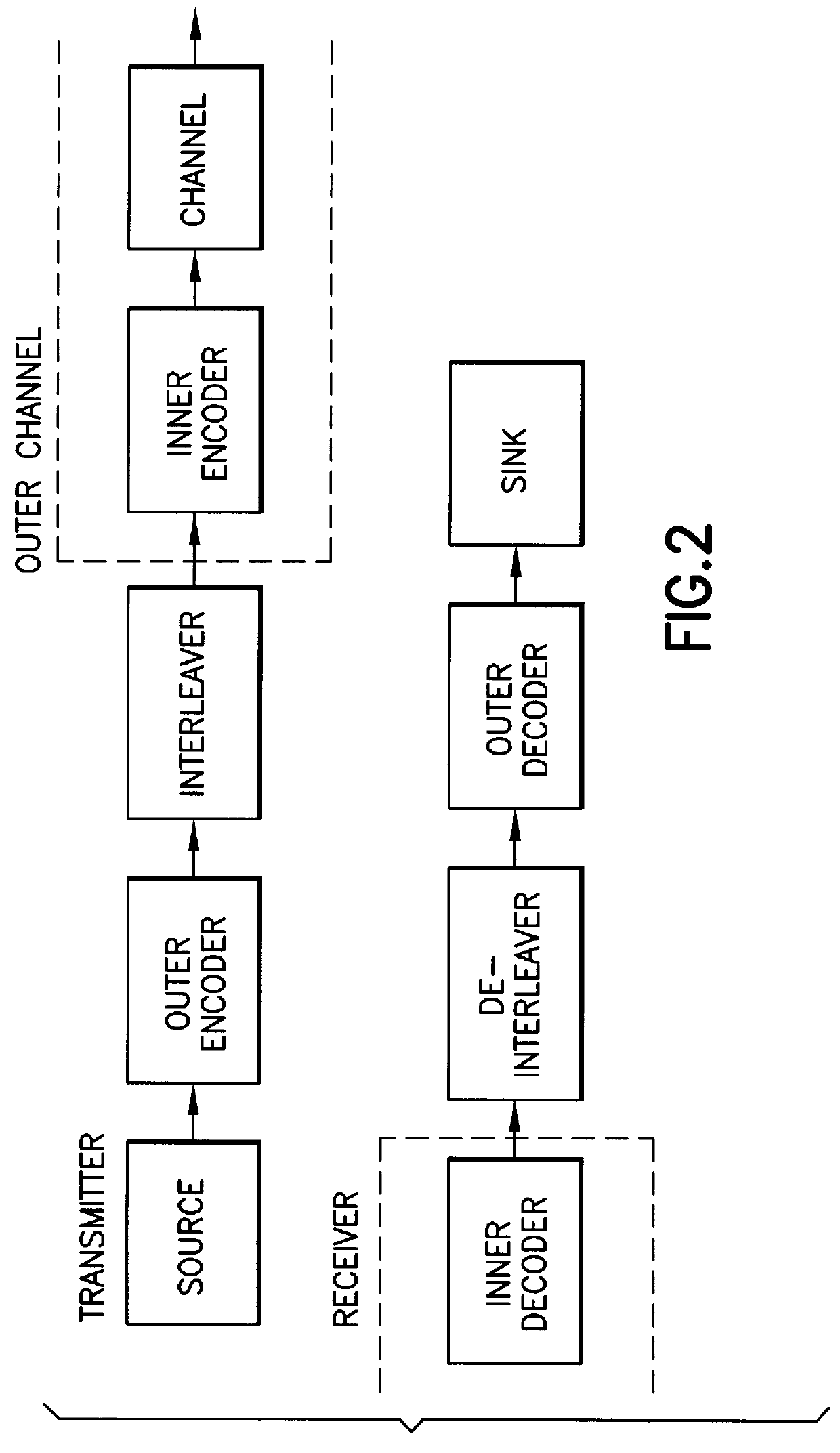
A received signal is first converted into a digital sequence that may contain "erasures" (or ambiguity symbols) as well as errors. Then iterative decoding is applied in order to eliminate or reduce the erasures. This decoding procedure works effectively with the associated transmitter that adopts a concatenation of an outer coder, a permutation and an inner coder. The principal of the invention is also applicable to a system in which the inner coder is replaced by a "digital modulator" that introduces some constraint, or a channel that introduces some memory such as partial response signaling, intersymbol interference or multipath propagation. The invention can be applied to many existing systems while maintaining "backward compatibility" in the sense that the transmitter side need not be modified.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
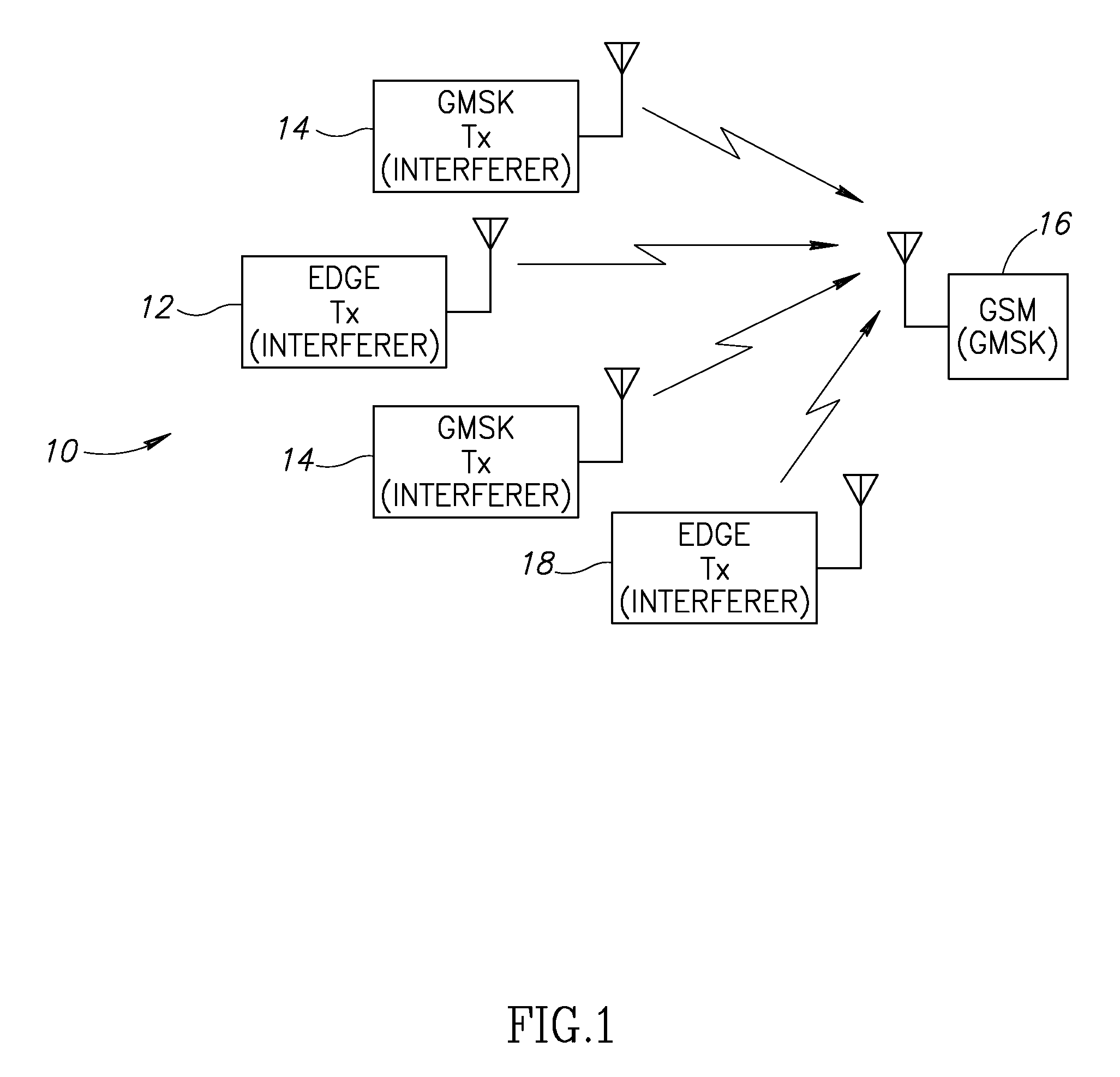
Blind interference mitigation in a digital receiver
InactiveUS20070127608A1Improve acceleration performanceReduce computational complexityError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionEngineeringCo-channel interference
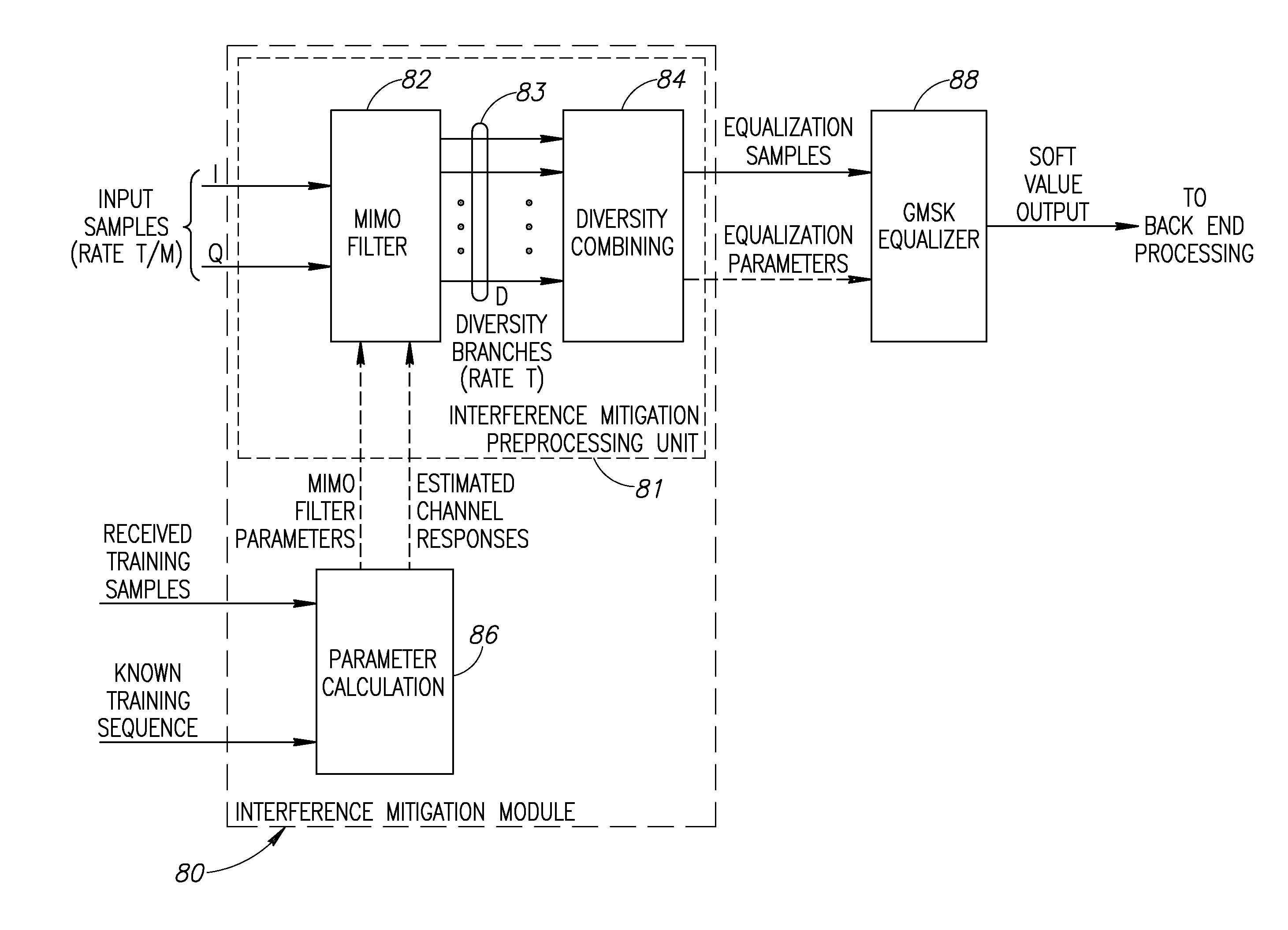
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK) single antenna interference cancellation (SAIC) for use in a digital receiver. The invention comprises an interference mitigation module that treats the problem of GMSK SAIC in a blind manner. The interference mitigation mechanism is operative to compensate for the co-channel interference added in the communications channel which is subject to multipath propagation and fading, receiver filter and any pre-channel estimation filtering. The interference mitigation module takes advantage of the spatial diversity making up multiple branches of the received signal. The branches comprise the in-phase and quadrature elements of the received signal, the sampling phases if over sampling is applied (i.e. T / m sampling) and / or multiple antennas. The invention utilizes the spatial diversity of these multiple representations of the received signal and combines (i.e. collapses) the information in the plurality of branches into a single branch that is input to the equalizer.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
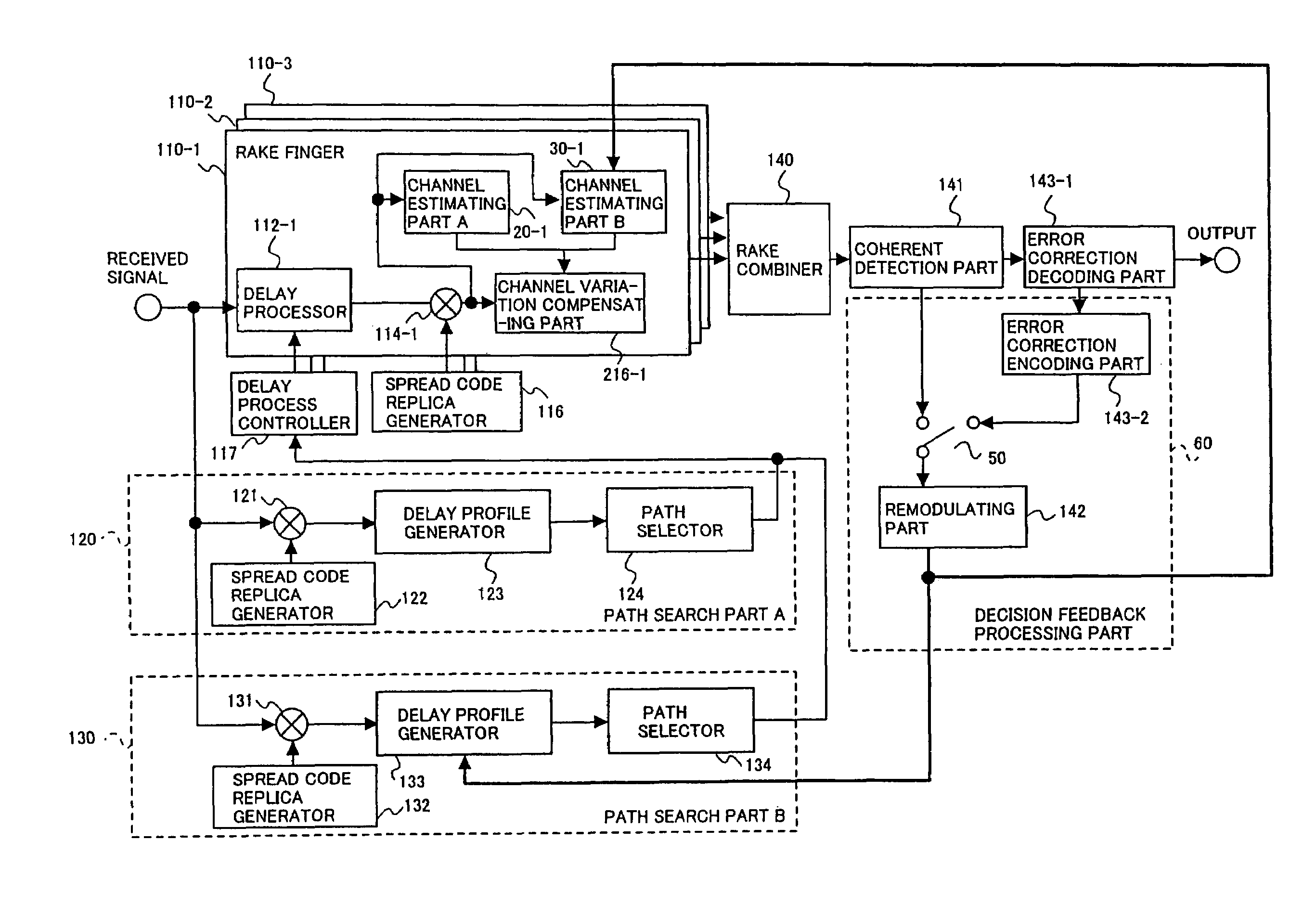
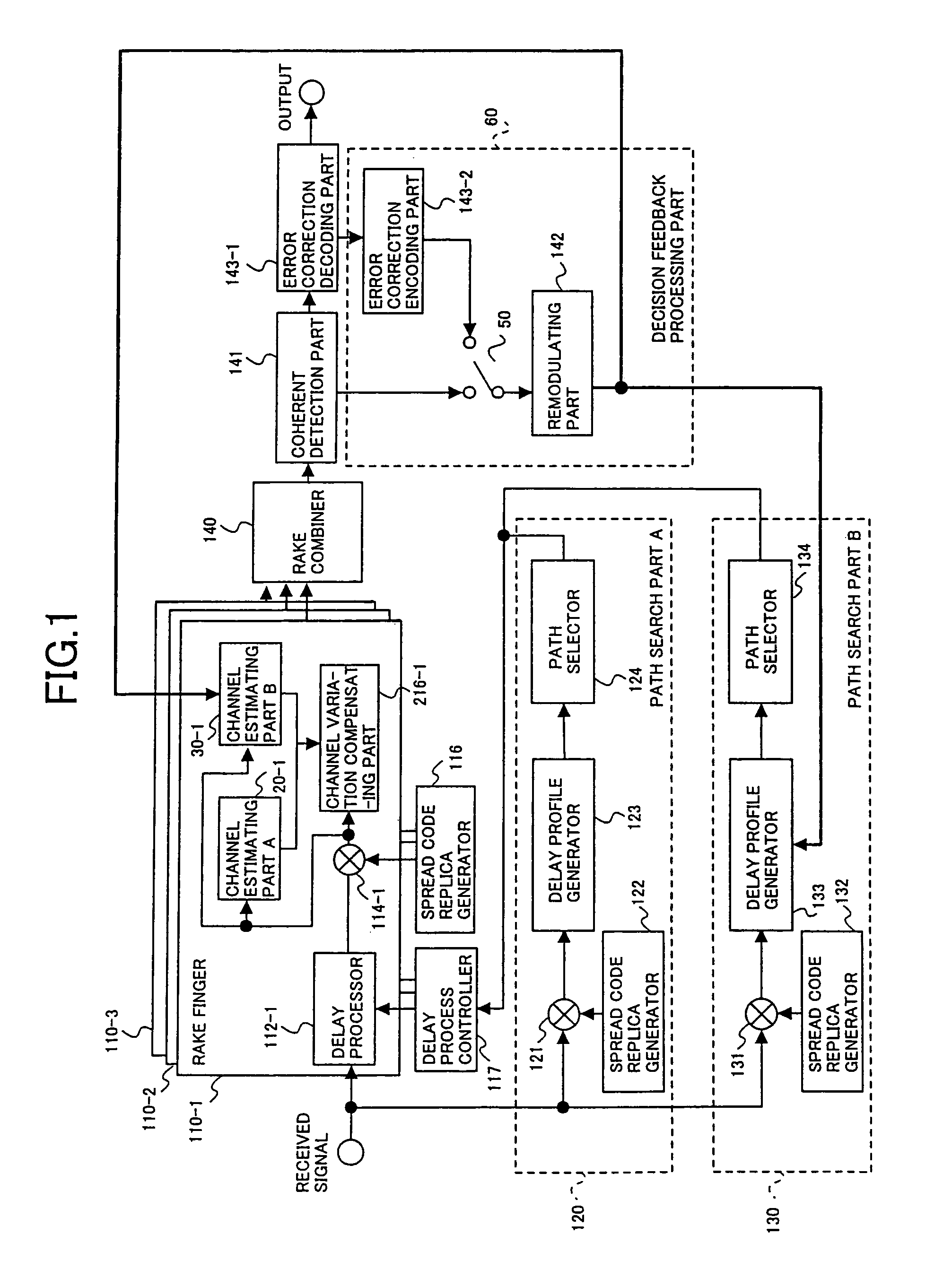
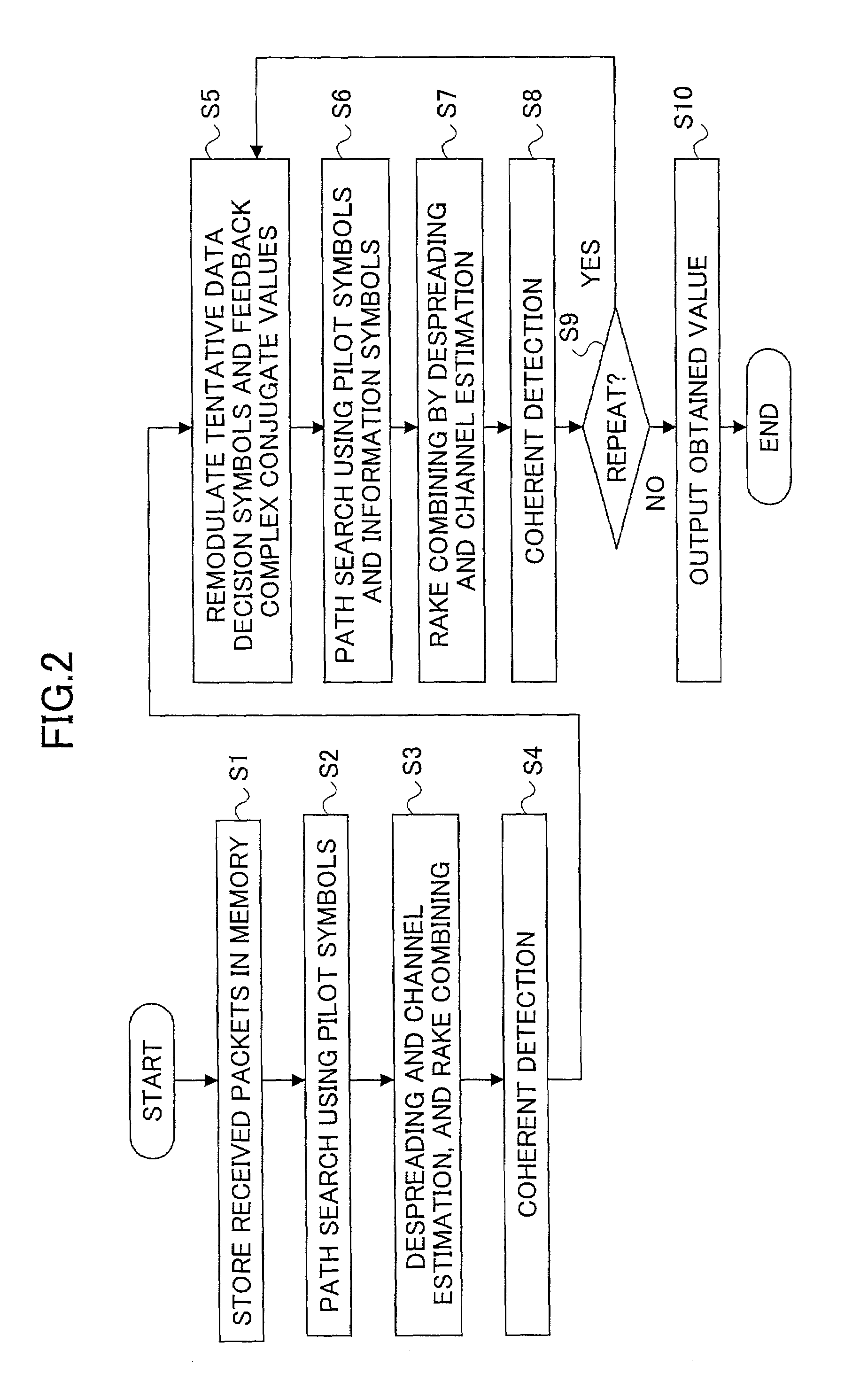
Path search method, channel estimation method and communication device
InactiveUS7072381B2High-accuracy path searchBaseband system detailsNetwork traffic/resource managementEstimation methodsComputer science
A communication device includes at least one of path search means for detecting respective timings of path components included a signal received via a multipath propagation path using pilot symbols of a known phase included in said received signal and channel estimation means for estimating channel variation using the pilot symbols. The path search means includes a first path search part for detecting respective timings of path components using pilot symbols and a second path search part for detecting respective timings of path components using information symbols derived from a signal demodulated according to the timings detected in the first path search part and pilot symbols. The channel estimation means includes a pilot symbol acquiring part for acquiring pilot symbols included in the received signal and a channel estimation part for implementing channel estimation using the acquired pilot symbols.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
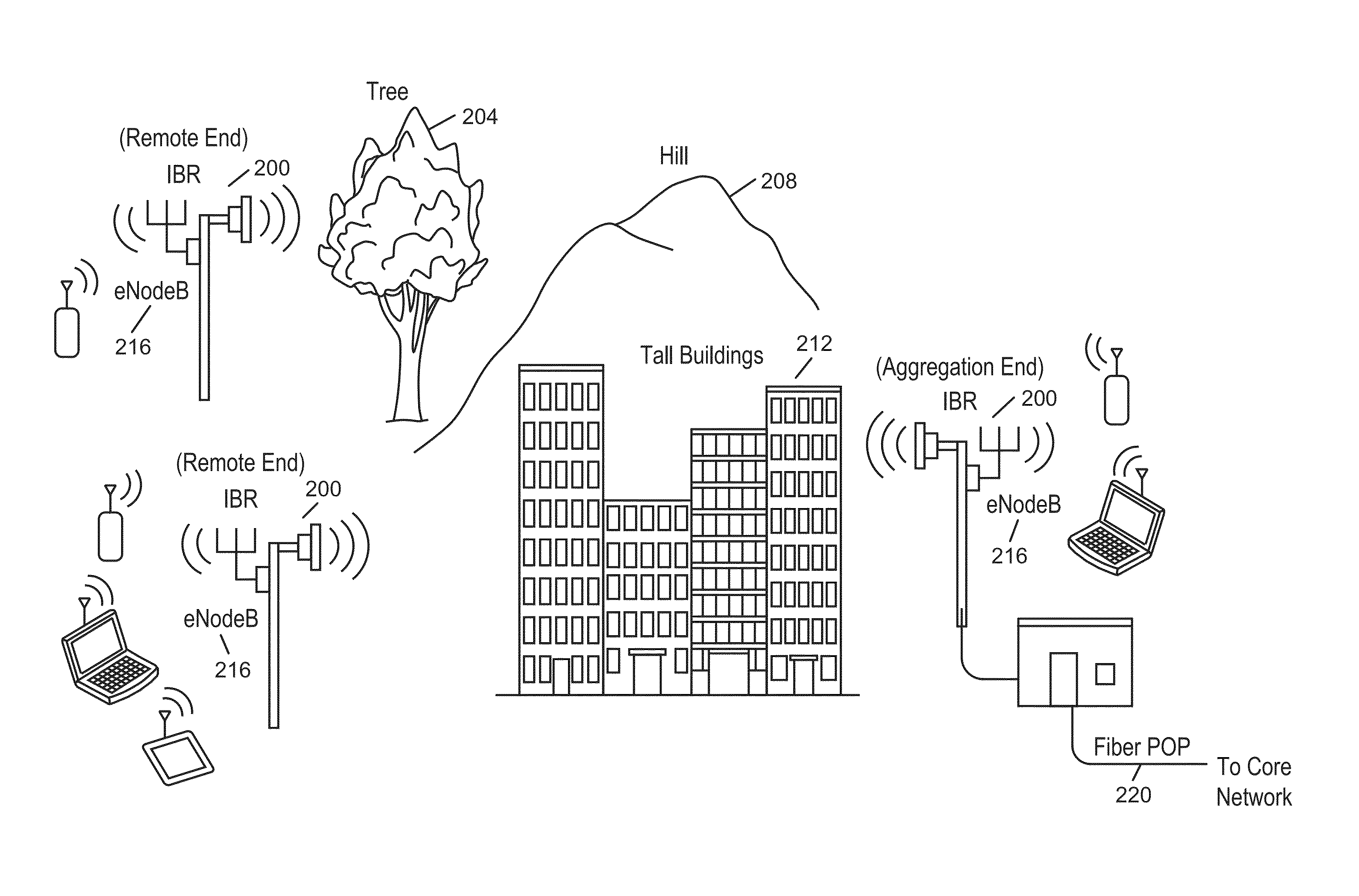
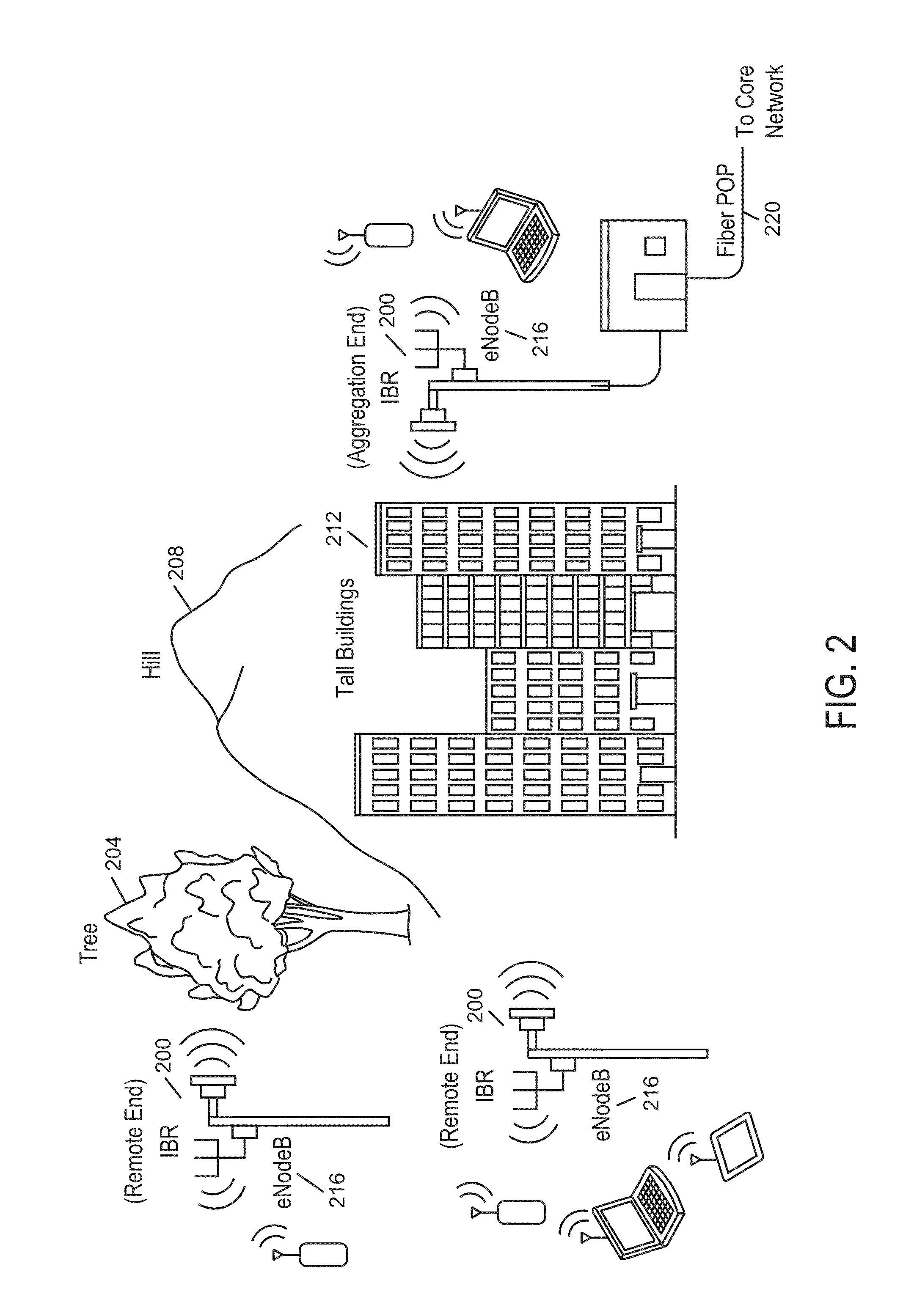
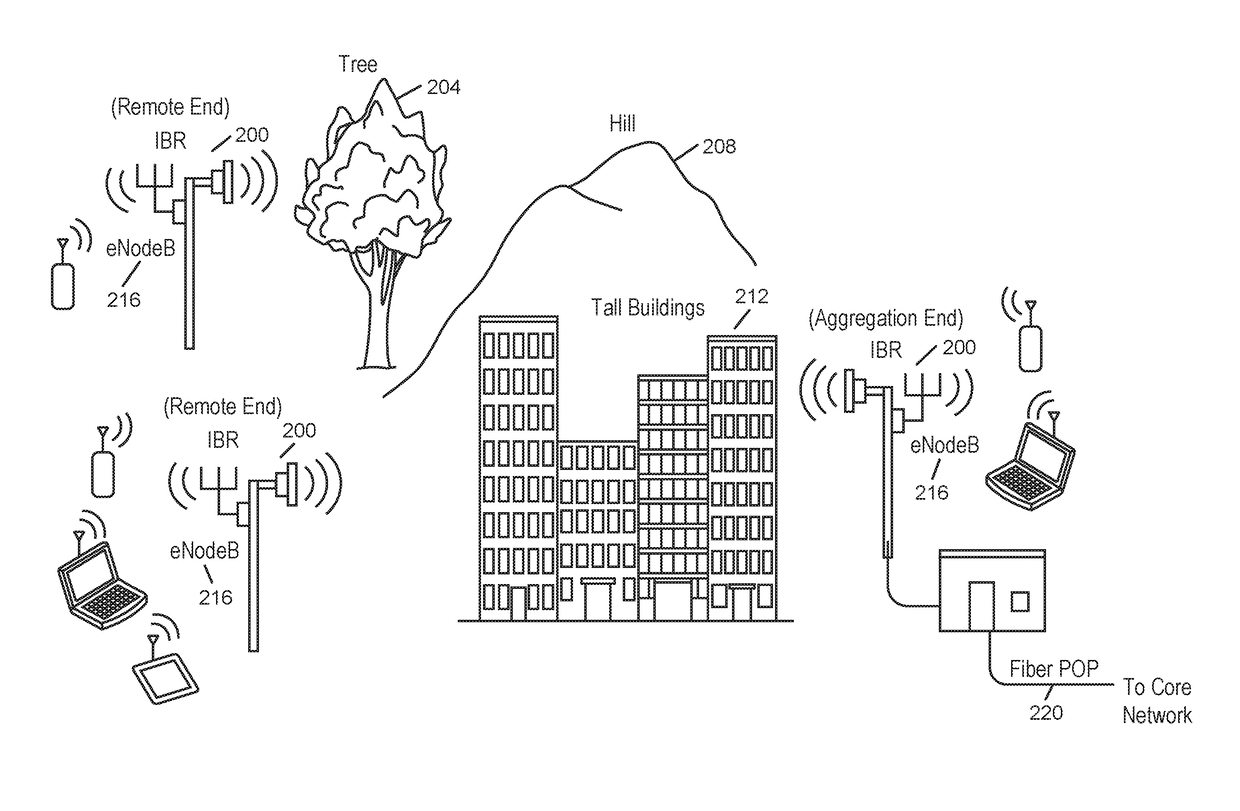
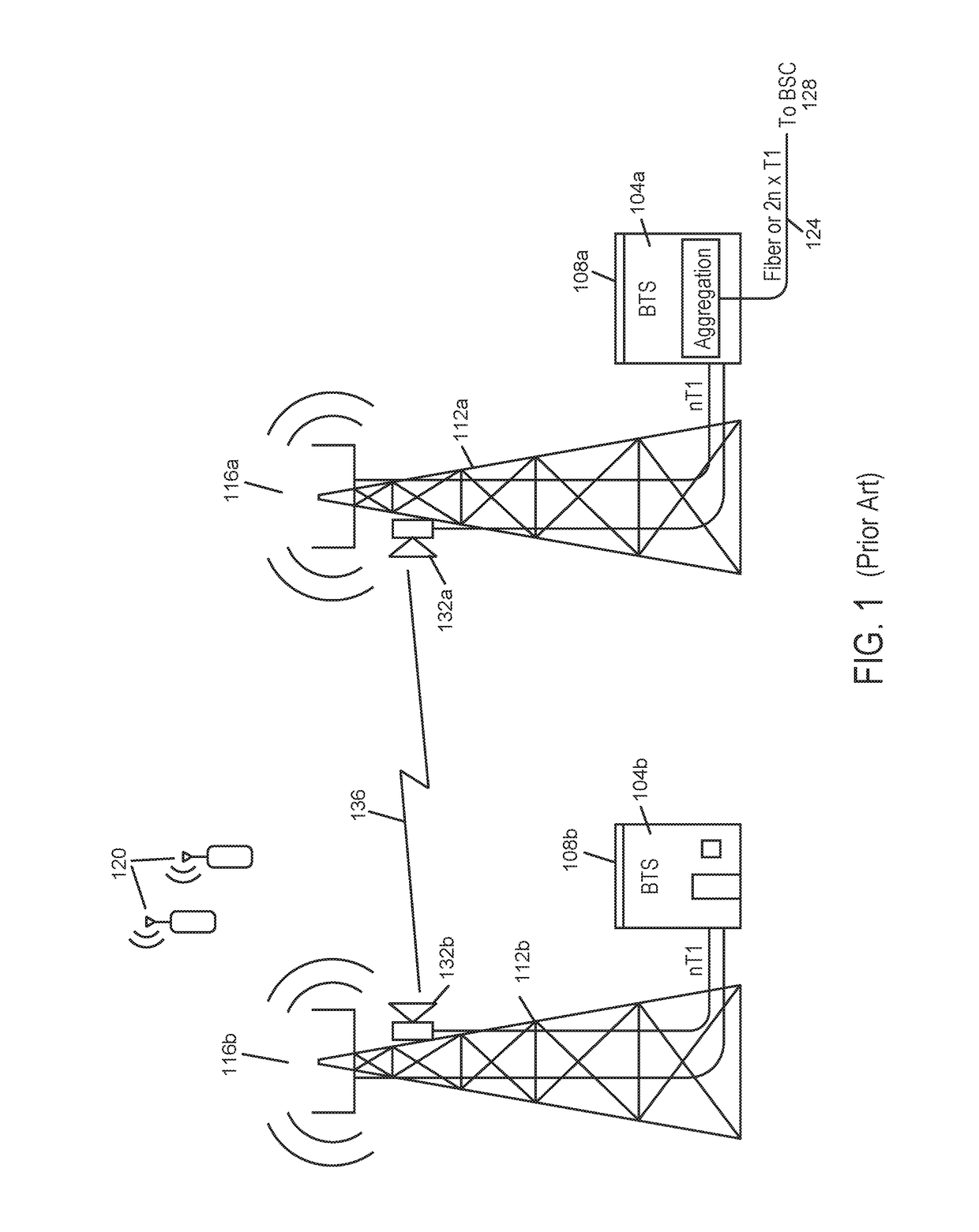
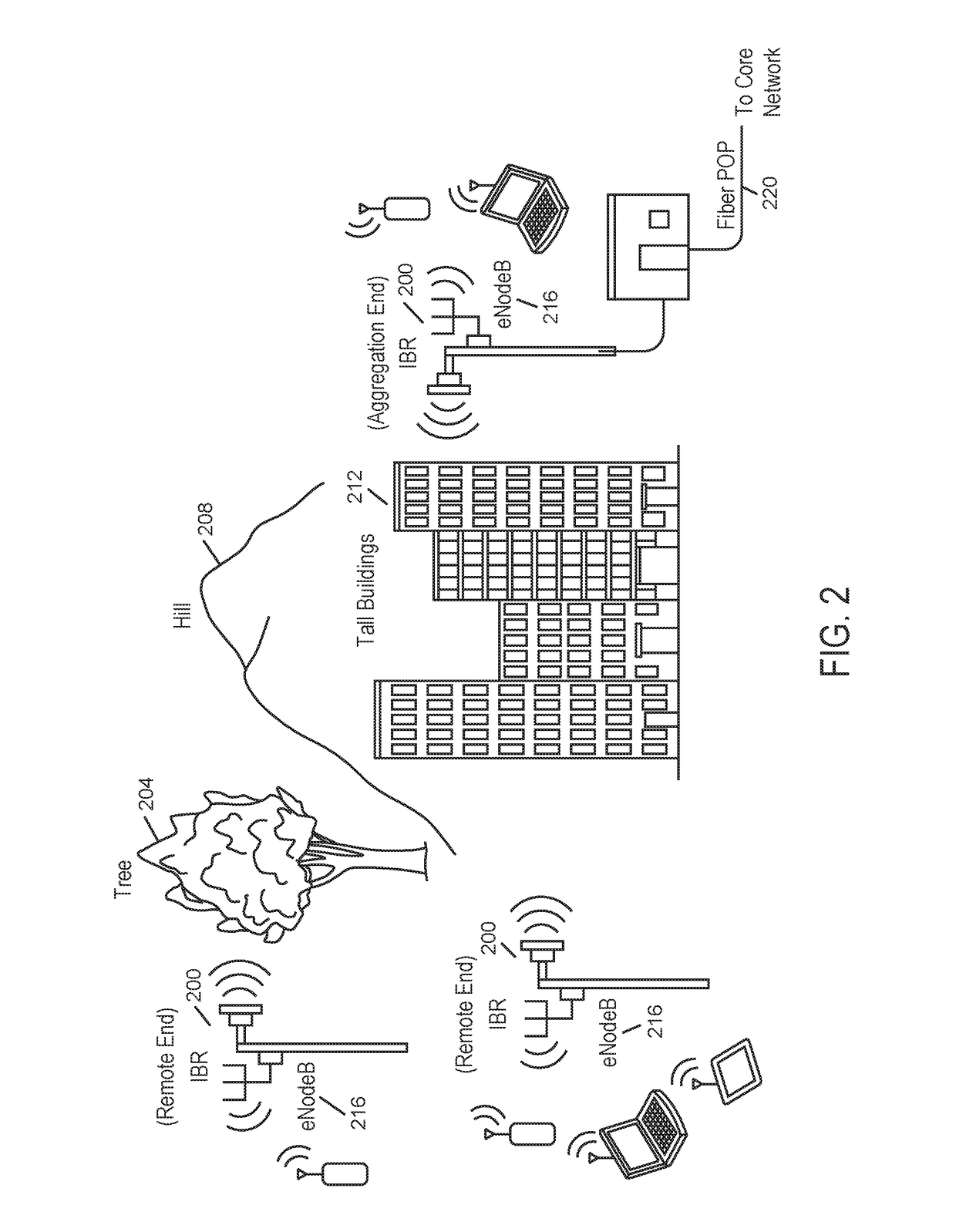
Backhaul radio with extreme interference protection
ActiveUS9049611B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelAntenna supports/mountingsRadio resourceMultipath propagation
A backhaul radio is disclosed that operates in multipath propagation environments such as obstructed LOS conditions with uncoordinated interference sources in the same operating band. Such a backhaul radio may use a combination of interference mitigation procedures across multiple of the frequency, time, spatial and cancellation domains. Such backhaul radios may communicate with each other to coordinate radio resource allocations such that accurate interference assessment and channel propagation characteristics assessment may be determined during normal operation.
Owner:COMS IP HLDG LLC
Backhaul radio with extreme interference protection
ActiveUS20150049720A1Channel coding adaptationPolarised antenna unit combinationsEngineeringResource allocation
A backhaul radio is disclosed that operates in multipath propagation environments such as obstructed LOS conditions with uncoordinated interference sources in the same operating band. Such a backhaul radio may use a combination of interference mitigation procedures across multiple of the frequency, time, spatial and cancellation domains. Such backhaul radios may communicate with each other to coordinate radio resource allocations such that accurate interference assessment and channel propagation characteristics assessment may be determined during normal operation.
Owner:COMS IP HLDG LLC
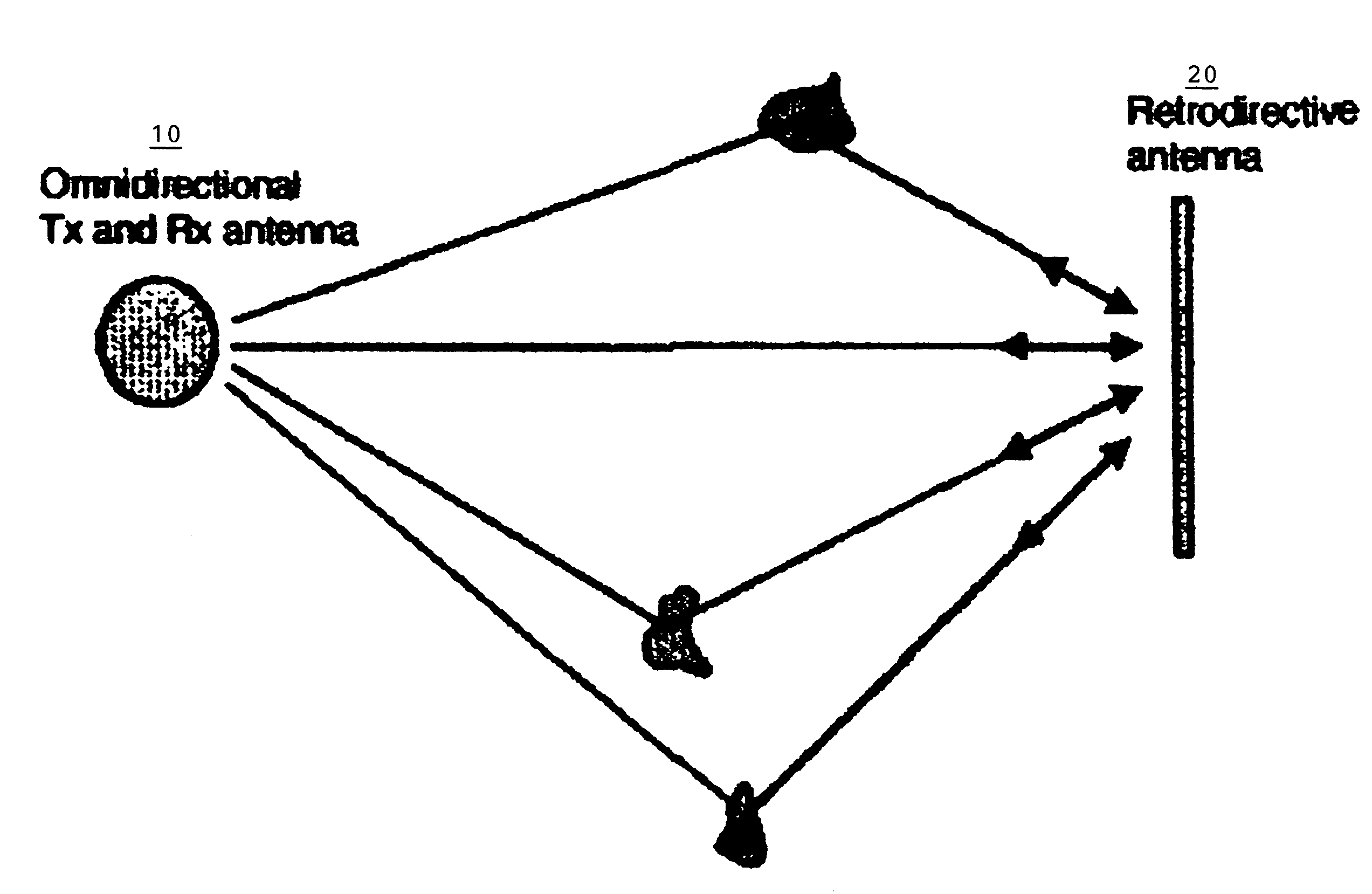
Method for employing multipath propagation in wireless radio communications
InactiveUS7440766B1Reduce negative impactAntenna supports/mountingsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsOmnidirectional antennaSimplex communication
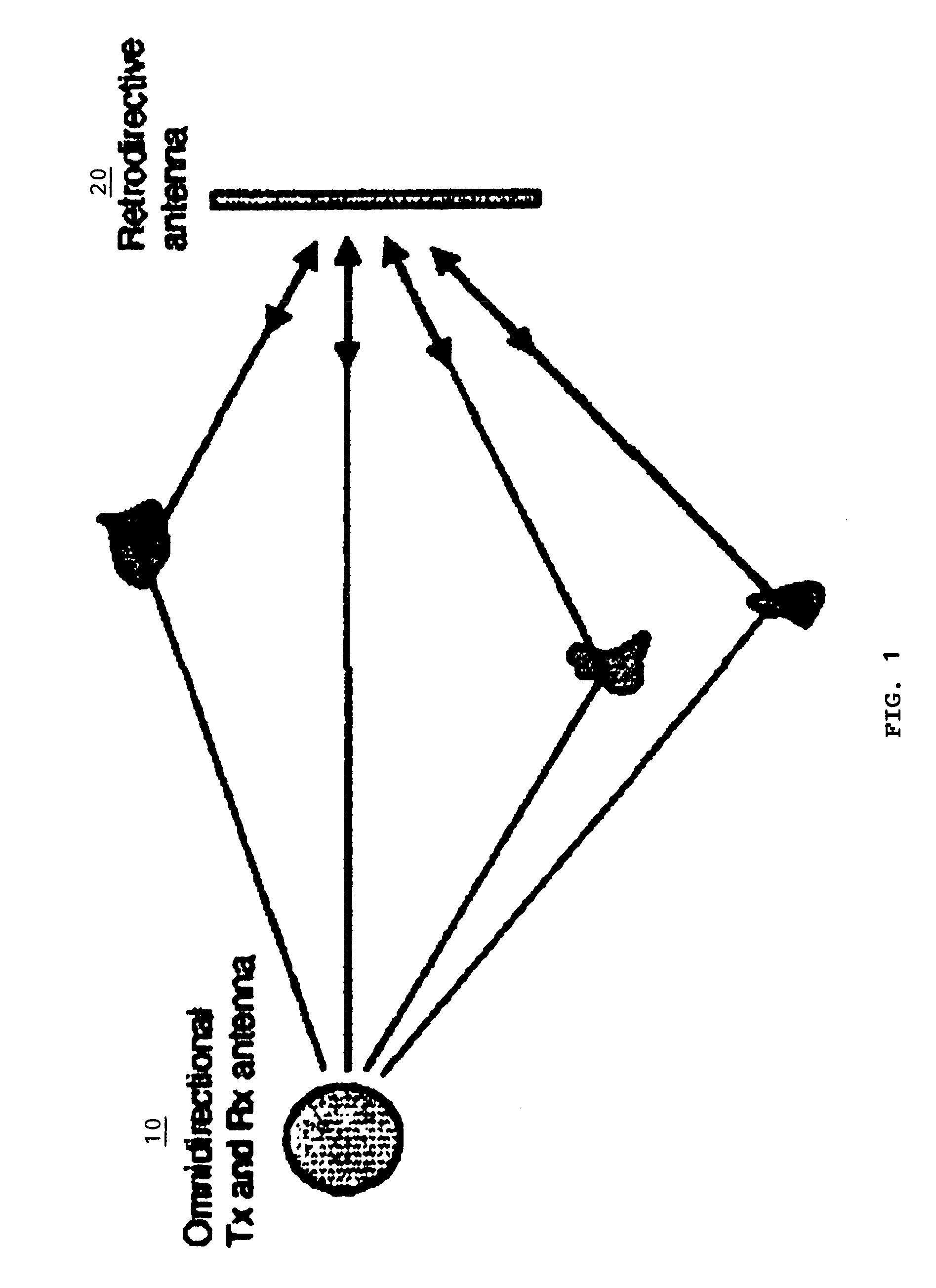
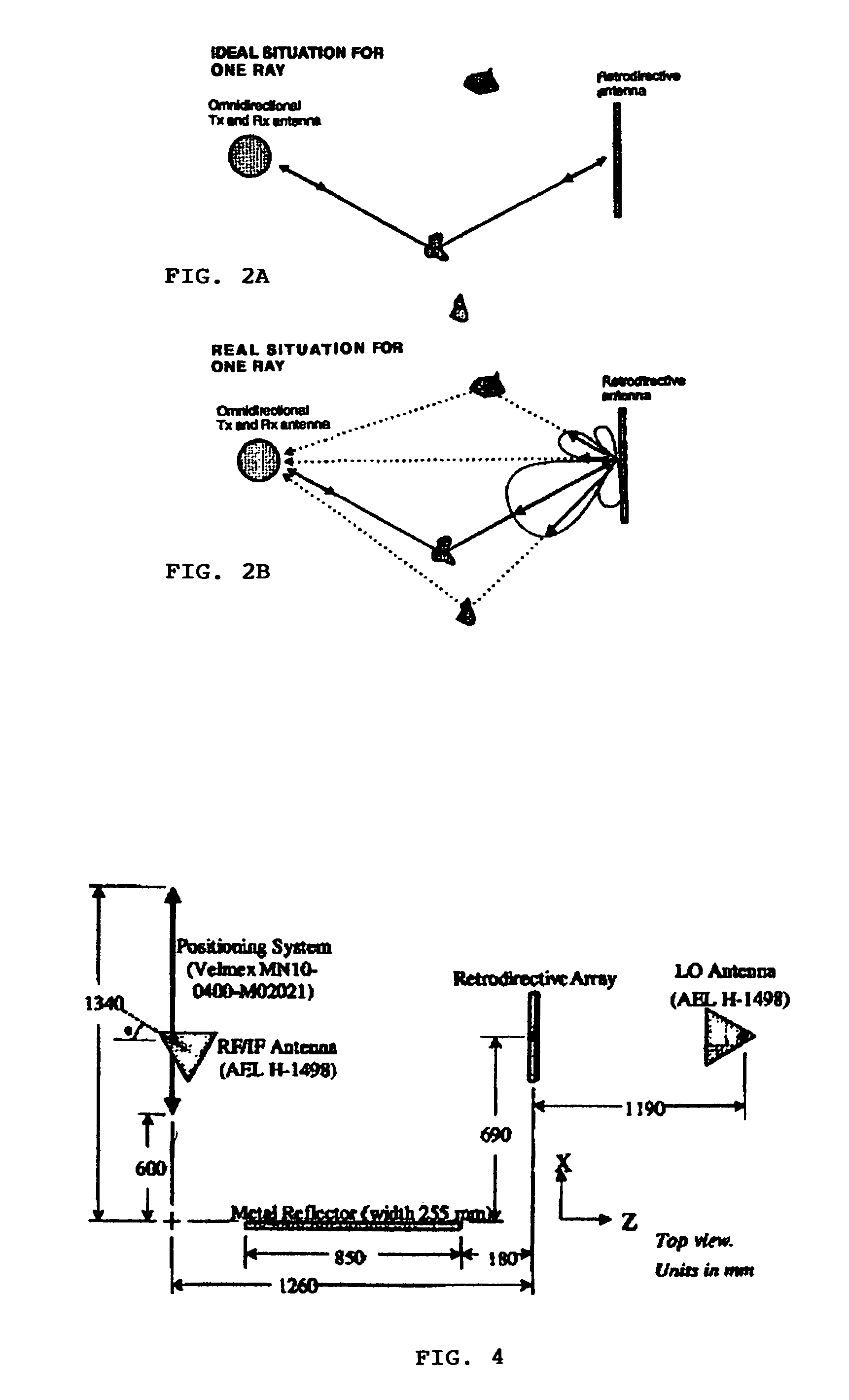
A method of employing multipath propagation in wireless radio communications uses an omnidirectional transmitting / receiving antenna at one end of a transmission link to send an interrogating signal across an environment subject to multipath disturbances to a phase-conjugating retrodirective antenna, and the retrodirective antenna returns a communication signal along the multiple pathways taken by the interrogating signal to the omnidirectional antenna despite the multipath disturbances. In a simplex communication mode, the retrodirective antenna sends a return signal mixed with a communication signal to the omnidirectional antenna. In a duplex communication mode, both an omnidirectional antenna and a phase-conjugating retrodirective antenna are operated in tandem at each end of the transmission link to provide effective two-way wireless radio transmissions.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
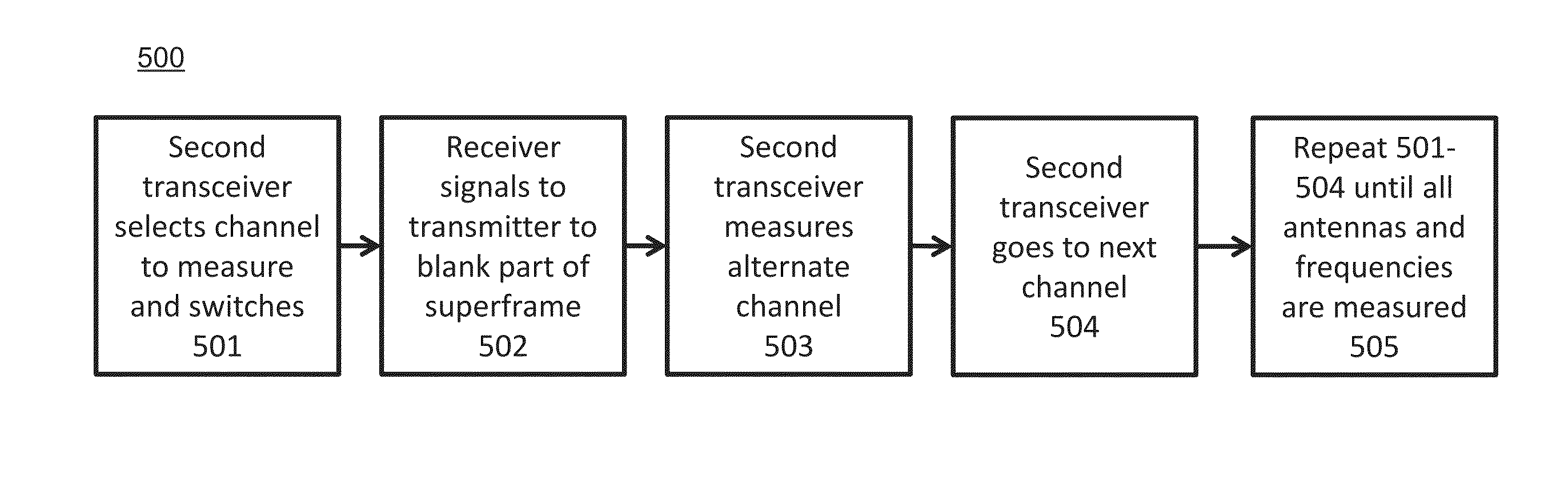
Full duplex backhaul radio with interference measurement during a blanking interval
ActiveUS20160192374A1Network traffic/resource managementCriteria allocationRadio resourceMultipath propagation
A backhaul radio is disclosed that operates in multipath propagation environments such as obstructed LOS conditions with uncoordinated interference sources in the same operating band. Such a backhaul radio may use a combination of interference mitigation procedures across multiple of the frequency, time, spatial and cancellation domains. Such backhaul radios may communicate with each other to coordinate radio resource allocations such that accurate interference assessment and channel propagation characteristics assessment may be determined during normal operation.
Owner:COMS IP HLDG LLC
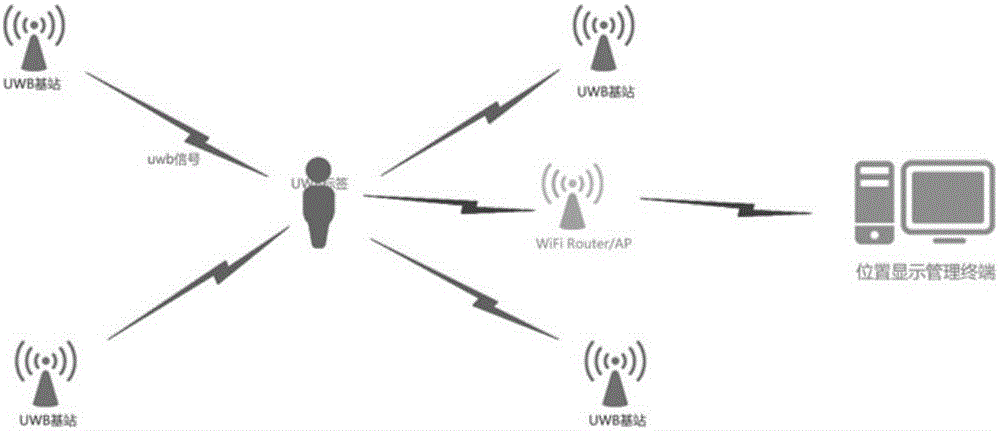
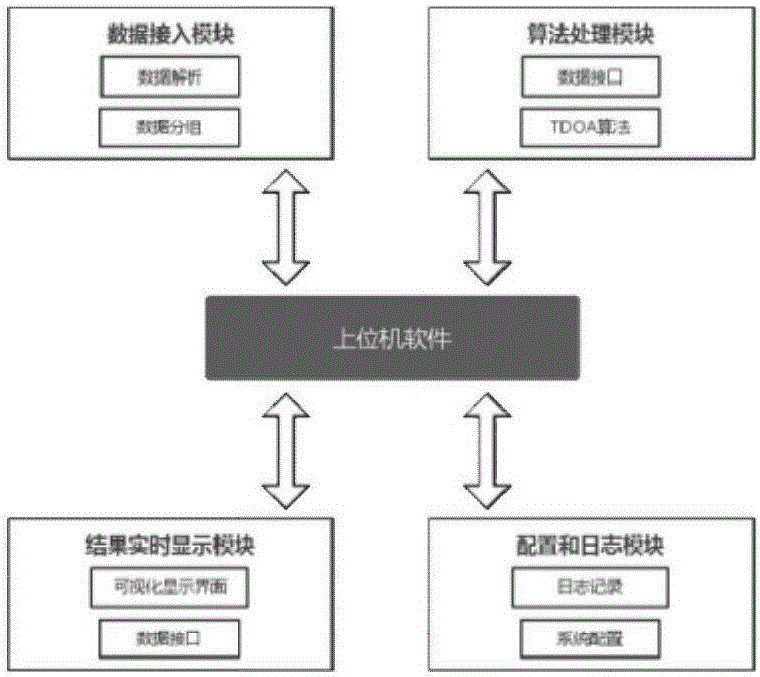
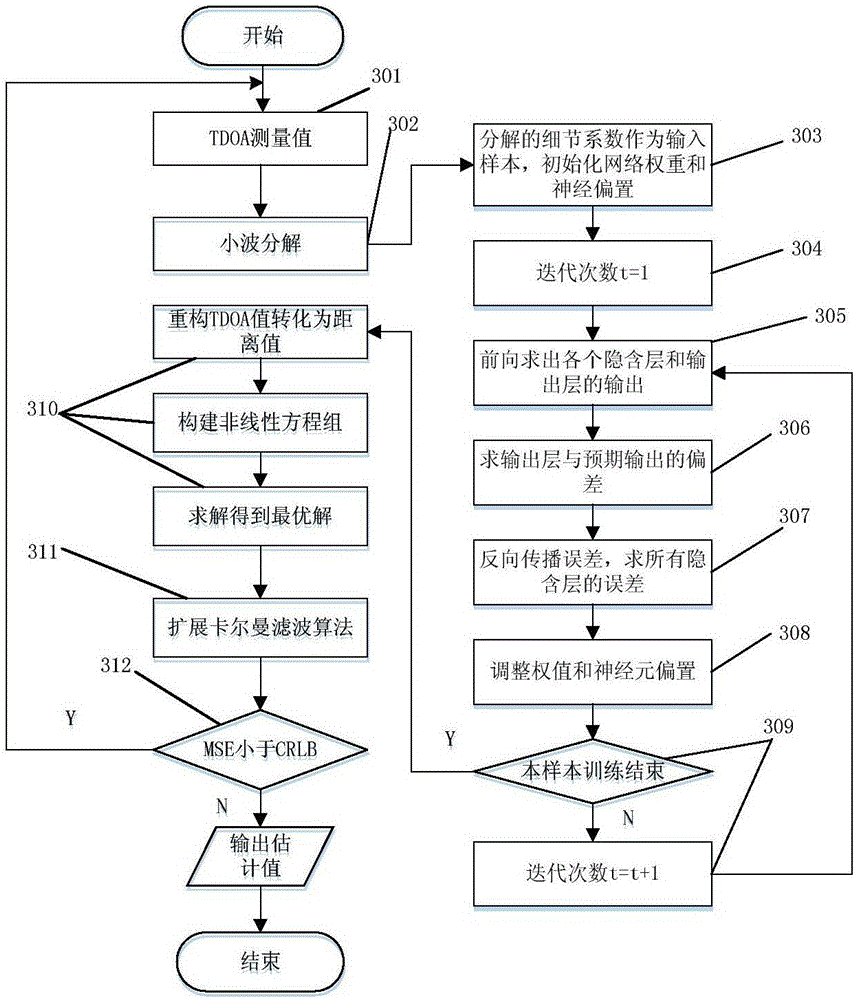
Adaptive indoor dynamic target UWB positioning method and adaptive indoor dynamic target UWB positioning system
ActiveCN106793077AAchieve positioningAchieve precise positioningPosition fixationWireless communicationNonlinear systems of equationsAdaptive denoising
The invention discloses an adaptive indoor dynamic target UWB positioning method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly measuring a TDOA value by using a UWB positioning system; then, processing the measured TDOA value by using a wavelet analysis adaptive denoising method, outputting a reconstructed TDOA value, converting the reconstructed TDOA value into a distance difference, establishing a nonlinear equation set, and obtaining an optimal solution of the equation set; then using the optimal solution as an initial value, performing tracking and positioning on a dynamic target by using an extended Kalman filtering algorithm, and figuring out a final estimated value; and finally outputting the final estimated value. By virtue of the adaptive indoor dynamic target UWB positioning method provided by the invention, a distance measuring error caused by the influence of multipath propagation (Multipath) and non-line-of-sight interference (NLOS) in a UWB signal propagation process can be weakened and even eliminated, the positioning precision is improved, and the accurate positioning of the dynamic target in a non-line-of-sight indoor environment can be realized. The ultra wide band positioning system verifies the validity of the positioning method and realizes the indoor positioning of the dynamic target.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
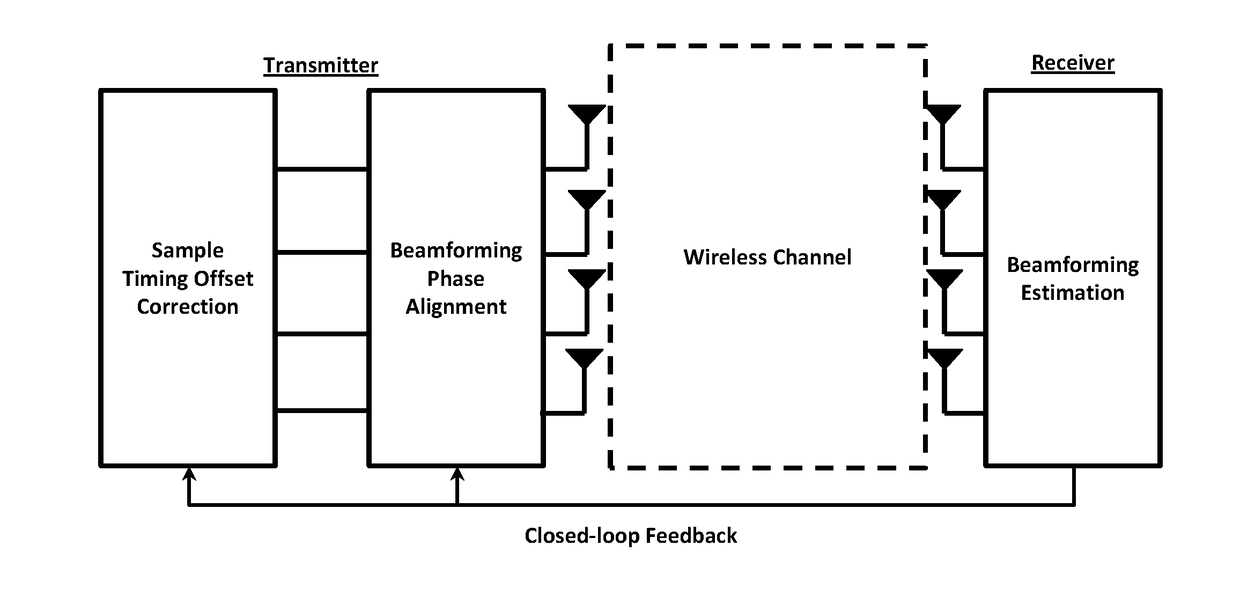
Backhaul radio with adaptive beamforming and sample alignment
ActiveUS20180092099A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityClosed loop feedbackSelf adaptive
A backhaul radio is disclosed that operates in multipath propagation environments such as obstructed LOS conditions with uncoordinated interference sources in the same operating band. Such a backhaul radio may use adaptive beamforming and sample alignment at the transmitter to enhance the link performance. Such backhaul radios may communicate with each other to compute and apply optimal beamforming parameters for a particular propagation environment through a closed-loop feedback mechanism.
Owner:COMS IP HLDG LLC
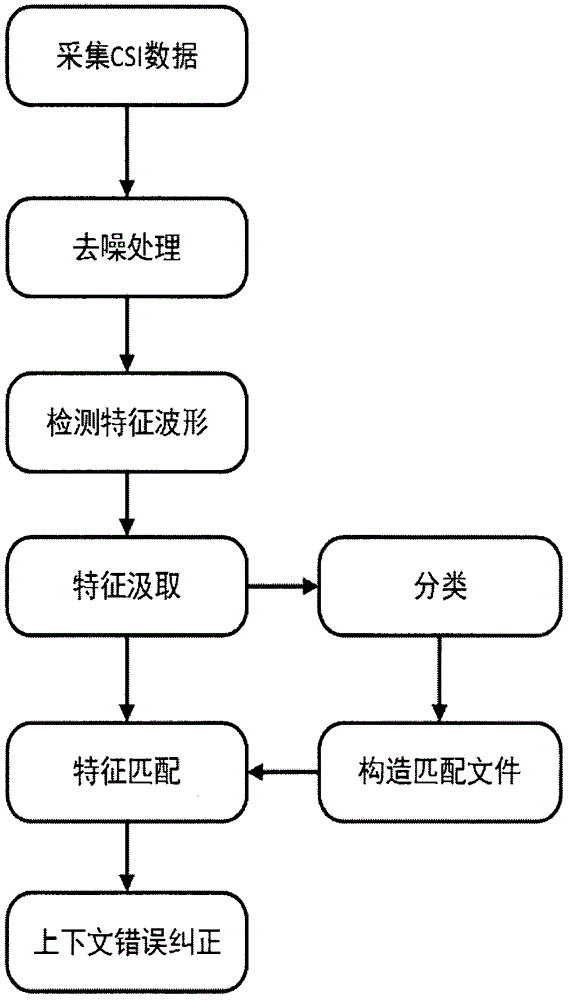
Detection and matching mechanism for recognition of handwritten letters using WiFi signals
ActiveCN105844216AGuarantee authenticitySpatial transmit diversityCharacter and pattern recognitionCorrection algorithmChannel state information
The invention discloses a detection and matching mechanism for recognition of handwritten letters using WiFi signals. The invention mainly makes use of the characteristics of wireless signal multipath propagation, and acquires CSI (Channel State Information) data that carry information reflecting external environmental characteristics, including hand movements when letters are written. The CSI data after de-noising (via Butterworth filtering and principal component analysis filtering) show that in the stage of writing letters, the CSI data fluctuate significantly, and the CSI data are relatively stable in the stage without handwriting, and on the basis of the characteristics, the invention provides a waveform feature extraction algorithm to detect and extract waveforms only including information on 26 handwritten letters. Finally, the invention provides a solution combining feature matching and context error correction, takes the waveform as a matching feature, carries out machine learning classification for the extracted 26 feature waveforms, matches the waveforms by using a DTW (dynamic time warping), and improves the recognition accuracy of the system through the context error correction algorithm.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
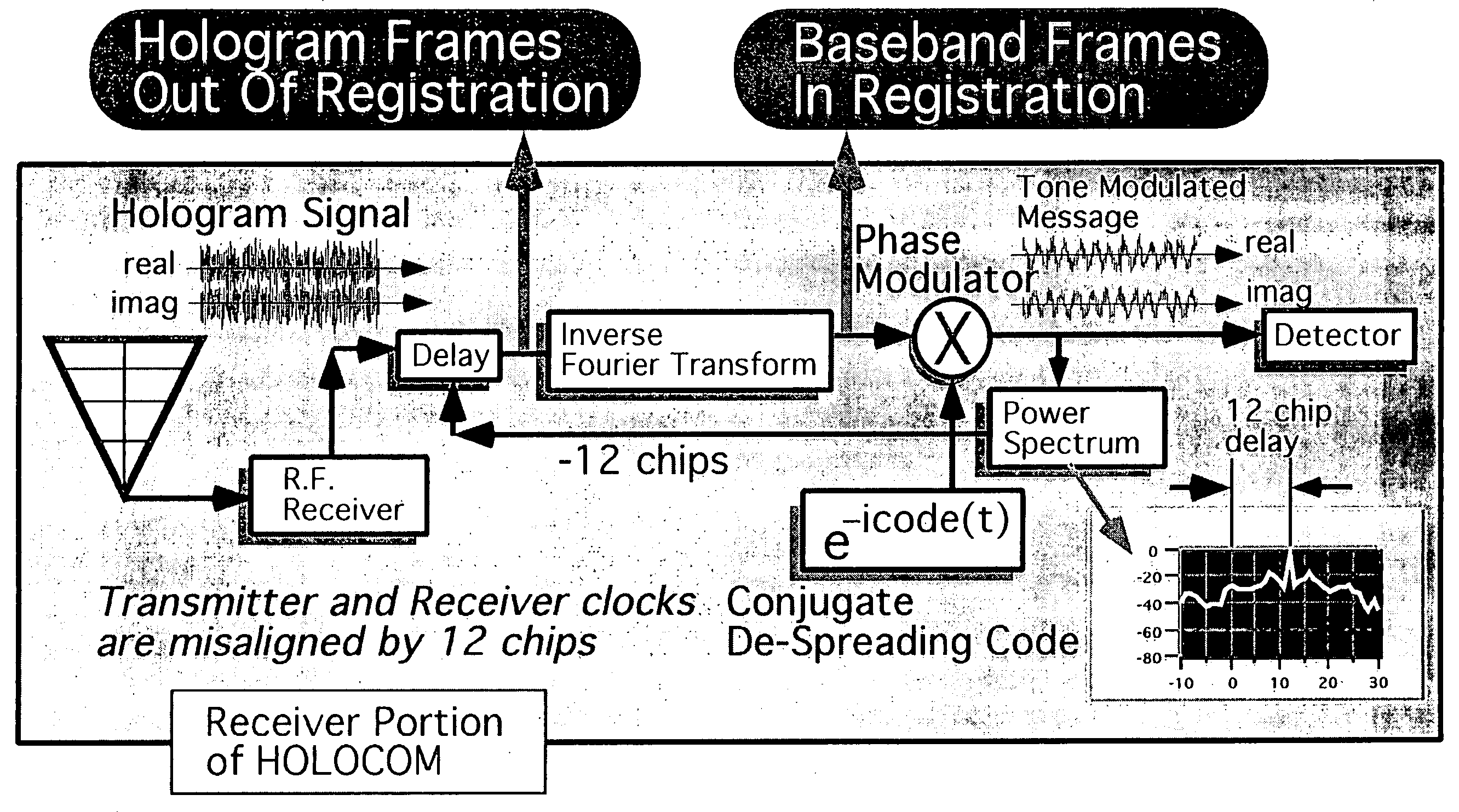
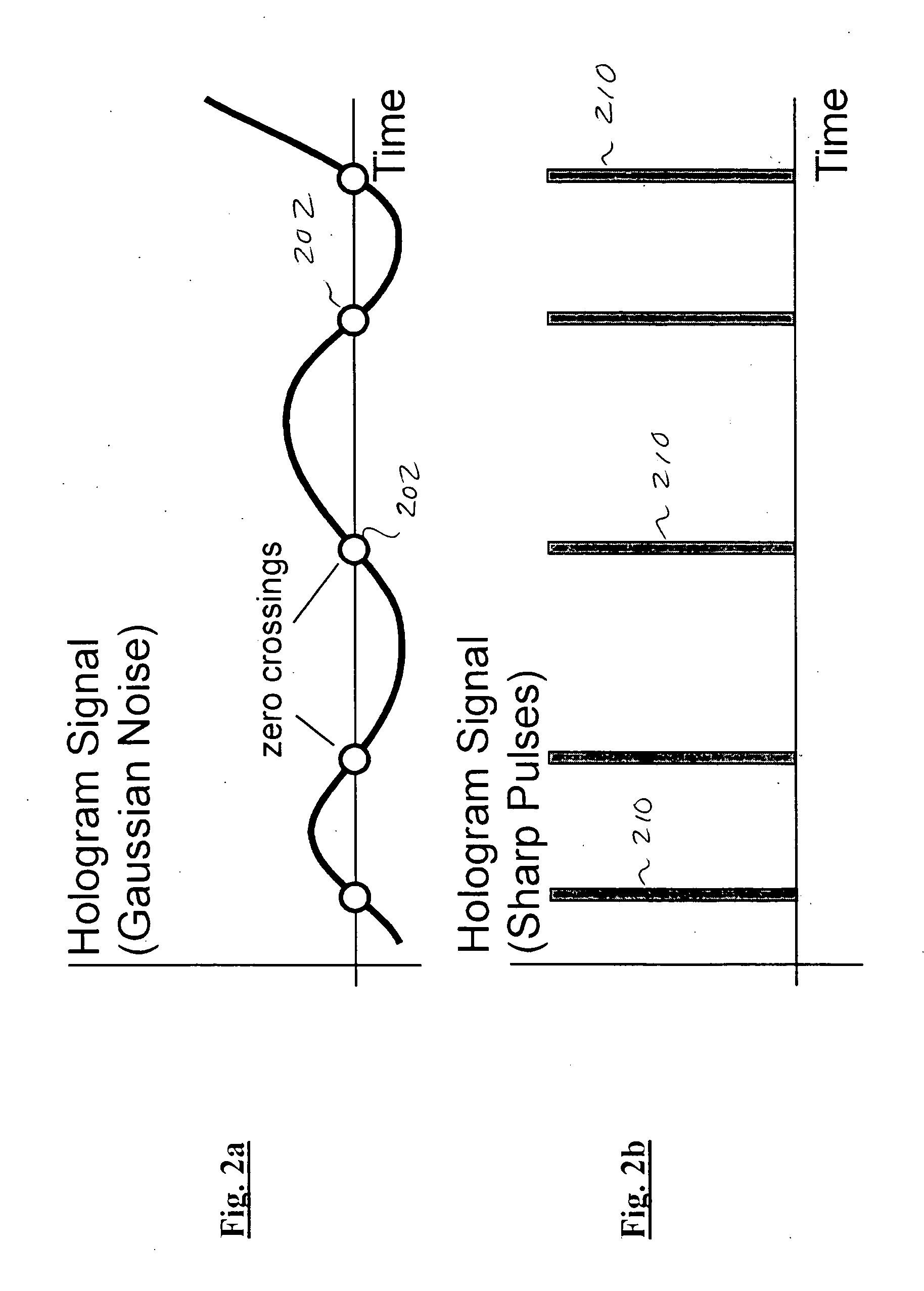
Multipath-adapted holographic communications apparatus and methods
InactiveUS20050100077A1Simultaneous amplitude and angle modulationModulation with suppressed carrierTransceiverRadar systems
Improved apparatus and methods for utilizing holographic waveforms for a variety of purposes including communication, ranging, and detection. In one exemplary embodiment, the holographic waveforms are transmitted over an RF bearer medium to provide, inter alia, highly covert communications, radar systems, and microwave data links. Multipath propagation is compensated for by either filtering the multipath signals in the decoded baseband, or alternatively adding the various signals, using a power spectrum. Methods of providing multiple access and high bandwidth data transmission are also disclosed. Improved apparatus utilizing these features; e.g., a wireless miniature covert transceiver / locator, are also disclosed.
Owner:HOLOWAVE
Backhaul radio with advanced error recovery
ActiveUS20180084553A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityFrequency bandMultipath propagation
A backhaul radio is disclosed that operates in multipath propagation environments such as obstructed LOS conditions with uncoordinated interference sources in the same operating band. Such a backhaul radio may use an advanced ARQ protocol, which uses an ACK_MAP, constructed by a combination of implicit and explicit signaling, and performs a combination of proactive and reactive retransmissions.
Owner:COMS IP HLDG LLC
Radio with interference measurement during a blanking interval
A backhaul radio is disclosed that operates in multipath propagation environments such as obstructed LOS conditions with uncoordinated interference sources in the same operating band. Such a backhaul radio may use a combination of interference mitigation procedures across multiple of the frequency, time, spatial and cancellation domains. Such backhaul radios may communicate with each other to coordinate radio resource allocations such that accurate interference assessment and channel propagation characteristics assessment may be determined during normal operation.
Owner:COMS IP HLDG LLC
Method and apparatus for controlling interference suppressing receivers
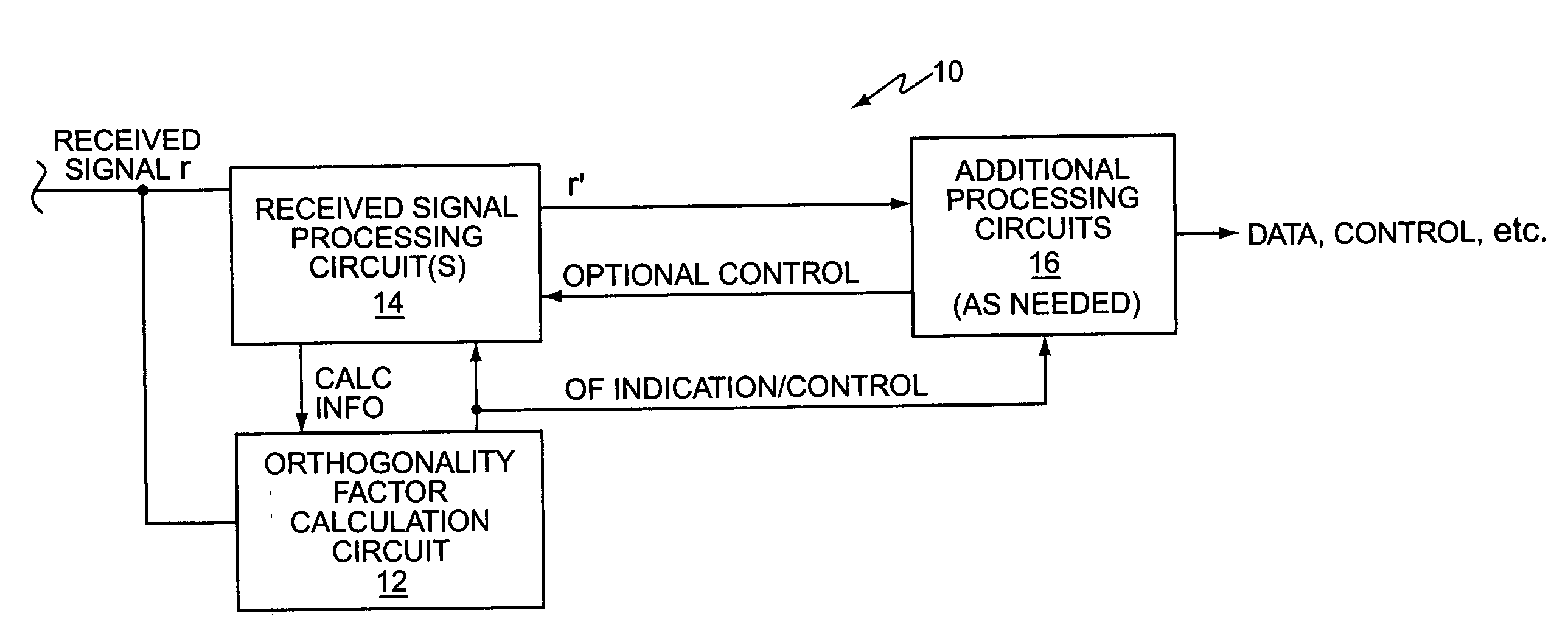
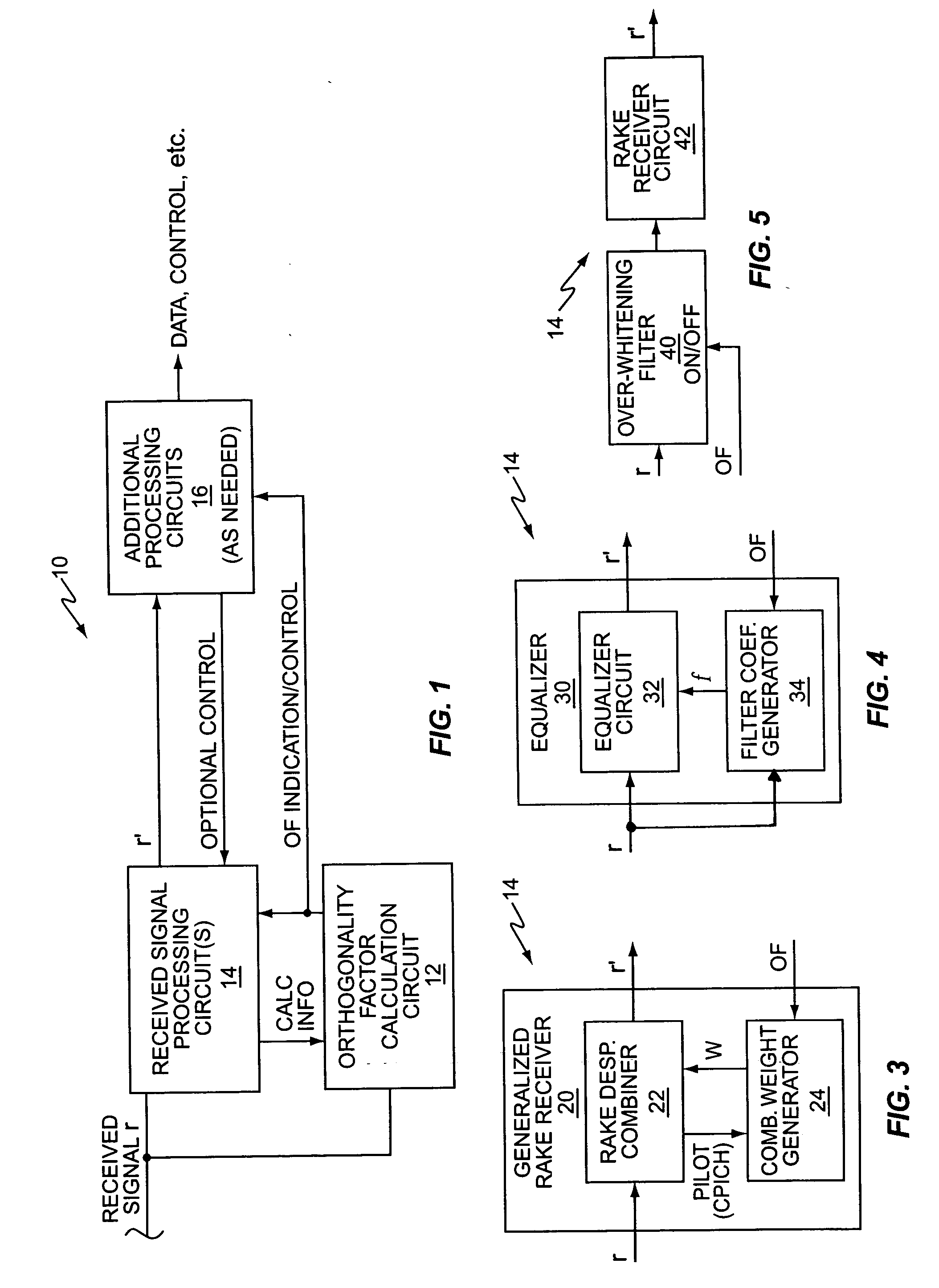
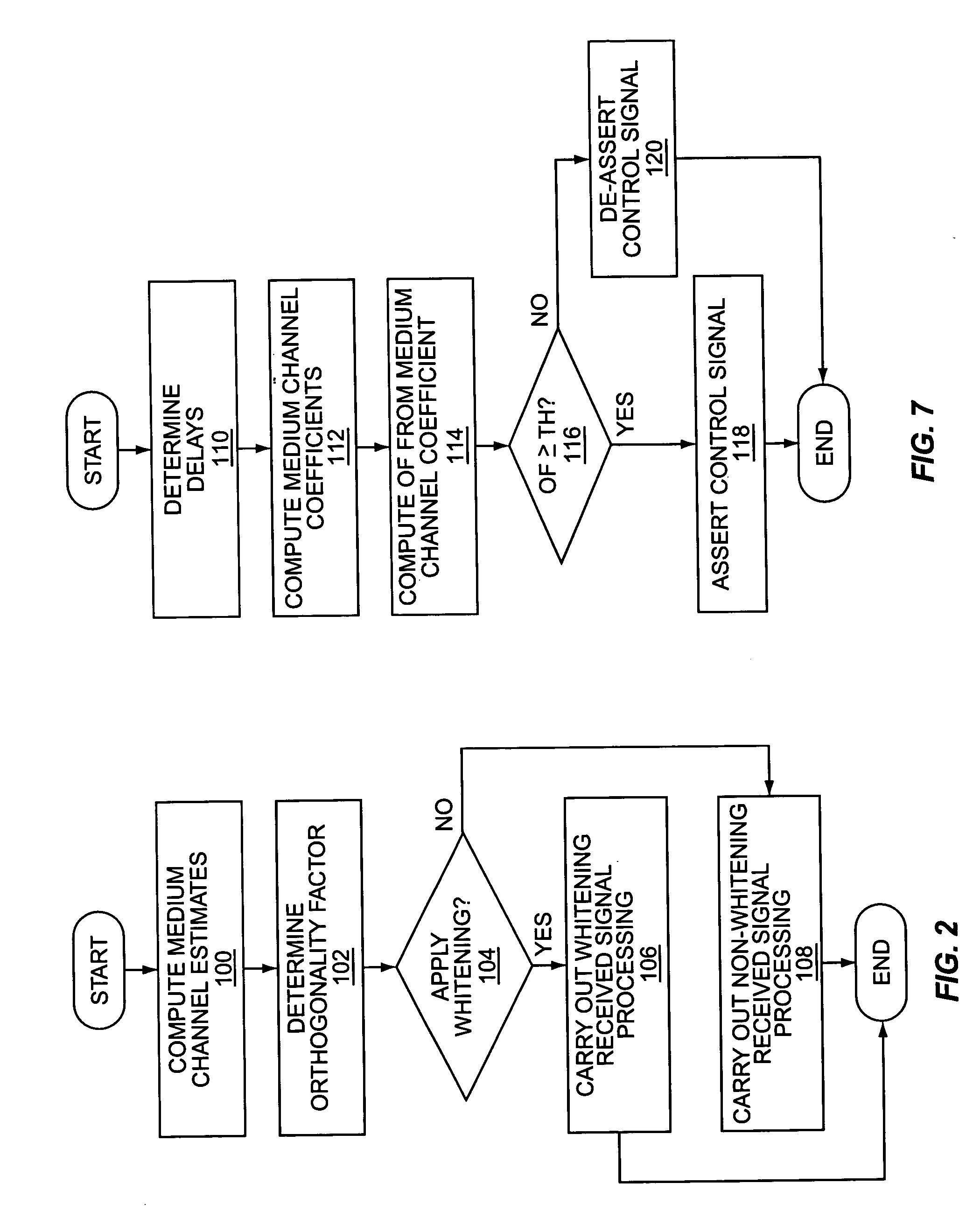
InactiveUS20060063505A1Controlling interference suppressionImprove reception performanceError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionCode division multiple accessSignal of interest
A wireless communication receiver is configured to suppress interference with respect to a received signal of interest on a selective basis responsive to evaluating whether the receiver currently is or is not operating in a colored noise / interference environment. For example, an exemplary Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) mobile station activates or deactivates interference suppression responsive to determining and evaluating an orthogonality factor, which, in this context, serves as a measure of how much downlink power gets converted into same-cell interference via multipath propagation. The orthogonality factor thus serves as an indicator of noise plus interference coloration. In one or more exemplary embodiments, then, an exemplary receiver circuit is configured to determine the orthogonality factor, evaluate it, and selectively enable or disable received signal whitening based on that evaluation. The exemplary receiver circuit and associated selective whitening method can be applied to various receiver architectures and signal types.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Multipath propagation detection and avoidance method and system
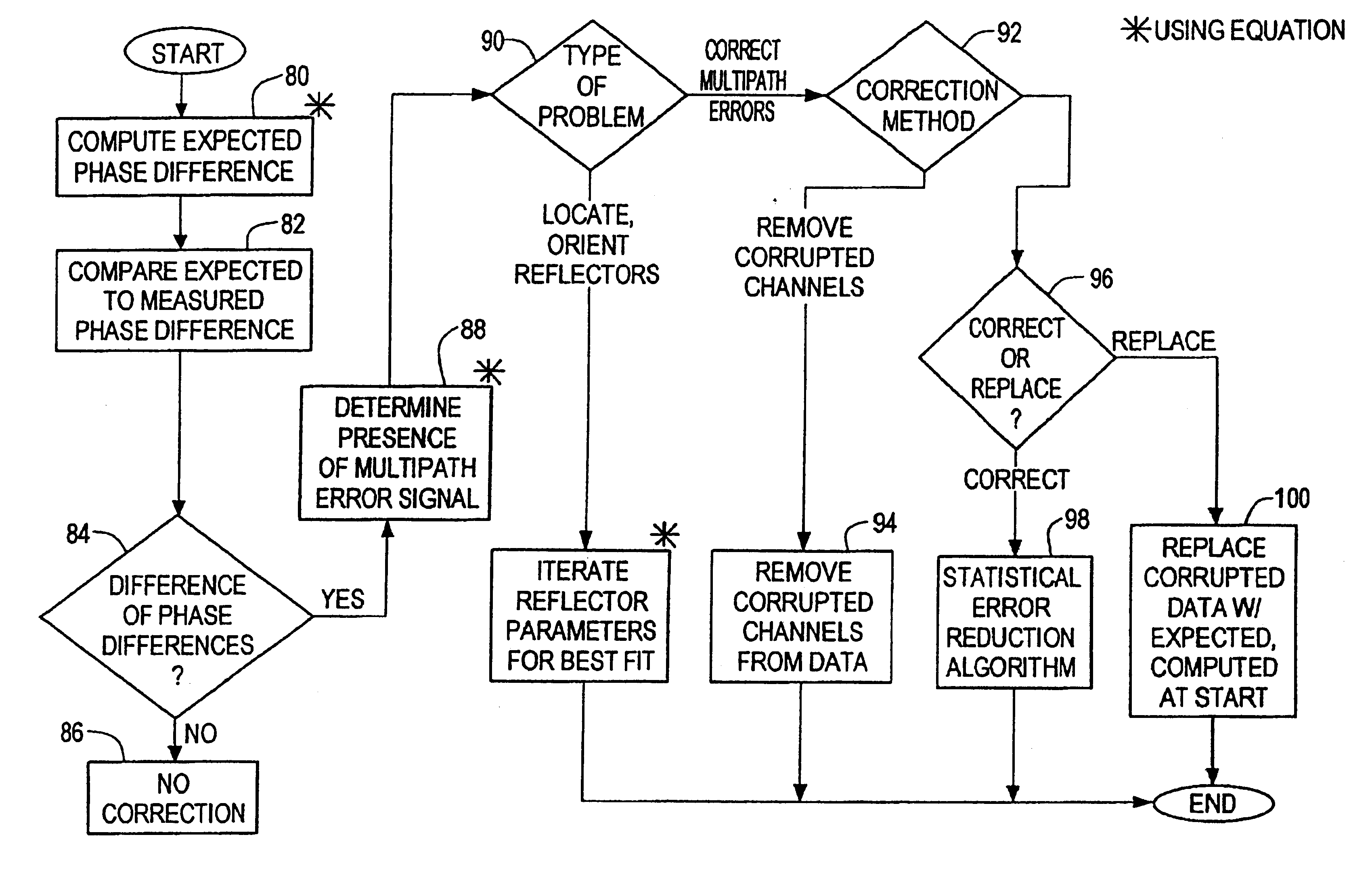
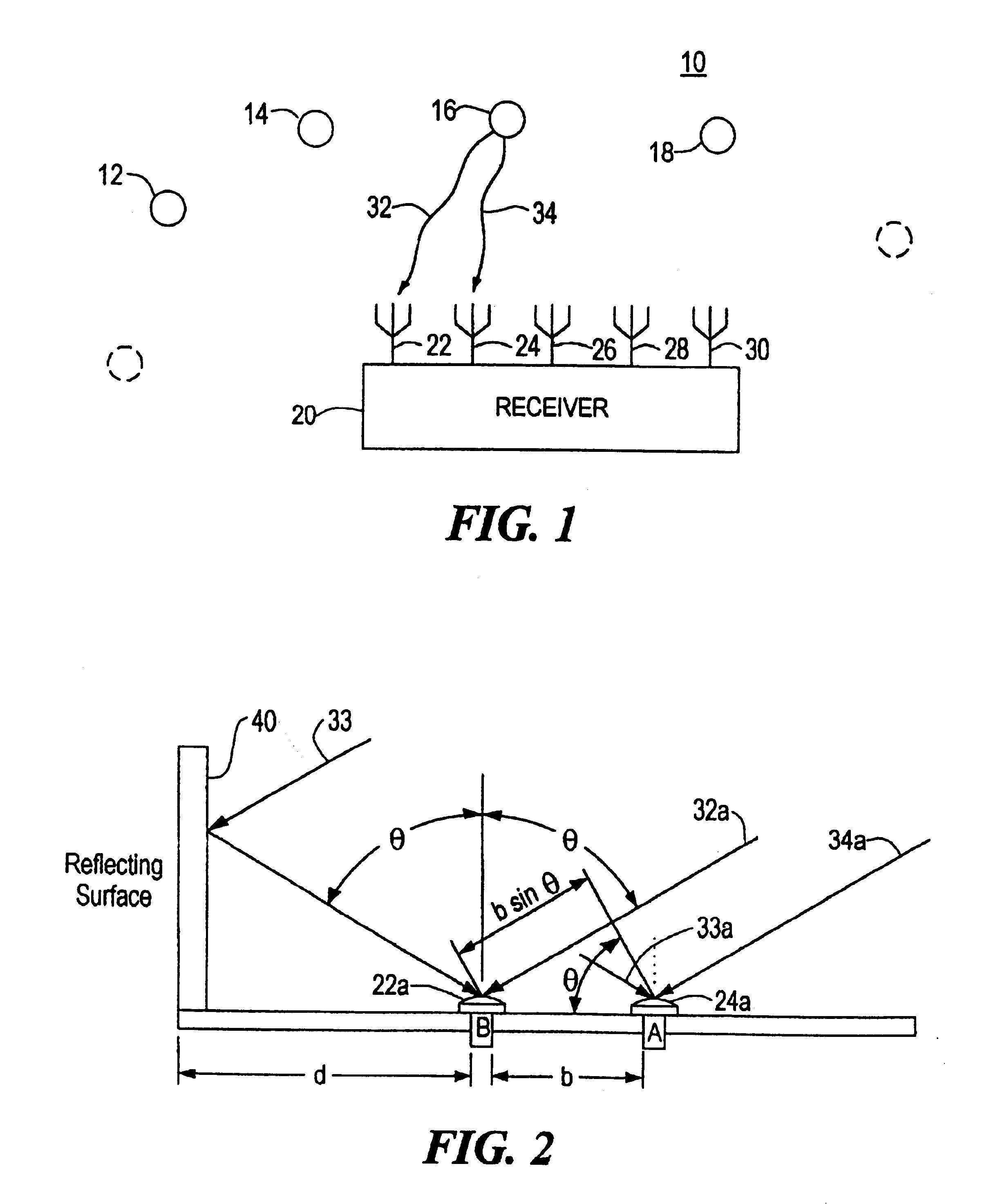
InactiveUS6362782B1Suppress errorRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsBeacon systems using radio wavesPhase differenceCarrier signal
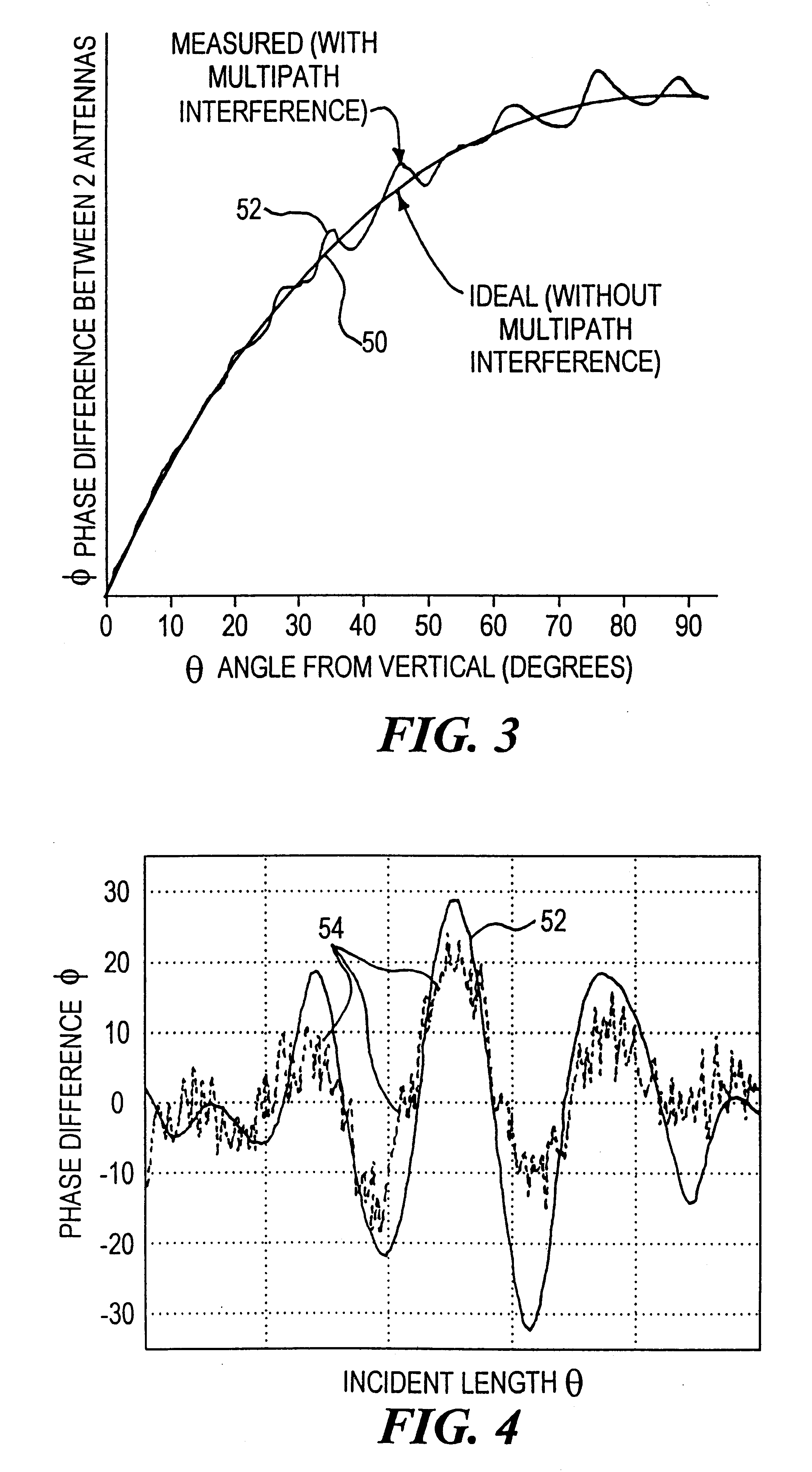
Multipath propagation detection can be accomplished using first and second spaced antennas which receive a carrier signal from a moving radiation source and produce a carrier phase difference representative of the location of the source; a difference signal representative of the difference between the measured carrier phase difference and a predetermined phase difference for the source in that location is generated; and the presence of multipath distortion in that difference signal is determined. Furthermore, when a multiplicity of source signals are tracked as in reception of navigation signals from the Global Positioning Satellite System, the receiver may be programmed to eliminate or suppress errors arising from measurements that have been distorted by multipath propagation.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Iterative localization techniques
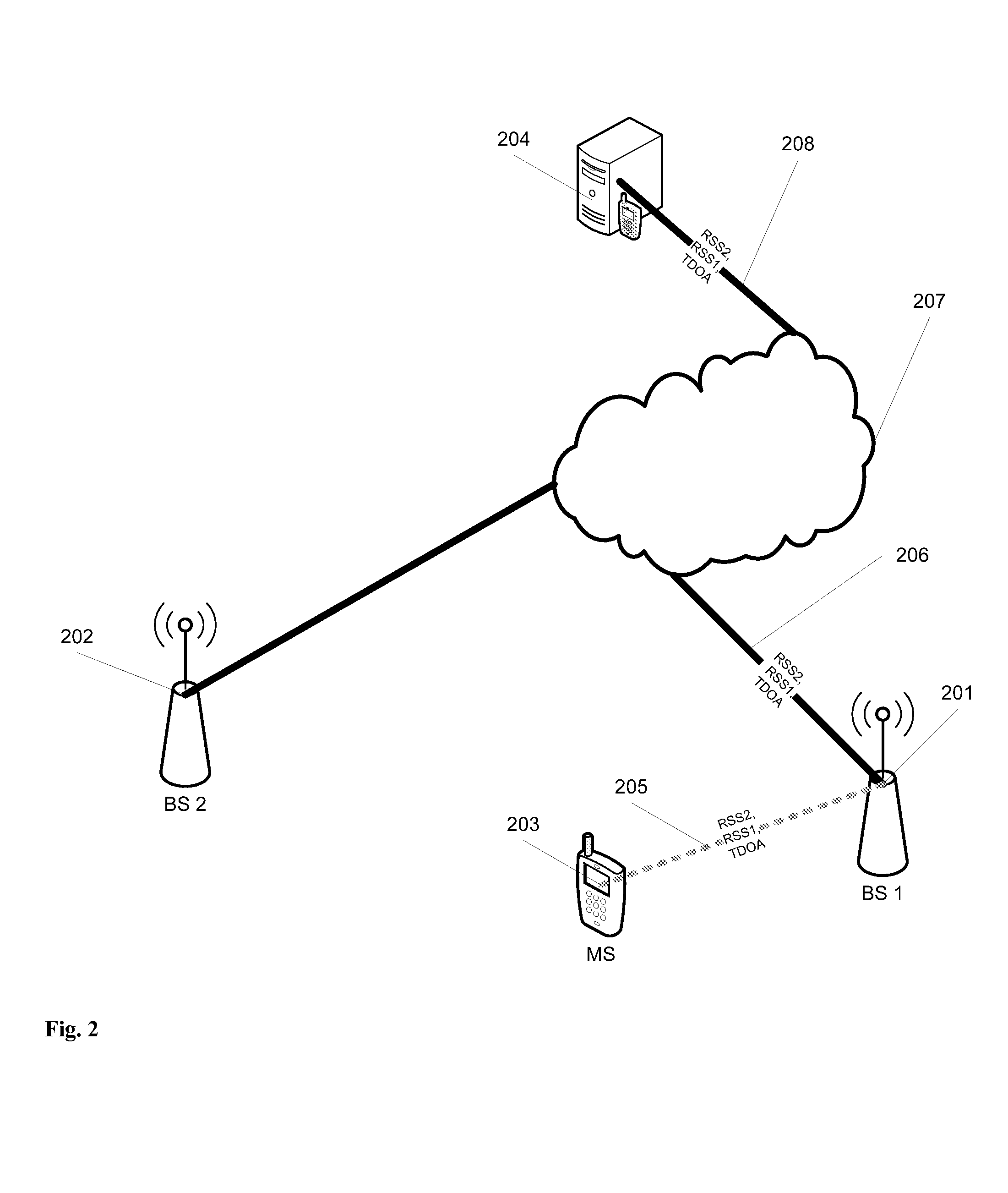
The present invention refers to iterative localization techniques with wireless communication systems for rural environment with limited number of base stations in the range of the mobile station and urban environment with multipath propagation channel and several base stations in the range of mobile station.
Owner:WILDFIRE EXCHANGE
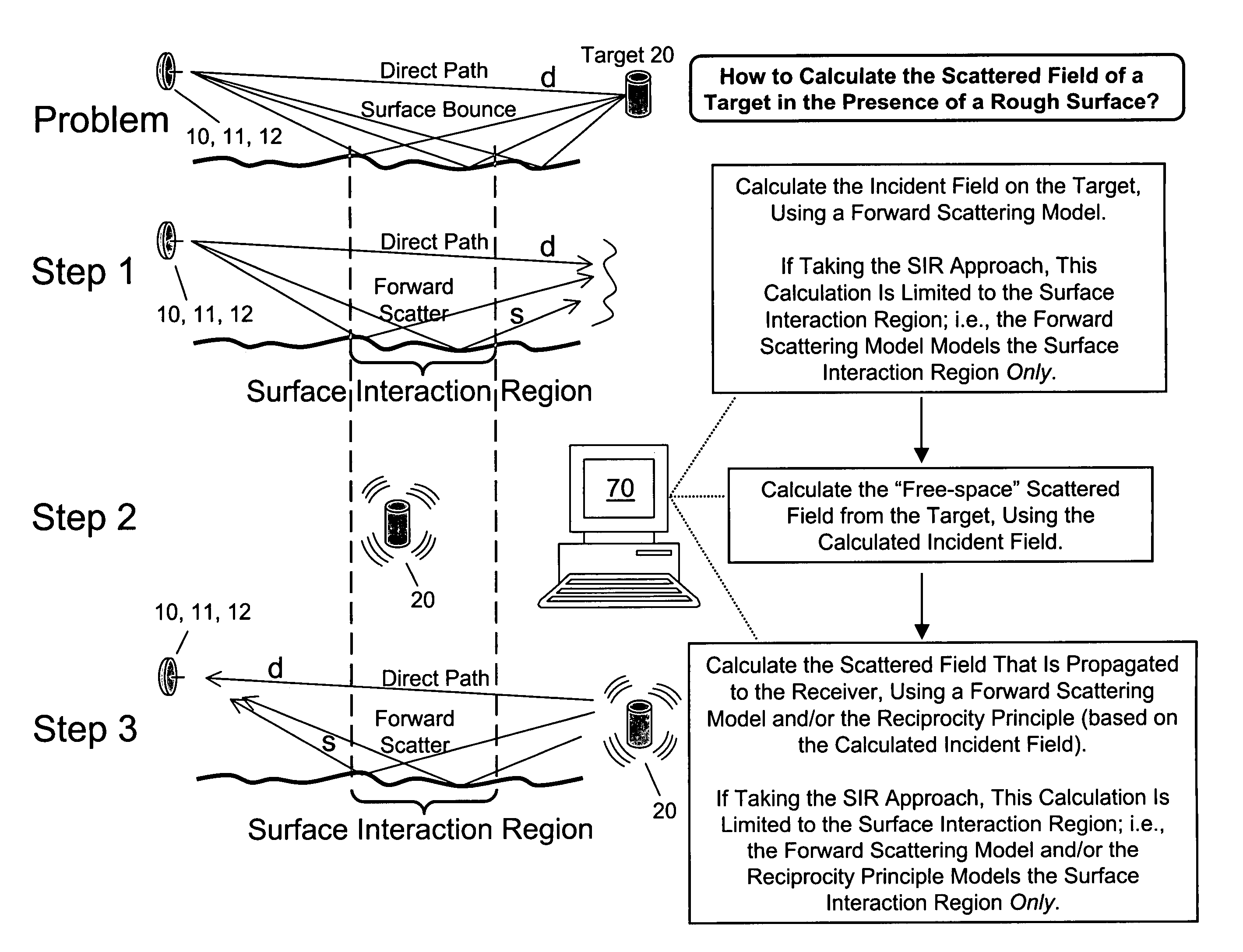
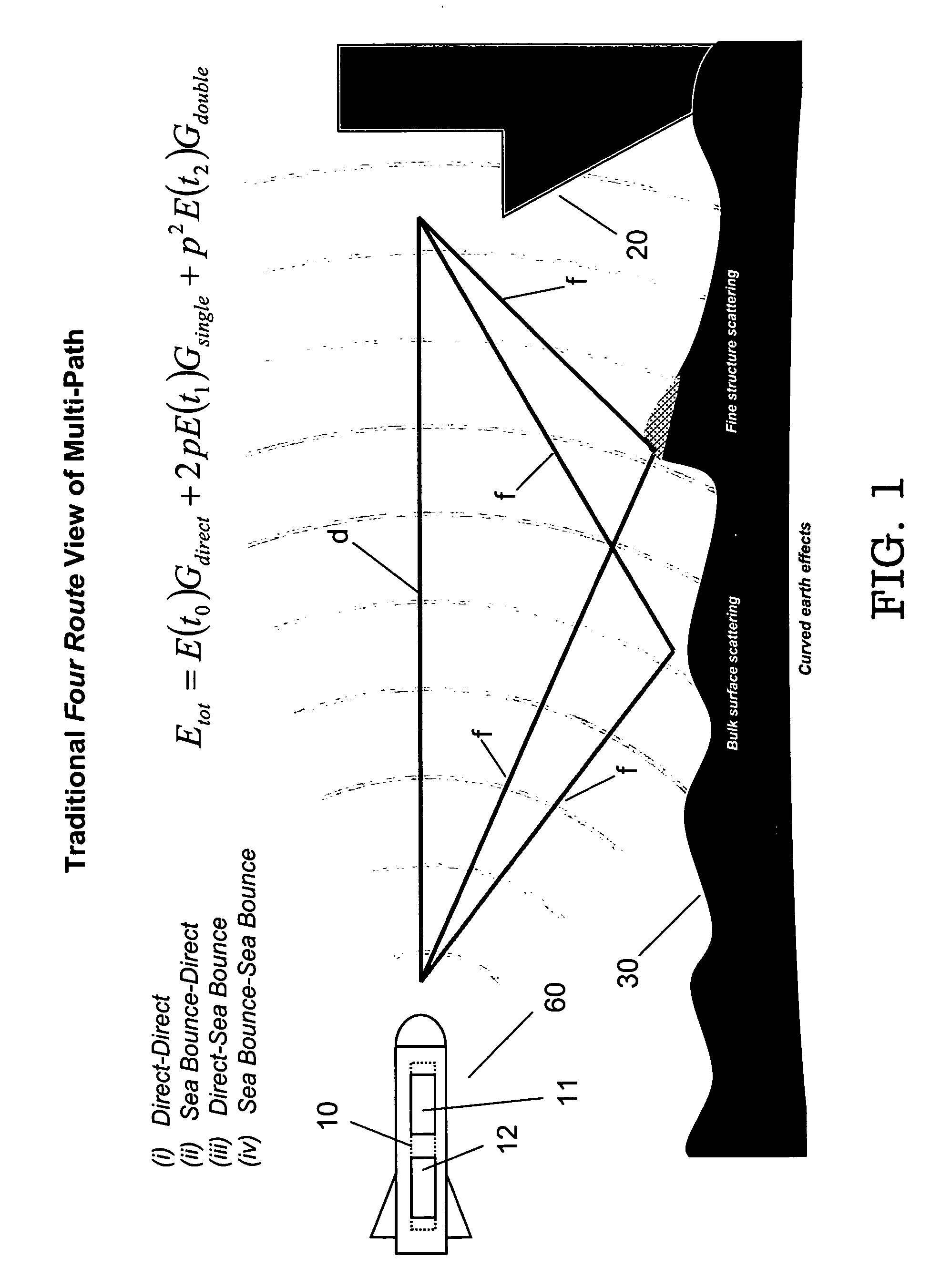
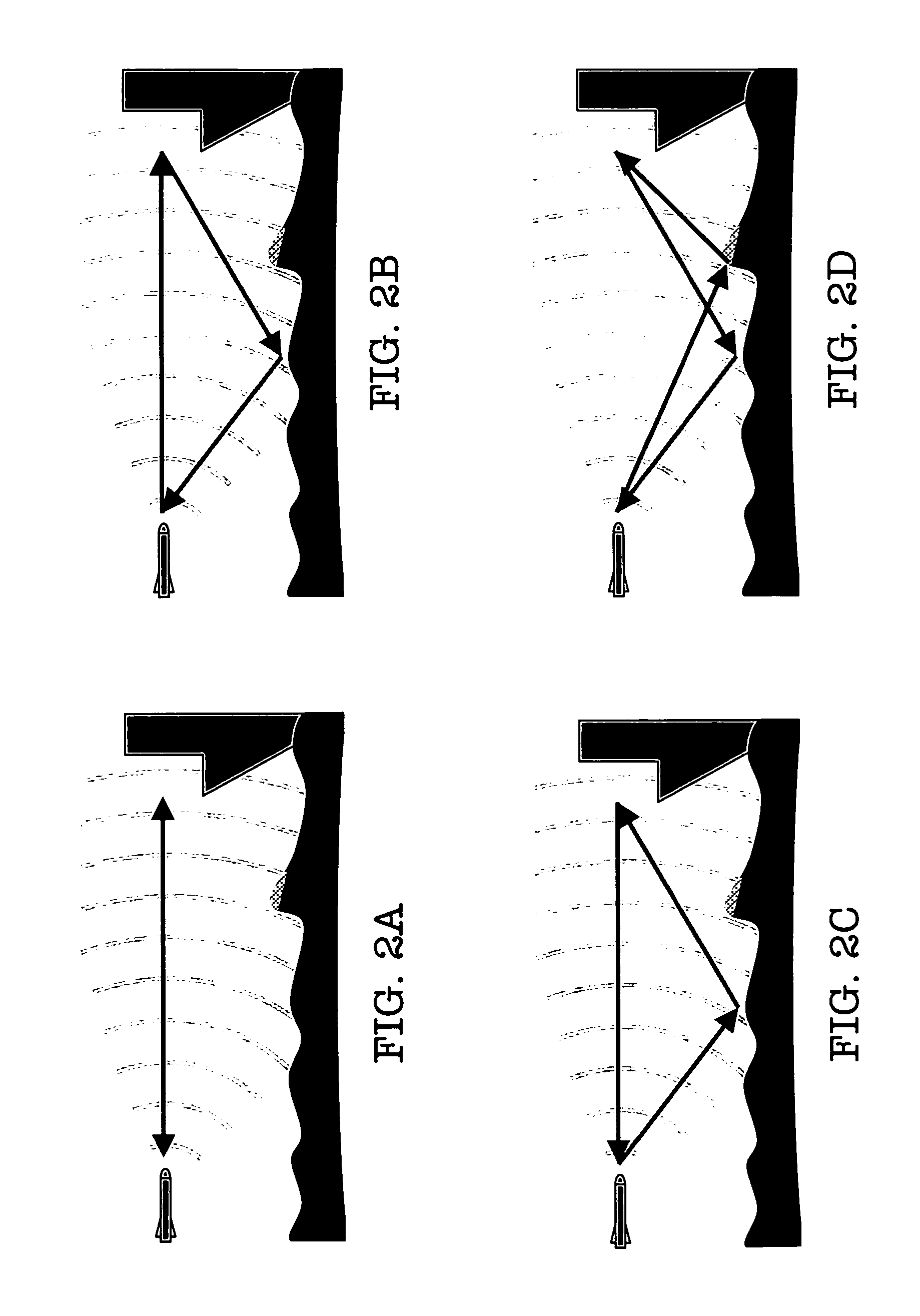
Dual forward scattering method for modeling multipath propagation
InactiveUS7161529B1Accurate calculationReducing modeled domainRadio wave reradiation/reflectionForward scatterClassical mechanics
Analysis of electromagnetic (or acoustic) multipath propagation inventively focuses upon the transmitter-to-target propagation (transmitted propagation reaching target via both direct pathway and forward scattered pathway) and the target-to-receiver propagation (re-transmitted propagation reaching receiver via both direct pathway and forward scattered pathway). Transmitter-to-target propagation is calculated using conventional multipath modeling technique. The target's overall scattered field is calculated using the calculated transmitter-to-target propagation in conjunction with qualitative electromagnetic / acoustic target information. Target-to-receiver propagation is calculated using conventional multipath modeling technique and / or the reciprocity principle as applied to the calculated transmitter-to-target propagation. Jointly disclosed (practicable therewith or thereapart) is inventive confinement of the assessment of multipath propagation to a “surface interactive region” (“SIR”), intermediate the target and transmitter and / or the target and receiver. The down range time of the propagation, translatable to range distance, is related to error associated with such restriction. A SIR scope is selected commensurately with acceptable error.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
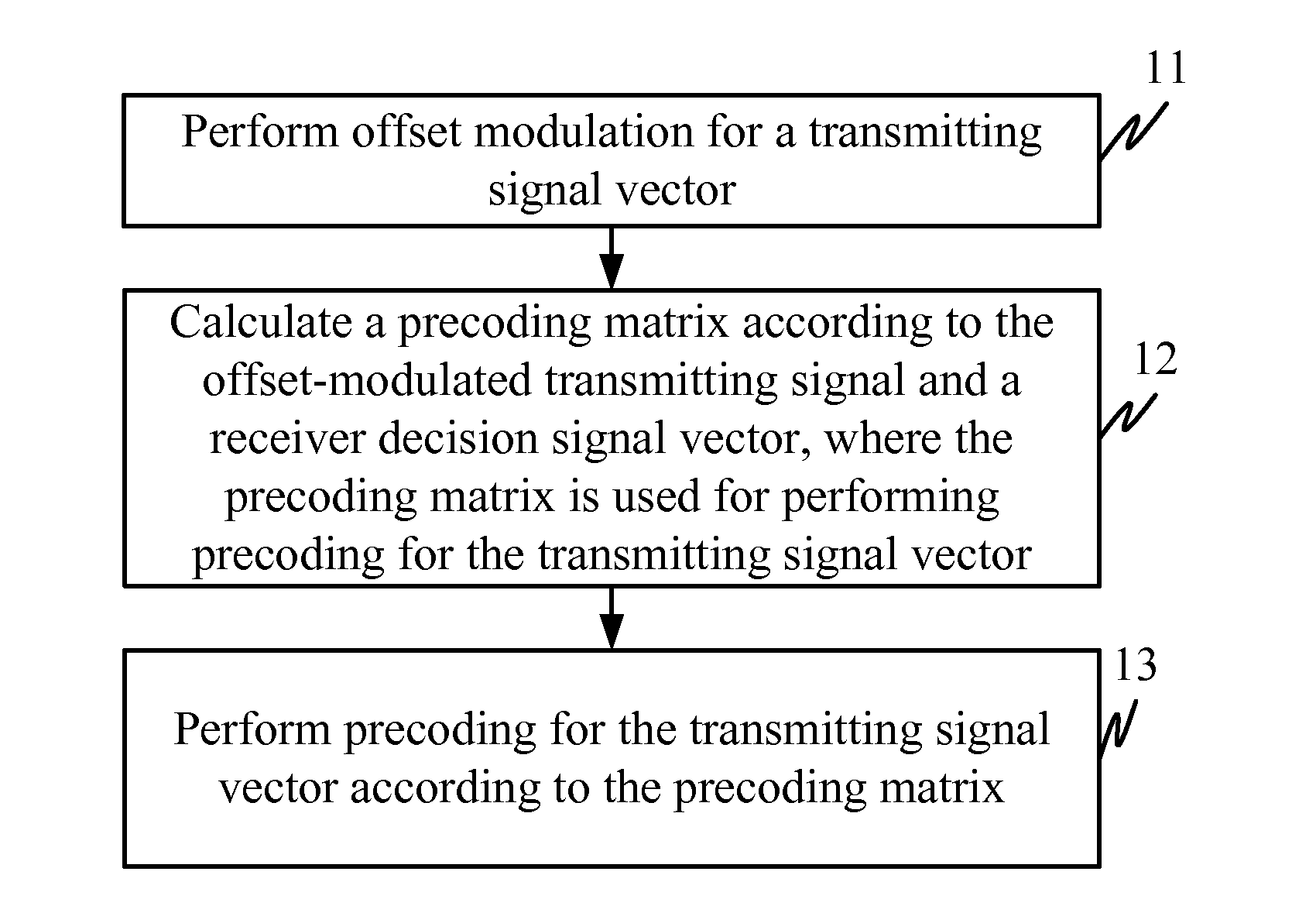
Channel state information transmission method appraratus and system
InactiveUS20120087382A1Reduce distractionsReduce complexityMultiple-port networksFrequency-division multiplexChannel state informationSignal on
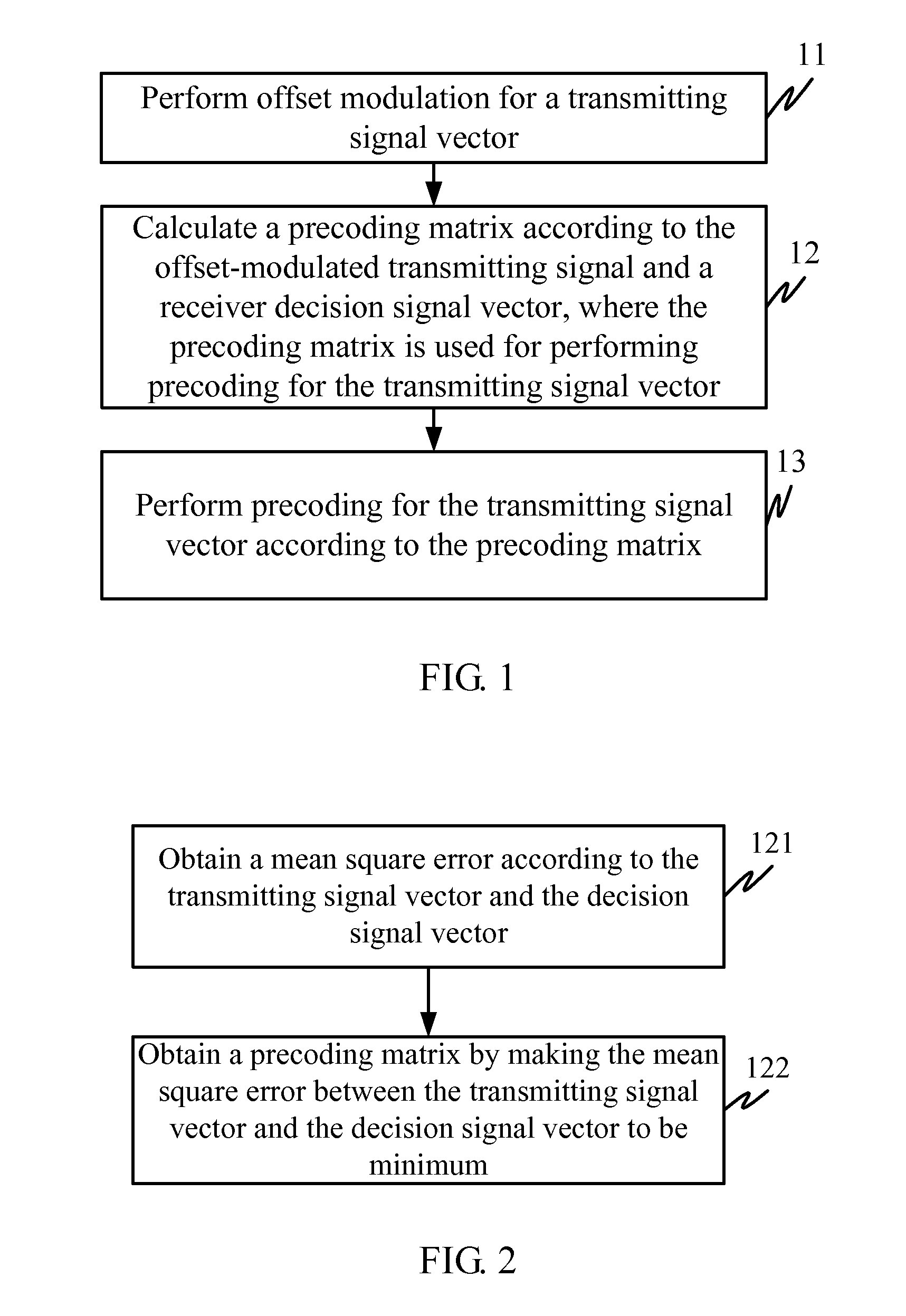
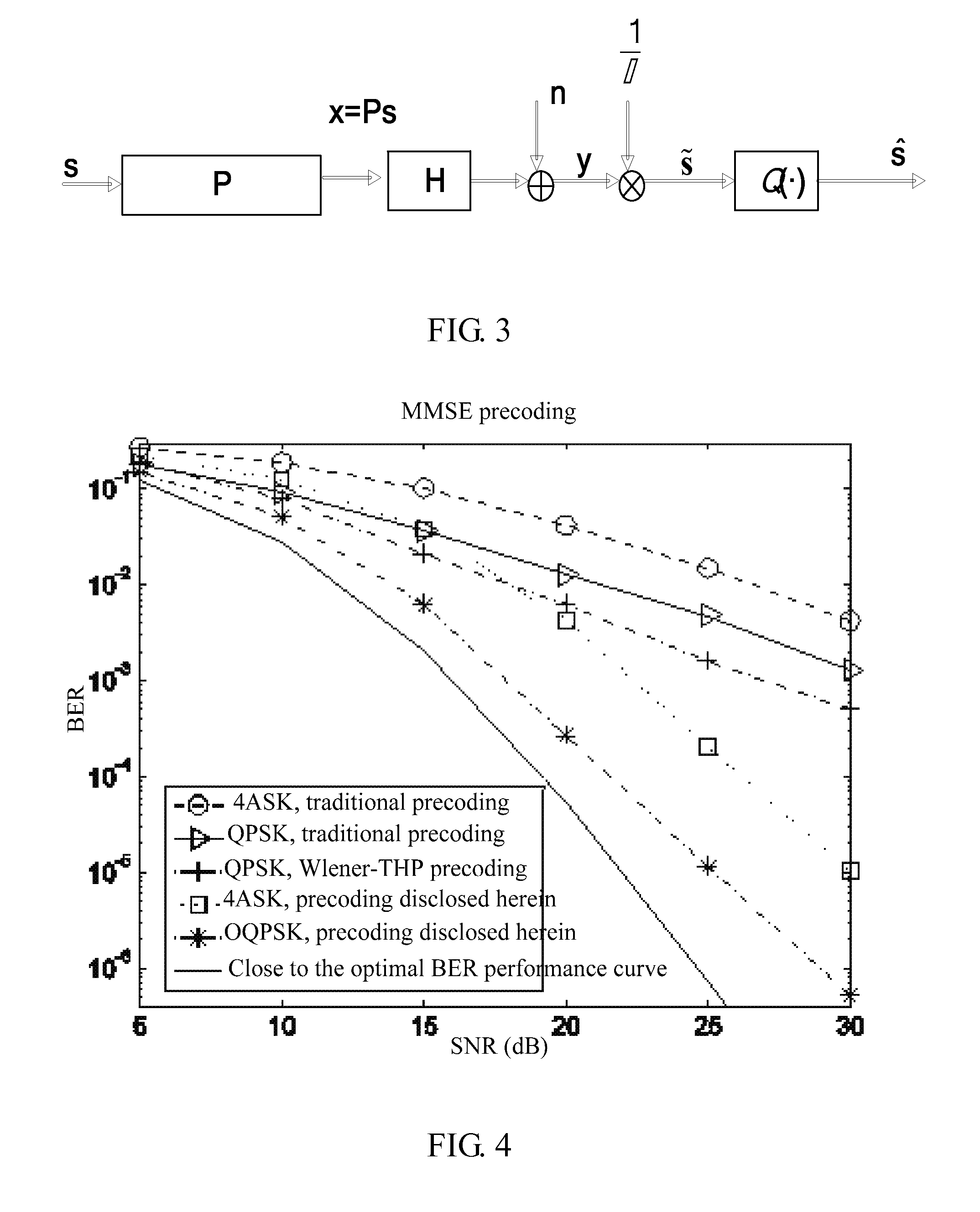
A precoding method, a precoding apparatus, a Frequency Domain Equalization (FDE) method, and an FDE apparatus are provided in the embodiments of the present invention. The precoding method includes: performing offset modulation for a transmitting signal vector; calculating a precoding matrix according to the offset-modulated transmitting signal vector and a receiver decision signal vector, where the precoding matrix is used for performing precoding for the transmitting signal vector; and performing precoding for the transmitting signal vector according to the precoding matrix. Linear precoding is performed by using the offset-modulated signal on the transmitter, and therefore, the interference caused by multiple antennas and multipath propagation is reduced, the system BER is reduced, and the complexity of implementation is low.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Ka-band satellite channel modeling method integrated with meteorological factors
InactiveCN103188011AVerify accuracyVerify validityNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionFuzzy clustering analysisPrincipal component analysis
The invention provides a Ka-band satellite channel modeling method integrated with meteorological factors and aims at solving the problems that data classification is lack of theoretical basis and simulation data are difficult to obtain in a traditional Ka-band satellite channel modeling process. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, analyzing the propagation characteristic of a Ka-band satellite channel and the influences of multipath propagation, rainfall, atmospheric absorption, atmospheric scintillation and other factors to satellite channel modeling; and secondly, establishing a multistate Markov model of the Ka-band satellite channel by using a principal component analysis and fuzzy clustering analysis method. Through comparing the electrical level crossing-over rate and the average decay time of the established model with the electrical level crossing-over rate and the average decay time of a former model, the accuracy and the effectiveness of the channel model are checked, the theoretical basis is provided for resisting the rain attenuation of the Ka-band satellite channel, and meanwhile, Ka-band satellite channel modeling method has great practical significance in technical research on the aspects of signal modulation, coding mode and power control of Ka-band satellite communication.
Owner:紫光陕数大数据有限公司
Radio with interference measurement during a blanking interval
A backhaul radio is disclosed that operates in multipath propagation environments such as obstructed LOS conditions with uncoordinated interference sources in the same operating band. Such a backhaul radio may use a combination of interference mitigation procedures across multiple of the frequency, time, spatial and cancellation domains. Such backhaul radios may communicate with each other to coordinate radio resource allocations such that accurate interference assessment and channel propagation characteristics assessment may be determined during normal operation.
Owner:COMS IP HLDG LLC
Method for clustering wireless channel mpcs based on a kpd doctrine
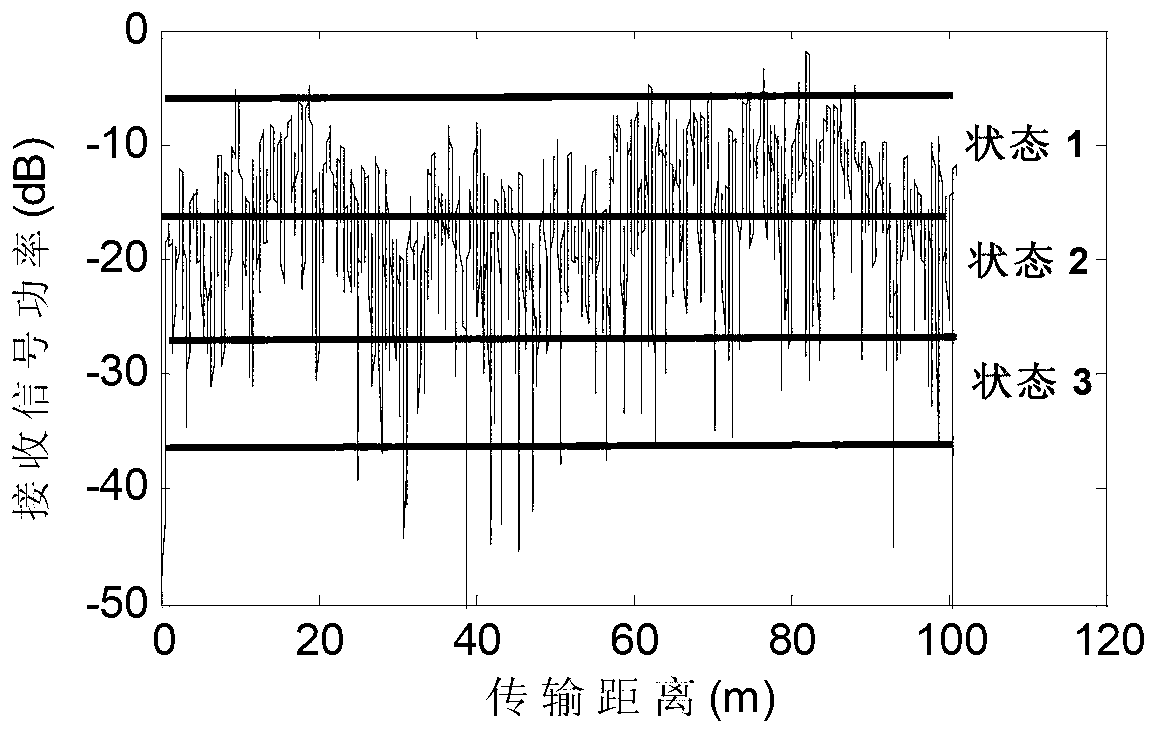
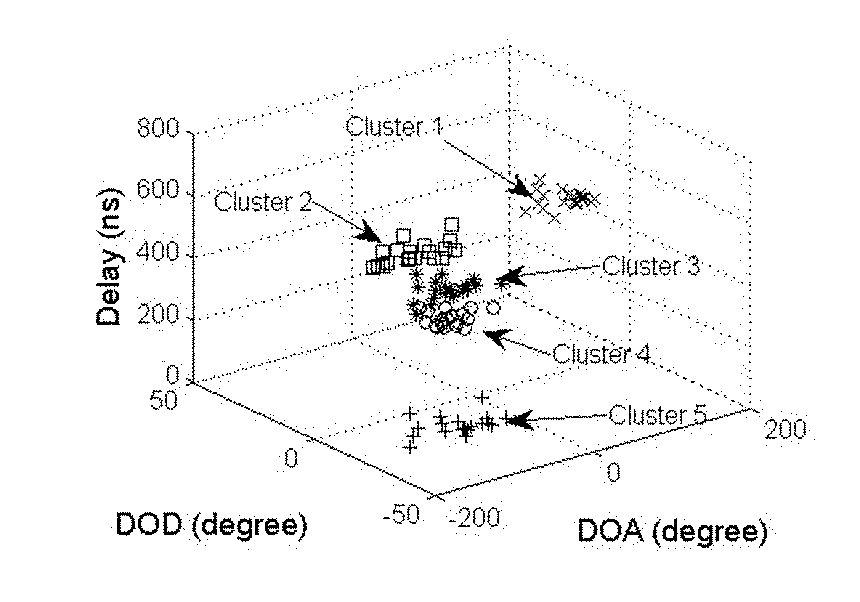
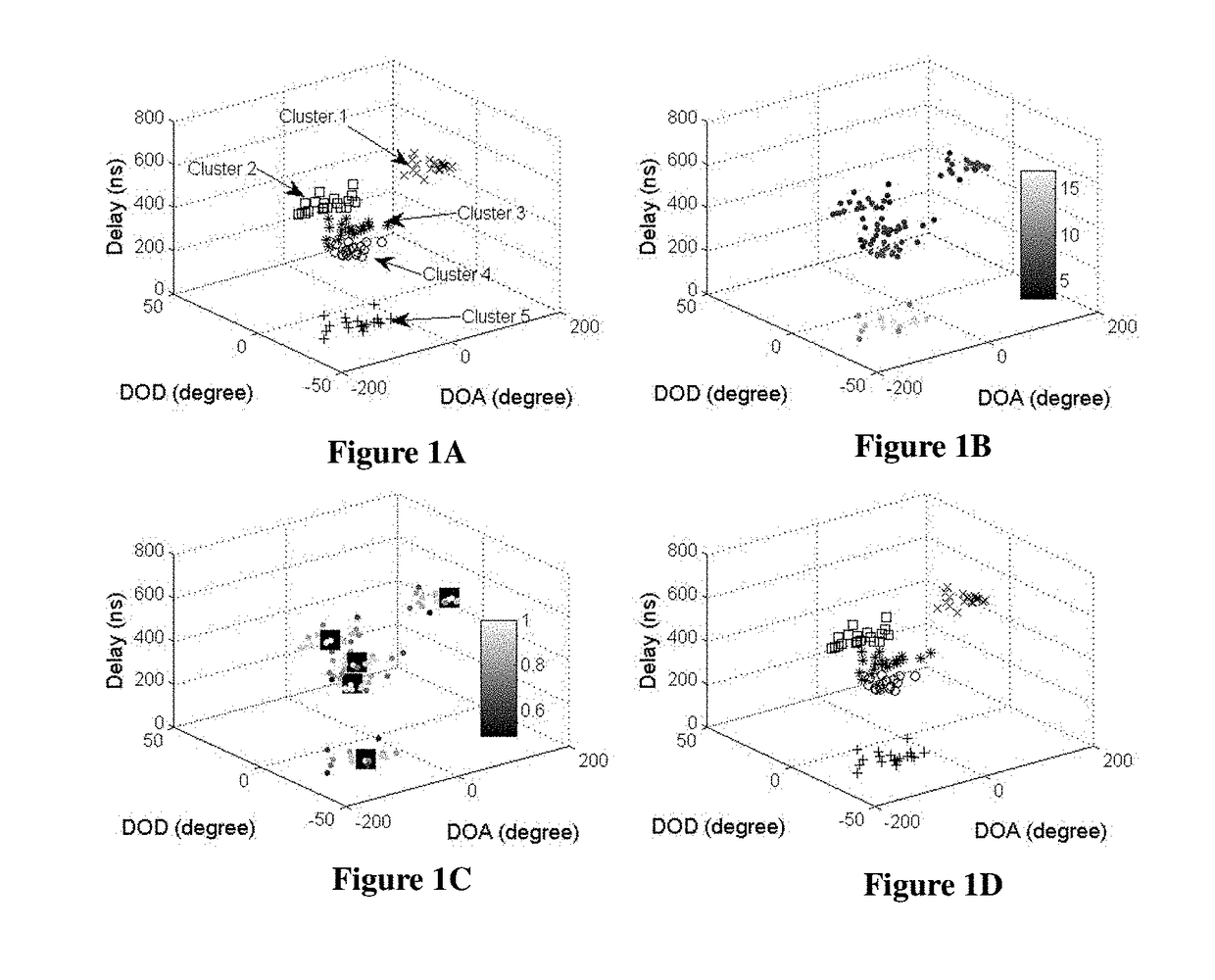
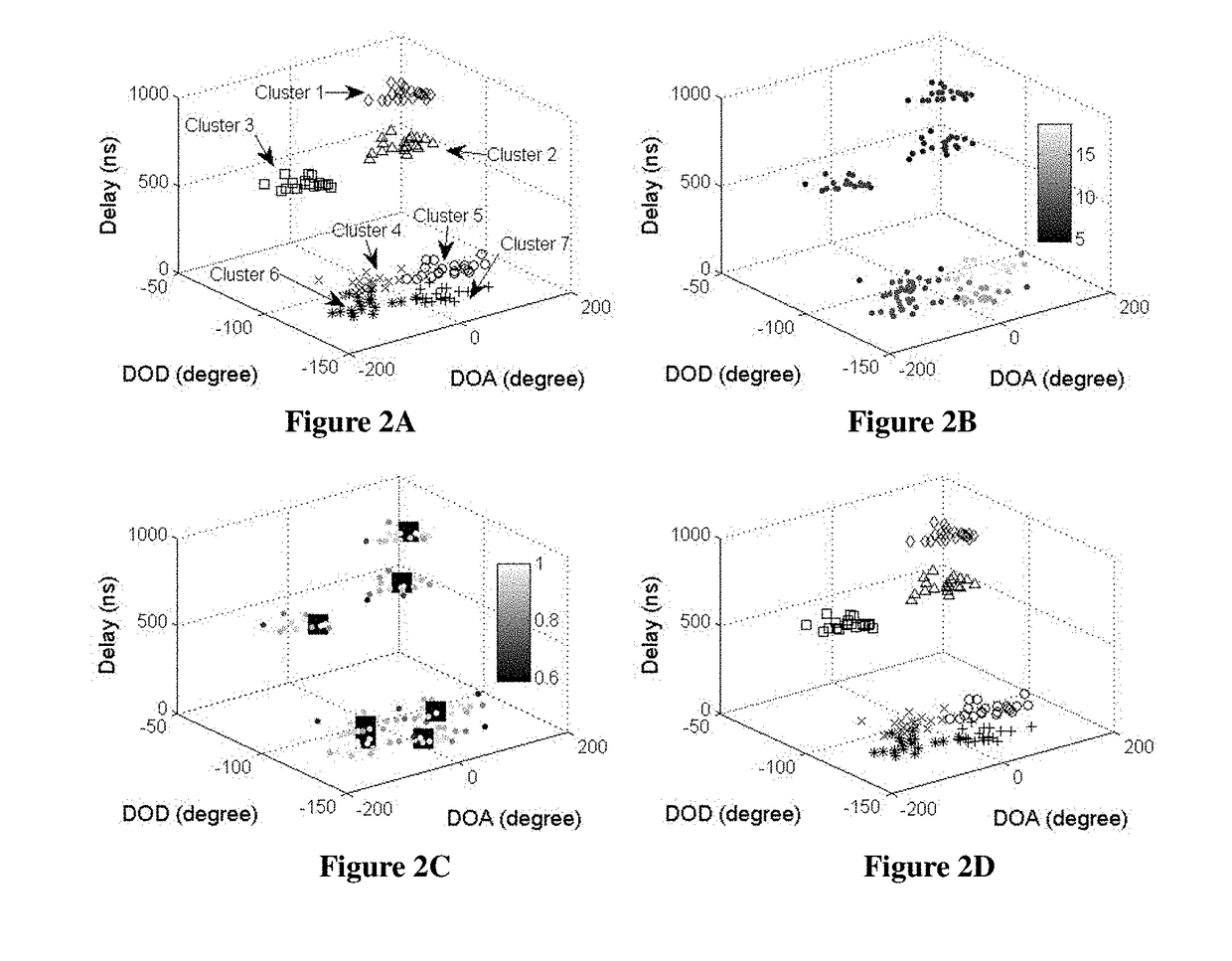
A Kernel-power-density based method for wireless channel multipath components (MPCs) clustering. Signals get to the receiver from a transmitter via multipath propagation. MIMO channels can be modeled as double-directional, which contains the information of power, delay, direction of departure (DOD) and direction of arrival (DOA) of MPCs. The MPCs tend to appear in clusters. All the parameters of MPCs can be estimated by using high-resolution algorithms, such as MUSIC, CLEAN, SAGE, and RiMAX. Considering a data snapshot for a certain time with several clusters, which include a number of MPCs, where each MPC is represented by its power, delay, DOD and DOA. This invention adopts a novel clustering framework by using a density based method, which can better identify the local density variations of MPCs and requires no prior knowledge about clusters. It can work for the cluster oriented channel processing technology in future wireless communication field.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
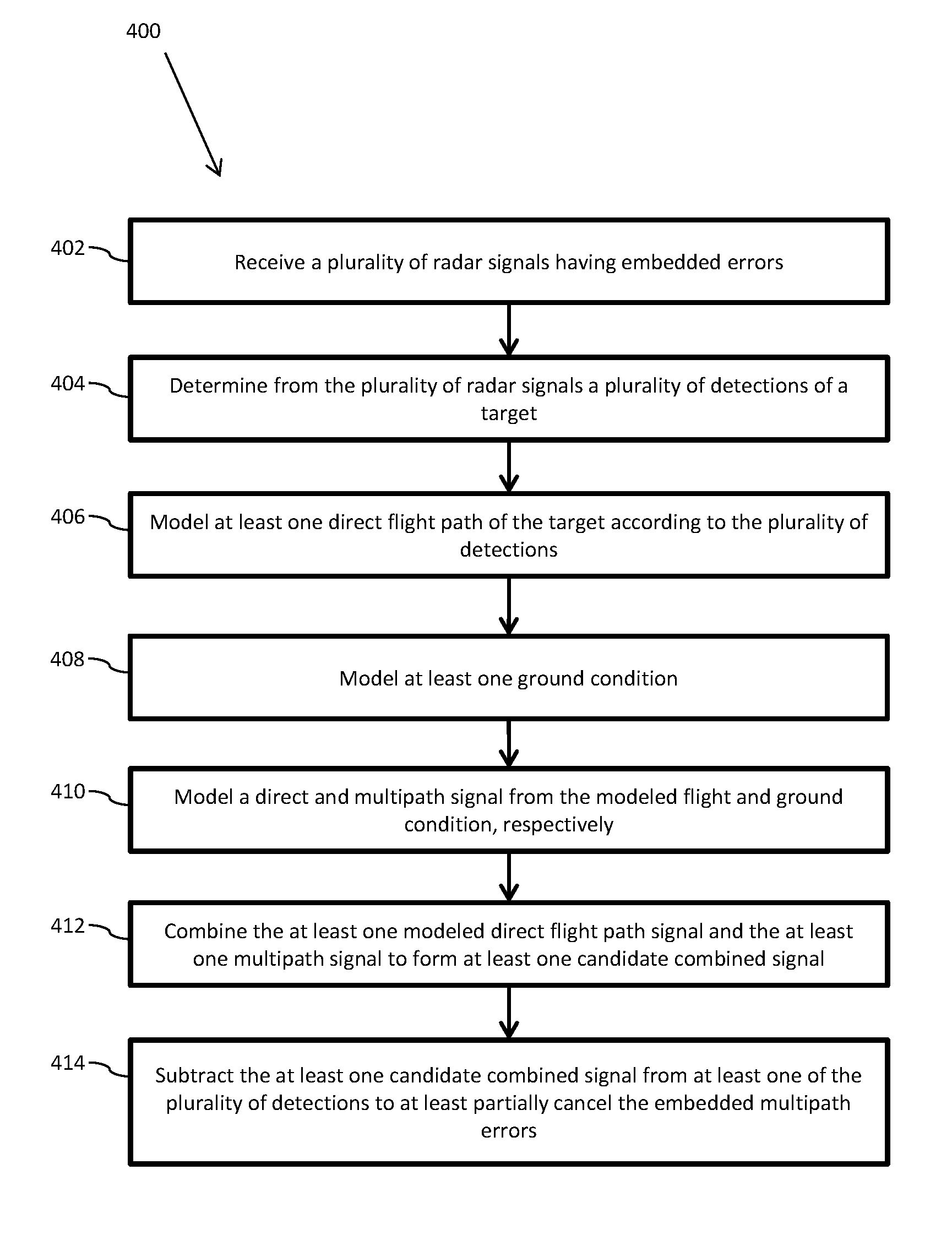
Methods And Systems For Mitigating Multipath Propagation
ActiveUS20170031003A1Satellite radio beaconingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionEngineeringMultipath propagation
A system and method for mitigating multipath propagation are disclosed herein. The method may include collecting a plurality of detections of a target, forming a plurality of models each assuming at least one parameter causing multipath propagation, determining which model best fits the detections of the target, using the best fit model to approximate the ground conditions, and using the approximated ground conditions to remove the multipath error from the observed signals.
Owner:SRC INC
Method for prediction of a channel coefficient
ActiveUS20050118955A1Accurate predictionVariable amount of dataTransmission monitoringRadio transmissionMobile radio channelMobile radio
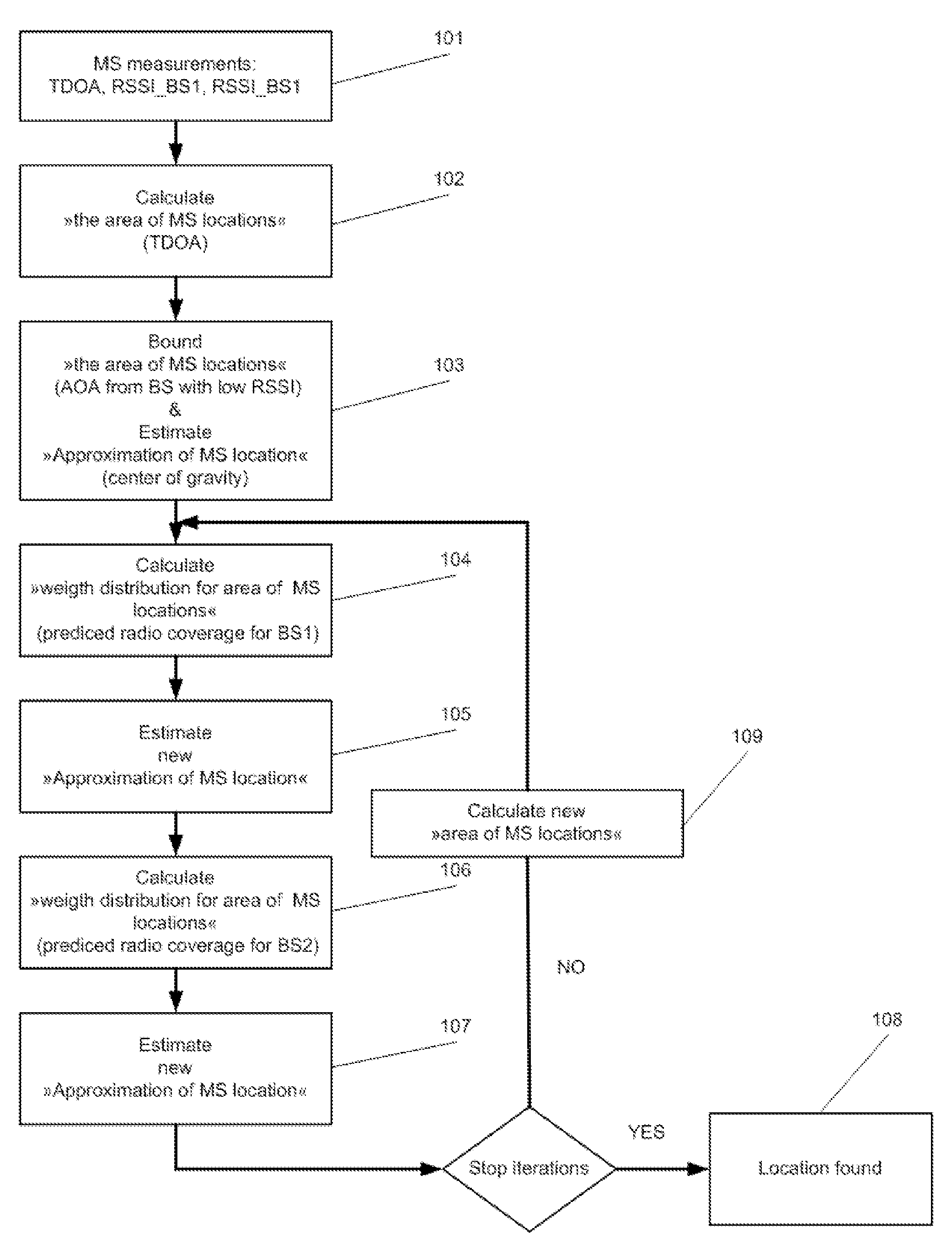
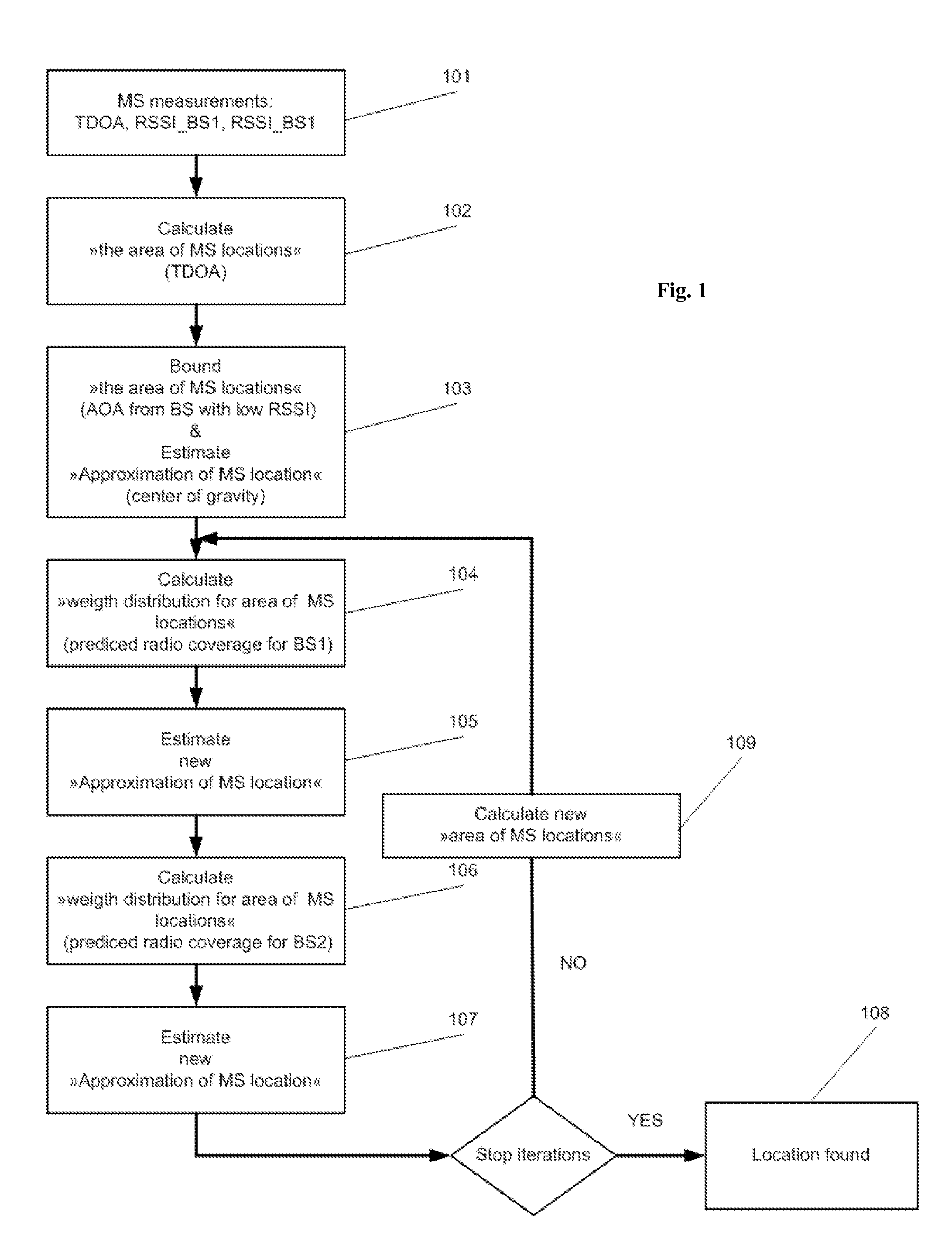
The present invention provides a method for prediction of a channel coefficient for a propagation path in a mobile radio channel with multipath propagation, in which a canonical random variable analysis is used for prediction of the channel coefficient. The method is preferably used in an estimator for channel coefficients in a base station or in a mobile station in a mobile radio system.
Owner:APPLE INC
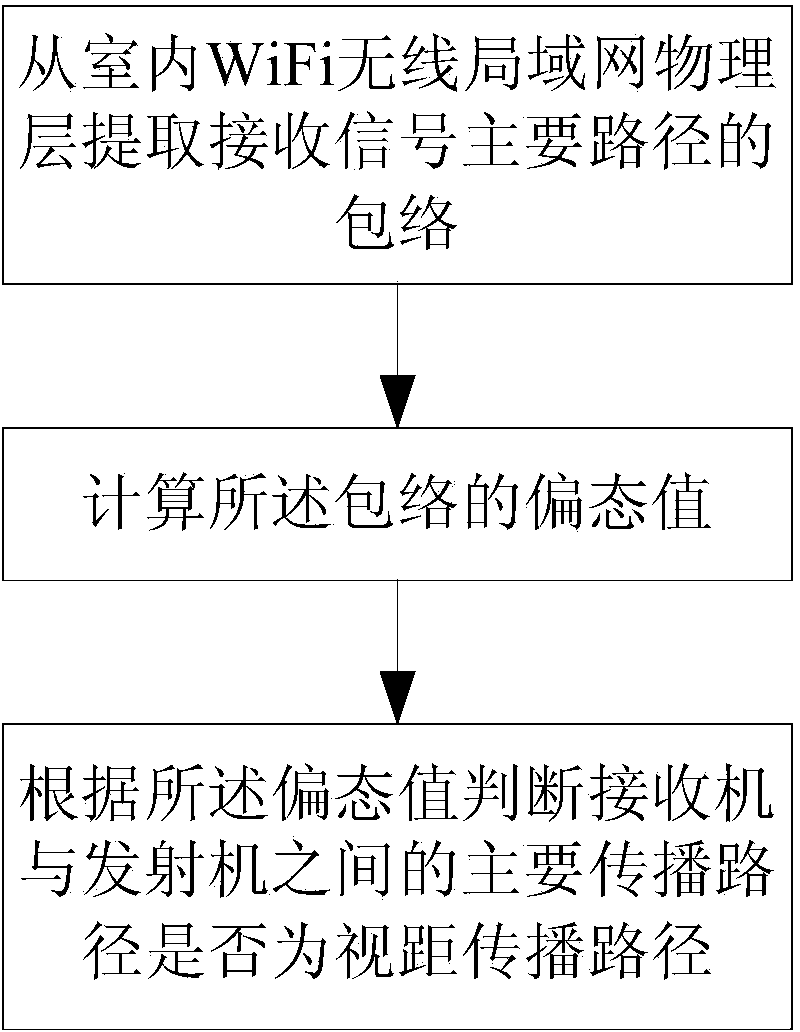
Sight distance propagation path judging method and system on basis of time domain features of WiFi (Wireless Fidelity) physical layer
ActiveCN103532647AImprove discriminationAccurate identificationNetwork topologiesPropogation channels monitoringTime domainChannel impulse response
The invention provides a sight distance propagation path judging method on the basis of time domain features of a WiFi (Wireless Fidelity) physical layer, which comprises the following steps of: extracting an envelope of a main path of a receiving signal from an indoor WiFi wireless local area network physical layer; calculating a skewness value of the envelope; and according to the skewness value, judging whether a main propagation path between a receiver and a transmitter is a sight distance propagation path. According to the invention, by extracting multipath propagation time domain information from the physical layer, channel impulse response is utilized to filter out noise and influence of a non-sight-distance propagation path delayed for long time, movement of the receiver is utilized to improve randomness of the non-sight-distance propagation path and simultaneously main determinacy of the sight distance propagation path, accuracy and robustness of judging the sight distance propagation path are improved, and judgment on the sight distance path propagation is implemented on universal wireless local area network equipment and in a typical indoor environment.
Owner:WUXI TSINGHUA NAT LAB FOR INFORMATIONSCI & TECH INTERNET OF THINGS TECH CENT
Method and apparatus for suppressing adjacent channel interference and multipath propagation signals and radio receiver using said apparatus
ActiveUS20080084953A1Reduce channel interferenceSimple structureError preventionModulated-carrier systemsAdjacent-channel interferenceRadio receiver
A method detects multipath propagation in a modulated digital signal. The method provides a first value of channel frequency, representing the modulated digital signal free of multipath propagation, providing a second value of said channel frequency, representing the modulated digital signal with multipath propagation, and comparing the first and second values. A method detects adjacent channel interference in a modulated digital signal by comparing first and second values of a characteristic parameter of the digital signal, respectively representing the digital signal free of adjacent channel interference and the digital signal affected by adjacent channel interference. In particular, the method obtains a derivative signal, applies a non-linear Teager-Kaiser function to the digital signal and the derivative signal for generating first and second signals respectively representing energy content of the digital signal and energy content of the derivative signal, and processes the first and second signals for generating the second value.
Owner:MICROELECTRONIC INNOVATIONS LLC
Broadband wireless transmission method and system, transmitter and method, receiver and method
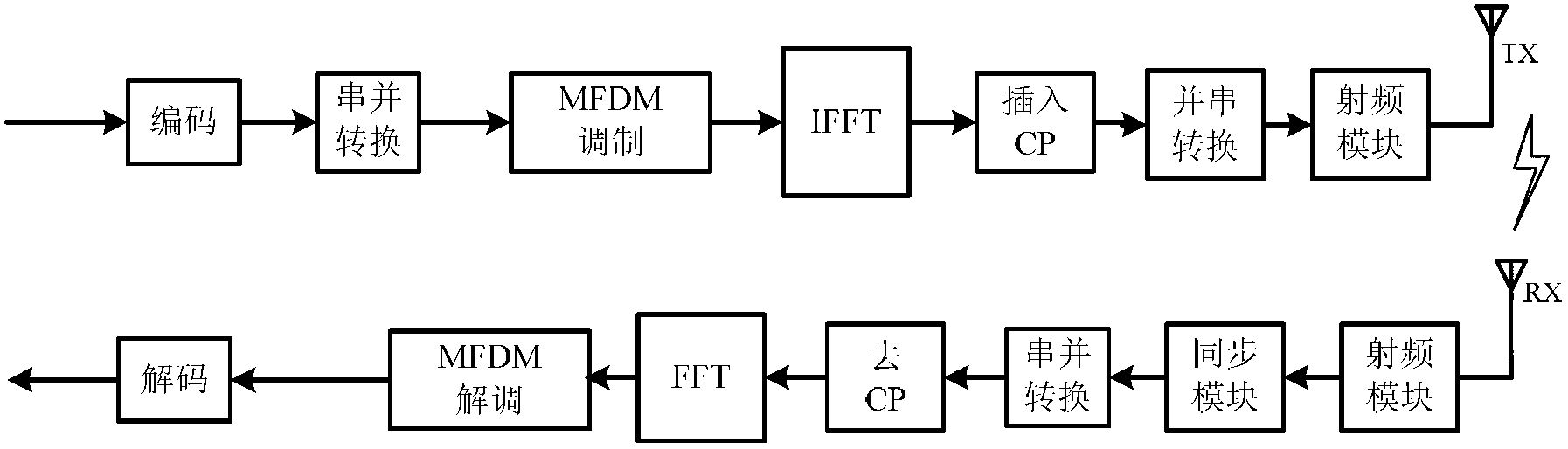
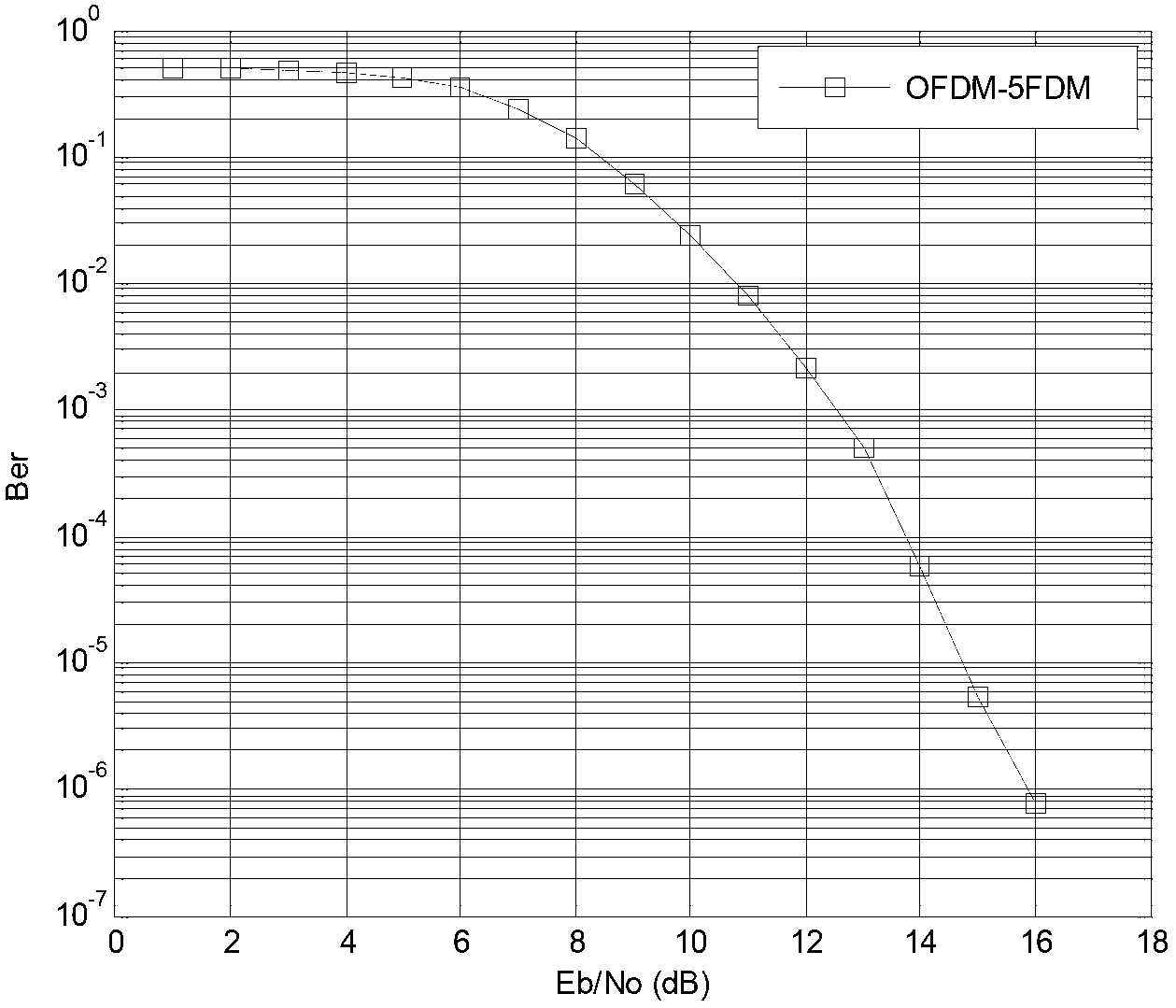
InactiveCN102710574AOvercoming intersymbol interferenceInterference will notMulti-frequency code systemsHardware structureCyclic prefix
The invention discloses a broadband wireless transmission method and a broadband wireless transmission system, a transmitter and a method, as well as a receiver and a method under high-speed movement environment. High-speed baseband signals serially input by a transmitting end are converted to be low-speed parallel baseband signals by series-to-parallel conversion, then MFDM (Multi-Frequency Difference Modulation) mapping is conducted, time-domain baseband signals are converted to be frequency-domain baseband signals which are converted to be time domain signals by IFFT (Inverse Fast Fourier Transform), a CP (Cyclic Prefix) is inserted and the parallel-to-series conversion is conducted, then the signals are sent to a radio frequency module and then are sent to an antenna to be transmitted, a receiving end converts the signals received by the antenna into digital baseband signals through the radio frequency module, the position synchronization is realized by a synchronization module, then the signals are subjected to series-to-parallel conversion, the CP is removed, the signals are sent to an FFT (Fast Fourier Transform) module and are converted to be frequency-domain baseband signals, then the MFDM mapping is removed, and time-domain baseband information is recovered. The Doppler frequency deviation caused by intersymbol interference and high-speed movement due to multipath propagation can be overcome, and the hardware structure of the receiver is simplified greatly due to the avoidance of channel estimation.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Matching locating method based on wireless channel frequency domain amplitude response
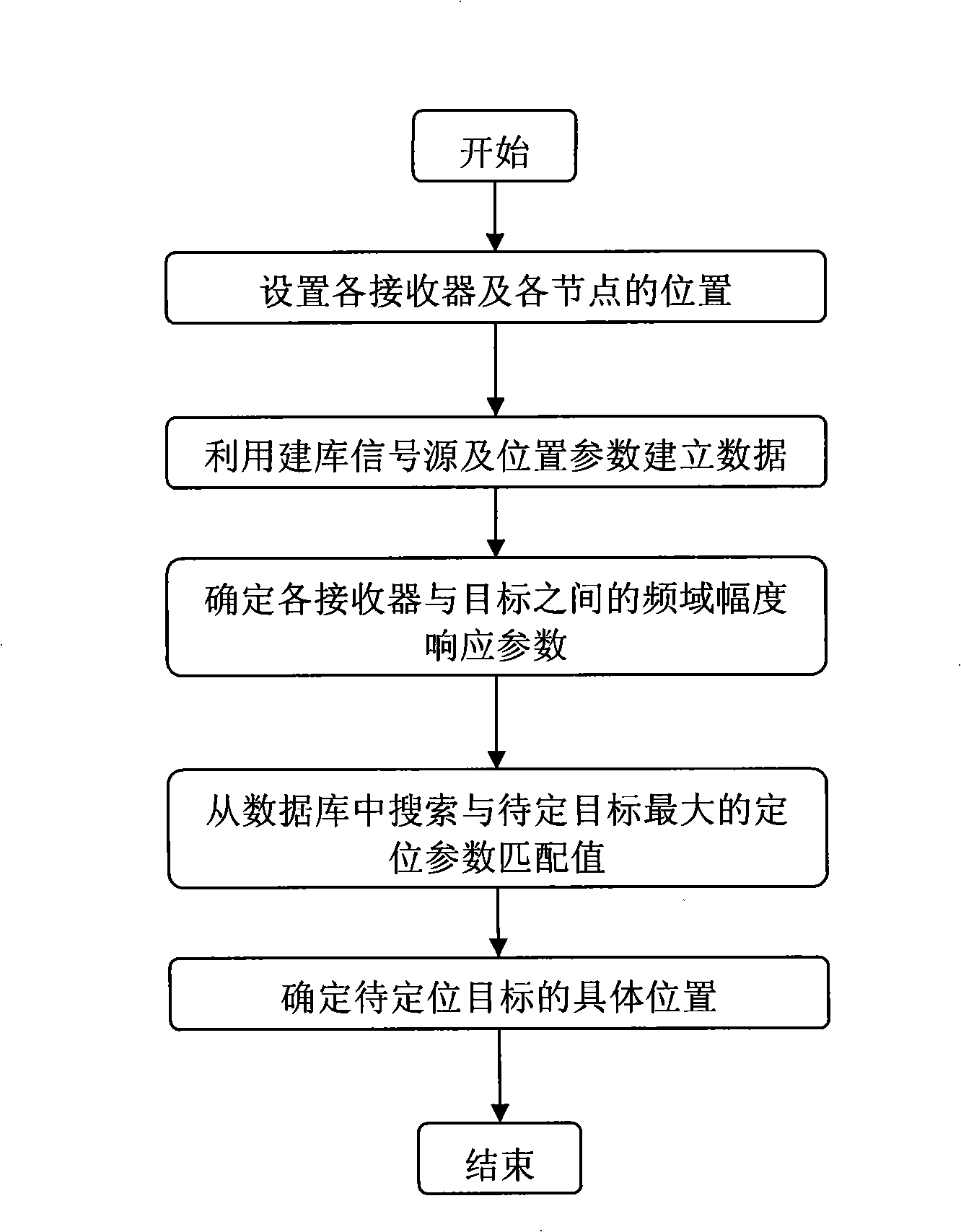
InactiveCN101526609AImprove accuracyHigh positioning accuracyPosition fixationAmplitude responseLocation area
The invention belongs to a method for locating indoor wireless propagated signal source, comprising the following steps of: adopting a database-setting signal source to set up a location database, defining a frequency domain amplitude response parameter between each receiver and each target, and defining the position of the targets which are to be located. Because the invention adopts a signal with the shape of normalized gammagram as a database-setting signal to define a normalized frequency domain amplitude response parameter of wireless propagation channel between each node and each receiver, define a first location parameter corresponding thereto and the database for setting up location, and locate the targets which are to be located, and uses the space difference of multipath propagation and indirect wave propagation between the targets which are to be located and each signal receiver in the location method to conquer negative effects, the invention has the advantages that the sensitivity to position difference in location area can be effectively improved, time synchronicity demand and location cost can be reduced, as well as location accuracy and location precision can be promoted, etc.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Device for receiving secondary radio signals with quasi-dynamic or dynamic sectoring of space to be monitored and corresponding method
ActiveCN102227647AEasy detectionInterference CancellationMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsRocket
The invention relates to a device for secondary radar signal reception with quasi-dynamic or dynamic sectoring of a space to be monitored and a method used therein. In conventional radar tracking systems, e.g. of rockets, antenna arrays are used, with only one beam being used for one object. One device for receiving secondary radar signals is configured or such a secondary radar system is designed in such a manner that objects can be better separated, especially when there is a large number of objects in the monitored space, thereby making systems less susceptible to interfering signals and achieving multipath propagation.
Owner:IAD GESELLSCHAFT FUER INFORMATIK AUTOMATISIERUNG & DATENVERARBEITUNG MBH
Iterative Localization Techniques
ActiveUS20110317570A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemMobile station
The present invention refers to iterative localization techniques with wireless communication systems for rural environment with limited number of base stations in the range of the mobile station and urban environment with multipath propagation channel and several base stations in the range of mobile station.
Owner:WILDFIRE EXCHANGE
Method and device for determining the position of at least one second transmitting and receiving device in respect of a first transmitting and receiving device in a passive access control system operating in the ghz range
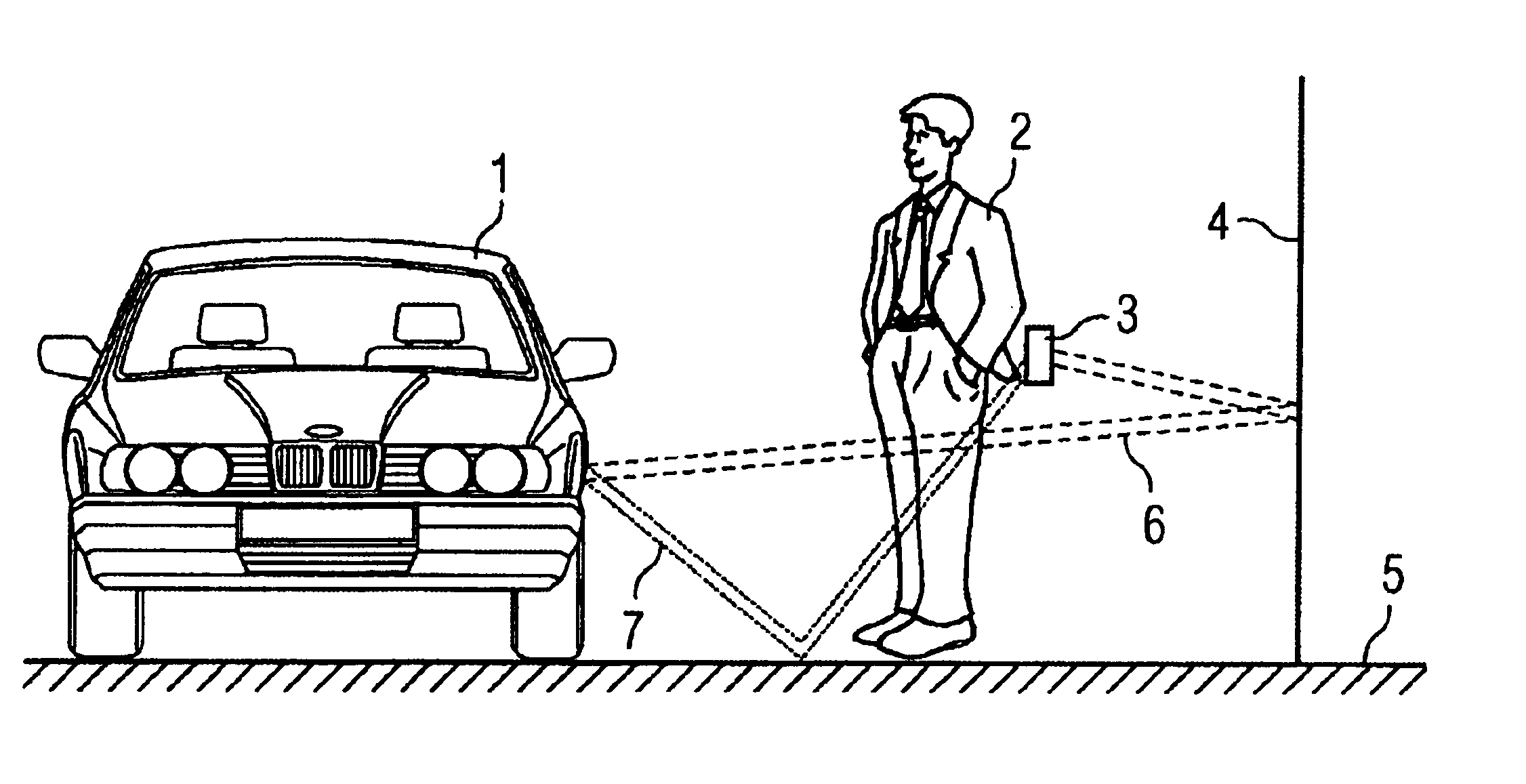
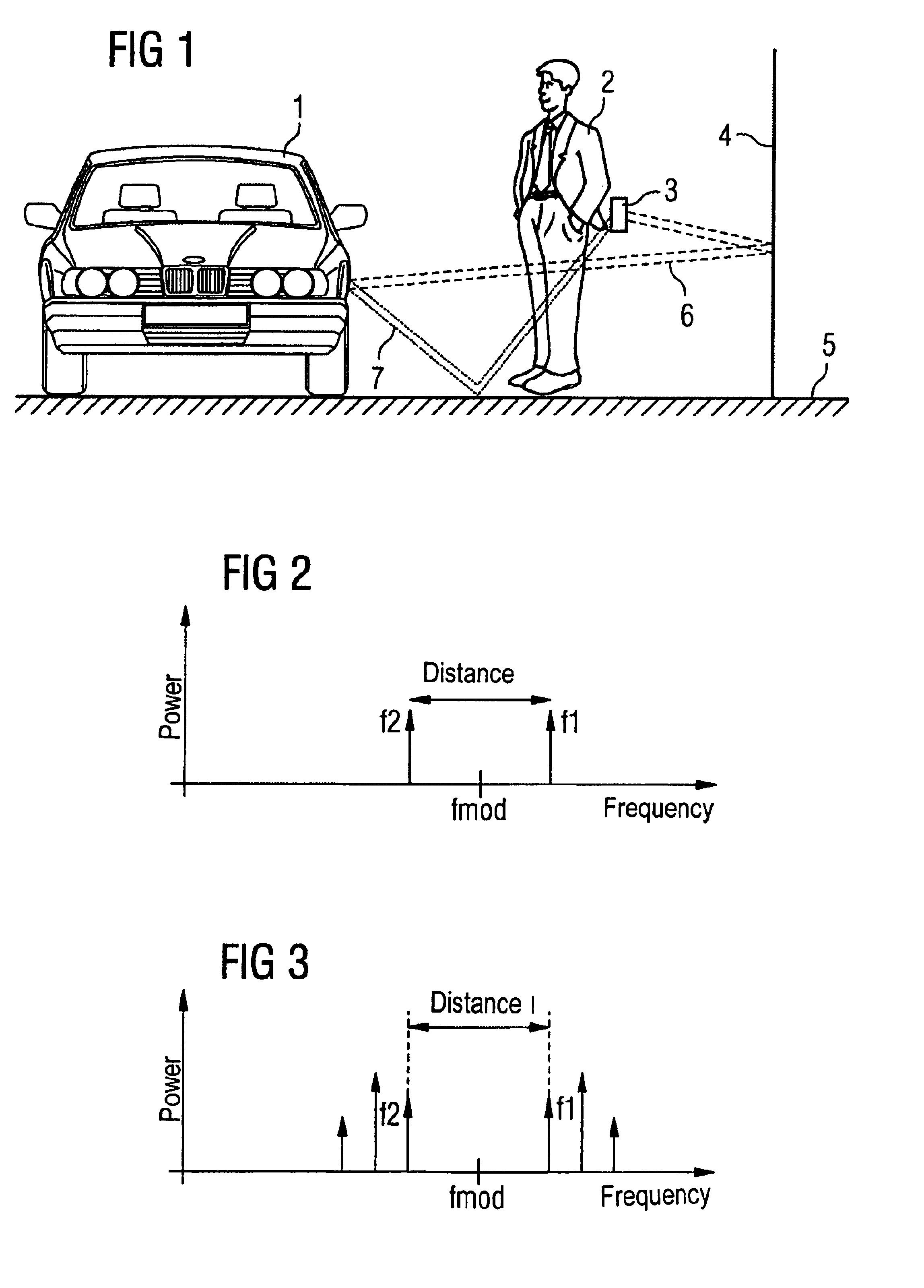
InactiveUS6909396B2Precise positioningElectric signal transmission systemsMultiple keys/algorithms usageRadarControl system
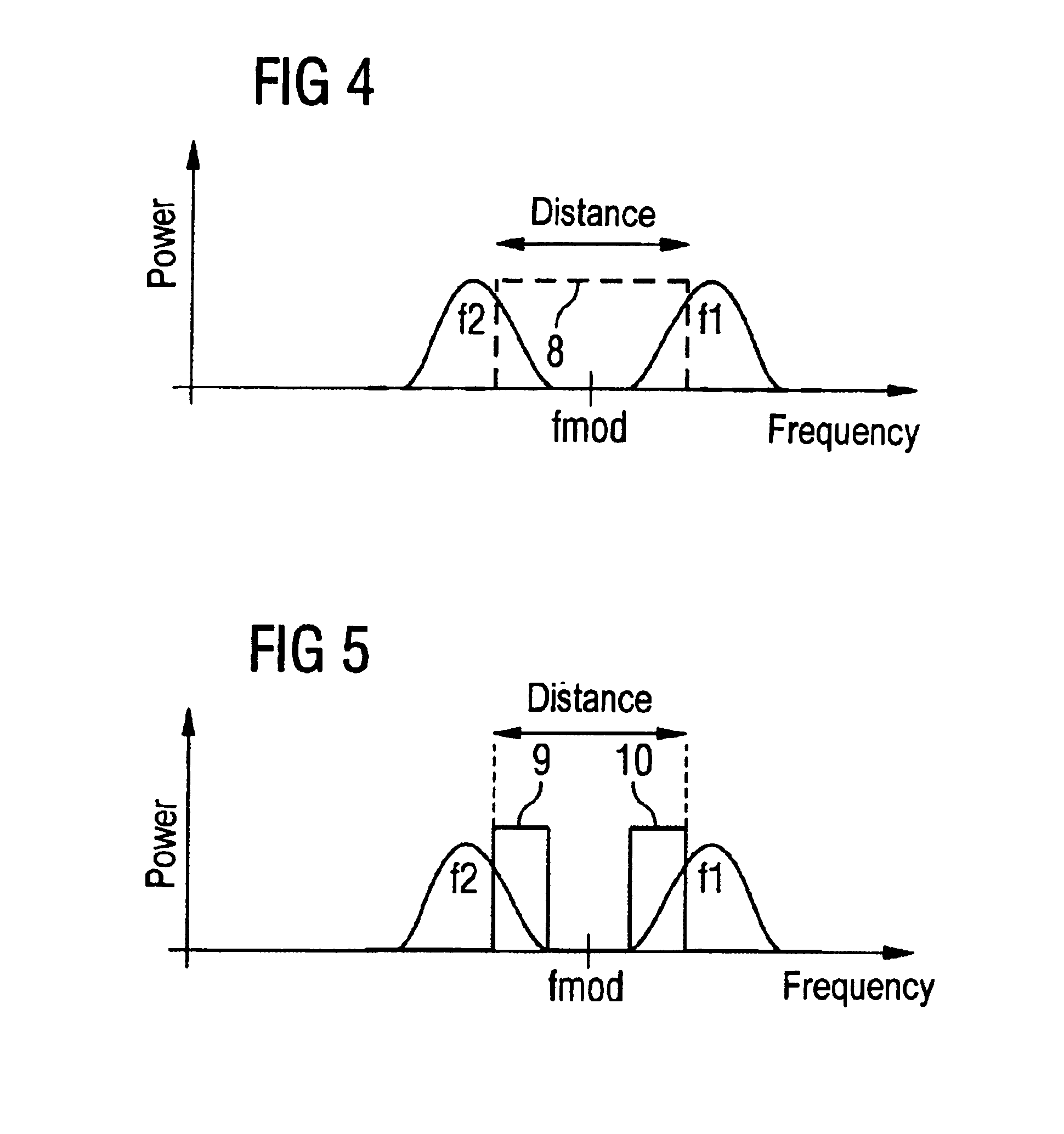
A method for determining the position of at least one second transmitting and receiving device (3) in respect of a first transmitting and receiving device in a passive access control system operating in the GHz range, comprising the steps of using a radar method, wherein signals (f1, f2) are received in the first transmitting and receiving device on the left-hand side and right-hand side of a modulation frequency (fmod), determining the distance of two signals (f1, f2) closest to the left-hand side and right-hand side modulation frequency (fmod) wherein the distance is proportional to the distance between the first transmitting and receiving device and at least one second transmitting and receiving device (3), so that multipath propagations are not taken into consideration.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com