Patents
Literature
489 results about "Co-channel interference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Co-channel interference or CCI is crosstalk from two different radio transmitters using the same channel. Co-channel interference can be caused by many factors from weather conditions to administrative and design issues. Co-channel interference may be controlled by various radio resource management schemes.
Method for database driven channel quality estimation in a cognitive radio network
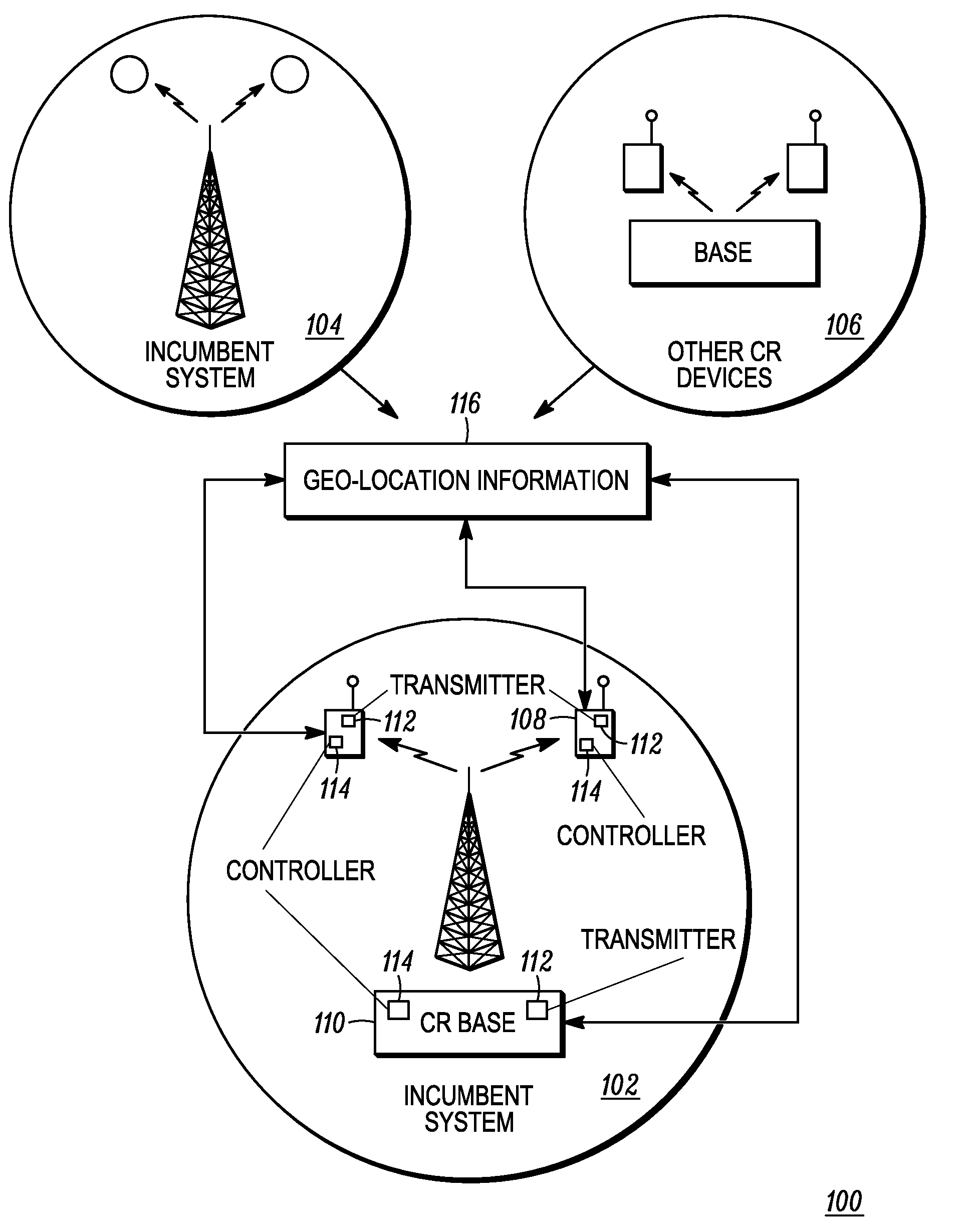
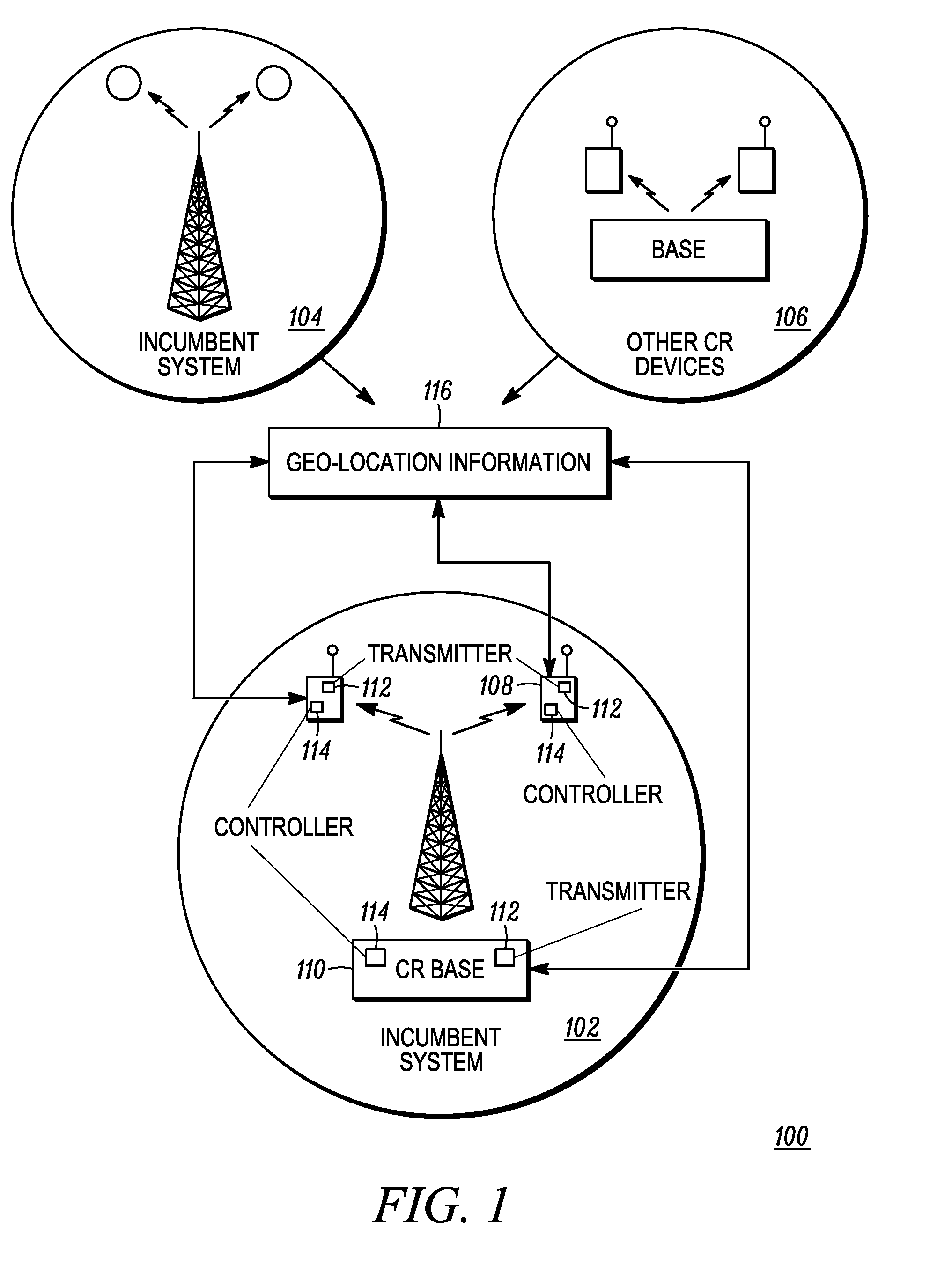
ActiveUS20100330919A1Power managementTransmission monitoringCo-channel interferenceGeolocation database
A method of determining operating parameters for a secondary system transmitter is described. The transmitter characteristics, including location and operating frequency band, are provided to a geo-location database. The database determines the maximum allowable transmission power that meets various specifications for different channels and conveys the power and channel(s) to the transmitter. The database estimates channel incumbent signal strengths based on the transmitter location and primary and higher-priority secondary incumbent systems, estimates the splatter levels, determines whether adjacent and co-channel interference protection ratios are met, and adjusts the allowable power level accordingly. The database also estimates aggregate co- and adjacent channel primary and secondary incumbent system interference levels at the transmitter location and predicts channel quality for each allowable channel. The estimated levels are updated using measurements of actual levels at the transmitter location. The database dynamically allocates channels using the secondary system priorities.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC +1
System and Method for Co-Channel Interference Measurement and Managed Adaptive Resource Allocation for Wireless Backhaul
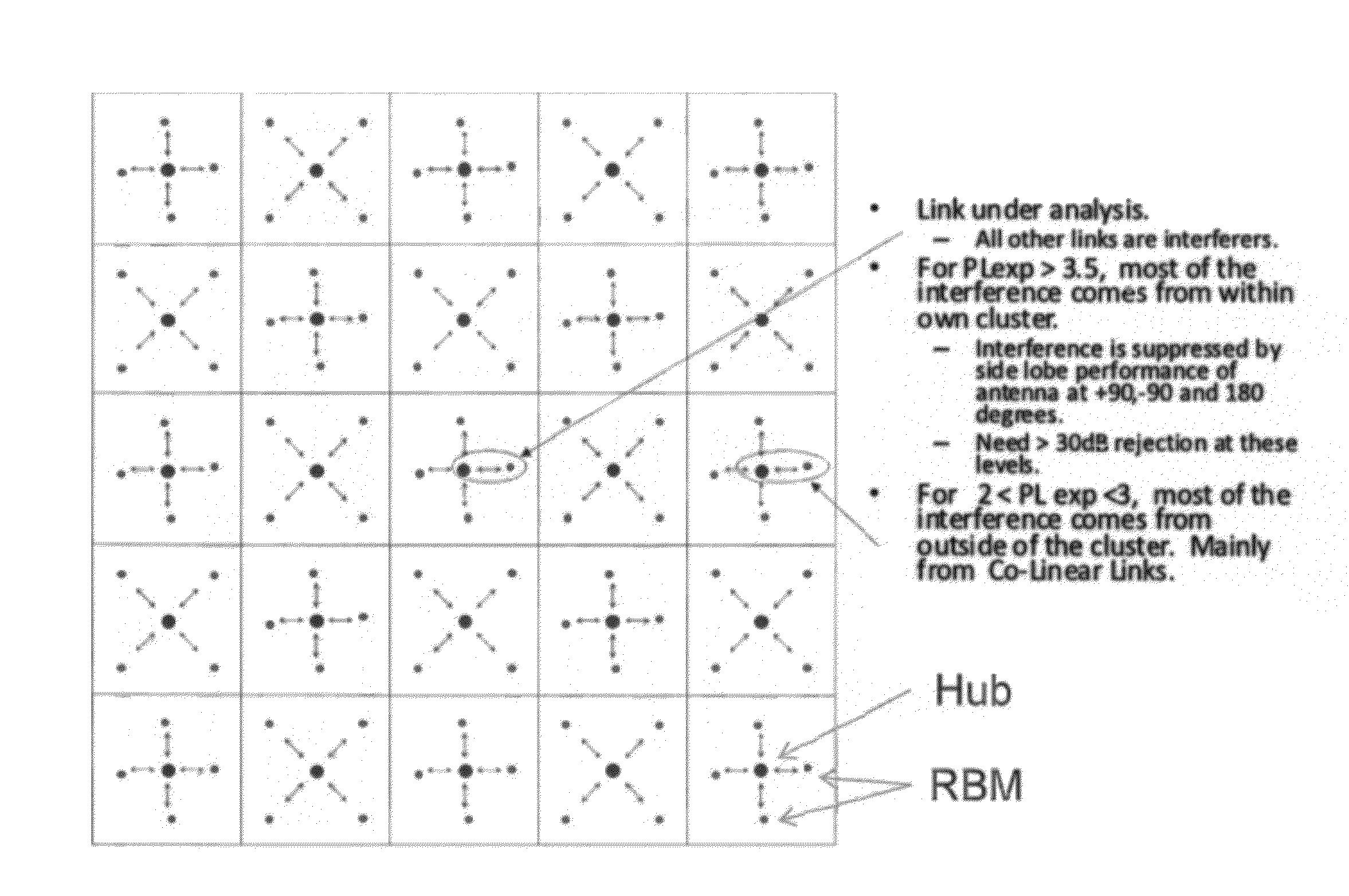
ActiveUS20120236731A1Reduce disadvantagesReduce co-channel interferenceError preventionTransmission systemsResource blockPublic resource
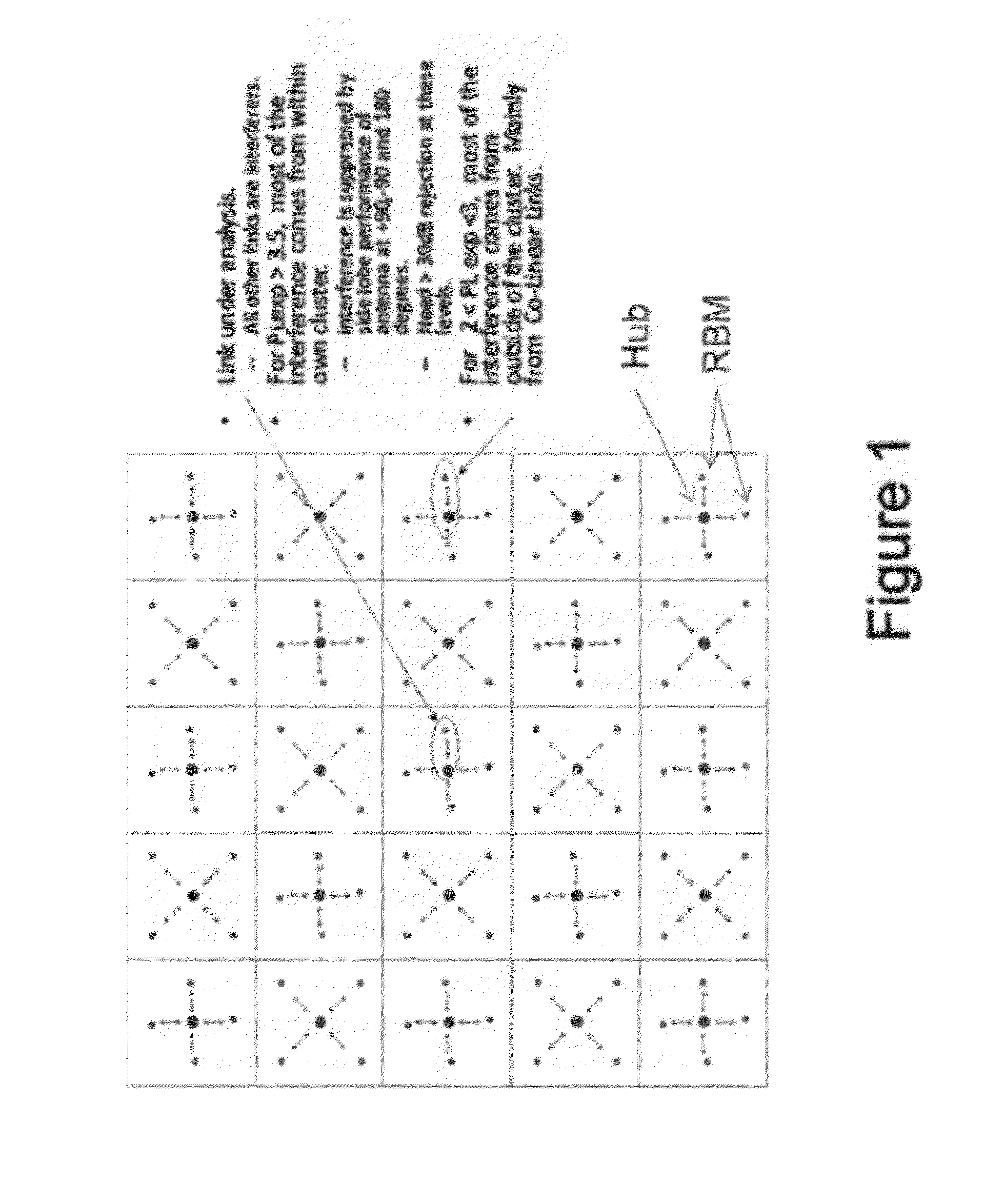
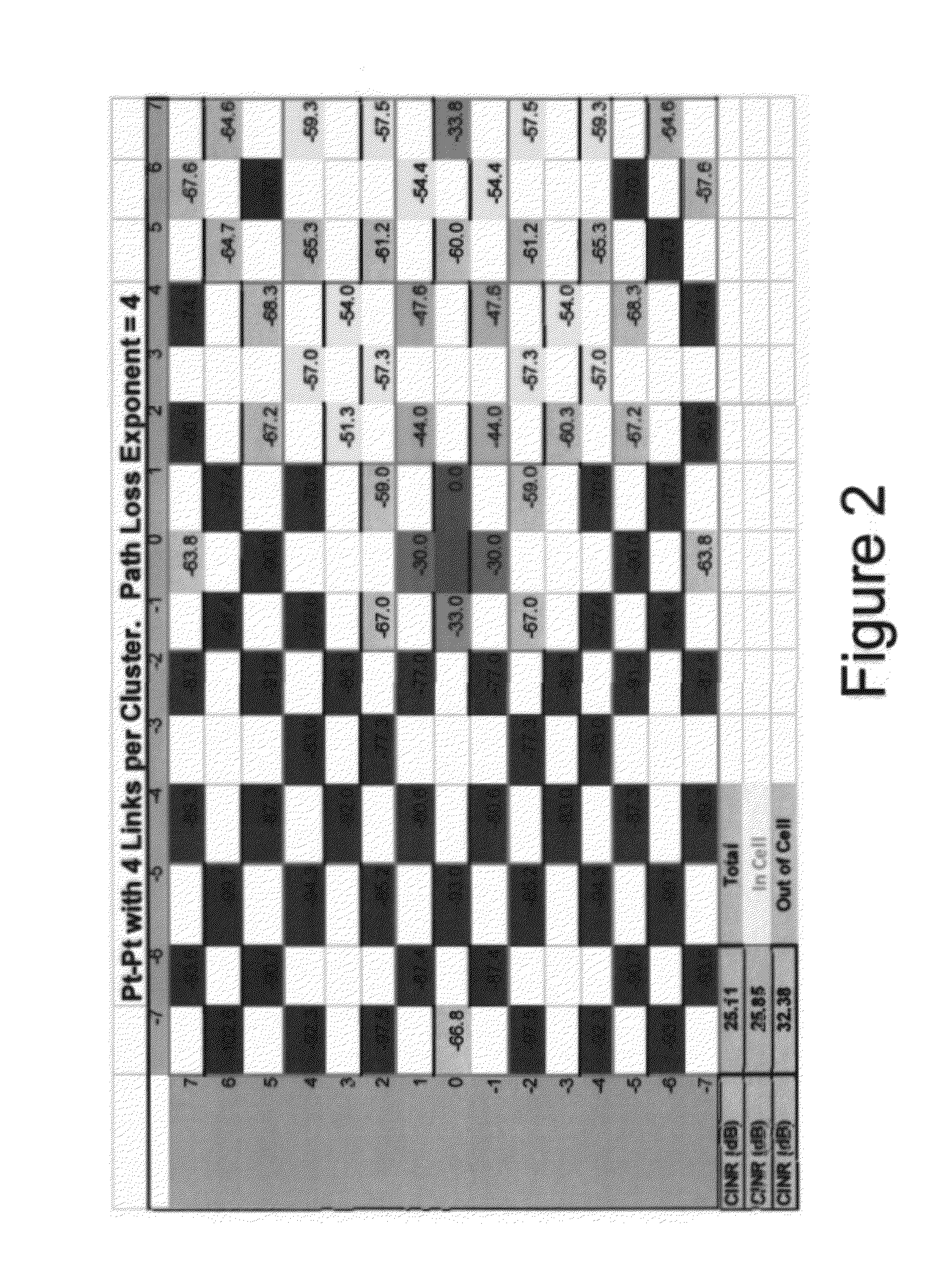
A system, method, and software are provided for measuring co-channel interference in a wireless network with particular application for management of resource allocation for Non Line of Sight (NLOS) wireless backhaul in MicroCell and PicoCell networks. Given the difficulty of predicting the mutual interference between multiple links, DownLink and UpLink co-channel interference are characterized between each Hub and each Remote Backhaul Module Unit periodically during active service. Beneficially, the co-channel interference metrics are used as the basis for intelligently and adaptively managing network resources to substantially reduce interference and increase the aggregate data capacity of the network e.g. by grouping of interfering and / or non-interfering links, and managing resource block allocations accordingly, i.e. assigning common resource blocks preferentially to weakly interfering links or groups of links and allocating different resource blocks or orthogonal channels to strongly interfering links or groups of links.
Owner:BLINQ NETWORKS
Method and apparatus for reducing co-channel interference in a communication system
InactiveUS7016319B2Multiplex communicationInter user/terminal allocationCommunications systemResource block
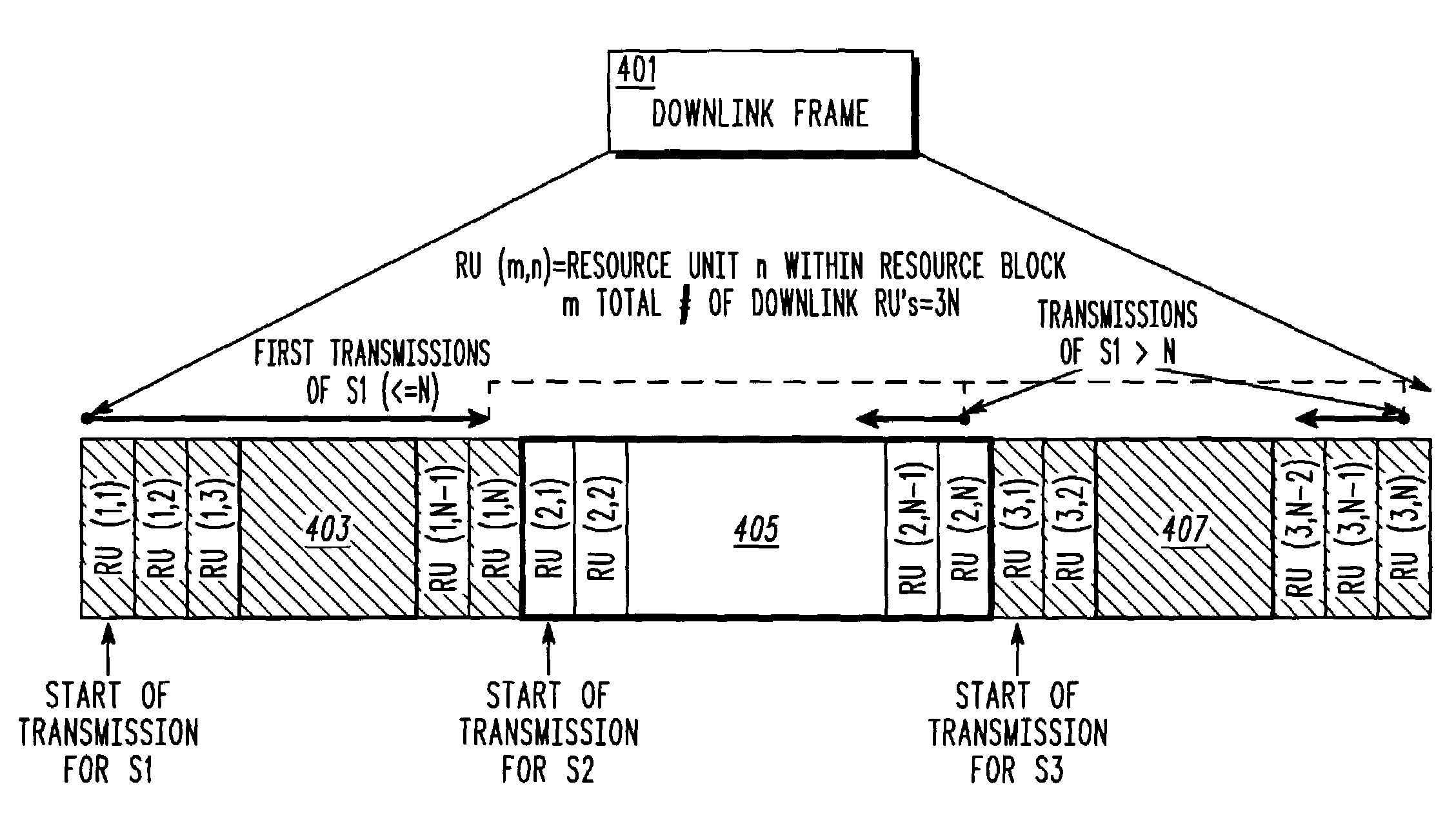
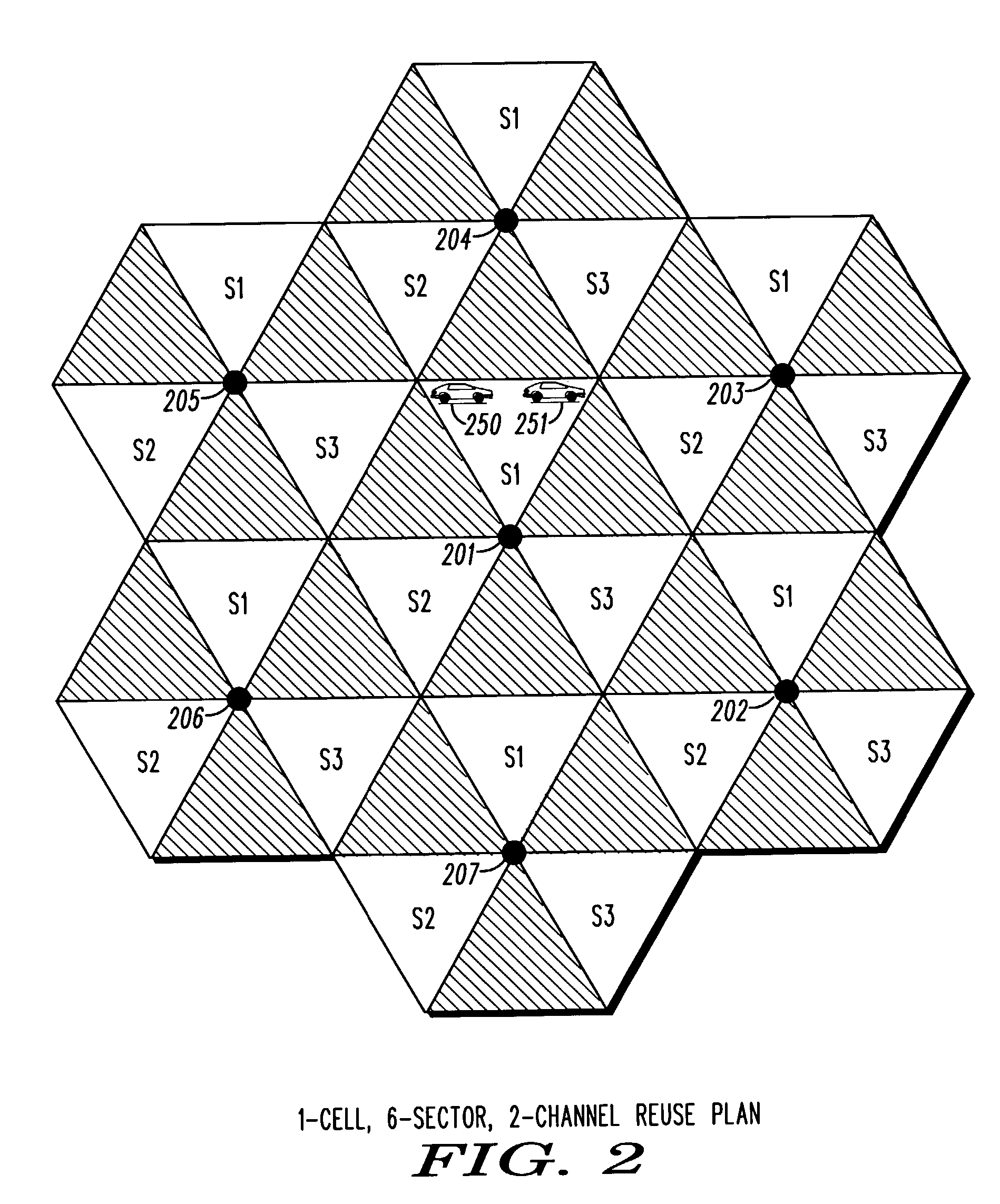
A downlink frame (401) is divided in to similar sized resource blocks (403, 405, 407) with each co-channel sector scheduled to transmit from the beginning of its respective assigned resource block. Transmissions to remote units within the particular sector will occur only within the particular resource block, up to a point where all N resource units have been utilized. Beyond that point, additional transmissions are scheduled to be transmitted at the end of the resource blocks assigned to the other sectors.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
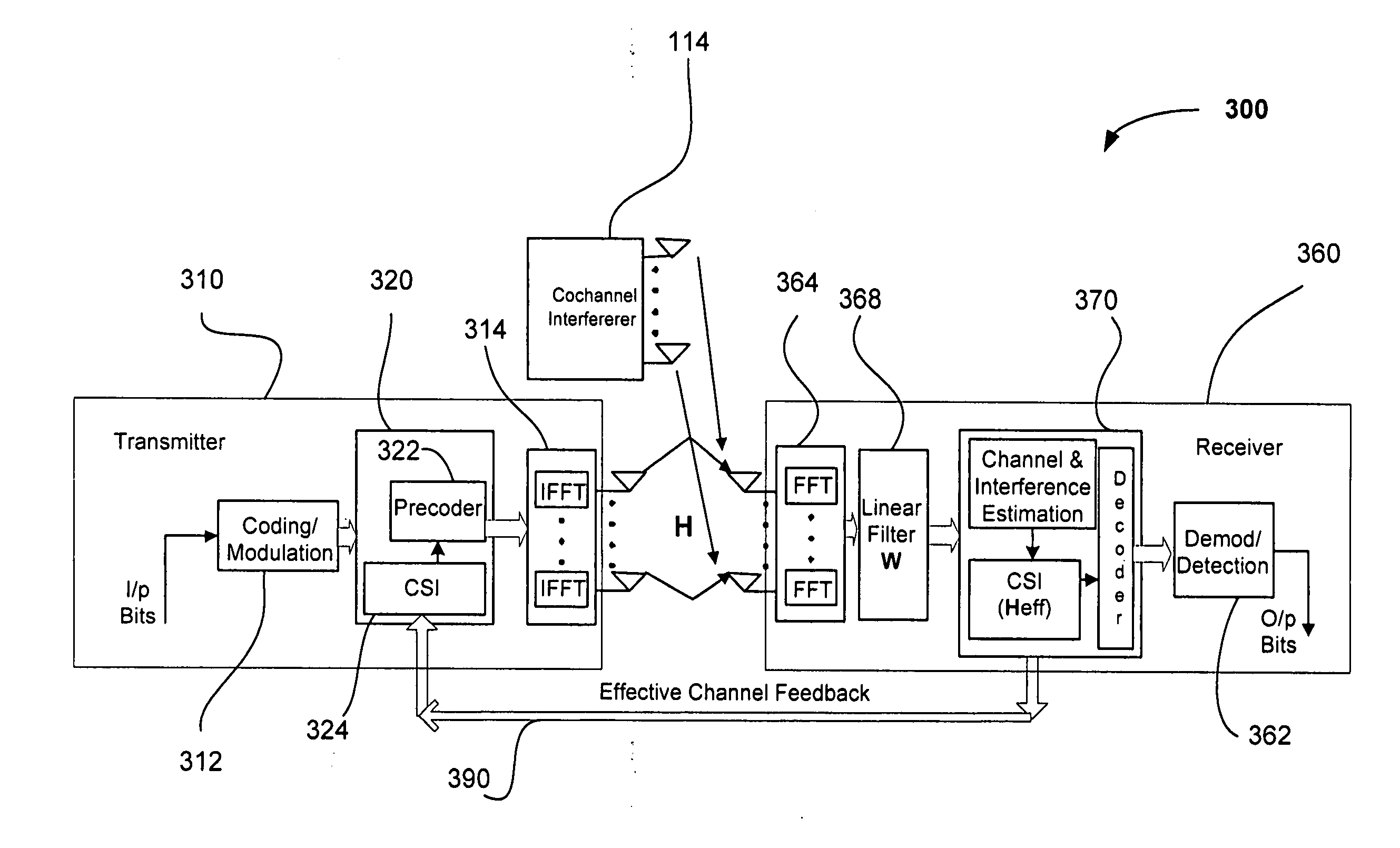
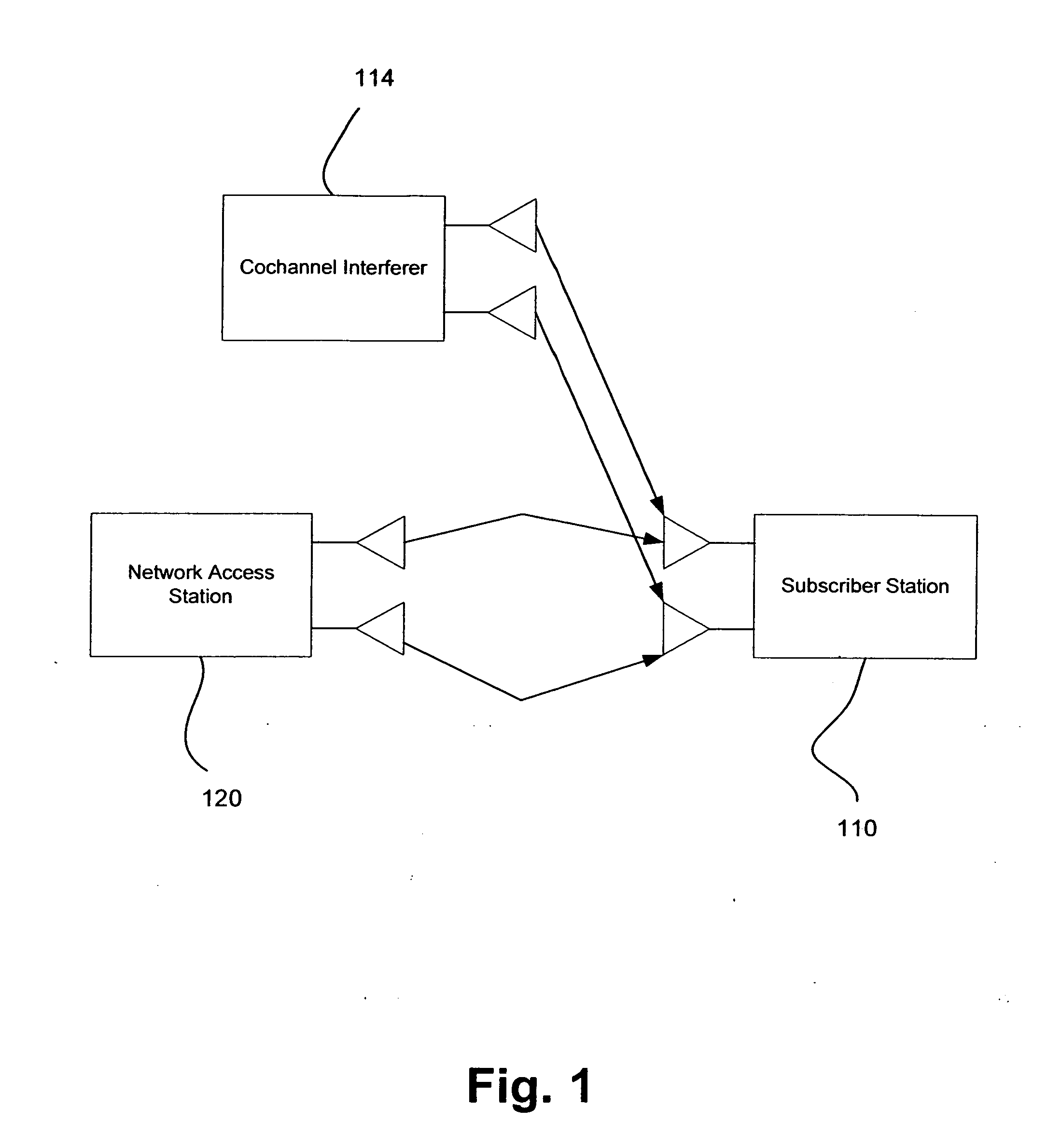
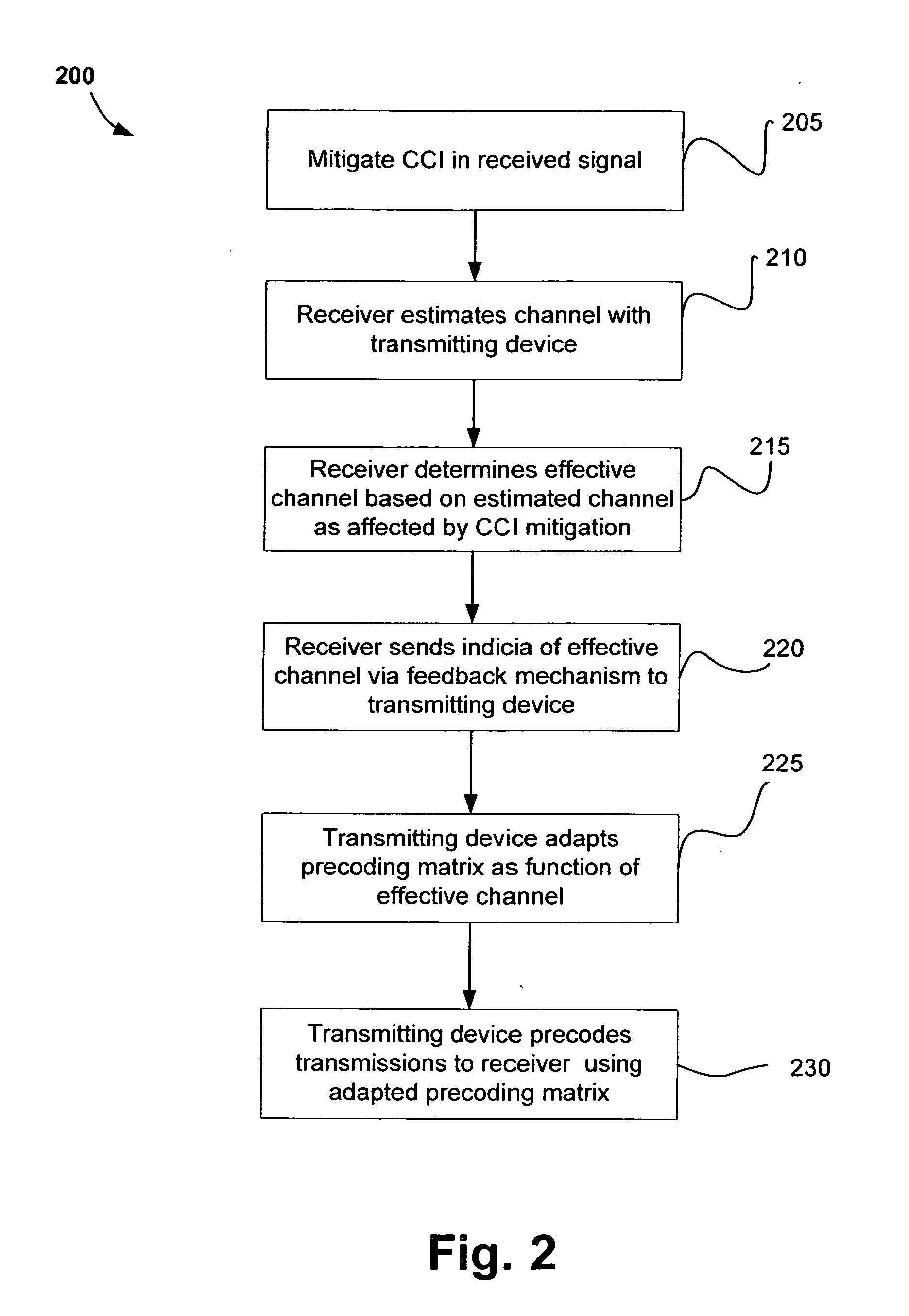
MIMO precoding in the presence of co-channel interference
InactiveUS20070211813A1Modulated-carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsPrecodingChannel state information
Methods and systems for communicating in a wireless network include mitigating co-channel interference (CCI) for precoded multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems and incorporating the effect of CCI mitigation on channel characteristics in the design of channel state information (CSI) feedback mechanisms. Various embodiments and variants are also disclosed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
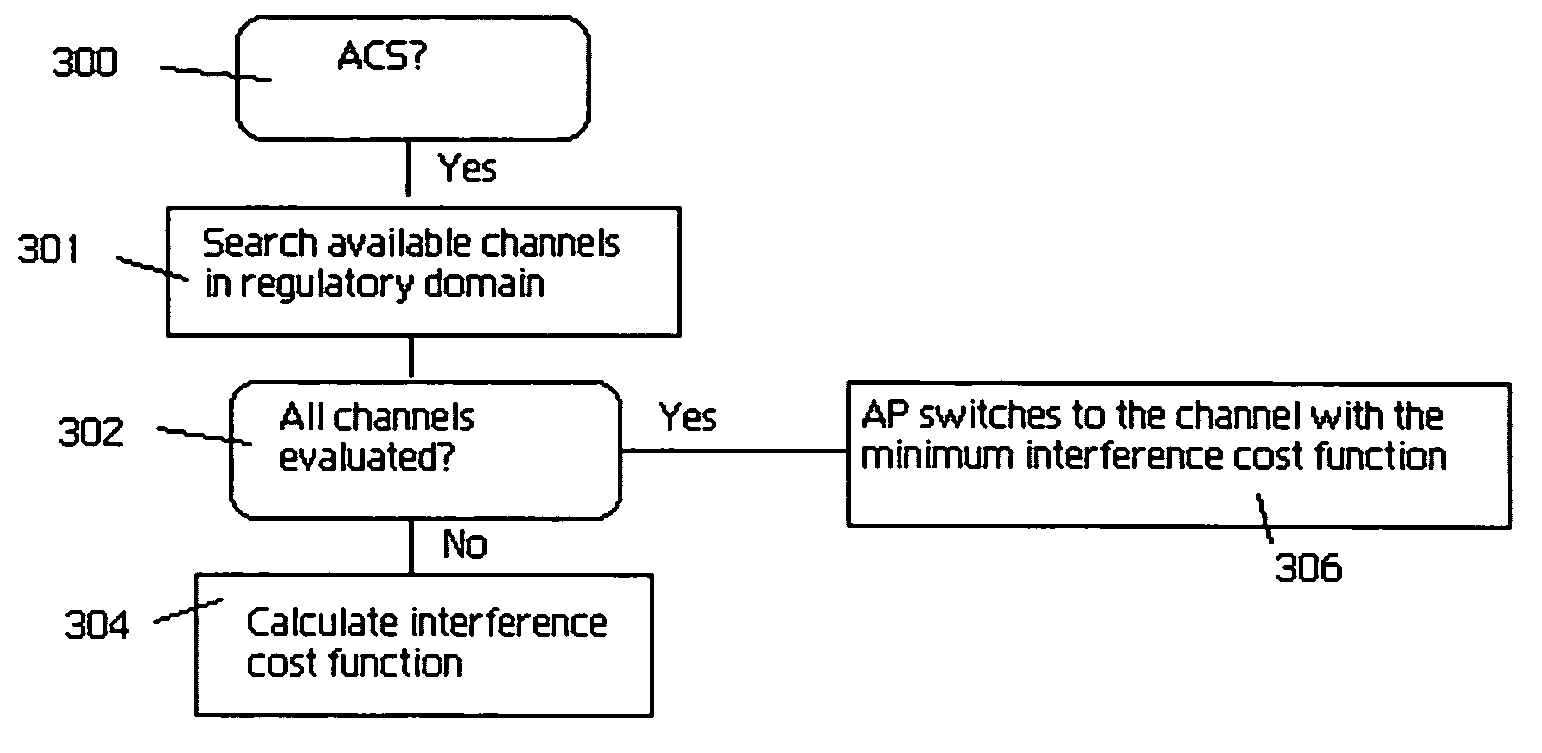
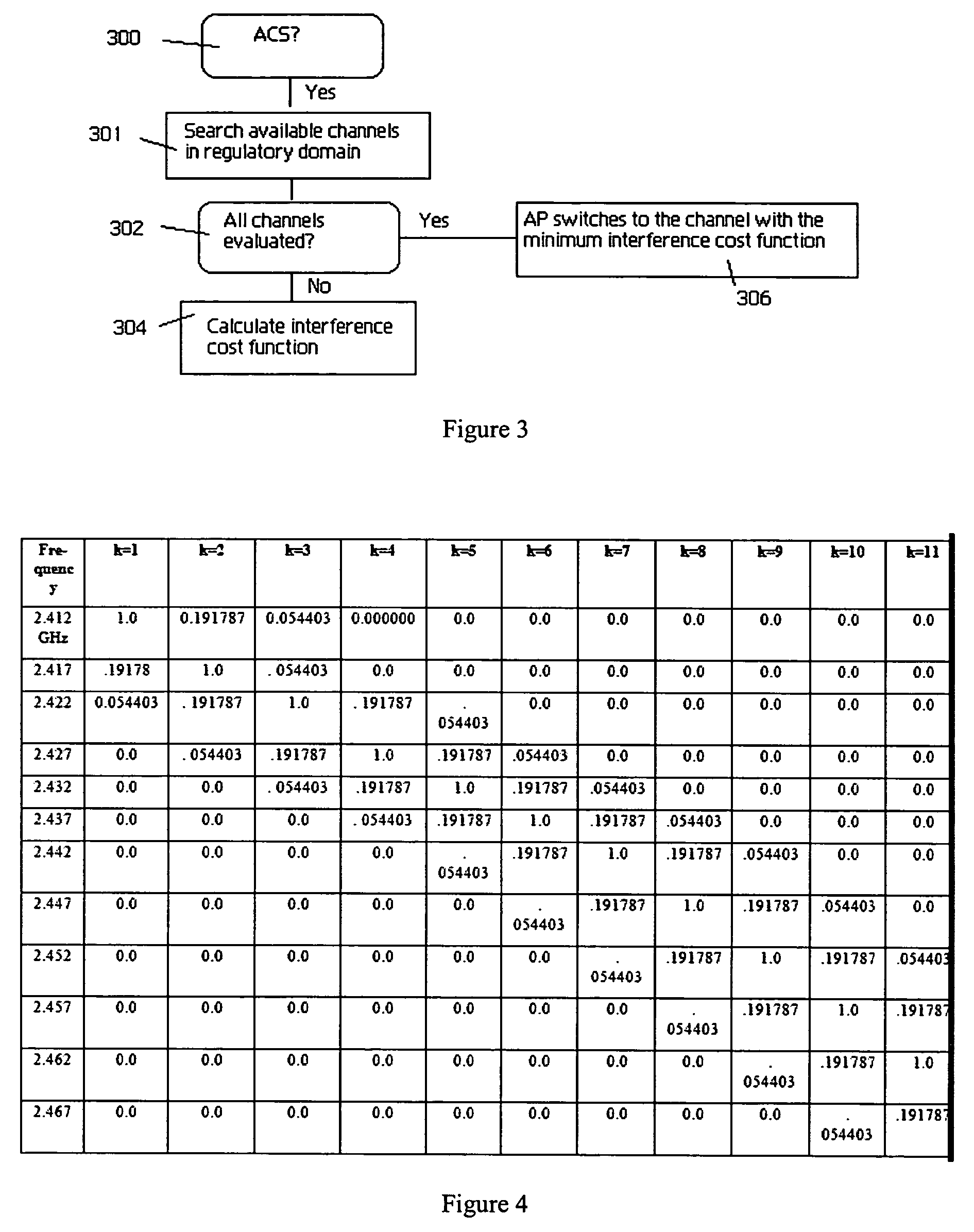
Wireless access point (AP) automatic channel selection
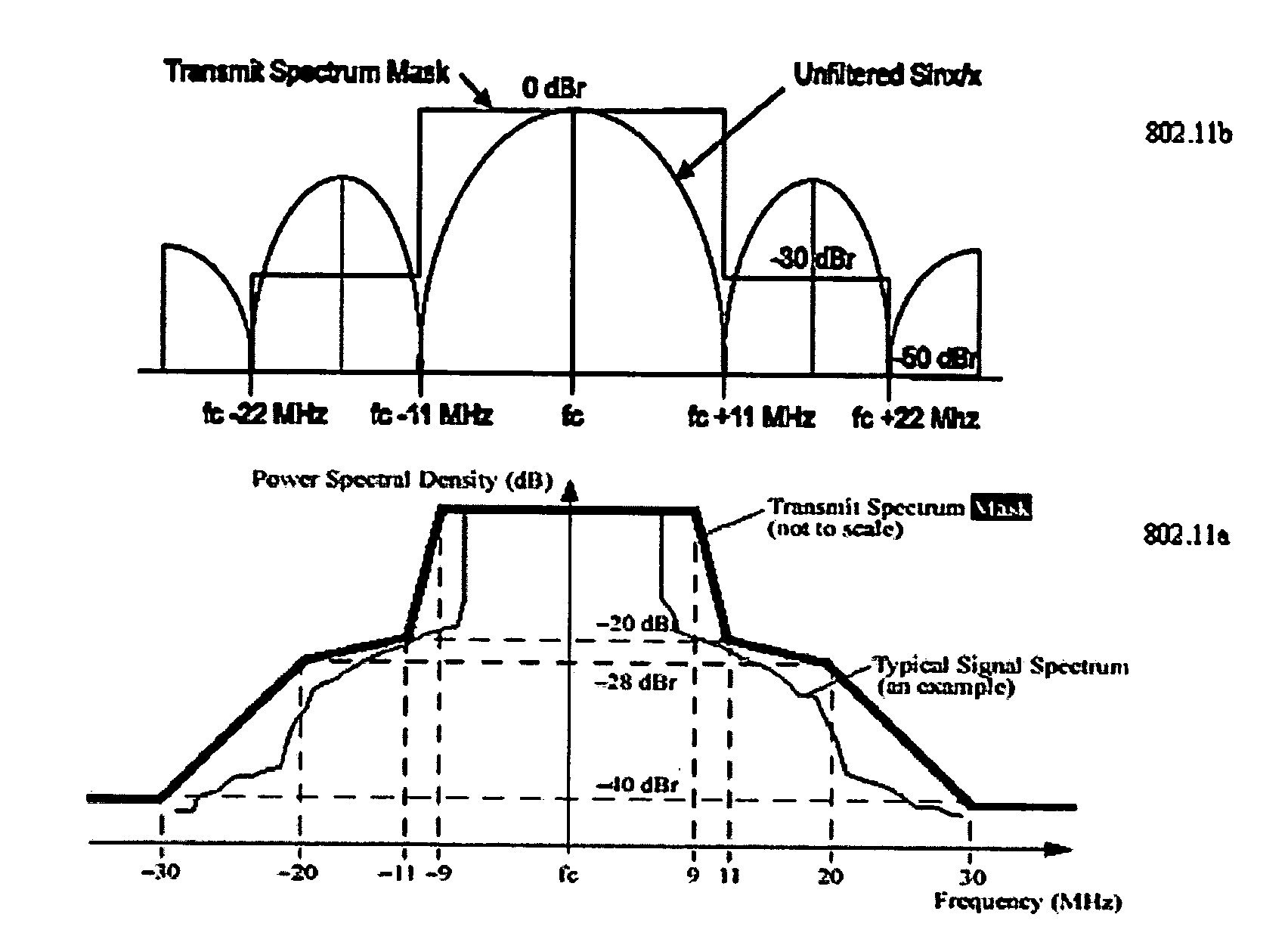
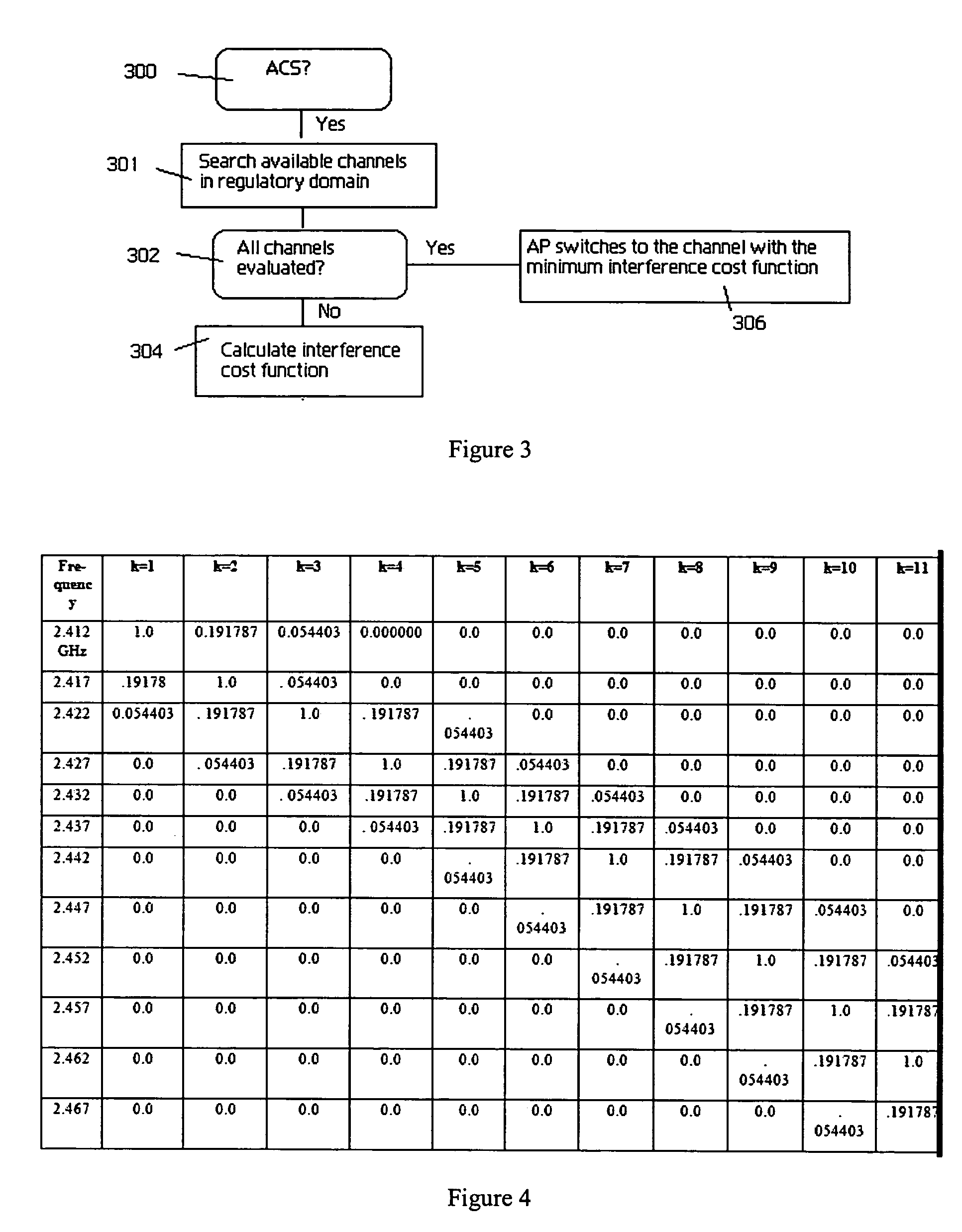
An automatic channel selection (ACS) process enables an access point to determine a best channel available, i.e., the channel with a least amount of interference, for it operation. When ACS is enabled, the access point scans frequencies for all neighboring access points and their signal strengths. Based on this data, the access point then determines which frequency is least likely to be interfered with by these other access points. The access point switches itself to this frequency and begins operation. During normal operation, the access point may periodically rescan the air space and reevaluate its current operating channel. Preferably, every neighboring access point has its own channel, and the co-channel interference levels should be low enough so that there is a maximum coverage and high throughput for the network. If these characteristics cannot be achieved, the access point may then adjust its power automatically to reduce the interference level in the network. This automatic power adjustment (APA) feature preferably operates across a set of access points, each of which has the function. In this manner, the transmitting power of the neighboring access points in the wireless network is “cooperatively” adjusted to minimize the channel interference and maximize the coverage and throughput for the network. A method of determining optimal access point locations for access points that perform the ACS and APA functions is also described.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method and apparatus for adaptive non-linear self-jamming interference cancellation
InactiveUS20110149714A1Reduce impactInterfere with removalFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexNonlinear filterLinear filter
Certain embodiments of the disclosure propose a method for cancelling co-channel interference (self-jamming) generated by nonlinearities in the radio-frequency (RF) front-end devices. The proposed method utilizes an adaptive non-linear filter to generate a distorted version of the transmitted signal. The self-jamming interference may be mitigated utilizing the distorted signal through adaptive cancellation.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Blind interference mitigation in a digital receiver
InactiveUS20070127608A1Improve acceleration performanceReduce computational complexityError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionEngineeringCo-channel interference
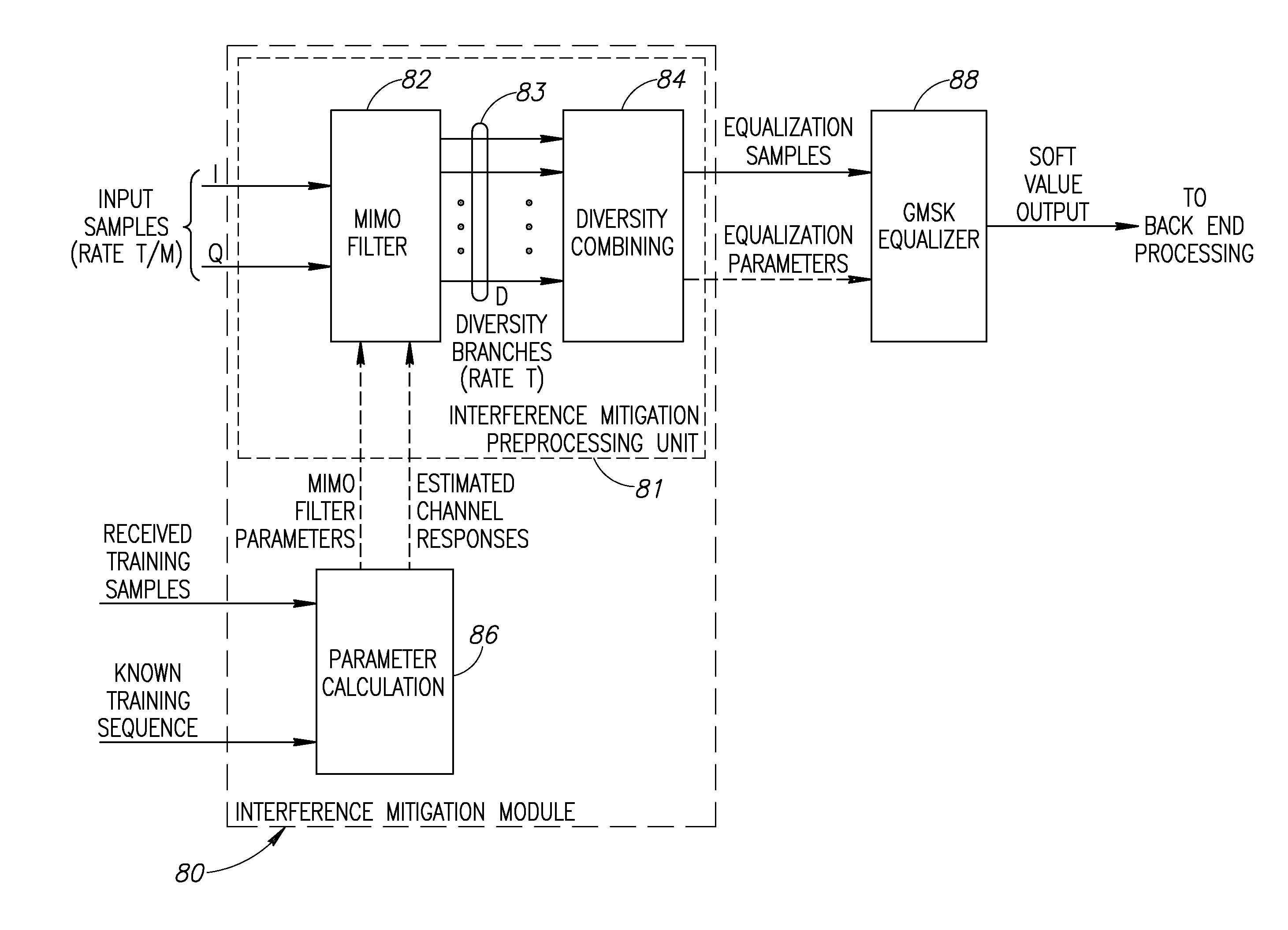
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK) single antenna interference cancellation (SAIC) for use in a digital receiver. The invention comprises an interference mitigation module that treats the problem of GMSK SAIC in a blind manner. The interference mitigation mechanism is operative to compensate for the co-channel interference added in the communications channel which is subject to multipath propagation and fading, receiver filter and any pre-channel estimation filtering. The interference mitigation module takes advantage of the spatial diversity making up multiple branches of the received signal. The branches comprise the in-phase and quadrature elements of the received signal, the sampling phases if over sampling is applied (i.e. T / m sampling) and / or multiple antennas. The invention utilizes the spatial diversity of these multiple representations of the received signal and combines (i.e. collapses) the information in the plurality of branches into a single branch that is input to the equalizer.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
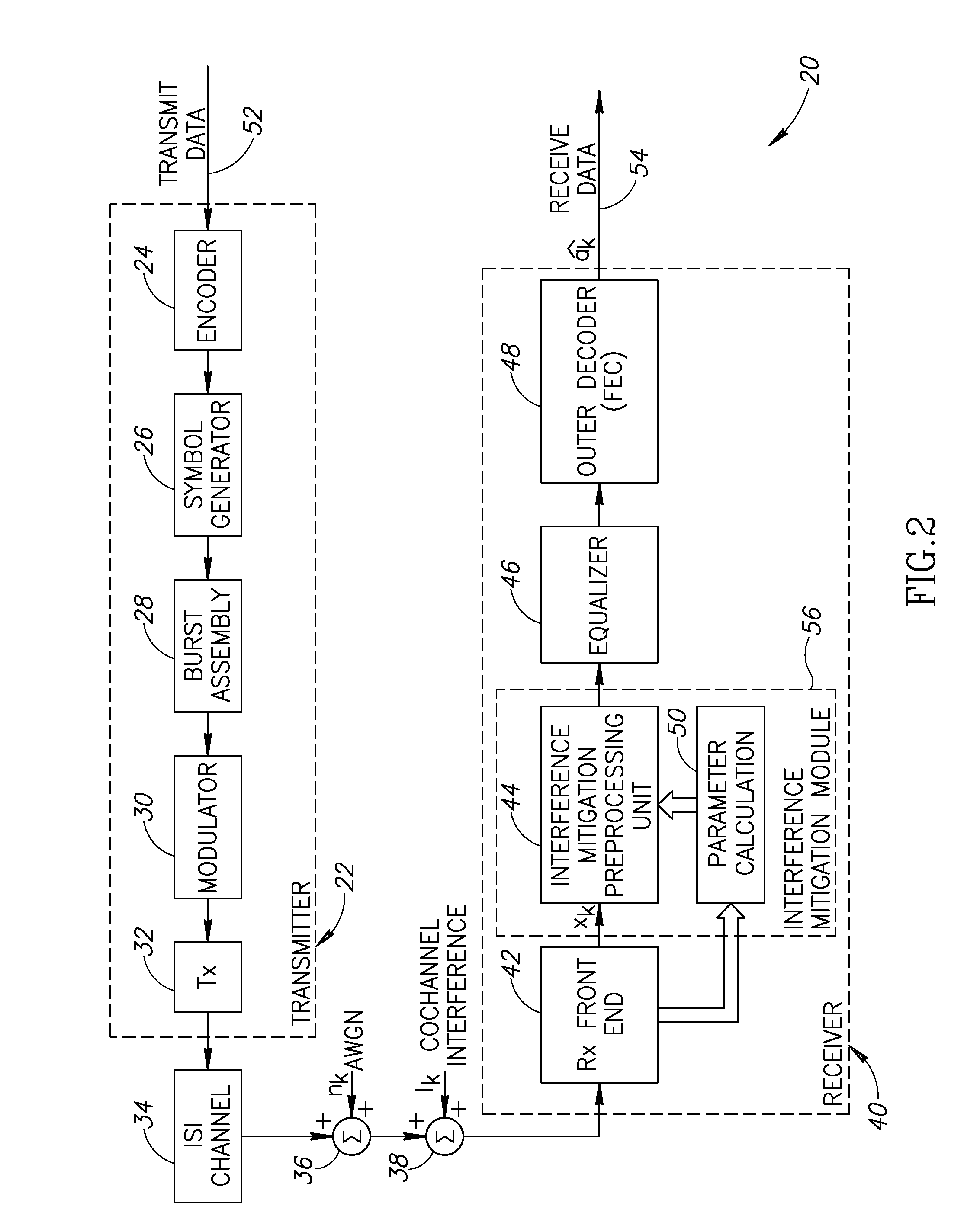
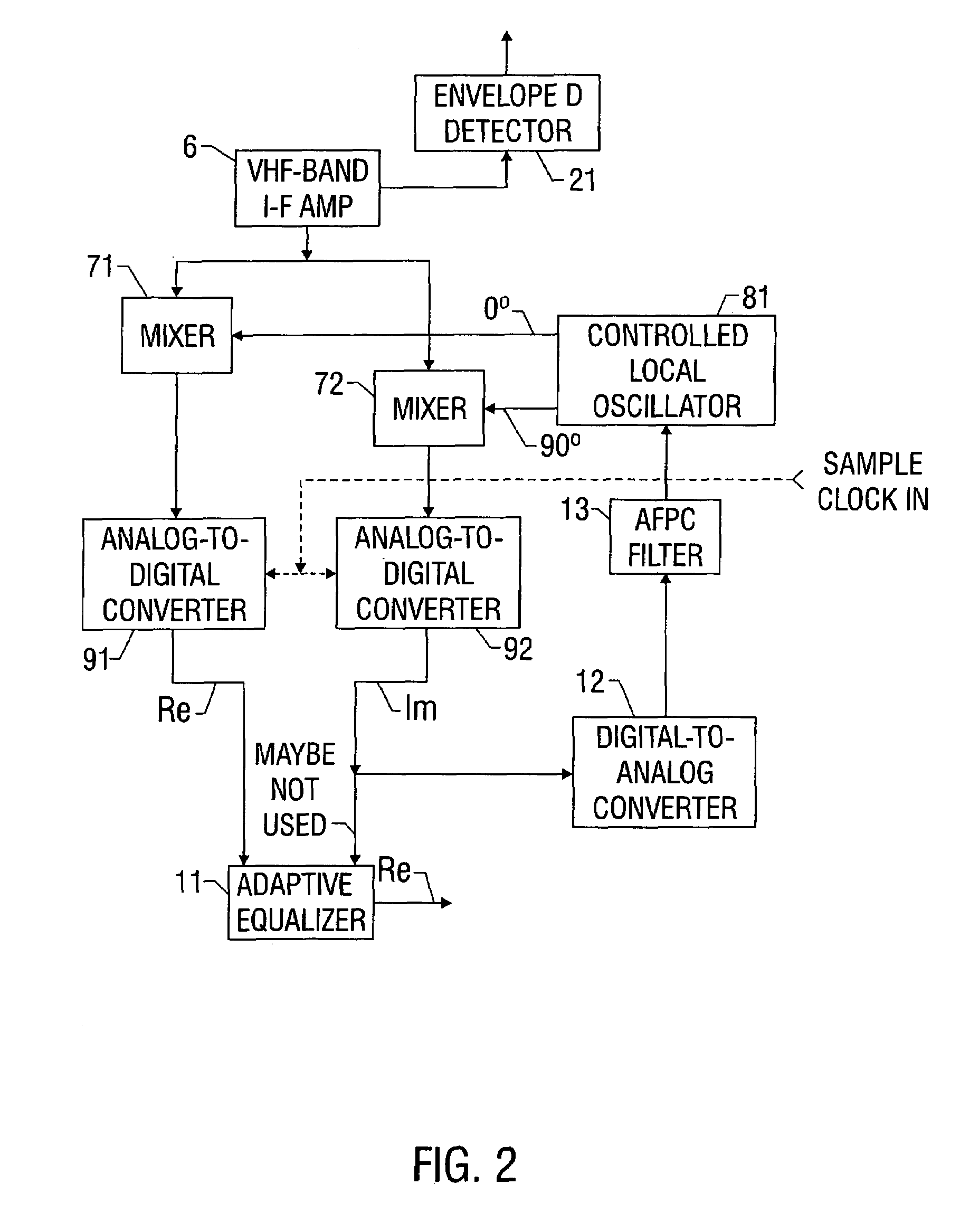
DTV signal with GCR components in plural-data-segment frame headers and receiver apparatus for such signal
InactiveUS7038732B1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionData segmentScan line
A DTV signal has a plural-data-segment frame header including complementary first and second ghost-cancellation reference signals differentially delayed by the duration of two NTSC horizontal scan lines. A receiver for such DTV signal has an adaptive equalizer for baseband symbol code with kernel weights calculated by a computer operative on the equalizer response after comb filtering. The comb filter combines the equalizer response as differentially delayed by the duration of two NTSC horizontal scan lines to cancel artifacts of co-channel NTSC interference in the comb filtered equalizer response supplied to the computer. This reduces the undesirable influence of such artifacts on equalization to reduce intersymbol interference.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Interference and noise estimation in an OFDM system
ActiveUS20050002324A1Quantity minimizationQuality improvementError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission monitoringMultiuser systemCarrier signal
Noise and interference can be independently measured in a multiple user Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) system. Co-channel interference is measured in a frequency hopping, multiple user, OFDM system by tracking the sub-carriers assigned to all users in a particular service area or cell. The composite noise plus interference can be determined by measuring the amount of received power in a sub-carrier whenever it is not assigned to any user in the cell. A value is stored for each sub-carrier in the system and the value of noise plus interference can be a weighted average of the present value with previously stored values. The noise component can be independently determined in a synchronous system. In the synchronous system, all users in a system may periodically be prohibited from broadcasting over a sub-carrier and the received power in the sub-carrier measured during the period having no broadcasts.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
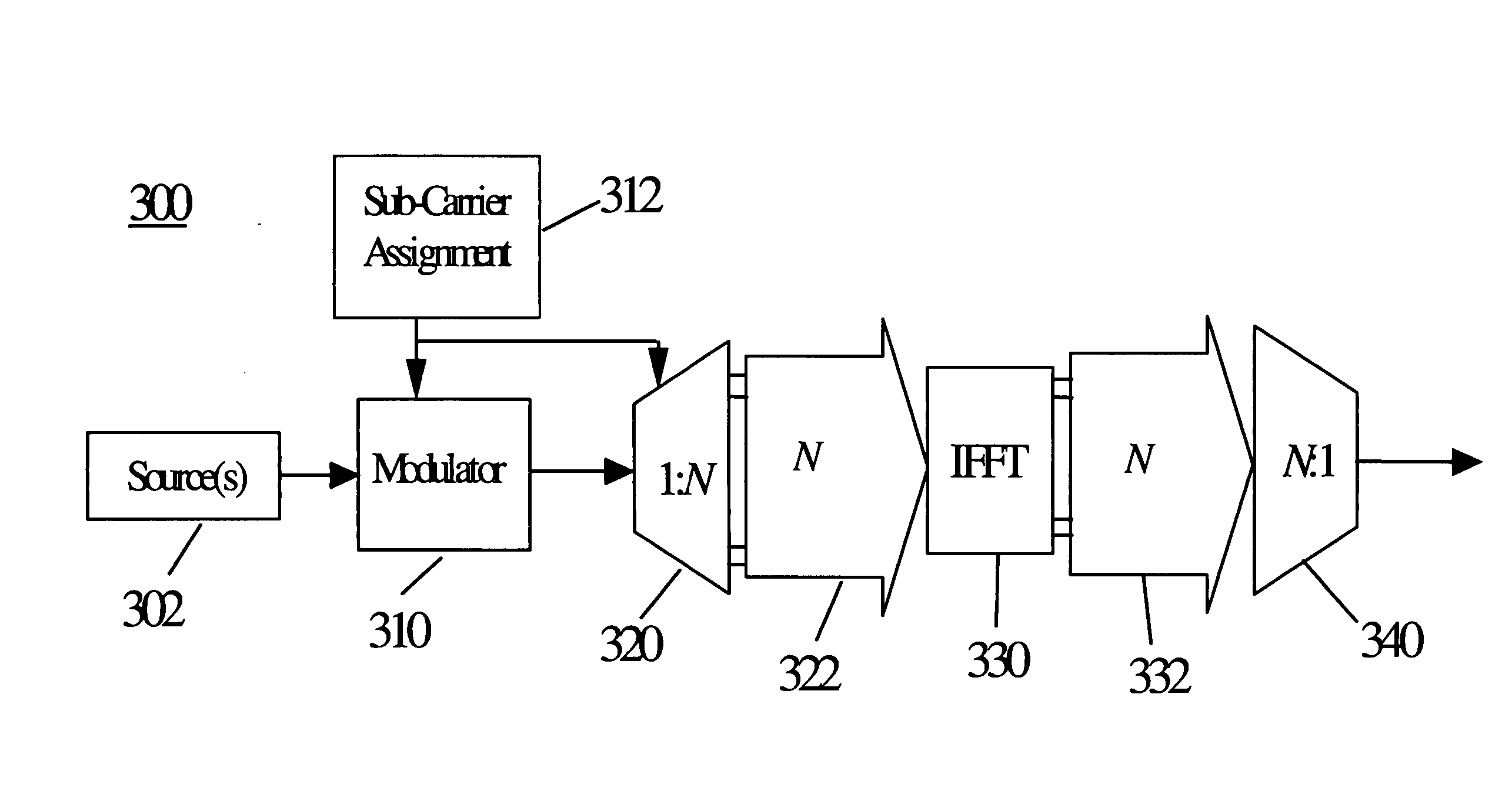
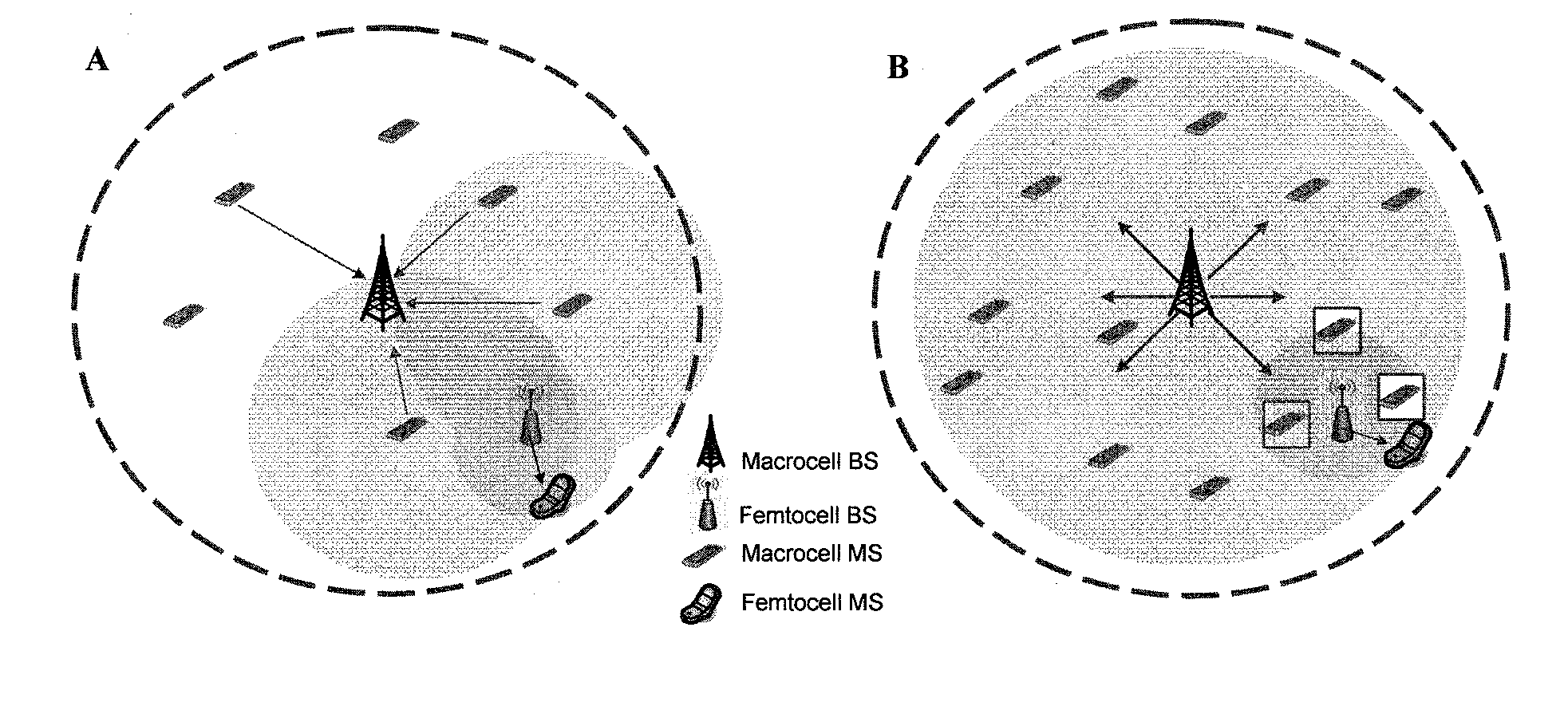
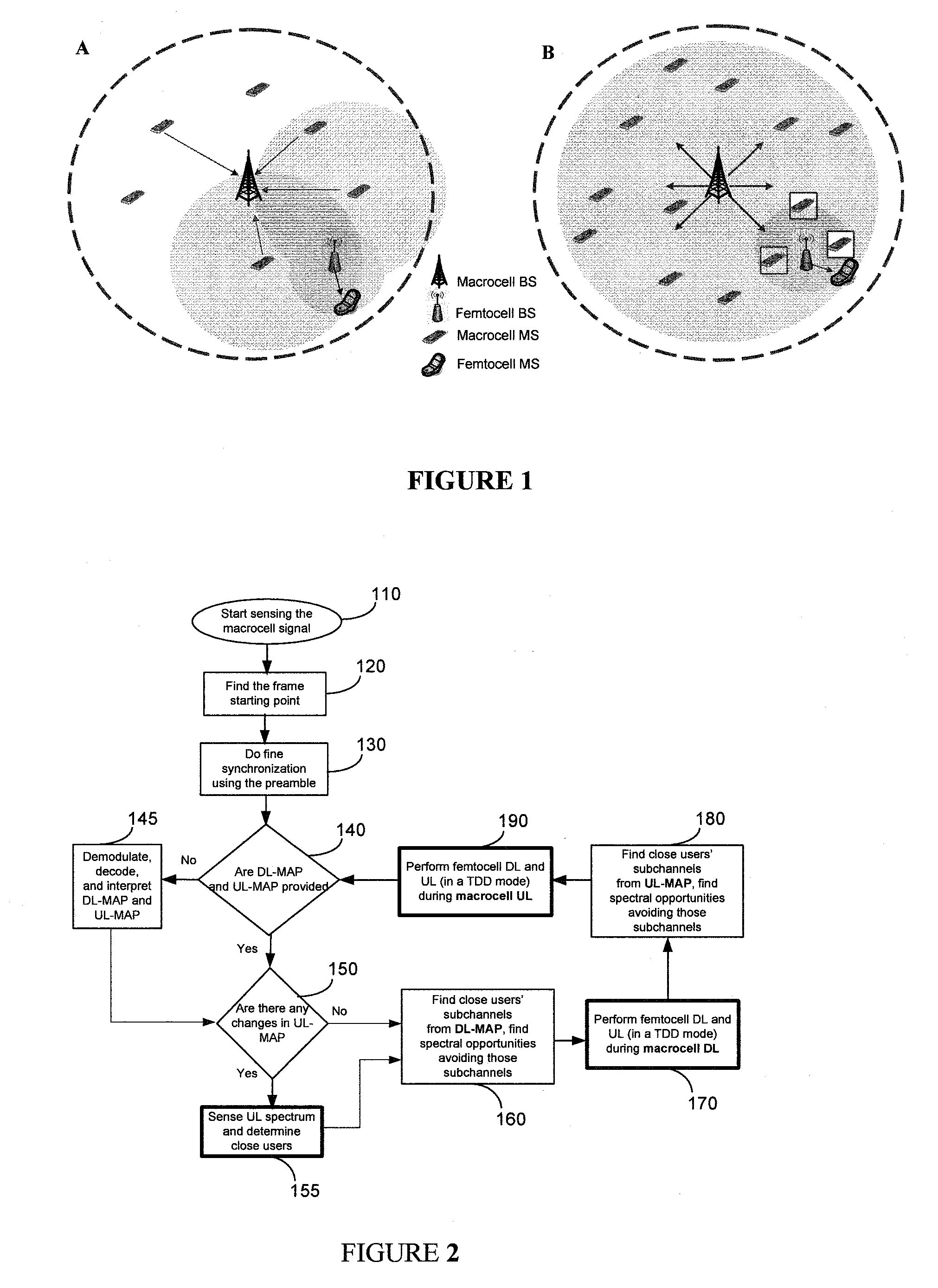
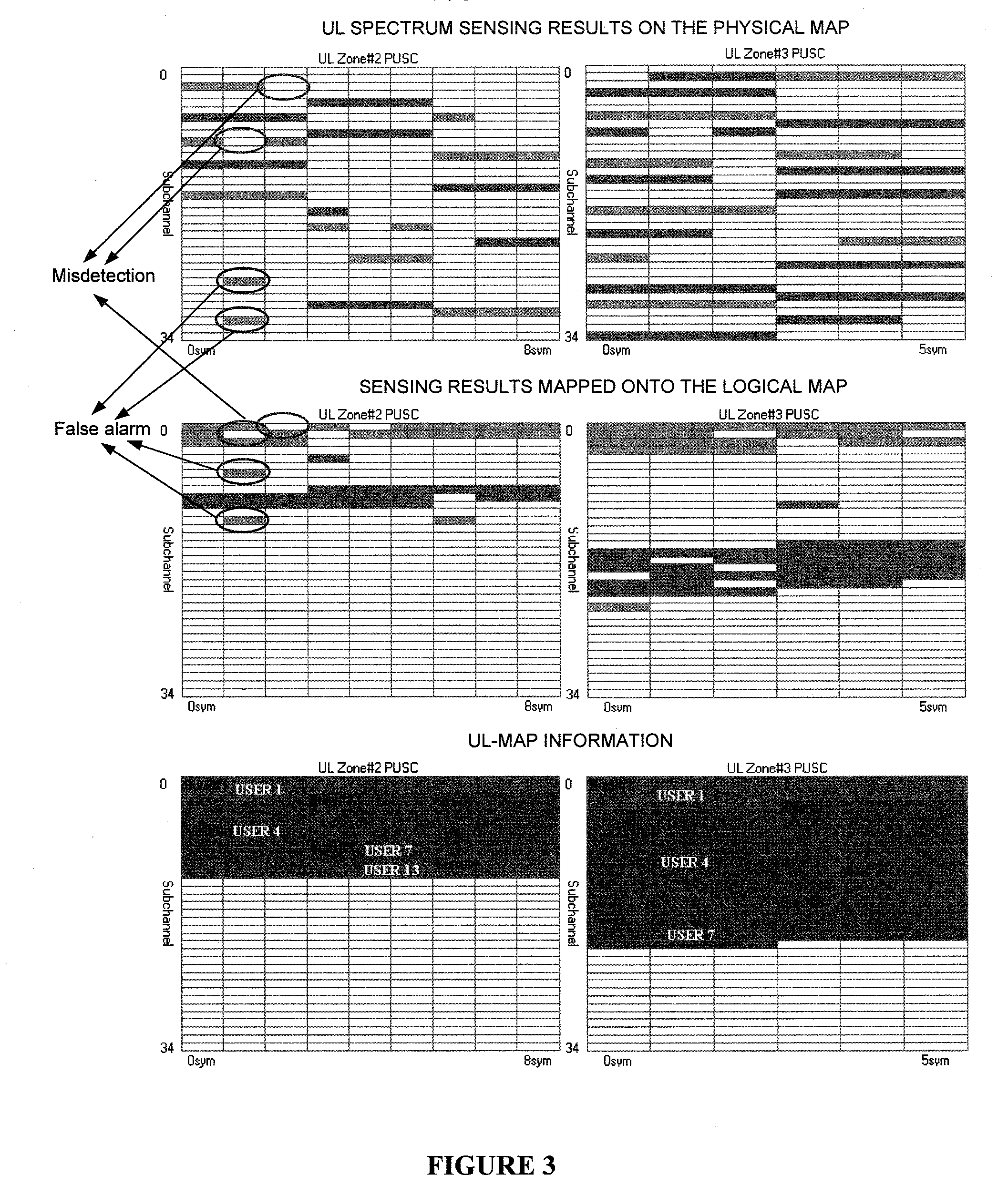
OFDMA-based co-channel femtocell
ActiveUS20090221295A1Improve efficiencyExpand coverageTransmission path divisionNetwork topologiesFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
A femtocell increases efficiency and coverage of a macrocellular network operating in a co-channel manner within the macrocell spectrum by selecting subcarriers for its mobile station using both the subcarrier allocation map received from the macrocell and a spectrum sensing operation. Interference is avoided by selecting only subcarriers not allocated by the macrocell and subcarriers allocated to users not nearby to the femtocell. Interference is eliminated from the received signals using co-channel interference avoidance techniques. Selection of subcarriers for femtocell use may take into consideration inter-carrier interference detected.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
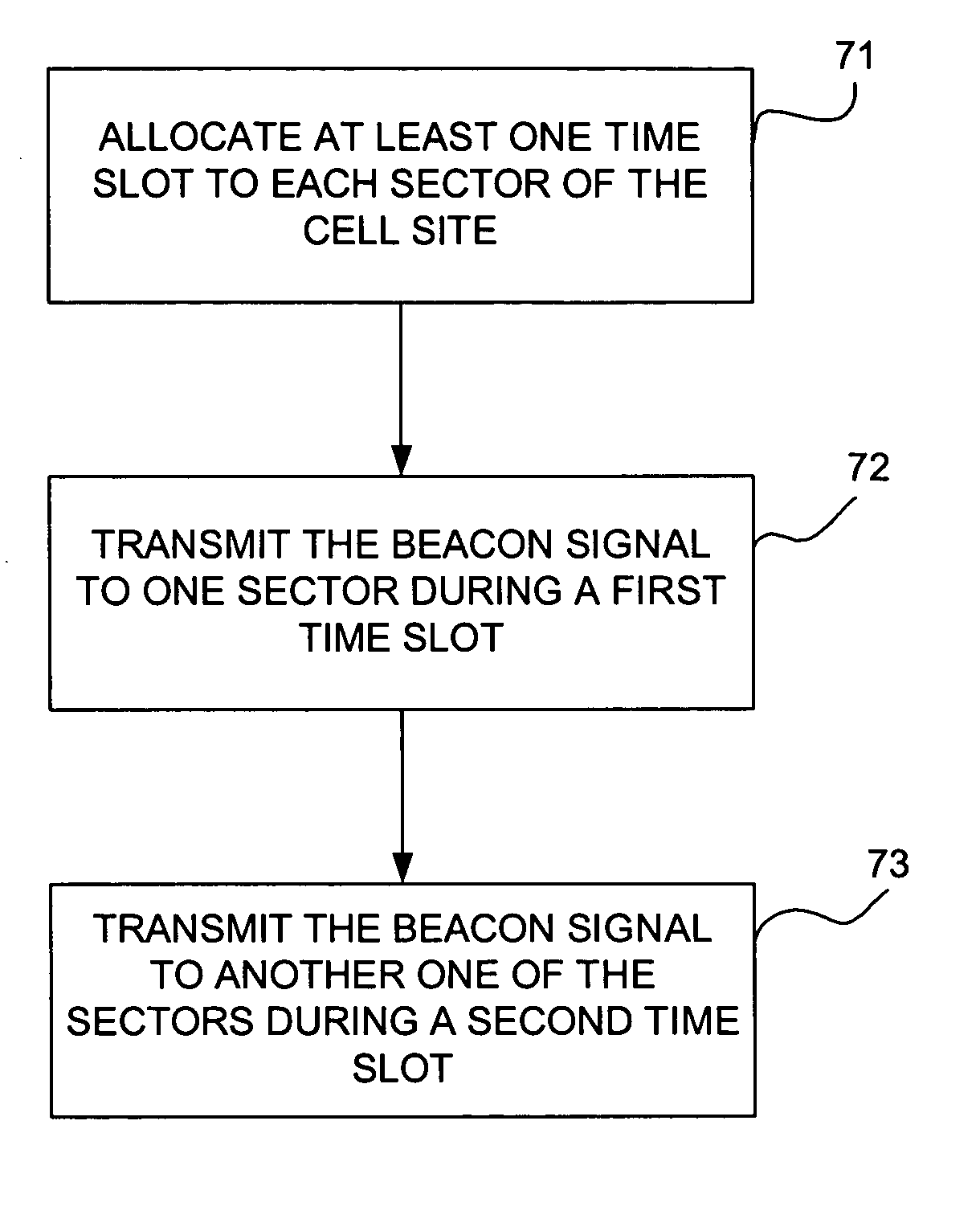
Method and apparatus for allocating a beacon signal in a wireless communications network
InactiveUS20060089141A1Improve spectral efficiencyReduce power consumptionAssess restrictionPosition fixationAdjacent-channel interferenceFrequency spectrum
A method and apparatus for transmitting beacon signals in a wireless communications network. For a given cell site, a single frequency may be used for the beacon signal by assigning different beacon signal time slots to different sectors of the cell site. During one time slot, the beacon signal is transmitted to one of the sectors, and during another one of the time slots, the beacon signal is transmitted to a different one of the sectors. Because a single frequency can be used for all of the sectors of a cell site, more frequencies are available for other purposes, such as for user traffic, for example. The invention improves spectral efficiency, reduces adjacent channel interference and co-channel interference and allows power consumption to be controlled.
Owner:CINGULAR WIRELESS II LLC
Wireless access point (AP) automatic channel selection
An automatic channel selection (ACS) process enables an access point to determine a best channel available, i.e., the channel with a least amount of interference, for it operation. When ACS is enabled, the access point scans frequencies for all neighboring access points and their signal strengths. Based on this data, the access point then determines which frequency is least likely to be interfered with by these other access points. The access point switches itself to this frequency and begins operation. During normal operation, the access point may periodically rescan the air space and reevaluate its current operating channel. Preferably, every neighboring access point has its own channel, and the co-channel interference levels should be low enough so that there is a maximum coverage and high throughput for the network. If these characteristics cannot be achieved, the access point may then adjust its power automatically to reduce the interference level in the network. This automatic power adjustment (APA) feature preferably operates across a set of access points, each of which has the function. In this manner, the transmitting power of the neighboring access points in the wireless network is “cooperatively” adjusted to minimize the channel interference and maximize the coverage and throughput for the network. A method of determining optimal access point locations for access points that perform the ACS and APA functions is also described.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
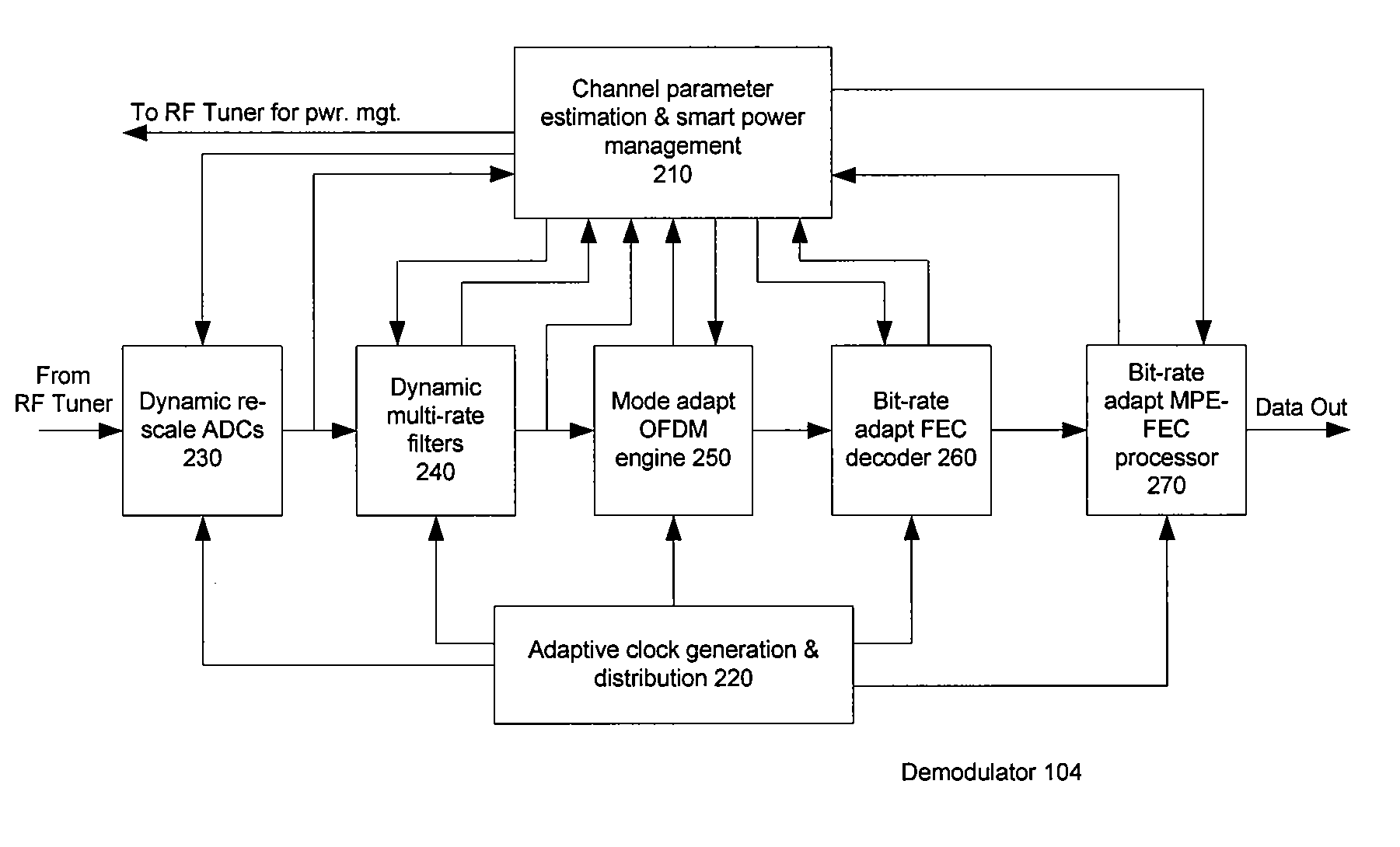
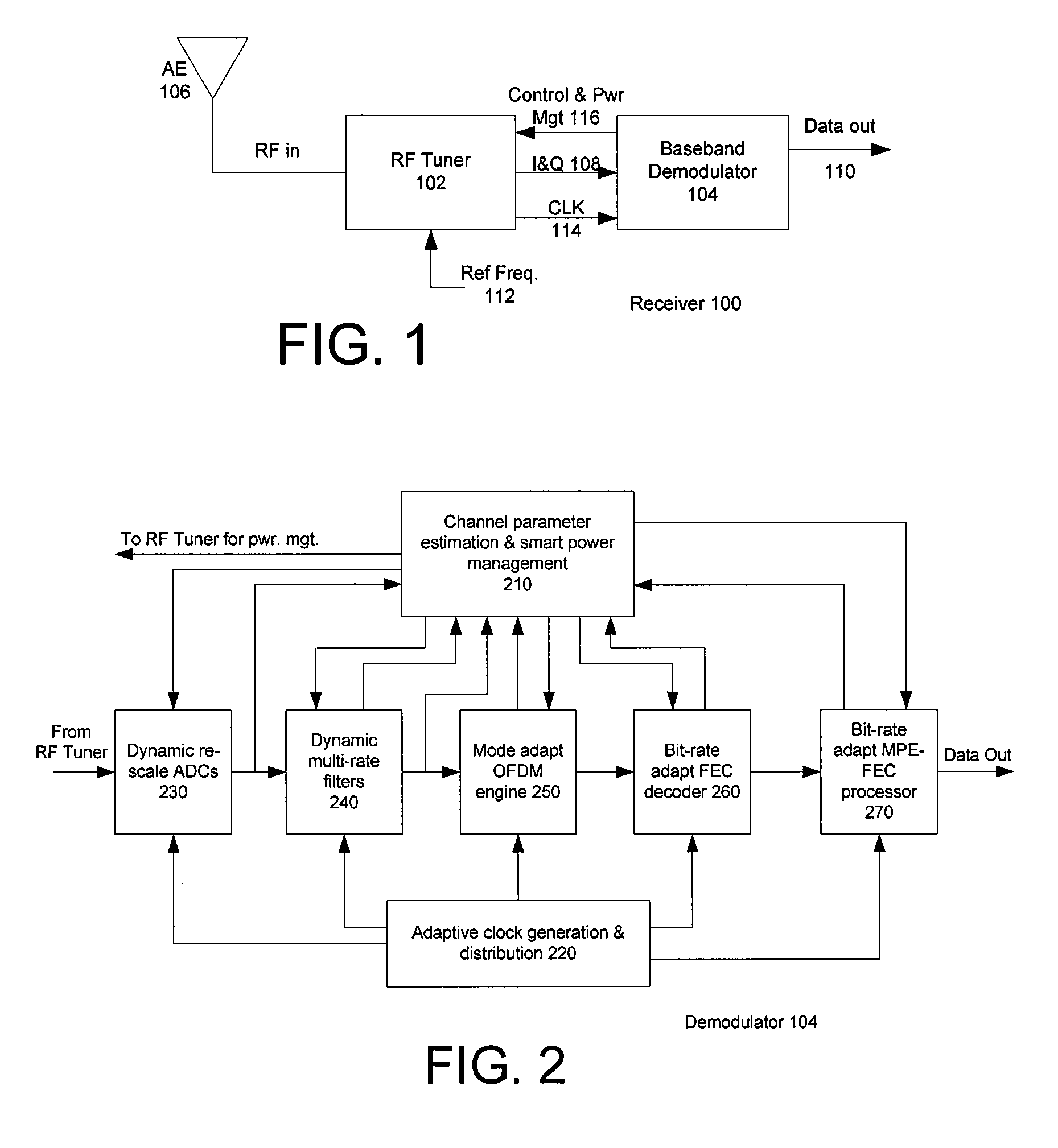
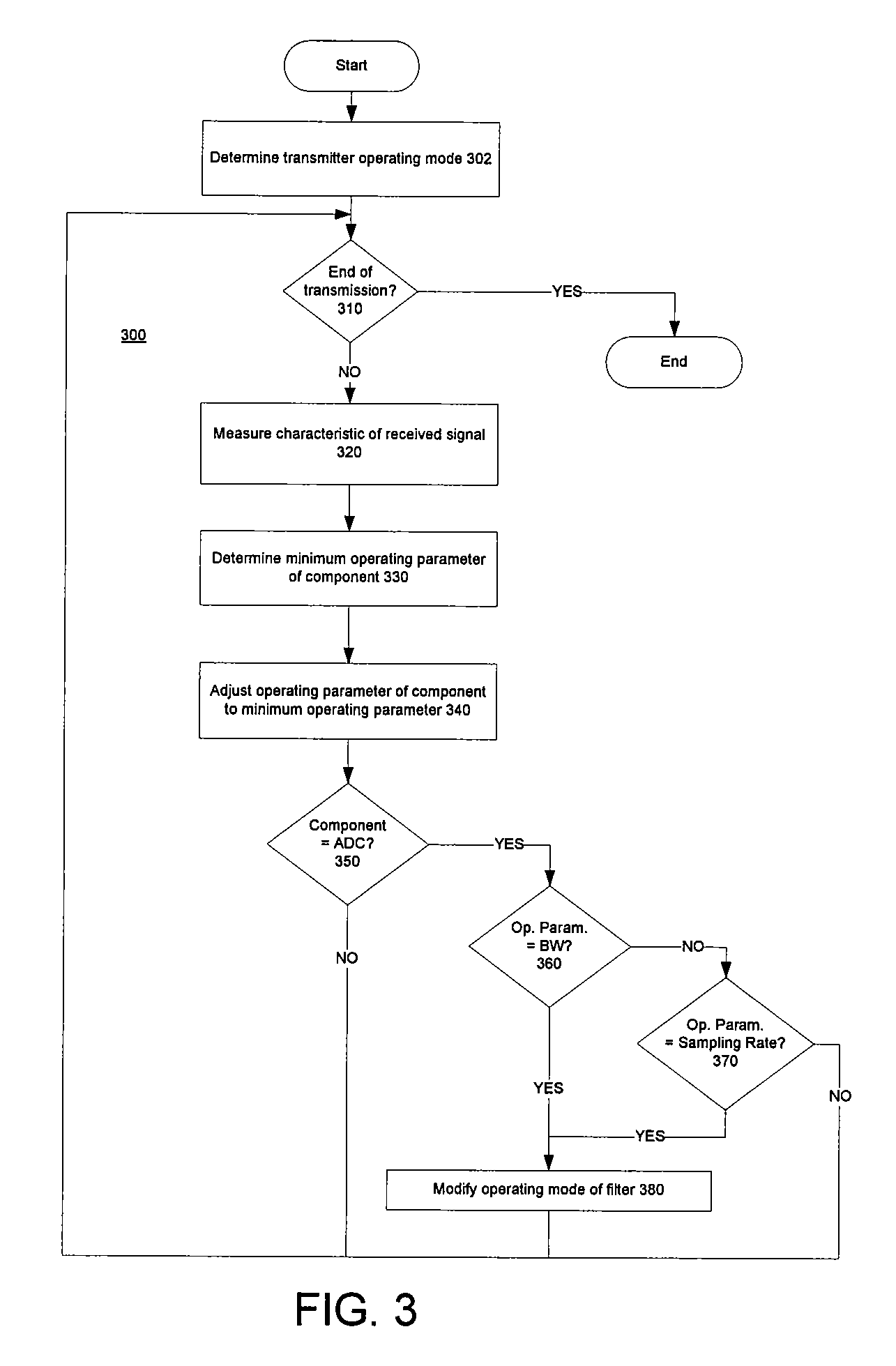
Power Management in Digital Receivers
ActiveUS20070064839A1Unnecessary power consumptionVolume/mass flow measurementAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAdjacent-channel interferenceControl power
Methods and systems consistent with the present invention provide a method for dynamically controlling power consumption in a digital demodulator circuit by varying clock rates and bit widths of demodulator components including an analog to digital converter, decimation filter, OFDM operating engine, FEC decoder, and MPE-FEC processor, according to parameters and conditions of the received signal including modulation mode, signal to noise ratio, effective bit transmission rate, bit error rate, packet error rate, adjacent channel interference, and co-channel interference.
Owner:CSR TECH INC
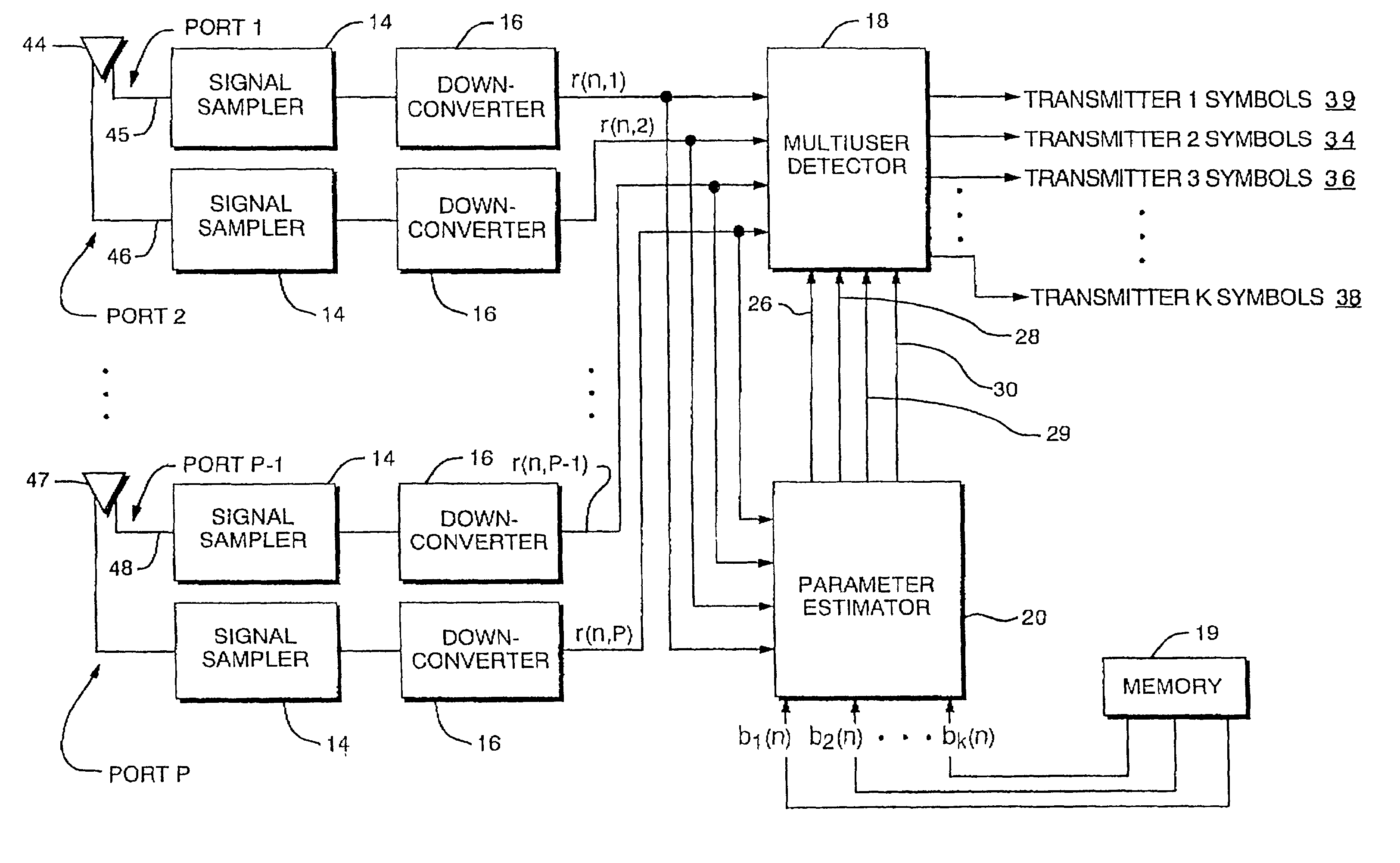
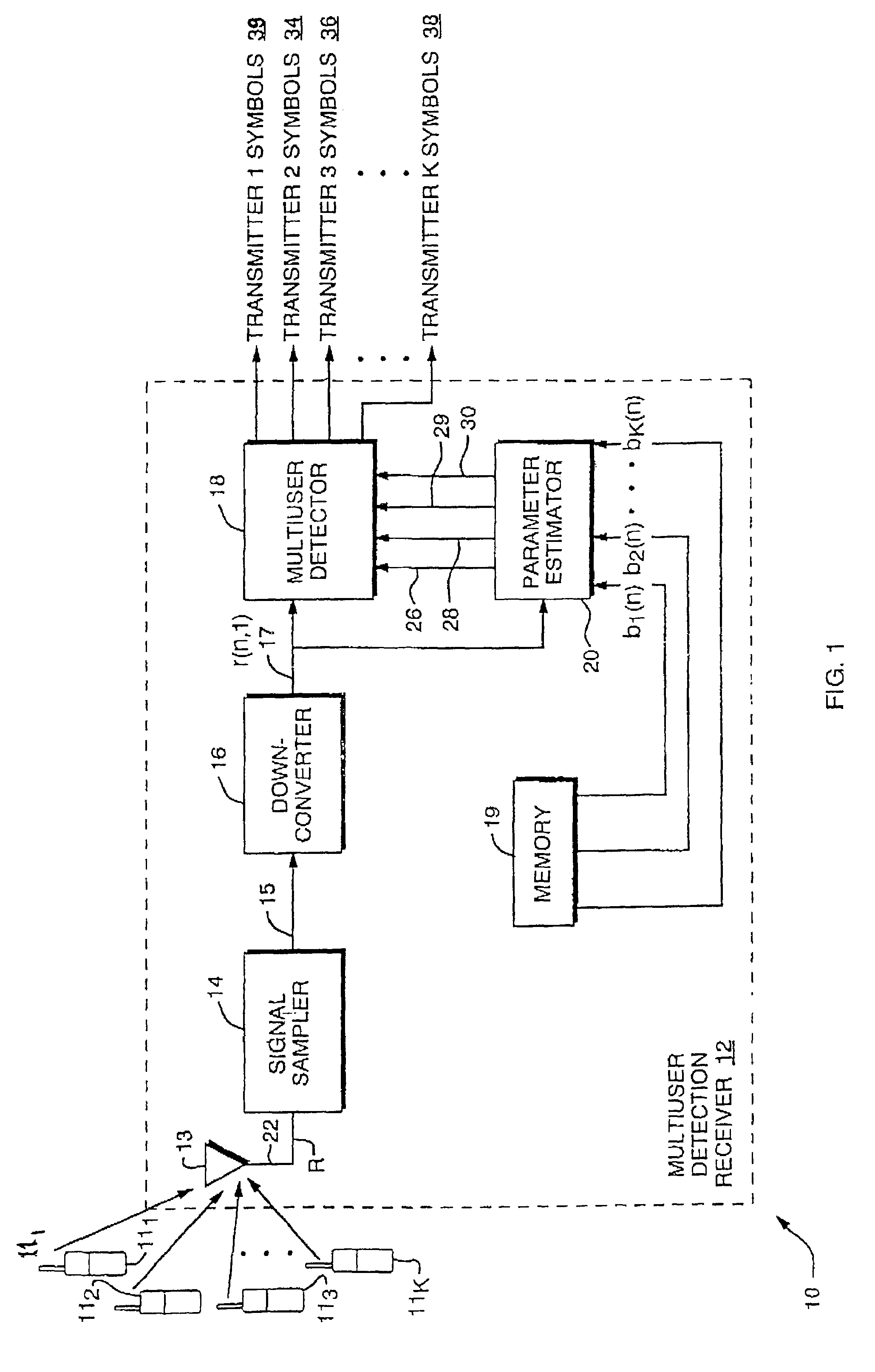
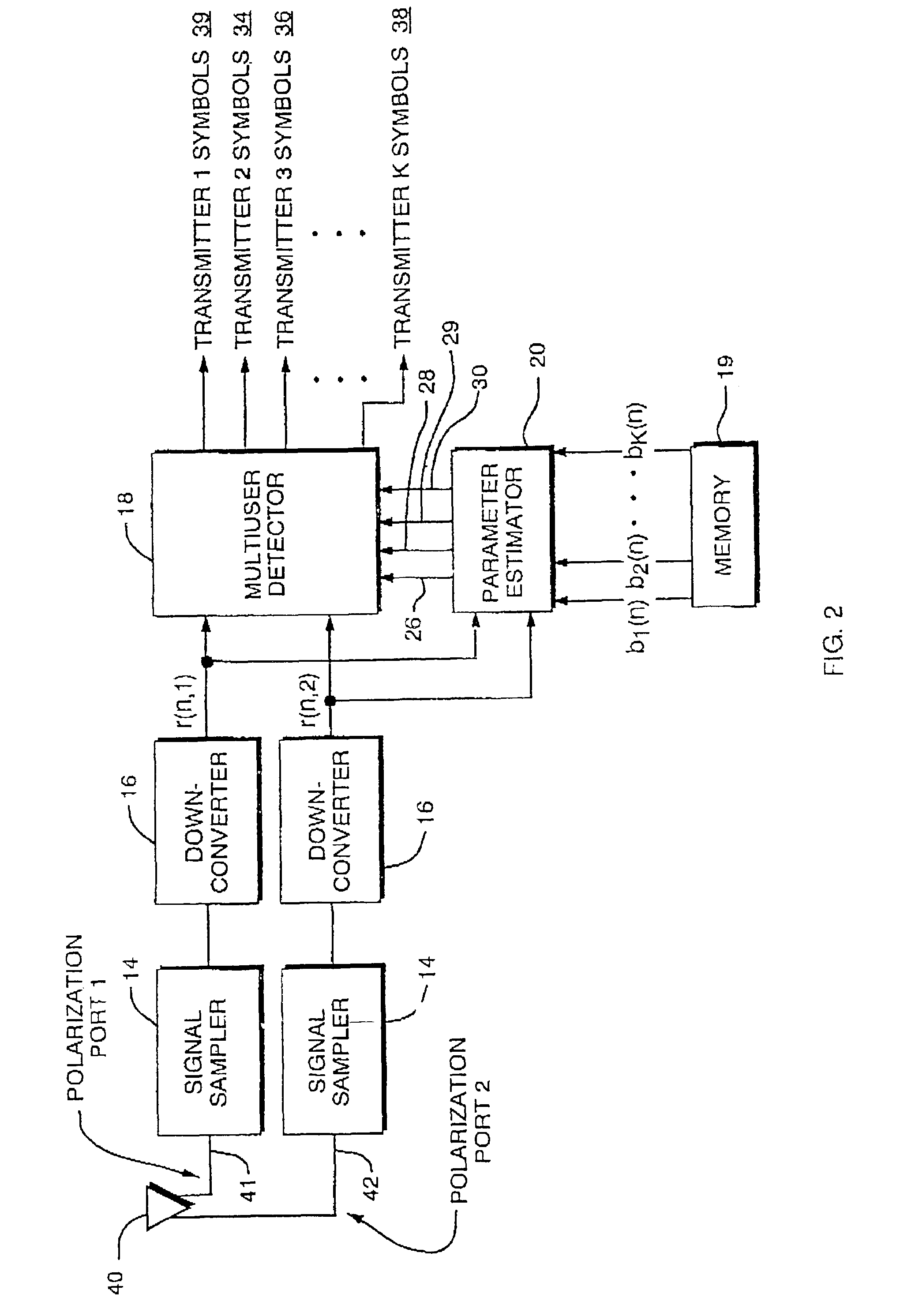
Co-channel interference receiver
InactiveUS7092452B2Providing polarization diversityReduce in quantityPolarisation/directional diversityLine-faulsts/interference reductionPrior informationCo-channel interference
A digital receiver automatically detects and non-coherently demodulates a multiplicity of interfering digitally modulated signals transmitted simultaneously at approximately the same carrier frequency. The receiver includes one or more antenna inputs (e.g., polarization and / or space diverse), a parameter estimator module, and a multiuser detector for estimating the data transmitted by each interfering signals and adapted to operate with at least one of a MUD algorithm with partially quantized prior information and a MUD algorithm based on prewhitened data.
Owner:COLLISION COMM
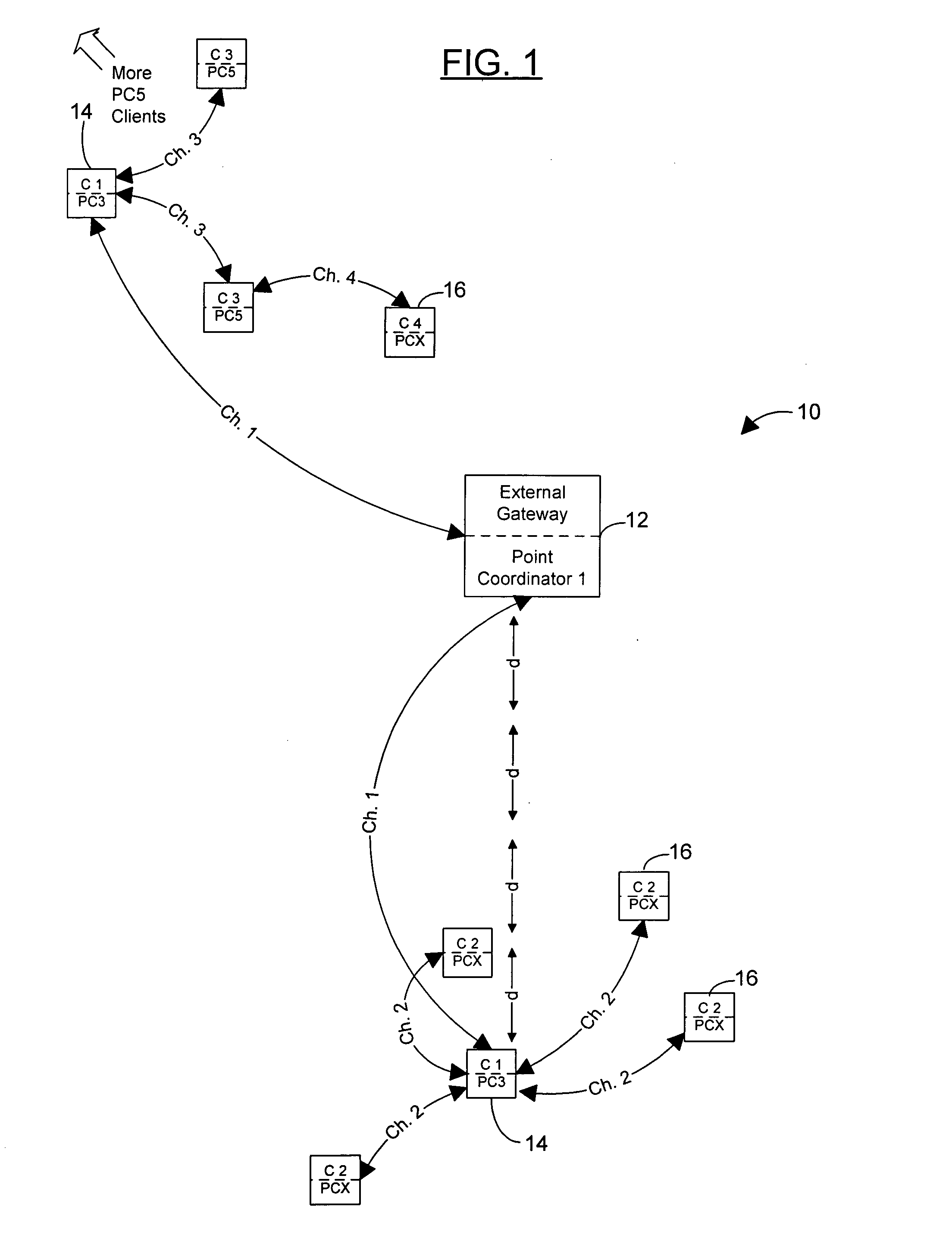
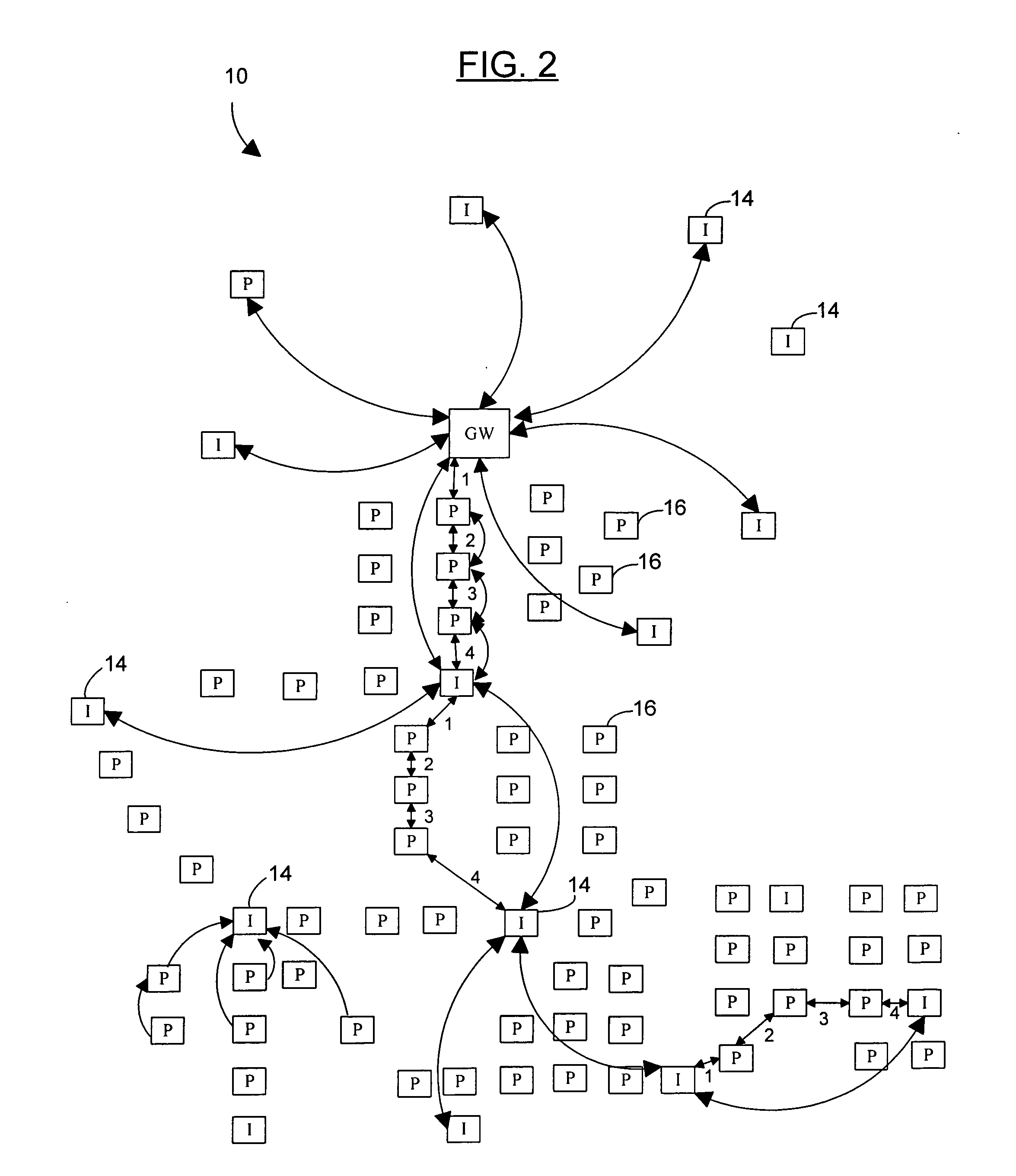
Multi-hop peer-to-peer wireless local loop phone system and method
InactiveUS20050036470A1Lower latencyLarge installationEnergy efficient ICTNetwork traffic/resource managementTransmitted powerCo-channel interference
A peer-to-peer wireless phone system with peer-to-peer units and network configuration algorithms by which a virtual circuit data path is established by minimizing the latency added at each hop starting with the external network gateway or the most loaded hop and choosing closest time slots for each next hop until a the virtual circuit is completed. Also, certain embodiments of the present invention include network configuration algorithms by which traffic around any external network gateway(s) is optimized to maximize throughput around the gateway by allocating certain of many available channels to a group of P2P units around the gateway, these units acting as an “infrastructure” through which other units route virtual circuits through the gateway. The network topology is also configured to let these units transmit at higher power levels and ranges than other P2P units in the network, and thereby help minimize the number of hops needed to reach the external network gateway. Further, other sets of units can be configured with similar larger transmit ranges (around 4 of the standard P2P hop ranges), positioned at such a range on the opposite side of from the gateway to also act as “infrastructure units”, both to pass calls forward to the group of units in the gateway's Point Coordinator group, and to also route circuits that are internal to the network around the Point Coordinator group on the gateway, thereby maximizing efficient use of the gateway capacity. Such rings or layers of infrastructure can be repeated as necessary to minimize hops as the network grows larger, making the tradeoff between minimizing hops (which maximizes transmit power and increases co-channel interference) and minimizing power (which maximizes the number of hops and produces poor latency).
Owner:CALVERT NATHAN HUNTER
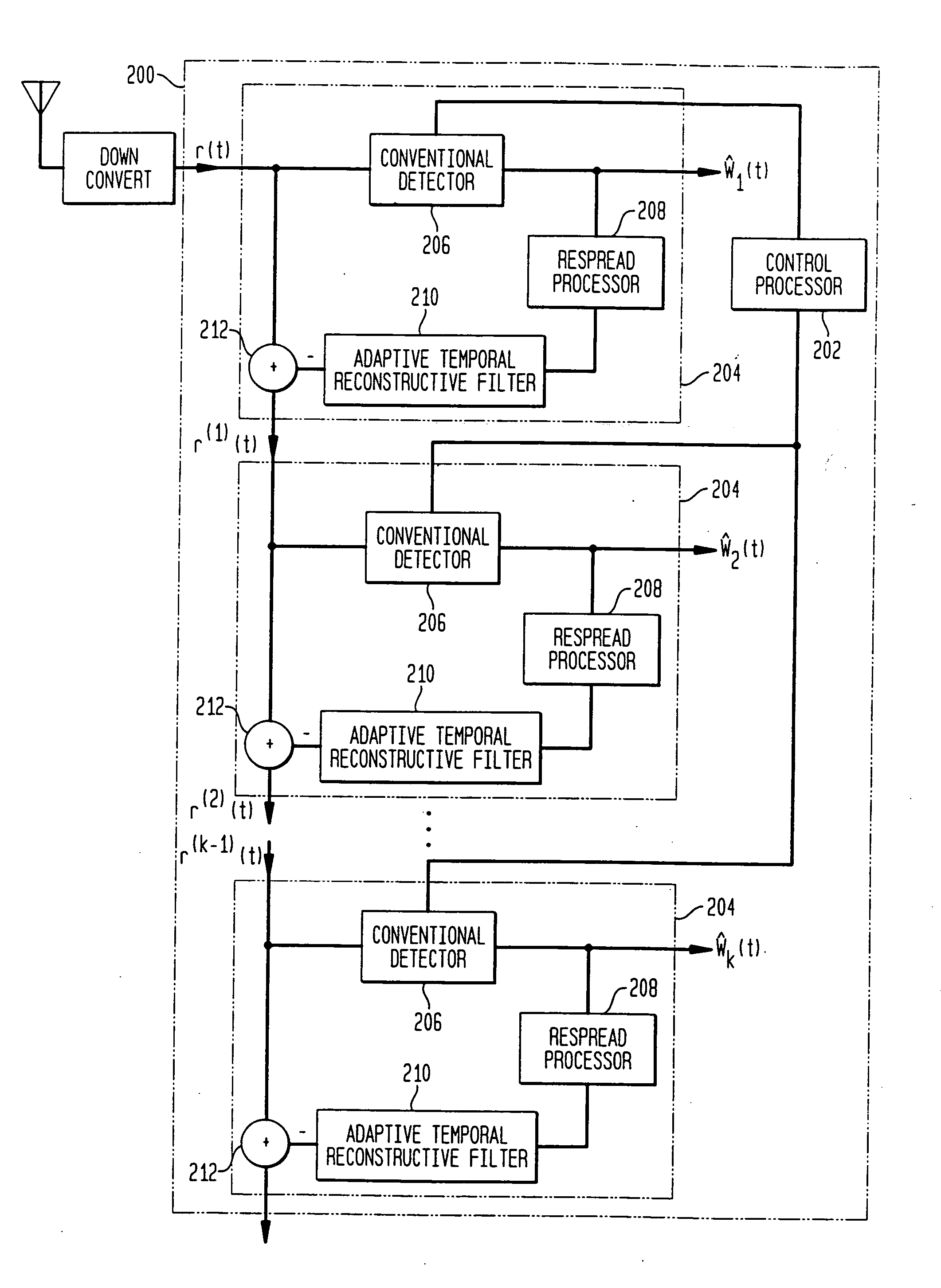
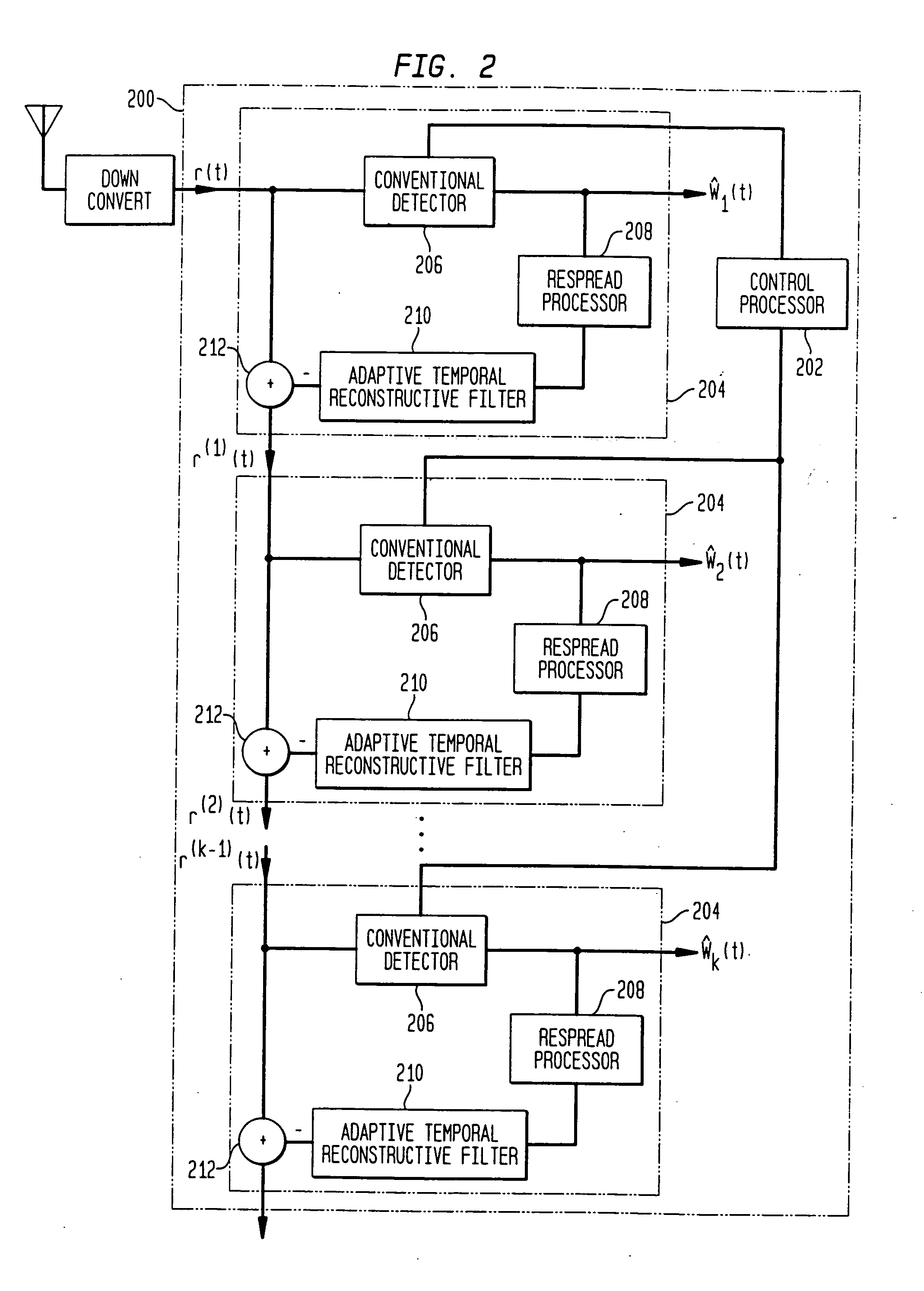
Combined adaptive spatio-temporal processing and multi-user detection for CDMA wireless systems
ActiveUS20050128985A1Reduce cancellationAccurate estimateRadio transmissionWireless commuication servicesEngineeringCo-channel interference
Methods and systems in a wireless receiver for enabling the reception of input signals at varied power levels in the presence of co-channel interference utilizing combinations of space-time adaptive processing (STAP), interference cancellation multi-user detection (MUD), and combined STAP / MUD techniques. In MUD, code, timing, and possibly channel information of multiple users are jointly used to better detect each individual user. The novel combination of adaptive signal reconstruction techniques with interference cancellation MUD techniques provides accurate temporal cancellation of interference with minimal interference residuals. Additional methods and systems extend adaptive signal reconstruction techniques to take Doppler spread into account. STAP techniques permit a wireless receiver to exploit multiple antenna elements to form beams in the direction of the desired signal and nulls in the direction of the interfering signals. The combined STAP-MUD methods and systems increase the probability of successful user detection by taking advantage of the benefits of each reception method. An additional method and system utilizes STAP techniques in the case where no pilot signal is available. This method compares the outputs of various hypothesized STAP solutions.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
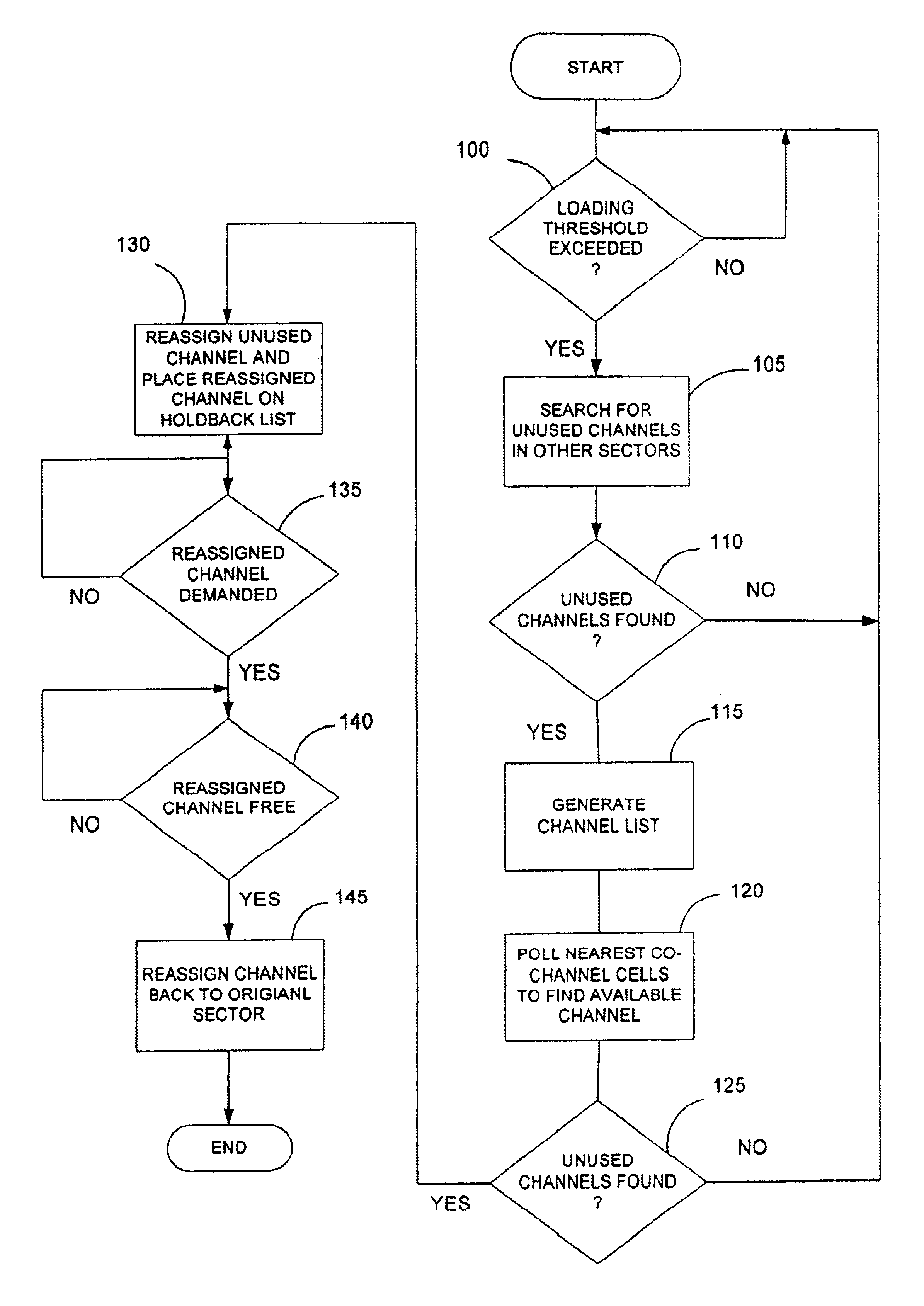
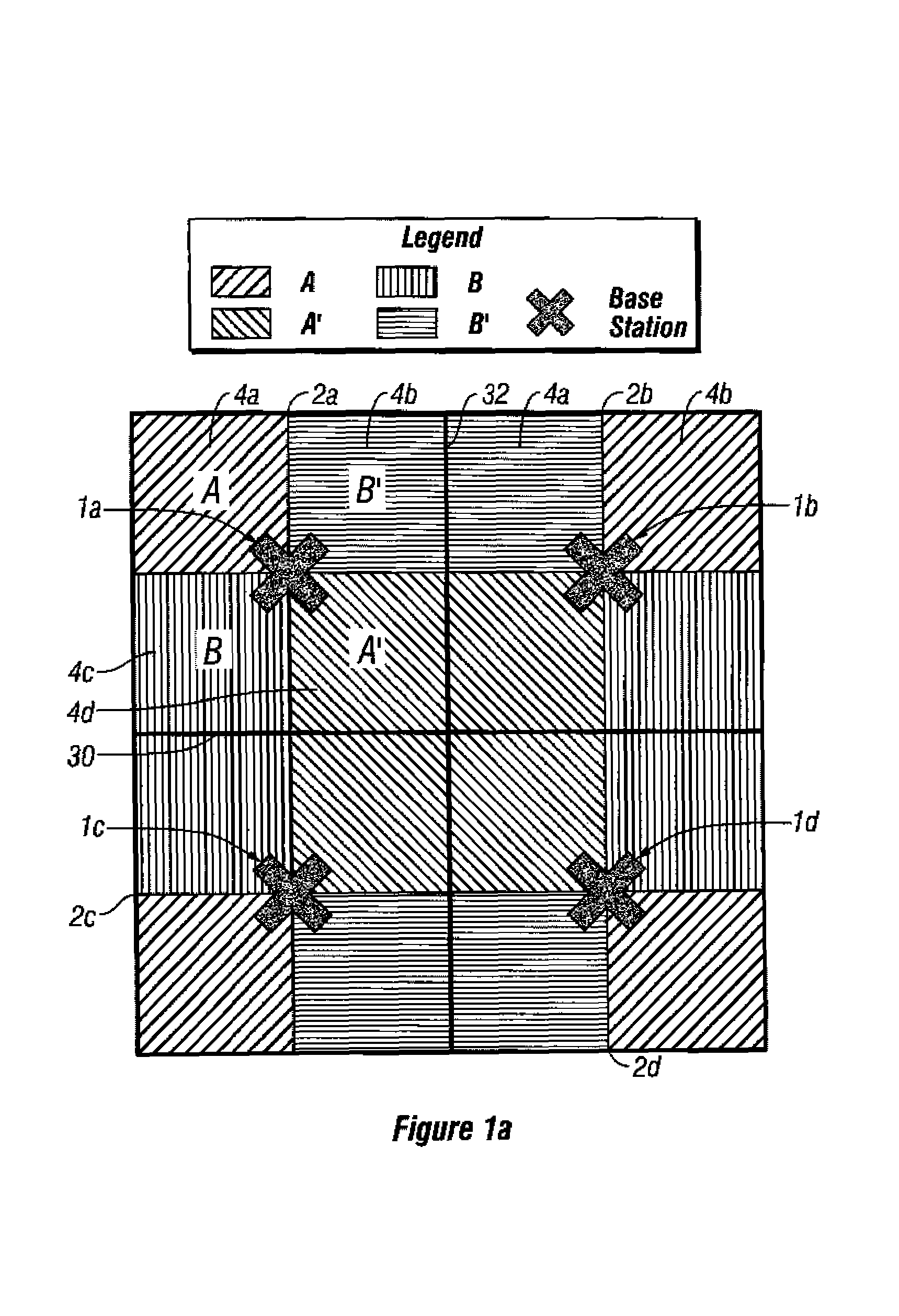
Dynamic channel allocation in a sectored cell of a cellular communication system
InactiveUS6898431B1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionDynamic channelCellular communication systems
In a sectored cell of a cellular communication network, channels are dynamically reassigned from a first sector in the cell to a second sector in the same cell when the loading in the first sector reaches a predetermined threshold. The channels allocated to the cell are further subdivided into subgroups and assigned initially to respective sectors in the cell. During normal operation, the channels in each sector are allocated to users in that sector in the usual manner. When the number of channels allocated in a first sector of the cell reaches a predetermined threshold, the base station controller polls the remaining sectors for unused channels. If an unused channel is found, that channel may be reassigned to the first sector. In one embodiment, the base station controller polls the controller in the nearest co-channel cells before reassigning the channel to prevent co-channel interference.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
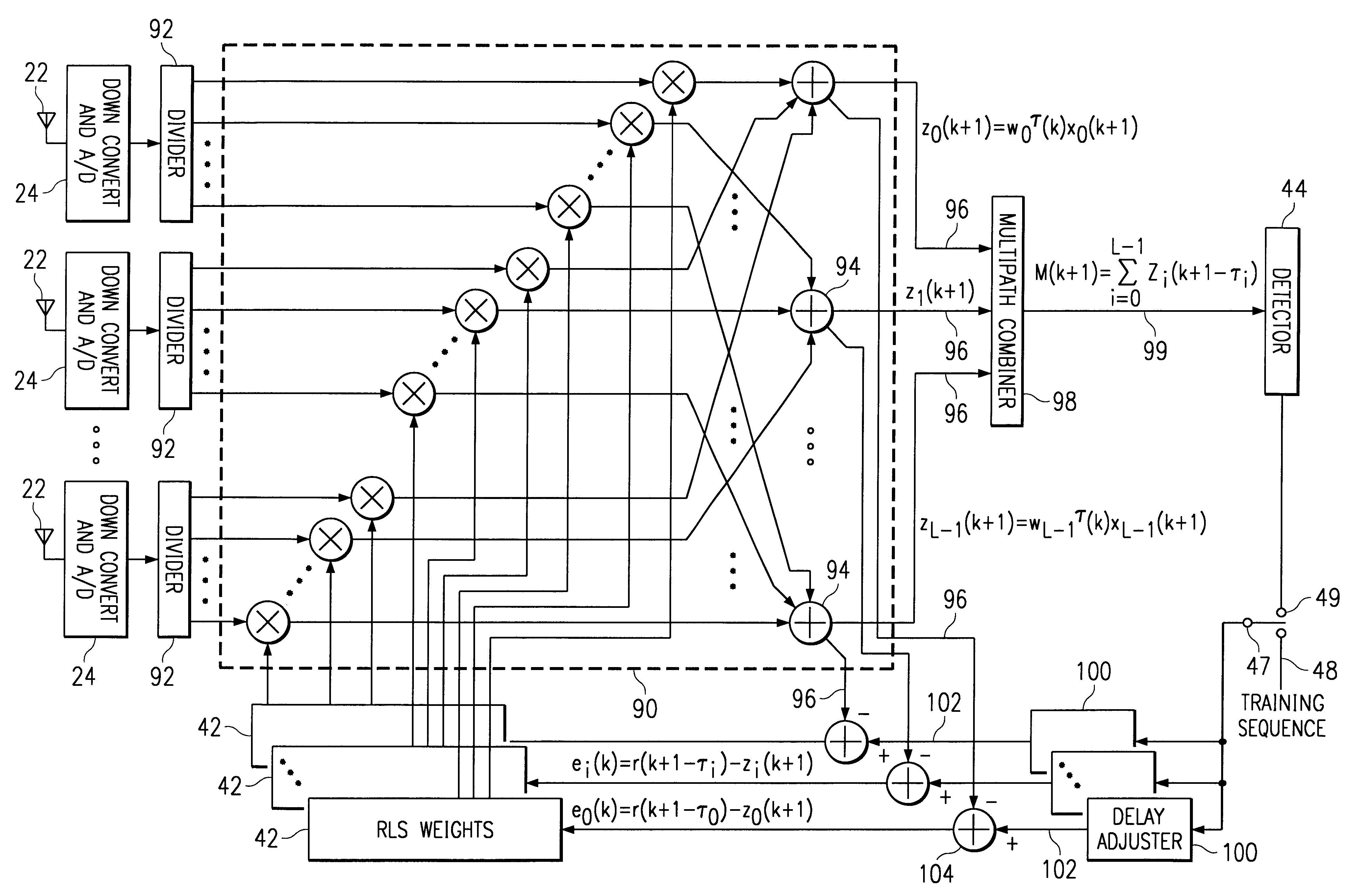
Method and apparatus for high rate data communication utilizing an adaptive antenna array
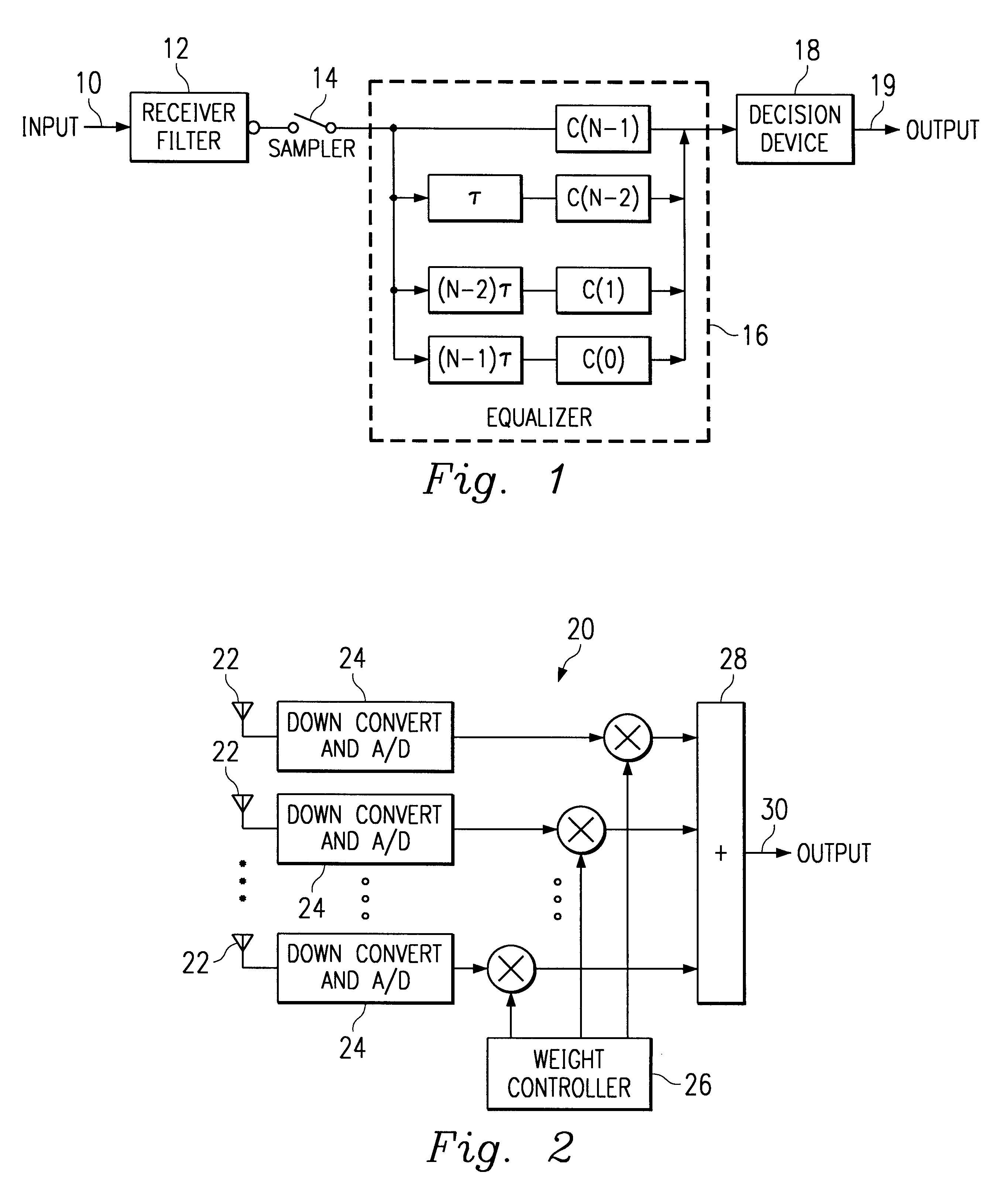
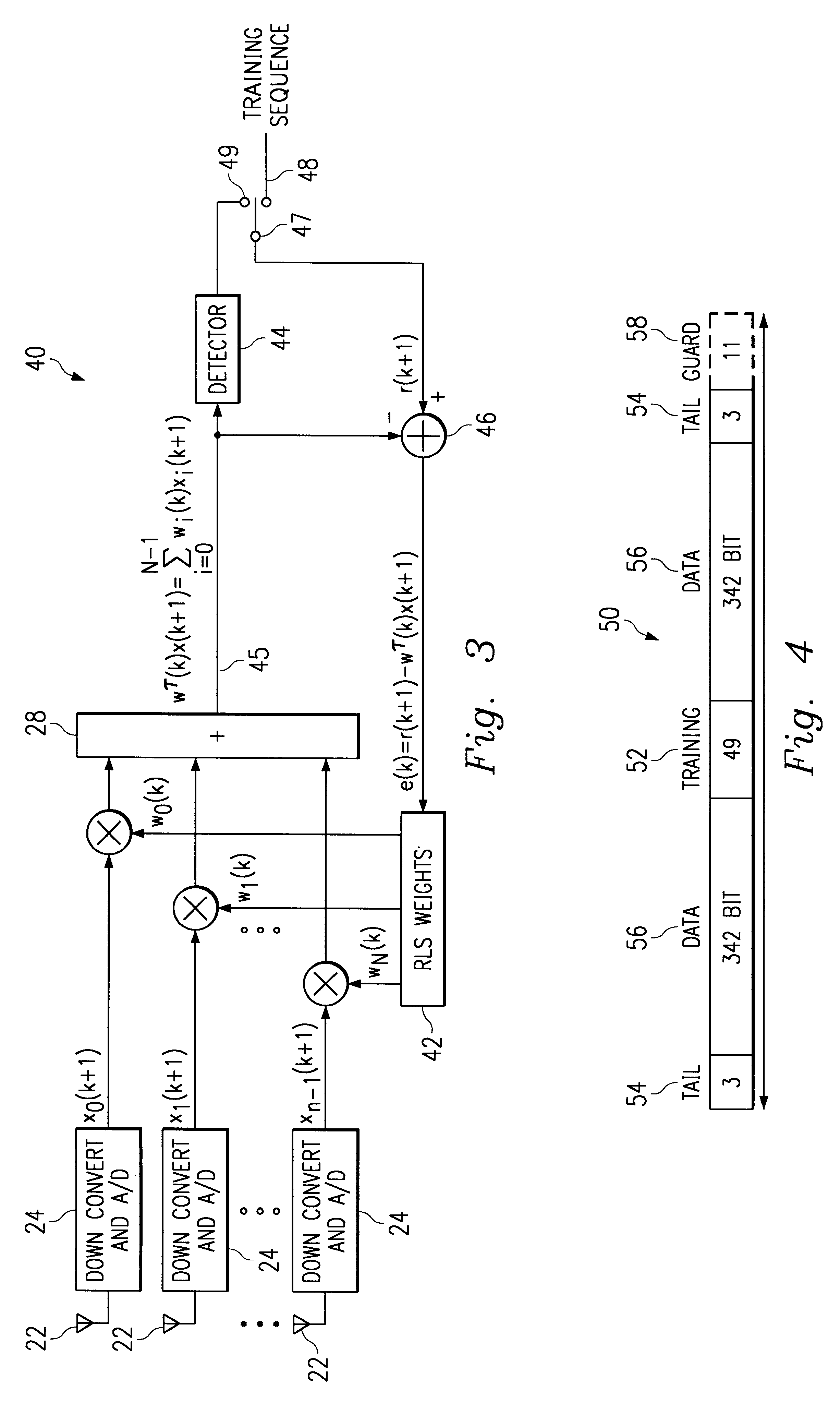
In a wideband Personal Communication Services system, a method and system are proposed for suppressing co-channel interference and reducing inter-symbol interference generated during the transfer of a data packet through a selected radio frequency channel. The system includes a weight controller utilizing recursive least squares algorithm to generate a plurality of appropriate weights to be integrated into received signals in order to maximize signal-to-noise ratio. A detected signal or a training sequence is intelligently switched in as a reference sequence in order to generate a plurality of appropriate weights. To further enhance the adaptive array system and take advantage of the multi-path radio frequency communication environment, two multi-path diversity schemes are included. One embodiment includes an adaptive array system with parallel array processors and another embodiment includes a system with tapped delay line processors.
Owner:APPLE INC
Reducing co-channel interference in satellite communications systems by antenna re-pointing
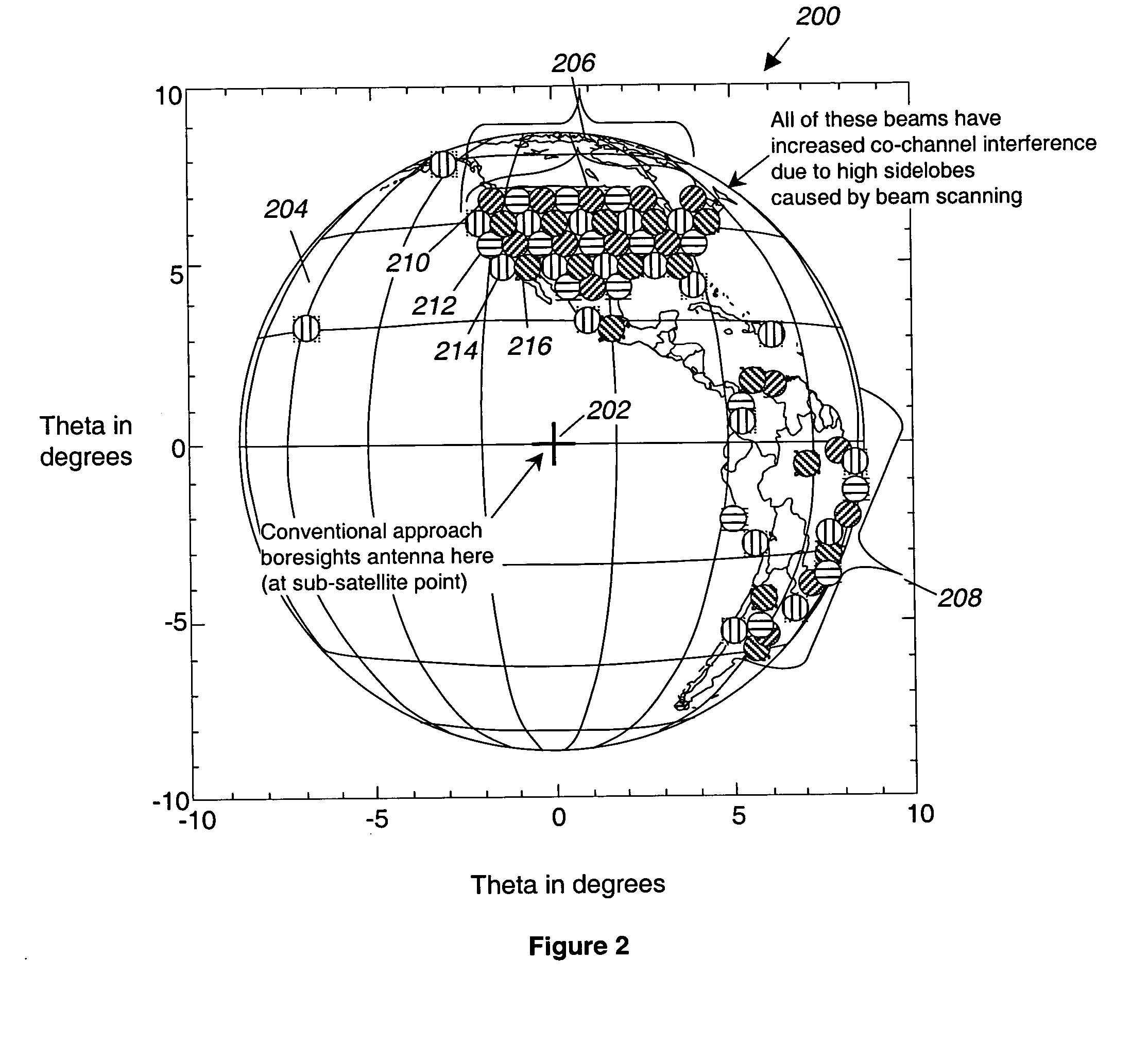
ActiveUS20050068230A1Improve performanceMinimizes CCIAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesRadio transmissionCommunications systemHigh density
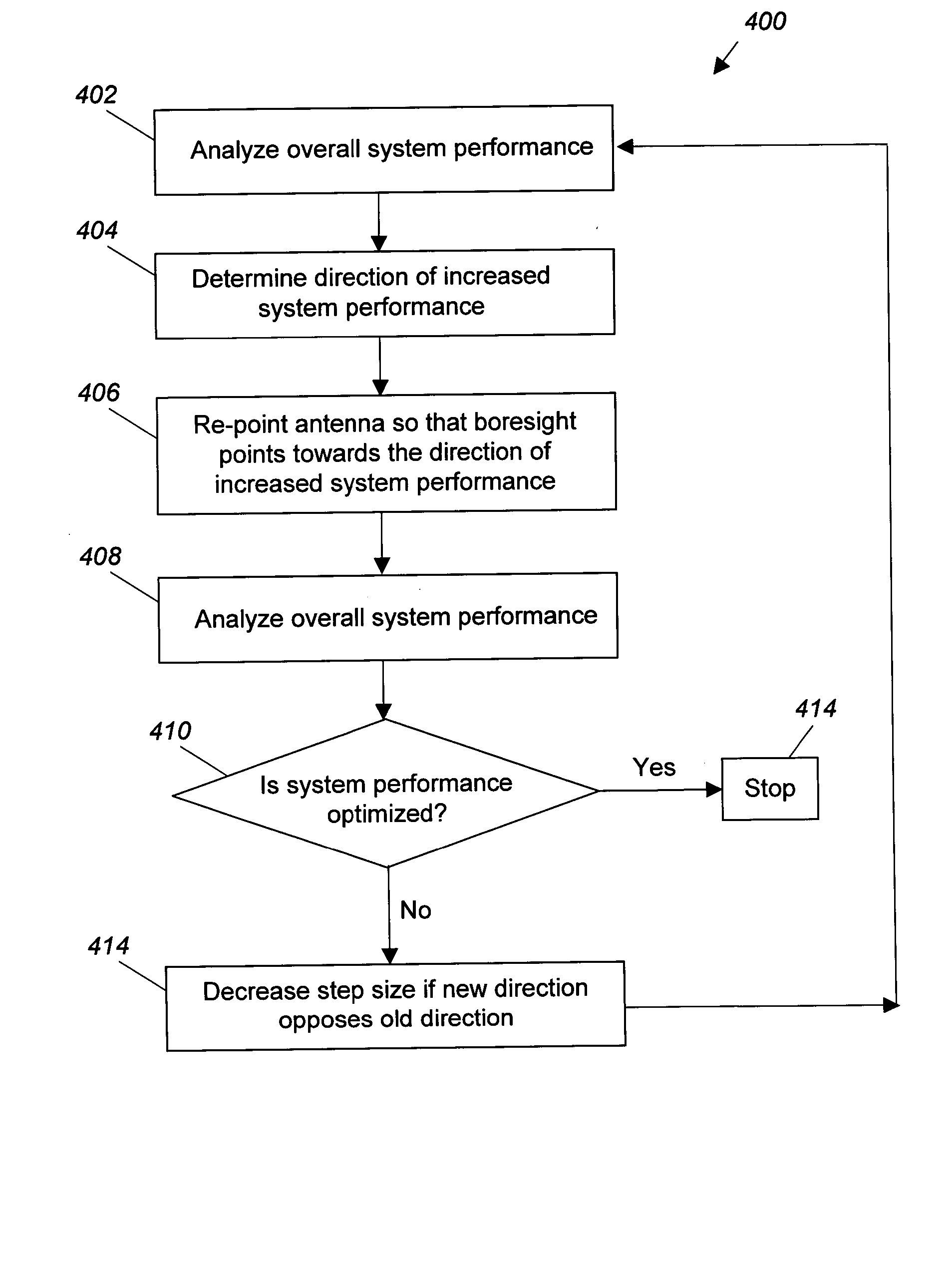
A system and method for increasing the performance of a satellite communication system by using a multivariate analysis approach to optimize the pointing of the boresight of a satellite-mounted antenna. Optimizing the pointing of the boresight of the antenna minimizes sidelobe generation, and thus Co-Channel Interference (CCI) in geographic areas served by the system. By minimizing CCI, the overall system performance of the communication system is optimized. To optimize the pointing of the boresight of the antenna, the overall performance of the satellite communication system is determined, and the boresight of the antenna is iteratively repointed in the direction of increasing system performance until the optimized boresight pointing is determined. Alternatively, the frequency re-use plan of the satellite communication system may be analyzed to determine a high density cell region and the boresight may be pointed to the high density cell region.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
SC-OFDMA-based satellite mobile communication system for forward link
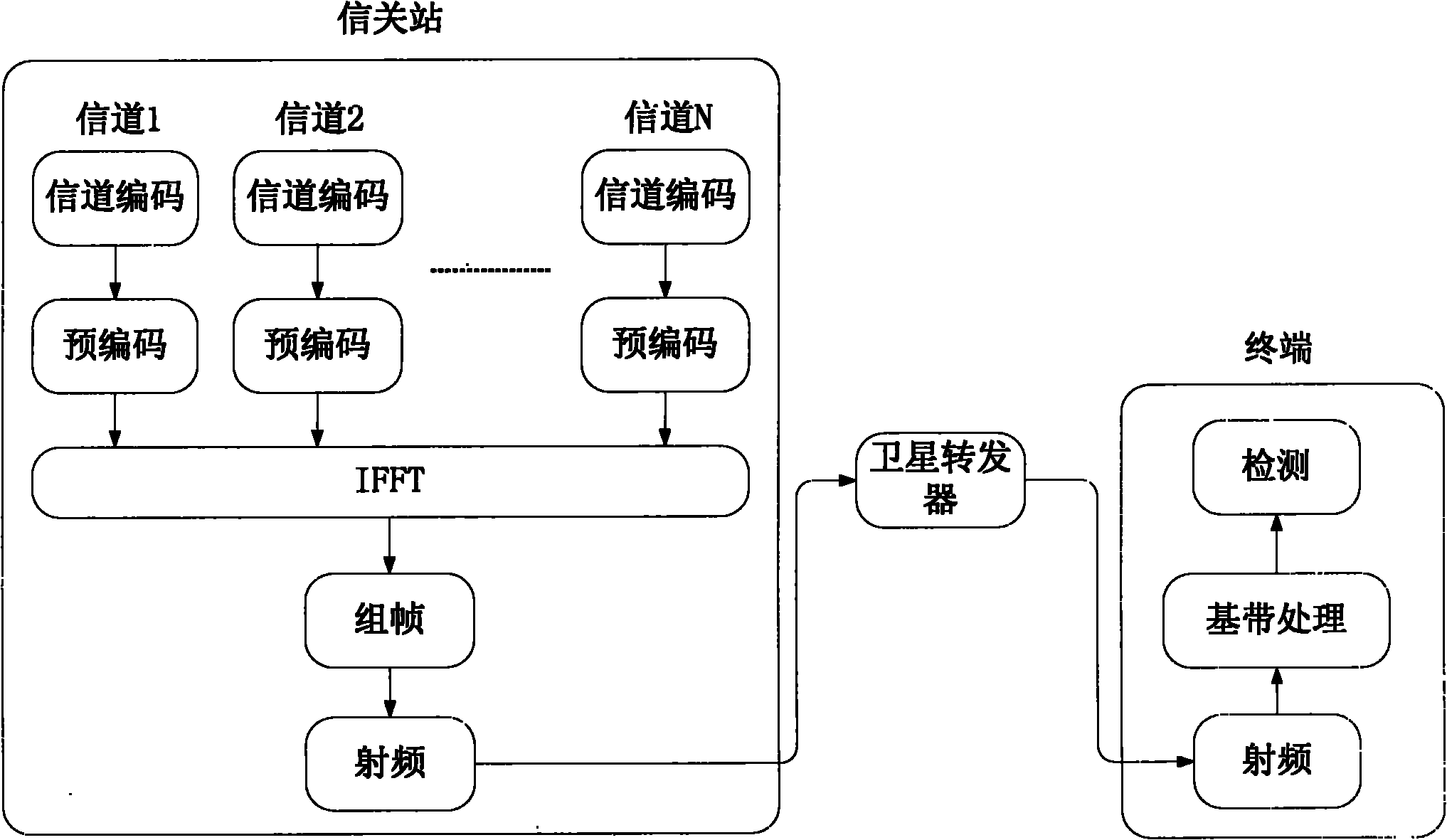
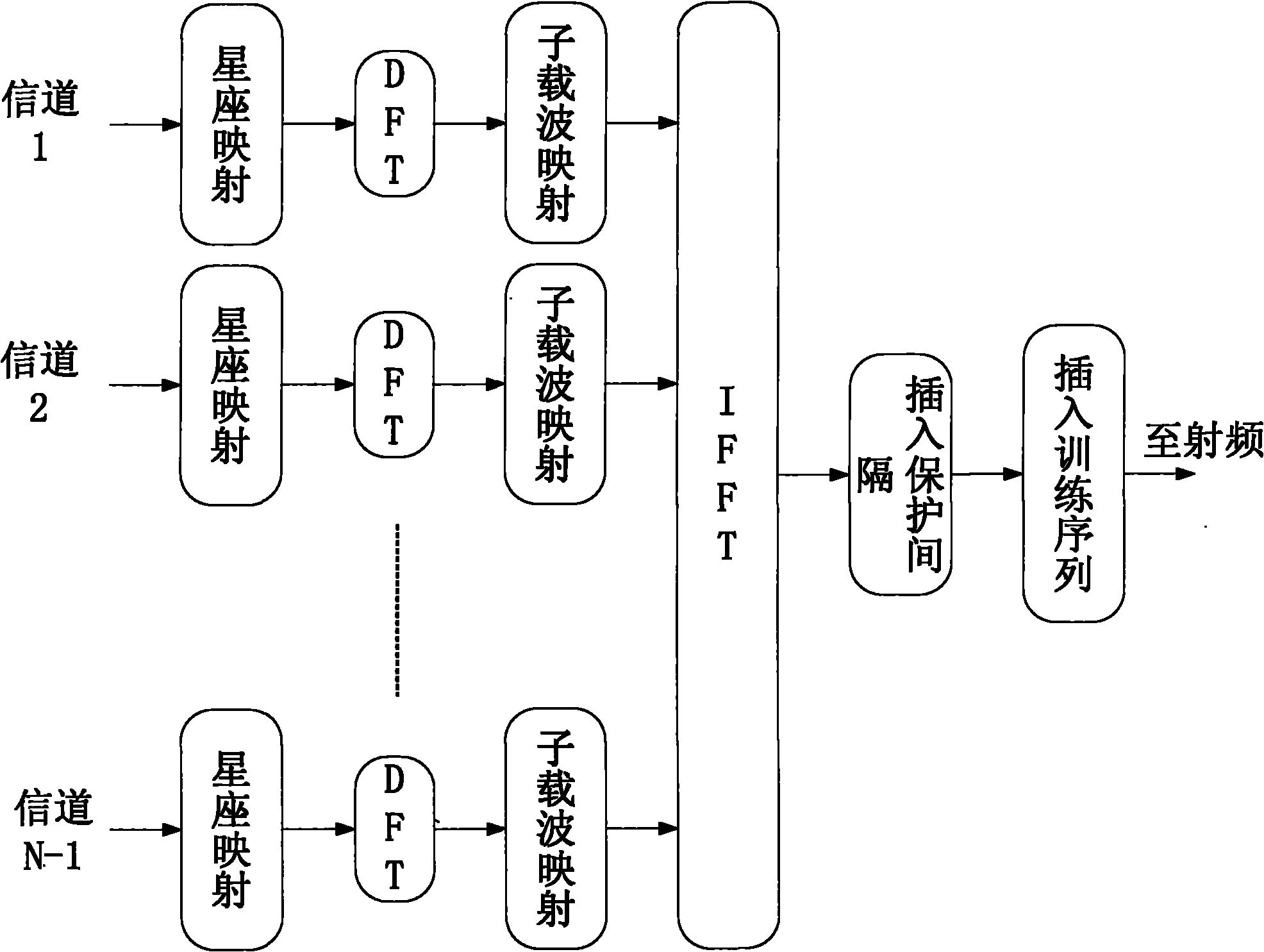
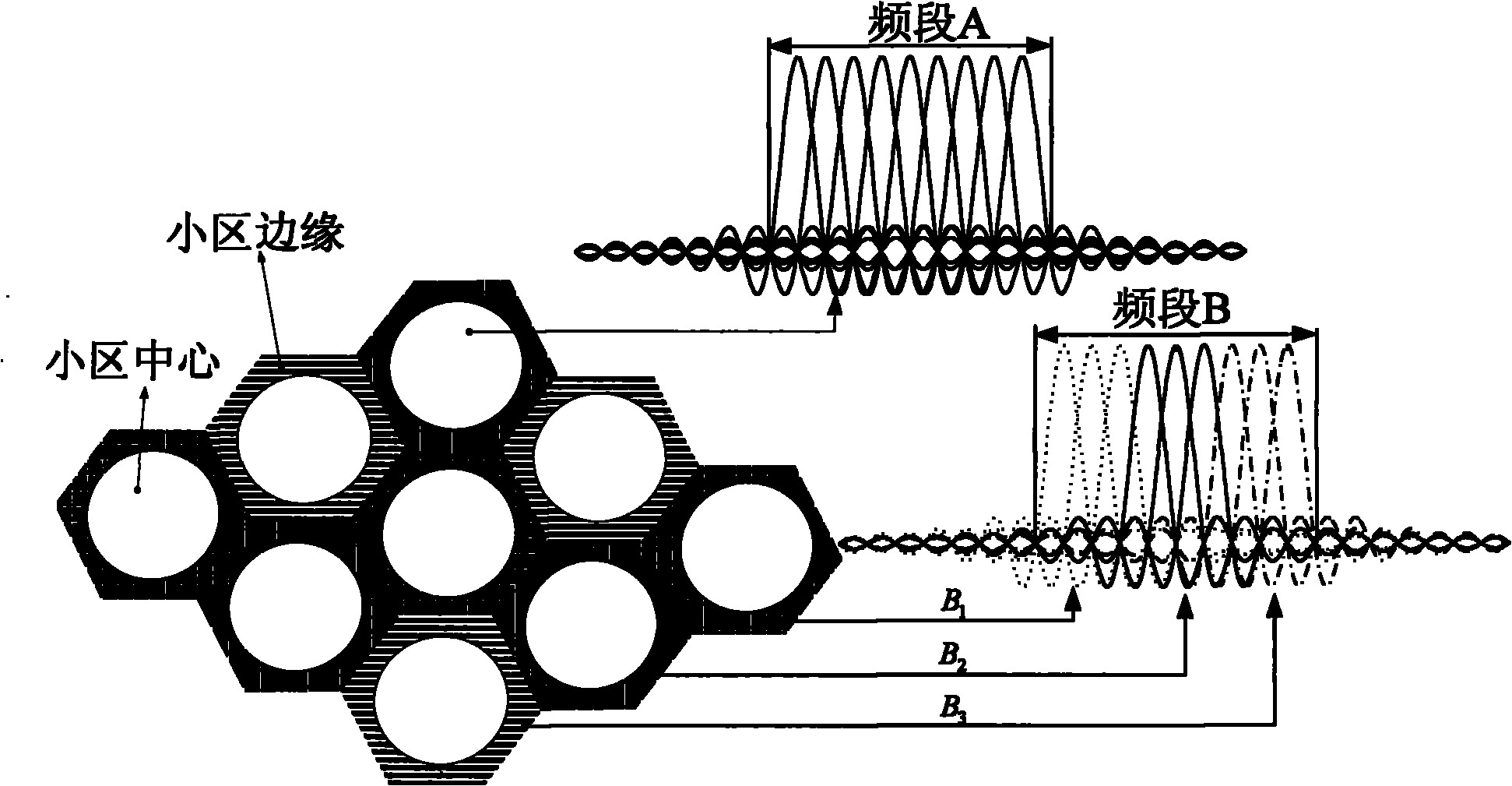
ActiveCN101795152AGuaranteed transmission qualitySolve the problem of high load peak-to-average power ratioRadio transmissionMulti-frequency code systemsFrequency spectrumResource utilization
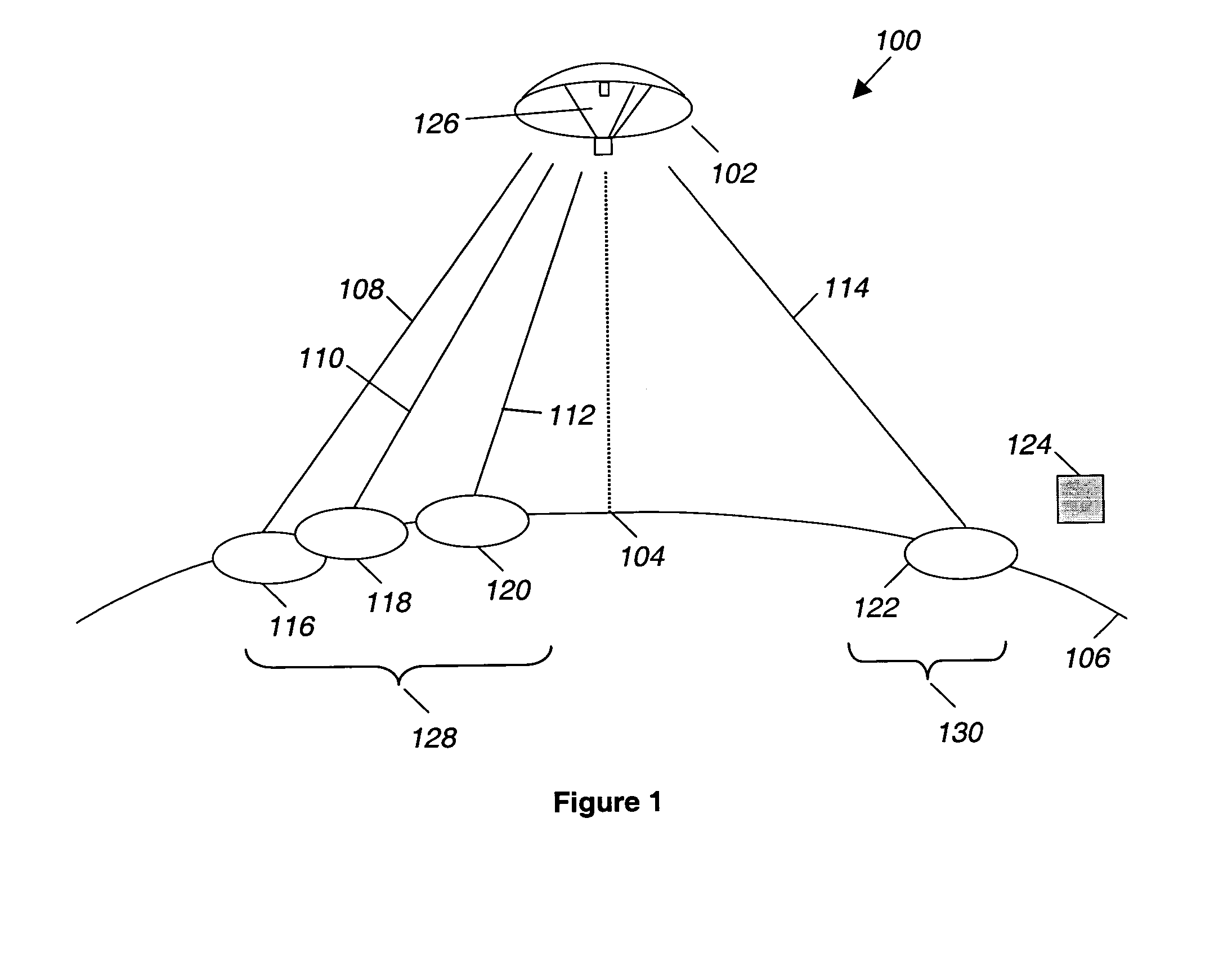
The invention discloses an SC-OFDMA-based satellite mobile communication system for a forward link, which belongs to the field of satellite mobile communication. The SC-OFDMA-based system for the forward link is characterized in that single carrier signals of a user are mapped to different sub-carriers through DFT (discrete Fourier transform) or FFT (fast Fourier transform) and then subjected to IFFT (inverse fast Fourier transform) to realize orthogonal transmission of each user signal so as to improve the utilization rate of high frequency spectrum resources and reduce the peak-to-average power ratio of the satellite forward link; and in the multi-beam-based satellite mobile communication system, different sub-carrier groups are distributed to the users in a beam overlapped area according to the beams belonging to the users so as to reduce the co-channel interference between the low beams and fulfill the aim of improving the capacity of the system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
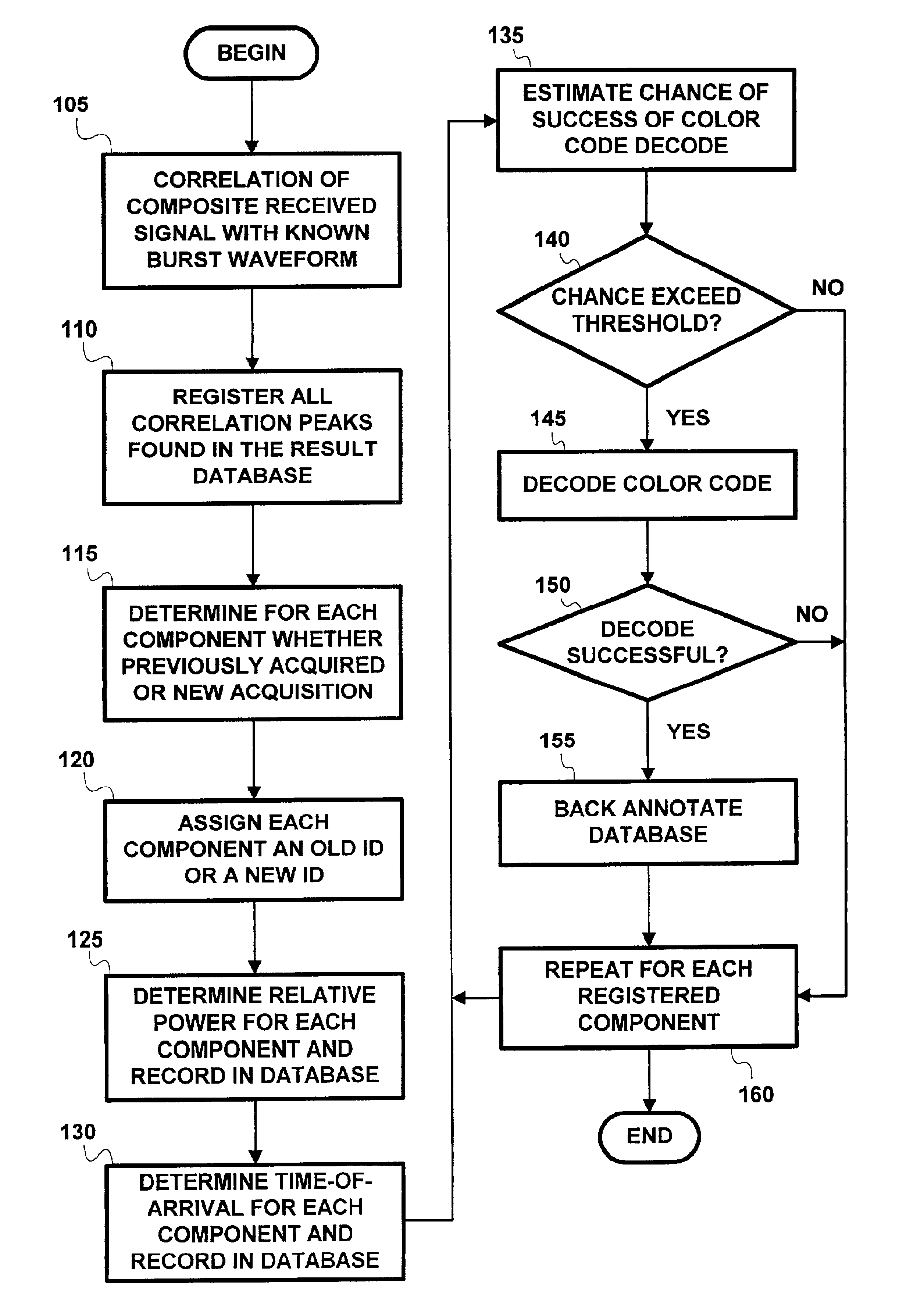
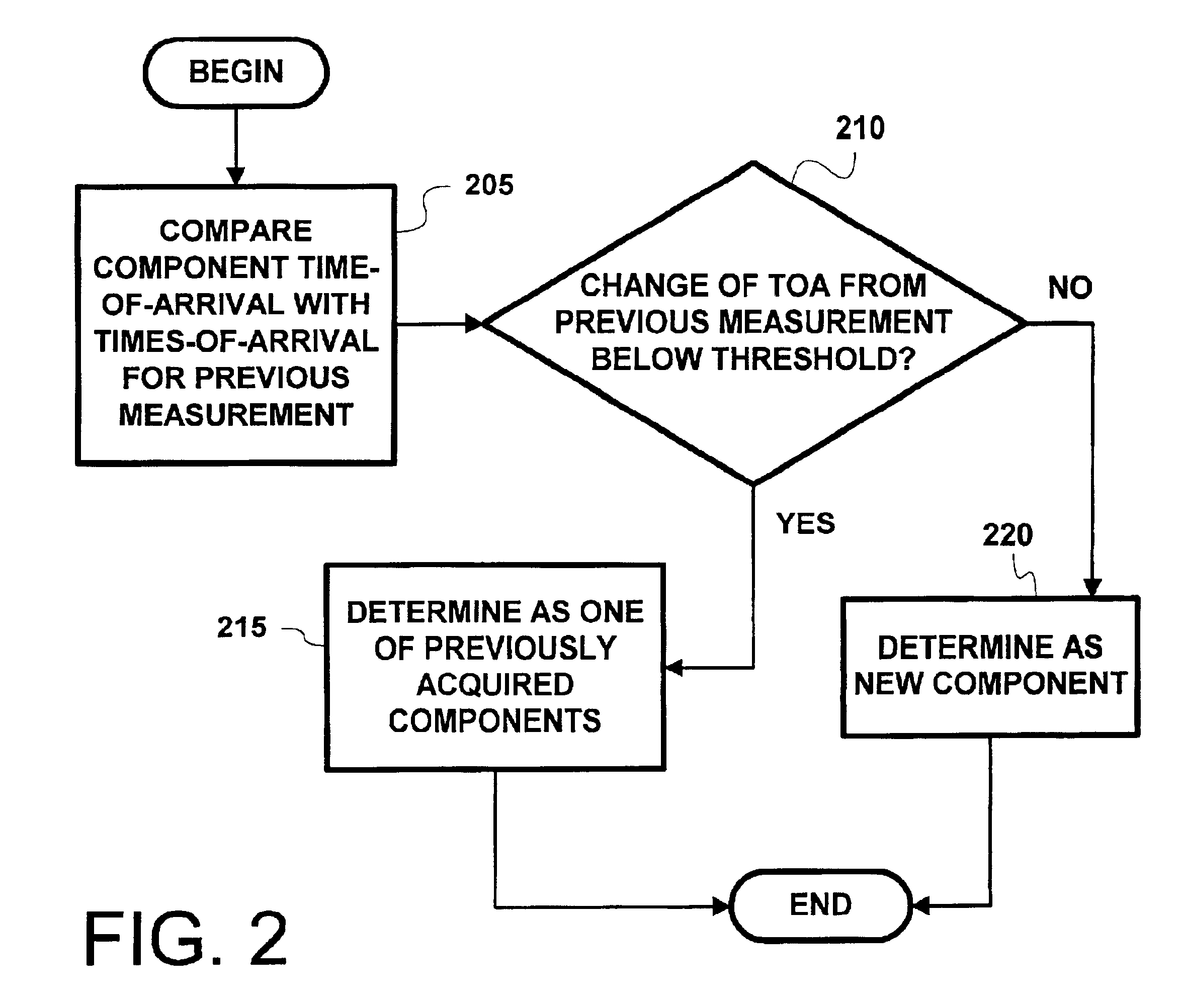
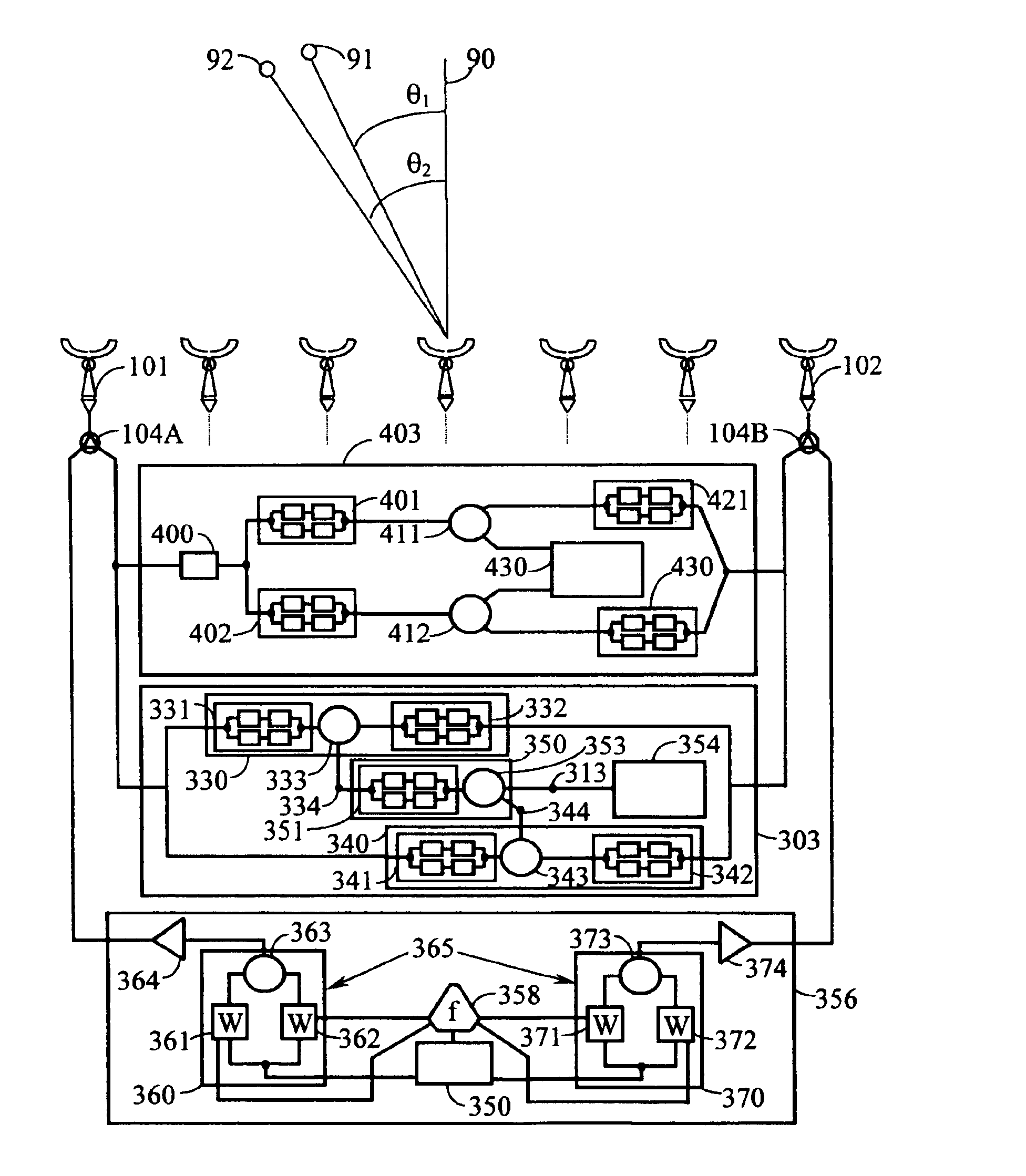
Method and apparatus for co-channel interference measurements and base station color code decoding for drive tests in TDMA, cellular, and PCS networks
InactiveUS6931235B2Improve reliabilityReduce in quantitySpatial transmit diversitySatellite radio beaconingGeolocationCo-channel interference
Co-channel interference in a wireless network is identified and quantified. Rather that using color code identification, a more reliable identification property of each co-channel component of the received composite signal is used, namely, the time of arrival of a known part of a signal. Detection and timing measurement is performed even in presence of stronger signals by focusing selectively on bursts having fixed contents (e.g., the FCCH burst used in GSM for frequency correction). The repetitive measurements of the time-of-arrival of each of the interfering components of the signal during a drive test enables determination of the geographical location of the interfering co-channel base stations.
Owner:PCTEL INC
Cancellation system for frequency reuse in microwave communications
InactiveUS6882868B1Good than fifty percent transmit efficiencyWeakening rangeRadio wave finder detailsSpatial transmit diversityNonlinear distortionFrequency reuse
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
Cancellation system for frequency reuse in microwave communications
InactiveUS20050239406A1Weakening rangeKeep shapeRadio wave finder detailsSpatial transmit diversityNonlinear distortionAntenna impedance
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC
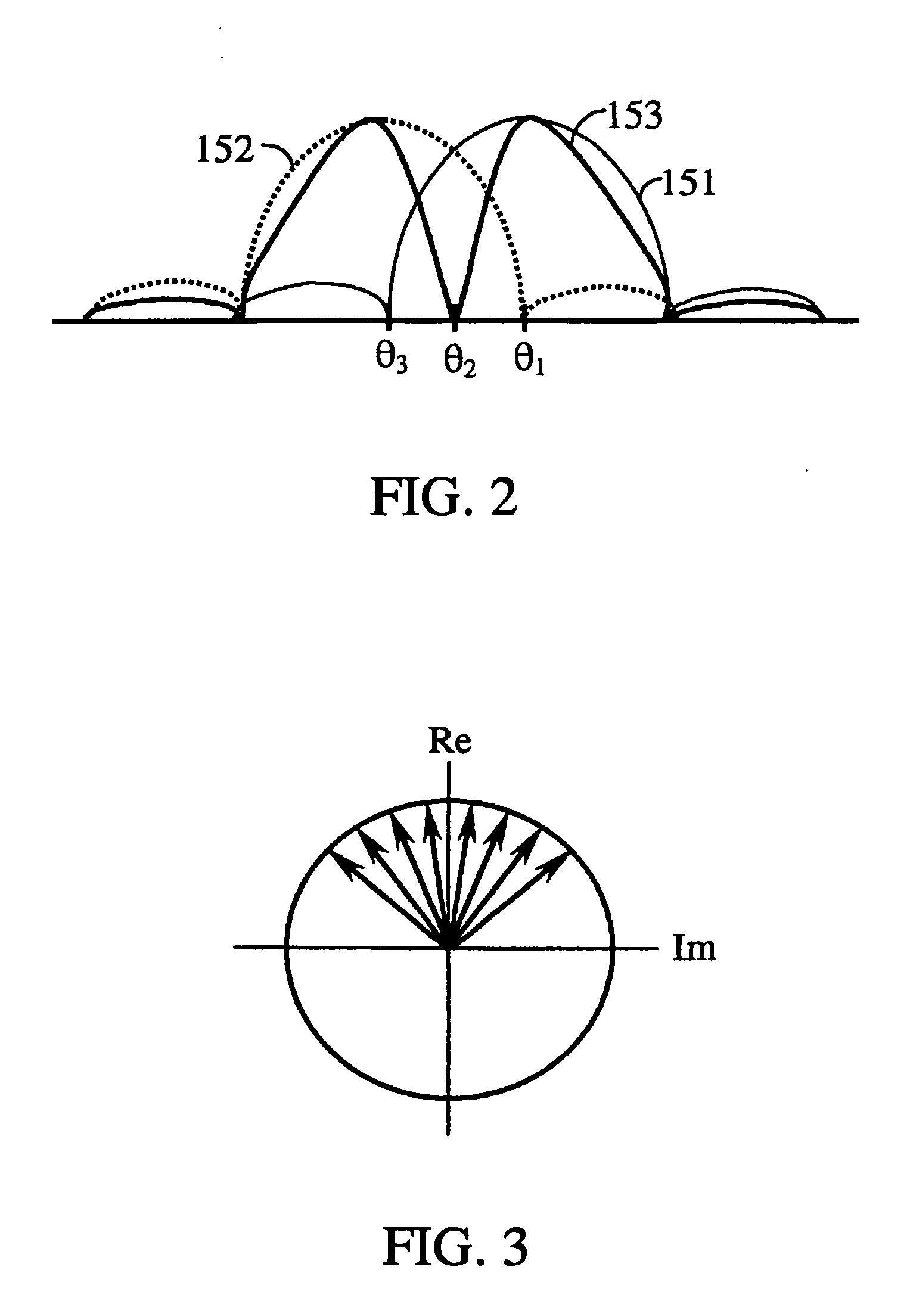
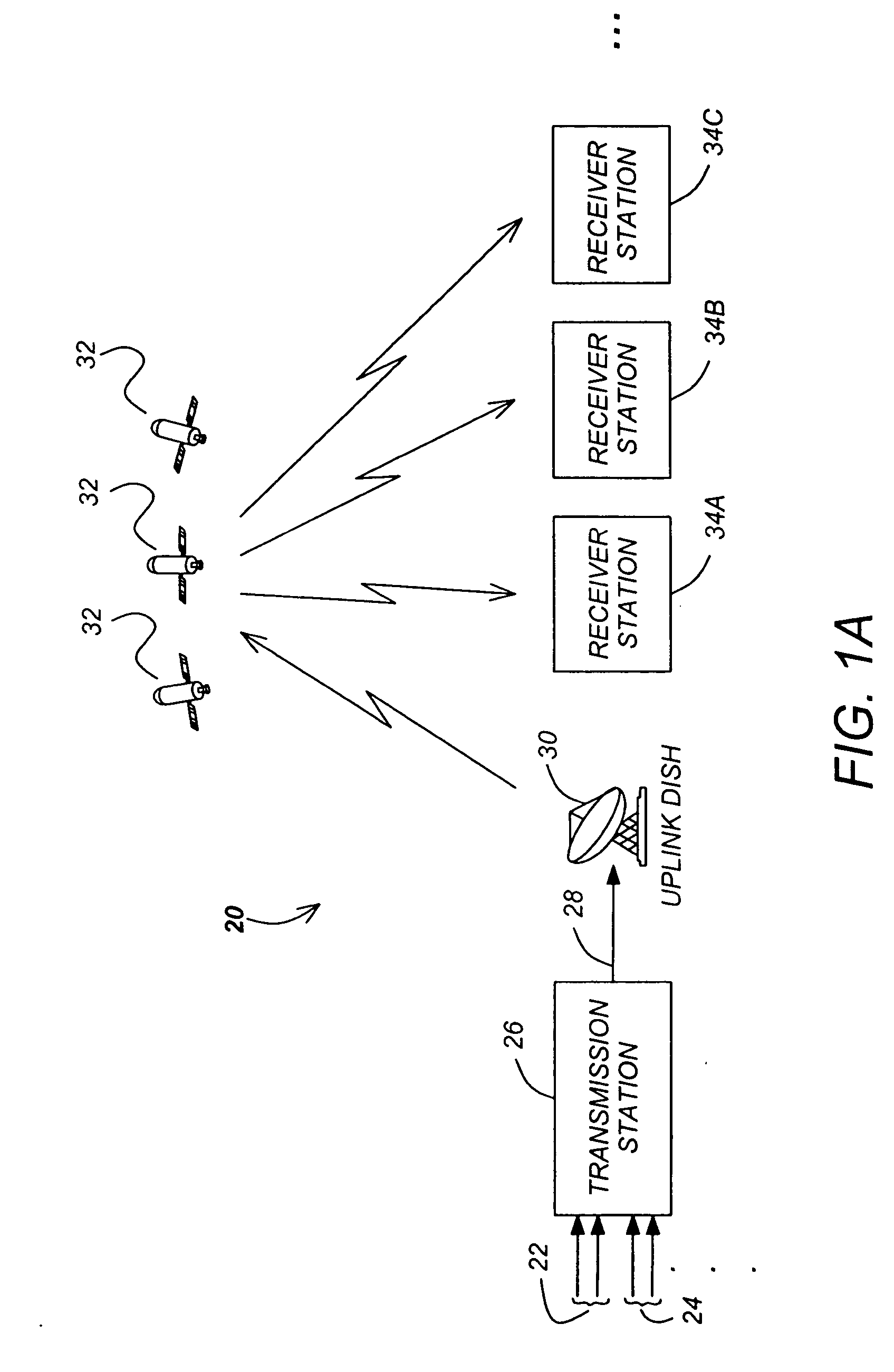
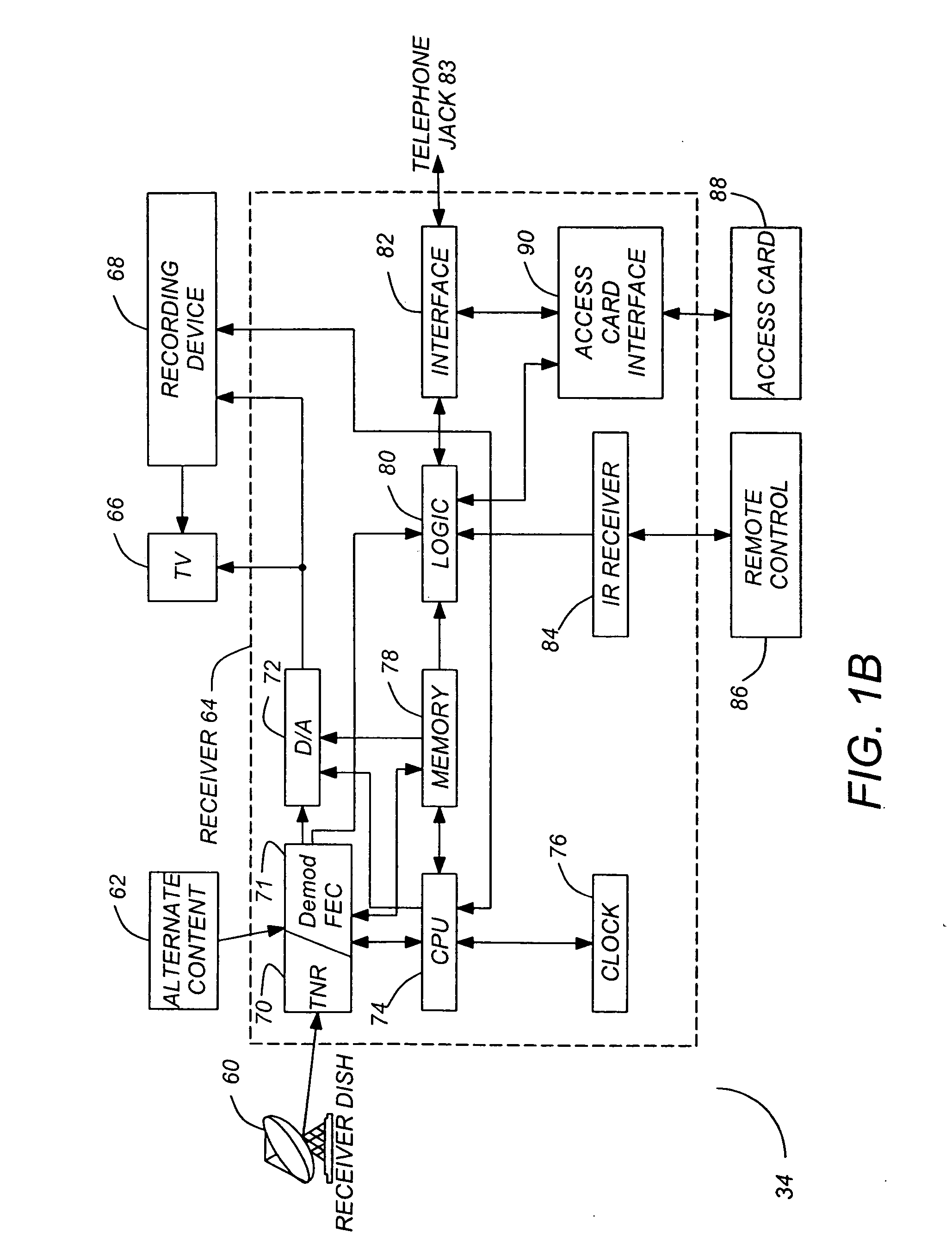
Methods and apparatuses for minimizing co-channel interference
ActiveUS20050226414A1Minimizing co-channel interferenceInterference minimizationTelevision system detailsError preventionComputer hardwareCommunications system
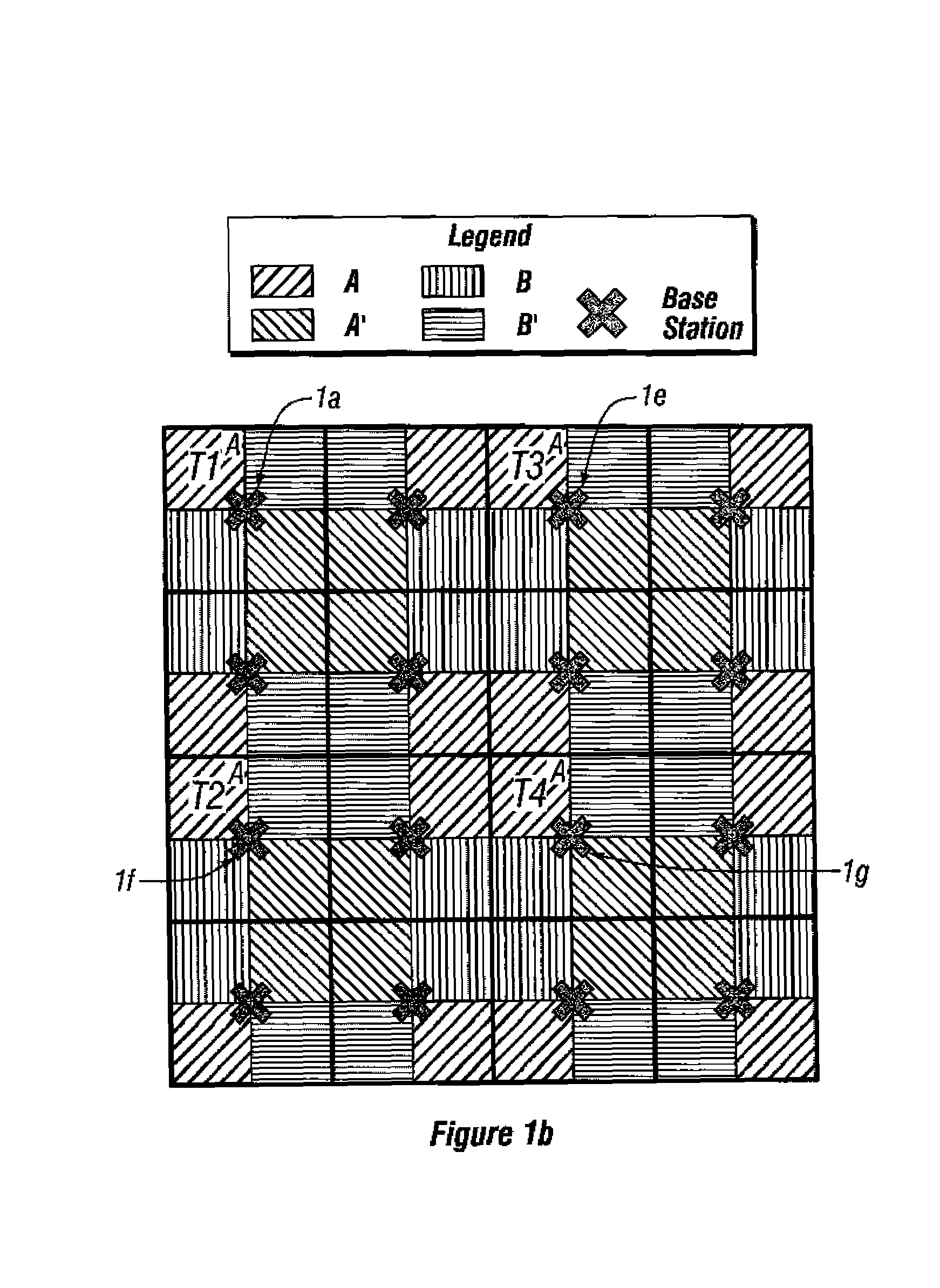
Methods and apparatuses for minimizing co-channel interference in communications systems are disclosed. A method in accordance with the present invention comprises scrambling a first frame using a first scrambling code, attaching a first header to the first frame to create the first signal, scrambling a second frame using a second scrambling code, attaching a second header to the second frame to create the second signal, and transmitting the first signal and the second signal over different channels of the communication system.
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
Repeater system for strong signal environments
ActiveUS6993287B2Reduce co-channel interferenceEasy to installActive radio relay systemsRepeater circuitsEngineeringCo-channel interference
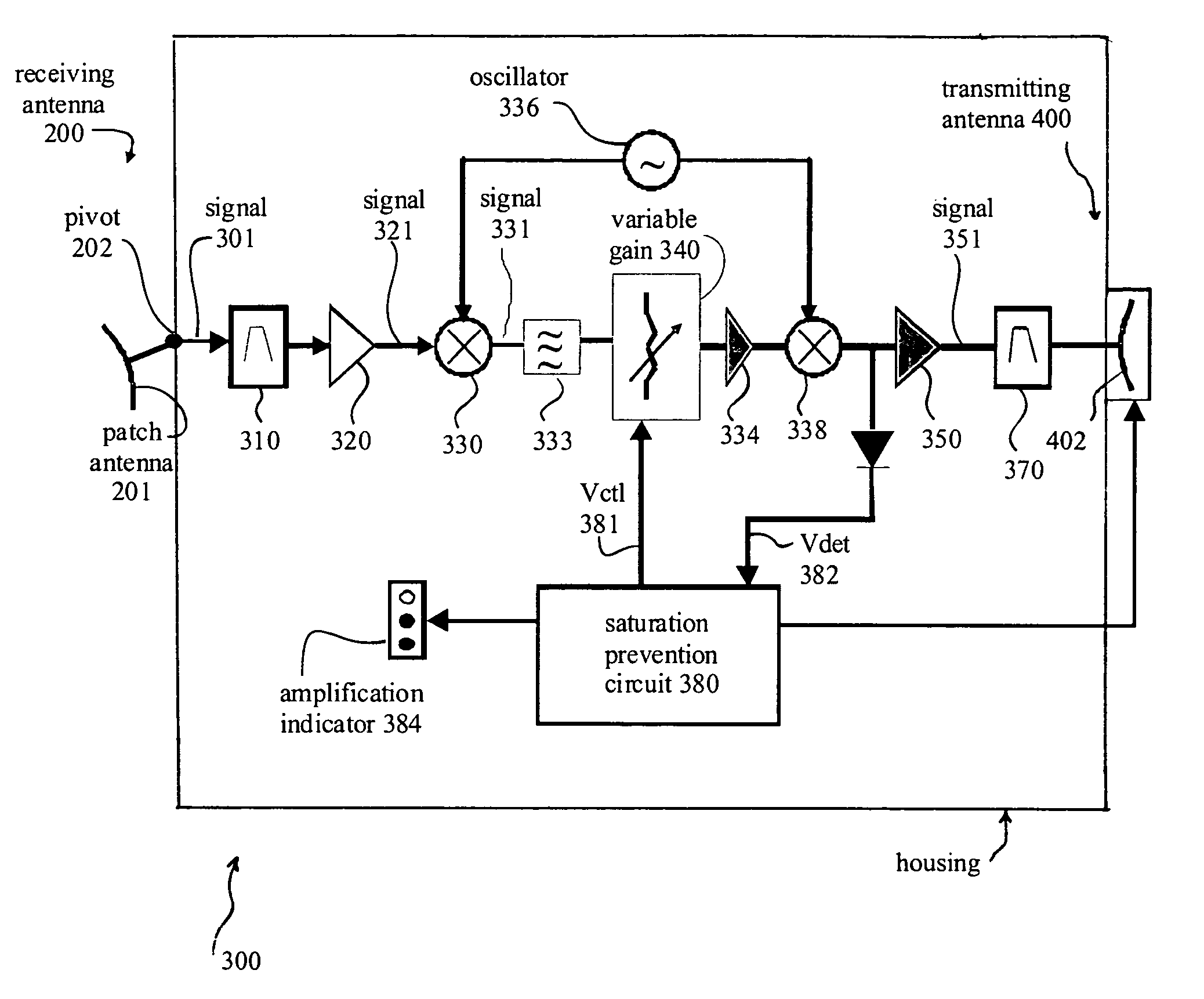
A repeater system combines co-located antennas, limited and controlled downlink signal amplification, stability management and an amplification indicator to create a user-installed solution to co-channel interference within cellular systems, in strong signal environments such as elevated locations or high-rise building. The invention may be particularly relevant to cellular systems, such as CDMA, that allow limited imbalance between uplink and downlink path losses, thus enabling the design of an inexpensive downlink repeater which creates moderate signal amplification for selected line-of-sight signals, defeating co-channel interference over a small area. Signal amplification is maintained at a level below the capacity of the system to support imbalance, guaranteeing reliable cellular calls.
Owner:CUFER ASSET LTD LLC
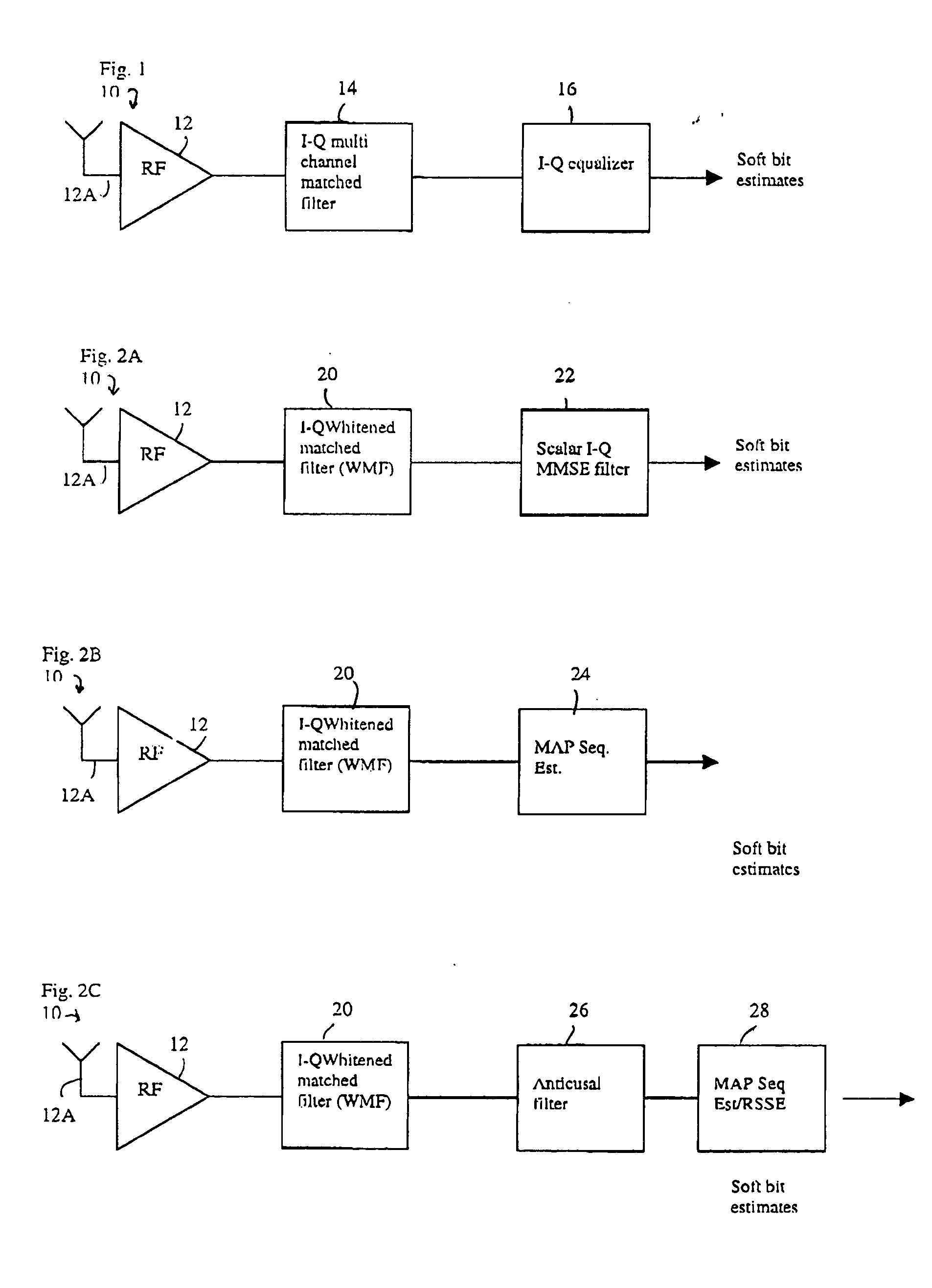
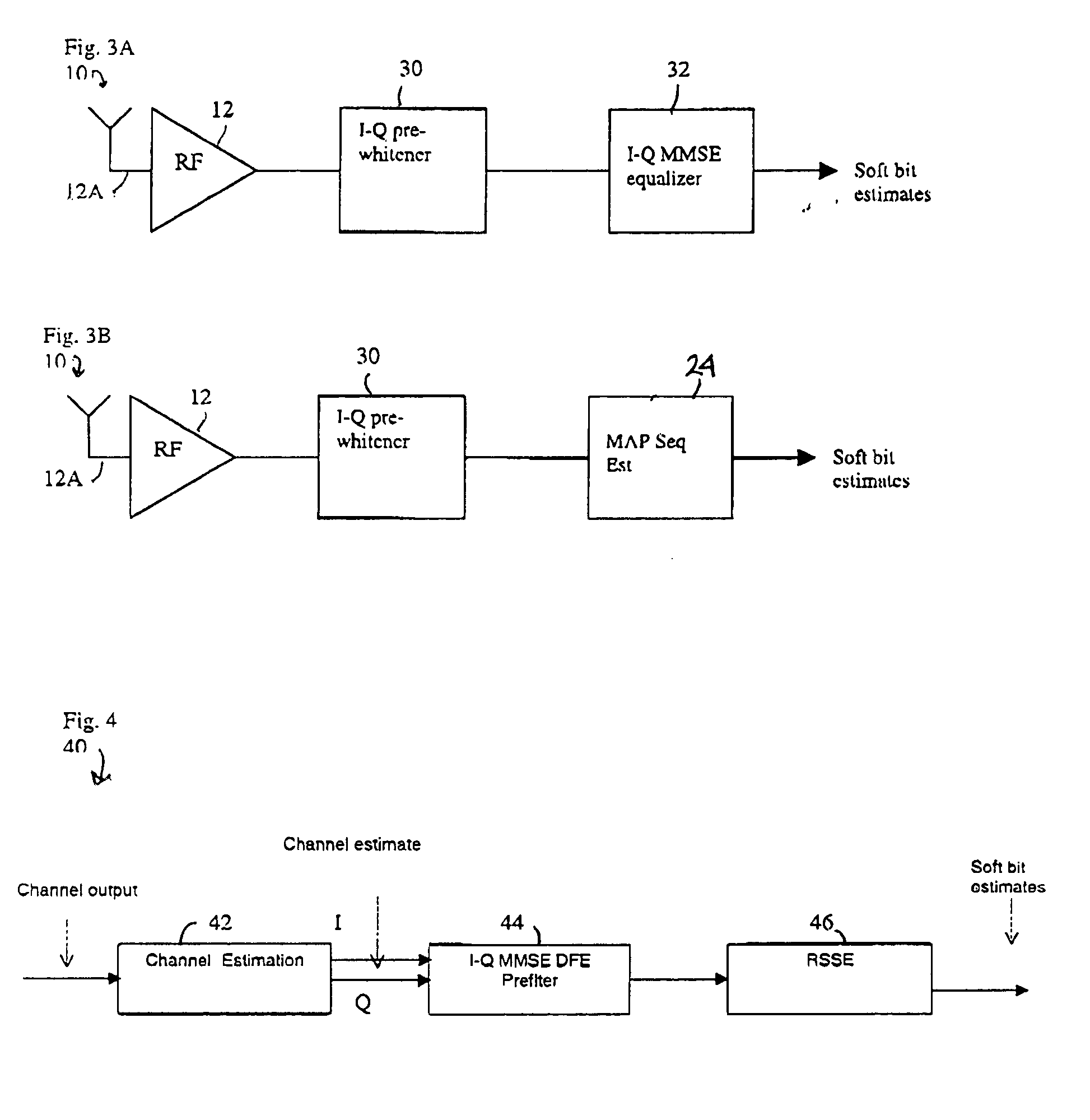
Method and apparatus providing low complexity equalization and interference suppression for SAIC GSM/EDGE receiver
InactiveUS20050036575A1Improve performanceReduce complexityError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionEngineeringCo-channel interference
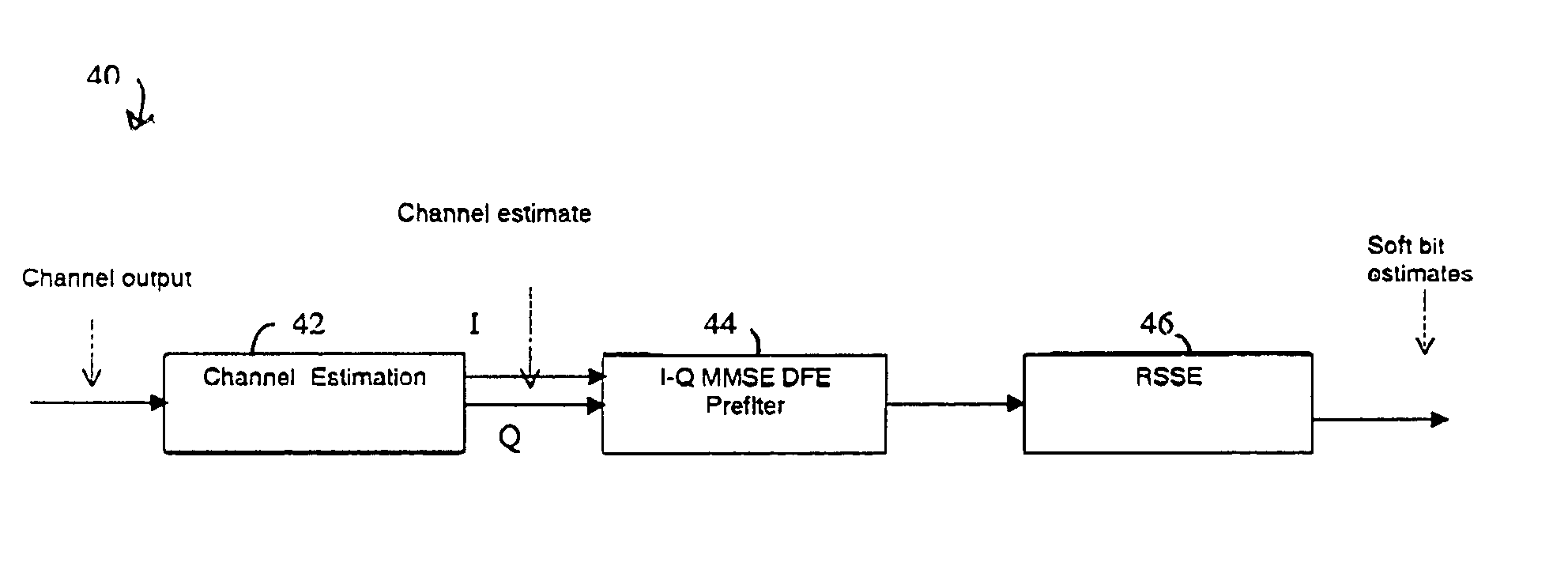
Disclosed is a RF receiver that includes baseband circuitry for performing Minimum Mean-Square Error (MMSE) optimization for substantially simultaneously suppressing inter-symbol interference (ISI) and co-channel interference (CCI) on a signal stream that comprises real and imaginary signal components. In a preferred embodiment the receiver includes a single receive antenna, and operates as a single / multi antenna interference cancellation (SAIC) receiver. The baseband circuitry operates to determine a set of In-Phase and Quadrature Phase (I-Q) MMSE vector weights that are used to perform the ISI suppression and the CCI suppression. A method for operating the receiver is also disclosed.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
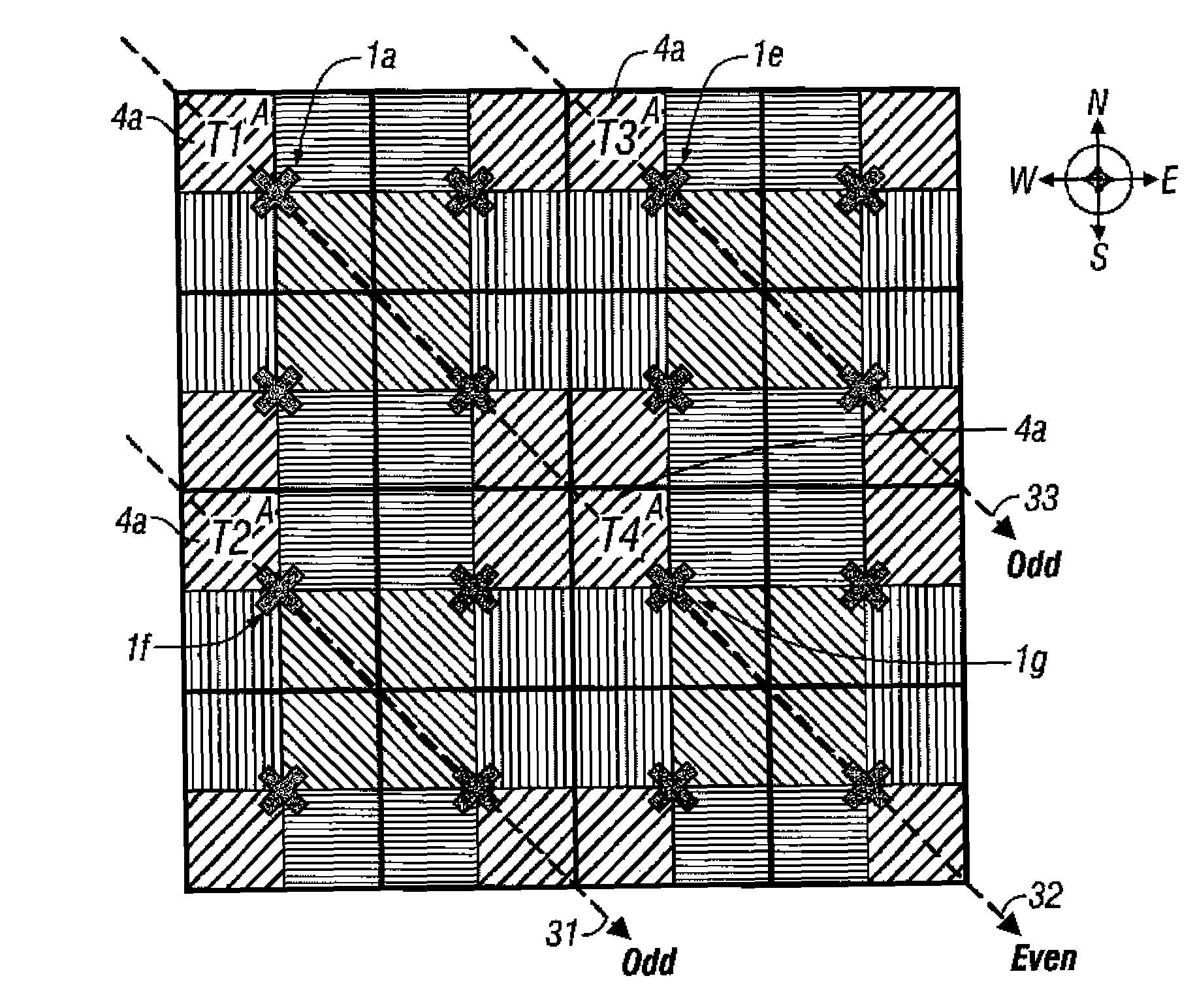
Method and system for reducing channel interference in a frame-synchronized wireless communication system
InactiveUS7177598B2Reduce channel interferenceReduce co-channel interferenceFrequency-division multiplexTransmission monitoringAdjacent-channel interferenceCommunications system
Base stations having potentially interfering terminal stations that are geographically located on the same or similar diagonal or Line of Sight (relative to the base station) operate on a first set of time frames (e.g., “even” time frames). Similarly, base stations having potentially interfering terminal stations that are not geographically located on the same or similar diagonals operate on a second set of time frames (e.g., “odd” time frames). By alternating in their use of the even and odd frames, the potential for co-channel interference between terminal stations is minimized. Systems and methods are disclosed which reduce co-channel and adjacent channel interference between terminal stations of different cells as well as adjacent channel interference between terminal stations of adjacent cells. The methods and systems so described can be used during the deployment or expansion of a communication system in a region.
Owner:WI LAN INC
Physical layer header scrambling in satellite broadcast systems
ActiveUS20050226418A1Minimizing co-channel interferenceInterference minimizationTelevision system detailsError preventionComputer hardwareCommunications system
Methods and apparatuses for minimizing co-channel interference in communications systems are disclosed. A method in accordance with the present invention comprises scrambling a first header of the first signal using a first scrambling code, scrambling a second header of the second signal using a second scrambling code, and transmitting the first signal and the second signal with the scrambled first header and the scrambled second header over different channels of the communication system.
Owner:DTVG LICENSING INC
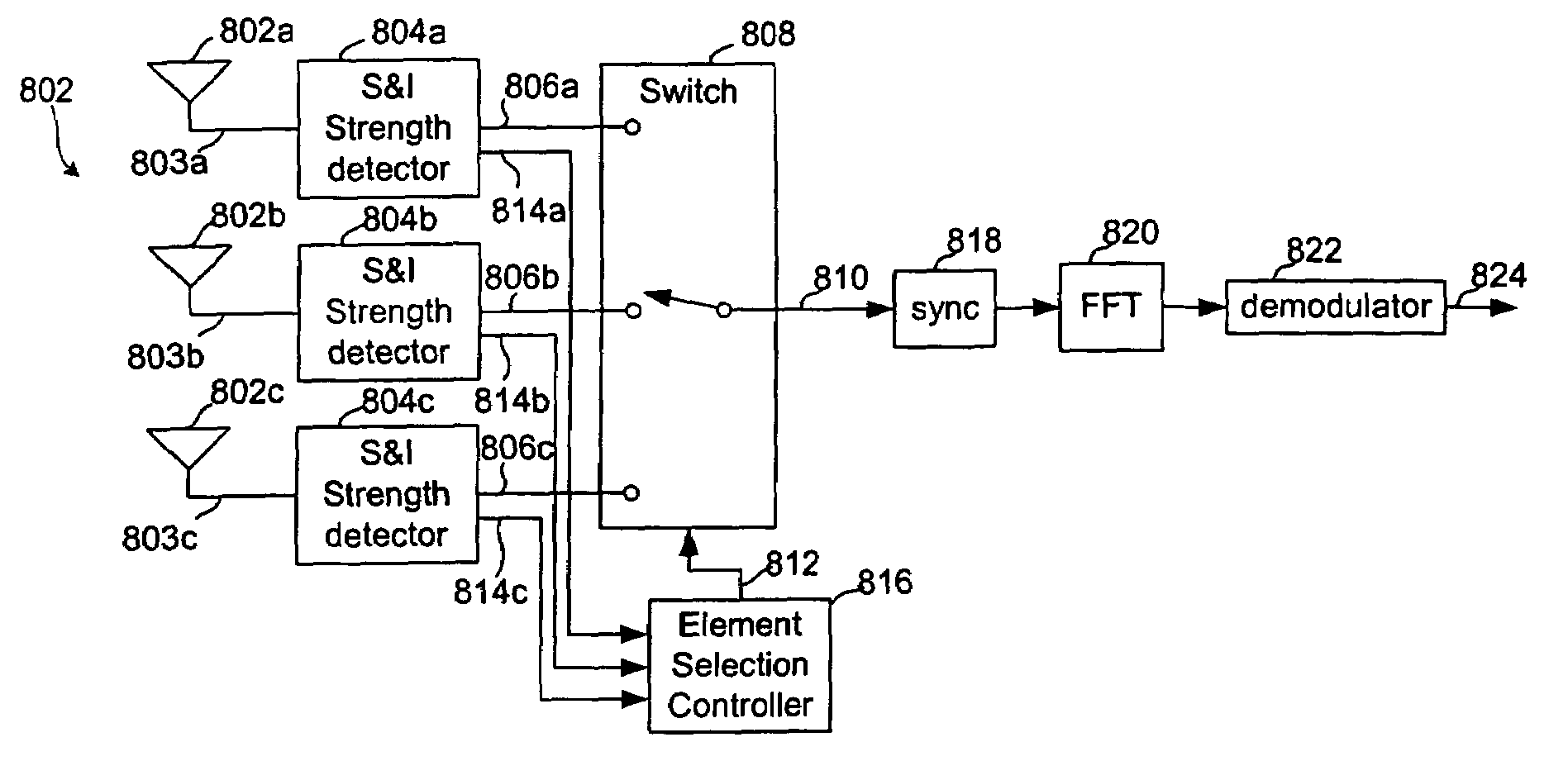
Signal selection systems
ActiveUS7426232B2Reduce the impactImprove data throughputSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityCarrier signalCo-channel interference
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
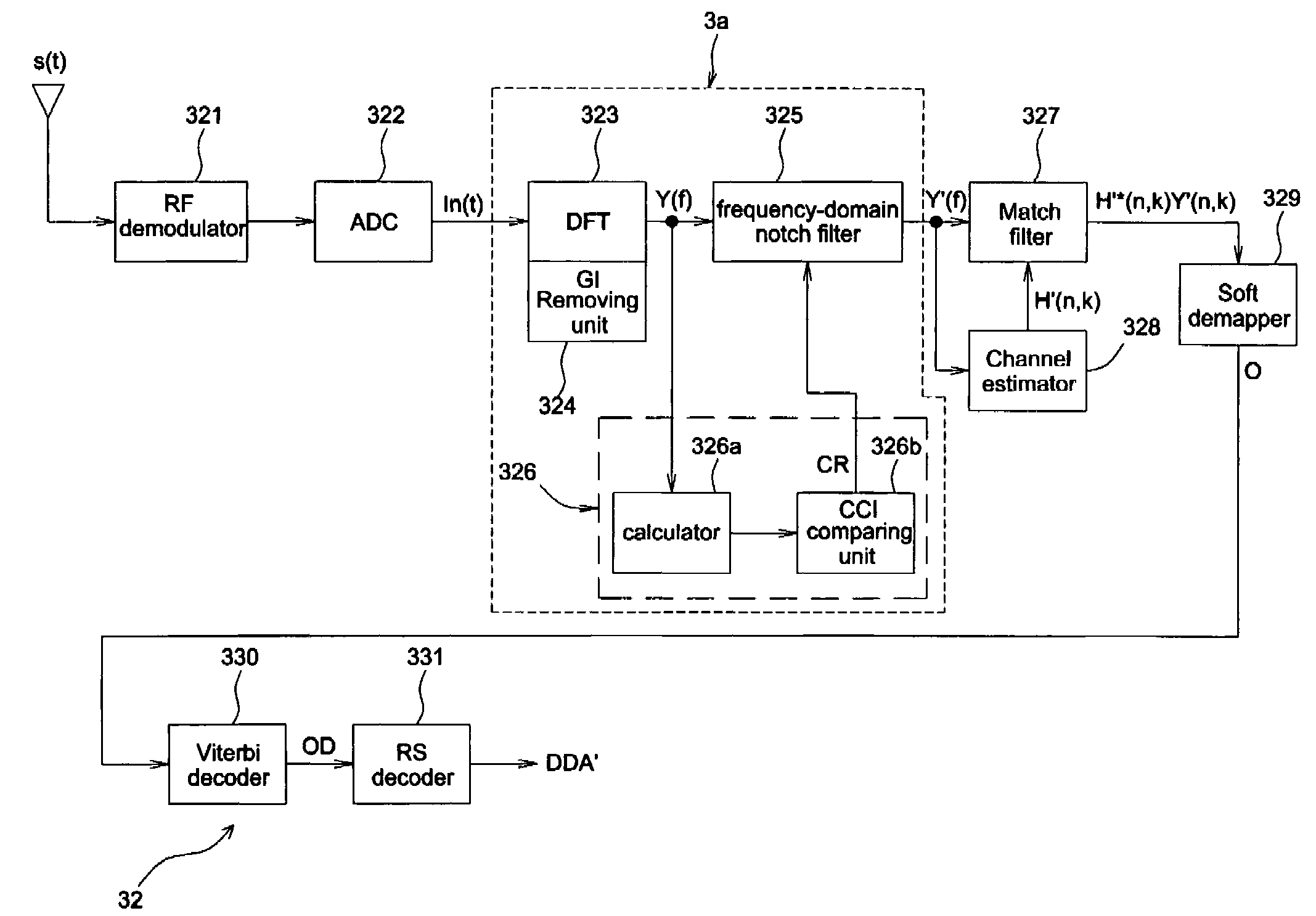
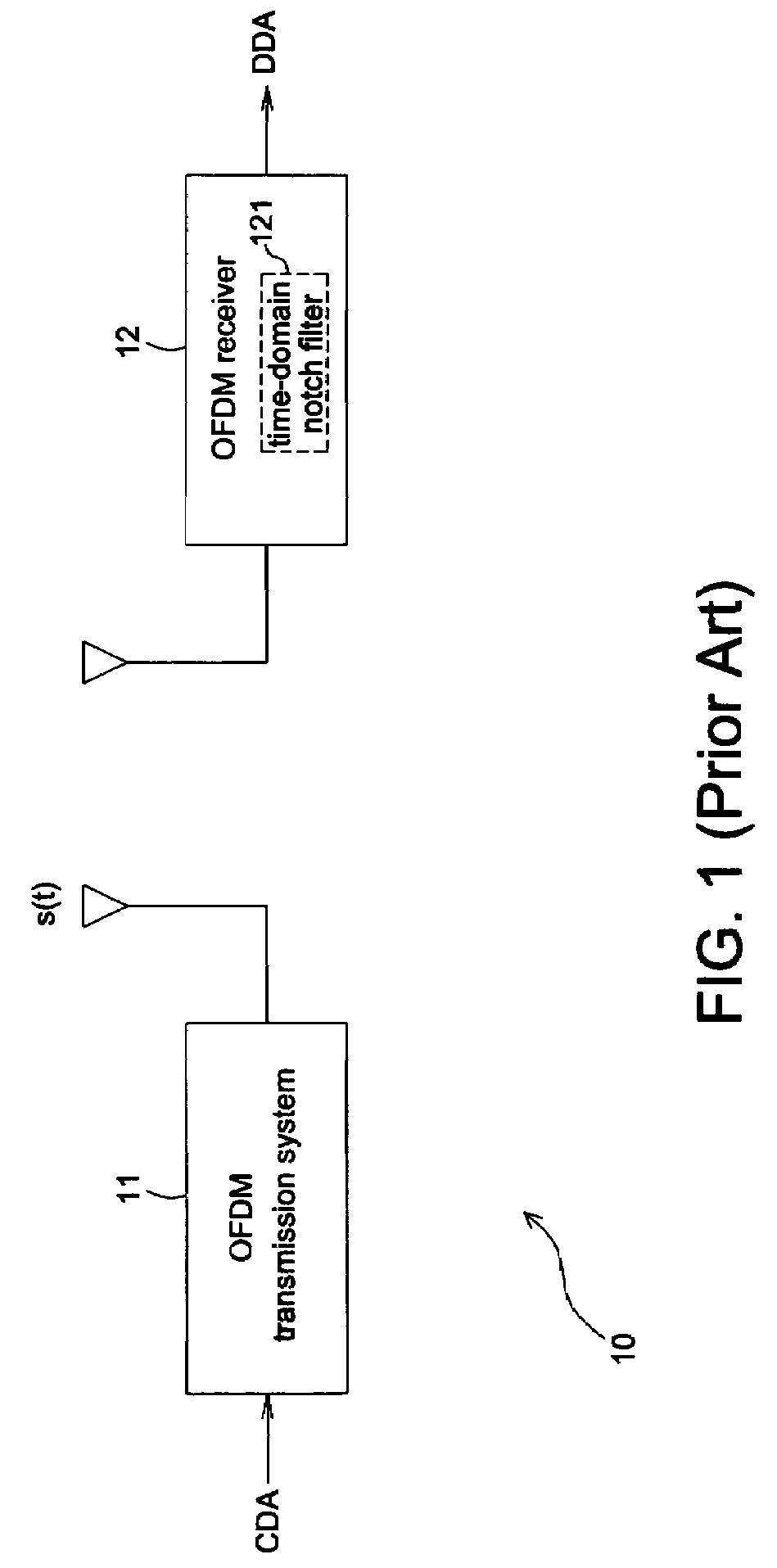
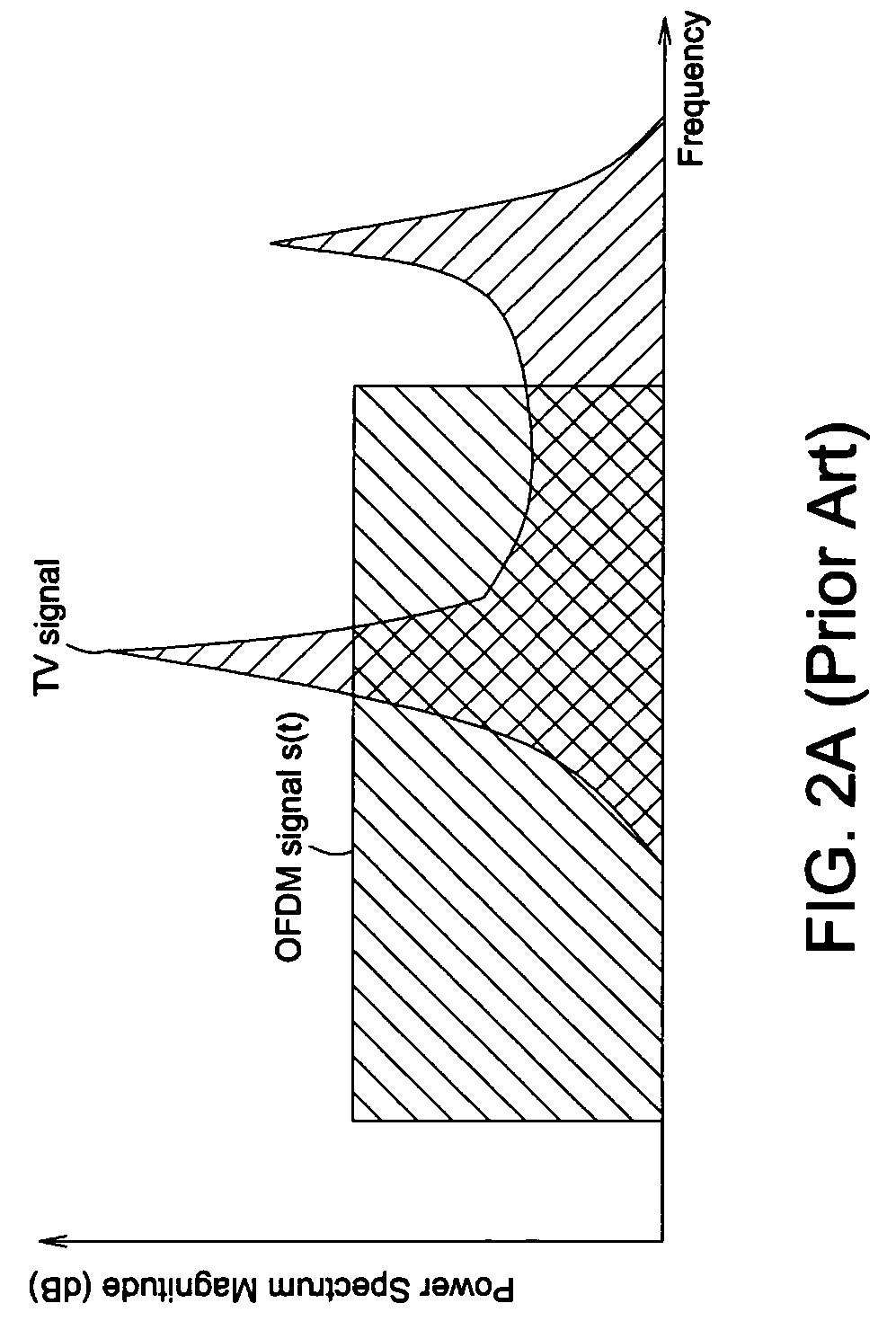
OFDM receiver
InactiveUS20080084940A1Exclude influenceSecret communicationChannel estimationCarrier signalCo-channel interference
An OFDM receiver includes a CCI detector and a frequency-domain notch filter. The CCI detector detects whether or not the co-channel interference exists in a sub-carrier and lowers the weight of a distorted sub-carrier to eliminate the influence of the co-channel interference. The frequency-domain notch filter receives a frequency-domain signal and generates a notched frequency-domain signal.
Owner:SILICON INTEGRATED SYSTEMS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com