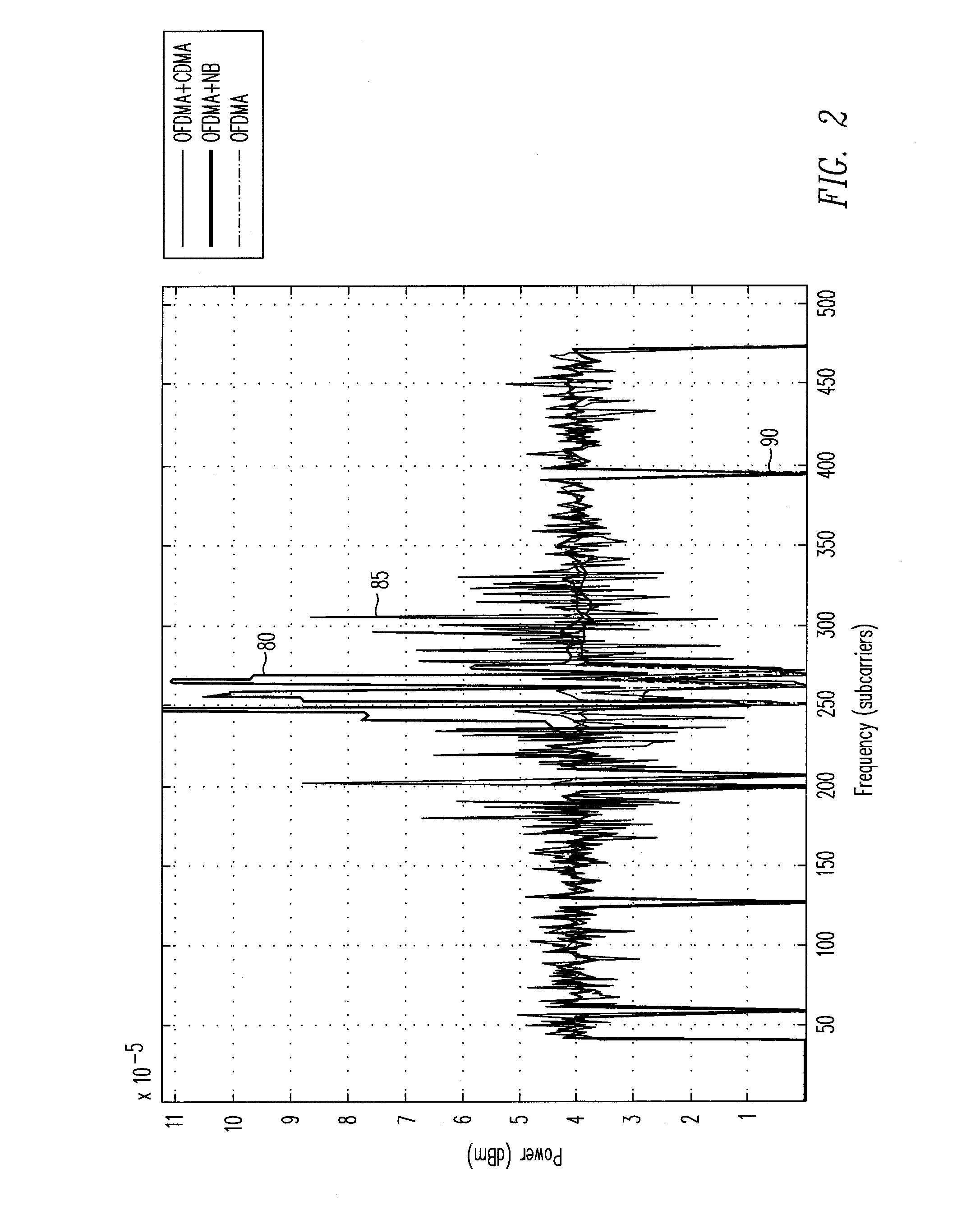
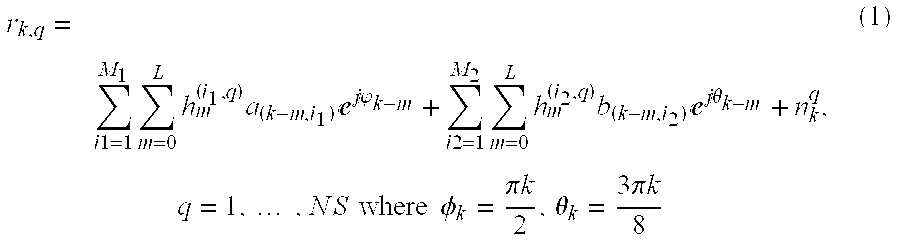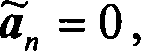Patents
Literature
97 results about "Single antenna interference cancellation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Single antenna interference cancellation (SAIC) is a technology used to boost the capacity of GSM networks without any other changes needed in the network.
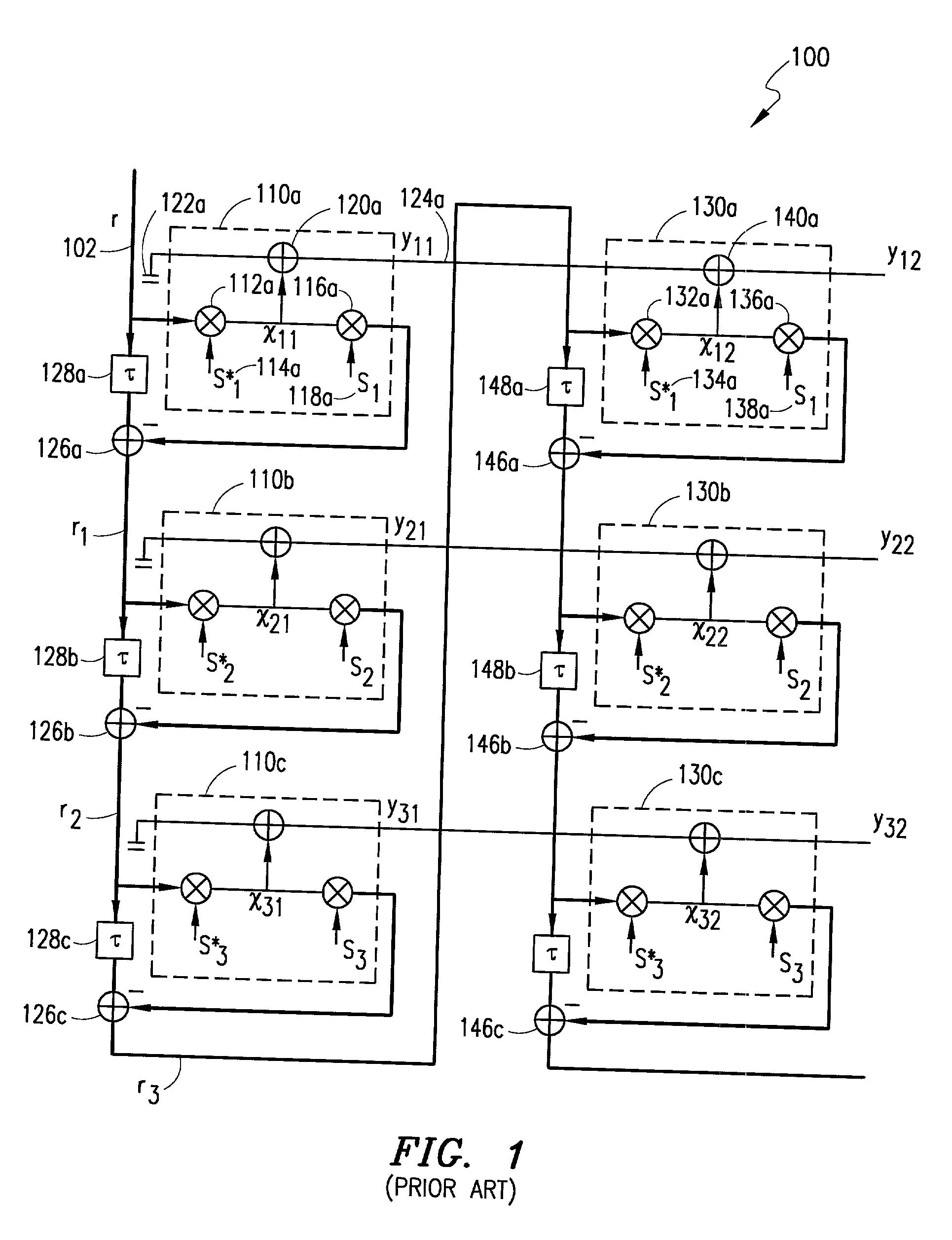
Method and system for antenna interference cancellation
InactiveUS20050226353A1Improve signal qualityHigh bandwidthCorrect operation testingLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemSignal on
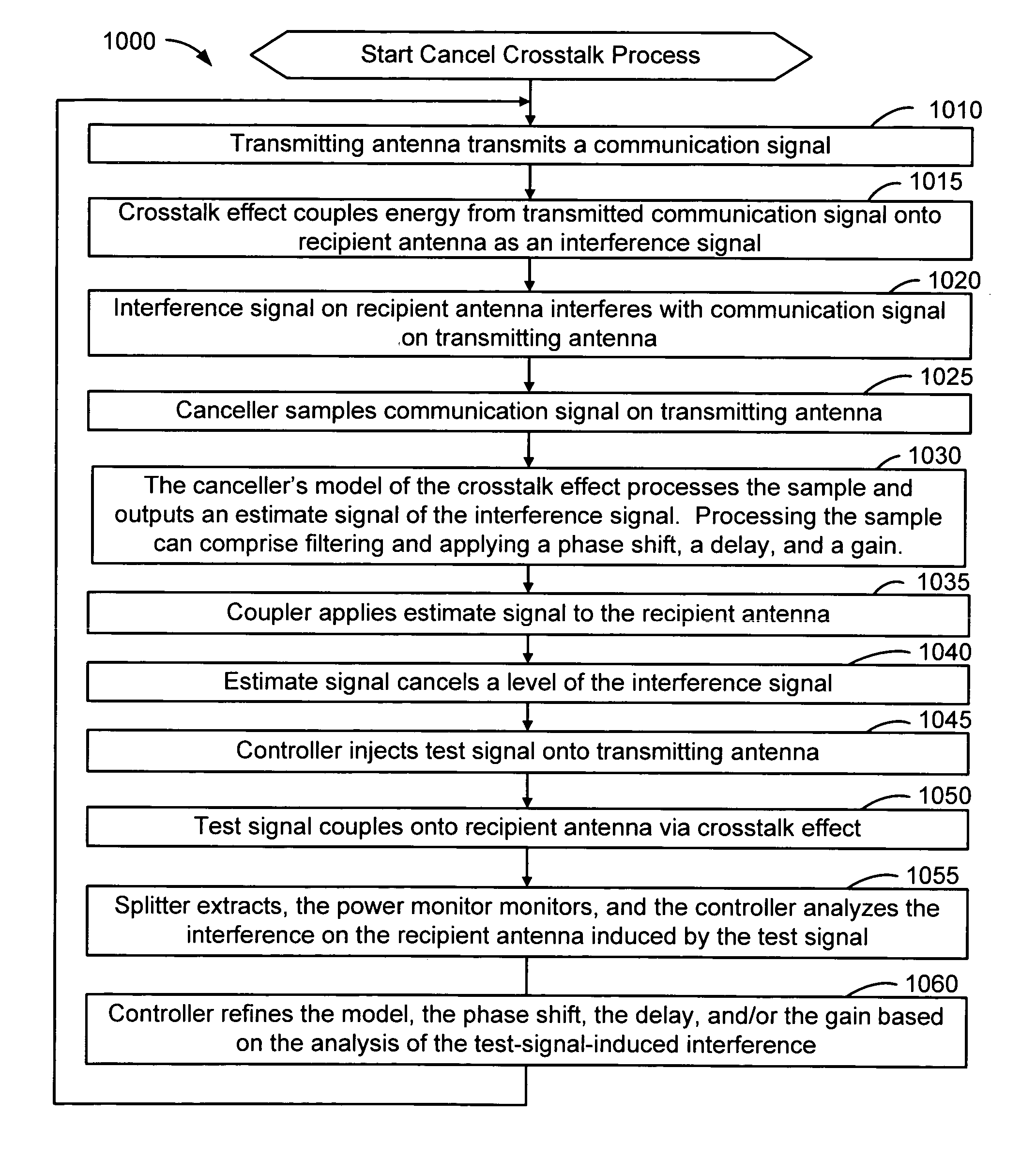
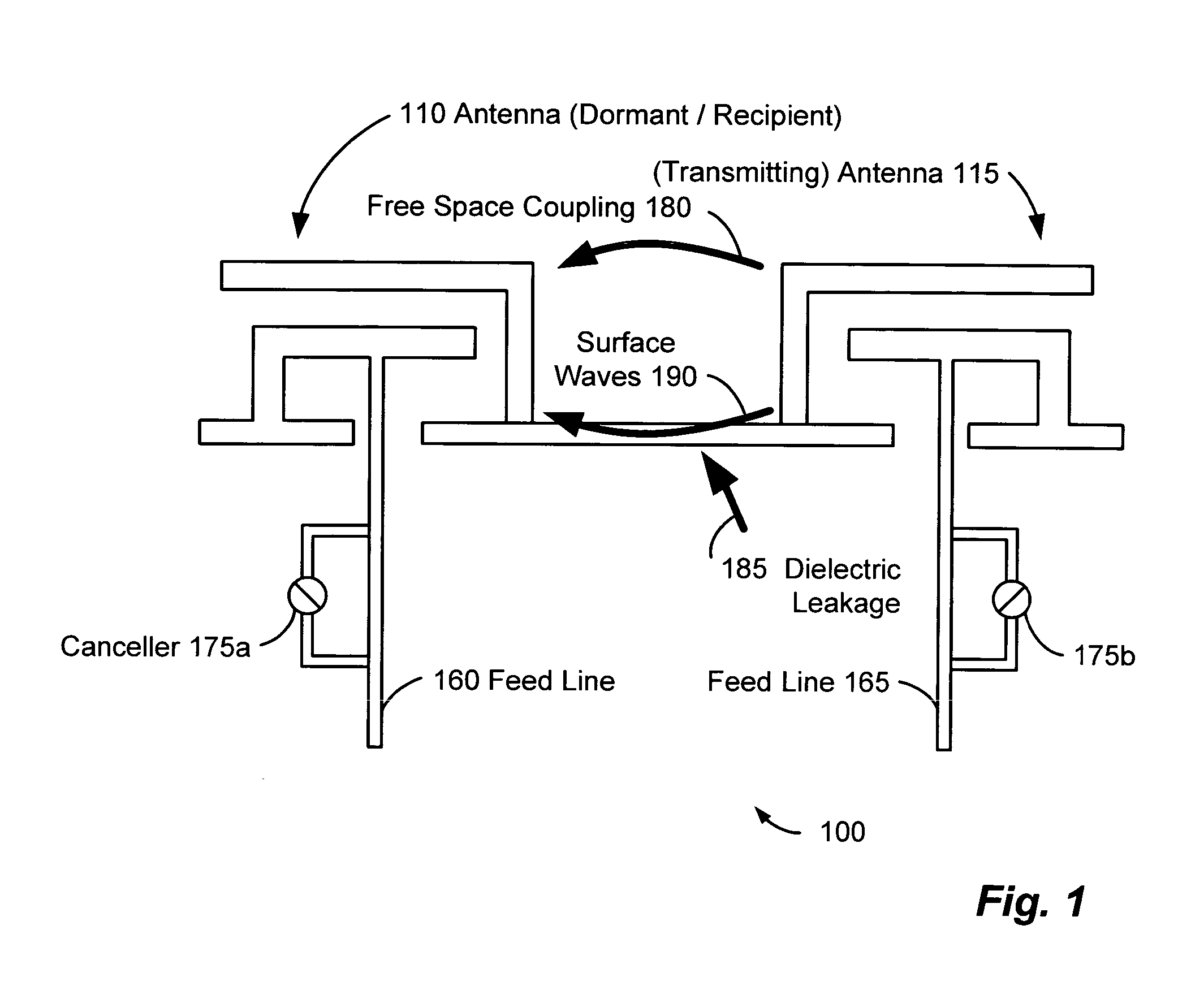
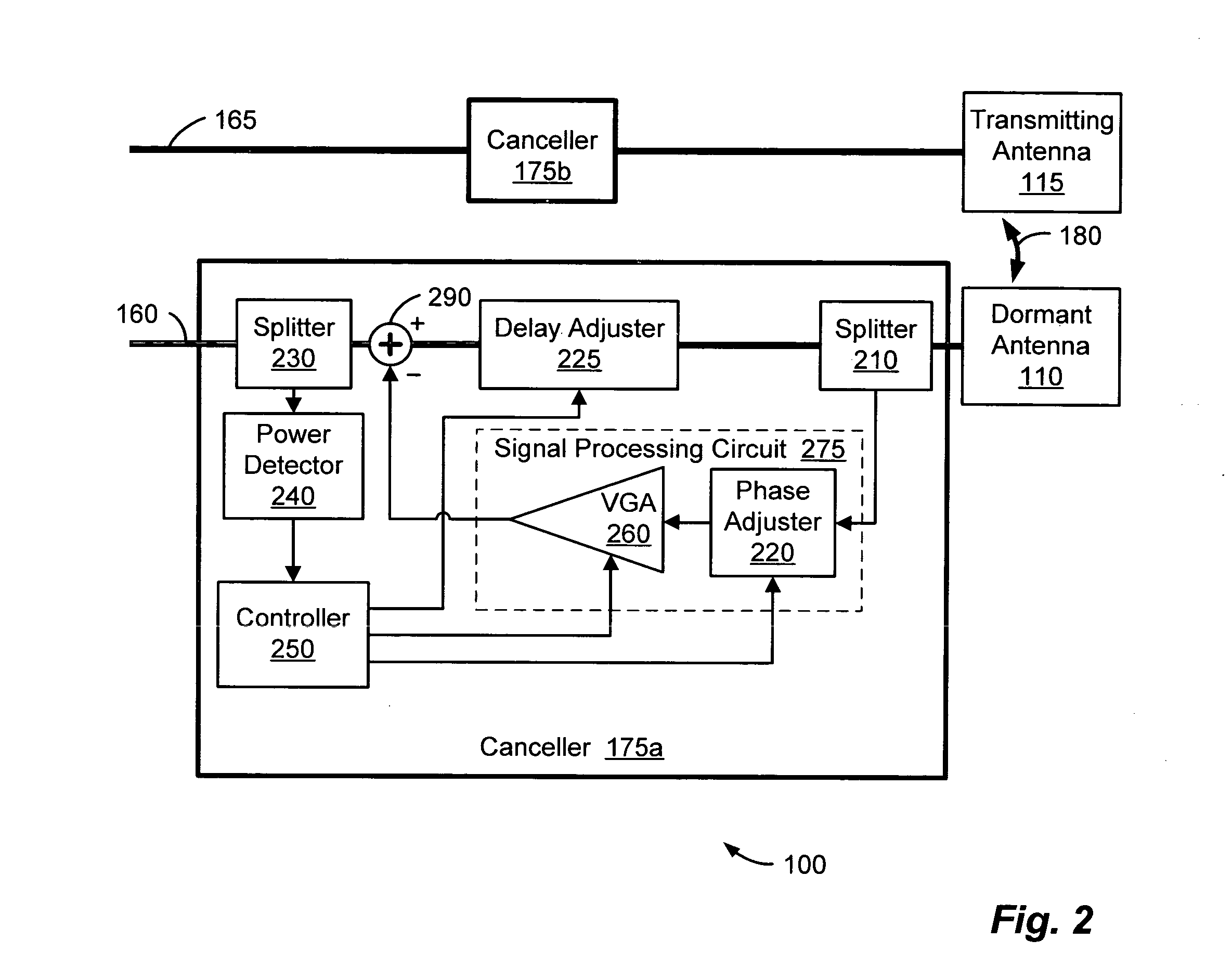
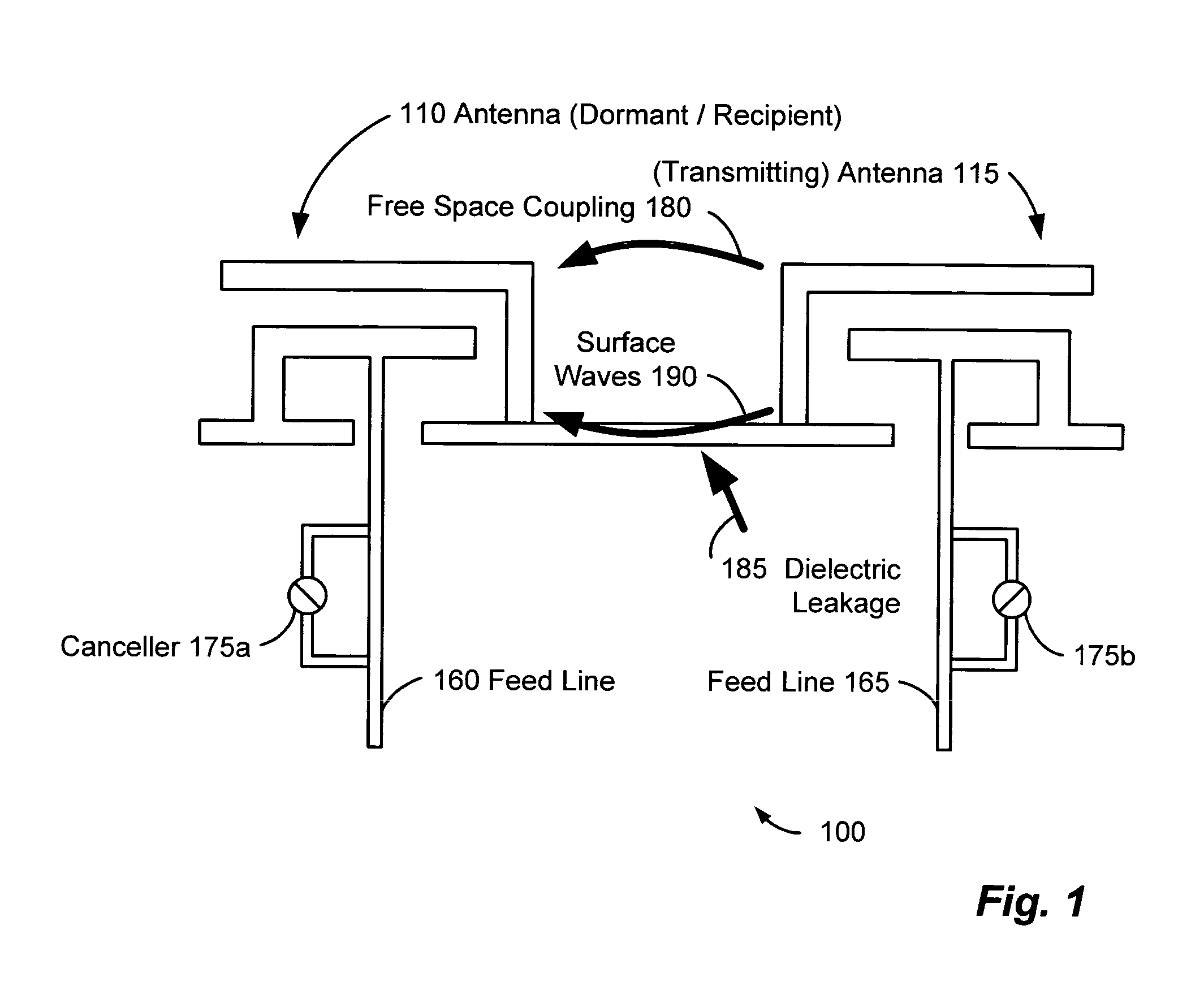
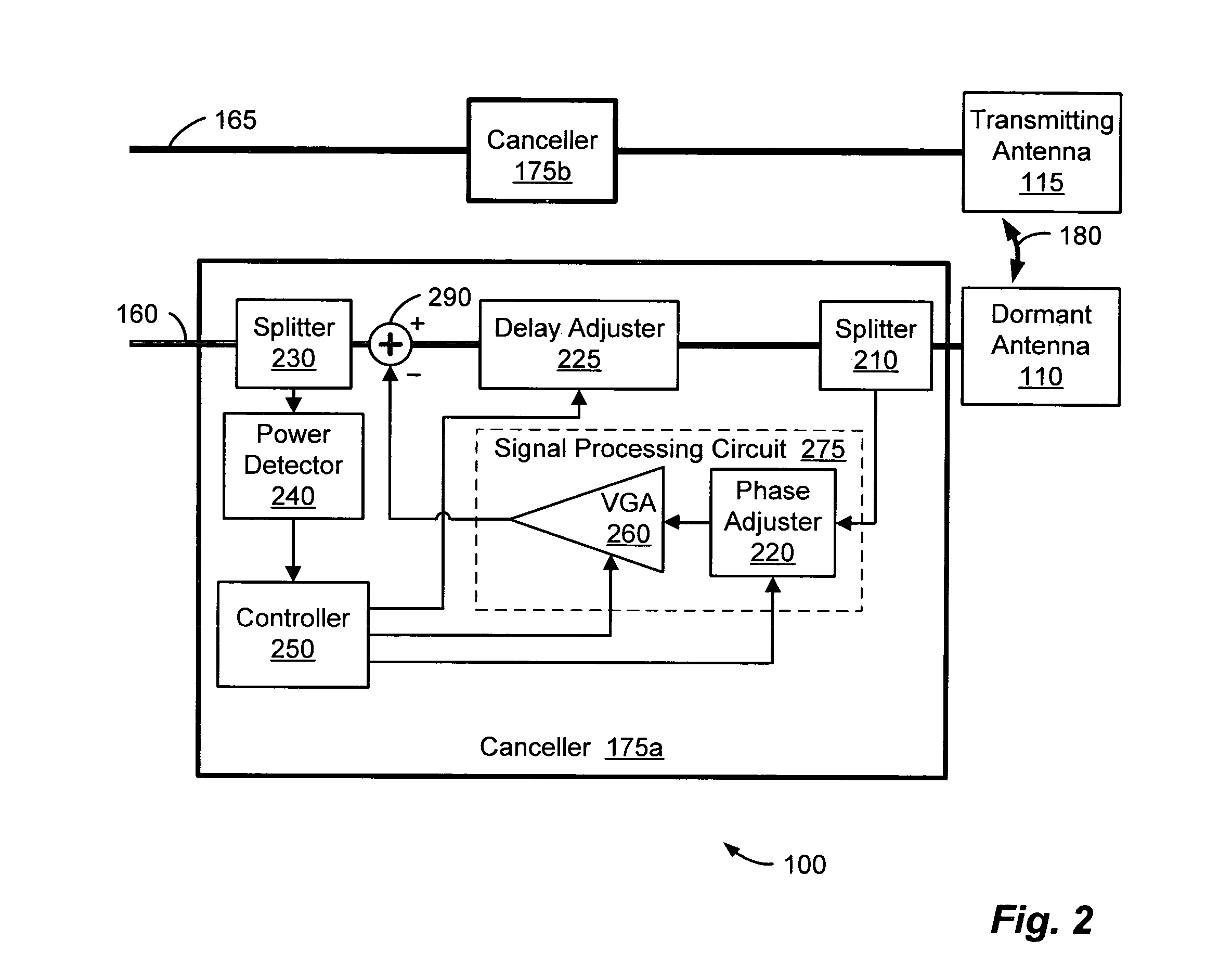
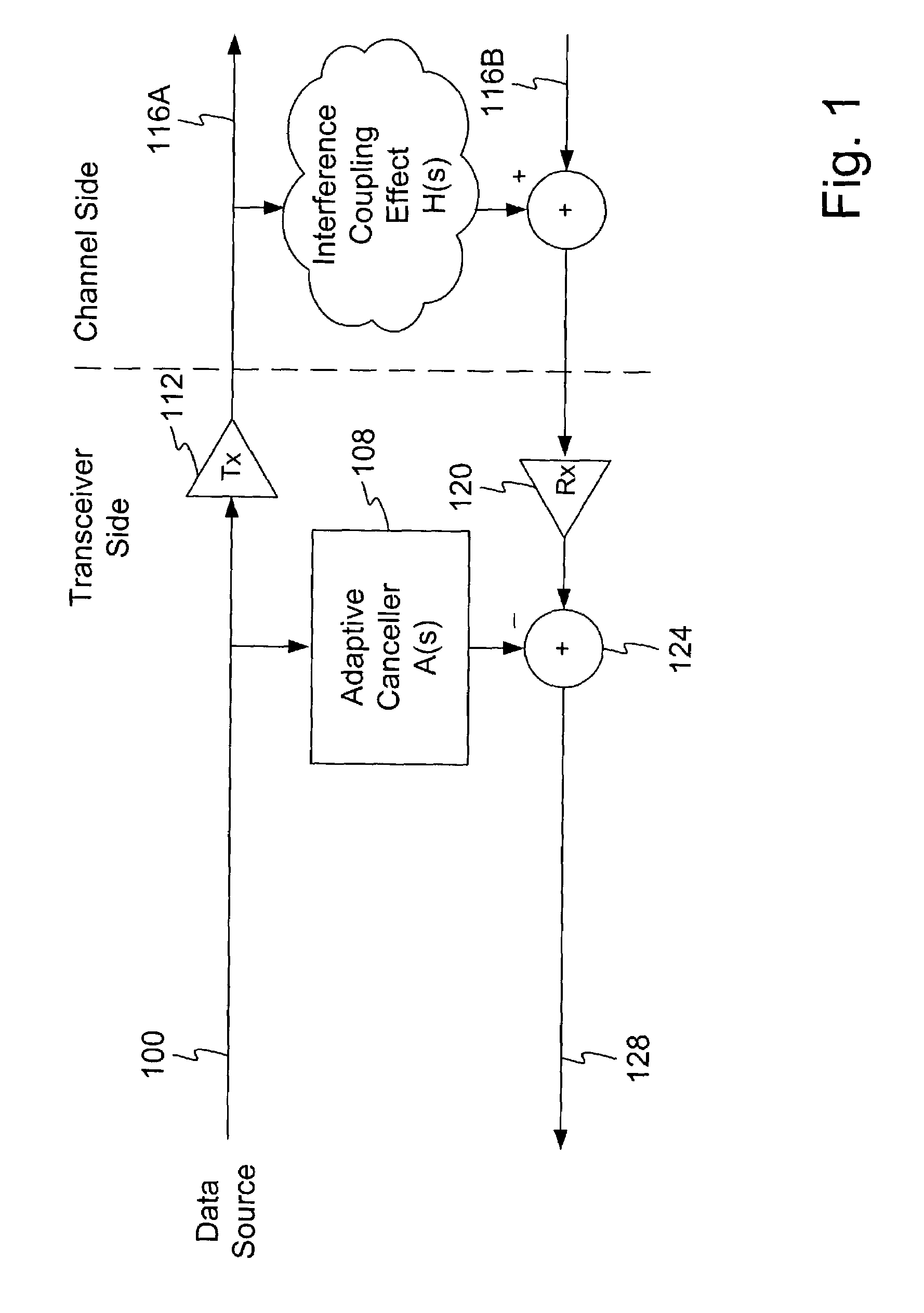
A wireless communication system can comprise two or more antennas that interfere with one another via free space coupling, surface wave crosstalk, dielectric leakage, or other interference effect. The interference effect can produce an interference signal on one of the antennas. A cancellation device can suppress antenna interference by generating an estimate of the interference signal and subtracting the estimate from the interference signal. The cancellation device can generate the estimate based on sampling signals on an antenna that generates the interference or on an antenna that receives the interference. The cancellation device can comprise a model of the crosstalk effect. Transmitting test signals on the communication system can define or refine the model.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Blind interference mitigation in a digital receiver
InactiveUS20070127608A1Improve acceleration performanceReduce computational complexityError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionEngineeringCo-channel interference
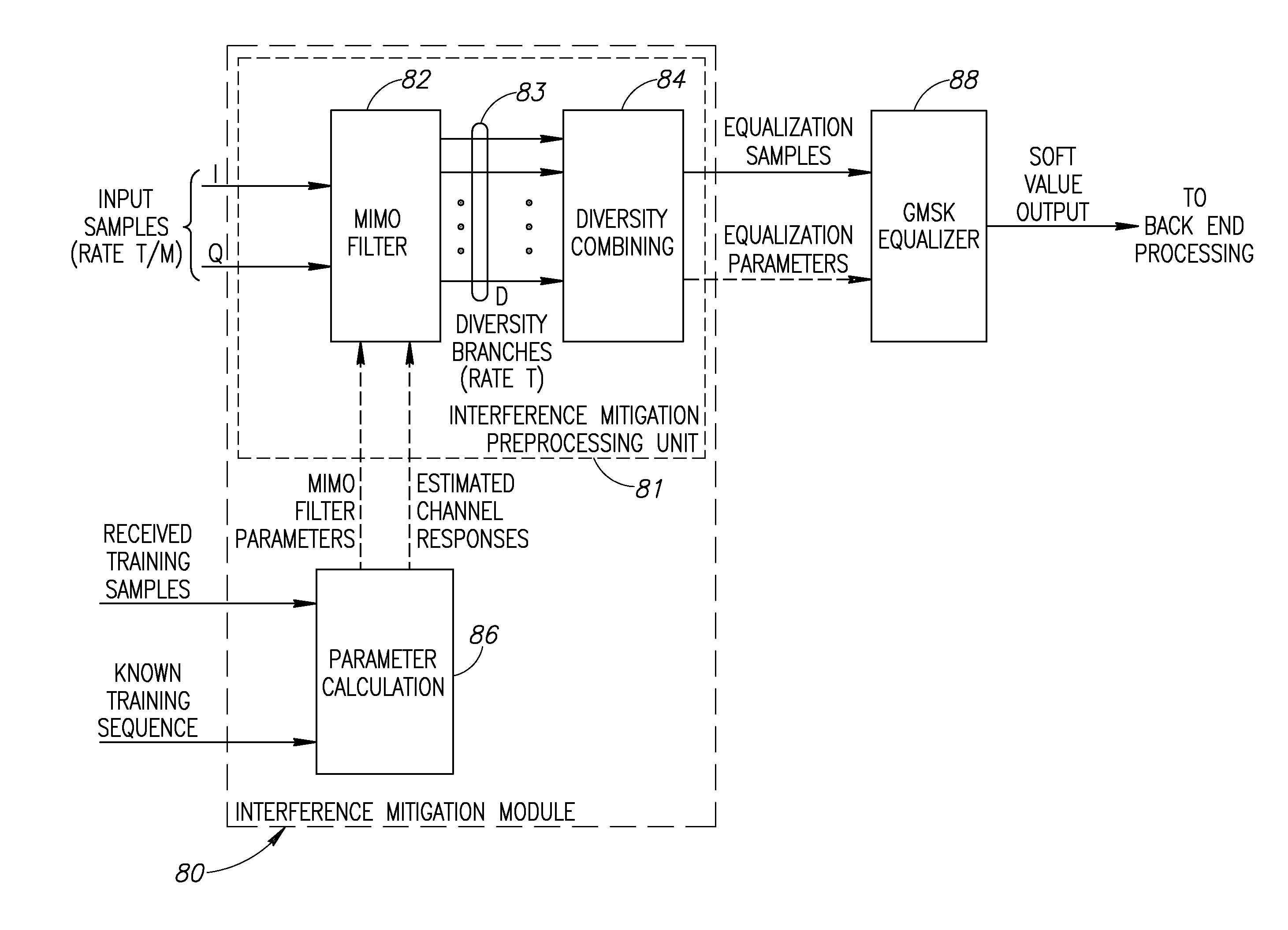
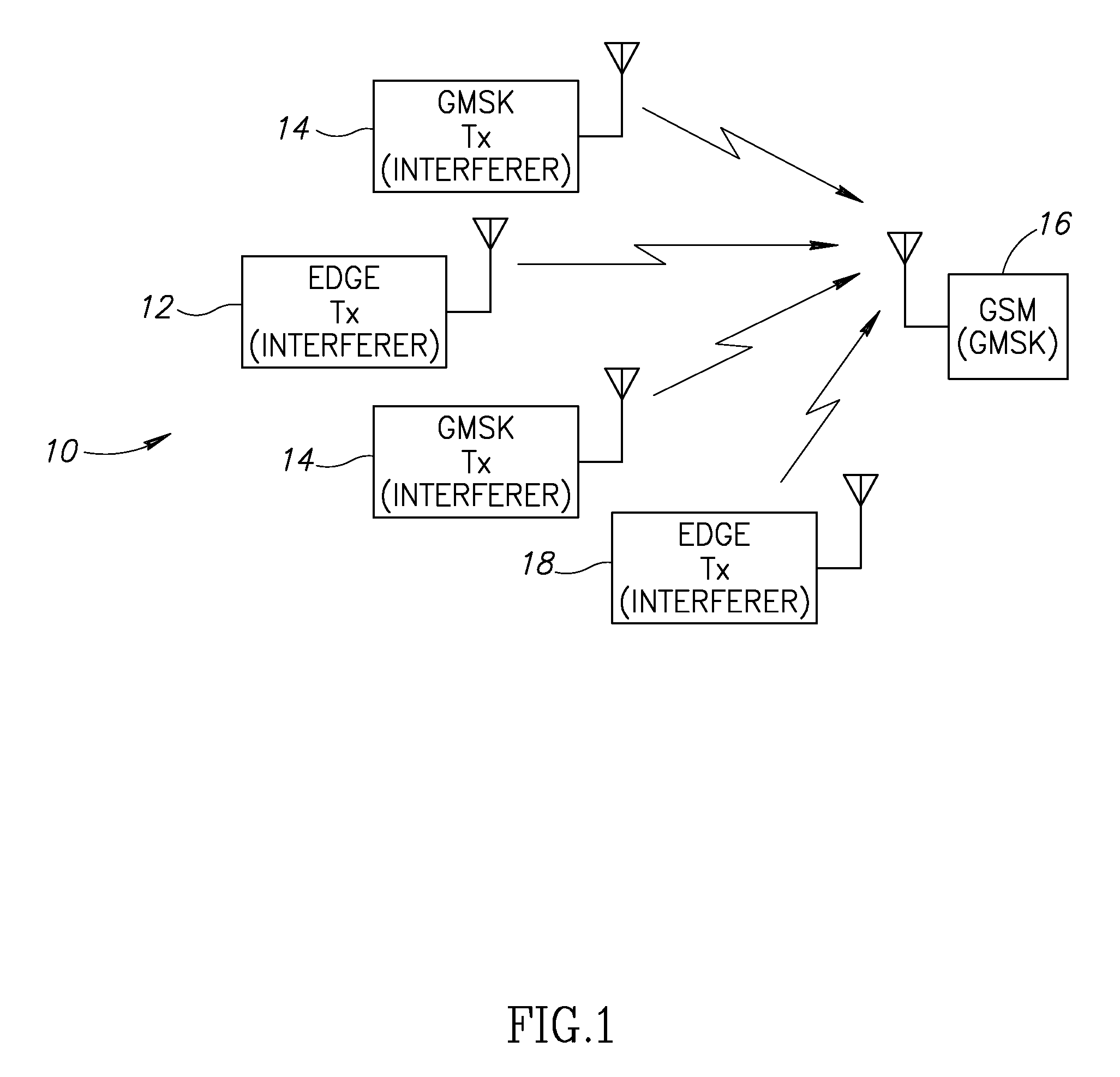
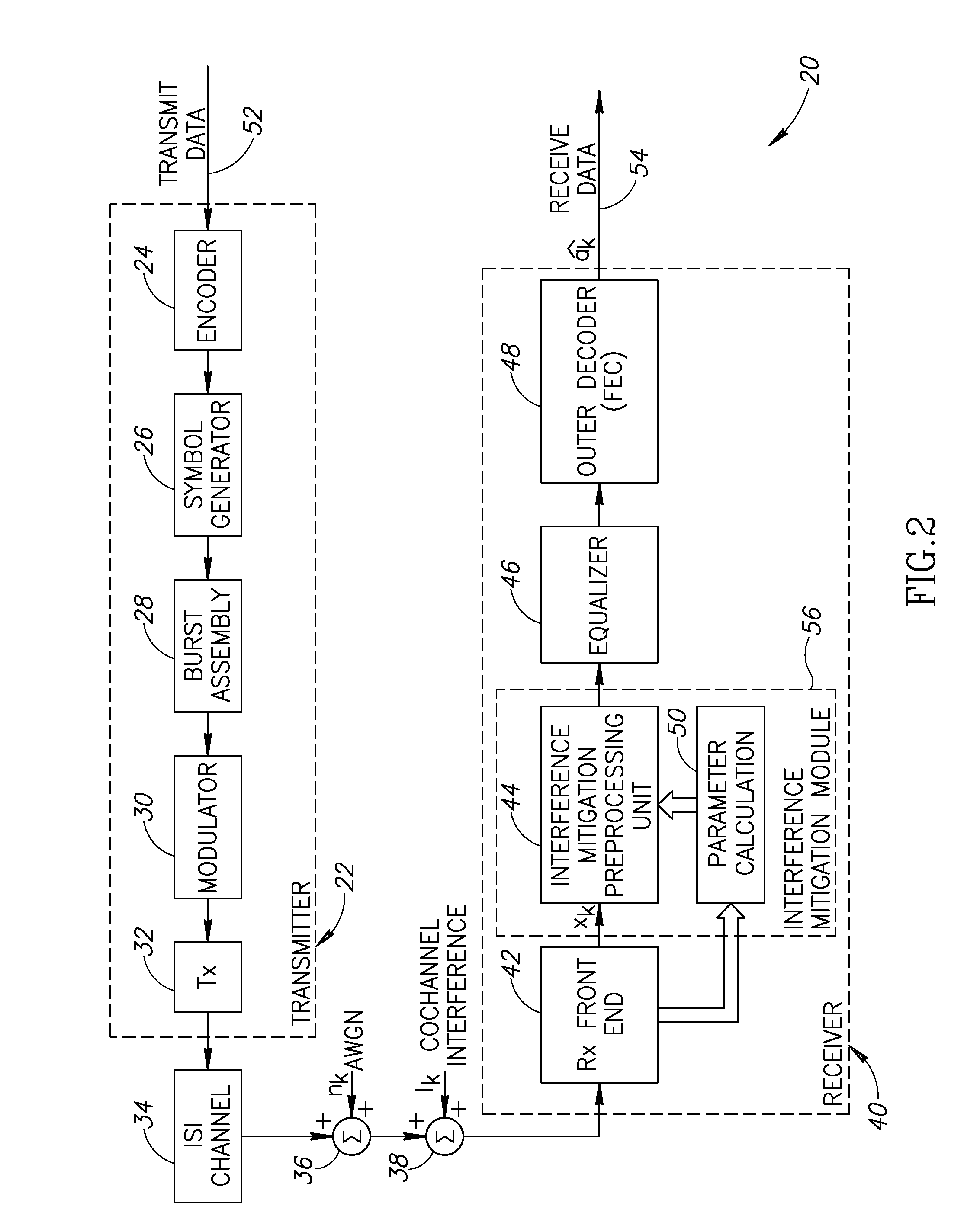
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying (GMSK) single antenna interference cancellation (SAIC) for use in a digital receiver. The invention comprises an interference mitigation module that treats the problem of GMSK SAIC in a blind manner. The interference mitigation mechanism is operative to compensate for the co-channel interference added in the communications channel which is subject to multipath propagation and fading, receiver filter and any pre-channel estimation filtering. The interference mitigation module takes advantage of the spatial diversity making up multiple branches of the received signal. The branches comprise the in-phase and quadrature elements of the received signal, the sampling phases if over sampling is applied (i.e. T / m sampling) and / or multiple antennas. The invention utilizes the spatial diversity of these multiple representations of the received signal and combines (i.e. collapses) the information in the plurality of branches into a single branch that is input to the equalizer.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
System and method for digital interference cancellation
ActiveUS8055235B1Increase effective dynamic rangeEfficient implementationTransmissionRadio frequency signalAnalog signal
A system and method for receiving a signal, comprising an input adapted to receive a radio frequency signal having a strong interferer; a signal generator, adapted to produce a representation of the interferer as an analog signal generated based on an oversampled digital representation thereof; and a component adapted to cancel the strong interferer from radio frequency signal based on the generated analog signal to produce a modified radio frequency signal substantially absent the interferer. The system typically has a nonlinear component that either saturates or produces distortion from the strong interferer, which is thereby reduced. The system preferably employs high speed circuits which digitize and process radio frequency signals without analog mixers.
Owner:HYPRES
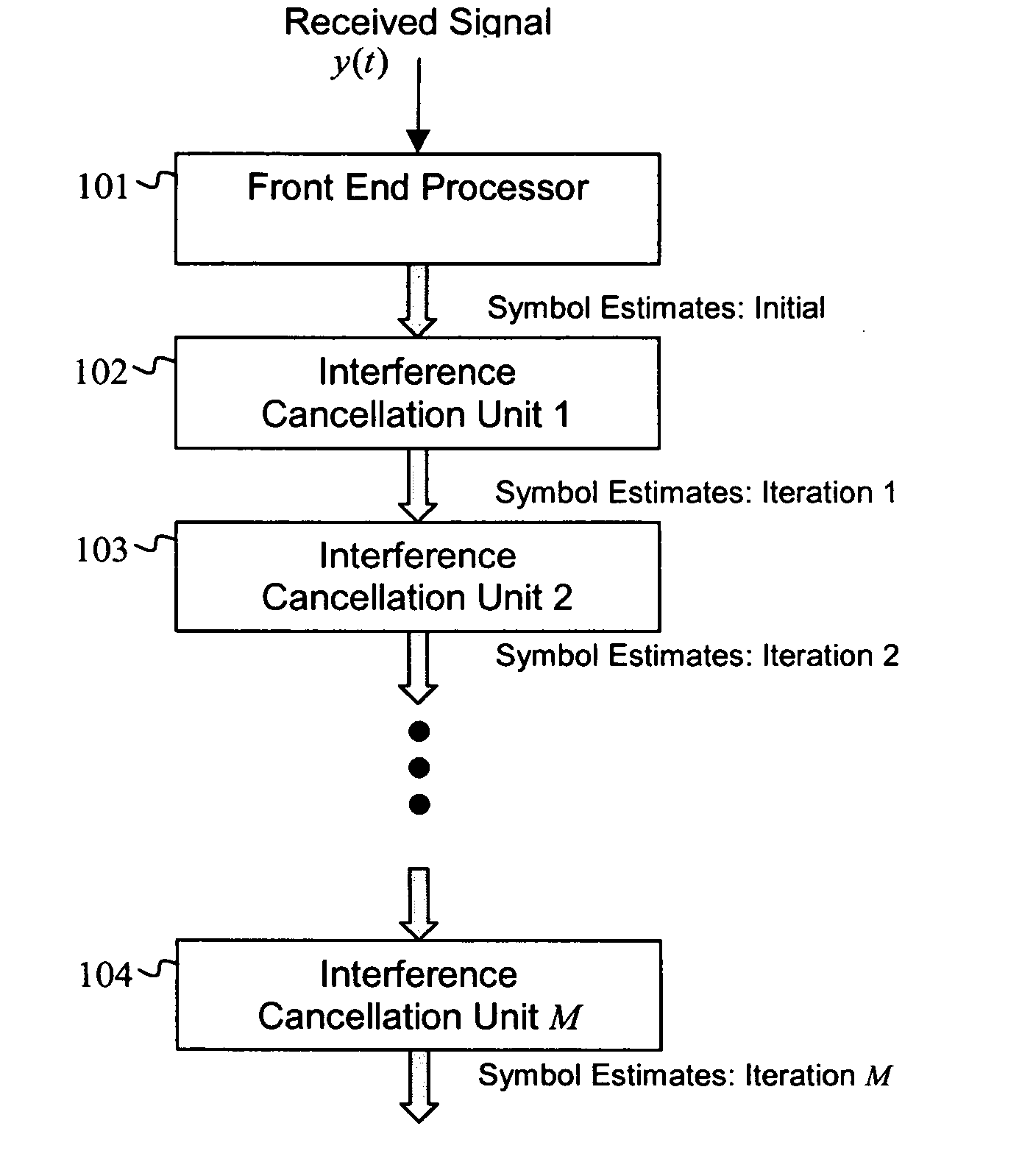
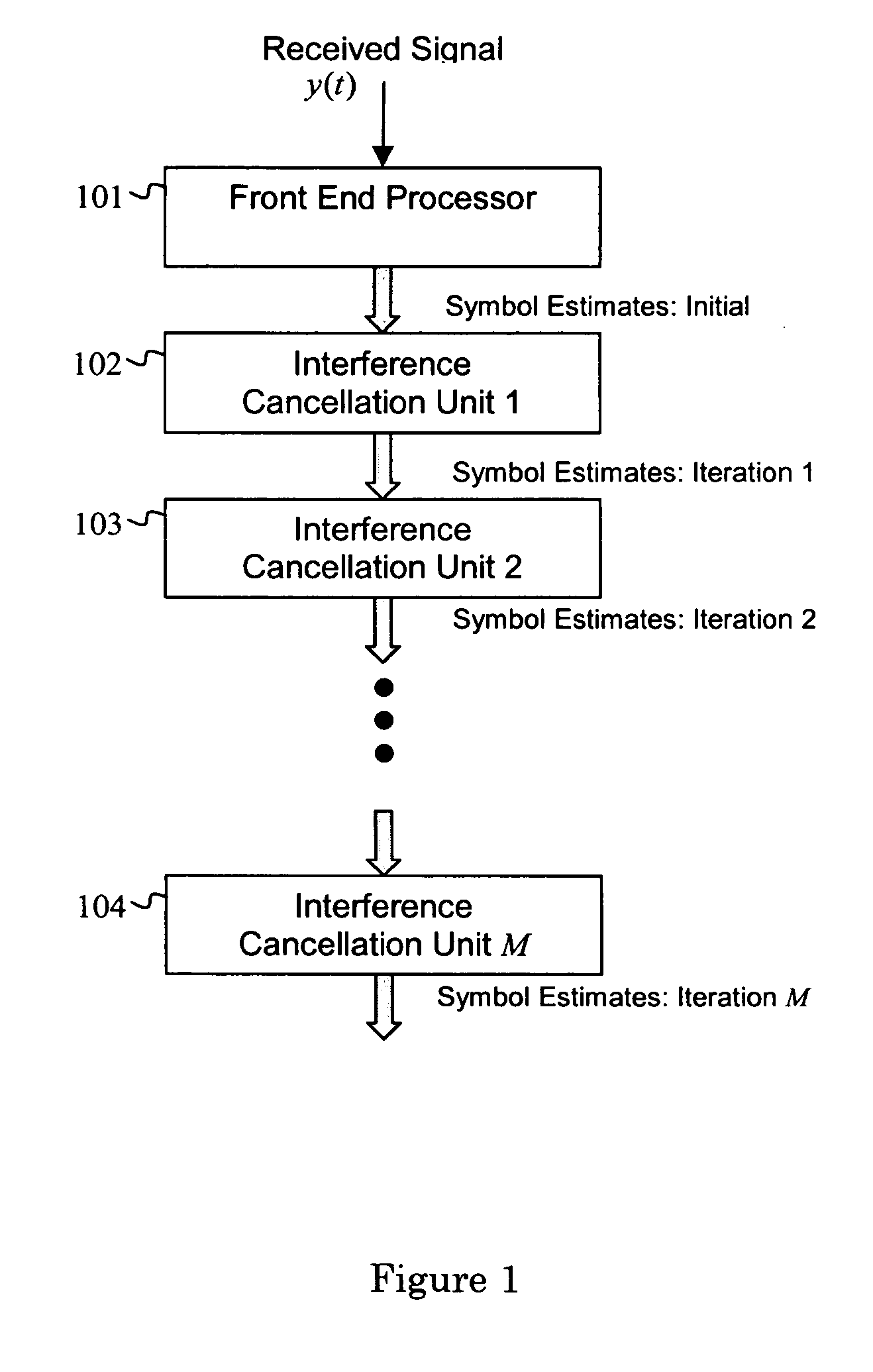
Iterative interference cancellation using mixed feedback weights and stabilizing step sizes
ActiveUS20070110131A1Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionSingle antenna interference cancellationEngineering
A receiver is configured for canceling intra-cell and inter-cell interference in coded, multiple-access, spread-spectrum transmissions that propagate through frequency-selective communication channels. The receiver employs iterative symbol-estimate weighting, subtractive cancellation with a stabilizing step-size, and mixed-decision symbol estimates. Receiver embodiments may be implemented explicitly in software or programmed hardware, or implicitly in standard Rake-based hardware either within the Rake (i.e., at the finger level) or outside the Rake (i.e., at the user or subchannel symbol level).
Owner:III HLDG 1
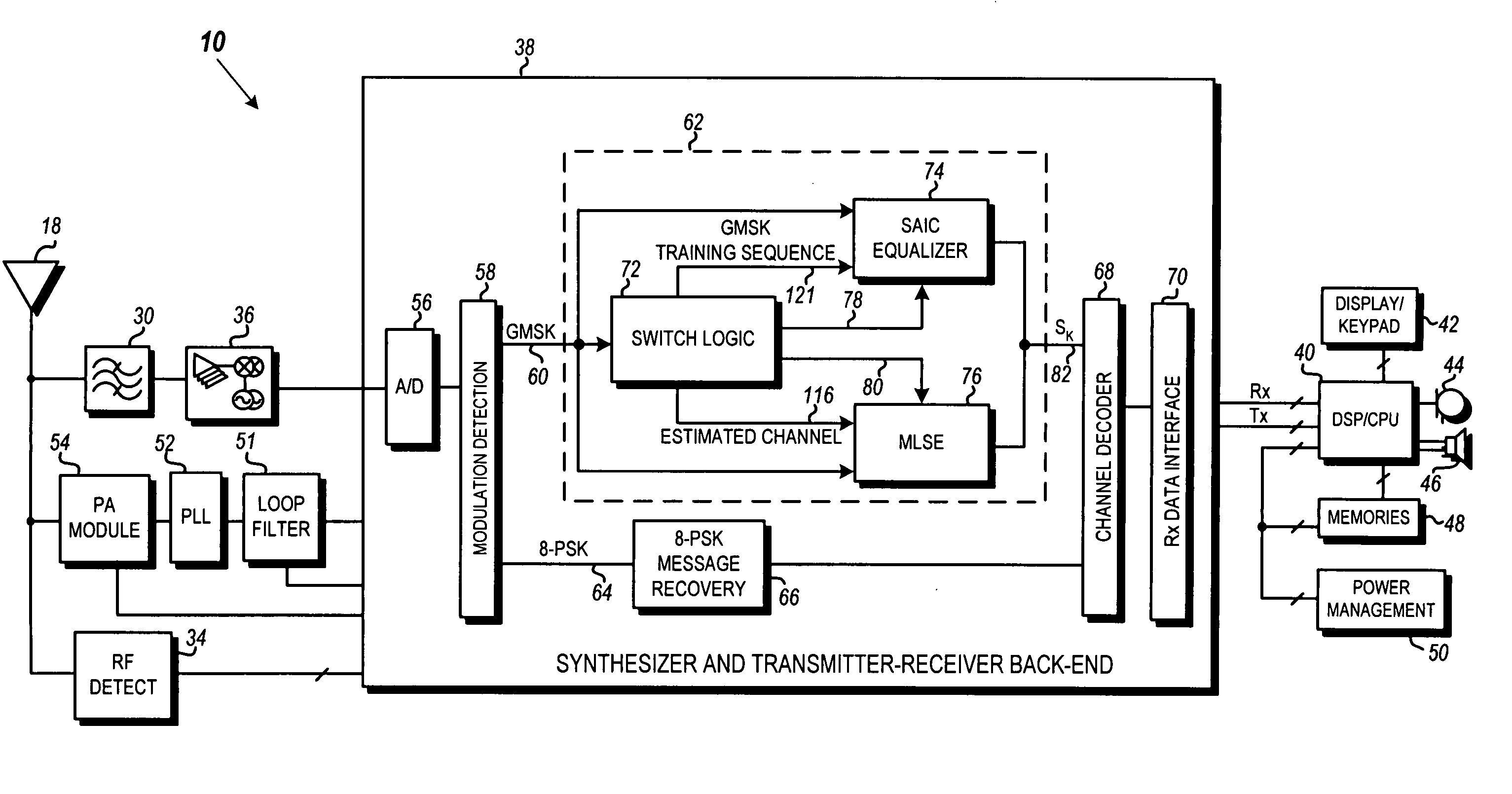
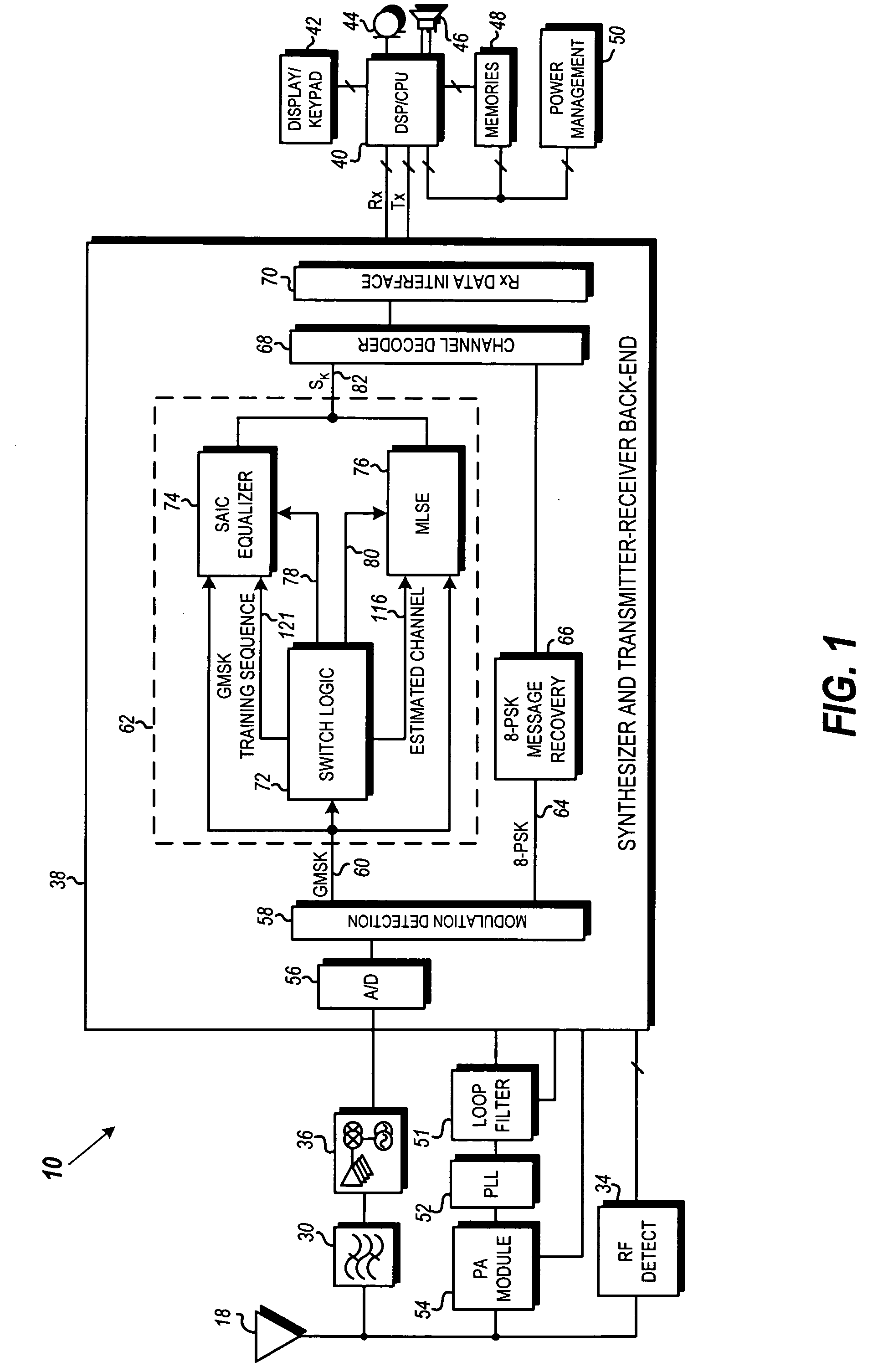
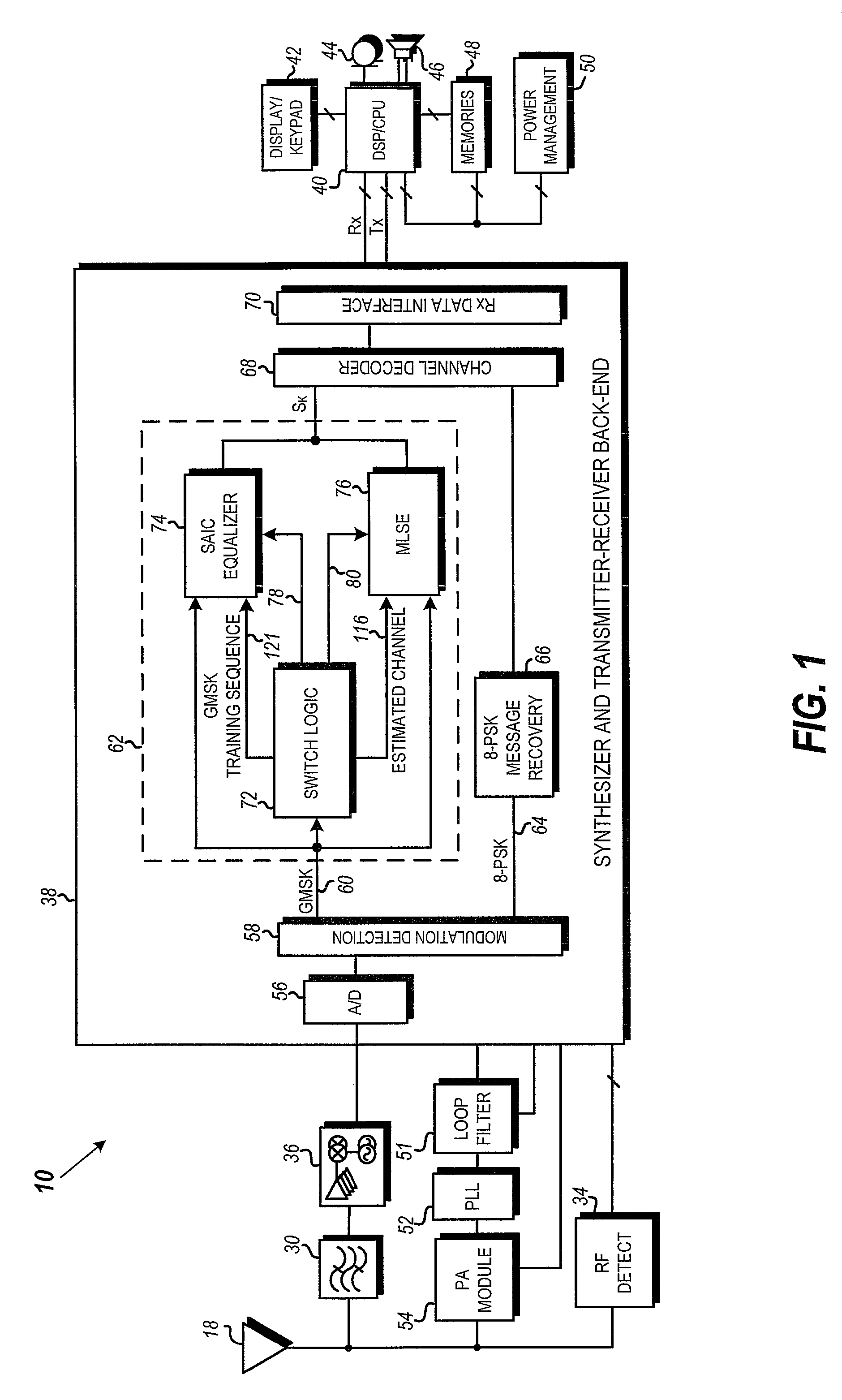
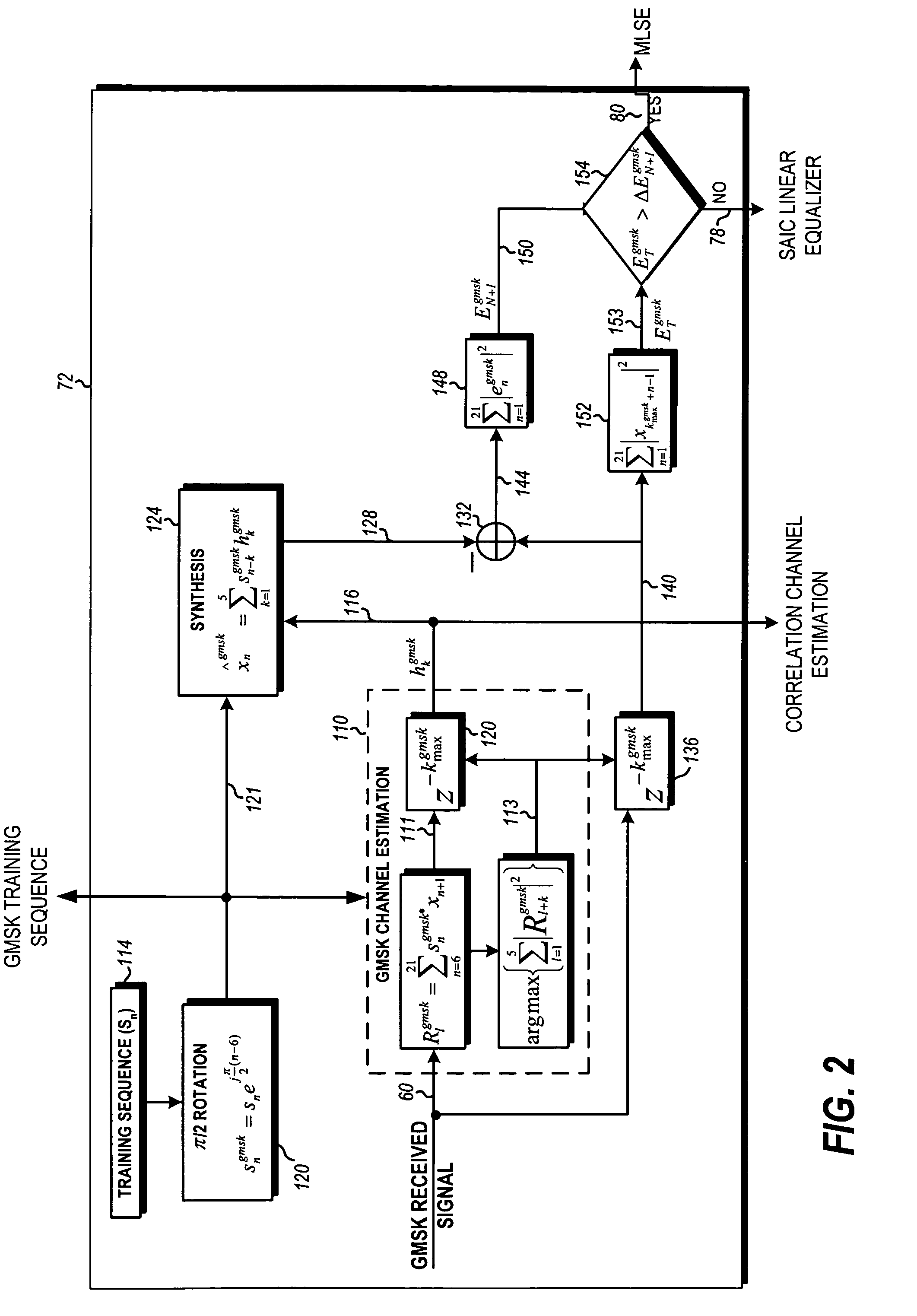
Dynamic switching between MLSE and linear equalizer for single antenna interference cancellation in a GSM communication system
ActiveUS20070058709A1Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsCommunications systemMobile station
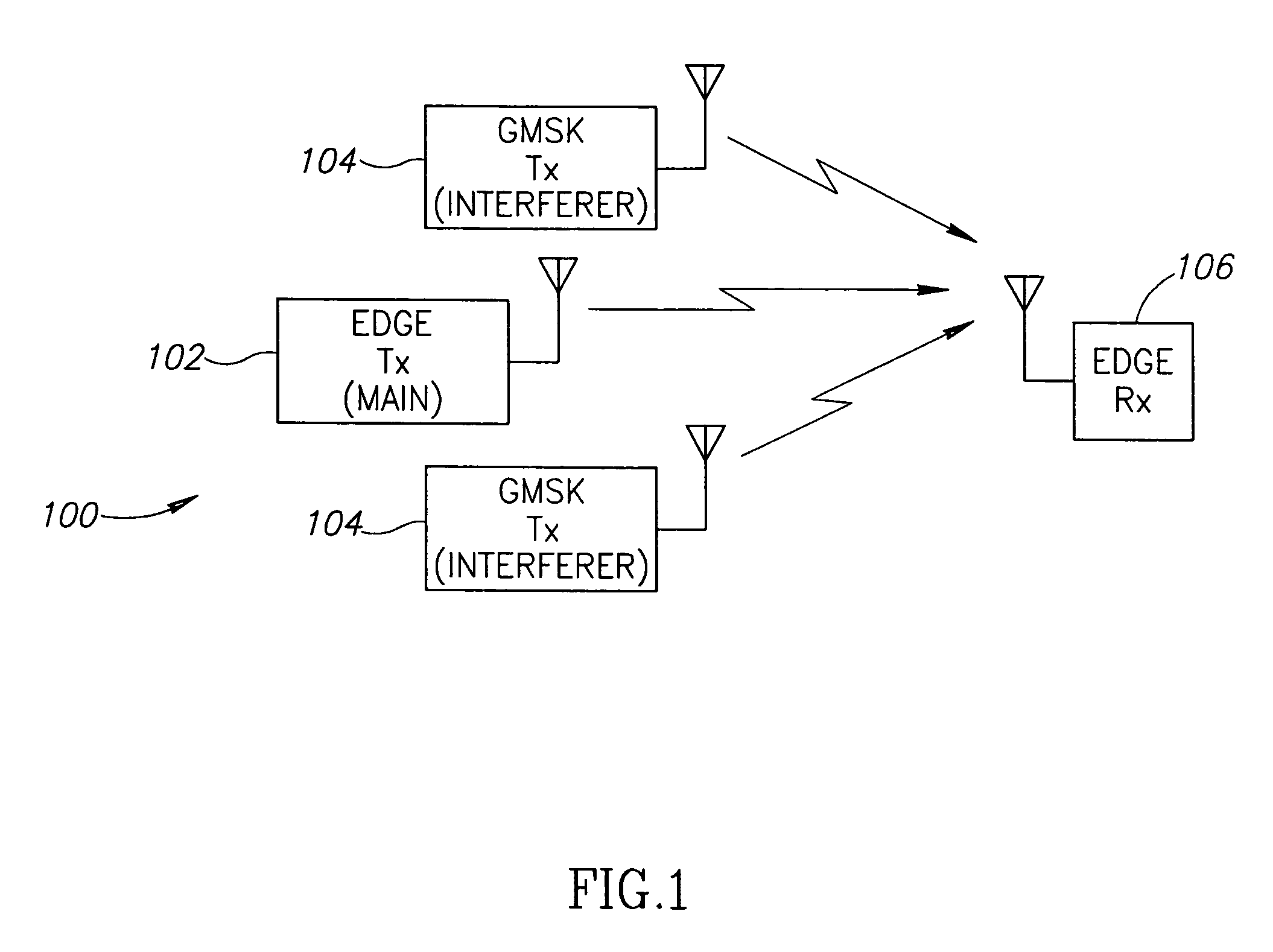
In a GSM / EDGE Single Antenna Interference Cancellation (SAIC) operation environment, a mobile station is required to operate in a wide range of interference levels. An SAIC linear equalizer that takes advantage of the GMSK signal structure performs better than a conventional Maximum Likelihood Sequence Estimation (MLSE) equalizer in high interference levels, while it performs worse in low interference levels. A dynamic selection between the SAIC linear equalizer and the MLSE equalizer for each received burst is achieved to provide the optimal performance across the entire required operation environments. The dynamic selection is based on the estimated noise plus interference energy relative to the total received signal energy. The soft information calculated by the two categories of equalizers is properly scaled to generate soft information with balanced magnitude.
Owner:APPLE INC
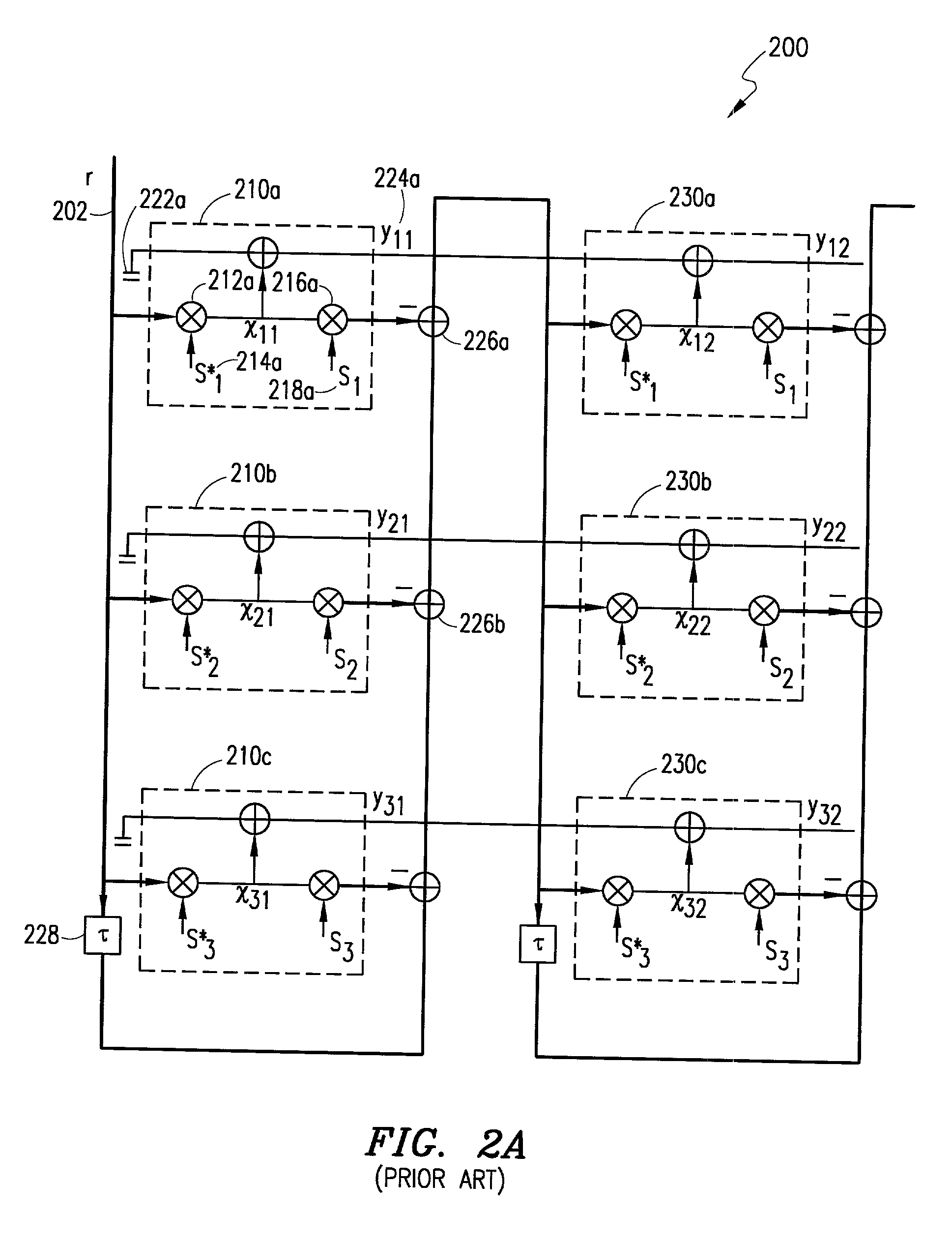
Method and system for antenna interference cancellation
InactiveUS7123676B2Enhance bandwidth and information carrying capabilityImprove signal qualityCorrect operation testingSynchronisation signal speed/phase controlCommunications systemCoupling
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Method for iterative interference cancellation for co-channel multi-carrier and narrowband systems
ActiveUS8155595B2Improve performanceInherent signal separationError preventionTransmission path divisionChannel impulse responseCarrier signal
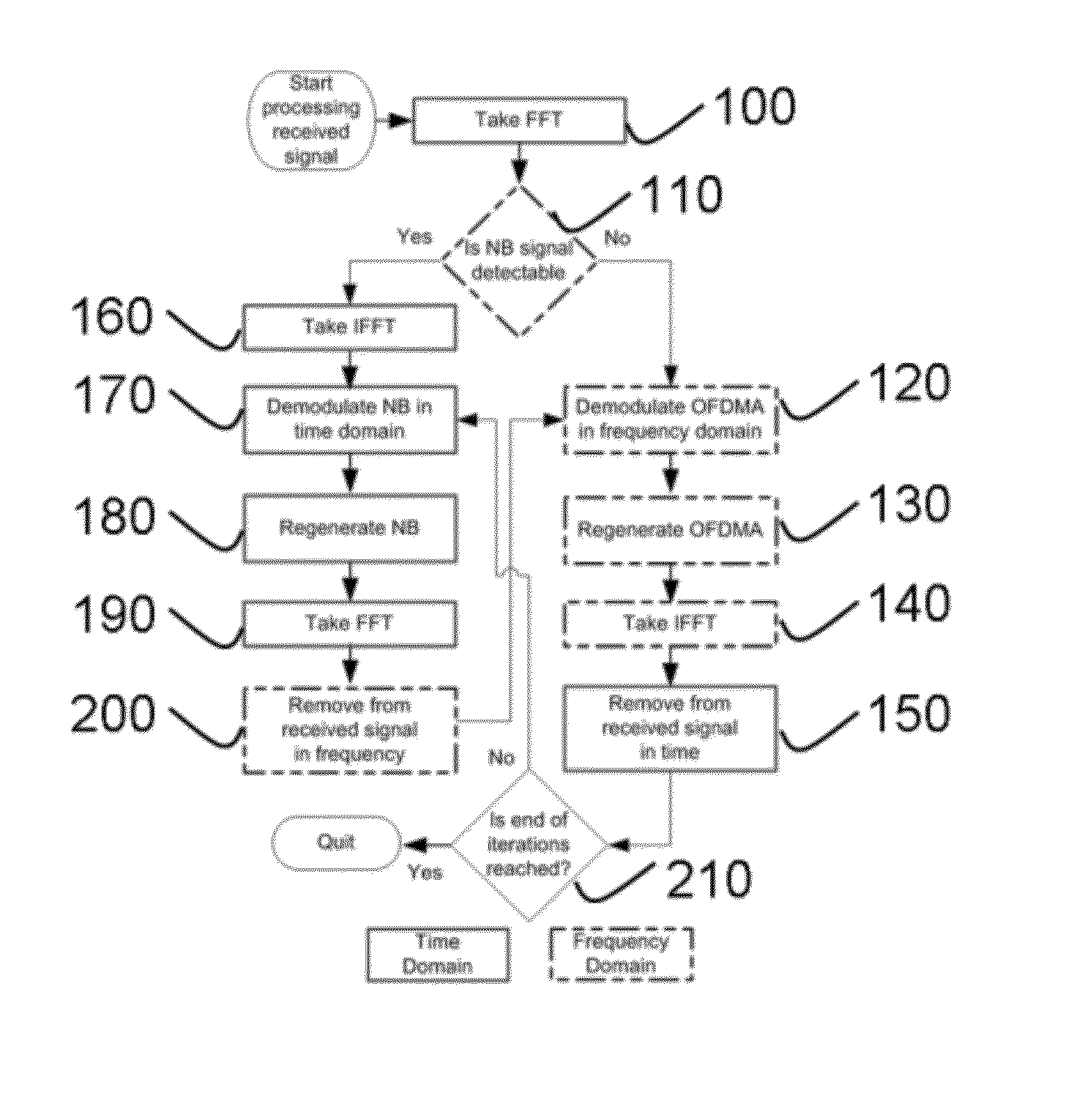
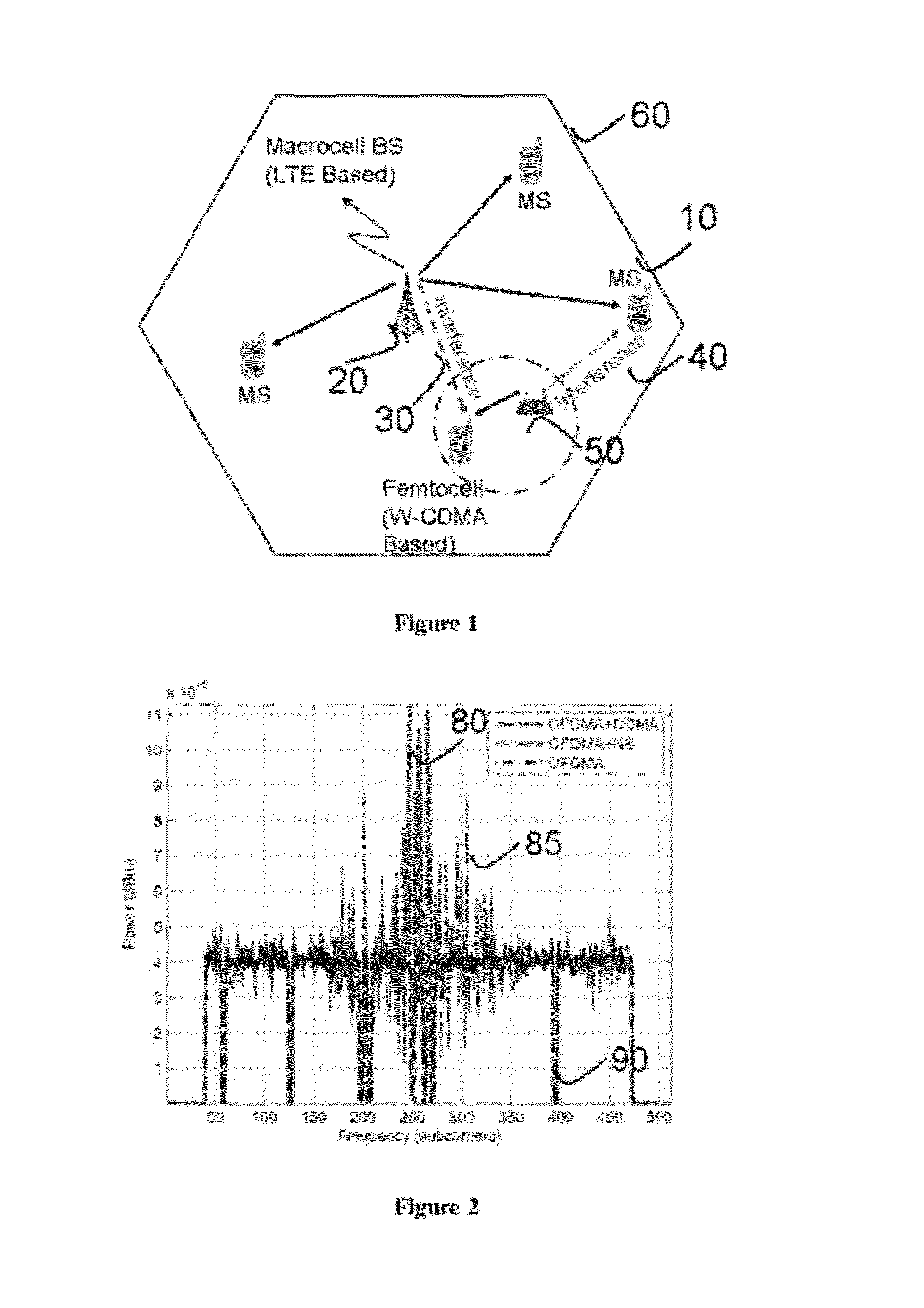
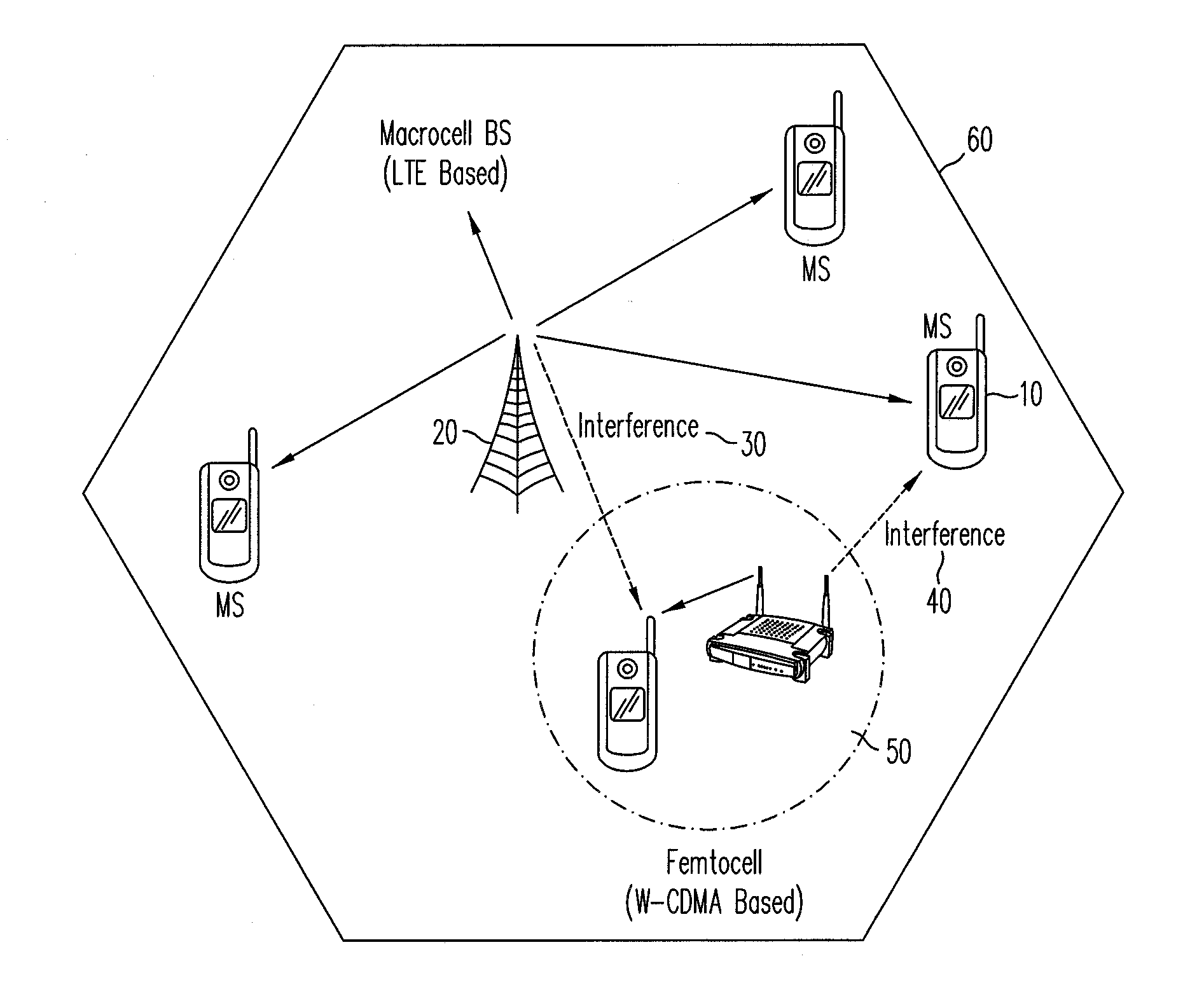
In a co-channel deployment of narrowband and multi-carrier technologies (e.g., a femtocell and a macrocell), a method provides cancelling of interference which treats the co-channel signals as desired signals and enhances each of them iteratively. At each iteration, each signal is demodulated and regenerated based on symbol decisions already made and a predetermined channel impulse response. To estimate the other (interfering) co-channel signal, the regenerated signal is subtracted from the aggregate signal. Simulations have shown that a method of the present invention can provide fundamental improvement in the performances of both interfering systems in as few as two iterations. The fundamental performance gain that can be obtained outweigh the required computational burden.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
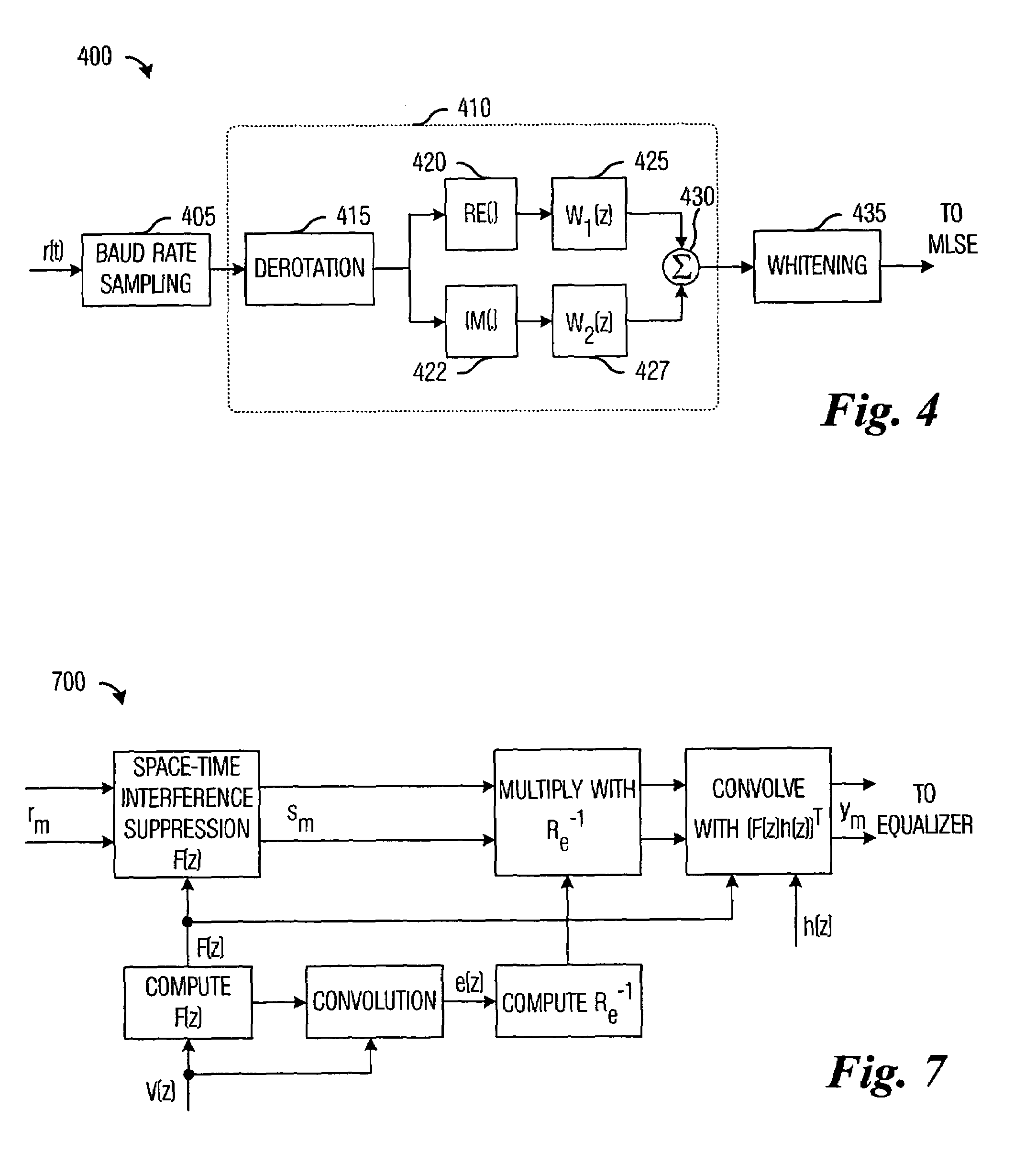
Frequency error estimation and correction in a SAIC linear equalizer
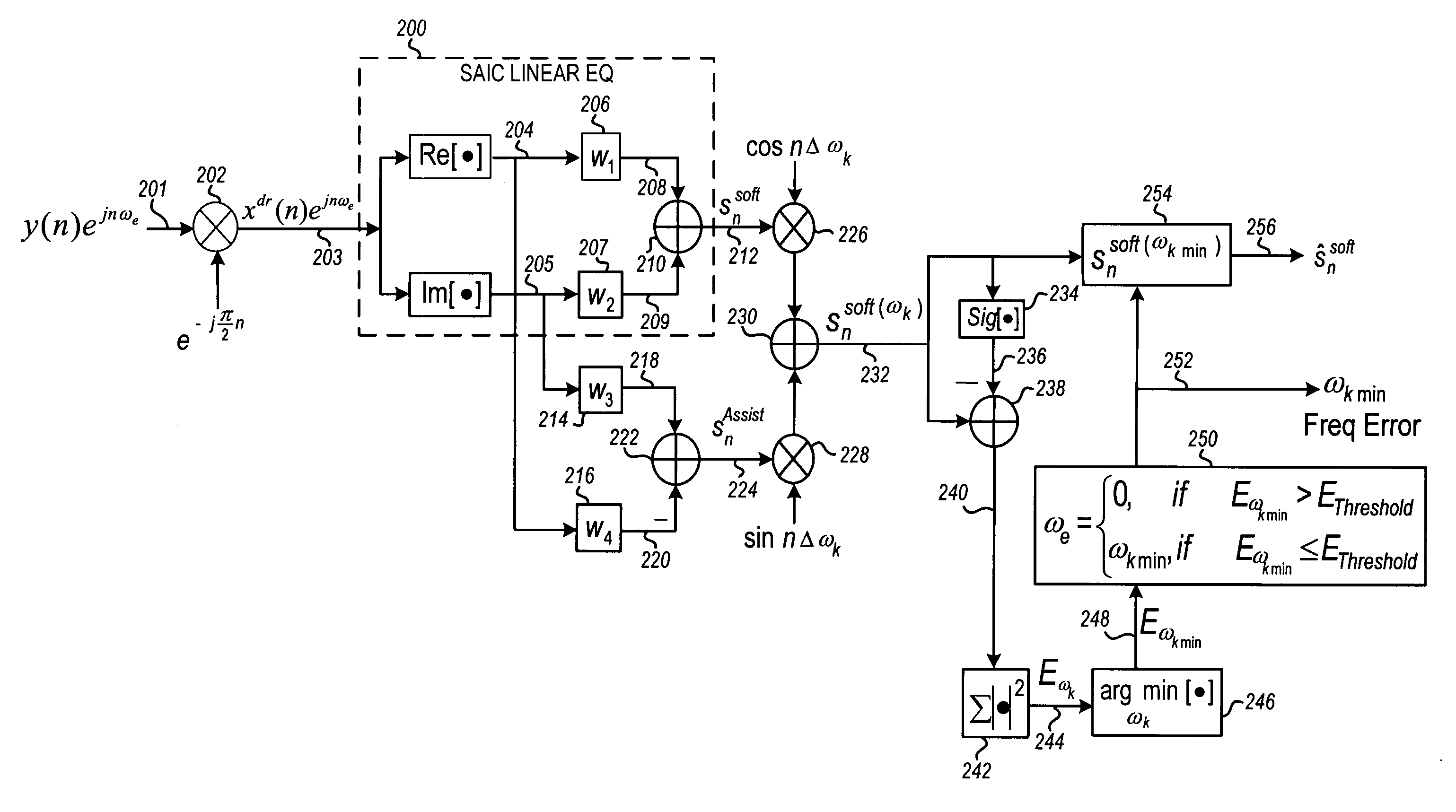
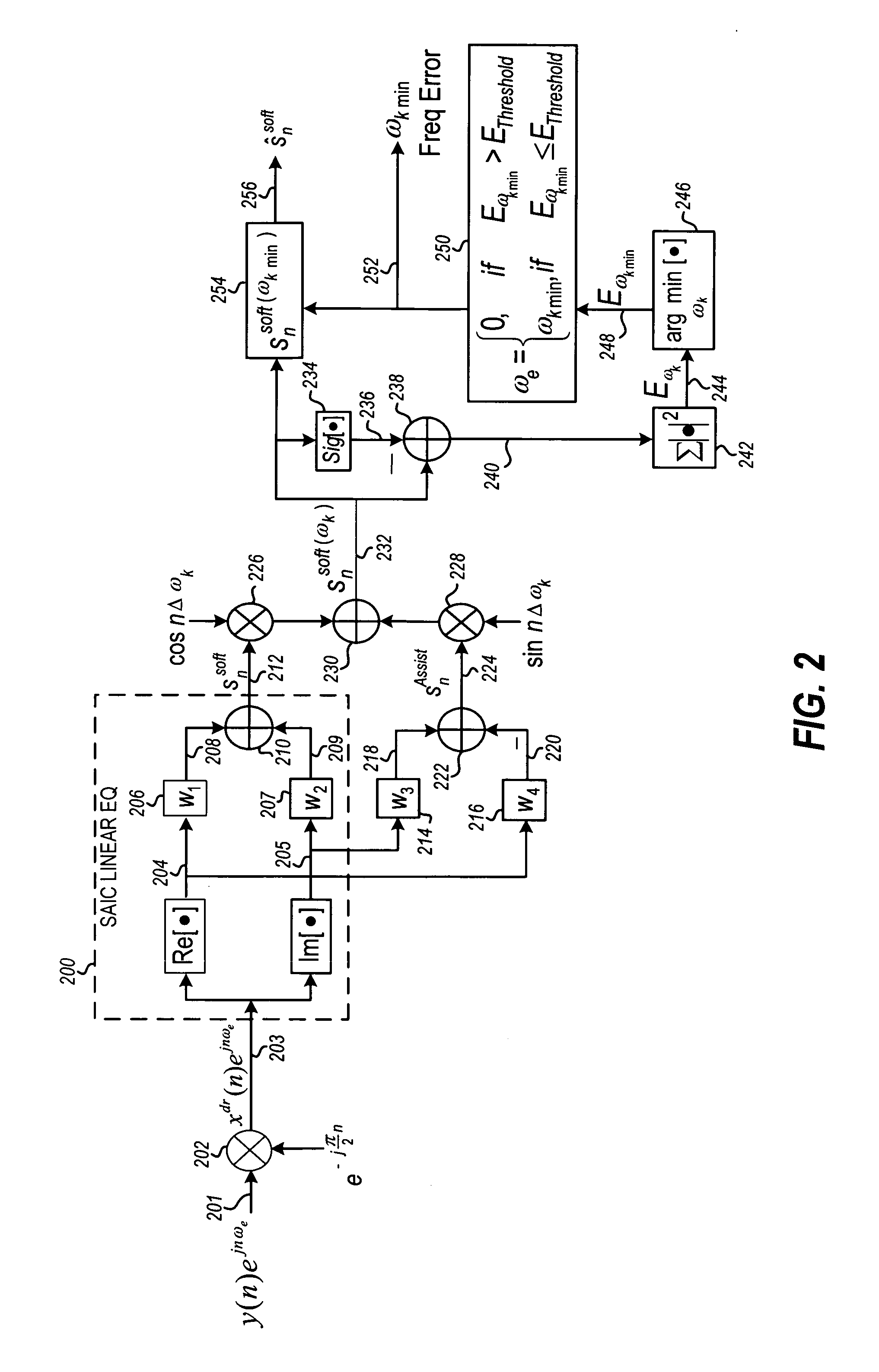
ActiveUS20070121764A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsAmplitude demodulationEffective solutionFinite impulse response
Different from conventional equalizers, the output of an SAIC (Single Antenna Interference Cancellation) linear equalizer in GSM / EDGE wireless communication systems is a real signal combined from two real FIR (Finite Impulse Response) filter outputs. Each of the FIRs separately uses the real and imaginary components of the ½π de-rotated received signal as input. The real-valued output of the SAIC equalizer creates difficulty to estimate and correct the frequency errors due to receiver LO and Doppler shift. Disclosed is an efficient and effective solution to the estimation and correction of the frequency error through an assistant signal generated by two additional FIR filters. The assistant signal and the SAIC equalizer output are used to estimate the frequency error, which is combined with the SAIC equalizer output and the assistant signal to give the frequency error corrected SAIC equalizer output.
Owner:APPLE INC
Linear single-antenna interference cancellation receiver
ActiveUS7295636B2Eliminate distractionsSuppress interferenceError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionCommunications systemEngineering
System and method for interference cancellation in a digital wireless communications system. A preferred embodiment comprises sampling a received signal wherein the received signal is real-valued, rotating the sampled received signal by a specified amount, extracting in-phase and quadrature phase streams from the rotated, sampled received signal, applying an interference suppression filter and combining the filtered streams. The output of the combining operation can be de-correlated (by whitening) if there is excessive correlation.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
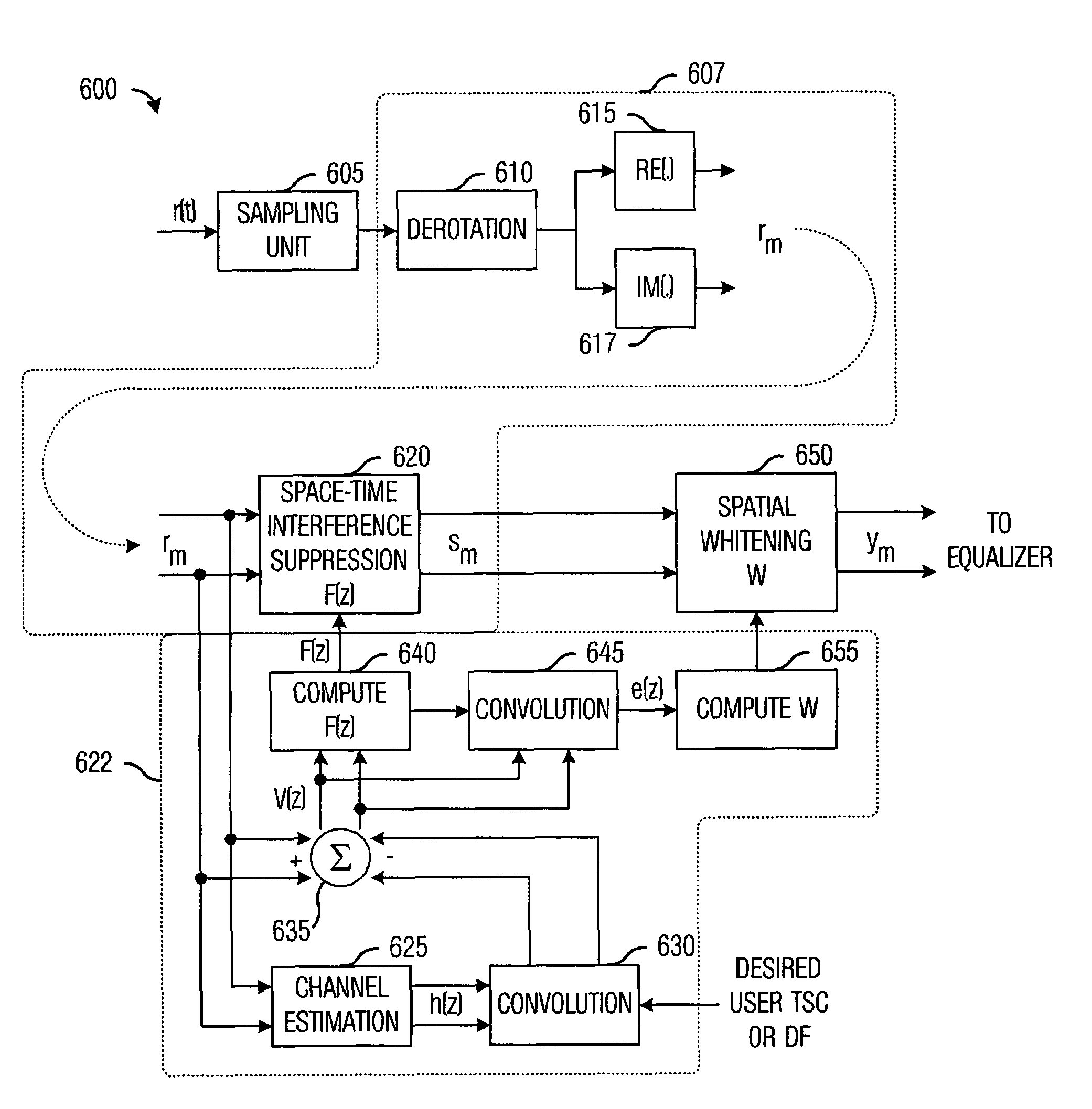
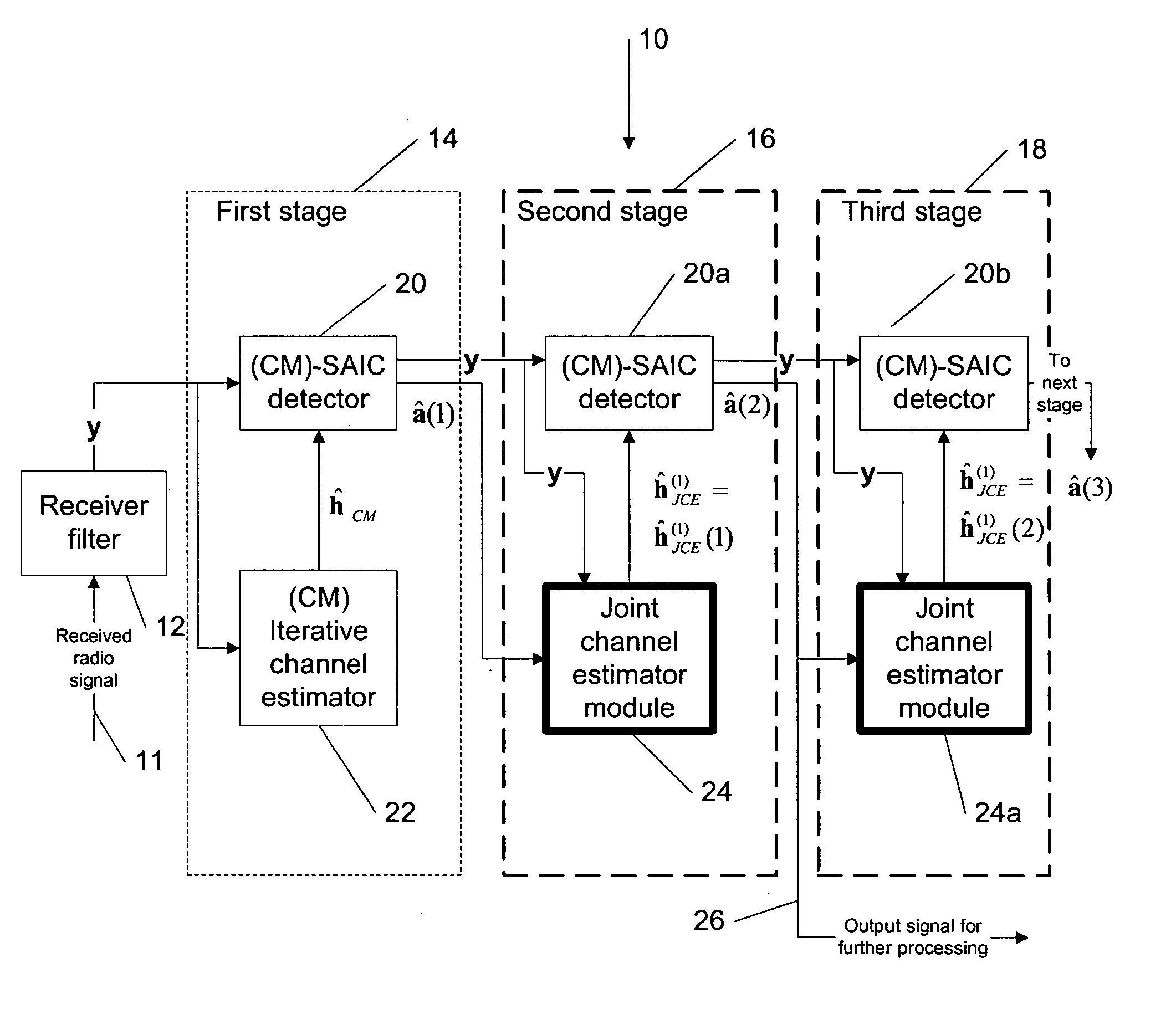
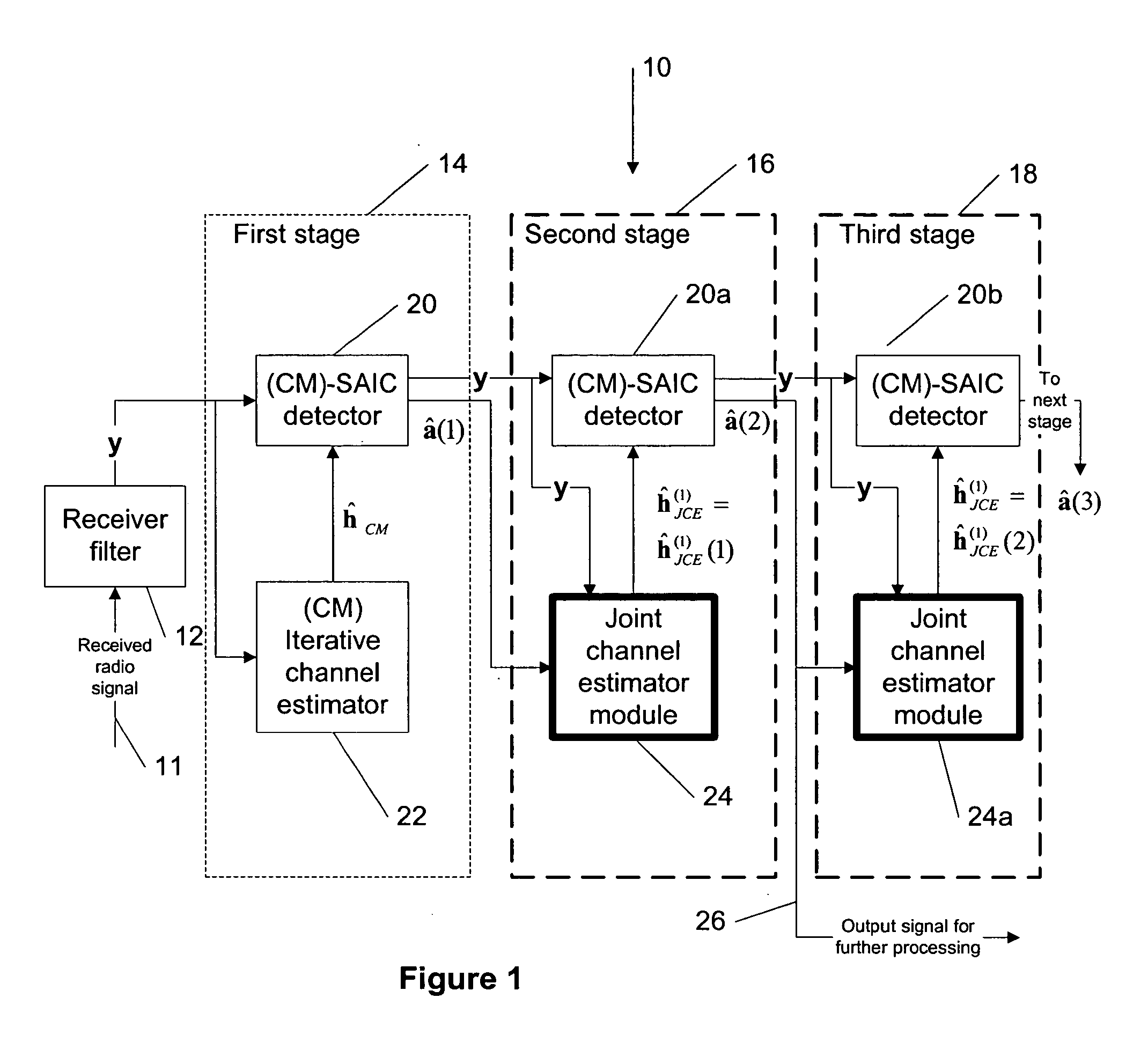
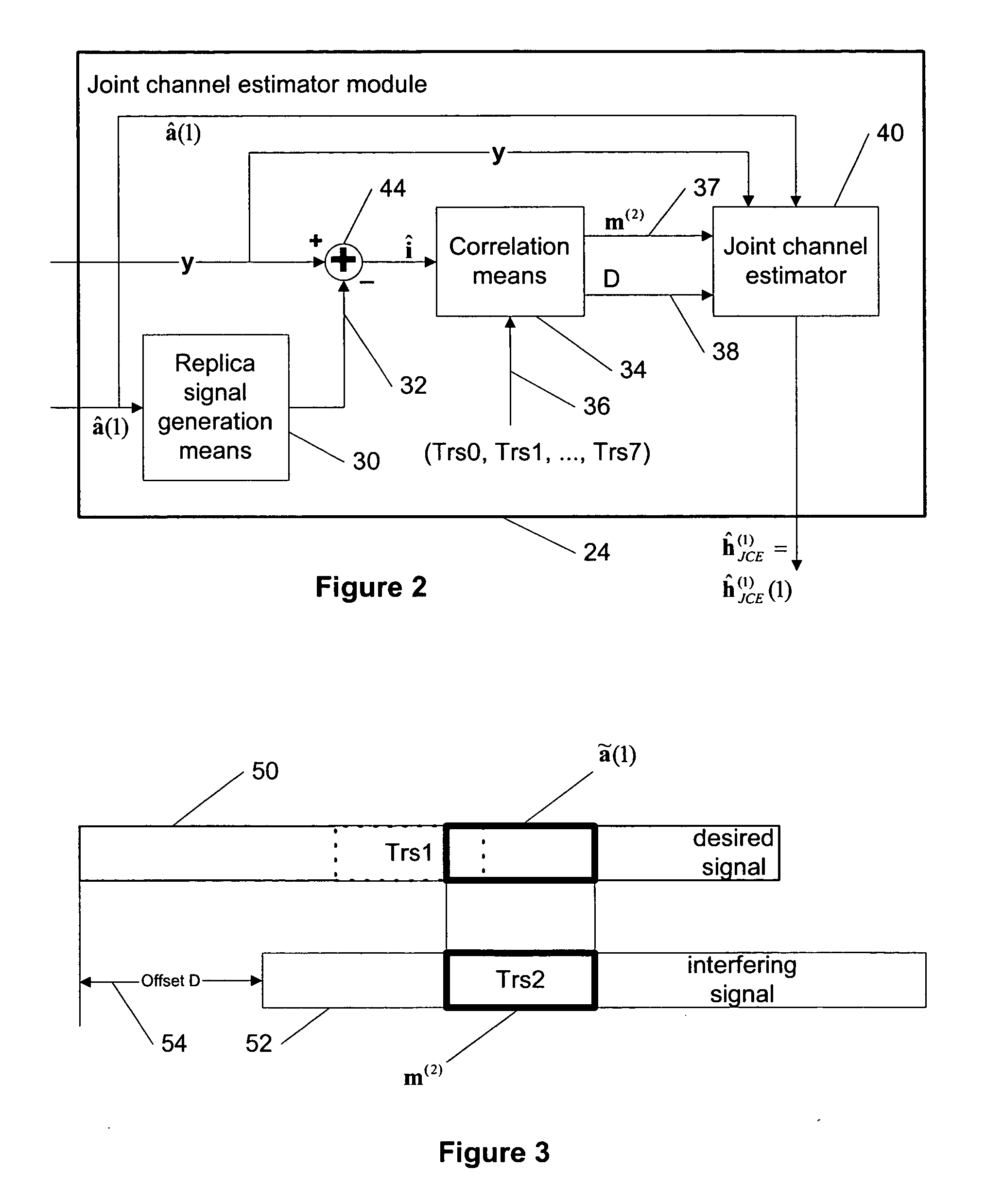
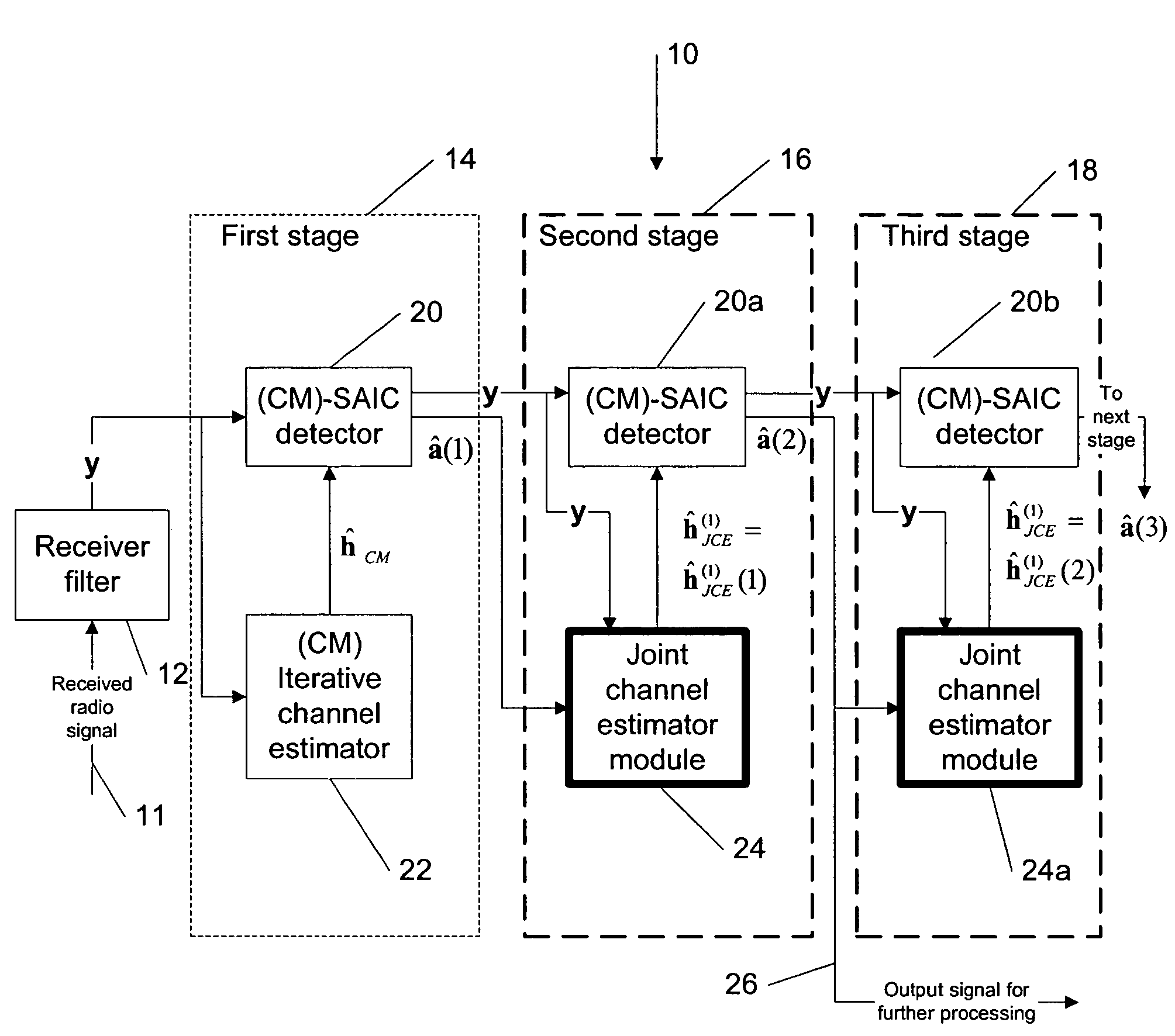
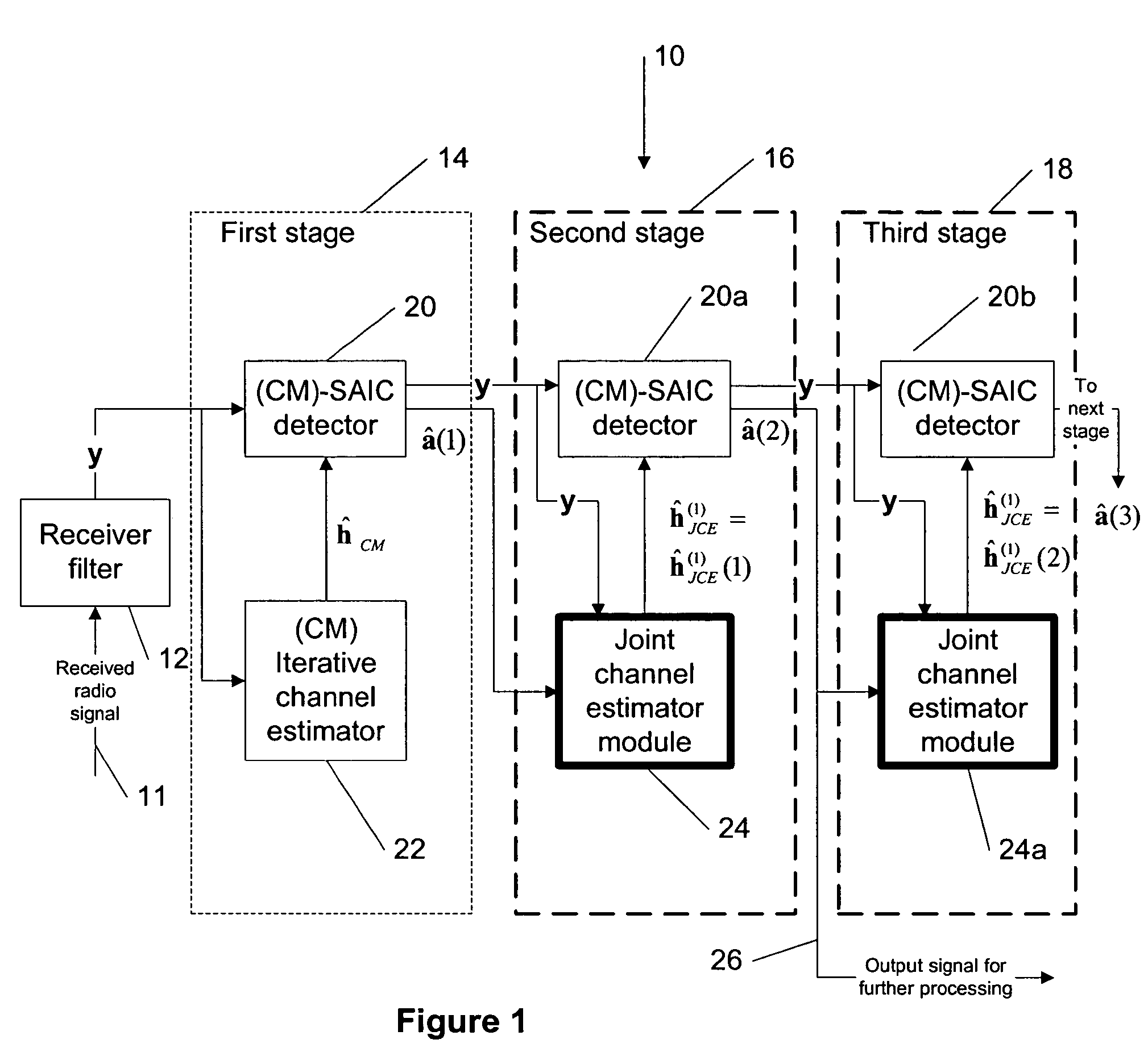
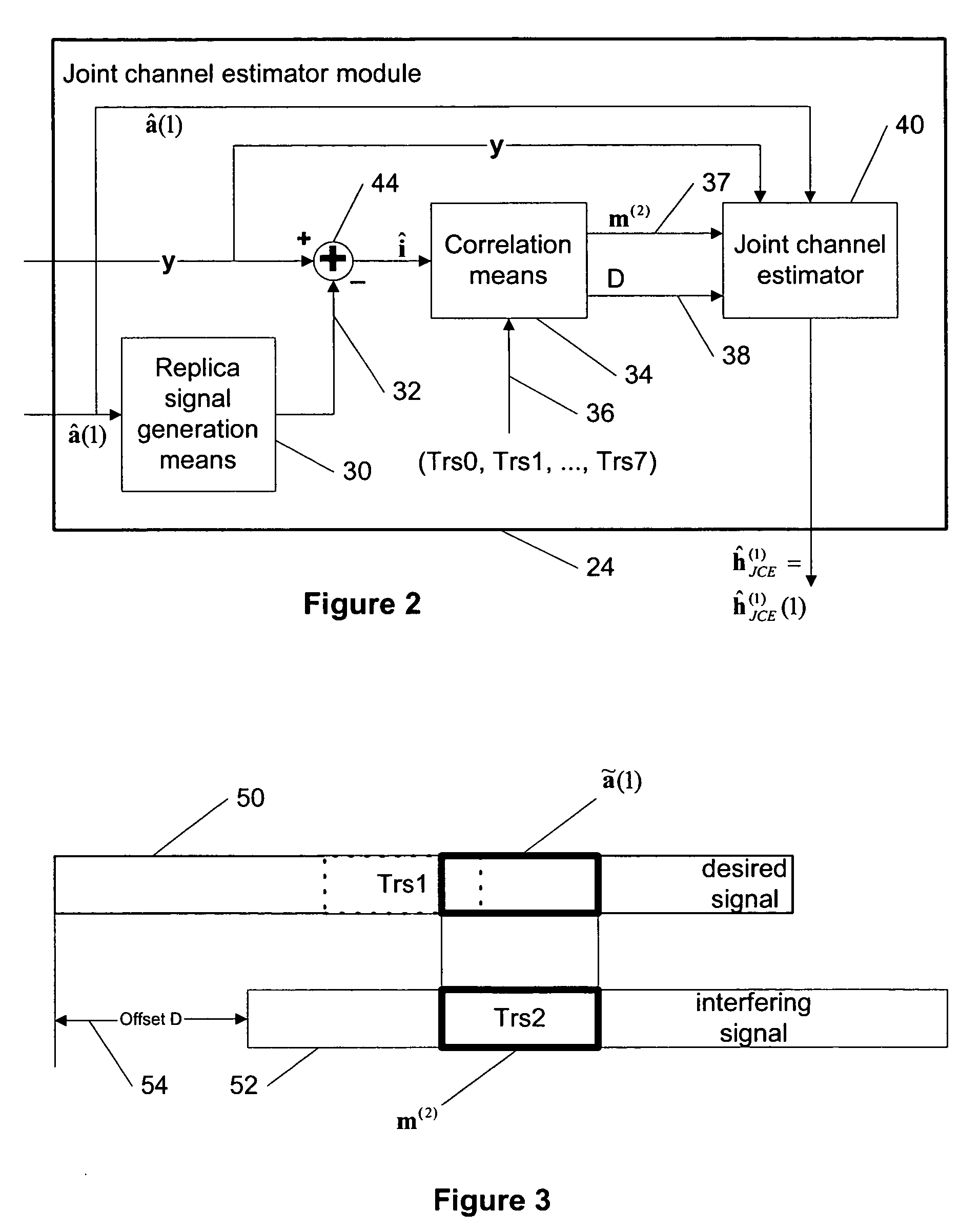
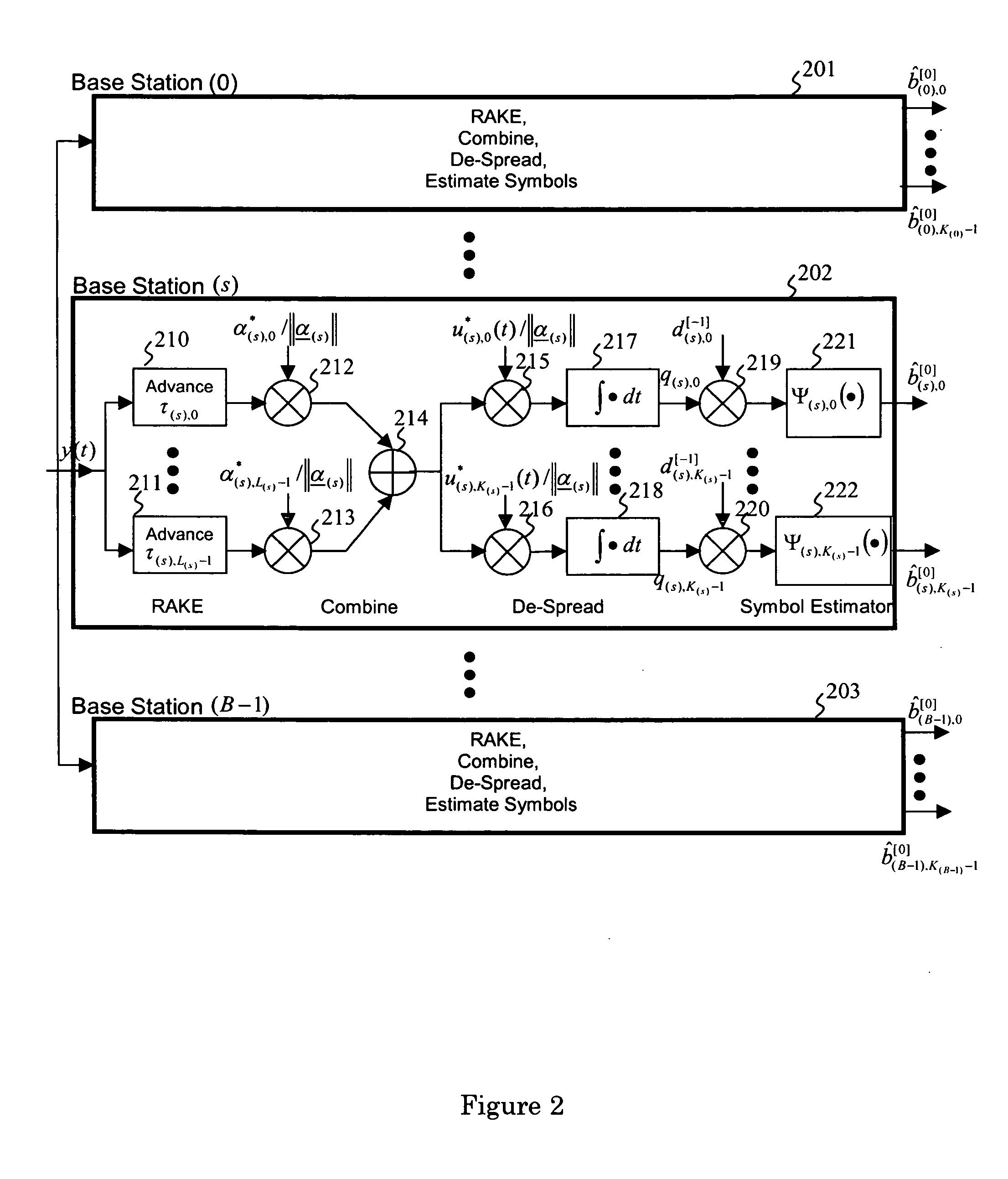
Joint channel estimator for synchronous and asynchronous interference suppression in SAIC receiver
ActiveUS20050152485A1Easy to optimizeError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionEngineeringEqualization
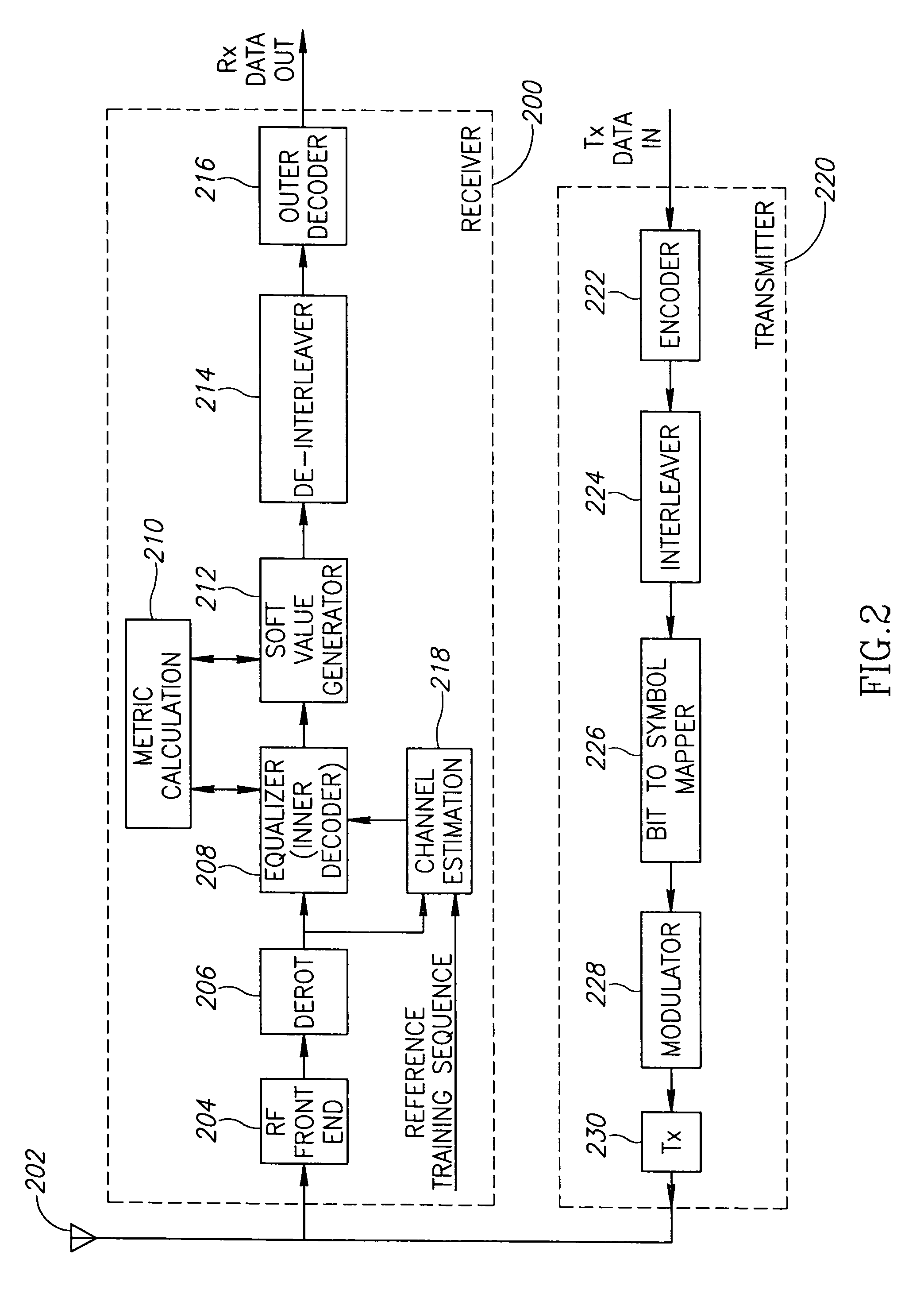
This invention discloses improved single antenna interference cancellation (SAIC) receivers utilizing joint channel estimation for suppression of interference of co-channel signals. This invention describes the technique to perform joint channel estimation for either synchronous or asynchronous co-channel signals without a prior knowledge of the interfering training sequence or its timing position. The invented joint channel estimation can require initial detection of the desired signal and can be implemented as a multistage equalization structure.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method for iterative interference cancellation for co-channel multi-carrier and narrowband systems
ActiveUS20100226356A1Improve performanceInherent signal separationError preventionTransmission path divisionChannel impulse responseInterference elimination
In a co-channel deployment of narrowband and multi-carrier technologies (e.g., a femtocell and a macrocell), a method provides cancelling of interference which treats the co-channel signals as desired signals and enhances each of them iteratively. At each iteration, each signal is demodulated and regenerated based on symbol decisions already made and a predetermined channel impulse response. To estimate the other (interfering) co-channel signal, the regenerated signal is subtracted from the aggregate signal. Simulations have shown that a method of the present invention can provide fundamental improvement in the performances of both interfering systems in as few as two iterations. The fundamental performance gain that can be obtained outweigh the required computational burden.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
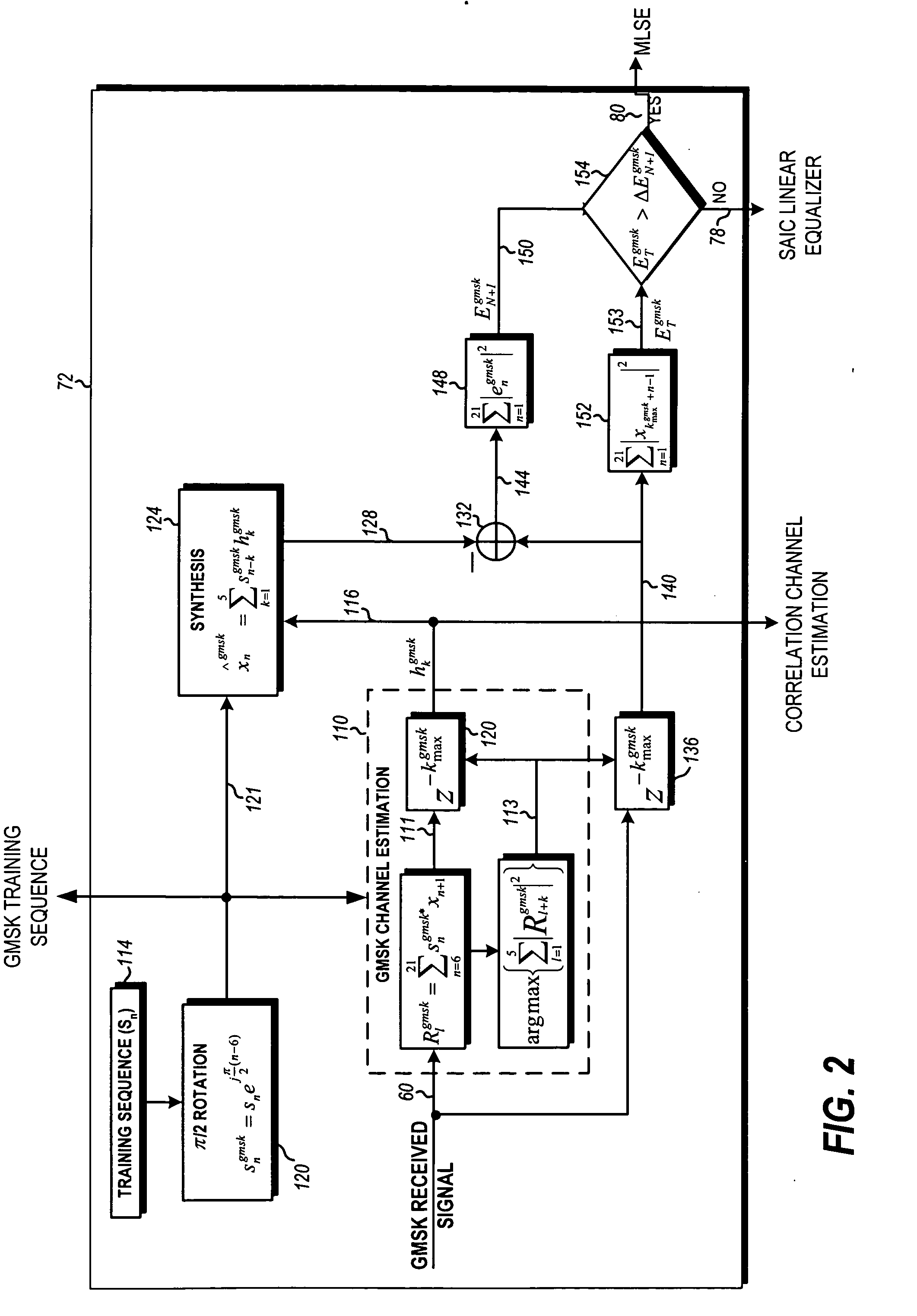
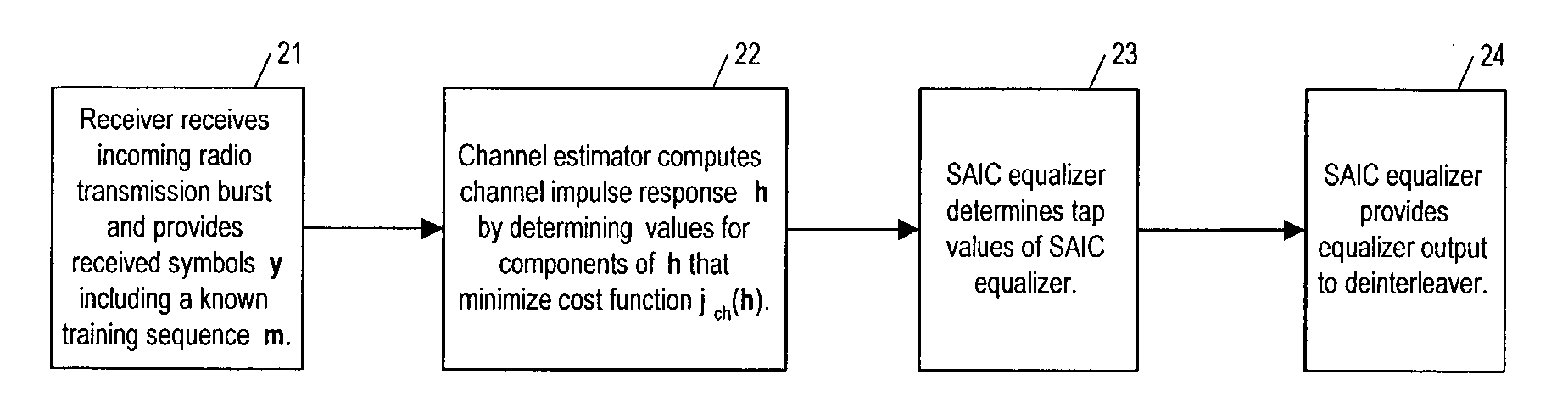
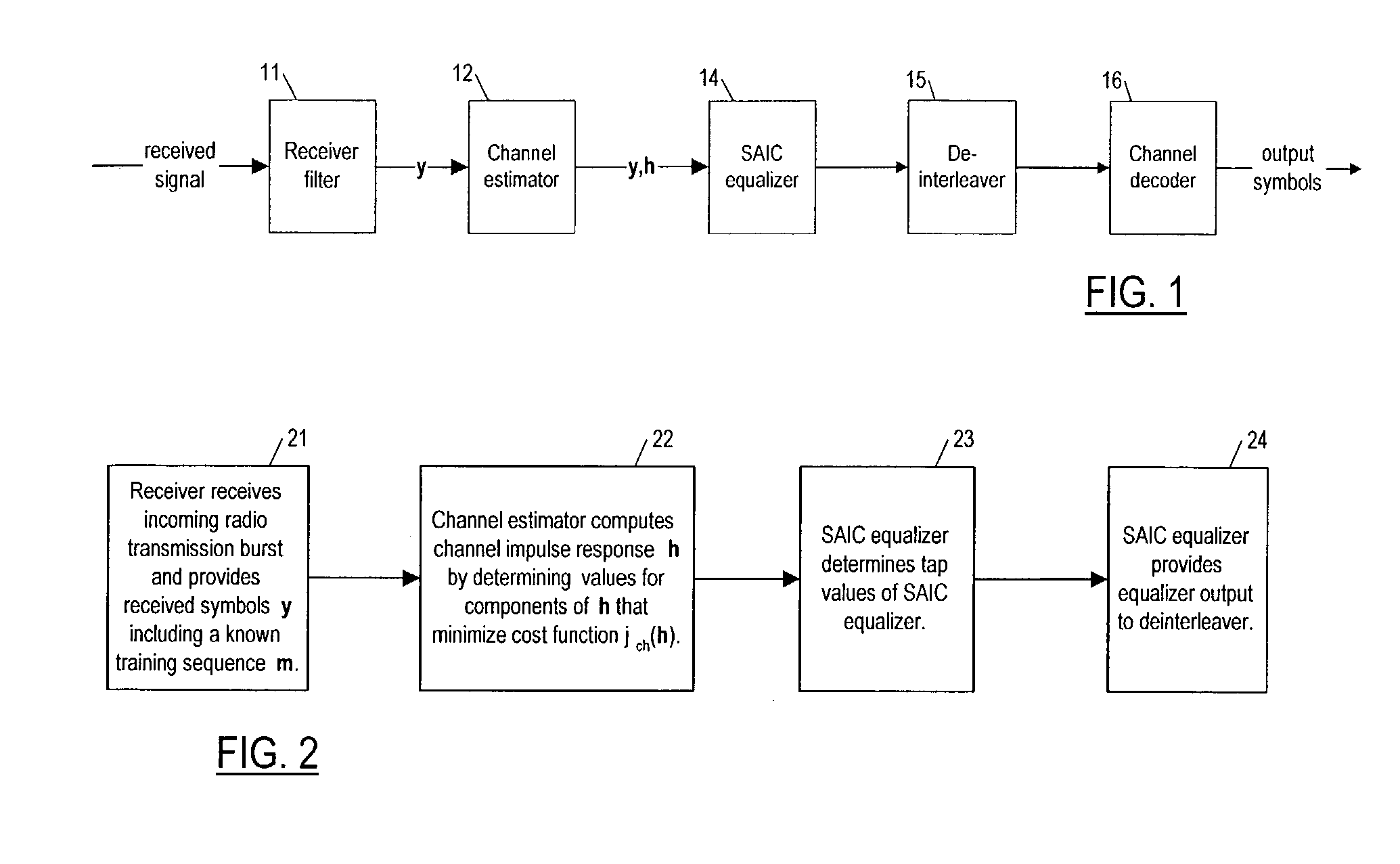
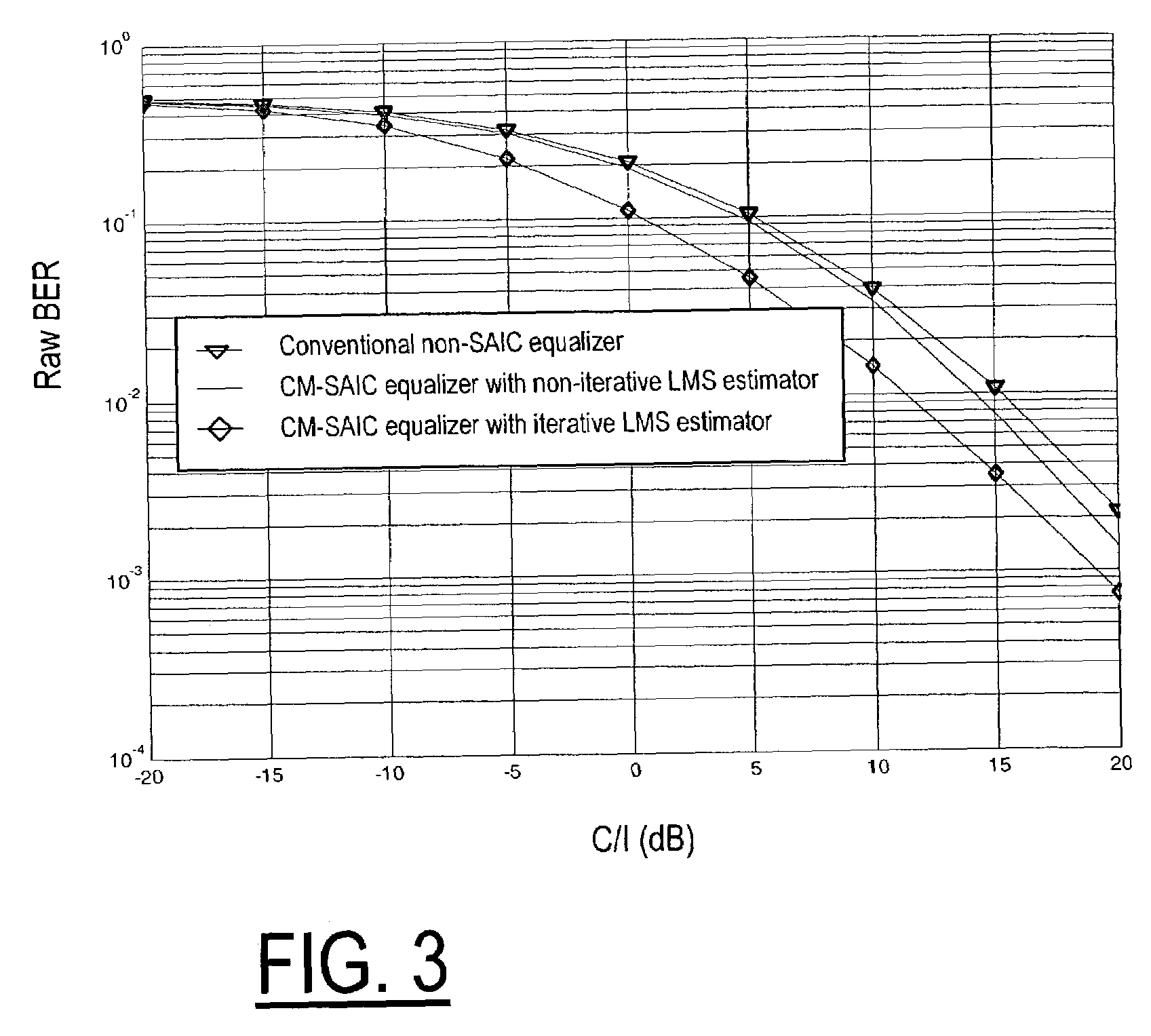
Method and apparatus for determining components of a channel impulse response for use in a SAIC equalizer
InactiveUS7200172B2Minimize cost functionMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsMean squareChannel impulse response
A method of operation of a receiver of a mobile station or a base station of a radio access network and corresponding equipment, the method for especial use in providing interference cancellation according to a single antenna interference cancellation (SAIC) algorithm. The method includes a step (22) in which a channel estimator (12) estimates channel impulse response components for use by a SAIC equalizer (14); in estimating the channel impulse response components, the channel estimator (12) minimizes a special cost function (Jch(h)) with respect to the components of the channel impulse response h. In some embodiments, the method uses an iterative least mean squares procedure to minimize the cost function (Jch(h)).
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Reduction of linear interference canceling scheme
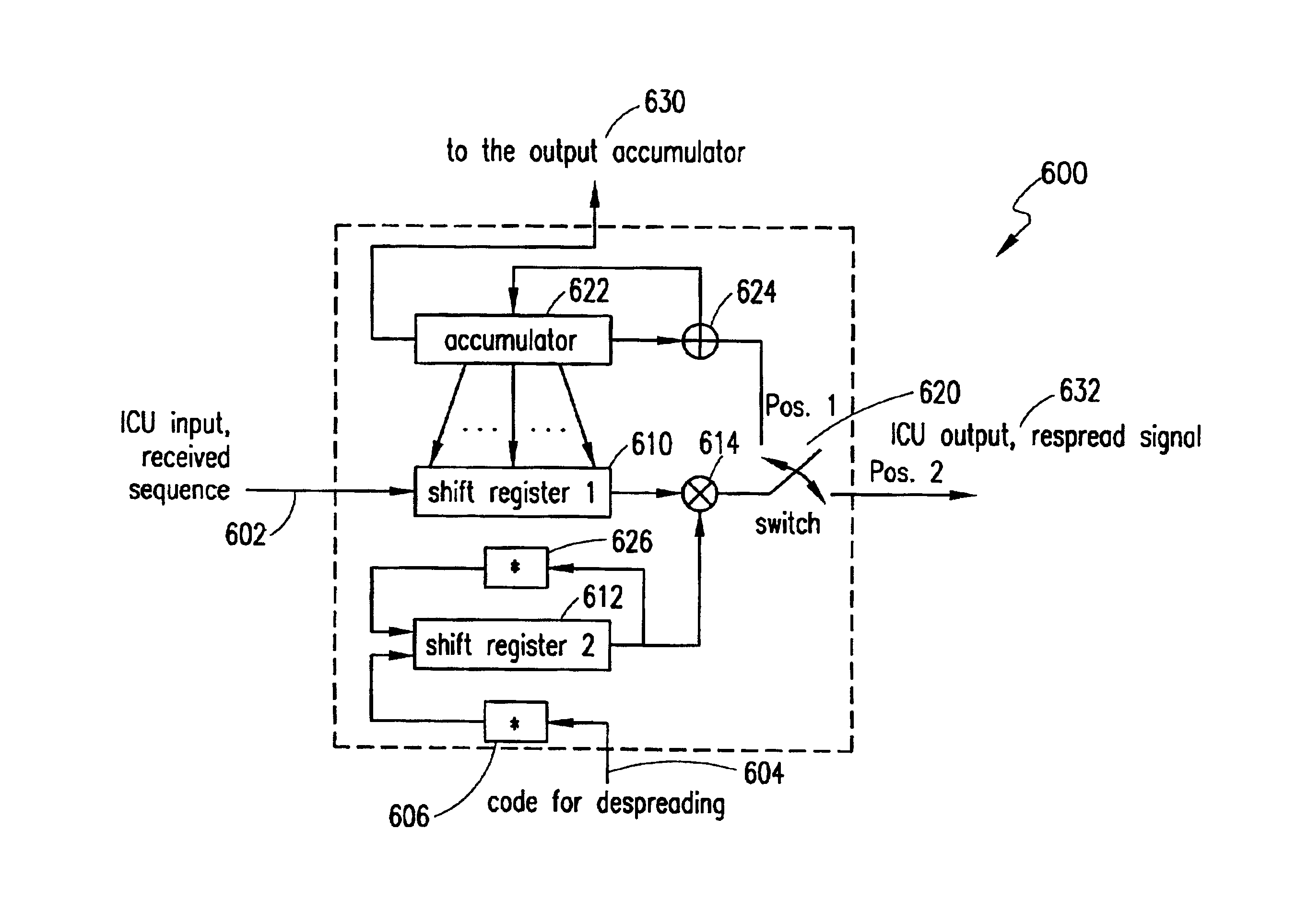
A system, method and apparatus for demodulating a received signal using a configurable receiver. The receiver performs the demodulation of a signal according to a selected interference cancellation demodulation scheme. The same receiver can be configured, by setting certain parameters, to behave as a successive interference cancellation (SIC) scheme receiver, a parallel interference cancellation (PIC) scheme receiver, or a hybrid interference cancellation (HIC) scheme receiver. In another aspect of the present invention, the receiver performs its demodulation operation using a single interference cancellation unit (ICU). In addition, the ICU's despreading and respreading functions may be performed by the same processing element.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Multiple channel interference cancellation
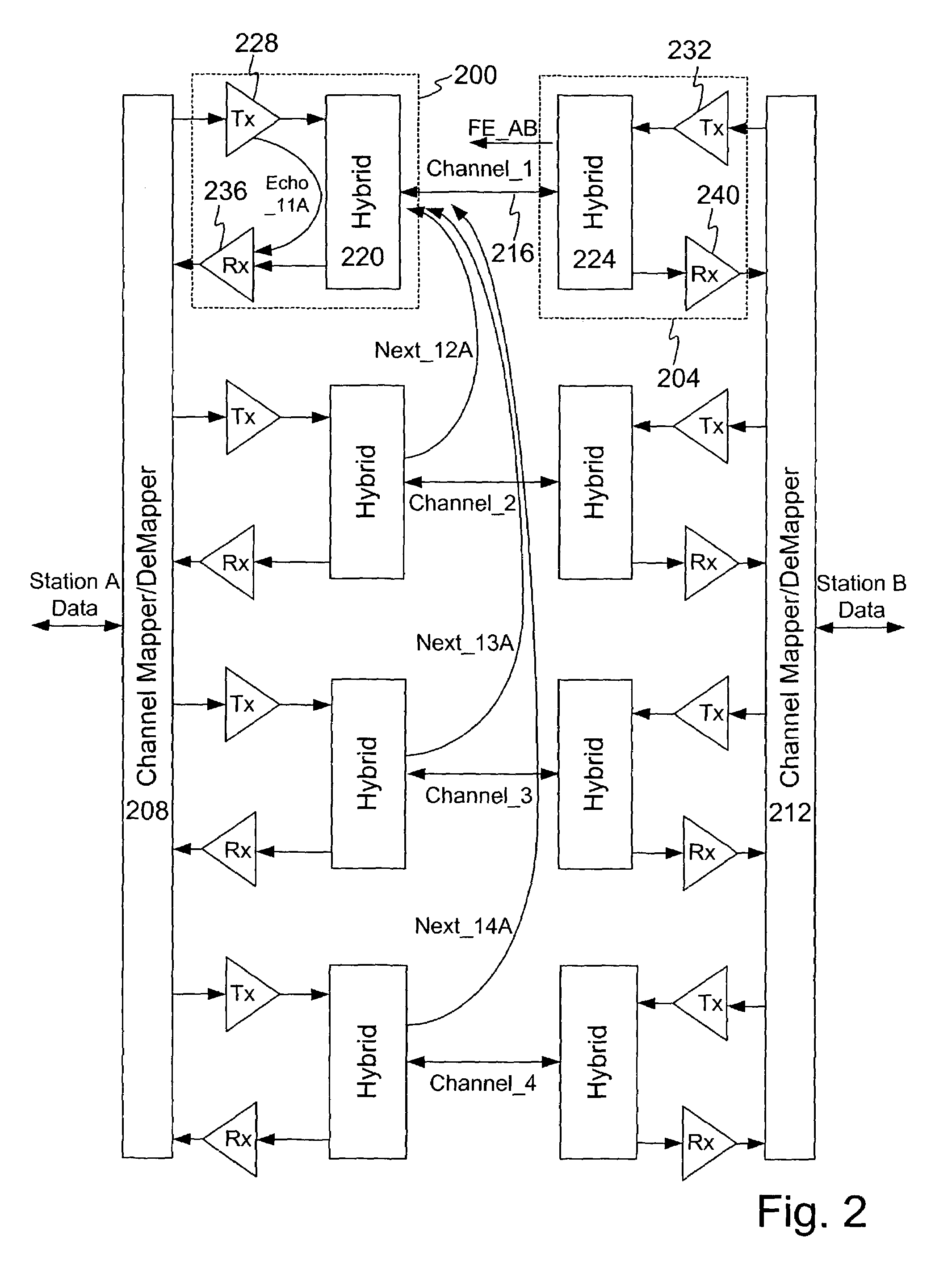
InactiveUS7002897B2Reduce or eliminate crosstalk, coupling, or echoReduce complexityTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsFrequency-division multiplex detailsCrosstalk cancellationHandling system
A method and apparatus for reducing crosstalk in a multi-channel communication system is disclosed. In one embodiment, outgoing signals in a multi-channel environment are manipulated into a transform domain, such as the frequency domain. Thereafter, the signals may be combined and modified based on a weighting variable to create a cancellation signal. Combined processing greatly reduces system complexity and increases processing speed. After processing in the transform domain, the cancellation signal undergoes further processing to return the cancellation signal into the time domain. The cancellation signal may then be combined with received signals to cancel crosstalk or echo. A method and apparatus for crosstalk cancellation in the analog domain and digital domain is also disclosed. Cancellation at least partially in the analog domain reduces the dynamic range requirements for digital to analog converters within the front-end processing system of a receiver and thereby reducing clipping and increasing operating speed.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Interference parameter signaling for efficient interference cancellation and suppression
ActiveUS20170078126A1Efficiently obtainedReduce distractionsReceiver specific arrangementsSignal allocationInterference cancelationCommunications system
The present invention relates to transmission and reception of downlink control information in a communication system. In particular, a serving base station transmits to a terminal a downlink control information which includes a first field with a scheduling information and a second field with interference parameters (interference information). The receiver employs the interference parameters for interference estimation used in interference cancellation or suppression.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
System and scheduler for intercell interference cancellation
ActiveUS20080009256A1Reduce distractionsTransmission control/equalisingCriteria allocationData streamRadio channel
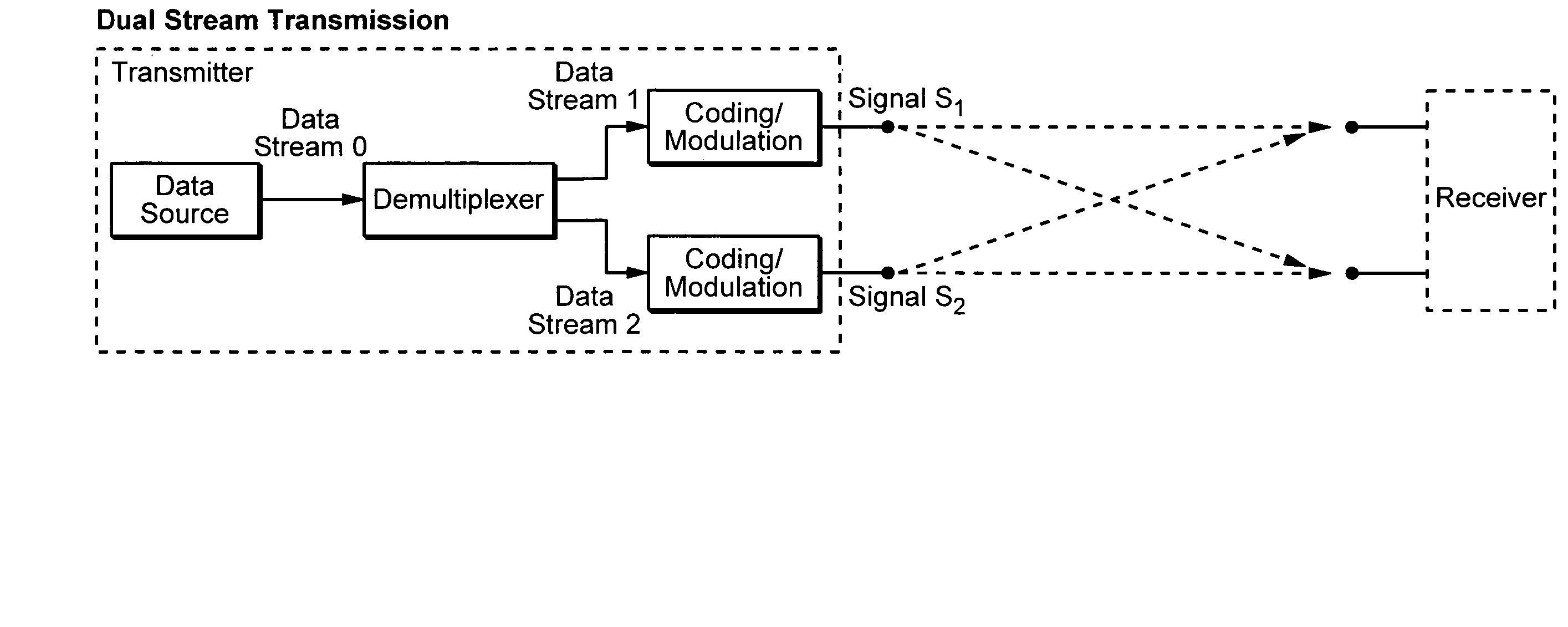
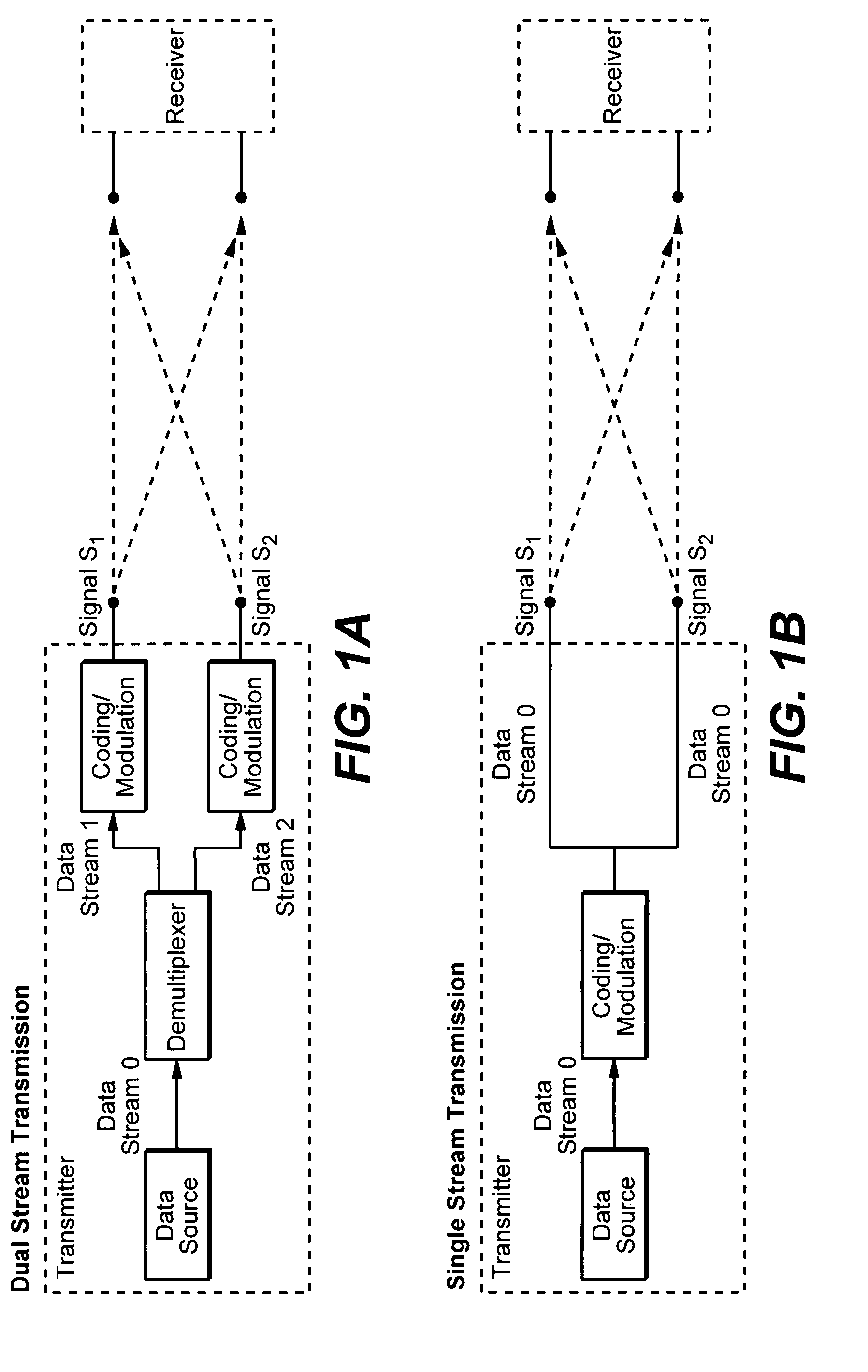
Embodiments of the invention provide a controller, in a cellular wireless network for cancellation of interference from neighboring cells. Logic in the controller determines channel quality of a radio channel between a first base station and a UE. Scheduling logic causes the first base station and a second base station to adjust the number of data streams used for communication within a time period, as a function of the channel quality. Other embodiments provide an apparatus for reducing interference in a receiver that receives N data streams. Signal processing logic receives the N data streams, where N-M of the data streams represent interference with respect to M desired data streams, and cancels the N-M data streams so as to receive the M desired data streams. The N data streams may be received from multiple base stations, or multiple UEs.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES II
Joint channel estimator for synchronous and asynchronous interference suppression in SAIC receiver
This invention discloses improved single antenna interference cancellation (SAIC) receivers utilizing joint channel estimation for suppression of interference of co-channel signals. This invention describes the technique to perform joint channel estimation for either synchronous or asynchronous co-channel signals without a prior knowledge of the interfering training sequence or its timing position. The invented joint channel estimation can require initial detection of the desired signal and can be implemented as a multistage equalization structure.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
Iterative interference cancellation using mixed feedback weights and stabilizing step sizes
A receiver is configured for canceling intra-cell and inter-cell interference in coded, multiple-access, spread-spectrum transmissions that propagate through frequency-selective communication channels. The receiver employs iterative symbol-estimate weighting, subtractive cancellation with a stabilizing step-size, and mixed-decision symbol estimates. Receiver embodiments may be implemented explicitly in software or programmed hardware, or implicitly in standard Rake-based hardware either within the Rake (i.e., at the finger level) or outside the Rake (i.e., at the user or subchannel symbol level).
Owner:III HLDG 1
System and method for digital interference cancellation
ActiveUS8301104B1Increase rangeEfficient implementationTransmissionRadio frequency signalAnalog signal
A system and method for receiving a signal, comprising an input adapted to receive a radio frequency signal having a strong interferer; a signal generator, adapted to produce a representation of the interferer as an analog signal generated based on an oversampled digital representation thereof; and a component adapted to cancel the strong interferer from radio frequency signal based on the generated analog signal to produce a modified radio frequency signal substantially absent the interferer. The system typically has a nonlinear component that either saturates or produces distortion from the strong interferer, which is thereby reduced. The system preferably employs high speed circuits which digitize and process radio frequency signals without analog mixers.
Owner:HYPRES
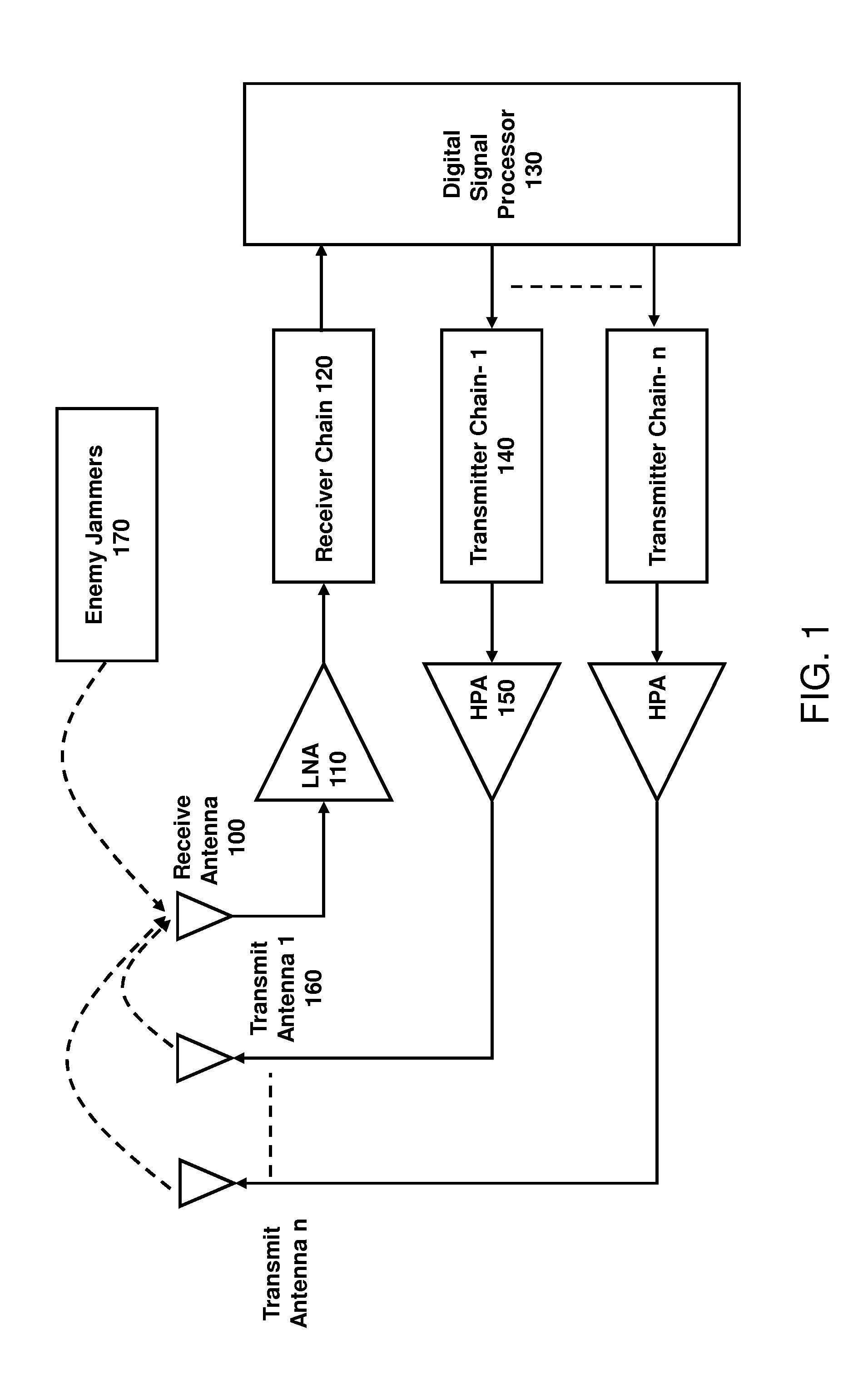
Timing offset compensation for inter-link interference cancellation
ActiveUS20180102807A1Reduce distractionsSynchronisation arrangementMulti-frequency code systemsInterference cancelationSingle antenna interference cancellation
Aspects of the disclosure relate to inter-link interference cancellation for reducing or mitigating interference from signals in different directions (e.g., uplink and downlink directions). A wireless communication device (i.e., a victim device subject to inter-link interference) may determine a time offset or lead time of an interfering signal from an offending device. Based on the determined time offset, the victim device may perform interference cancellation or suppression to reduce or mitigate the interference of the interfering signal. Other aspects, embodiments, and features are also claimed and described.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
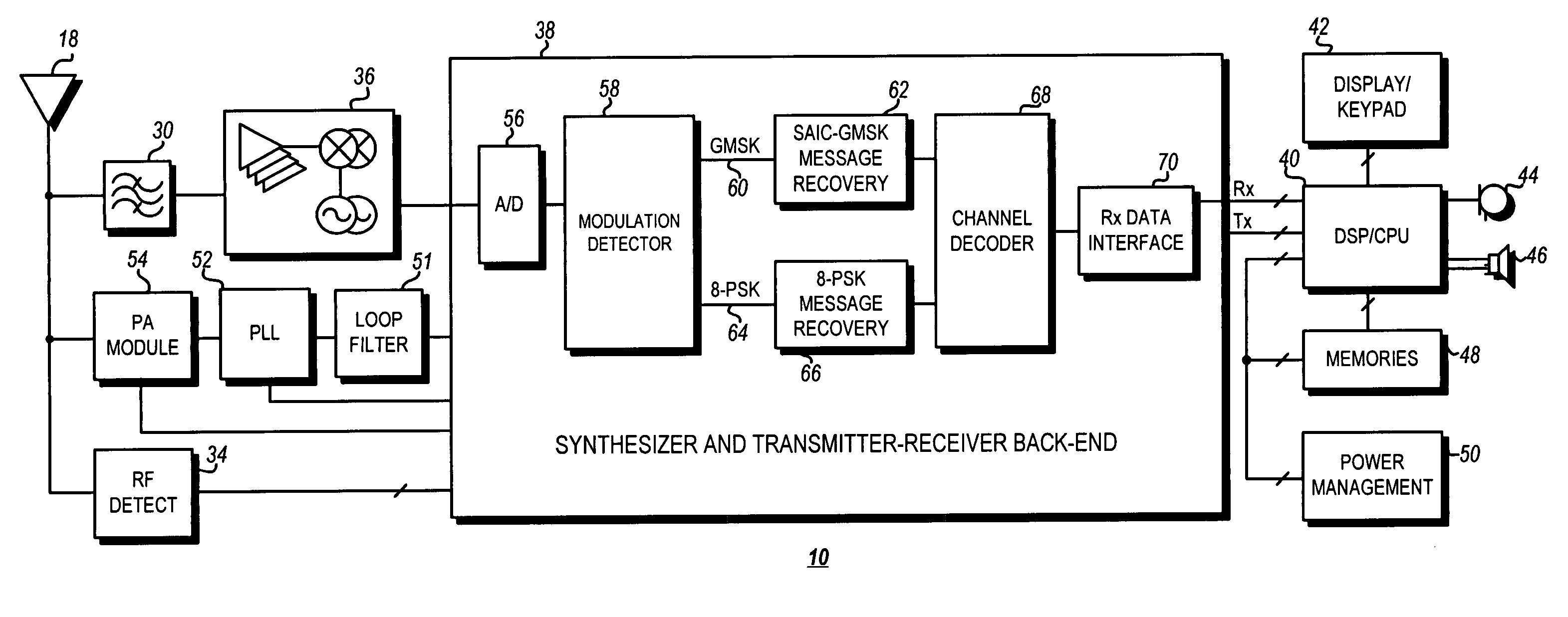
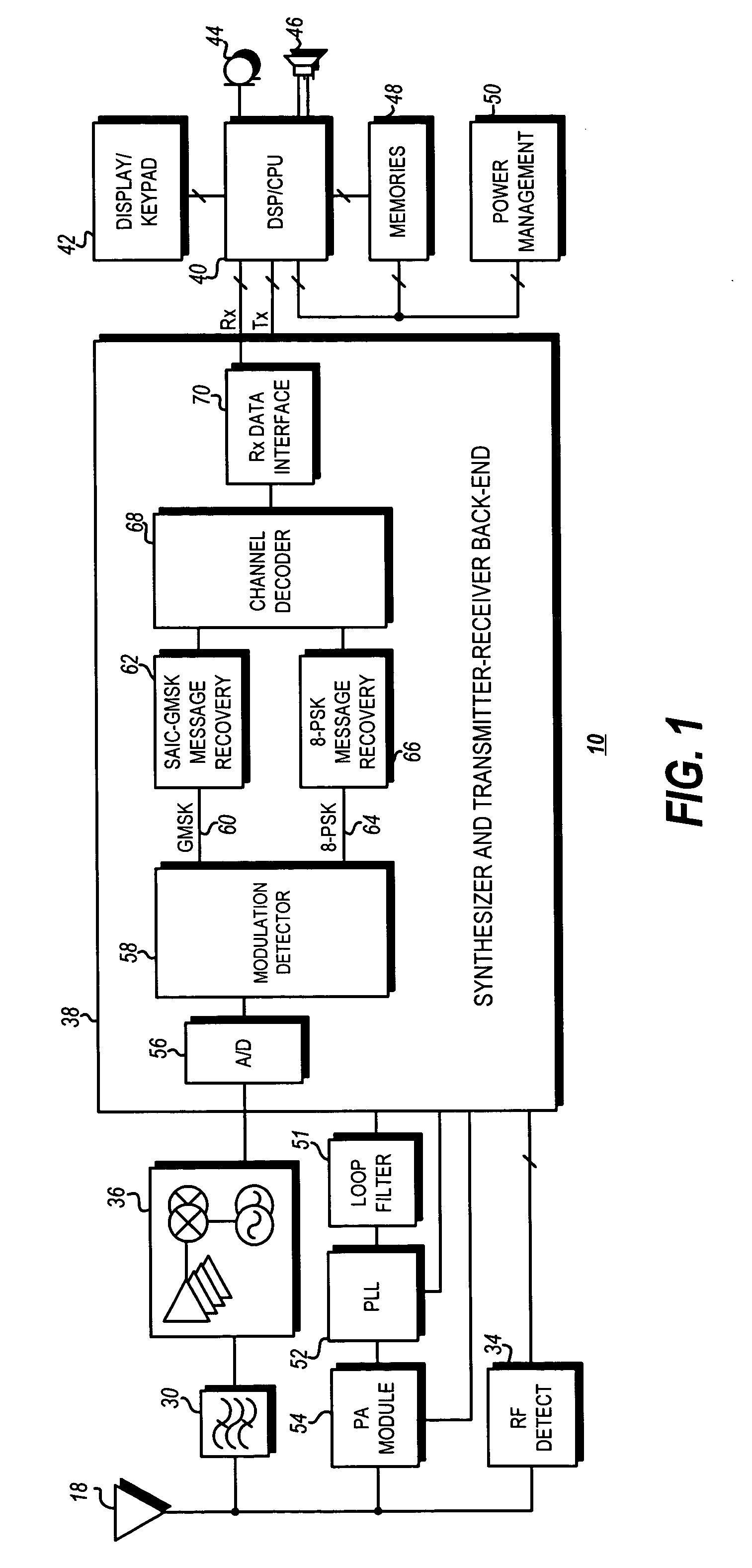
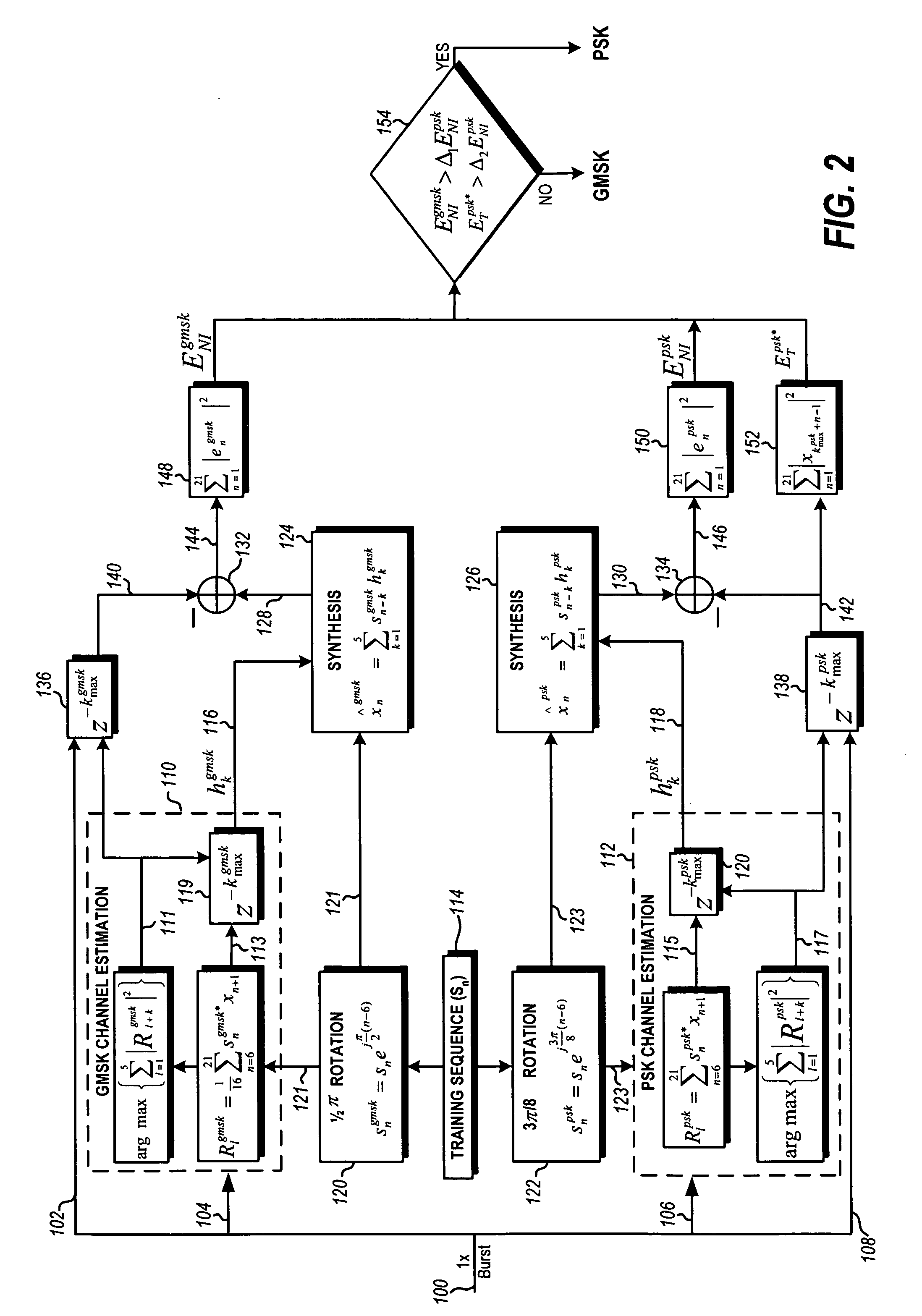
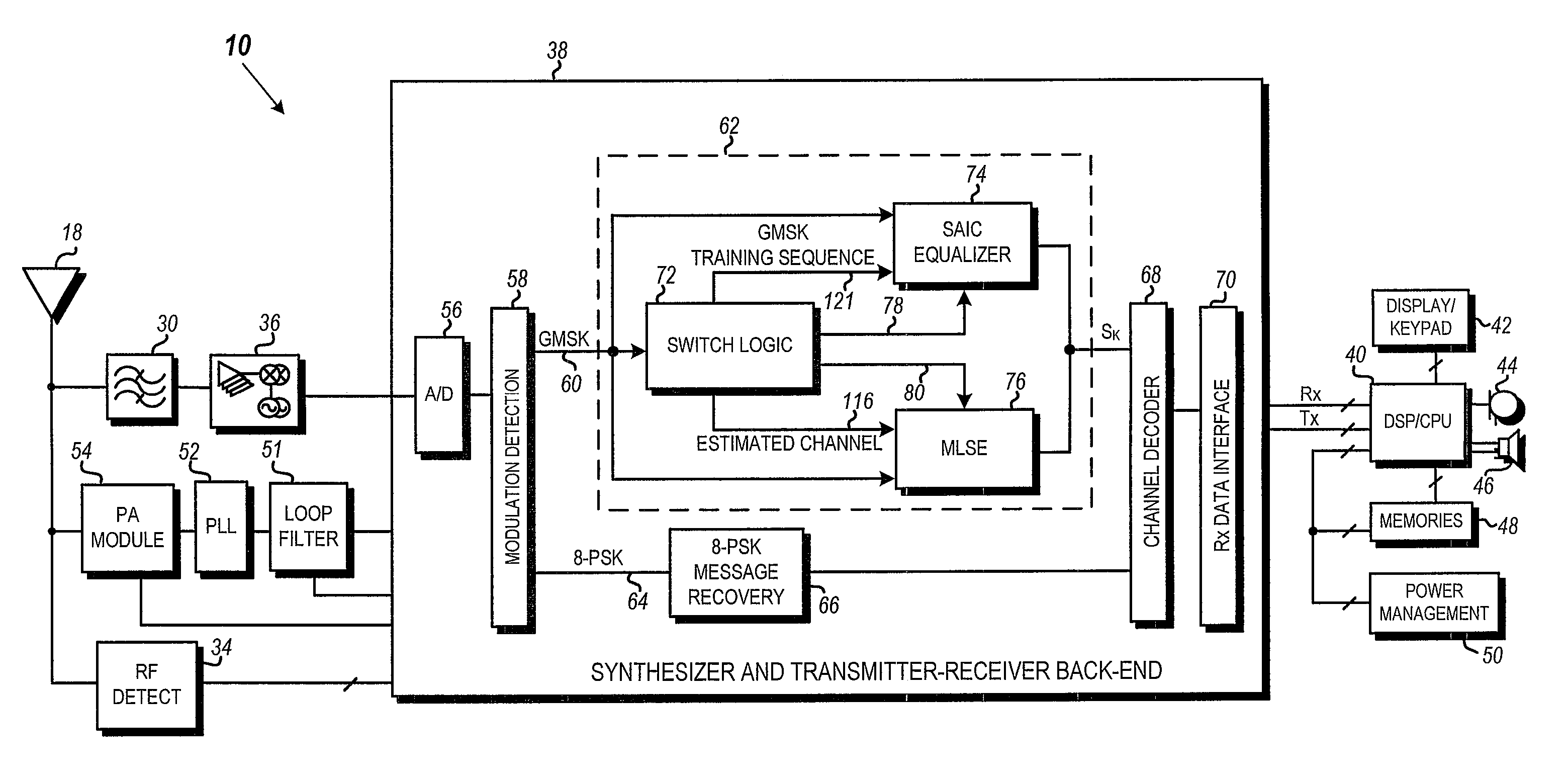
Modulation detection in a saic operational environment
InactiveUS20070041473A1Modulation type identificationPhase-modulated carrier systemsSequence signalEngineering
Blind modulation detection in a receiver of a wireless communication device calculates error energies for PSK and GMSK based on differences between a received training sequence signal and synthesized training signals generated from PSK and GMSK channel estimations and a known training sequence phase rotated by 3π / 8 and π / 2 per symbol, respectively. A highly reliable modulation detection in an Single Antenna Interference Cancellation (SAIC) operational environment is achieved by a dual comparison of a total energy value of the received signal and the two error energies. PSK is determined if the PSK error energy value is found to be lower than both the GMSK error energy value and the total energy value by predetermined thresholds; otherwise the modulation type is determined to be GMSK.
Owner:APPLE INC
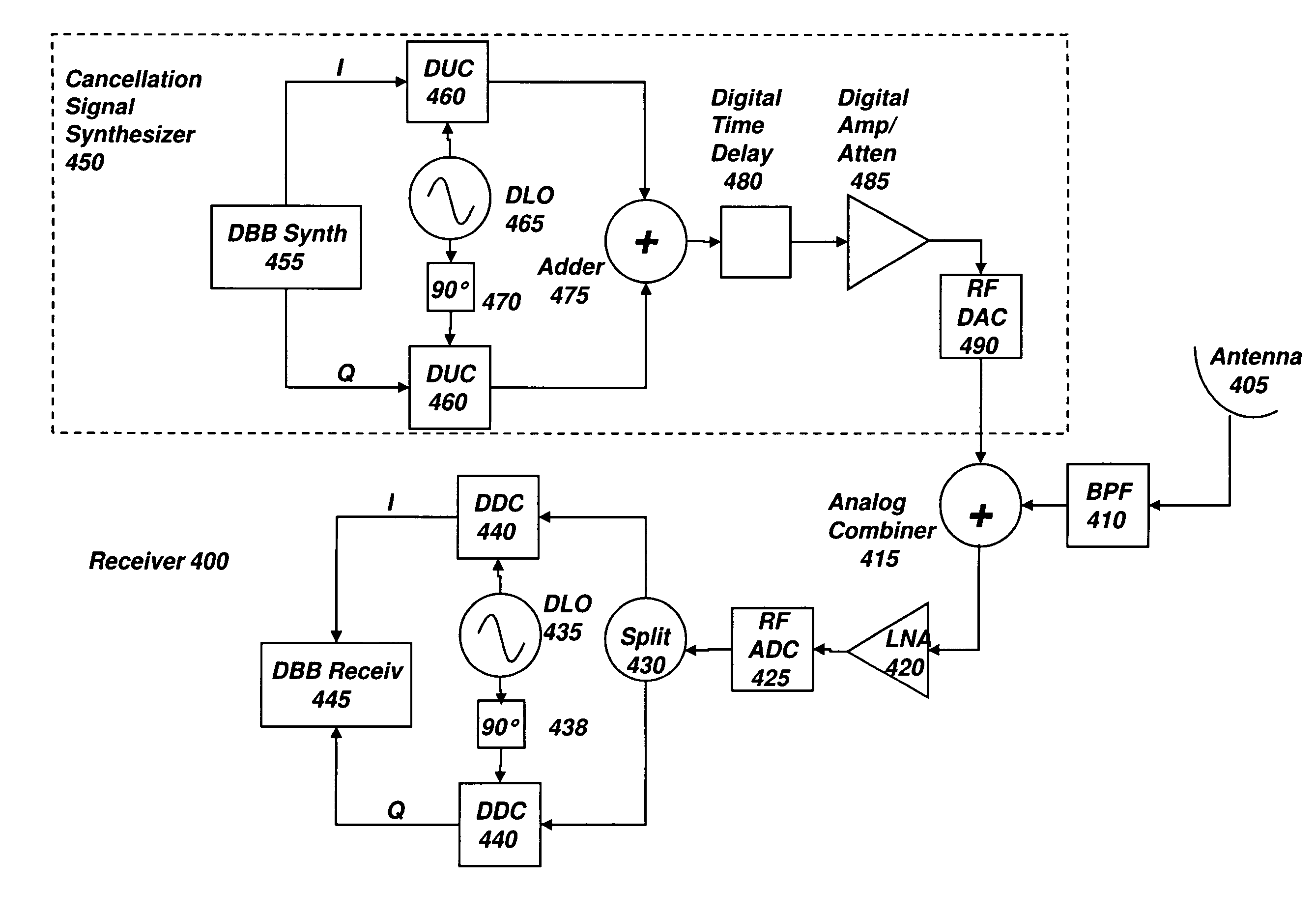
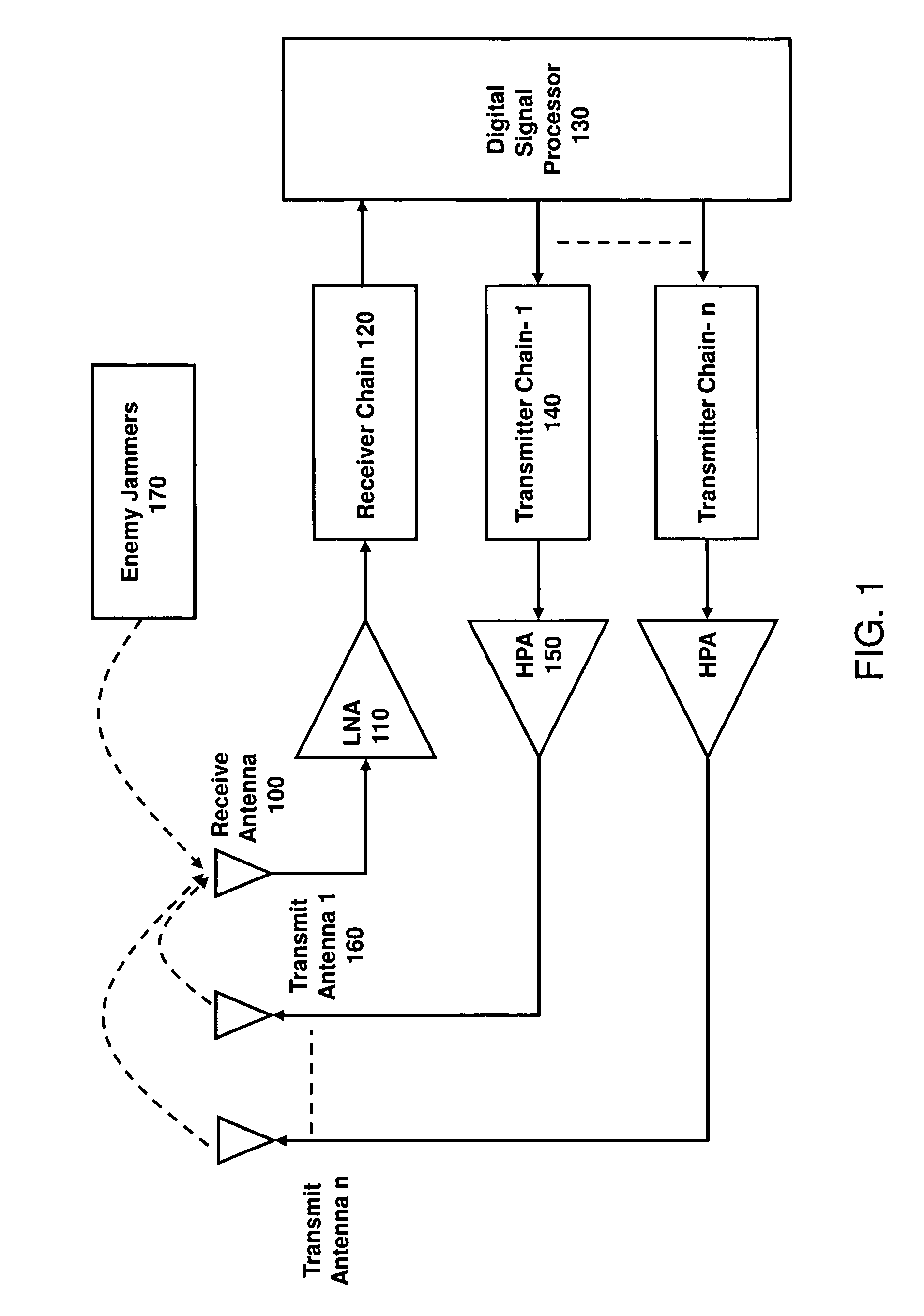
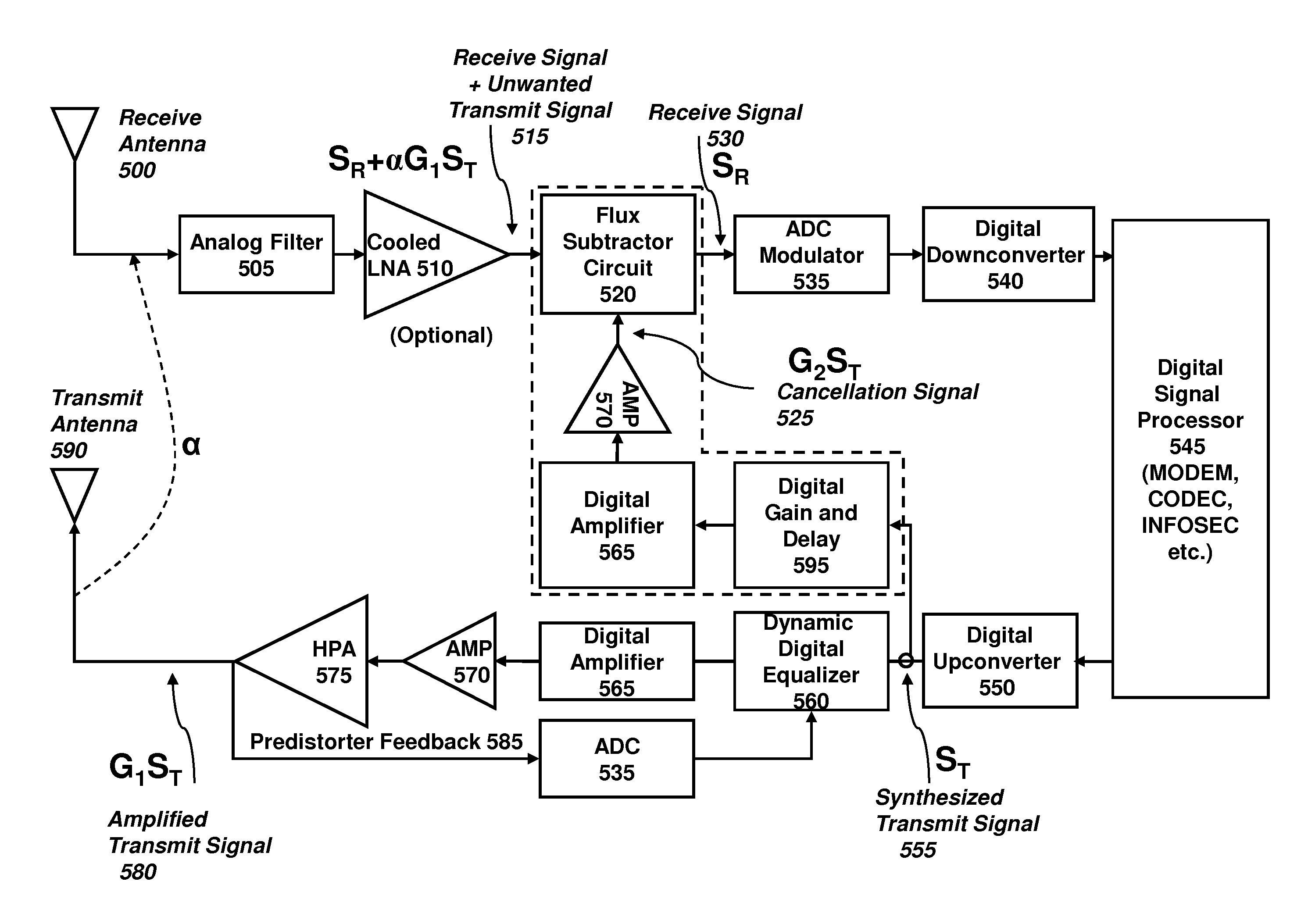
Active interference cancellation in analog domain
InactiveUS20150065064A1Reduce distractionsTransmissionEngineeringSingle antenna interference cancellation
A method of performing interference cancellation (IC) in a communication device having a plurality of transmitters and a plurality of receivers includes detecting a co-existence issue between a first transmitter and a first receiver; selecting the first transmitter for providing an input signal to IC circuit; selecting the first receiver, wherein each of the receivers has a corresponding filter, the first receiver having a filter for filtering a signal received by the first receiver to provide a first filtered signal; configuring the IC circuit based on parameters of the co-existence issue; generating an output signal based on the input signal and the parameters; selecting a filter, based on the filter of the first receiver, the selected filter configured to filter the output signal to provide a second filtered signal; and generating a cancellation signal based on the first and second filtered signals.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
I/Q MIMO detection for single antenna interference cancellation
InactiveUS20050226344A1High data ratePeak data rate can be improvedDiversity/multi-antenna systemsPhase-modulated carrier systemsSynchronous networkGSM
An I / Q MIMO detection framework is a practical means to realize interference cancellation (IC) gains when GMSK, 8PSK signals interfere with each other in synchronous GSM / EDGE networks, thereby providing coverage, capacity, and throughput gain. Further, the presented algorithm applies to a high data rate system concept, in which multiple signals are transmitted from the base station (BTS) through multiple antennas.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method and apparatus for switching on and off interference cancellation in a receiver
ActiveUS7006811B2Polarisation/directional diversityLine-faulsts/interference reductionRadio access networkSingle antenna interference cancellation
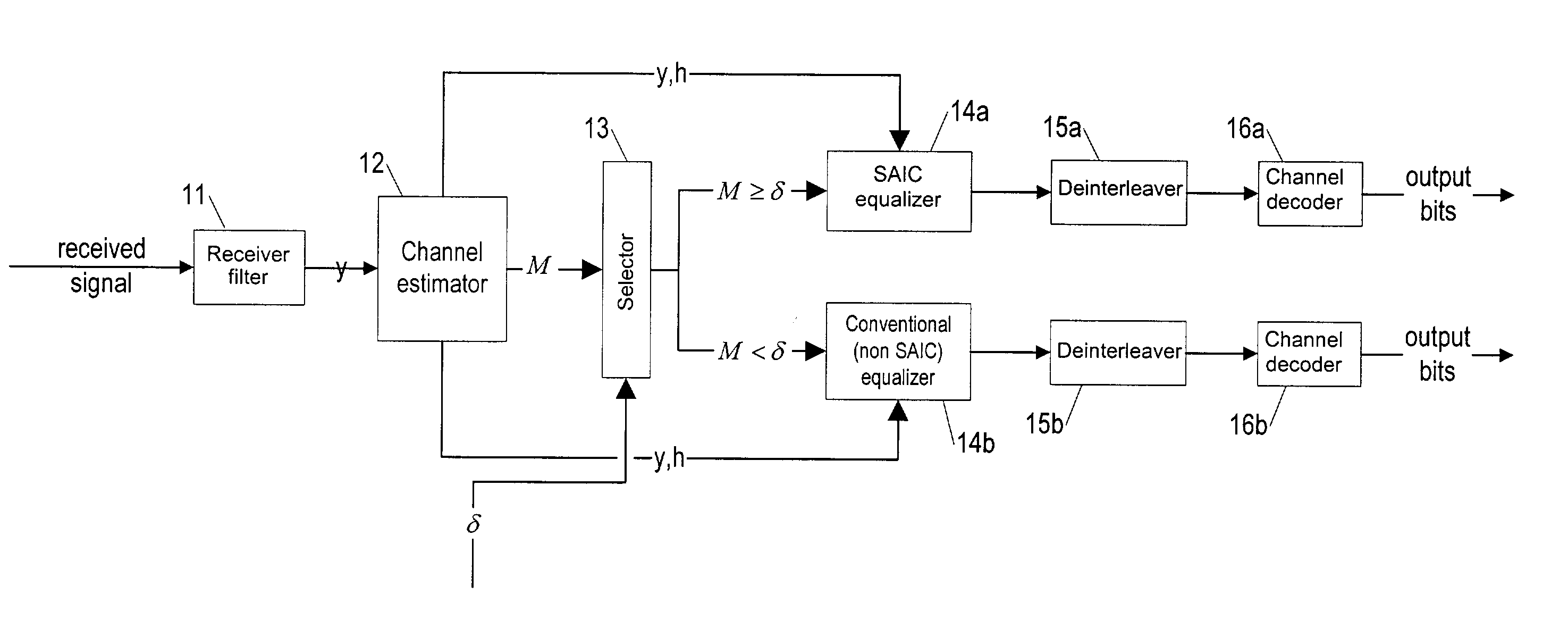
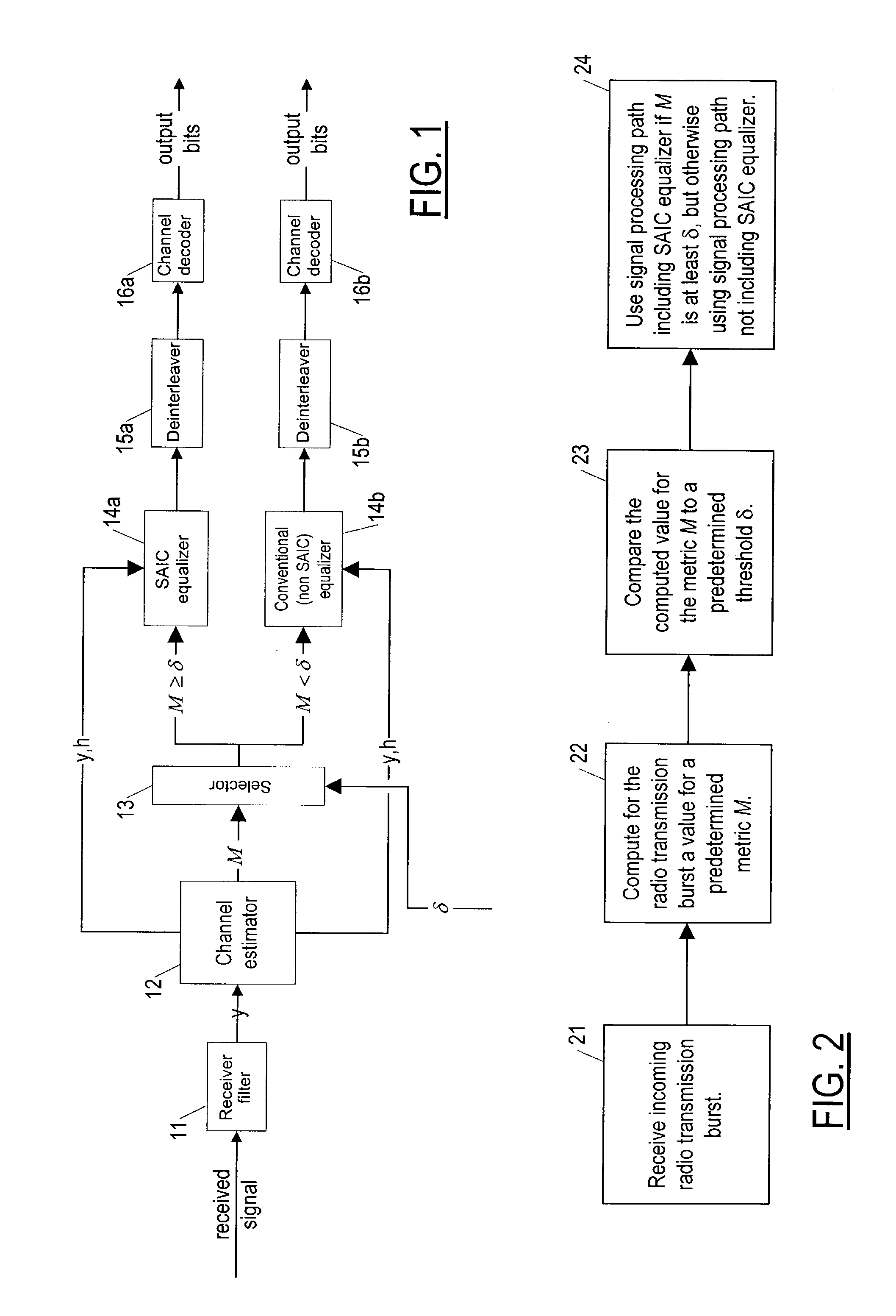
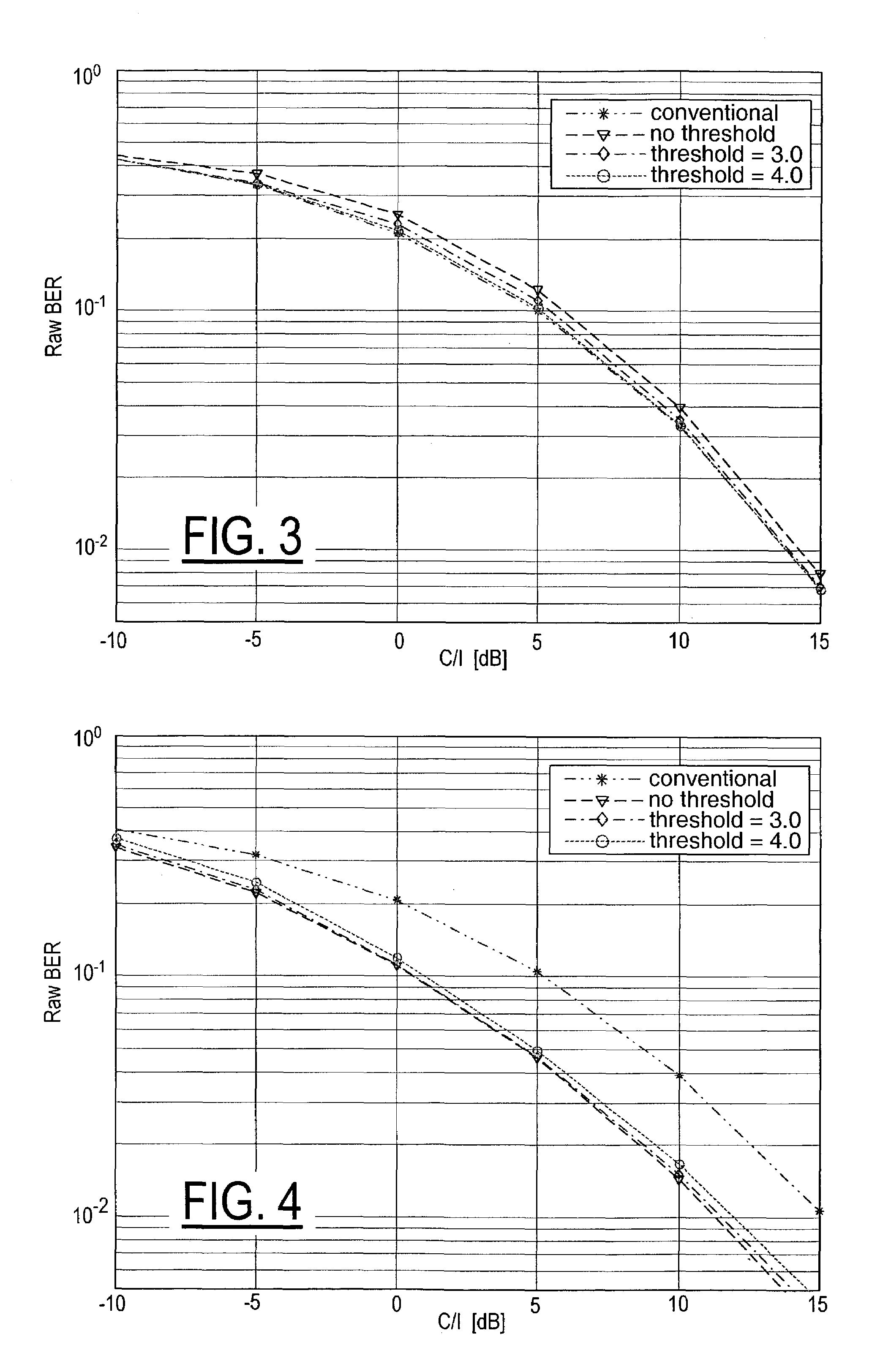
A method of operation of a receiver of a mobile station or a base station of a radio access network and corresponding equipment, the method for use in providing interference cancellation according to a single antenna interference cancellation (SAIC) algorithm without degrading performance in case of little or no interference. The method uses a metric M (having a value that is large when there is strong interference) to gauge whether or not to process an incoming signal burst using a processing path (14a–16a) including a module implementing a SAIC algorithm or instead to process the incoming signal burst using a conventional equalizer processing path (14b–16b). A selector module (13) selects one or the other path based on comparing the metric M with a threshold δ. Various metrics M are possible.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
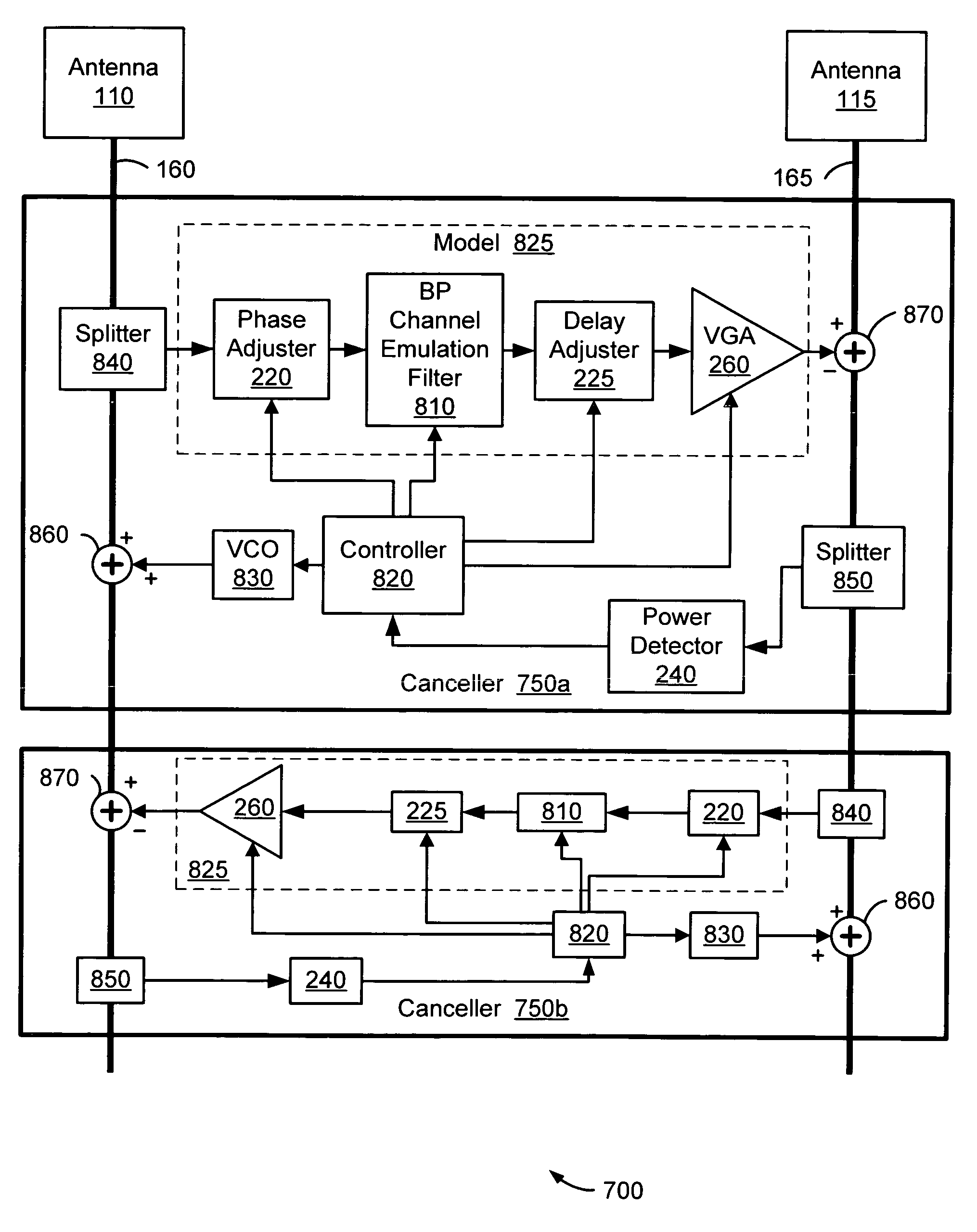
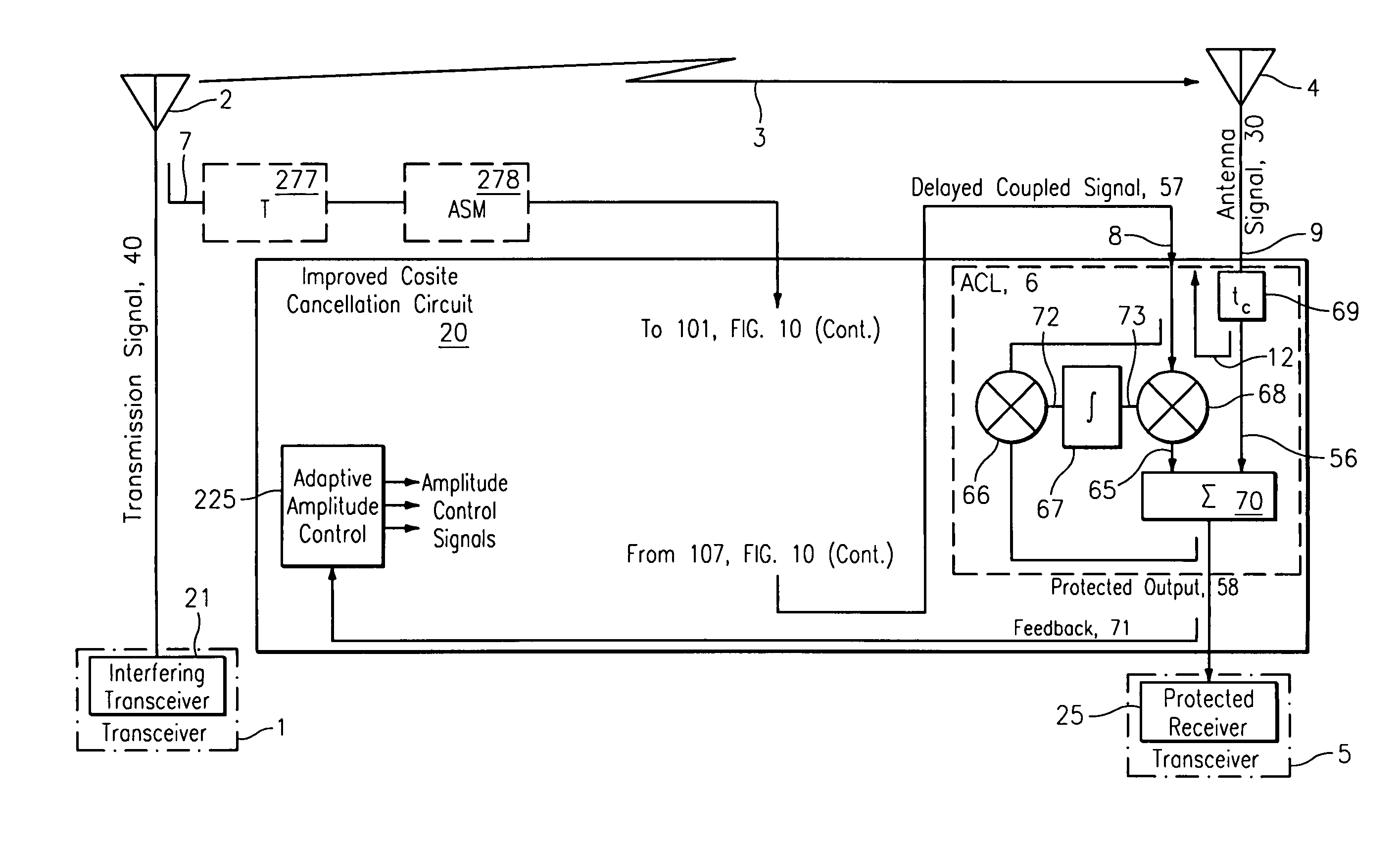
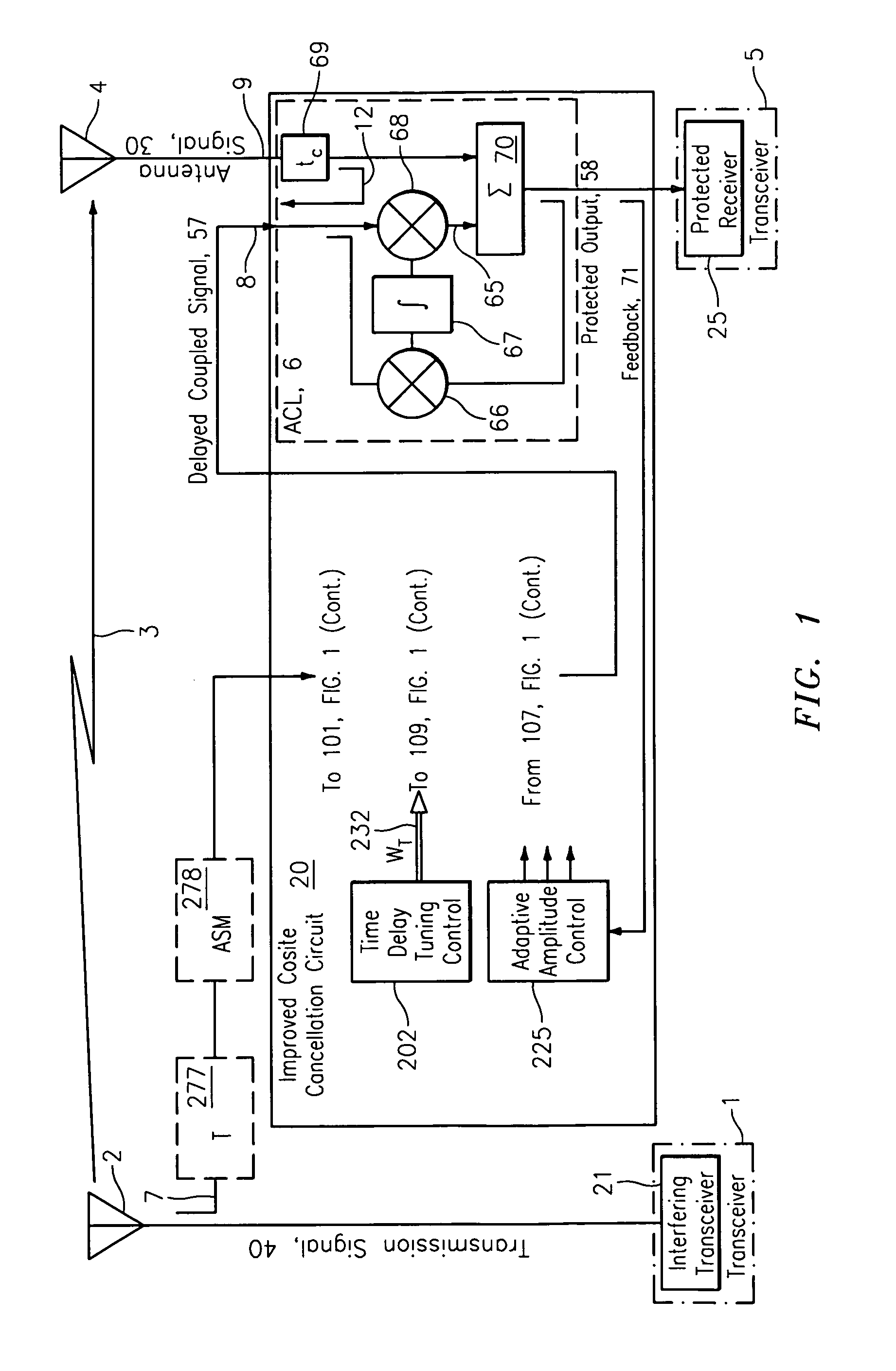
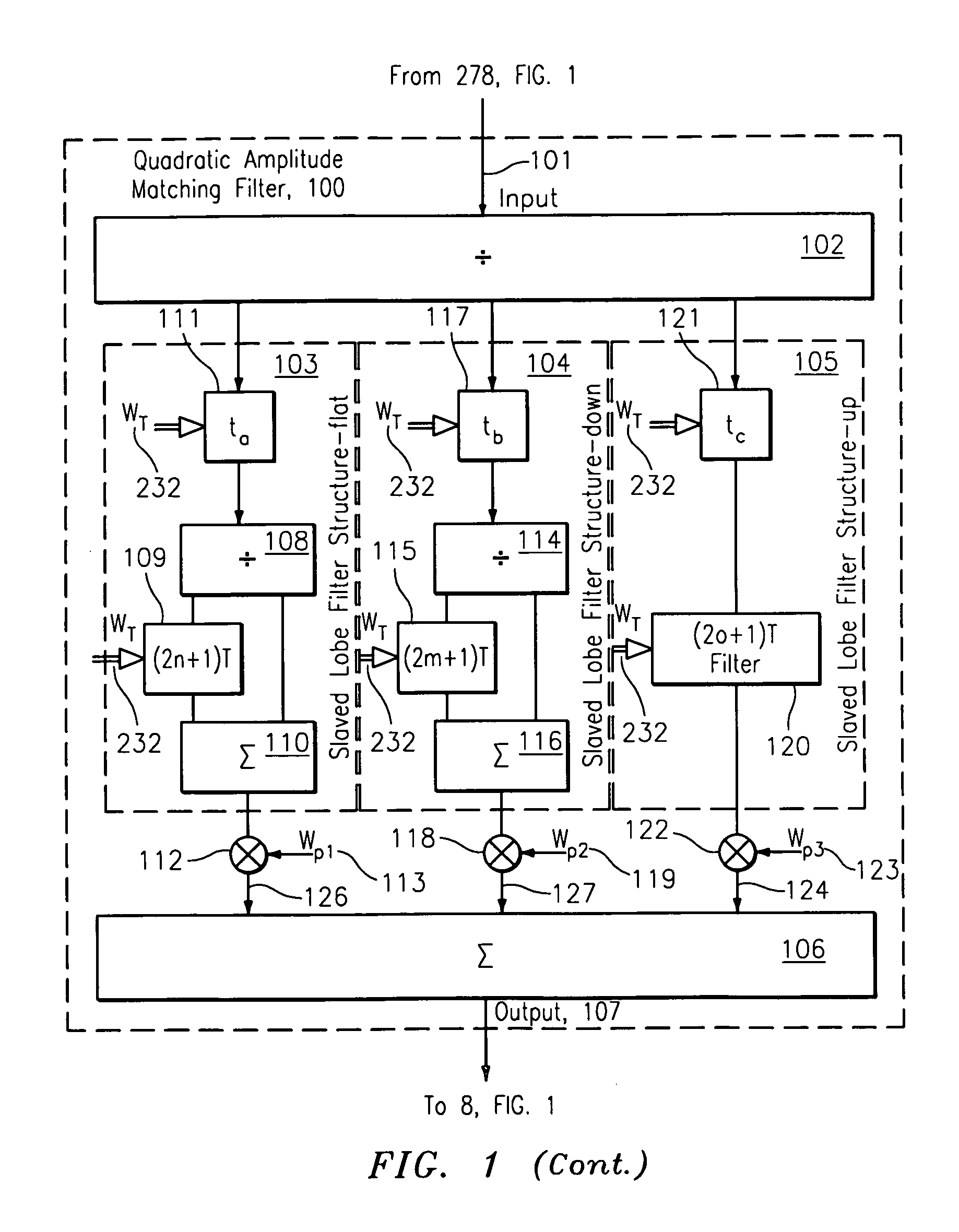
Quadratic amplitude control circuit for cosite interference cancellation
A quadratic amplitude matching system and associated method with an associated tuning control system is provided for continuously and automatically tuning a quadratic amplitude matching filter (QAMF) to a band center of an interfering signal to provide improved rejection of an interfering signal coupled from a transmission antenna into a local receive antenna in the presence of local multi-path, thereby providing improved interference cancellation system performance. The matching control system is provided as an element of an interference cancellation system.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Reduction of linear interference canceling scheme
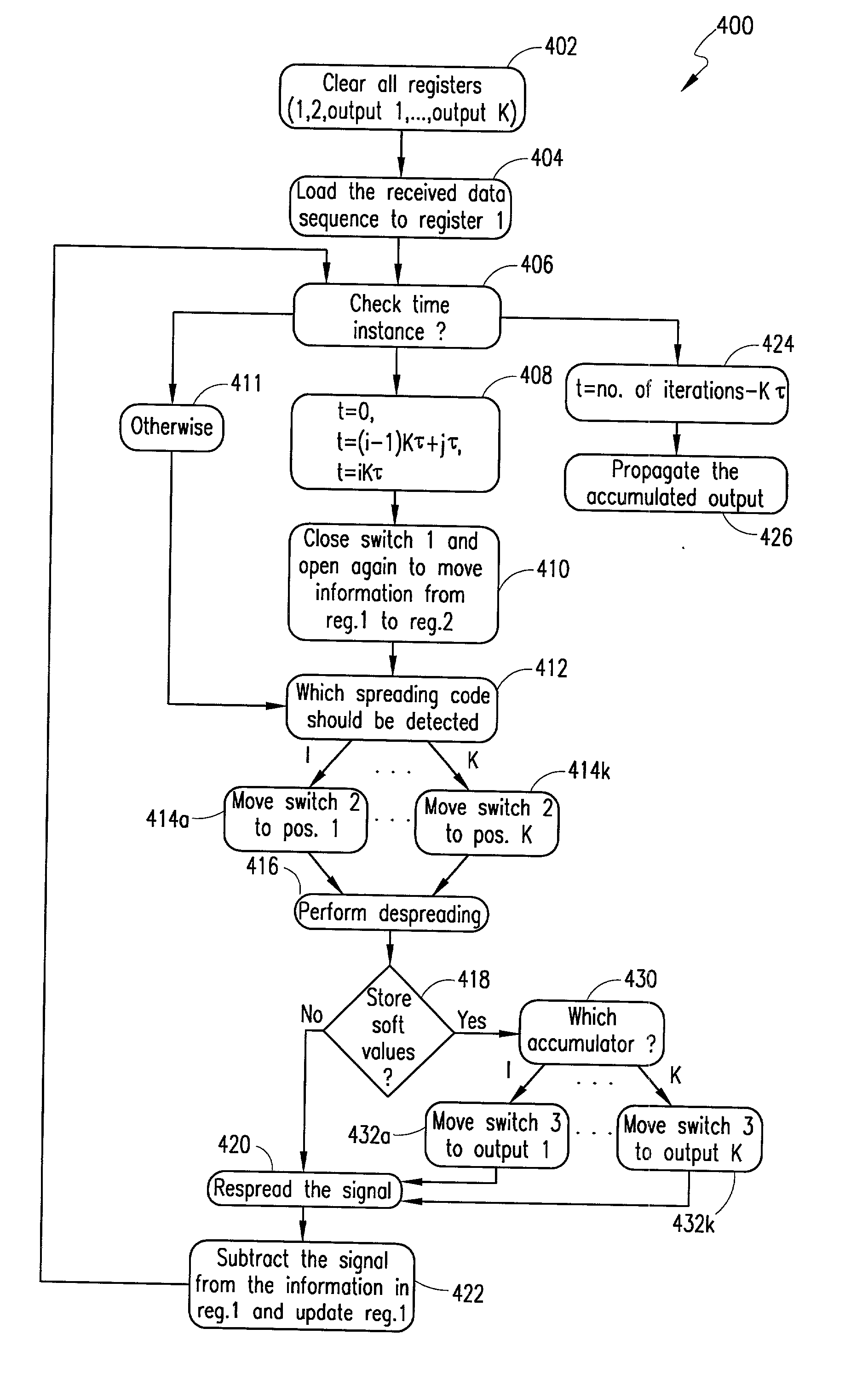
A system, method and apparatus for demodulating a received signal using a configurable receiver. The receiver performs the demodulation of a signal according to a selected interference cancellation demodulation scheme. The same receiver can be configured, by setting certain parameters, to behave as a successive interference cancellation (SIC) scheme receiver, a parallel interference cancellation (PIC) scheme receiver, or a hybrid interference cancellation (HIC) scheme receiver. In another aspect of the present invention, the receiver performs its demodulation operation using a single interference cancellation unit (ICU). In addition, the ICU's despreading and respreading functions may be performed by the same processing element.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Low complex degree equalization method based on iteration jam deleting in spread spectrum communication system
InactiveCN101232303AReduce implementation complexityImprove performanceTransmissionCoded elementEqualization
The invention relates to a low-complexity balancing method which is used in a spread spectrum communication system based on iterative interference cancellation, and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The method includes the following steps: in the pilot stage when receiving a signal, a channel is estimated using such methods as glide correlation and least square to get an estimation value of compound channel responses; for each compound channel response, L paths with maximum amplitude are selected from KNc paths, and the values of the other paths are assigned as zero; the channel responses are fragmented, Nc paths in each section form a channel response vector, and M vectors belonging to the k section form a channel response matrix; a correlation value register and a provisional decision variable register are initialized; in a numeric data code element stage when receiving the signal, the iterative interference cancellation is acted according the sequence of the numeric data code element to get a final decision value of an emitting code element. The invention greatly reduces the calculation amount of the tap selection and the coefficient training, but the performance thereof surpasses a linear balancing method which arranges the tap according to the maximum path position.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Single antenna interference suppression in a wireless receiver
InactiveUS7567635B2Reduce impactReduce co-channel interferenceError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementTime errorCommunications system
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of single antenna interference cancellation (SAIC) in a wireless communications system. A class of algorithms is disclosed for Downlink Advanced Receiver Performance (DARP) receivers based on a novel metric calculation used during equalization and optionally in other portions of the receiver as well, e.g., soft value generation. A DARP receiver for 8PSK EDGE modulation is presented wherein the interfering signals comprise GMSK modulated signals. The modified metric takes into account the rotation remaining in the noise component of the received signal after de-rotation of the 8PSK signal. Considering the interferer to be a GMSK signal, the I / Q elements of the noise are correlated and this fact is used to modify the decision rule for the received signal thus improving the performance of the equalizer. The model is further extended to take into account temporal error correlation.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
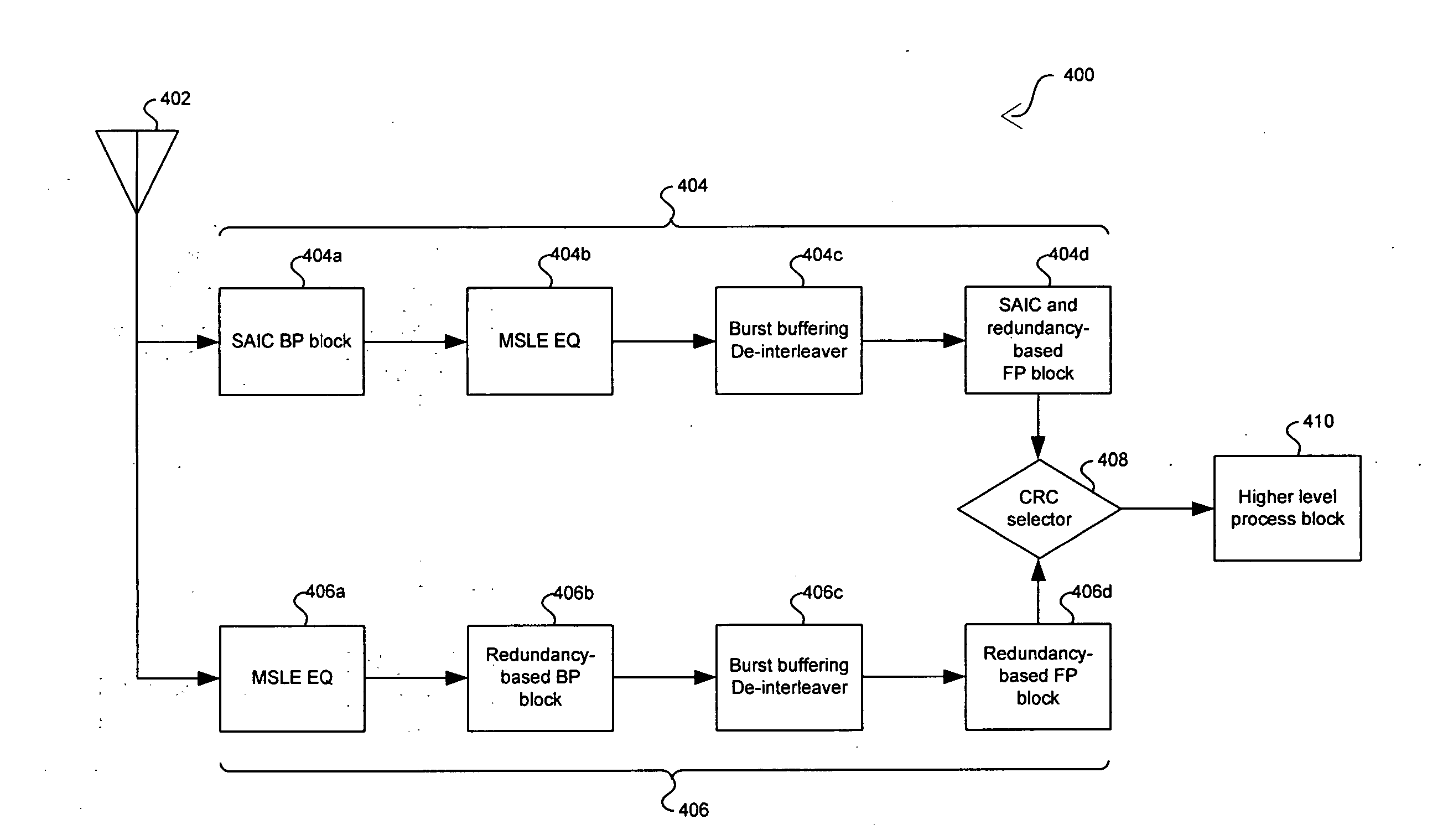
Method and system for decoding single antenna interference cancellation (SAIC) and redundancy processing adaptation using frame process
InactiveUS20070153942A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsComputer scienceSingle antenna interference cancellation
Aspects of a method and system for decoding single antenna interference cancellation (SAIC) and redundancy processing adaptation using frame process are provided. A receiver may decode video, voice, and / or speech bit sequences based on a first decoding algorithm that may utilize data redundancy and that may impose physical constraints. The receiver may also decode a bit sequence based on a second decoding algorithm that utilizes SAIC. The first and second decoding algorithms may be adapted to perform in parallel and a decoded received bit sequence may be selected based on a redundancy verification parameter. The first and second decoding algorithms may also be adapted to be performed sequentially where the subsequent decoding operation may be conditioned to the initial decoding operation. Moreover, either the first or the second decoding algorithm may be selected for decoding the received bit sequence. The selection may be based on noise and / or interference measurements.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Dynamic switching between maximum likelihood sequence estimation (MLSE) and linear equalizer for single antenna interference cancellation (SAIC) in a global system for mobile communications (GSM) system
ActiveUS7724816B2Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsEngineeringMobile communication systems
In a GSM / EDGE Single Antenna Interference Cancellation (SAIC) operation environment, a mobile station is required to operate in a wide range of interference levels. An SAIC linear equalizer that takes advantage of the GMSK signal structure performs better than a conventional Maximum Likelihood Sequence Estimation (MLSE) equalizer in high interference levels, while it performs worse in low interference levels. A dynamic selection between the SAIC linear equalizer and the MLSE equalizer for each received burst is achieved to provide the optimal performance across the entire required operation environments. The dynamic selection is based on the estimated noise plus interference energy relative to the total received signal energy. The soft information calculated by the two categories of equalizers is properly scaled to generate soft information with balanced magnitude.
Owner:APPLE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com